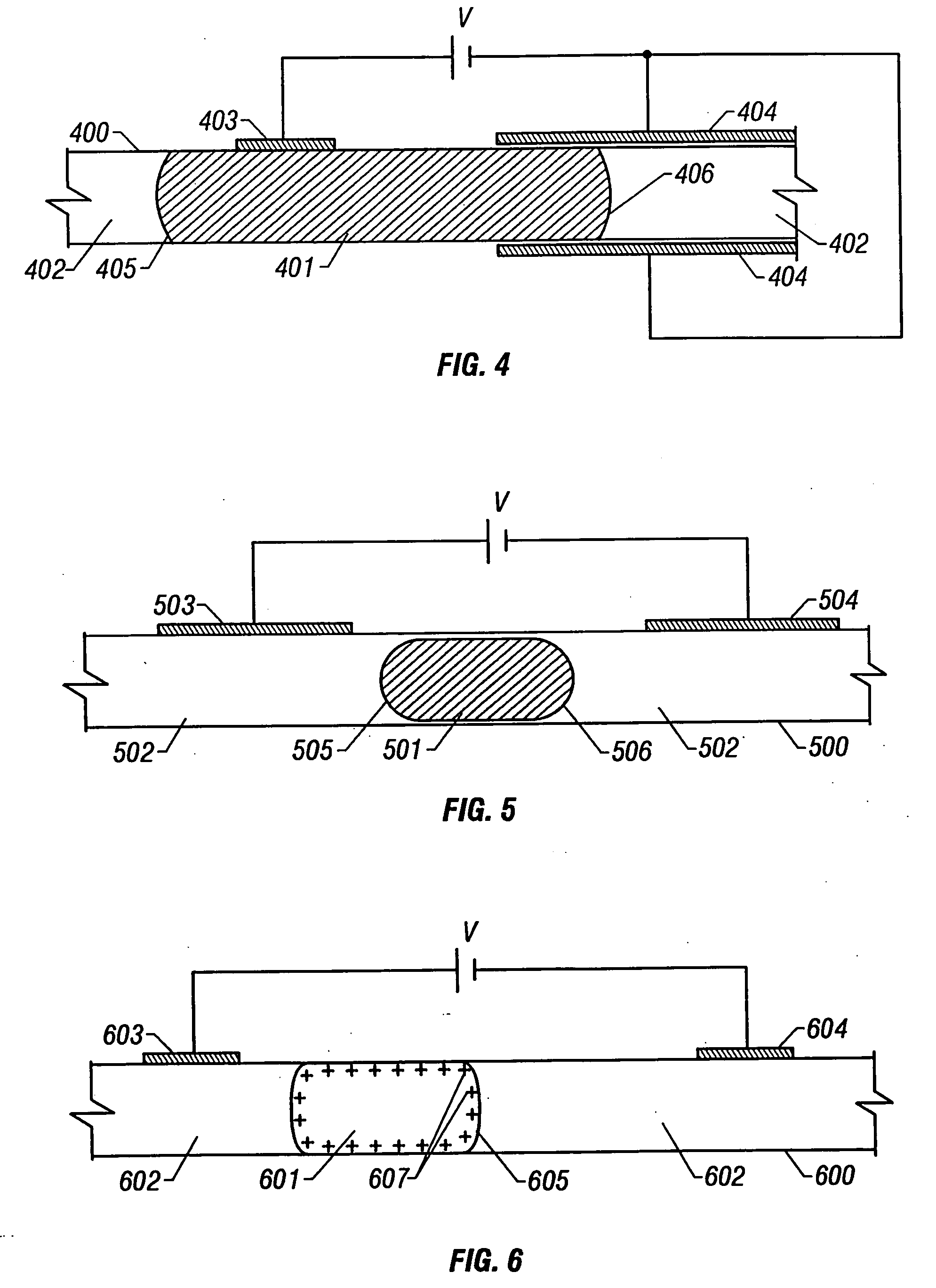
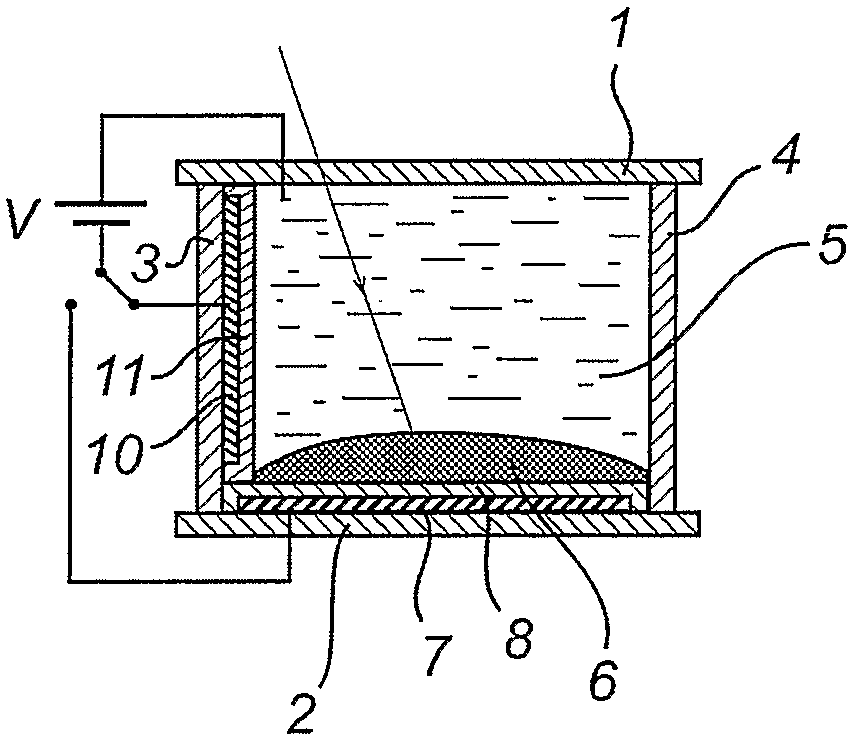
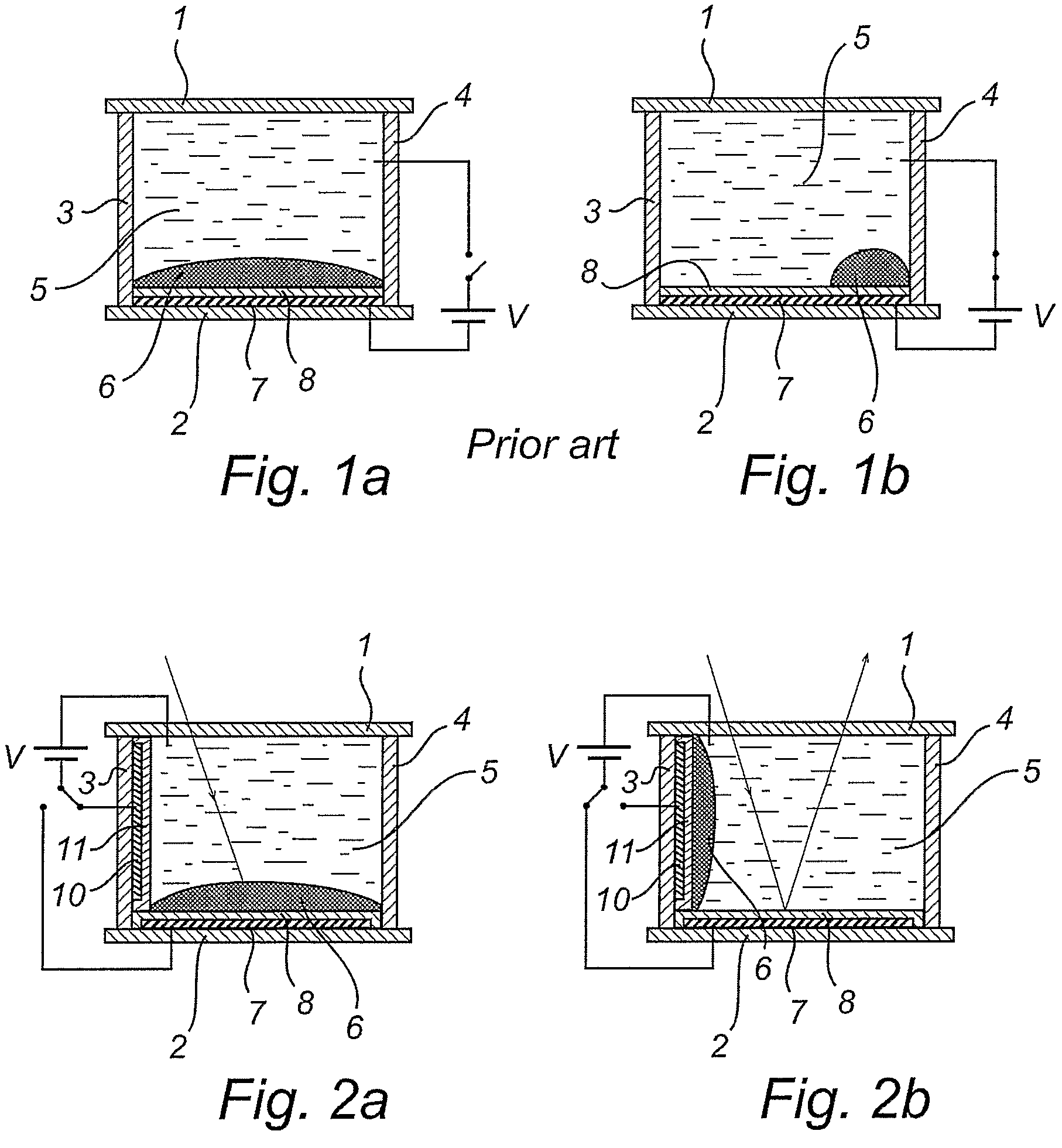
Patents
Literature
314 results about "Electrowetting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
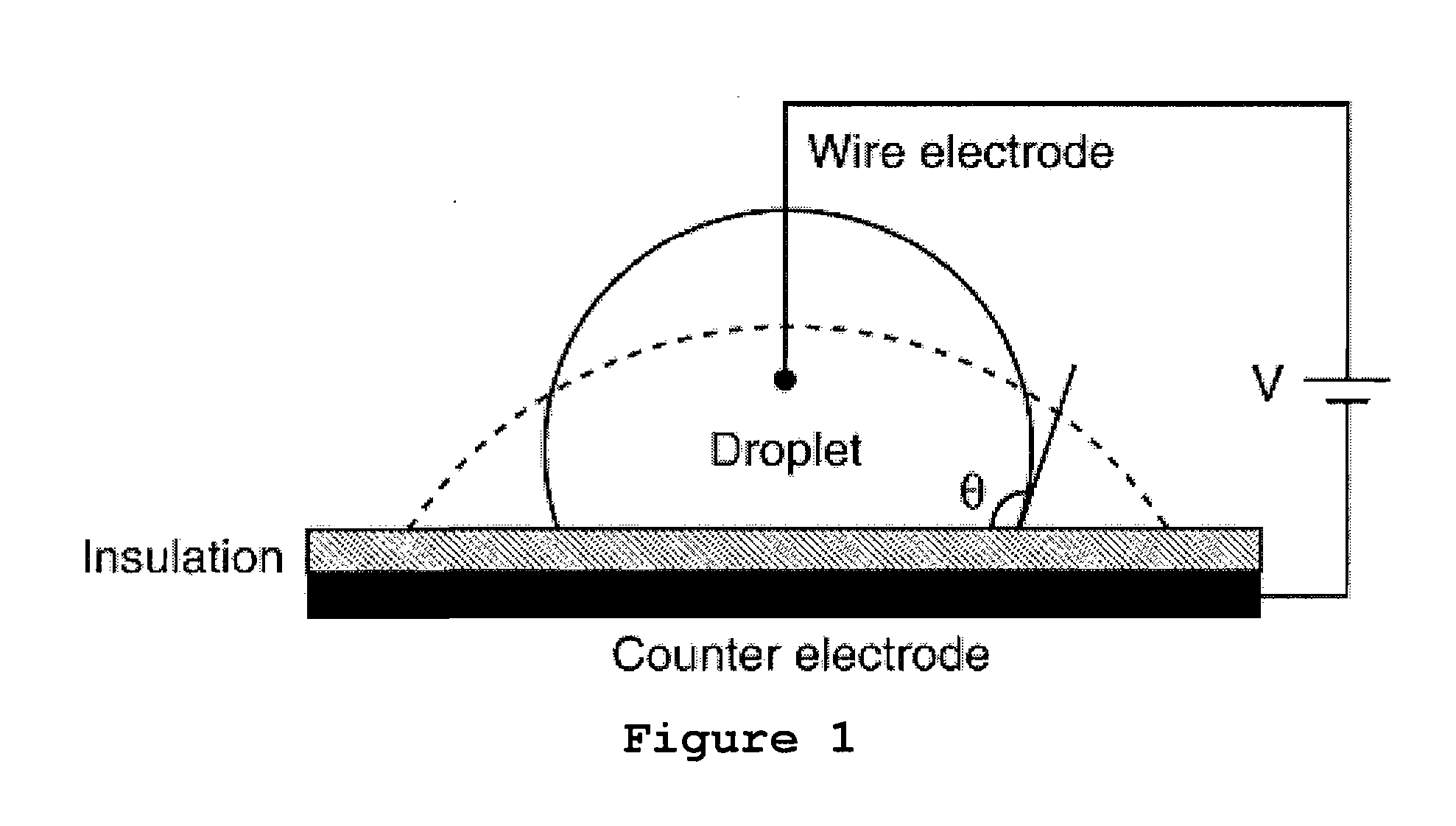
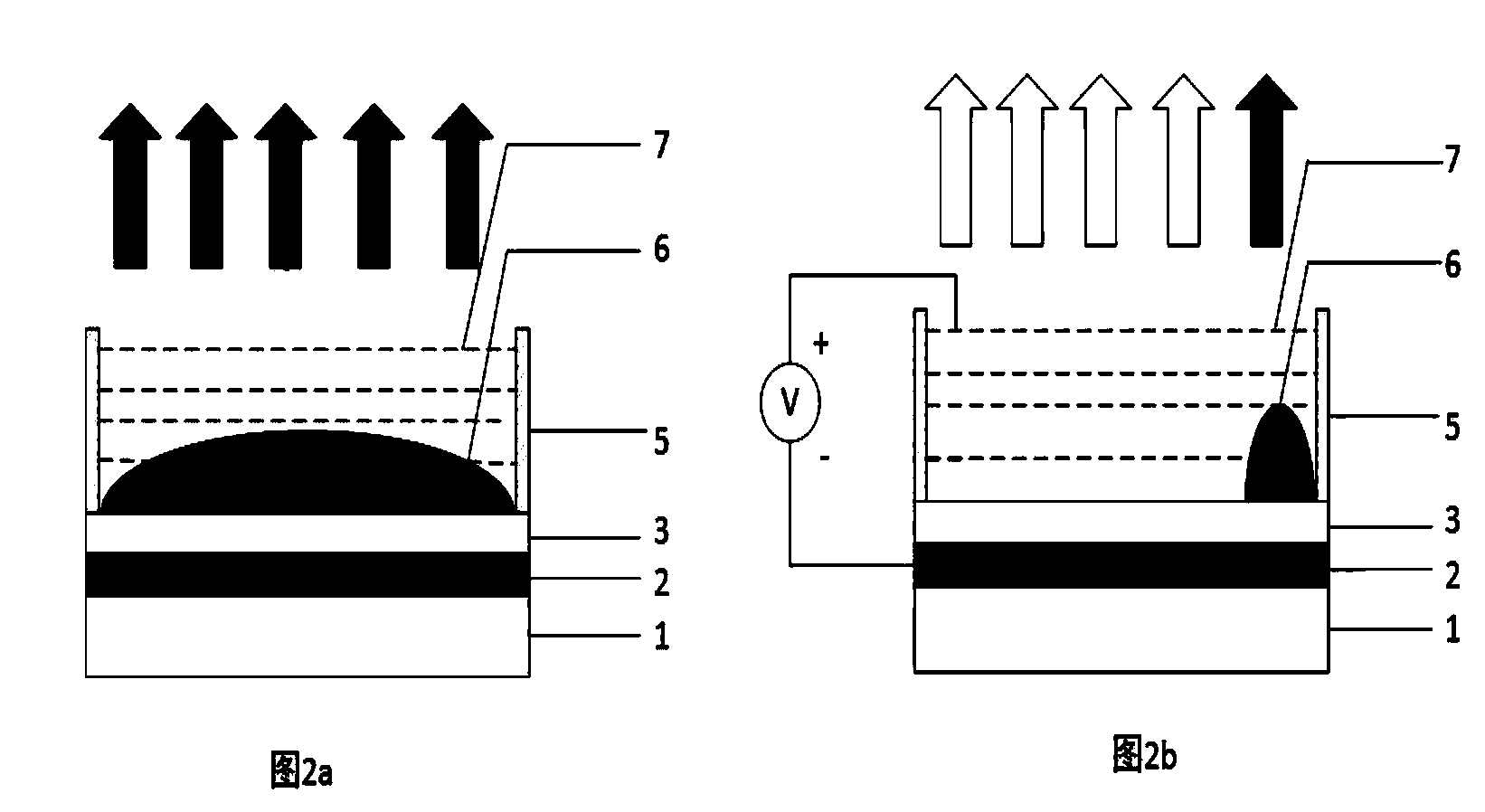
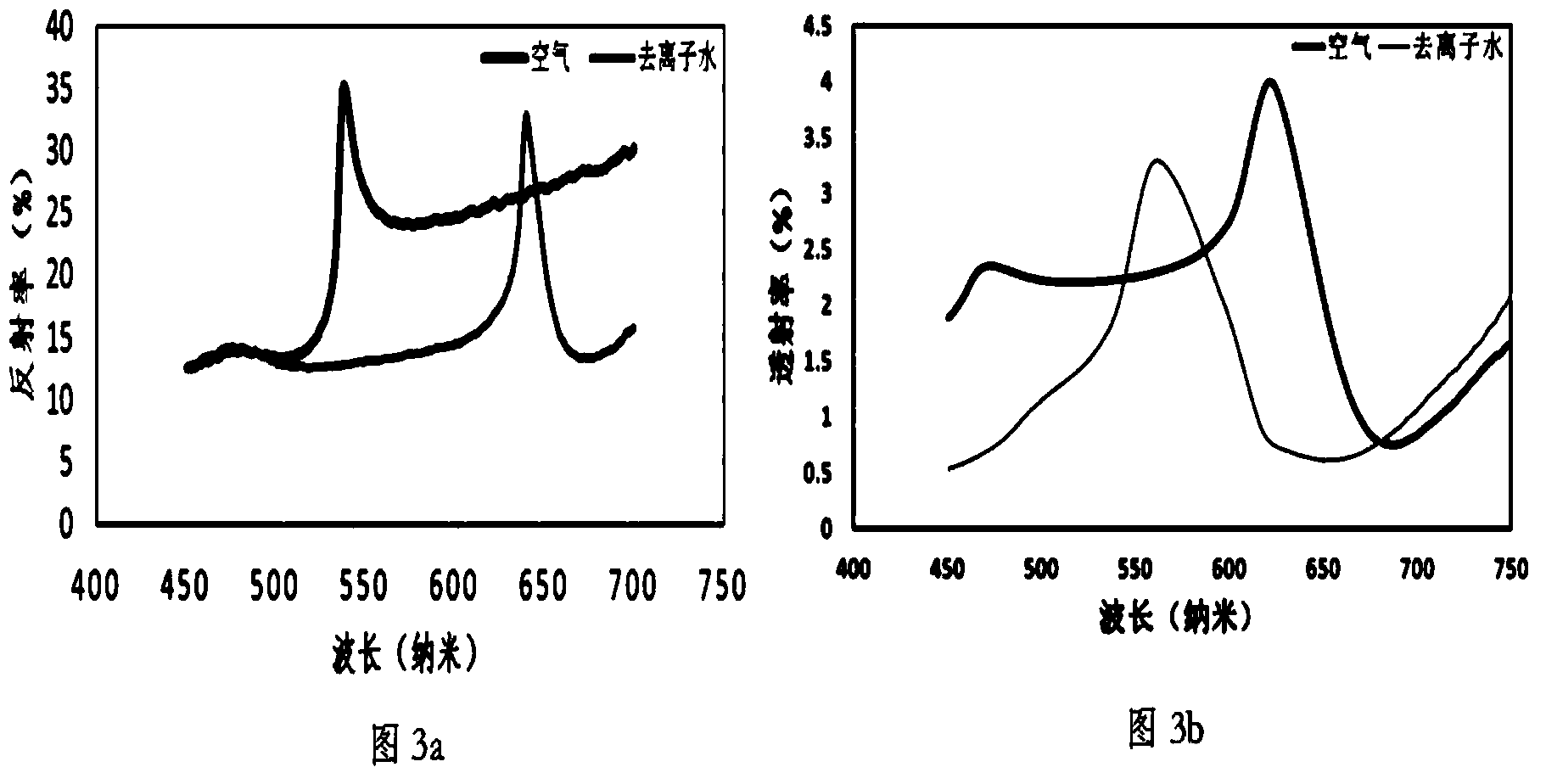
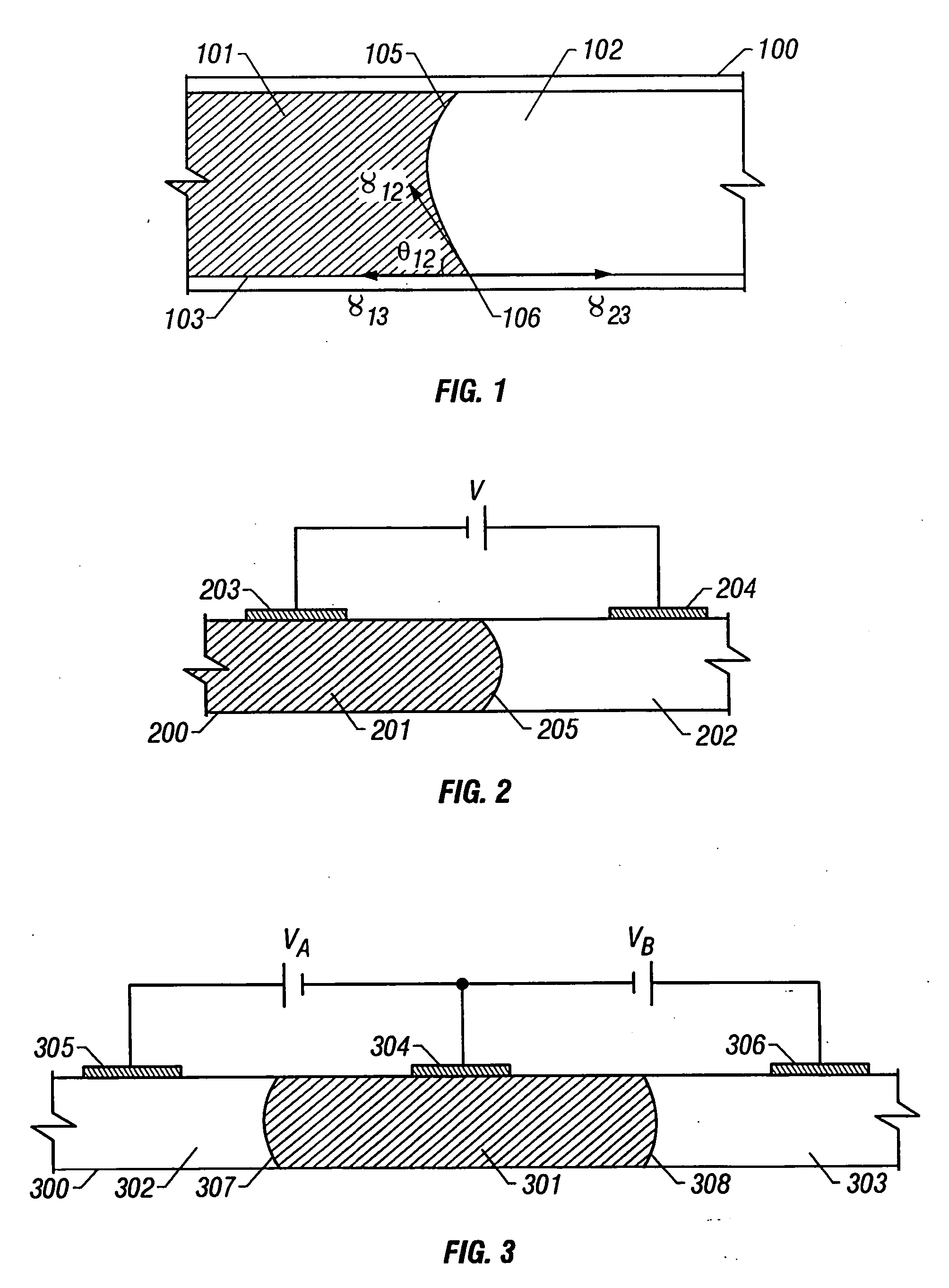
Electrowetting is the modification of the wetting properties of a surface (which is typically hydrophobic) with an applied electric field.
