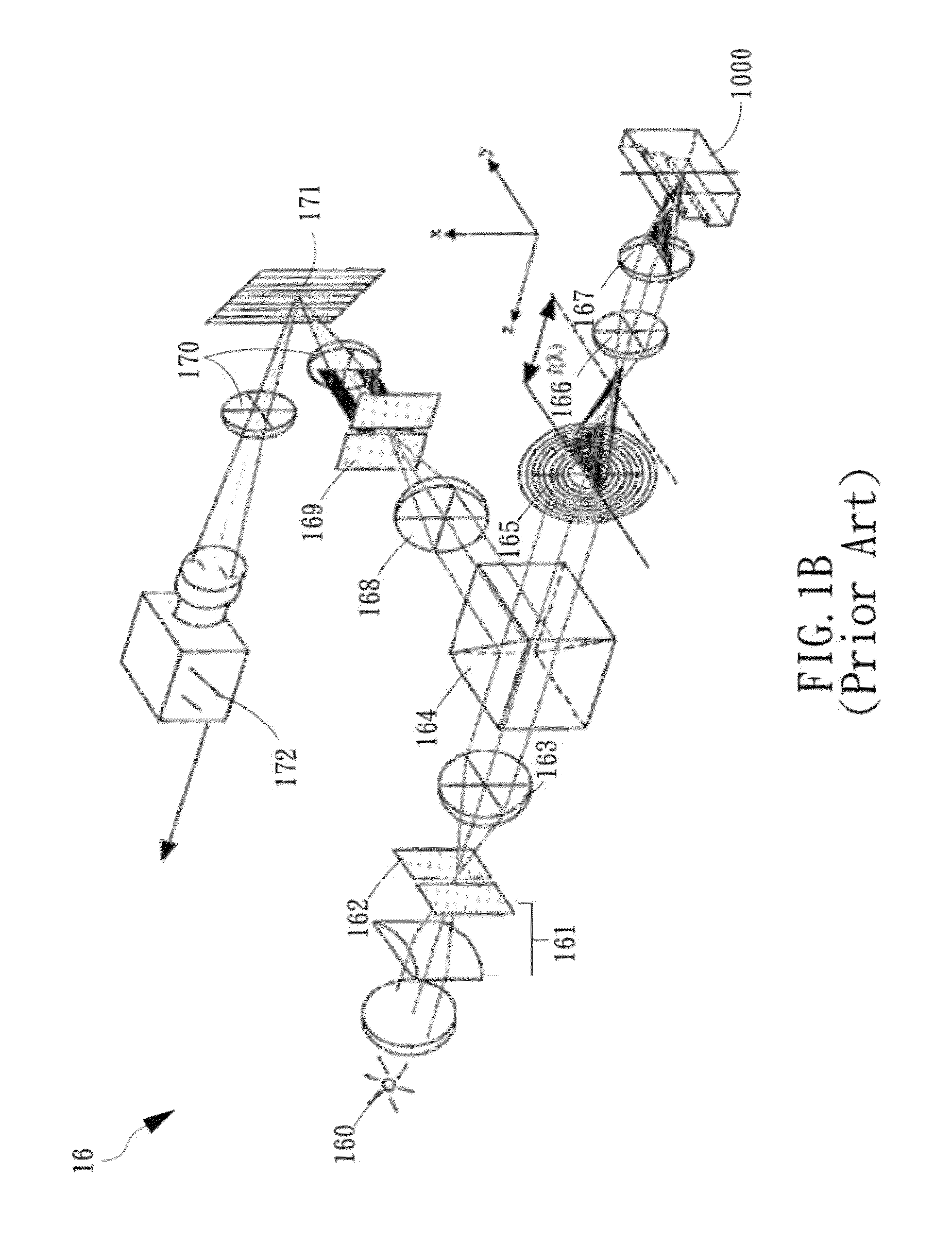
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Optical sectioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical sectioning is the process by which a suitably designed microscope can produce clear images of focal planes deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for thin sectioning using instruments such as the microtome. Many different techniques for optical sectioning are used and several microscopy techniques are specifically designed to improve the quality of optical sectioning.
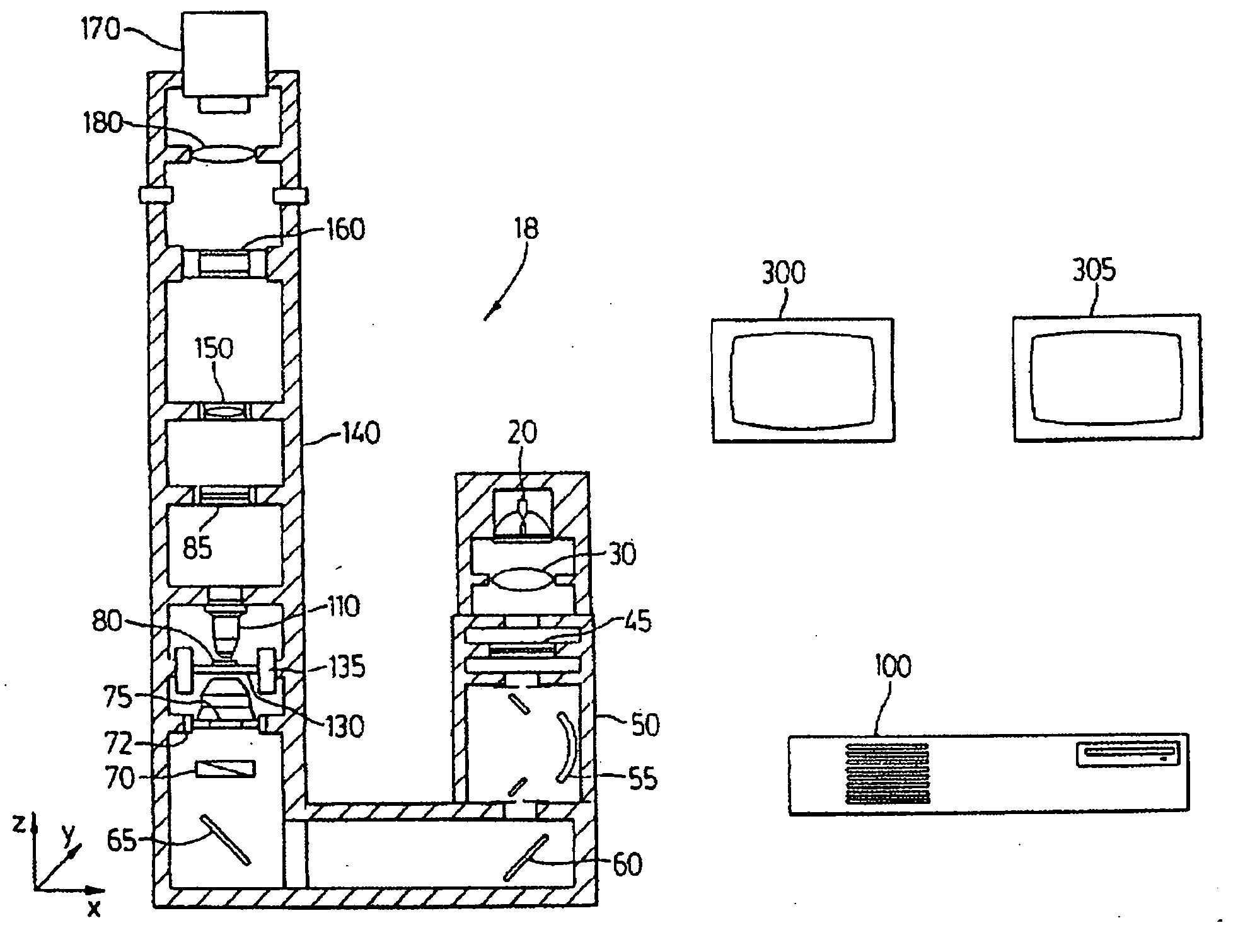
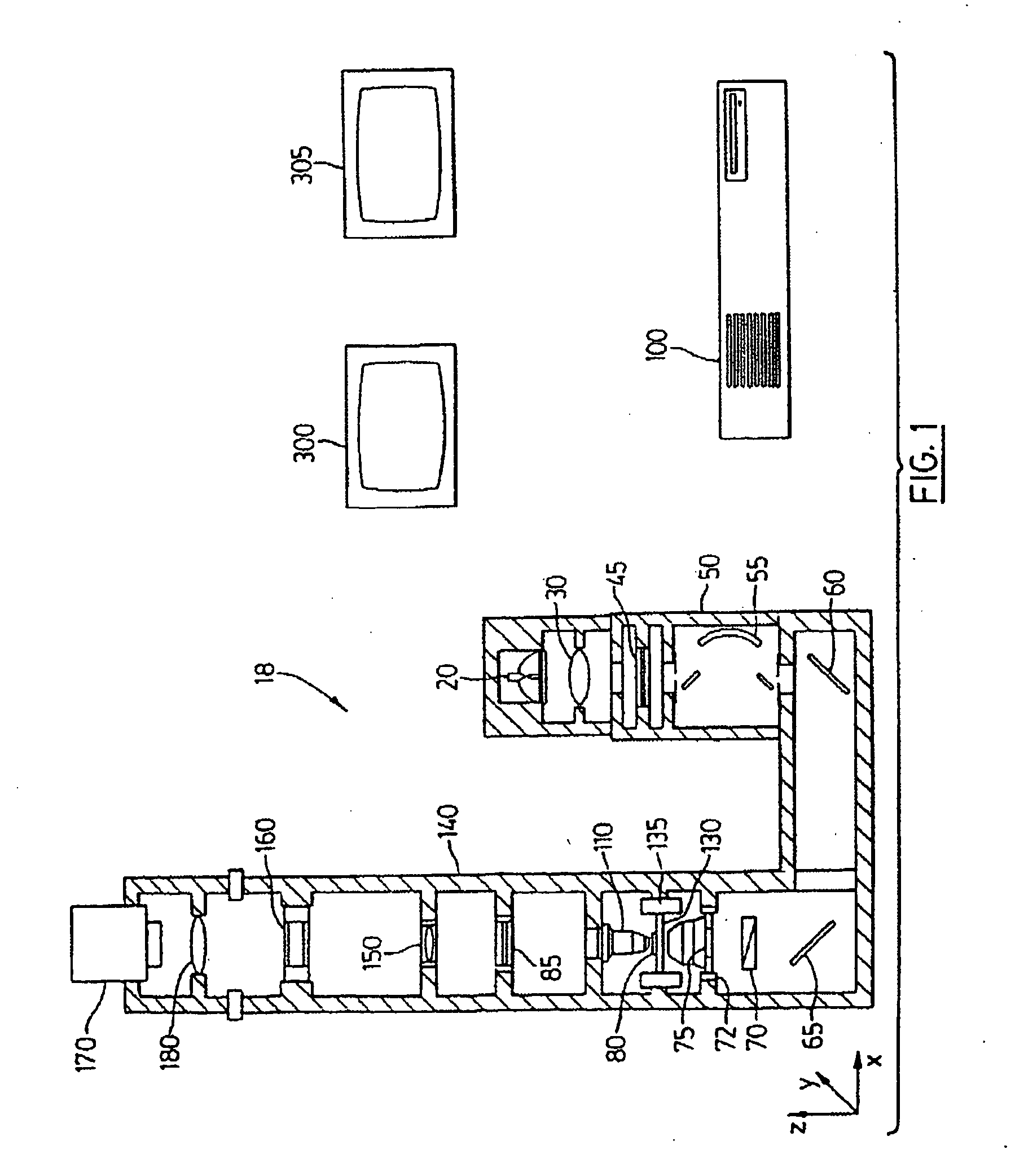
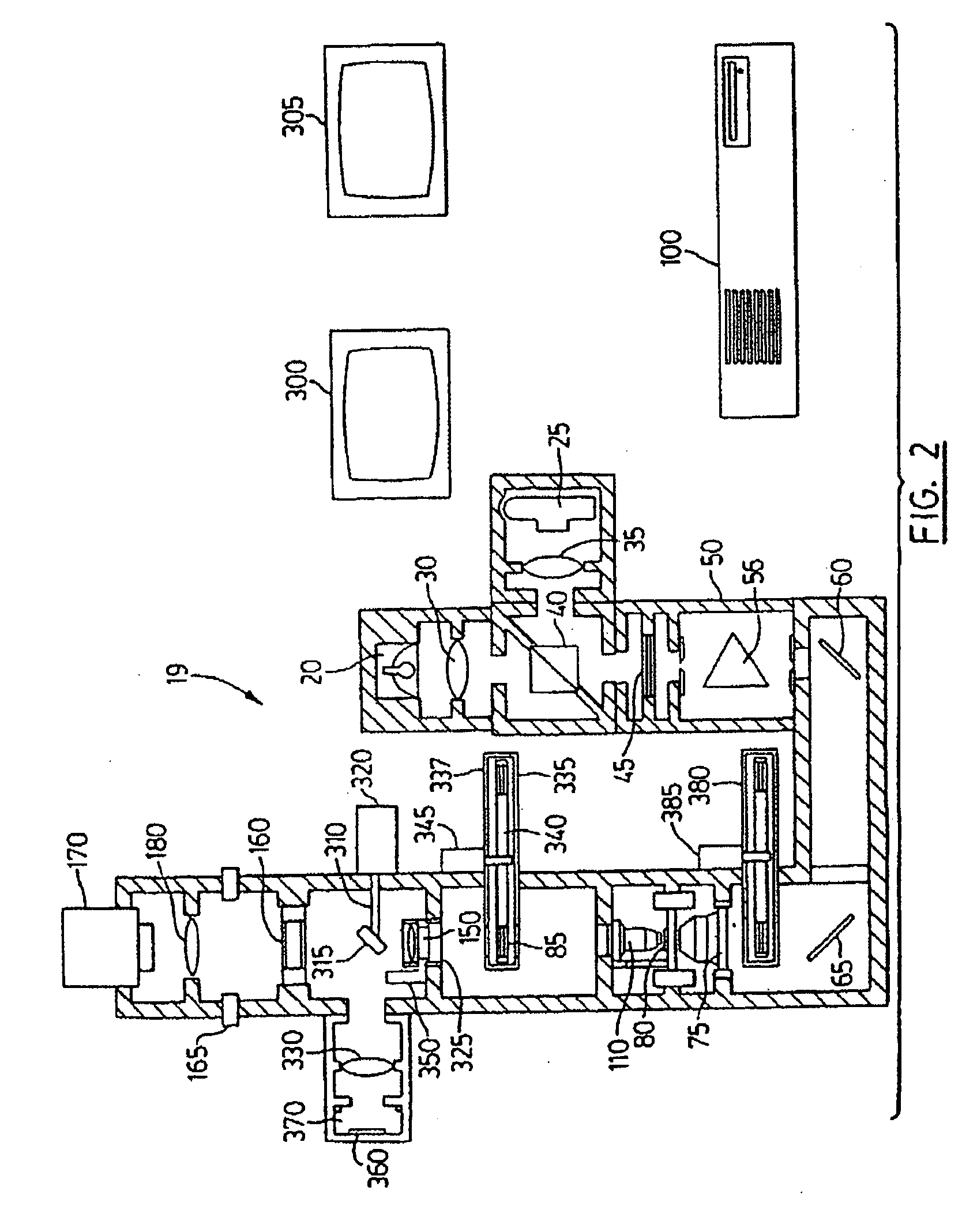
Color translating UV microscope
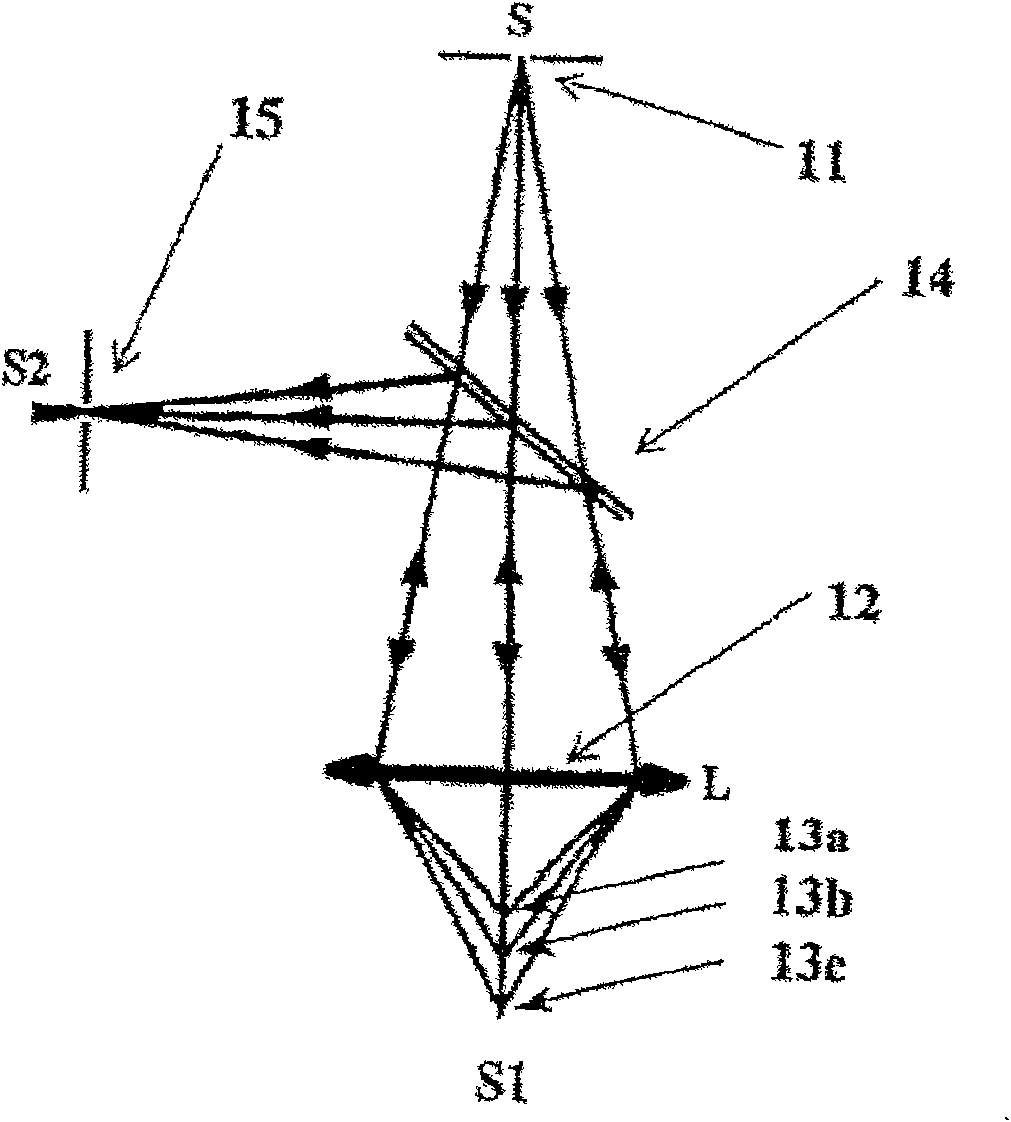
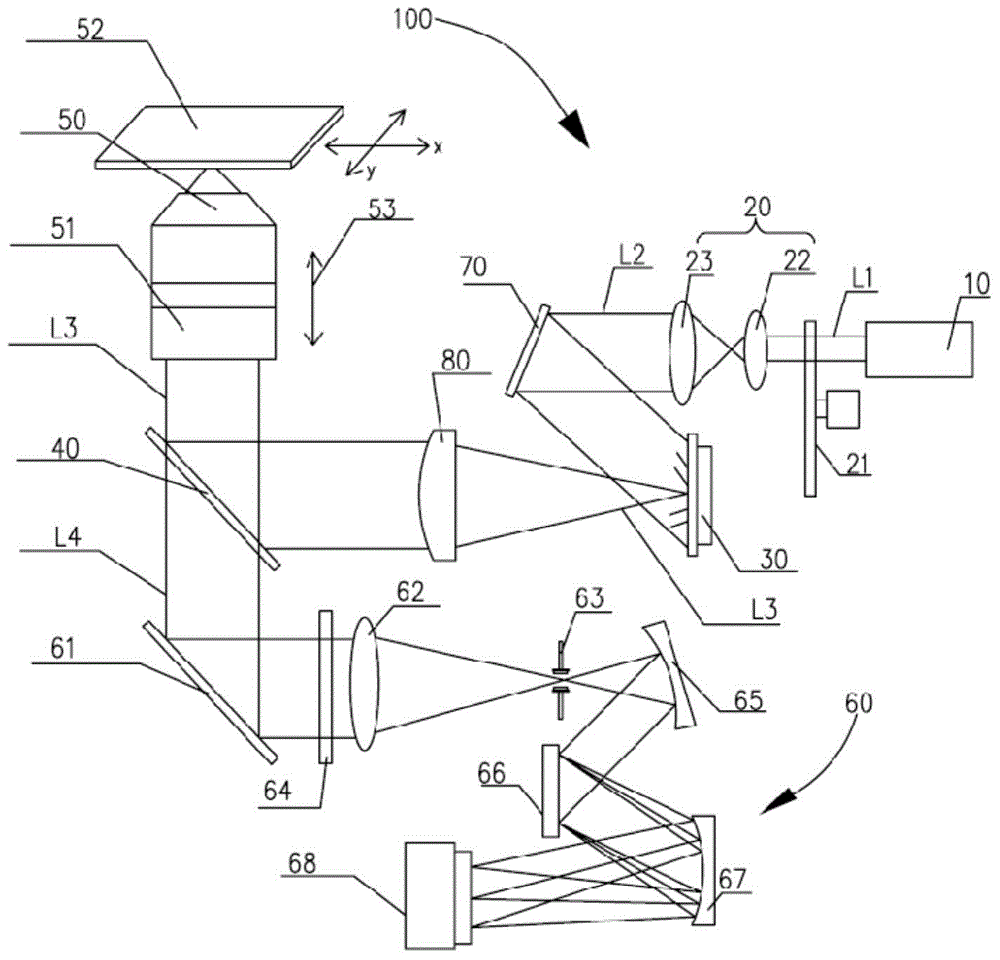
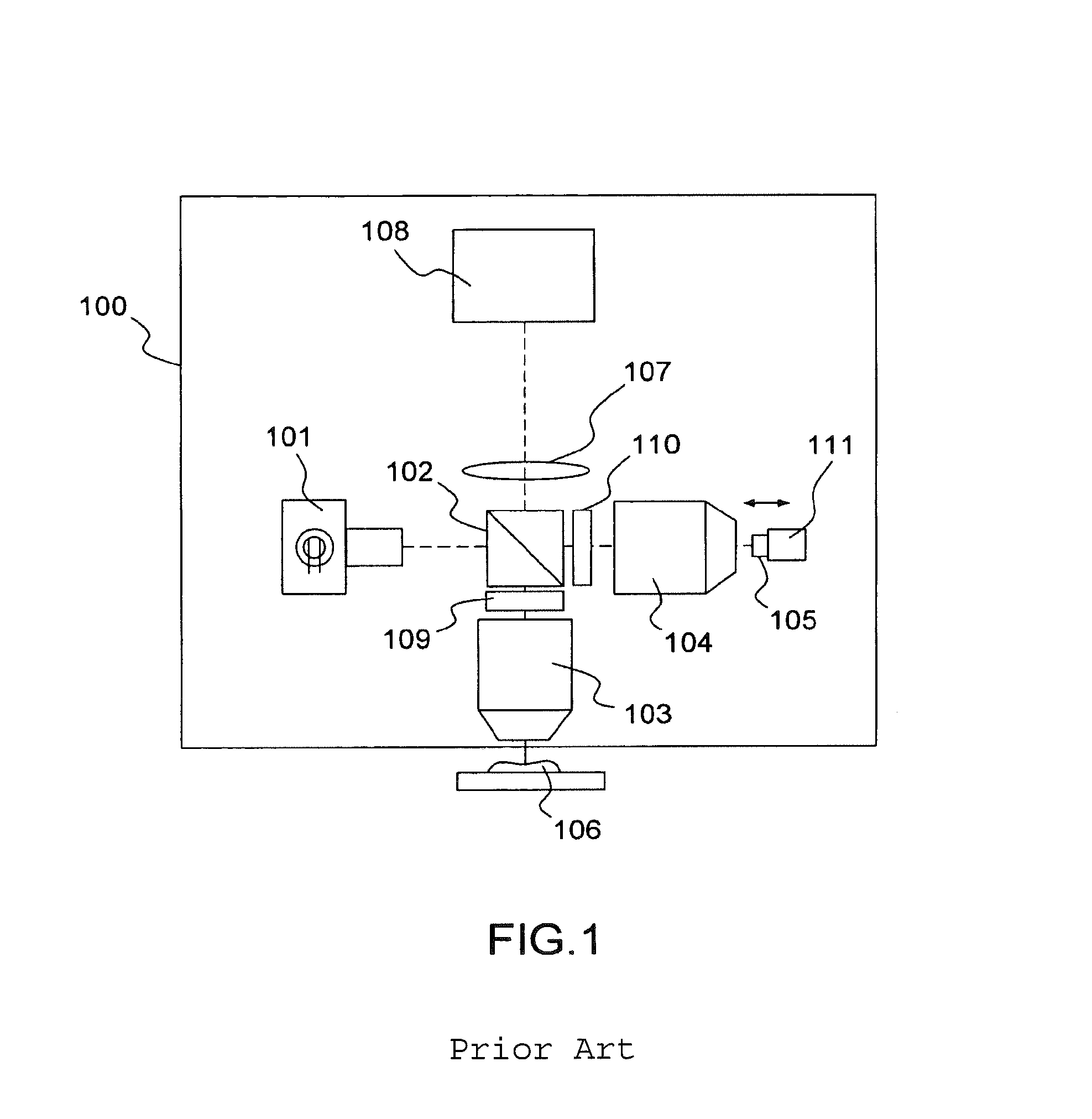
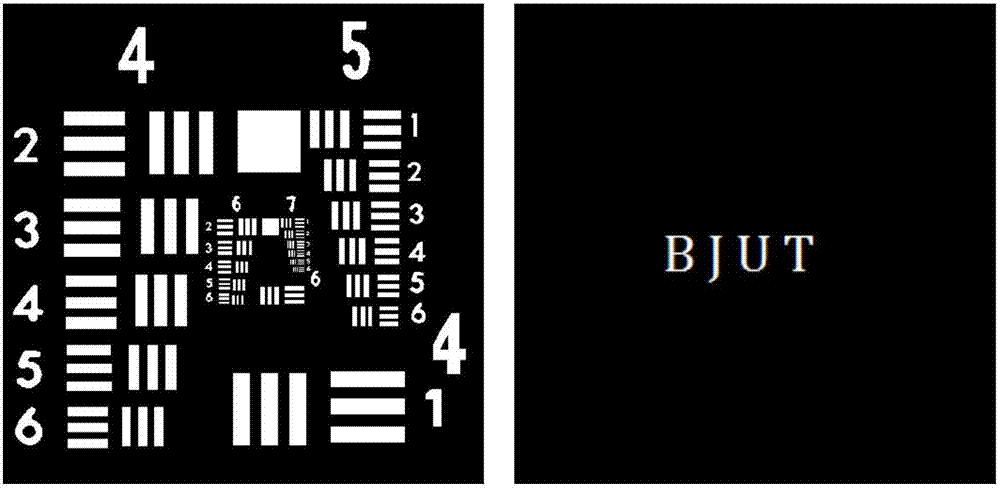
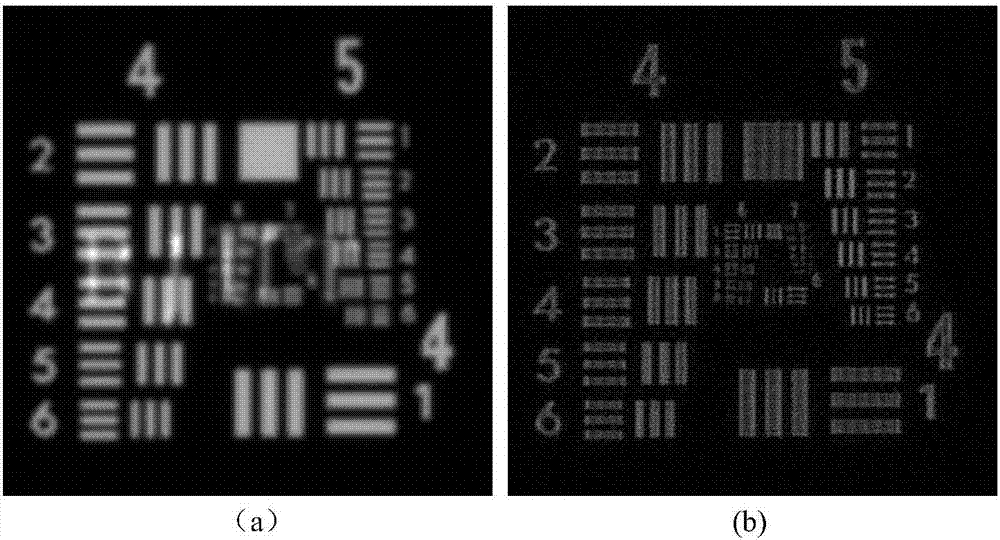
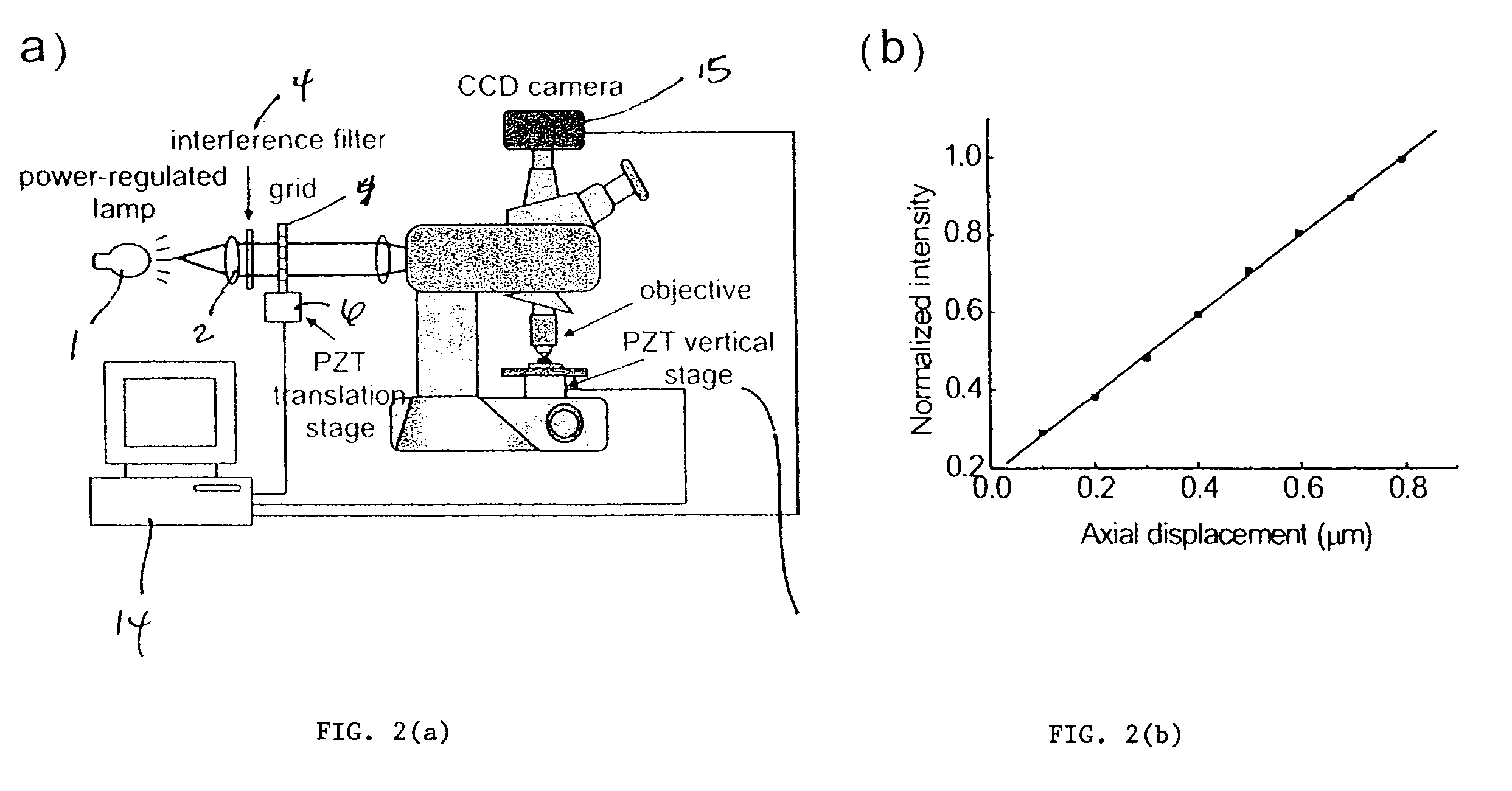
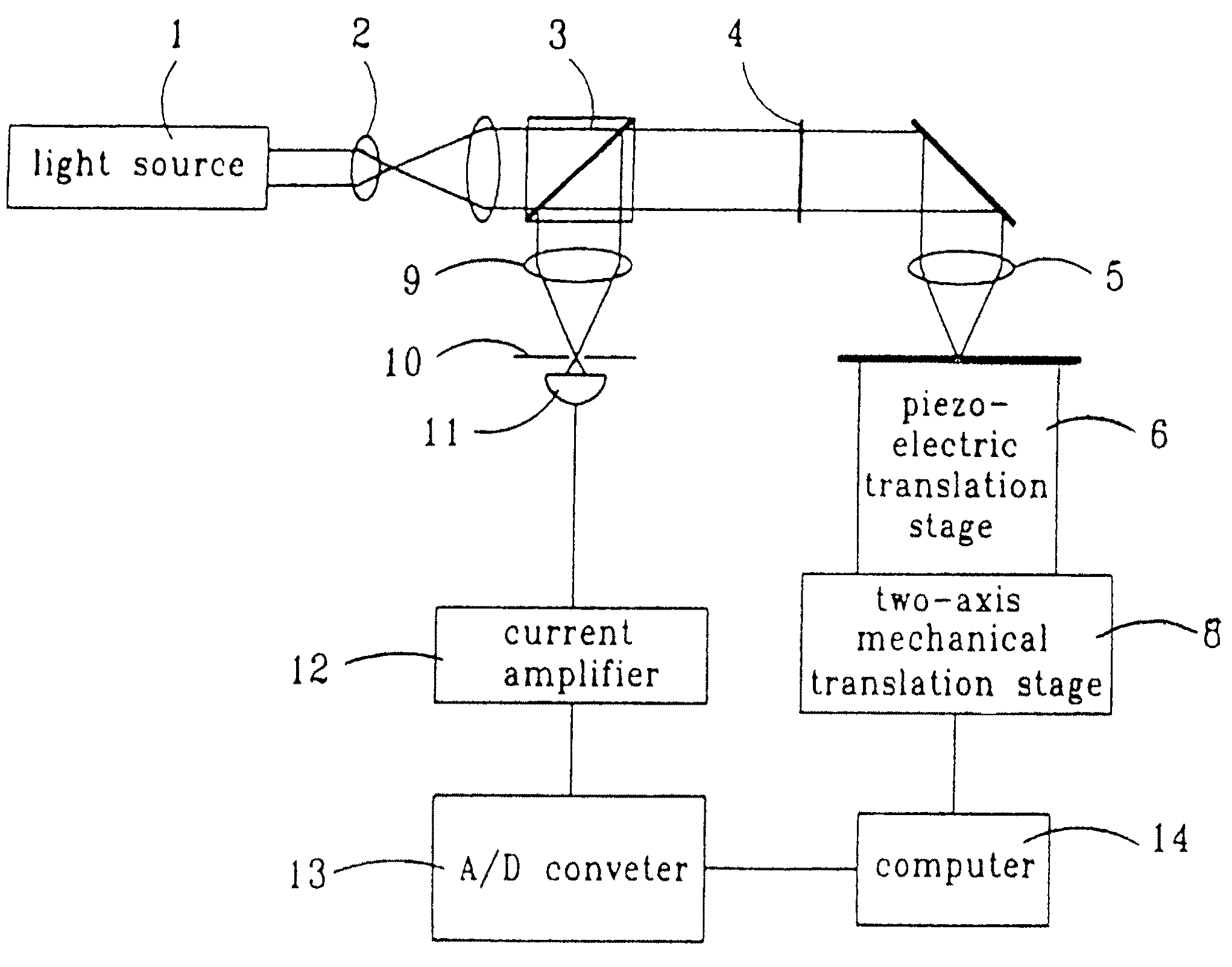
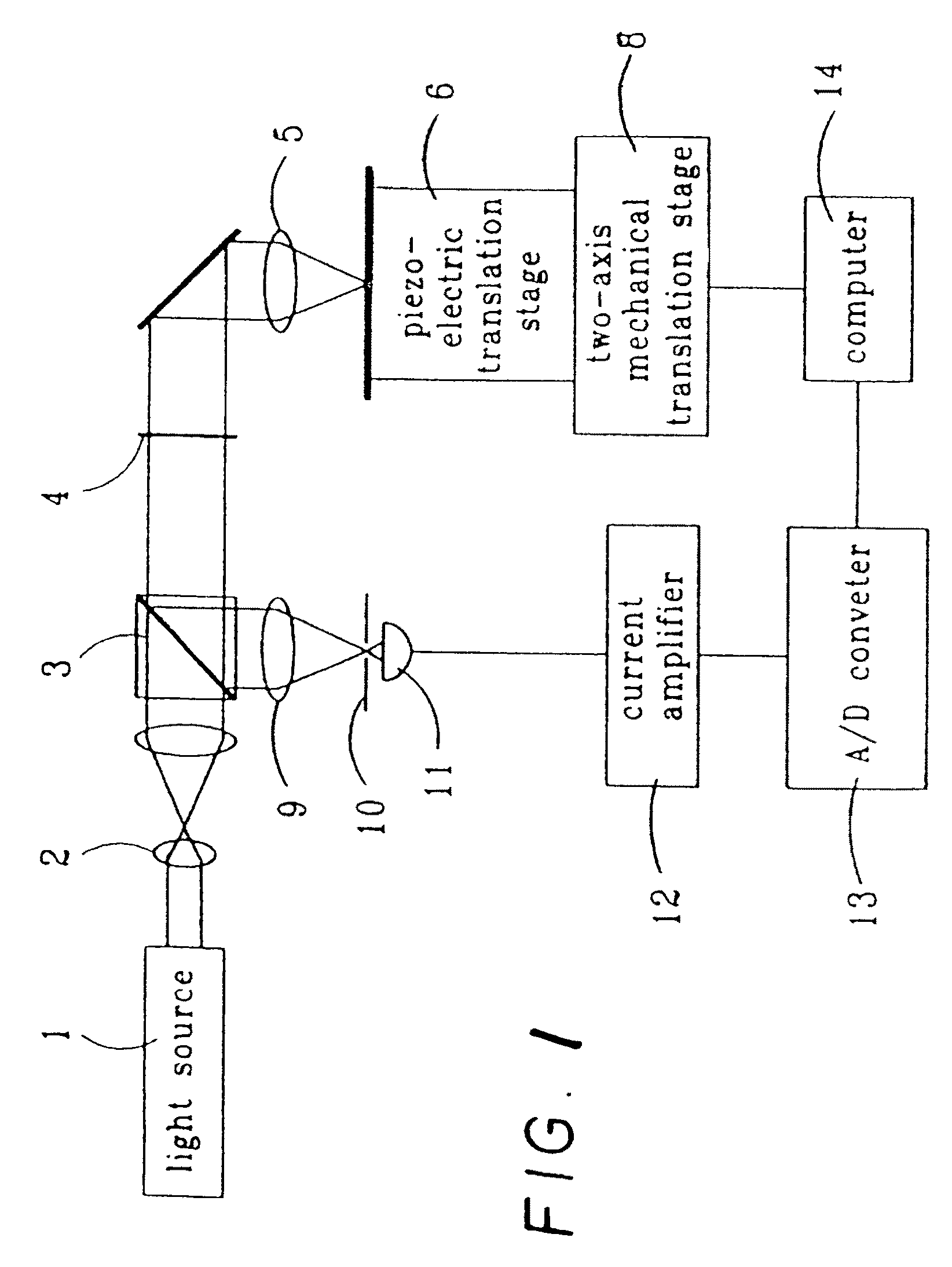
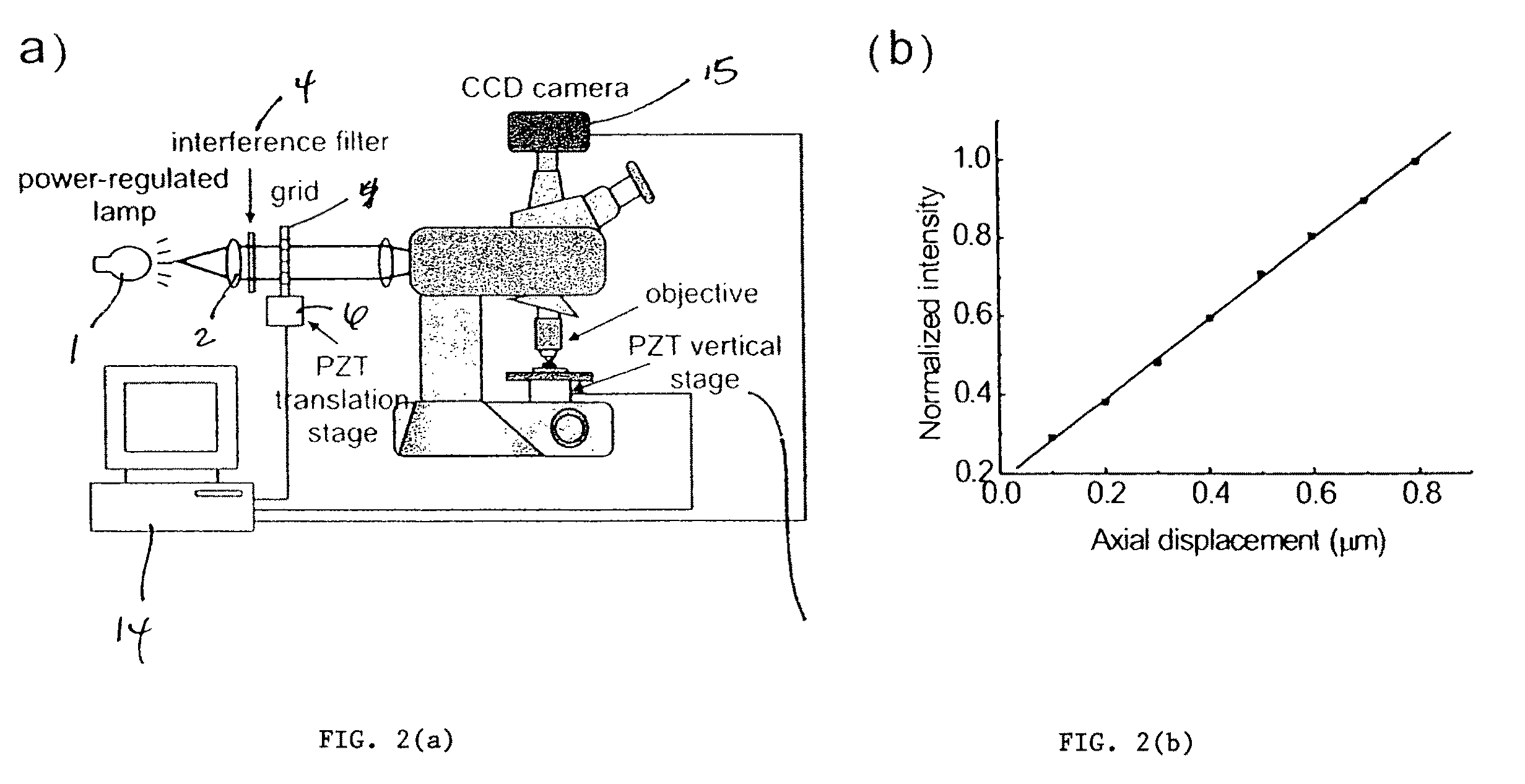
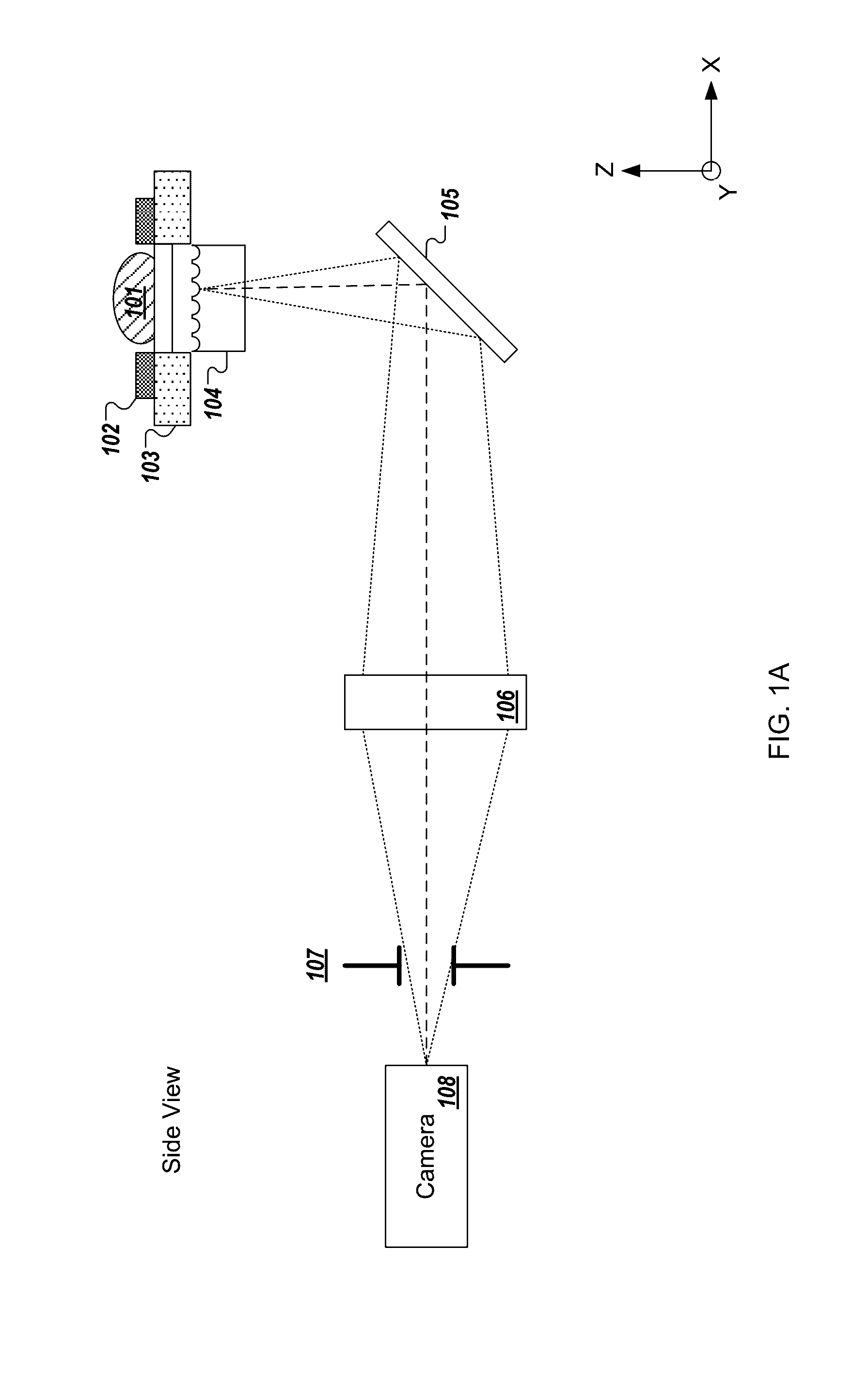
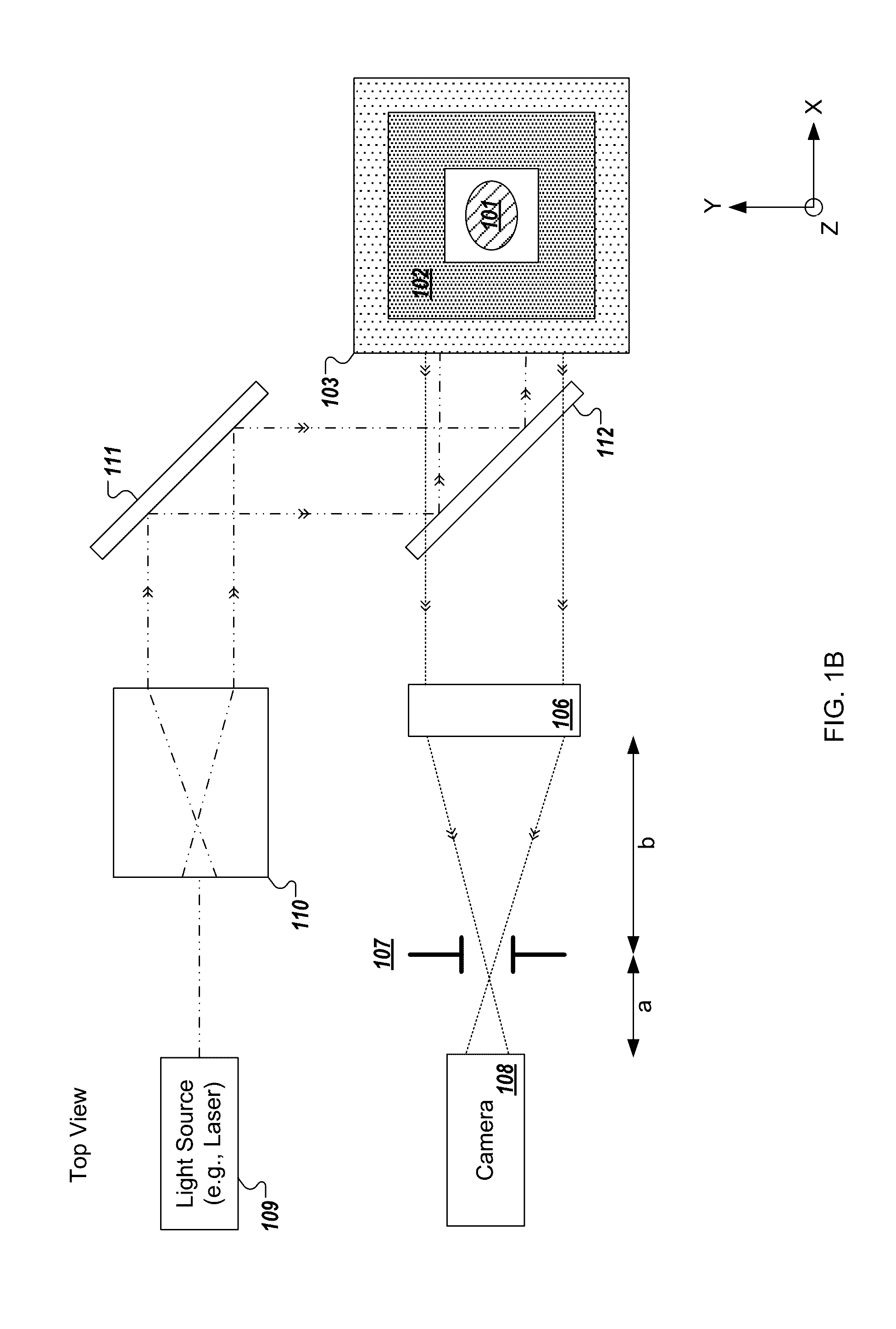
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
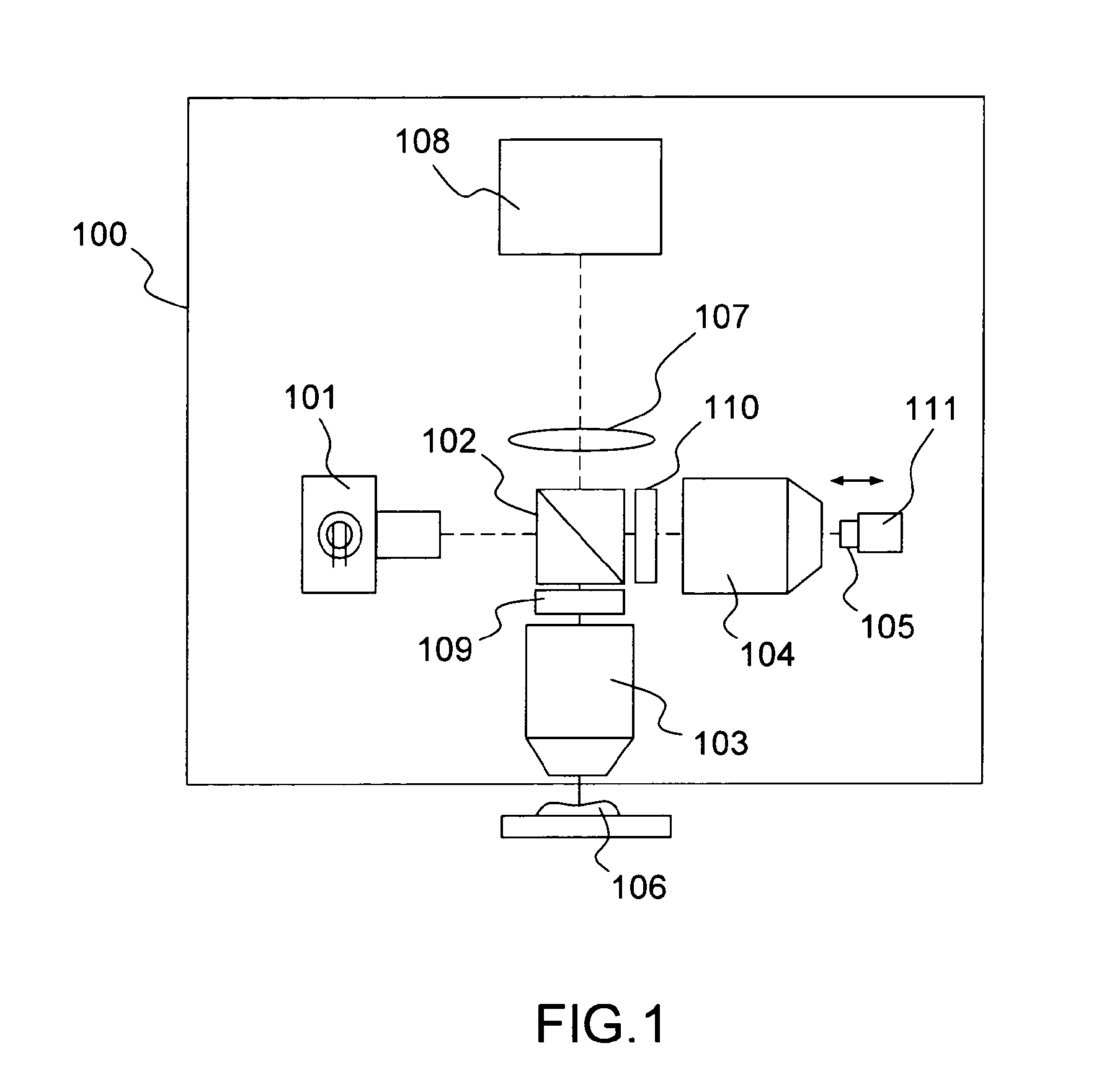
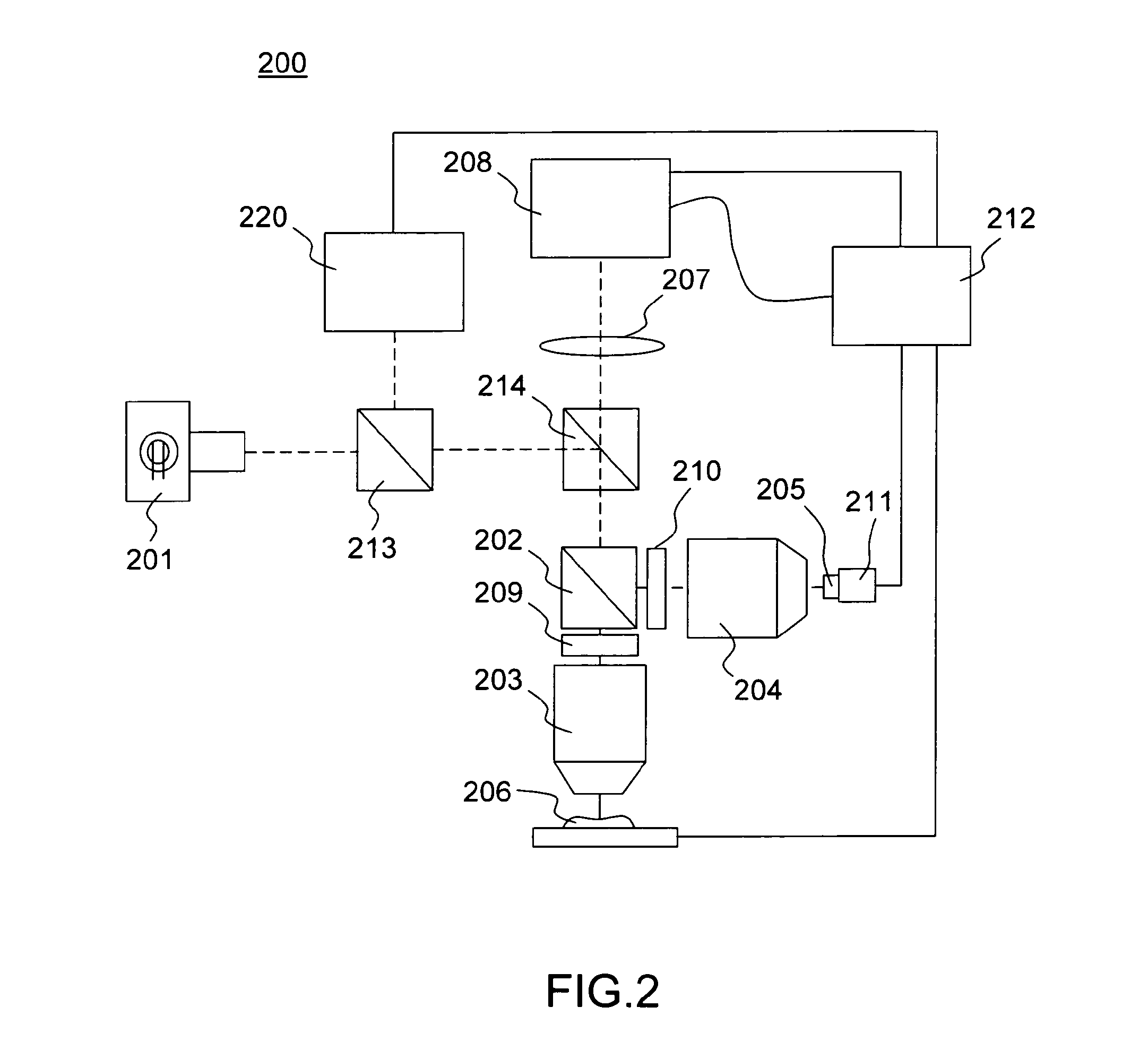
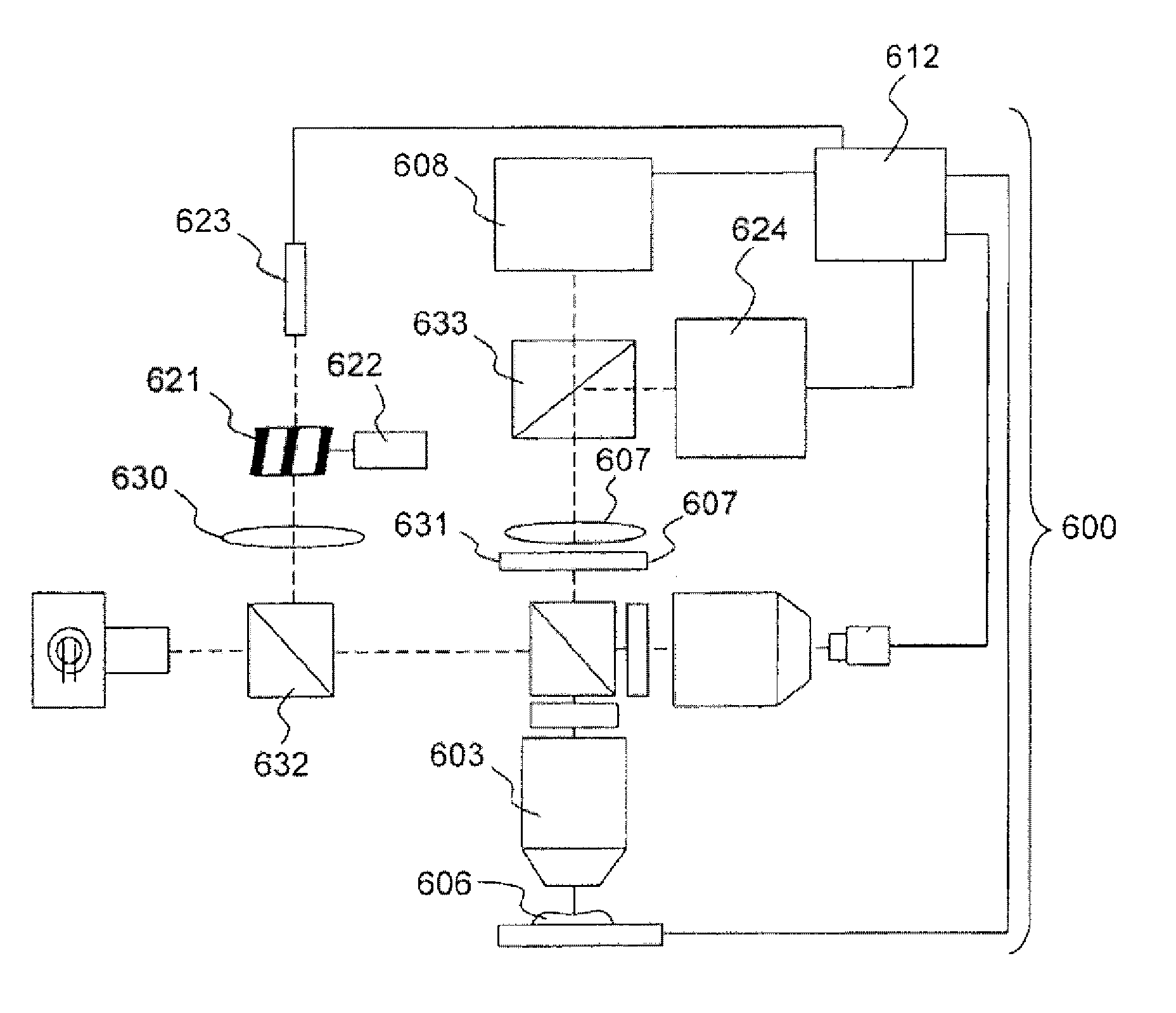
Optical tissue sectioning using full field optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20130182096A1Easy to combineEasy to separateColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsFluorescenceStructured illumination microscopy
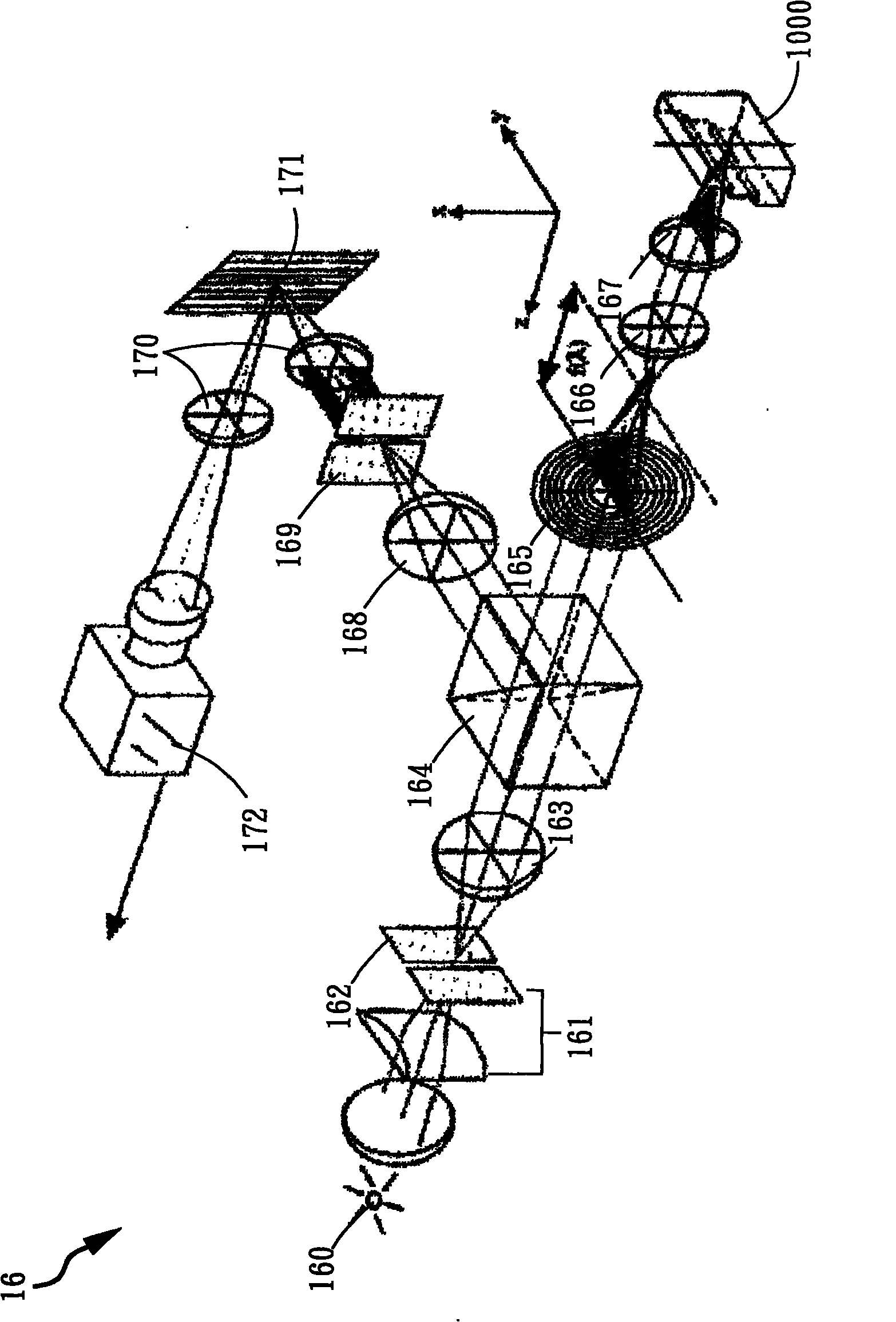
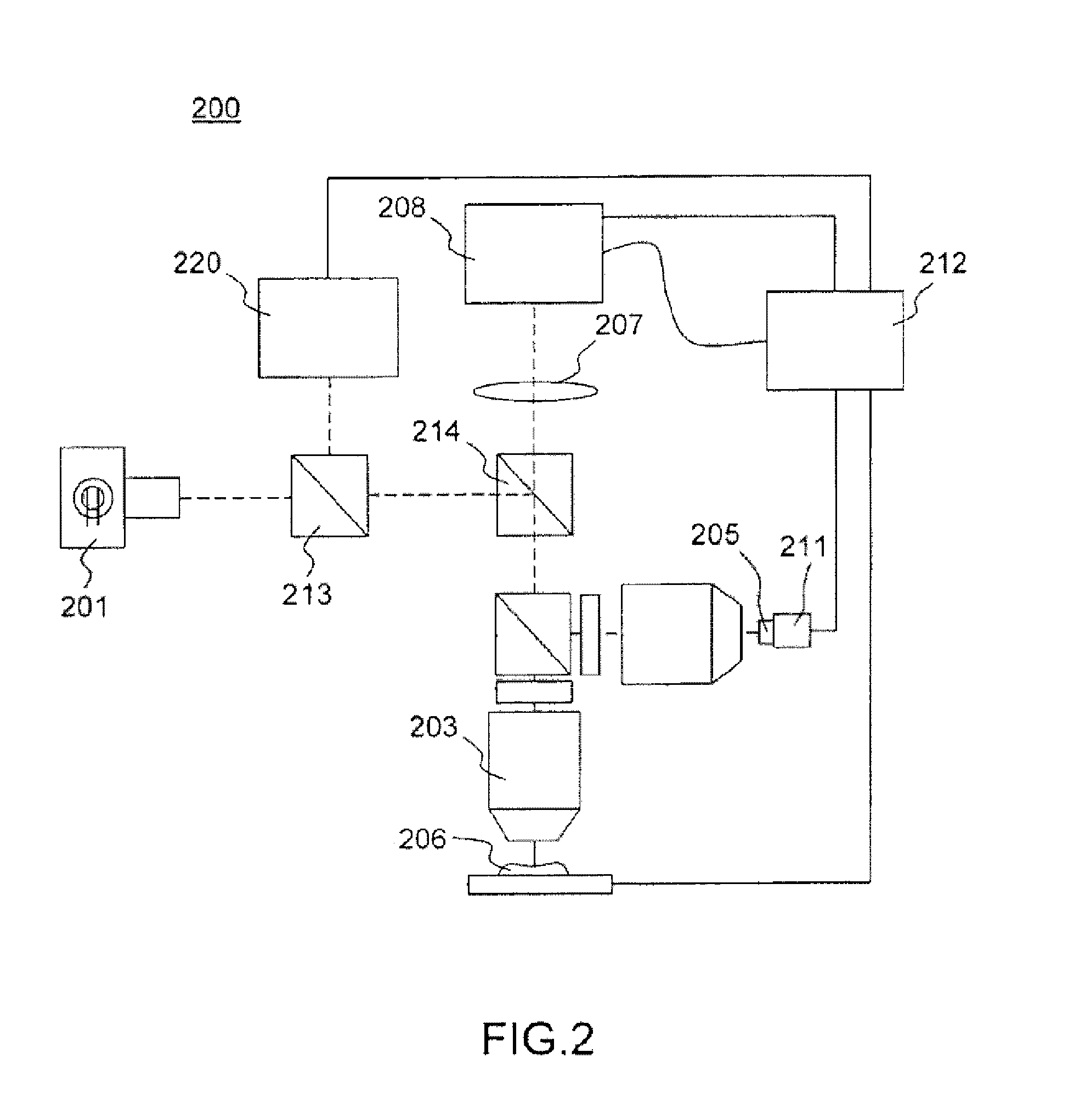
According to a first aspect, the invention relates to a multimodal optical sectioning microscope (200, 400, 600) for full-field imaging of a volumic and scattering sample comprising:—a full-field OCT system for providing an image of a first section in depth of the sample comprising an illumination sub-system (201, 401, 601) and a full-field imaging interferometer with a detection sub system (208, 408, 608) and an optical conjugation device for optically conjugating the sample and said detection sub system, wherein said optical conjugation device comprises a microscope objective (203, 403, 603),—a supplementary full-field optical sectioning imaging