Patents
Literature
71 results about "QT interval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
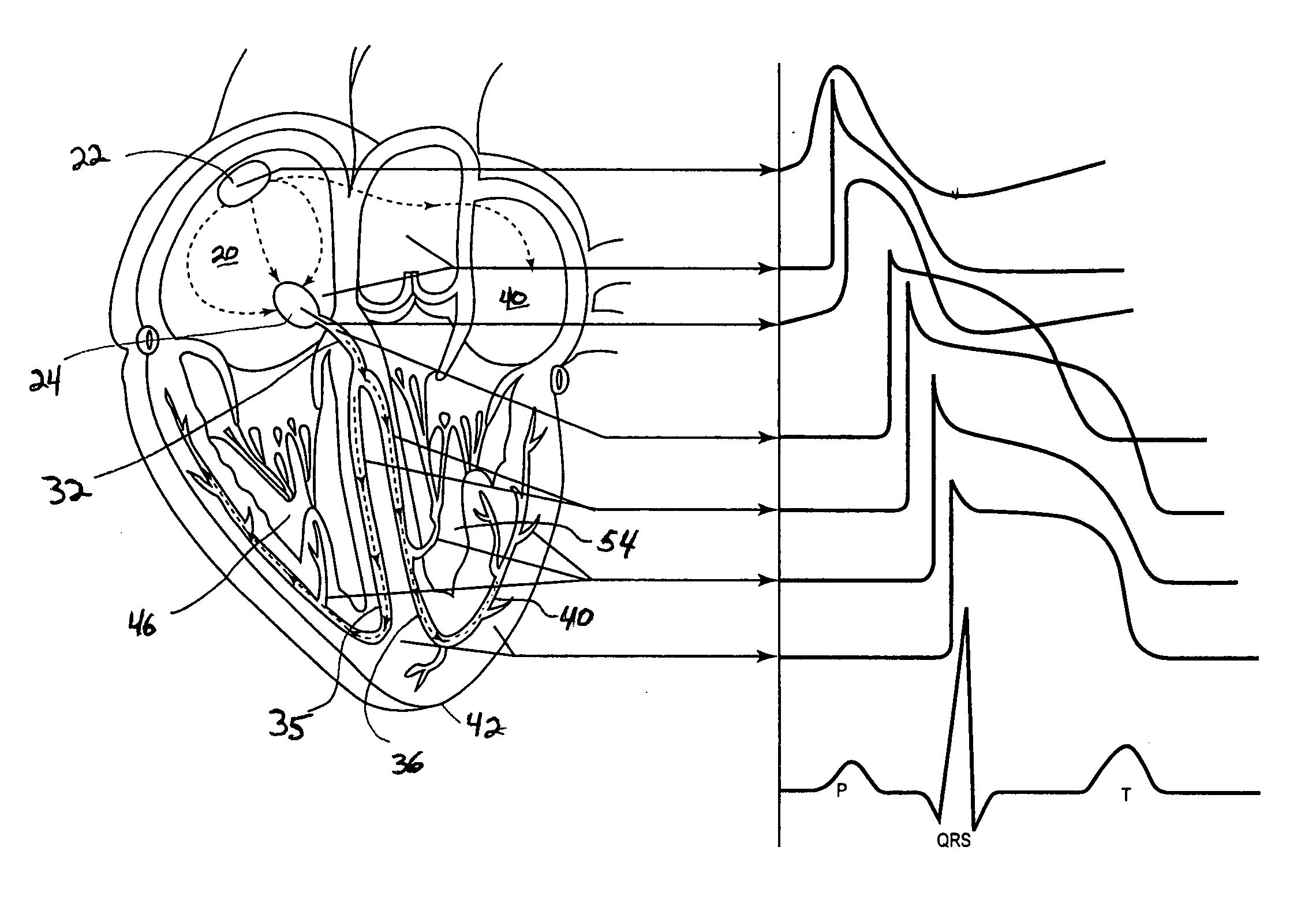
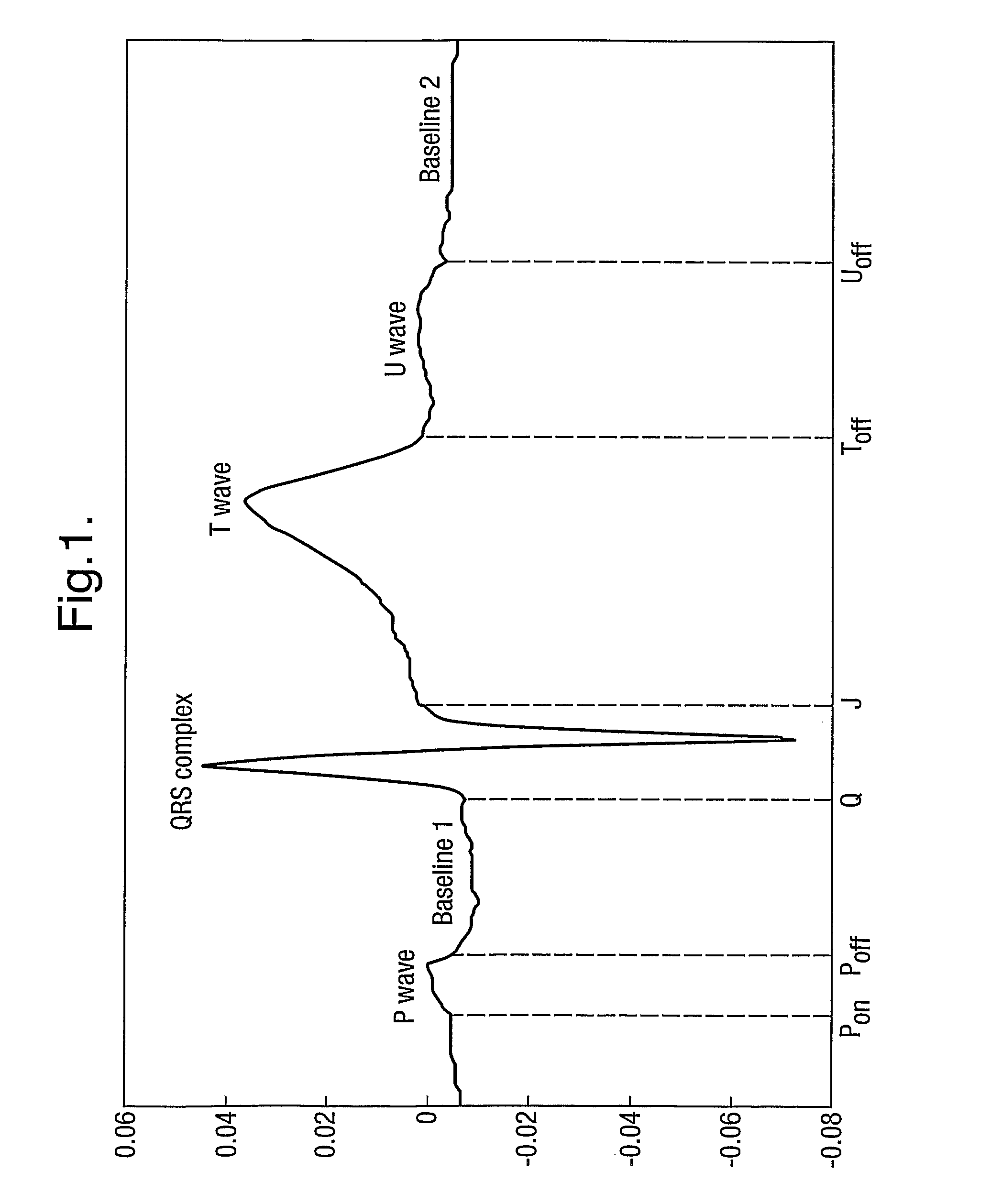
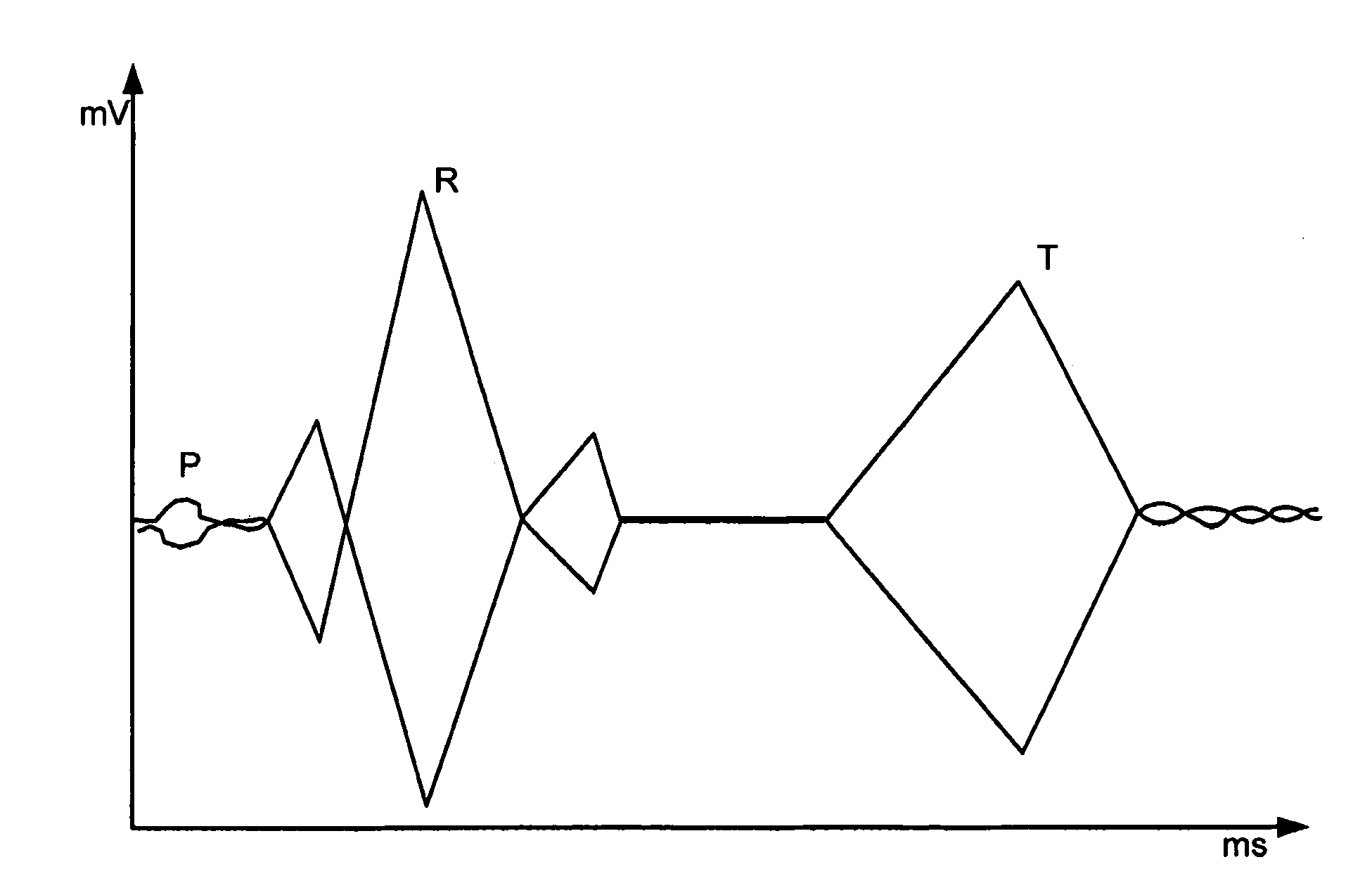
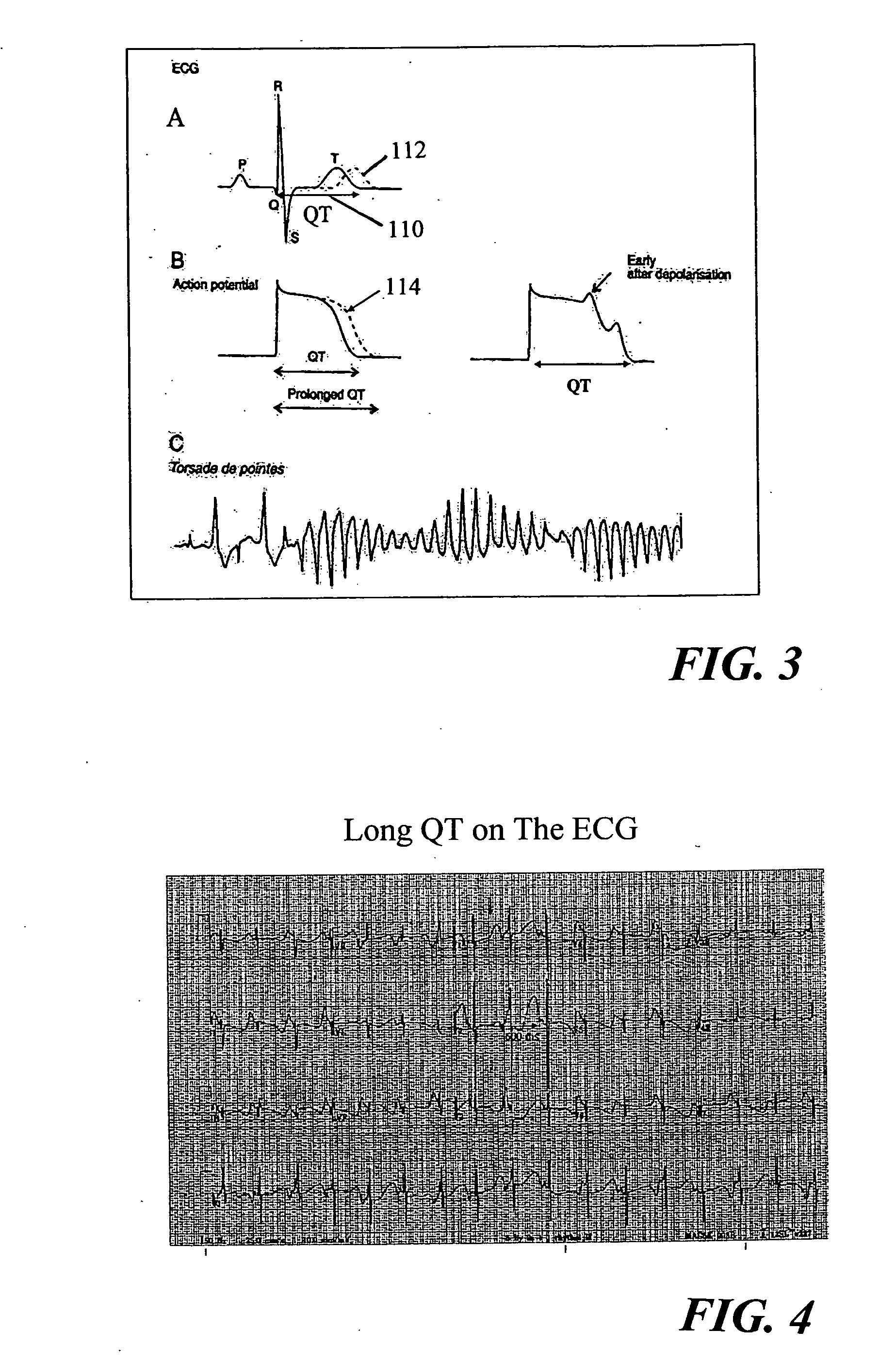
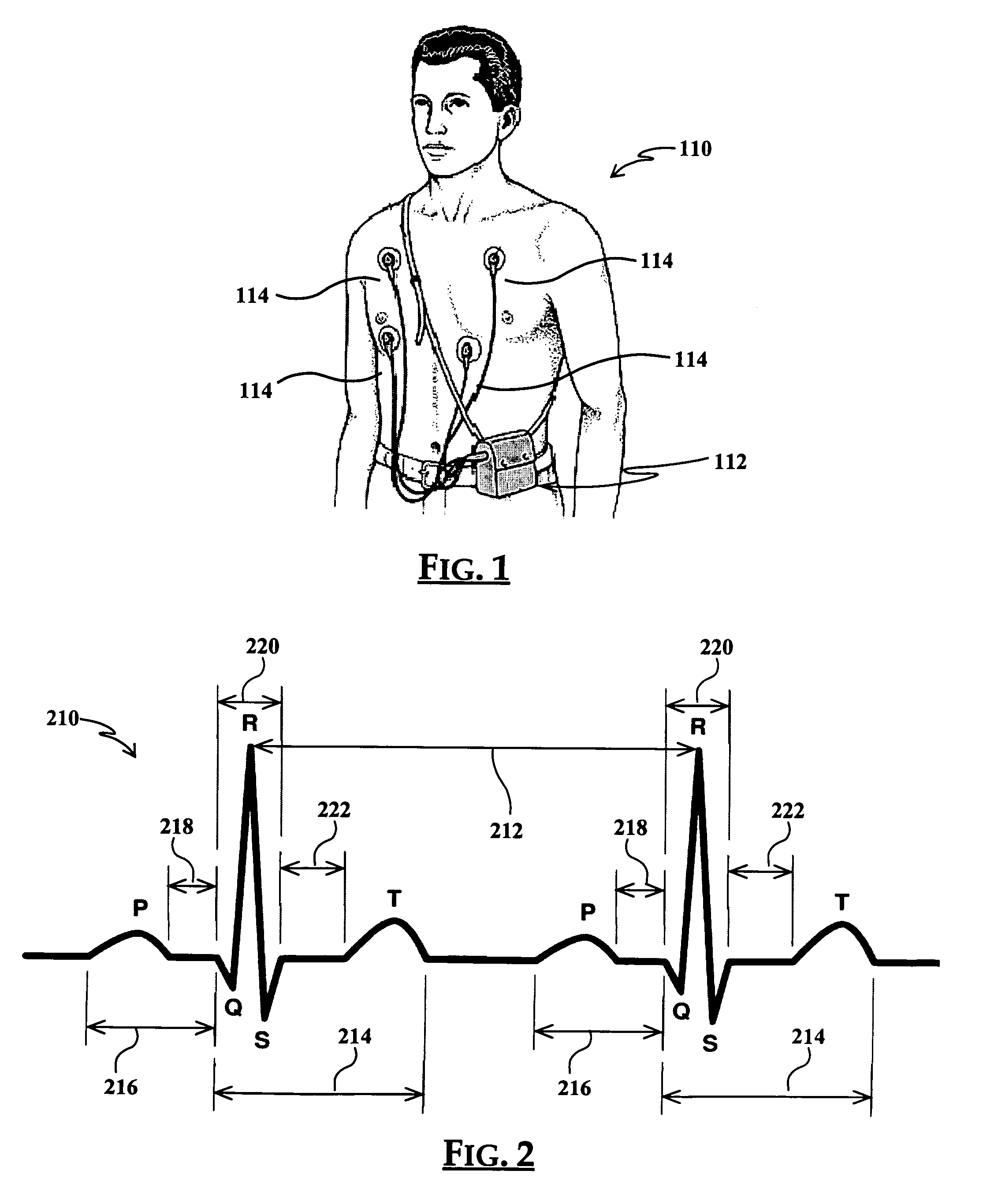
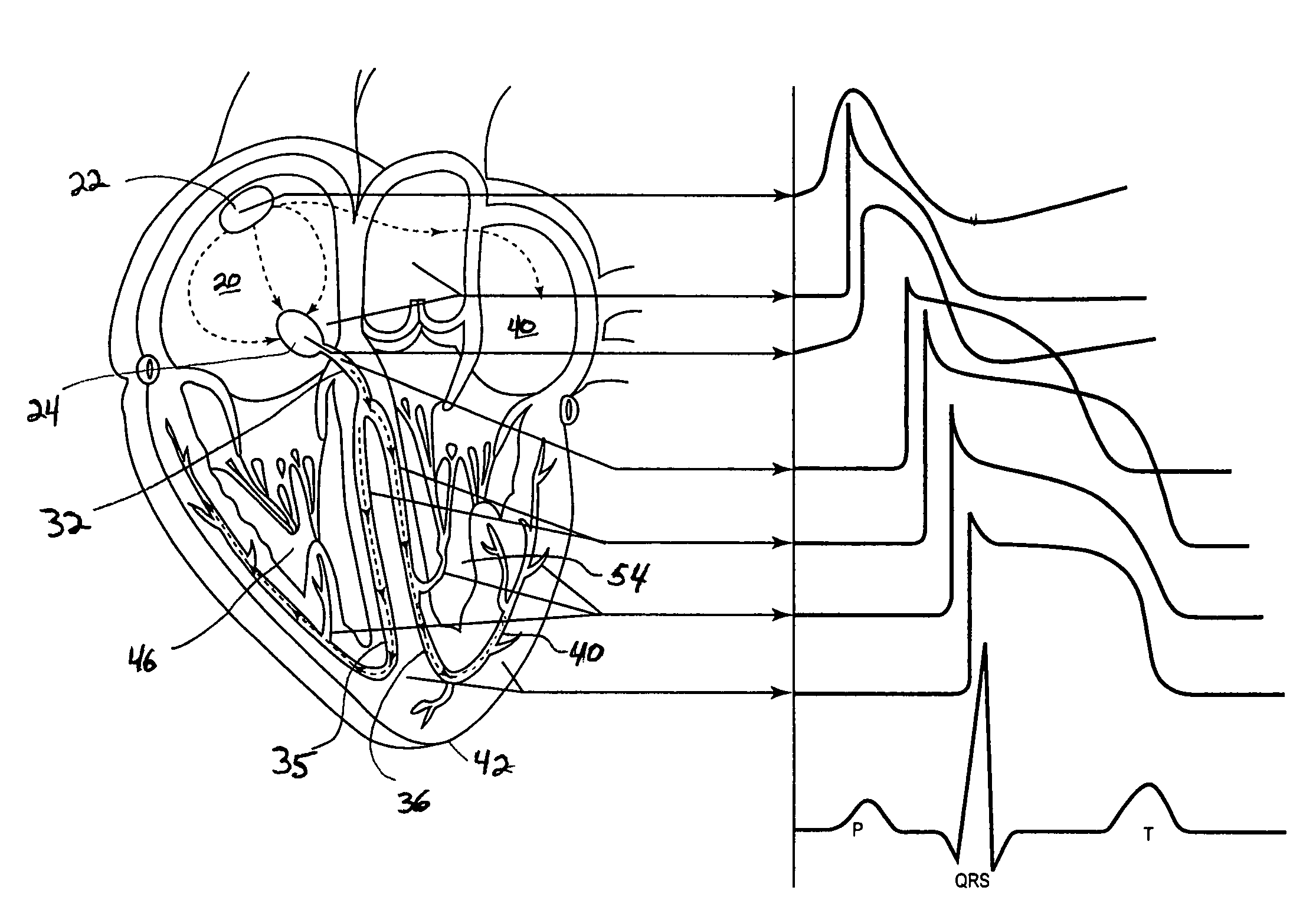
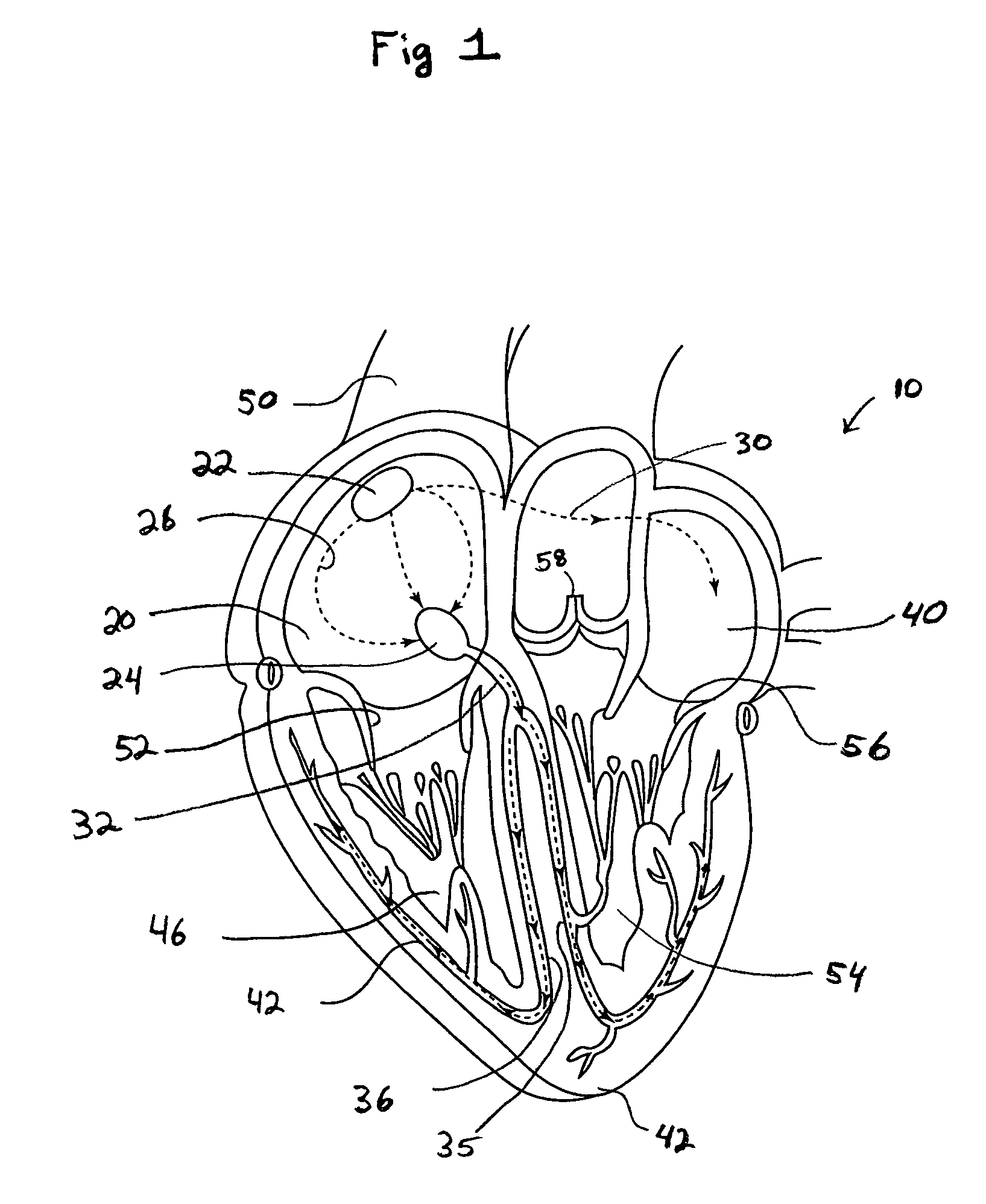
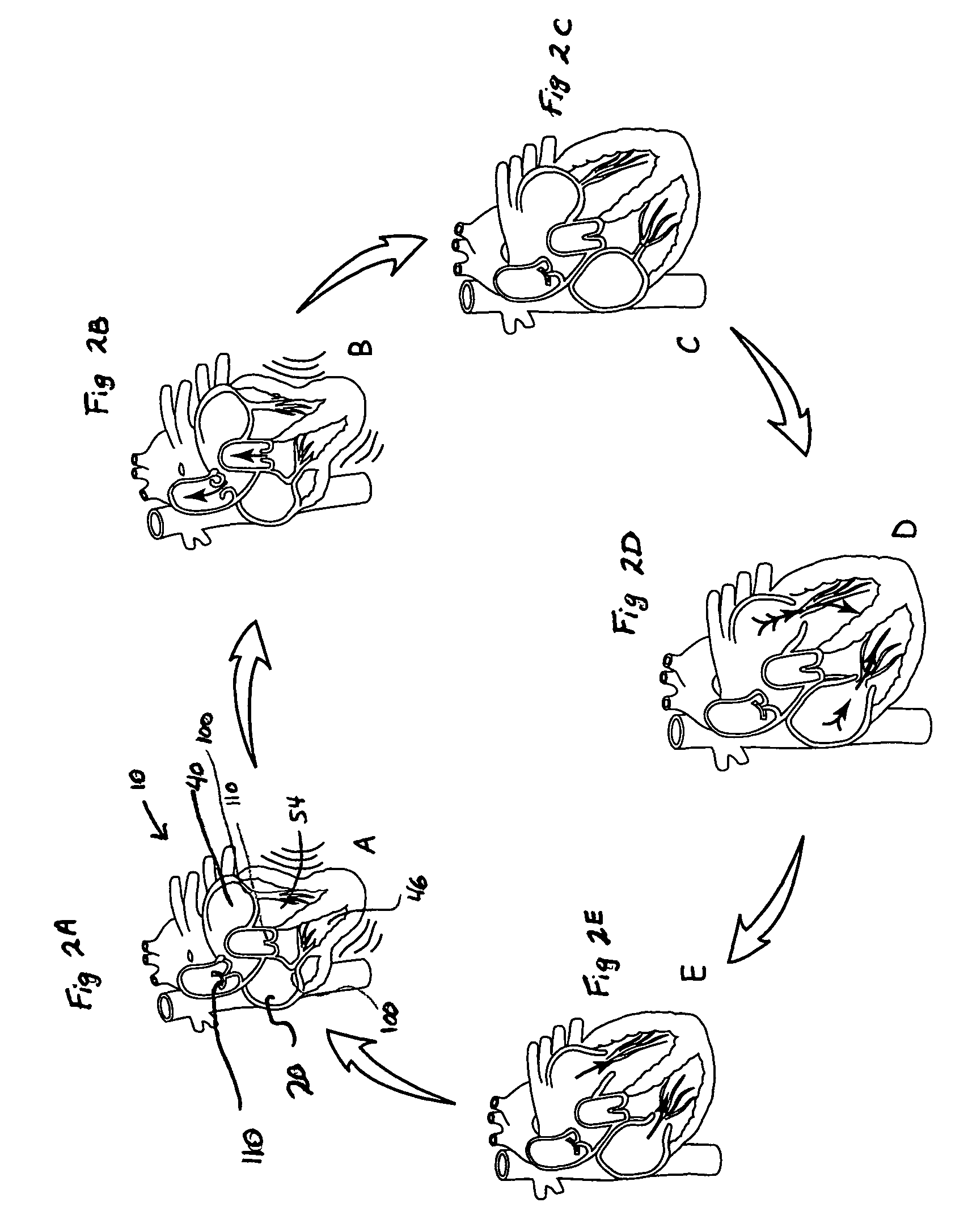
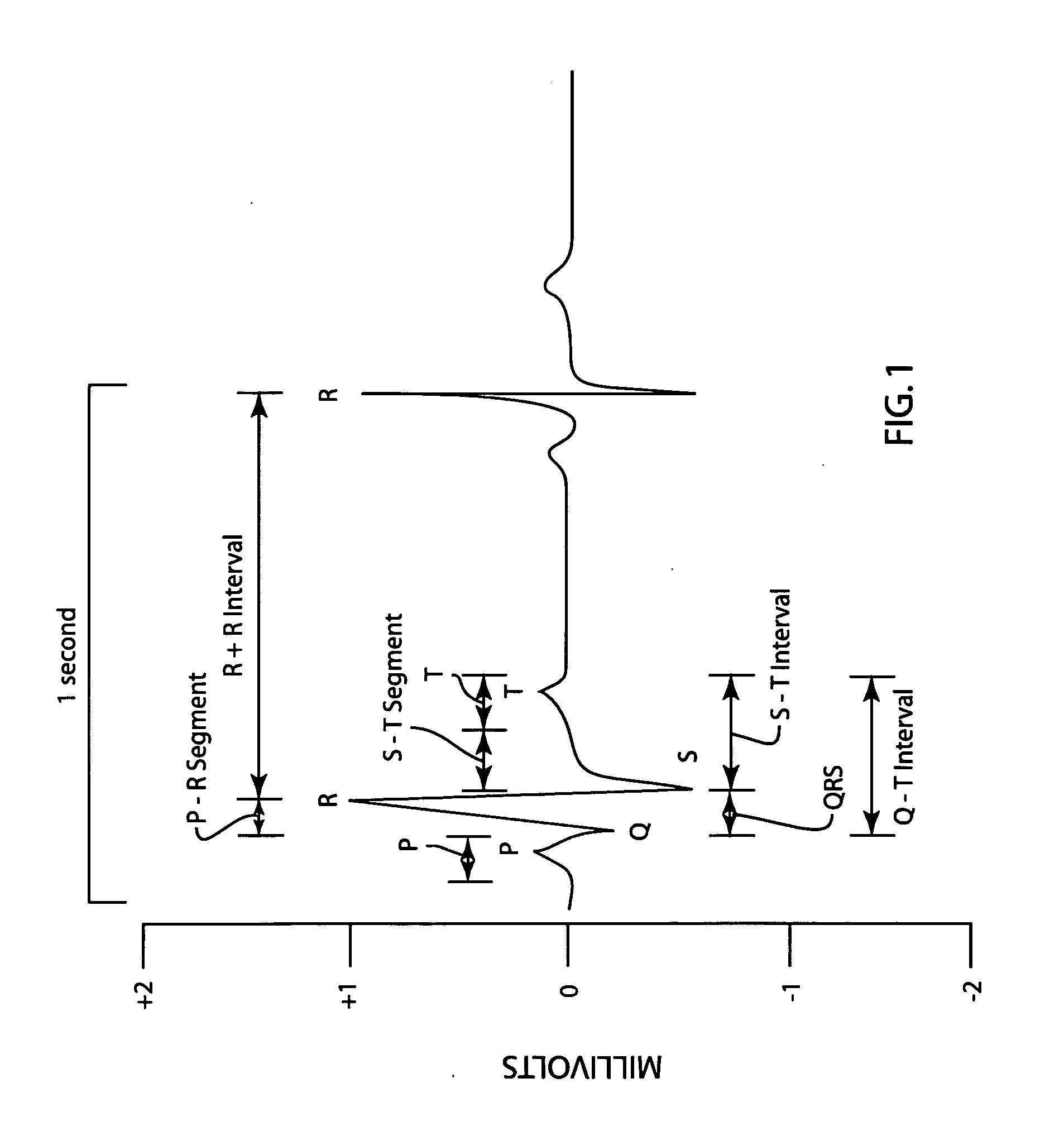
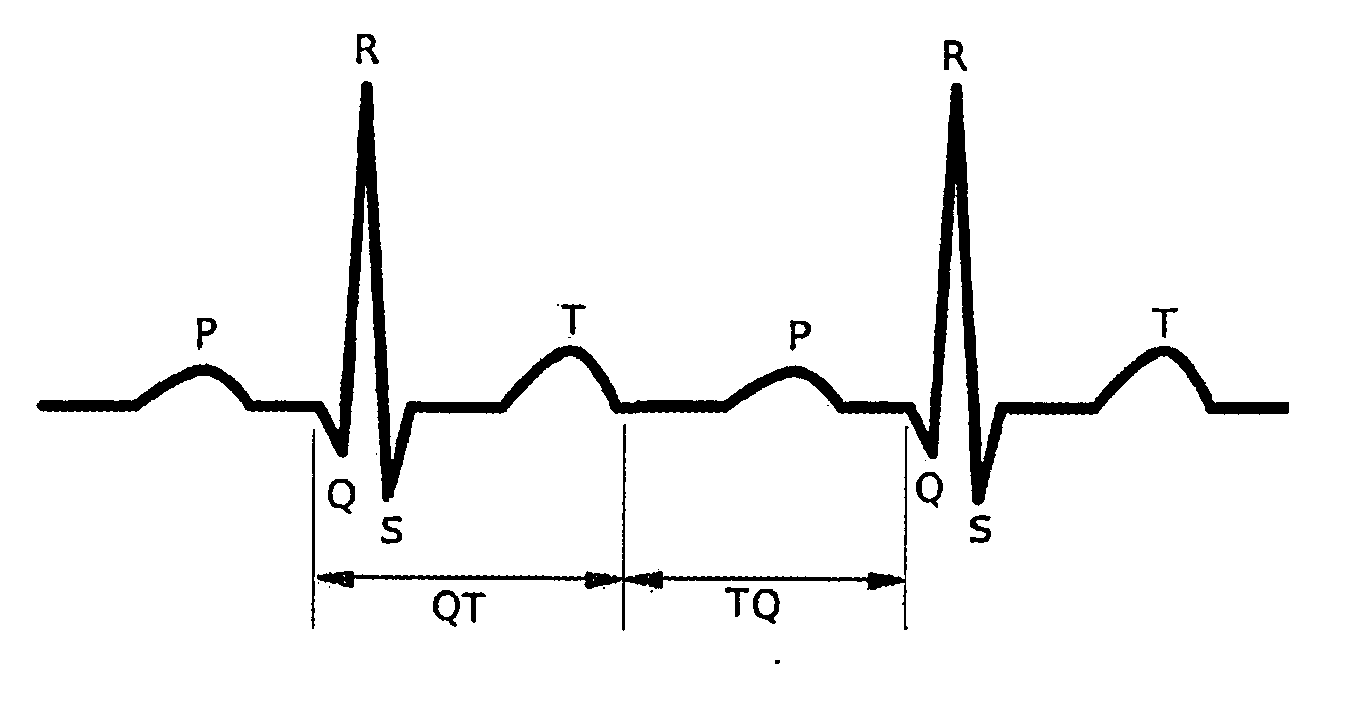
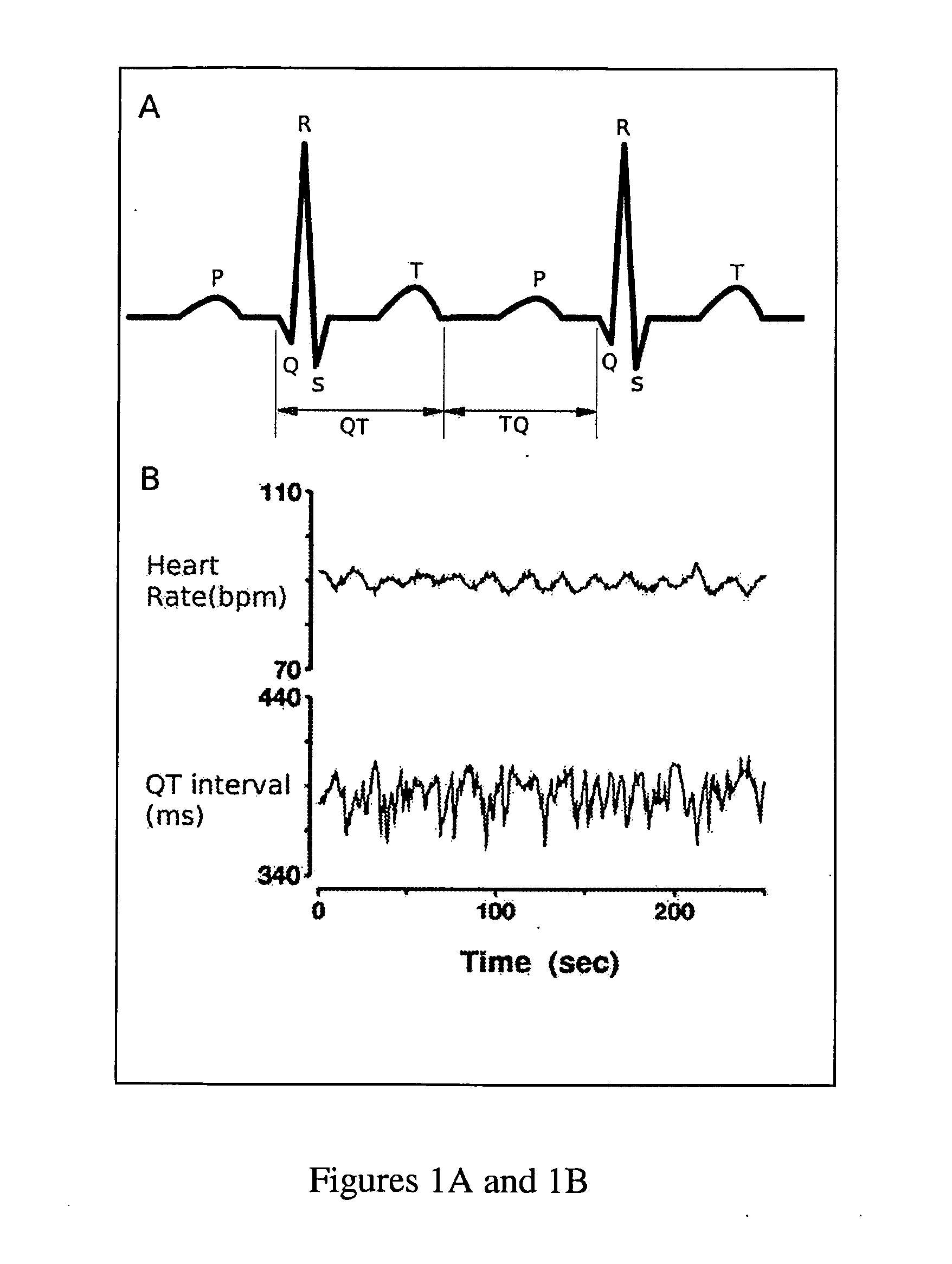
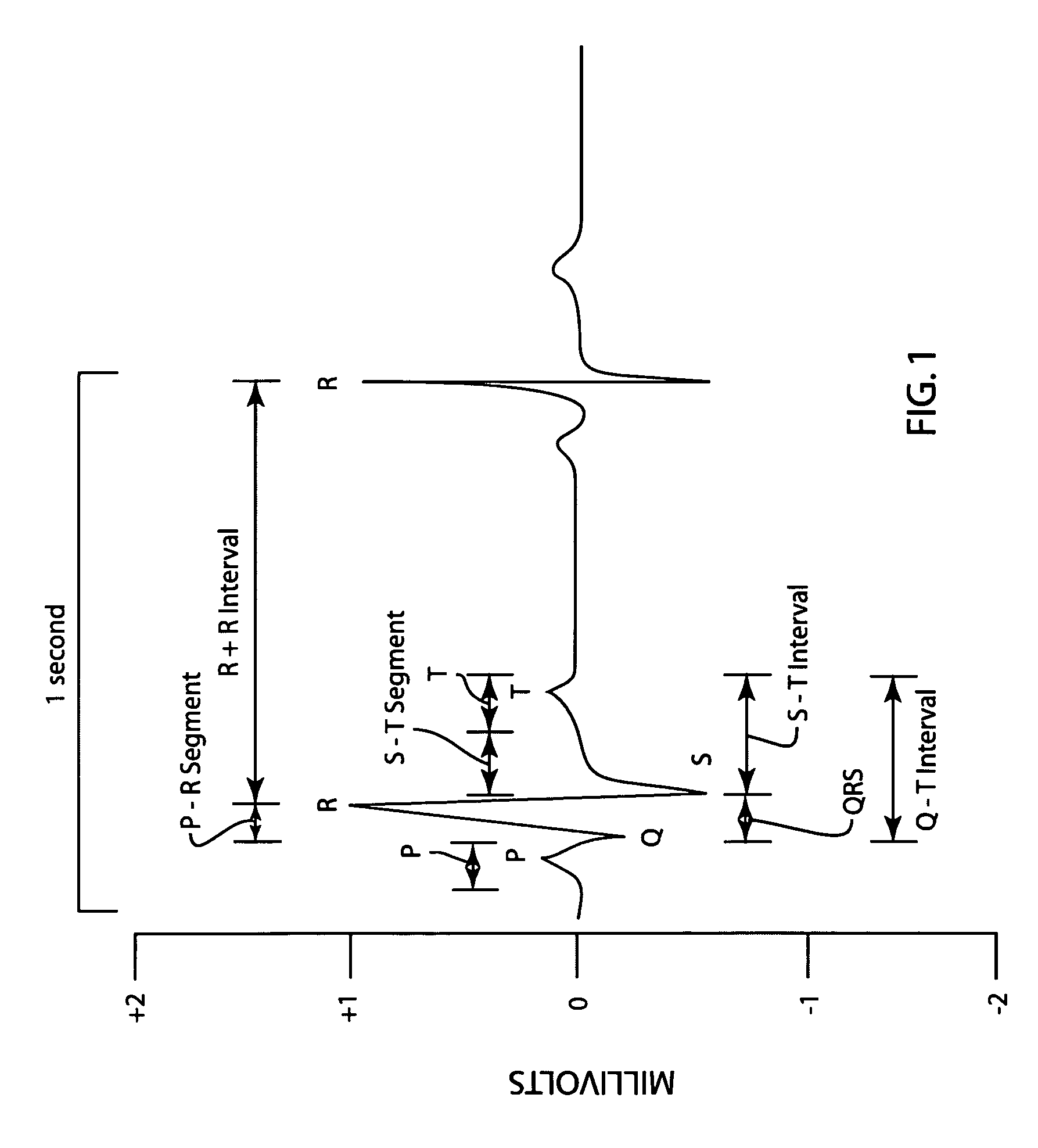
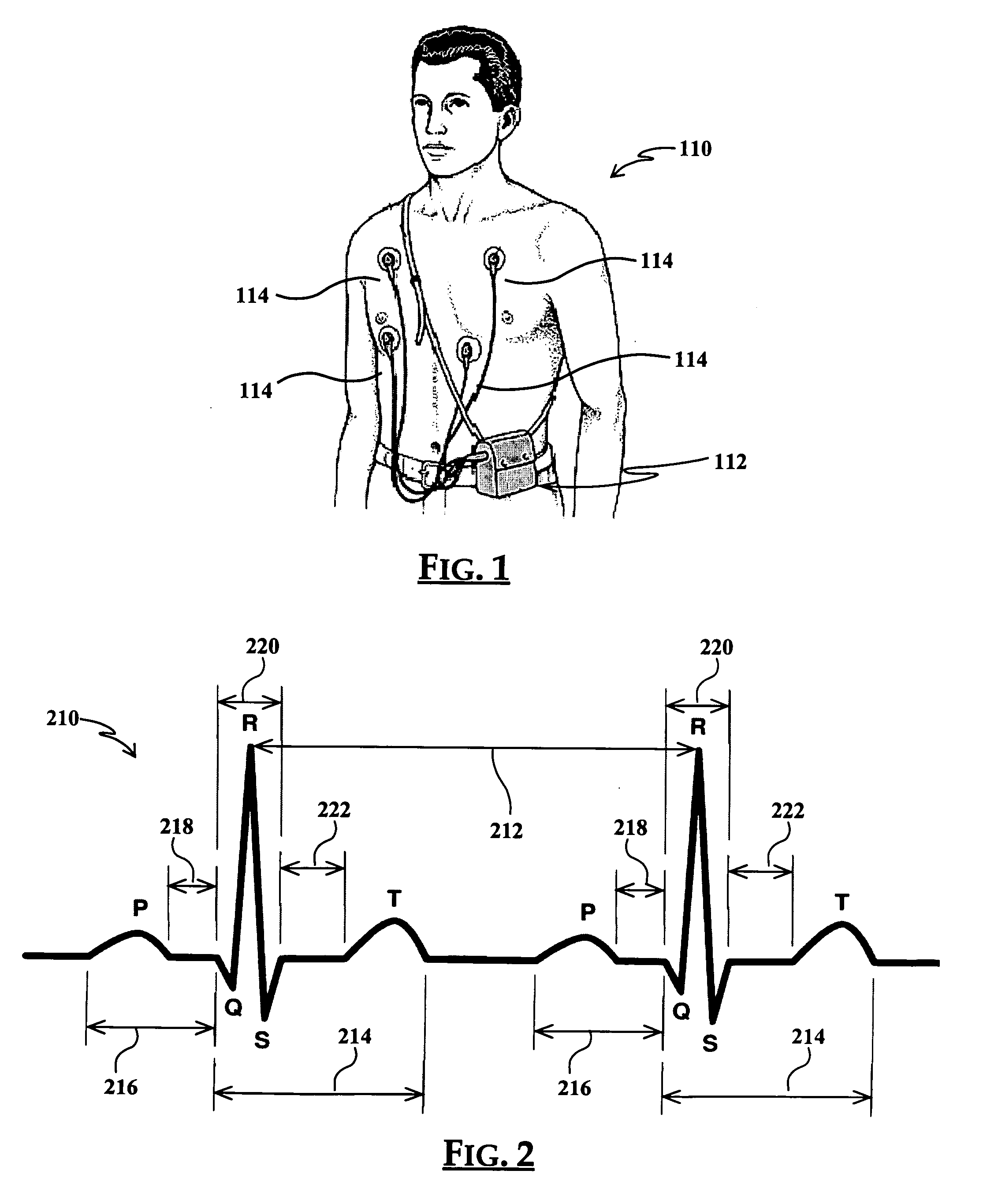
The QT interval is a measurement made on an electrocardiogram used to assess some of the electrical properties of the heart. It is calculated as the time from the start of the Q wave to the end of the T wave, and approximates to the time taken from when the cardiac ventricles start to contract to when they finish relaxing. An abnormally long or abnormally short QT interval is associated with an increased risk of developing abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Abnormalities in the QT interval can be caused by genetic conditions such as Long QT syndrome, by certain medications such as sotalol or pitolisant, by disturbances in the concentrations of certain salts within the blood such as hypokalaemia, or by hormonal imbalances such as hypothyroidism.
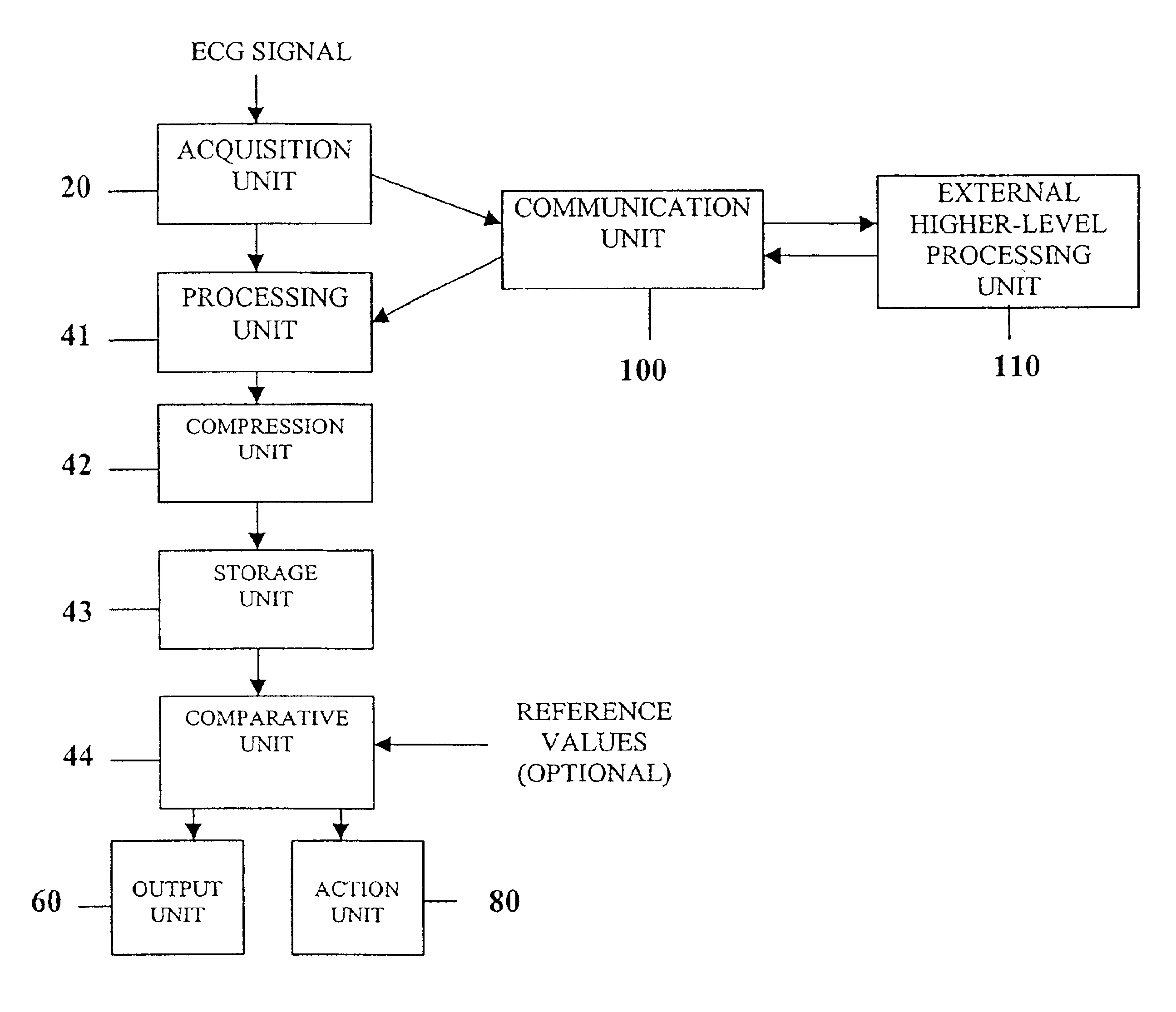
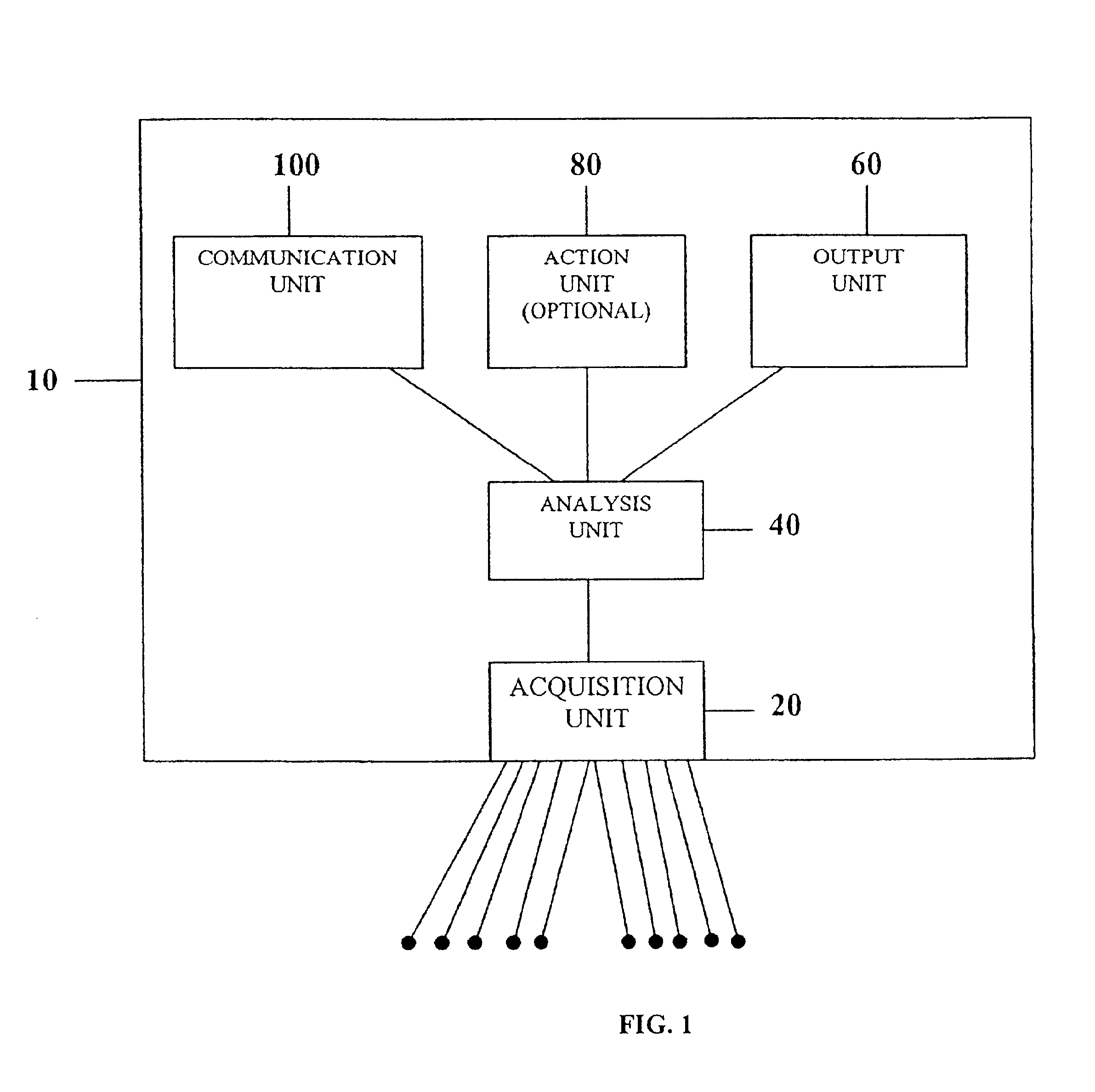
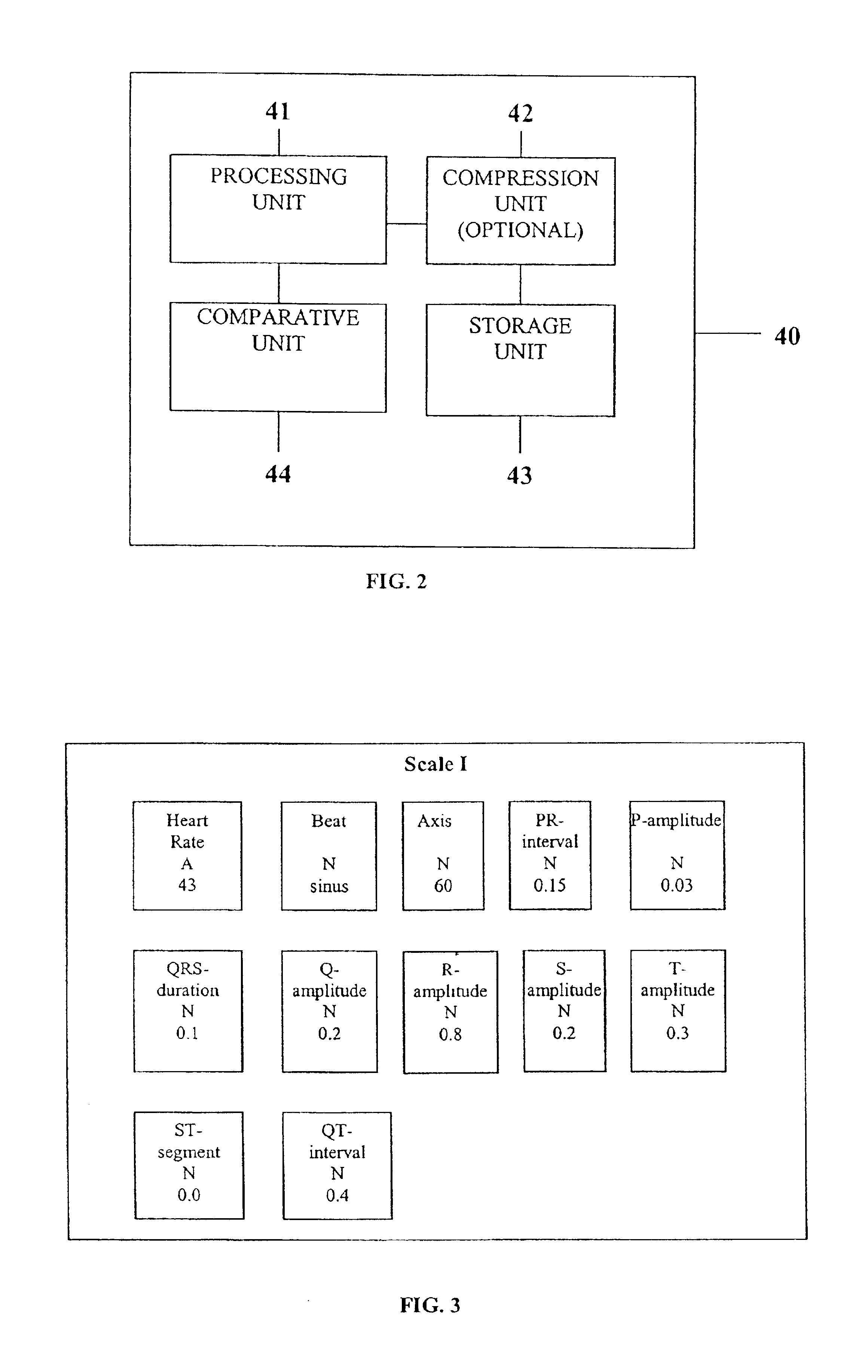
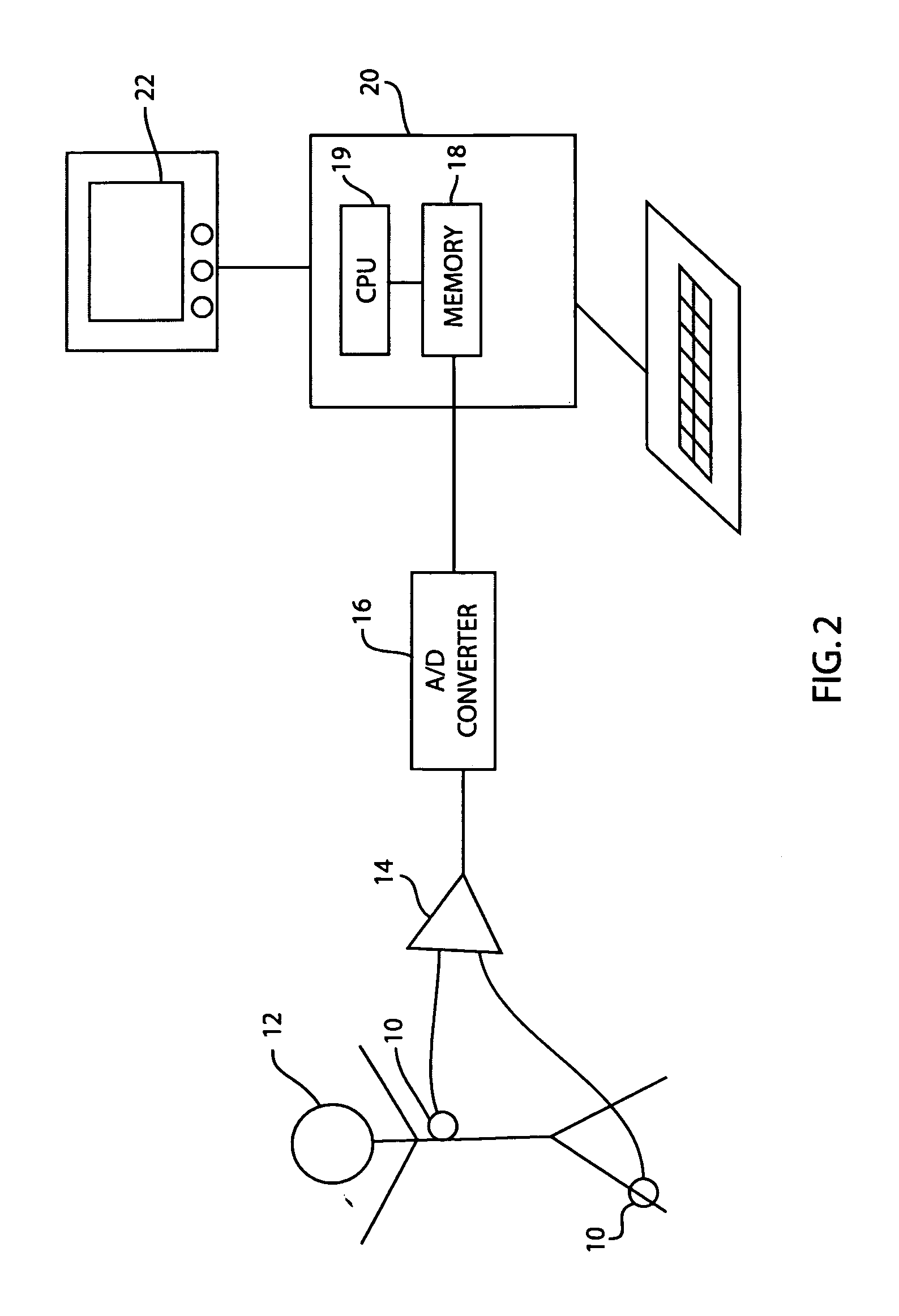
System and device for multi-scale analysis and representation of physiological data
InactiveUS6925324B2Easy to analyzeIncrease computing resourcesElectrocardiographySensorsReal time analysisT wave
System comprised of a medical device and method for analyzing physiological and health data and representing the most significant parameters at different levels of detail which are understandable to a lay person and a medical professional. Low, intermediate and high-resolution scales can exchange information between each other for improving the analyses; the scales can be defined according to the