Patents
Literature
614 results about "Fluoroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
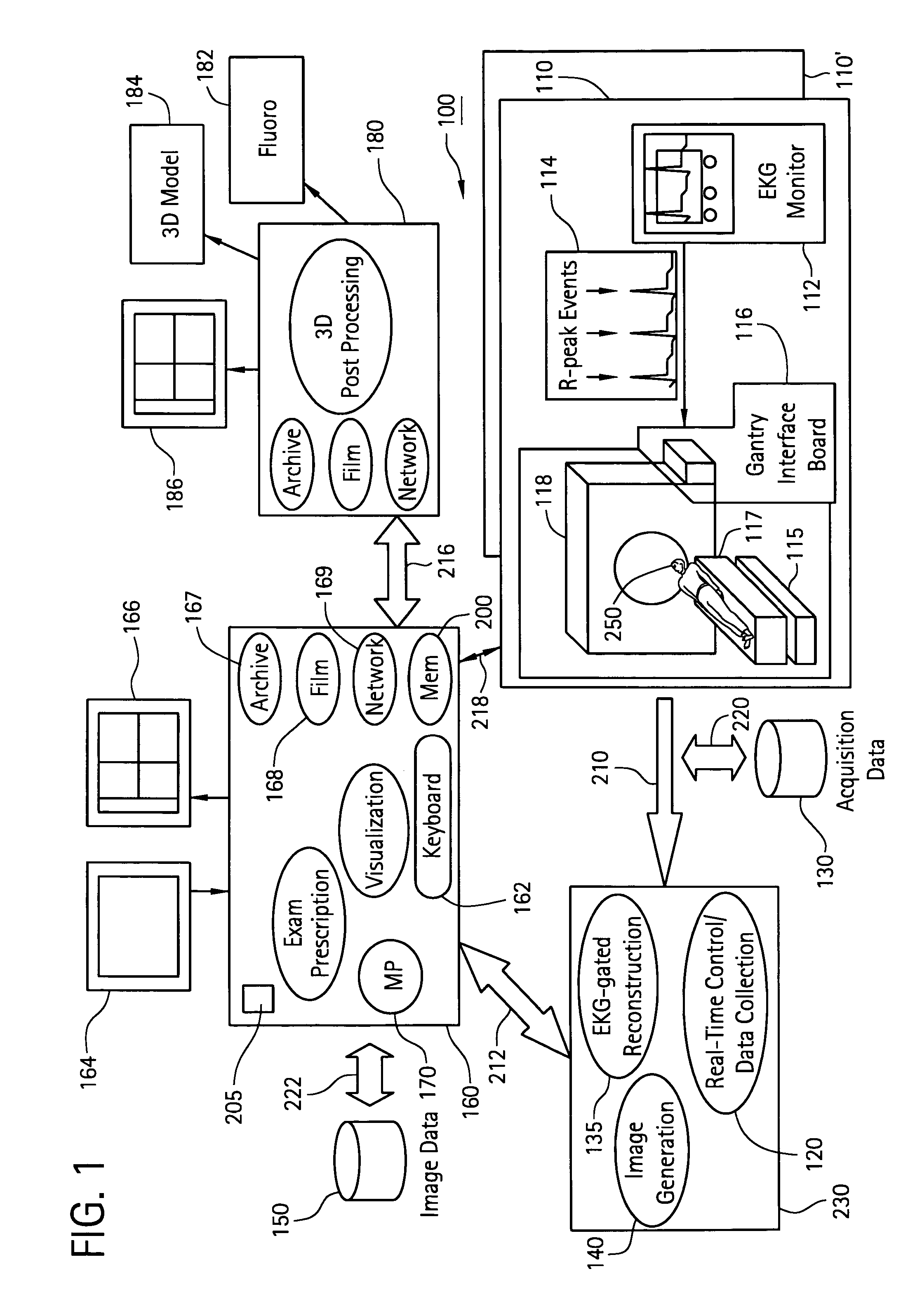
Fluoroscopy (/flʊəˈrɒskəpi/) is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope (/ˈflʊərəskoʊp/) allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.
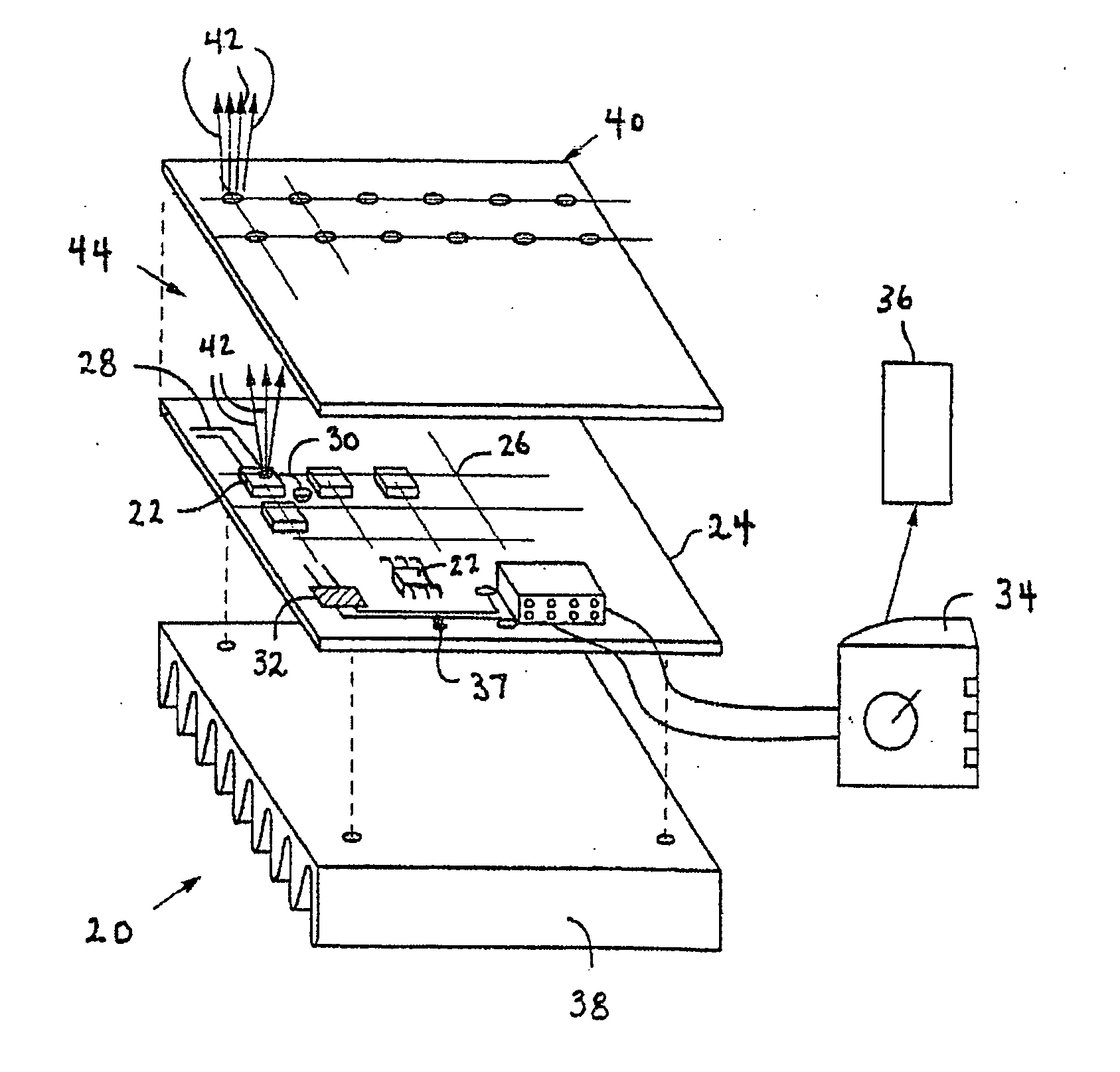
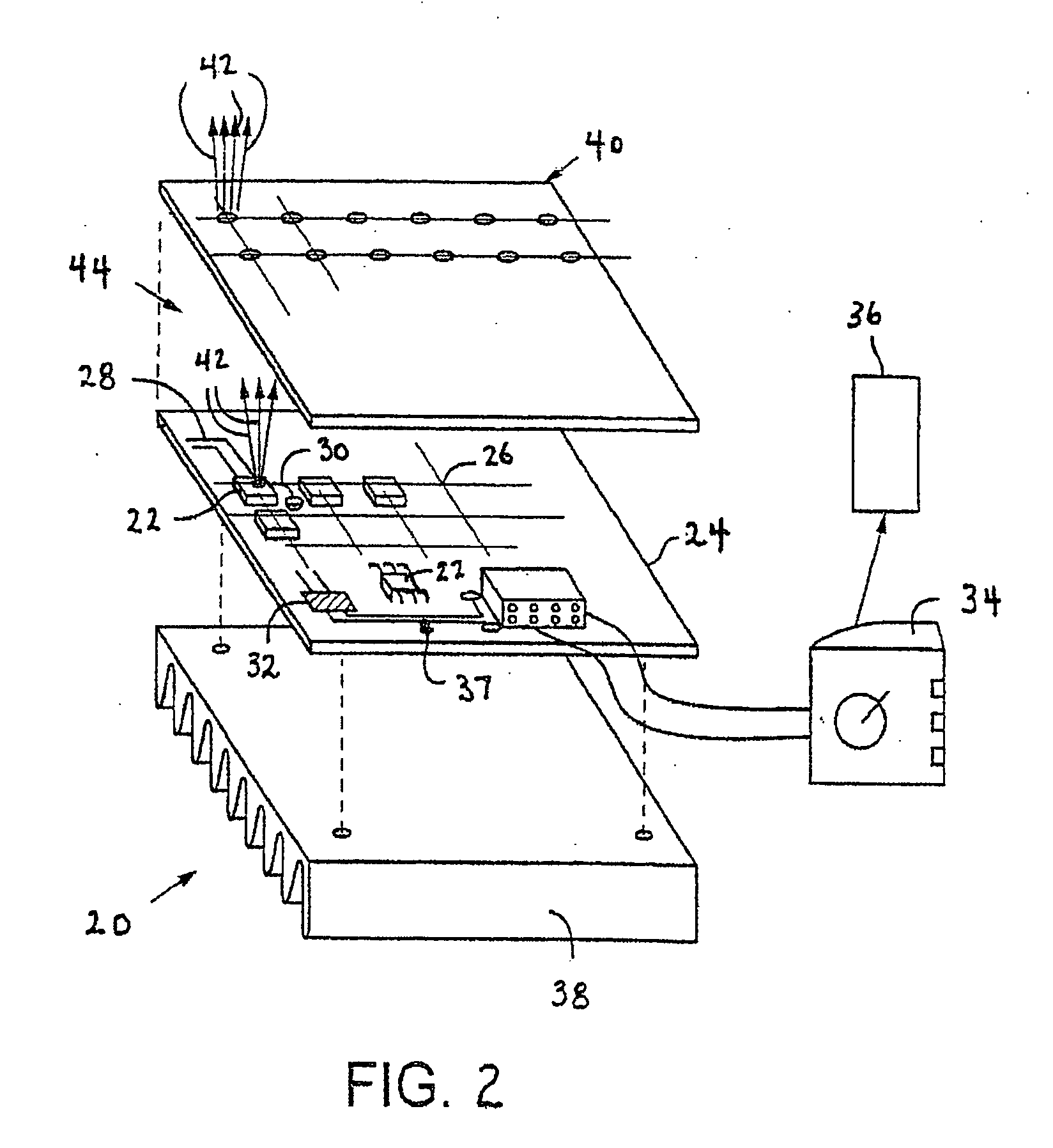
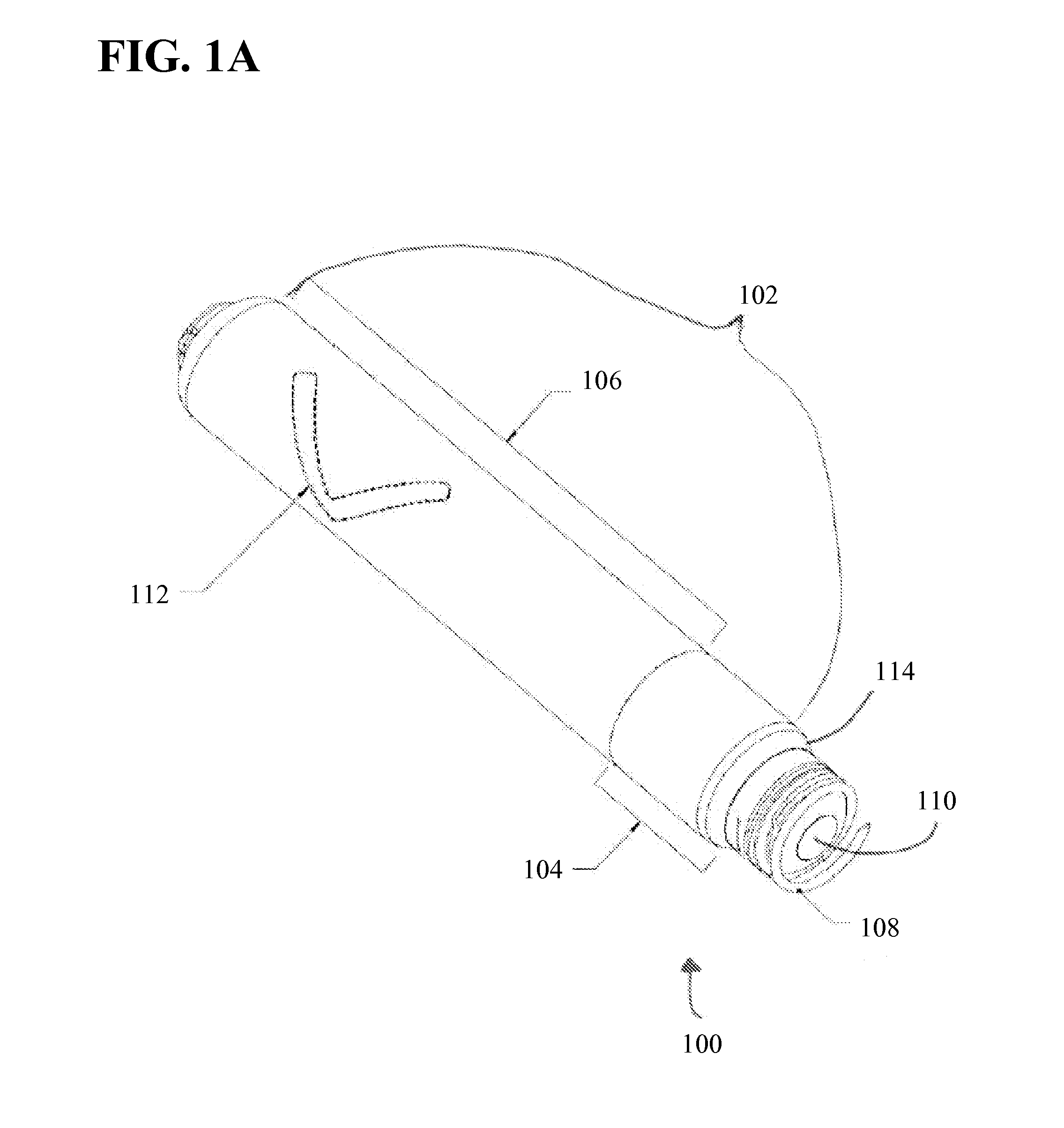
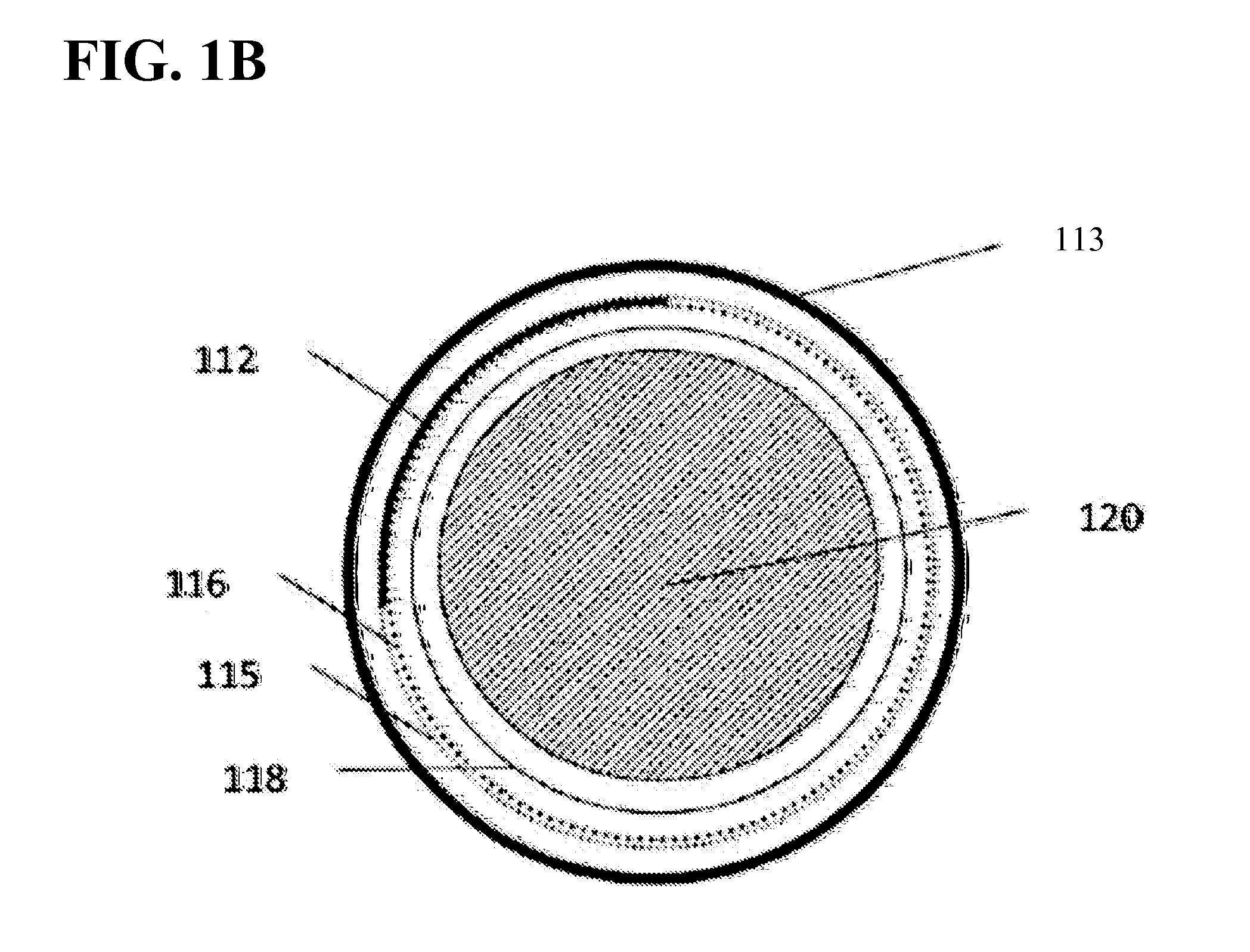
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS20050152146A1Eliminate needImprove light outputOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceDevice materialFluorescence
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
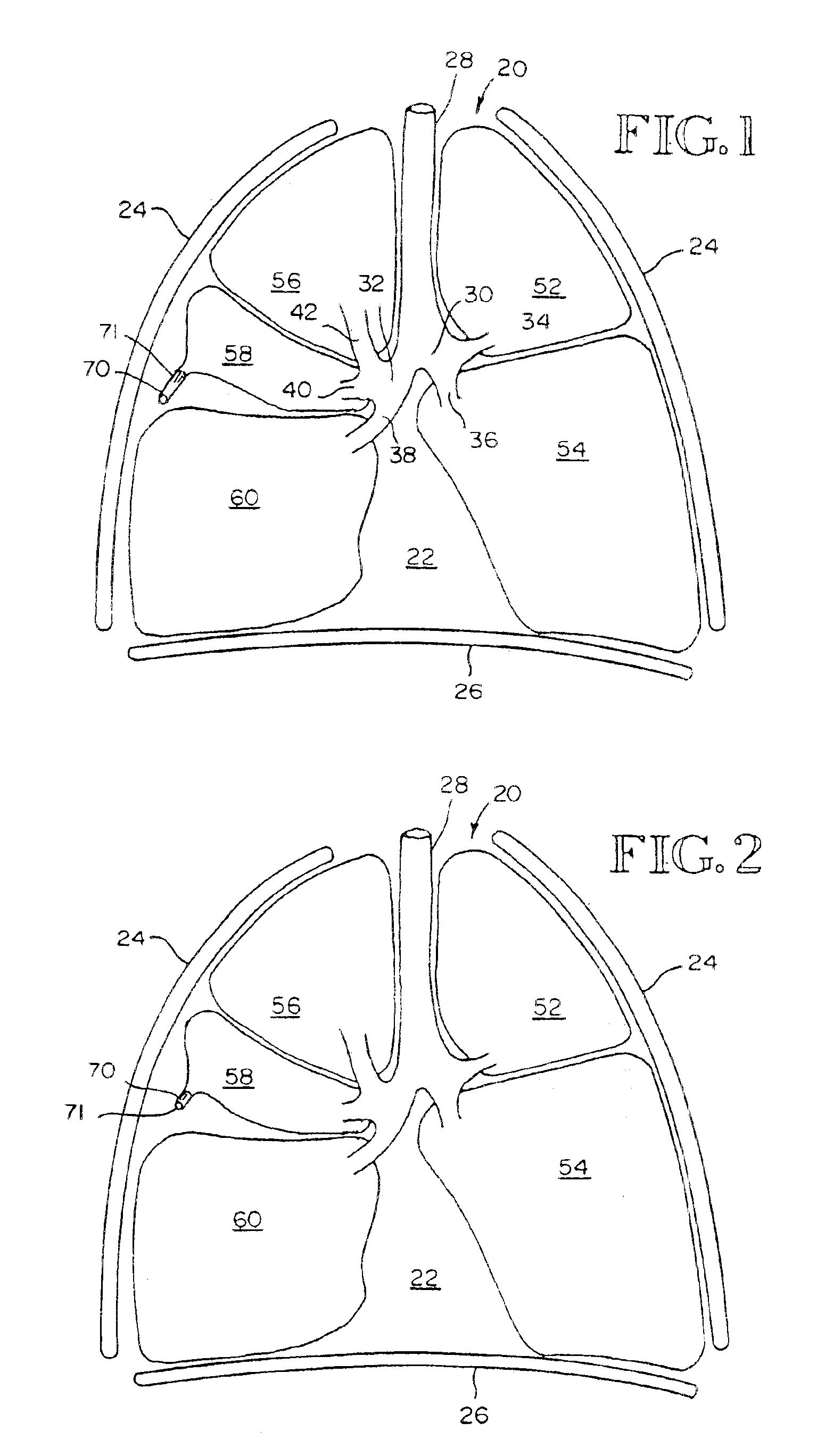
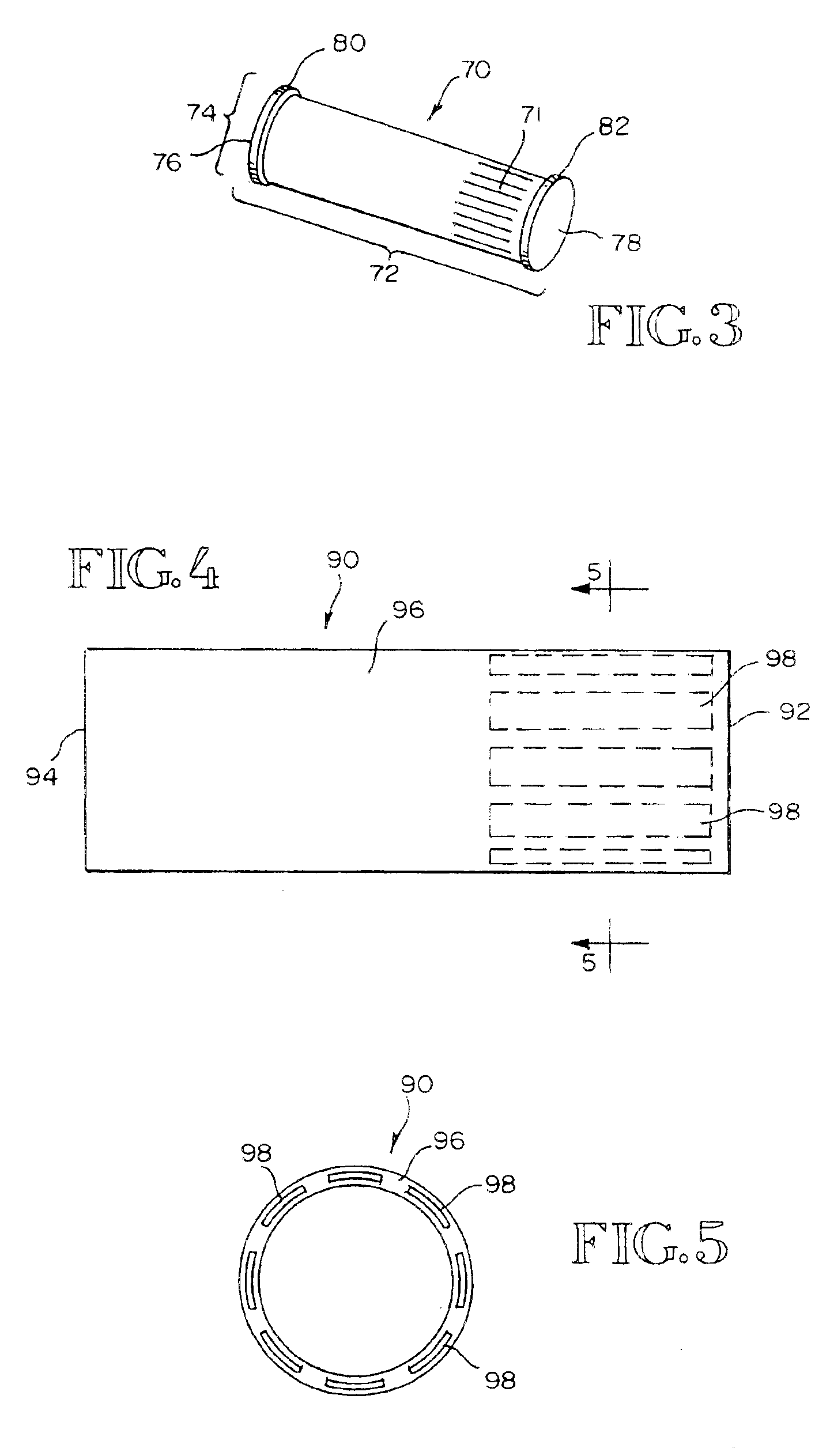
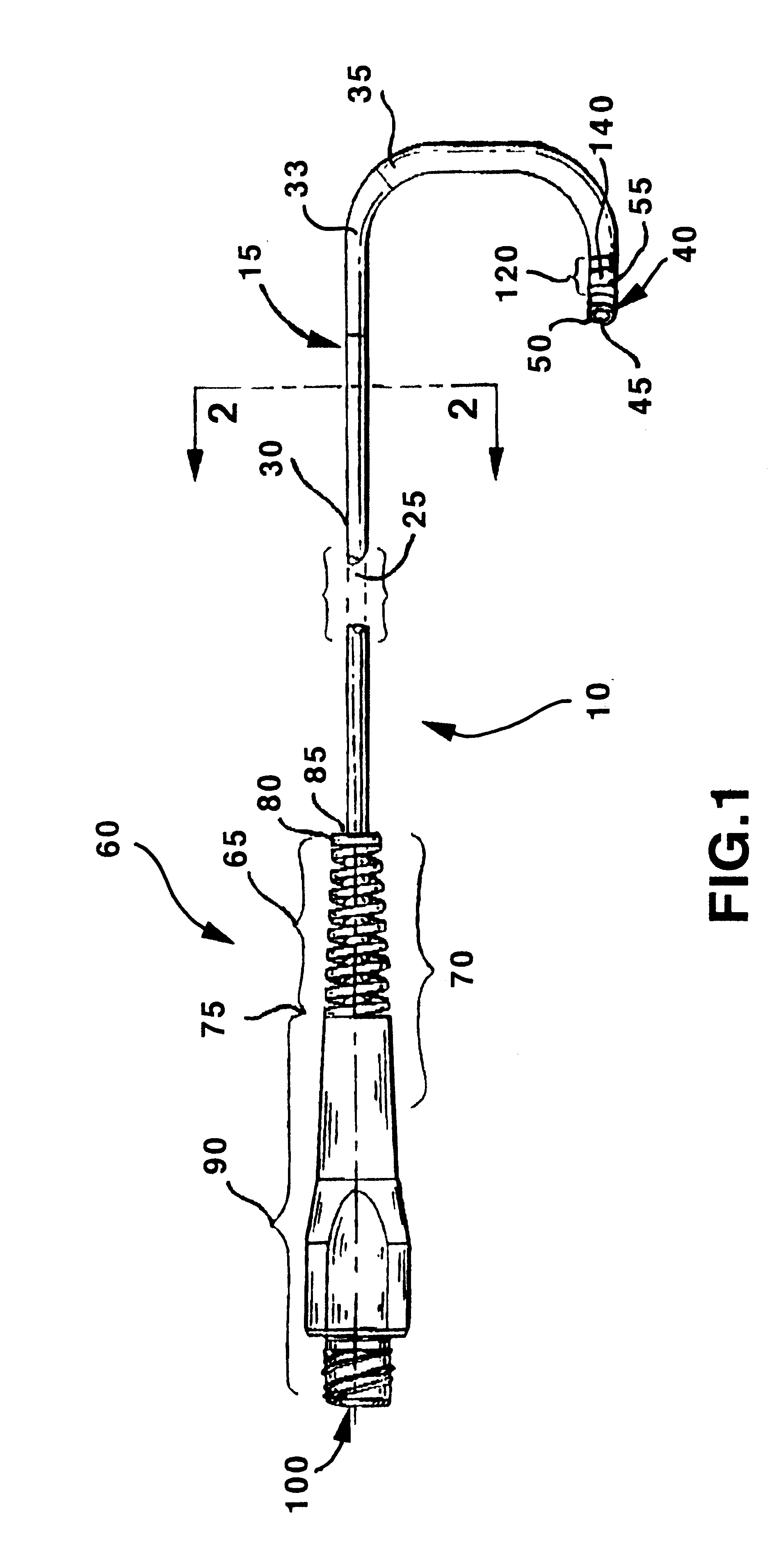
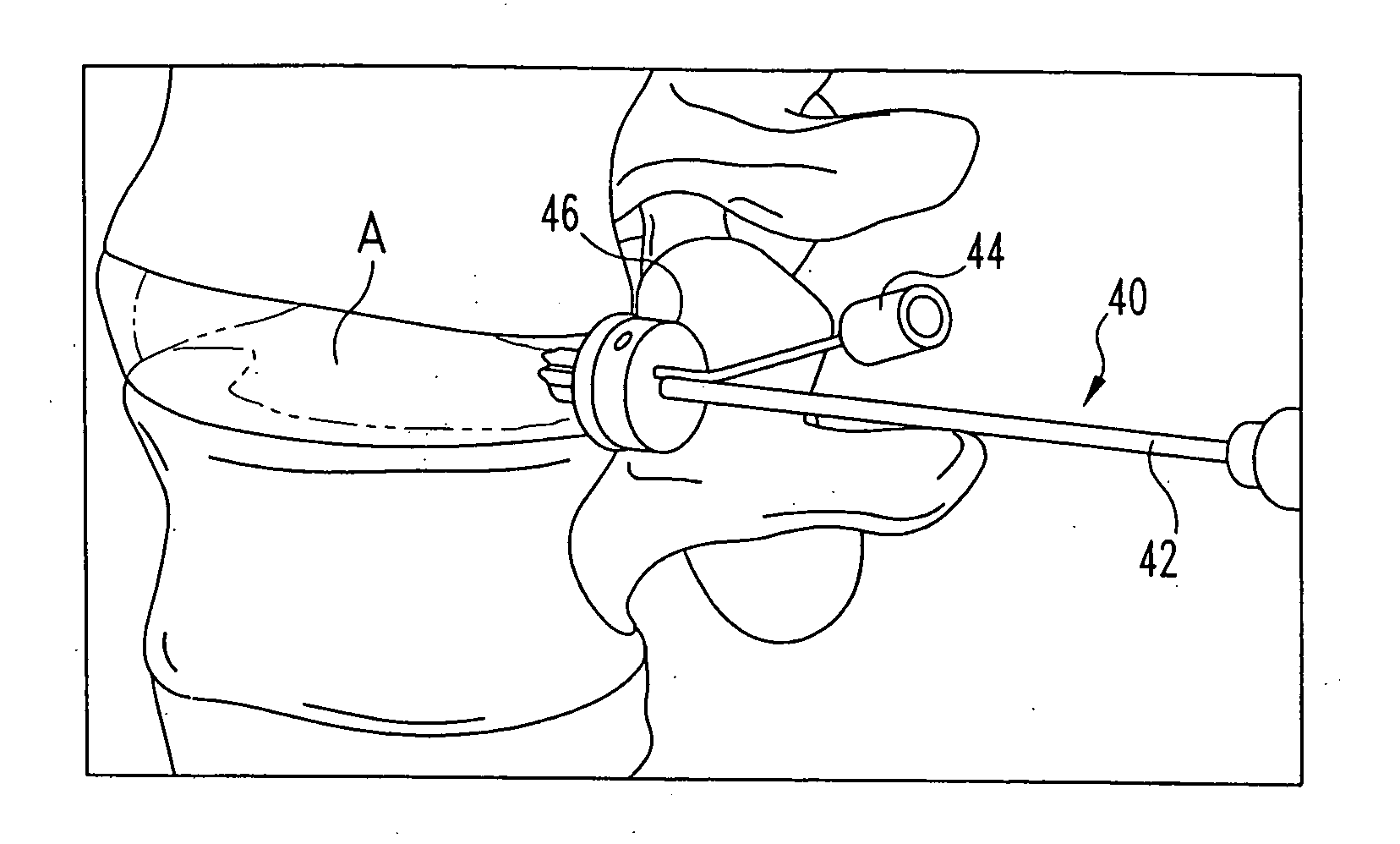
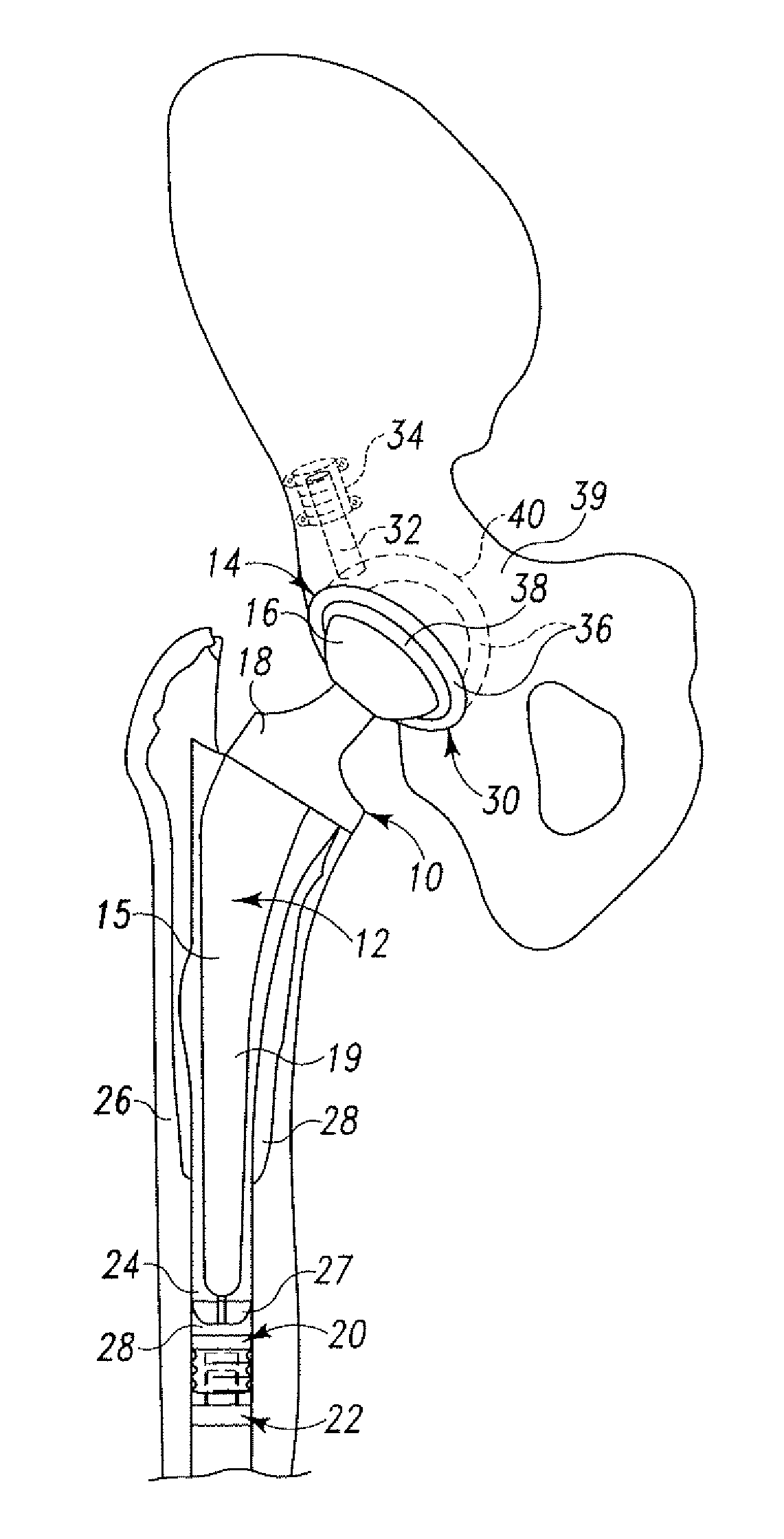
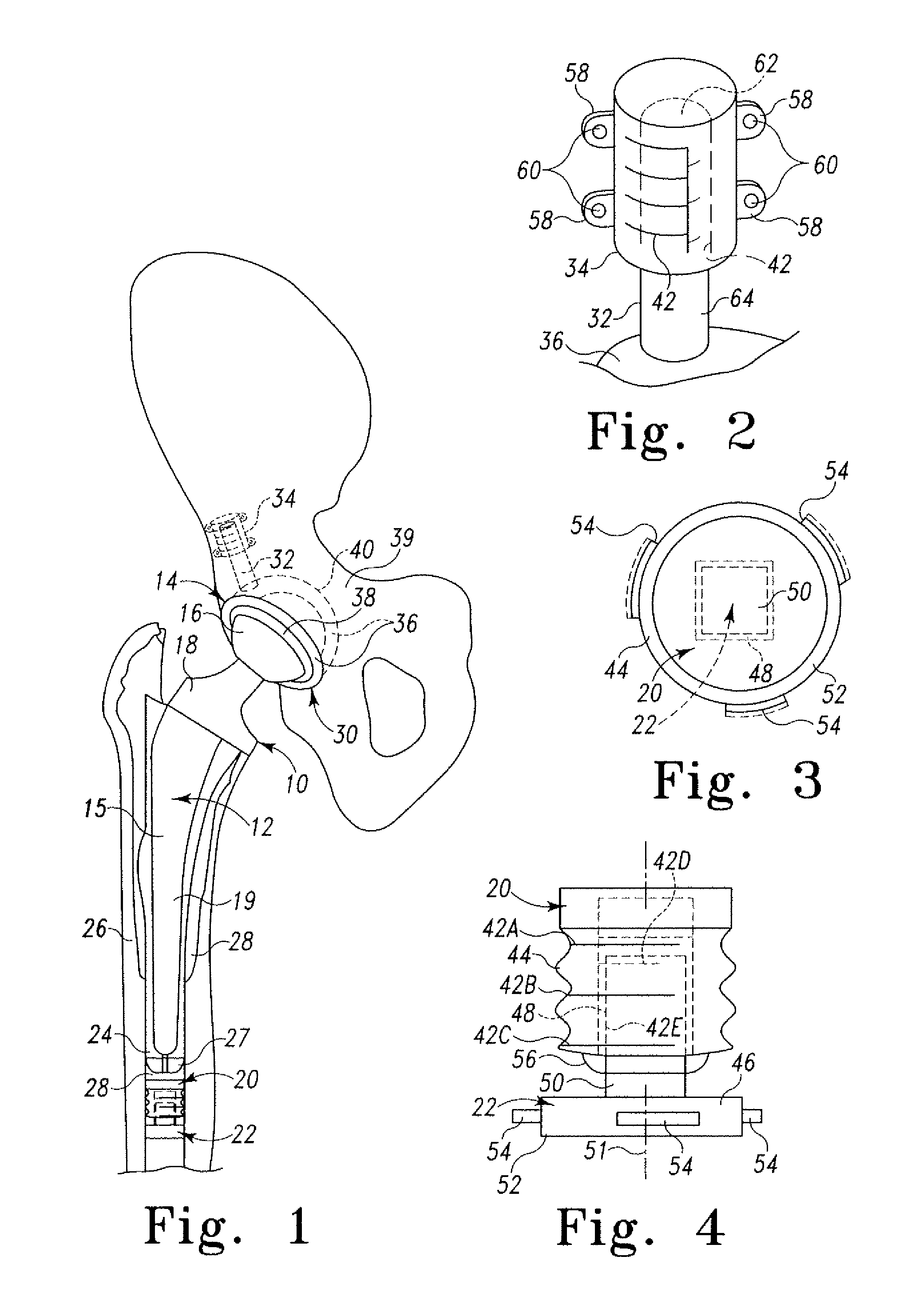
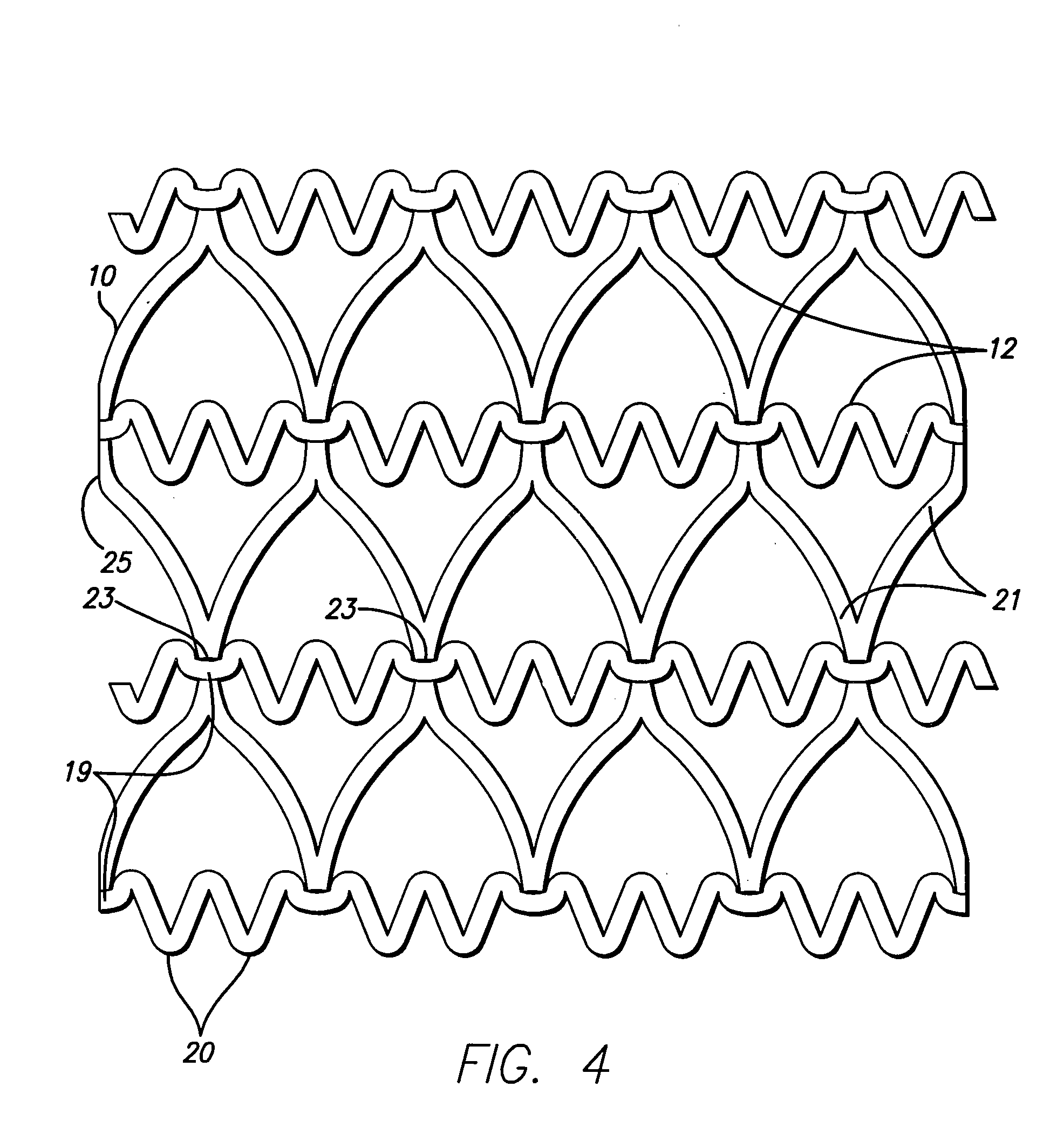
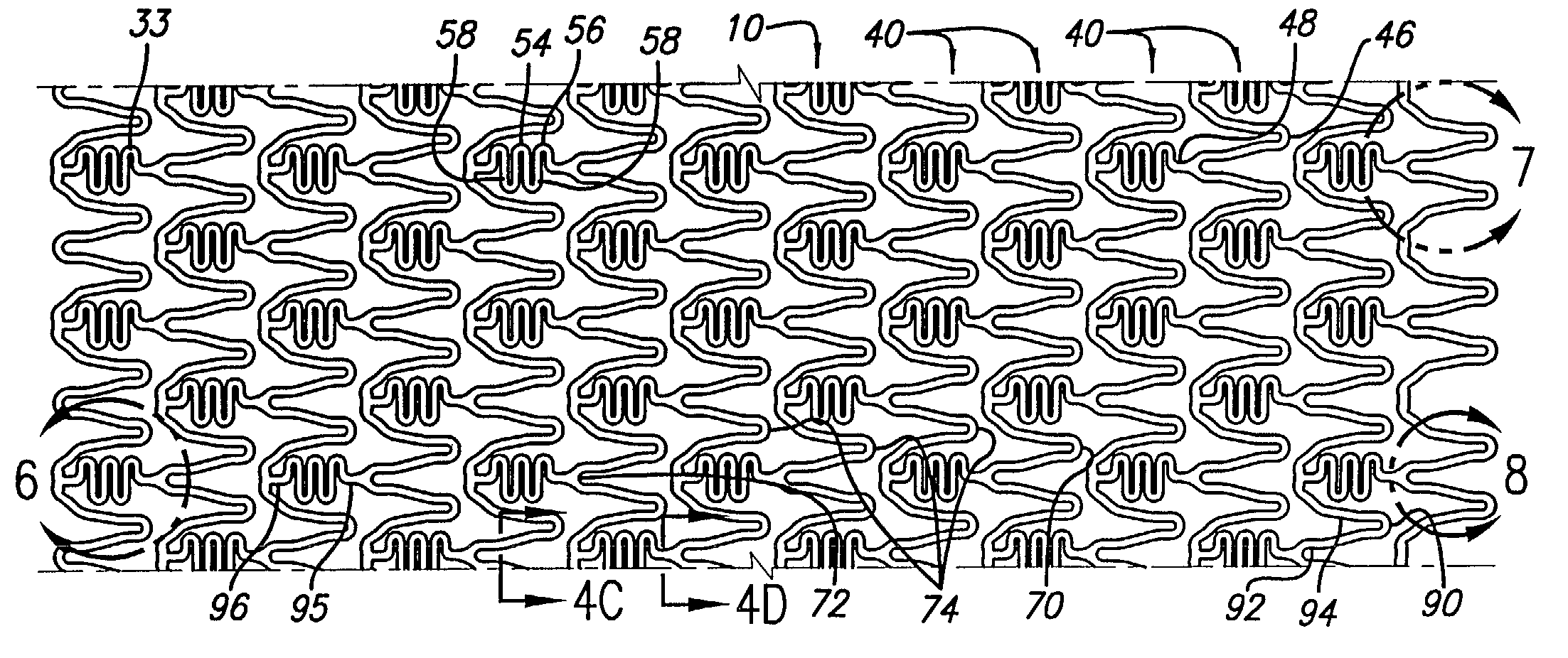
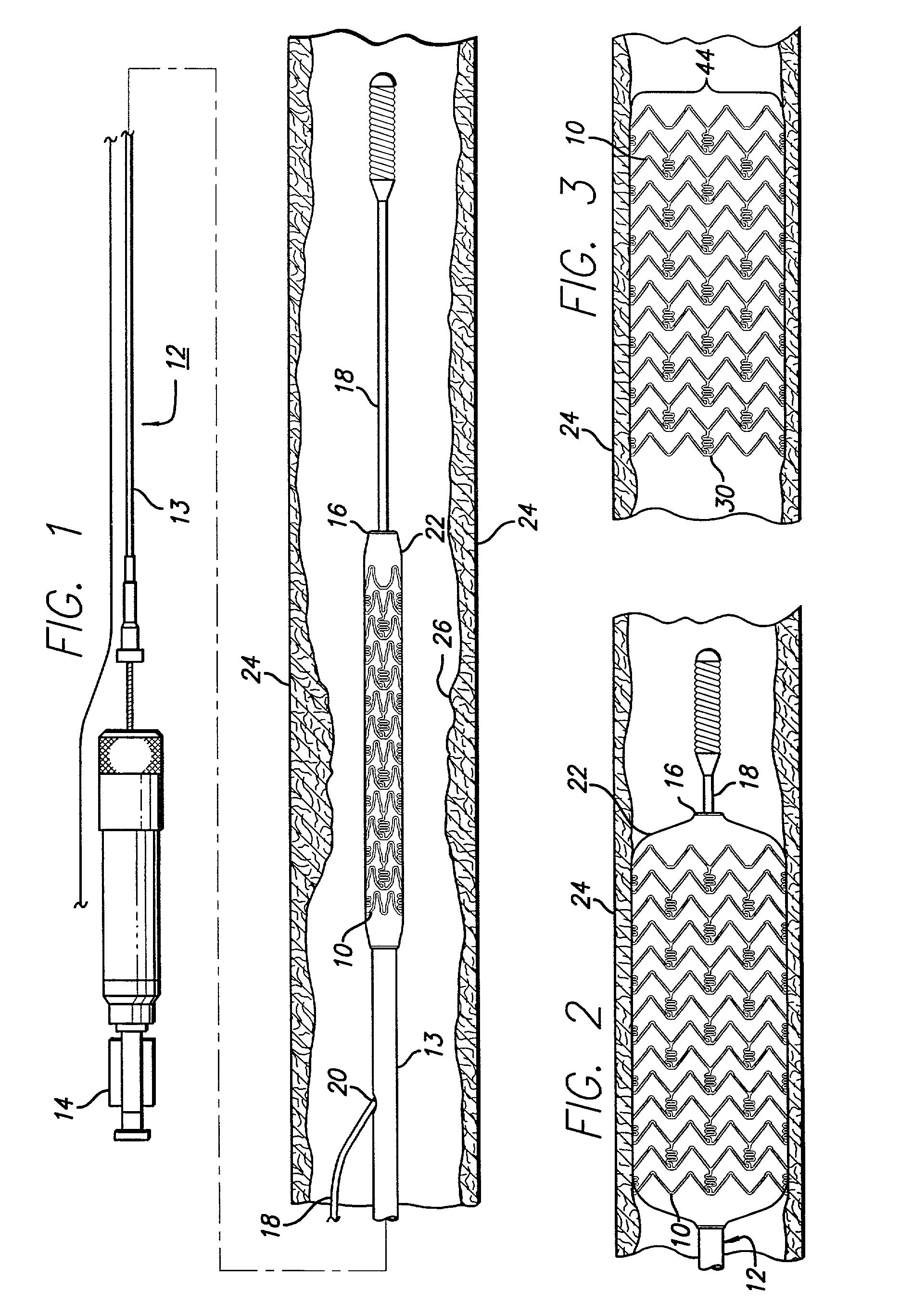
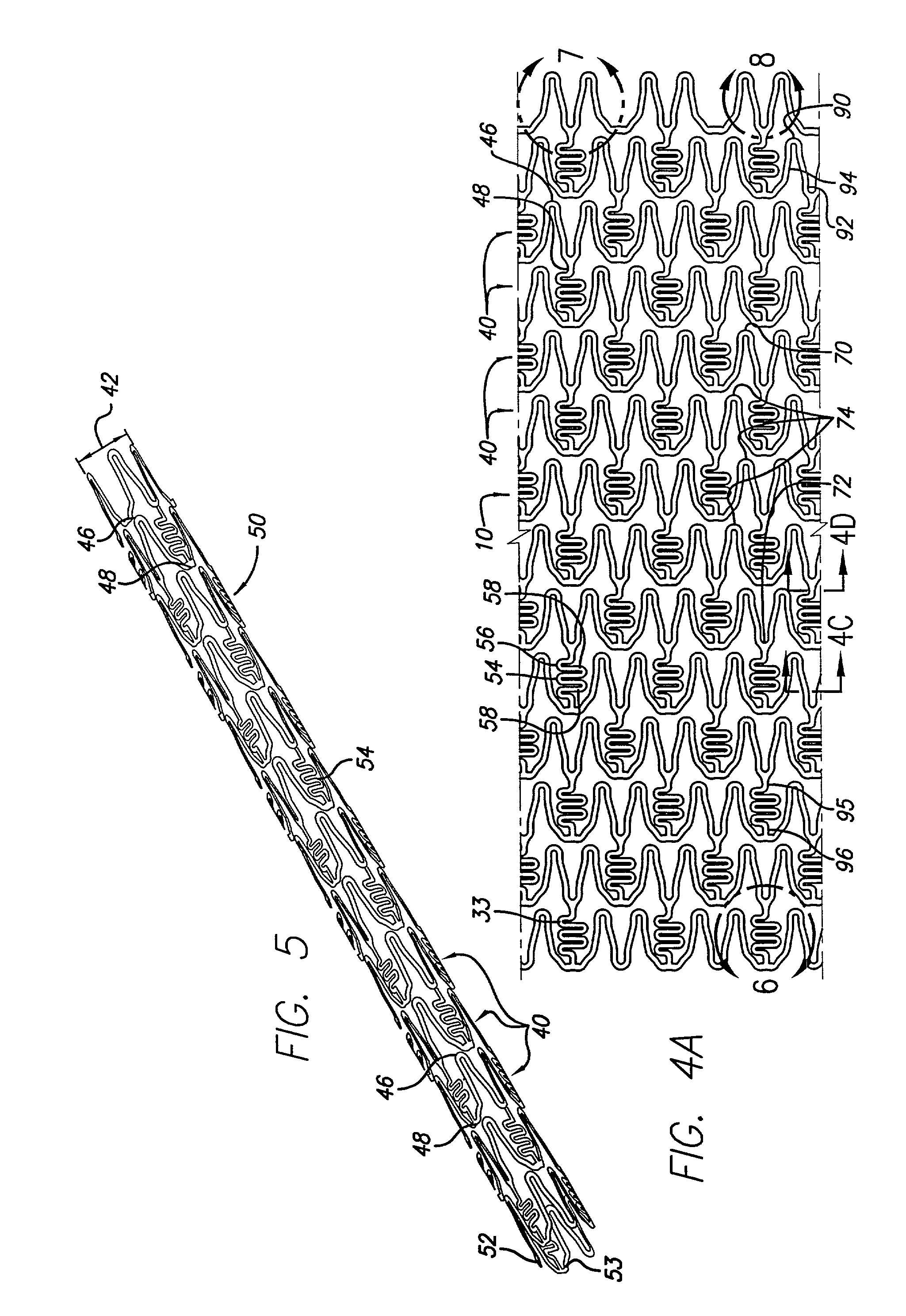
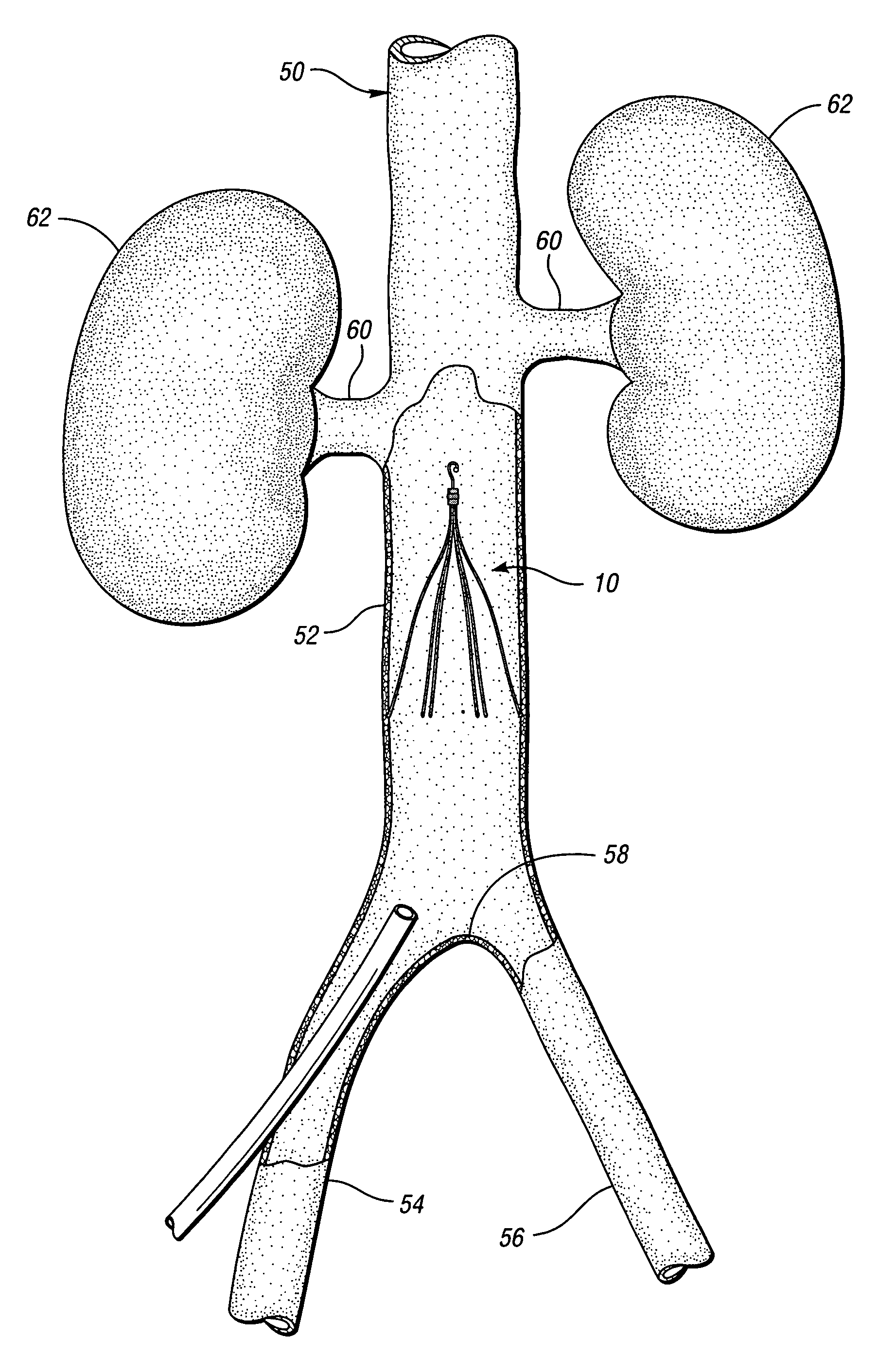
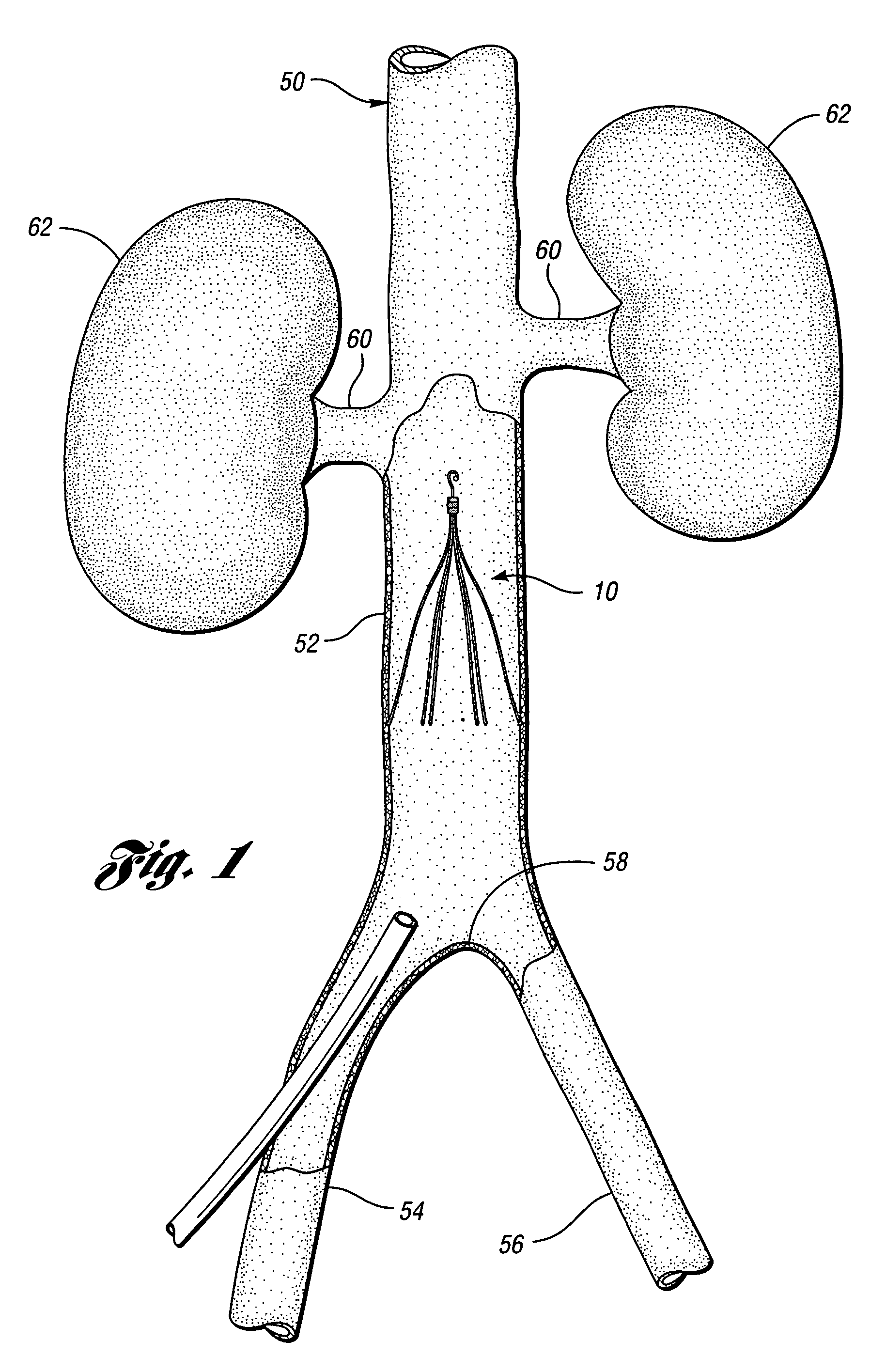
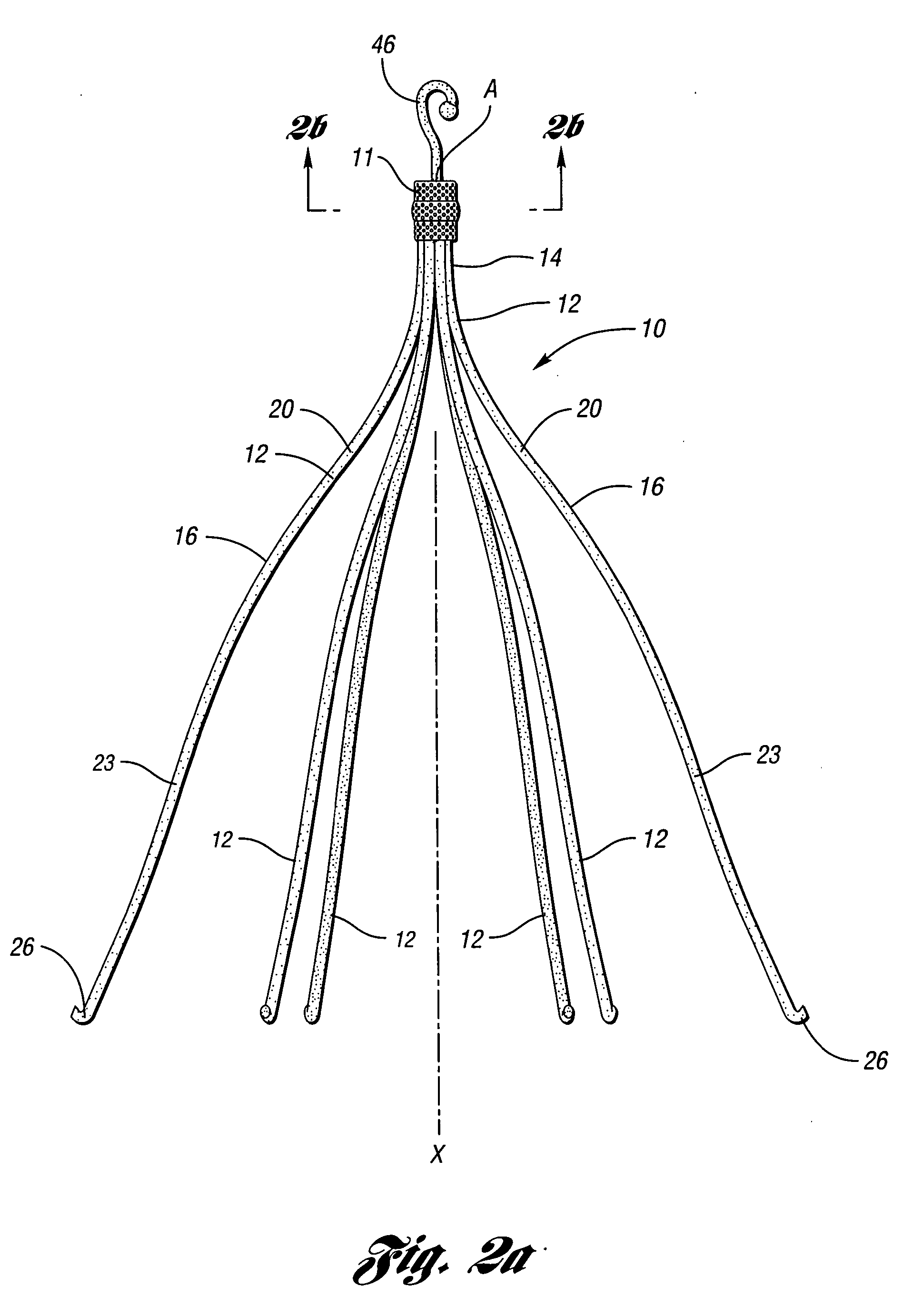
Constriction device viewable under X ray fluoroscopy
A constriction device that constricts body tissue is viewable under X ray fluoroscopy. The device includes an elongated sleeve. The sleeve includes opposed opened ends and is formed from expandable or elastic material to receive therein, when in an expanded