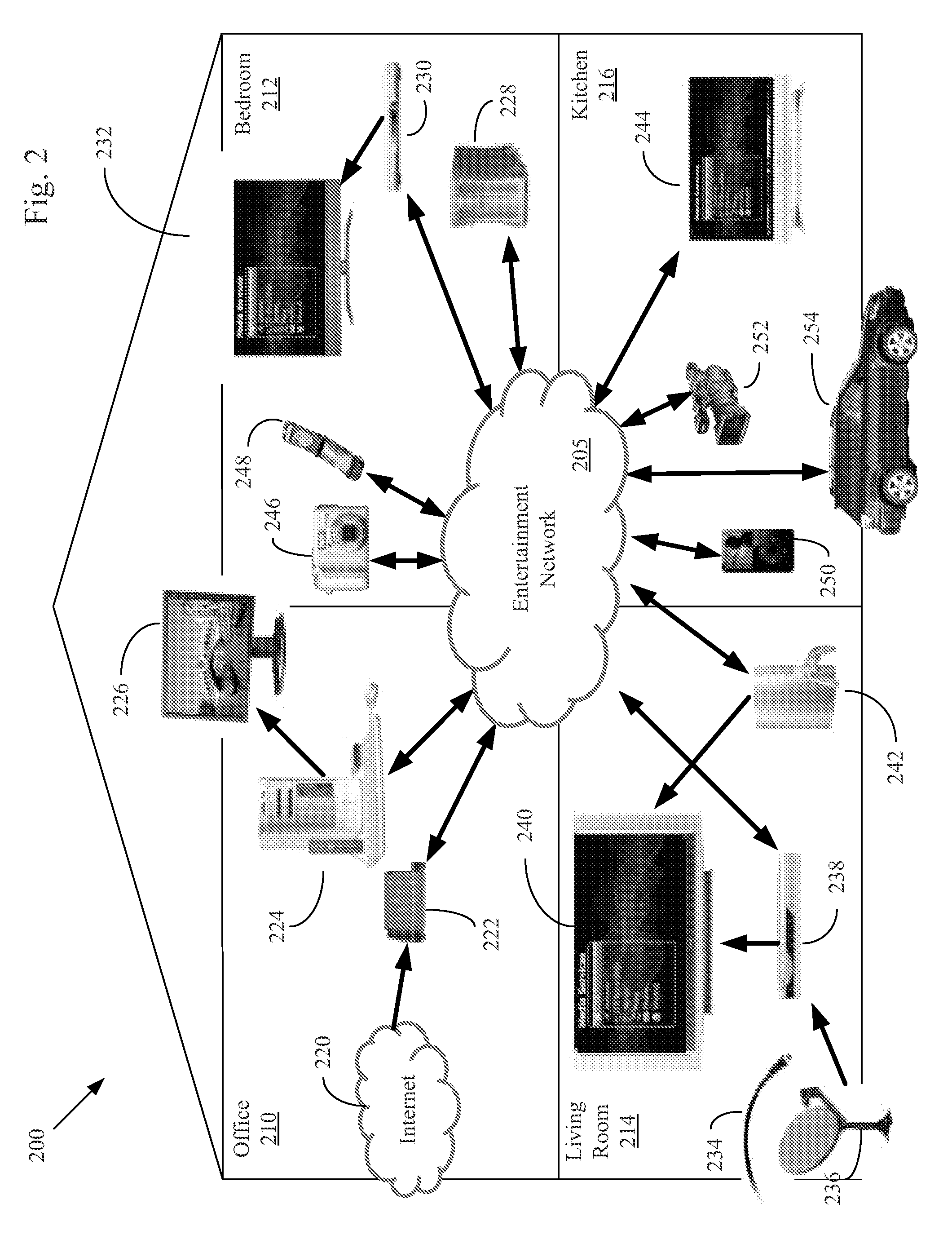
Patents
Literature
165 results about "Bandwidth reservation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
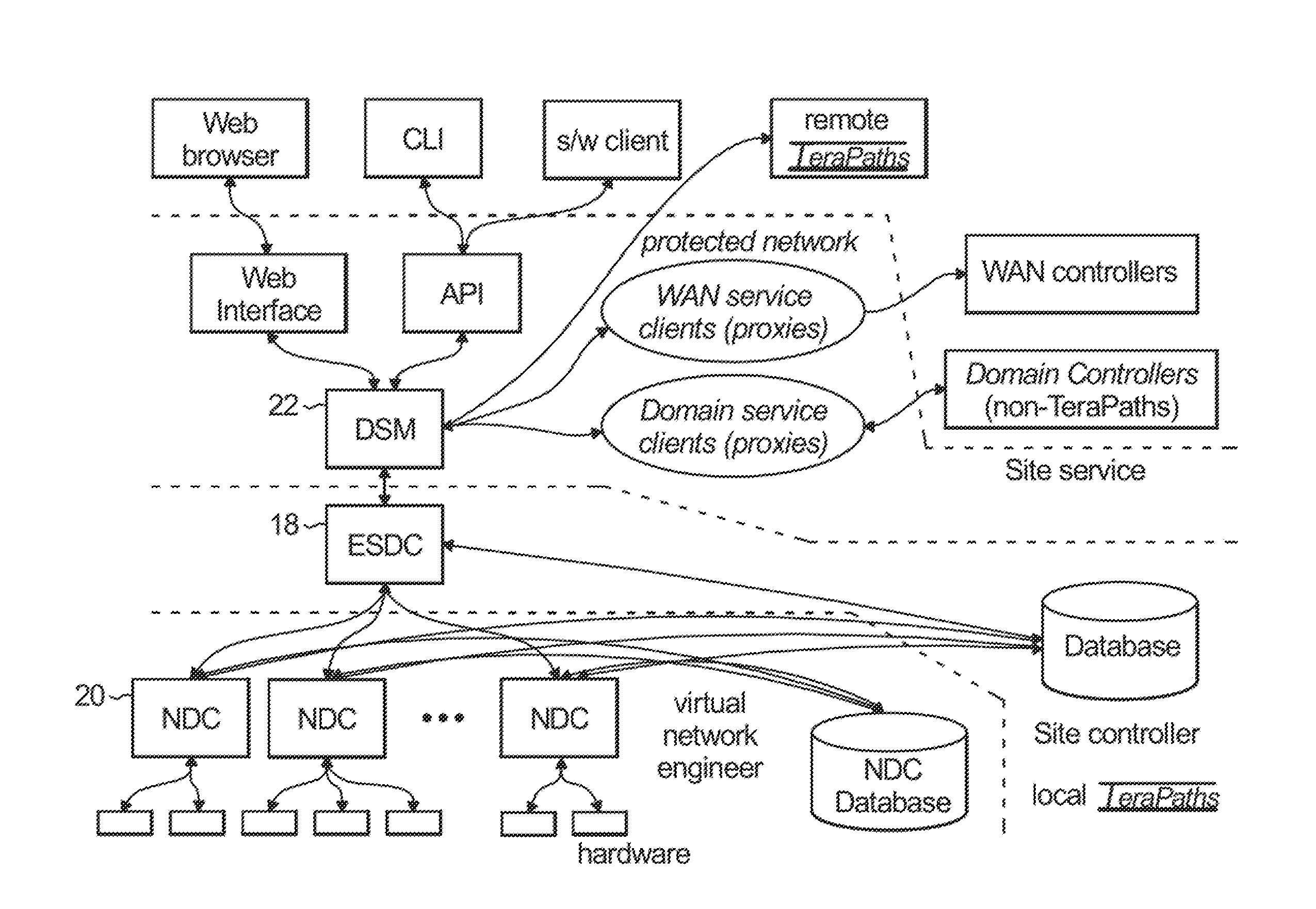
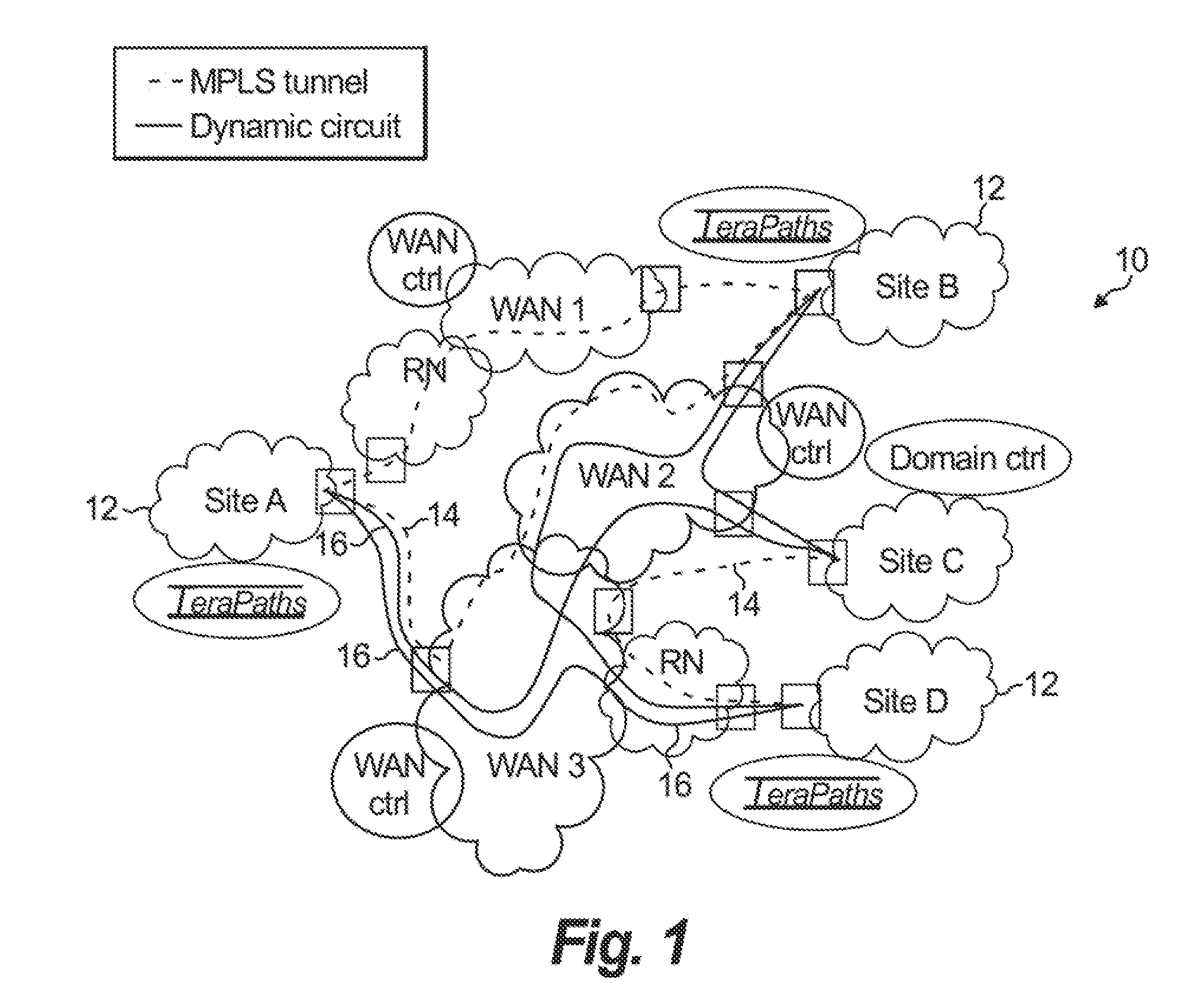
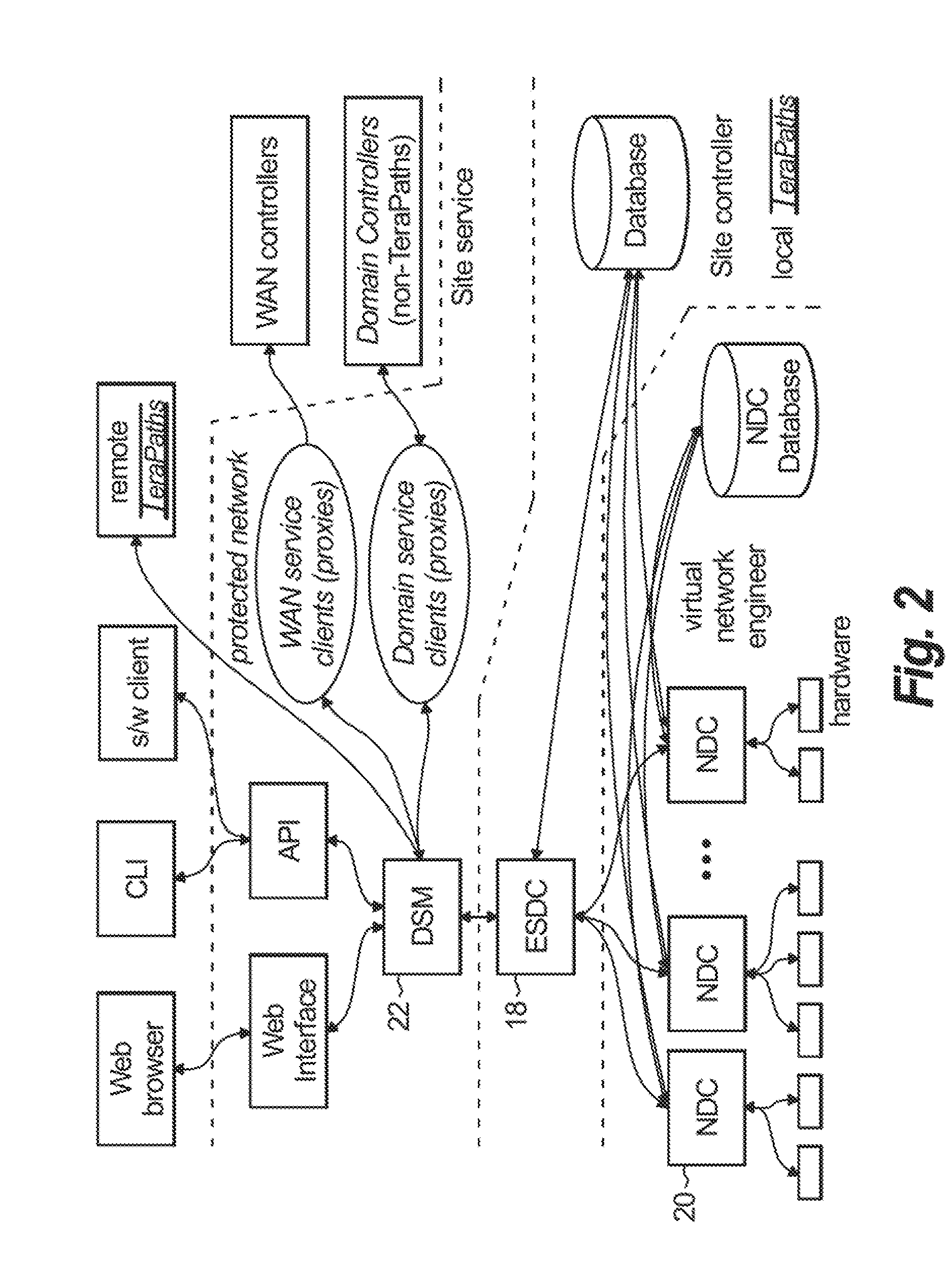
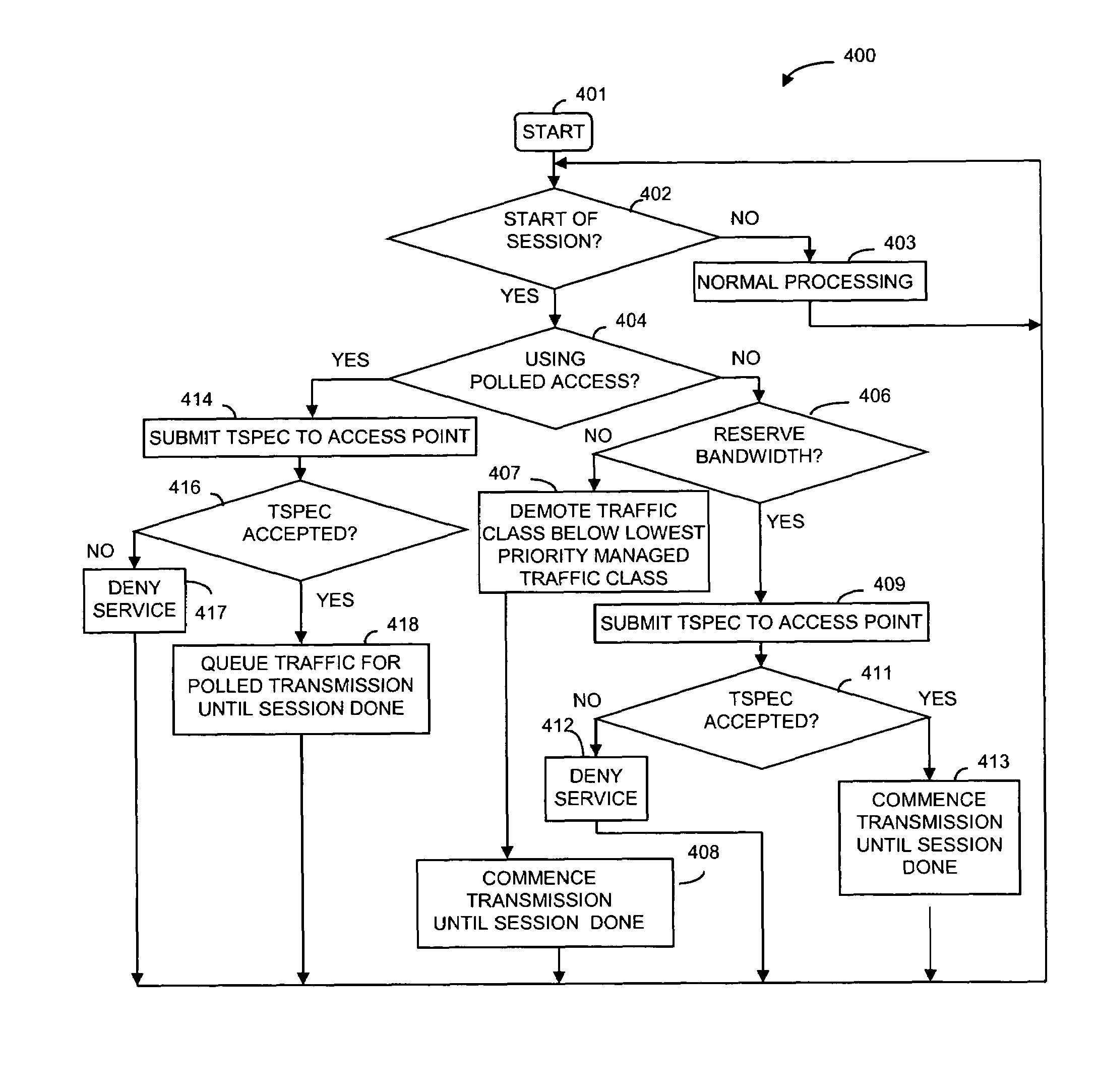
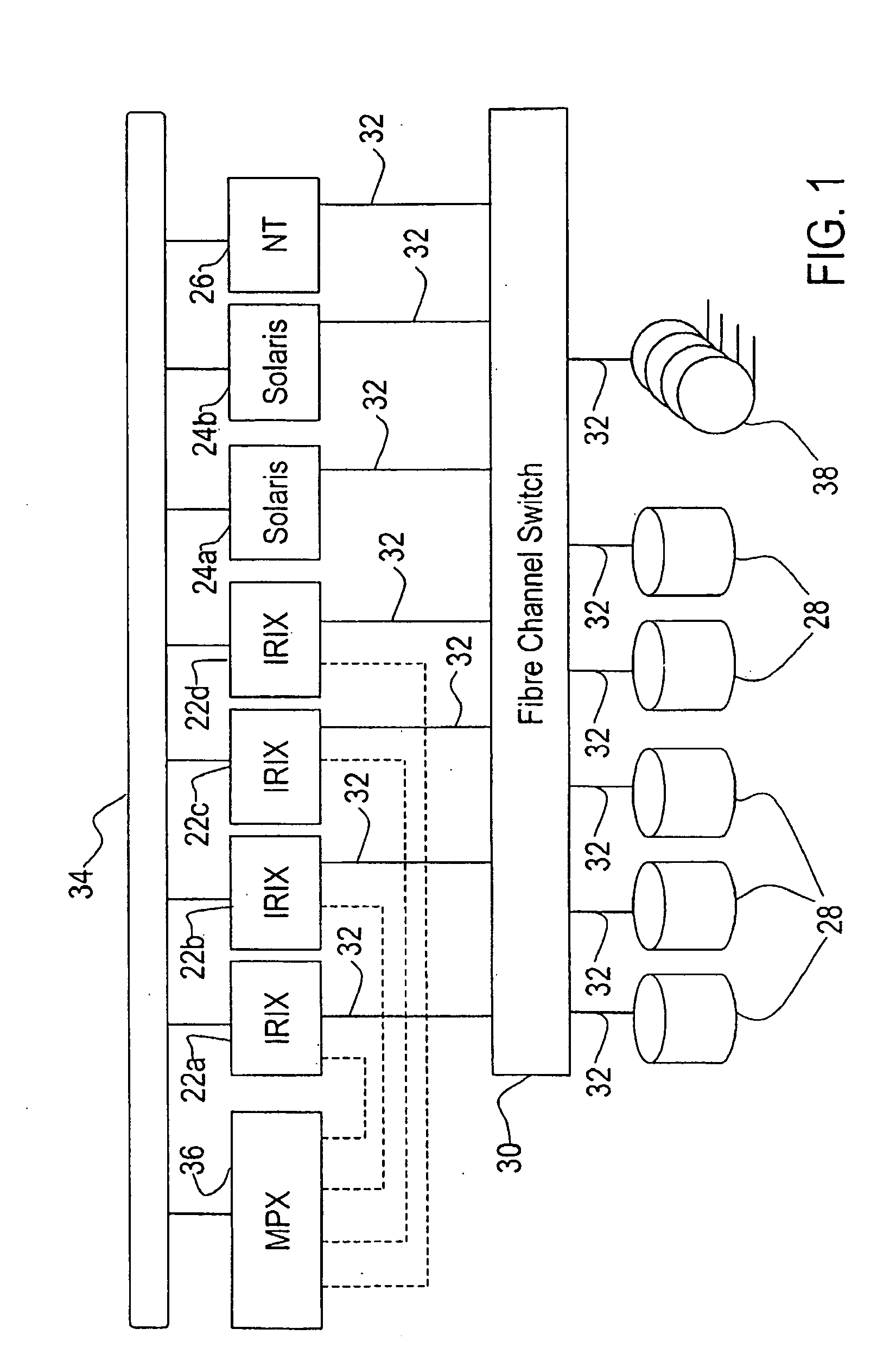
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
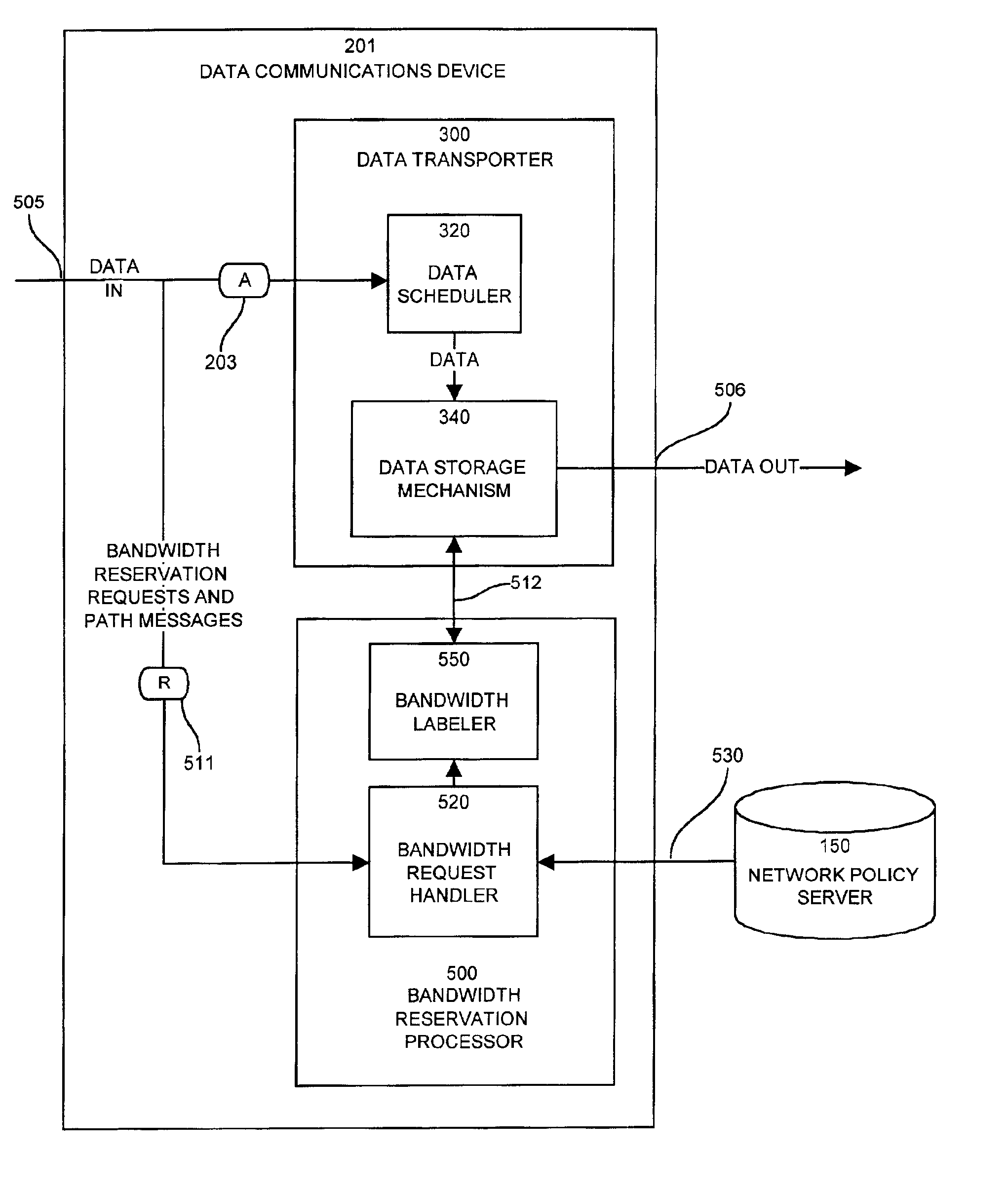
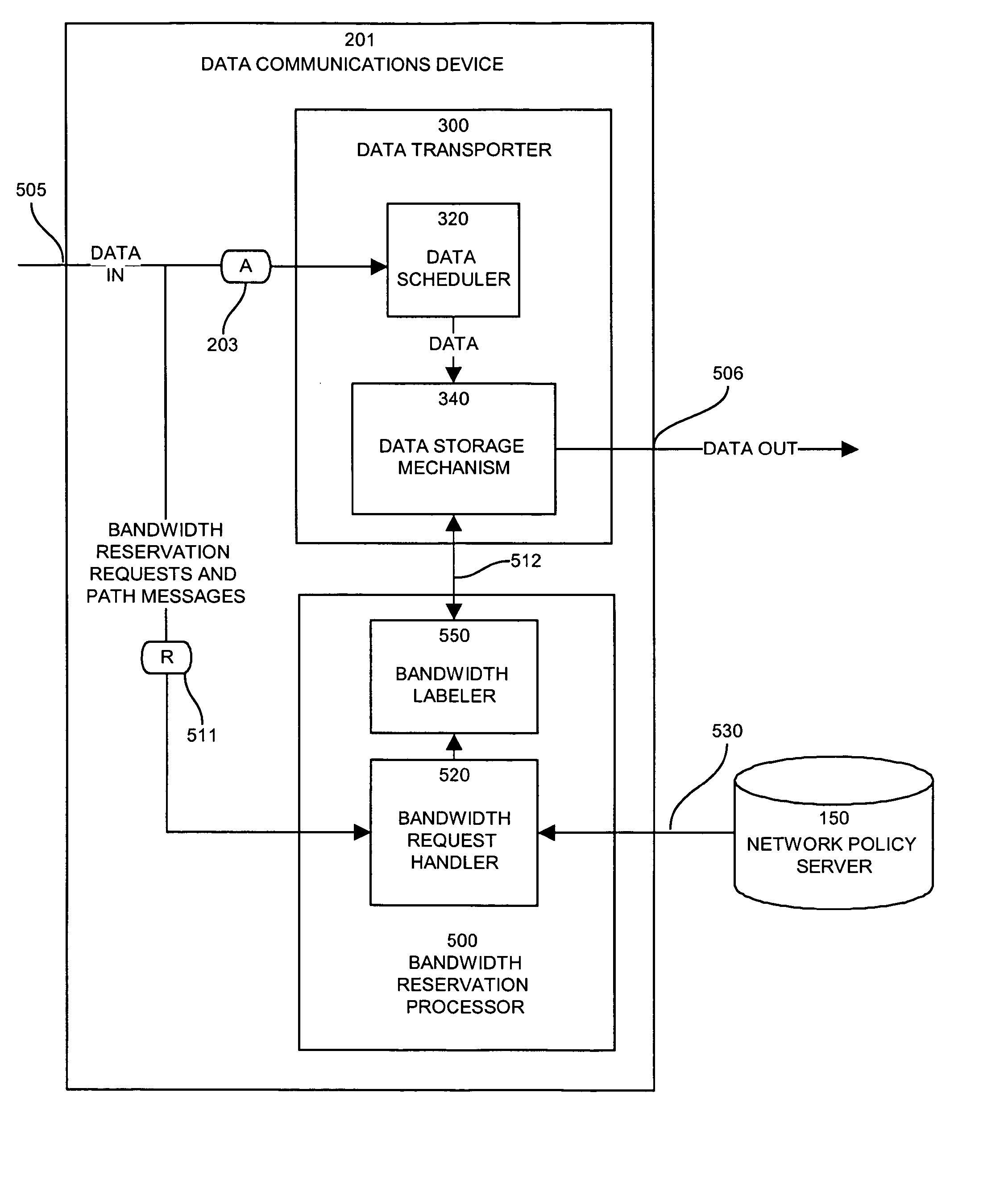
A system capable of dynamically reserving bandwidth and adjusting bandwidth reservations for active sessions of data communication in a data communications device is provided. The system generally separates the operation of bandwidth allocation and adjustment from the operation of data transport through the device, thereby allowing bandwidth reservations and adjustments to be made without disturbing sessions of data communication that are actively being transported through the device. The system can accept requests to allocate or reserve bandwidth in a data communications device using bandwidth reservation protocols such as RSVP. The reservation requests create sender state data that can be used to compute resource allocation data. The resource allocation data can be used to label data storage locations in a data storage mechanism according to the required bandwidth reservations. A data scheduling apparatus, which is ignorant of particular sessions and specific amounts of reserved bandwidth, examines data and deposits data into data storage locations having a label corresponding to a session identification specified in the data, if any. If an unknown or no session identification is specified in the data, the data scheduler deposits data into a data storage location that is unlabeled or that has an unreserved label. Thus session bandwidth is determined by the percentage of labeled data storage locations for the session. Changes in bandwidth reservations are reflected in the separate operation of alterations made in the data storage labeling scheme, and do not affect the data scheduler, or data dequeuing mechanisms, thus allowing data sessions to continue without interruption during bandwidth adjustments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
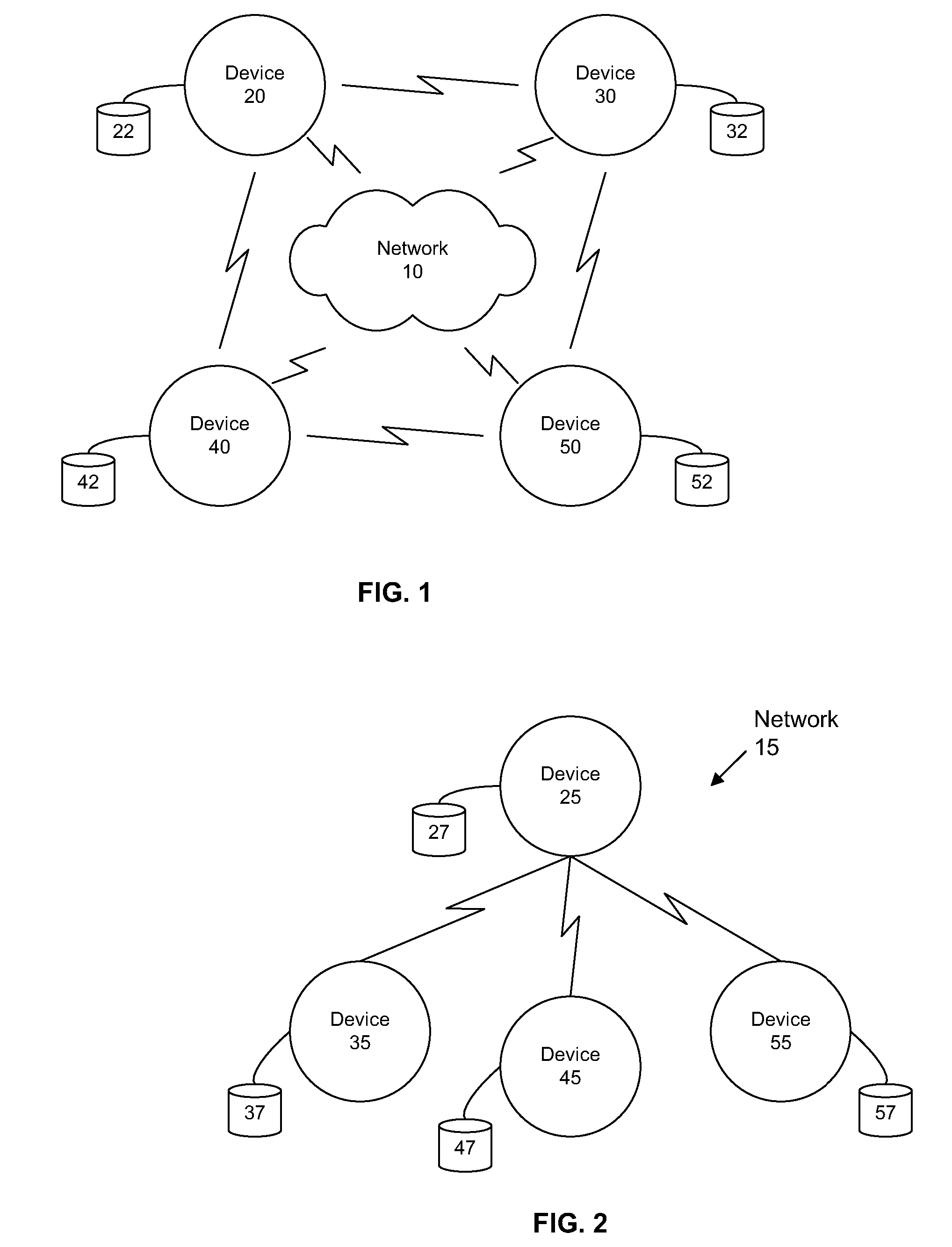
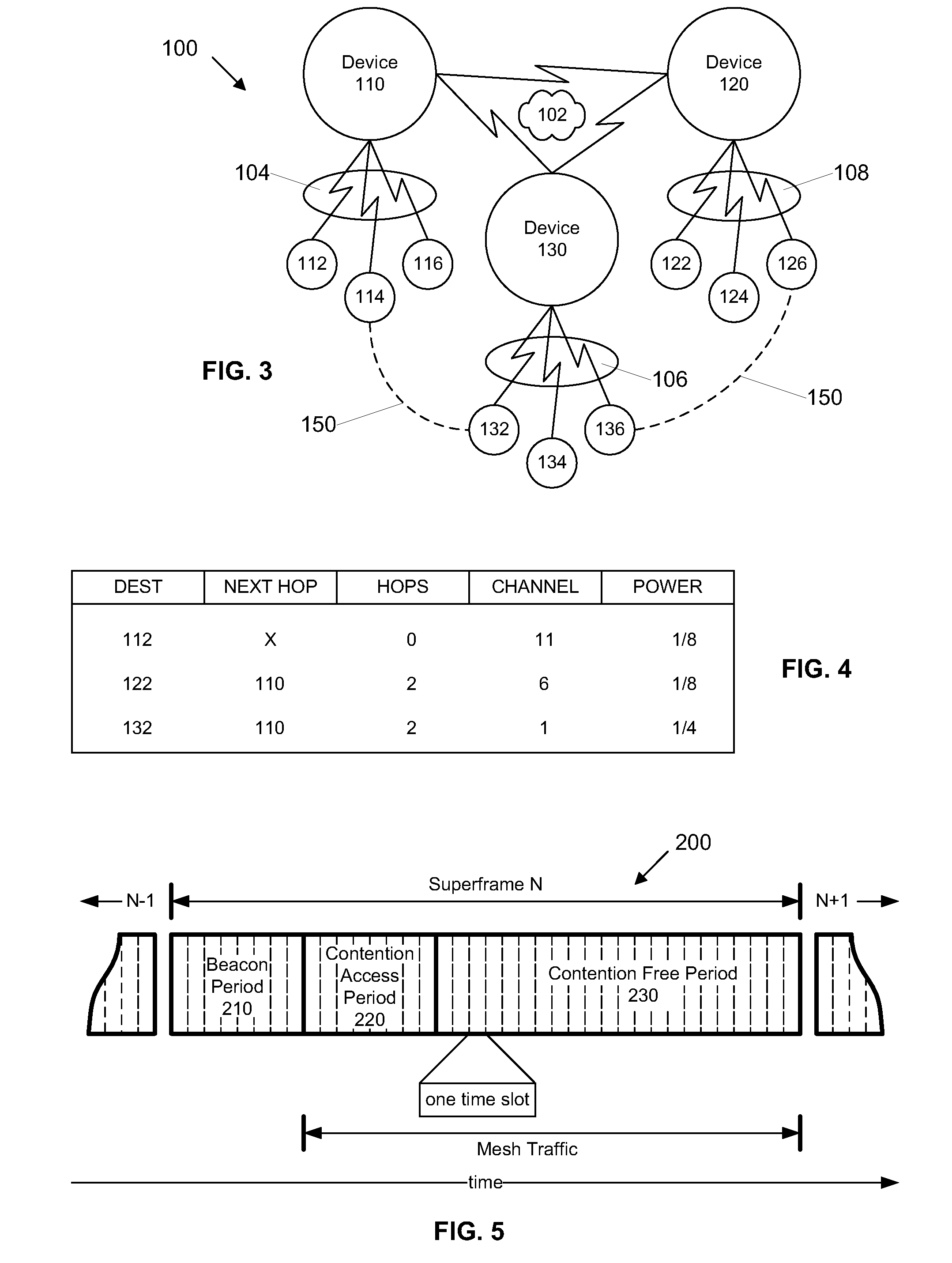
Multi-Hop Ultra Wide Band Wireless Network Communication
InactiveUS20070104215A1Avoid bandwidth reservation conflictImprove utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionFrequency spectrumCommunication device
A wireless communication system is provided that has at least three nodes arranged in a multi-hop ultra wide band (UWB) communication network such that communications from a first node destined for a third node pass through a second node. Each of the devices in the system includes a radio and a media access control (“MAC”) module that is configured to establish multi-hop UWB wireless communications between the three or more wireless communication devices that enables high bandwidth applications such as Voice Over Internet Protocol (“VoIP”); multiplayer gaming; Wireless High Definition Television; and Internet Protocol Television (“IPTV”) among others. The MAC module is configured to avoid bandwidth reservation conflicts so that network performance does not degrade as the number of hops or the number of nodes in the wireless communication system increases. The MAC also facilitates utilization of multiple channels to maximize the available spectrum and is further configured to dynamically switch between channels to maximize throughput and meet or exceed quality of service (“QoS”) requirements such that QoS is guaranteed and network resources are efficiently utilized.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Multiplexing several individual application sessions over a pre-allocated reservation protocol session
InactiveUS7013338B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksMultiplexingCommunity based
Apparatus and methods are provided for multiplexing application flows over a pre-allocated bandwidth reservation protocol session. According to one embodiment, a pre-allocated reservation protocol session, such as an RSVP session, is shared by one or more application sessions. The reservation protocol session is pre-allocated over a path between a first network device associated with a first user community and a second network device associated with a second user community based upon an estimated usage of the path for application sessions between users of the first and second user communities. Subsequently, the one or more application sessions are dynamically aggregated by multiplexing application flows associated with the one or more individual application sessions onto the pre-allocated reservation protocol session at the first network device and