Patents
Literature
38 results about "Surface ecg" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface ECG. Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) measures the heart's electrical activity by using surface or needle electrodes. ECG signals are employed to examine heart rate, heart rate variability, analysis of the waveform morphology, surgical monitoring, and other similar functions.
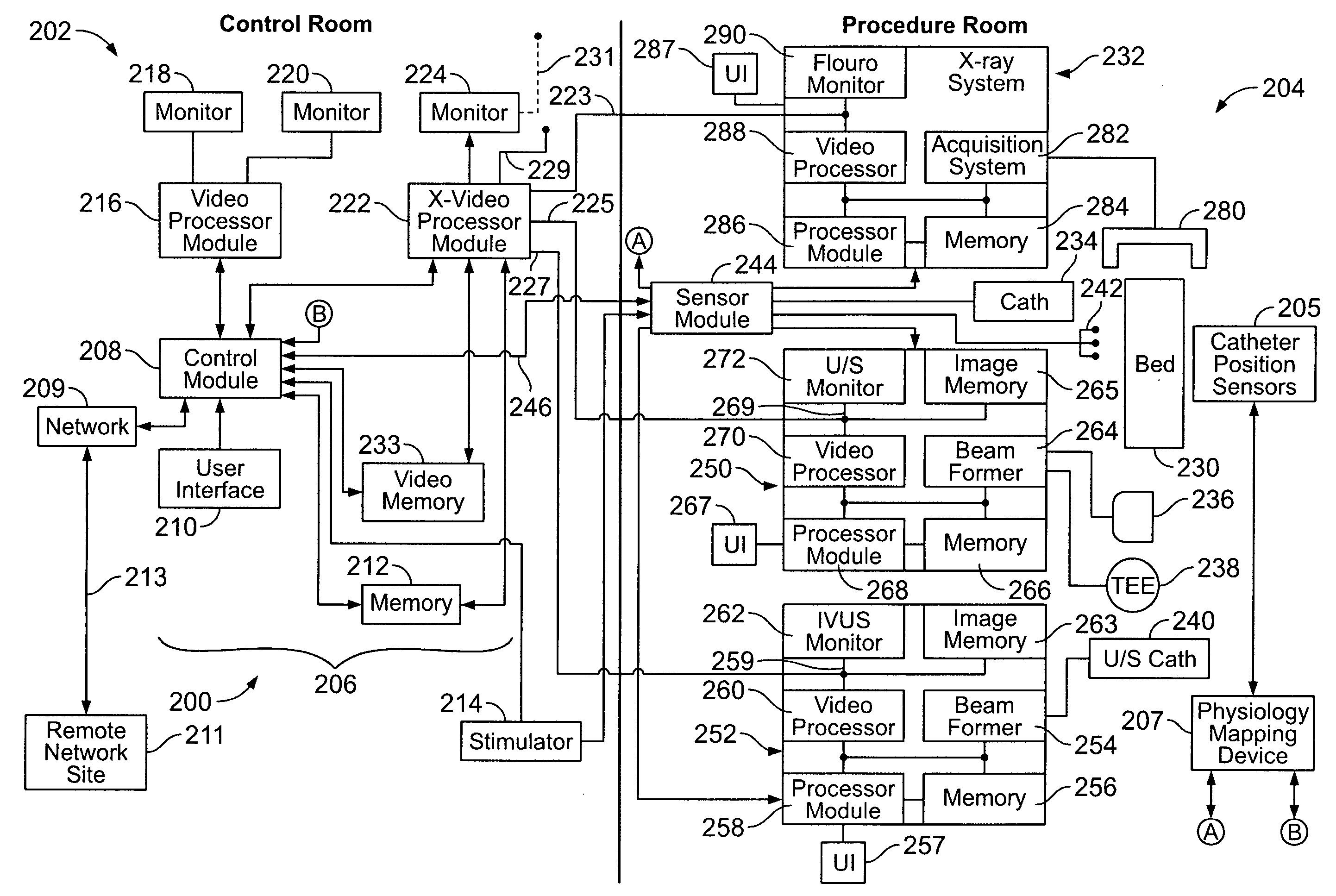
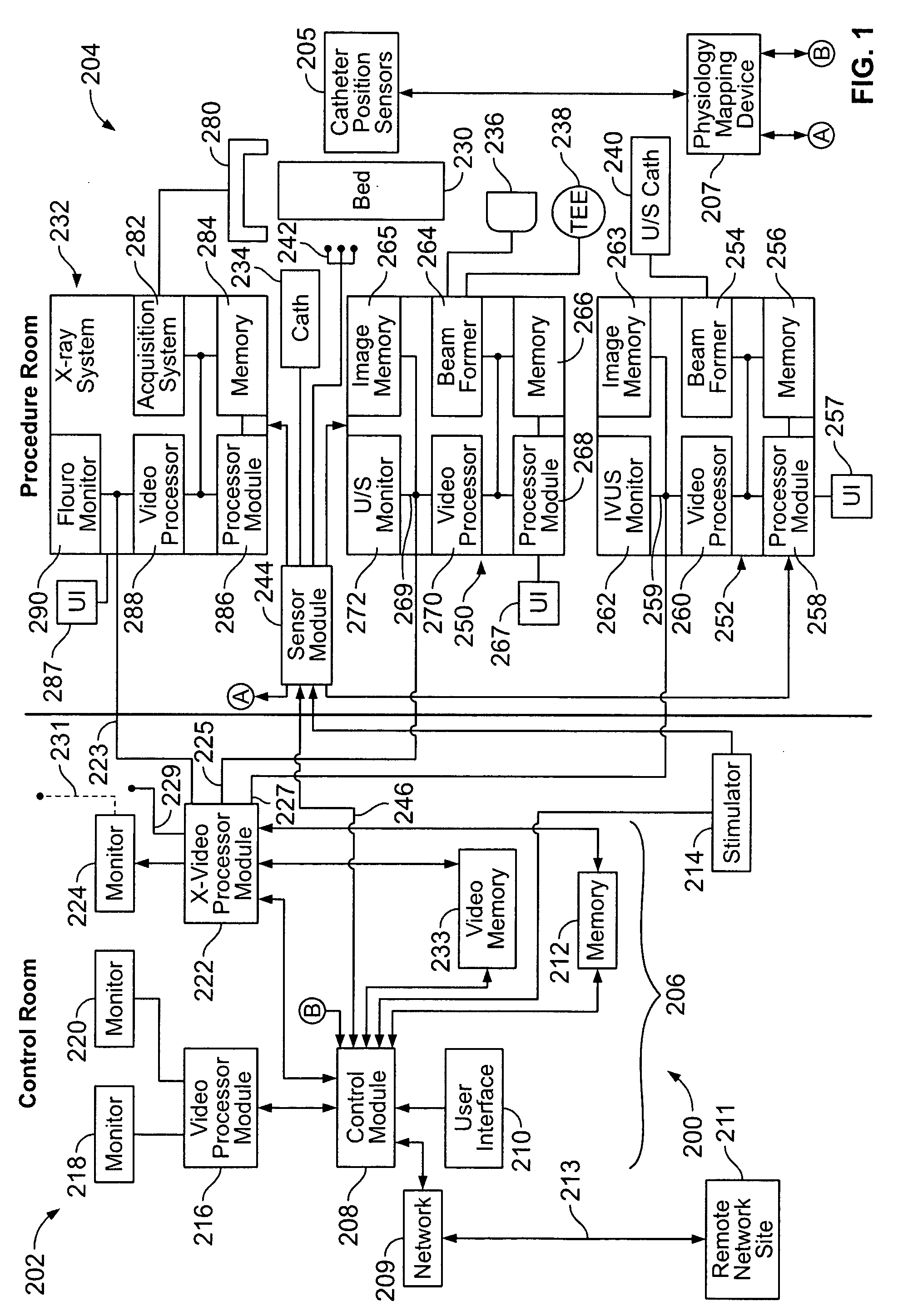
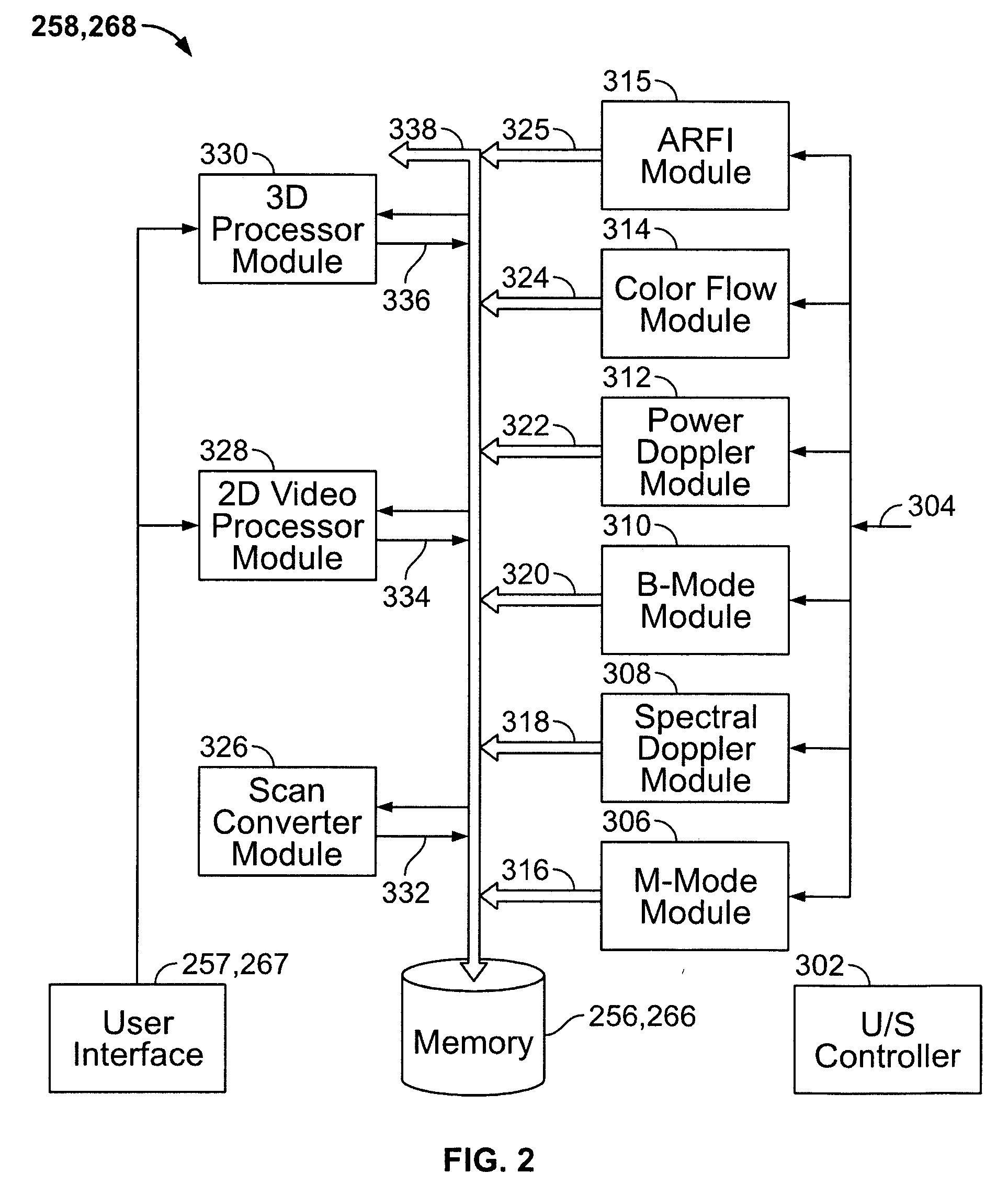
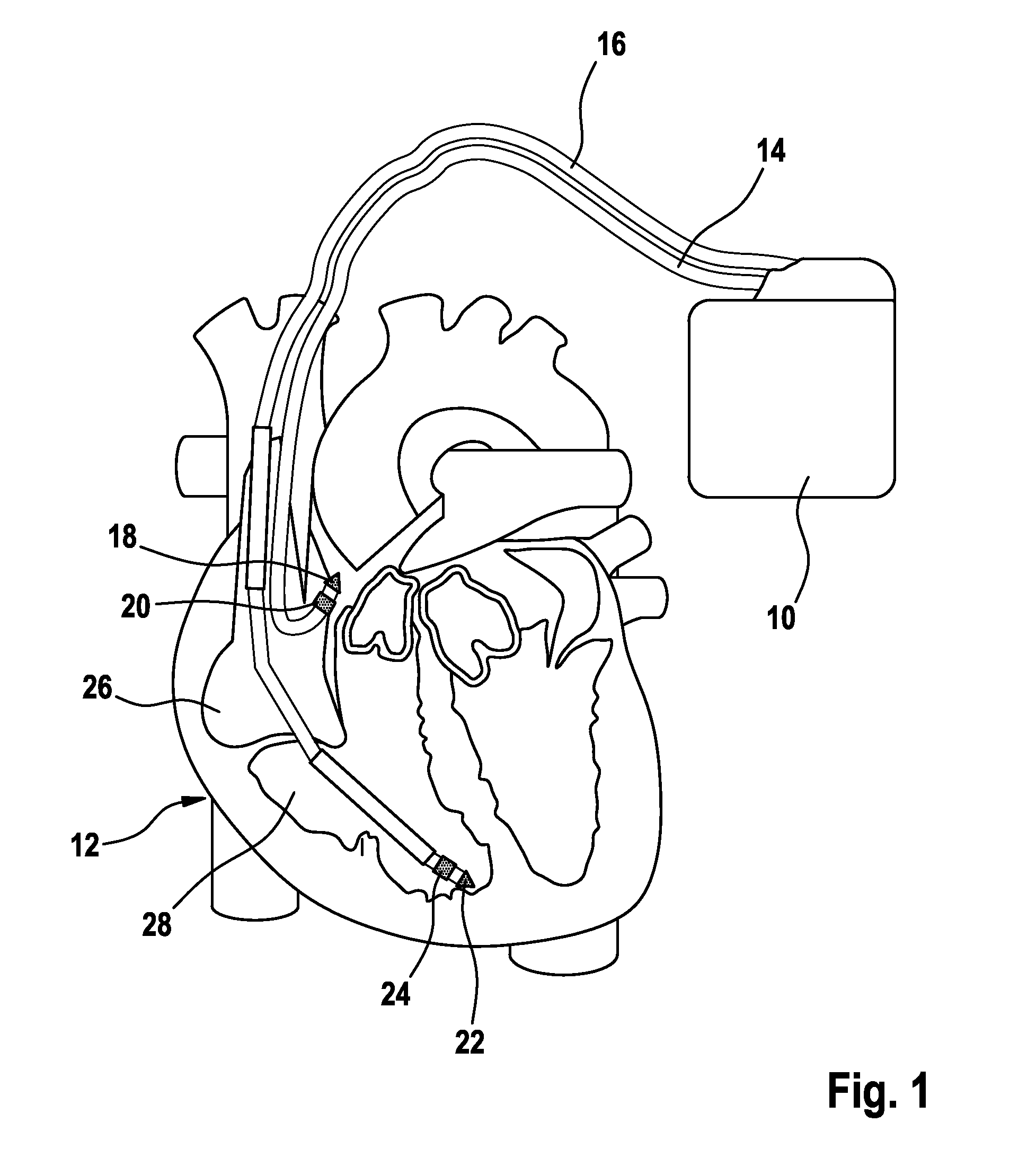
Physiology workstation with real-time fluoroscopy and ultrasound imaging
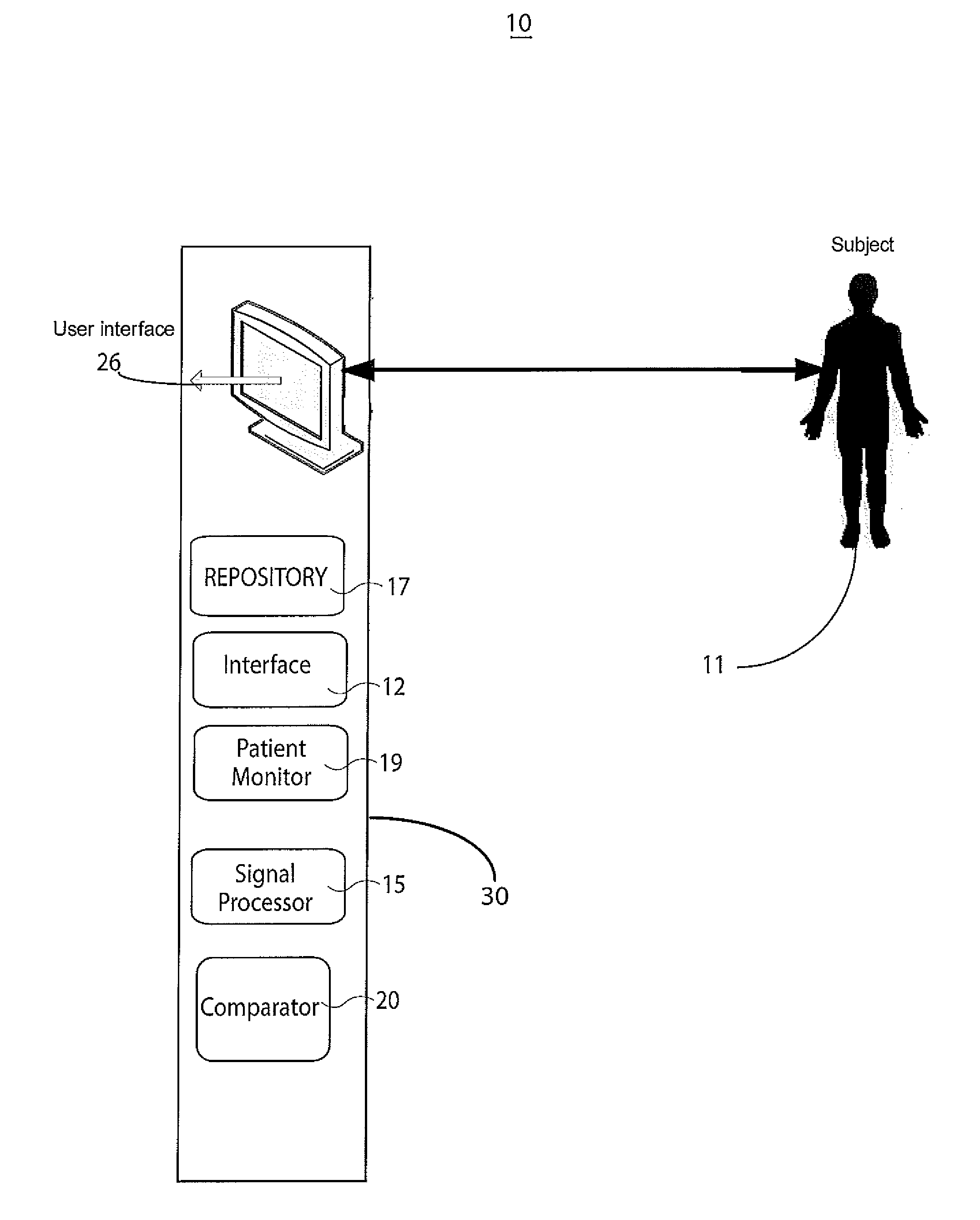
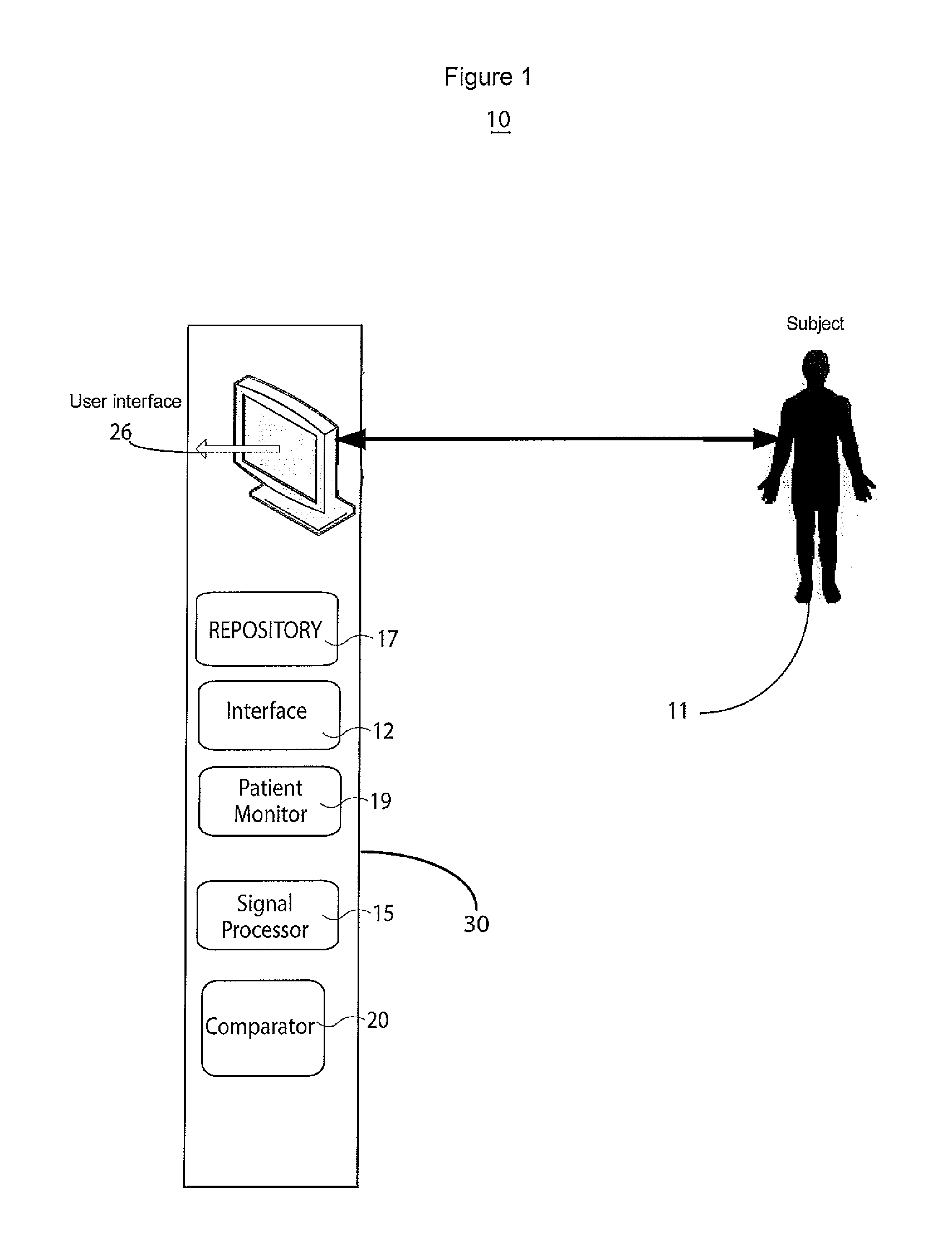
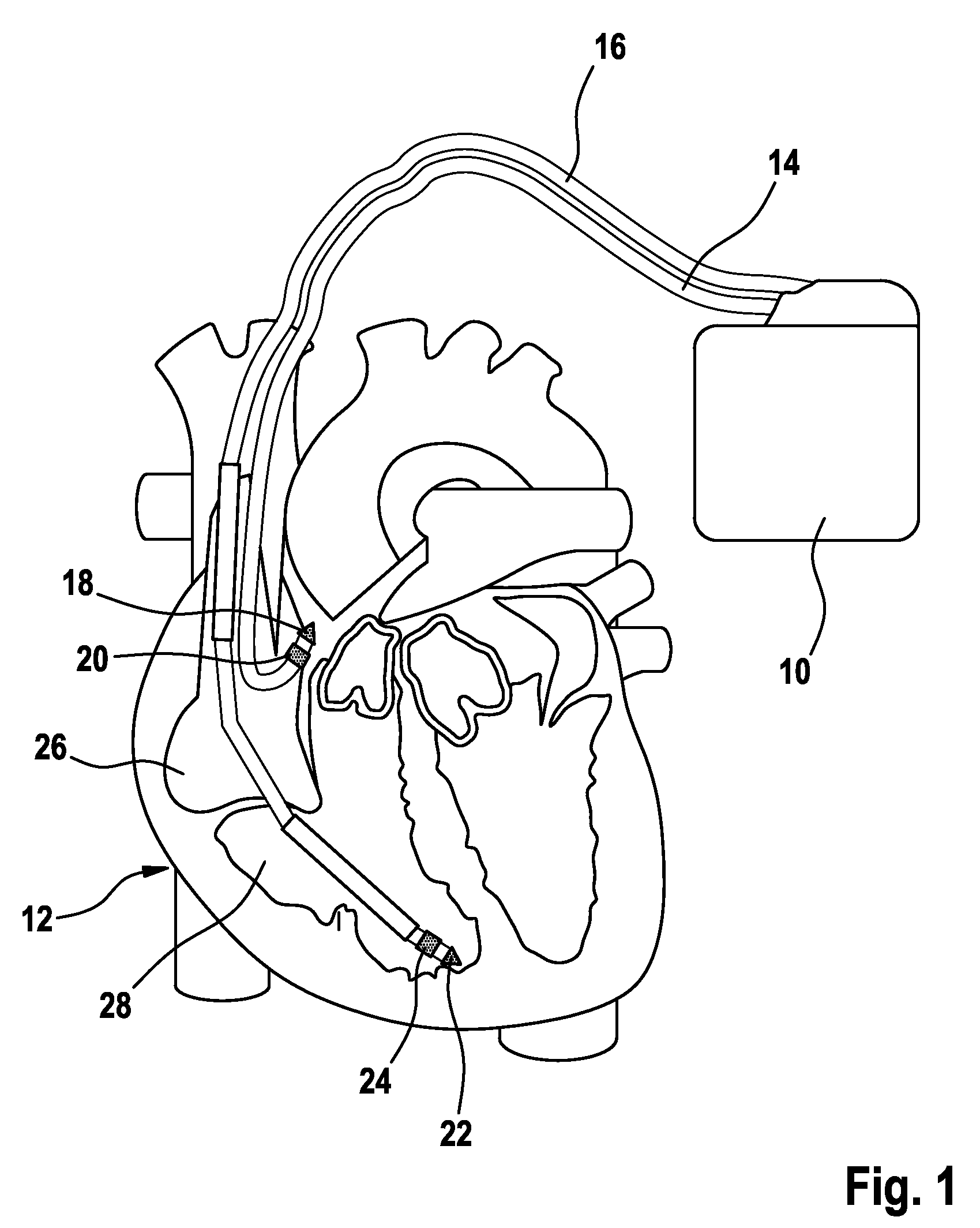
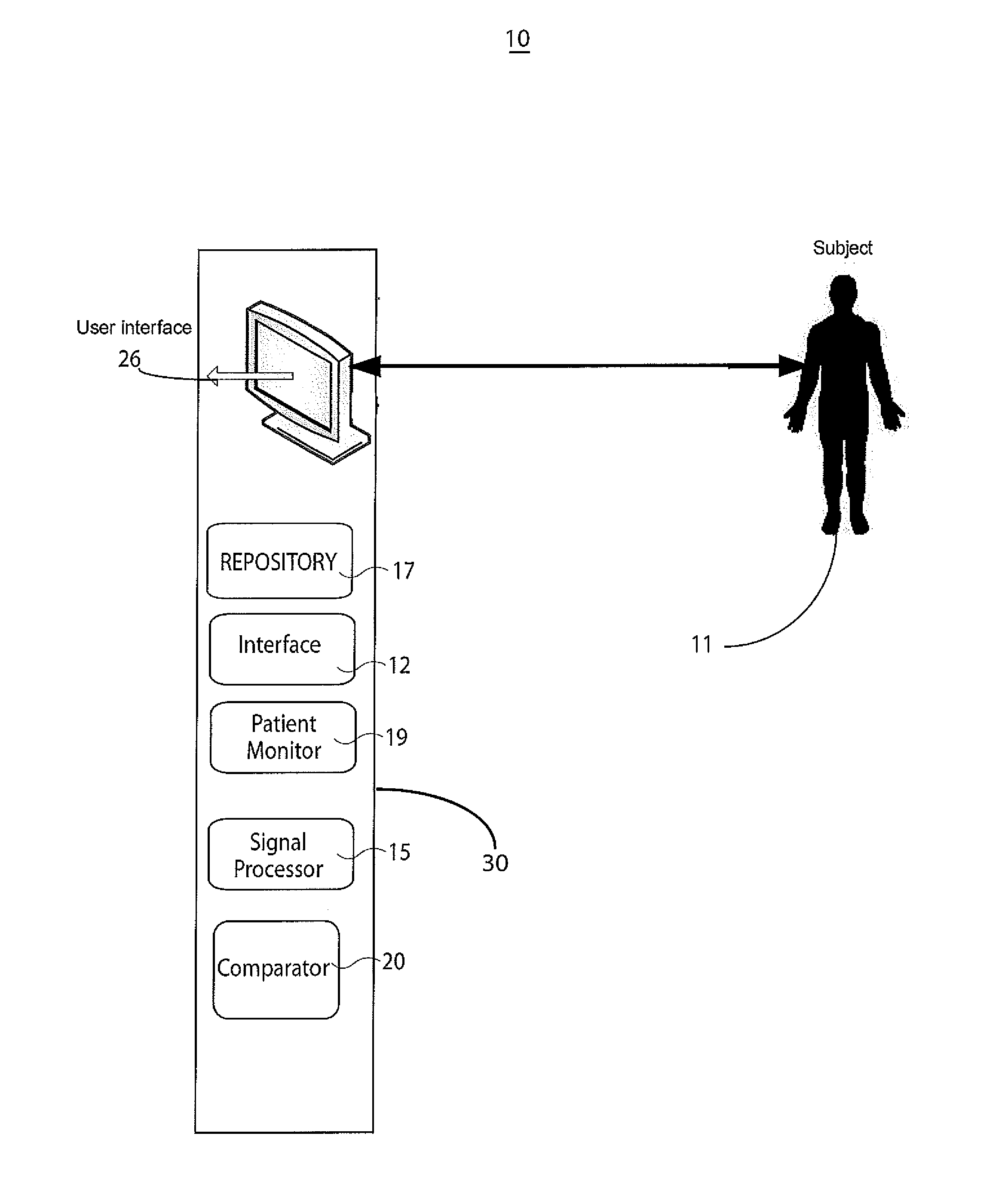
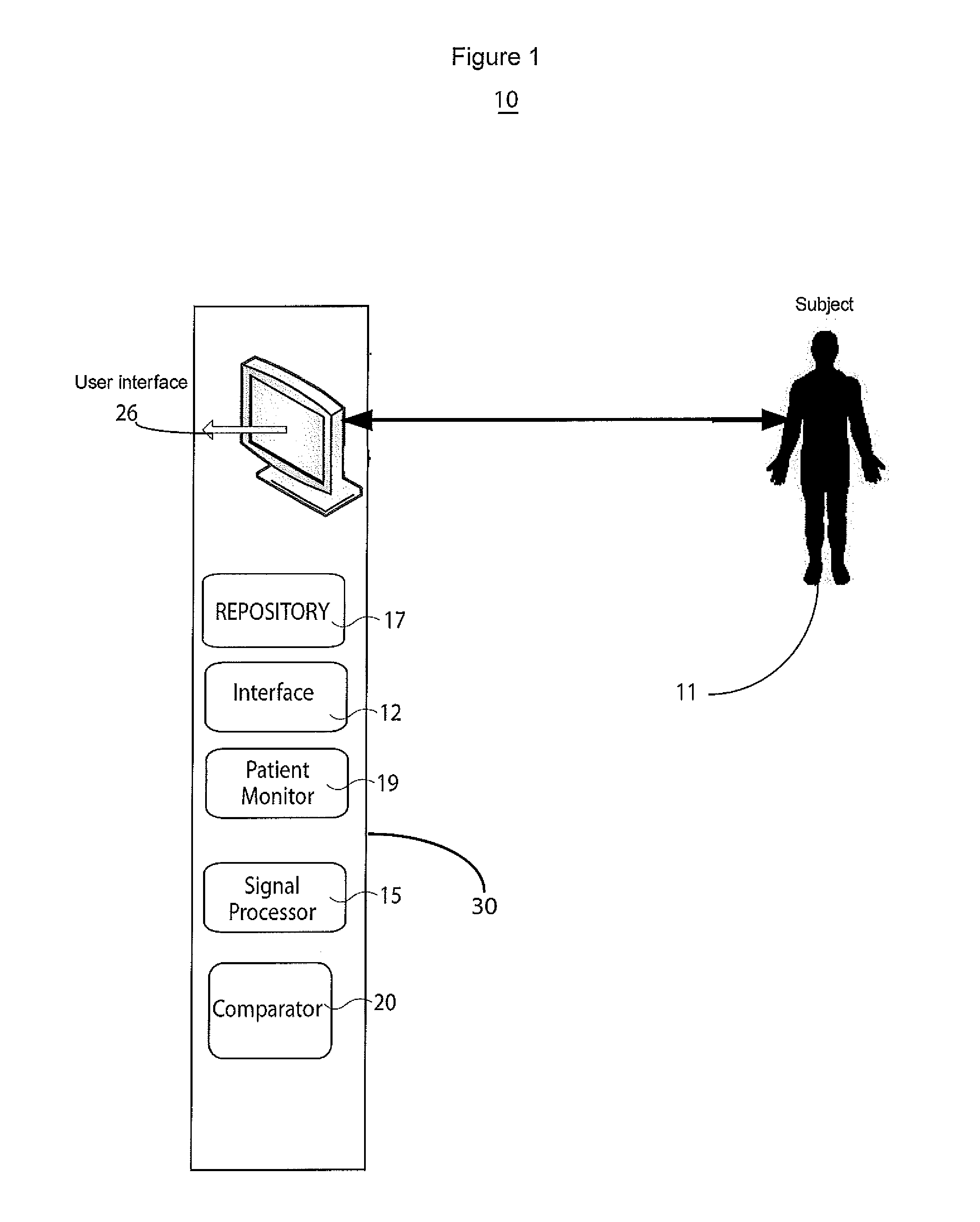
A physiology workstation is provided that comprises an physiology input configured to receive physiology signals from at least one of an intracardiac (IC) catheter inserted in a subject and surface ECG leads provided on the subject. The physiology signals are obtained during a procedure. A video input is configured to receive image frames, in real-time during the procedure. The image frames contain diagnostic information representative of data samples obtained from the subject during the procedure. A control module controls physiology operations based on user inputs. A display module is controlled by the physiology control module. The display module displays the physiology signals and the image frames simultaneously, in real-time, during the procedure. Optionally, the workstation may include a video processor module that formats the physiology signals into a display format. The video processor module may include an video processor and an external video processor that receive and control display of the physiology signals and image frames, respectively. The image frames may include at least one of ultrasound images obtained from a surface ultrasound probe, intravenous ultrasound images obtained from an ultrasound catheter and fluoroscopy images obtained from a fluoroscopy system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
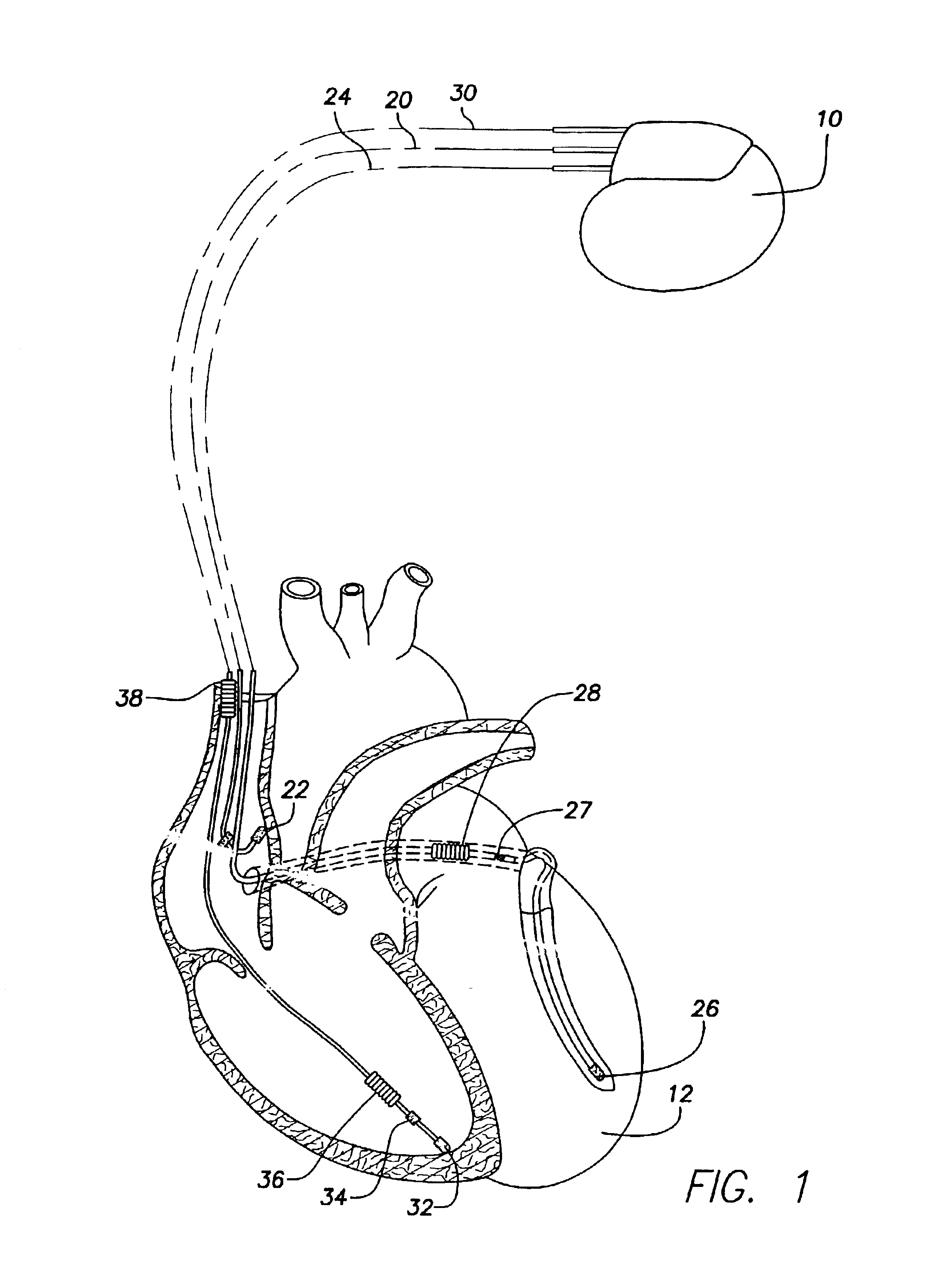
Catheterization method and system for controlling tip displacement
ActiveUS7640053B2Effectively avoid drawback and limitation of X-rayRapidly catheterizationElectrocardiographyEar treatmentControl signalSignal on
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
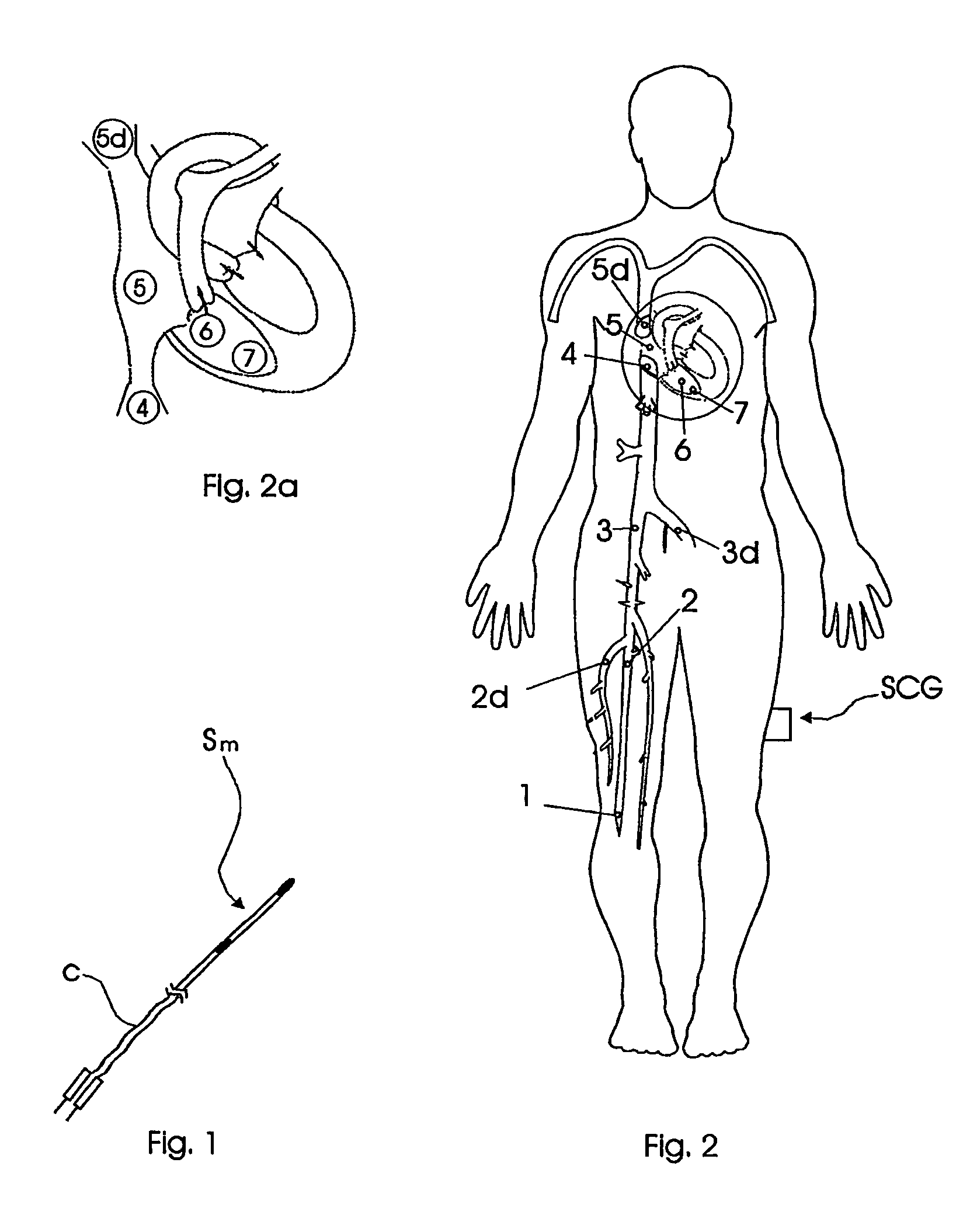
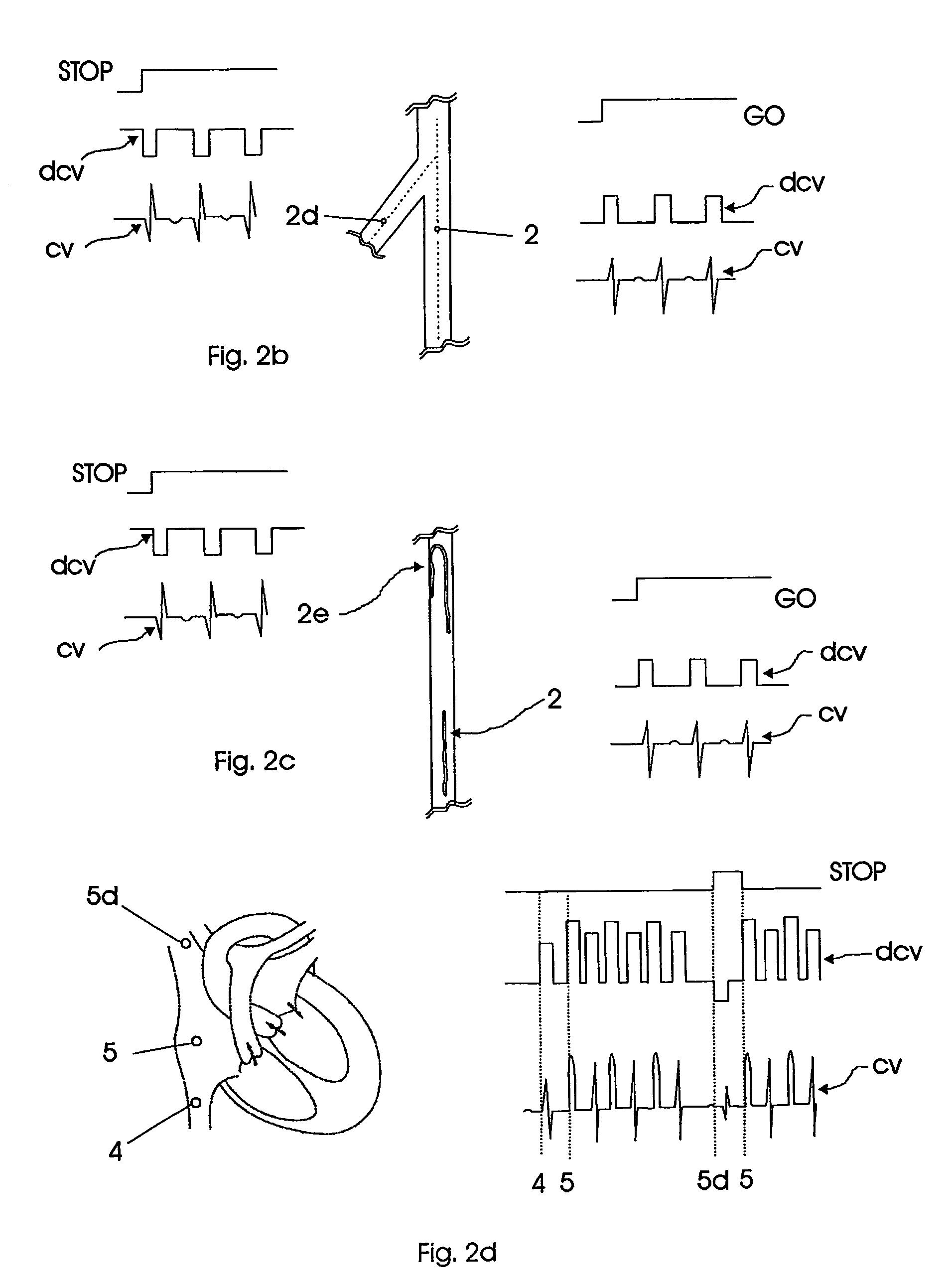
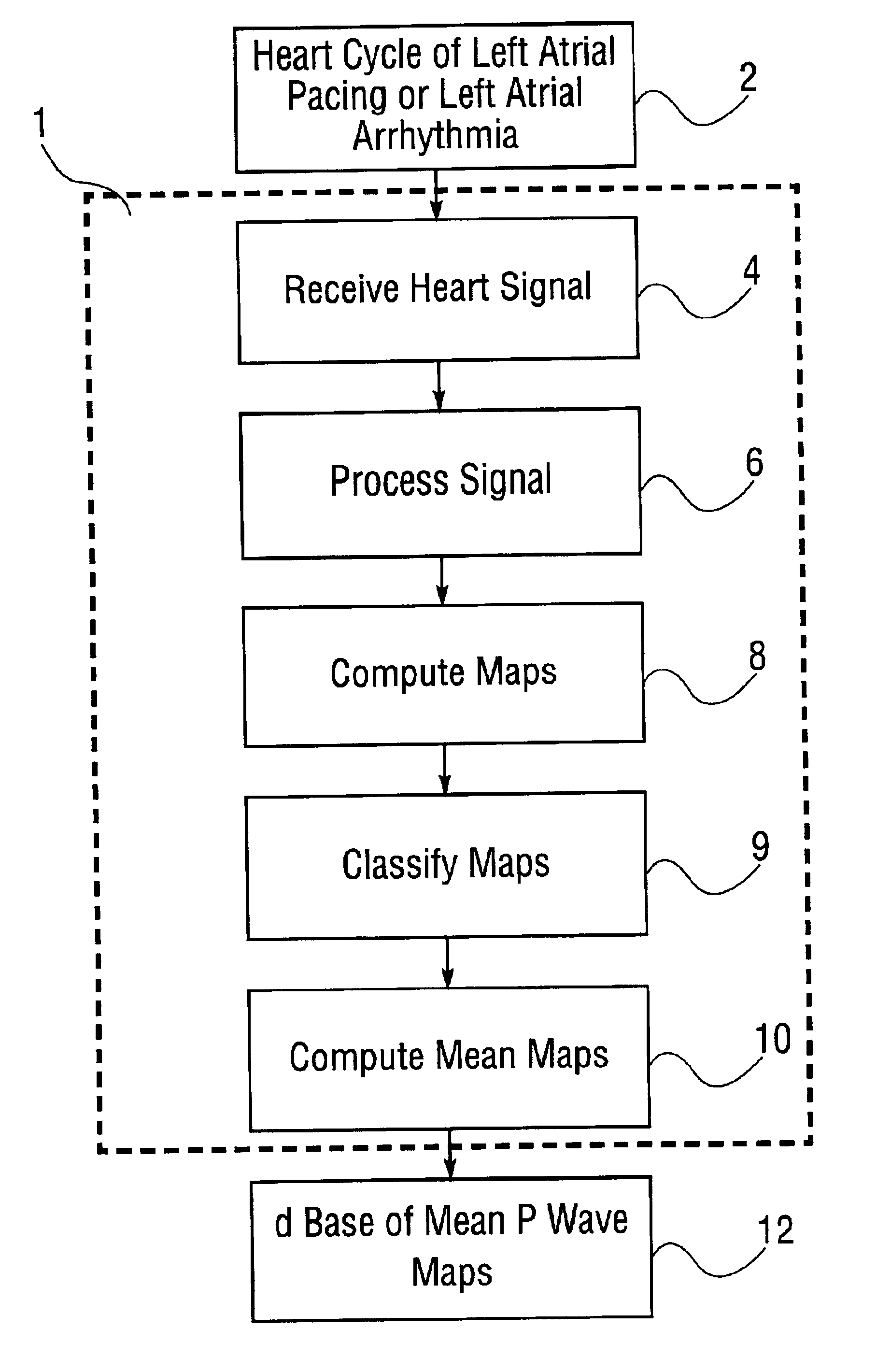
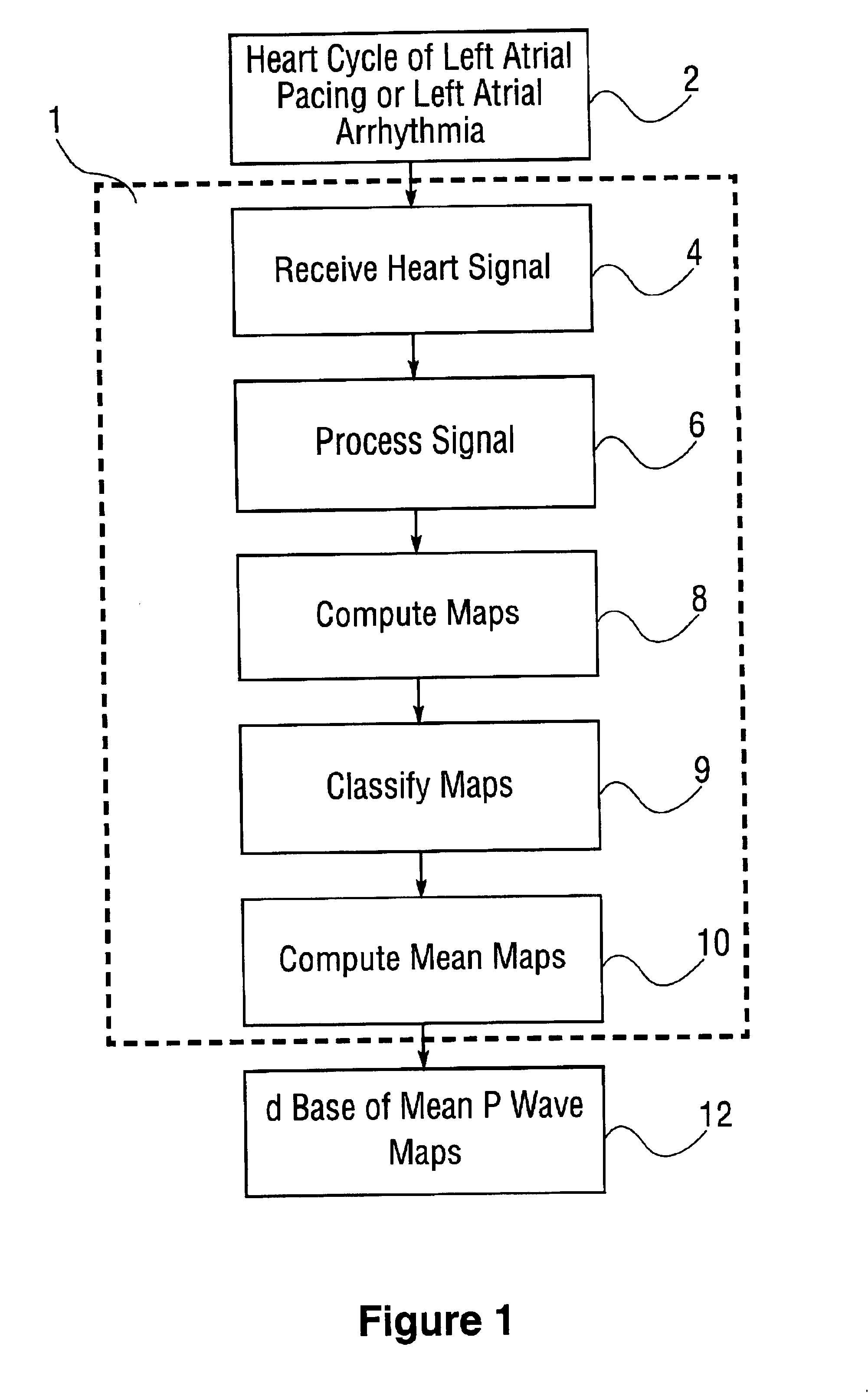
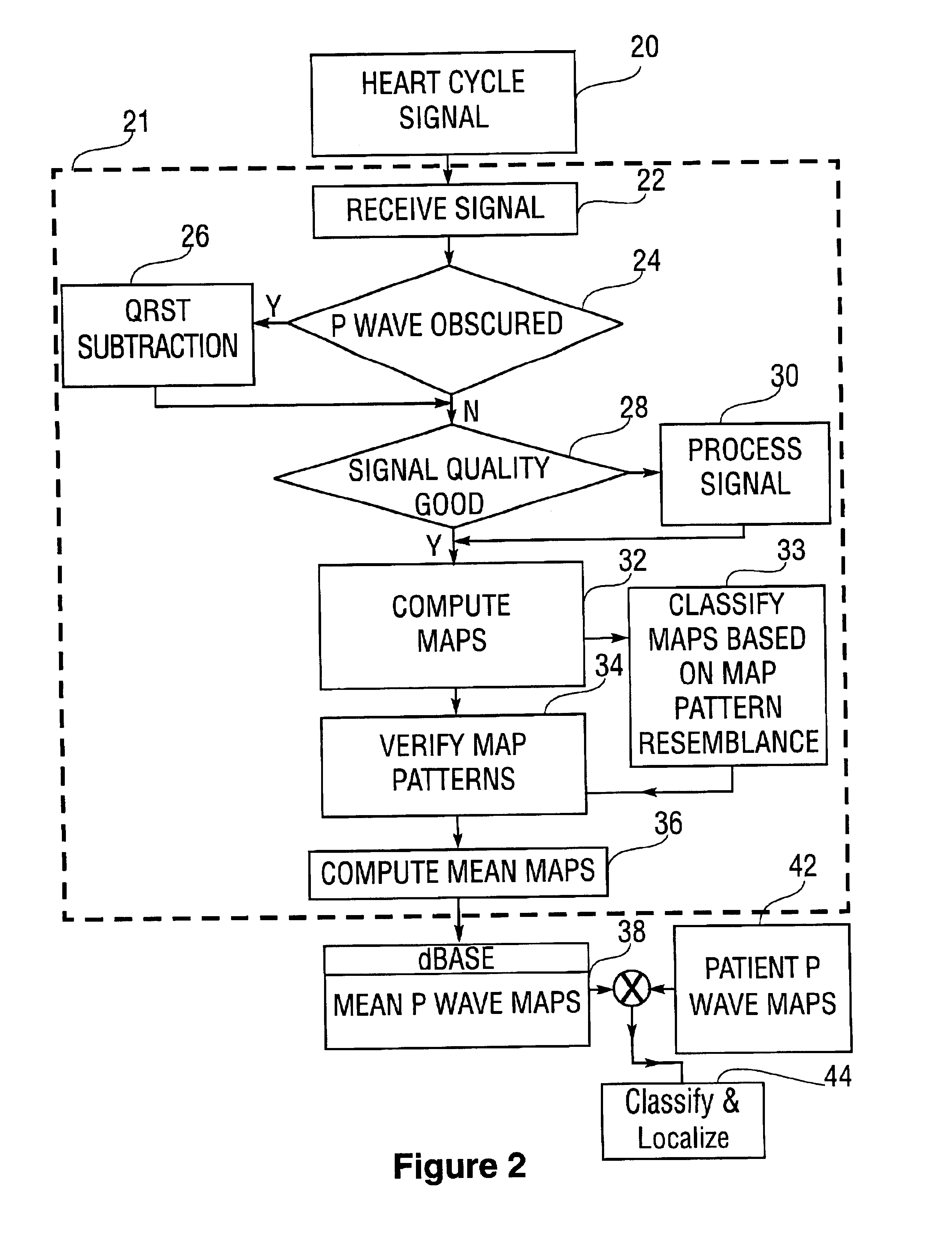
Database of body surface ECG P wave integral maps for localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias
InactiveUS6931273B2ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyIsorhythmic Atrioventricular DissociationHypsarrhythmia