condition, body tissue to be constricted and to constrict the body tissue therein when released from the expanded condition. At least a portion of the sleeve includes X ray opaque material rendering the device visible under X ray fluoroscopy.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
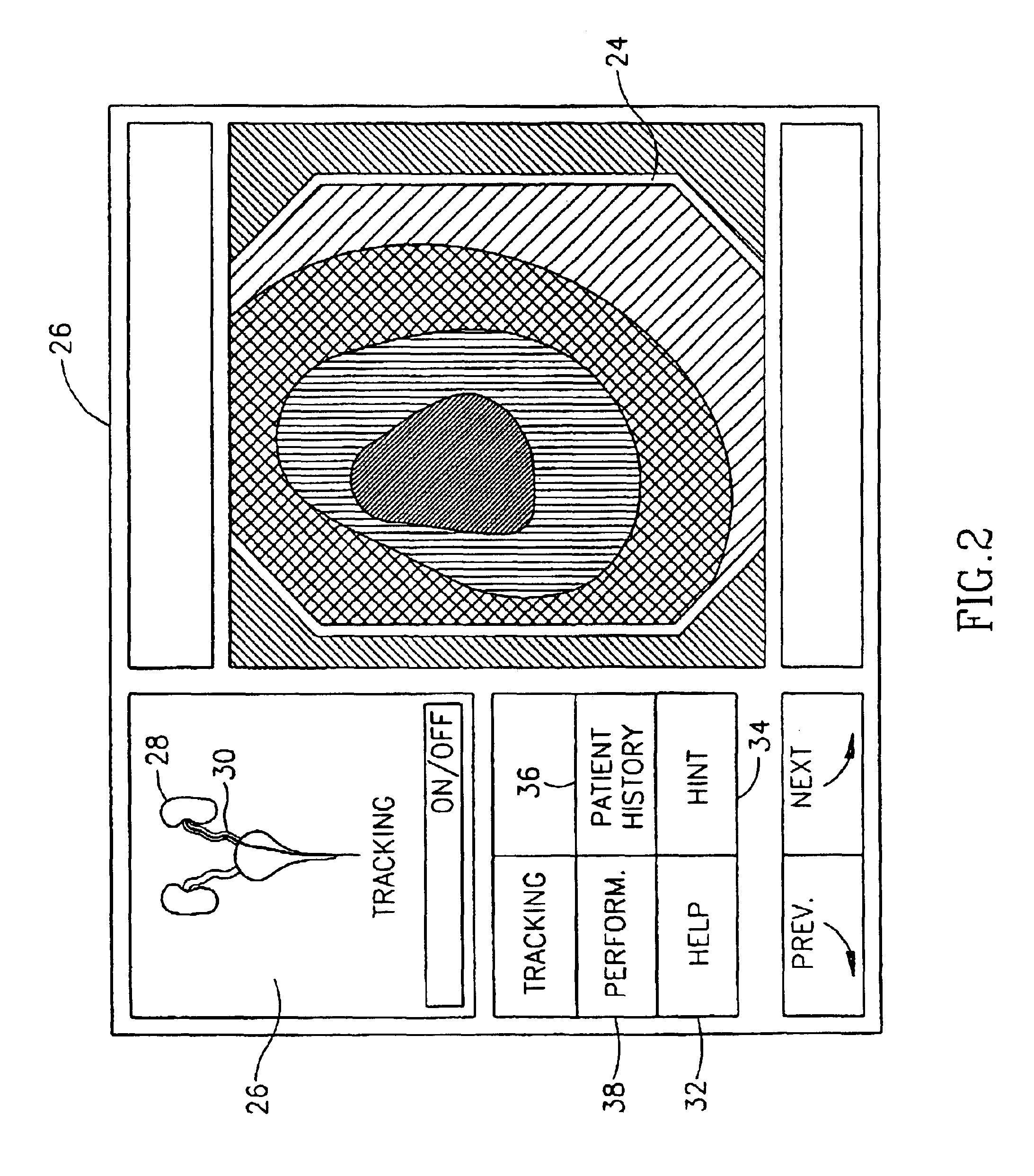
Videotactic and audiotactic assisted surgical methods and procedures
InactiveUS20080243142A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresSurgical operation
The present invention provides video and audio assisted surgical techniques and methods. Novel features of the techniques and methods provided by the present invention include presenting a surgeon with a video compilation that displays an endoscopic-camera derived image, a reconstructed view of the surgical field (including fiducial markers indicative of anatomical locations on or in the patient), and / or a real-time video image of the patient. The real-time image can be obtained either with the video camera that is part of the image localized endoscope or with an image localized video camera without an endoscope, or both. In certain other embodiments, the methods of the present invention include the use of anatomical atlases related to pre-operative generated images derived from three-dimensional reconstructed CT, MRI, x-ray, or fluoroscopy. Images can furthermore be obtained from pre-operative imaging and spacial shifting of anatomical structures may be identified by intraoperative imaging and appropriate correction performed.