corresponding software and hardware resources. A low-resolution Scale I represents a small number of primary elements such as intervals between the heart beats, duration of electrocardiographic PQ, QRS, and QT-intervals, amplitudes of P-, Q-, R-, S-, and T-waves. This real-time analysis is implemented in a portable device that requires minimum computational resources. The set of primary elements and their search criteria can be adjusted using intermediate or high-resolution levels. At the intermediate-resolution Scale II, serial changes in each of the said elements can be determined using a mathematical decomposition into series of basis functions and their coefficients. This scale can be implemented using a specialized processor or a computer organizer. At the high-resolution Scale III, combined serial changes in all primary elements can be determined to provide complete information about the dynamics of the signal. This scale can be implemented using a powerful processor, a network of computers or the Internet. The system can be used for personal or group self-evaluation, emergency or routine ECG analysis, or continuous event, stress-test or bed-side monitoring.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
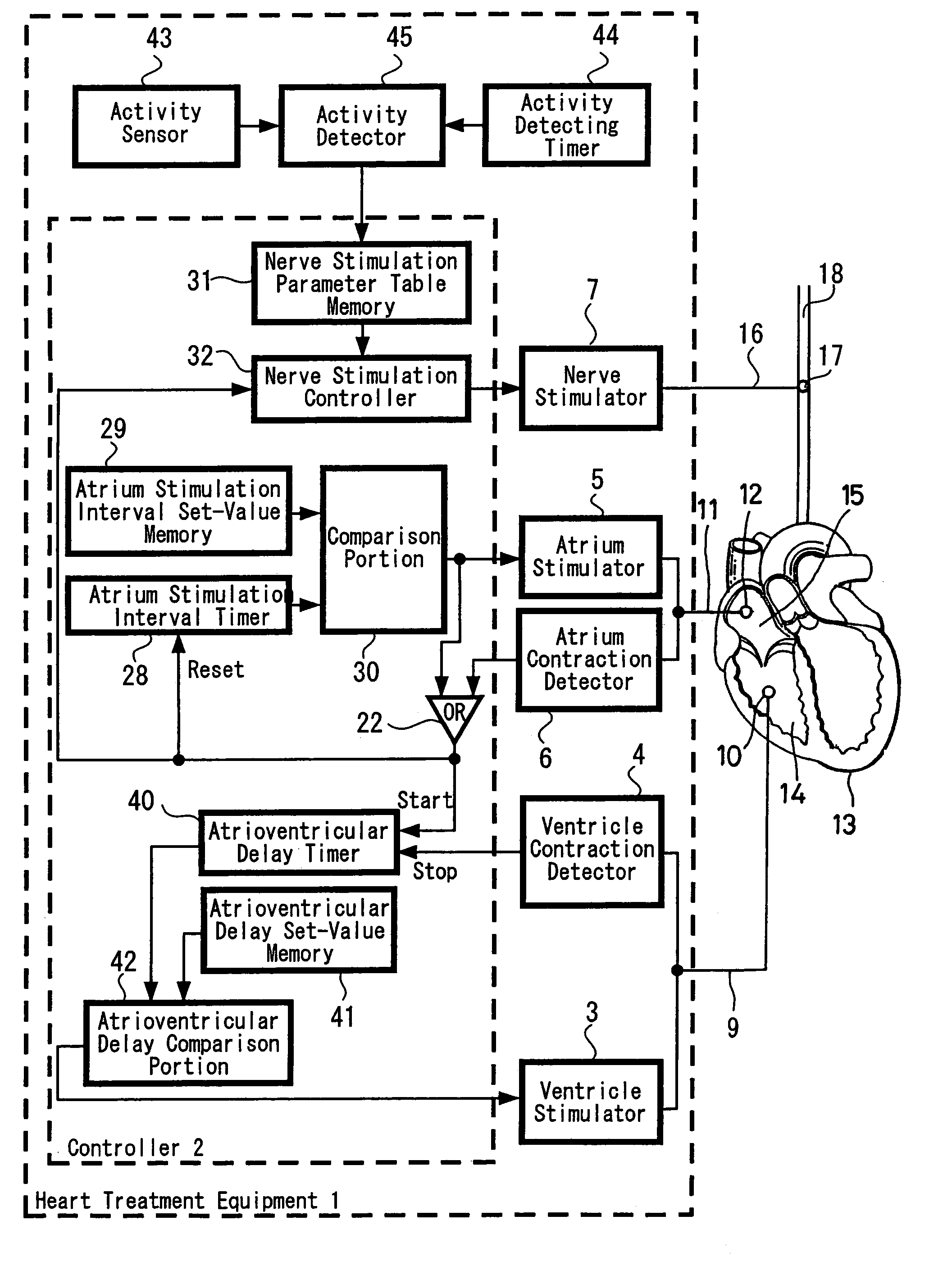
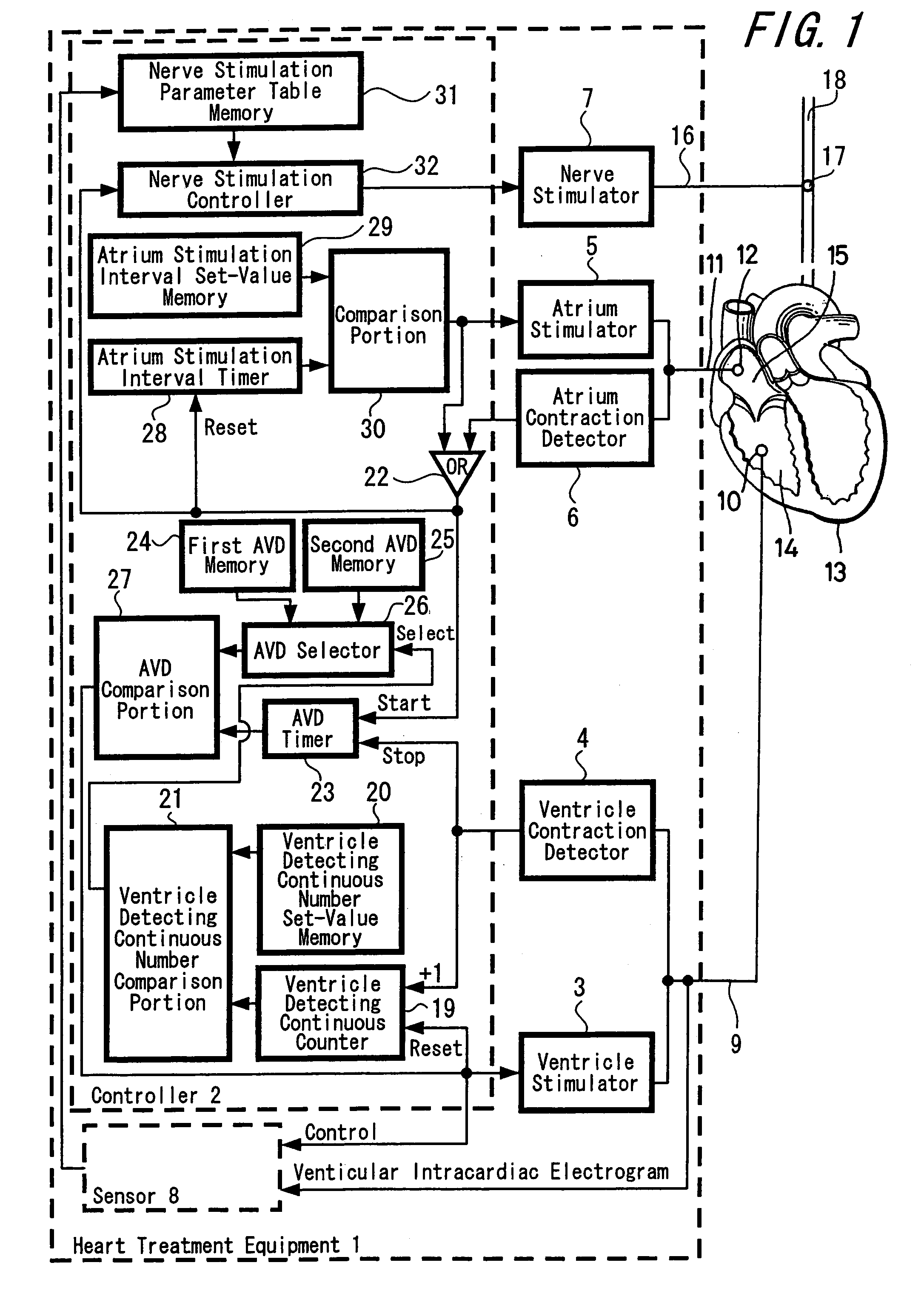
Heart treatment equipment and method for preventing fatal arrhythmia
InactiveUS7142917B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringBiological bodyVentricular premature contractions
In order to avoid a sudden cardiac death by a fatal arrhythmia, various living body information for generating a signal which shows a level of an autonomic tone is detected by a sensor or a VT / VF risk event is detected so as to control the stimulation of the vagus nerve or the nerve stimulation waveform. For this purpose, the parameter of the nerve stimulation signal is controlled according to a detection of the living body information represented by a QT interval which is measured by intracardiac information of the heart or a detection of a VT / VF risk event represented by a ventricular premature contraction which is picked up from spontaneous cardiac events.