demultiplexing at the second network device. According to another embodiment, a network device enables multiple applications, such as VoIP applications, that require real-time performance to share an aggregated reservation protocol session, such as an RSVP session. The network device includes a storage device having stored therein one or more routines for establishing and managing the aggregated reservation protocol session. A processor coupled to the storage device executes the one or more routines to pre-allocate the aggregated reservation protocol session and thereafter share the aggregated reservation protocol session among multiple application sessions of individual application sessions. The aggregated reservation protocol session is pre-allocated based upon an estimate of the bandwidth requirements to accommodate the multiple application sessions. The aggregated reservation protocol session is shared by multiplexing, onto the aggregated reservation protocol session, outbound media packets (e.g., packetized voice data) originated by local application / endpoints associated with the application sessions, and demultiplexing, from the aggregated reservation protocol session, inbound media packets (e.g., packetized voice data) originated by remote application / endpoints.
Owner:WINTERSPRING DIGITAL LLC
Policy-based admission control and bandwidth reservation for future sessions
ActiveUS20050228892A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksBandwidth reservationContent server
A method for delivering content over a network, the method involving: receiving a request to establish a session at a future time T1 over the network, the requested session for transferring content between a content server and a subscriber's equipment; reserving network capacity necessary to support the requested future session; acknowledging to the requestor that network resources have been reserved for said requestor for time T1; and when current time reaches time T1, causing the requested session to be set up for transferring content between the content server and the subscriber's equipment.
Owner:CAMIANT INC
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS20050128951A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transport
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
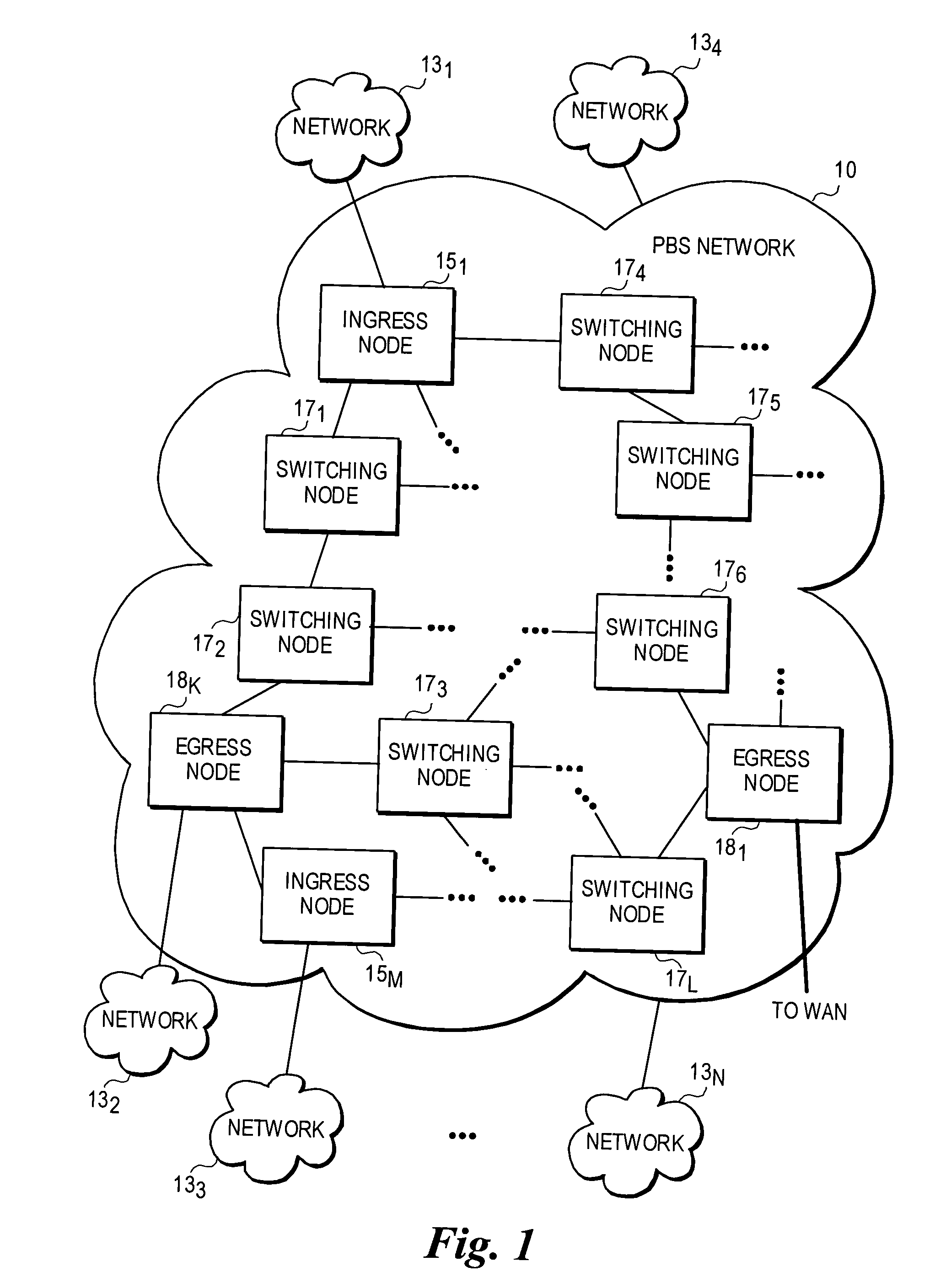
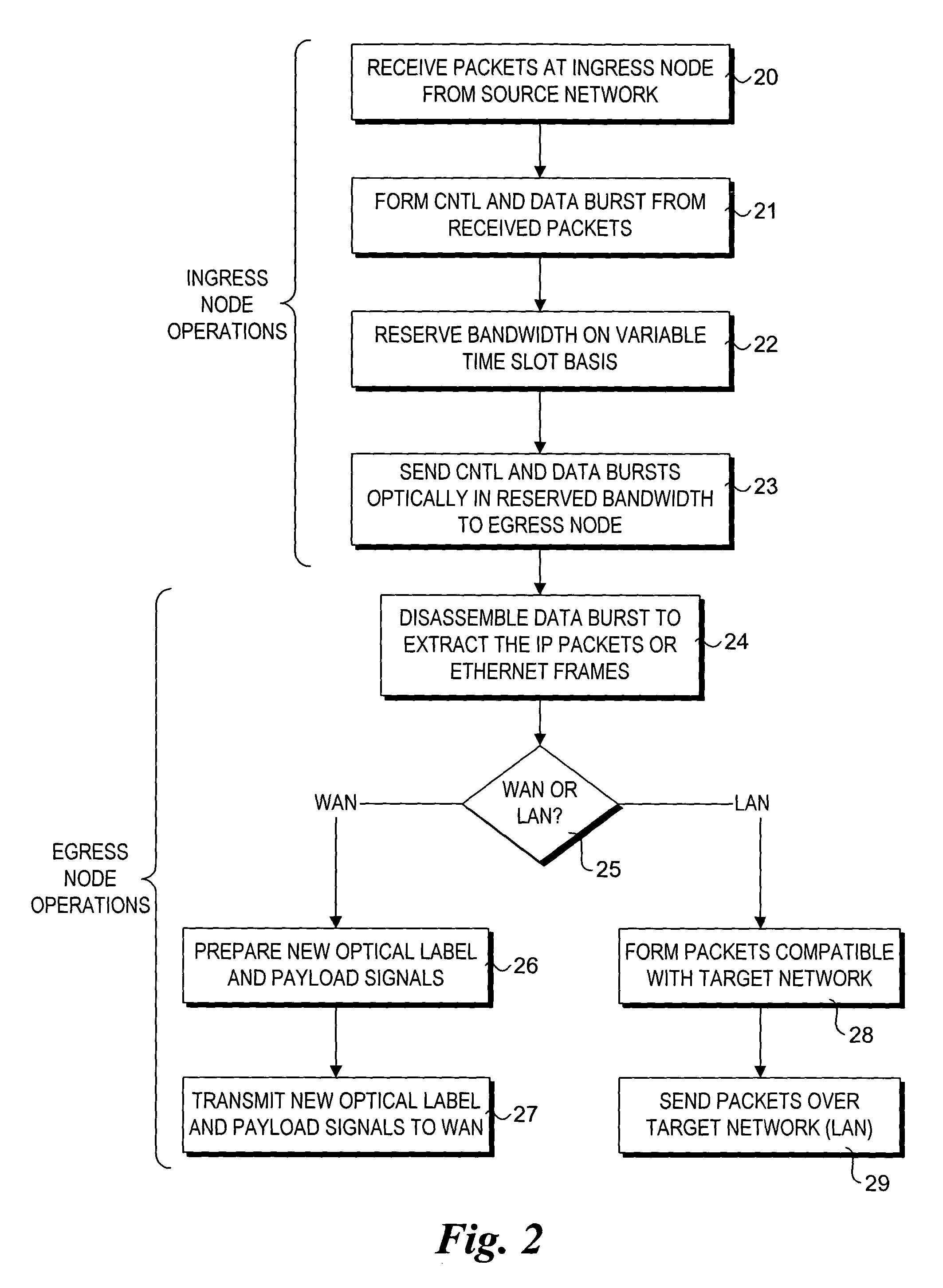
Method and system to recover resources in the event of data burst loss within WDM-based optical-switched networks
InactiveUS20050063701A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexExchange networkEdge node
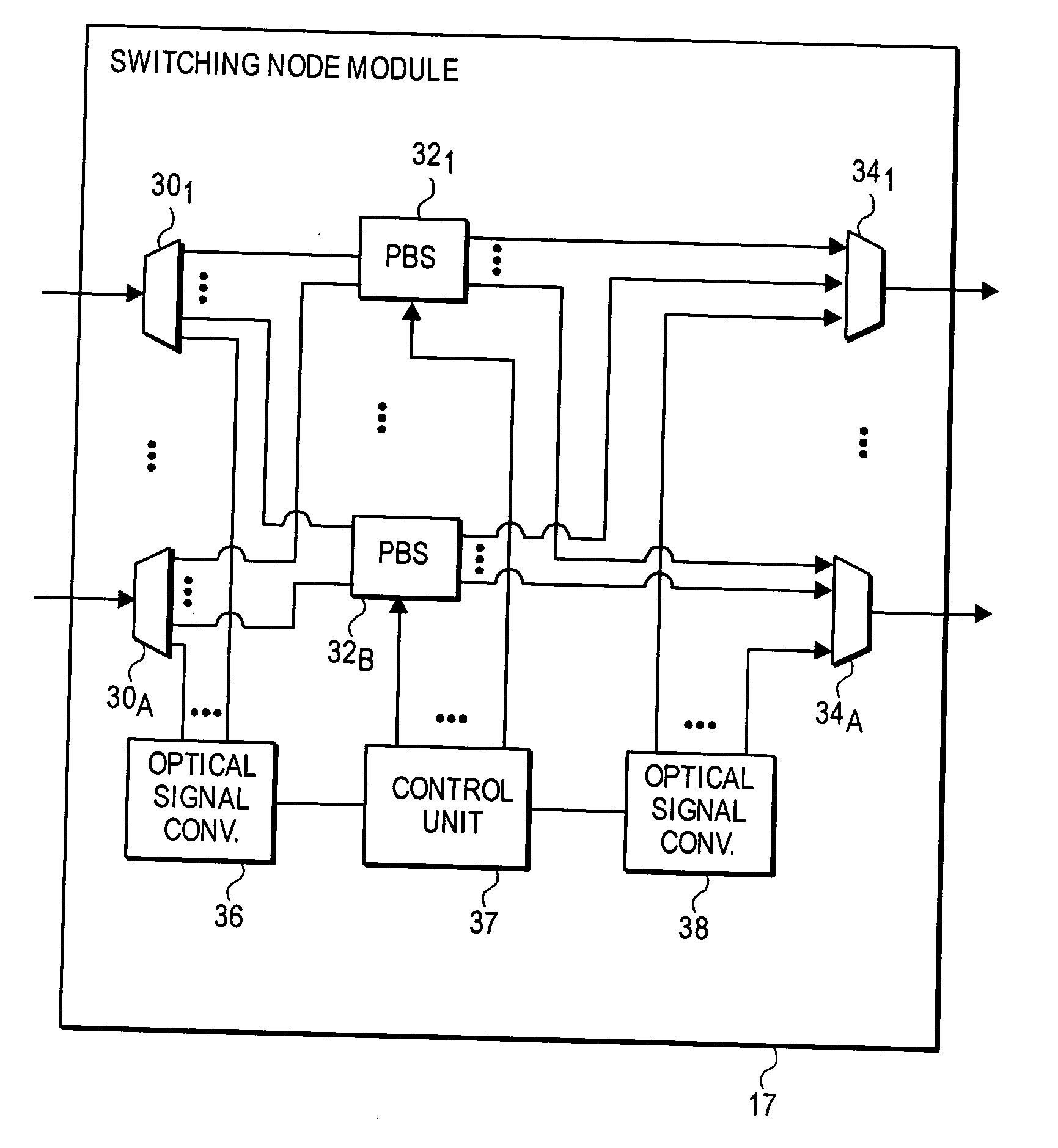
A mechanism for recovering reserved resources in a wavelength-division-multiplexed based photonic burst switched (PBS) network in response to resource non-availability. The PBS network includes edge and switching nodes, which optically communicate information formatted into PBS control and data burst frames. Each PBS data burst frame is associated with a PBS control burst frame. A PBS control burst is sent to reserve resources along a lightpath comprising a concatenation of lightpath segments linked between in ingress edge nodes, switching nodes and egress edge nodes. During a subsequent data burst, an unavailable resource is detected at one of the switching nodes. In response, a resource cancellation message (RCM) comprising a control burst is sent to upstream and / or downstream nodes along the lightpath. Upon receiving the RCM, the corresponding resource reservation is cancelled, freeing the network resources for subsequent bandwidth reservations and access.
Owner:INTEL CORP
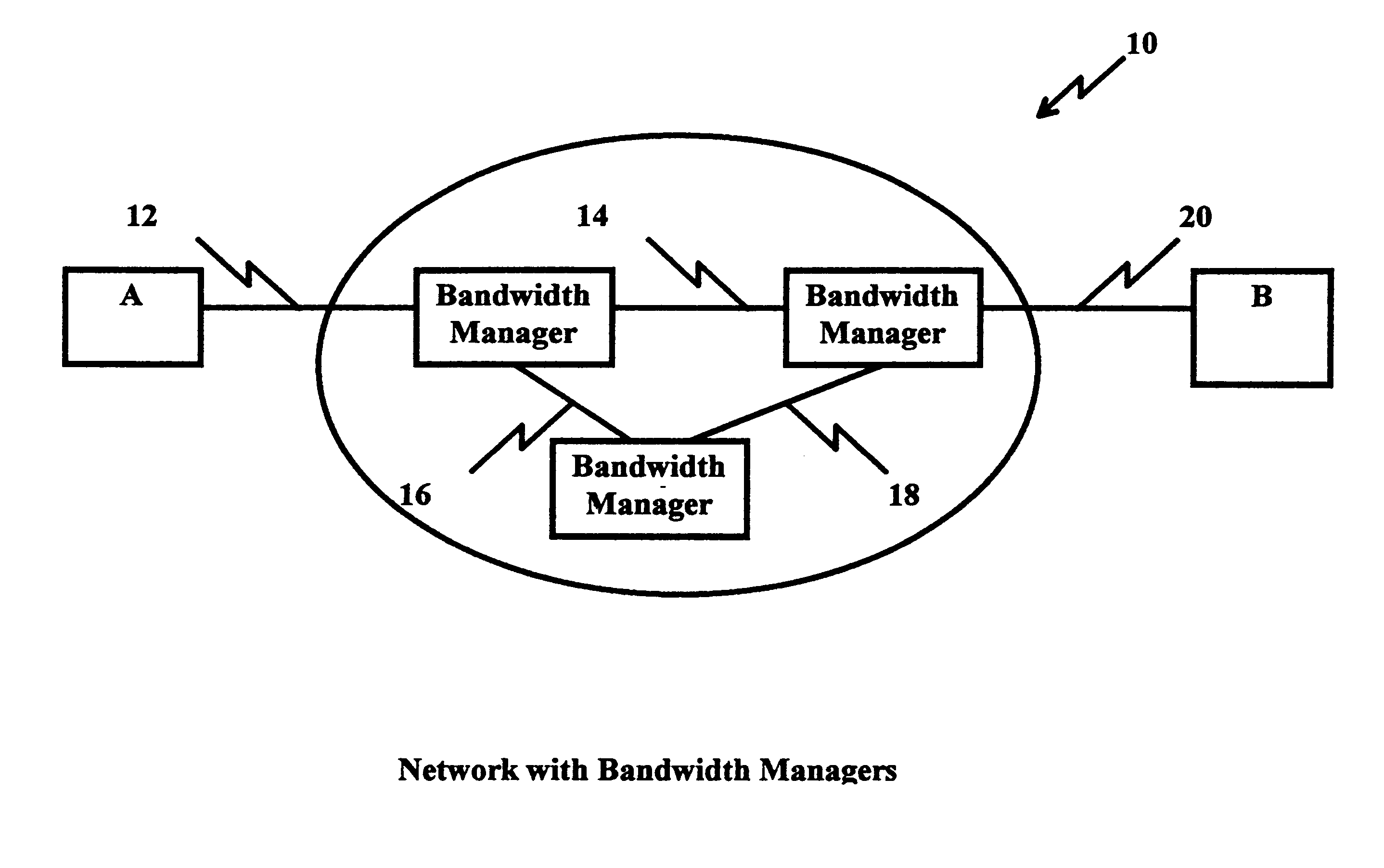
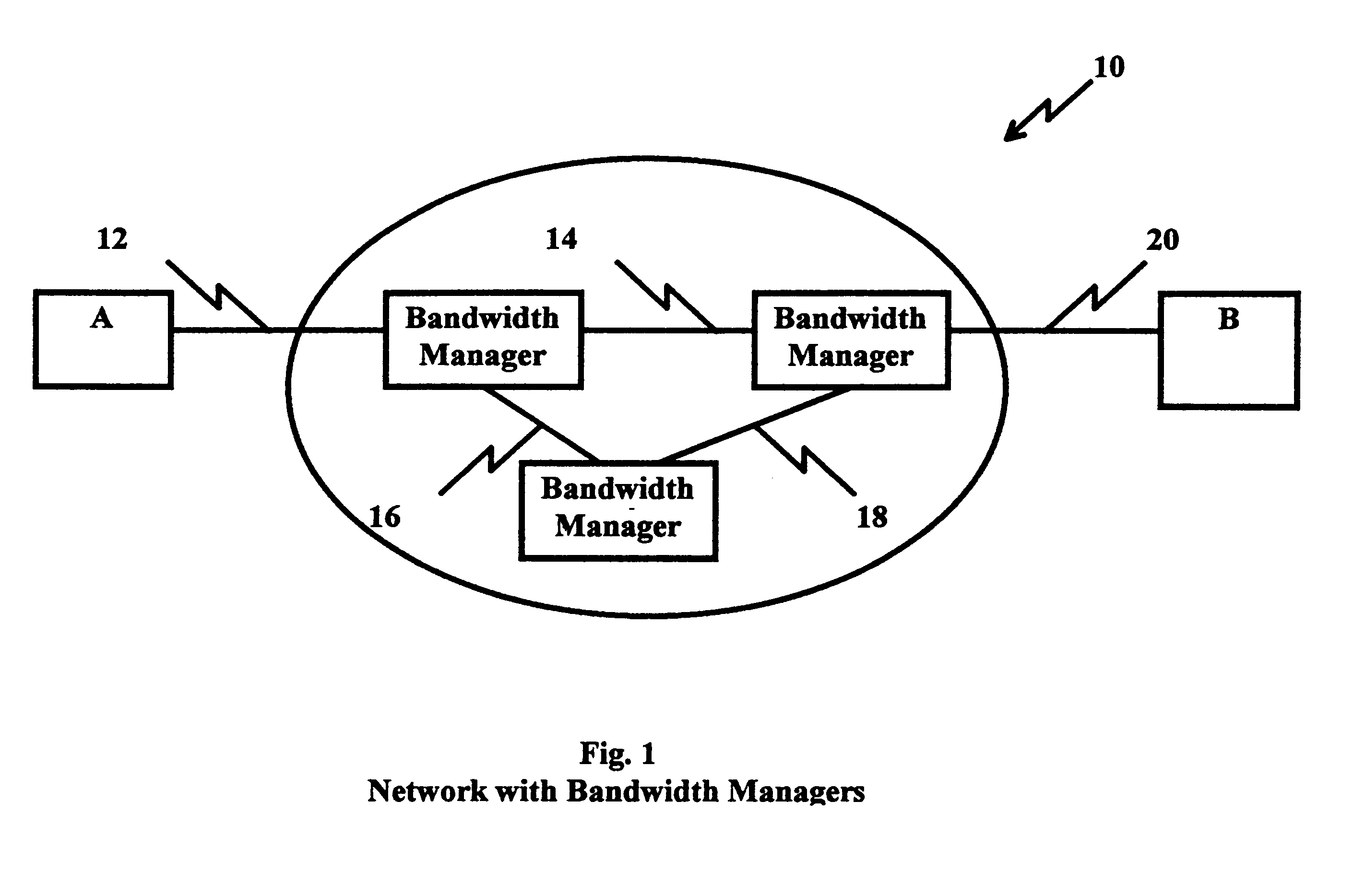
System and method for large file transfers in packet networks
A packet switching network, e.g., the Internet, employs bandwidth managers to provide guaranteed bandwidth reservations to paired forwarding and receiving agents interfacing with sending and receiving stations in the transfer of large data files therebetween. The forwarding agents obtain guaranteed reservations from the bandwidth manager for segments of the large data file which are transmitted to the receiving station in accordance with the respective reservations. The receiving agent reassembles the segments into the large data file for delivery to the receiving station. By segmenting the large data files, using guaranteed bandwidth reservations on different links or multiple networks, the transmission of large data files through packet switching networks is accomplished without adversely impacting the service requirements of other network users. Reservations and concomitant transmissions are arranged up to the capacity of the network for the attachment which maximizes the transmission ability and allows the network to distribute the bandwidth usage to prevent network congestion.