Owner:GILDENBERG PHILIP L
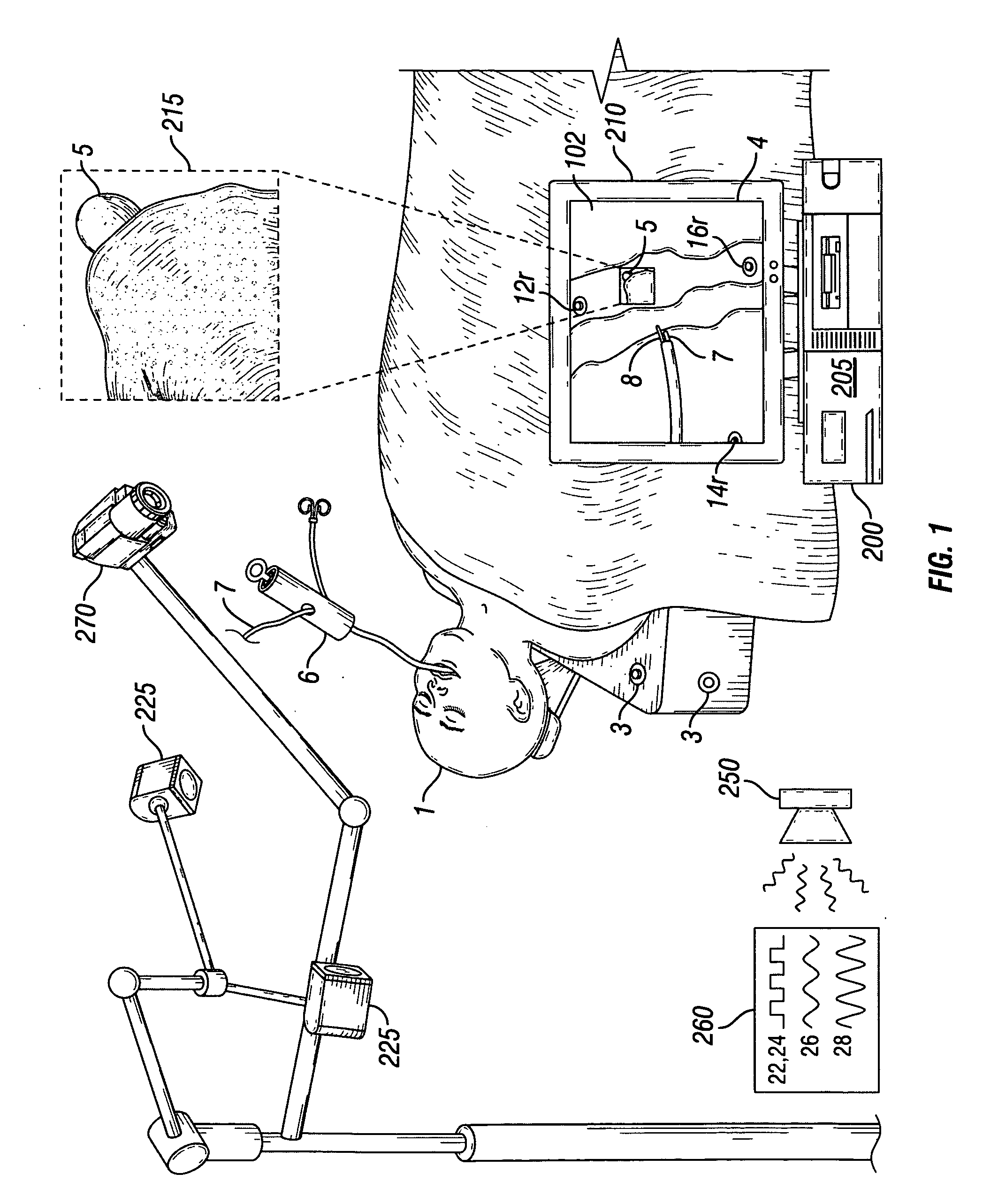
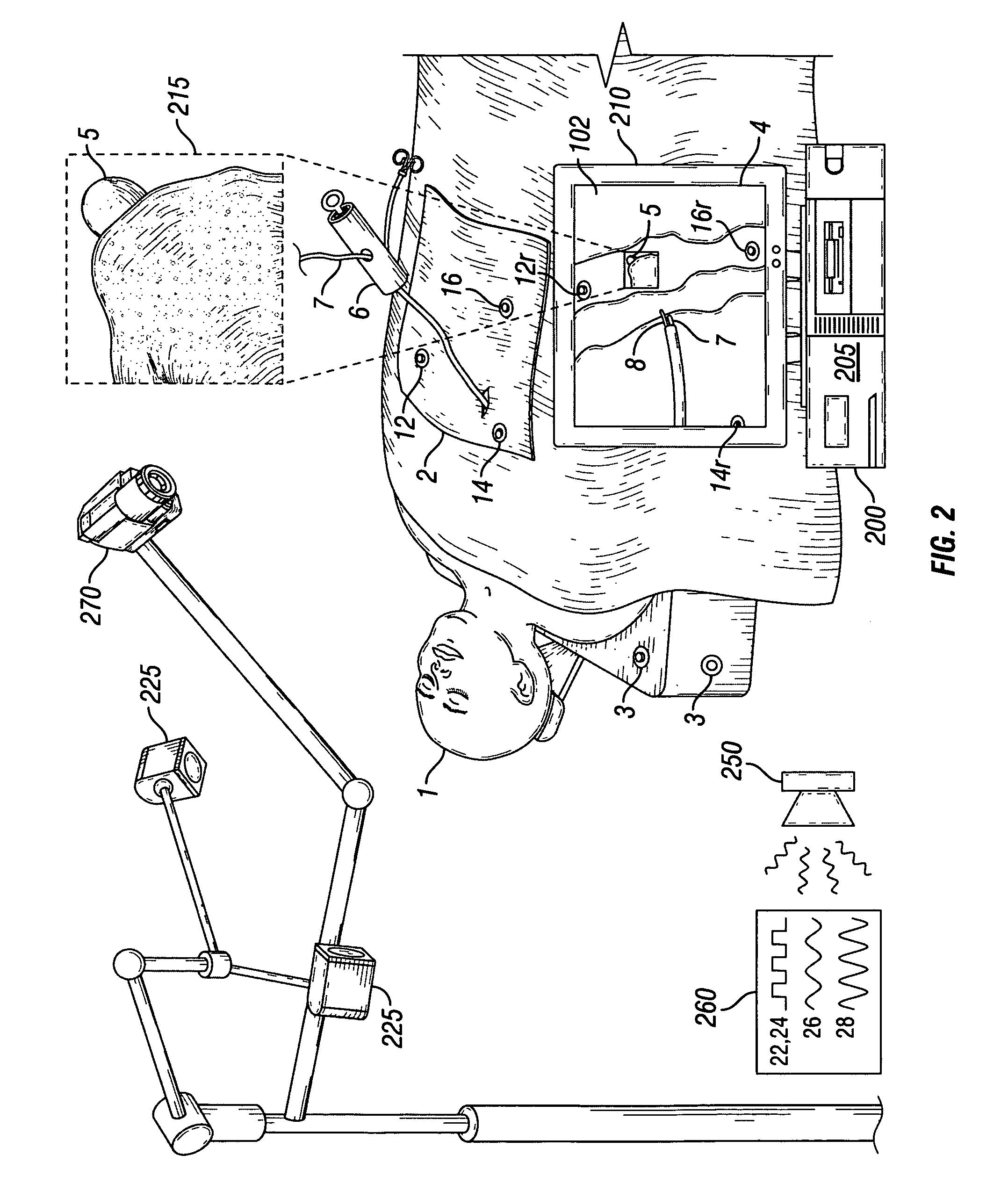
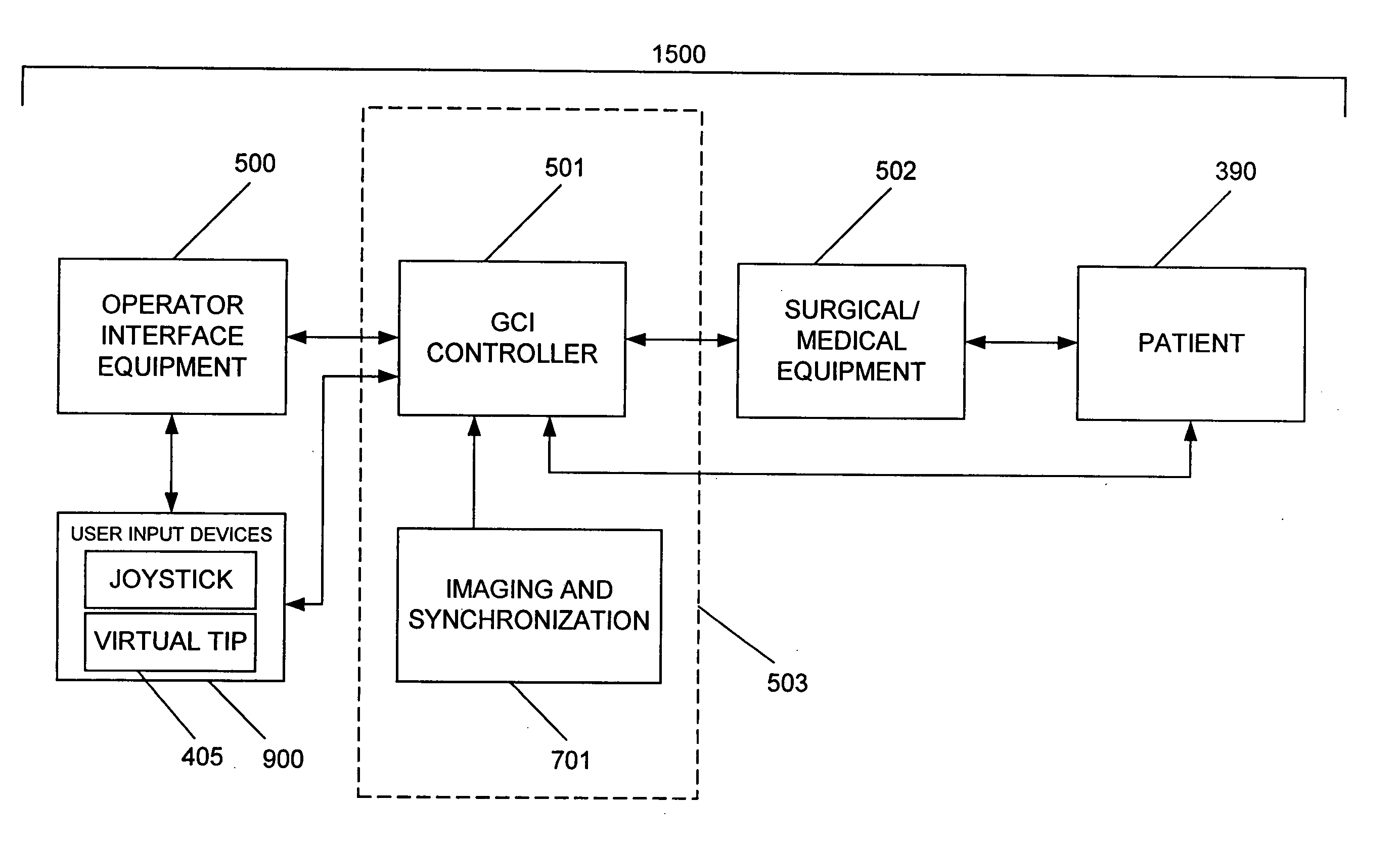
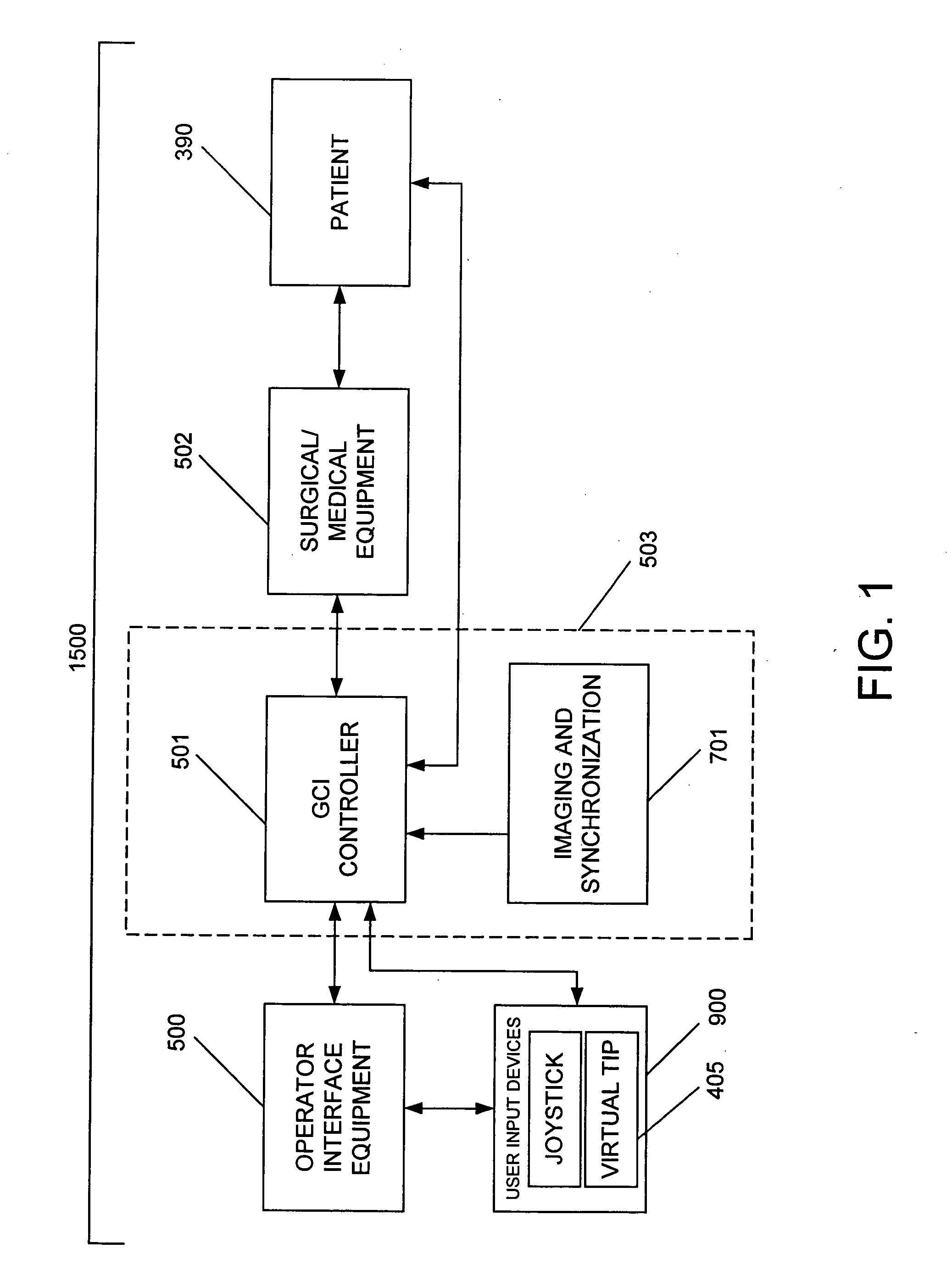
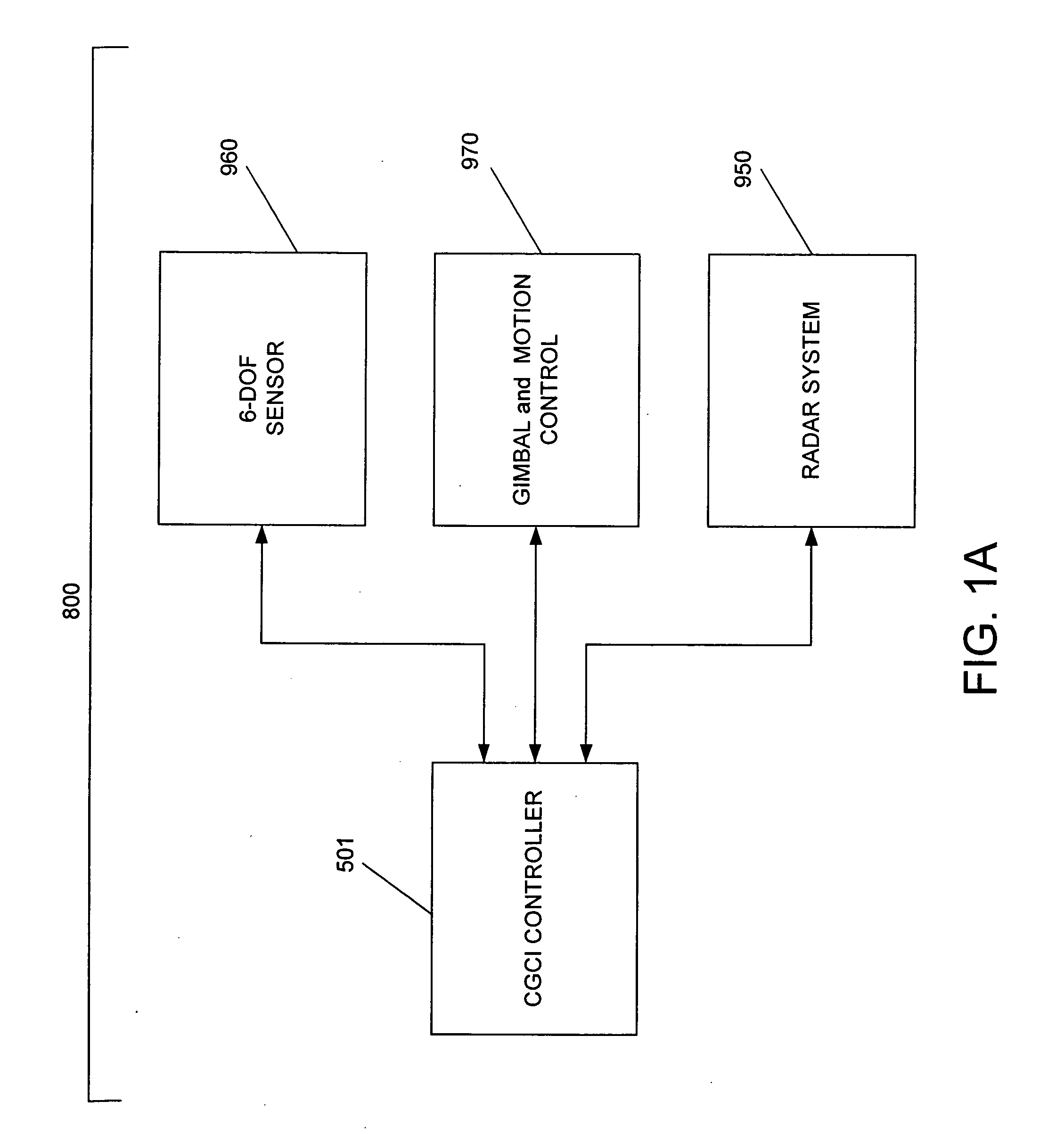
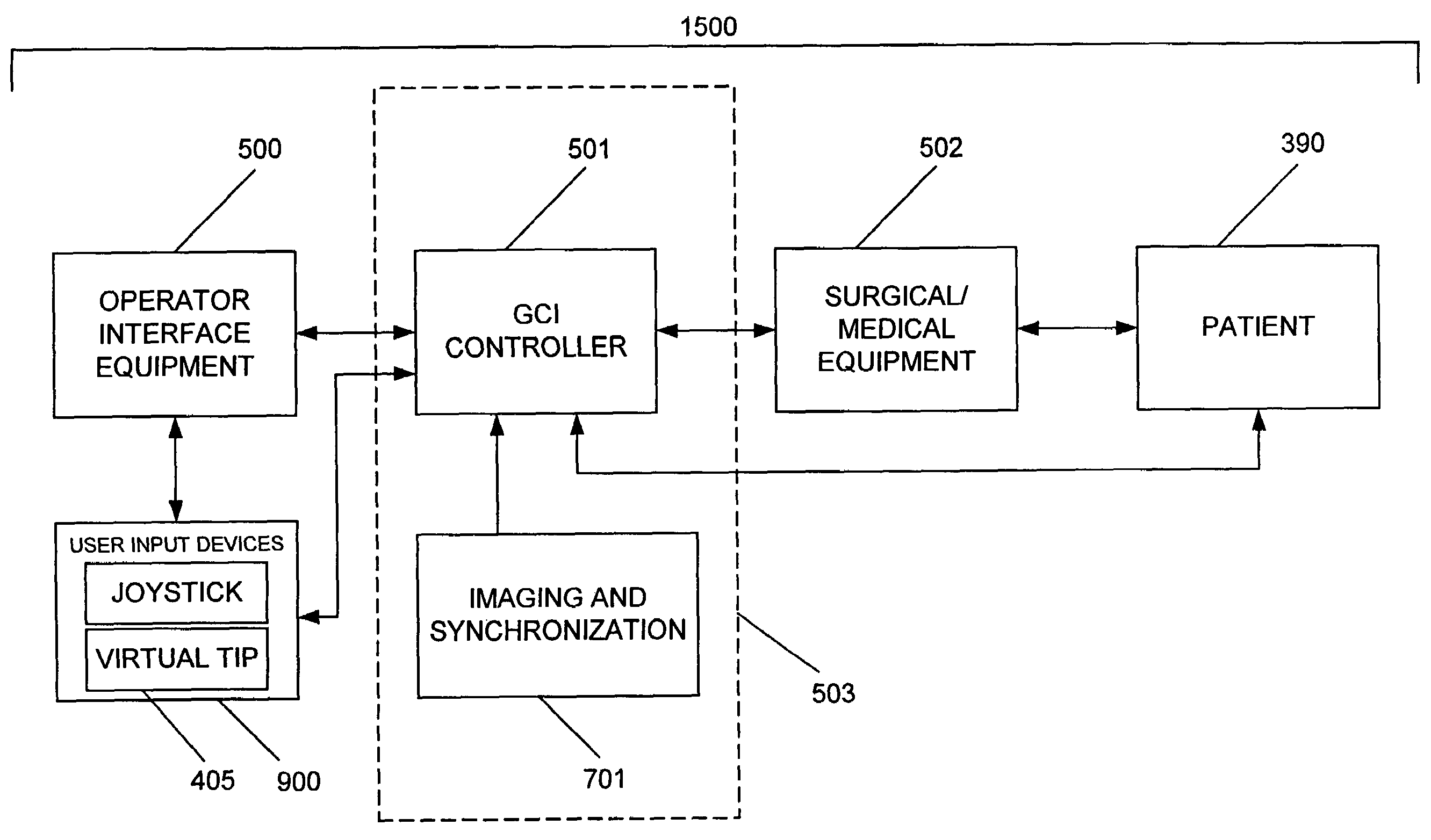
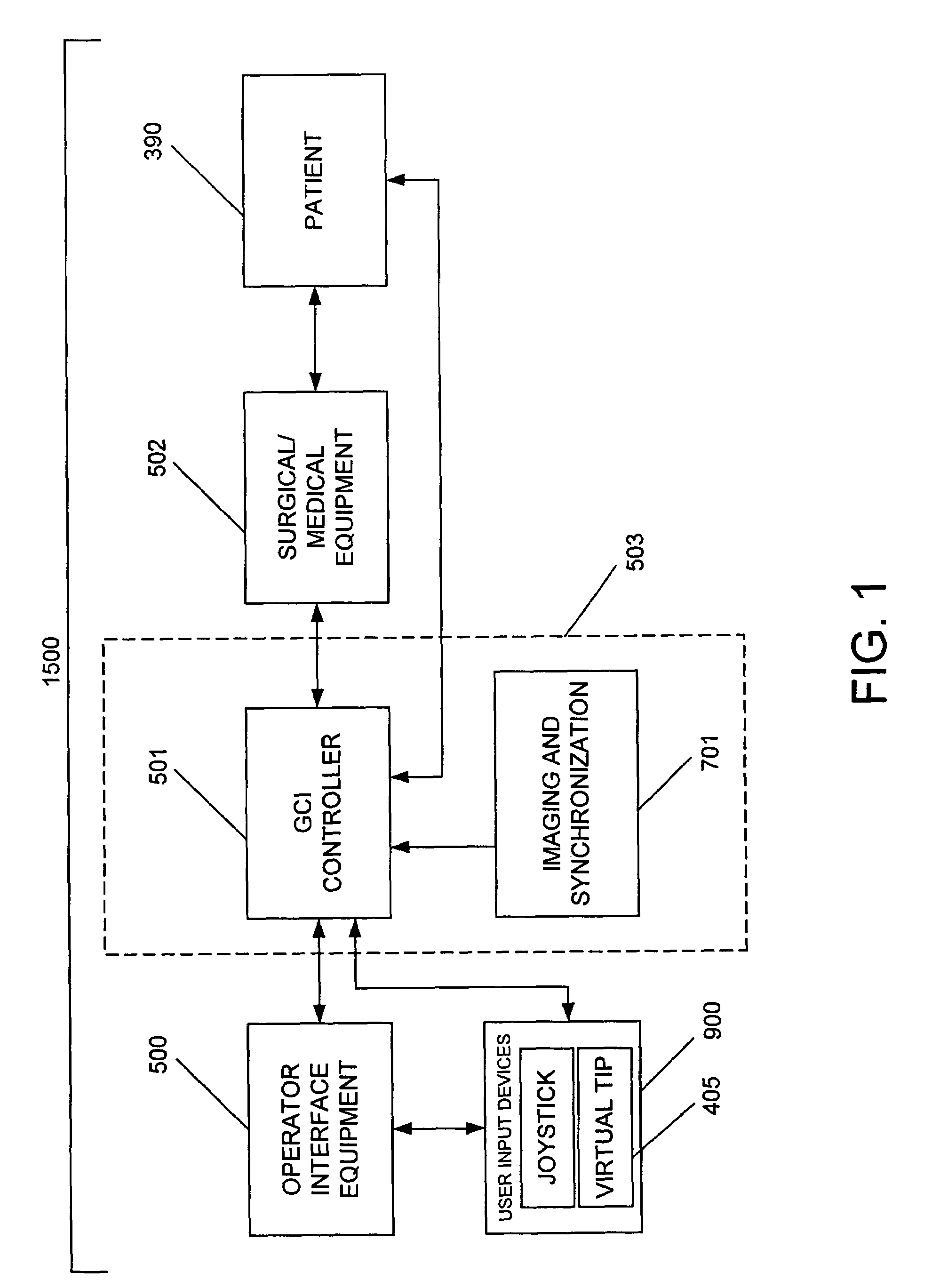
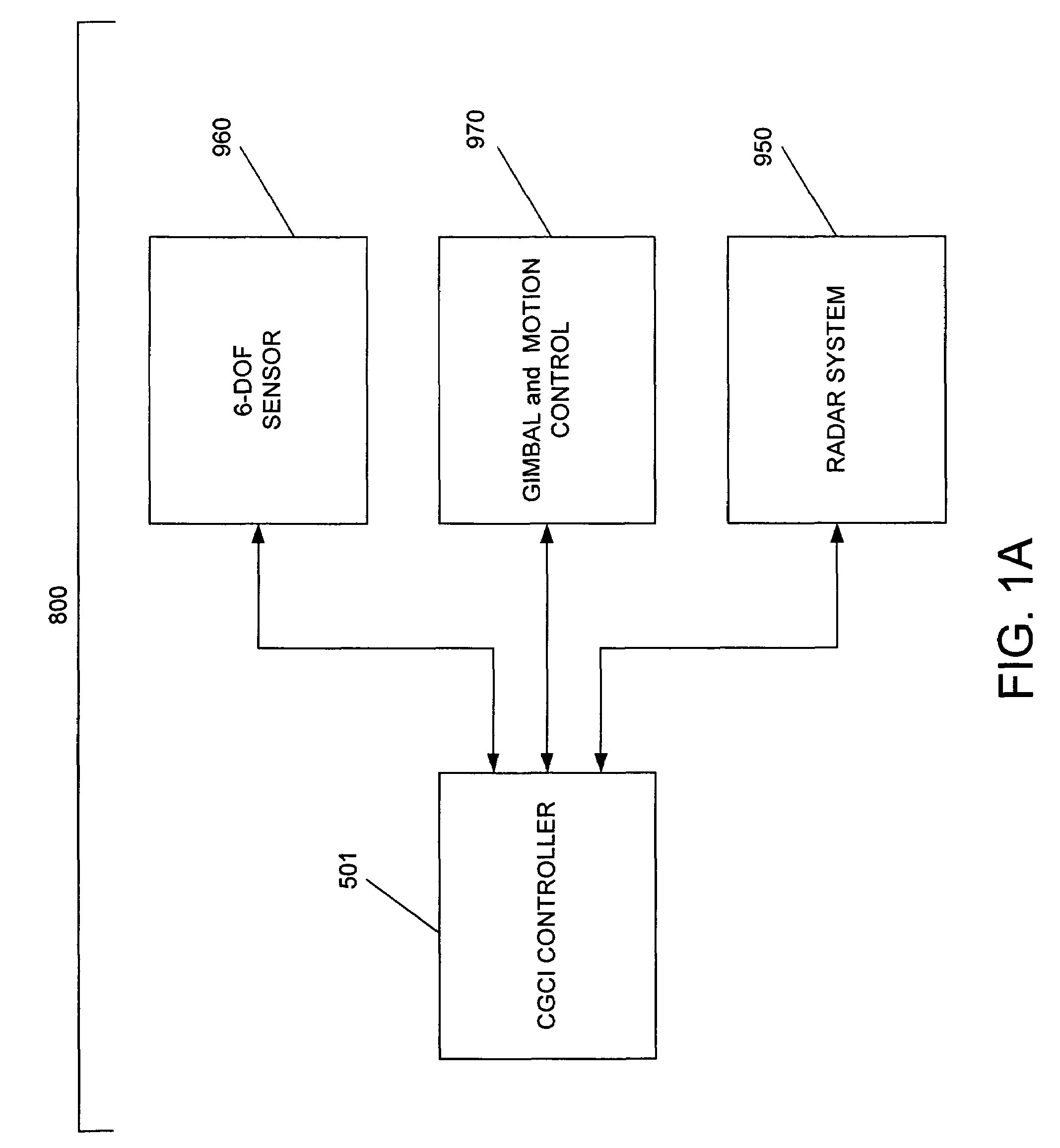
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS20050096589A1Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useEndoscopesMedical devicesRadar systemsGuidance control
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
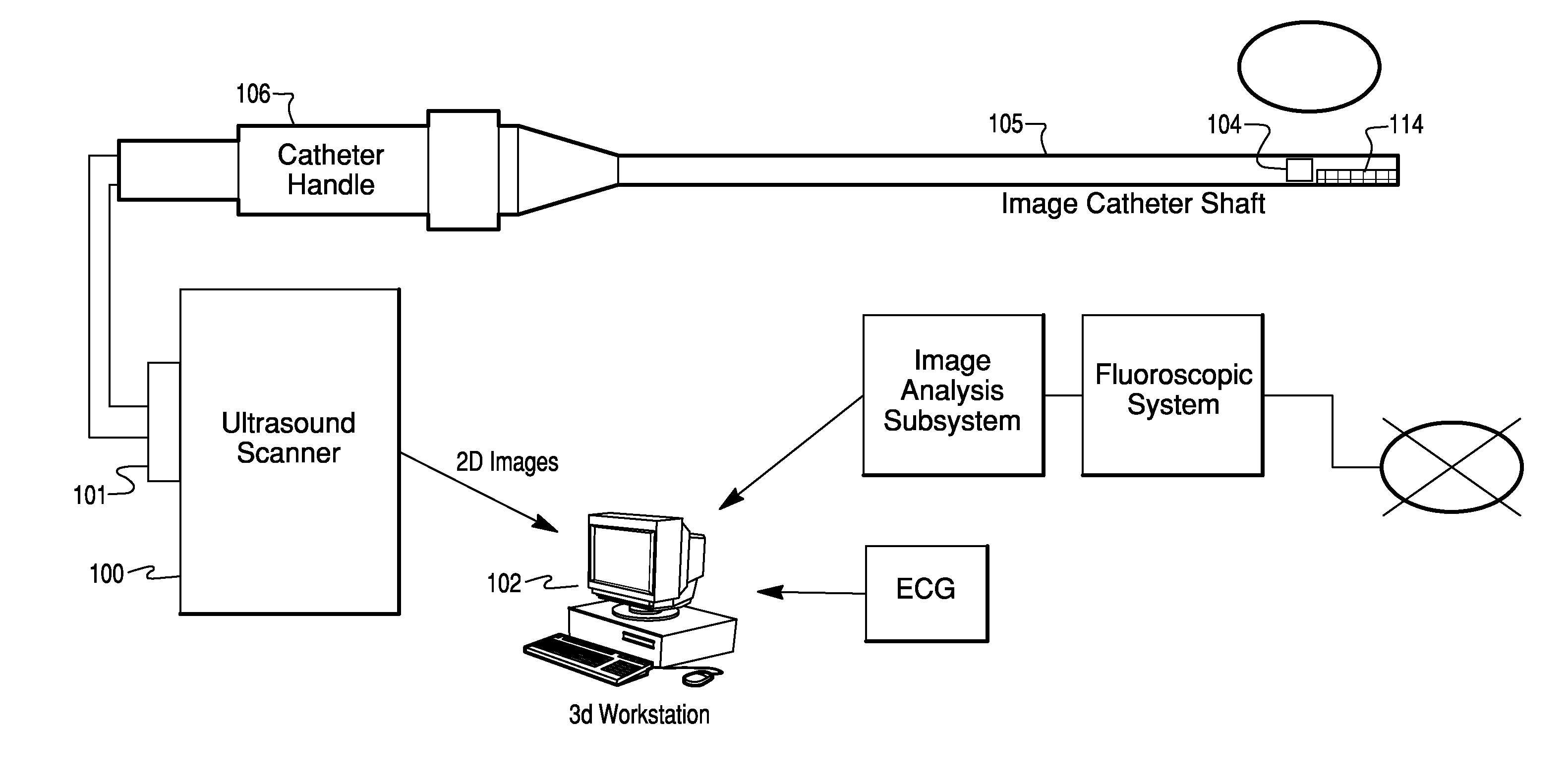
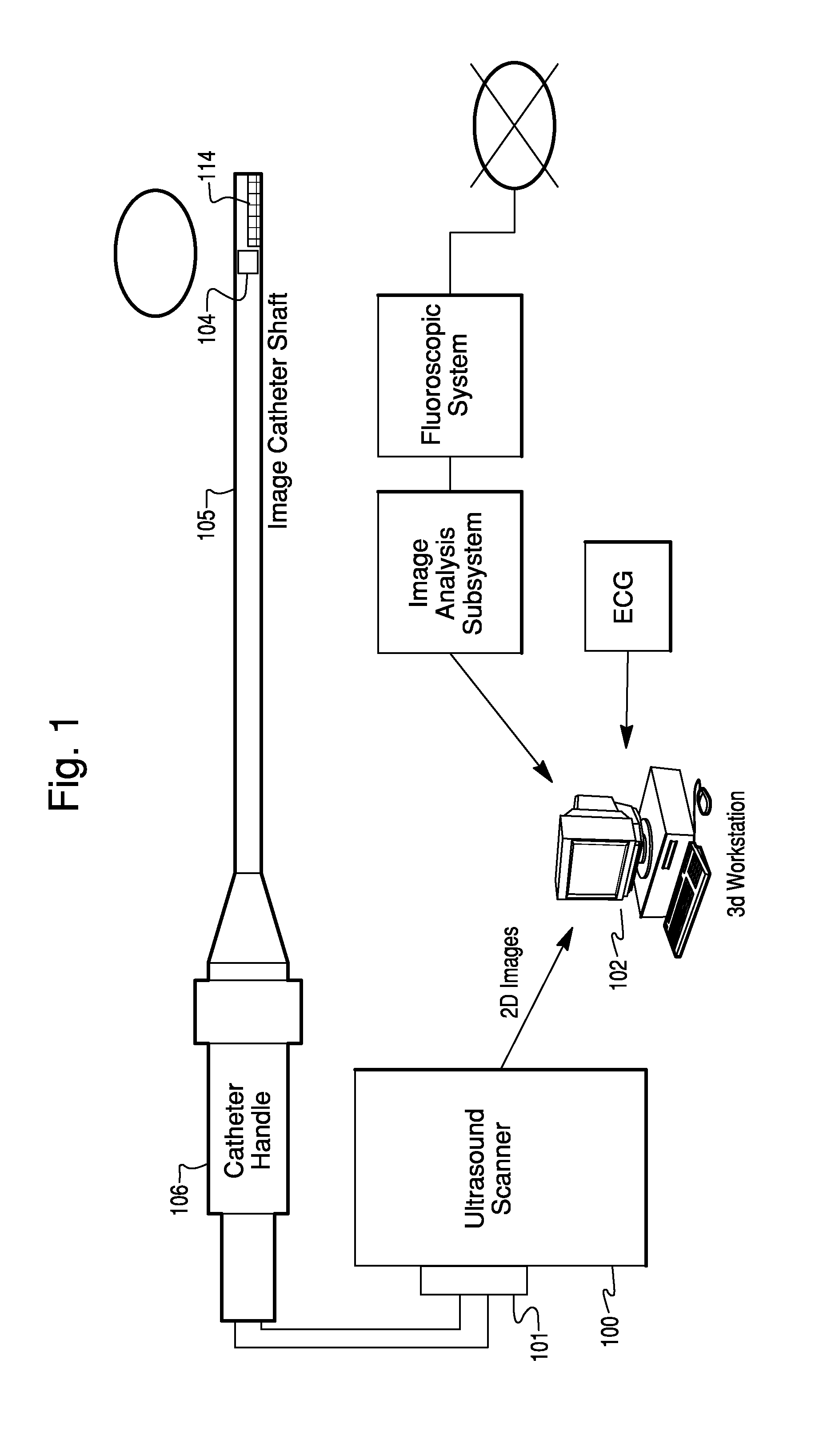
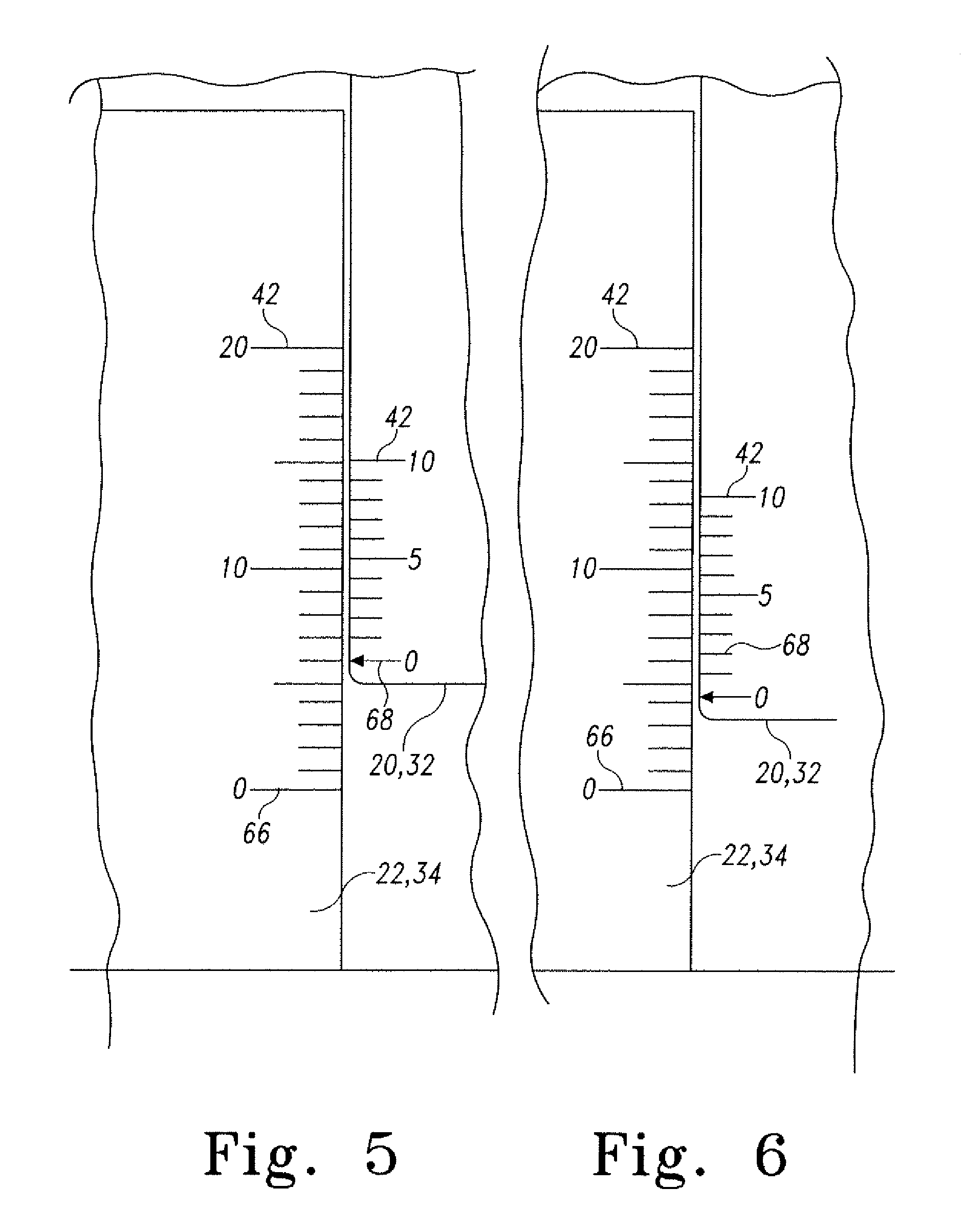
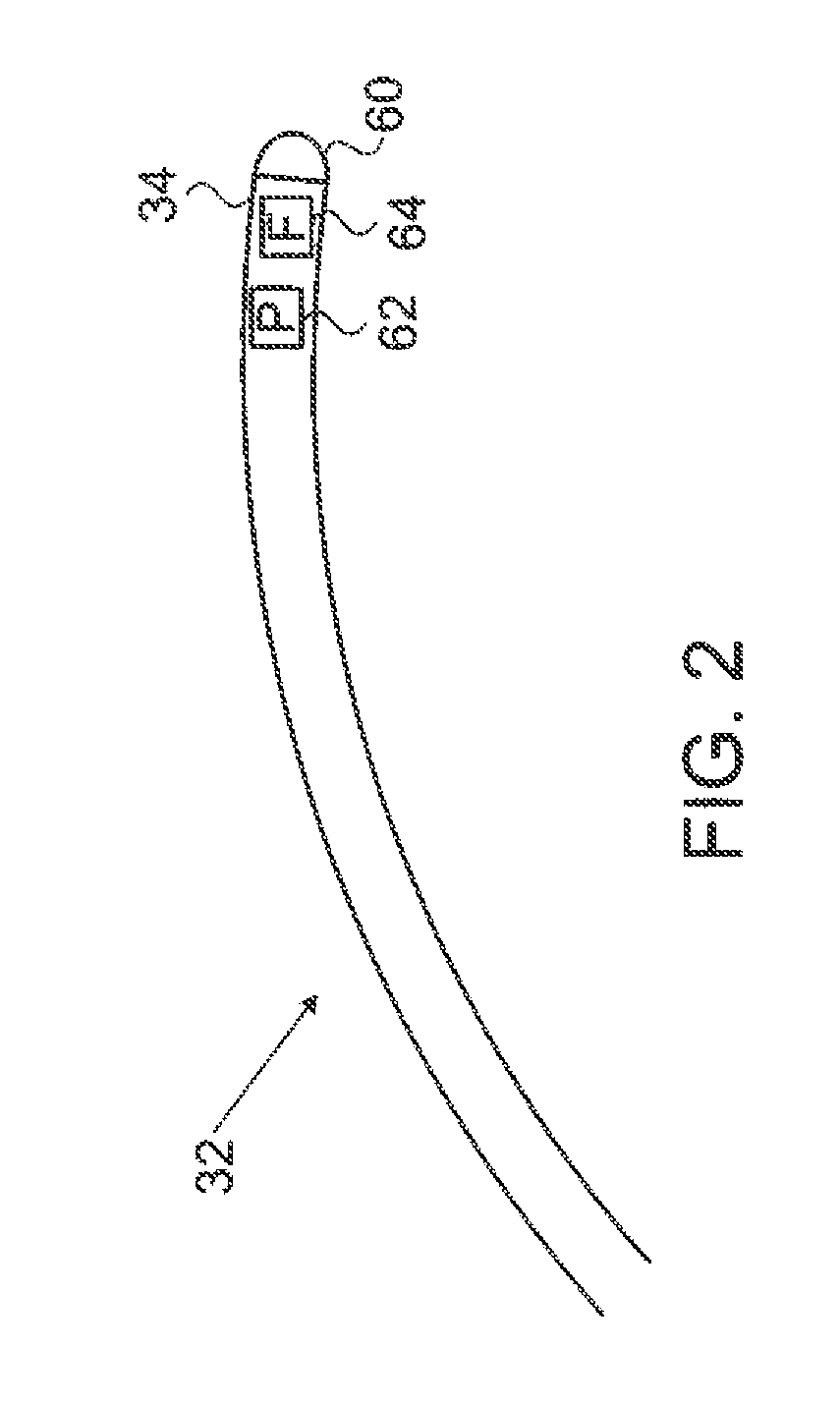
Catheter Position Tracking Methods Using Fluoroscopy and Rotational Sensors
Methods for determine the position and rotational orientation of the transducer array of an ultrasound imaging catheter within a patient include imaging the distal end of the catheter using fluoroscopy and determining the angular orientation based upon the shape and dimensions of the image of the transducer array and wire connecting harness. Additional rotational and translational information may be obtained from sensors located at the proximal end of the catheter. By combining position information obtained using fluoroscopy with information from relative rotation / translation sensors, the imaging transducer position and orientation can be determined more accurately. The resulting accurate imaging transducer position information enables