Owner:TERUMO KK
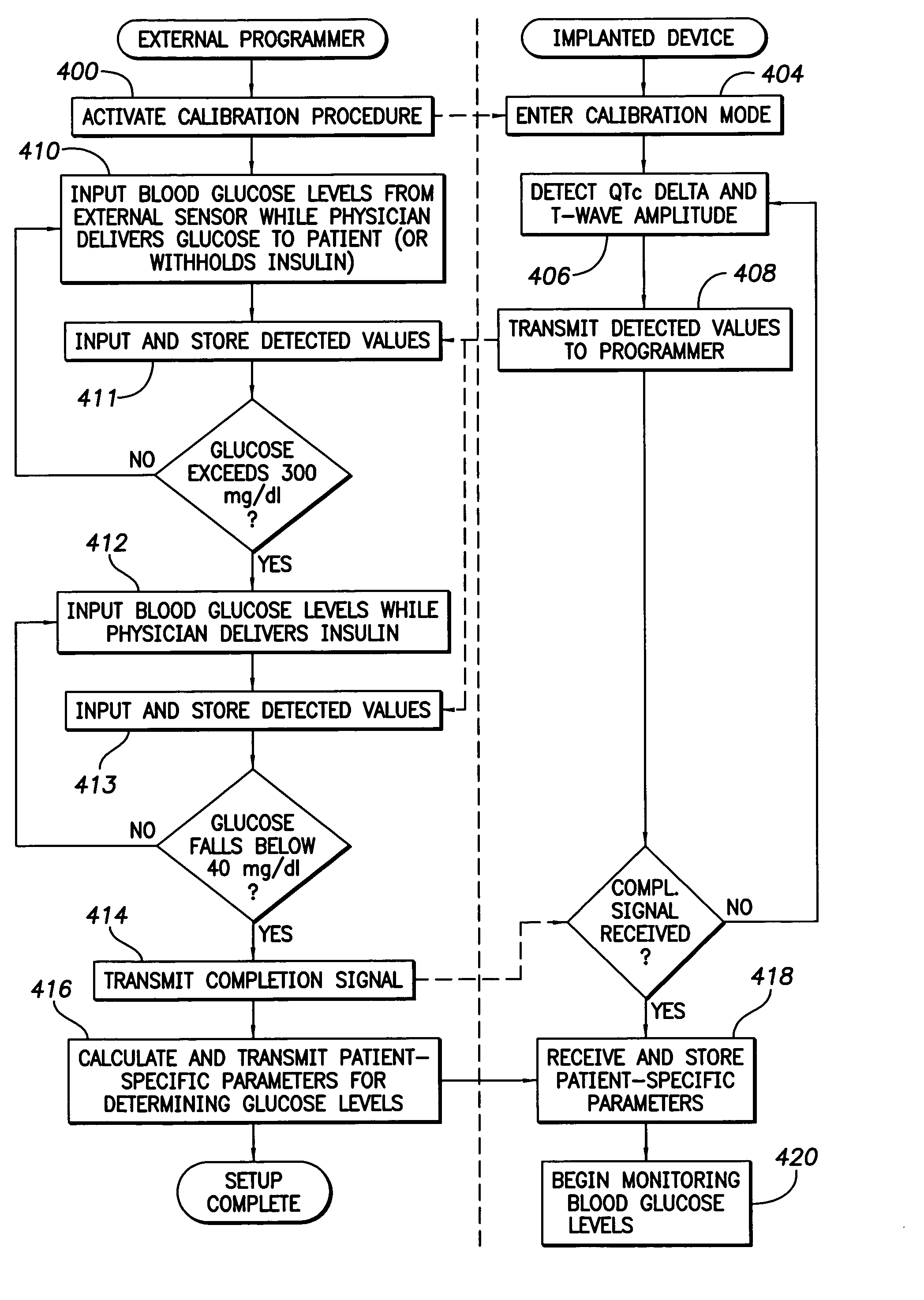
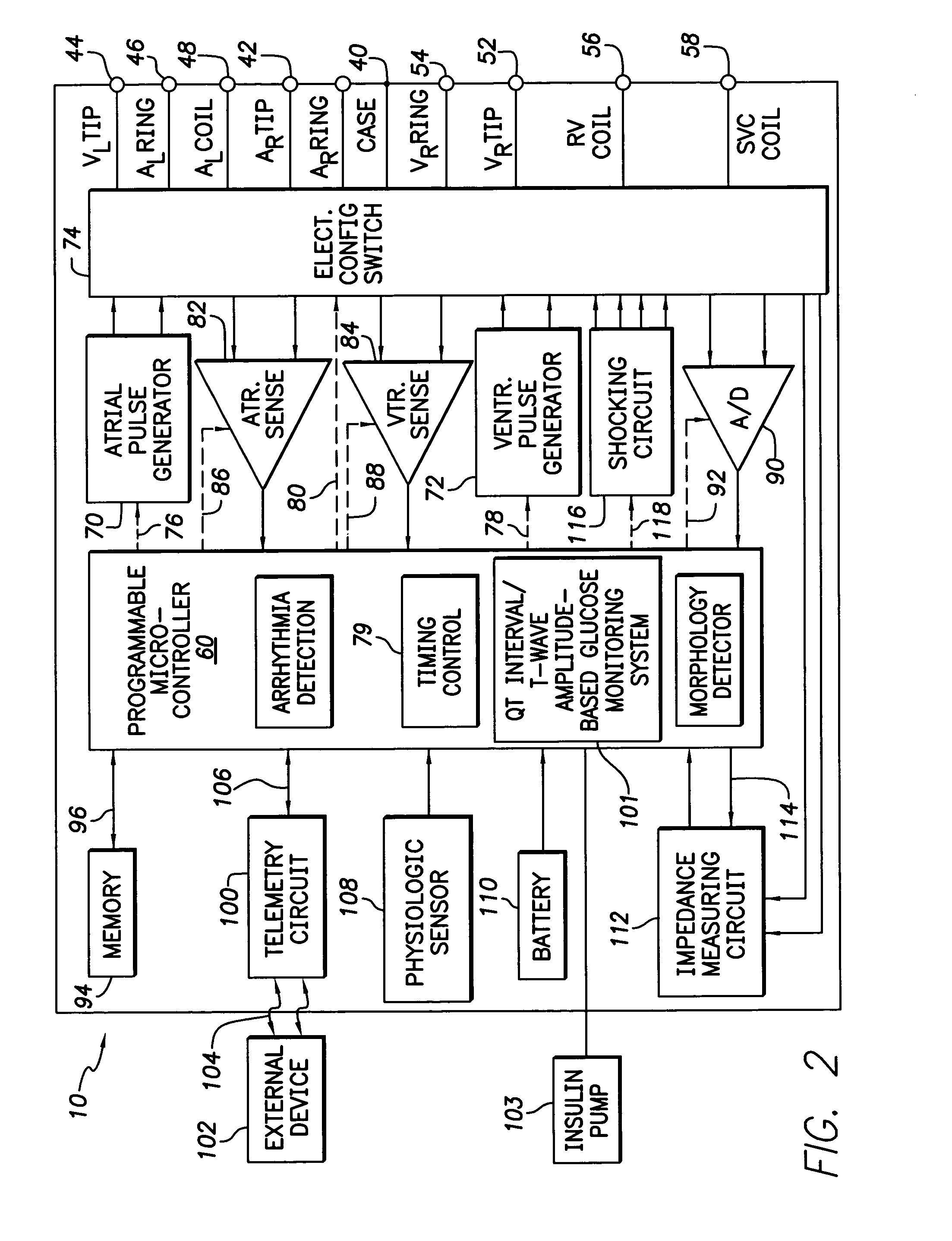
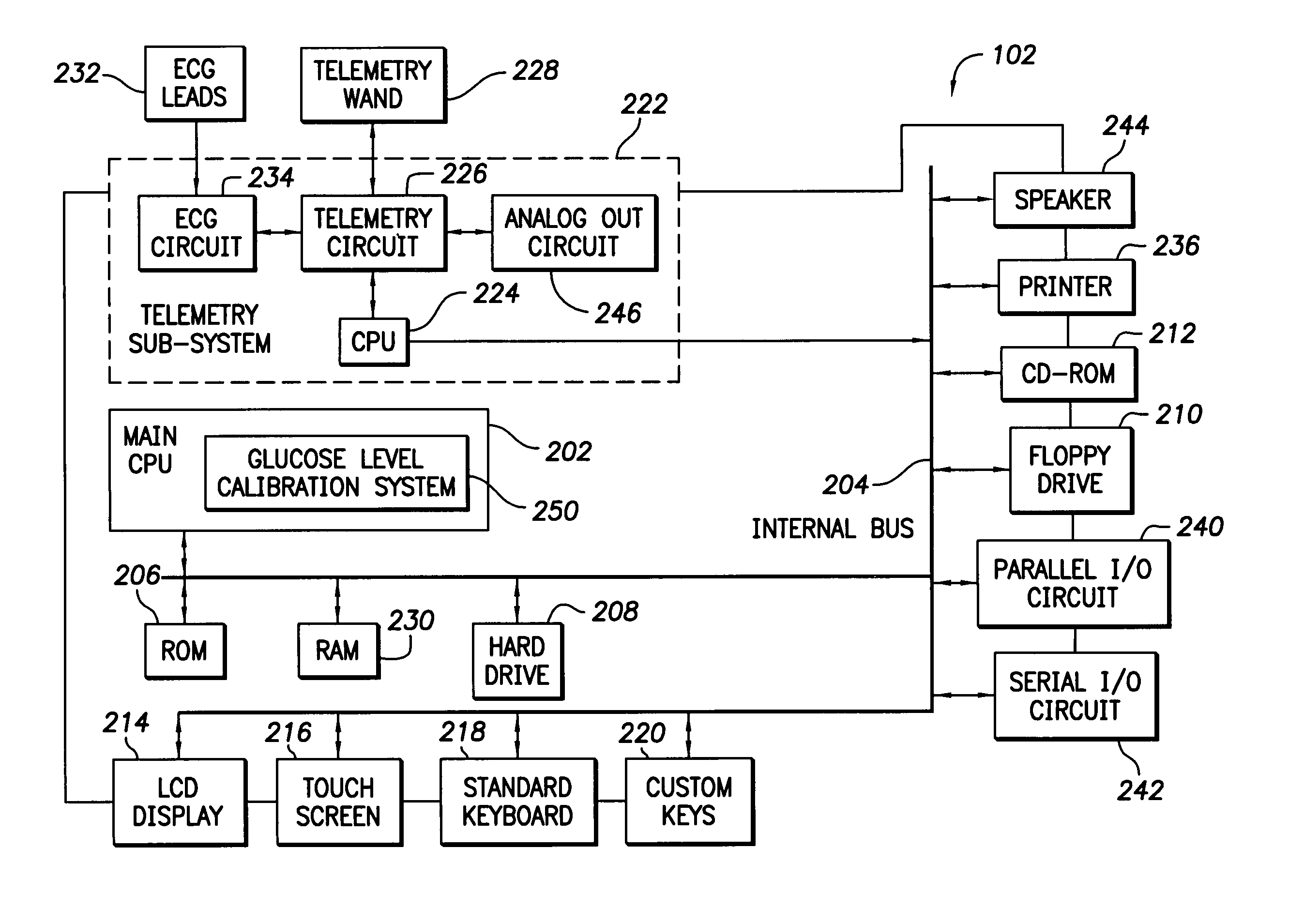
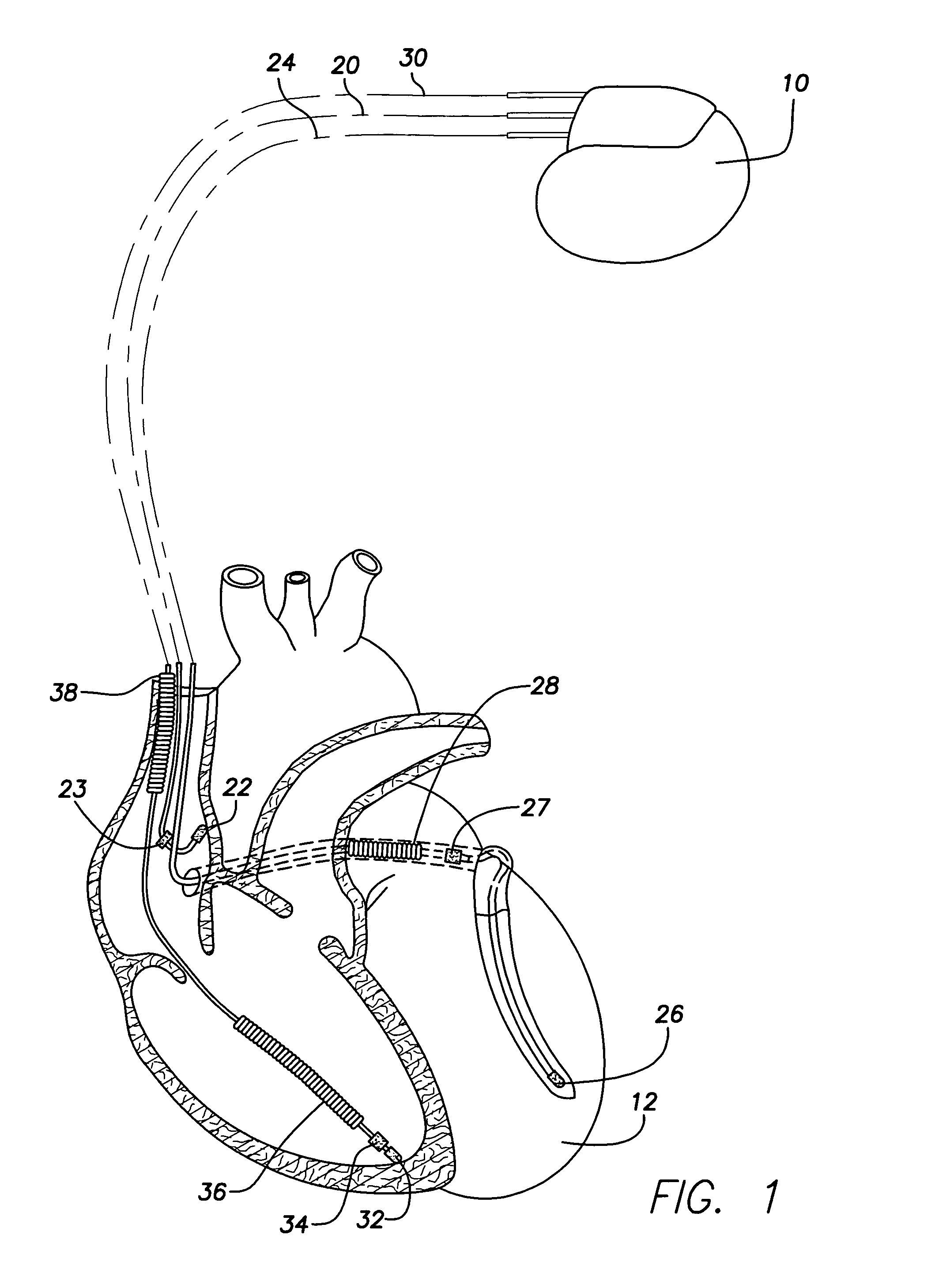
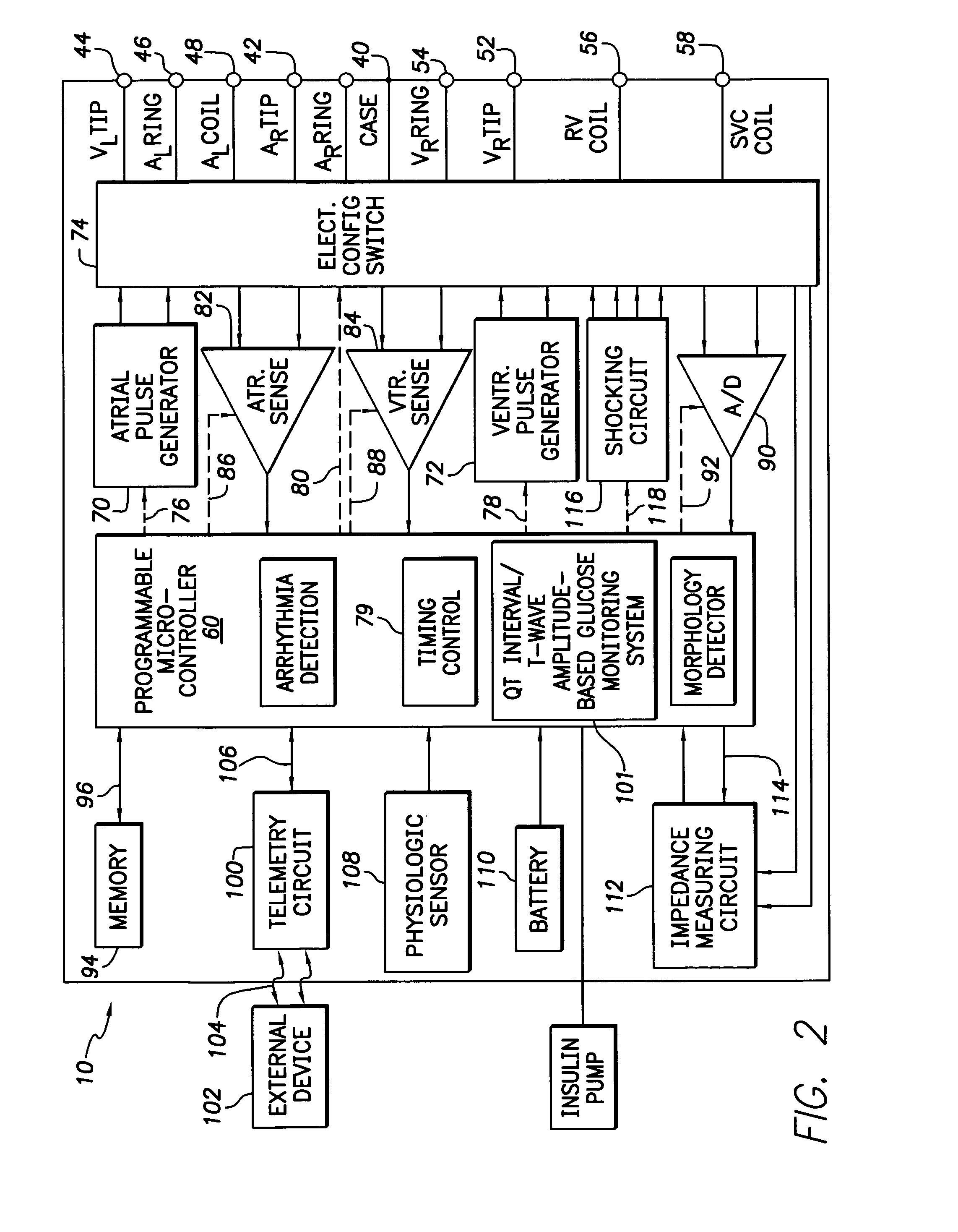
System and method for monitoring blood glucose levels using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7029443B2Reliable levelingImprove the level ofElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsT waveQT interval
T-wave amplitude and QT interval are derived from patient cardiac signals. Then blood glucose levels are determined based on a combination of the T-wave amplitude and the QT interval. By using a combination of both T-wave-based and QT interval-based signals, blood glucose levels can be reliably detected throughout a wide range of blood glucose levels. Once the blood glucose level has been detected, the implanted device compares the blood glucose level against upper and lower acceptable bounds and appropriate warning signals are generated if the level falls outside the bounds. In one example, wherein an implantable insulin pump is additionally provided, the pump is controlled based on the detected blood glucose level to maintain glucose levels within an acceptable range. A calibration technique is also provided for determining patient-specific parameters for use in the detection of blood glucose levels.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for monitoring blood glucose levels using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7016720B2Optimal blood glucose levelReliable levelingElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsT waveQT interval
T-wave amplitude and QT interval are derived from patient cardiac signals. Then blood glucose levels are determined based on a combination of the T-wave amplitude and the QT interval. By using a combination of both T-wave-based and QT interval-based signals, blood glucose levels can be reliably detected throughout a wide range of blood glucose levels. Once the blood glucose level has been detected, the implanted device compares the blood glucose level against upper and lower acceptable bounds and appropriate warning signals are generated if the level falls outside the bounds. In one example, wherein an implantable insulin pump is additionally provided, the pump is controlled based on the detected blood glucose level to maintain glucose levels within an acceptable range. A calibration technique is also provided for determining patient-specific parameters for use in the detection of blood glucose levels.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
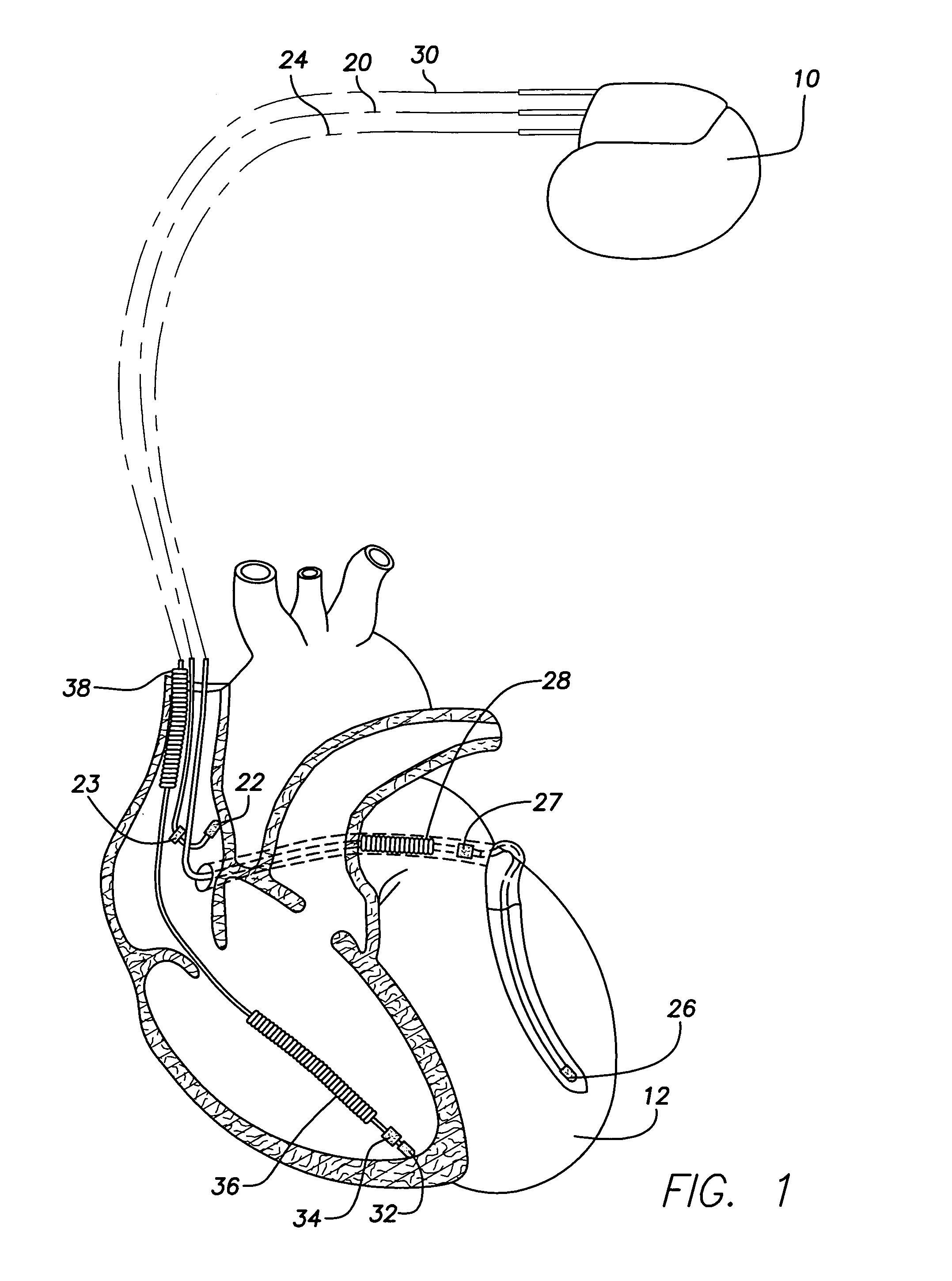
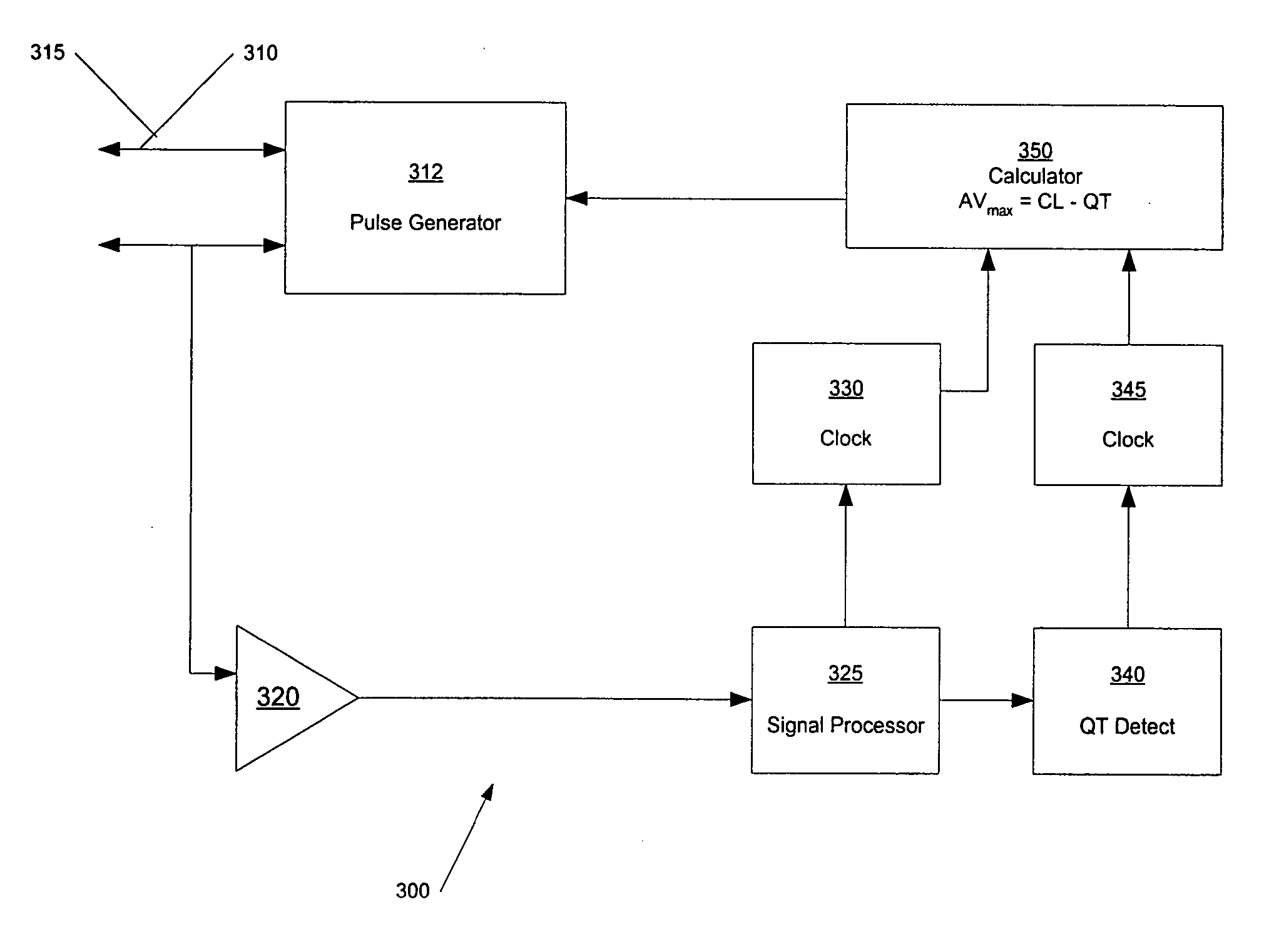
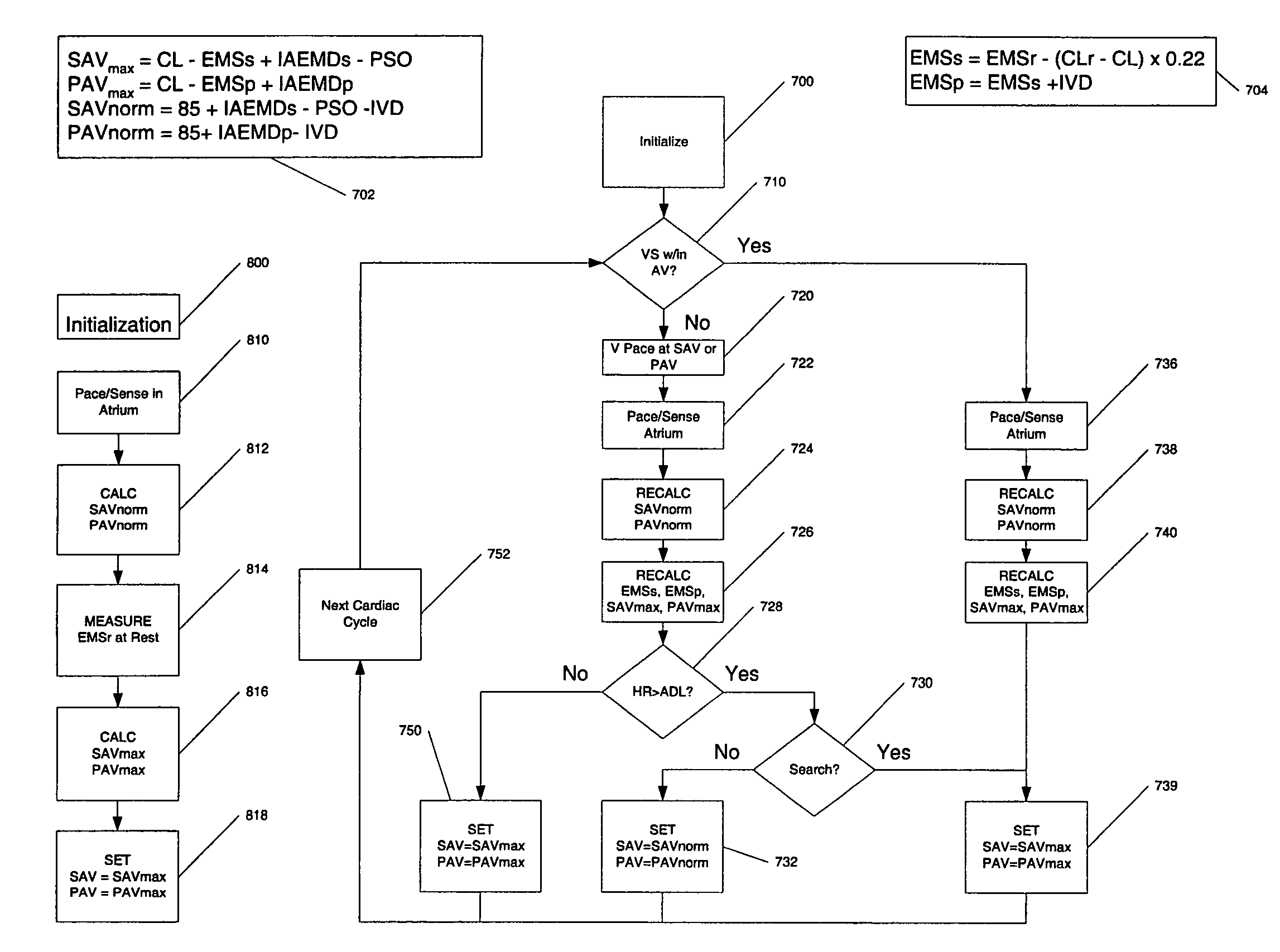
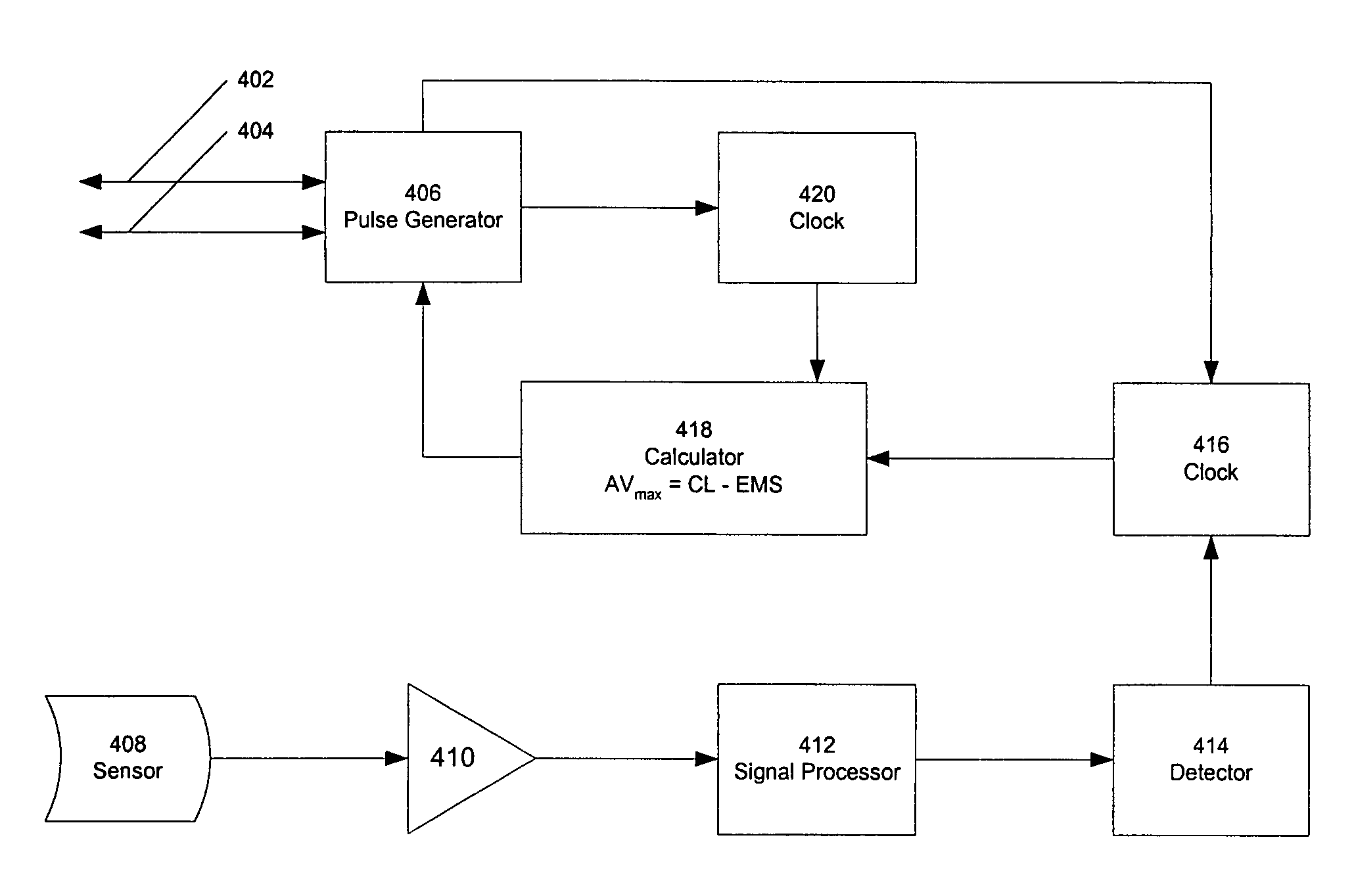
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of biomedical signal analysis including improved automatic segmentation
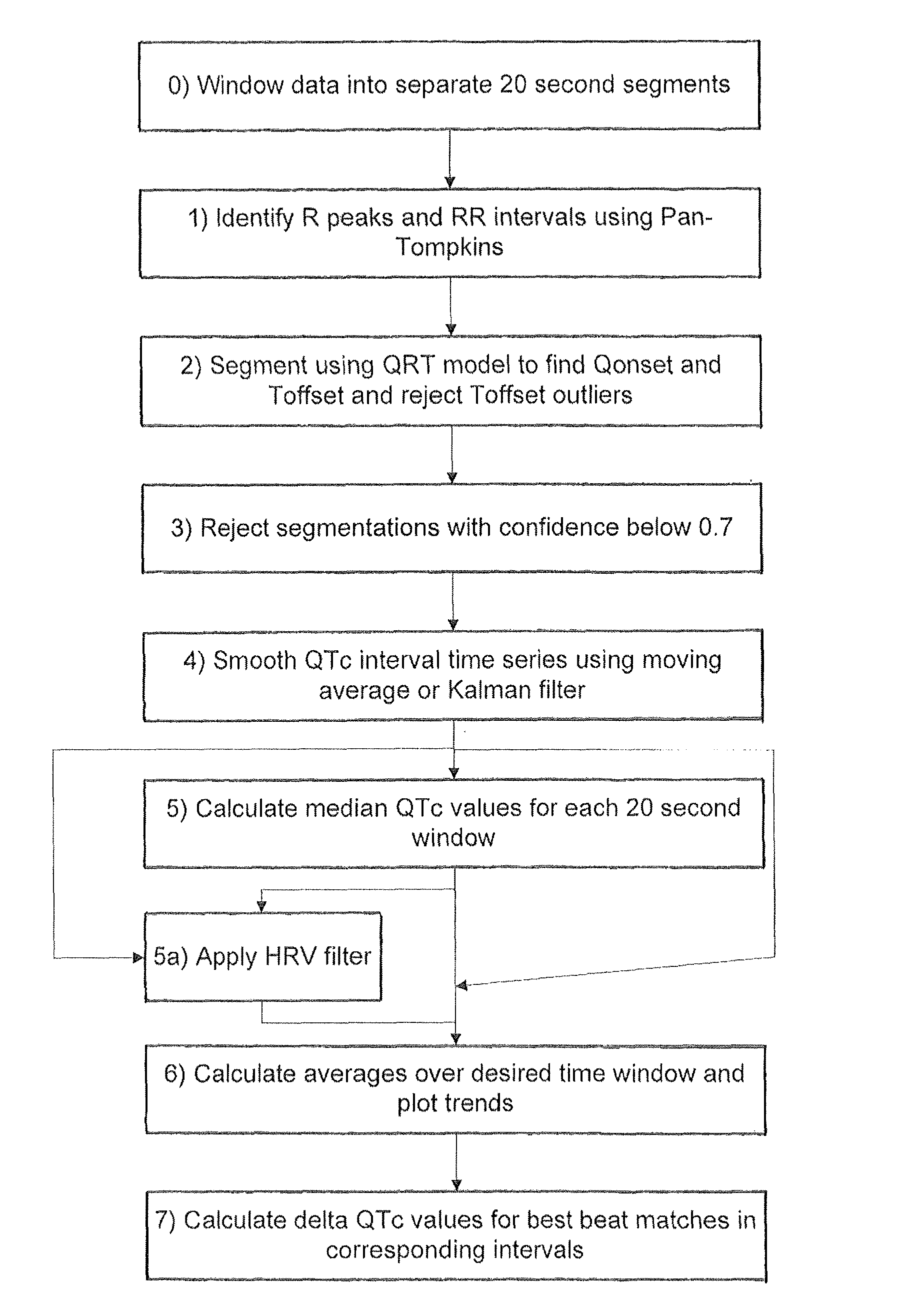
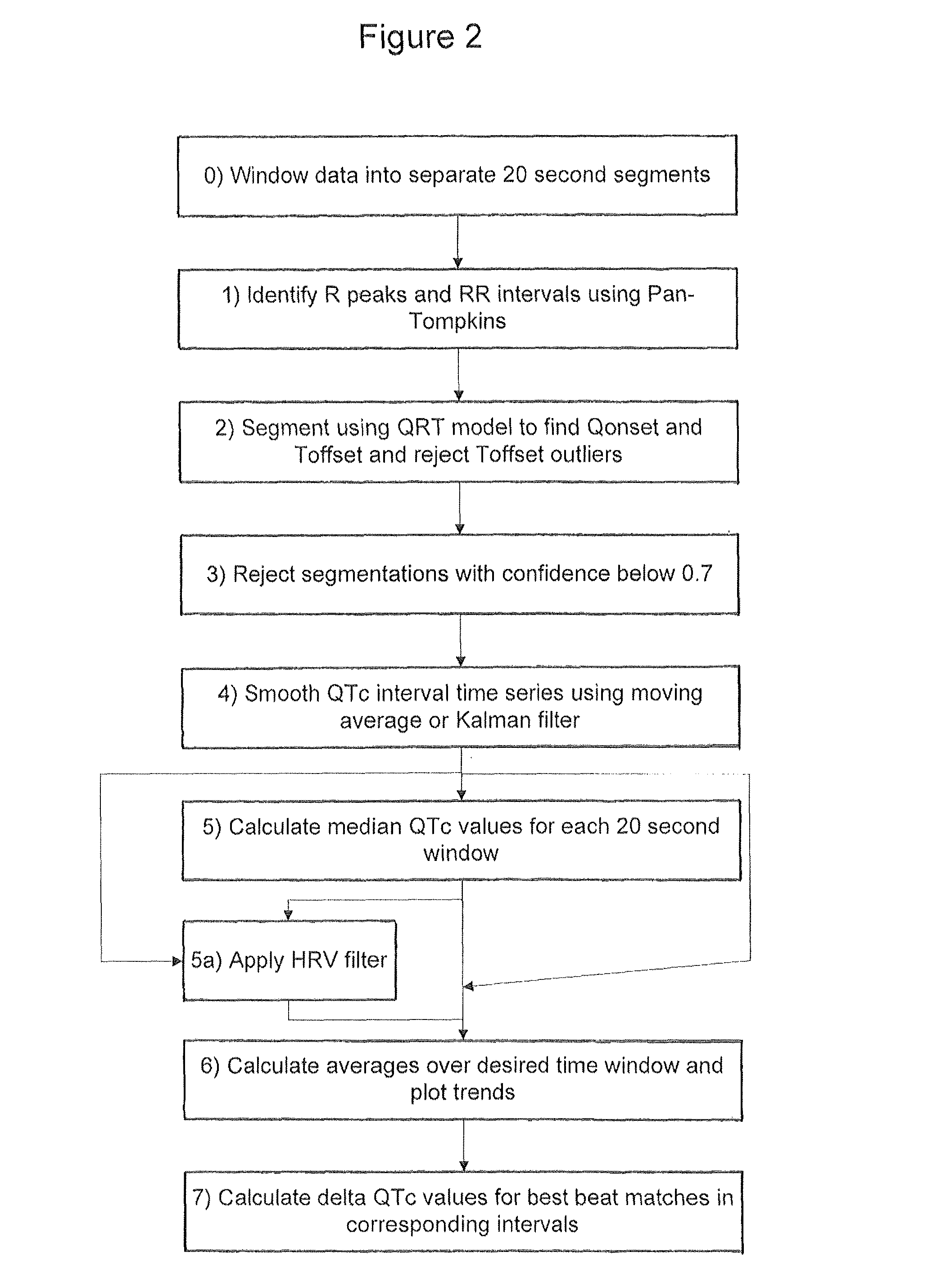
InactiveUS8332017B2Great confidenceIncrease contentMedical data miningElectrocardiographySliding time windowAutomatic segmentation
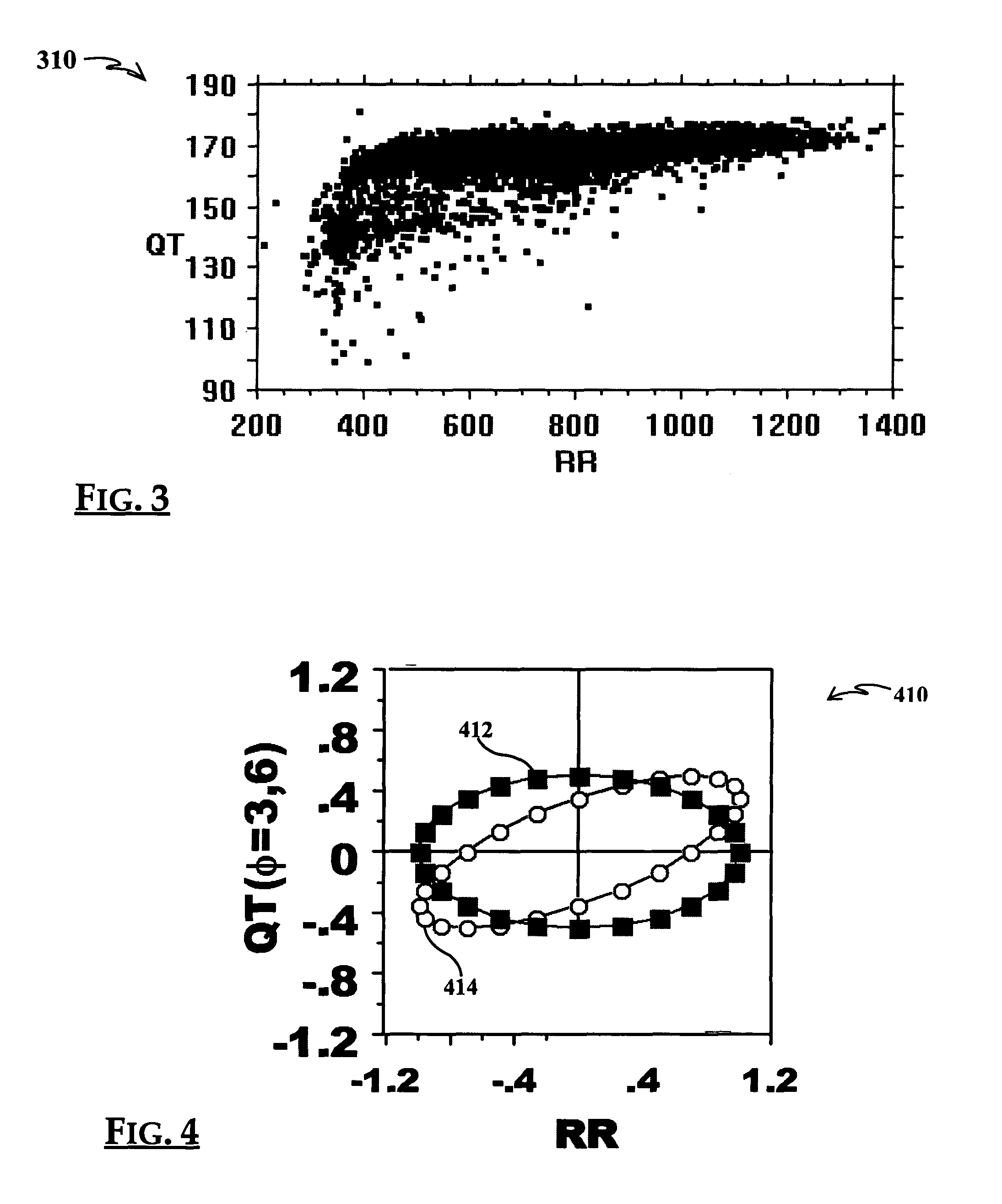
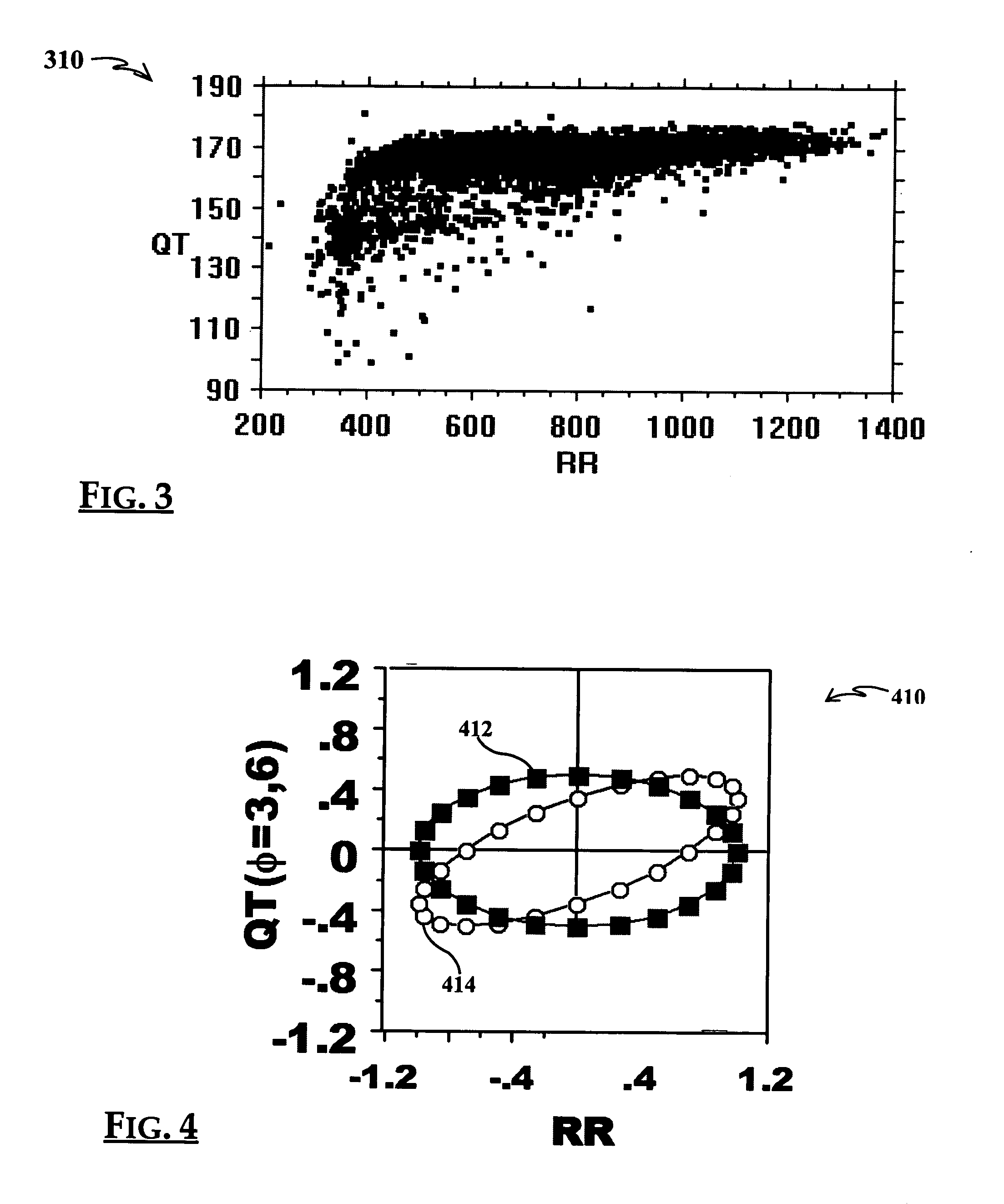
A method of analysing biomedical signals, for example electrocardiograms, by using a Hidden Markov Model for subsections of the signal. In the case of an electrocardiogram two Hidden Markov Models are used to detect respectively the start and end of the QT interval. The relationship between the QT interval and heart rate can be computed and a contemporaneous value for the slope of this relationship can be obtained by calculating the QT / RR relationship for all of the beats in a sliding time window based on the current beat. Portions of electrocardiograms taken on different days can efficiently and accurately be compared by selecting time windows of the ECGs at the same time of day, and looking for similar beats in those time windows.
Owner:OBS MEDICAL
Multi-Channel System for Beat to Beat QT Interval Variability
