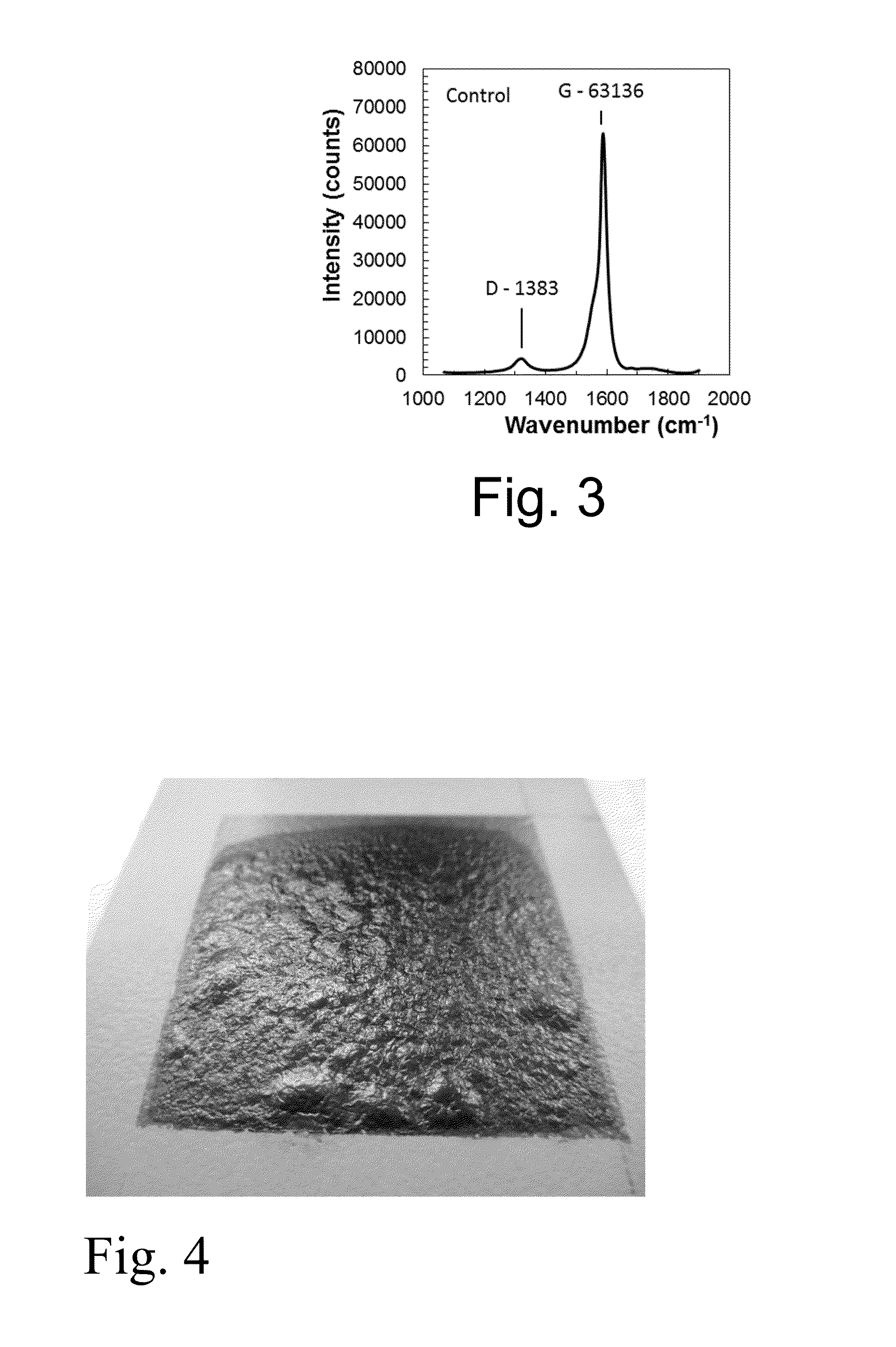
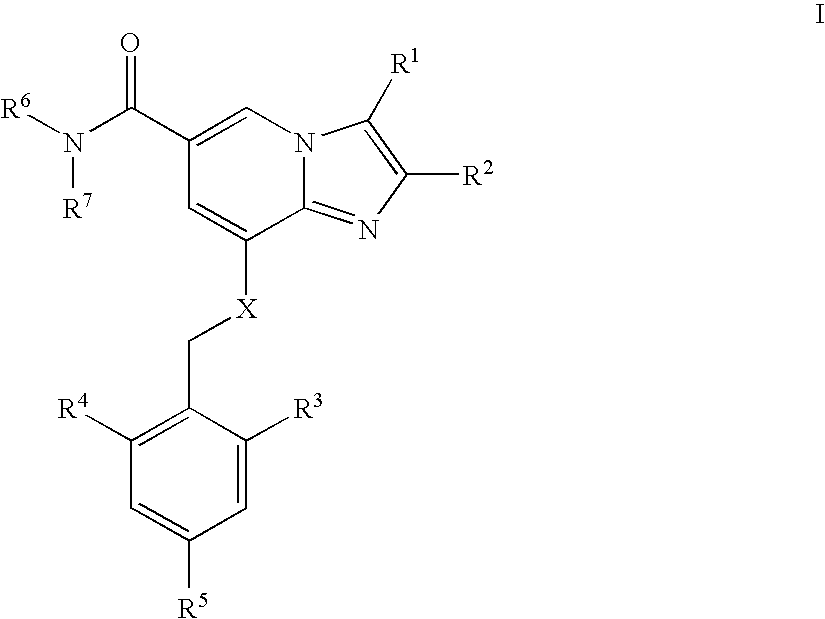
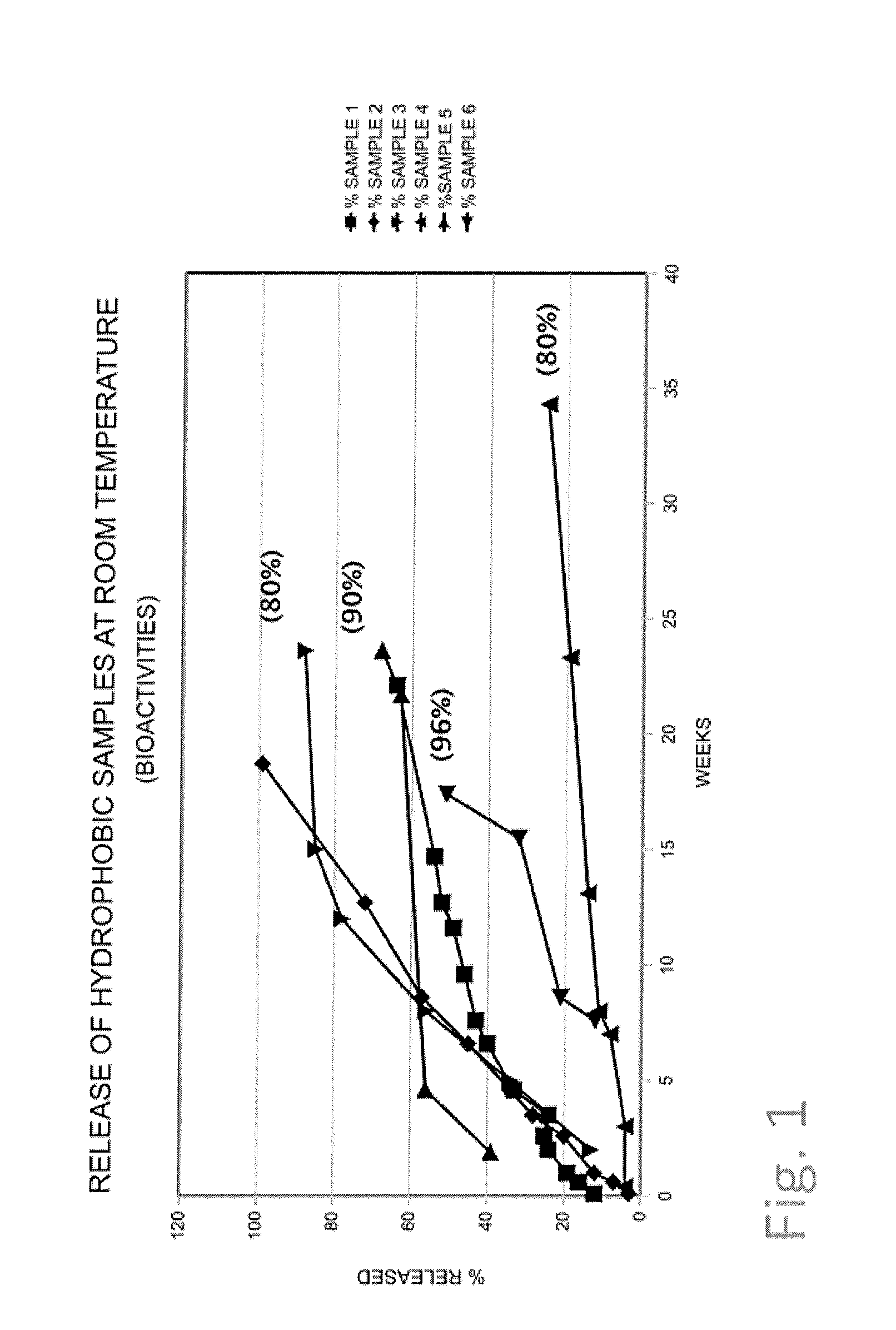
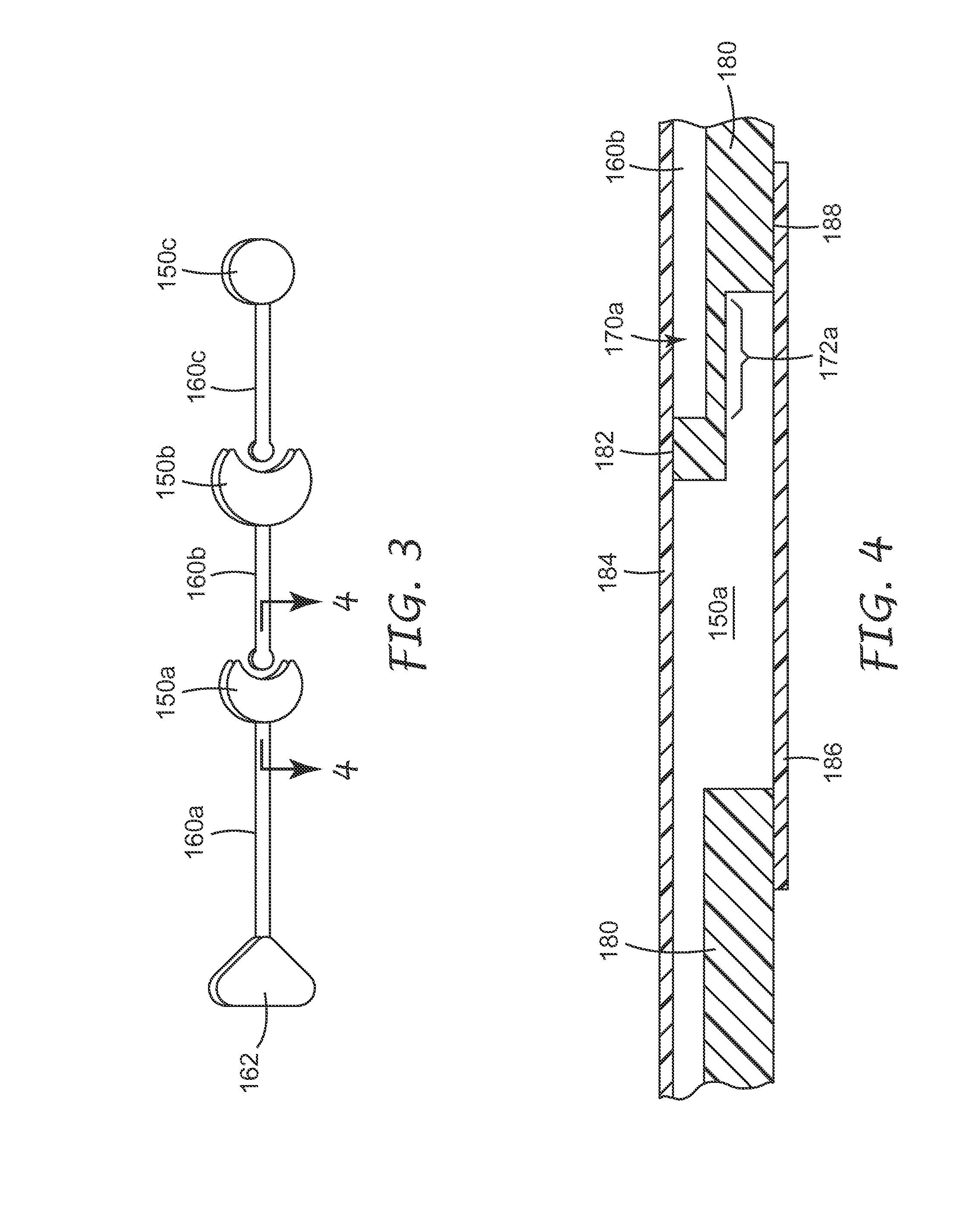
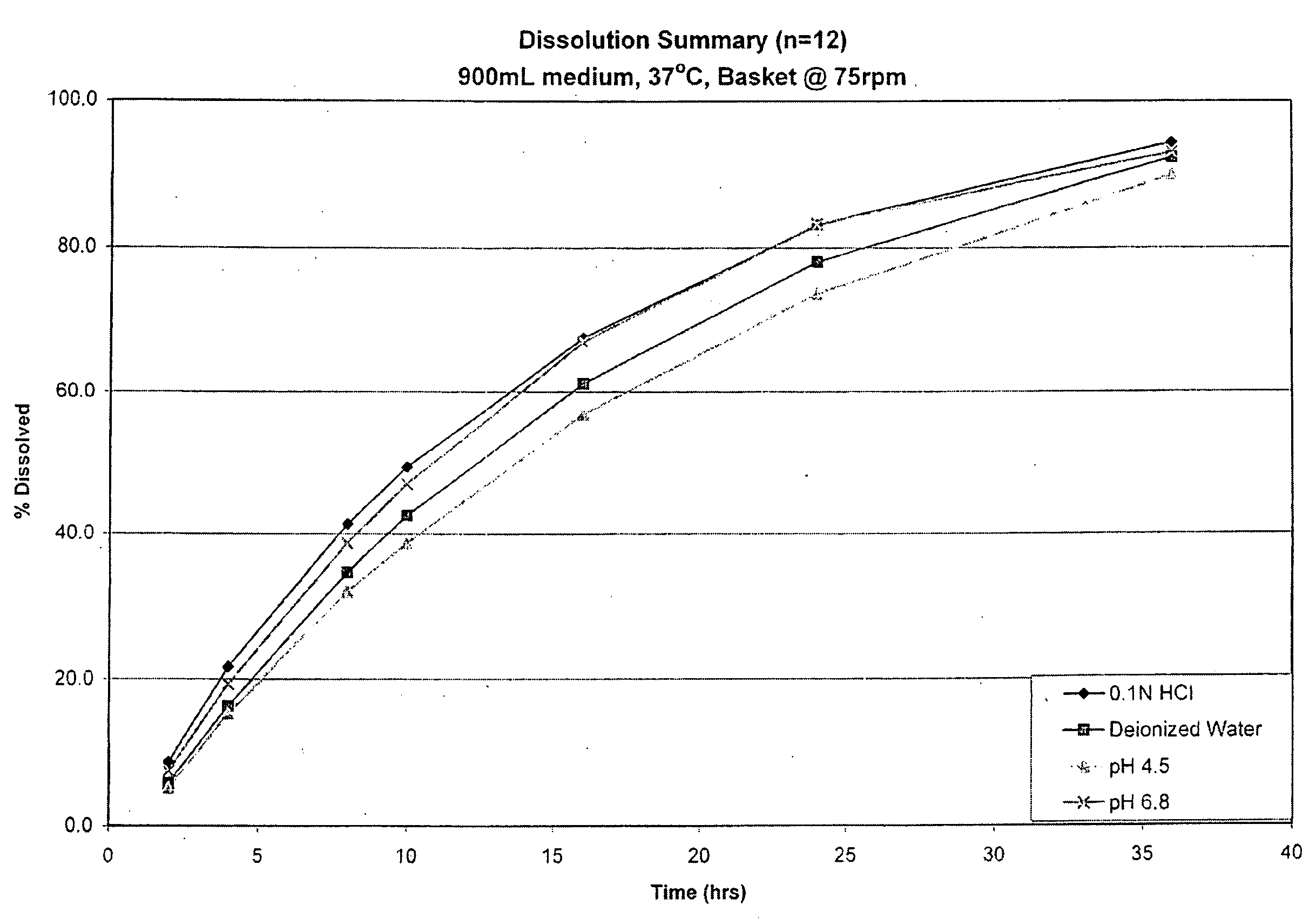
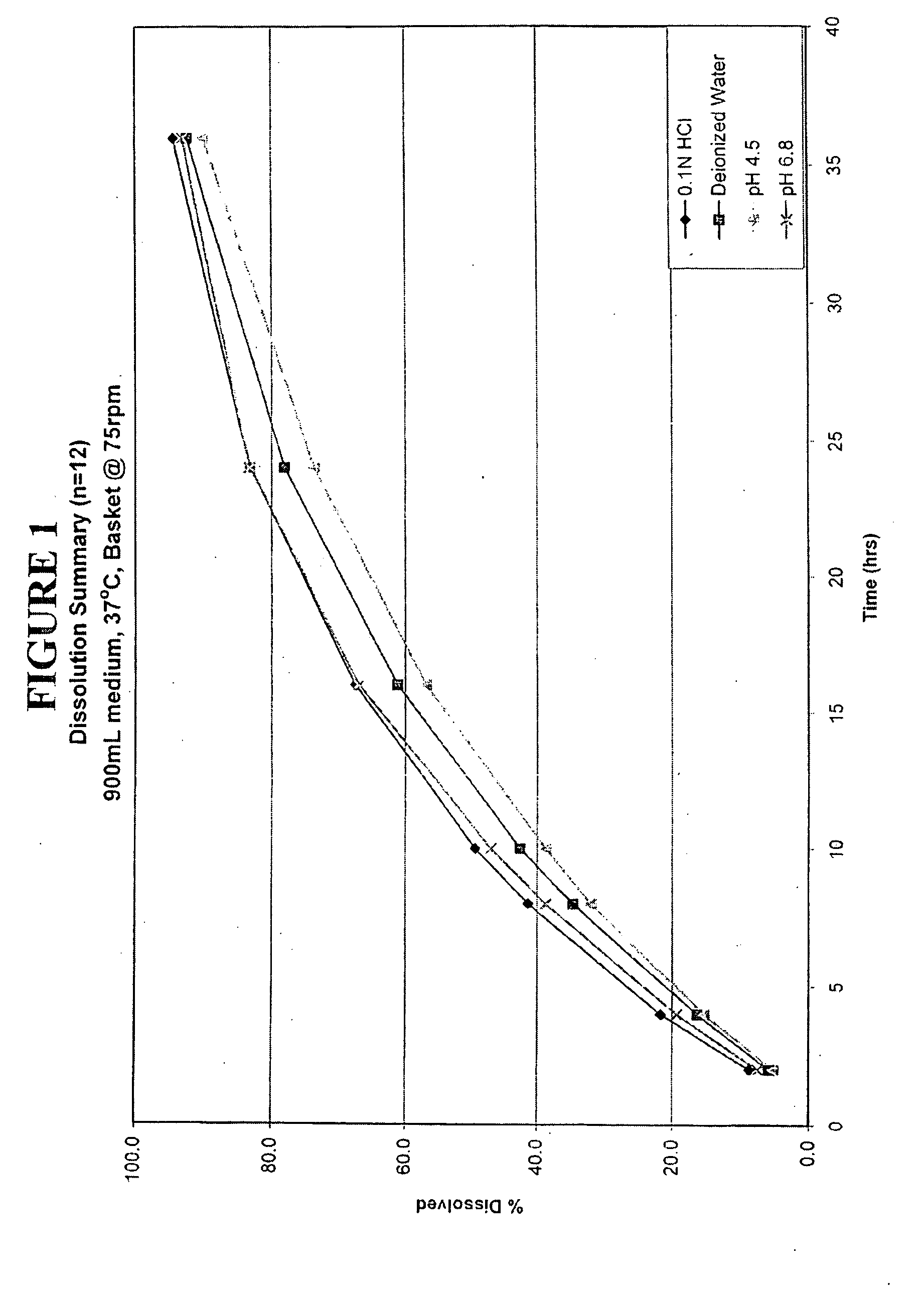
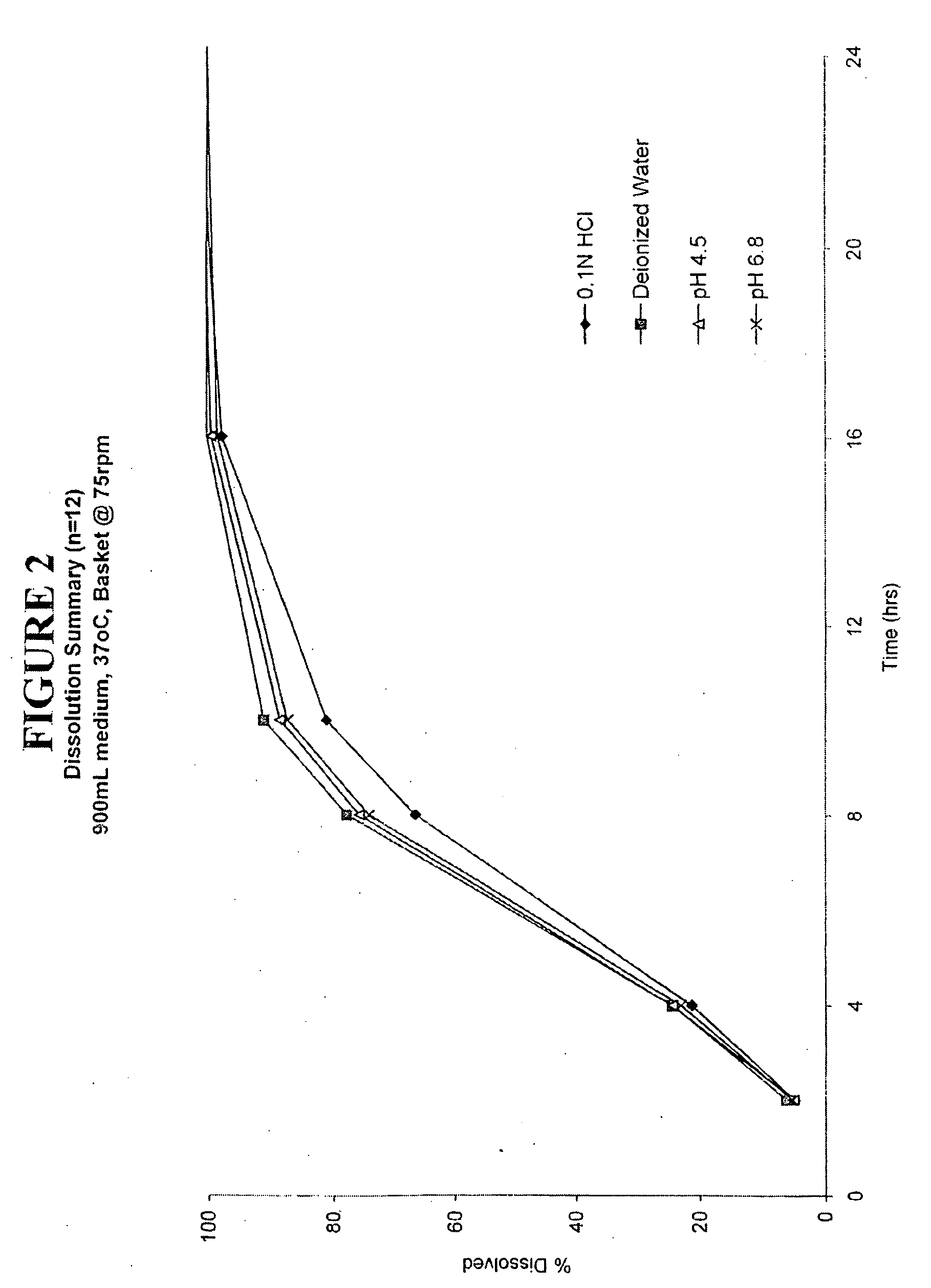
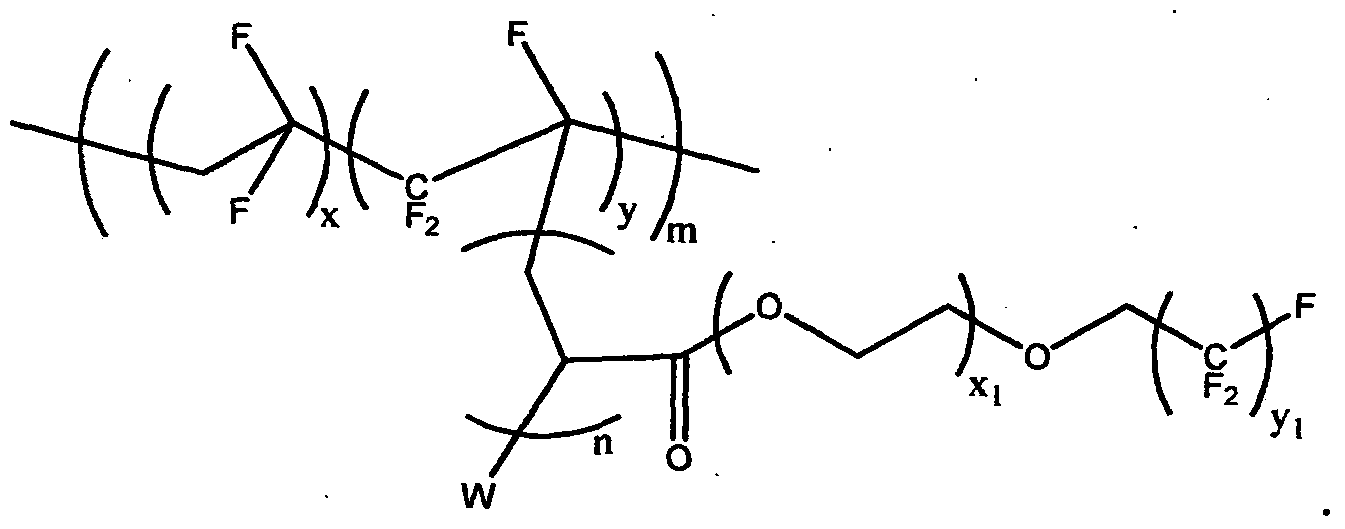
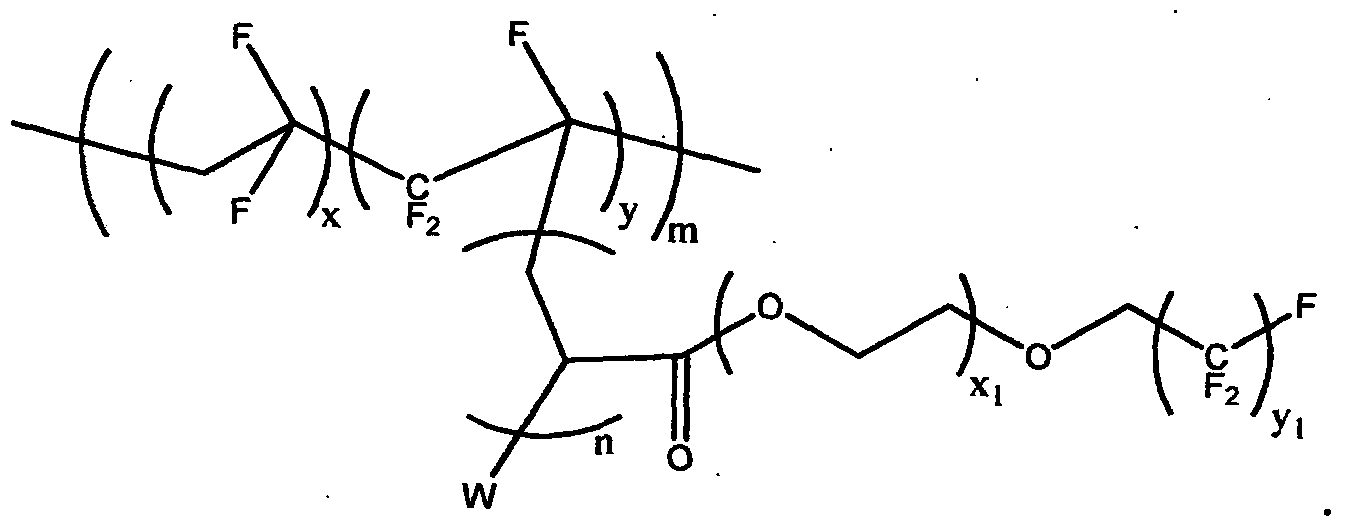
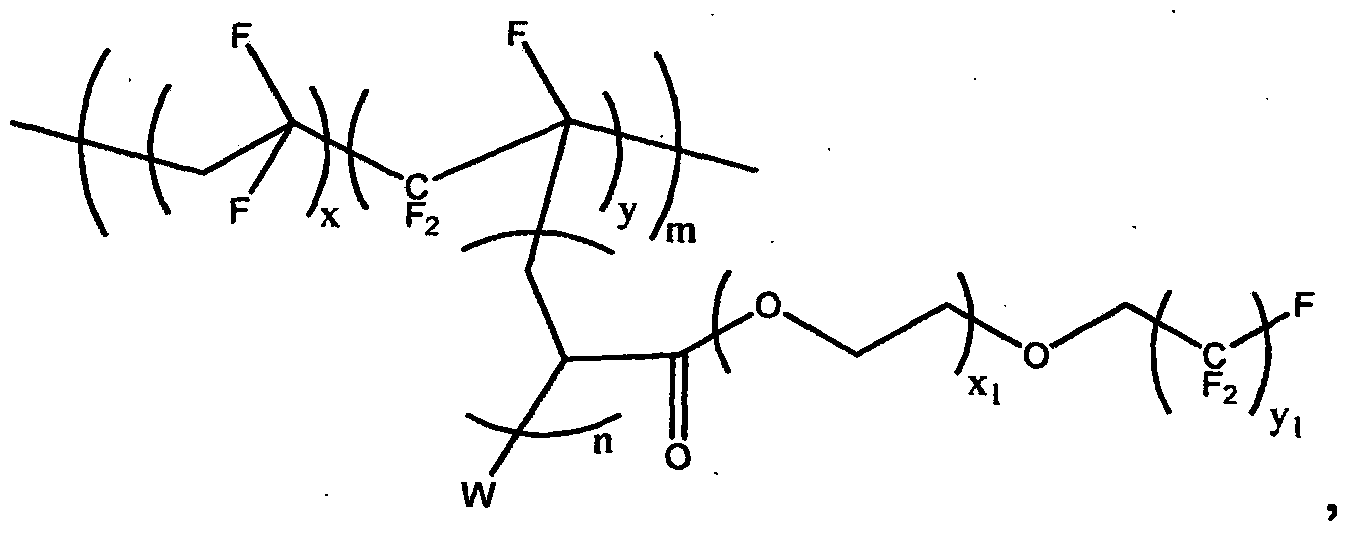
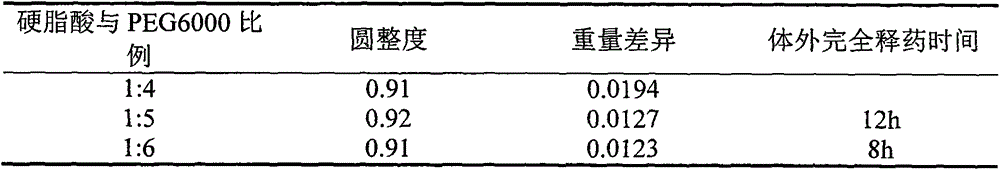
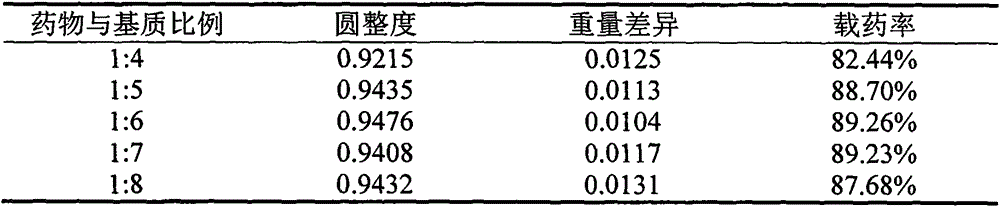
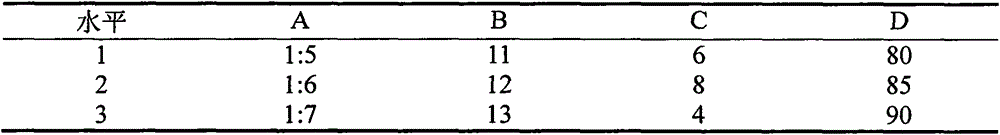
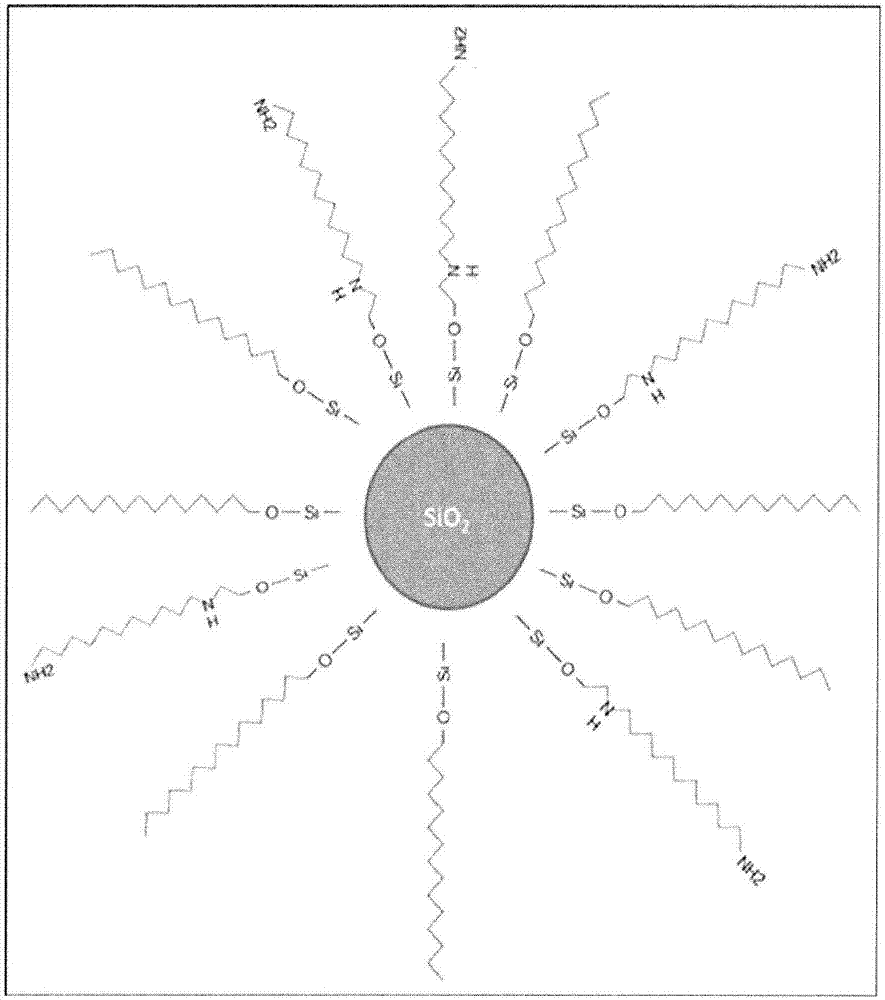
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Hydrophobic matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Techniques to improve polyurethane membranes for implantable glucose sensors
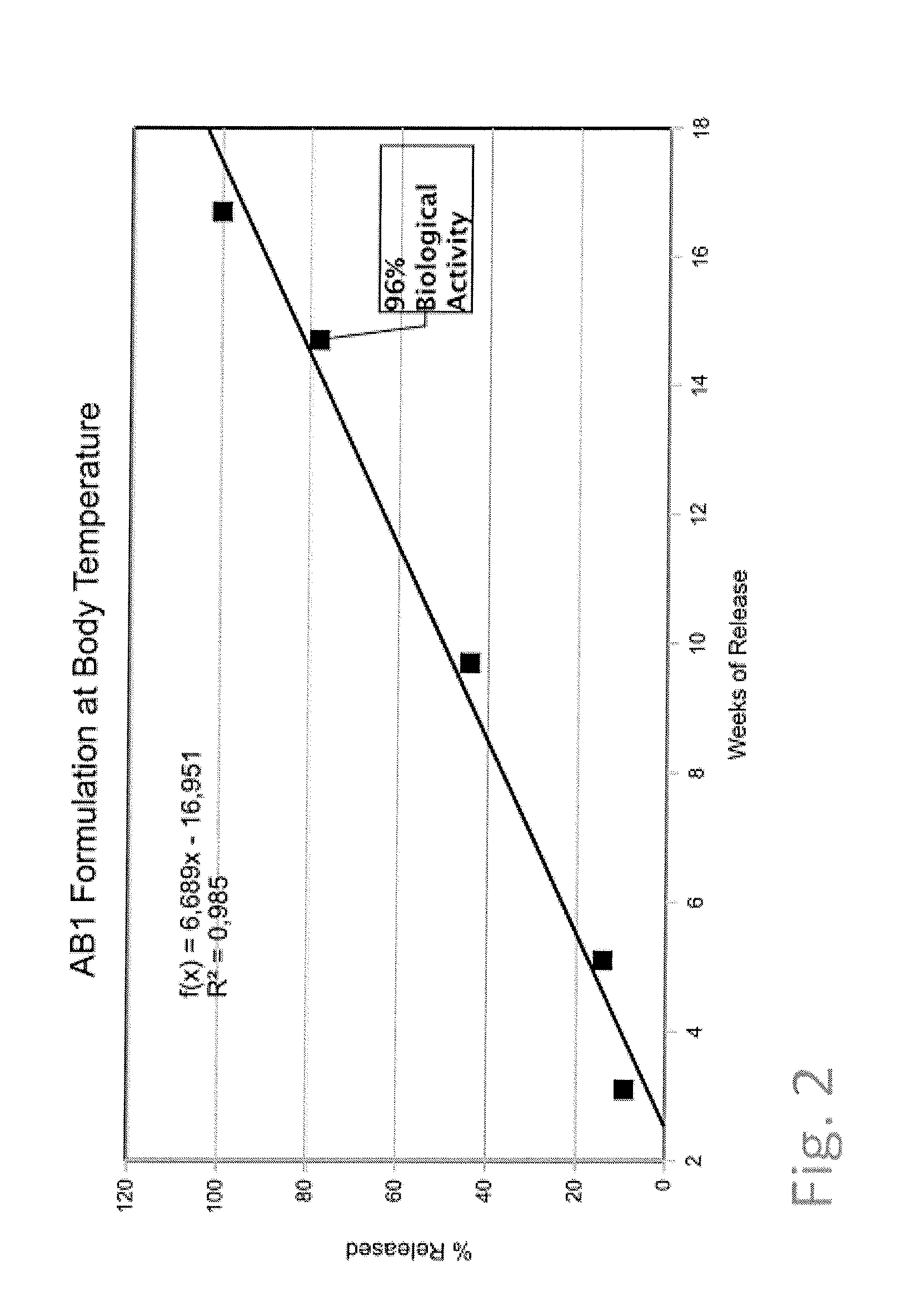
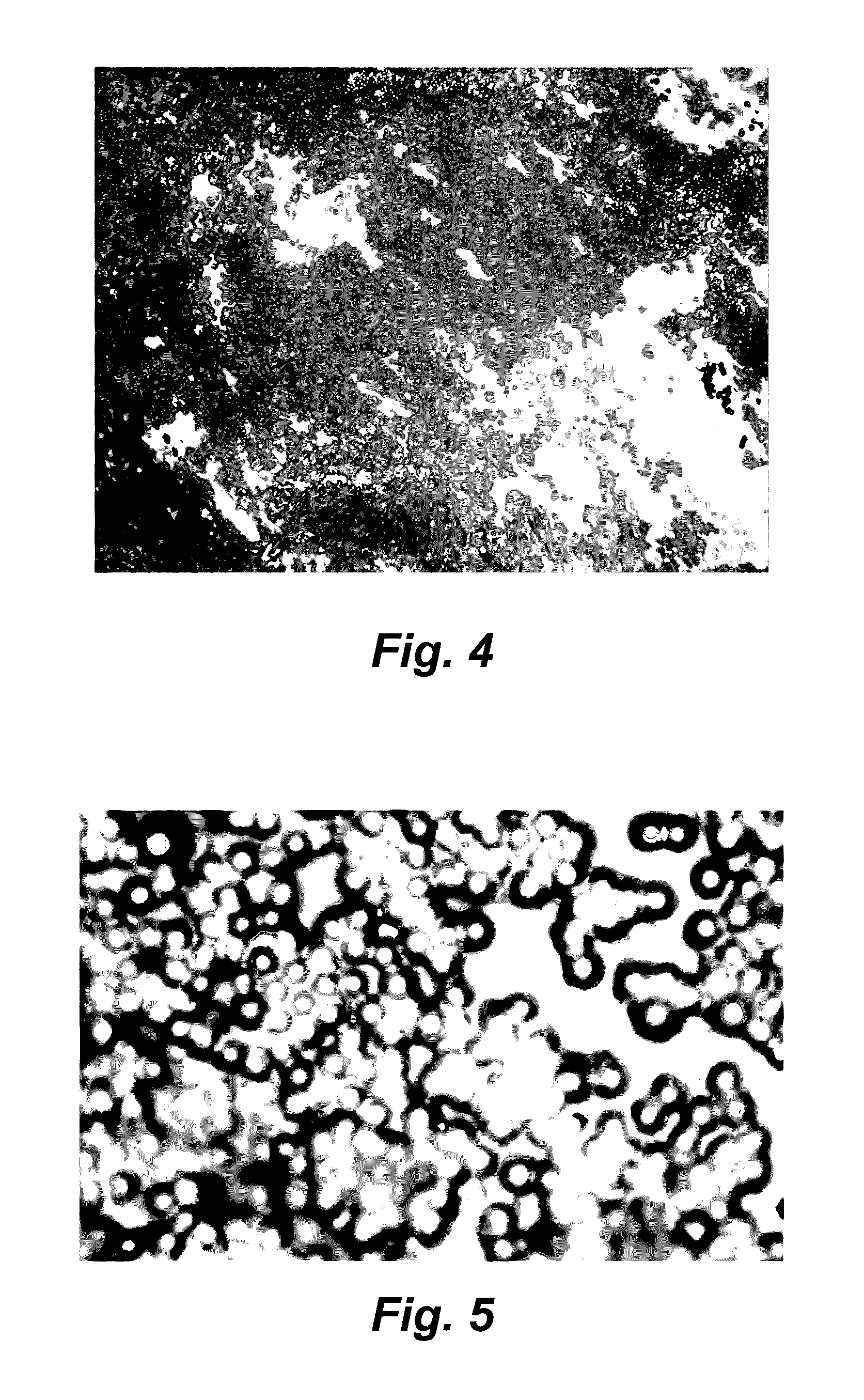
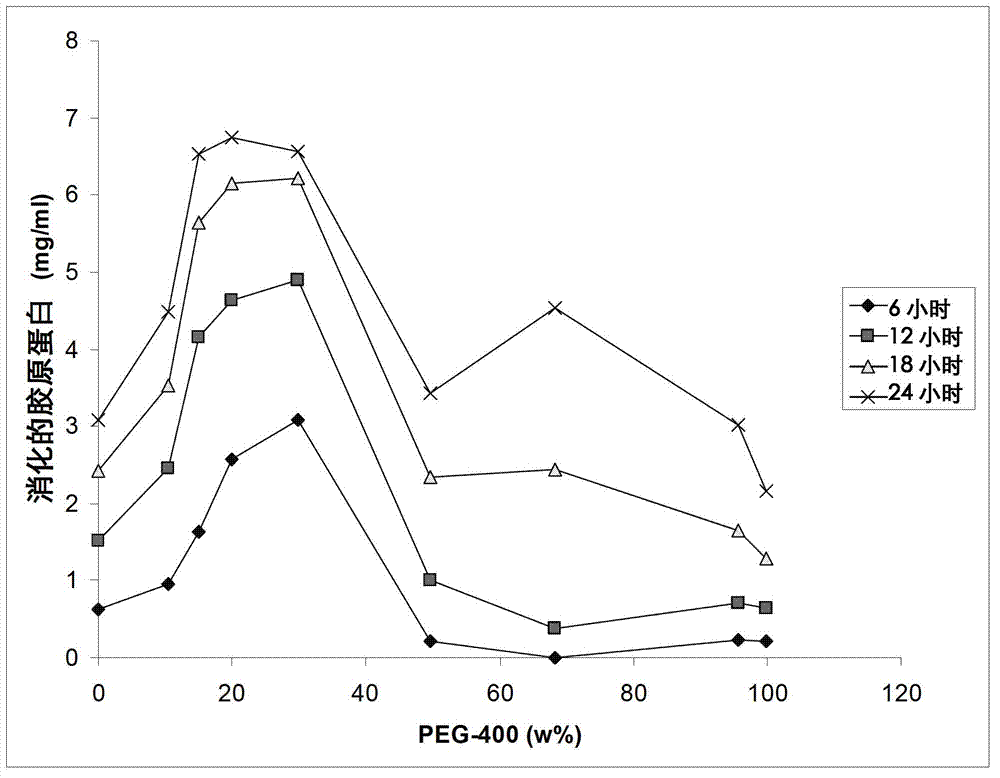
The invention provides an implantable membrane for regulating the transport of analytes therethrough that includes a matrix including a first polymer; and a second polymer dispersed throughout the matrix, wherein the second polymer forms a network of microdomains which when hydrated are not observable using photomicroscopy at 400× magnification or less. In one aspect, the homogeneous membrane of the present invention has hydrophilic domains dispersed substantially throughout a hydrophobic matrix to provide an optimum balance between oxygen and glucose transport to an electrochemical glucose sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Techniques to improve polyurethane membranes for implantable glucose sensors