combining multiple images from different positions or orientations to generate multi-dimensional images. Catheters including rotation and translation motion sensors at the proximal end, and radio-opaque materials near the distal end can be provided to enhance the methods.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS7280863B2Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useMedical devicesEndoscopesRadar systemsTip position
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
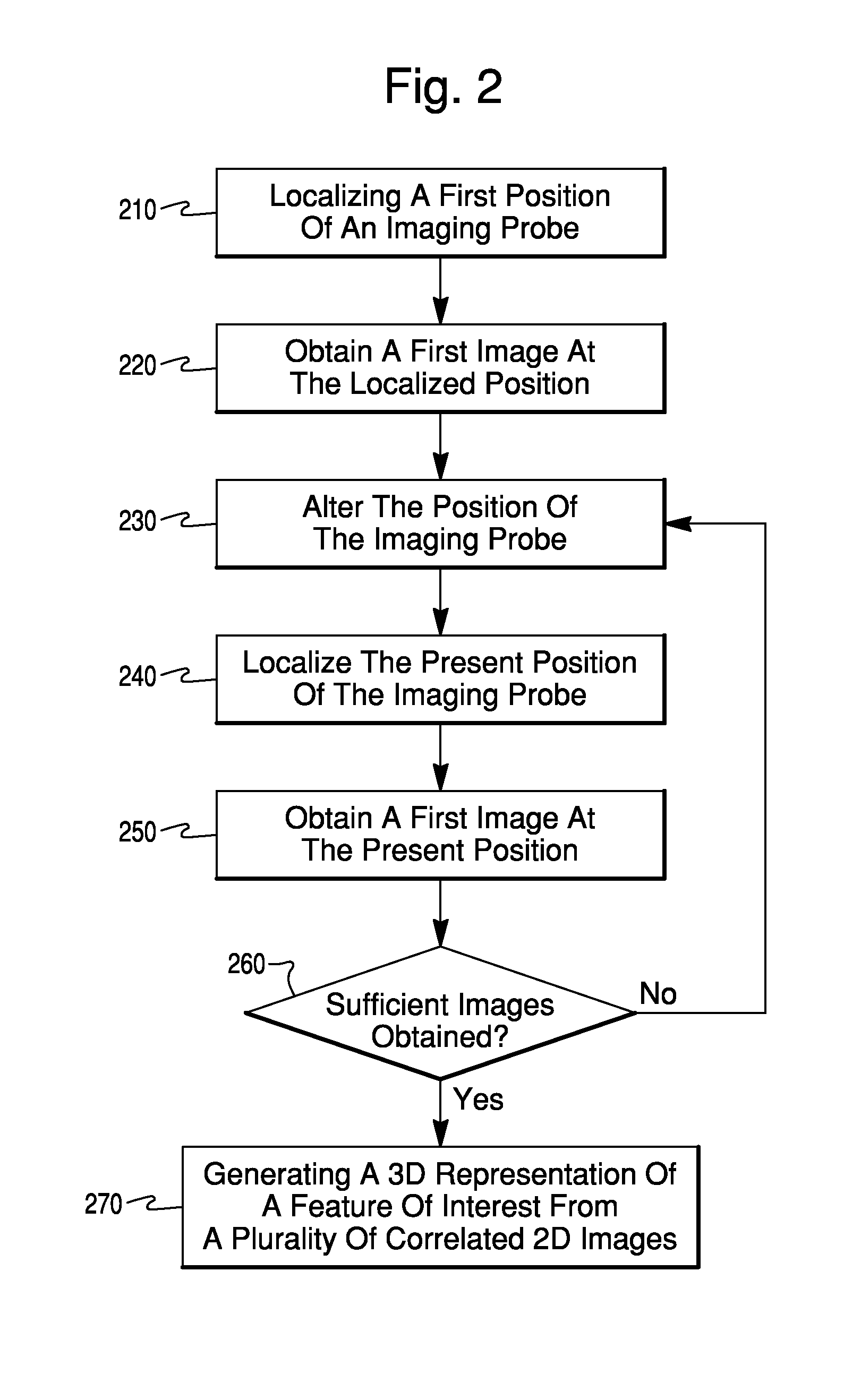
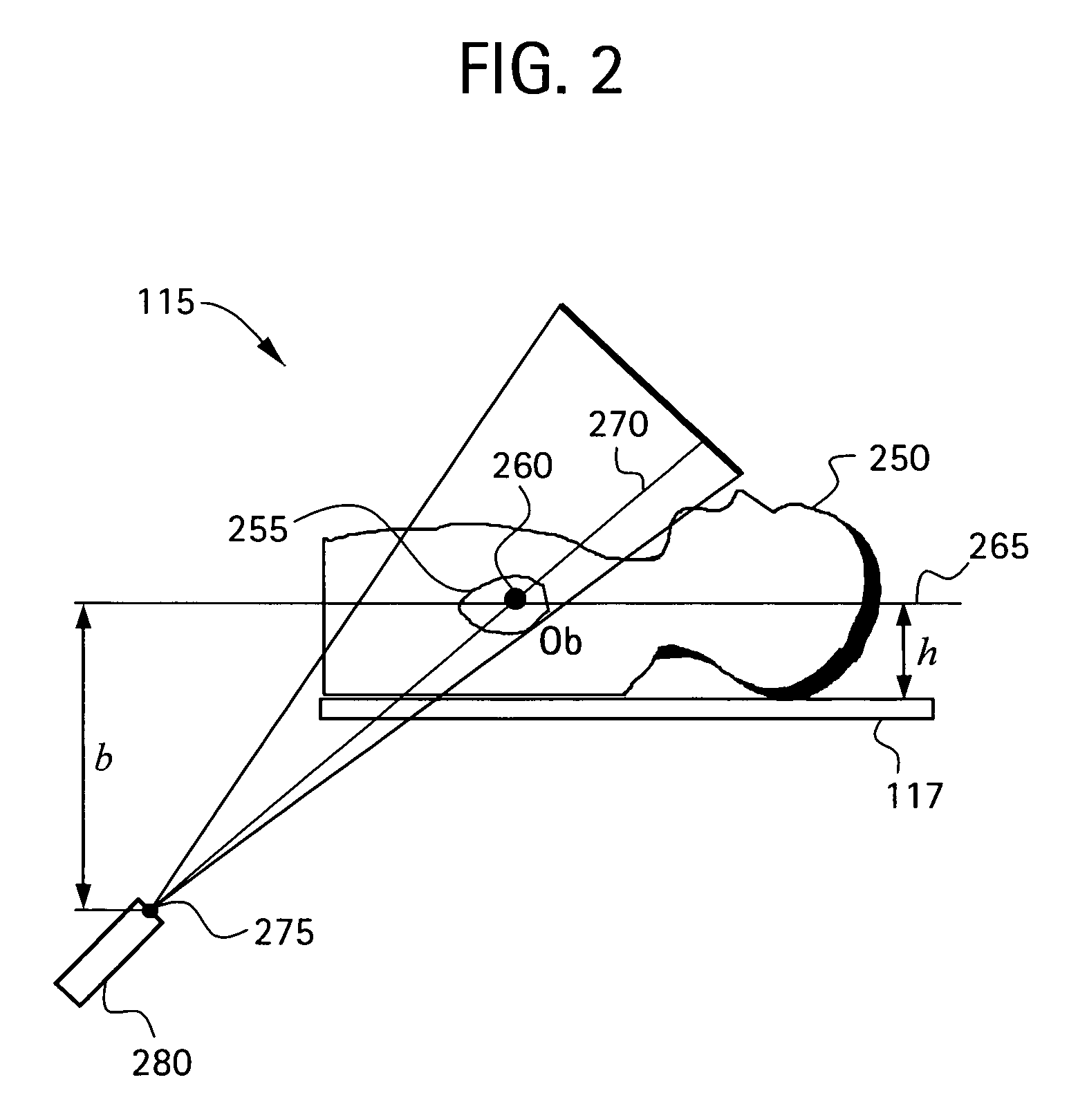
Method and system for generating three-dimensional model of part of a body from fluoroscopy image data and specific landmarks
InactiveUS20060004284A1Overcome disadvantagesSimpler and less-elaborate calculationSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsData setNavigation system
A method for generating a three-dimensional model of a part of the body with the aid of a medical and / or surgical navigation system, comprising the steps of identifying to the navigation system landmarks on the part of the body that are characteristic of the model of the part of the body; obtaining at least two fluoroscopy image data sets for each of one or more predetermined, individual and delimited regions of the part of the body; ascertaining characteristic body part data by processing and combining the landmark positions and parameters of the fluoroscopy data sets; and generating a three-dimensional and positionally determined model of the part of the body from the characteristic body part data.