A system and method are provided for developing a database of body surface ECG P-wave maps for classification and localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias. The system and method include generating and receiving P-wave data in a subject by left atrial pacing or receiving P-wave data in a subject during spontaneously occurring or induced left atrial arrhythmias; computing (e.g. potential or integral) maps of the P-wave data; classifying the maps specific to a left atrial ectopic origin; verifying the classification procedure; averaging the classified maps into mean maps; and storing and accessing the mean maps in the database. The mean maps of the P-wave data in the database can be used to automatically classify and localize P-wave data from a patient obtained during a left atrial arrhythmia such as atrial tachycardia, focal atrial fibrillation, or orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
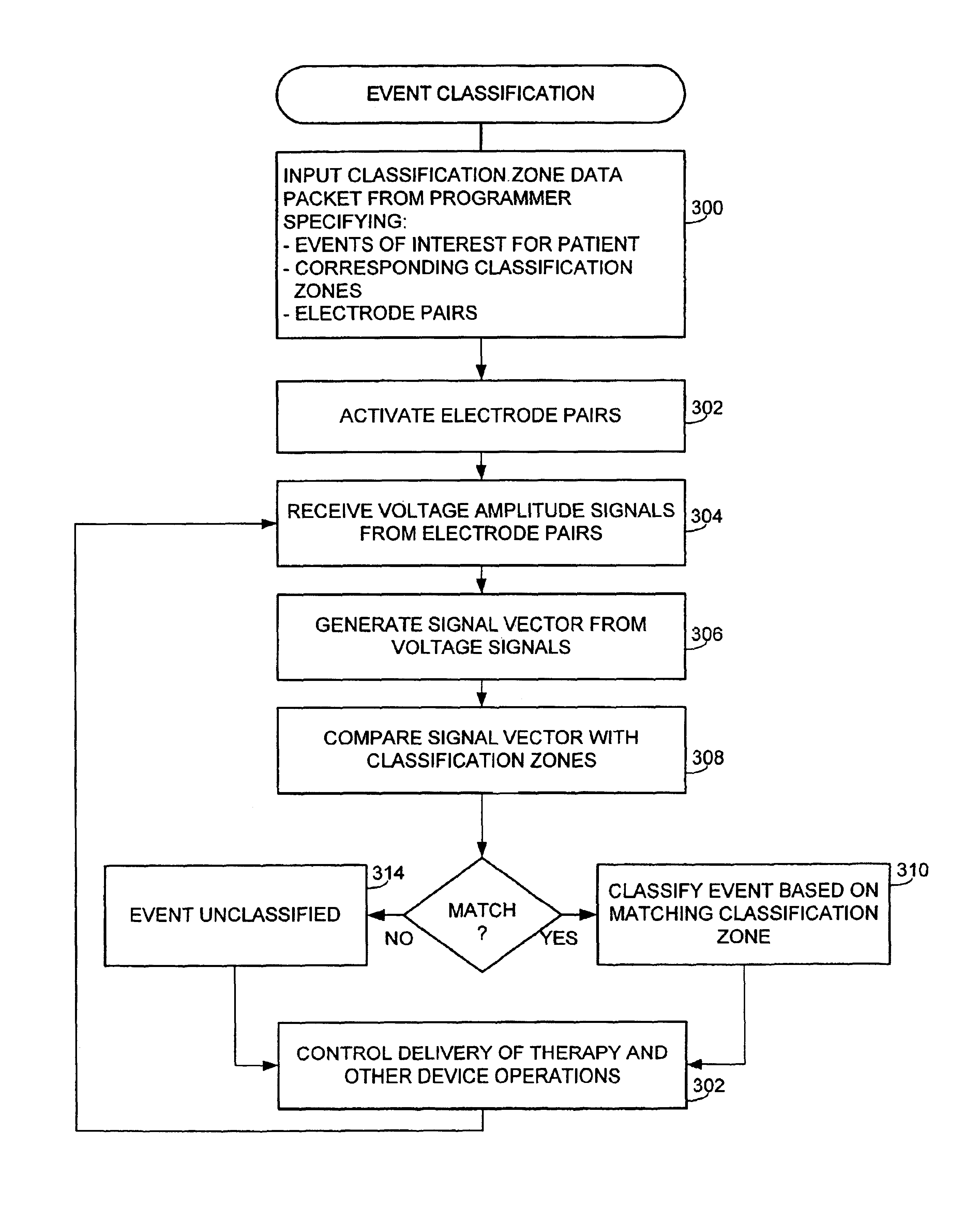
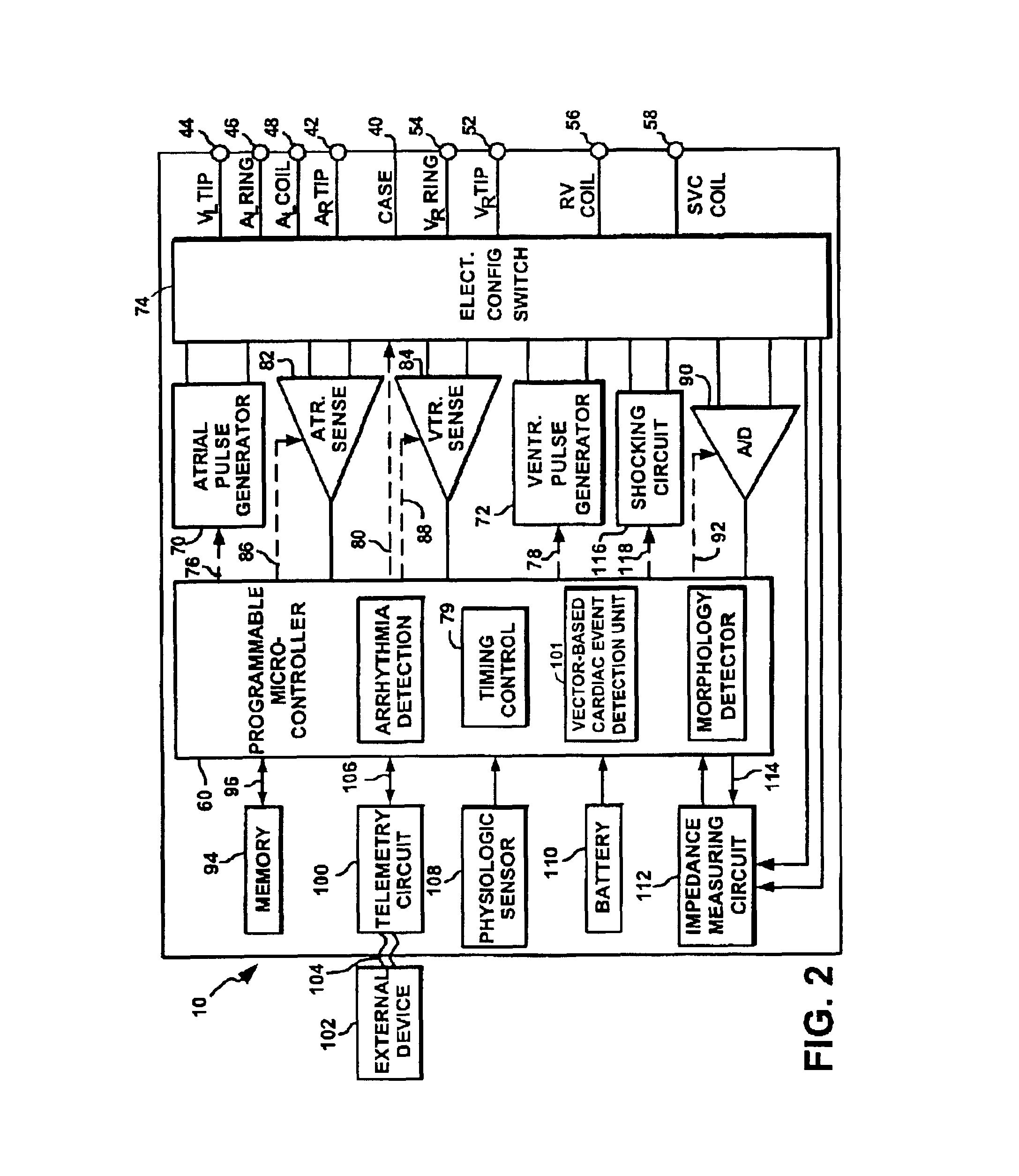
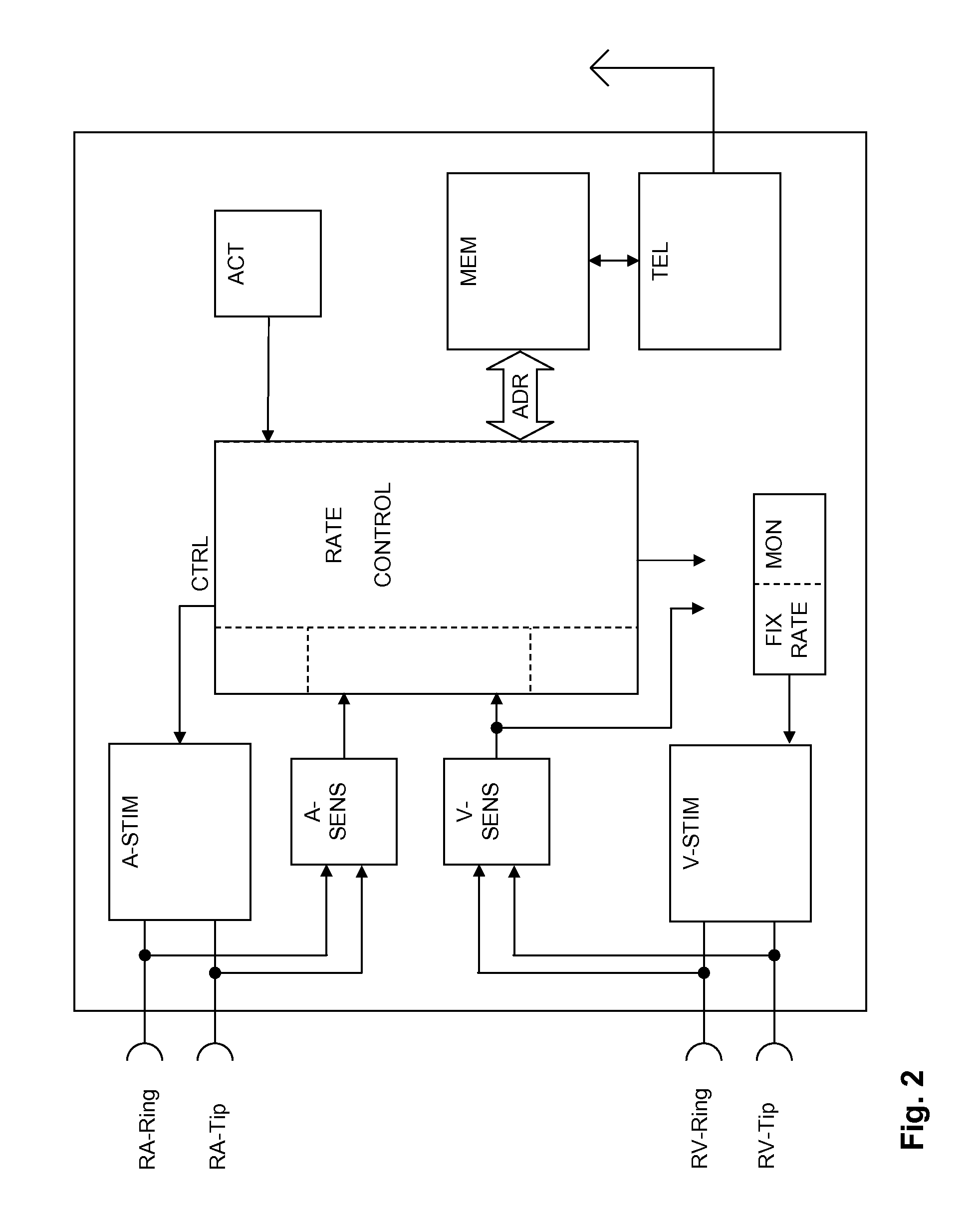
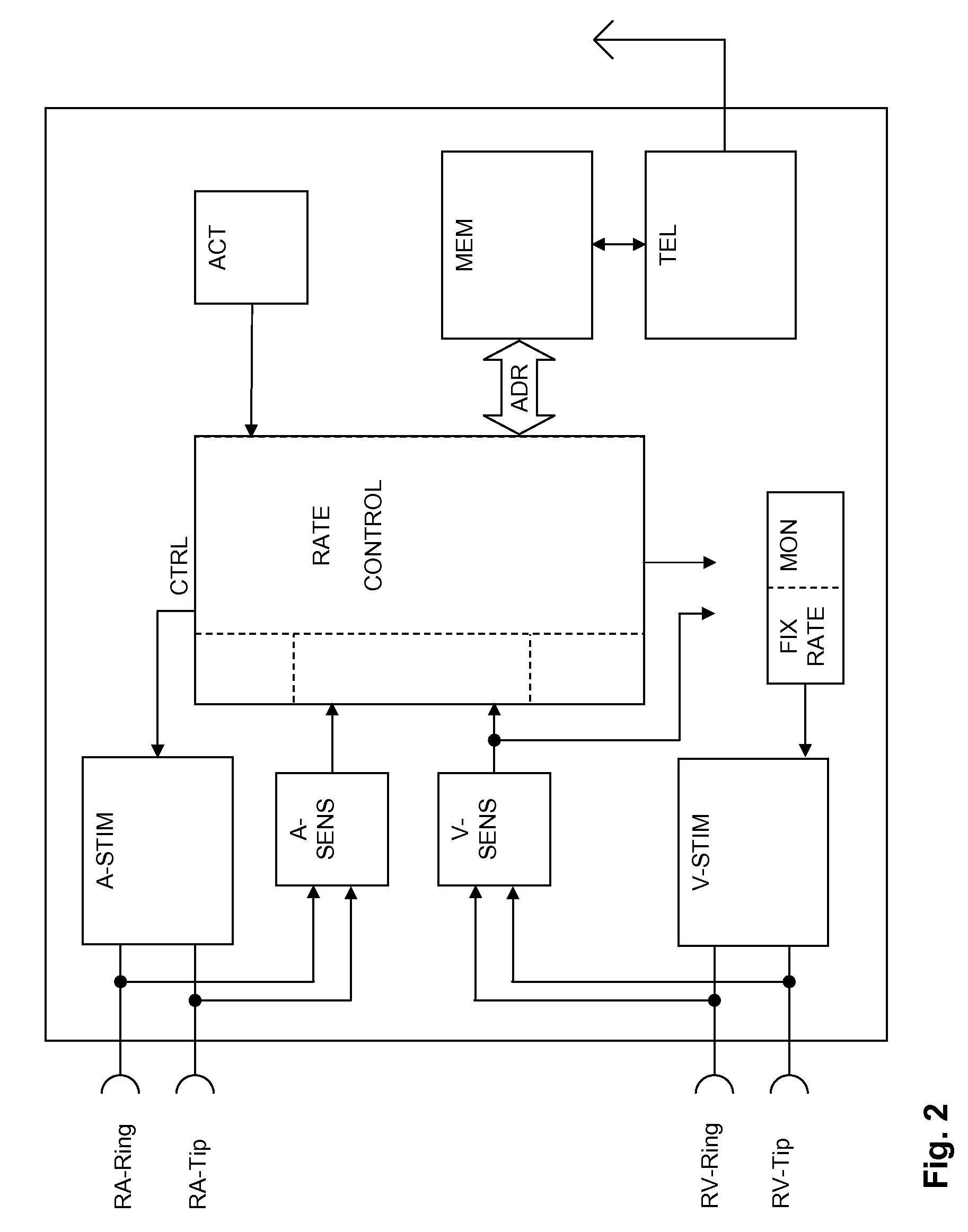
Implantable medical device and method for detecting cardiac events without using of refractory or blanking periods
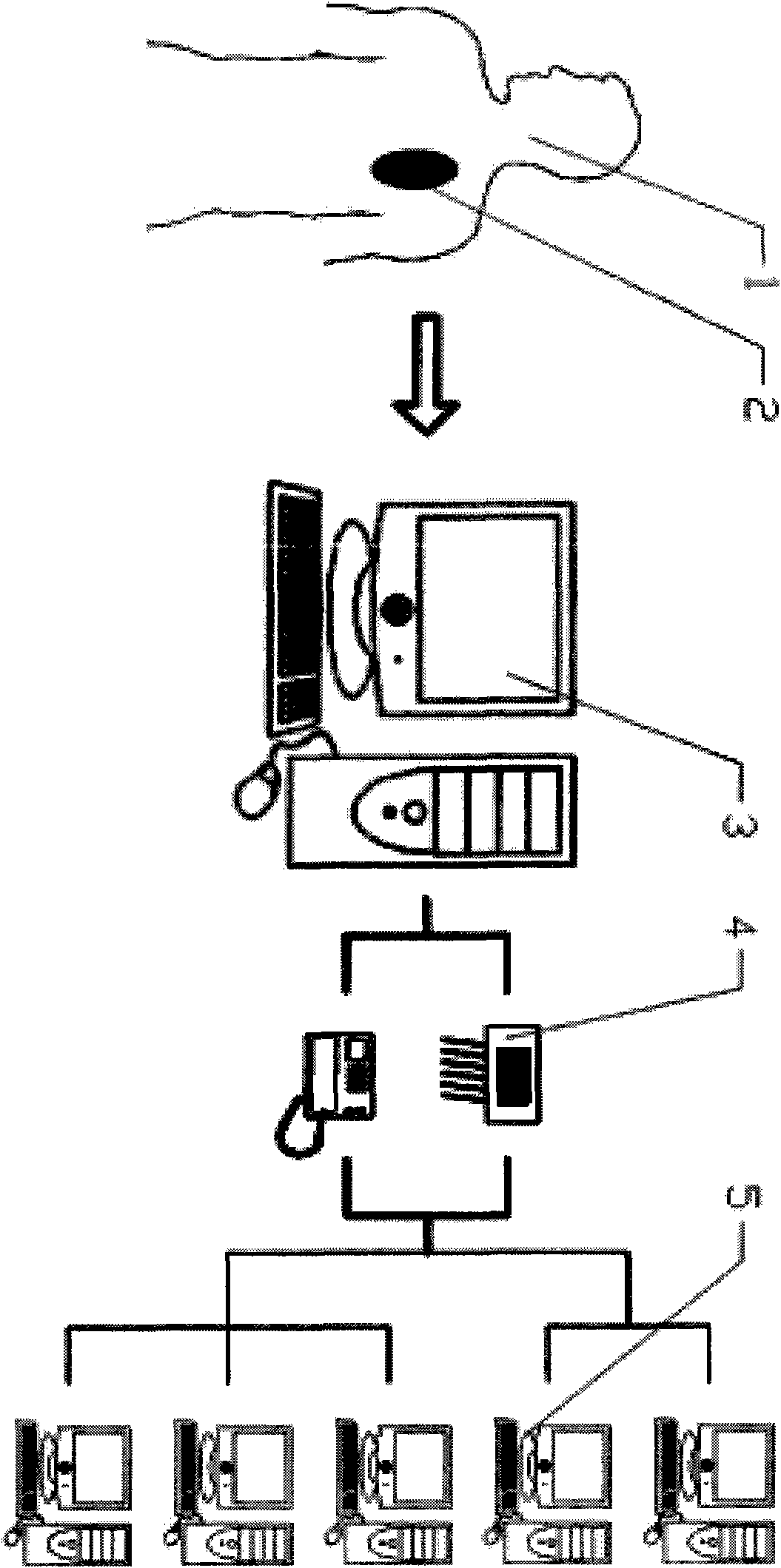
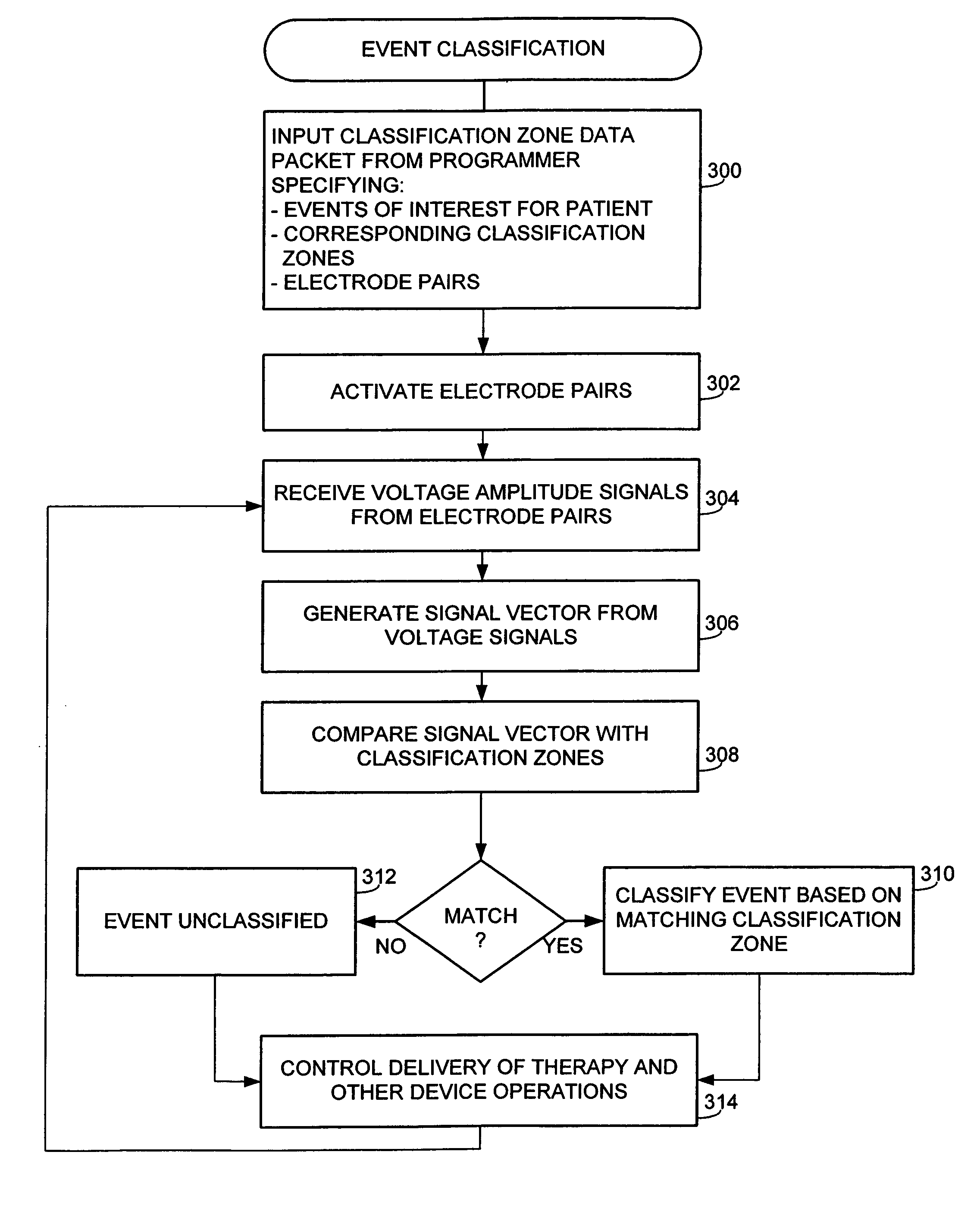
Cardiac electrical events are detected by comparing signal vectors with pre-determined classification zones representative of different cardiac events. The signal vector is generated by sensing the voltages between various combinations of electrodes, such as A-tip to V-tip, A-tip to A-ring, and A-ring to V-ring. The signal vector is compared with a set of classification zones corresponding to different events, such as P-waves, R-waves, T-waves, A-pulses, and V-pulses, to determine whether the vector lies within any of the classification zones. In this manner, cardiac events are detected using only the voltages received from the electrodes and no refractory periods or blanking periods are required to distinguish one event from another. The classification zones vary from patient to patient and a technique is provided herein for generating a set of vector classification zones for a particular patient. Signal vectors corresponding to various unknown cardiac events are generated by the implanted device and are transmitted to an external device programmer. ECG signals, generated by a surface ECG detector, are simultaneously received by the external programmer. The external programmer identifies the cardiac electrical event corresponding to each signal vector based on the ECG signals and then generates classification zones for each event type using only the signal vectors corresponding to the event.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Standalone systemic arterial blood pressure monitoring device
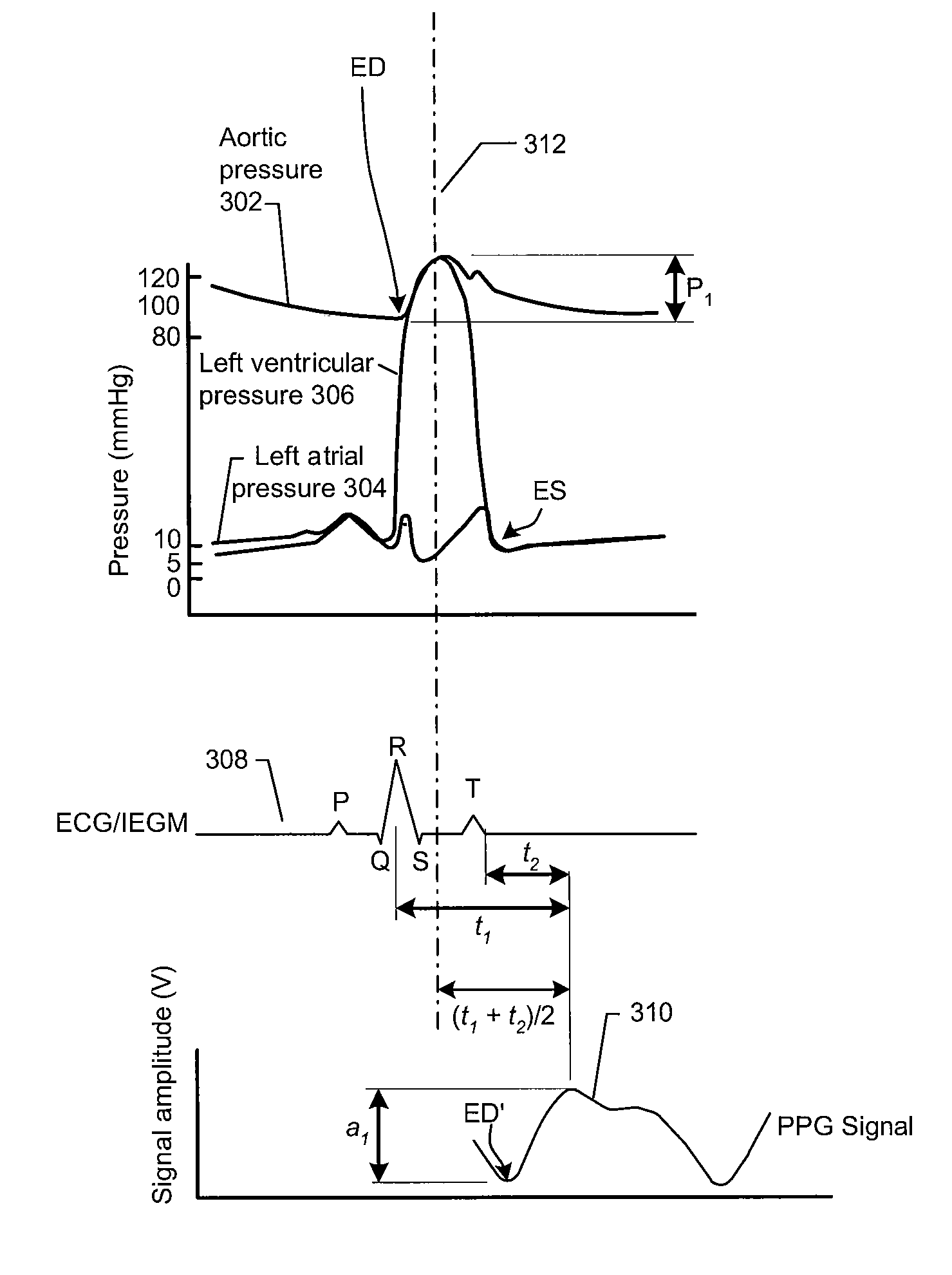
Certain embodiments of the present invention are related to an implantable monitoring device to monitor a patient's arterial blood pressure, where the device is configured to be implanted subcutaneously. The device includes subcutaneous (SubQ) electrodes and a plethysmography sensor. Additionally, the device includes an arterial blood pressure monitor configured to determine at least one value indicative of the patient's arterial blood pressure based on at least one detected predetermined feature of a SubQ ECG and at least one detected predetermined feature of a plethysmography signal. Alternative embodiments of the present invention are directed to a non-implantable monitoring device to monitor a patient's arterial blood pressure based on features of a surface ECG and a plethysmography signal obtained from a non-implanted sensor.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
