Patents
Literature
341 results about "Message switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
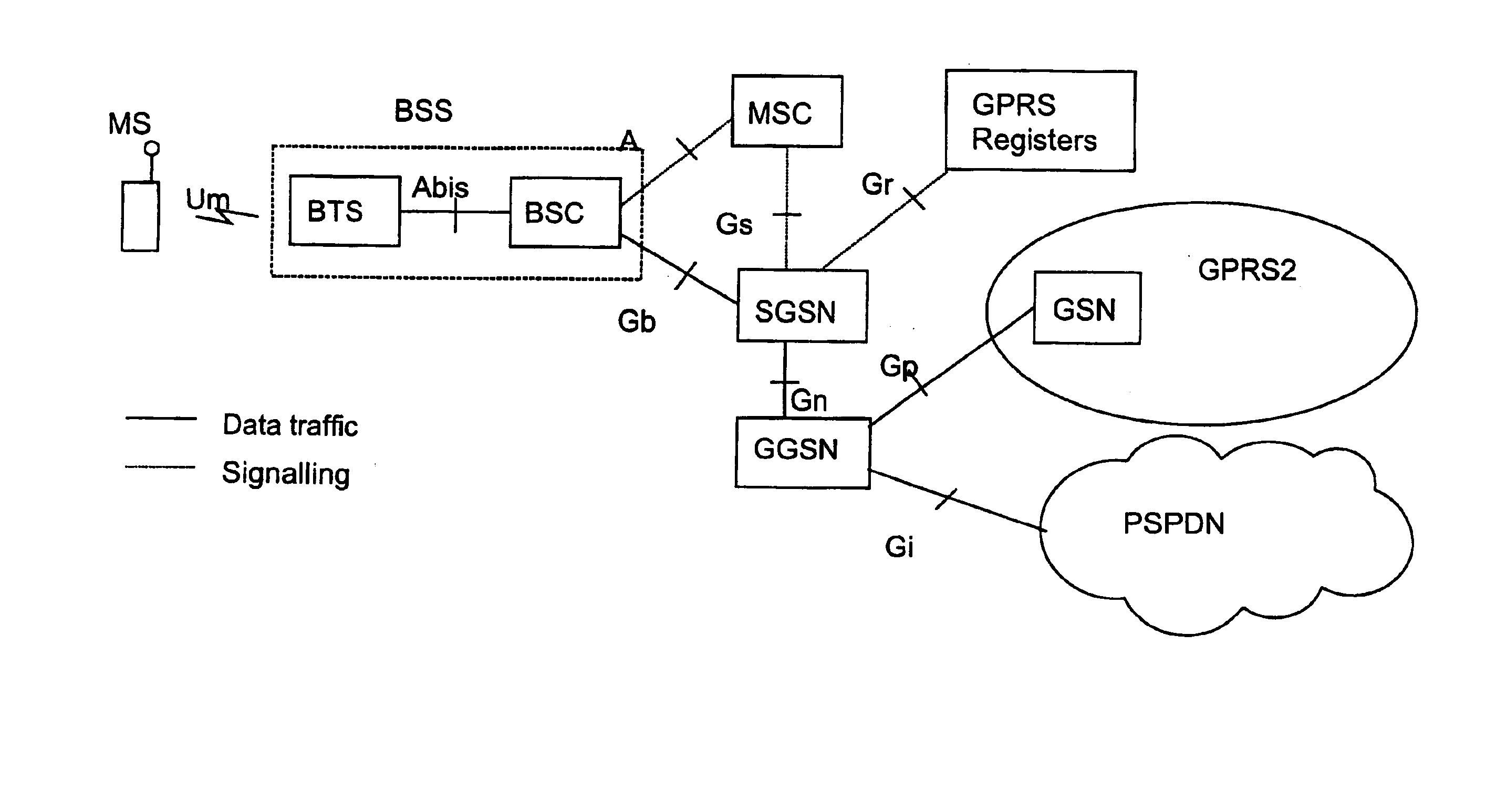
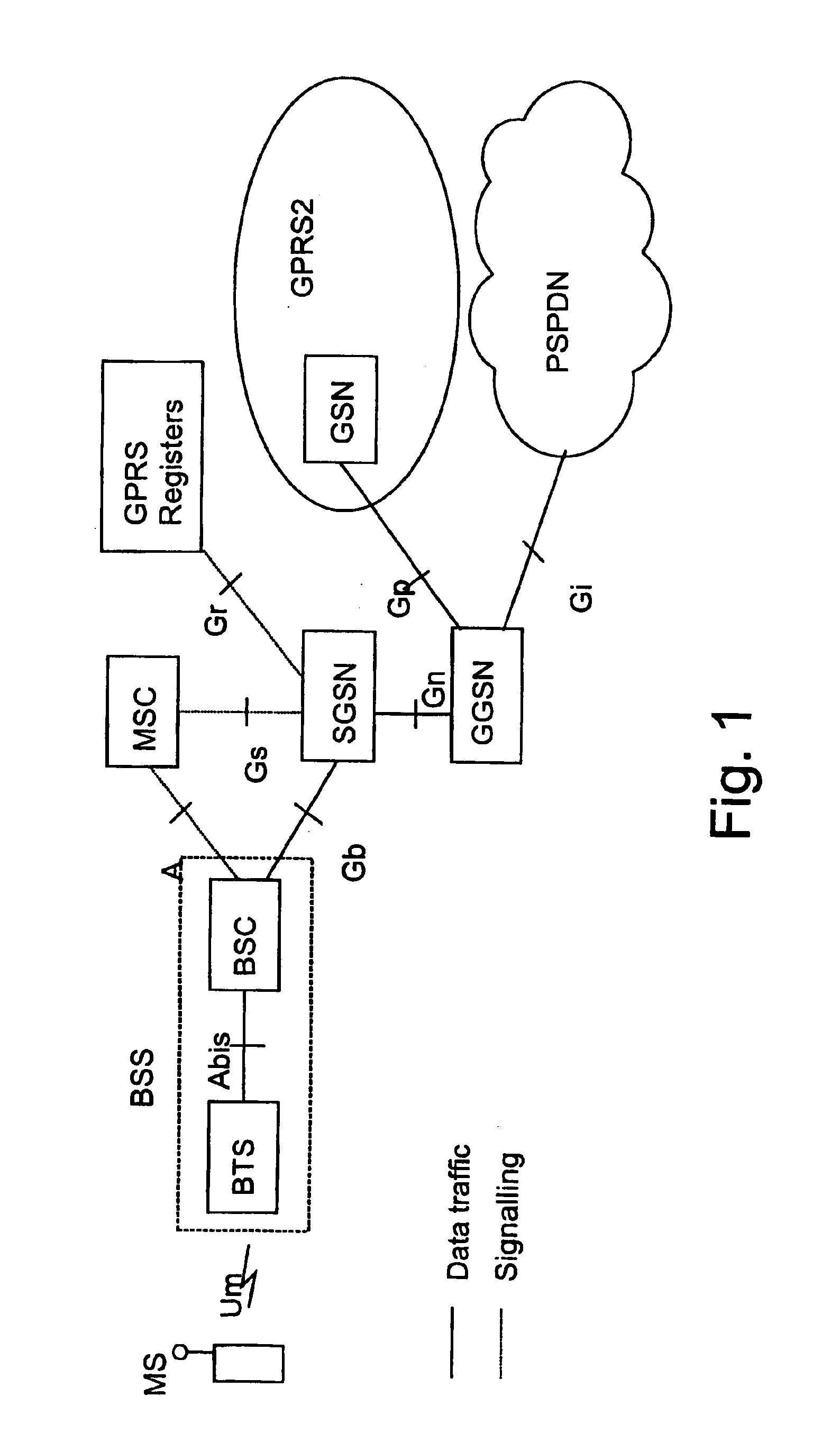
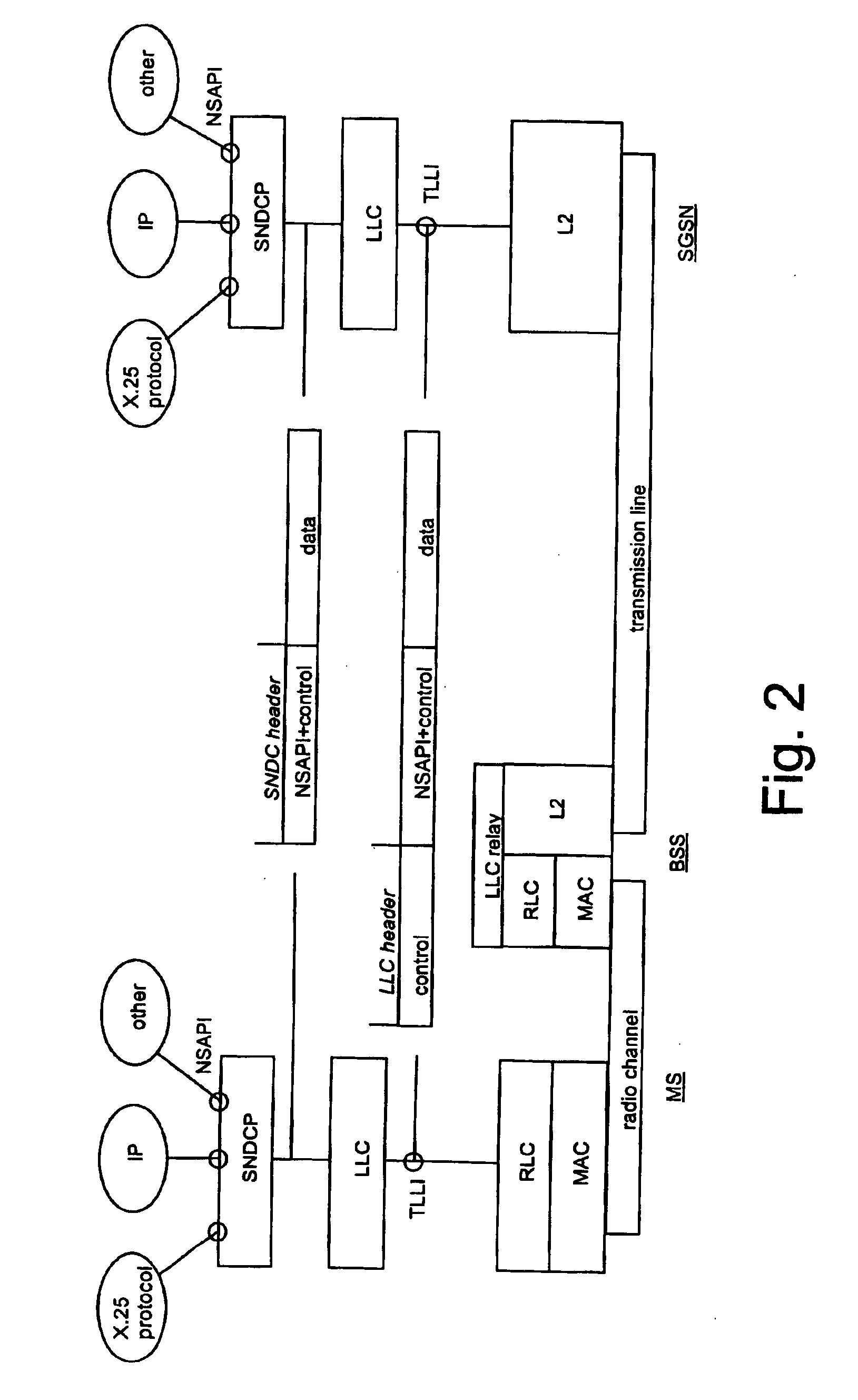
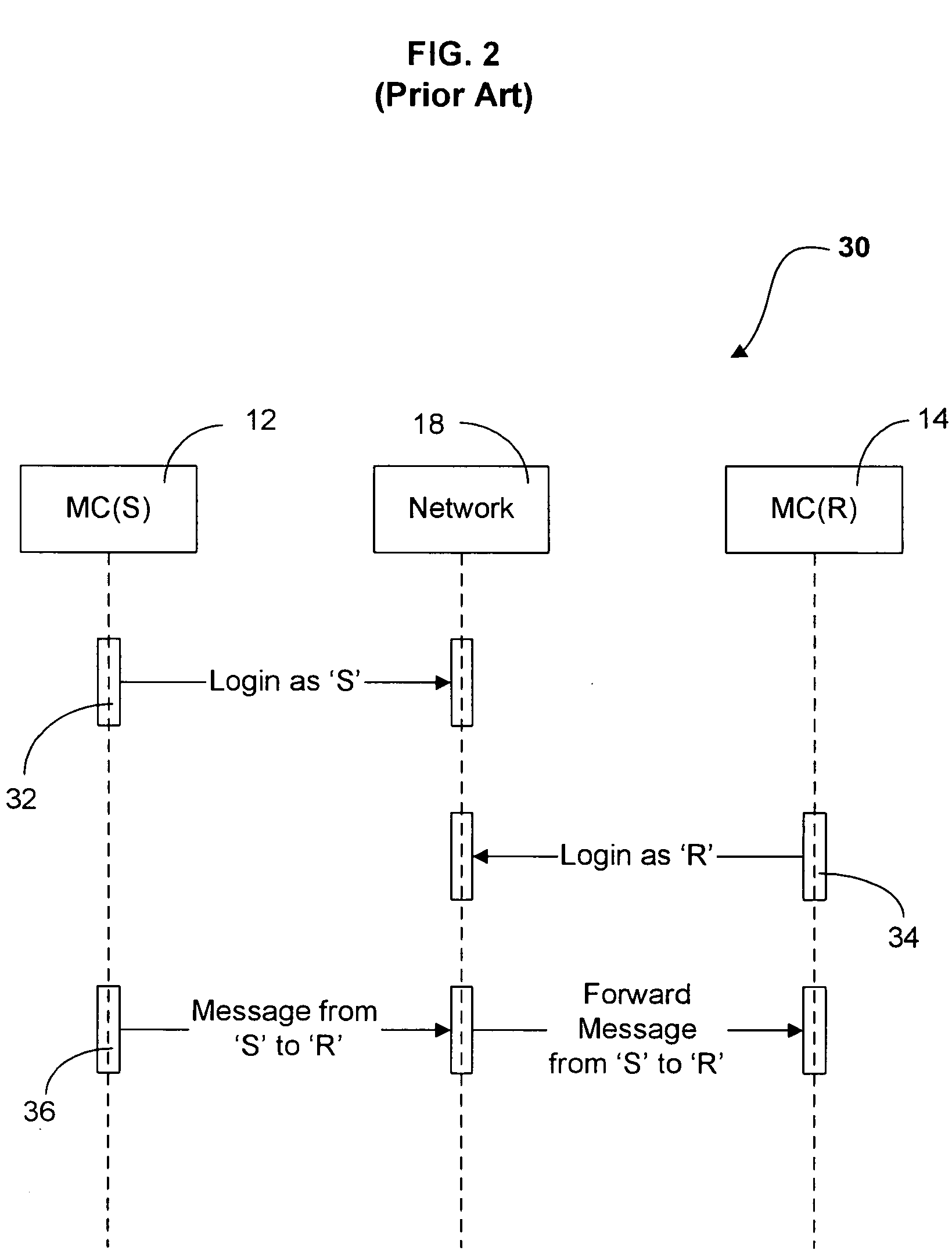
In telecommunications, message switching was the precursor of packet switching, where messages were routed in their entirety, one hop at a time. It was first built by Collins Radio Company, Newport Beach, California, during the period 1959–1963 for sale to large airlines, banks and railroads. Message switching systems are nowadays mostly implemented over packet-switched or circuit-switched data networks. Each message is treated as a separate entity. Each message contains addressing information, and at each switch this information is read and the transfer path to the next switch is decided. Depending on network conditions, a conversation of several messages may not be transferred over the same path. Each message is stored (usually on hard drive due to RAM limitations) before being transmitted to the next switch. Because of this it is also known as a 'store-and-forward' network. Email is a common application for message switching. A delay in delivering email is allowed, unlike real-time data transfer between two computers.
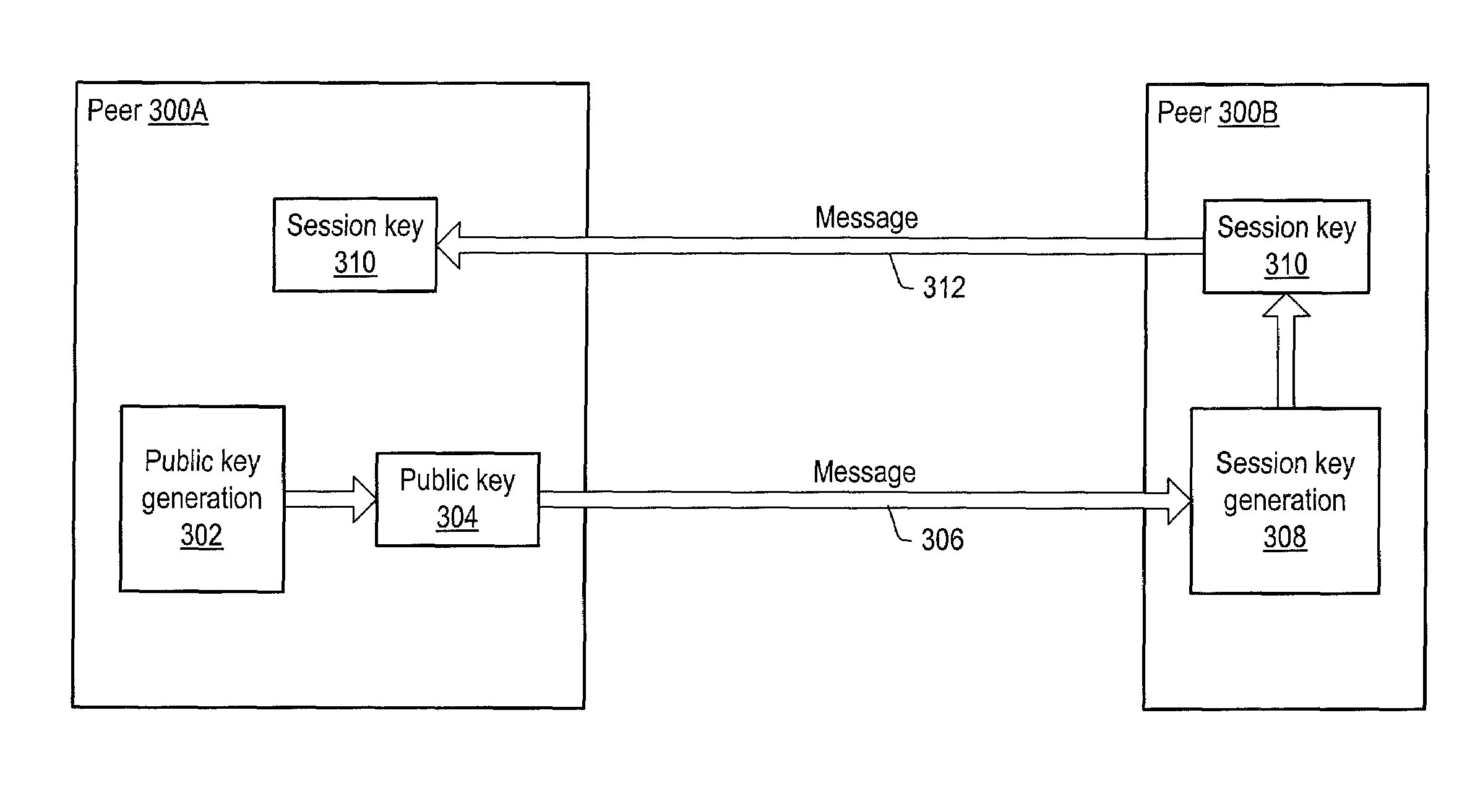
Secured peer-to-peer network data exchange
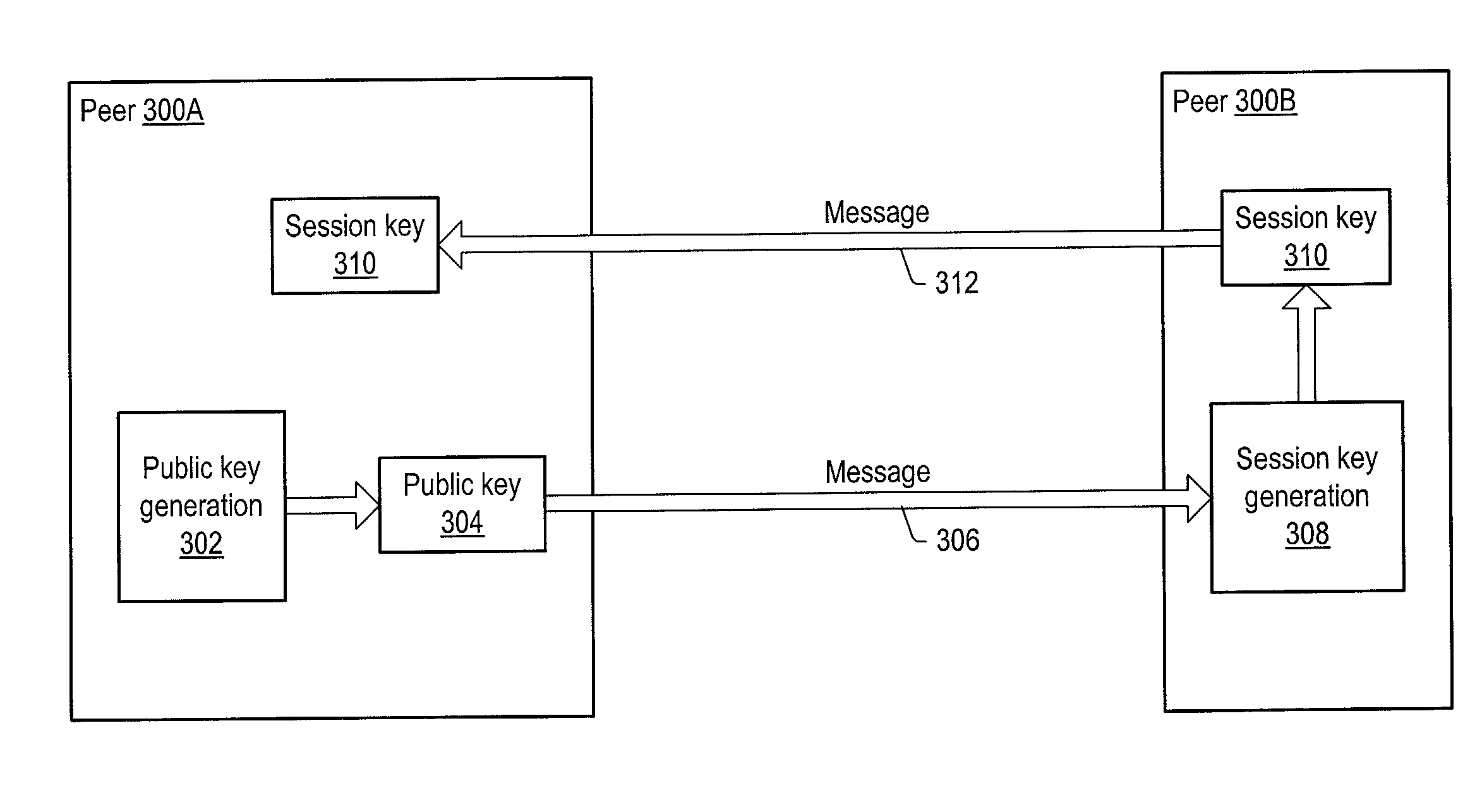
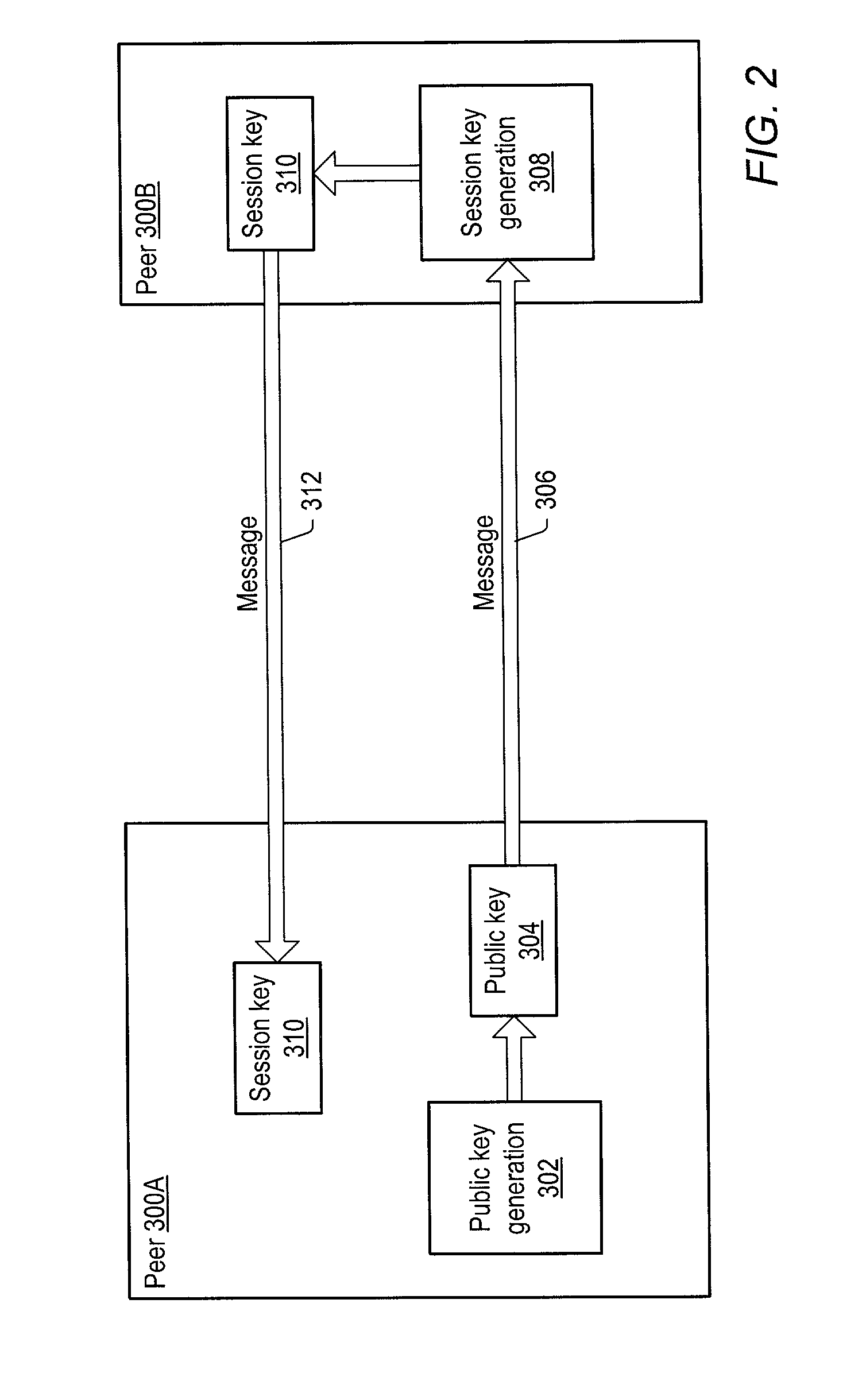
ActiveUS20030163697A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGroup sessionPeer-to-peer
A system and method for providing secure exchange of messages between peers in peer groups. Embodiments may be used to provide secured sessions between peers in the peer-to-peer network. Embodiments may also be used to provide secured group sessions among a plurality of peers. A first peer may generate and send a public key to a second peer. The second peer may generate a session key from the public key. The second peer may send the session key to the first peer, or alternatively to two or more peers in a group session. The session key may be secured when sending. Messages and / or other data exchanged between the two peers may be encrypted and decrypted using the session key.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
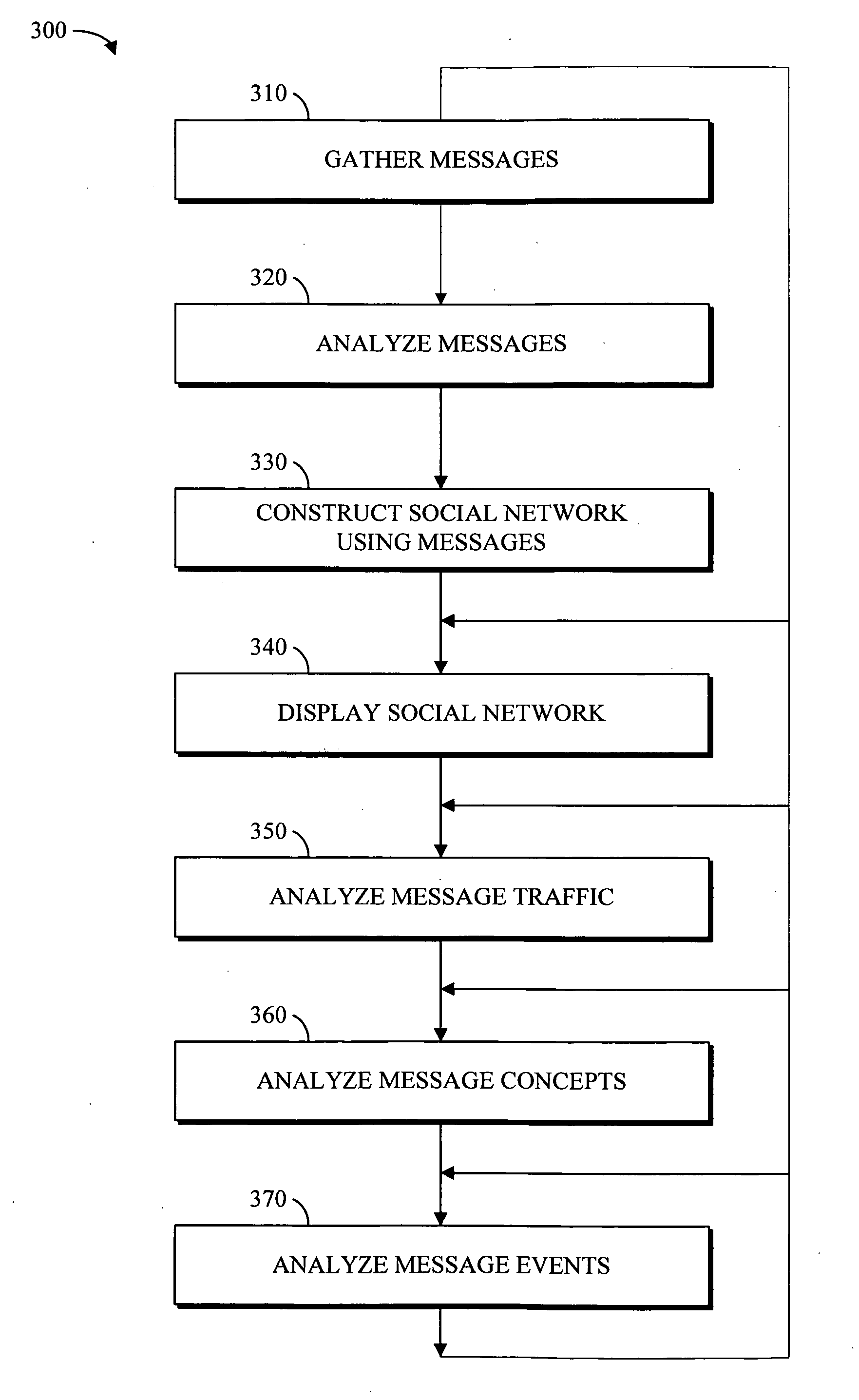
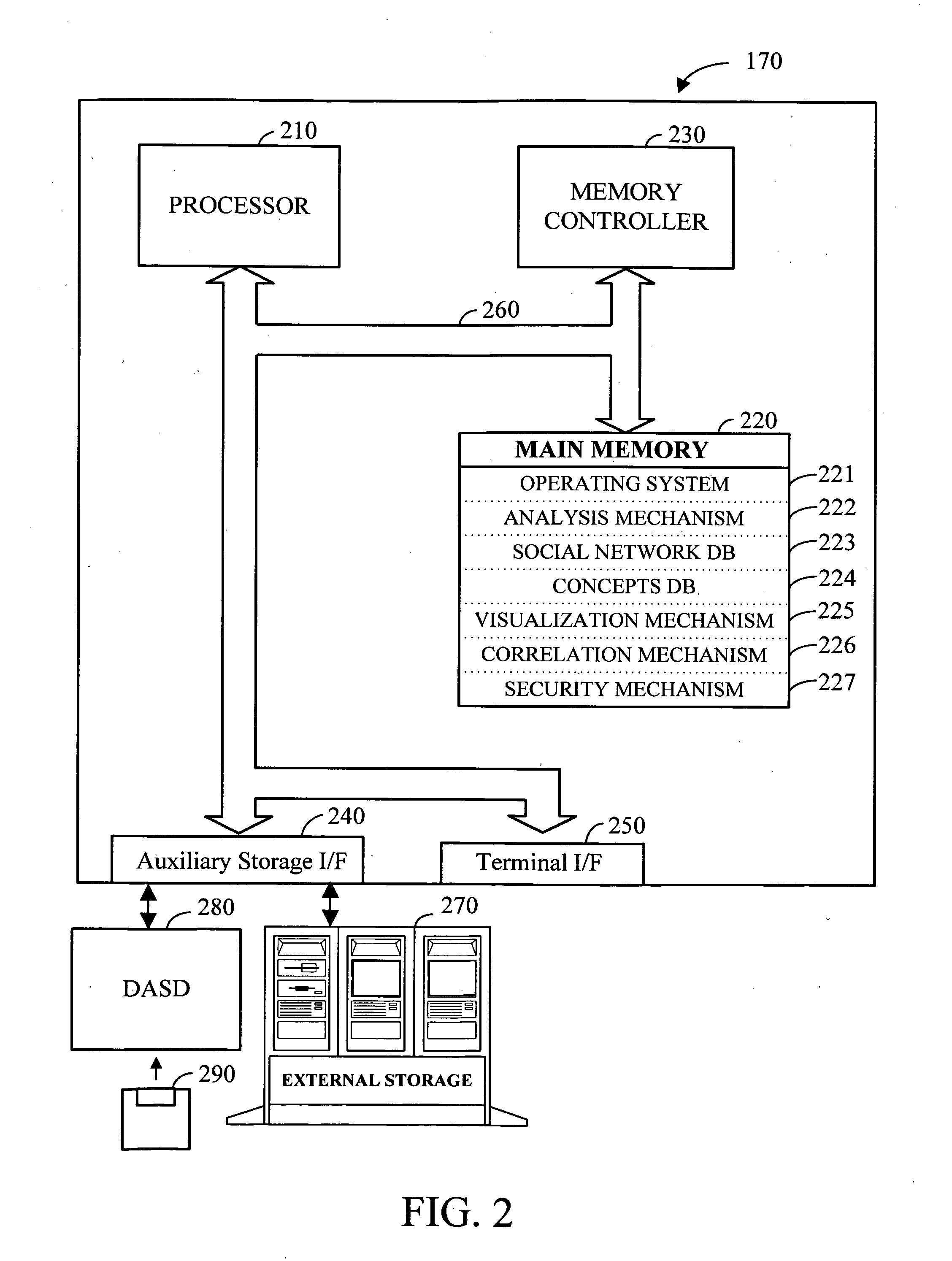
Apparatus and method for message-centric analysis and multi-aspect viewing using social networks
ActiveUS20060173957A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsReference modelMulti aspect
Electronic data files are broadly characterized as “messages” and a social network is constructed by analyzing one or more messages exchanged between various entities. Additionally, messages from structured and / or unstructured data stores are correlated using one or more common / related data elements from two or more messages. Further, the social network and the concepts contained in the exchanged messages (i.e. semantic network) can be visualized using a series of multi-aspect viewing tools. Finally, in conjunction with the social network and the semantic network, a message network based on the chronological relationship of the messages (event network) can be constructed to analyze and visualize how the messages relate to each other in a time-based reference model. Once visualized, the relationship of the concepts contained in the messages as well as the relationship between the entities and the timing involved in the exchange of messages can be analyzed for desired information.