Owner:BRAINLAB
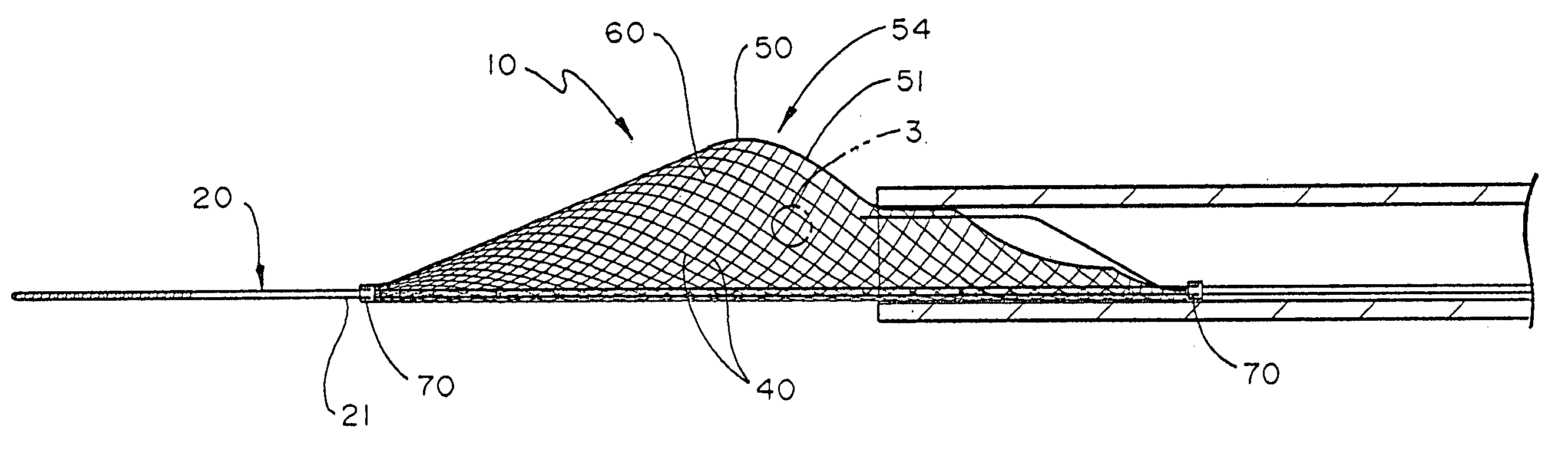
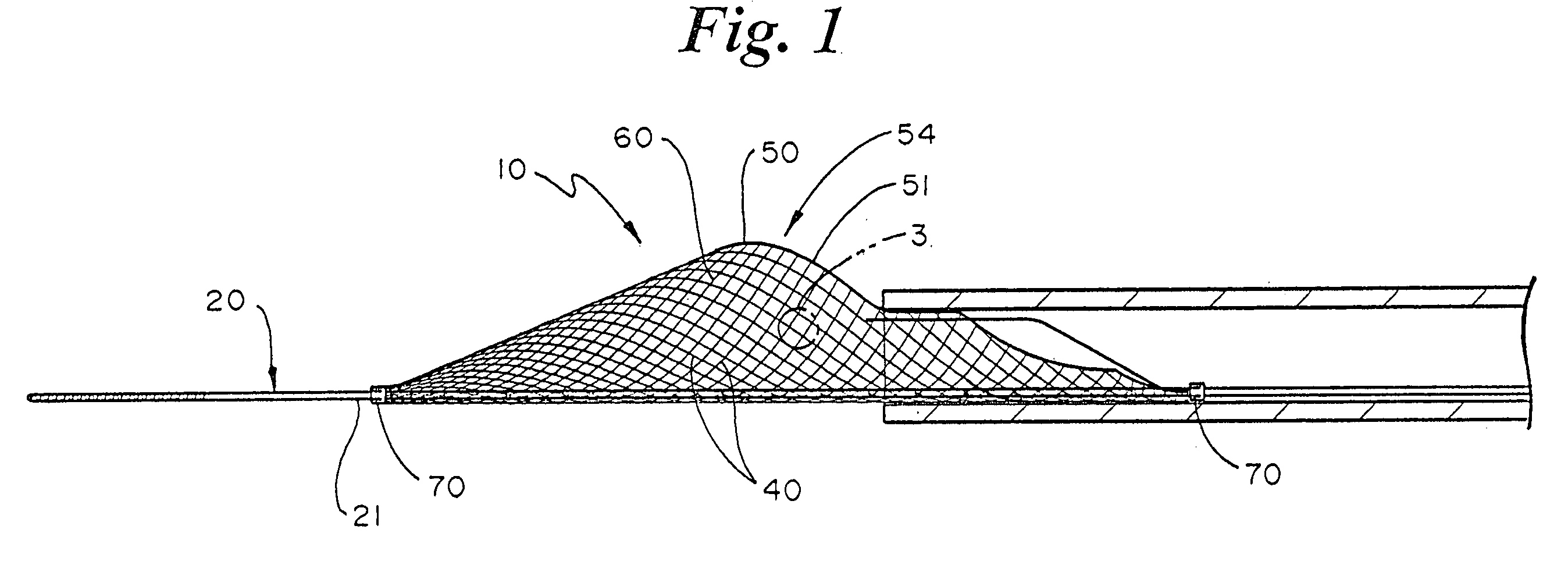
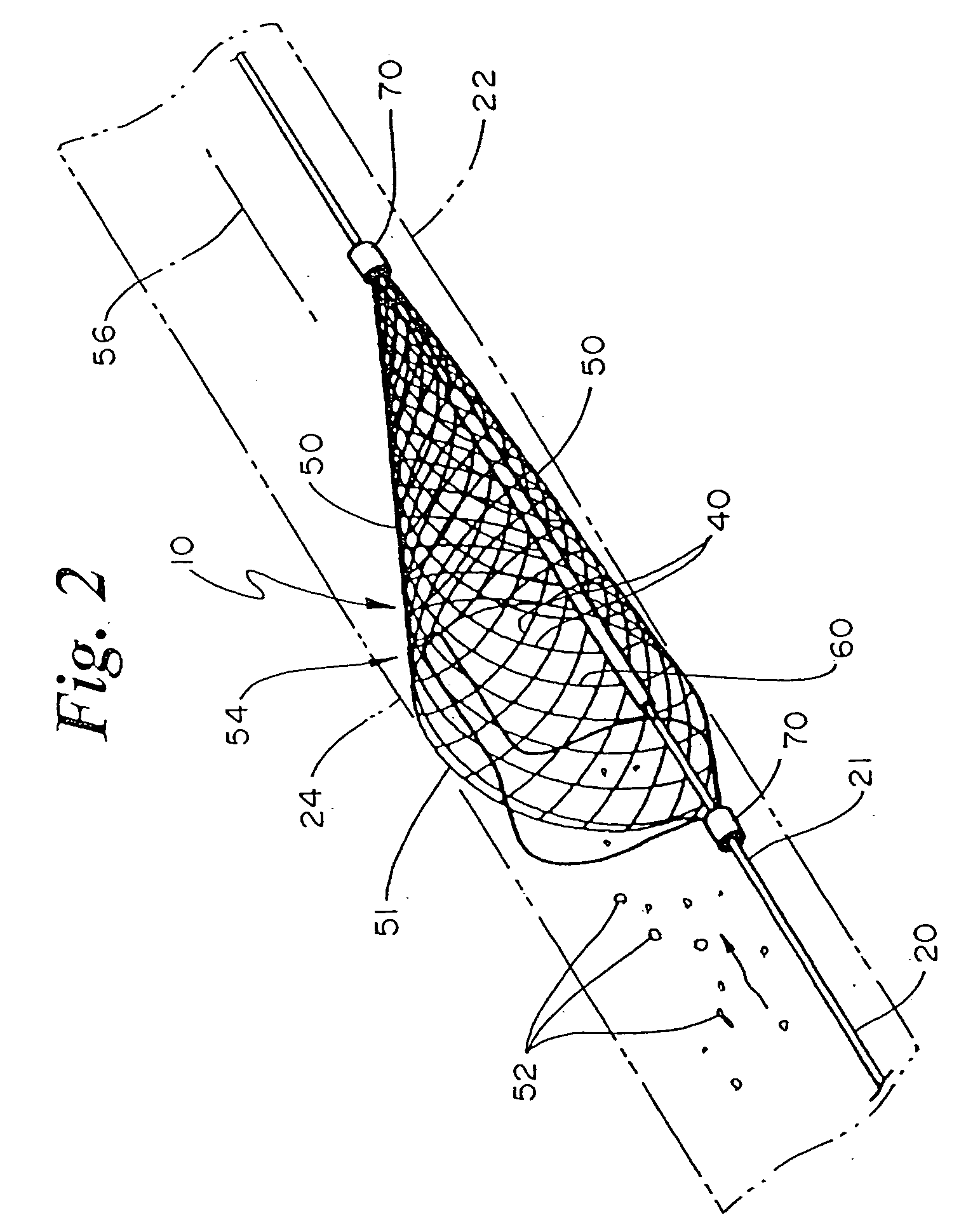
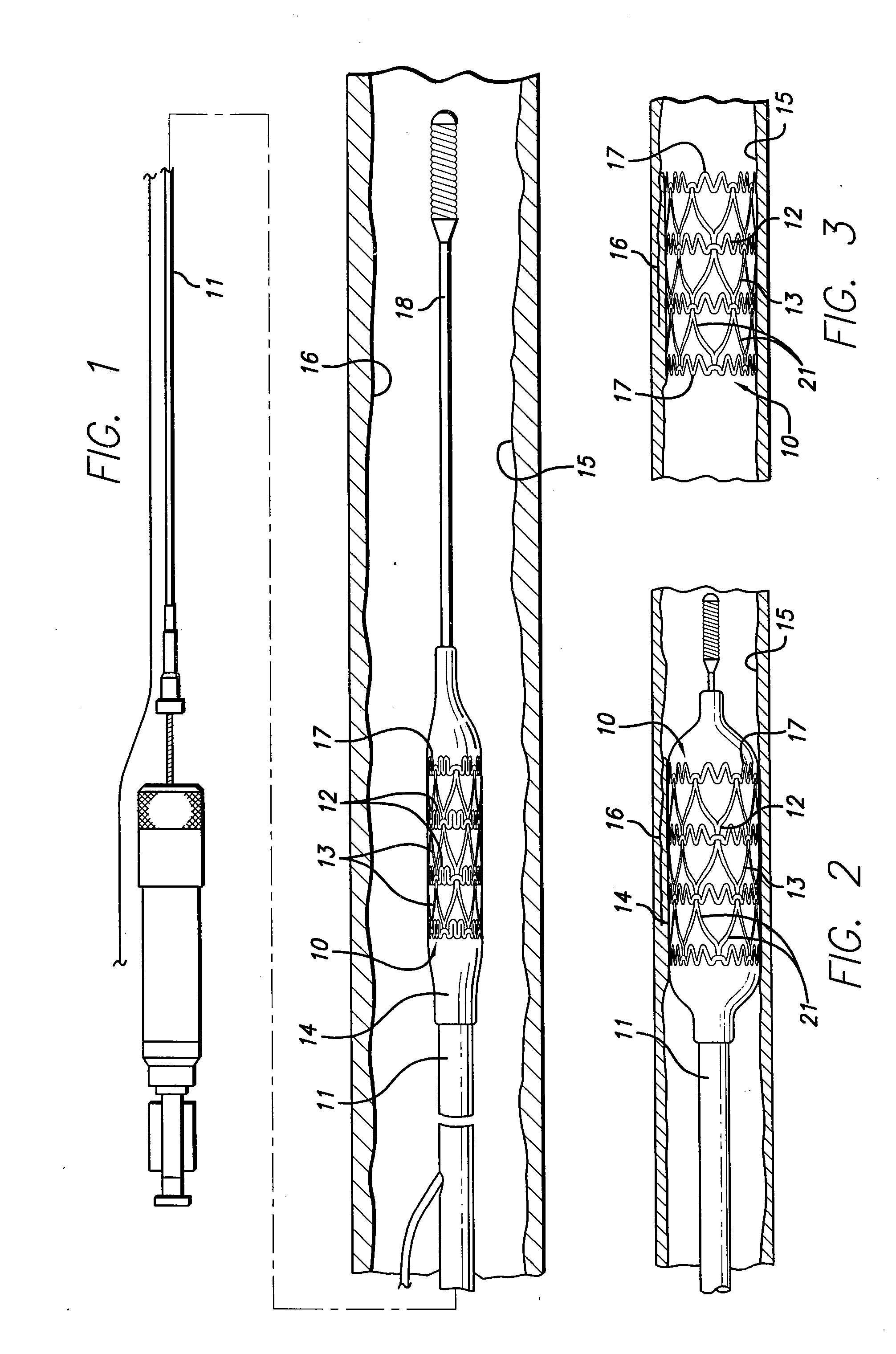
Temporary intraluminal filter guidewire and methods of use
InactiveUS6866677B2Restrict movementPrevent movementDilatorsCatheterRelative displacementEngineering
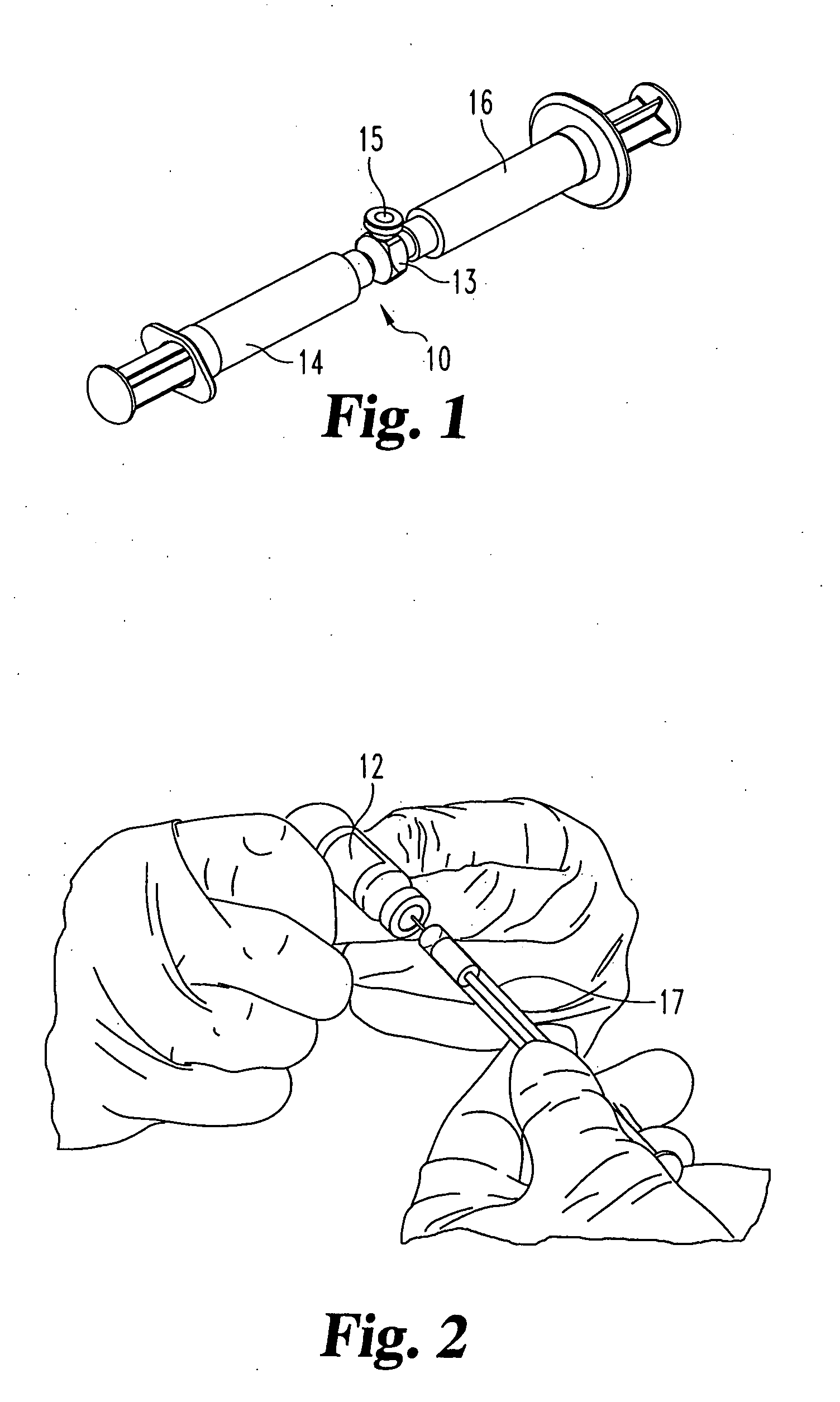
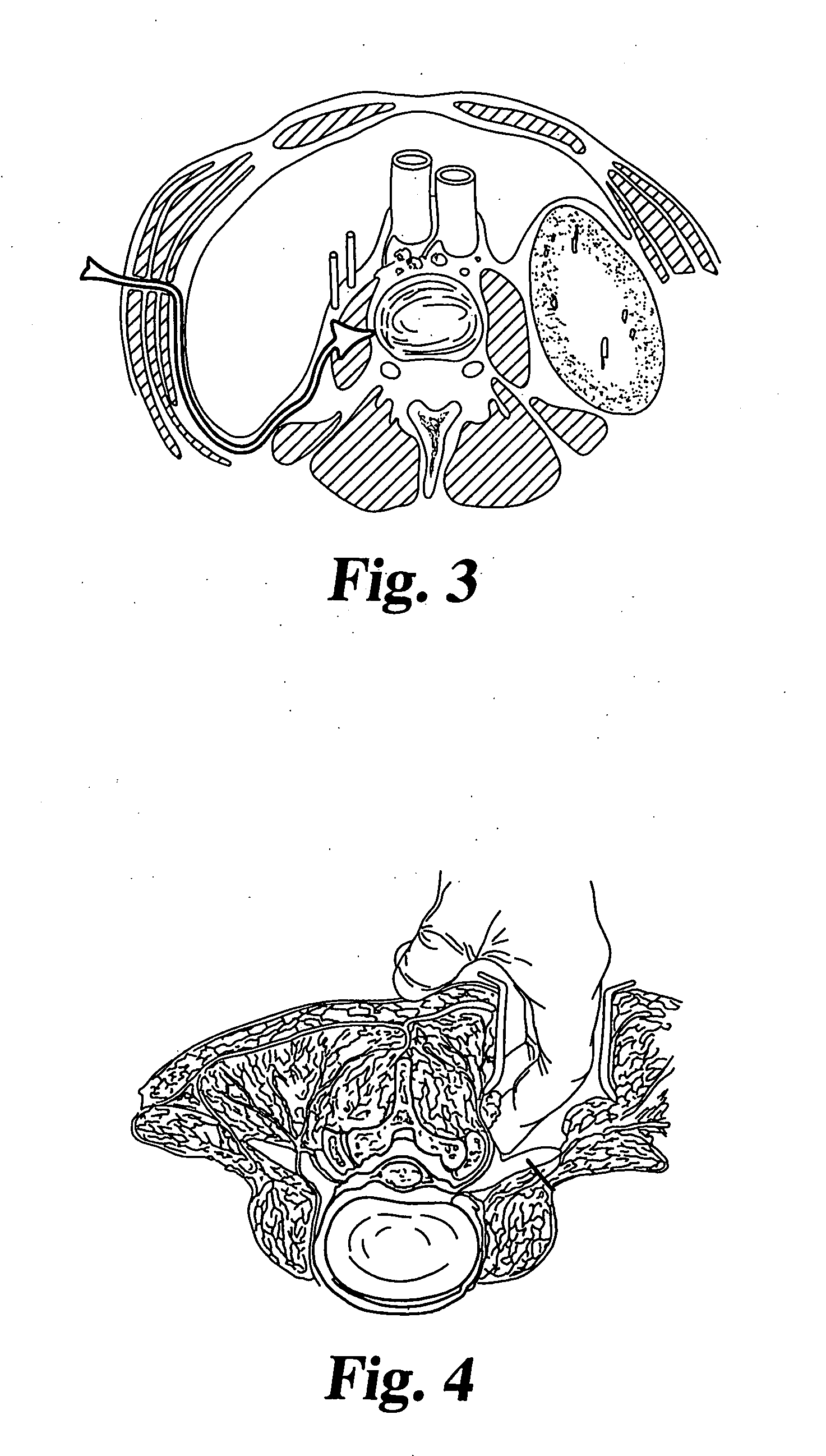
The present invention is a temporary intraluminal filter guidewire for use during interventional procedures, such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A braided filter is mounted near the distal end of a steerable guidewire, which guides a therapeutic catheter. An actuator rod slides over the guidewire and is removably connected to the filter. The rod controls relative displacement of the filter ends, causing transformation of the filter between a deployed configuration and a collapsed configuration. Wire having enhanced radiopacity is included in the filter to provide visualization under fluoroscopy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Radiopacity intraluminal medical device
A stent or other intraluminal medical device having markers formed from housings integral with the stent and marker inserts having a higher radiopacity than the stent provides for more precise placement and post-procedural visualization in a vessel, by increasing the radiopacity of the stent under X-ray fluoroscopy. The housings are formed integral to the stent and the marker inserts are made from a material close in the galvanic series to the stent material and sized to substantially minimize the effect of galvanic corrosion.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
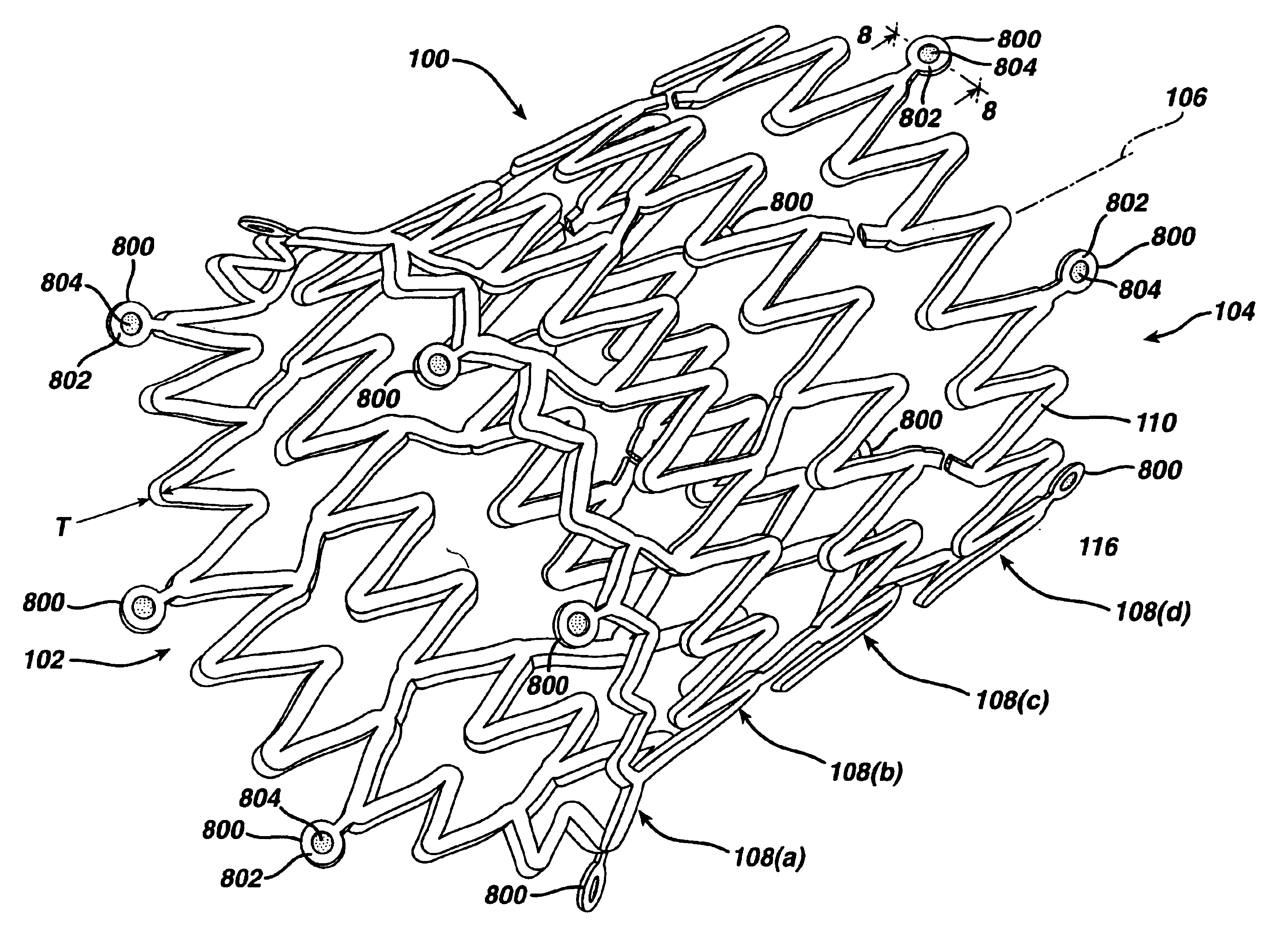
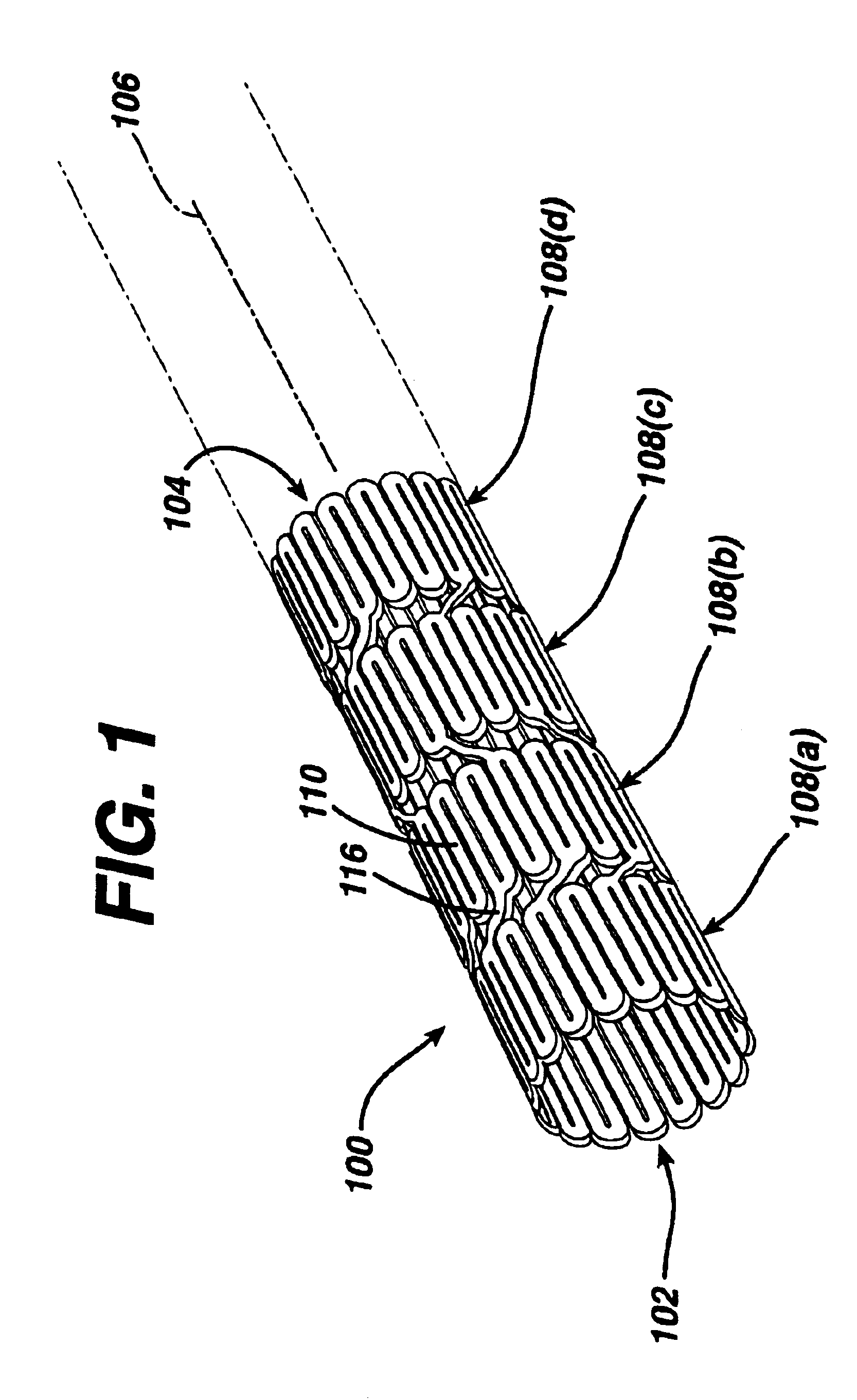
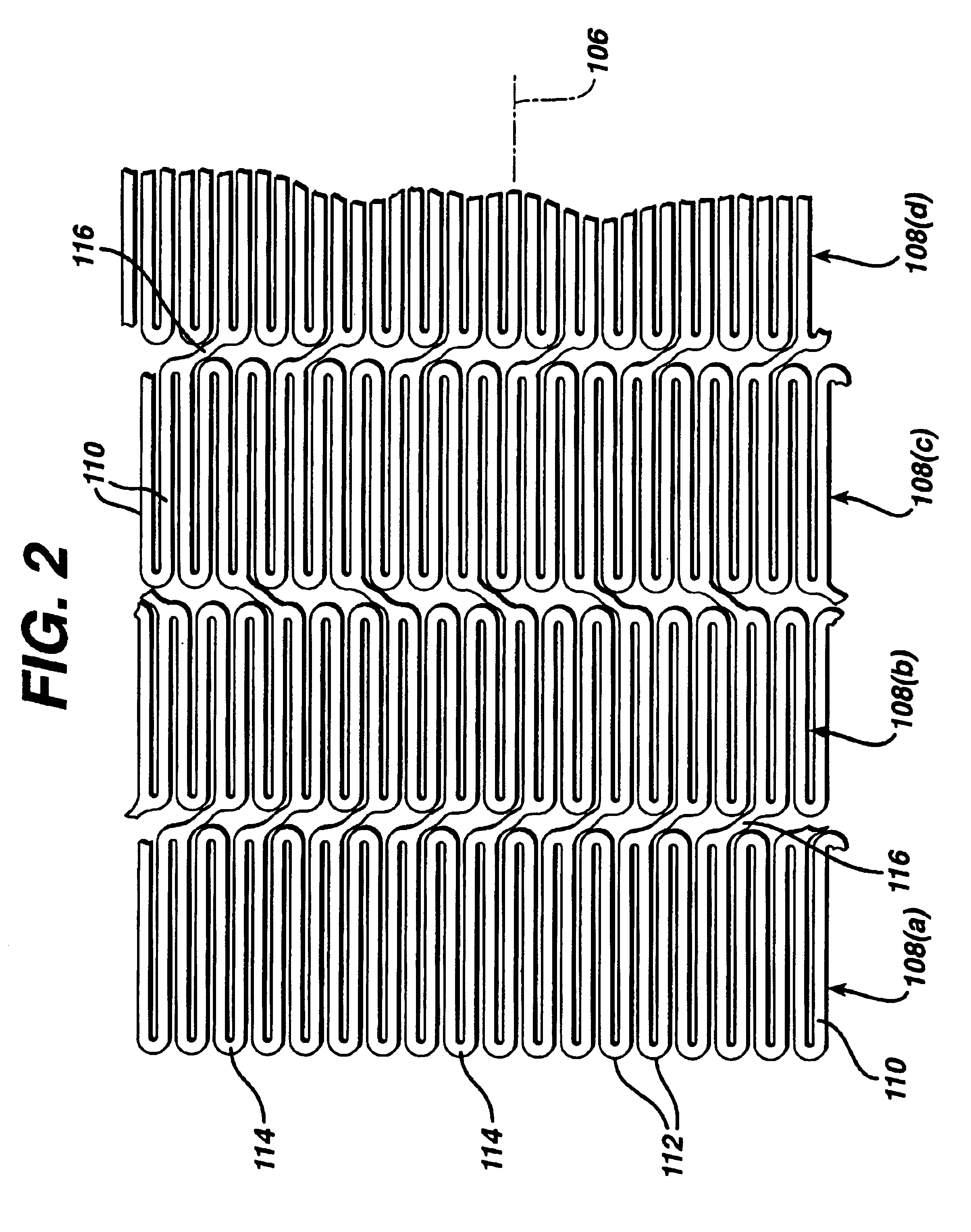
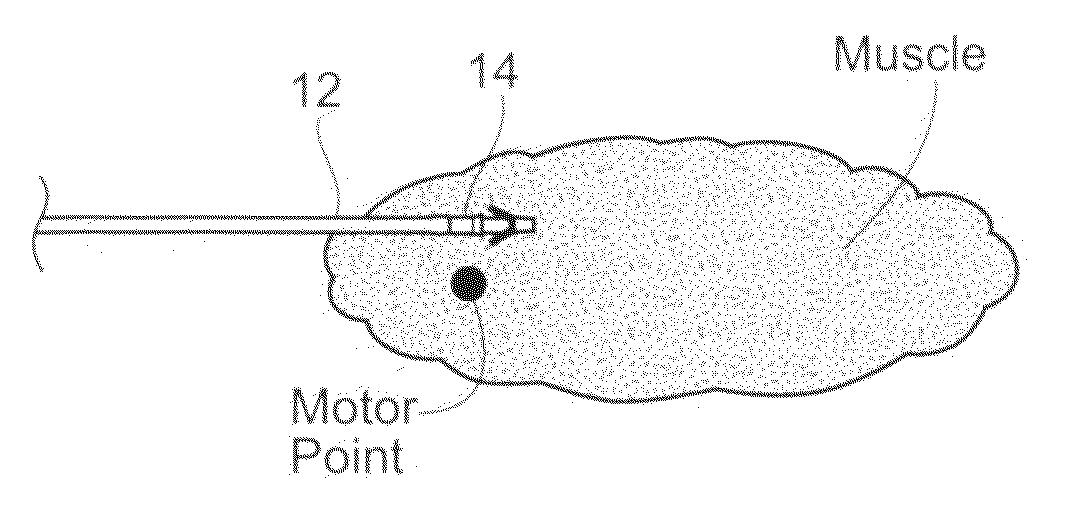
Systems and methods to place one or more leads in muscle for providing electrical stimulation to treat pain
InactiveUS20100036454A1Relief the painPain reliefInternal electrodesExternal electrodesElectricityPhysical therapy
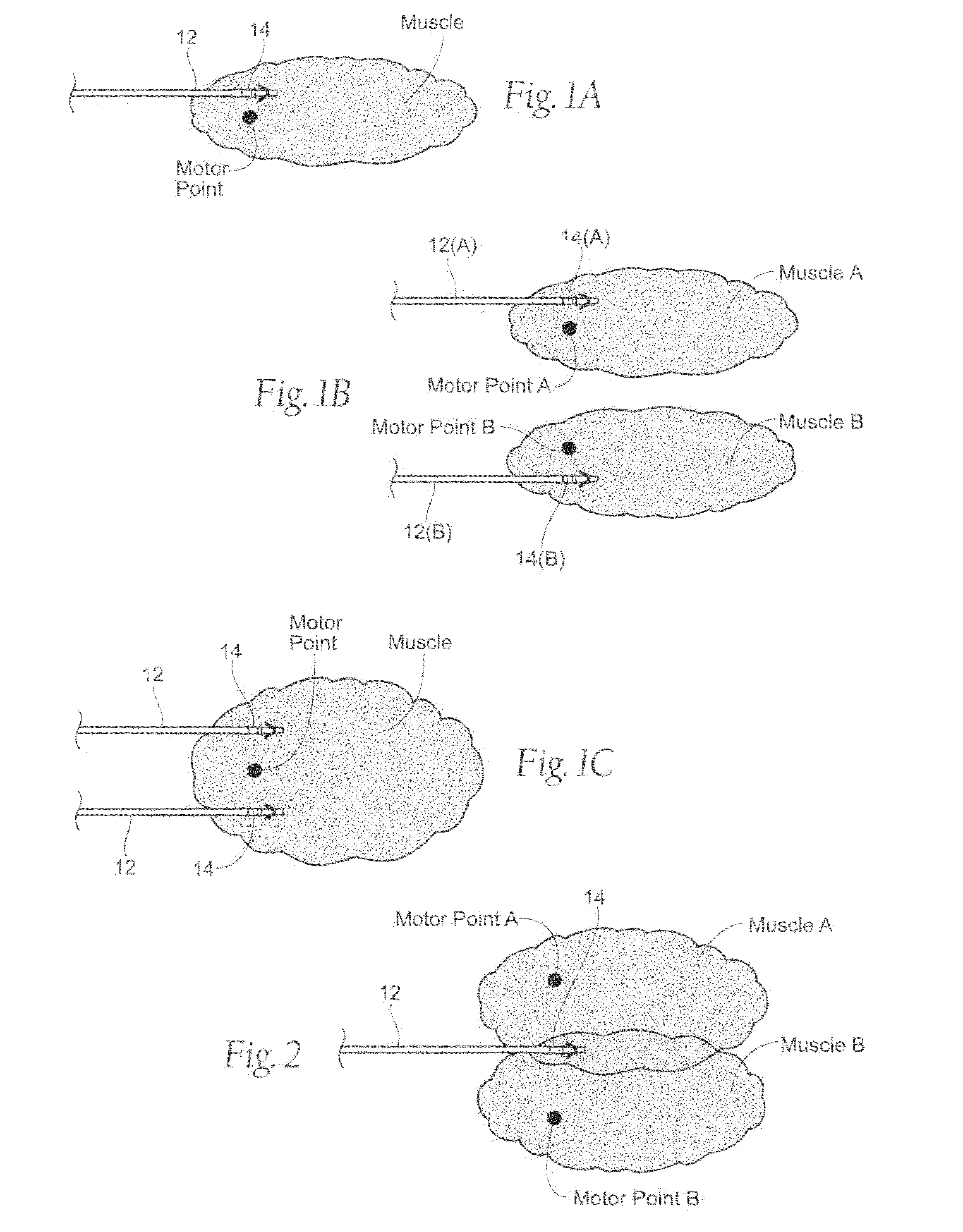
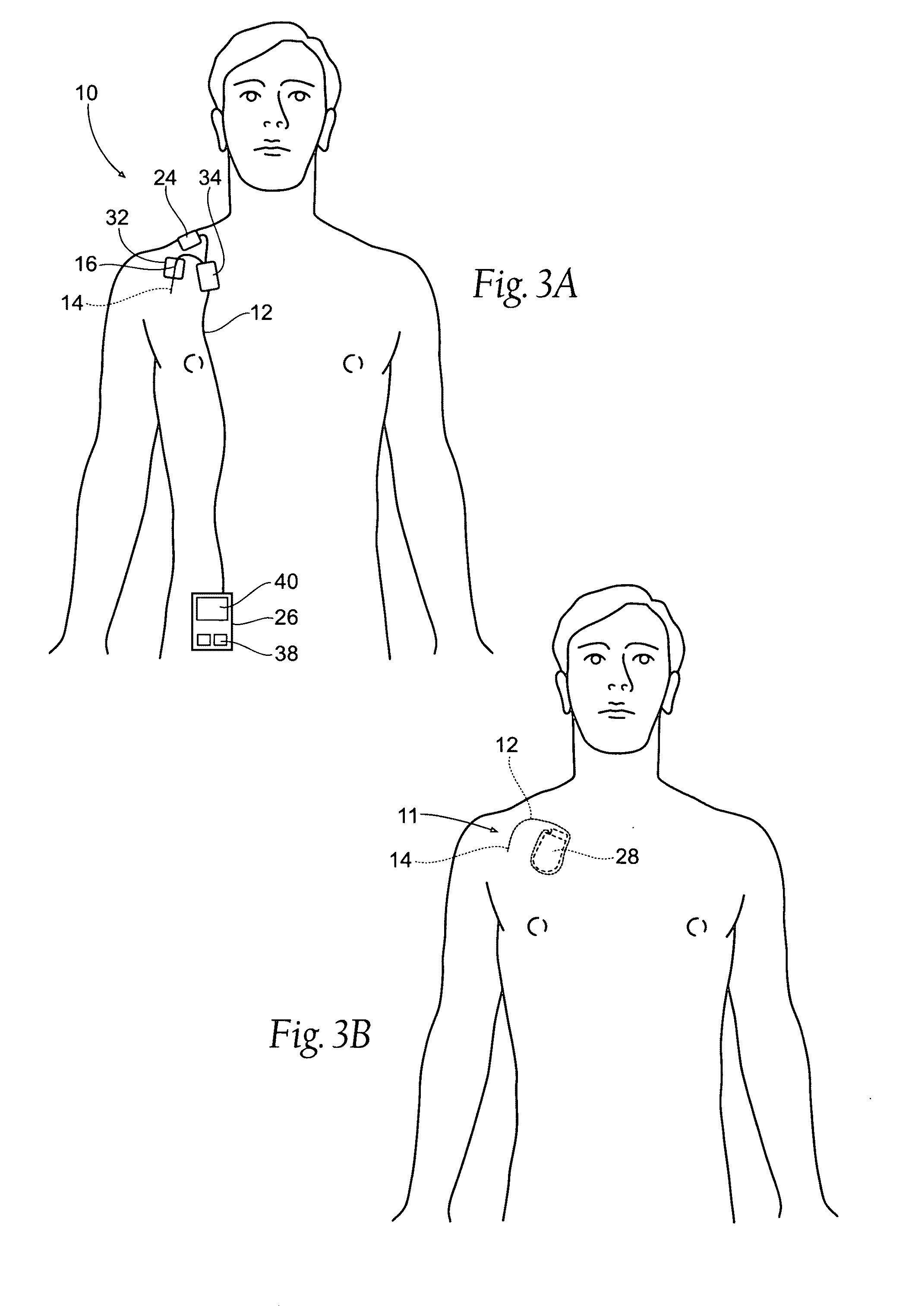
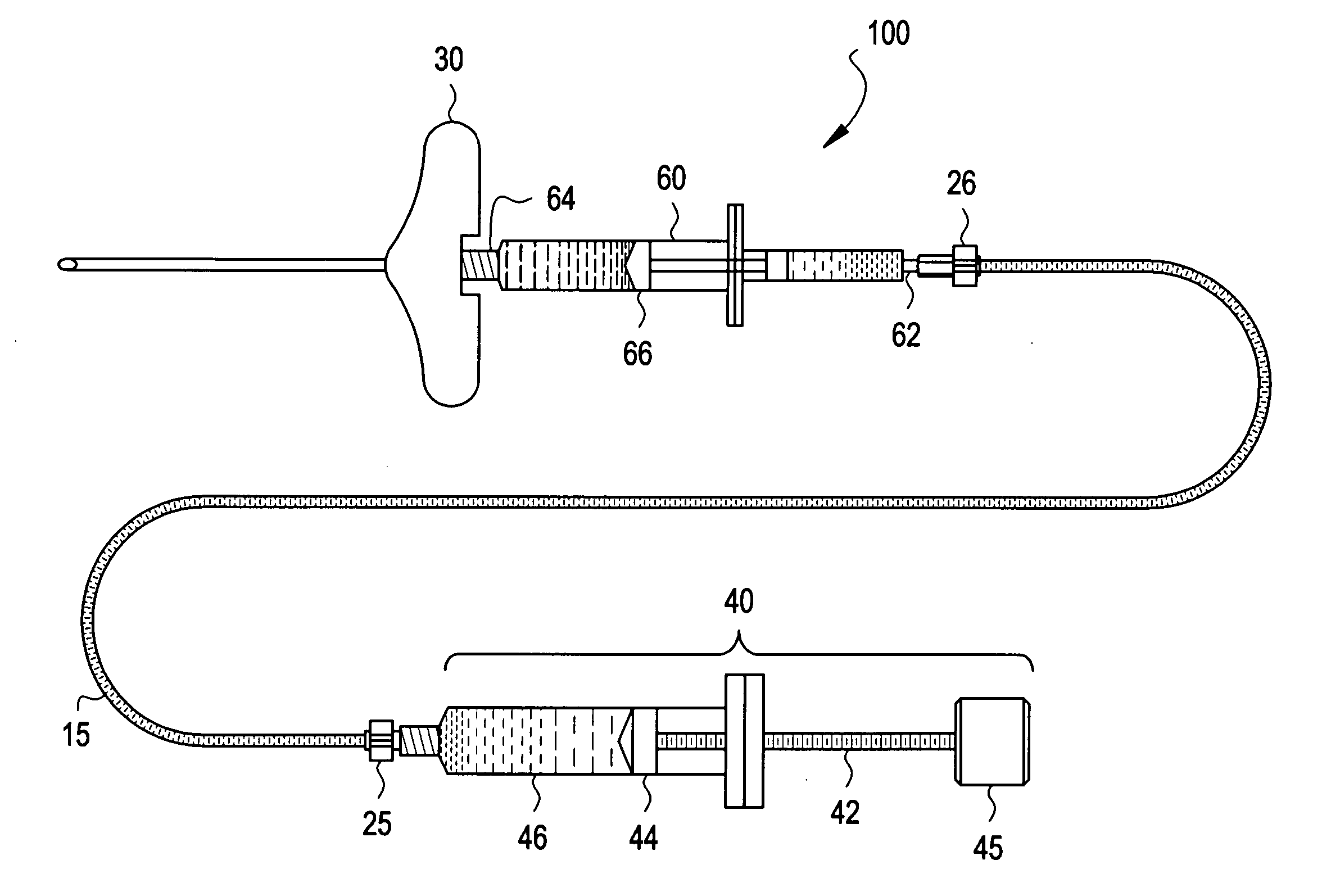
Systems and methods are adapted to provide the relief of pain. The systems and methods make possible the percutaneous placement of one or more intramuscular leads, without the need for fluoroscopy, for providing electrical stimulation to activate a motor point innervating the muscle, to provide the therapeutic relief of pain. The one or more intramuscular leads may be placed in muscle(s) to resist migration. The target nerves and their motor points innervate the muscles in which the one or more leads are placed. The systems and methods can include a two-stage solution. The first stage may include temporary systems and methods, including the use of an external pulse generator. The second stage may include more permanent systems and methods, including the use of an implanted pulse generator.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