system for providing a fluorescent image of a second section in depth of said sample comprising a structured illumination microscope with an illumination sub system (623), means (421, 422) for generating at the focal plane of said microscope objective of said full-field imaging interferometer a variable spatial pattern illumination and a detection sub system (624), optically conjugated with said focal plane of the microscope objective.
Owner:LLTECH MANAGEMENT
Slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module and slit-scan microscopic system and method using the same
ActiveUS20100188742A1Improve performanceMinimized in sizePrismsMicroscopesBroadbandLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module, which utilizes at least two lenses having chromatic aberration for splitting a broadband light into continuously linear spectral lights having different focal length respectively. The present invention utilizes the confocal lens module employing slit-scan confocal principle and chromatic dispersion techniques and the confocal microscopy with optical sectioning ability and high resolution in spectral dispersion to establish a confocal microscopy method and system with long DOF and high resolution, capable of modulating a broadband light to produce the axial chromatic dispersion and focus on different depths toward an object's surface for obtaining the reflected light spectrum from the surface. Thereafter, the spectrum is spatially filtered by a slit and then a peak position with respect to the filtered spectrum along the scanning line is detected by a spectral image sensing unit for generating the sectional profile of the measured surface.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
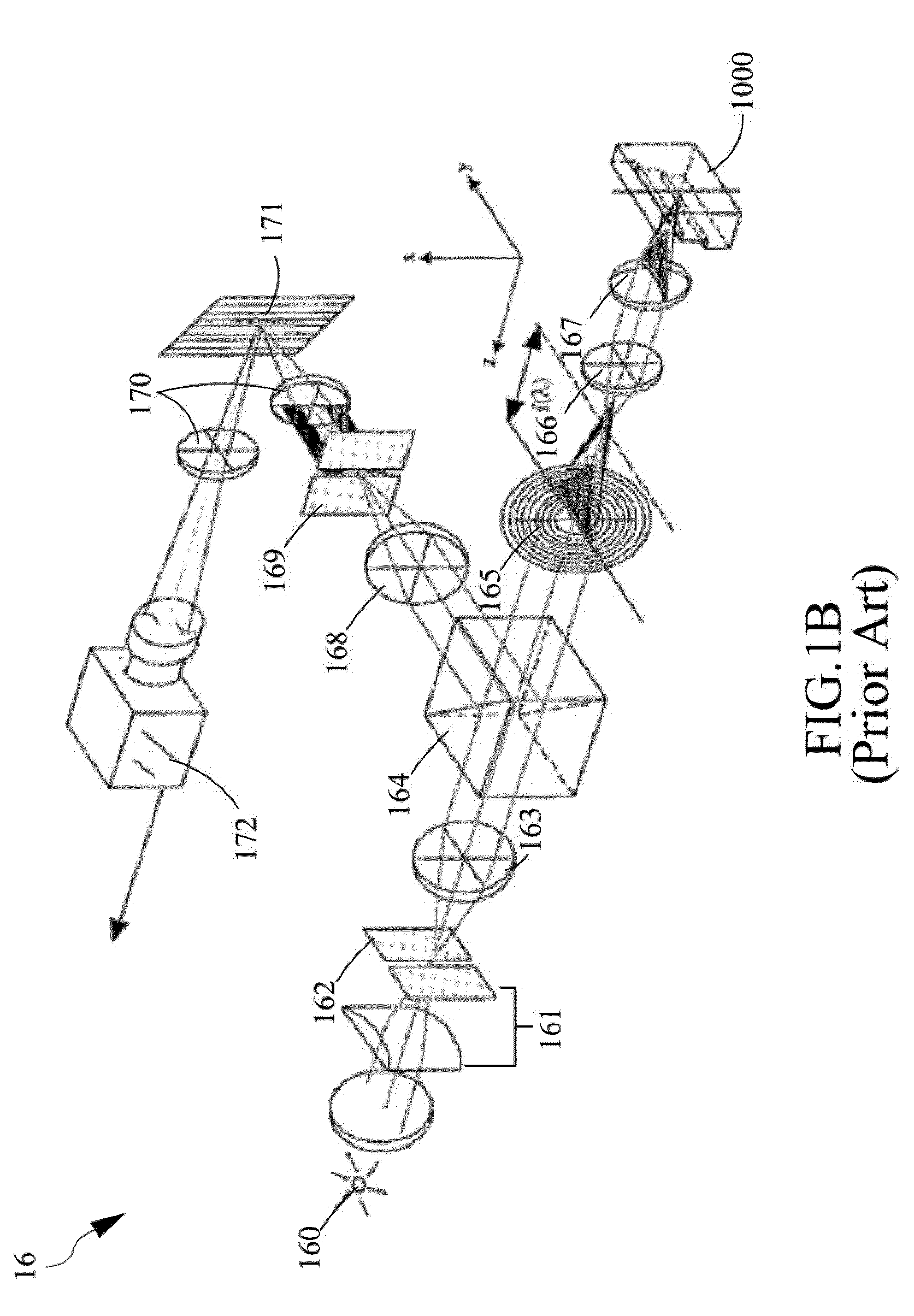
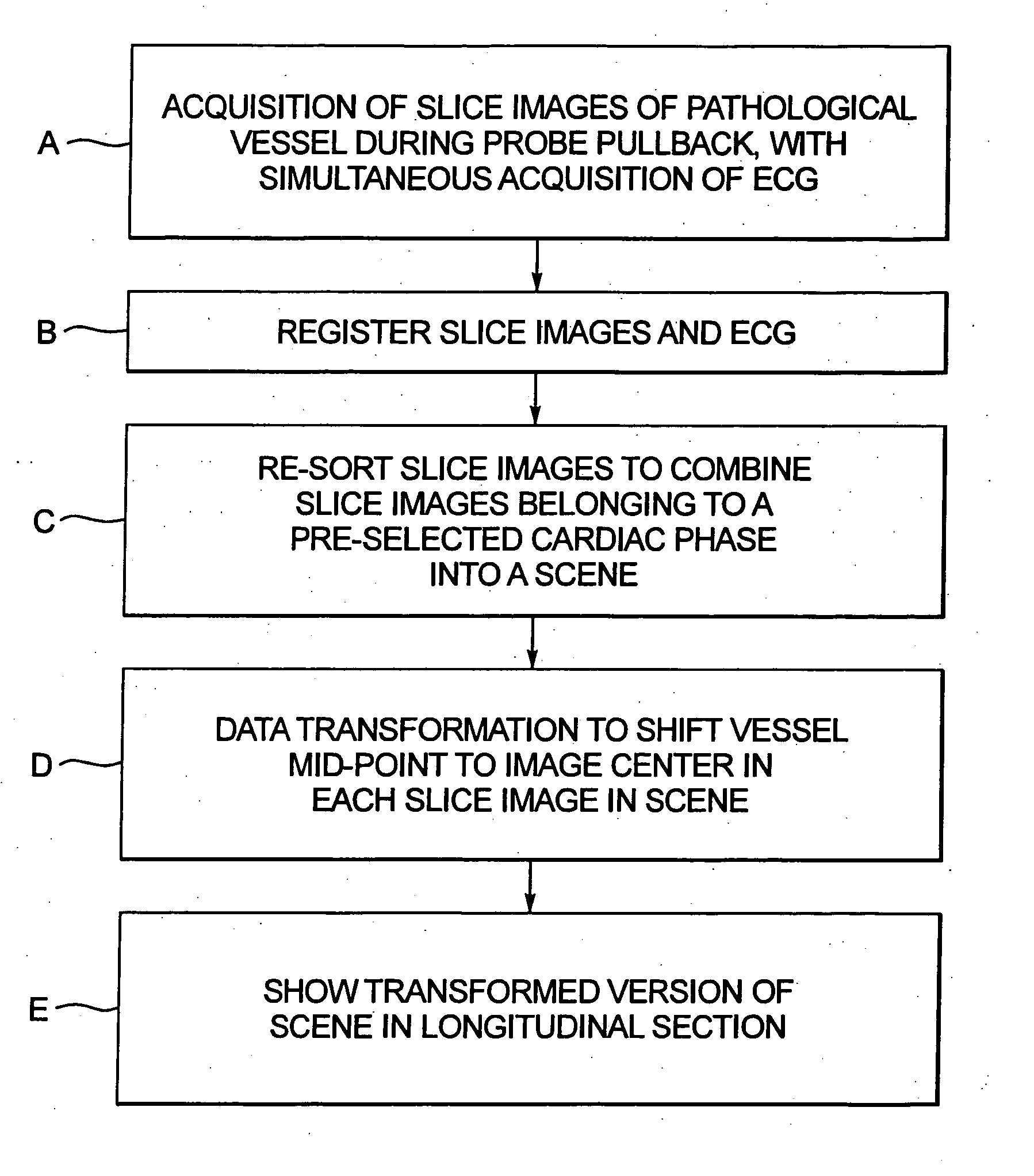
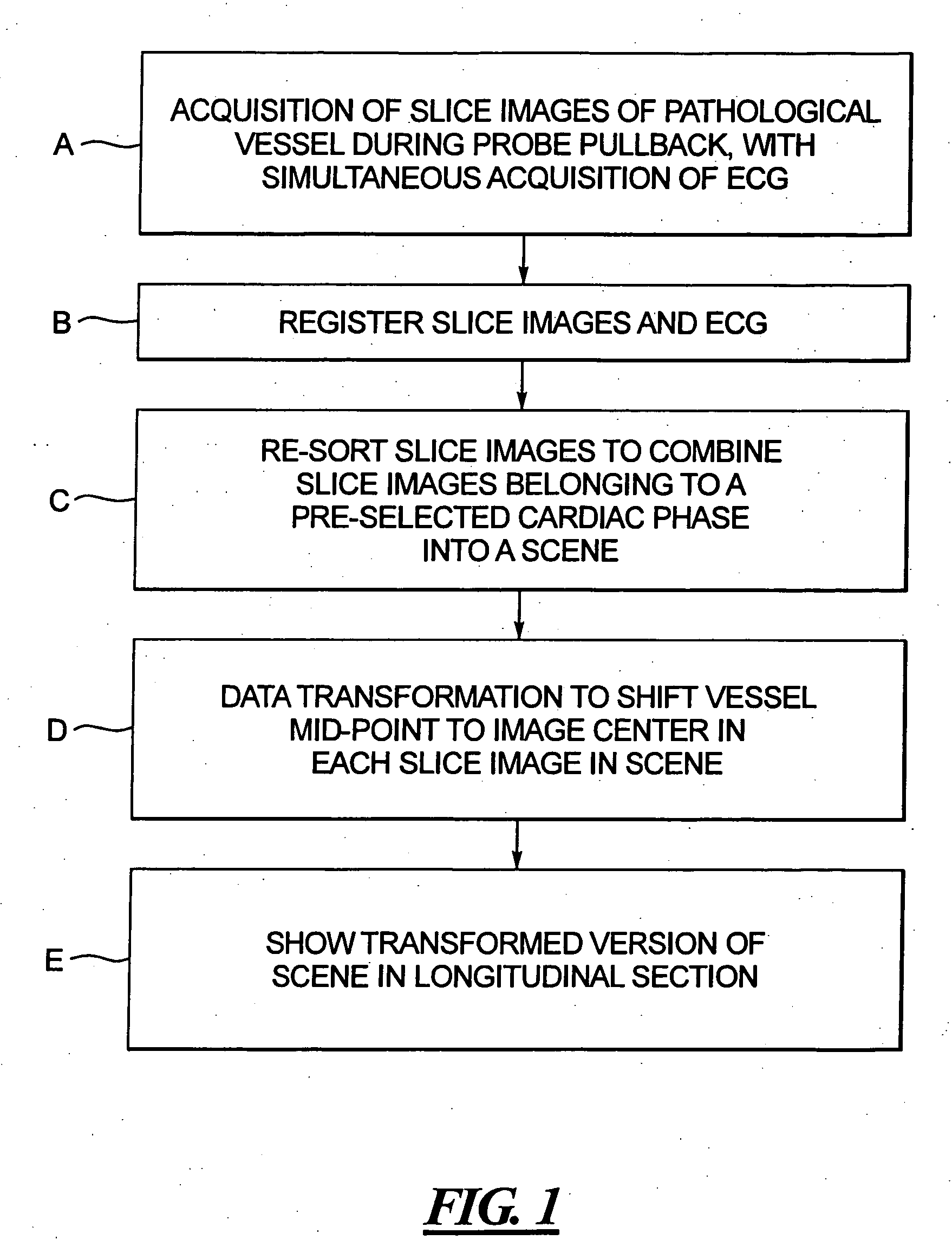
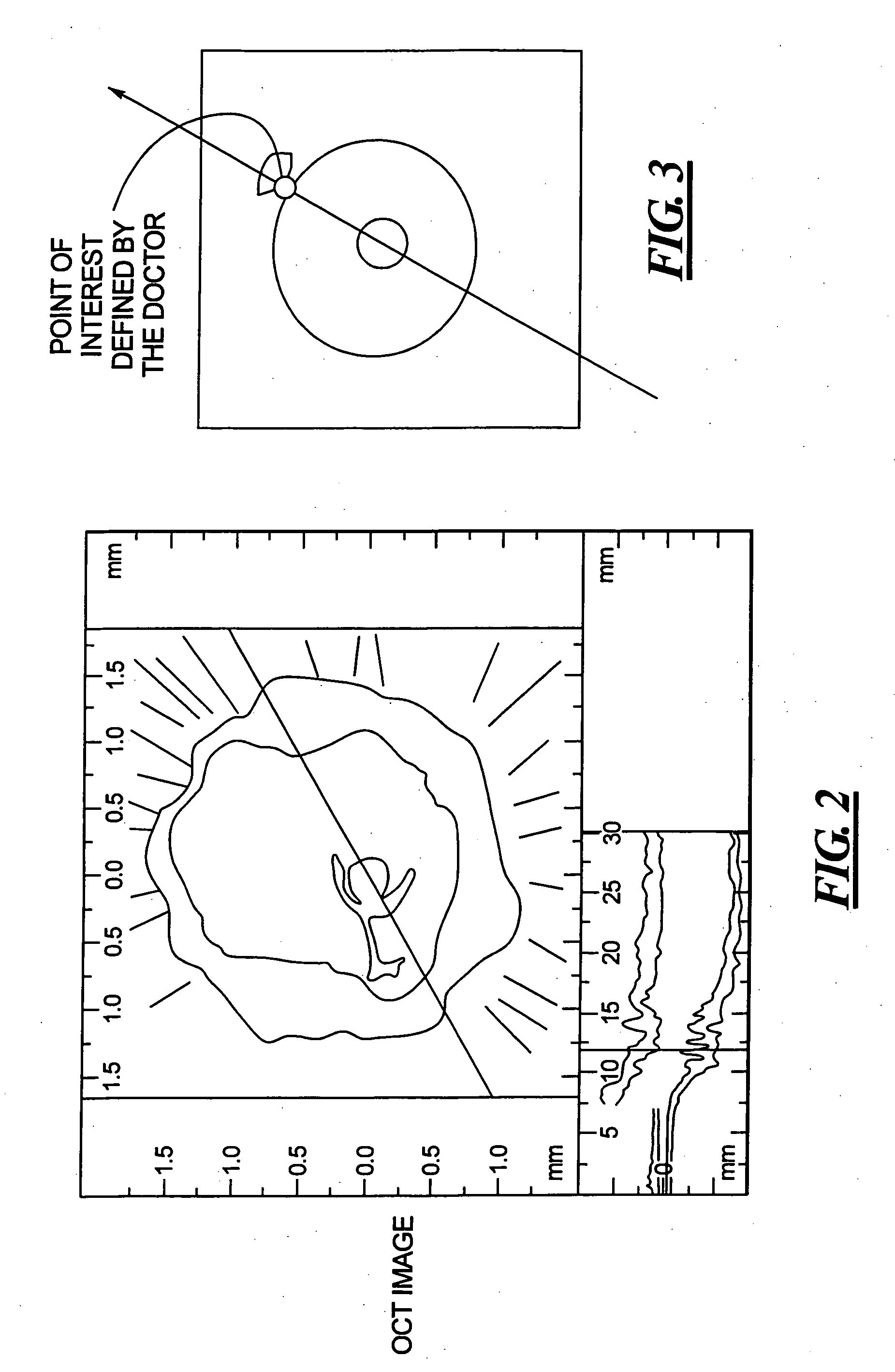
Method and apparatus for ECG-synchronized optically-based image acquisition and transformation
InactiveUS20070167833A1Increased radiation exposureSolve the lack of resolutionElectrocardiographyCatheterEcg signalData transformation
