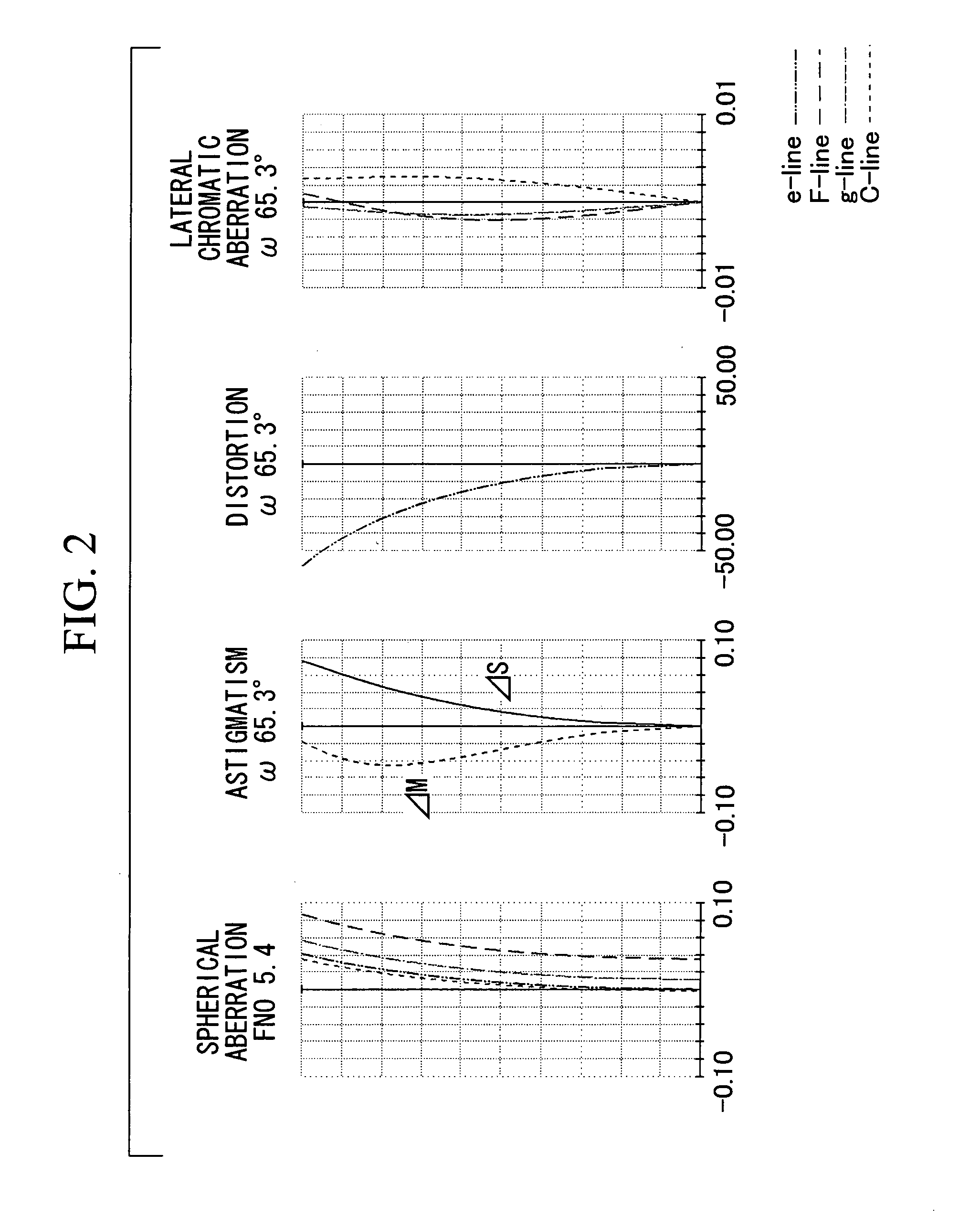
Patents
Literature
1308 results about "Microscopic observation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microscopic Observation Drug Susceptibility assay. The Microscopic Observation Drug Susceptibility assay (MODS) is a culture method shown to be more sensitive, faster and cheaper test than current culture-based tests for Tuberculosis.
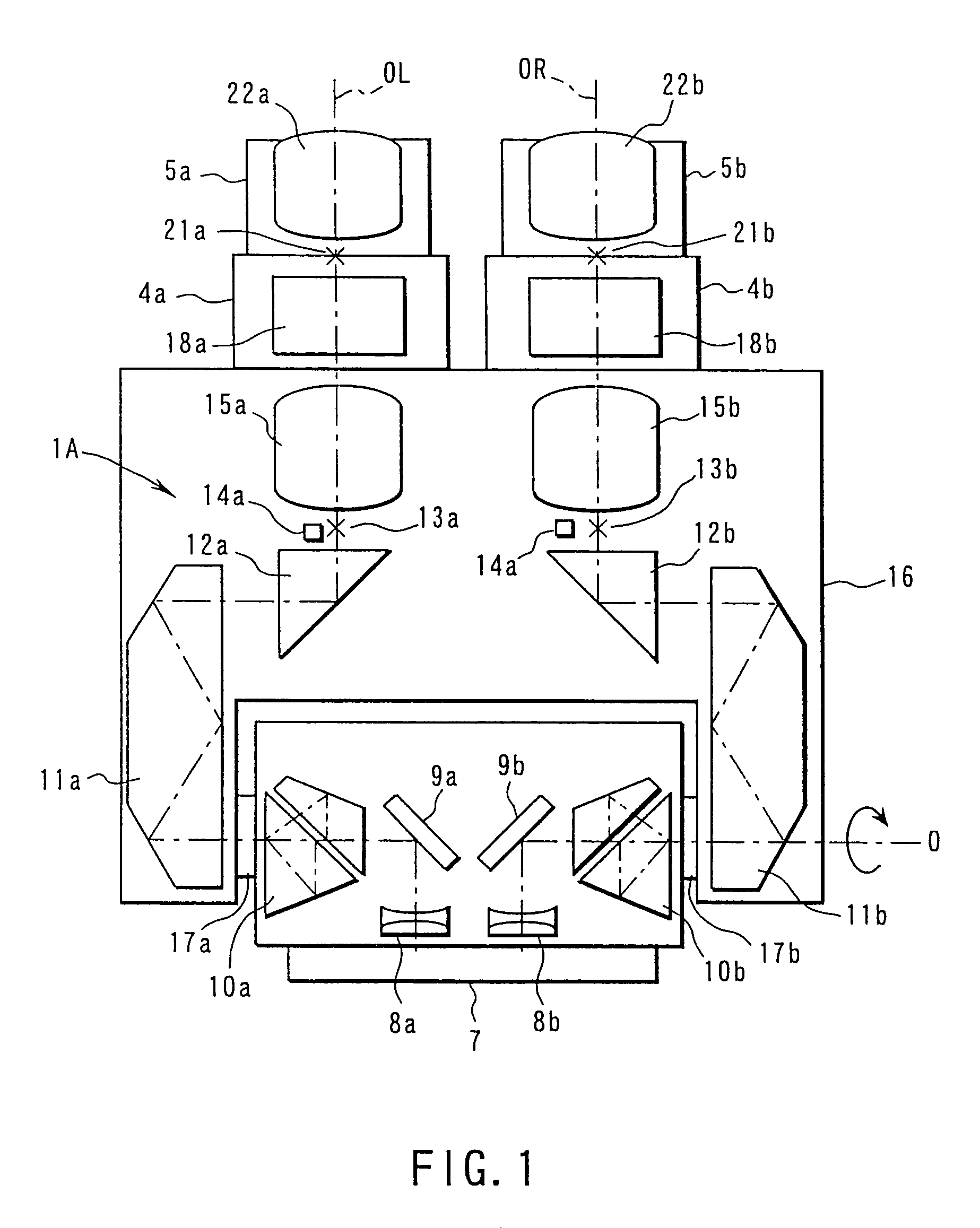
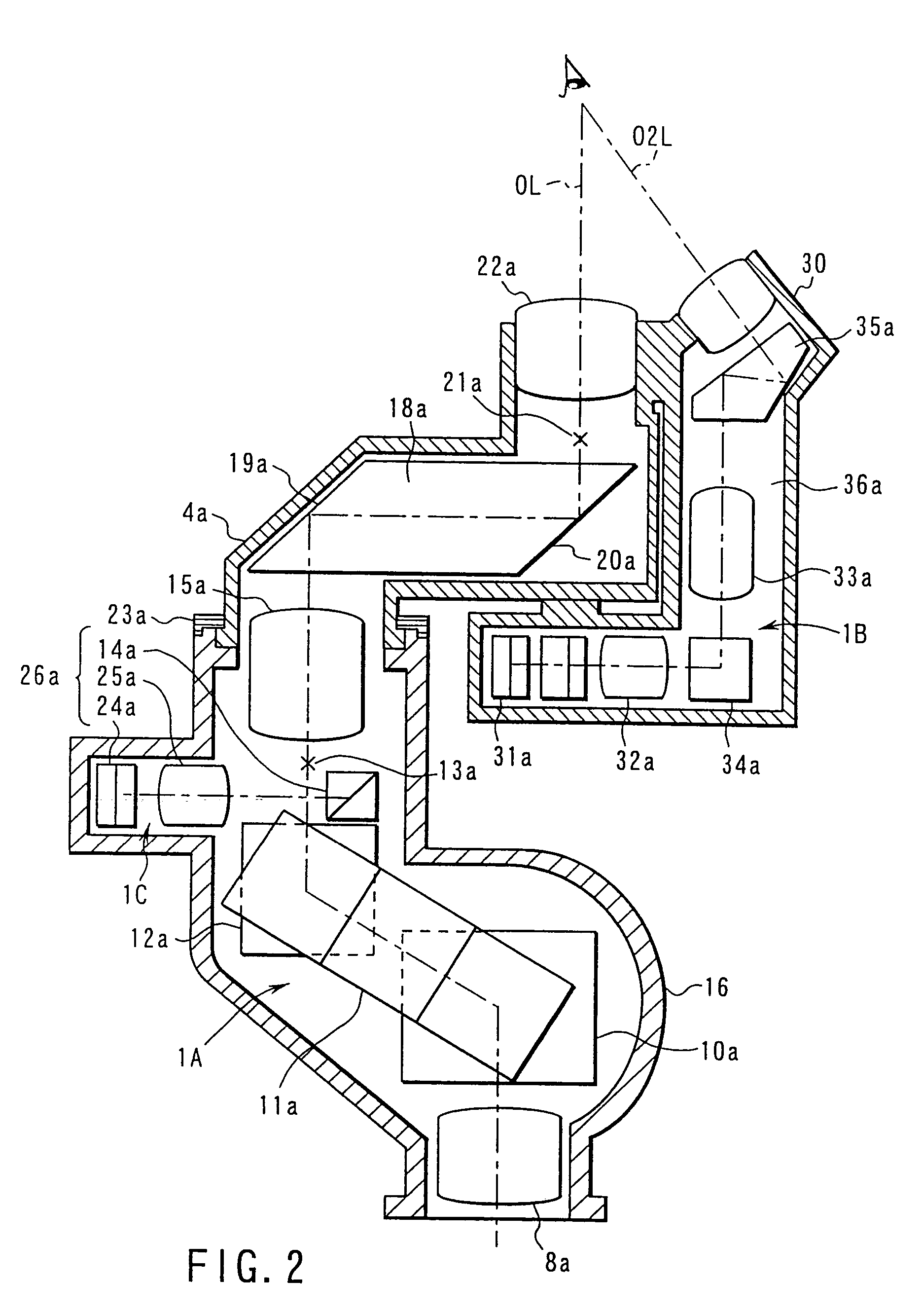
Microsurgical robot system
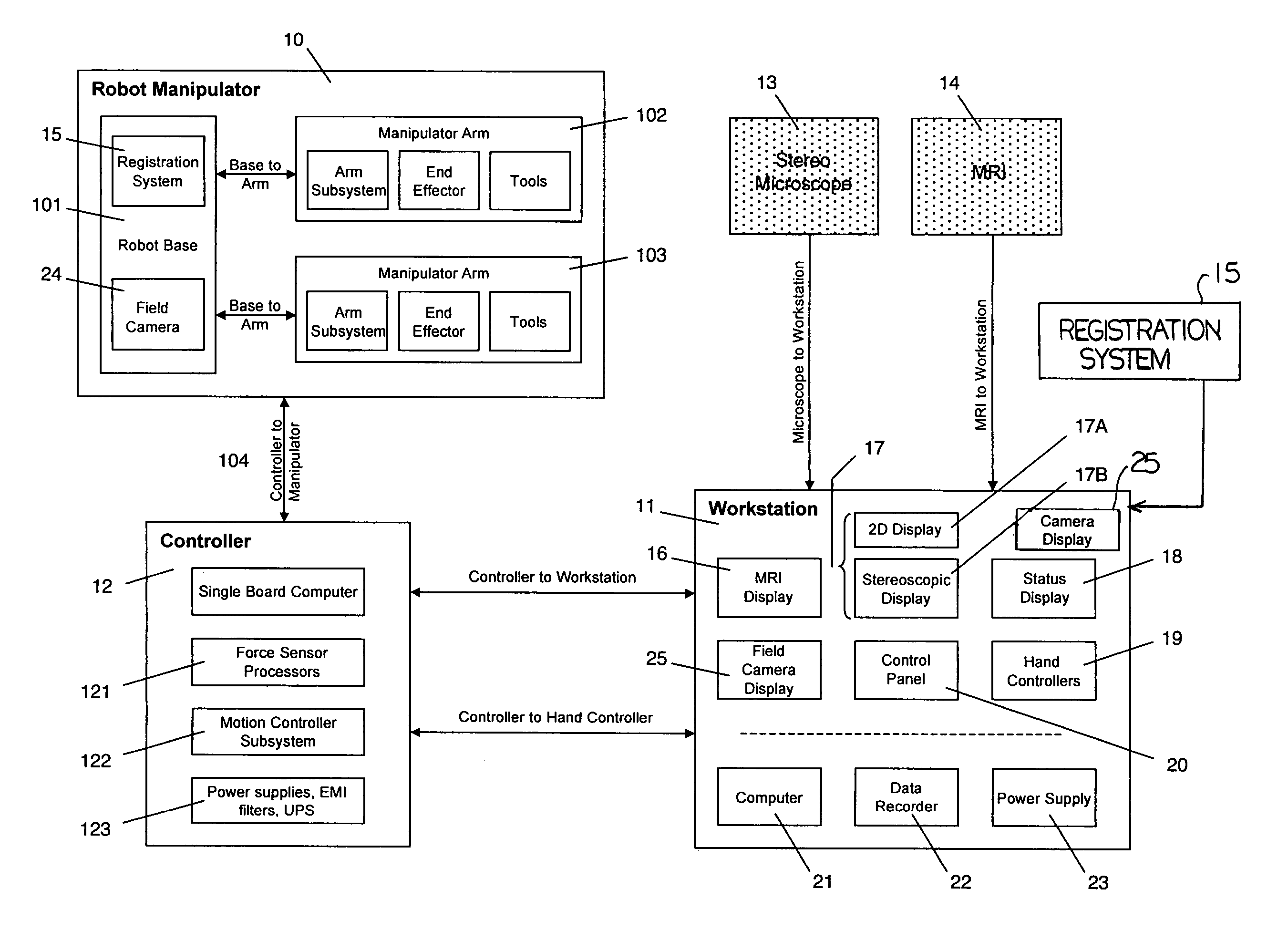
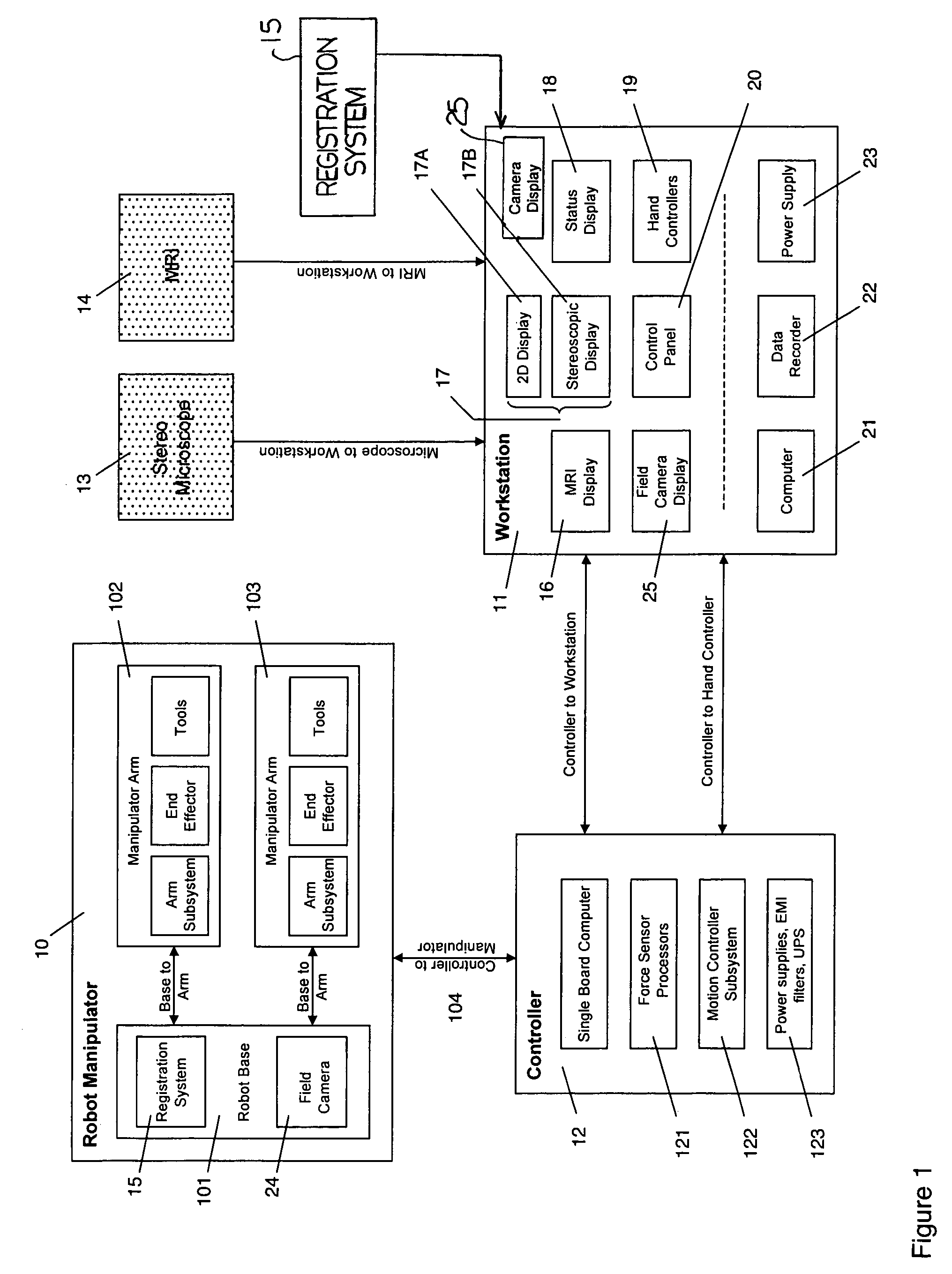
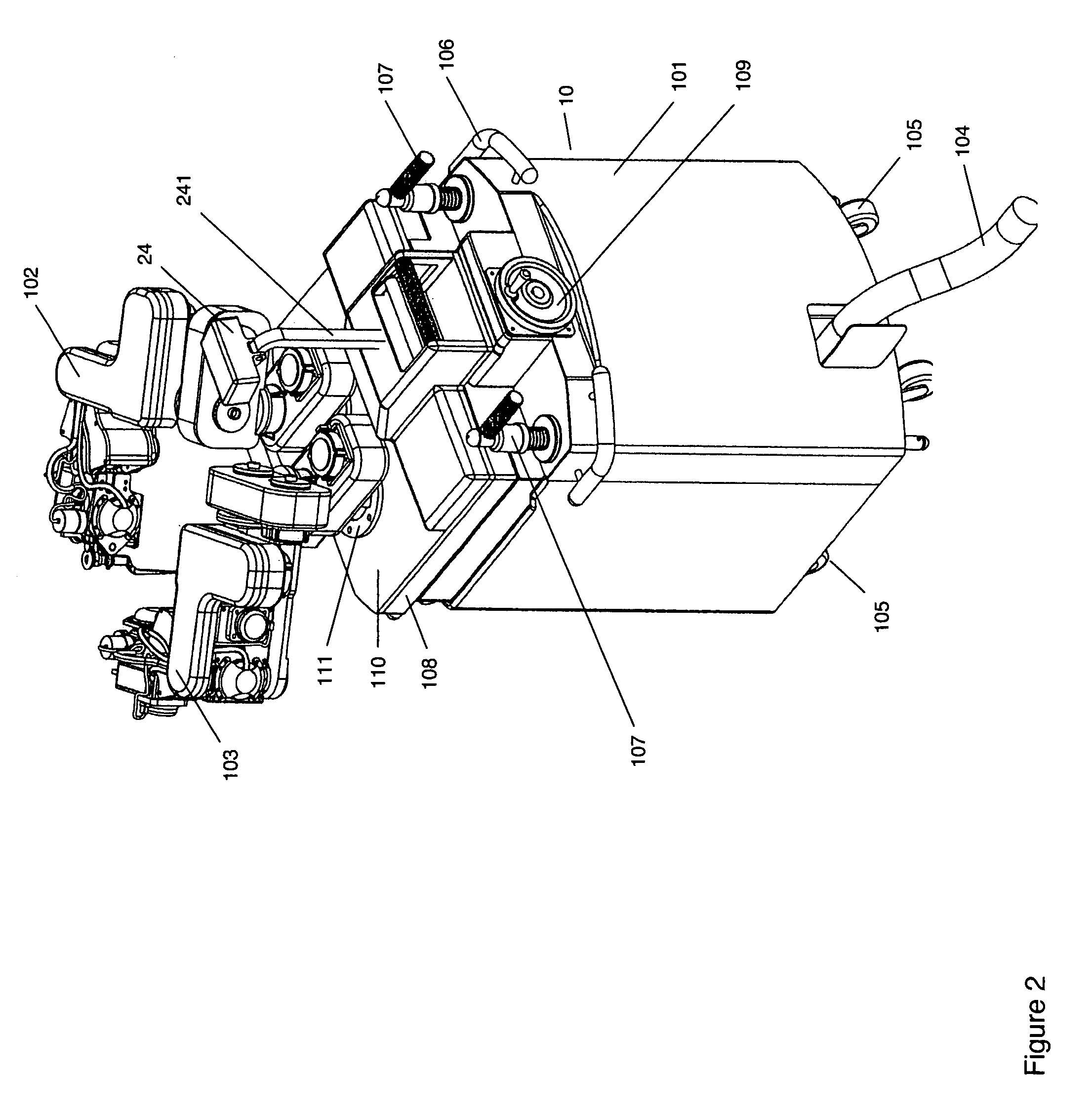
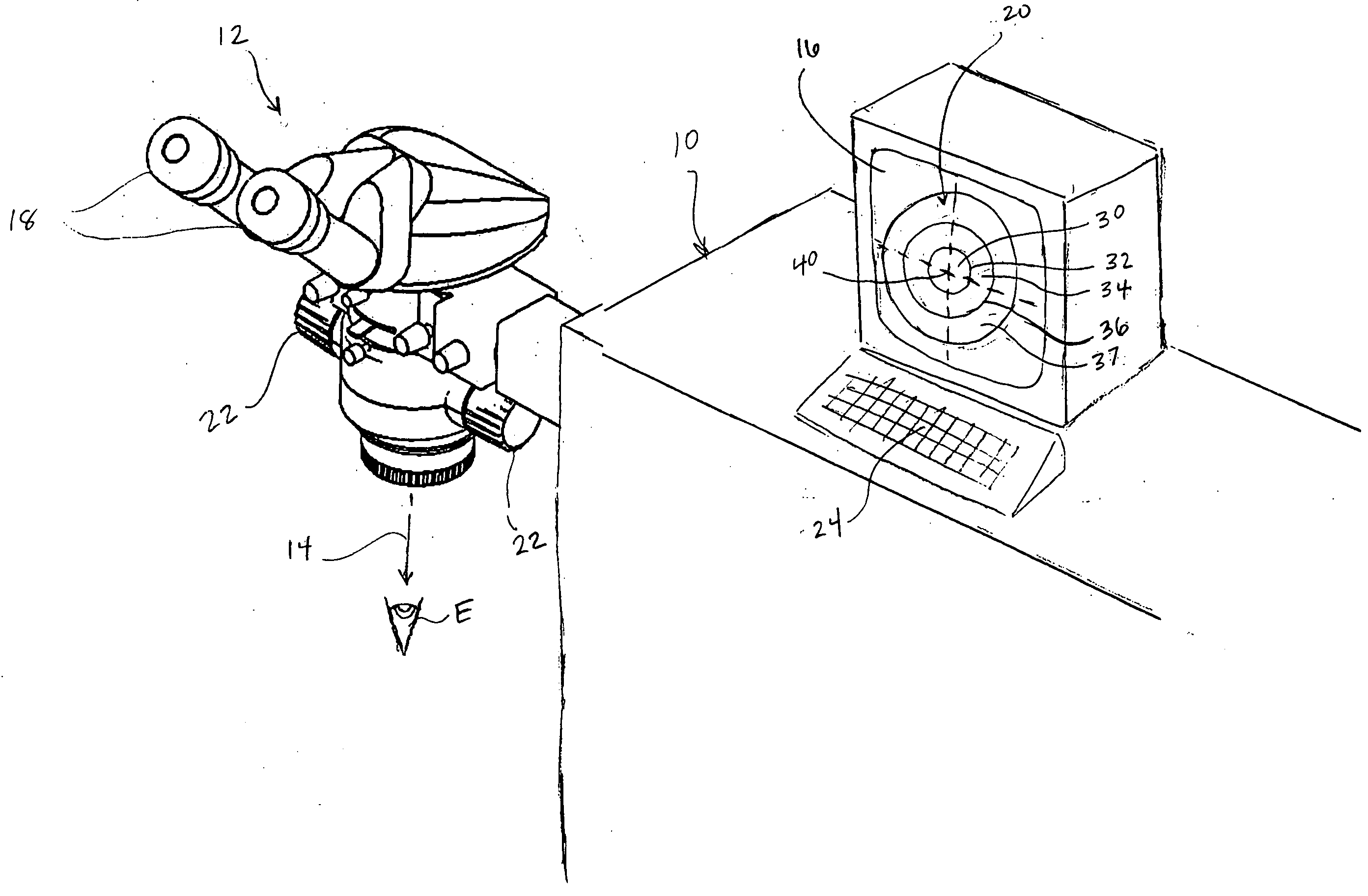
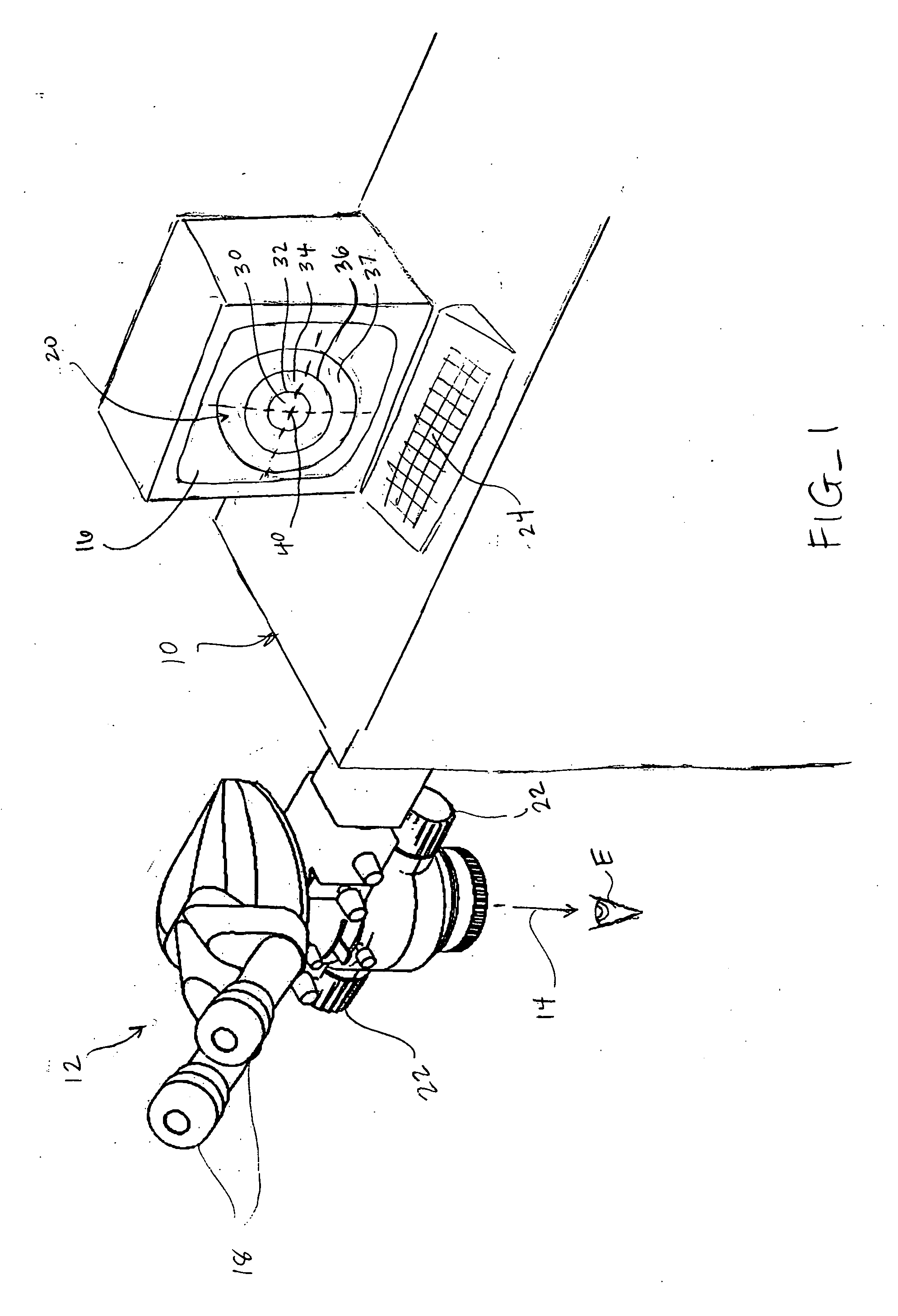
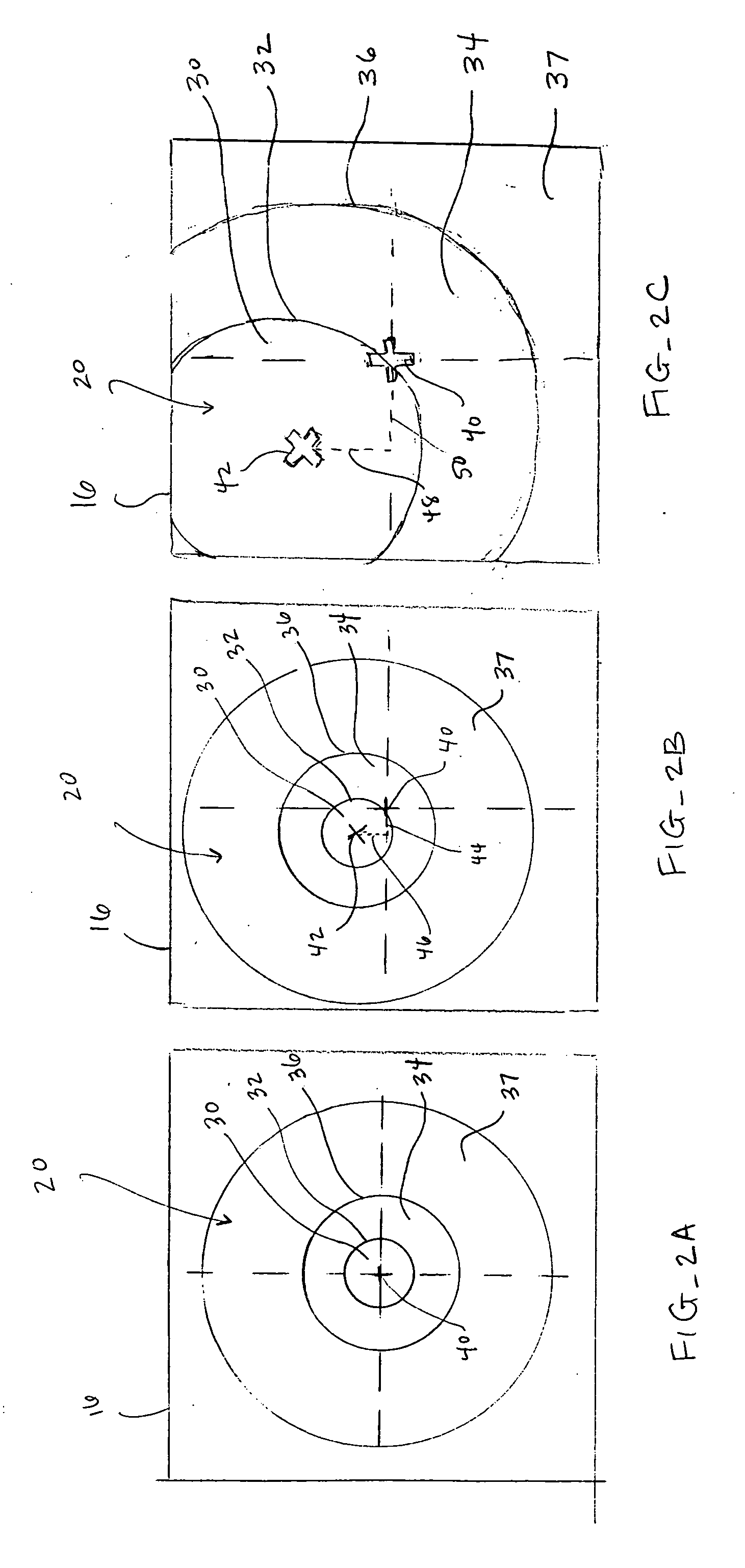
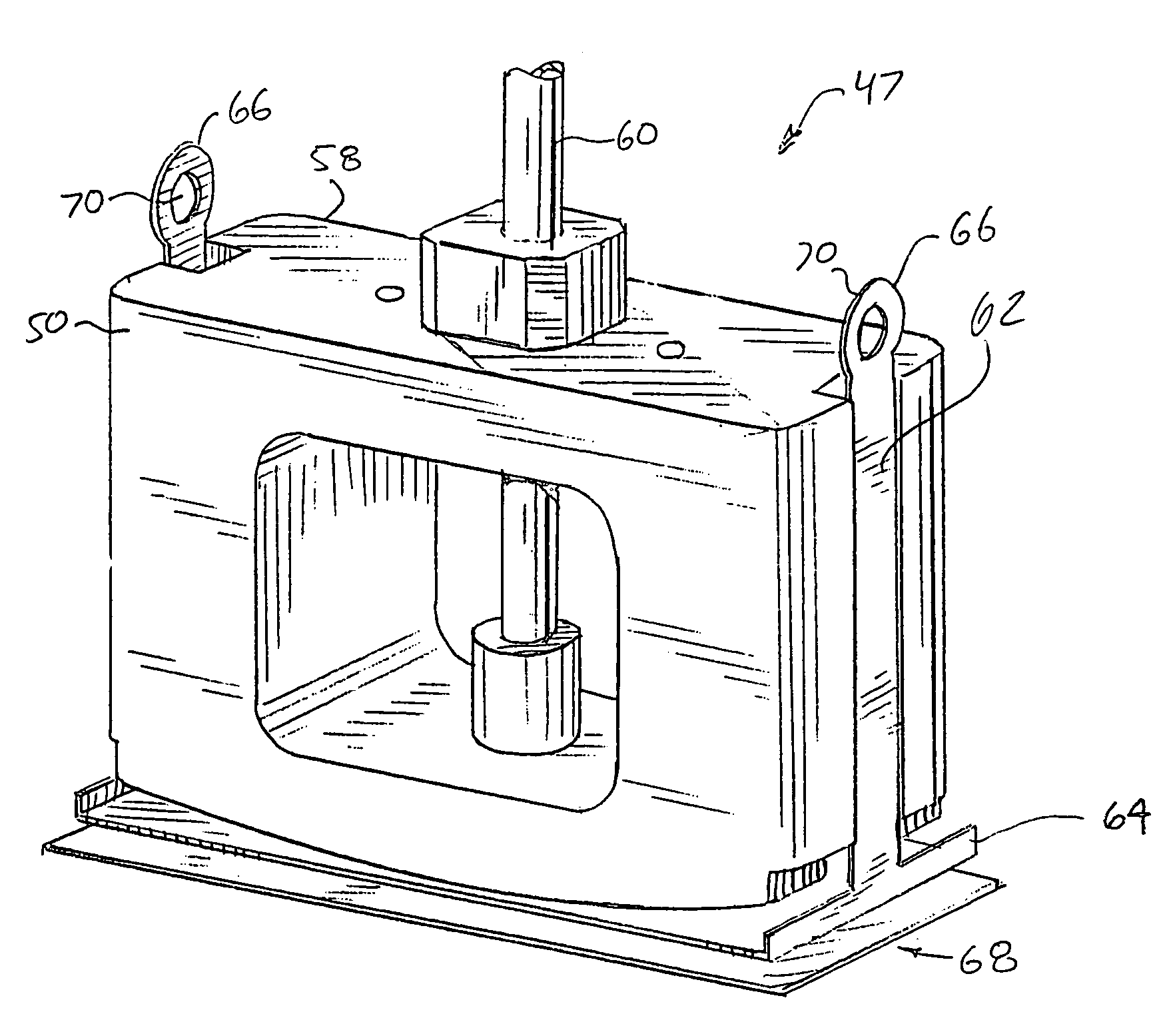