InactiveUS20070203418A1Reduce the impact of noiseRapid and regular updatingElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySingular value decompositionT wave
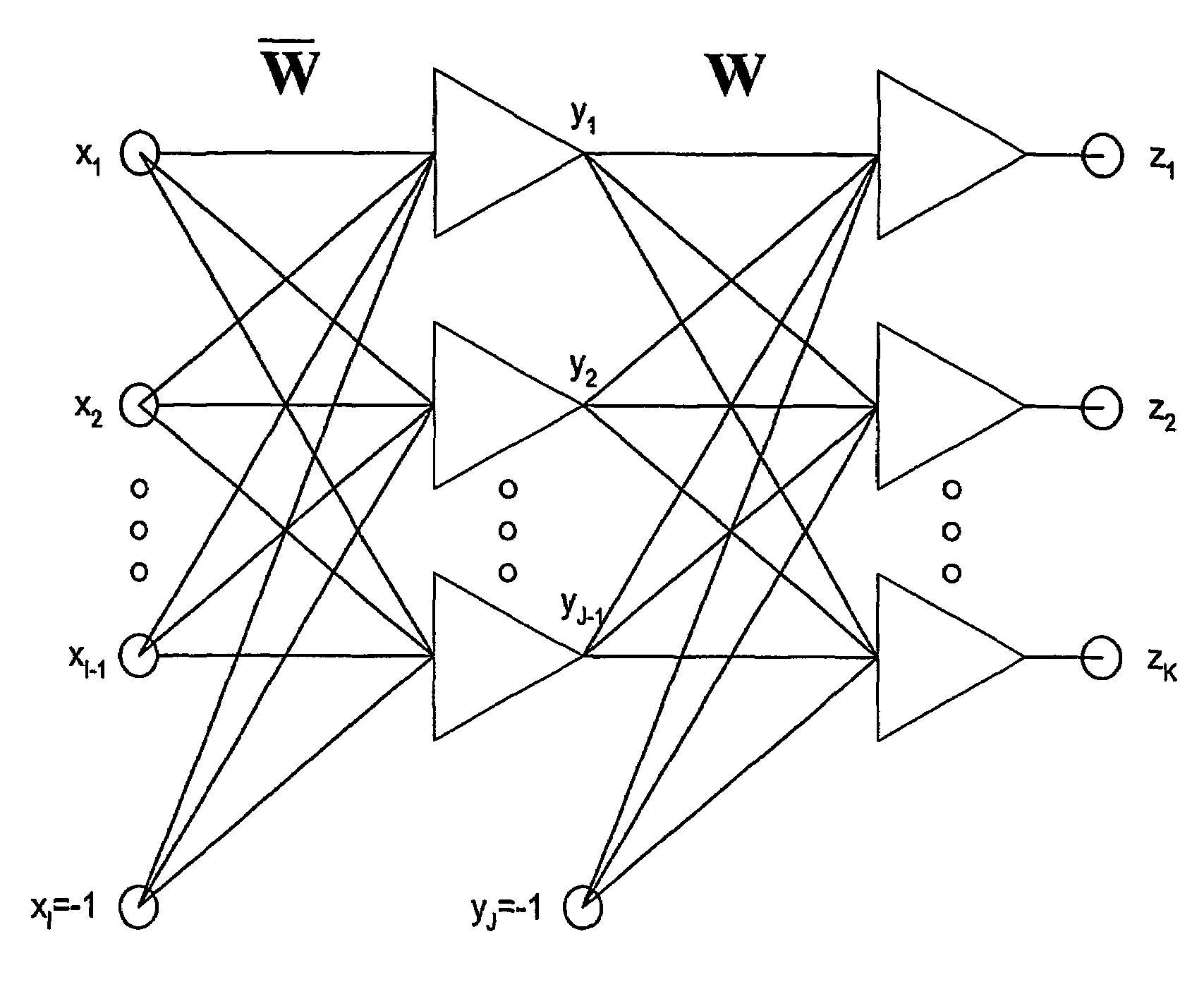
The measurement of beat-to-beat QT interval variability (QTV) shows clinical promise for identifying several types of cardiac pathology. However, until now, there has been no device capable of displaying, in real time on a beat-to-beat basis, changes in QTV in all 12 conventional leads in a continuously monitored patient. While several software programs have been designed to analyze QTV, heretofore, such programs have all involved only a few channels (at most) and / or have required laborious user interaction or off-line calculations and post-processing, limiting their clinical utility. This invention discloses a PC-based ECG software program that in real time, acquires, analyzes and displays QTV and PQ interval variability (PQV) in each of the independent channels that constitute the 12-lead conventional and / or Frank X, Y, Z lead ECG. The system also analyzes and displays the QTV and PQV from QT and PQ interval signals that are derived from multiple channels and from singular value decomposition such that the effect of noise and other artifacts on the QTV and PQV results are substantially reduced compared to existing single-channel methods. Moreover, this invention also discloses certain new parameters of T-wave (and QRS and P-wave) morphology, that in initial studies have improved clinical diagnostic utility and / or reproducibility and reliability compared to known existing parameters of T-wave morphology. Finally, it also discloses a method for determining the beat-to-beat variability these T, QRS and P-wave morphologic parameters.
Owner:CARDIOSOFT
Methods and systems for determining pacing parameters based on repolarization index
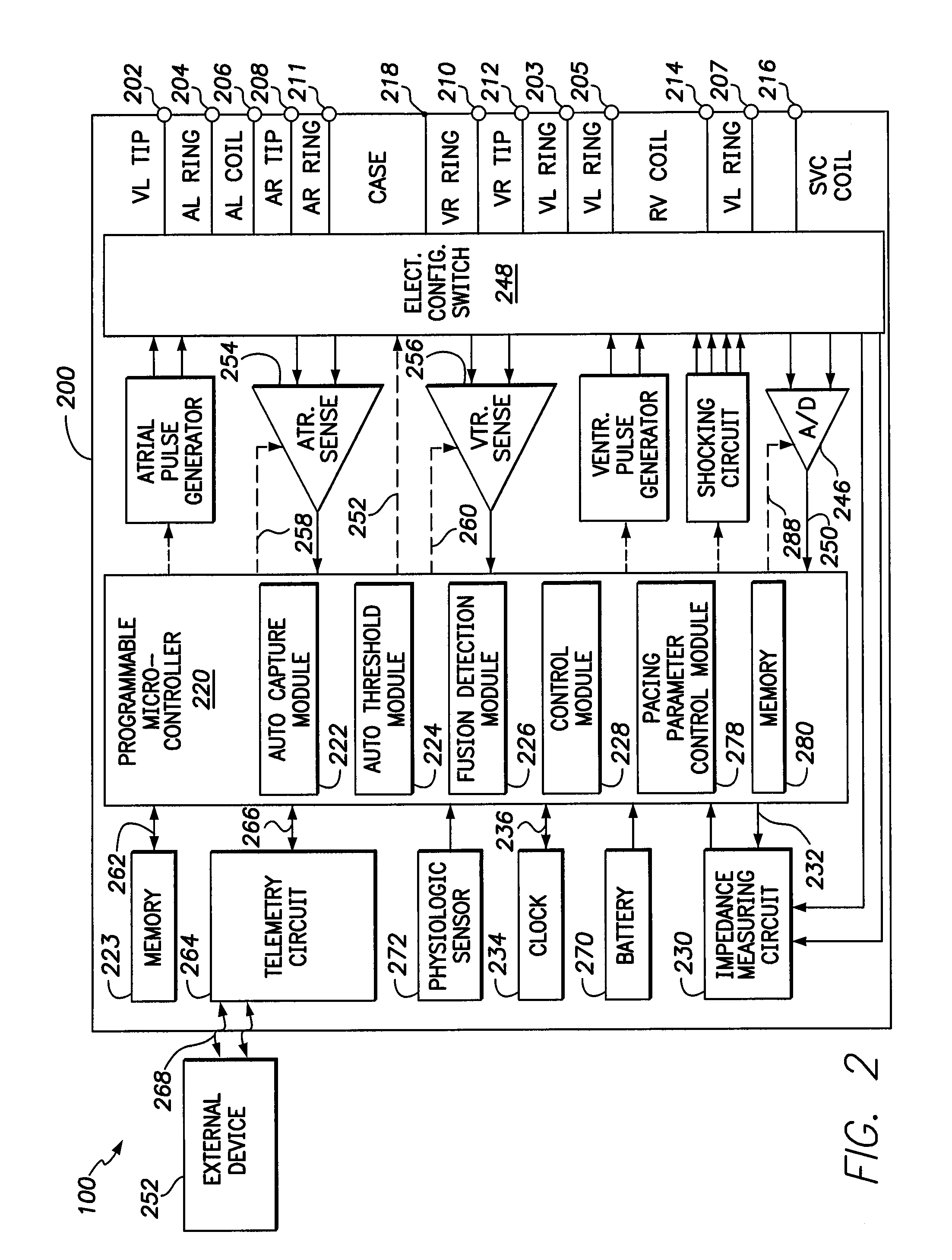
Methods and systems are provided for determining pacing parameters for an implantable medical device (IMD). The methods and systems provide electrodes in the right atrium (RA), right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV). The methods and systems sense RV cardiac signals and LV cardiac signals at an RV electrode and an LV electrode, respectively, over multiple cardiac cycles, to collect global activation information. The methods and systems identify a T-wave in the LV cardiac signal. The methods and systems calculate a repolarization index based at least in part on a timing of the T-wave identified in the LV cardiac signal. The methods and systems set at least one pacing parameter based on the repolarization index, wherein the at least one pacing parameter that is set represents at least one of an AV delay, an inter-ventricular interval and an intra-ventricular interval. Optionally, the methods and systems may deliver an RV pacing stimulus at the RV electrode such that the LV cardiac signal sensed thereafter includes the RV pacing stimulus followed by a T-wave. The methods and systems determine a waveform metric such as at least one of a QT interval, T-wave duration, and T-wave amplitude, and utilize the waveform metric to determine as the repolarization index.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
QT-interval measurement in the electrocardiogram
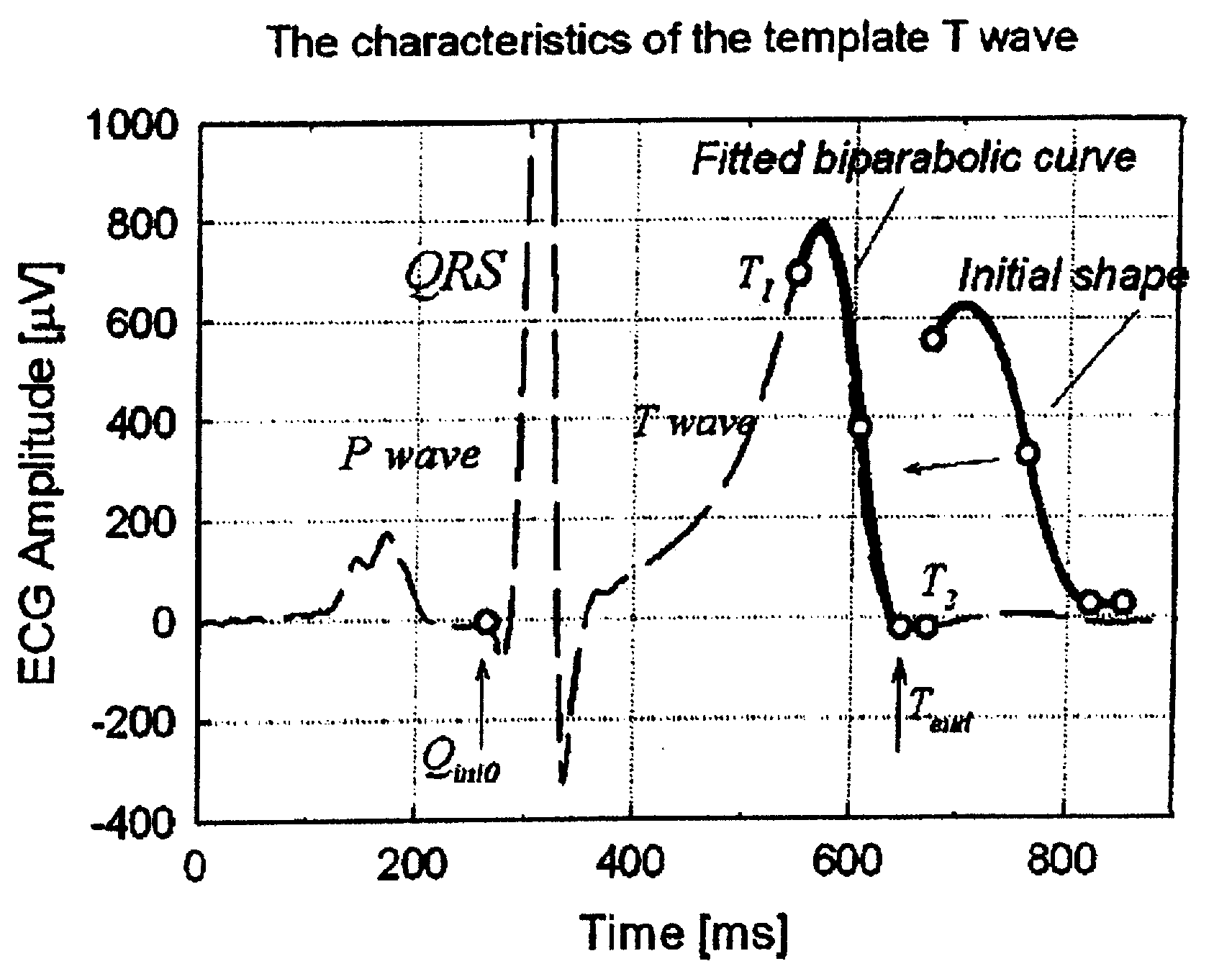
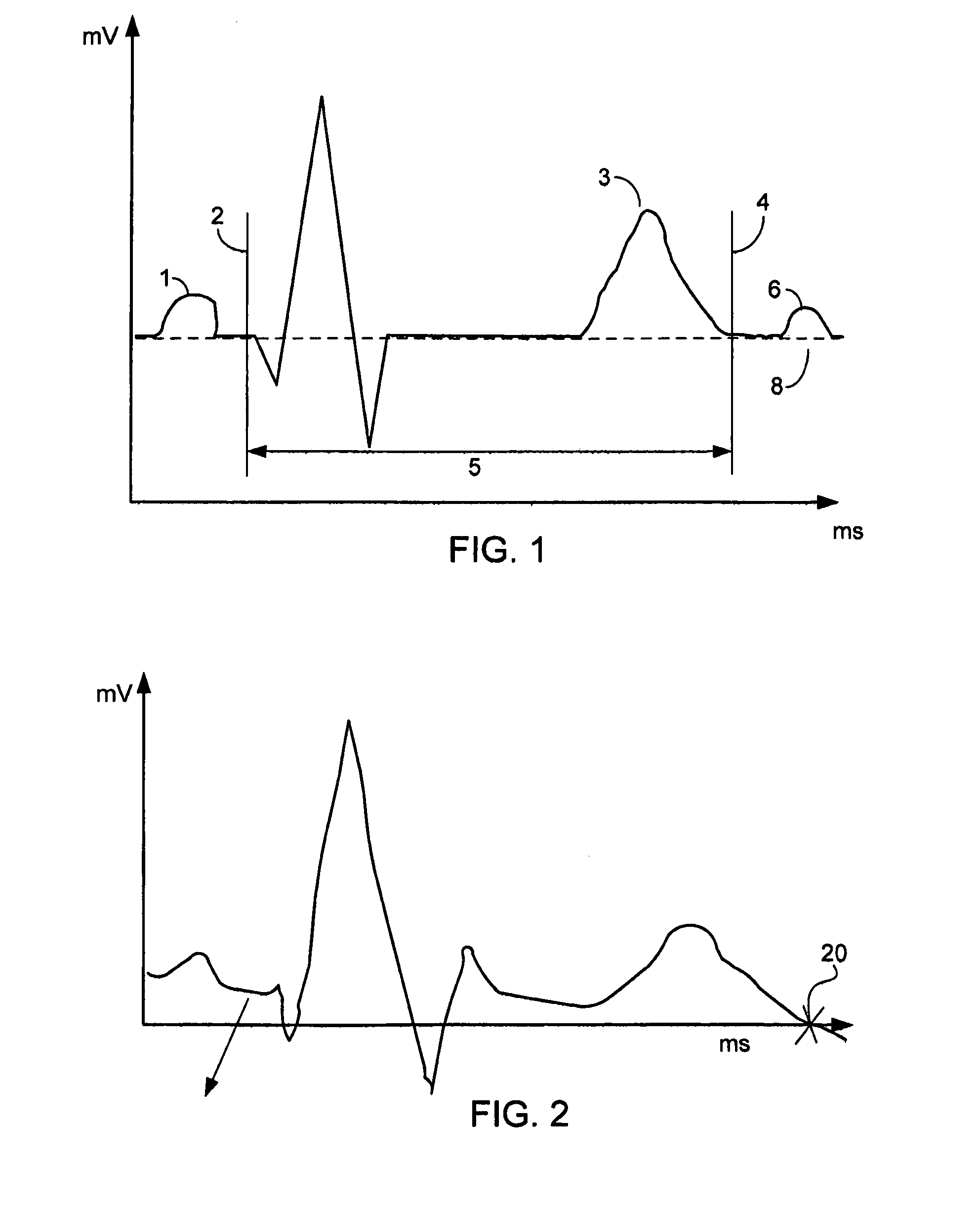
InactiveUS7627369B2Reduce low frequency baseline noiseReduce high frequency noiseElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalElectricity
A method and apparatus for measuring the QT interval of an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is provided wherein the end of the T wave is identified from ECG data. The end of the T wave is defined as the first time of intersection at which an upright T wave of a first set of derived ECG signal data intersects an inverted T wave of a second set of derived ECG signal data. The intersection of the two sets of ECG data is along an isoelectric line within the trough after the positive T wave peak when the superimposed isoelectric baselines from the upright and inverted ECG signals demonstrate the best least squares fit.