ActiveUS20060086624A1Easy to makeImmobilised enzymesVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteGlucose sensors
The invention provides an implantable membrane for regulating the transport of analytes therethrough that includes a matrix including a first polymer; and a second polymer dispersed throughout the matrix, wherein the second polymer forms a network of microdomains which when hydrated are not observable using photomicroscopy at 400× magnification or less. In one aspect, the homogeneous membrane of the present invention has hydrophilic domains dispersed substantially throughout a hydrophobic matrix to provide an optimum balance between oxygen and glucose transport to an electrochemical glucose sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
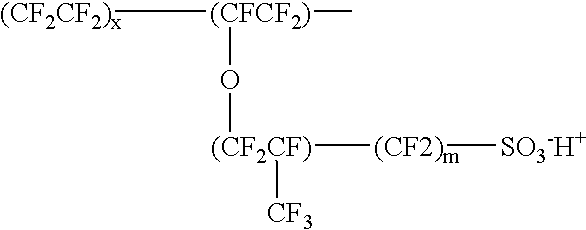
Proton-selective conducting membranes
InactiveUS20020127474A1Easy to operateSelective operationIon-exchanger regenerationSolid electrolyte cellsHydrophobic polymerProton
A membrane comprising: (a) a hydrophobic matrix polymer, and (b) a hydrophilic non-ionic polymer, wherein the hydrophobic polymer and the hydrophilic polymer are disposed so as to form a dense selectively proton-conducting membrane. The microstructure of such a membrane can be tailored to specific functionality requirements, such as proton conductivity vs. proton selectivity, and selectivity to particular species.