ActiveUS7155316B2Minimize patient riskComplete efficientlyProgramme-controlled manipulatorEndoscopesMicroscopic observationDisplay device
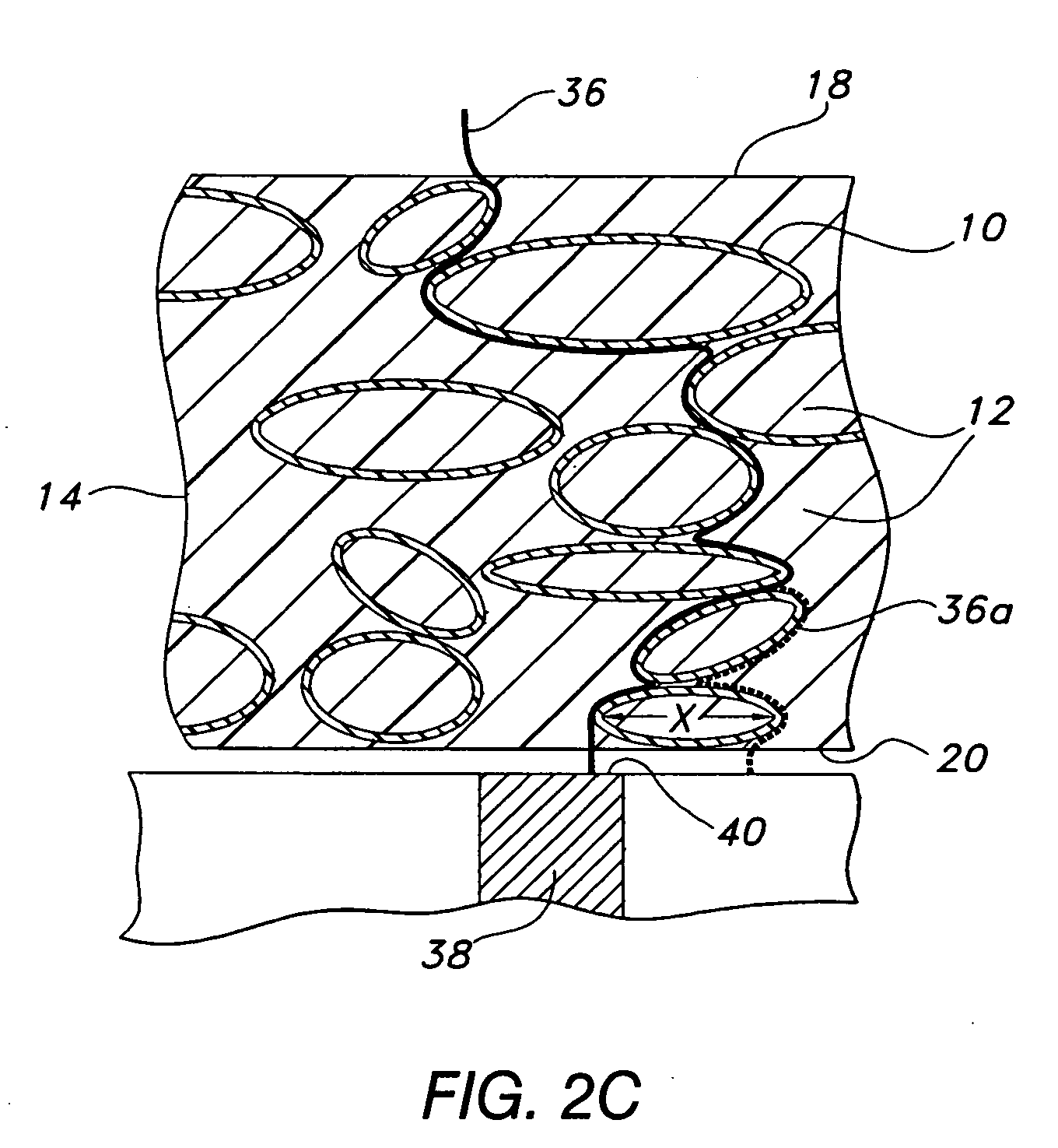
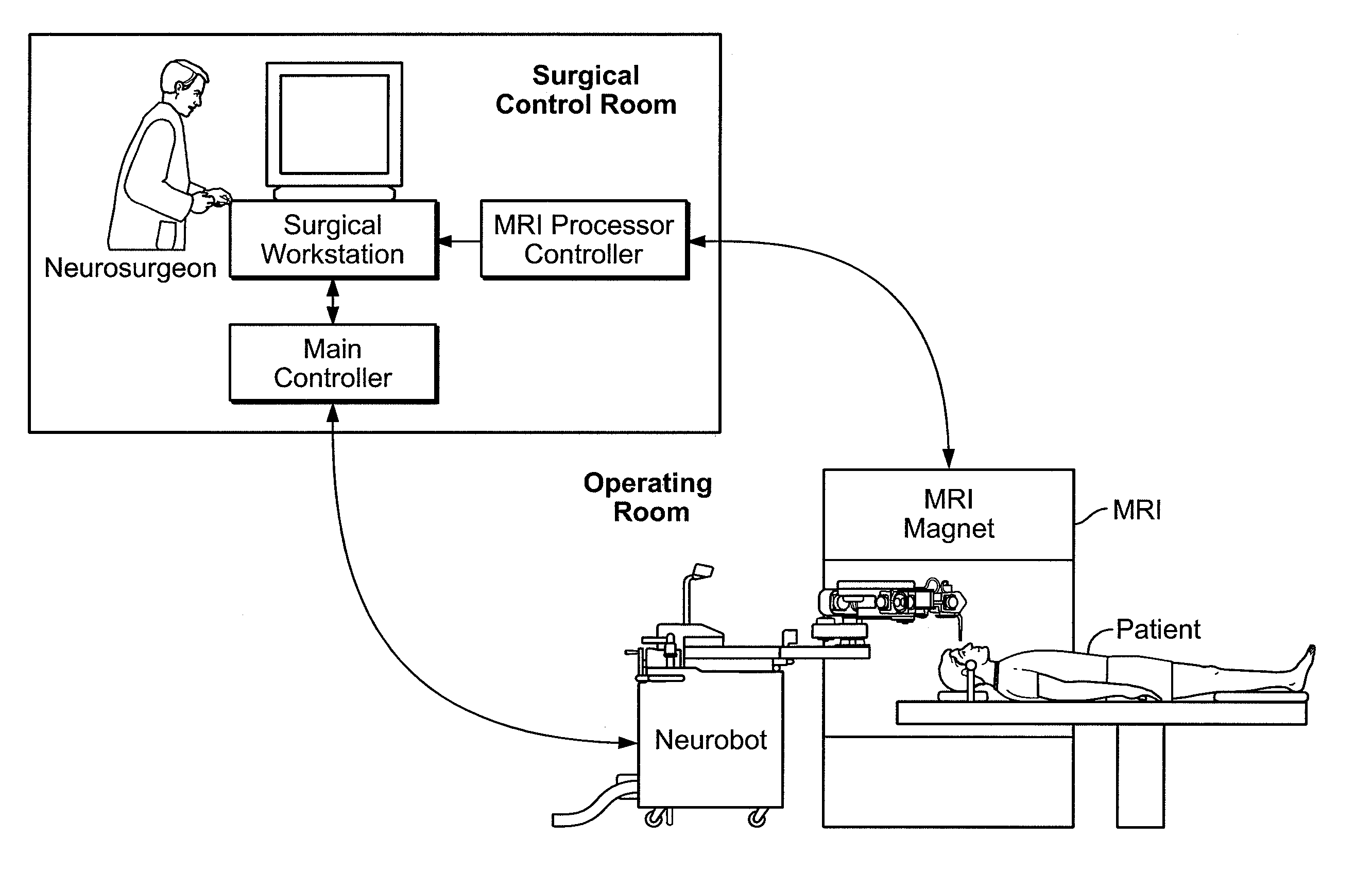
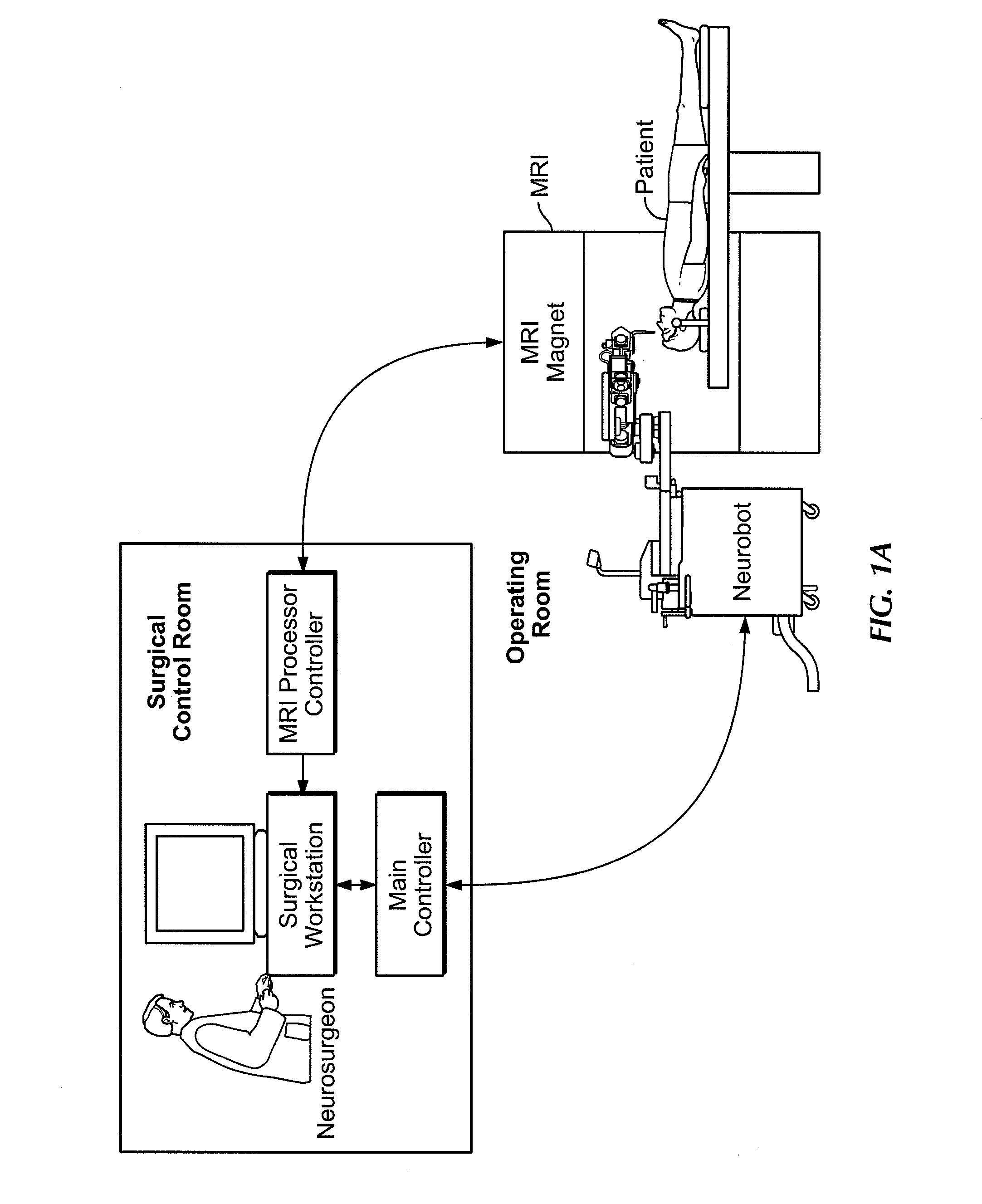
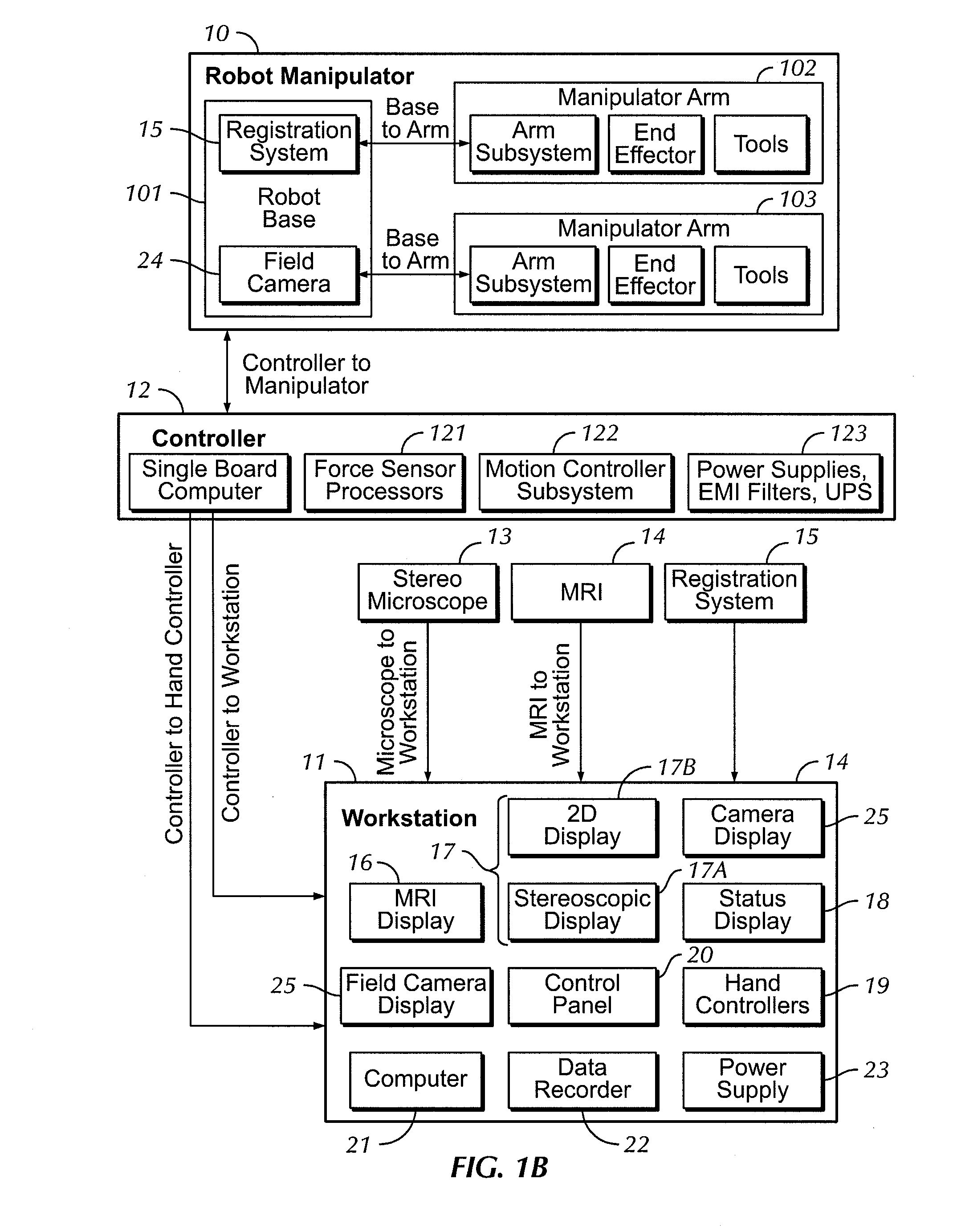
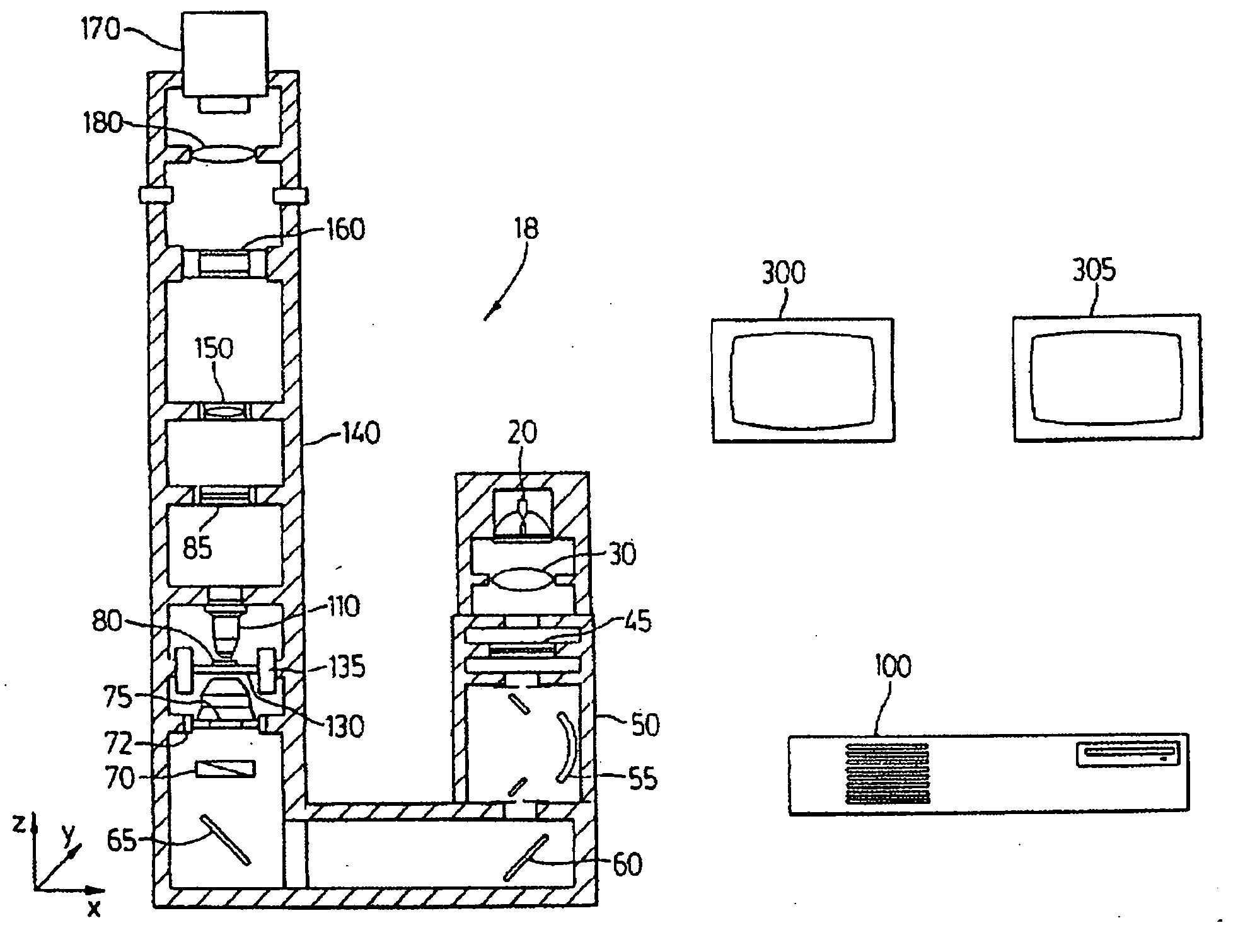
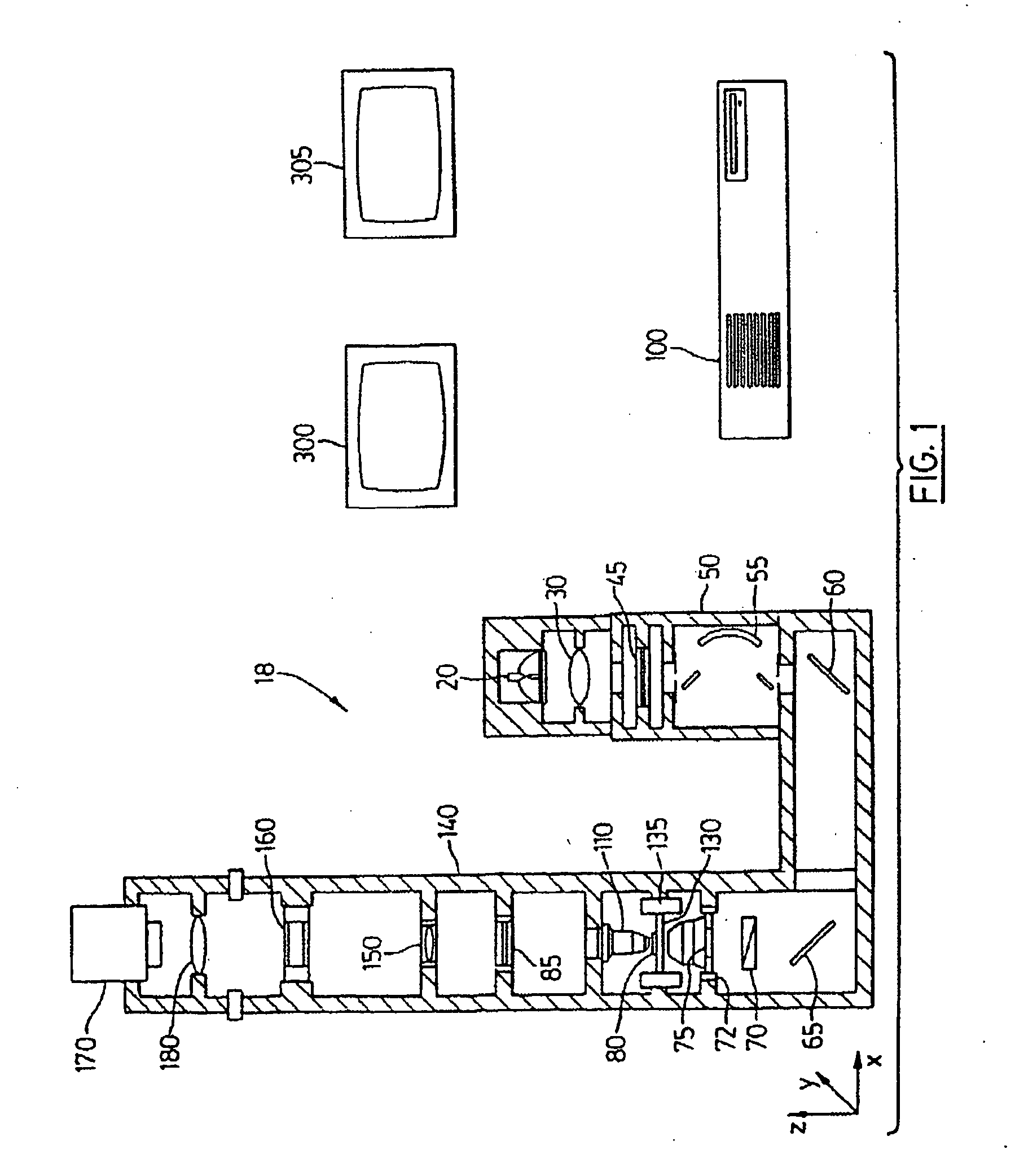
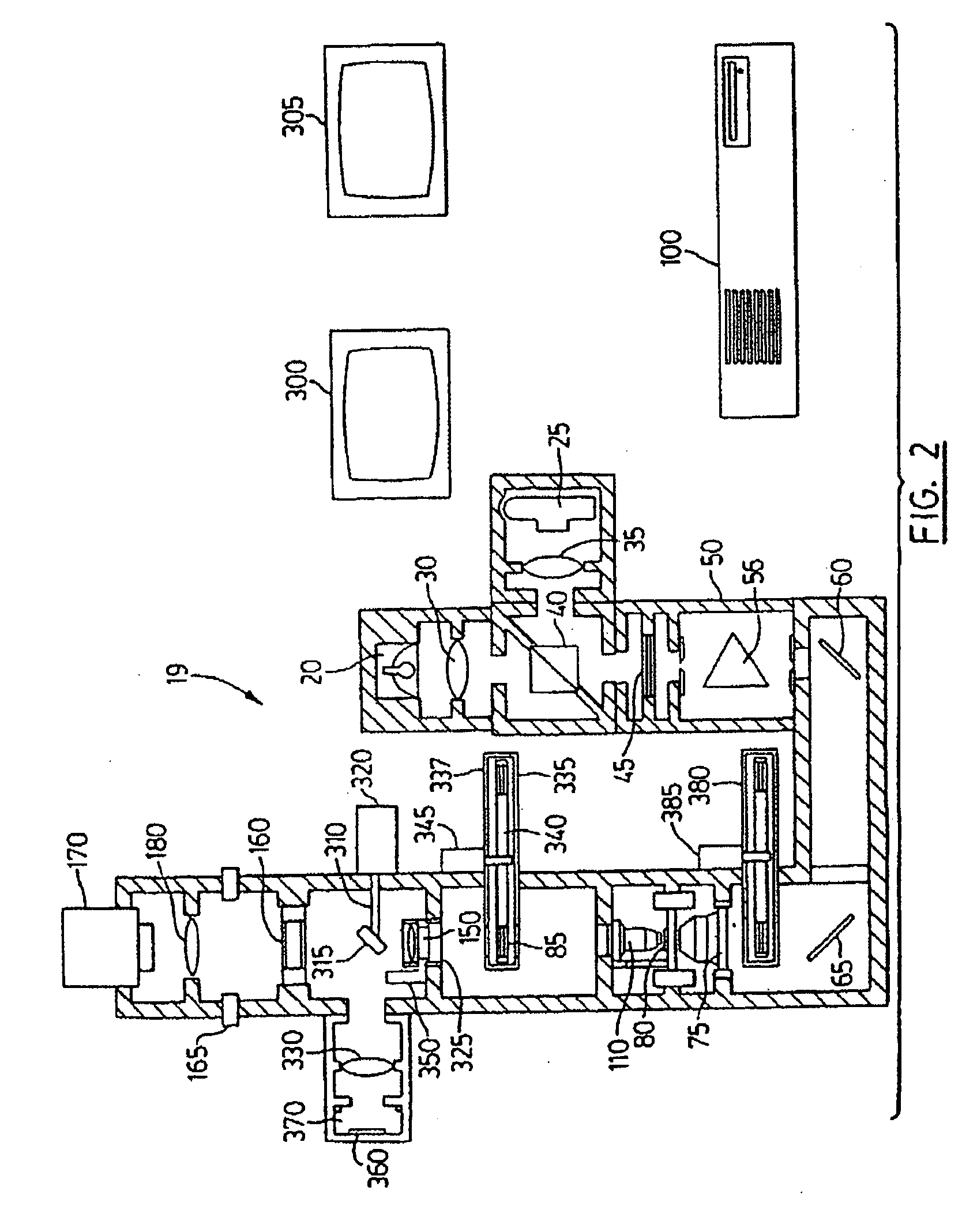
A robot system for use in surgical procedures has two movable arms each carried on a wheeled base with each arm having a six of degrees of freedom of movement and an end effector which can be rolled about its axis and an actuator which can slide along the axis for operating different tools adapted to be supported by the effector. Each end effector including optical force sensors for detecting forces applied to the tool by engagement with the part of the patient. A microscope is located at a position for viewing the part of the patient. The position of the tool tip can be digitized relative to fiducial markers visible in an MRI experiment. The workstation and control system has a pair of hand-controllers simultaneously manipulated by an operator to control movement of a respective one or both of the arms. The image from the microscope is displayed on a monitor in 2D and stereoscopically on a microscope viewer. A second MRI display shows an image of the part of the patient the real-time location of the tool. The robot is MRI compatible and can be configured to operate within a closed magnet bore. The arms are driven about vertical and horizontal axes by piezoelectric motors.
