Patents
Literature
1983results about How to "Small surface area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
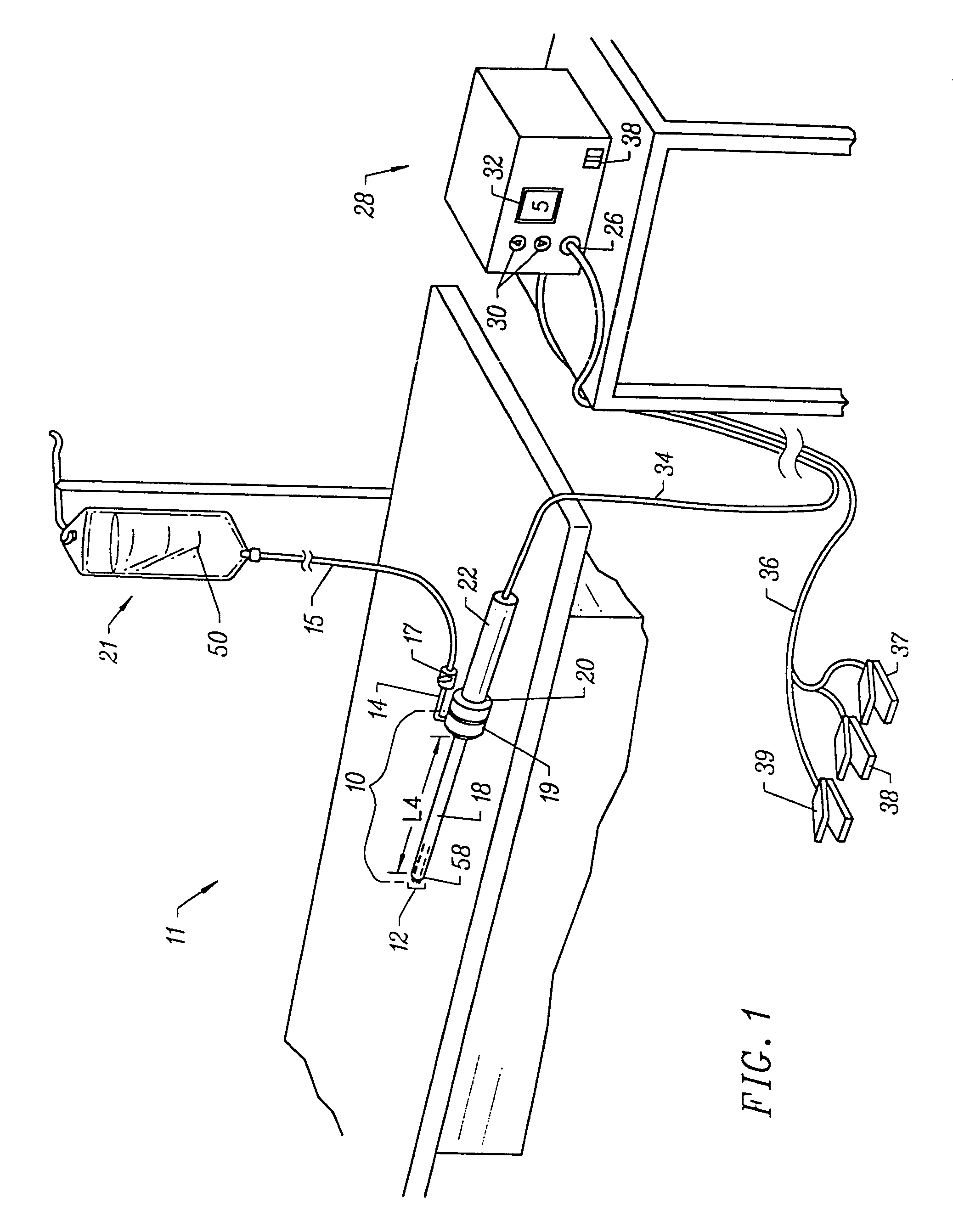
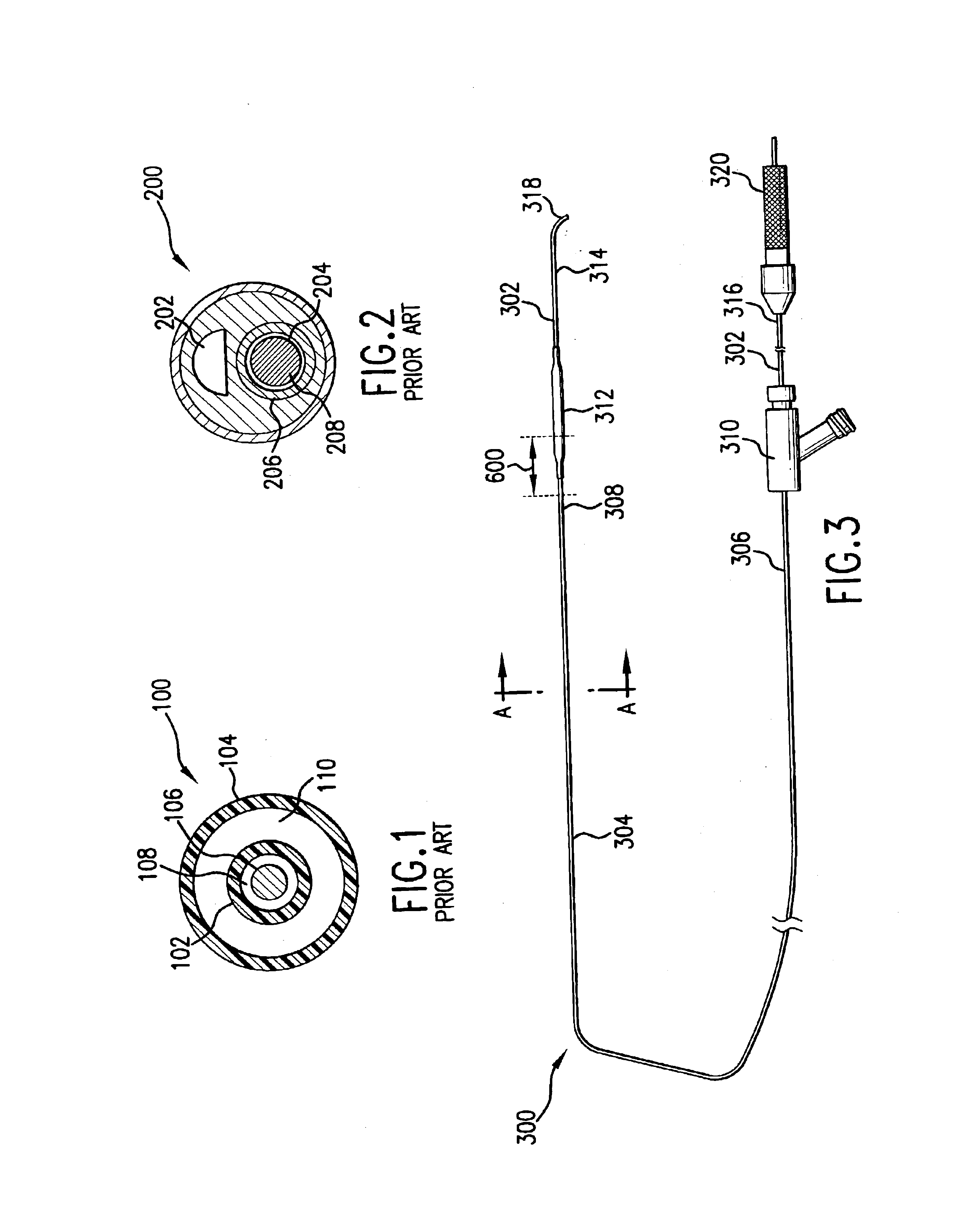
Methods for targeted electrosurgery on contained herniated discs
InactiveUS7179255B2Reduce pressureReduced neckingEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesFibrous ringCorneal ablation
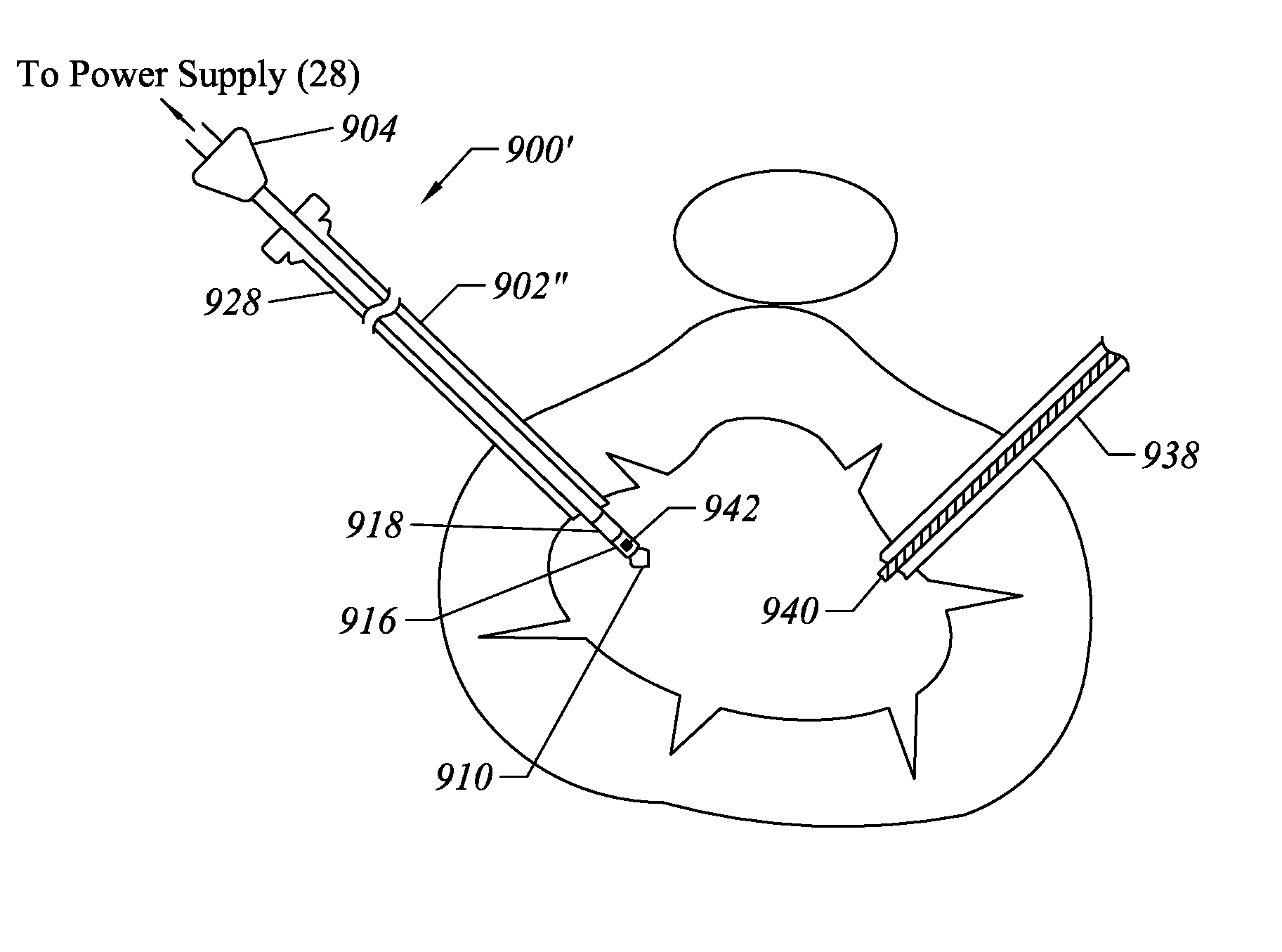
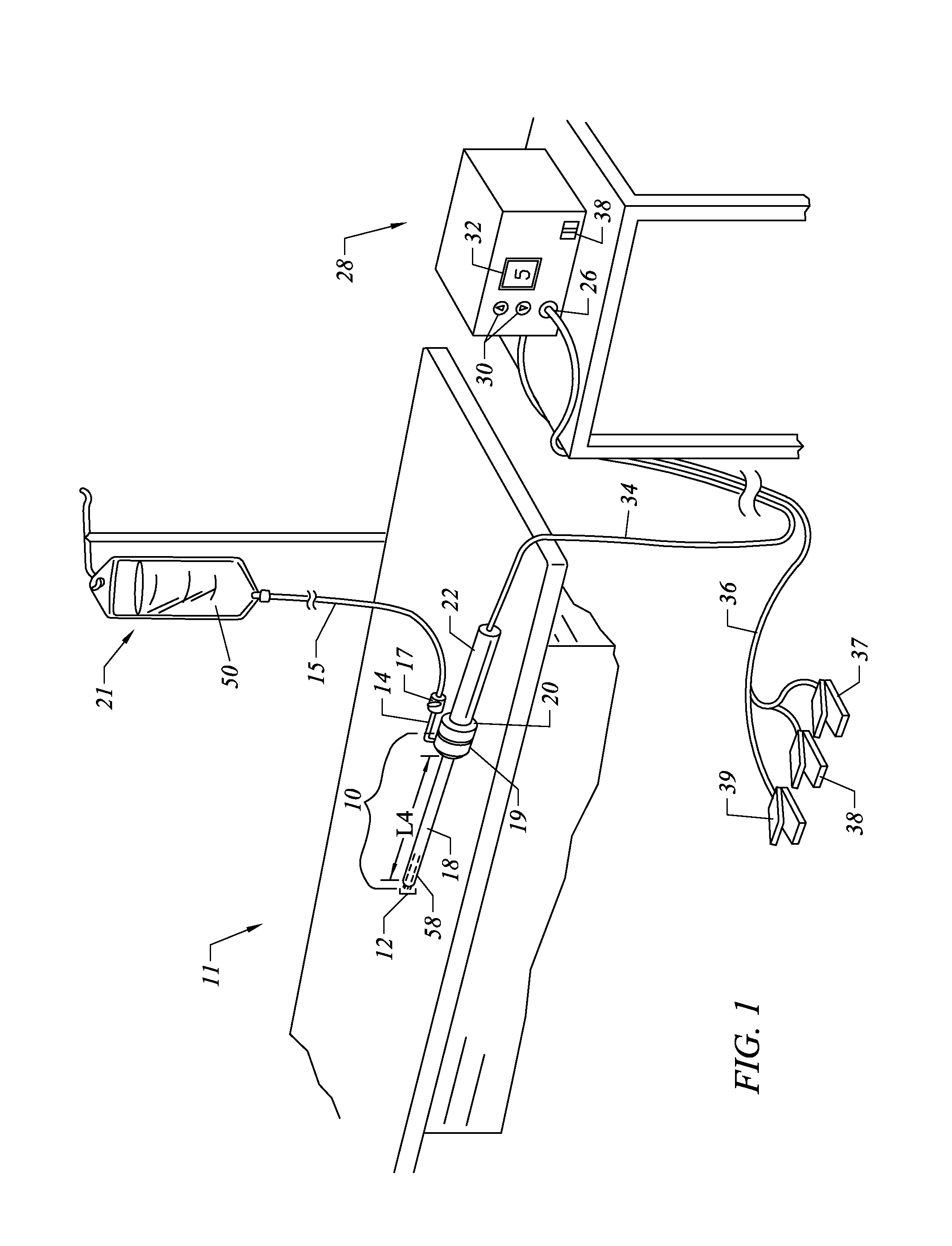
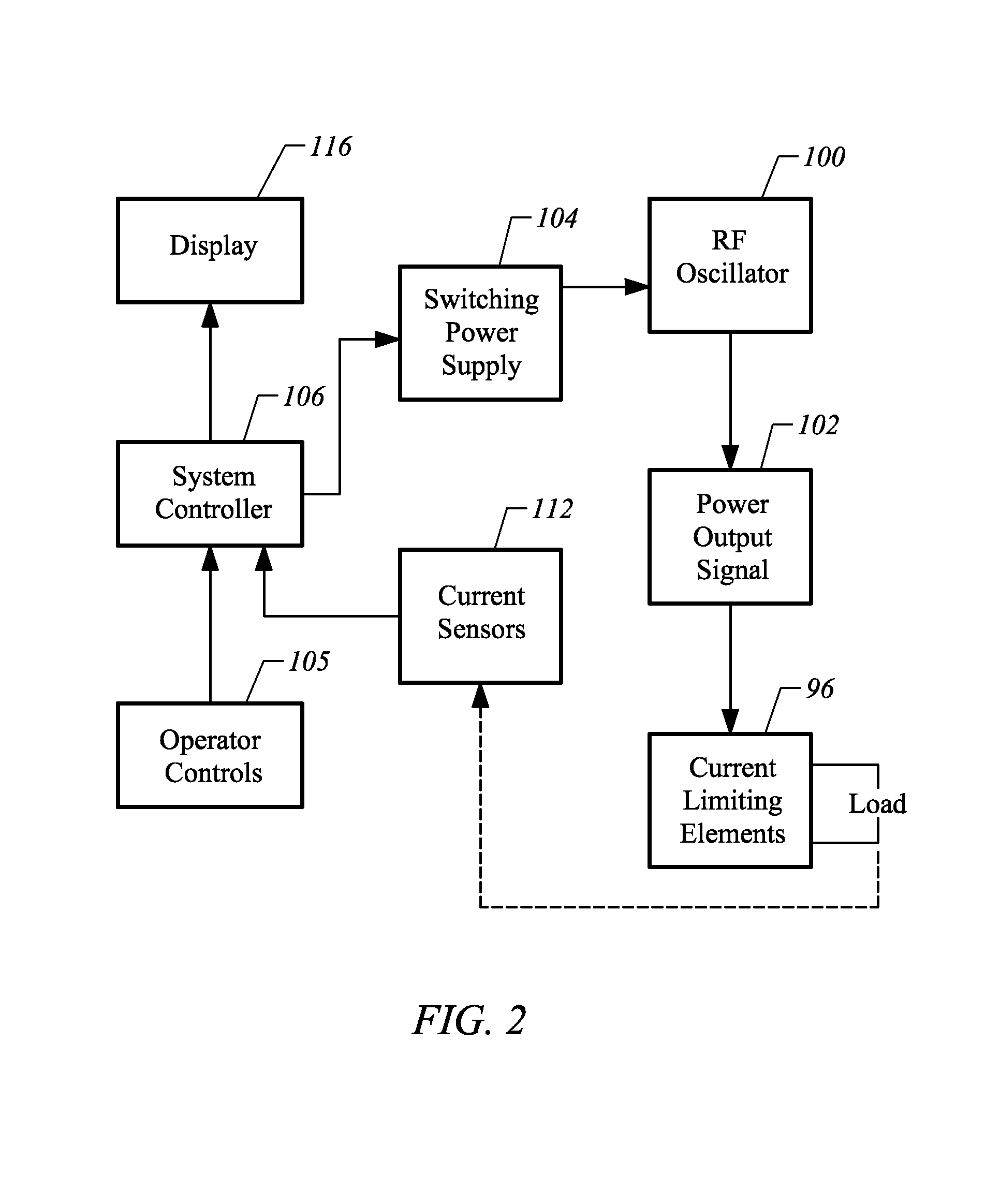
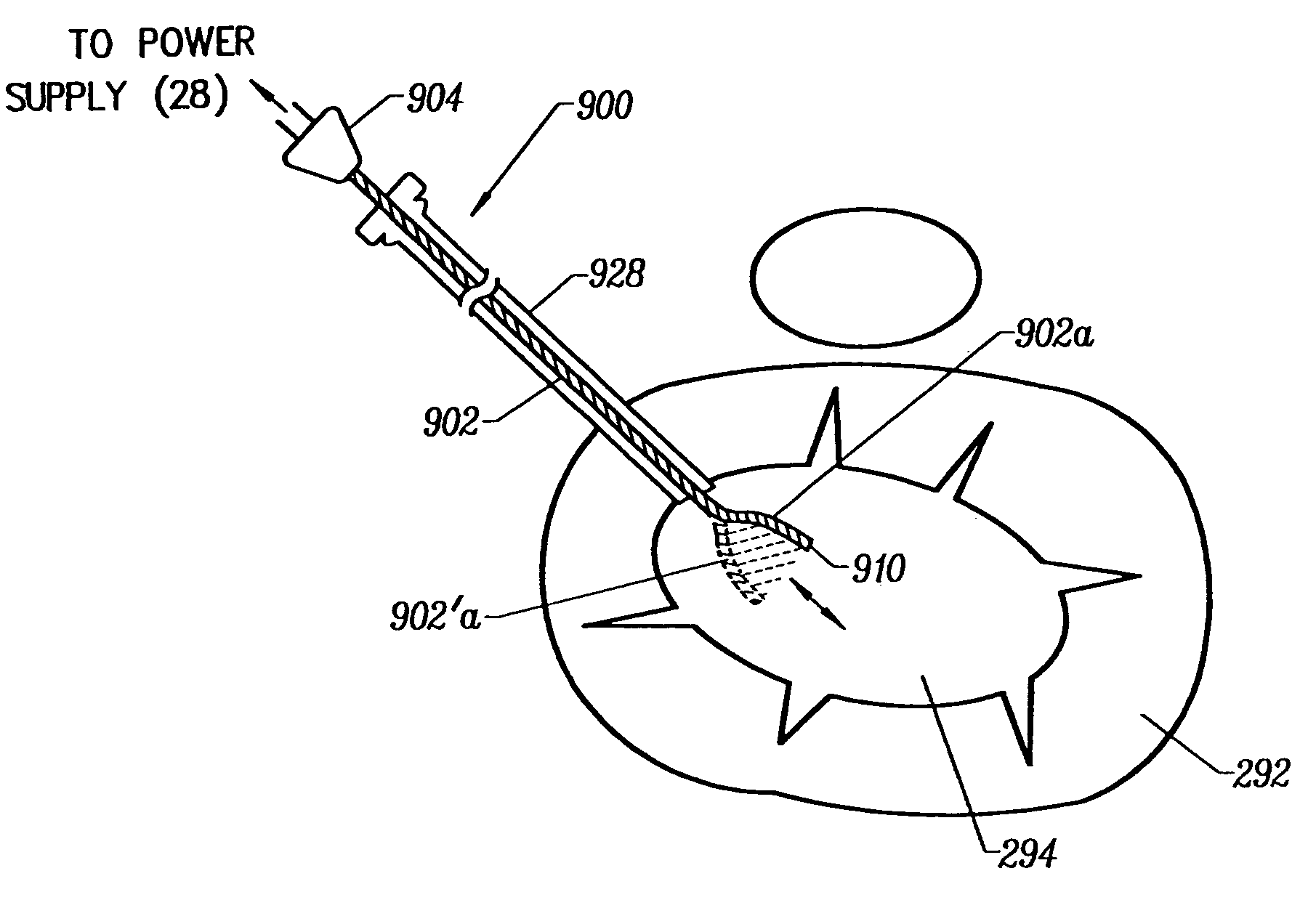
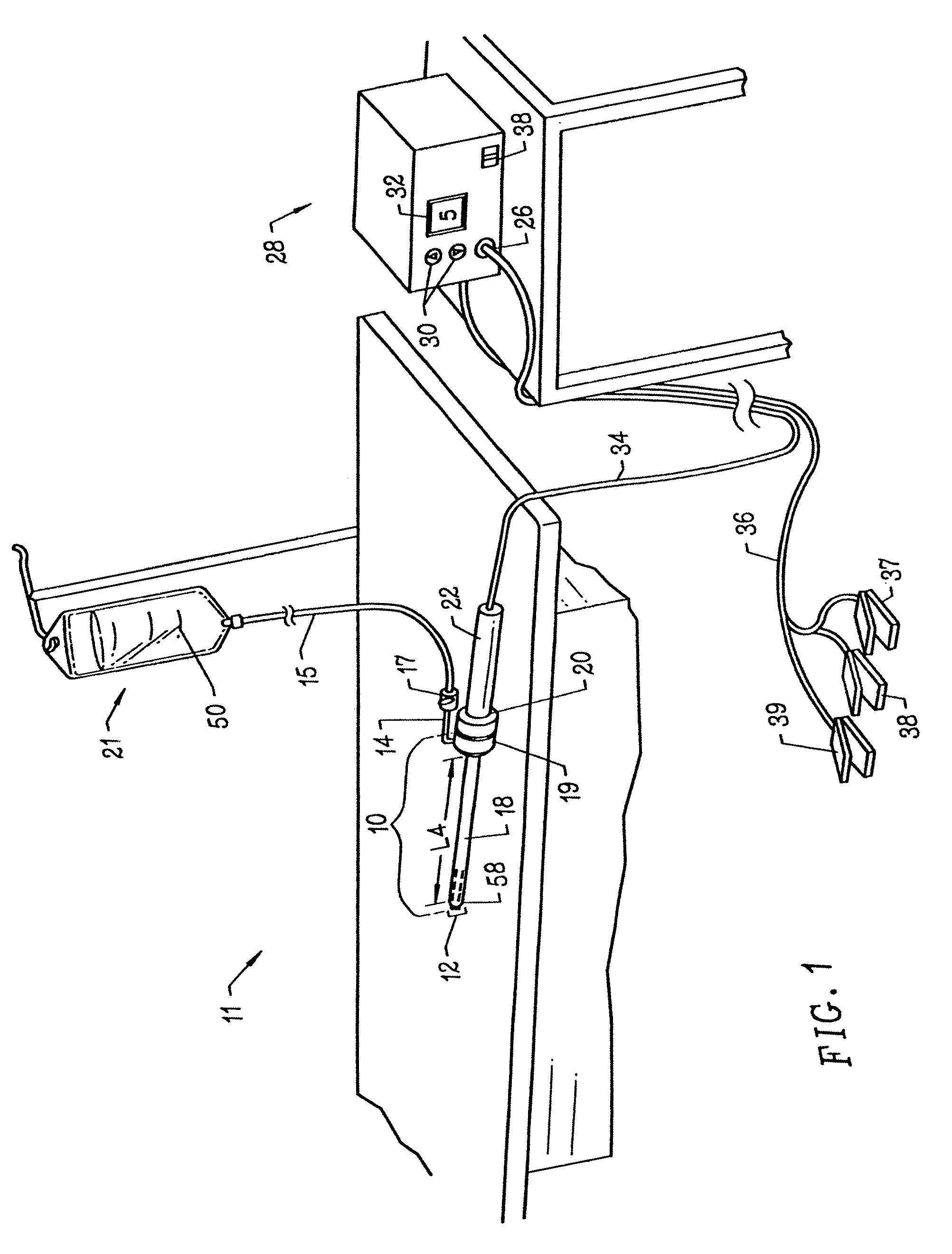
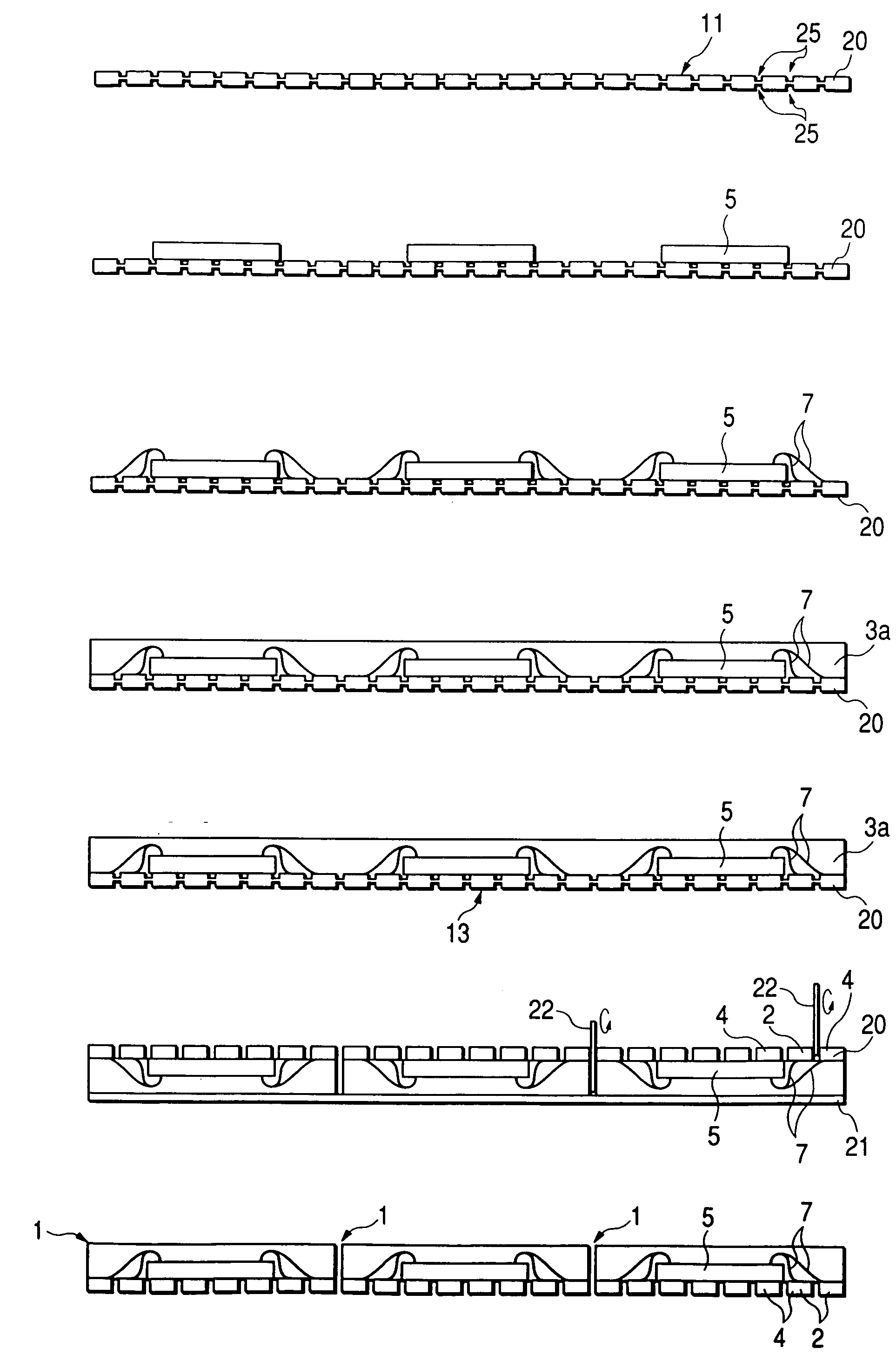
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
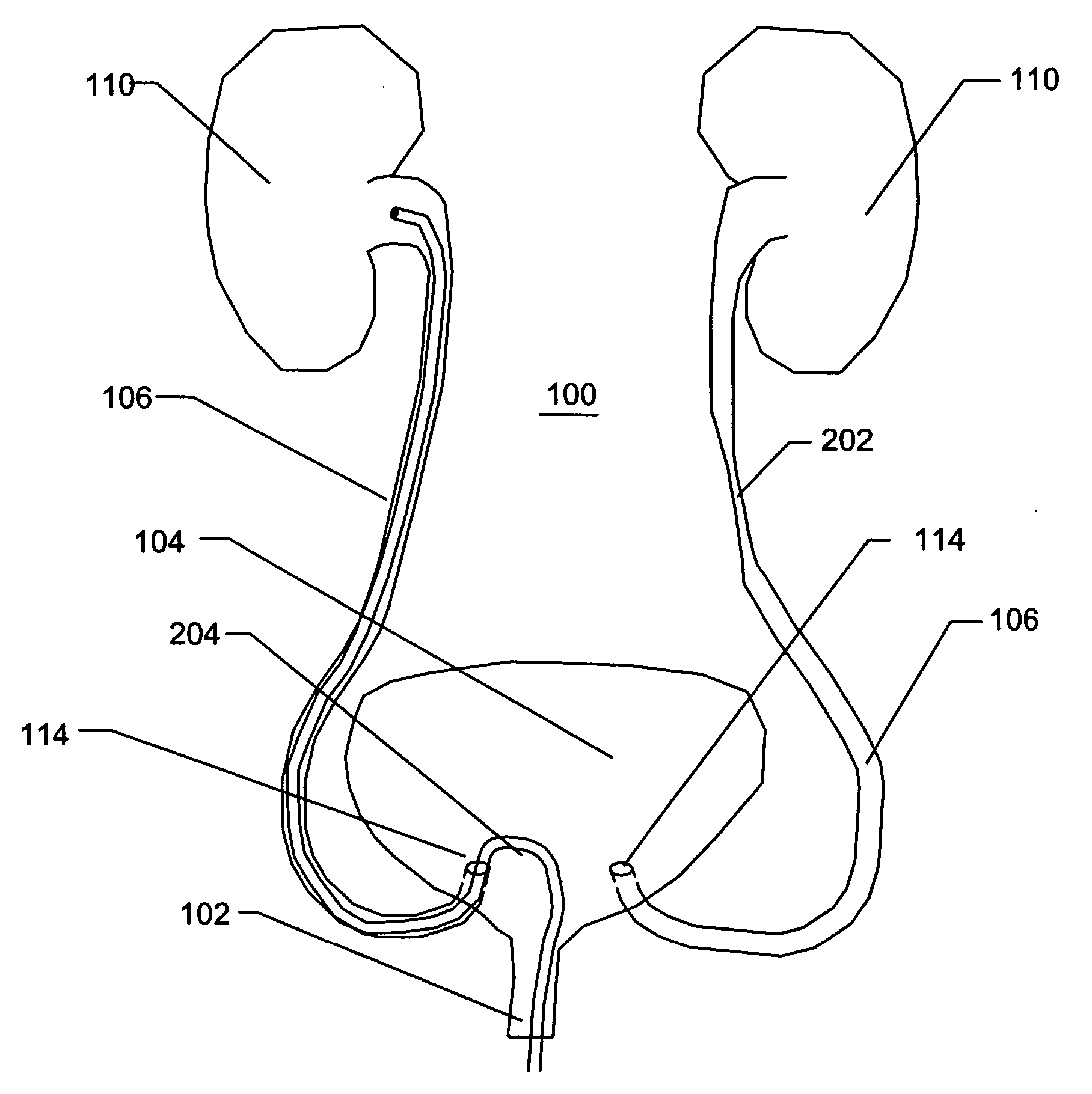
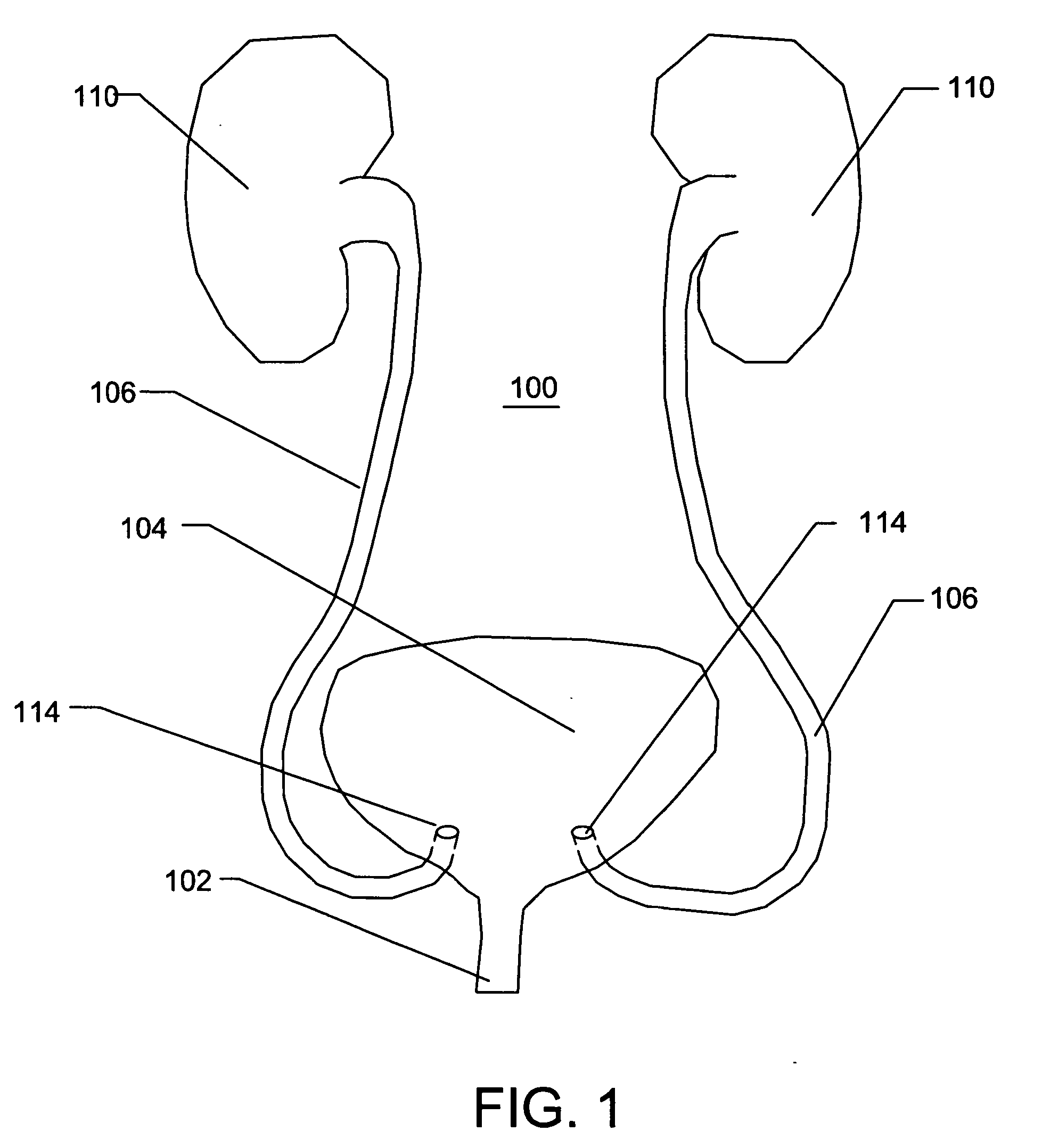
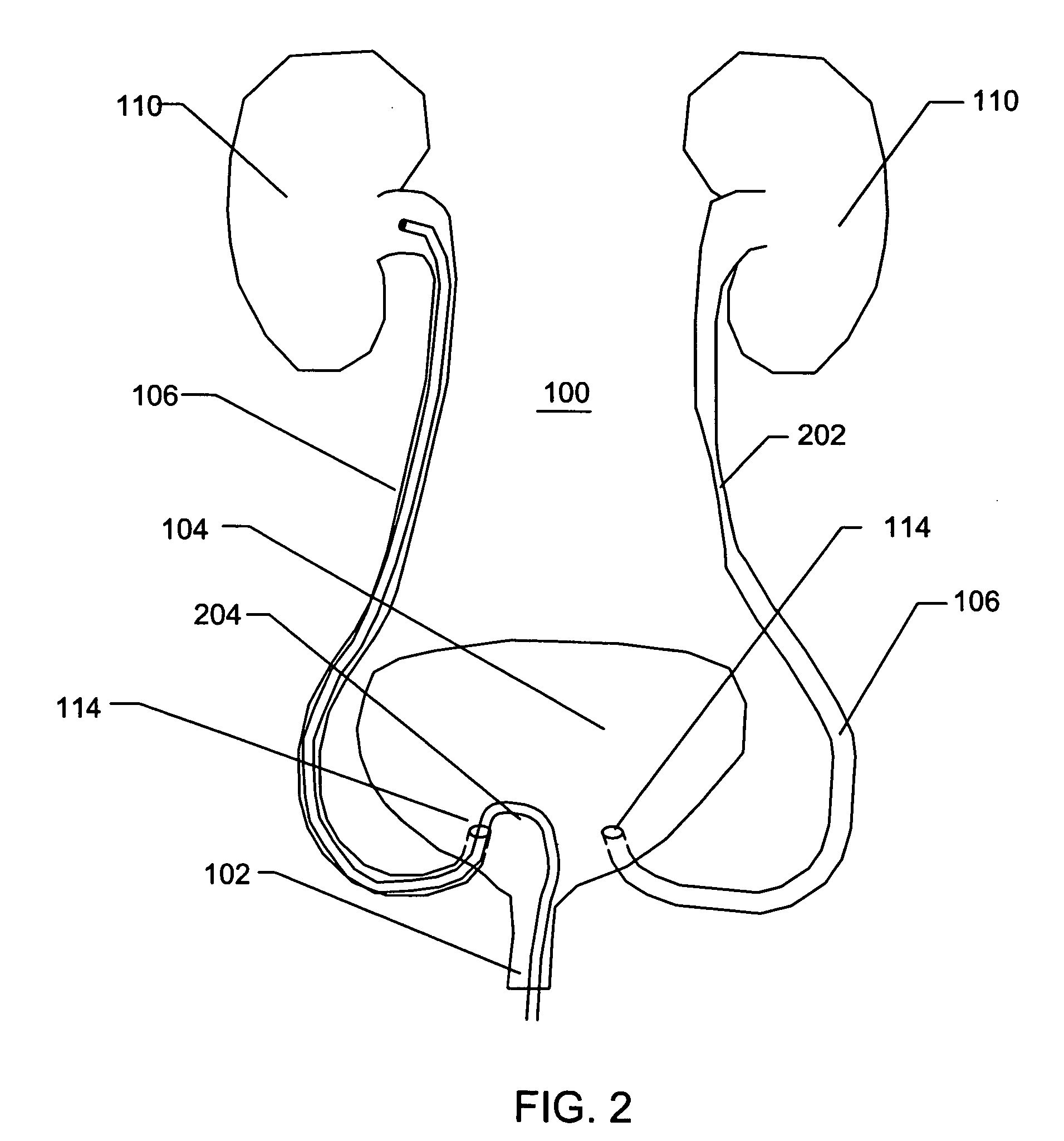
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUS7318823B2Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Devices for reconfiguring a portion of the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS20150127021A1Reducing circumferenceReducing gastric volumeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsFolded formPERITONEOSCOPE
The present invention involves new interventional methods and devices for reconfiguring a portion of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedures are generally performed laparoscopically and may generally be described as laparoscopic plication gastroplasty (LPG) in which, after obtaining abdominal access, spaced apart sites on a gastric wall are engaged, approximated and fastened to create one or more tissue folds forming one or more plications projecting into the gastrointestinal space. The serosal tissue may optionally be treated during the procedure to promote the formation of a strong serosa-to-serosa bond that ensures the long-term stability of the tissue plication. These procedures are preferably carried out entirely extragastrically (i.e. without penetrating through the gastrointestinal wall), thereby minimizing the risks of serious complications.