In a method and apparatus for optically-based acquisition of slice images from a vessel of a subject, and for combining the slice images to provide an intuitively recognizable visualization of a pathology in the vessel, slice images of the vessel are acquired during pullback of an optical probe of the optically-based slice imaging system, while simultaneously acquiring an ECG signal from the subject. The slice images and the ECG signal are registered, and slice images acquired at a selected cardiac phase are combined into a scene. The slice images in the scene are subjected to a first data transformation to shift the vessel midpoint in each slice image to the image center of each slice image. After the first data transformation, the slice images in the scene are subjected to a second data transformation to produce the visualization. The second transformation, for example, can be a curved planar reformation to allow the vessel to be shown in longitudinal section.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module and confocal microscopic method and system thereof
ActiveCN101872064AAccurate and fast profile measurementMeasurement rate increaseOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansSpectral dispersionMulti wavelength
The invention provides a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscopic system, which uses more than two chromatic lenses to enable a linear incident light field to generate dispersed rays and to enable rays with different wavelengths to be focused at different positions. Moreover, the invention utilizes a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module with a linear scanning confocal principle and a light source dispersion technique to develop a long-field-depth high-definition optical micro-morphological profile microscopic method and a system by using a confocal microscopic technique with optical sectioning capacity and in combination with the high definition of spectral dispersion. The method and the system of the invention use a broadband light source. By adopting a dispersion objective module, the broadband light source is enabled to generate axially dispersed rays which are focused at different depths, the focused surface reflectance spectrum is obtained simultaneously, spatial filtering is conducted through a slit, the peak position of a spectral focusing response curve is accurately sensed by a linear spectral image sensing unit and thereby sectional profile measurement can be finished accurately and rapidly.