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
Techniques to improve polyurethane membranes for implantable glucose sensors
The invention provides an implantable membrane for regulating the transport of analytes therethrough that includes a matrix including a first polymer; and a second polymer dispersed throughout the matrix, wherein the second polymer forms a network of microdomains which when hydrated are not observable using photomicroscopy at 400× magnification or less. In one aspect, the homogeneous membrane of the present invention has hydrophilic domains dispersed substantially throughout a hydrophobic matrix to provide an optimum balance between oxygen and glucose transport to an electrochemical glucose sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Techniques to improve polyurethane membranes for implantable glucose sensors
ActiveUS20060086624A1Easy to makeImmobilised enzymesVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteGlucose sensors
The invention provides an implantable membrane for regulating the transport of analytes therethrough that includes a matrix including a first polymer; and a second polymer dispersed throughout the matrix, wherein the second polymer forms a network of microdomains which when hydrated are not observable using photomicroscopy at 400× magnification or less. In one aspect, the homogeneous membrane of the present invention has hydrophilic domains dispersed substantially throughout a hydrophobic matrix to provide an optimum balance between oxygen and glucose transport to an electrochemical glucose sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Microsurgical robot system
InactiveUS20070032906A1Enhanced Situational AwarenessReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorEndoscopesMicroscopic observationHorizontal axis
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
Color translating UV microscope
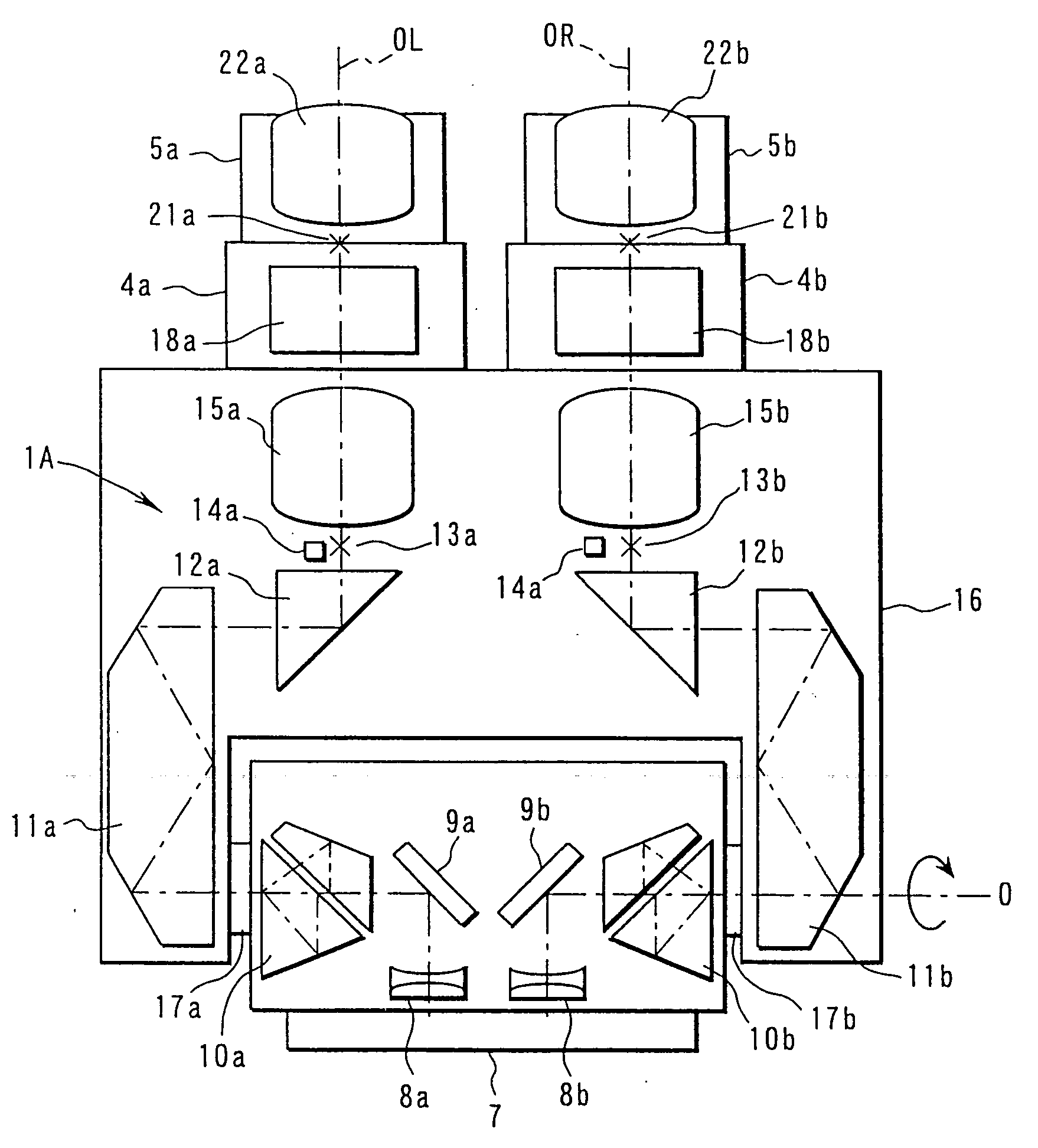
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
Operation microscope
InactiveUS20050020876A1Efficient executionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryMicroscopic observationNuclear medicine
There is disclosed an operation microscope in which an observing and displaying system of an operating instrument are selected, and an endoscope image for observing a dead angle of the microscope and a navigation image are selectively displayed in a microscope observation field, so that a tomographic image, three-dimensionally constructed image, and the like can be selectively displayed in a display screen in accordance with a treatment position displayed in a monitor or an observation position of the operation microscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Monolayer and/or Few-Layer Graphene On Metal or Metal-Coated Substrates
InactiveUS20100255984A1Easy to disassembleMaterial nanotechnologyParticle separator tubesHigh concentrationIn plane
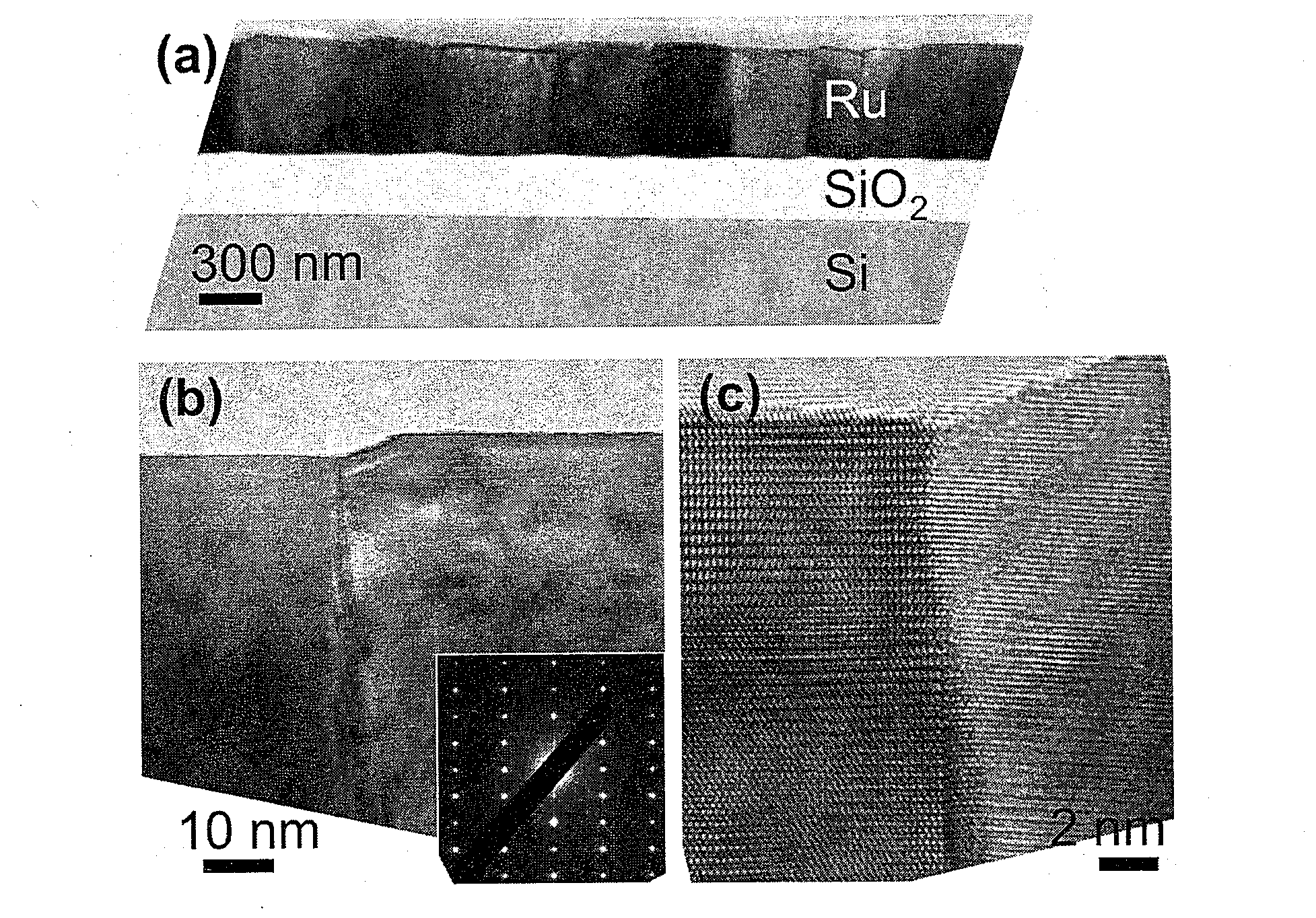
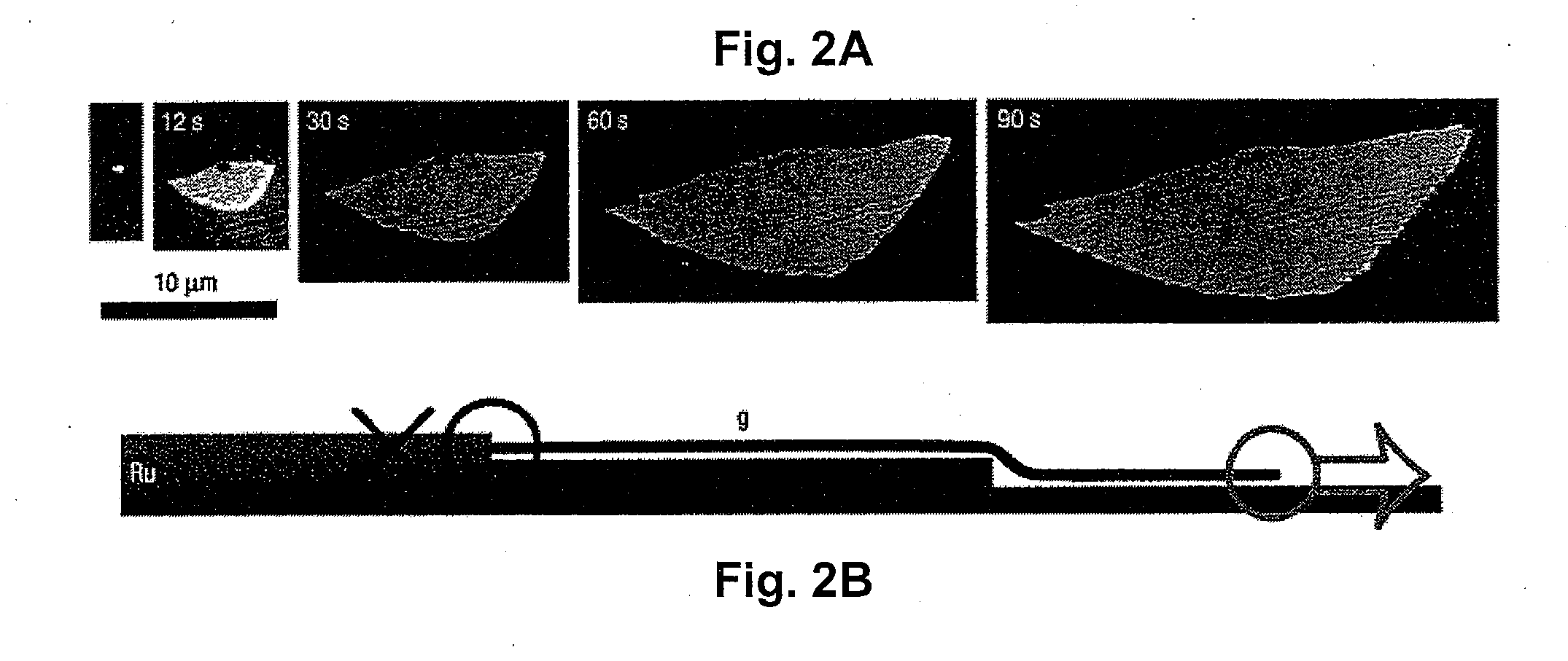
Graphene is a single atomic layer of sp2-bonded C atoms densely packed into a two-dimensional honeycomb crystal lattice. A method of forming structurally perfect and defect-free graphene films comprising individual mono crystalline domains with in-plane lateral dimensions of up to 200 μm or more is presented. This is accomplished by controlling the temperature-dependent solubility of interstitial C of a transition metal substrate having a suitable surface structure. At elevated temperatures, C is incorporated into the bulk at higher concentrations. As the substrate is cooled, a lowering of the interstitial C solubility drives a significant amount of C atoms to the surface where graphene islands nucleate and gradually increase in size with continued cooling. Ru(0001) is selected as a model system and electron microscopy is used to observe graphene growth during cooling from elevated temperatures. With controlled cooling, large arrays of macroscopic single-crystalline graphene domains covering the entire transition metal surface are produced. As the graphene domains coalesce to a complete layer, a second graphene layer is formed, etc. By controlling the interstitial C concentration and the cooling rate, graphene layers with thickness up to 10 atomic layers or more are formed in a controlled, layer-by-layer fashion.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Operation microscope
InactiveUS8221304B2Efficient executionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryOperation microscopesMicroscopic observation
There is disclosed an operation microscope in which an observing and displaying system of an operating instrument are selected, and an endoscope image for observing a dead angle of the microscope and a navigation image are selectively displayed in a microscope observation field, so that a tomographic image, three-dimensionally constructed image, and the like can be selectively displayed in a display screen in accordance with a treatment position displayed in a monitor or an observation position of the operation microscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Marking diamond
InactiveUS6187213B1Avoid overall overheatingAvoid necessityBranding equipmentPolycrystalline material growthMicroscopic observationGemstone
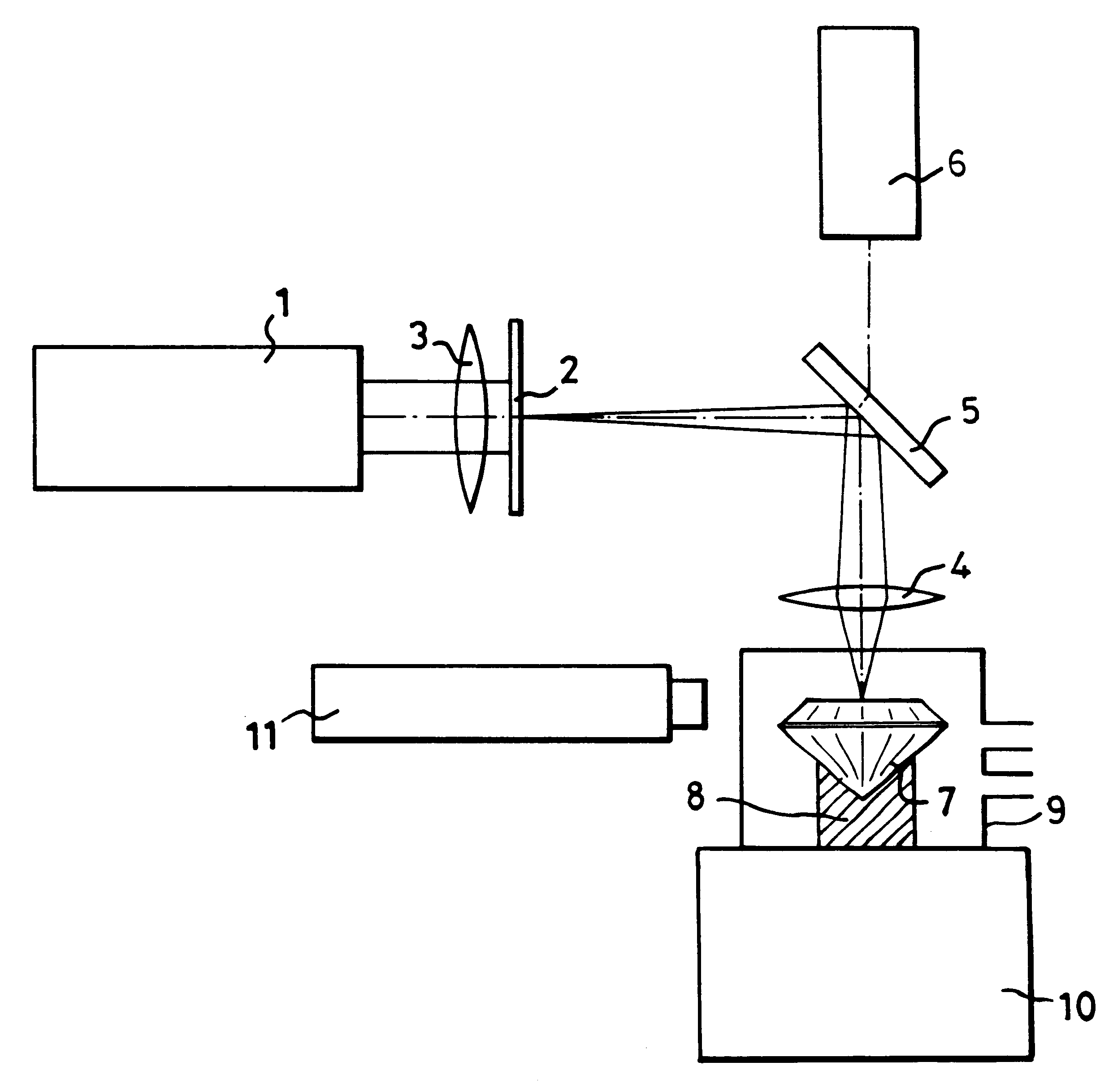
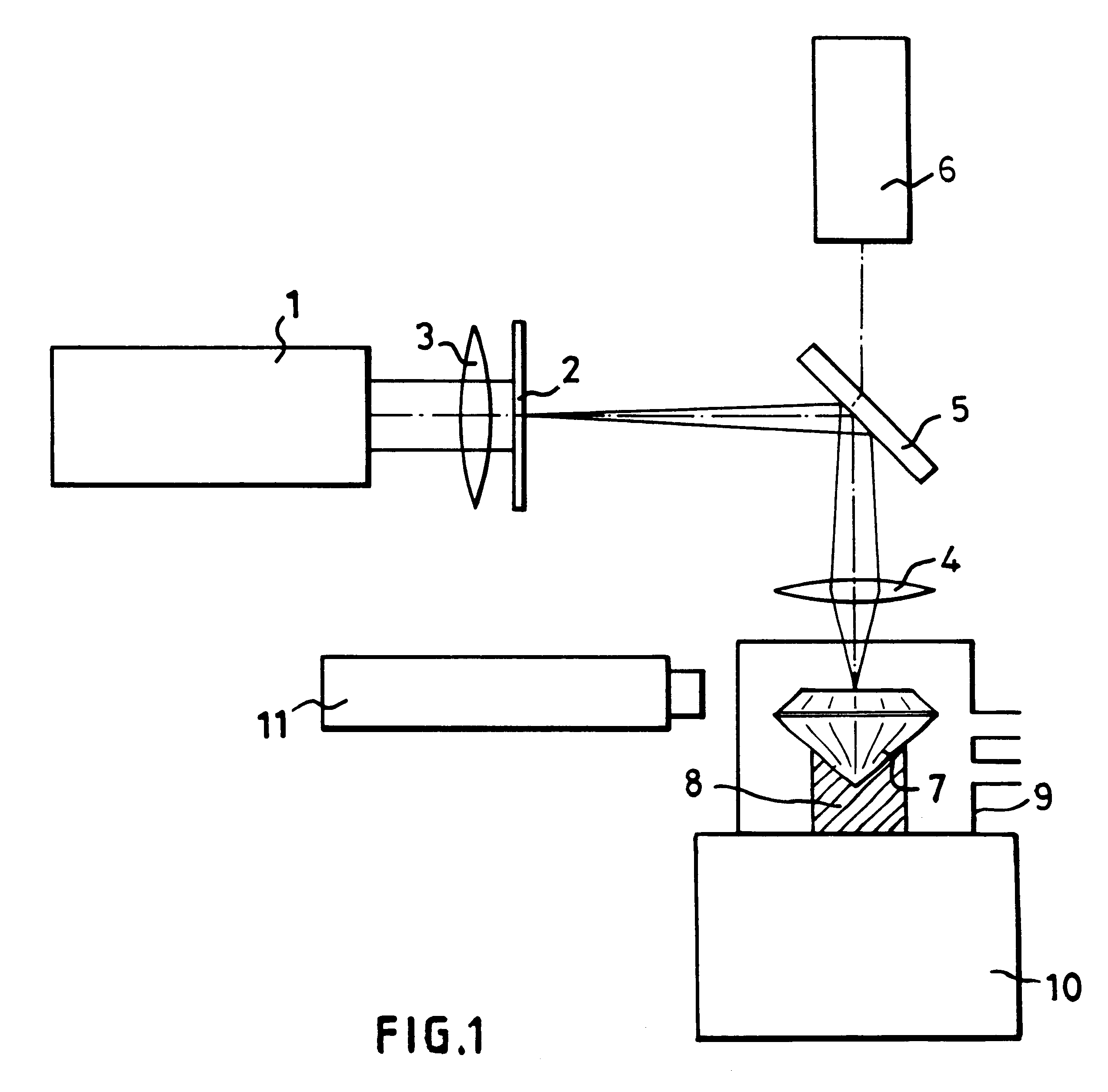
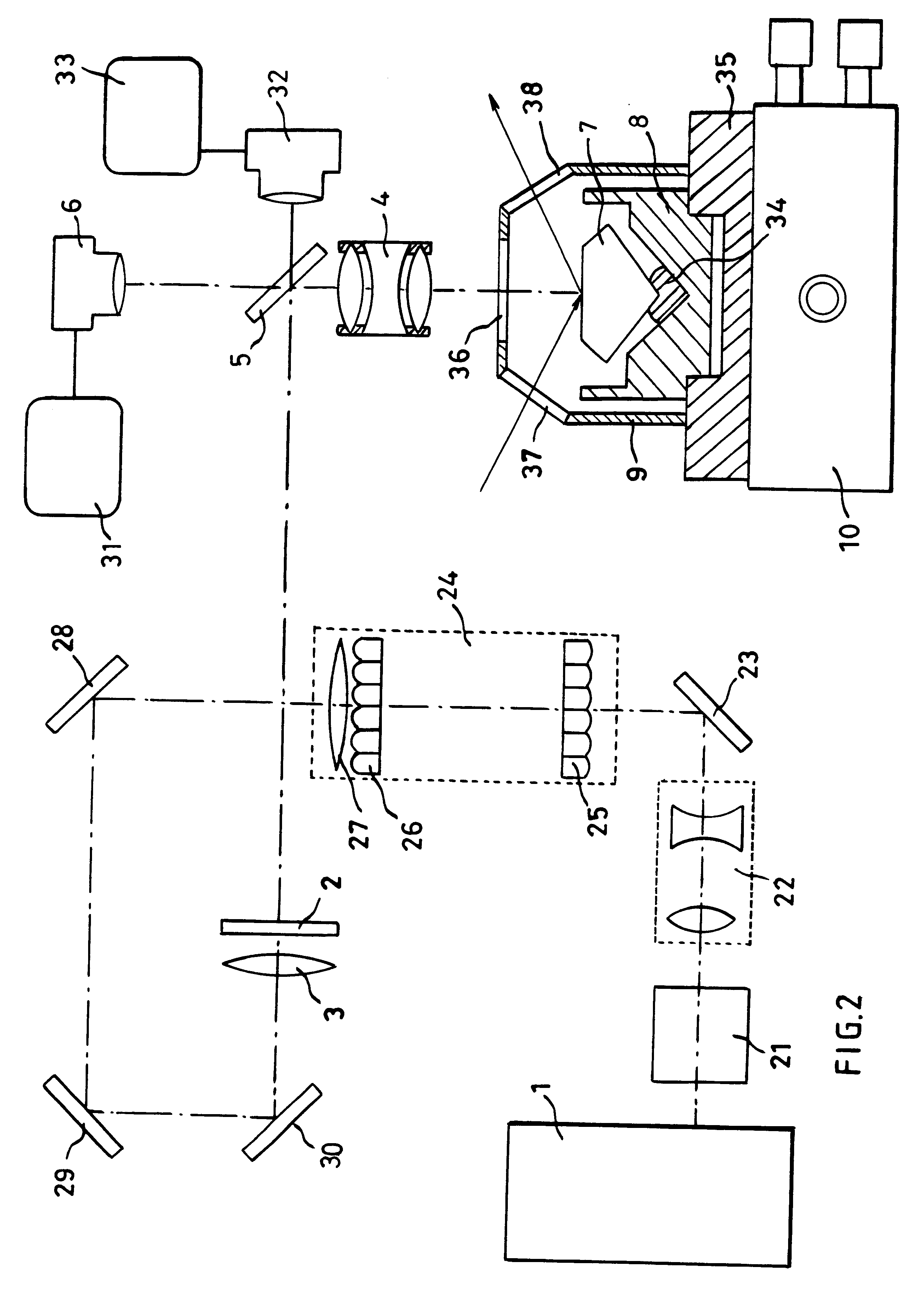
In order to produce on the table of a diamond gemstone (7), an information mark which is invisible to the naked eye using a x10 loupe, an ultraviolet laser (1) having a wavelength of 193 nm is used in association with a mask (2) to irradiate the surface of the stone (7) at a fluence of less than 2 J / cm2 per pulse and with not fewer than 100 pulses, in the presence of air which reacts with the diamond (7) and causes the mark to be formed without any darkening which is visible when viewing using a microscope.
