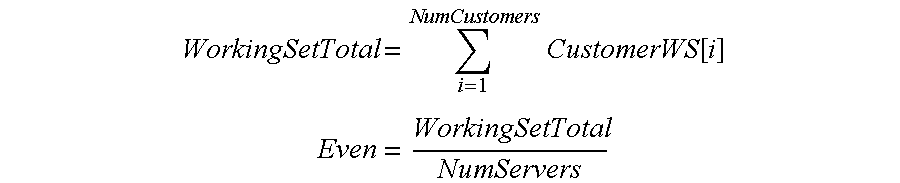Patents
Literature
4456 results about "Computational resource" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computational complexity theory, a computational resource is a resource used by some computational models in the solution of computational problems. The simplest computational resources are computation time, the number of steps necessary to solve a problem, and memory space, the amount of storage needed while solving the problem, but many more complicated resources have been defined.
Method and apparatus of specifying and performing speech recognition operations
ActiveUS7720683B1Efficient executionShorten cycle timeSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
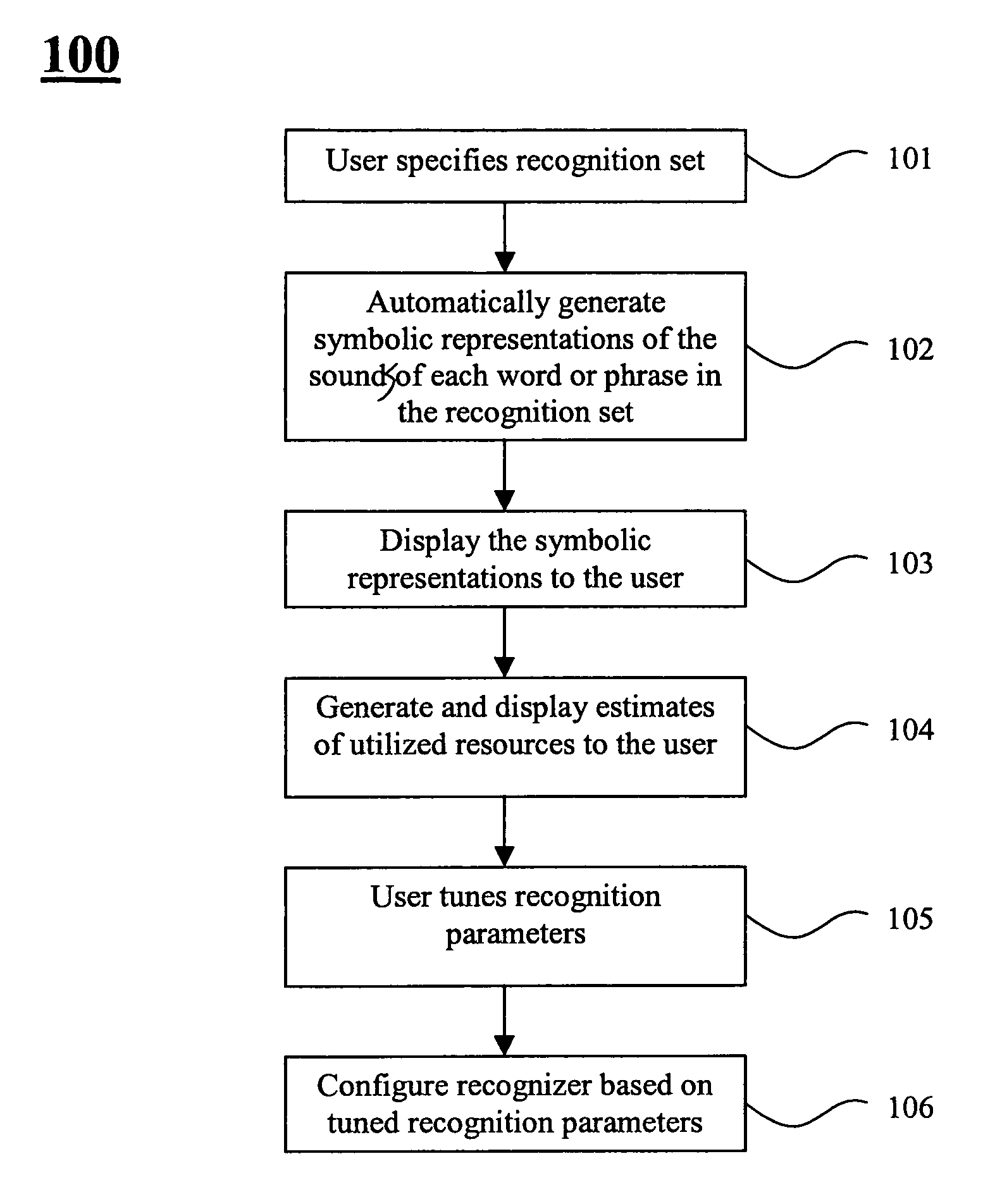
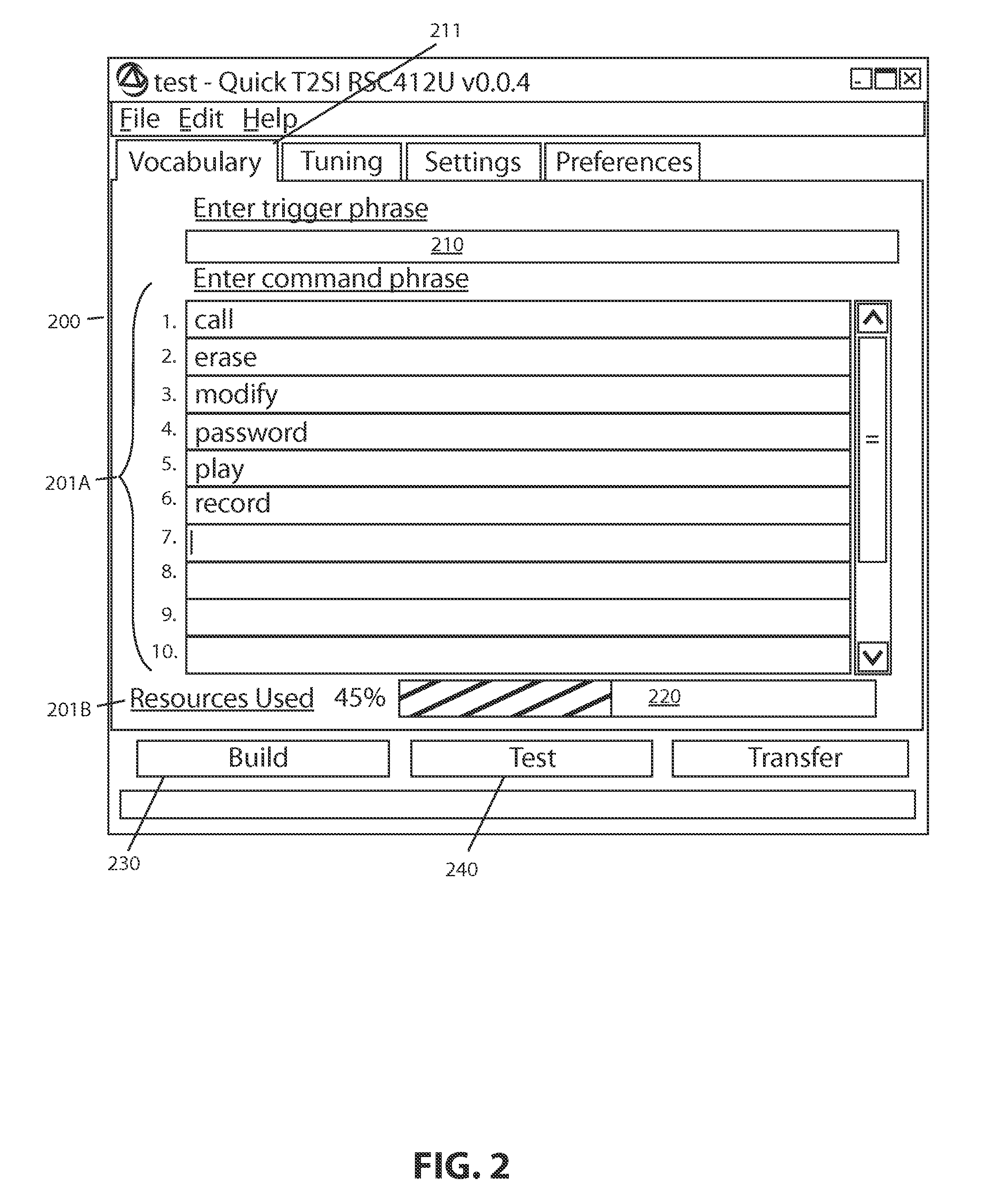
A speech recognition technique is described that has the dual benefits of not requiring collection of recordings for training while using computational resources that are cost-compatible with consumer electronic products. Methods are described for improving the recognition accuracy of a recognizer by developer interaction with a design tool that iterates the recognition data during development of a recognition set of utterances and that allows controlling and minimizing the computational resources required to implement the recognizer in hardware.
Owner:SENSORY
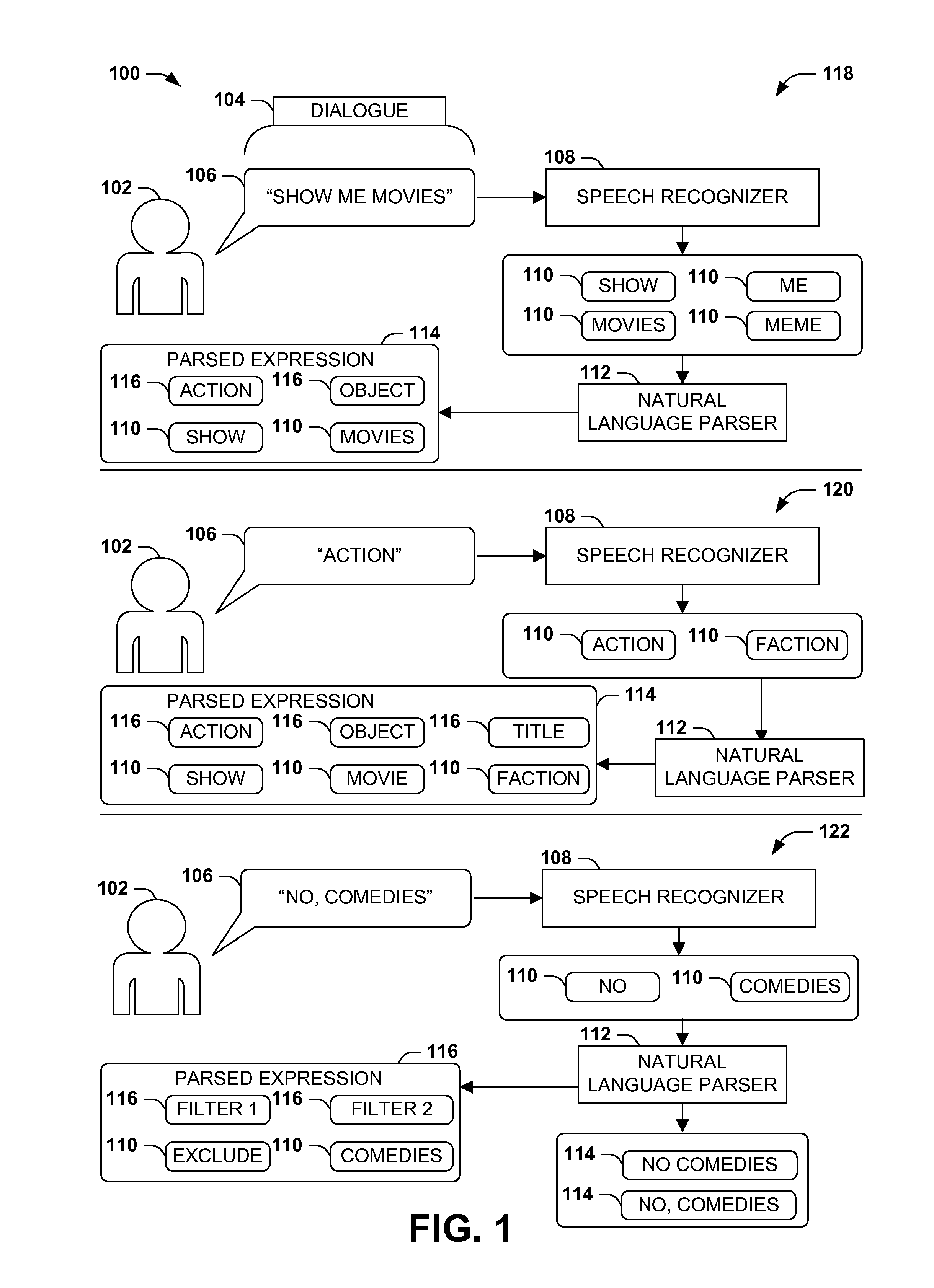
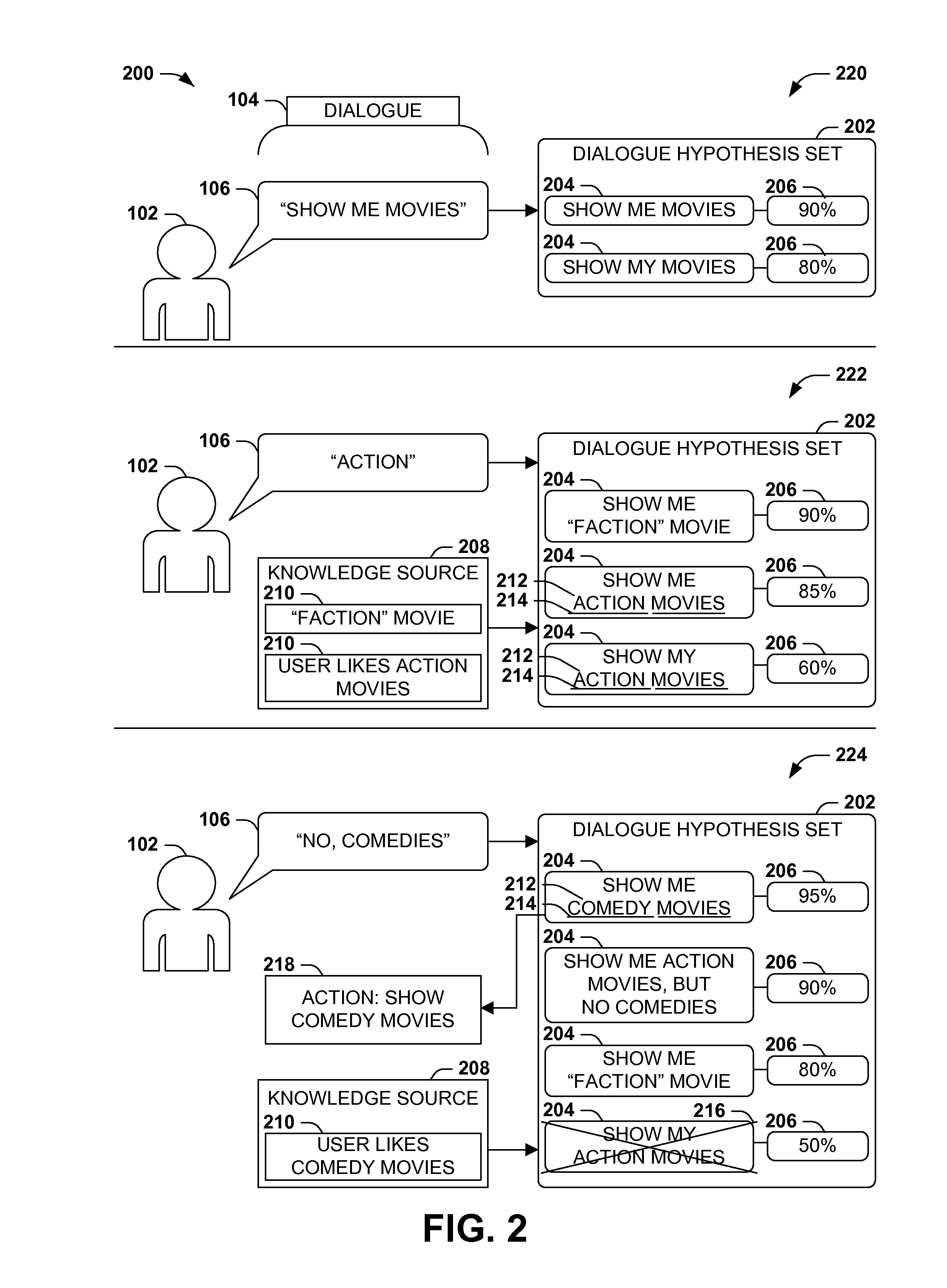
Dialogue evaluation via multiple hypothesis ranking
ActiveUS20150142420A1Reduce settingsNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionKnowledge sourcesMultiple hypothesis
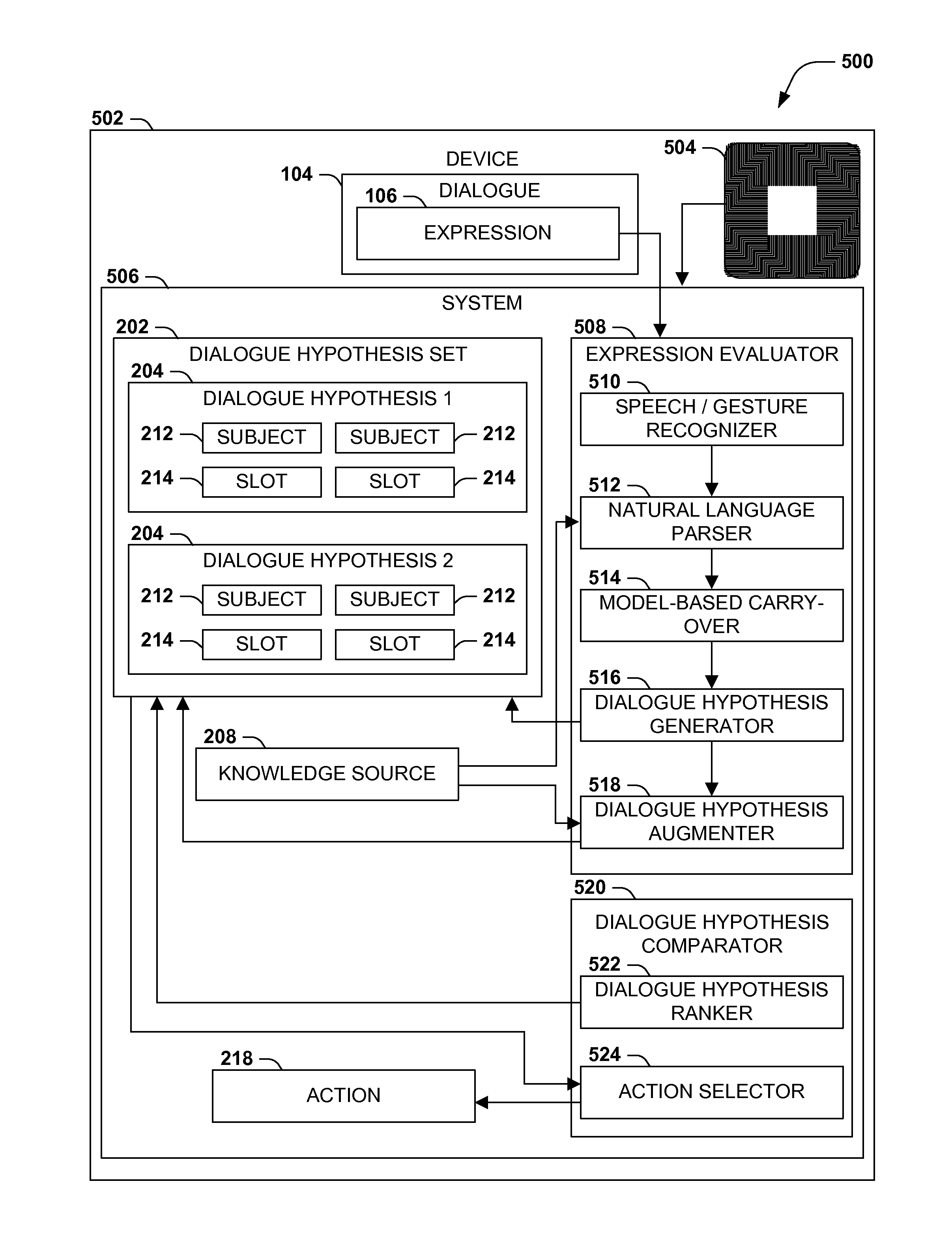
In language evaluation systems, user expressions are often evaluated by speech recognizers and language parsers, and among several possible translations, a highest-probability translation is selected and added to a dialogue sequence. However, such systems may exhibit inadequacies by discarding alternative translations that may initially exhibit a lower probability, but that may have a higher probability when evaluated in the full context of the dialogue, including subsequent expressions. Presented herein are techniques for communicating with a user by formulating a dialogue hypothesis set identifying hypothesis probabilities for a set of dialogue hypotheses, using generative and / or discriminative models, and repeatedly re-ranks the dialogue hypotheses based on subsequent expressions. Additionally, knowledge sources may inform a model-based with a pre-knowledge fetch that facilitates pruning of the hypothesis search space at an early stage, thereby enhancing the accuracy of language parsing while also reducing the latency of the expression evaluation and economizing computing resources.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
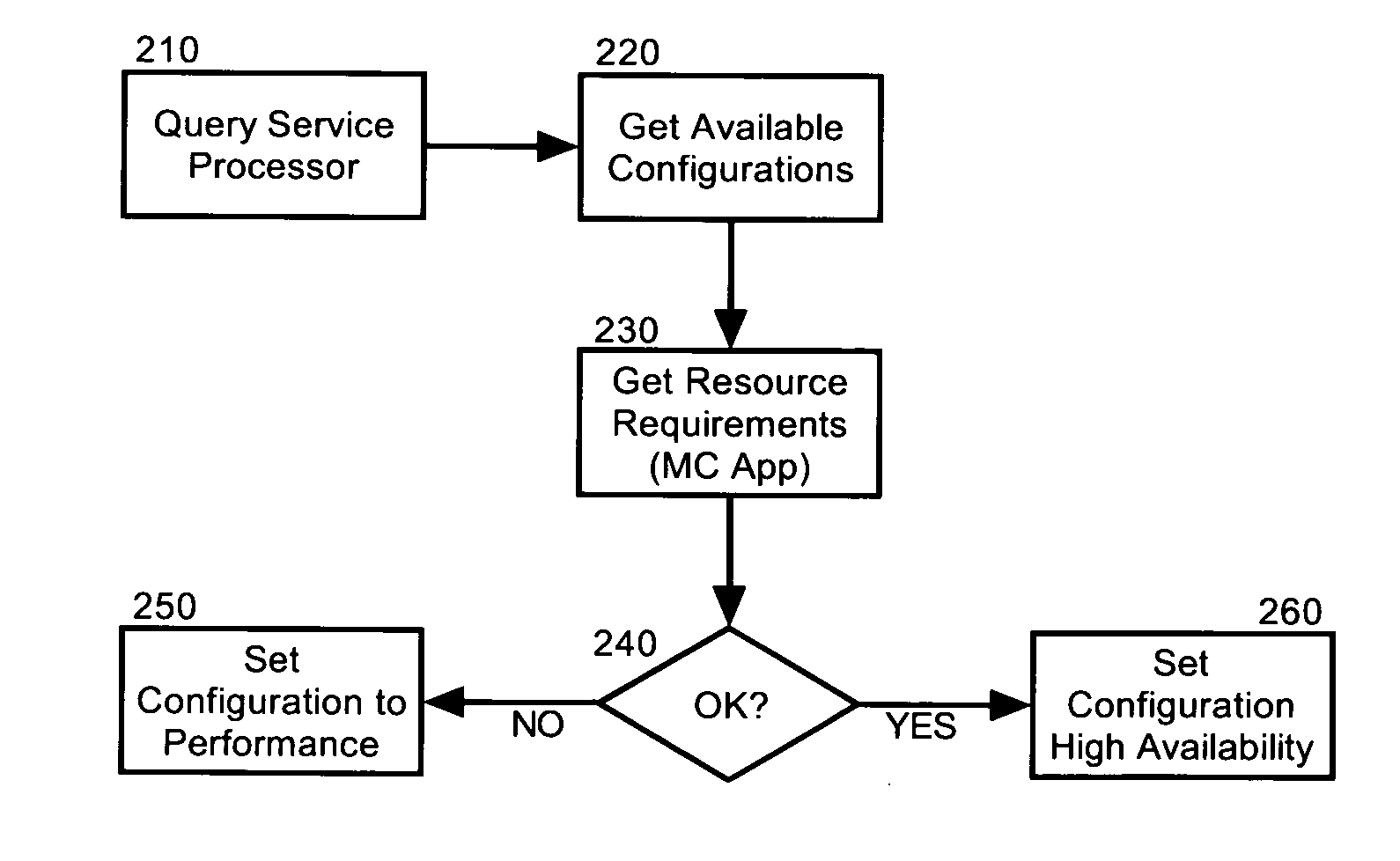
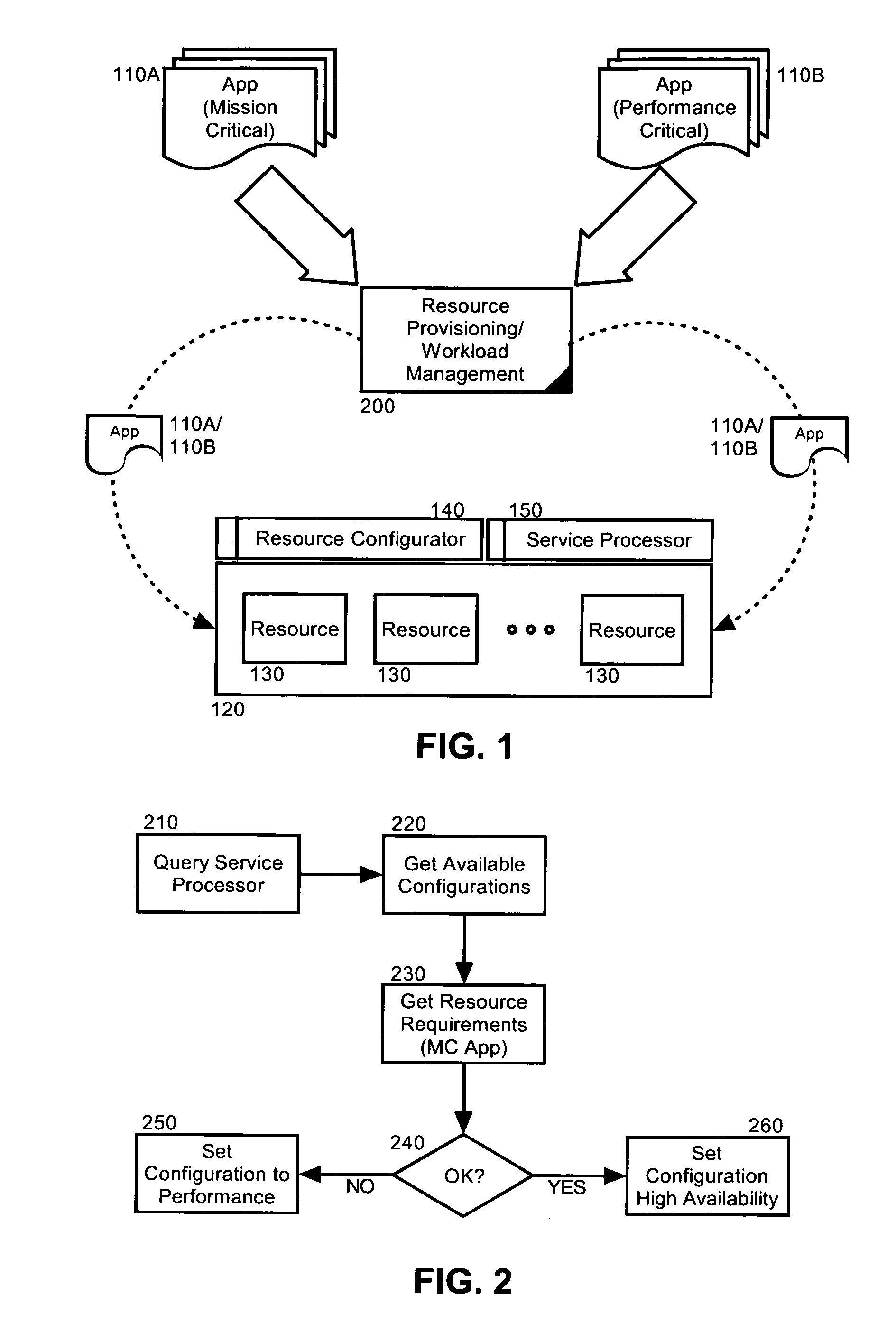
Dynamic resource allocation for disparate application performance requirements
InactiveUS20070198982A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsResource poolData processing system
Embodiments of the invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to dynamic computing resource allocation, and provide a method, system and computer program product for dynamic resource allocation for disparate application performance requirements. In one embodiment of the invention, a resource allocation data processing system can include a shared resource pool including resources and a resource configurator coupled to the shared resource pool. The system further can include a service processor coupled to the resource configurator, wherein the service processor can include an application programming interface (API) exposing methods for commanding the resource configurator to configure the resources in the shared resource pool.