Owner:NUIX NORTH AMERICA
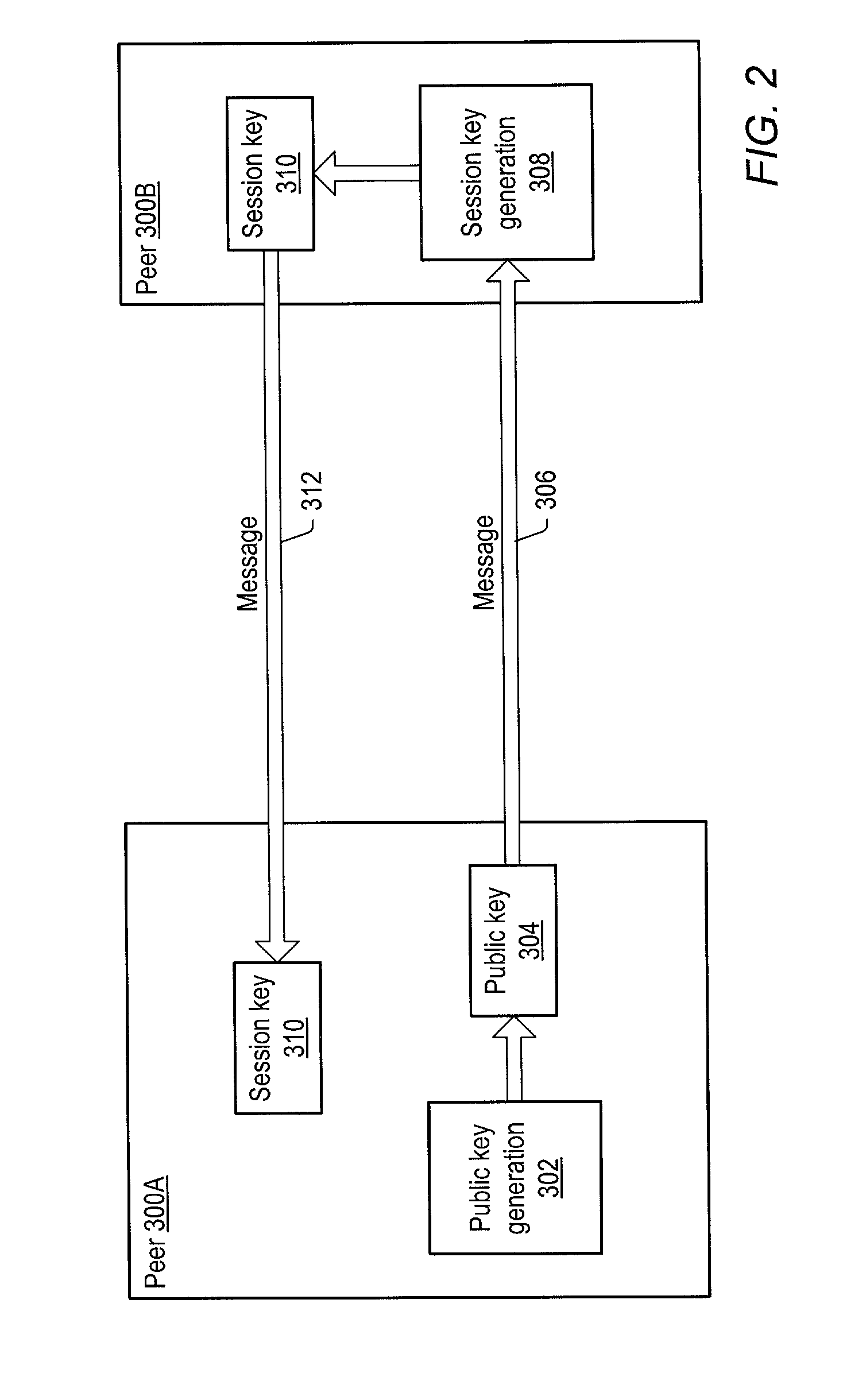
Secured peer-to-peer network data exchange
ActiveUS7127613B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGroup sessionMessage switching
A system and method for providing secure exchange of messages between peers in peer groups. Embodiments may be used to provide secured sessions between peers in the peer-to-peer network. Embodiments may also be used to provide secured group sessions among a plurality of peers. A first peer may generate and send a public key to a second peer. The second peer may generate a session key from the public key. The second peer may send the session key to the first peer, or alternatively to two or more peers in a group session. The session key may be secured when sending. Messages and / or other data exchanged between the two peers may be encrypted and decrypted using the session key.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
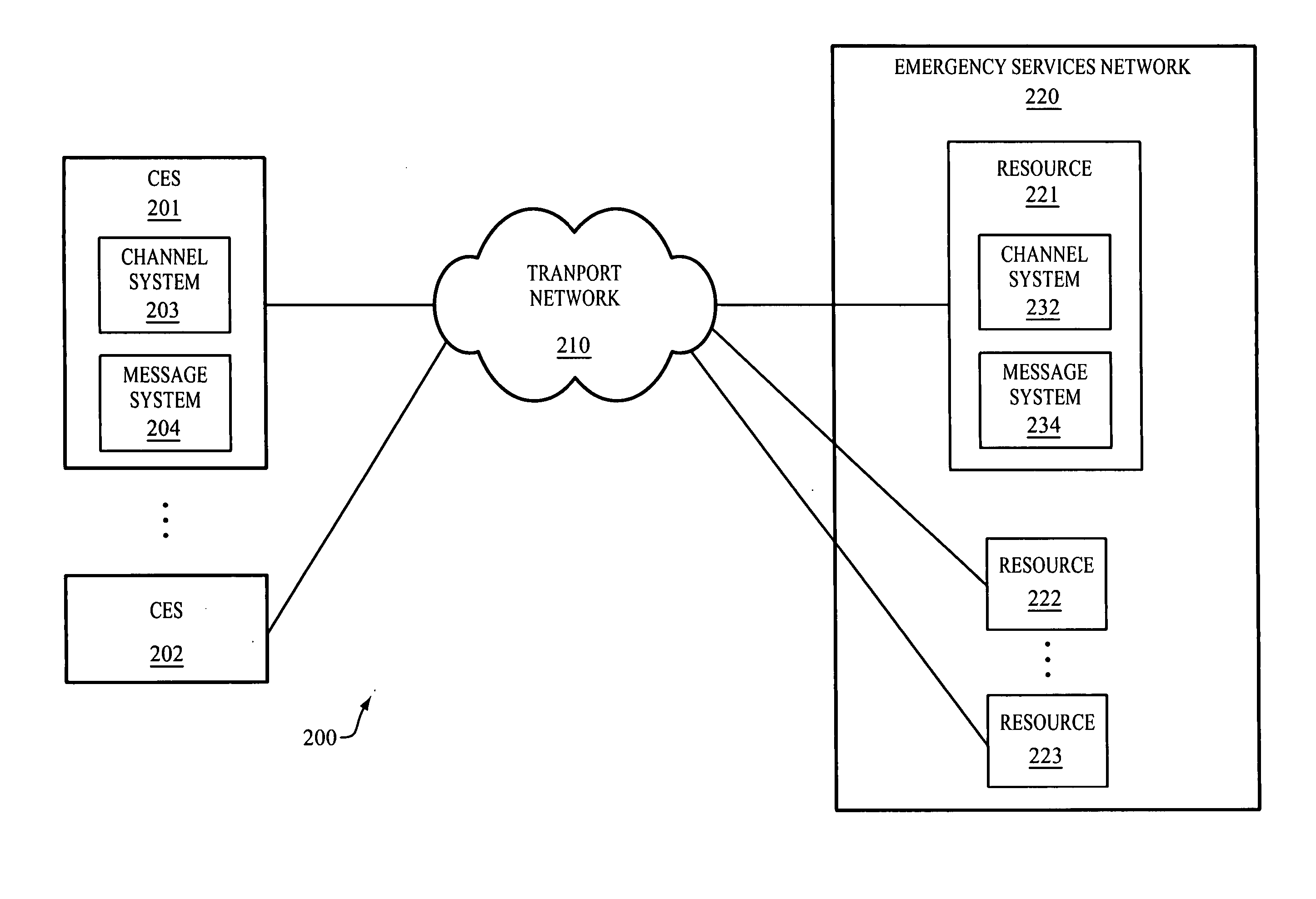
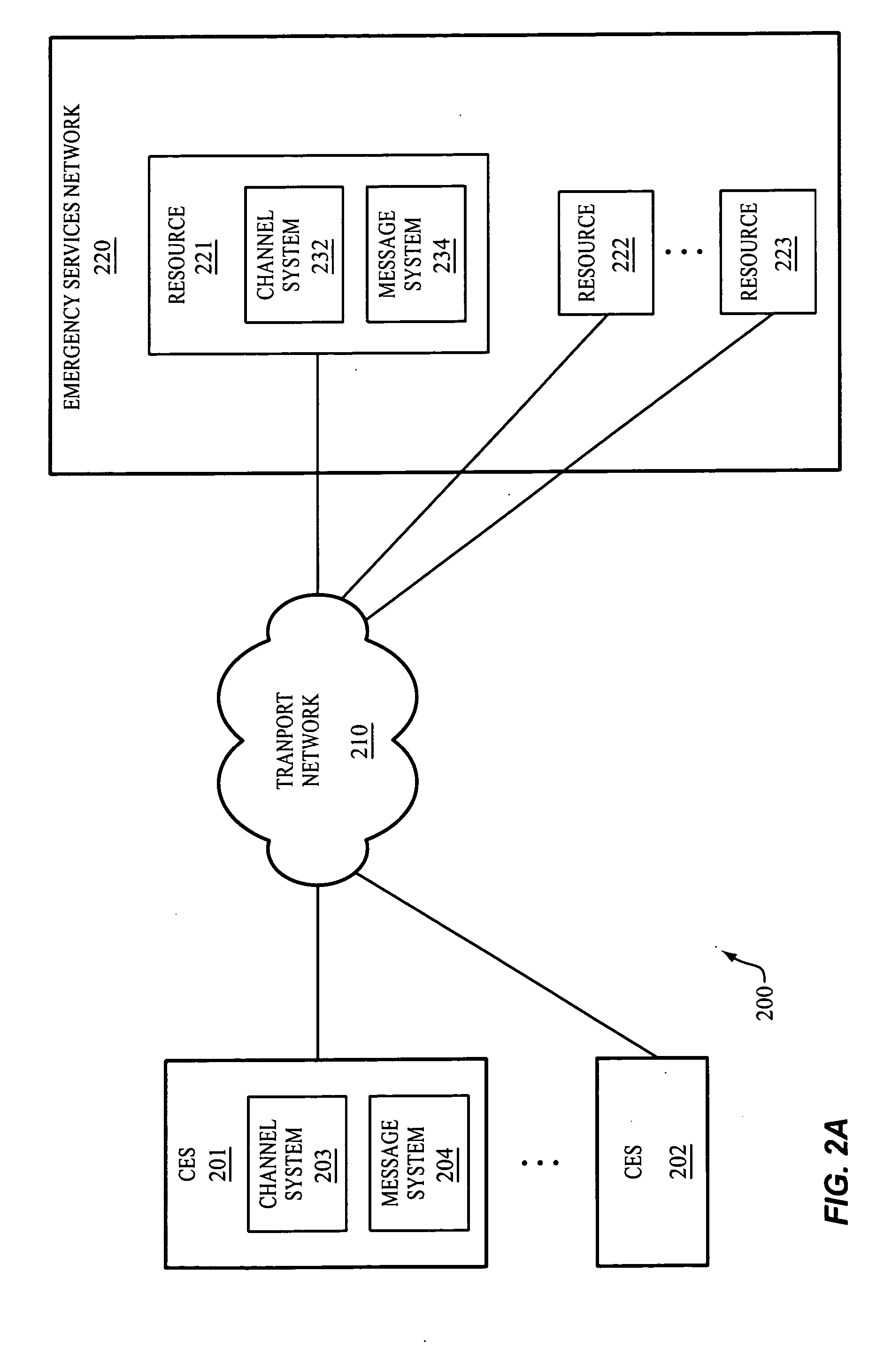
Rotating media channels between resources of an emergency services network and conforming emergency systems
InactiveUS20050201358A1Easy to addTelephonic communicationData switching by path configurationMessage switchingTransport network
The invention includes a communication network for rotating media channels between resources of an emergency services network and a conforming emergency system (CES). A conforming emergency system and one of the resources of the emergency services network dynamically establish a first media channel between one another over a transport network. With the first media channel established, the conforming emergency system and the resource exchange messages over the first media channel to facilitate the CES in handling emergency events. Responsive to a triggering event, the CES and one of the resources (the same or another resource) dynamically establish a second media channel between one another over the transport network. With the second media channel established, the conforming emergency system and the resource exchange messages over the second media channel to facilitate the CES in handling emergency events. The first media channel may be torn down.
Owner:WEST SAFETY SERVICES INC
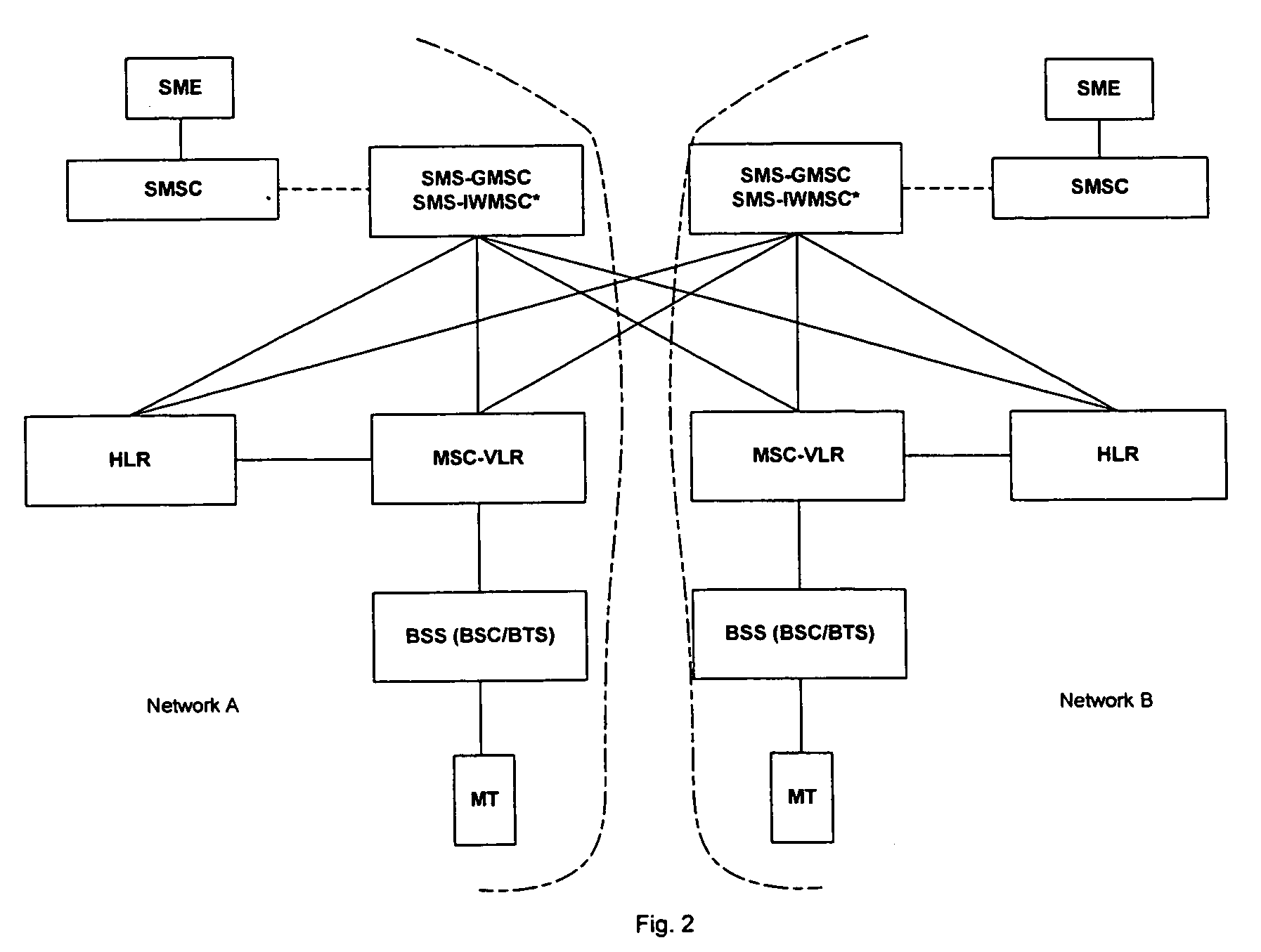
Method for the transmission of multimedia messages
InactiveUS6848008B1Versatile in useBig advantageData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemMessage switching
The invention relates to a method for the transmission of multimedia messages in a communication system from a transmitting terminal (MS1) to a receiving terminal (RH, MS2). The communication system comprises at least a first communication network (NW1), a second communication network (NW2) and a multimedia message switching centre (MMSC). In the first communication network (NW1), at least a first address type is used as the terminal address, and in the second communication network (NW2), at least a second address type is used as the terminal address. In the method, the address of the receiving terminal (RH, MS2) is annexed to said multimedia message. The multimedia message is further supplemented with data on the type of said address, wherein the multimedia message is transmitted from the transmitting terminal (MS1) to said multimedia message switching centre (MMSC), in which the type of the address of the receiving terminal (RH, MS2) is examined, and said address type is used to select the communication network (NW1, NW2) to be used in the transmission of the message from the multimedia message switching centre (MMSC) to the receiving terminal (RH, MS2).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
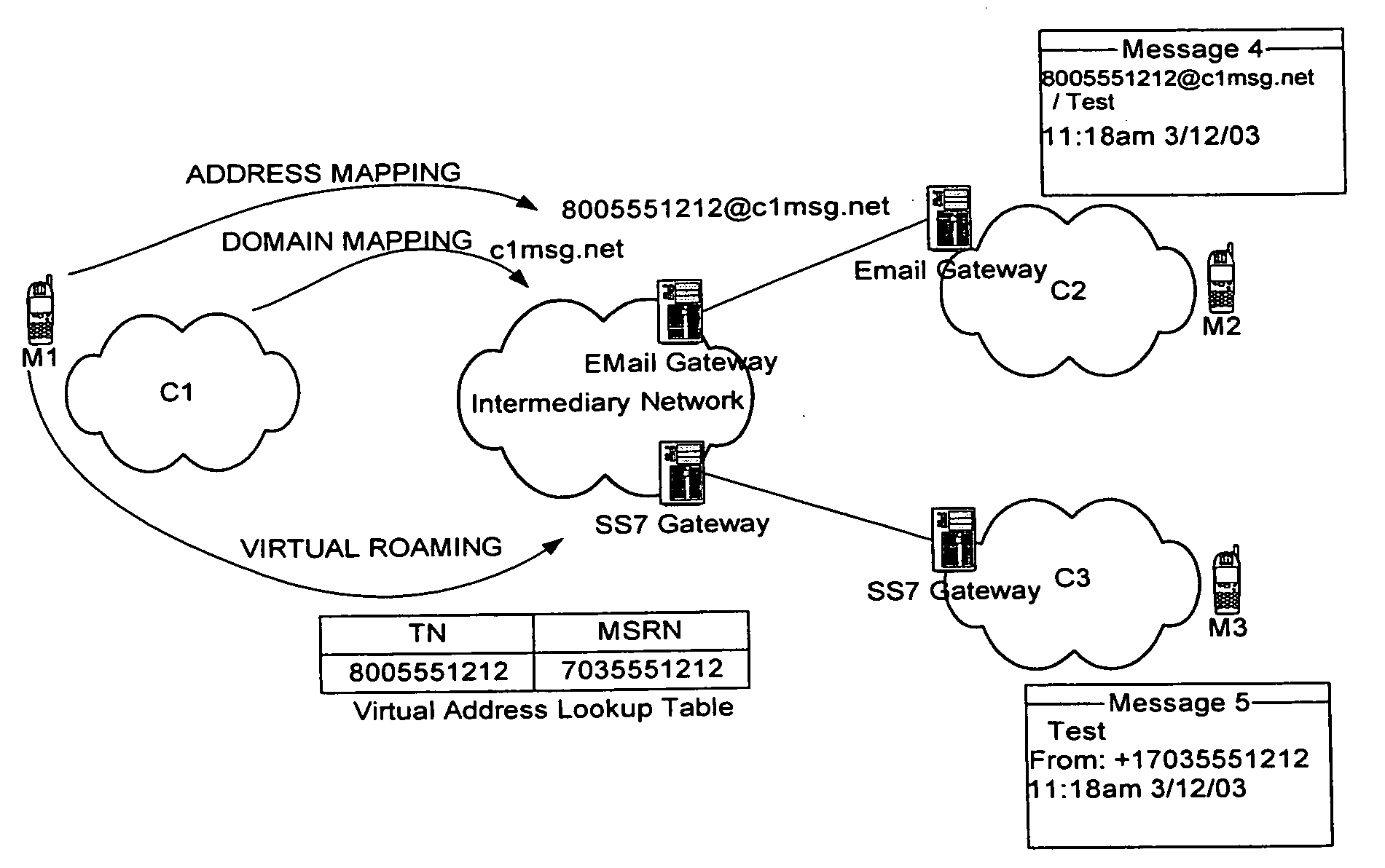
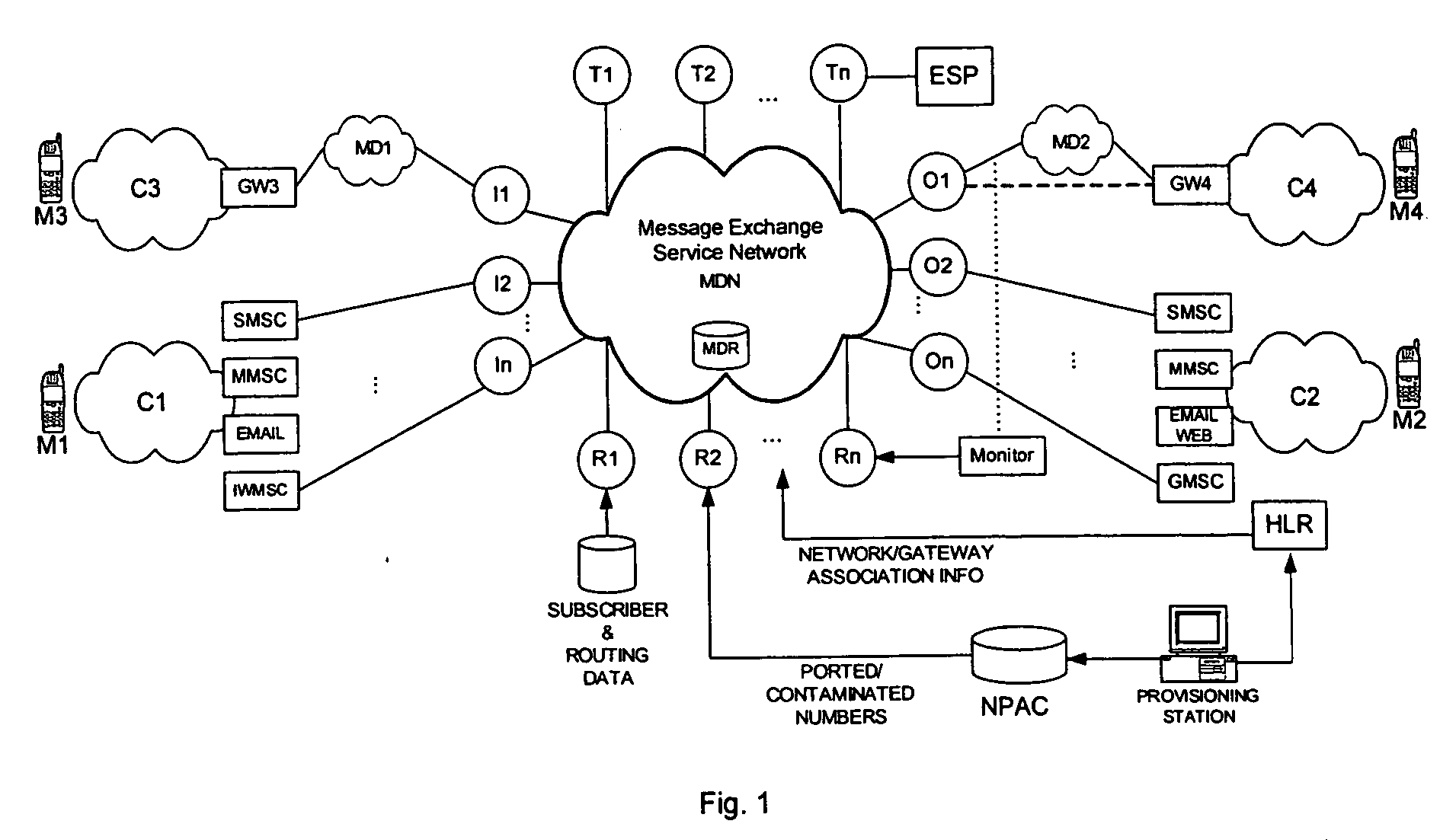
Intermediary network system and method for facilitating message exchange between wireless networks
ActiveUS20050215250A1Raise the possibilityInformation formatData switching by path configurationRouting decisionPublic land mobile network
Network System and Method for facilitating message exchange between mobile subscribers belonging to the same or different public land mobile networks, possibly incorporating different standards. Message exchange between two subscribers of the same or different networks may involve one or more lookups on subscription data, zero or more message transformations, one or more routing decisions including application of costing functions, and, storage and propagation of the message in one or more Core or Intermediary networks. The messages may be of type, among others, SMS (Short Message Service), MMS (Multimedia Message Service), or EMAIL.