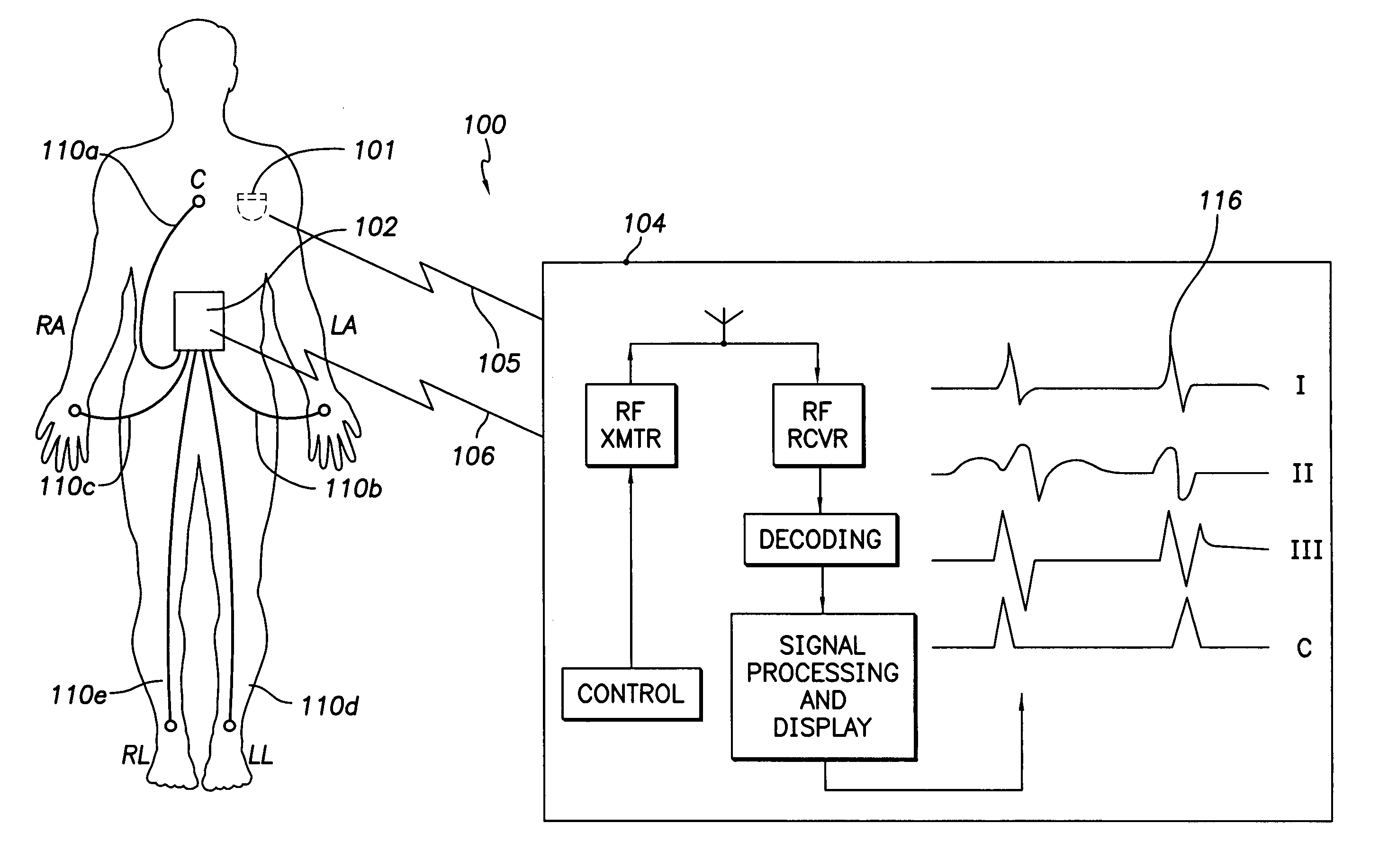
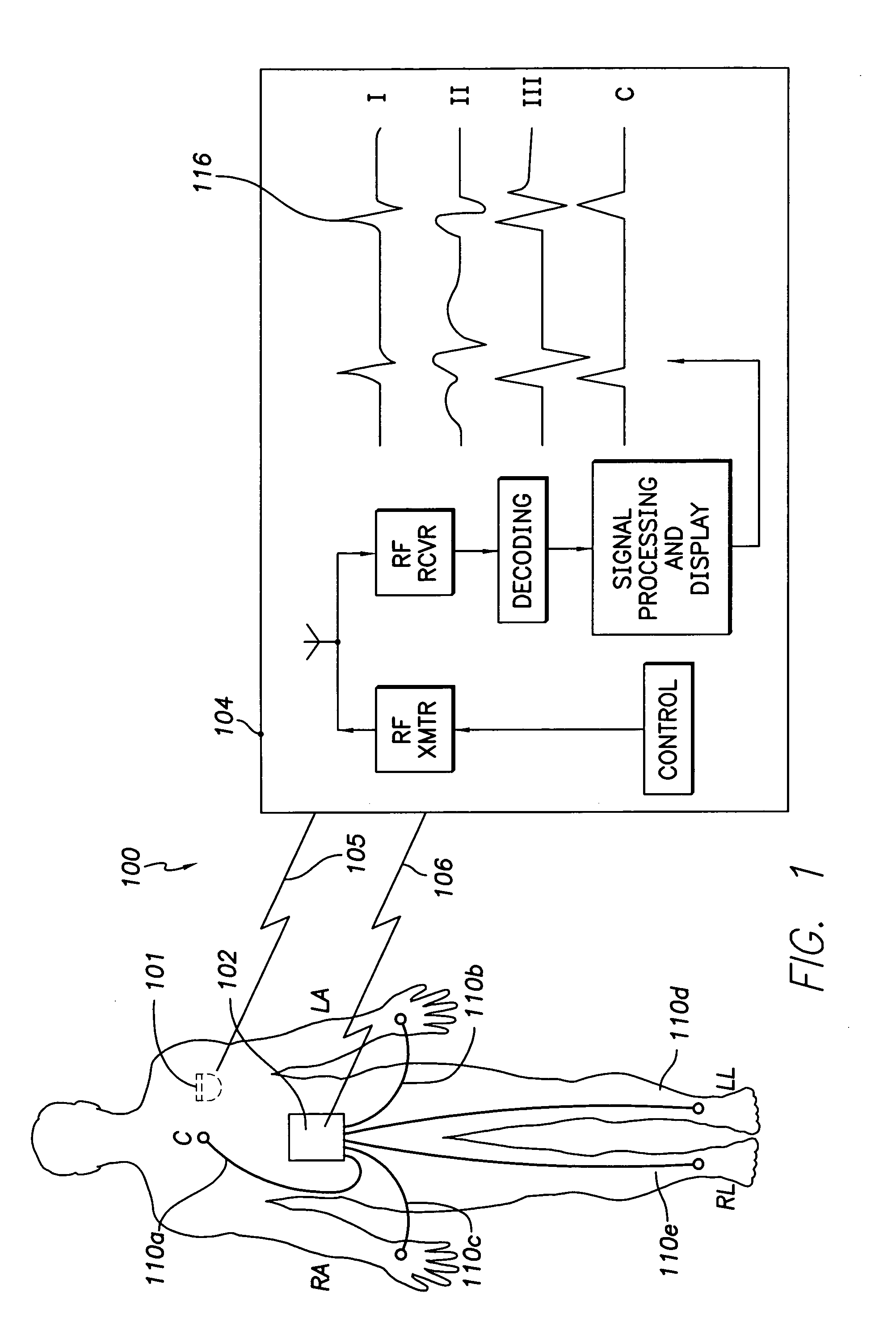
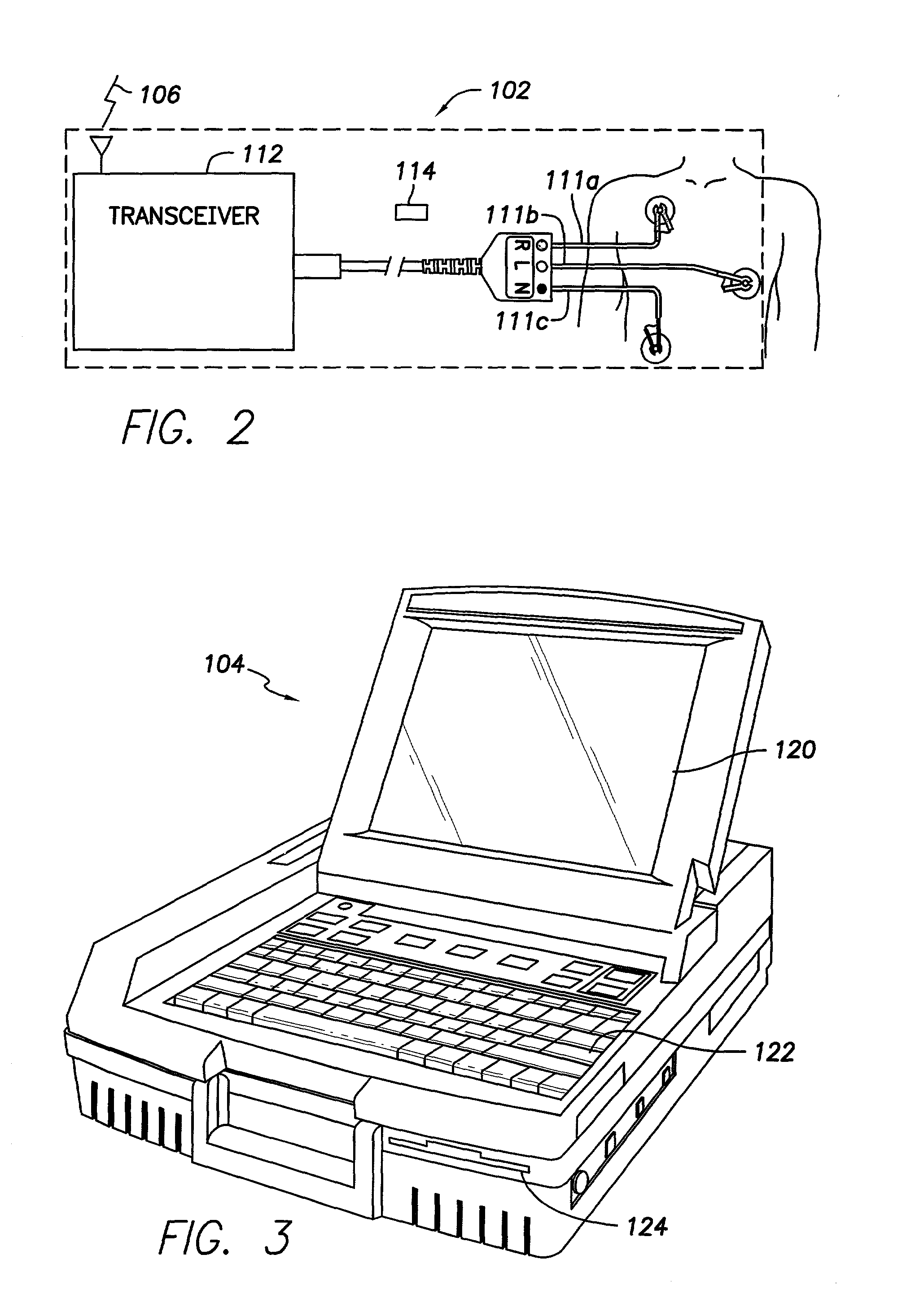
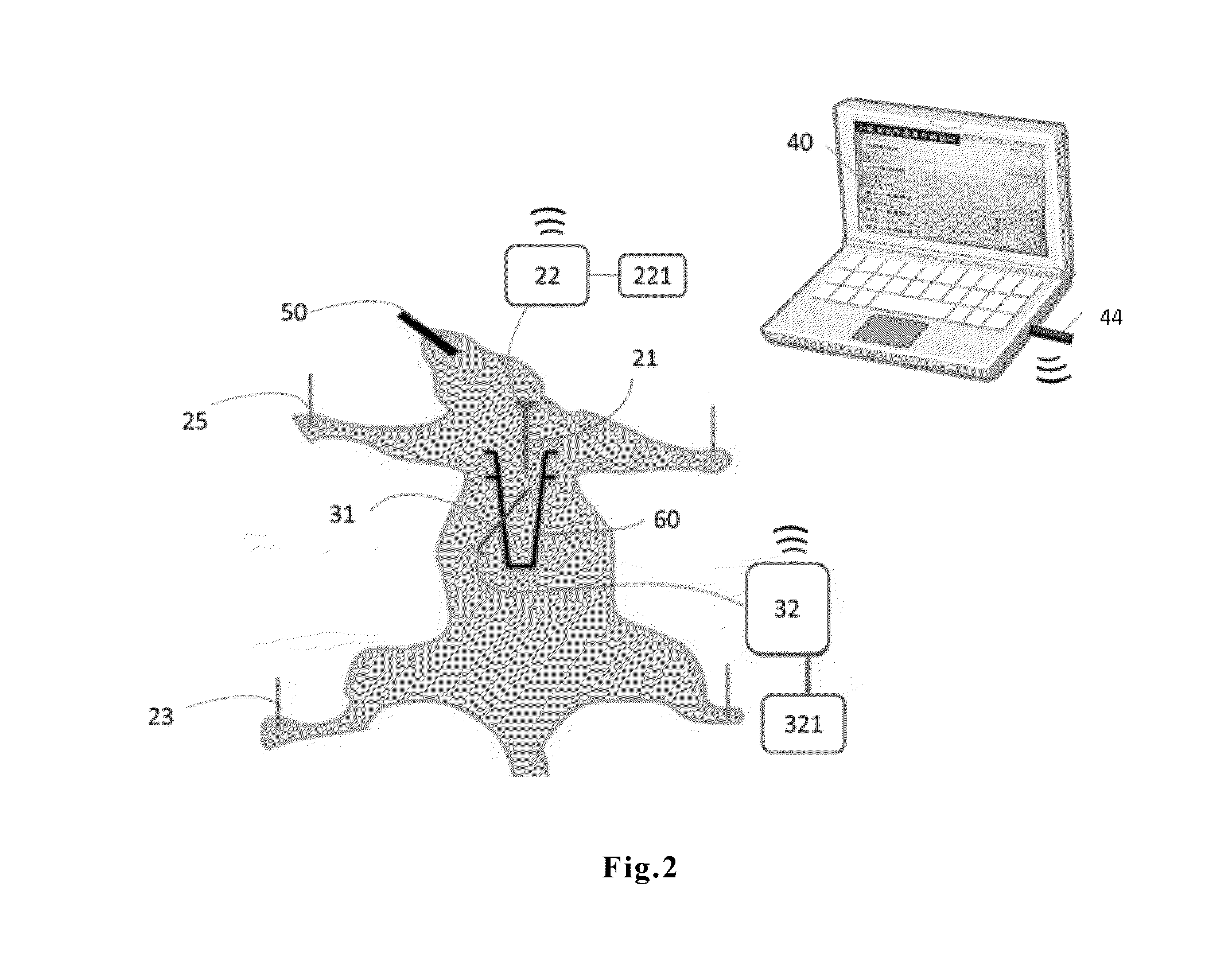
Programmer and surface ECG system with wireless communication
A programmer for implantable stimulation devices and surface ECG system in wireless communication with each other. A self-powered ECG monitor with conventional surface electrodes transceives signals from and to a programmer provided with a radio frequency transceiver to eliminate hardwiring between the surface electrodes and the programmer. The system reduces the need for supply line frequency filtering and isolation circuitry to protect against high voltage defibrillation shocks.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
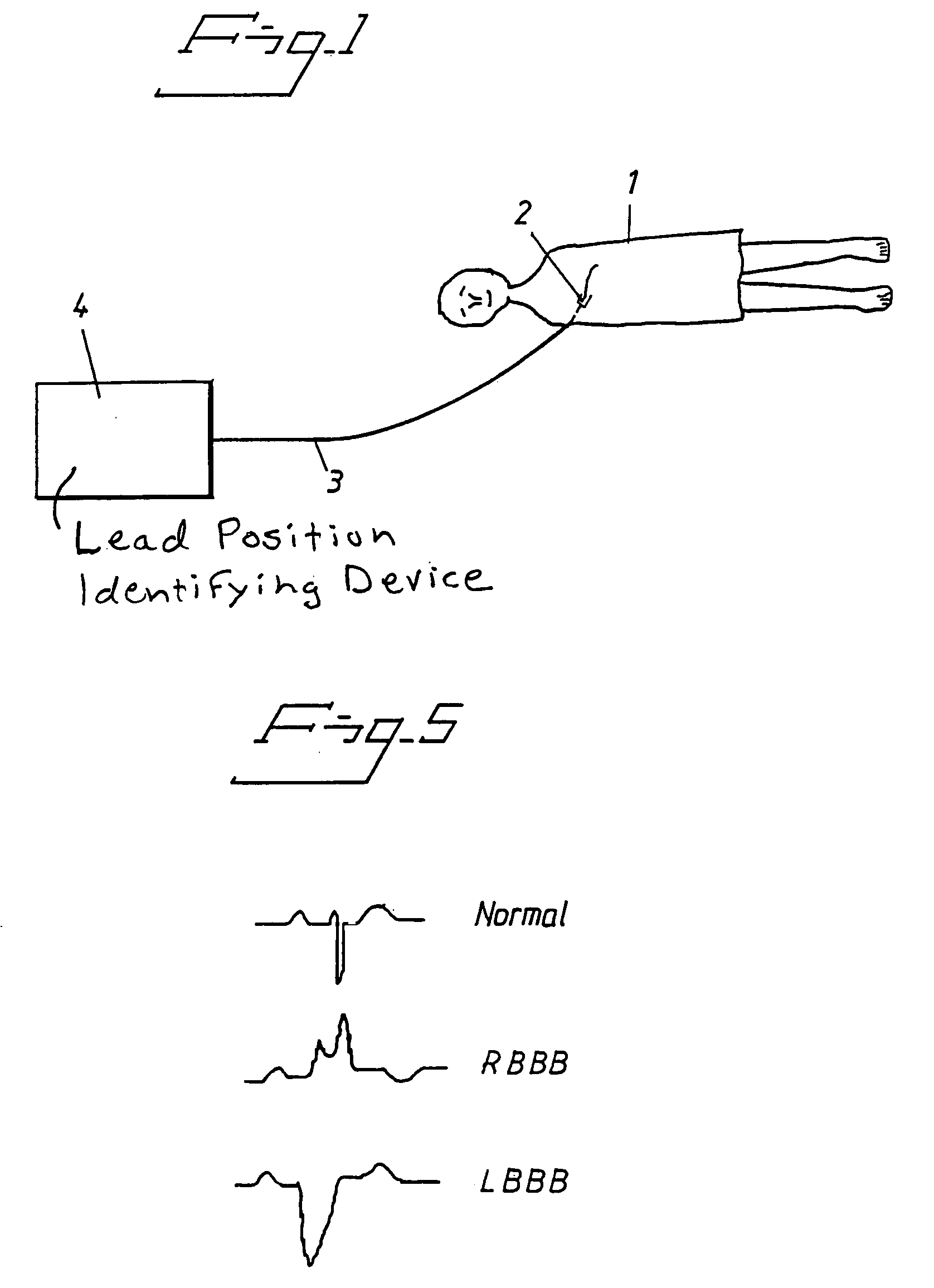
Arrangement and Method for Evaluating Operational Effectiveness of Implantable Medical Electrode Leads for Different Lead Placements
InactiveUS20080249375A1Improved and simplifiedElevated PSAElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalOperational effectiveness
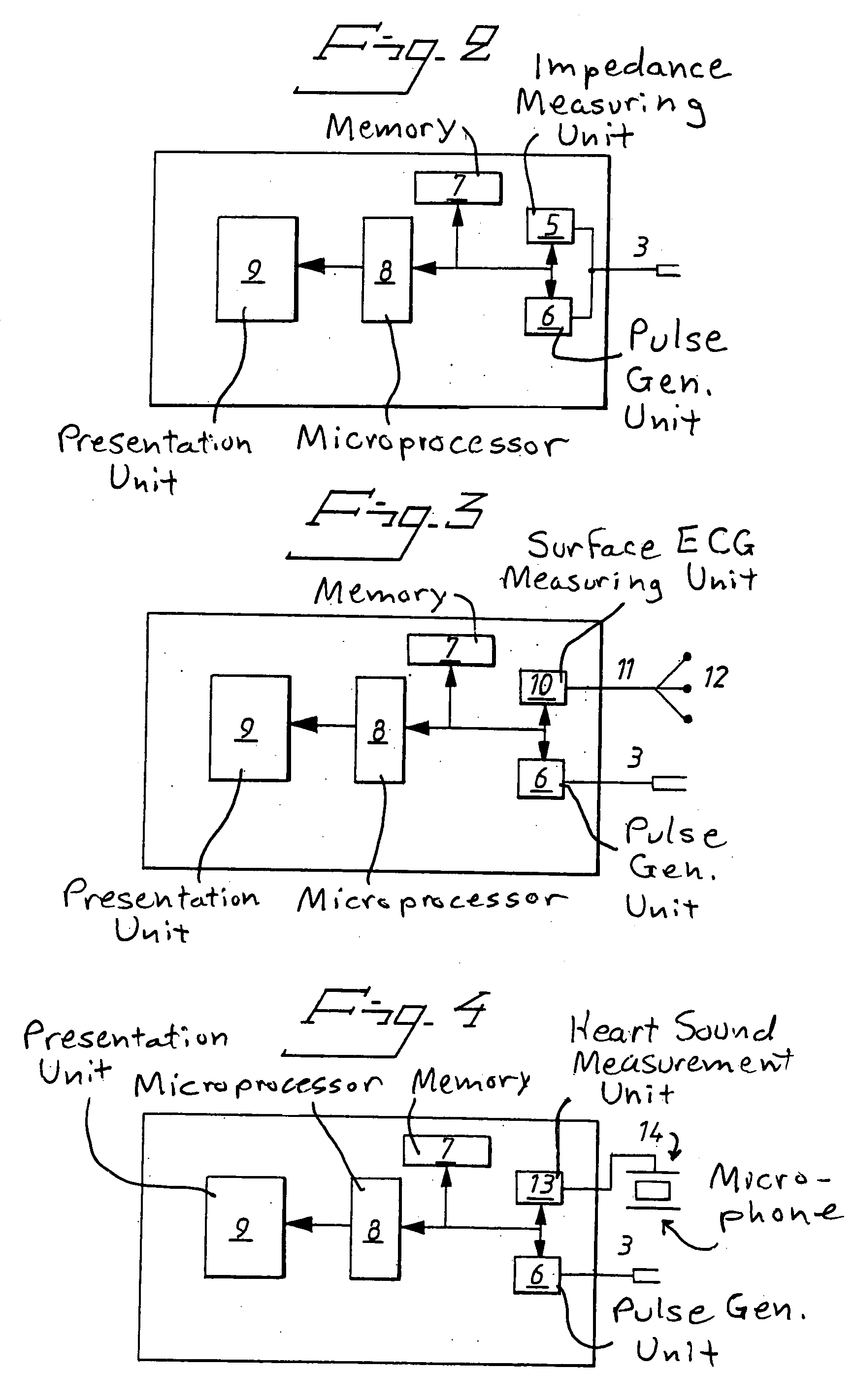
In a method and an arrangement for evaluating operational effectiveness of an implantable medical device for different lead placements associated with the medical device, a measuring unit records signals that are characteristic of cardiac activity at respectively different lead positions, and these signals are stored. A processor accesses the stored signals and, from the stored signals, determines a measure of cardiac activity at each of the lead positions. The recorded signals may be intracardiac ECG signals, surface ECG signals, heart sound signals obtained from a microphone, or impedance signals. The lead position at which the best hemodynamic behavior of the heart is identified from the analysis of the stored signals, and is determined as being the optimum site for placement of the electrode leads.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
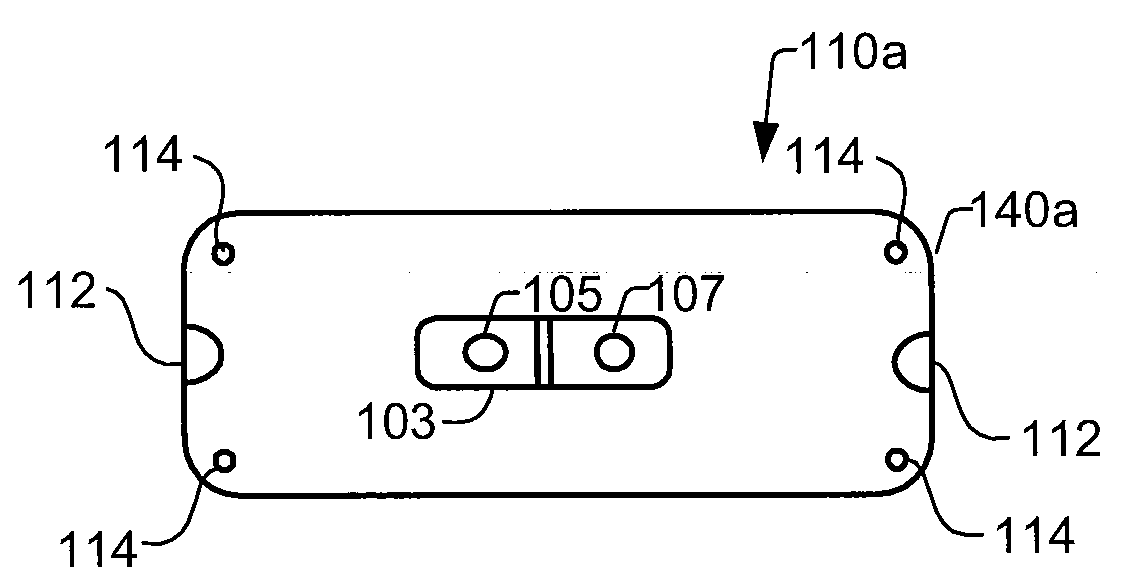
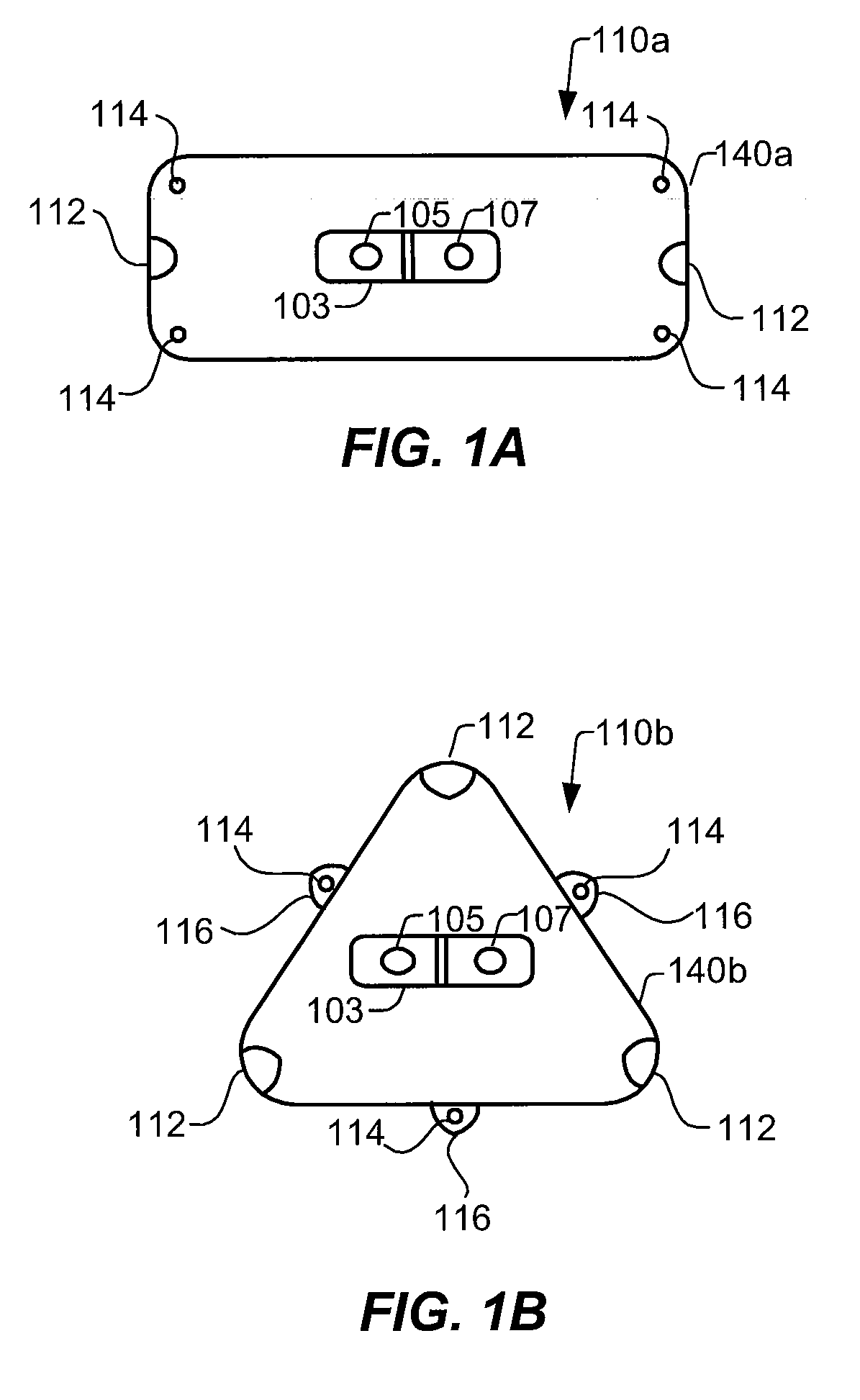
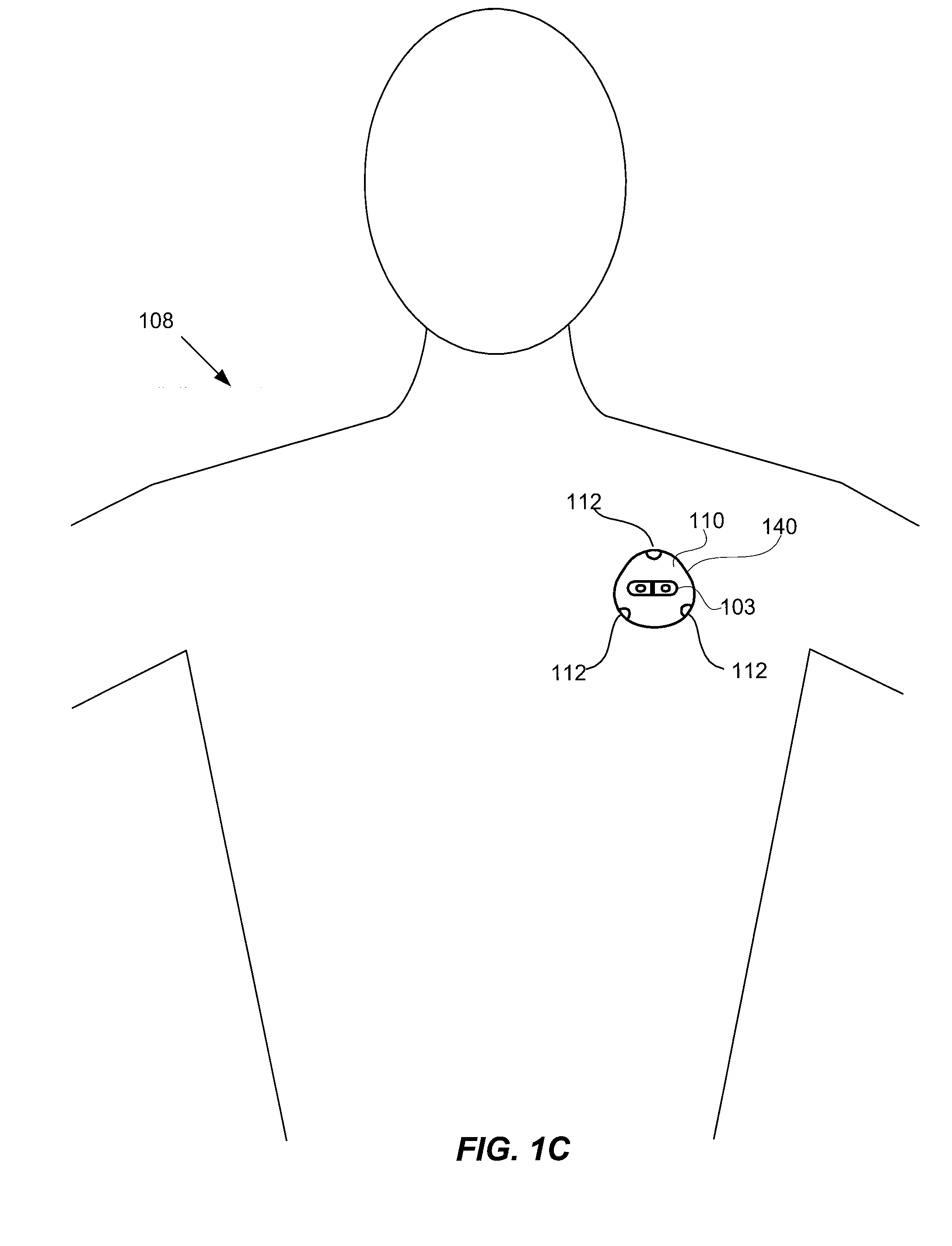
Method for generating three standard surface ECG leads derived from three electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the torso
A method for a 3-lead electrocardiographic (ECG) recording comprising three signal electrodes contained in the mid-horizontal plane of the human torso and the calculation of the standard leads I, II and III. Such electrodes are placed in-line as in a chest belt instead of the traditional positioning of electrodes in the upper and low parts of the frontal plane of the torso.
Owner:MISCZYNSKI DALE J +3
System for Heart Performance Characterization and Abnormality Detection
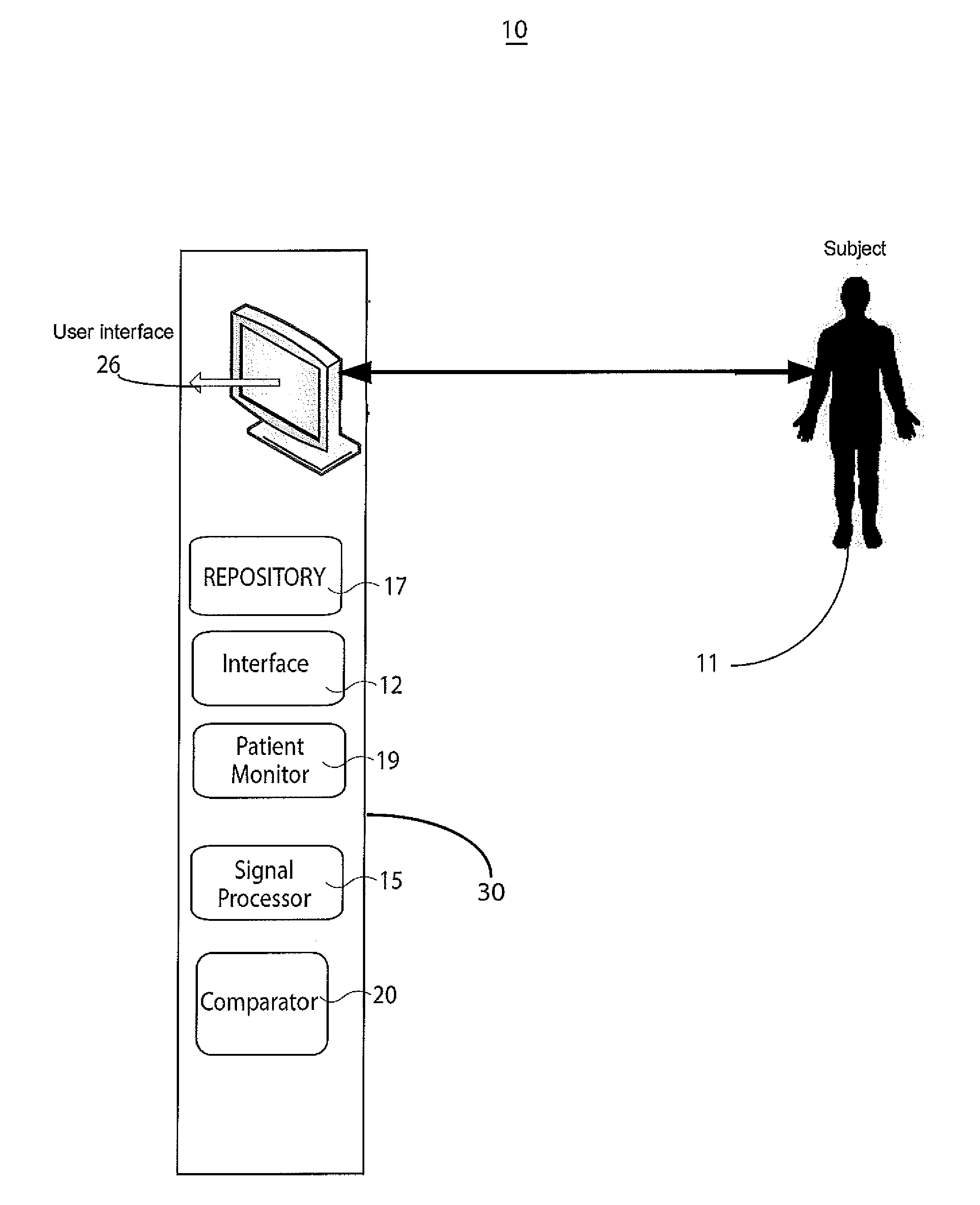
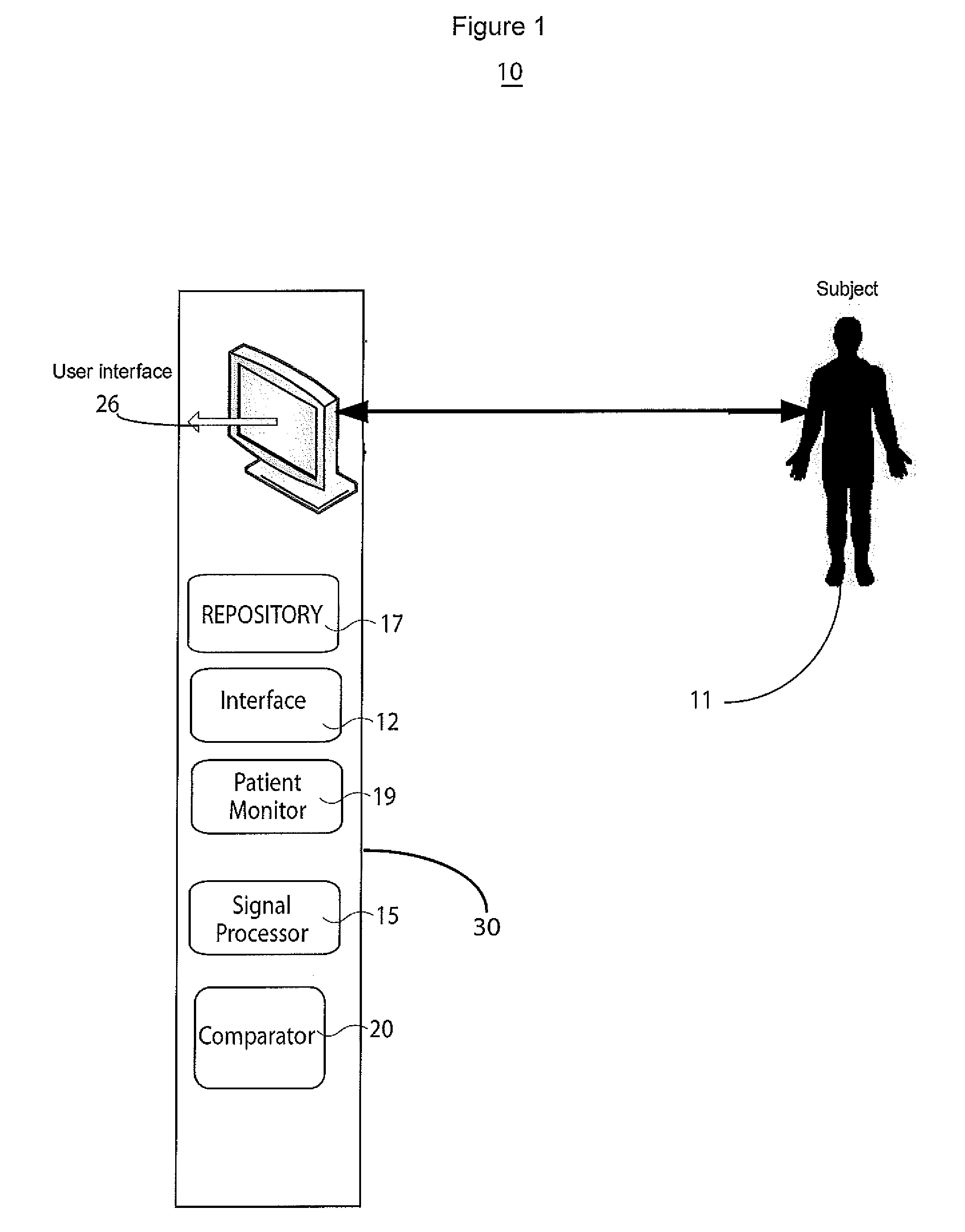
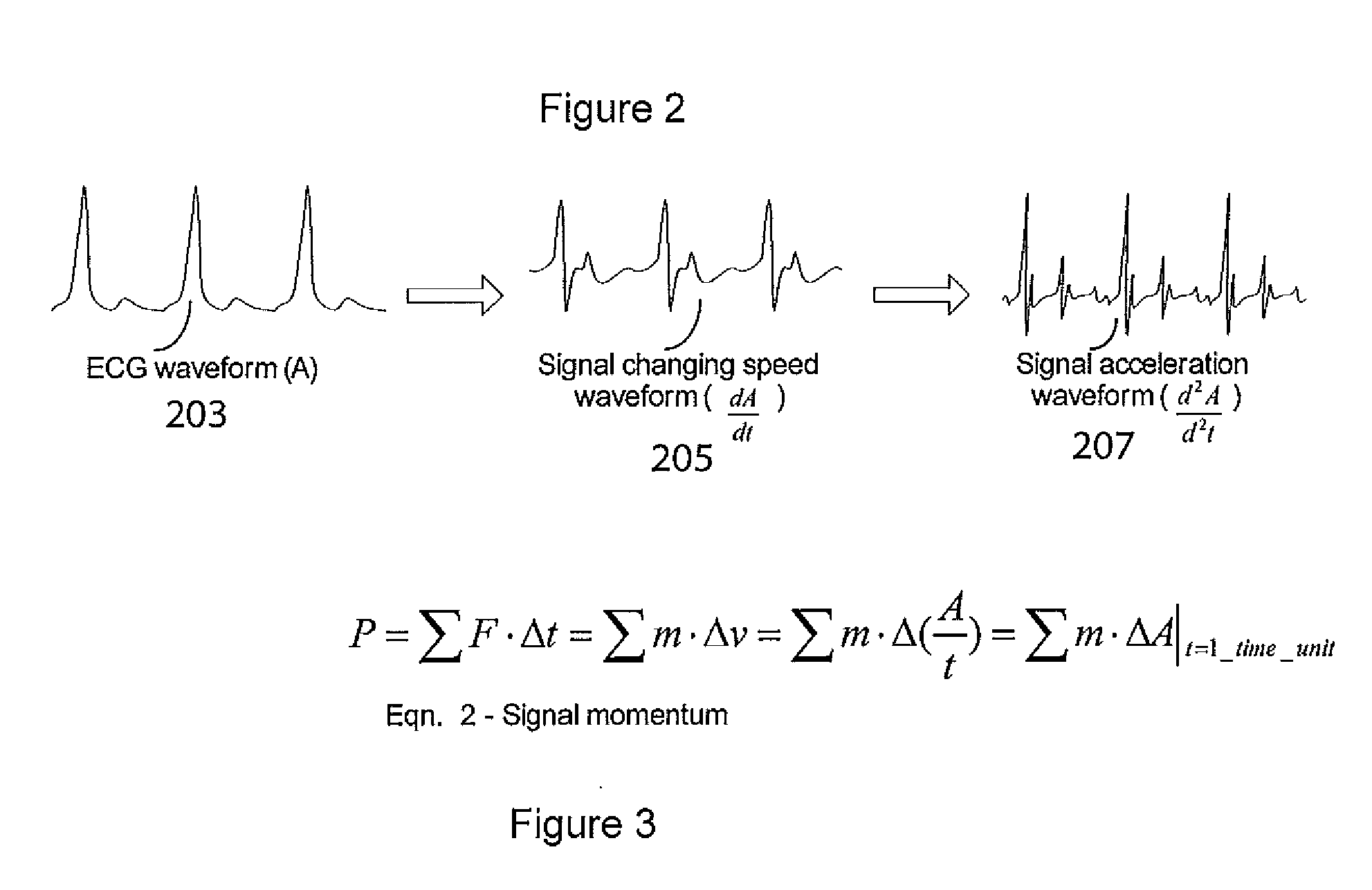
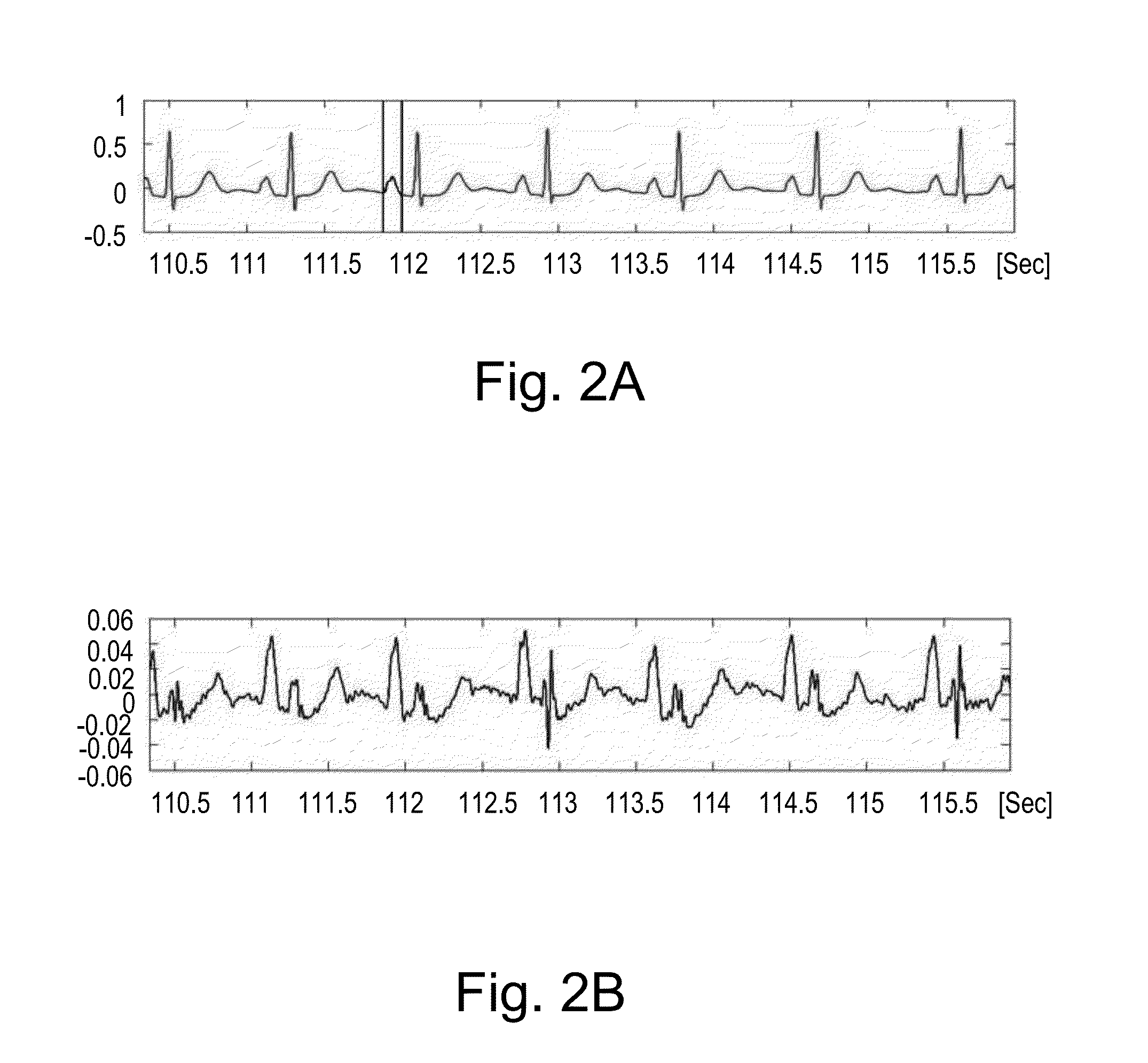
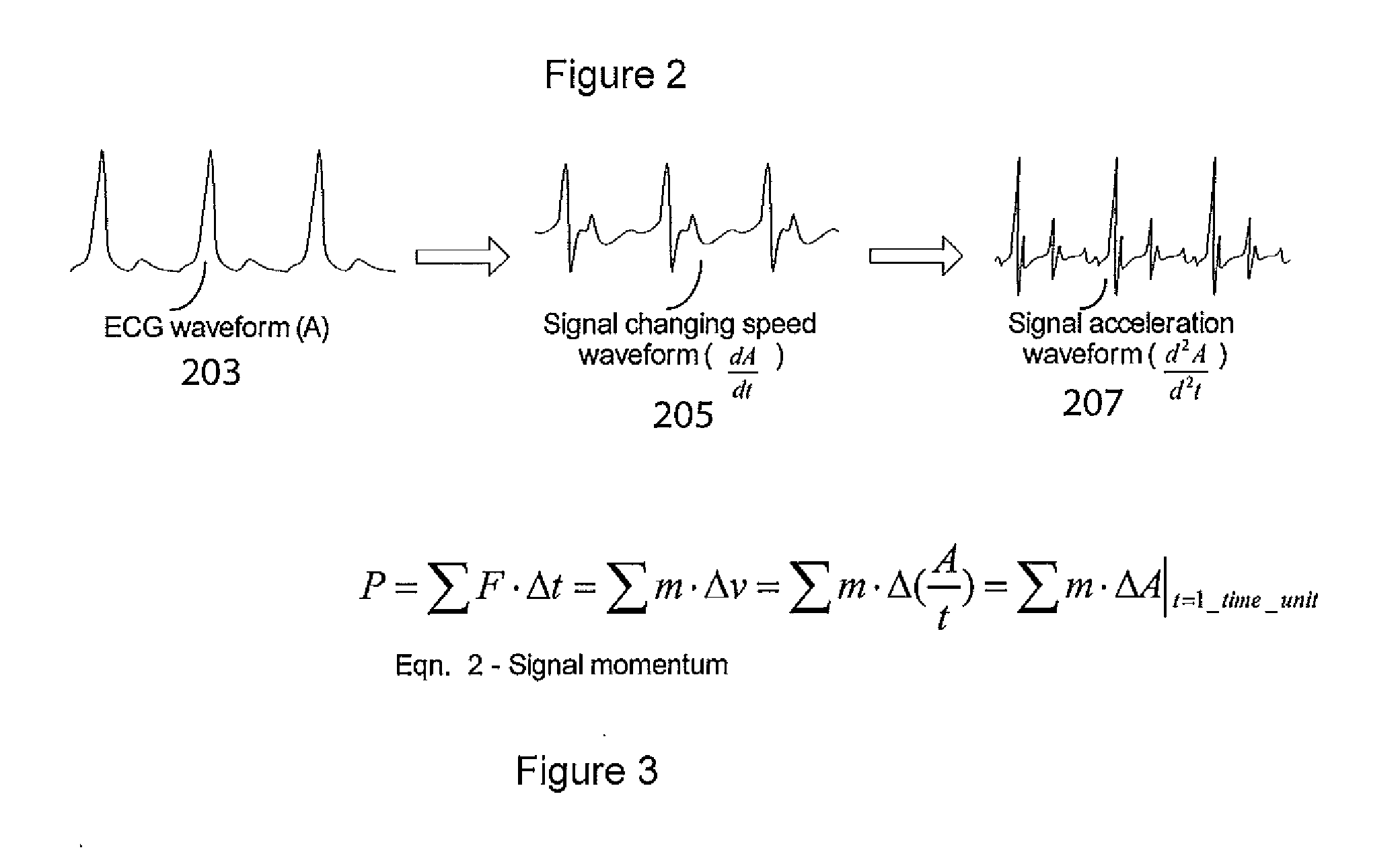
A system improves analysis, diagnosis and characterization of cardiac function signals (including surface ECG signals and intra-cardiac electrograms) based on cardiac electrophysiological activity momentum computation, characterization and mapping. The system calculates an electrophysiological signal momentum of different portions of cardiac signals including a timing, location and severity of cardiac pathology and improves reliability of diagnosis, detection, mapping to an identified medical condition, and characterization. The system improves identification of cardiac disorders, differentiation of cardiac arrhythmias, characterization of pathological severity, prediction of life-threatening events and supports evaluation of drug administration effects.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Heart stimulator