Owner:LONGEVITY SURGICAL
Methods and apparatus for treating intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20050010205A1Minimal and collateral damageLower the volumeDiagnosticsSurgical needlesMedicineIntervertebral disc
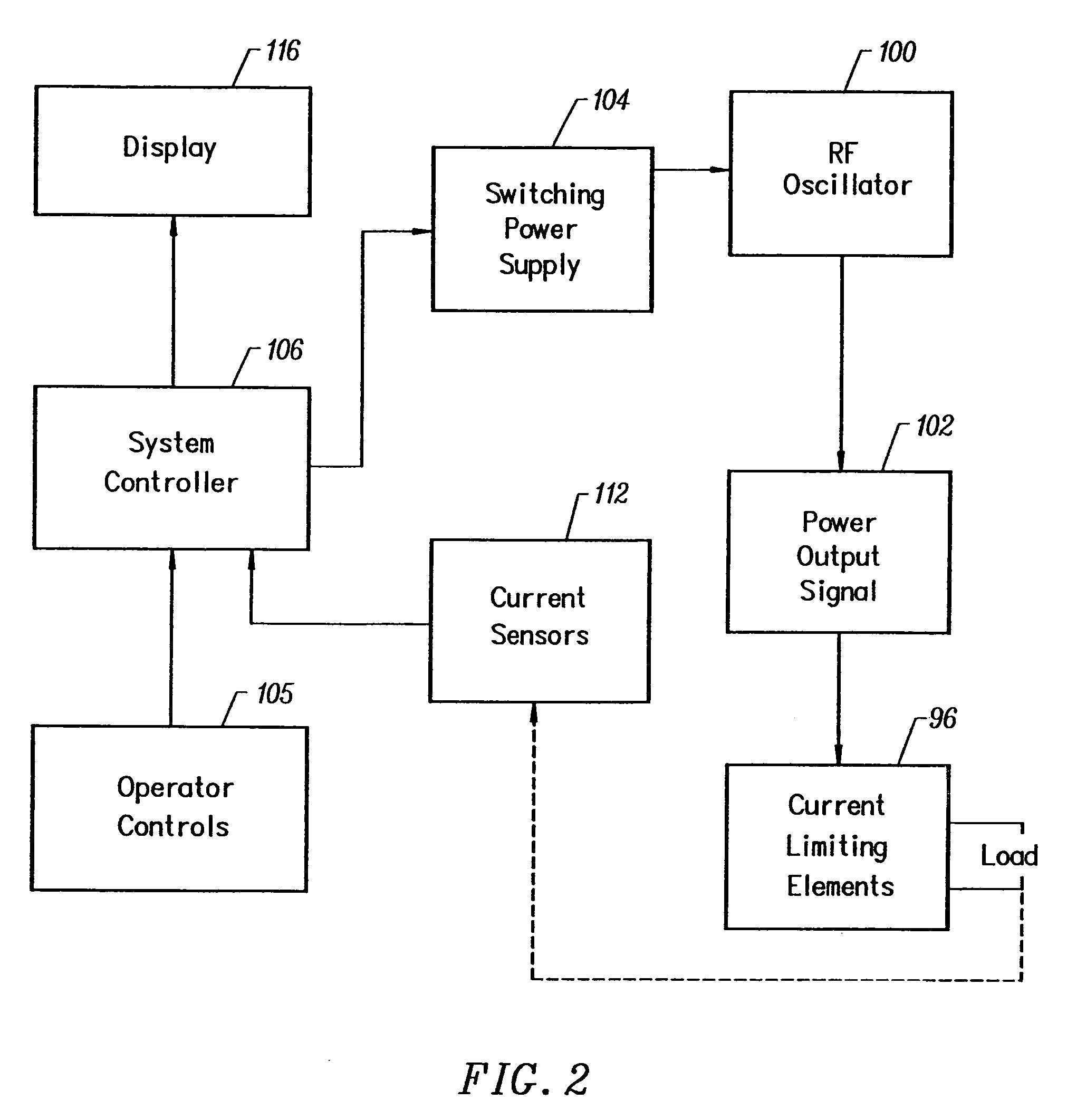
Apparatus and methods for treating a target tissue by delivering a fluid at a defined temperature to a patient's body. An apparatus of the invention includes a fluid delivery unit for delivering fluid in at least close proximity to the target tissue, an aspiration unit for withdrawing the fluid, and a fluid source unit for providing the fluid at the defined temperature. A method of the invention includes forming a void in at least close proximity to the target tissue, and circulating a preheated fluid through the void, wherein the target tissue undergoes adjustment from body temperature to a treatment temperature due to heat exchange between the fluid and the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Lighting device
ActiveUS7614759B2Maximizing light extractionReduce probabilityPoint-like light sourceLighting elementsElement spaceEffect light
A lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element surface being at least twice as large as and substantially parallel to the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface area of a projection of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as a surface area of a projection of the light emitter.
Owner:CREELED INC
Electronic fuse with conformal fuse element formed over a freestanding dielectric spacer
InactiveUS20070210890A1Small surface areaFuse device manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIntegrated circuitEngineering
An electronic fuse for an integrated circuit and a method of fabrication thereof are presented. The electronic fuse has a first terminal portion and a second terminal portion interconnected by a fuse element. The fuse element has a convex upper surface and a lower surface with a radius of curvature at a smallest surface area of curvature less than or equal to 100 nanometers. Fabricating the electronic fuse includes forming an at least partially freestanding dielectric spacer above a supporting structure, and then conformably forming the fuse element of the fuse over at least a portion of the freestanding dielectric spacer, with the fuse element characterized as noted above. The dielectric spacer may remain in place as a thermally insulating layer underneath the fuse element, or may be removed to form a void underneath the fuse element.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUSRE40156E1Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