Owner:SYBASE 365 INC
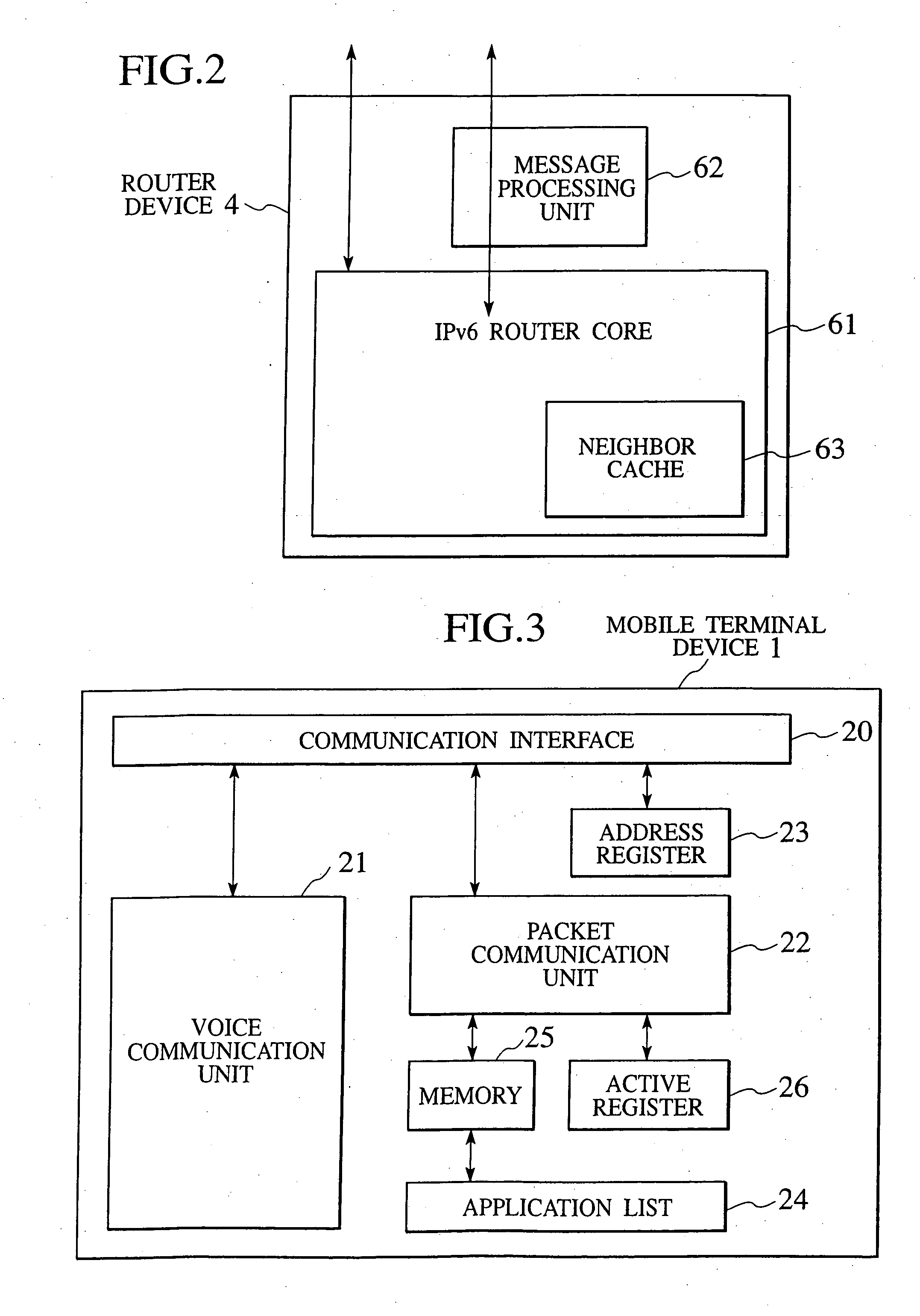
Packet transfer scheme using mobile terminal and router for preventing attacks using global address
In a mobile communication network providing an Internet service, the arrived packets are delivered from the nearest neighbor router device to the mobile terminal device according to the need such as when a prescribed application is activated or when a prescribed packet has arrived, by using message exchanges between the nearest neighbor router device and the mobile terminal device, so that it becomes possible to prevent the unnecessary packet attacks from the global Internet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
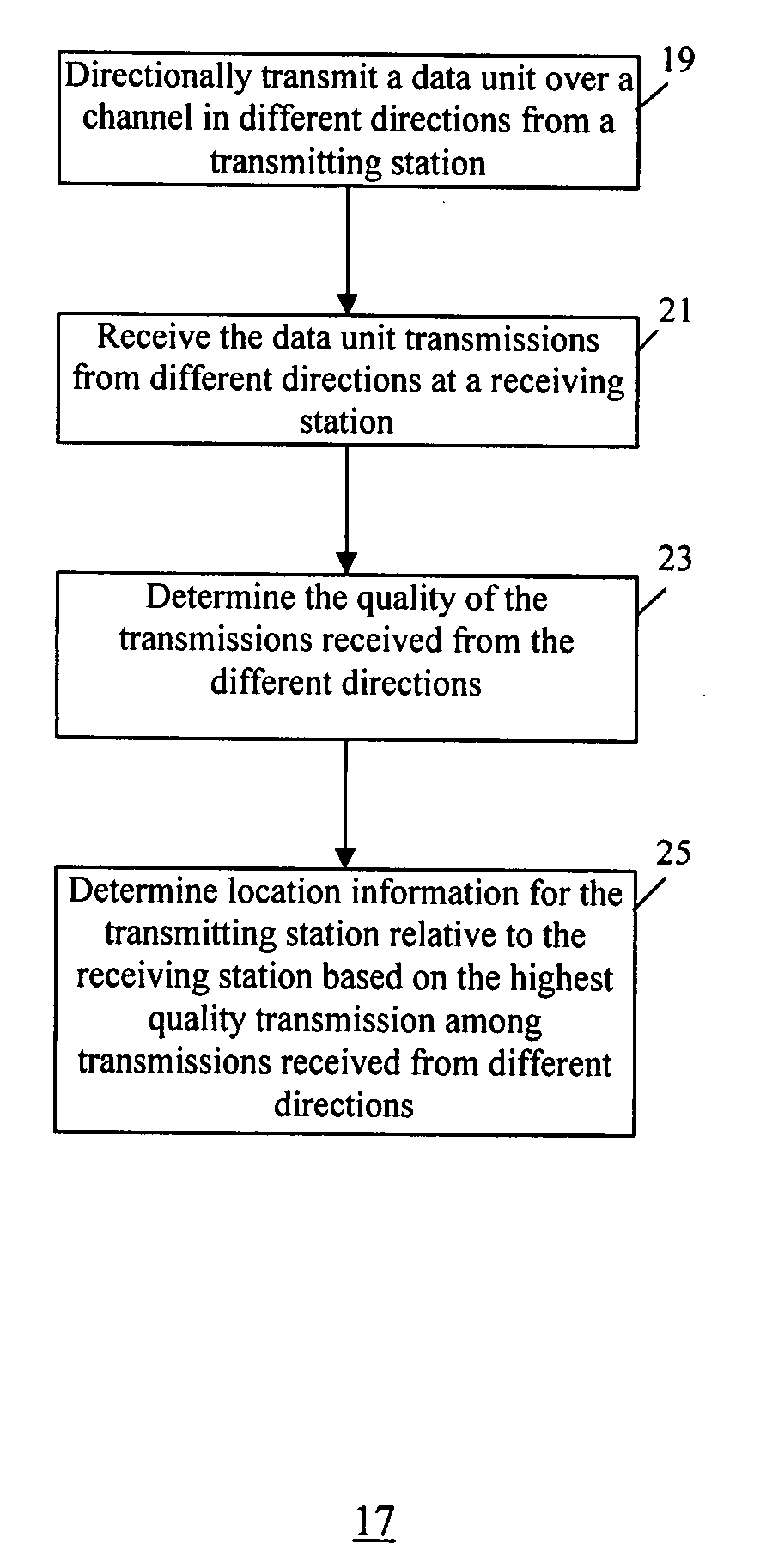
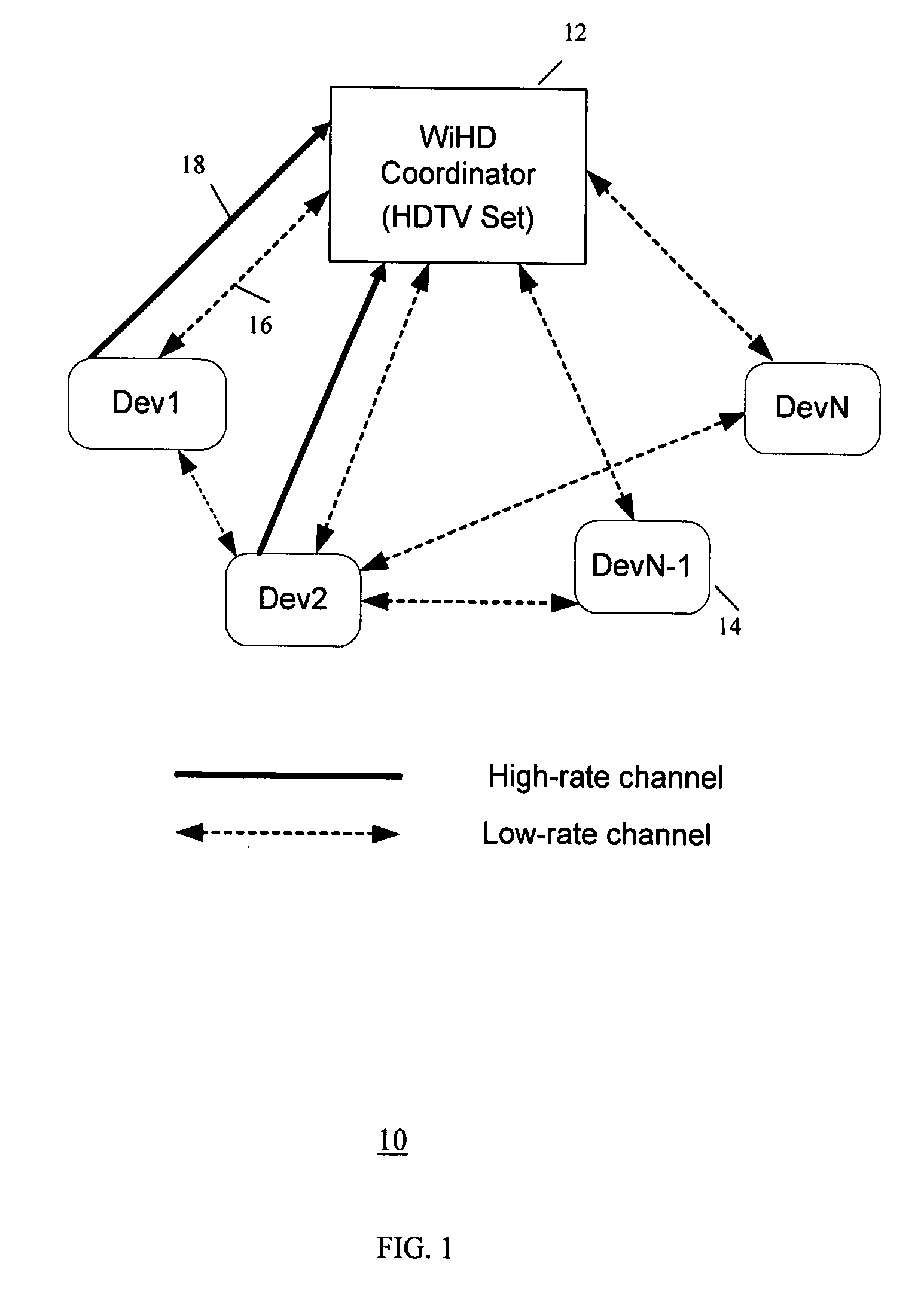
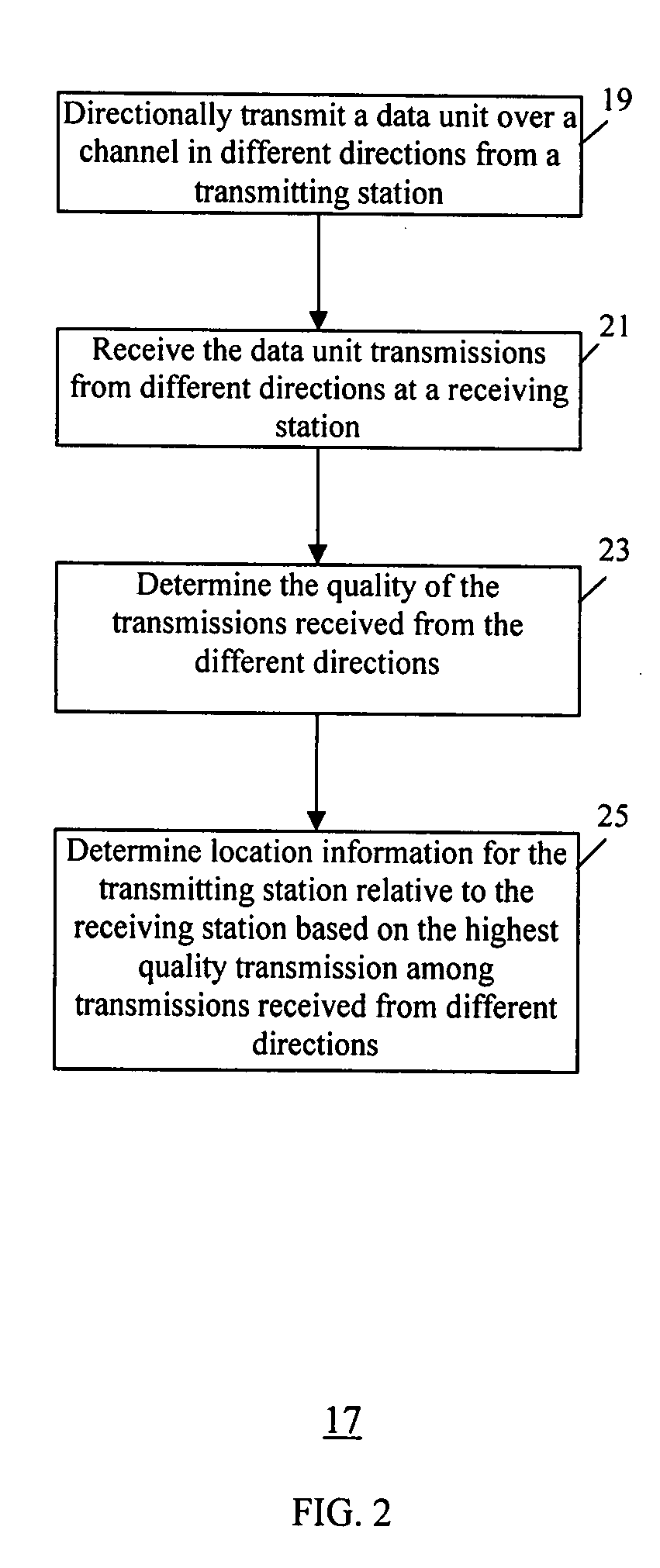
Method and system for device discovery in a wireless video area network
InactiveUS20080095072A1Quality improvementTelephonic communicationData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsTelecommunications link
A method and system for device discovery in a wireless network is provided. The device discovery involves directionally transmitting a data unit from a transmitting station over a channel in different directions to emulate omni-directional transmission, receiving the data unit transmissions from different directions at a receiving station, determining the quality of the transmissions received from the different directions, and detecting location information for the transmitting station relative to the receiving station based on the highest quality transmission among the transmissions received from the different directions. Further, if a channel has sufficient bandwidth to satisfy direct link communication between two stations, then during a direct link set-up stage, the two stations conduct a probing message exchange using omni-direction transmission, and upon successful probing, obtain communication link status information and set proper communication configurations for the two stations based on the communication link status information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
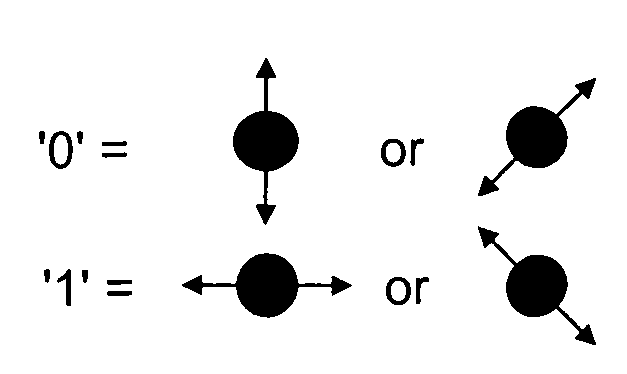
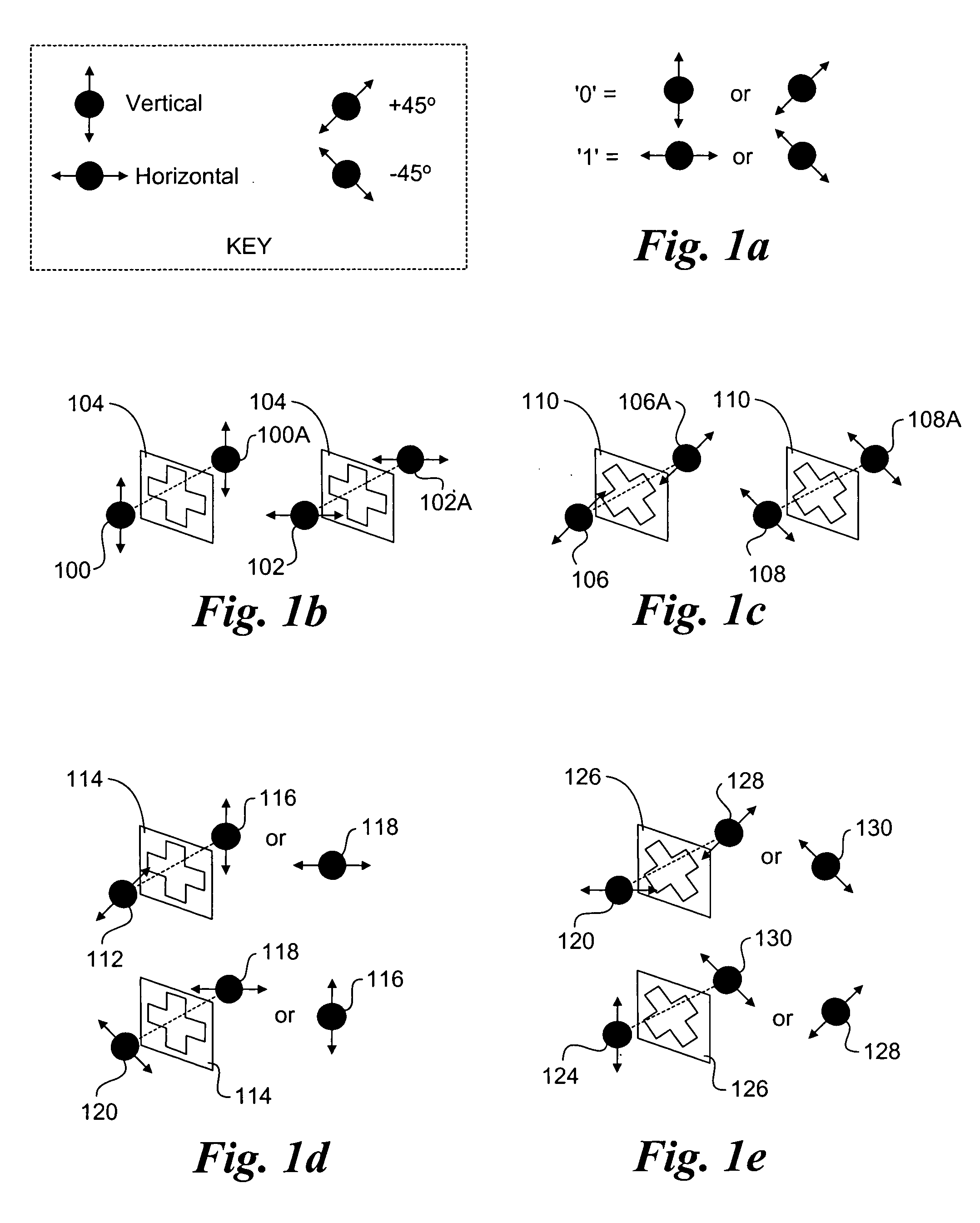
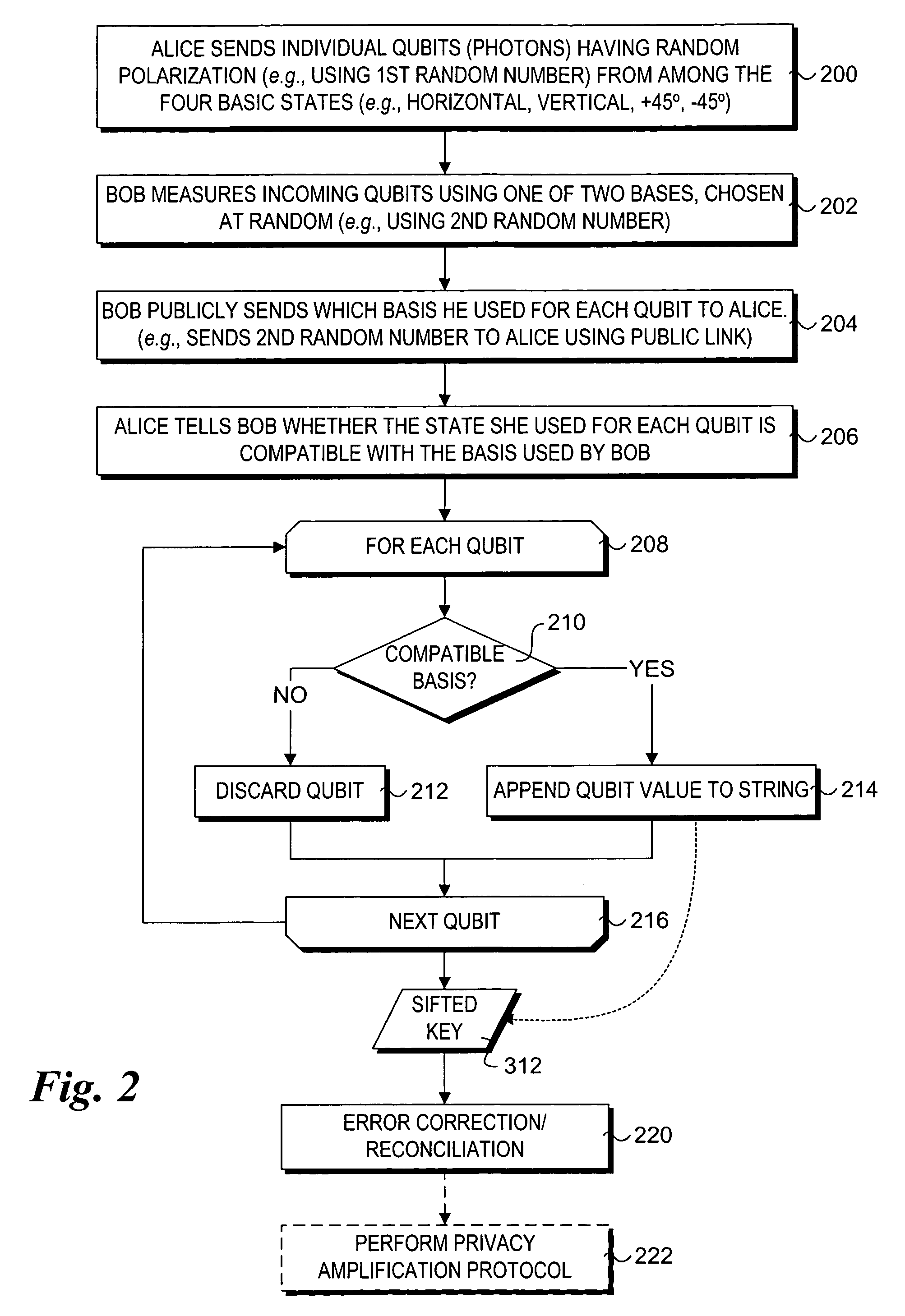
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
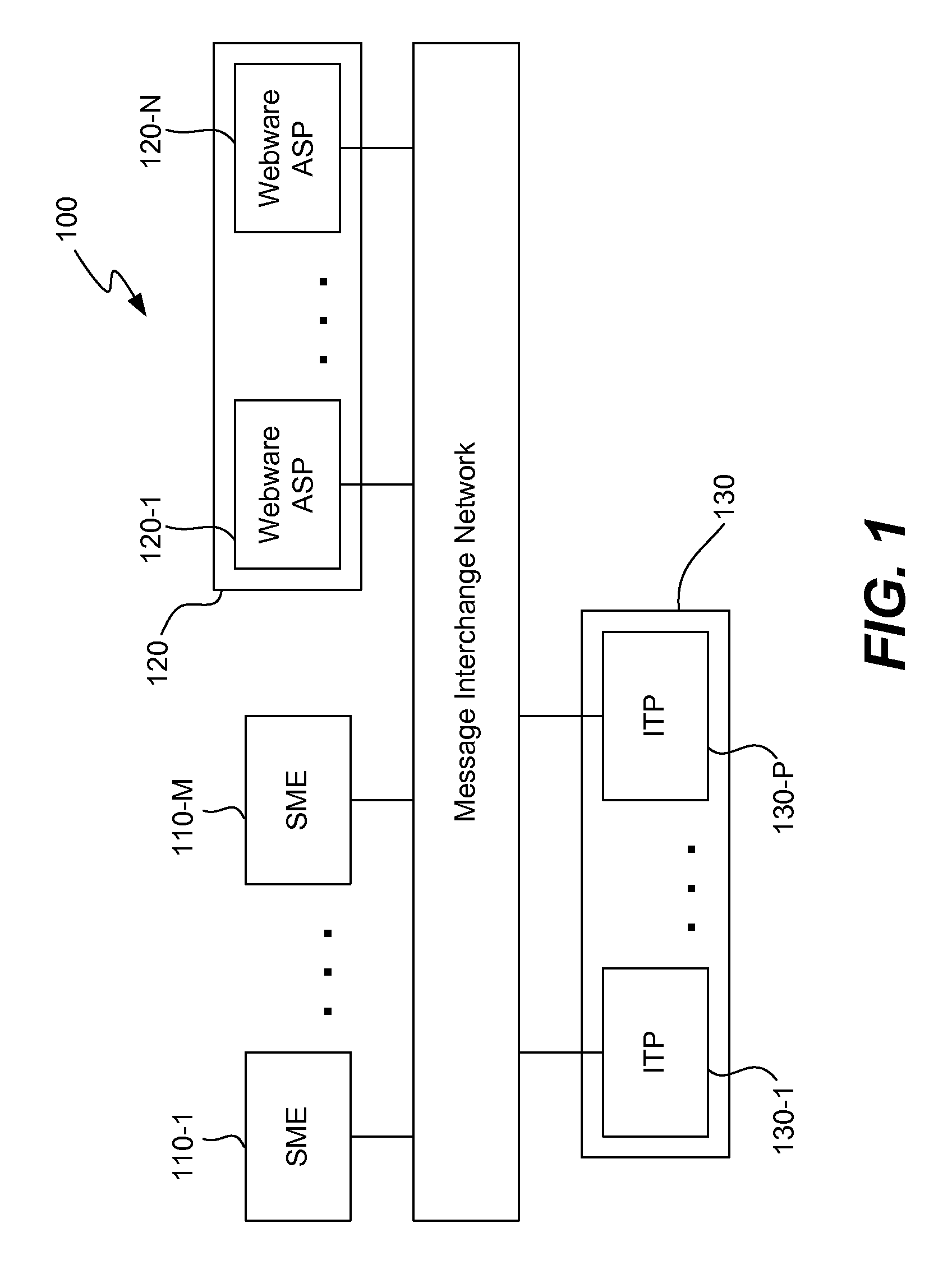
Apparatus and methods for managing messages sent between services
InactiveUS20080016242A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterprogram communicationRelevant informationMessage switching
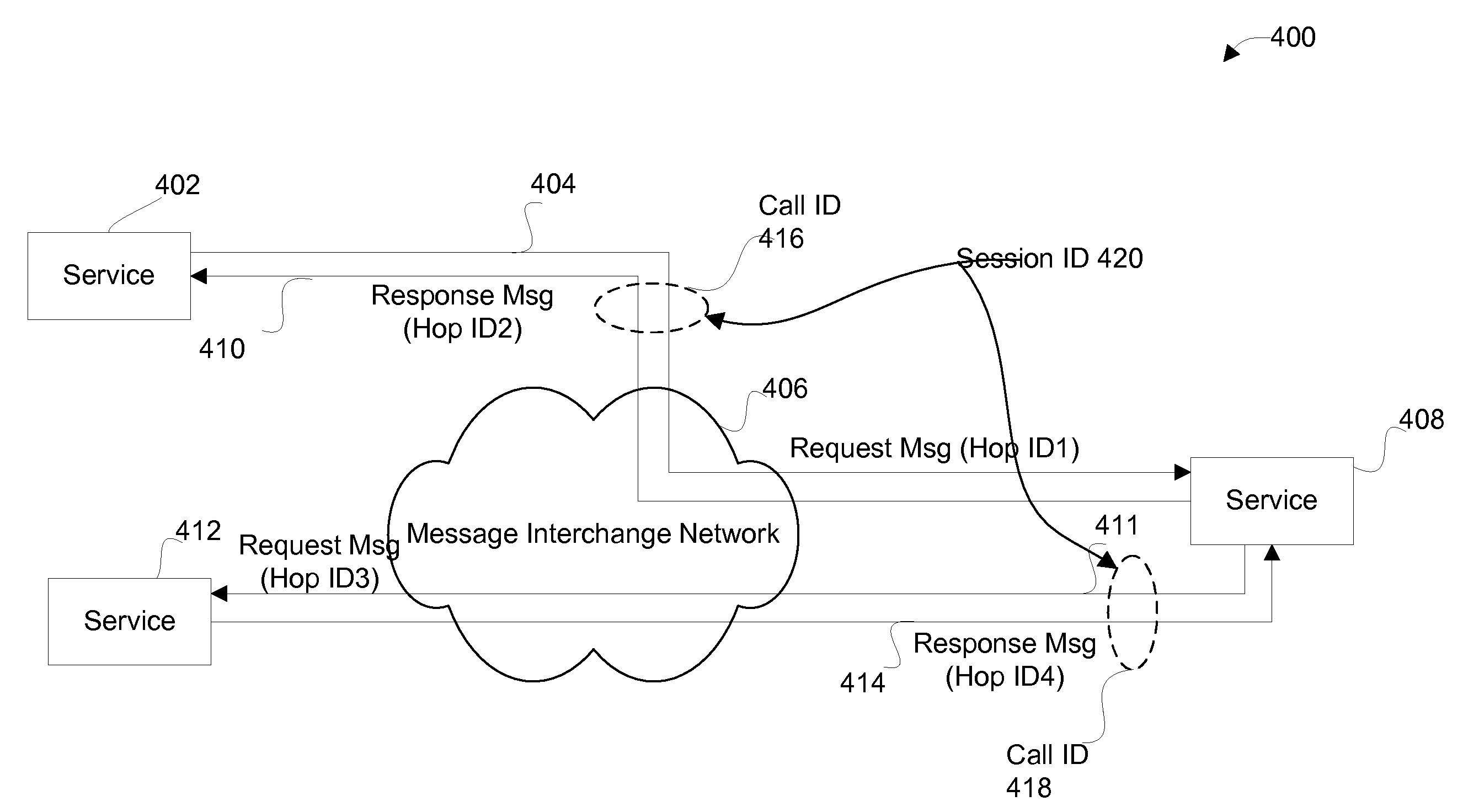
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for managing services within a computer network. In one embodiment, a message interchange network for exchanging application-level messages between services, which are located outside the message interchange network, is provided. At the message interchange network, a plurality of application-level messages, which each specify which one or more receiving services are to receive the each application-level message, are received. Each received application-level message is forward towards the one or more receiving services. Correlation information regarding each application-level message that is received into message interchange network is retained. The application-level messages are sent between pairs of the services, and the retained correlation information for each application-level message pertains to each application-level message and any other application-level messages related to the each application-level message. A query can then be received, at the message interchange network from a first service, to search the retained correlation information for specific one or more portions of the retained correlation information. A response to the query, which includes the specific one or more portions of the retained correlation information, is sent to the first service.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
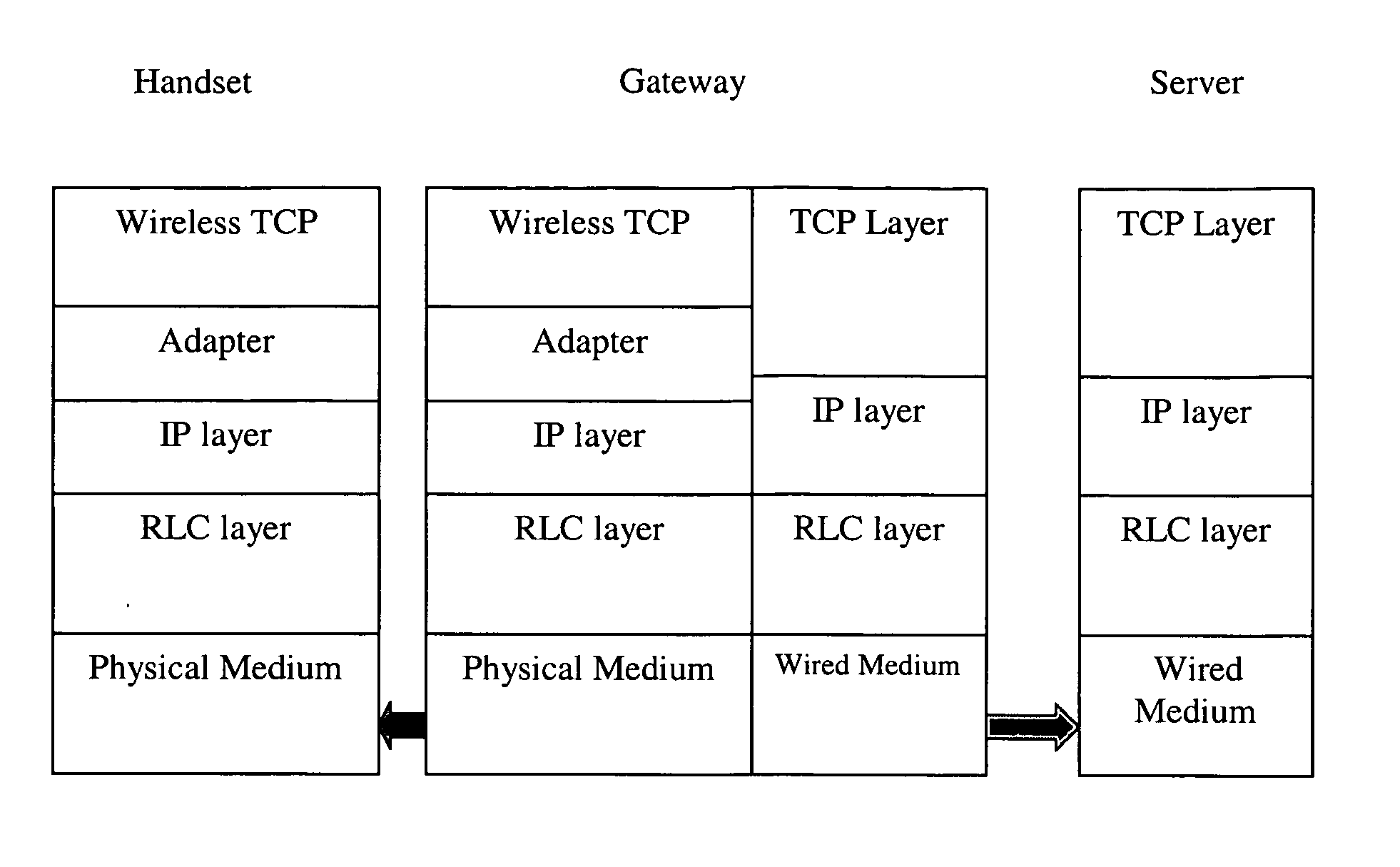
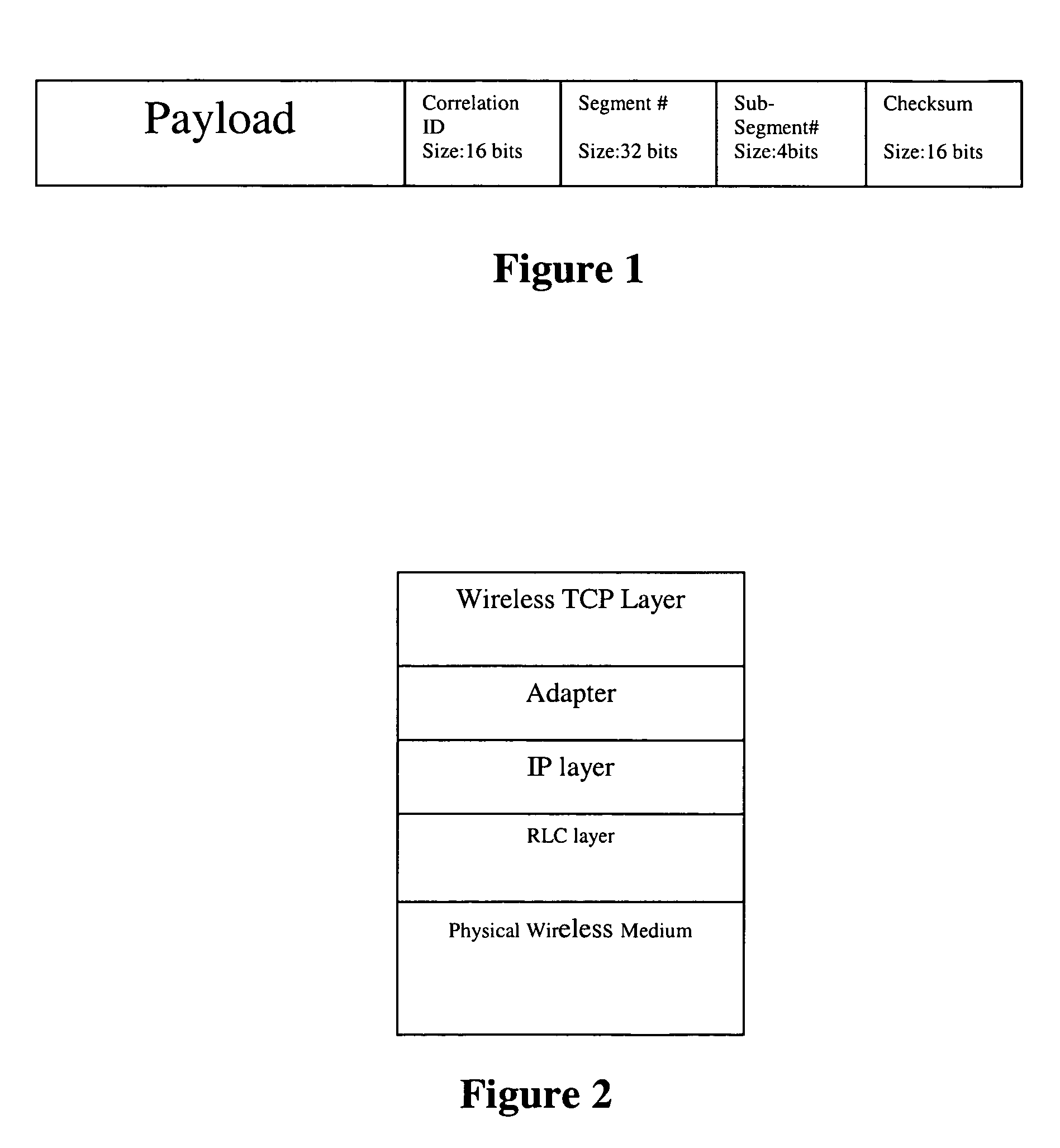
Sub-segment based transport layer protocol for wireless medium
InactiveUS20050265353A1Maximum performanceSave bandwidthEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementTransport layerPacket loss
The invention enables the use of TCP protocol for reliable transport of data over a wireless network, resolving the problems associated with frequent packet loss. Additional benefits include delivery of significant performance improvement, bandwidth saving and backward compatibility compared to the wire-line TCP protocol, and contribution to power savings in wireless handsets and devices. To make the retransmission process more granular, transport layer segments are subdivided into sub-segments. The invention utilizes a split TCP based approach and produces a series of smaller-sized segments that share the same transport layer header. A NACK-based message exchange, a new header format and a special windowing protocol are used to achieve reliability, flow-control, and efficient buffer handling.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
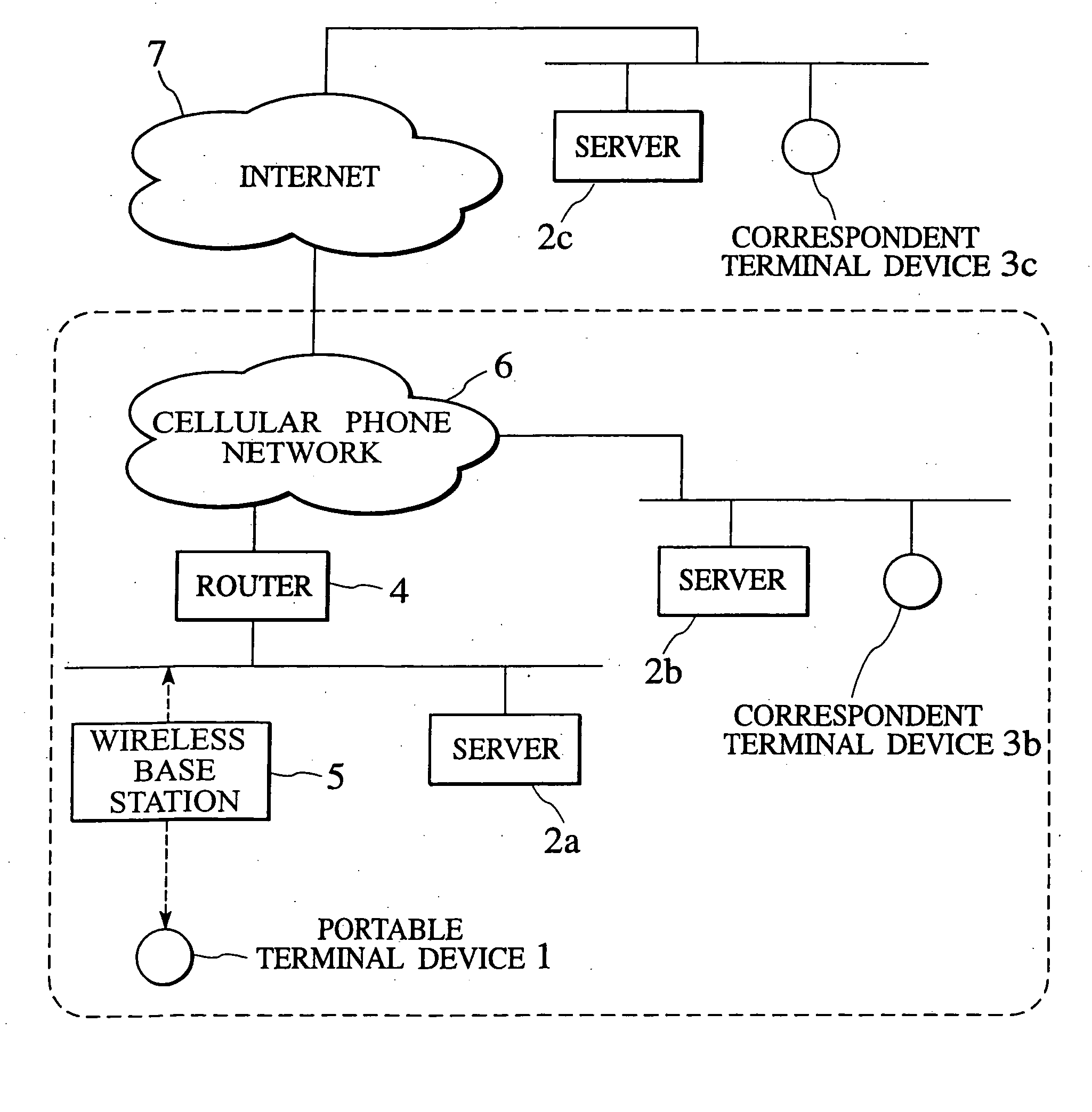
Interactive Electronic Commerce and Message Interchange System
InactiveUS20070299728A1Facilitates collection and redemptionDiscounts/incentivesSpecial service for subscribersPrint mediaThe Internet
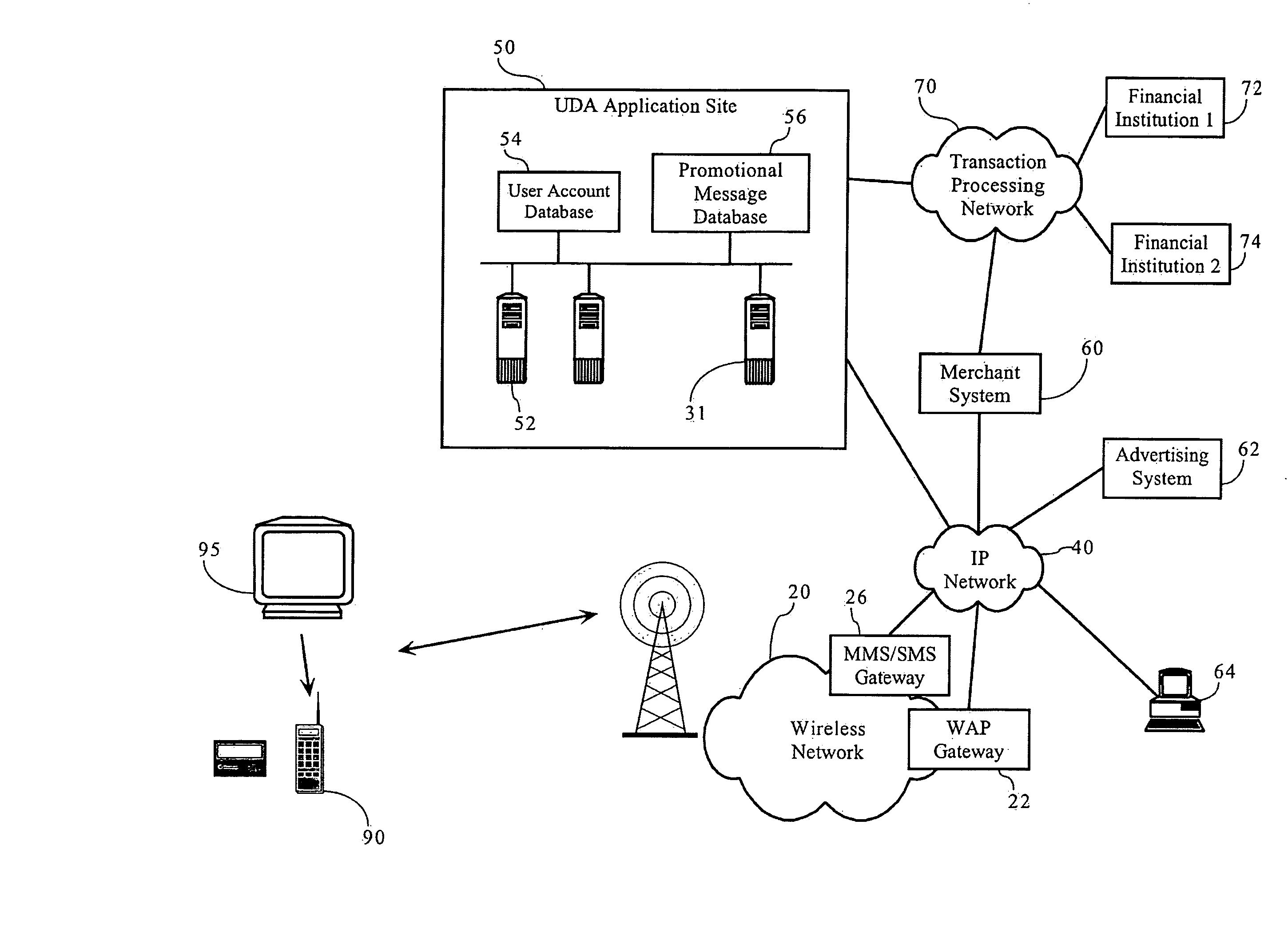
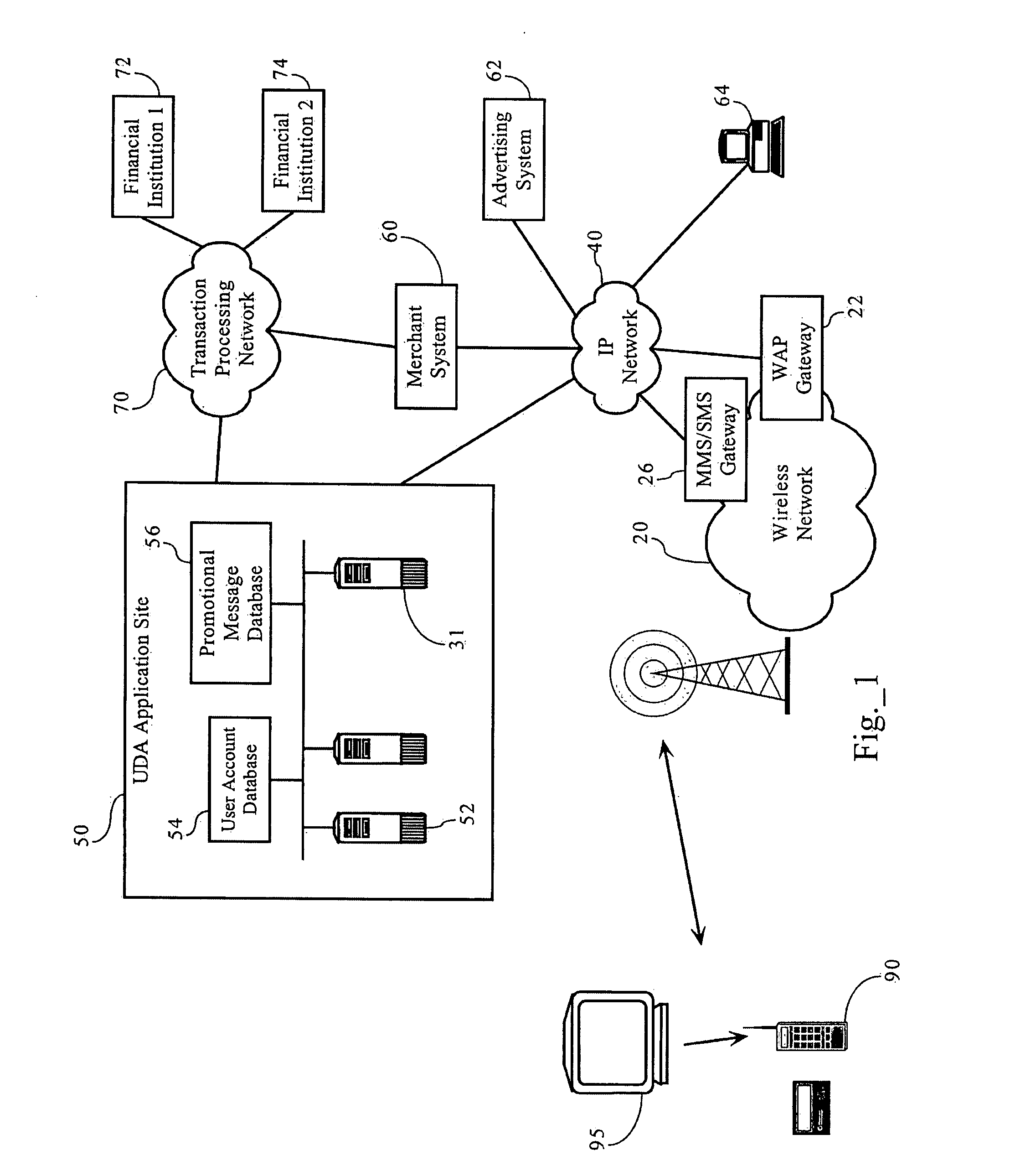
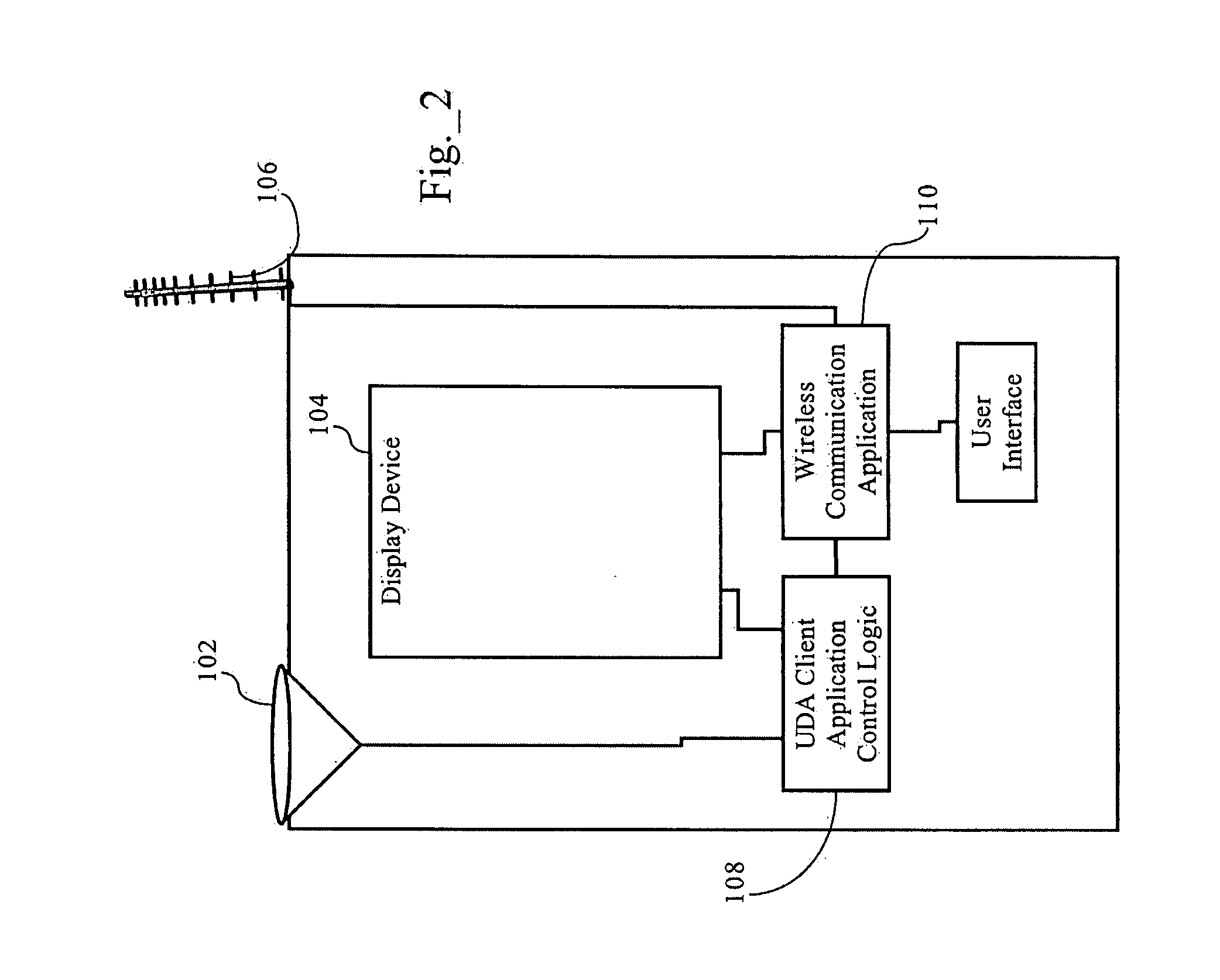