Owner:GERSAN ESTAB
Modified graphite particles derived from scaly natural ones, production thereof and secondary battery
InactiveUS6139990APigmenting treatmentNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsMicroscopic observationX-ray
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Capturing of cell fluid and analysis of its components under observation of cells and instruments for the cell fluid capturing and the analysis
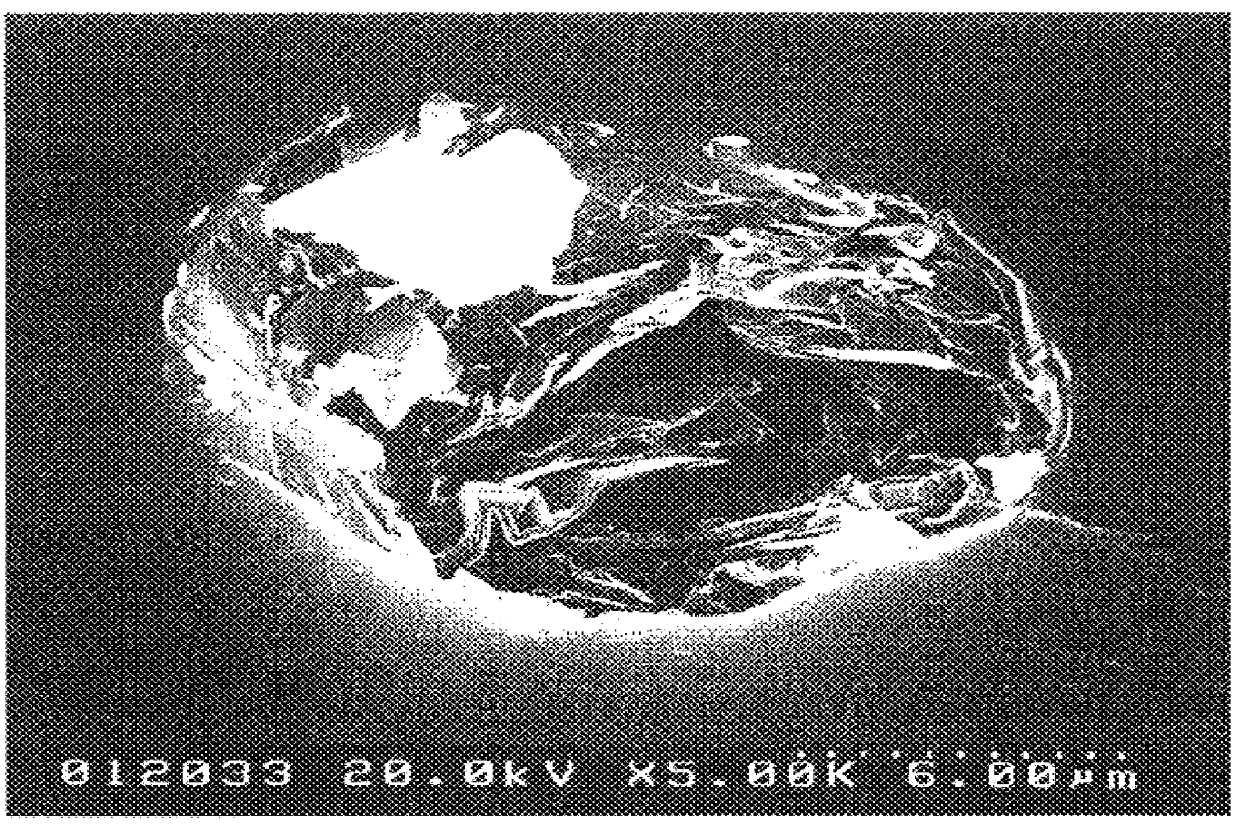
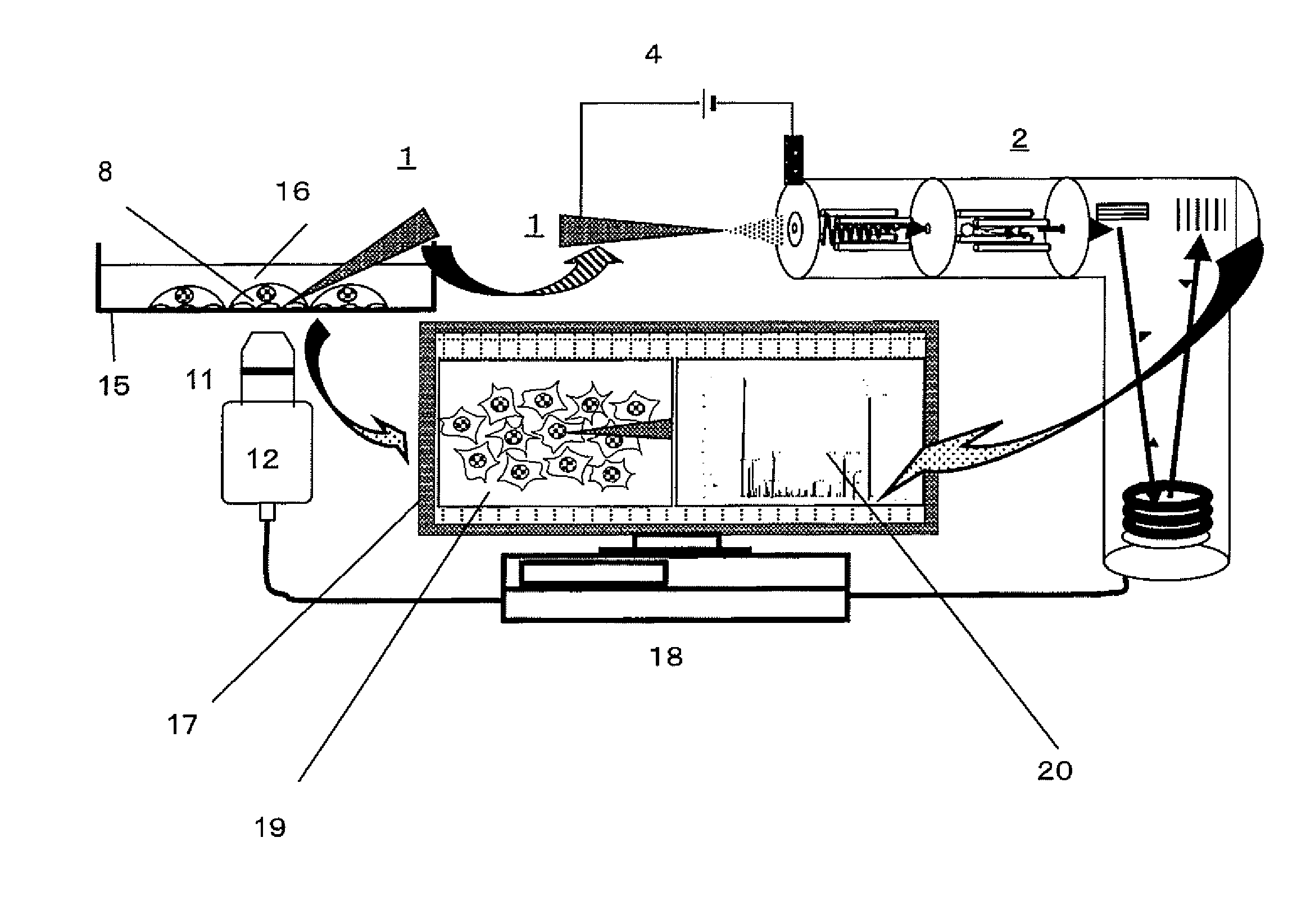
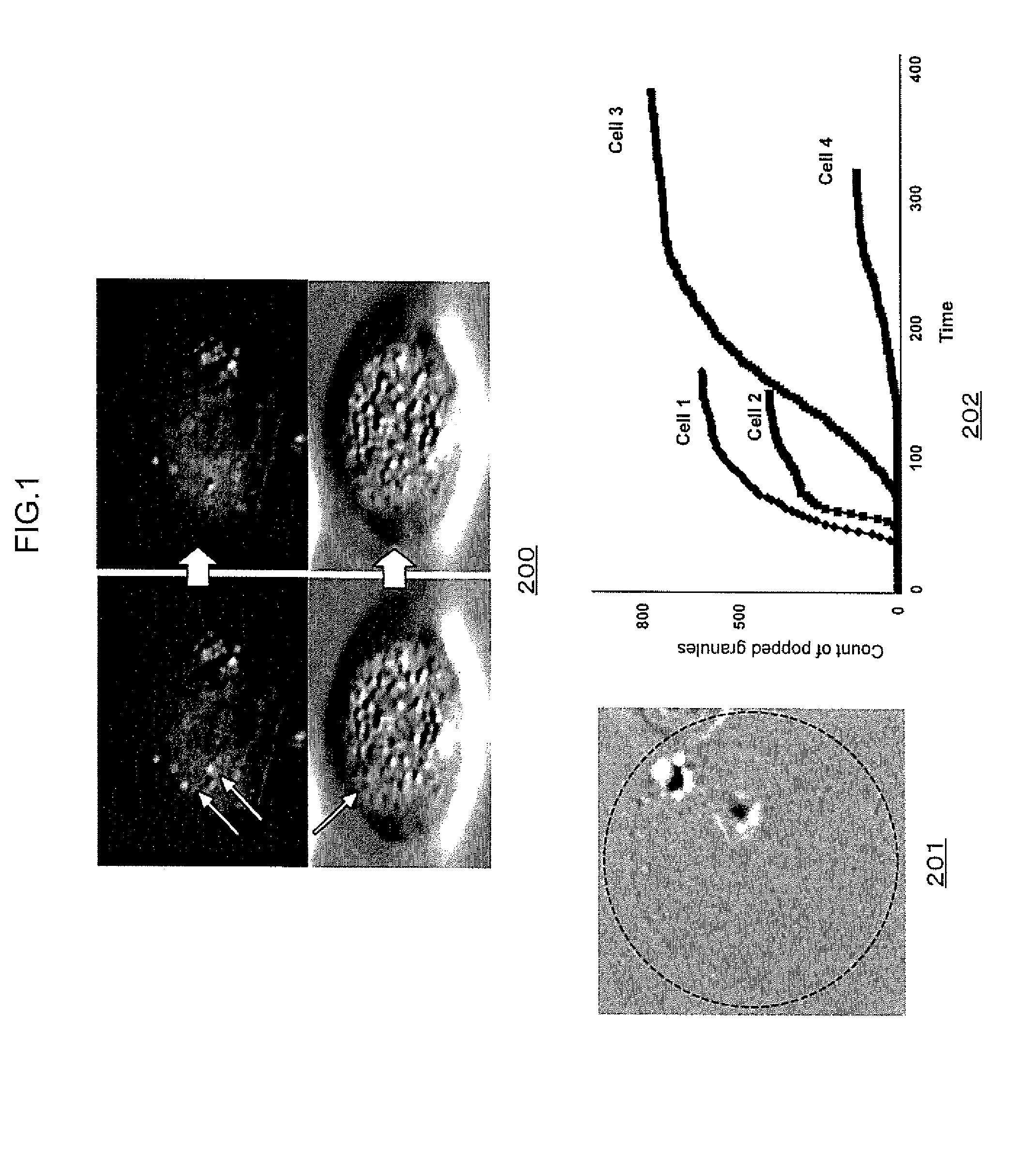
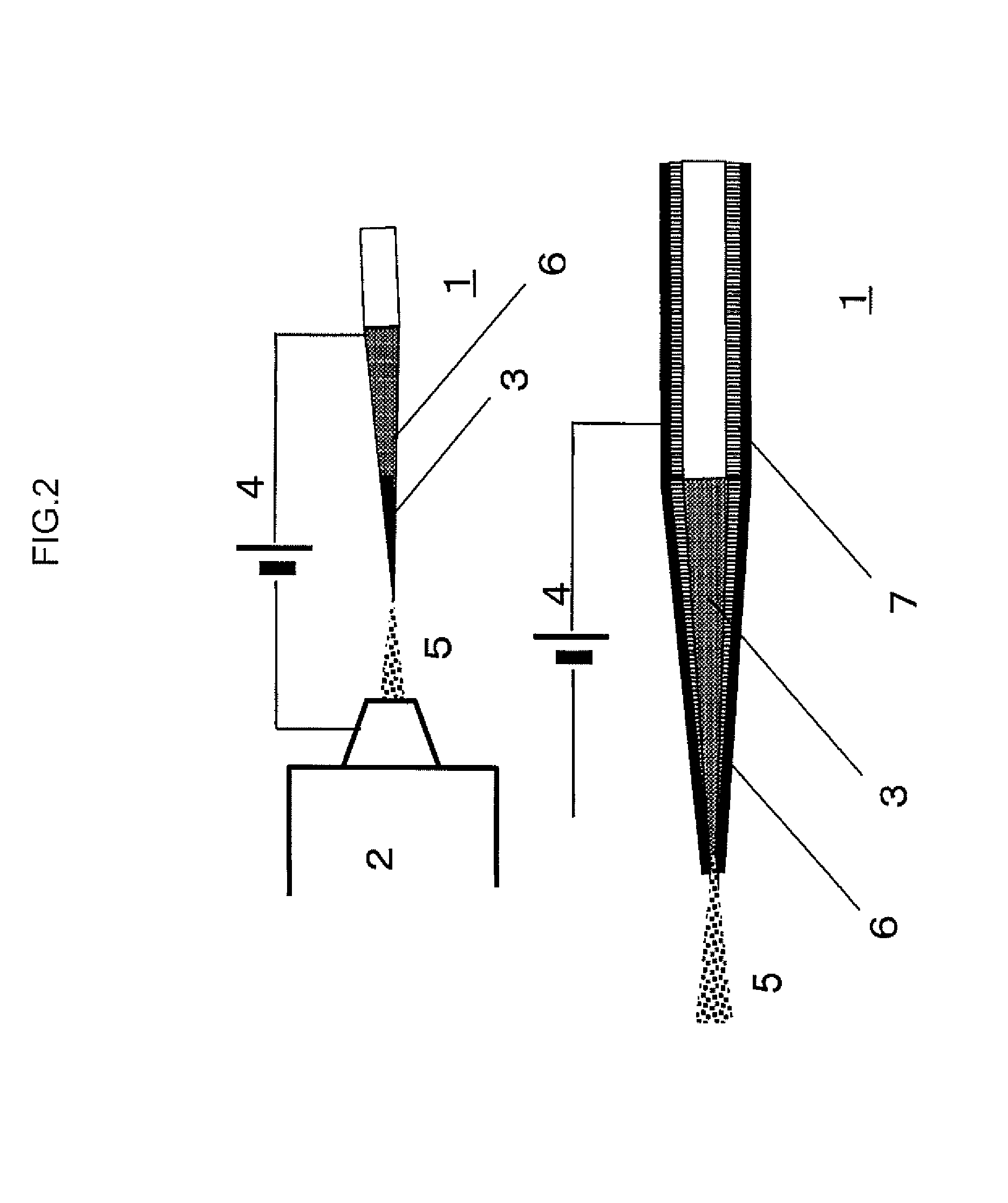
ActiveUS20140315237A1Clarify causeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentMicroscopic observation
A method captures cellular components from a single cell and performs mass spectrometry on the components. The method includes inserting a nanospray ionization capillary tip into a specific region of the cell under observation with a microscope. The nanospray ionization capillary tip can include a filament in the interior. The method further includes capturing the cellular components of the specific region of the cell into the opening of the nanospray ionization capillary tip and keeping the components at the nanospray ionization capillary tip, supplying an ionization supporting solvent from a back-end of the nanospray ionization capillary tip, applying an electric field between a sample inlet of a mass spectrometer and the nanospray ionization capillary tip, whereby nanospray ionization to the cellular components is implemented, and performing the mass spectrometry on the cellular components captured at the nanospray ionization capillary tip.
Owner:HUMANIX
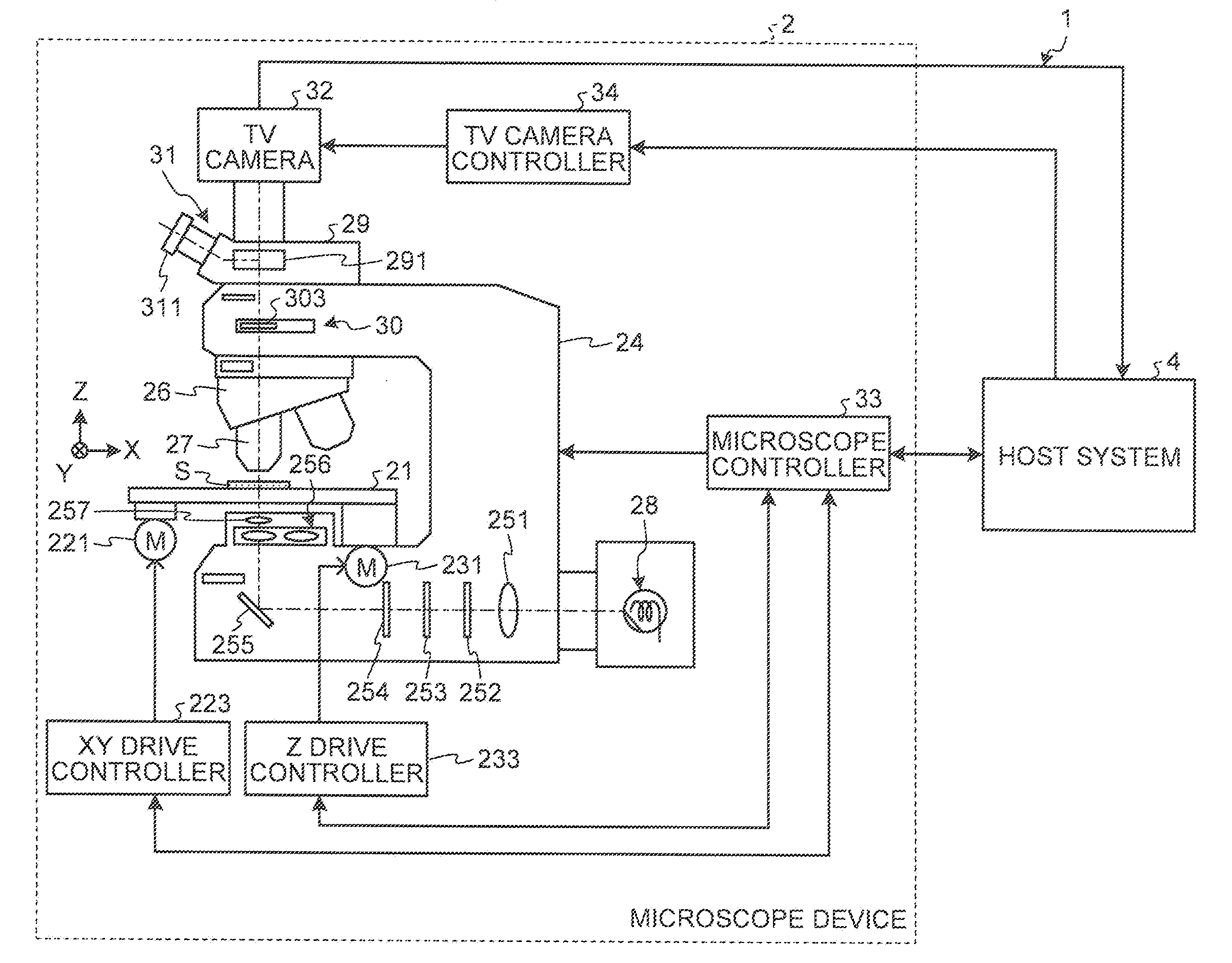
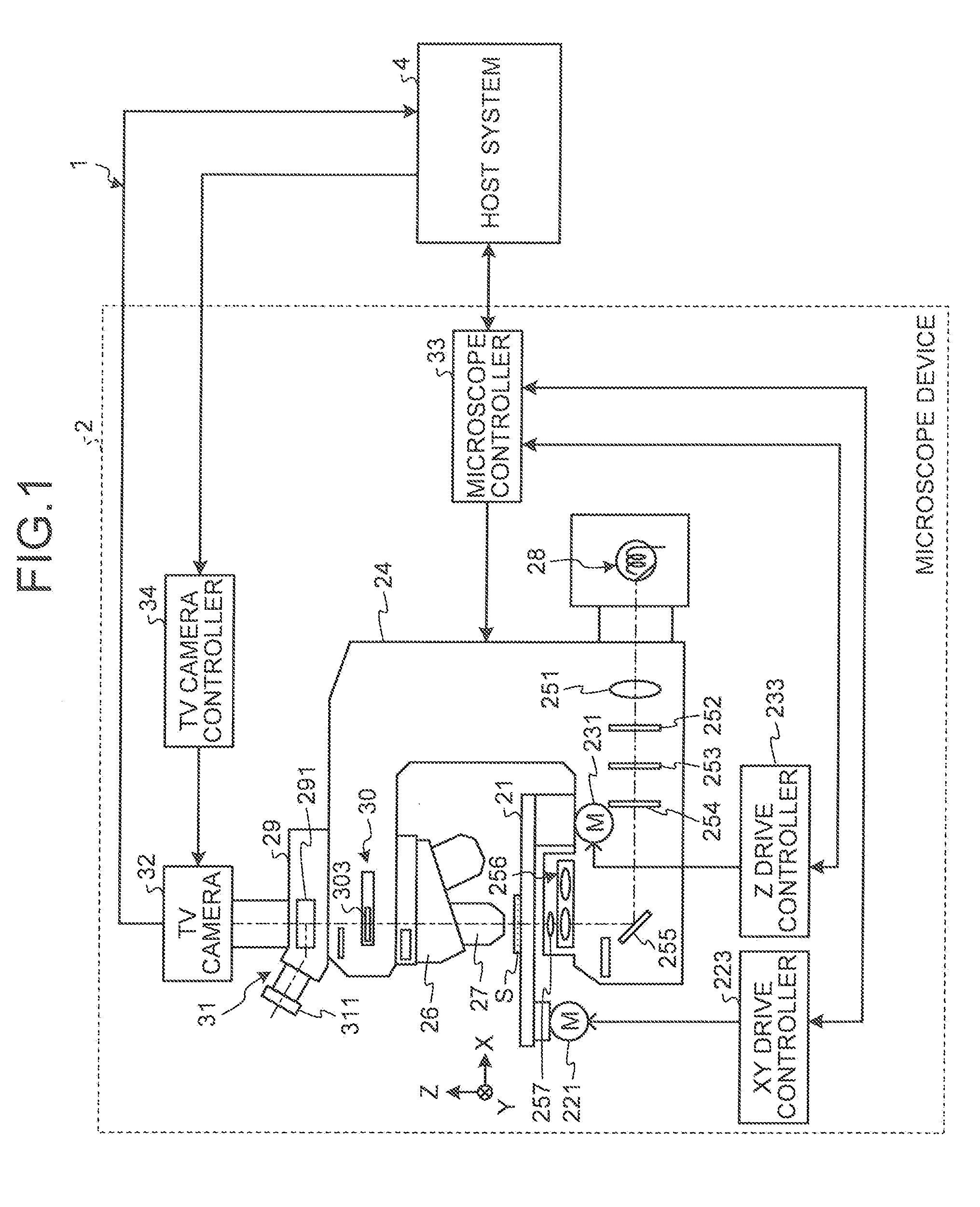
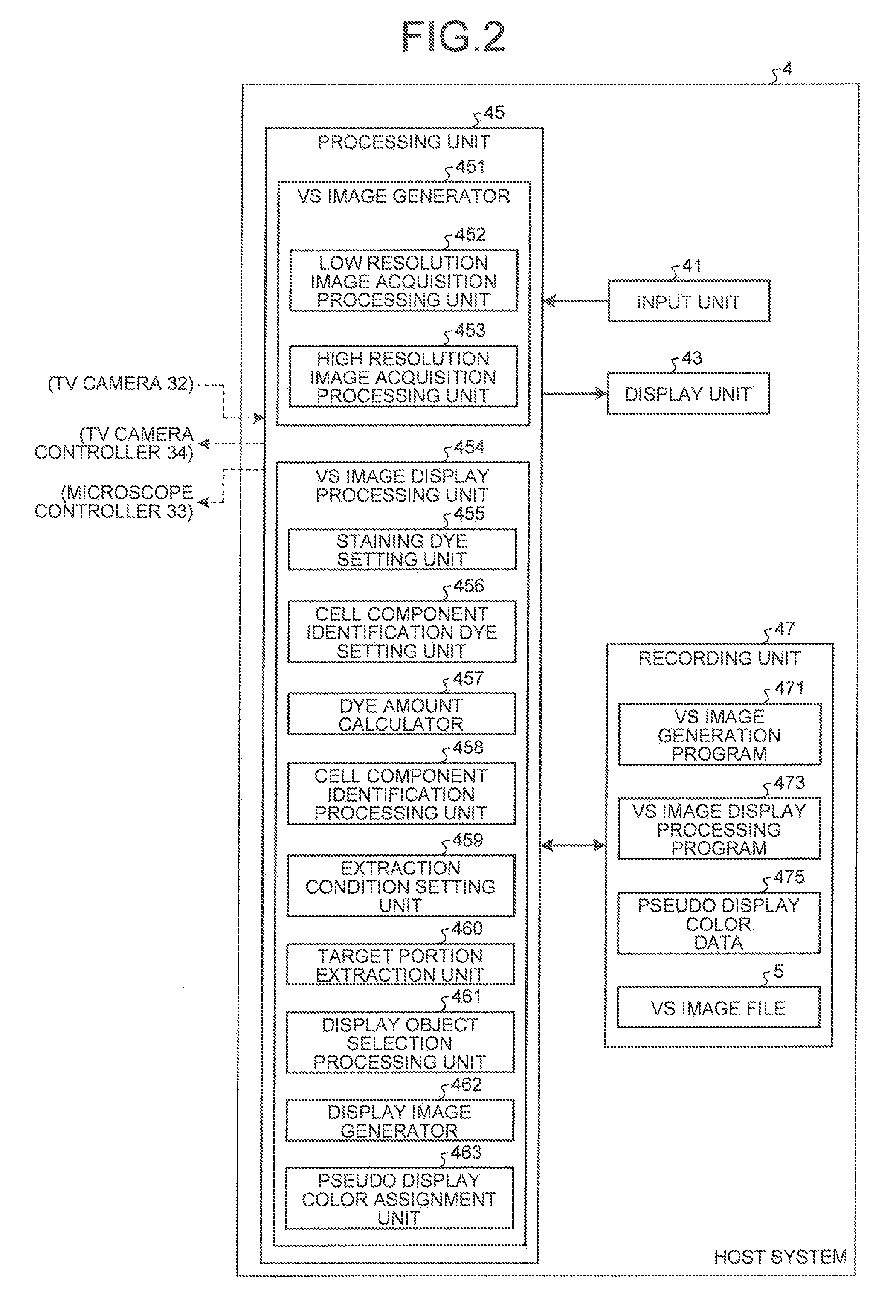
Microscope System, Specimen Observation Method, and Computer Program Product
ActiveUS20110212486A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscopic observationMicroscope
A microscope system includes an acquisition unit that obtains a specimen image acquired by capturing the specimen stained by an element identification dye that visualizes a predetermined cell constituent element and a molecule target dye that visualizes a predetermined target molecule by using a microscope; a dye amount unit that obtains dye amounts of the element identification dye and the molecule target dye that stain corresponding positions on the specimen for each pixel of the image; an element area identification unit that identifies an area of the cell constituent element based on the dye amount of the element identification dye; a condition setting unit that sets the presence or absence of the predetermined target molecule on the cell constituent element as a condition; and an extraction unit that extracts an area of a target portion that satisfies the condition based on the dye amount of the molecule target dye.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP +1
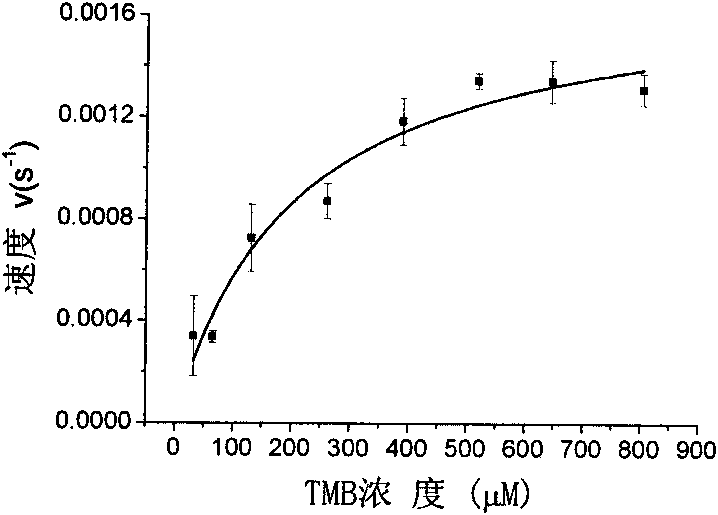
Method for applying gold nanoparticles mimetic enzyme in biological detection
InactiveCN101706504AEasy to synthesizeDimensionally stableMaterial analysisMicroscopic observationHorse radish peroxidase
A method for applying gold nanoparticles mimetic enzyme in biological detection adopts gold nanoparticles instead of horse radish peroxidase (HRP) in the biological detection. The detection comprises the following steps: coupling the gold nanoparticles and a specific molecular probe to construct a specific nano-probe; performing specific binding between the nano-probe and the corresponding target molecule to be detected; developing with coloring solution containing peroxide and hydrogen-donating substrate, and measuring absorbance or performing microscopic observation so as to realize the qualitative and quantitative detection of the target molecule. The method belongs to the nanometer material and biomedical nanometer technical field. In the method, the size of the used gold nanoparticles mimetic enzyme is 1-1000nm, the gold nanoparticles mimetic enzyme can imitate HRP to catalyze peroxide and hydrogen-donating substrate to perform a color development reaction, and the enzymatic activity increases with the decrease of the size of the gold nanoparticles. The method of the invention uses the gold nanoparticles to label antibody and other biological molecules to build the similar enzyme labeled antibody and other diagnose preparations, thus having extensive application value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Microscope Stage and Microscope Observing Unit
InactiveUS20090141345A1Reduce humidityTemperature controlHeating or cooling apparatusMicroscopesMicroscopic observationEngineering
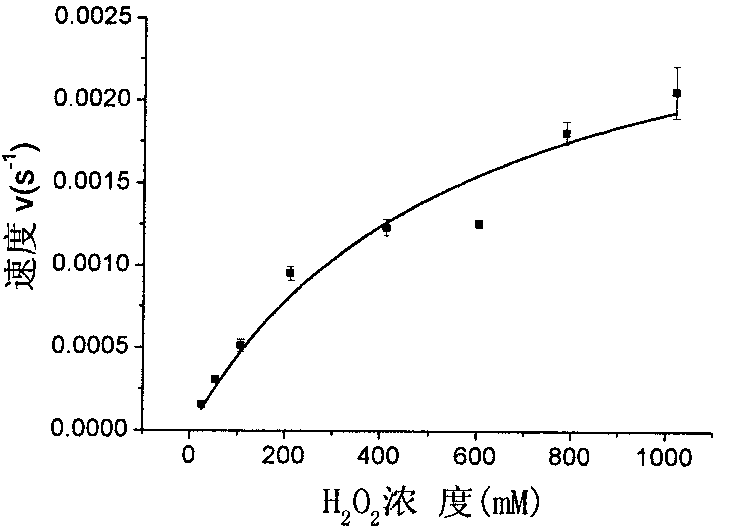
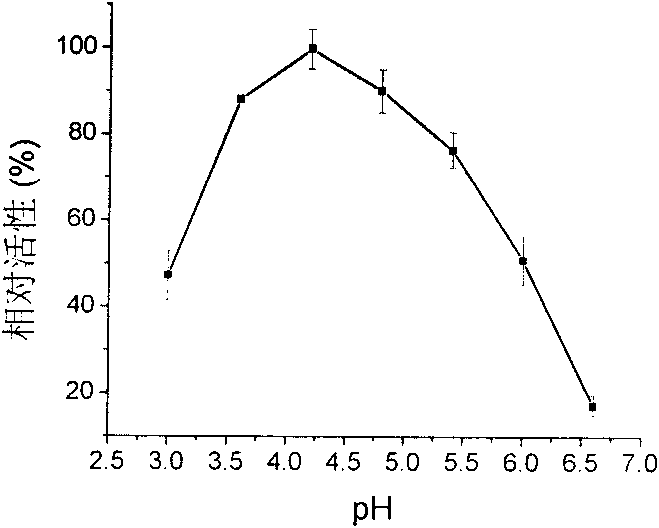
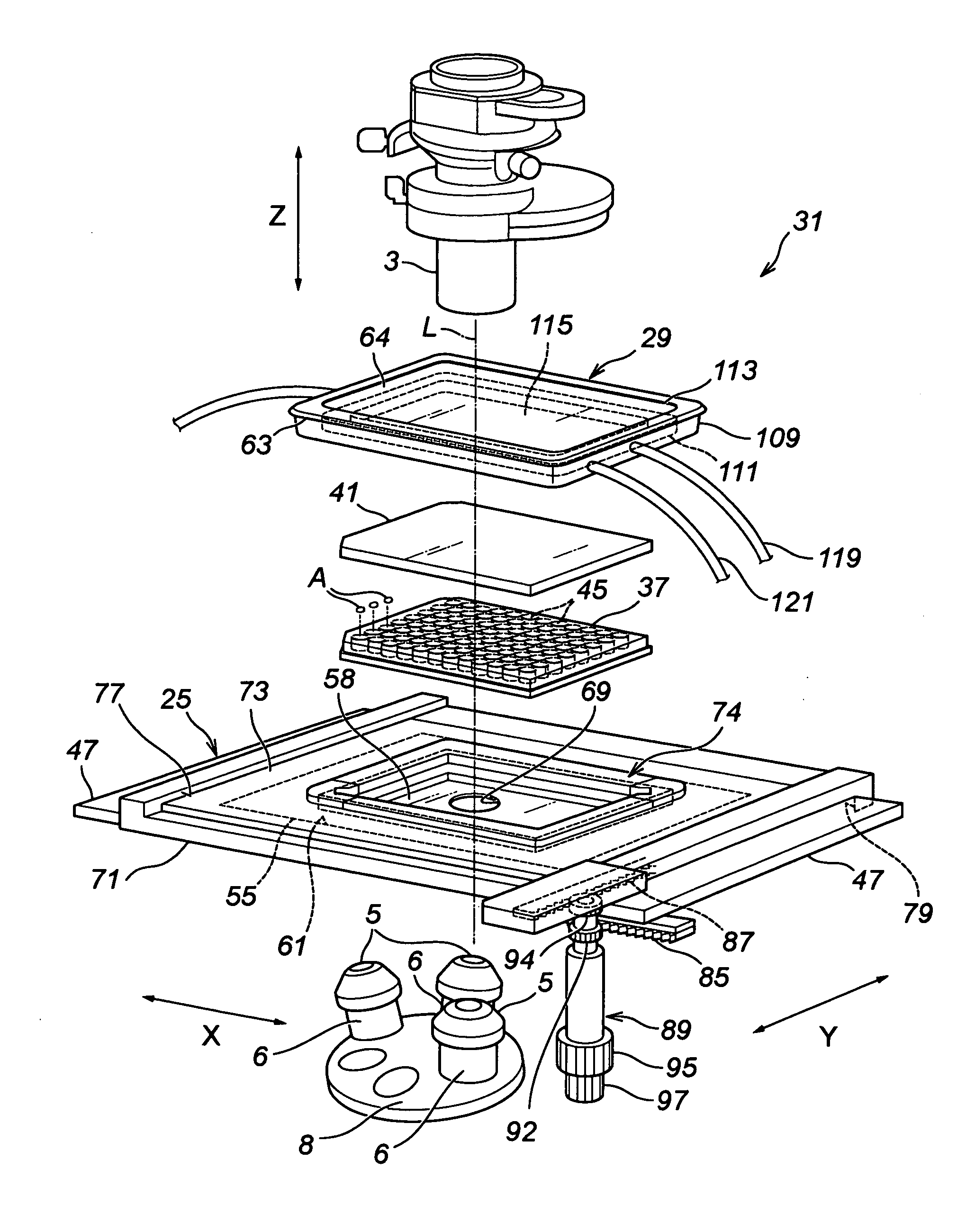
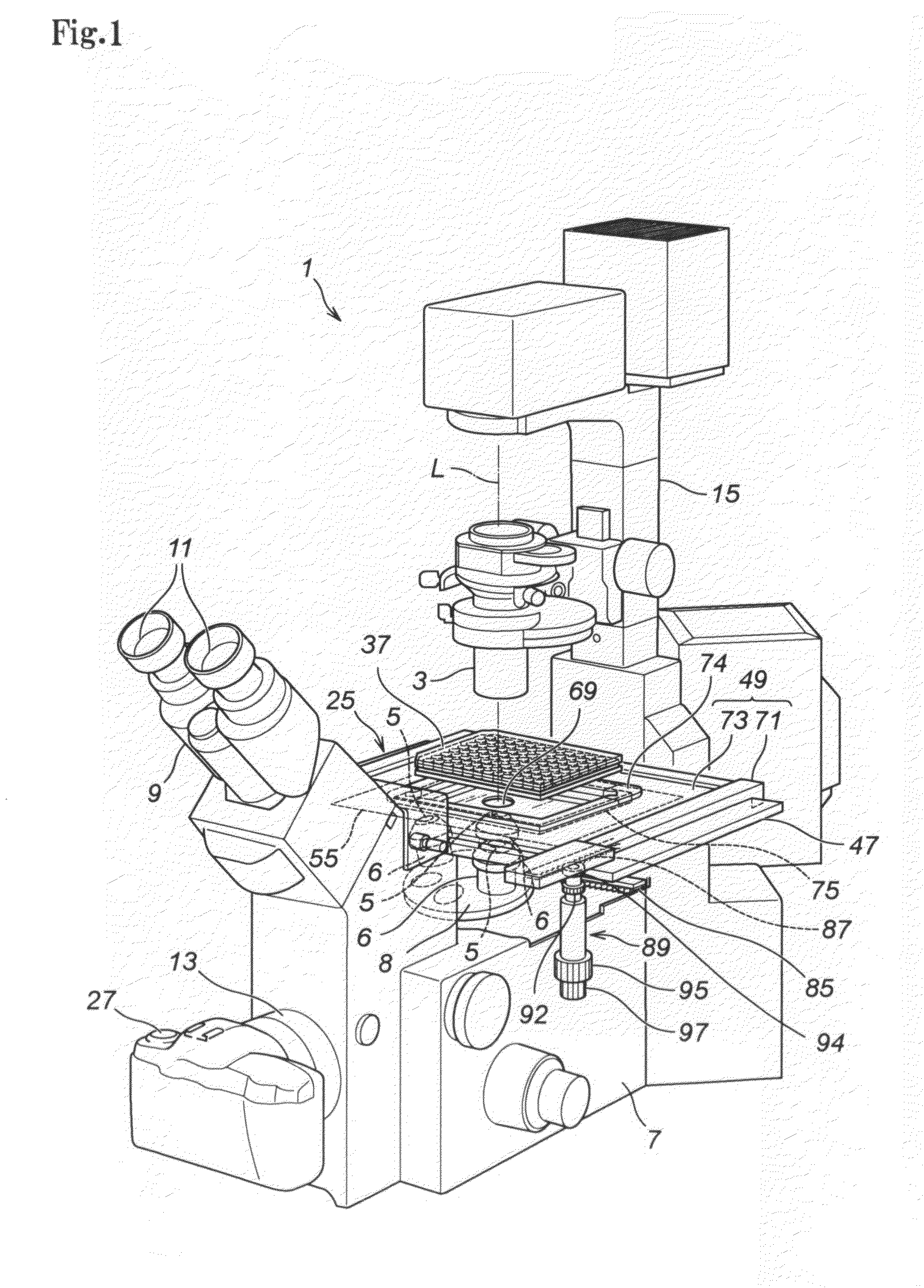
A microscope stage capable of always heating the entire culture vessel even when the culture vessel is moved in two-dimensional directions, and allowing an object lens and a condenser even in a high-power microscope to approach an object of observation such as a cell until they come into focus. A heating unit (58) faces a well plate (37) on a drive base (49) even when the drive base (49) is driven to any position in two-dimensional directions. Therefore, all the cells A in the small compartments (45) of the well plate (37) are always heated. Since the microscope stage (25) is constituted such that a lower-side base (71) houses an upper-side base (73) and a fixed base (47) in recessed portions, its thickness is considerably small. Accordingly, an object lens (5) and a condenser (3) can approach close to the cells A. Therefore, it is possible for high-power object lens (5) and condenser (3) to focus on the cells A.
Owner:TOKAI HITKK
Visual simulation shale micro-crack plugging capacity test system and method
ActiveCN103485762AIntuitive visual macro analysisImprove general applicabilityConstructionsBorehole/well accessoriesMicroscopic observationMicroscopic scale
The invention relates to a visual simulation shale micro-crack plugging capacity test system and a visual simulation shale micro-crack plugging capacity test method. Displacement evaluation experiment is performed on a single or combined micro-crack rock sample by a solution or a drilling fluid which contains the plugging agents with different concentrations and different types at different experiment conditions, such as pressure differences and times, indexes, such as the invasion depth, are compared, the formation conditions of inner mud cakes in drilling are directly described, and microscopic observation and analysis are performed on percolation substances invade into the micro-cracks by utilizing amplification imaging instruments, such as a high-definition microscope, so that the plugging mechanisms and the effects of various drilling fluid plugging agents and drilling fluids are analyzed and researched intuitively and microscopically, a proper drilling fluid plugging agent is selected preferably, a drilling fluid system formula is optimized, the problem about the experimental conditions that the visual simulation evaluation cannot be performed on shale micro-crack plugging in the past is solved, and a new evaluation experimental research means is provided for related research and production in the technical field of fractured shale strata borehole wall stability in petroleum engineering.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Microscope magnification sensor
