Patents
Literature
1010 results about "Partial filling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Partial fill. Definition. An order that is not completely executed. With a partial fill, a certain portion of the order has been completed and a portion remains in the system as an open order.
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
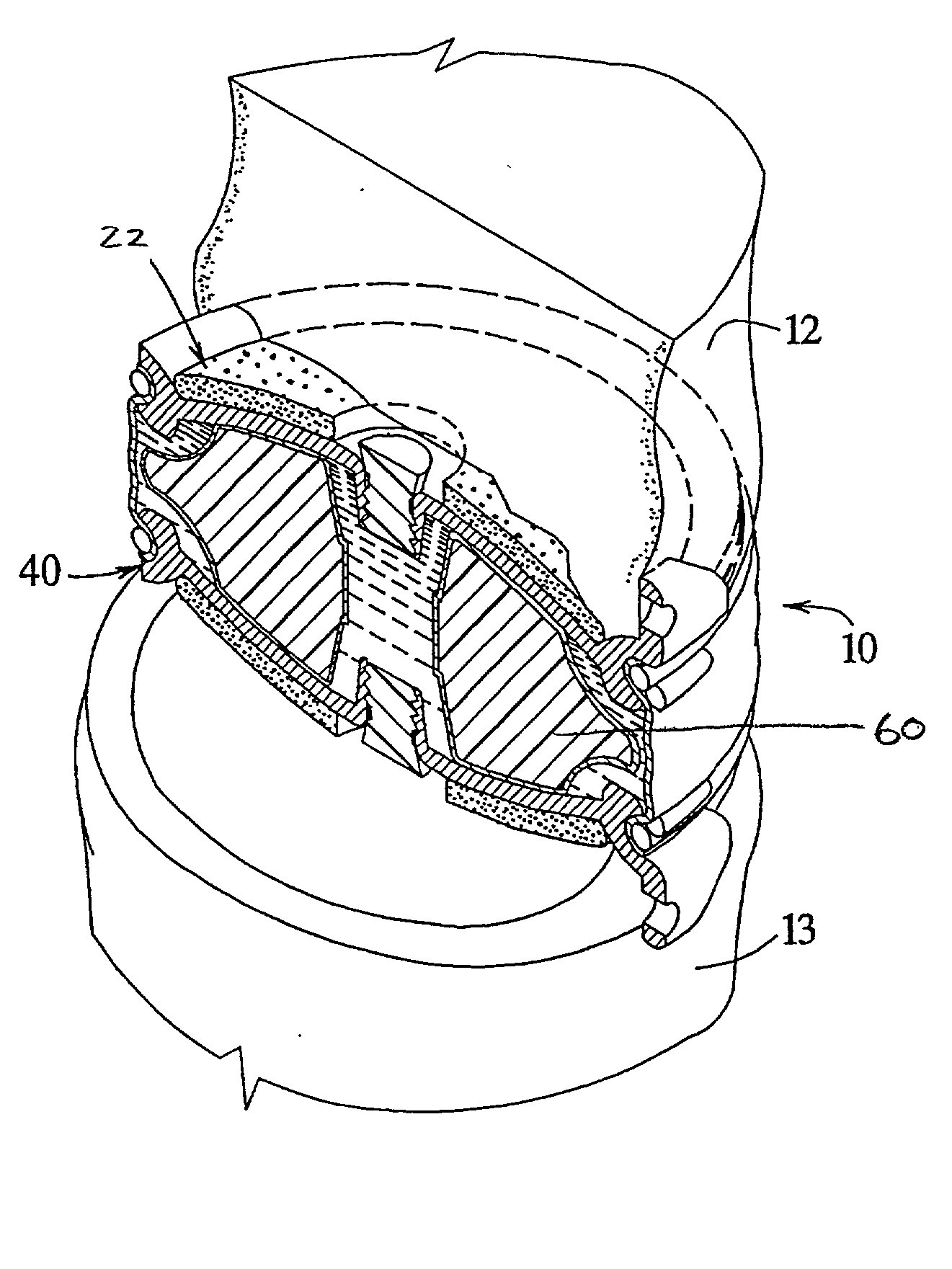
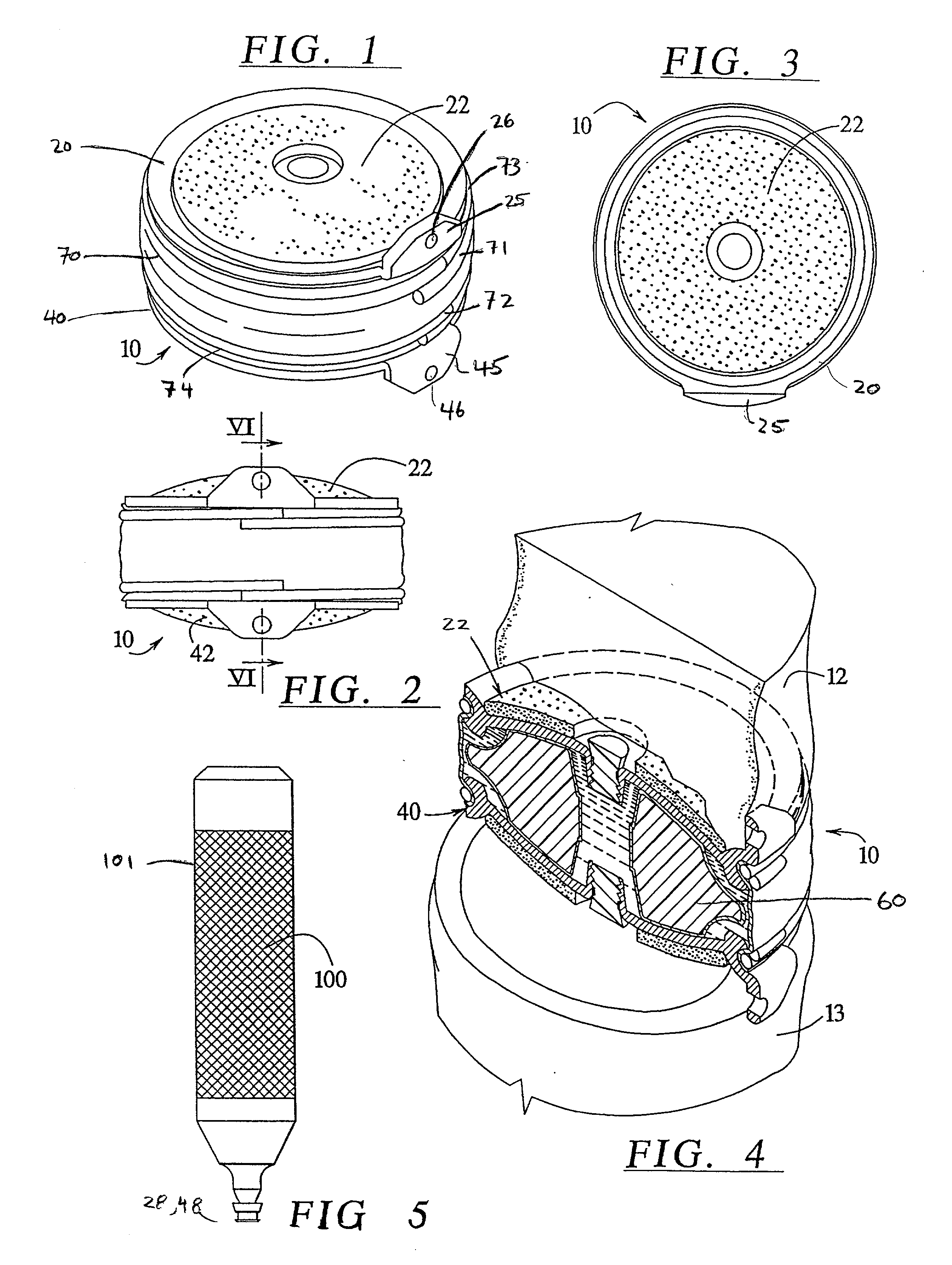
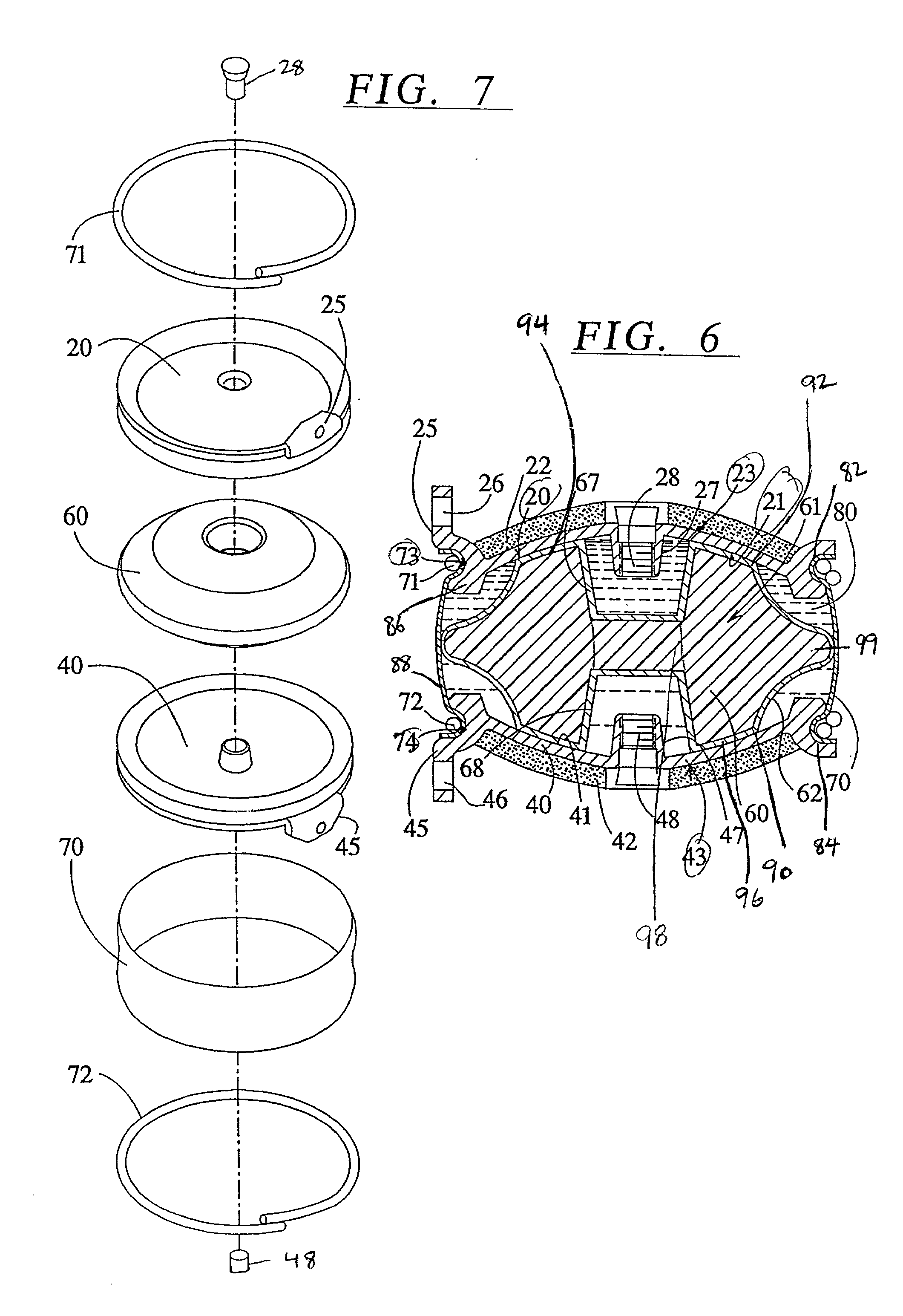
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
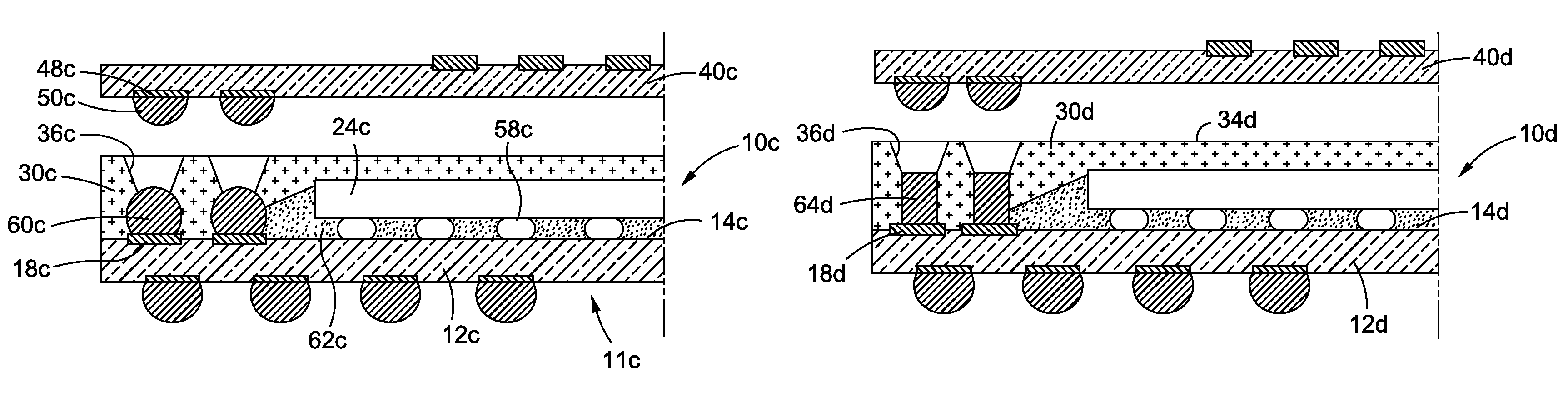
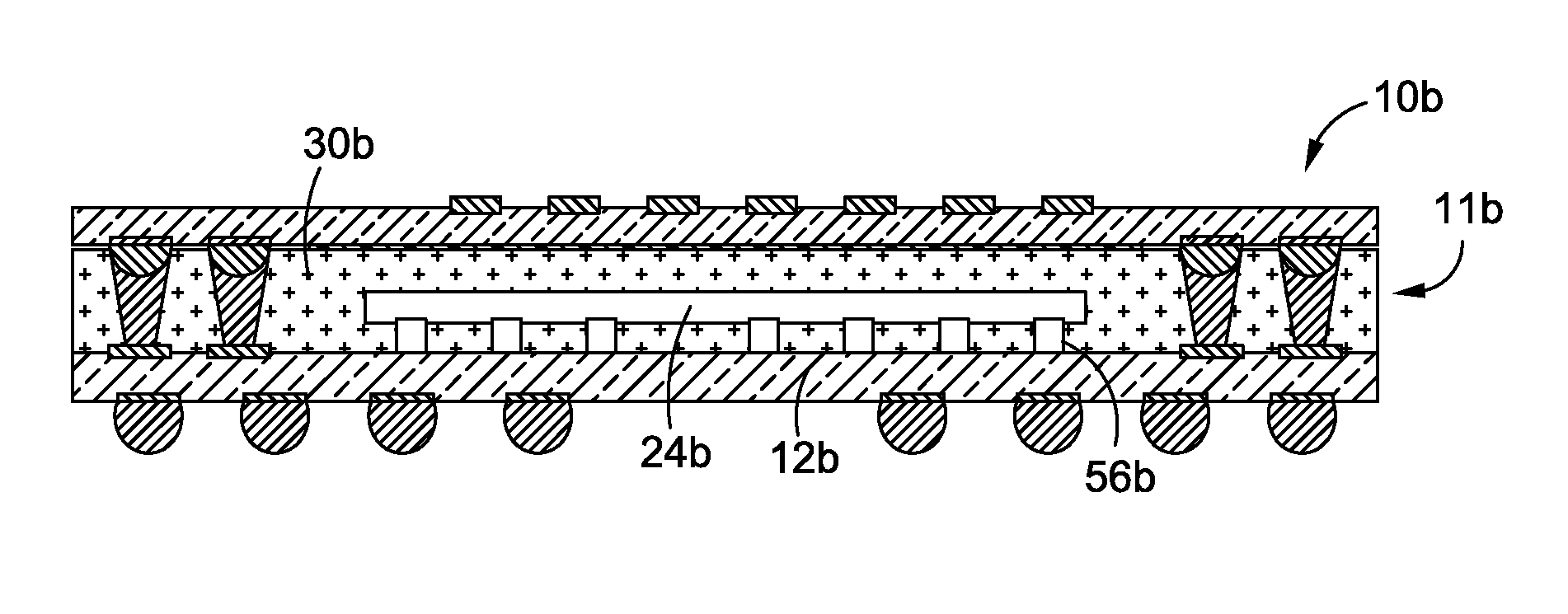
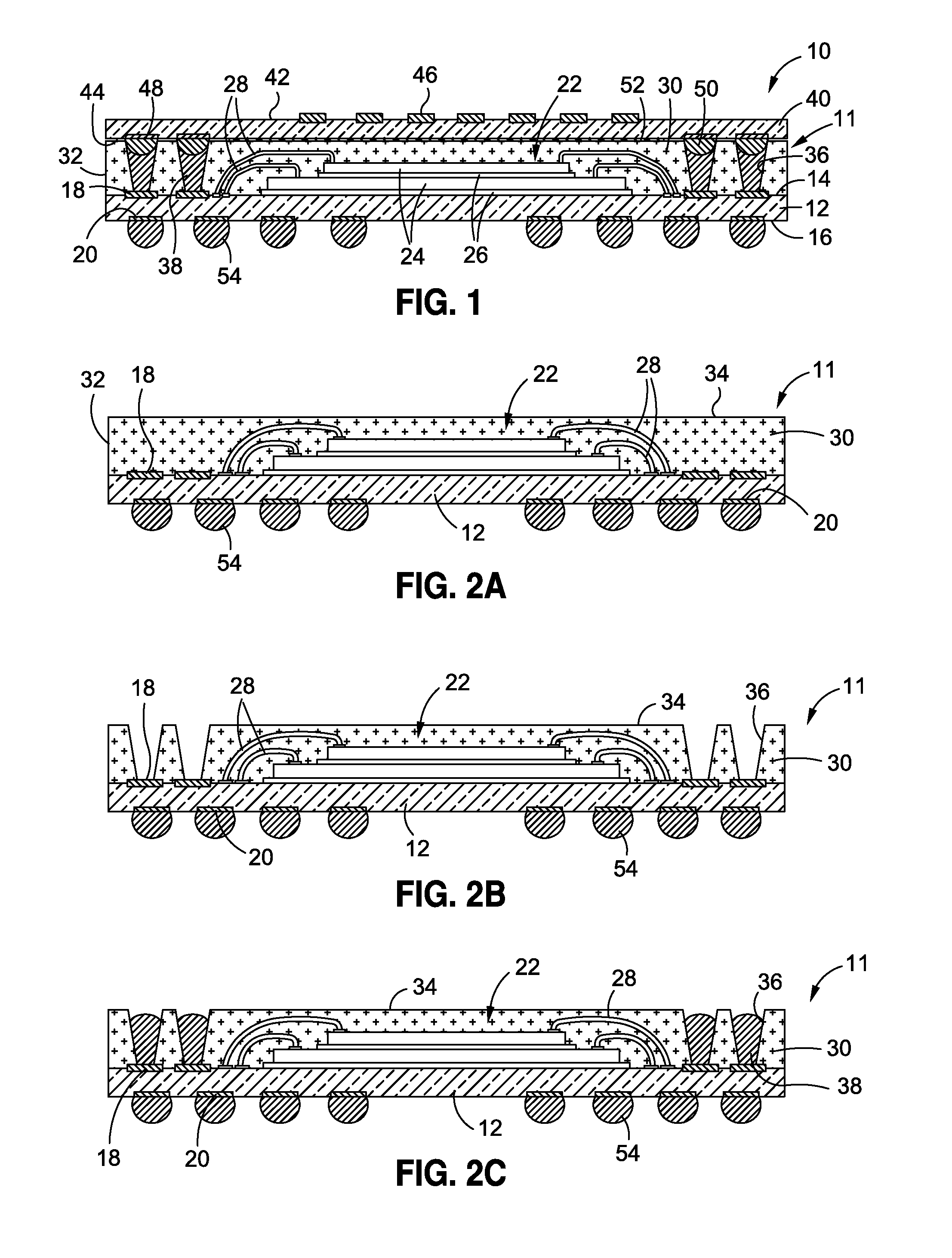
Thin stacked interposer package
ActiveUS7777351B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageElectronic component
The present invention comprises a semiconductor package comprising a bottom semiconductor package substrate which is populated with one or more electronic components. The electronic component(s) of the bottom substrate are covered or encapsulated with a suitable mold compound which hardens into a package body of the semiconductor package. The package body is provided with one or more vias through the completion of laser drilling process, such via(s) providing access to one or more corresponding conductive contacts of the bottom substrate. These vias are either lined or partially filled with a conductive metal material. Subsequently, a top semiconductor package substrate (which may optionally be populated with one or more electronic components) is mounted to the package body and electrically connected to the conductive metal within the via(s) of the package body.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
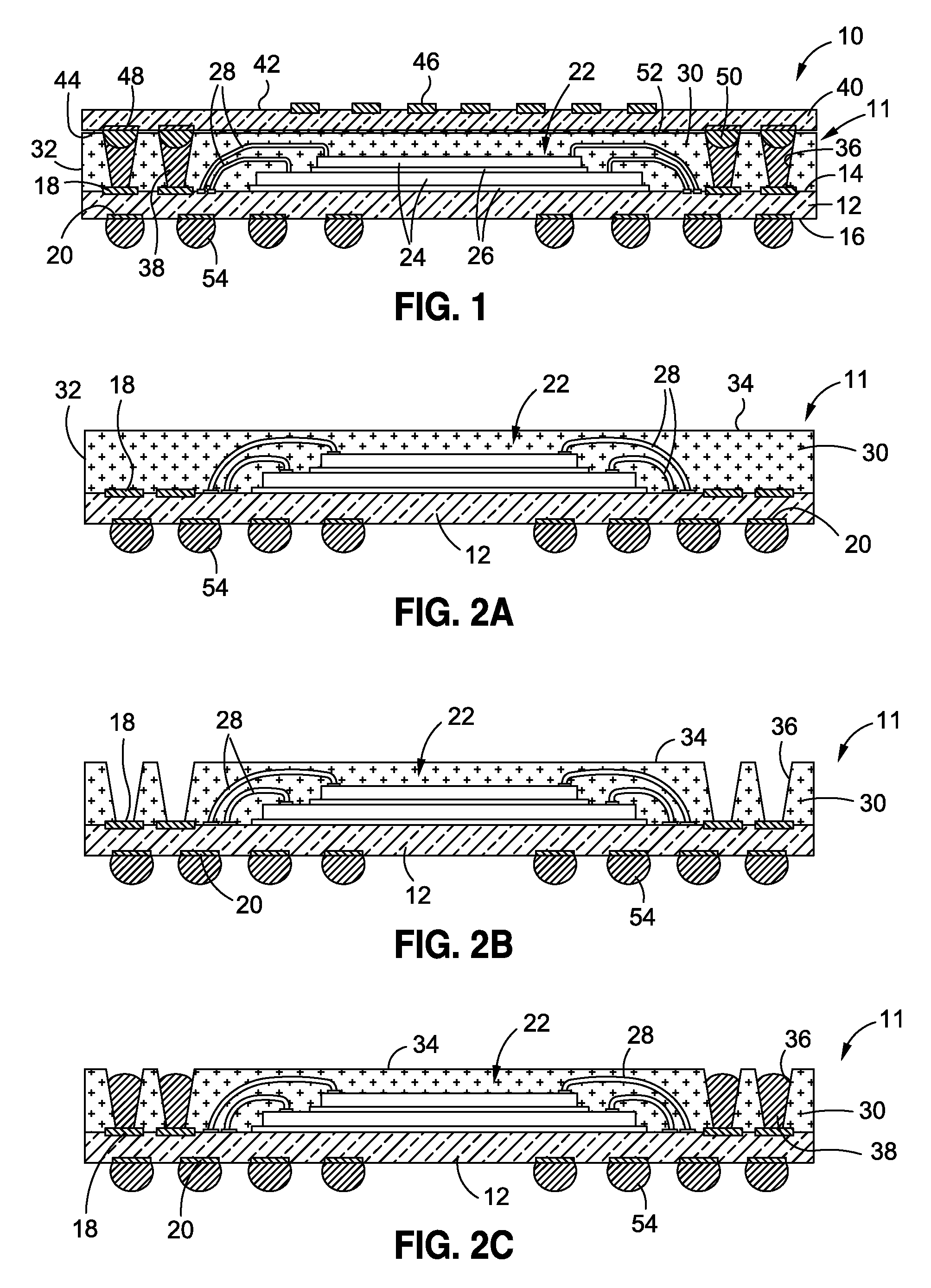
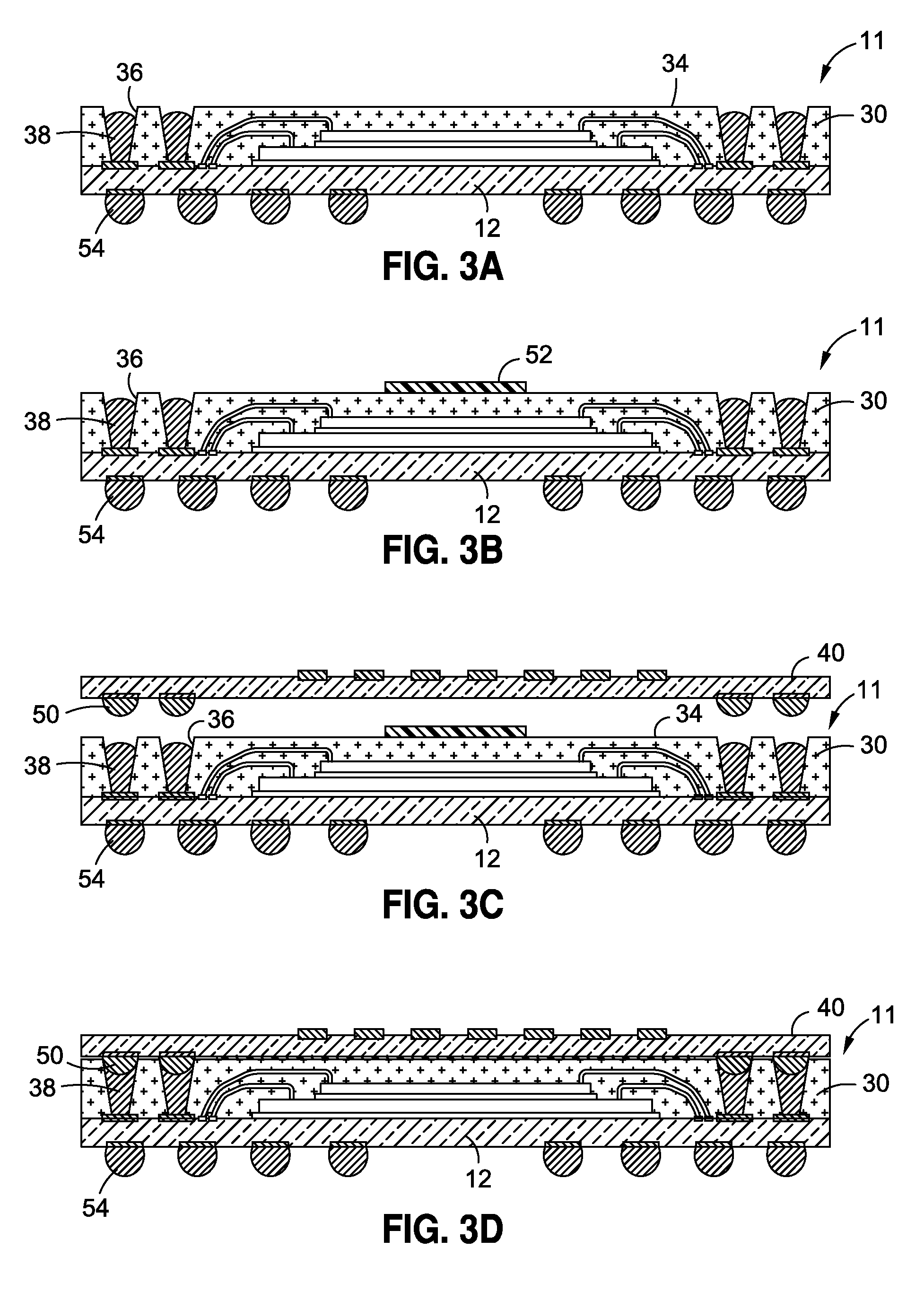
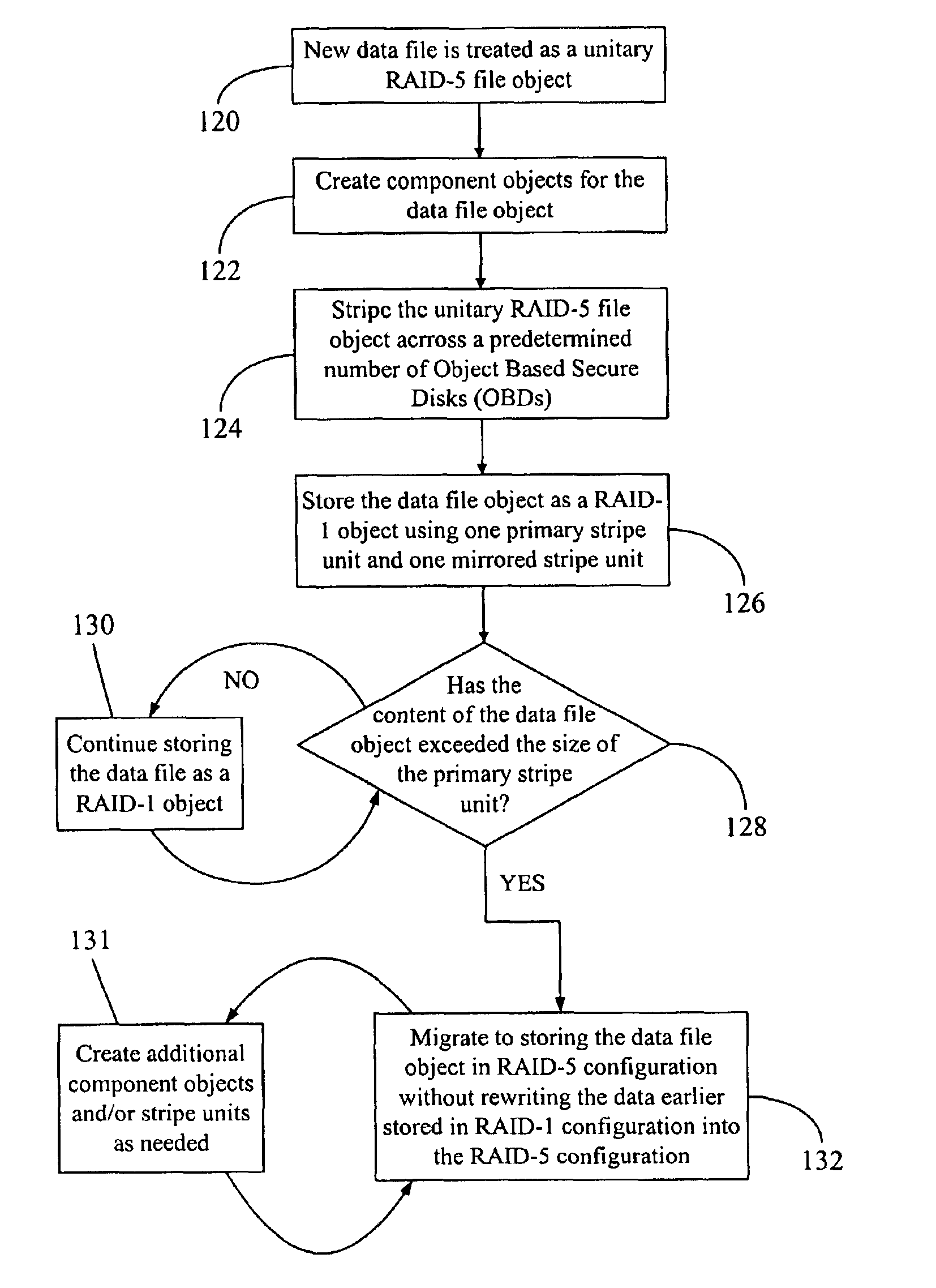
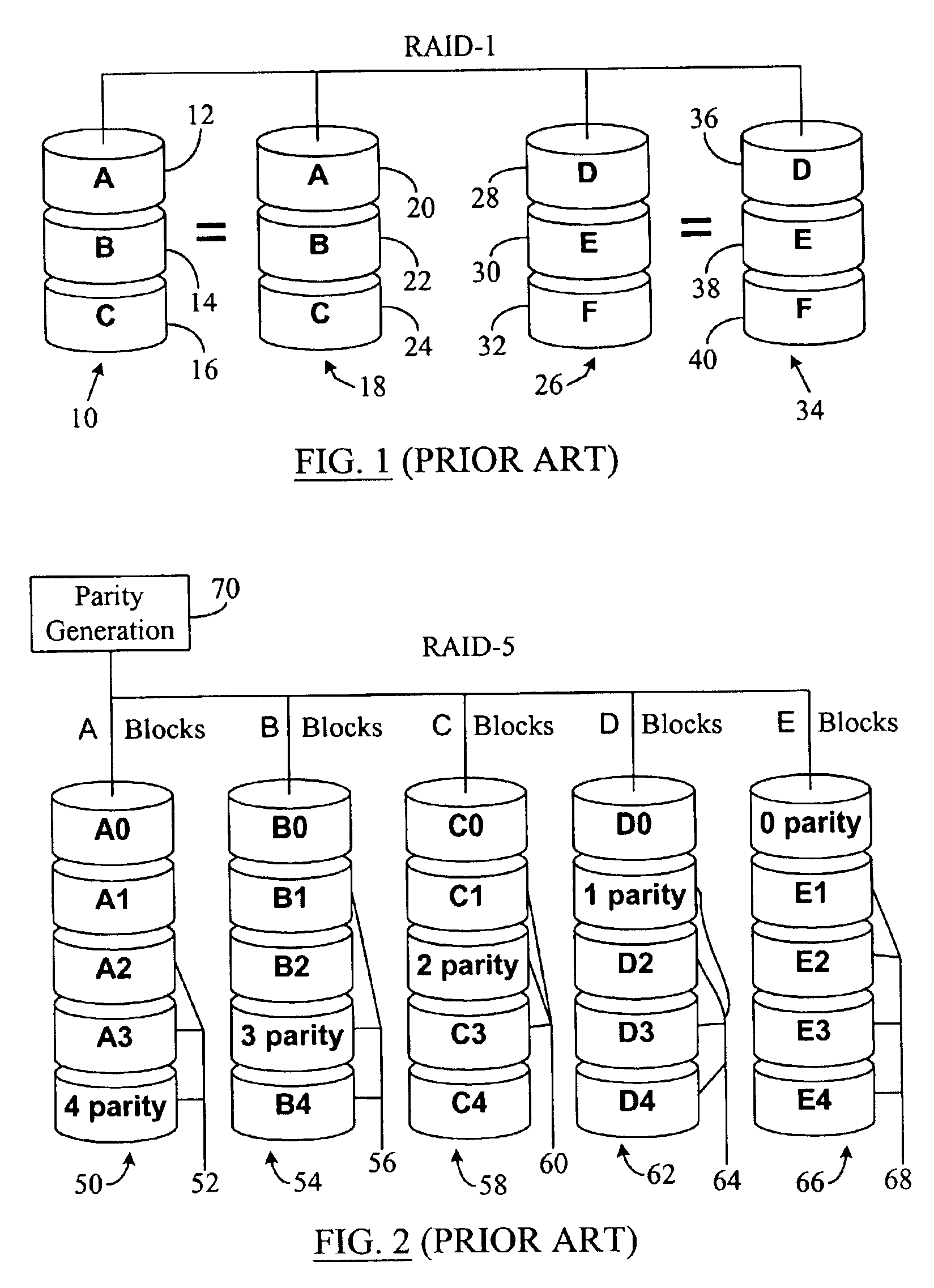
Data file migration from a mirrored RAID to a non-mirrored XOR-based RAID without rewriting the data
InactiveUS6985995B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionRAIDObject based
A data storage methodology wherein a data file is initially stored in a format consistent with RAID-1 and RAID-X and then migrated to a format consistent with RAID-X and inconsistent with RAID-1 when the data file grows in size beyond a certain threshold. Here, RAID-X refers to any non-mirrored storage scheme employing XOR-based error correction coding (e.g., a RAID-5 configuration). Each component object (including the data objects and the parity object) for the data file is configured to be stored in a different stripe unit per object-based secure disk. Each stripe unit may store, for example, 64 KB of data. So long as the data file does not grow beyond the size threshold of a stripe unit (e.g., 64 KB), the parity stripe unit contains a mirrored copy of the data stored in one of the data stripe units because of the exclusive-ORing of the input data with “all zeros” assumed to be contained in empty or partially-filled stripe units. When the file grows beyond the size threshold, the parity stripe unit starts storing parity information instead of a mirrored copy of the file data. Thus, the data file can be automatically migrated from a format consistent with RAID-1 and RAID-X to a format consistent with RAID-X and inconsistent with RAID-1 without the necessity to duplicate or rewrite the stored data.
Owner:PANASAS INC
System and method for measuring an analyte in a sample
ActiveUS20090184004A1Interference minimizationLess of concentration profileImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Methods of determining a corrected analyte concentration in view of some error source are provided herein. The methods can be utilized for the determination of various analytes and / or various sources of error. In one example, the method can be configured to determine a corrected glucose concentration in view of an extreme level of hematocrit found within the sample. In other embodiments, methods are provided for identifying various system errors and / or defects. For example, such errors can include partial-fill or double-fill situations, high track resistance, and / or sample leakage. Systems are also provided for determining a corrected analyte concentration and / or detecting some system error.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Atomic layer deposition for filling a gap between devices