Owner:LENOVO ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SINGAPORE
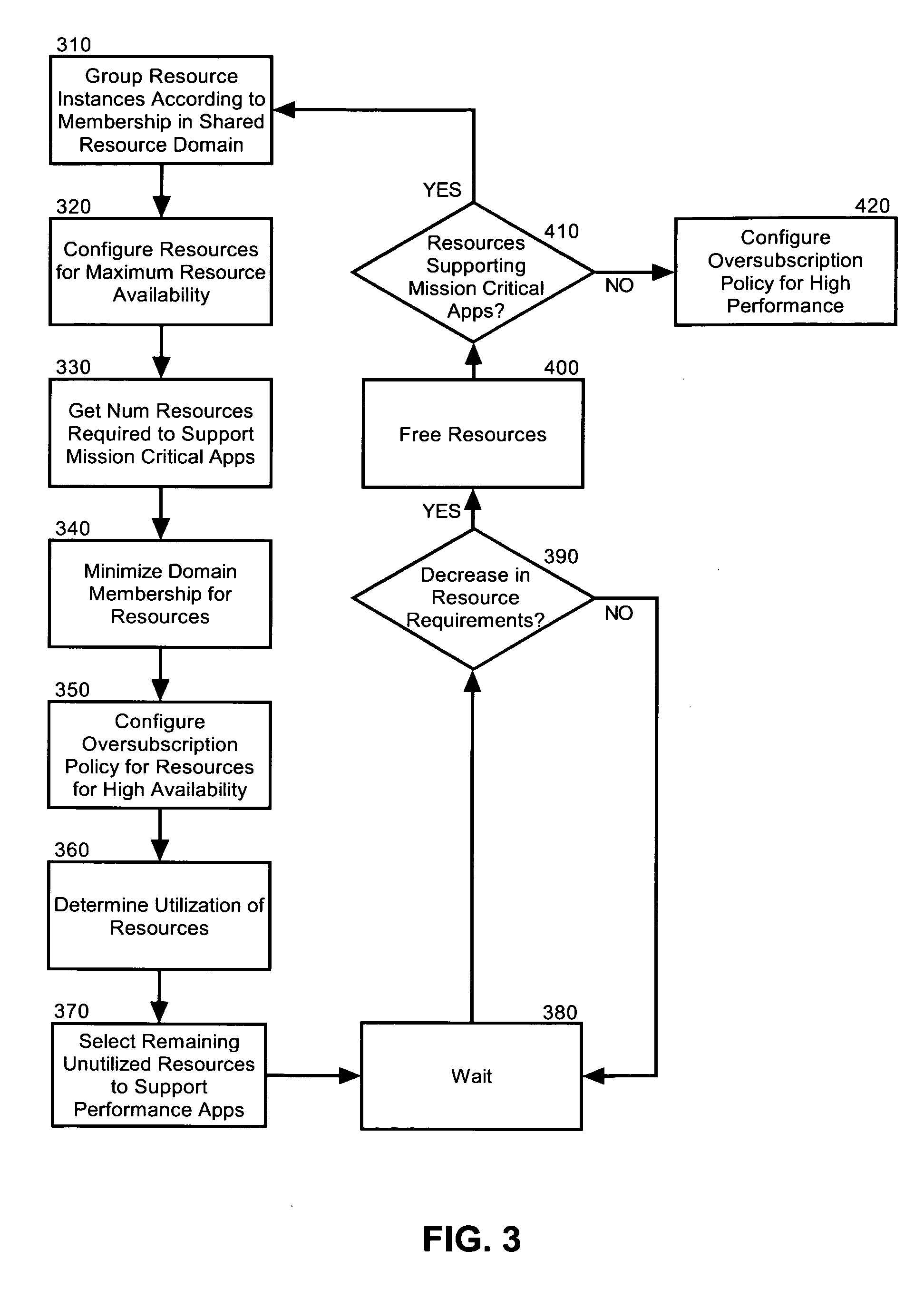
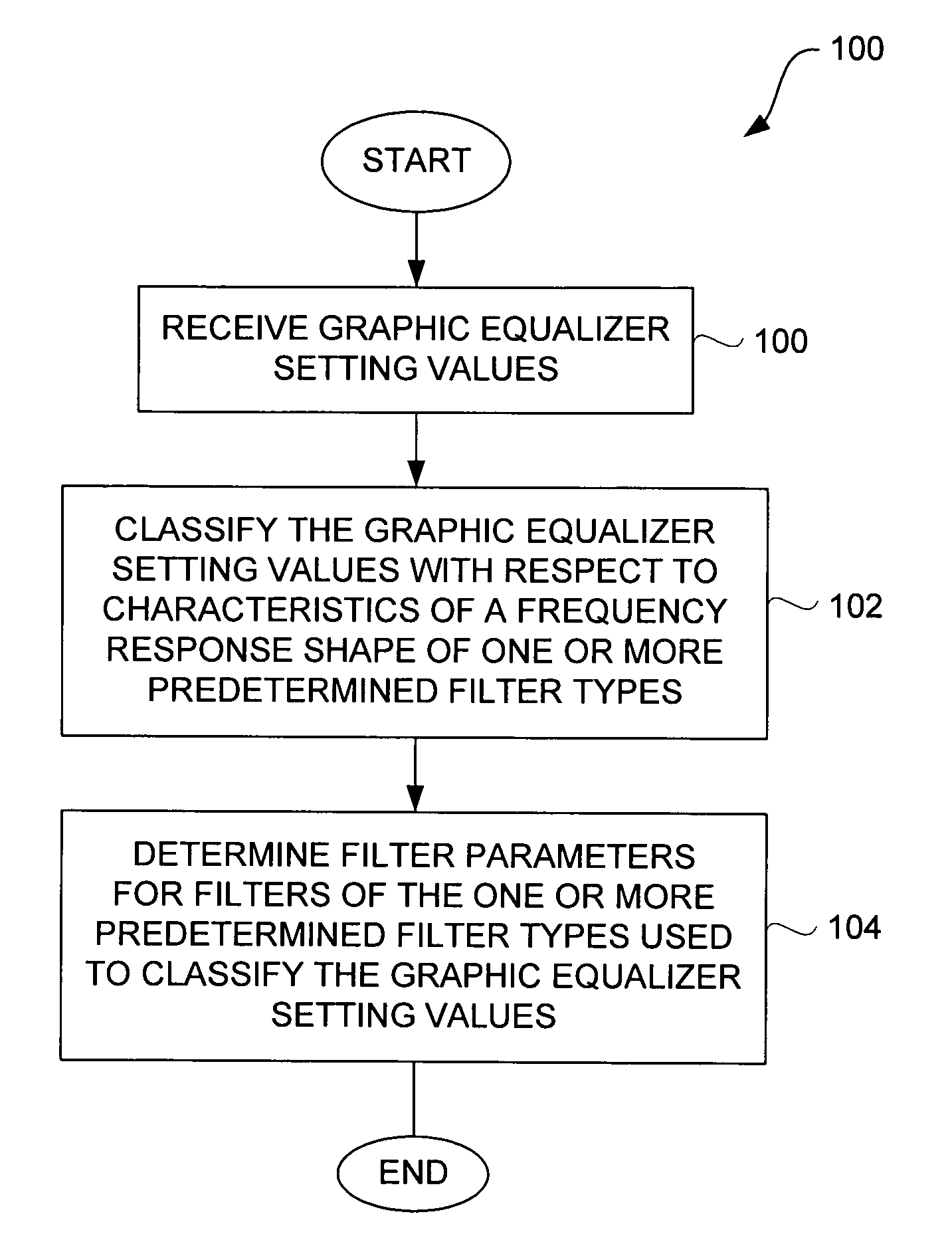
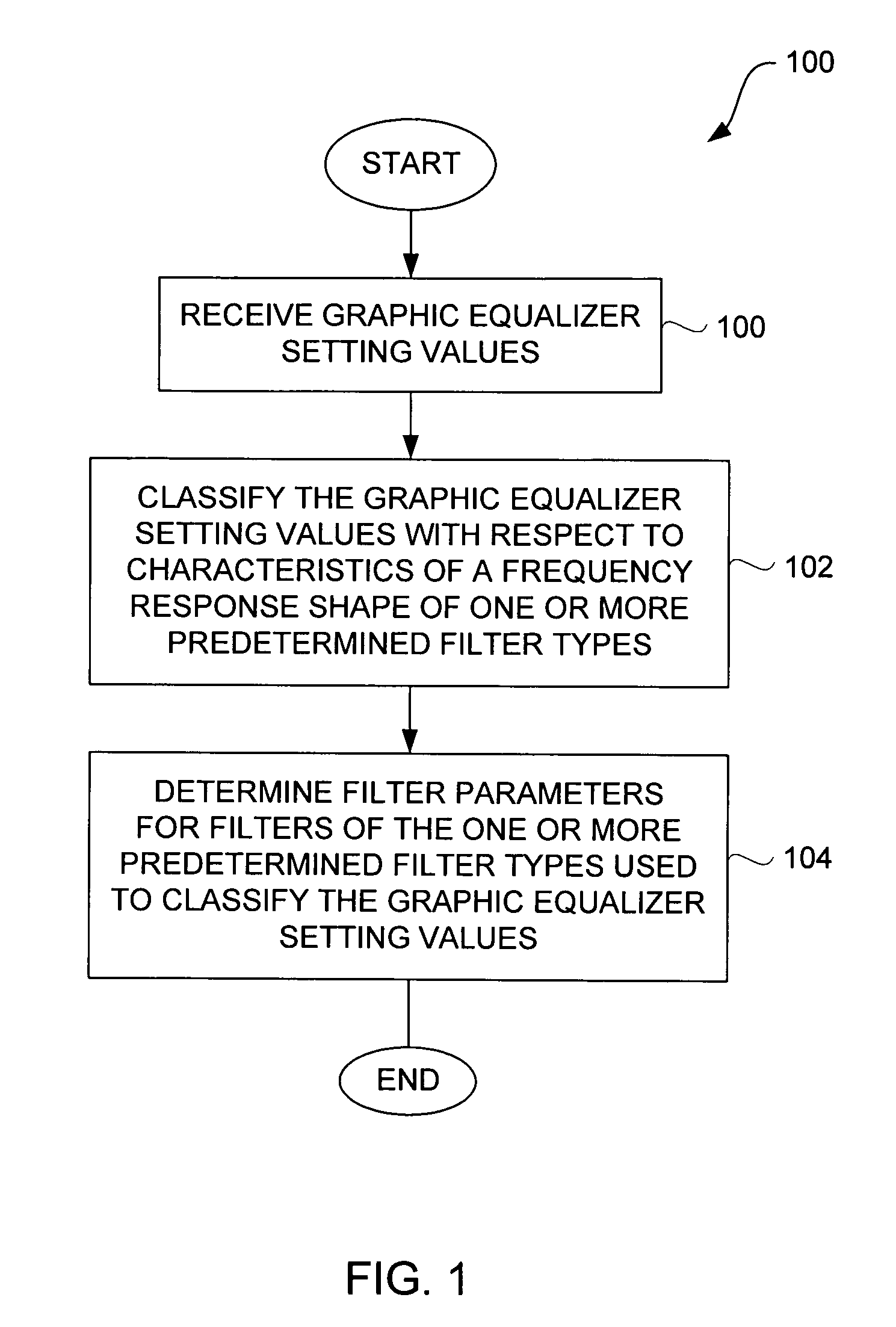
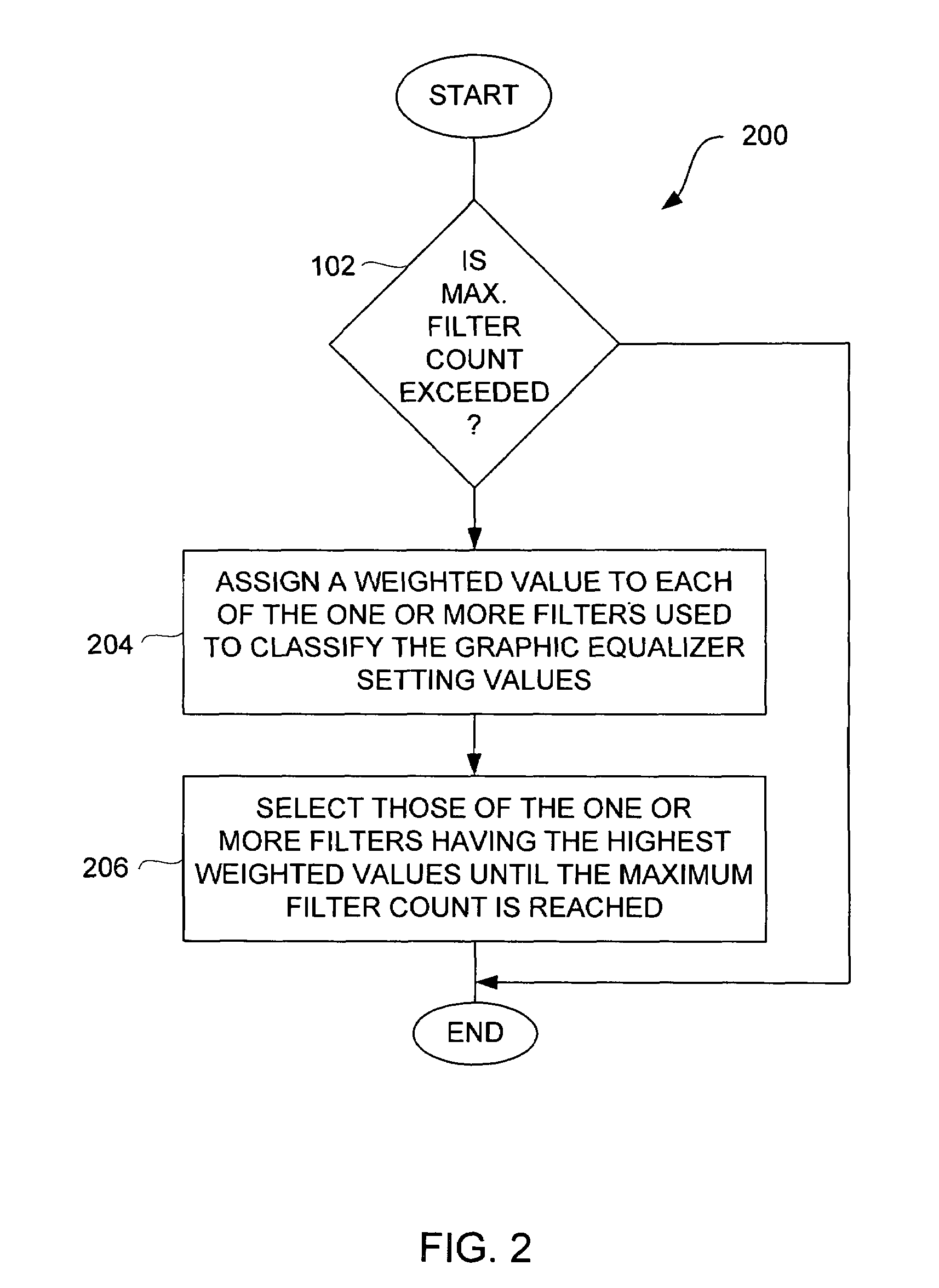
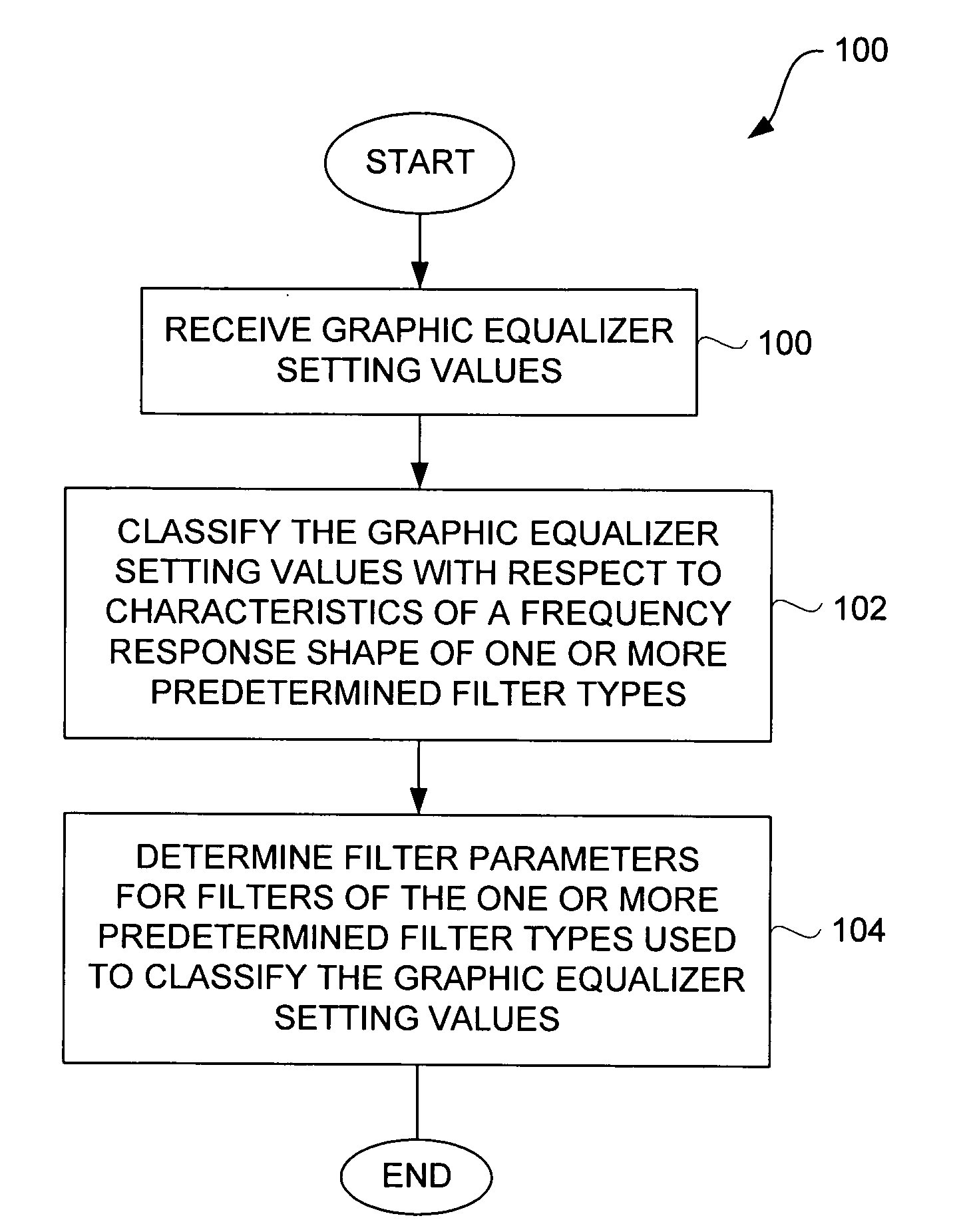
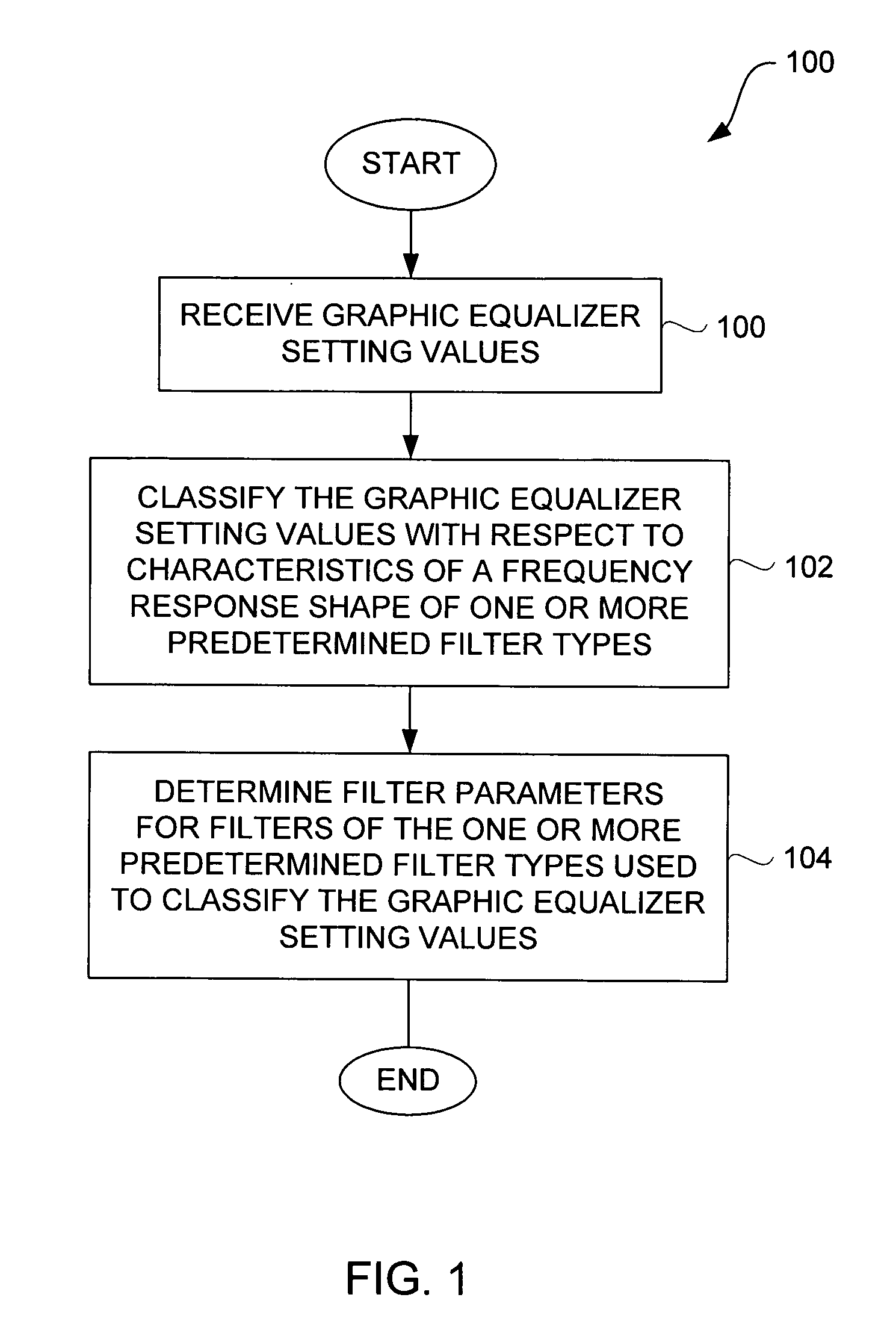
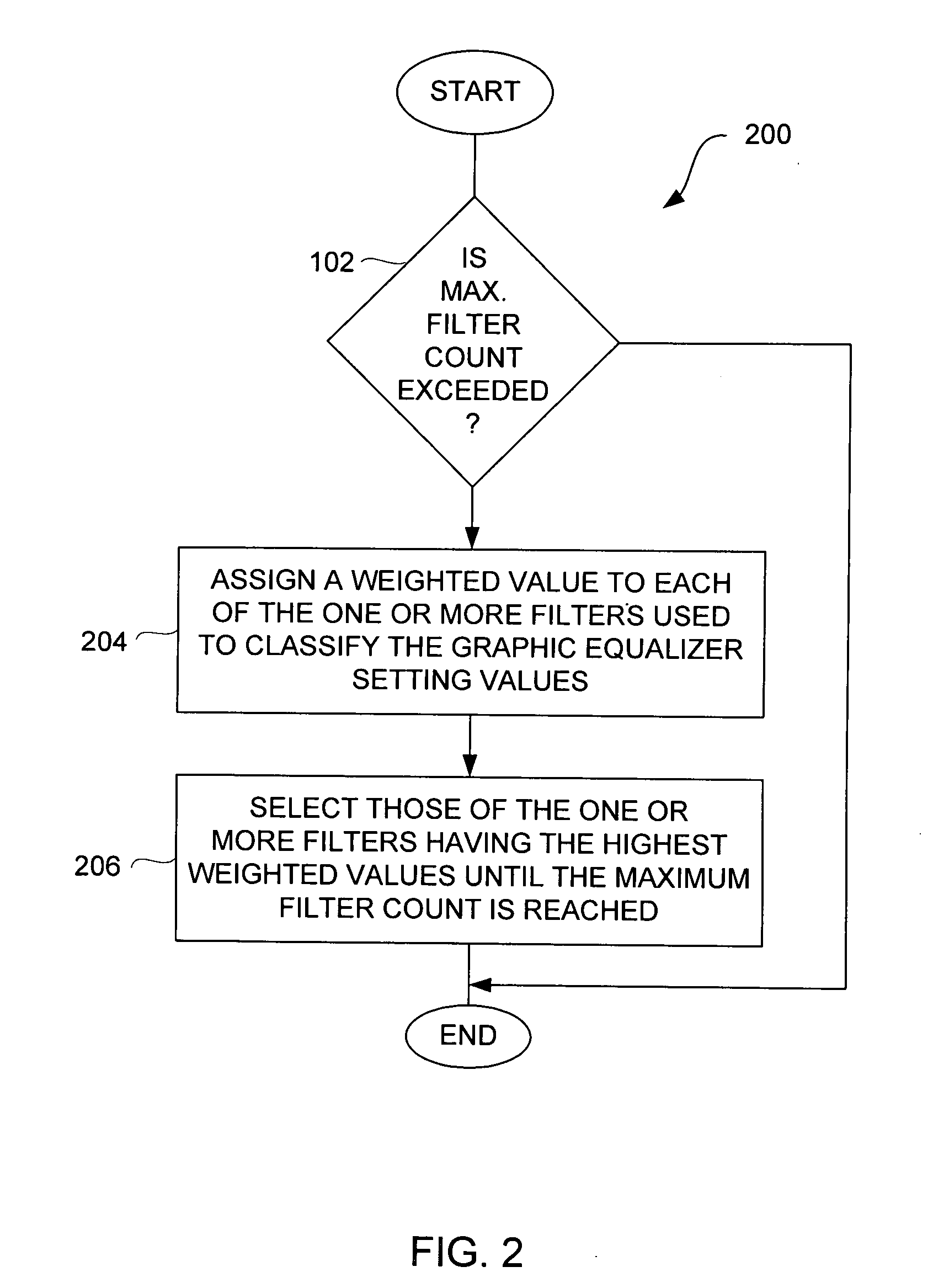
Method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction
InactiveUS7711129B2Limited computing resourceImprove approachSpecial data processing applicationsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsGraphicsMulti band
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive network traffic compression mechanism including dynamic selection of compression algorithms
ActiveUS7420992B1Reduce impactImprove performanceTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsAdaptive compressionSelf adaptive
An adaptive compression mechanism that dynamically selects compression algorithms applied to network application traffic to improve performance. One implementation includes an arbitration scheme that reduces the impact on computing resources required to analyze different compression algorithms for different network applications. The adaptive compression functionality of the present invention can be integrated into network application traffic management or acceleration systems.