Microfluidic method and device for transferring mass between two immiscible phases
InactiveUS20060231398A1Mass productionLow costSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityElectrophoresis
A method of transferring mass of at least one solute between a liquid first phase and a fluid second phase that is immiscible with the first phase, the method comprising moving at least one droplet of said liquid first phase in a microfluidic device by using electric-type forces (electrowetting or dielectrophoresis) within a space that is filled with said fluid second phase. Said droplet is preferably moved by said electric-type forces along a path between a point for injecting said droplet into said microfluidic device, and an extraction and / or analysis zone, said path being defined in such a manner that said droplet sweeps through a significant fraction of said space filled with said fluid second phase. The method may include a step of transferring said droplet using said electric-type forces to a chemical analysis device integrated in said microfluidic device, and a step of chemically analyzing said droplet. The invention also provides a device for implementing such a method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Frequency-addressable Apparatus and Methods for Actuation of Liquids
InactiveUS20080169195A1Uniform thicknessSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsDielectricWorking fluid
Embodiments of the invention are directed to apparatus, methods, and applications involving the actuation of a semi-insulative working fluid by electromechanical forces based on electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and liquid dielectrophoresis (liquid DEP) mechanisms that are controlled by the frequency, but not the magnitude, of an AC voltage (i.e., ‘frequency-addressable). In the various apparatus embodiments of the invention, a single, frequency-addressable electrode pair includes at least one electrode that has a spatially-varying dielectric coating thickness and thus a spatially-varying electrode gap wherein at least a portion of which a volume of a working fluid can stably reside under no influence of an applied voltage. In an exemplary aspect, a frequency-addressable, bistable apparatus includes at least one wider gap and one narrower gap associated, respectively, with a thicker and a thinner dielectric coating thickness of the electrode(s). The working fluid resides in only one of the at least two gap regions only under the influence of capillary force. A brief burst of AC voltage at a selected high frequency or low frequency will move the liquid from one gap region to another (and back) by one of an EWOD-based and a DEP-based force. In an alternative aspect, an analog apparatus has a continuous, spatially-varying electrode gap in which the dielectric coating thickness on the electrodes varies smoothly in an inverse manner. Various applications to a display device, fiber optic coupler and attenuator, controlled liquid volume dispensers, spotting arrays, well plate apparatus, and others are presented, along with control methods.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Microfluidic method and device for transferring mass between two immiscible phases
InactiveUS8236156B2Mass productionLow costSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringPartial filling
A method of transferring mass of at least one solute between a liquid first phase and a fluid second phase that is immiscible with the first phase, the method comprising moving at least one droplet of said liquid first phase in a microfluidic device by using electric-type forces (electrowetting or dielectrophoresis) within a space that is filled with said fluid second phase. Said droplet is preferably moved by said electric-type forces along a path between a point for injecting said droplet into said microfluidic device, and an extraction and / or analysis zone, said path being defined in such a manner that said droplet sweeps through a significant fraction of said space filled with said fluid second phase. The method may include a step of transferring said droplet using said electric-type forces to a chemical analysis device integrated in said microfluidic device, and a step of chemically analyzing said droplet. The invention also provides a device for implementing such a method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Microfluidic control for waveguide optical switches, variable attenuators, and other optical devices
