Patents
Literature
511 results about "Virtual router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
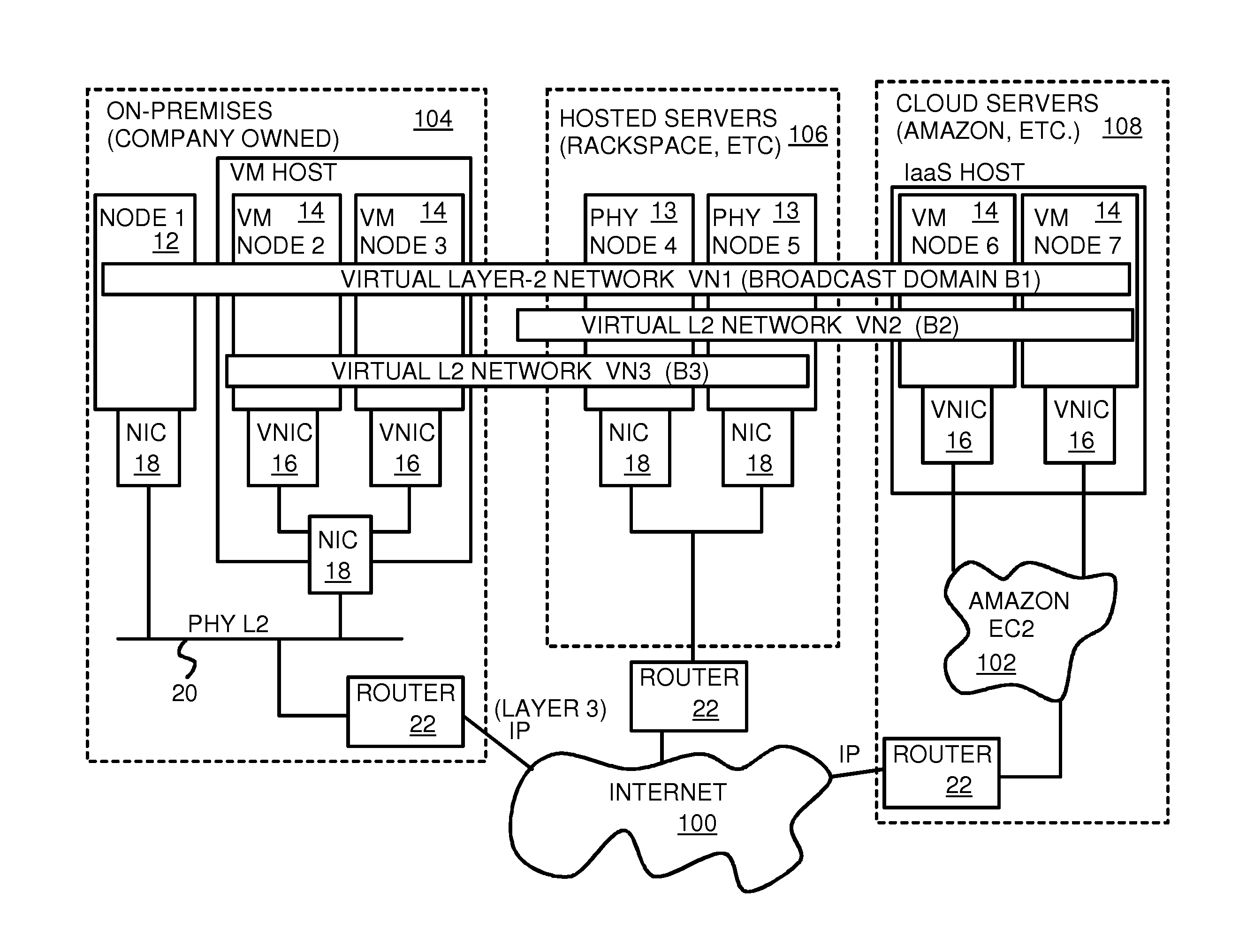
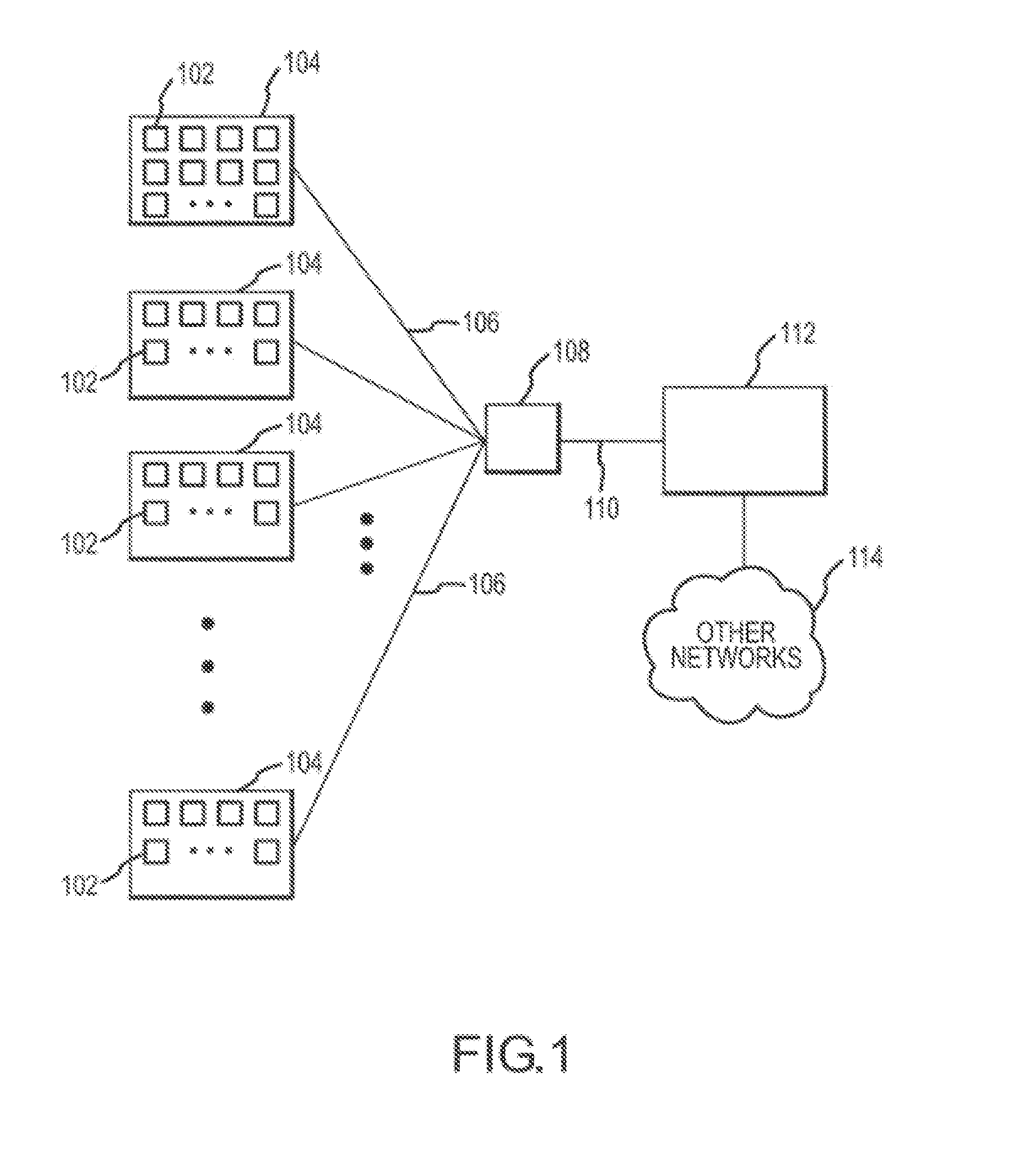
Fully distributed routing over a user-configured on-demand virtual network for infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) on hybrid cloud networks
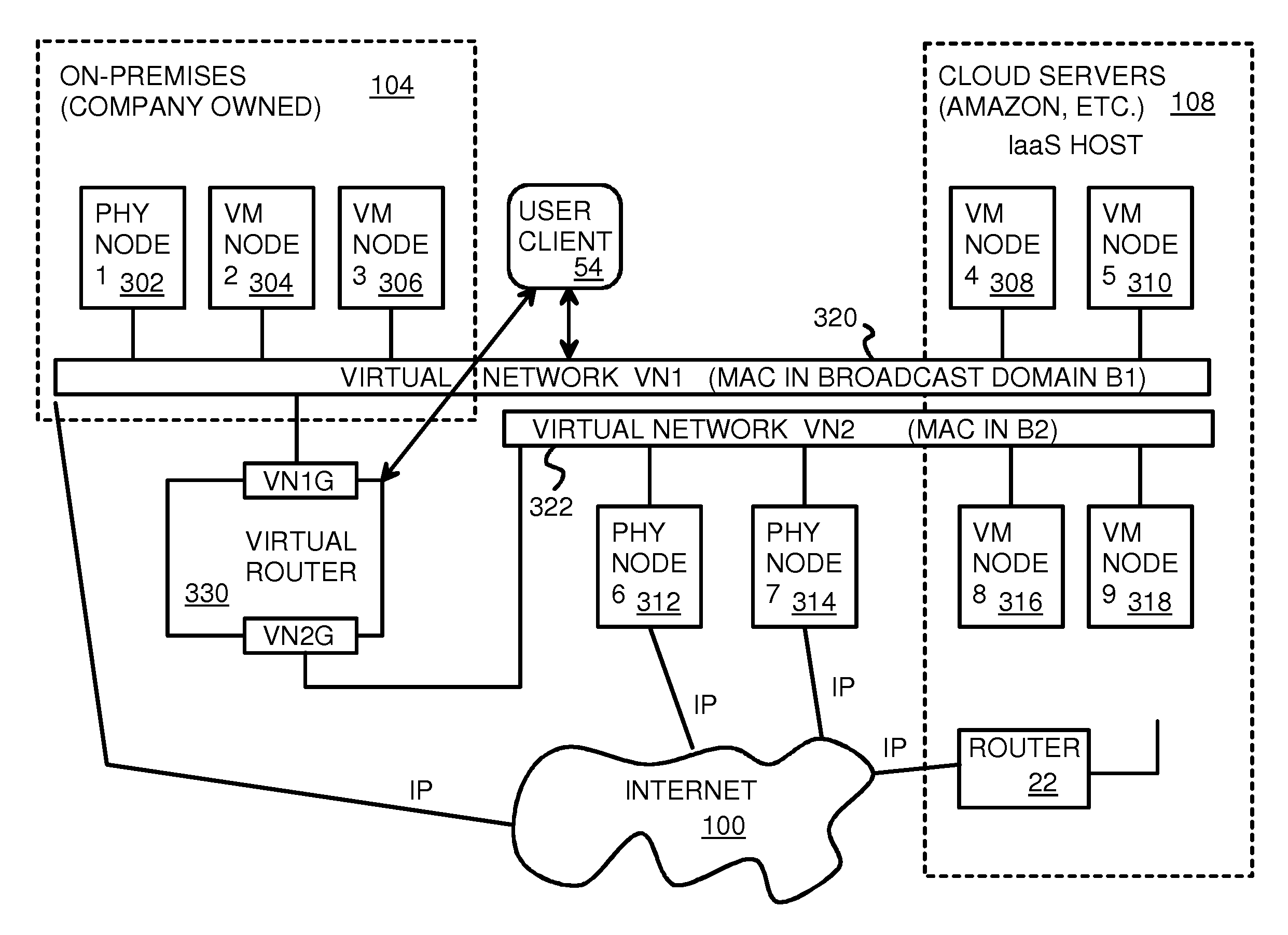
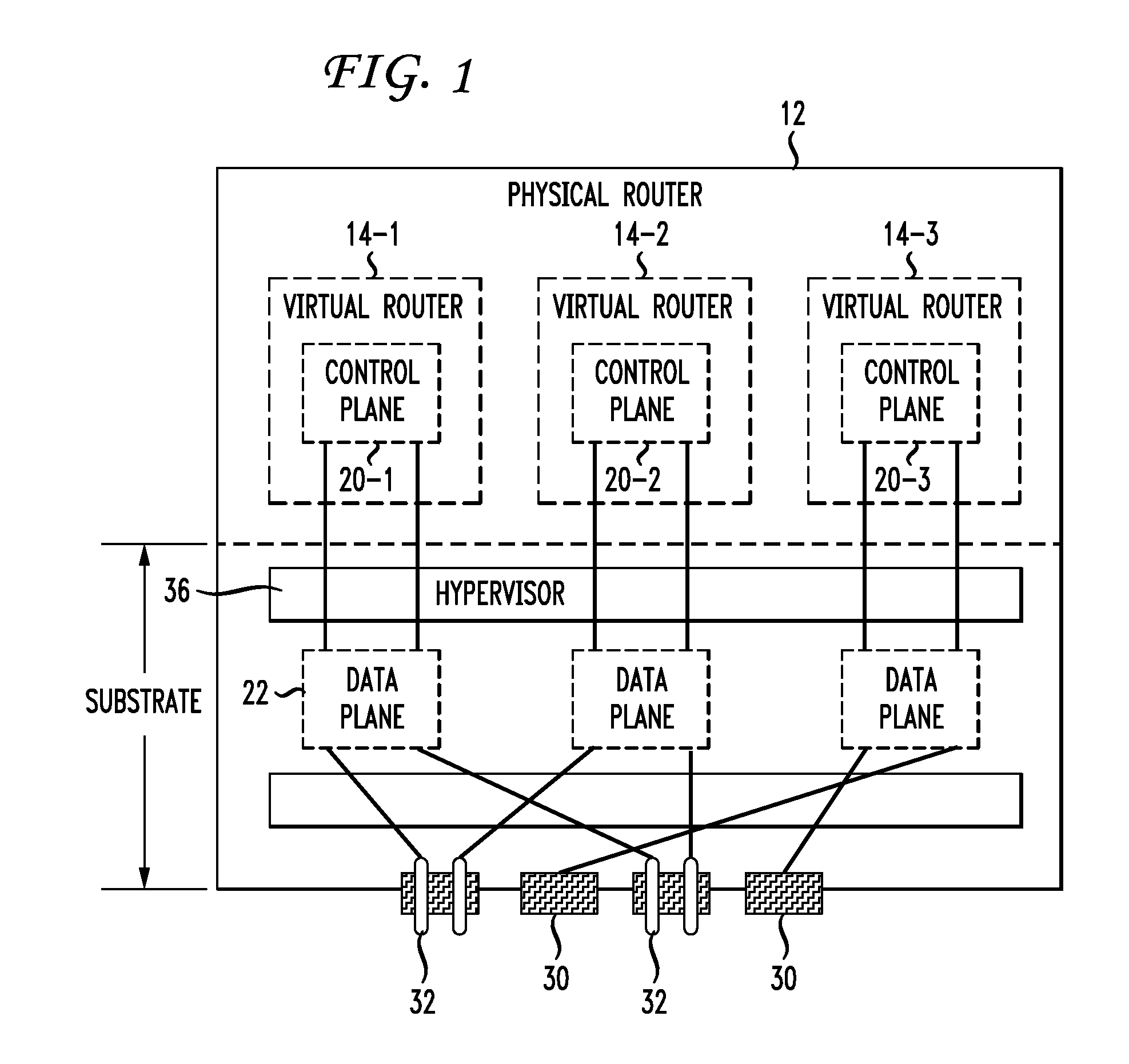
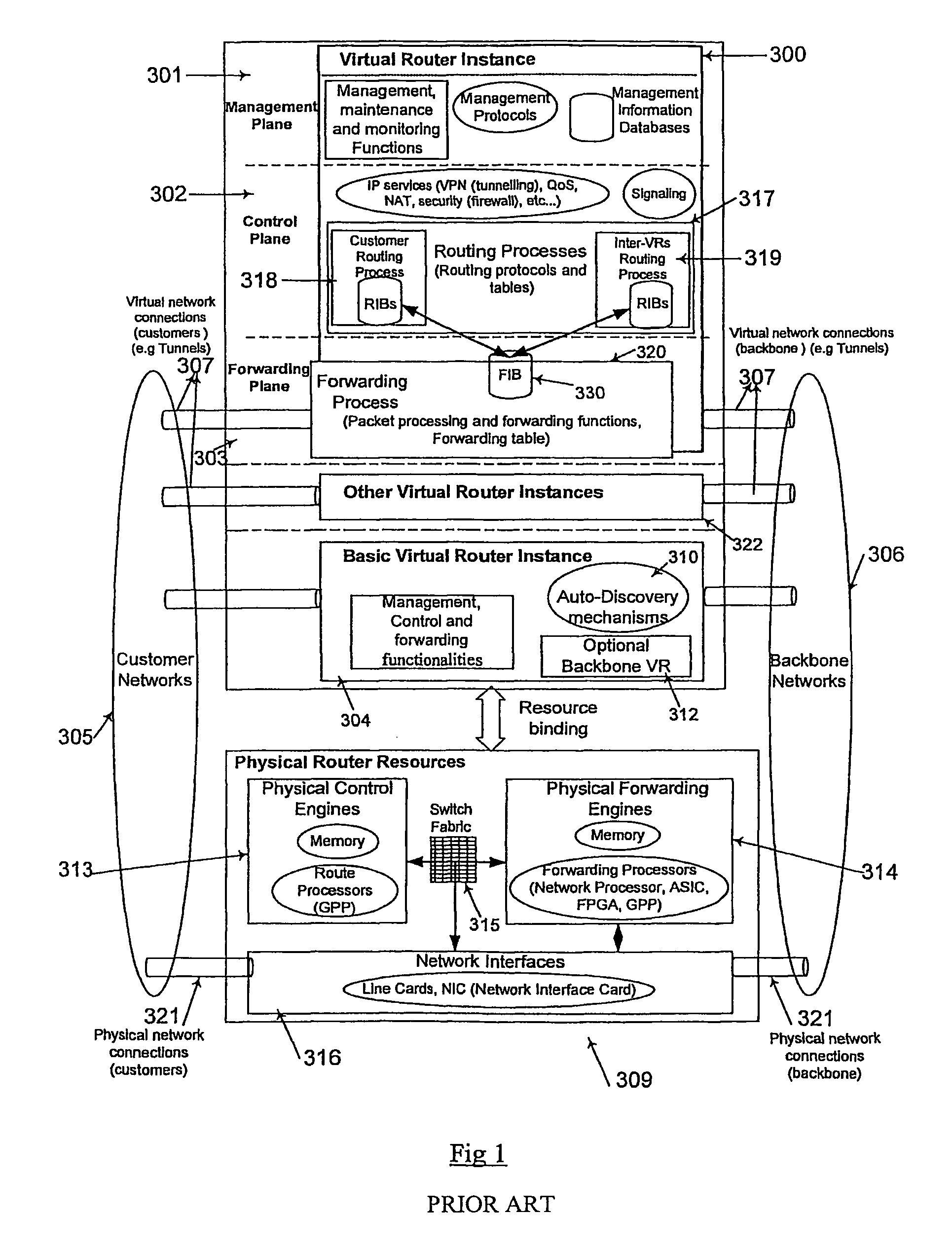
A layer-3 virtual router connects two or more virtual networks. Virtual networks are overlaid upon physical networks. Each virtual network (VN) is a layer-2 network that appears to expand an organization's LAN using virtual MAC addresses. The network stack forms a virtual-network