Owner:PSI HEARTSIGNALS GLOBAL
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining onset of physiological conditions
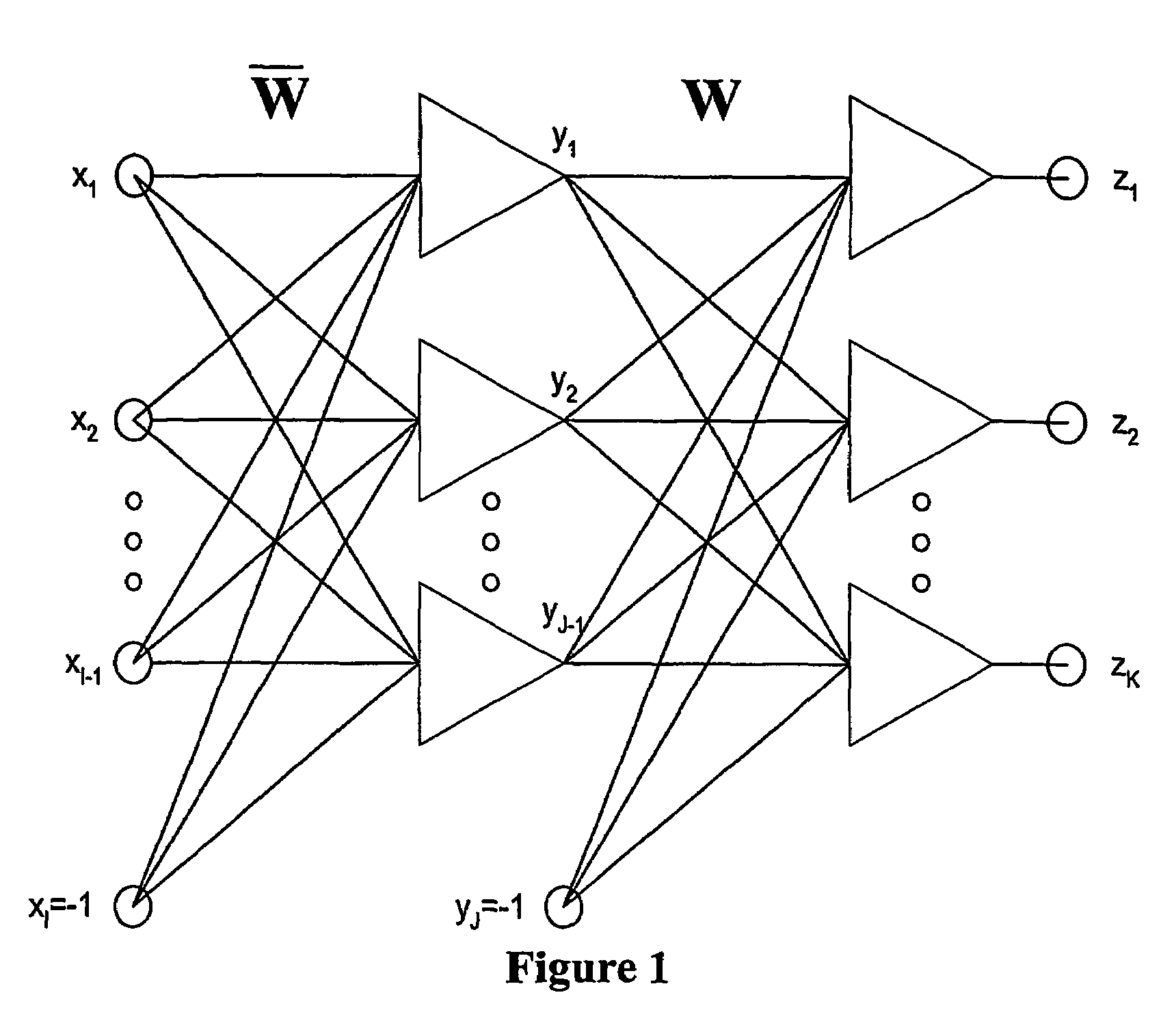
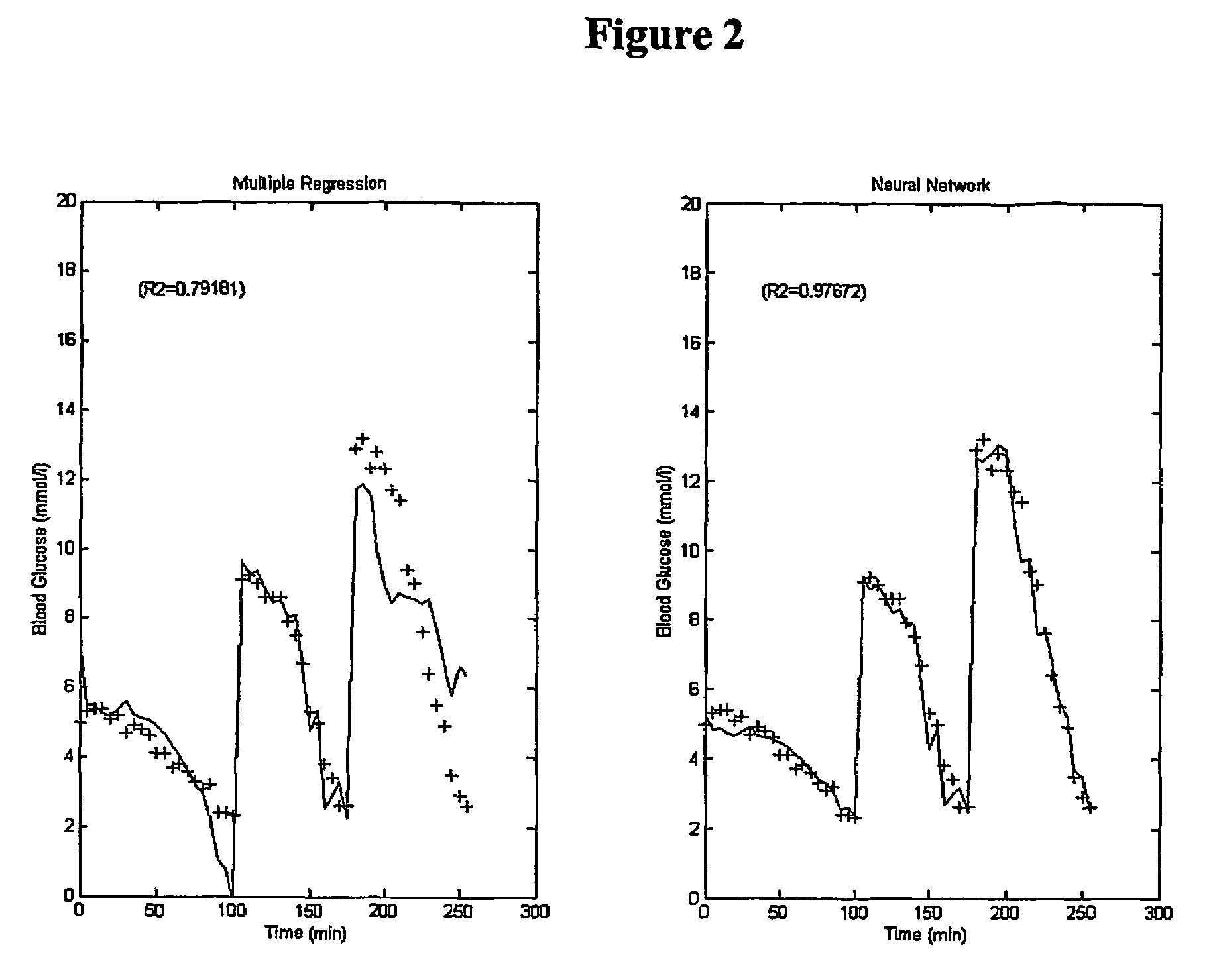
The invention relates to the modelling and design of early warning systems for detecting medical conditions using physiological responses. The device comprises sensors for monitoring physiological parameters such as skin impedance, heart rate, and QT interval of a patient, means for establishing when those parameters change, the rate of change of the parameters, and a neural network processor for processing the information obtained by the sensors. The neural network processor is programmed with a fast learning algorithm. When the neural network establishes that a physiological condition is present in the patient an alarm signal will be generated. The invention extends to a method of non-invasive monitoring of a person using a neural network programmed with a fast learning algorithm. A non-invasive hypoglycaemia monitor is specifically described.
Owner:UNIV OF TECH SYDNEY
Method and system for performing superposition analysis on exercise load electrocardio waveforms
ActiveCN102397067AAccurate judgmentAccurate Waveform DataDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsT waveQT interval
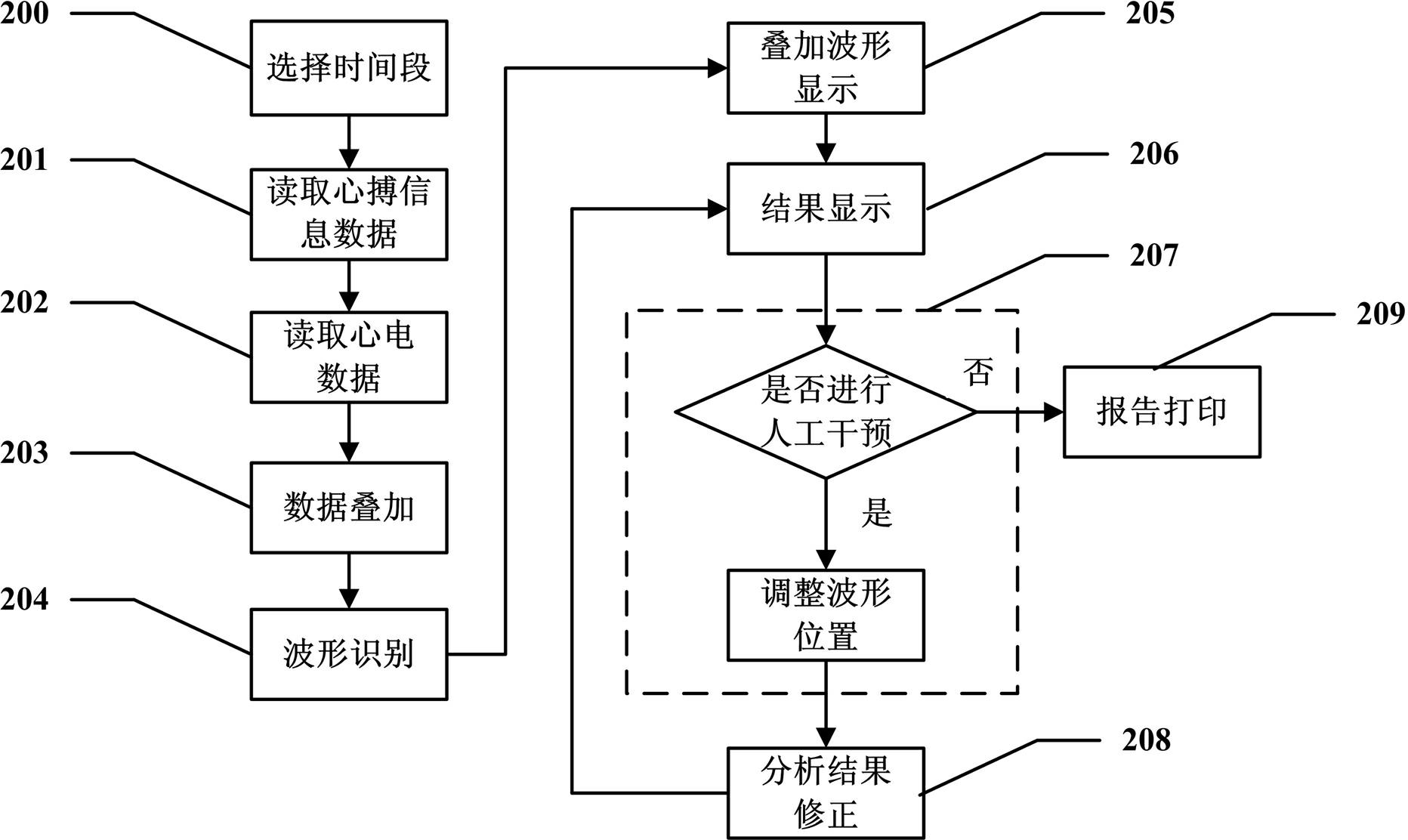
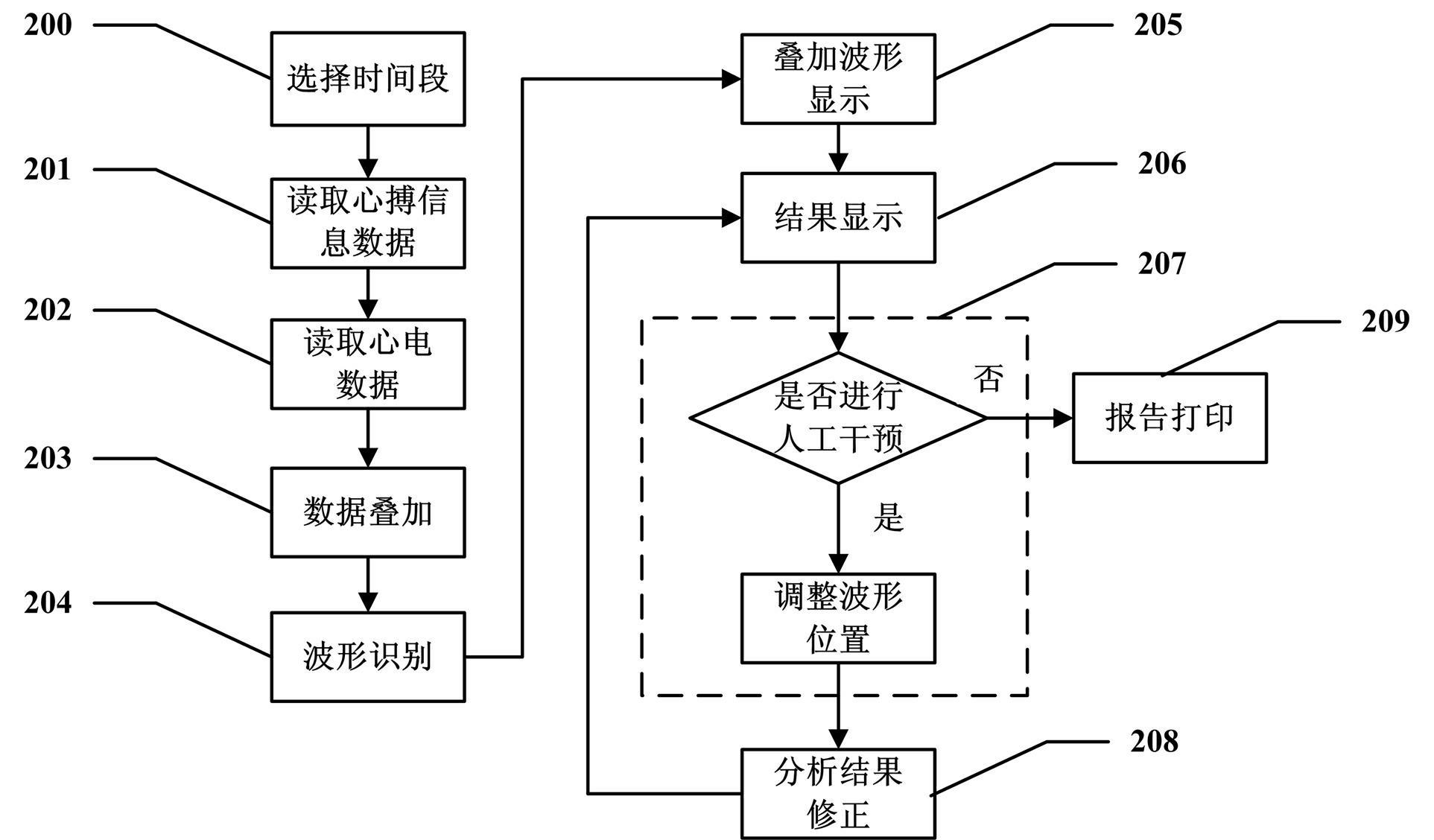
The invention discloses a method for performing superposition analysis on electrocardio data of any time segment. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting any segment of representative waveforms from an electrocardiogram; reading electrocardio data and waveform information in the time period; superposing the waveform of each heart beat in the time period and analyzing the waveform type of the superposed waveforms, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a P wave, the voltage of a Q wave, an R wave and an S wave, the average voltage of an ST segment, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a T wave, the time limit of the P wave, the Q wave, the R wave, the S wave and the T wave, a QT interval and other data; and providing a human-computer interaction interface, displaying an analysis result obtained after waveforms are superposed, and allowing a user to perform manual intervention on the analysis result. The application scope of an exercise load test is broadened, the accuracy of the test result is improved, and the diagnostic report has higher reference value.
Owner:CONTEC MEDICAL SYST
Methods for acute and long-term treatment of substance abuse
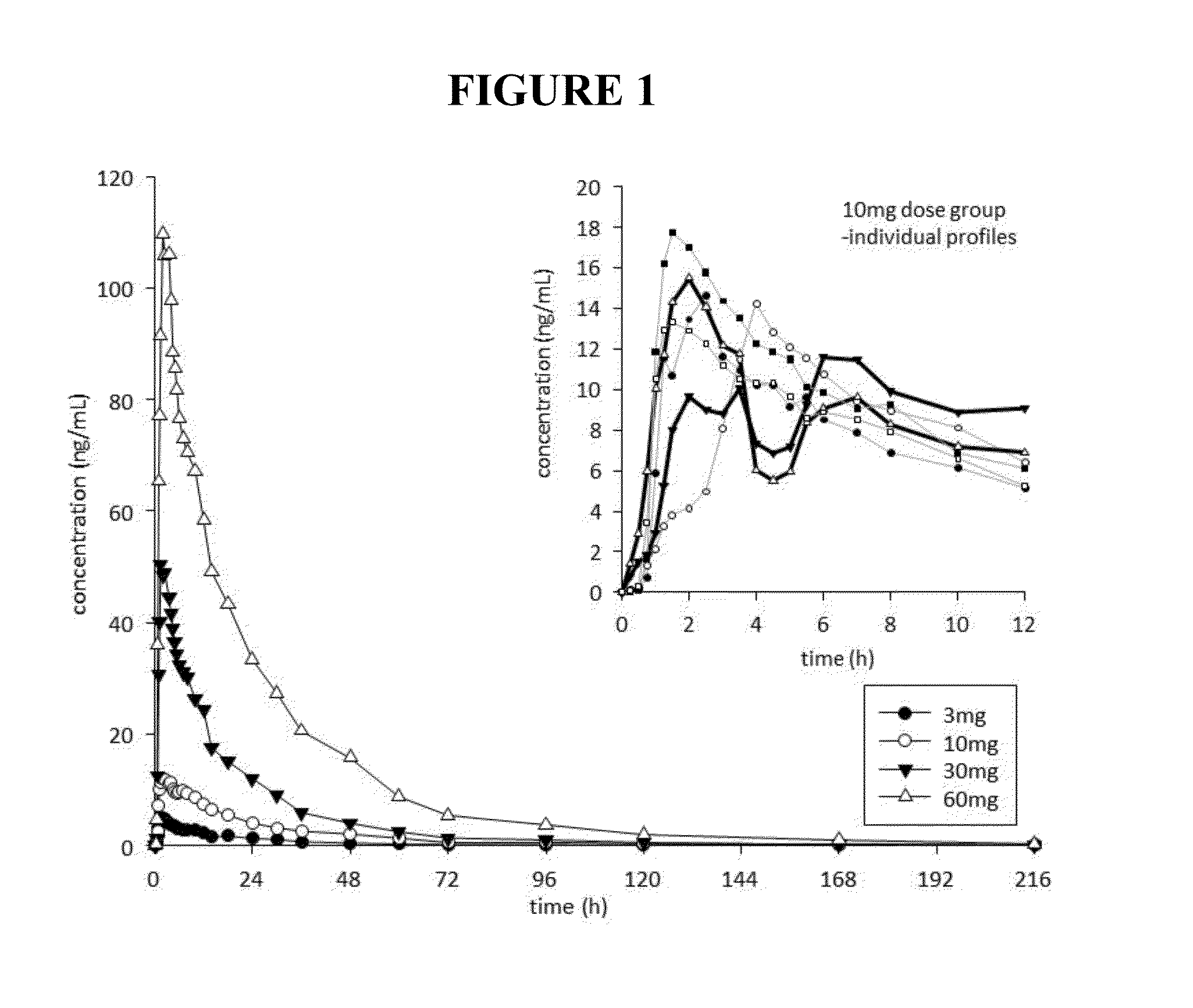
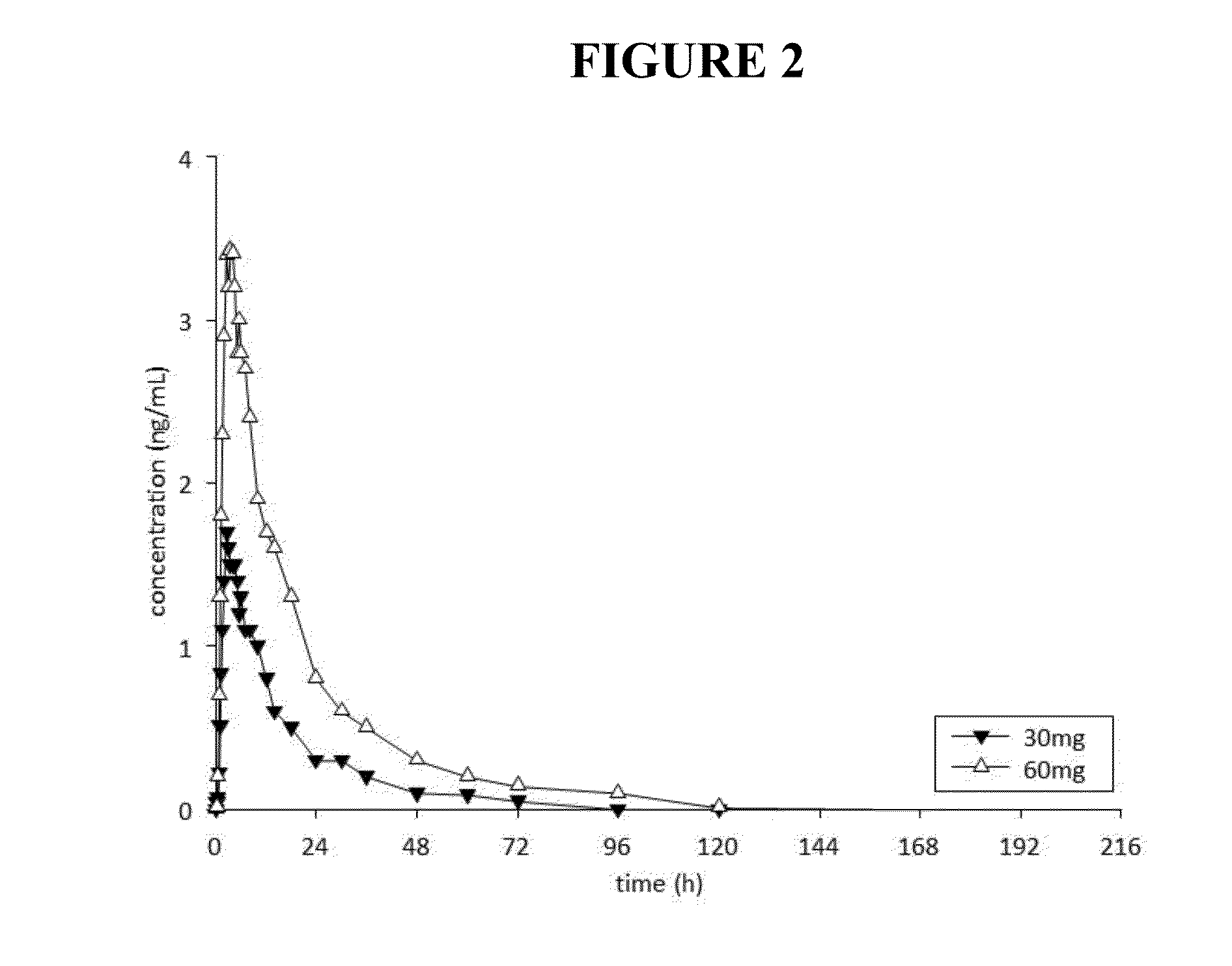
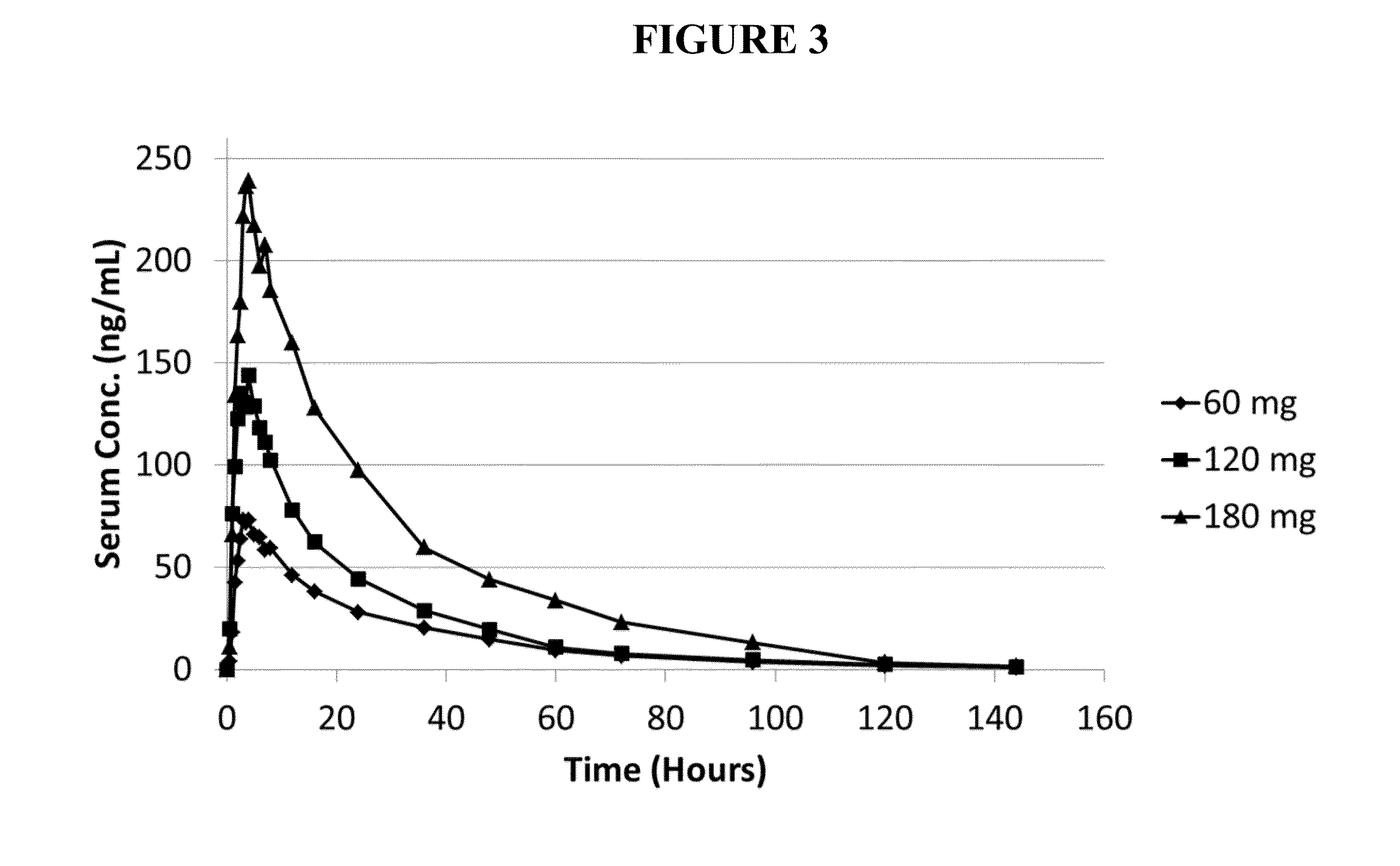
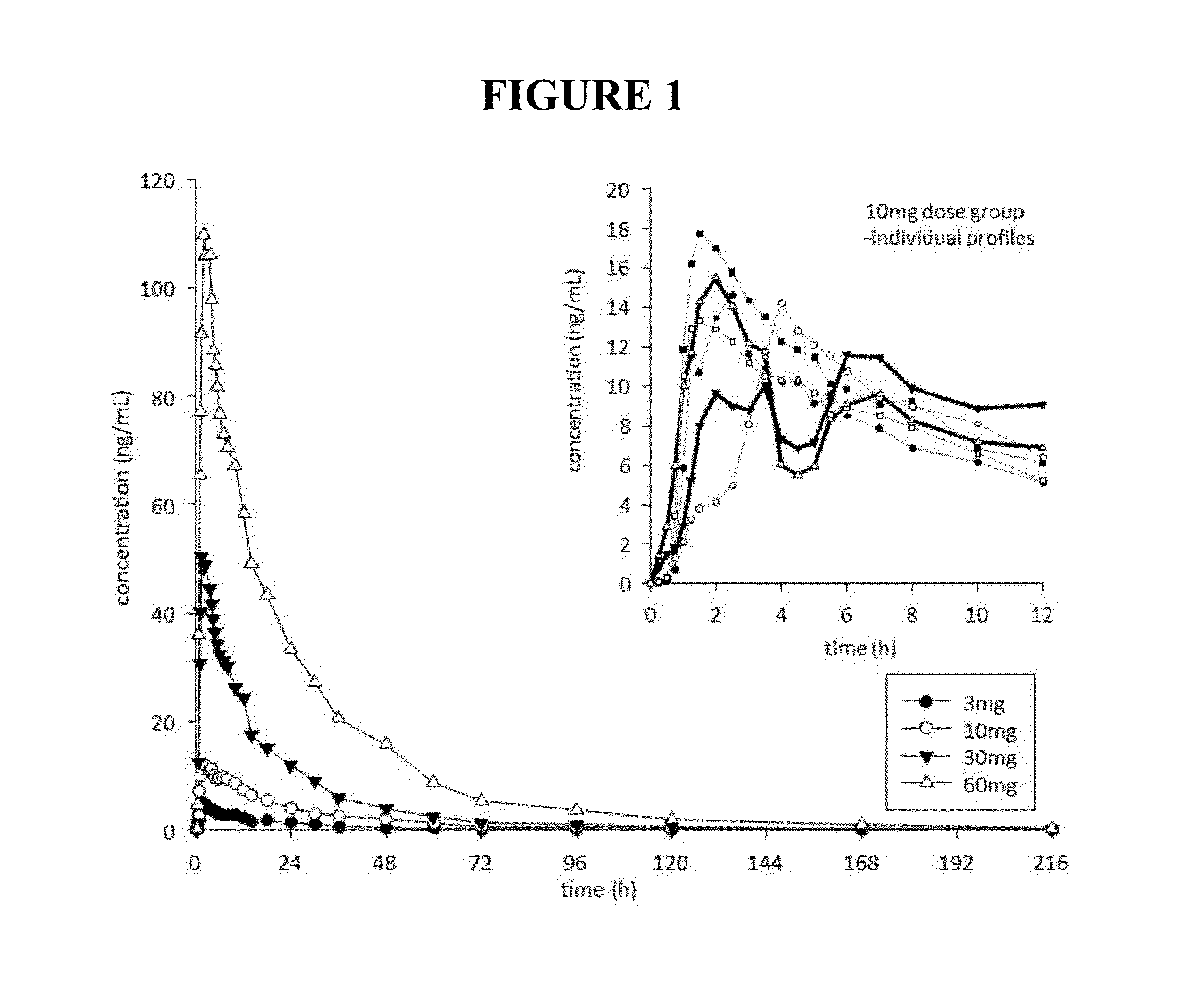
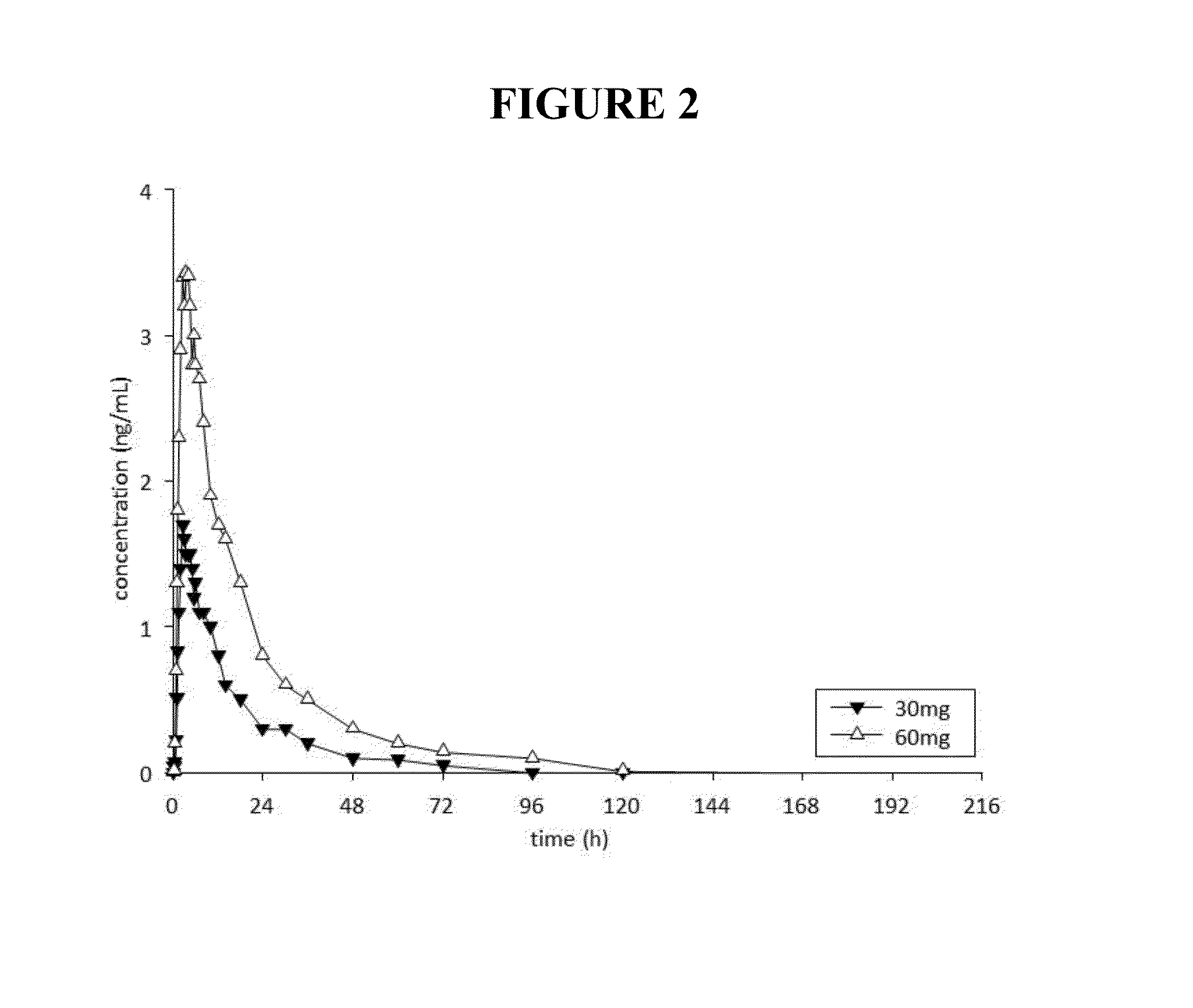
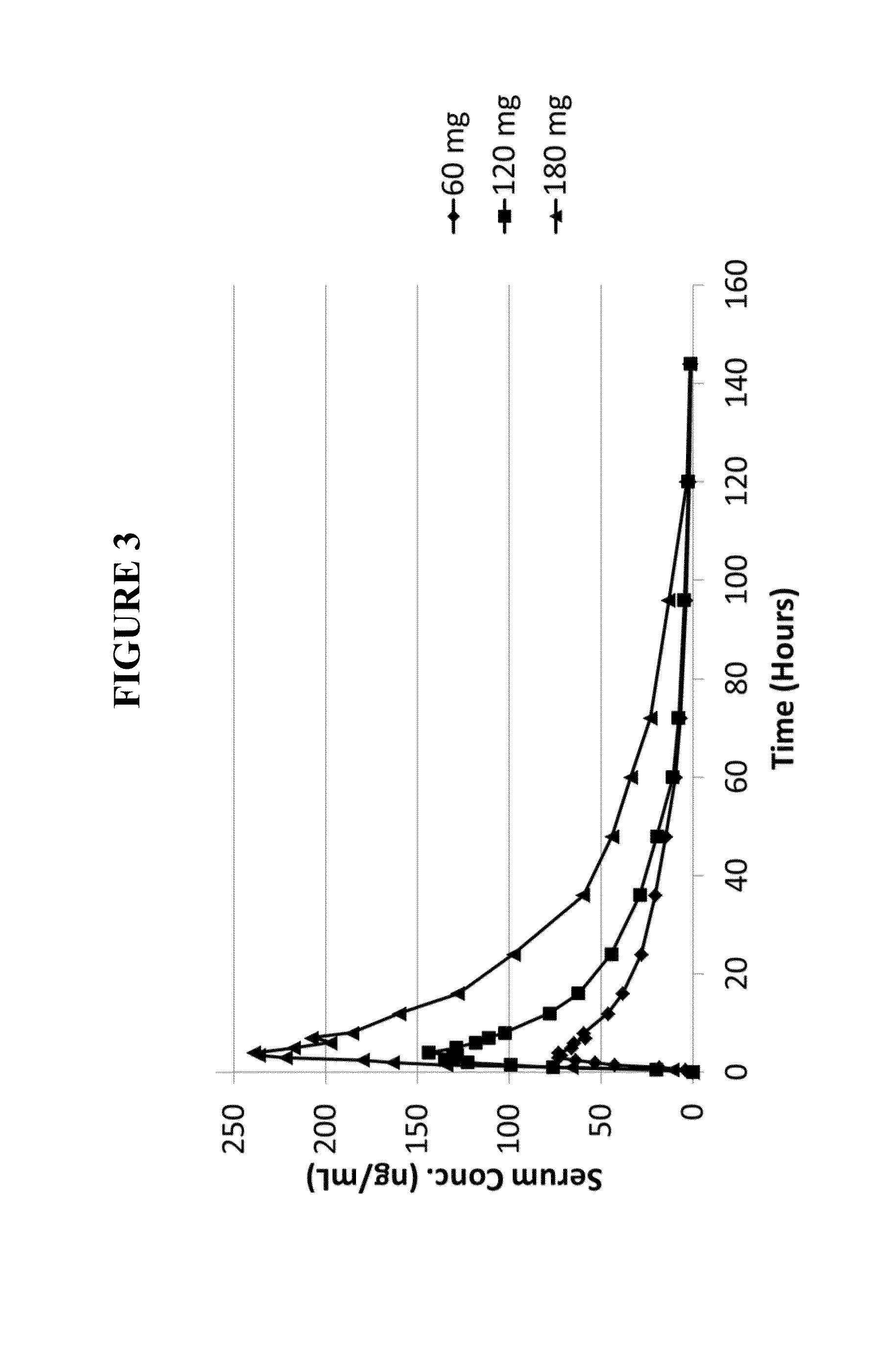
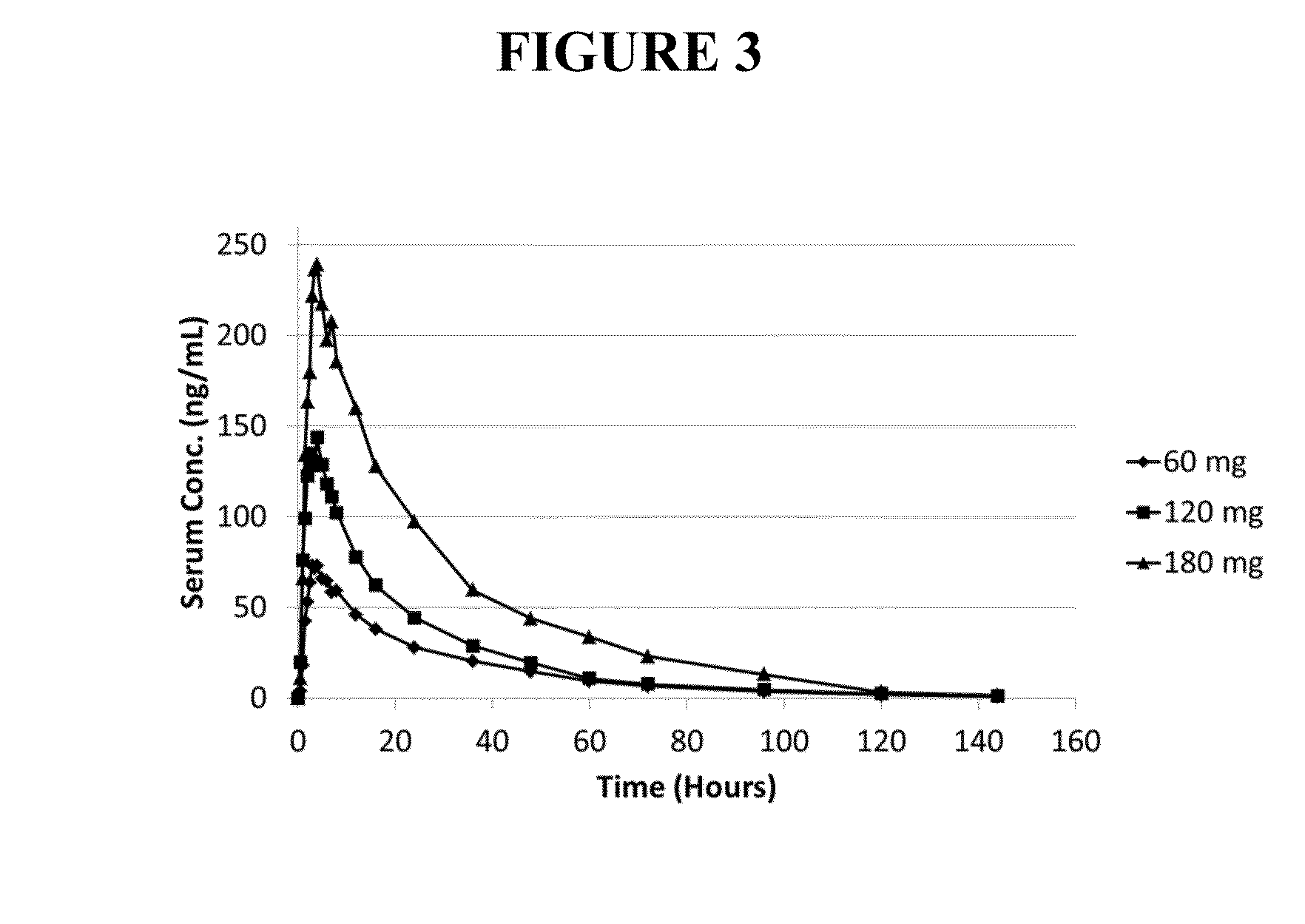
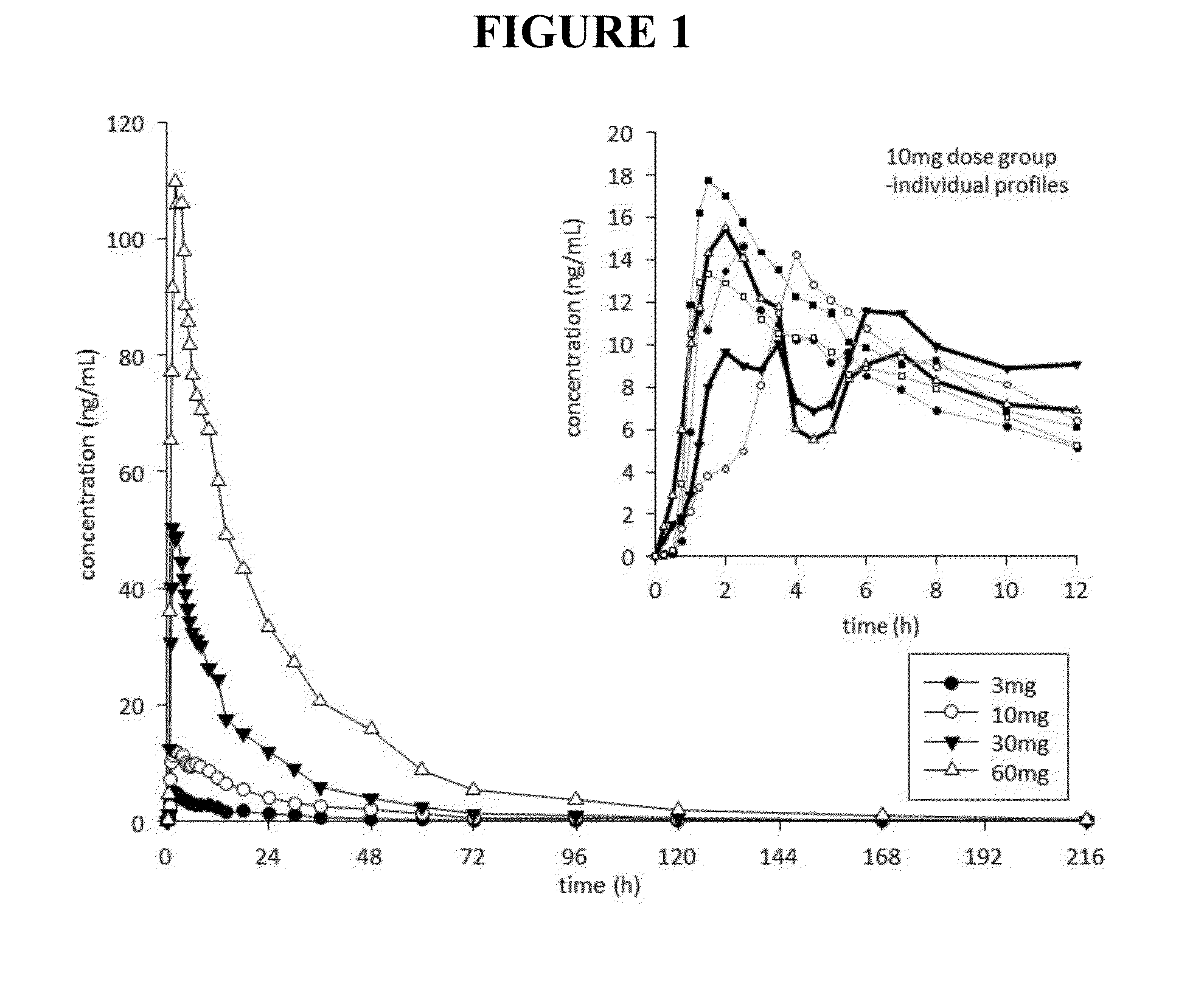