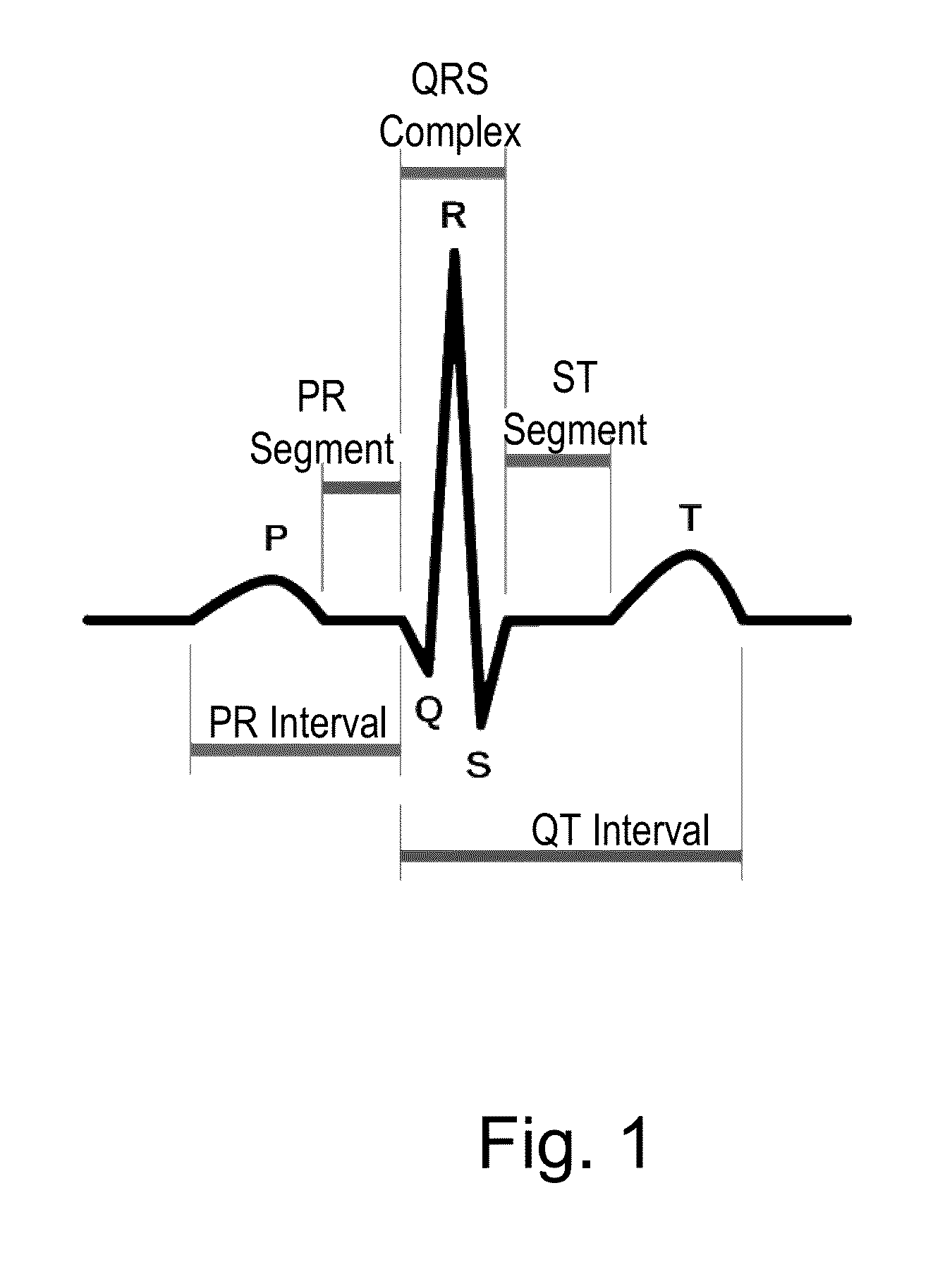
InactiveUS20080114411A1Risk minimizationTerminate stable ventricular tachycardiaElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsPR intervalVentricular tachycardia
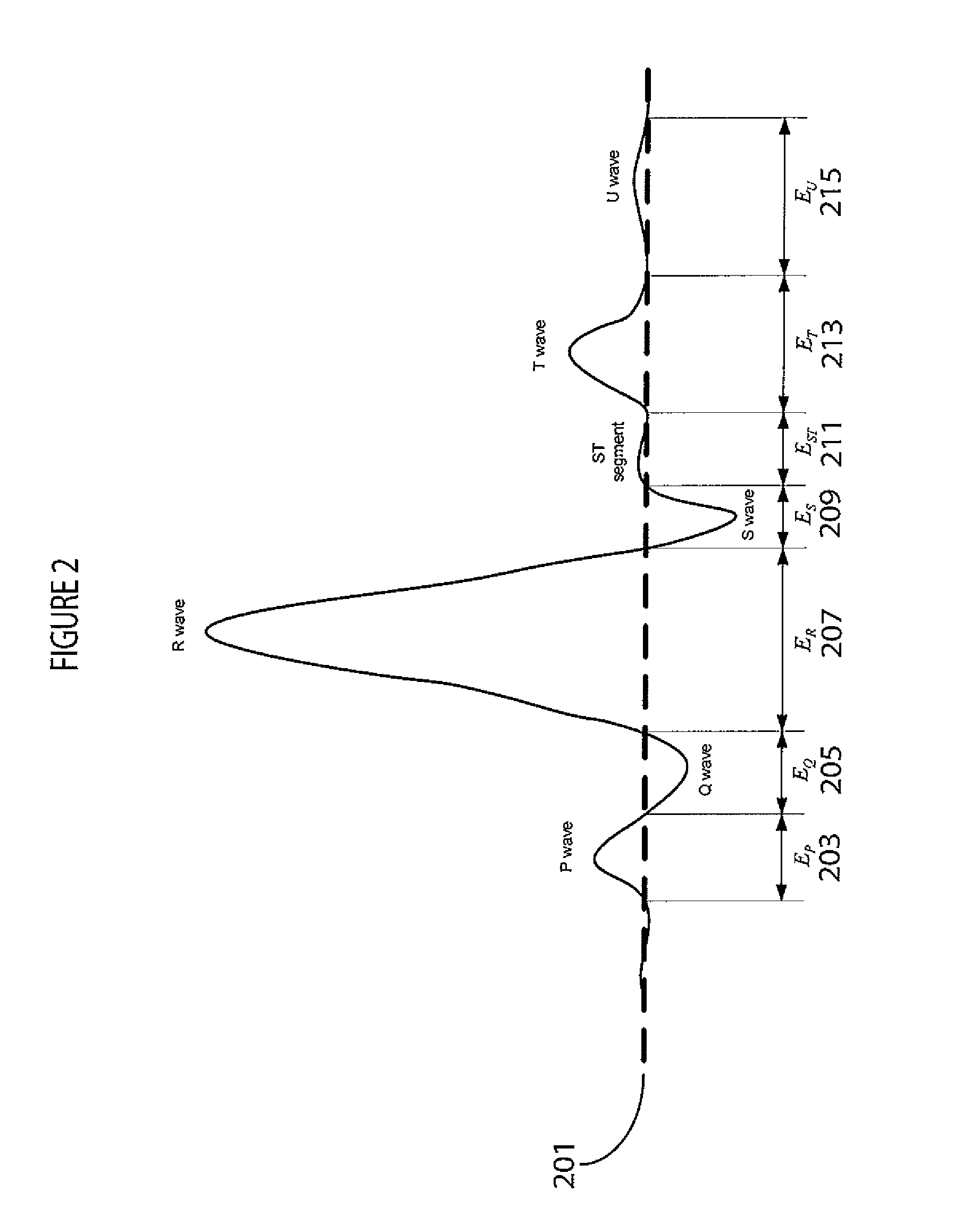
Heart stimulator that provides for timing a premature stimulation pulse for anti-tachycardia pacing outside the vulnerable phase of a ventricle, to terminate stable ventricular tachycardia while minimizing the risk of accelerating stable ventricular tachycardia into unstable ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. RT interval is determined instead of QT interval. Conventional QT interval is defined to end at T wave offset, which is difficult to measure because inherent imprecision in identifying the end of T wave from surface ECG. For safe ATP, such problems may be avoided. Because the VP usually refers to the portion of the T wave near the peak and early downslope (FIG. 3), in order to avoid the VP, only need to determine the peak of T wave, then set an blanking window or safety margin (e.g., 20 ms before to 20 ms after the peak of T wave) during which ATP pulses should not be delivered.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
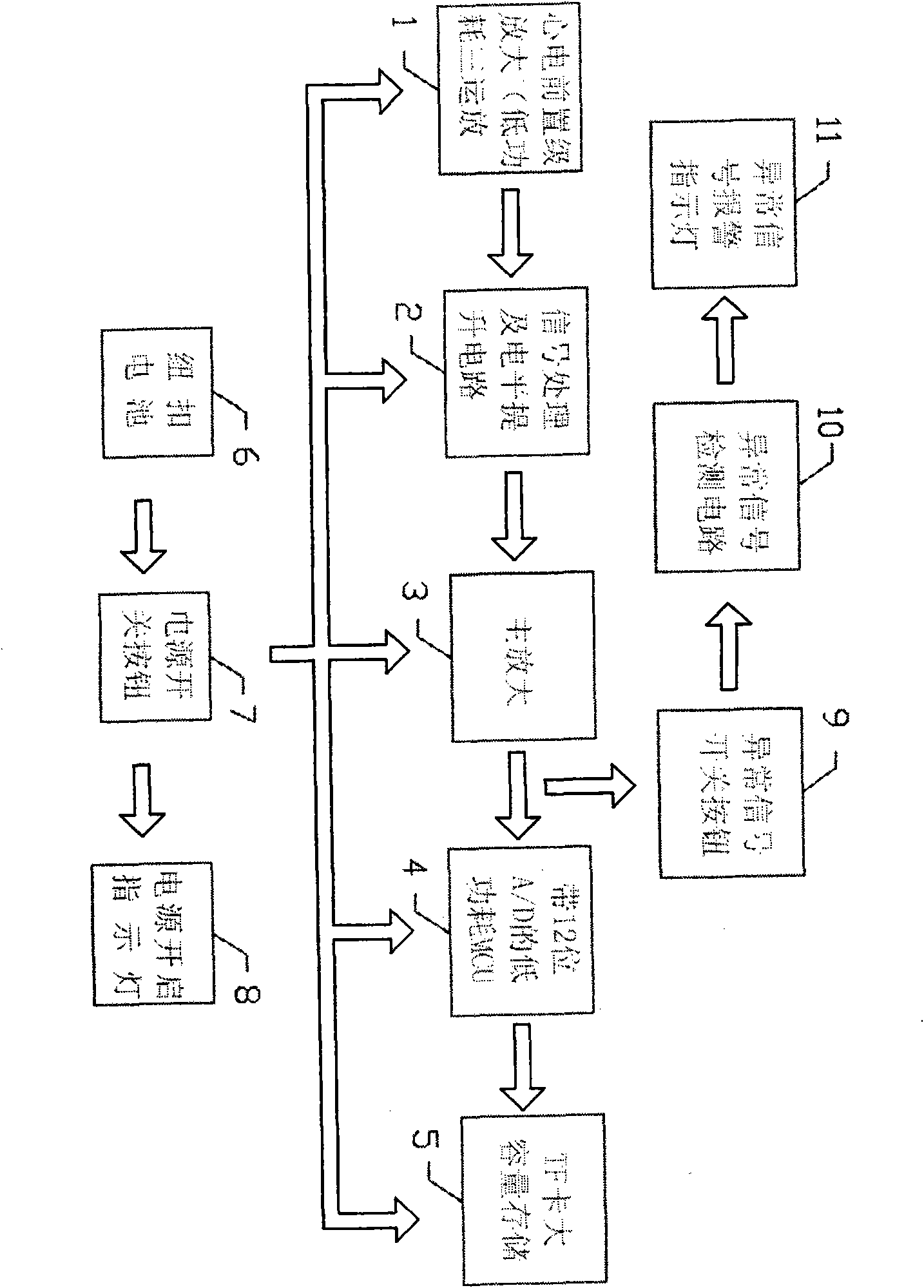
Non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method and system having ultra-long record period and ultra-high storage capacity
InactiveCN102485171AAchieve playbackRealize monitoringDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMass storageConvalescence
The invention relates to a non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method having an ultra-long record period and an ultra-high storage capacity. By using the method, characteristic values of electrocardiographic waves can be safely, stably and clearly acquired under the natural physiological state of a human body within a long period (more than 15 days), microvolt-level measurements of T-wave alternans can be acquired, and the collection, processing and high-capacity storage of electrocardiographic waves can be completed; and multiple electrocardiographic recording pasters can be used to realize the simultaneous recording of multi-channel body surface electrocardiograms, and a computer data processing and analysis system can complete the data monitoring and analysis, image display, data storage and printing and output of the recorded signals and realize the networking transmission of the electrocardiosignals. The clinical indications of the device include: symptoms related to suspected arrhythmia; determination of arrhythmia property, and completion of reasonably evaluating anti-arrhythmia treatment and monitoring myocardial ischemia; evaluation of anemic heart disease treatment measures; instructions to acute myocardial infarction patients before leaving hospital and during convalescence; and installation, detection and function assessment of sudden cardiac death and heart pacemakers.