InactiveUS7016560B2Reduce power consumptionGood workmanshipTransportation and packagingMixersDifferential pressureThermal expansion
Devices utilize elements carried by a fluid in a microchannel toswitch, attenuate, shutter, filter, or phase shift optical signals. In certain embodiments, a microchannel carries a gaseous or liquid slug that interacts with at least a portion of the optical power of an optical signal traveling through a waveguide. The microchannel may form part of the cladding of the waveguide, part of the core and the cladding, or part of the core only. The microchannel may also have ends or may be configured as a loop or continuous channel. The fluid devices may be self-latching or may be semi-latching. The fluid in the microchannel is moved using e.g., e.g., electrocapillarity, differential-pressure electrocapillarity, electrowetting, continuous electrowetting, electrophoresis, electroosmosis, dielectrophoresis, electro-hydrodynamic electrohydrodynamic pumping, magneto-hydrodynamic magnetohydrodynamic pumping, thermocapillarity, thermal expansion, dielectric pumping, and / or variable dielectric pumping.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
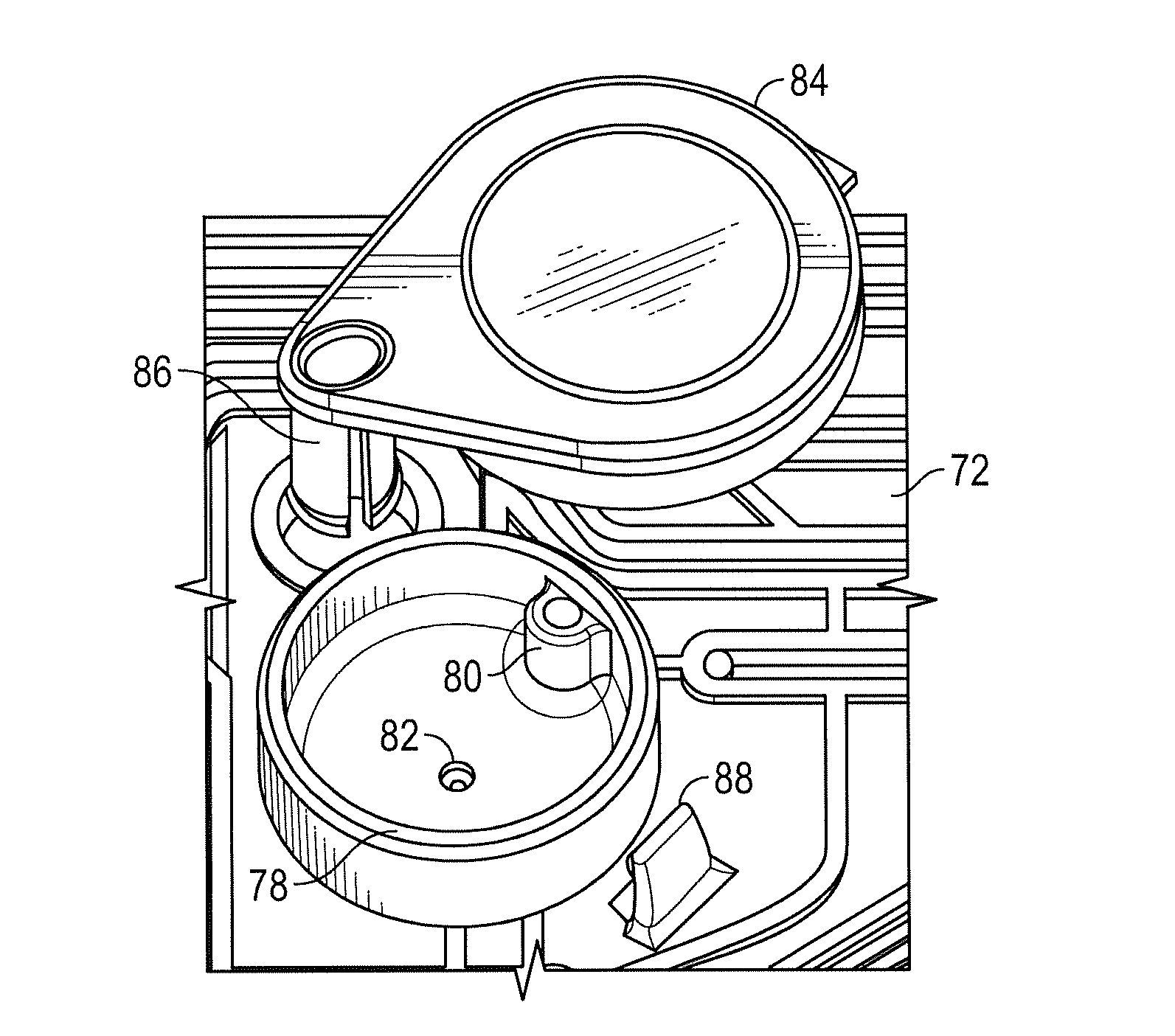
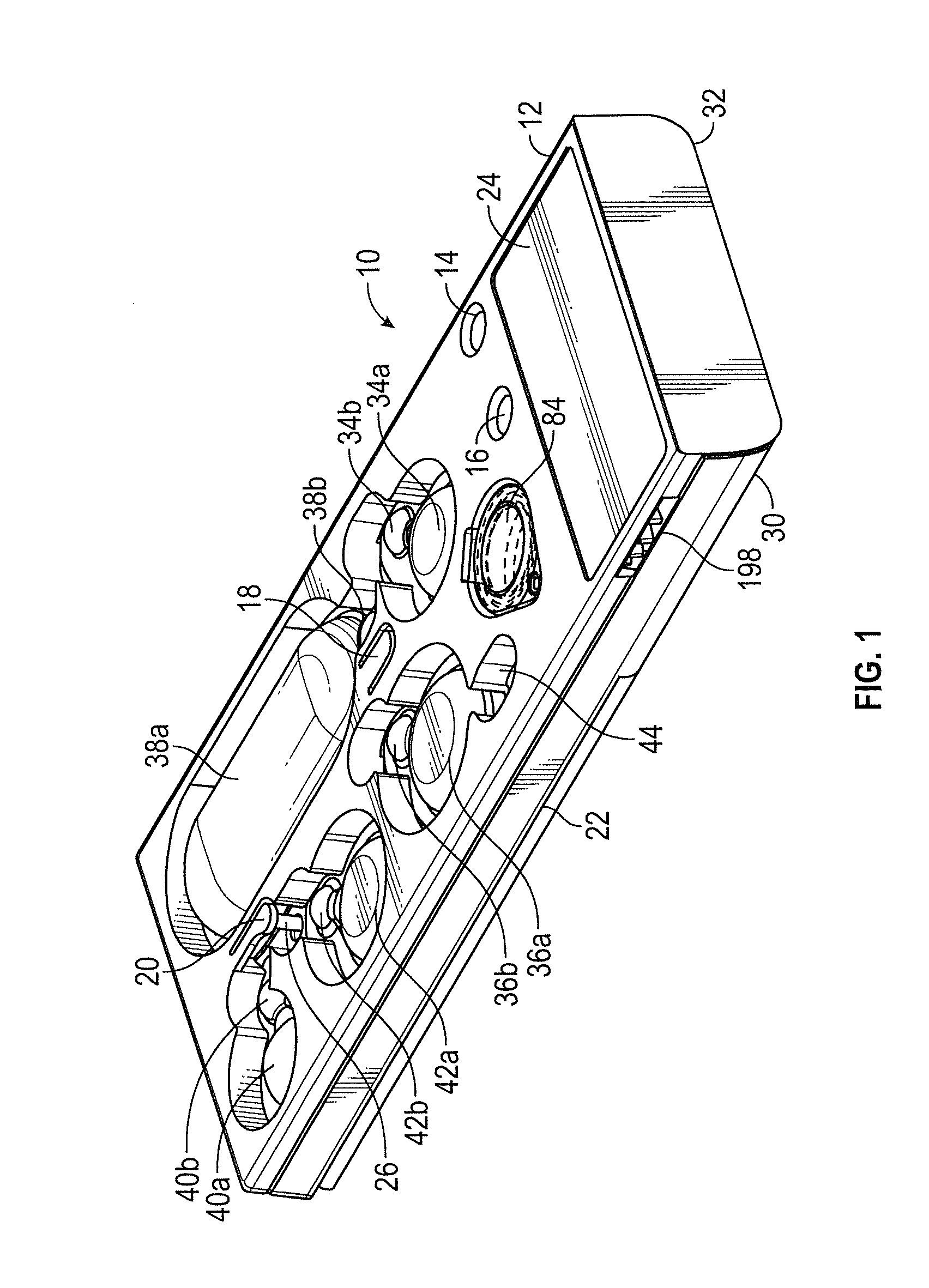
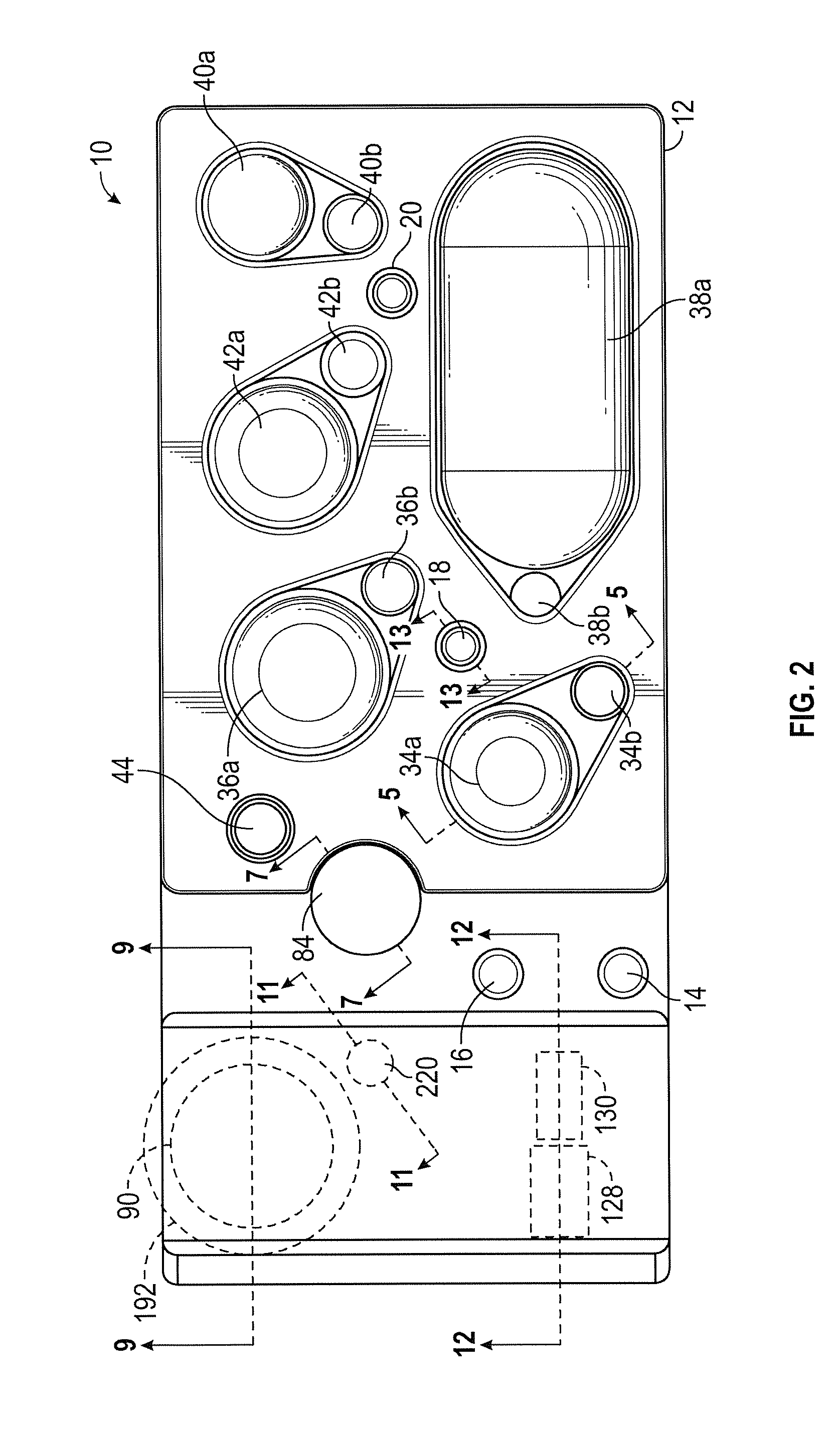
Cartridge for performing assays in a closed sample preparation and reaction system
ActiveUS20160130640A1Ease and rapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusThermal energyLysis
In one embodiment, a multiplex fluid processing cartridge includes a sample well, a deformable fluid chamber, a mixing well with a mixer disposed therein, a lysis chamber including a lysis mixer, an electrowetting grid for microdroplet manipulation, and electrosensor arrays configured to detect analytes of interest. An instrument for processing the cartridge is configured to receive the cartridge and to selectively apply thermal energy, magnetic force, and electrical connections to one or more discrete locations on the cartridge and is further configured to compress the deformable chamber(s) in a specified sequence.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
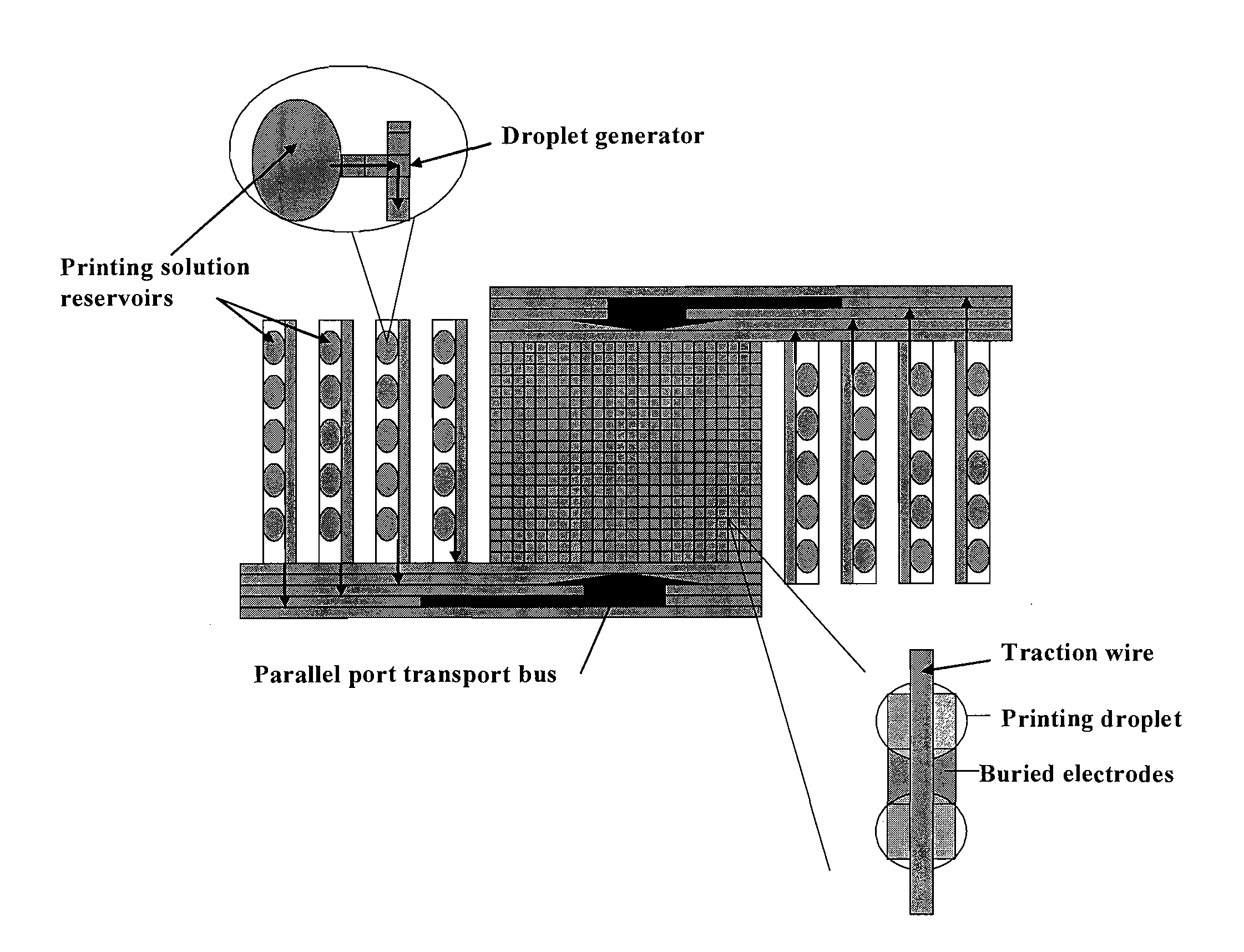
Electrowetting Microarray Printing System and Methods for Bioactive Tissue Construct Manufacturing
InactiveUS20110076734A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAdditive manufacturing apparatusDielectricTissue construct
Apparatuses and methods for manufacturing three-dimensional, bioactive, tissue scaffold fabrications with embedded cells and bioactive materials, such as growth factors, using biomimetic structure modeling, solid freeform fabrication, biocompatible hydrogel material, and electrowetting on dielectric-based multi-microarray printing.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Optical shutter for plasma display panel and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20050128370A1Prevent weak emissionIncrease contrastCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersStatic indicating devicesHigh contrastElectricity
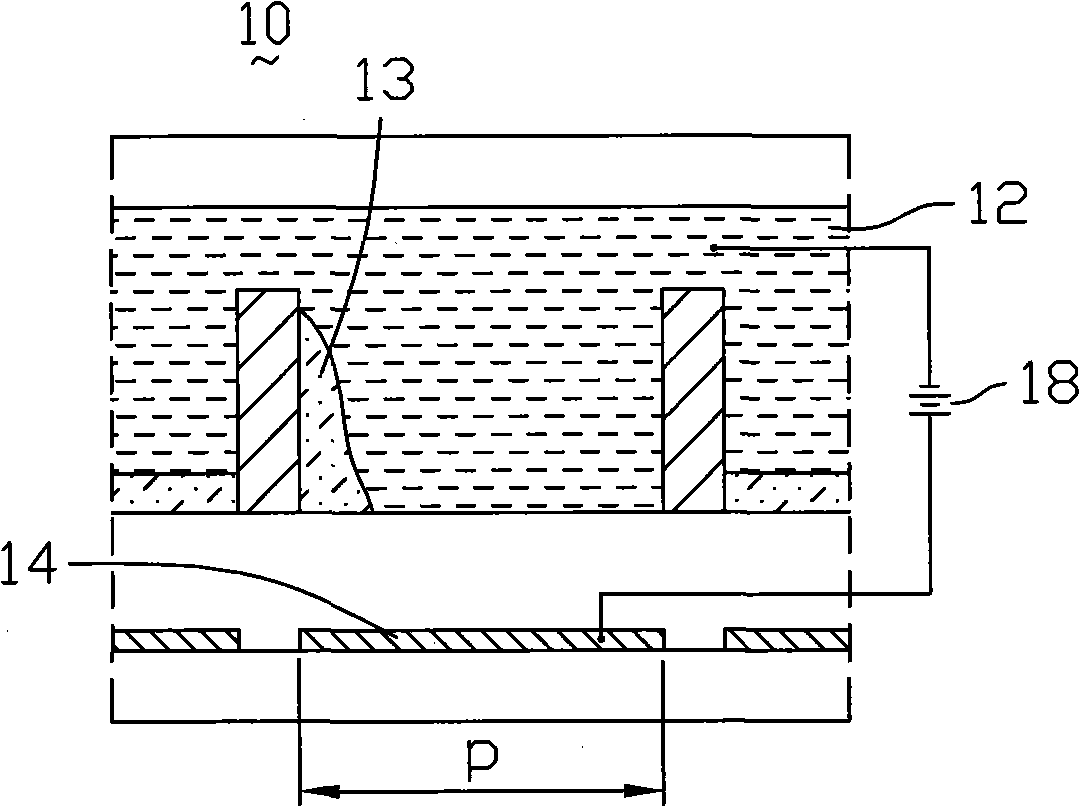
Disclosed herein are an optical shutter for a plasma display panel and driving method thereof. According to the present invention, an optical shutter, which employs a black organic solution that moves according to the electrowetting phenomenon and a pair of electrodes for providing voltages, is disposed on a display surface of the plasma display panel. In this state, during the non-display period, voltages are not applied to the optical shutter so that light emitted from the panel cannot transmit the optical shutter. During the display period, voltages having a different polarity are applied to the electrodes of the optical shutter so that light emitted from the panel can transmit the optical shutter. It is thus possible to completely prevent weak emission generating during the non-display period where cells are initialized and selected. Accordingly, there are effects in that contrast can be improved and the picture quality can be thus enhanced.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method And Apparatus For Characterizing And Counting Particles, In Particular, Biological Particles
ActiveUS20090218223A1Manipulation is accurateAccurately characterizeSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsDielectricElectricity