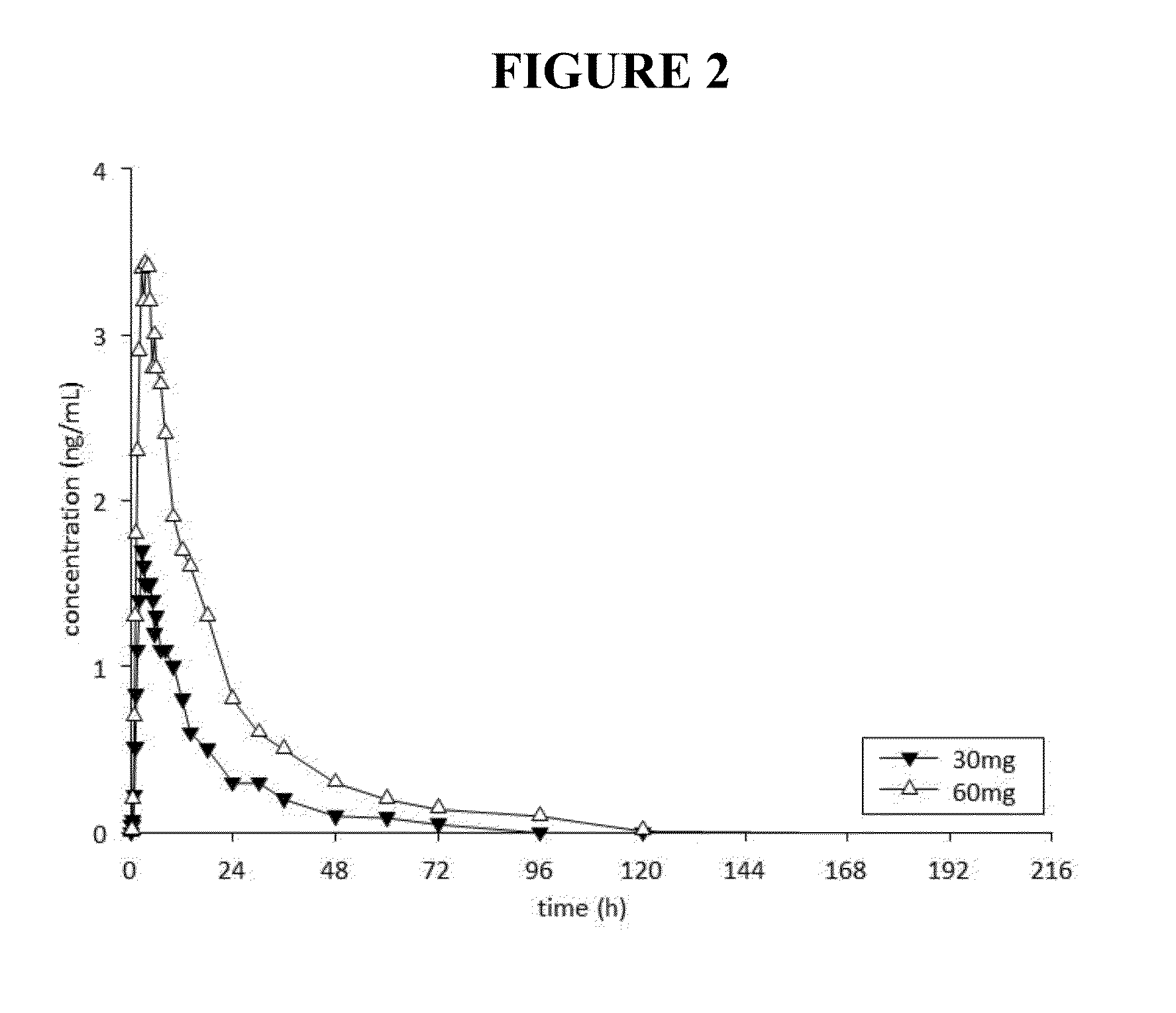
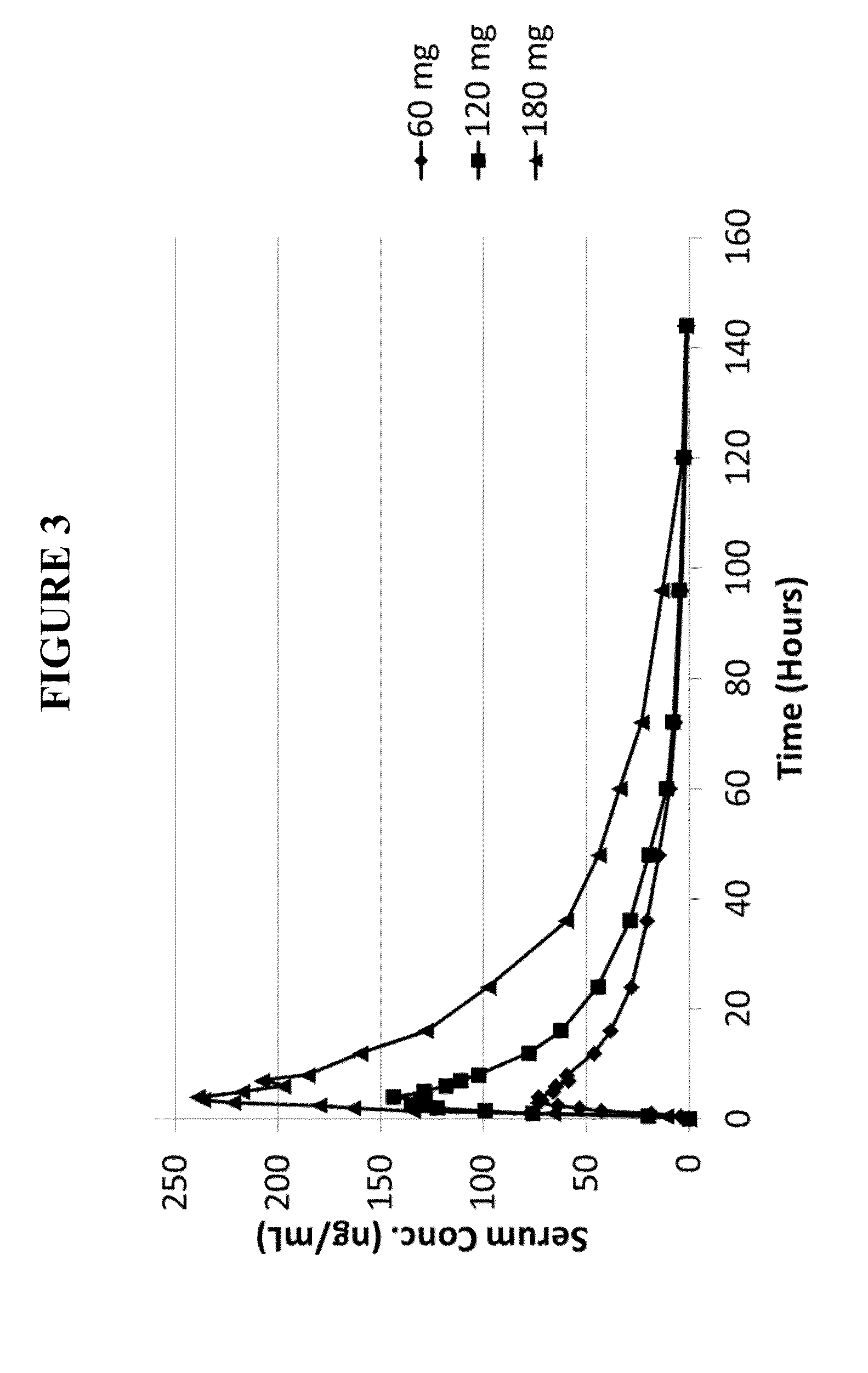
This invention is directed to a method of treating drug addiction, including acute and post-acute withdrawal symptoms, comprising treating an addicted patient with noribogaine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or solvate thereof at a dosage that provides a therapeutic serum concentration. In one embodiment, the average serum concentration is 50 ng / mL to 180 ng / mL under conditions where the QT interval prolongation does not exceed about 50 milliseconds, and preferably about 30 milliseconds.
Owner:DEMERX
Heart stimulator
InactiveUS20080114411A1Risk minimizationTerminate stable ventricular tachycardiaElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsPR intervalVentricular tachycardia
Heart stimulator that provides for timing a premature stimulation pulse for anti-tachycardia pacing outside the vulnerable phase of a ventricle, to terminate stable ventricular tachycardia while minimizing the risk of accelerating stable ventricular tachycardia into unstable ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. RT interval is determined instead of QT interval. Conventional QT interval is defined to end at T wave offset, which is difficult to measure because inherent imprecision in identifying the end of T wave from surface ECG. For safe ATP, such problems may be avoided. Because the VP usually refers to the portion of the T wave near the peak and early downslope (FIG. 3), in order to avoid the VP, only need to determine the peak of T wave, then set an blanking window or safety margin (e.g., 20 ms before to 20 ms after the peak of T wave) during which ATP pulses should not be delivered.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
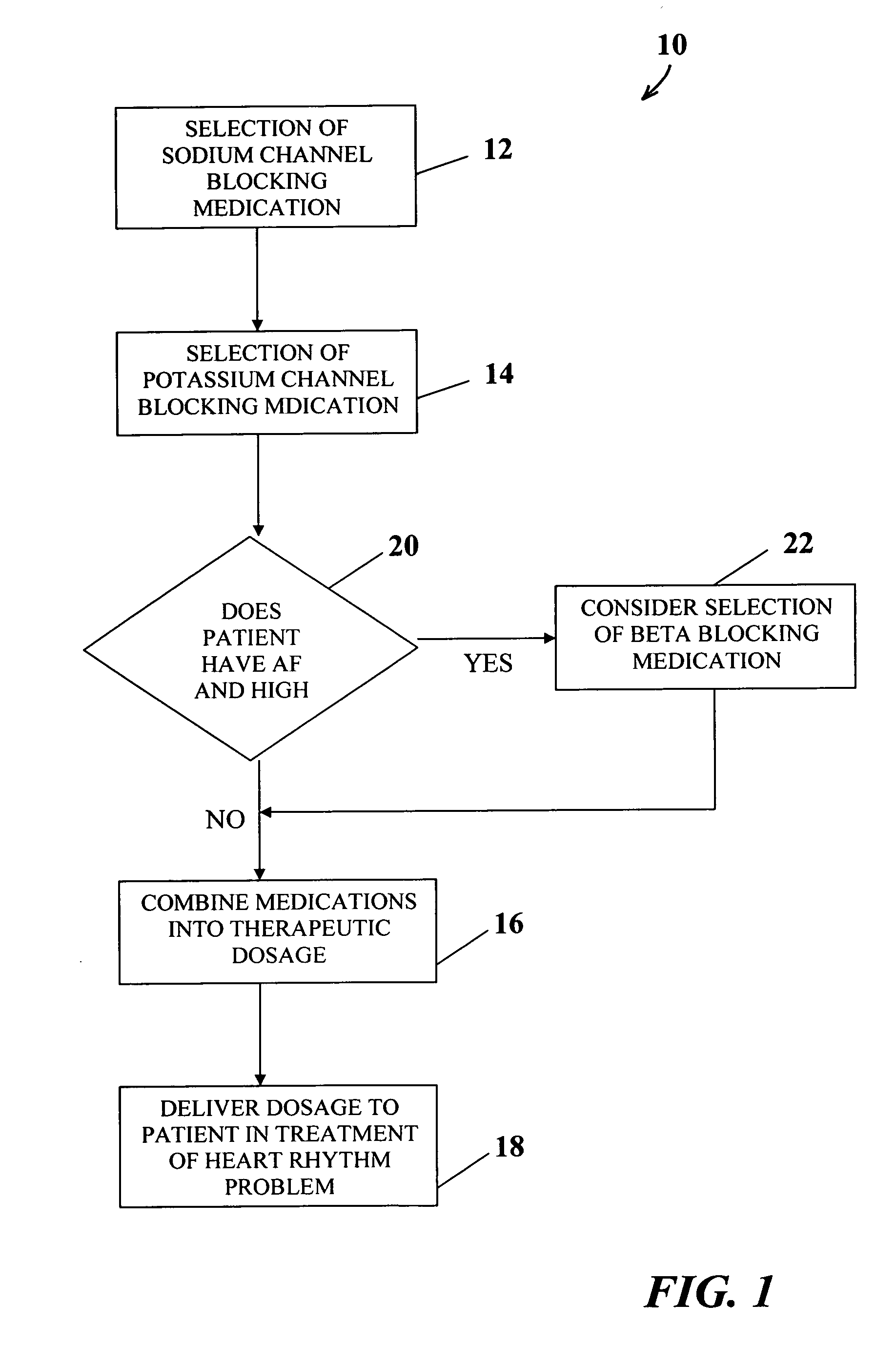
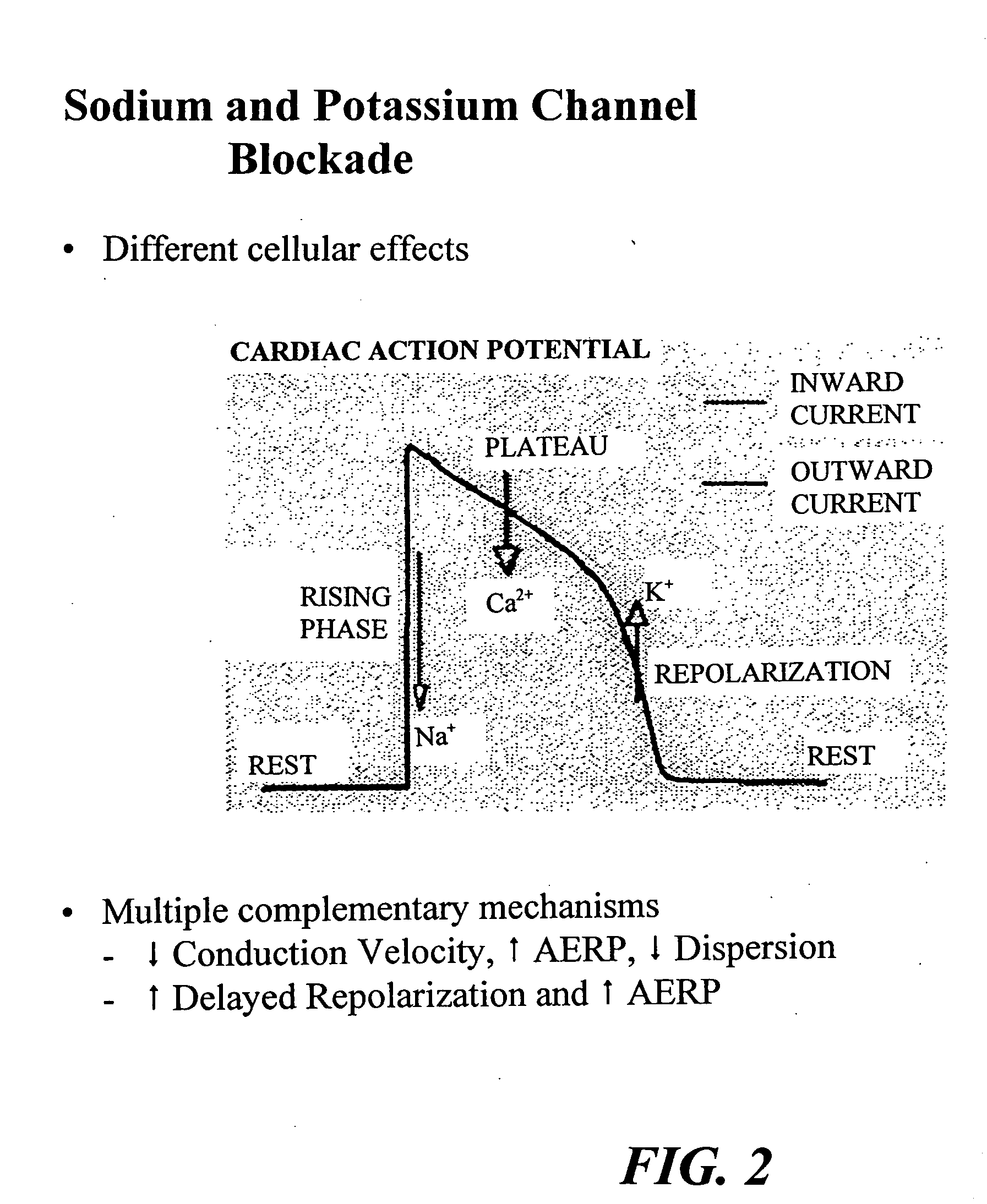
Method of drug therapy in treatment of cardiac arrhythmias
A method for treatment of cardiac arrhythmias is disclosed. The method comprises the combining of a sodium channel blocking medication and a potassium channel blocking medication into a therapeutic dosage and the delivery of the therapeutic dosage to a patient in treatment of a heart rhythm problem. The heart rhythm problems being treated include atrial fibrillation and atrial or ventricular tachycardia. Preferably, the therapeutic dosage is at least one tablet and the concentration of each medication is determined based upon the heart problem being treated, the underlying heart rate, the QT interval and other comorbid conditions of the patient. A pharmaceutical composition for the therapeutic treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in a patient is also provided having a combination of a sodium channel blocking medication and a potassium channel blocking medication. Under certain conditions of the patient, the composition can also include a beta blocking medication.