Methods, apparatuses and systems enabling an interactive electronic commerce system enabling the targeted exchange of messages with interested users presented with message codes in conventional media, such as television, radio, and printed publications. The present invention allows for the targeted dissemination of information, such as advertising, promotions, sales announcements, coupons, and the like. The present invention, in one embodiment, provides an end-to-end ecommerce solution that transforms the cell phone / PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) into a Universal Digital Assistant which can receive data including advertising, promotions, sales announcement information based on message identifiers encoded into advertising and content from and including the analog and digital TV, TV set-top box, Internet, wireless, radio, satellite and print media. In one embodiment, the present invention enables an interactive electronic coupon system that facilitates the collection and redemption of electronic coupons.
Owner:NEMIROFSKY FR ROBERT +1
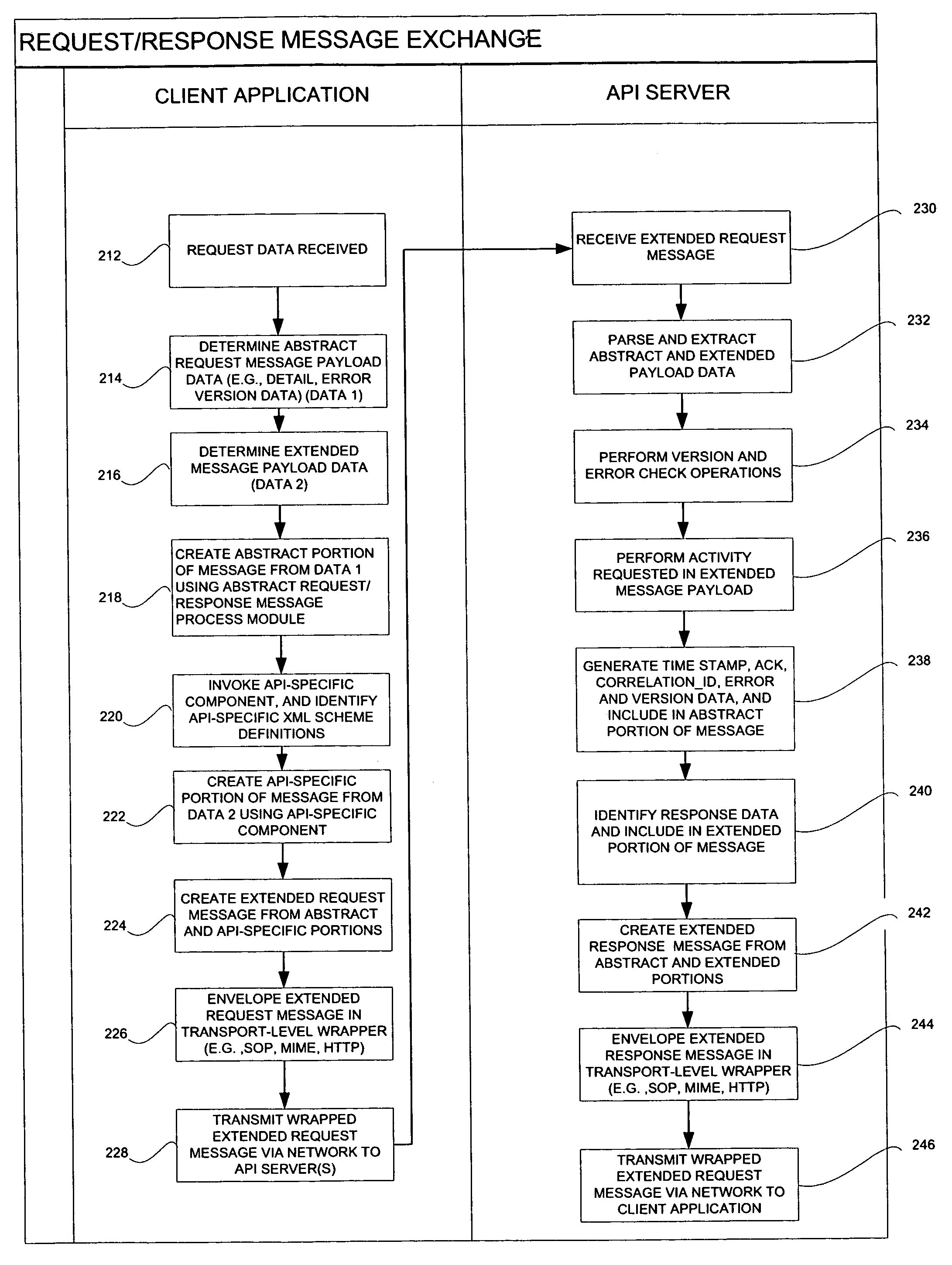
API and business language schema design framework for message exchanges
ActiveUS20050138648A1Facilitate communicationInterprogram communicationTransmissionApplication serverMessage switching
A server system facilitates an exchange of messages with a remote client application. The server system includes a plurality of application servers hosting a plurality of applications. A plurality of Application Program Interfaces (APIs) provides programmatic access to the plurality of applications, each of the APIs being configured to receive request messages compiled by the remote client application. First and second request messages, respectively addressed to first and second APIs of the plurality of APIs by a remote client application, each comprise at least one common data component. Further, the first request message includes a first payload specific to the first API, and the second request message includes a payload specific to the second API.
Owner:EBAY INC
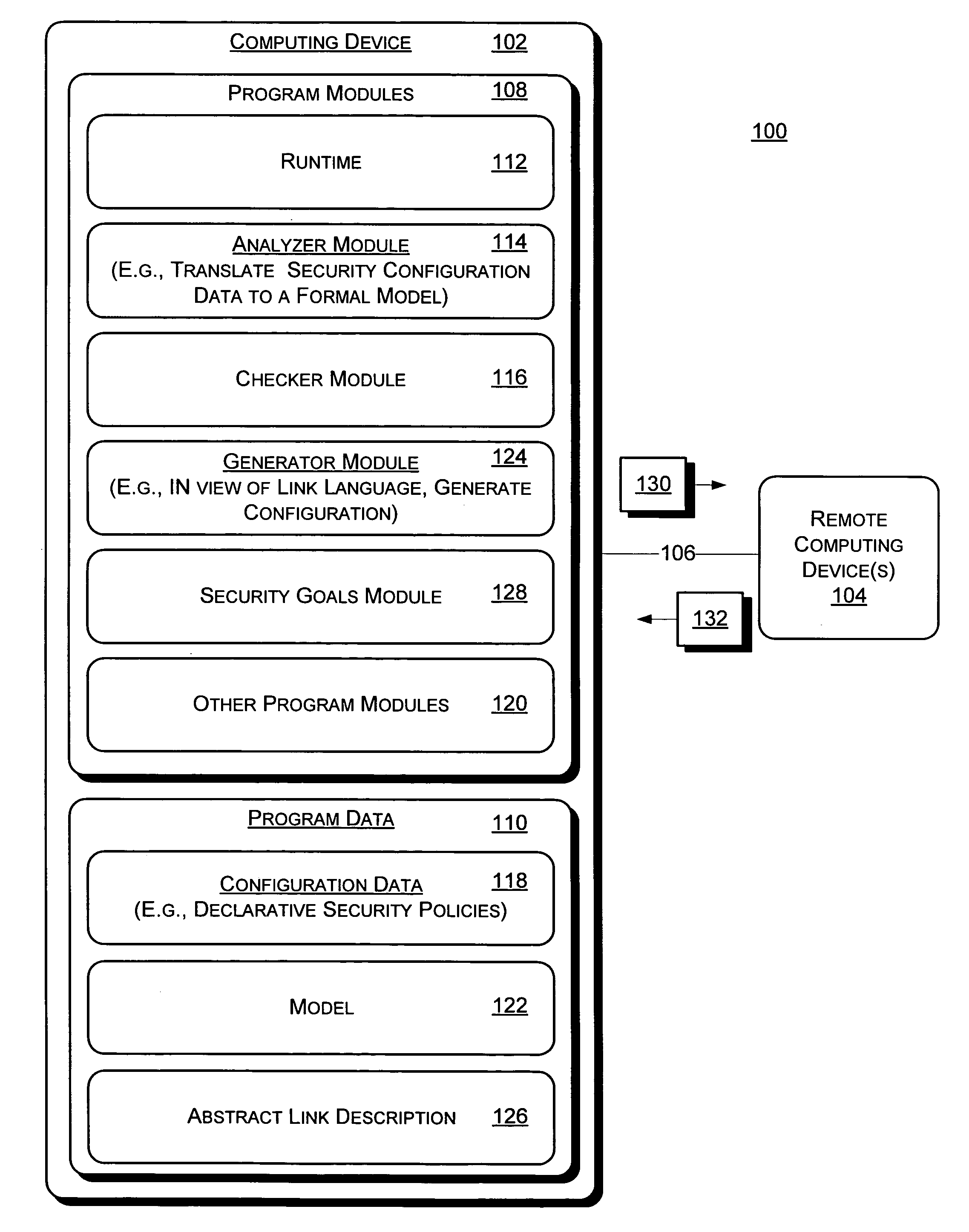
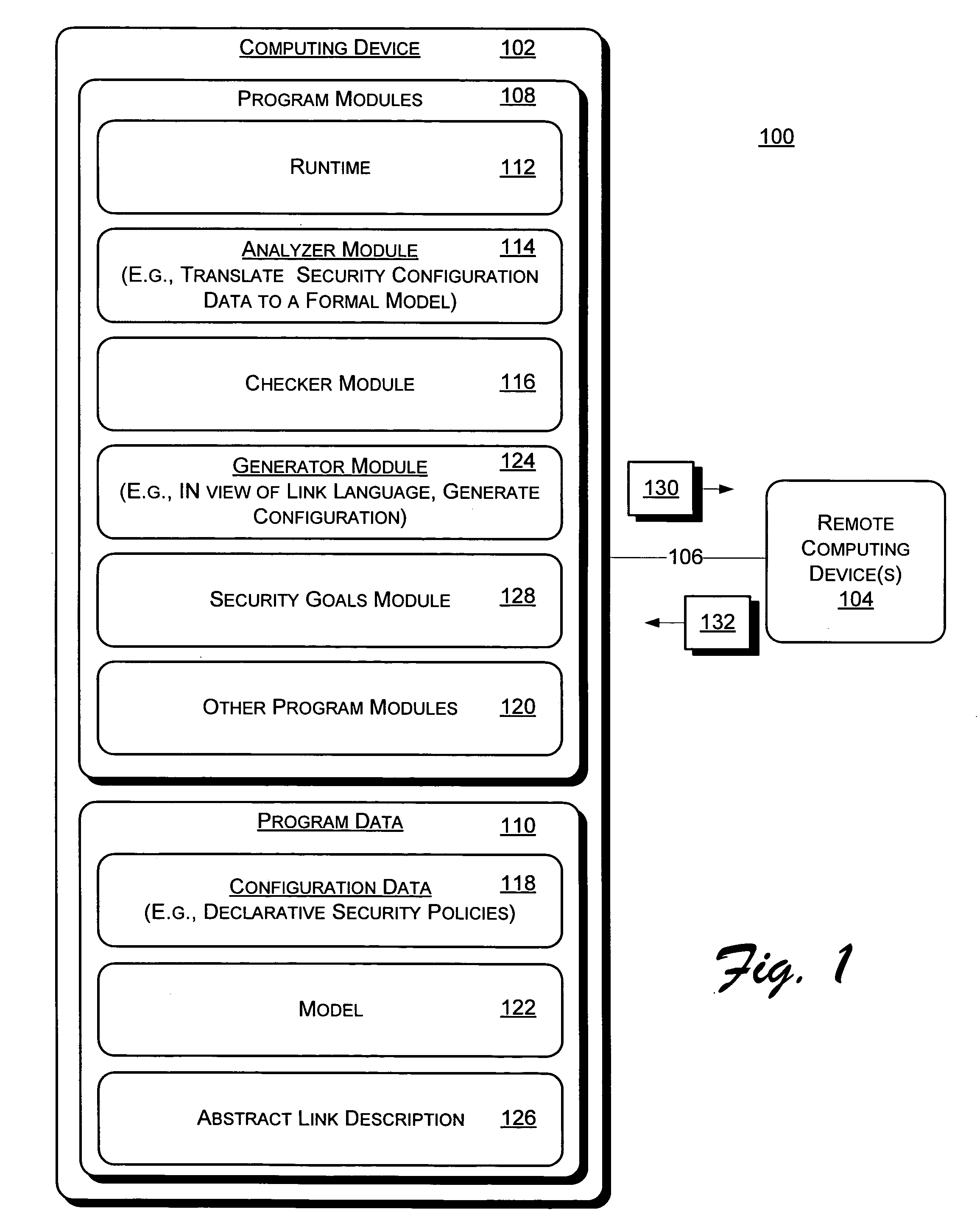
Automatically generating security policies for web services
InactiveUS20050251853A1User identity/authority verificationData switching networksWeb serviceMessage switching
Systems and methods for automatically generating security policy for a web service are described. In one aspect, one or more links between one or more endpoints are described with an abstract link description. The abstract link description describes, for each link of the one or more links, one or more security goals associated with exchange of message(s) between the one or more endpoints associated with the link. The one or more endpoints host respective principals networked in a distributed operating environment. Detailed security policies for enforcement during exchange of messages between the one or more endpoints are automatically generated from the abstract link description.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
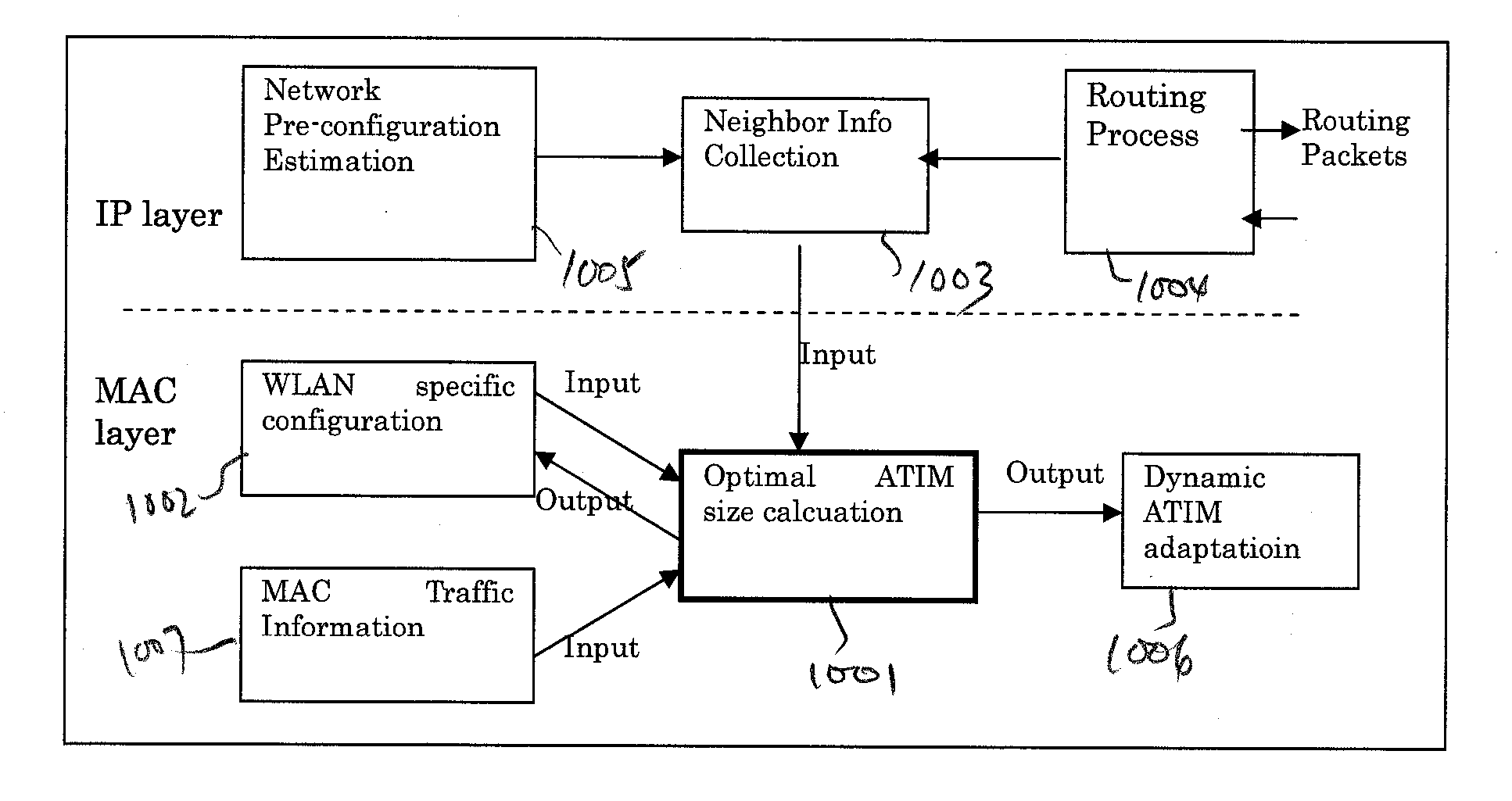
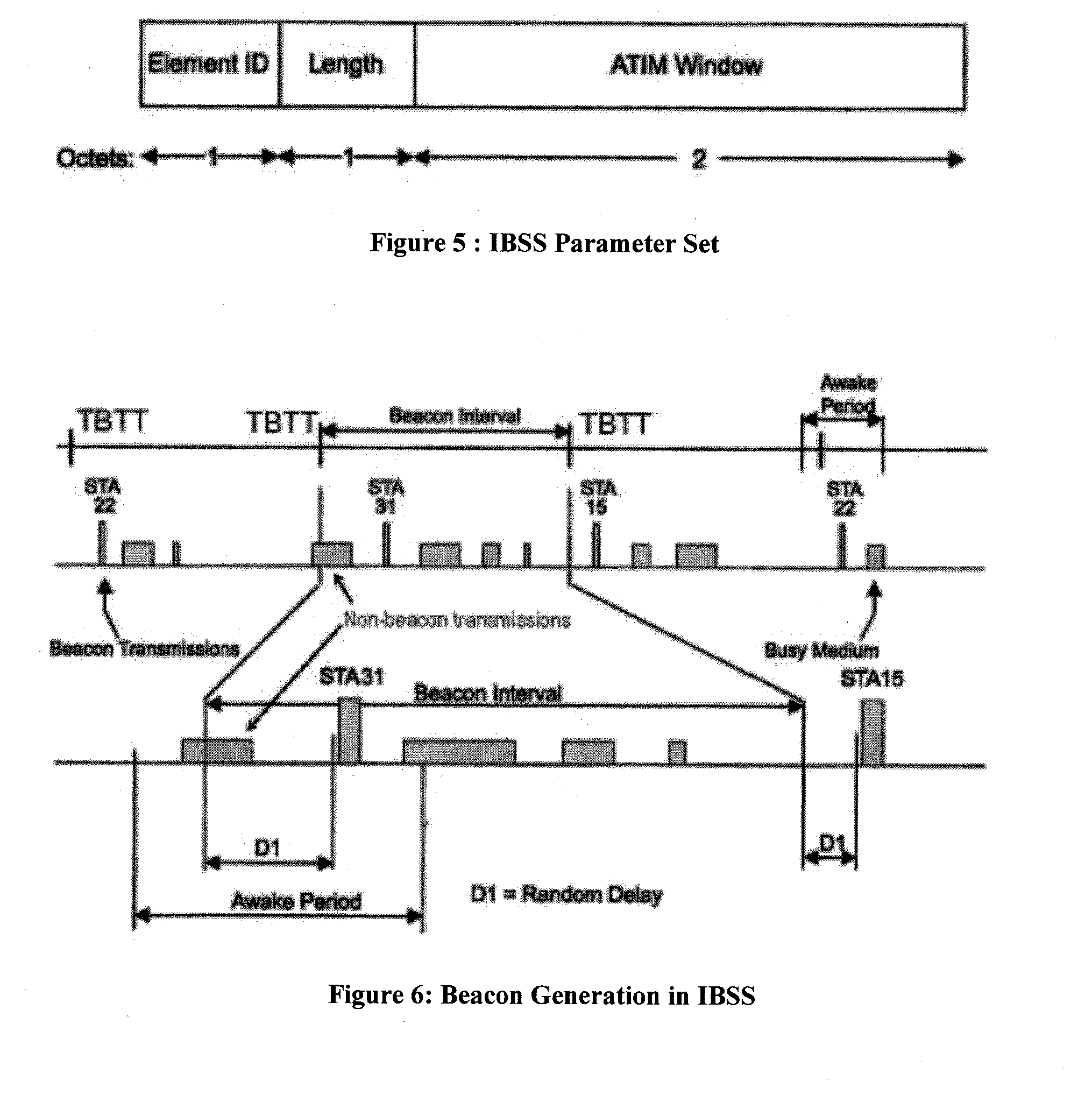
Method and apparatus for optimal atim size setup for 802.11 networks in an ad hoc mode
InactiveUS20070133448A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMessage switchingNetsniff-ng
A method for power saving in an ad hoc wireless computer network determines an optimal ATIM message exchange window. The method (a) determines an effective number of nodes that participate in exchanges of ATIM messages during an ATIM window; (b) using the effective number of nodes, calculating a length for a data frame transmission window; and (c) calculates a length for the ATIM window using the calculated data frame transmission window. In one instance, the method determines the effective number of nodes based on the number of senders of ATIM messages. In another instance, the effective number of nodes is determined based on both senders and recipients of the ATIM messages. The method may determine the effective number of nodes from a number of successful ATIM message transmissions in a given time period. The calculated ATIM window size can be provided as an initial value to other methods that dynamically adjust the ATIM window size.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
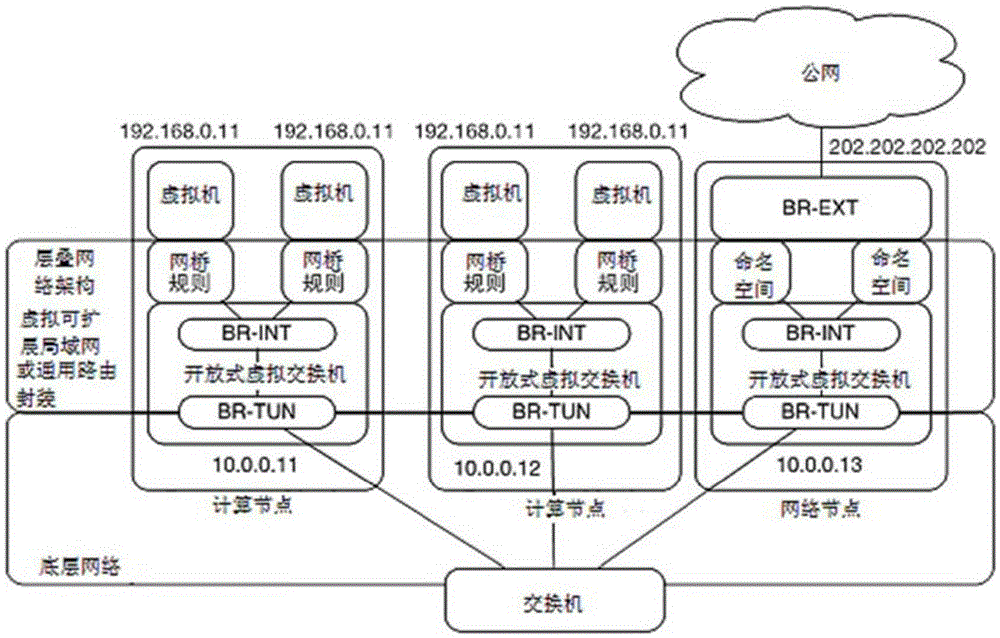
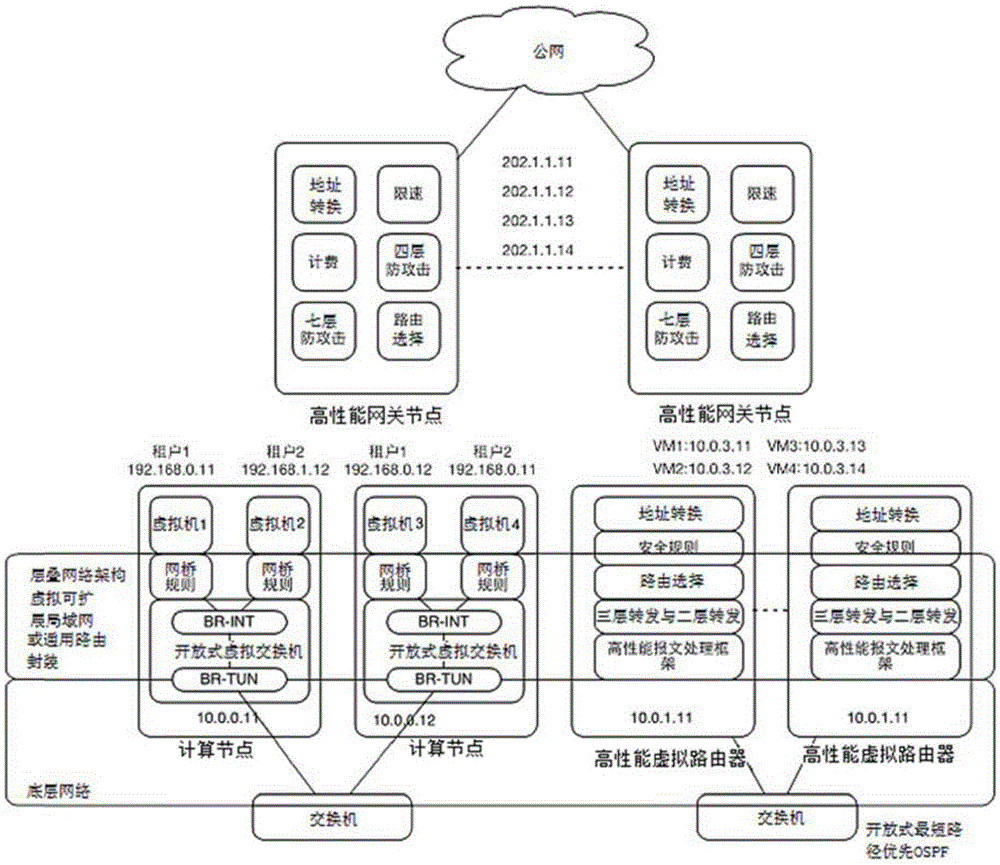
Multi-tenant-oriented cloud network architecture
ActiveCN105391771ADoes not affect availabilityImprove performanceData switching networksPrivate networkIp address
The invention discloses a multi-tenant-oriented network architecture. The cloud network architecture comprises computing nodes, a virtual router cluster and a cloud gateway. Virtual machines which are included in the computing nodes perform message exchange with a public server in a private network through the virtual router cluster. Furthermore message exchange between the virtual machines and a public network is realized through the virtual router cluster and the cloud gateway, wherein the virtual router cluster comprises at least two virtual routers, and each virtual router transmits a same IP address to a private network switch. The cloud gateway comprises at least two gateway nodes. Each gateway node transmits an equivalent default router to the private network switch. Furthermore each gateway node transmits a same floating IP address to a public network router or a public network switch, thereby realizing cluster expansion of the cloud network architecture, preventing serviceability reduction of the whole network caused by fault of a single node and improving defensive capability of the network to attacks.