Owner:E C R ELECTRO CHEM RES
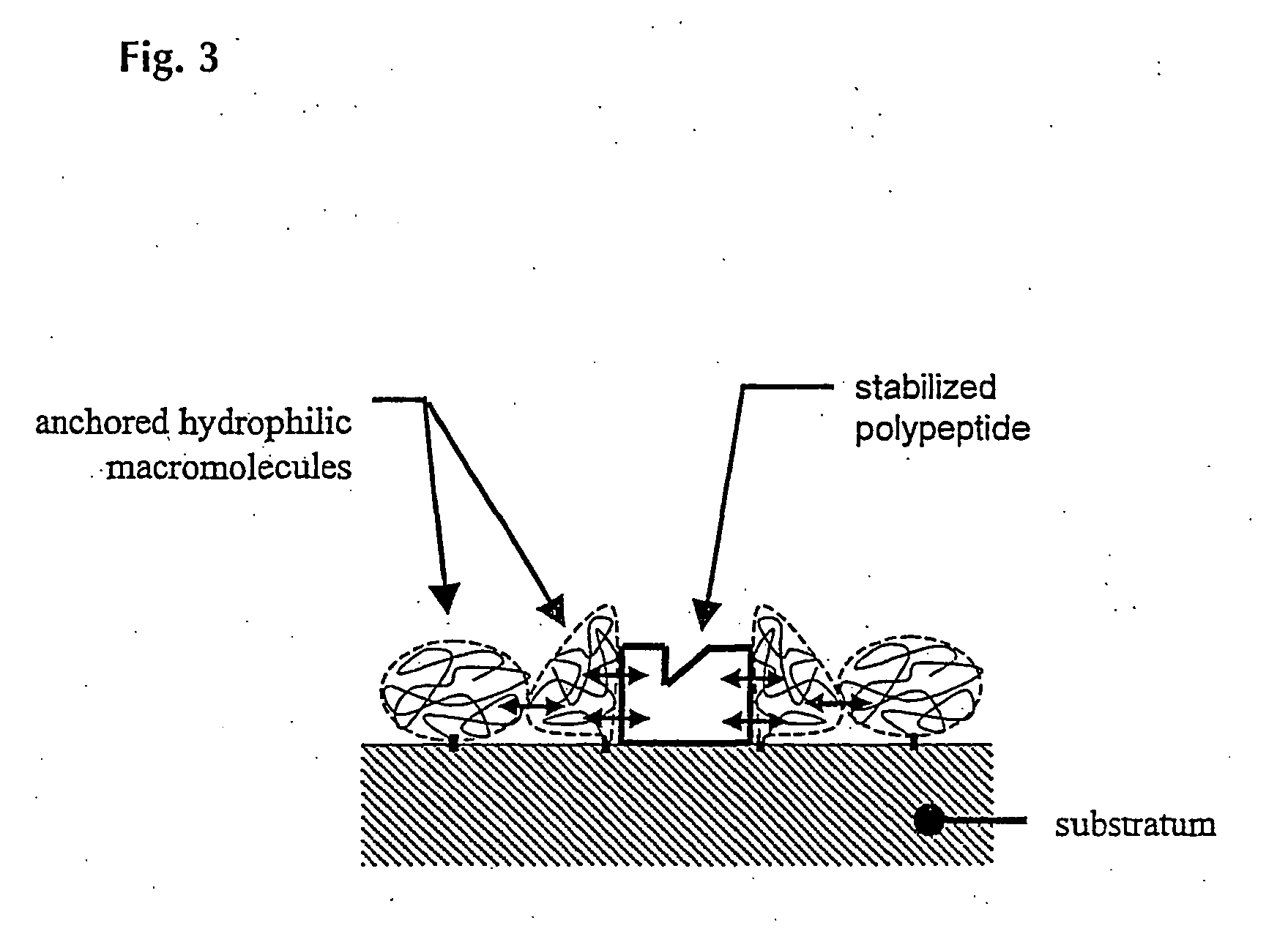
Biocompatible materials
InactiveUS20050053642A1Reduce in quantityTime-stabilising natural conformationMaterial nanotechnologyPharmaceutical containersBiological interactionChemisorption
The present invention teaches a novel approach of creating biocmpatible surfaces, said surfaces being capable of functionally interact with biological material. SAid biocompatible surfaces comrise at least two comonents, such as a hydrophobic substratum and a macromolecule of hydrophilic nature, which, in a cooperativity, form together the novel biocoompatible surfaces. The novel approach is ased on contacting said hydrophobic substratum with a laterally patterned monomolecular layer of said hydrophilic and flexible macromolecules, exhibiting a pronounced excluded volume. The htus formed two component surface is, in respect to polarity and morphology, a molecularly heterogeneous surface. Structural features of said macromolecular monolayer (as e.g. the layer thickness or its lateral density) are determined by: i) the structural features of the layer forming macromolecules (as e.g. their MW or their molecular architecture) and ii) the method of creating said monomolecular layer (as e.g. by physi- or chemisorbing, or by chemically binding said macromolecules). The structural features of the layer forming macromolecules(s) is in turn determined by synthesis. AMount and conformation and thus also biological activity of biological material (as e.g. polypeptides) which contact the novel biocompatible surface, is determined and maintained by the cooperative action of the underlying hydrophobic substratum and the macromolecular layer. In this way it becomes possible to maintain and control biological interactions between said contacted polypeptides and other biological compounds as e.g. cells, antibodies and the like. Consequently, the present invention aims to reduce and / or eliminate the deactivation and / or denaturation associated with the contacting of polypeptides and / or other biological material to a hydrophobic substratum surface.
Owner:BIOSURF APS
Multi component controlled delivery system for soap bars
InactiveUS7208460B2Increase depositionImprove skinPowder deliverySoap detergents with organic compounding agentsControlled releaseMicrosphere
Owner:SALVONA IP
Multi component controlled delivery system for soap bars
InactiveUS20050065047A1Increase depositionHigh densitySoap detergents with organic compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsControlled releaseMicrosphere