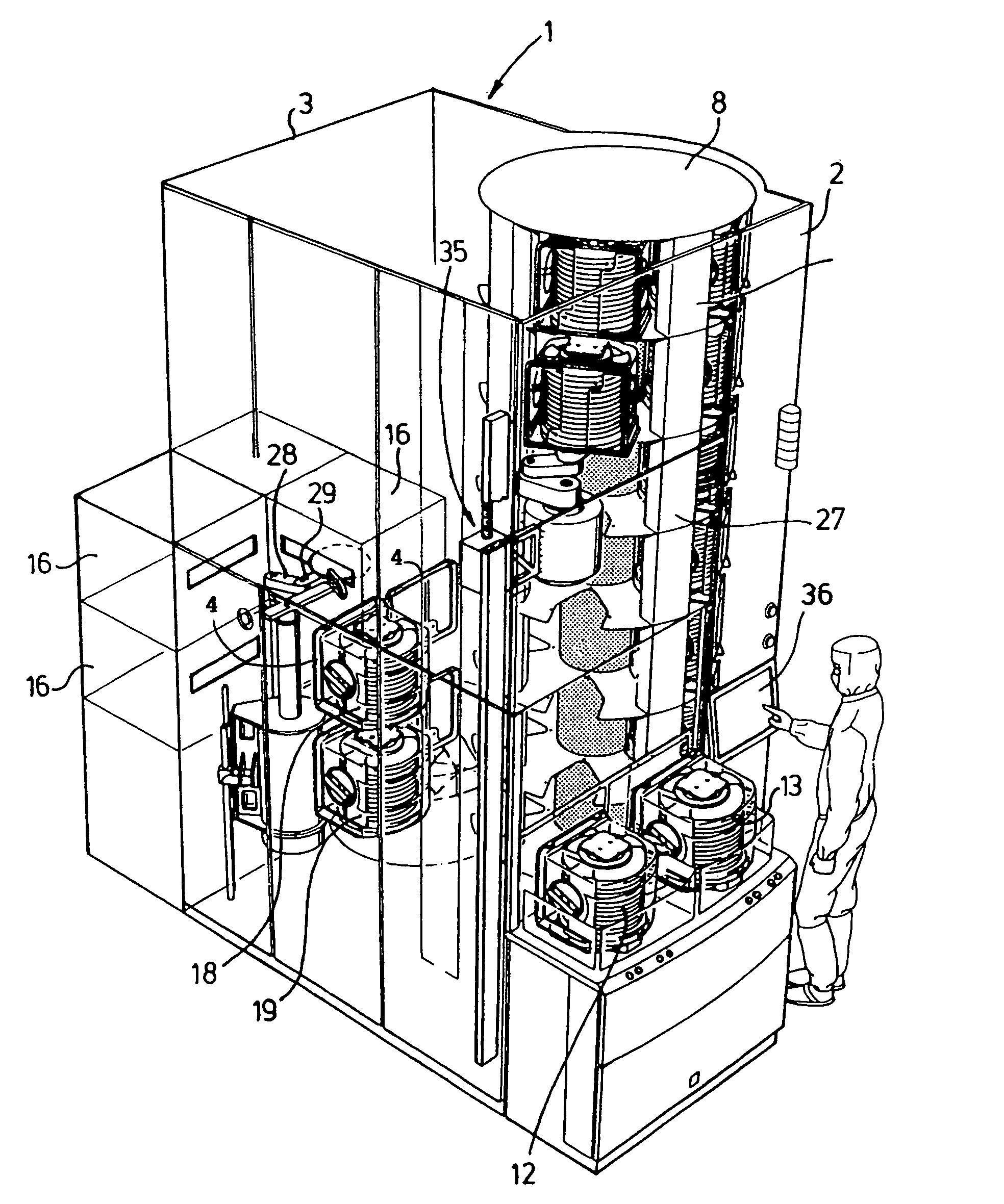
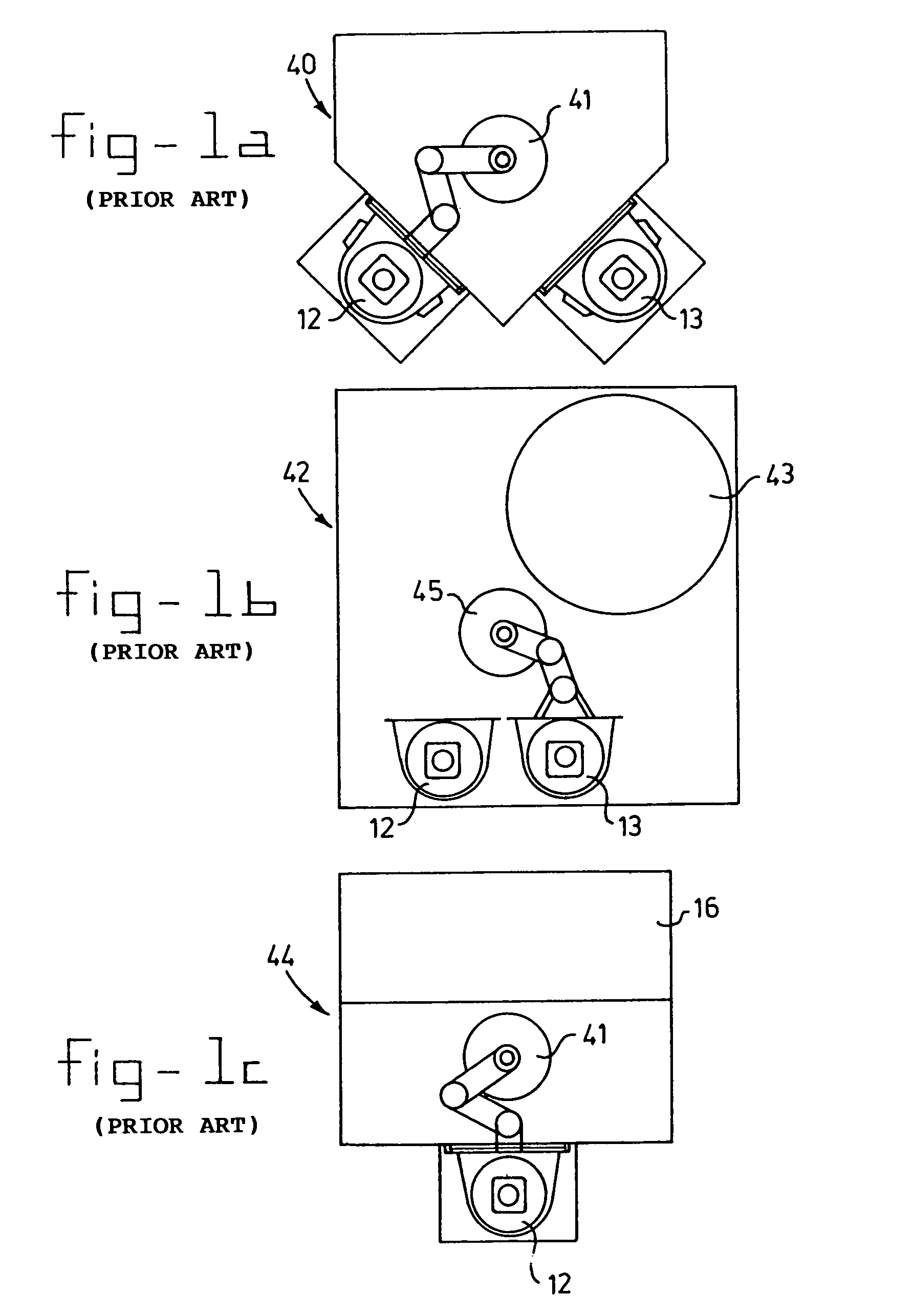
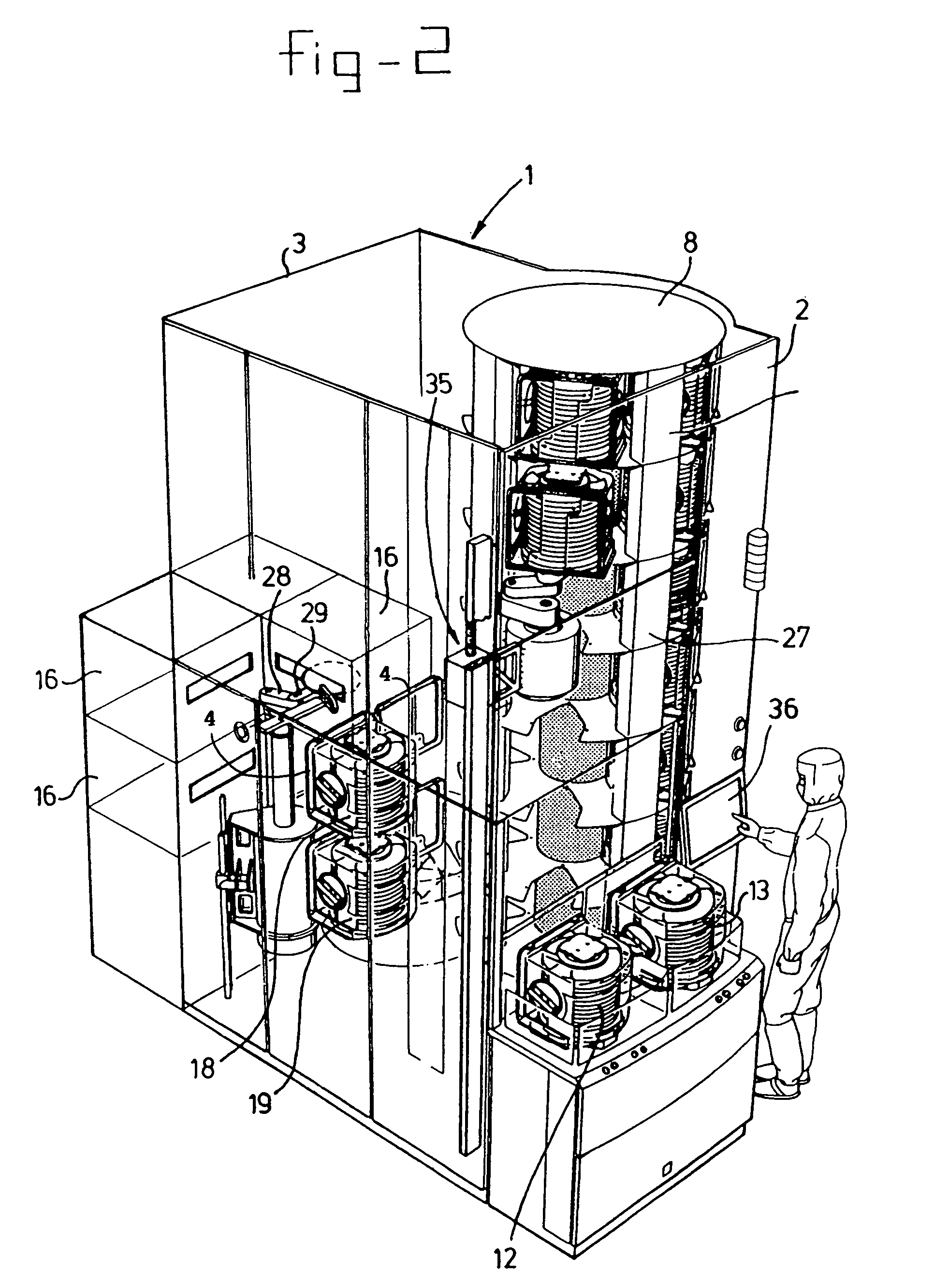
Sorting/storage device for wafers and method for handling thereof
InactiveUS7077614B1Easy and less-expensive to produceReducing throughout capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationMeasurement stationBiomedical engineering
Sorting / storage device for wafers. A sorting device is provided in which at least two cassettes containing wafers may be present and the wafers are moved from one cassette to the other cassette or vice versa. If appropriate, a measuring station may be present in the sorting device. In the immediate vicinity of the sorting device, the cassettes are stored in a magazine which is designed for this purpose and the cassettes are moved using a handling device for cassettes.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
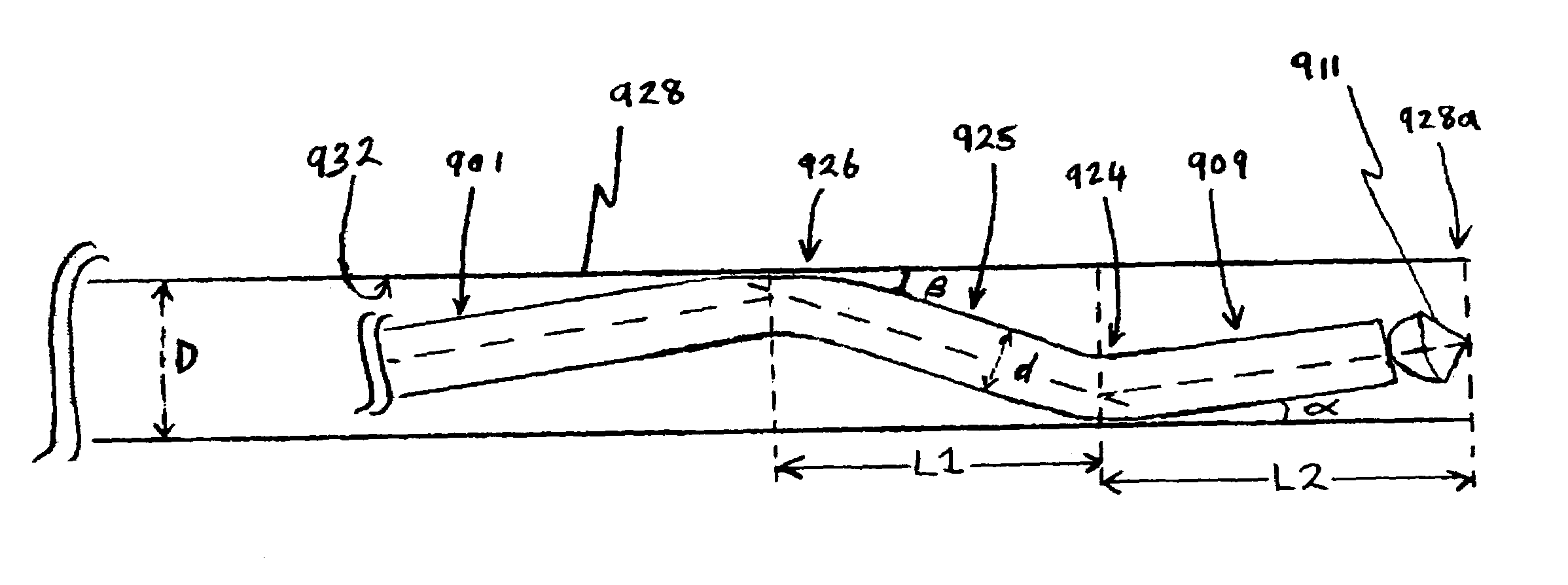
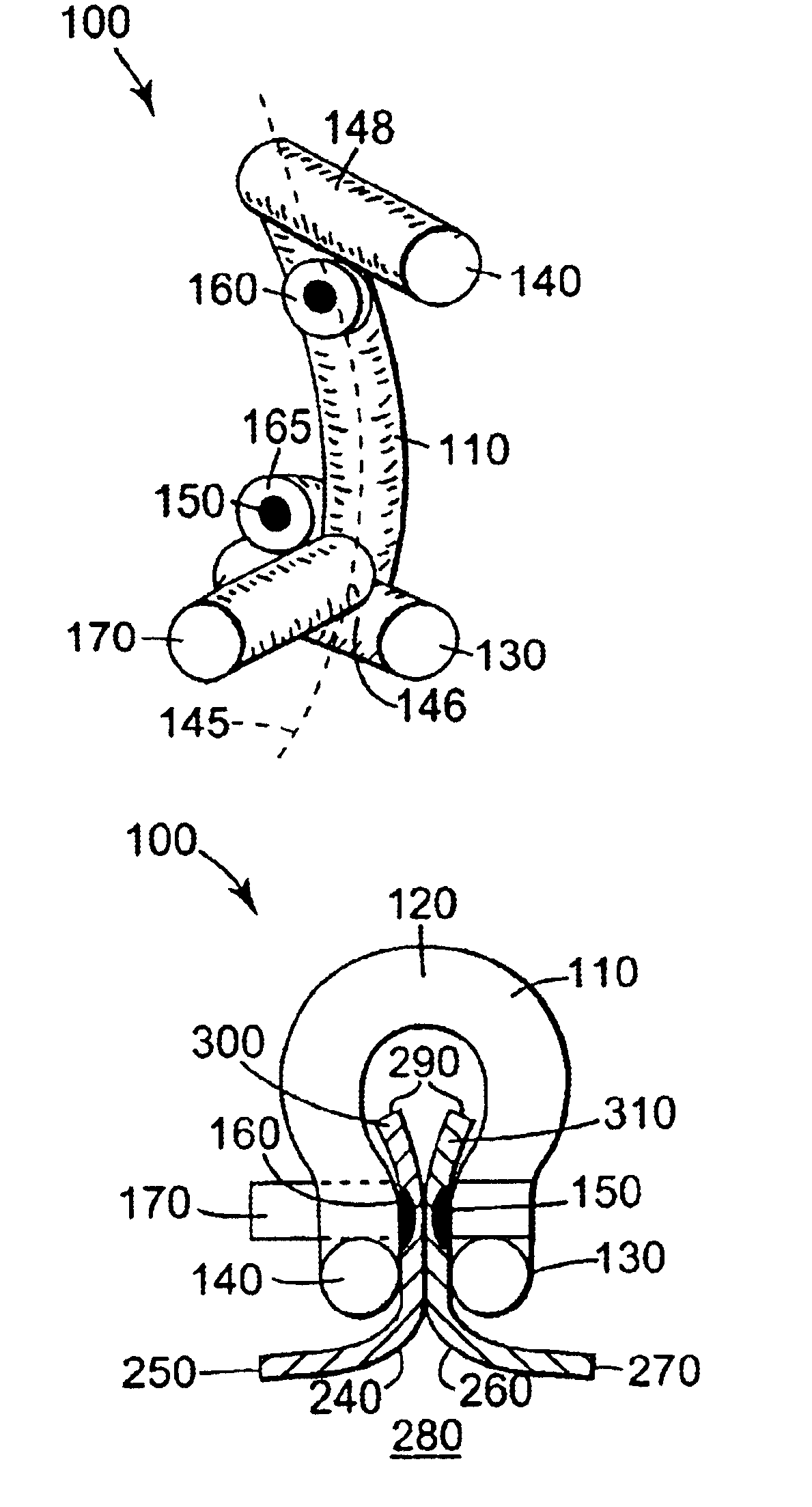
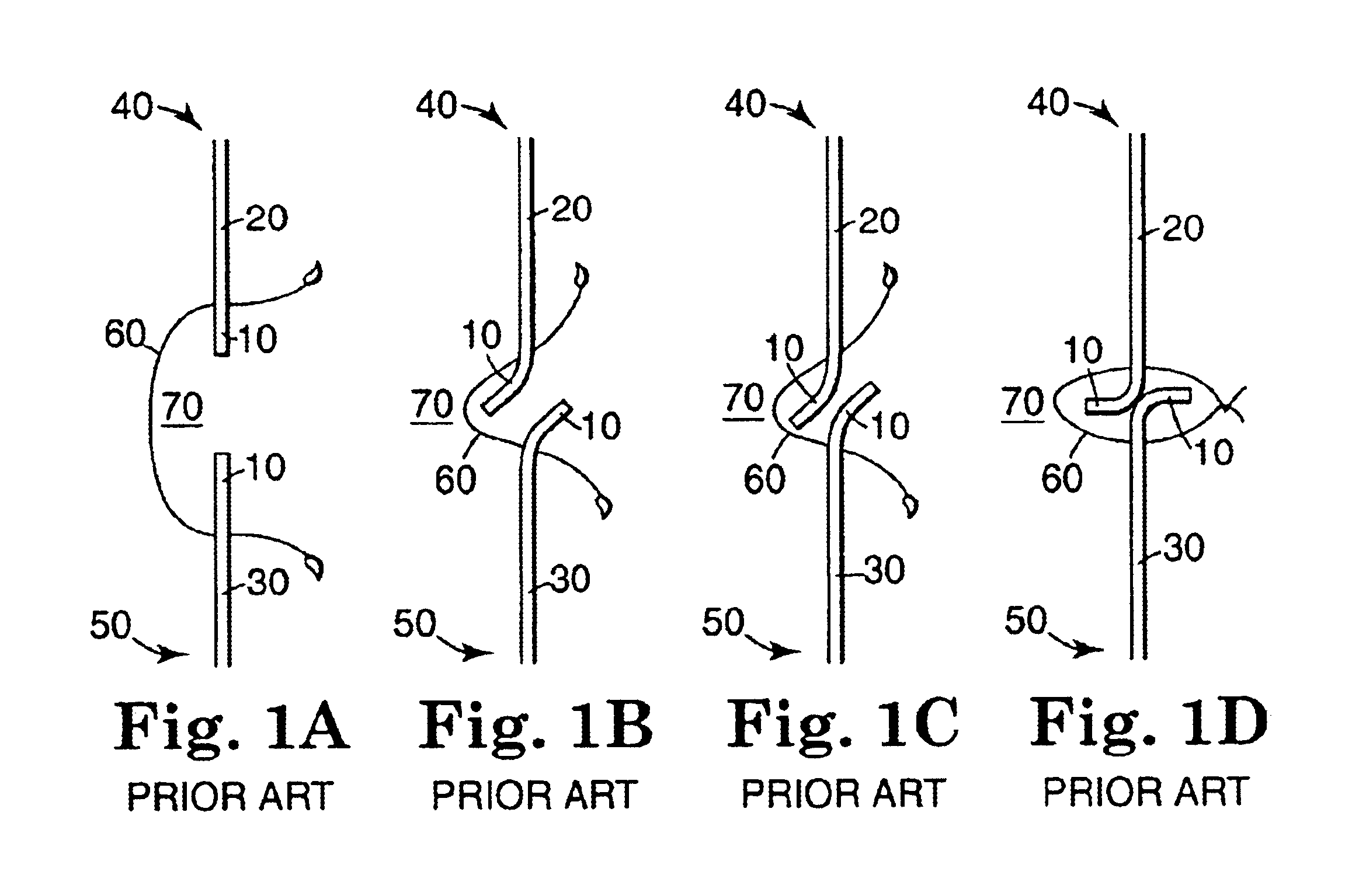
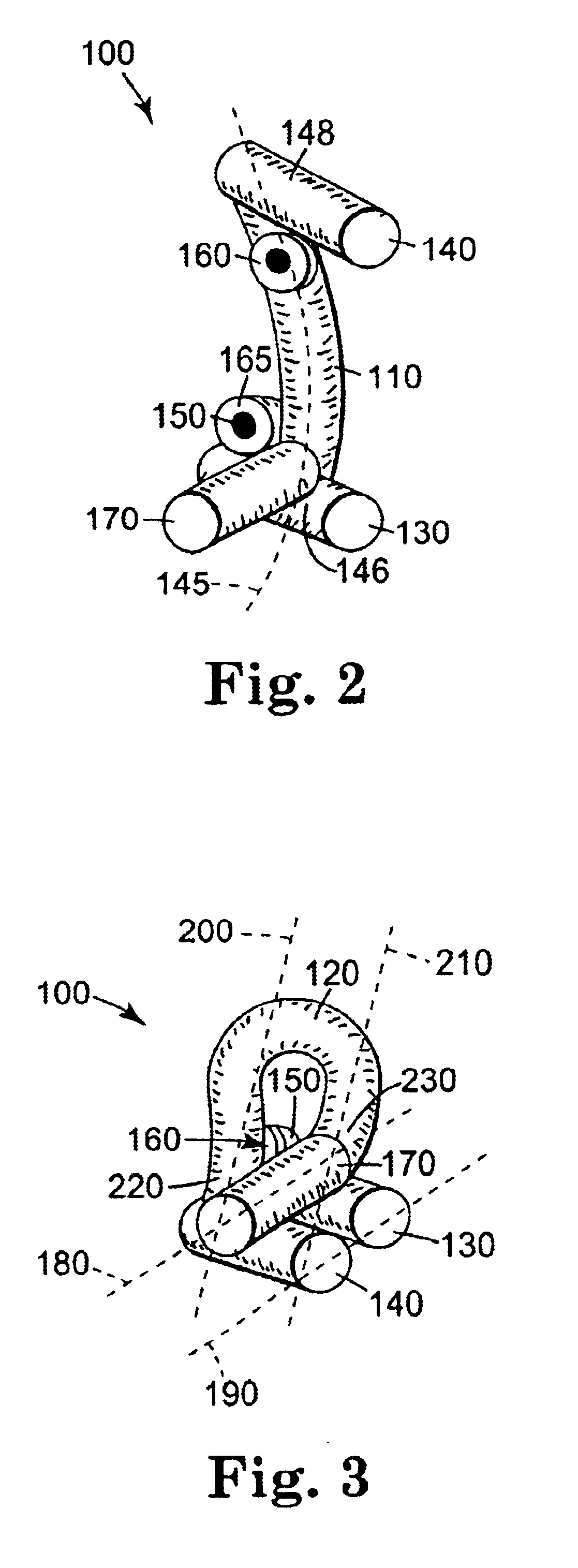
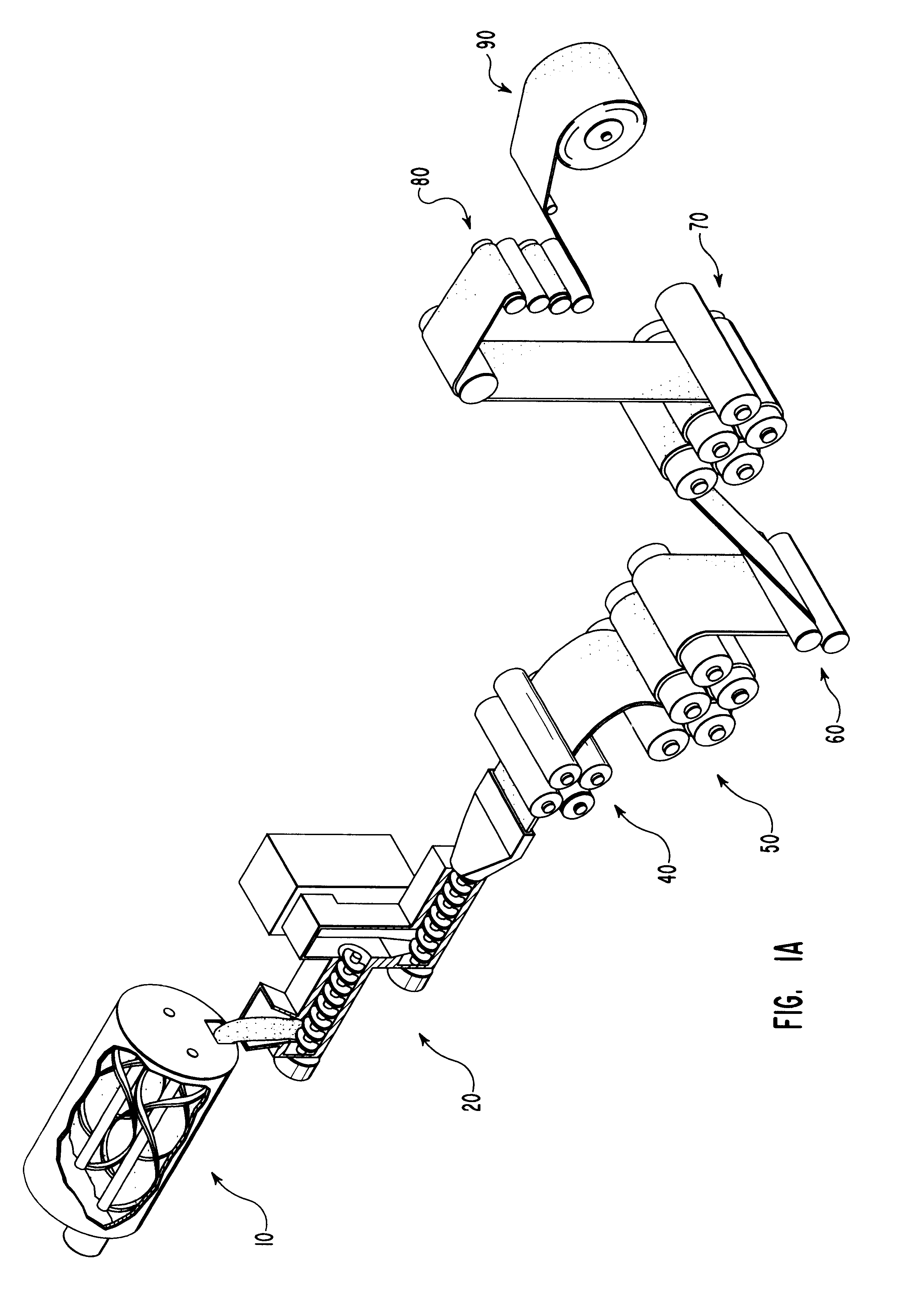
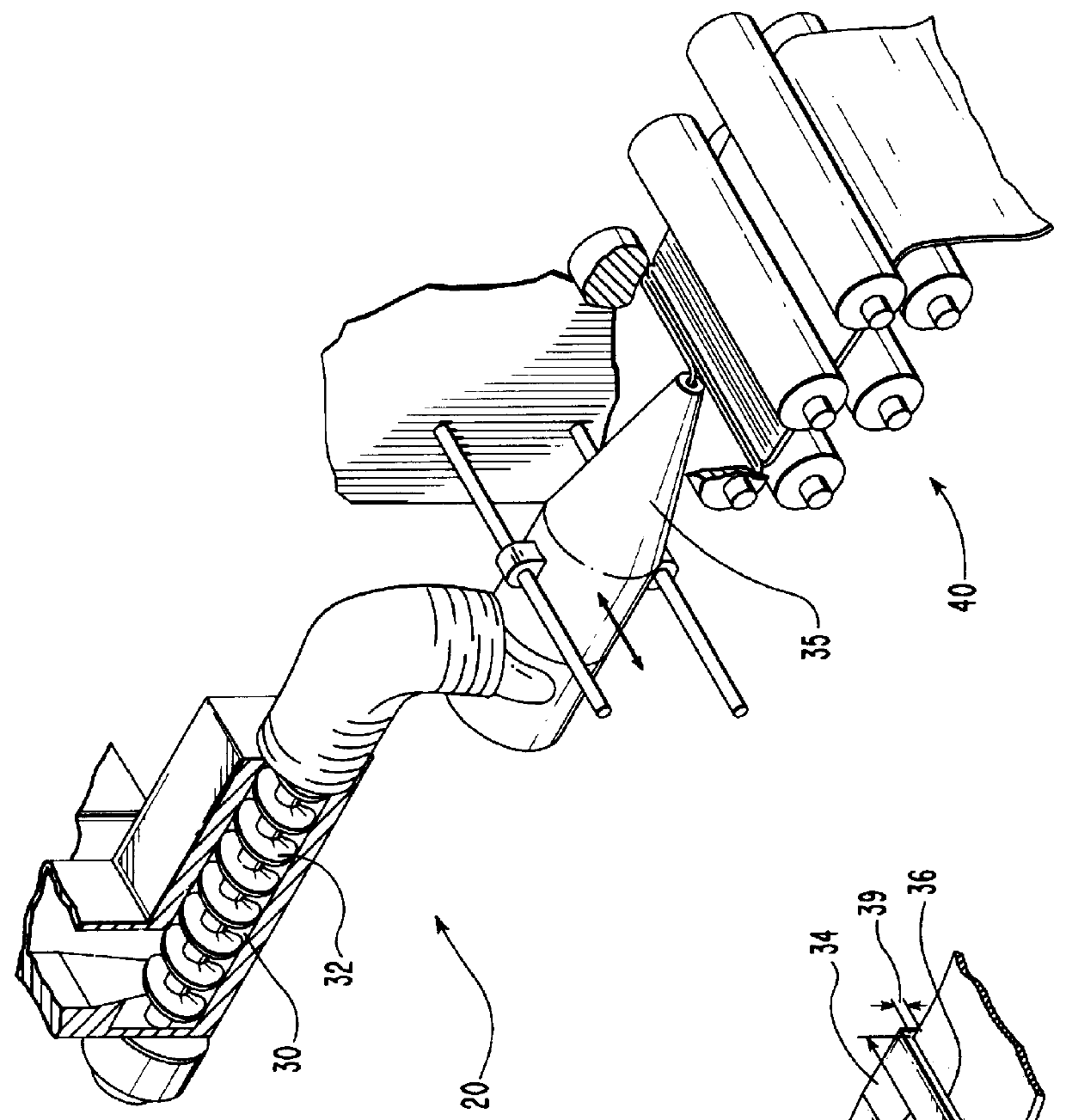
Electrosurgical apparatus having a curved distal section
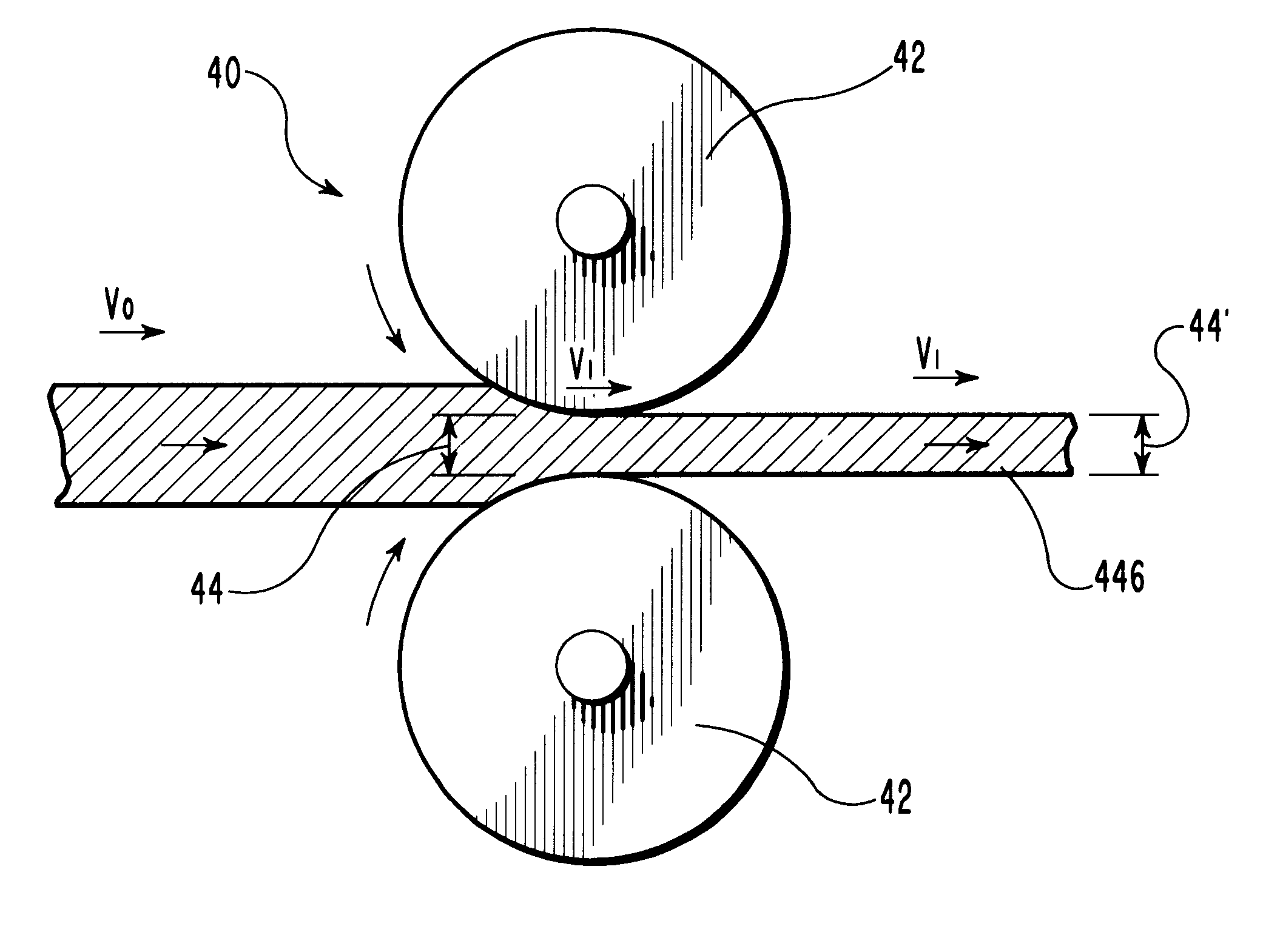
InactiveUS7070596B1Reduce pressureReduced neckingDiagnosticsSurgical needlesIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for advancing and retracting a medical instrument within an introducer device, wherein the instrument includes a distal tip, a distal linear portion, a first distal curve, a substantially linear inter-curve portion, and a second proximal curve. The length of the distal linear portion and the angle of the first curve determine the position of the distal tip within a lumen of the introducer device, such that the distal tip occupies a substantially central transverse location within the lumen and the distal tip avoids contact with the introducer device. The length of the inter-curve portion and the angle of the second curve determine deflection of the distal tip from a longitudinal axis of the shaft when the second curve is extended distally beyond a distal end of the introducer device. Also, methods and apparatus for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Radio frequency identification transponder antenna
ActiveUS20070052613A1Lower input impedanceLower resistanceRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationImpedance matchingElectric field
A RFID transponder having a microchip or integrated circuit, an impedance-matching structure and a resonant structure mounted on at least one substrate and connected to each other by an electric field.