Device for delivering viscous material
ActiveUS20050070915A1Safe removalMinimize safety concernIntravenous devicesProsthesisSurgical siteField of view
Methods and devices are described for delivering a viscous material to a surgical site in a patient while keeping the clinician outside the fluoroscopy field.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
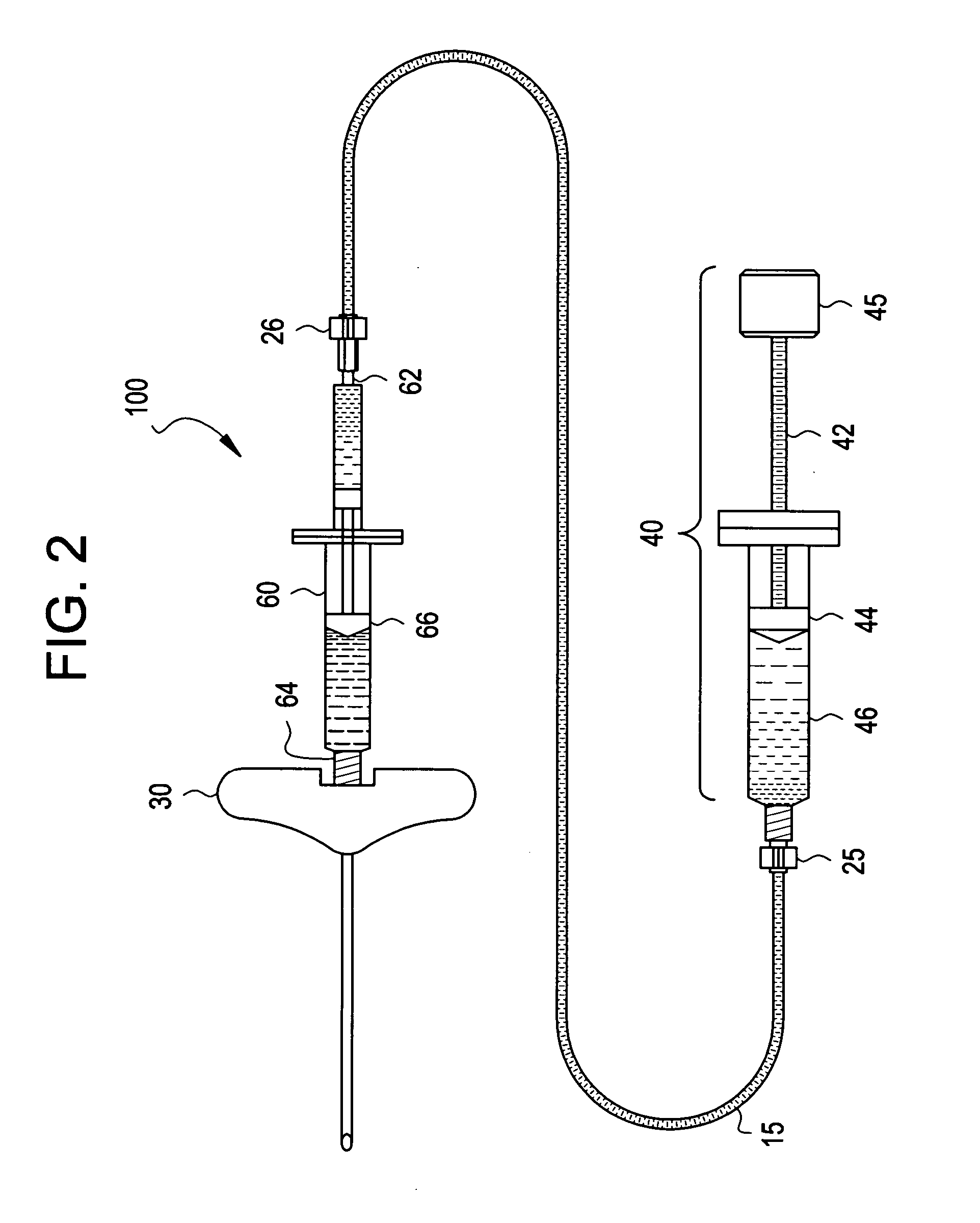
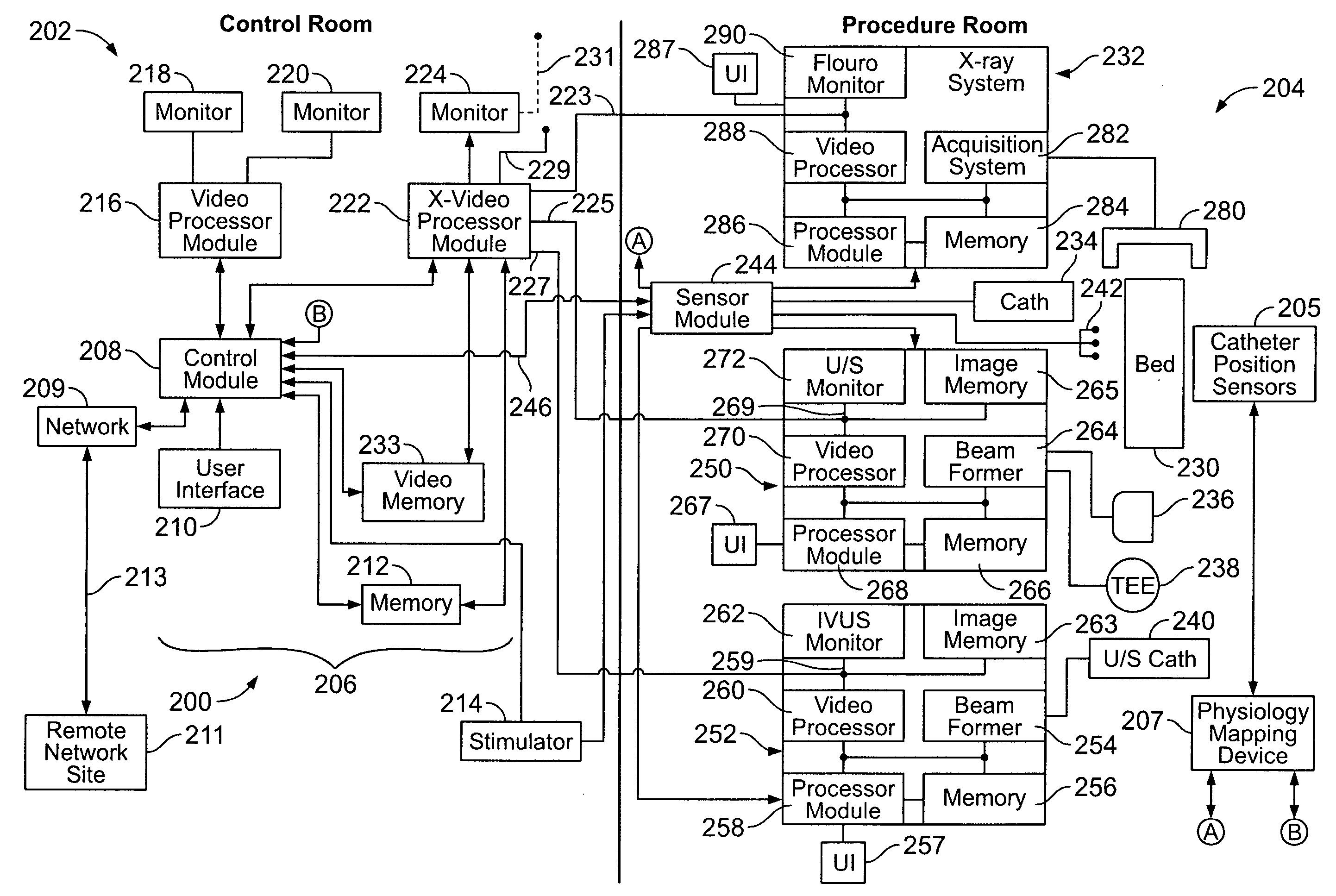
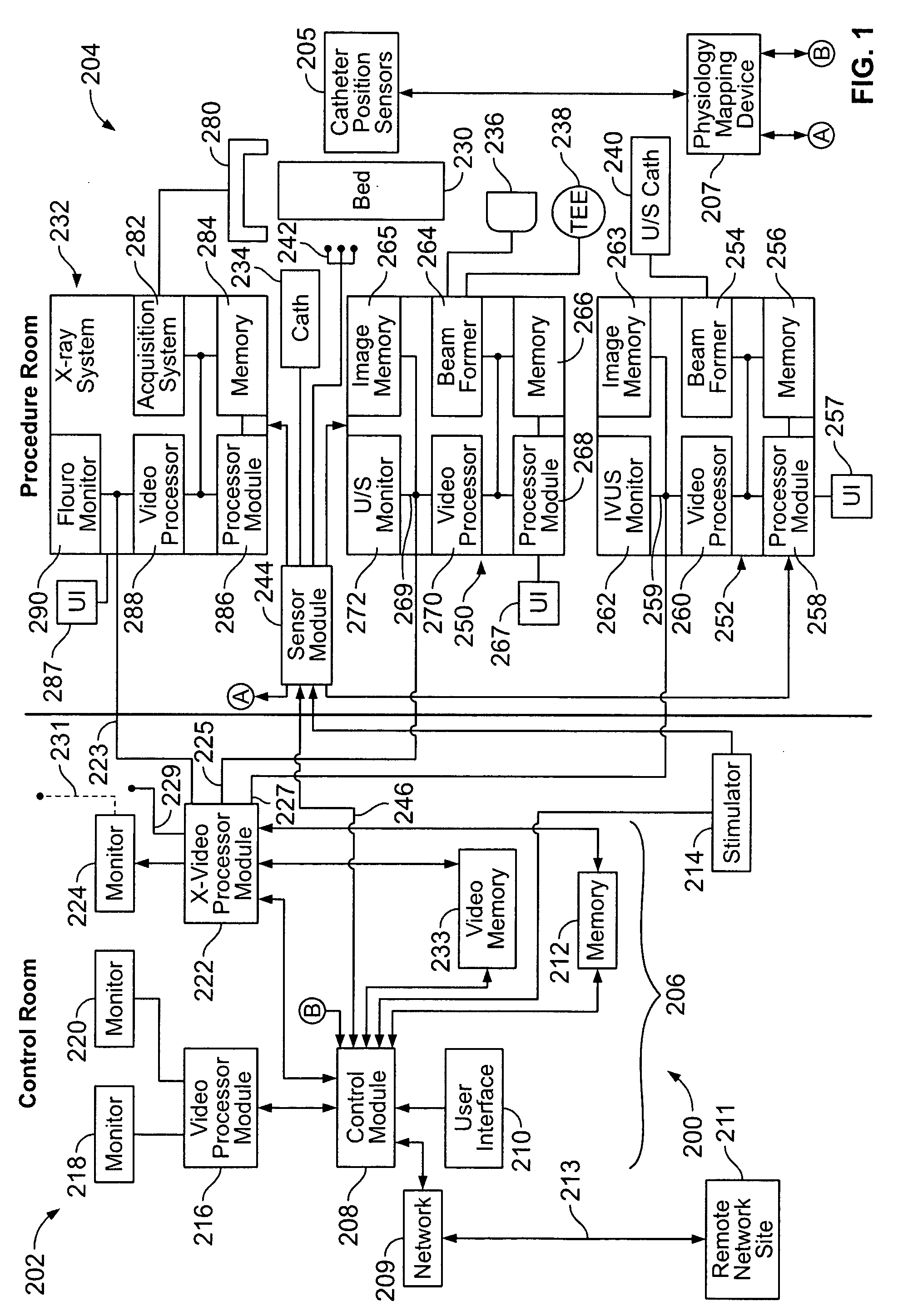
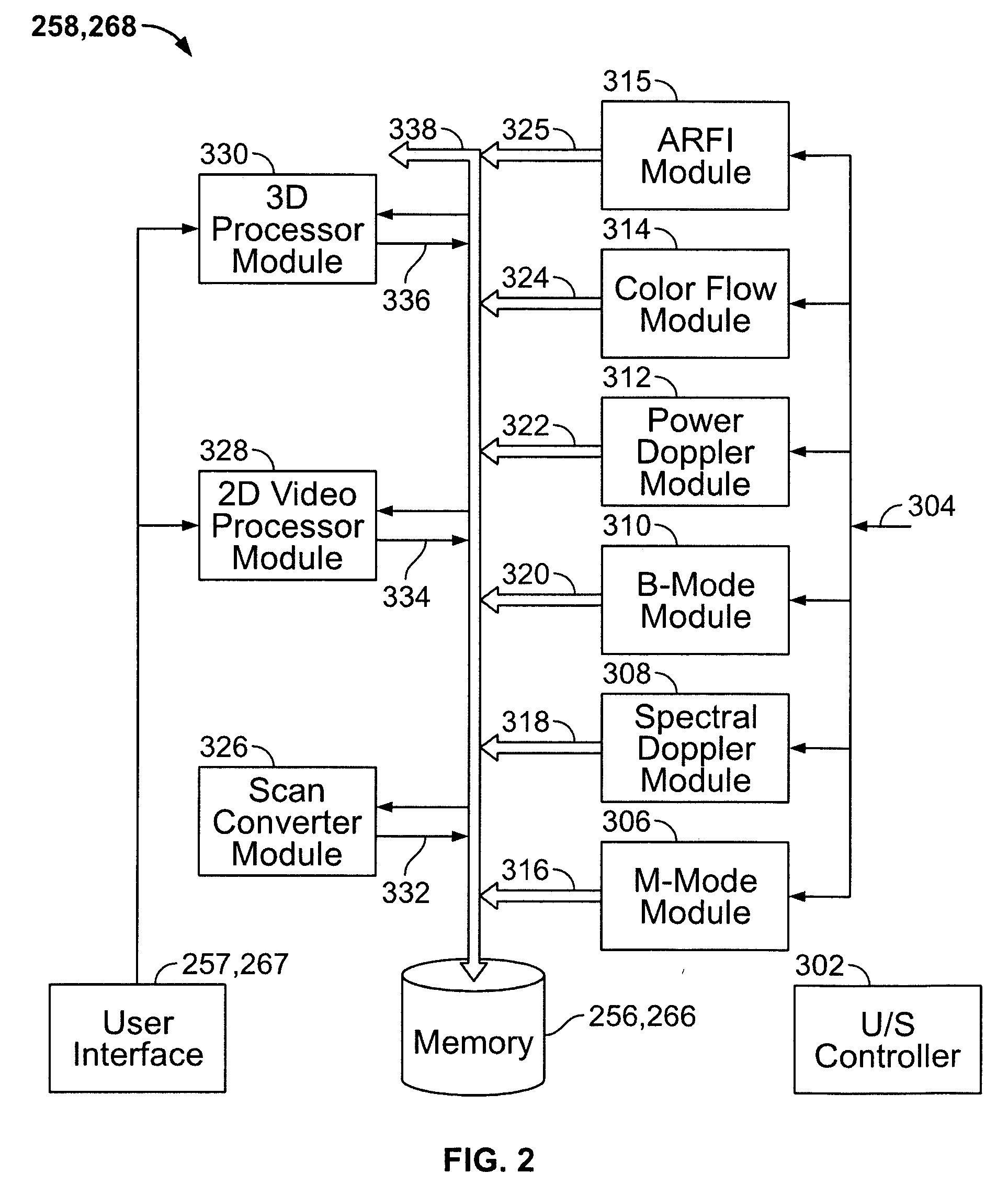
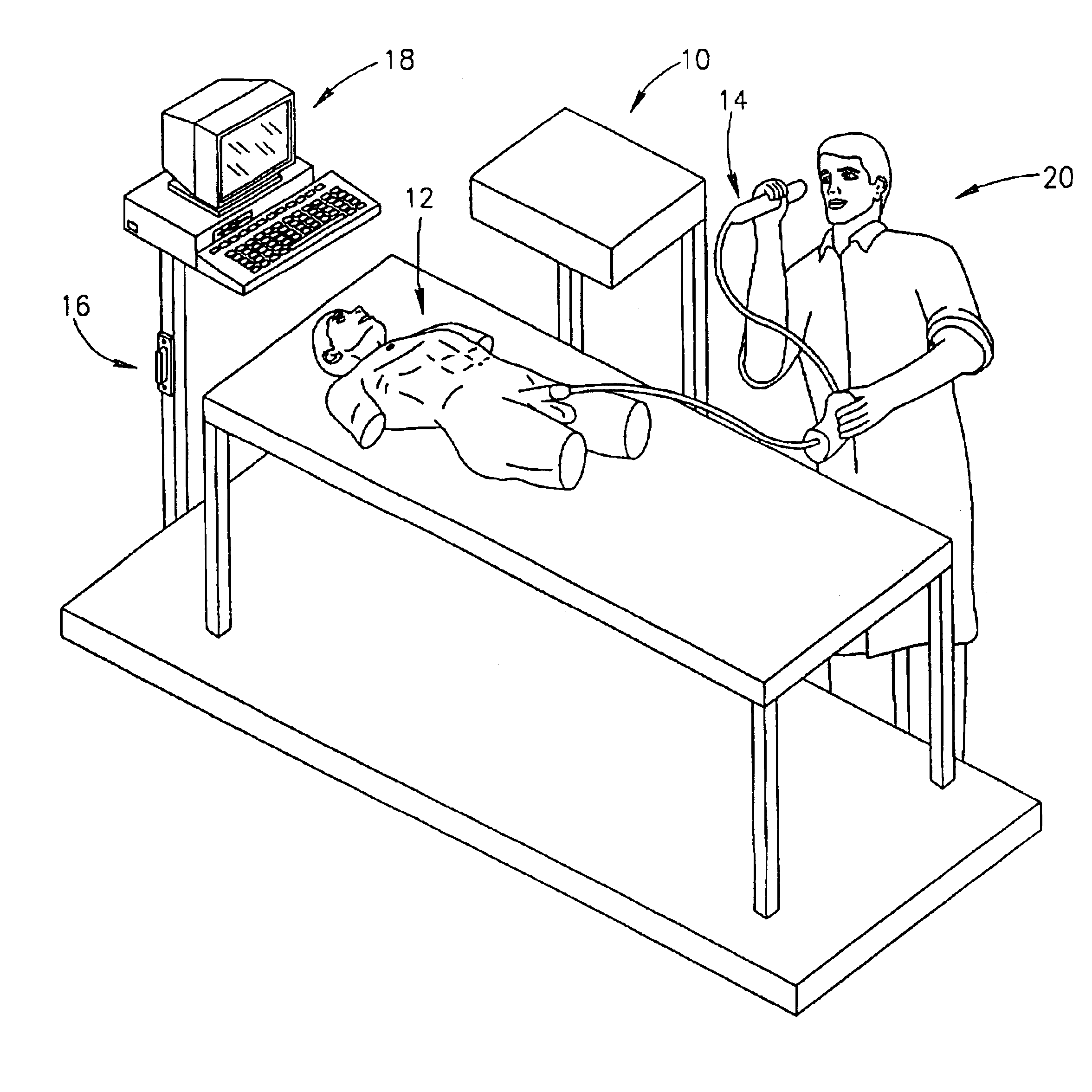
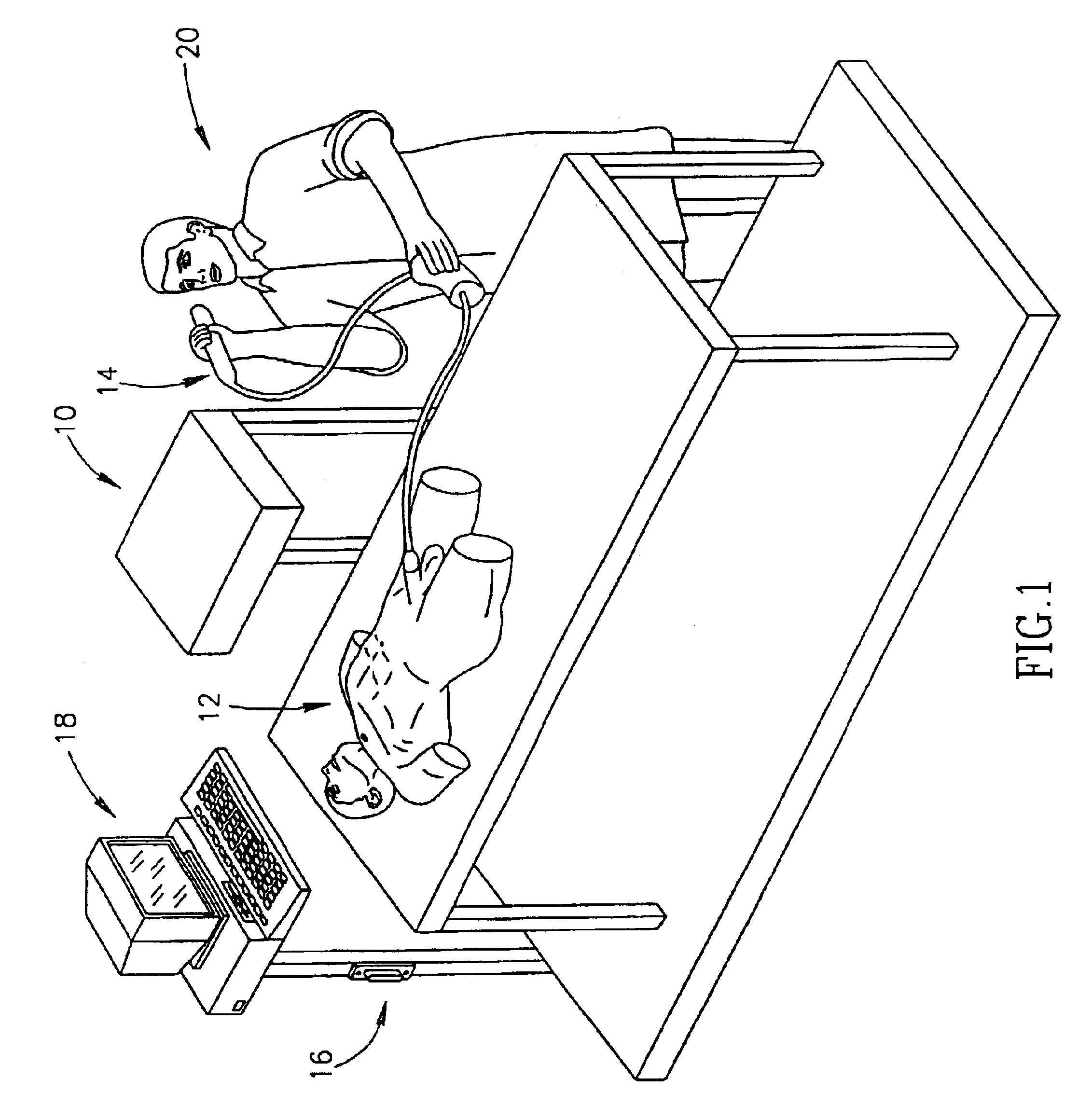
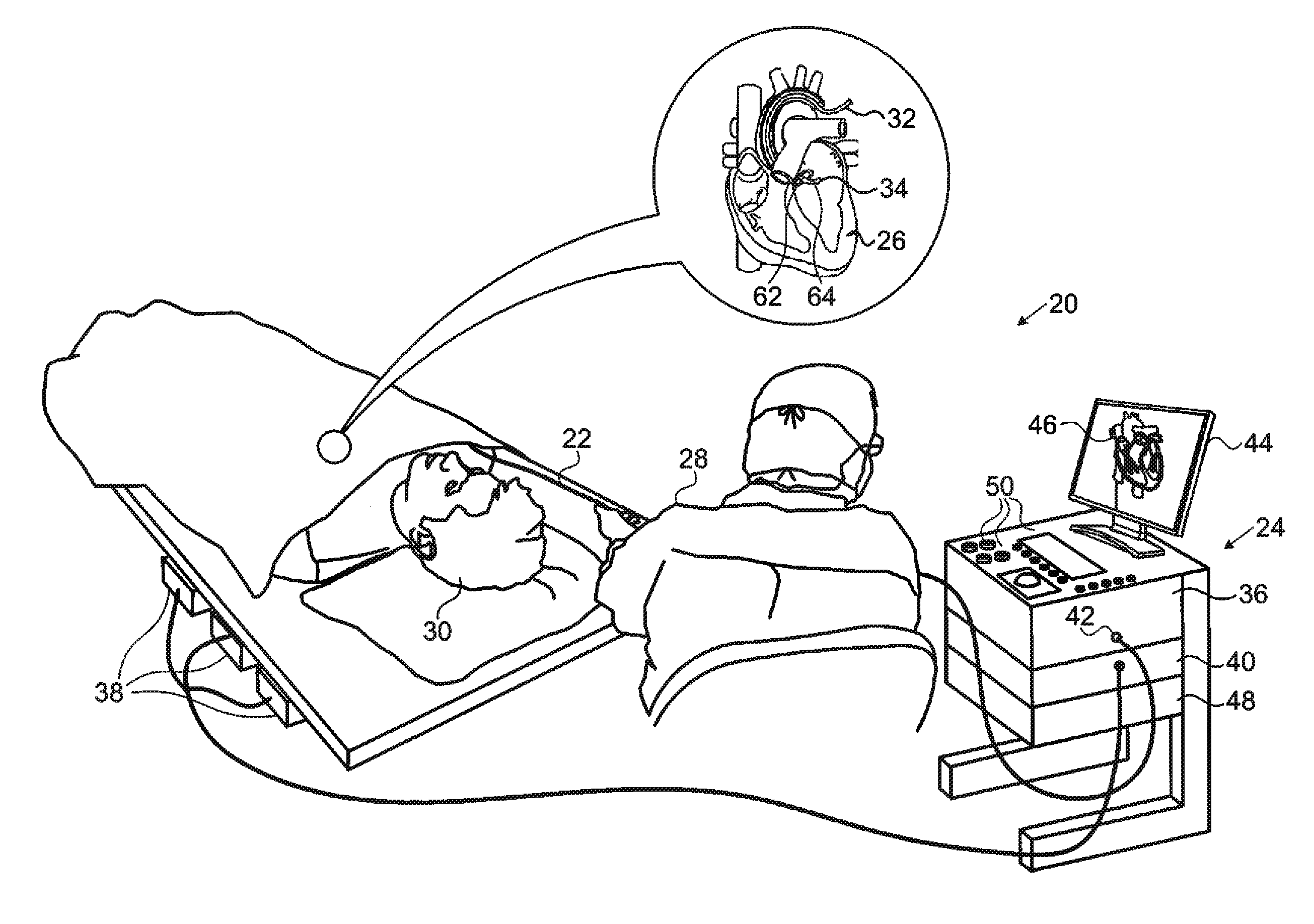
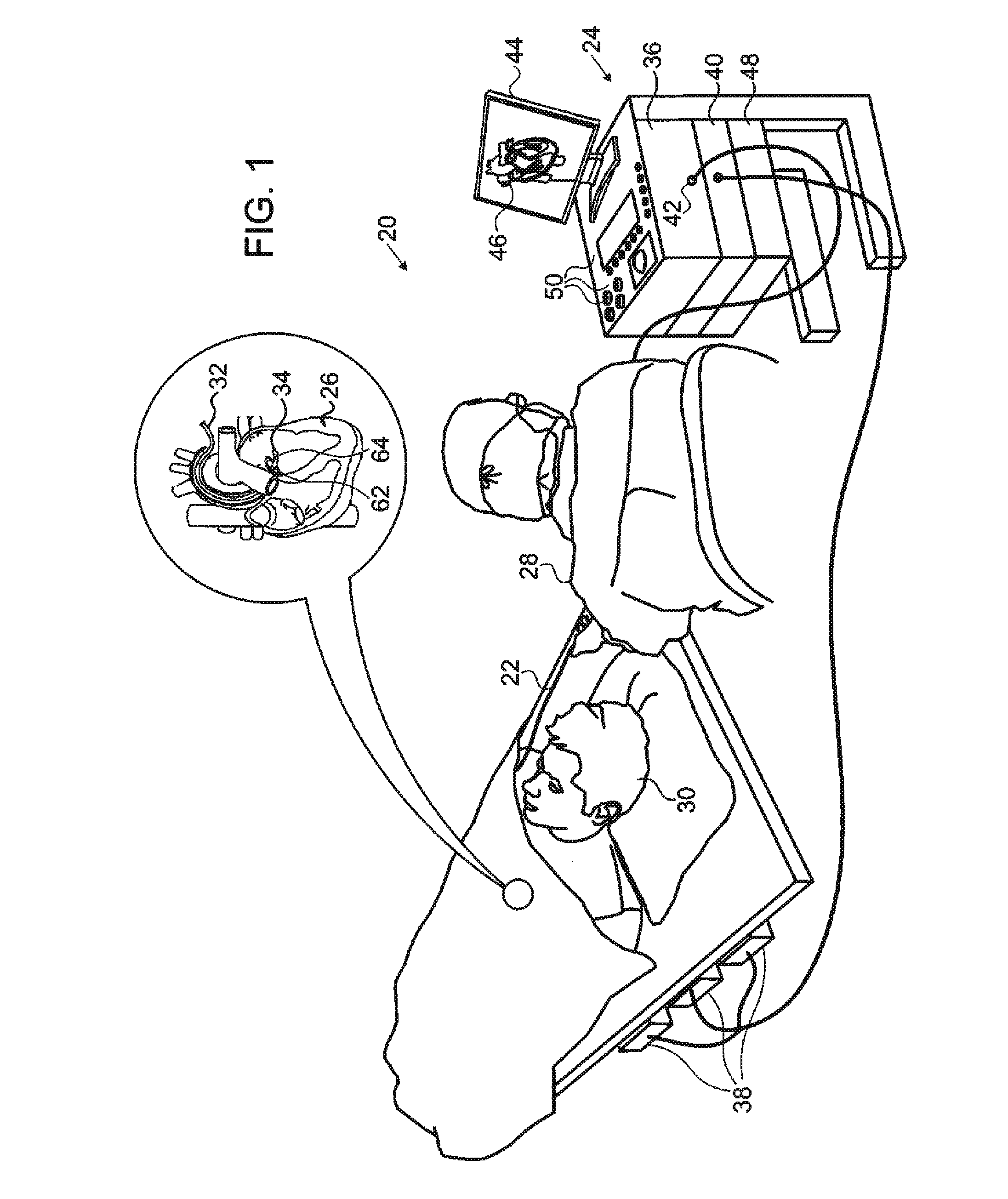
Physiology workstation with real-time fluoroscopy and ultrasound imaging
A physiology workstation is provided that comprises an physiology input configured to receive physiology signals from at least one of an intracardiac (IC) catheter inserted in a subject and surface ECG leads provided on the subject. The physiology signals are obtained during a procedure. A video input is configured to receive image frames, in real-time during the procedure. The image frames contain diagnostic information representative of data samples obtained from the subject during the procedure. A control module controls physiology operations based on user inputs. A display module is controlled by the physiology control module. The display module displays the physiology signals and the image frames simultaneously, in real-time, during the procedure. Optionally, the workstation may include a video processor module that formats the physiology signals into a display format. The video processor module may include an video processor and an external video processor that receive and control display of the physiology signals and image frames, respectively. The image frames may include at least one of ultrasound images obtained from a surface ultrasound probe, intravenous ultrasound images obtained from an ultrasound catheter and fluoroscopy images obtained from a fluoroscopy system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for registering 3D models of anatomical regions with projection images of the same
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
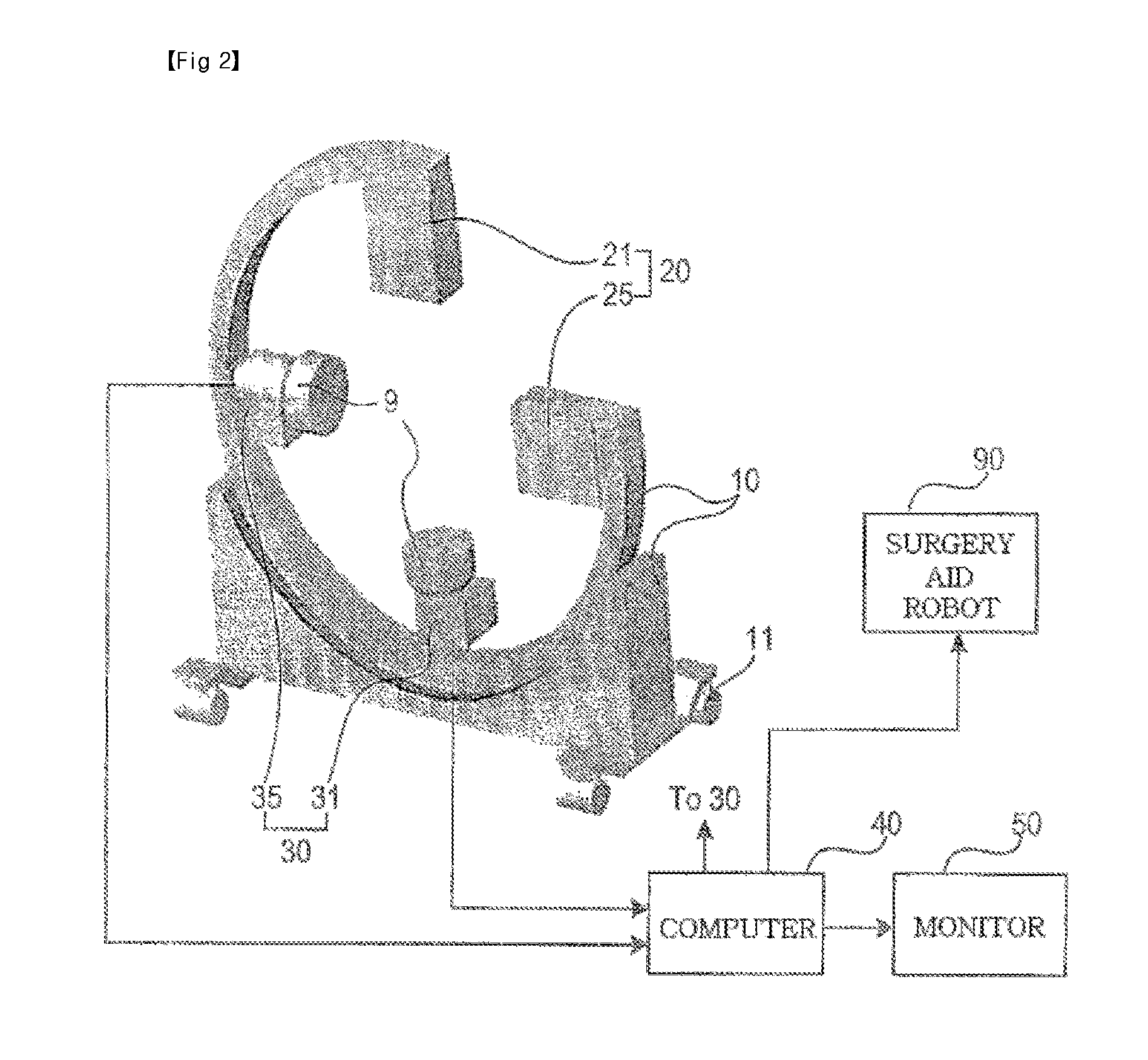
Bi-planar fluoroscopy guided robot system for minimally invasive surgery and the control method thereof
InactiveUS8046054B2Accurate three-dimensional surgery planAccurate surgery planMasksUmbrellasLess invasive surgeryProgram planning