A method is provided for filling a trench or gap between a pair of semiconductor devices formed above a substrate. A liner is applied in a trench or gap between a pair of devices by atomic layer deposition to partially fill the trench or gap. The trench or gap is filled by a bulk fill process.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for restoring and maintaining solid-state drive performance
InactiveUS20110119462A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataTerm memory
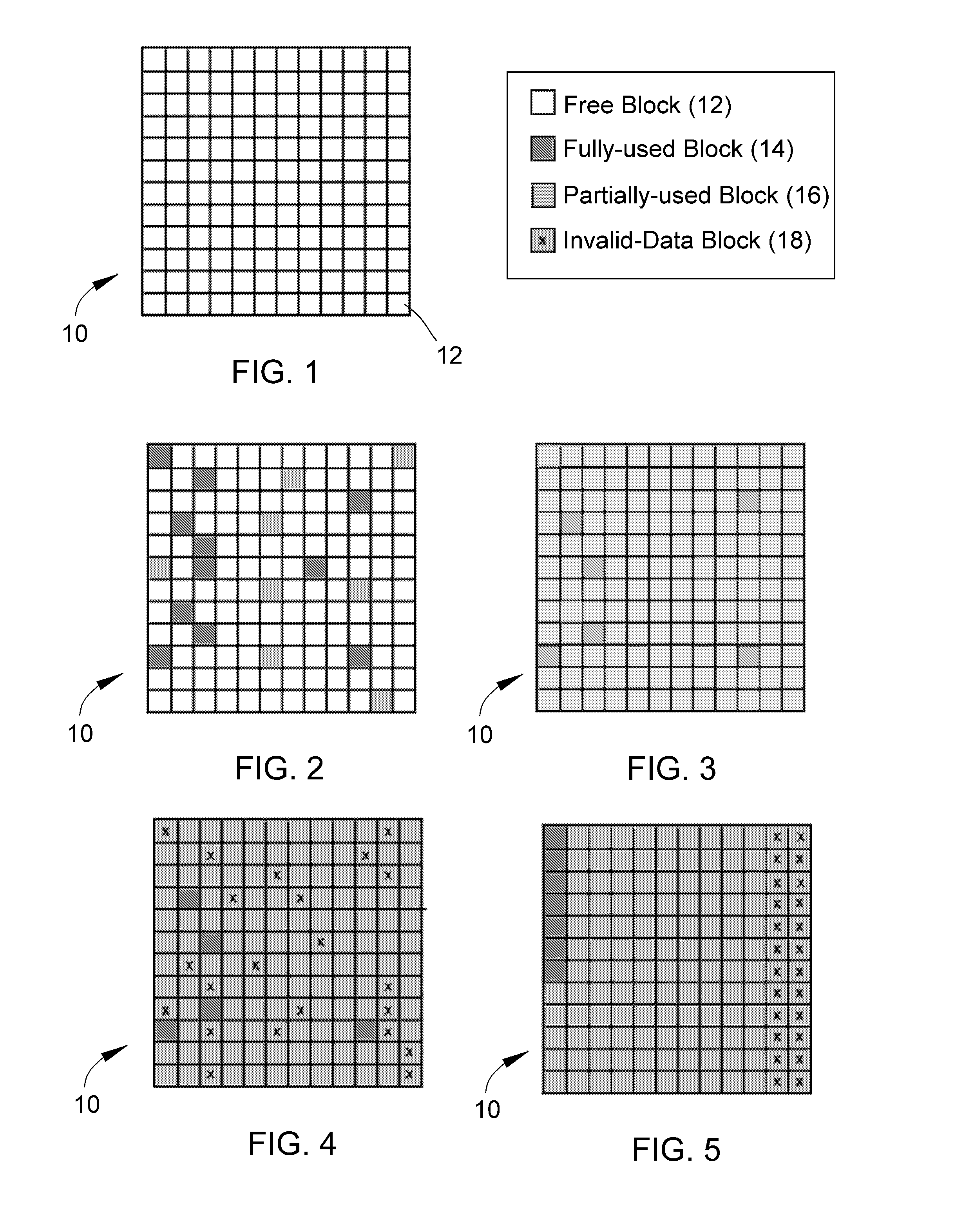
A method of maintaining a solid-state drive so that free space within memory blocks of the drive becomes free usable space to the drive. The drive comprises cells organized in pages that are organized in memory blocks in which at least user files are stored. A defragmentation utility is executed to cause at least some of the memory blocks that are partially filled with data and contain file fragments to be combined or aligned and to cause at least some of the memory blocks that contain only invalid data to be combined or aligned. A block consolidation utility is then executed to eliminate at least some of the partially-filled blocks by consolidating the file fragments into a fewer number of the memory blocks. The consolidation utility also increases the number of memory blocks that contain only invalid memory. All of the memory blocks containing only invalid data are then erased.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Stressed barrier plug slot contact structure for transistor performance enhancement
ActiveUS20080157208A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStress inducedPerformance enhancement
A method for forming a slot contact structure for transistor performance enhancement. A contact opening is formed to expose a contact region, and a slot contact is disposed within the contact opening in order to induce a stress on an adjacent channel region. In an embodiment, a stress inducing barrier plug is disposed within a portion of the contact opening and the remainder of the contact opening is filled with a lower resistivity contact metal. By selecting the proper materials and deposition parameters, the slot contact can be tuned to induce a tensile or compressive stress on the adjacent channel region, thus being applicable for both p-type and n-type devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for supplying bulk product to an end user
InactiveUS7214028B2Eliminate needEfficient transportTank vehiclesMixing operation control apparatusMarine engineeringEngineering
A method and apparatus for supplying bulk material to an end user includes the step of providing a bulk material source that is at a location distant from the end user and a specially configured vessel and trailer apparatus for transporting the bulk material to the end user. The vessel is filled with bulk material at the bulk material source and then transported with a specially configured trailer. Alternatively, at source or destination, the vessel can remain as a temporary storage device, free-standing from the trailer. During transport between the bulk material source and the end user, the vessel is filled or partially filled with a selected bulk material. During transport, the vessel is in a generally horizontal position, supported by the trailer and a specially configured elevator. The vessel is unloaded from the trailer by moving the vessel longitudinally along the trailer and by transferring the vessel from a generally horizontal position upon the trailer to an elevated upright position.