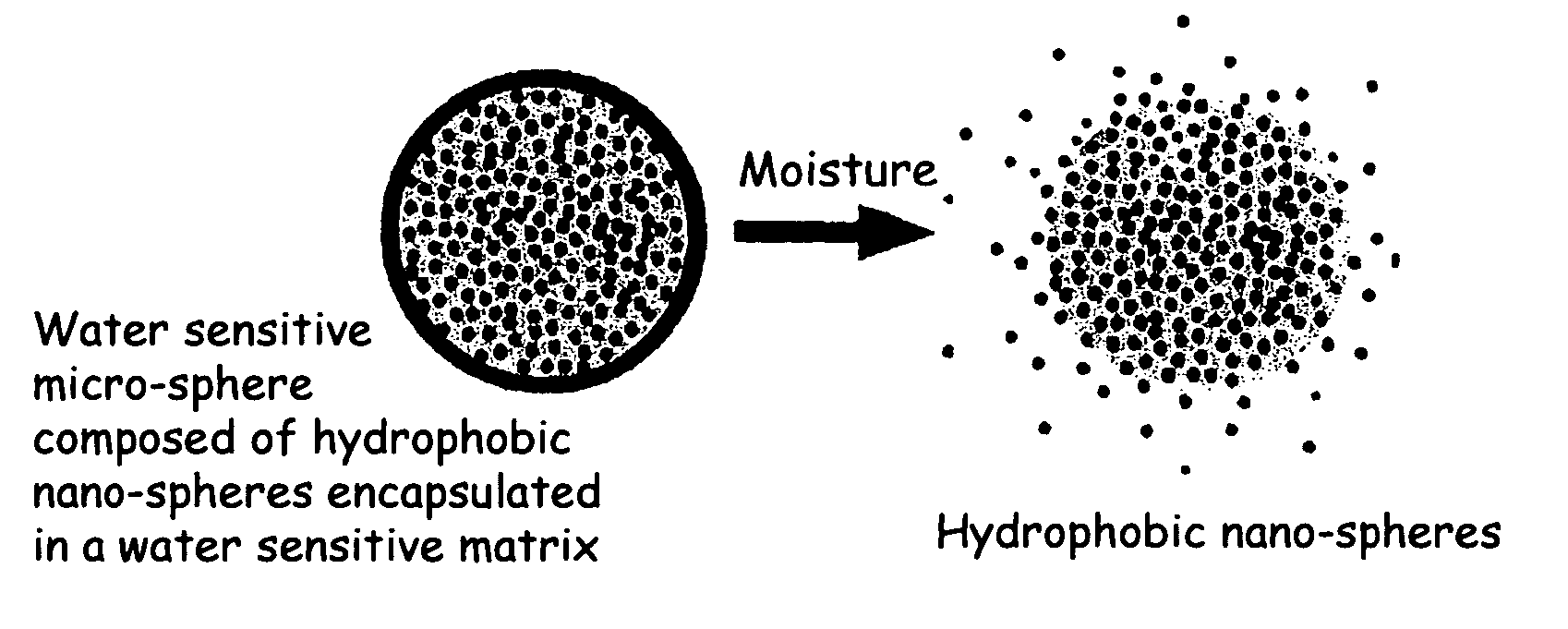
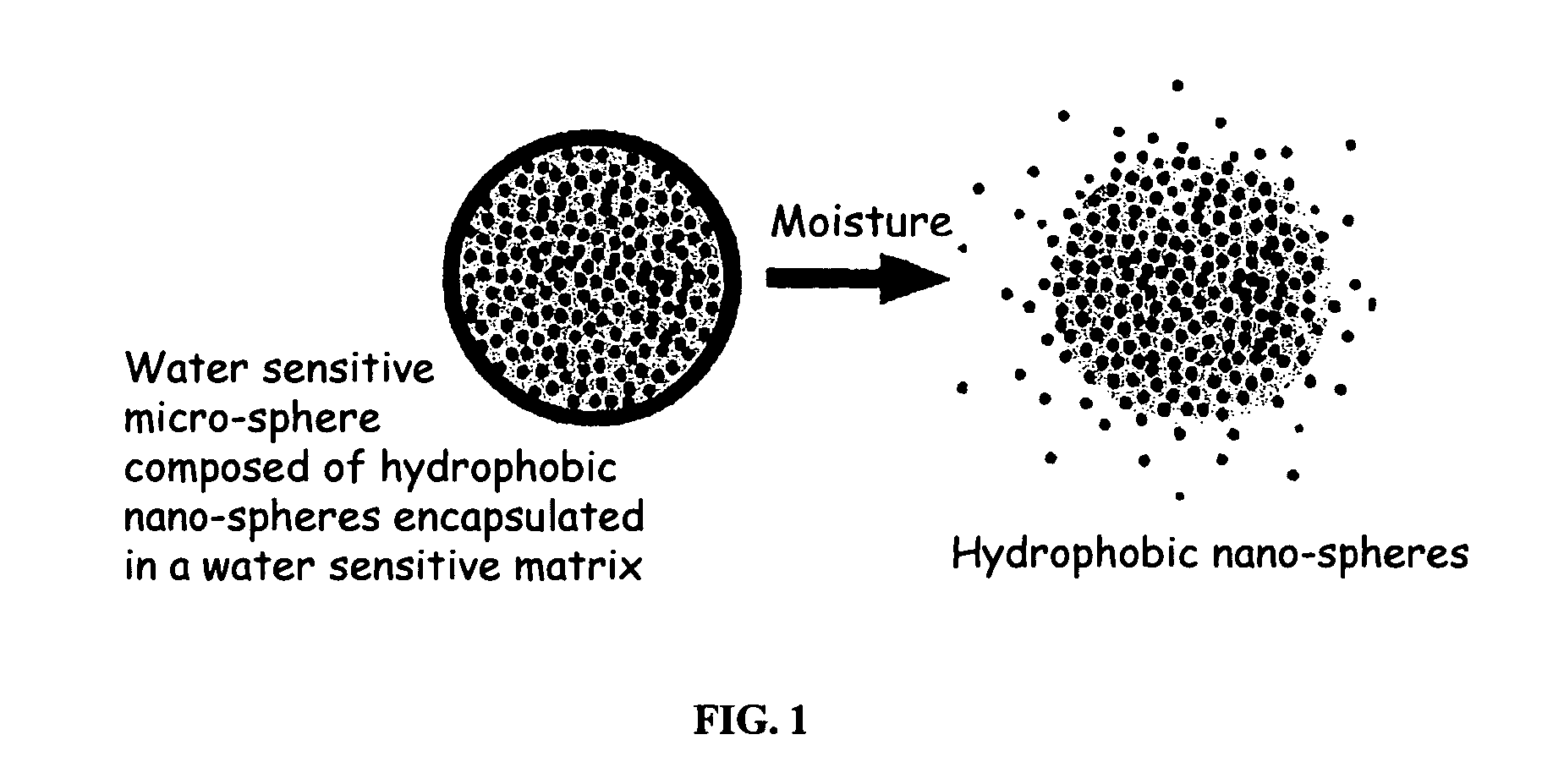
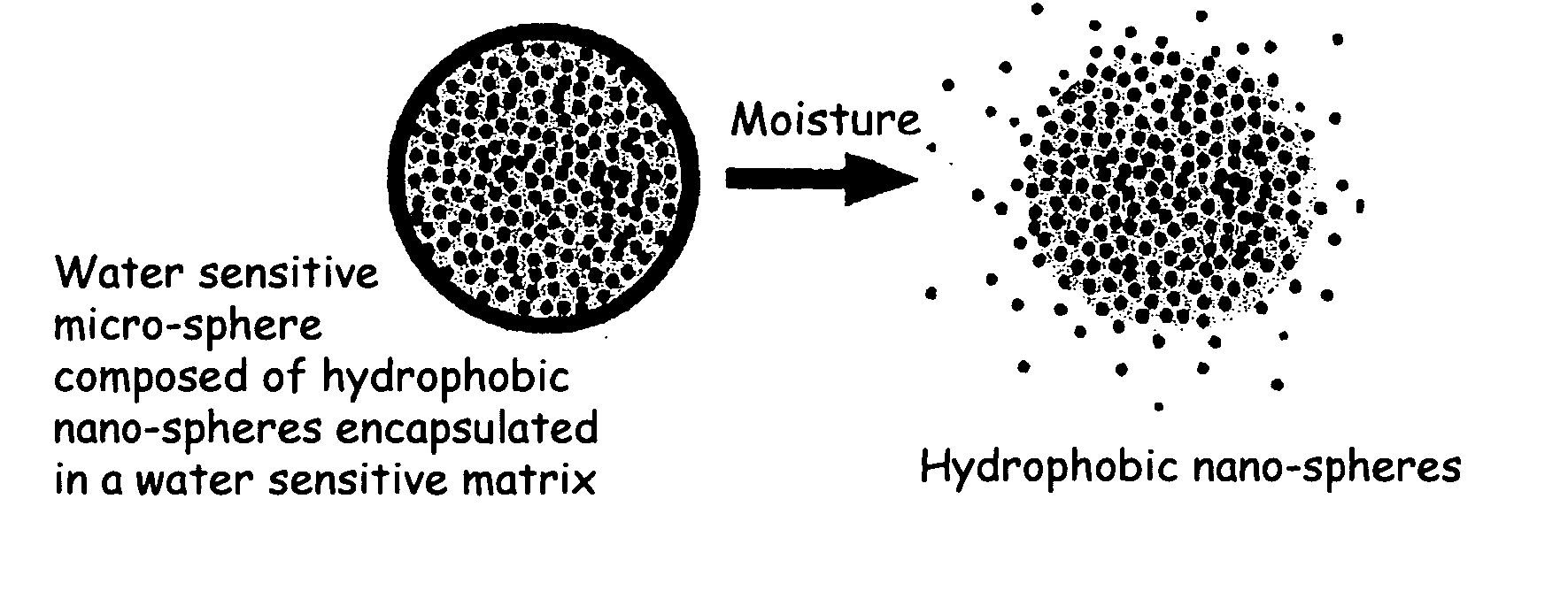
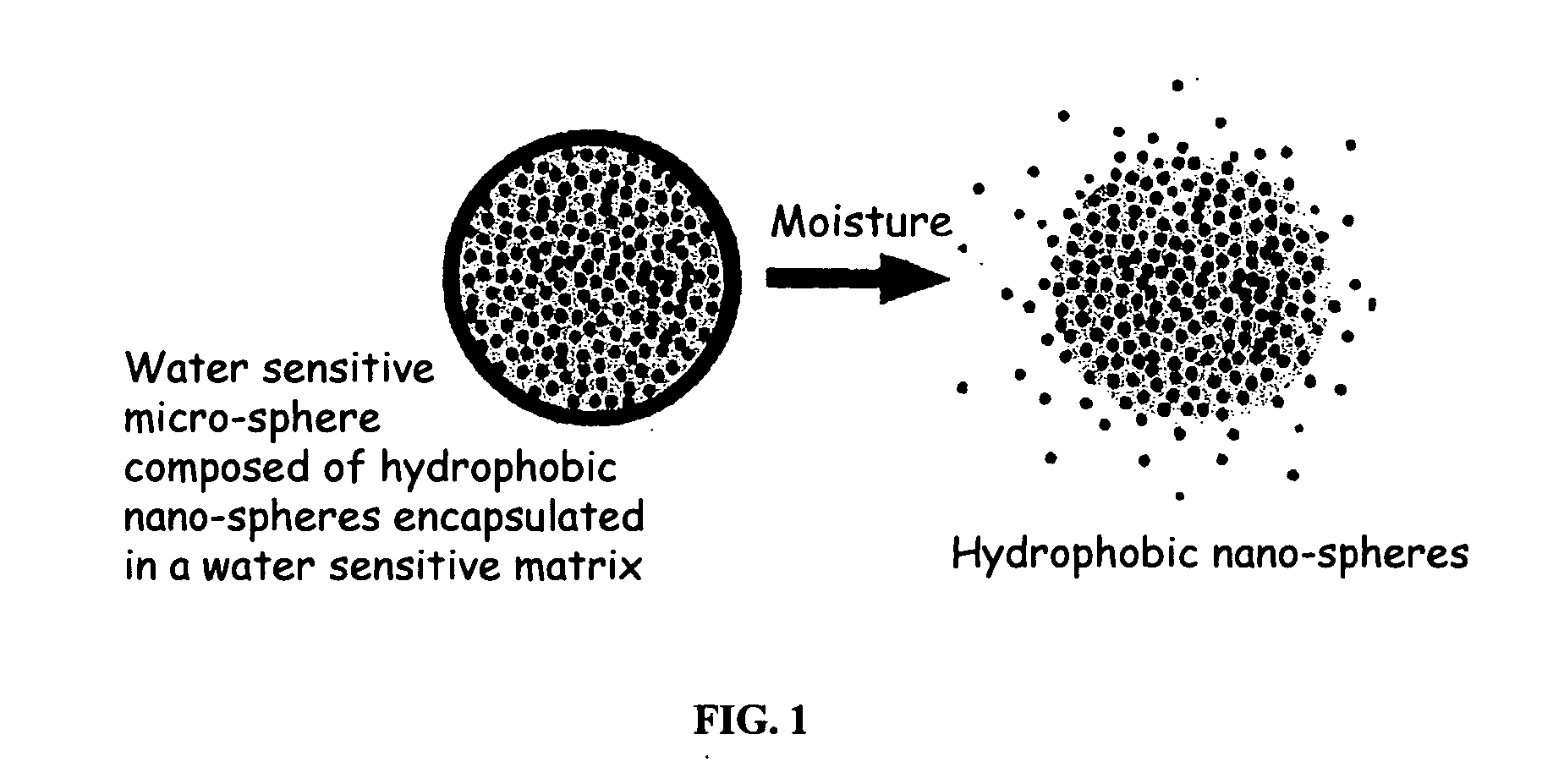
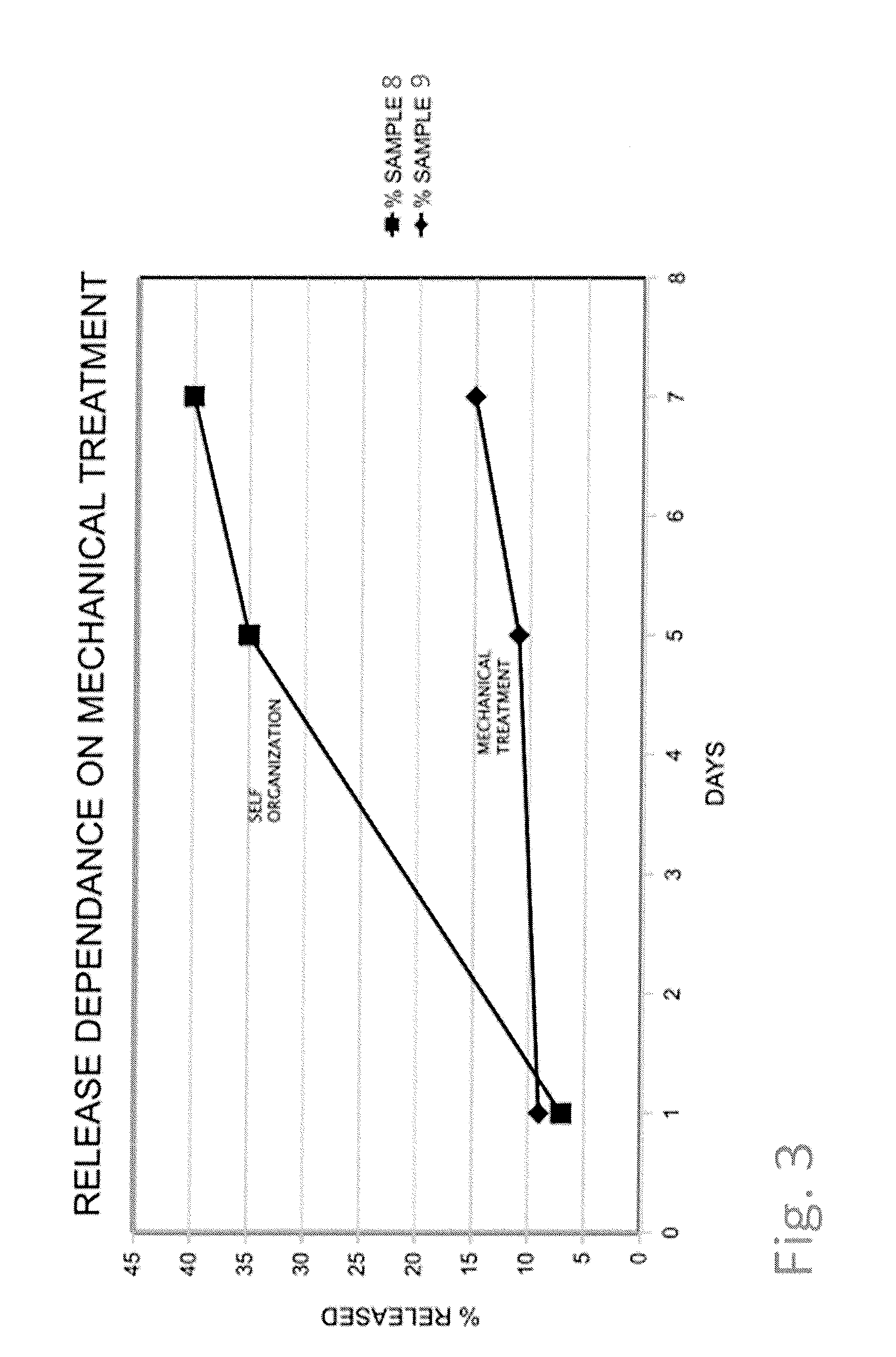
The present invention relates to an improved controlled delivery system that can be incorporated in soap bars to enhance deposition of active ingredients and sensory markers onto skin. The carrier system also provides controlled release or prolonged release of these actives from the skin over an extended period of time. The controlled delivery system of the present invention comprises substantially free-flowing, powder formed of solid hydrophobic, positively charged, nanospheres of encapsulated active ingredients, that are encapsulated in moisture sensitive microspheres. The high cationic charge density of the nanosphere improves deposition of active ingredients onto skin. The high cationic charge density on the nanosphere surface is created by incorporating a cationic conditioning agent into the solid hydrophobic matrix of the nanospheres, by incorporating a cationic charge “booster” in the moisture sensitive microsphere matrix, or by using a cationic conditioning agent in the nanosphere matrix in conjunction with a cationic charge “booster” in the microsphere matrix. The invention also pertains to soap products comprising the controlled release system of the present invention.
Owner:SALVONA IP
Oral pharmaceutical extended release dosage form
An enteric coated pharmaceutical extended release dosage form of a H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor giving an extended plasma concentration profile of a H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor. The extended plasma profile is obtained by a pharmaceutical composition which comprises a core material of a hydrophilic or hydrophobic matrix, and the H+, K+-ATPase inhibitor and optionally pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The dosage form may be administered once daily.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Patterning device
InactiveUS20140378339A1Promote sportsIncrease trappingMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsEvaporationEngineering
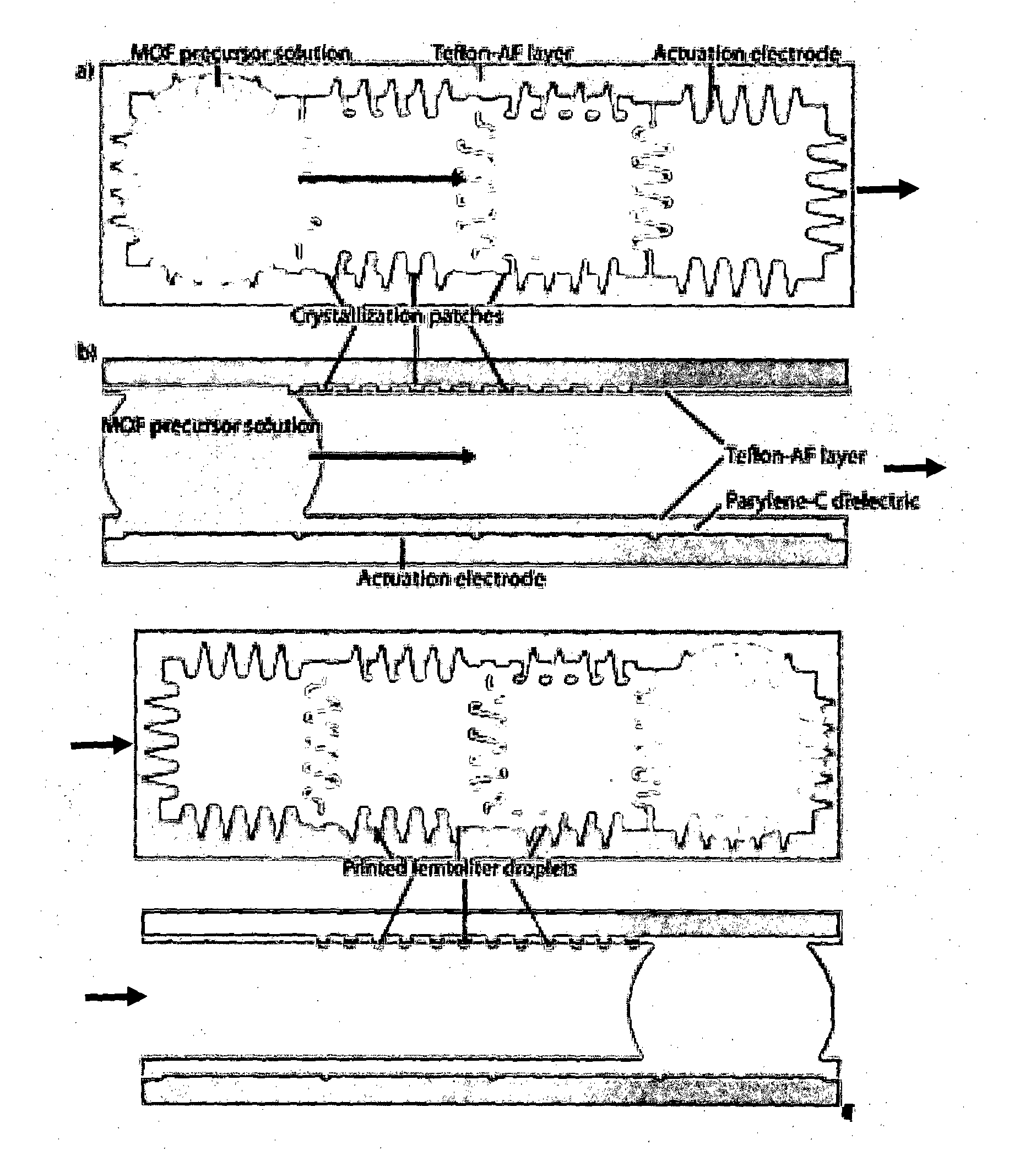
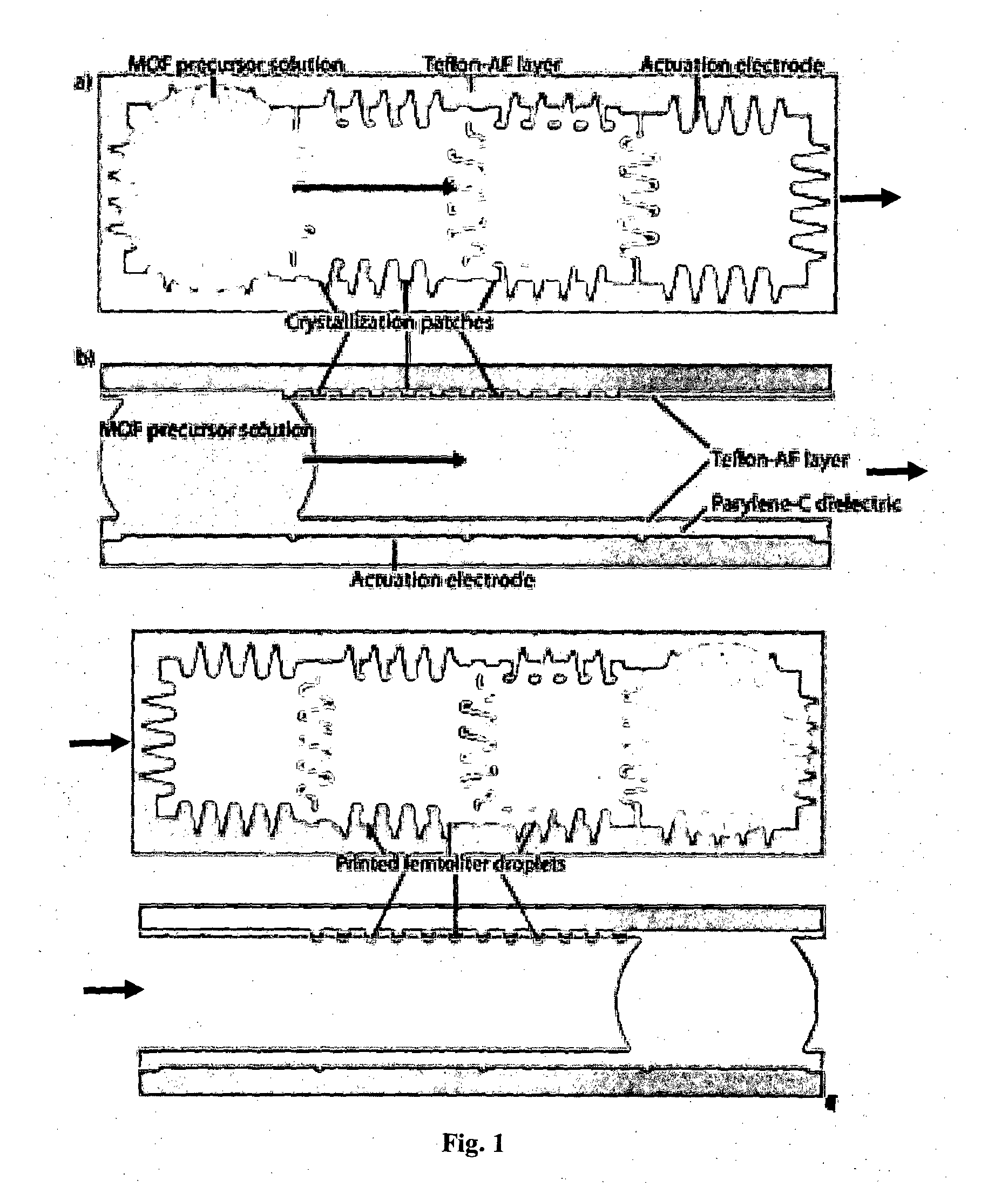
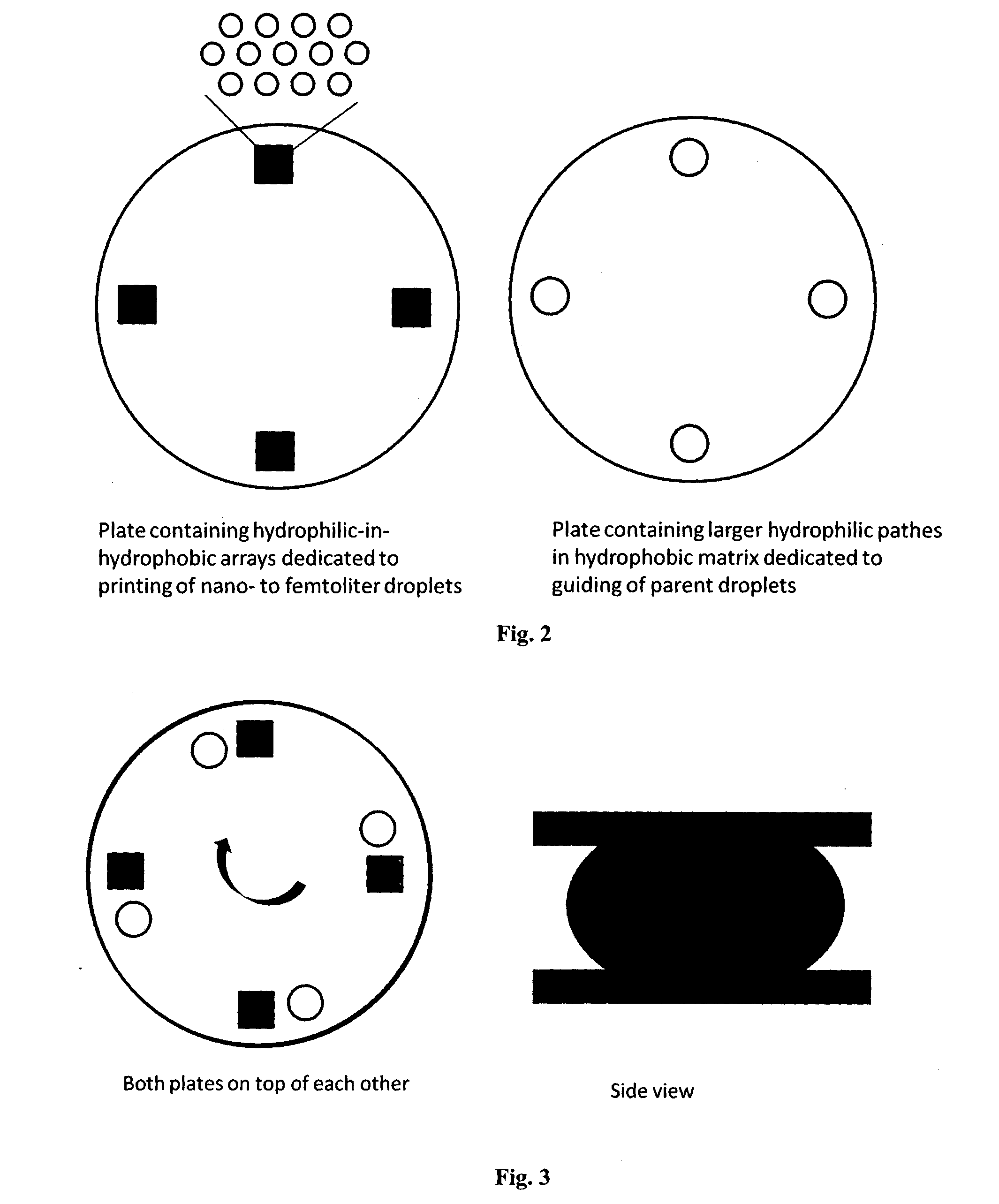
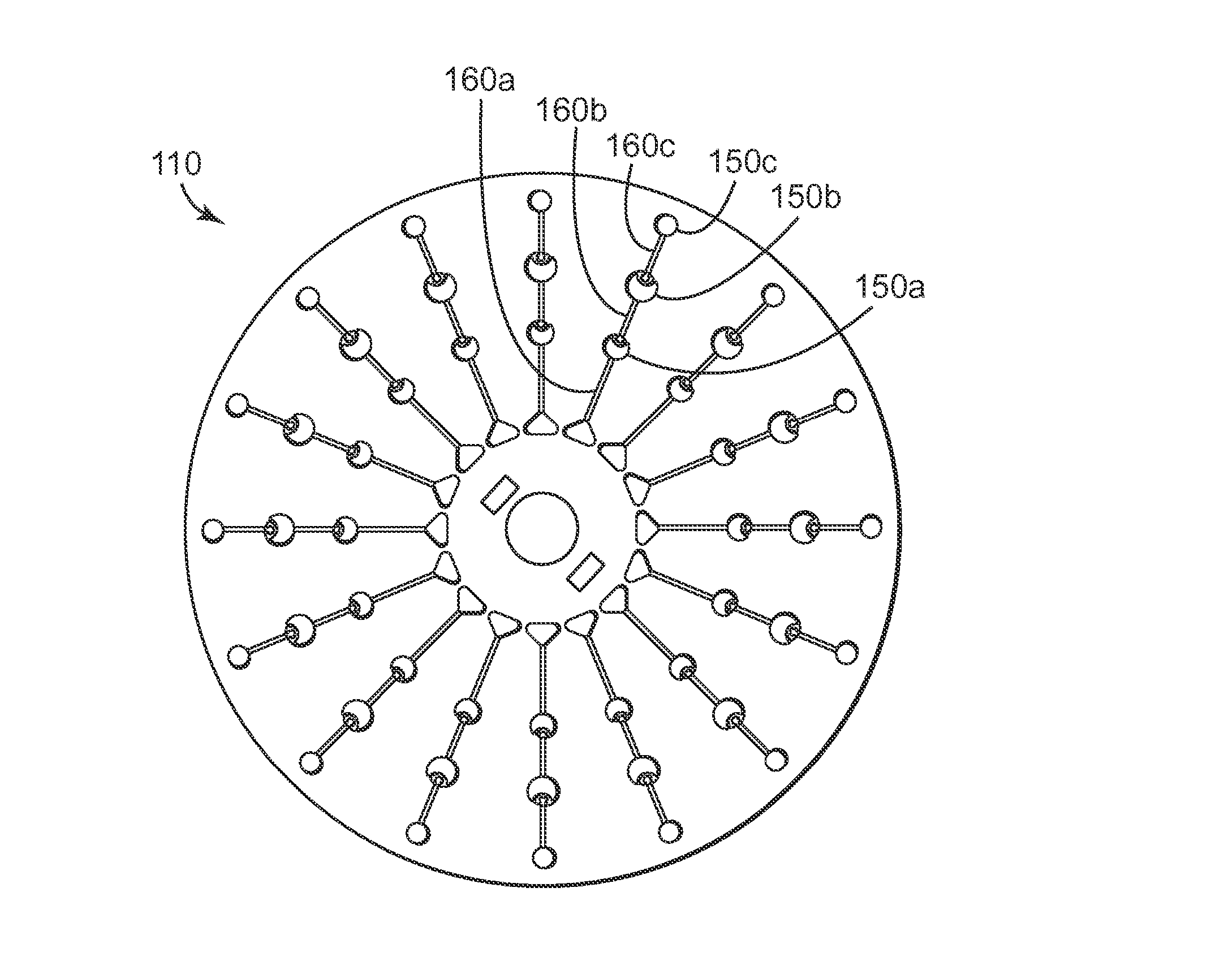
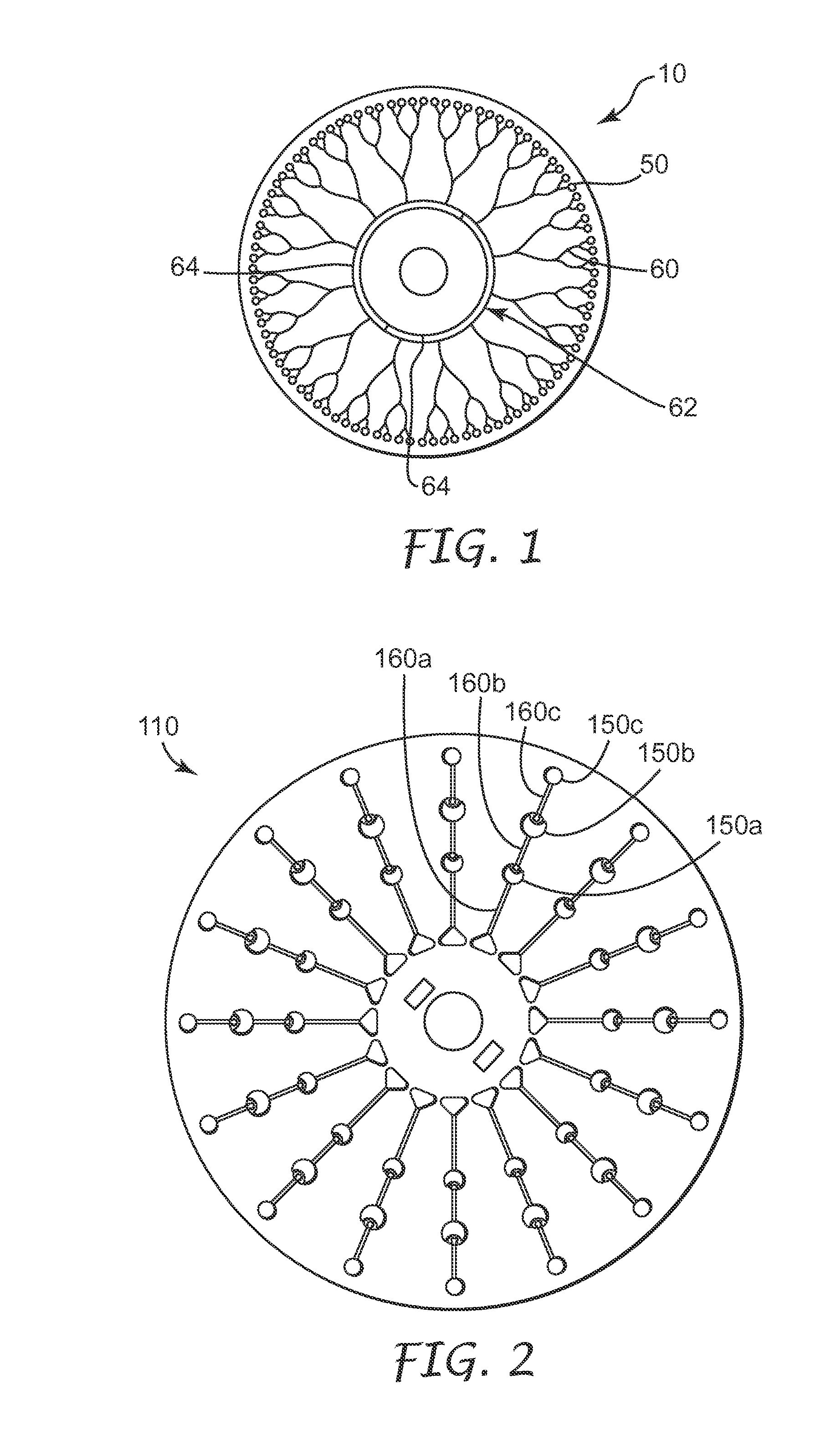
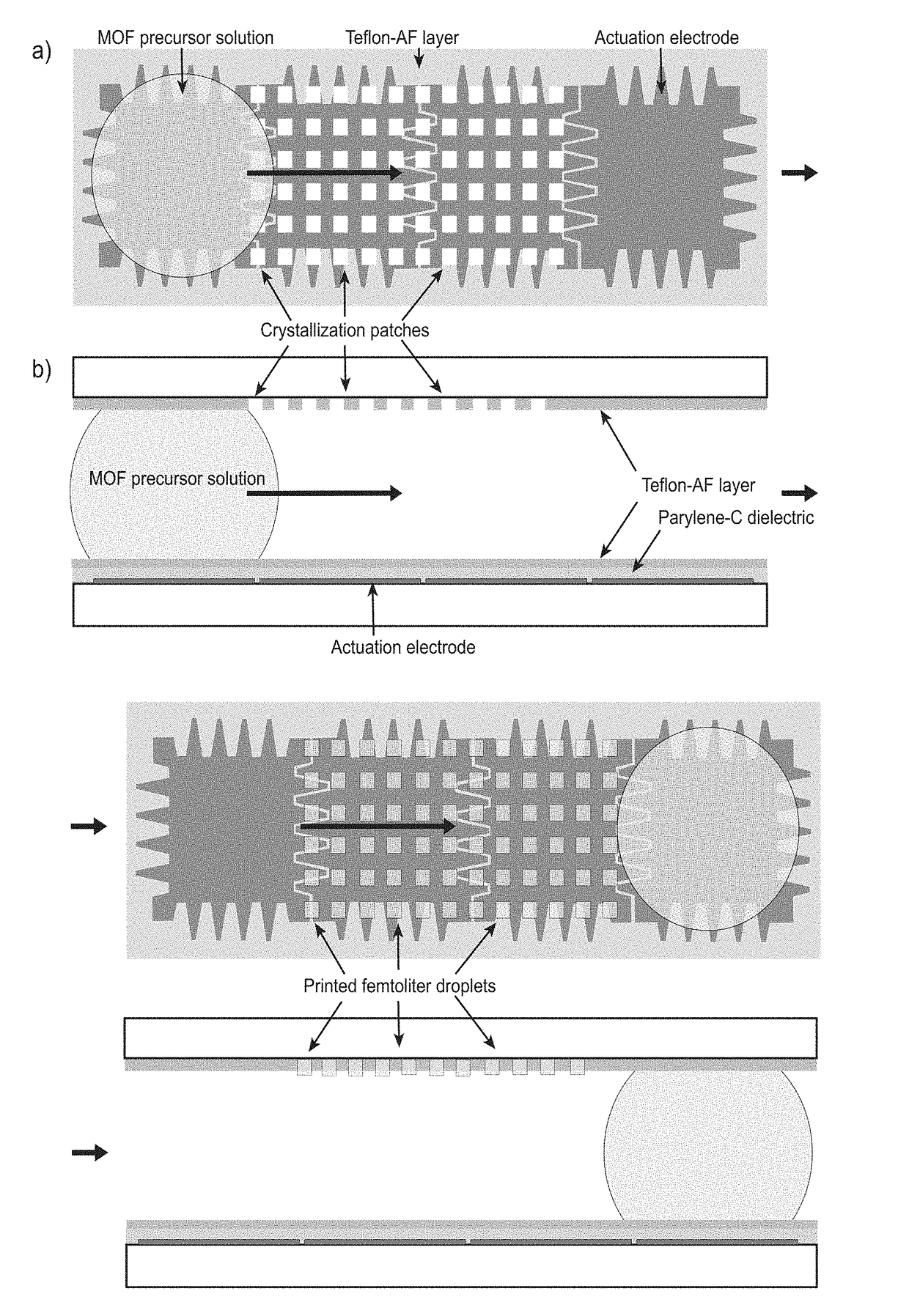
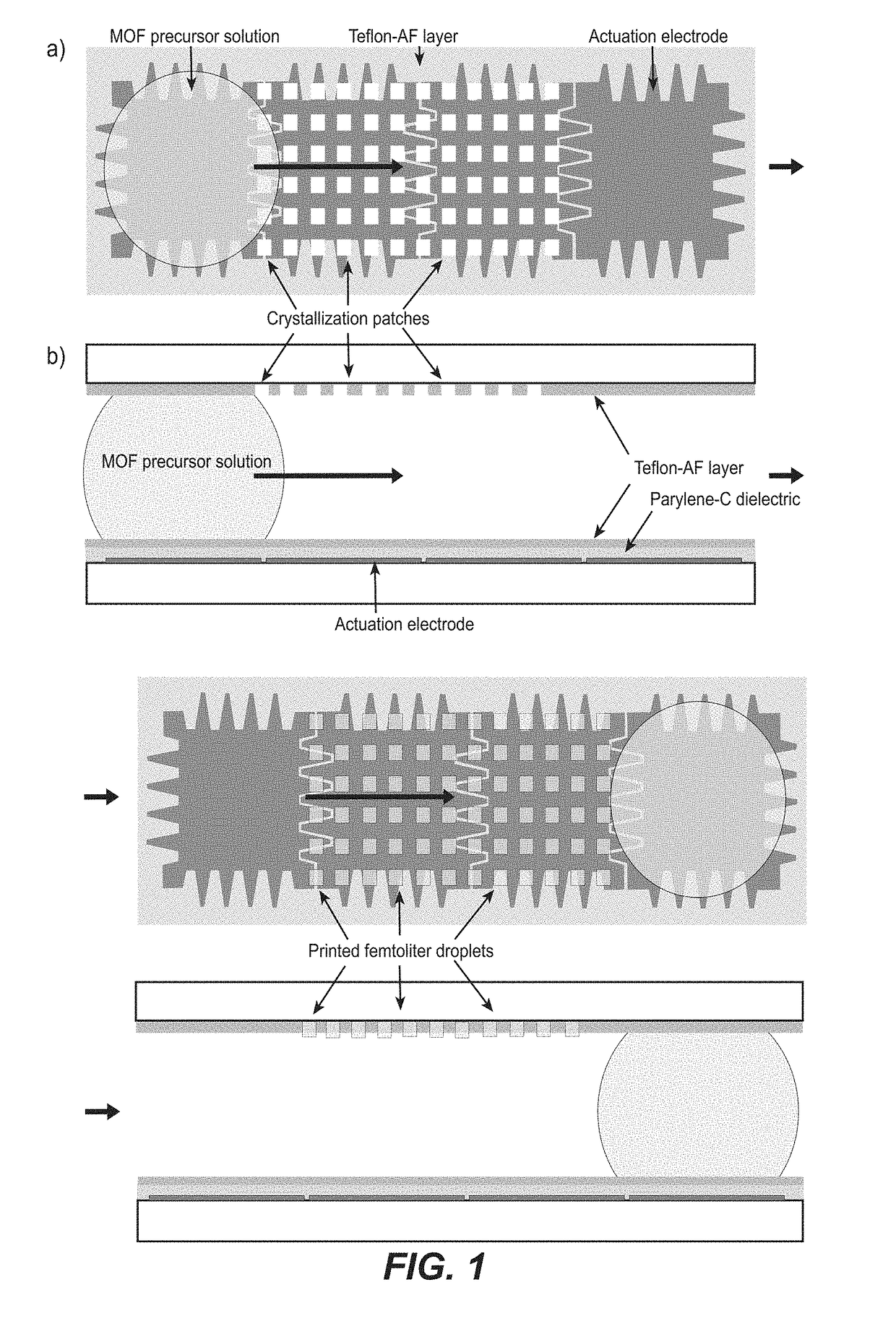