Owner:陈亮嘉
Optical sectioning of a sample and detection of particles in a sample
ActiveUS8780181B2Low statistical uncertaintyEasy to useImage enhancementImage analysisOptical axisOptical sectioning
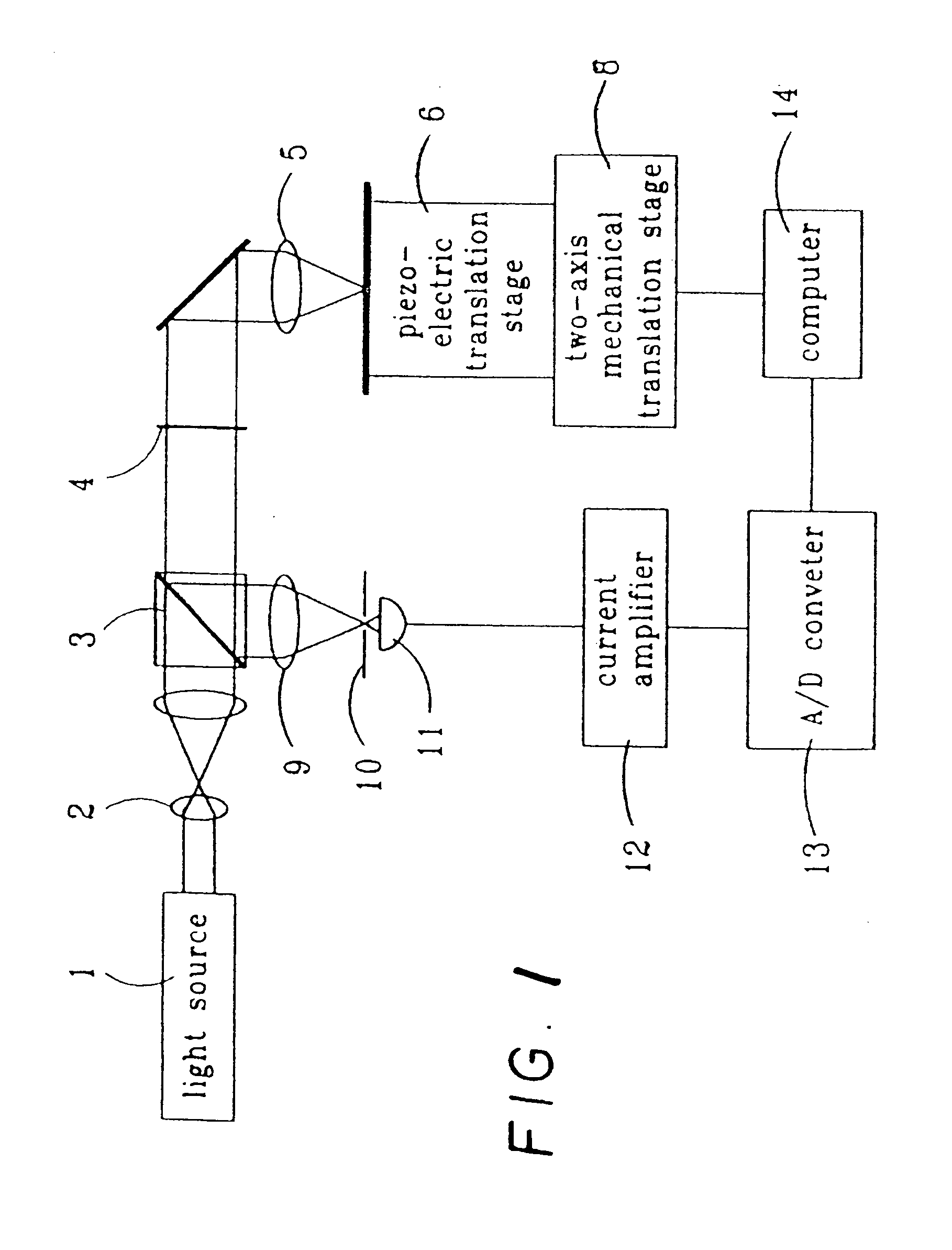
The invention relates to an apparatus, a method and a system for obtaining a plurality of images of a sample arranged in relation to a sample device. The apparatus comprises at least a first optical detection assembly having an optical axis and at least one translation unit arranged to move the sample device and the first optical detection assembly relative to each other. The movement of the sample device and the first optical detection assembly relative to each other is along a scanning path, which defines an angle theta relative to the optical axis, wherein theta is larger than zero.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system and method
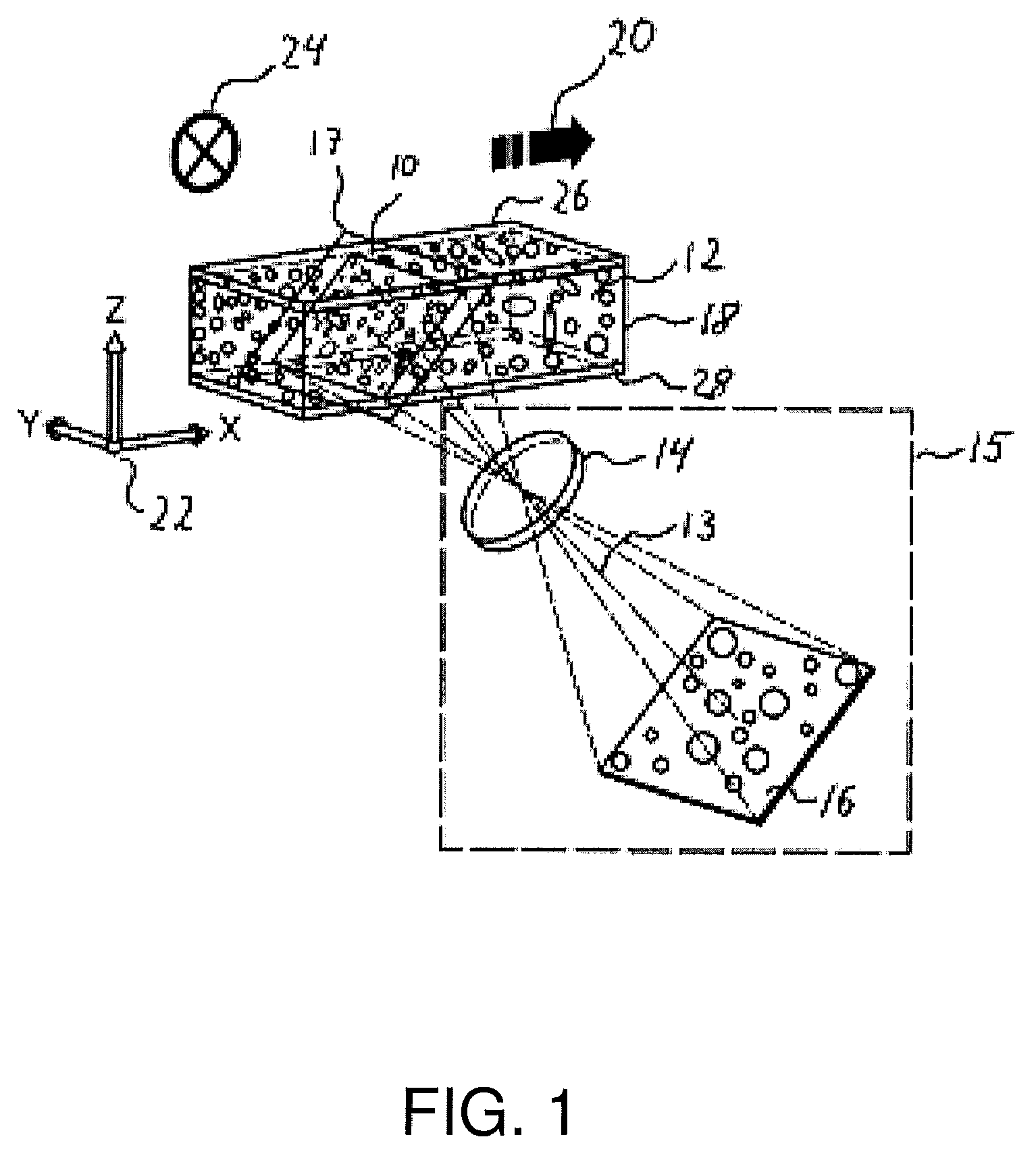
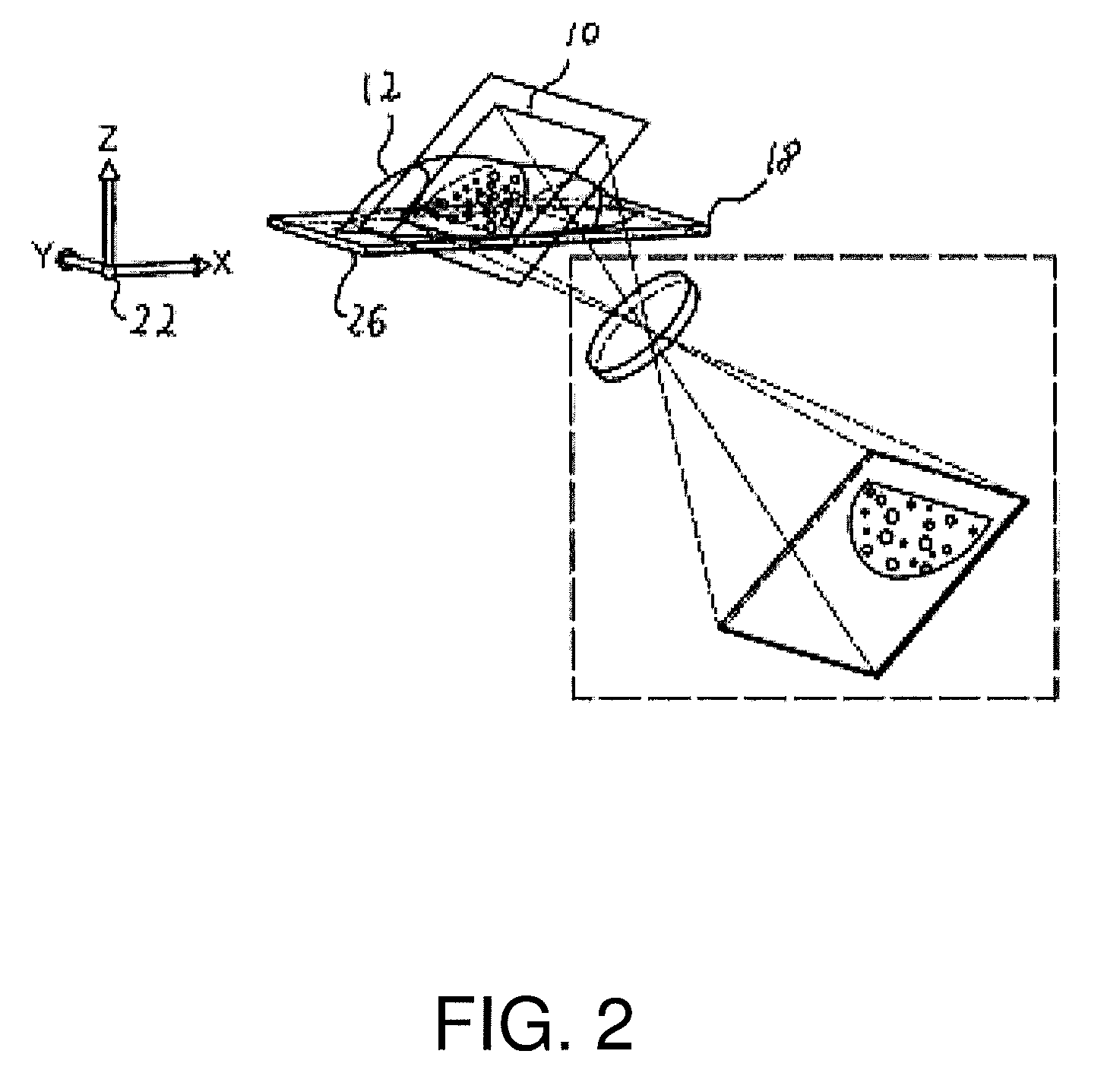
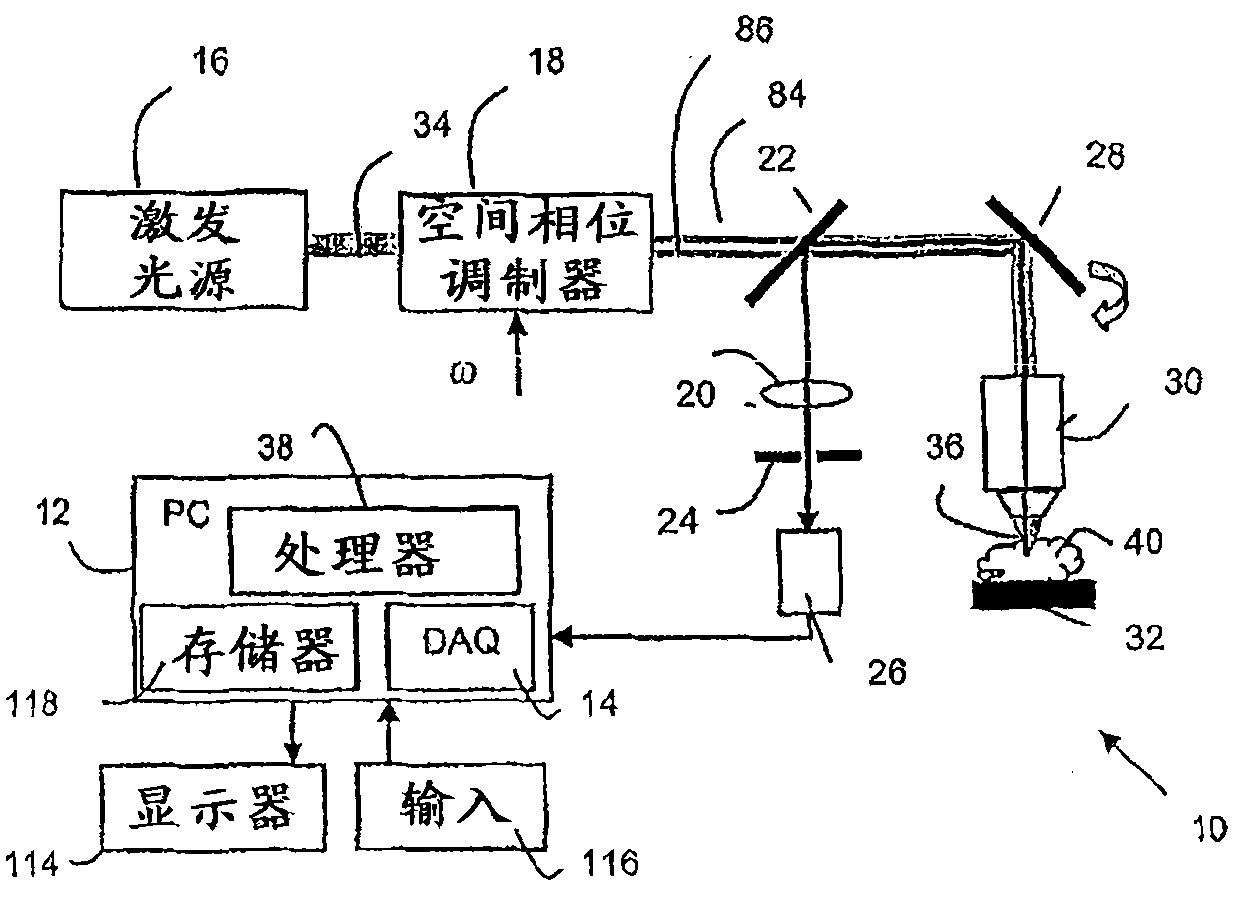
A fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system (10) and method (200) is disclosed for high resolution molecular imaging of thick biological tissues (40) with single photon excited fluorescence. Optical sectioning and diffraction limited spatial resolution are retained for imaging inside a multiple-scattering medium by the use of focal modulation, a technique for suppressing the background fluorescence signal excited by the scattered light. The focal modulation microscopy system has a spatial phase modulator (18) inserted in the excitation light path (34), which varies the spatial distribution of coherent excitation light around the focal volume periodically at a preset frequency. A fluorescence focal modulation image (122,142) is formed on a display (114) with the demodulated fluorescence, while a confocal image (120,140) is available simultaneously.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Non-contact type optical sectioning imaging method
InactiveCN101692971AEnables non-contact optical tomography processEnables non-contact optical tomographyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCamera lensAnatomical structures
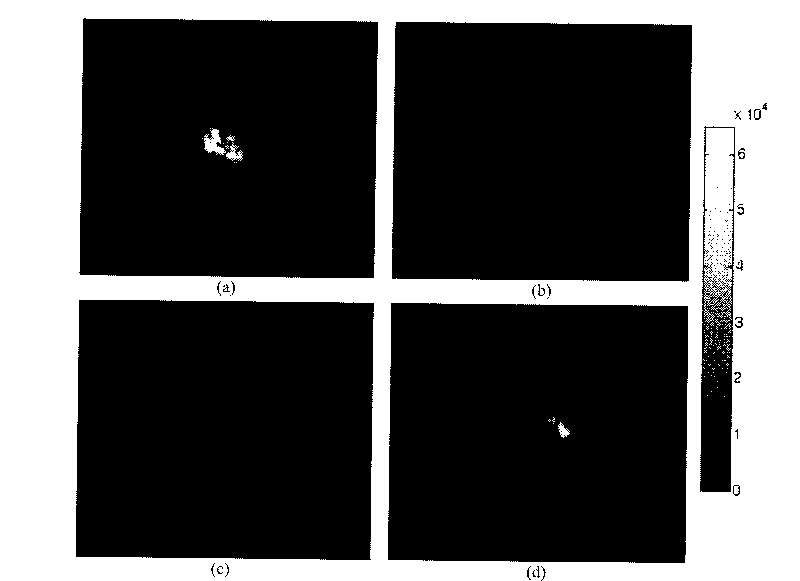
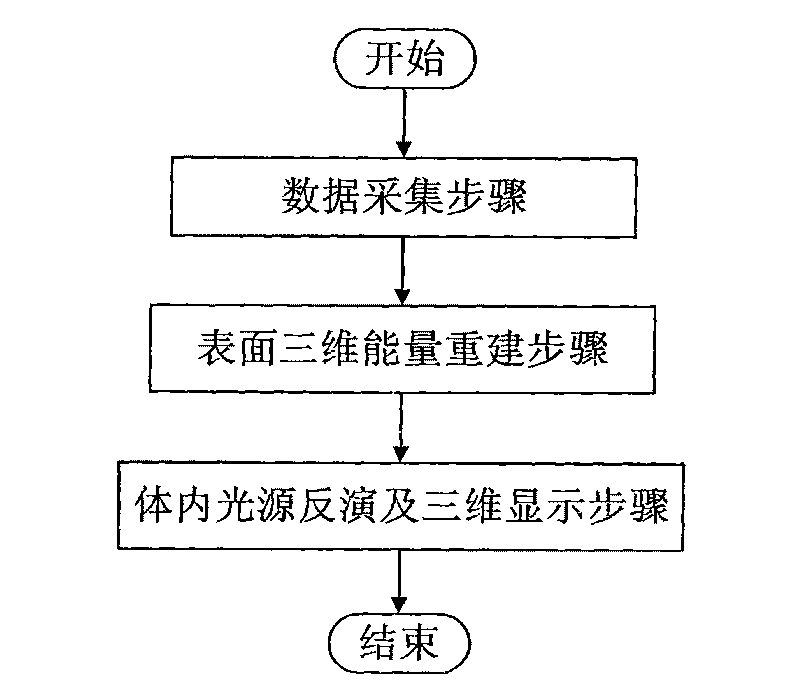
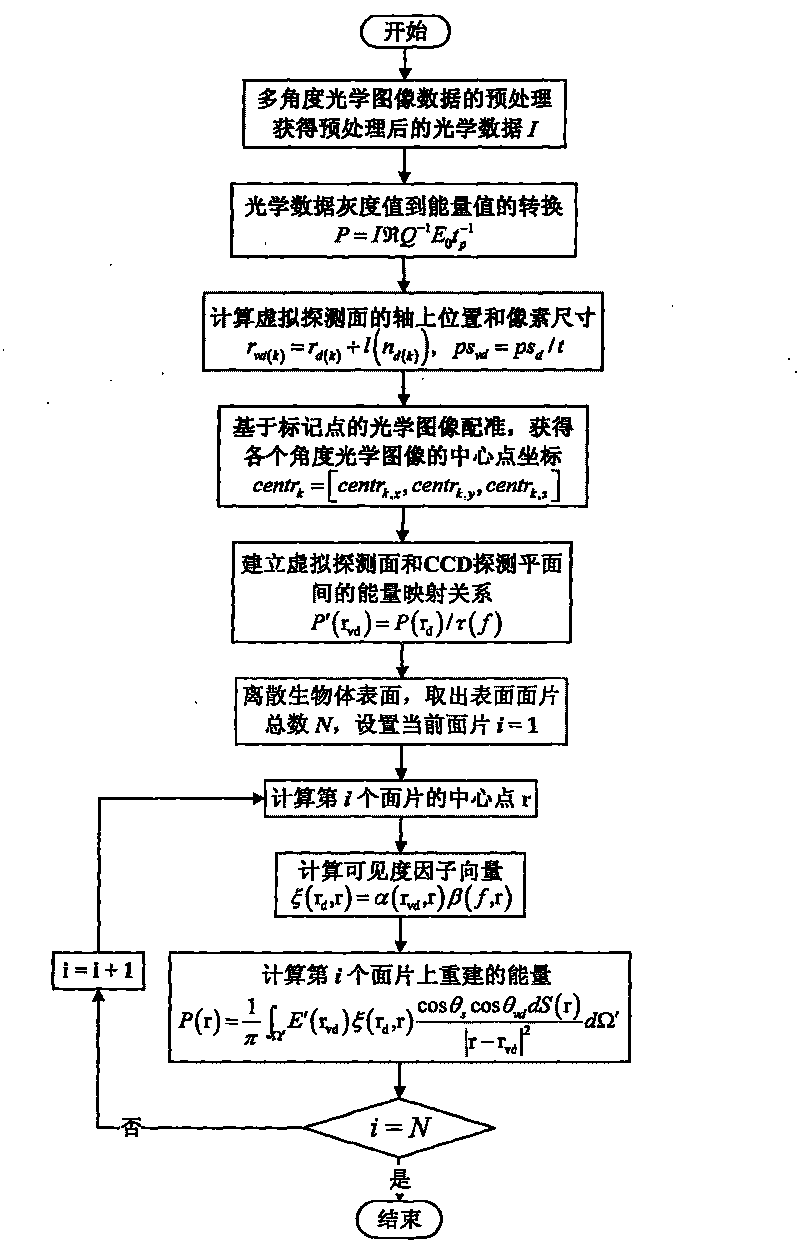
The invention discloses a non-contact type optical sectioning imaging method, and solves the problem of the non-contact type optical sectioning imaging which can not be realized in the prior art under high-aperture lenses. The method comprises the following realization steps: firstly, using a multimode optical molecule imaging system to collect multi-angle optical images, organism surface three-dimensional shapes and anatomical structure information, then, reconstructing organism surface three-dimensional energy, including: (1) preprocessing optical images and conversing from gray value to energy value, (2) registering the optical images and organism surface three-dimensional shape information, (3) confirming virtual detecting surface position and pixel size, and mapping energy of CCD cameras to the virtual detecting surface, (4) computing visible factors, (5) reconstructing surface three-dimensional energy distribution, finally, inverting the internal light source, and displaying three-dimensionally and solidly. The method has the advantages of realizing surface three-dimensional energy reconstruction under high-aperture lenses and non-contact type sectioning imaging under high-aperture lenses, and can be used in the field of non-contact type optical molecule imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
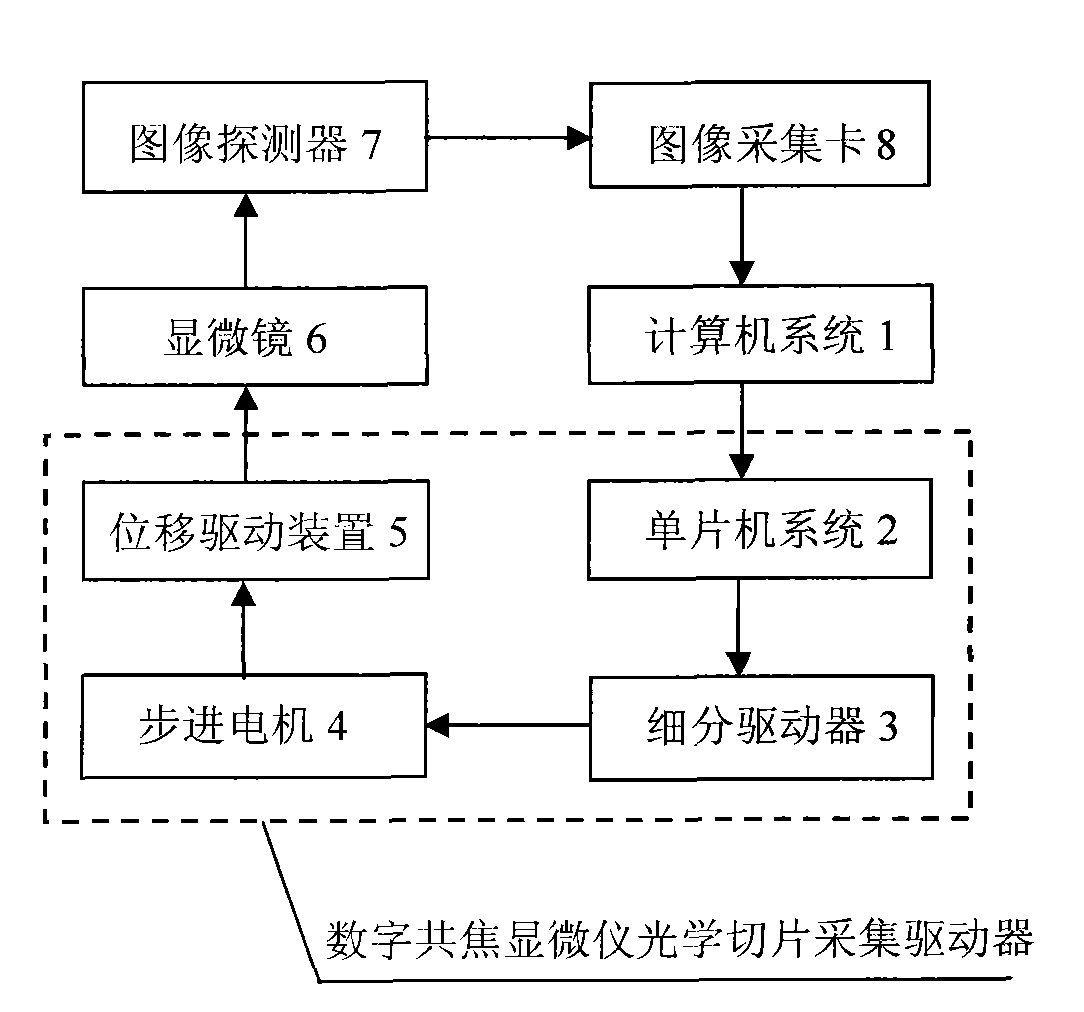
Digital confocal microscope optical section collecting device
The invention provides a driver of a digital confocal microscope optical section collecting device. The driver comprises a single-chip system, a sub-division driver, a stepping motor and a displacement driving device, and the driver arranged on the microscope and controlled by a computer drives a stage to acquire the sequenced optical section images of cells on the stage by an image detector. The method for the driver to acquire the optical section images is to carry out the submicron equidistant stepping control on the stage of the microscope by setting the section distance, collected section number and other parameters. By using the definition-based evaluation for the function value and the change rate thereof as the evaluation standards, the method of the invention is capable of automatically focusing on cells and locating the upper and lower edges, and acquiring the sequenced optical section images of intact cells.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:1192062 ALBERTA
Fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging system with optical sectioning strength
The invention discloses a fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging system with optical sectioning strength. The fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging system comprises a laser emitter, a beam-expanding light path component, a micro-reflector, a dichroscope, a fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging assembly and a spectrograph, wherein the laser emitter is used for emitting a laser beam to the beam-expanding light path component, and the beam-expanding light path component is used for carrying out speckle suppression to obtain an illuminating beam; the illuminating beam generates a structure light field through the micro-reflector; the structure light field is reflected to the fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging assembly through the dichroscope; the fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging assembly comprises an objective lens, an objective lens drive device and an objective table; the objective lens is used for receiving the structure light field and focusing on a sample on the objective table, and exciting a fluorescent beam; the objective lens drive device drives the objective lens to move along the optical axis, so that the objective lens carries out the optical axis scanning; and the spectrograph analyzes and separates the fluorescent beam to obtain spectrum and image information. By virtue of the fluorescent micro-spectrum imaging system with the optical sectioning strength, a three-dimensional image and corresponding one-dimensional spectrum information of the sample structure can be obtained.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES SHENZHEN
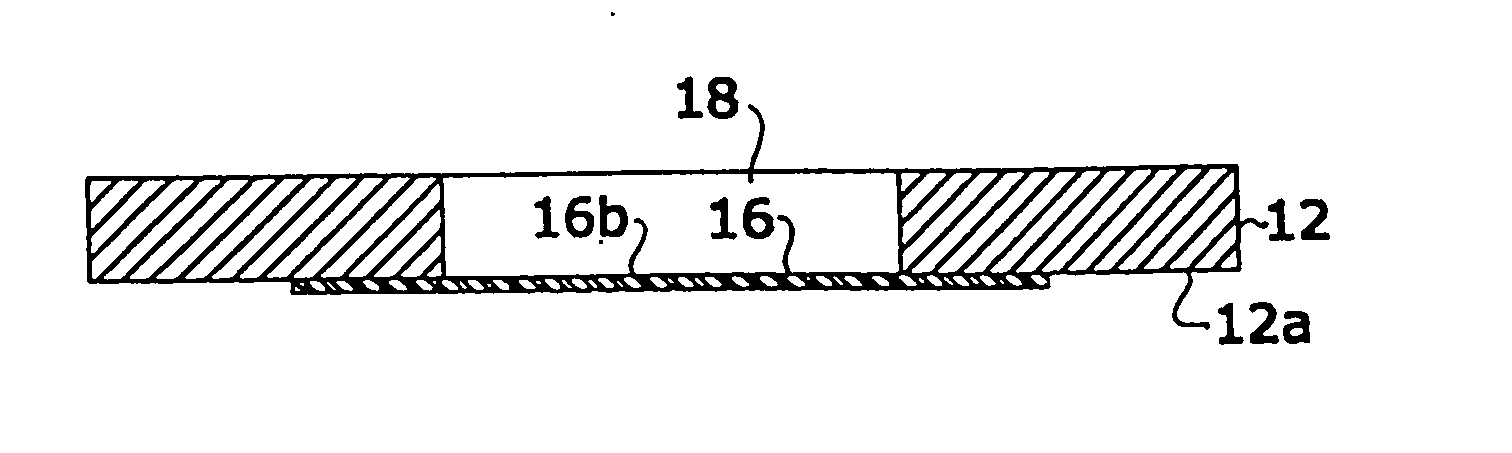
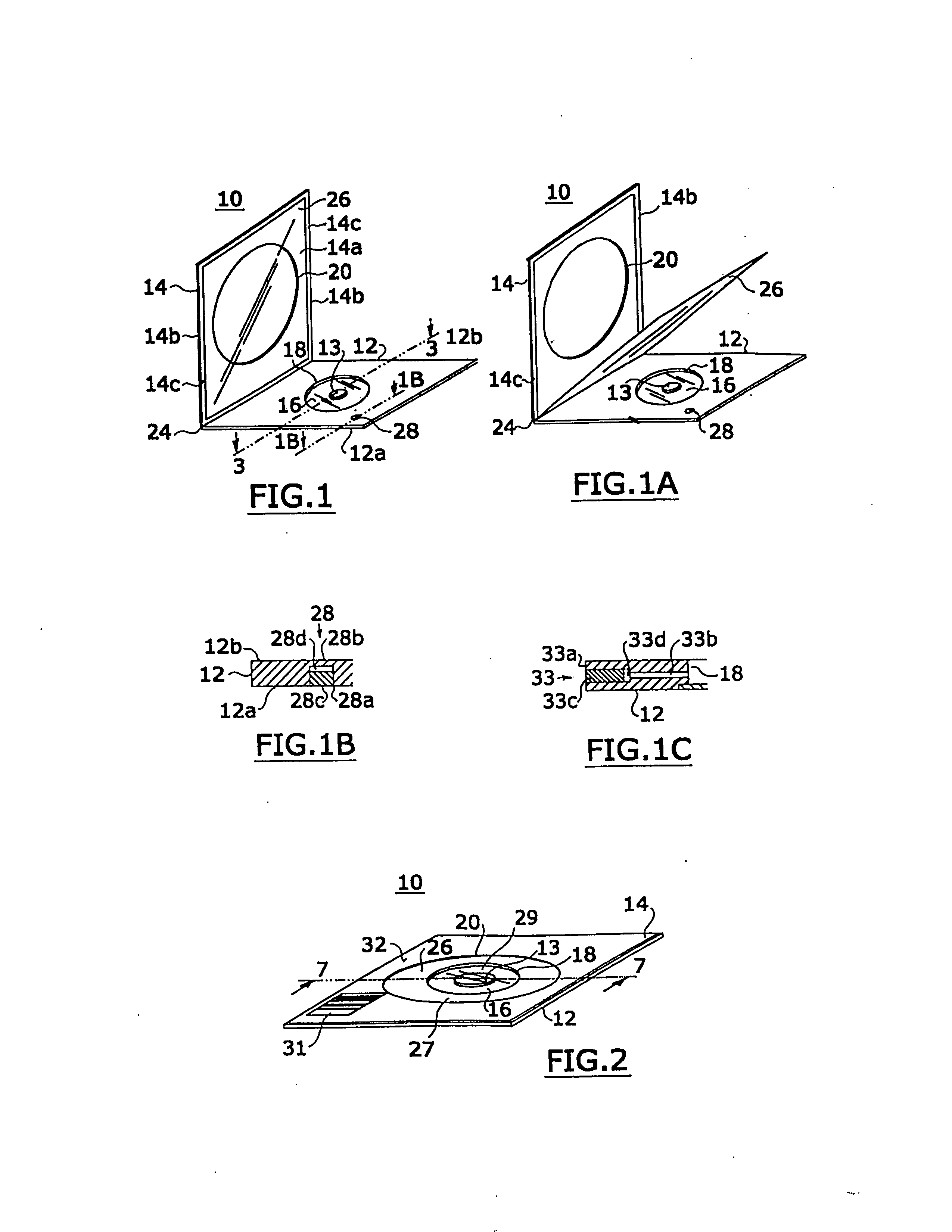
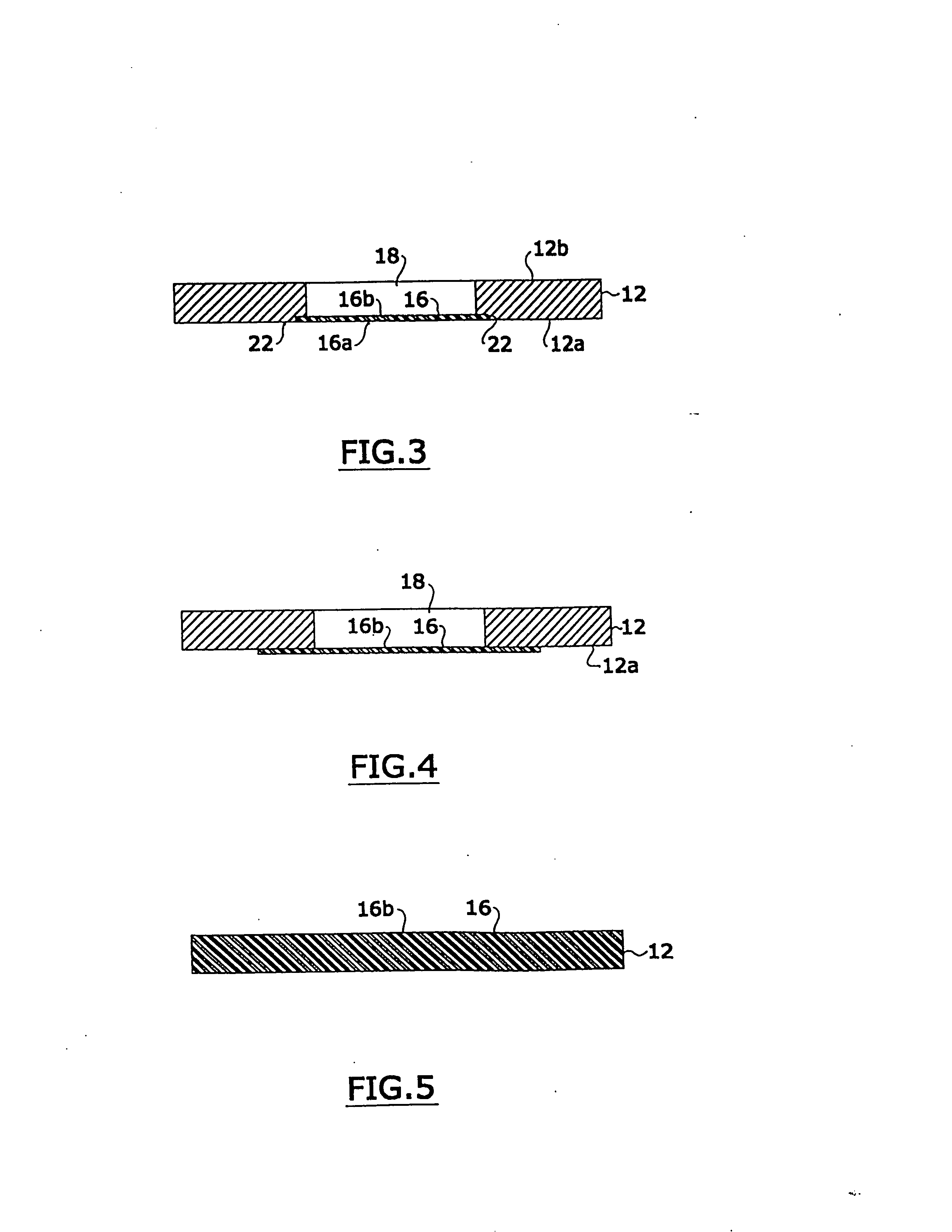
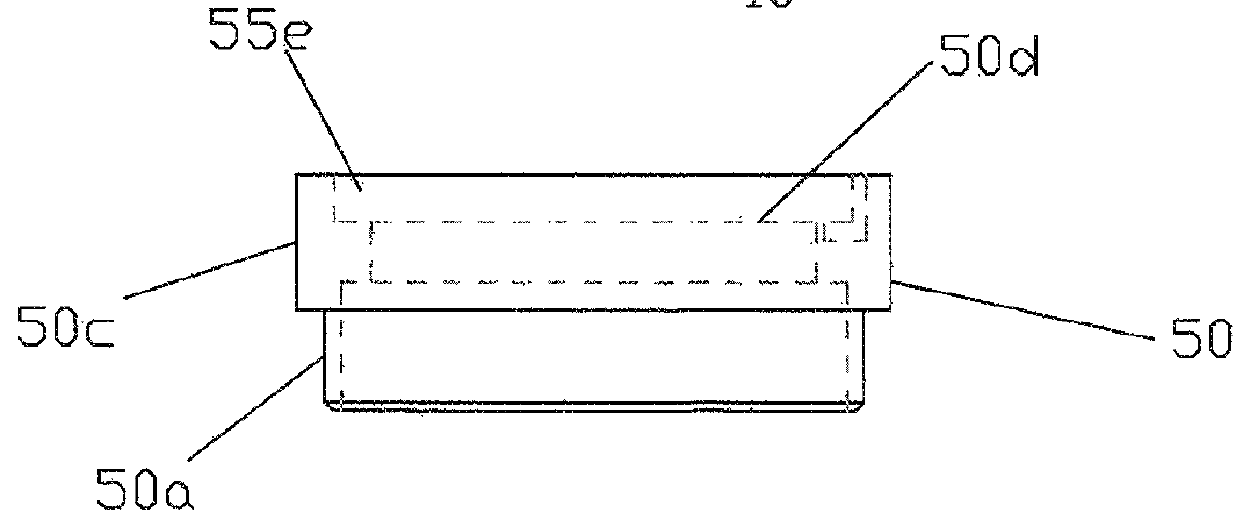
Cassette for facilitating optical sectioning of a retained tissue specimen
InactiveUS20130182318A1Facilitates optical examinationEnhance the imagePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue specimenMultiple point
A cassette for retaining a specimen of surgically exposed tissue from a patient in an orientation that facilitates optical sectioning of the tissue by a confocal microscopic or other optical imaging microscope. The cassette includes a base member having a rigid optically transparent window upon which a tissue specimen is situated, a pliable membrane locatable over a substantial portion of the base member including the window, and an upper member, having an aperture therethrough, which can cover the base member to provide an enclosed cavity between the membrane and the window sealing the tissue specimen therein. The edges of the tissue specimen may be positioned planar against the window and retained in that position by bonds formed between the membrane and window at multiple points or locations around the tissue specimen. The specimen retained in the cavity is imagible a microscope through the window of the base member.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
Optical tissue sectioning using full field optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS9185357B2Increase contrastEasy to combineColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsFluorescenceFull field
According to a first aspect, the invention relates to a multimodal optical sectioning microscope (200, 400, 600) for full-field imaging of a volumic and scattering sample comprising:—a full-field OCT system for providing an image of a first section in depth of the sample comprising an illumination sub-system (201, 401, 601) and a full-field imaging interferometer with a detection sub system (208, 408, 608) and an optical conjugation device for optically conjugating the sample and said detection sub system, wherein said optical conjugation device comprises a microscope objective (203, 403, 603), —a supplementary full-field optical sectioning imaging system for providing a fluorescent image of a second section in depth of said sample comprising a structured illumination microscope with an illumination sub system (623), means (421, 422) for generating at the focal plane of said microscope objective of said full-field imaging interferometer a variable spatial pattern illumination and a detection sub system (624), optically conjugated with said focal plane of the microscope objective.