Owner:SMARTRAC TECHNOLOGY GMBH
Methods and apparatus for treating intervertebral discs
InactiveUS7387625B2Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureDiagnosticsSurgical needlesIntervertebral discTreatment targets
Apparatus and methods for treating a target tissue by delivering a fluid at a defined temperature to a patient's body. An apparatus of the invention includes a fluid delivery unit for delivering fluid in at least close proximity to the target tissue, an aspiration unit for withdrawing the fluid, and a fluid source unit for providing the fluid at the defined temperature. A method of the invention includes forming a void in at least close proximity to the target tissue, and circulating a preheated fluid through the void, wherein the target tissue undergoes adjustment from body temperature to a treatment temperature due to heat exchange between the fluid and the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Device for creating an anastomosis, including penetration structure and eversion structure
InactiveUS6916327B2Improve patencyImprove the quality of lifeStaplesNailsAnatomical structuresSurgical staple
A surgical staple for use in creating an everted anastomosis of at least two anatomical structures includes a bendable staple body. At least two evening elements protrude from the staple body. Spacing elements and a penetrating element also are provided. In use, the evening elements and spacing elements are apposed, and inner layers of the anatomical structures are held together to form an evened anastomosis. The evening platforms are disposed on an outer radius of the closed staple, and the penetrating element is disposed on a different, inner radius, to ensure that the penetrating element is excluded from the lumen of the anastomosis. Embodiments of the invention substantially ensure intima-to-intima approximation completely circumferentially at the anastomotic site, with no portion of cut tissue edges, suture or staple exposed to the lumen of the anastomosis. Cut tissue edges, as well as the staple, are completely extra-lumenal. Related methods provide similar advantages.
Owner:METACARDIA
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based compositions
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Touch screen
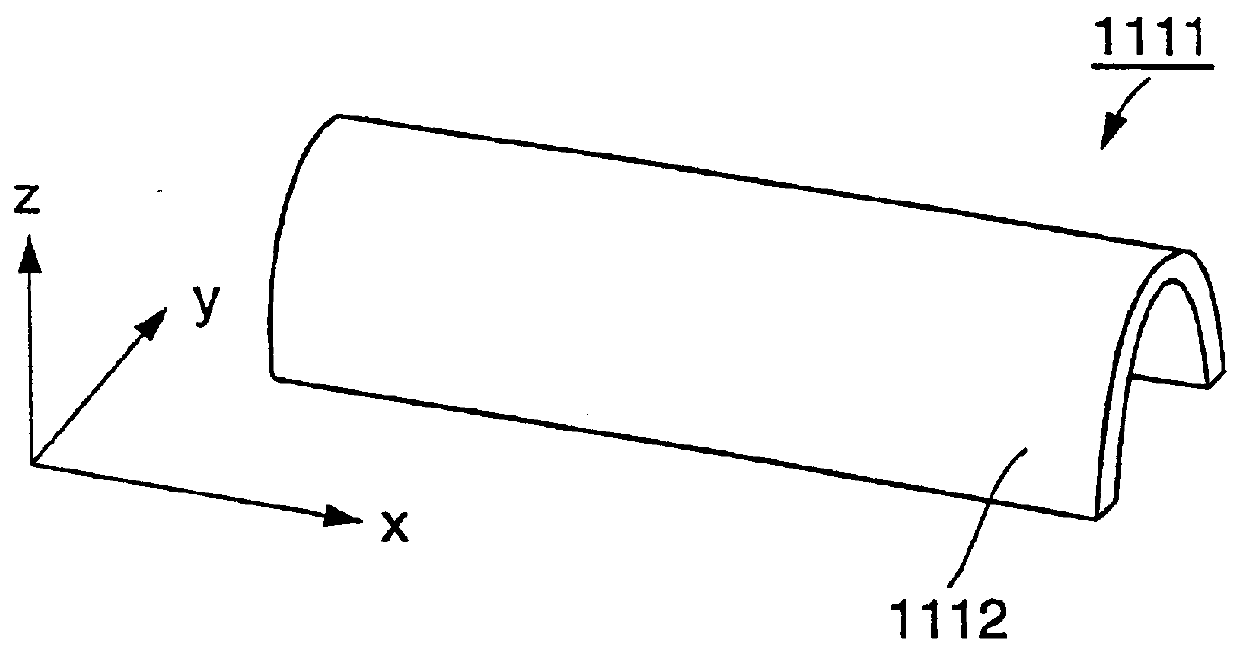
InactiveUS6072475AEasy to useSmall surface areaInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency actuatorsTouch SensesHand held
A touch screen 1111 having an active surface area 1112 which extends in three physical dimensions (x-, y- and z-dimensions) is provided. In the figure the active surface area has an U-shaped form. When a user slides his finger over the active surface area the tactile feedback gives him information about the position of the finger. The touch screen is activated when the active surface area senses a certain pressure from the finger. The use of the touch screen is facilitated especially when the user is on the move or when the touch screen is out of sight. Such use is common when operating hand-held terminals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Magnetic coupling using halbach type magnet array
InactiveUS6841910B2Reduce leakageIncrease the magnetic field strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesCouplingMagnetization
A magnetic coupling having two opposed annular arrays of angularly spaced permanent magnets magnetized to create magnetic north poles and magnetic south poles alternately spaced about each array. The north-pole and south-pole magnets of each array are tapered in cross-section from their surfaces at the gap to an annular surface of the array spaced from the gap, and permanent magnet spacer magnets completely fill in the space between the north-pole and south-pole magnets from the annular surface of the array at the gap to the spaced annular surface with the spacer magnets being magnetized generally transversely to the direction of magnetization of the adjacent north-pole, south-pole magnets so that the magnetic field created by the permanent magnets extends across the gap and annularly through each array to cause one of the arrays to rotate in synchronism with the other array.
Owner:QUADRANT TECH CORP
Formable bone plate, clamping apparatus, osteotomy system and method for reconstructing a bone
ActiveUS20090281543A1Prolong surgery timeFacilitate optimum clampingSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsOsteotomyBiomedical engineering
A system and method are provided that use a formable bone plate and a clamping apparatus for small bone reconstruction. The formable bone plate includes a plate body having a plurality of nodes separated by internodes. Each node includes a hole formed therein for receiving a screw, wire, tack, or other fixation device screwed or placed into a bone. A clamp engages an engagement section of the node to facilitate bending of at least one of the internodes to contour the plate to the bone in-situ or ex-situ and when at least partly screwed to or not screwed to the bone.
Owner:SKELETAL DYNAMICS INC
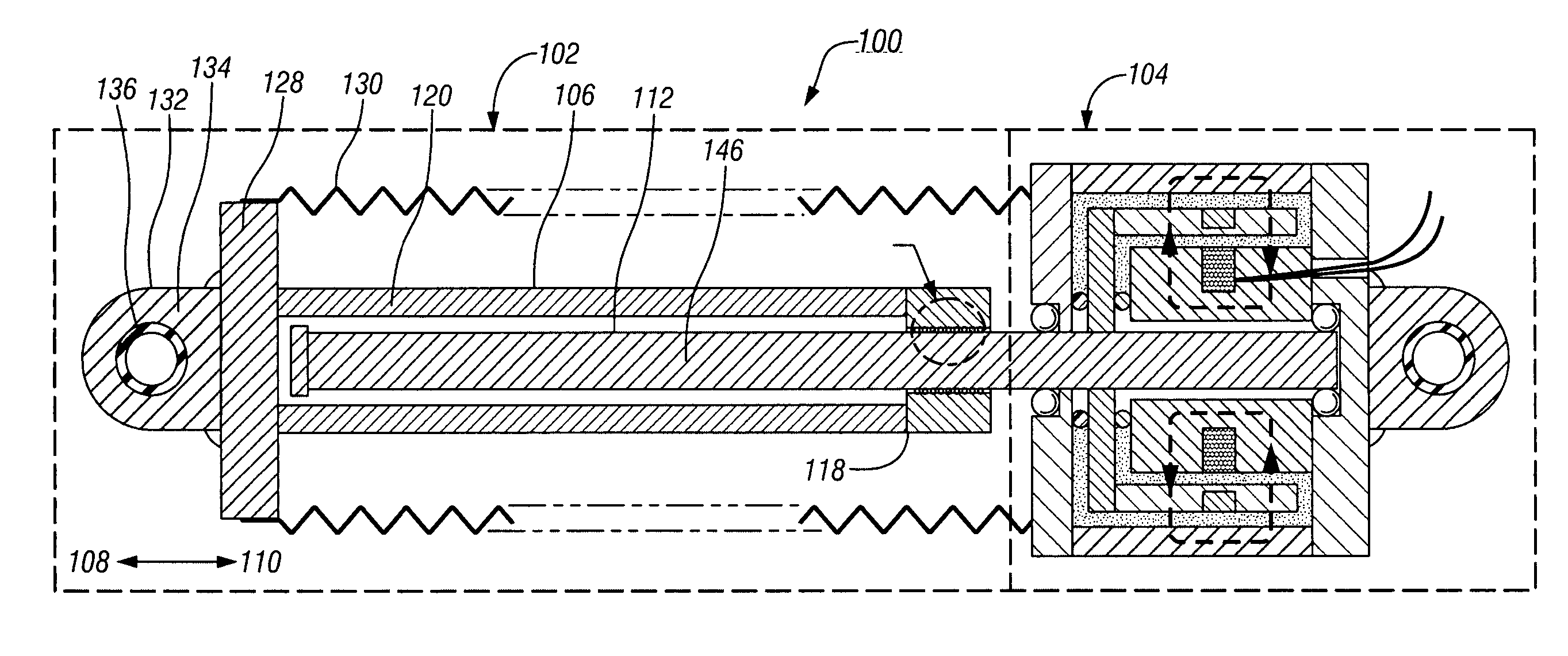
Fluid damper having continuously variable damping response
ActiveUS20050121269A1Reduce manufacturing costLower the volumeSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
An improved damping apparatus that utilizes a fluid having a viscosity that may be varied by the application of an electromagnetic field, such as a magnetorheological fluid or an electrorheological fluid, to provide the damping response. The damping apparatus includes a linear to rotary conversion mechanism which comprises a translatable member that is adapted for linear translation in a forward and a reverse direction and a rotatable member comprising a rotatable shaft that is rotatably coupled to the translatable member; wherein translation of the translatable member in one of the forward or the reverse directions produces a forward or a reverse rotation of the rotatable member and shaft, respectively. The damping apparatus also includes a damping mechanism which comprises a hub that is fixed to the shaft, a means for generating a variable electromagnetic field in response to an applied electrical signal that may be continuously varied in response to an input signal that is representative of a desired damping force and a fluid having a viscosity that may be continuously varied by application of the electromagnetic field that is in touching contact with the hub. Application of the variable electromagnetic field to the fluid produces changes in the viscosity of the fluid that in turn provides variable resistance to rotation of the hub and resistance to translation of the translatable member, thereby providing a damping apparatus with a continuously variable damping response.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Sheets having a starch-based binding matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix, optionally reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, a cellulosic ether, optionally fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the cellulosic ether to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and cellulosic ether form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Non-expandable transluminal access sheath