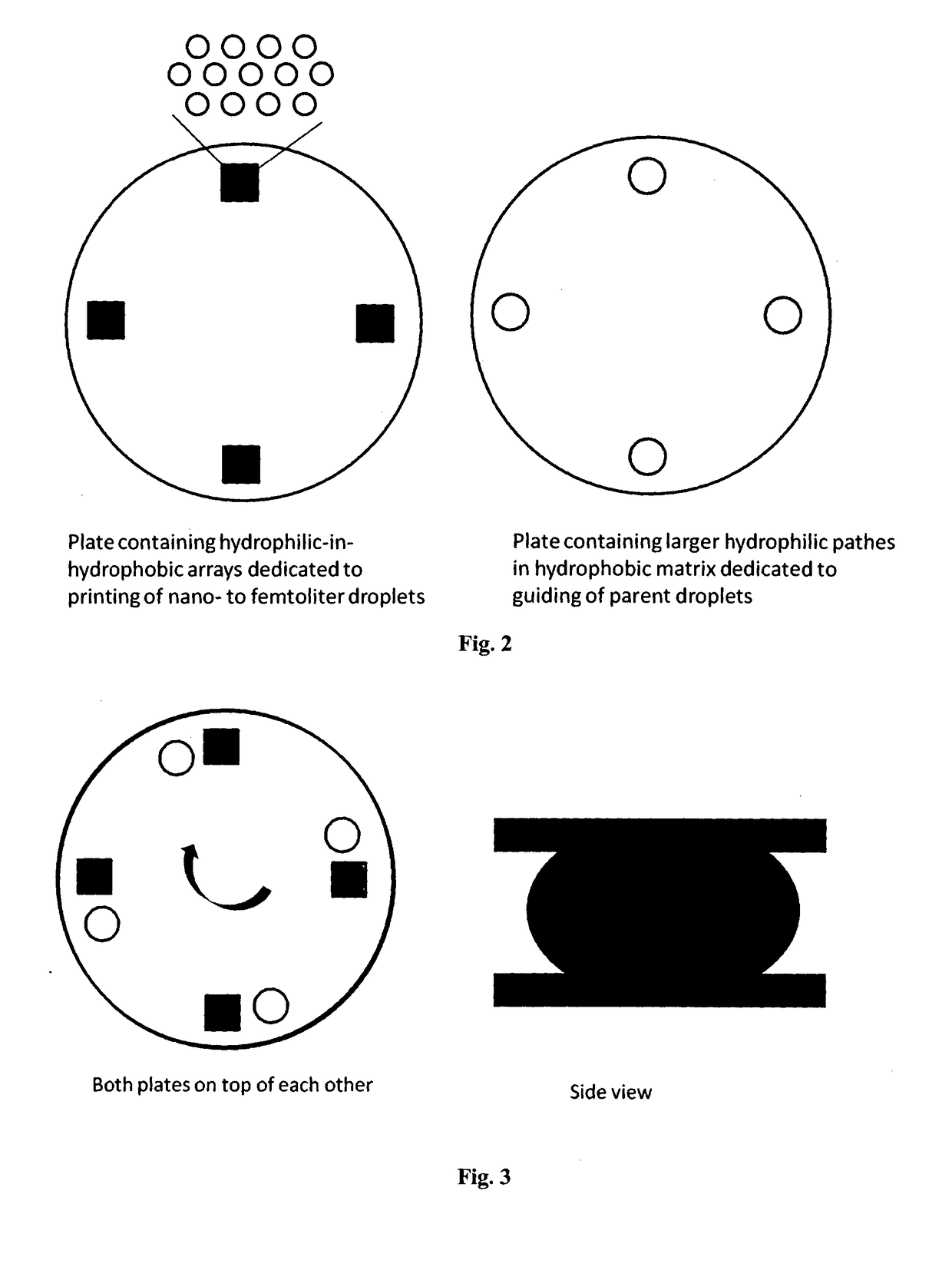
A novel miniaturized and highly automated method for the controlled printing of large arrays of nano- to femtoliter droplets is presented by actively transporting mother droplets over hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic micropatches. The proposed technology consists of single plate or double-plate devices where mother droplets can be actuated and hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic micropatches on one or both plates of the device where nano- to femtoliter droplets are printed. Due to the selective wettability of the more wettable hydrophilic micropatches in a hydrophobic matrix, large nano- to femtoliter droplet arrays are created when mother droplets are transported over these arrays. The parent droplets can be moved by different droplet actuation principles, for example, by using the principle of electrowetting-on-dielectric droplet actuation. We propose another method that uses two plates that are placed on top of each other while being separated by a spacer. One plate is dedicated to confirming and guiding of parent droplets by using hydrophilic patches in a hydrophobic matrix, while the other plate contains hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic arrays dedicated to the printing of nano- to femtoliter droplets. When the plate dedicated to parent droplet guiding is rotated over the plate dedicated to printing of nano- to femtoliter droplets, nano- to femtoliter droplets are dispensed inside the hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic array due to their selective wettability. All these proposed methods allow the parent droplets to be moved over the hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic arrays many times, providing unique advantages for performing bio-assays or miniaturized materials synthesis in nano- to femtoliter sized droplets. Upon the controlled evaporation of the dispensed droplets of solution, large arrays of the printed material can be generated on an automated way in seconds of time on a very flexible way. The method disclosed herein provides a distinct nano- to femtoliter droplet printing technique for a wide variety of applications such as protein- or cell-based bio-assays or printing of crystalline structures, suspensions of nanoparticles or components for microelectronics.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Methods for making and using particulate pharmaceutical formulations for sustained release