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for the characterization and / or the counting of particles by means of non uniform, time variable force fields and integrated optical or impedance meter sensors. The force fields can be of positive or negative dielectrophoresis, electrophoresis or electro-hydrodynamic motions, characterized by a set of stable equilibrium points for the particles (solid, liquid or gaseous); the same method is suitable for the manipulation of droplets (liquid particles) by exploiting effects known to the international scientific community with the name of Electro-wetting on dielectric. The aim of the present invention is to act on the control of the position of each particle which is present in the sample, for the purpose of displacing such particles in a deterministic or statistical way, in order to detect their presence with the integrated optical or impedance meter sensors and / or characterize their type, for the purpose of counting or manipulating them in an efficient way.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Digital Microfluidic Platform for Actuating and Heating Individual Liquid Droplets
A digital microfluidic platform utilizes dual active matrix circuitry to actuate and heat liquid droplets on a biochip. Liquid droplets are introduced into a droplet handling area of the biochip where they can be actuated by electrodes residing in pixels of an actuating active matrix array according to the electrowetting on dielectric phenomenon and heated by heating elements residing in pixels of a heating active matrix array. Pixels of the actuating active matrix array and the heating active matrix array are independently addressable such that droplets in the droplet handling area can be selectively heated and actuated according to their location. The actuating active matrix array and heating active matrix array can be formed on the same or different substrates with the droplet handling area disposed above or between the substrates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
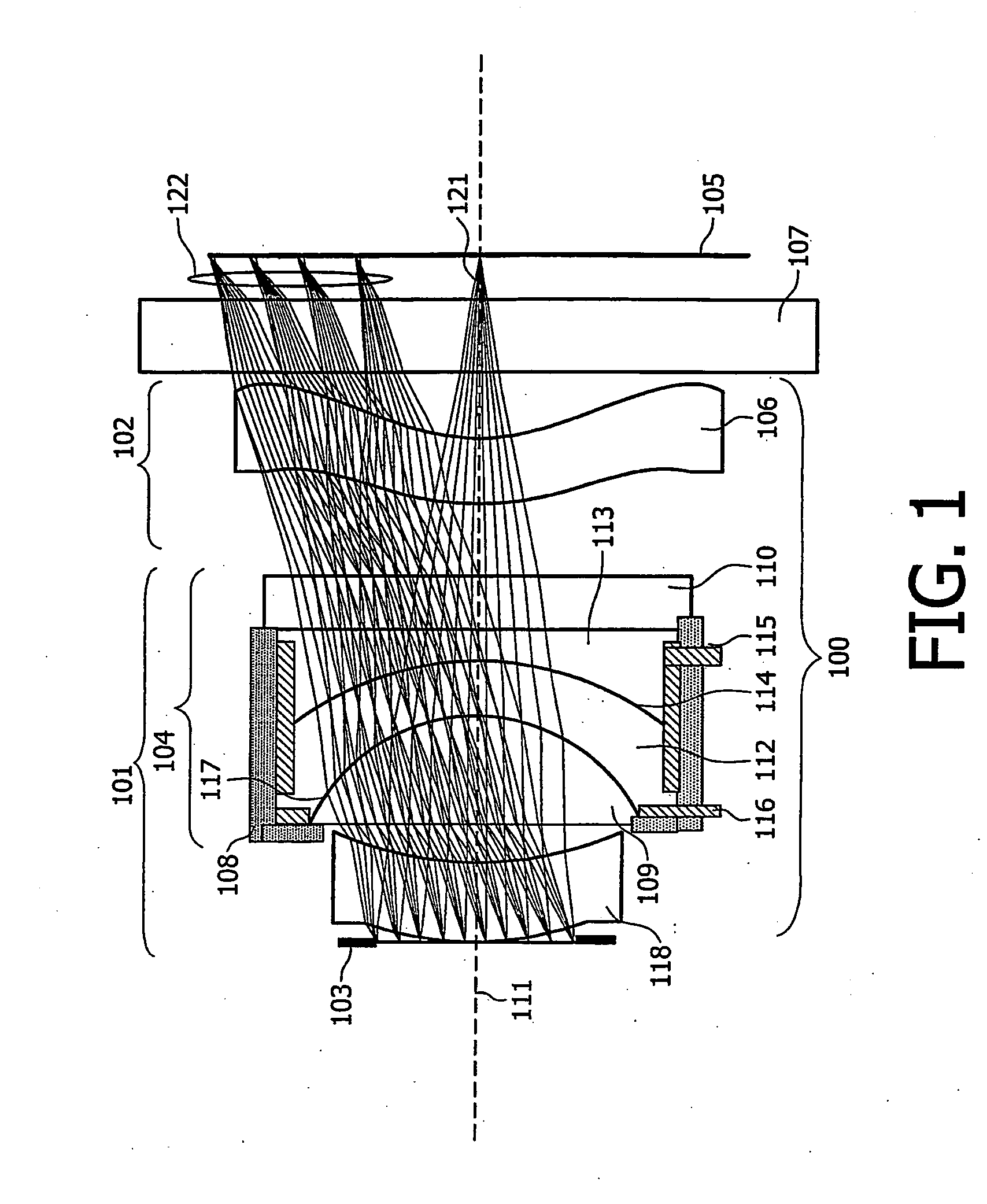
Variable Lens System
InactiveUS20080231966A1Reduce building heightLong focal lengthTelevision system detailsMountingsMaterials scienceOptics
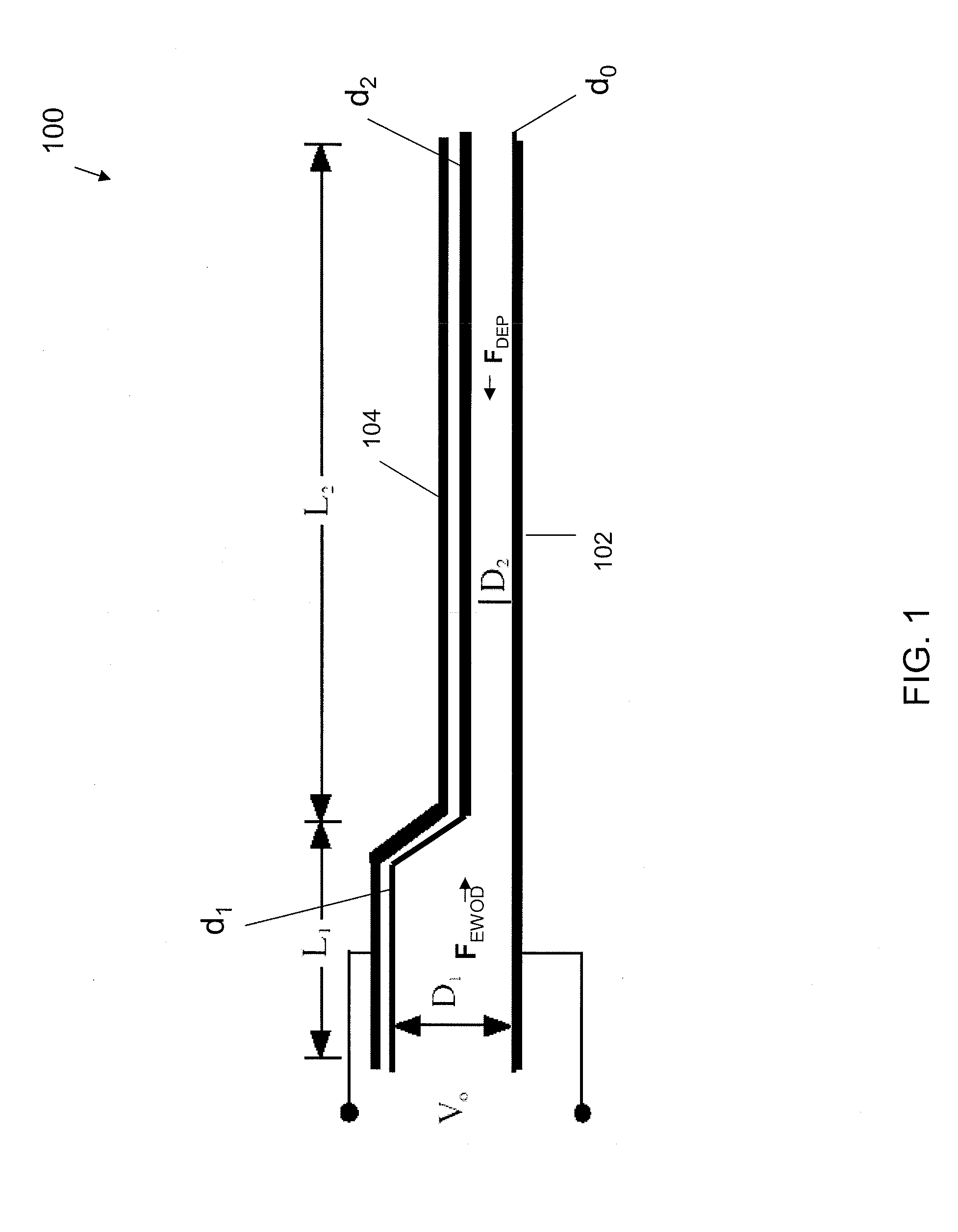
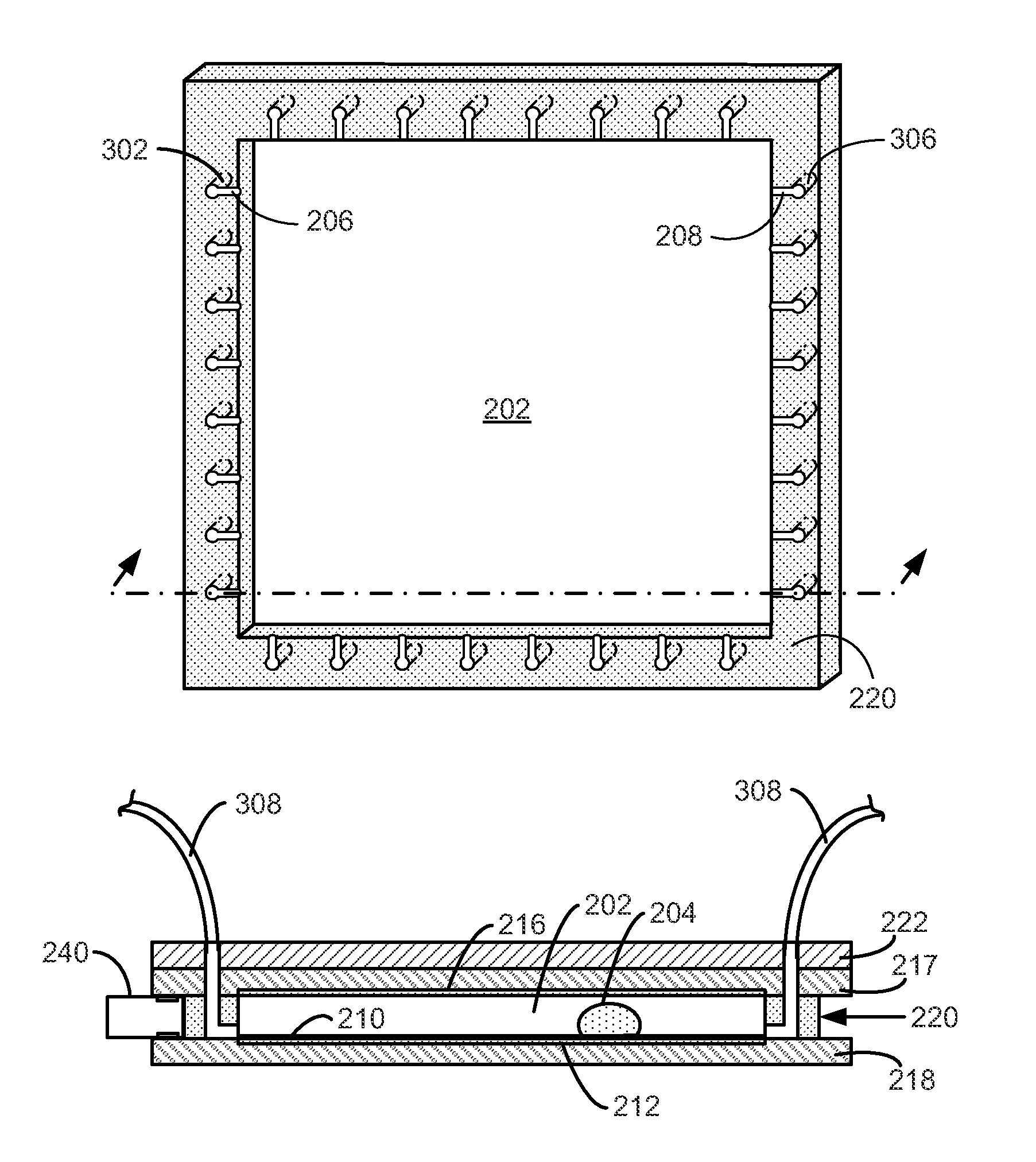
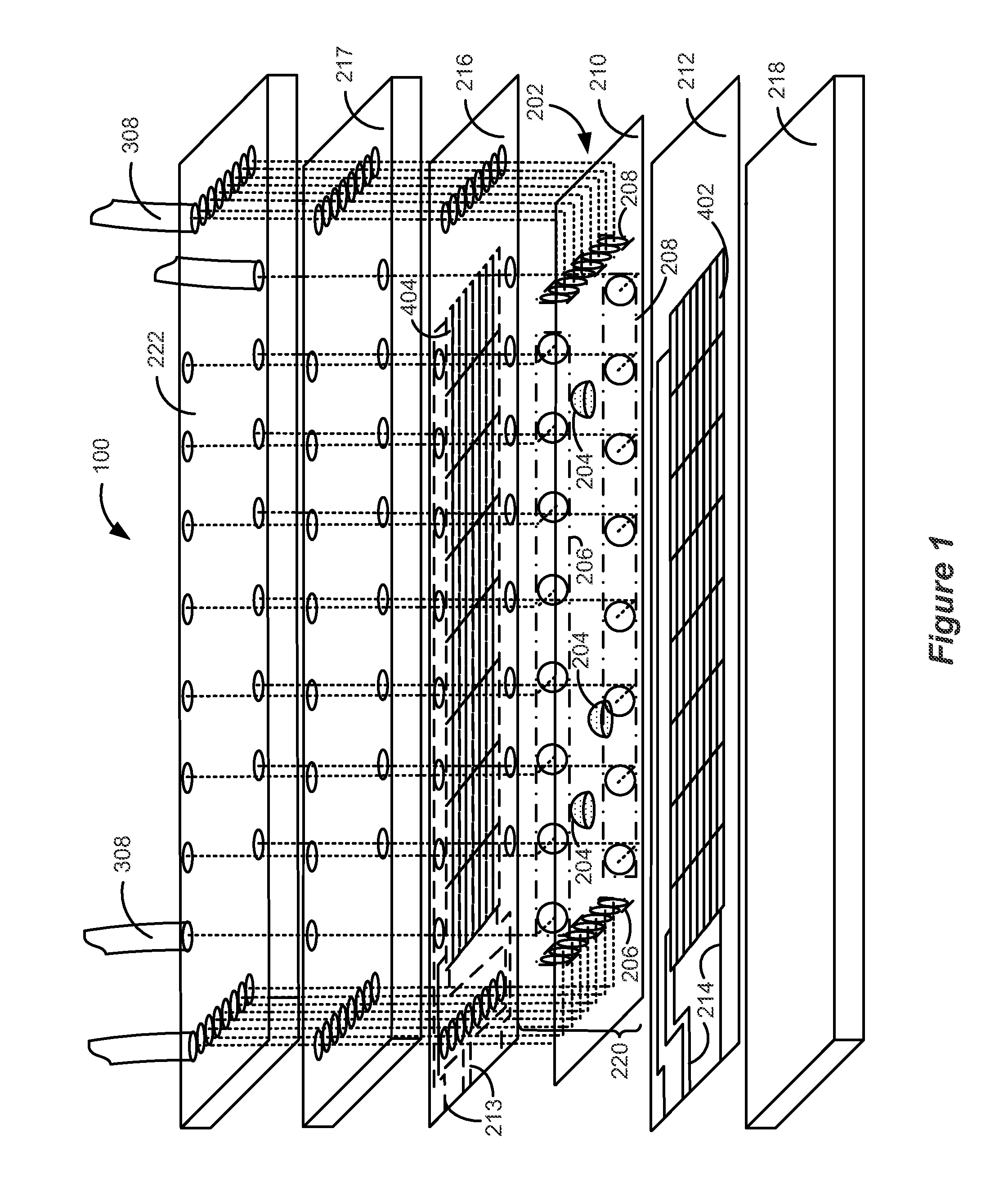
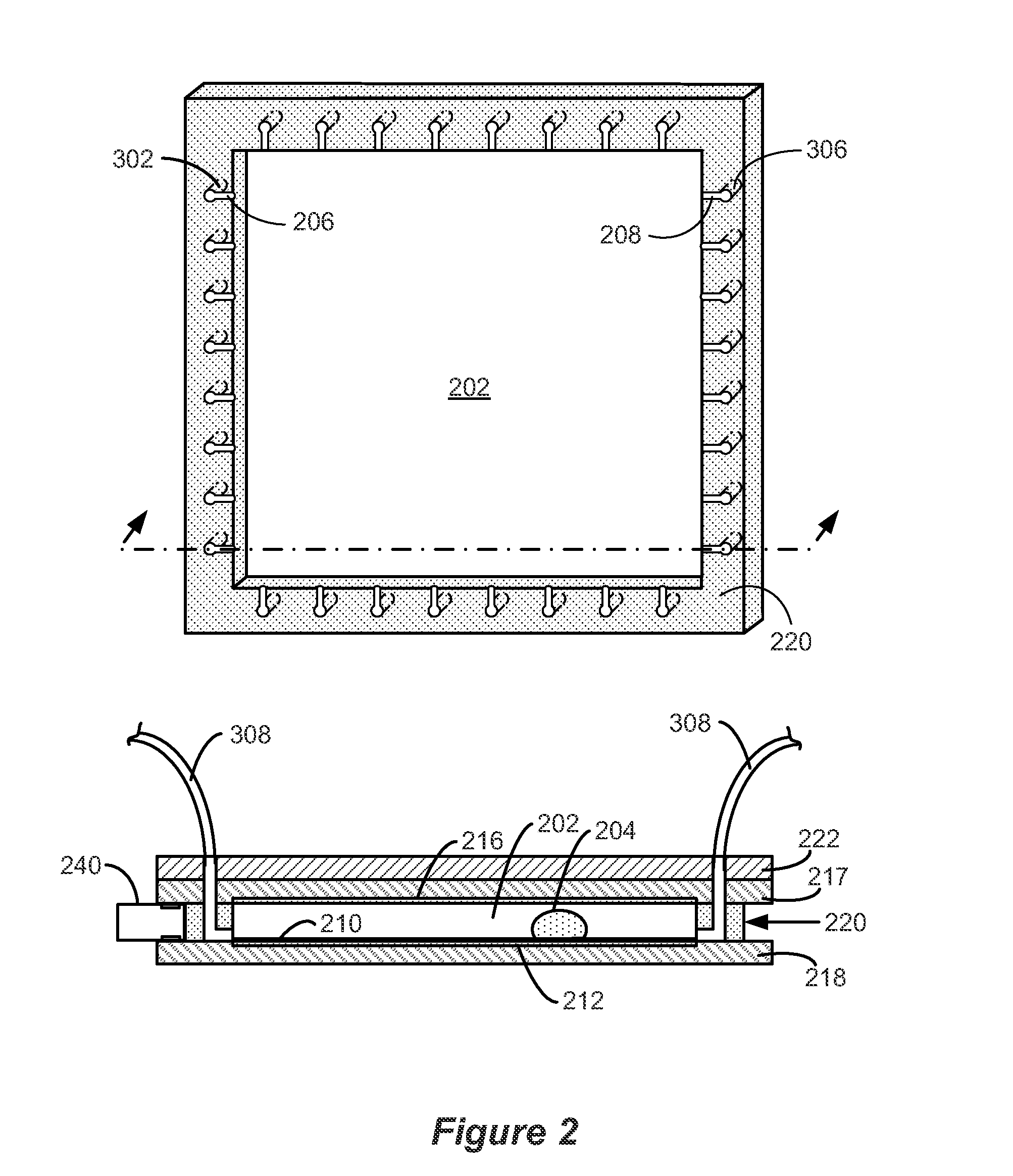
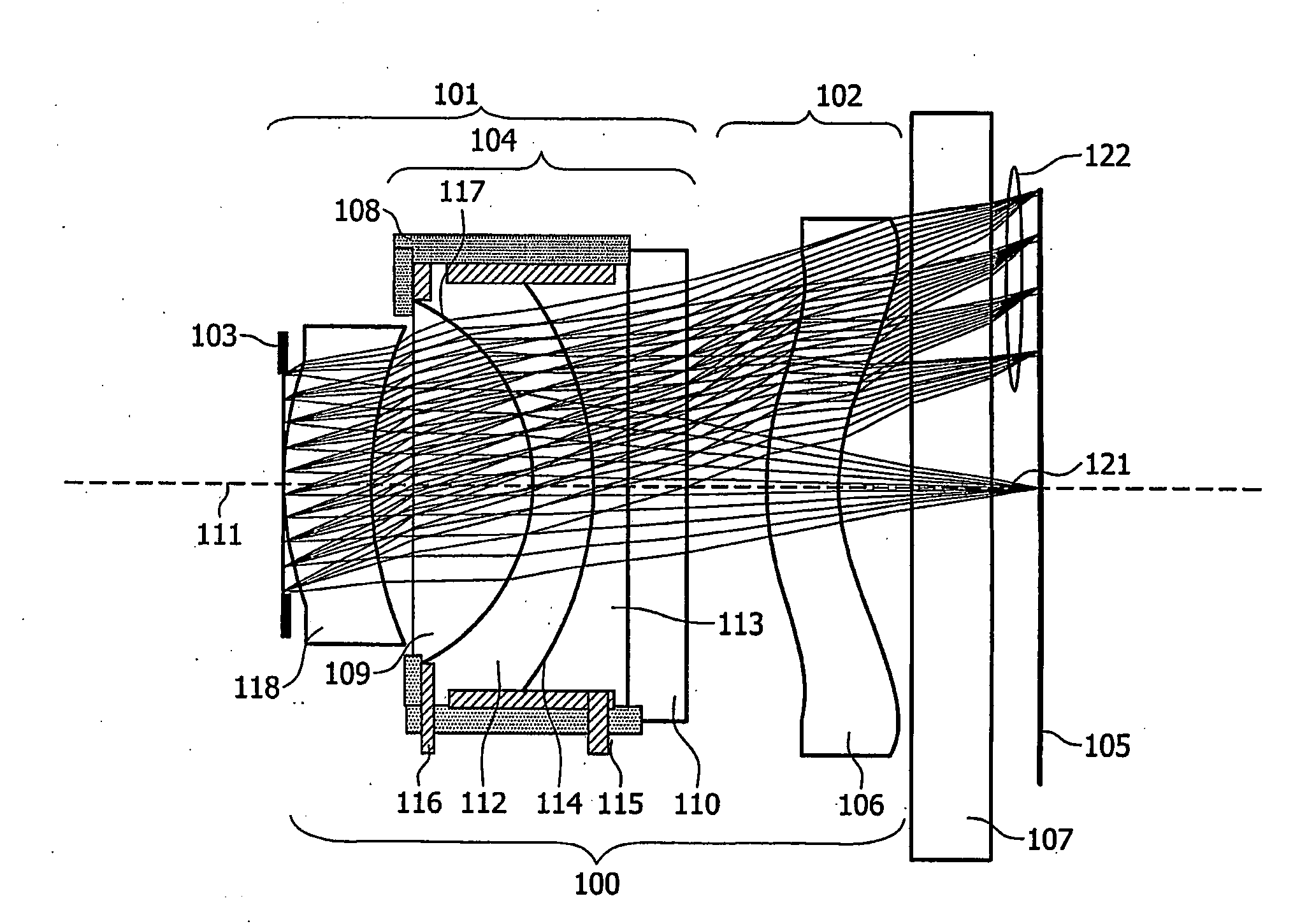
A compact and substantially achromatic optical lens system (100, 200) comprising an electrowetting lens (104, 204) is provided. The optical lens system is using an electrowetting lens in which at least one of the entrance window surface (117, 217) or exit window surfaces (219), being in contact with one of the fluids (112, 212, 113, 213), has a curvature. When the sign of the curvature of that surface has the same sign as the curvature of the meniscus when no voltage is applied, a low building height is achieved. The optical element (104, 204) not only acts as a focussing or zooming device, but that it also acts as an aberration reduction element for the other elements in the optical lens system (100, 200).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
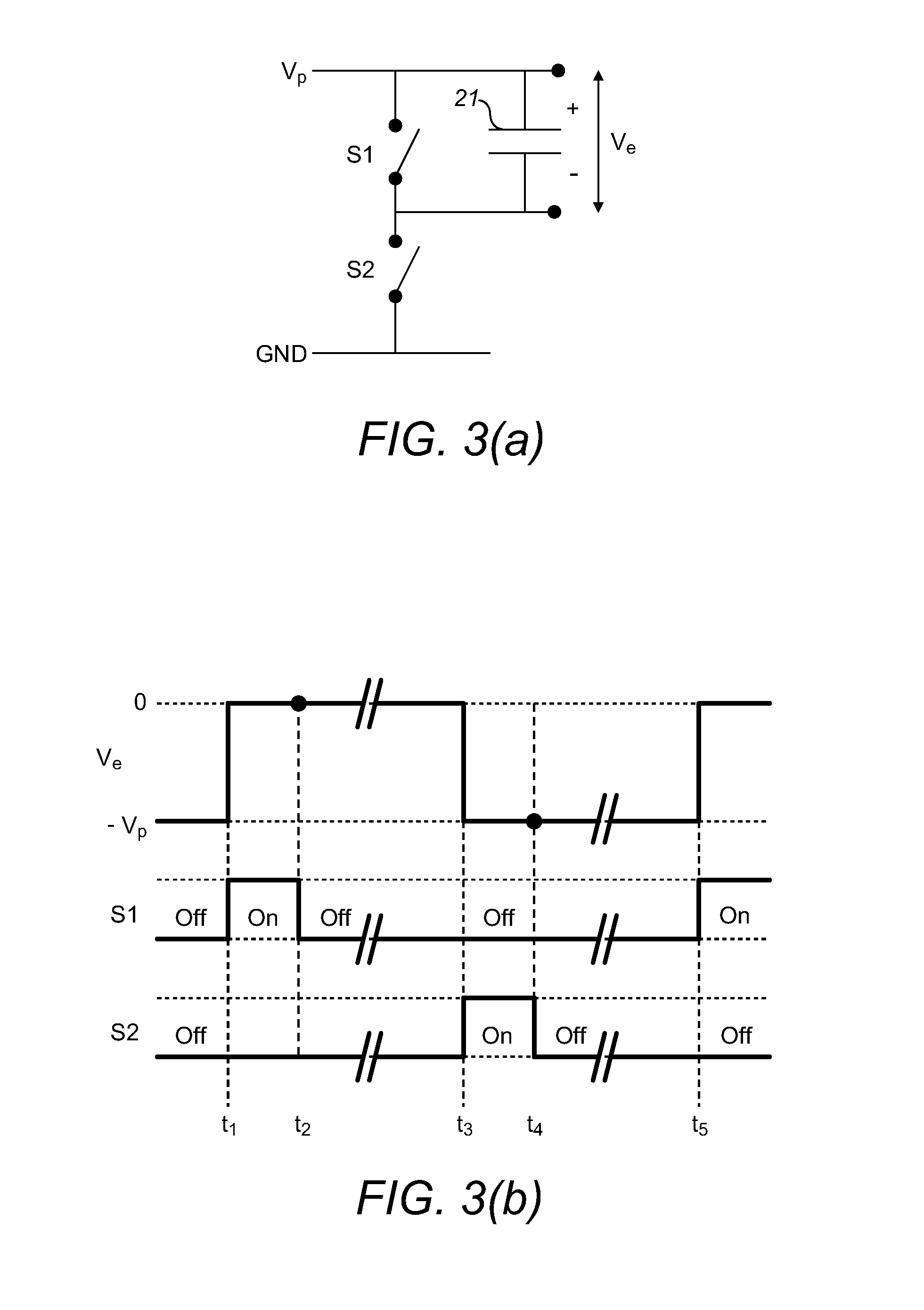
A method of driving an active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric device and an active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric device
ActiveUS20180078934A1Minimizes physical sizeMinimizing size of whole arrayCellsStatic indicating devicesDielectricElectricity
A method of driving an active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric (AM-EWOD) device comprises (i) setting a reference electrode to a first reference voltage; (ii) writing a set of data to array element electrodes of array elements of the device; and (iii) either (a) maintaining the voltages written to the array element electrodes until a time t0 or (b) re-writing the set of data N−1 times (where N≧2). The reference electrode is then set to a second reference voltage different from the first reference voltage, and features (i) to (iii) are repeated. When the data are first written, there is a delay between the time when the voltage on the reference electrode is transitioned and the time when a given array element is next written with data. Feature (iii) allows the time for which the correct data values are held to be increased relative to the time for which incorrect data values may possibly be held, so that the time for which an element may be in an incorrect state can be made insignificant in terms of its effect on unwantedly perturbing droplet operations.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
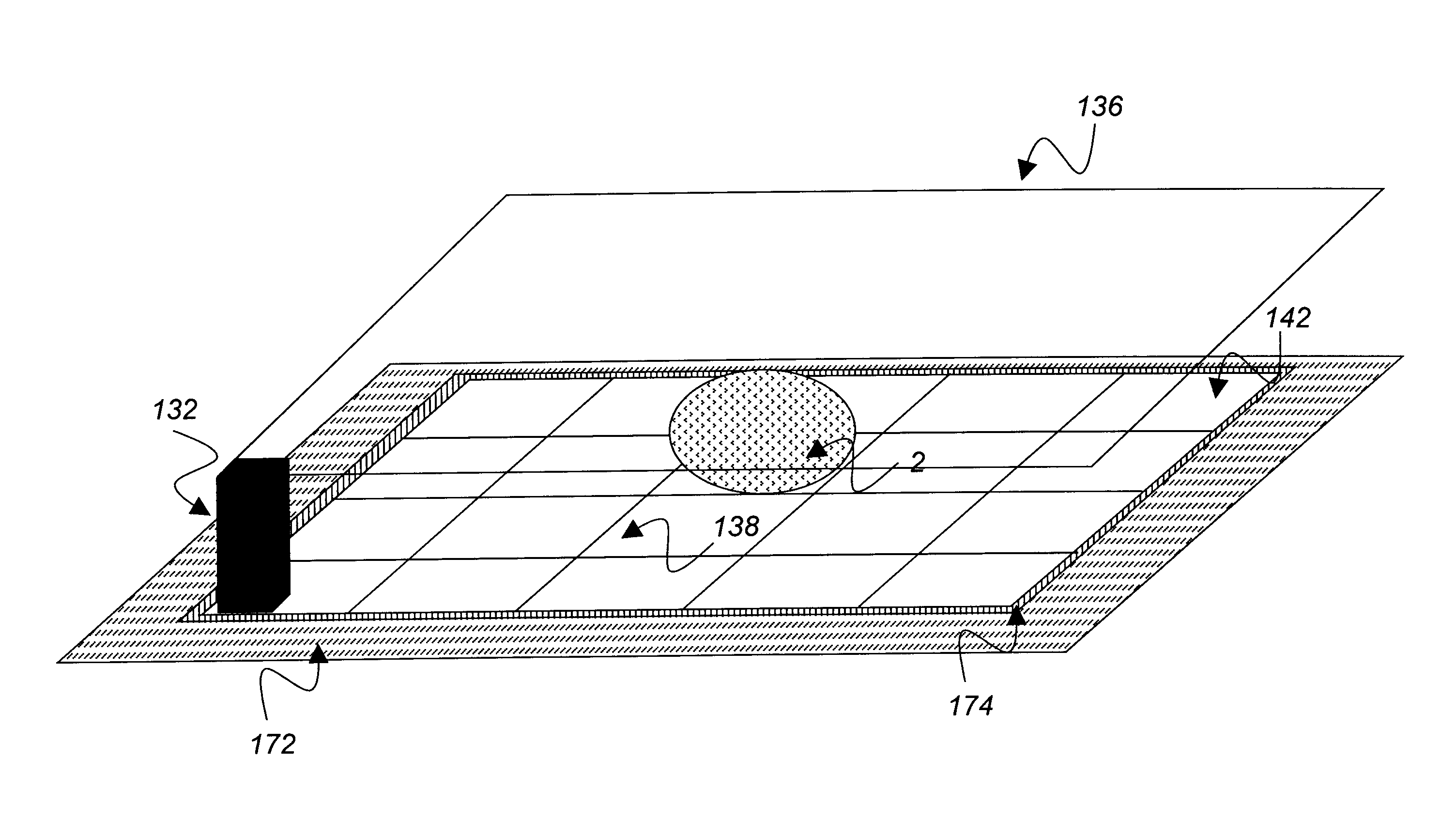