Owner:TILT TANK L L C
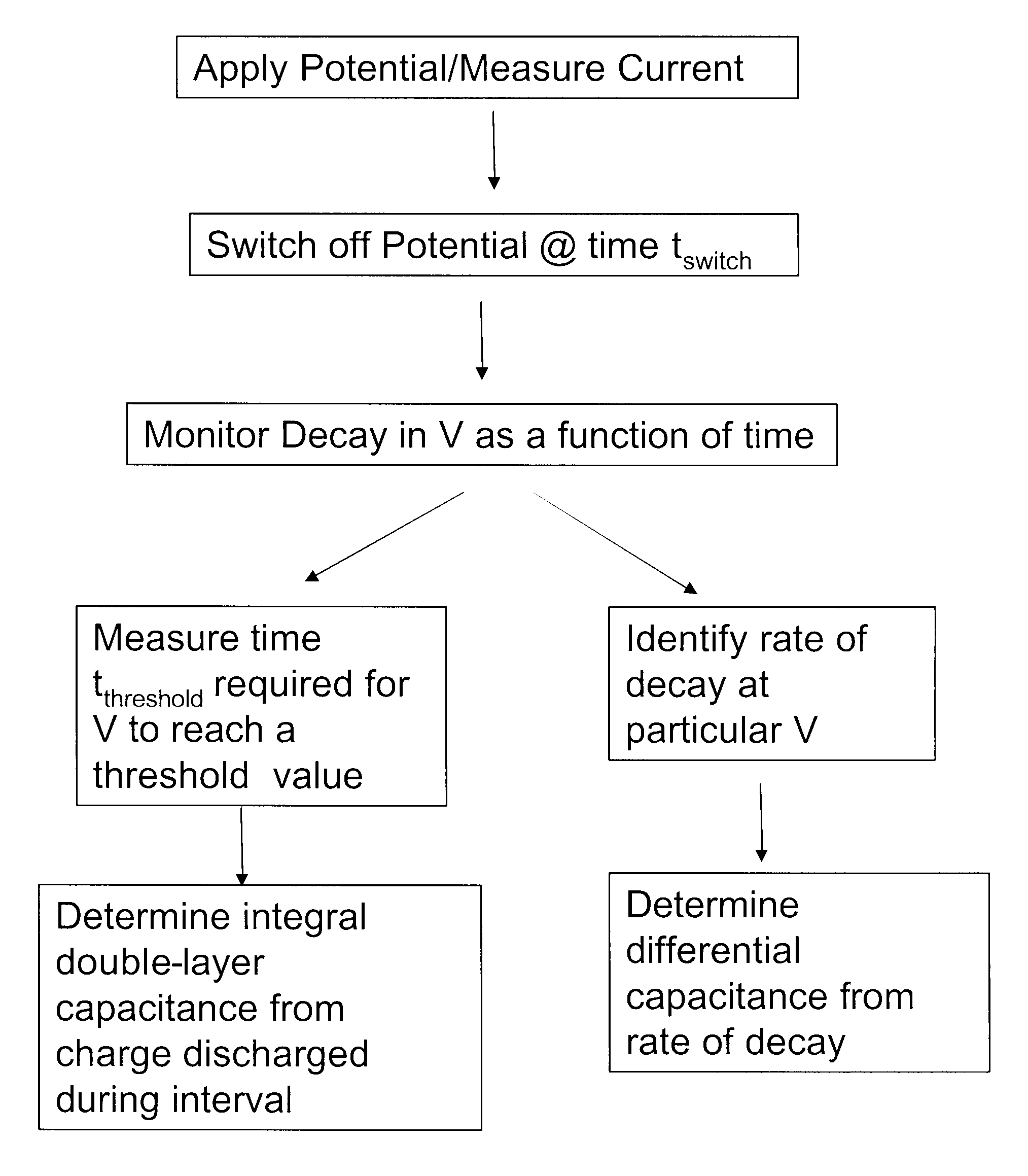
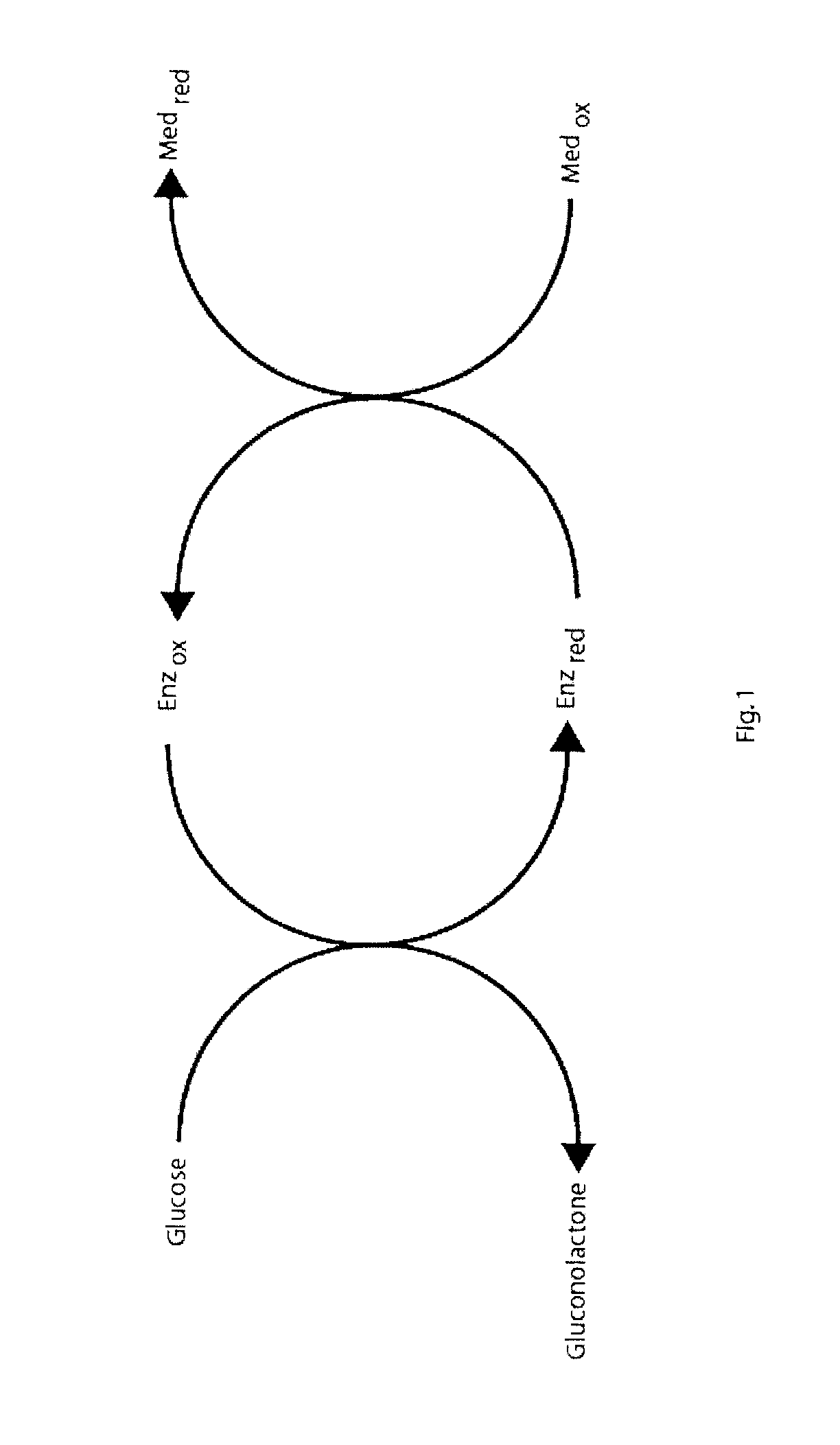
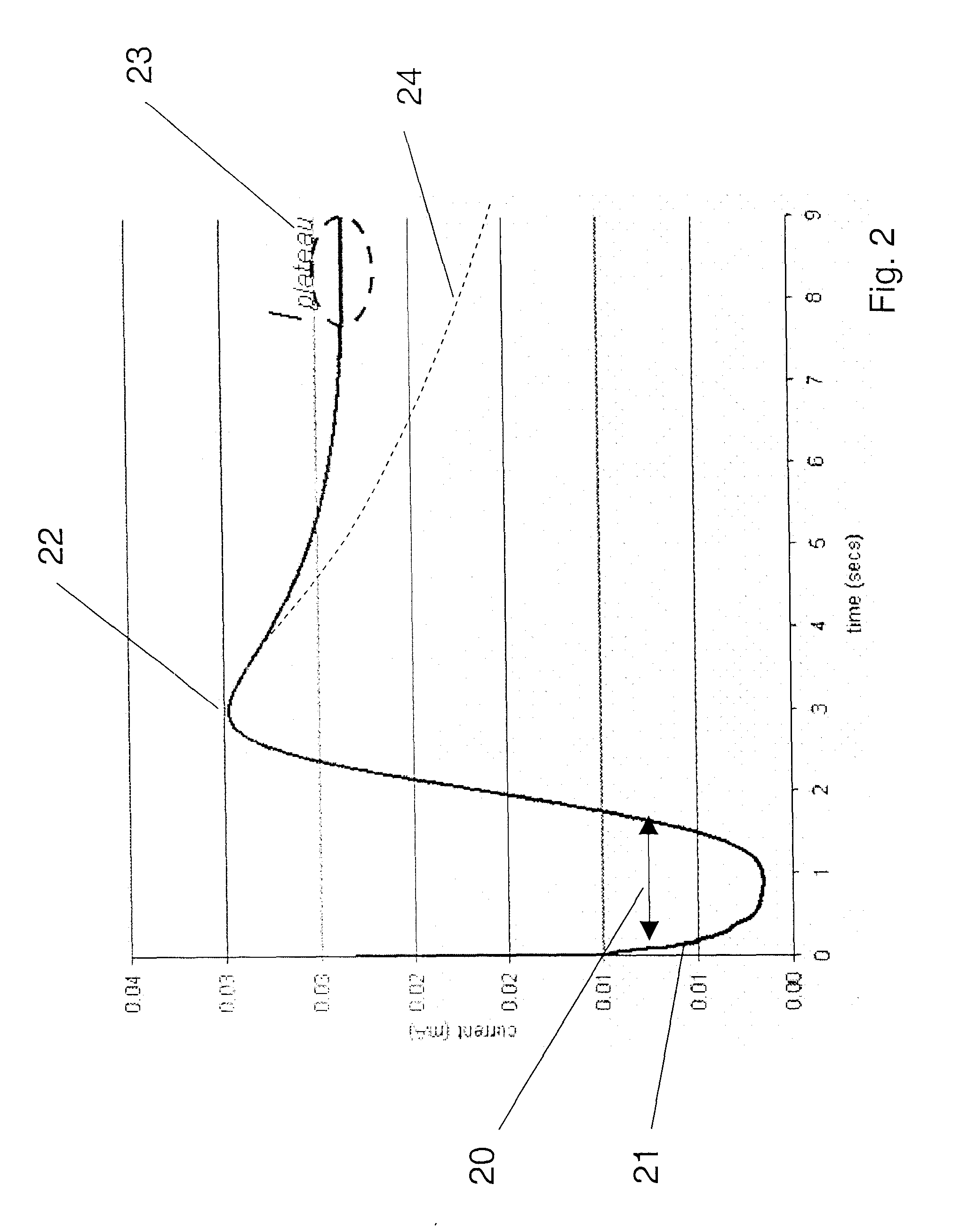
Determination of Partial Fill in Electrochemical Strips
Partial fill of an electrochemical test strip is determined by making a DC determination of double layer capacitance from charging or discharging charge on a test strip containing sample, for example a blood sample to be tested for glucose. The measured double layer capacitance is compared to a reference value. The double layer capacitance may be determined as an integral or differential capacitance. Double layer capacitance may also be used for quality control to monitor the quality of electrode formation, particularly in strips using screen printed electrodes.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
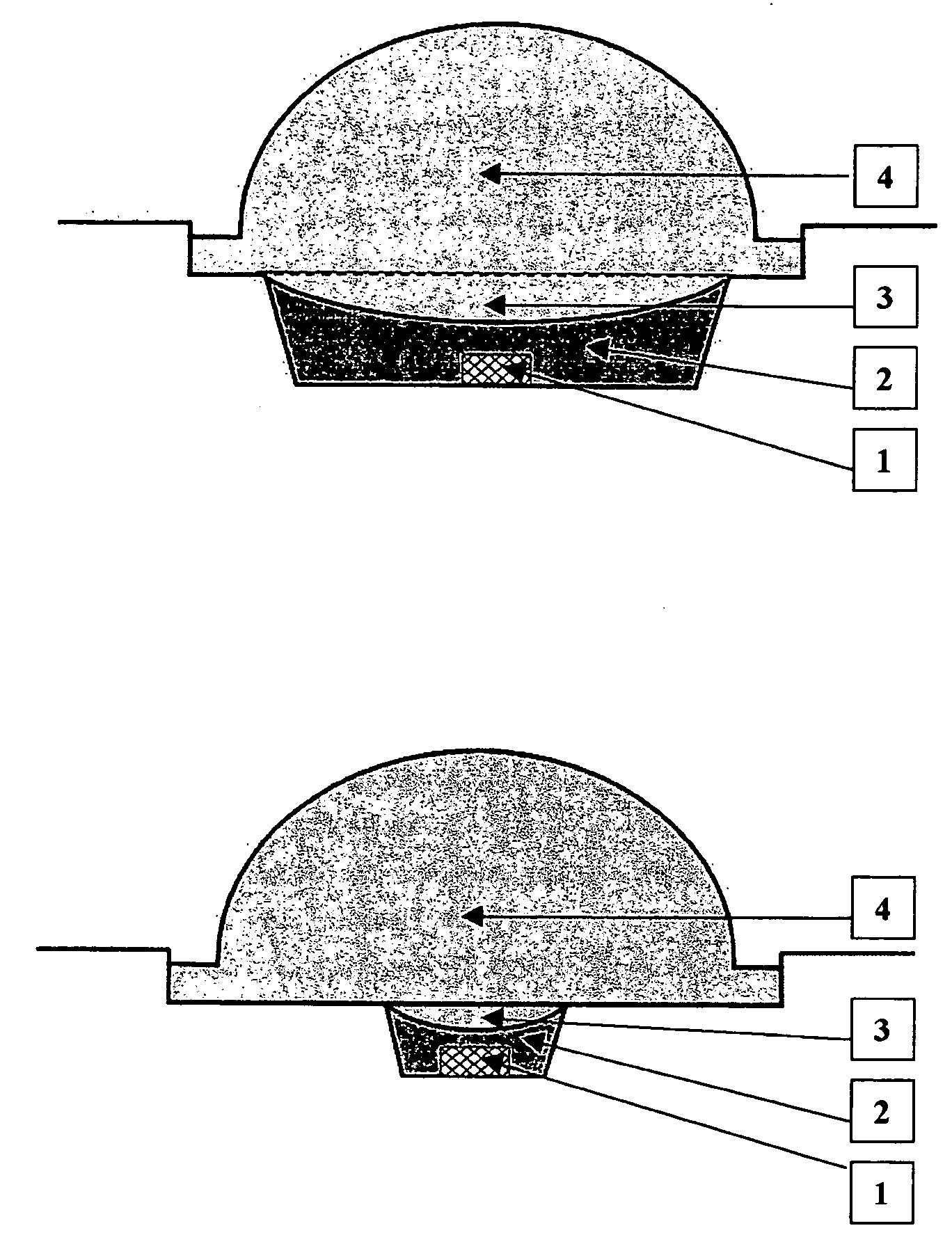
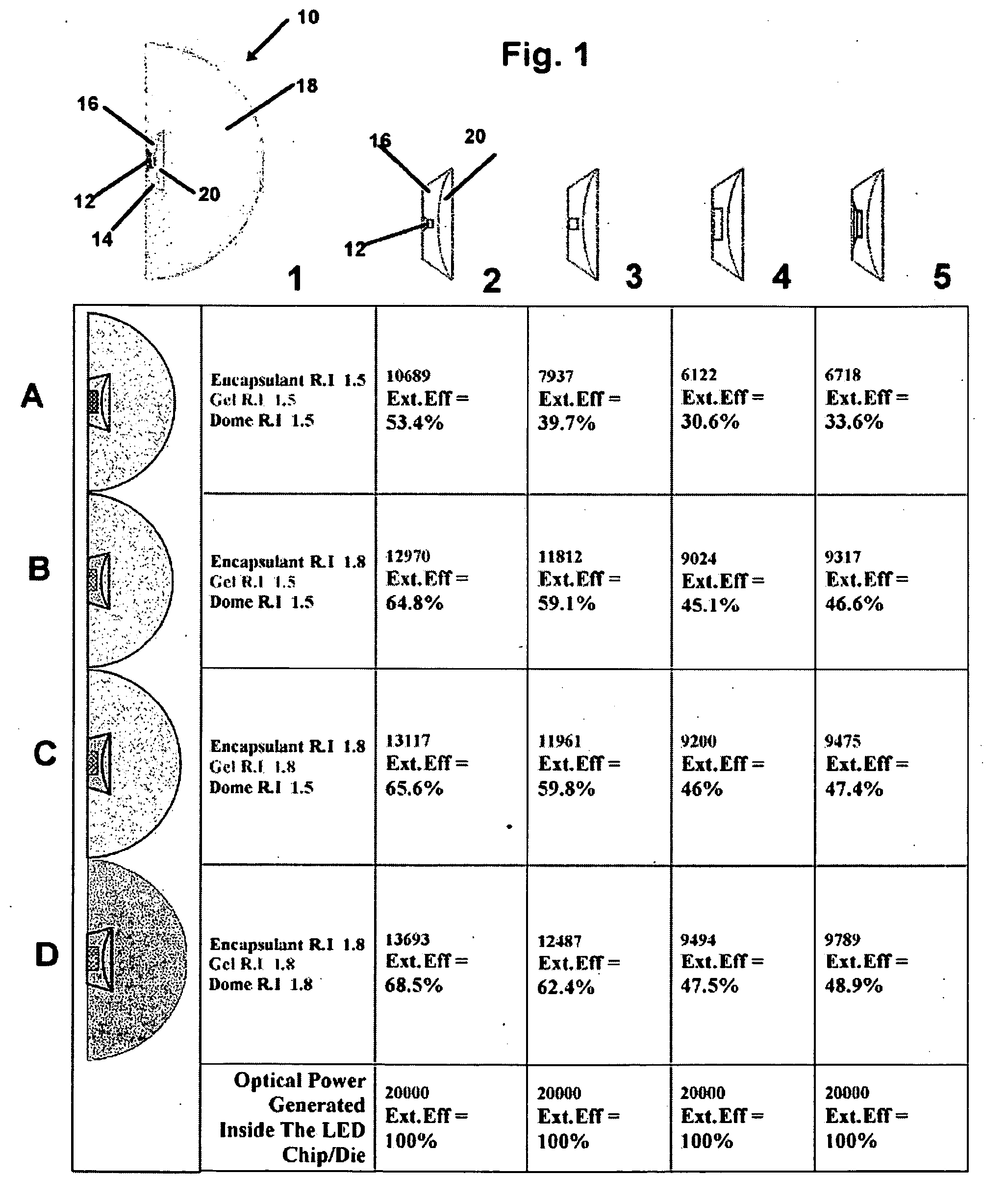
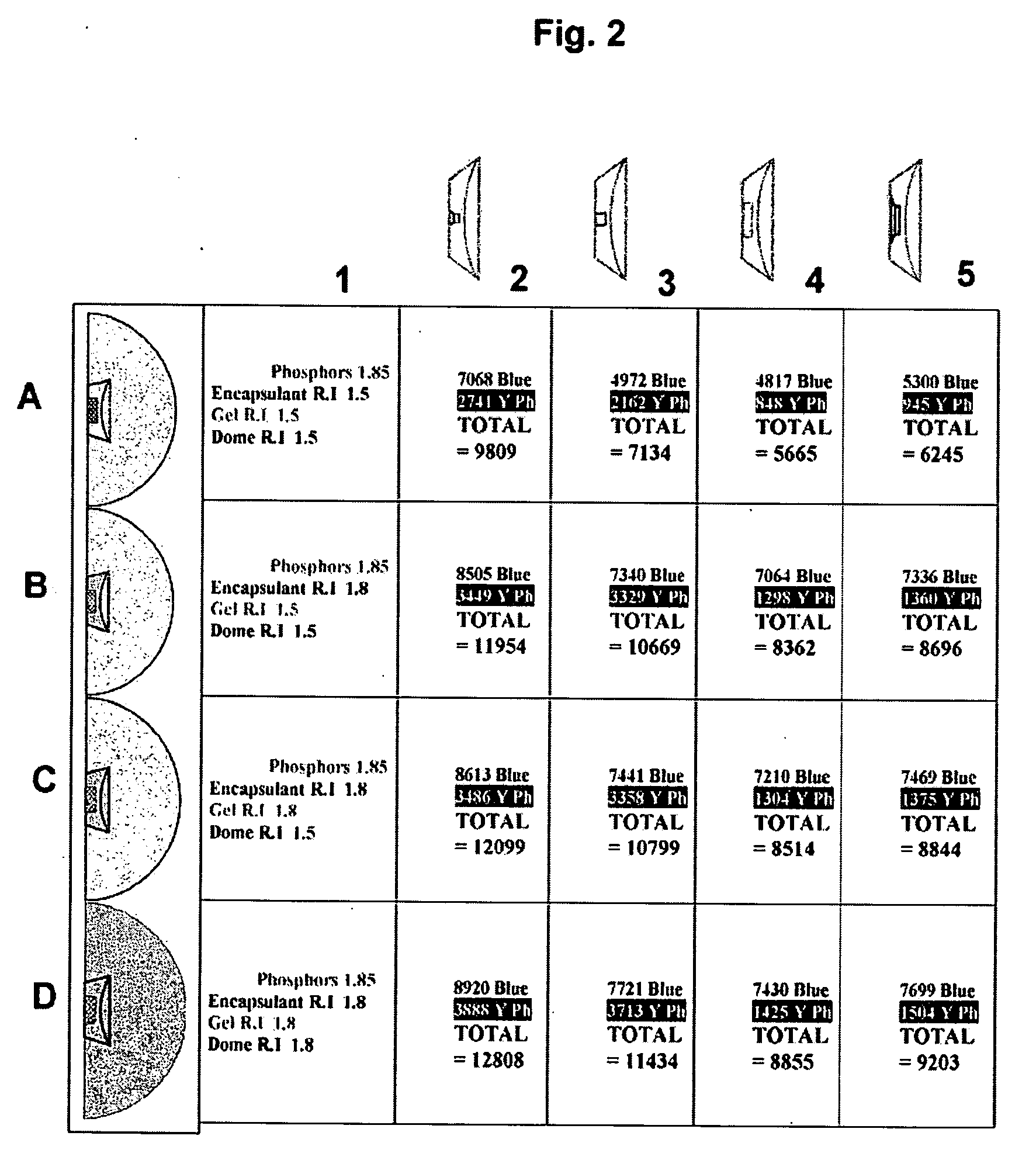
Light efficient packaging configurations for LED lamps using high refractive index encapsulants
InactiveUS20060255353A1High refractive indexImprove optical efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceSurface mountingRefractive index
Light efficient packaging configurations for LED lamps using high refractive index encapsulants. The packaging configurations including dome (bullet) shaped LED's, SMD (surface mount device) LED's and a hybrid LED type, including a dome mounted within a SMD package. In another embodiment used with SMD LED devices a relatively small semi-hemispherical “blob” of HRI encapsulant surrounds the LED chip with the remainder of the SMD cavity filled with conventional encapsulant. The packaging configurations increase the LED's light emission efficiency at a reasonable cost and in a commercially viable manner, by maximizing the light efficiency while minimizing the amount of high refractive index encapsulant used.
Owner:TASKAR NIKHIL R +3
Thin stacked interposer package
ActiveUS8319338B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageElectronic component
The present invention comprises a semiconductor package comprising a bottom semiconductor package substrate which is populated with one or more electronic components. The electronic component(s) of the bottom substrate are covered or encapsulated with a suitable mold compound which hardens into a package body of the semiconductor package. The package body is provided with one or more vias through the completion of laser drilling process, such via(s) providing access to one or more corresponding conductive contacts of the bottom substrate. These vias are either lined or partially filled with a conductive metal material. Subsequently, a top semiconductor package substrate (which may optionally be populated with one or more electronic components) is mounted to the package body and electrically connected to the conductive metal within the via(s) of the package body.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Magnetic field shielding sheet for a wireless charger, method for manufacturing same, and receiving apparatus for a wireless charger using the sheet
ActiveUS20150123604A1Reduce lossesHigh quality factorNear-field transmissionShielding materialsElectric power transmissionTerminal equipment
Provided are a magnetic field shield sheet for a wireless charger, which blocks an effect of an alternating-current magnetic field generated when a charger function for a portable mobile terminal device is implemented in a non-contact wireless manner on a main body of the portable mobile terminal device and exhibits excellent electric power transmission efficiency, a method of manufacturing the sheet, and a receiver for the wireless charger by using the sheet. The sheet includes: at least one layer thin magnetic sheet made of an amorphous ribbon separated into a plurality of fine pieces; a protective film that is adhered on one surface of the thin magnetic sheet via a first adhesive layer provided on one side of the protective film; and a double-sided tape that is adhered on the other surface of the thin magnetic sheet via a second adhesive layer provided on one side of the double-sided adhesive tape, wherein gaps among the plurality of fine pieces are filled by some parts of the first and second adhesive layers, to thereby isolate the plurality of fine pieces.
Owner:AMOSENSE
Method for tuning a work function of high-k metal gate devices
InactiveUS20100068877A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesWork functionEngineering
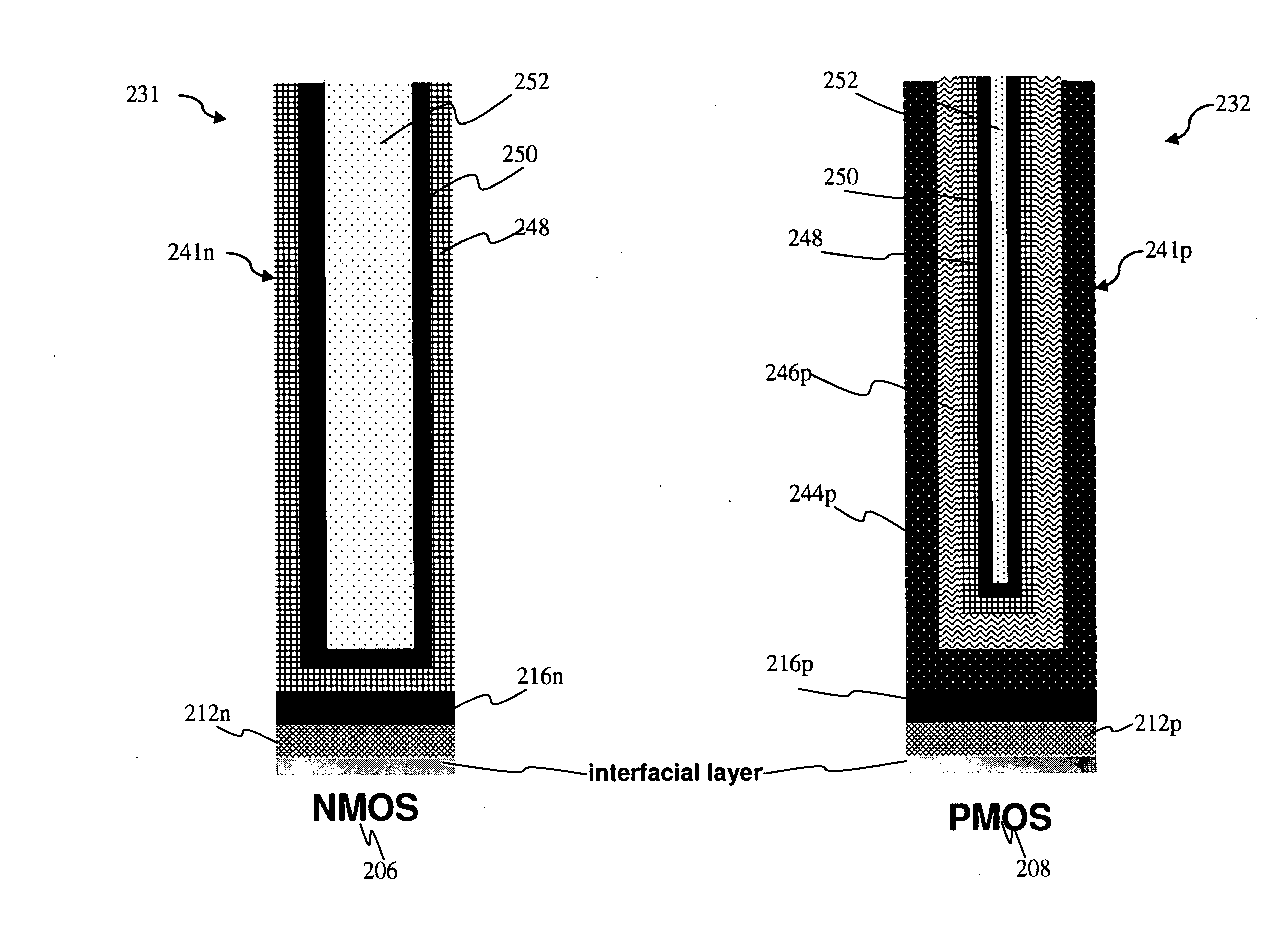
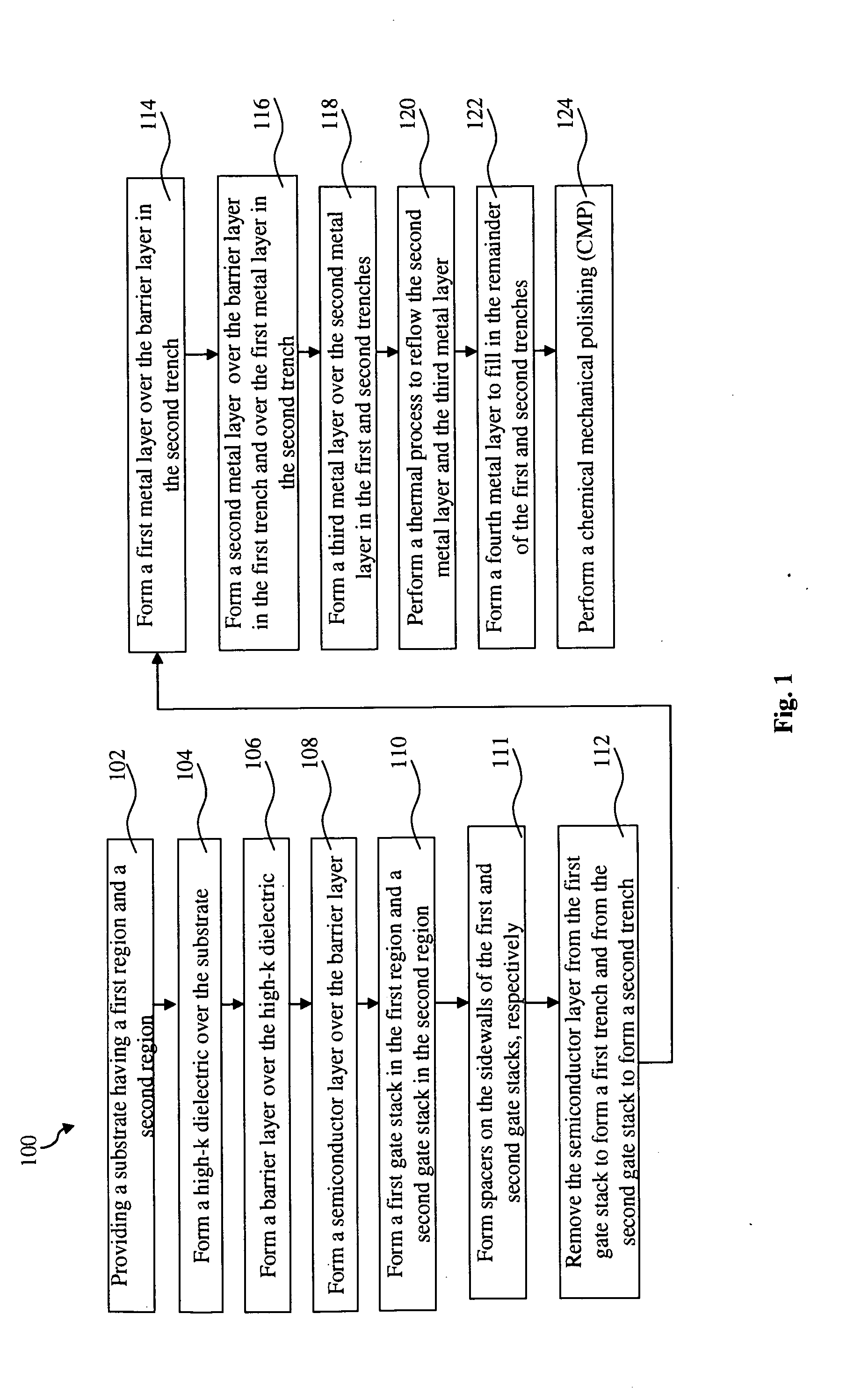
The present disclosure provides a method of fabricating a semiconductor device that includes providing a semiconductor substrate, forming first and second transistors in the substrate, the first transistor having a first gate structure that includes a first dummy gate, the second transistor having a second gate structure that includes a second dummy gate, removing the first and second dummy gates thereby forming a first trench and a second trench, respectively, forming a first metal layer to partially fill in the first and second trenches, removing the first metal layer within the first trench, forming a second metal layer to partially fill in the first and second trenches, forming a third metal layer to partially fill in the first and second trenches, reflowing the second metal layer and the third metal layer, and forming a fourth metal layer to fill in the remainder of the first and second trenches.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Beverage portioned package for preparing a foamy beverage from soluble powder
InactiveUS20050158426A1Sufficient pressureSufficient amountPackaging foodstuffsWater insolubleWadding
A beverage portioned package for preparing a beverage in an extraction device of which the package is held or clamped between a water supplying part and a receiver of the device. The package has a first surface for the water to be forced to flow there through under pressure when the package is held or clamped in the device; a second surface for the flow of beverage to be forced to flow there through so to be collected in the receiver, wherein the package contains a portion of water-soluble beverage material and a portion of a filler. The filler comprising water insoluble material adapted to maintain the extraction pressure above the pressure created by the sole resistance of the first and second surfaces when the package is emptied of said soluble material.