Owner:IBM CORP
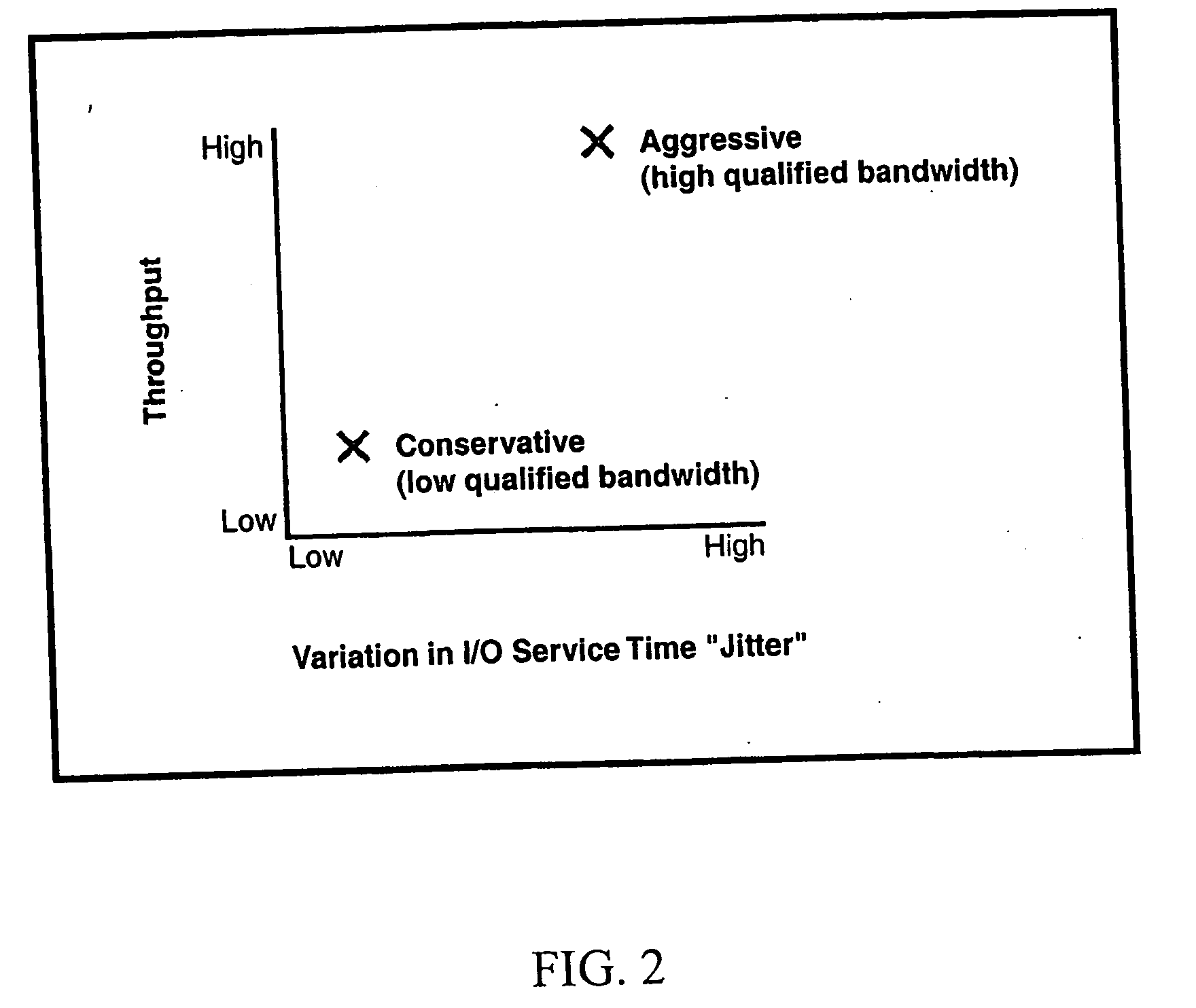
Flow control for very bursty connections in high speed cell switching networks
In high speed cell switching networks, a Call Admission Control (CAC) procedure is performed on each connection according to a specified Traffic Descriptor. A mandatory parameter of the Traffic Descriptor is the Peak Cell Rate (PCR), associated with a Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT). Connections which specify a high CDVT value may potentially send into the network bursts of cells at a rate much higher than the declared Peak Cell Rate, which may lead to congestion in cell buffers of intermediate network nodes. Guaranteeing the Quality of Service (QoS) for such connections may require the reservation of a high amount of resources in the network, leading to poor utilization of those resources. A Call Admission Control procedure, associated with an Usage Parameter Control / Network Parameter Control mechanism, provides: accepting not bursty connections and guaranteeing the Quality of Service requested at connection setup, accepting very bursty connections and guaranteeing a minimal Quality of Service rather than simply rejecting them, protecting the network from potentially too bursty traffic, determining a bandwidth reservation method based on a Mean Burst Length, for every connection, minimizing the bandwidth reservation while satisfying the required Quality of Service.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
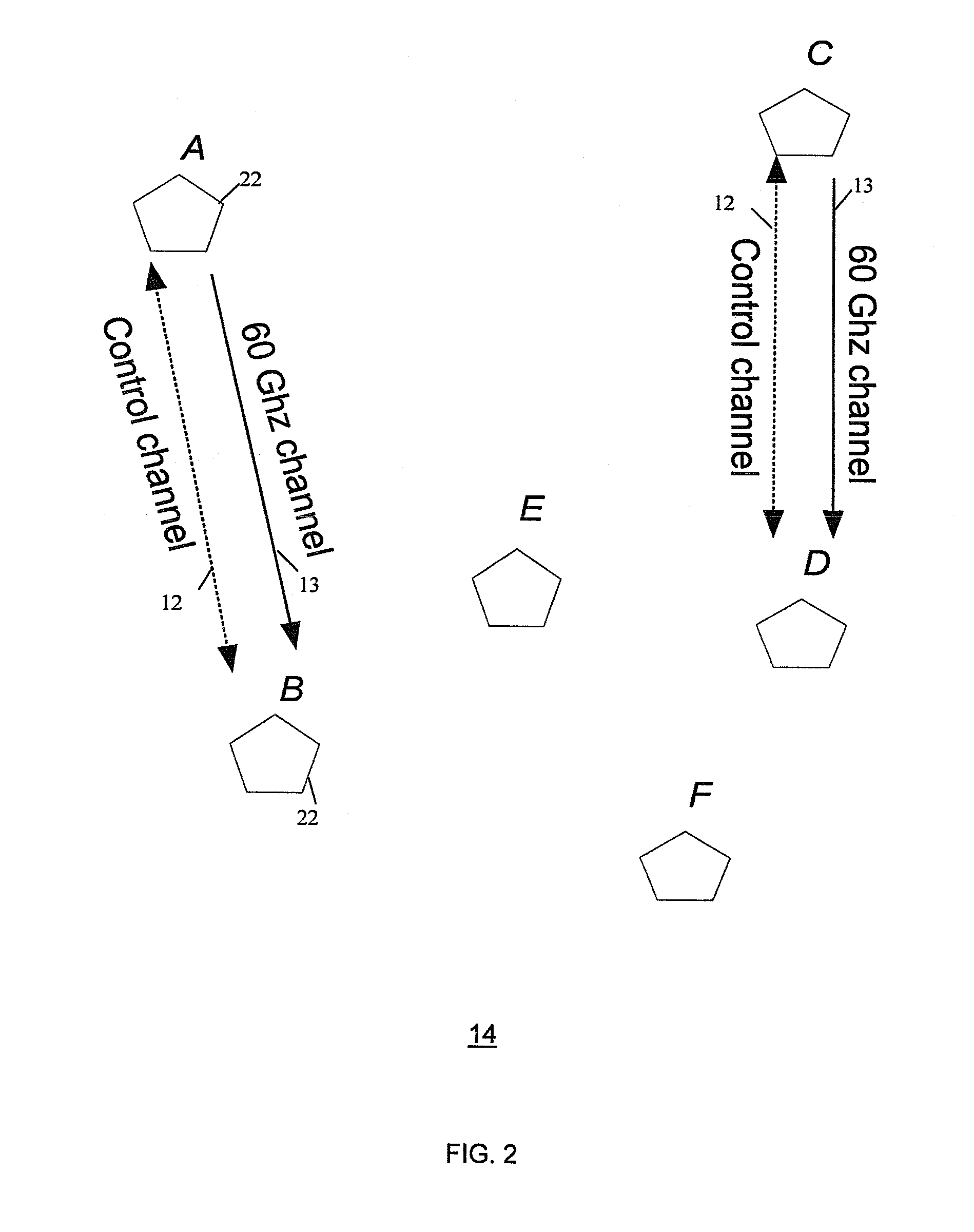
Method and system for wireless communication using channel selection and bandwidth reservation
ActiveUS20080175199A1Avoid interferenceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesWireless dataControl channel
A method and system for wireless communication involves communicating via a control channel the channel occupation information with a discovered wireless station, based on the occupation information, selecting a wireless data channel for a new transmission with the discovered station and reserving bandwidth for the new transmission on the data channel simultaneous with one or more ongoing transmissions on the data channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
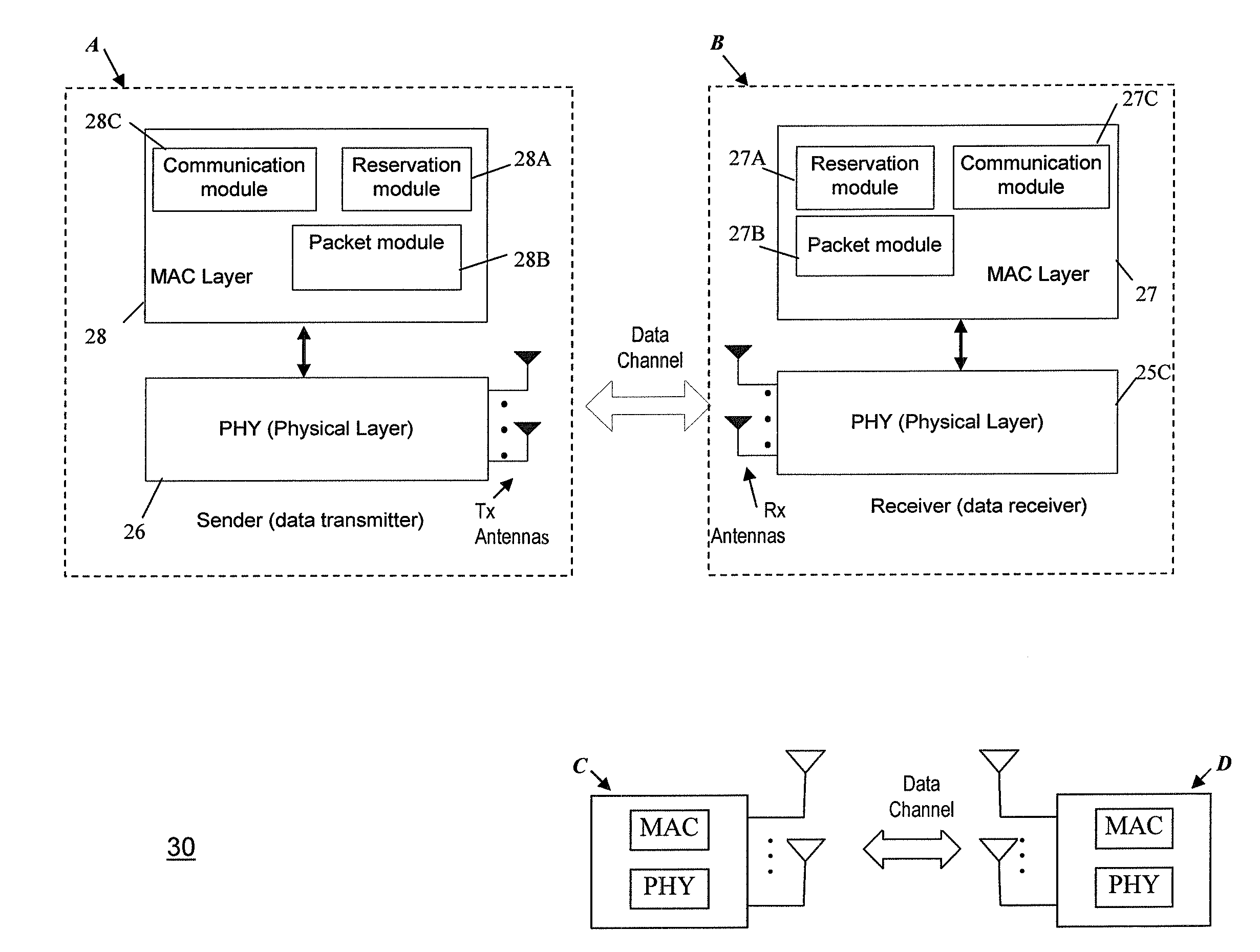
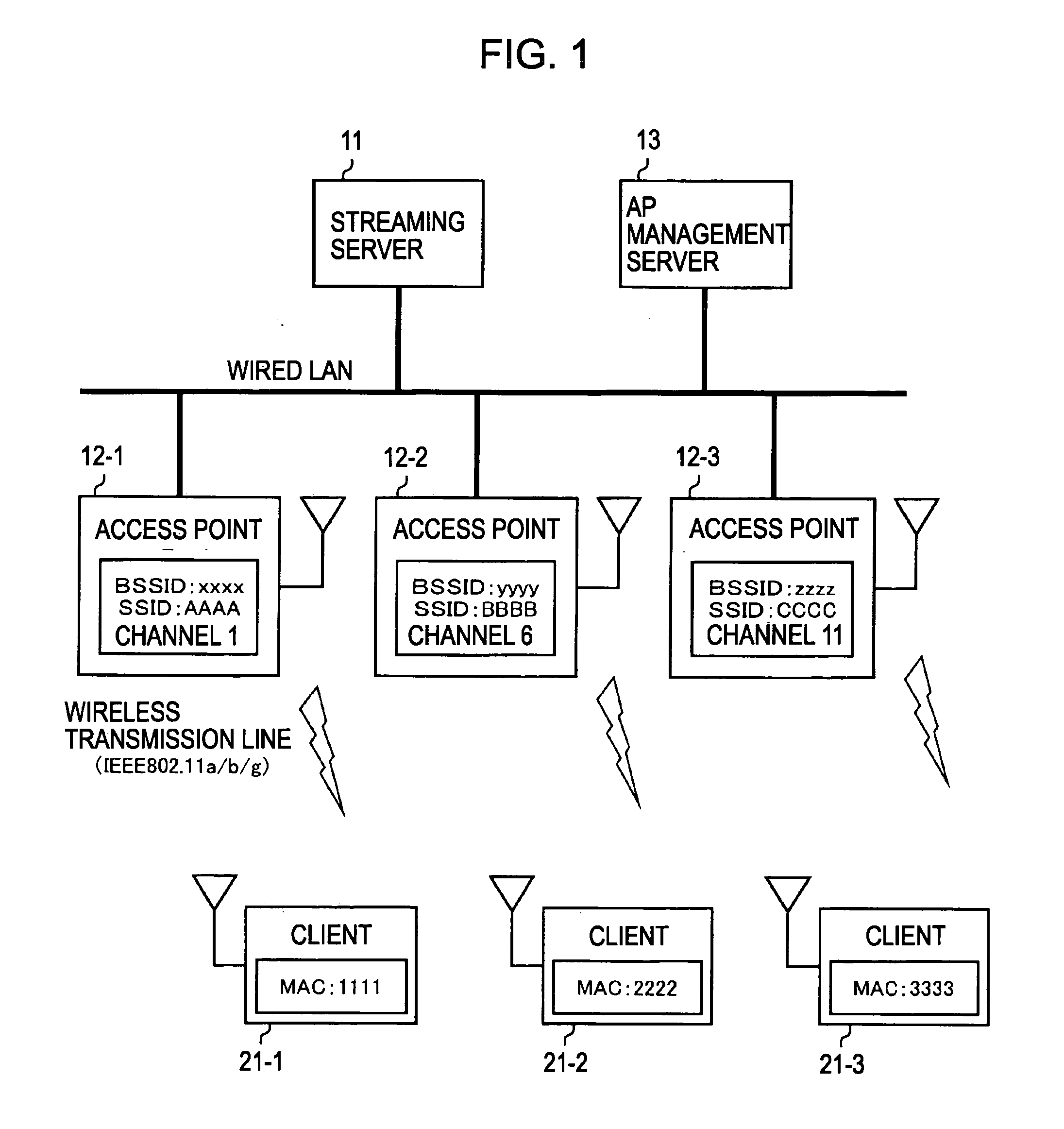
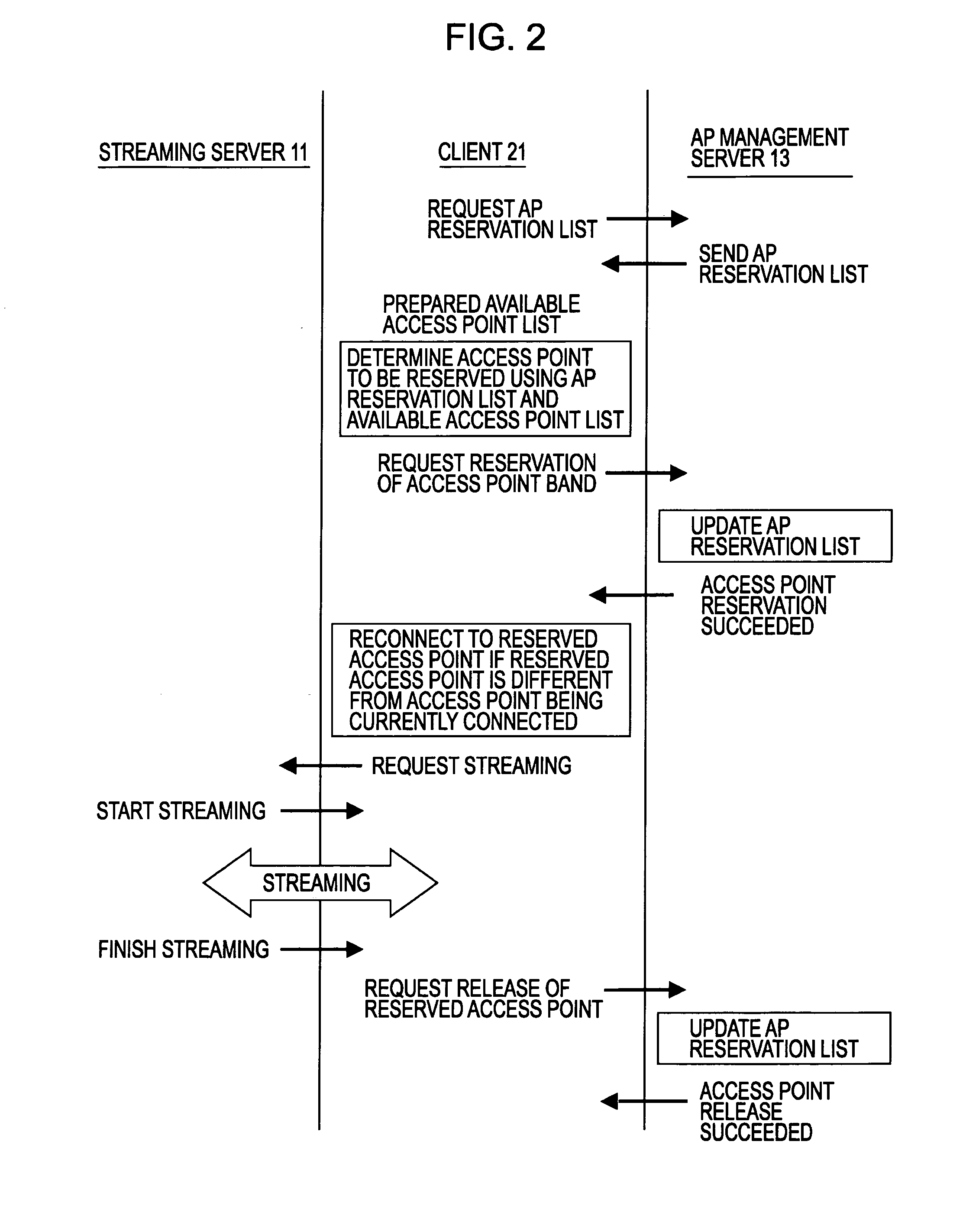
Wireless communication system, access point management device and access point management method, wireless communication device and wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS20060268767A1Secure bandwidth requiredNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCommunication device
A wireless communication device includes: an available access point managing section managing available access point information relating to access points to which connection can be made; an access point selecting section selecting an access point to which connection is made when performing data communication with the server, on the basis of information relating to a reservable bandwidth for each of the access points, and the available access point information relating to the access points to which connection can be made; a bandwidth reservation requesting section making a request for reserving, from within a reservable bandwidth for the selected access point, a bandwidth required when performing data communication with the server; and a data communication section performing data communication with the server by using the bandwidth reserved for the access point.