System for manipulating samples in liquid droplets
ActiveUS20130126358A1CellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesVoltage pulseElectrode array
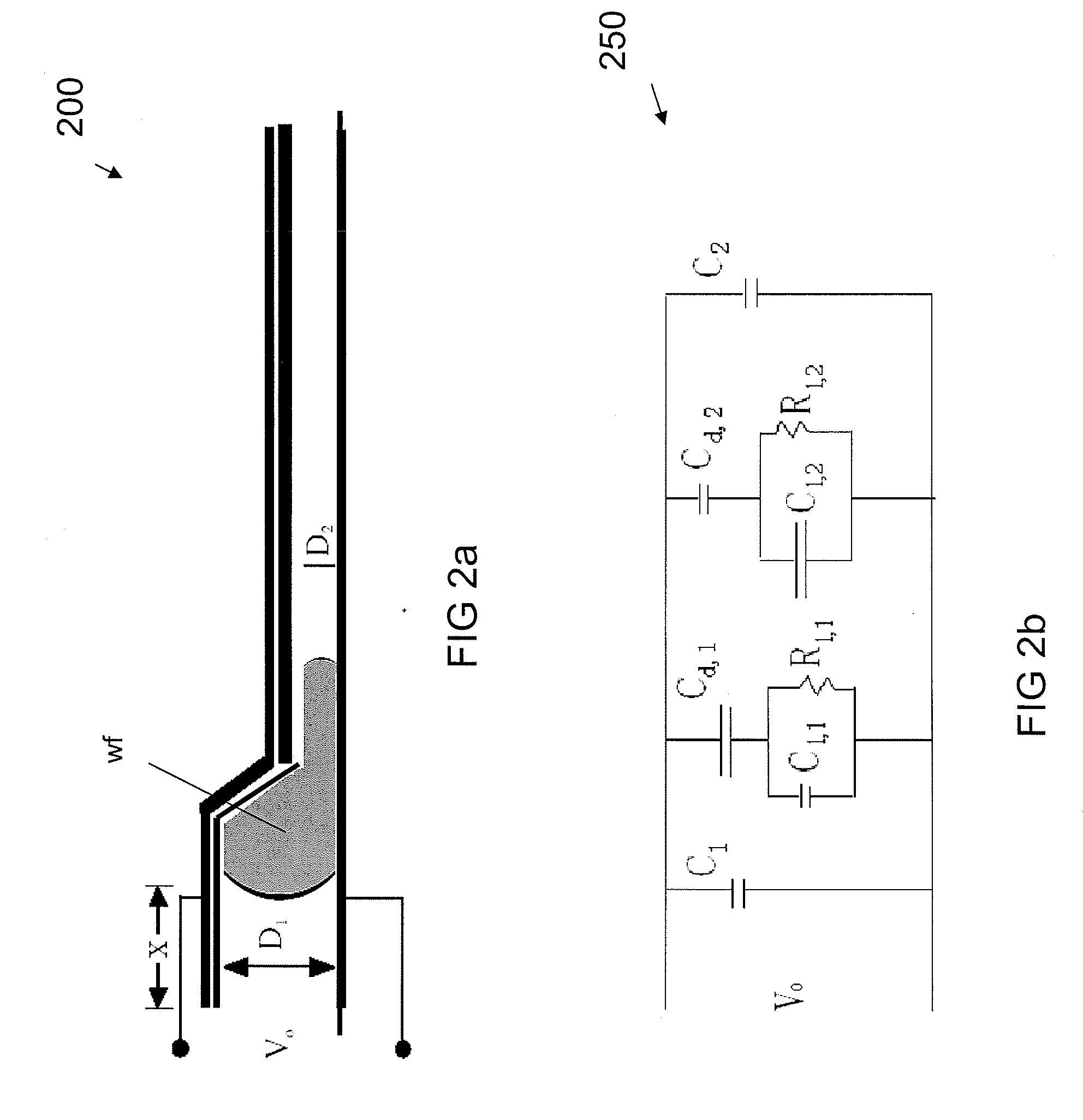
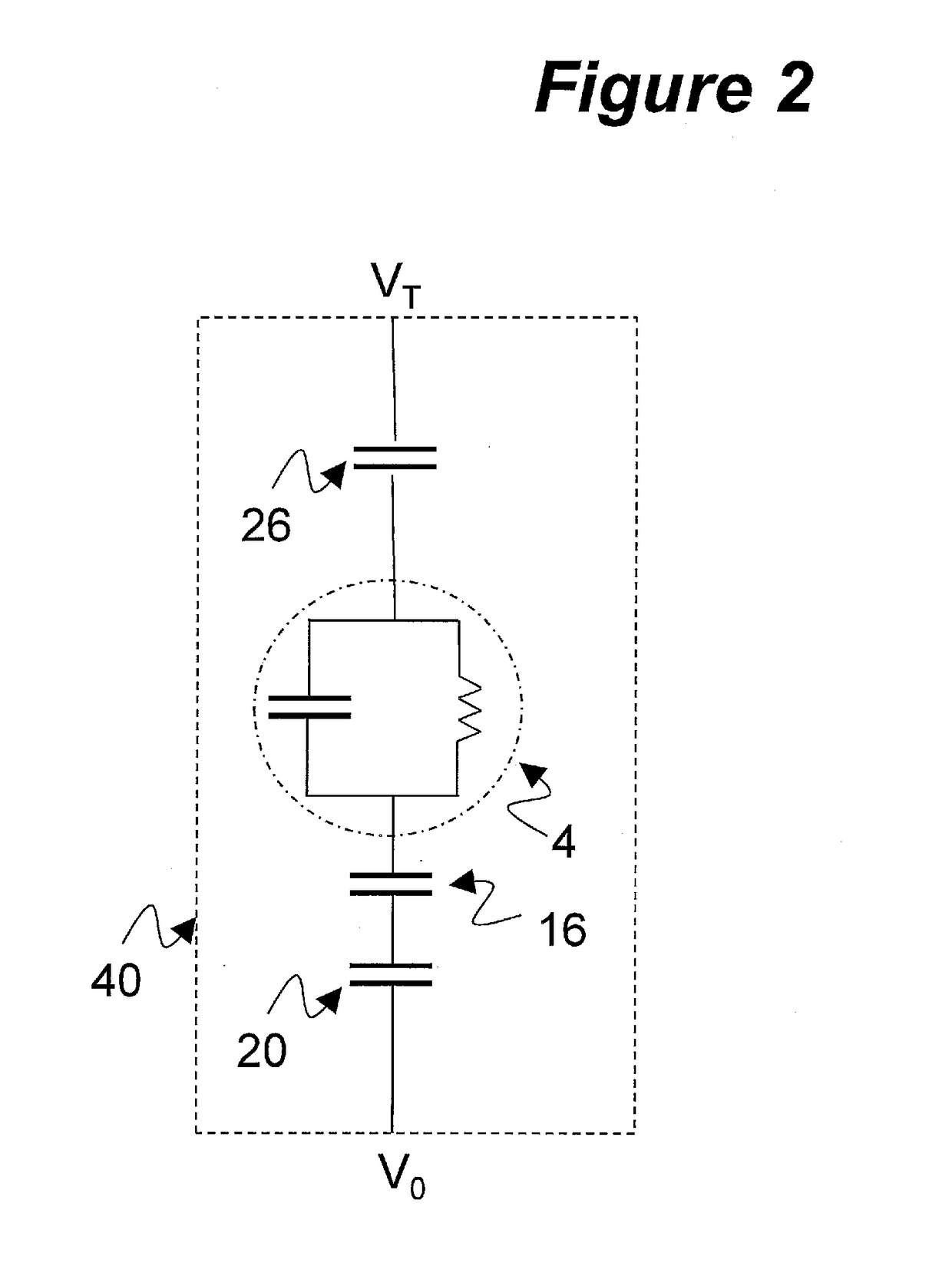
A liquid droplet manipulation system has a substrate with at least one electrode array and a central control unit for controlling selection of individual electrodes of the electrode array and for providing the electrodes with individual voltage pulses for manipulating liquid droplets by electrowetting. A working film is placed on top of the electrodes for manipulating samples in liquid droplets with the electrode array. At least one selected individual electrode of the electrode array is configured to be penetrated by light of an optical detection system for the optical inspection or analysis of samples in liquid droplets that are located on the working film. Also disclosed is working film that is to be placed on the electrode array and a cartridge that includes such a working film for manipulating samples in liquid droplets.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
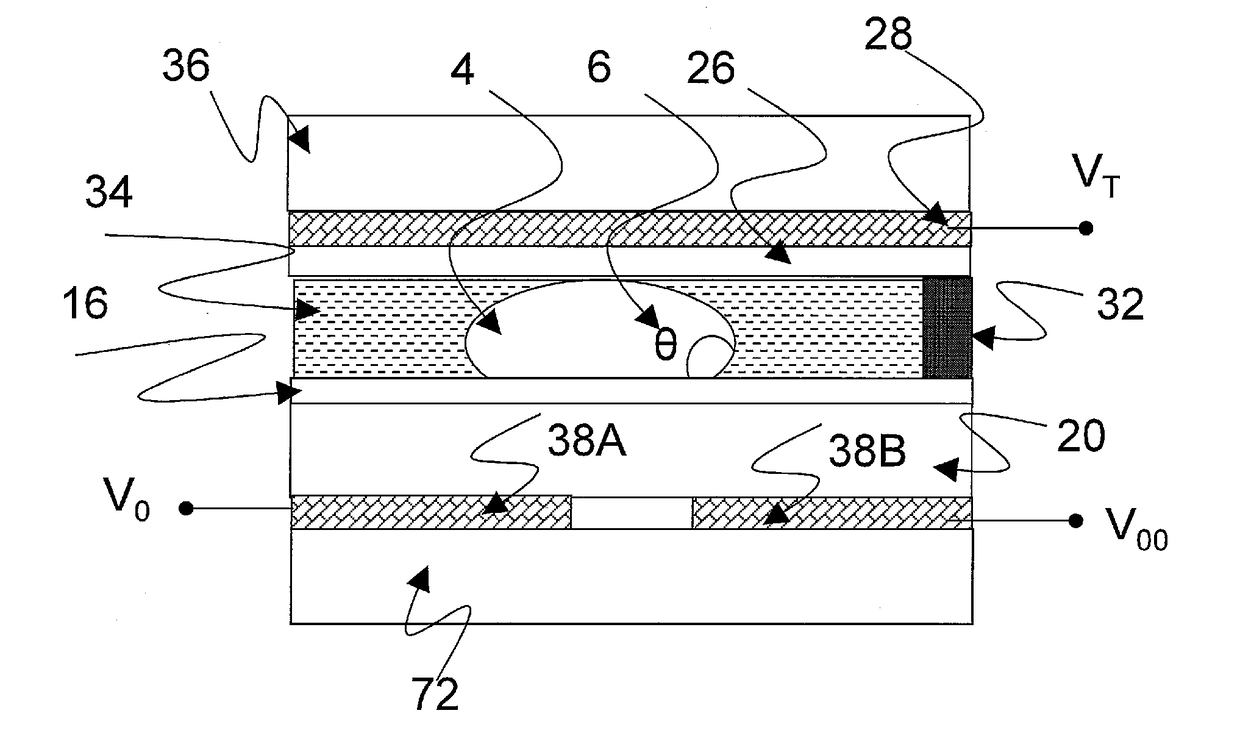
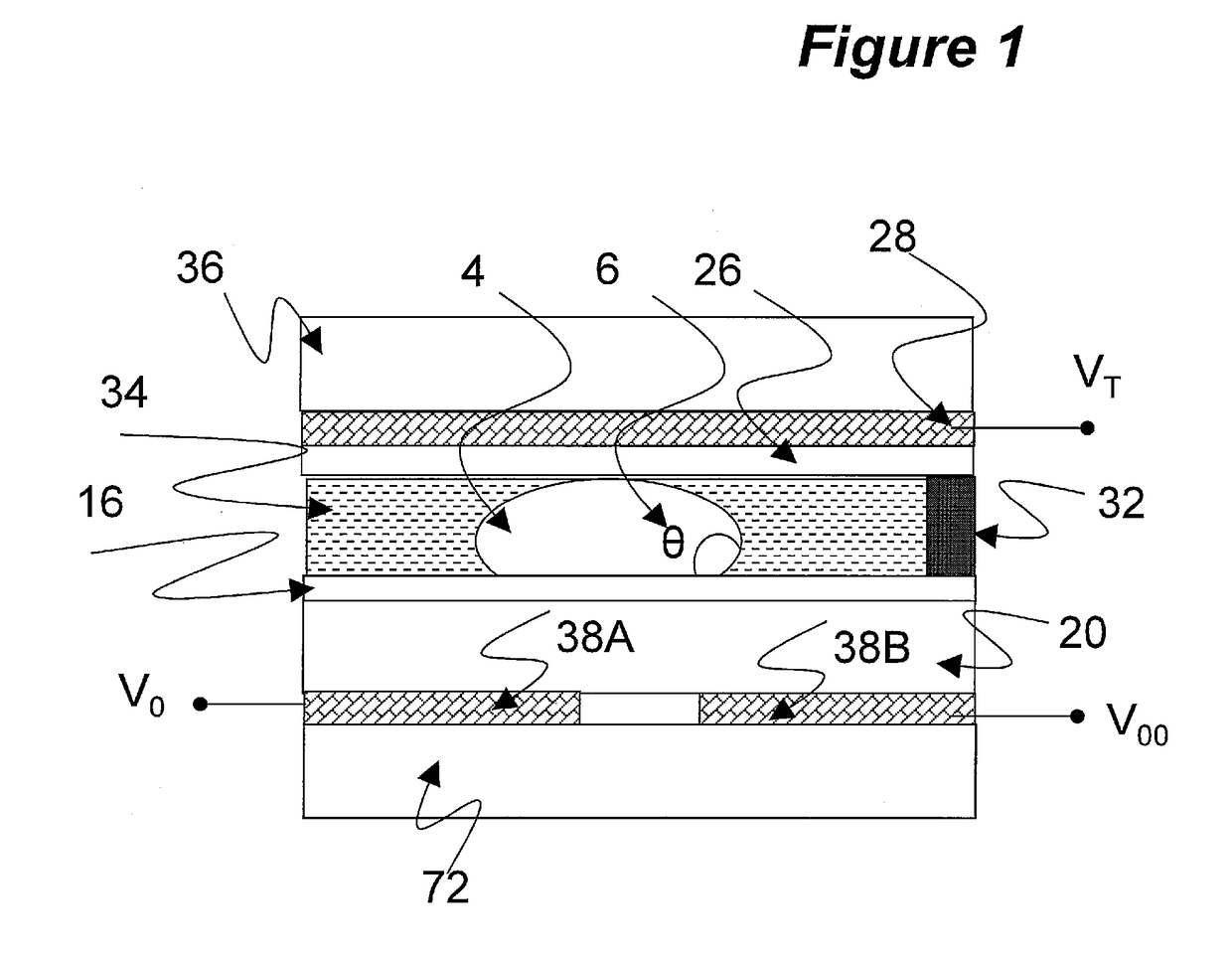
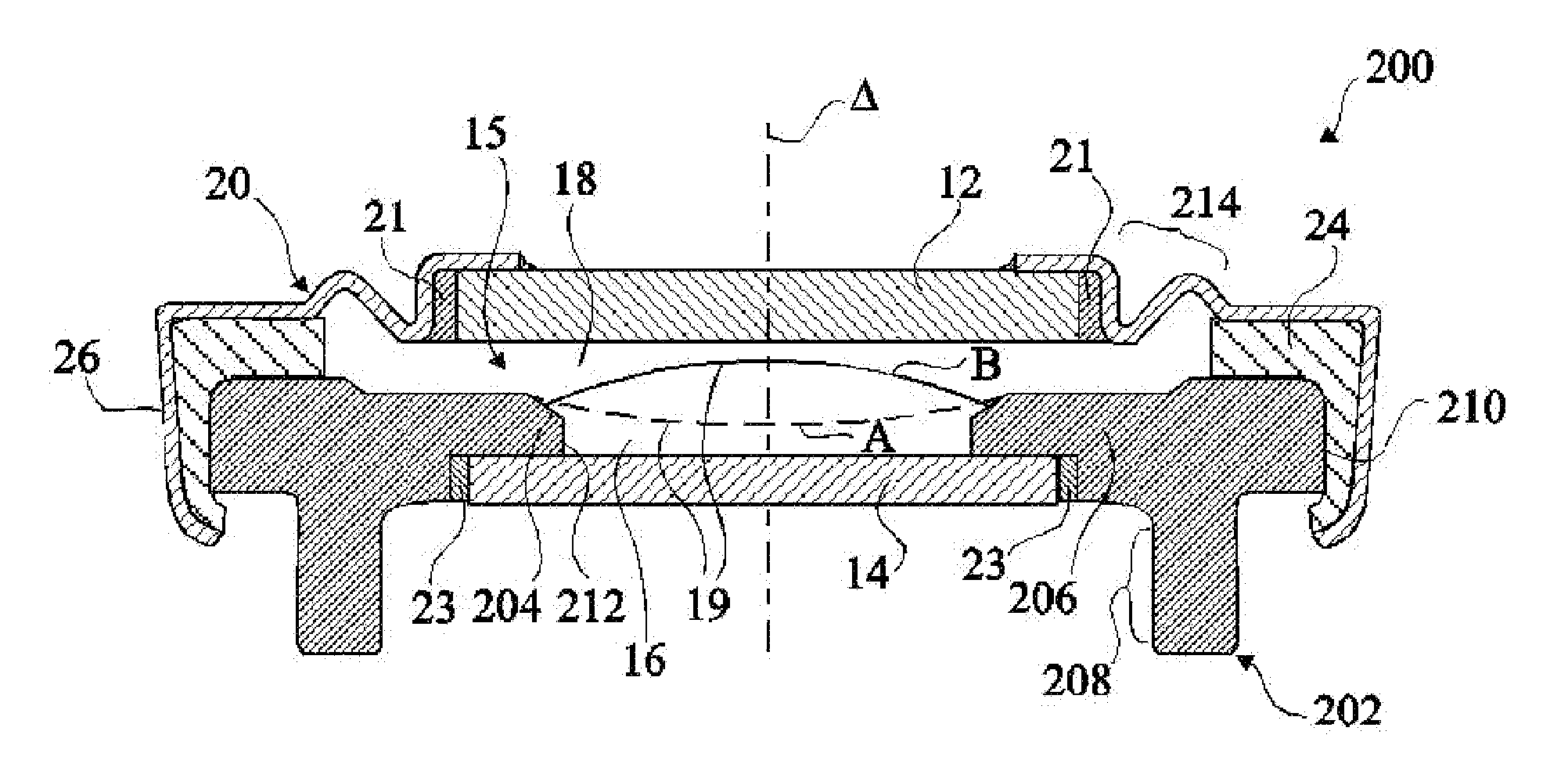
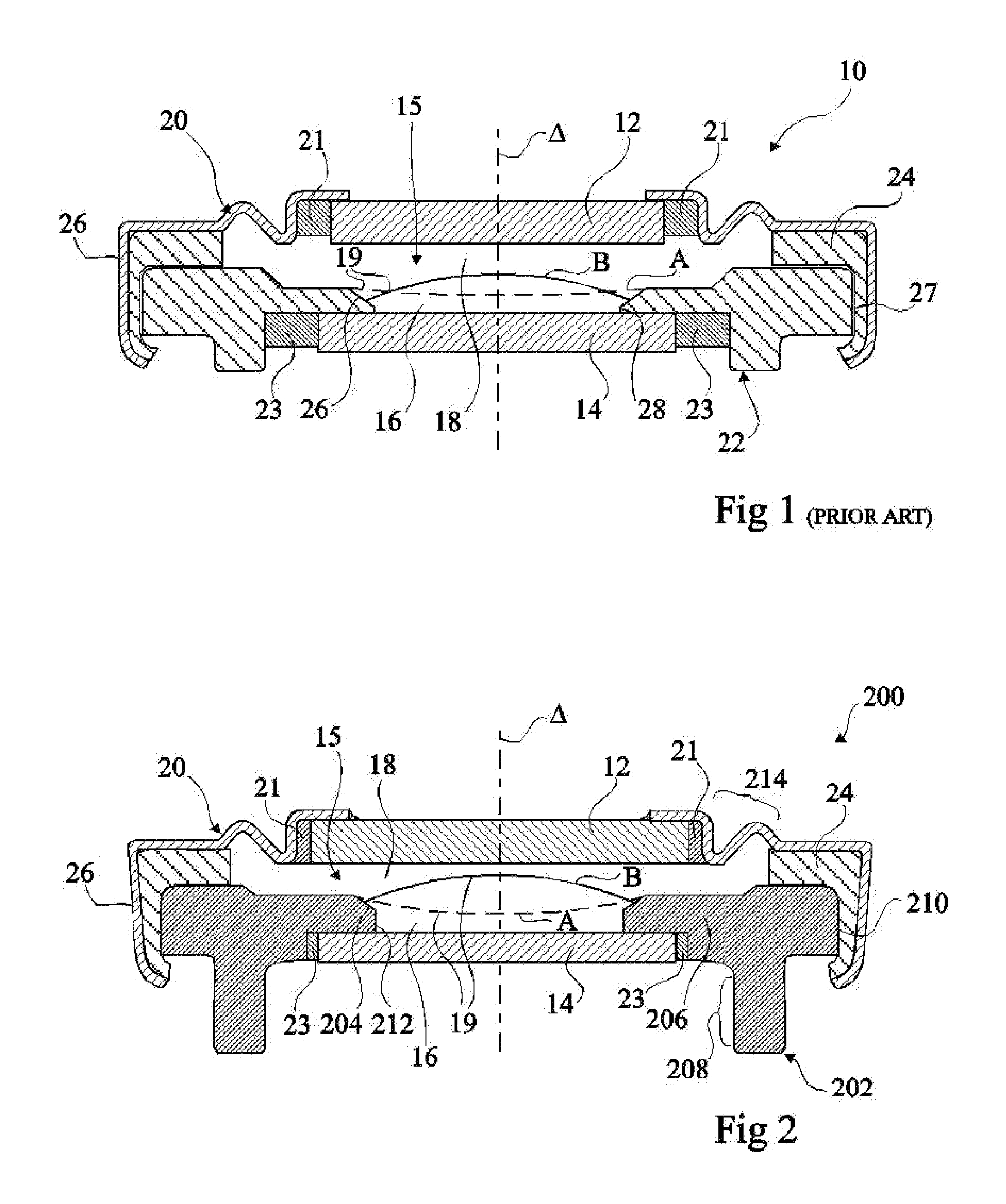
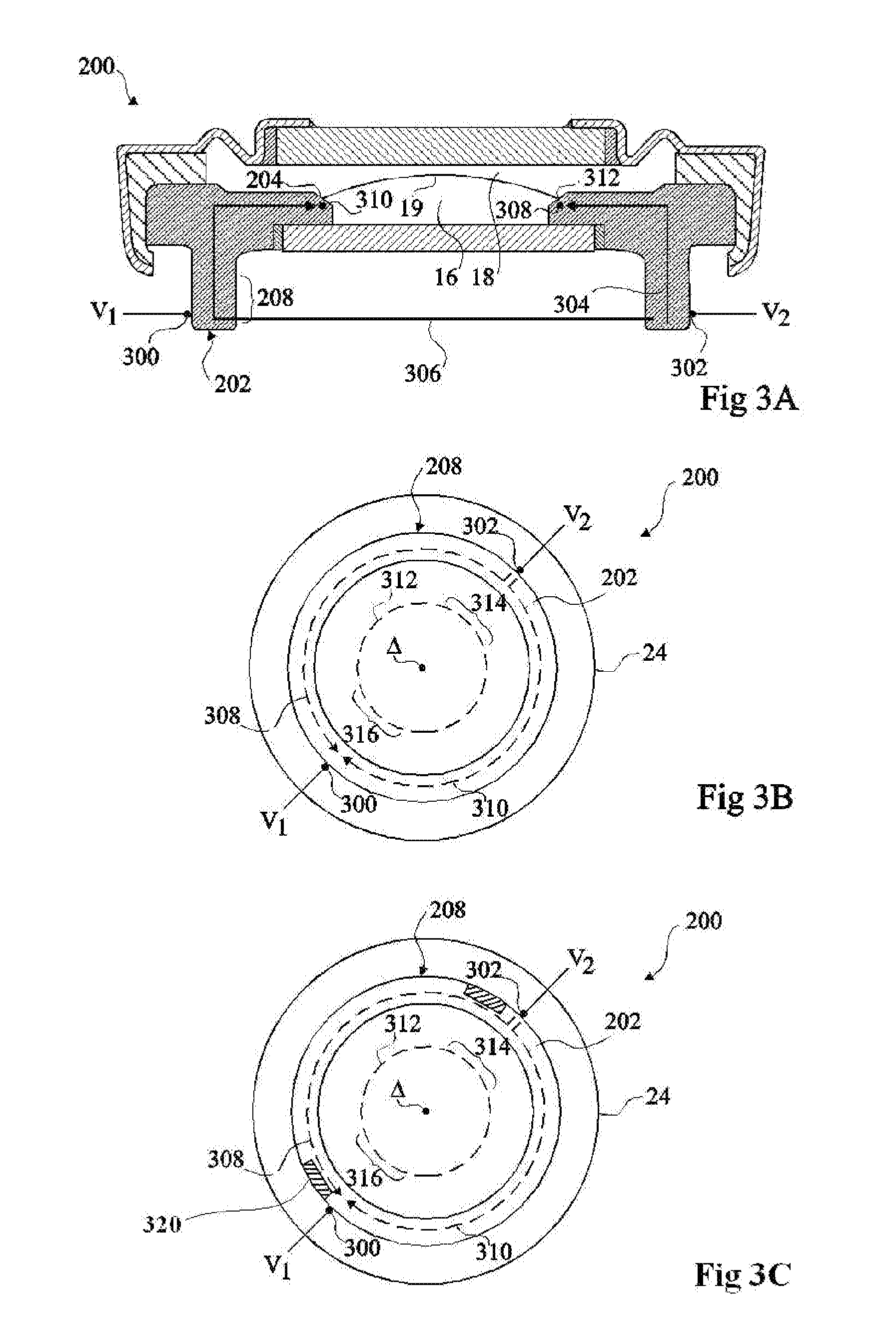
Electrowetting device with polymer electrode
The invention concerns an electrowetting optical device comprising a chamber (15) comprising first and second immiscible liquids (16, 18) contacting each other at a liquid-liquid interface (19), the first liquid being an insulating liquid and the second liquid being a conducting liquid; a first electrode (20) in the contact with the second liquid; and a second electrode (202) insulated from the first and second liquids by an insulating layer, wherein the second electrode is formed of a conductive molded polymer material, wherein the curvature of said liquid-liquid interface is controllable by application of a voltage between said first and second electrodes.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
Active matrix device and method of driving the same
ActiveUS20120268804A1Easy to manufactureLow costHeating or cooling apparatusLaboratory glasswaresDriver circuitActive matrix
An electrowetting on dielectric (EWOD) device which includes a plurality of array elements configured to manipulate one or more droplets of fluid on an array, each of the array elements including a corresponding array element driver circuit, wherein each array element driver circuit includes: a top substrate electrode and a first drive electrode between which the one or more droplets may be positioned, the top substrate electrode being formed on a top substrate, and the first drive electrode being formed on a lower substrate; and circuitry configured to selectively provide drive voltages to the first drive electrode to move the one or more droplets among the plurality of array elements, and wherein at least one of the plurality of array elements includes: a heater element also formed on the lower substrate and configured to heat the one or more droplets when positioned between the top substrate electrode and the first drive electrode of the at least one array element; and circuitry configured to control the heater element.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Electrowetting system
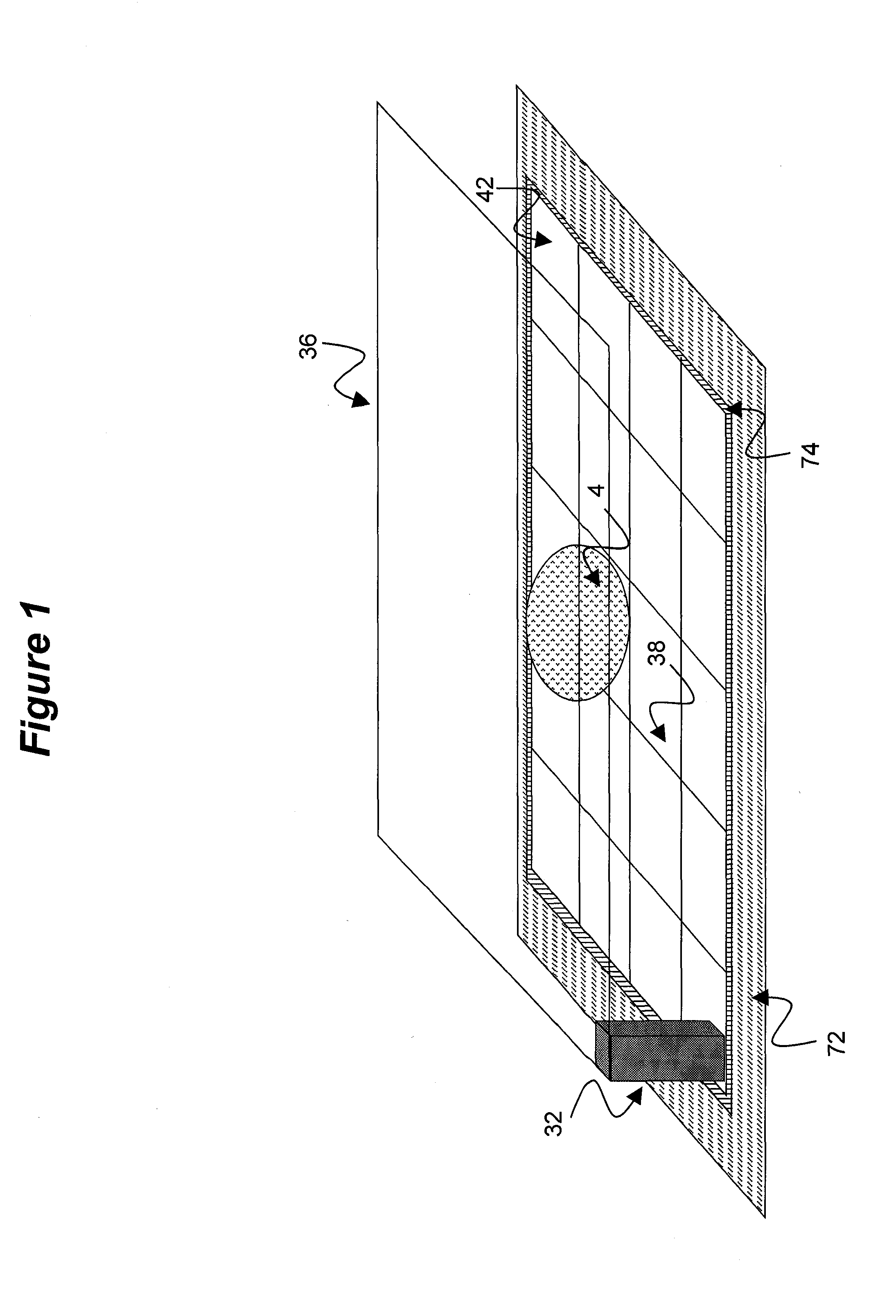
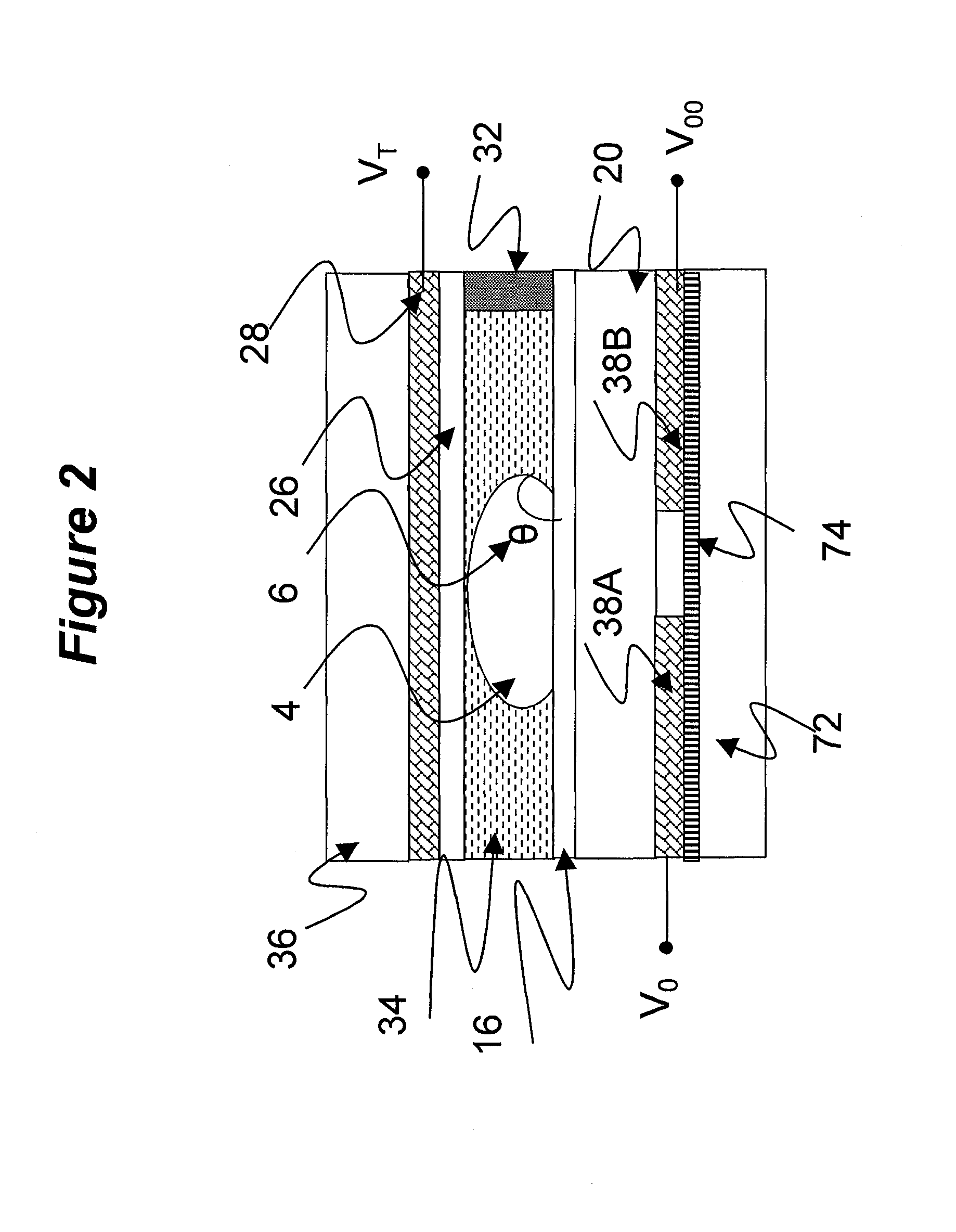
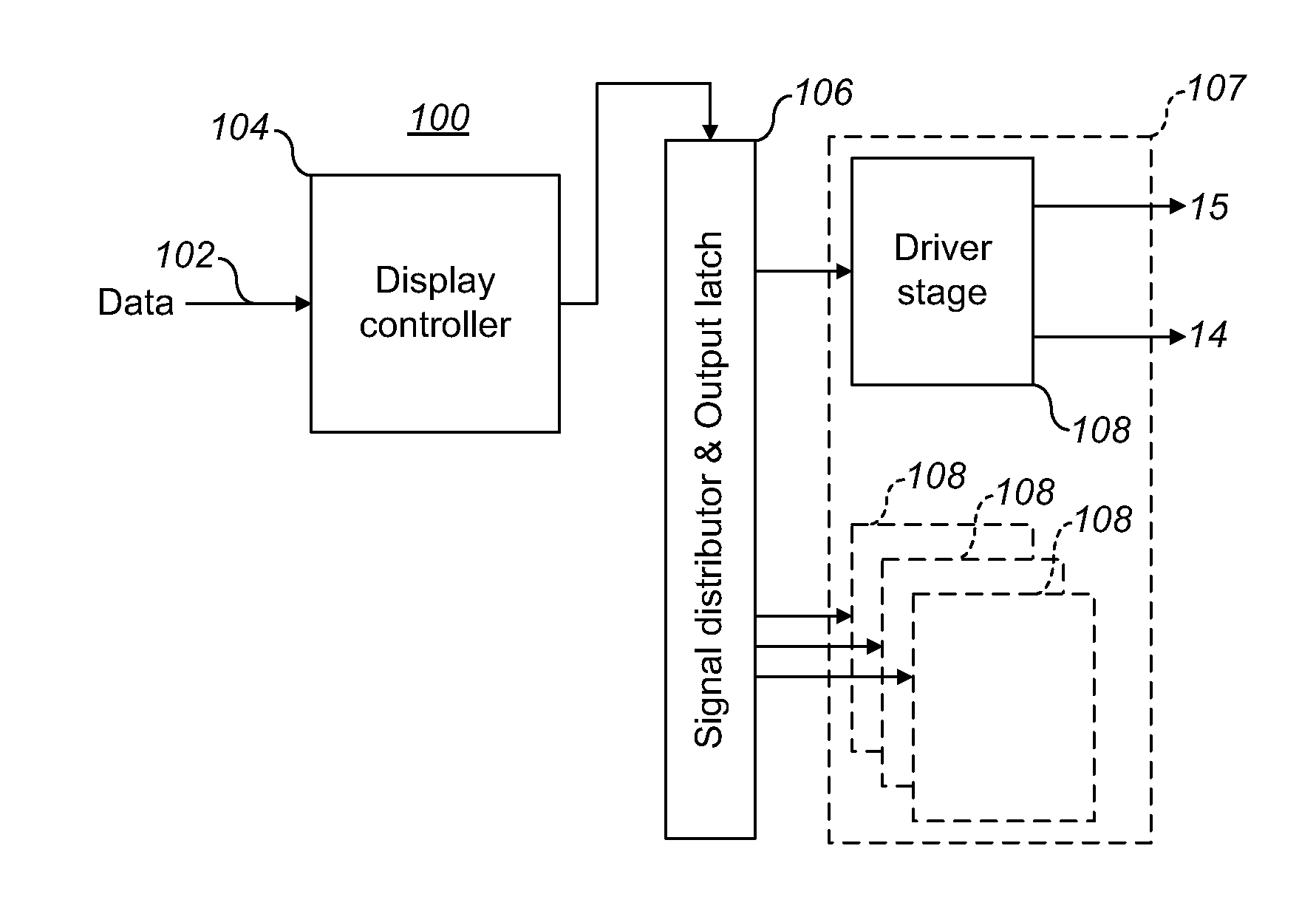
InactiveUS20110187696A1Reduce power consumptionReduce memory sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDisplay device
An electrowetting system including a display device having a plurality of electrowetting elements, including a first electrowetting element and a second electrowetting element, each being configurable in a plurality of different display states; and a display controller for electrical addressing of the plurality of electrowetting elements in order to switch the plurality of electrowetting elements between different display states. The display controller is arranged to address the first electrowetting element twice subsequently, separated by a first addressing interval, and to address the second electrowetting element twice subsequently, separated by a second addressing interval, the second addressing interval being longer than the first addressing interval. The present invention further relates to a display controller, a driver stage and a method of controlling a display device.