Owner:北京云启志新科技股份有限公司
Authentication in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS7660772B2Easy to usePrevent forgeryAccounting/billing servicesData taking preventionTelecommunications networkTelecommunications link
The invention relates to an authentication method intended for a telecommunications network, especially for an IP network. From a terminal (TE1) in the network a first message (RR) containing an authenticator and a data unit is transmitted to the network, the data unit containing information relating to the manner in which the authenticator is formed. For carrying out authentication in the network, the data unit contained in the first message is used for determining a check value, which is compared with the said authenticator. To make it unnecessary for the terminal to perform any complicated and heavy exchange of messages when attaching to the network and for still obtaining the desired security characteristics for use, such an identification unit is used in the terminal which receives as input a challenge from which a response and a key can be determined essentially in the same manner as in the subscriber identity module of a known mobile communications system, a set of authentication blocks is generated into the network, of which each contains a challenge, a response, and a key, whereby the generation is performed in the same manner as in the said mobile communication system, at least some of the challenges contained by the authentication blocks are transmitted to the terminal, one of the challenges is chosen for use at the terminal, and, based on it, a response and key for use are determined with the aid of the terminal's identification unit, in the said first message (RR) the network is notified with the aid of the said data unit of which key corresponding to which challenge was chosen, and the authenticator of the first message and the said check value are determined with the aid of the chosen key.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
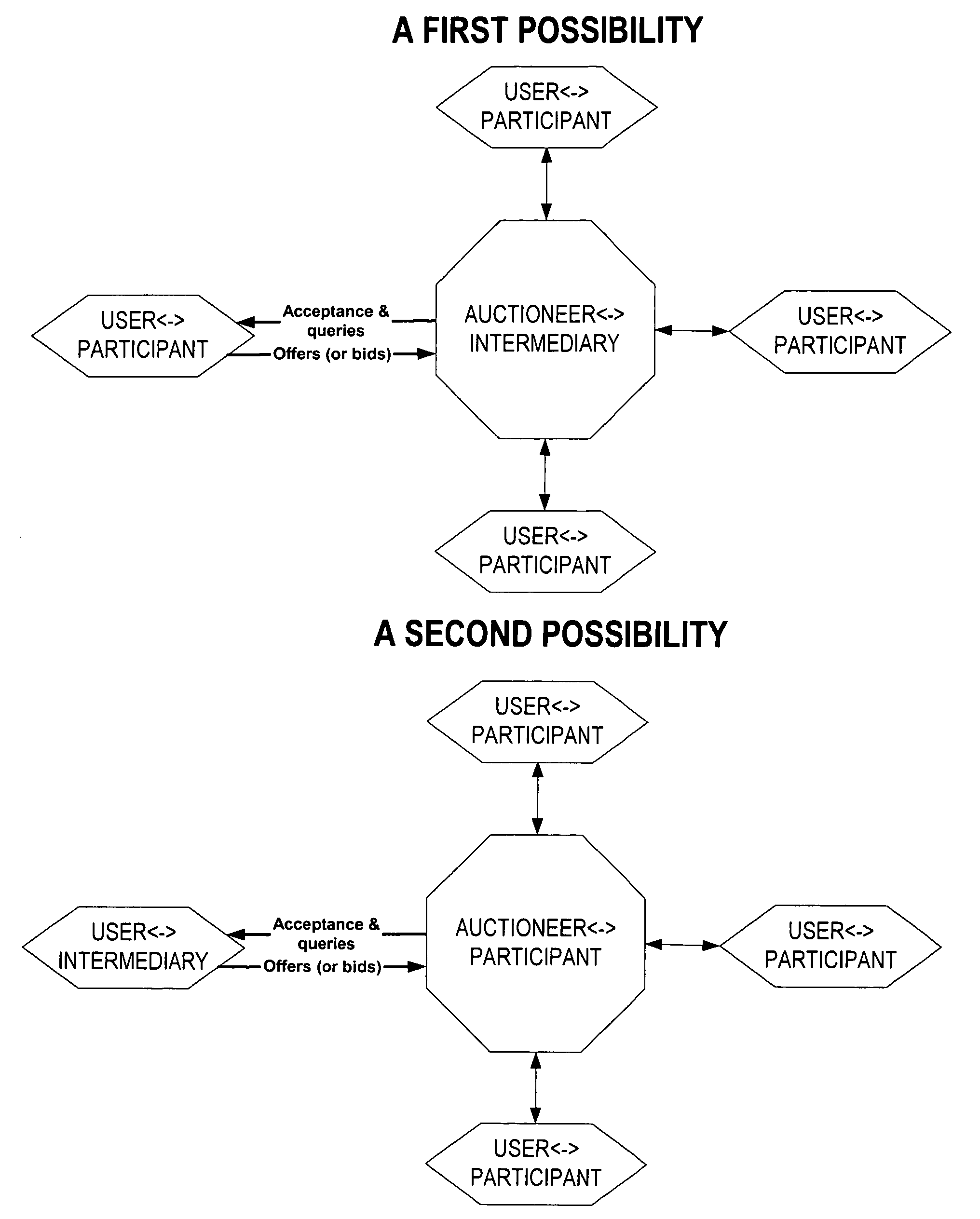
Computer method and system for intermediated exchanges
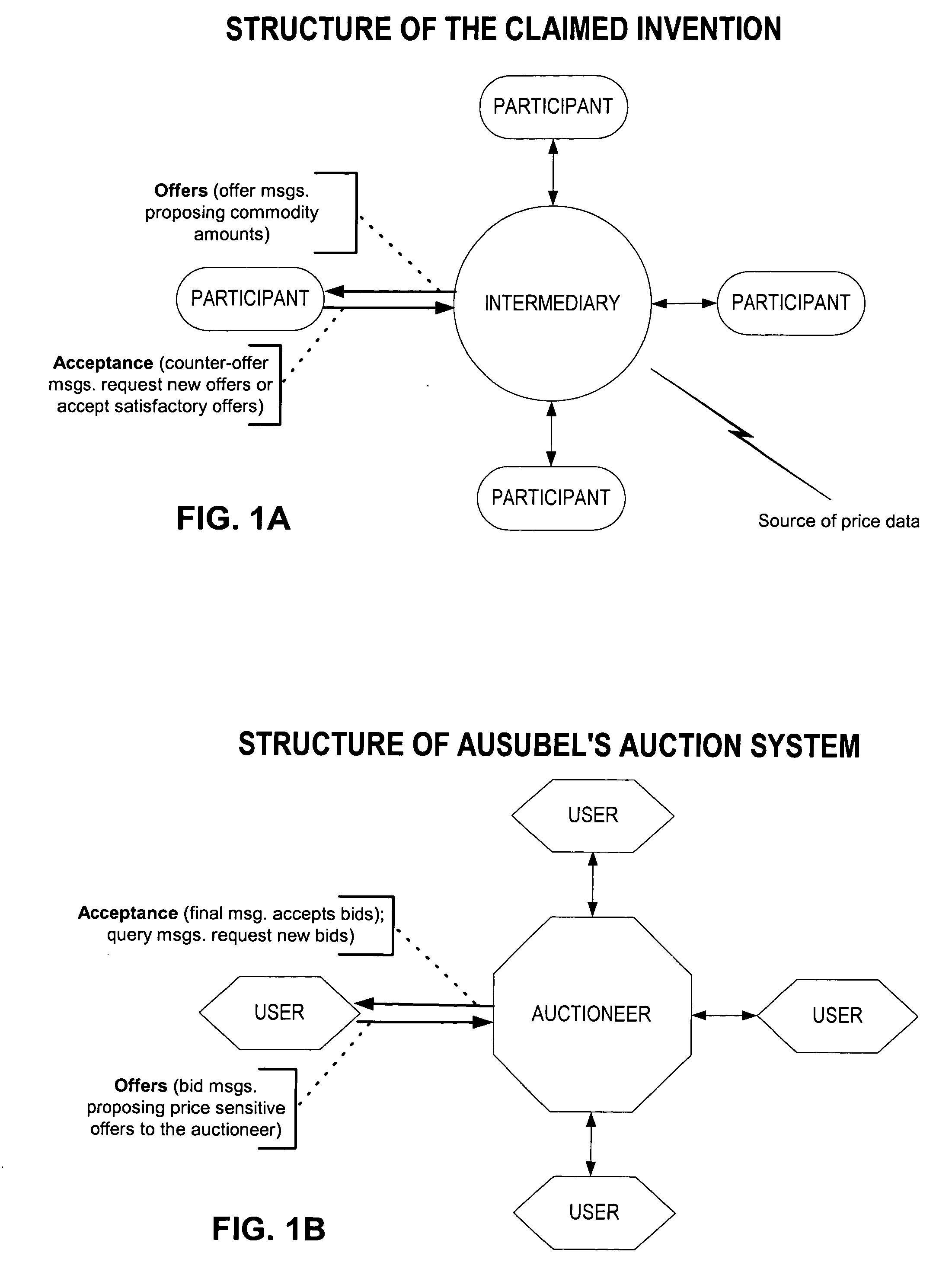
InactiveUS6968318B1Maximize tradeoffMaximizes number of unitFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsComputer methodsSoftware
In a preferred embodiment, this invention includes software processes distributed on one or more computer systems that exchange messages in order to facilitate an intermediated exchange of financial commodities between a plurality of participants. The messages are exchanged according to a preferred protocol that leads to a satisfactory exchange that meets the objectives of the participants, and that substantially maximizes in a fair manner the total amount of financial commodities exchanged. Optionally, the invention employs heuristic rules in association with the preferred protocol that adapt the protocol to the time and exchange requirements of financial commodities. In other embodiments, this invention is equally applicable to the exchange of any tangible or intangible commodities. In a general embodiment, this invention further includes a preferred message-exchange protocol for the construction of computer programs representing exchange participants and an intermediary. These constructed computer programs exchange messages such that a satisfactory intermediated exchange of commodities is substantially certain to be achieved.
Owner:ITG SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS INC
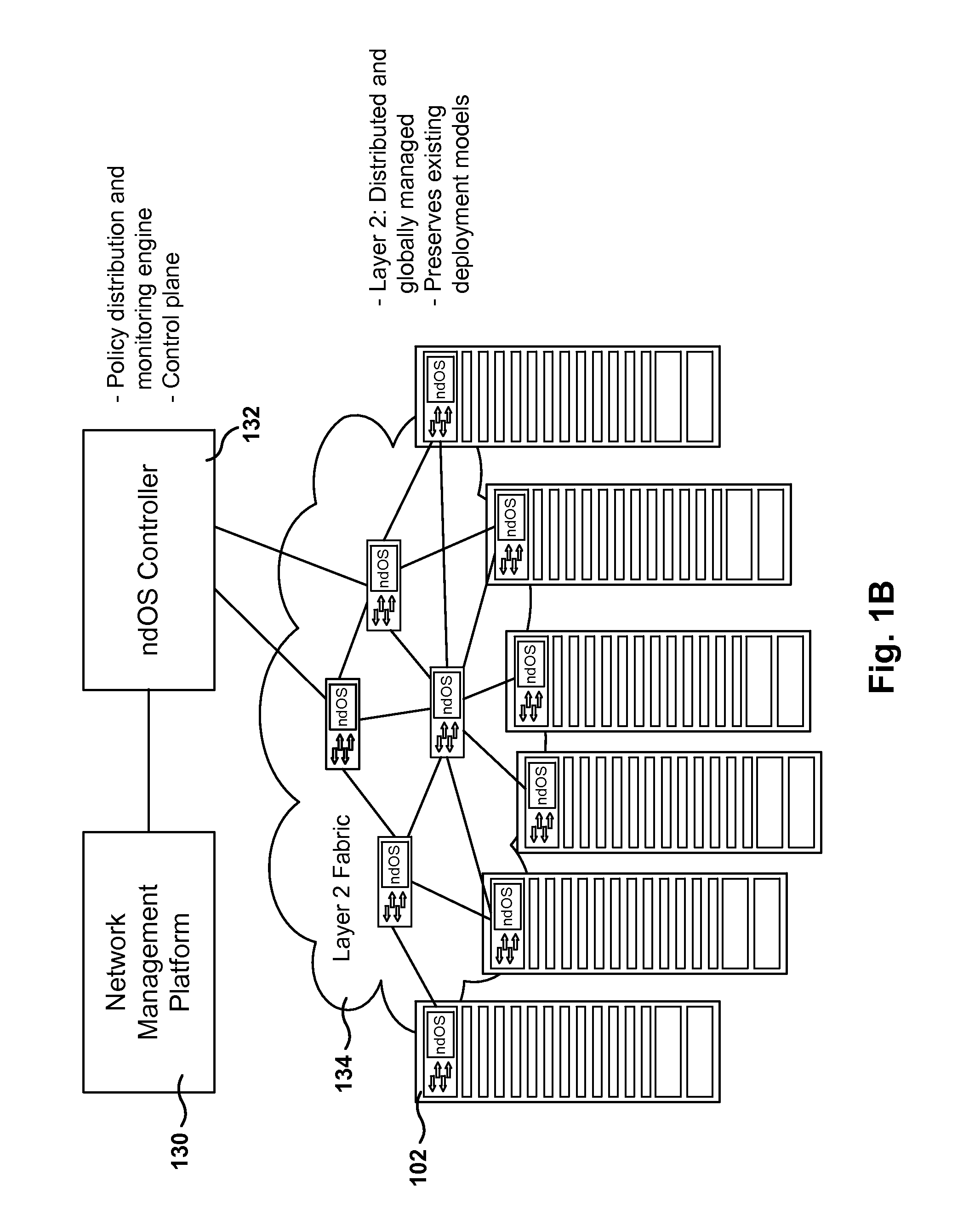
Methods, Systems, and Fabrics Implementing a Distributed Network Operating System
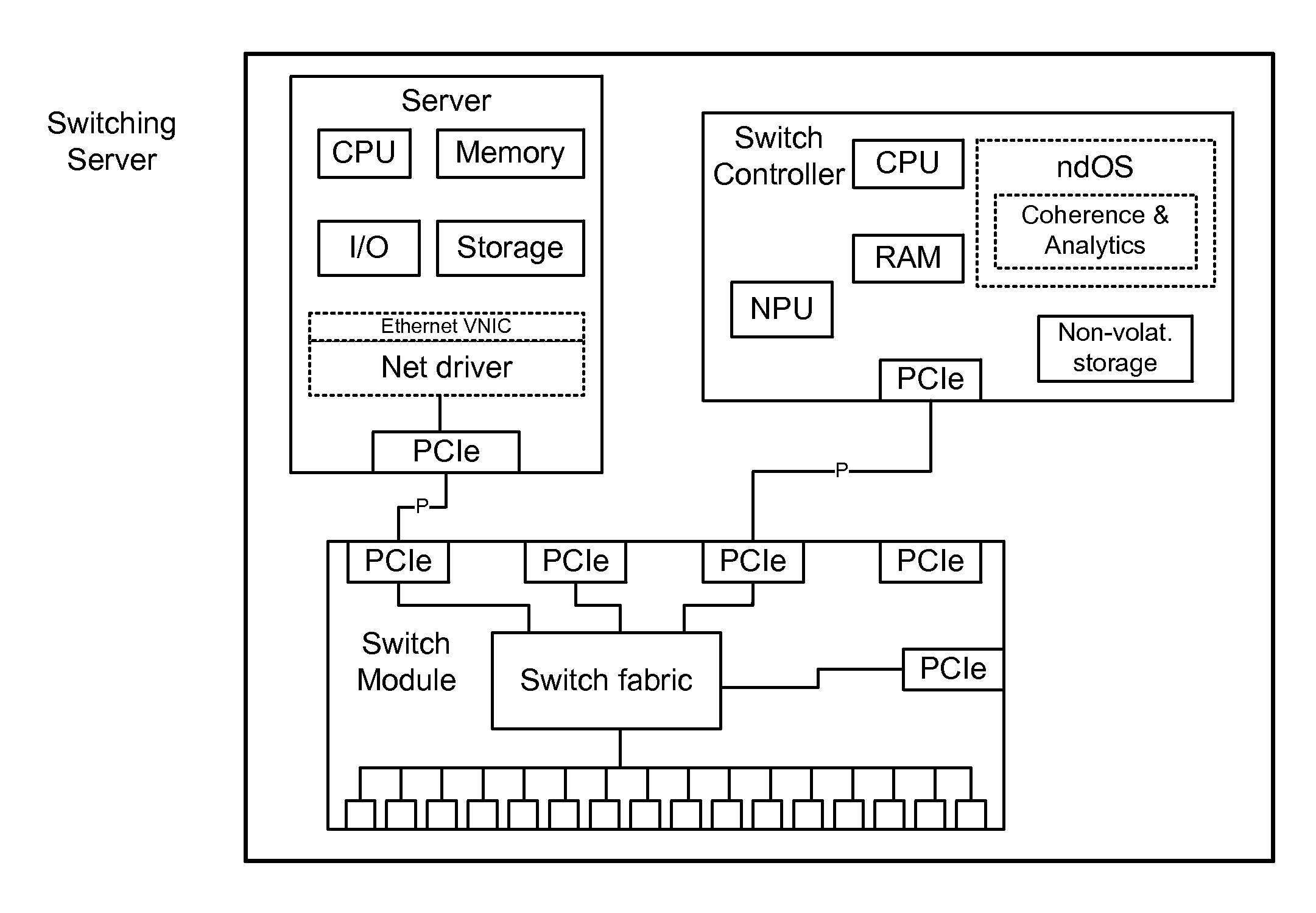
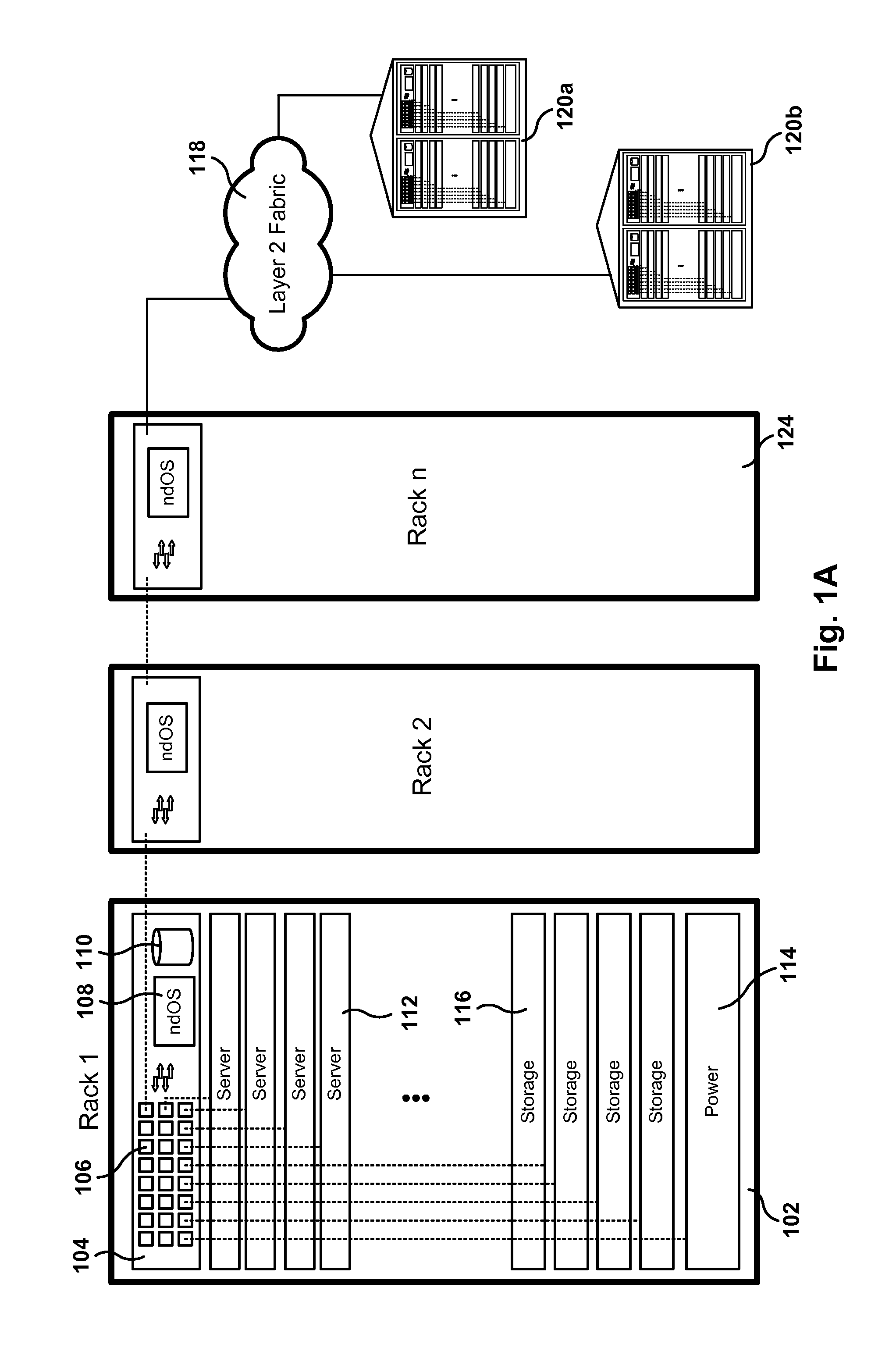
ActiveUS20130235870A1Data switching by path configurationService-level agreementNetwork operating system
Methods, systems, and computer programs are presented for managing a switching layer fabric. A network device operating system (ndOS) program includes program instructions for exchanging switching policy regarding a switching of network packets in a plurality of ndOS switching devices having respective ndOS programs executing therein. The first ndOS program is executed in a first ndOS switching device, and the switching policy is exchanged with other ndOS programs via multicast messages. Further, the ndOS program includes program instructions for exchanging resource control messages with the other ndOS switching devices to implement service level agreements in the switching layer fabric, where the ndOS switching devices cooperate to enforce the service level agreements. Further yet, the ndOS program includes program instructions for receiving changes to the switching policy, and program instructions for propagating the received changes to the switching policy via message exchange between the ndOS programs. The ndOS switching devices are managed as a single logical switch that spans the plurality of ndOS switching devices.
Owner:PLURIBUS NETWORKS
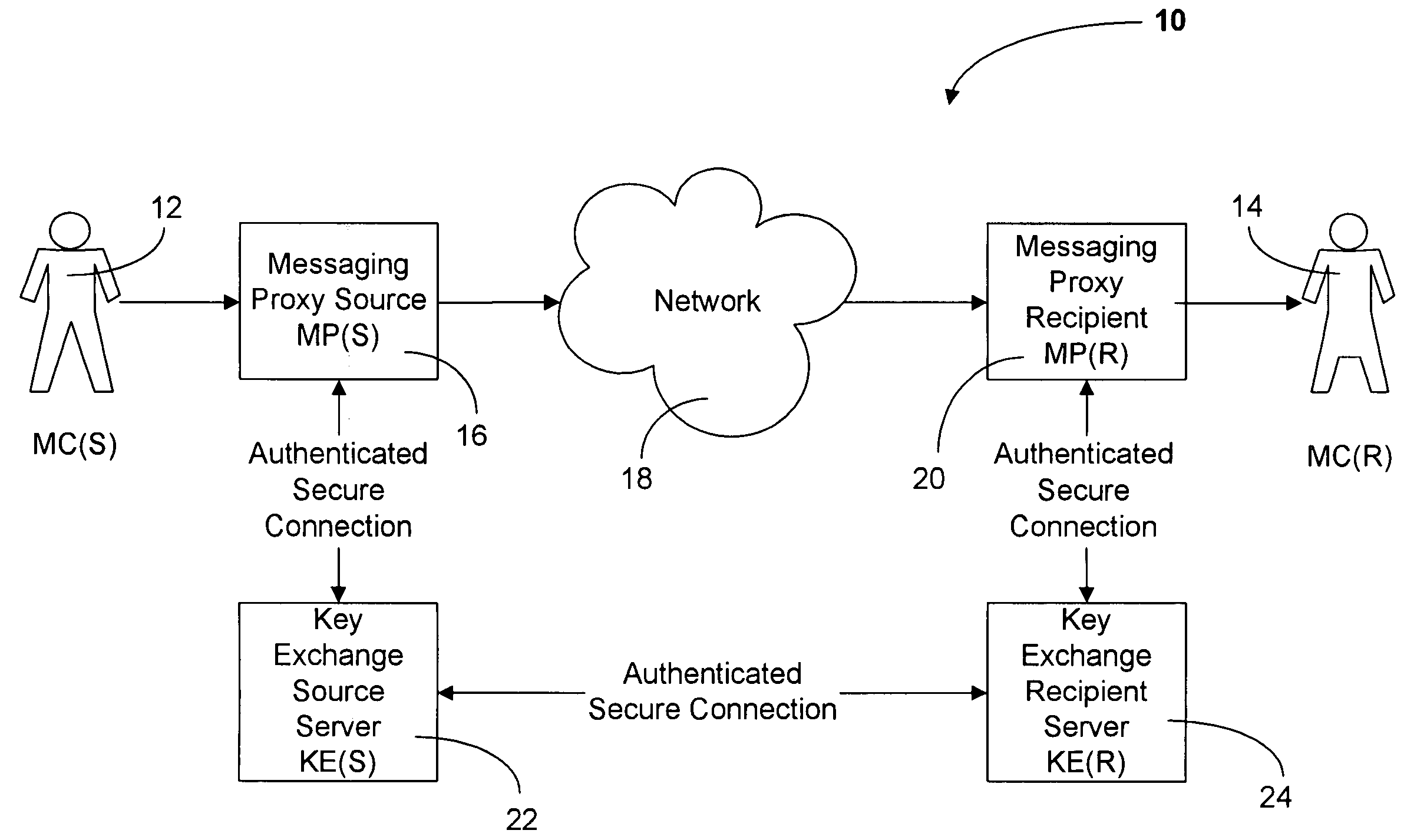
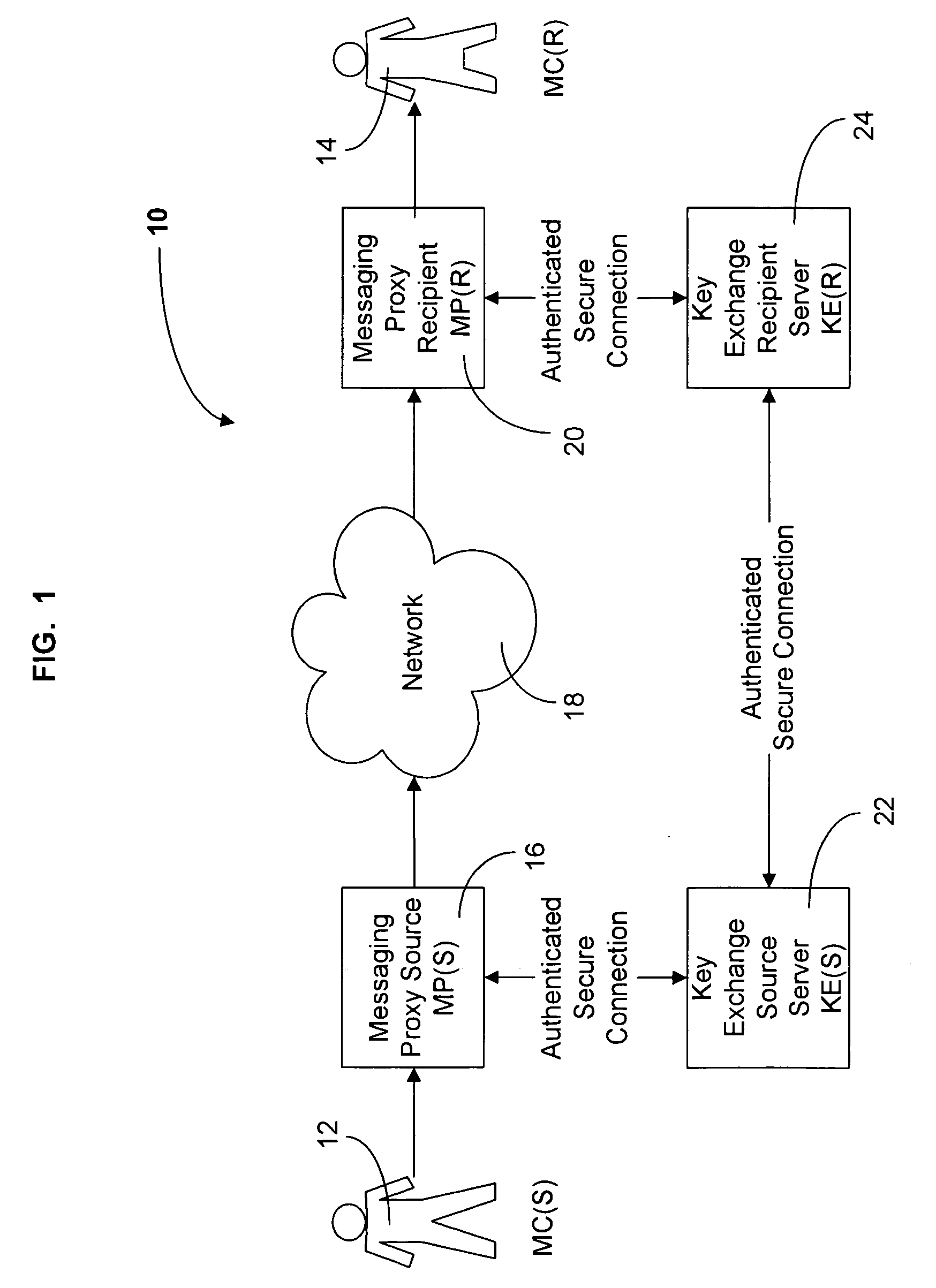
Method and system for sending secure messages over an unsecured network
InactiveUS20050182937A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeMessage delivery
The present invention is directed to a system and method for providing the secure exchange of messages utilizing an existing unsecured messaging network such as the Internet. A messaging proxy is provided between a sender of a message and the unsecured messaging network. In sending a secure message, the messaging proxy contacts a key exchange server via an authenticated secure connection. The messaging proxy generates a key with which to encrypt the message. The key is sent via an authenticated secure connection to a messaging proxy of a recipient. If the sender receives an acknowledgement of the recipient receiving the key, the message is encrypted and sent via the unsecured messaging network. The recipient then uses the key to decrypt the message. Should the recipient not have a proxy in place to receive encrypted messages and a corresponding key exchange server, the message is sent unencrypted.