Owner:SONY CORP
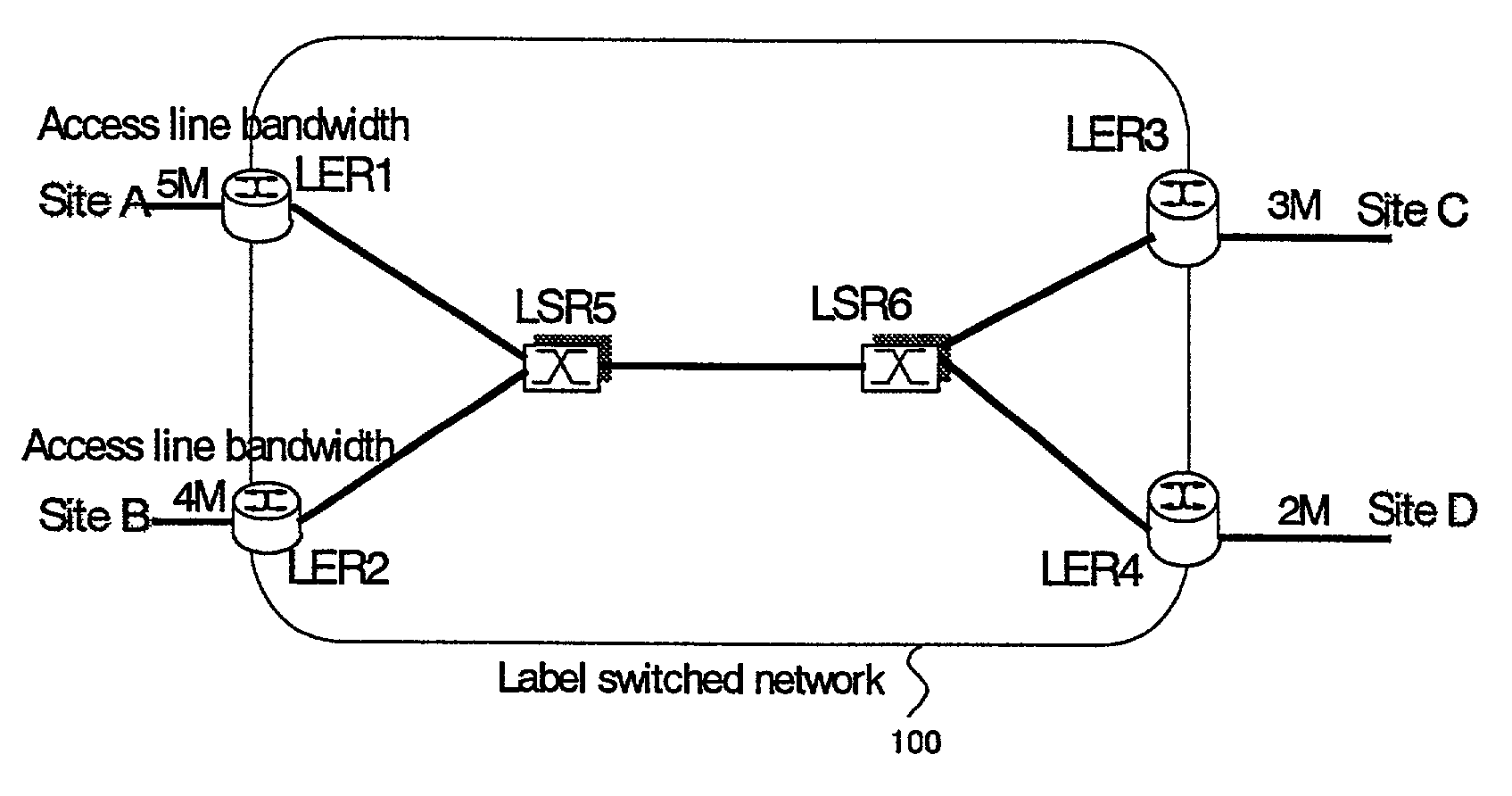
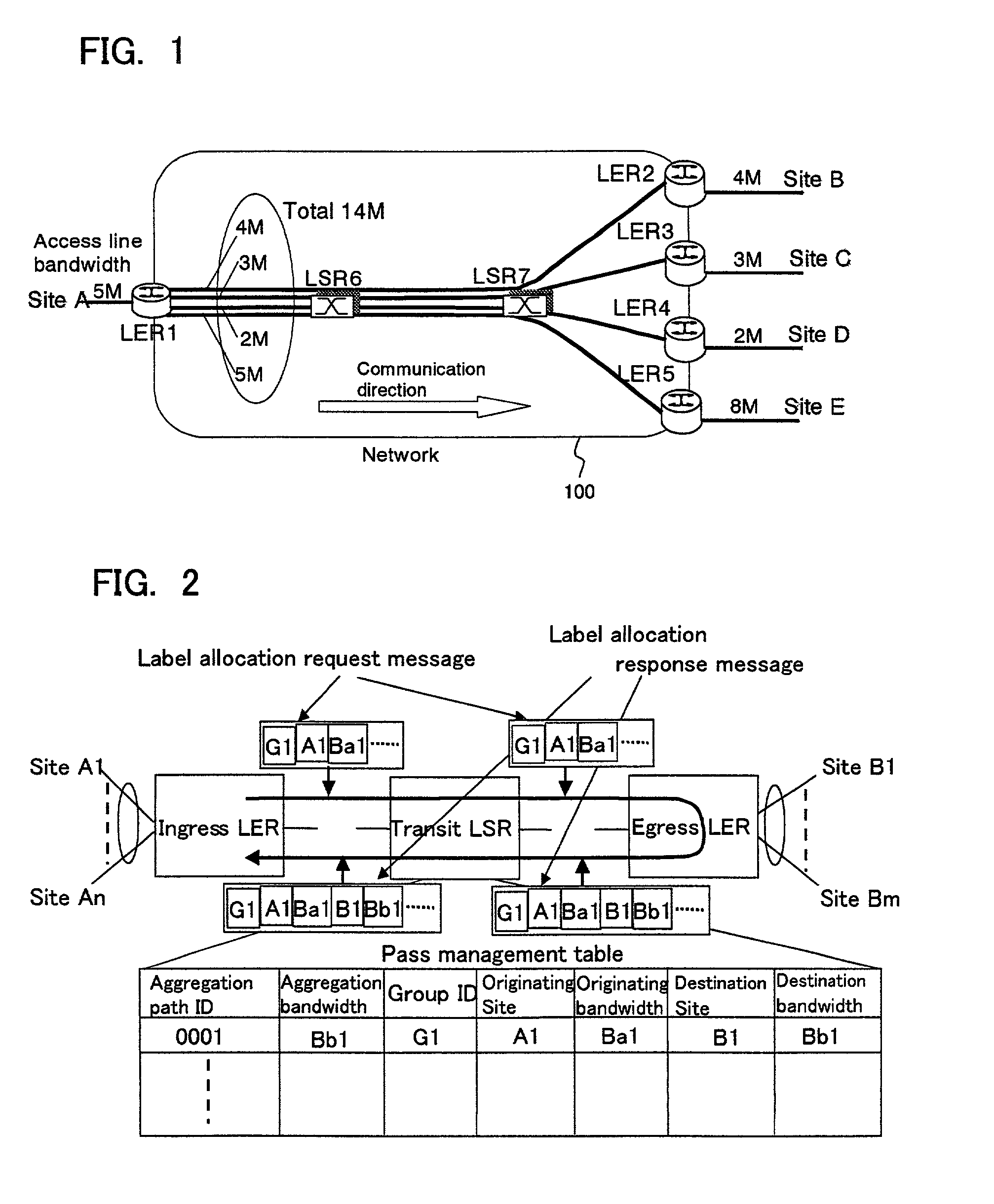
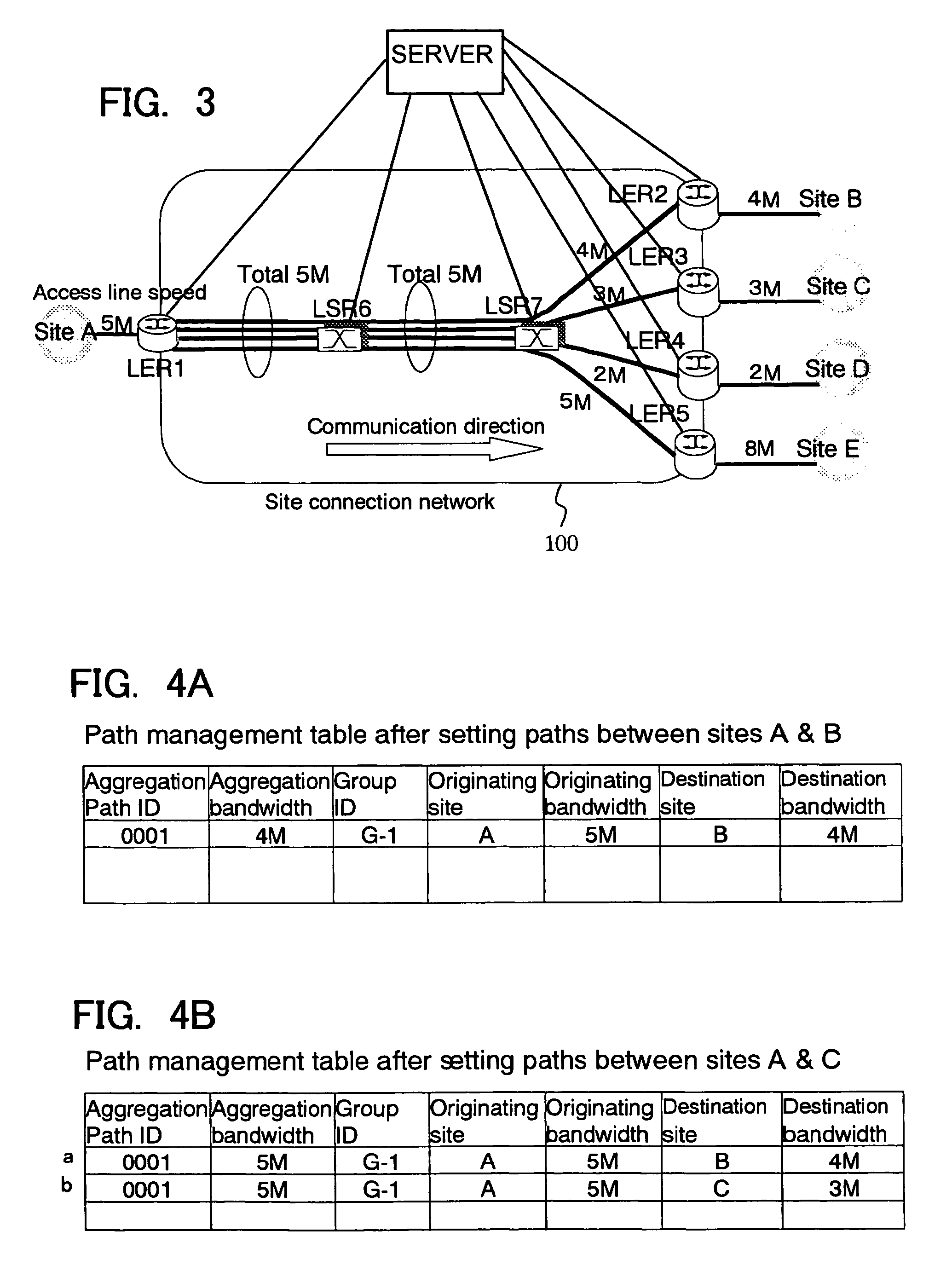
Method for allocating network aggregation bandwidth and a network system using the same
A method and a system using the method enabling to decrease required resource for the bandwidth reservation in an inter-site connection network used for communication between communication sites. The aggregation of bandwidth is considered for allocating bandwidth in the inter-site connection network. The network consists of a plurality of nodes each having a packet switch, and a plurality of user sites each constituted by a host or an internal network respectively connected to the plurality of nodes via access lines. With respect to the plurality of user sites, when one user site is to be connected to the other site through the network, a necessary and sufficient bandwidth for interconnecting between the user site and the other is calculated according to the bandwidth of the access line connecting the user site to the network considered as a minimal bandwidth. Based on the calculated result, the bandwidth is allocated to the plurality of nodes.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
MAC protocol employing multiple data rates
InactiveUS7379494B2Maximize effective useOperation moreNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex communicationFrequency spectrumWireless transmission
Method and apparatus for combining high data rate traffic and low data rate traffic on a common transmission medium while maximizing efficient use of available spectrum. Since spectrum is an economically valuable resource and transport of data generates revenue, the present invention directly leads to more profitable network operation. The disclosed systems are applicable to both wired and wireless transmission media. In one embodiment, a bandwidth reservation scheme provides that data rate may be varied so that when a particular data communication device is allocated a frame, it is also assigned a data rate for use in that frame. Because bandwidth usage varies with data rate, the division of available spectrum into channels for use by individual data communication devices may also vary among frames.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Co-Scheduling of Network Resource Provisioning and Host-to-Host Bandwidth Reservation on High-Performance Network and Storage Systems
A cross-domain network resource reservation scheduler configured to schedule a path from at least one end-site includes a management plane device configured to monitor and provide information representing at least one of functionality, performance, faults, and fault recovery associated with a network resource; a control plane device configured to at least one of schedule the network resource, provision local area network quality of service, provision local area network bandwidth, and provision wide area network bandwidth; and a service plane device configured to interface with the control plane device to reserve the network resource based on a reservation request and the information from the management plane device. Corresponding methods and computer-readable medium are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA THROUGH THE ERNEST ORLANDO LAWRENCE BERKELEY NAT LAB +1
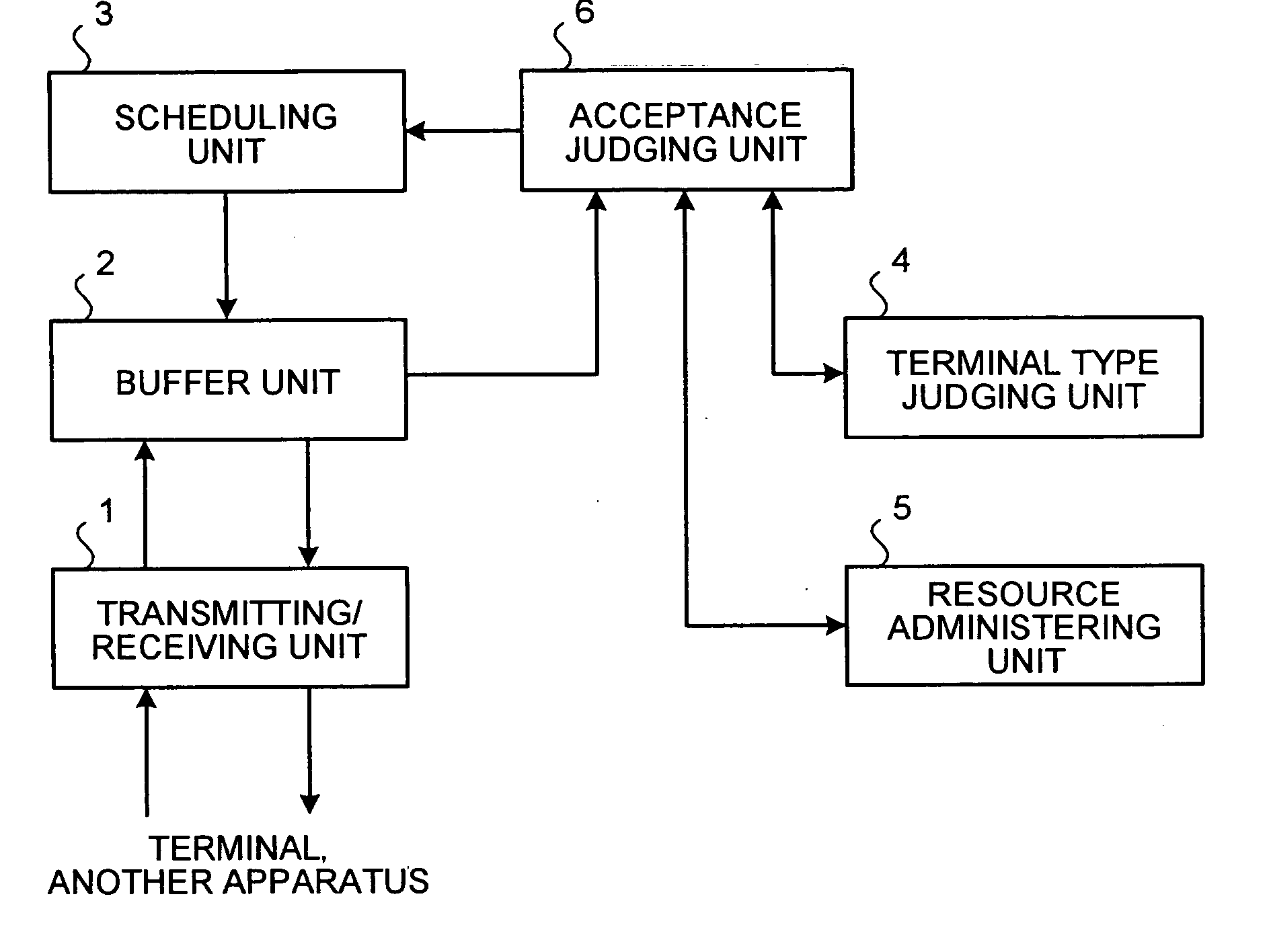
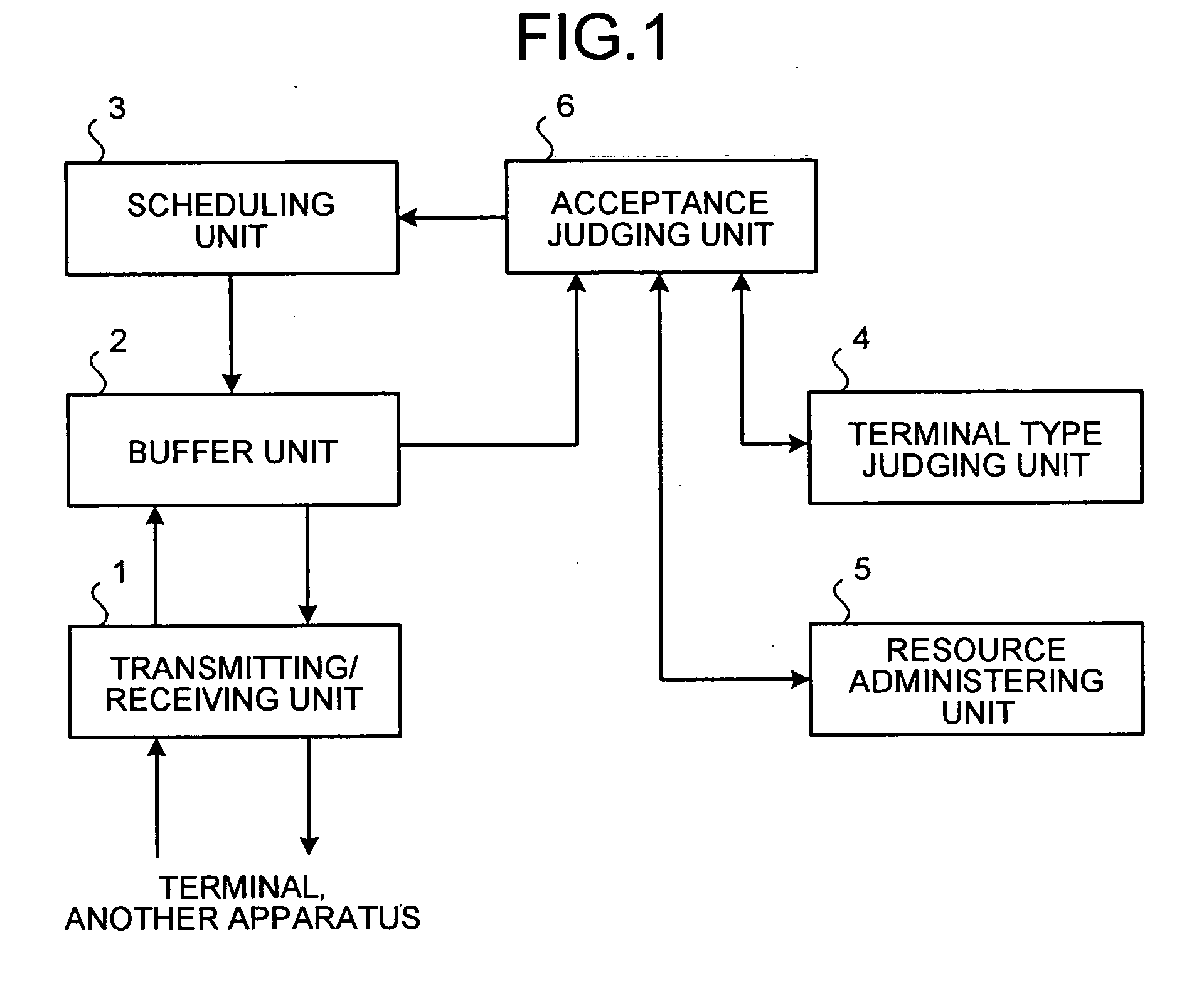
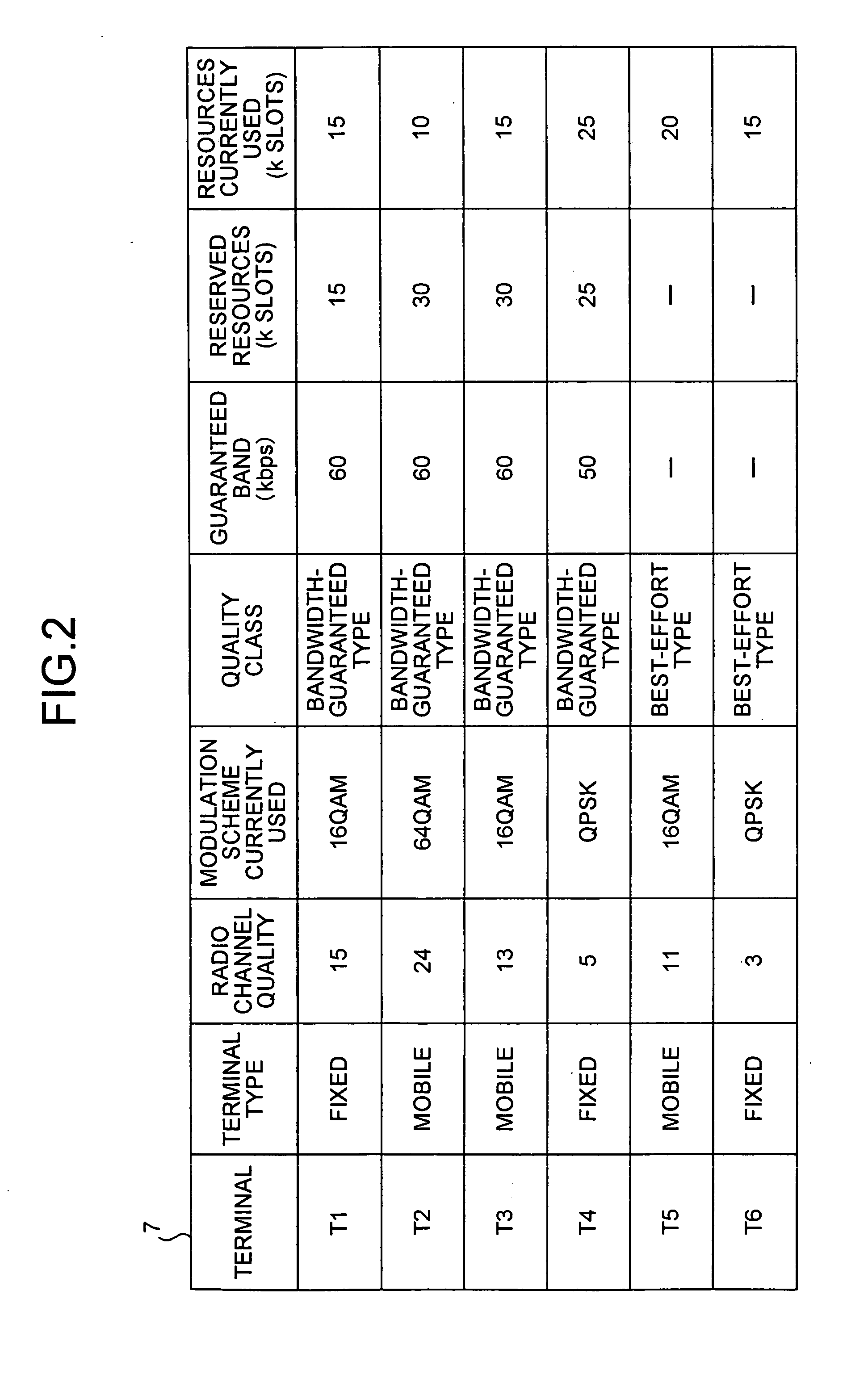
Base station apparatus, terminal, and bandwidth control method
InactiveUS20070223427A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesBandwidth reservationBase station
A terminal-type judging unit judges whether a terminal is a mobile terminal or a fixed terminal. For a connection with the fixed terminal, an acceptance judging unit and a scheduling unit convert a requested bandwidth into a first resource amount using a modulation scheme used at the time of receiving a bandwidth reservation request and reserve the first resource amount. For a connection with the mobile terminal, the acceptance judging unit and the scheduling unit convert a requested bandwidth into a second resource amount using the slowest modulation scheme and reserve the second resource amount. If a higher-speed modulation scheme is usable for the connection with the mobile terminal, the scheduling unit assigns a difference between a resource amount for using the higher-speed modulation scheme and the second resource amount, to a best-effort-type connection.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for device discovery in wireless communication
ActiveUS20080176561A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionWireless dataMessage switching
The present invention provides a method and a system for device discovery in wireless communication. One implementation involves scanning one or more wireless channels to discover a partner wireless station for a new transmission, by detecting peak energy and beacons on each scanned channel. If a beacon is not detected, then selecting the clearest channel among the scanned channels, and transmitting beacons on the clearest channel. Upon detecting a beacon from a partner station, establishing association with the partner station and selecting a wireless data channel for communication with the partner station. Another implementation involves discovering a partner wireless station to establish a data channel for communication with a discovering station that is associated with a coordinator station, and transmitting a bandwidth reservation request to the coordinator to reserve channel time for control message exchange between the discovering station and the partner station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bandwidth reservation-based VSAT satellite communication system bandwidth distribution method
InactiveCN101986619AEasy to implementAllocation is fastRadio transmissionData switching networksTime delaysEffective management
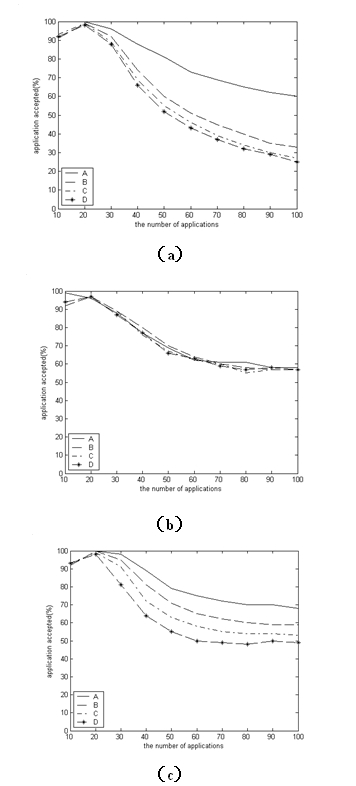
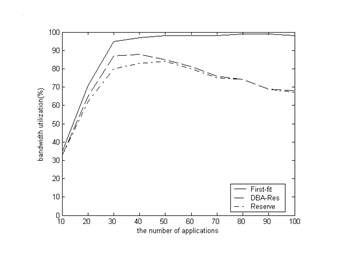
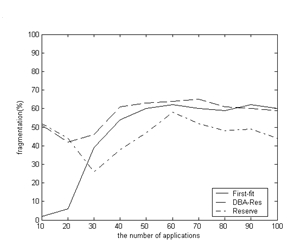
The invention discloses a bandwidth reservation-based very small aperture terminal (VSAT) satellite communication system bandwidth distribution method, and relates to the technical field of satellite communication. In the method, different applications are endowed with different priorities based on the conventional bandwidth reservation-based dynamic bandwidth distribution method, and the high-priority application can occupy the bandwidth section occupied by the low-priority application, vice is not; and in actual distribution, when the bandwidth section corresponding to the application has no enough idle bandwidth, and the bandwidth sections with low priorities are searched in turn from high priorities to low priorities. The method keeps the advantages of the conventional bandwidth reservation-based dynamic bandwidth distribution method such as simple implementation, few channel fragments and high distribution speed, coordinates different QoS (quality of service) demands and application scenes, realizes effective management of channel resources, improves the utilization rate of satellite channel resources in a network environment of multiple service types, meanwhile, simplifies star-earth interaction and reduces the time delay caused by bandwidth distribution.
Owner:NANJING DANAO TECH
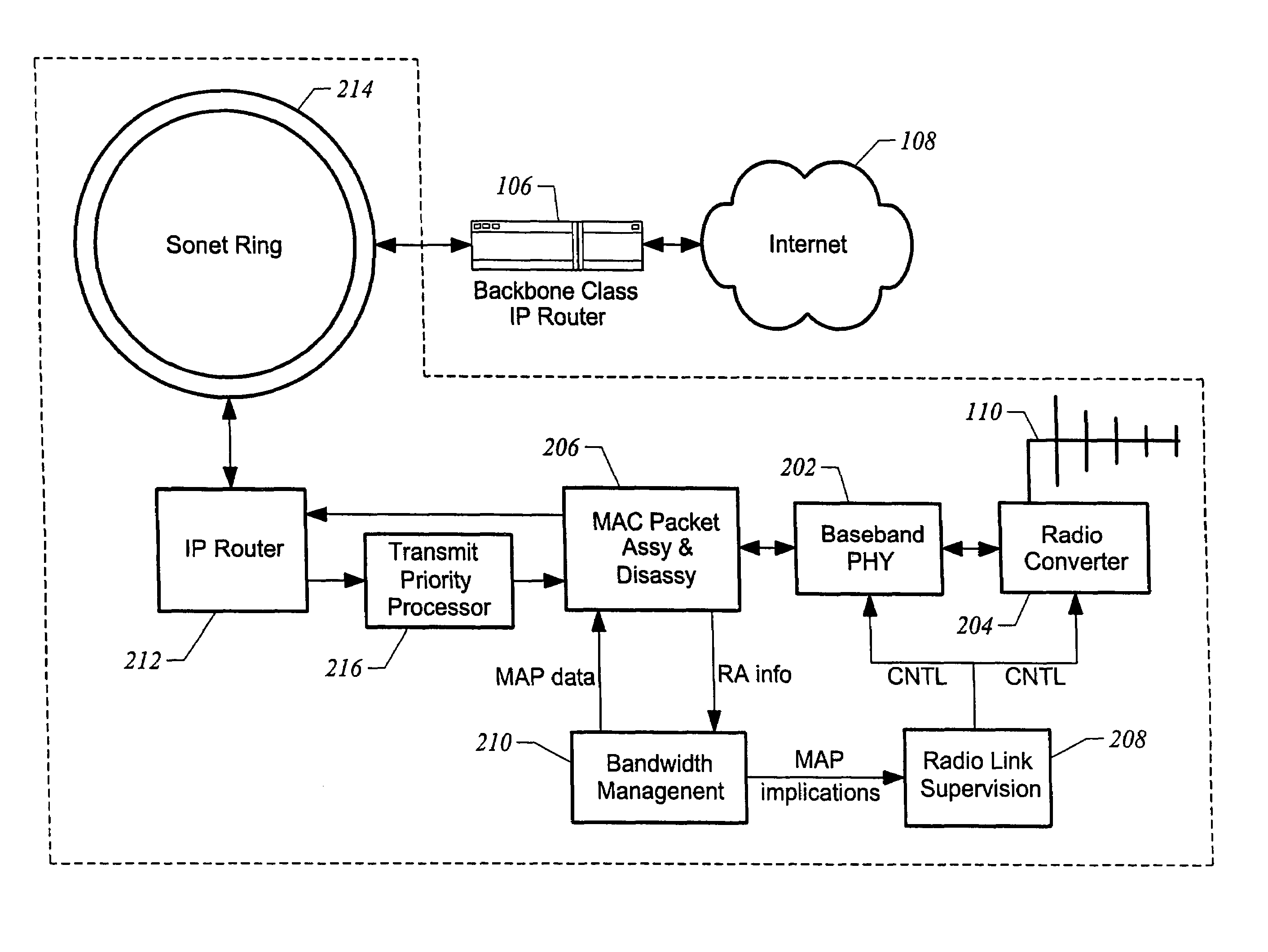
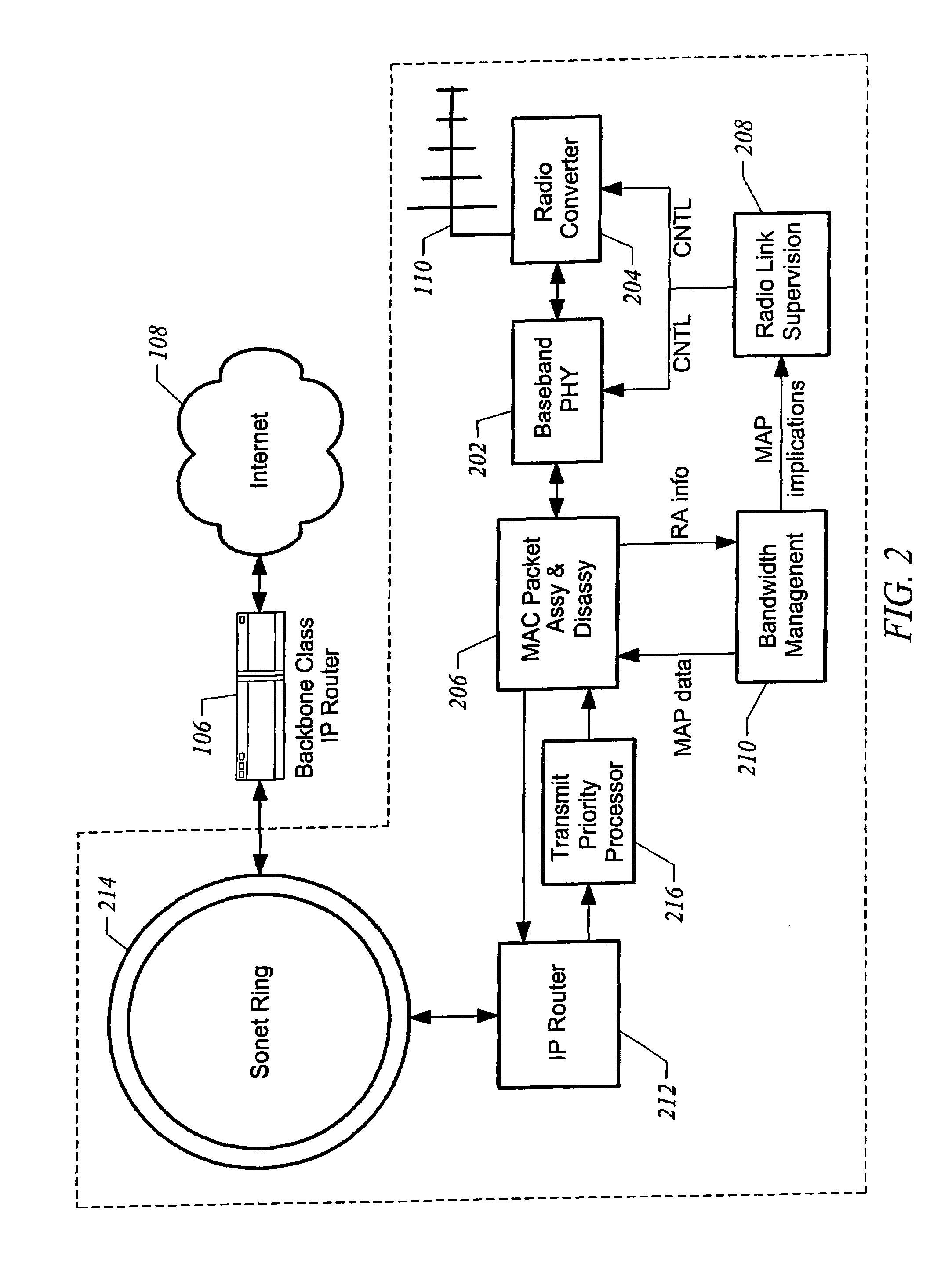
Method and apparatus for over-the-air bandwidth reservations in wireless networks
ActiveUS7324491B1Quality assuranceGuaranteed service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexWireless mesh networkWireless traffic
Embodiments control access to a wireless network providing communication for wireless traffic and controlled by a wireless access point to assure quality of service for designated traffic by assigning all communication of the designated traffic to use one of the priorities on the wireless network, requiring that ones of the wireless traffic wanting to communicate using the one of the priorities and higher ones of the priorities and using a distributed medium access protocol submit bandwidth reservation requests to the wireless access point, granting a bandwidth reservation to one of the wireless traffic for communication by the wireless access point in response to a bandwidth reservation request upon bandwidth being available on the wireless network, and allowing other ones of the wireless traffic to communicate using lower ones of the priorities without requiring bandwidth reservation requests.