InactiveUS20060253102A1Improved radiopaque characteristicMinimize potential for damageCannulasInfusion syringesFluid transportVisibility
A transluminal sheath is disclosed that permits instrumentation to be passed therethrough. The transluminal sheath comprises a composite structure with an inner layer, an outer layer, and a reinforcing layer. The materials comprising the inner and outer layer are plastically deformable and maintain their shape, once bent into a specific configuration. The reinforcing layer further has radiopacity enhancing coatings to improve visibility under fluoroscopy and a system of flutes running longitudinally, to enhance fluid transport and reduce friction.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based sheets
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
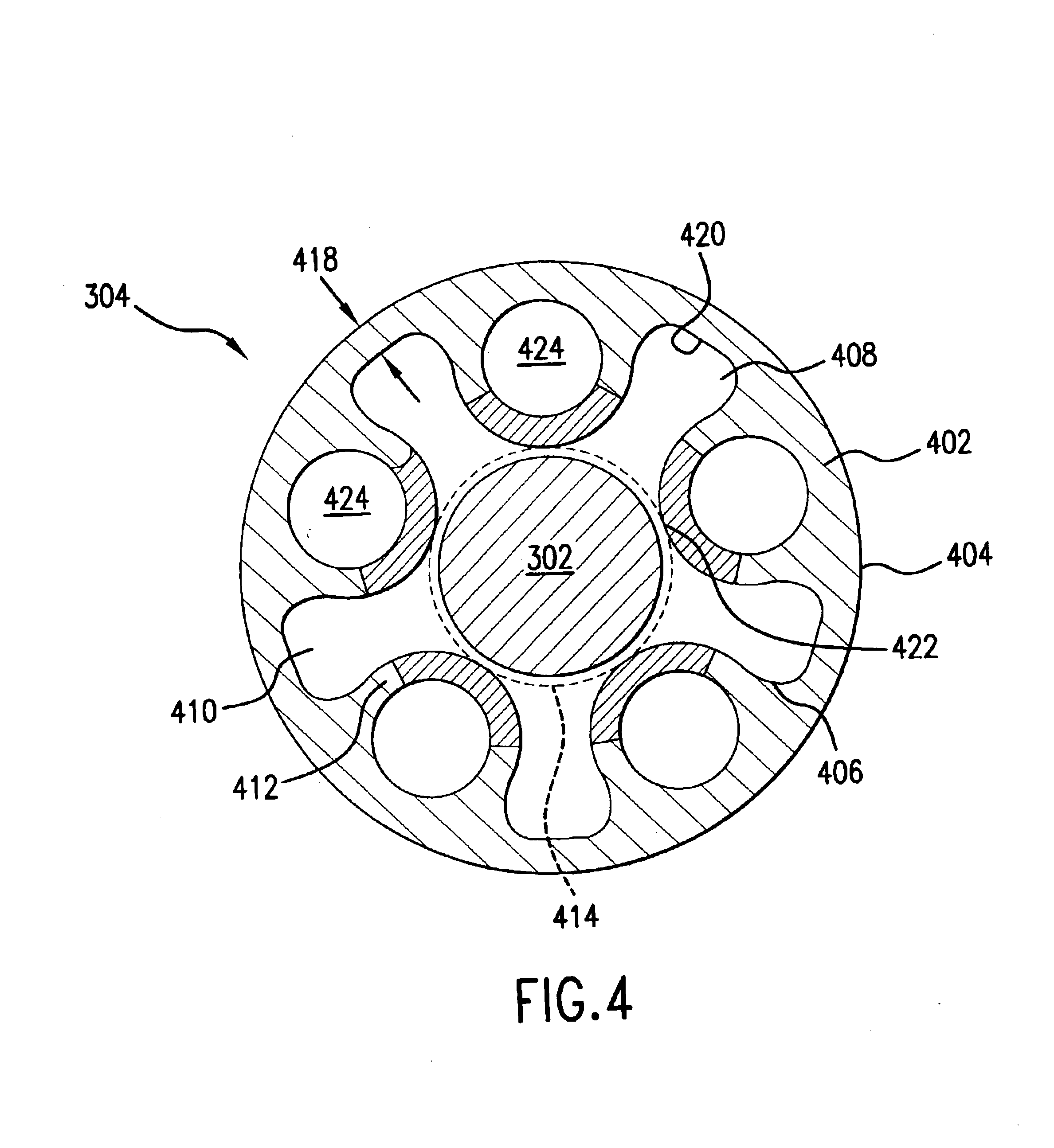
Catheter having a low-friction guidewire lumen and method of manufacture
InactiveUS6849062B2Reduce surface areaIncrease thicknessStentsBalloon catheterLow frictionBalloon catheter
A catheter shaft for a balloon catheter includes a centrally-located guidewire lumen. A body portion of the catheter shaft includes arc-shaped nodes that define a guidewire track within the guidewire lumen. Each node provides a single contact point for a guidewire within the guidewire lumen, thereby limiting frictional contact due to “rolling” friction, rather than “sliding” friction, between the catheter shaft and an inserted guidewire. The nodes include a crown region that includes the contact point. The crown region may be formed of a material having a lower coefficient of friction than the remaining portion of the catheter shaft. At least one node has an inflation lumen extending therethrough. The inflation lumen is in fluid communication with an interior of an inflatable balloon.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Electronic component and method for manufacturing the same
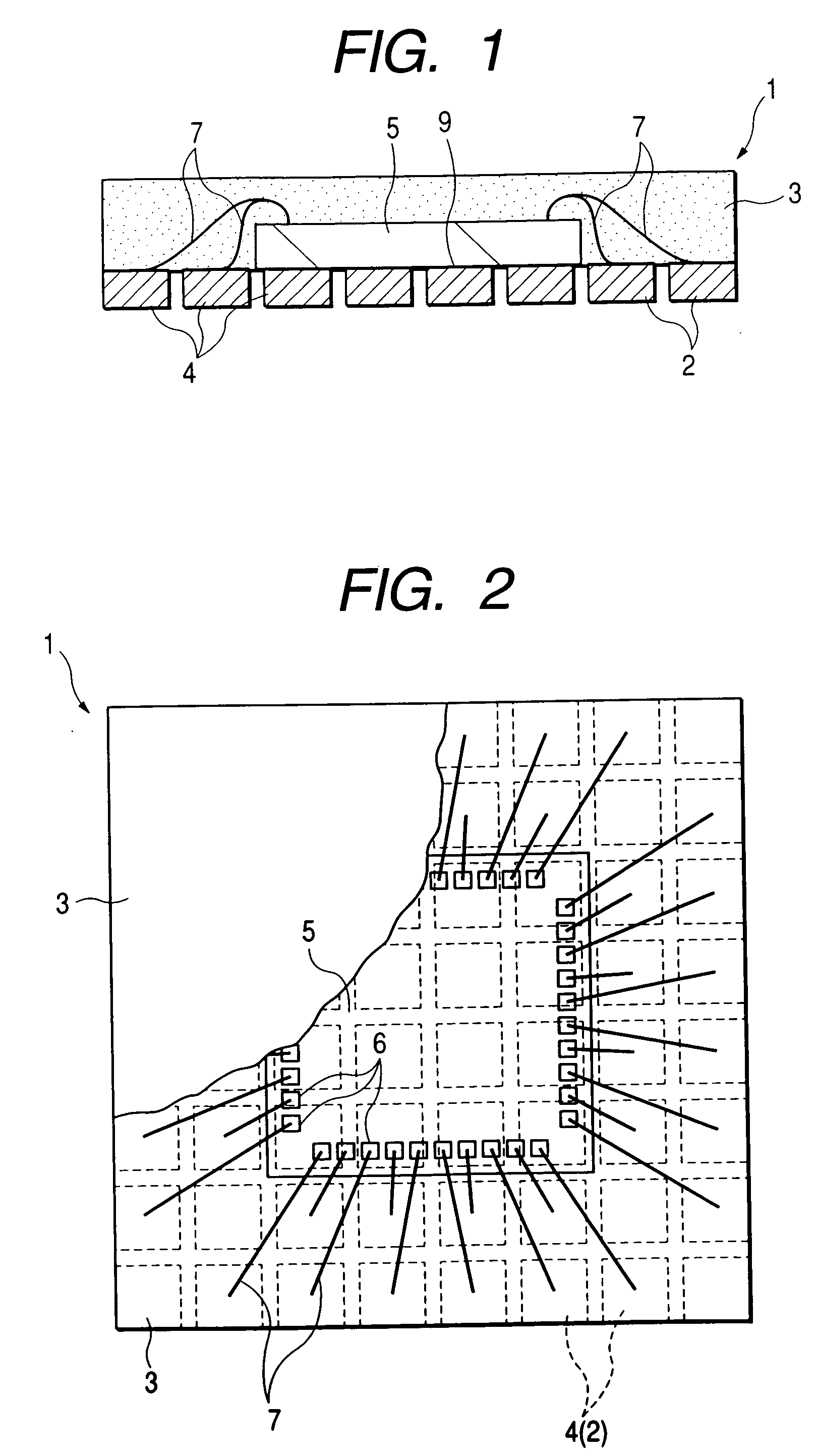
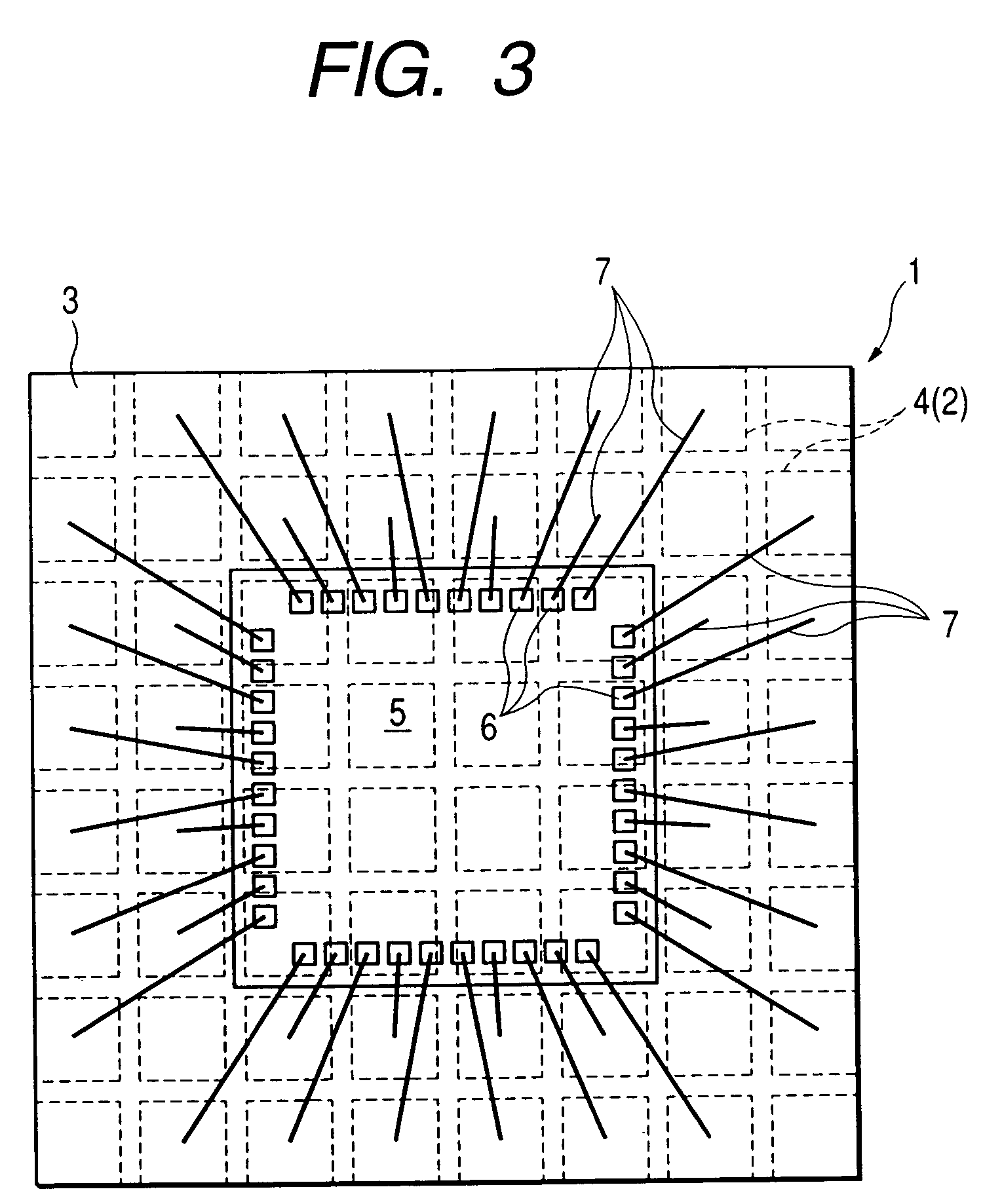
InactiveUS7170215B2Small surface areaPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResonanceElectronic component
An electronic component includes a substrate; a piezoelectric material layer supported directly or indirectly by the substrate; a first electrode arranged on a surface of the piezoelectric material layer on an opposite side of the substrate; and a second electrode arranged on a surface of the piezoelectric material layer on the substrate side. The piezoelectric material layer is sandwiched between the first electrode and the second electrode. The first electrode has a smaller surface area than the piezoelectric material layer. A portion where the piezoelectric material layer is exposed from the first electrode includes a portion that is thinner than a thickness of the piezoelectric material layer between the first electrode and the second electrode. Thus, it is possible to configure a resonator with a higher frequency than its ordinary resonance, and it is easy to achieve an adjustment of the resonance frequency of the resonator, as well as improving the yield of the component and enabling the configuration of an electronic component that includes a plurality of resonators of different frequencies.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Instant beverage cartridges and methods
InactiveUS20120070542A1Improve convenienceReduce wasteMilk preparationAlcoholic beverage preparationEngineering
Present embodiments generally relate to a single-serve beverage cartridge for use with a single-serve coffee brewer. In some embodiments, the cartridge includes a cup, a lid, and a single serving of instant coffee or another instant beverage component. In some embodiments, the cartridge is configured to be pierced by one or more piercing members, which can provide an opening for liquid to flow into and / or out of the cartridge. In certain instances, the cartridge includes an insert configured to facilitate mixing of the instant beverage component with the liquid. In some embodiments, the instant beverage component is compressed. In certain embodiments, the cartridge does not include a filter or a barrier configured to retain non-liquid matter within the cartridge.
Owner:STARBUCKS
Manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050003586A1Compact processAvoid bendingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialAdhesive
A non-leaded resin-sealed semiconductor device is manufactured by the steps of providing a conductive flat substrate (metal plate) of copper plate or the like, fixing semiconductor elements respectively to predetermined positions on the principal surface of the substrate by an insulating adhesive, electrically connecting electrodes on the surfaces of the semiconductor elements with predetermined partition parts of the substrate separate from the semiconductor elements by conductive wires, forming an insulating resin layer on the principal surface of the substrate to cover the semiconductor elements and wires, selectively removing the substrate from the rear of said substrate to form electrically independent partition parts whereof at least some are external electrode terminals, and selectively removing said resin layer to fragment the device into regions containing the semiconductor elements and the plural partition parts around the semiconductor elements. Thus, there is provided a compact non-leaded semiconductor device having a large number of electrode terminals.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
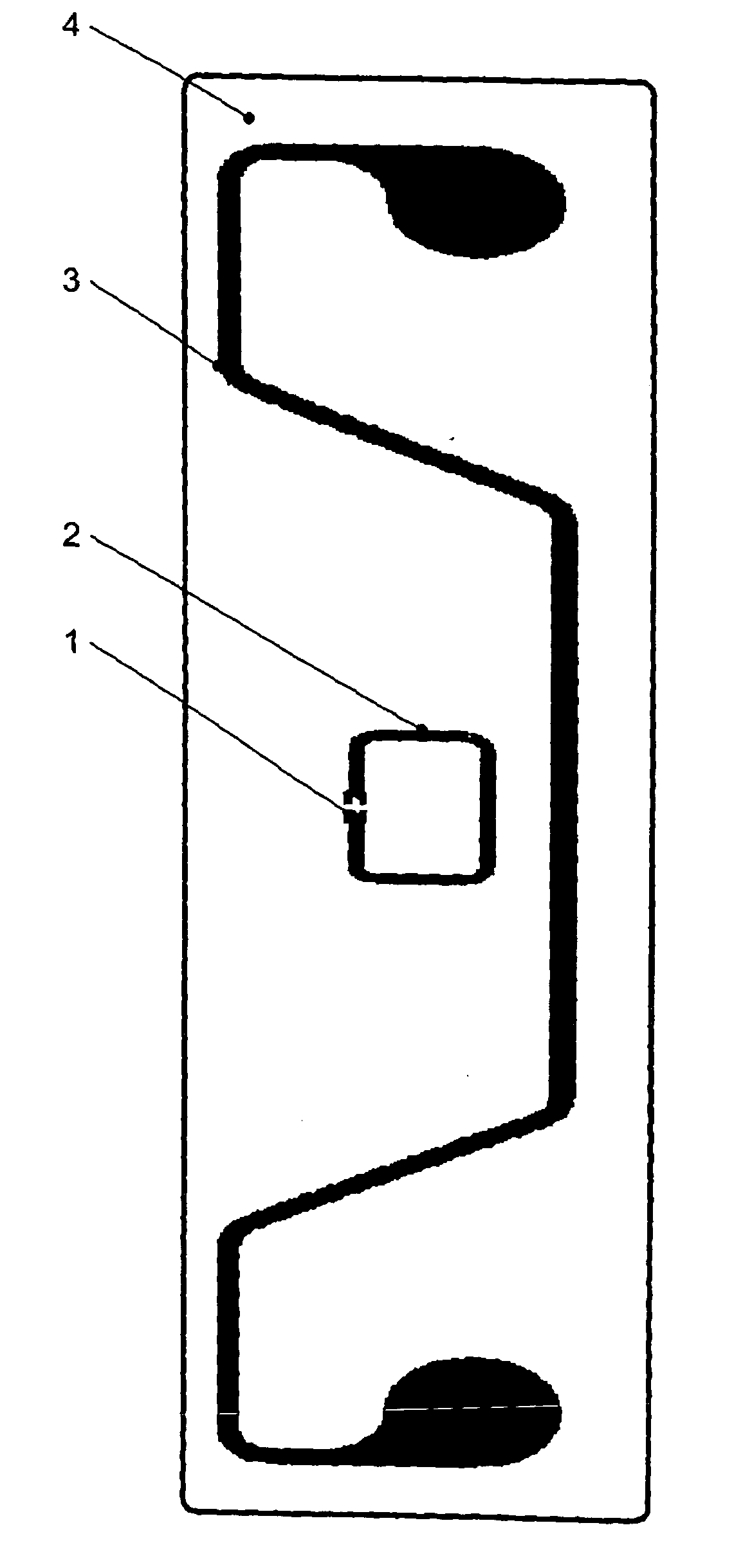
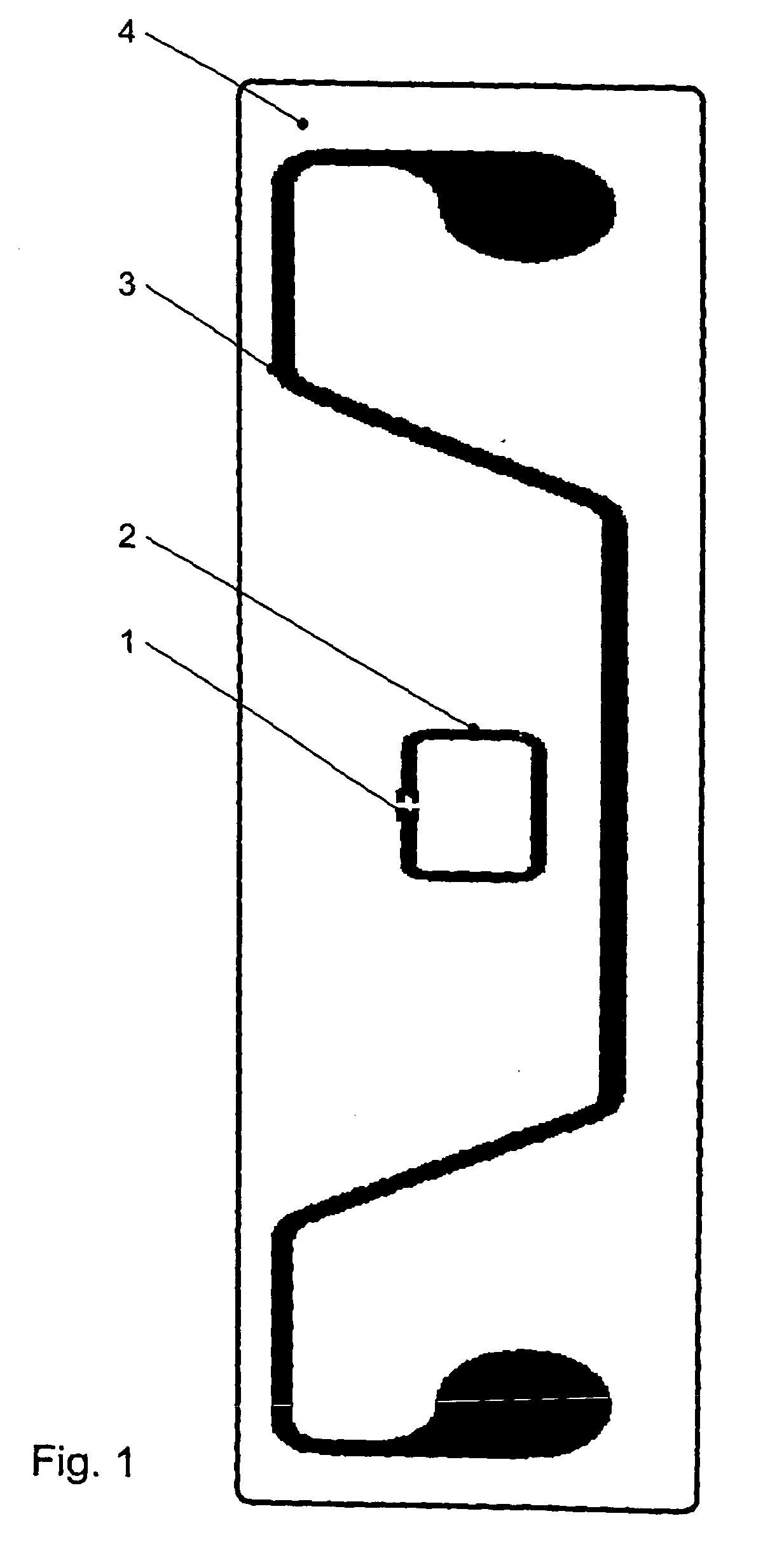
Fragrance release system
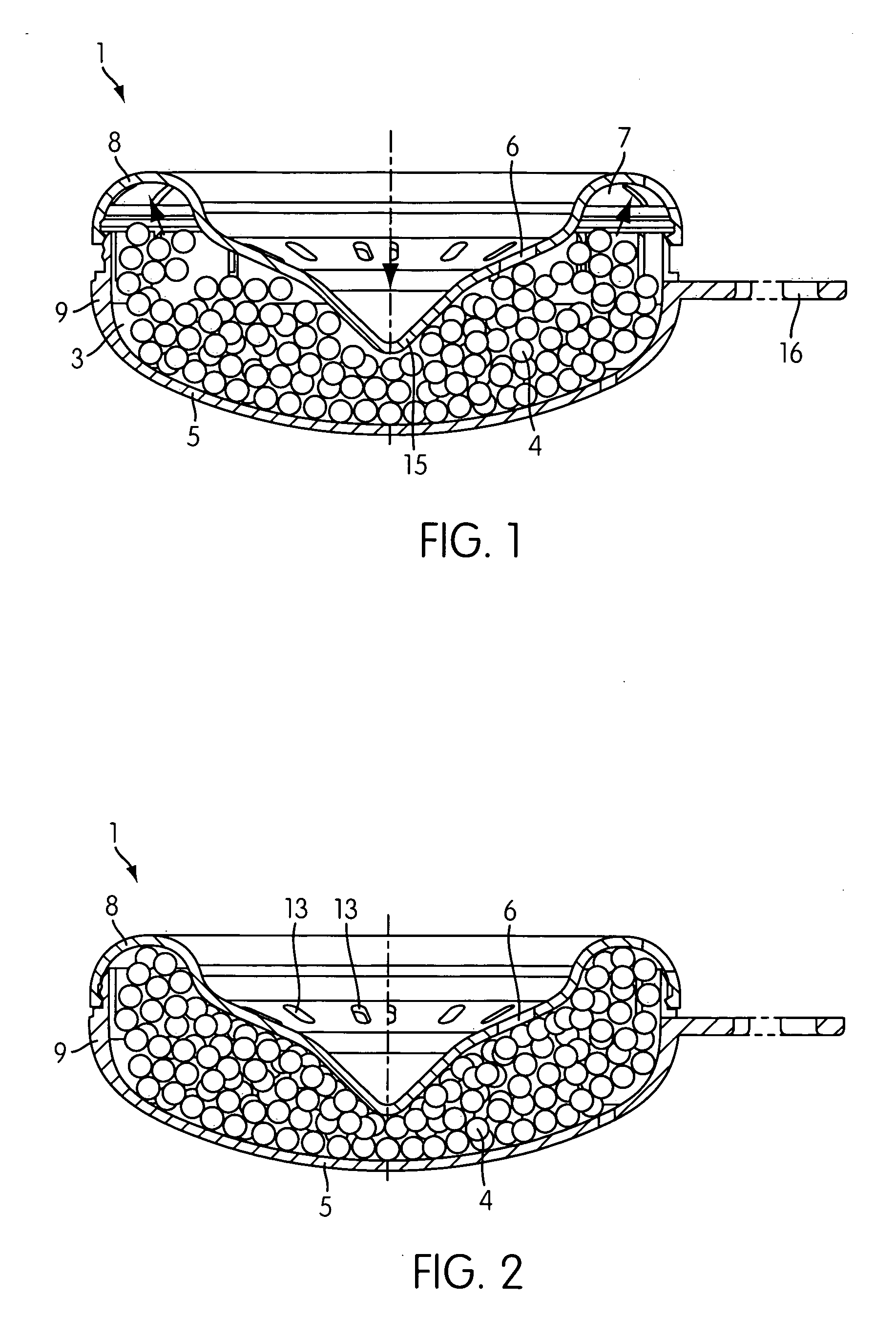
InactiveUS20050148479A1Increased fragrance releaseConstant fragrancingCosmetic preparationsTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsEngineeringCarrier material
A fragrance release system having a substantially rotationally symmetric container having a chamber accommodating a multitude of particles for deodorizing or fragrancing an open or closed space, the particles comprising a carrier material and at least one fragrance, and the container having a plurality of orifices through which emission of the fragrances of the particles from the accommodation chamber outward is possible, wherein the accommodation chamber (3) of the substantially rotationally symmetric container (2) has a crescent-like cross-sectional shape with a convex front wall (5) and a concave back wall (6).