Owner:CA TECH INC
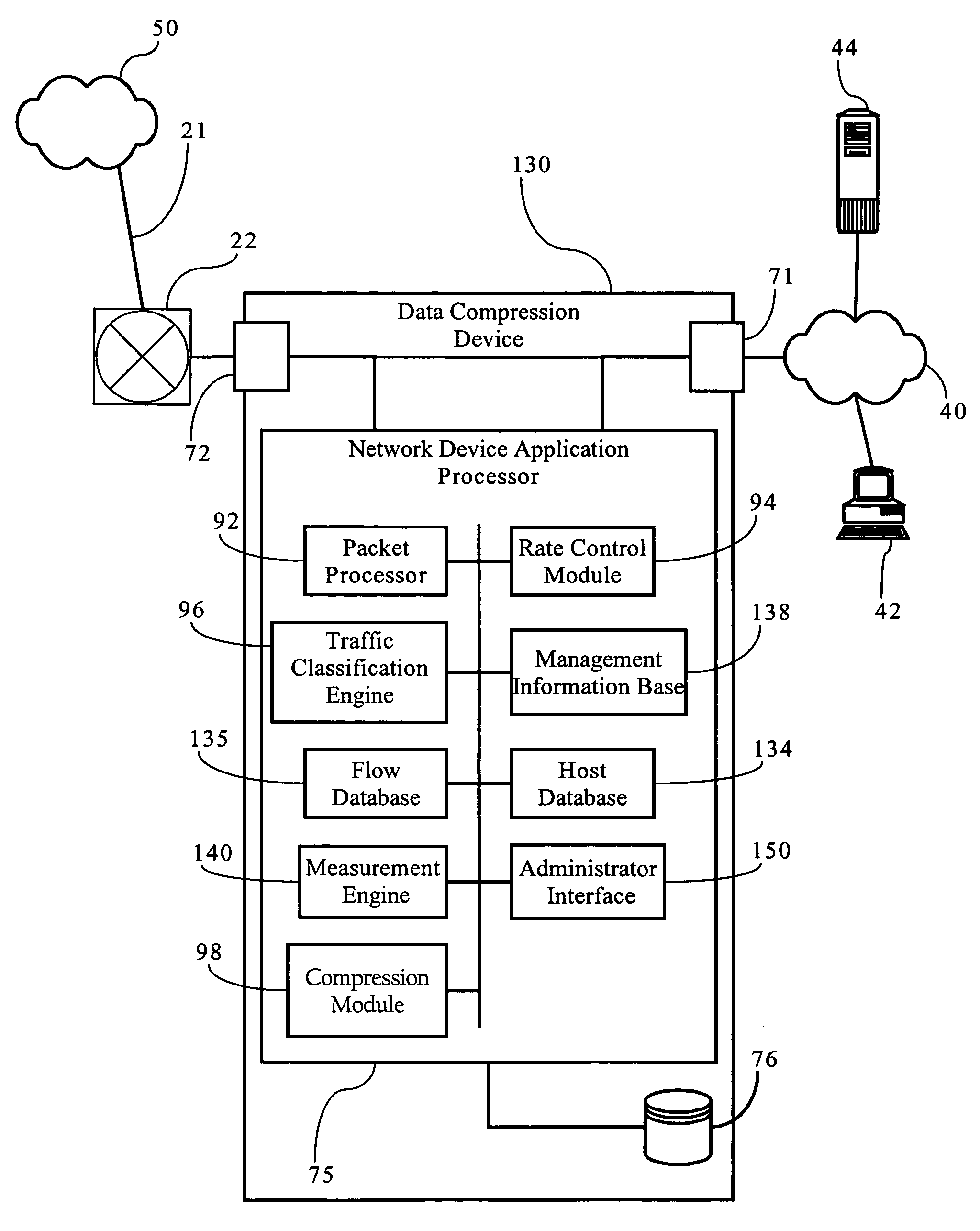
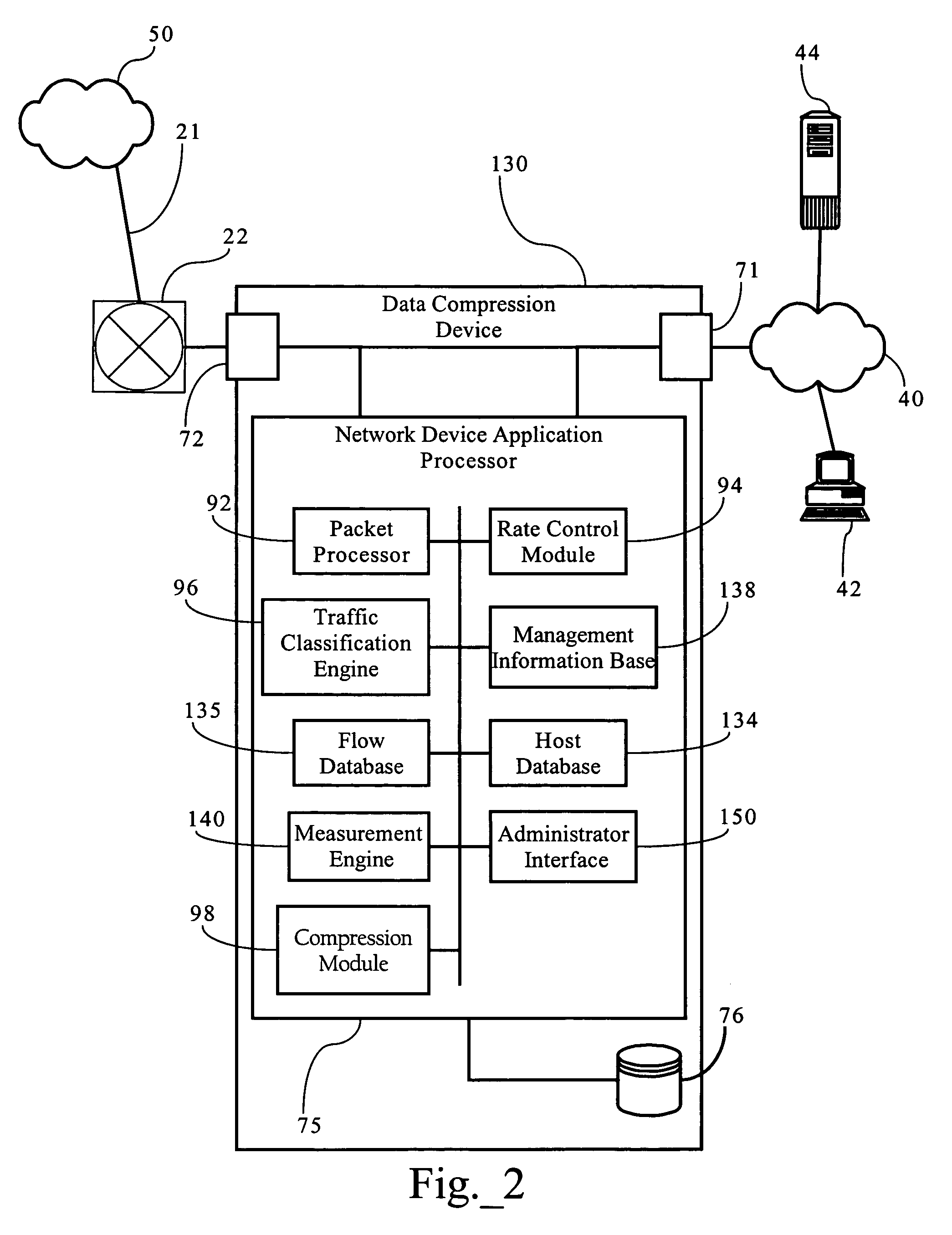
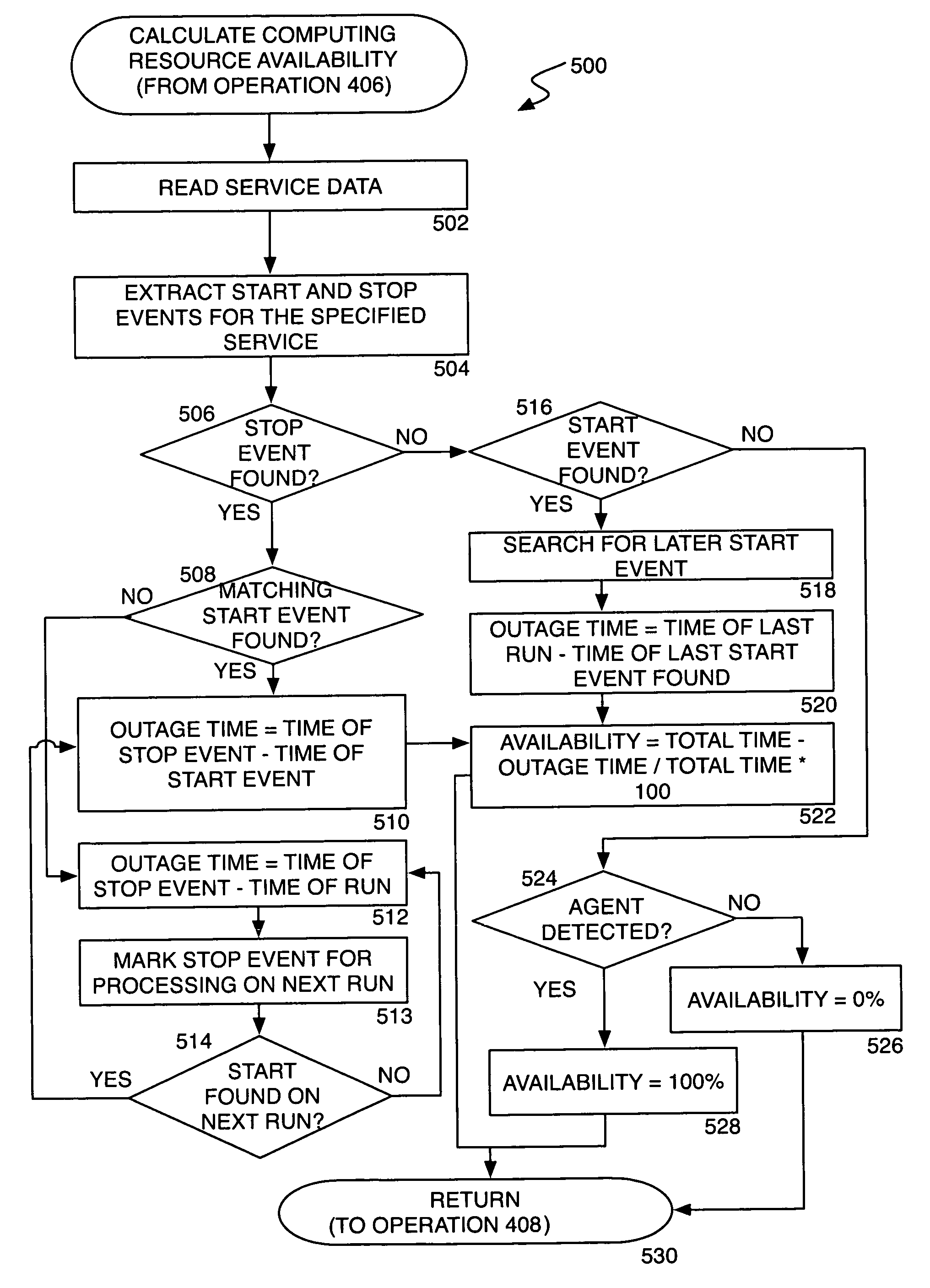
Determining the level of availability of a computing resource
ActiveUS7500150B2Well formedHardware monitoringMultiprogramming arrangementsComputational resourceReal-time computing
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Real-time mission adaptable route planner
InactiveUS6259988B1Easy to customizeInstruments for road network navigationEnergy saving arrangementsTurn angleSearch problem
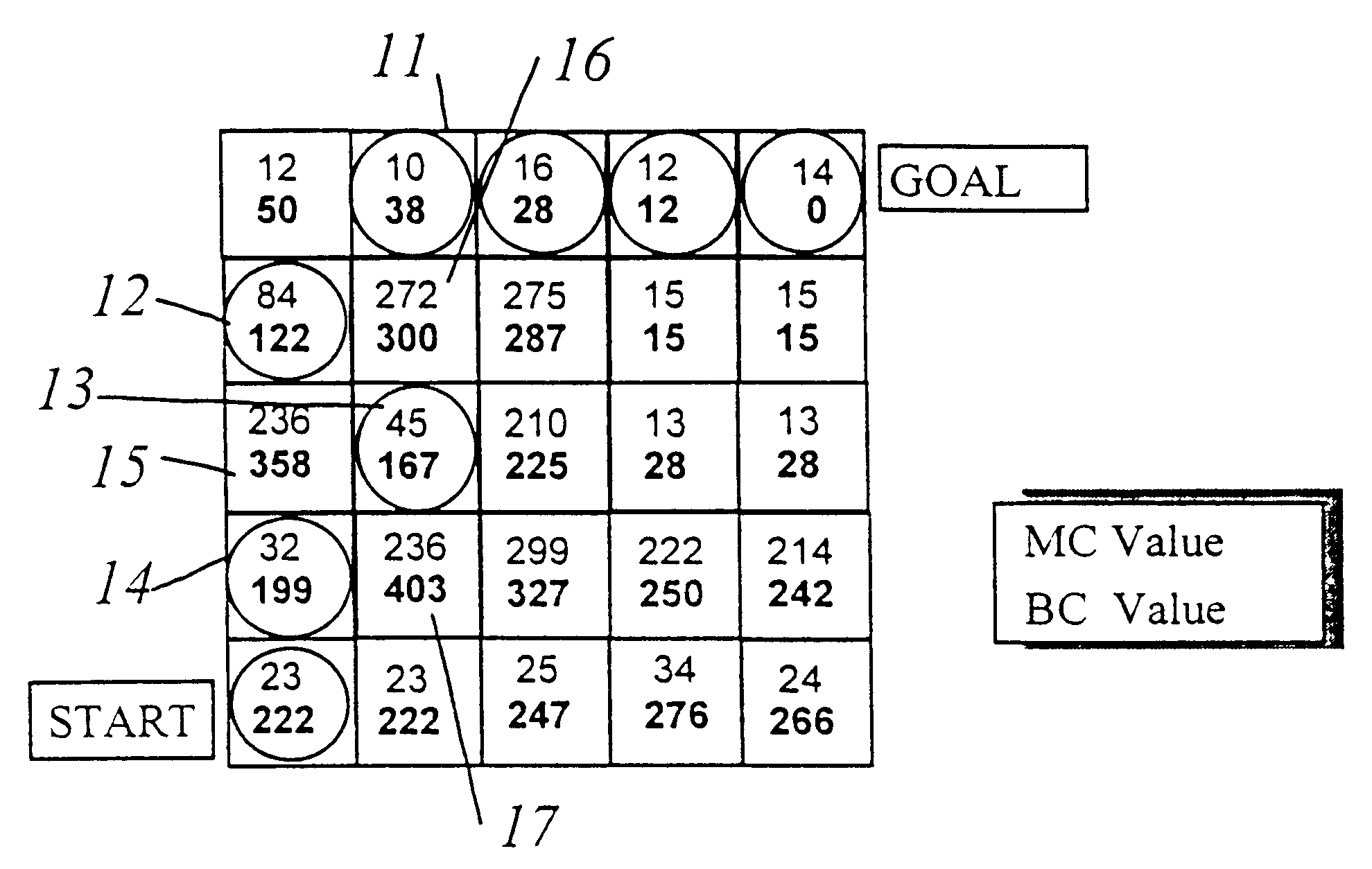
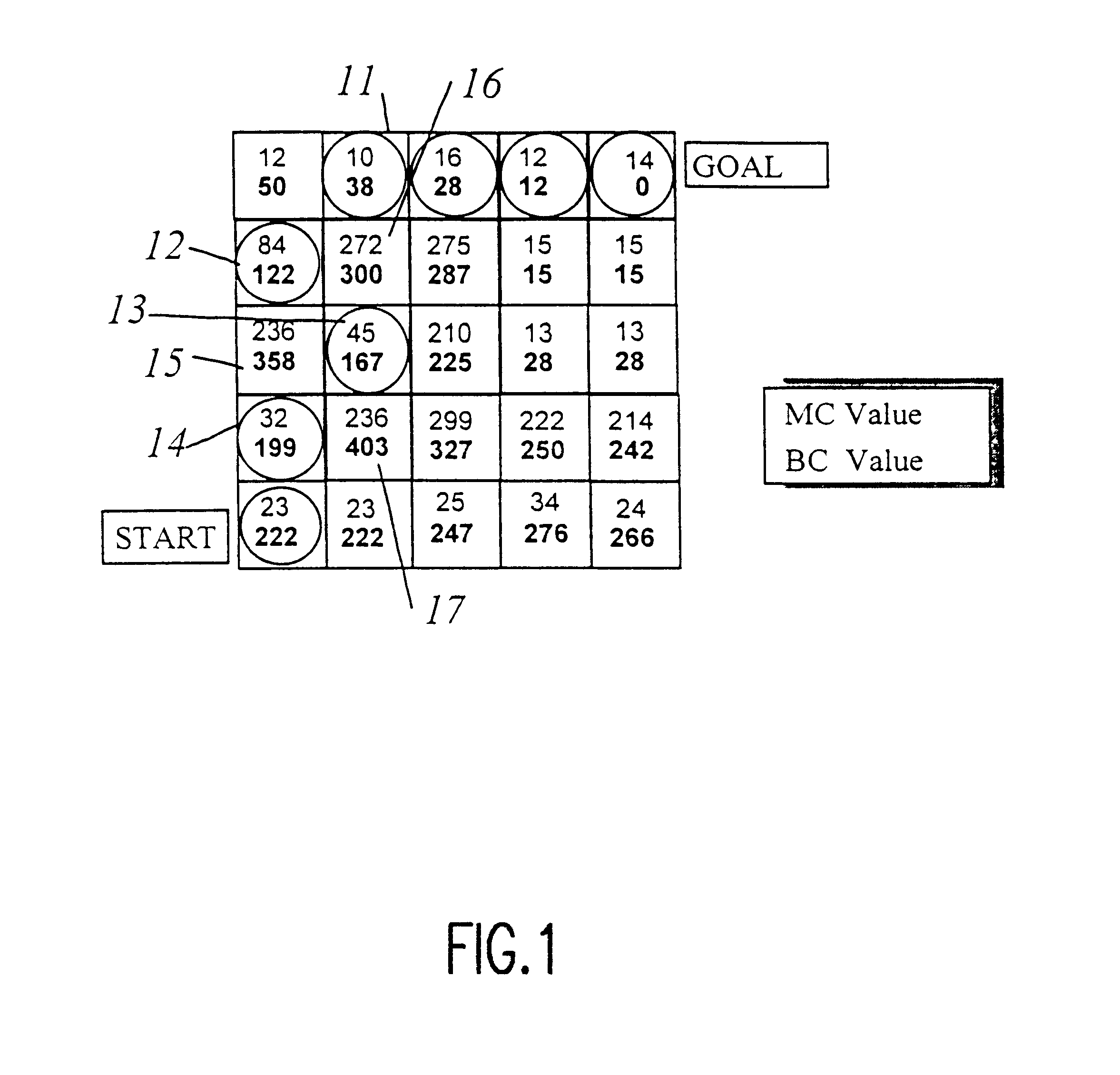
A hybrid of grid-based and graph-based search computations, together with provision of a sparse search technique effectively limited to high-probability candidate nodes provides accommodation of path constraints in an optimization search problem in substantially real-time with limited computational resources and memory. A grid of best cost (BC) values are computed from a grid of map cost (MC) values and used to evaluate nodes included in the search. Minimum segment / vector length, maximum turn angle, and maximum path length along a search path are used to limit the number of search vectors generated in the sparse search. A min-heap is preferably used as a comparison engine to compare cost values of a plurality of nodes to accumulate candidate nodes for expansion and determine which node at the terminus of a partial search path provides the greatest likelihood of being included in a near-optimal complete solution, allowing the search to effectively jump between branches to carry out further expansion of a node without retracing portions of the search path. Capacity of the comparison engine can be limited in the interest of expediting of processing and values may be excluded or discarded therefrom. Other constraints such as approach trajectory are accommodated by altering MC and BC values in a pattern or in accordance with a function of a parameter such as altitude or by testing of the search path previously traversed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
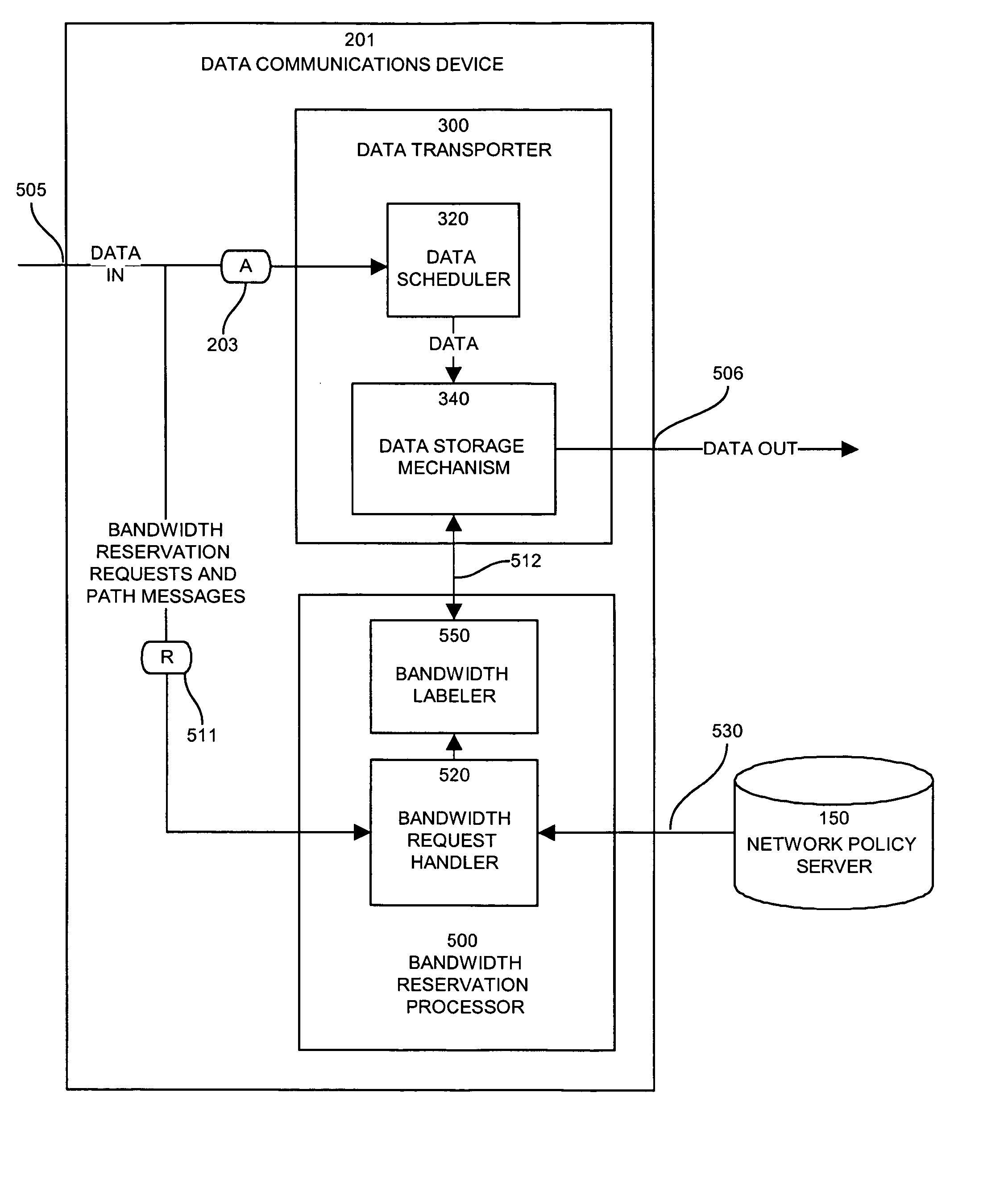
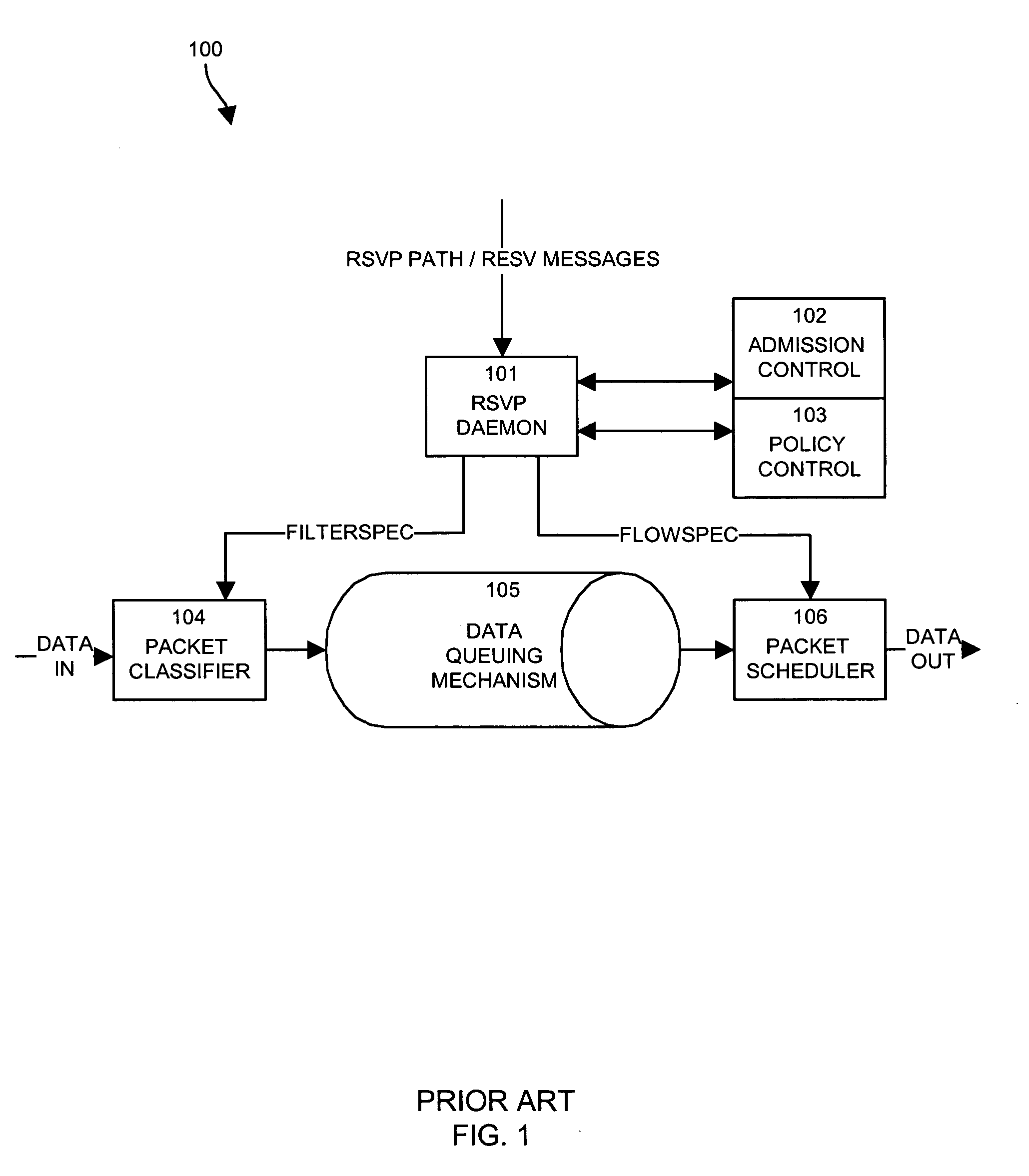
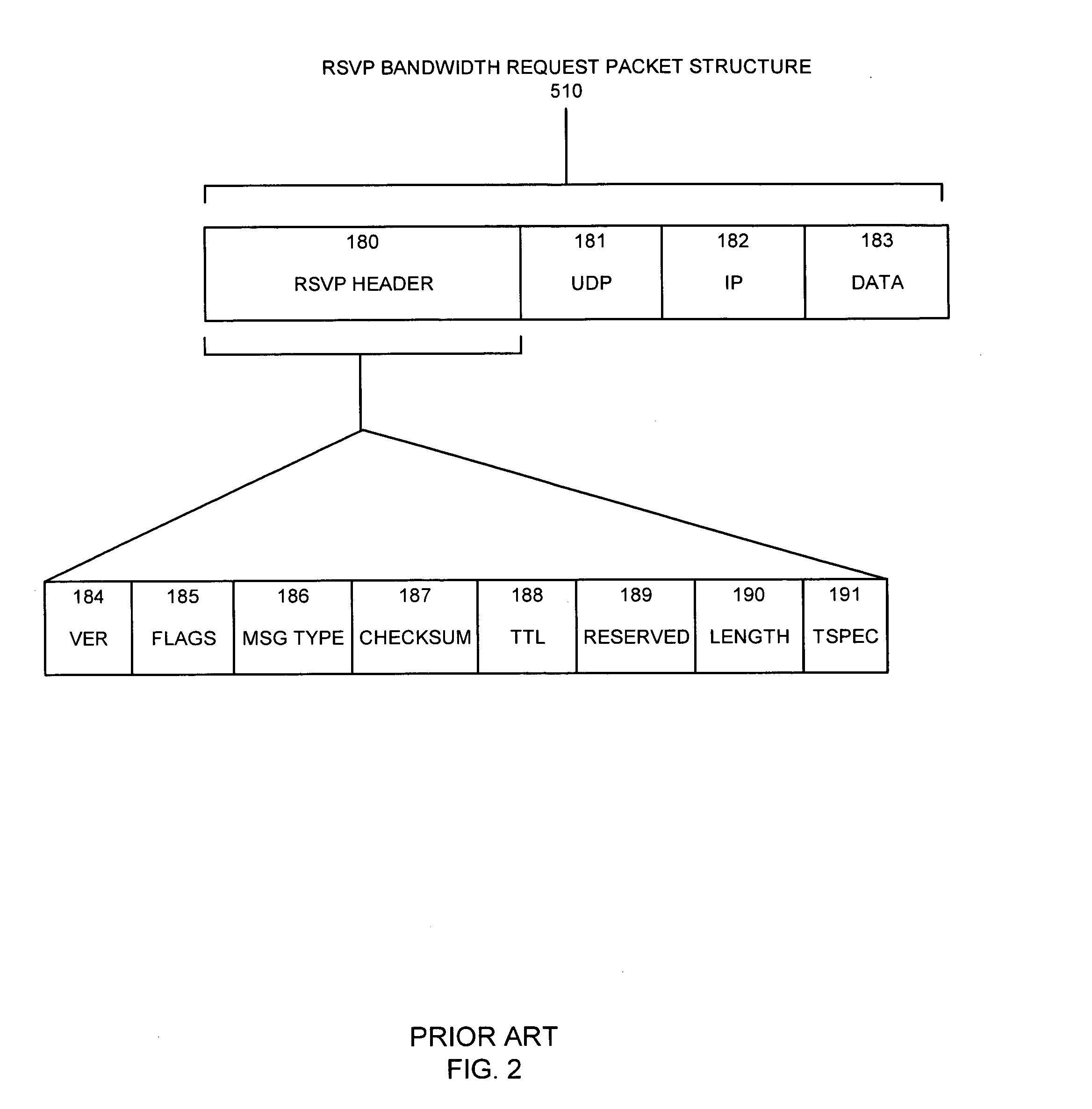
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
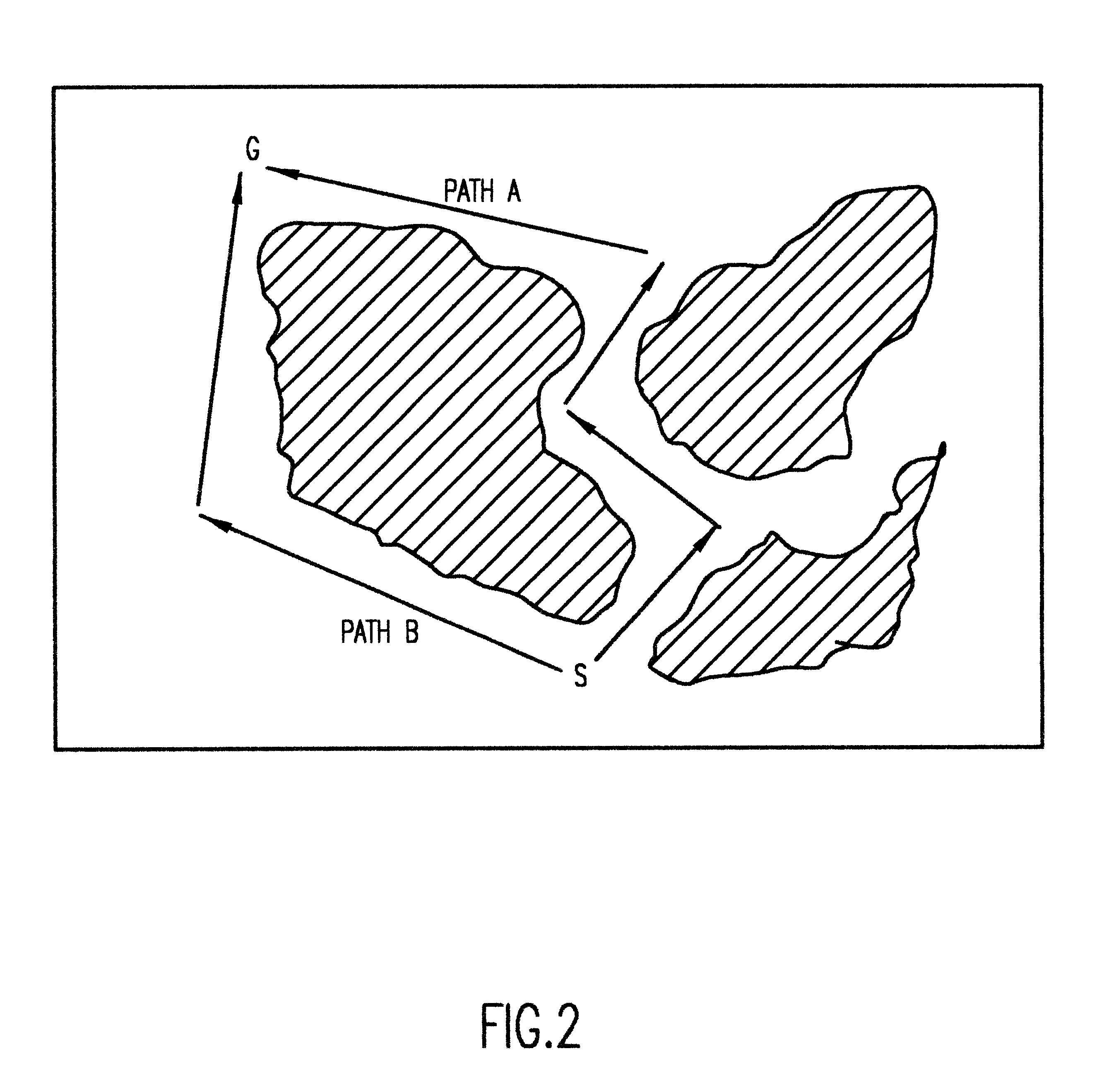
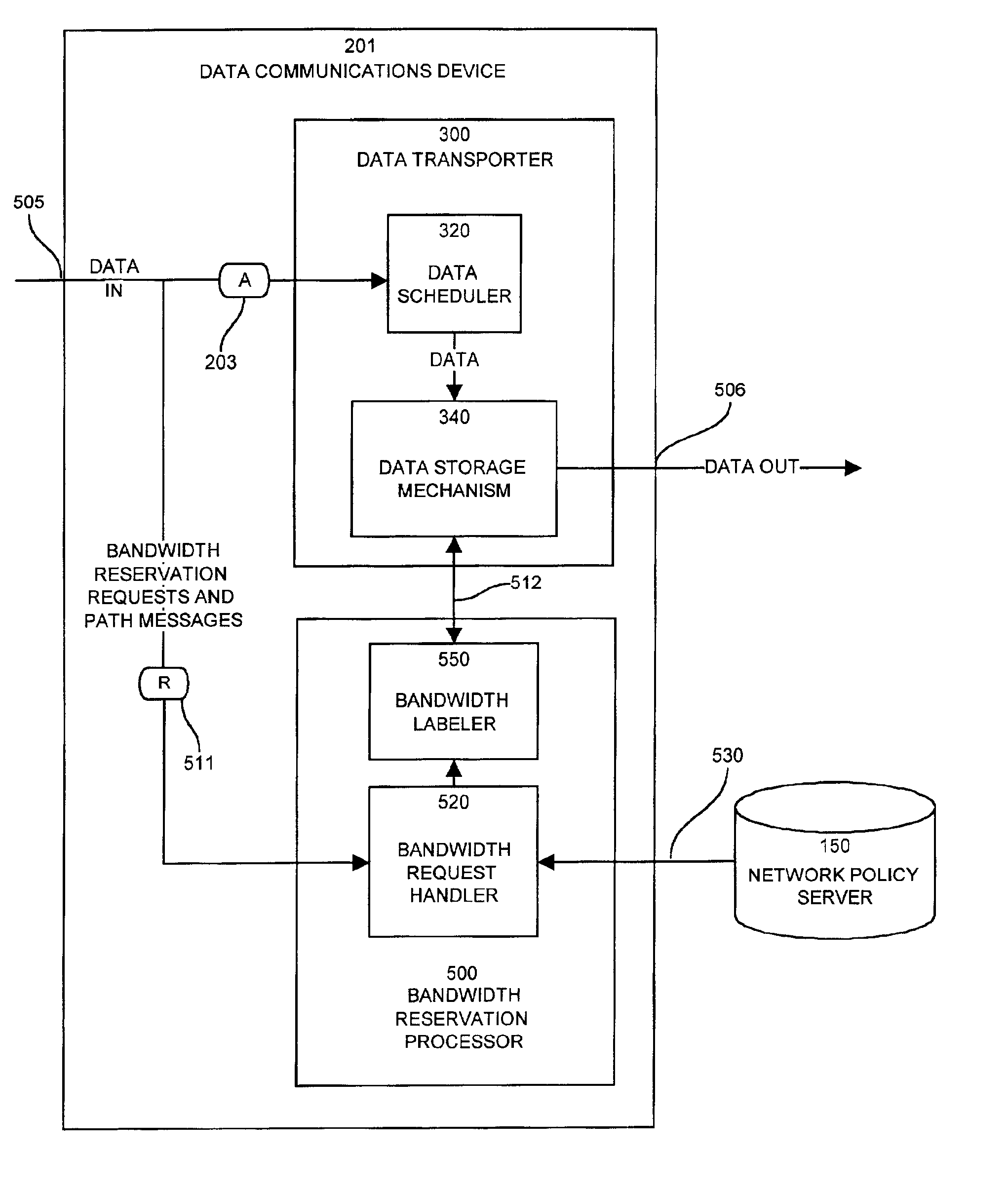
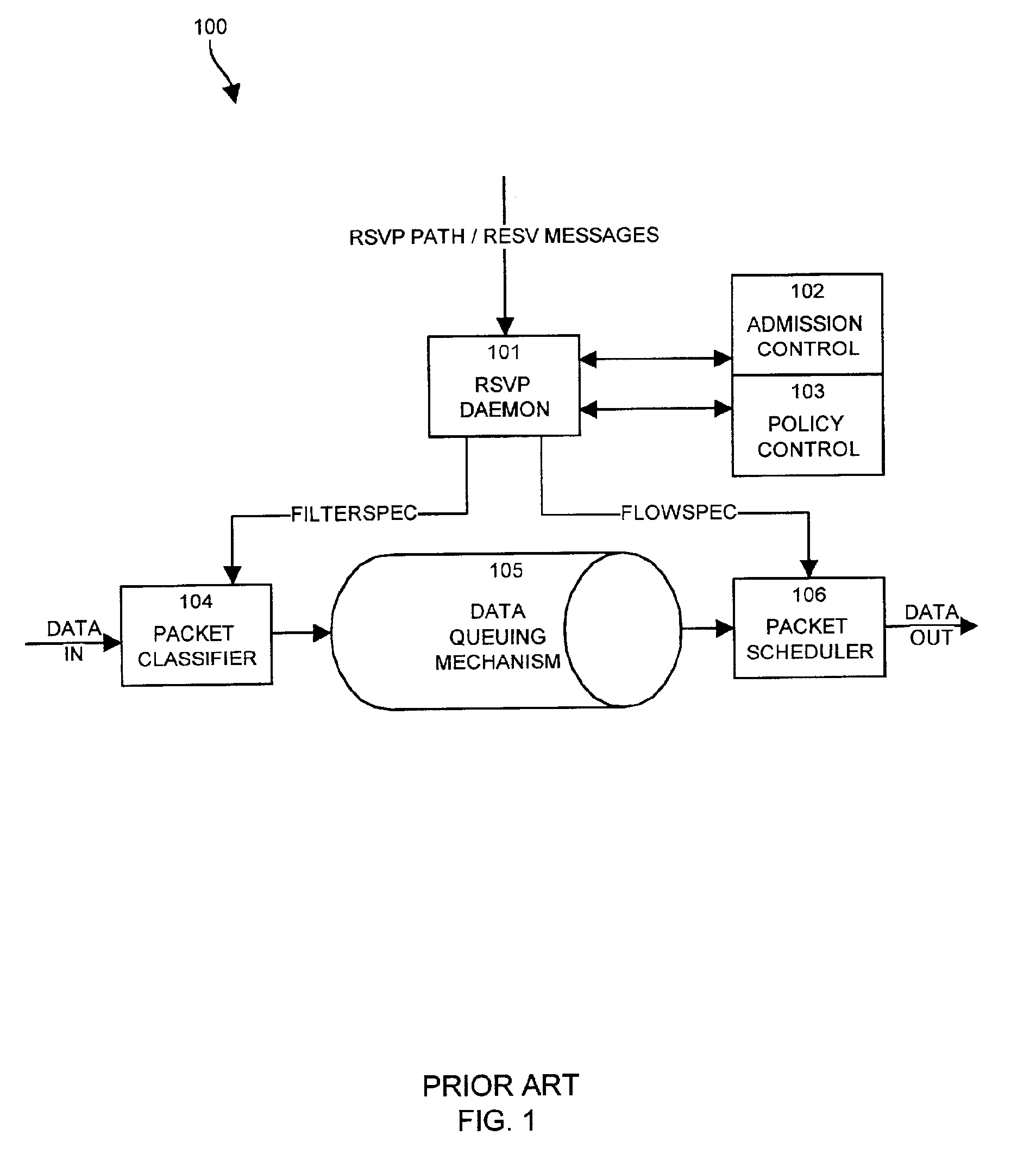
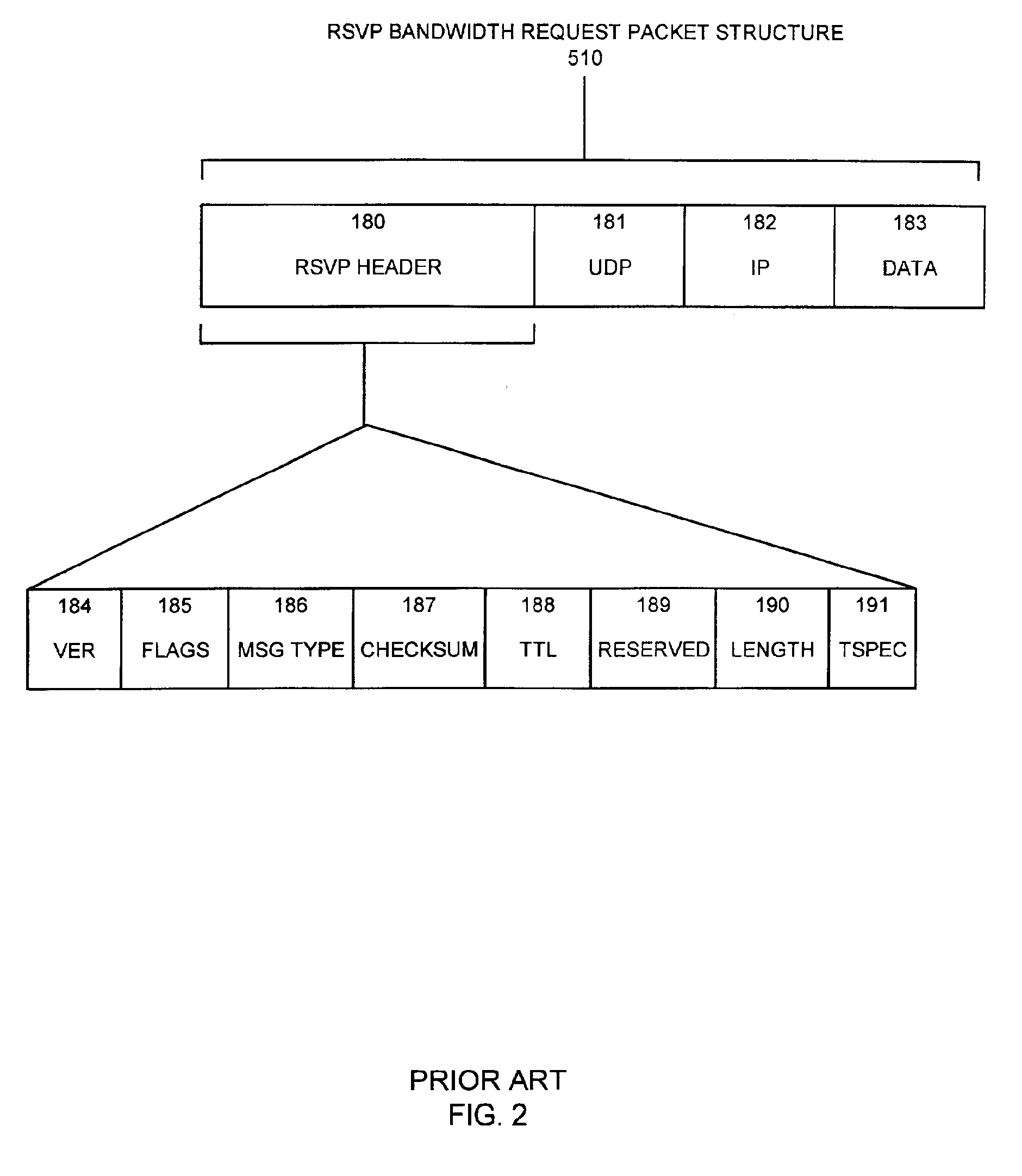
A system capable of dynamically reserving bandwidth and adjusting bandwidth reservations for active sessions of data communication in a data communications device is provided. The system generally separates the operation of bandwidth allocation and adjustment from the operation of data transport through the device, thereby allowing bandwidth reservations and adjustments to be made without disturbing sessions of data communication that are actively being transported through the device. The system can accept requests to allocate or reserve bandwidth in a data communications device using bandwidth reservation protocols such as RSVP. The reservation requests create sender state data that can be used to compute resource allocation data. The resource allocation data can be used to label data storage locations in a data storage mechanism according to the required bandwidth reservations. A data scheduling apparatus, which is