packet with a virtual gateway MAC address of the virtual router to reach a remote virtual network. A VN device driver shim intercepts packets and their virtual MAC and IP addresses and encapsulates them with physical packets sent over the Internet. A VN switch table is expanded to include entries for nodes on the remote virtual network so that all nodes on both virtual networks are accessible. A copy of the VN switch table is stored on each node by a virtual network management daemon on the node. A Time-To-Live field in the virtual-network packet is decremented for each virtual hop and a checksum recalculated.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Virtual network in server farm
ActiveUS7802000B1Telephonic communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionTraffic capacityVirtual switch
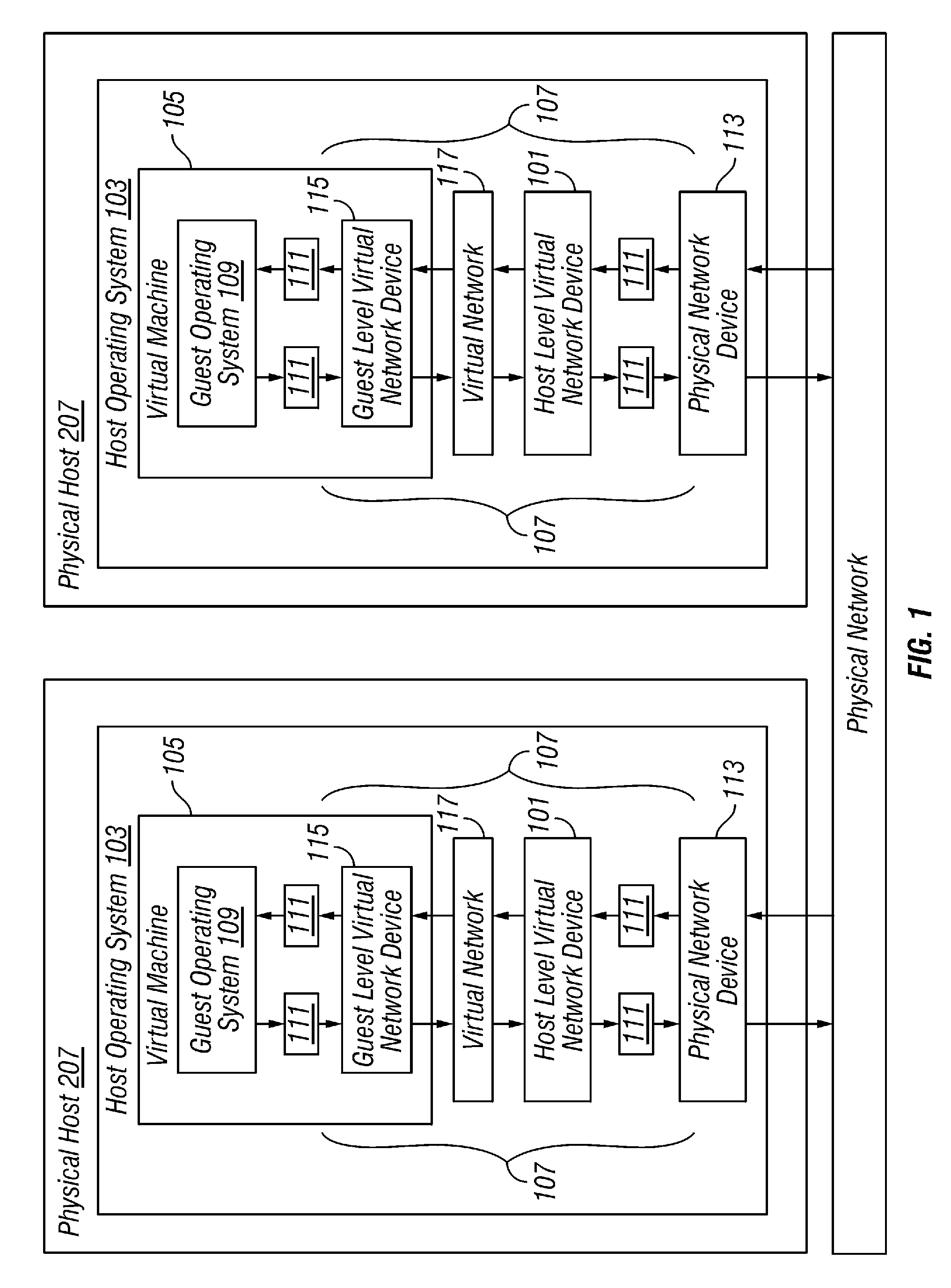
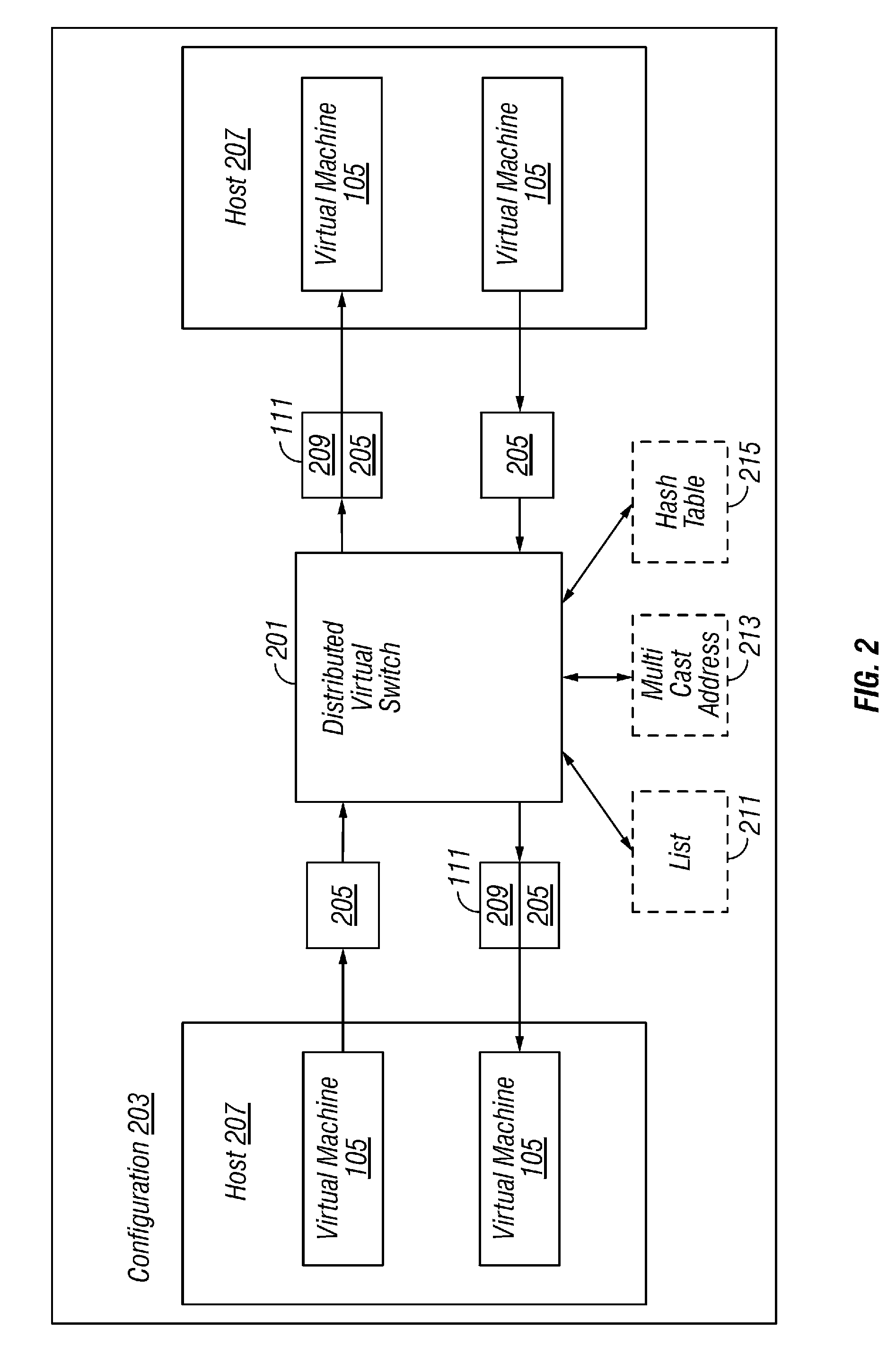
A plurality of virtual machines execute on a network of physical computers. The virtual machines are deployed in fenced and unfenced configurations across multiple physical computers. Host level virtual network devices execute on the physical computers, and intercept the virtual machine network traffic. For each fenced configuration of virtual machines, a distributed virtual switch transmits network traffic between the virtual machines deployed in that fenced configuration, and a virtual router routes network traffic between virtual machines deployed in that fenced configuration and external components.