Owner:杰升生物科技(上海)有限公司 +2
Implantable medical device and method for detecting cardiac events without using of refractory or blanking periods
Cardiac electrical events are detected by comparing signal vectors with pre-determined classification zones representative of different cardiac events. The signal vector is generated by sensing the voltages between various combinations of electrodes, such as A-tip to V-tip, A-tip to A-ring, and A-ring to V-ring. The signal vector is compared with a set of classification zones corresponding to different events, such as P-waves, R-waves, T-waves, A-pulses, and V-pulses, to determine whether the vector lies within any of the classification zones. In this manner, cardiac events are detected using only the voltages received from the electrodes and no refractory periods or blanking periods are required to distinguish one event from another. The classification zones vary from patient to patient and a technique is provided herein for generating a set of vector classification zones for a particular patient. Signal vectors corresponding to various unknown cardiac events are generated by the implanted device and are transmitted to an external device programmer. ECG signals, generated by a surface ECG detector, are simultaneously received by the external programmer. The external programmer identifies the cardiac electrical event corresponding to each signal vector based on the ECG signals and then generates classification zones for each event type using only the signal vectors corresponding to the event.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Standalone systemic arterial blood pressure monitoring device
Certain embodiments of the present invention are related to an implantable monitoring device to monitor a patient's arterial blood pressure, where the device is configured to be implanted subcutaneously. The device includes subcutaneous (SubQ) electrodes and a plethysmography sensor. Additionally, the device includes an arterial blood pressure monitor configured to determine at least one value indicative of the patient's arterial blood pressure based on at least one detected predetermined feature of a SubQ ECG and at least one detected predetermined feature of a plethysmography signal. Alternative embodiments of the present invention are directed to a non-implantable monitoring device to monitor a patient's arterial blood pressure based on features of a surface ECG and a plethysmography signal obtained from a non-implanted sensor.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
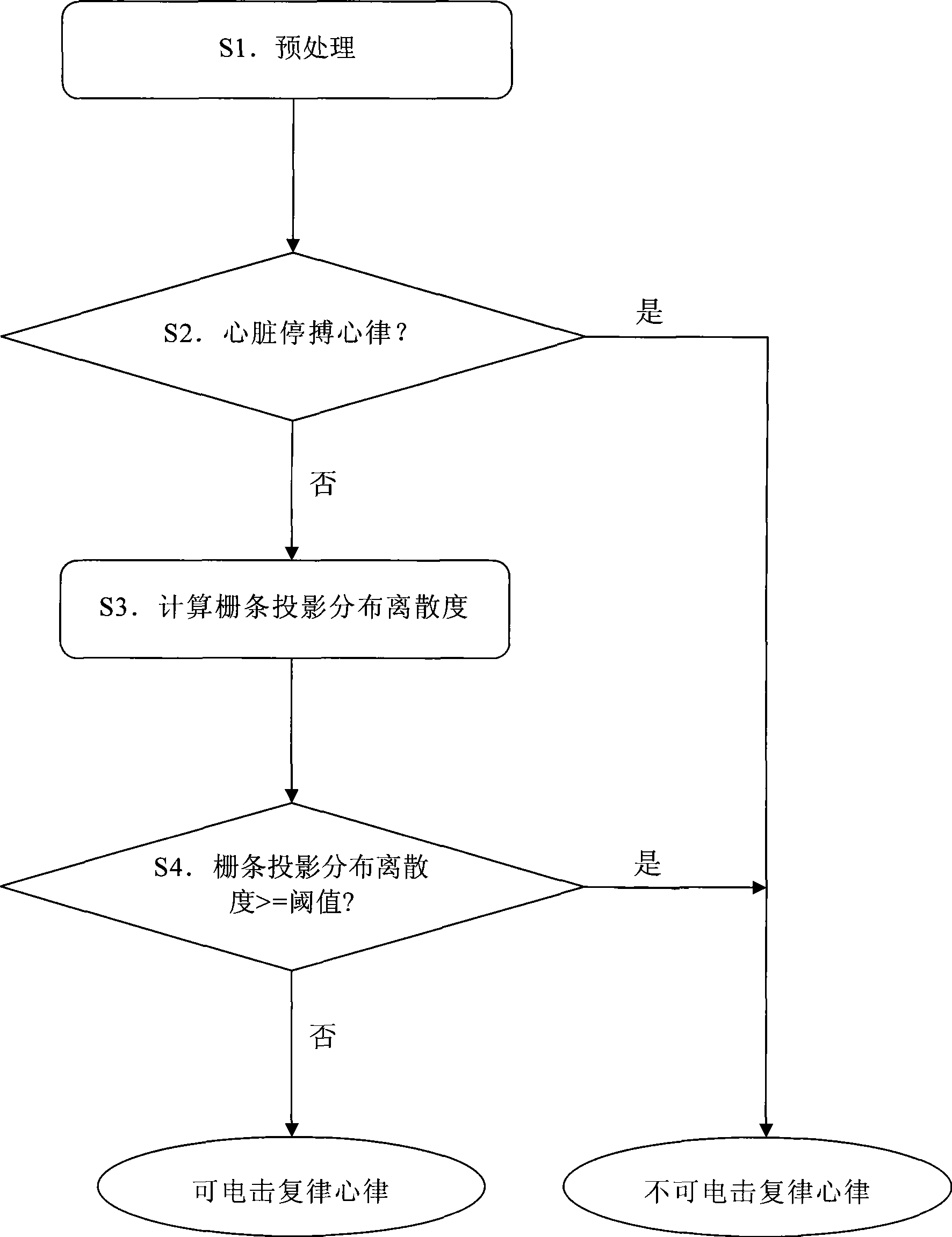
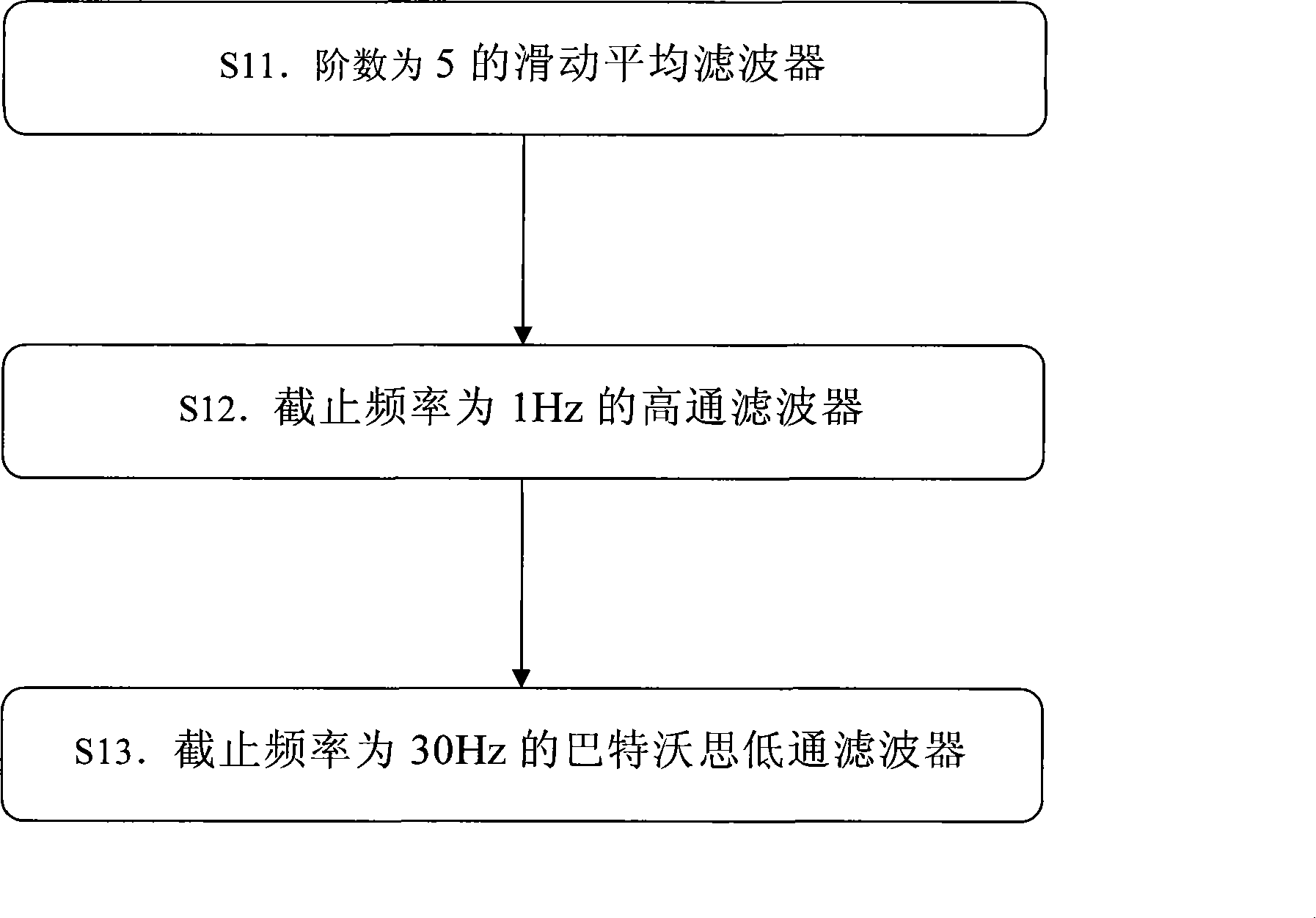
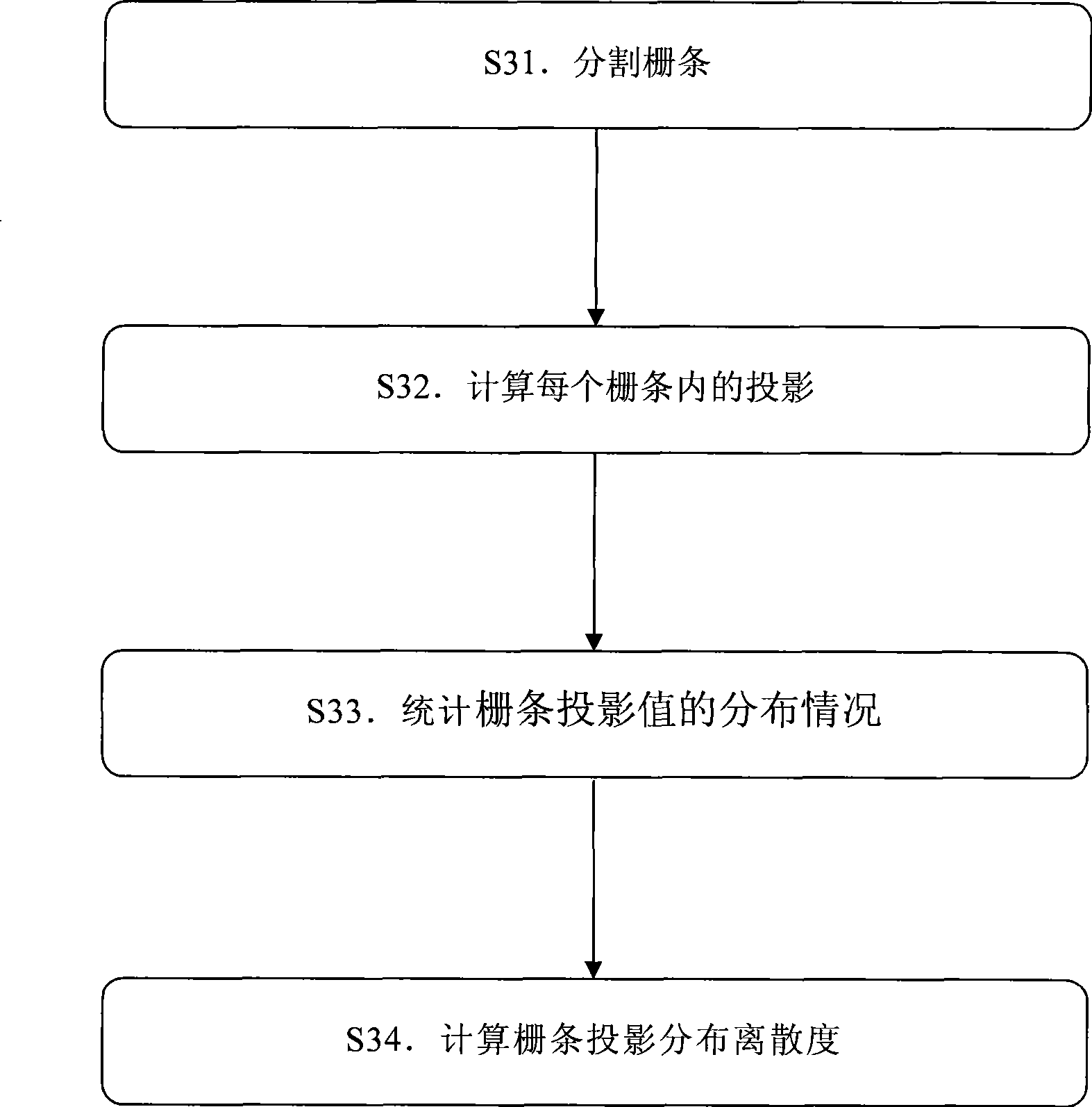
Shockable rhythm recognition algorithm based on grid projection distribution dispersion
InactiveCN101461710AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseEcg signal
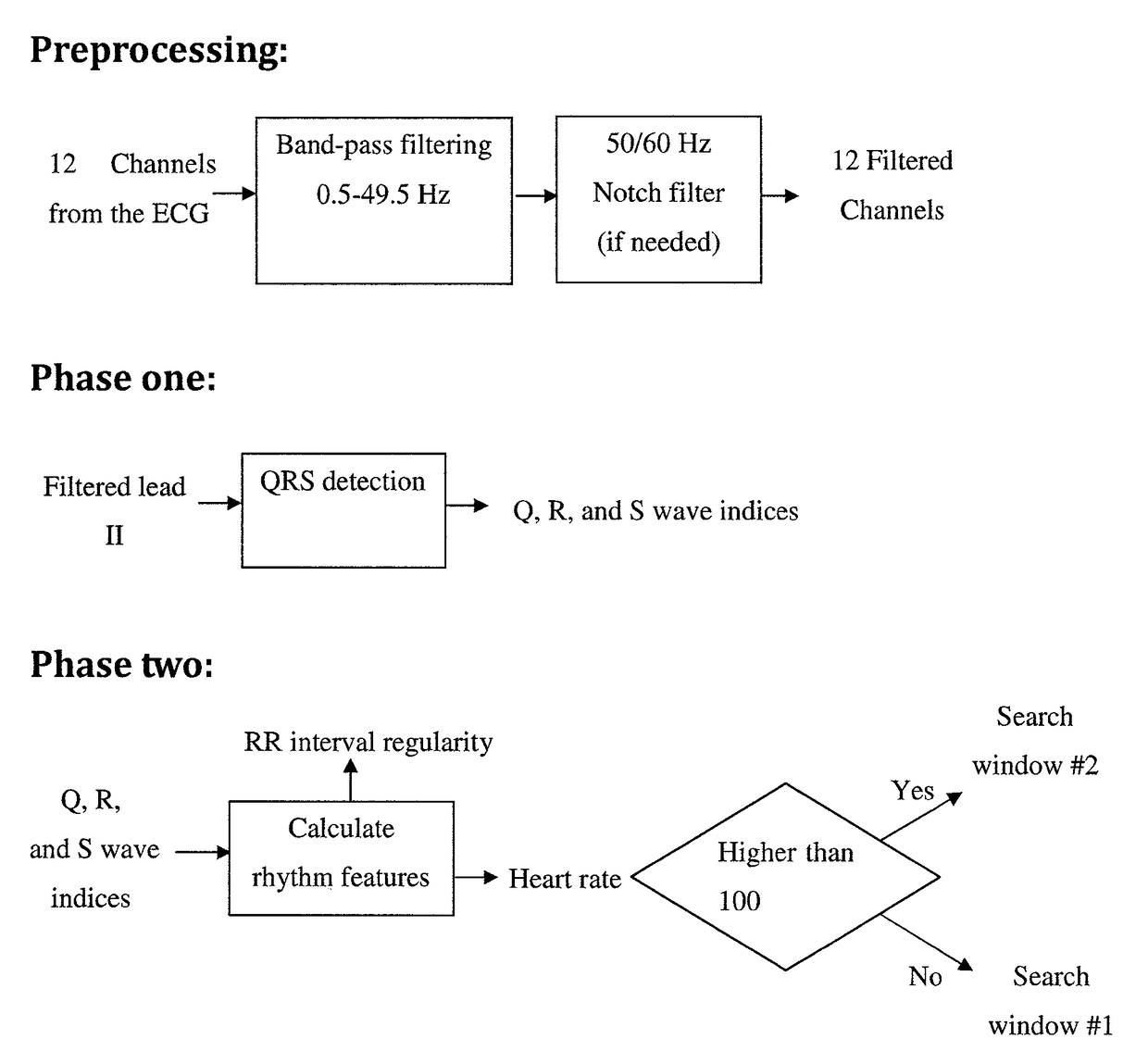
A recognition algorithm of heart rhythm capable of electric shock cardioversion based on grid projection distribution dispersion, is suitable for disease diagnosis and treatment instrument or apparatus, including the steps: S1, preprocessing the electrocardiosignal; S2, recognizing whether the electrocardiosignal is the heart rhythm of cardiac arrest, if so, judging the heart rhythm as the heart rhythm incapable of electric shock cardioversion, otherwise, continuing the follow-up steps S3 and S4; S3, calculating the distribution dispersion of the grid projection; S4, determining whether it pertains to the heart rhythm incapable of electric shock cardioversion or the heart rhythm capable of electric shock cardioversion based on the distribution dispersion of the grid projection. The invention improves the sensitivity and specificity of recognizing the heart rhythm capable of electric shock cardioversion, simplifies the computational complexity of the algorithm, can be applied to the existing ECG guardianship equipment and automatic external defibrillator, and the like instruments requiring body surface electrocardiogram for recognizing the heart rhythm capable of electric shock cardioversion.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
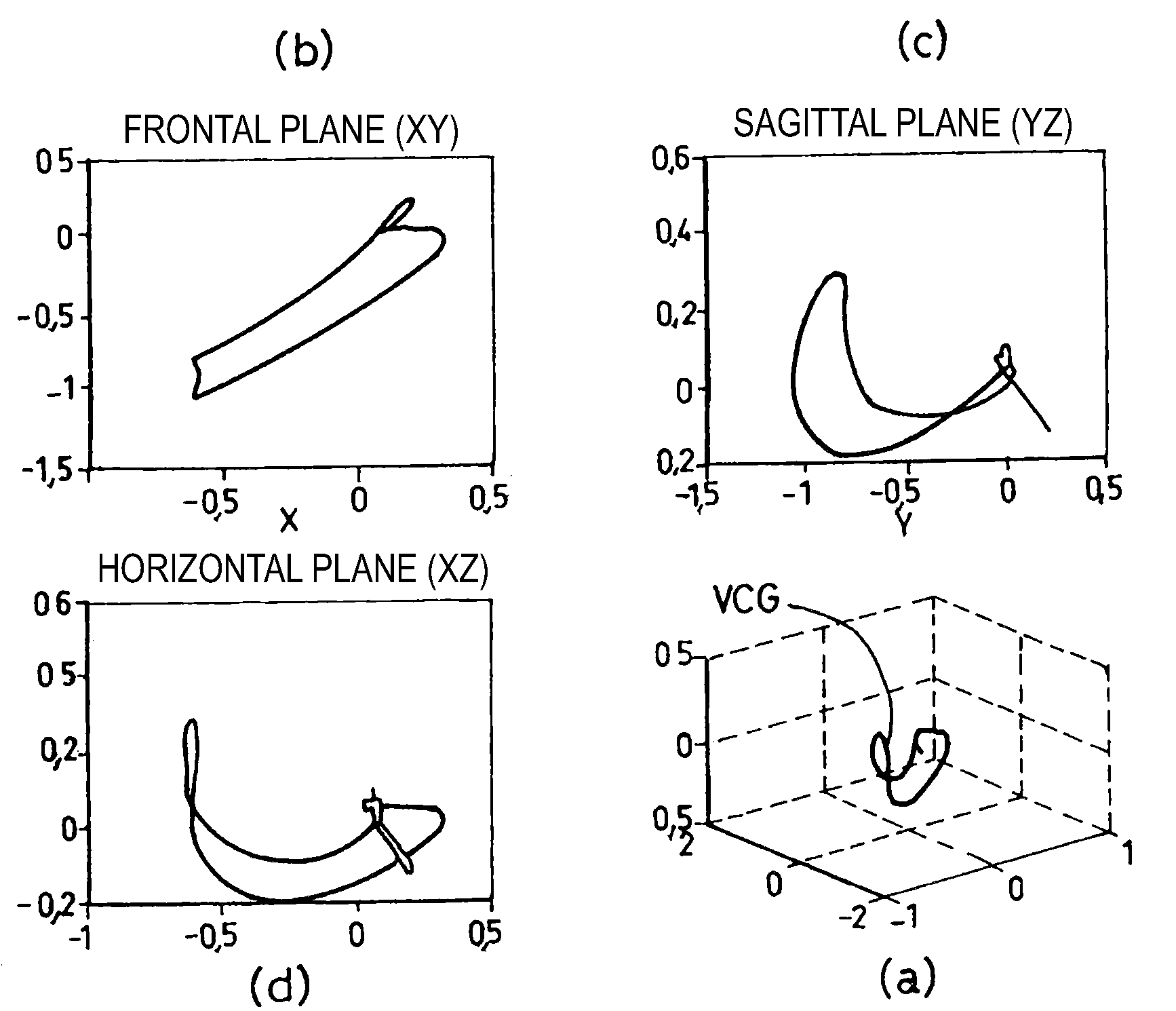
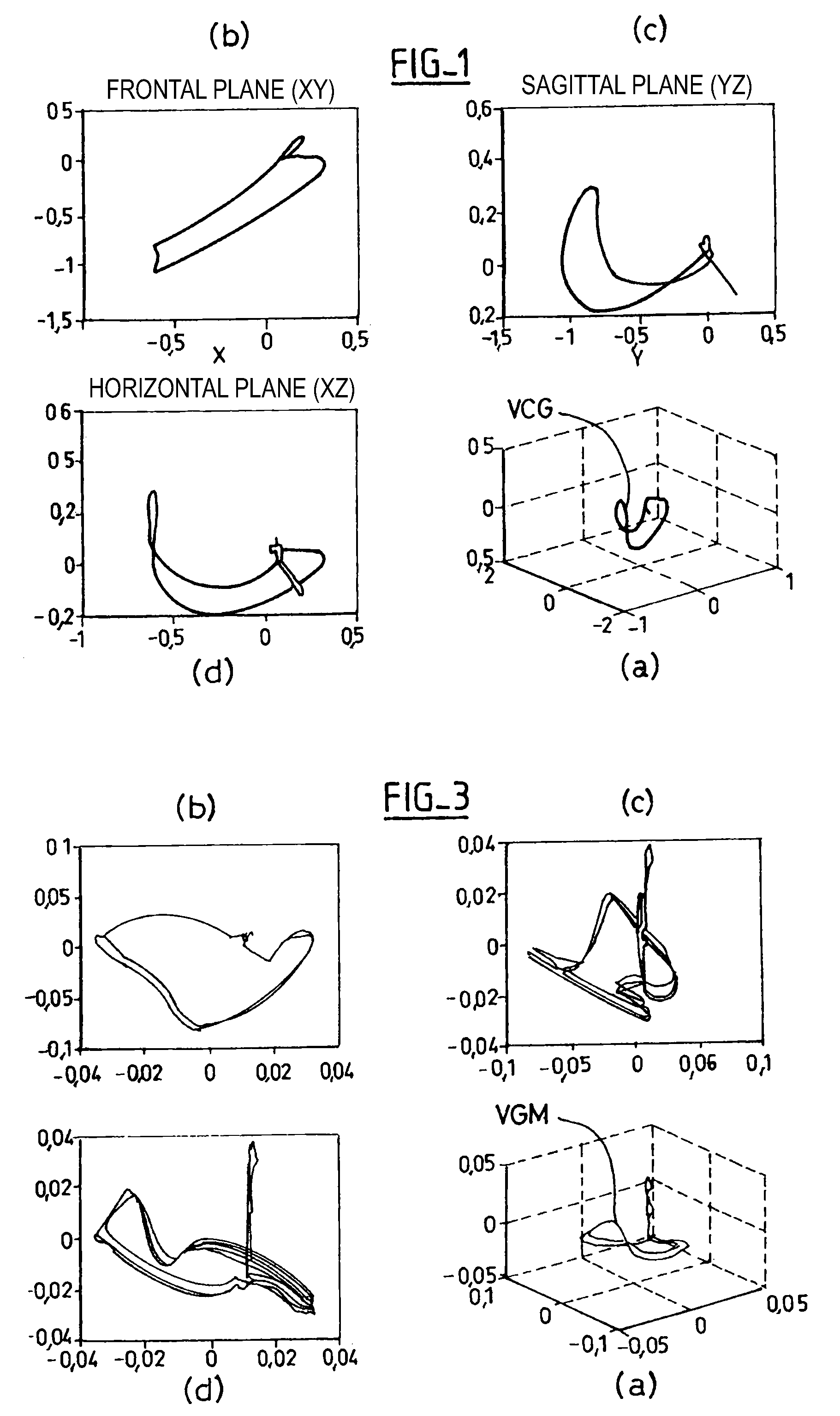
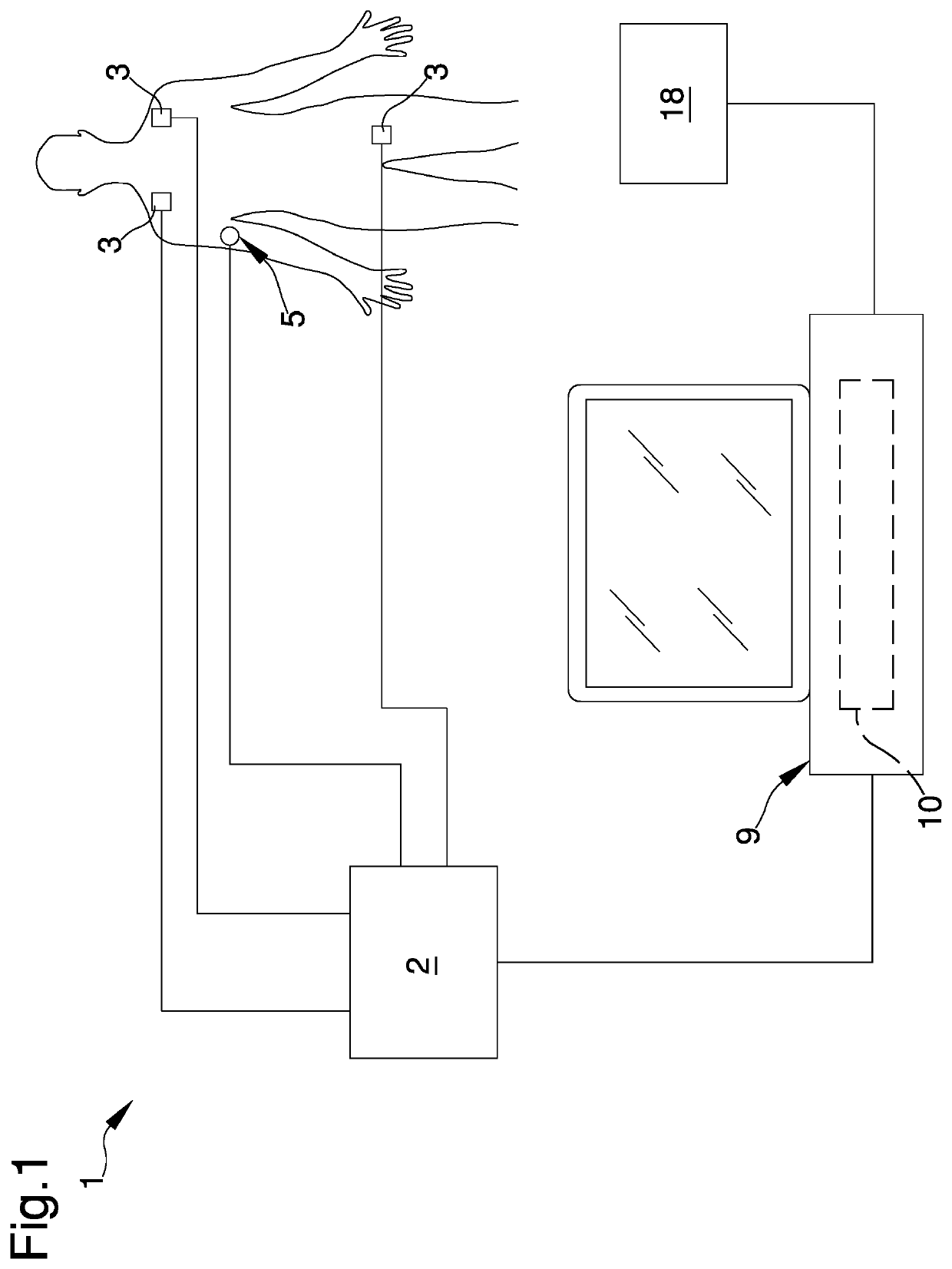
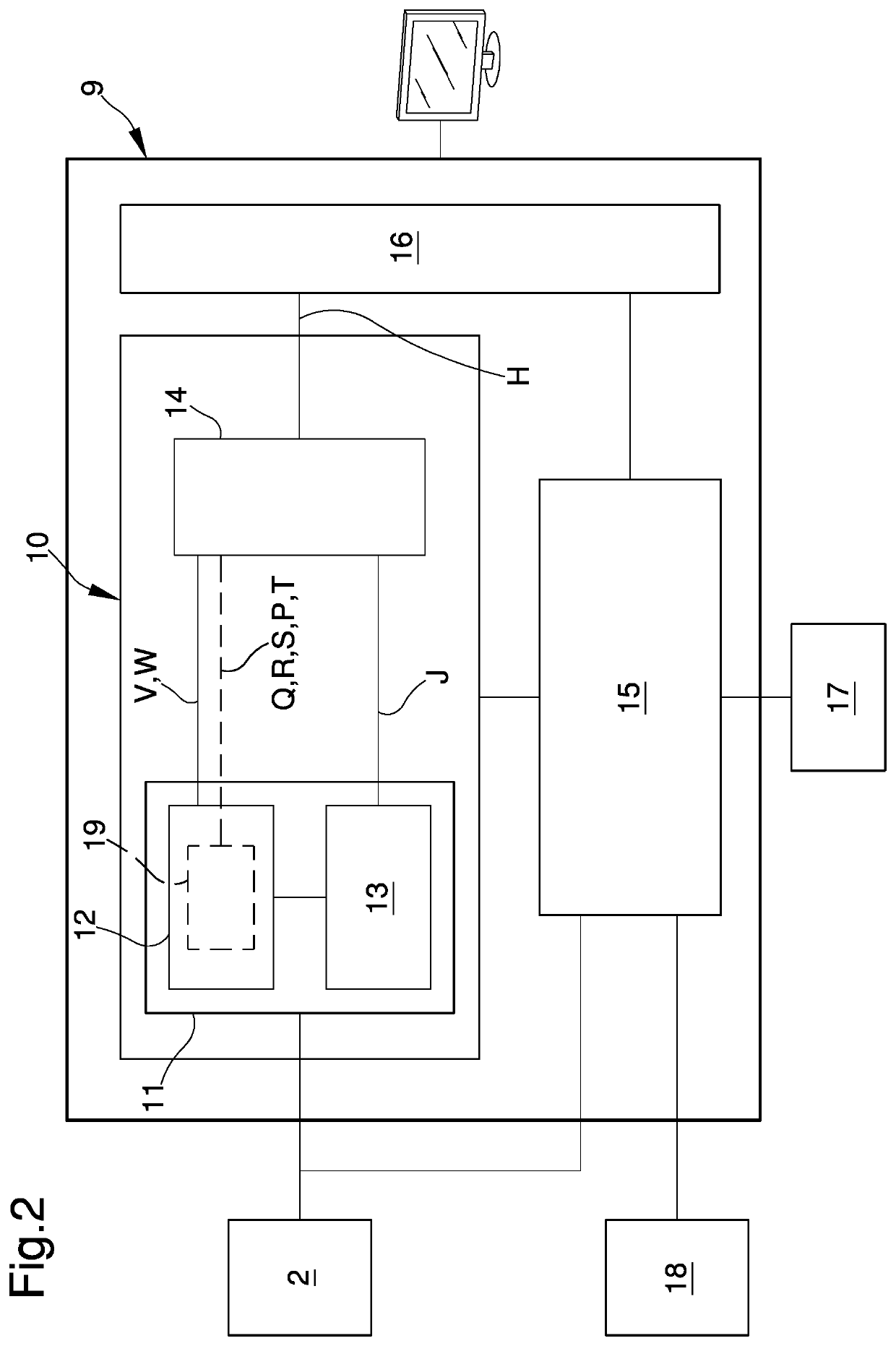
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram
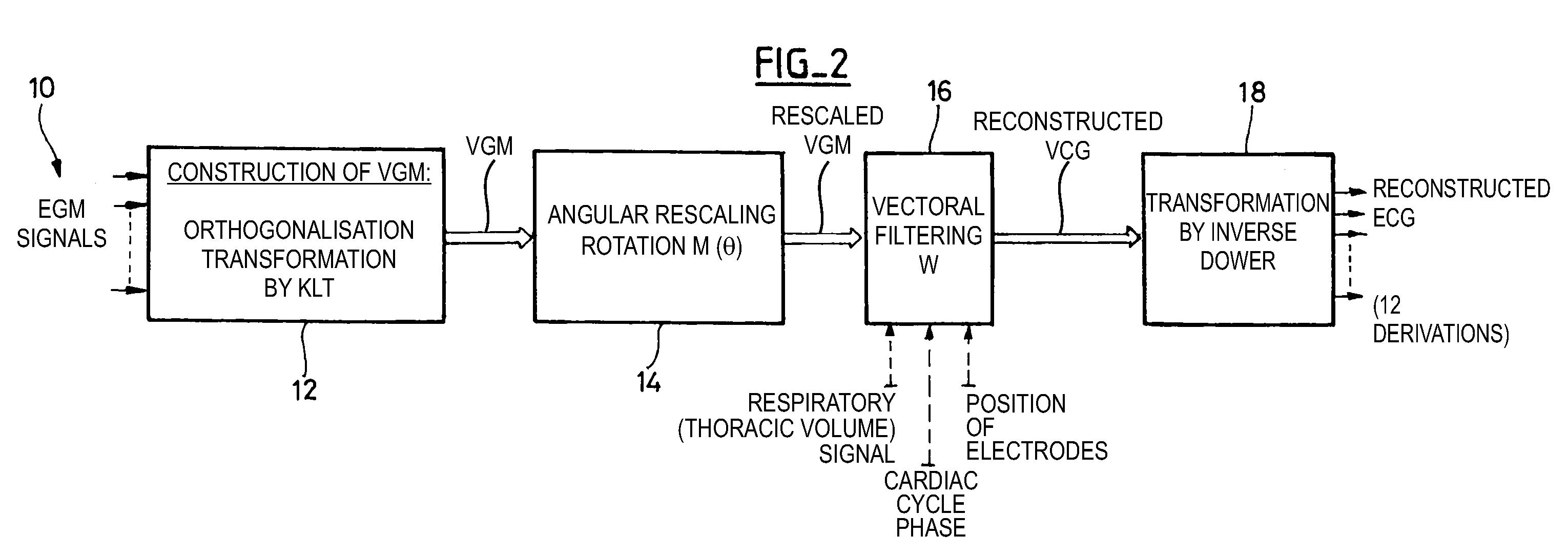
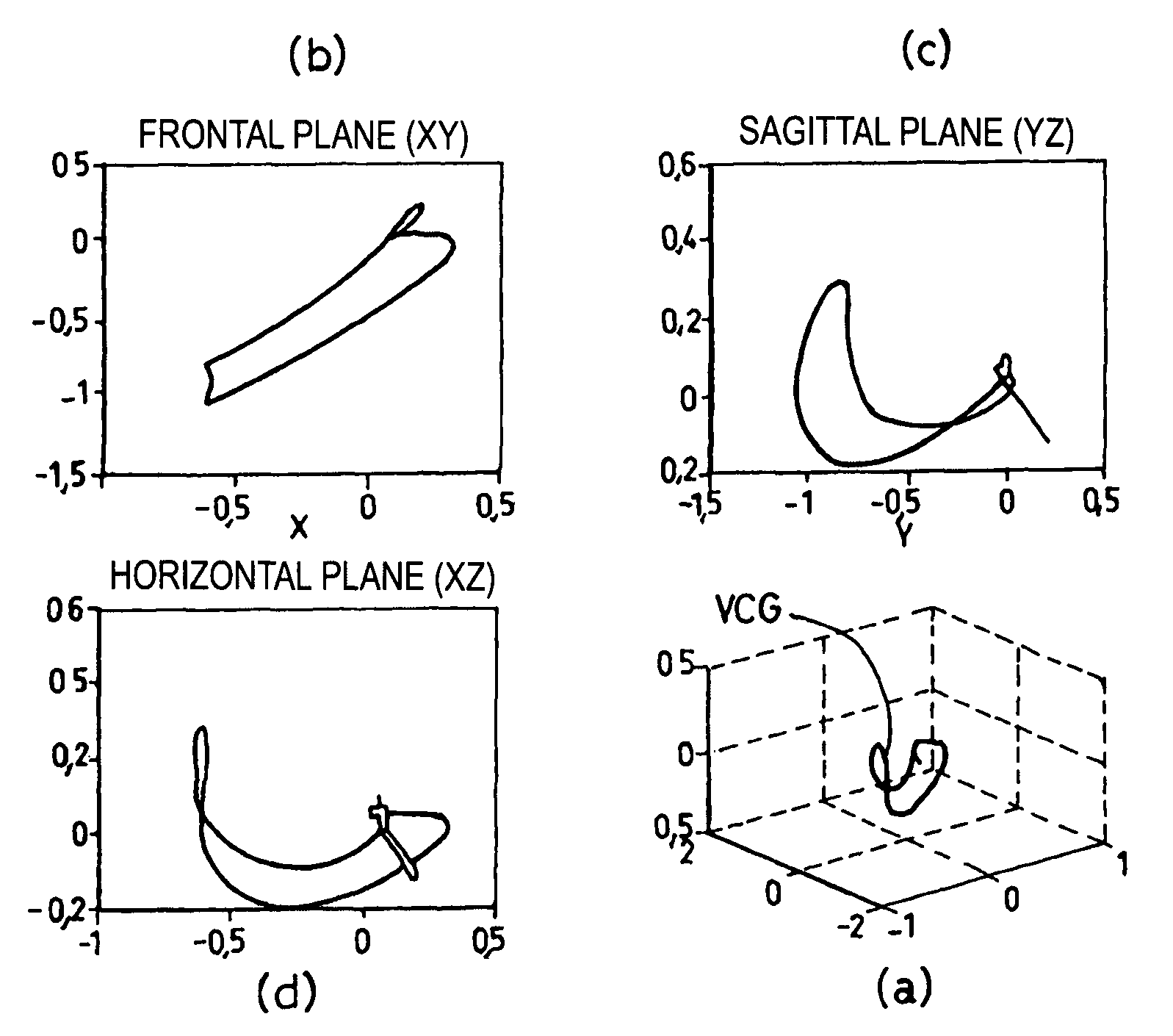
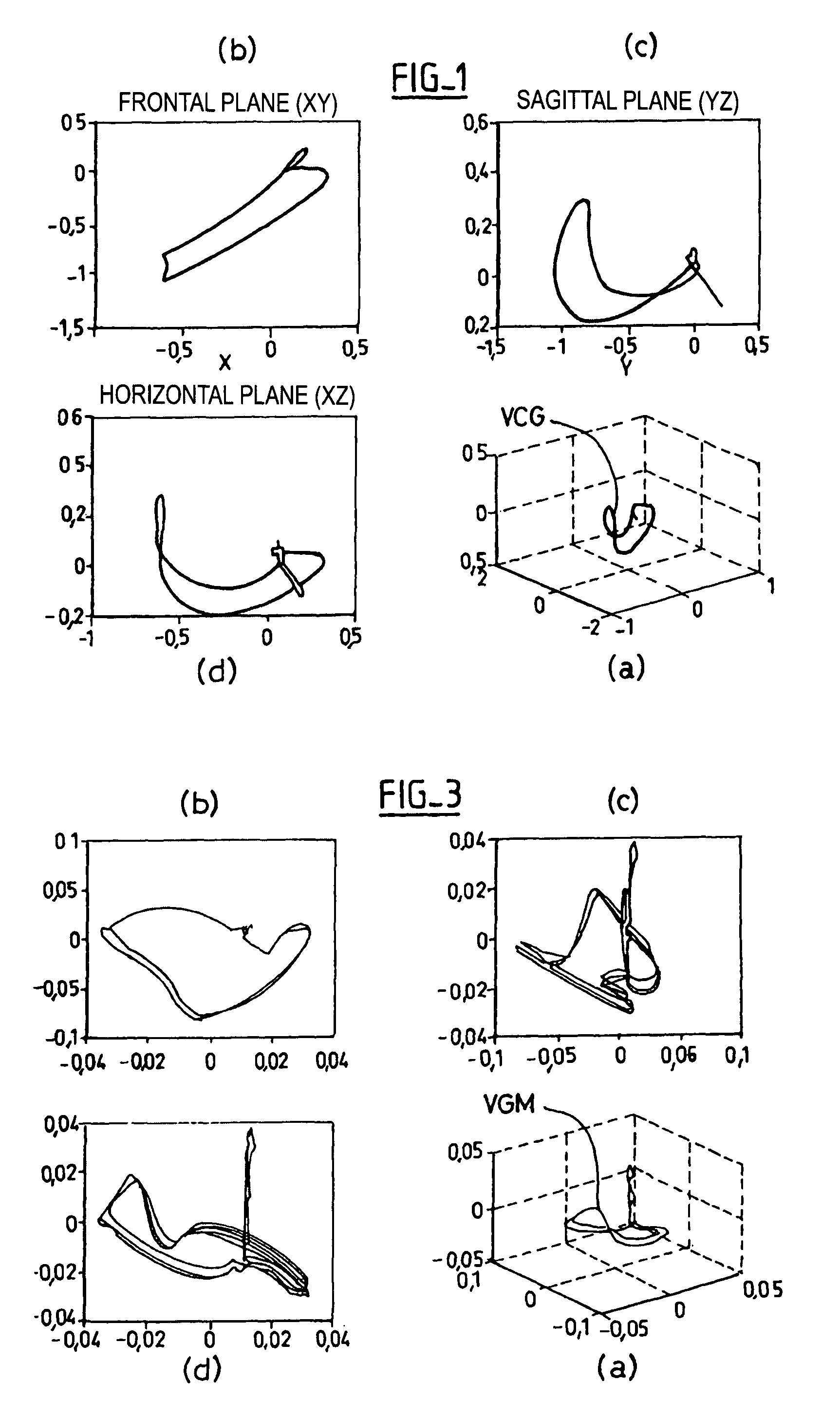
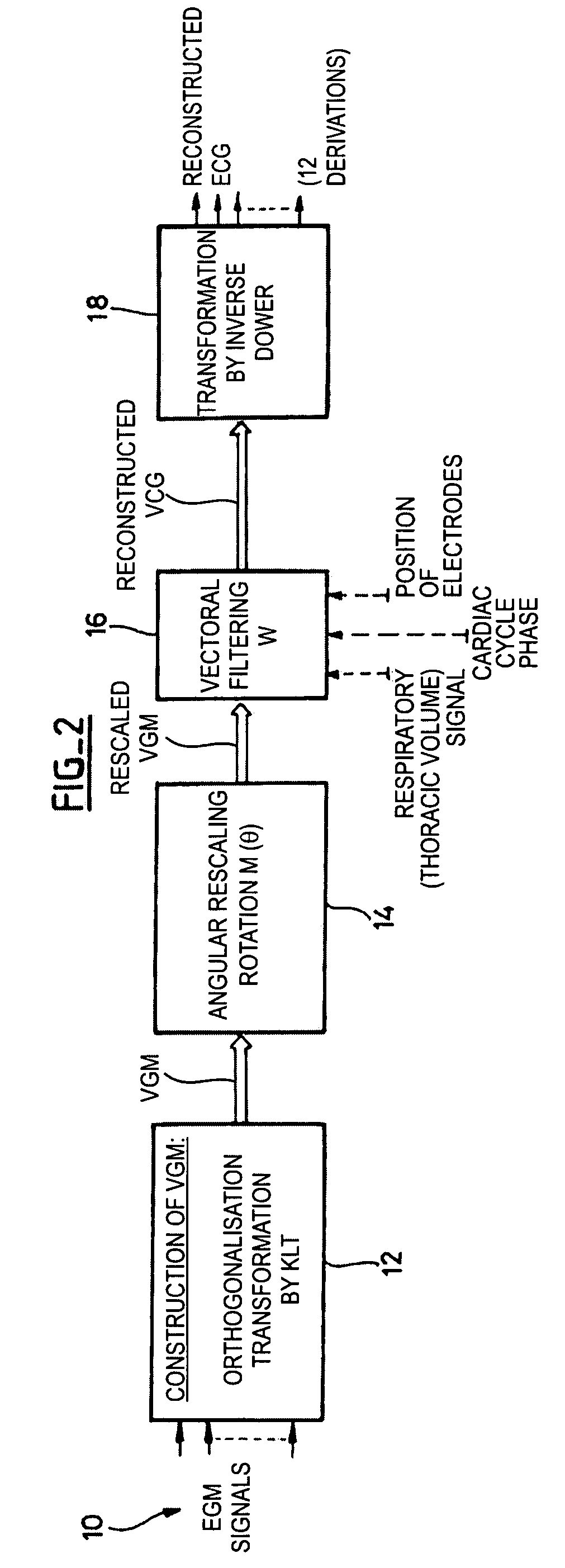
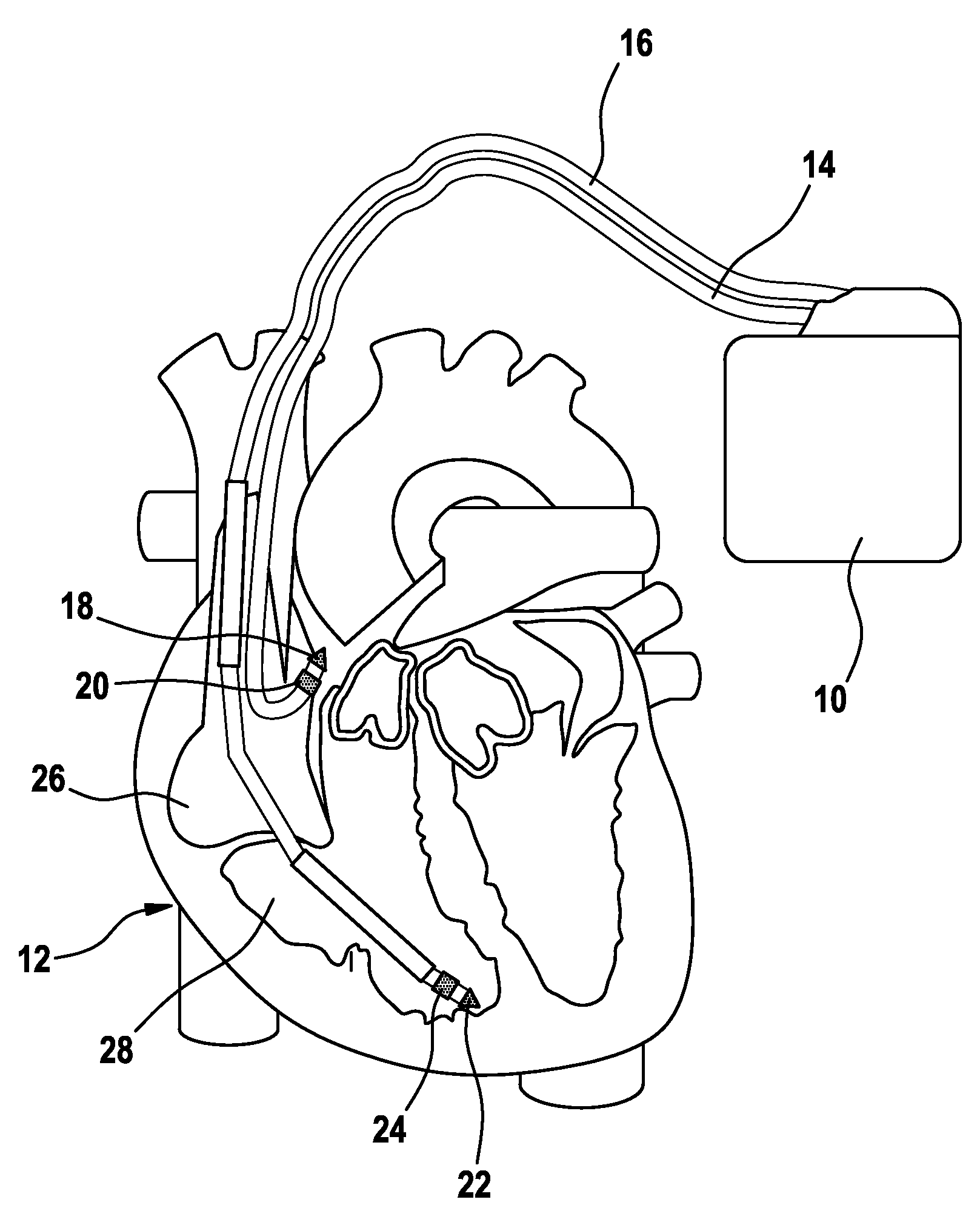
The reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram. This method includes: (a) acquisition (10) of a plurality of endocardial electrogram signals (EGM) through a plurality of endocardial derivations defined based upon endocardial electrodes; (b) calculation (12), by combining the endocardial electrogram (EGM) signals acquired at step (a), of the corresponding endocardial vectogram (VGM); (c) angular resealing (14) of the orthonormated mark of the endocardial vectogram (VGM) with that of the surface vectocardiogram (VCG); (d) estimation (16), based upon the endocardial vectogram (VGM) calculated at step (b), of a reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed), and (e) calculation (18) of the surface electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to said reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Separating clinically relevant sources of electrical activity in ECG signals
This invention provides a fully automatic method and a system for detecting and classifying cardiac arrhythmias from a surface ECG record. The method defines four relevant parameters whose values are extracted from said ECG record. Clinically relevant conclusions are assigned to various combinations of the obtained values of said parameters. The method can be employed for detecting fetal QRS complexes from abdomen ECG of a pregnant woman.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
System for cardiac pathology detection and characterization
InactiveUS8364248B2Easy to identifyData processing applicationsElectrocardiographyEnergy variationDisease
A system improves characterization and diagnosis of cardiac electrophysiological activities by analyzing and characterizing cardiac function signals (including surface ECG signals and intra-cardiac electrograms) based on cardiac electrophysiological energy mode and pattern identification and mapping. The system accurately determines a time stamp, location and severity of cardiac pathology and clinical events by calculating a cardiac signal energy mode and energy variation and distribution. The system identifies cardiac disorders, differentiates cardiac arrhythmias, characterizes pathological severity, predicts life-threatening events, and supports evaluation of administration of drugs.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Separating clinically relevant sources of electrical activity in ECG signals
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
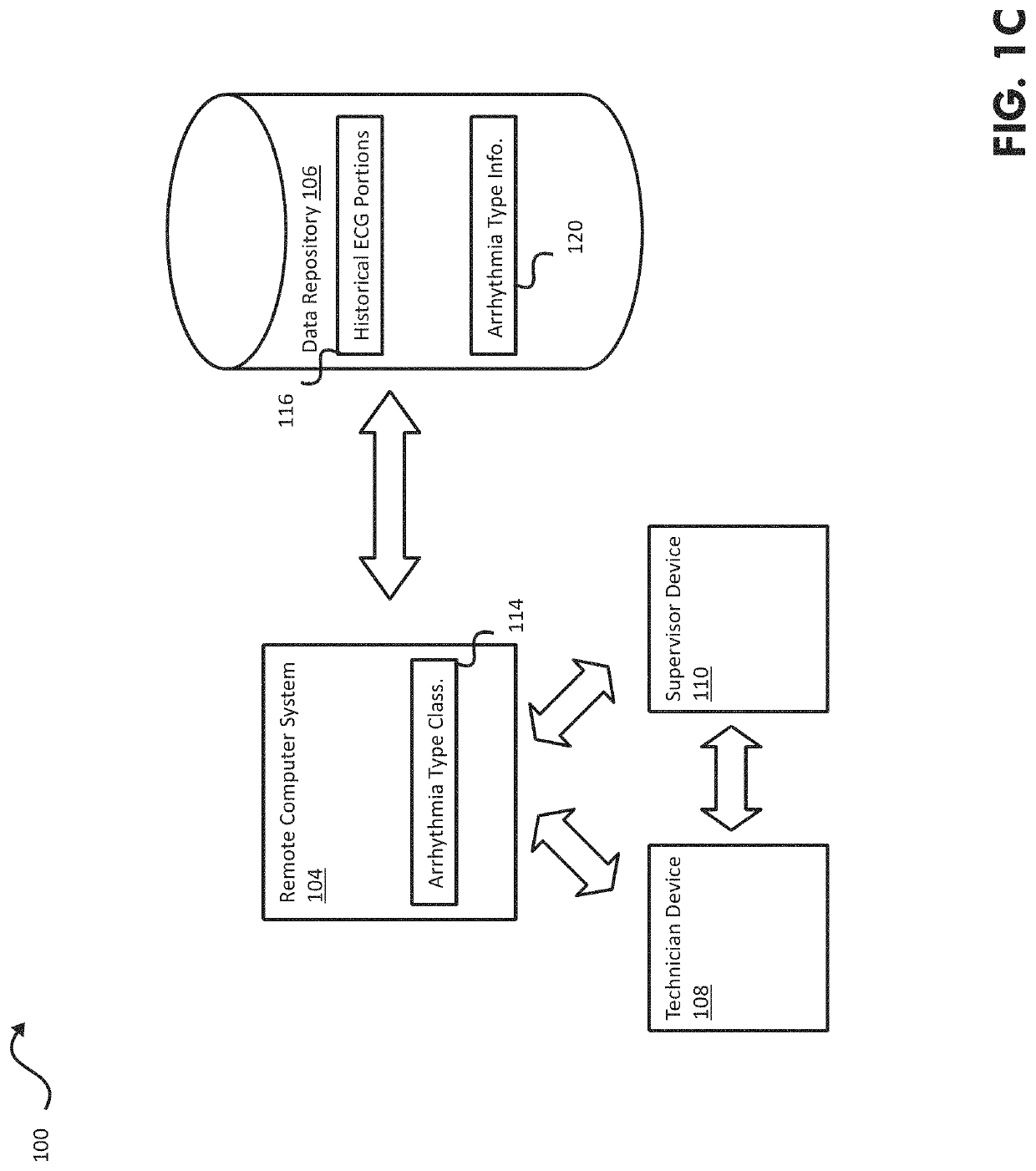
Systems, Devices, and Methods for Cardiac Diagnosis and/or Monitoring
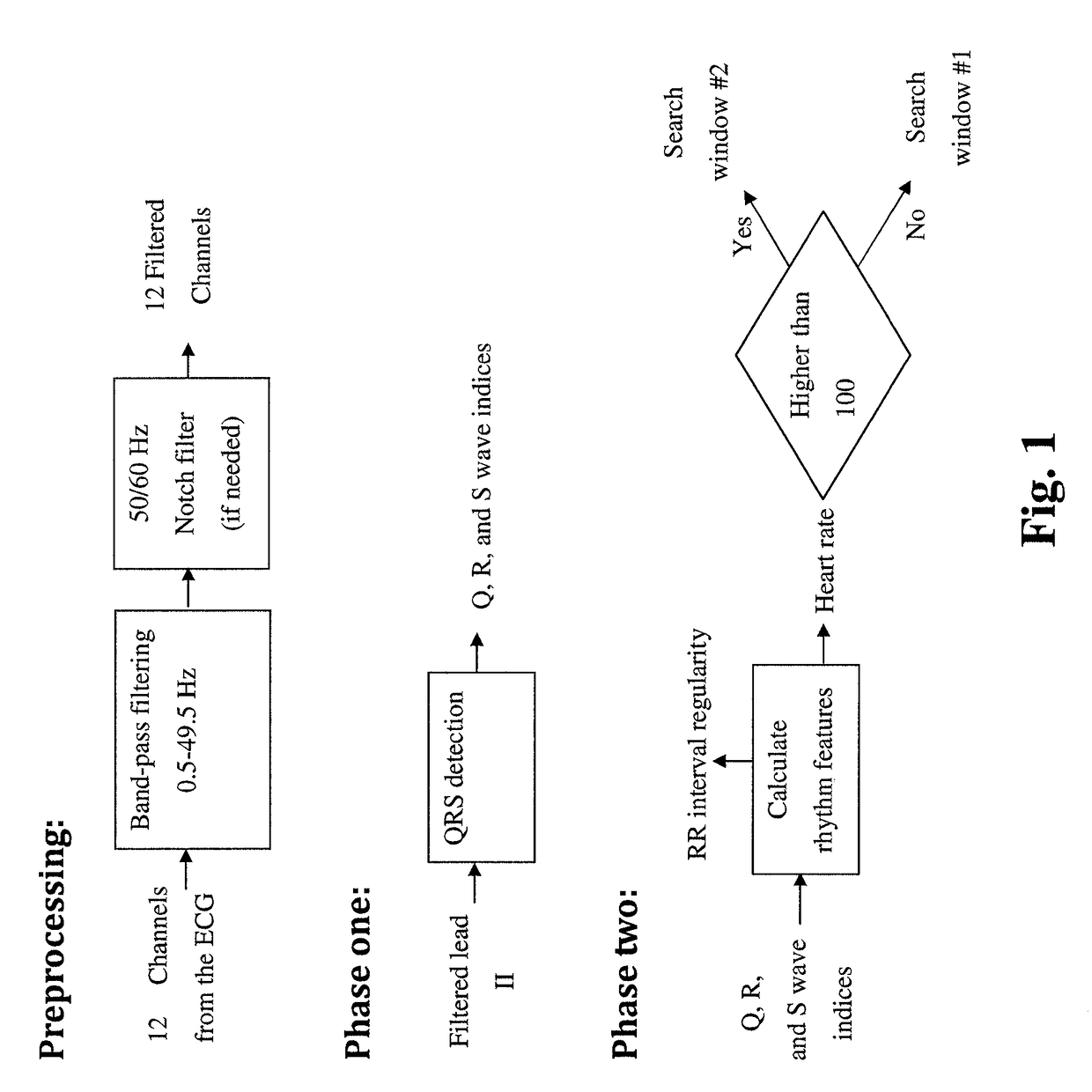
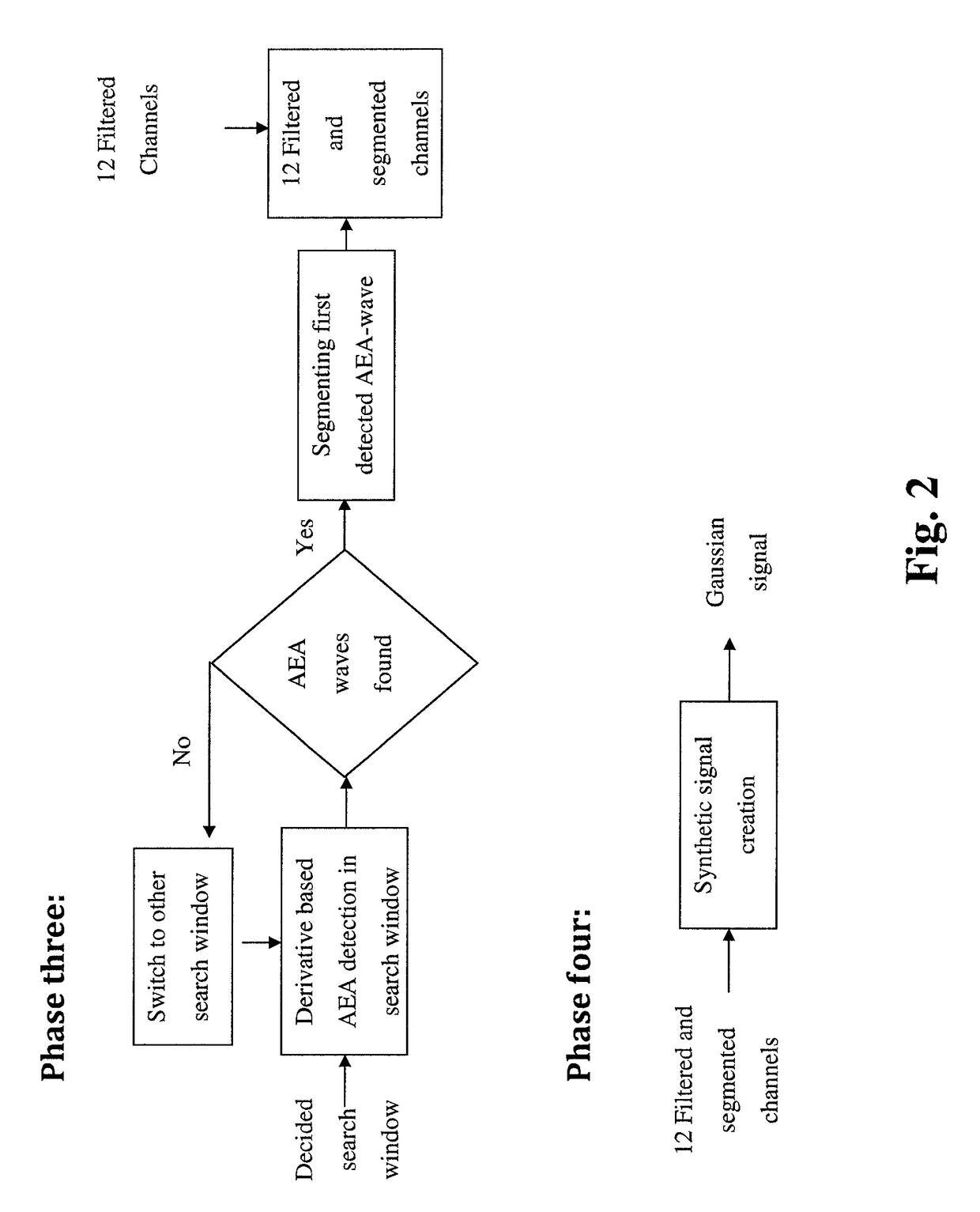
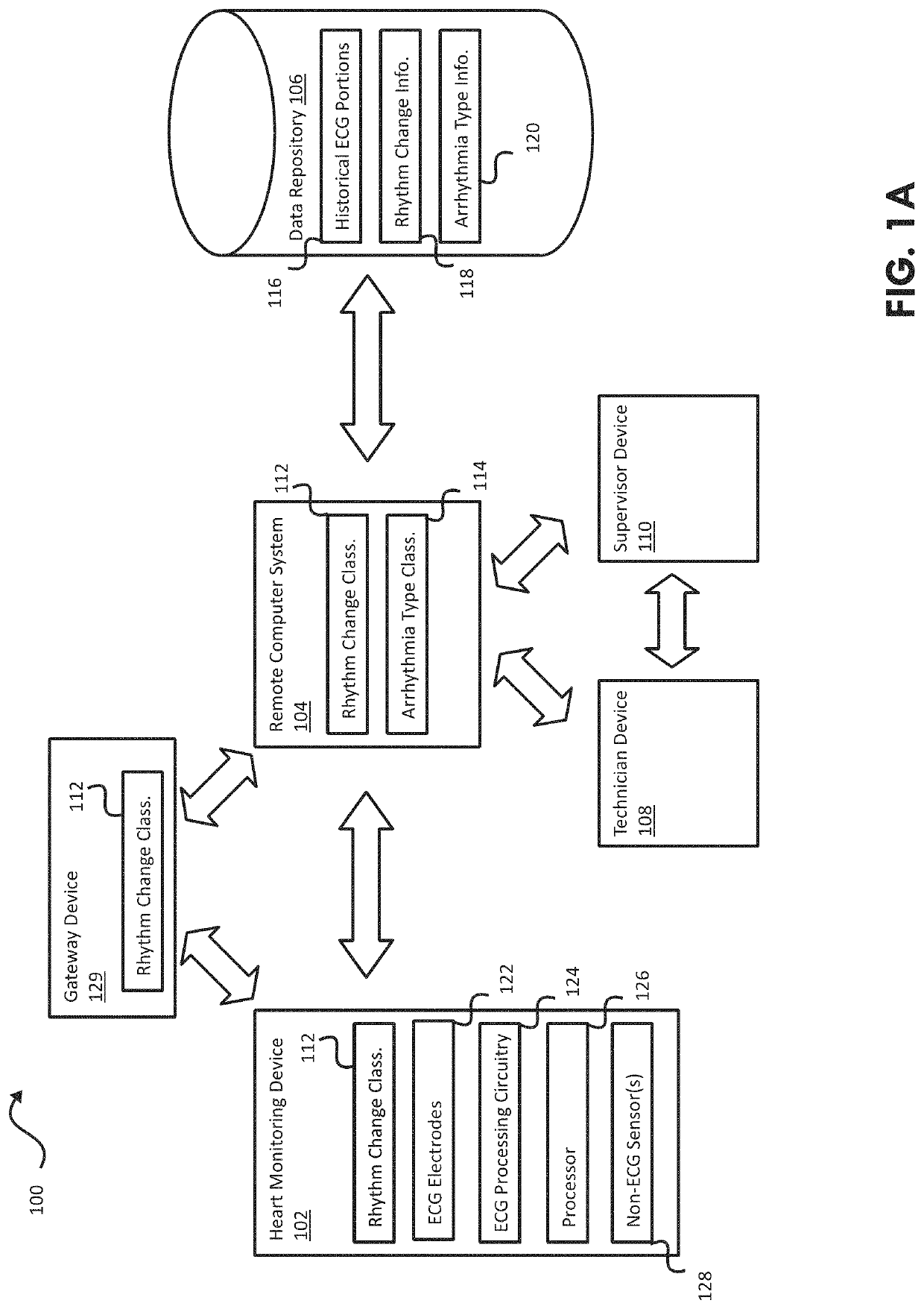
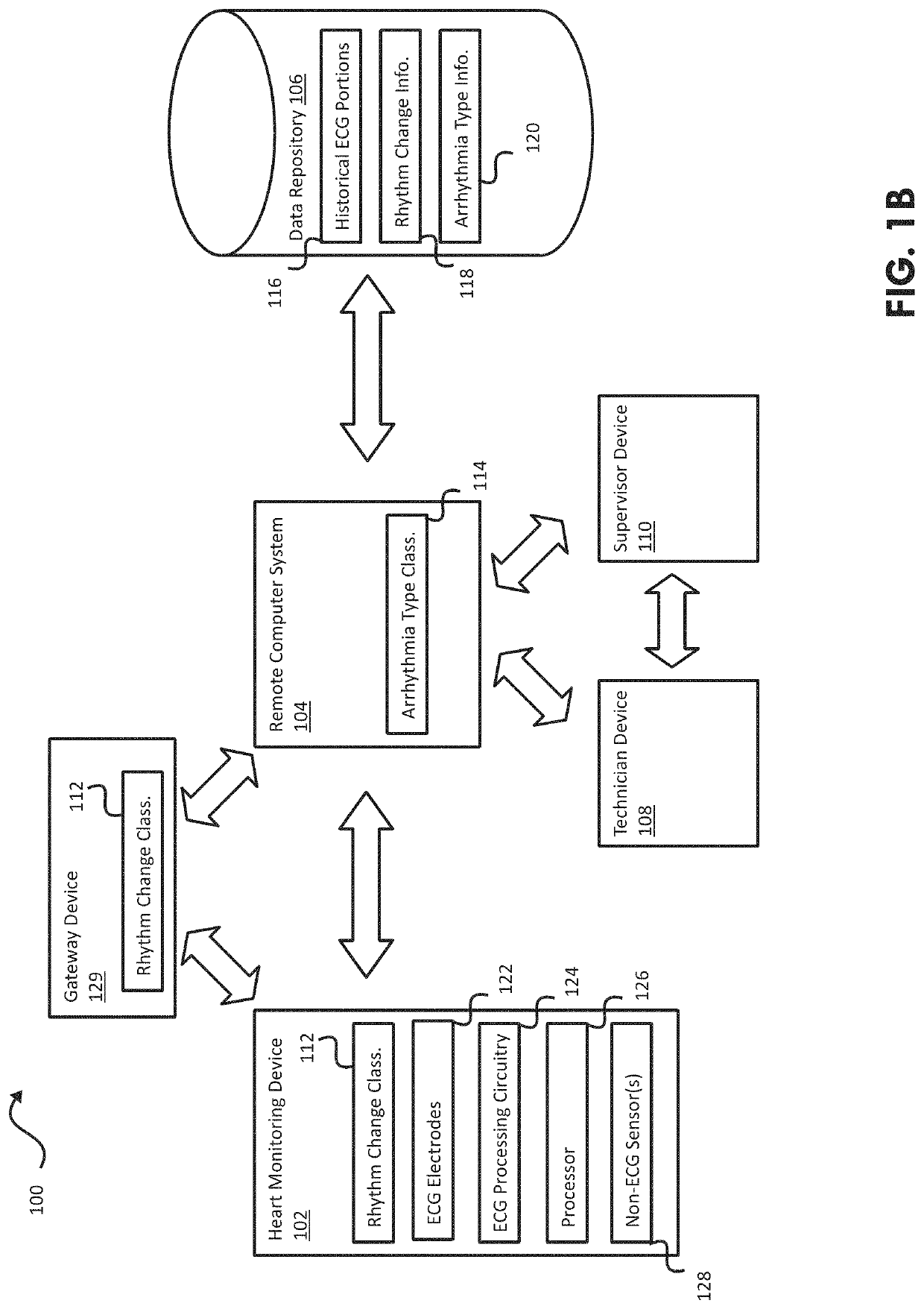
Some embodiments of the current disclosure are directed toward cardiac diagnosis and / or arrhythmia monitoring, and more particularly, systems, devices and methods for arrhythmia monitoring with a trained classifier including at least one neural network. In some embodiments, an external heart monitoring device may include a plurality ECG electrodes to sense surface ECG activity, ECG processing circuitry to process the surface ECG activity to provide at least one ECG signal, a non-transitory computer-readable medium comprising a rhythm change classifier comprising at least one neural network, and at least one processor to receive the ECG signal(s), detect with the rhythm change classifier time data corresponding to a predetermined rhythm change in the ECG signal(s), determine based on the detected time data at least one ECG signal portion corresponding to the predetermined rhythm change, and transmit the at least one determined ECG signal portion to a remote computer system.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL ISRAEL LTD
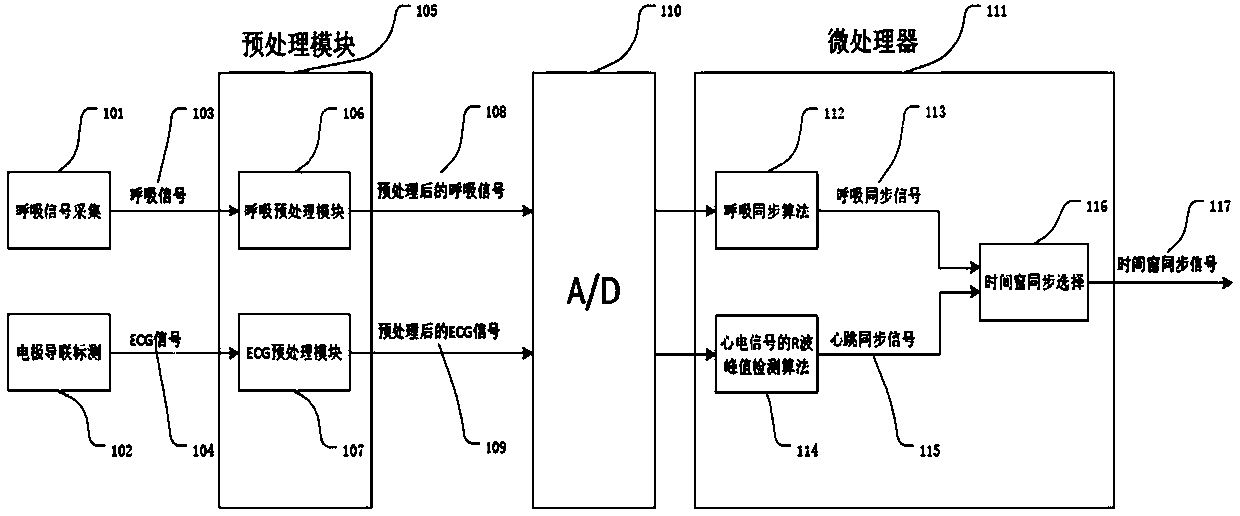
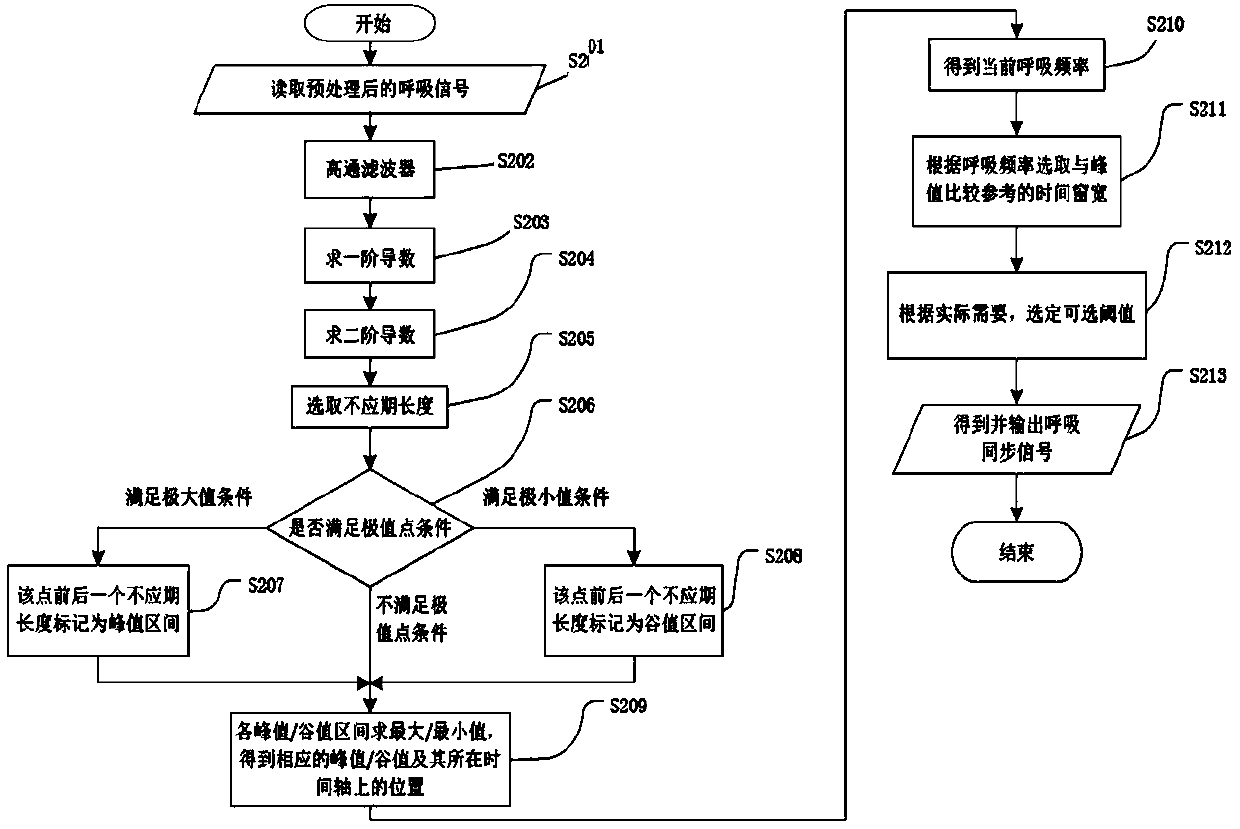
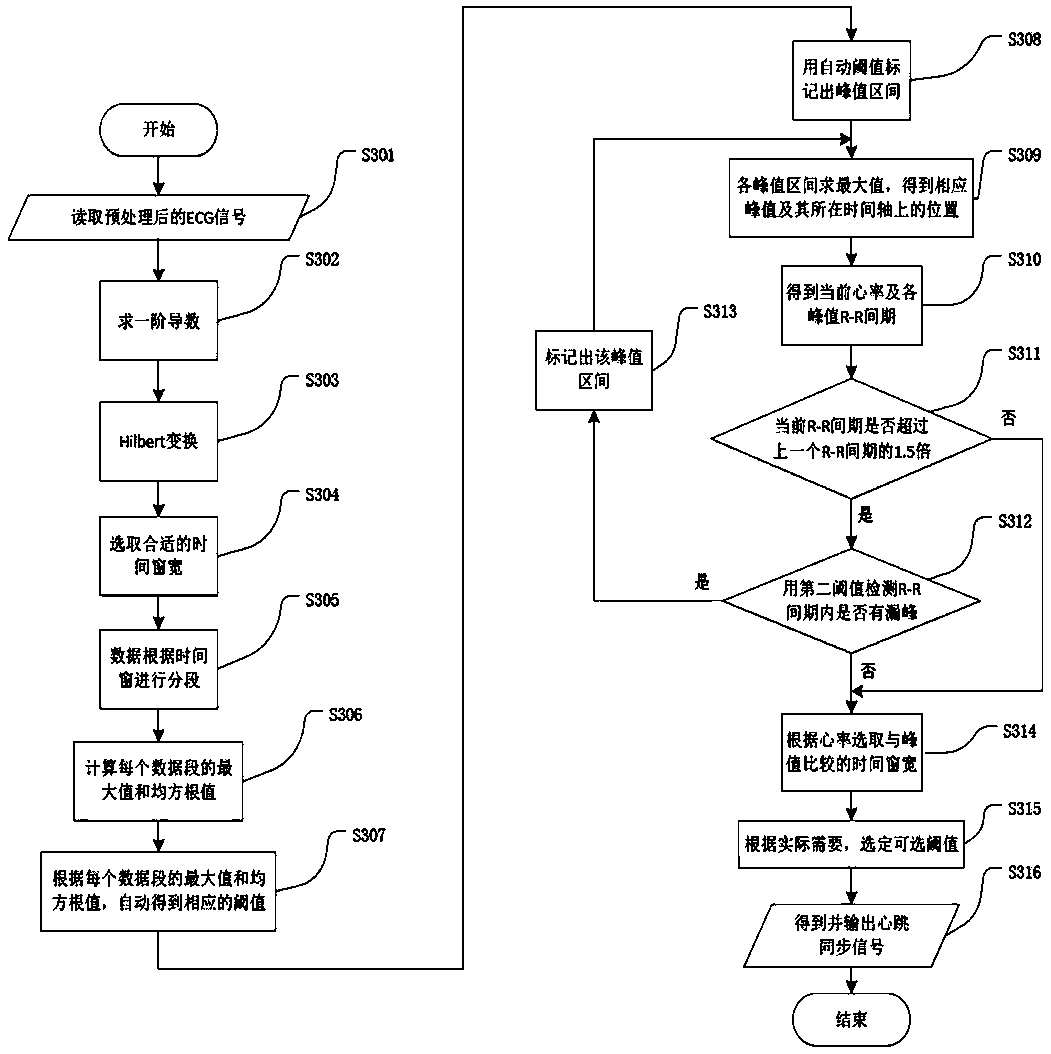
Synchronous breath and heartbeat signal extraction method and synchronous breath and heartbeat signal extraction device for collecting multiple medical signals
InactiveCN105326477APrevent false peak interferenceHigh accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVIT signalsEcg signal
The invention belongs to the field of medical signal collection, and specifically relates to a method and a device for extracting a synchronous breath and heartbeat signals. The device consists of a signal collection module, a signal pre-processing module and a synchronous signal extraction module, wherein the signal collection module is used for completing the collection of a breath signal and a body surface ECG(Electrocardiogram) signal; the signal pre-processing module is used for carrying out amplifying-filtering pre-processing on the breath signal and the ECG signal; the synchronous signal extraction module is used for extracting a synchronous signal according to requirements through recognizing characteristic points of the breath signal and the ECG signal, i.e., providing a time window for collecting other medical signals. According to the method and the device for extracting the synchronous breath and heartbeat signals, disclosed by the invention, a suitable time window can be set for collecting the other medical signals through the synchronous breath and heartbeat signals, the interference, which is caused by breath and heartbeats, on the other medical signals can be effectively restrained, and the method is simple and effective.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram
The reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram based upon an endocardial electrogram. This method includes: (a) acquisition (10) of a plurality of endocardial electrogram signals (EGM) through a plurality of endocardial leads defined based upon endocardial electrodes; (b) calculation (12), by combining the endocardial electrogram (EGM) signals acquired at step (a), of the corresponding endocardial vectogram (VGM); (c) angular resealing (14) of the orthonormalized mark of the endocardial vectogram (VGM) with that of the surface vectocardiogram (VCG); (d) estimation (16), based upon the endocardial vectogram (VGM) calculated at step (b), of a reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed), and (e) calculation (18) of the surface electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to said reconstructed surface vectocardiogram (VCGreconstructed).
Owner:SORIN CRM
System and method of using regression models to estimate vulnerable periods for heart stimulation parameters
InactiveUS7603172B2Terminate stable ventricular tachycardiaRisk minimizationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsSustained ventricular tachycardiaT wave
Heart stimulator that provides for timing a premature stimulation pulse for anti-tachycardia pacing outside the vulnerable phase of a ventricle, to terminate stable ventricular tachycardia while minimizing the risk of accelerating stable ventricular tachycardia into unstable ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. RT interval is determined instead of QT interval. Conventional QT interval is defined to end at T wave offset, which is difficult to measure because inherent imprecision in identifying the end of T wave from surface ECG. For safe ATP, such problems may be avoided. Because the VP usually refers to the portion of the T wave near the peak and early downslope (FIG. 3), in order to avoid the VP, only need to determine the peak of T wave, then set an blanking window or safety margin (e.g., 20 ms before to 20 ms after the peak of T wave) during which ATP pulses should not be delivered.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
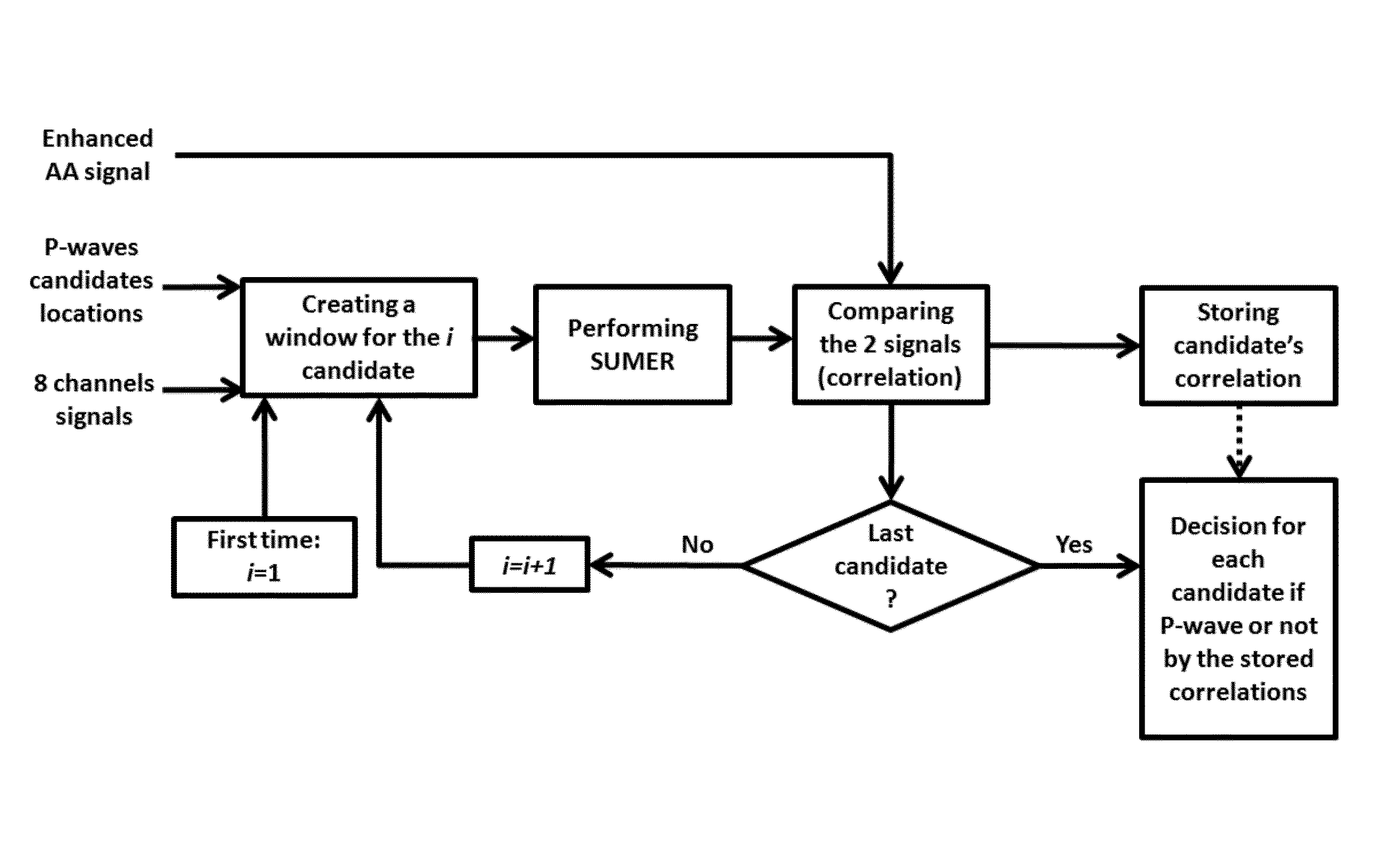
Method and system for detecting P-waves in the surface ECG signal
InactiveUS8750973B2Reduce noiseMaximizing energy ratioElectrocardiographySensorsSurface ecgCardiac arrhythmia
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
System for Heart Performance Characterization and Abnormality Detection
A system improves analysis, diagnosis and characterization of cardiac function signals (including surface ECG signals and intra-cardiac electrograms) based on cardiac electrophysiological activity momentum computation, characterization and mapping. The system calculates an electrophysiological signal momentum of different portions of cardiac signals including a timing, location and severity of cardiac pathology and improves reliability of diagnosis, detection, mapping to an identified medical condition, and characterization. The system improves identification of cardiac disorders, differentiation of cardiac arrhythmias, characterization of pathological severity, prediction of life-threatening events and supports evaluation of drug administration effects.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods and systems for the delivery of accurate and precise measurements from the body-surface electrocardiogram
ActiveUS10610115B1Facilitate efficient reviewImprove the level ofElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalSurface ecg
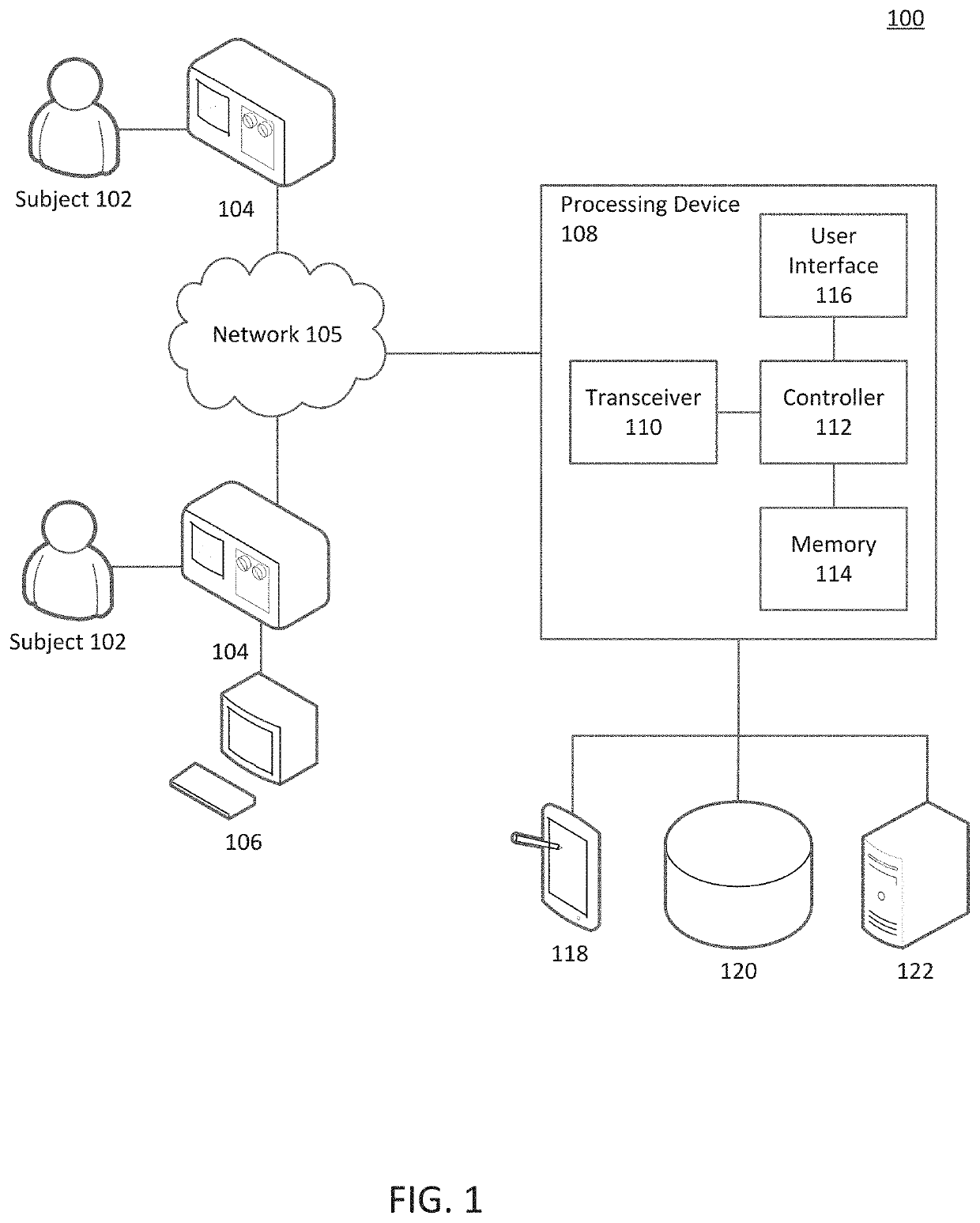
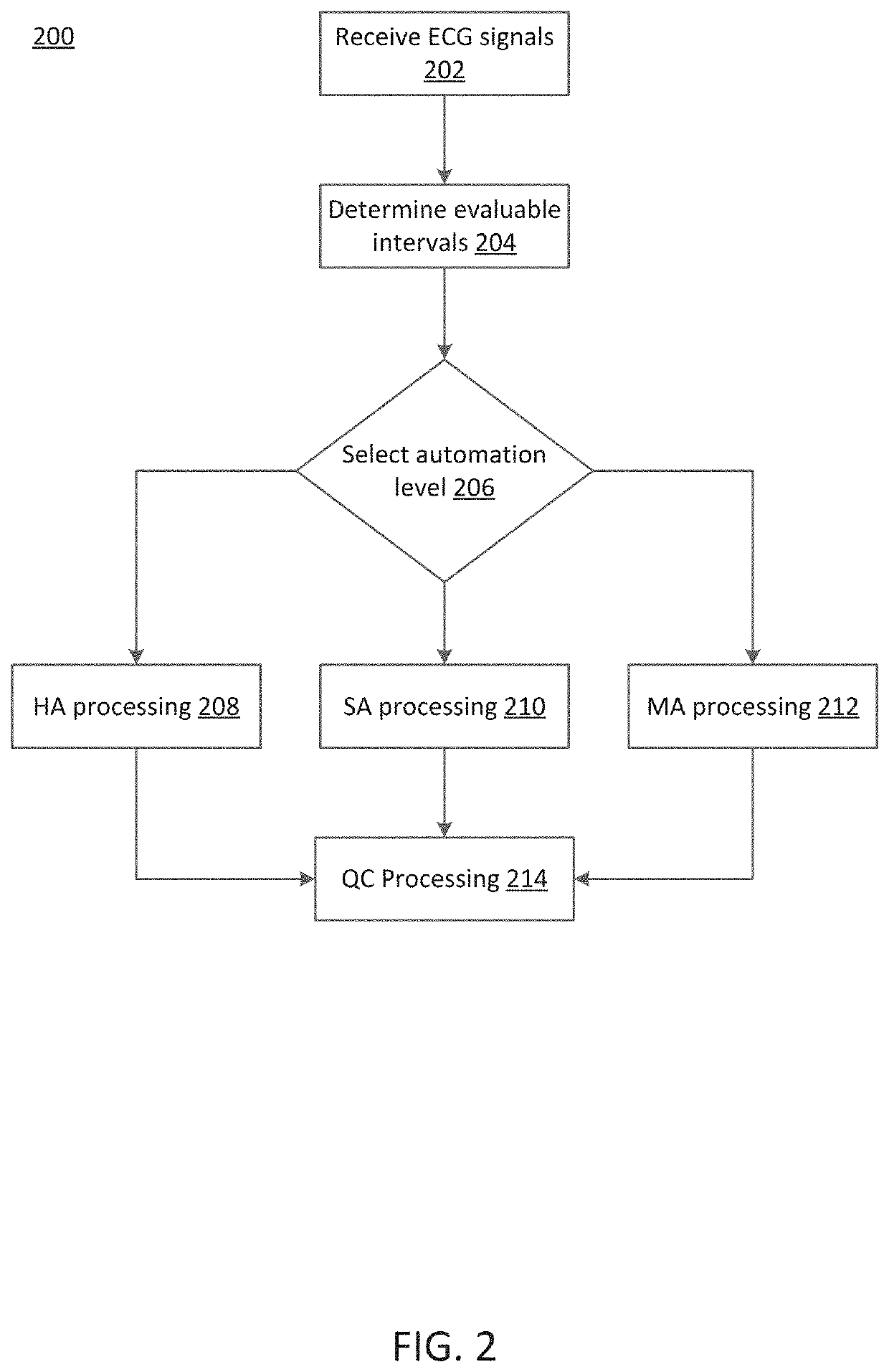
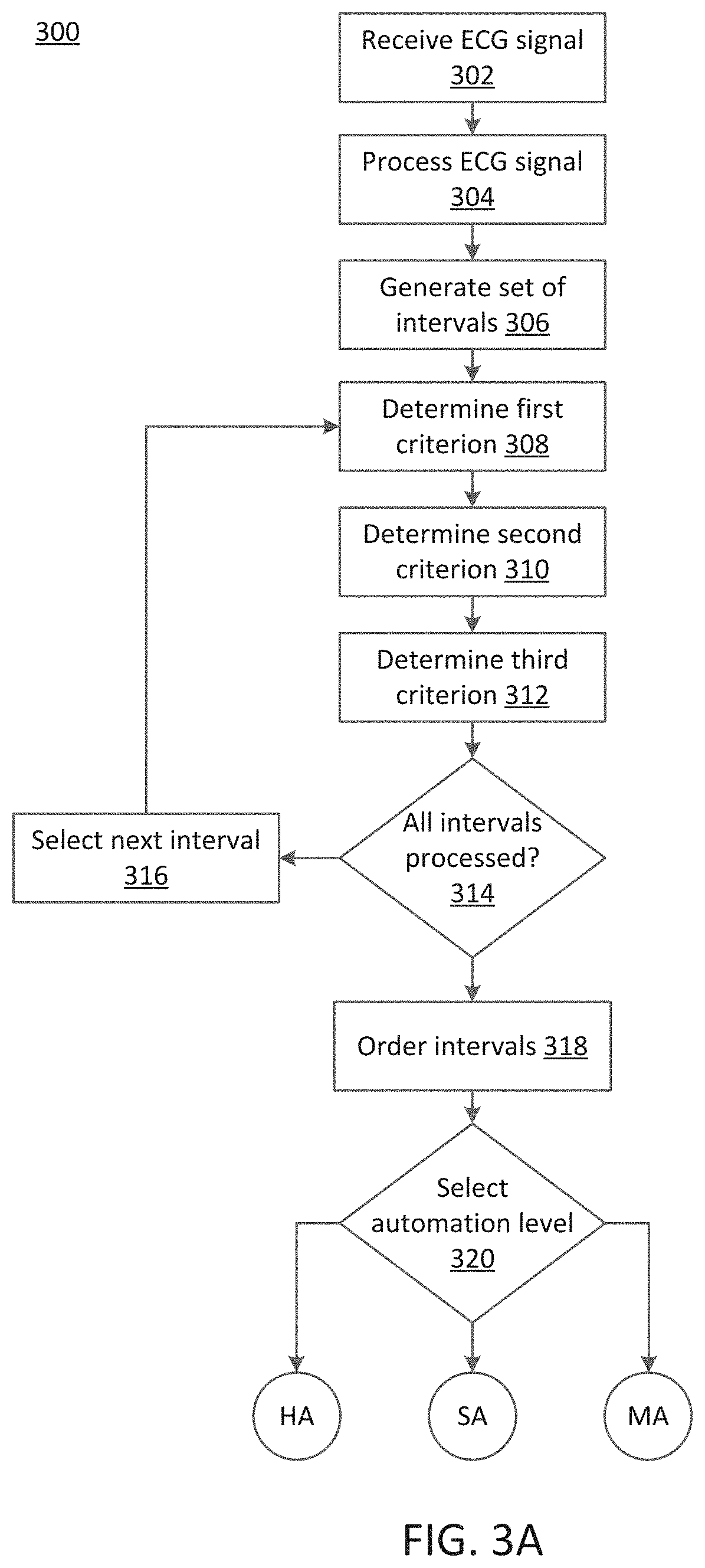
Described here are methods, devices, and systems for characterizing a physiological signal, and more specifically an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. Generally, the method includes receiving an ECG signal generated by an ECG device coupled to a patient. The ECG signal may comprise a plurality of cardiac beat intervals. A set of evaluable replicates may be identified using a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for each cardiac beat, a repolarization signal, and an isoelectric line. Interval measurements may be determined from the set of evaluable multi-beat sequences. An ECG signal characteristic may be determined from the interval measurements.