Owner:SRA JASBIR S
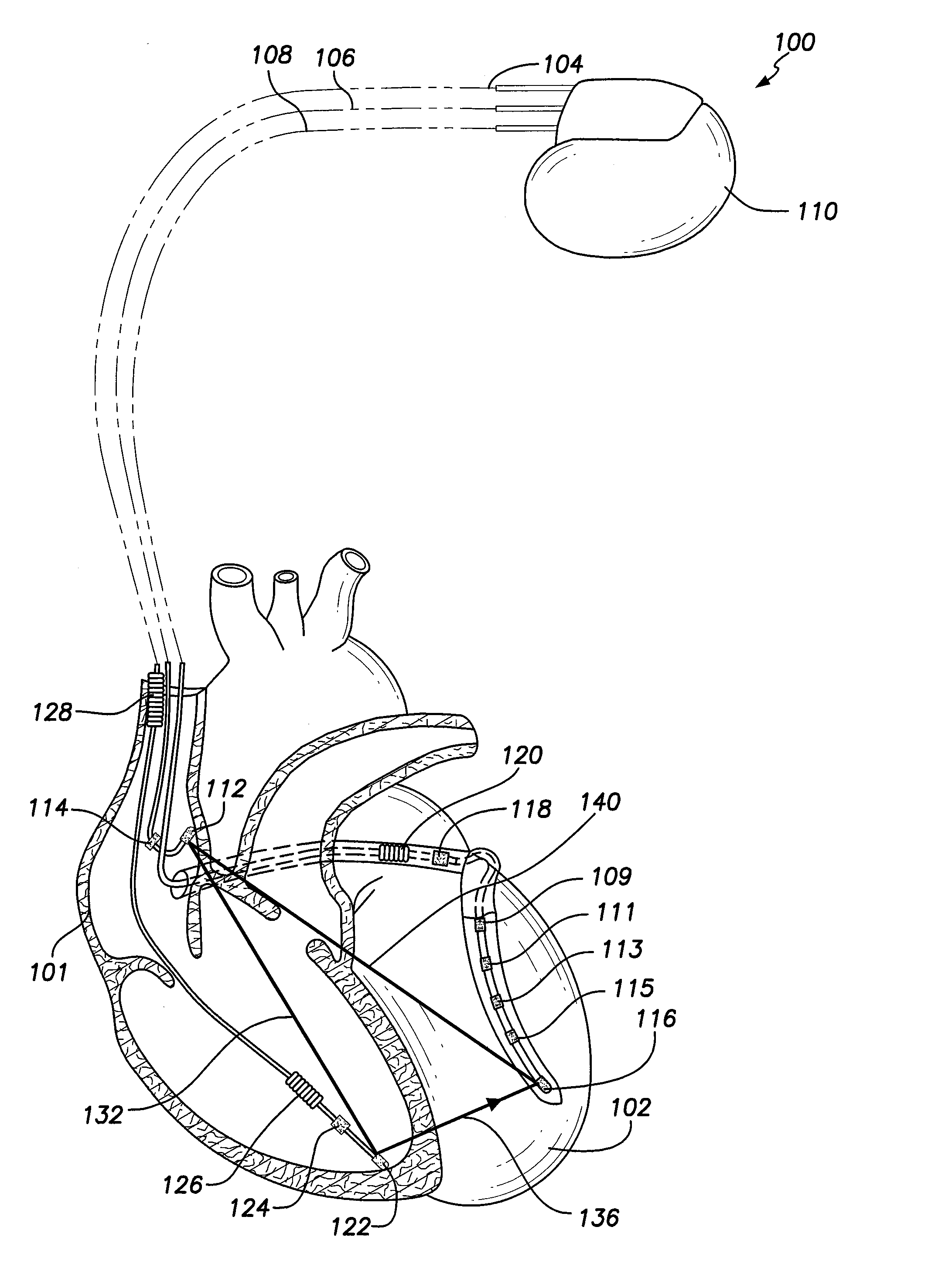
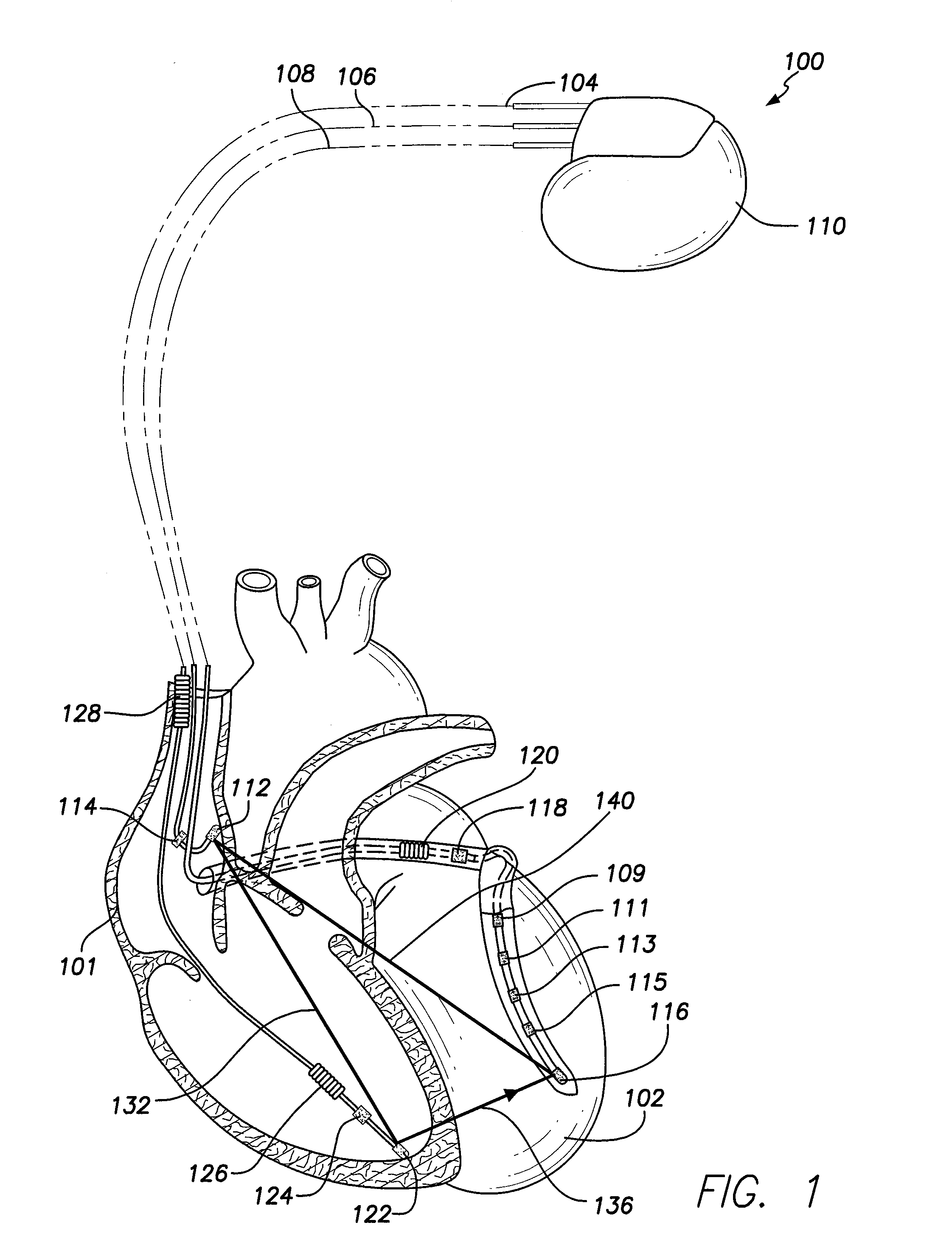
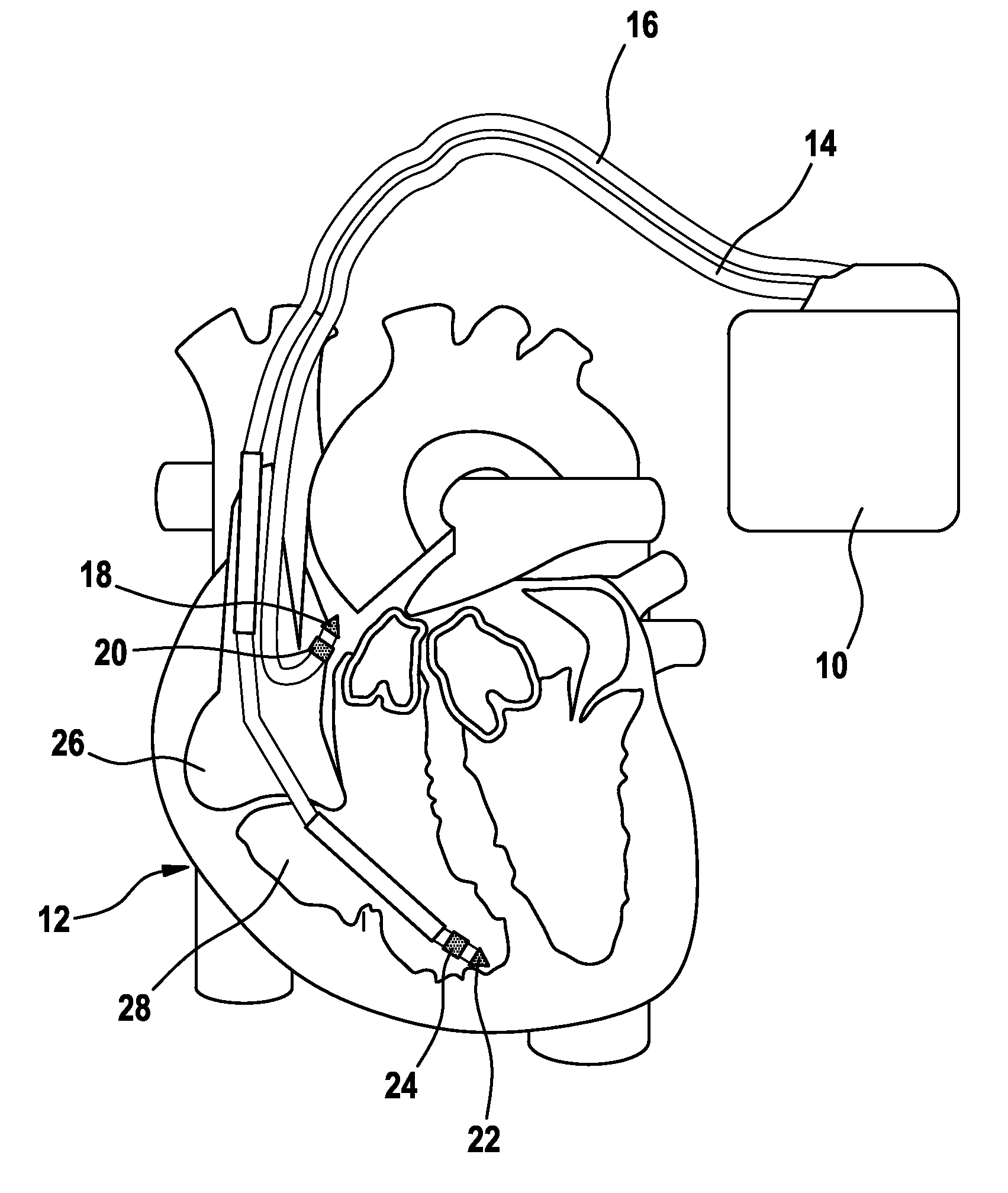
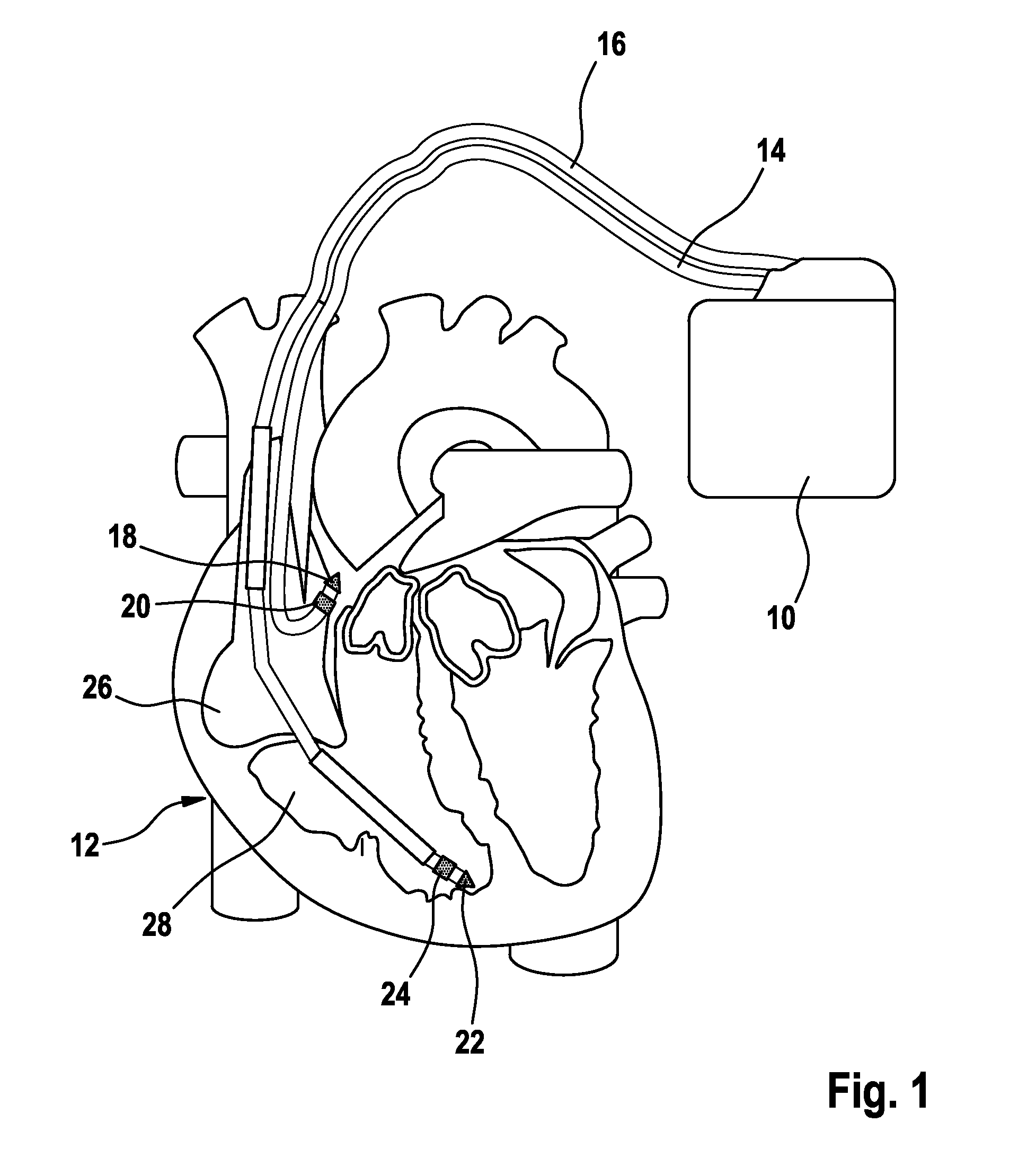
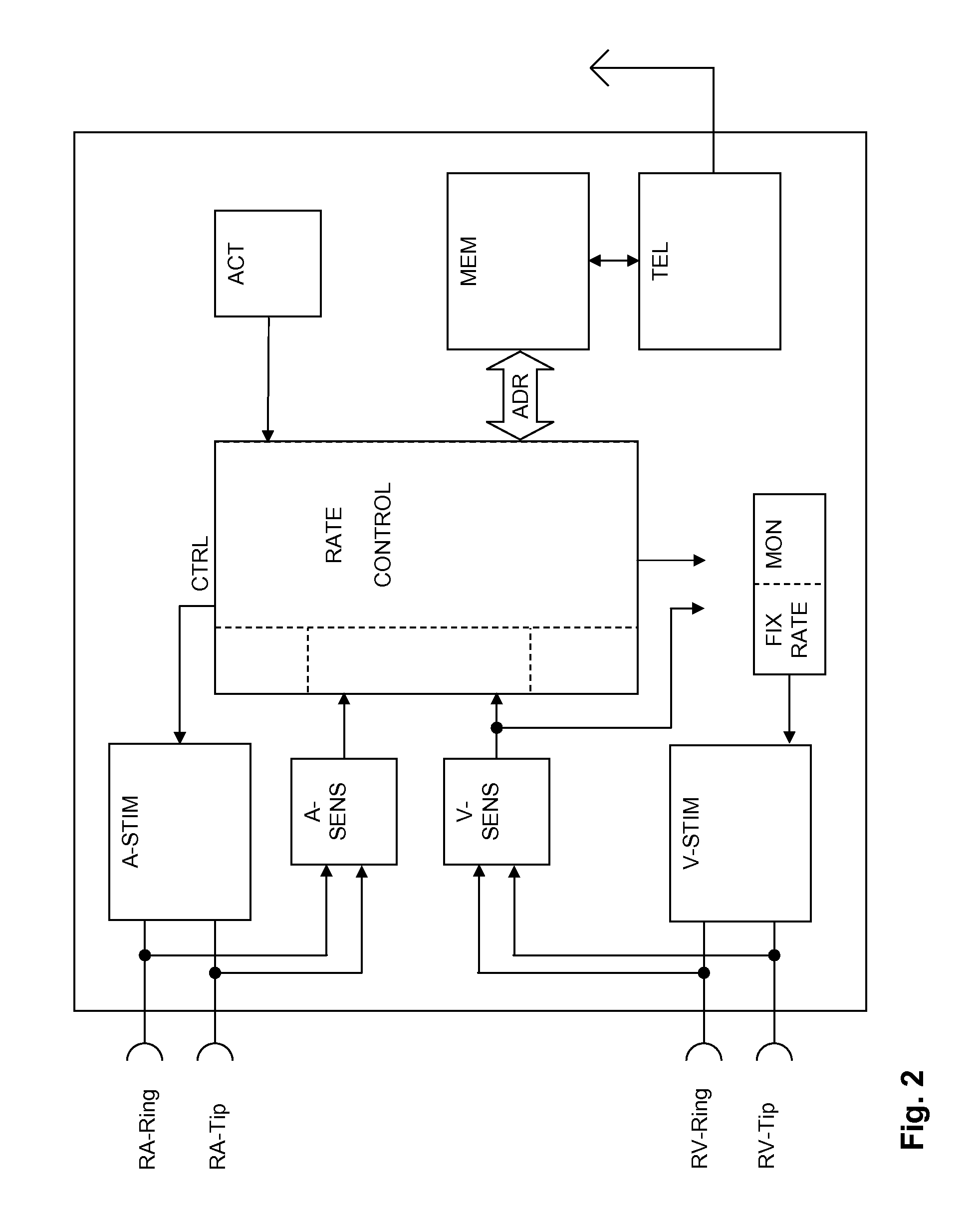
System and method for treating abnormal ventricular activation-recovery time
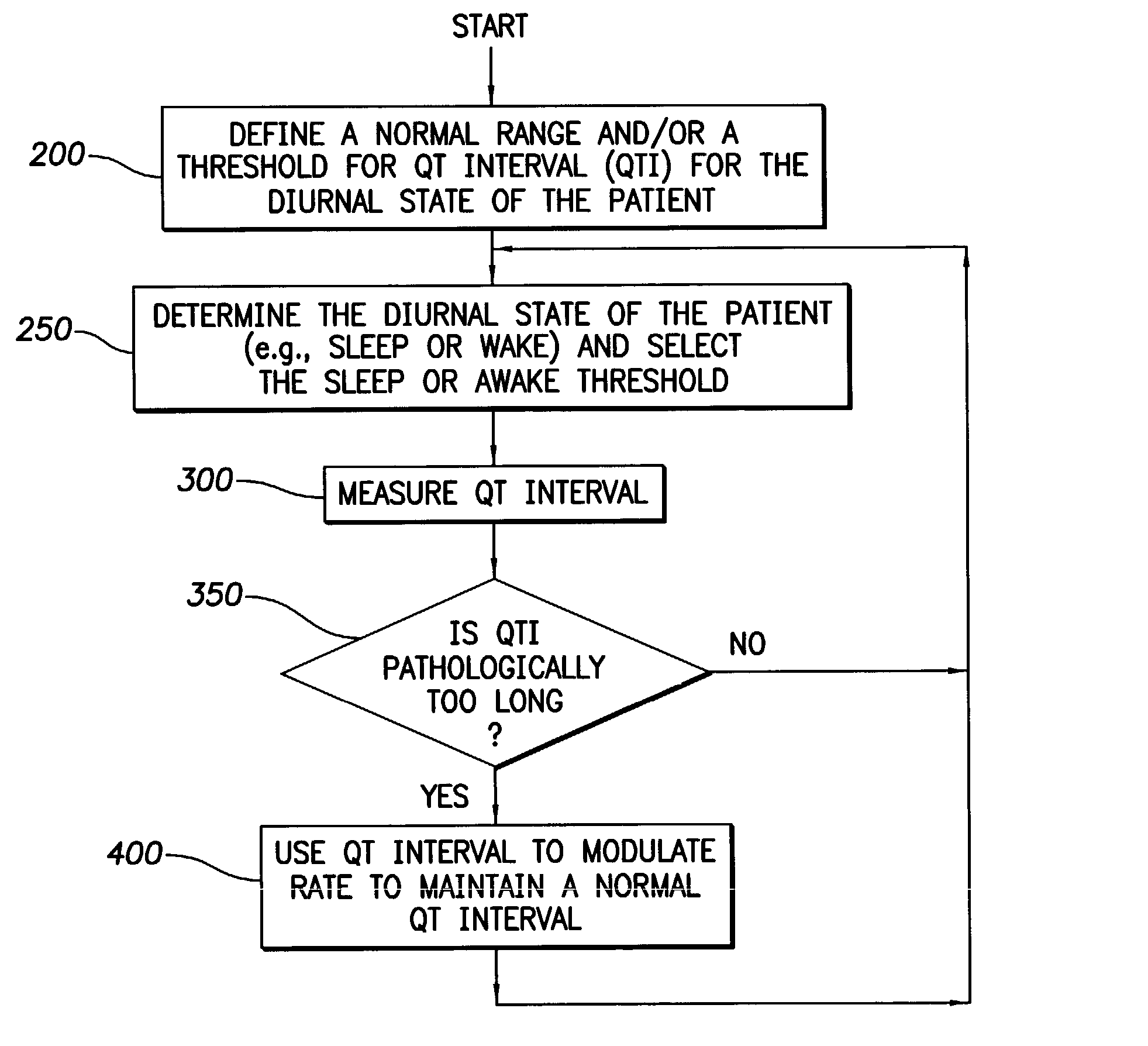
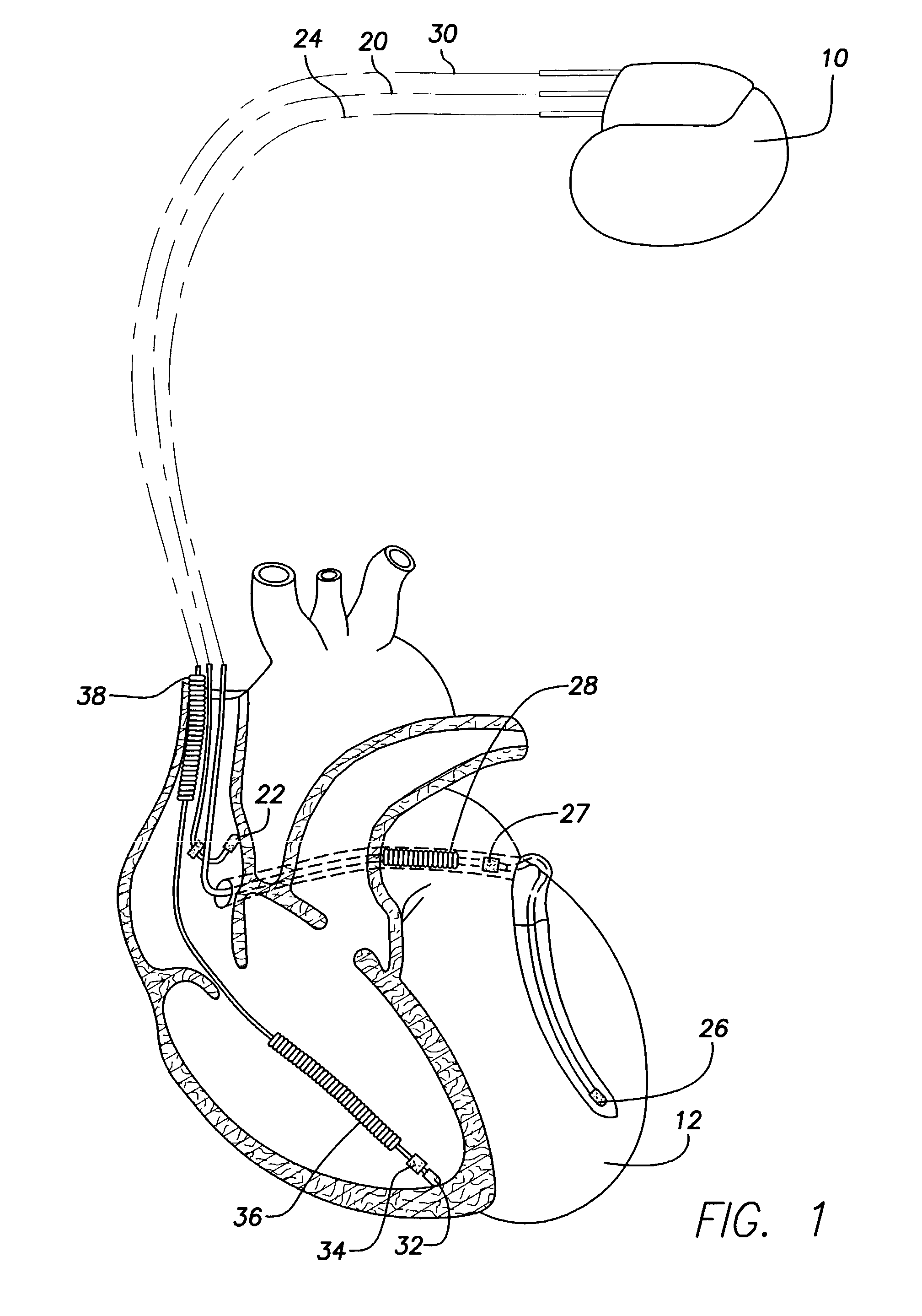
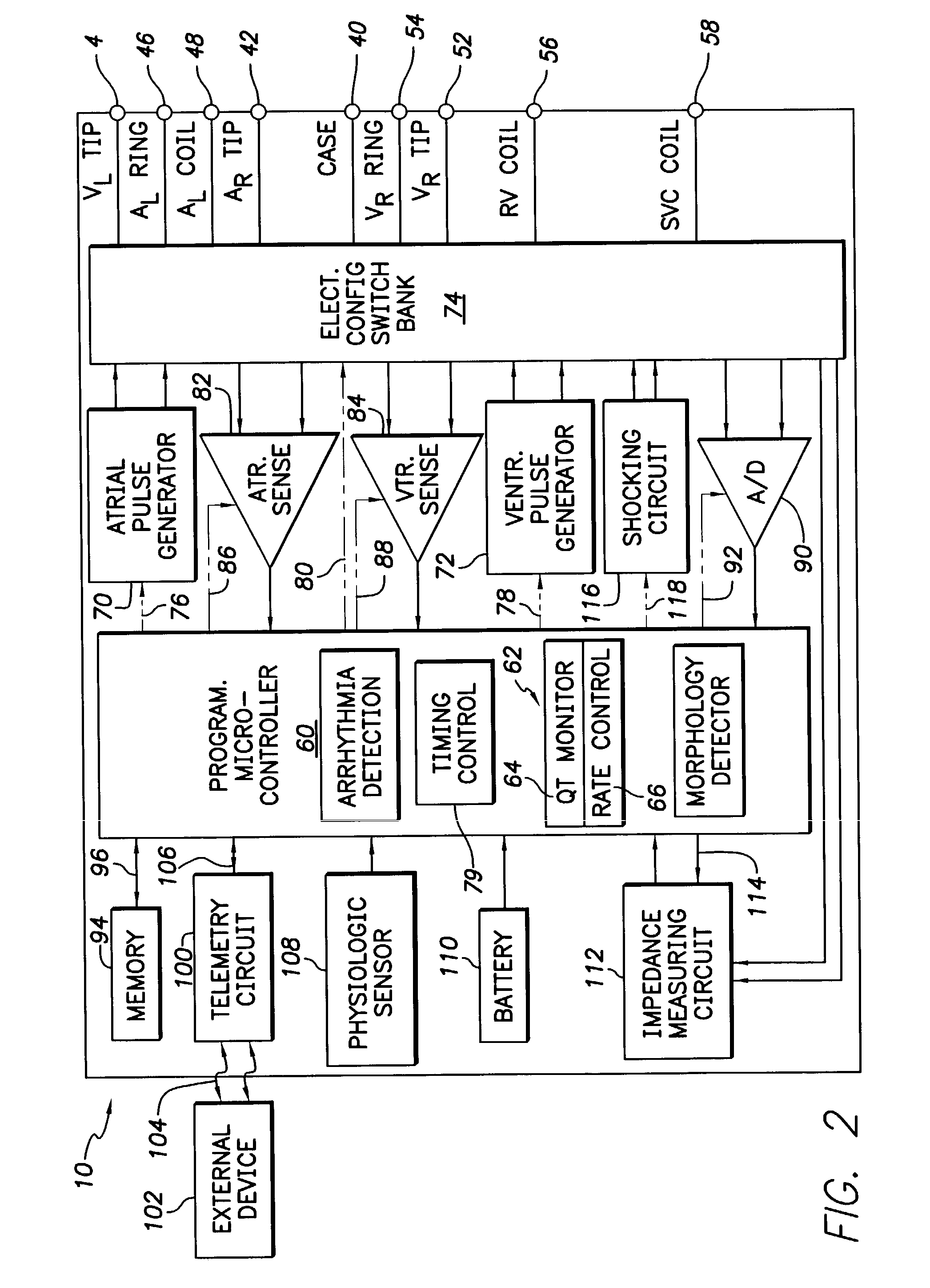
An implantable cardiac stimulation device provides long QT interval therapy for preventing abnormal ventricular activation-recovery time and ultimately ventricular arrhythmias. The device includes a sensing circuit that senses intracardiac activity of a heart and that generates electrical signals representing electrical activity of the heart. The device includes a physiologic sensor, such as body motion, or other diurnally varying sensor that reliably detects a diurnal state of the patient (i.e., not the QT interval itself). The device further includes a measuring circuit that measures a QT interval of the electrical signals, a control circuit that determines whether the QT interval is appropriate for the diurnal state, and a pulse generator that delivers pacing pulses to at least one chamber of the heart at a pacing rate when the QT Interval is pathologically too long. Furthermore, the pacing rate control circuit varies the pacing rate of the pulse generator responsive to the measured QT interval according to the measured diurnal state.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Use of noribogaine for the treatment of pain
InactiveUS20150258104A1Alleviate and inhibit painBiocideAnimal repellantsSerum concentrationQT interval
This invention is directed to methods of treating pain in patients comprising treating patients with noribogaine at a dosage that provides an average serum concentration of 50 ng / mL to 180 ng / mL, including under conditions where the QT interval prolongation does not exceed about 50 milliseconds.
Owner:DEMERX
Cardiac function circadian variation analysis system and method
InactiveUS8391962B2Increase cost-effective deploymentTargeted optimizationElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationRR intervalQT interval
Systems and Methods for stratifying relative risks of adverse cardiac events by processing a duration of electrocardiograph recordings generally recorded by a Holter type of device. The duration of electrocardiograph recordings are processed to resolve RR interval related data, QT interval related data, and are fitted to formulas to at least partially establish fitting related measures. The fitting formulas incorporate circadian related periodic factors, and can further incorporate additional processing including utilizing Lissajous analysis techniques, among others.
Owner:WATANABE MARI ALFORD
Methods and compositions for reducing tolerance to opioid analgesics
InactiveUS20150258108A1Effective analgesiaReduced Tolerance RequirementsBiocideAnimal repellantsSerum concentrationTolerability
A method for modulating tolerance to an opioid analgesic in a patient undergoing opioid analgesic therapy, the method comprising interrupting or administering concurrently with said opioid analgesic therapy an amount of noribogaine, noribogaine derivative, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or solvate thereof that provides a therapeutic serum concentration of noribogaine. In some embodiments, the therapeutic average serum concentration is 50 ng / mL to 180 ng / mL, said concentration being sufficient to re-sensitize the patient to the opioid as an analgesic while maintaining a QT interval of less than about 500 ms during said treatment.
Owner:DEMERX
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and compositions for sustained noribogaine treatment
This invention is directed to a method of treating opioid or opioid-like drug addiction, including acute and post-acute withdrawal symptoms, comprising treating an addicted patient with noribogaine at a dosage that provides an average serum concentration of 50 ng / mL to 180 ng / mL under conditions where the QT interval prolongation does not exceed about 50 milliseconds.