ignorant of particular sessions and specific amounts of reserved bandwidth, examines data and deposits data into data storage locations having a label corresponding to a session identification specified in the data, if any. If an unknown or no session identification is specified in the data, the data scheduler deposits data into a data storage location that is unlabeled or that has an unreserved label. Thus session bandwidth is determined by the percentage of labeled data storage locations for the session. Changes in bandwidth reservations are reflected in the separate operation of alterations made in the data storage labeling scheme, and do not affect the data scheduler, or data dequeuing mechanisms, thus allowing data sessions to continue without interruption during bandwidth adjustments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction
InactiveUS20050201572A1Limited computing resourceImprove approachTransmission control/equlisationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMulti bandGraphics
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-tenant audit awareness in support of cloud environments
ActiveUS20120179646A1Facilitate compliance analysisEasy to analyzeDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsData miningComputer science
A cloud enablement aggregation proxy (CEAP) receives and processes audit data from audited resources before such data is stored in a database. The CEAP manages log data for resources hosted in a multi-tenant shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., a compute cloud). A method for managing log data begins by the proxy aggregating and normalizing log information received from a plurality of the resources. The aggregated and normalized log information is then parsed to identify a tenant associated with each of a set of transactions. For each of the set of transactions, the CEAP annotates log data associated with the tenant and the particular transaction to include a tenant-specific identifier. An optional tenant separation proxy (TSP) separates the annotated log data on a per tenant basis prior to storage, and the tenant-specific log data may be stored in per tenant data structures or dedicated tenant log event databases to facilitate subsequent compliance or other analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
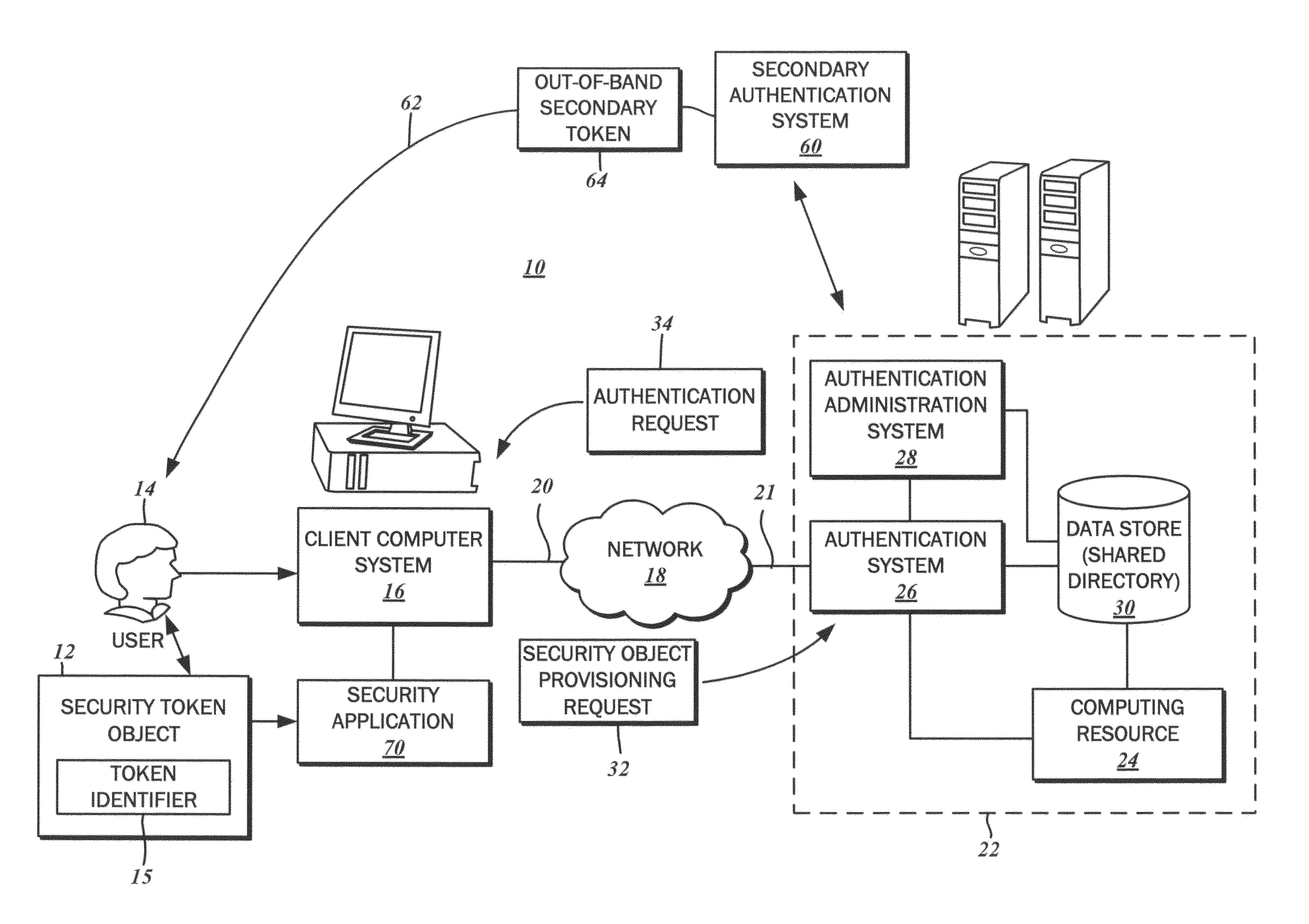
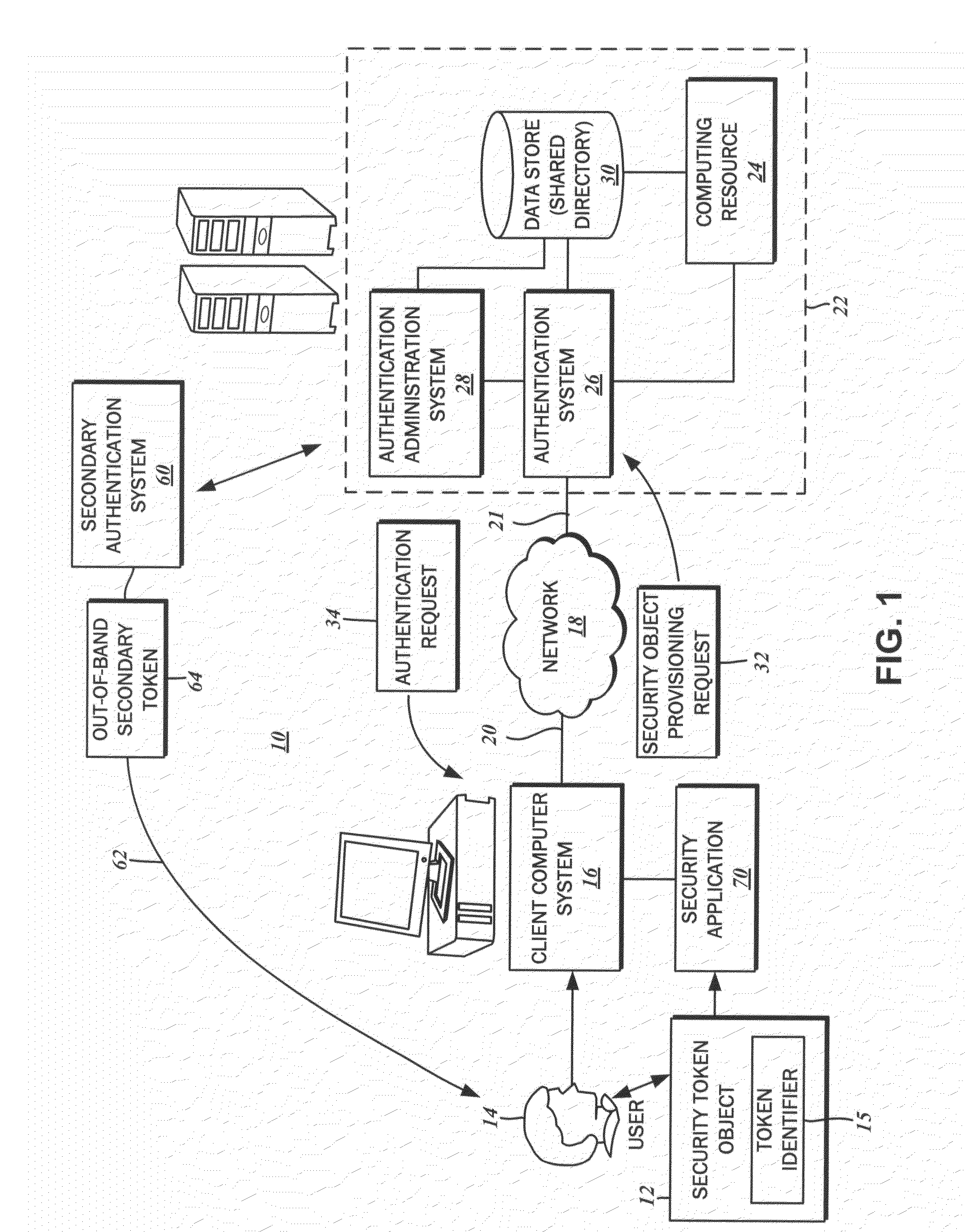
Security device provisioning
ActiveUS8510816B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUnique identifierClient-side
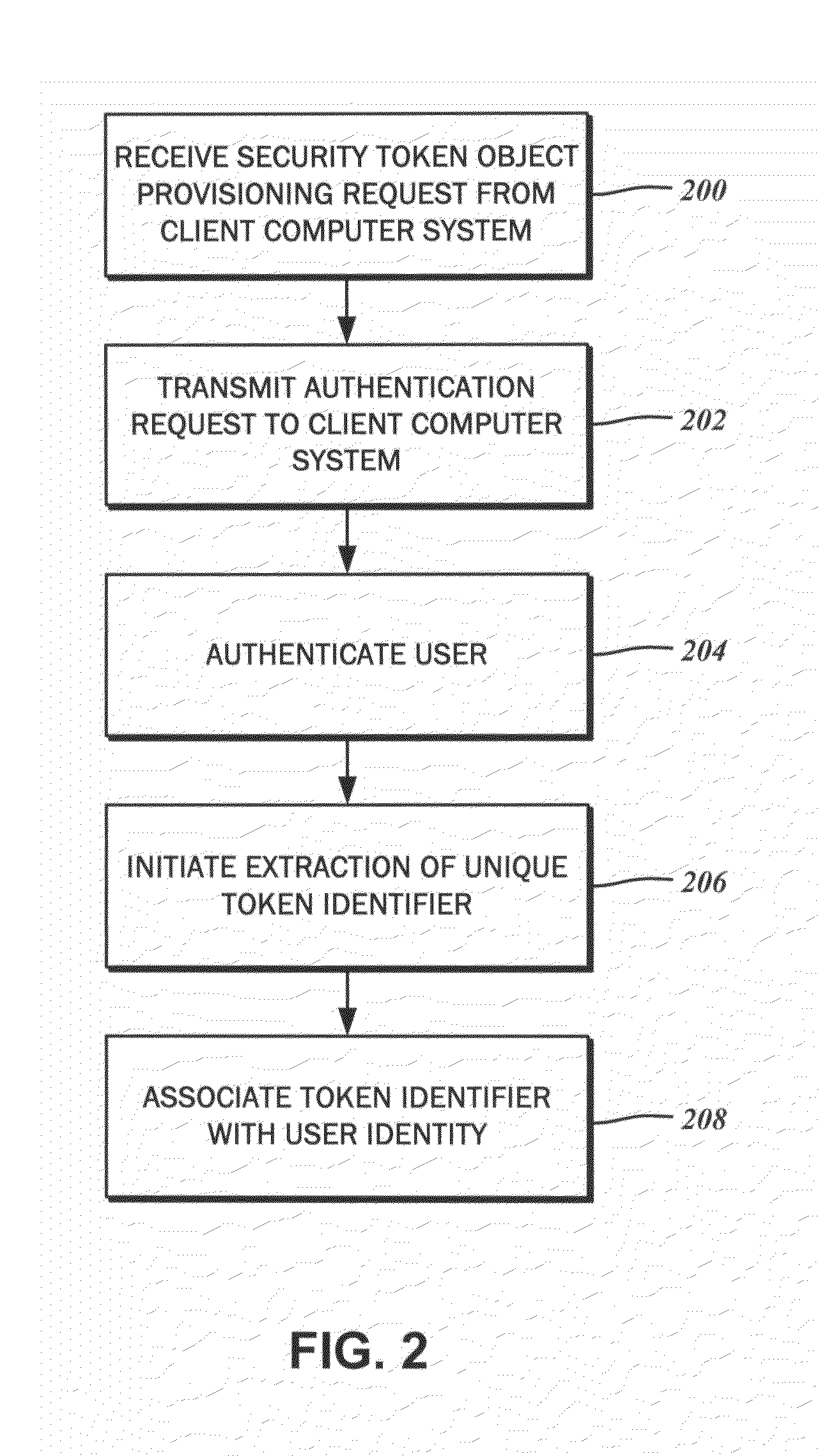
The provisioning of a security token object to a user is disclosed. The security token object is used for accessing a computing resource through a client computer system. A security token object provisioning request may be received from the client computer system. In response, an authentication request may be transmitted. The user is authenticated against a user identity based upon a set of received identity credentials provided by the user. The extraction of a unique token identifier from the security token object is initiated, and completed without intervention from the user. The unique token identifier received from the client computer system is associated with to the user identity in a data store. By providing the security token object, the user can gain access to the computing resource.