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
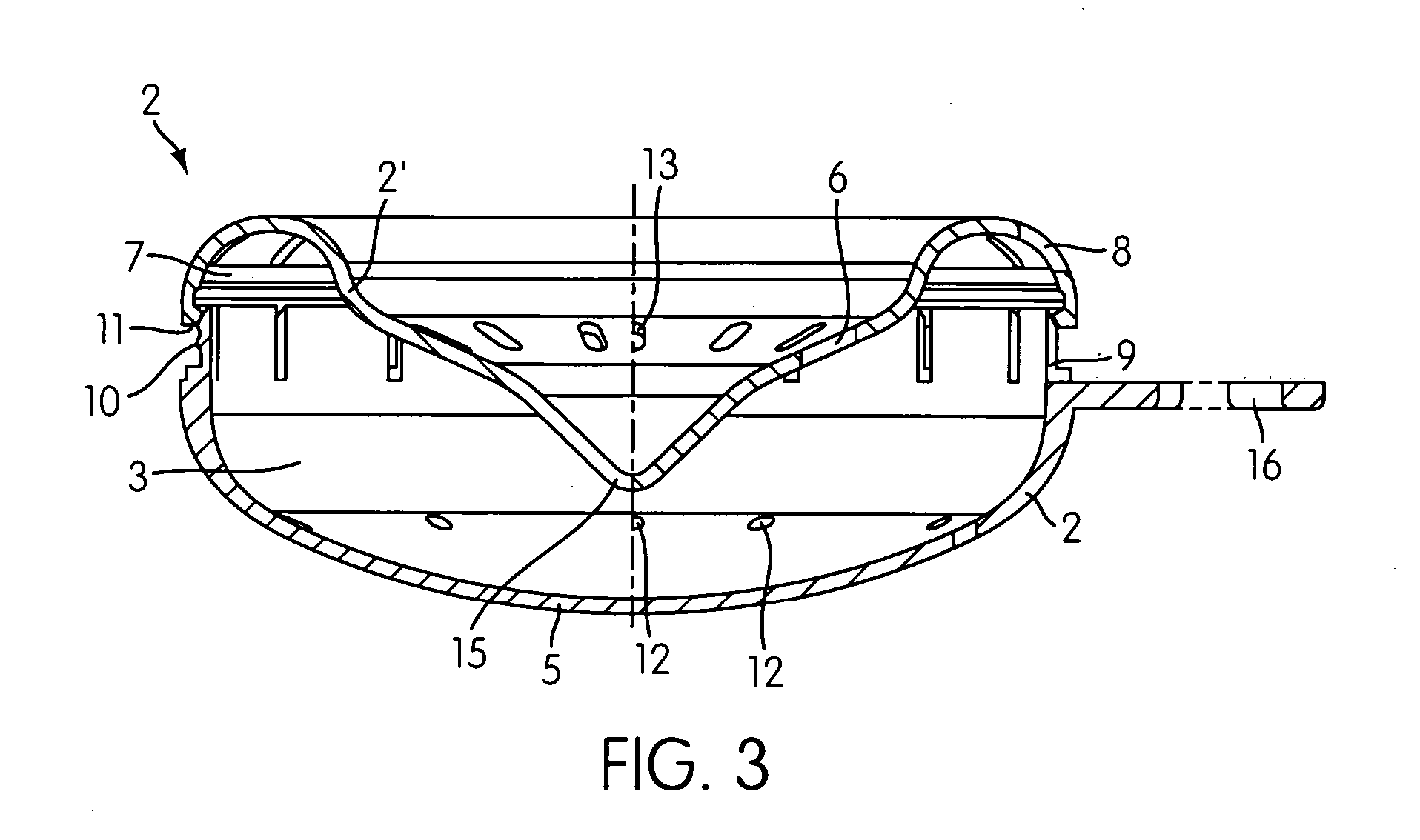
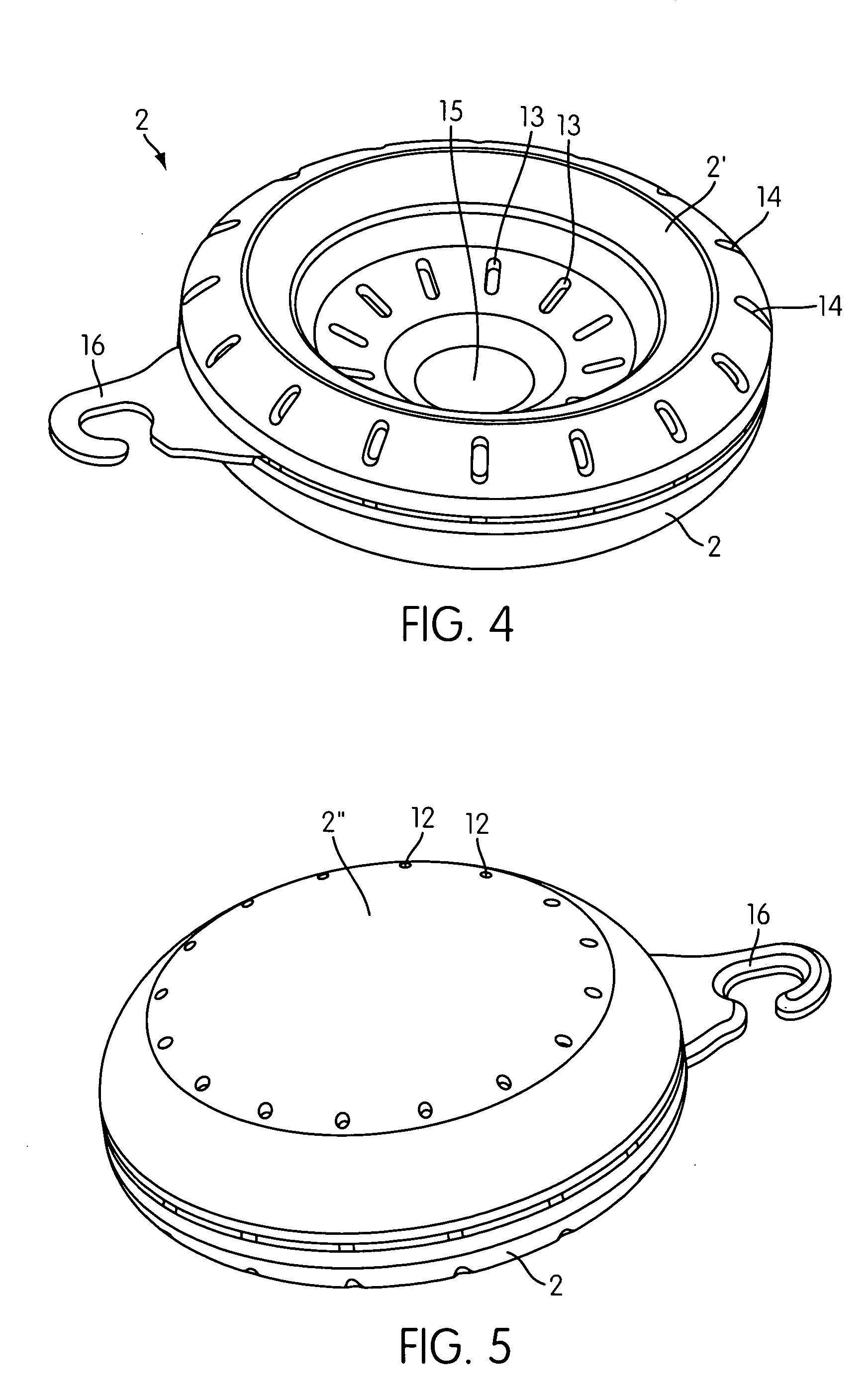
Absorbent article
InactiveUS20070073253A1Low elastic modulusAvoid separationSanitary towelsBaby linensEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Porous carbons from carbohydrates
ActiveUS20050207962A1Small surface areaIncreased proportion of mesoporesHybrid capacitor electrodesCeramicwarePorous carbonPore diameter
A porous carbon characterized by a volumetric pore size distribution having two peaks, a first of said peaks being between 0.5 and 1.0 nm and a second of said peaks being between 1.0 and 5.0 nm. The porous carbon may have a volumetric capacitance in an organic electrolyte of at least 40 F / cm3, an average pore diameter between about 2 nm and about 30 nm, a surface area of at least 900 m2 / g, and / or a density of at least 0.4 g / cm3. A method for making such a carbon includes a) curing a mixture comprising a carbohydrate, a dehydrating component, and a nonmetallic cationic pore-forming agent and b) carbonizing the cured carbon under conditions effective to provide a porous carbon having a surface area between about 100 m2 / g and about 3000 m2 / g. The the dehydrating component and nonmetallic cationic component may comprise two moieties of one compound.
Owner:TDA RES
Transdermal pharmaceutical formulation for minimizing skin residues
InactiveUS20060153905A1Reduce transferLoss of therapyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderActive agentBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
This invention relates to novel transdermal or transmucosal pharmaceutical formulation which reduces the occurrences of contamination of other individuals and the transference to clothing of the user. The novel formulation includes at least one pharmacologically active ingredient, and a solvent system having a monoalkylether of diethylene glycol and a glycol present in specified ratios, and a mixture of water and alcohol. The invention also relates to a method for inhibiting or delaying crystallization of an active agent in a pharmaceutical formulation.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
High density integrated circuit module
InactiveUS6919626B2Improve cooling effectImprove space efficiencyPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsAdhesiveFlexible circuits
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for fabricating densely stacked ball-grid-array packages into a three-dimensional multi-package array. Integrated circuit packages are stacked on one another to form a module. Lead carriers provide an external point of electrical connection to buried package leads. Lead carriers are formed with apertures that partially surround each lead and electrically and thermally couple conductive elements or traces in the lead carrier to each package lead. Optionally thin