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Stabilization of carbon nanotube coatings to moisture
ActiveUS20160137854A1Easy to wetReduce resistanceNon-metal conductorsCarbon compoundsCarbon nanotubeAqueous solution
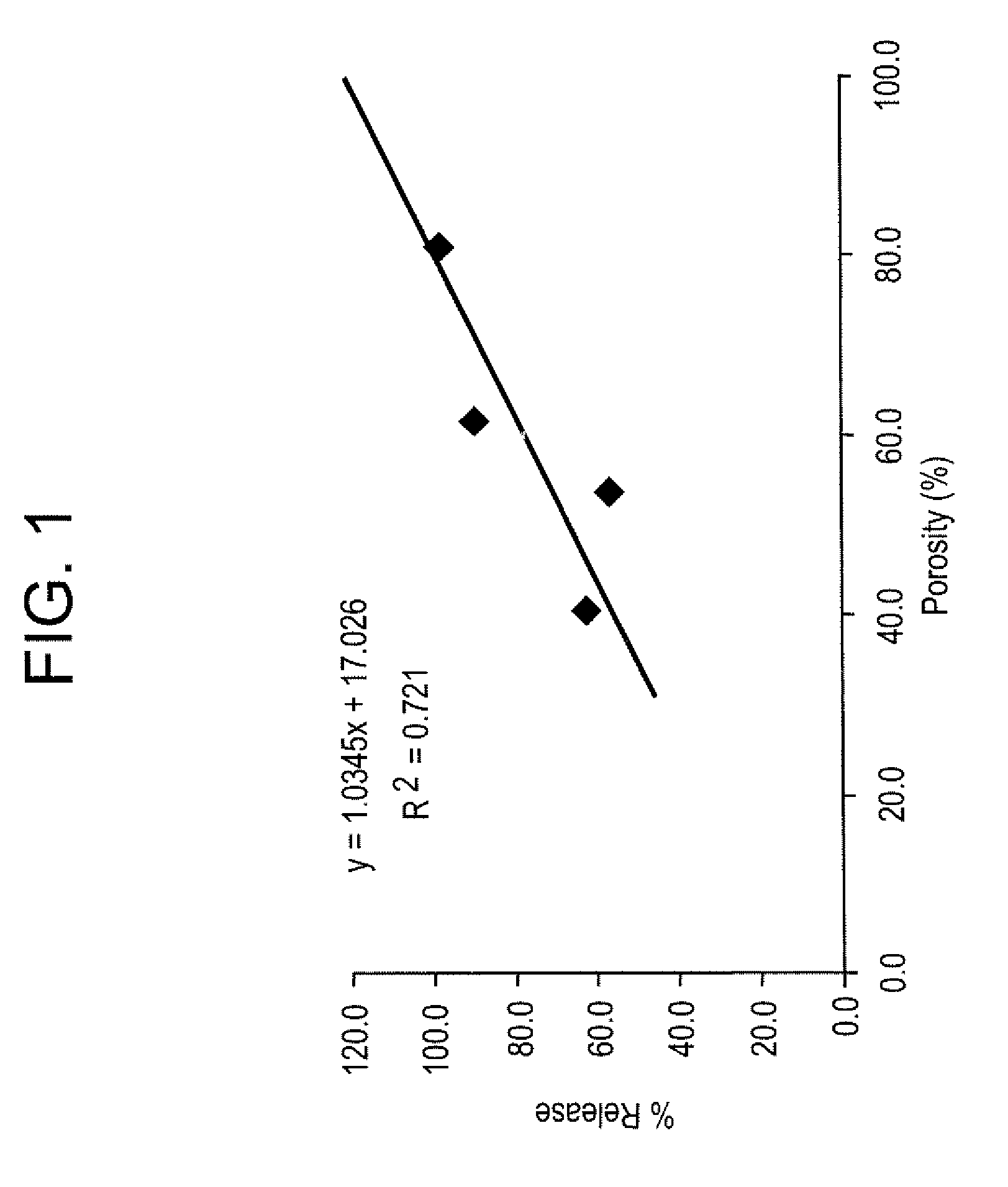
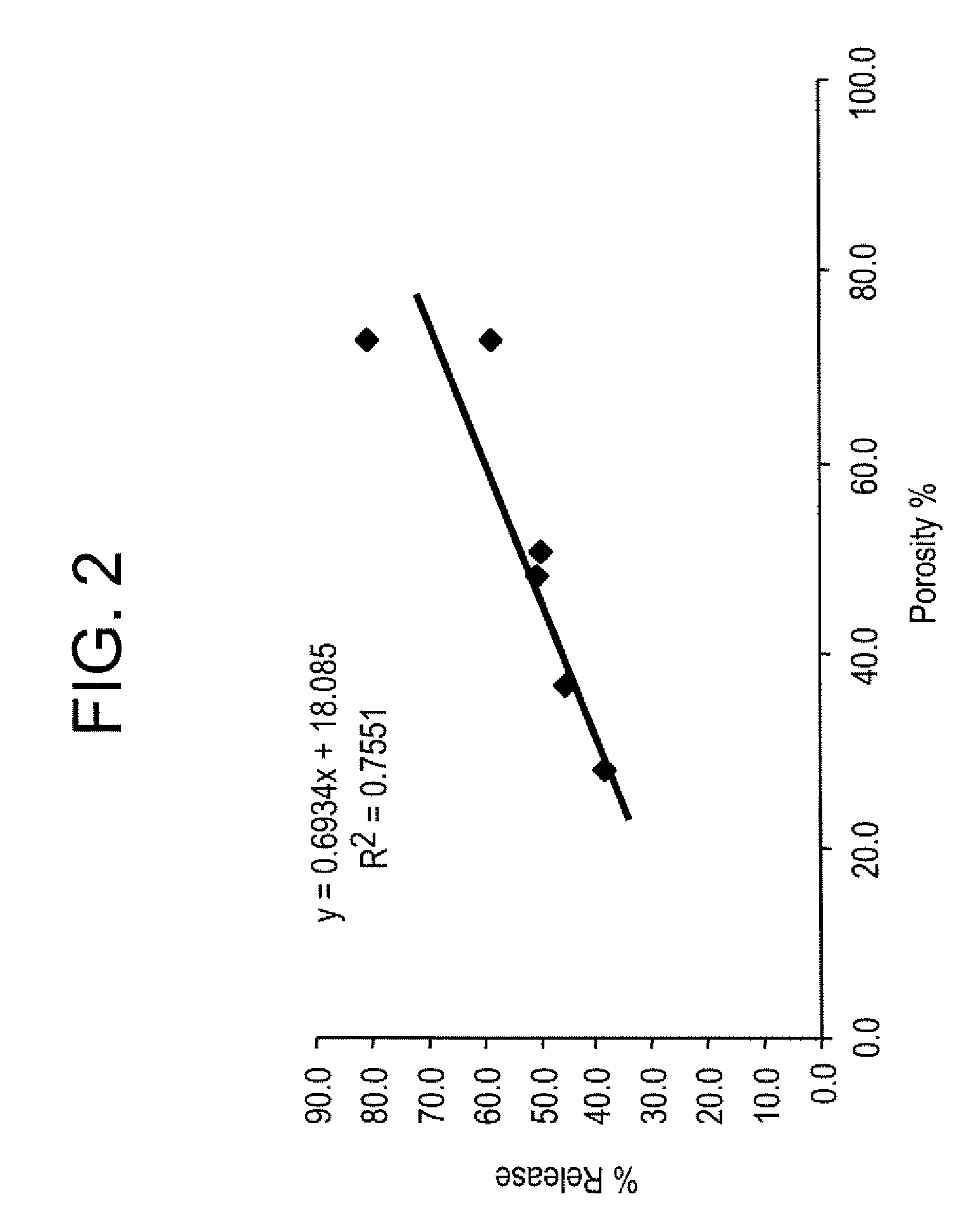
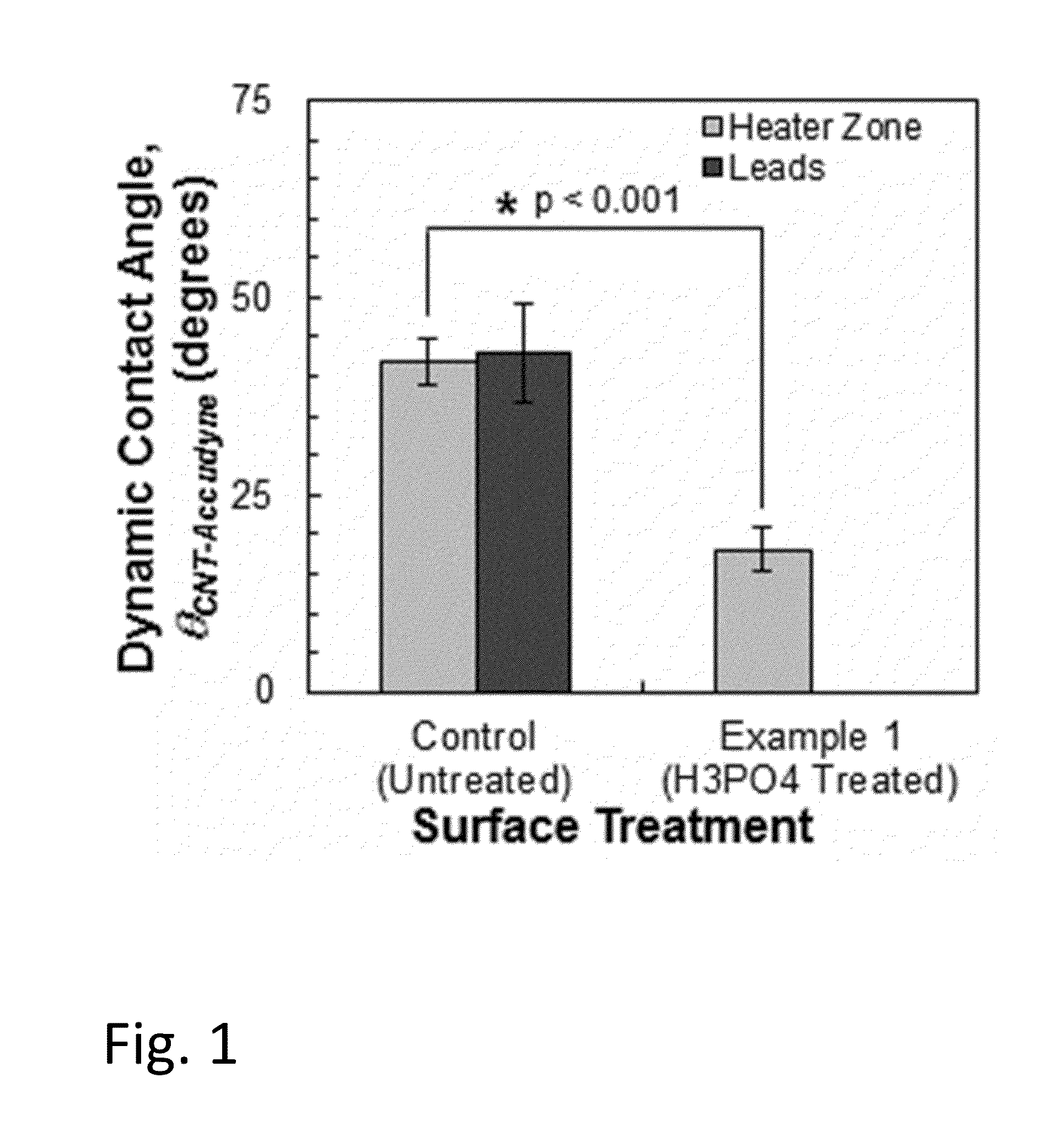
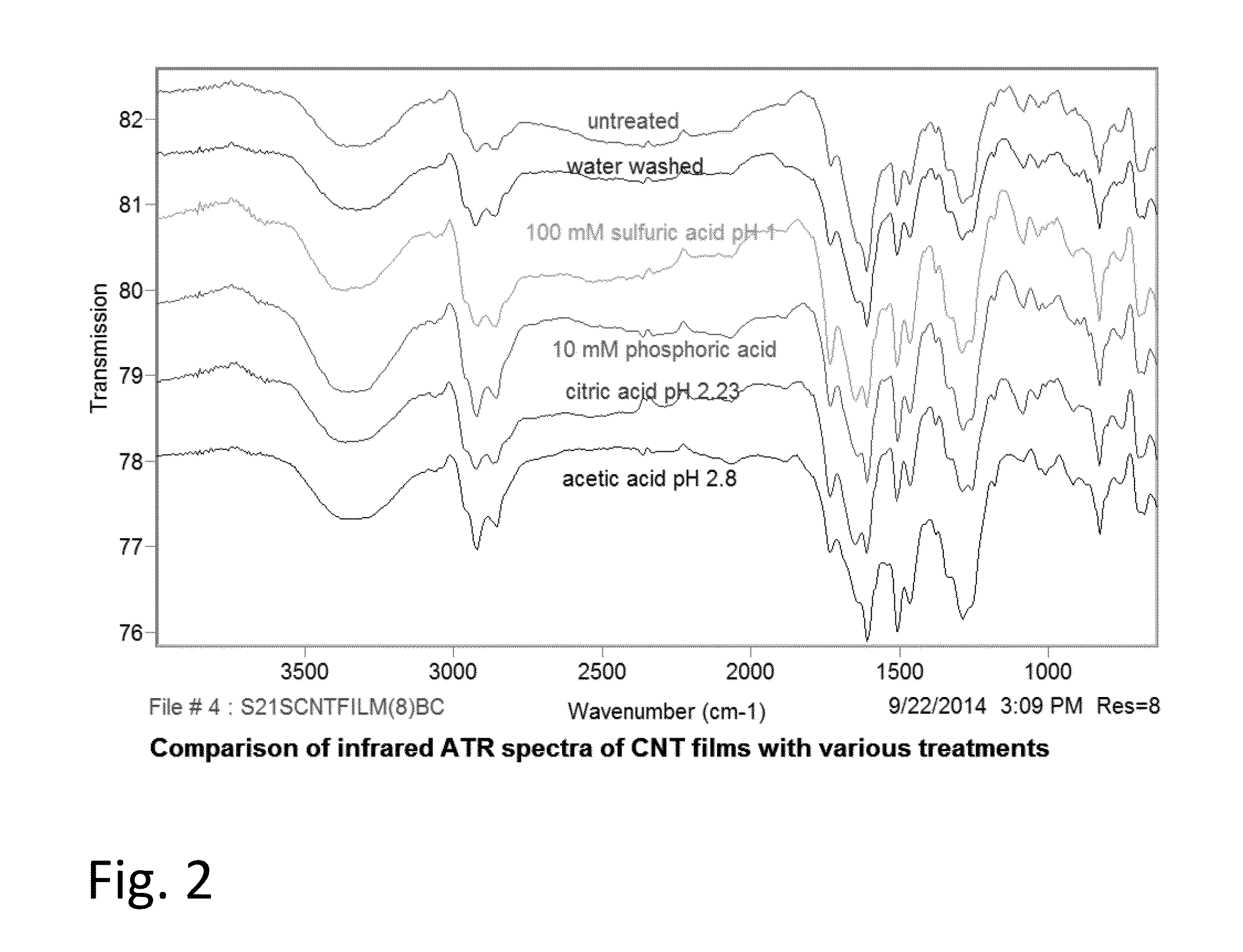
A method of making CNT films is described in which the film is washed with a mild acid treatment. The method generates a CNT film that is not sensitive to moisture or fluctuations in moisture. The method involves the use of anionic polysaccharides or anionic glycosaminoglycans such as hyaluronic acid, sodium salt, as aqueous dispersing agents and their modification to a hydrophobic matrix after deposition. In the course of conducting the work described here, we made the surprising discovery that washing with an aqueous acidic solution resulted in a decrease in resistance through the material. The invention also includes CNT composites made by the inventive methods and a CNT composite comprising CNTs and anionic polysaccharides or anionic glycosaminoglycans further characterized by a low cationic content and a high conductivity and / or small CNT particle size as measured by SEM.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Novel modified release formulation
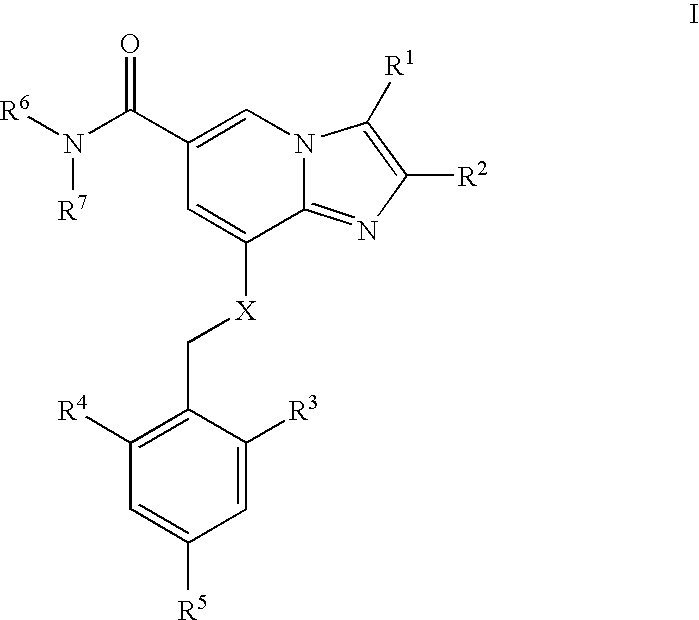
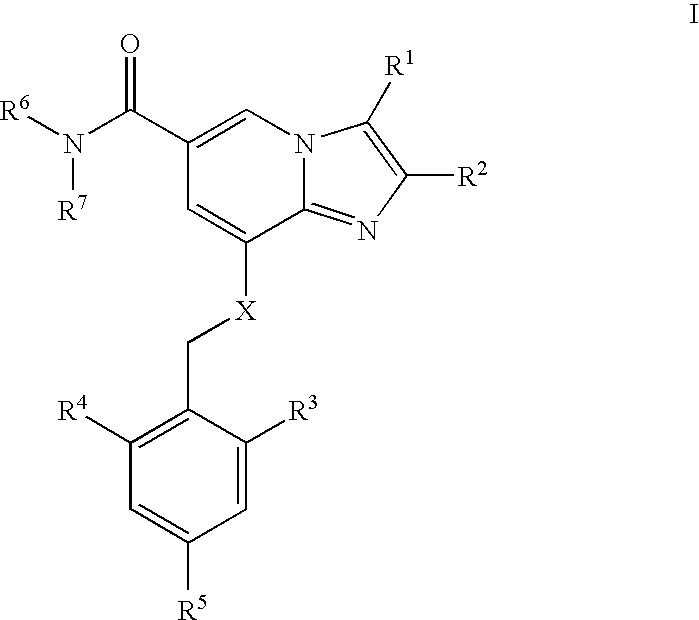
The present invention is directed to a multiparticulate, modified release solid dispersion formulation, comprising a drug substance having a pH-dependent solubility, said drug substance being a compound of the formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; a hydrophobic matrix former which is a water-insoluble, non-swelling amphiphilic lipid; and a hydrophilic matrix former which is a meltable, water-soluble excipient; wherein the weight ratio hydrophobic matrix former / hydrophilic matrix former is ≧1; and the particle size is less than 300 μm. Also a unit dosage of the same, as well as a process for the preparation thereof and the use of the formulation and unit dosage is claimed.
Owner:JUPPO ANNE
Hydrophobic drug-delivery material, method for manufacturing thereof and methods for delivery of a drug-delivery composition
A method for manufacturing a drug-delivery composition includes providing at least a pharmaceutically active composition, providing a hydrophobic matrix; and mixing the hydrophobic matrix and the pharmaceutically active composition to form a paste-like or semi-solid drug-delivery composition.