Disclosed is a computer-integrated surgery aid system for minimally invasive surgery and a method for controlling the same. The system includes a surgery planning system for creating three-dimensional information from two-dimensional images obtained by means of biplanar fluoroscopy so that spinal surgery can be planned according to the image information and a scalar-type 6 degree-of-freedom surgery aid robot adapted to be either driven automatically or operated manually.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Transcoronary Sinus Pacing System, LV Summit Pacing, Early Mitral Closure Pacing, and Methods Therefor
ActiveUS20080082136A1Optimize early closureShorten the timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMulti-lumen catheterCoronary sinusPericardium tissue
A transcoronary sinus pacing system comprising a sheath having a lumen, a pacing catheter having a pacing needle, wherein the catheter can be advanced within the lumen and placed in the LV summit, and a right ventricular pacing device. A LV summit pacing device. An early mitral valve closure pacing device configured to operate with a right ventricular apex pacing device. A method for implanting a pacing device at a target coronary sinus tissue location, wherein the target can be the posterior LV summit. A method for achieving early closure of a mitral valve. A method for using visualization devices such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound and / or catheter features such as a radiopaque marker to locate a target location for LV pacing and to avoid piercing an artery or the pericardium when anchoring the LV pacing electrode.
Owner:GAUDIANI VINCENT
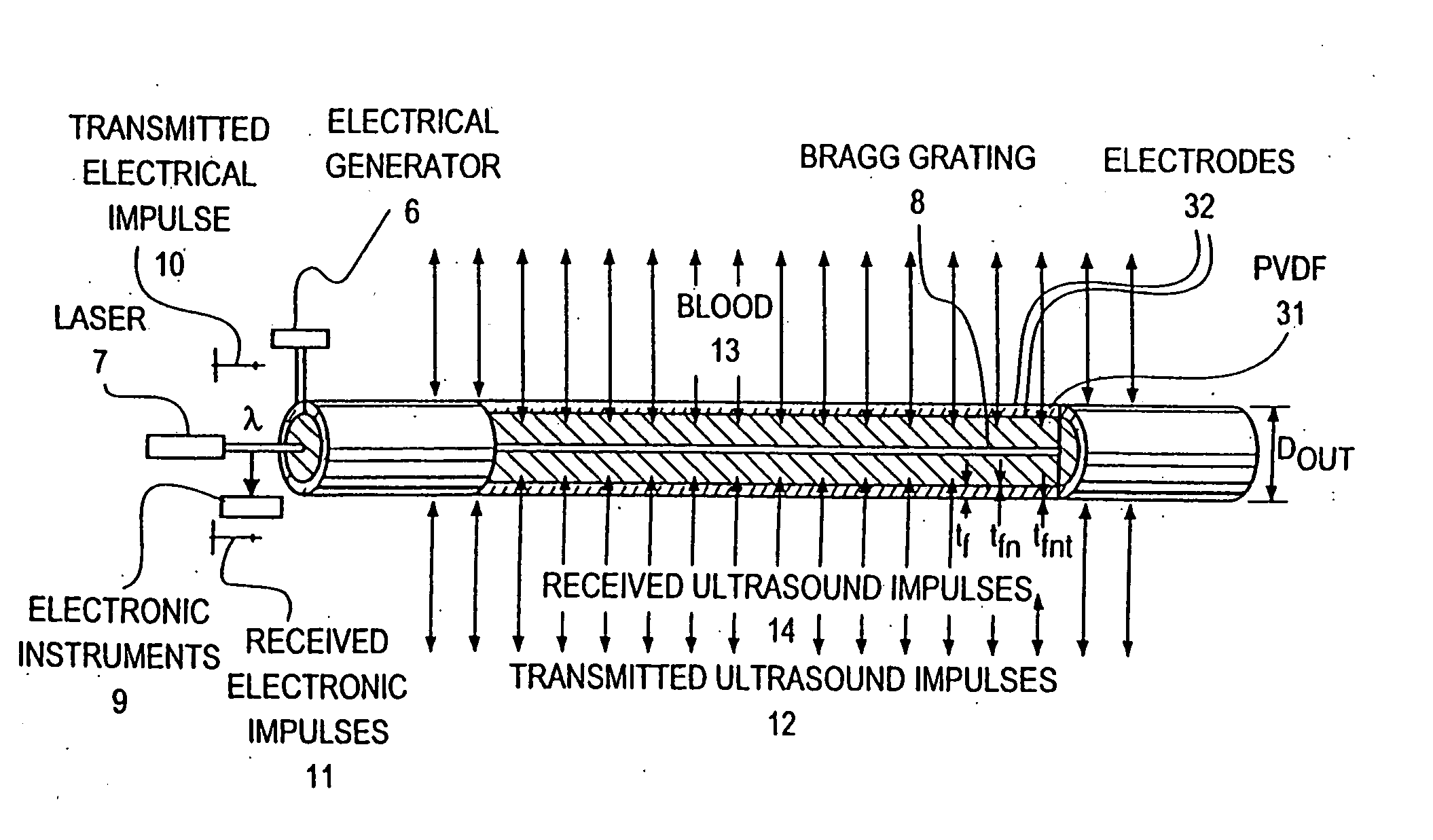
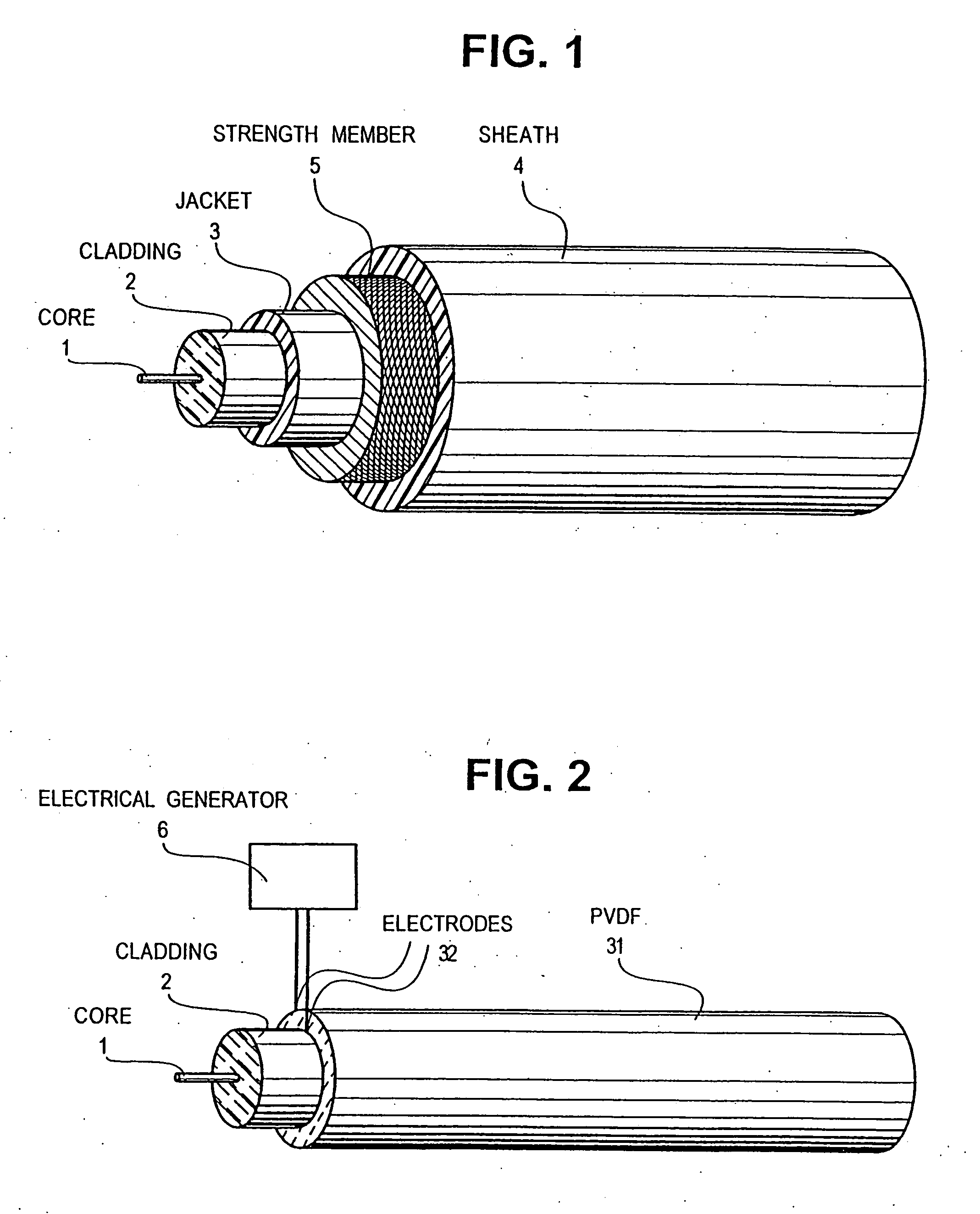
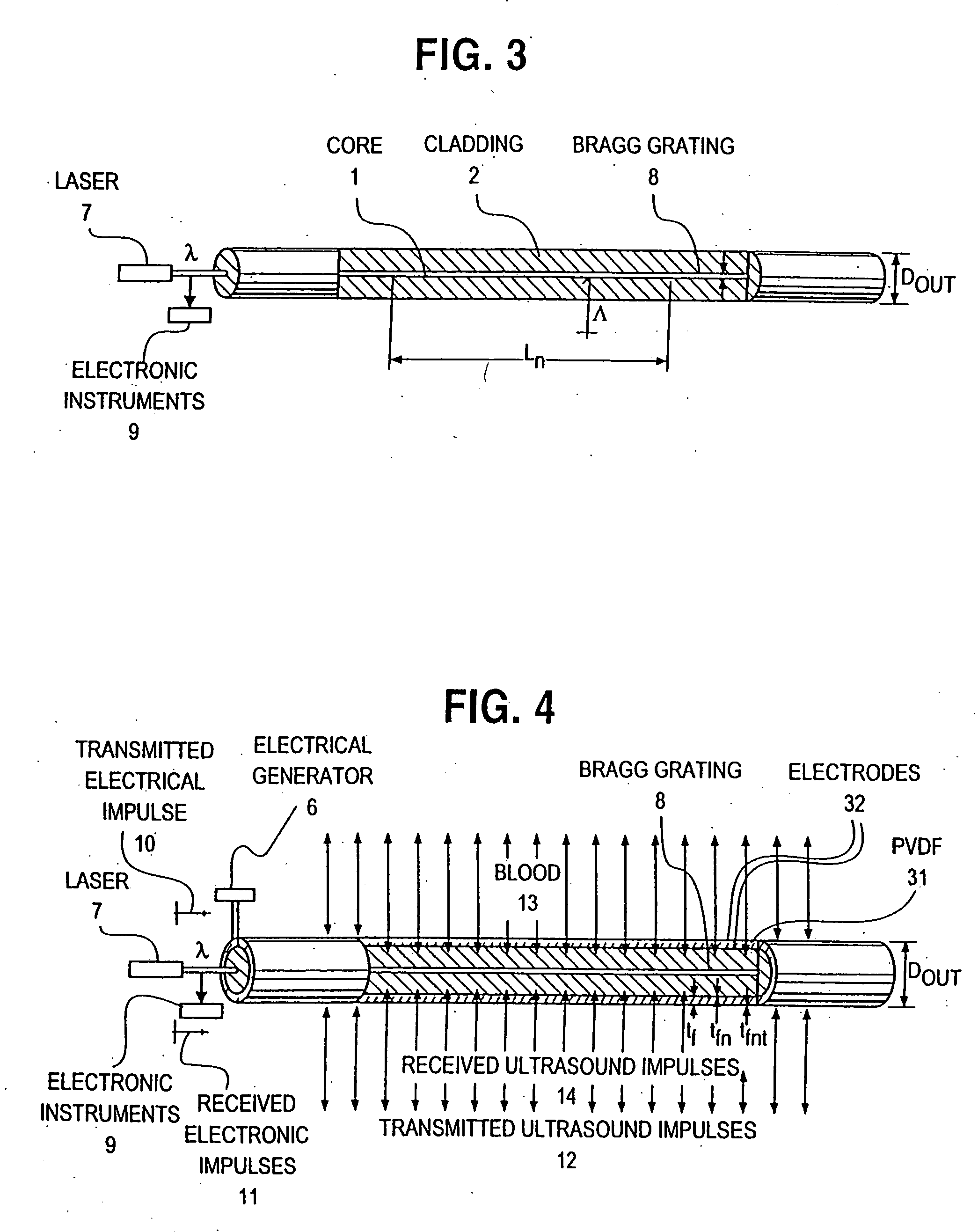
Optical-acoustic imaging device
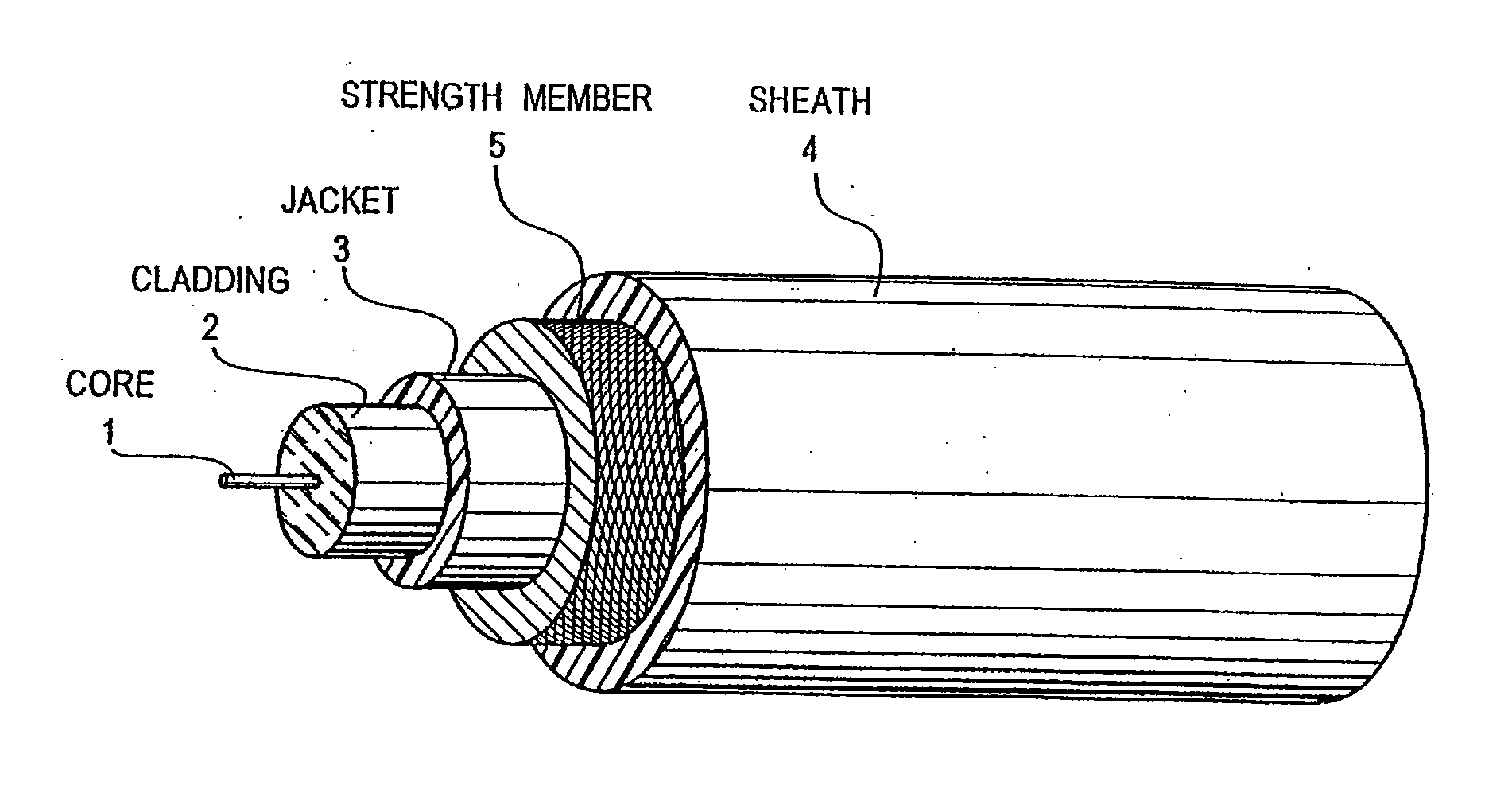
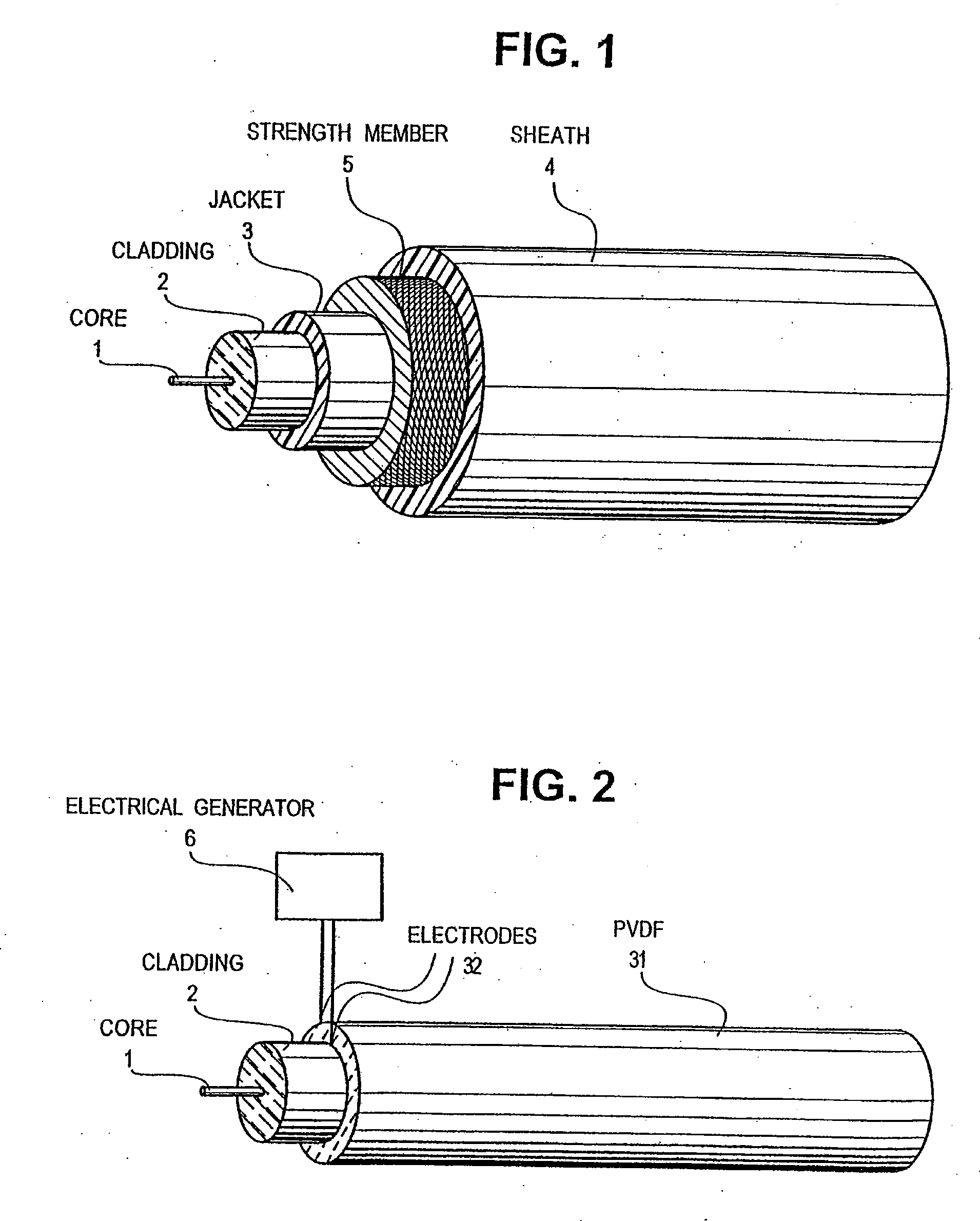
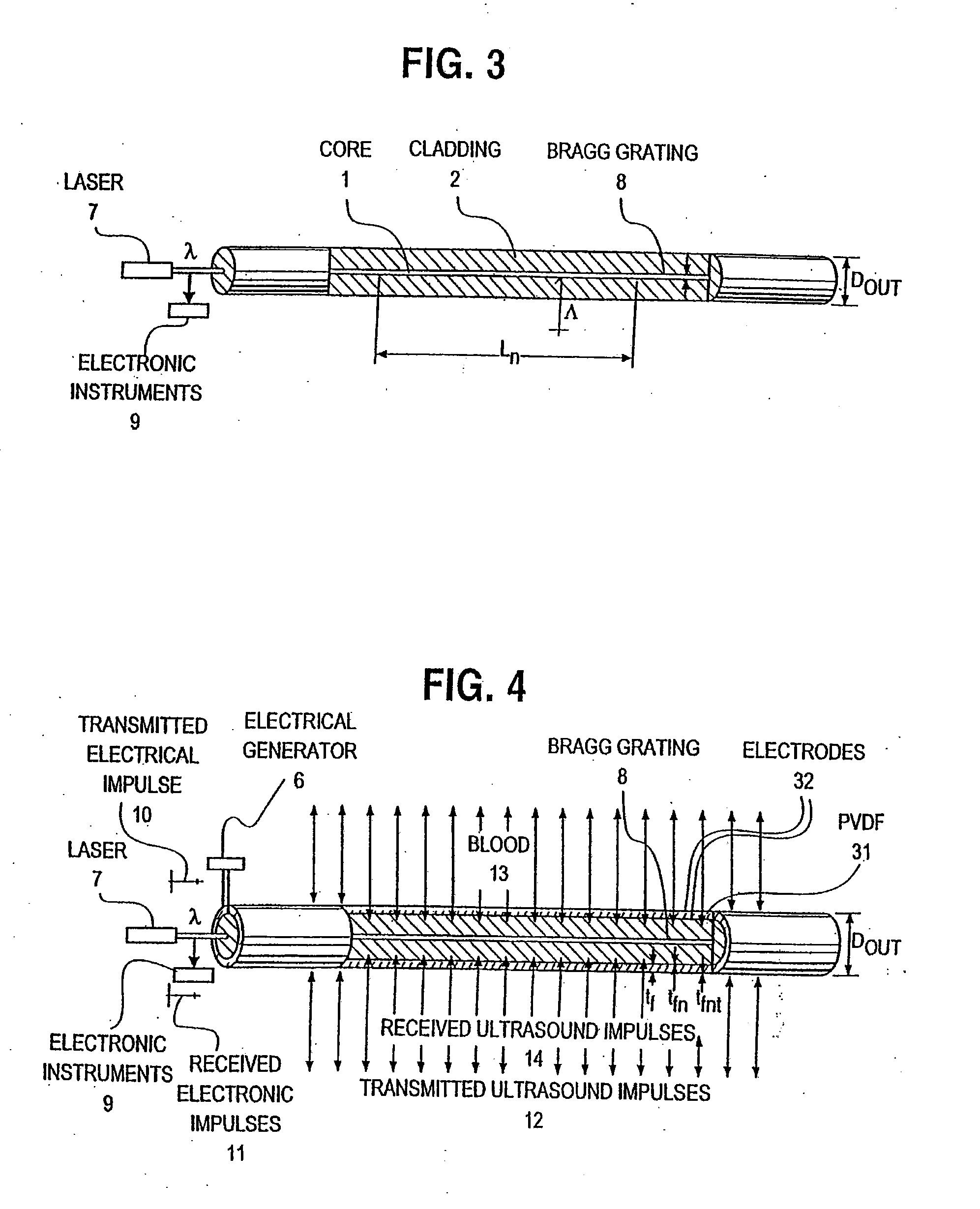
InactiveUS20080119739A1Reduce radiation exposureShorten operation timeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGratingRadiation exposure
The present invention is a guide wire imaging device for vascular or non-vascular imaging utilizing optic acoustical methods, which device has a profile of less than 1 mm in diameter. The ultrasound imaging device of the invention comprises a single mode optical fiber with at least one Bragg grating, and a piezoelectric or piezo-ceramic jacket, which device may achieve omnidirectional (360°) imaging. The imaging guide wire of the invention can function as a guide wire for vascular interventions, can enable real time imaging during balloon inflation, and stent deployment, thus will provide clinical information that is not available when catheter-based imaging systems are used. The device of the invention may enable shortened total procedure times, including the fluoroscopy time, will also reduce radiation exposure to the patient and to the operator.