layers of thermally conductive adhesive located between the lead carrier and adjacent packages facilitates the transfer of heat between packages and to the lead carrier. Lead carriers may be formed of custom flexible circuits having multiple layers of conductive material separated by a substrate to provide accurate impedance control and providing high density signal trace routing and ball-grid array connection to a printed wiring board.
Owner:OVID DATA CO
Expandable stent having plurality of interconnected expansion modules
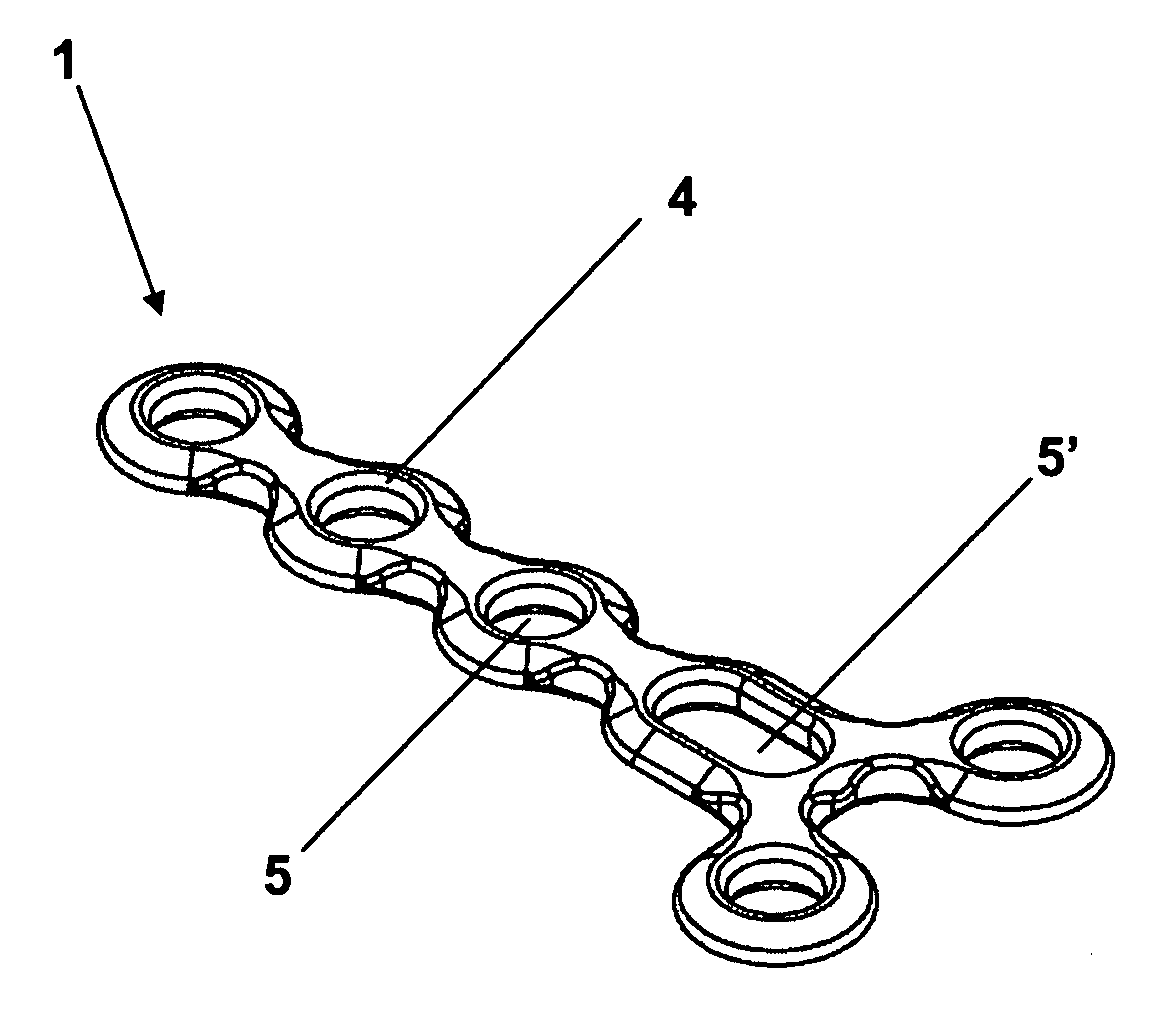
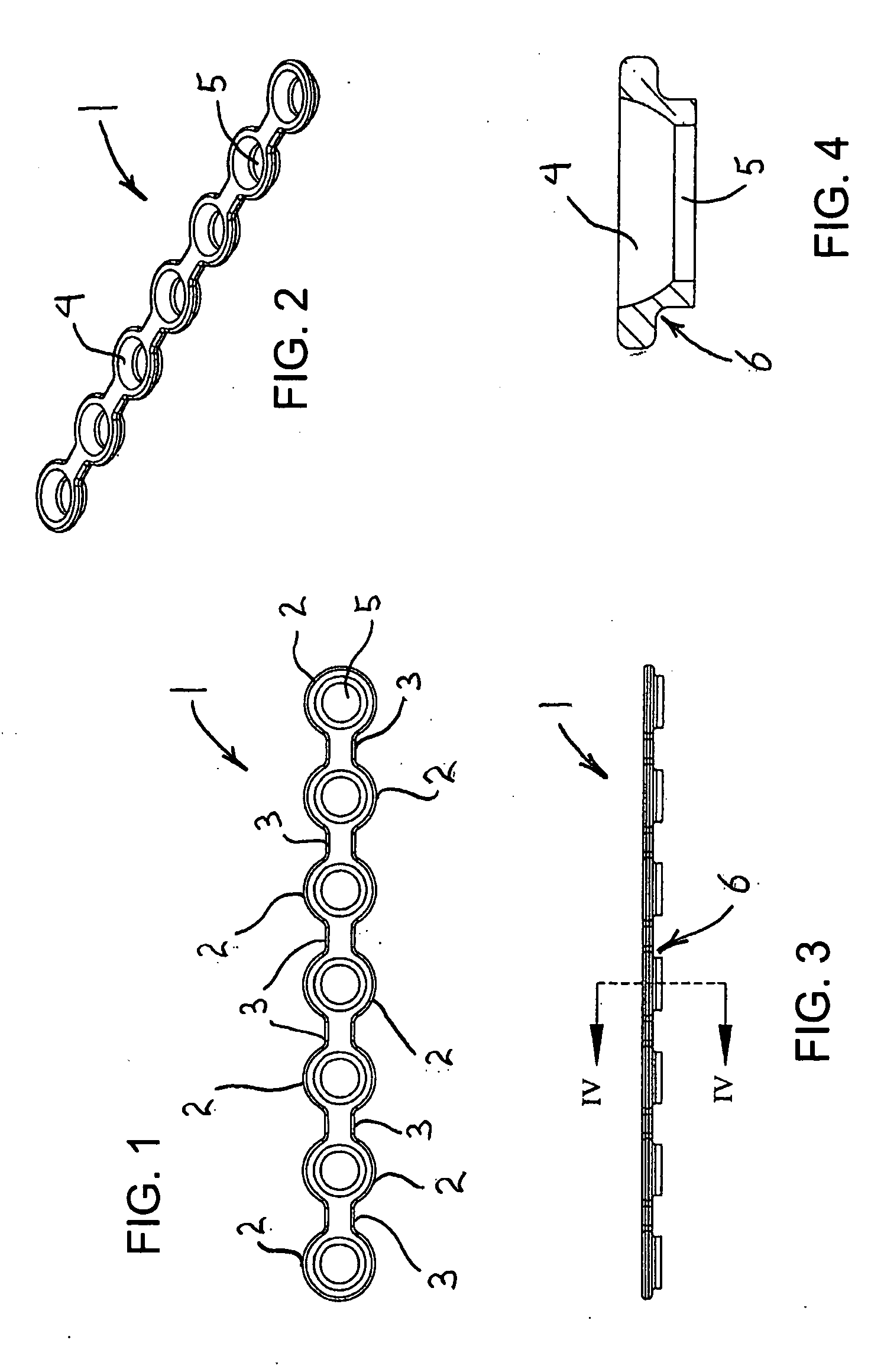
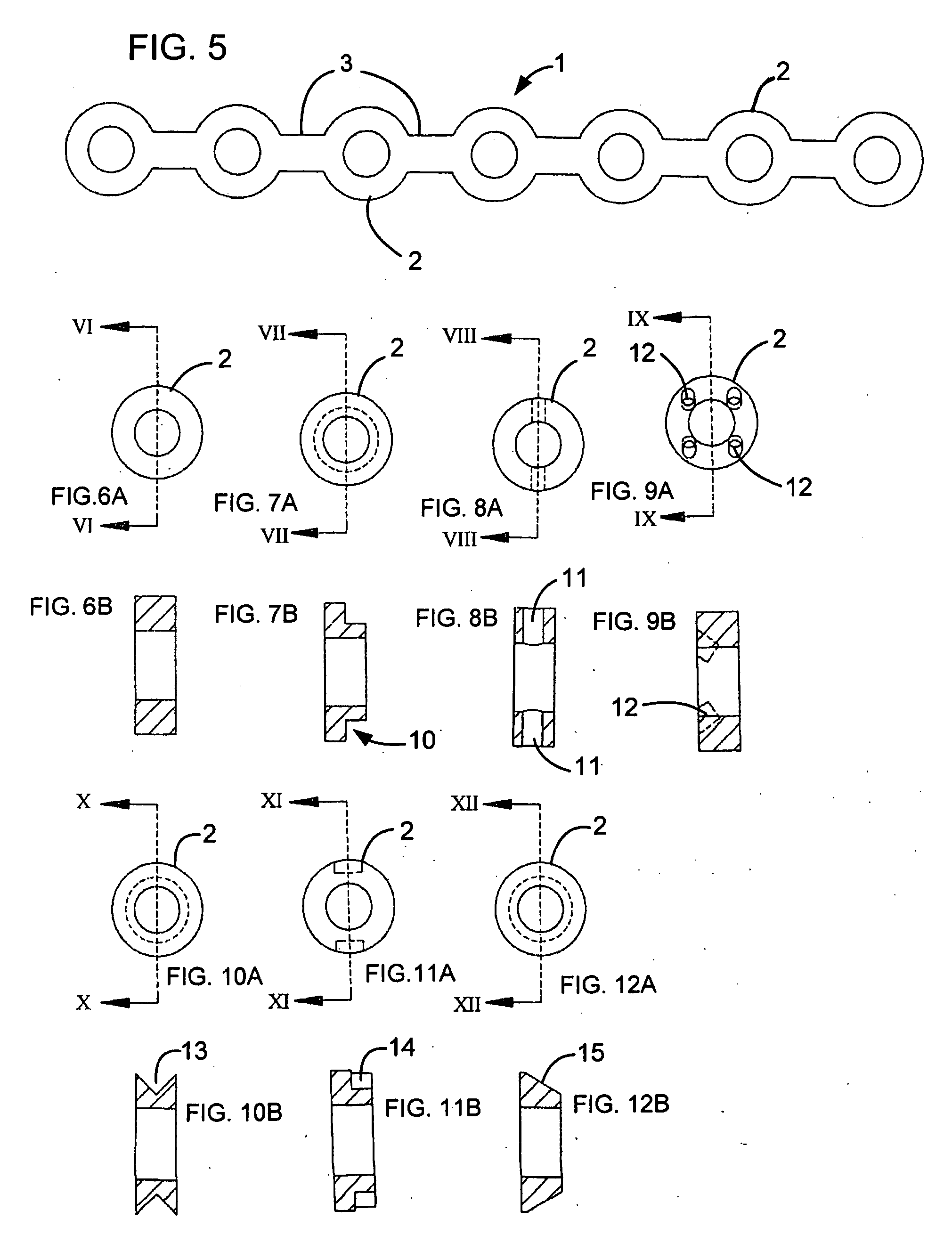
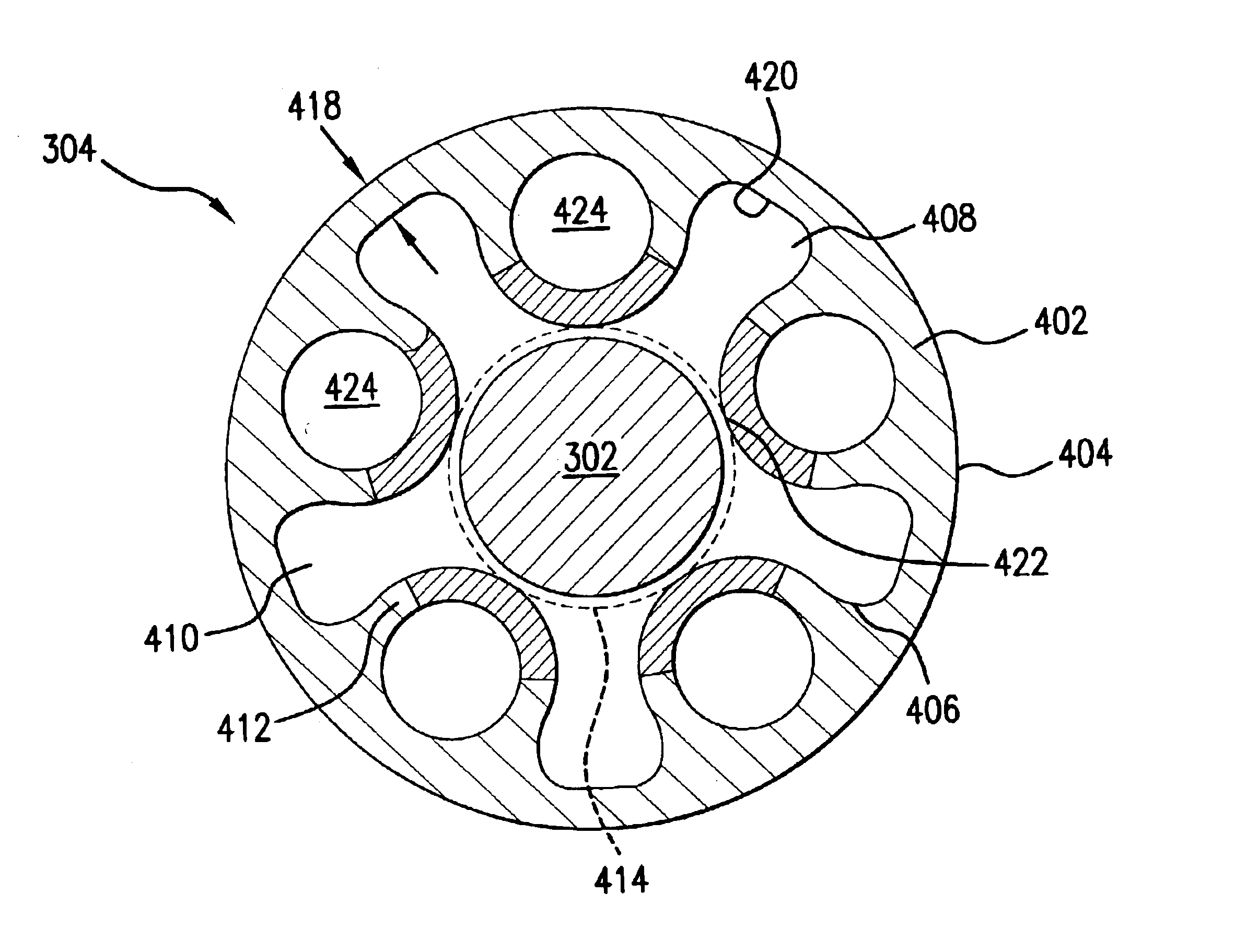
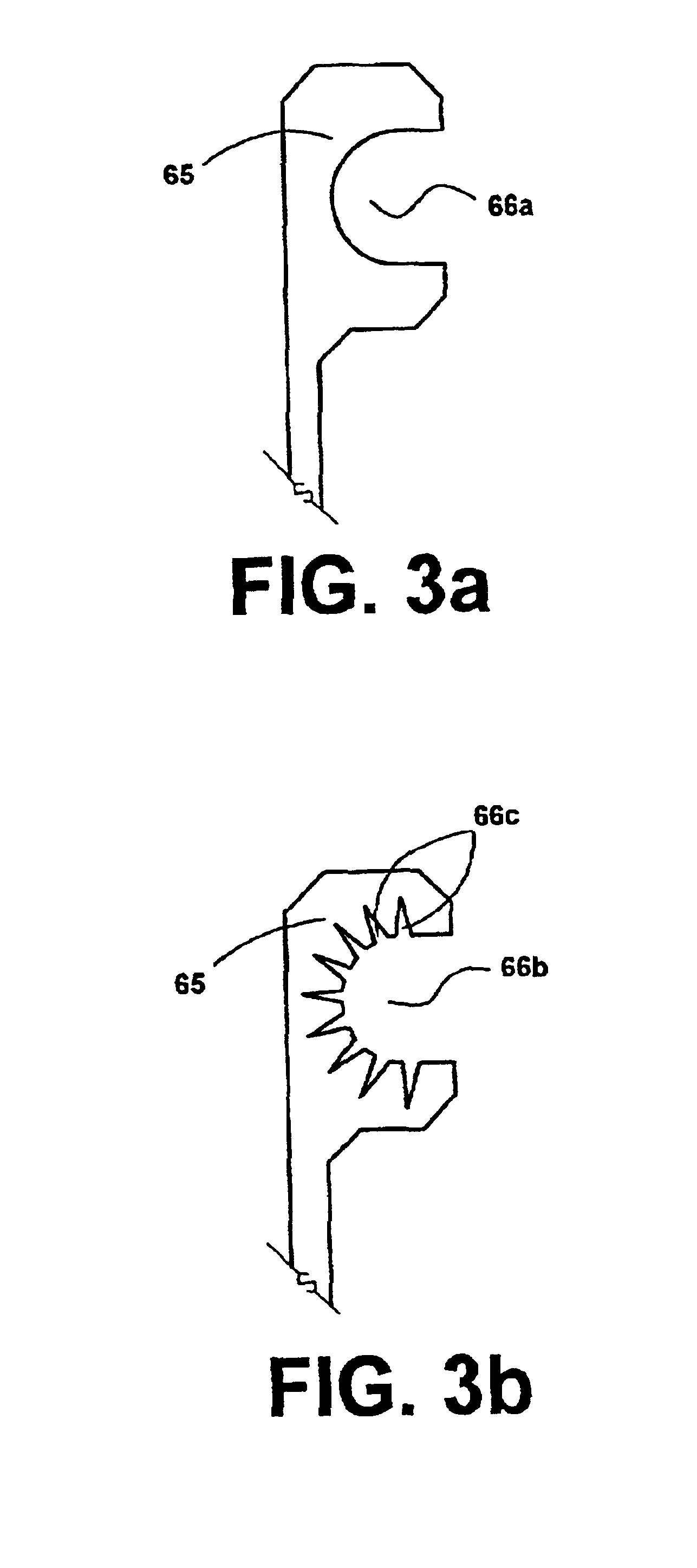
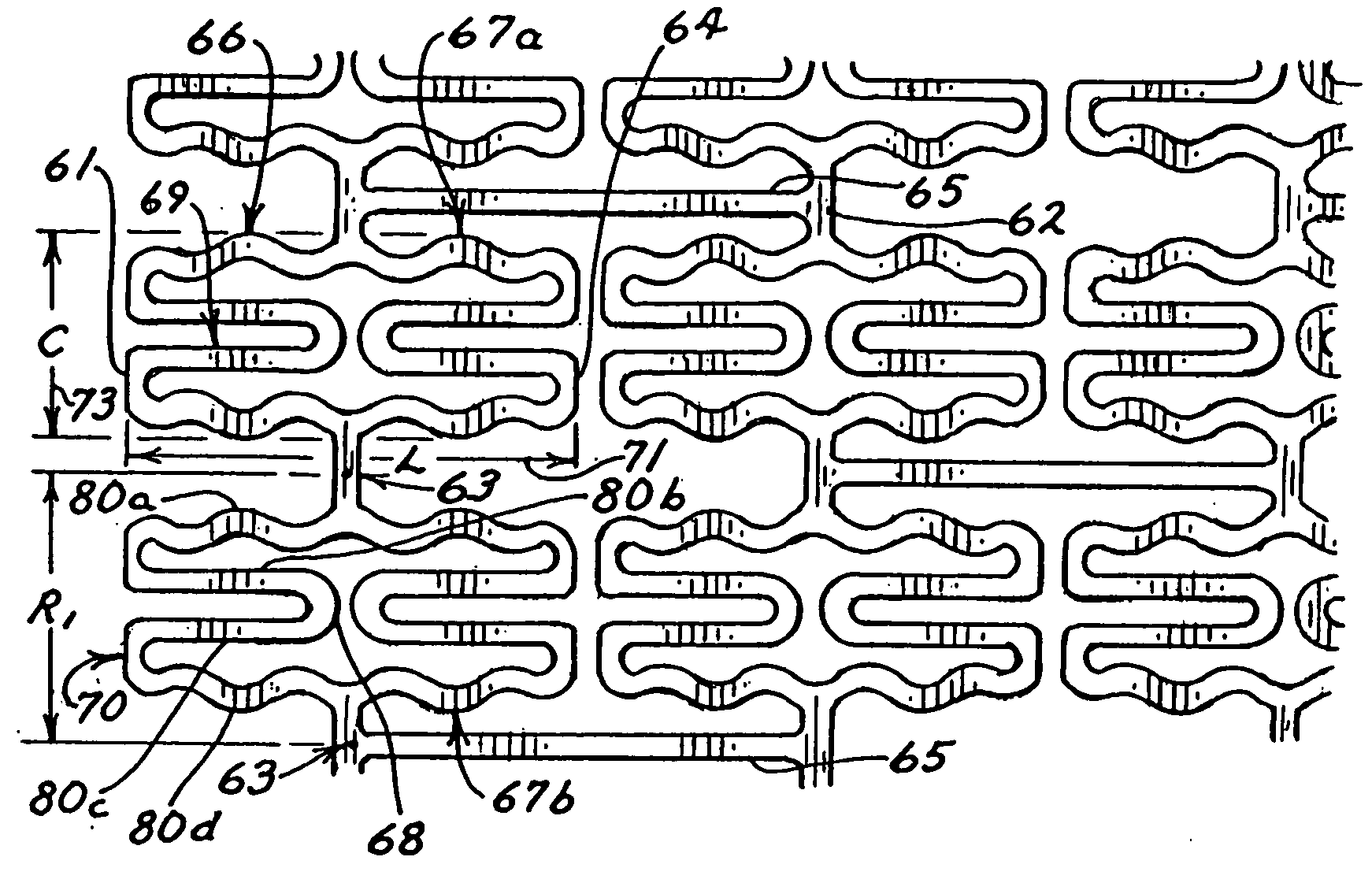
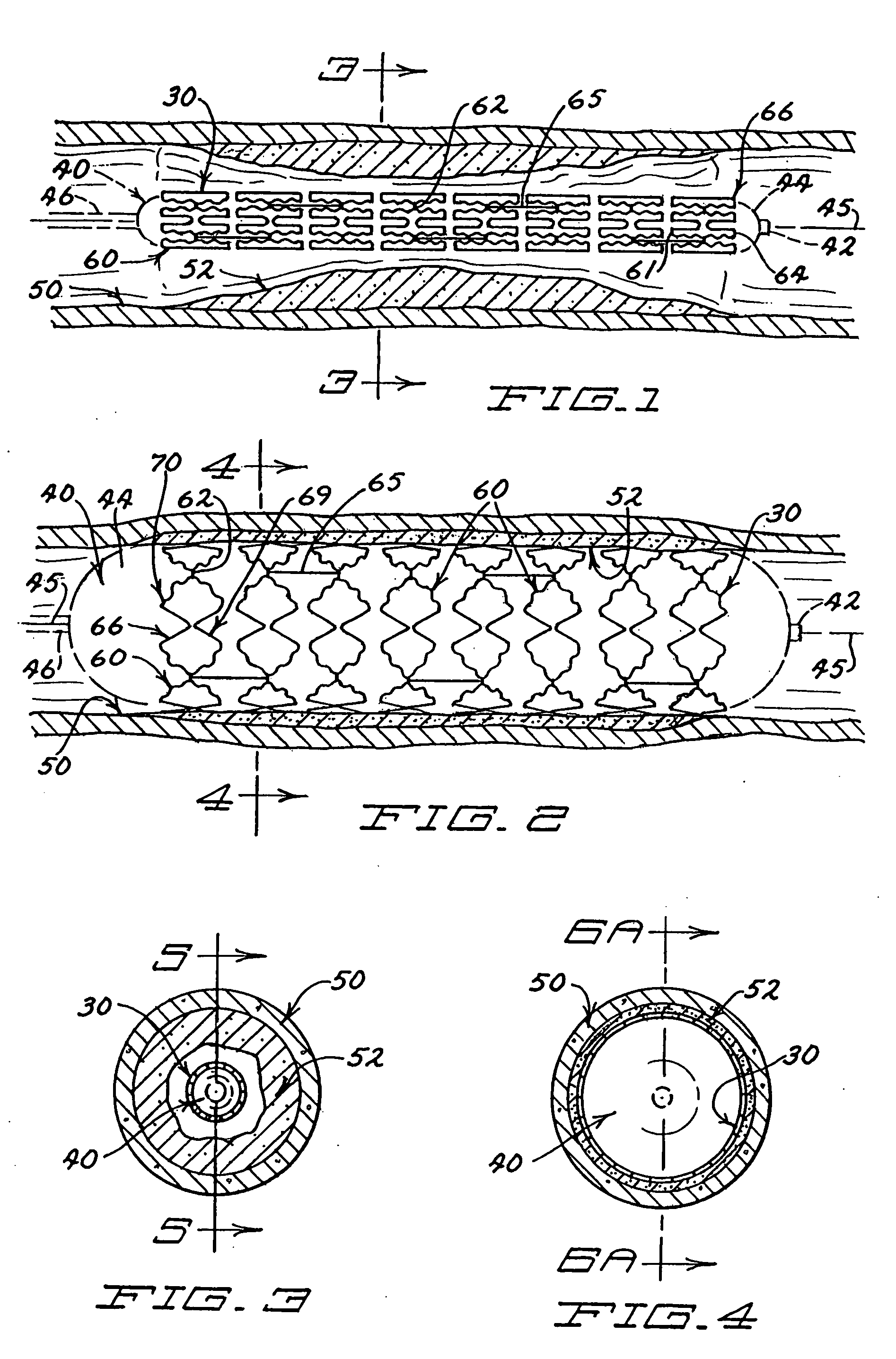
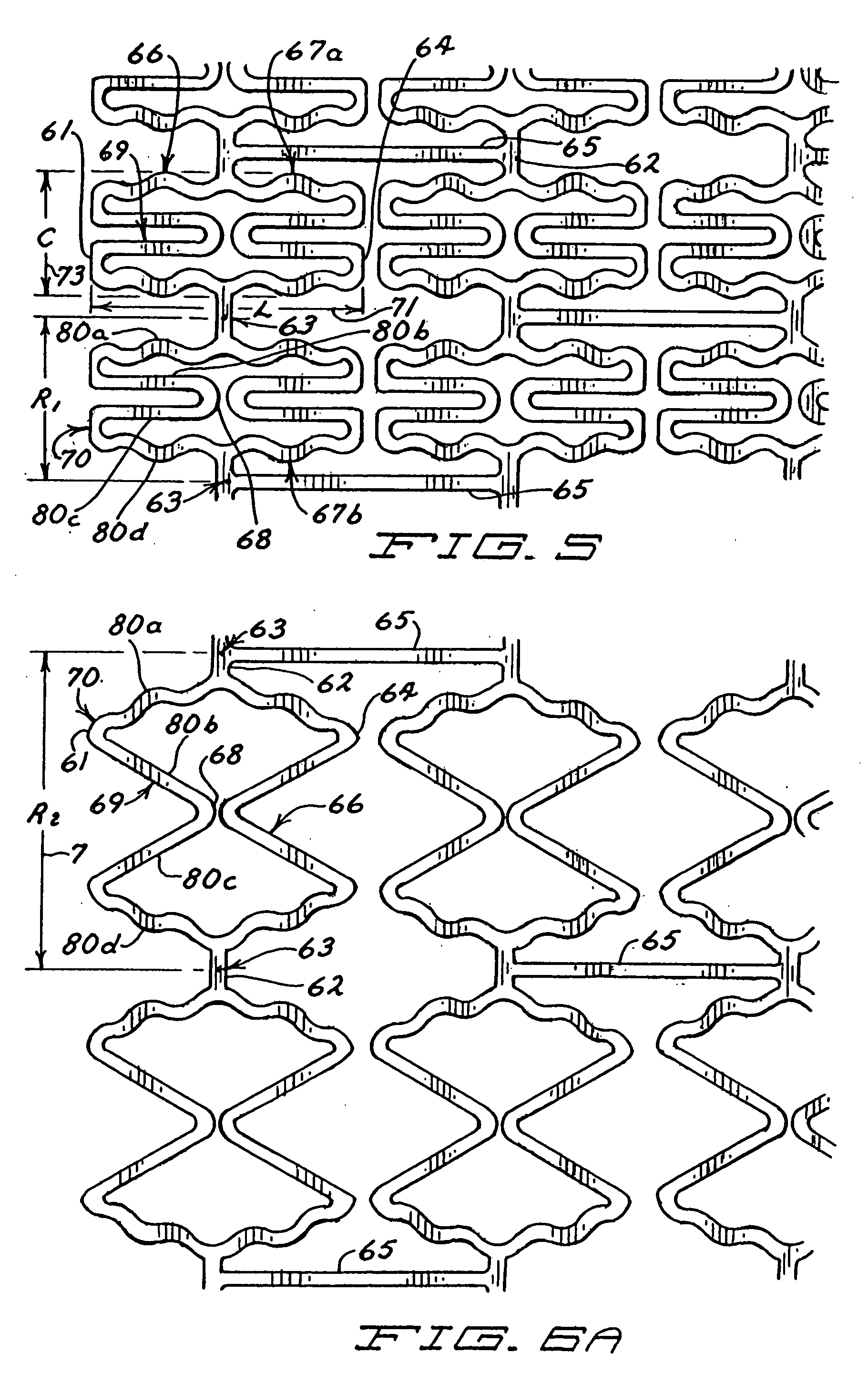
InactiveUS20050004656A1Significantly improvedSmall surface areaStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentInterconnection
Expandable stents are disclosed. The stents have a plurality of rings or modules interconnected in series, with selectable links between the rings to provide for articulation. The preferred stent includes a plurality of modules, each of the modules being radially interconnected to form a ring configured to be expandably interconnected and being interconnected to each other in series by respective interconnection bridges. Each ring including a continuous strand of a material, the continuous strand of material being interconnected end to end so as to generally encompass a radial space within the ring. The strand of material being configured to include a repeating series of interconnected repeating W-shaped strand configurations having a repeating dip, rise, dip, rise, loop, dip, rise, dip, rise, loop patterned configuration. Preferably, the continuous strand of a material has an outer surface including cavities being at least partially filled with compositions containing medicinal agents selected to provide medically desirable effects upon positioning within a patient. Preferably, the continuous strand of a material has a series of narrowings that facilitate the bending of the strand. Alternate rings have at least one and preferably a number of expansion cells. The expansion cells preferably have at least one accordion structure on each side of the cell, which allows for significant expansion. The material of the respective stents being deformable such that each ring can be deformed from a first configuration wherein each ring has a first circumference and, in certain embodiments, each expansion cell has a first radial length, to a second configuration wherein each ring has a second circumference greater than the first circumference. Methods of producing the devices are also disclosed, including various etching methods.
Owner:STENT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com