Owner:AVAYA TECH LLC
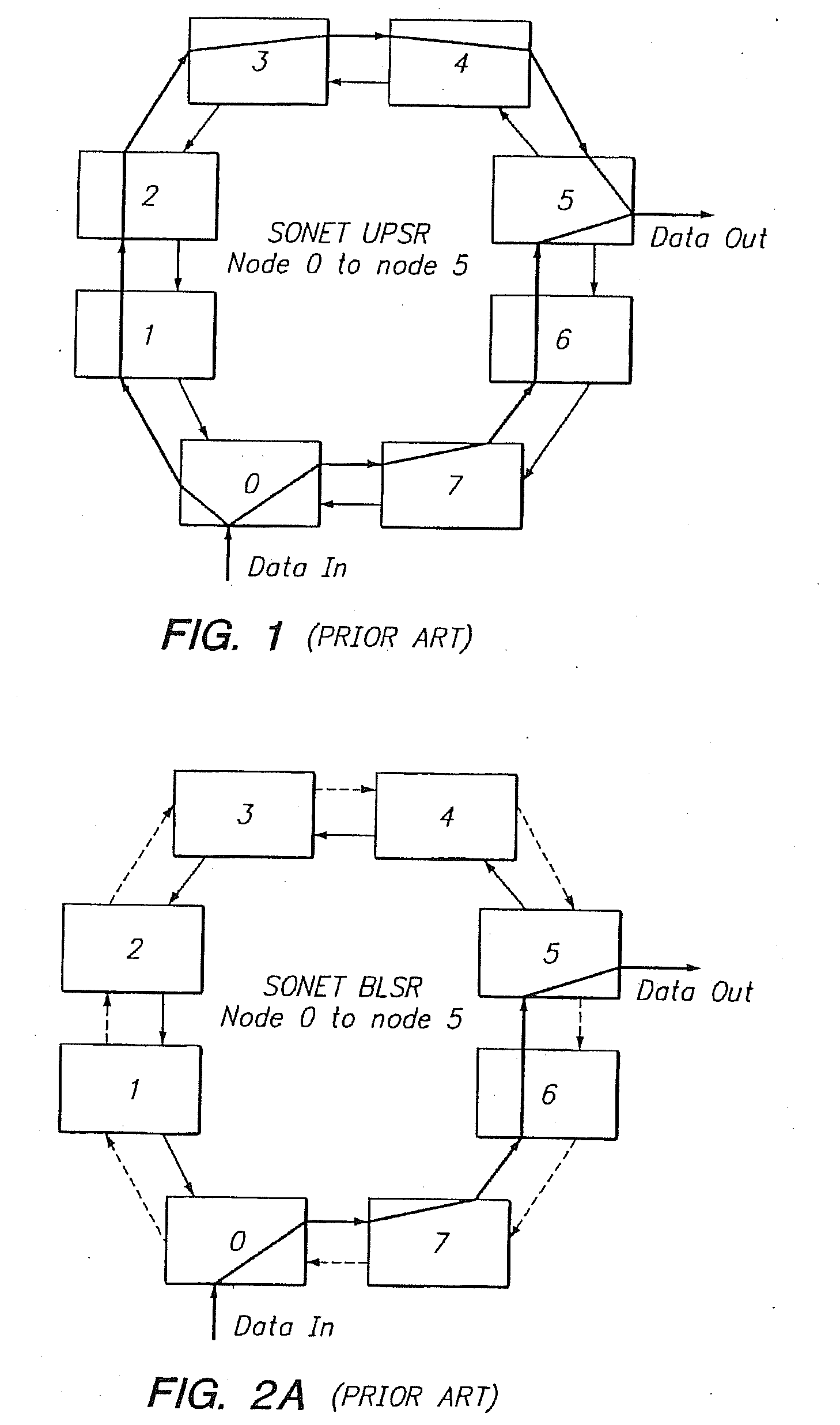
Bandwidth reservation reuse in dynamically allocated ring protection and restoration technique
InactiveUS20090141621A1Maximize switching speedError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableRing protection
The disclosed network includes two rings, wherein a first ring transmits data in a clockwise direction, and the other ring transmits data in a counterclockwise direction. The traffic is removed from the ring by the destination node. During normal operations (i.e., all spans operational), data between nodes can flow on either ring. Thus, both rings are fully utilized during normal operations. The nodes periodically test the bit error rate of the links (or the error rate is constantly calculated) to detect a fault in one of the links. The detection of such a fault sends a broadcast signal to all nodes to reconfigure a routing table within the node so as to identify the optimum routing of source traffic to the destination node after the fault.
Owner:ADTRAN
Bandwidth reservation for data flows in interconnection networks
ActiveUS20090028186A1Constant bandwidthTime-division multiplexSelective content distributionPacket arrivalData stream
A method and apparatus for bandwidth reservation for data flows in interconnection networks. Some embodiments of an apparatus for transmitting a data stream include a transmitter to transmit a data stream to a recipient apparatus, the data stream including a plurality of data packets. The apparatus further includes a receiver to receive a response from the recipient apparatus regarding data packet arrival status, and a network unit to direct the operation of the transmitter, the network unit to direct the transmitter to maintain the data stream with a constant bandwidth.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
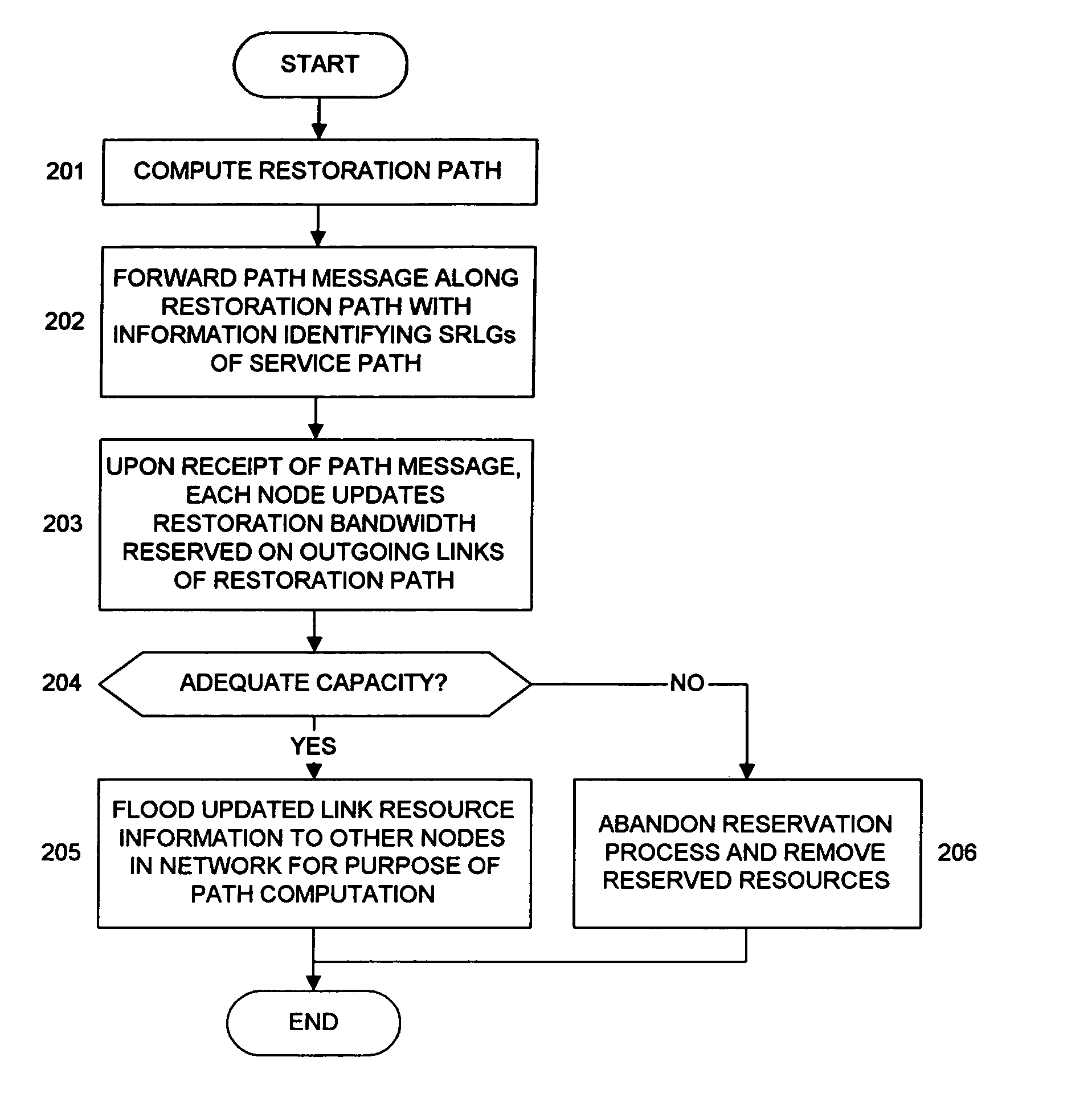
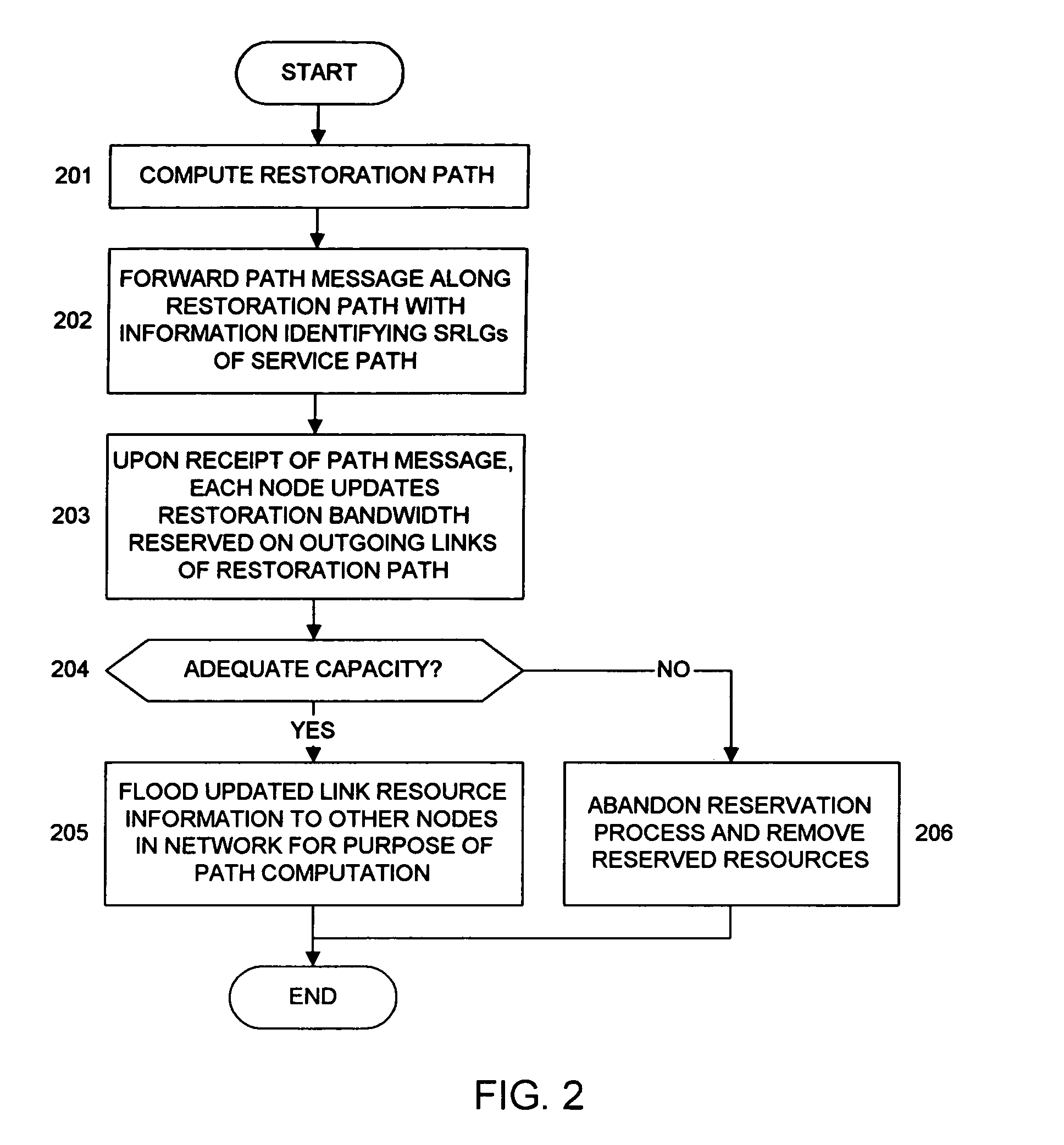
Method for restoration and normalization in a mesh network
InactiveUS7652983B1Minimal service traffic interruptionAchieve performanceLaser detailsError preventionBandwidth reservationDistributed computing
The present invention is directed to methods for signaling that enable bandwidth reservation, path restoration, path normalization, and path removal in a mesh network that supports shared mesh restoration.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
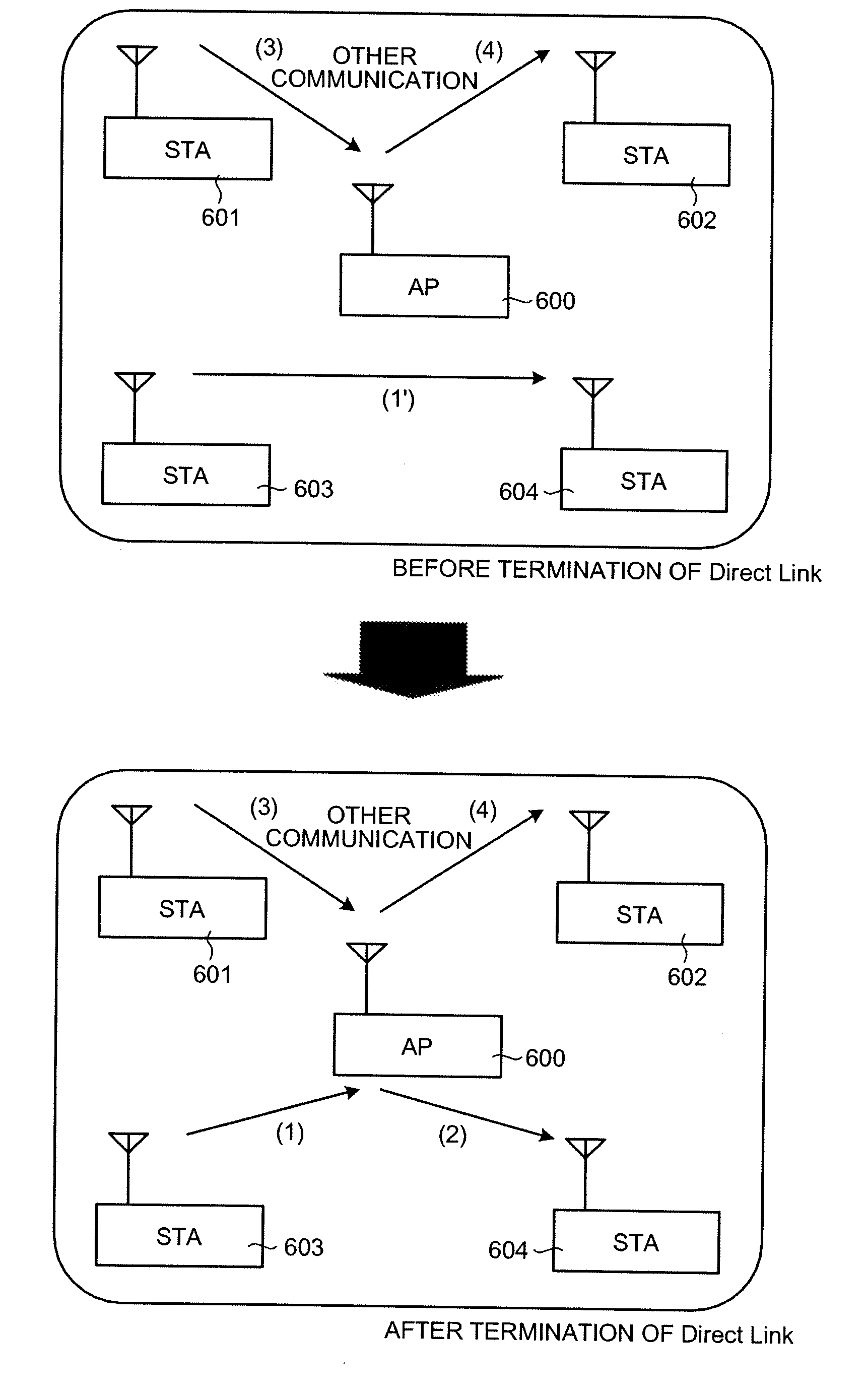
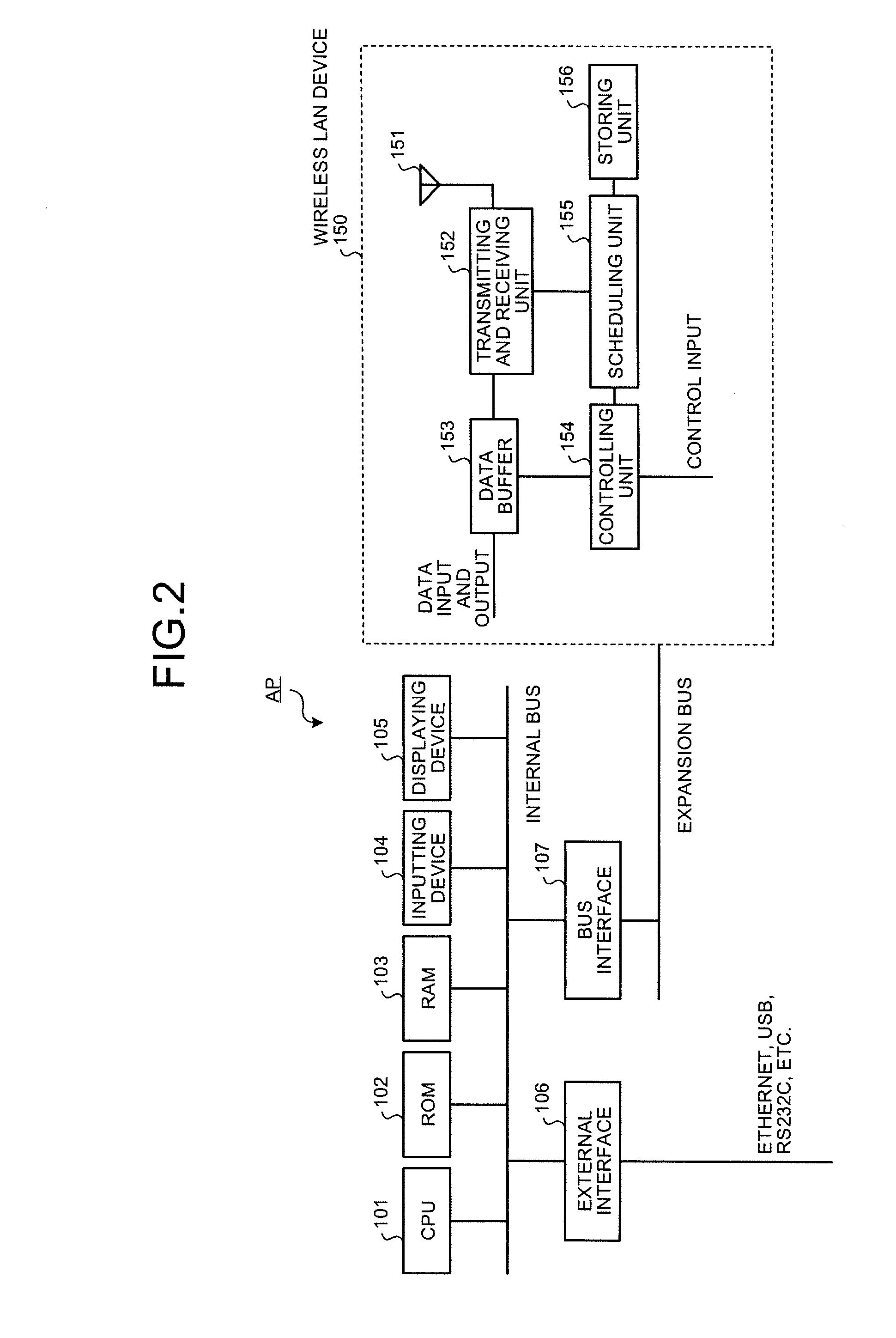
Radio Lan System, and Base Station and Terminal Station Thereof
InactiveUS20080259853A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesWireless lanData transmission
A wireless LAN system that includes a plurality of stations and an access point, interconnected via a network, and supports QoS has infrastructure mode and a Direct Link. In the infrastructure mode, data communication is performed between stations STA via an access point AP. In the Direct Link, data communication is performed directly between the stations STA. The access point AP performs a process for reserving a bandwidth 2W that is twice a bandwidth W required when the Direct Link is used, in response to a QoS bandwidth reservation request when the Direct Link is used from a station STA. As a result, the QoS of data transfer can be ensured even when the Direct Link is terminated.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Dynamic flow division scheduling system and method
InactiveCN102710489ABalanced UtilizationAggregated Bandwidth IncreaseData switching networksData centerGranularity
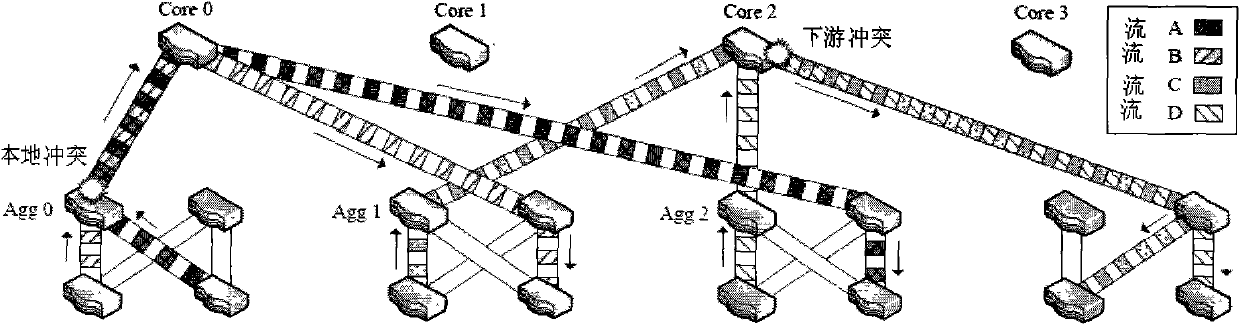