Owner:LLTECH MANAGEMENT
Slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module and slit-scan microscopic system and method using the same
ActiveUS8773757B2Improve performanceMinimized in sizePrismsMicroscopesReflectance spectroscopyLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module, utilizing at least two lenses having chromatic aberration for splitting a broadband light into continuously linear spectral lights having different focal length respectively. The present invention utilizes the confocal lens module employing slit-scan confocal principle and chromatic dispersion techniques and the confocal microscopy with optical sectioning ability and high resolution in spectral dispersion to establish a confocal microscopy method and system with long DOF and high resolution, capable of modulating a broadband light to produce the axial chromatic dispersion and focus on different depths toward an object's surface for obtaining the reflected light spectrum from the surface. Thereafter, the spectrum is spatially filtered by a slit and then a peak position with respect to the filtered spectrum along the scanning line is detected by a spectral image sensing unit for generating the sectional profile of the measured surface.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
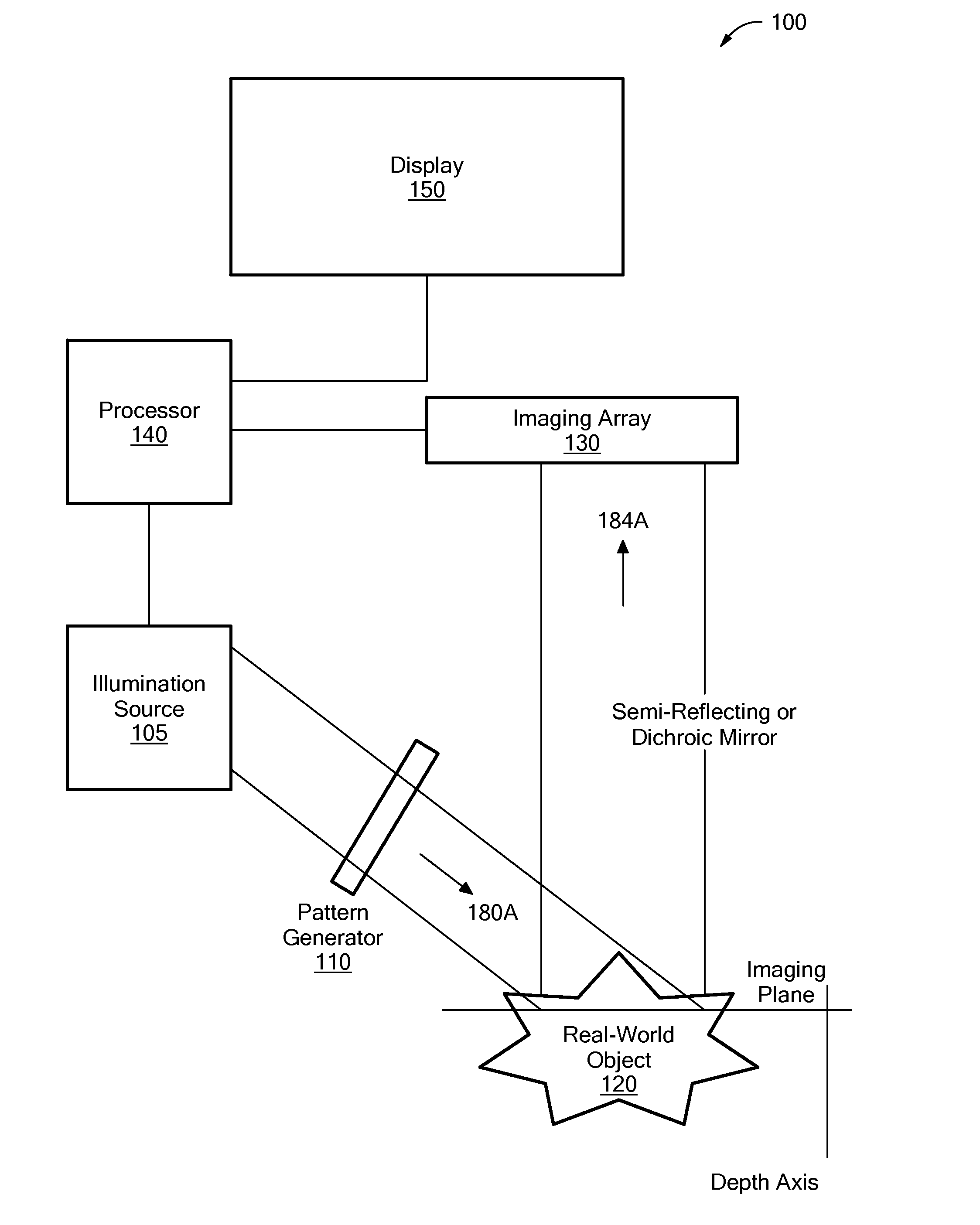
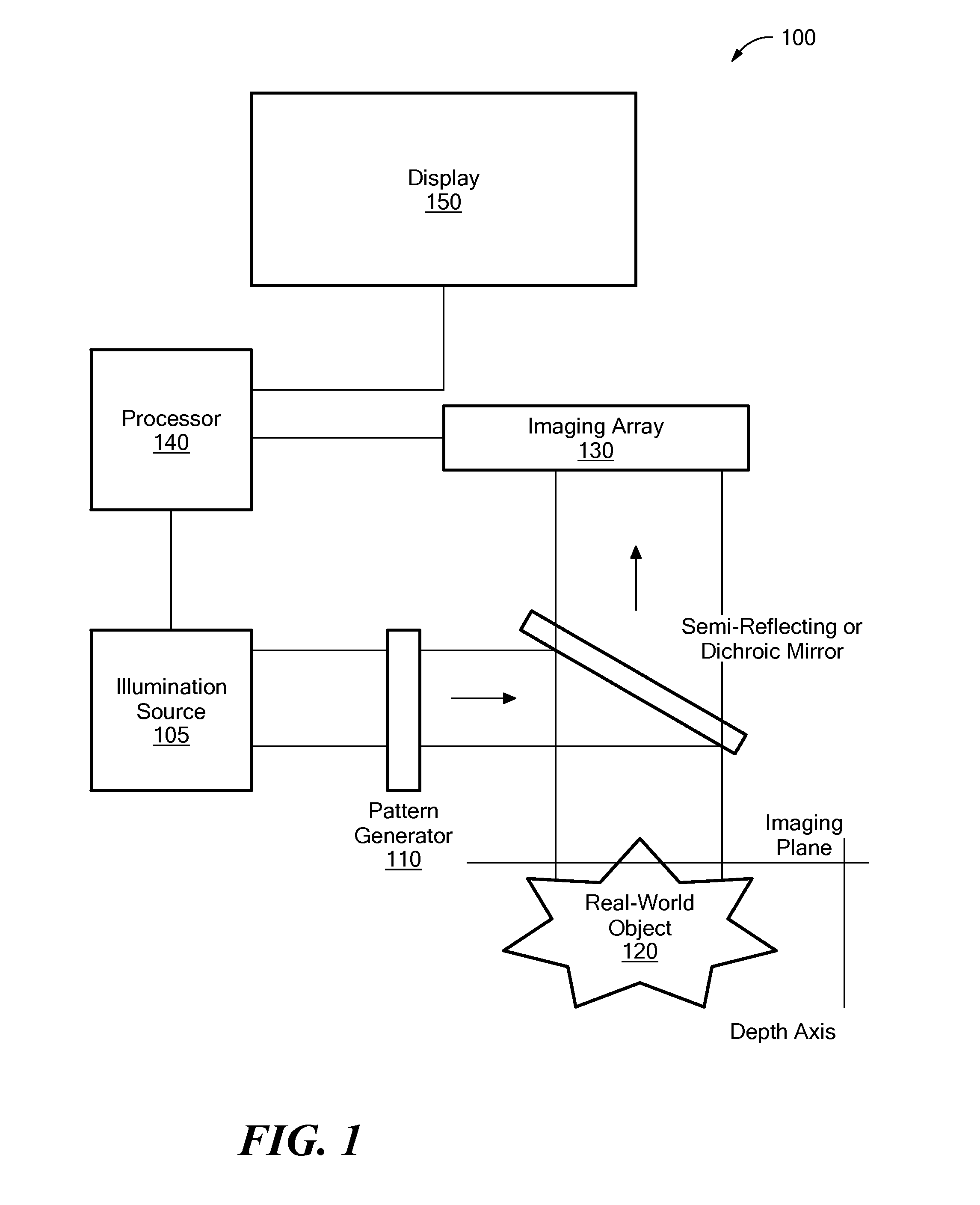
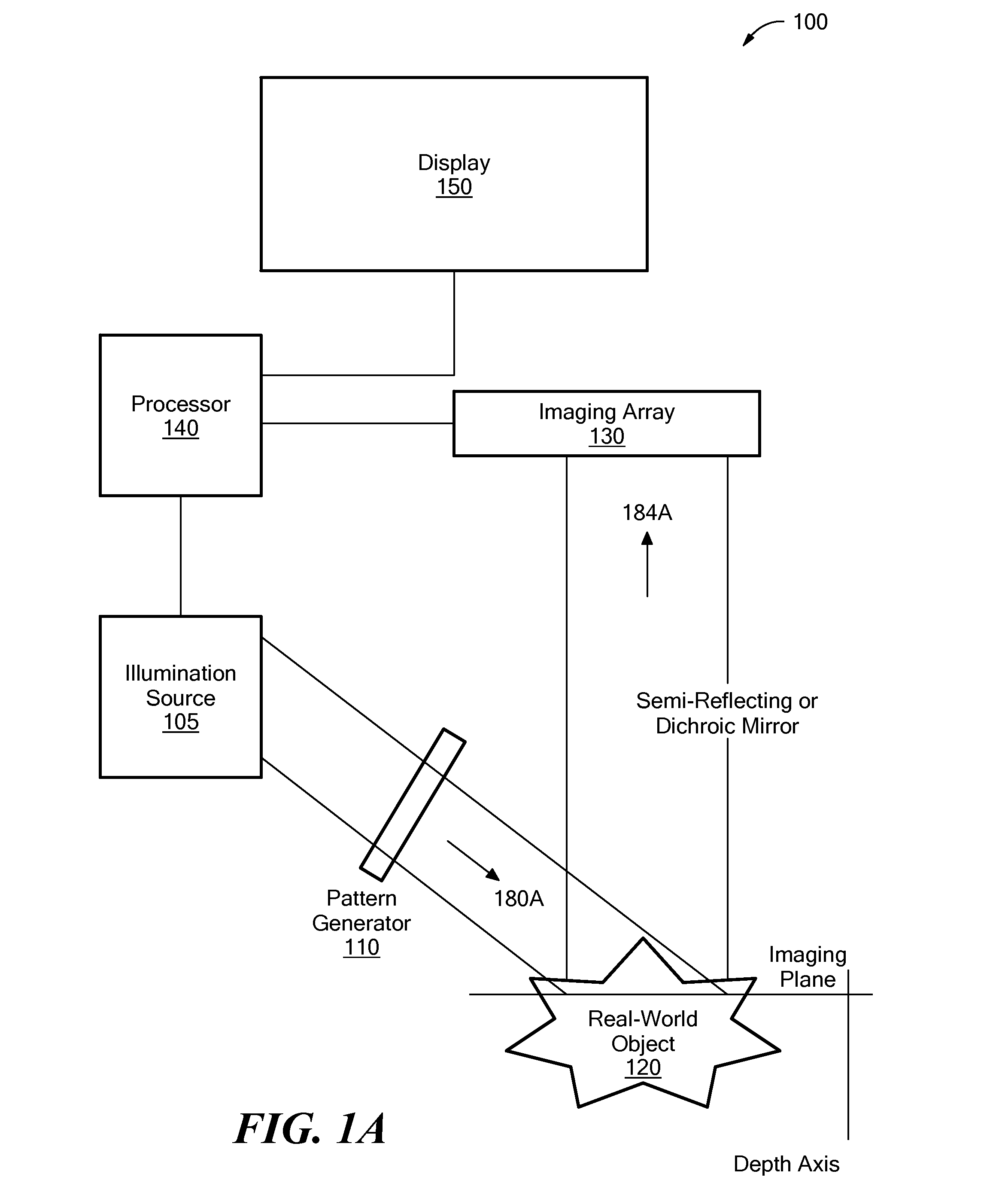
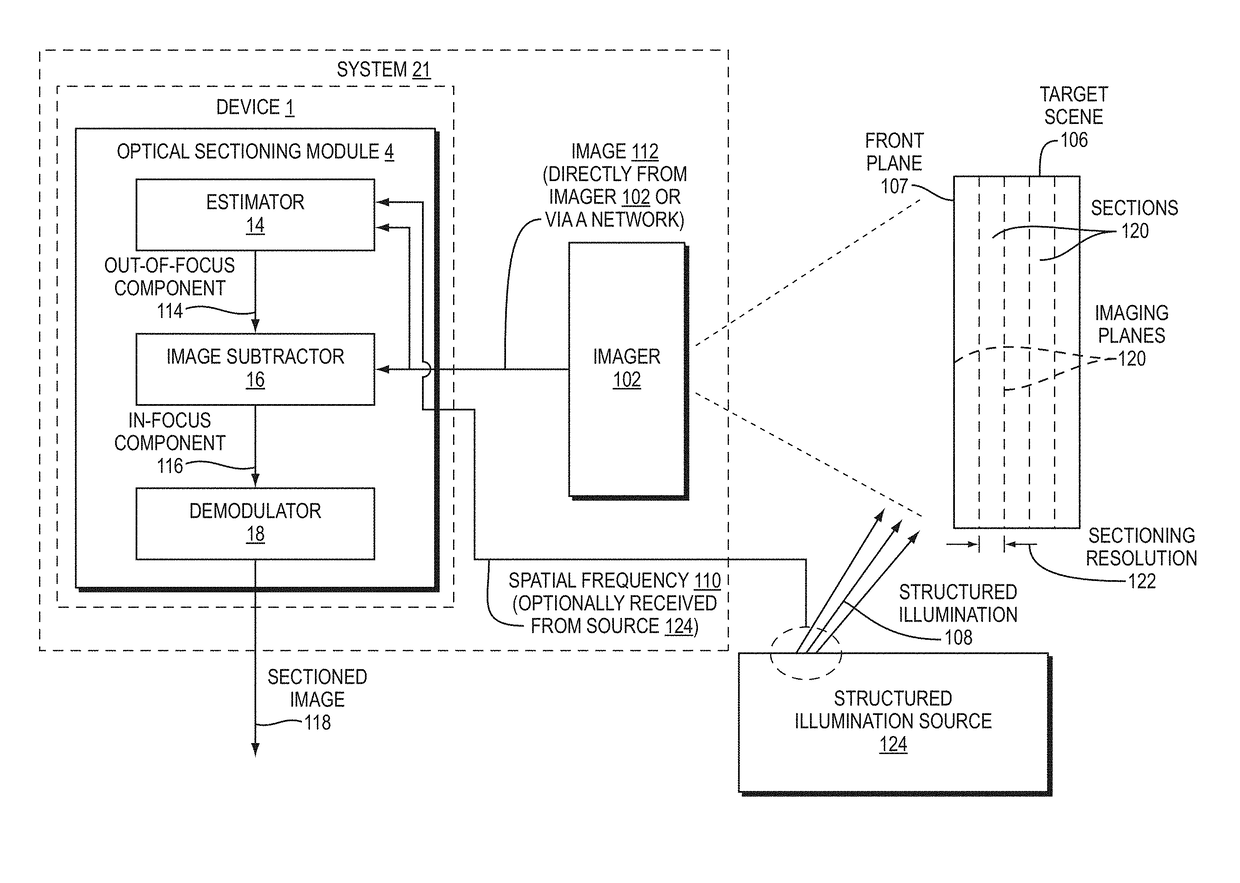
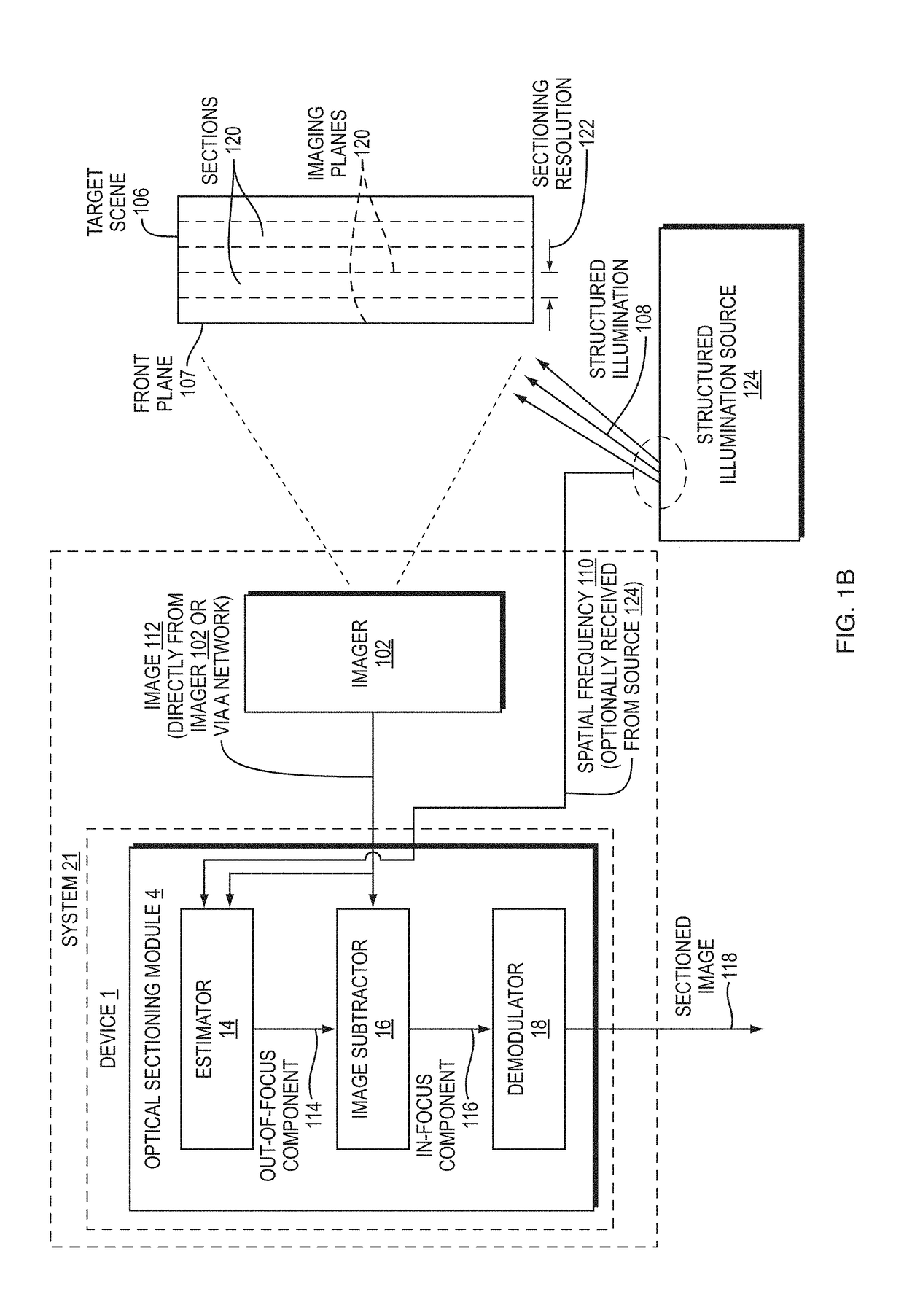
System and Method for Producing an Optically Sectioned Image Using Both Structured and Uniform Illumination
A first image data set of the real-world object is received at a processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially uniform illumination. A second image data set of the real-world object is received at the processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially structured illumination. A high pass filter is applied to the first-image data set to remove out-of-focus content and retrieve high-frequency in-focus content. The local contrast of the second-image data set is determined producing a low resolution local contrast data set. The local contrast provides a low resolution estimate of the in-focus content in the first-image data set. A low pass filter is applied to the estimated low resolution in-focus data set, thus making its frequency information complementary to the high-frequency in-focus data set. The low and high frequency in-focus data sets are combined to produce an optically-sectioned data set of the real-world object.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
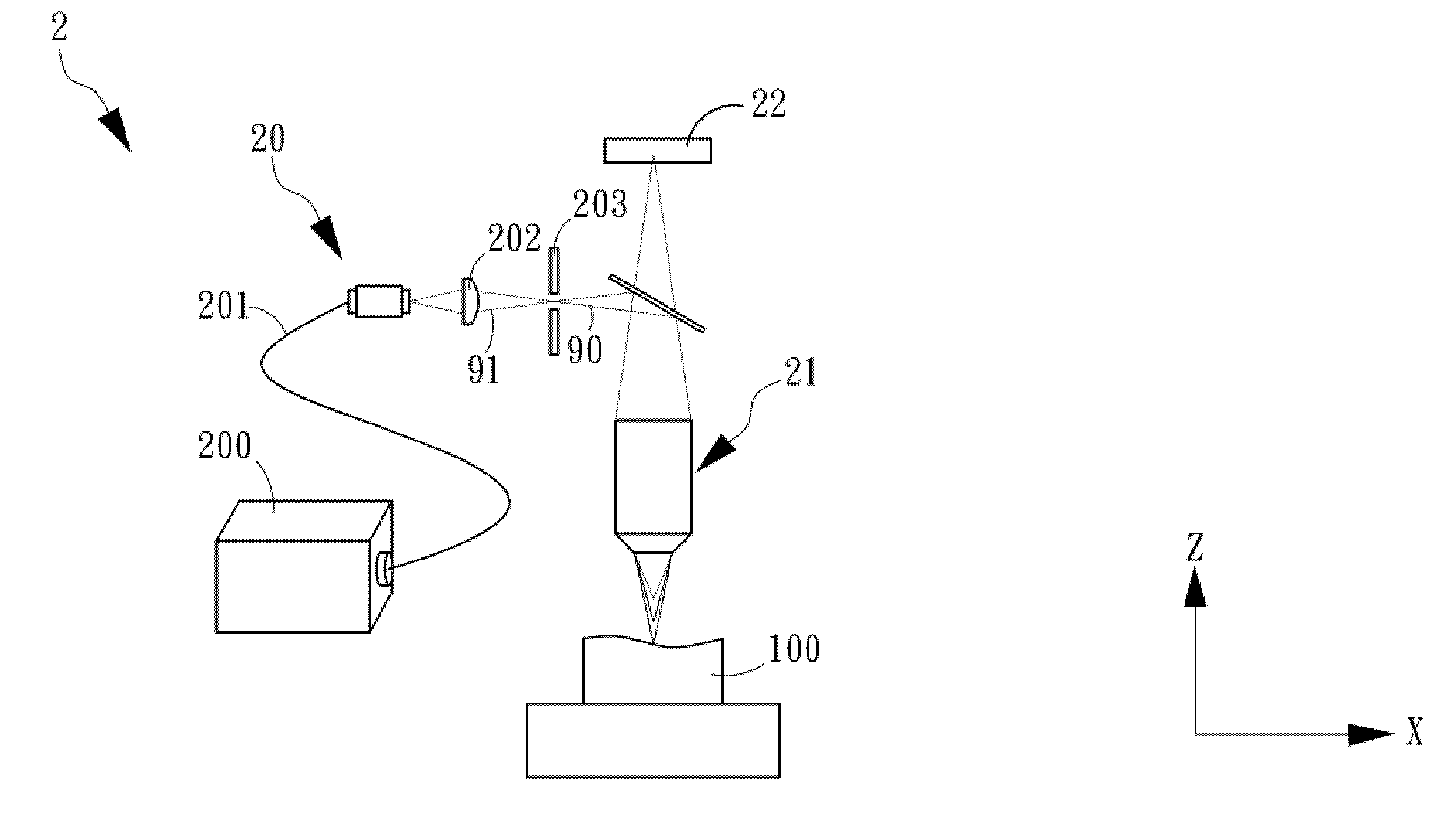
Super-resolution fluorescent digit holographic sectioning microimaging system and method
ActiveCN106885796ARealize 3D renderingAchieving super-resolution optical tomographyFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingSpatial light modulator
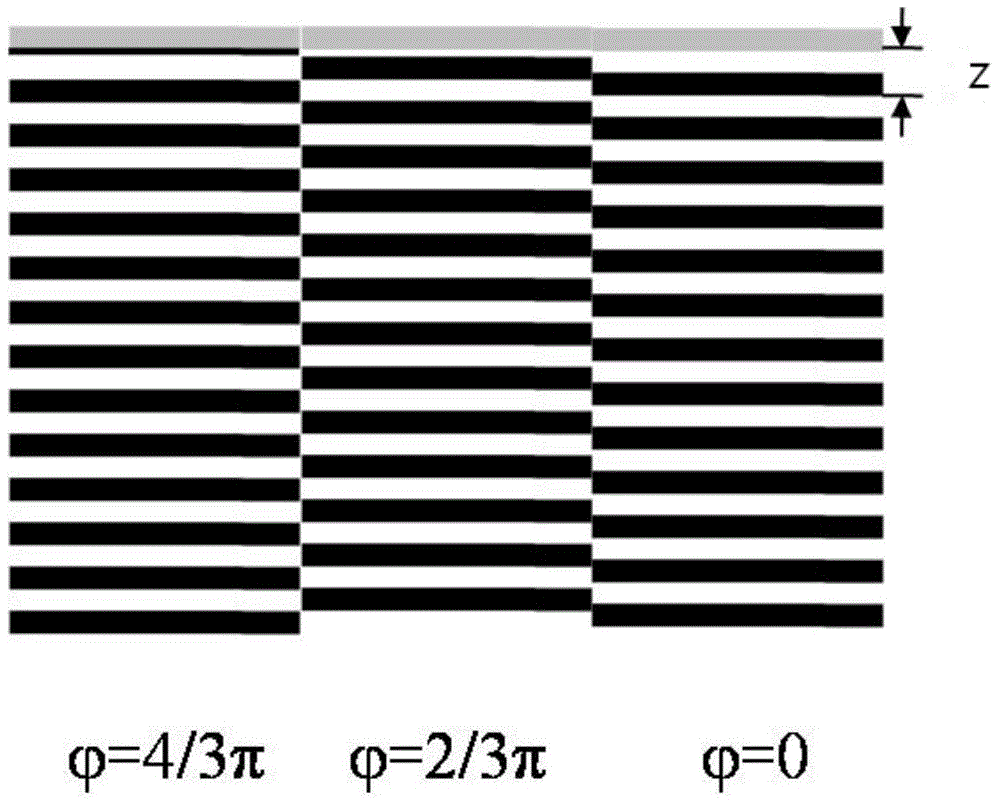
The invention relates to a super-resolution fluorescent digit holographic sectioning microimaging system and method and belongs to the field of fluorescent digit holographic and super-resolution imaging. Laser after amplitude modulation through a spatial light modulator loading a proper mask structure enters a microobjective to generate exciting light in a three-dimensional structure on a to-be-image sample; excited fluorescence of the sample is collected by the microobjective, and is then diffracted and divided and shifted in phase through the spatial light modulator through a dichroscope and an imaging system, and the two beans of light intervene in a position where an image detector is located to form a hologram which is recorded; the recorded hologram is reconstructed through a numerical algorithm in a computer, and for a structure in certain depth in the sample, reconstructed images of super-resolution and optical section can be separately acquired; the reconstructed images of super-resolution and optical section are fused by means of the numerical algorithm, so that super-resolution optical sectioning imaging is realized; and the reproducing distance of the hologram is changed, so that three-dimensional imaging of the super-resolution optical sections of structures in different depths of the sample can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for characterizing transparent thin-films using differential optical sectioning interference microscopy
InactiveUS20080266548A1Easy constructionEasy CalibrationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhase-affecting property measurementsLinear regionImage resolution
An imaging, differential optical sectioning interference microscopy (DOSIM) system and method for measuring refractive indices and thicknesses of transparent thin-films. The refractive index and thickness are calculated from two interferometric images of the sample transparent thin-film having a vertical offset that falls within the linear region of an axial response curve of optically sectioning microscopy. Here, the images are formed by a microscope objective in the normal direction, i.e., in the direction perpendicular to the latitudinal surface of the thin-film. As a result, the lateral resolution of the transparent thin-film is estimated based on the Rayleigh criterion, 0.61λ / NA.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method of characterizing transparent thin-films using differential optical sectioning interference microscopy
InactiveUS7545510B2Easy constructionEasy CalibrationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhase-affecting property measurementsLinear regionImage resolution
An imaging, differential optical sectioning interference microscopy (DOSIM) system and method for measuring refractive indices and thicknesses of transparent thin-films. The refractive index and thickness are calculated from two interferometric images of the sample transparent thin-film having a vertical offset that falls within the linear region of an axial response curve of optically sectioning microscopy. Here, the images are formed by a microscope objective in the normal direction, i.e., in the direction perpendicular to the latitudinal surface of the thin-film. As a result, the lateral resolution of the transparent thin-film is estimated based on the Rayleigh criterion, 0.61λ / NA.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method for quantitatively characterizing pores in shale
ActiveCN108956424AAccurate three-dimensional fluorescent stereoscopic displayPermeability/surface area analysisEpoxyFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively characterizing pores in shale. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting a shale sample and injecting epoxy resin into the collectedshale sample in a high-temperature and high-pressure state; then grinding the shale sample with the injected epoxy resin into a laser confocal optical sheet; S2, carrying out optical slicing on the laser confocal optical sheet prepared by S1 in a laser scanning mode, so as to obtain a series of two-dimensional laser confocal photomicrographs; S3, based on identification of pores in the shale in S2, classifying the pores in the identified shale; and S4, carrying out three-dimensional modeling and quantitative characterization on the pores in the shale by applying three-dimensional modeling software. According to the method provided by the invention, the pores with different formation factors in the shale are identified by applying a fluorescent technology, and different pore types in the shale are divided; and a two-dimensional fluorescent confocal slice is subjected to three-dimensional fluorescent modeling and quantitative characterization of the pores in the shale.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Systems and methods for in-operating-theatre imaging of fresh tissue resected during surgery for pathology assessment
ActiveUS20160305926A1Time necessaryFacilitates in-operating-theater analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicroscopesFresh TissueOperating theatres
The disclosed technology brings histopathology into the operating theatre, to enable real-time intra-operative digital pathology. The disclosed technology utilizes confocal imaging devices image, in the operating theatre, “optical slices” of fresh tissue—without the need to physically slice and otherwise process the resected tissue as required by frozen section analysis (FSA). The disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, includes a simple, operating-table-side digital histology scanner, with the capability of rapidly scanning all outer margins of a tissue sample (e.g., resection lump, removed tissue mass). Using point-scanning microscopy technology, the disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, precisely scans a thin “optical section” of the resected tissue, and sends the digital image to a pathologist rather than the real tissue, thereby providing the pathologist with the opportunity to analyze the tissue intra-operatively. Thus, the disclosed technology provides digital images with similar information content as FSA, but faster and without destroying the tissue sample itself.