InactiveUS20050094262A1Maintain positionLaser surgeryDiagnosticsMicroscopic observationDisplay device
Devices, systems and methods for scaling the size and / or position of a marker on a magnified image of an object. In preferred embodiments, the object is an eye that is undergoing laser eye surgery. The eye is viewed through a magnification system or microscope and an image of the eye is presented on a display. One or more markers are present on the image, each identifying a specific target location or landmark on the eye. When a desired magnification setting is selected, the image is scaled accordingly. In addition, one or more of the markers is scaled in size and / or position to reflect the magnification setting. This allows the marker to maintain identification of the target location while reflecting the selected magnification level.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Multiple microchannels chip for biomolecule imaging
InactiveUS20020015149A1Eliminate statistical testExtensive testingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous substrateMicroscopic observation
A panel chip for supporting biological samples for observation with an imaging microscope. The glass panel defines a top flat surface, a bottom bearing surface, and at least a few channels extending generally parallel to each other from top to bottom surfaces. Each of the channels defines a top access mouth for ingress of biological. The channels are arranged in subgroups made of a number of unit cells. Instead of being cylindroid, these channels may form cross sectional rectangular or arcuate channels, or cross sectionally water droplet like channels. Each channel has such an inner diameter as to accommodate flow through viscosity of a biological sample containing fluid. The porous substrate that is created by slot channel can provide the maximum binding surface area per unit cell or pixel, as compared to cylindrical pores, thus achieving higher sensitivity and better imaging. Also, this panel chip is capable of being used as direct in situ synthesizing of molecules and drugs. Other impurities in test solutions are however allowed to pass freely therethrough and be least prone to blockage.
Owner:ROYCE TECH
Pattern printed sheet
InactiveUS9213929B2Low priceReduce working spaceRecord carriers used with machinesNon-linear opticsMicroscopic observationDisplay device
The pattern printed sheet 1 of the present invention includes a substrate 2 and a non-visible light-reflective transparent pattern 3 printed on a surface of the substrate, wherein an ink for forming the transparent pattern 3 contains a non-visible light-reflective material capable of selectively reflecting a light having a wavelength in a non-visible light range, and the transparent pattern 3 printed on the surface of the substrate 2 has a multilayer structure in section which is repeated at predetermined intervals as observed by a scanning electron microscope, and reflects only a circular polarization component in a predetermined rotation direction relative to an incident light applied thereto. The pattern printed sheet is usable as a coordinate detecting means which is applicable a data input system of a type capable of directly hand-writing input data on an image screen of a display device, and has a reduced weight and a low price, and is readily obtained in the form of a large area sheet and can be mass-produced.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Systems and methods for intra-operative stimulation within a surgical field
InactiveUS20110060242A1Accurate assessmentElectrotherapySurgical needlesMuscle contractionRange of motion
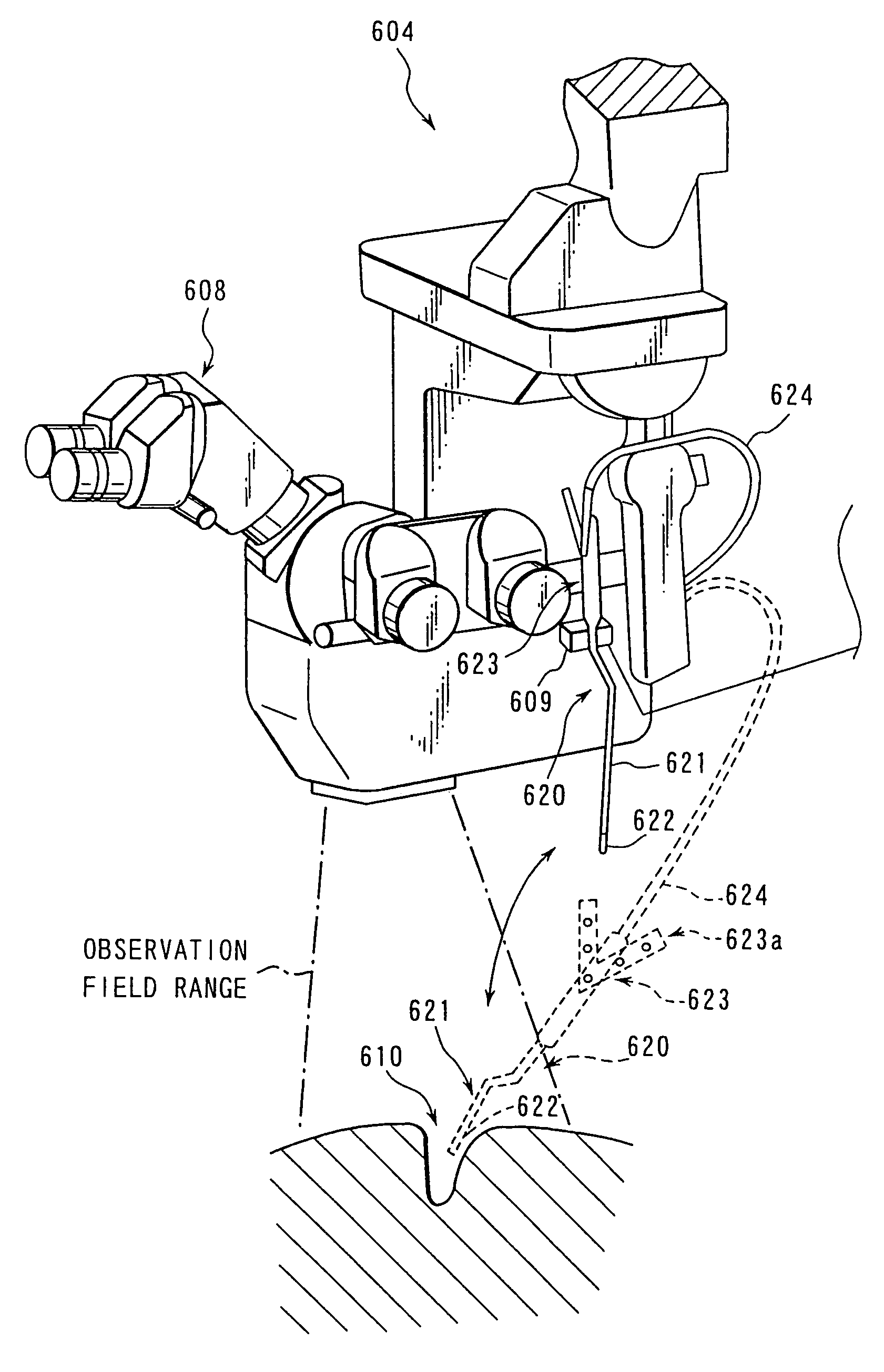
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide safeguarding against tissue injury during surgical procedures and / or identify nerve damage occurring prior to surgery and / or verify range of motion or attributes of muscle contraction during reconstructive surgery. Such improved assemblies may be utilized in embodiments of methods according to the present invention allowing, preferably by a single hand, manipulation, carrying, parameter adjustment and / or informational feedback generation from within a surgical field. Single-handed operation and easily identifiable feedback generation is desirable especially where focused attention is required, such as during surgery observed through a microscope.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SURGICAL
Method and apparatus for automated coverslipping
ActiveUS7271006B2Reduce the possibilitySmall restoring forceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesMicroscopic observationCapillary action
An apparatus and method for selecting and dispensing coverglasses over specimens on slides for the purpose of viewing specimens through a microscope. The selecting device contains a suctioning mechanism for picking up a coverglass from a stack of coverglasses. It also contains the ability to bend the coverglass to assist in separating the coverglasses. The apparatus further contains a matched barrier to eliminate any coverglasses that may stick to the selected coverglass. The selecting device also contains spring members which aid in the dispensing of the coverglass. After the suctioning mechanism releases the coverglass, the spring members exert a force onto the coverglass to insure that it is released from the selecting device and placed onto the slide. After placement of the coverglass onto the slide, capillary action pushes air bubbles out from underneath the coverglass.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
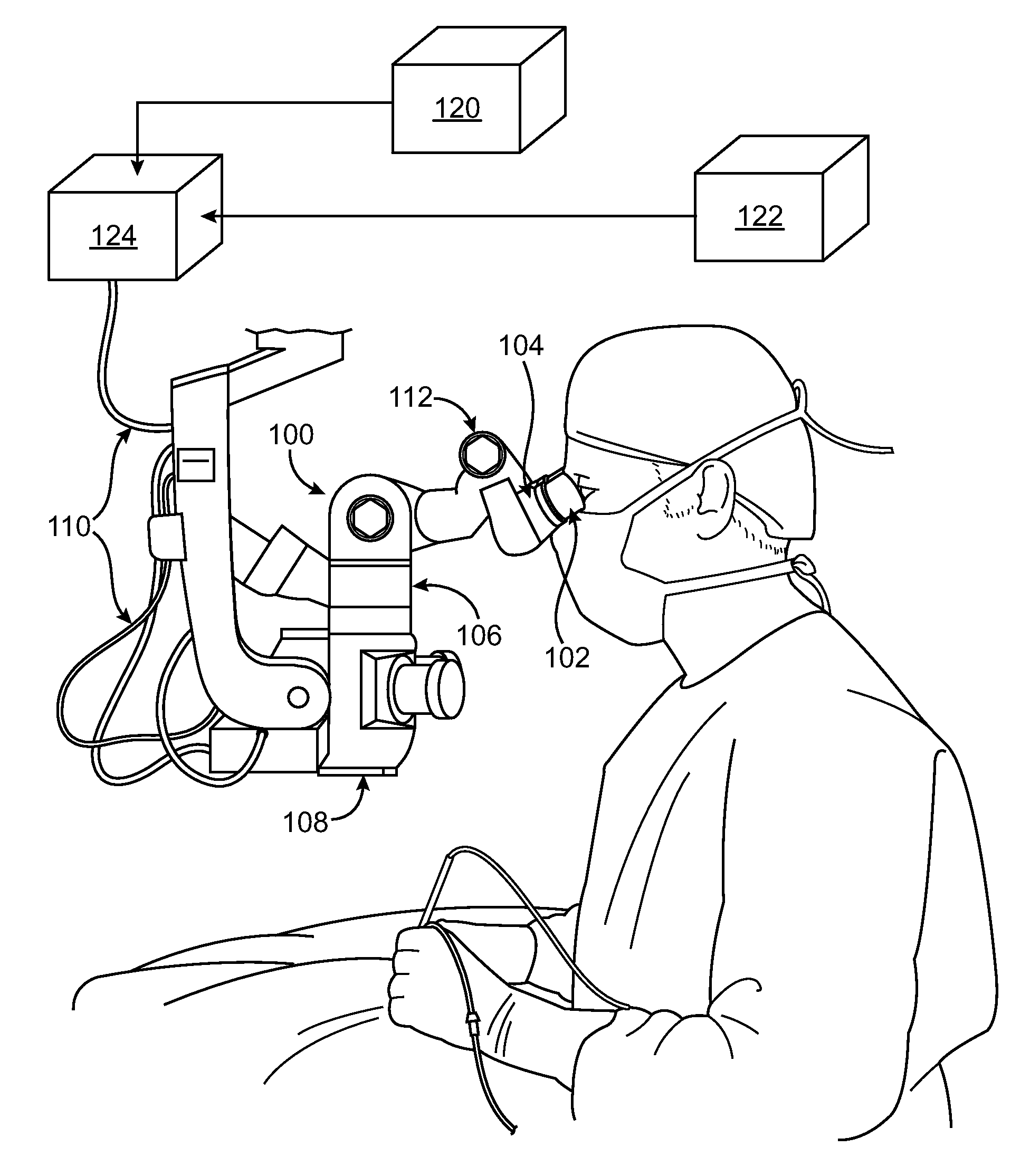
Microscope Viewing Device
A microscope, e.g., a surgical microscope, includes an image generation device in the light path or light paths of the microscope. Images based on real-time or static data concerning the object in view, e.g., a patient's MRI data and / or parameters of one or more surgical instruments being used to operate on the patient, are projected into the microscope's light path so the surgeon does not need to look away from the surgical field and does not require other personnel to read outloud the settings and data from the machines being used in the surgery.