Owner:NESTEC SA
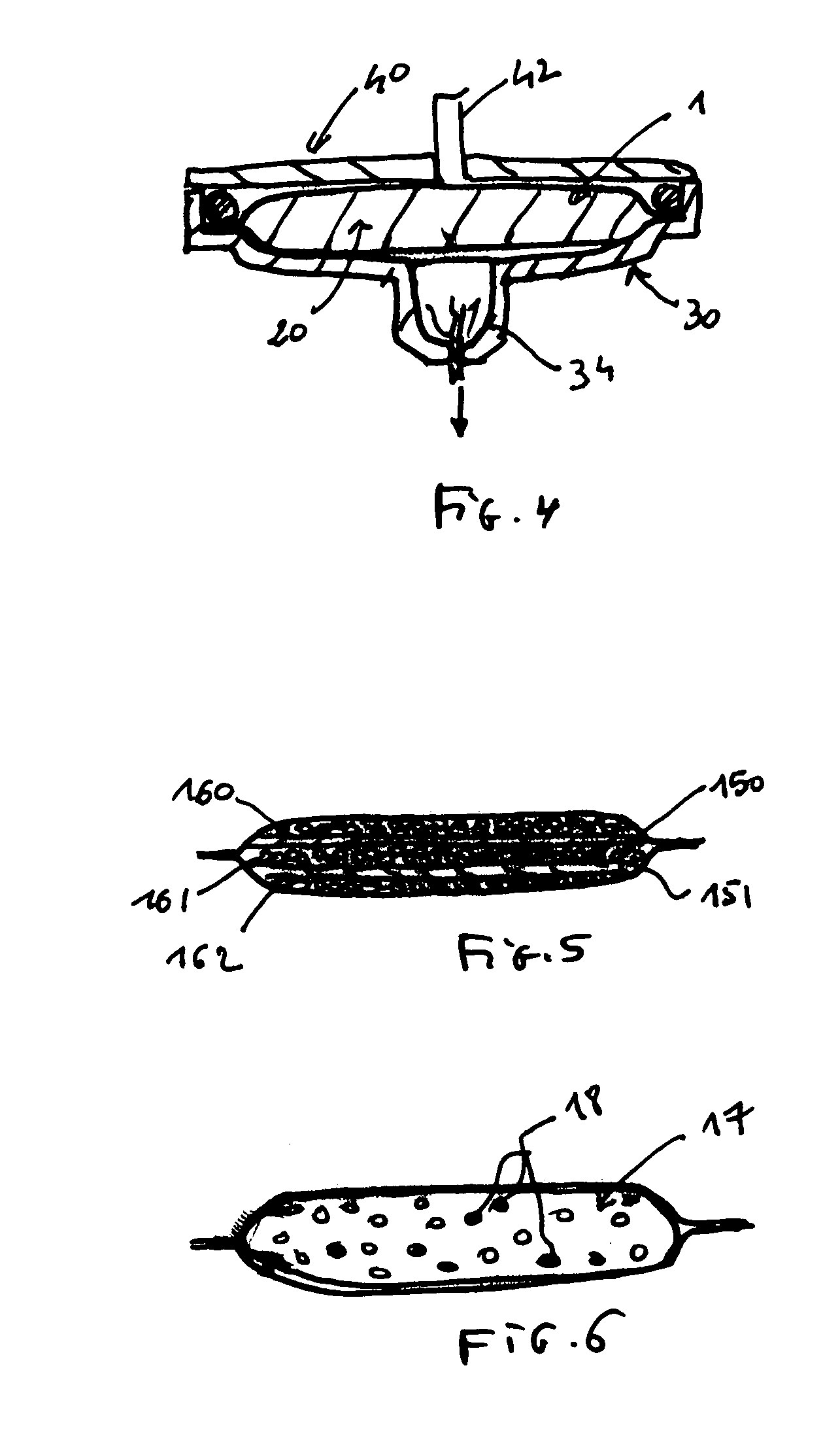
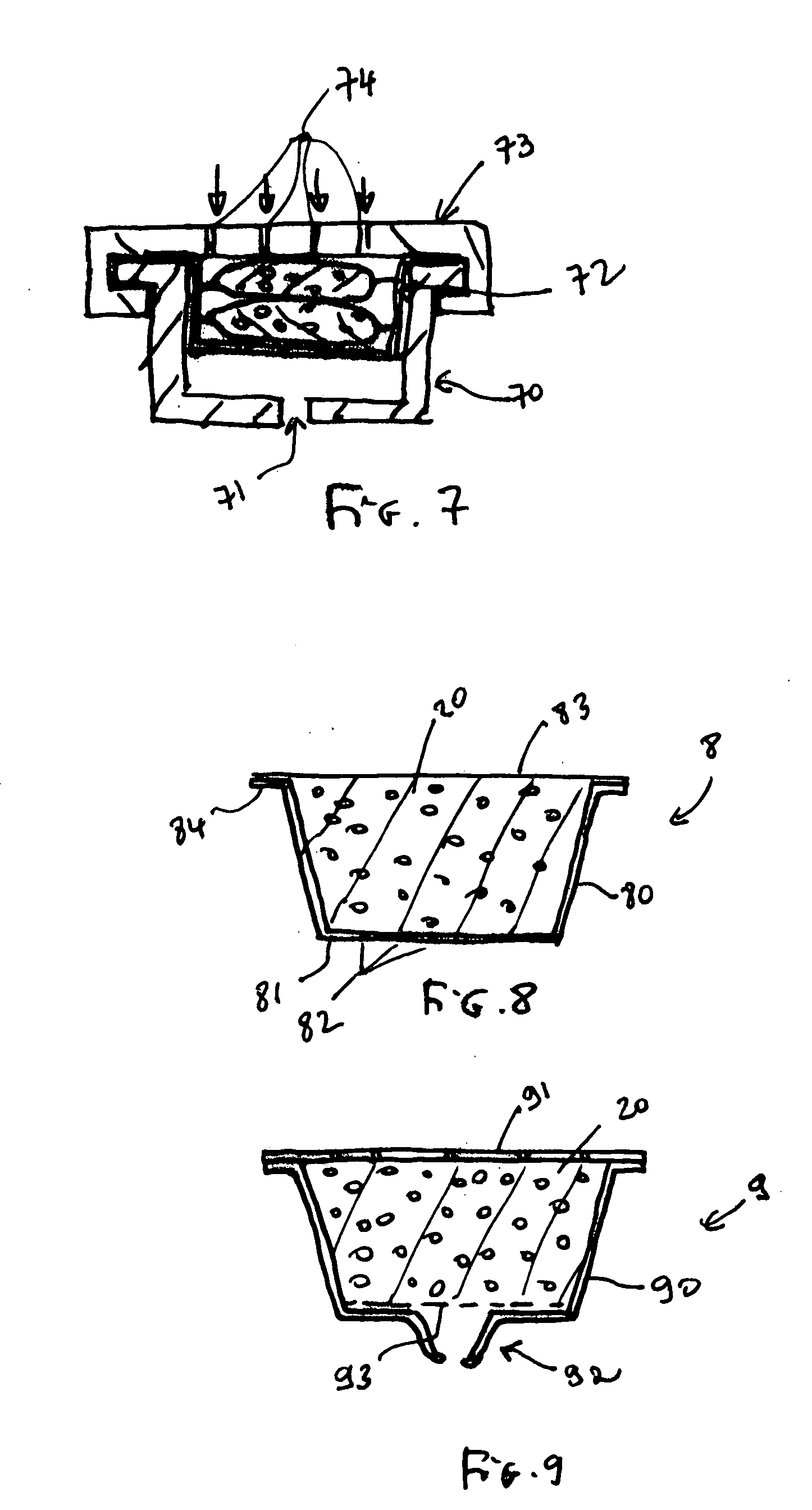
Storage management system and method for increasing capacity utilization of nonvolatile storage devices using partially filled substitute storage devices for continuing write operations
InactiveUS6199146B1Improve capacity utilizationInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsData setMagnetic tape
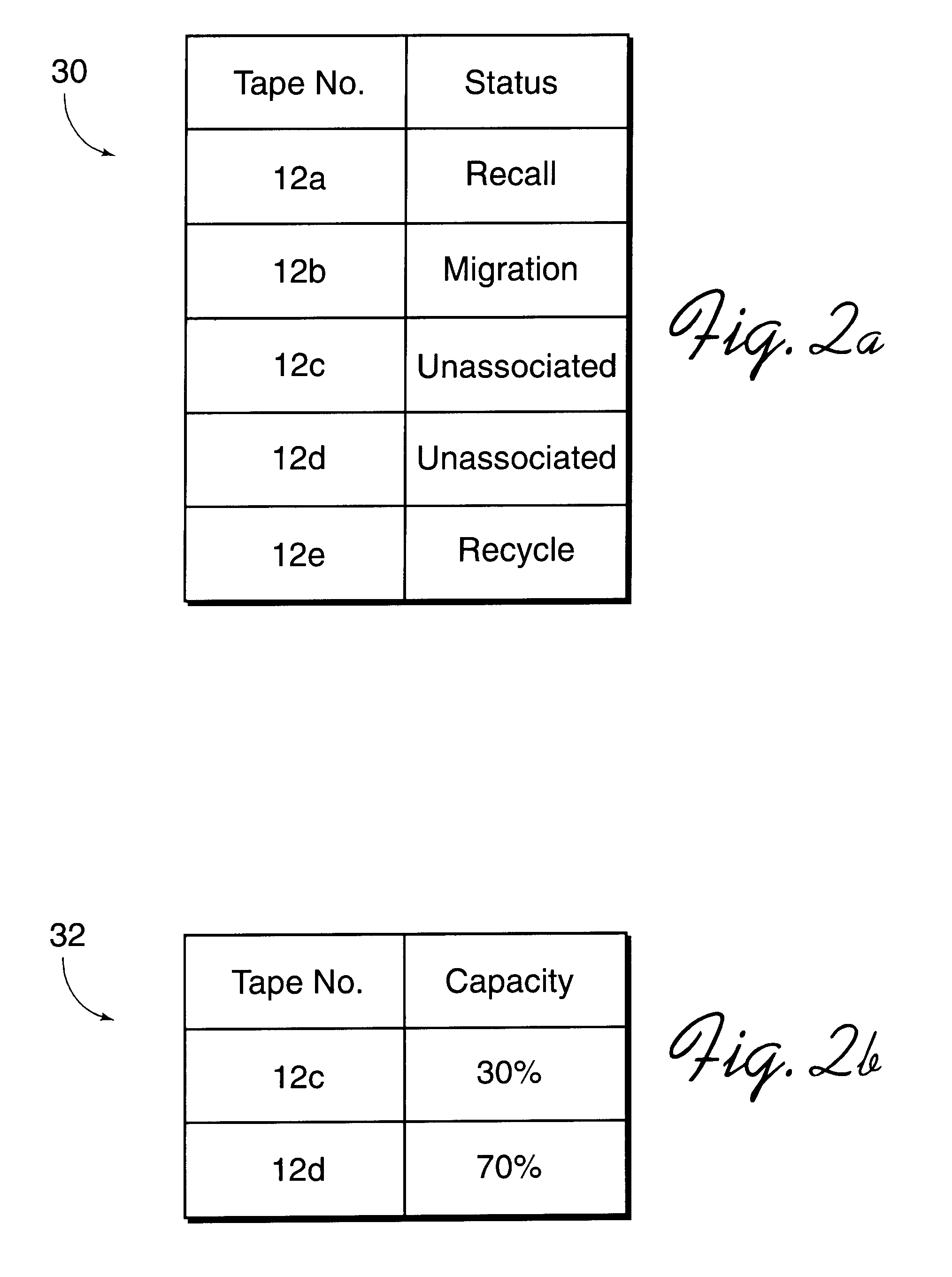
A system and method for increasing capacity utilization of non-volatile storage devices within a group of non-volatile storage devices used to store data from at least one attached system are disclosed. A group of data sets is written to a first storage device as part of a write operation such as migration. A plurality of storage devices partially filled with data are designated as substitutes. The write operation to the first storage device is suspended upon receiving a request to read a data set stored in the first storage device, such as occurs in a recall operation. A second storage device is then selected from the plurality of substitute storage devices. The write operation is continued by writing data sets from the group of data sets included in the write operation that were not written to the first storage device to the selected second storage device. The requested data is then read from the first storage device. After data has been read from the first storage device, the first storage device may be designated as a substitute storage device so that the partially filled first storage device may be selected for continuing write operations. Data sets from substitute storage devices may be transferred or merged into a lesser number of storage devices during recycle operations to prevent the number of substitute storage devices from increasing beyond a predetermined limit or goal. Recycling operations in which data sets from different storage devices are transferred or merged may be performed by building a first queue including a list of filled tapes ordered according to the least amount of valid data and a second queue including all unassociated partially filled storage devices ordered by the amount of available storage space, and merging. The non-volatile storage devices may include tapes or tape libraries.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device incorporating a defect controlled strained channel structure and method of making the same
InactiveUS6919258B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierSingle crystal substrate
A semiconductor device includes a single crystal substrate and a dielectric layer overlying the substrate. The dielectric layer includes at least one opening having a first portion and an overlying second portion. The first portion has a depth and width, such that an aspect ratio of the depth to width is greater than one. The semiconductor device further includes a first material having a first portion and a second portion, the first portion of the first material filling the first portion of the at least one opening. Defects for relaxing strain at an interface between the first material and the substrate material exist only within the first portion of the first material due to the aspect ratio being greater than one. The second portion of the first material is substantially defect free. Furthermore, the second portion of the first material and an overlying second material different than the first material fill the overlying second portion of the at least one opening. The second material has a thickness which is less than a critical thickness to maintain the second material in a strained state. The strained second material functions as a channel for charge carriers.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC +1
Multi-valving sample injection apparatus
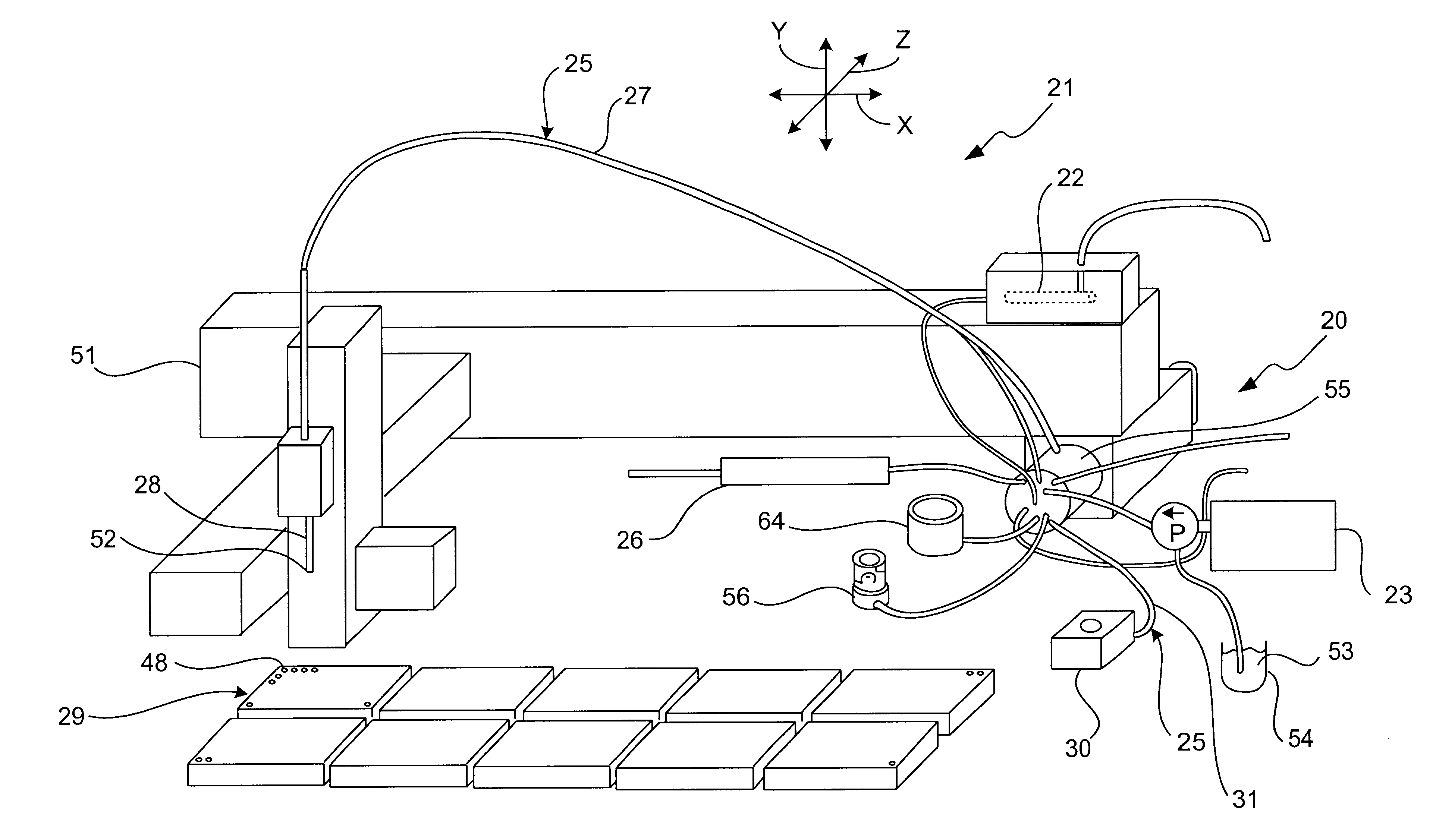
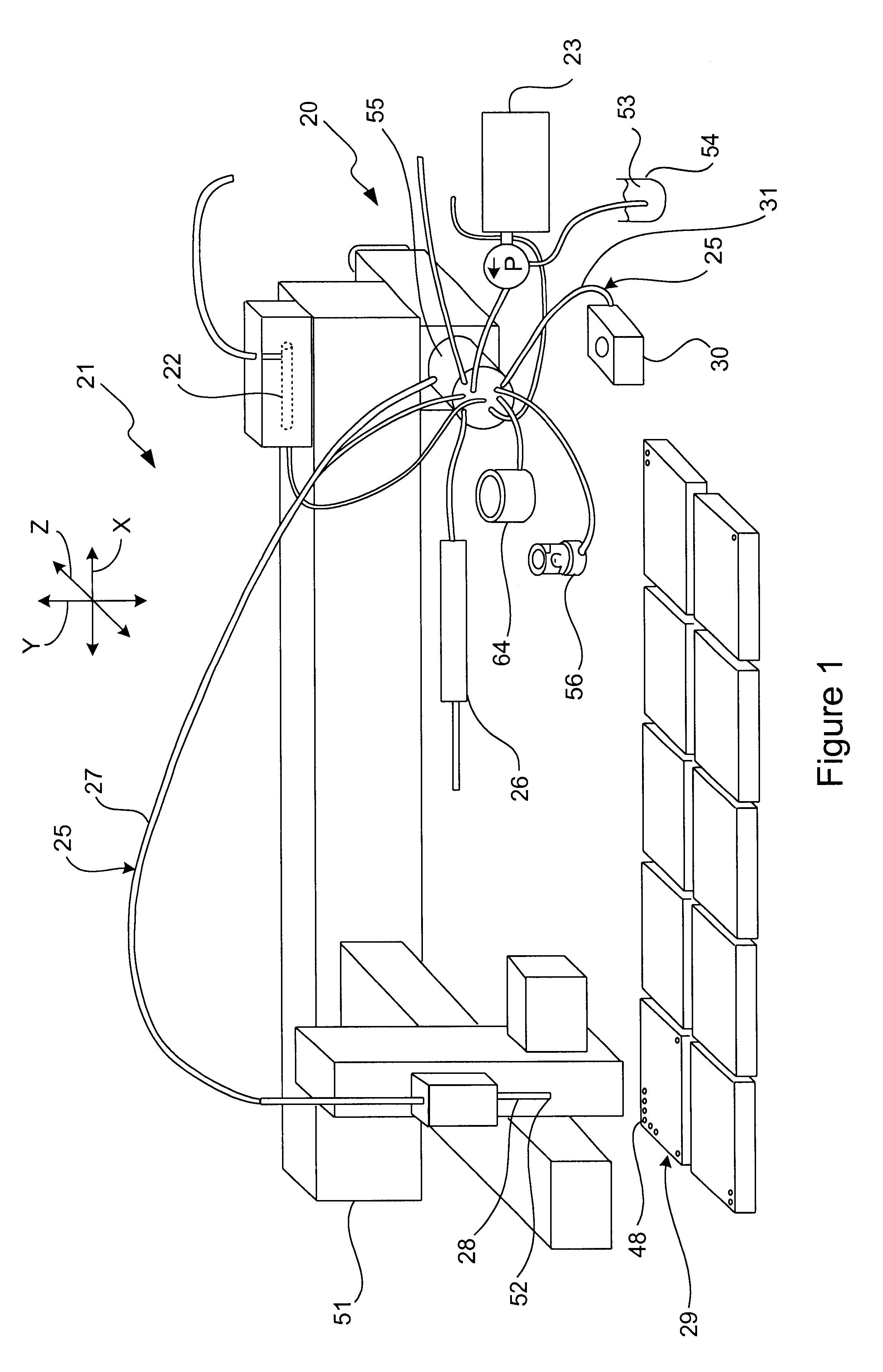
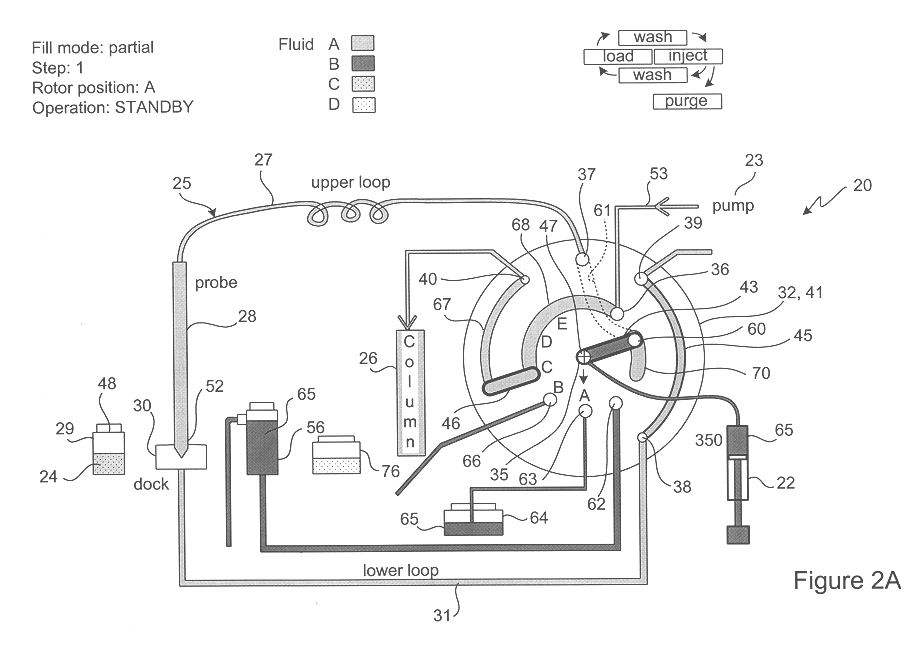
A multi-function valve apparatus for use with a Probe-In-Loop (PIL) architecture sample injection assembly which enables both Partial-Fill and Complete-Fill injections. The rotor element is rotatable about a rotation axis relative the stator between: a Load Position, an Overfill Position, and an Injection Position. In the Load Position, a first bridge channel fluidly couples a metering syringe to the sample loop assembly enabling the probe to aspirate one of a discrete volume of sample into the probe, during a Partial-Fill Mode, and a second volume of sample into the probe, during a Complete-Fill Mode. In the Overfill Position, in the Complete-Fill Mode, a second bridge channel fluidly couples a downstream loop portion to a waste port, and the first bridge channel fluidly couples the metering syringe to an upstream loop portion of the sample loop assembly. This enables the metering pump to dispense the sample from the probe into the downstream loop portion and out the waste port to completely fill the downstream loop portion and the second bridge channel with a substantially precise known volume. In the Injection Position, the second bridge channel fluidly couples the downstream loop portion to the analyzing device to inject the sample into the analyzing device, in either the Partial-Fill Mode or and the Complete-Fill Mode.