Owner:SAMANTREE MEDICAL SA
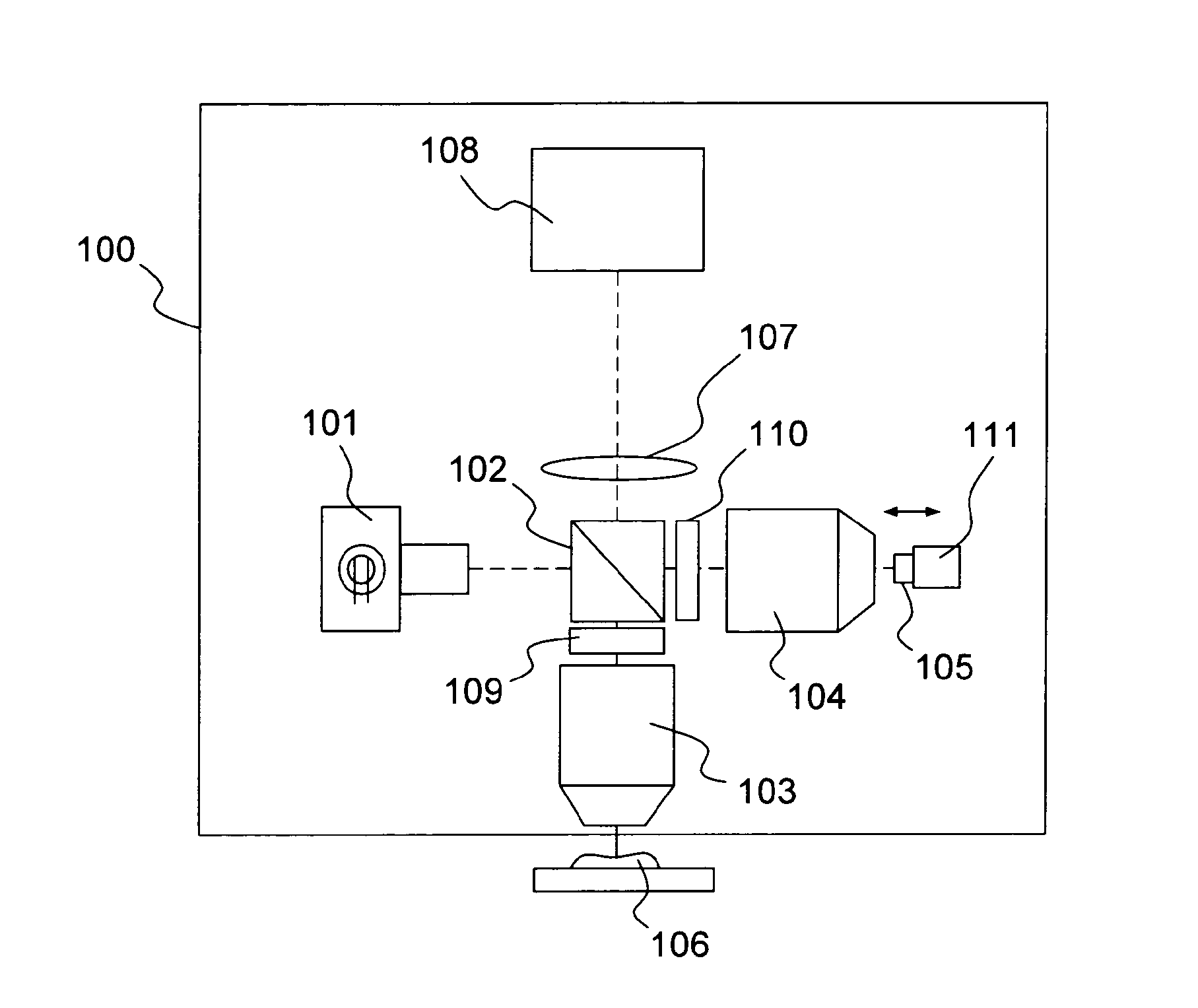
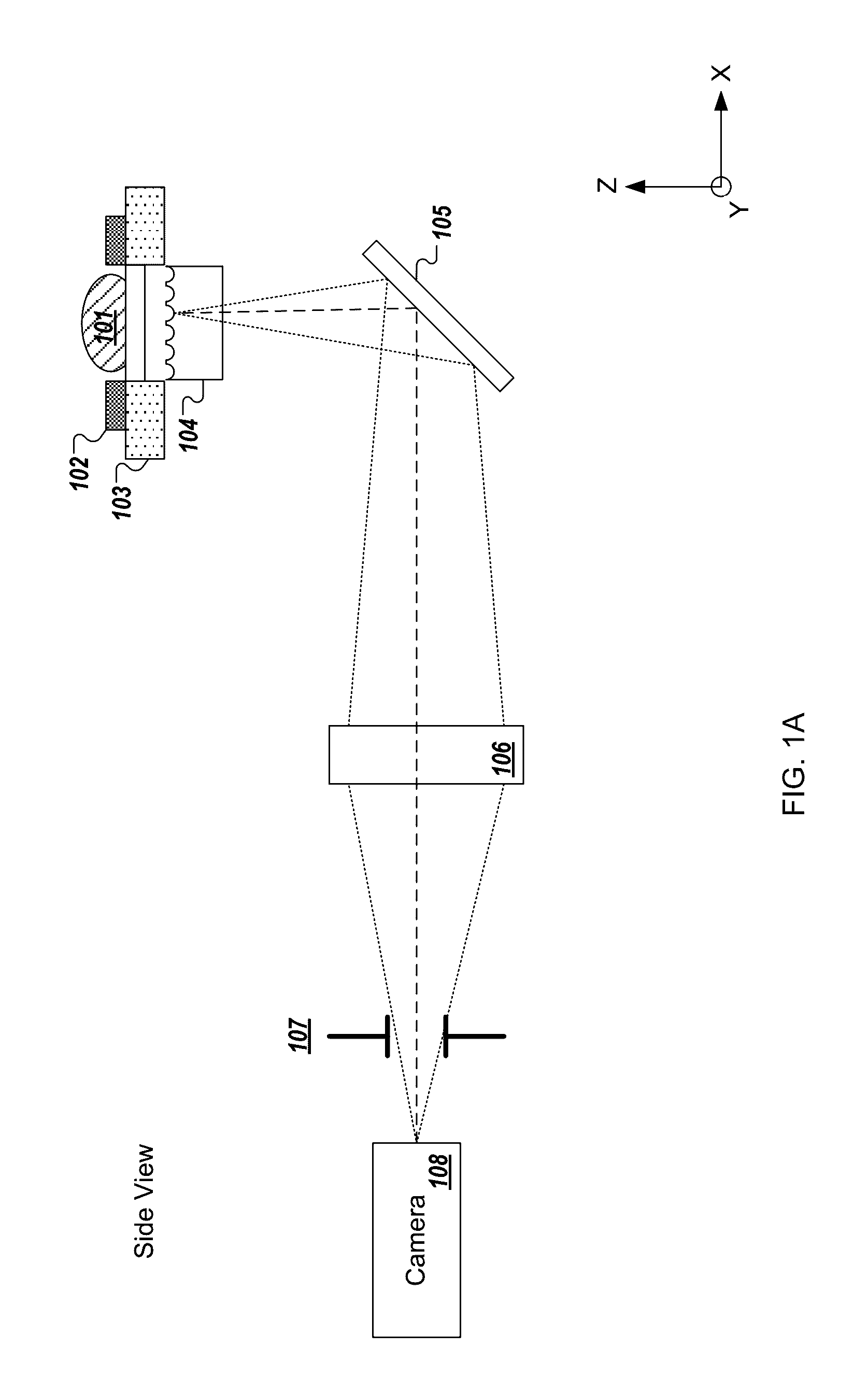
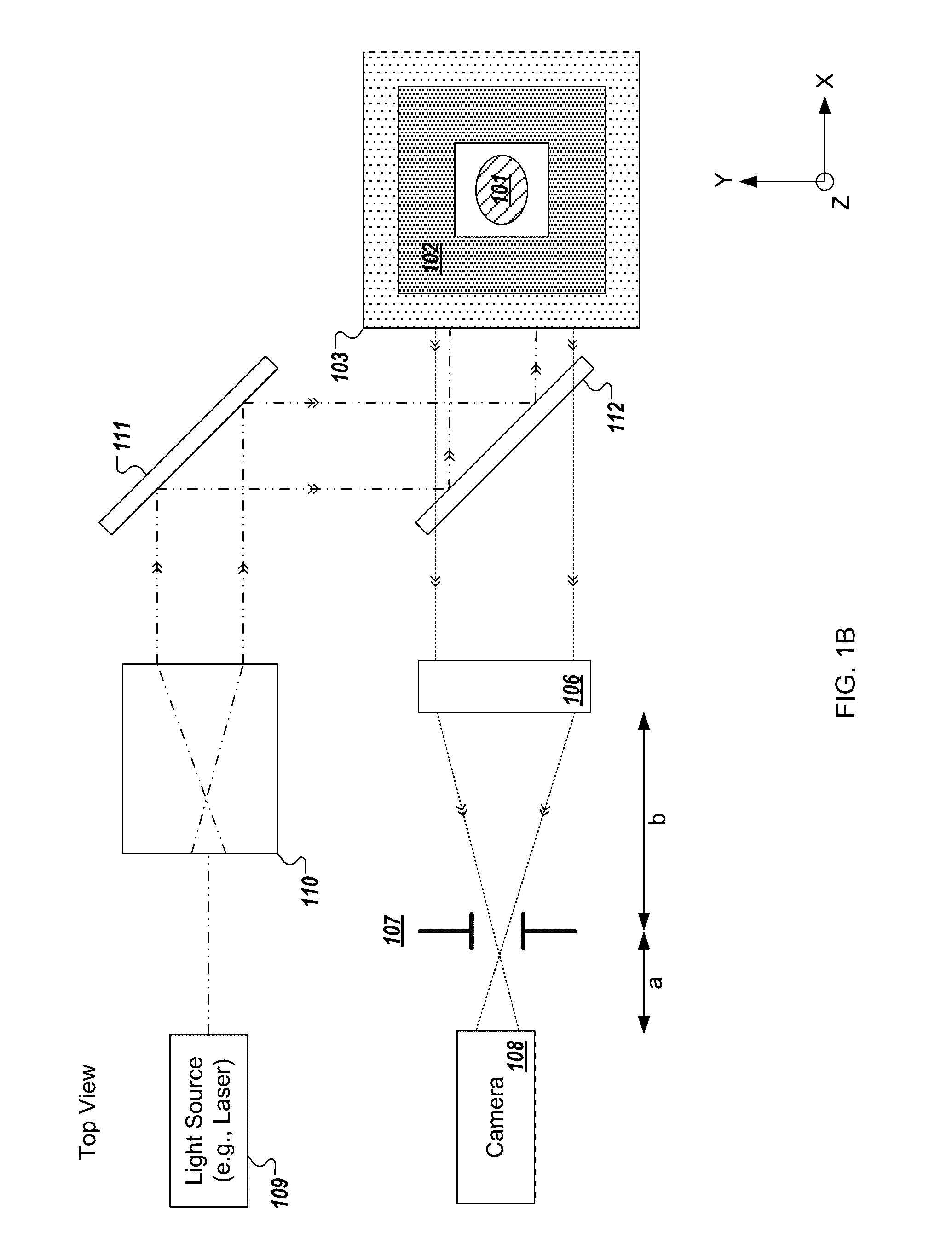
Low Numerical Aperture Exclusion Imaging
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention an apparatus for a low numerical aperture exclusion imaging apparatus is provided. The apparatus may include an electromagnetic illumination source for illuminating a portion of a specimen, and for collecting an image created by the electromagnetic radiation an objective lens optically coupled to the electromagnetic illuminated portion of the specimen. The apparatus also includes an optical blocking plate disposed between the objective lens and a focusing lens. The optical blocking plate is positioned to substantially block undesired electromagnetic radiation from image sources distally aligned in the same optical axis as the specimen. This invention enhances narrow depth of field characteristics in imaging. It also enhances discreet imaging in a narrow focus field by eliminating some of most of the light which contributes to wide depth of field focus. This is useful for optical sectioning ranging from microscopy to photography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
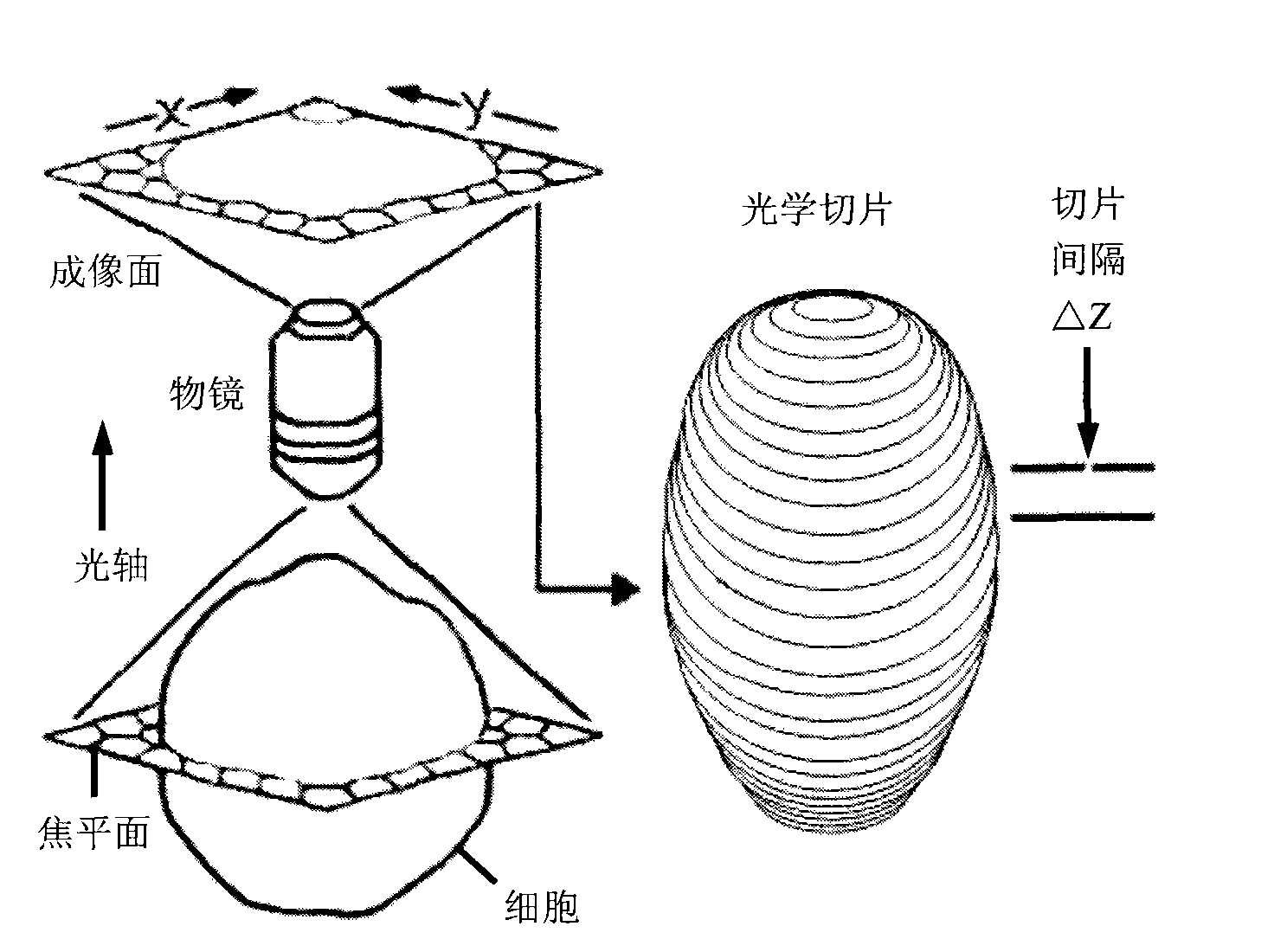
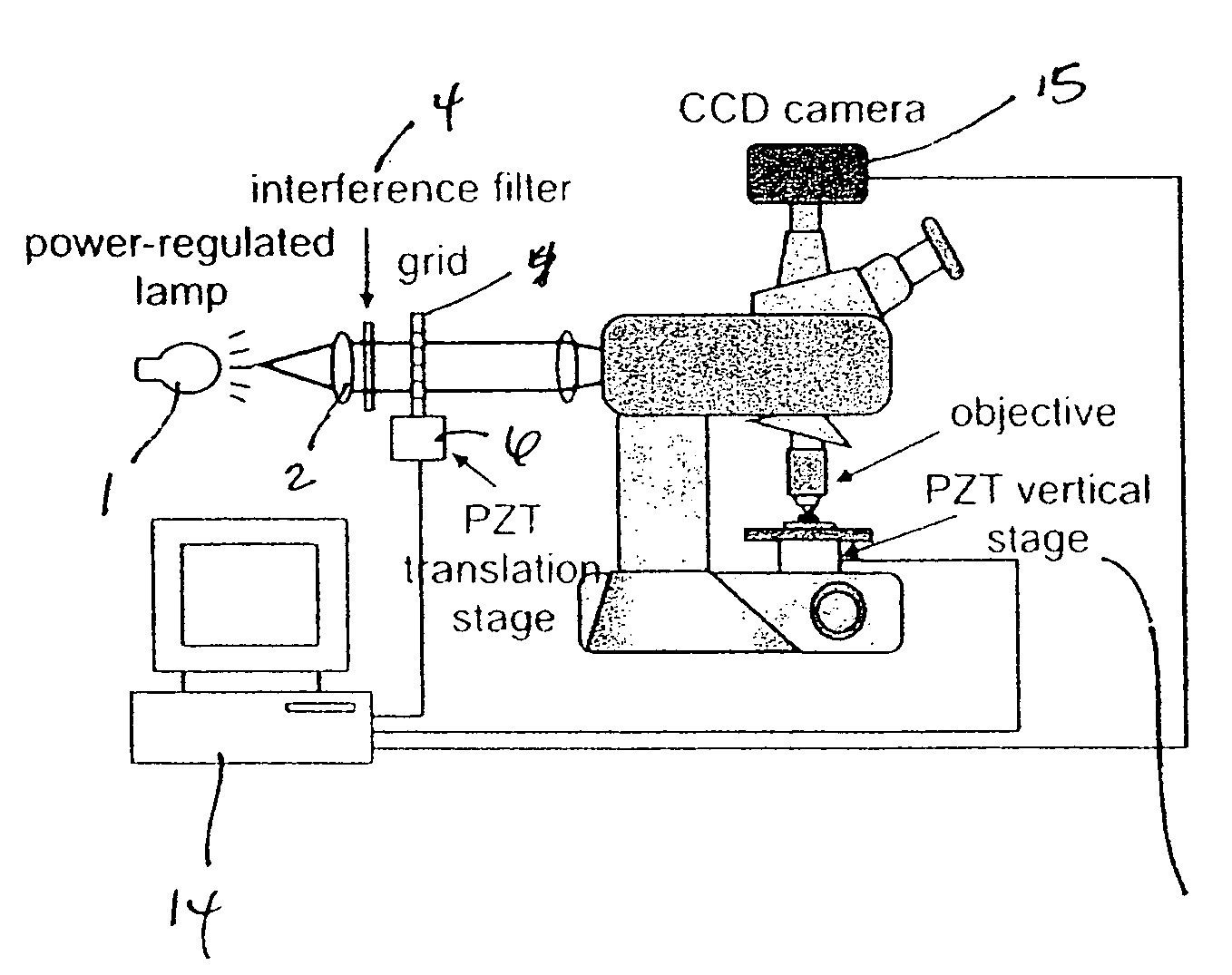
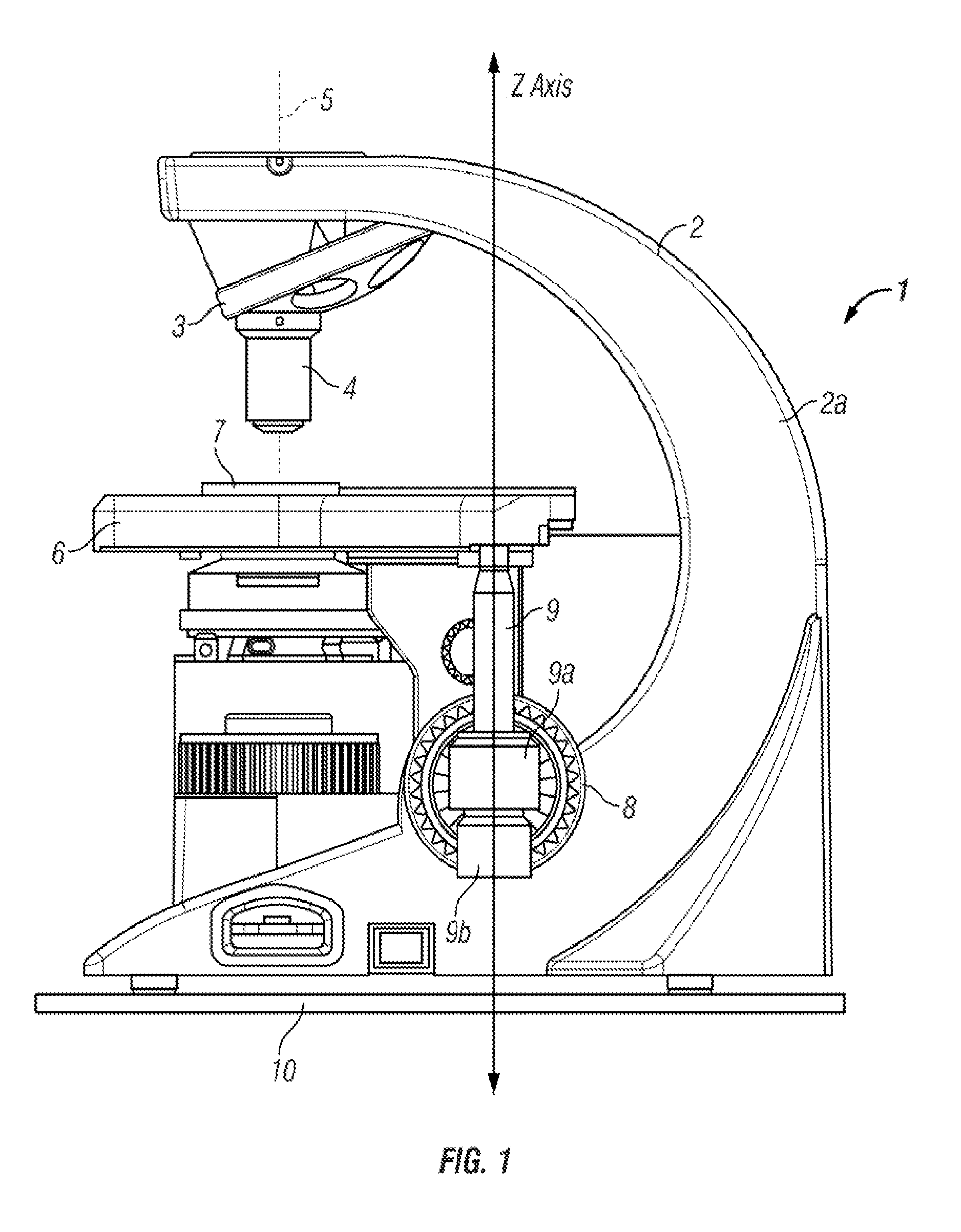
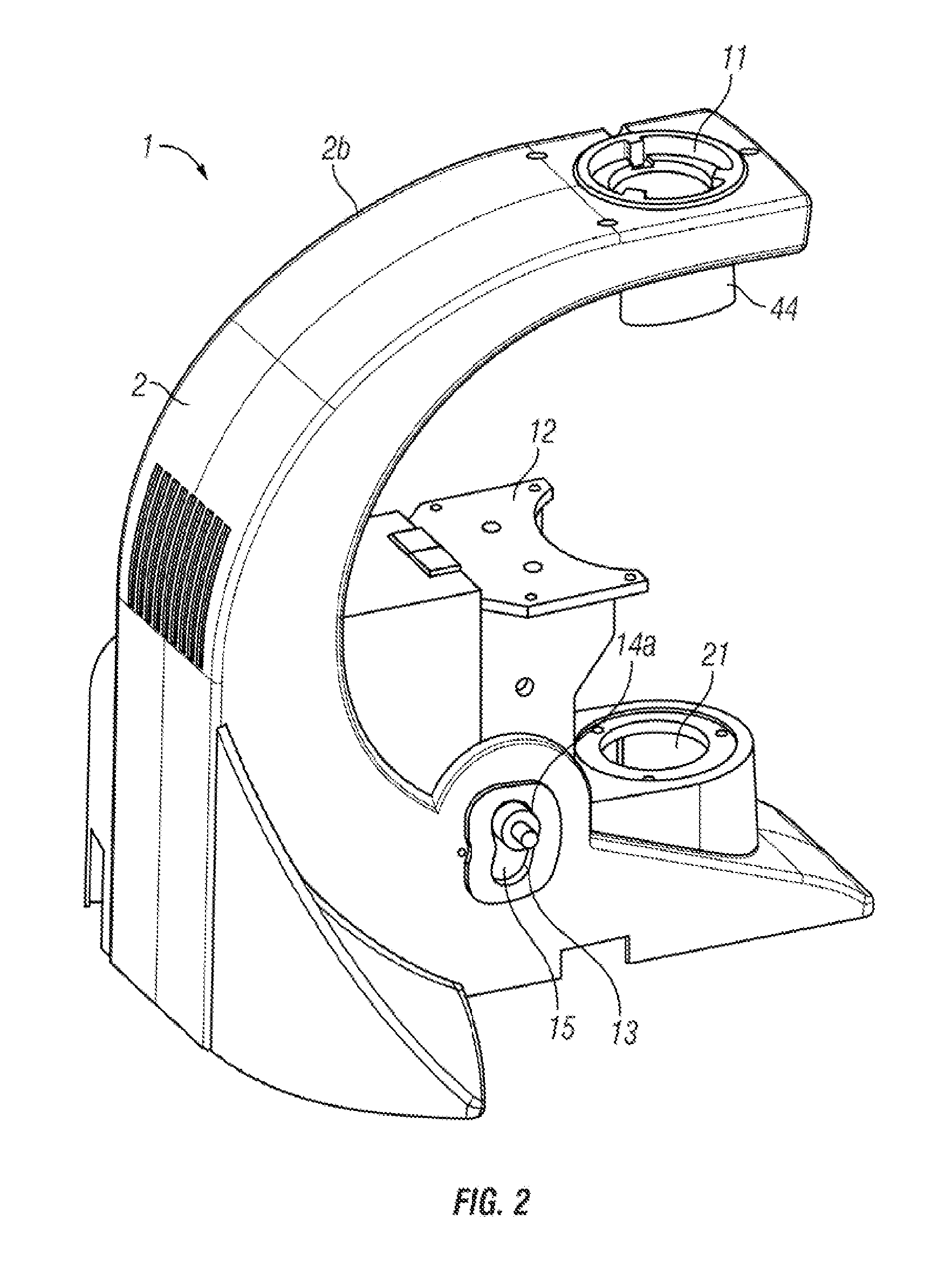
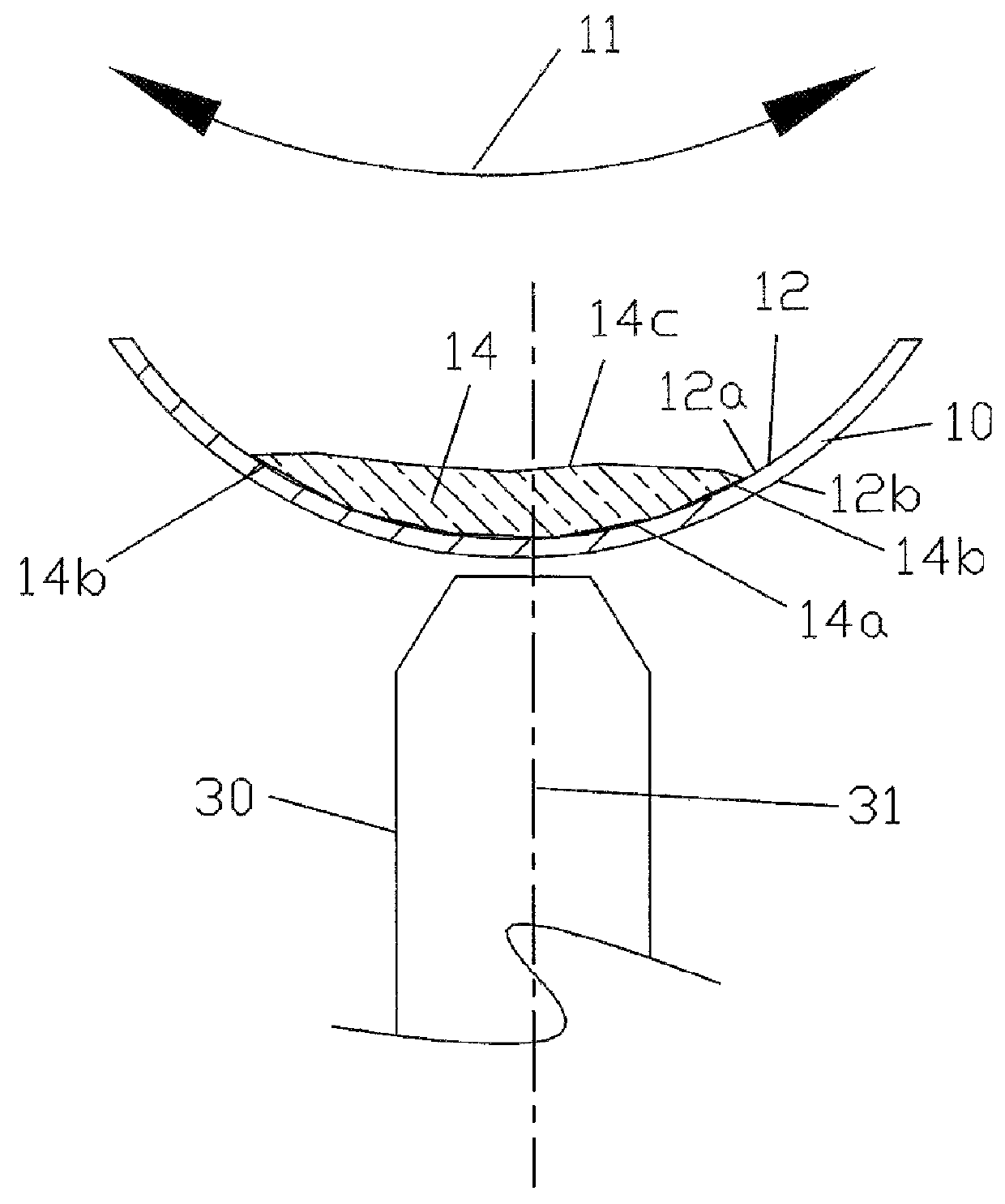
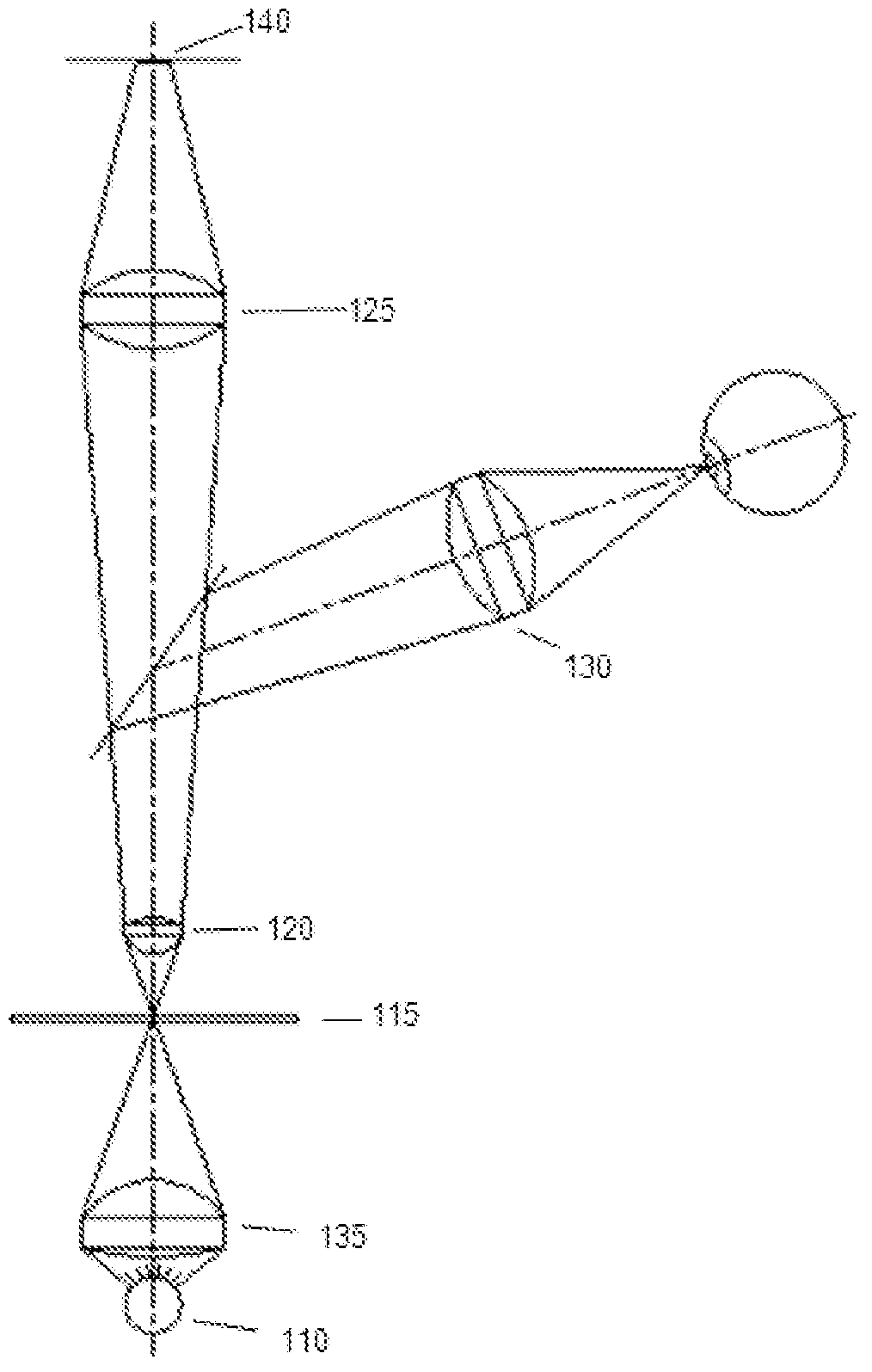
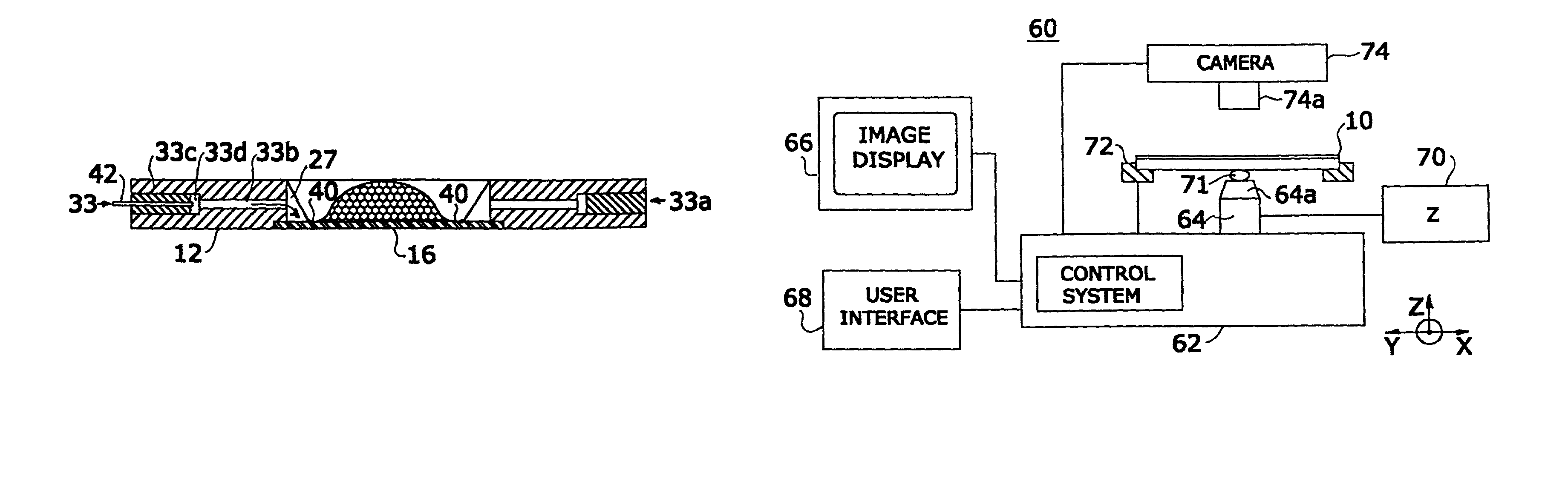
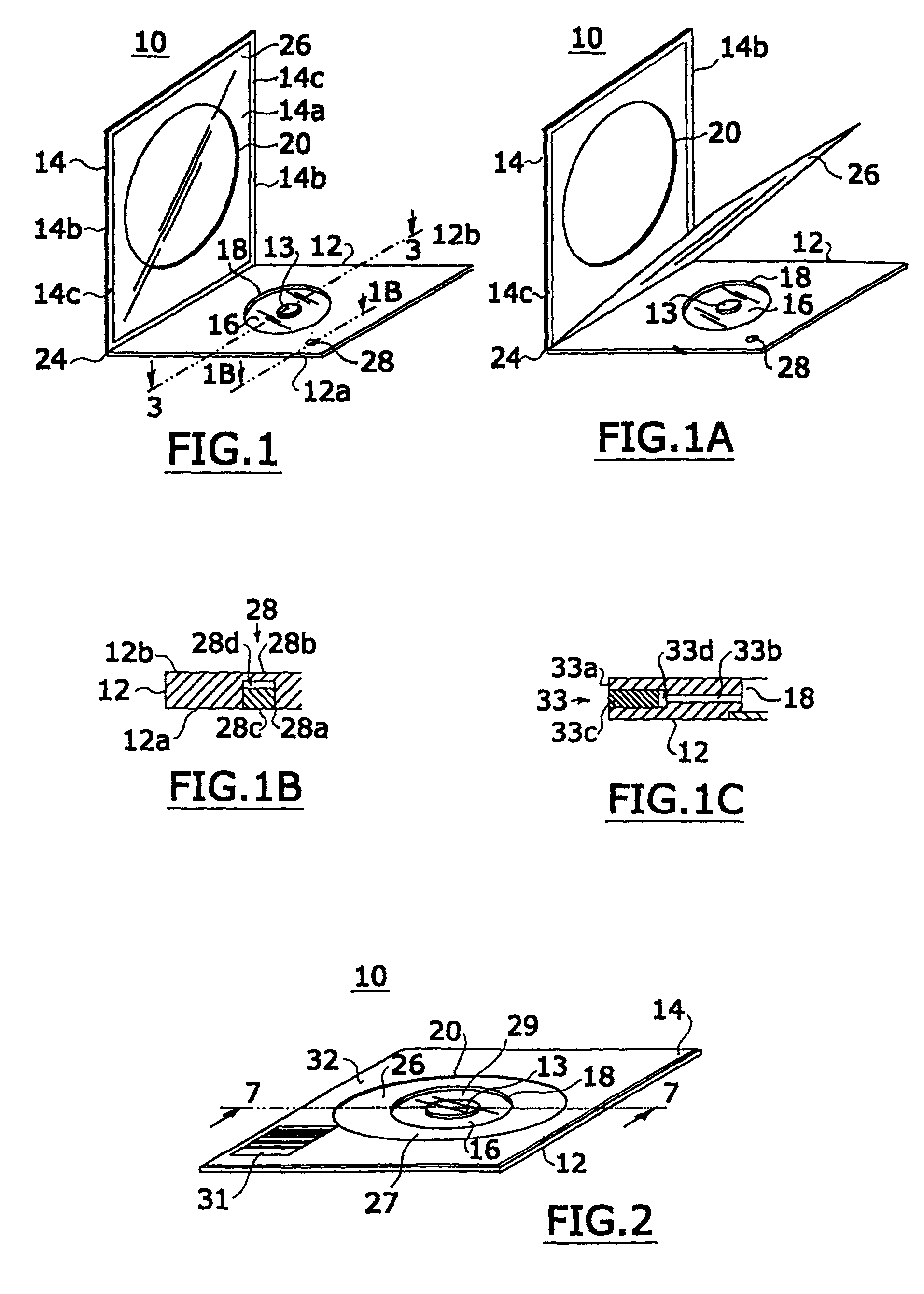
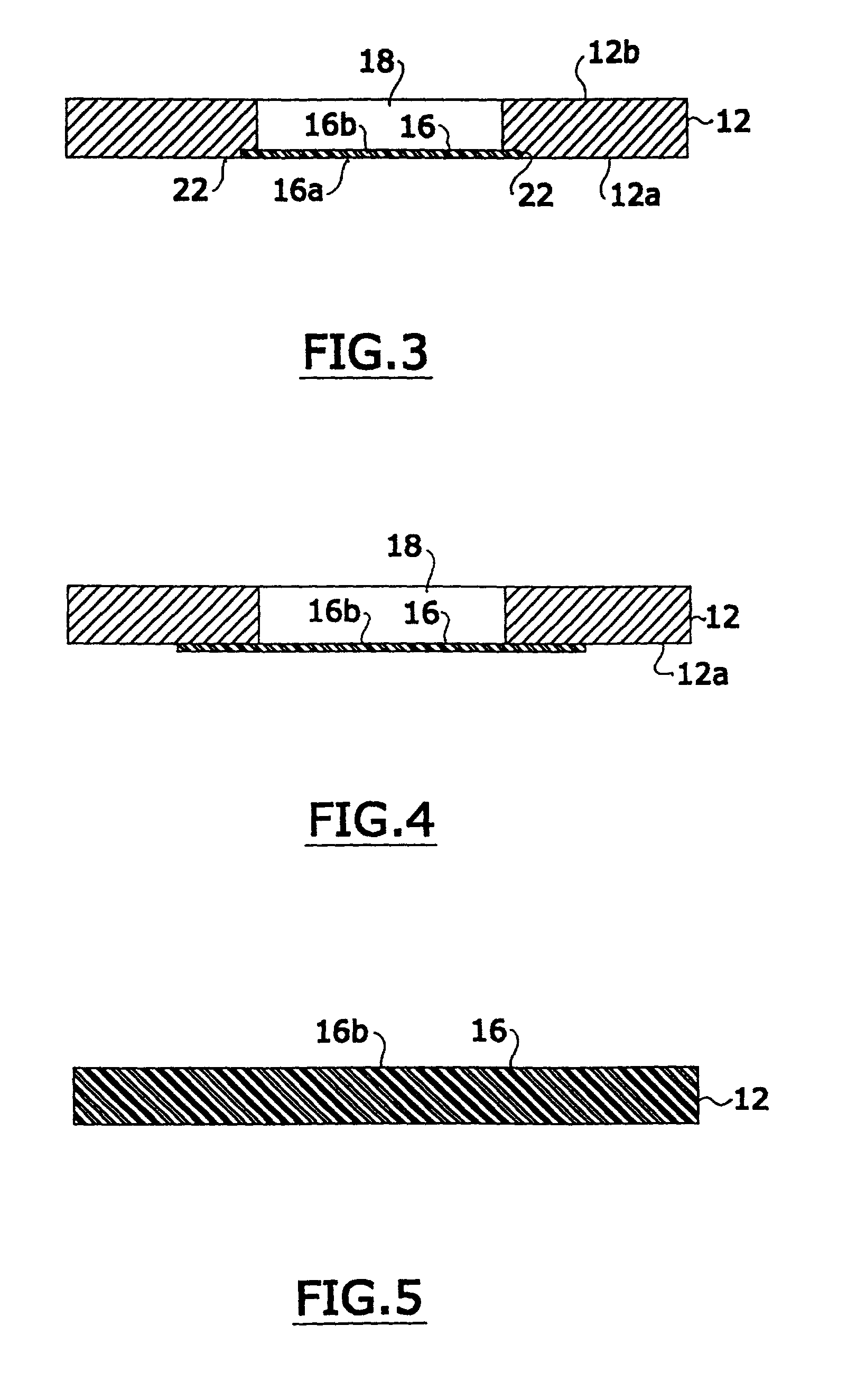
Tissue specimen stage for an optical sectioning microscope
A tissue specimen stage is provided having a window with surface curvature upon which an excised tissue specimen is locatable, a carriage having a tissue specimen receptacle to which the window is mounted, and a platform supporting the carriage and presenting the window to the objective lens of an optical sectioning microscope. The carriage is mounted to the platform for movement along two rotational axes so that the carriage's movement follows the curvature of all or part of the window while maintaining the same optical geometry of the window with respect to the objective lens. The window has surface curvature adapted to at least approximate the shape or curvature of the non-histologically prepared tissue specimen to be placed thereupon.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
System and method for time-related microscopy of biological organisms
ActiveCN102782561AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
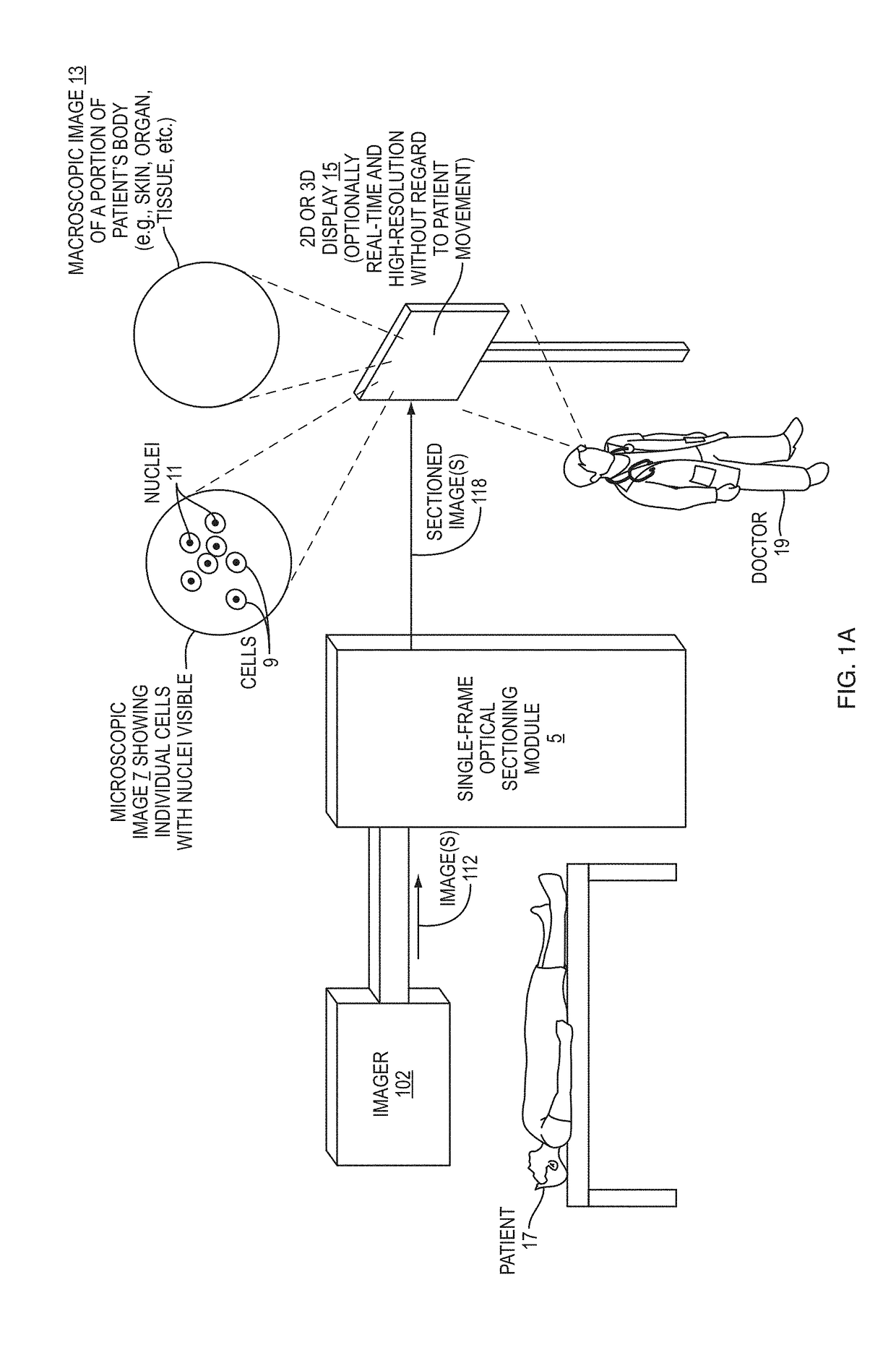
Methods, Systems, and Devices for Optical Sectioning
ActiveUS20180239946A1Reduce capacityHigh resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopesGratingBiological imaging
Methods, systems, and devices described herein enable single-image optical sectioning, even at depth within turbid media, such as human skin or other tissue. Embodiments can eliminate the need for multiple image samples or raster scans, making in-vivo or live biological imaging easier and faster than multi-image sectioning techniques. Better contrast and resolution than traditional three-phase structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is possible in turbid media. Embodiments enable imaging of cell nuclei. Resolution and contrast resulting from disclosed embodiments are less sensitive to motion of or within patients or other targets than confocal microscopy and three-phase SIM techniques. Three-dimensional images of target specimens can be provided based on a group of single-image optical sections. Real-time imaging can also be provided.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
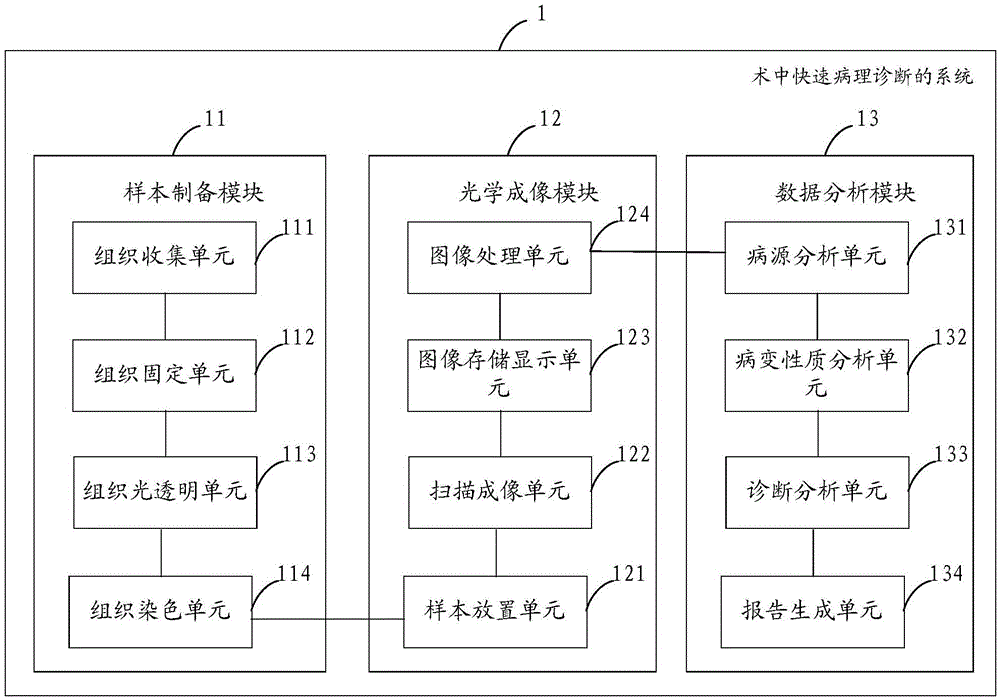
Rapid intraoperative pathological diagnosis system and method
ActiveCN105606573ARealize the function of optical sectioningAvoid taking timePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical clearingFluorescence