Owner:LIQUAVISTA BV
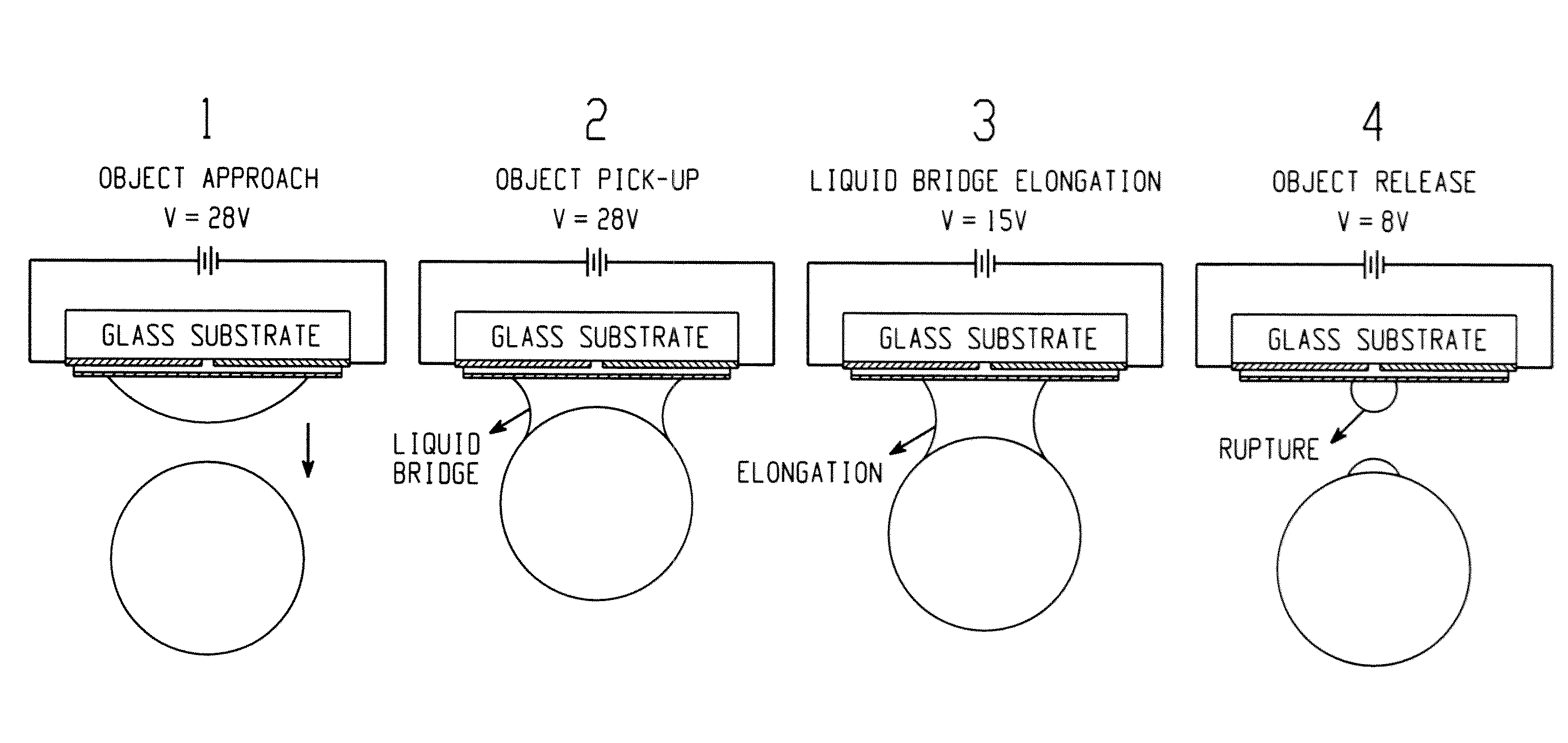
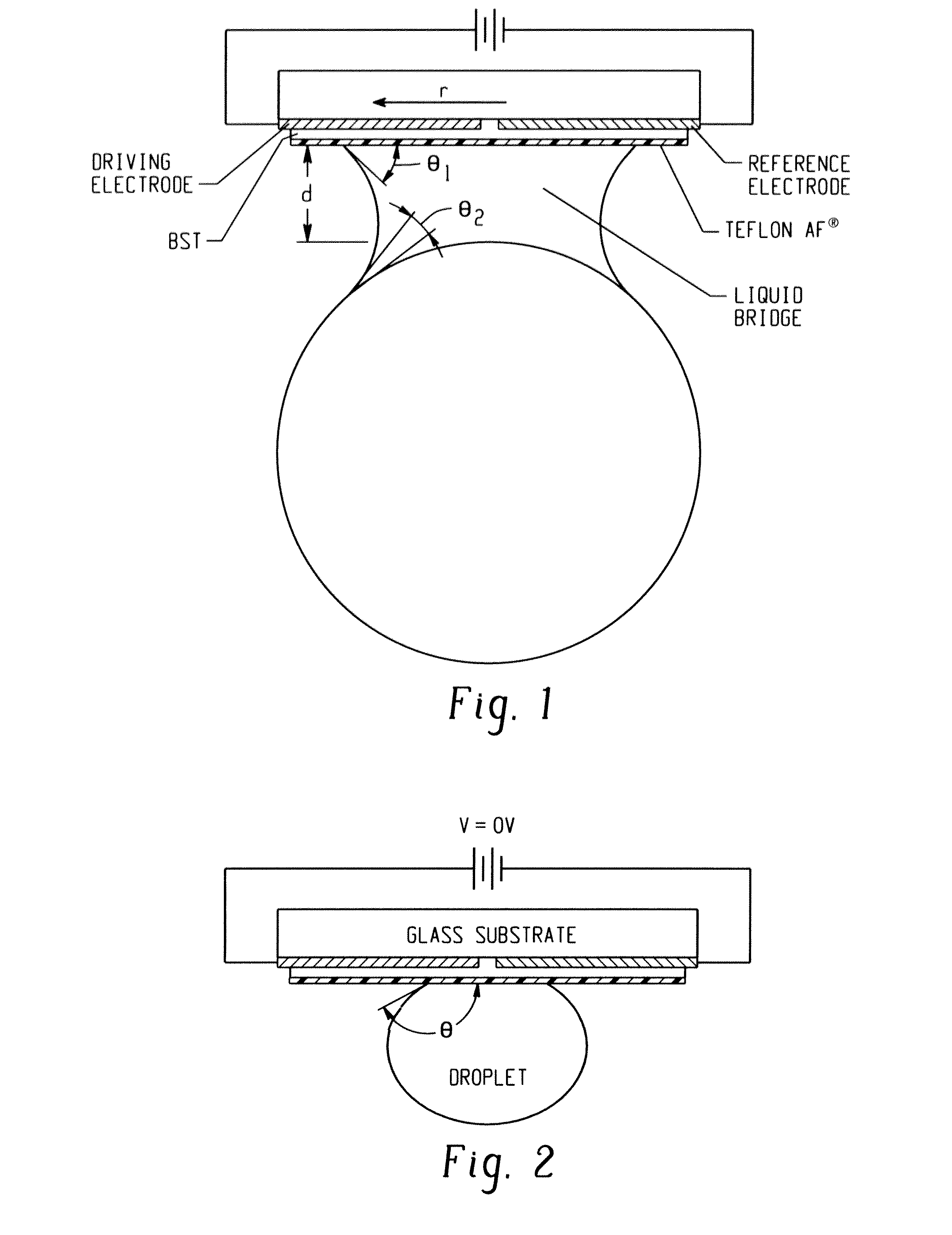
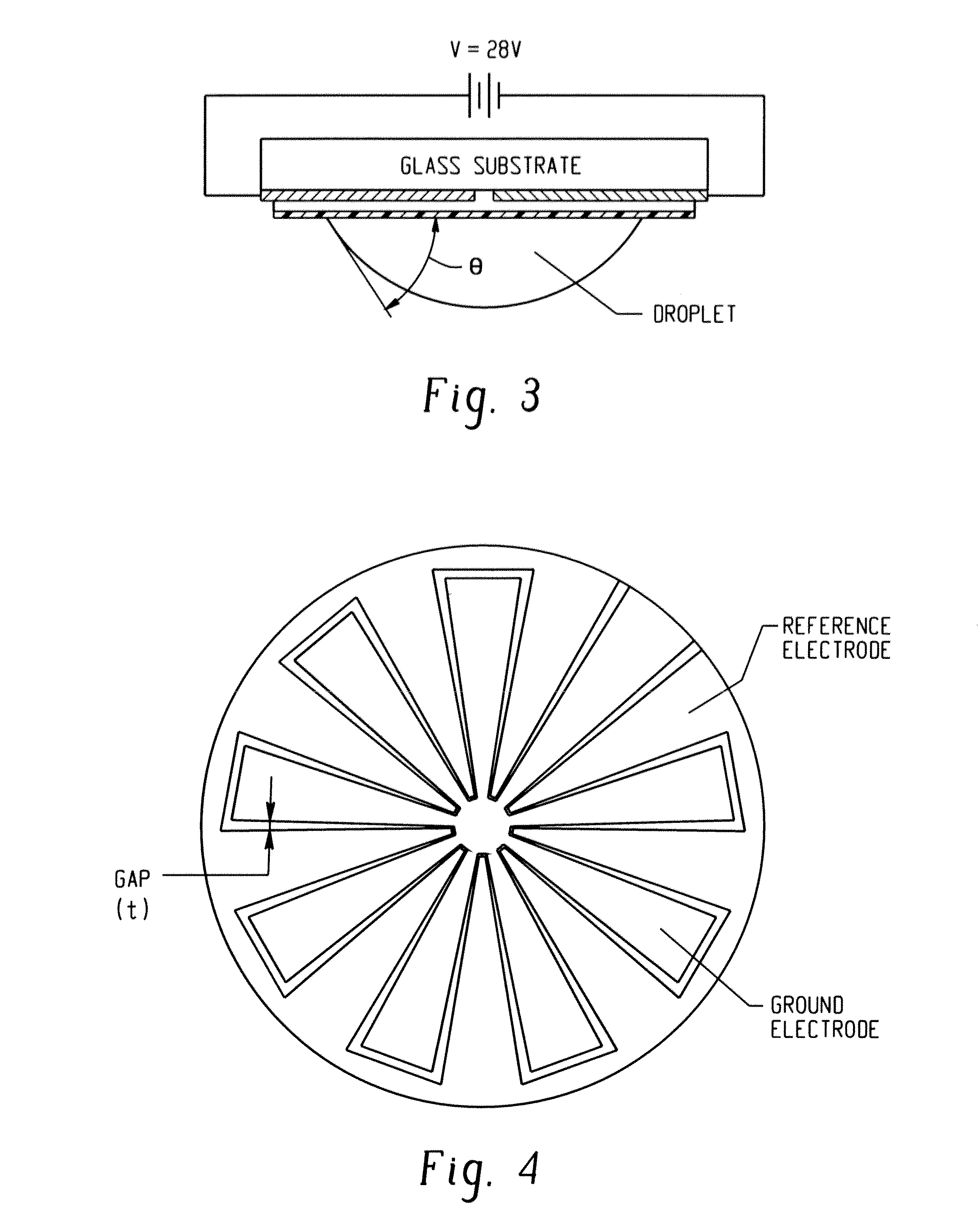
Apparatus and method for manipulating micro component
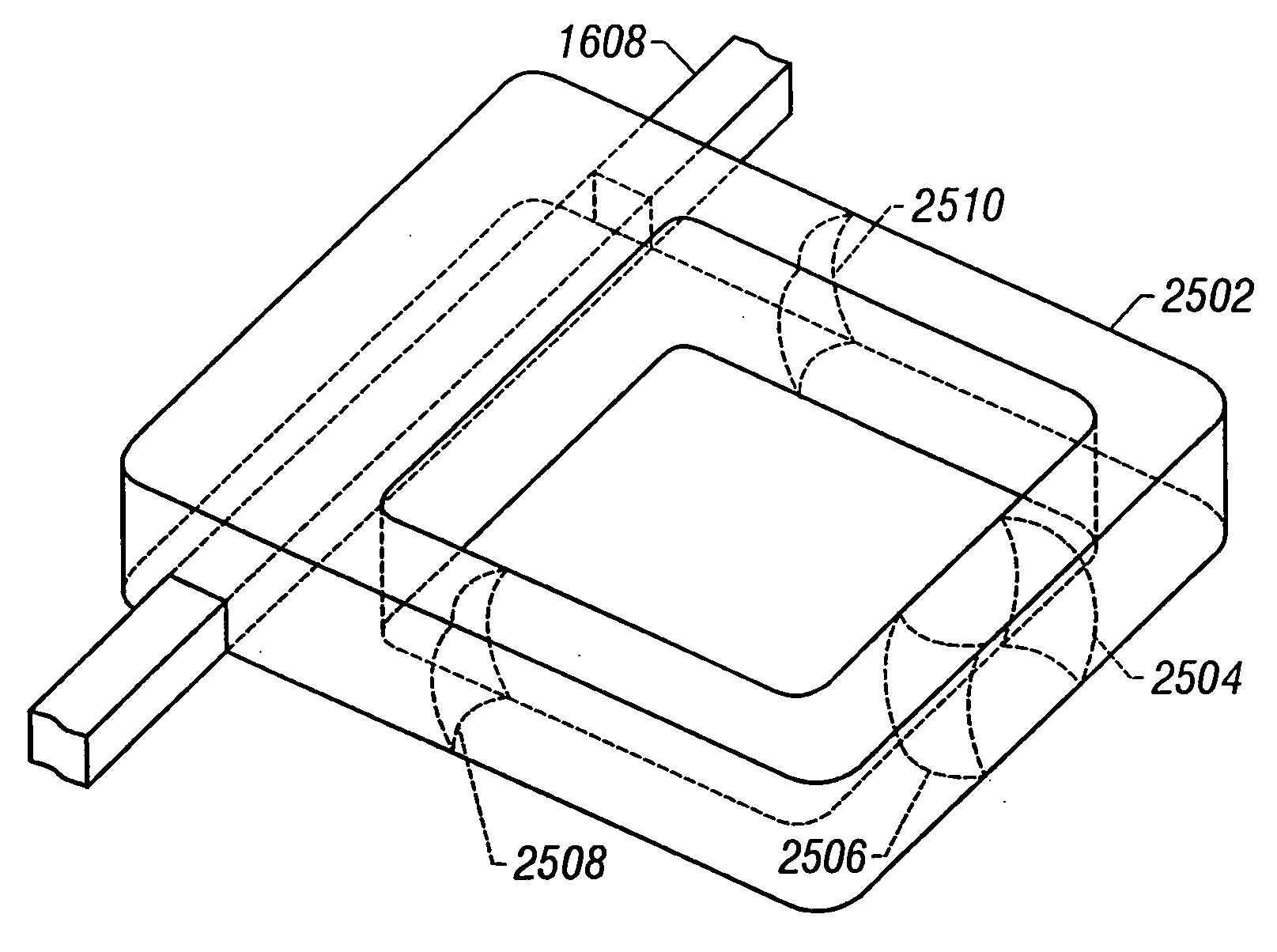
In one embodiment, a system for manipulation of a micro component includes a gripper subsystem for lifting, holding, and releasing a micro component. The gripper subsystem includes a base substrate having a work side and an opposing side, a positive electrode secured to the work side of the base substrate, a negative electrode suitably spaced from the positive electrode and secured to the work side of the base substrate, a dielectric layer formed over the work side of the base substrate and the positive and negative electrodes, and a hydrophobic layer comprising a hydrophobic material with predictable electrowetting behavior formed over the dielectric layer such that the dielectric layer is between the work side of the base substrate and the hydrophobic layer. A method for manipulation of a micro component is also provided as well as a method of manufacturing the system for manipulation of a micro component.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Method And Apparatus For The Manipulation And/Or The Detection Of Particles
ActiveUS20090205963A1High measurement sensitivitySludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsDielectricElectricity
Method and apparatus for the manipulation and / or control of the position of particles by means of time-variable fields of force. The fields of force can be of dielectrophoresis (positive or negative), electrophoresis, electrohydrodynamic or electrowetting on dielectric, characterized by a set of stable points of equilibrium for the particles.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
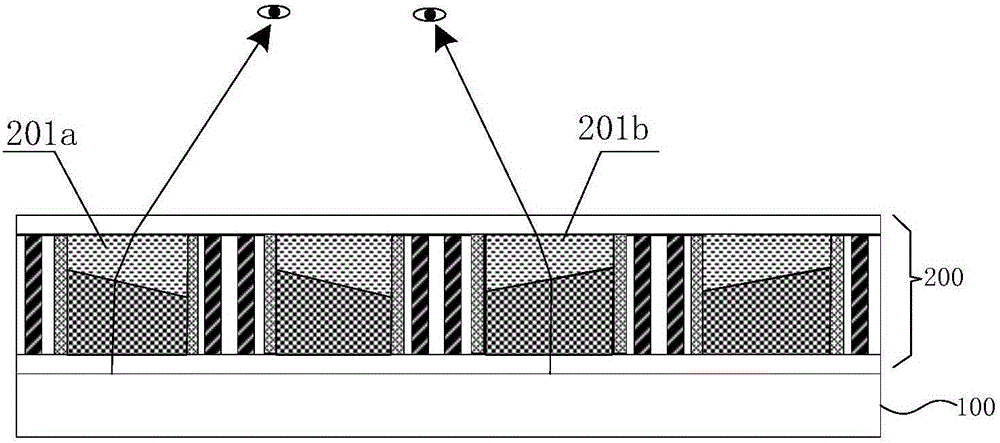
Display device for driving liquid drops to move on basis of electrowetting effect
ActiveCN103592759ASolve absorptionImprove optical efficiencyOptical elementsDisplay deviceRefractive index
A display device for driving liquid drops to move on the basis of an electrowetting effect is characterized by comprising a lower substrate, an electrode plate, a nano-metal grating, a plurality of liquid drops, a super-hydrophobic coating layer, a dielectric layer, an electrode array and an upper substrate in sequence from bottom to top. A cofferdam is added on the periphery between the upper substrate and the lower substrate to form a sealed chamber, the chamber is filled with a second fluid insoluble with the liquid drops, and the single liquid drops in a chamber between the electrode array and the electrode plate which are parallel to each other at least cover two adjacent electrodes of the electrode array. The characteristic that the nano-metal grating is extremely sensitive to changes of the refractive index of an adjacent material is utilized, color filtering is finished by changing the material refractive index, active modulation of transmission and reflection spectrums of the nano-metal grating is achieved, and simultaneously due to the hydrophobic characteristic of the nano-metal grating structure, the electrowetting display modulation contrast and speed can be improved.