Owner:IDEX HEALTH & SCI
Method and apparatus for automatic filling of forms with data
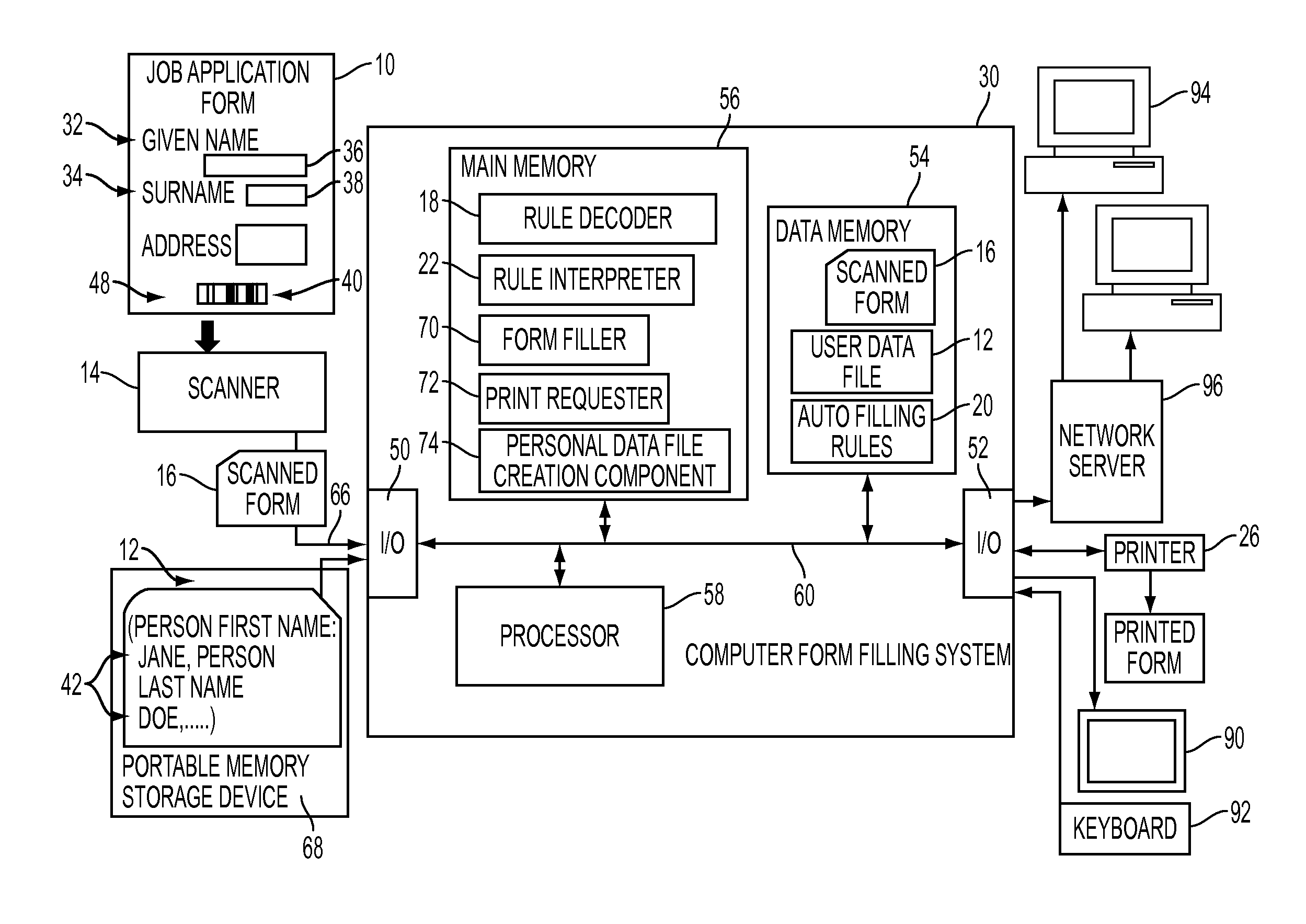
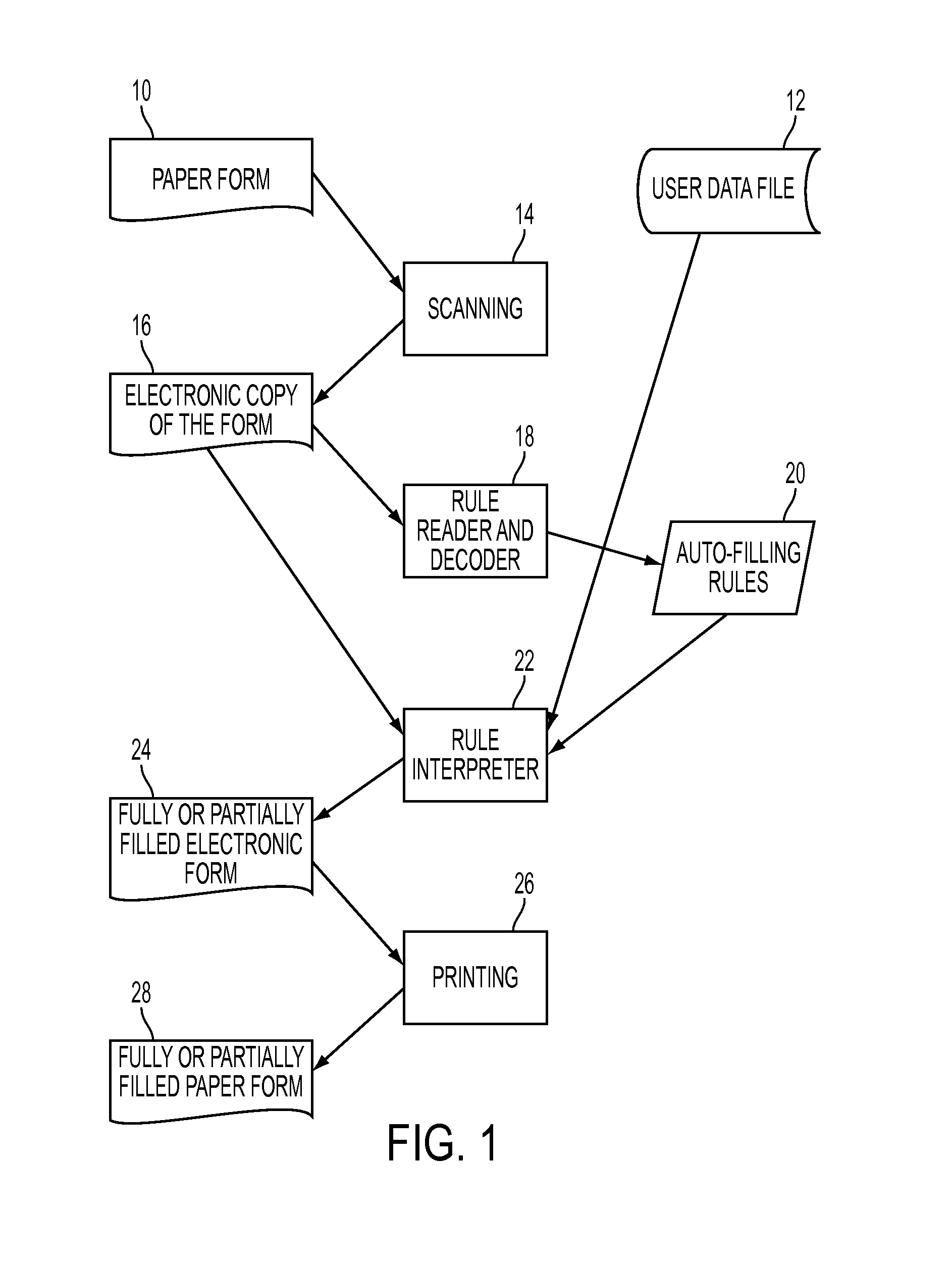
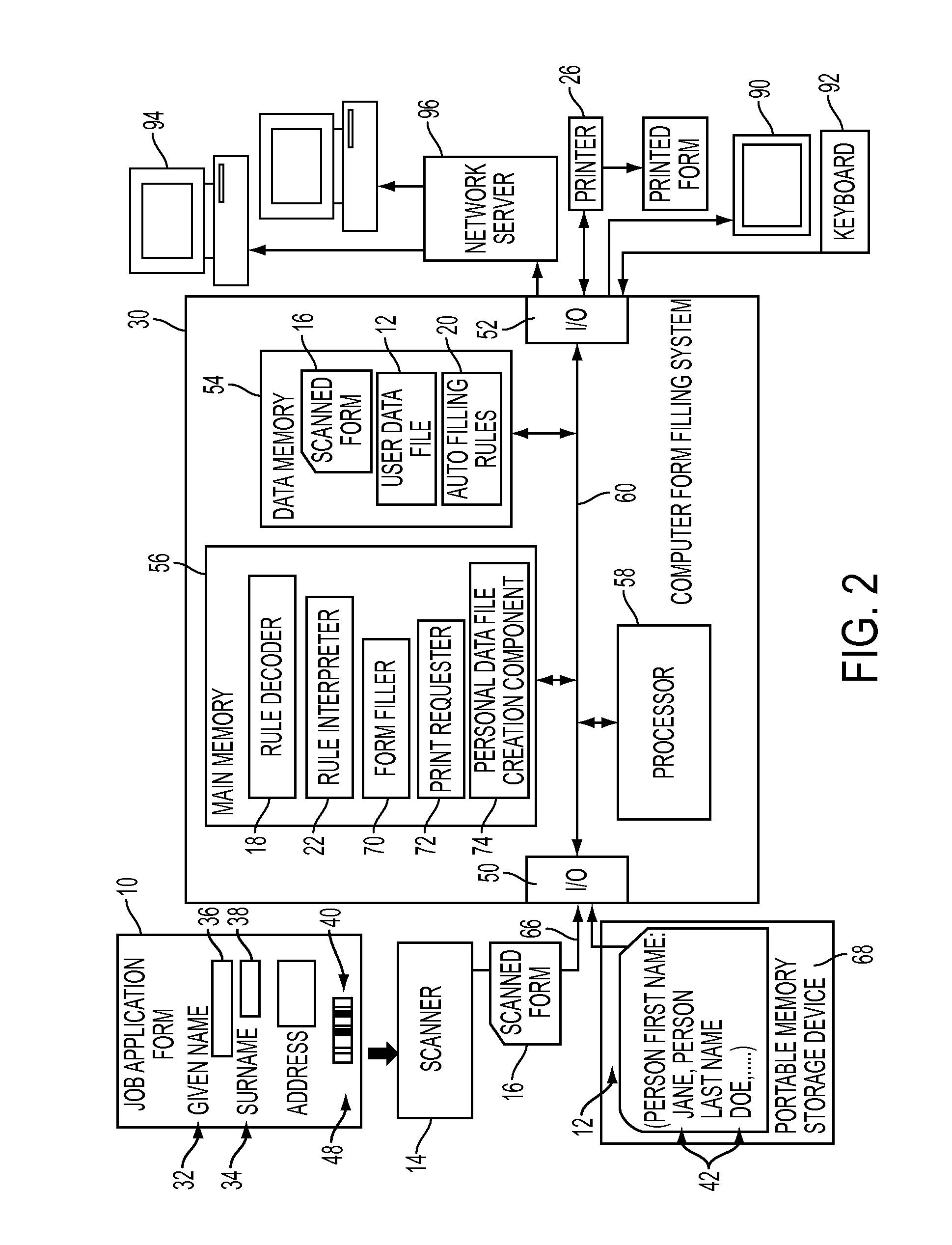
InactiveUS20110271173A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData fileDisplay device
A system and a method for filling a form are provided which take as input a user's data file, which is configured for use in filling in forms, and an image of an original form to be filled in using the user's personal data. Form filling rules encoded in the image are decoded and used to determine values of a plurality of fields of the form by applying the decoded rules to the user's data. The plurality of fields of the form are filled with the determined values to generate an at least partially filled form, which is then output, e.g., to a printer or a display. The exemplary system and method are able to operate independently of the language used in the text of the form, have the capability of filling in previously unseen forms, and are particularly suited to filling in paper forms.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Expandable stent having plurality of interconnected expansion modules
InactiveUS20050004656A1Significantly improvedSmall surface areaStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentInterconnection
Expandable stents are disclosed. The stents have a plurality of rings or modules interconnected in series, with selectable links between the rings to provide for articulation. The preferred stent includes a plurality of modules, each of the modules being radially interconnected to form a ring configured to be expandably interconnected and being interconnected to each other in series by respective interconnection bridges. Each ring including a continuous strand of a material, the continuous strand of material being interconnected end to end so as to generally encompass a radial space within the ring. The strand of material being configured to include a repeating series of interconnected repeating W-shaped strand configurations having a repeating dip, rise, dip, rise, loop, dip, rise, dip, rise, loop patterned configuration. Preferably, the continuous strand of a material has an outer surface including cavities being at least partially filled with compositions containing medicinal agents selected to provide medically desirable effects upon positioning within a patient. Preferably, the continuous strand of a material has a series of narrowings that facilitate the bending of the strand. Alternate rings have at least one and preferably a number of expansion cells. The expansion cells preferably have at least one accordion structure on each side of the cell, which allows for significant expansion. The material of the respective stents being deformable such that each ring can be deformed from a first configuration wherein each ring has a first circumference and, in certain embodiments, each expansion cell has a first radial length, to a second configuration wherein each ring has a second circumference greater than the first circumference. Methods of producing the devices are also disclosed, including various etching methods.