Owner:BEDI HARMEET SINGH
Identification information protection method in wlan inter-working
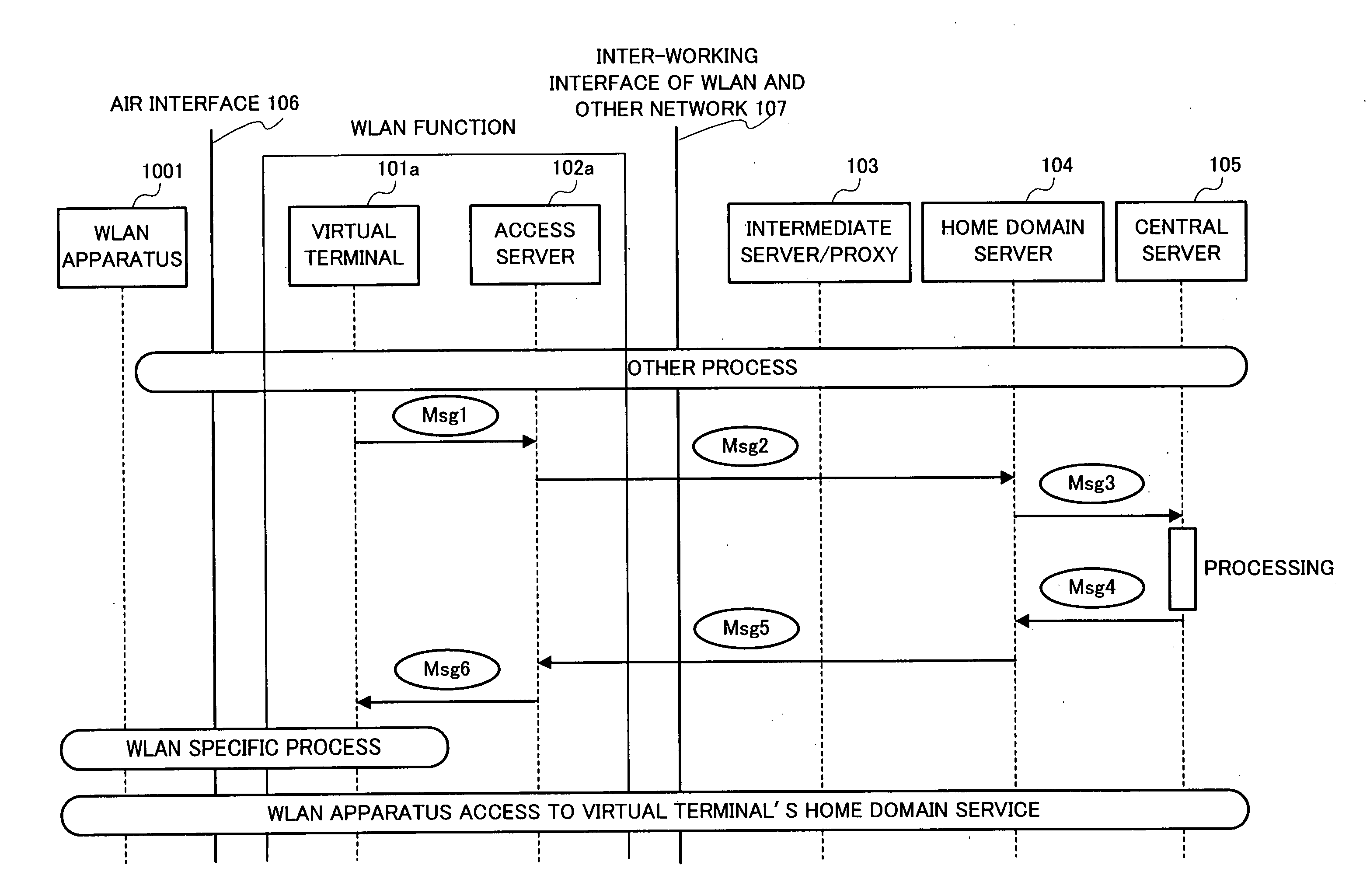
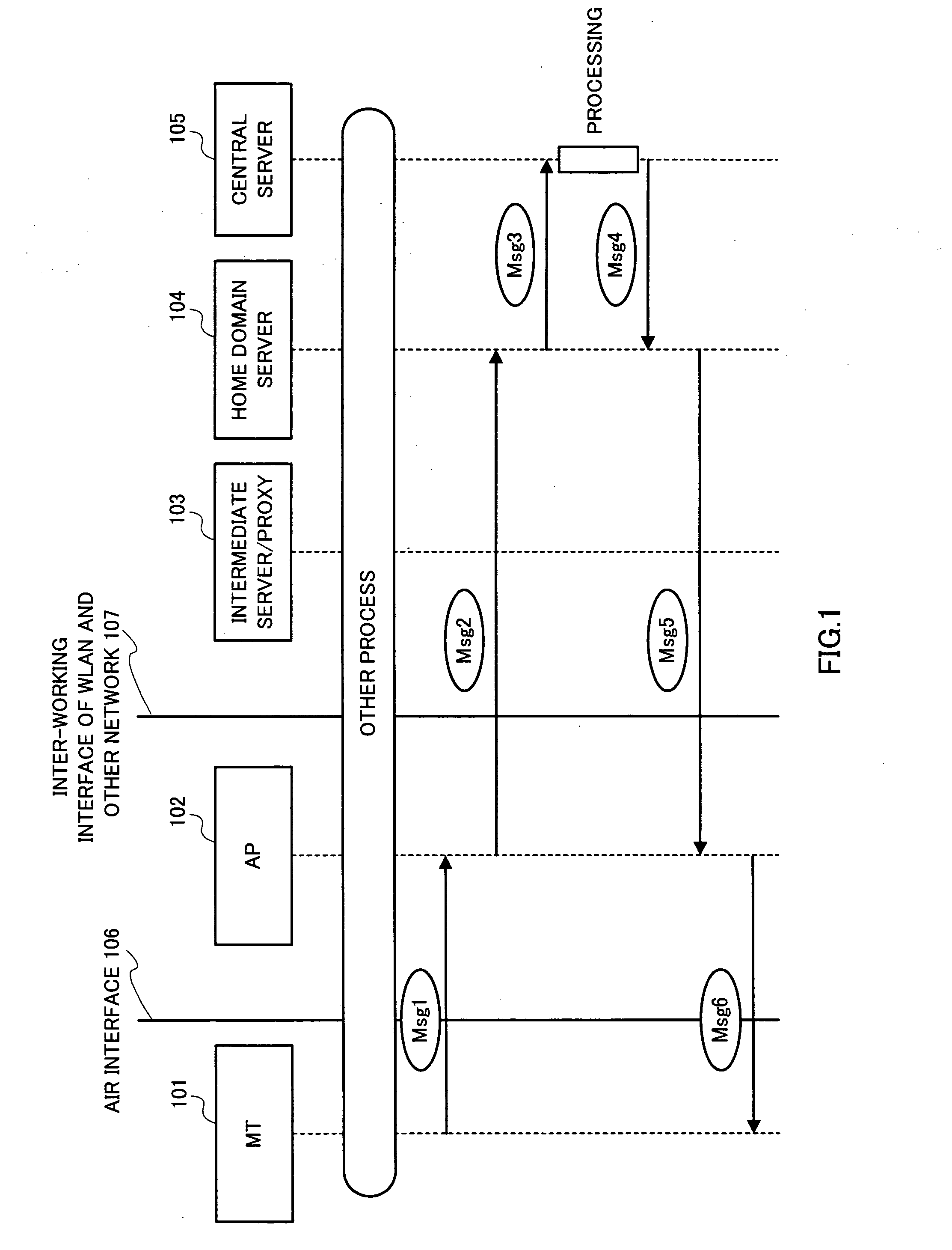
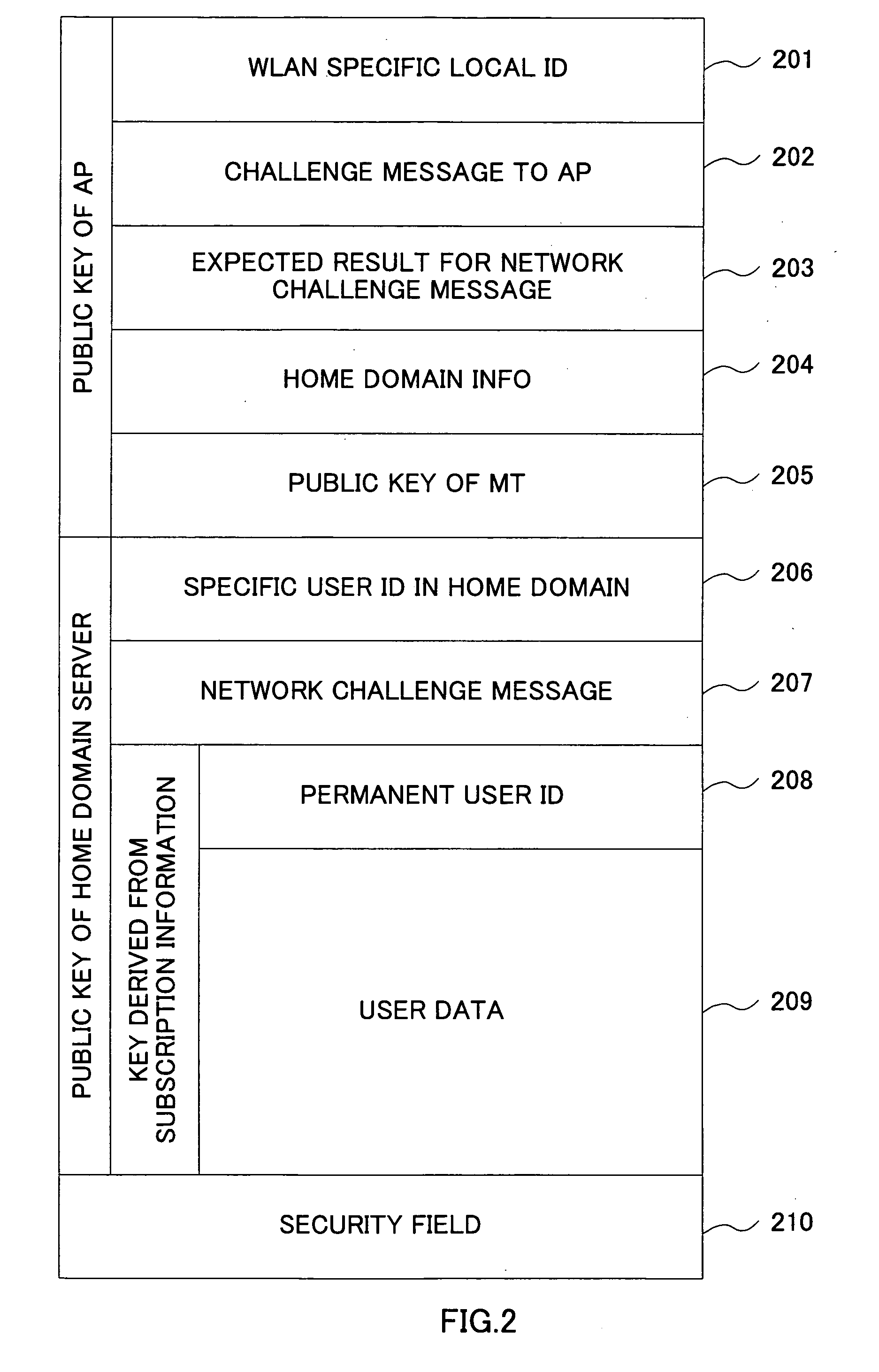
ActiveUS20060101273A1Save network resourcesAdd supportDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationMan-in-the-middle attackMessage switching
By introducing a hierarchical encryption scheme and the use of asymmetric cryptography, the critical information in message exchanges is concealed from unauthorized entities. This helps greatly in preventing man-in-the-middle attacks faced by inter-working. In addition, access control is conducted by introducing a network structure having a rule interpreter that is capable of mapping general rules to WLAN specific commands. It obviates the needs for mobile user's home network to understand information about every WLAN it is inter-worked with. A common interface independent of WLAN technologies could be used by the home network for all the WLANs. The above conception provides a solution to the problems of the protection of user identification information and access control in the inter-working of WLAN.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for device discovery in wireless communication
ActiveUS20080176561A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionWireless dataMessage switching
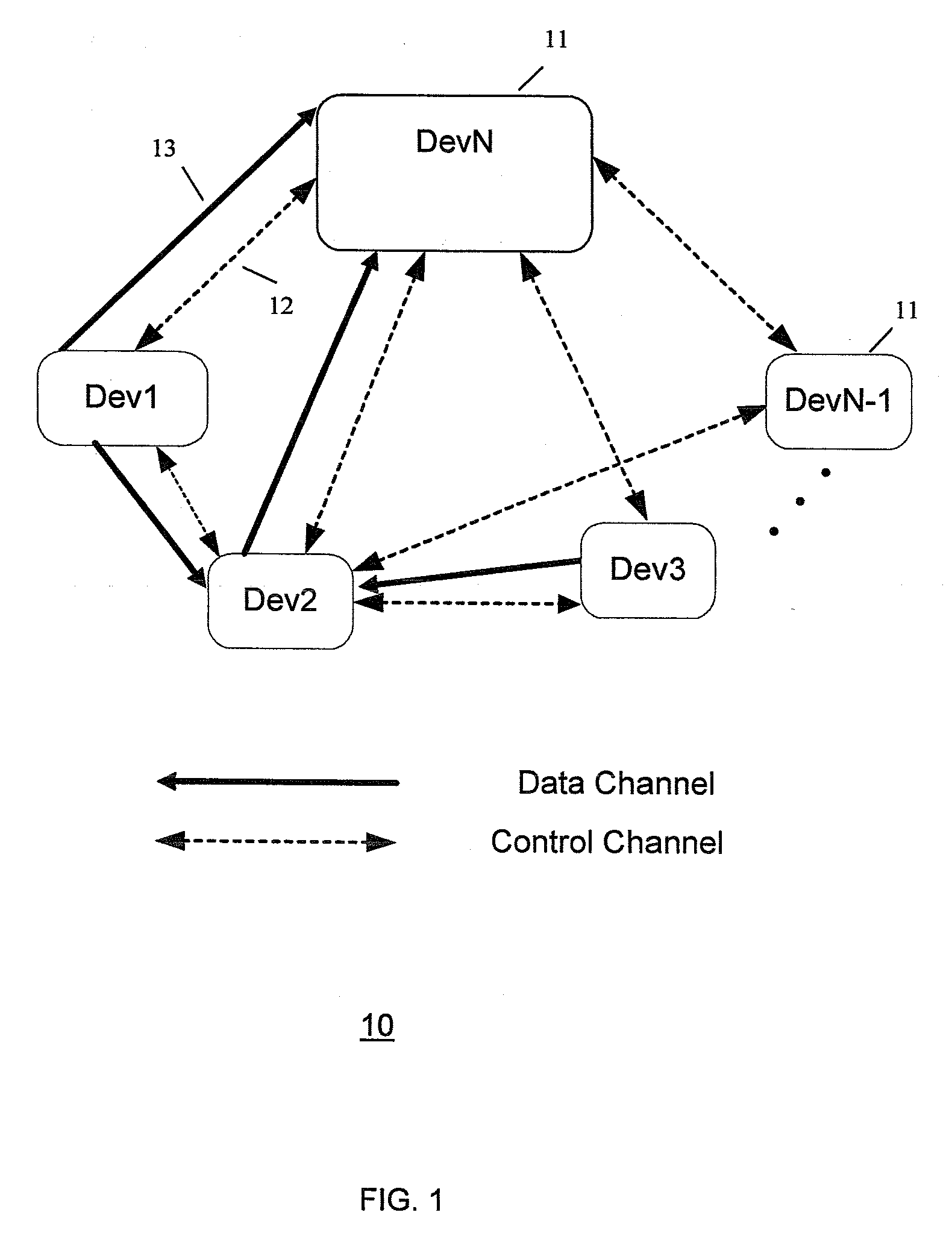
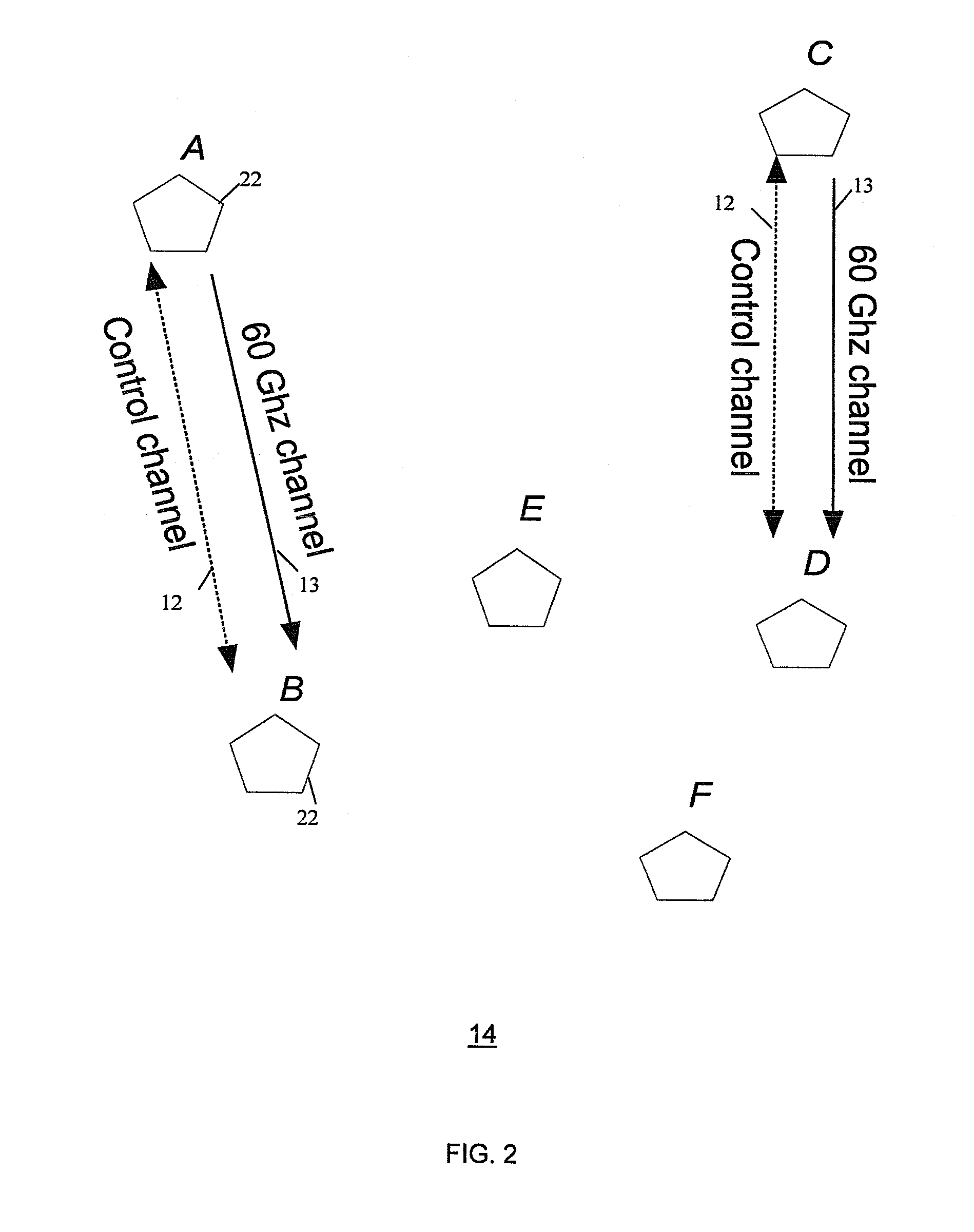
The present invention provides a method and a system for device discovery in wireless communication. One implementation involves scanning one or more wireless channels to discover a partner wireless station for a new transmission, by detecting peak energy and beacons on each scanned channel. If a beacon is not detected, then selecting the clearest channel among the scanned channels, and transmitting beacons on the clearest channel. Upon detecting a beacon from a partner station, establishing association with the partner station and selecting a wireless data channel for communication with the partner station. Another implementation involves discovering a partner wireless station to establish a data channel for communication with a discovering station that is associated with a coordinator station, and transmitting a bandwidth reservation request to the coordinator to reserve channel time for control message exchange between the discovering station and the partner station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
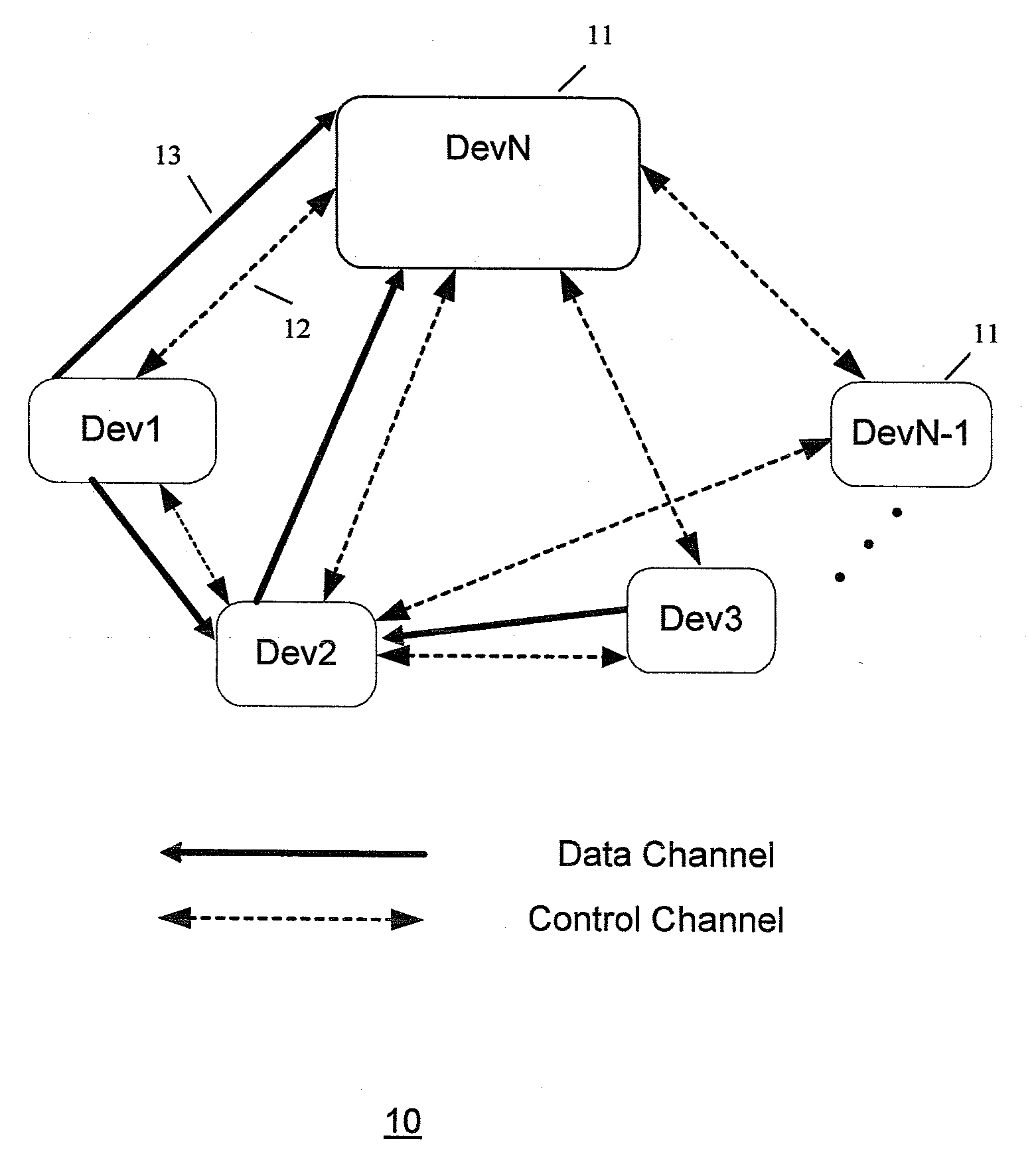
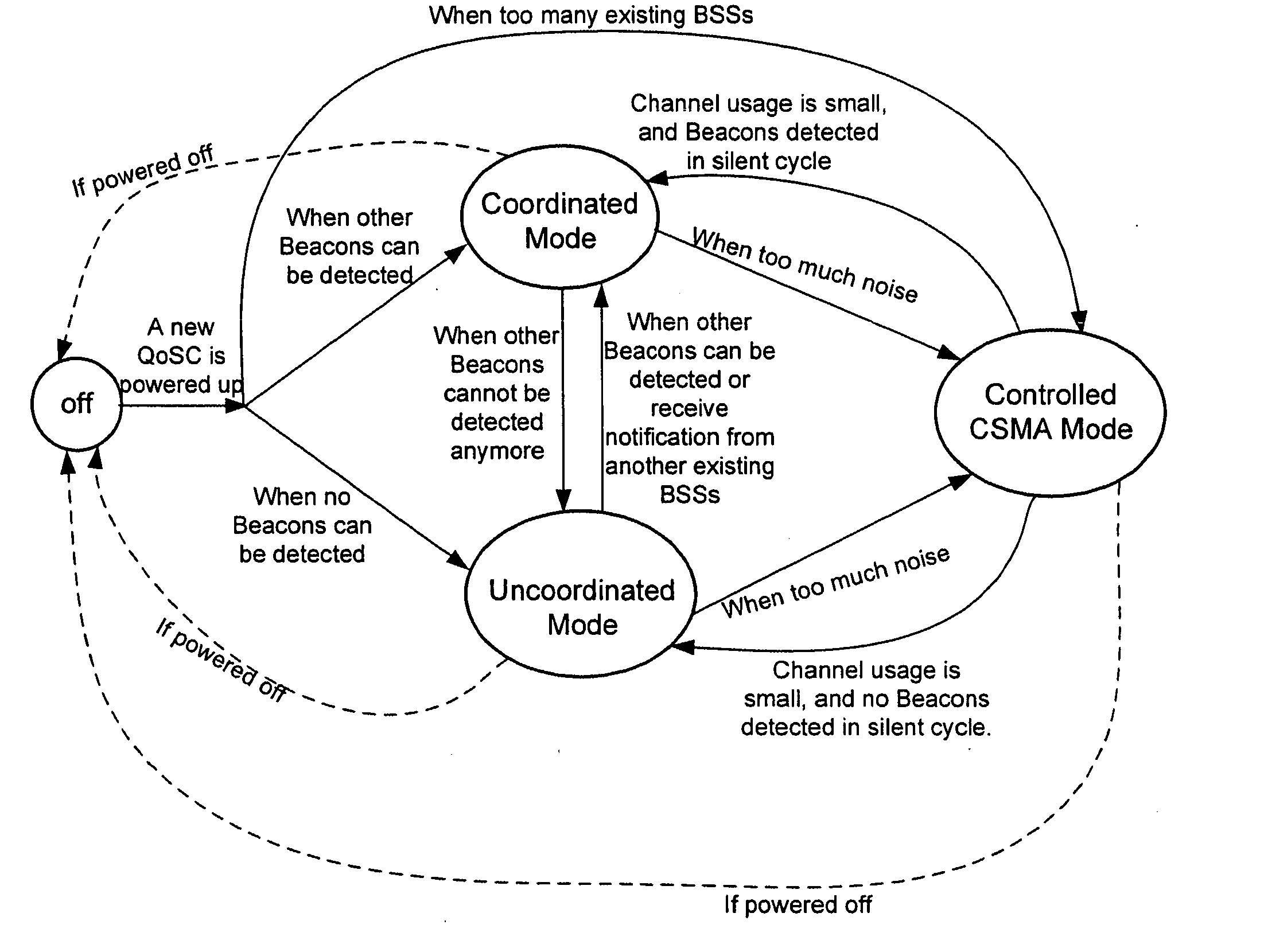
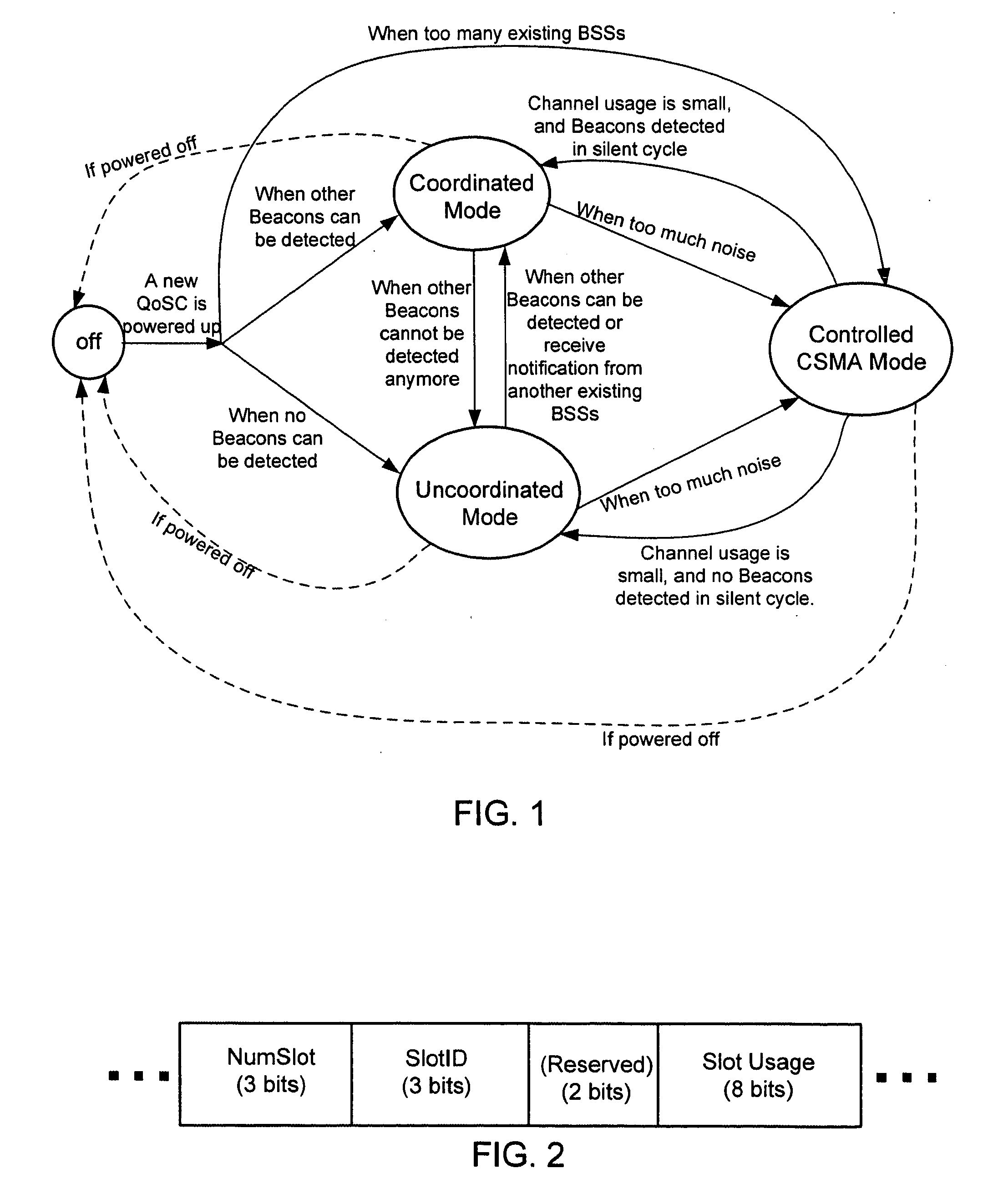
Systems and methods for network coordination with limited explicit message exchange
ActiveUS20050170835A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionMessage switchingDistributed computing
Owner:SHARP KK
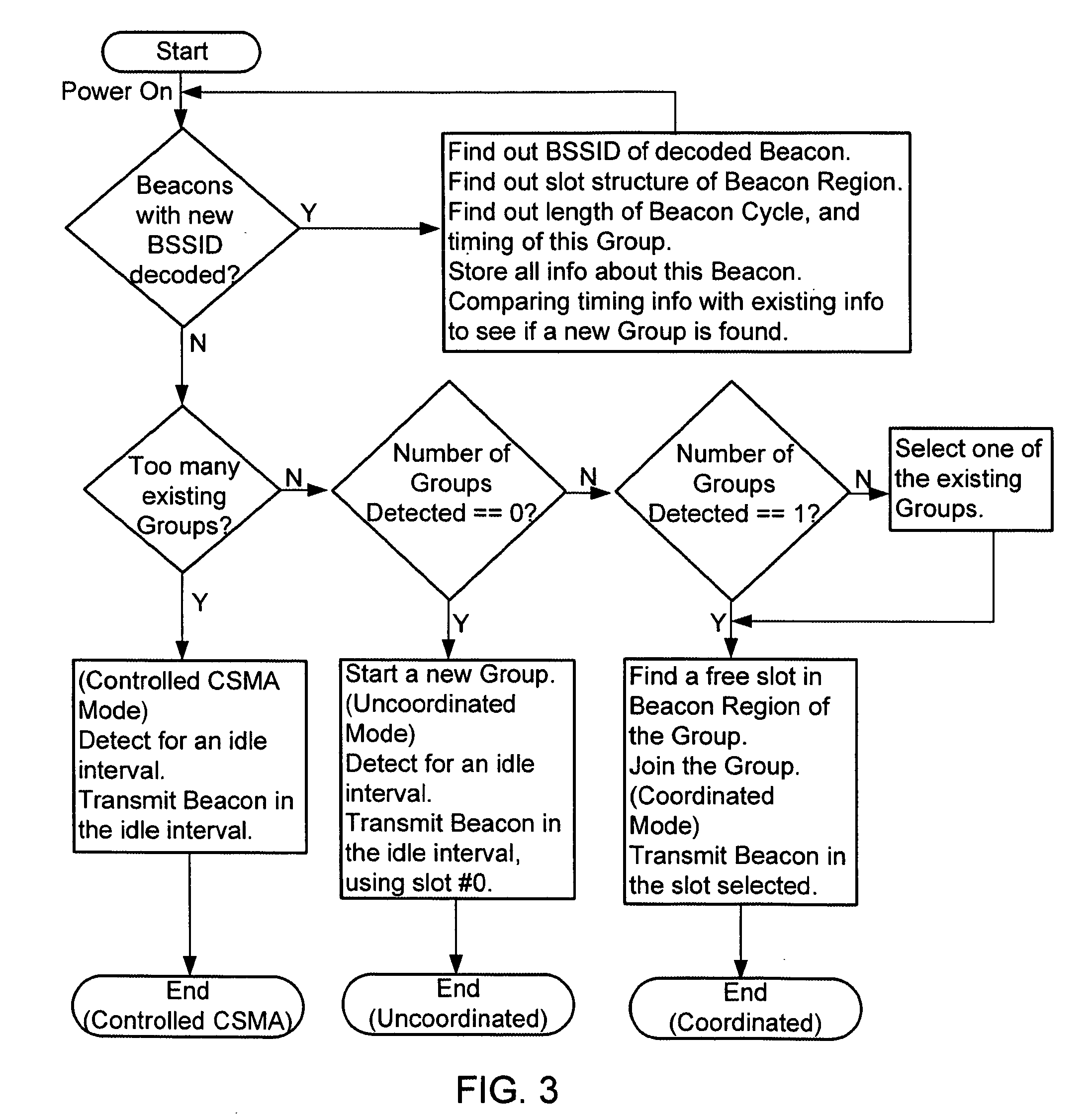
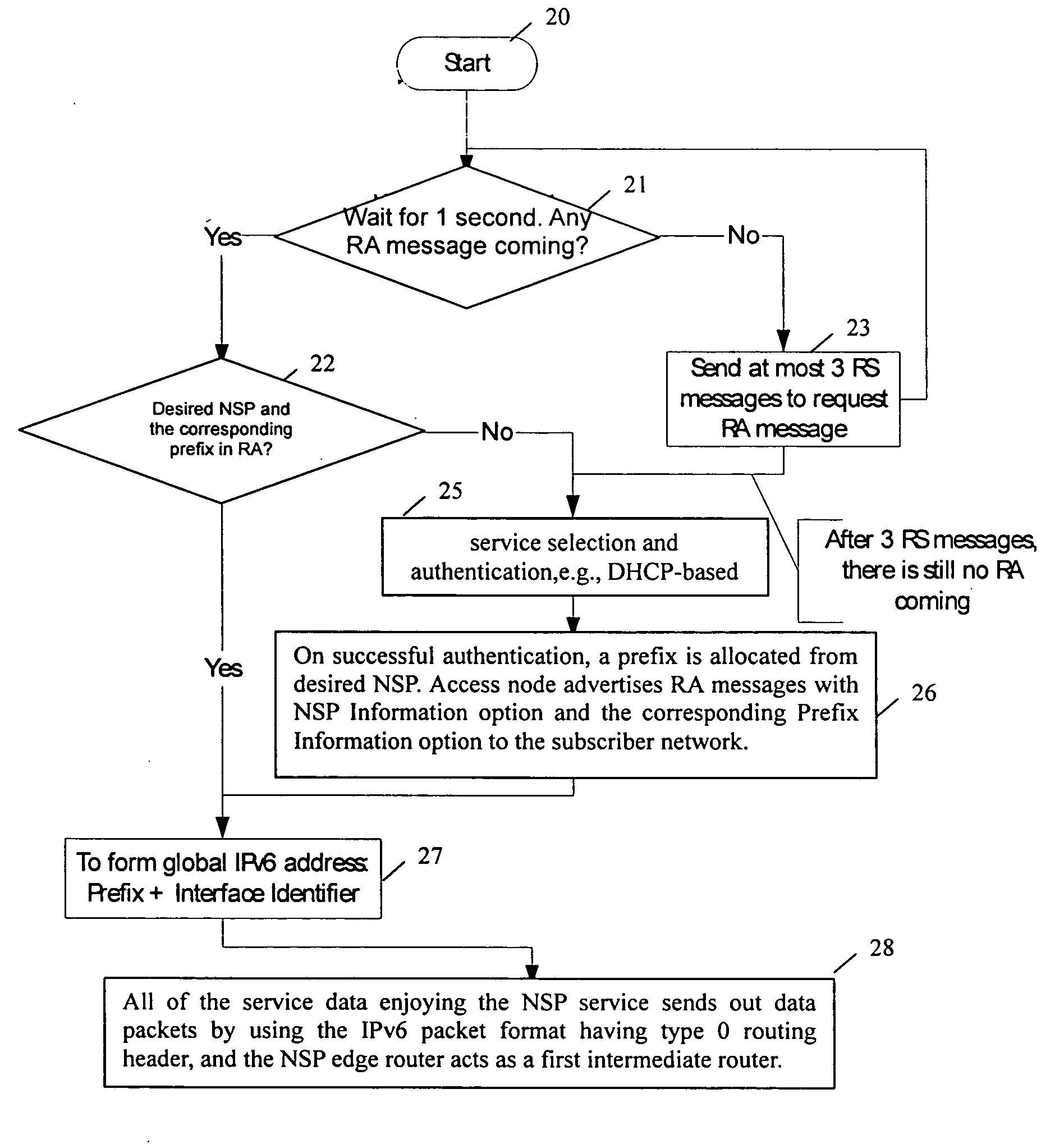
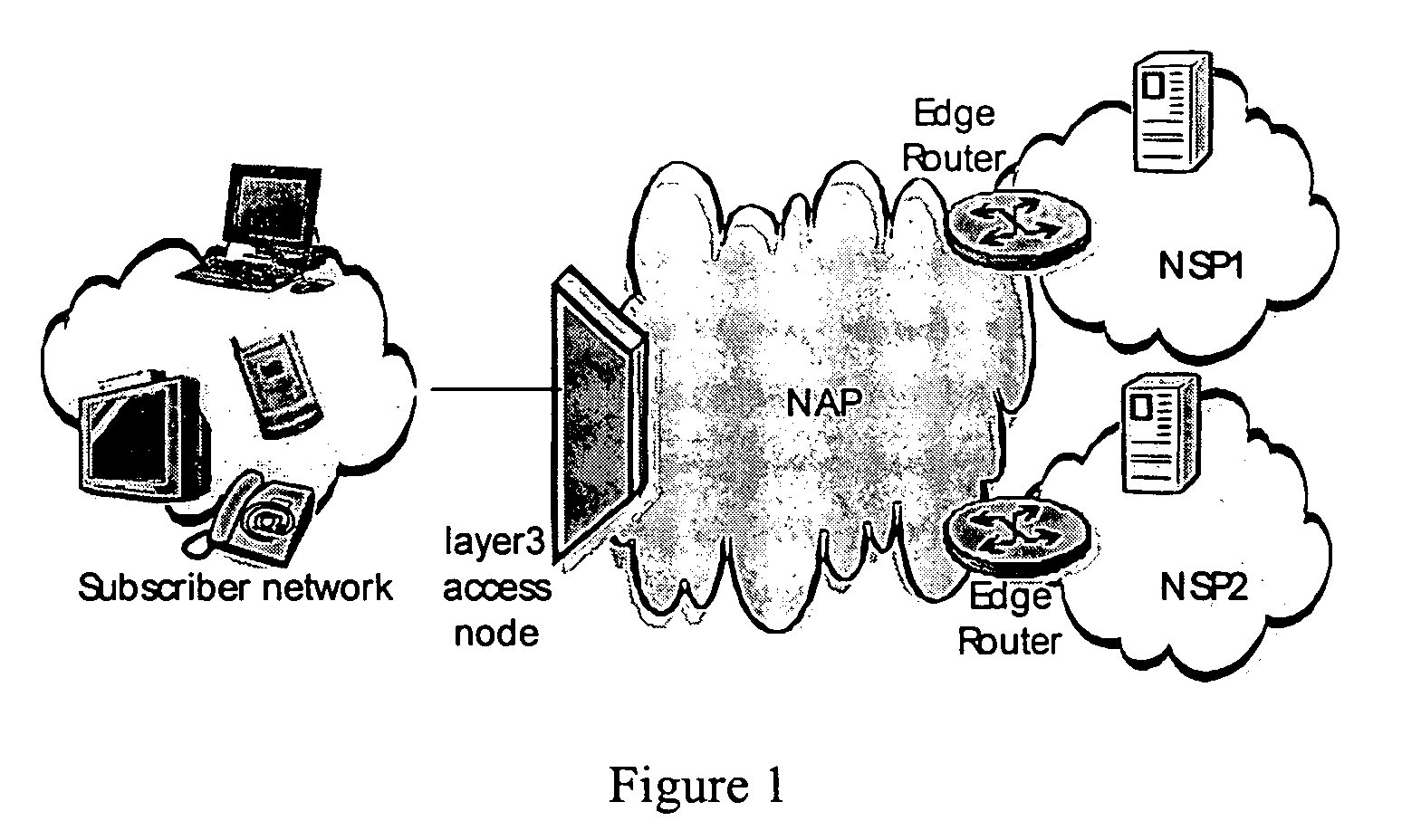
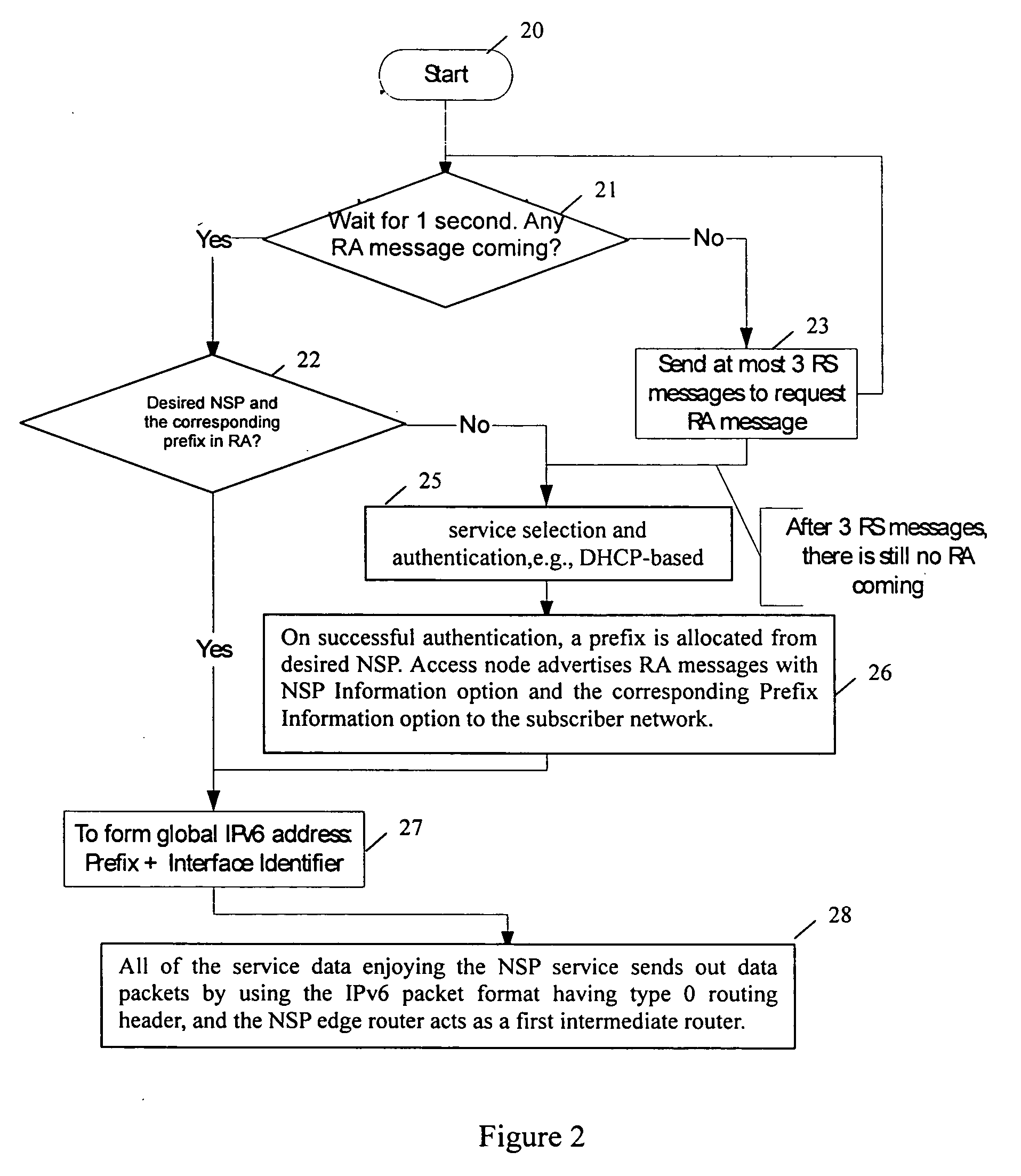
Network service selection and authentication and stateless auto-configuration in an IPv6 access network
InactiveUS20060080728A1Easy to useMore manageable for the operatorDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTraffic volumeAuto-configuration