Owner:BIOCORRX INC +1
Formation of hydrophilic polysaccharide coatings on hydrophobic substrates
InactiveUS7052776B2Good biocompatibilityReduce static chargeSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsDye absorptionHydrophobic polymer
Articles produced from hydrophobic polymers (e.g., polyethylene) are surface-coated with thin films of starch in order to render the surfaces hydrophilic. The thin coatings form on the surfaces of plastic objects when the objects are placed in contact with hot, aqueous solutions of starch. These starch coatings are adherent to the hydrophobic plastic surfaces under both wet and dry conditions, and they permit the surfaces to be uniformly wet with water. The coatings may be rendered even more adherent when wet by graft polymerizing the starch with a synthetic monomer. Resultant products have the potential for improved biocompatibility, improved compatibility with hydrophilic reagents, reduced build-up of electrostatic charge, reduced blocking, reduced friction, improved absorption of water-based dyes, and improved adhesion properties. The starch coatings are non-toxic, inexpensive and biodegradable.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods and devices for removal of organic molecules from biological mixtures using a hydrophilic solid support in a hydrophobic matrix
InactiveUS20080103297A1Improve throughputSugar derivativesLayered productsSolid phase extractionHydrophobic matrix
Methods and devices for removing small negatively charged molecules from a biological sample mixture that uses a solid-phase extraction material that includes a hydrophilic solid support at least partially embedded within a hydrophobic matrix.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Enteric coated hydrophobic matrix formulation
InactiveUS20100003322A1Quicker TmaxReduce the amount of coatingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrophobic matrixEnteric coated
Owner:IMPAX LAB INC
A highly hydrophilic and highly oleophobic membrane for oil-water separation
InactiveCN103534011AFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater contaminantsPolymer scienceSide chain
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Self-gelling tunable drug delivery system
InactiveUS20080102123A1Rapid drug releaseQuick releasePowder deliveryAnaestheticsMedicineHydrophilic matrix
A self-gelling tunable drug delivery system is disclosed. The self-gelling tunable drug delivery system is comprised of a hydrophilic matrix and a hydrophobic matrix.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
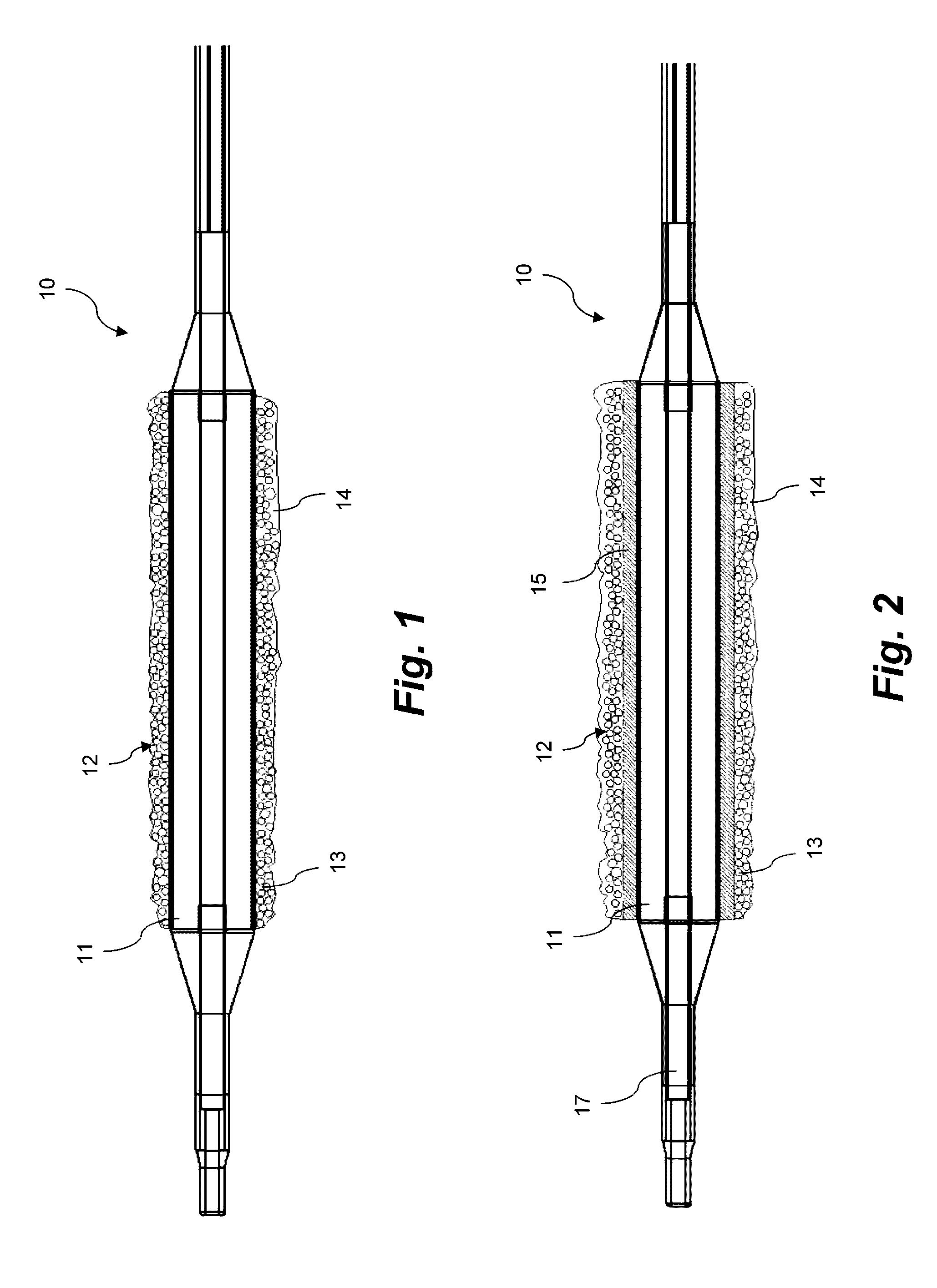
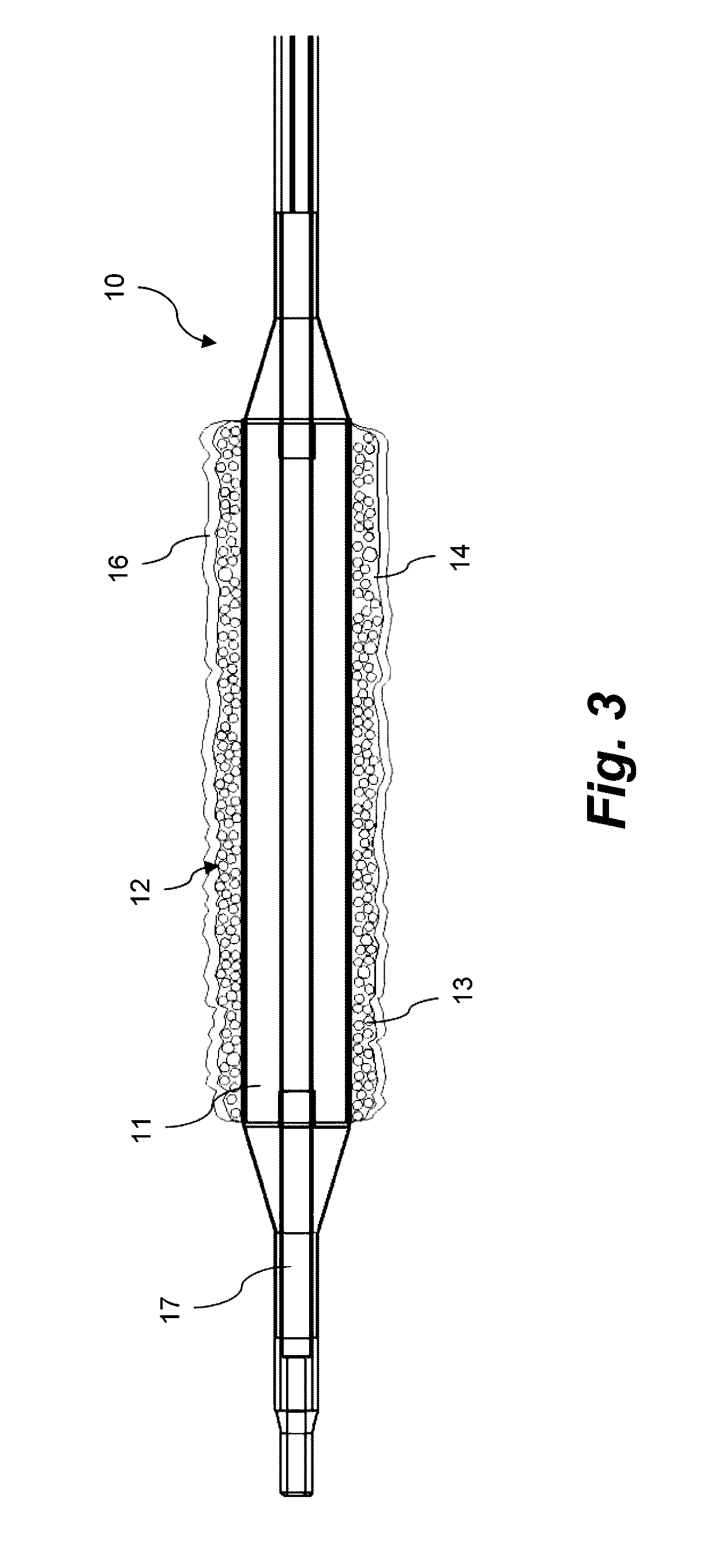
Coating for intraluminal expandable catheter providing contact transfer of drug micro-reservoirs
A coating for an expandable portion of a catheter comprising a hydrophobic matrix and a dispersed phase is disclosed. The dispersed phase comprises a plurality of micro-reservoirs dispersed in the hydrophobic matrix, wherein the plurality of micro-reservoirs comprises a first active agent and a first biodegradable or bioerodable polymer. A coating formulation and a method for forming the coating are also disclosed. A catheter comprising the coating on the expandable portion and a method for treating a condition are also provided.
Owner:M A MED ALLIANCE
Silicified electrolyte material for fuel cell, method for its preparation and fuel cell using same
InactiveUS20090068529A1Increase deposition rateSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureHydrogenFuel cells
This material suitable for constituting an electrolyte for a fuel cell has a hydrophobic matrix comprising carbon, fluorine, oxygen and hydrogen, and silicon.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
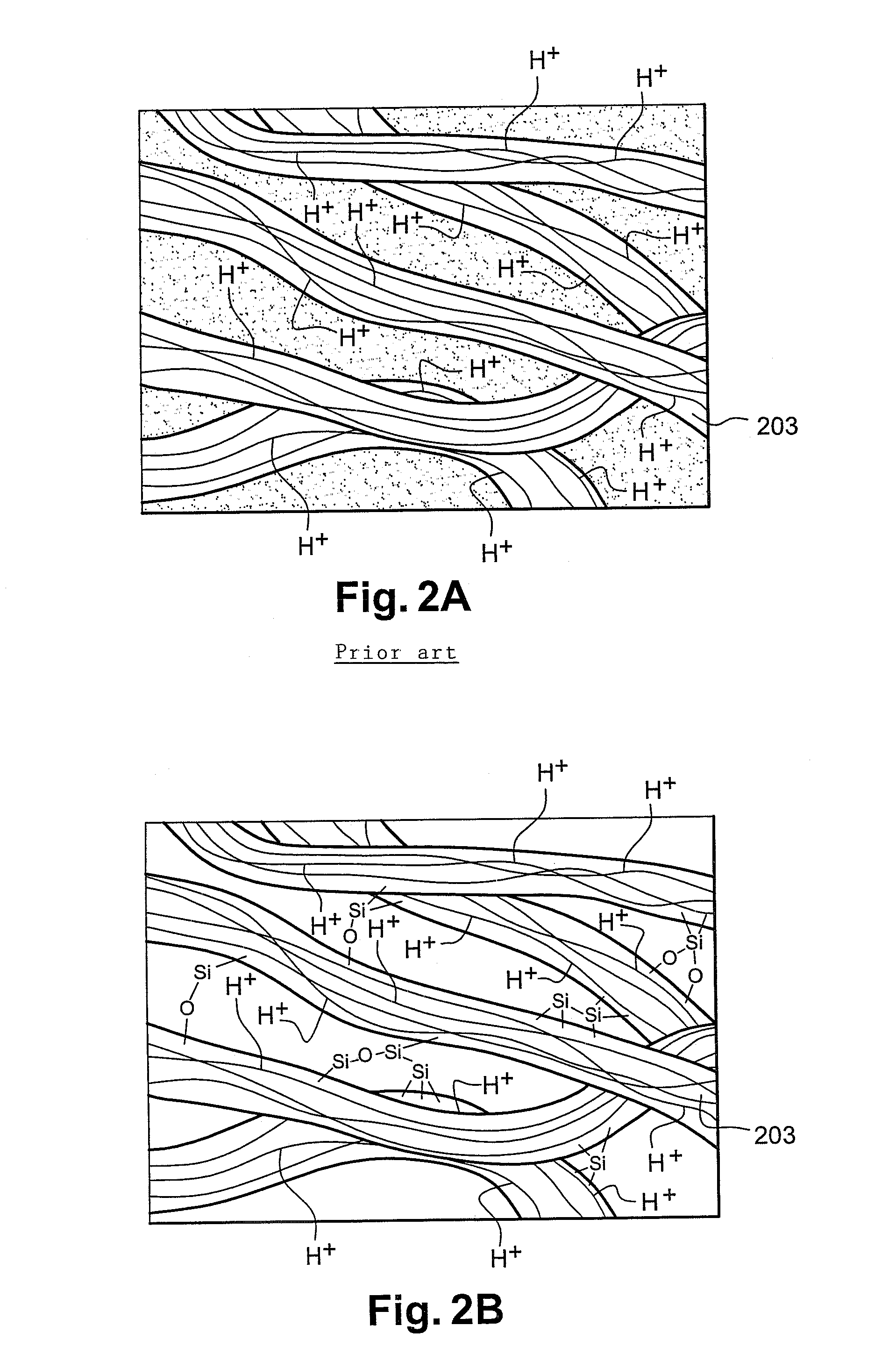
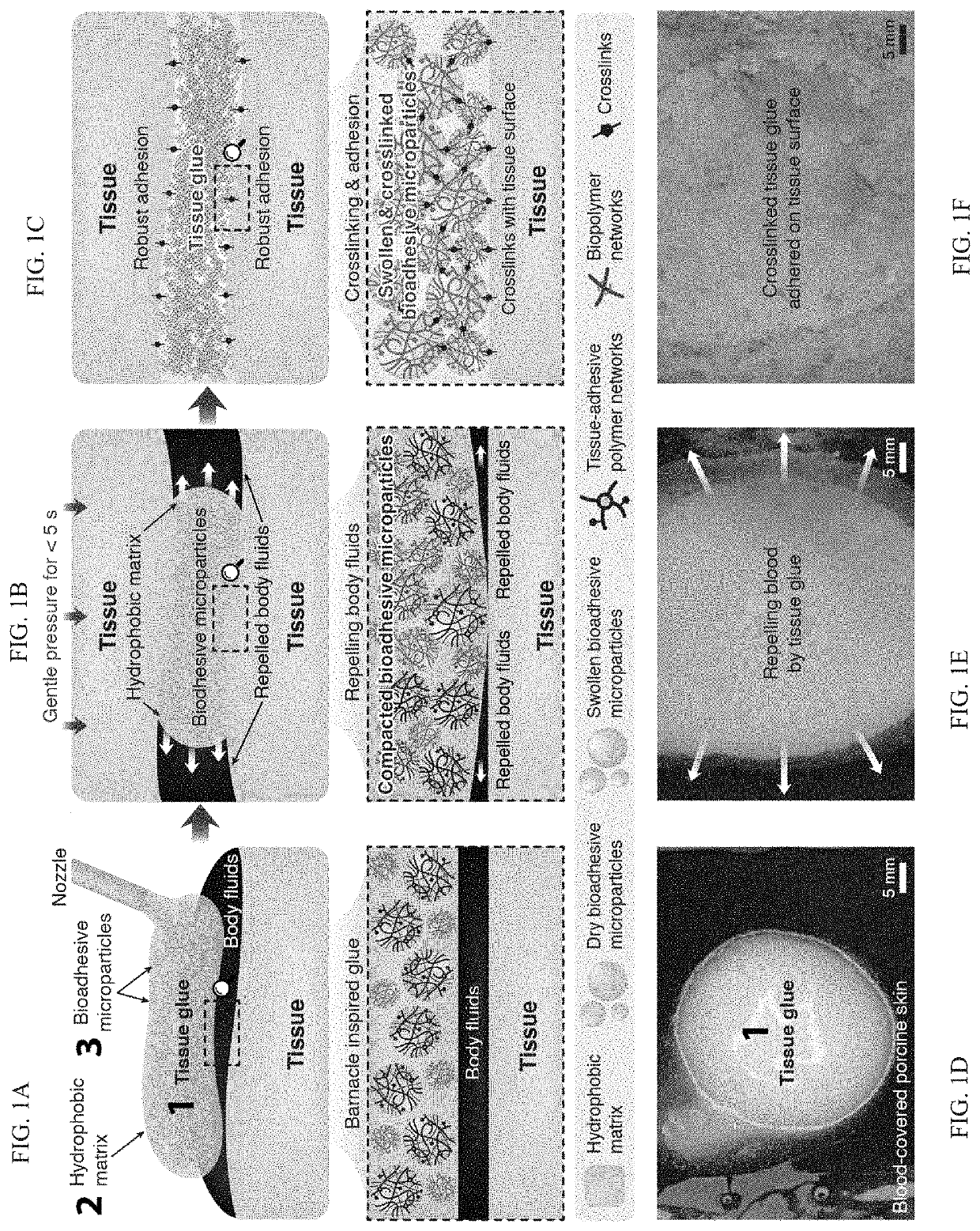
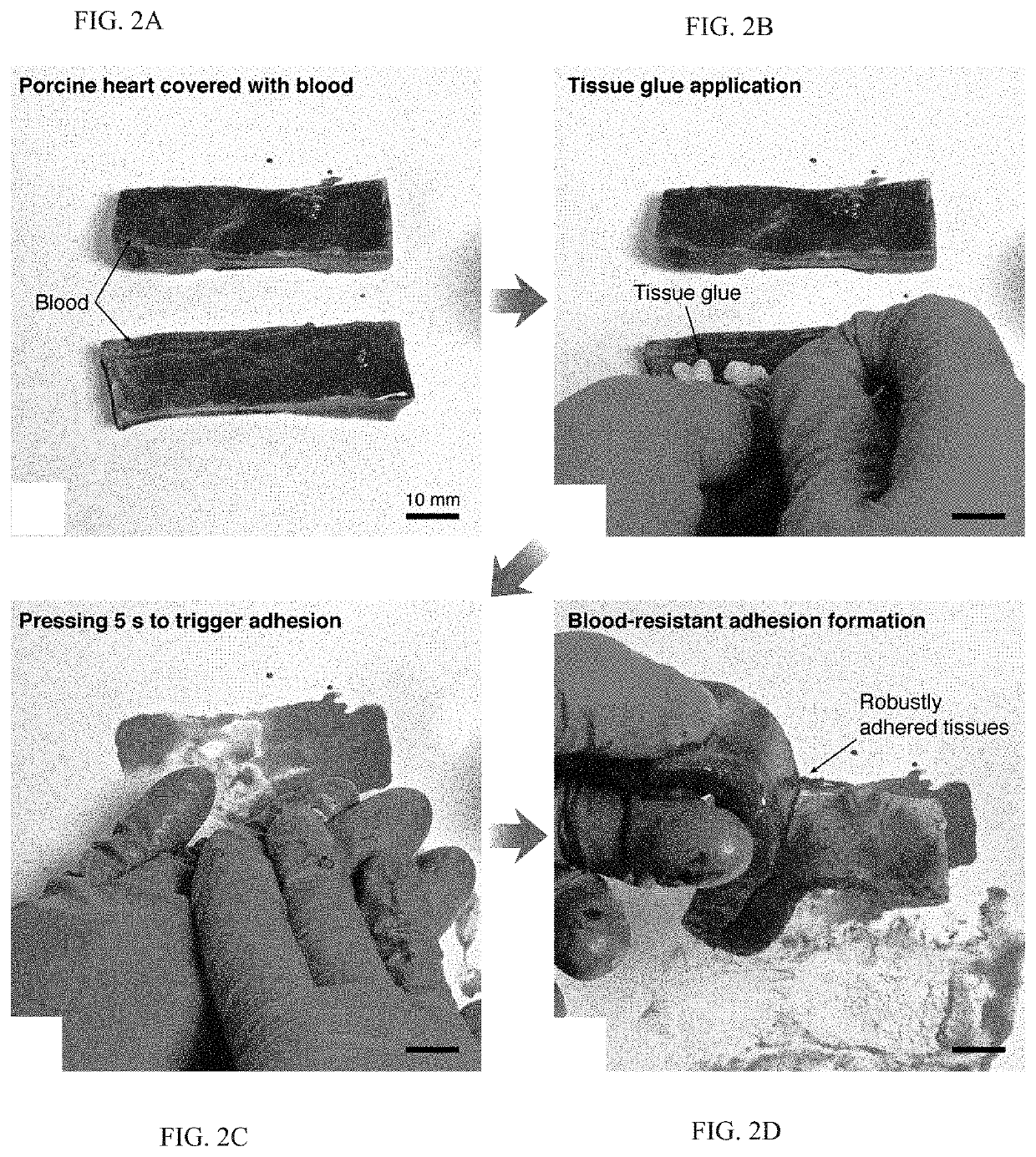
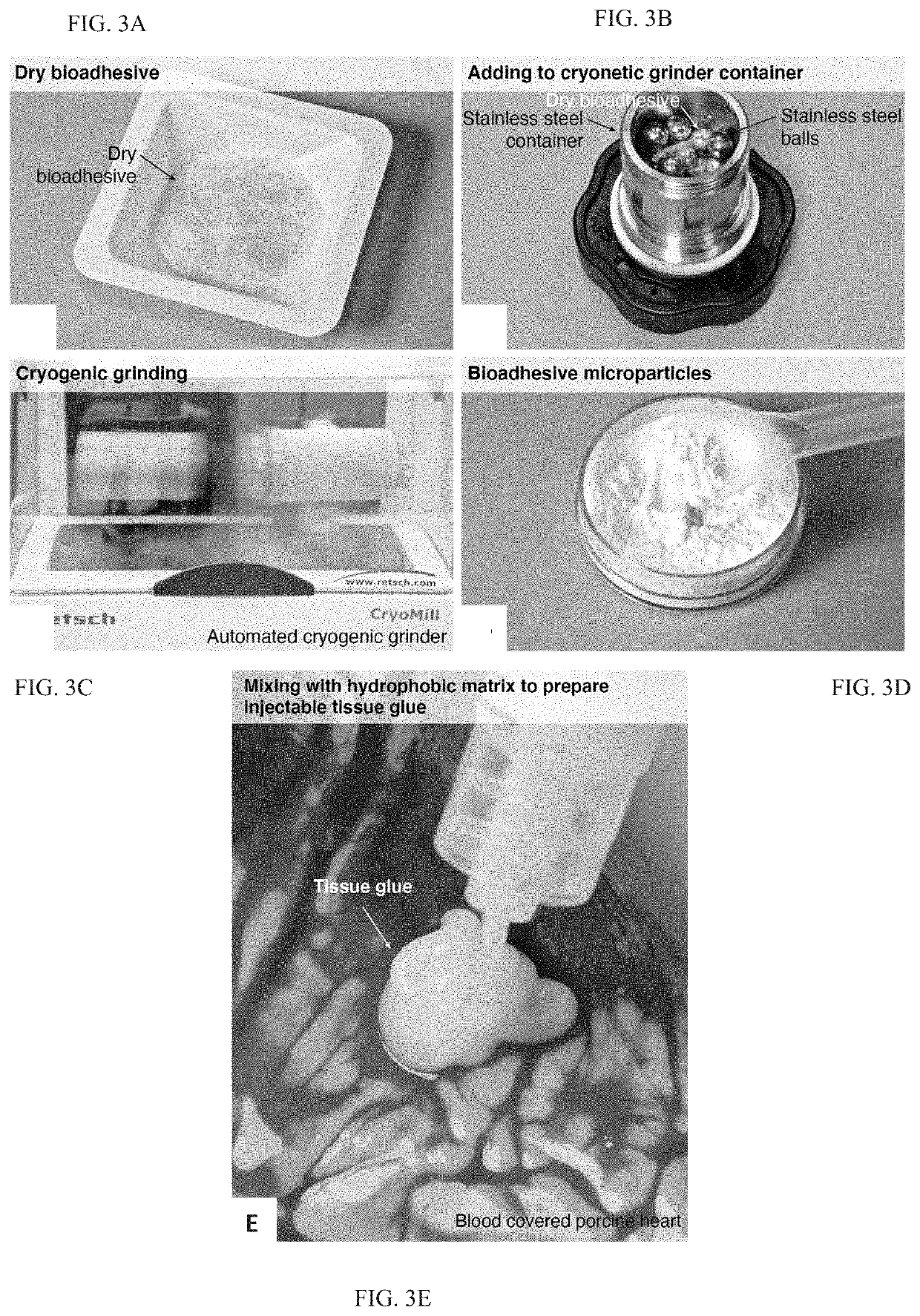
Body fluid resistant tissue adhesives
PendingUS20210163797A1Fast and robust adhesionFast and reliableNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSurgical adhesivesPolymer scienceBioadhesive
A tissue adhesive material that provides fast and robust adhesion even on tissue surfaces covered in bodily fluids. The tissue adhesive material is formed of a hydrophobic matrix and a plurality of bioadhesive microparticles dispersed within the hydrophobic matrix configured such that disposing the adhesive material directly on a fluid covered surface and applying pressure causes the (a) hydrophobic matrix to repel the fluid, (b) the bioadhesive particles to compress forming an adhesive layer, and (c) the bioadhesive particles to form temporary crosslinks followed by covalent crosslinks with the surface.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
Self-supporting interface dressing
The present invention relates to a self-supporting interface dressing formed by a thin layer of a composition comprising a hydrophobic matrix and having through-holes. According to the invention, this hydrophobic matrix comprises, for 100 parts by weight of a styrene / saturated olefin / styrene triblock copolymer with a viscosity of between 0.2 and 2 Pa.s, as measured in a 10% (weight / weight) solution in toluene, from 400 to 1,220 parts by weight of a plasticizer, preferably a plasticizer oil, and from 0 to 720 parts by weight of petroleum jelly, it being additionally specified that the total quantity of plasticizer and of petroleum jelly is greater than or equal to 750 parts by weight, and the quantity of petroleum jelly is between 400 and 720 parts by weight when the quantity of plasticizer is between 1,000 and 1,220 parts by weight. Application to the treatment of wounds.