Owner:STENT TECH
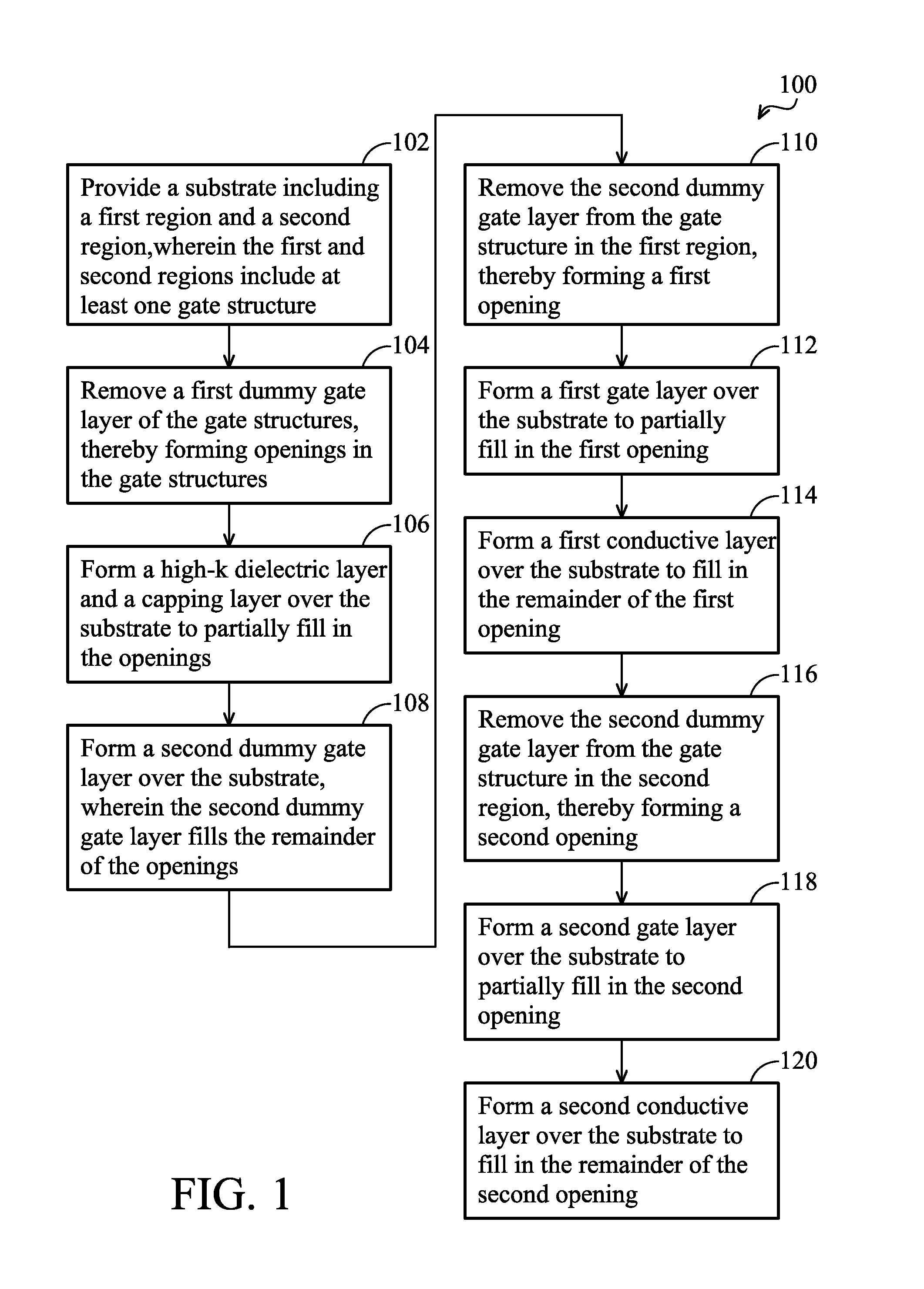
Methods for a gate replacement process
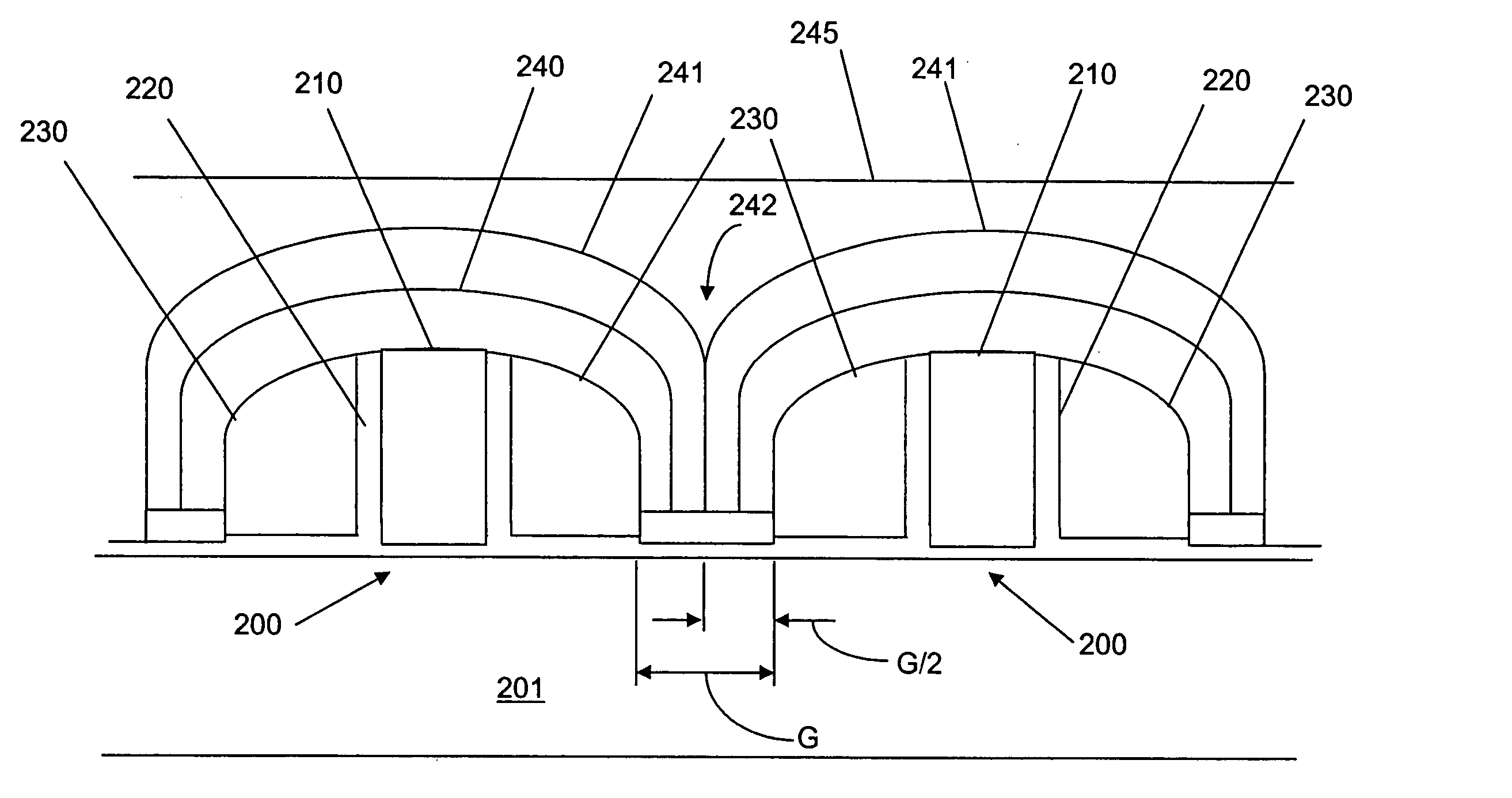
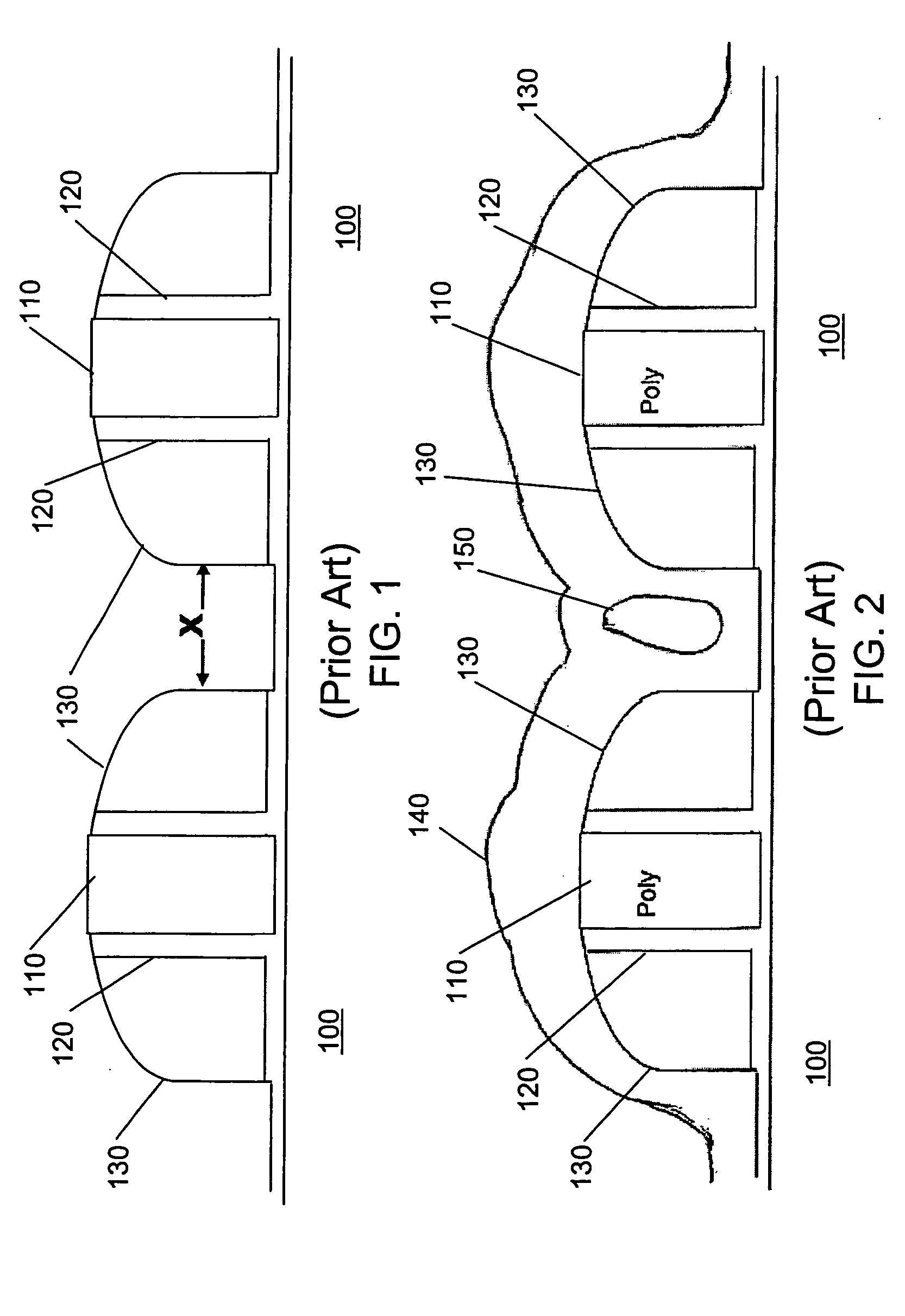
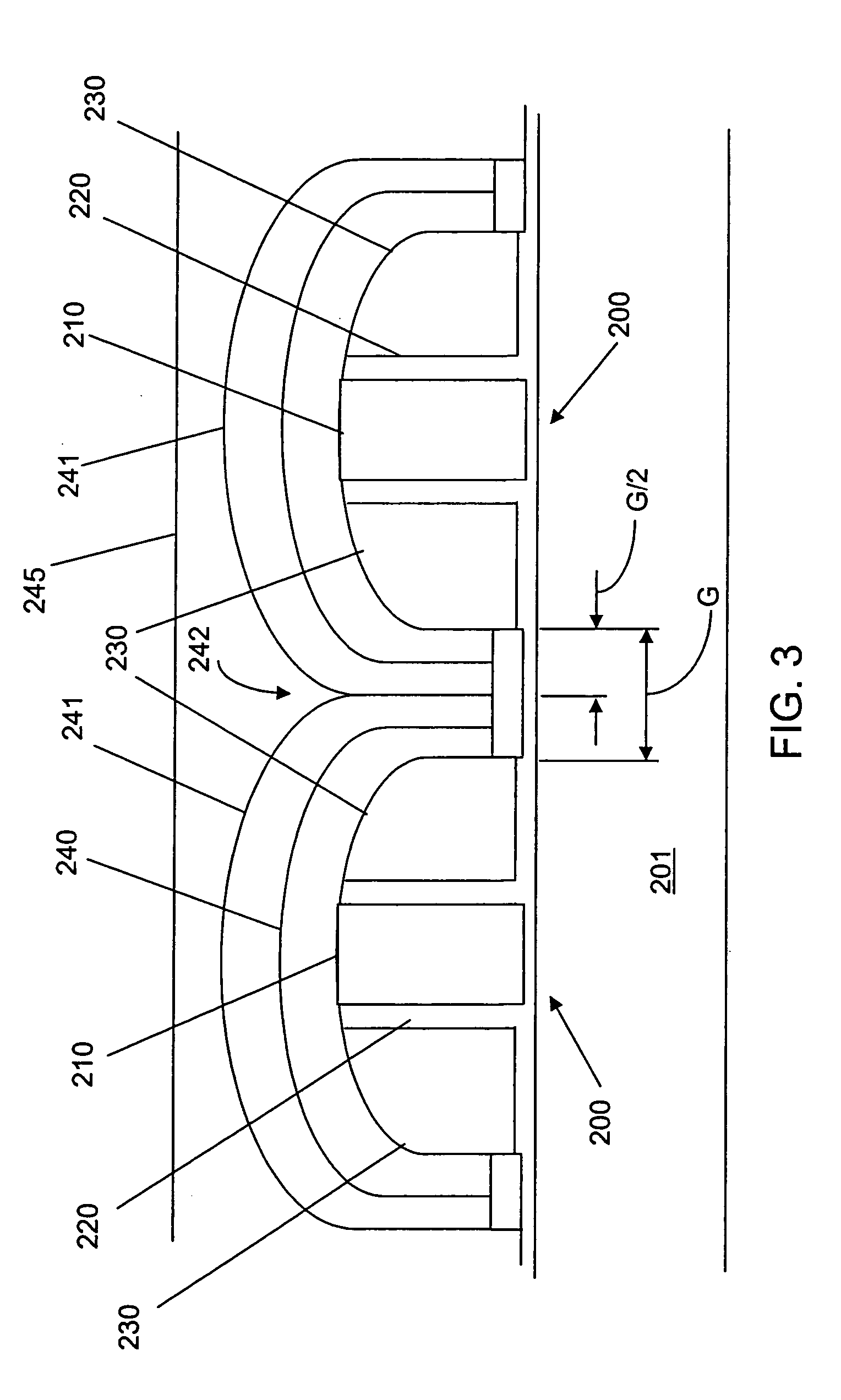
ActiveUS20110081774A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectric layerPartial filling
A method for fabricating a semiconductor device is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method may include providing a substrate; forming a gate structure including a first dummy gate over the substrate; removing the first dummy gate from the gate structure to form a trench; forming an interfacial layer, high-k dielectric layer, and capping layer to partially fill in the trench; forming a second dummy gate over the capping layer, wherein the second dummy gate fills the trench; and replacing the second dummy gate with a metal gate. In one embodiment, the method may include providing a substrate; forming an interfacial layer over the substrate; forming a high-k dielectric layer over the interfacial layer; forming an etch stop layer over the high-k dielectric layer; forming a capping layer including a low thermal budget silicon over the etch stop layer; forming a dummy gate layer over the capping layer; forming a gate structure; and performing a gate replacement process.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
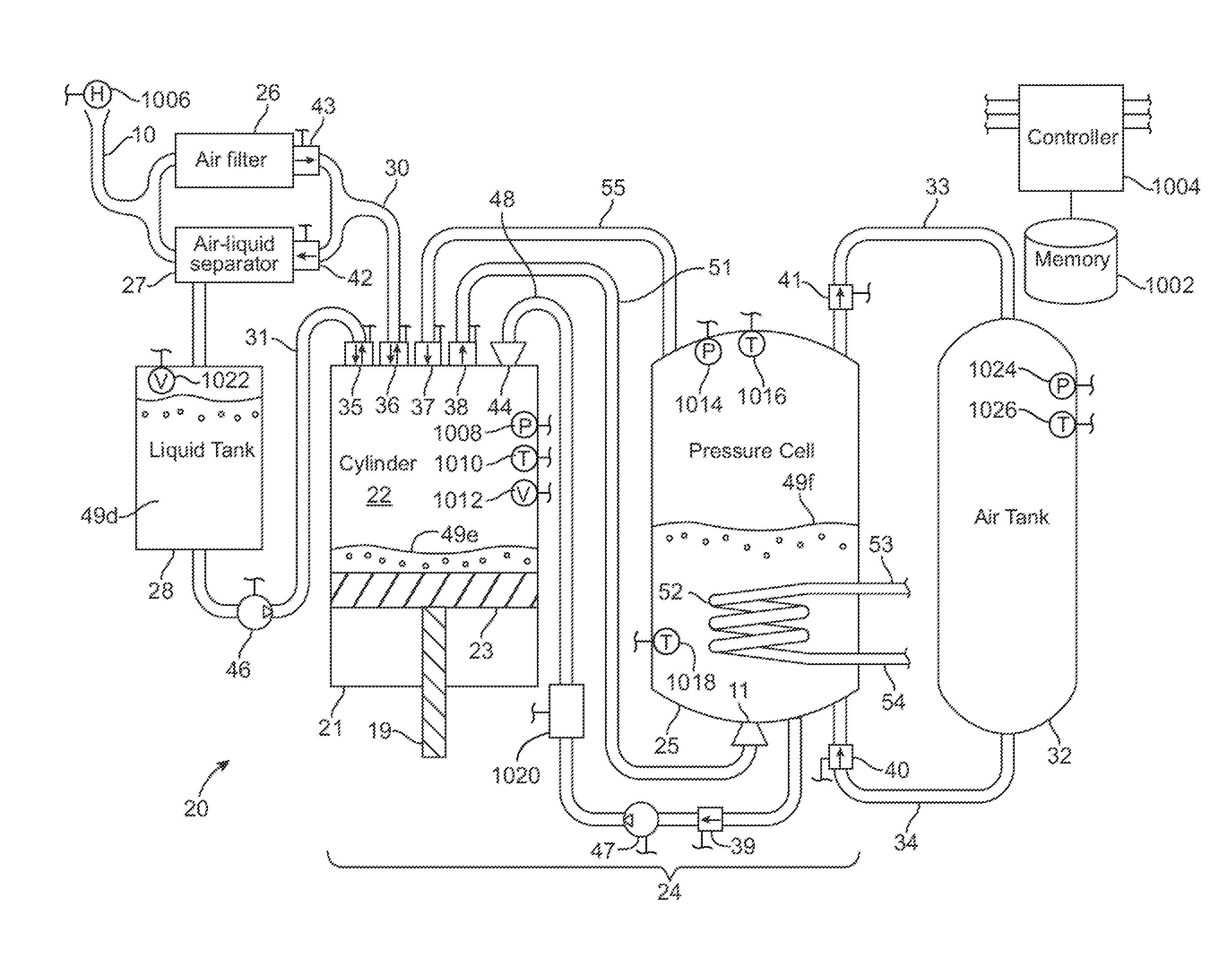
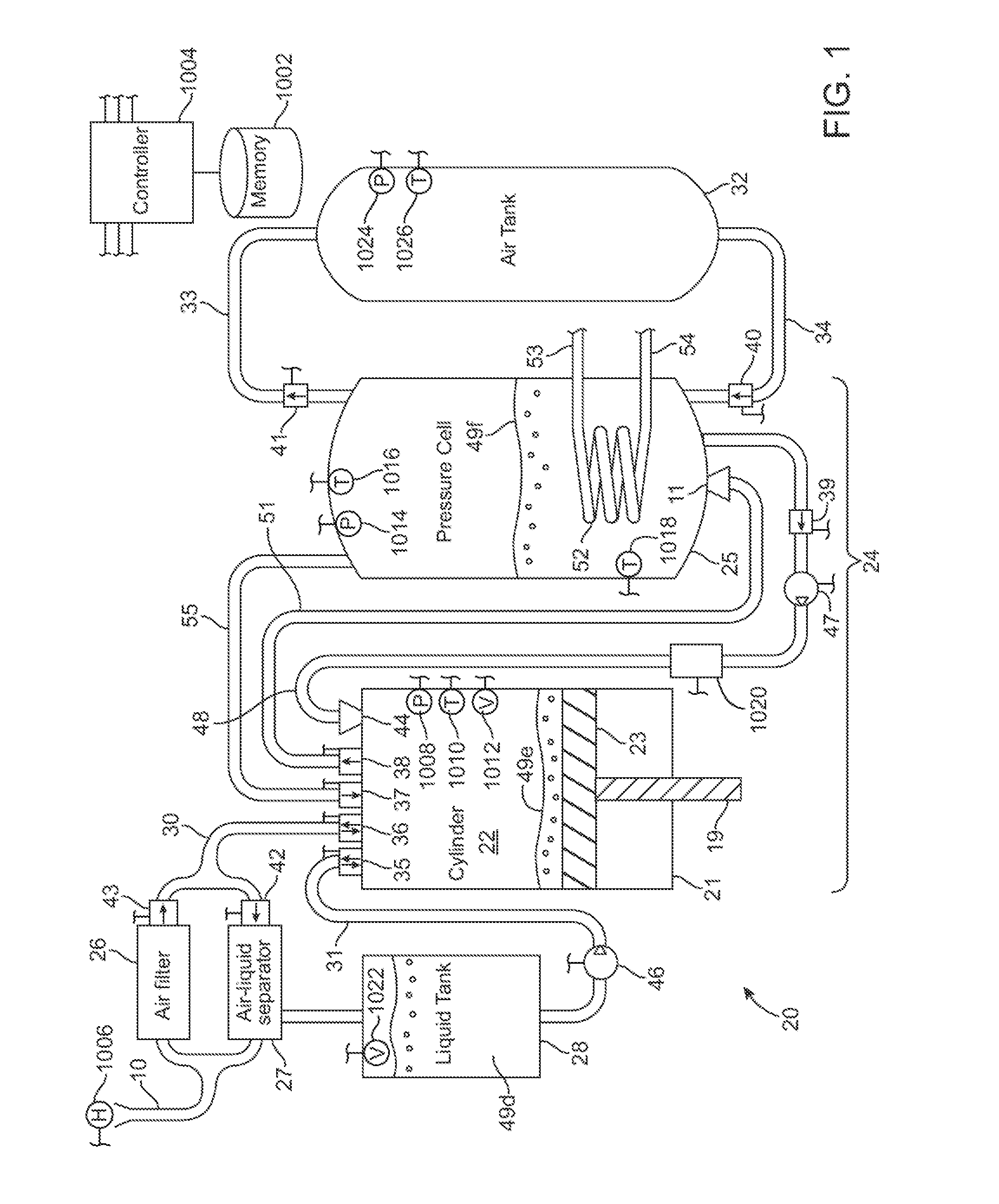
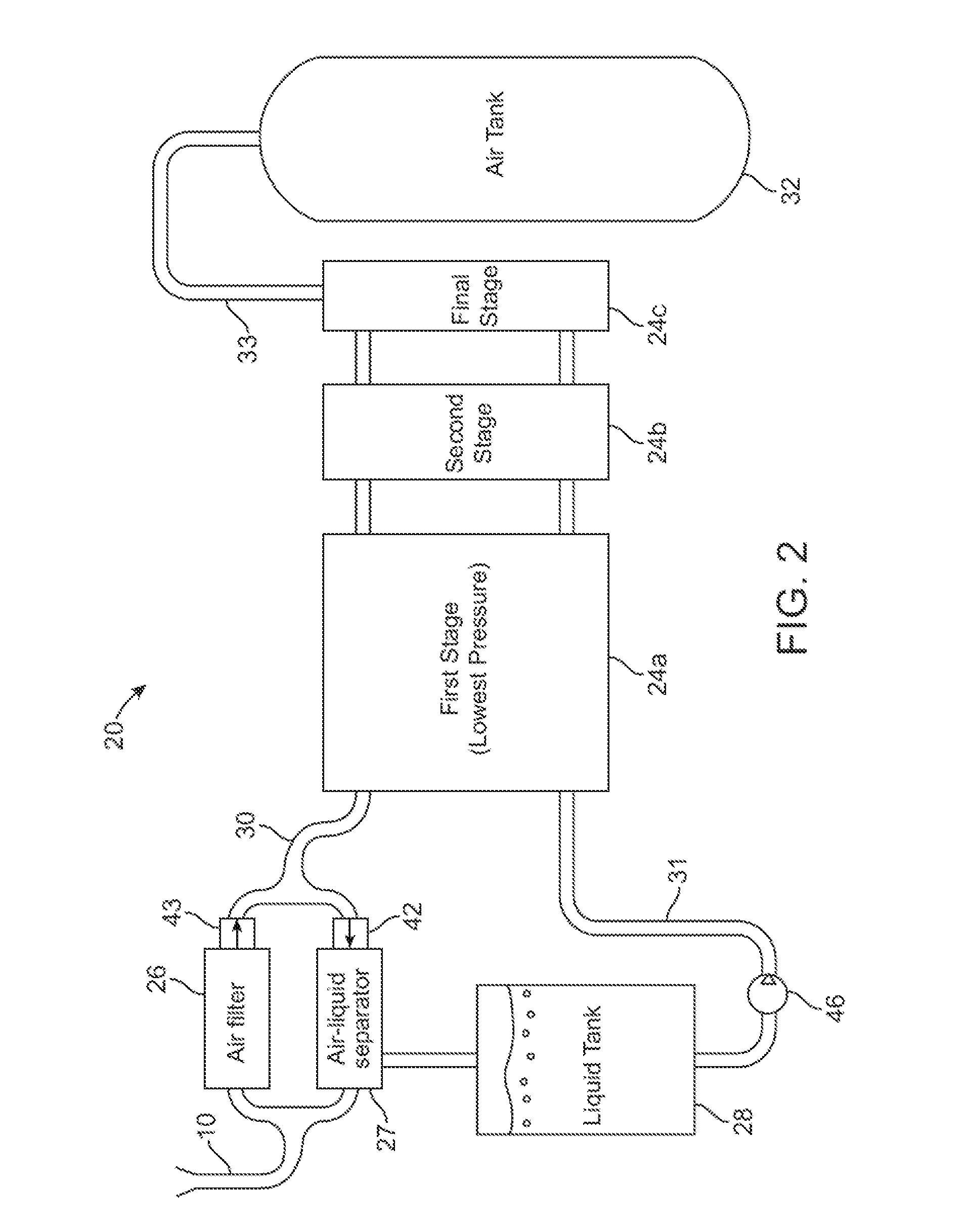
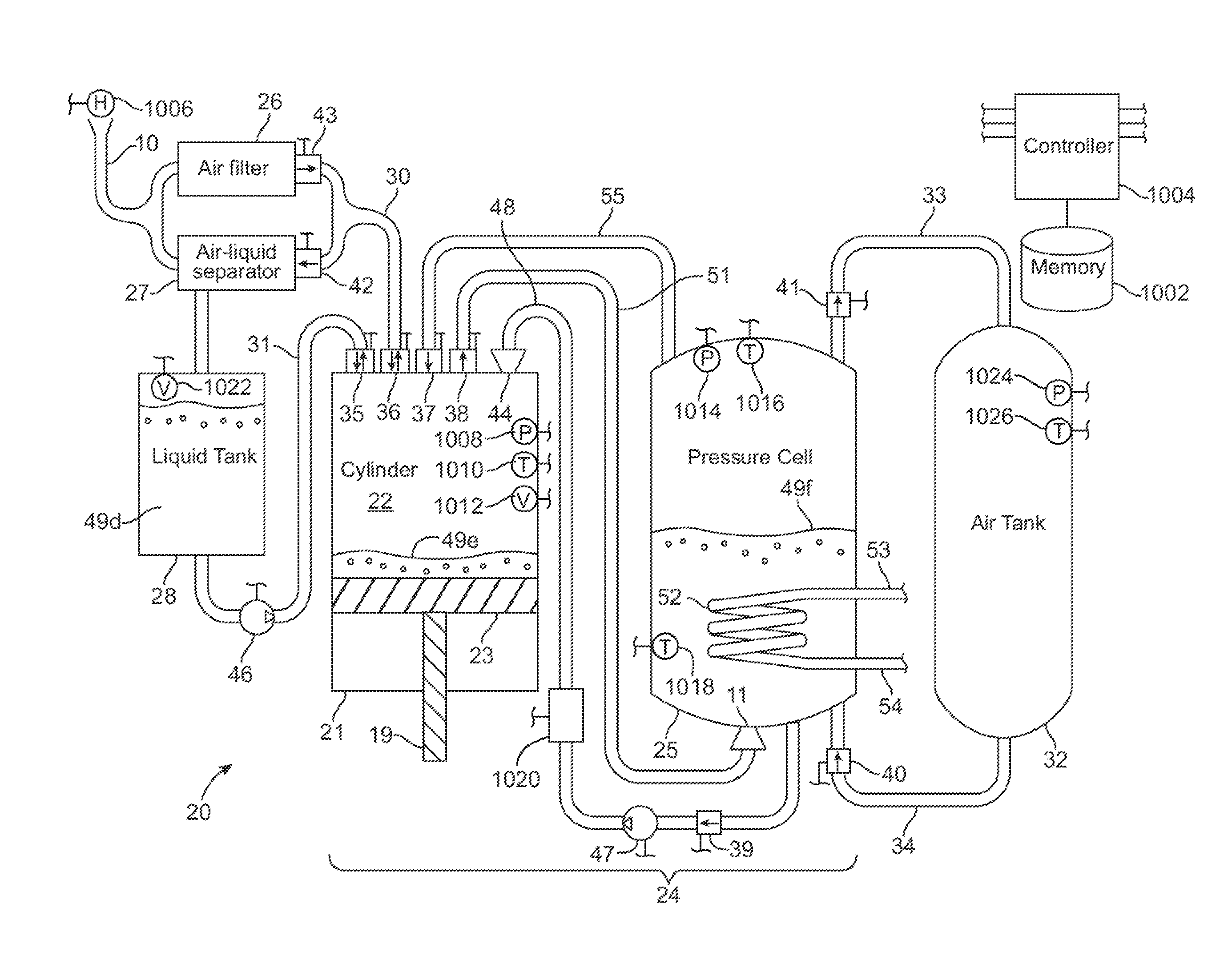
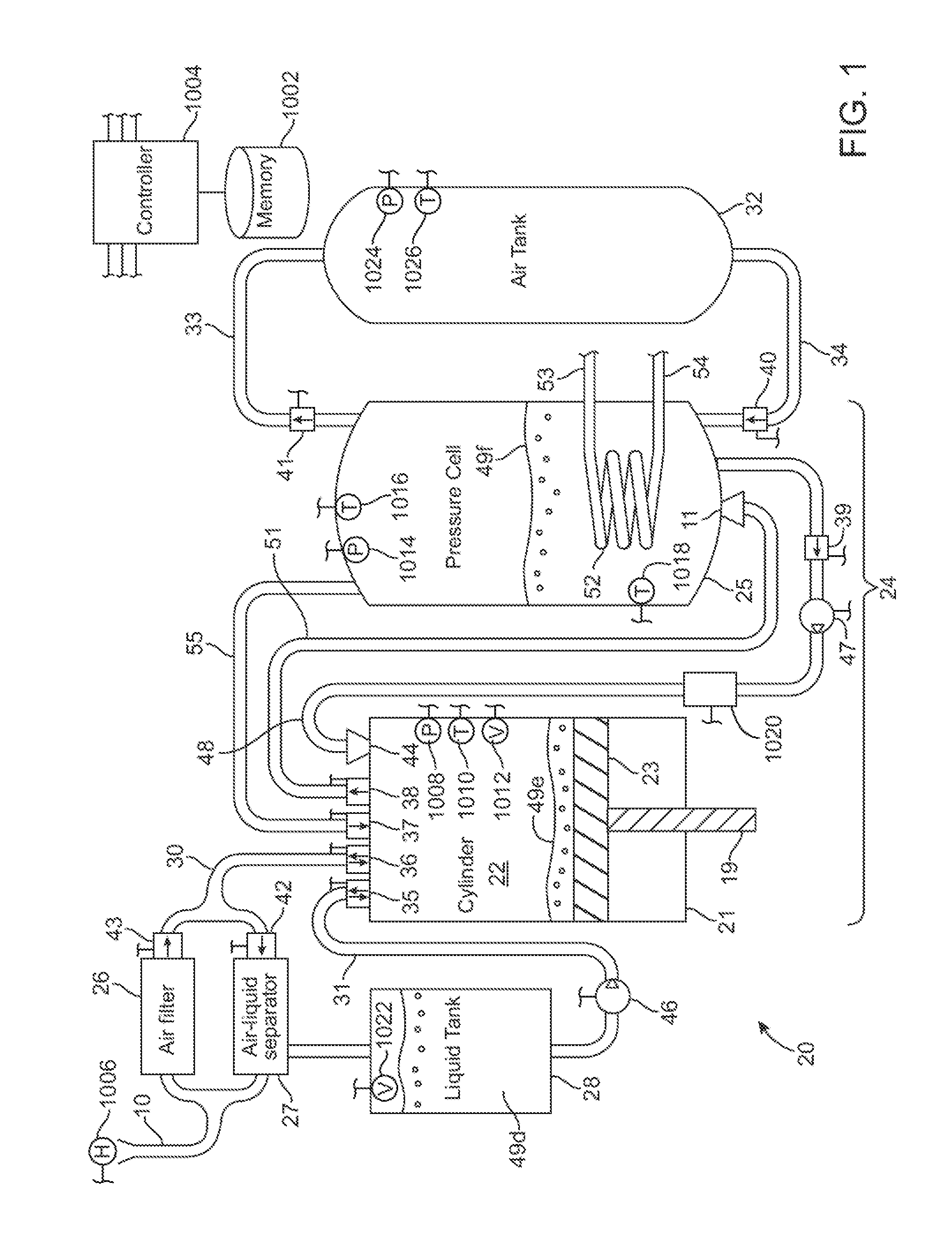
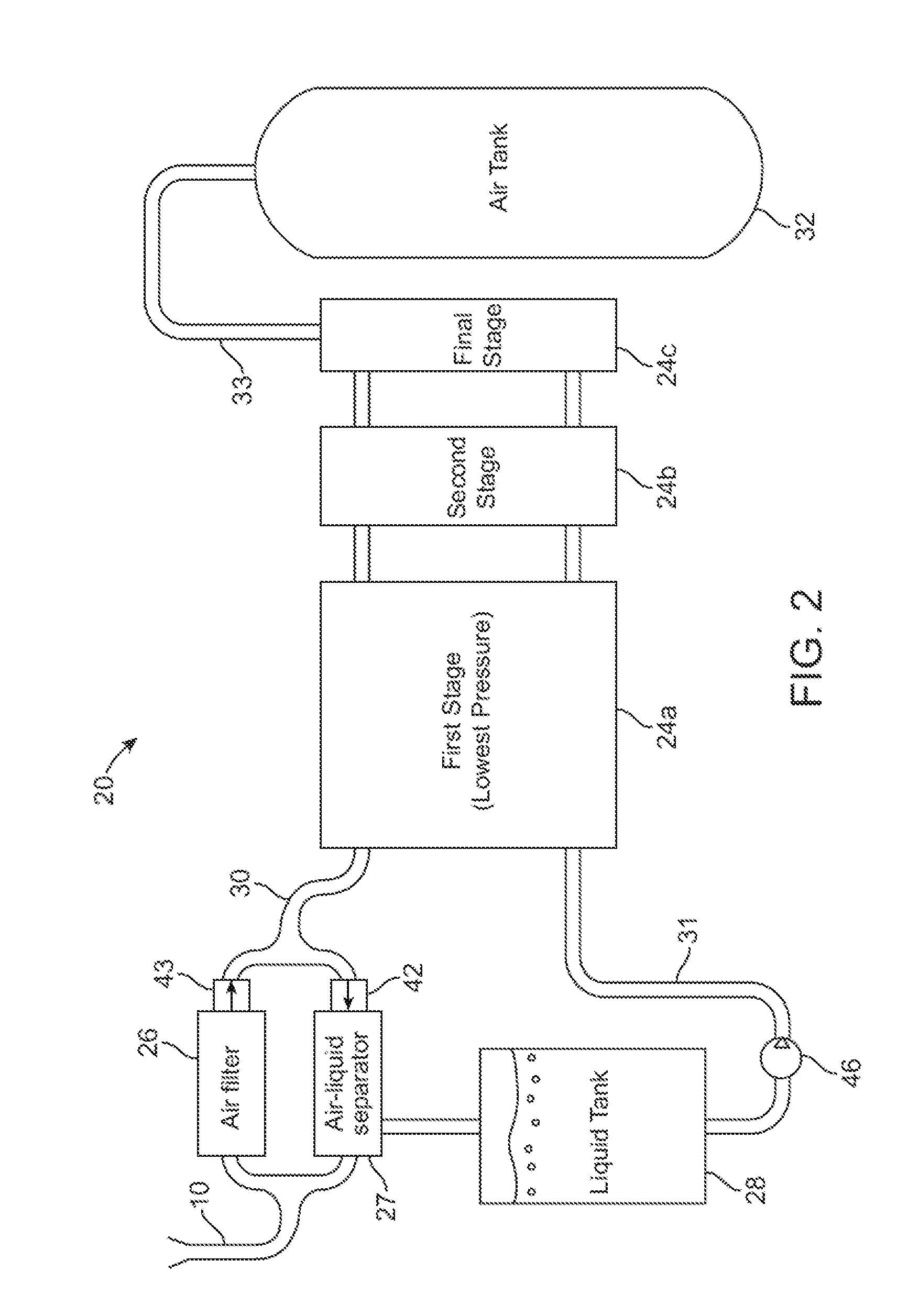
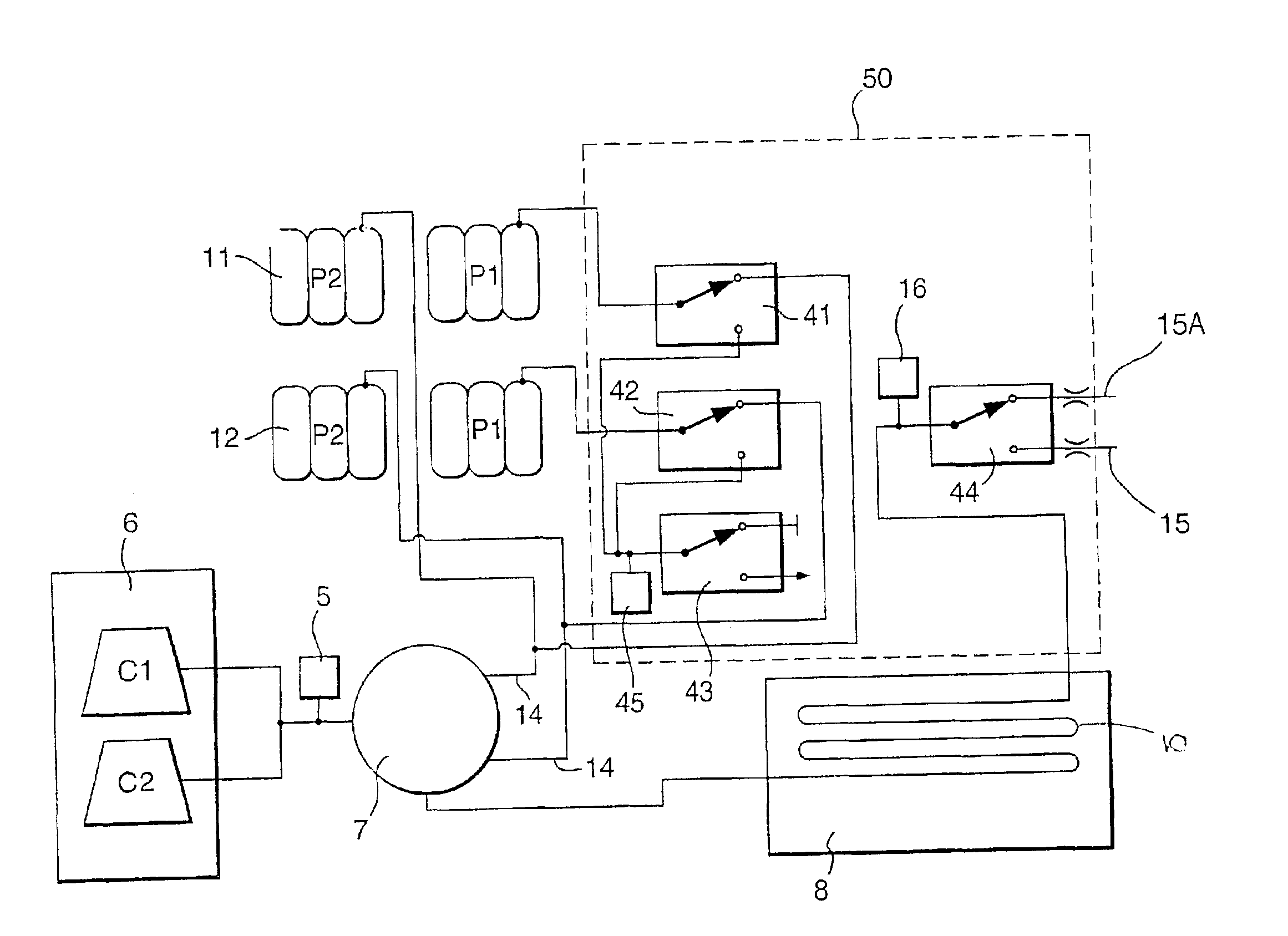
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326062A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Microfluidic method and device for transferring mass between two immiscible phases
InactiveUS8236156B2Mass productionLow costSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringPartial filling
A method of transferring mass of at least one solute between a liquid first phase and a fluid second phase that is immiscible with the first phase, the method comprising moving at least one droplet of said liquid first phase in a microfluidic device by using electric-type forces (electrowetting or dielectrophoresis) within a space that is filled with said fluid second phase. Said droplet is preferably moved by said electric-type forces along a path between a point for injecting said droplet into said microfluidic device, and an extraction and / or analysis zone, said path being defined in such a manner that said droplet sweeps through a significant fraction of said space filled with said fluid second phase. The method may include a step of transferring said droplet using said electric-type forces to a chemical analysis device integrated in said microfluidic device, and a step of chemically analyzing said droplet. The invention also provides a device for implementing such a method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Environmental Control System and Method
InactiveUS20080120335A1Enhances and simplifies comprehensionImprove efficiencyComputer controlElectric testing/monitoringGraphicsControl system