Owner:厦门市为纳光电科技有限公司
Display device
The invention relates to a display device which comprises a display panel and an electric wetting prism component, wherein the electric wetting prism component is arranged along a light emitting direction of the display panel; the electric wetting prism component comprises a plurality of micro-lens structures and a mode control line; each of micro-lens structures is corresponding to a pixel unit of the display panel; each of the micro-lens structures comprises a sealing chamber, a nonpolar insulating solution and an electrolyte solution; the nonpolar insulating solution and the electrolyte solution are sealed in the sealing chamber; a first lateral inner wall and a second lateral inner wall of the sealing chamber both comprise a hydrophobic layer and electrode pillar located on one side of the hydrophobic layer away from the nonpolar insulating solution and the electrolyte solution; the first side and the second side are two opposite sides; the electrode pillar in each of the micro-lens structures is connected with the mode control line; the nonpolar insulating solution and the electrolyte solution are in different refractive indexes. The display device provided by the invention is used for applying different voltages to the electrode pillar of each of the micro-lens structures through the mode control line, so that the display can be switched between different work modes.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Efficient dilution method, including washing method for immunoassay
ActiveUS20140197028A1Efficient dilutionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringElectrowetting
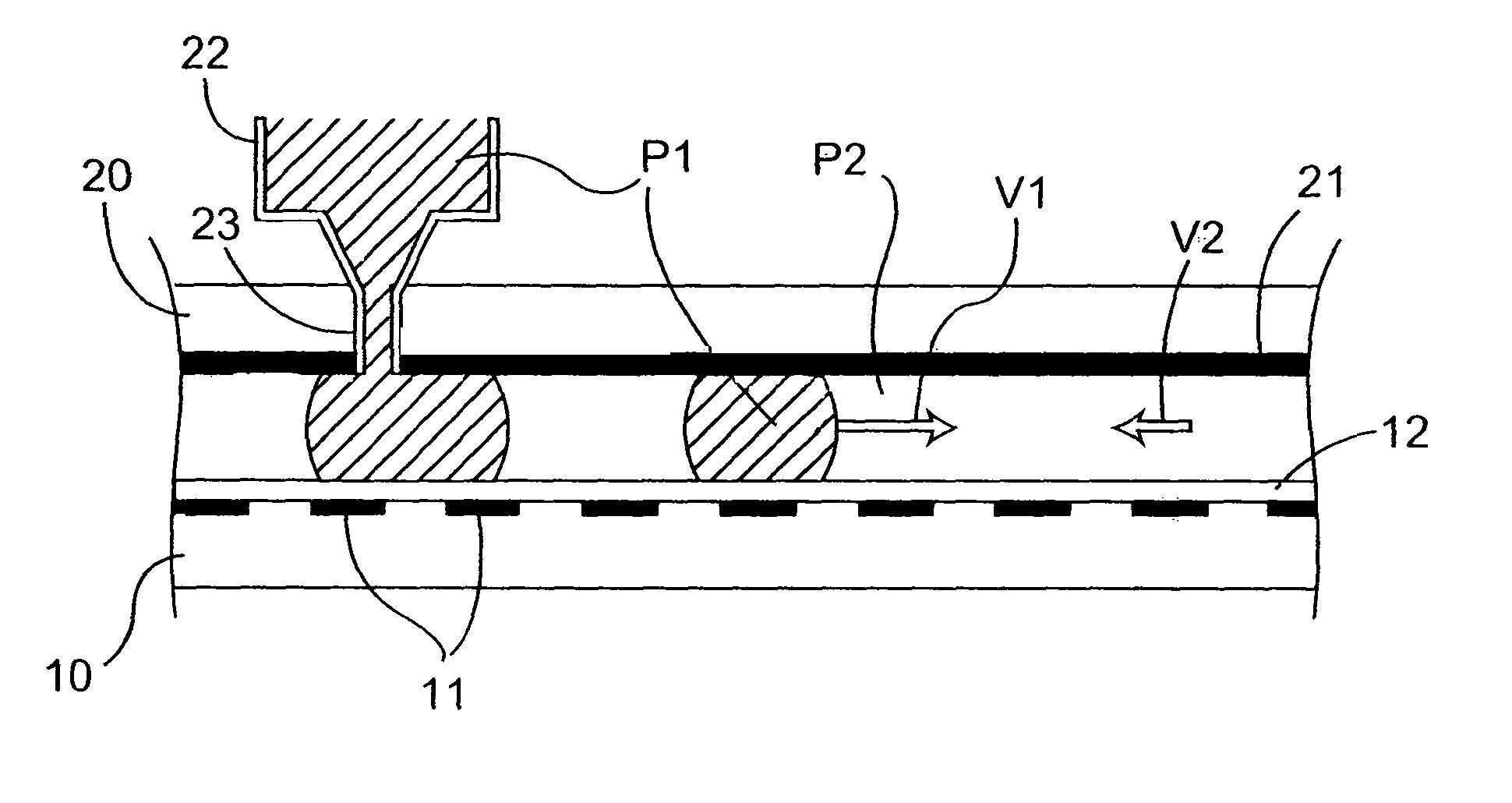
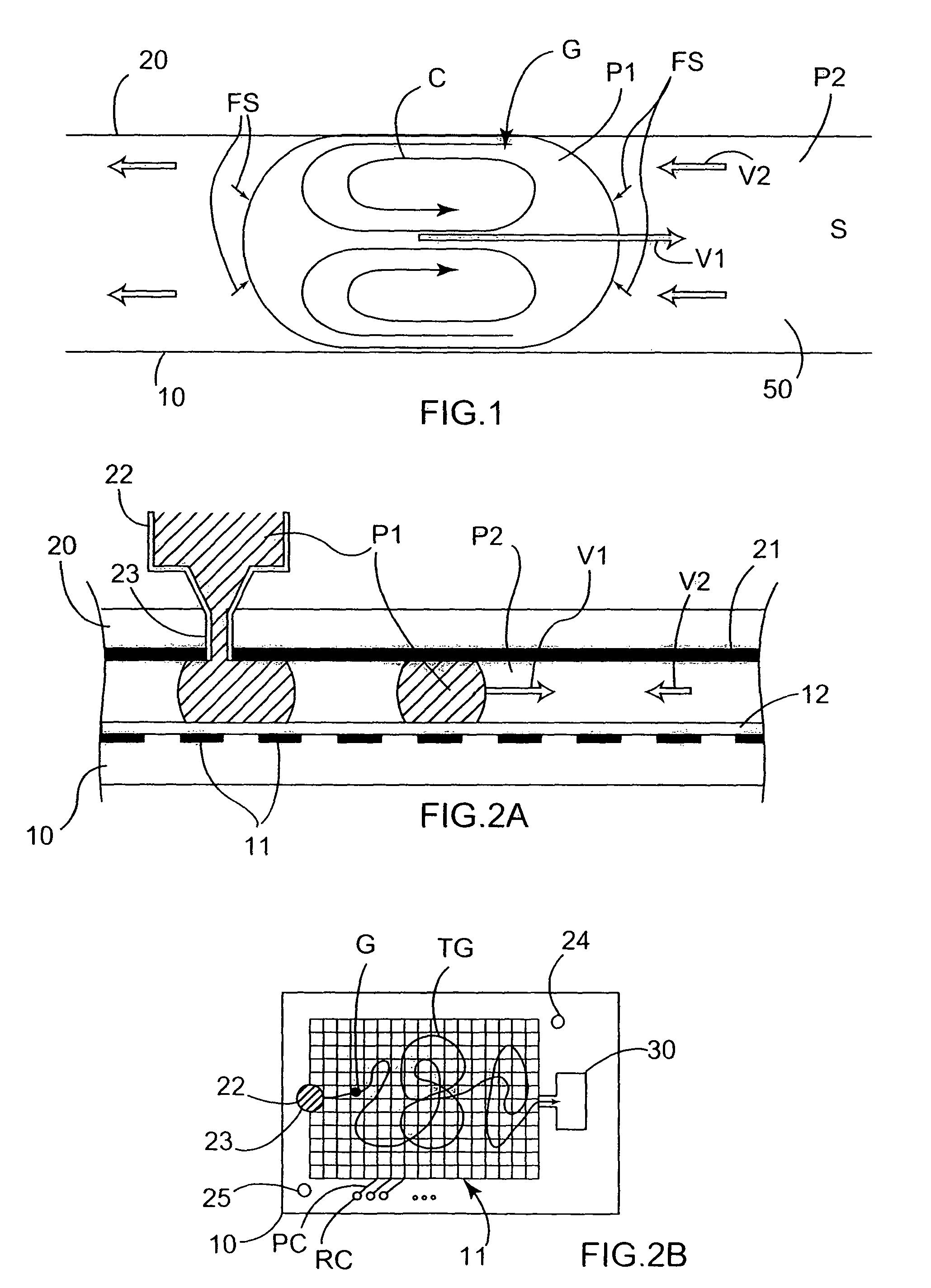
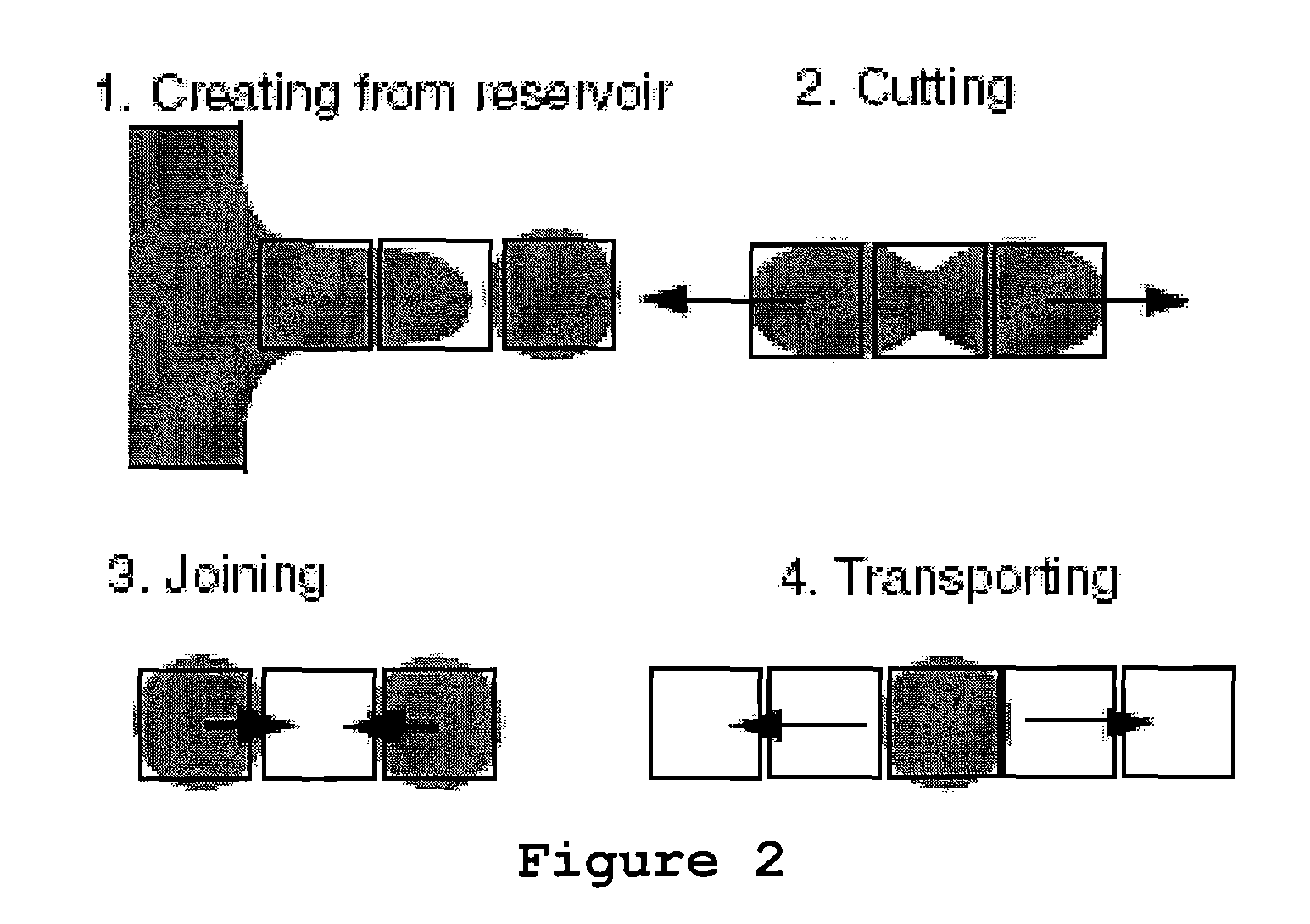
A method of droplet manipulation utilizing a droplet manipulation device includes activating elements of the device to bring a first droplet into proximity of a second droplet, controlling the elements of the device to alter the shape of at least one of the first and second droplets, and further controlling the elements of the device to move at least one of the first or second droplets until the droplets are in contact about an aggregate area. The elements are controlled in a manner so as to control the area of contact and the degree of mixing of the fluid between the first and second droplets. The method may be employed to move particles of a particulate suspension from the first droplet to the second droplet. The droplet manipulation device may be an electrowetting on dielectric (EWOD) device, which includes shaping electrodes activated to shape droplets, and a bridging electrode activated to join the droplets to transfer fluid between the shaped droplets
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Ultrafine fluid jet apparatus
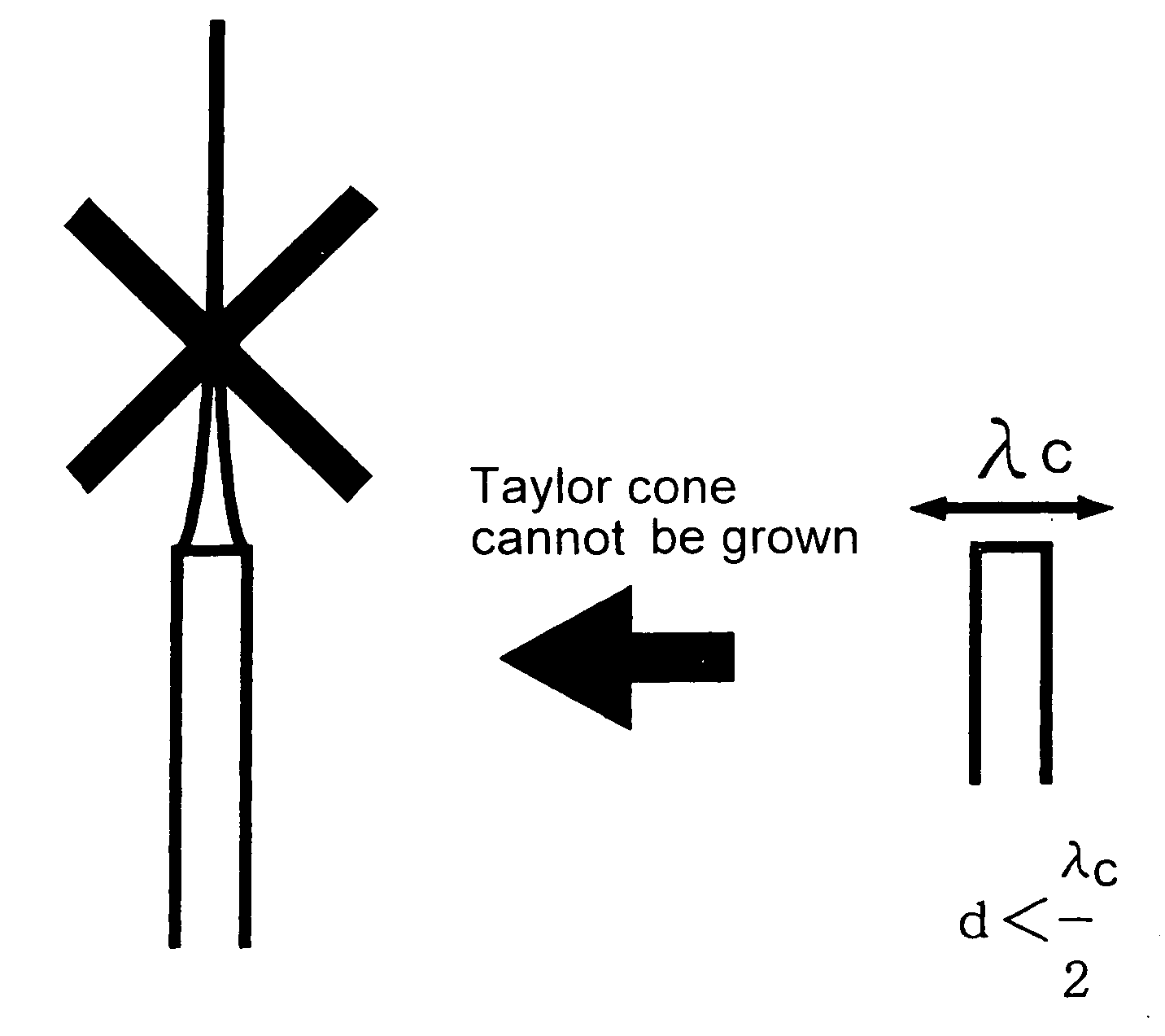
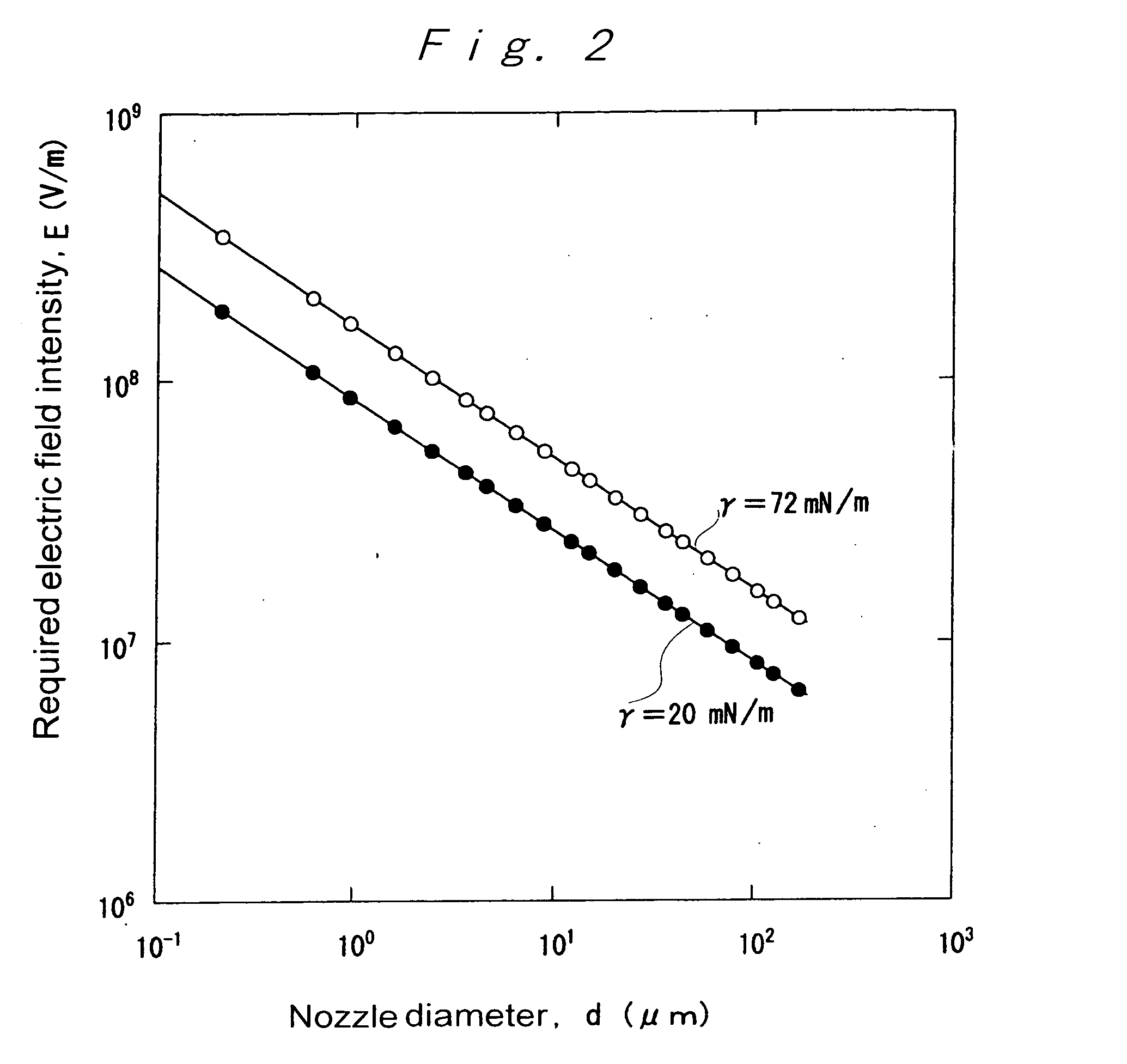
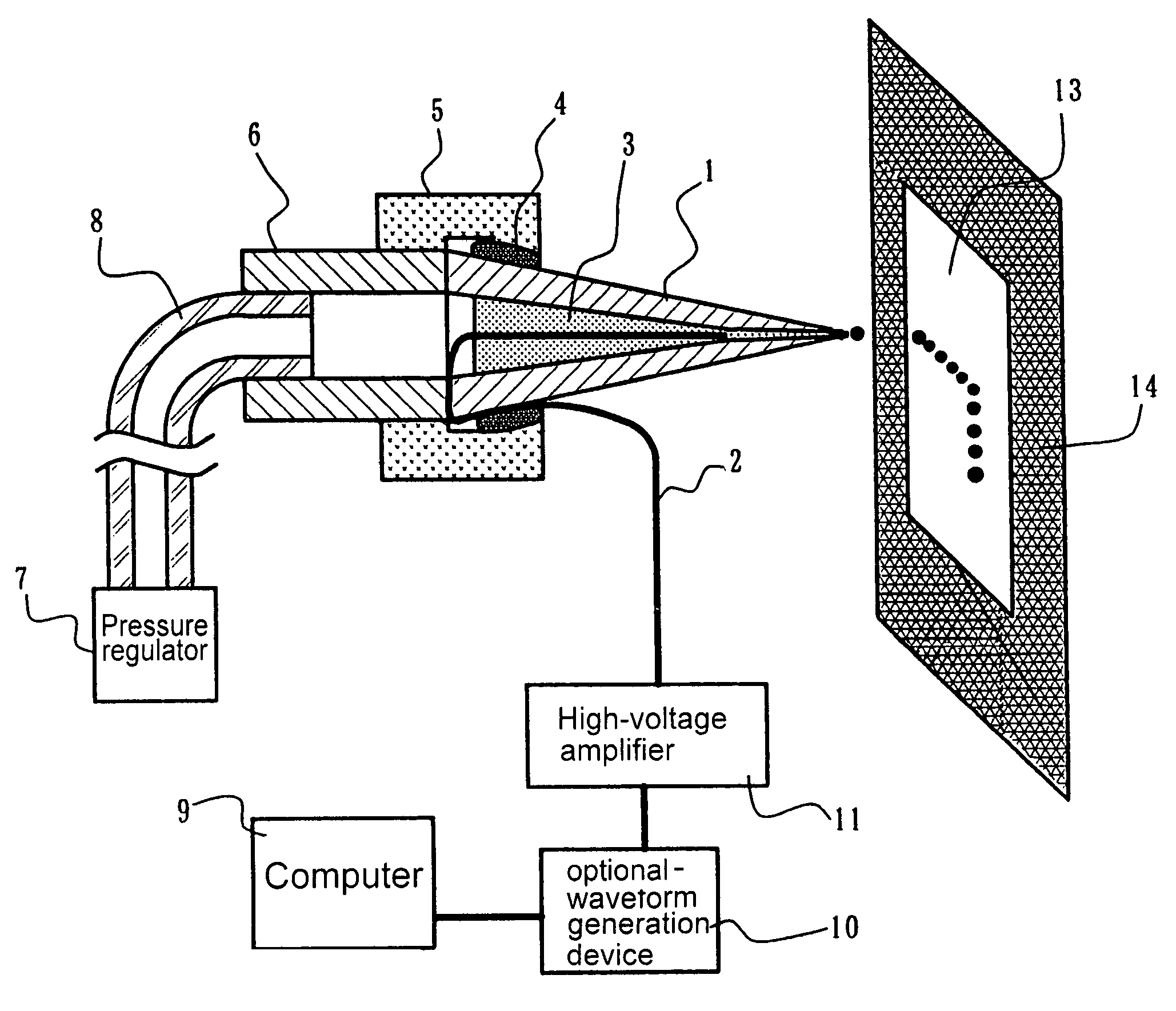
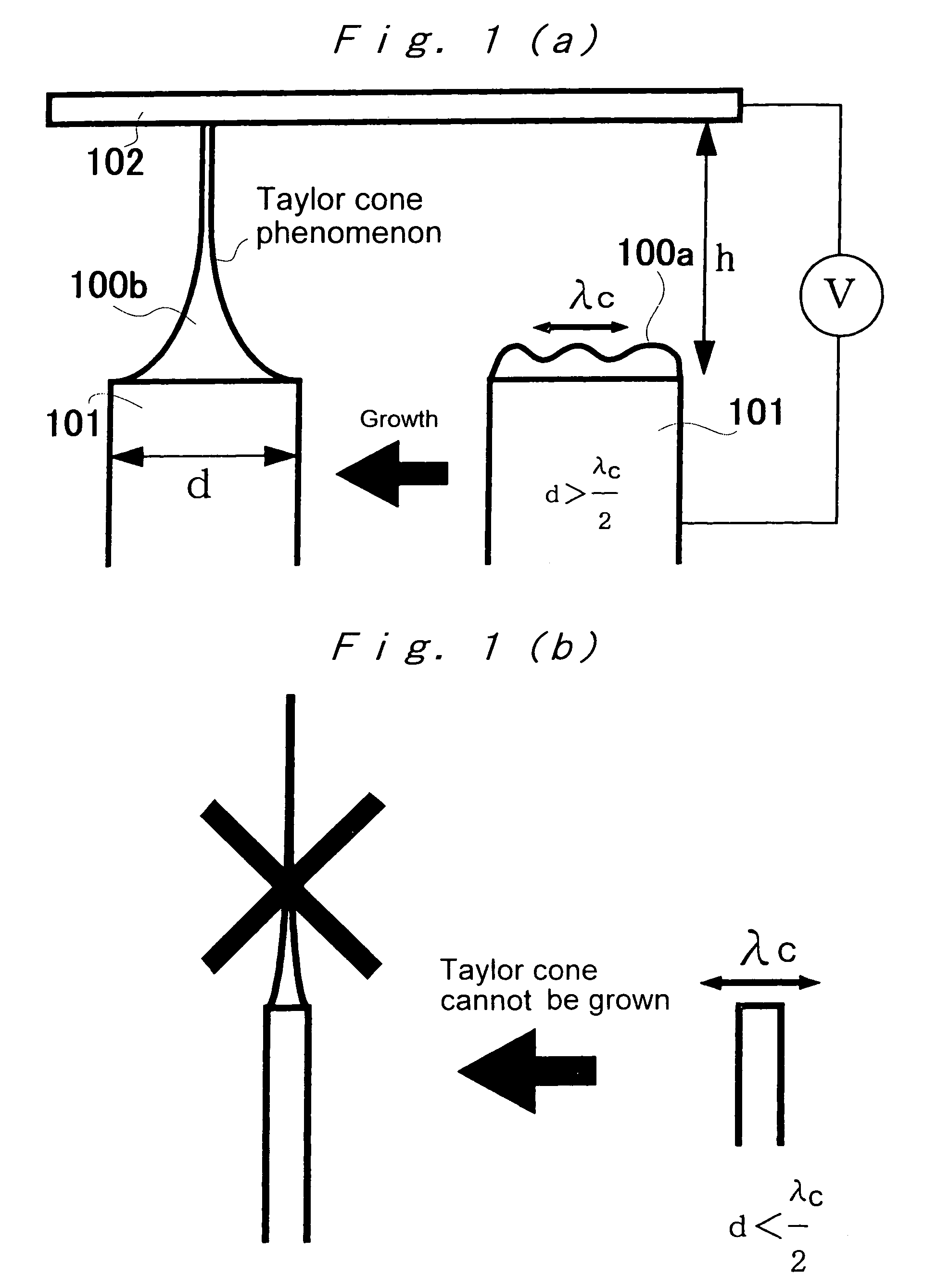
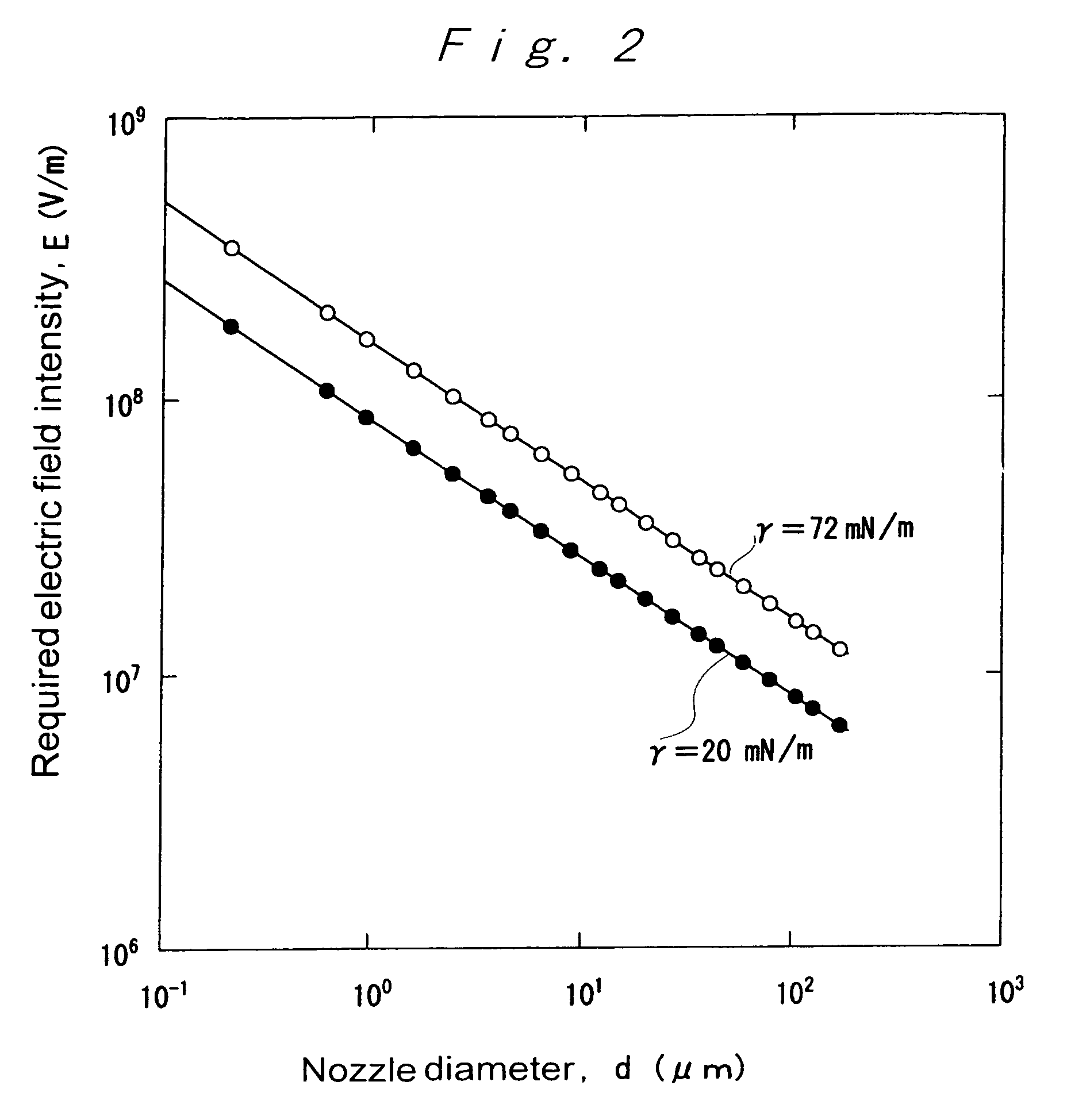
ActiveUS20050116069A1Improve the immunityReduce the overall diameterBurnersLiquid spraying plantsElectrical field strengthEvaporation
An ultrafine fluid jet apparatus comprising a substrate arranged near a distal end of an ultrafine-diameter nozzle to which a solution is supplied, and an optional-waveform voltage is applied to the solution in the nozzle to eject an ultrafine-diameter fluid droplet onto a surface of the substrate; wherein an electric field intensity near the distal end of the nozzle according to a diameter reduction of the nozzle is sufficiently larger than an electric field acting between the nozzle and the substrate; and wherein Maxwell stress and an electro-wetting effect being utilized, a conductance is decreased by a reduction in the nozzle diameter or the like, and controllability of an ejection rate by a voltage is improved; and wherein landing accuracy is exponentially improved by moderation of evaporation by a charged droplet and acceleration of the droplet by an electric field.