Owner:SECUREAUTH CORP
System and method for allocating computing resources of a distributed computing system
In certain aspects, the invention features a system and method for (1) receiving reservations for a first subset of computing resources of a distributed computing system (DCS), wherein each of the reservations specifies a time period, (2) allocating the first subset according to the reservations, (3) receiving requests for use of at least a second subset of the DCS's computing resources, wherein each of the requests specifies a time period, (4) determining whether enough unallocated resources are available to fulfill all of the requests, wherein the unallocated resources include the DCS's resources not allocated according to the reservations, (5) allocating resources according to the requests, if there are enough unallocated resources available, and (6) allocating resources in accordance with an allocation criteria if there are not enough unallocated resources available.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
System and device for multi-scale analysis and representation of physiological data
InactiveUS6925324B2Easy to analyzeIncrease computing resourcesElectrocardiographySensorsReal time analysisT wave
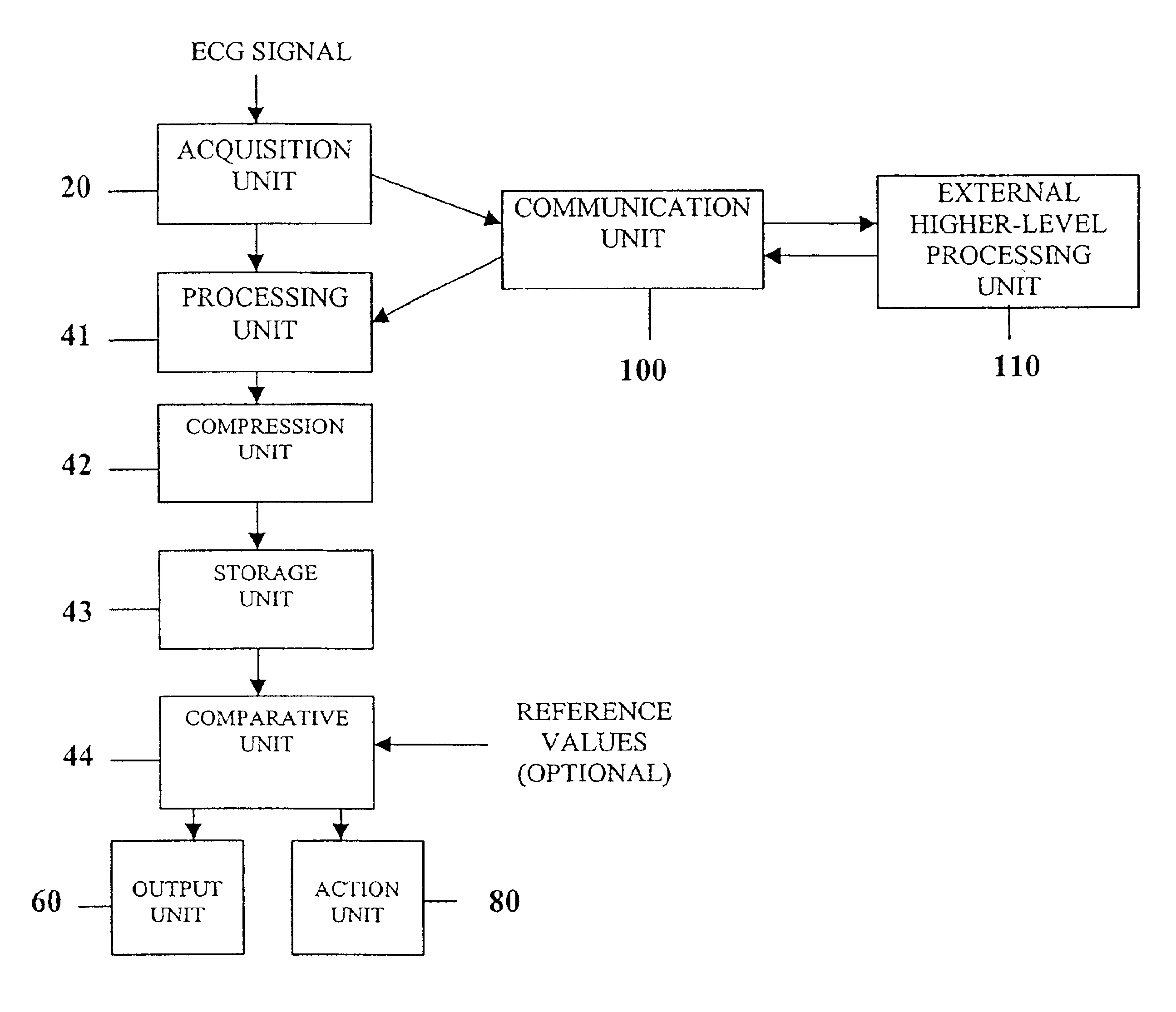
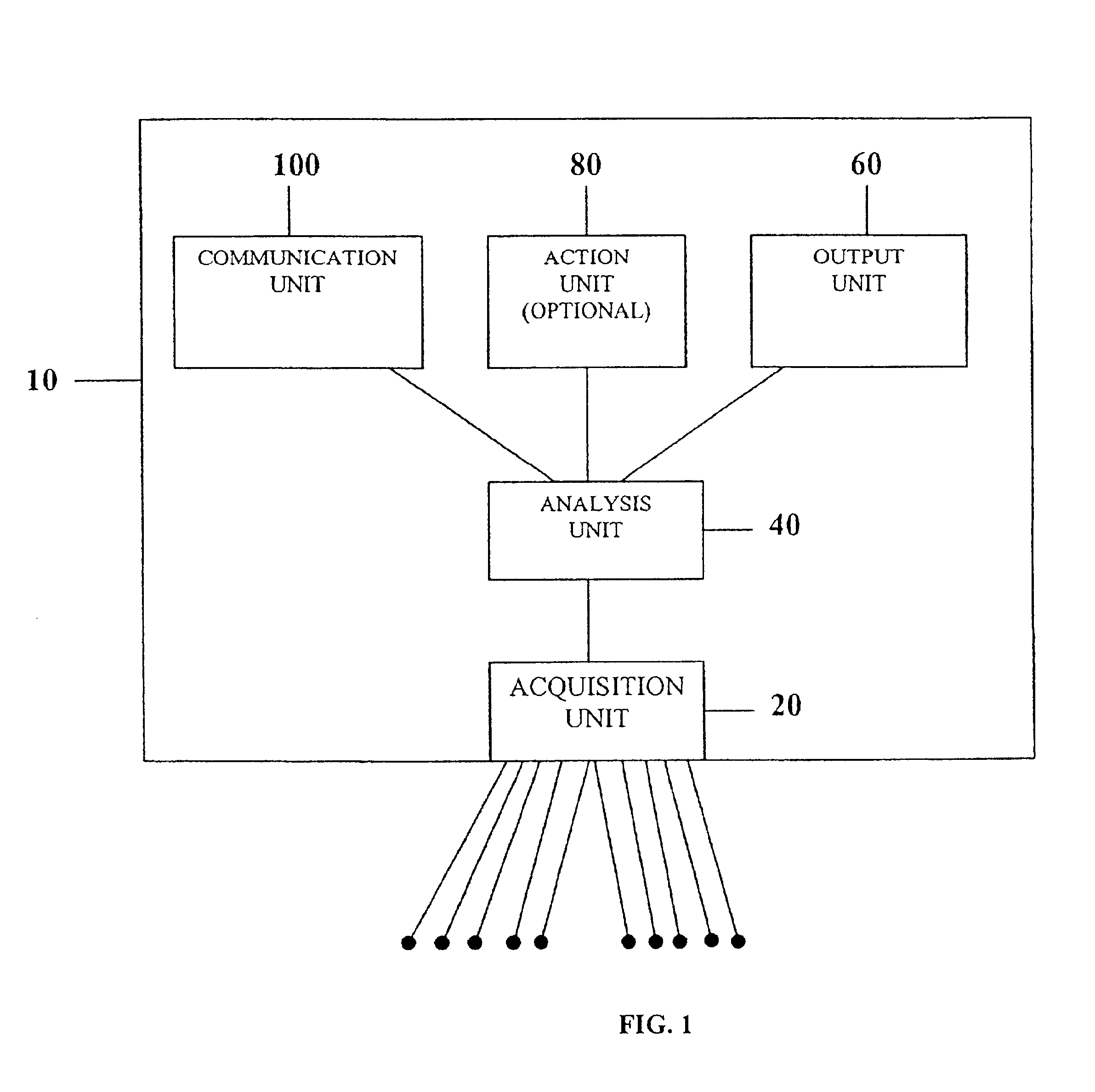
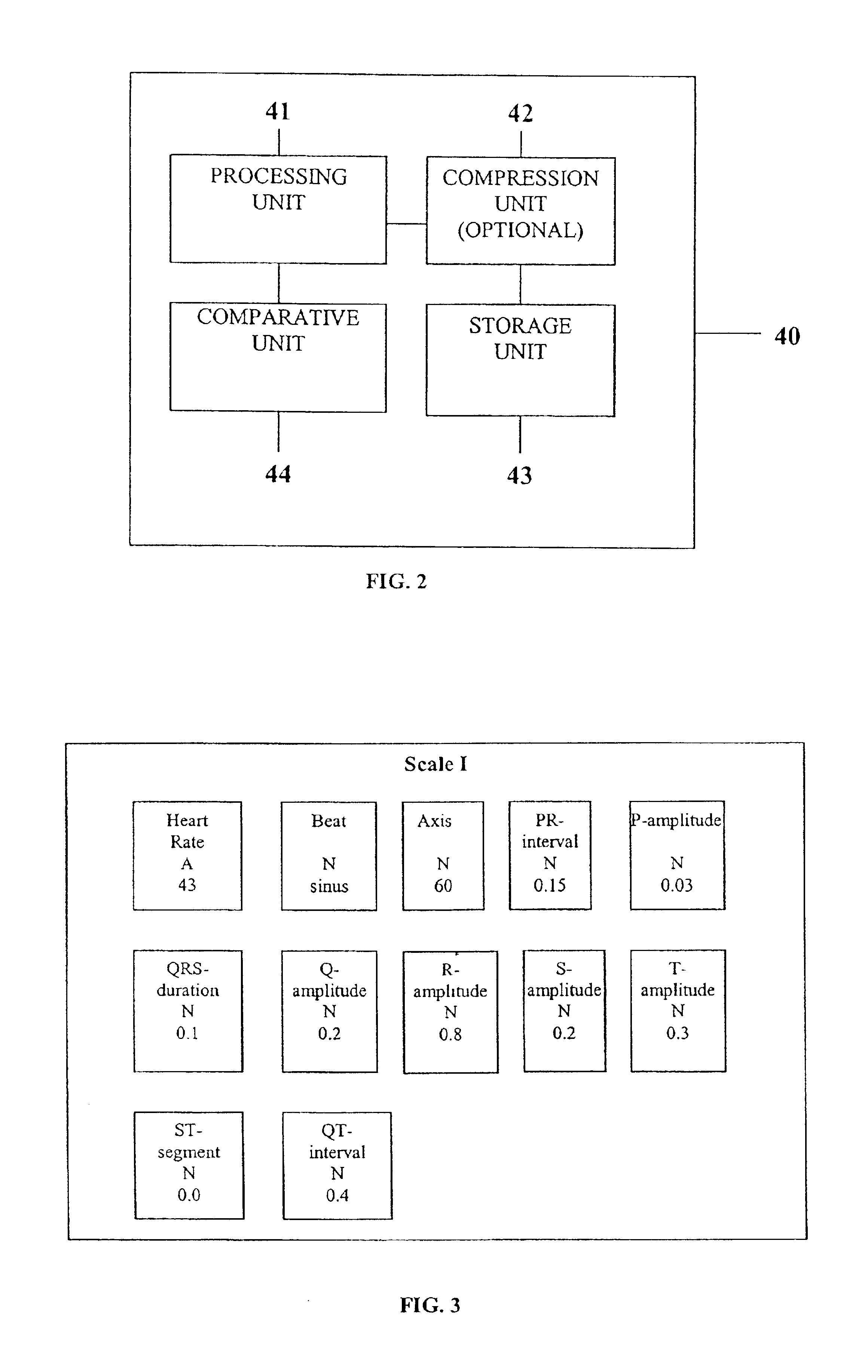
System comprised of a medical device and method for analyzing physiological and health data and representing the most significant parameters at different levels of detail which are understandable to a lay person and a medical professional. Low, intermediate and high-resolution scales can exchange information between each other for improving the analyses; the scales can be defined according to the corresponding software and hardware resources. A low-resolution Scale I represents a small number of primary elements such as intervals between the heart beats, duration of electrocardiographic PQ, QRS, and QT-intervals, amplitudes of P-, Q-, R-, S-, and T-waves. This real-time analysis is implemented in a portable device that requires minimum computational resources. The set of primary elements and their search criteria can be adjusted using intermediate or high-resolution levels. At the intermediate-resolution Scale II, serial changes in each of the said elements can be determined using a mathematical decomposition into series of basis functions and their coefficients. This scale can be implemented using a specialized processor or a computer organizer. At the high-resolution Scale III, combined serial changes in all primary elements can be determined to provide complete information about the dynamics of the signal. This scale can be implemented using a powerful processor, a network of computers or the Internet. The system can be used for personal or group self-evaluation, emergency or routine ECG analysis, or continuous event, stress-test or bed-side monitoring.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Realtime kernel
ActiveUS20100146085A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsData streamNetwork connection
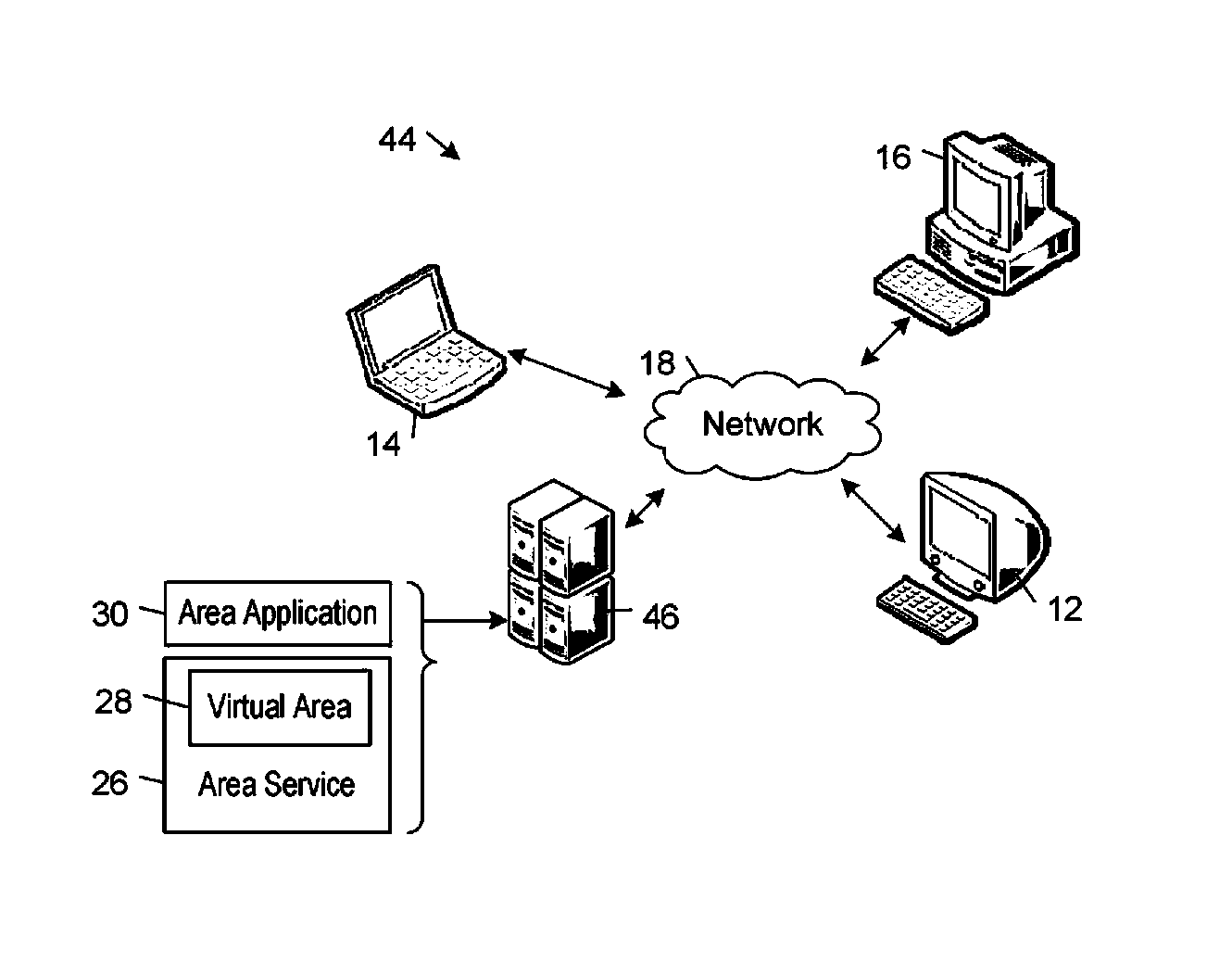
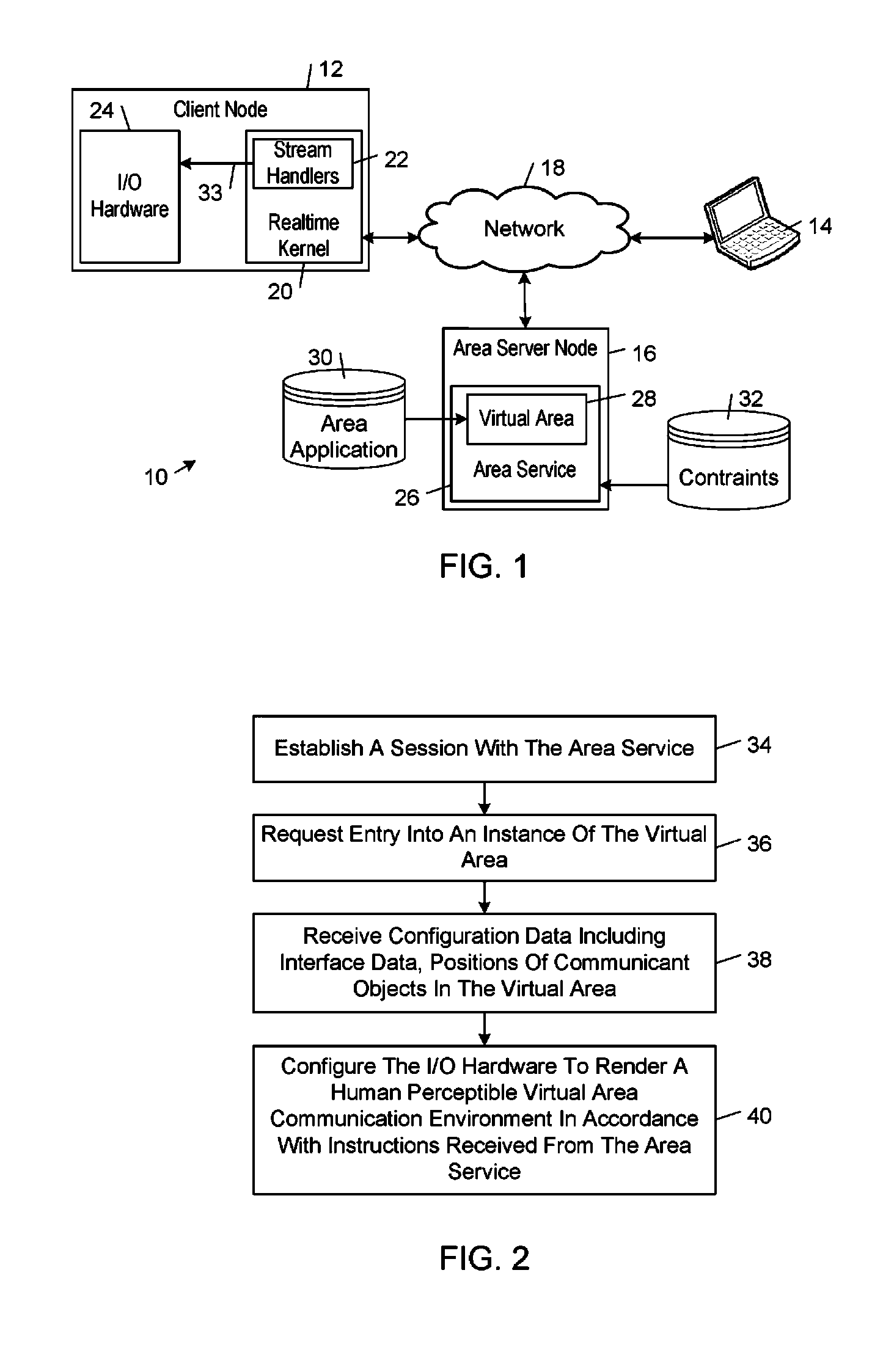
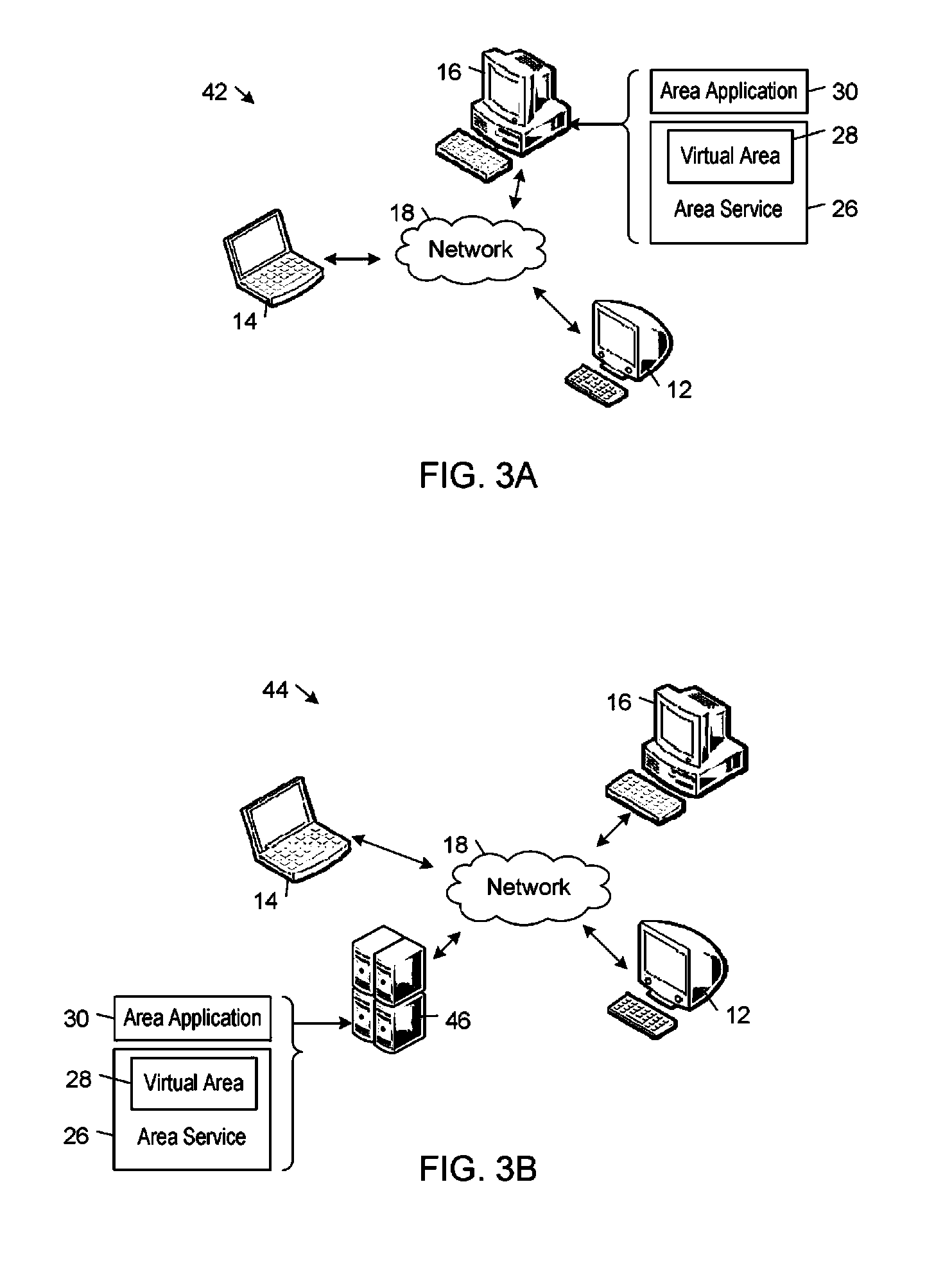
A realtime kernel supports realtime communications between communicants operating on respective network nodes. The realtime kernel handles the complex tasks of connecting to communicants, virtual areas, and other network resources, switching those connections in response to user inputs, and mixing realtime data streams. The realtime kernel enables developers to focus on developing high-level communications functionality instead of low-level plumbing code. The realtime kernel imposes relatively low computational resource requirements so that realtime communications performance can be achieved using a wide range of computing devices and network connections that currently are available.