The sensors dialog box (100) can be used to serve two purposes, according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. First, it can allow the user to specify and change most of the settings of the sensors used in the system. When the user selects a sensor from the list of available sensors (1002), the rest of the sensors dialog (100) fills with information that describes and relates to the selected sensor. The name, type calibration, and check period of the sensor can be entered into the edit boxes (1004), in the preferred embodiment, manual entry can occur as long as the sensor is not linked to the calendar from the sensor log generator dialog box. This embodiment can also include an apply button (1006) and change sensor color for graphics button (1008). When the sensor is of type “EQUATION”, the information in an equation window (1010) will be parsed to tell the program how to interpret what the reading of the sensor is at any given time.
Owner:DOLGOFF ALEXEI
Lithium storage battery comprising a current-electrode collector assembly with expansion cavities and method for producing same
InactiveUS20080153000A1Improve performanceEasy to implementFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsLithiumPartial filling
A lithium storage battery comprises a stack formed by a current collector comprising recessed zones, an electrode and a plurality of expansion cavities for the material forming the electrode. Each expansion cavity comprises at least one wall formed by a part of the electrode. Preferably the electrode is an electrode formed by at least one material able to insert and de-insert Li+ ions, the volume of which material increases when Li+ ions are inserted. The empty volume of the expansion cavities can thus be at least partially filled by a part of the material forming the electrode when Li+ cations are inserted in the material. The expansion cavities are formed in the recessed zones of the current collector.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
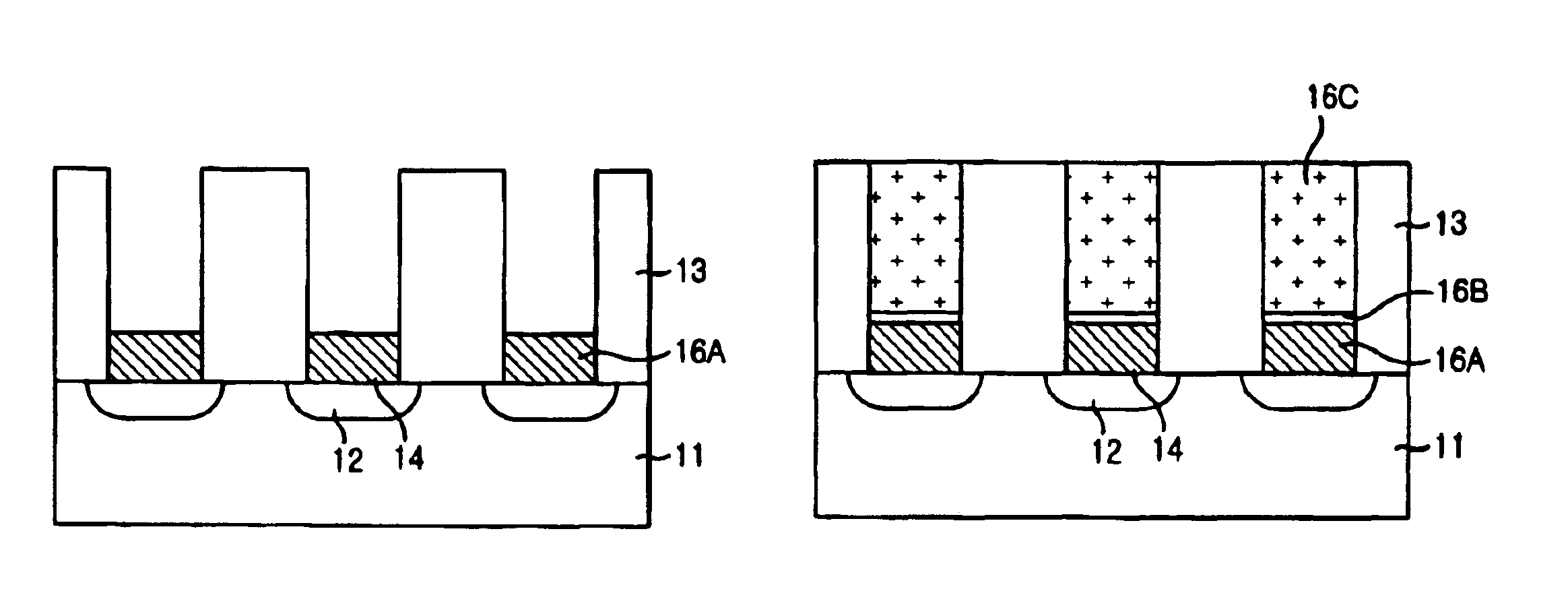
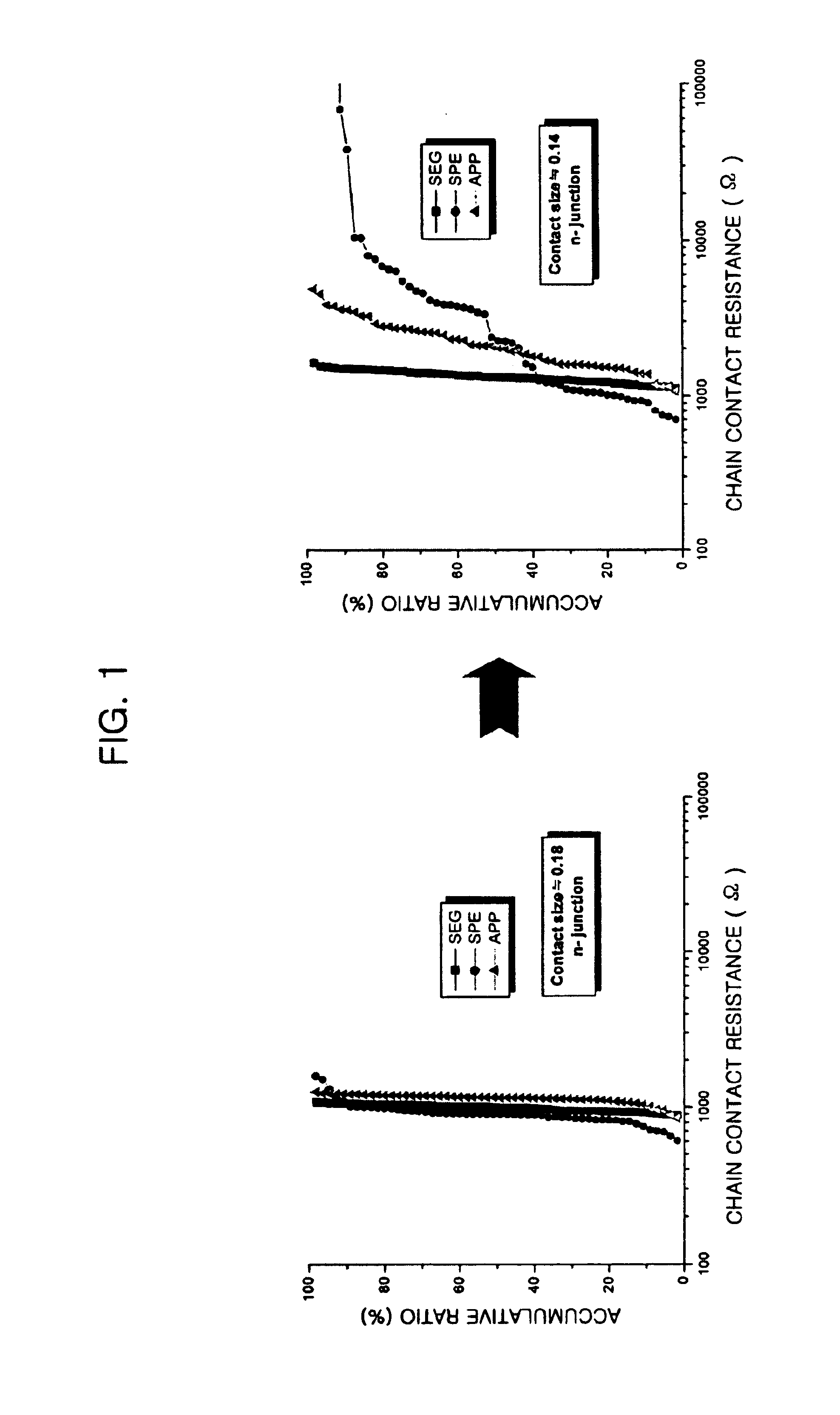
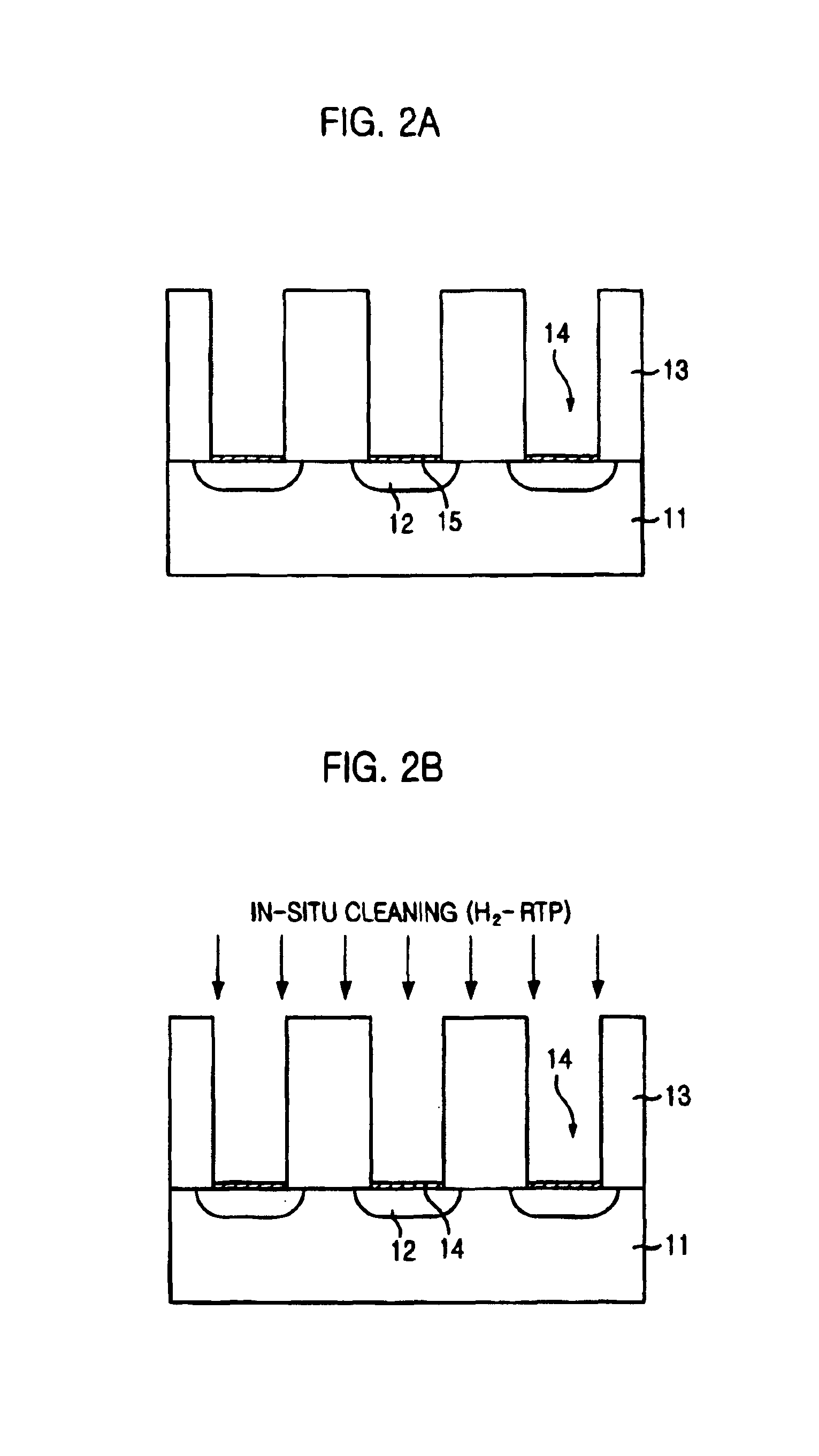
Method for forming contact plug in semiconductor device
InactiveUS6844259B2Reduce contact resistanceReduce uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon membraneEngineering
The present invention provides a method for forming a contact plug in a semiconductor device capable of preventing an increase of contact resistance even if the contact size becomes smaller and degradation of a step coverage property and of suppressing a decrease of uniformity in the contact resistance. The inventive method includes the steps of: a method for forming a contact plug in a semiconductor device, comprising the steps of: forming a contact hole by etching an insulating layer on a substrate; forming a first silicon film with a first doping concentration on the substrate in the contact hole so that the contact hole is partially filled; flushing a doping gas on a surface of the first silicon film; and forming a second silicon film having a second doping concentration higher than the first doping concentration on the first silicon film until filling the contact hole.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