Owner:AWDEH RICHARD
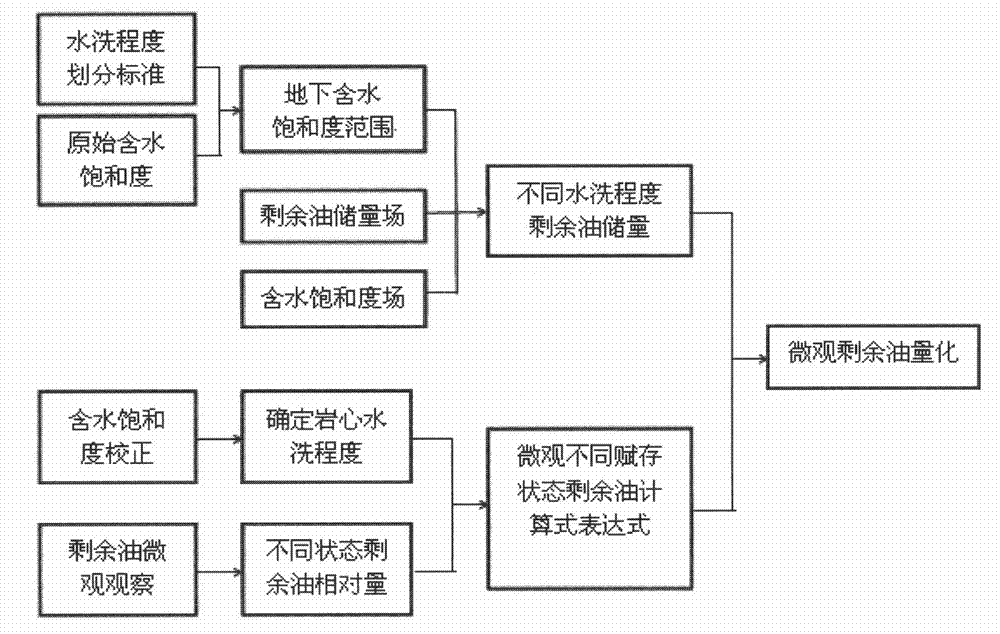
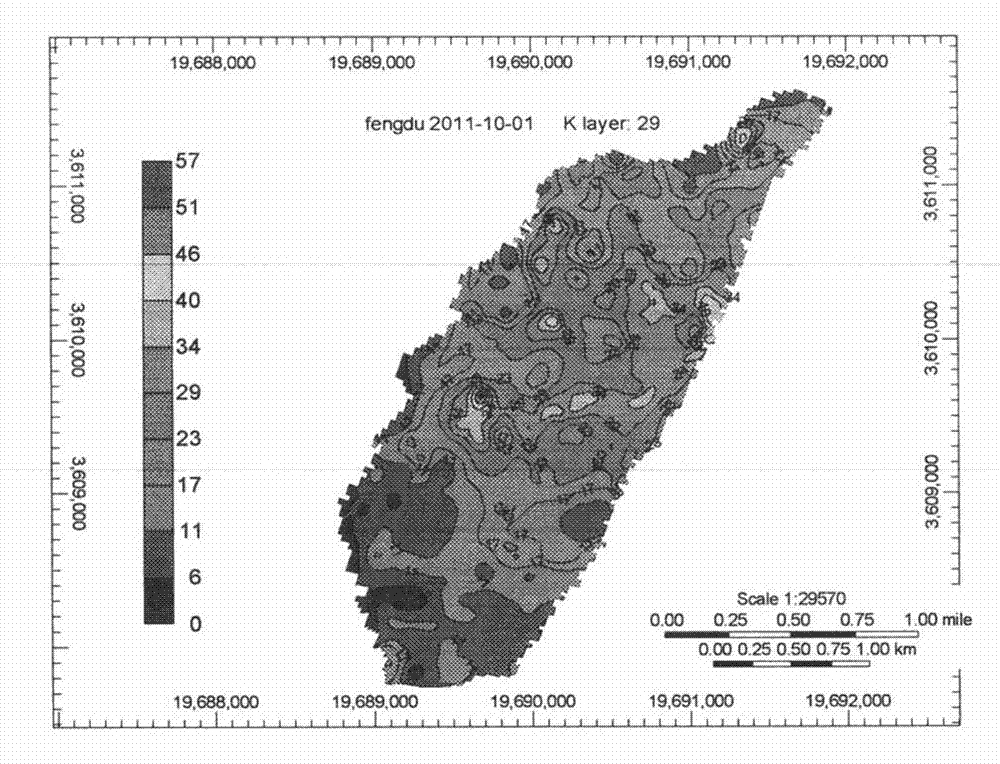
Method for macroscopically quantizing microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states
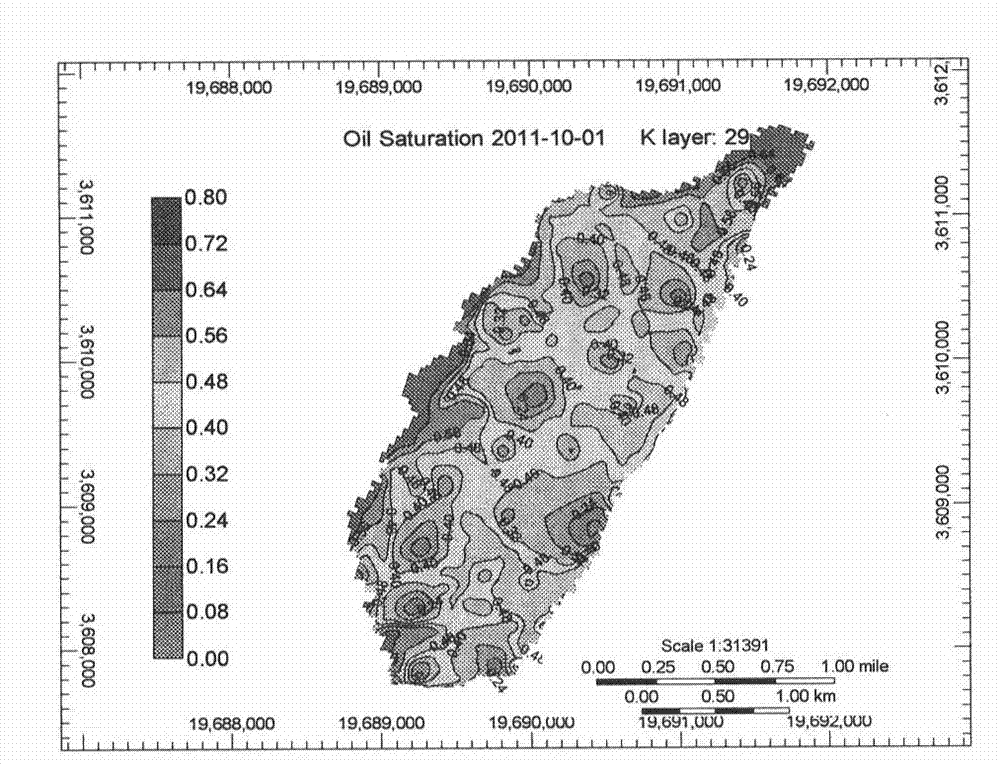
ActiveCN103206208ARaise the level of researchMeet the actual needs of developmentBorehole/well accessoriesRock coreMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a method for macroscopically quantizing microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states. The method includes the steps: acquiring a remaining oil reserve distribution field and a water saturation distribution field by macroscopic numerical simulation; determining the range of underground water saturation under the condition of different washing degrees according to washing degree differentiating standards and original water saturation, and obtaining macroscopic remaining oil reserve with different washing degrees according to the remaining oil reserve distribution field and the water saturation distribution field; determining the washing degree of a rock core in a current state by water saturation correction test for a coring well, determining the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states by microscopic observation test for oily slices of the coring well, and counting to obtain the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states under different washing degrees; and macroscopically quantizing the microscopic remaining oil by applying computation expression for microscopic remaining oil mass in different occurrence states according to the macroscopic remaining oil reserve with different washing degrees and the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states under different washing degrees.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM EXPLORATION DEELOPMENT INST OF HENAN OILFIELD BRANCH SINOPEC
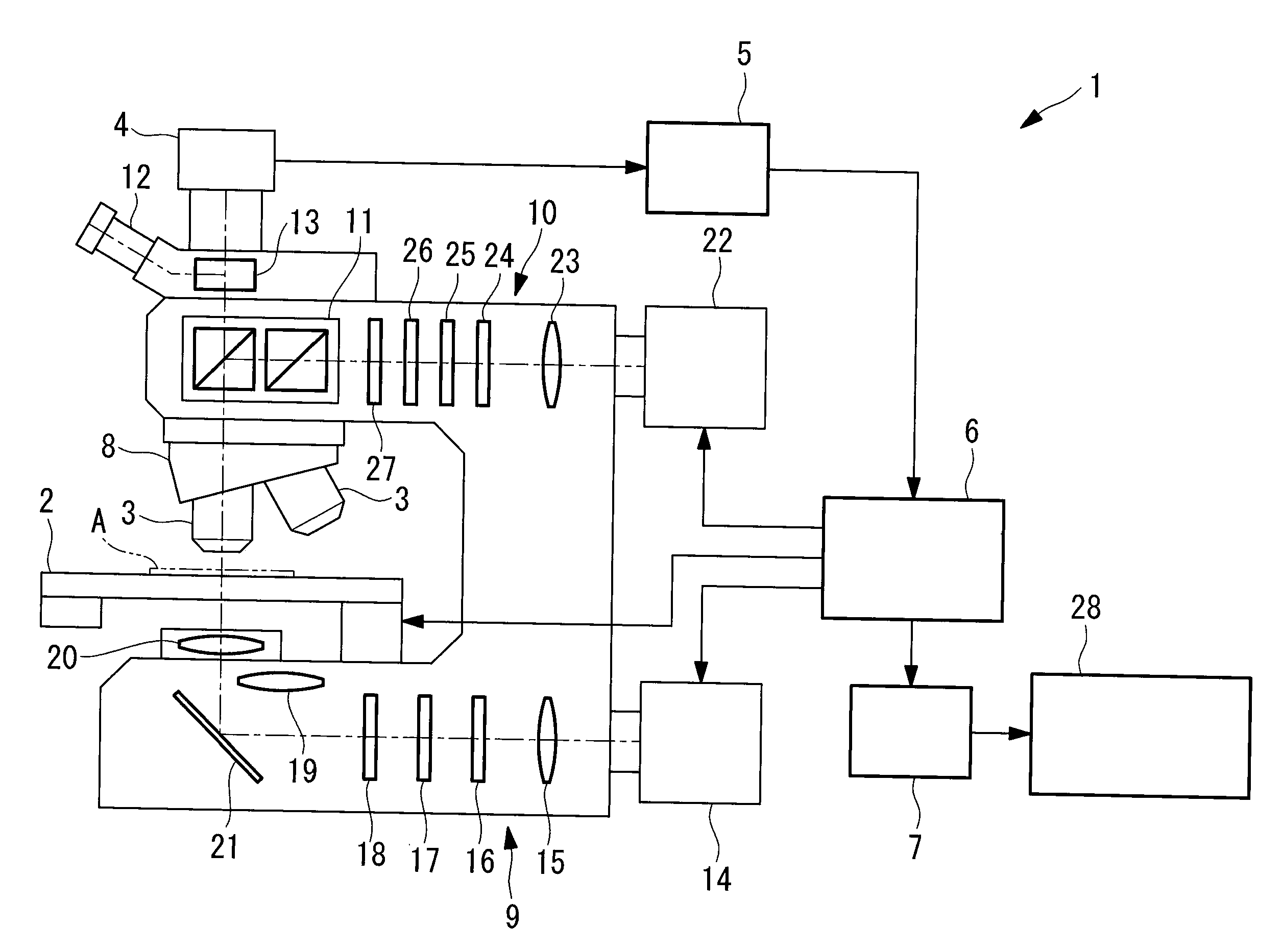
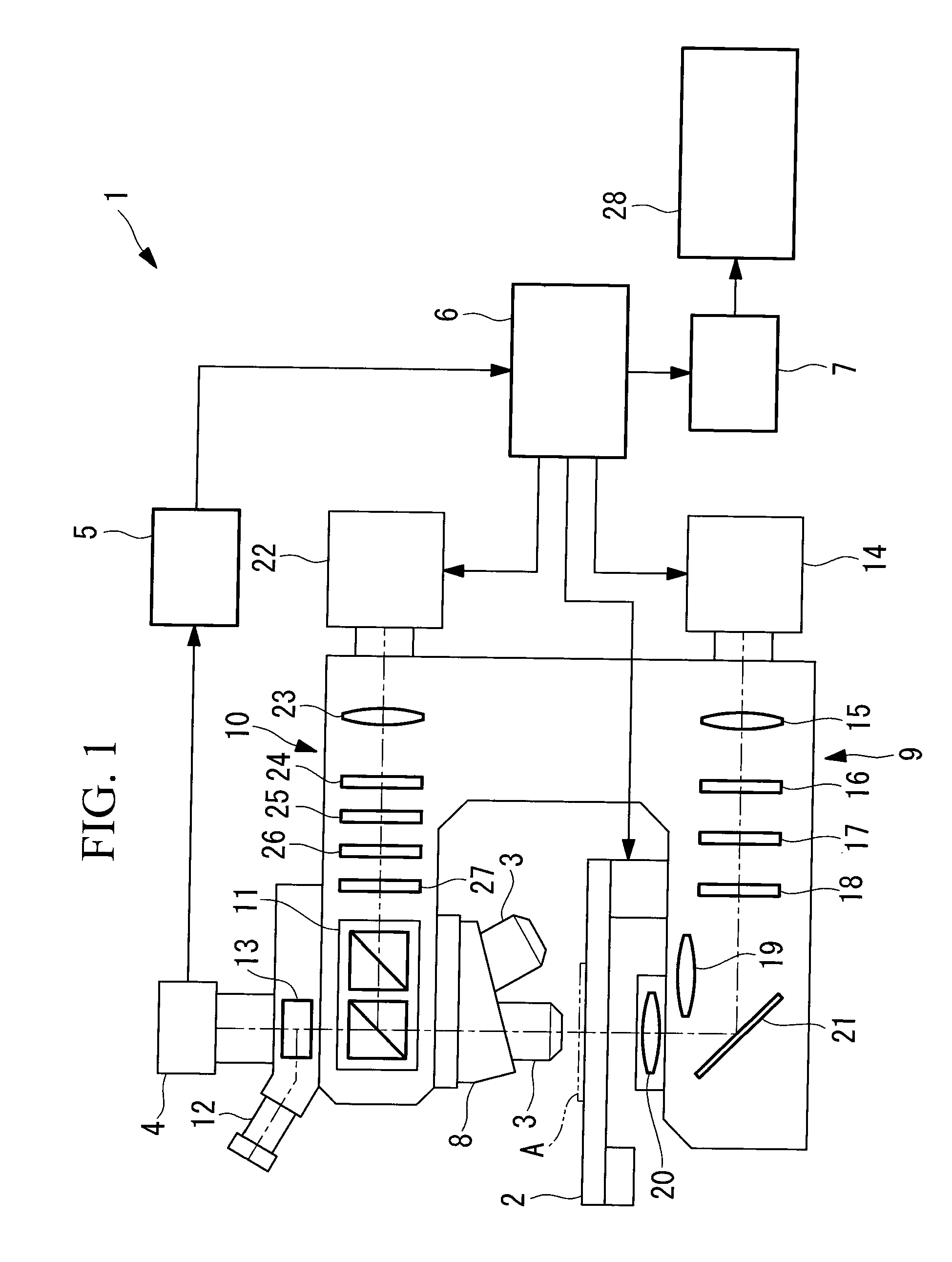
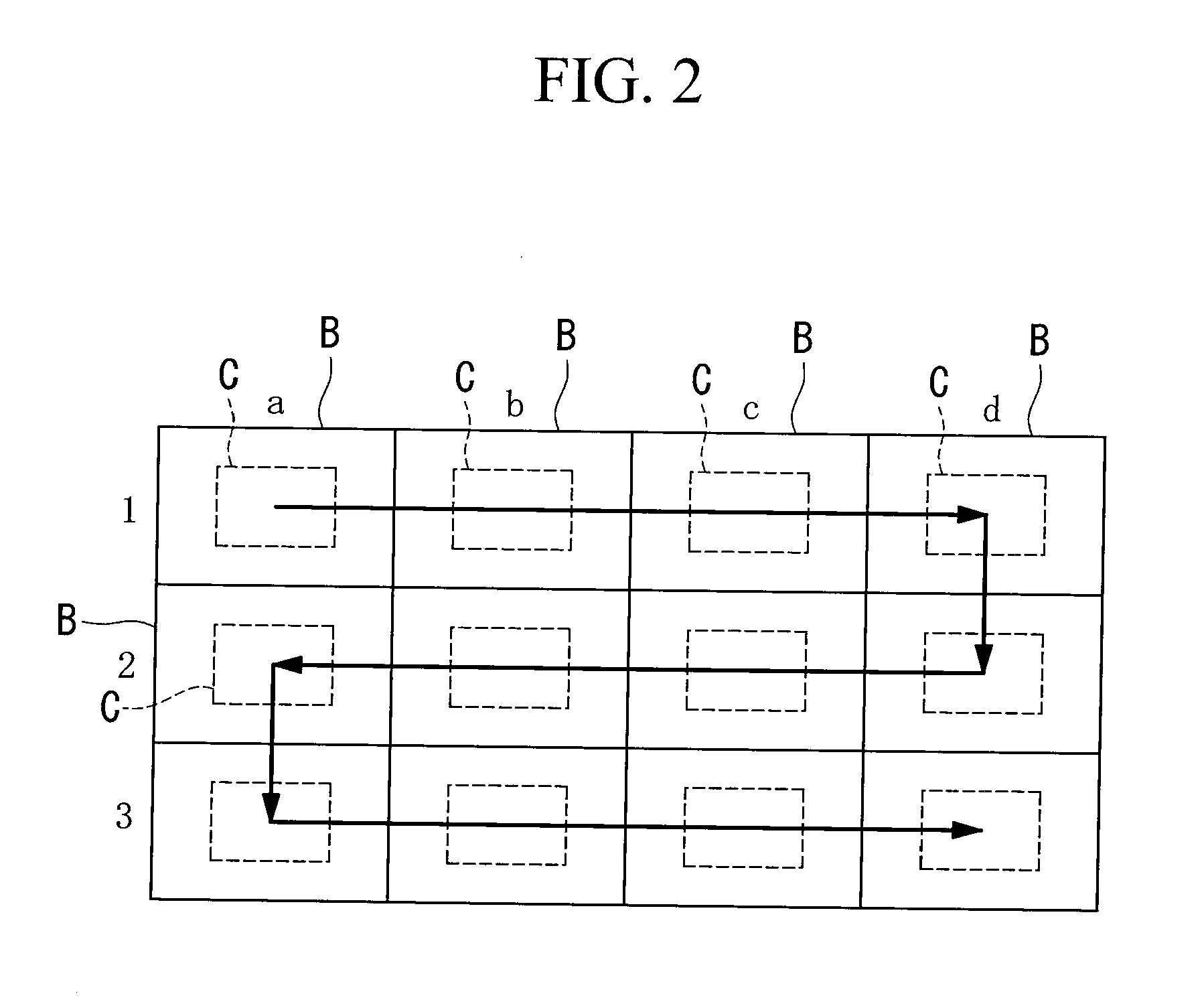
Microscope Apparatus and Microscope Observation Method
ActiveUS20110102571A1Adjustment is limitedColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVirtual slideMicroscopic observation
The number of seams between magnified images in a created virtual slide is reduced to make the virtual slide clear and sharp. Provided is a microscope apparatus including an objective lens that collects light from a sample on a slide; a focus position detecting section that detects a focus position of the objective lens with respect to the sample; a focus state adjustment section that adjusts a focus state with respect to the sample based on a detection result from the focus position detecting section; and a magnified-image acquisition section that acquires a magnified image of each part of the sample, in which, if the focus position detected by the focus position detecting section is changed by more than a predetermined threshold with respect to a focus state in which an adjacent magnified image was obtained, the focus state adjustment section limits the adjustment in the focus state to the predetermined threshold or less.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
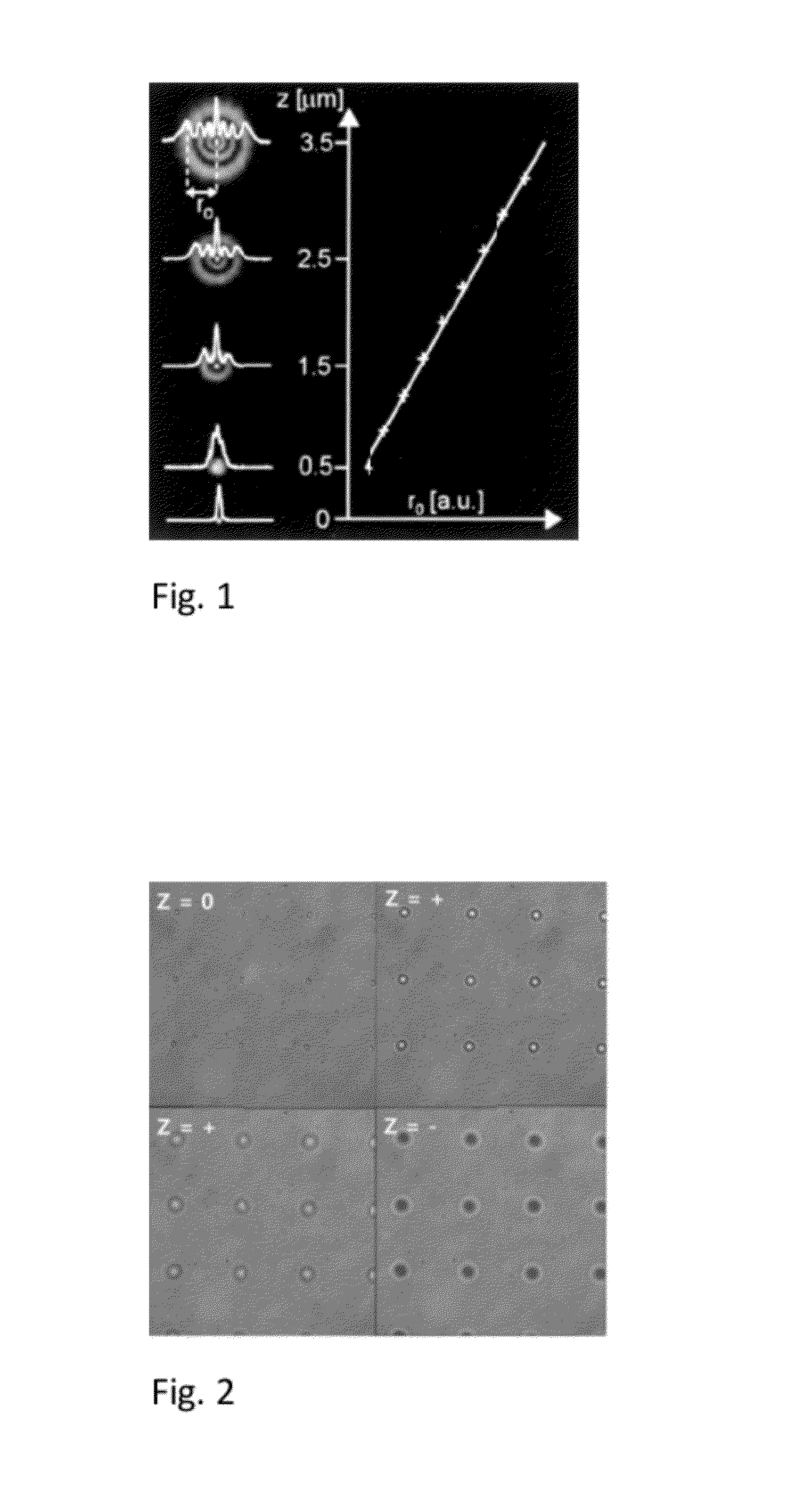
Simple Ultra-Stable Stage with Built-in Fiduciary Markers for Fluorescence Nanoscopy
ActiveUS20120300293A1Efficient and cost-effective and simple provisionEasy to detectCeramic shaping apparatusMicroscopesFluorescenceMicroscopic observation
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
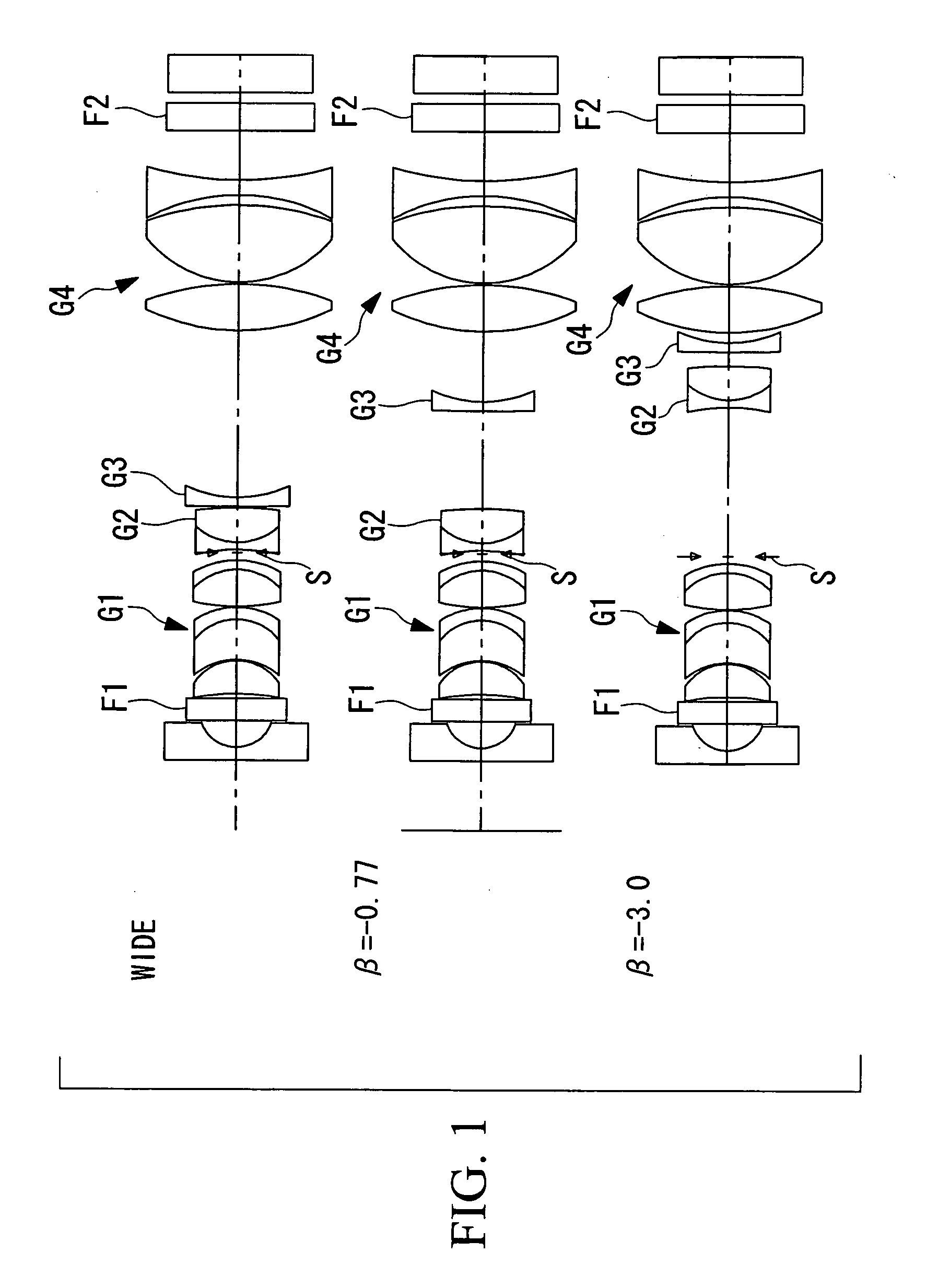
Image-acquisition optical system
ActiveUS20070258150A1Shorten the lengthSmall outer diameterMicroscopesTelescopesOptical axisMicroscopic observation
There is provided a compact image-acquisition optical system which is capable of observing from normal observation to microscopic observation with a single image-acquisition optical system, whose overall length is short, and whose lens outer diameter is small. The invention provides an image-acquisition optical system comprising a plurality of lens groups, wherein, by moving at least one of the plurality of lens groups on the optical axis, it is possible to change a state from a normal observation state (wide-angle end) to a close-up magnified-observation state (telephoto end), and wherein the magnification of the image-acquisition optical system at the telephoto end satisfies βTELE<−2.0.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Pattern printed sheet
InactiveUS20070290047A1Reduce working spaceReduce weightRecord carriers used with machinesNon-linear opticsMicroscopic observationDisplay device
The pattern printed sheet 1 of the present invention includes a substrate 2 and a non-visible light-reflective transparent pattern 3 printed on a surface of the substrate, wherein an ink for forming the transparent pattern 3 contains a non-visible light-reflective material capable of selectively reflecting a light having a wavelength in a non-visible light range, and the transparent pattern 3 printed on the surface of the substrate 2 has a multilayer structure in section which is repeated at predetermined intervals as observed by a scanning electron microscope, and reflects only a circular polarization component in a predetermined rotation direction relative to an incident light applied thereto. The pattern printed sheet is usable as a coordinate detecting means which is applicable a data input system of a type capable of directly hand-writing input data on an image screen of a display device, and has a reduced weight and a low price, and is readily obtained in the form of a large area sheet and can be mass-produced.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Cmp polishing liquid and polishing method