Owner:SOCOCO INC
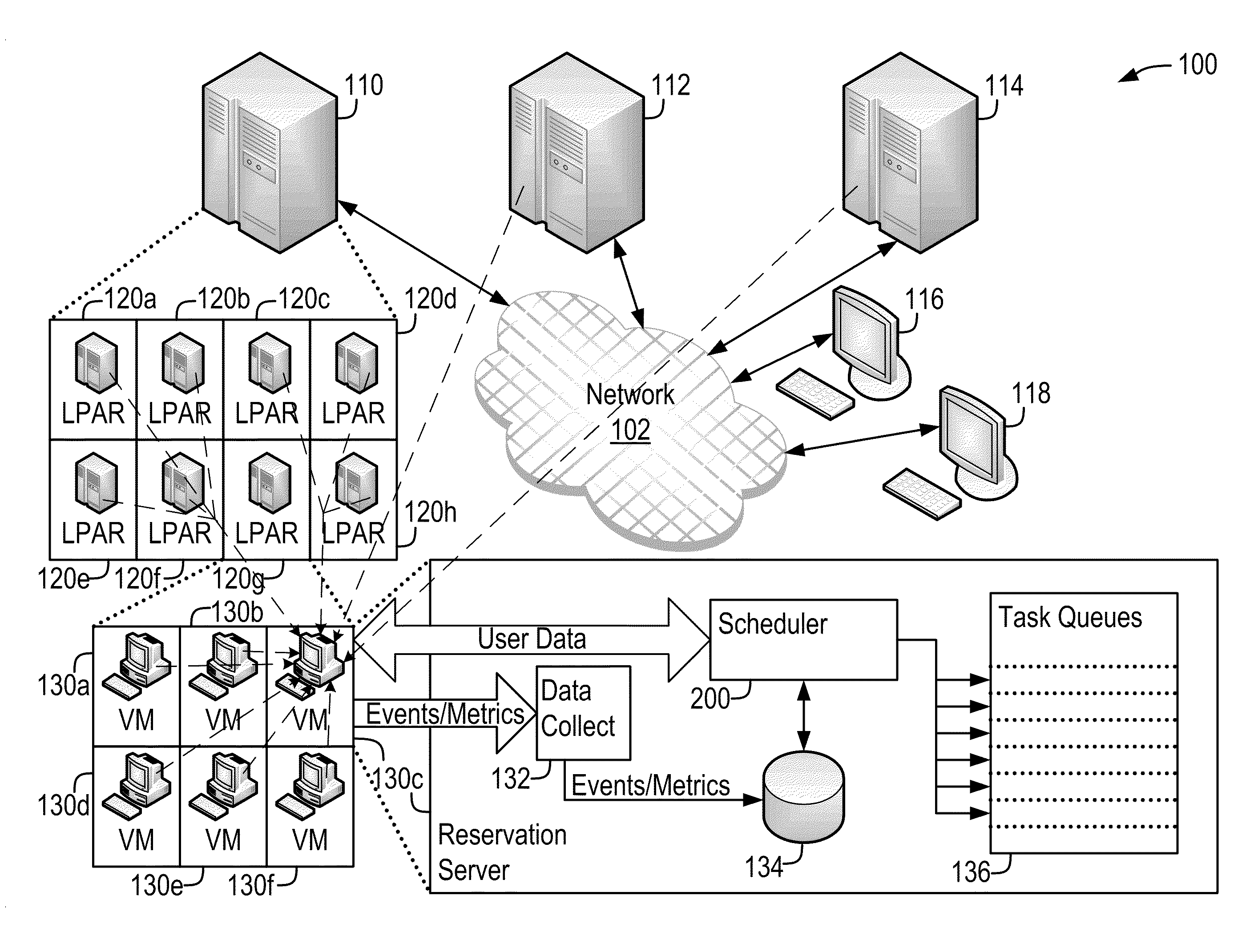
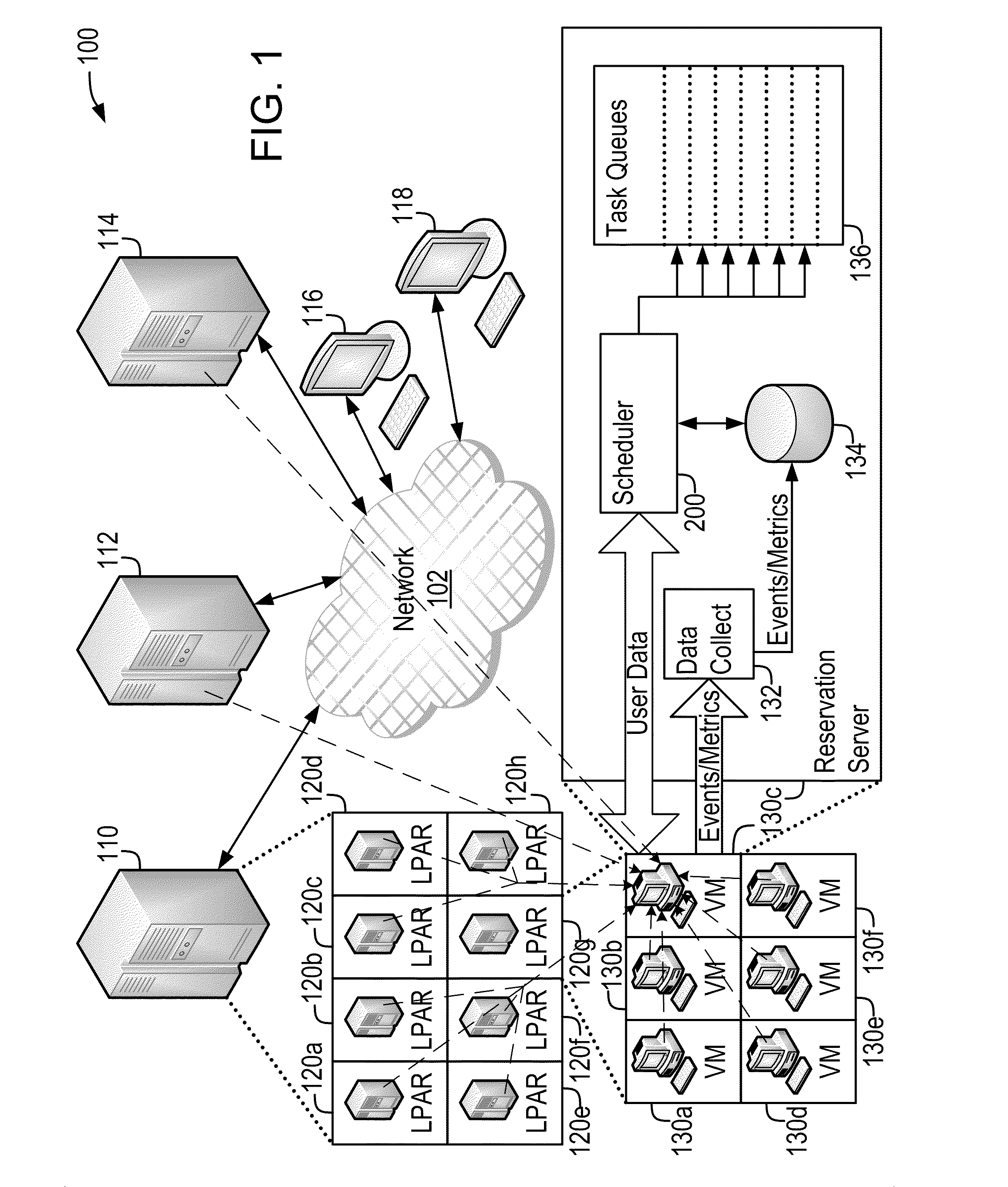
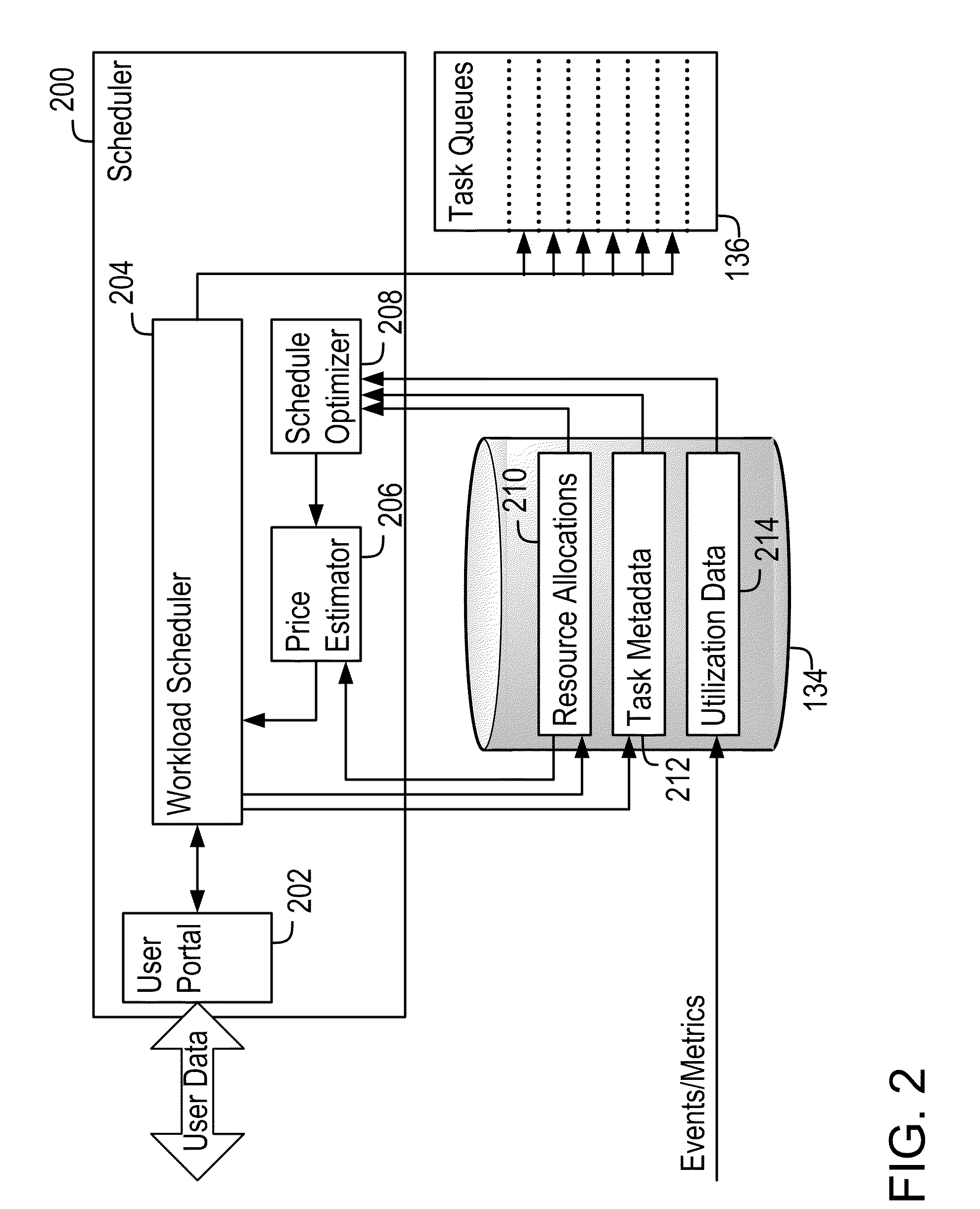
Demand-Driven Workload Scheduling Optimization on Shared Computing Resources
InactiveUS20110154353A1Low costHinder taskResource allocationMemory systemsTime scheduleProgram planning
Systems and methods implementing a demand-driven workload scheduling optimization of shared resources used to execute tasks submitted to a computer system are disclosed. Some embodiments include a method for demand-driven computer system resource optimization that includes receiving a request to execute a task (said request including the task's required execution time and resource requirements), selecting a prospective execution schedule meeting the required execution time and a computer system resource meeting the resource requirement, determining (in response to the request) a task execution price for using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule, and scheduling the task to execute using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule if the price is accepted. The price varies as a function of availability of the computer system resource at times corresponding to the prospective execution schedule, said availability being measured at the time the price is determined.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
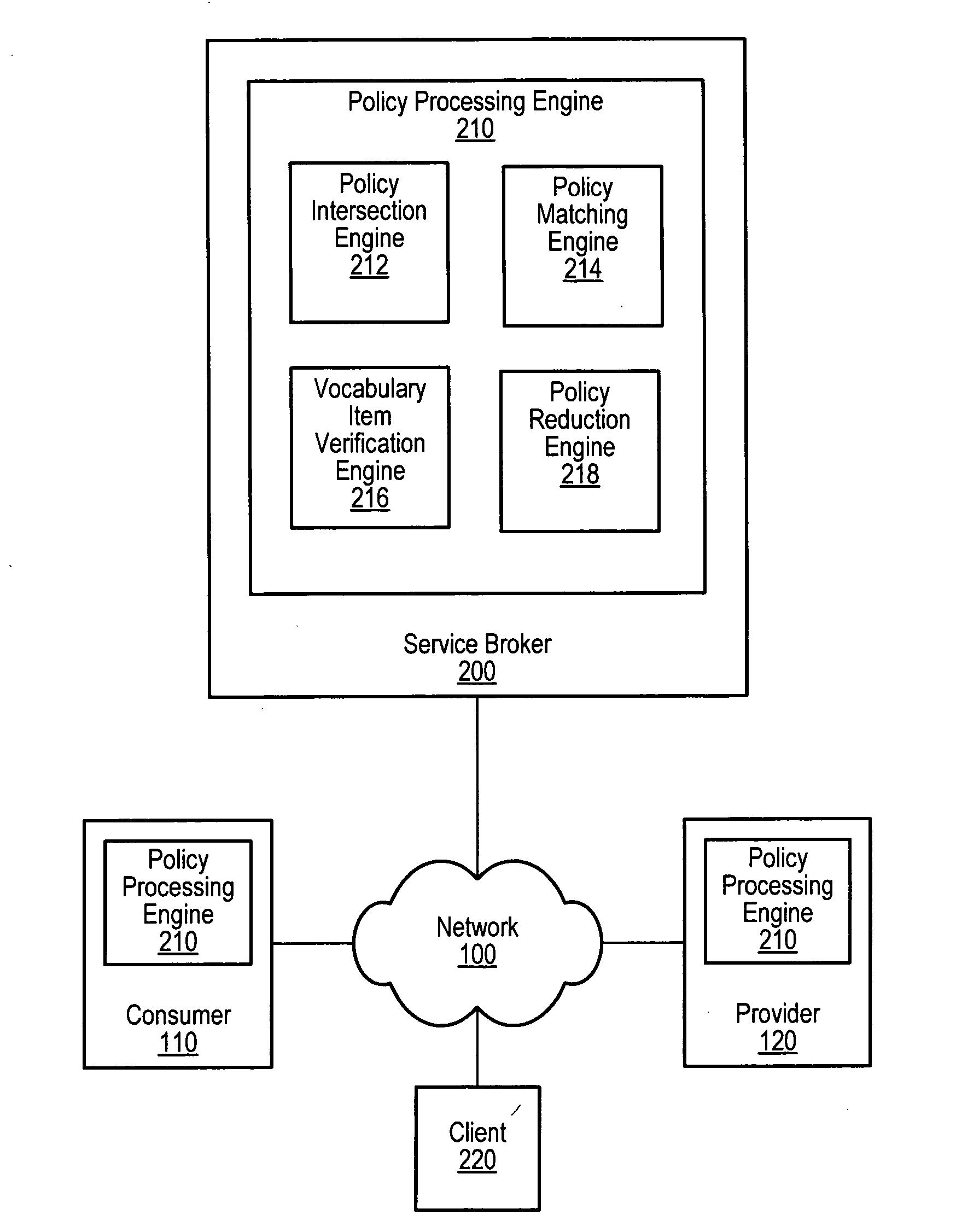
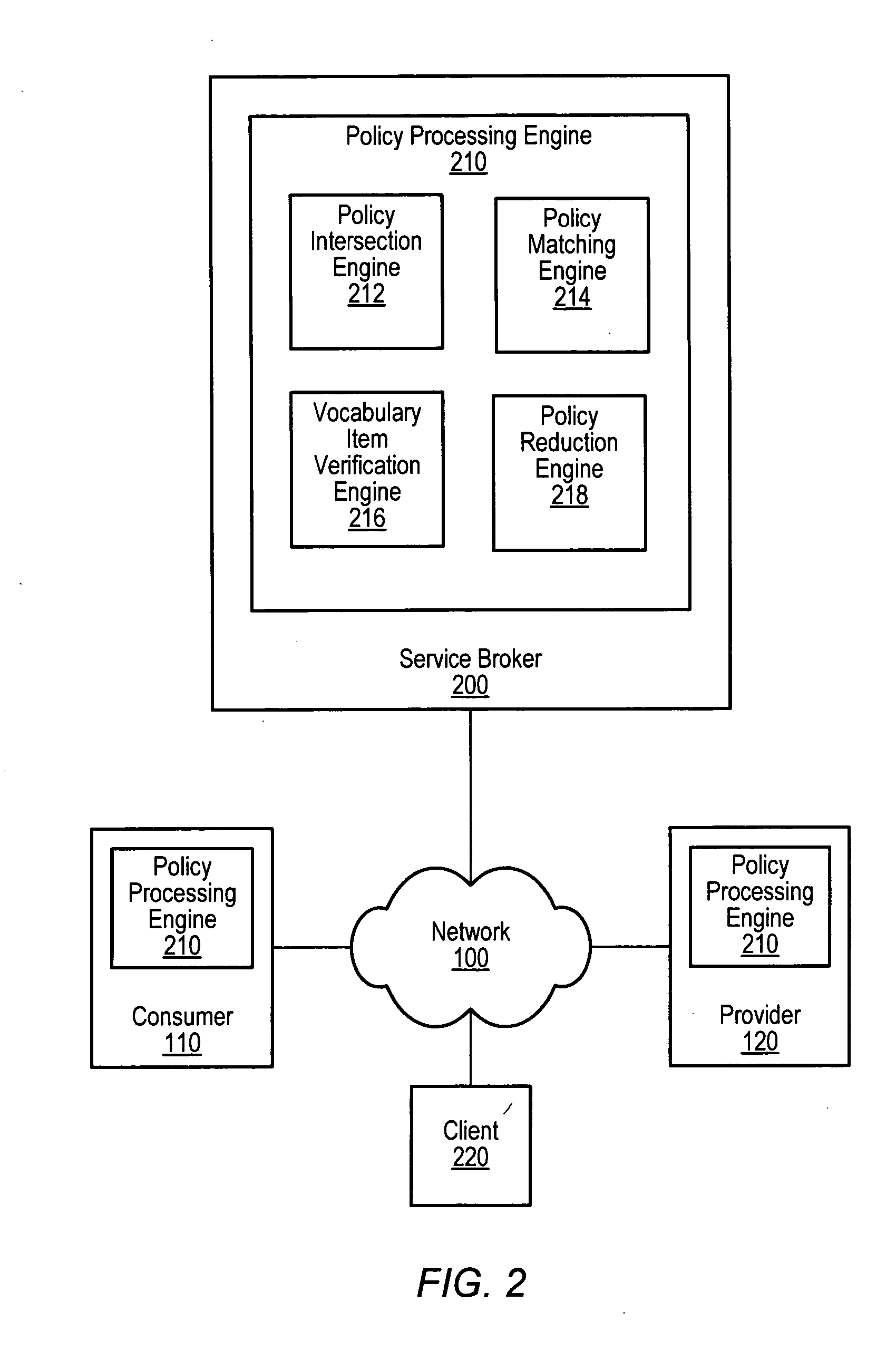
Automated policy constraint matching for computing resources
Web services interface policy constraints may be specified in a policy constraints language and policy processing, such as generating an intersection policy of two policies may be automated by a policy-processing engine. A policy constraint may be a specification of a value, range of values, or set of values that a particular requirement or offering is allowed to have. Hierarchies of requirements and / or offerings may also be expressed and matched such that a more specific case of a requirement or offering may be matched against a more general case of the same requirement or offering. Also, preferences among vocabulary items, vocabulary item values, policy constraints, and other elements of a policy may be specified and automatically determined by a policy-processing engine. Automated matching of consumer requirements against provider offerings may allow a policy-processing engine to process policies with specifications of requirements or offerings from any domain-specific schema.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for promotion of calculations to cloud-based computation resources
ActiveUS20100057831A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsHigh bandwidthElectronic form
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for the promotion of calculations to cloud-based computation resources. One or more applications, such as spreadsheet applications, can prepare the calculation of a relatively large-scale computation, such as running statistical reports on large (e.g., greater than 1000 by 1000 cell) spreadsheets or other data objects. If the pending calculation is determined to be greater than a computation threshold for instance in computation intensity or data size, a computation request can be sent to a promotion engine. The promotion engine can identify a set of computation resources located in a cloud or other network and transmit the data request and subject data to the set of computation resources, which afford greater computation speed than the local machine hosting the requesting application. A set of results is returned from the cloud to the requesting application, thereby creating higher bandwidth and faster calculation times for the user.
Owner:RED HAT
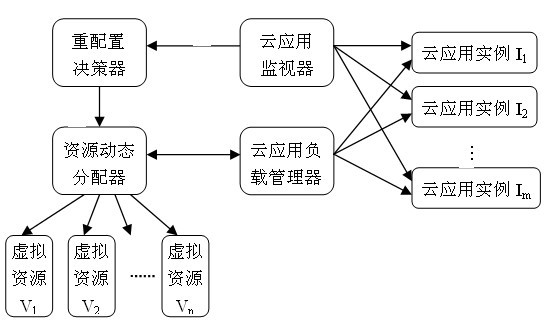
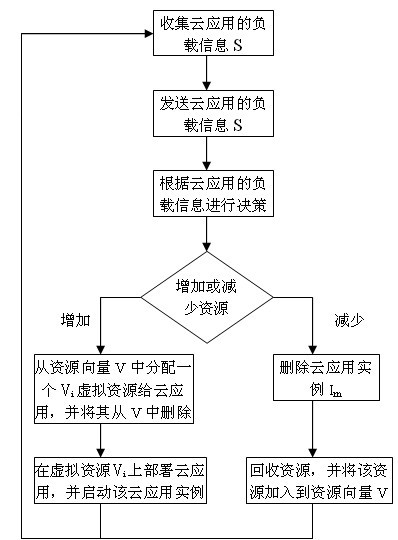
Cloud computing resource scheduling method based on dynamic reconfiguration virtual resources
InactiveCN101938416ADynamic Allocation OptimizationMeeting the Need for Dynamic ScalabilityData switching networksCurrent loadDecision taking
The invention relates to a cloud computing resource scheduling method based on dynamic reconfiguration virtual resources. The method comprises the steps of: using cloud application load information collected by a cloud application monitor as a basis; making a dynamic decision based on the load capacity of the virtual resources for running cloud application and the current load of the cloud application; and dynamically reconfiguring virtual resources for cloud application based on the decision result. Dynamic adjustment of resources is realized by a method for reconfiguring virtual resources for cloud application, without needing dynamic redistribution of physical resources or stopping executing cloud application. The method can dynamically reconfigure the virtual resources according to the load variation of the cloud application, optimize allocation of the cloud computing resources, realize effective use of the cloud computing resources, and meet the requirements on dynamic scalability of cloud application. In addition, the method can avoid waste of the cloud computing resources, and save the cost for using resources for cloud application users.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Techniques for pruning a data object during operations that join multiple data objects
InactiveUS7020661B1Reduce consumptionReduced computing resourceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData miningDigital object
Techniques for eliminating one or more portions of a data object from any join step of an operation that joins multiple data objects include determining that an operation joins a first data object and a second data object. The second data object includes multiple portions. Each of multiple data units of the first data object is scanned. Based on data in the data units of the first data object, information is generated. The information indicates a portion of the second data object for exclusion. The indicated portion is excluded from an output of the operation. Only one or more portions of the second data object that are not indicated for exclusion in the information are included in a particular join step involving the second data object. By pruning a large second table, such as a fact table, the computational resources consumed by the joins are substantially reduced.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
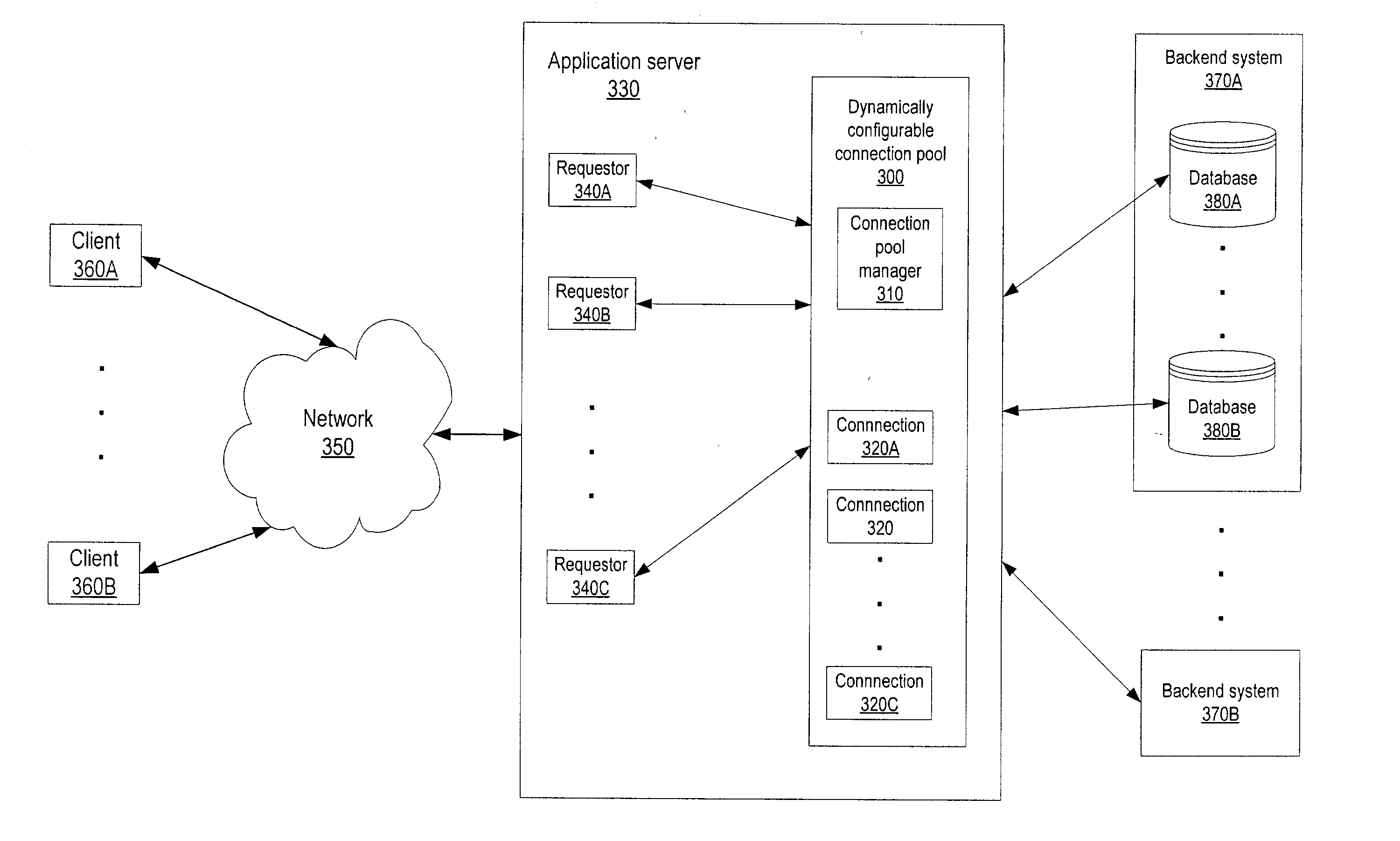
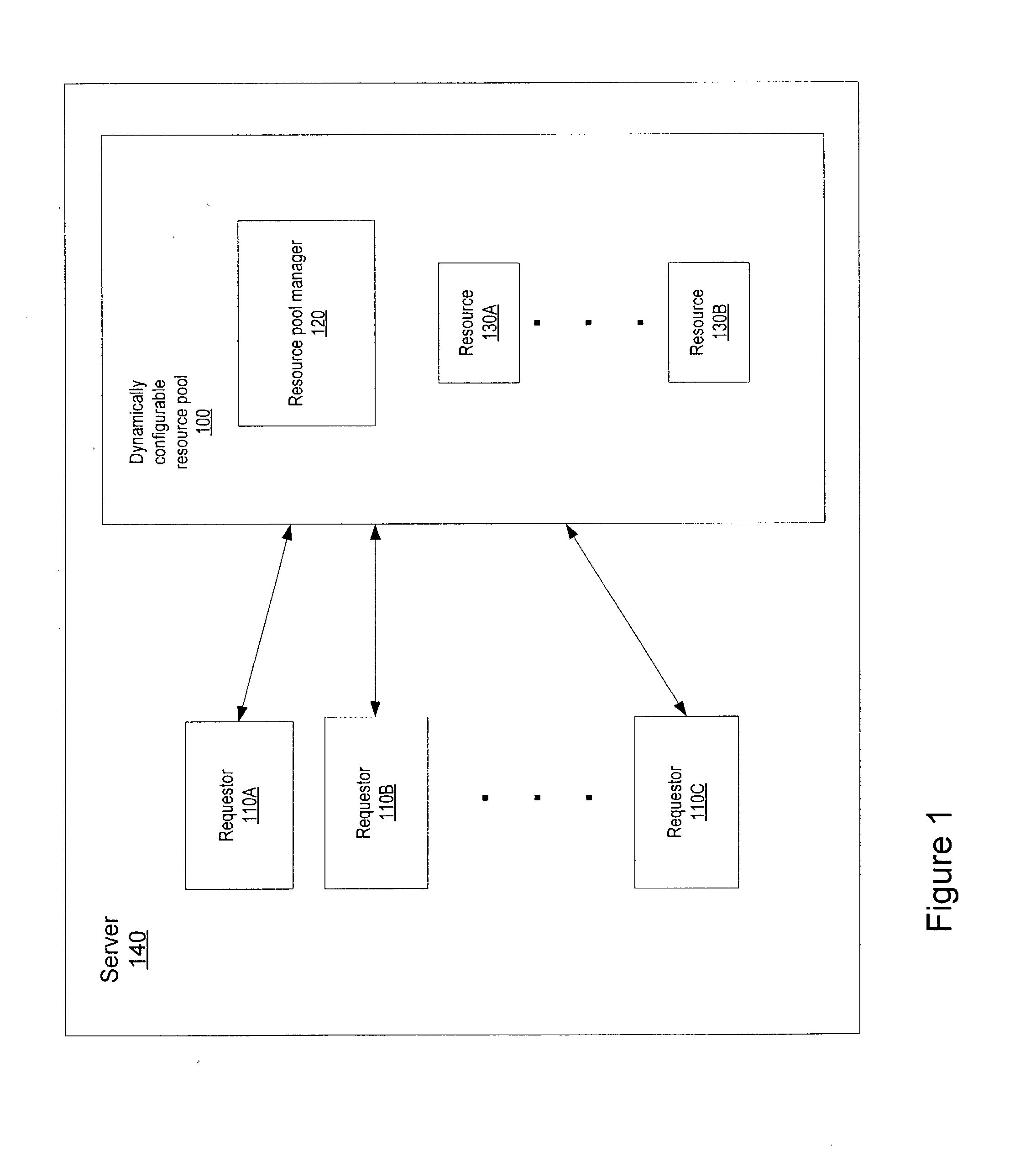
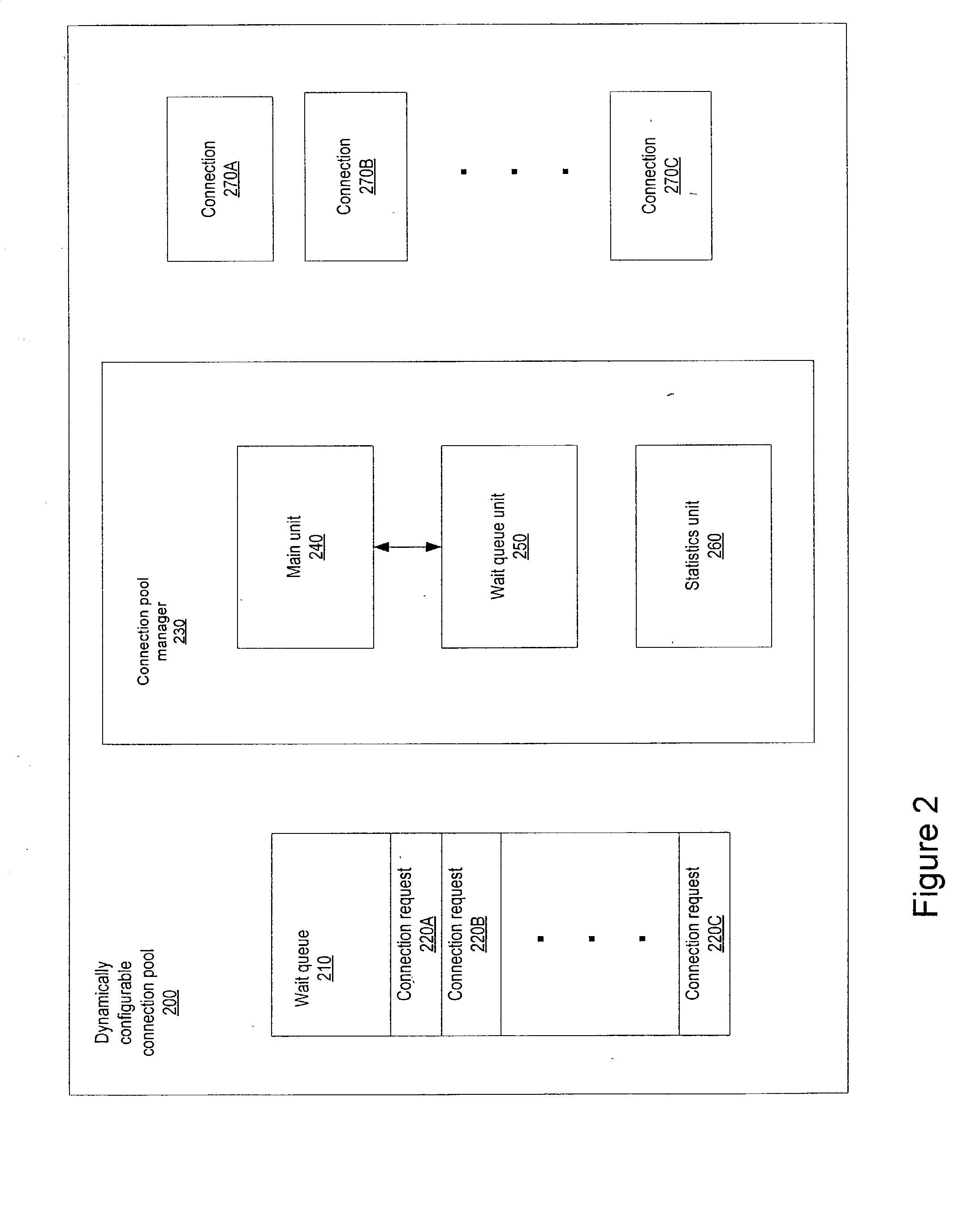
Dynamically configurable resource pool
ActiveUS20040088413A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsResource poolWeb service
A dynamically configurable resource pool may provide a pool of computing resource for use in a computing system or application, such as a connection pool or a thread pool for server systems such as application and web server systems. In one embodiment, a server may include a resource pool configured to provide a plurality of computing resources. Other components in the server may be configured to request use of one of the computing resources from the connection pool. The resource pool may include a resource pool manager configured to service requests for the computing resources. The resource pool manager may manage configuration of the resource pool. The resource pool manager may also be configured to receive a configuration change request to change the configuration of the resource pool while the resource pool is available for use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Using execution statistics to select tasks for redundant assignment in a distributed computing platform
InactiveUS7093004B2Minimizes unnecessary network congestionImprove deploymentResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsOff the shelfSelf adaptive
The invention provides an off-the-shelf product solution to target the specific needs of commercial users with naturally parallel applications. A top-level, public API provides a simple “compute server” or “task farm” model that dramatically accelerates integration and deployment. A number of described and claimed adaptive scheduling and caching techniques provide for efficient resource and / or network utilization of intermittently-available and interruptible computing resource in distributed computing systems.