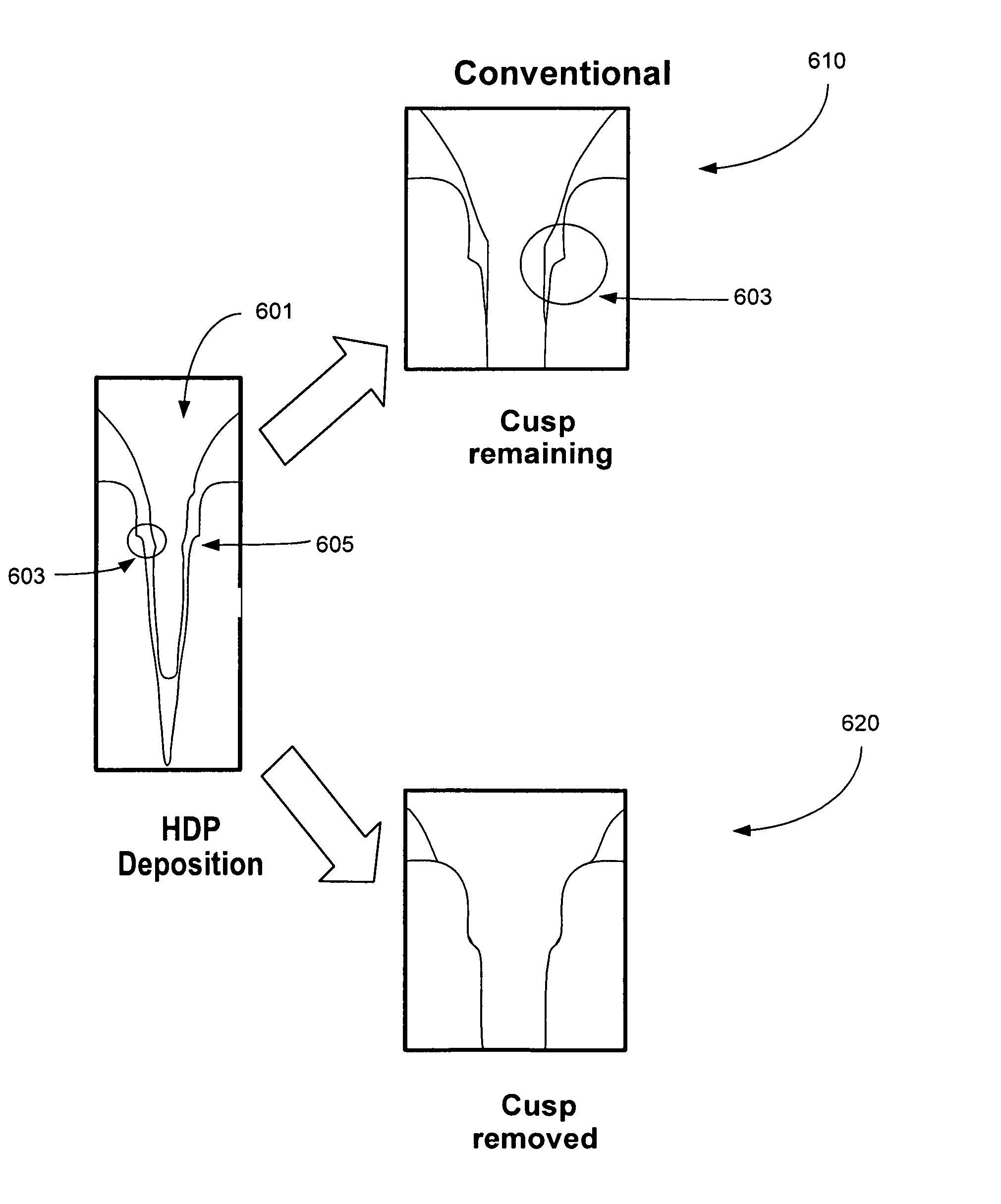
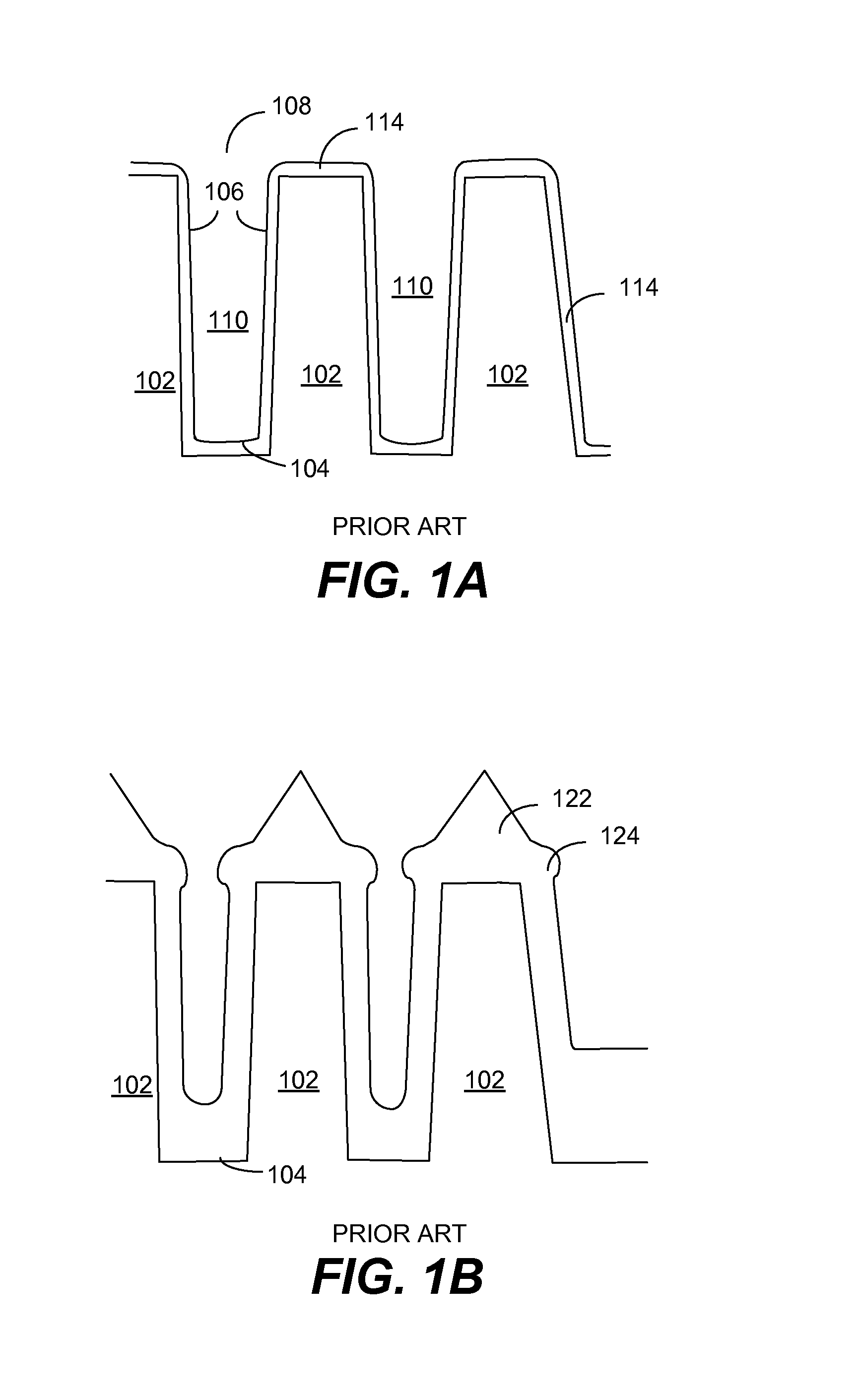
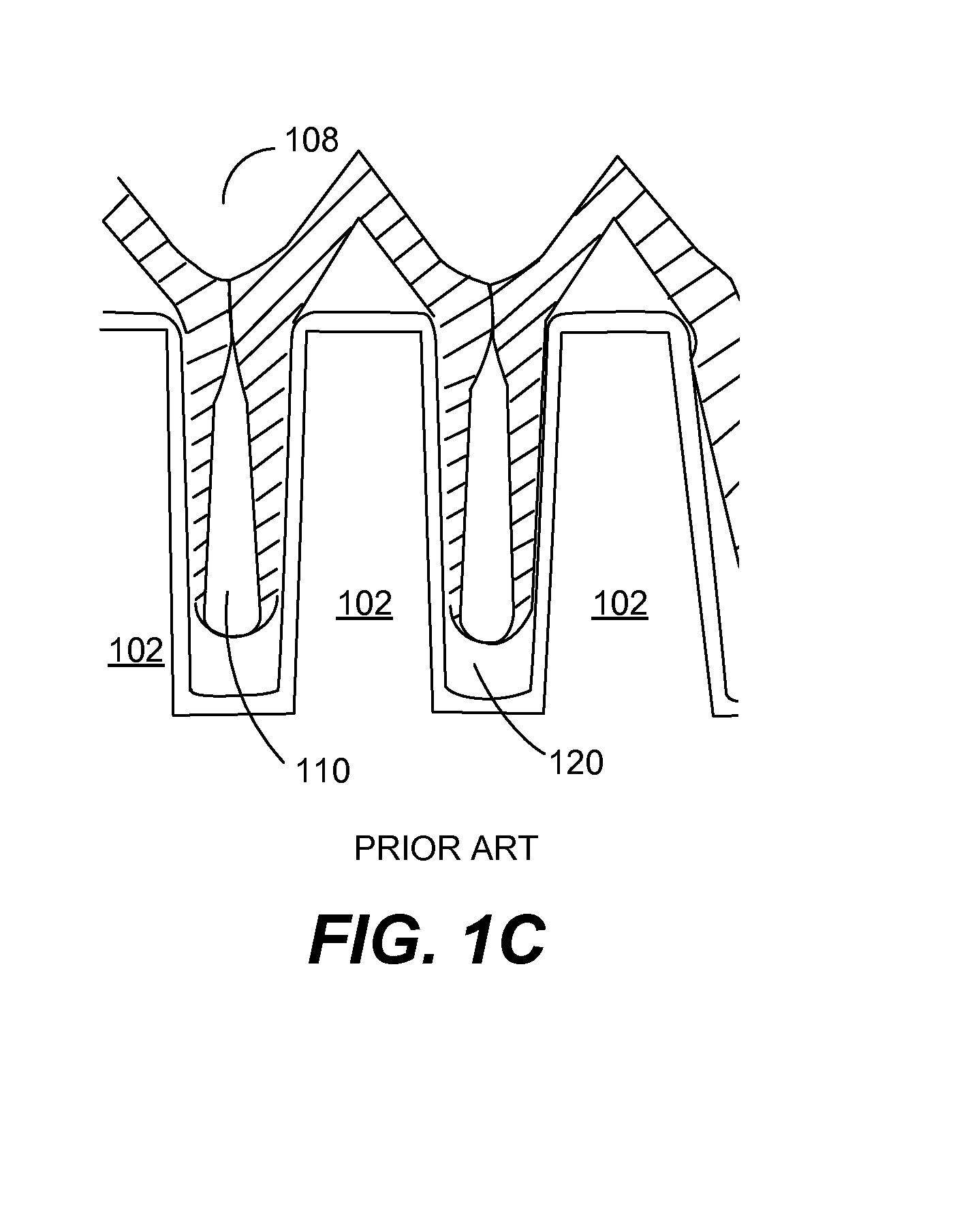
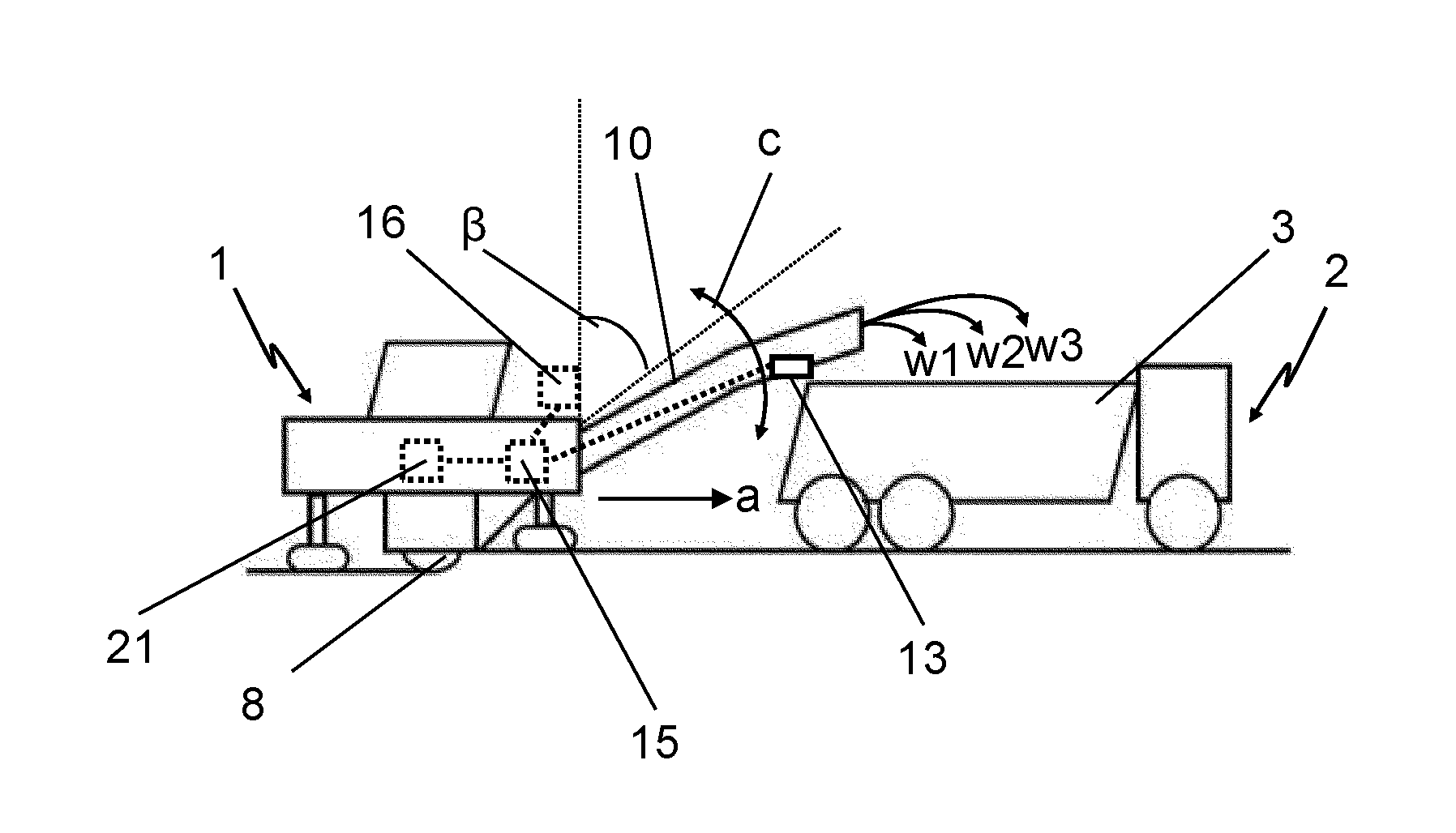
Atomic layer removal for high aspect ratio gapfill
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method For Controlling A Loading Process Of A Transport Vehicle With Milled Material, Device For Implementing Such A Method And A Milling Device
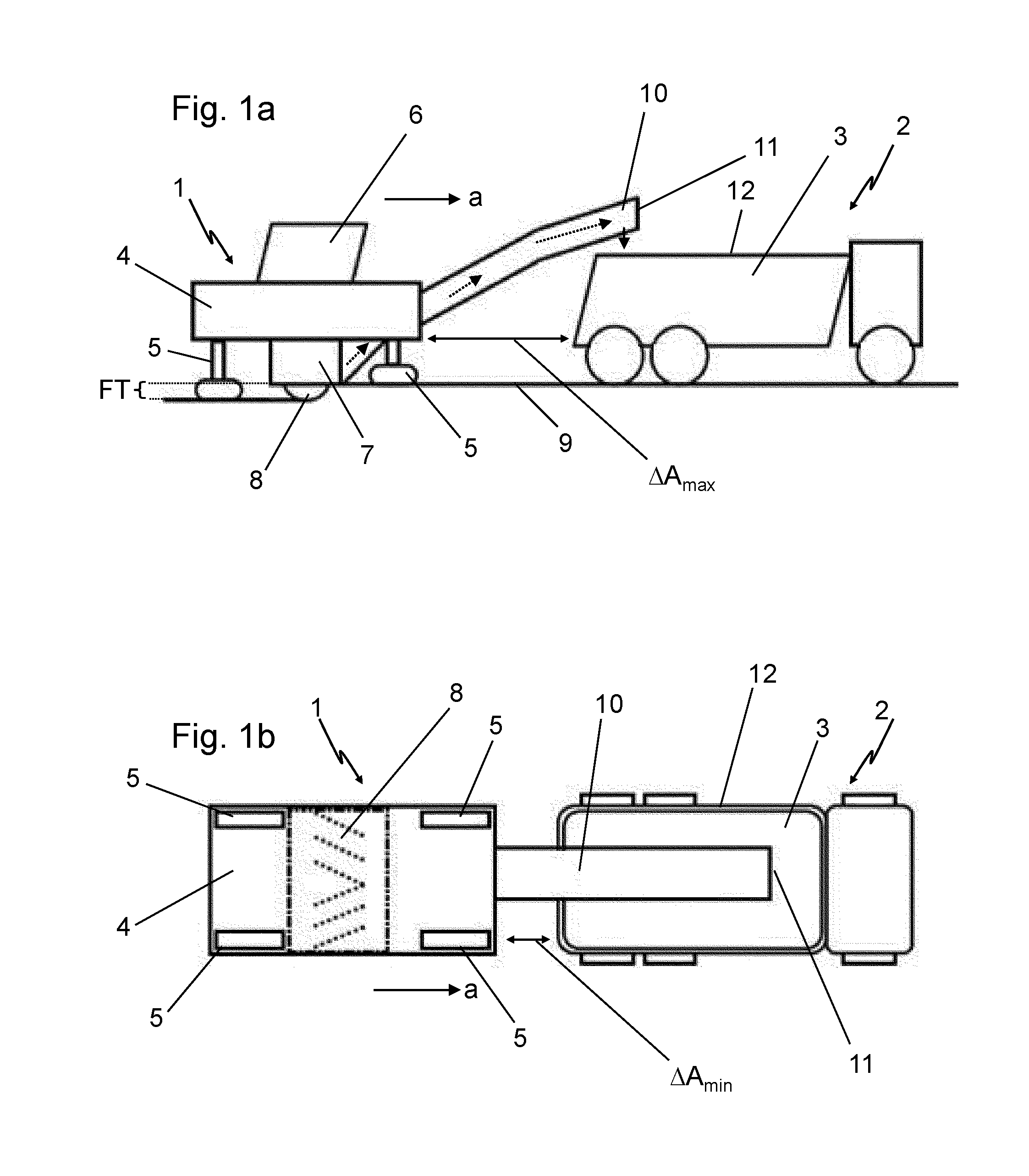
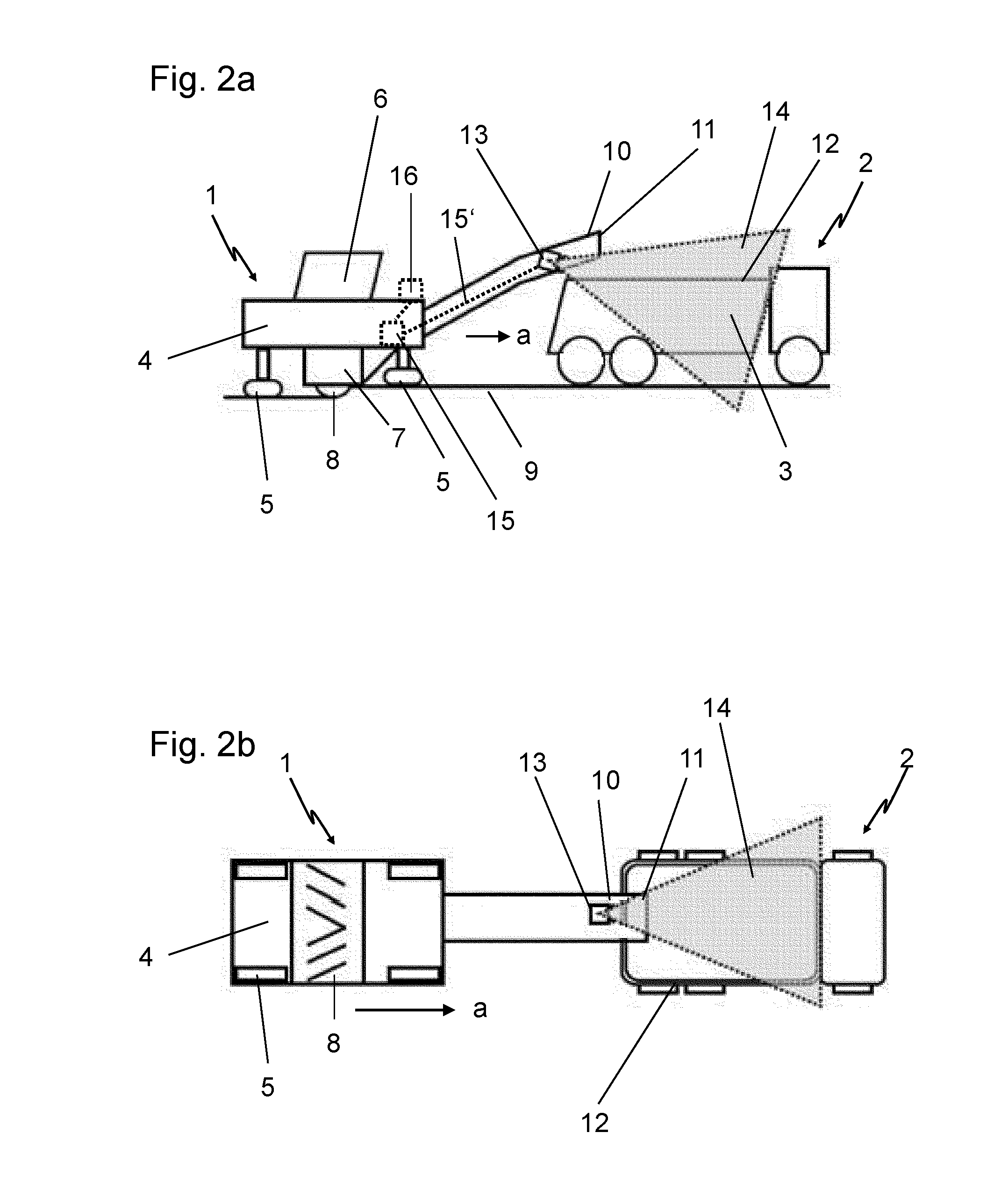
ActiveUS20130080000A1Improve accuracyMake fastRoads maintainenceLoading/unloadingRoad surfacePartial filling
The invention relates to a method for controlling a loading process of a transport vehicle by a milling device in milling operation, a device for implementing this method and a road milling machine or a device for the removal of soil material with such a device. An essential aspect of the invention is a sensor device by means of which the position and partially also the fill level of the transport container of the transport vehicle can be determined.
Owner:BOMAG
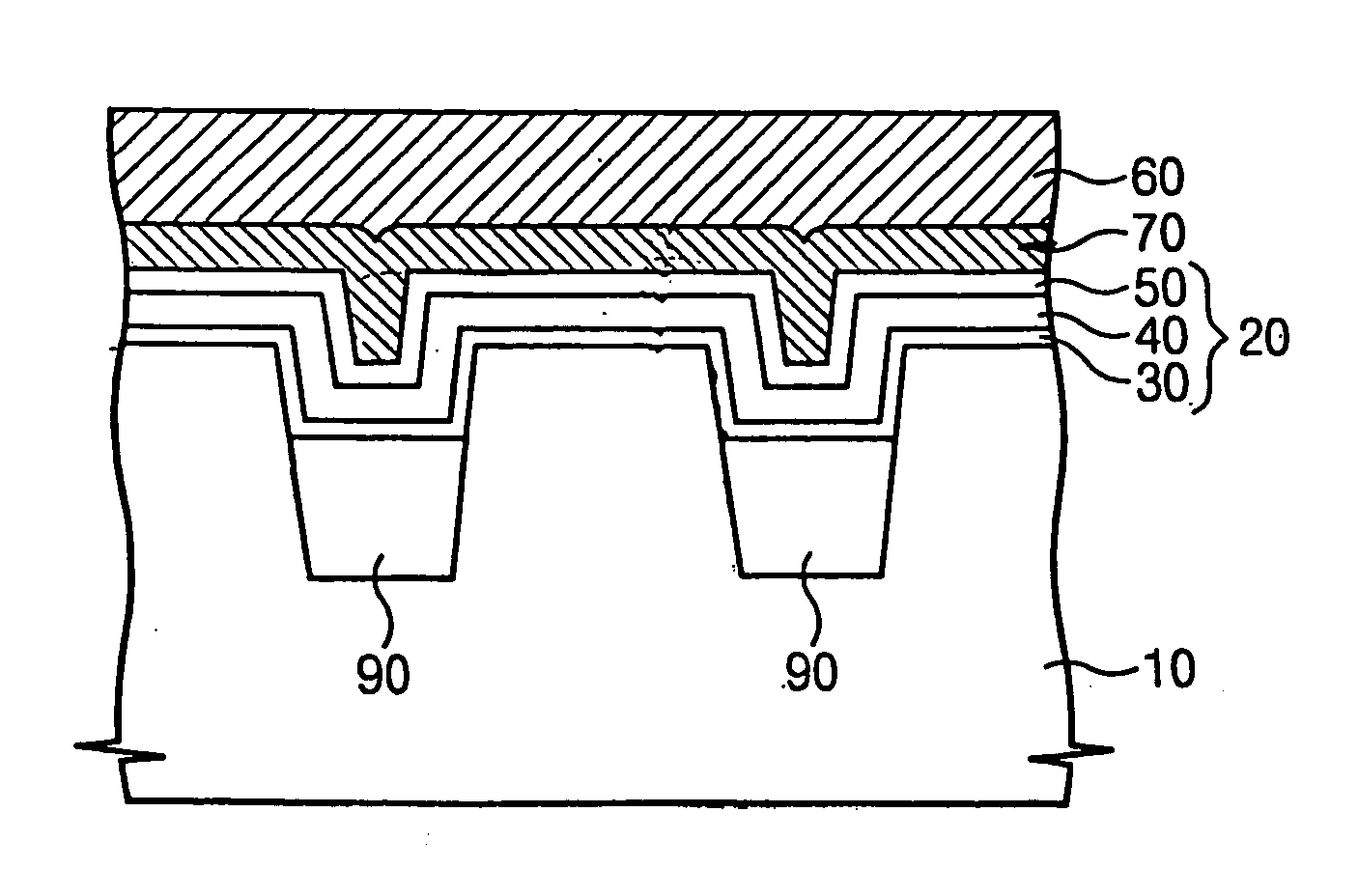
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and method of fabricating the same
In an example embodiment, a semiconductor substrate has a plurality of active regions separated by a plurality of trenches. A gate insulation film fills at least a portion of the trenches, and a conductive gate film is formed over the gate insulation film. In an example embodiment, the gate insulation film, may include a tunneling insulation film, a charge storage film, and a blocking insulation film. The example embodiment may also include field isolation films, which partially fill the trenches of the semiconductor substrate, such that the upper surfaces of the active regions or the substrate are higher than the upper surfaces of the field isolation films.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326069A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Inflatable support
InactiveUS6877178B2Small sizeEasy to decompressStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesDifferential pressureTransducer
A pressure pad has two sets of cells with a sensor pad positioned under the pad. During inflation, part of the flow goes to the sensor pad to exhaust and the rest fills the cells. Any change in patient position / weight causing a change in airflow in tube will alter the differential pressure measured at a pressure transducer. Based on this feedback a microprocessor directly controls the power level to the pump, thus adjusting the airflow to the cells to prevent bottoming or to rung at a minimum pressure. The pressure pad is segmented into a heel section, upper leg section, torso section, and a head section. The heel, head, and upper leg sections are maintained at a lower pressure, and the torso section at a higher pressure. A control module to control the flow in the segments is provided inside the pressure pad. The pressure pad can be an alternating or static pad.
Owner:HUNTLEIGH TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com