The present invention provides a method for network service selection and authentication in an IPv6 access network, a scheme for stateless auto-configuration and devices thereof. A NSP Information option containing the IPv6 address of a NSP edge router and a NSP name is defined in RA messages. A NSSA Information option is defined in RS option fields. The present invention enables IPv6 stateless auto-configuration in an access network. The new NSP Information option, the way of “one time authentication per subscriber network per NSP” and the use of IPv6 routing header promote the efficiency of IPv6 stateless auto-configuration and reduce the NSP selection and authentication traffic. The present invention provides an efficient solution for network service selection and authentication without introducing any other message exchange between terminals and access nodes. In short, the scheme of network service selection and authentication according to the present invention is piggybacked on RS / RA messages, which is very simple.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
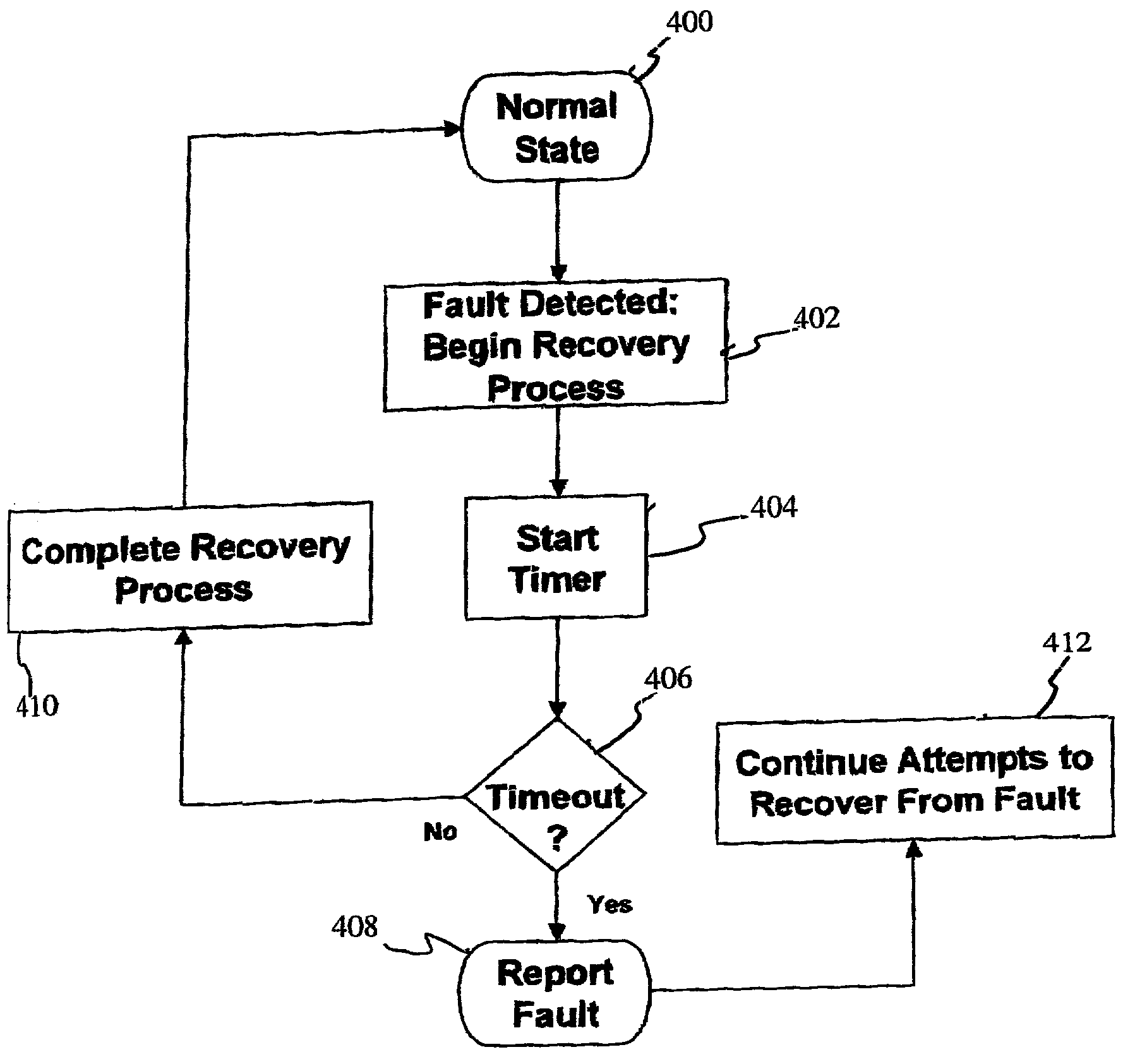
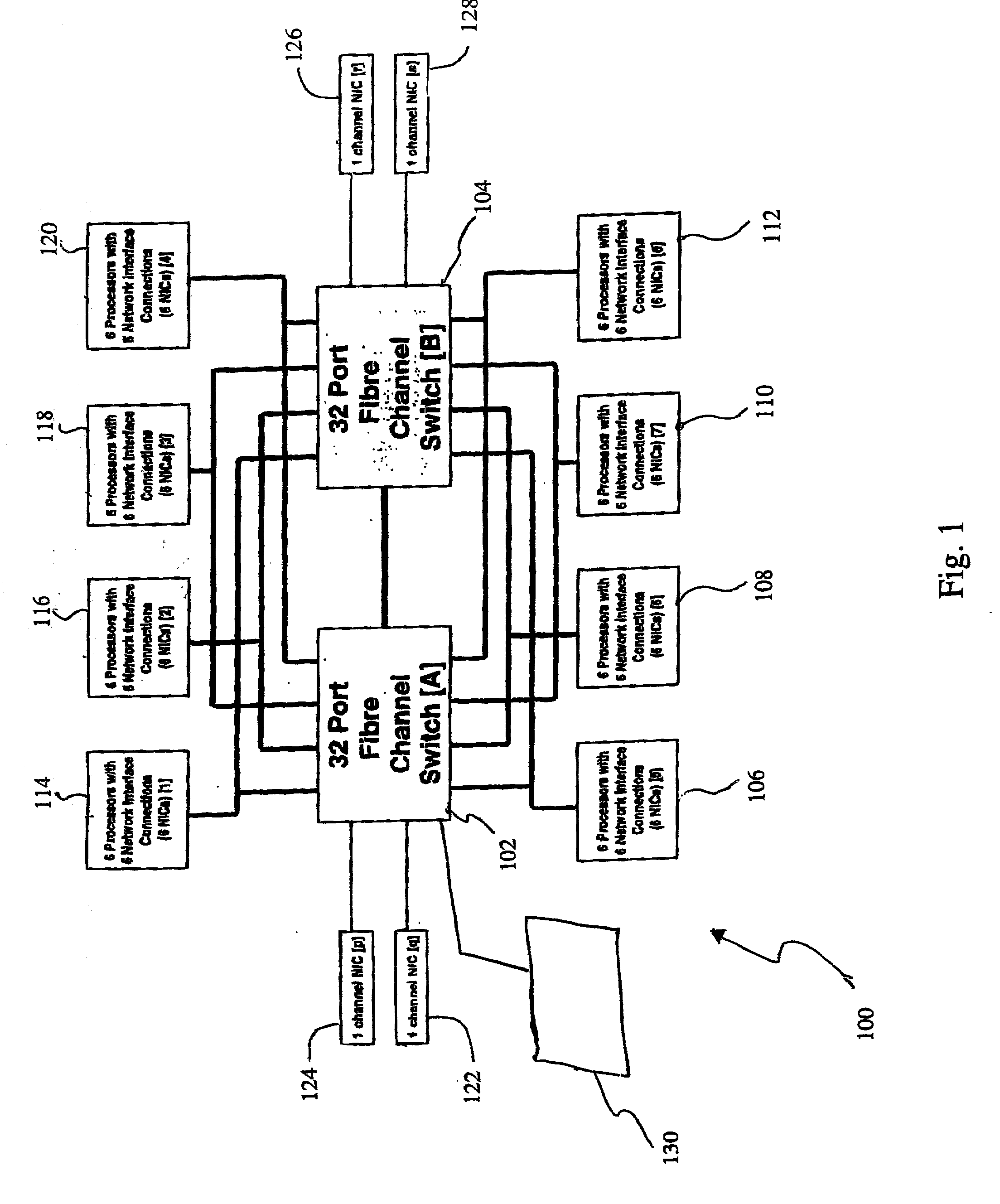
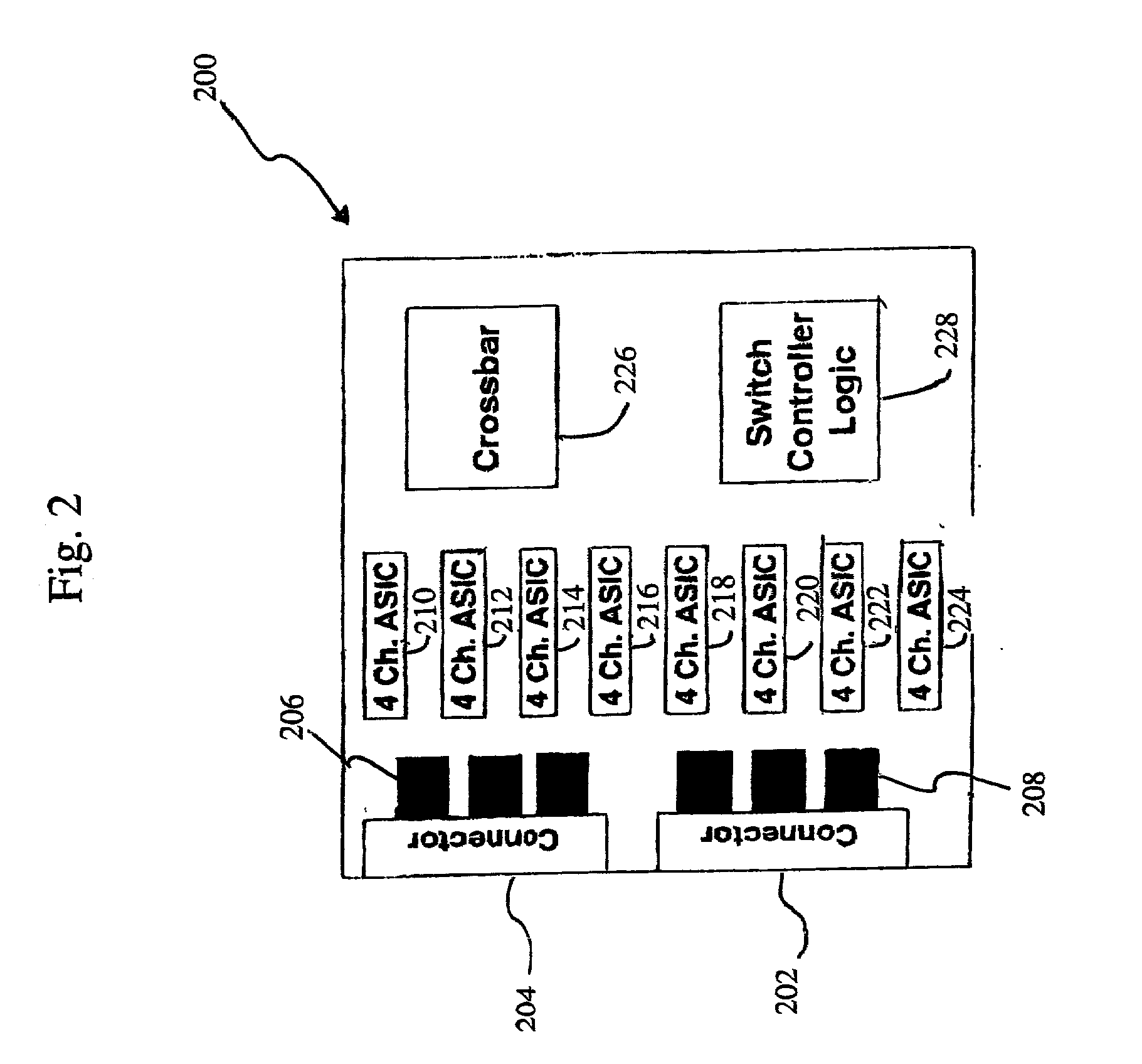
System and method for real-time fault reporting in switched networks
A method and apparatus for fault management in a network. A network architecture is disclosed including at least one network switch, several network interface cards, several processors (host) and a network manager. Fault reporting and detection logic is implemented in each switch and in each network interface card. In addition, multiple fault reporting pathways are provided for each switch and each network interface card. As a result, utilizing message exchanges such as Fibre Channel exchange messages, the switch, the network interface cards and the processors (host) are able to autonomously generate and report faults to the network manager. The combined fault reporting enables the network manager to more accurately isolate faults. In addition, because of the autonomous nature of the fault reporting, faults may be detected and corrected prior to the initiation of a communication session.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
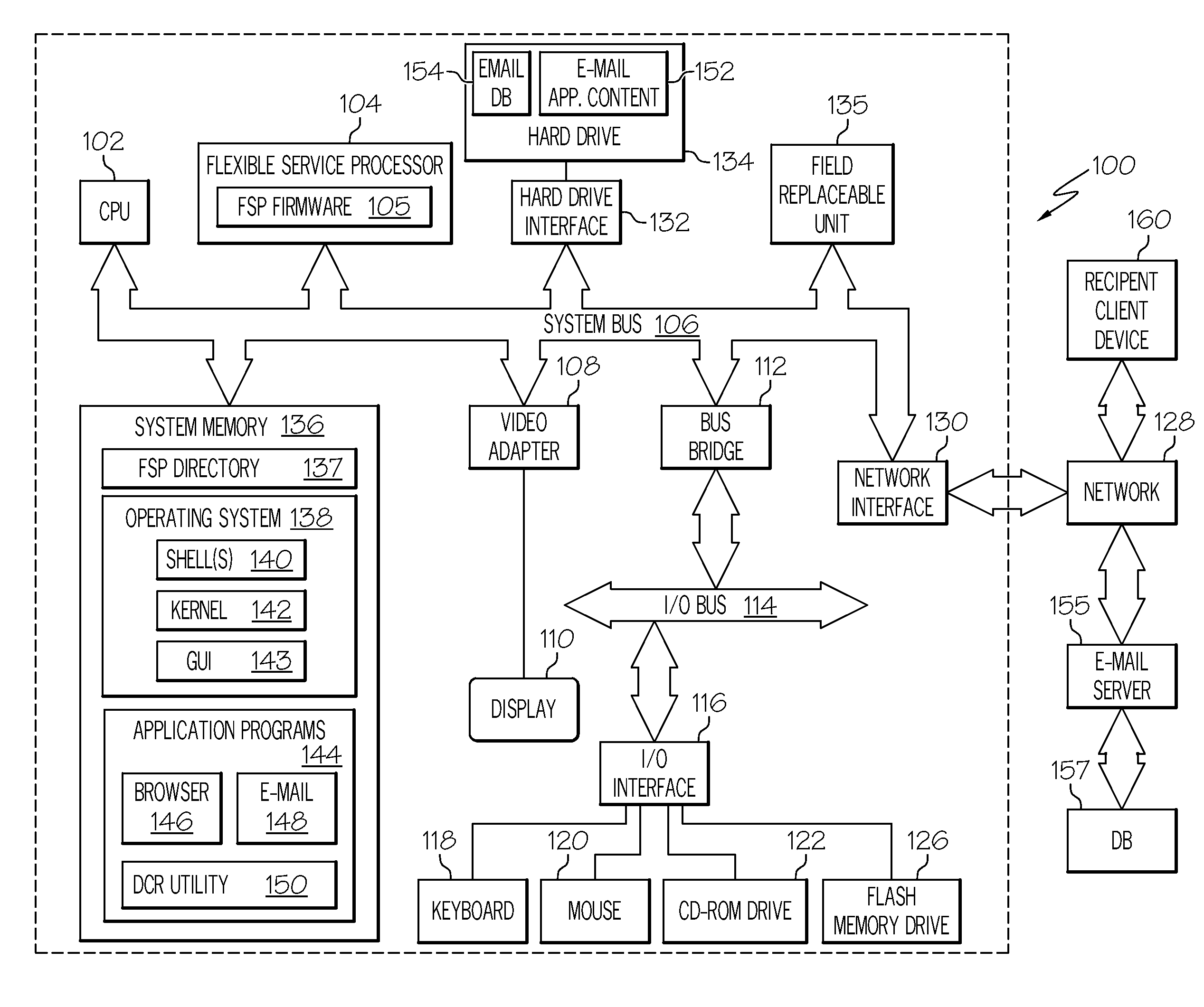
Image rescale based on defined characteristics
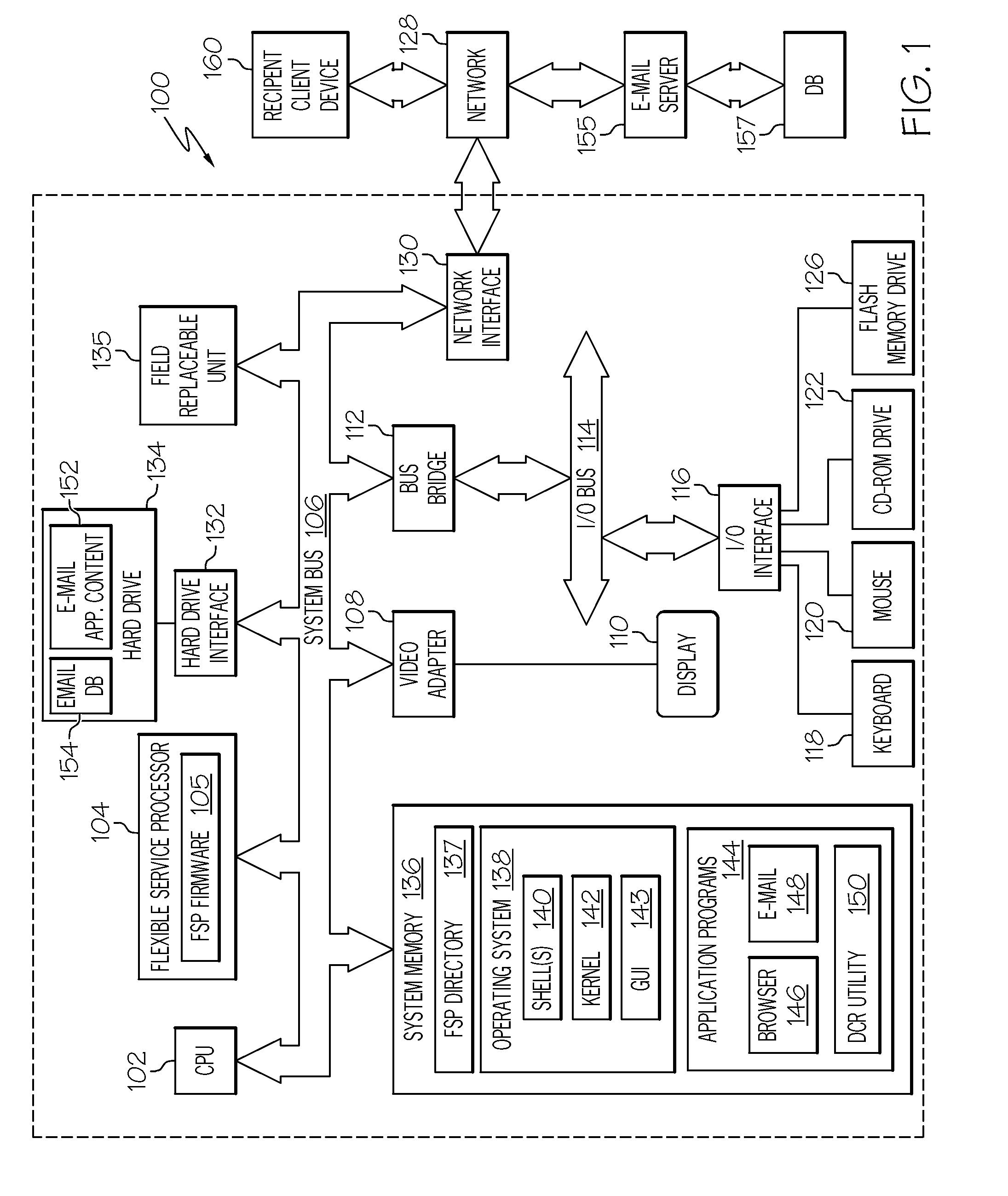
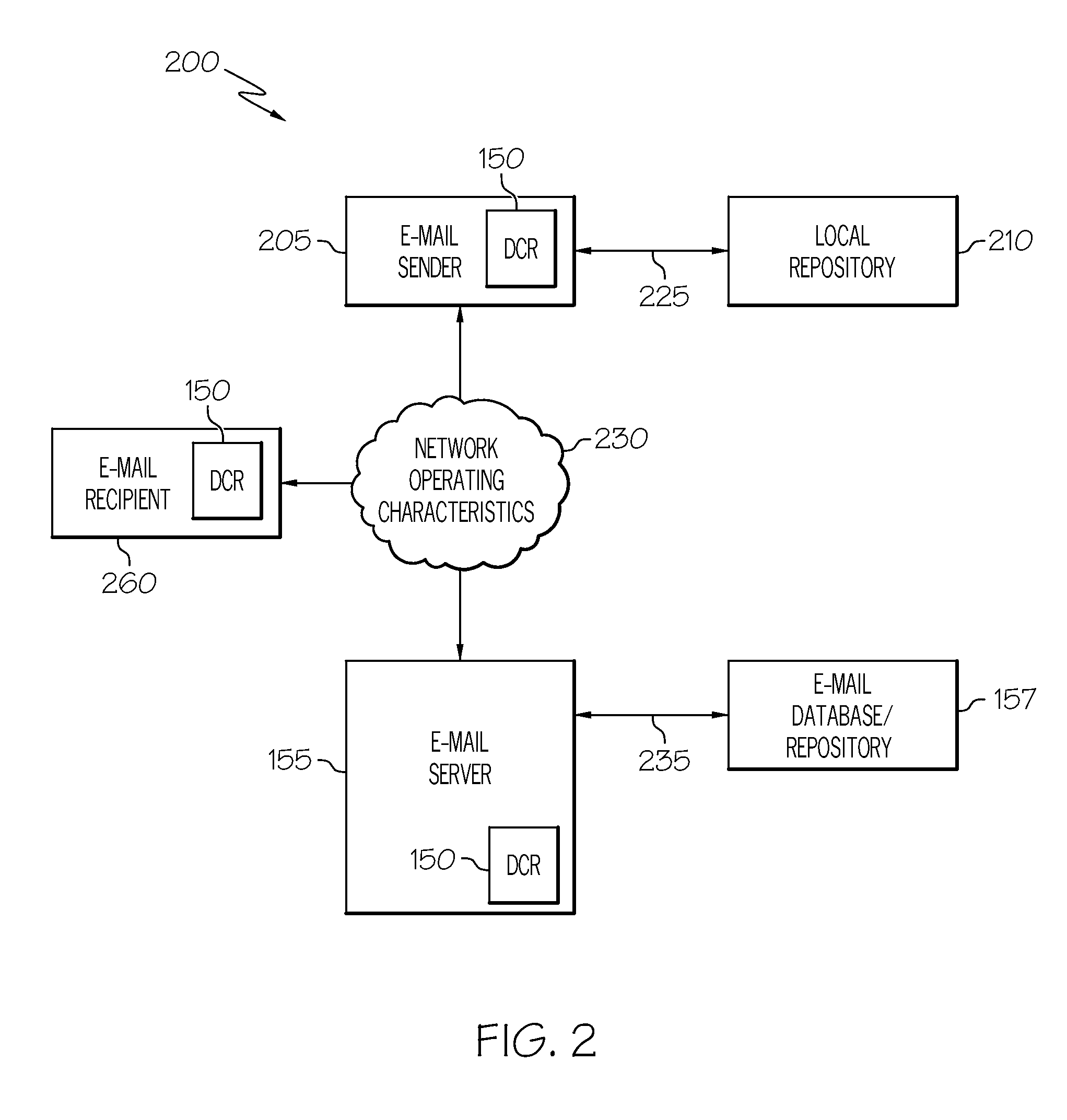
InactiveUS20110066687A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksClient-sideElectronic mail
A system and method automatically rescales an electronic message having one or more associated content. When the electronic message is generated and the associated content connected to the message, an agent of the electronic message application checks predefined settings / configurations of the message client. The sender's e-mail client checks a plurality of conditions, such as, the condition of the network, the type of network, the status or capacity of the receiving inbox of an intended recipient client, and the geographic destination of the message. Based on these dynamic content rescale settings, the sender's client dynamically and optimally rescales the associated content before forwarding the electronic message with the rescaled content to the recipient client. Rescaling of the associated content may be performed by the message exchange server or the recipient client. The recipient client may later request and receive a copy of the associated content without rescaling.