The invention provides a dynamic flow division scheduling system and a dynamic flow division scheduling method for a data center network. A host machine applies for bandwidth reservation of specific flow for a flow scheduler of a data center; the flow scheduler checks the bandwidth using conditions of all paths which can be selected by the specific flow; if the sum of bandwidths retained on the paths meets the demand for the bandwidth of the specific flow, the flow is divided into one or more sub-flows, and then the sub-flows are forwarded on the corresponding paths; and if the bandwidths retained on all the paths cannot meet the demand for the bandwidth of the specific flow, the current flows on the paths are transferred to other paths, so that a space is reserved for forwarding the specific flow. According to the dynamic flow division scheduling system and the dynamic flow division scheduling method, the actual bandwidth demand of the flow can be timely and accurately obtained, and scheduling can be performed on the granularity which is thinner than the flow, so that the utilization rate of the whole data center network is balanced, and the convergence bandwidth of the whole data center network is increased.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
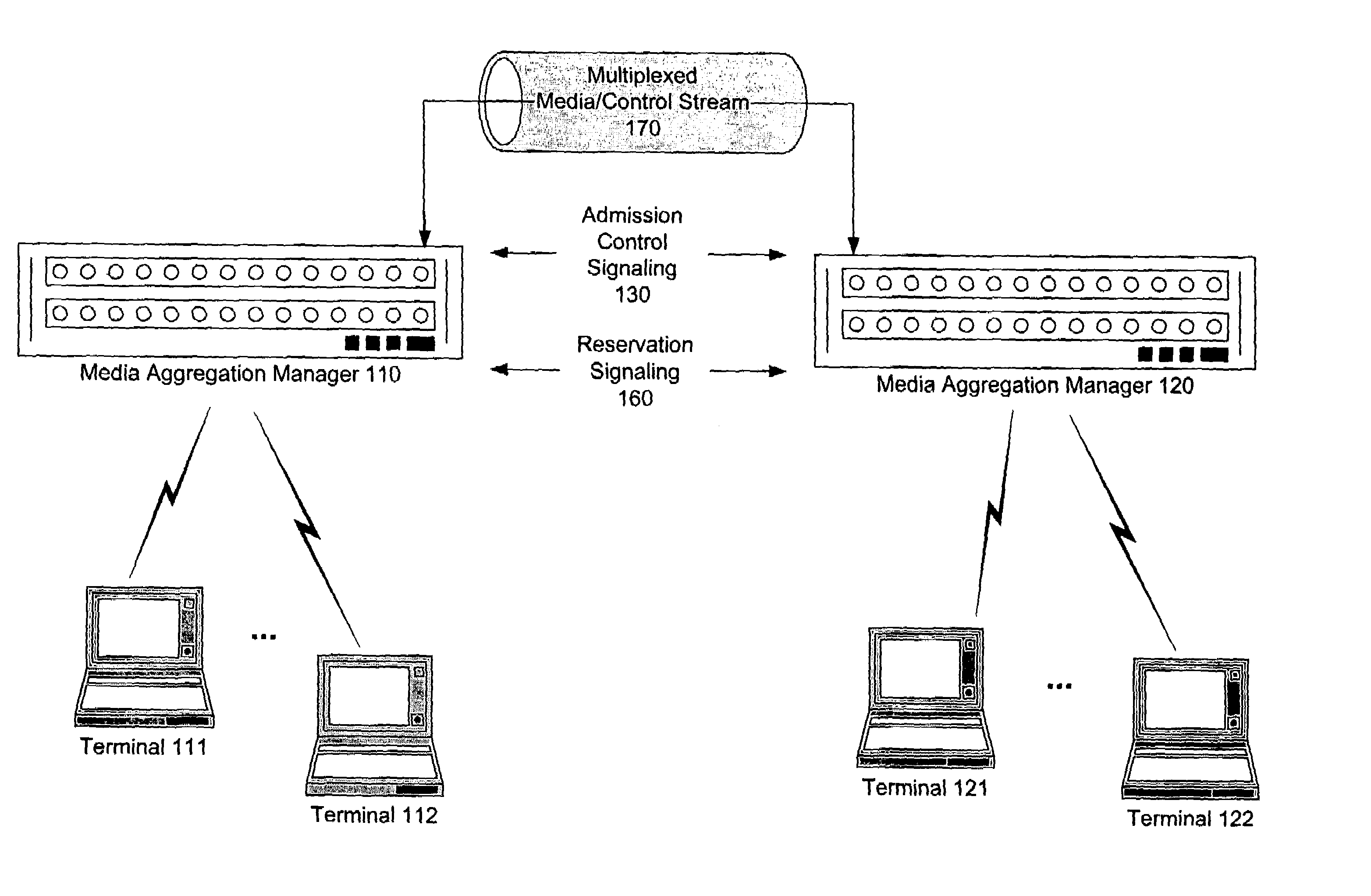
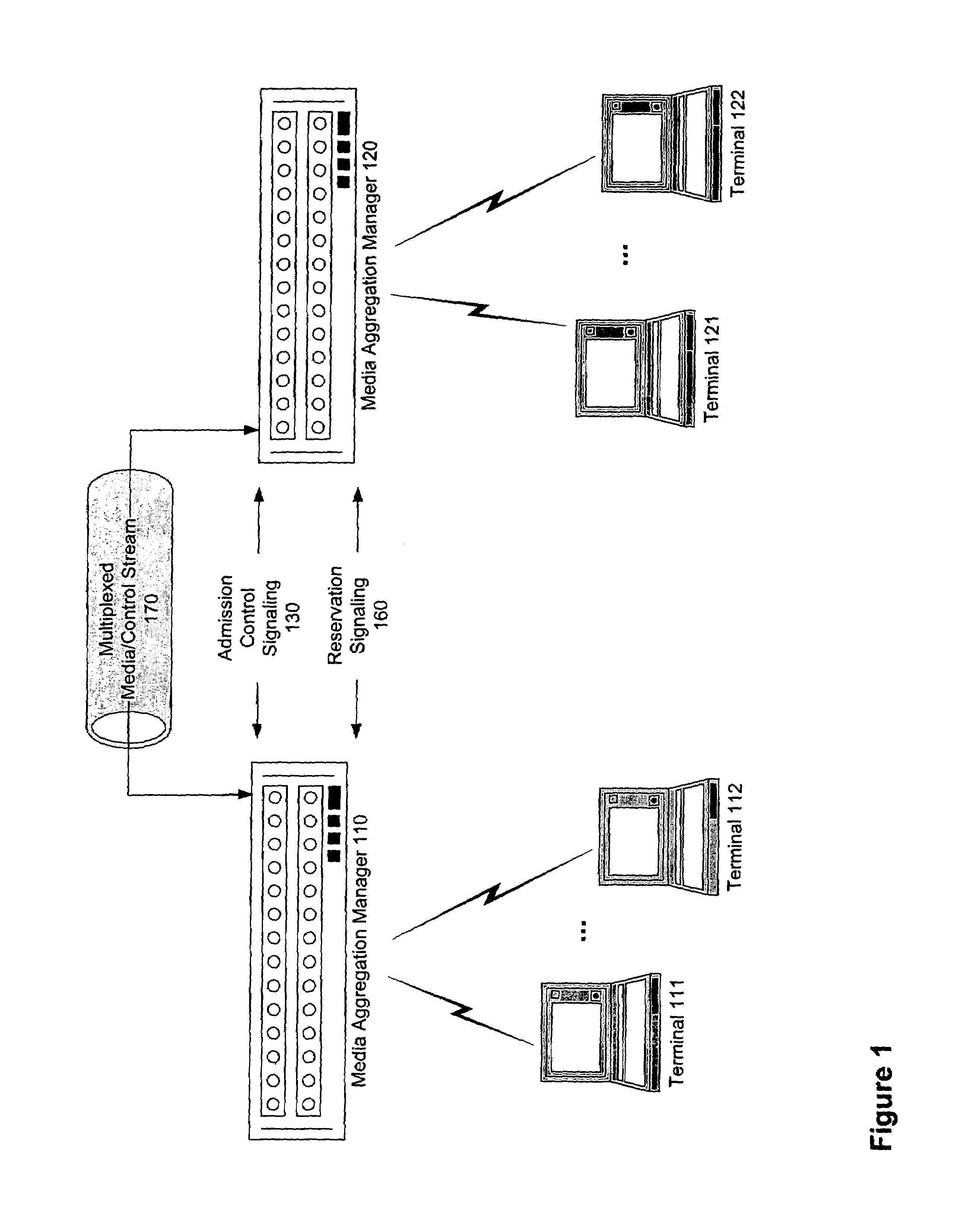
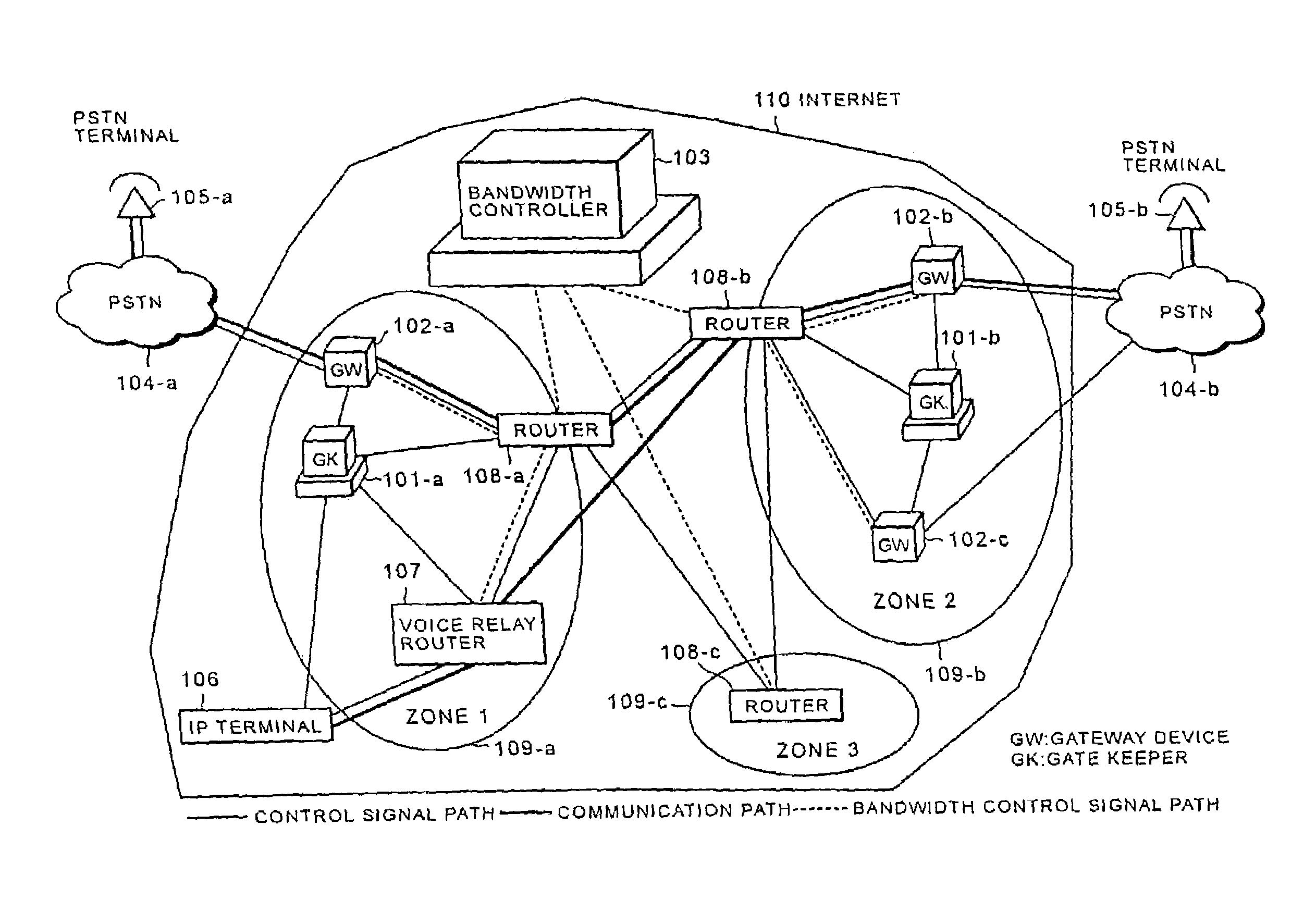
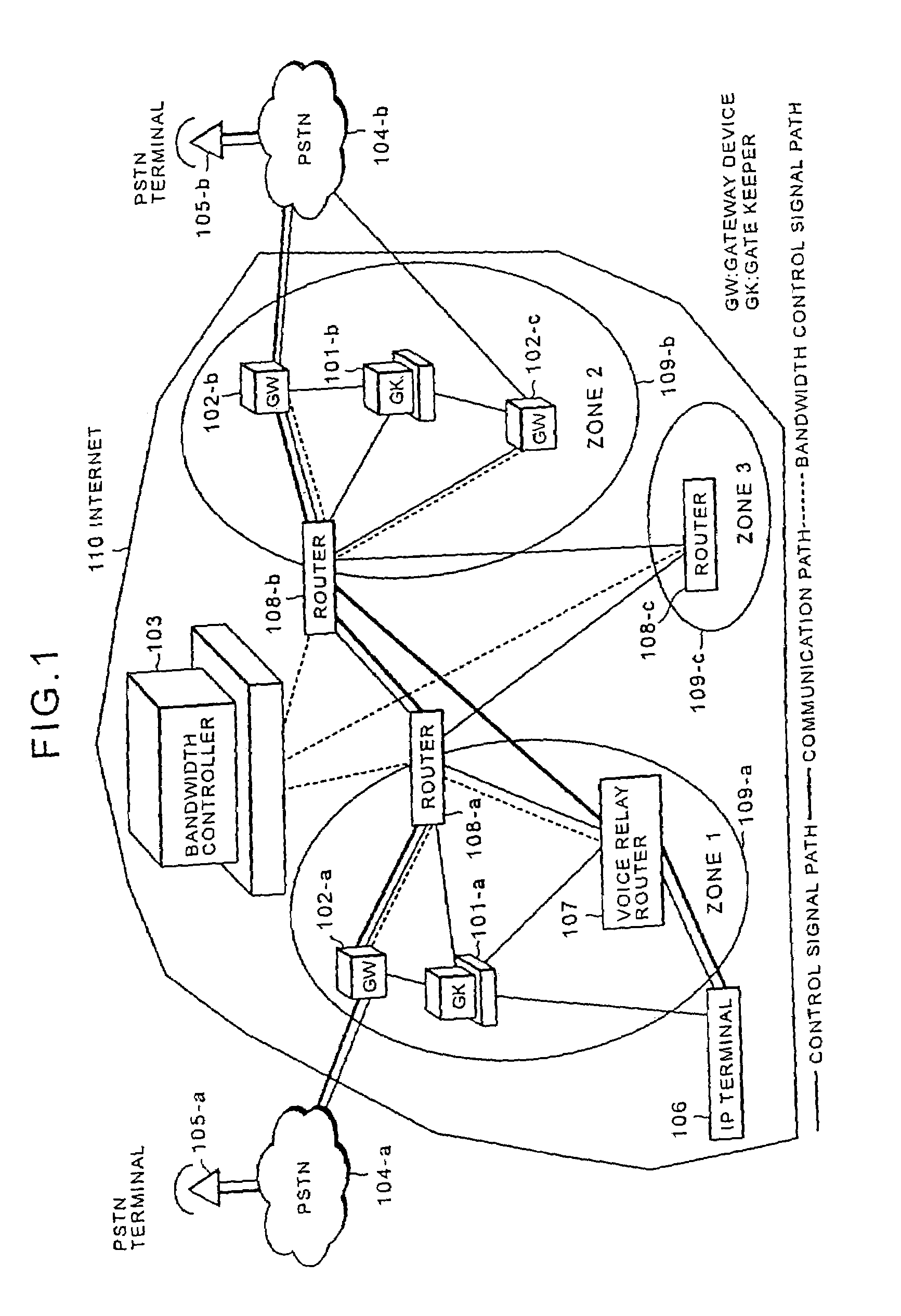
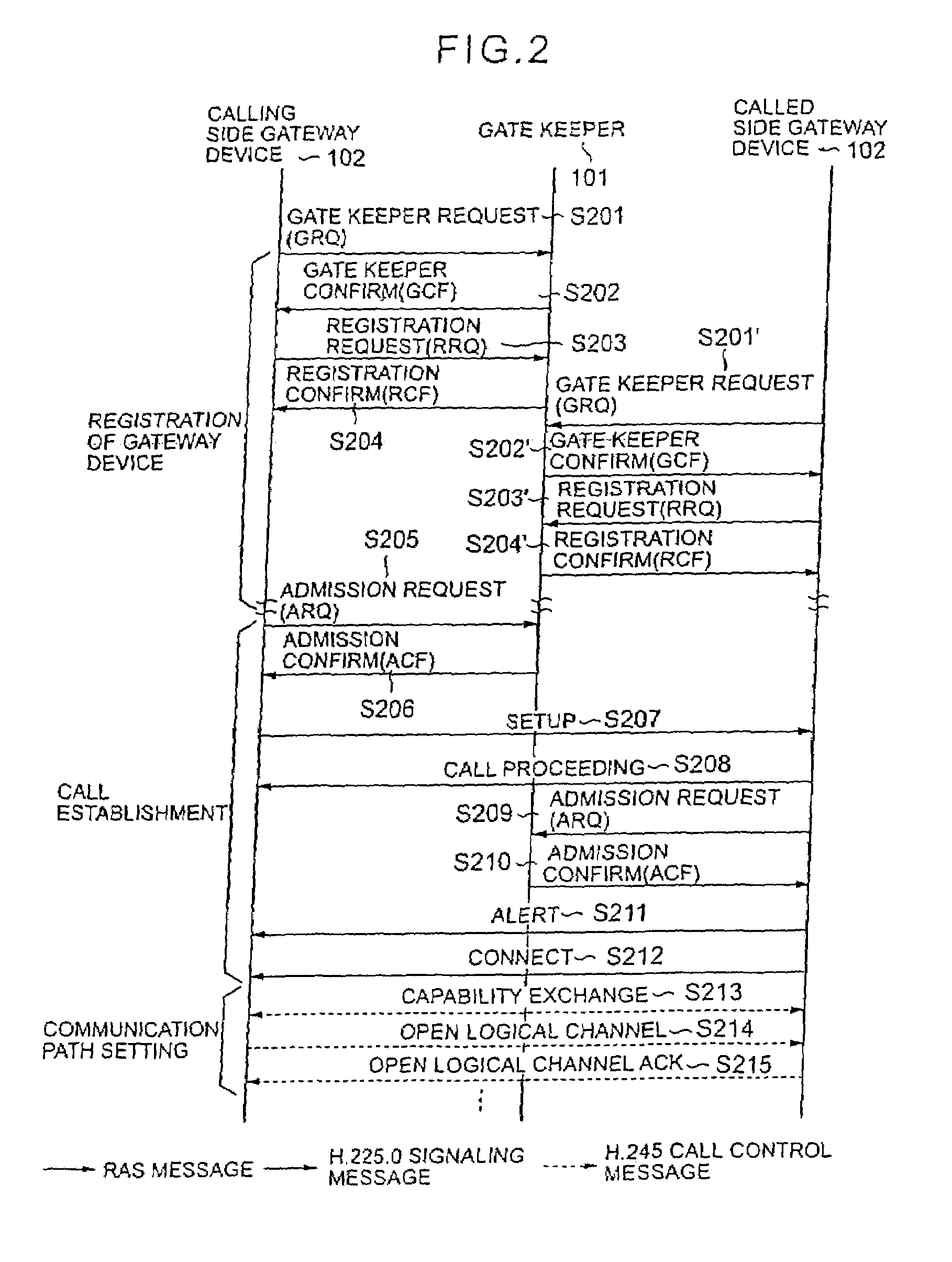
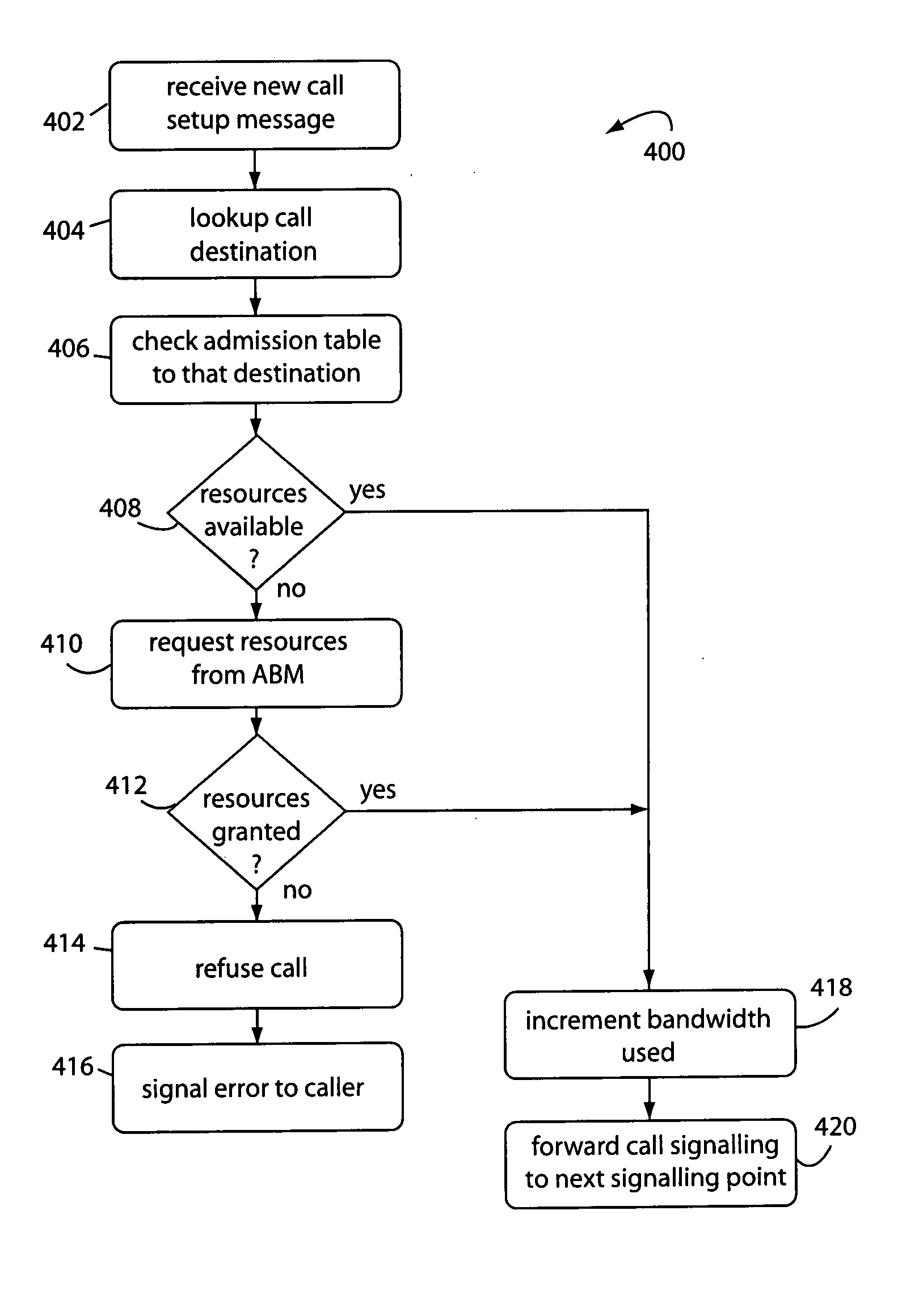
Internet telephone connection method, bandwidth controller and gate keeper
InactiveUS7272134B2Improve reliabilityFlexibly variationInterconnection arrangementsTelevision system scanning detailsCommunication qualityGate-keeper
In an Internet telephone connection method, a communication bandwidth is managed by using a bandwidth controller, gateway devices and voice relay routers to monitor communication quality under bandwidth reservation. A communication path under bandwidth reservation is preferentially selected by using gate keepers and the voice relay routers, and the connection of the Internet telephone is performed. A problematic device is prohibited from being selected as a connection-destination device at the time of a call setup and the problem restoration is monitored by using the gate keepers and the gateway devices. Further, a device having invalid attribute information is prohibited from being selected as a connection-destination device at the time of call-setup, and the restoration of the attribute information is notified to the overall network. Accordingly, the reservation of the communication bandwidth can be performed under the control of the overall network, fixed communication quality can be maintained and reliability can be enhanced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
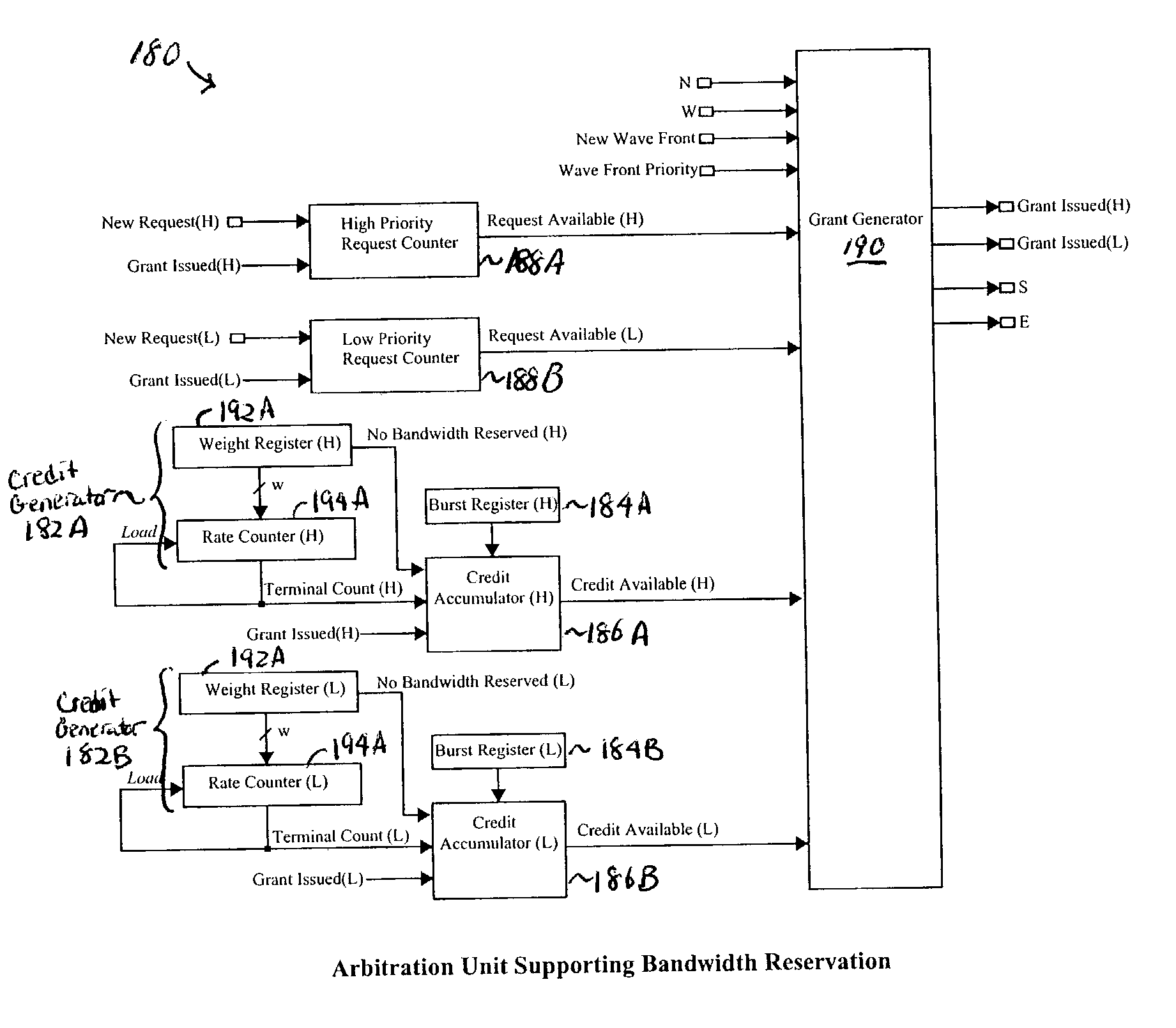
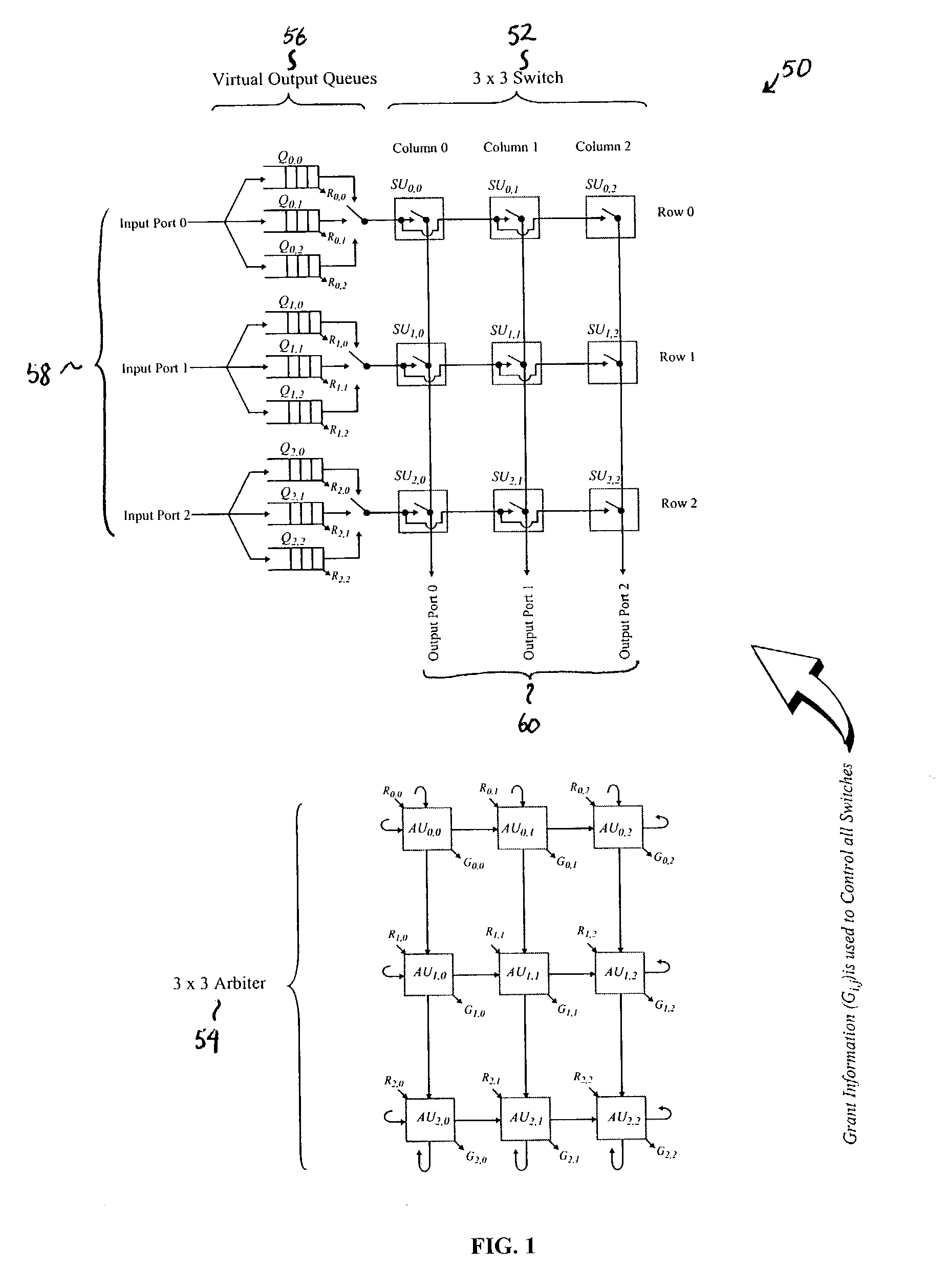
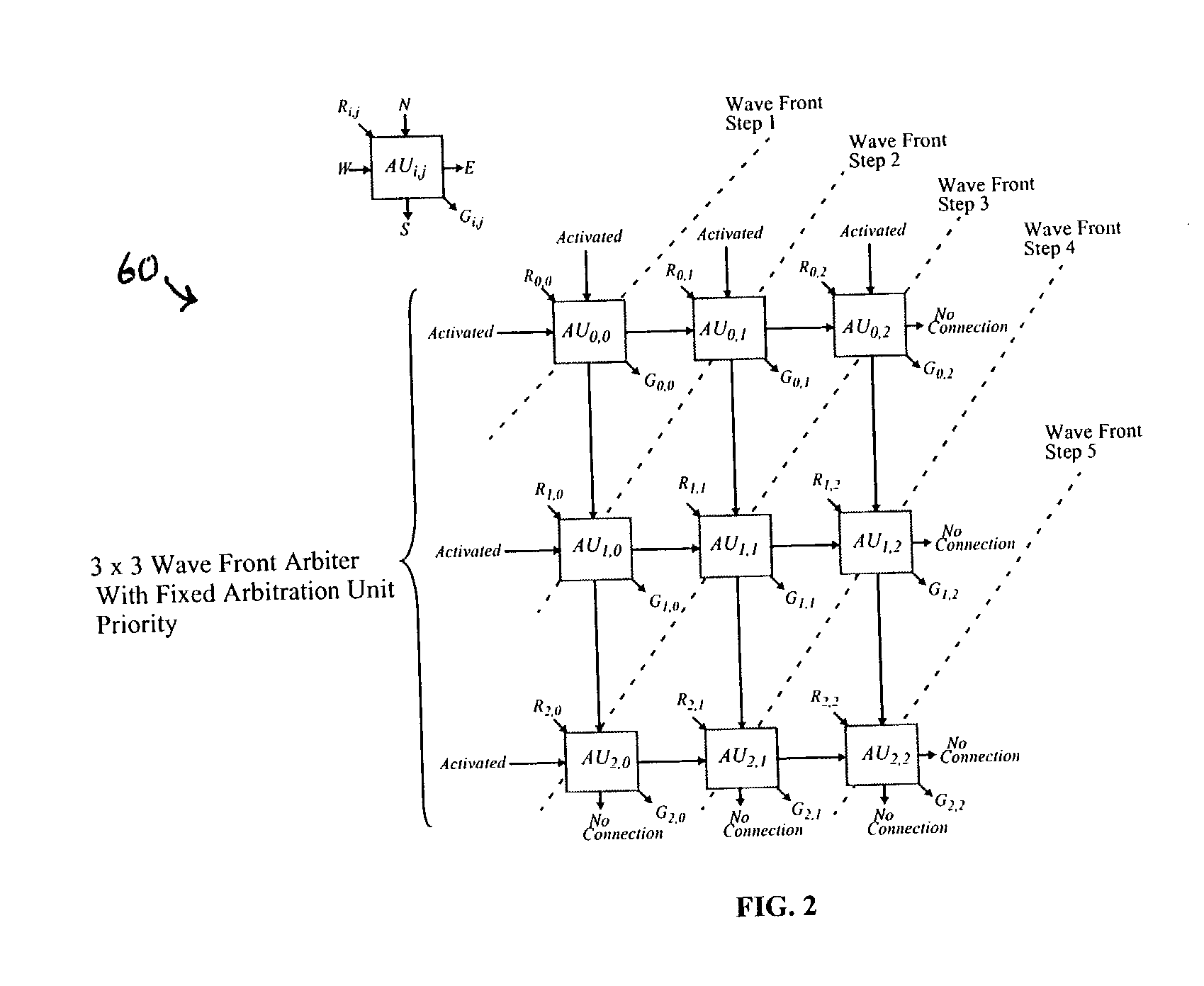
Cell based wrapped wave front arbiter (WWFA) with bandwidth reservation
InactiveUS20040085967A1Data switching by path configurationCircuit switching systemsProcessor registerCell based
A system and method for a cell based wrapped wave front arbiter (WWFA) with bandwidth reservation are disclosed. The method for reserving bandwidth of a given priority using the WWFA for arbitrating bandwidth among virtual links between input and output ports, each virtual link supporting one or more priorities and corresponding to an arbitration unit (AU) of the WWFA generally comprises performing at least one arbitration pass of a wave front of the WWFA where AUs having a reserved bandwidth request of a given priority and reserved bandwidth credit of the given priority compete for the bandwidth associated with the wave front, and where AUs not having a reserved bandwidth request of the given priority and reserved bandwidth credit of the given priority do not compete for the bandwidth, and performing at least one subsequent arbitration pass where AUs having a reserved bandwidth request of the given priority compete for the bandwidth. Each virtual link preferably supports a high priority and a low priority such that the WWFA performs four passes. Each priority of each virtual link may be associated with a bandwidth credit accumulator register indicating the level of remaining reserved bandwidth credit, if any, a reserved bandwidth weight register for programming a predetermined level of reserved bandwidth, a request counter register for tracking the number of bandwidth requests, a rate counter register that is periodically incremented to generate reserved bandwidth credits for the bandwidth credit accumulator register, and an optional burst register having a predetermined value for limiting the maximum value of the bandwidth credit accumulator register.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