Owner:VMWARE INC
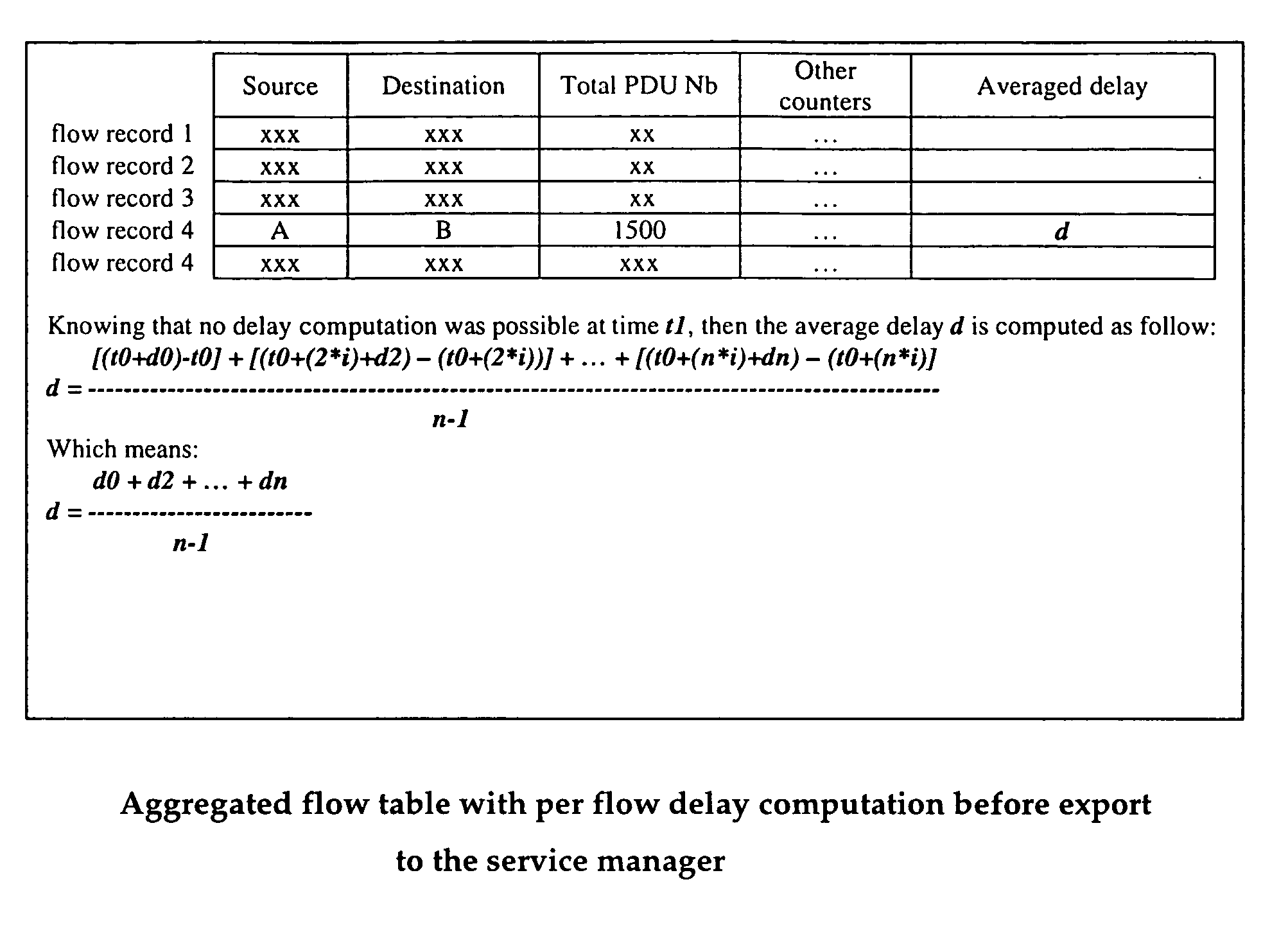
Distributed architecture for real-time flow measurement at the network domain level
ActiveUS20050132044A1Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsRelevant informationCommunications system
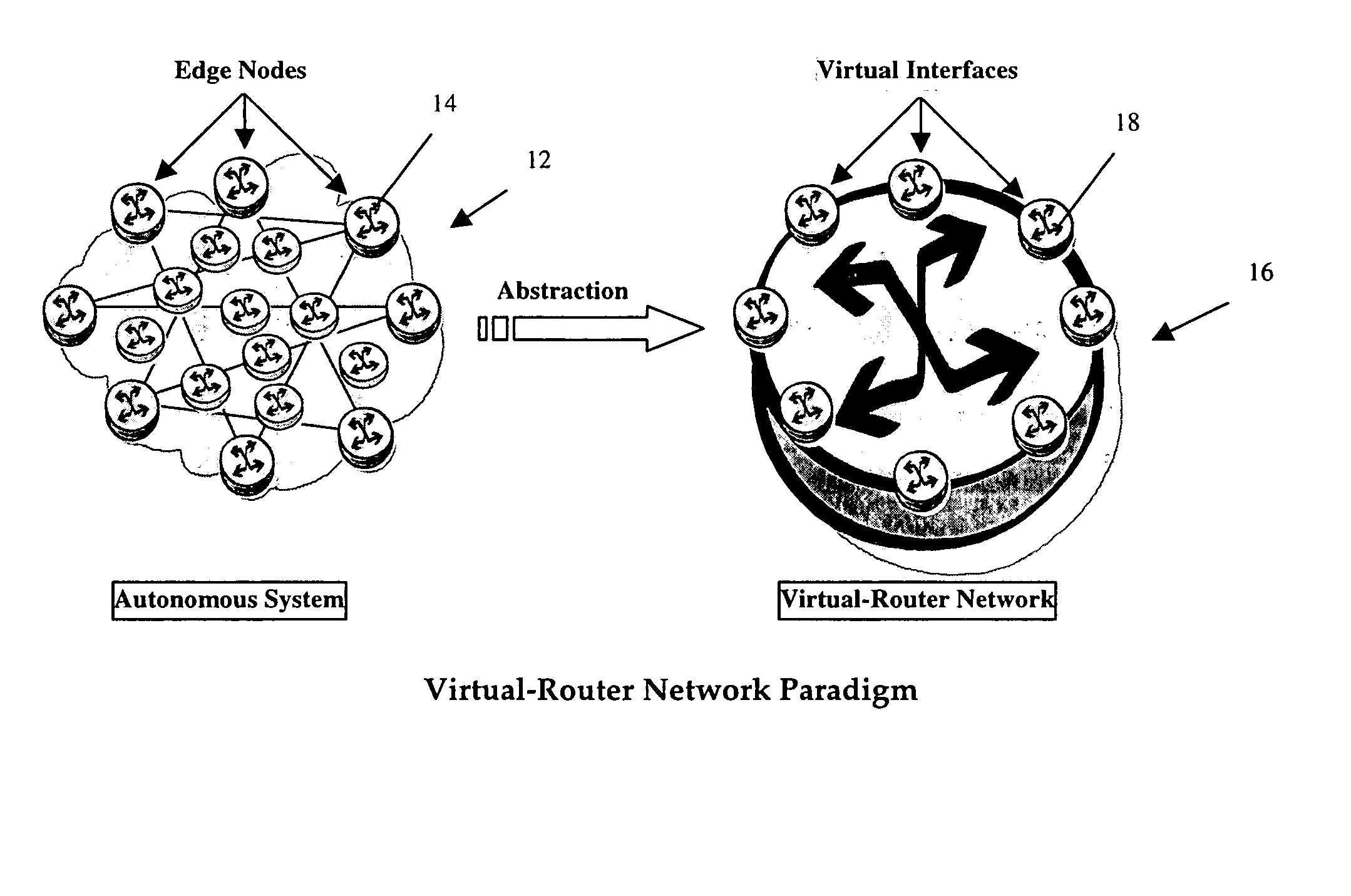
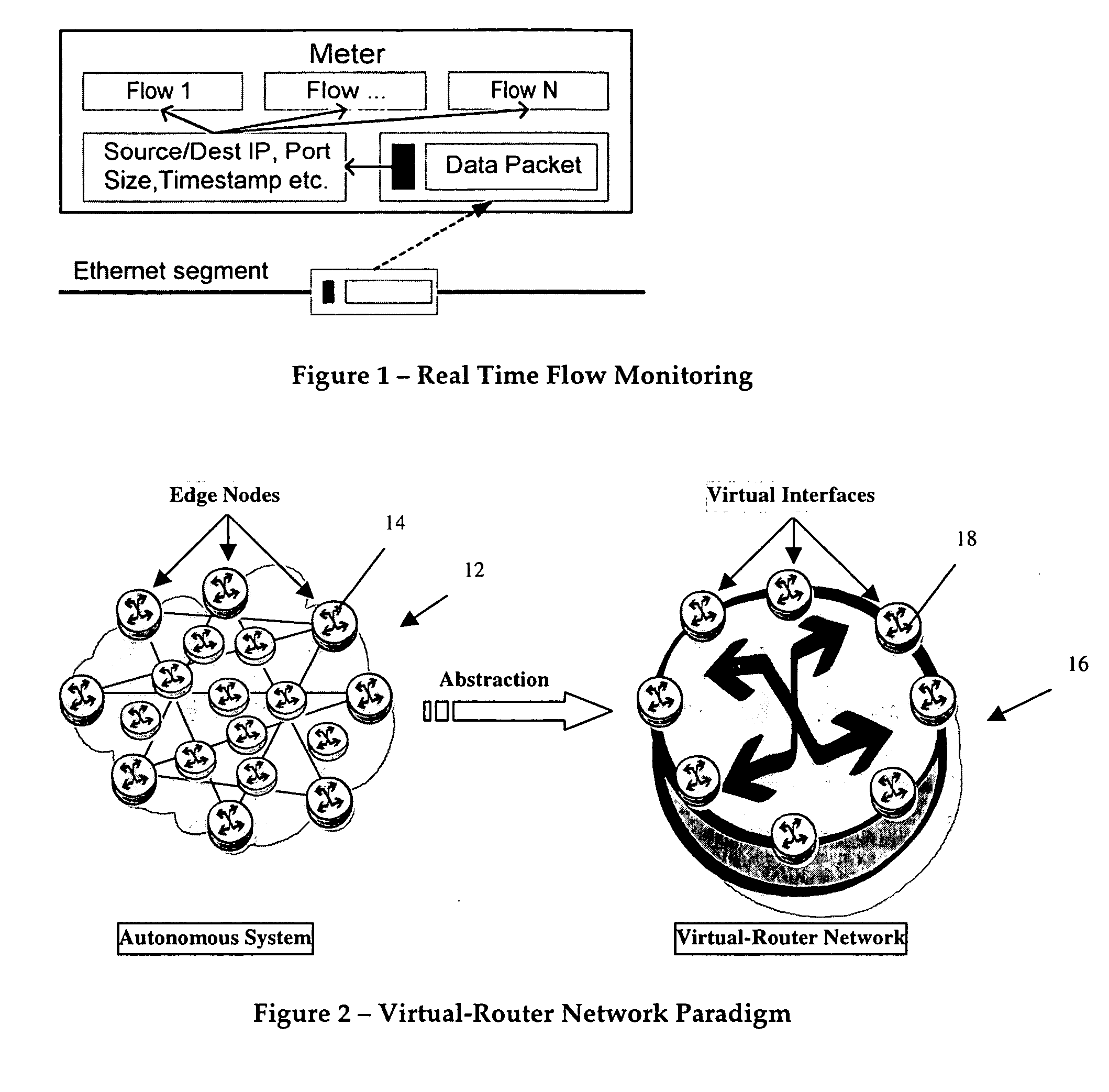
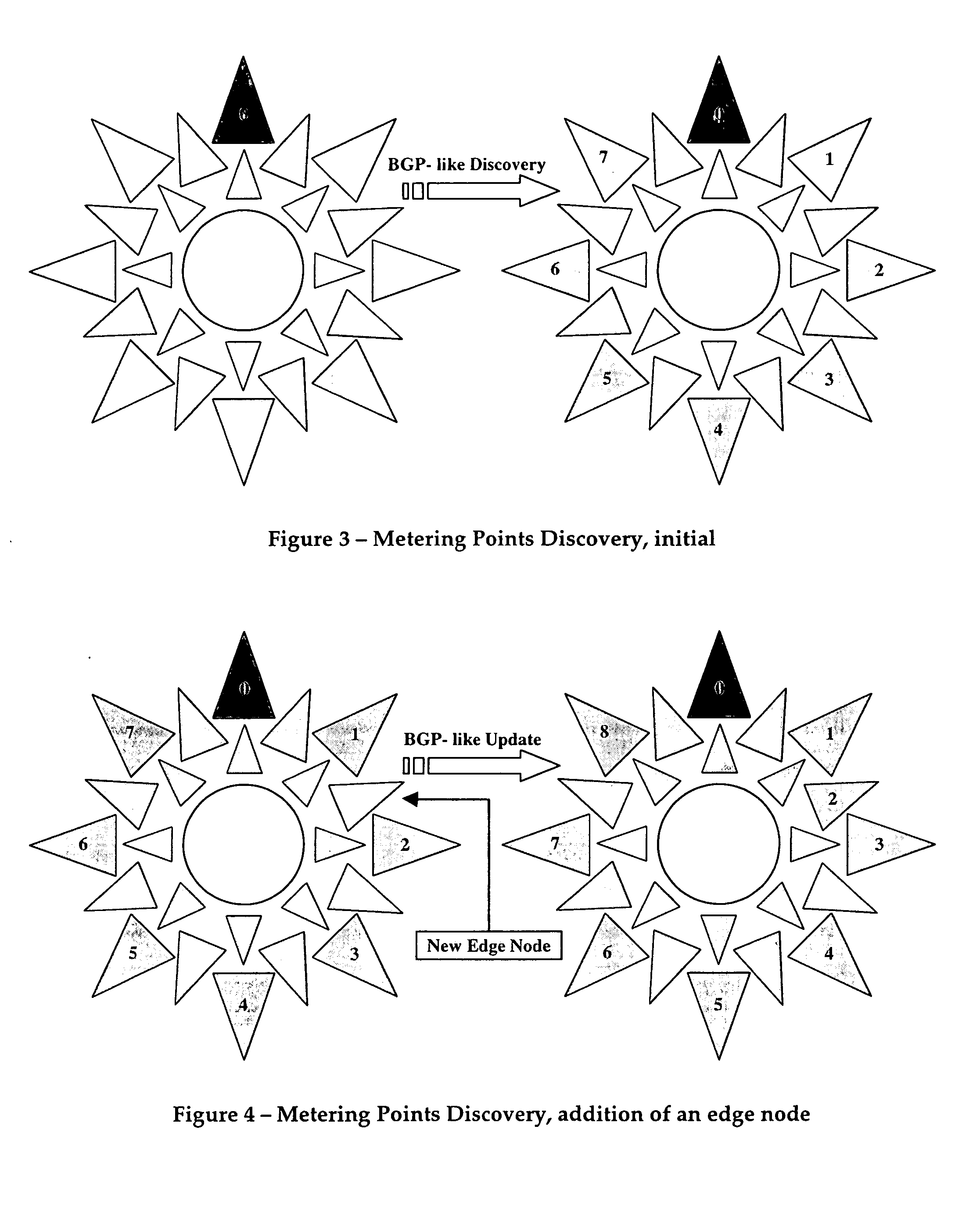
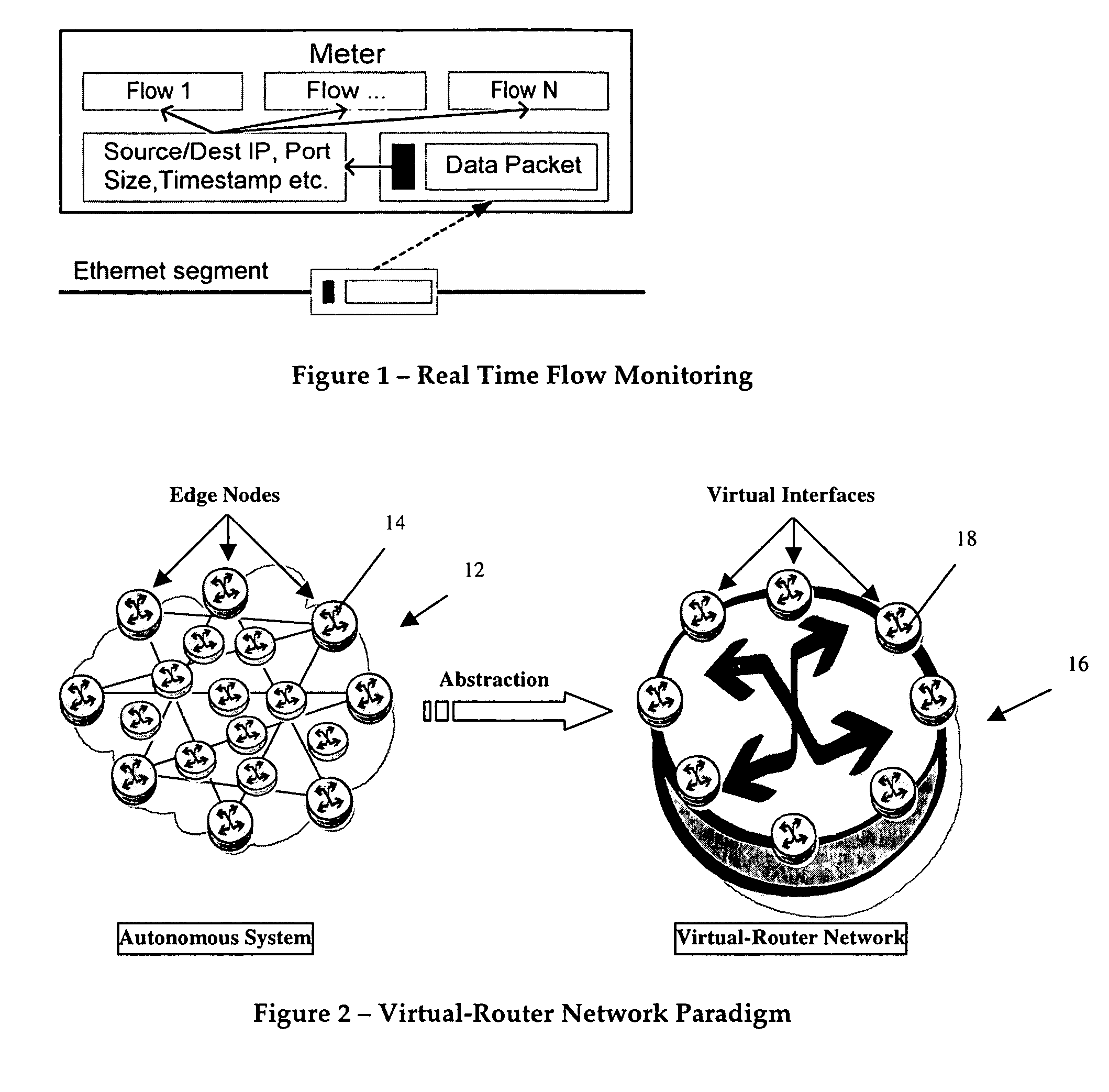
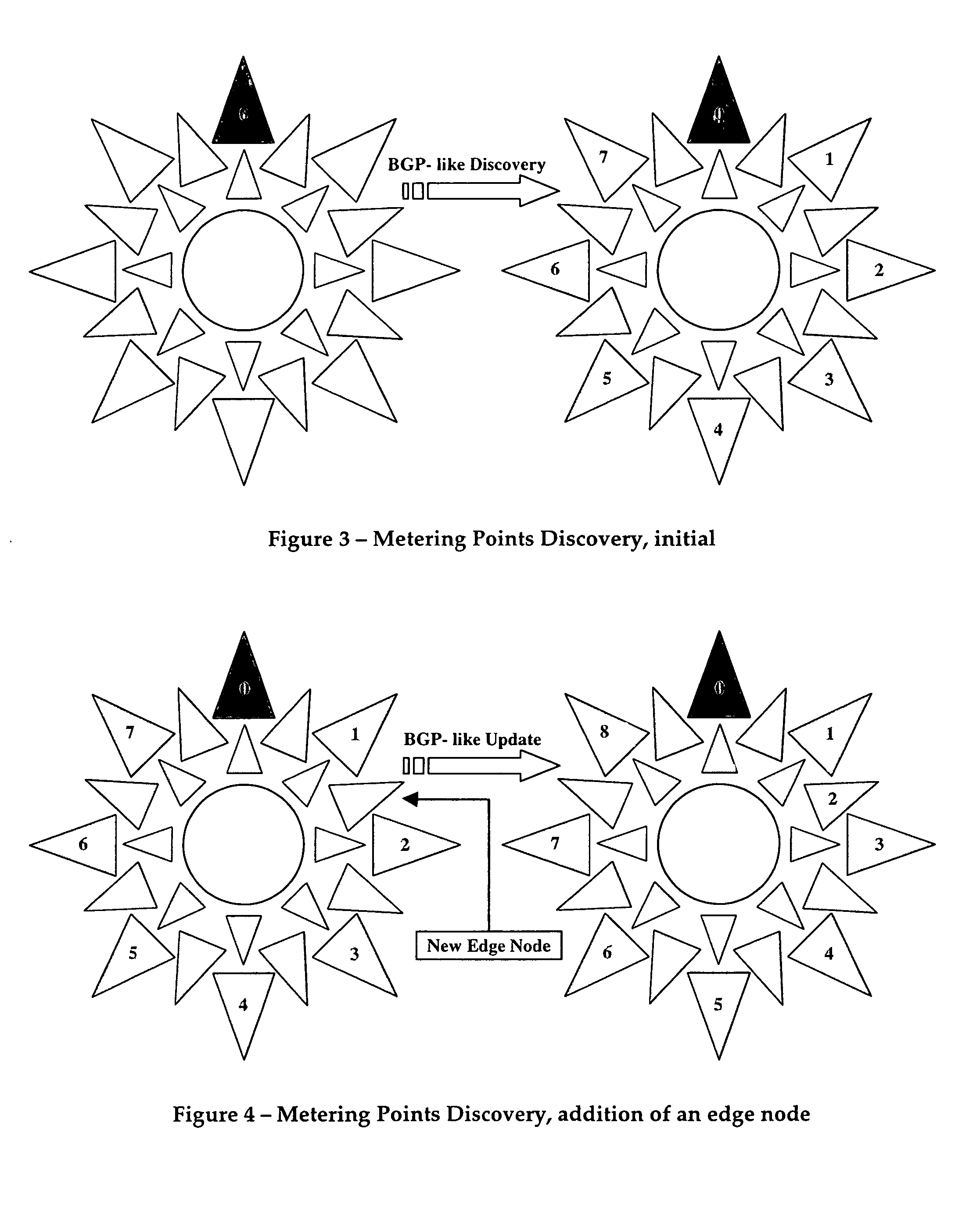
A virtual router network (VRN) for performing real-time flow measurements (RTFM) is provided. The VRN effectively reduces the number of traffic metering points required thereby simplifying the aggregation and exportation of flow records to a collector. The collector may be service manager in a network management system. The metering points, in a preferred embodiment, are at virtual interfaces (VI) which are edge nodes in VRN. One of the virtual interfaces is selected as a master virtual interface and act as a collector and distributor of flow related information. In one aspect of the invention the VRN is used to provide, non-invasively, per-flow delay monitoring in a communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Live Router Migration
InactiveUS20110032830A1Easily and quickly migrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData trafficReal time routing
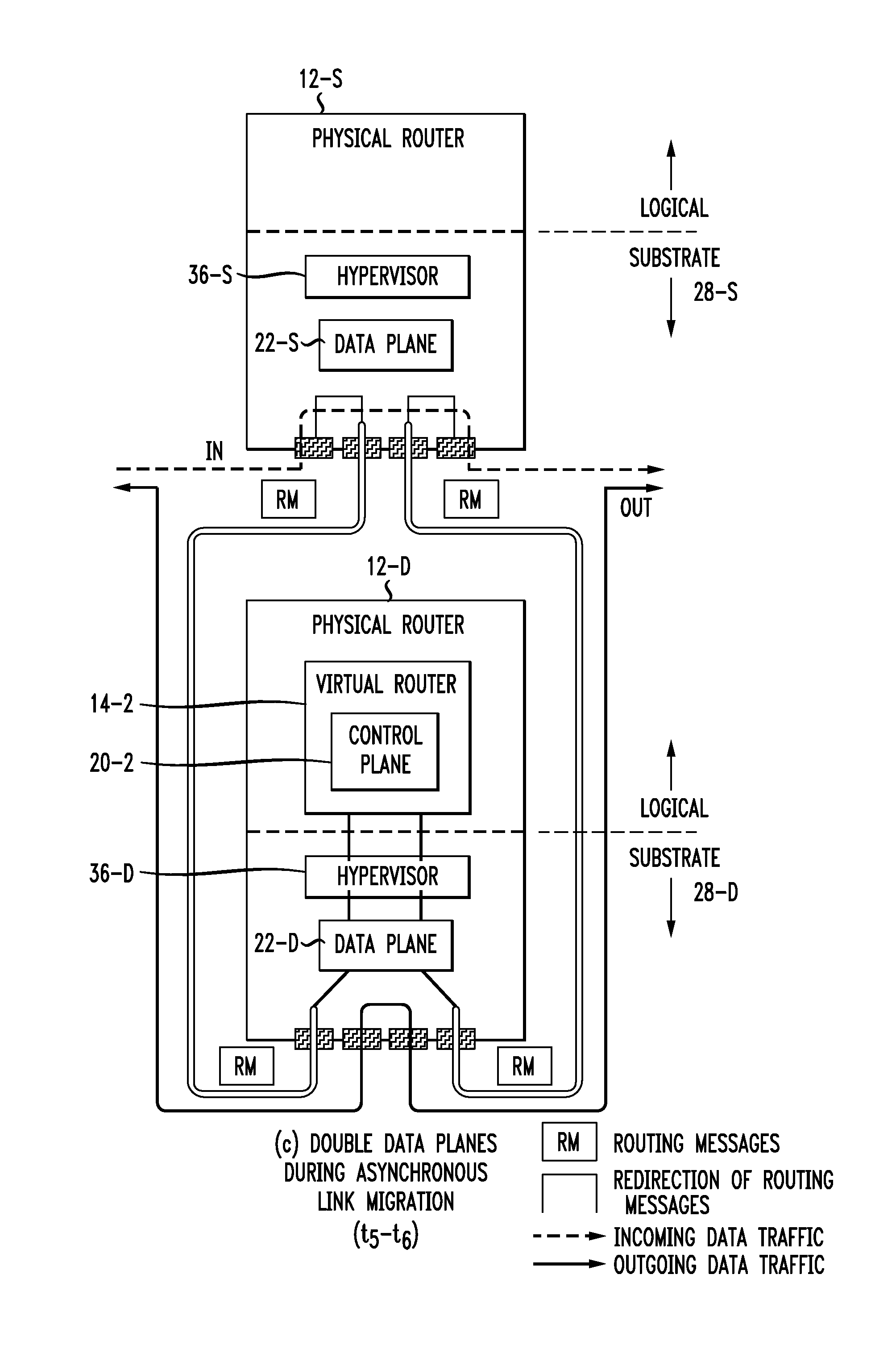
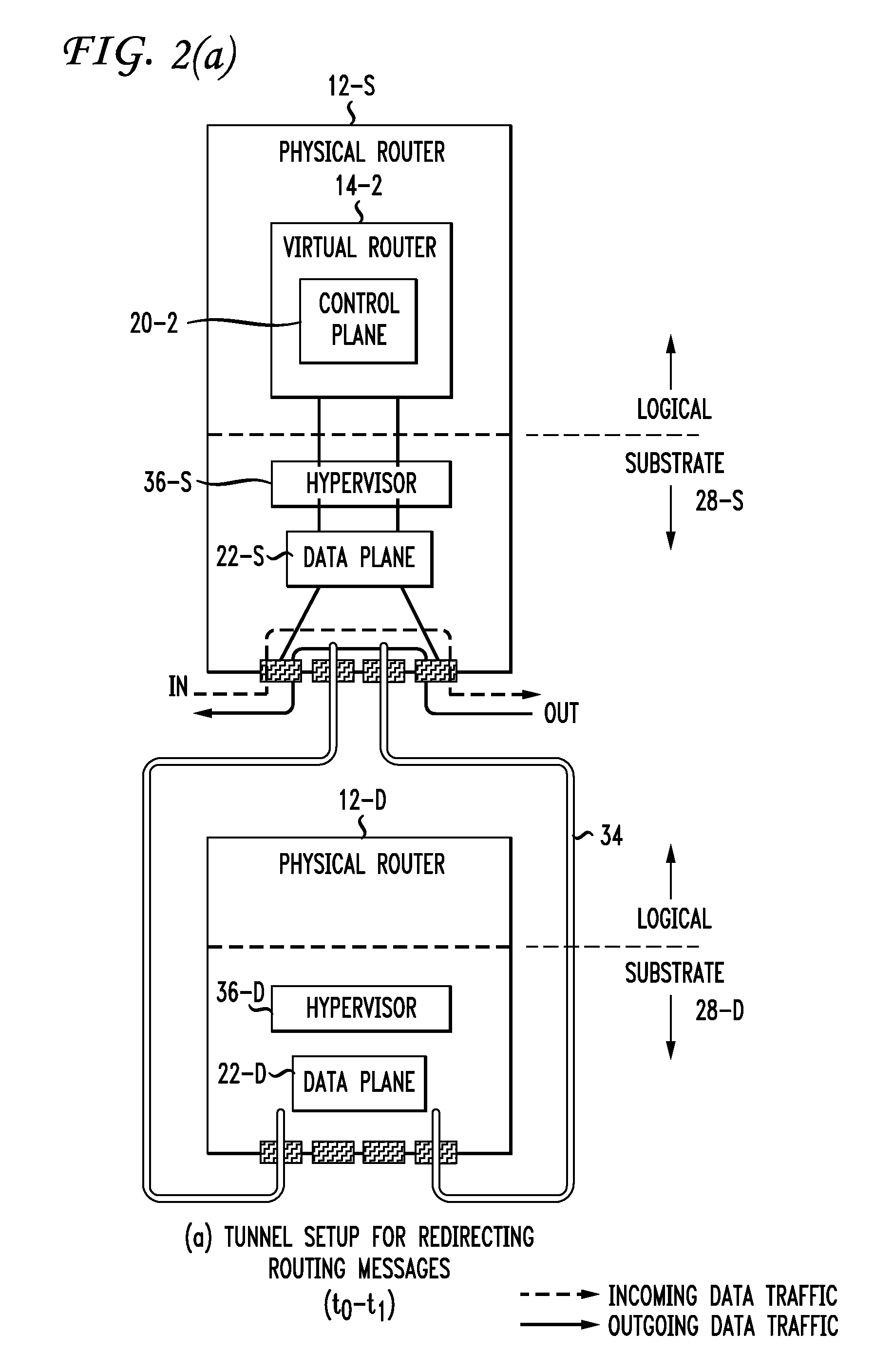
Live router migration is implemented by separating the logical features of a virtual router from its physical features. Tunnels are established between a source (physical) router and a destination (physical) router, allowing the control plane of the virtual router being migrated