Owner:DATASYNAPSE
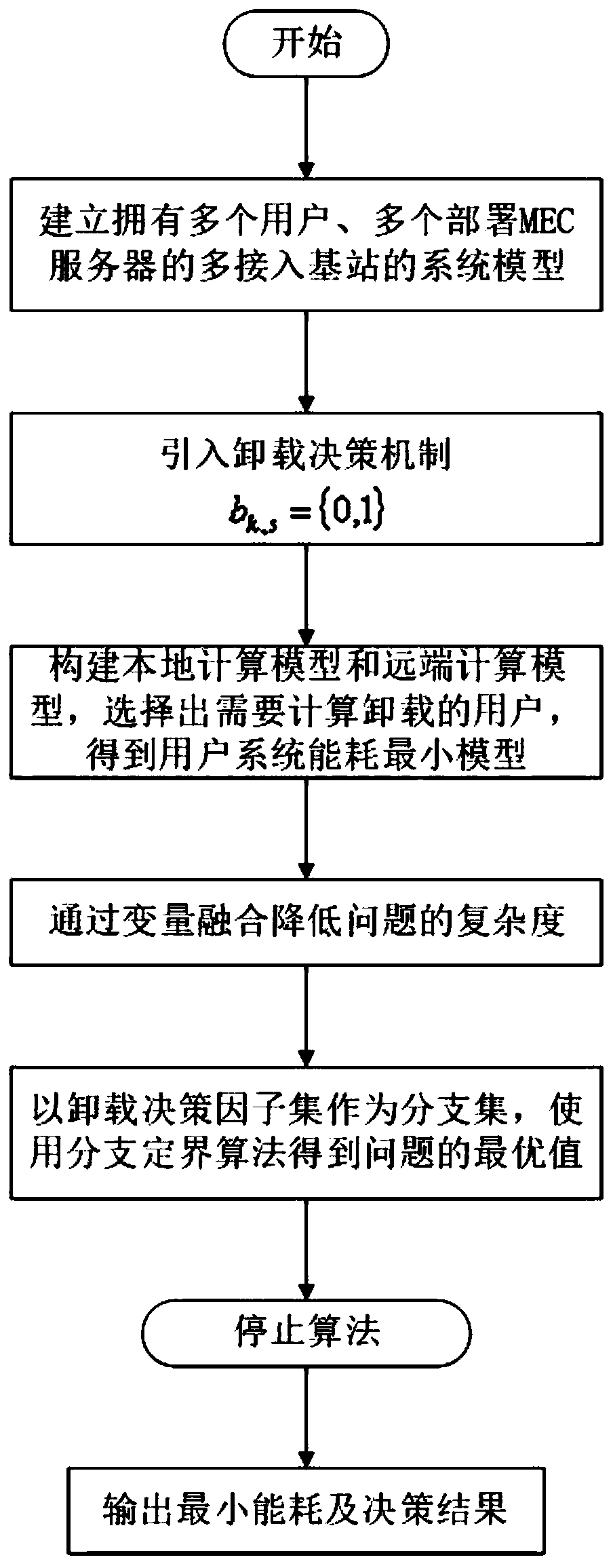
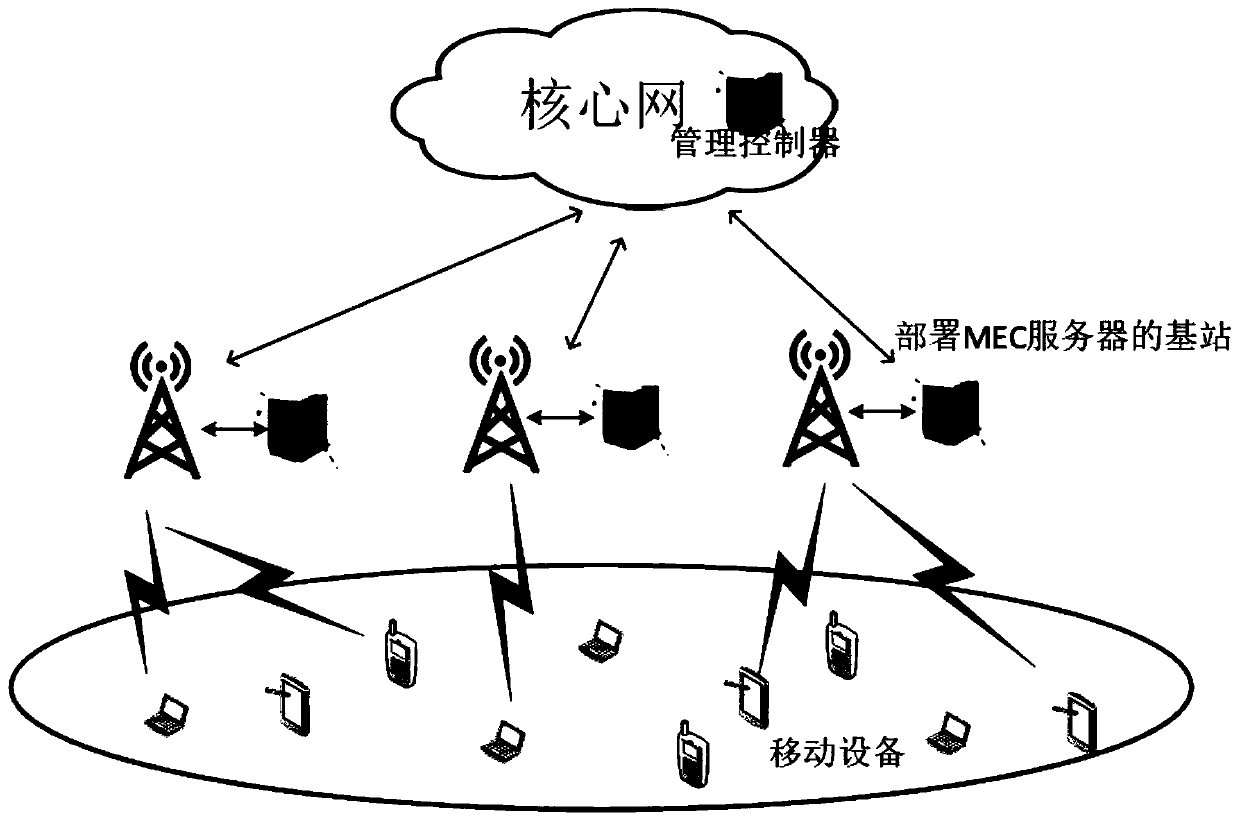
A joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network
ActiveCN109814951AFull restorationUniversalService provisioningProgram loading/initiatingDecision takingWireless resource allocation
The invention discloses a joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network, which comprises the following steps of 1, establishing an OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)-based multi-MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) base station and a multi-user scene model, wherein the MEC base station supports the multi-user access; 2, introducing an unloading decision mechanism; Meanwhile, constructing a local calculation model and a remote calculation model, selecting a user needing to perform calculation unloading, and establishing a calculation task unloading and resource allocation scheme based on minimum energy consumption under the condition of meeting the time delay constraint according to the conditions; 3, carrying out variablefusion on three mutually constrained optimization variables, namely an unloading decision variable, a wireless resource distribution variable and a computing resource distribution variable, so as to simplify the problem; and 4, obtaining an unloading decision and a resource allocation result which enable the total energy consumption of the user in the MEC system to be minimum through a branch andbound algorithm. The method has the advantage that the energy consumption of the system can be effectively reduced on the premise that strict time delay limitation is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
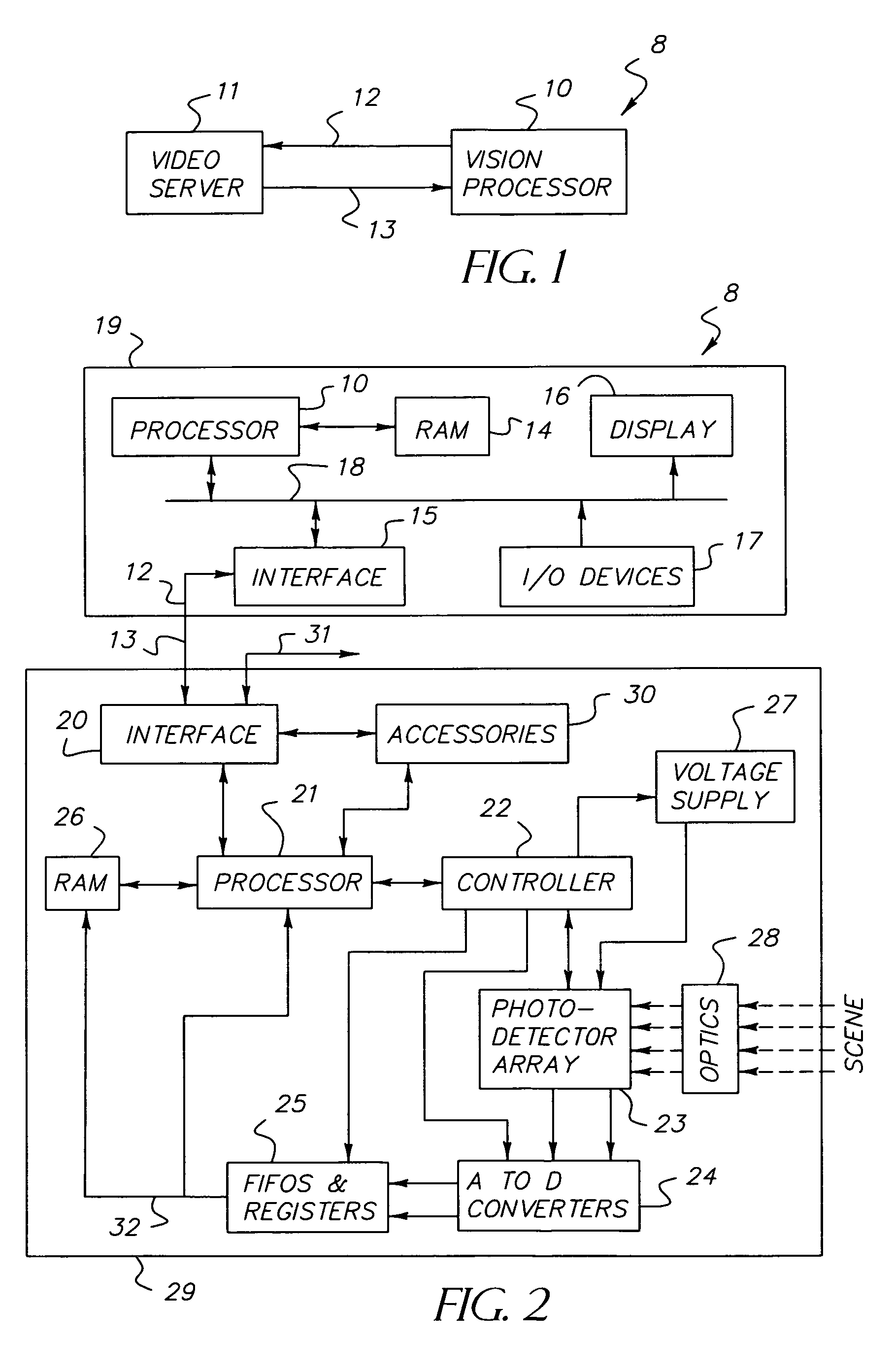
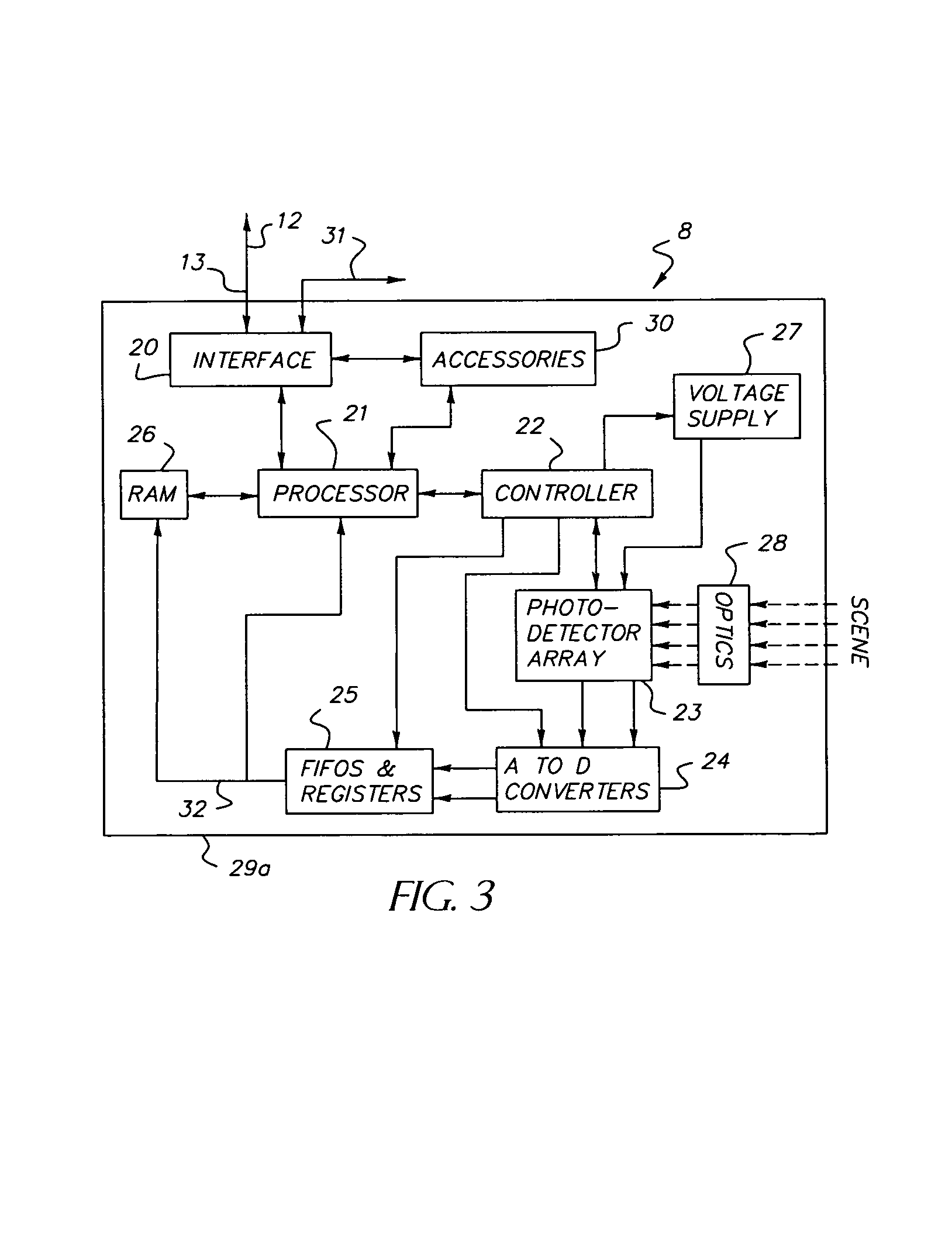
Dynamically reconfigurable vision system
InactiveUS7106374B1Efficiently usEffective resourcesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVision processingPhotodetector
A closed-loop vision system is disclosed that utilizes a concept known as Dynamically Reconfigurable Vision (DRV), which is adaptive image sensing driven by a computer or human operator's response to changing scenery. The system reduces the amount of irrelevant video information sensed and thus achieves more effective bandwidth and computational resource utilization, as compared to traditional vision systems. One or more reconfigurable photodetector arrays sensitive to either visible, infrared or ultraviolet radiation are present in the DRV system. These photodetector arrays feature on-chip means for spatial and temporal data reduction implemented through multiple independently controllable, time-correlated, frequently overlapping windows on the photodetector array that may be programmed according to their size, location, resolution, integration time, and frame rate. All photodetector array windows are dynamically reconfigurable in real time on a frame-by-frame basis. Furthermore, a DRV system is constructed in a client-server architecture in which a vision processor client passes window request command messages to the reconfigurable photodetector array server, which in turn delivers the requested video back to the client processor. The ability to simultaneously reconfigure, integrate, process, and readout multiple photodetector array video windows is an important characteristic of the DRV system.