Owner:LABORATOIRE URGO
Patterning device
ActiveUS20180015437A1Promote sportsIncrease trappingMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsEvaporationEngineering
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Preparation method of puerarin sustained-release dropping pill
InactiveCN104622828AImprove Medication AdherenceReduce releaseOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderWater bathsSide effect
The invention relates to a preparation method of a puerarin sustained-release dropping pill. The method comprises the following steps: (1) weighing hydrophobic matrix and hydrophilic matrix, fully melting and mixing evenly under a water bath heating condition, adding puerarin powder and mixing evenly; (2) starting the dropping pill, and preheating for 30 minutes; (3) starting a pill dropping machine stirring system and stirring for 10 minutes; (4) turning on a condensate liquid level adjusting knob and adjusting the dropping distance; (5) mounting a dripping head in a pill dropping machine; (6) dropping a liquid medicine into condensate; (7) collecting sustained-release dropping pills; and (8) sucking up condensate on the surfaces of the sustained-release dropping pills with filter paper and medical gauze, so as to obtain the puerarin sustained-release dropping pills. An optimal preparation technology of the novel puerarin sustained-release dropping pill is optimized; the targets of delaying drug release and reducing toxic and side effects can be reached; meanwhile, the medication frequency can be reduced; the medication compliance of patients is improved; the method has relatively large application value; and important reference is provided for pharmaceutical companies and clinical research and development.
Owner:TAIYUAN INST OF TECH
Multifunctional superhydrophobic particles for chemical adhesion and blooming
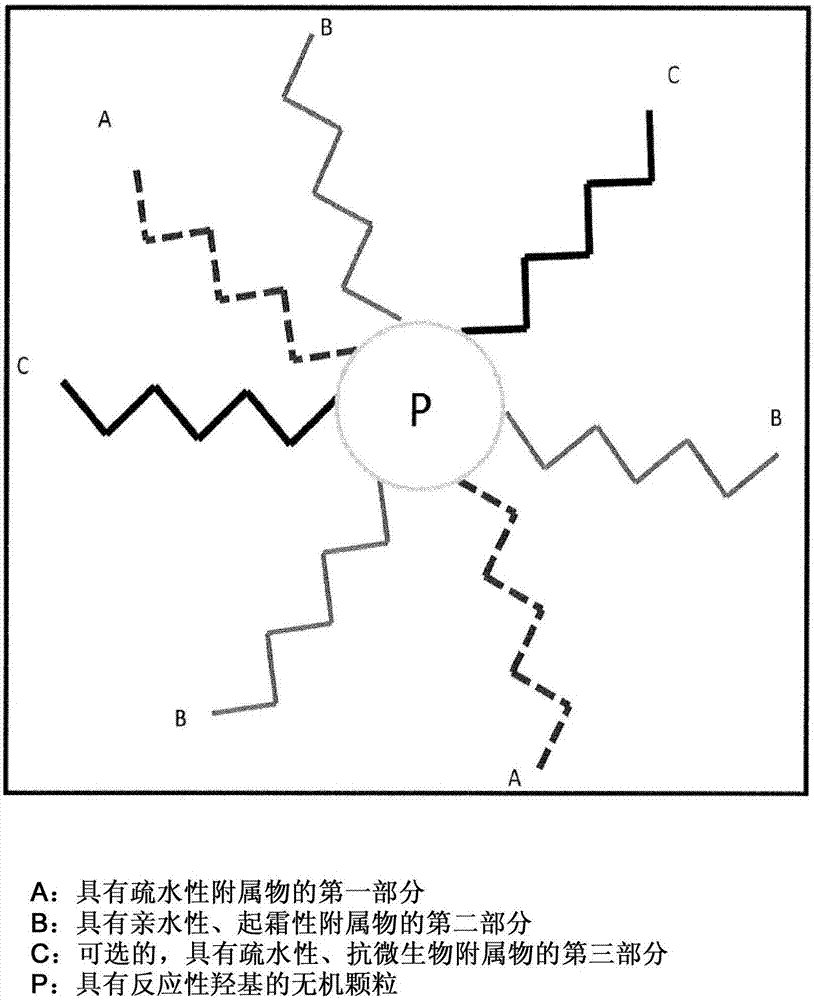
Provided herein is a multifunctional particle and methods of forming the same. The multifunctional particle includes a surface of the particle; a first moiety coupled to the surface and having at least one substantially hydrophobic appendage; and a second moiety coupled to the surface and having at least one appendage comprising a reactive functional group and a substantially hydrophilic repeating unit, whereby the particle is substantially superhydrophobic as a result of the substantially hydrophobic appendage, chemically reactive as a result of the reactive functional group, and migratory to a surface of a substantially hydrophobic matrix in which the particle may be included as a result of the substantially hydrophilic repeating unit. Additionally, antimicrobial functional groups may be coupled to the surface.
Owner:VELOX FLOW
Coating for intraluminal expandable catheter providing contact transfer of drug micro-reservoirs
A coating for an expandable portion of a catheter comprising a hydrophobic matrix and a dispersed phase is disclosed. The dispersed phase comprises a plurality of micro-reservoirs dispersed in the hydrophobic matrix, wherein the plurality of micro-reservoirs comprises a first active agent and a first biodegradable or bioerodable polymer. A coating formulation and a method for forming the coating are also disclosed. A catheter comprising the coating on the expandable portion and a method for treating a condition are also provided.
Owner:M A MED ALLIANCE
Tamsulosin sustained release pellet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102579359APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsUrinary disorderSustained release pelletsSolubility
The invention provides a tamsulosin sustained release pellet. The tamsulosin sustained release pellet comprises a medicine-containing pellet core and a sustained release coating layer, wherein the sustained release coating layer comprises a hydrophobic matrix and a hydrophilic polymer which is sensitive to pH values. The pH values of a high molecular polymer in the dissolving process are 1 to 14, so that medicines are released at different pH values; and simultaneously, the high molecular polymer can be used as a carrier for controlling tamsulosin to be released, so that a prescription is simplified, preparation difficulties are reduced, and the tamsulosin sustained release pellet is easy to industrially produce in batches. Surprisingly, the preparation can be used for preparing various tamsulosin sustained release formulations without dependence on the physicochemical property of the tamsulosin.
Owner:COSCI MED TECH CO LTD
Enzymatic wound debriding compositions with enhanced enzymatic activity
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Super-hydrophobic matrix material of monoclinic-phase celsian glass ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a super-hydrophobic matrix material of monoclinic-phase celsian glass ceramic and a preparation method thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: providing 25-55 wt% of barium salt, 8-22 wt% of aluminum powder, 8-26 wt% of silicon powder and 0-30 wt% of cosolvent according to the mass percentage of the raw materials; mixing the raw materials, melting to obtain clarified glass liquid, and / or quenching a part of the glass liquid to obtain glass frit; forming the molten glass to obtain a glass blank, and / or crushing and forming the glass frit to obtain a glass ceramic blank; putting the glass blank and / or the ceramic blank into a high-temperature furnace for sintering crystallization treatment to obtain glass ceramic with monoclinic celsian as a main crystal phase; performing corrosion treatment on the glass ceramic to corrode all or part of glass phase so that the glass ceramic super-hydrophobic base material with the monoclinic celsian as the main crystal phase is obtained. The method is simple, consumes less time and energy, and can be used for obtaining the ceramic material of which the principal crystalline phase is baryta feldspar and the surface is provided with a self-growing micro-nano convex frame structure.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Substained release formulation of protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20050175693A1High initial releaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSulfated polysaccharidesIn vivo
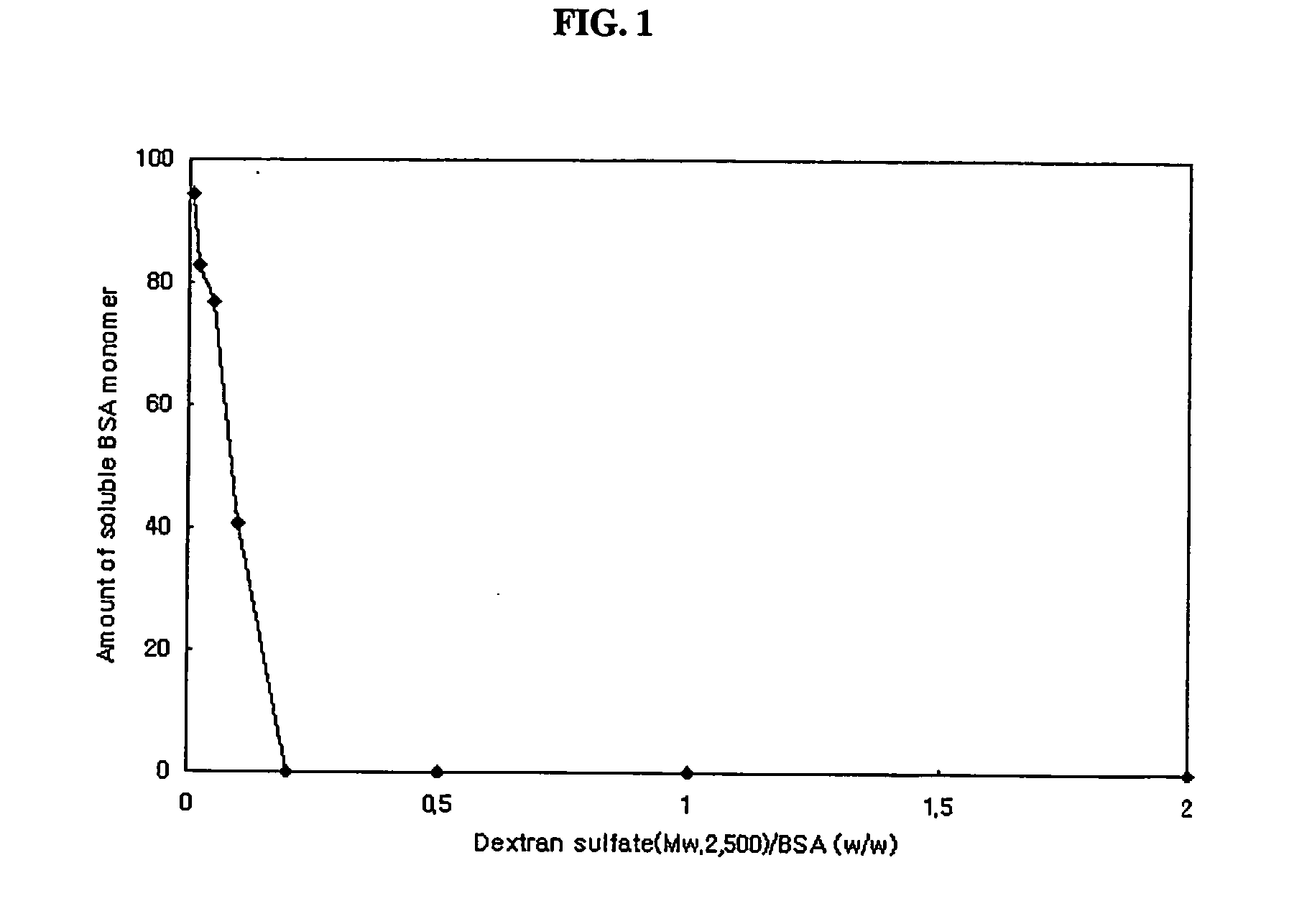
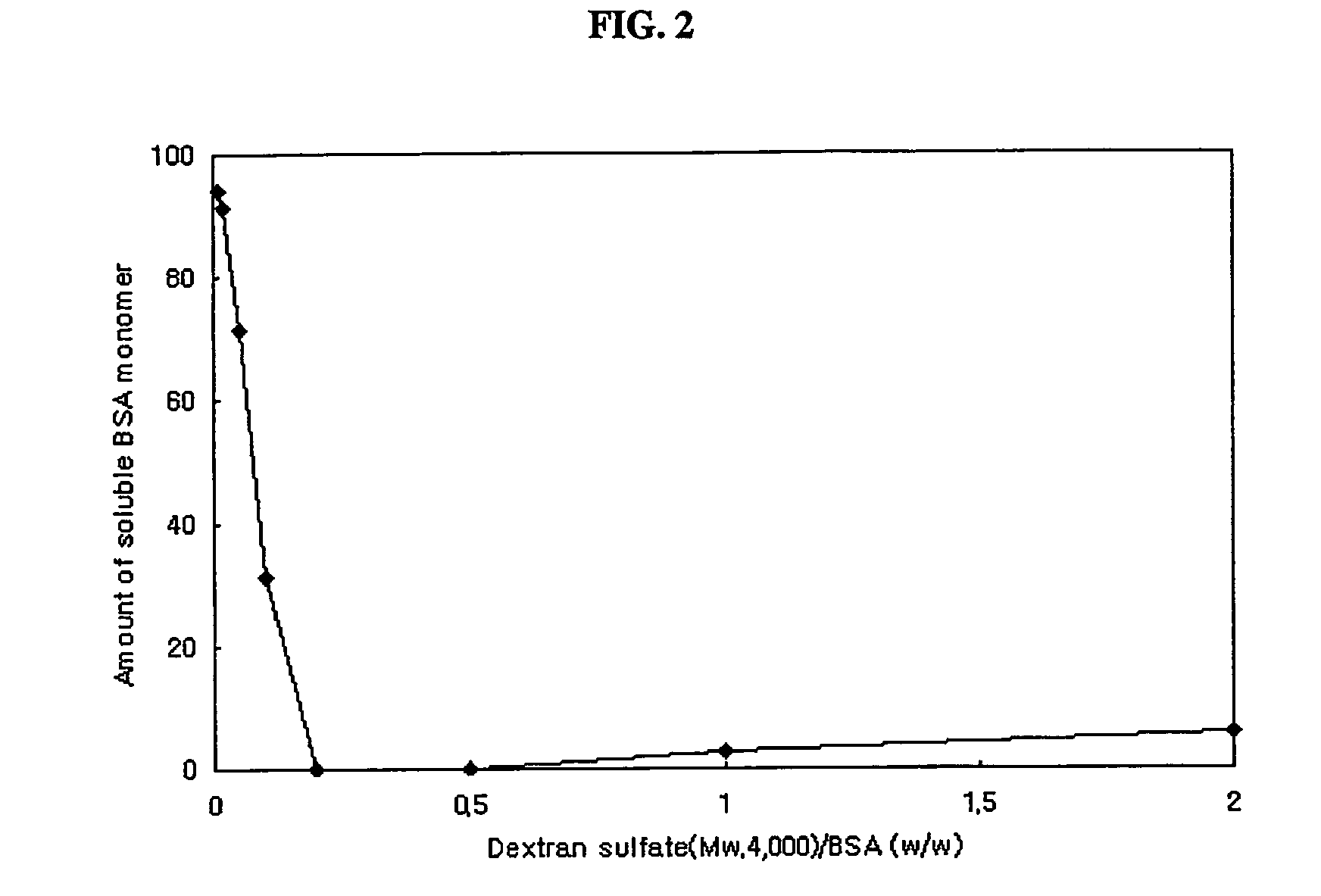
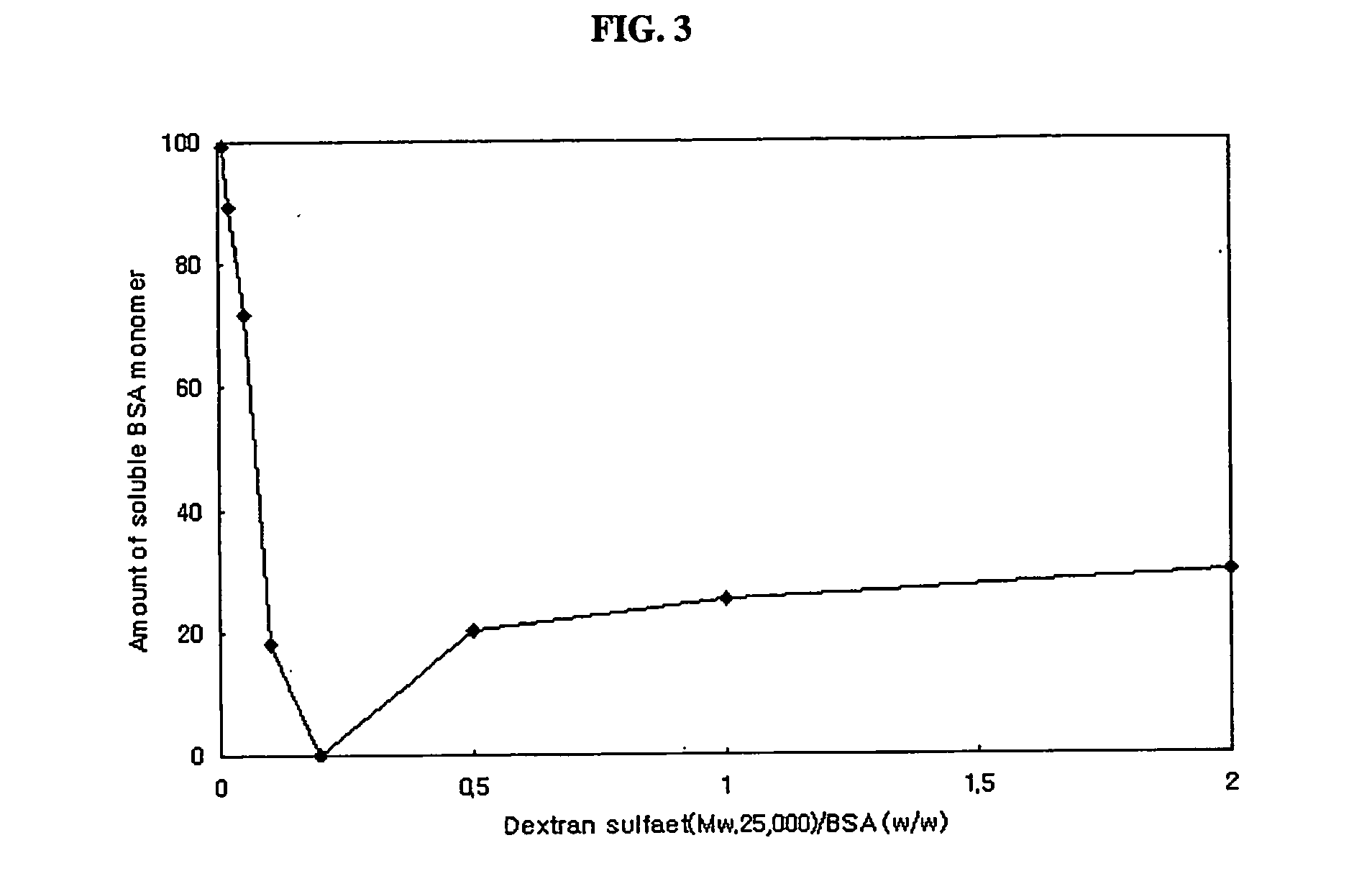
The present invention relates to a sustained release formulation comprising protein as an active ingredient, and a preparation method thereof. According to the present invention, the sustained release formulation contains protein drugs that are encapsulated in biodegradable hydrophobic matrices as pharmaceutically active forms by forming complexes with sulfated polysaccharides. The sustained release formulation prepared by the present invention can be used to effectively treat a disease without frequent injections by keeping the protein concentration at a sufficiently high level for a long period when injected in vivo once.
Owner:PEPTRON
Novel modified release formulation
InactiveUS20040067252A1Increase opportunitiesBiocidePowder deliveryPharmaceutical medicineHydrophilic matrix
The present invention is directed to a multiparticulate, modified release solid dispersion formulation, comprising a drug substance having a pH-dependent solubility, said drug substance being a compound of the formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; a hydrophobic matrix former which is a water-insoluble, non-swelling amphiphilic lipid; and a hydrophilic matrix former which is a meltable, water-soluble excipient; wherein the weight ratio hydrophobic matrix former / hydrophilic matrix former is >=1; and the particle size is less than 300 mum. Also a unit dosage of the same, as well as a process for the preparation thereof and the use of the formulation and unit dosage is claimed.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com