The invention is suitable for the technical field of medical information and provides a rapid intraoperative pathological diagnosis system and method. The system comprises a sample preparation module, an optical imaging module and a data analysis module, wherein the sample preparation module extracts a diseased sample tissue from a patient body, fixes the diseased sample tissue by adopting a chemical reagent, then performs optical clearing treatment on the diseased sample tissue by adopting an optical clearing agent and finally performs fluorescent staining treatment on the diseased sample tissue; the optical imaging module first arranges and fixes the diseased sample tissue subjected to the fluorescent staining treatment, and then performs optical scanning imaging treatment on the diseased sample tissue subjected to the fluorescent staining treatment, by adopting a functional microimaging system, so as to obtain a functional diagram and an optical section diagram of the diseased sample tissue; and the data analysis module performs comparative analysis on the functional diagram and the optical section diagram as well as existing disease database data to generate a diagnosis result report. The system and the method are high in section-making speed and high in section-making quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Cassette for facilitating optical sectioning of a retained tissue specimen
InactiveUS8149506B2Facilitates optical examinationEnhance the imagePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageTissue sample
A cassette for retaining a specimen of surgically exposed tissue from a patient in an orientation that facilitates optical sectioning of the tissue by a confocal microscopic or other optical imaging microscope. The cassette includes a base member having an optically transparent window upon which a tissue specimen is situated, a membrane locatable over a substantial portion of the base member including the window, and an upper member which can cover the base member to provide an enclosed cavity between the membrane and the window sealing the tissue specimen therein. The edges of the tissue specimen may then be positioned planar against the window and retained in that position by bonds formed between the membrane and window around the tissue specimen. The cassette may be part of a confocal imaging system to produce microscopic images of sections of the tissue specimen useful for Mohs surgery.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
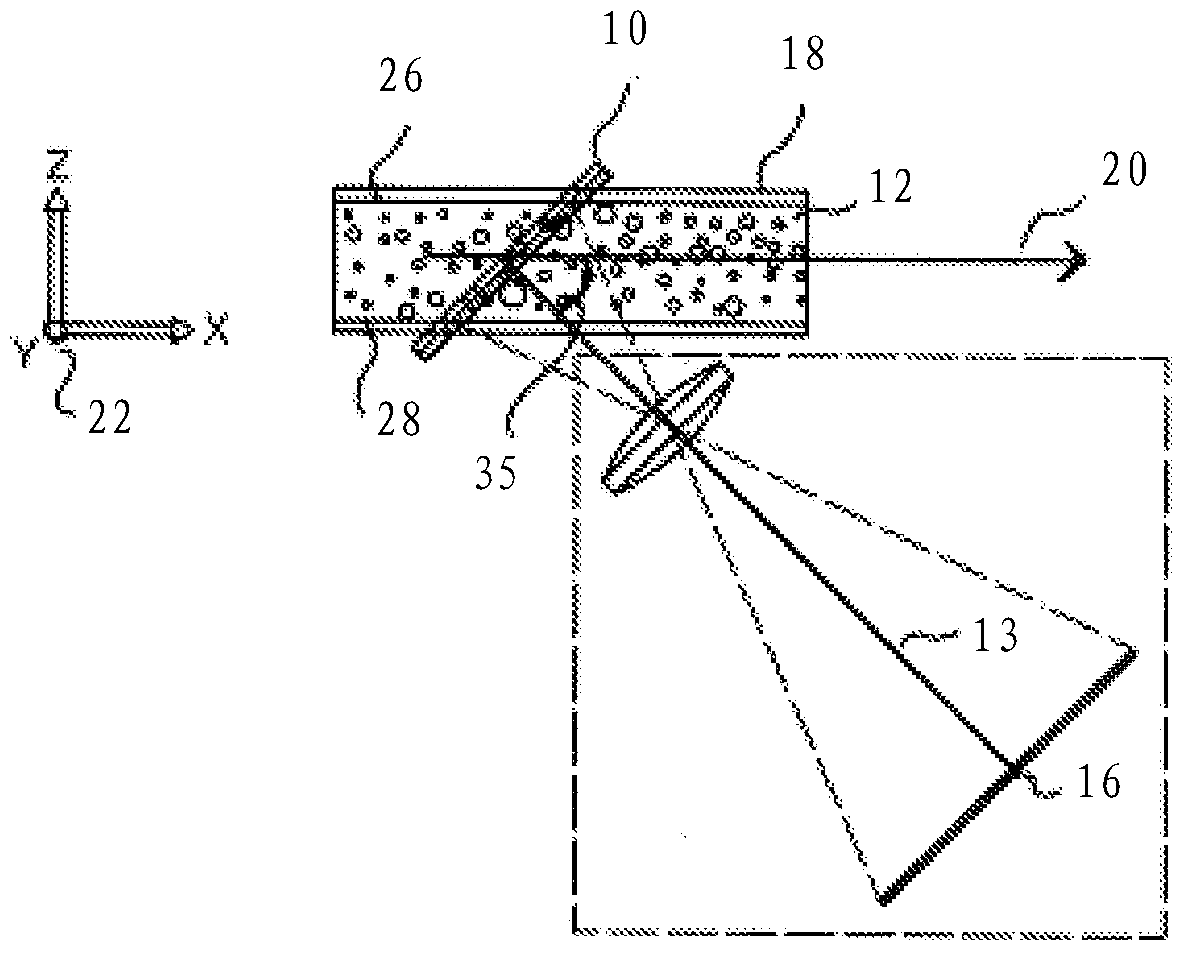
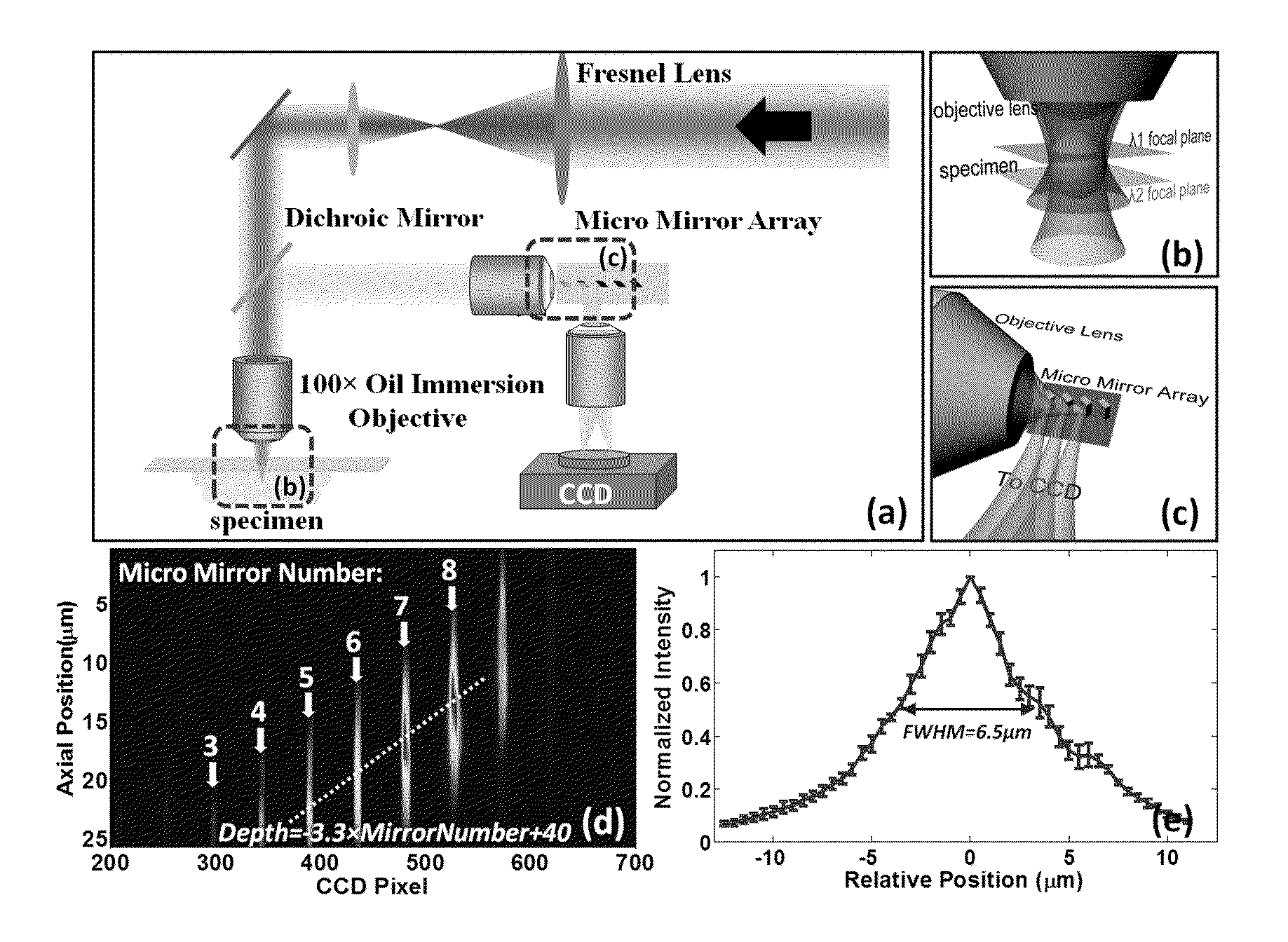
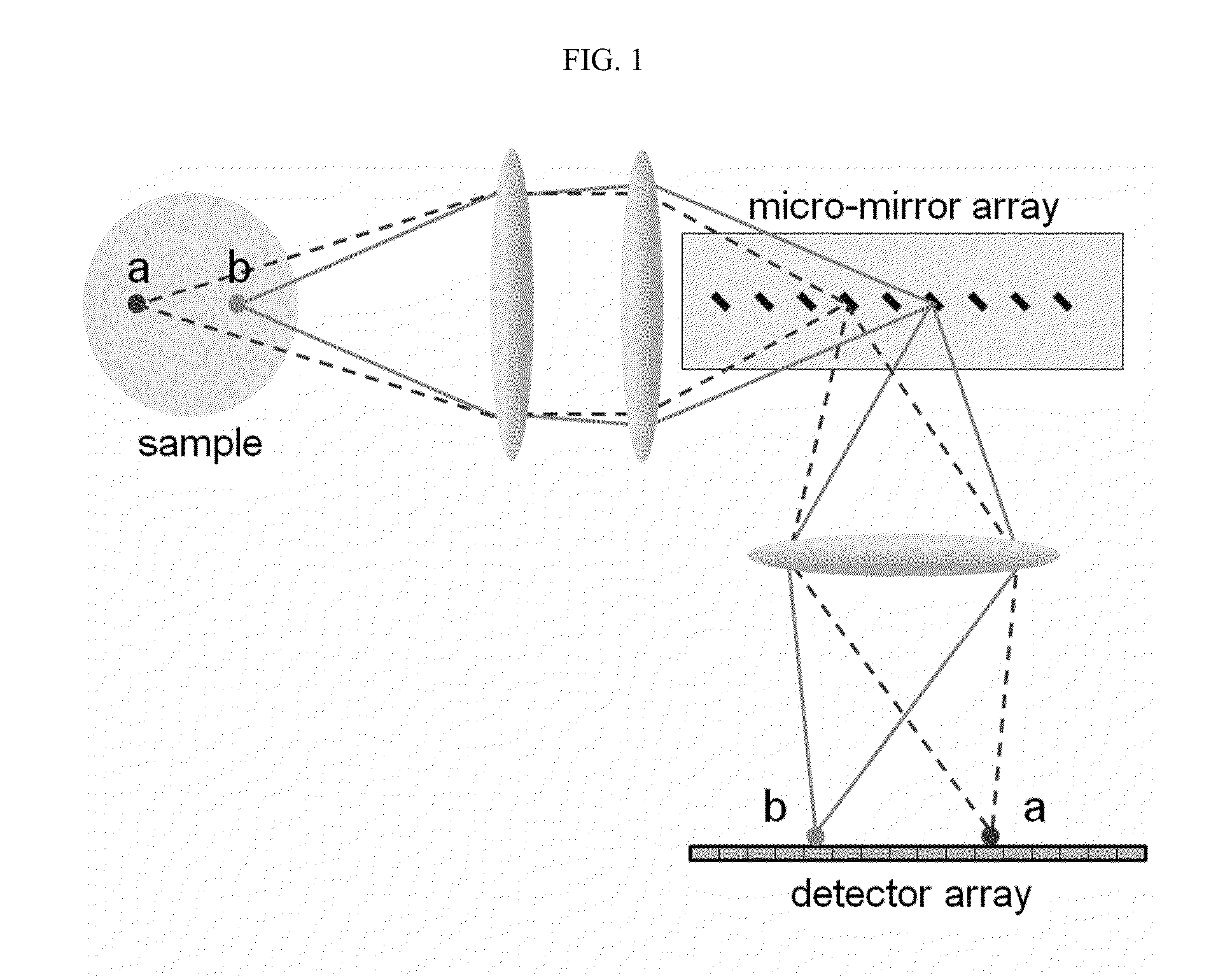
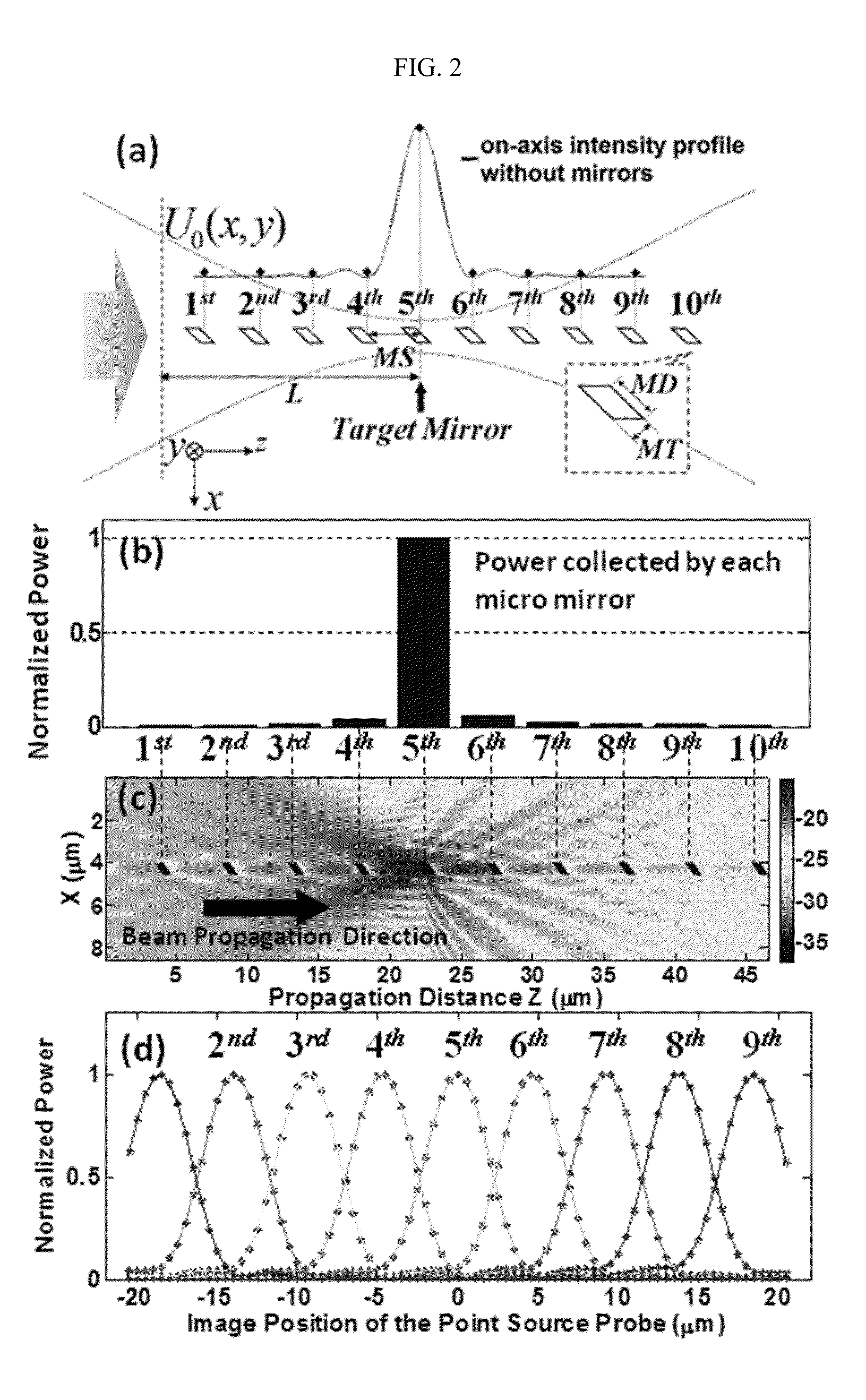
Z-microscopy
ActiveUS20140146159A1Efficient collectionIncrease the number ofColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsComputational physicsImage signal
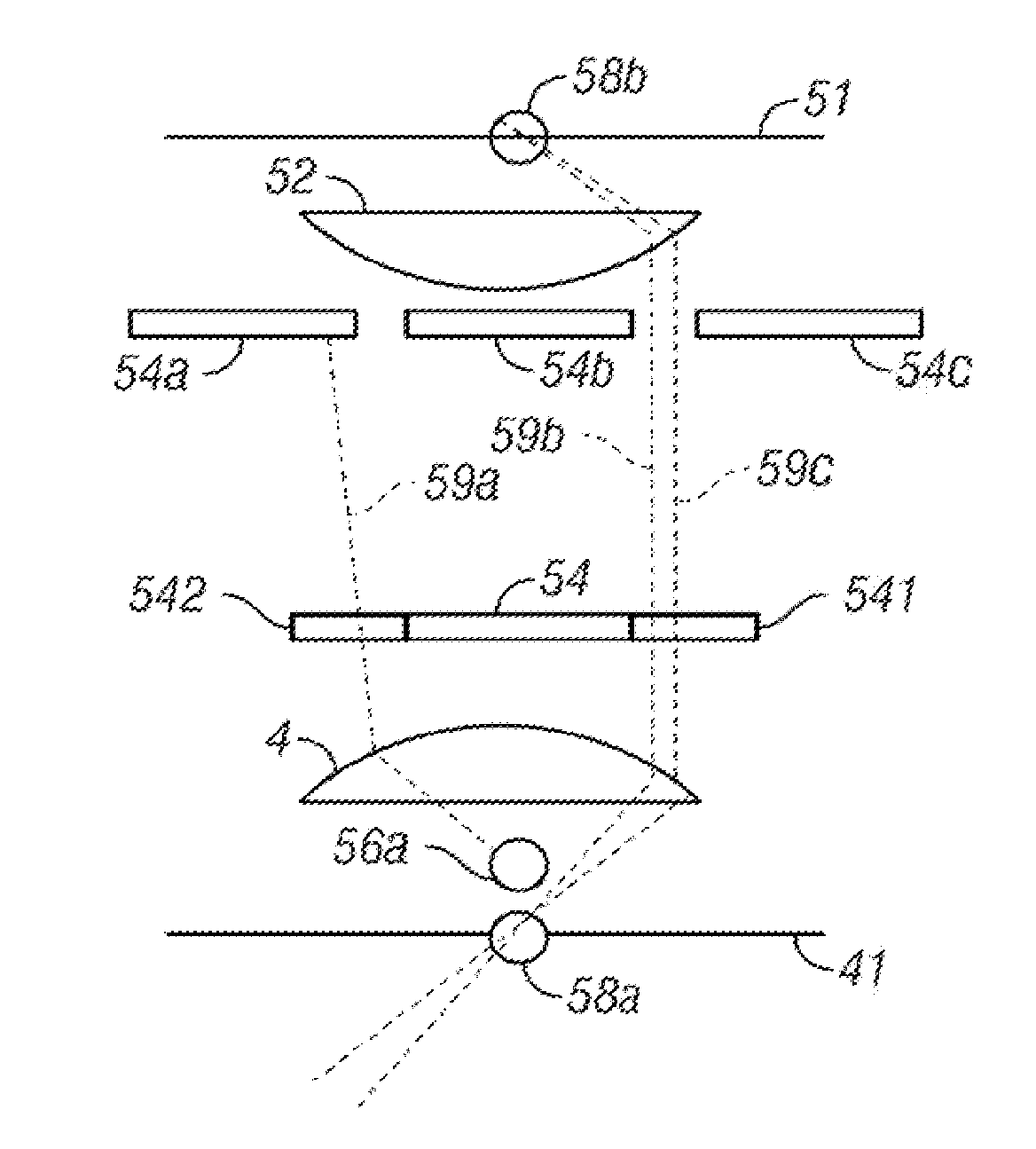
We present a method for parallel axial imaging, or z-microscopy, utilizing an array of tilted micro mirrors arranged along the axial direction. Image signals emitted from different axial positions can be orthogonally reflected by the corresponding micro mirrors and spatially separated for parallel detection, essentially converting the more challenging axial imaging to a lateral imaging problem. Each micro mirror also provides optical sectioning capability due to its finite dimension.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
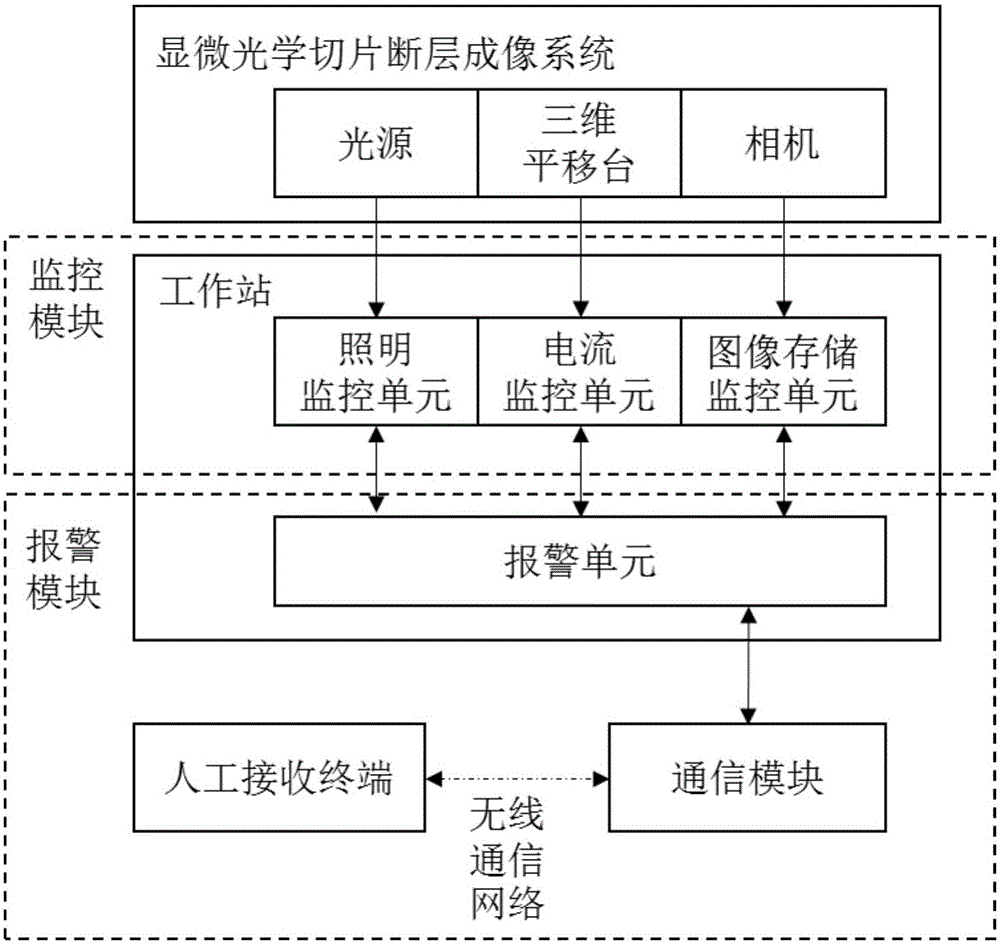
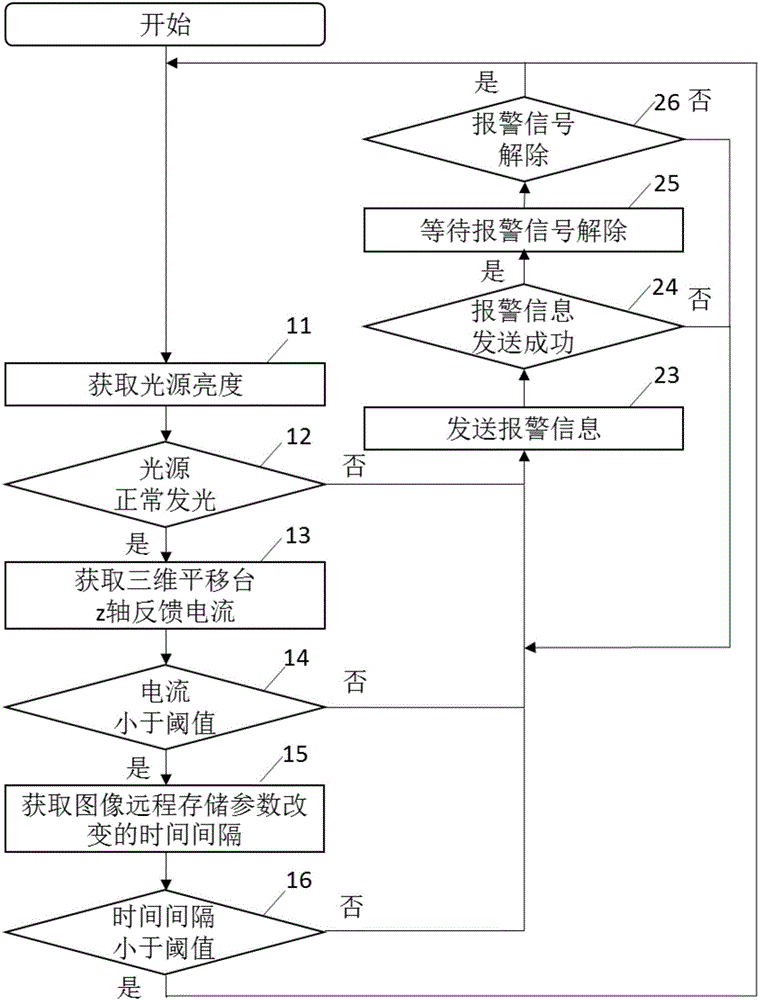
Monitoring alarm system and method for microscopic optical slice tomographic imaging system
ActiveCN106017872ATimely transmissionWaste less timeCurrent/voltage measurementTesting optical propertiesImaging conditionComputer science