Owner:ERESTECH
Reducing noise of intracardiac electrocardiograms using an autoencoder and utilizing and refining intracardiac and body surface electrocardiograms using deep learning training loss functions
PendingCN113749664AMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringSurface ecgComputer vision
The invention discloses a system and a method. The system includes a memory storing processor executable code for a denoised autoencoder, and one or more processors coupled to the memory to execute the processor executable code to receive raw signal data comprising signal noise, encode, by the denoised autoencoder, the raw signal data by performing a denoising autoencoder operation to produce a latent representation, and decode, by the denoised autoencoder, the latent representation to produce clean signal data reconstructed without the signal noise. A first filter is applied to a signal to emphasize activity within the signal and to produce a first modified signal, a rectifier and a second filter are applied to the first modified signal to smooth areas of the first modified signal with clinical importance and to produce a second modified signal, and high frequency energy zones of the second modified signal are automatically detected using an energy threshold to produce a weights vector.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBTER (ISRAEL) LTD
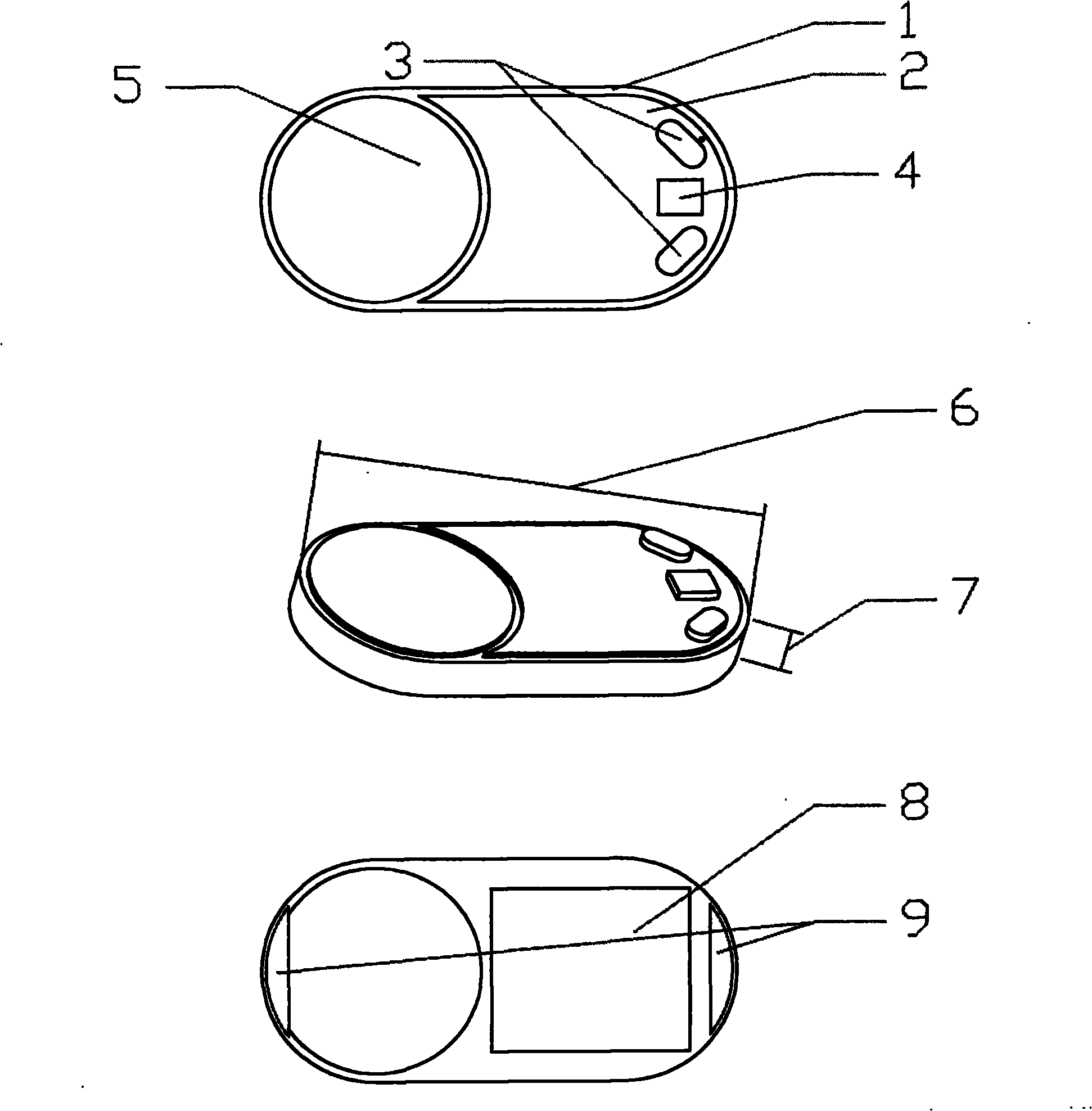
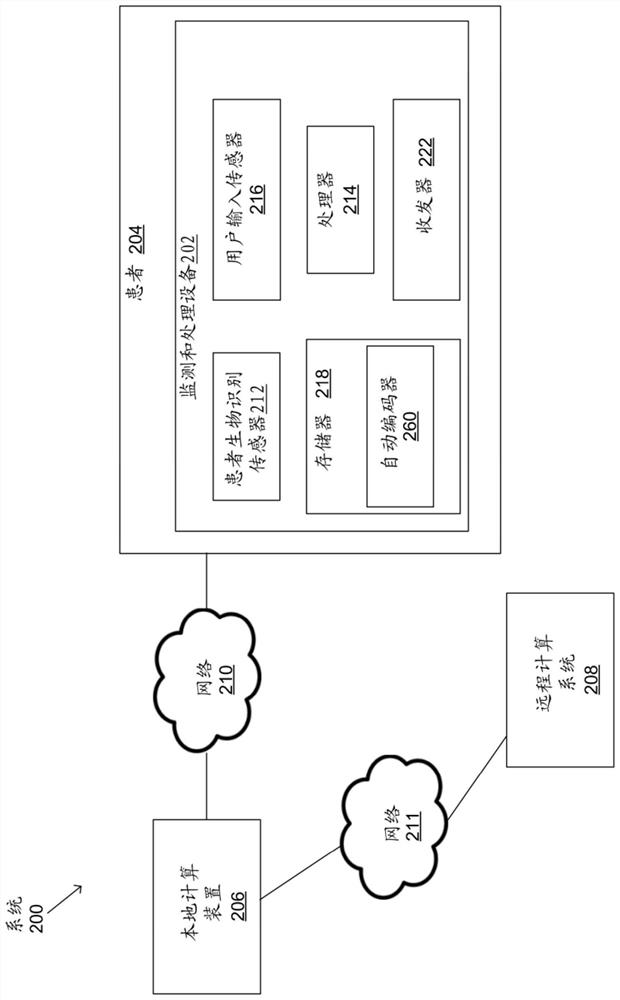
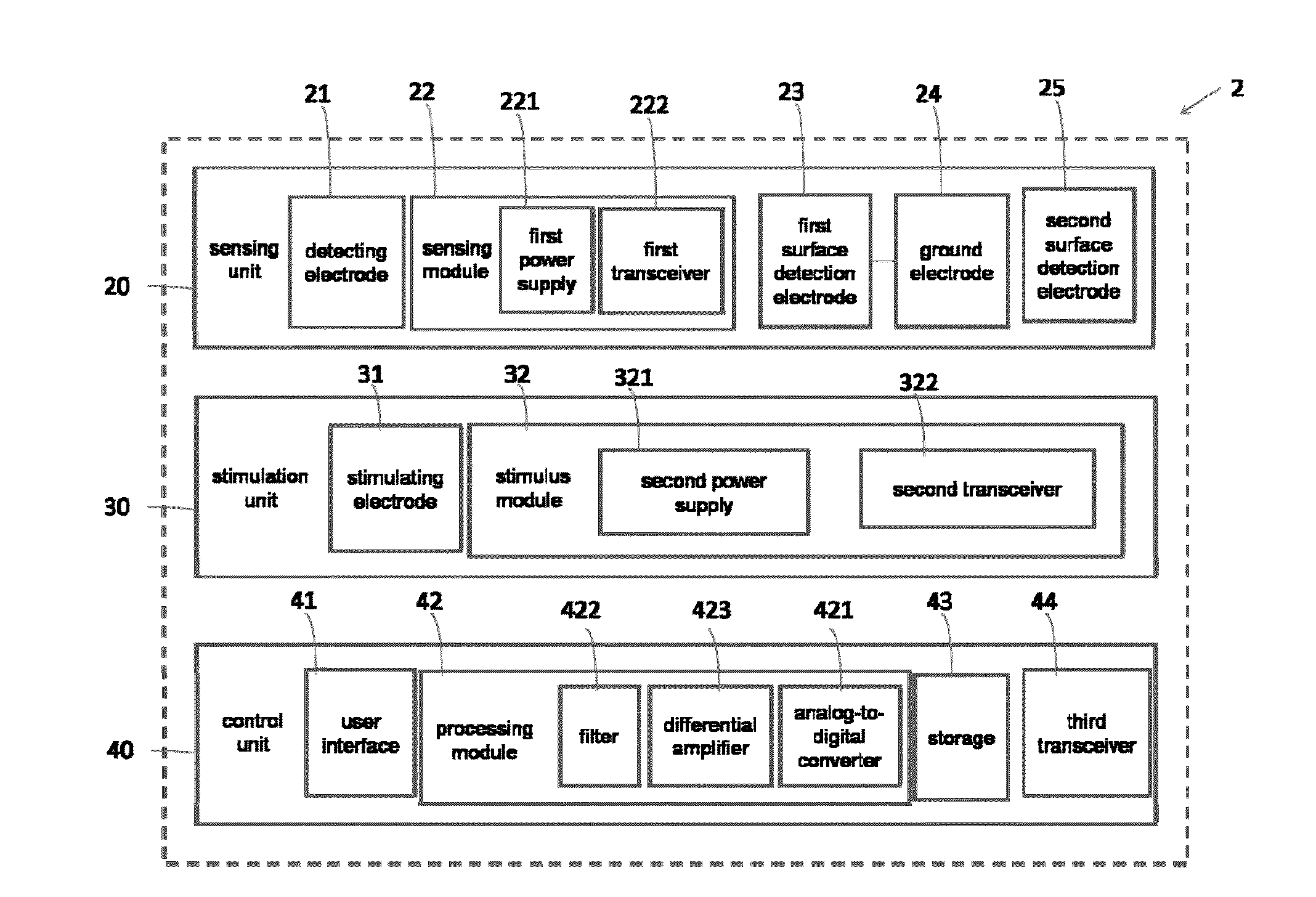
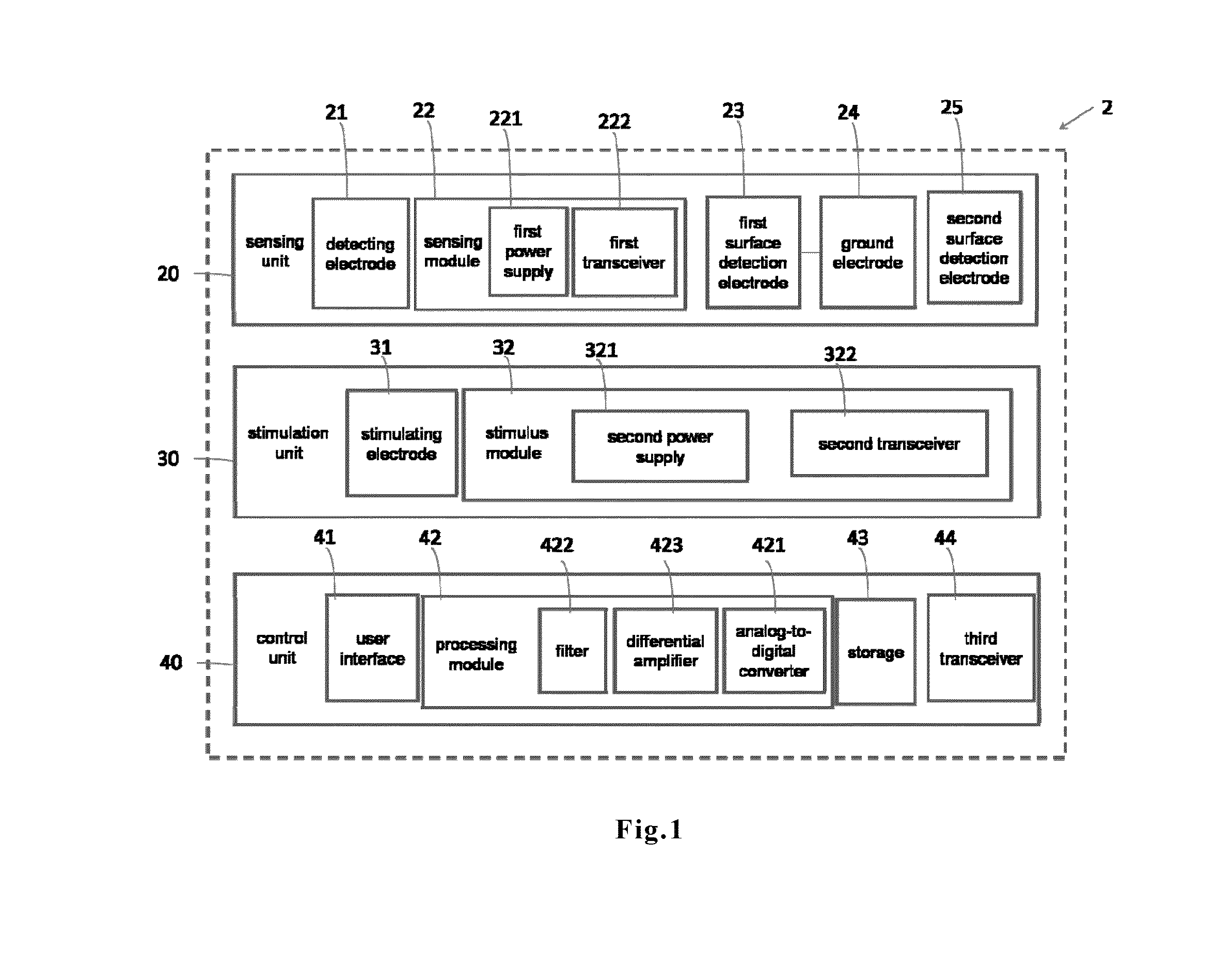
Physiological signal detection system
InactiveUS20140221804A1Increase heightSimple technologyElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalRemote system
The present invention provides a handy remote physiological signal detection system, comprising a sensing unit, a stimulation unit and a control unit. The sensing unit includes a detecting electrode, a first surface detection electrode, a second surface detection electrode and a sensing module. The sensing modules is used to detect the signals between the detection electrode and the first surface detection electrode to get an epicardial detection signal, and is also used to detect the signals between the second surface detection electrode and the first detection electrode to get a surface-ECG signal. The stimulus unit includes a stimulating electrode and a stimulus module used to provide a stimulus signal to the stimulating electrode. The control unit includes a user interface and a processing module used to convert the epicardial detection signal and the surface-ECG signal to digital signals and display the digital signals in the user interface. All systems were controlled through the remote system and are small and handy.
Owner:HU YU FENG
Medical apparatus for the introduction of catheters into the human body
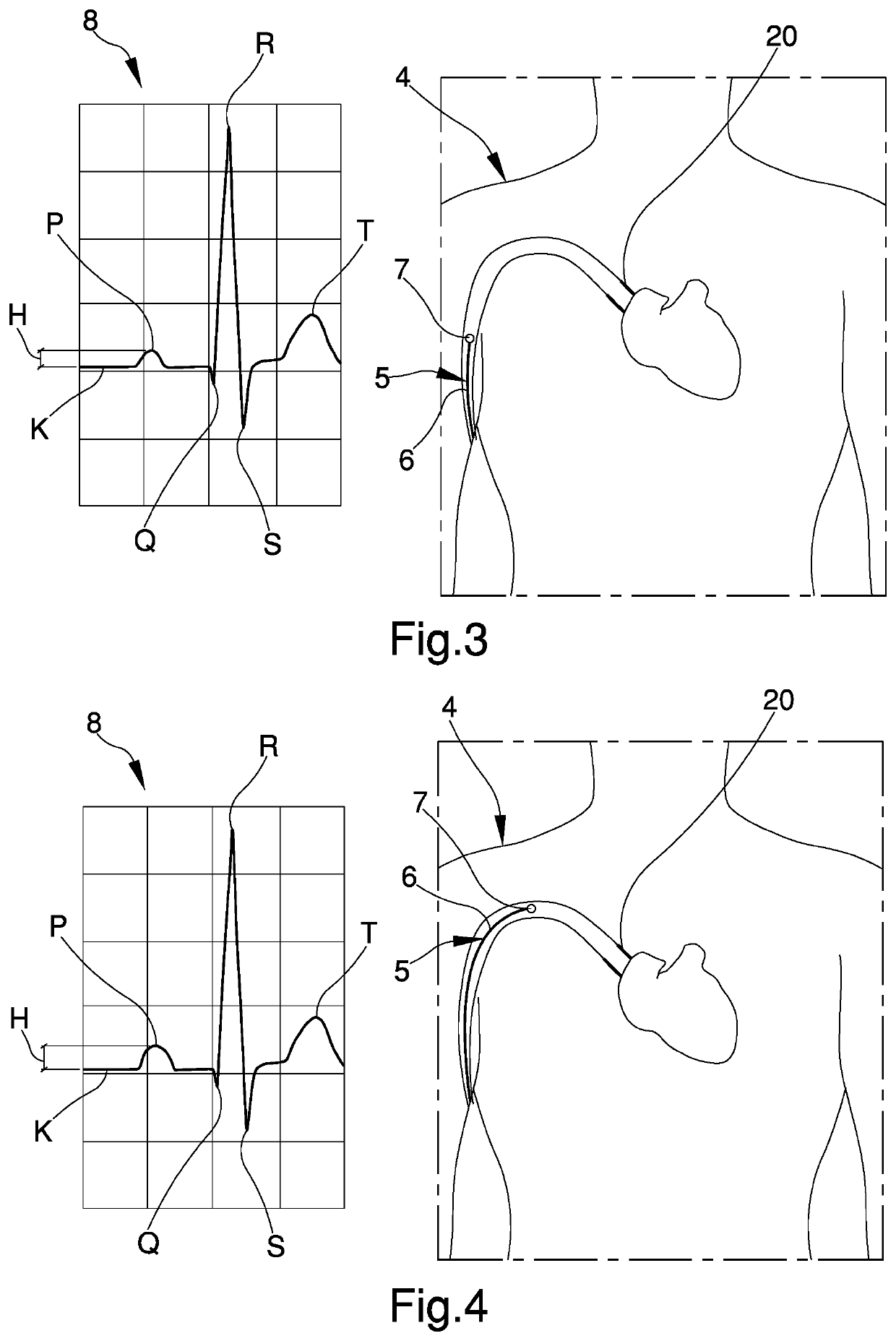
ActiveUS10722142B2Easy to optimizeImproving catheter implantsElectrocardiographySurgeryHuman bodySurface ecg
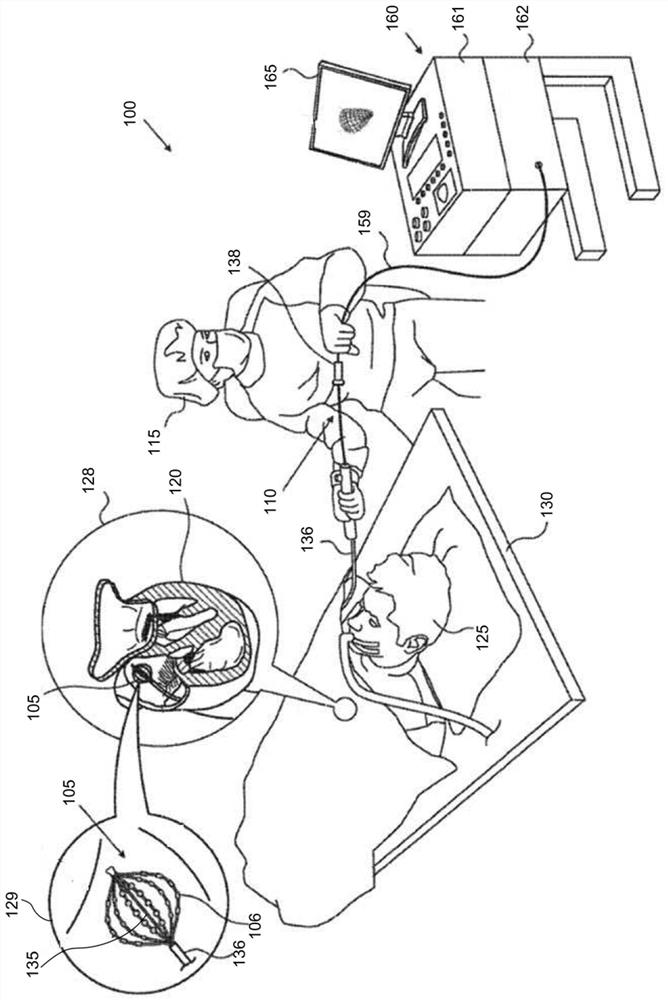
A medical apparatus for the introduction of catheters into the human body including: an ECG device having at least three electrodes, positionable on a human body for the detection of surface electrical potential data and adapted to provide at output at least one surface ECG strip; at least one catheter element having a distal ending part positionable inside the human body and having an auxiliary electrode element for the detection of intracavitary electrical potential data, associated with the ECG device for sending to the latter said intracavitary data, the ECG device being adapted to provide at output at least one intracavitary ECG strip; —an electronic device associated with the ECG device for the receipt of at least said intracavitary ECG strip and comprising a data processing module (10) adapted to process at least the intracavitary ECG strip to obtain usage information adapted at least to provide instructions on the insertion of the catheter element in the human body.
Owner:VYGON ITALIA SRL +1
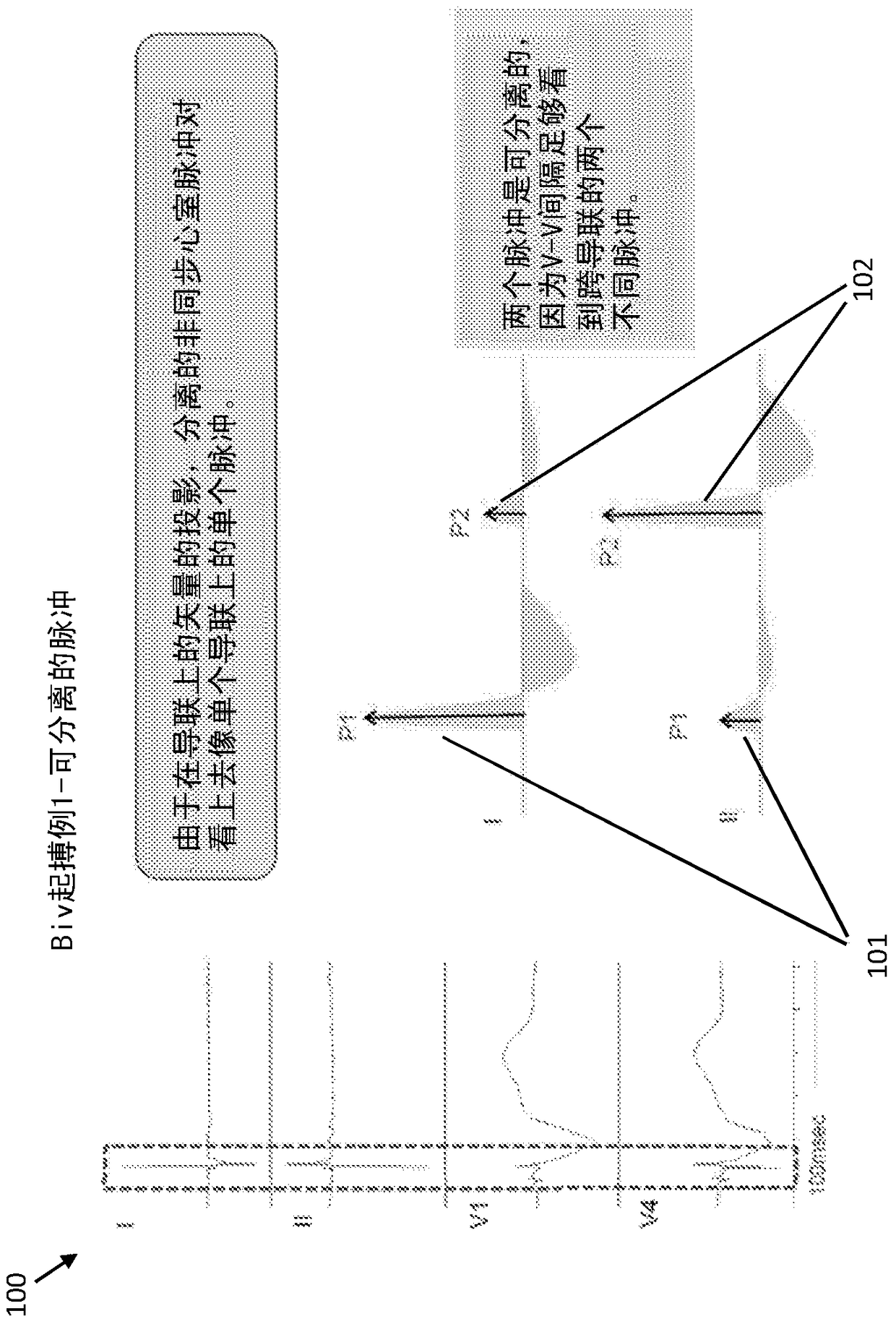
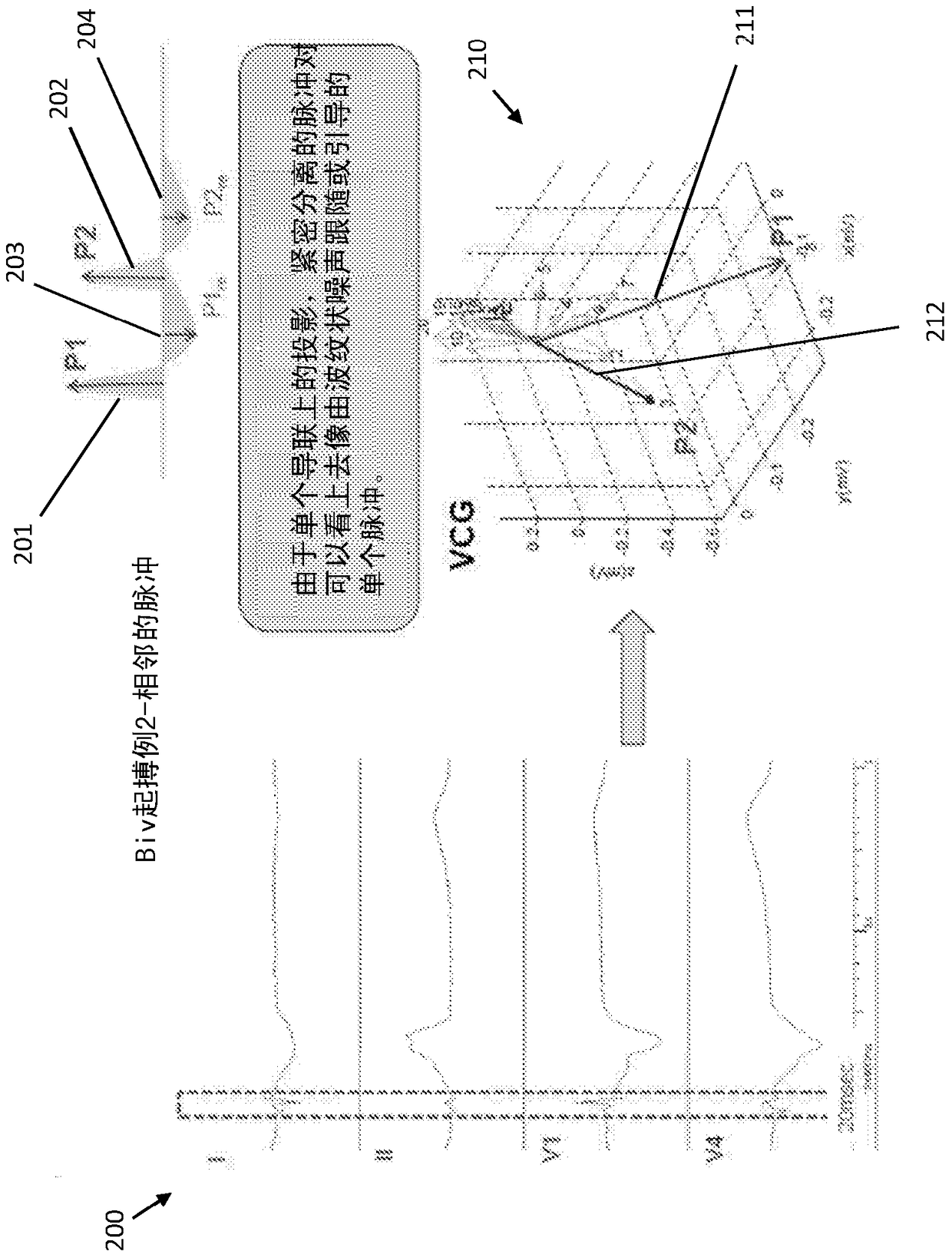
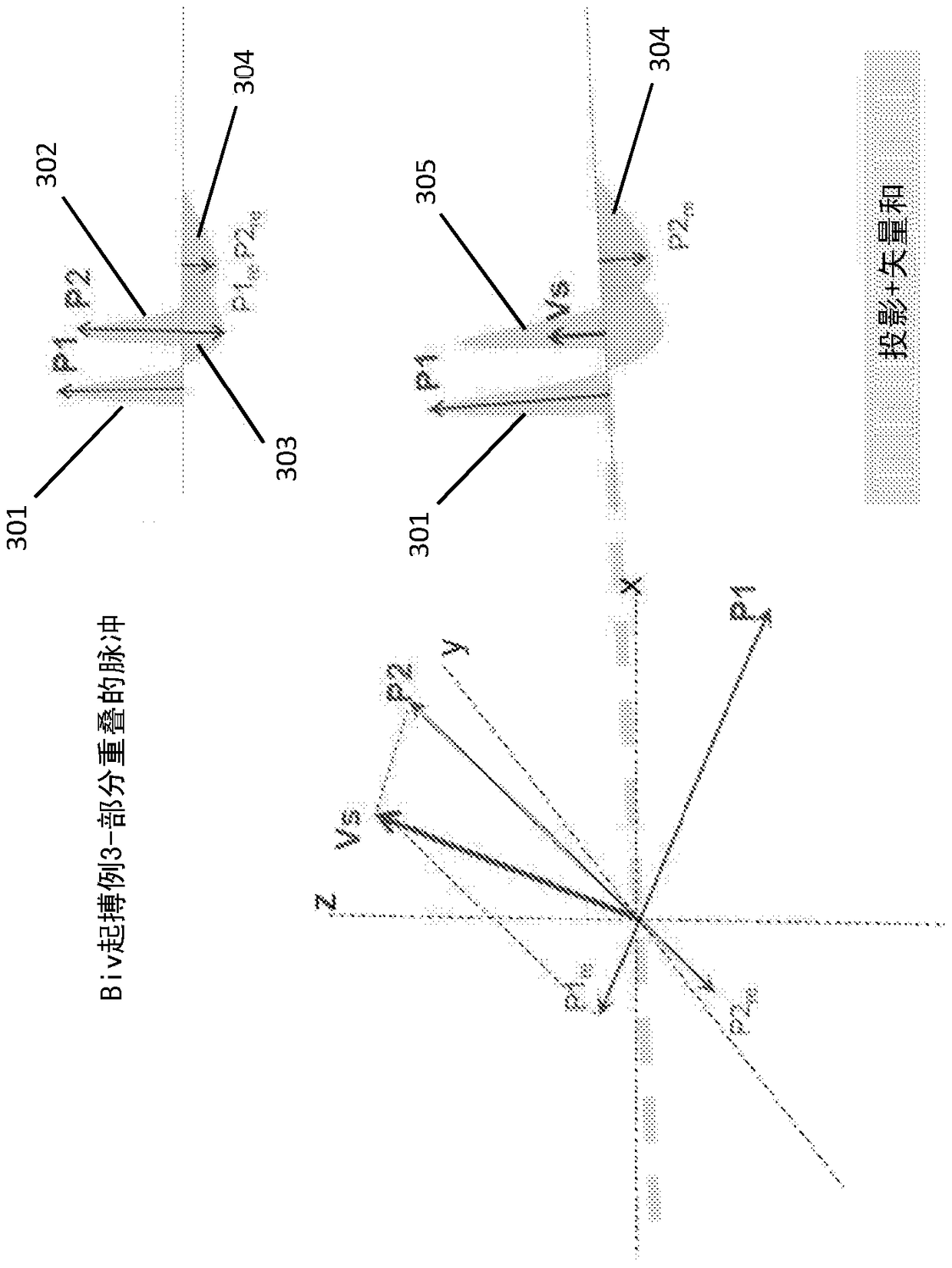
Systems and methods for biventricular pacemaker pulse detection in surface ecg
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
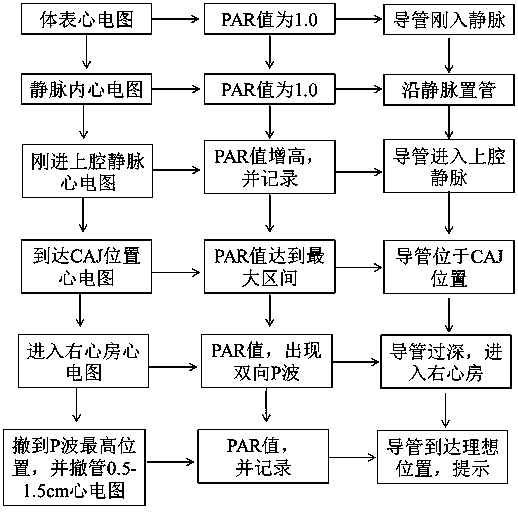
Peripherally inserted central catheter positioning algorithm based on intracardiac electrogram
The invention relates to a peripherally inserted central catheter positioning algorithm based on intracardiac electrogram, and belongs to the field of medical apparatuses. The peripherally inserted central catheter positioning algorithm based on intracardiac electrogram comprises the steps of firstly, performing checking to obtain the electrocardiograph of the head of a peripherally inserted central catheter at different positions, calculating the ratio of P wave amplitude of the electrocardiograph at different positions to P wave amplitude of the surface electrocardiogram to obtain PAR value;and calculating the amplitude ratio of P waves to QRS waves of the electrocardiograph at different positions to obtain PQAP, so as to establish the relationship of the position of the head of the peripherally inserted central catheter to the PAR value or the PQAP value. Through data statistics, a method for expressing the position of the head of the peripherally inserted central catheter with PARvalue or the PQAP value is finally established. In the process of placing the peripherally inserted central catheter, equipment can measure the electrocardiograph, can display the PAR value or the PQAP value and the expectation position of the corresponding peripherally inserted central catheter, can prompt the position of the peripherally inserted central catheter in a real time manner, and canperform voice prompt that the peripherally inserted central catheter achieves the expectation position. The electrocardiograph is directly changed into the PAR value or the PQAP value and the positionof the head of the corresponding peripherally inserted central catheter, medical personnel can directly read the position of the tip of the peripherally inserted central catheter, and positioning ofthe peripherally inserted central catheter can be quickly and conveniently completed.
Owner:SHANDONG BRANDEN MEDICAL DEVICE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com