ActiveUS20120094491A1High barrier film polishing speedGood dispersionOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilica particleDispersion stability
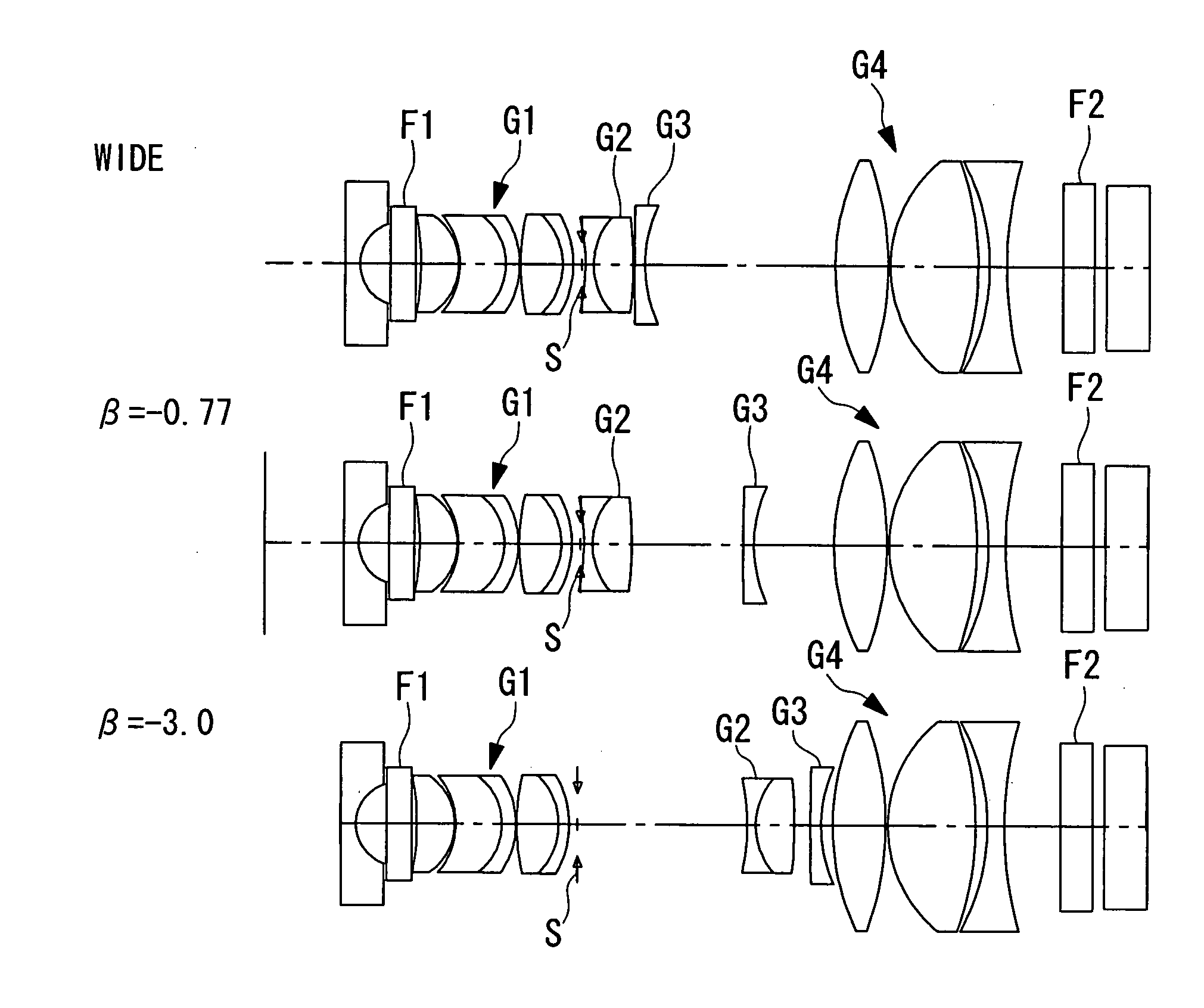
The invention relates to a CMP polishing liquid comprising a medium and silica particles as an abrasive grain dispersed into the medium, characterized in that:(A1) the silica particles have a silanol group density of 5.0 / nm2 or less;(B1) a biaxial average primary particle diameter when arbitrary 20 silica particles are selected from an image obtained by scanning electron microscope observation is 25 to 55 nm; and(C1) an association degree of the silica particles is 1.1 or more. The invention provides a CMP polishing liquid which has the high barrier film polishing speed, the favorable abrasive grain dispersion stability, and the high interlayer dielectric polishing speed, and a polishing method producing semiconductor substrates or the like, that have excellent microfabrication, thin film formation, dimension accuracy, electric property and high reliability with low cost.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Method for the electron-microscopic observation of a semiconductor arrangement and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20040065827A1Producing an excessive and uncompensatable image blurHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron microscopeSecondary electrons
A method for the electron-microscopic observation of a semiconductor arrangement is provided. It includes providing an electron microscopy optics for imaging secondary electrons emanating from the semiconductor arrangement within an extended object field on a position-sensitive detector, providing an illumination device for emitting a primary energy beam, directing the primary energy beam to at least the object field for extracting there secondary electrons from the semiconductor arrangement. The semiconductor arrangement comprises a region with an upper surface provided by a first material and a recess with a high aspect ratio which is surrounded by the upper surface and has a bottom provided by a second material.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Closed observational device for electron microscope
InactiveUS20070145289A1Easy and clear observationElectric discharge tubesMachines/enginesMicroscopic observationElectron microscope
A closed observational device for an electron microscope is formed of a housing. The housing includes a liquid chamber formed therein, at least one view hole formed at each of a top side thereof and a bottom side thereof and communicating with the liquid chamber and coaxially aligned with the other, and a film mounted to and sealing each of the view holes. Accordingly, a general specimen or a live cell can be placed into the liquid chamber for microscopic observation under the electron microscope. Besides, the present invention can enclose the liquid inside the housing to prevent the liquid from exhausting outward or volatilization.
Owner:CONTREL TECH CO LTD
In situ evaluation system and method of reliability of thin-film materials on flexible electronic substrate
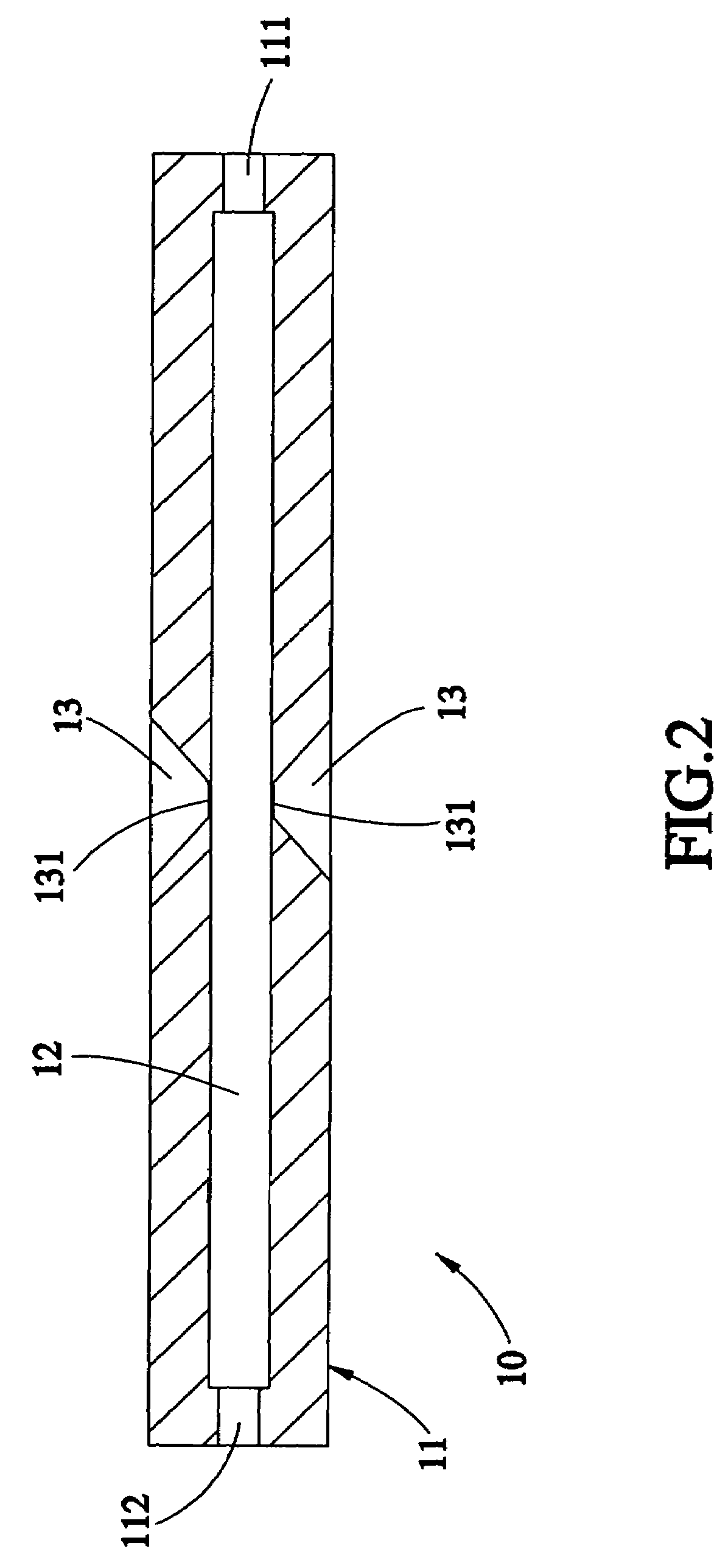
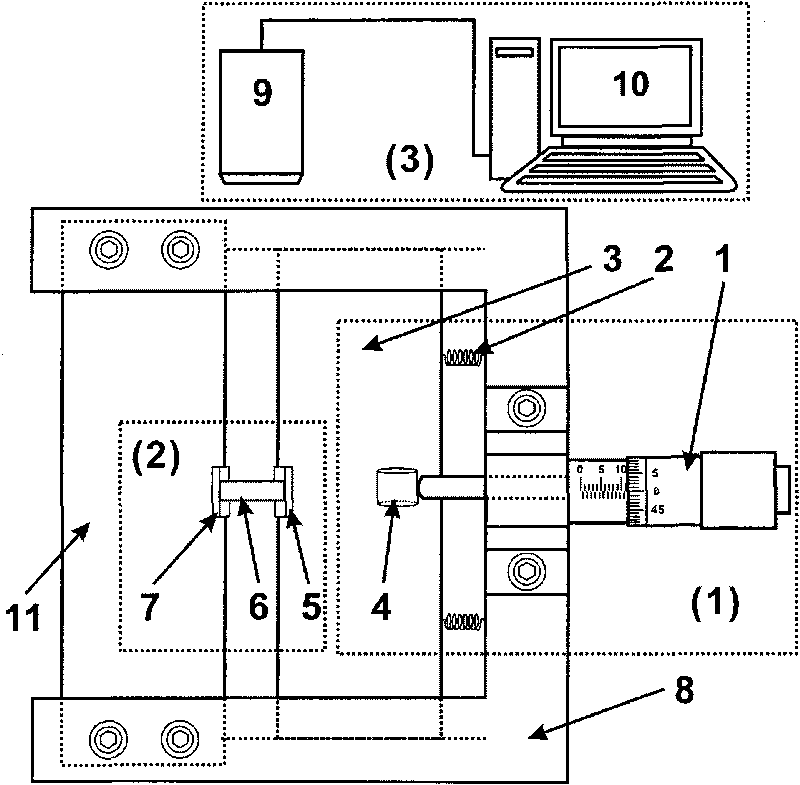
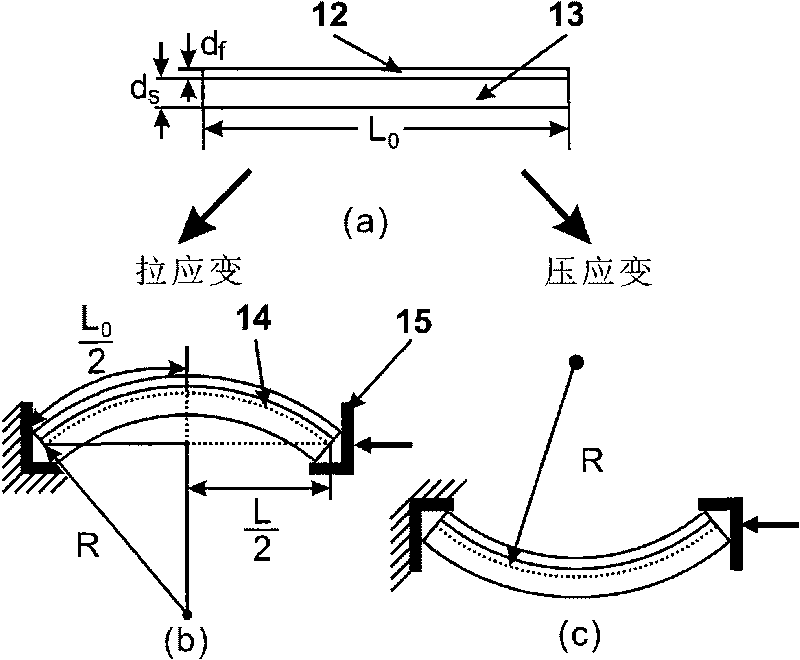
InactiveCN101726442AGet rid of the disadvantages of inaccurate resistance value measurementImprove test accuracyMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMicroscopic observationMechanical reliability
The invention relates to establishment for a test device and a test method for the bending fracture performance of thin-film materials, in particular to an in situ evaluation system and a method of the mechanical reliability of a layer or a plurality of layers of thin-film materials with the micron to nanometer thickness on a flexible electronic substrate. The system comprises a high-precision micrometer caliper, a balance spring, a translational slide block, a freely supported beam fixed end, a freely supported beam movable end, and the like, wherein a composite beam comprising the micrometer caliper and a flexible substrate exerts precise and controllable step displacement to implement freely supported beam bending experiments; real-time exerted strain corresponding to a freely supported beam span is computed according to parameters and geometrical relationship of the freely supported beam span, sample sizes, and the like; and the bending fracture performance and critical cracking strain of the kind of thin film are tested and evaluated by combining in situ microscopic observation and subsequent scanning electron microscope characterization. The invention does not need to consider the electroconductibility of the thin-film materials, and is still adaptable for non-conductive thin-film materials. The experiment operation is simple and fast, in situ real-time positioning observation and analysis can be carried out on samples.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com