Owner:IBM CORP
Server with message exchange accounting
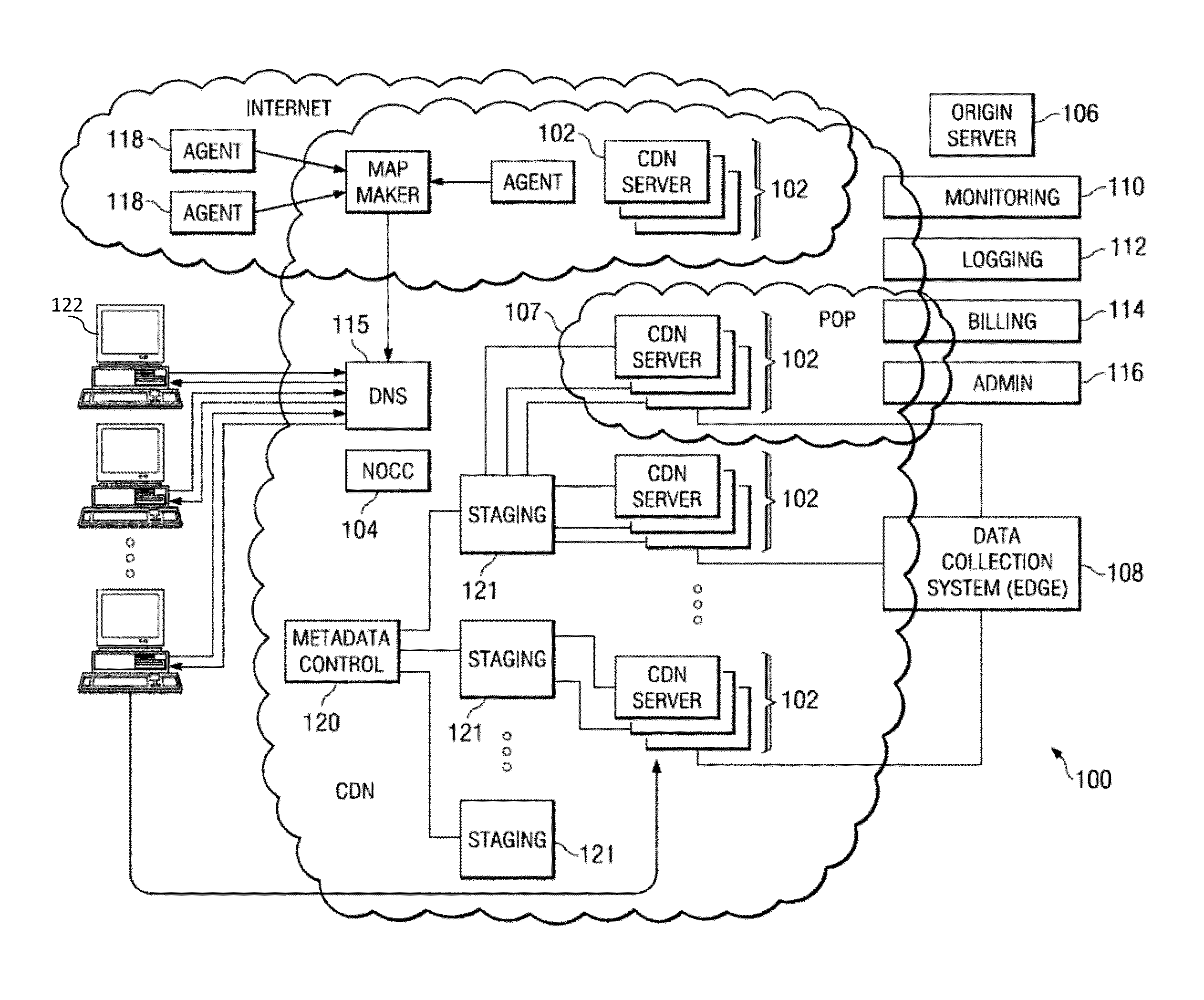
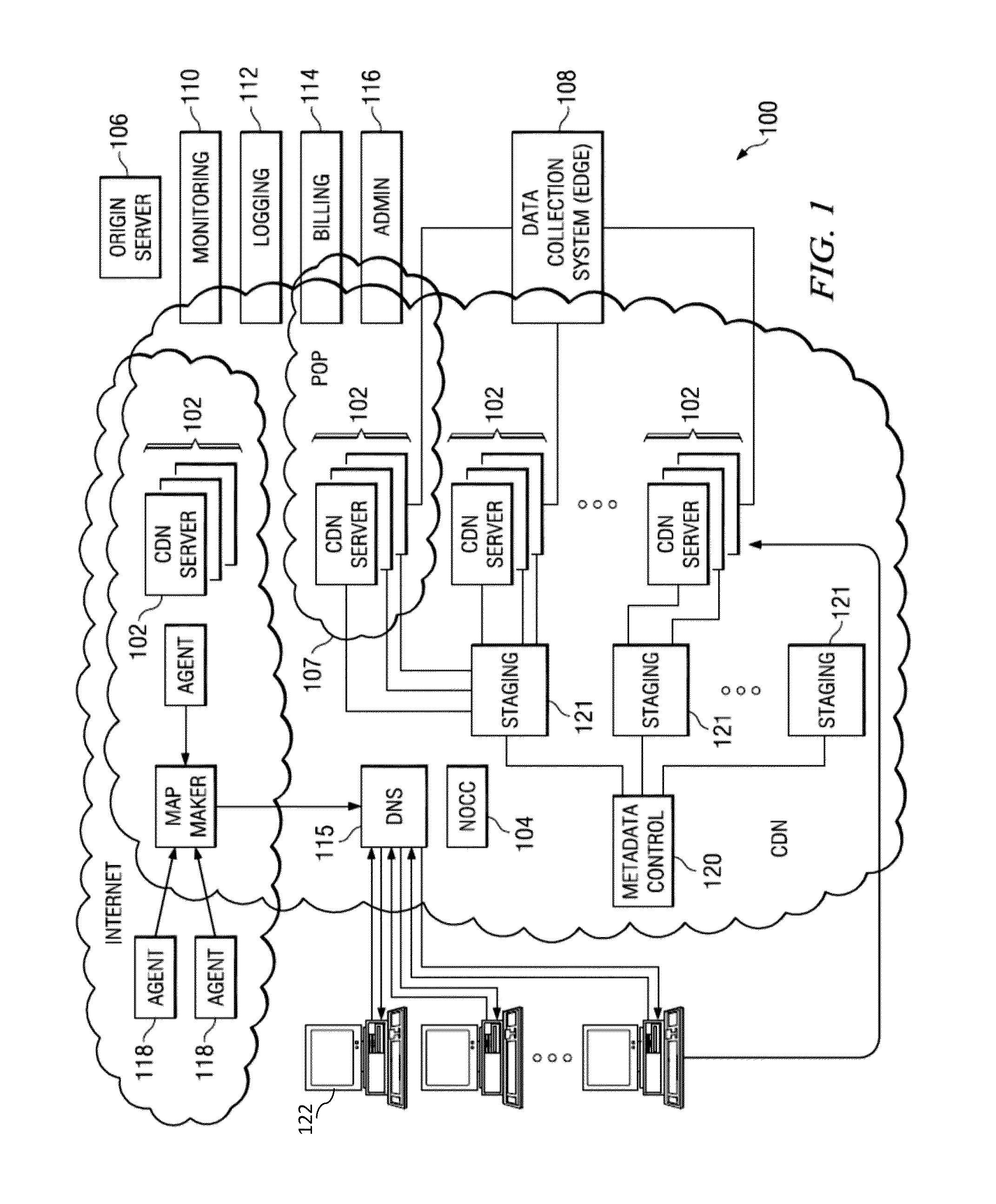
InactiveUS20130254343A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionExchange modelControl system
A server has a firewall module that performs accounting of traffic seen at the server. The traffic includes message exchanges, such as HTTP requests and HTTP responses. The server tests the message exchanges to determine if they match any of several message exchange categories. The server keeps statistics on matching traffic, for example the rate of matching traffic generated by a particular requesting client. Typically, the server is a proxy server that is part of a content delivery network (CDN), and the message exchanges occur between a client requesting content, the proxy server, other servers in the CDN, and / or an origin server from which the proxy server retrieves requested content. Using the message exchange model and the statistics generated thereby, the server can flag particular traffic or clients, and take protective action (e.g., deny, alert). In an alternate embodiment, a central control system gathers statistics from multiple servers for analysis.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Open flow switchboard system and message processing method of open flow switchboard system
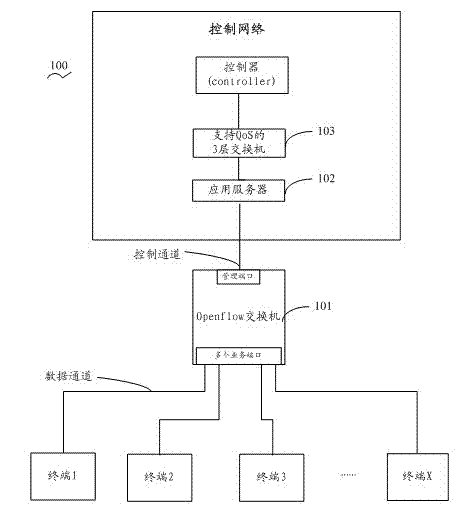
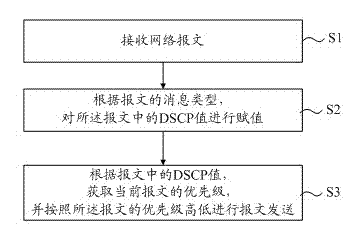
InactiveCN102868645AAvoid packet dropIncrease costData switching networksCode pointApplication server
The invention provides an open flow switchboard system and a message processing method of the open flow switchboard system. The open flow switchboard system comprises one or more of controllers, an open flow switchboard, an application server and a QoS (Quality of Service) three-layer switchboard, wherein the open flow switchboard is connected with the one or more of controllers, the application server is connected with the open flow switchboard and used for assigning differentiated services code point (DSCP) values in the messages according to message types of the messages, and the QoS three-layer switchboard is connected with the application server and used for acquiring priority level of current messages according to the DSCP values and sending the messages to the one or more of controllers according to the priority level of the messages. According to types of the messages, the open flow switchboard system and the message processing method of the open flow switchboard system perform dispatching of messages in the system according to certain priority level, do not improve cost of the whole system, simultaneously resolve the problem of high-priority-level message switching due to undersize of broadband, and further improve stability of the system.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
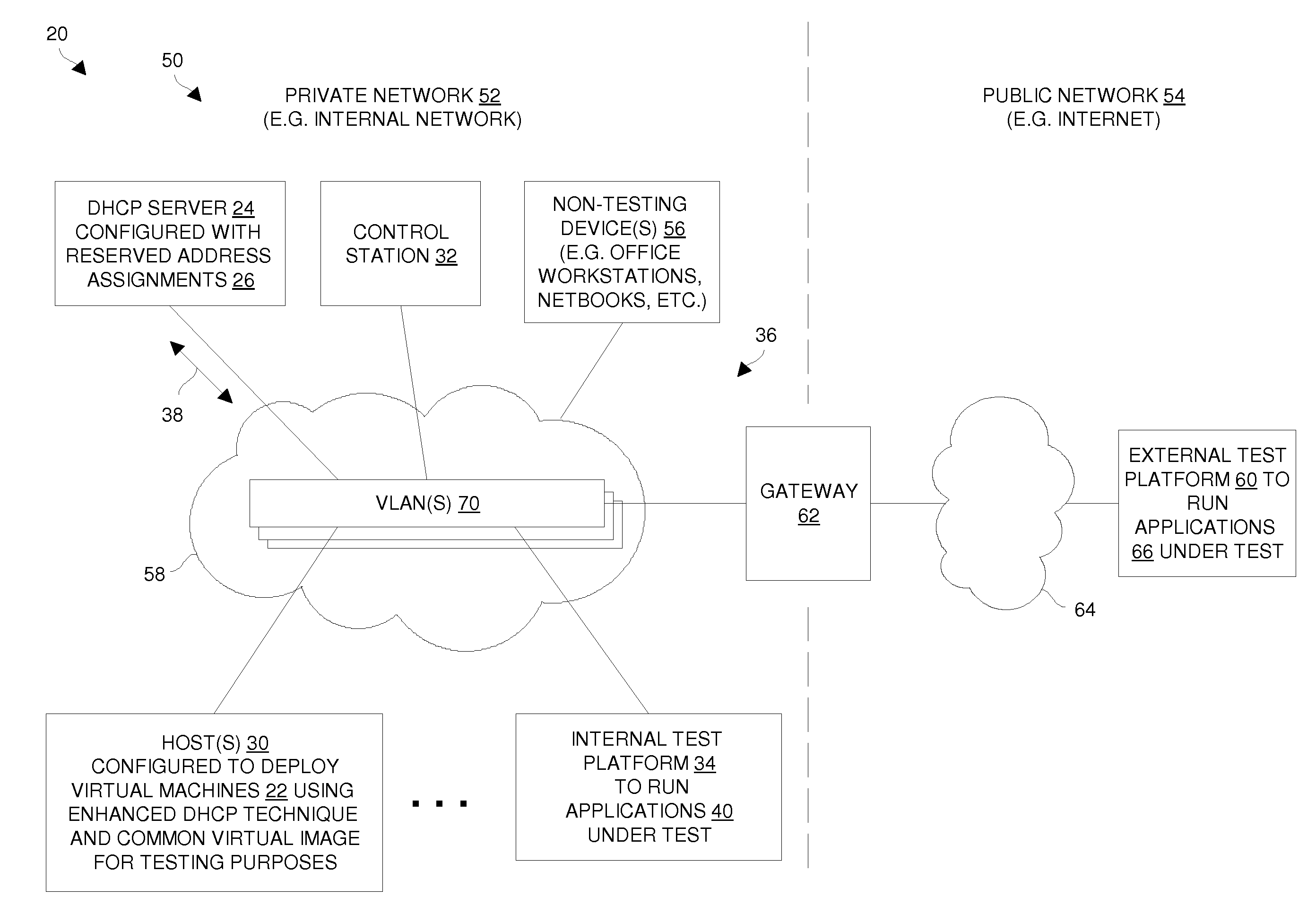
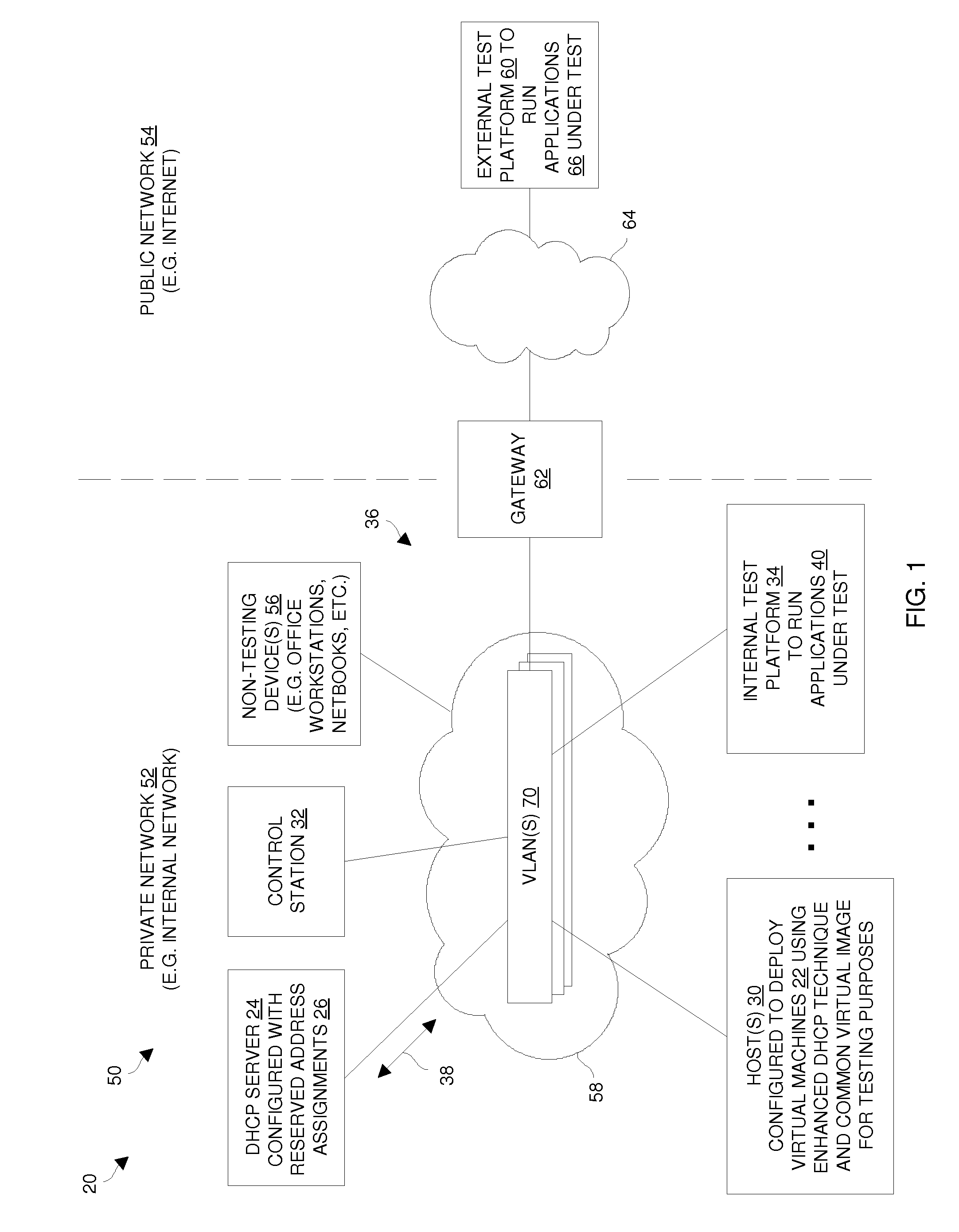
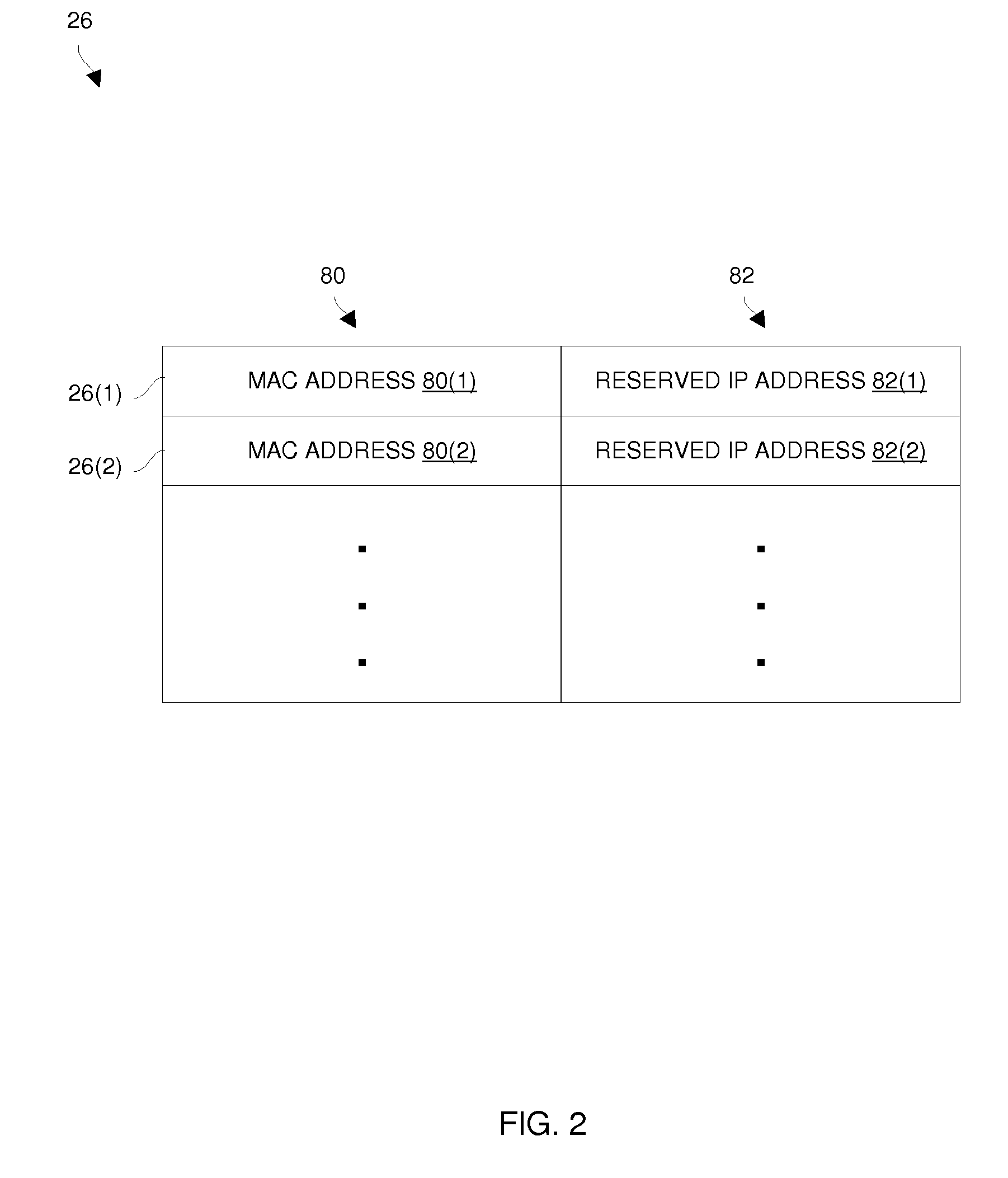
Techniques for deploying virtual machines using a DHCP server to assign reserved IP addresses
ActiveUS20110119382A1Efficient and effectiveLess susceptibleError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressReserved IP addresses
An improved technique involves providing a set of reserved address assignments to a DHCP server, each reserved address assignment including a unique MAC address and a reserved IP address which are associated with each other via that reserved address assignment. The technique further involves providing a base virtual machine image and a set of unique MAC addresses, and generating multiple virtual machines from the base virtual machine image and the set of unique MAC addresses. Each virtual machine (i) provides a particular unique MAC address of the set of unique MAC addresses to the DHCP server and obtains a particular reserved IP address from the DHCP server via an exchange of DHCP messages between that virtual machine and the DHCP server, and (ii) operates as a networked standalone computer using the particular unique MAC address and the particular reserved IP address.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
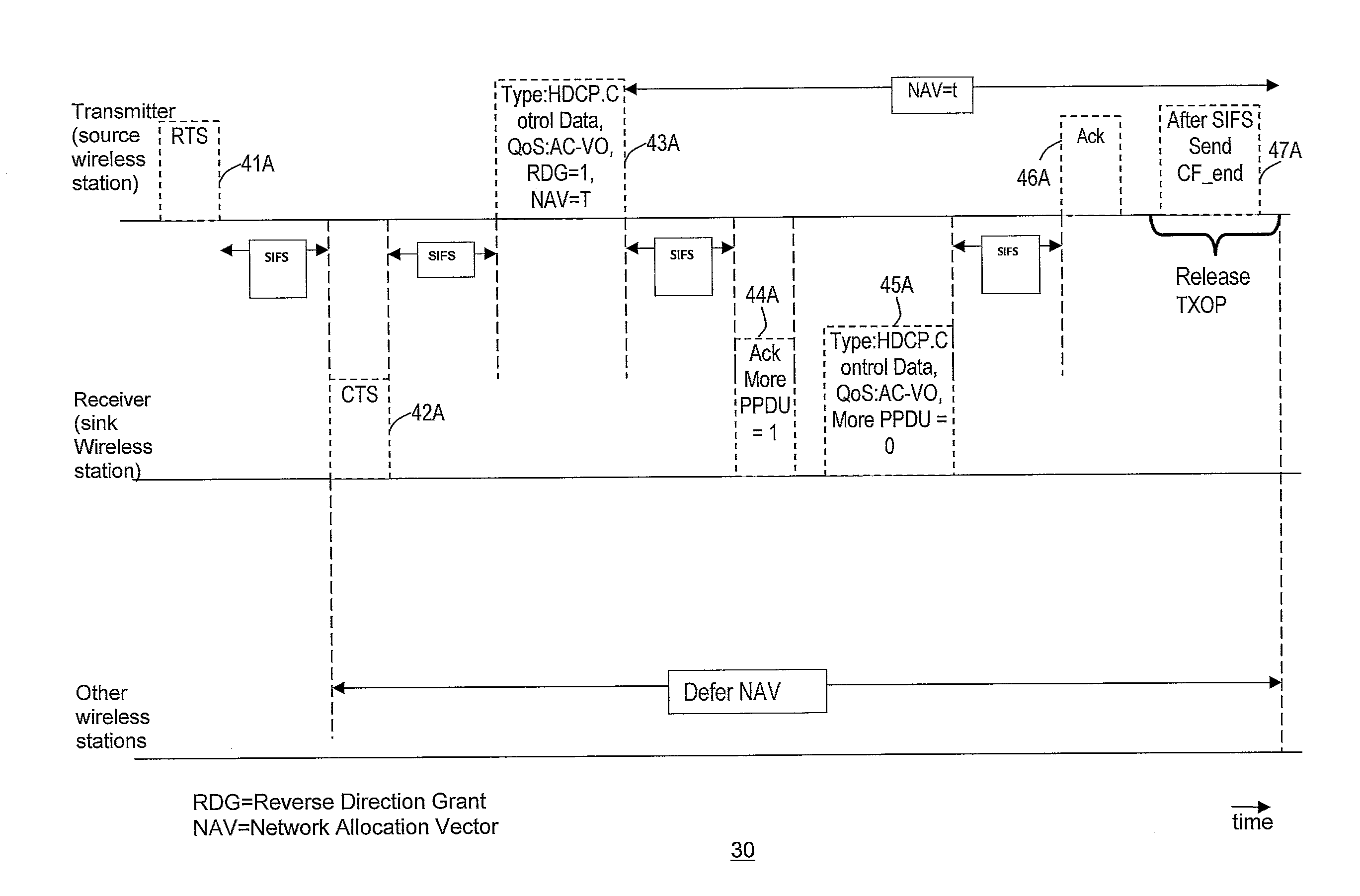
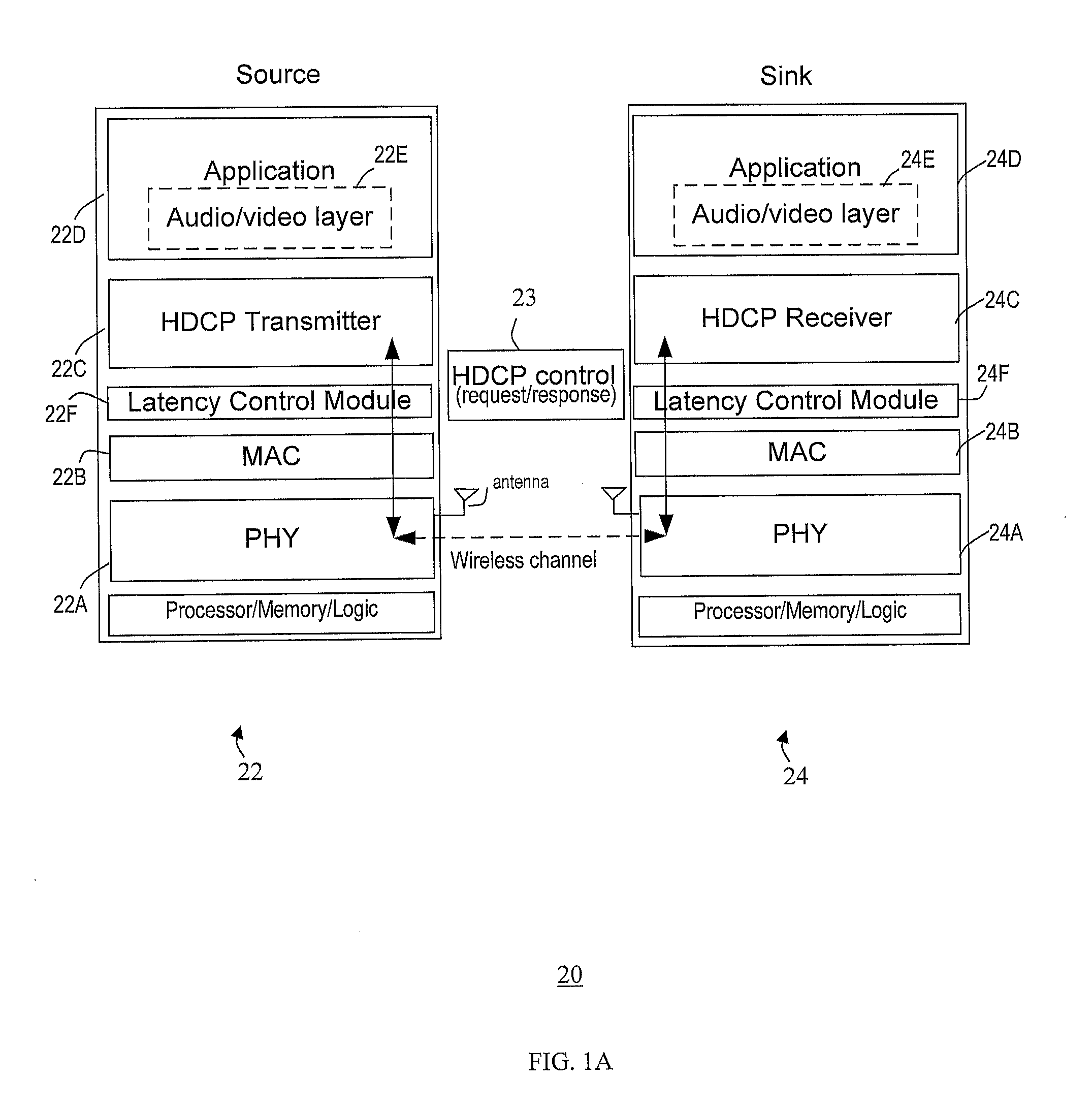
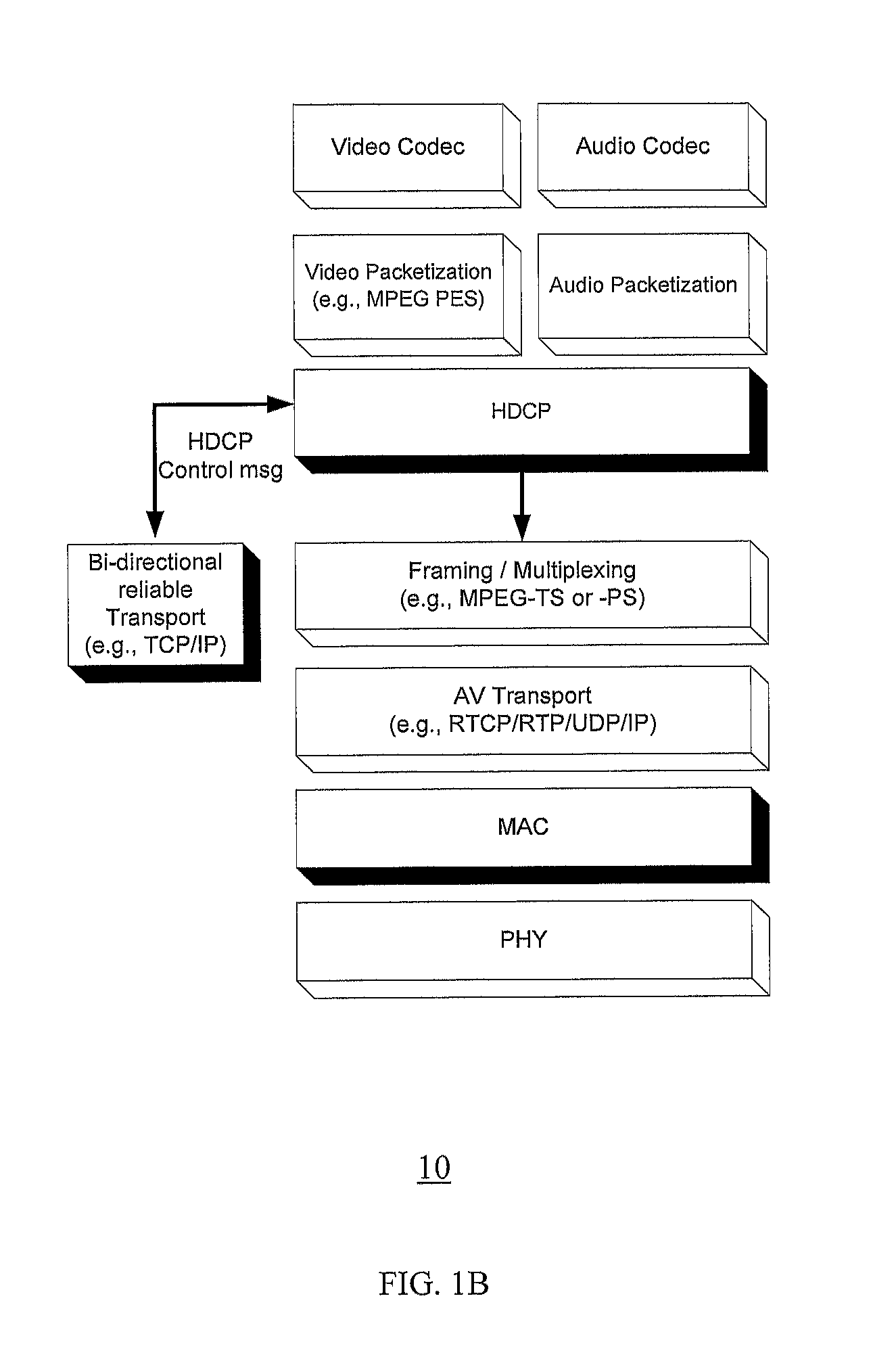
Method and system for minimizing latencies for content protection in audio/video networks
ActiveUS20120127937A1Lower latencyNetwork topologiesRadio transmission for post communicationMessage switchingAudio frequency
Reducing latencies for content protection in audio / video networks includes reserving a wireless channel for a time period to accommodate control message exchange for content protection in data communication between a wireless transmitter and wireless receiver over a wireless channel. The control message exchange includes wirelessly transmitting a control request message from the transmitter for content protection to the receiver, and transmitting a control response message from the receiver to the transmitter in reply. Reserving the wireless channel includes reserving the wireless channel for a time period that accommodates the control message exchange. The time period includes a single transmission opportunity period for communication on the wireless channel, to reduce latency for the control message exchange between the transmitter and receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com