Owner:PHYZHON HEALTH INC
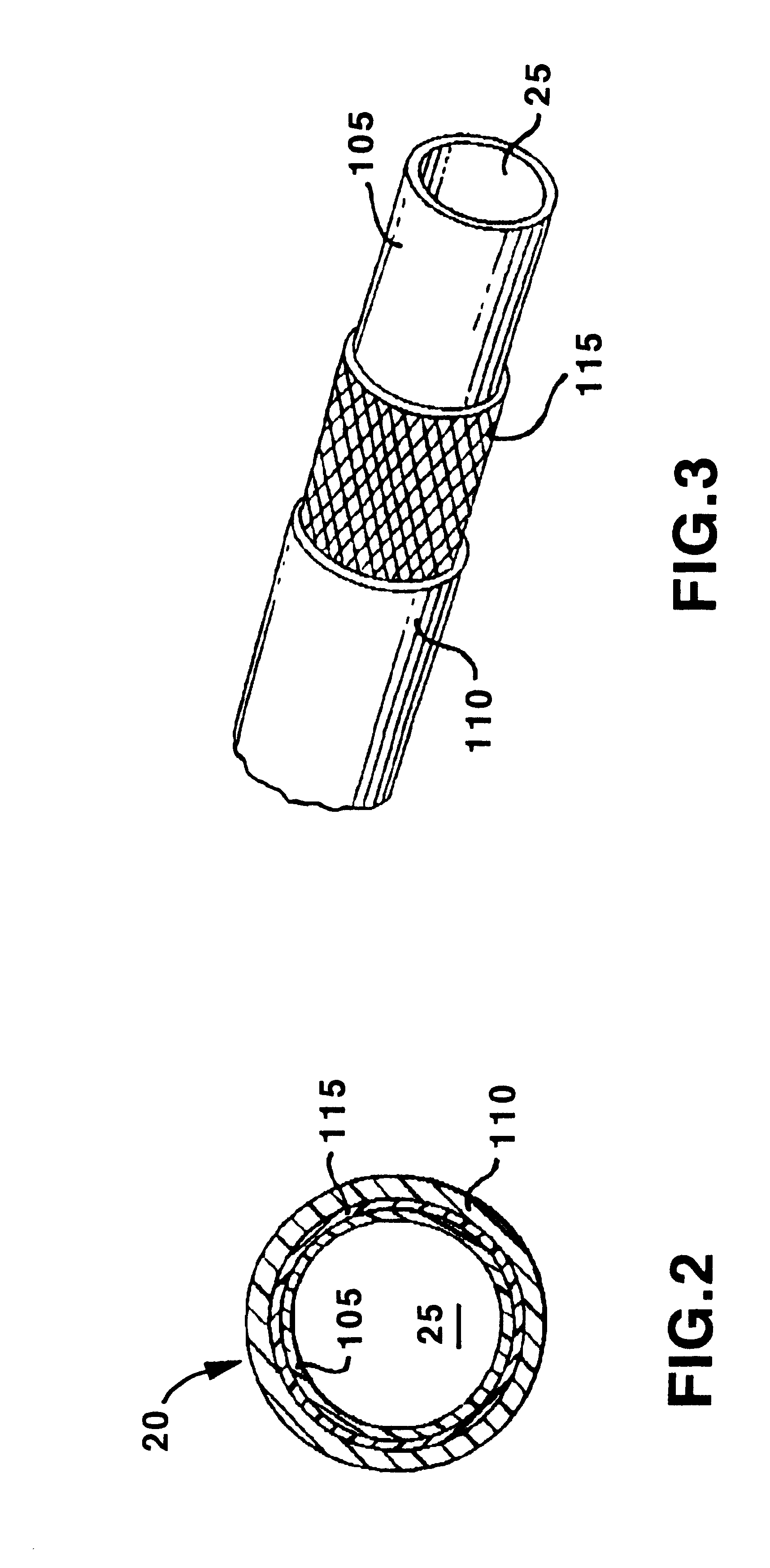
Guiding catheter with radiopaque band
The present invention comprises a tubular catheter shaft defining at least one catheter shaft lumen and a radiopaque band made of a polymeric material loaded with a radiopaque material of greater than 40% by weight, suitable for visualization under fluoroscopy in catheters in the range of 3 French to 5 French. The distal soft tip is formed of a relatively flexible polymeric material, loaded with radiopaque material which is less radiopaque than the radiopaque band. The radiopaque band's proximal end adjoins the distal end of the catheter shaft. The radiopaque band's distal end adjoins the proximal end of the distal tip to form an attachment junction. A tubular sleeve fits coaxially over the radiopaque band, the distal end of the catheter shaft and the proximal end of the distal soft tip. The tubular sleeve adheres the catheter shaft distal end to the proximal end of the radiopaque band and adheres the soft tip proximal end to the distal end of the radiopaque band thereby aligning the soft tip lumen, the radiopaque band lumen, and the catheter shaft lumen. The proximal end of the tubular sleeve is bonded to a distal portion of the catheter shaft. The distal end of the tubular sheath is bonded to the proximal end of the soft distal tip. The radiopaque band is bonded to the tubular sheath thereby bridging the attachment junction. The tubular sleeve is made of a polymeric material loaded with a radiopaque material which is less radiopaque than the radiopaque band. The tubular sleeve is melt compatible with the radiopaque band, the catheter shaft distal end and the distal soft tip such that the tubular sleeve, the distal end of the catheter shaft, the radiopaque band and the proximal end of the distal soft tip bond.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Markers for visualizing interventional medical devices
InactiveUS20050149002A1Avoid transmissionStentsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
A marking material that, when disposed upon medical devices used during interventional medical procedures with imaging modalities such as X-ray Fluoroscopy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging, renders such medical devices visible with minimal imaging artifacts. The material comprises a particulate material with generally higher atomic weight disposed within a matrix material with generally lower atomic weight. In one embodiment the particulate material is magnetic. In another embodiment the particulate material is non-magnetic.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
Non-expandable transluminal access sheath
InactiveUS20060253102A1Improved radiopaque characteristicMinimize potential for damageCannulasInfusion syringesFluid transportVisibility
A transluminal sheath is disclosed that permits instrumentation to be passed therethrough. The transluminal sheath comprises a composite structure with an inner layer, an outer layer, and a reinforcing layer. The materials comprising the inner and outer layer are plastically deformable and maintain their shape, once bent into a specific configuration. The reinforcing layer further has radiopacity enhancing coatings to improve visibility under fluoroscopy and a system of flutes running longitudinally, to enhance fluid transport and reduce friction.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
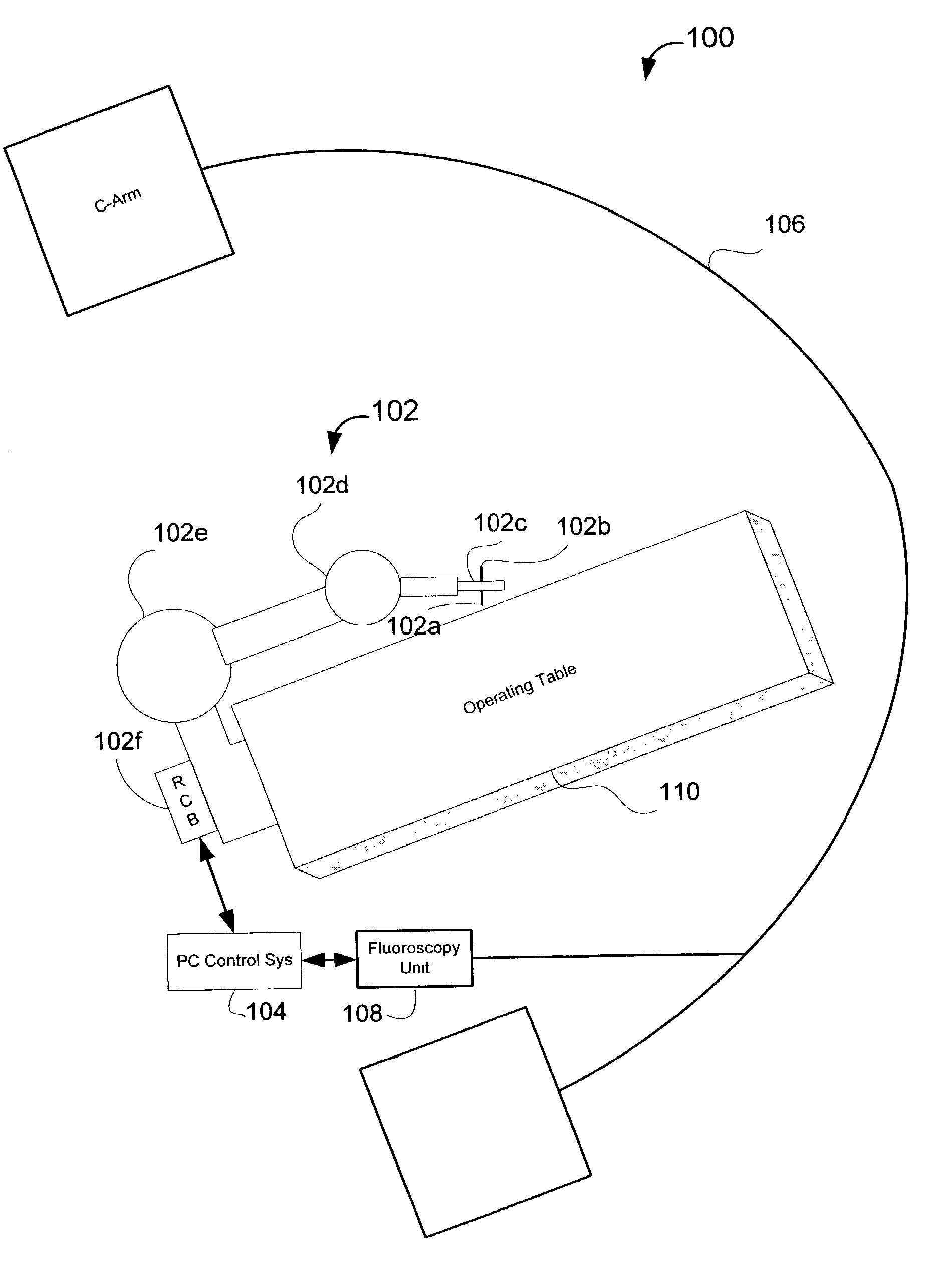
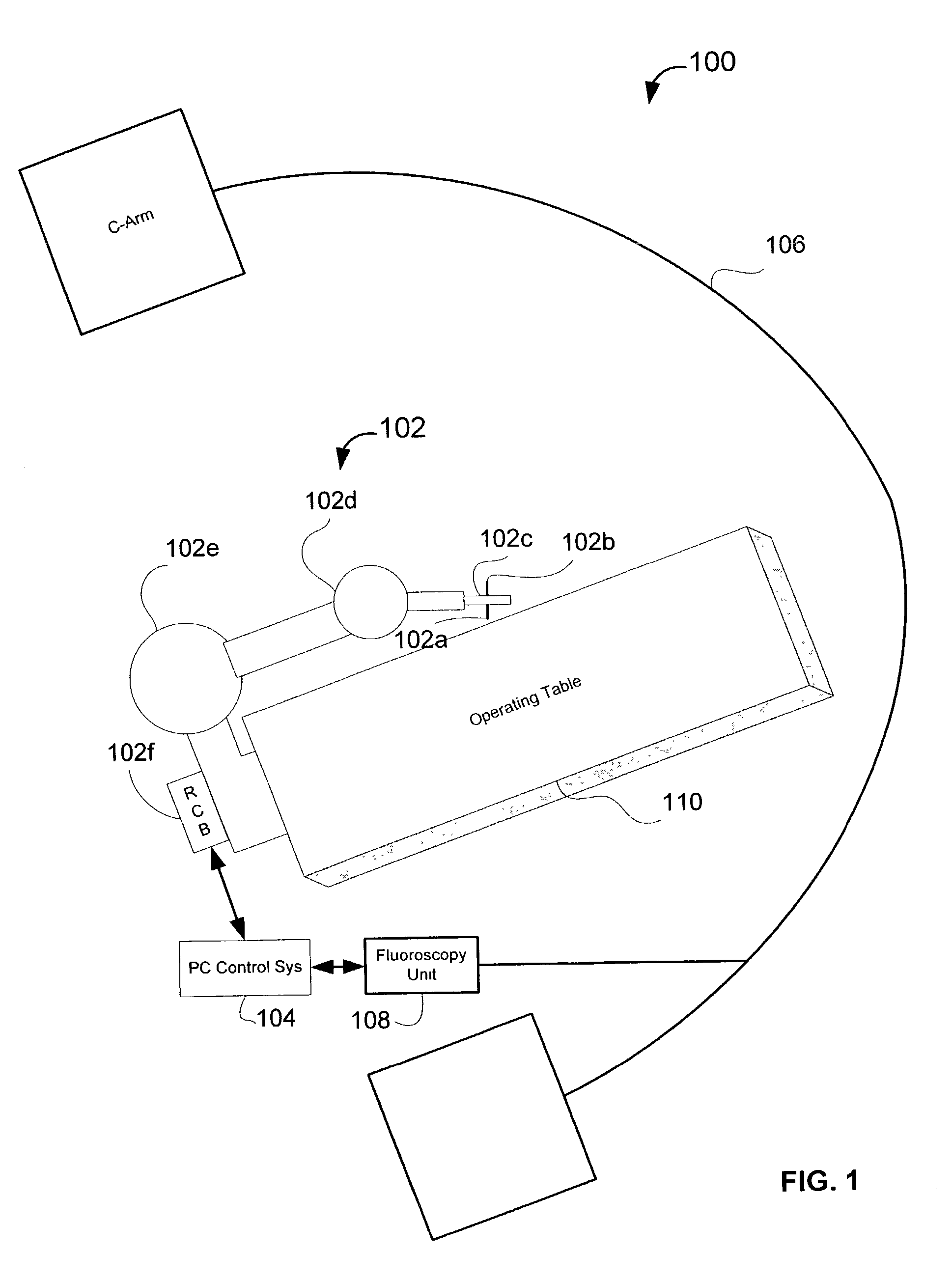
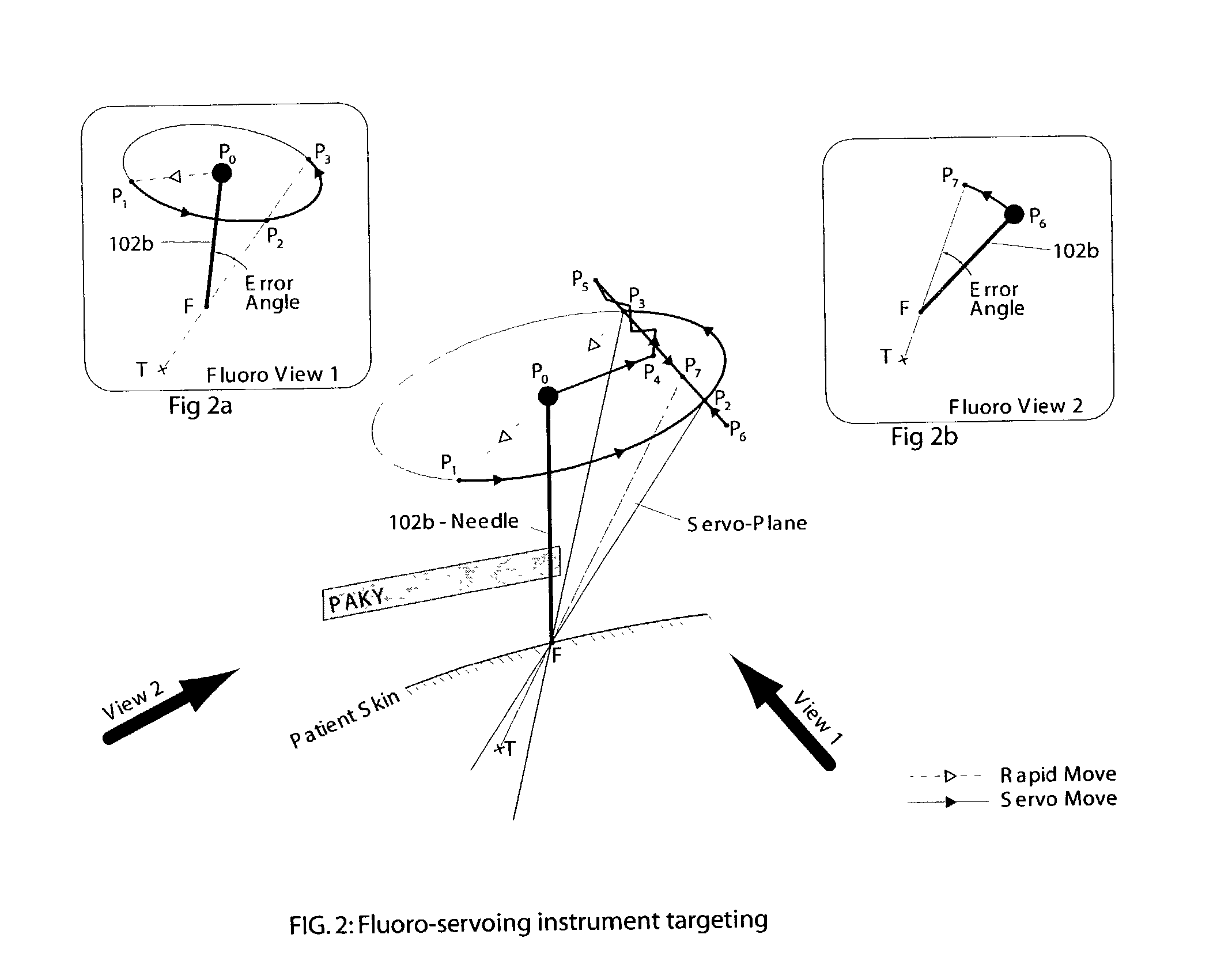
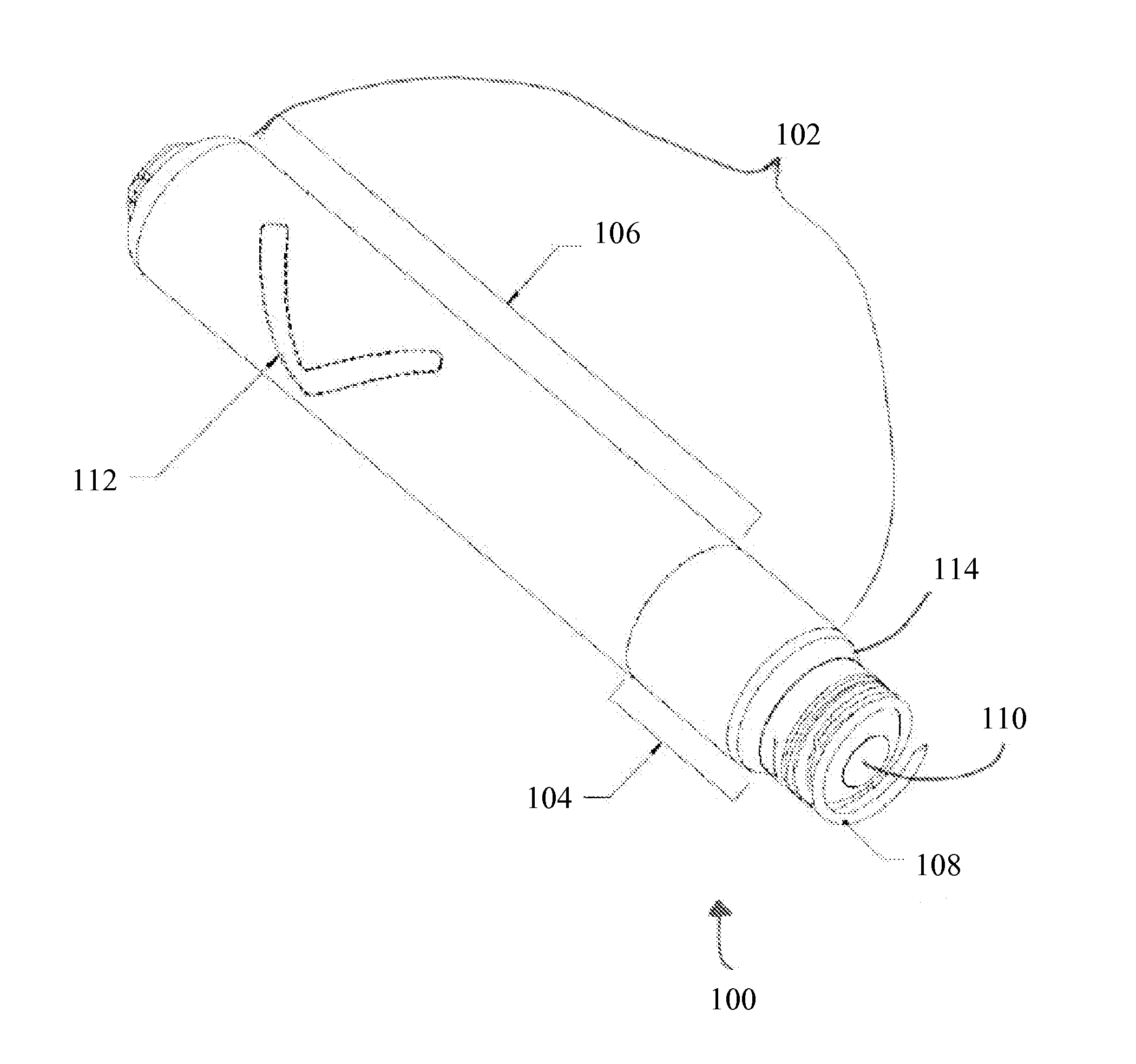
System and method for robot targeting under fluoroscopy based on image servoing
InactiveUS7008373B2Improve accuracyImprove simplicitySurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringFluorescenceEngineering
A system and method for image guided instrument targeting including a robot unit coupled with an instrument, an imaging unit, and a first control unit, which is coupled with the robot unit and coupled with the imaging unit. The control unit receives the imaging data about a target and about the instrument from the imaging unit and controls the robot unit to properly orienting the instrument for insertion, based upon the imaging data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
X-Ray Identification for Active Implantable Medical Device
An active implantable medical device is disclosed herein having a radio-opaque marker. The radio-opaque marker can be formed within an exterior wall of the device or within recesses on the outside of the exterior wall. The implantable medical device can be a leadless pacemaker. The shape of the radio-opaque marker can be designed to facilitate visualization and identification of the location, orientation, and rotation of the implanted medical device by conventional fluoroscopy. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Endoscopic tutorial system for urology
InactiveUS6939138B2Simulation is accurateEducational models3D-image renderingComplete resolutionDynamic contrast
A method and a system for simulating the minimally invasive medical procedure of urological endoscopy. The system is designed to simulate the actual medical procedure of urological endoscopy as closely as possible by providing botha simulated medical instrument, and tactile and visual feedback as the simulated procedure is performed on the simulated patient. Particularly preferred features include a multi-path solution for virtual navigation in a complex anatomy, the simulation of the effect of the beating heart on the urethra as it crosses the illiac vessel, and the simulated operation of a guidewire within the urethra In addition, the system and method optionally and more preferably incorporate the effect of dynamic contrast injection of dye into the urethra for fluoroscopy. The injection of such dye, and the subsequent visualization of the urological organ system in the presence of the endoscope, must be accurately simulated in terms of accurate visual feedback. Thus, the system and method provide a complete solution to the complex and difficult problem of training students in urological endoscopy procedures.
Owner:SIMBIONIX
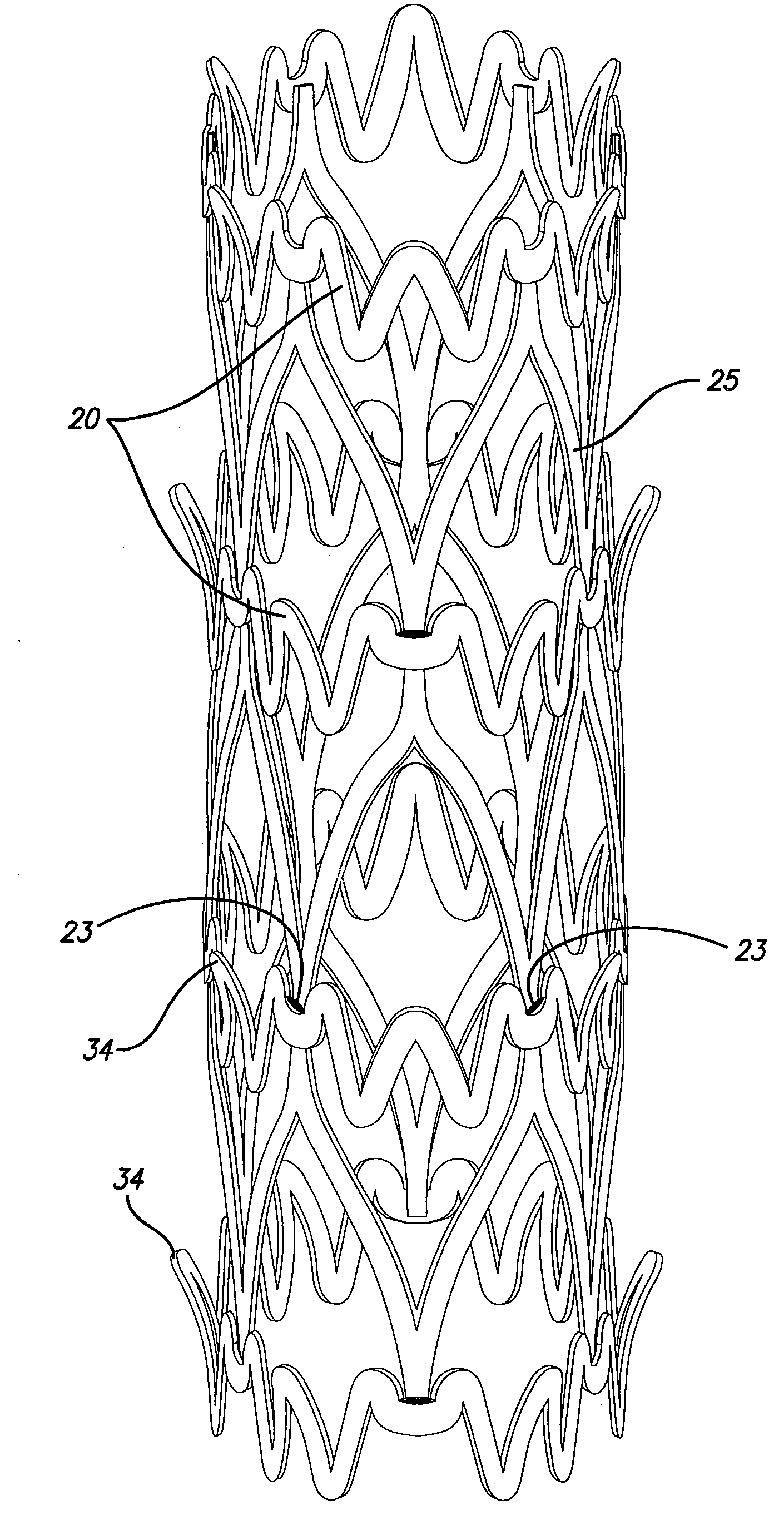
Radiopaque distal embolic protection device
InactiveUS20060030878A1Precise positioningSmall sizeSurgeryDilatorsDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
The present invention is a radiopaque distal embolic protection device for use in a lumen of a patient's body, such as a blood vessel. The protection device has an expandable and retractable filter attached to a distal portion of a guidewire. At least a portion of the filter has a radiopaque coating for viewing under fluoroscopy during use. The radiopaque coating allows the operator to ensure that the periphery of the filter has fully engaged the wall of a blood vessel and to take appropriate measures in recovery of the protection device after capture of emboli and particulate matter.
Owner:EV3
Methods for injecting a curable biomaterial into an intervertebral space
A method for treating a diseased or damaged spinal disc comprises the steps of: (a) providing access to the nucleus pulposus through the annulus; (b) removing at least a portion of the nucleus pulposus to create an intradiscal space; determining the size of the intradiscal space; and (c) sealably introducing under pressure a curable biomaterial through the annulus directly into the intradiscal space. The method may include the additional steps of applying a force to distract the opposing vertebral bodies about the intradiscal space and then removing the distraction force after the biomaterial has cured. The step of determining the size of the intradiscal space may be accomplished by expanding a compliant balloon within the intradiscal space using a contrast medium capable of visualization under fluoroscopy. The curable material is sealably introduced through a vented needle inserted through the opening. The curable biomaterial is introduced until a quantity of the material flows into the vent.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Implant system with migration measurement capacity
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Hybrid stent and method of making
InactiveUS20080188924A1Increase awarenessOvercomes shortcomingOrganic active ingredientsLayered productsMedicineFluorescence
A stent is formed by encasing or encapsulating metallic rings in an inner polymeric layer and an outer polymeric layer. At least one polymer link connects adjacent metallic rings. The stent is drug loaded with one or more therapeutic agent or drug, for example, to reduce the likelihood of the development of restenosis in the coronary arteries. The inner and outer polymeric materials can be of the same polymer or different polymer to achieve different results, such as enhancing flexibility and providing a stent that is visible under MRI, computer tomography and x-ray fluoroscopy.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
In-vivo calibration of contact force-sensing catheters using auto zero zones
A method for the in vivo re-calibration of a force sensing probe such as an electrophysiology catheter provides for the generation of an auto zero zone. The distal tip of the catheter or other probe is placed in a body cavity within the patient. Verification that there is no tissue contact is made using electrocardiogram (ECG) or impedance data, fluoroscopy or other real-time imaging data and / or an electro-anatomical mapping system. Once verification that there is no tissue contact is made, the system recalibrates the signal emanating from the force sensor setting it to correspond to a force reading of zero grams and this recalibrated baseline reading is used to generate and display force readings based on force sensor data.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Hybrid stent and method of making
InactiveUS7691461B1Increase awarenessOvercomes shortcomingOrganic active ingredientsLayered productsCoronary arteriesFluorescence
A stent is formed by encasing or encapsulating metallic rings in an inner polymeric layer and an outer polymeric layer. At least one polymer link connects adjacent metallic rings. The stent is drug loaded with one or more therapeutic agent or drug, for example, to reduce the likelihood of the development of restenosis in the coronary arteries. The inner and outer polymeric materials can be of the same polymer or different polymer to achieve different results, such as enhancing flexibility and providing a stent that is visible under MRI, computer tomography and x-ray fluoroscopy.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Anti-thrombus filter having enhanced identifying features
InactiveUS20060069405A1Easy to identifyReduced endotheliosis featureDiagnosticsSurgeryCeramic coatingThrombus
A removable filter for capturing thrombi in a body vessel. The filter has anti-thrombogenic, echogenic, and radiopaque features. The features of the filter provide for enhanced identifying and reduced endotheliosis in a body vessel of a patient. Generally, the anti-thrombogenic feature is preferably a fibrinolytic coating disposed on the filter to decrease the accumulation of fibrin thereon. The echogenic feature preferably is comprised of marks formed on the filter that give rise to reflections of ultrasound waves during ultrasonography. The radiopaque feature is preferably a polymeric coating, ceramic coating, or noble metal coating applied on the filter for enhanced fluoroscopy.
Owner:COOK INC
Optical-acoustic imaging device
InactiveUS20040082844A1Shorten operation timeReduce radiation exposureMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGratingRadiation exposure
The present invention is a guide wire imaging device for vascular or non-vascular imaging utilizing optic acoustical methods, which device has a profile of less than 1 mm in diameter. The ultrasound imaging device of the invention comprises a single mode optical fiber with at least one Bragg grating, and a piezoelectric or piezo-ceramic jacket, which device may achieve omnidirectional (360°) imaging. The imaging guide wire of the invention can function as a guide wire for vascular interventions, can enable real time imaging during balloon inflation, and stent deployment, thus will provide clinical information that is not available when catheter-based imaging systems are used. The device of the invention may enable shortened total procedure times, including the fluoroscopy time, will also reduce radiation exposure to the patient and to the operator.
Owner:PHYZHON HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com