The present invention discloses a monitoring alarm system and a method for a microscopic optical slice tomographic imaging system. The system comprises a monitoring module, and an alarm module. The monitoring module is used for monitoring the imaging condition of the microscopic optical slice tomographic imaging system, and then judging whether an abnormal condition occurs or not according to the acquired imaging condition information of the microscopic optical slice tomographic imaging system. If an abnormal condition occurs, the monitoring module sends out an alarm triggering signal. The alarm module is used for receiving the alarm triggering signal and then sending out an alarm. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the parameters of the microscopic optical slice tomographic imaging system during the imaging process, such as the brightness of a light source, the current of a three-dimensional translational platform and the like, can be acquired in real time. Meanwhile, the system sends out the alarm upon detecting the occurrence of the following abnormal conditions: the light source cannot provide a pre-set light source brightness; the air floating shaft of the three-dimensional translational platform cannot supply sufficient air during the imaging process, an acquisition program cannot control the normal imaging of a camera; and so on. Therefore, the time waste and the labor cost during the imaging process are effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the stability of the imaging process is improved, and the high-resolution characteristics of the imaging effect can be maintained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Confocal blood vessel imaging machine
ActiveCN106510629ATo offer comfortRelieve painDiagnostics using tomographySensorsAcupuncture treatmentLight beam
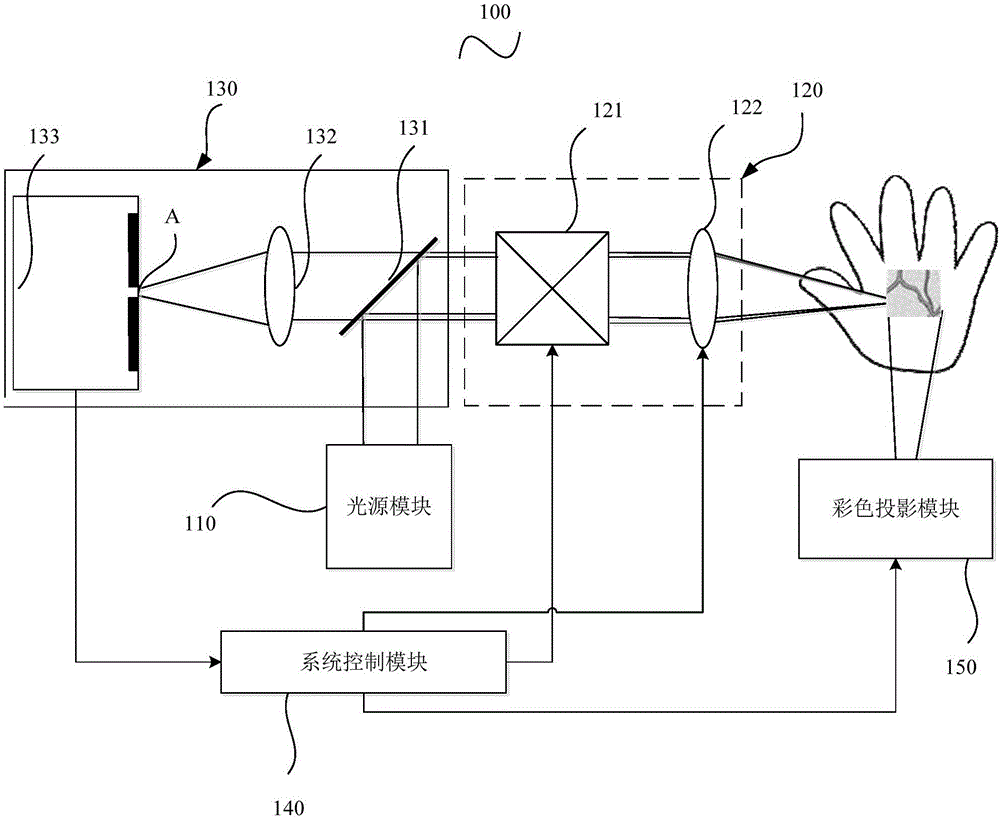
The invention provides a confocal blood vessel imaging machine, which comprises a light source module, a confocal scanning module, a detecting module, a color projection module and a system control module. The confocal scanning module comprises an XY light beam scanning mechanism and a scanning lens mechanism; and the detecting module comprises a detector with a pinhole, a focusing lens and a light splitting mechanism. The confocal blood vessel imaging machine provided by the invention utilizes lossless optical sectioning strength of a confocal technology for providing three-dimensional position information of blood vessels, can better provide blood vessel information of obese patients and infant patients for medical personnel, and is beneficial to providing convenience for the medical personnel to give an acupuncture treatment, relieving the pains of the patients, improving the success rate of puncture, shortening the puncture time, reducing the working intensity of the medical personnel, reducing the medical disputes and improving the hospital prestige.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Systems and methods for in-operating-theatre imaging of fresh tissue resected during surgery for pathology assessment
ActiveUS20160313252A1Time necessaryFacilitates in-operating-theater analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicroscopesFresh TissueOperating theatres
The disclosed technology brings histopathology into the operating theatre, to enable real-time intra-operative digital pathology. The disclosed technology utilizes confocal imaging devices image, in the operating theatre, “optical slices” of fresh tissue—without the need to physically slice and otherwise process the resected tissue as required by frozen section analysis (FSA). The disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, includes a simple, operating-table-side digital histology scanner, with the capability of rapidly scanning all outer margins of a tissue sample (e.g., resection lump, removed tissue mass). Using point-scanning microscopy technology, the disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, precisely scans a thin “optical section” of the resected tissue, and sends the digital image to a pathologist rather than the real tissue, thereby providing the pathologist with the opportunity to analyze the tissue intra-operatively. Thus, the disclosed technology provides digital images with similar information content as FSA, but faster and without destroying the tissue sample itself.
Owner:SAMANTREE MEDICAL SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com