Owner:SIJTECH +1
Electrowetting display and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101359091AReduce manufacturing costSimplify the manufacturing processOptical elementsElectricityDisplay device
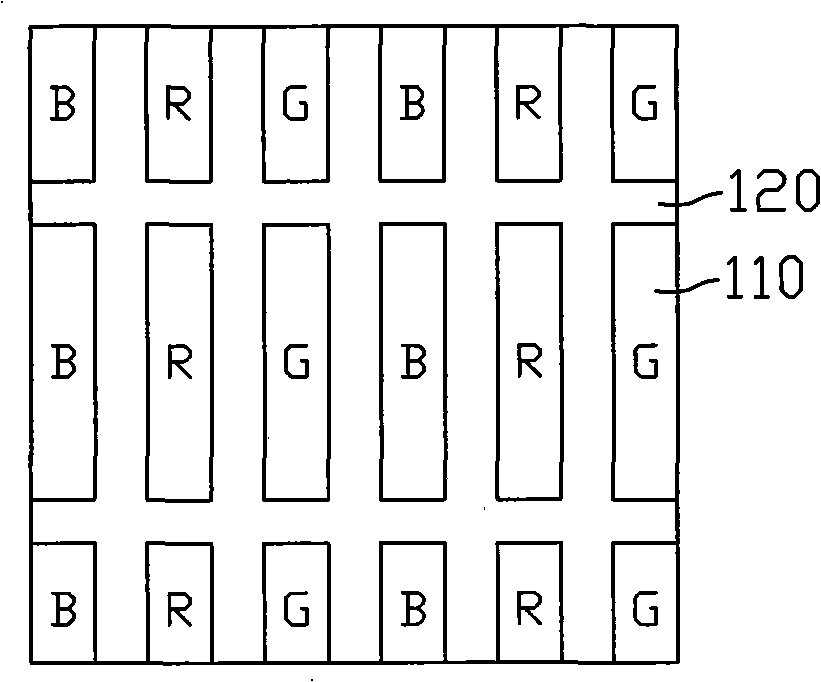
The invention relates to an electro-wetting display and a manufacturing method thereof. The electro-wetting display comprises a first substrate, a second substrate, a plurality of isolation walls arranged on the first substrate in a grid form, a plurality of pixel electrodes, lightproof masking fluid and various dyeing fluids of different colors. The minimum region structured by the adjacent isolation walls defines a sub-pixel unit. The pixel electrodes are arranged on the second substrate correspondingly to the sub-pixel units. The lightproof masking fluid fills in the sub-pixel units, and each dyeing fluid is the mixed solution of the transparent conductive solution and water-soluble dyes or water-soluble pigments; the mixed solution is incompatible with the masking fluid; all the mixed solutions respectively fill in the sub-pixel units. The incident rays from any substrate are filtered by the dyeing fluids. The electro-wetting display and the manufacturing method thereof can realize full-color display and the manufacturing cost is lower, and manufacturing method is also simpler.
Owner:INNOCOM TECH SHENZHEN +1
Microfluidic control for waveguide optical switches, variable attenuators, and other optical devices
InactiveUS20060083473A1Improve efficiencyIncrease functional densityTransportation and packagingMixersDifferential pressureEngineering
Devices utilize elements carried by a fluid in a microchannel to switch, attenuate, shutter, filter, or phase shift optical signals. In certain embodiments, a microchannel carries a gaseous or liquid slug that interacts with at least a portion of the optical power of an optical signal traveling through a waveguide. The microchannel may form part of the cladding of the waveguide, part of the core and the cladding, or part of the core only. The microchannel may also have ends or may be configured as a loop or continuous channel. The fluid devices may be self-latching or may be semi-latching. The fluid in the microchannel is moved using e.g., e.g., electrocapillarity, differential-pressure electrocapillarity, electrowetting, continuous electrowetting, electrophoresis, electroosmosis, dielectrophoresis, electro-hydrodynamic electrohydrodynamic pumping, magneto-hydrodynamic magnetohydrodynamic pumping, thermocapillarity, thermal expansion, dielectric pumping, and / or variable dielectric pumping.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
Bi-stable electrowetting optical element and driving method therefor
InactiveUS7548363B2Excellent power consumption characteristicsIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsIdentification meansPlanar electrodeDisplay device
An optical element used, e.g., in an electrowetting display device having a number of pixels, is arranged in an array. Each optical element includes a cell filled with a polar conductive fluid, such as a water solution, and a non-polar fluid, such as an oil. The cell further includes first and second planar electrodes covered with first and second hydrophobic layers. By applying a voltage between the first fluid and alternately the first or second electrodes, the oil is forced to migrate between the first and second hydrophobic layers. Thus a bi-stable, energy efficient optical element is provided.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
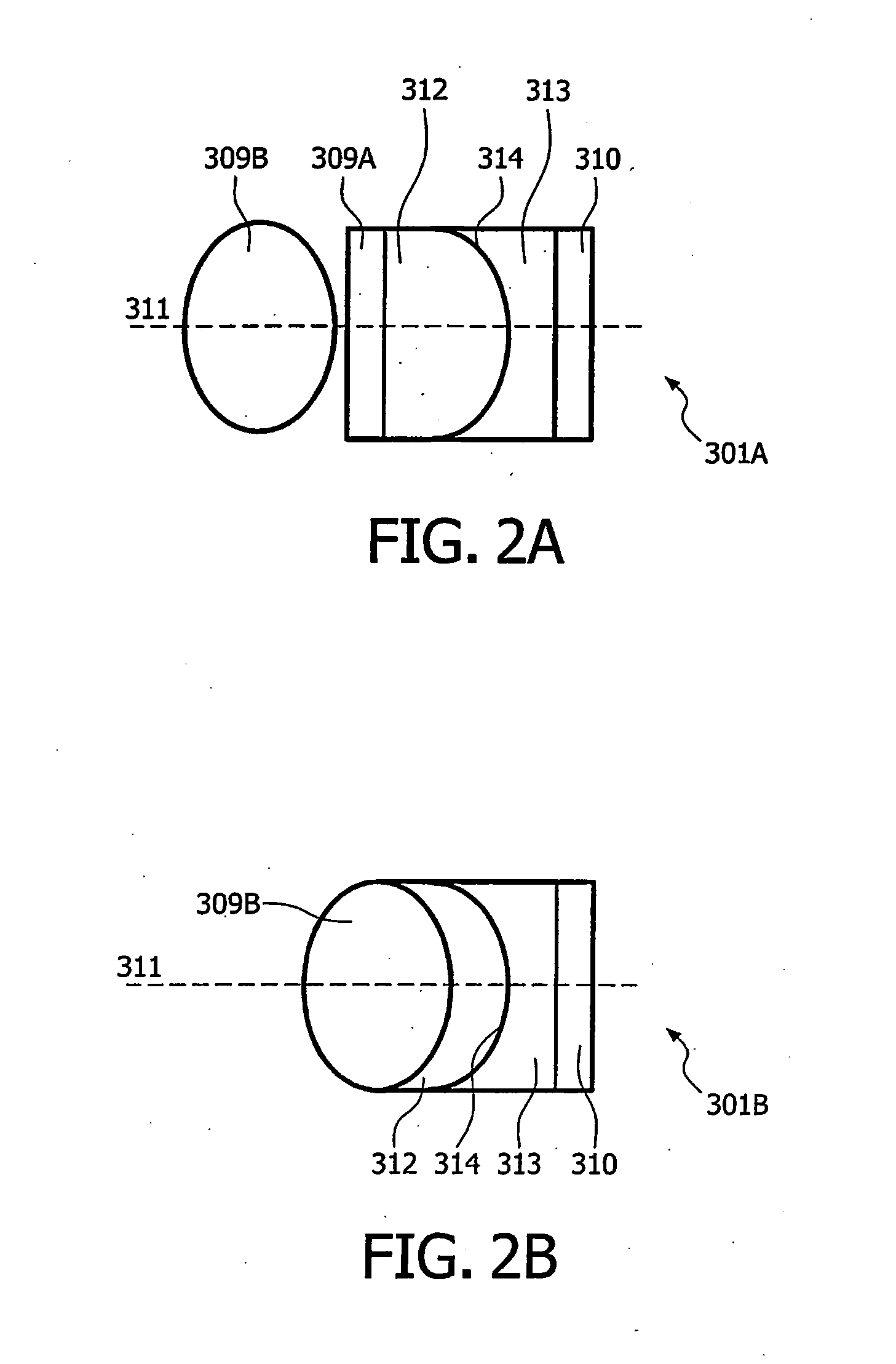
Method of manufacturing an electrowetting-based variable-focus lens
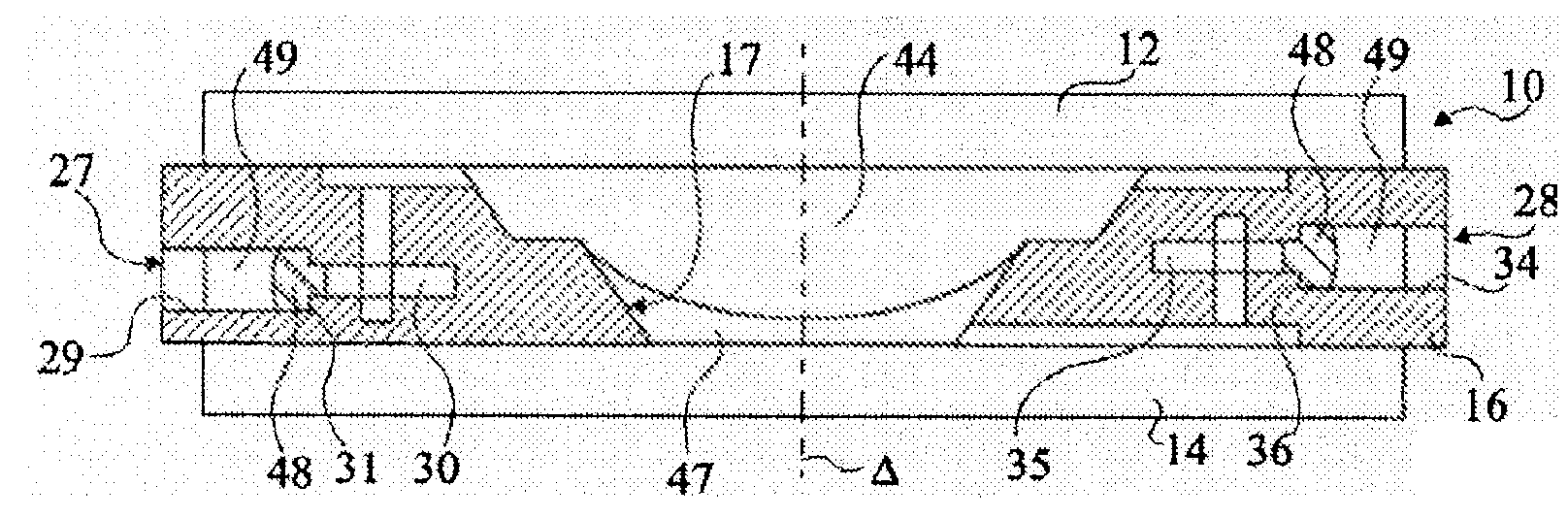
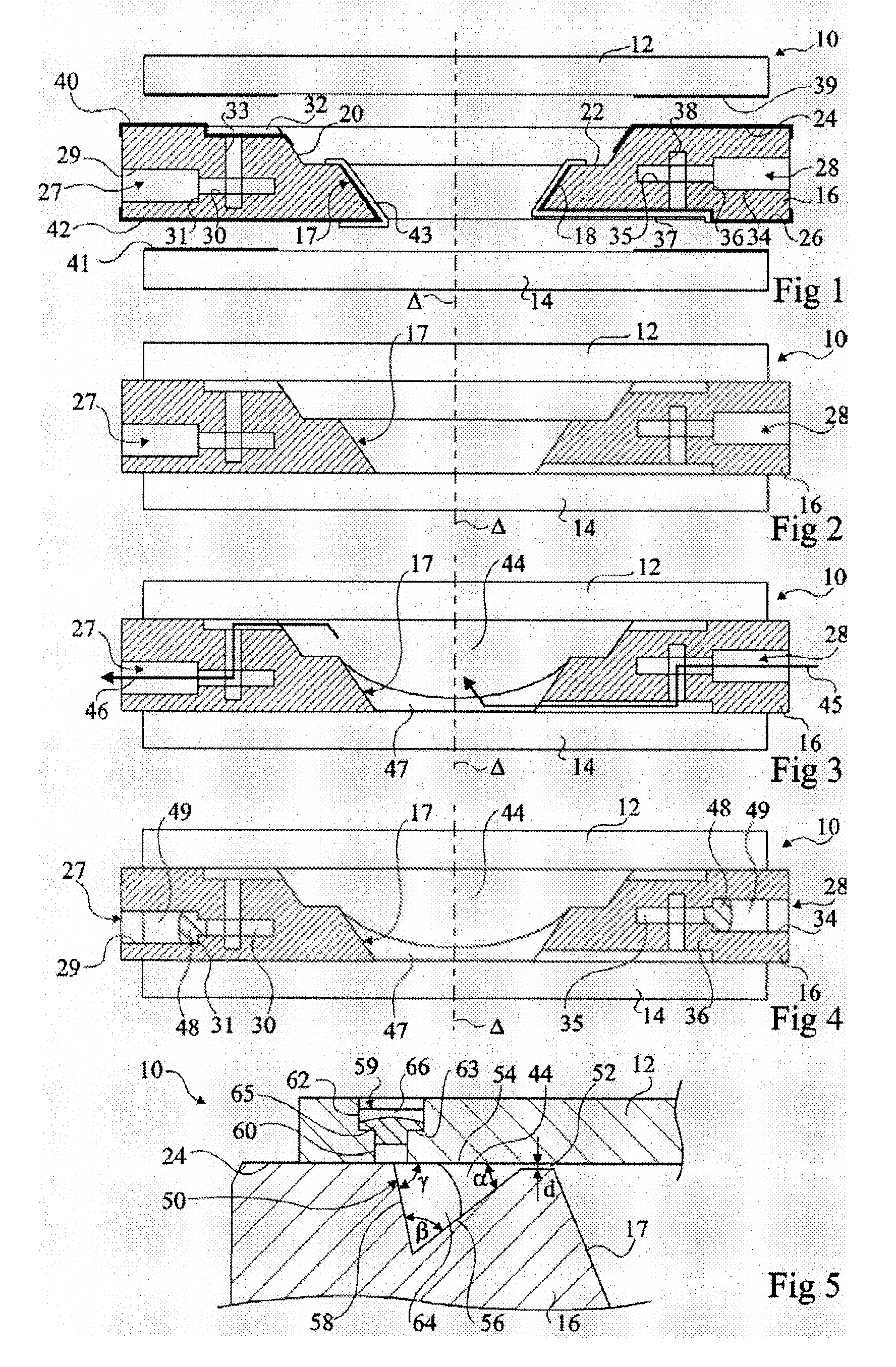
InactiveUS20090021842A1Precise positioningSimple and precise mannerOptical articlesLensElectricityRefractive index
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing an electrowetting-based variable-focus lens, comprising: (a) providing an enclosure having a cavity (17) and at least one channel (27, 28; 59) communicating at one end with the cavity and at the other end emerging at the exterior surface of the lens; (b) filling the cavity with first and second liquids (44, 47) that are immiscible and of different refractive indices via the channel; and (c) hermetically scaling the channel.
Owner:VARIOPTIC SA
Electrowetting display device
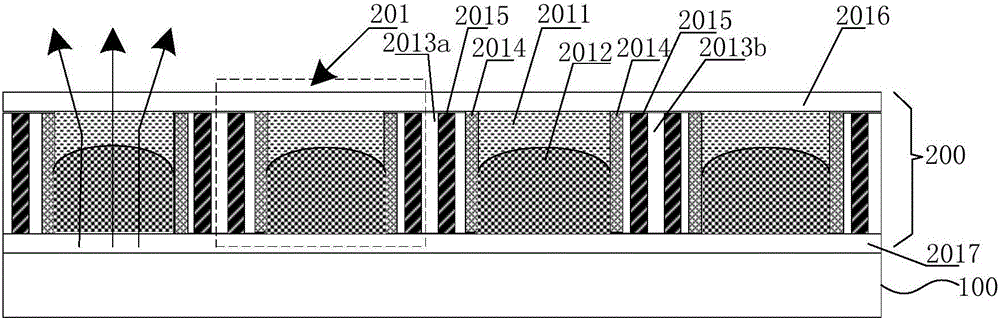
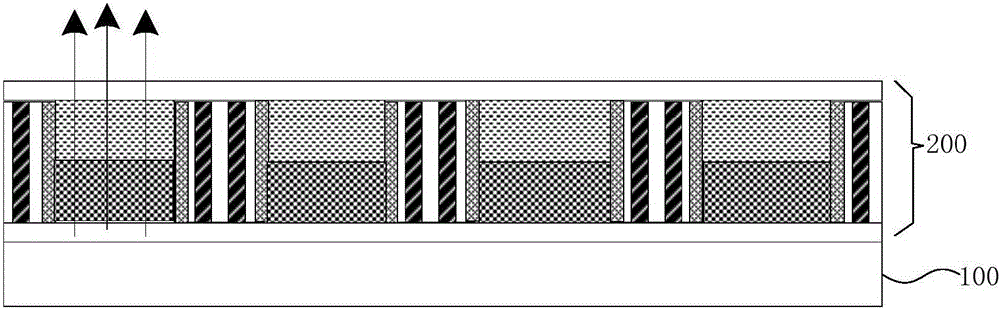
The disclosure provides an electrowetting display device. The electrowetting display device includes a first substrate and a second substrate disposed to each other. A first electrode layer may dispose on the first substrate. A second electrode layer may dispose on the second substrate. A hydrophobic dielectric layer is disposed on the first electrode layer. A first pixel rib is disposed on the first substrate. A second pixel rib is disposed on the first pixel rib. A water contact angle of the second pixel rib may be larger than that of the first pixel rib. A first liquid and a second liquid may be disposed in between the first substrate and the second substrate. The electrowetting display device can prevent the problem of an existing electrowetting display device that the second liquid with large injection amount will contract to generate overflow, can also improve uniformity after panel drive and reliability of panel operation without affecting contrast ratio of the electrowetting display device.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Ultrafine fluid jet apparatus
ActiveUS7434912B2Improve the immunityReduce the overall diameterBurnersLiquid spraying plantsElectrical field strengthEngineering
An ultrafine fluid jet apparatus including a substrate arranged near a distal end of an ultrafine-diameter nozzle to which a solution is supplied, and an optional-waveform voltage is applied to the solution in the nozzle to eject an ultrafine-diameter fluid droplet onto a surface of the substrate; wherein an electric field intensity near the distal end of the nozzle according to a diameter reduction of the nozzle is sufficiently larger than an electric field acting between the nozzle and the substrate; and wherein Maxwell stress and an electro-wetting effect being utilized, a conductance is decreased by a reduction in the nozzle diameter or the like, and controllability of an ejection rate by a voltage is improved; and wherein landing accuracy is exponentially improved by moderation of evaporation by a charged droplet and acceleration of the droplet by an electric field.
Owner:SIJTECH +1
Electrowetting display device
InactiveUS20130010348A1Reduce hydrophobicityAffects longevityLine/current collector detailsOptical elementsDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for making an electrowetting display device comprising a plurality of picture elements and a first support plate and a second support plate. Each picture element comprises a space between the first support plate and the second support plate. The method comprises the steps of: providing the first support plate with an electrode structure; arranging an insulating layer on the electrode structure, the insulating layer having a thickness and a hydropobic surface facing the space; temporarily applying an electric field across the thickness of the insulating layer to reduce permanently the hydrophobicity of a predetermined area of the surface. The invention further relates to an electrowetting display device and a use of an area of reduced hydrophobicity in an electrowetting device.
Owner:LIQUAVISTA BV
Method for improving packaging performance of electrowetting device and electrowetting device
The invention discloses a method for improving the packaging performance of an electrowetting device and the electrowetting device. A layer of attaching material good in hydrophobicity is arranged on the surfaces of pixel walls of a packaging attaching area, the problems that when a high-hydrophilic material is adopted to prepare the pixel walls to avoid the ink jumping phenomenon, the attaching performance of a rubber frame and the pixel walls is poor, and the packaging sealing performance is not good can be solved, an obtained packaging device is more reliable in quality, ink jumping is avoided, and the packaging sealing performance is guaranteed. Furthermore, the attaching material can cover the intersection of the longitudinal pixel walls and the transverse pixel walls, supporting columns are formed, and a series of display problems caused when base plates are bent due to gravity or stress are prevented. The method is simple in technology, low in cost and easy to control, and the obtained electrowetting device has superior packaging performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN GUOHUA OPTOELECTRONICS +2
Controlled flow of a thin liquid film by electrowetting
InactiveUS20110303541A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMechanical engineeringMaterials science
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com