Owner:DEMERX
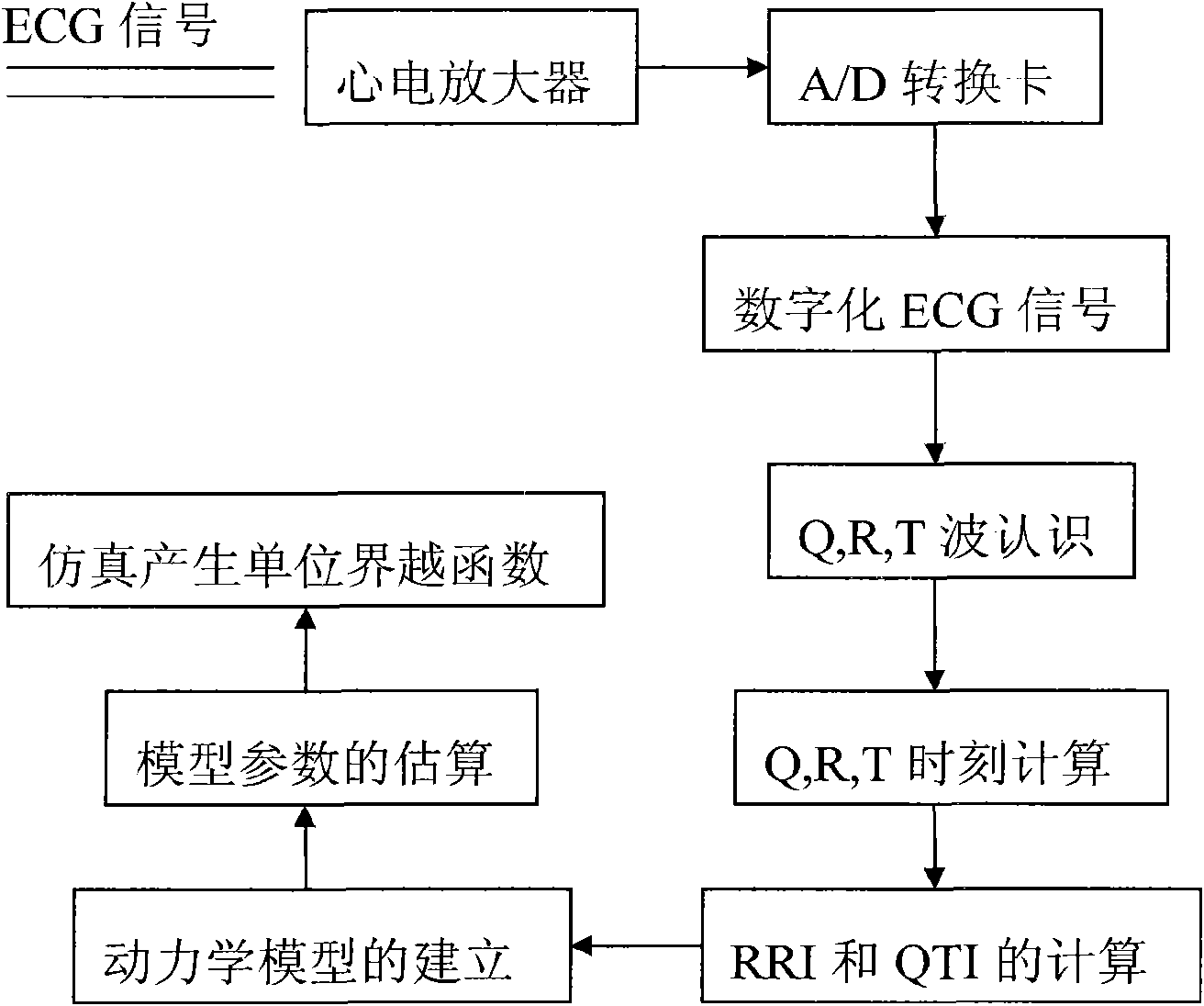
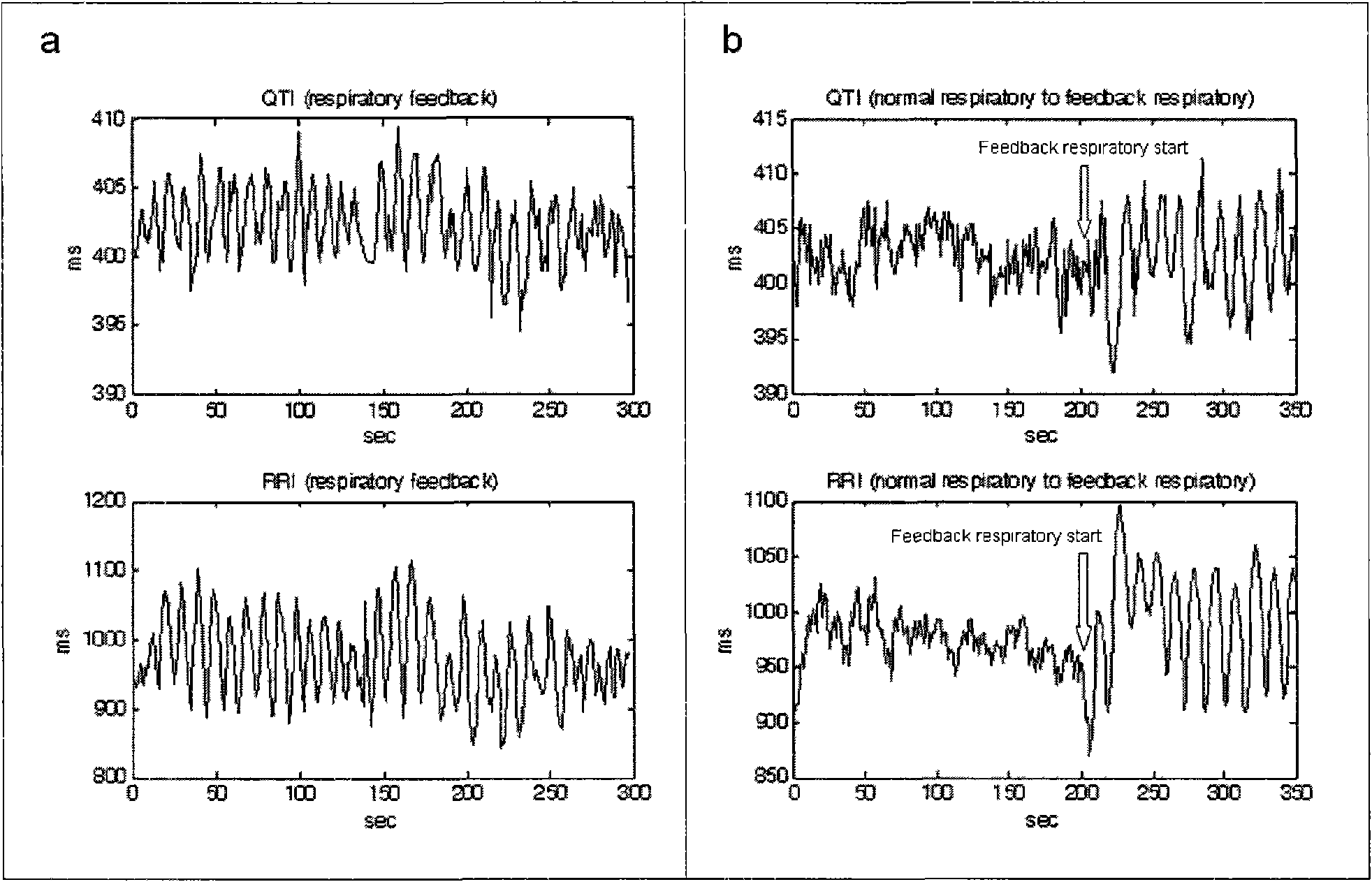
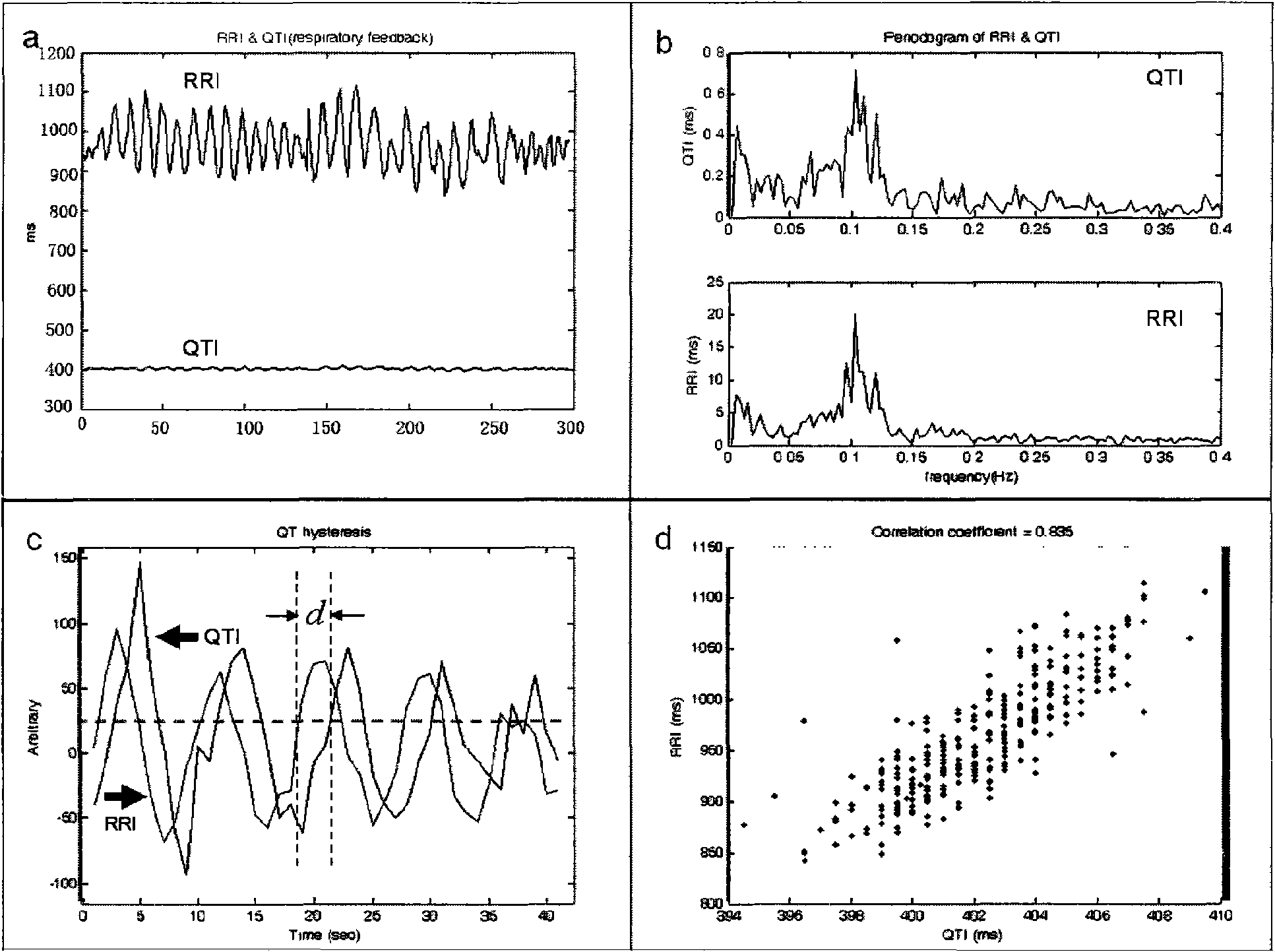
Method for building dynamic model of electrocardio signal RR interval and QT interval and applications thereof
The invention relates to a method for building a dynamic model of electrocardio signal RR interval and QT interval and applications thereof. The method for building the dynamic model of electrocardio signal RR interval and QT interval utilizes RRI as an input signal and QTI as an output signal to build a linear relation dynamic model between RRI signal and QTI signal, preferably a second order linear relation dynamic model. Based on the high correlation between RRI and QTI and the fact that QTI lags behind RRI, a linear model is built between RRI and QTI; according to the data of clients detected in experiments, systematic parameter estimation is carried out on a transfer function to obtain a special transfer function. And then, the system is simulated, QTI obtained from simulation is found to be very close to the actually measured QTI. The transfer characteristic between RRI and QTI reflects the functional state of hearts, and the heart function can correspondingly be evaluated by using the unit step of the transfer function, thus the system can have a certain clinical research prospect.
Owner:江依法
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods for QT interval control
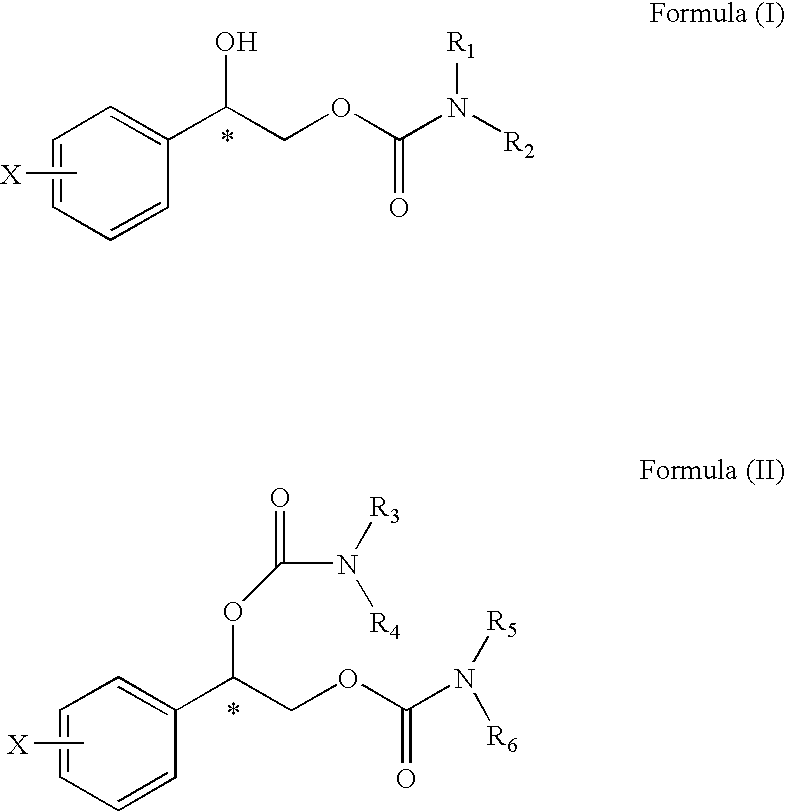
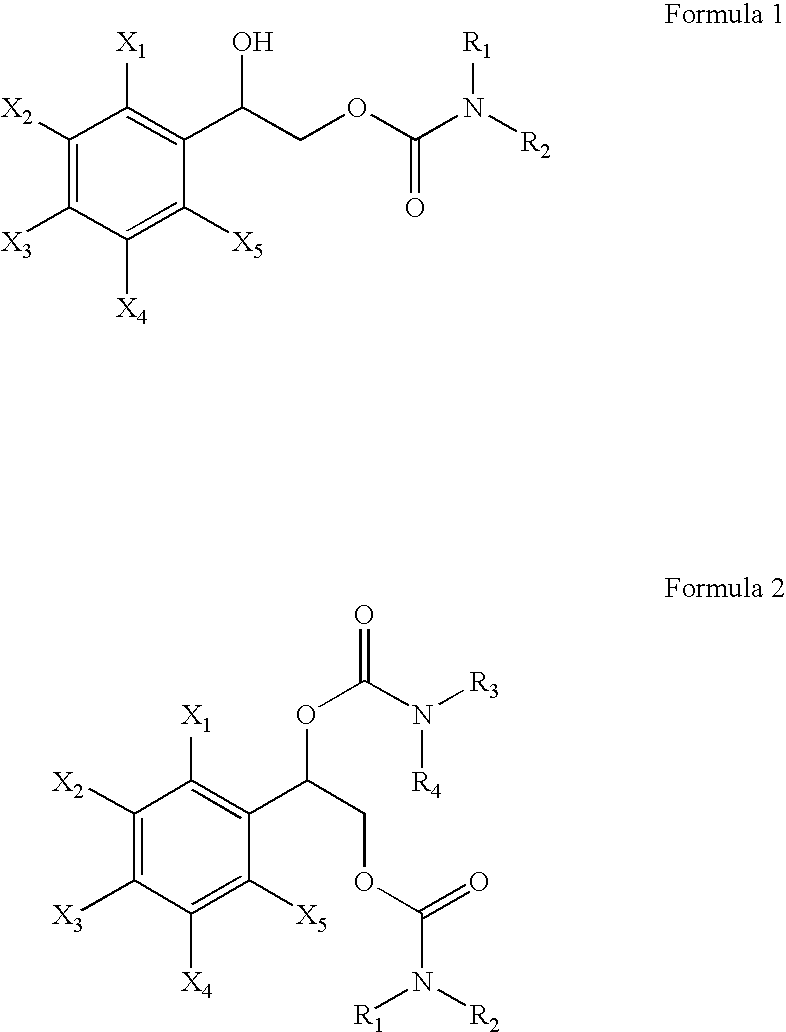
This invention is directed to methods for controlling the duration of the depolarization and repolarization of the cardiac ventricle and therefore the QT interval, in therapeutically useful ways in a subject, comprising administering to the subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a compound selected from the group consisting of Formula (I) and Formula (II), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof: wherein phenyl is substituted at X with one to five halogen atoms selected from the group consisting of fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine; and, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-C4 alkyl; wherein C1-C4 alkyl is optionally substituted with phenyl, wherein phenyl is optionally substituted with substituents independently selected from the group consisting of halogen, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, amino, nitro and cyano.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Method and apparatus for analyzing and editing ECG morphology and time series
ActiveUS20070244401A1Improve data qualityHigh measurement accuracyElectrocardiographySensorsQT intervalEcg waveforms
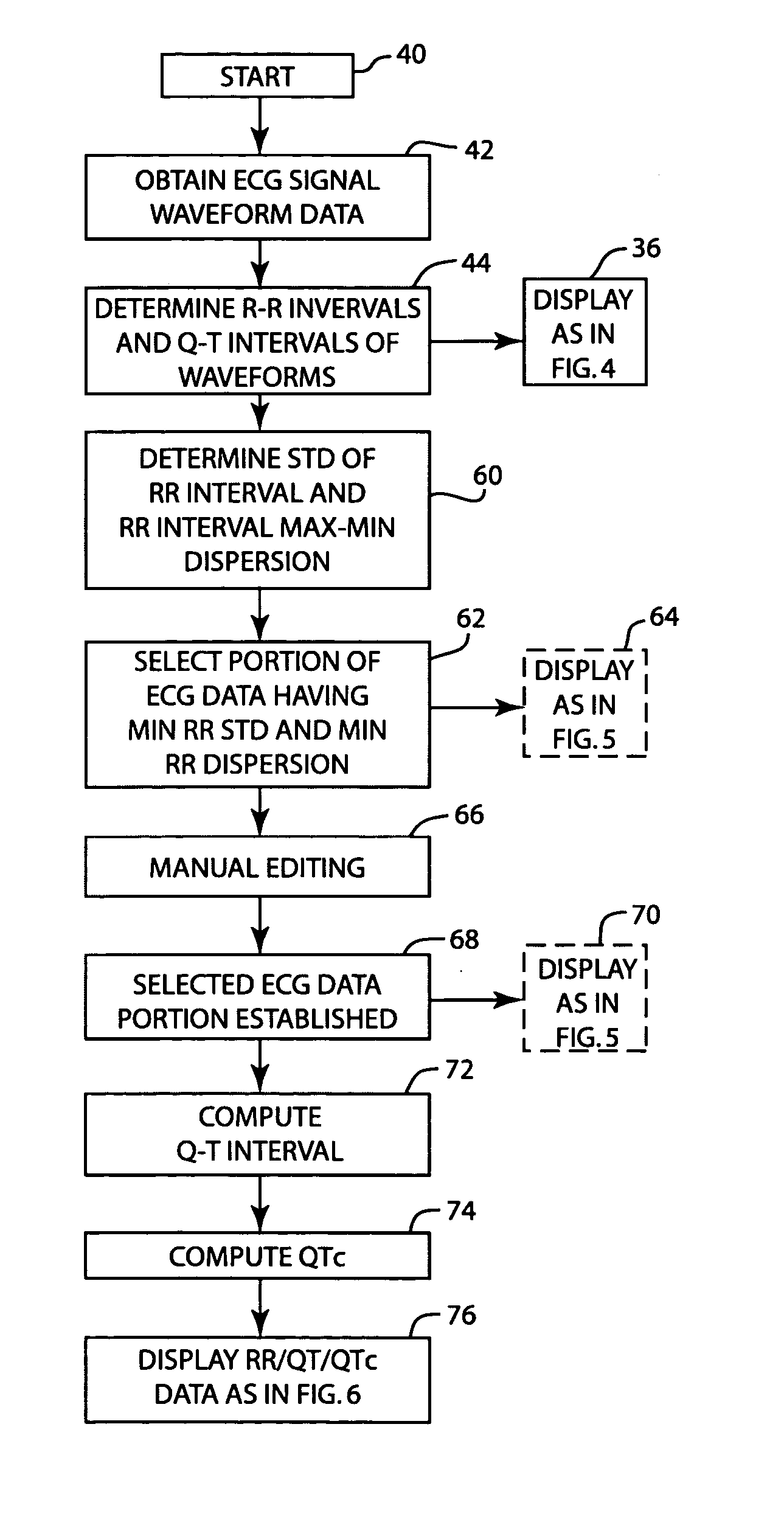
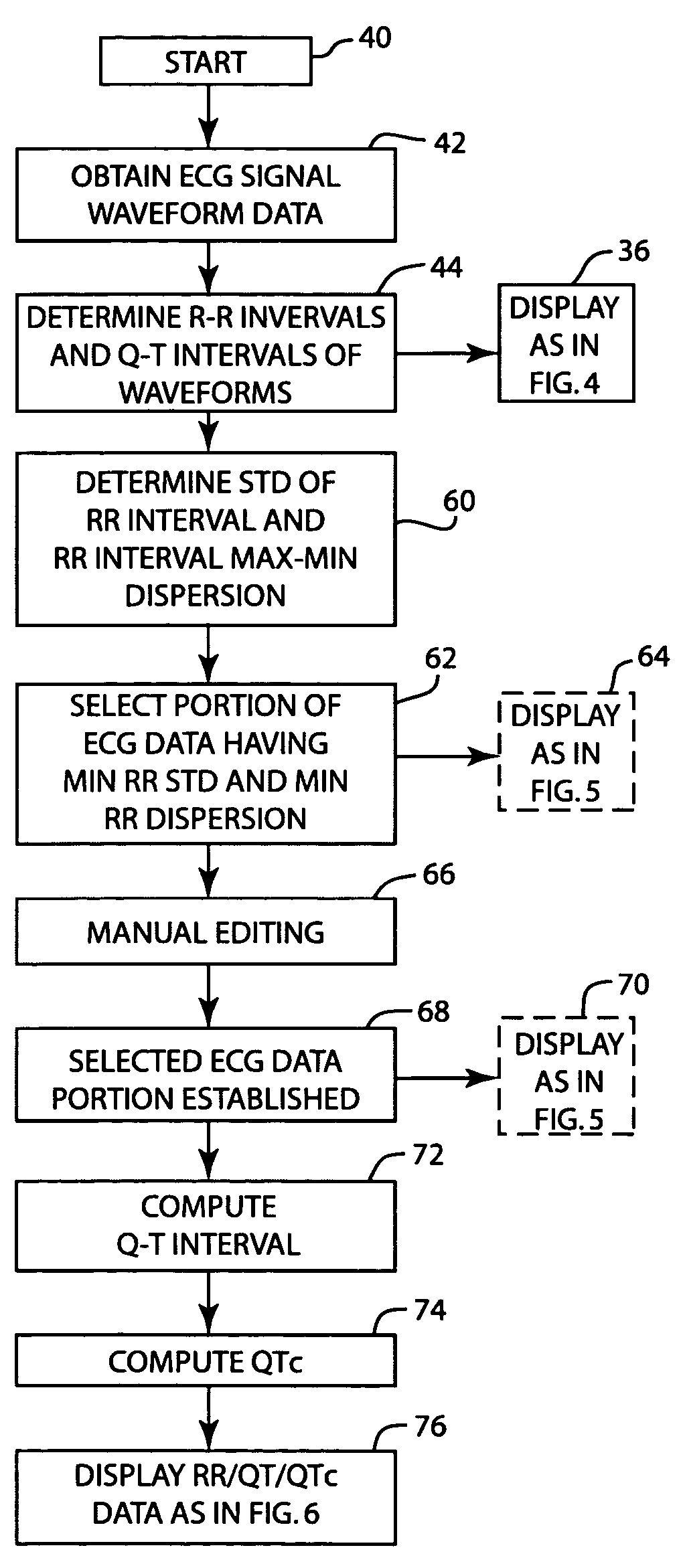
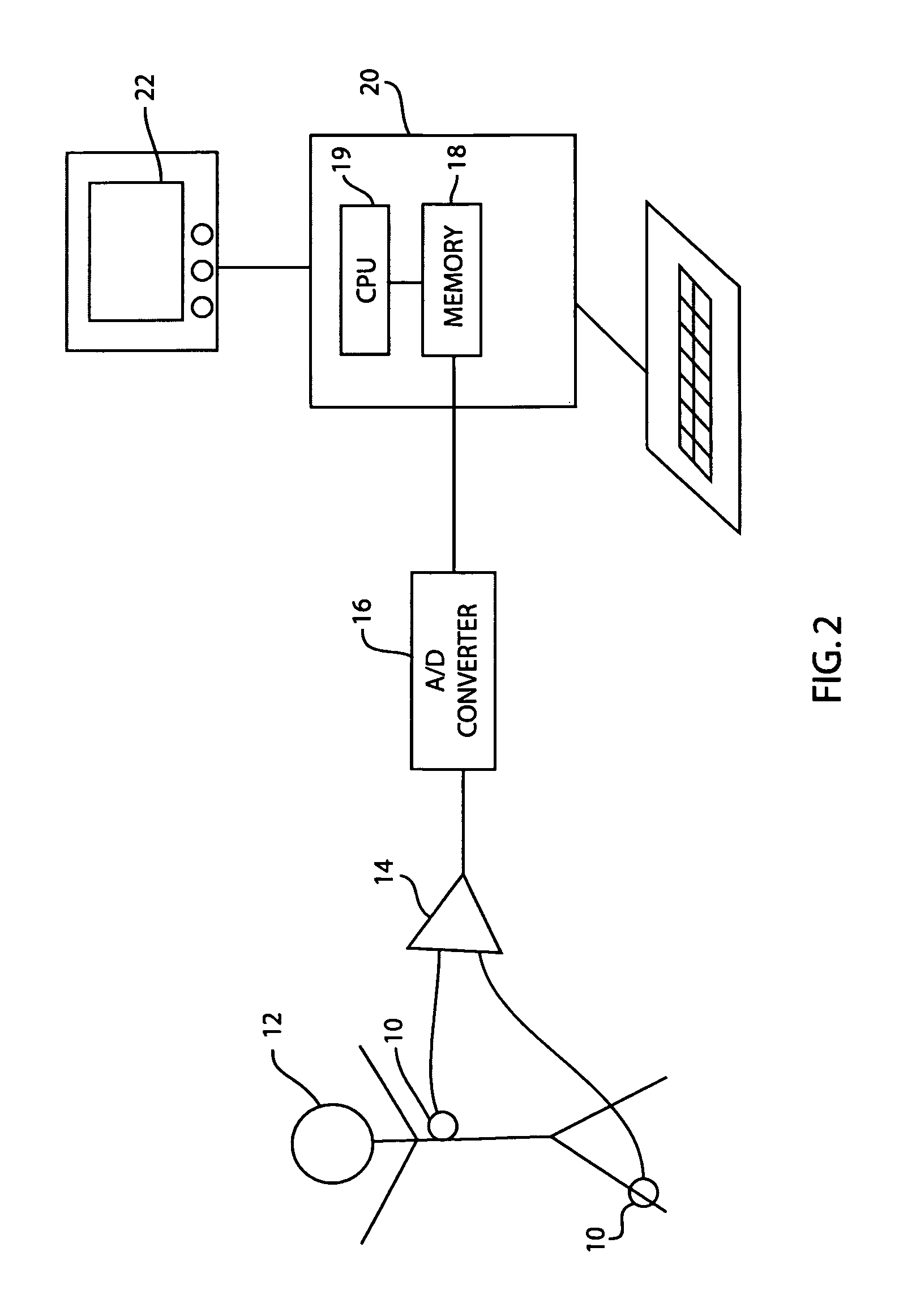
A method and apparatus for analyzing the QT interval characteristics of ECG signal data having a succession of waveforms produced by the beating of the heart. ECG signal data is obtained from a patient. The R-R interval and the QT intervals of the waveforms of the ECG signal data are determined. Waveforms of the ECG signal data having a stable heart rate are selected for use in determining the QT interval characteristics. Preferably, the waveforms selected are those having minimum R-R interval standard deviation and minimum R-R interval dispersion. The QT correction (QTc) is computed from the ECG signal data waveforms selected in the foregoing manner or on the basis of clinician editing. The R-R intervals, the QT intervals, and QTc for the heart beats of the selected waveforms are displayed for analysis and diagnosis purposes. The invention can also be used, in an analogous manner, to obtain and display other cardiac data from the ECG waveforms.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Arrhythmia classification method based on multi-feature fusion and Stacking-DWKNN
The invention relates to an arrhythmia classification method based on multi-feature fusion and Stacking-DWKNN. The arrhythmia classification method comprises the following steps: S1, removing noise inan electrocardiosignal by adopting continuous wavelet transform; S2, segmenting the electrocardiosignal processed in the step S1 to intercept a complete heart beat, then performing feature extractionon the intercepted heart beat, and establishing the following data sets for the extracted features according to categories, wherein the set A = {235 single heart beat morphological characteristics},the set B = {P-QRS-T wave}, the set C = {PR interval}, the set D = {QT interval}, the set E = {ST segment}, the set F = {RR interval}, the set G = {R amplitude}, and the set H = {T amplitude}; S3, inputting any one set or a combination of any multiple sets in the data set in the step S2 into a plurality of KNN algorithms which are integrated by Stacking and improved by weight values for heart beatclassification. The heart beat classification method provided by the invention can effectively improve the result accuracy of heart beat classification.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
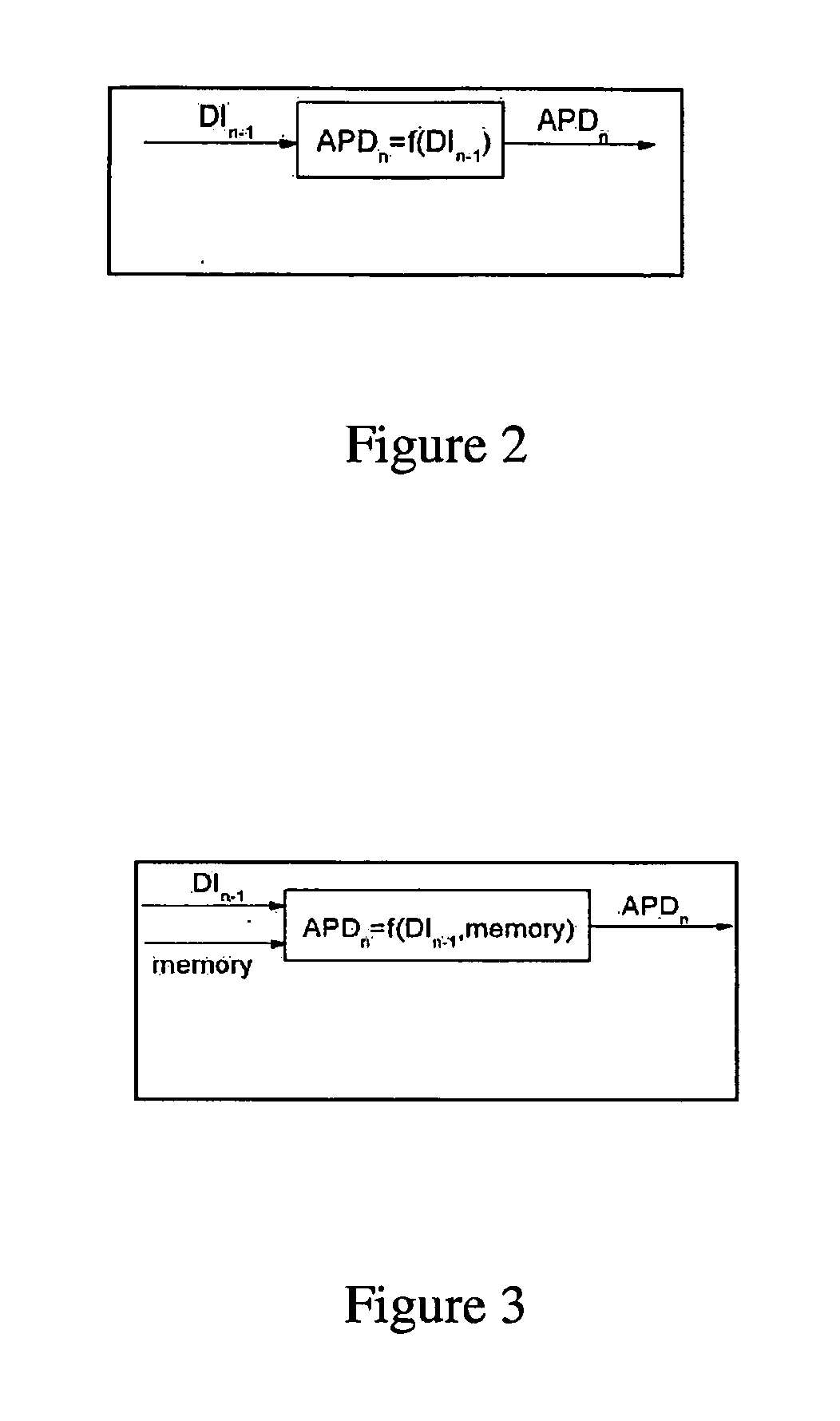
Novel methodology for arrhythmia risk stratification by assessing qt interval instability
A method of predicting ventricular arrhythmias includes receiving an electrical signal from a subject's heart for a plurality of heart beats, identifying characteristic intervals and heart beat durations of the electrical signal corresponding to each of the plurality of heart beats to provide a plurality of characteristic intervals with corresponding heart beat durations, representing dynamics of the plurality of characteristic intervals as a function of a plurality of preceding characteristic intervals and durations of corresponding heart beats over a chosen period time, assessing a stability of the function over the chosen period of time, and predicting ventricular arrhythmias based on detected instabilities in the dynamics of the characteristic intervals.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and apparatus for analyzing and editing ECG morphology and time series
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cardiac function circadian variation analysis system and method
InactiveUS20100292597A1Targeted optimizationIncrease cost-effective deploymentElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationPR intervalRR interval
Systems and Methods for stratifying relative risks of adverse cardiac events by processing a duration of electrocardiograph recordings generally recorded by a Holter type of device. The duration of electrocardiograph recordings are processed to resolve RR interval related data, QT interval related data, and are fitted to formulas to at least partially establish fitting related measures. The fitting formulas incorporate circadian related periodic factors, and can further incorporate additional processing including utilizing Lissajous analysis techniques, among others.
Owner:WATANABE MARI ALFORD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com