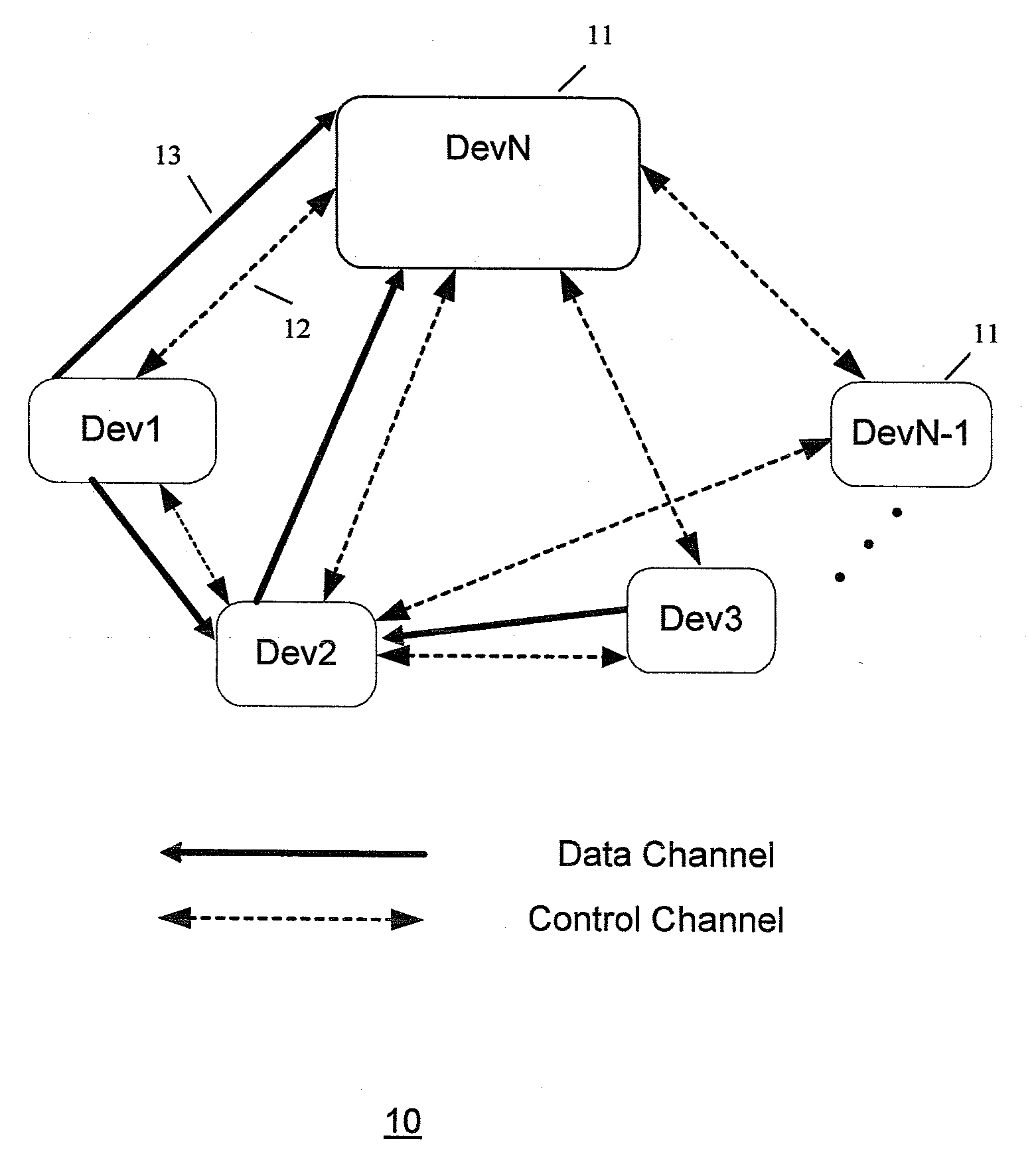
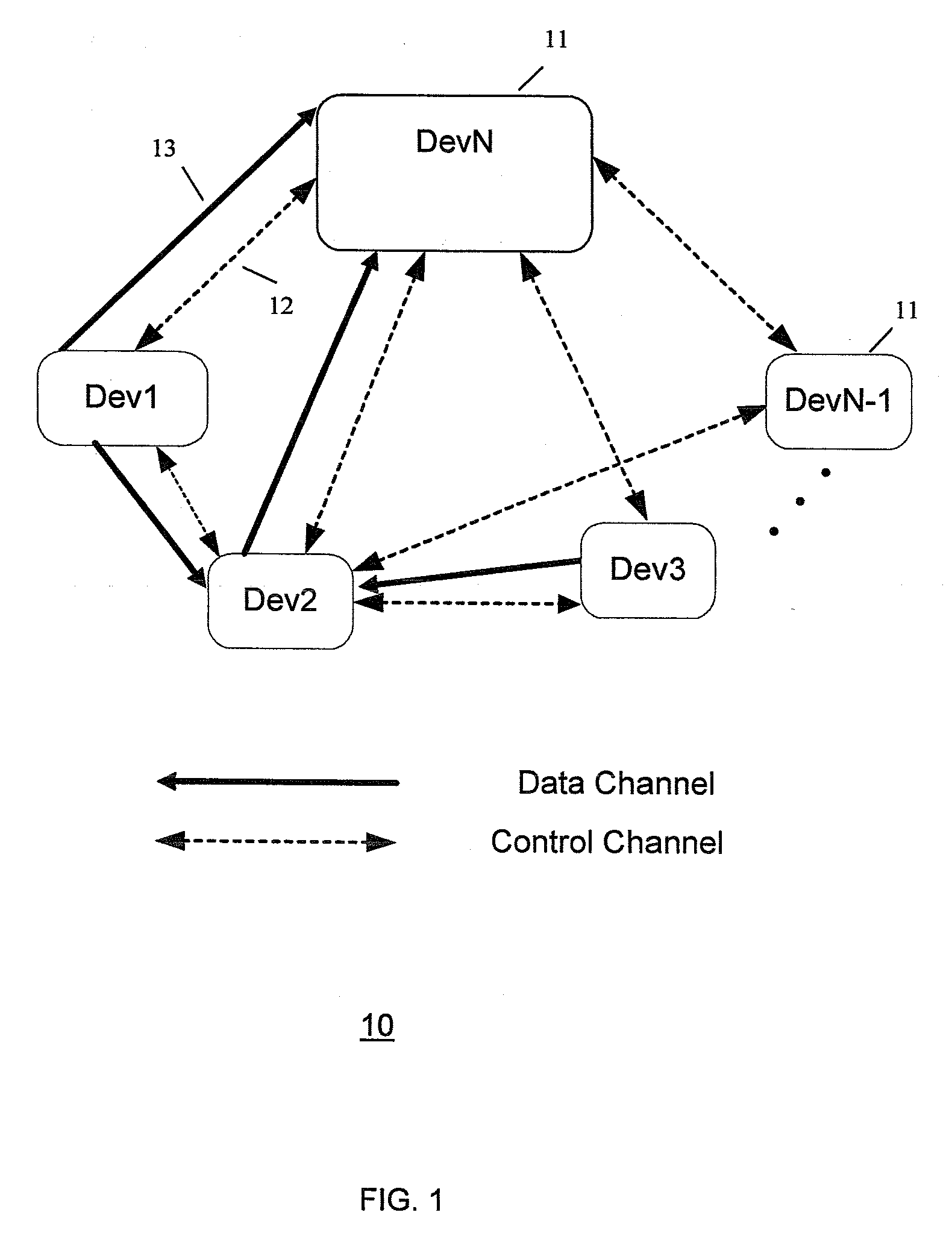
Multi-hop ultra wide band wireless network communication
InactiveUS7941149B2Promotes its utilizationHigh bandwidthError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementThroughputWireless network
A wireless communication system is provided that has at least three nodes arranged in a multi-hop ultra wide band (UWB) communication network such that communications from a first node destined for a third node pass through a second node. Each of the devices in the system includes a radio and a media access control (“MAC”) module that is configured to establish multi-hop UWB wireless communications between the three or more wireless communication devices that enables high bandwidth applications such as Voice Over Internet Protocol (“VoIP”); multiplayer gaming; Wireless High Definition Television; and Internet Protocol Television (“IPTV”) among others. The MAC module is configured to avoid bandwidth reservation conflicts so that network performance does not degrade as the number of hops or the number of nodes in the wireless communication system increases. The MAC also facilitates utilization of multiple channels to maximize the available spectrum and is further configured to dynamically switch between channels to maximize throughput and meet or exceed quality of service (“QoS”) requirements such that QoS is guaranteed and network resources are efficiently utilized.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Method and system for controlling utilisation of a file system
A method for preventing oversubscription to a file storage by multiple processes, whether such processes are operating on one node with directly attached storage or on several nodes of a computing cluster sharing a storage area network. Processes or nodes issue requests for bandwidth reservations to a controller daemon. The controller daemon maintains records of all existing bandwidth reservations and ensures that new reservations are granted only if a qualified bandwidth of the file storage will not be exceeded. The qualified bandwidth is empirically determined to take into account installation specific hardware configurations, workloads, and quality of service requirements. In conjunction with suitable enabled client kernels the controller daemon serves to encapsulate all I / O activity including non-reserved I / O activity to the file storage by issuing non-guaranteed bandwidth leases for use by each node in servicing non-guaranteed process I / O activity, such leases being revokable by the controller daemon in order to service new guaranteed bandwidth reservation requests.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
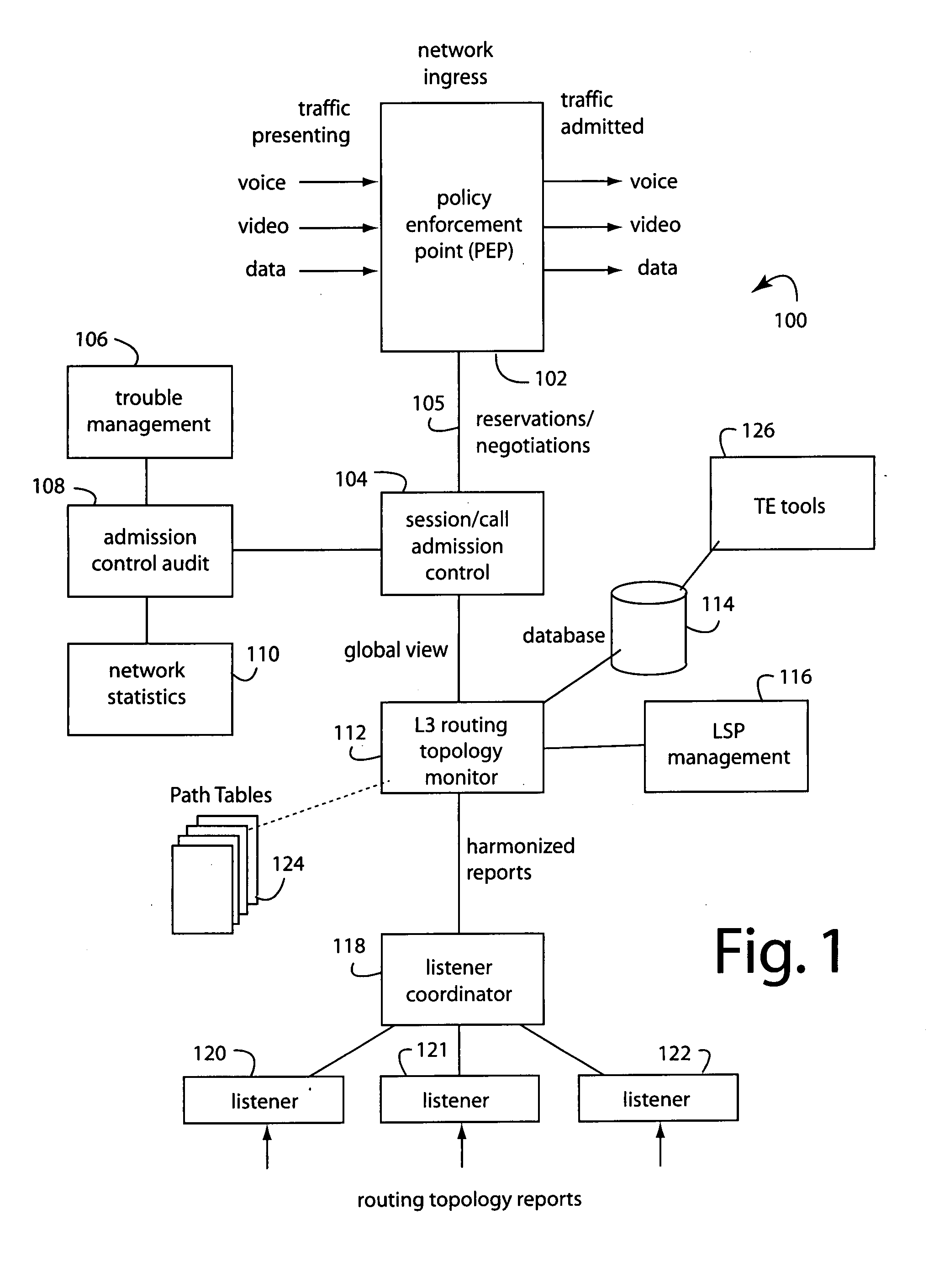
Under-assigning resources to video in triple-play virtual topologies to protect data-class traffic
ActiveUS20080225706A1Low costEasy to planError preventionTransmission systemsShort termsData traffic
A method for video-on-demand (VoD) admission control at a network edge assigns to a triple-play network virtual topology lesser resources than there exists in a corresponding underlying physical link bandwidth. This prevents video-on-demand (VoD) starvation of data-class traffic. At least one policy enforcement point (PEP) is attached to an edge of the network, providing for autonomous short-term, application-aware controls to be applied to corresponding network ingress traffic, and also providing for long-term controls on corresponding network ingress traffic. The network ingress traffic to the network comes under management when the traffic nears or exceeds network capacity. It is enabled to do so by computations of current network routing topology and bandwidth reservations. Path tables are used to calculate if a PEP may admit more, or must shed, sessions / calls to maintain service for other existing application traffic. The PEP and a session / call admission controller (S / CAC) may be independently located within the topology of the network, and together implement admission controls that differentiate between triple-play video, voice, and data traffic classes.