Owner:COMPTEK AMHERST SYST INC
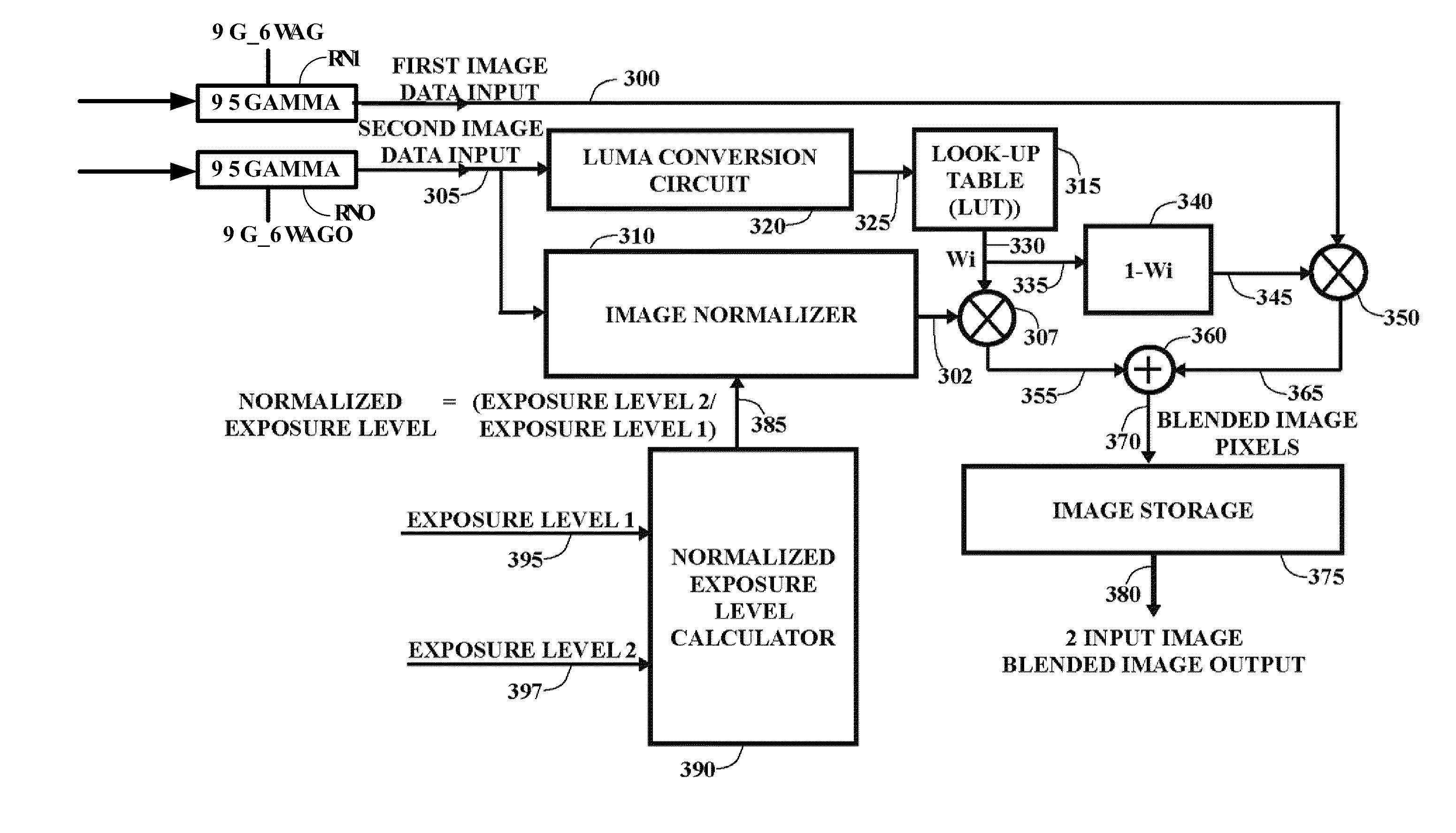
Multiple exposure high dynamic range image capture
ActiveUS20110254976A1Increase influenceIncrease valueTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceExposure level
Techniques for creating a High Dynamic Range (HDR) image within a consumer grade digital camera from a series of images of a scene captured at different exposure levels, and displaying the HDR image on the camera's built-in display are provided. The approach employs mixing images of the series to incorporate both scene shadow and highlight details, and the removing of “ghost” image artifacts appearing in the mixed HDR image resulting from movement in the scene over the time the series images are captured. The low computational resource utilization of the image mixing and ghost removal processing operations, along with the ability to commence image mixing and ghost removal prior to the acquisition of all series images, can significantly reduce the time required to generate and display a tone mapped HDR image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
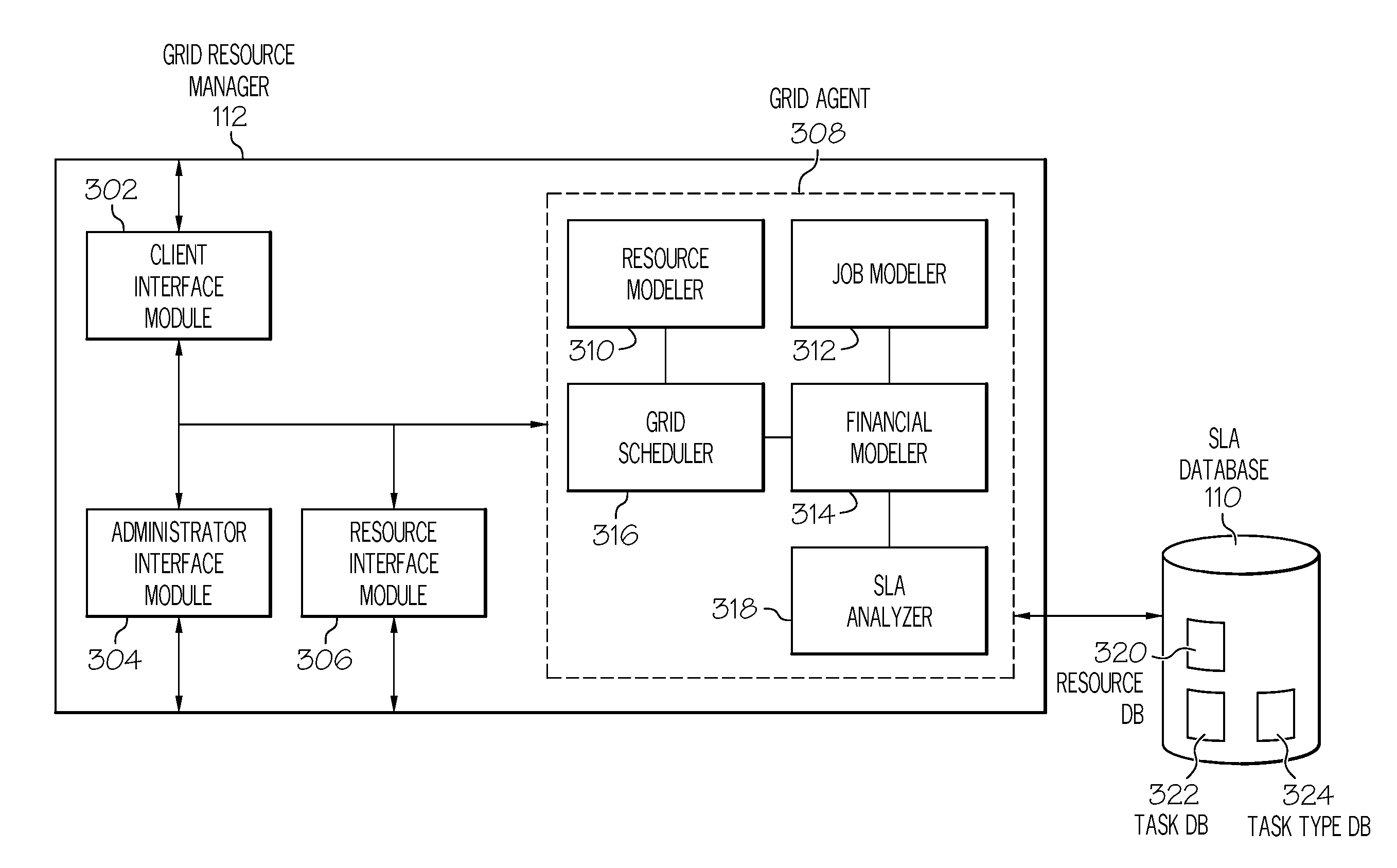
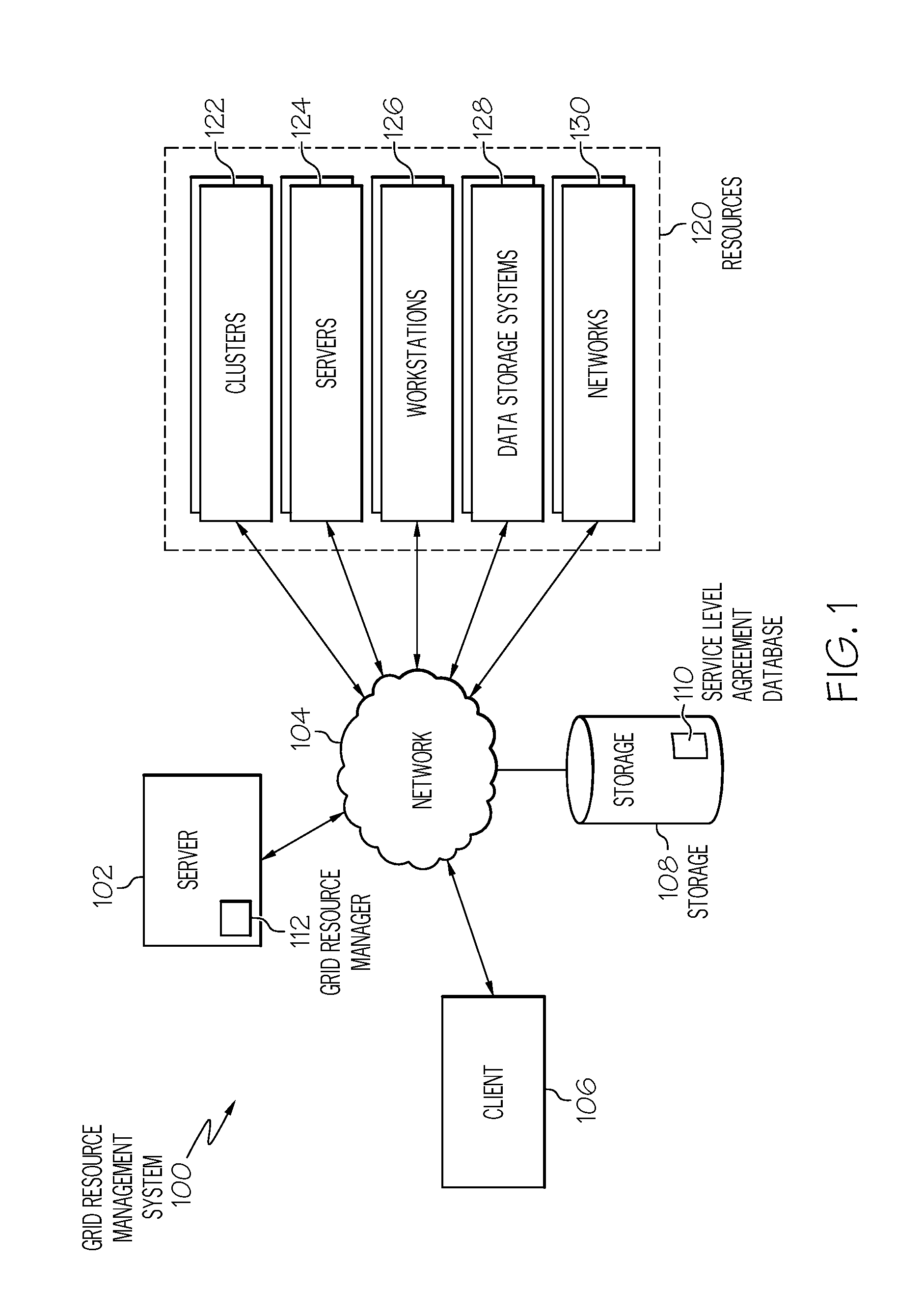
Management of grid computing resources based on service level requirements
InactiveUS20080320482A1Multiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionService level requirementRemedial action
Generally speaking, systems, methods and media for management of grid computing resources based on service level requirements are disclosed. Embodiments of a method for scheduling a task on a grid computing system may include updating a job model by determining currently requested tasks and projecting future task submissions and updating a resource model by determining currently available resources and projecting future resource availability. The method may also include updating a financial model based on the job model, resource model, and one or more service level requirements of an SLA associated with the task, where the financial model includes an indication of costs of a task based on the service level requirements. The method may also include scheduling performance of the task based on the updated financial model and determining whether the scheduled performance satisfies the service level requirements of the task and, if not, performing a remedial action.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and Systems for Evaluating Historical Metrics in Selecting a Physical Host for Execution of a Virtual Machine
ActiveUS20130042123A1Maximize power efficiencyMaximum efficiency of power useVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingResource consumptionCloud computing
Methods and systems for improved management of power utilization and resource consumption among physical hosts in a cloud computing environment. The management server may provide functionality facilitating the identification and optimized placement of a virtual machine within a cloud computing environment by evaluating historical and heuristic metrics data associated with both the physical hosts and the virtual machines. The management server utilizes the metrics data to generate scores for a plurality of physical host based on physical resources available in a cloud of computing resources. The management server identifies a physical host on which to place a virtual machine using the metrics data, generated scores, and numerous, configurable criteria. The management server responds to the identification of the physical host on which to place a virtual machine by adjusting processor performance and / or operating states for one or more of the physical hosts in the cloud computing environment.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method for allocating web sites on a web hosting cluster
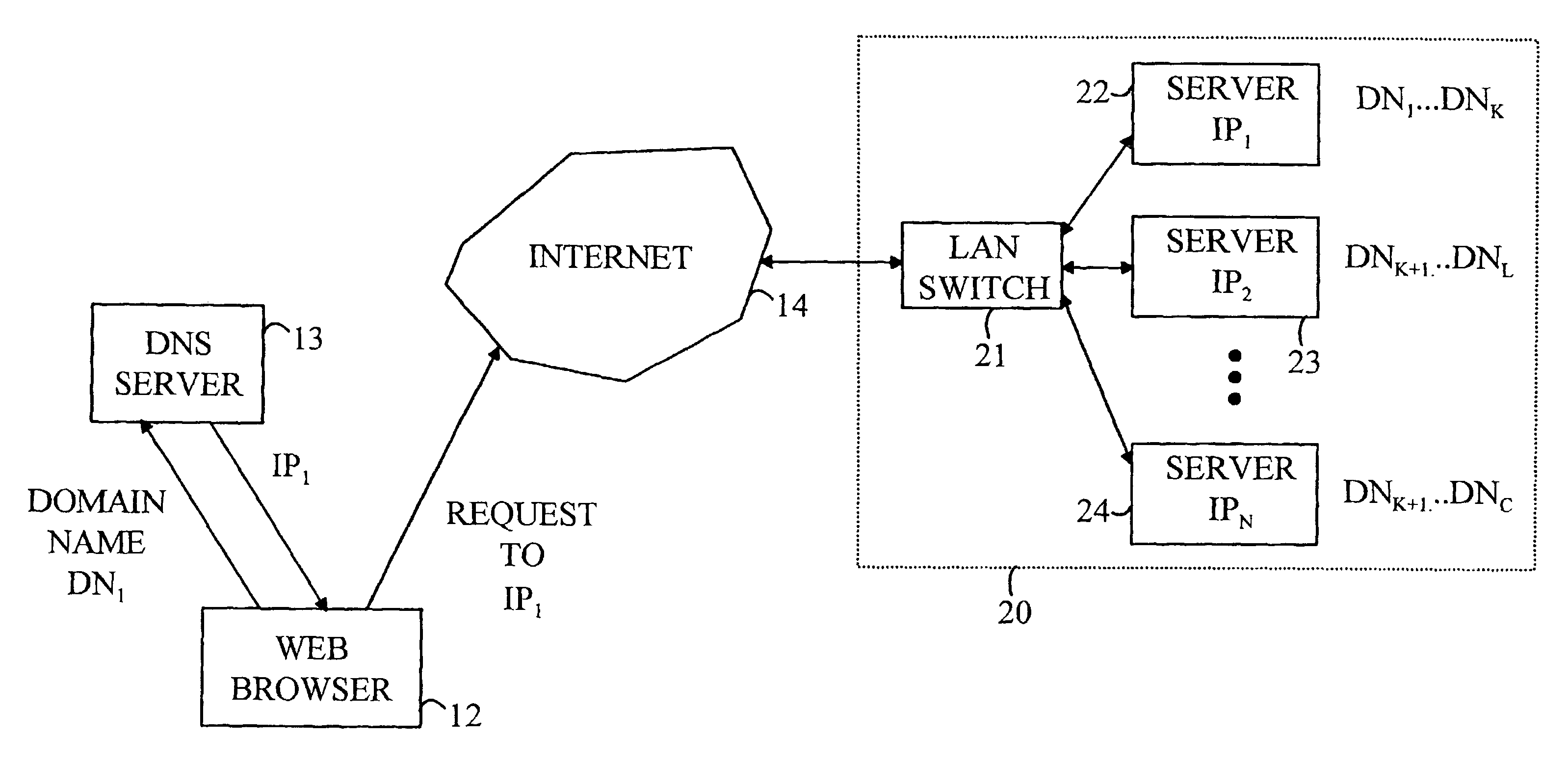
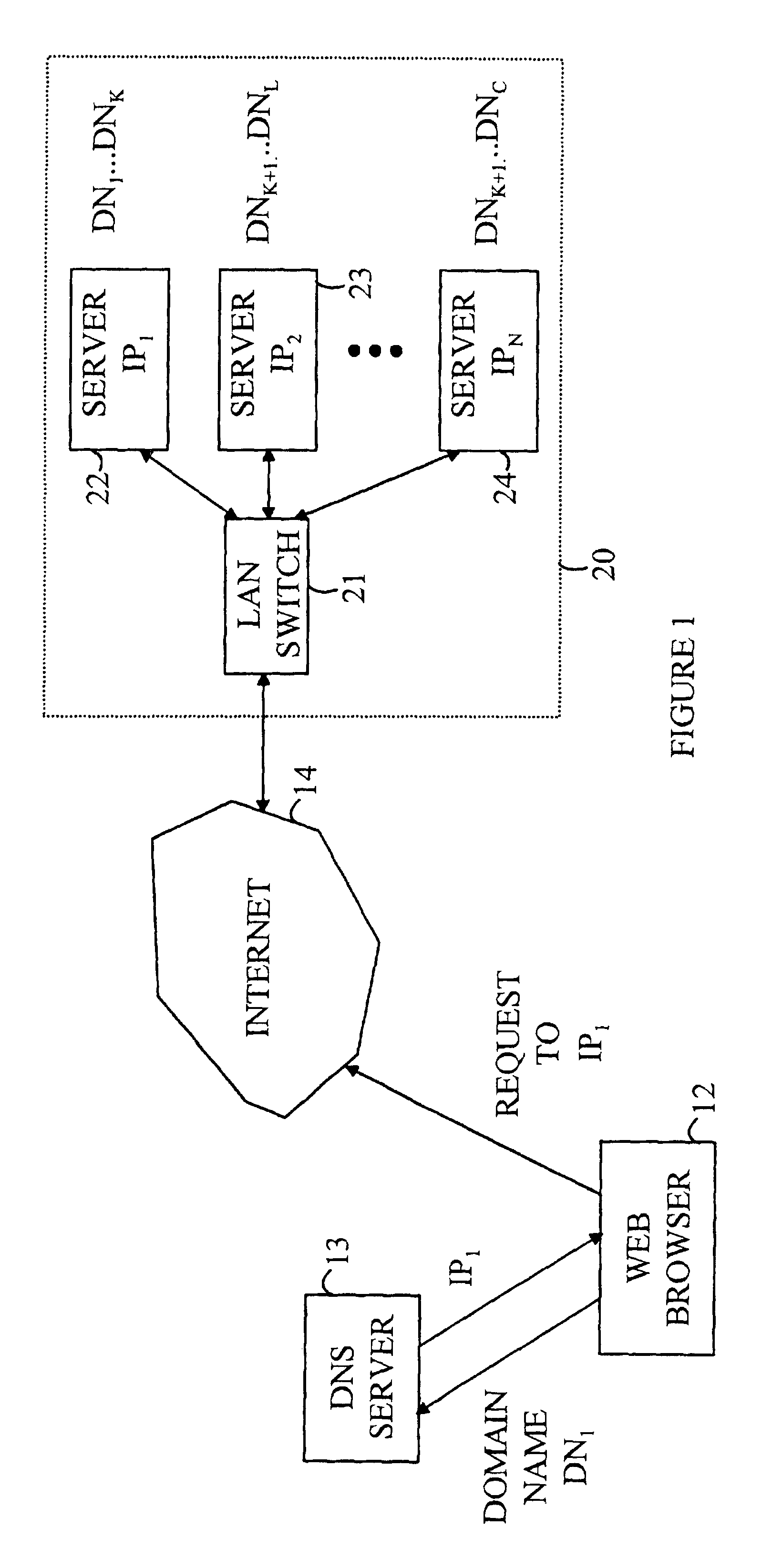
A method for operating a cluster of N server nodes to service client requests received on a network. Each client request is directed to one of C customers hosted on the server cluster. Each customer is identified by a domain name, and each server node is identified by an address on a network. In the method of the present invention, the customers are grouped into N groups, each group being assigned to a corresponding one of the server nodes. Configuration information is provided to a Domain Name Server (DNS), the information defining the correspondence between each of the customers and one of the server nodes assigned to one of the groups containing that customer. The DNS provides the address of the server node in response to a message specifying the domain name of the customer. The client then directs its request to the identified server node utilizing the address provided by the DNS. In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the grouping of the customers depends on a measurement of the computational resources required to service the client requests for each of the customers. In embodiments in which the activity associated with each request is primarily the return of files stored in the cluster, the measurement of computational resources includes the size of the files returned by each client—within a time period and the communication bandwidth needed to service the requests.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
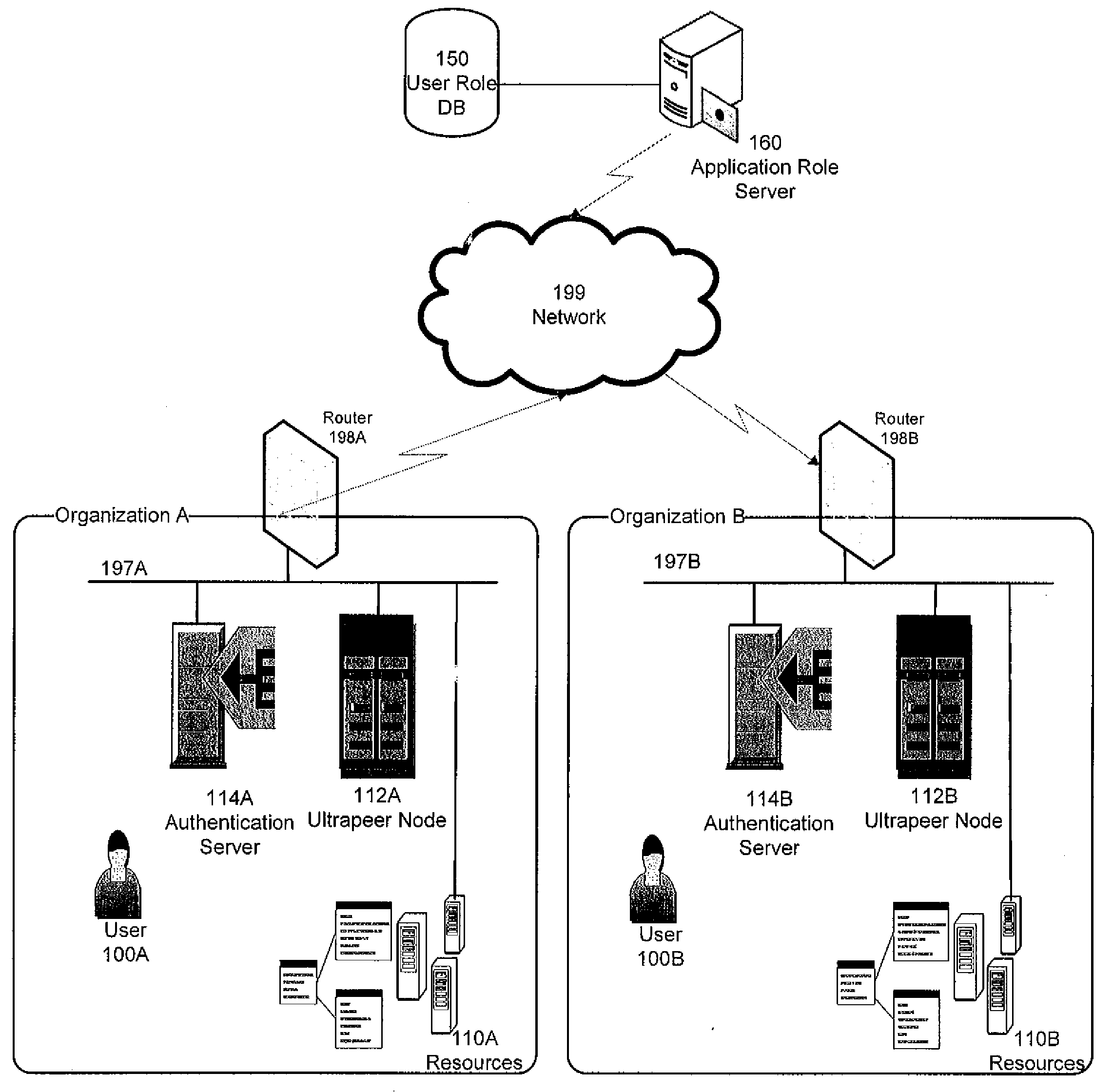
Role-based access control to computing resources in an inter-organizational community
ActiveUS20080313716A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsDistributed Computing EnvironmentInter organizational
A method for controlling access to a plurality of computing resources in a distributed computing environment can comprise the steps of: an application role server, responsive to receiving a certificate request, authenticating the requester and issuing a digital certificate to the requester; an access control node, responsive to receiving a resource access request, granting access to the computing resource to the requester upon ascertaining the requestor's access privileges, or forwarding the resource access request to another access control node.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS20050128951A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transport
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
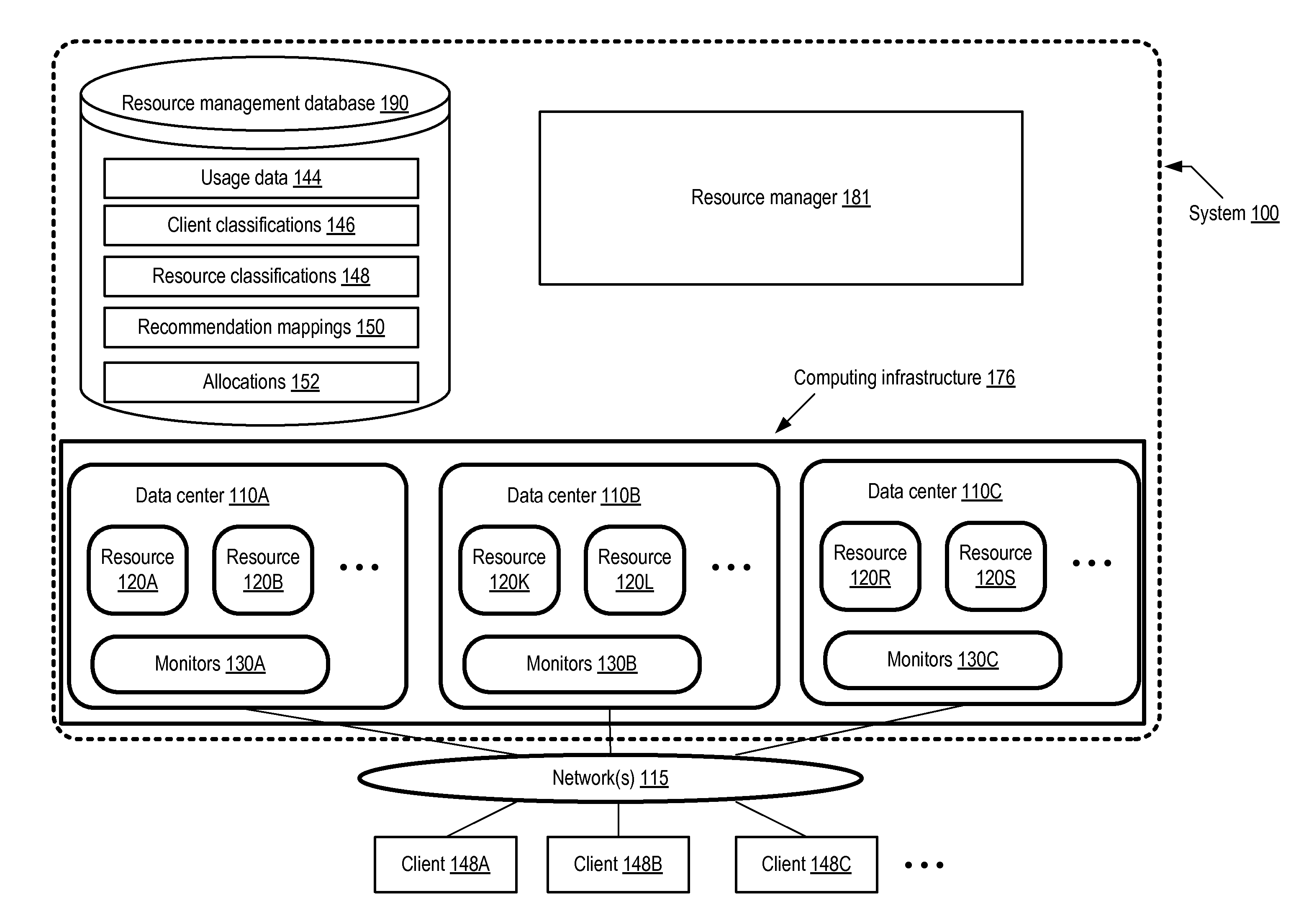
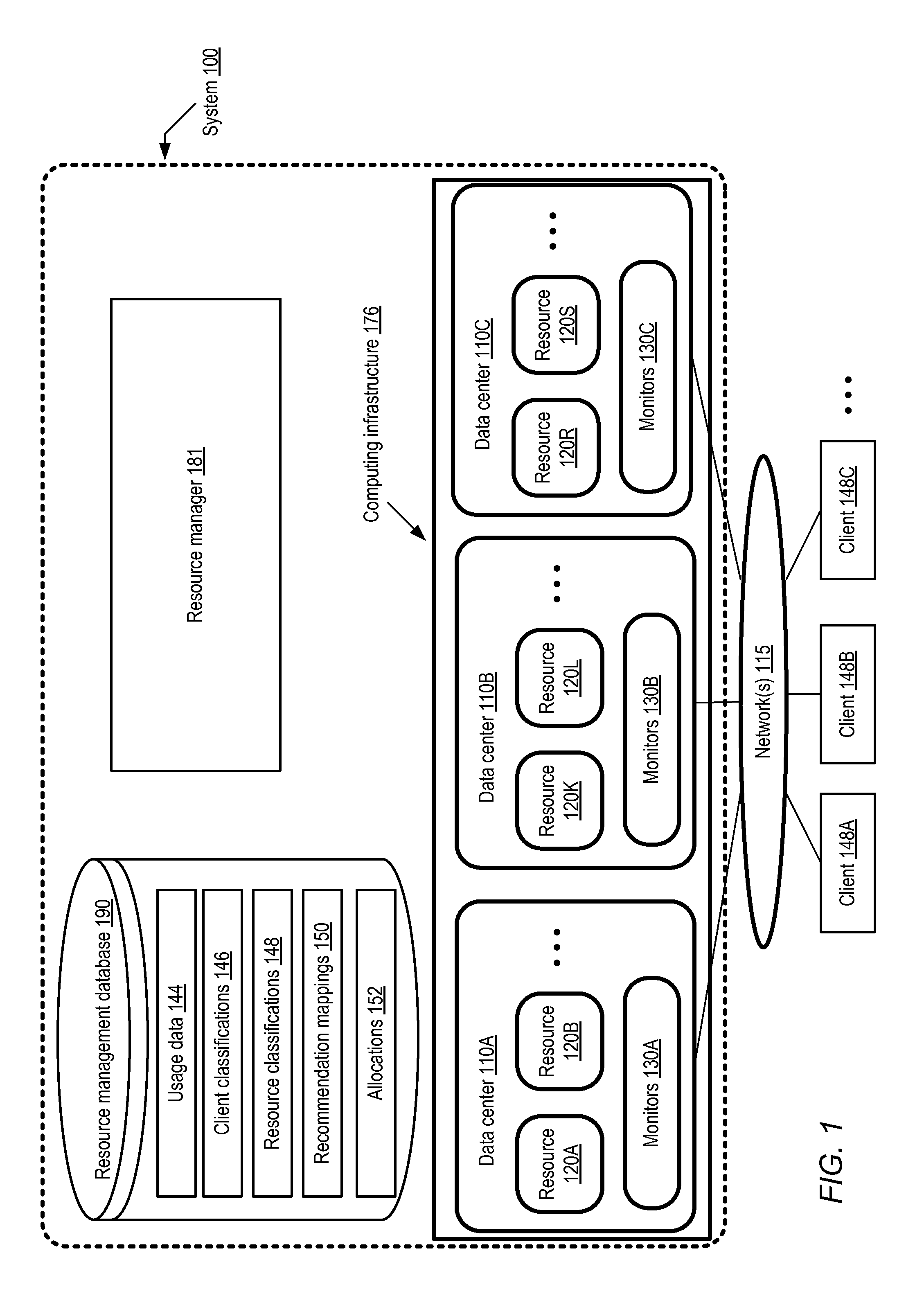
Client Classification-Based Dynamic Allocation of Computing Infrastructure Resources
Methods and apparatus for classification-based dynamic allocation of computing resources are described. A method comprises determining usage data sources corresponding to one or more clients of a computing infrastructure, and assigning values to client classification categories associated with a particular client based on metrics obtained from the particular client's usage data sources. The method includes generating a recommendation mapping between values of the client classification categories, and one or more resources of the infrastructure, based at least in part on resource classification information. The method further includes allocating at least a portion of the one or more resources to the particular client based at least in part on the recommendation mapping.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com