Owner:RPX CORP
Communication system to which multiple access control method is applied
InactiveUS6850489B1Efficient use ofShorten the timeTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemNetwork packet
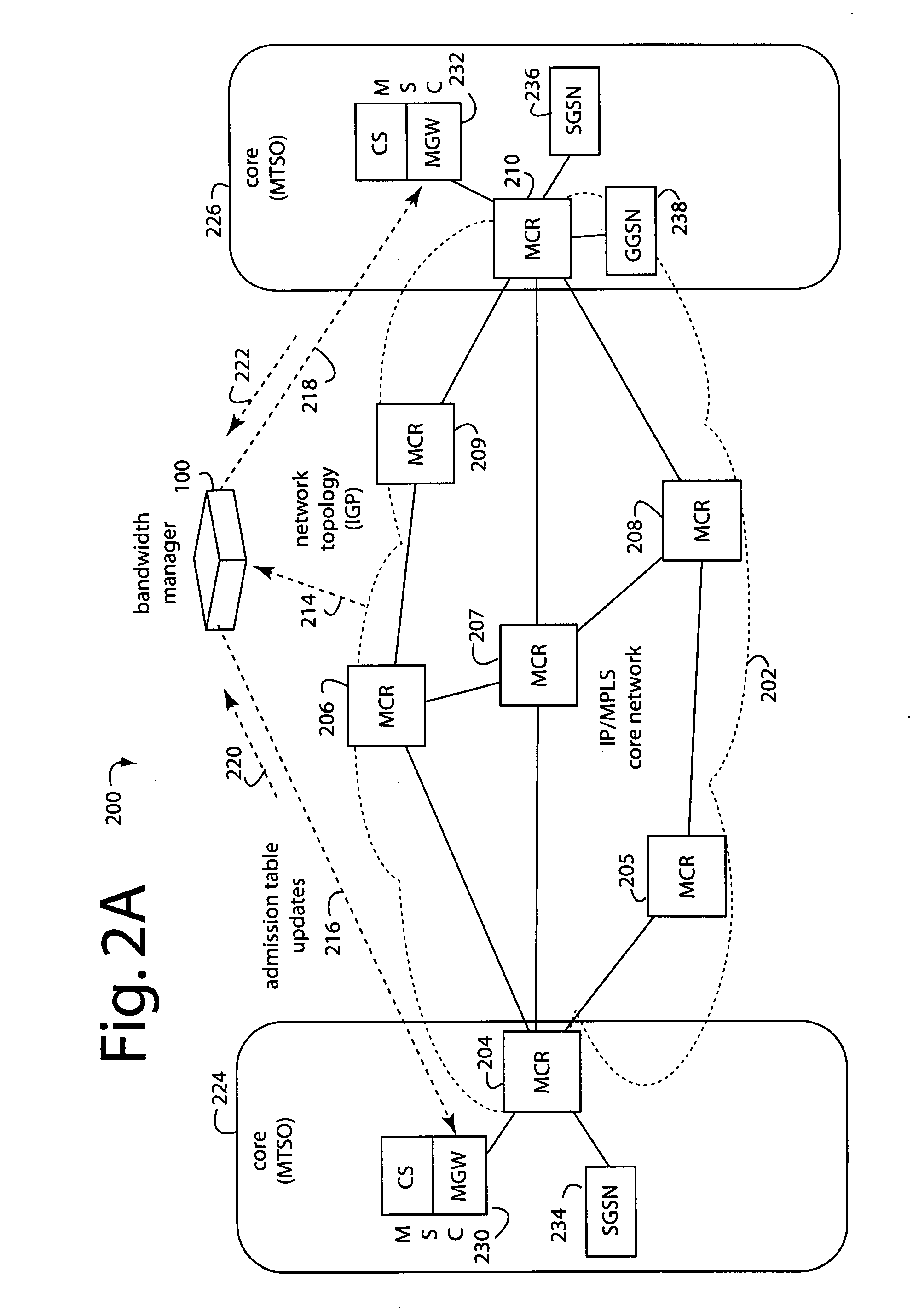
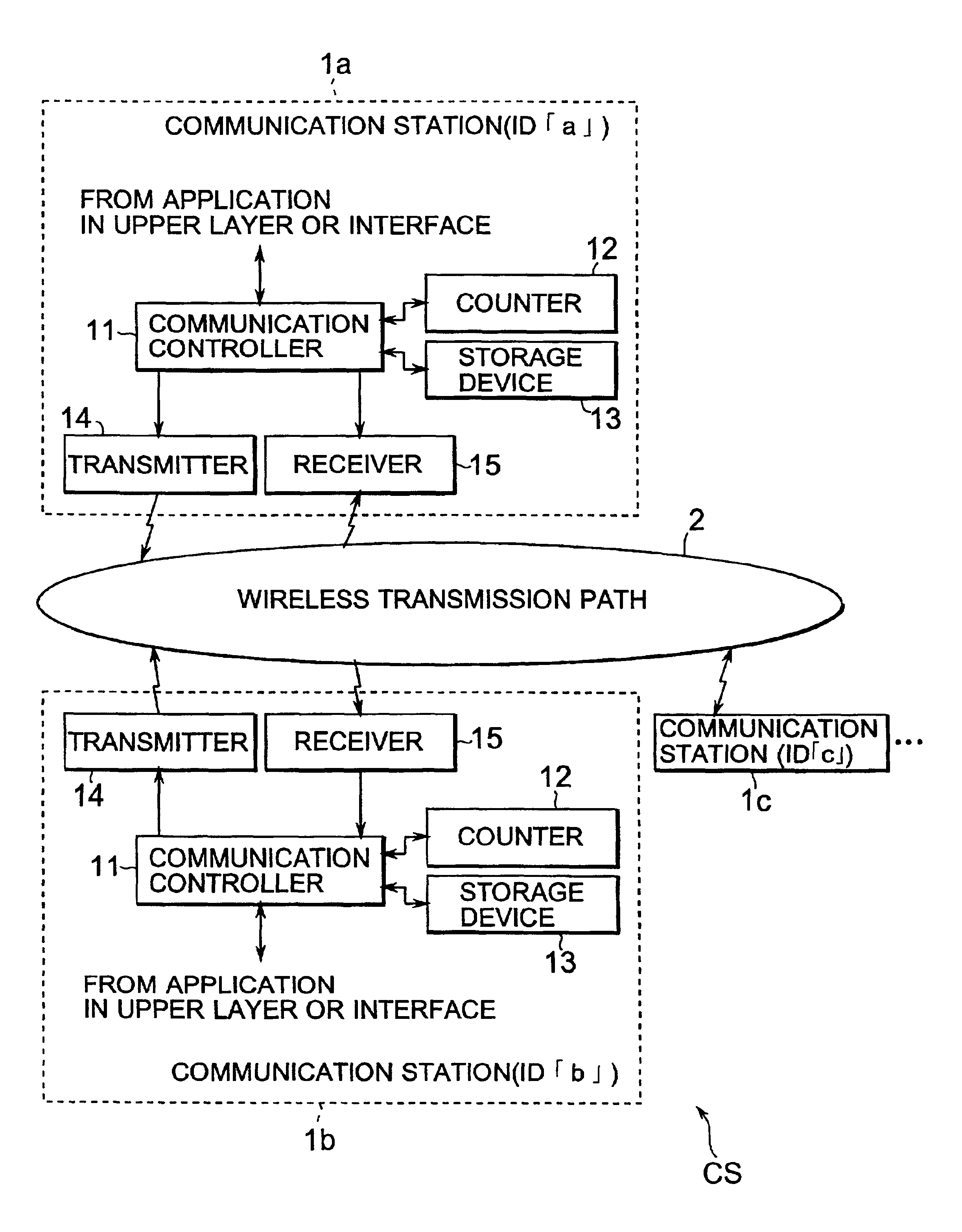
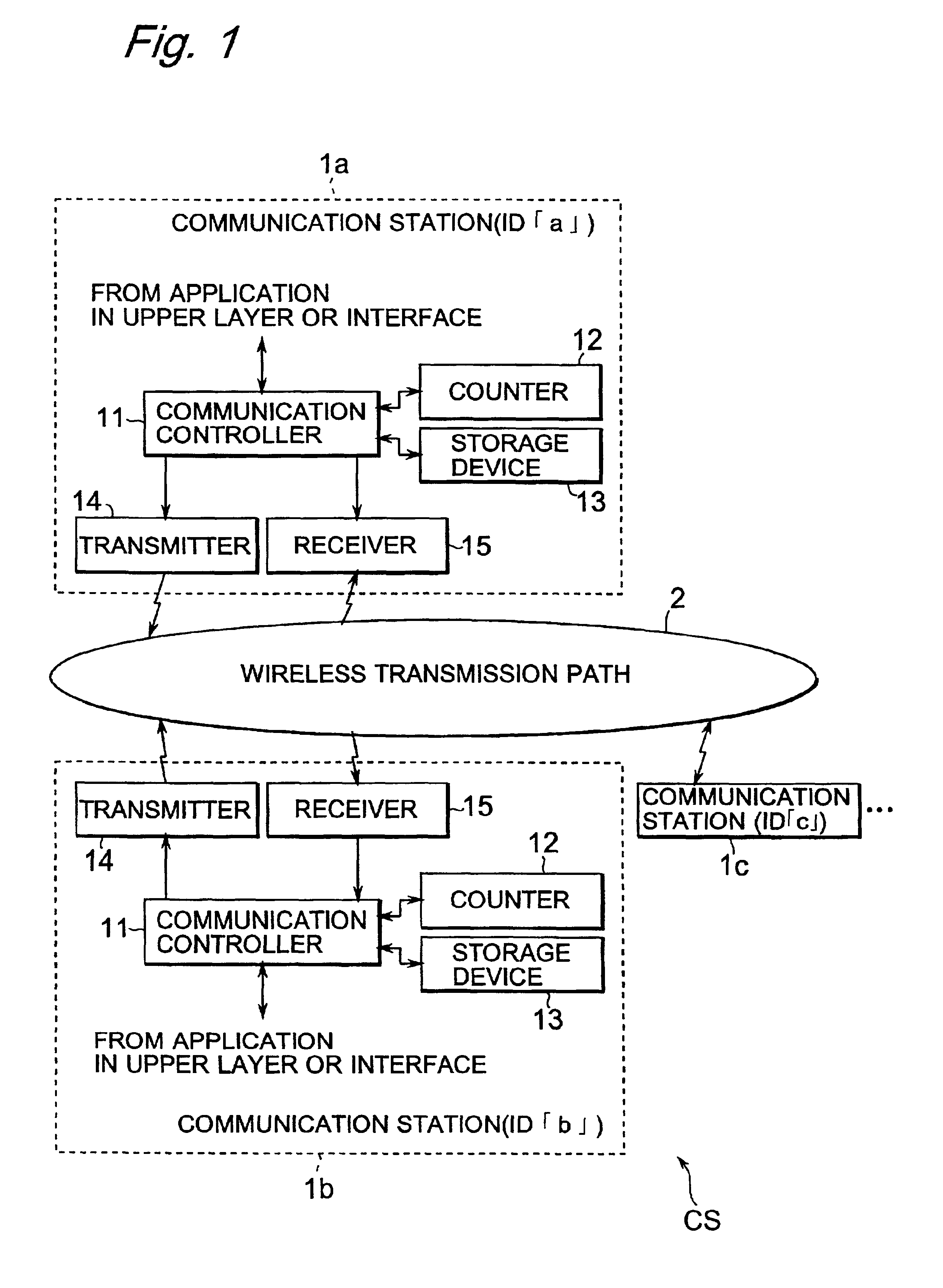
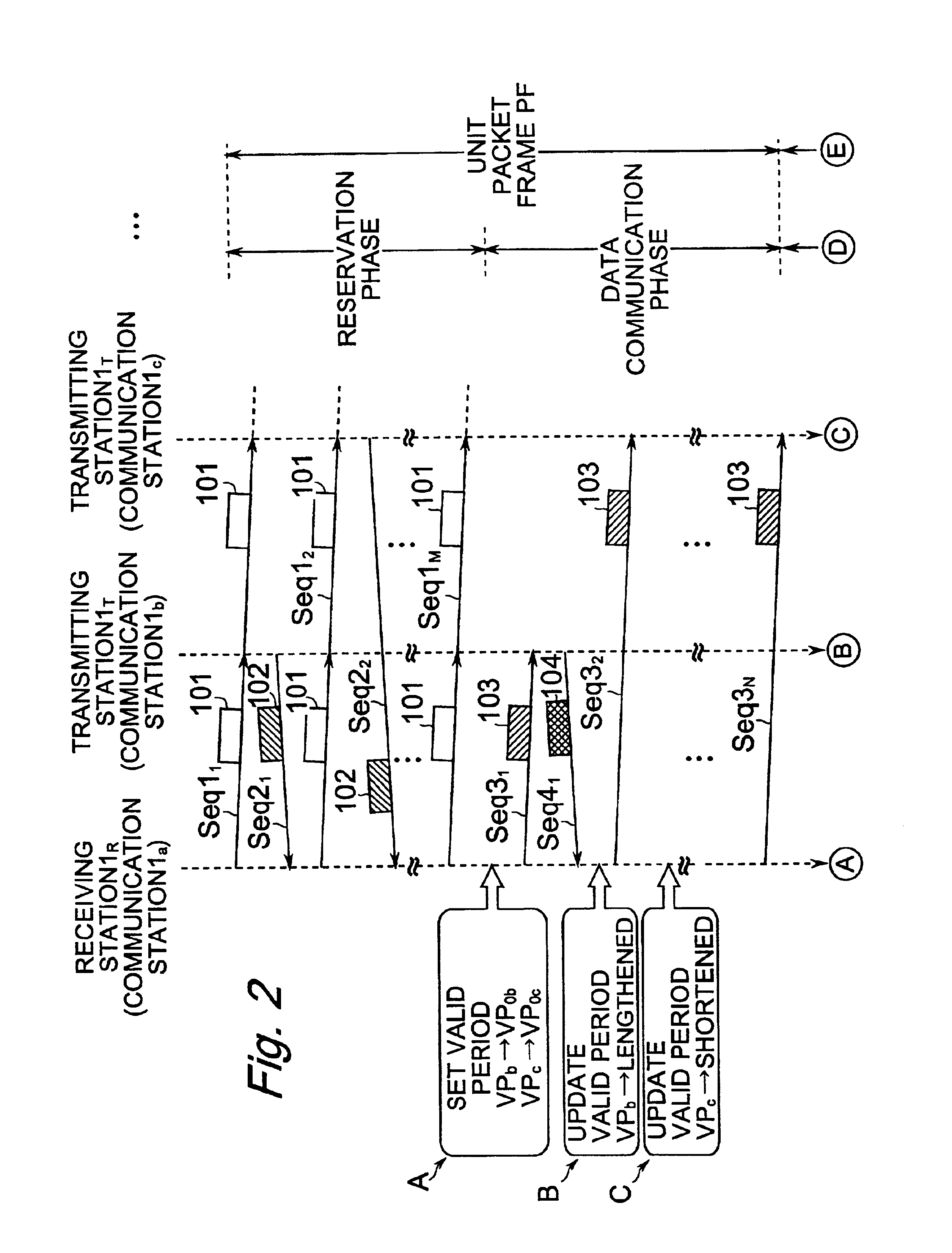
A communication system CS includes a plurality of communication stations and data communication is performed between any two communication stations, one is a transmitting station and the other is a receiving station. When any data for transmission is generated, the transmitting station transmits, to the receiving station, a reservation request packet for requesting bandwidth reservation. The receiving station reserves a bandwidth responding to the reservation request packet and then transmits a communication reservation packet to inform the transmitting station of the reserved bandwidth. The transmitting station creates a data packet and then transmits the created data packet through the informed bandwidth. The receiving station stores a valid period of the bandwidth reserved for the transmitting station, and voluntarily and repeatedly creates, for transmission, the communication reservation packet for the duration of the stored valid period. Accordingly, a communication system in which time for bandwidth reservation is shortened and thus bandwidths are effectively utilized is implemented.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
TCP congestion control method for bandwidth reservation network
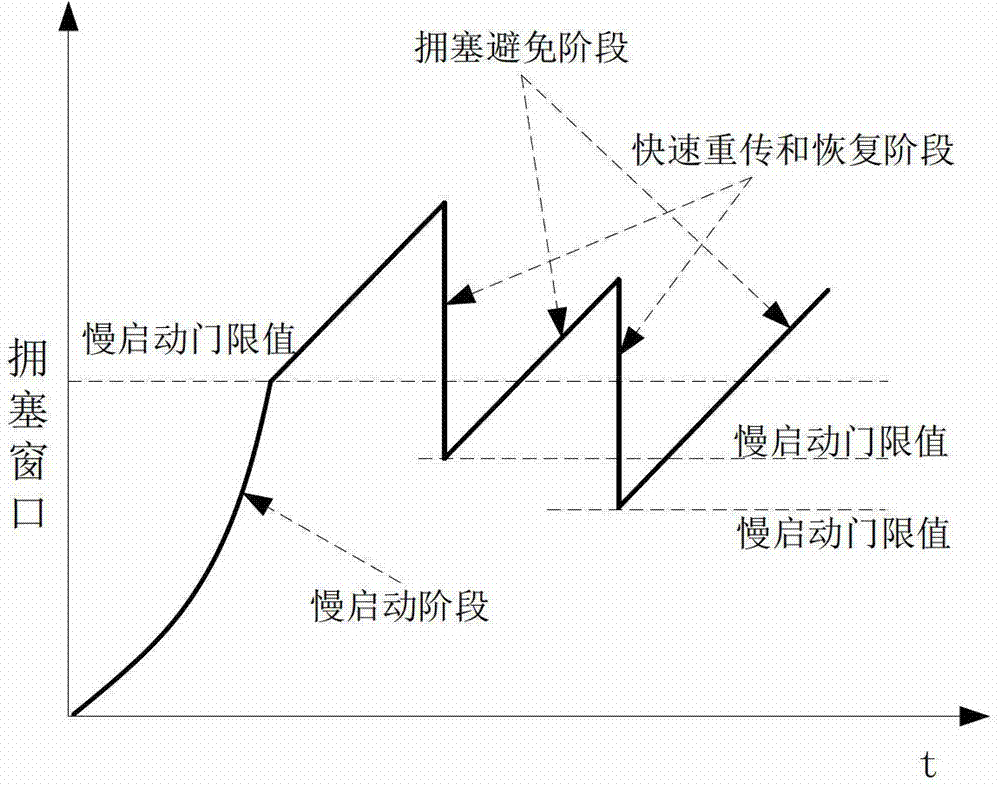
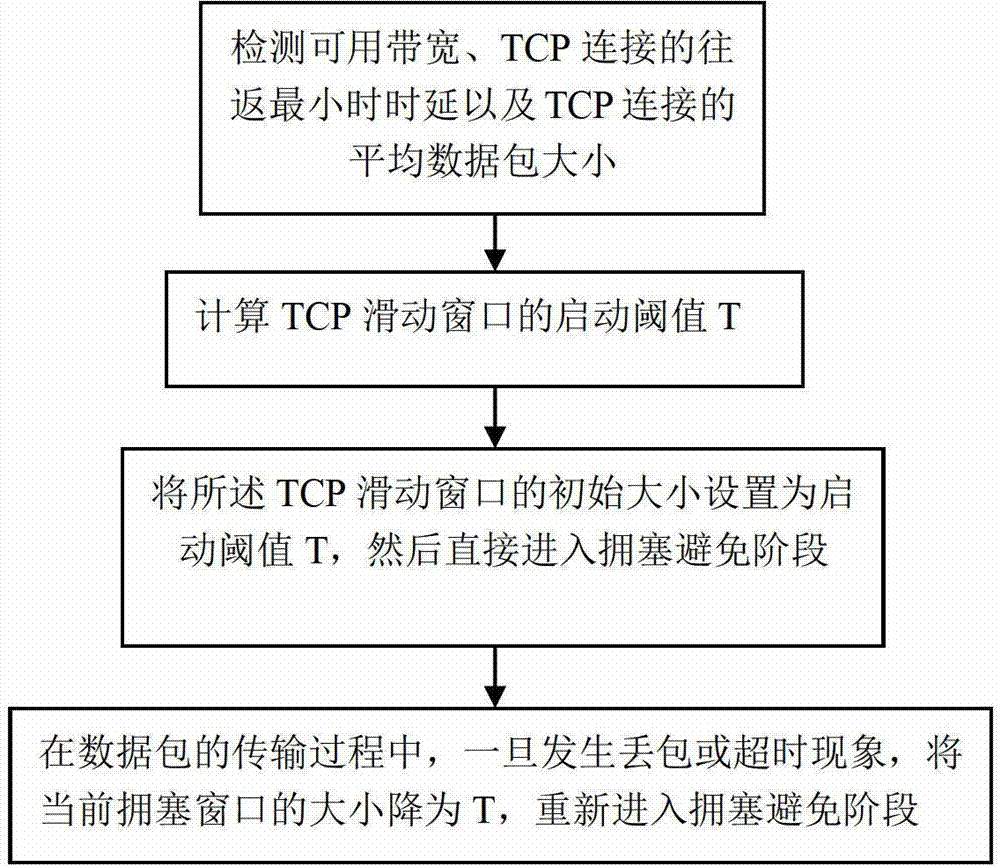
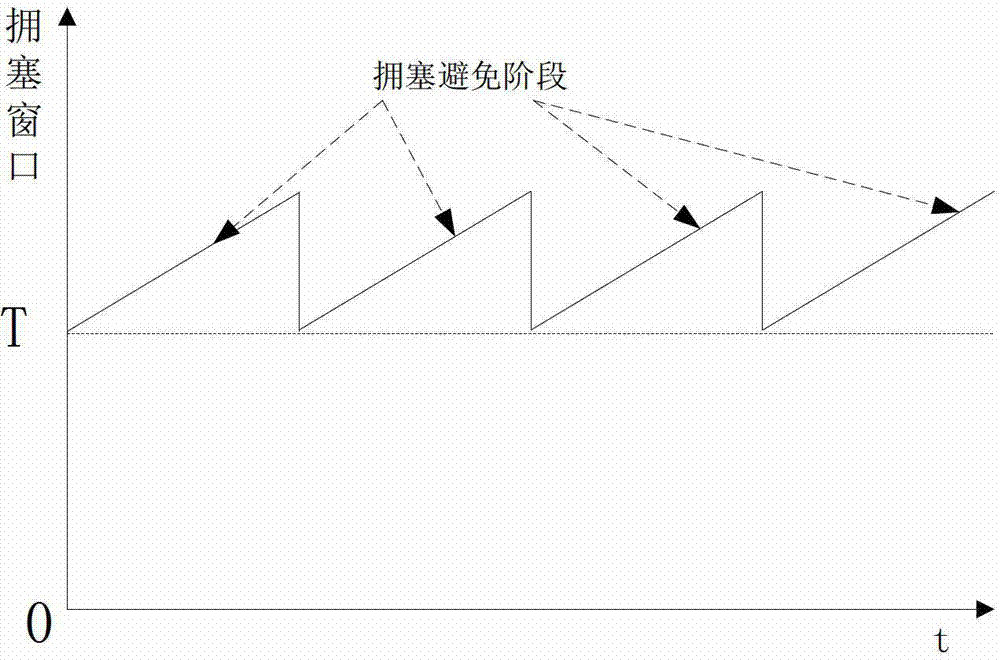
The invention relates to a TCP congestion control method for a bandwidth reservation network. The method comprises the steps of detecting the current usable bandwidth in a network link, the minimum round-trip delay for TCP connection, and the average data packet size for TCP connection; calculating the starting threshold T of a TCP sliding window according to the usable bandwidth, the minimum round-trip delay and the average data packet size; setting the initial size of the TCP sliding window as the starting threshold T and directly entering the congestion avoiding stage; reducing the size of the current congestion window to be T and reentering the congestion avoiding stage once packet loss or timeout occurs during data packet transmission.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
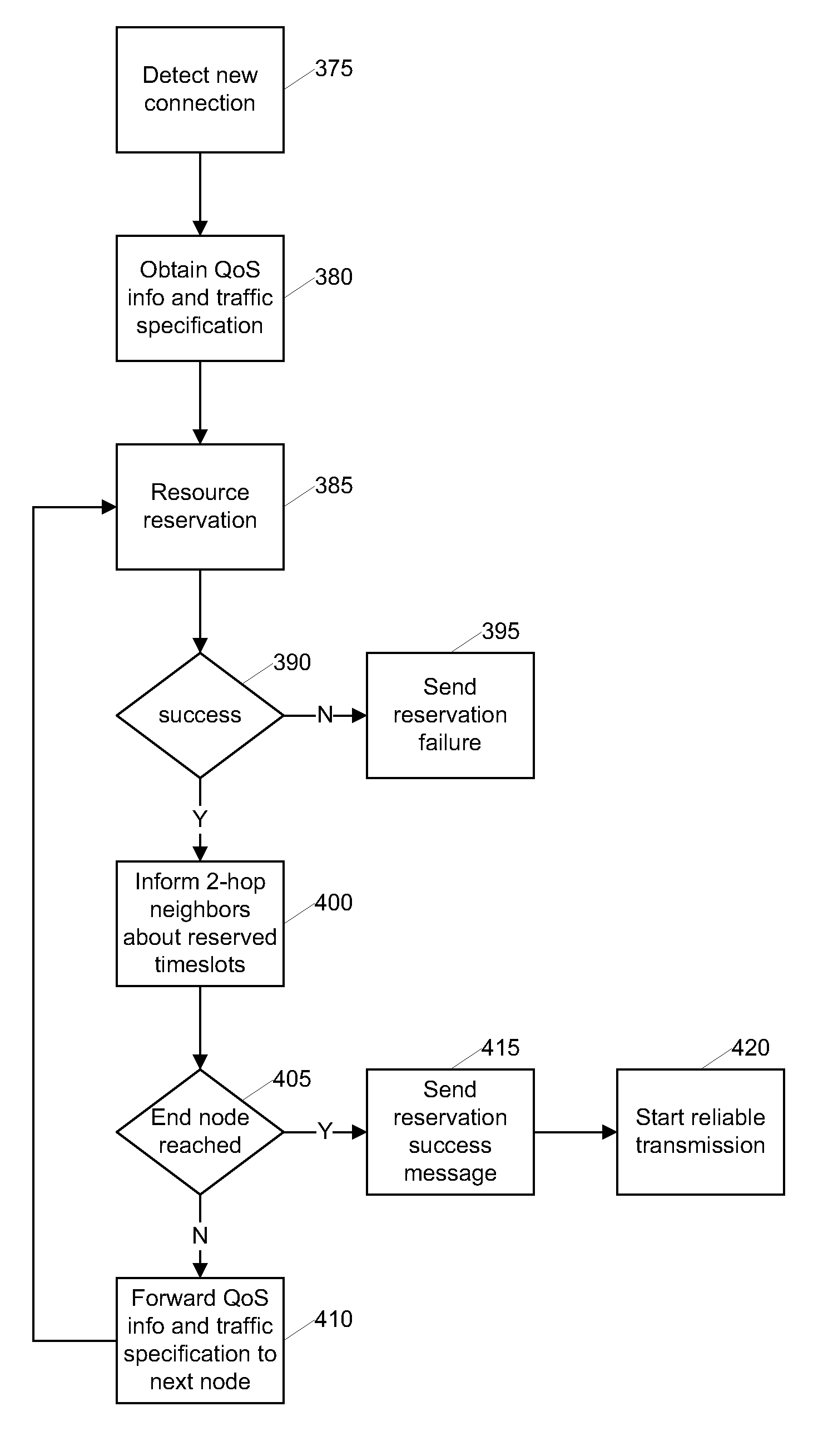
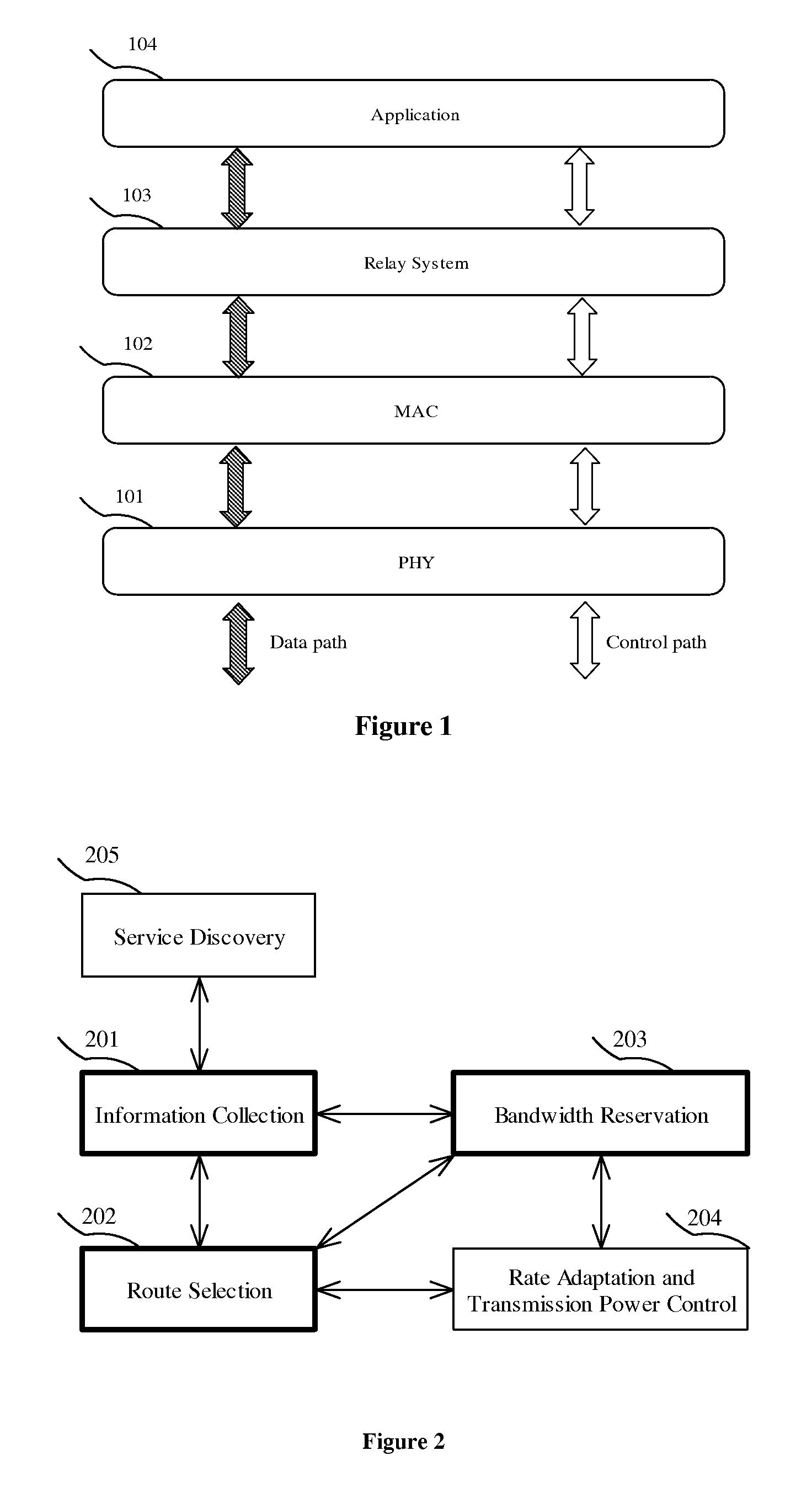
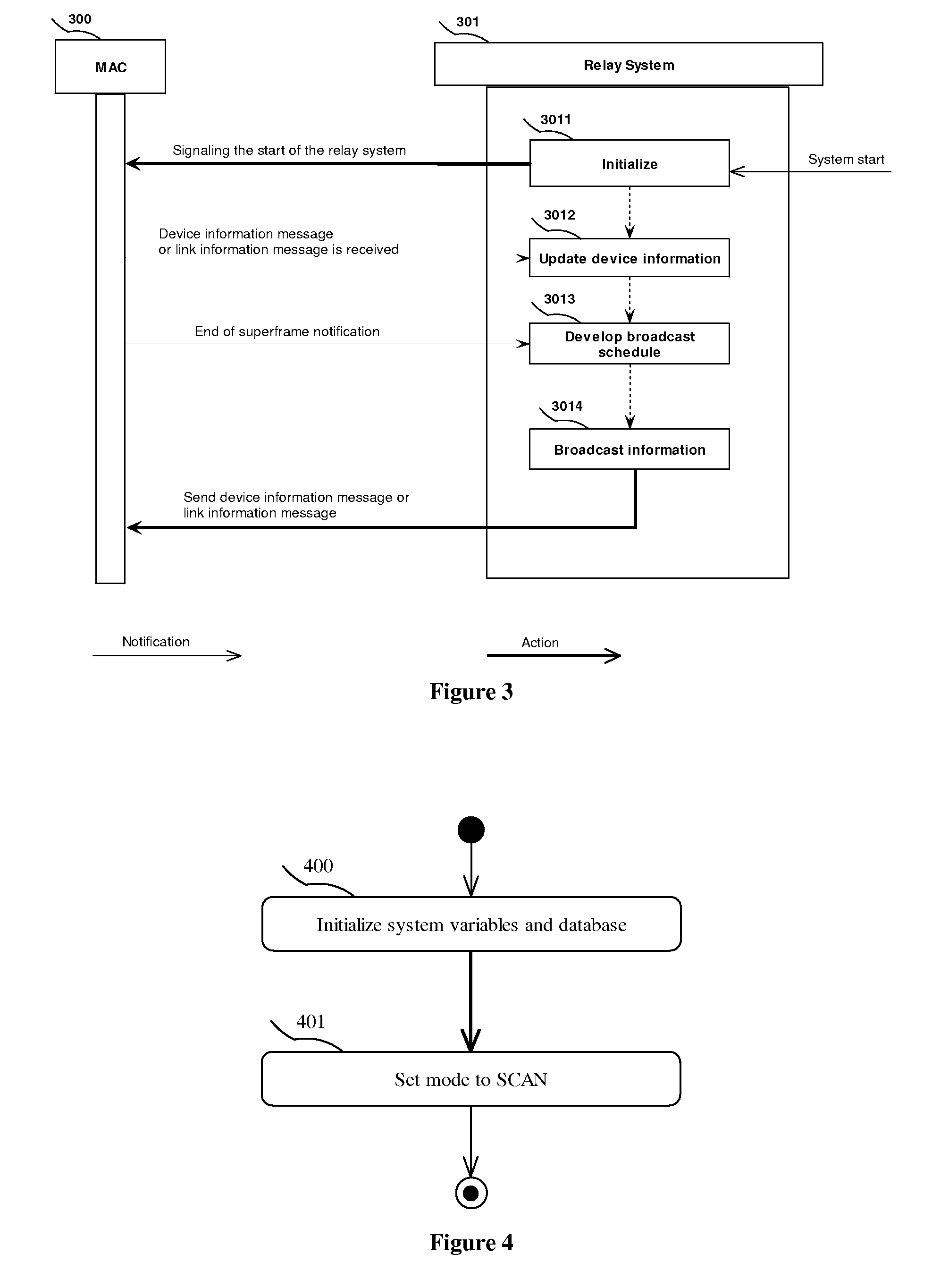
Method and Device for Data Routing and Bandwidth Reservation in Small Scale Distributed Networks
InactiveUS20090147723A1Reduce communication overheadEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsBroadcast schedulingNetwork topology
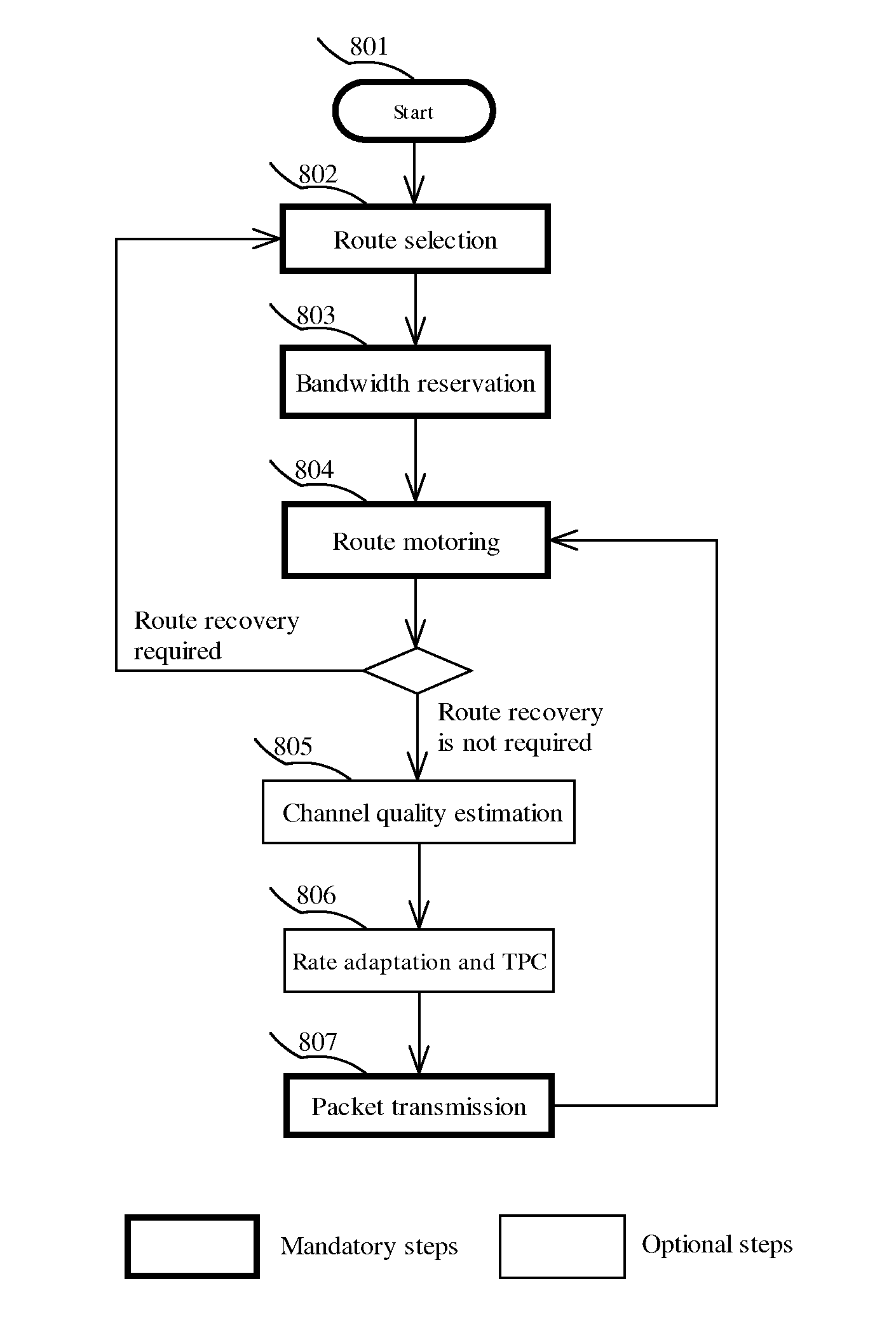
A data routing and / or bandwidth reservation method for small scale distributed network in which each member has a topological view of the whole network. Route selection is performed at a source member and bandwidth reservation is conducted along the selected route. Upon start up or joining the network each member of the network establishes and maintains a list of information for all other devices in the network, which serves as a topological view of the network. To reduce communication overhead during information collection, a priority based broadcast scheduling is adopted. When a device intends to establish a connection with another device it selects a route based on its own preference and current network topology. The device then reserves bandwidth along the selected route. Bandwidth reservation uses a mutually exclusive bandwidth reservation protocol which guarantees only one application can reserve bandwidth at a time.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com