to send and receive messages from the destination router. The control plane information is then transferred to the destination router, which functions to clone the data plane at the destination router. Outgoing links from the destination router are then be established. The double appearance of the data plane at both the source and destination routers allows for the data plane information to be transferred asynchronously over to the destination router. Once all of the data plane information has been transferred, incoming data traffic links at the destination router can be established and the tunnels between the routers taken down.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
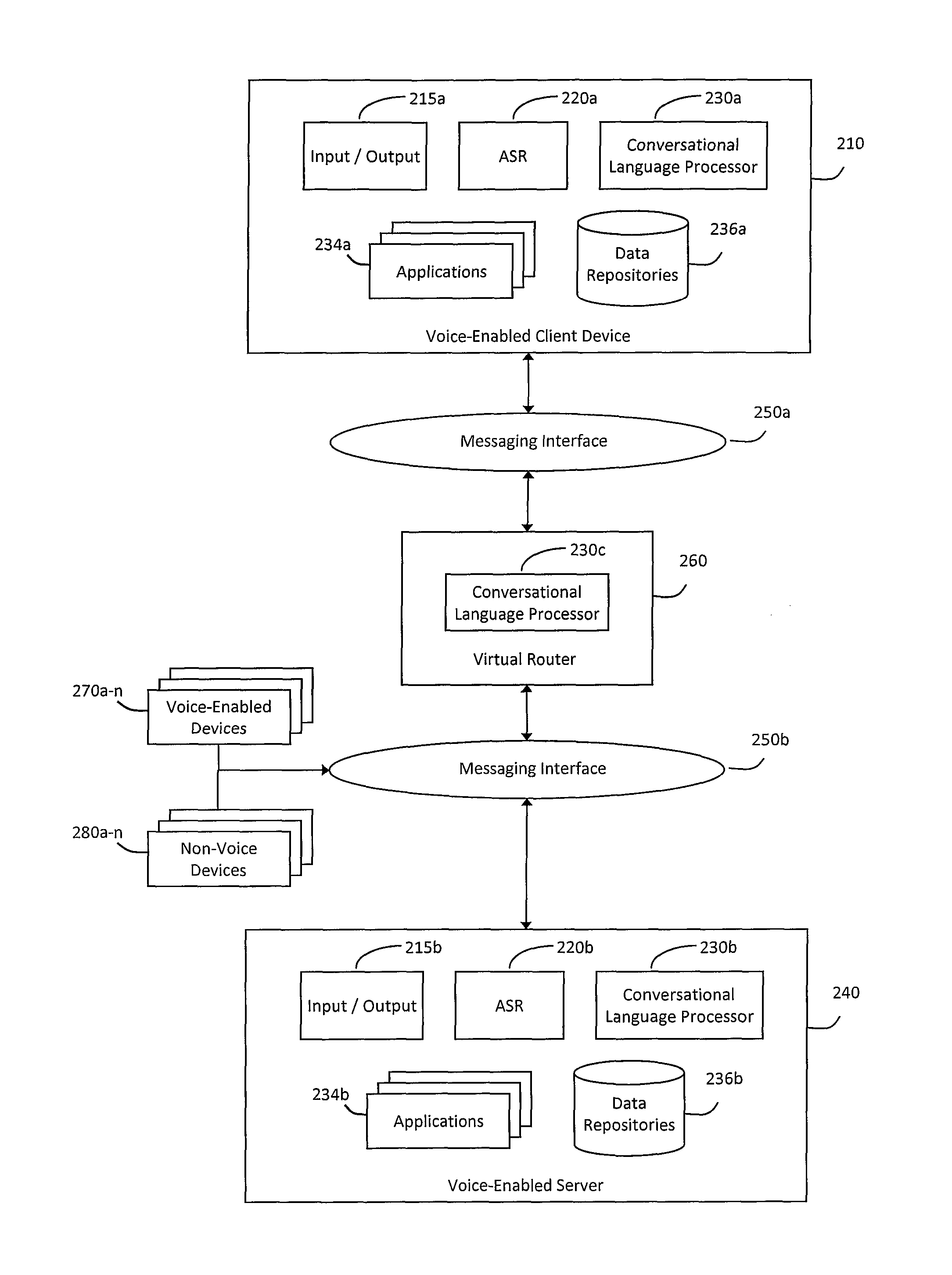
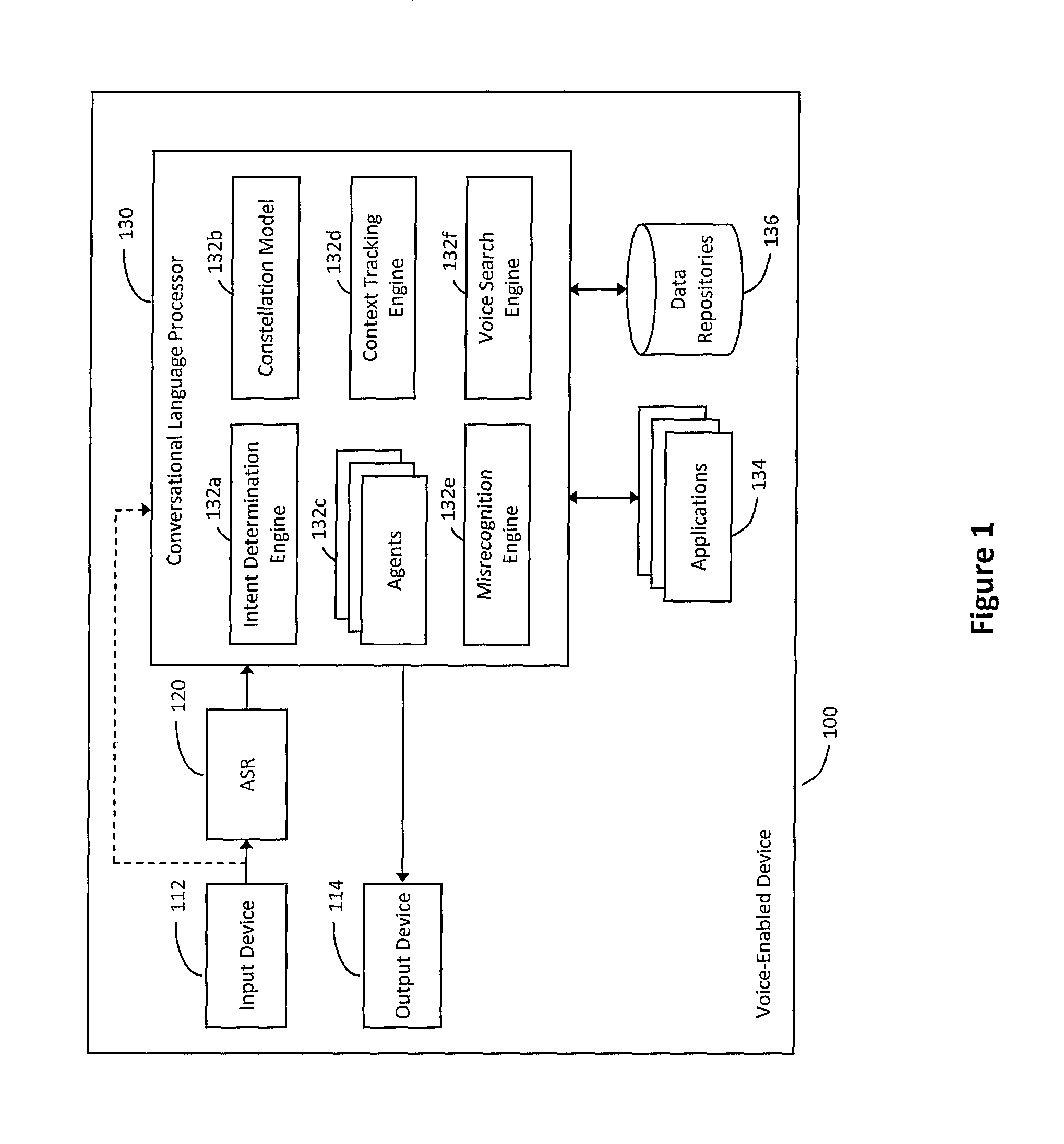
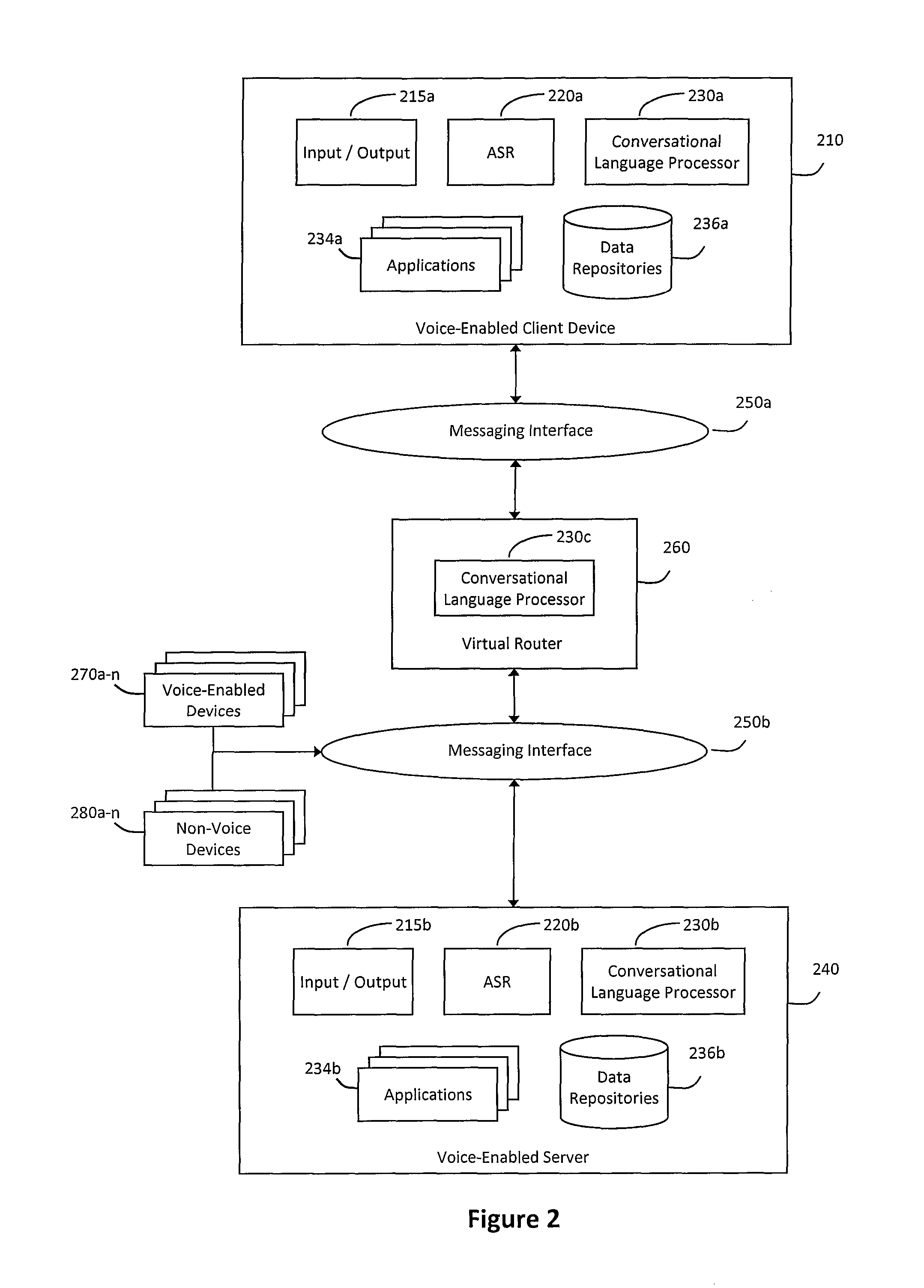
System and method for hybrid processing in a natural language voice services environment
ActiveUS9171541B2Input/output for user-computer interactionSpeech recognitionMultimodal interactionSpeech sound
A system and method for hybrid processing in a natural language voice services environment that includes a plurality of multi-modal devices may be provided. In particular, the hybrid processing may generally include the plurality of multi-modal devices cooperatively interpreting and processing one or more natural language utterances included in one or more multi-modal requests. For example, a virtual router may receive various messages that include encoded audio corresponding to a natural language utterance contained in a multi-modal interaction provided to one or more of the devices. The virtual router may then analyze the encoded audio to select a cleanest sample of the natural language utterance and communicate with one or more other devices in the environment to determine an intent of the multi-modal interaction. The virtual router may then coordinate resolving the multi-modal interaction based on the intent of the multi-modal interaction.
Owner:VOICEBOX TECH INC
Distributed architecture for real-time flow measurement at the network domain level
ActiveUS8095640B2Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsCommunications systemRelevant information
A virtual router network (VRN) for performing real-time flow measurements (RTFM) is provided. The VRN effectively reduces the number of traffic metering points required thereby simplifying the aggregation and exportation of flow records to a collector. The collector may be service manager in a network management system. The metering points, in a preferred embodiment, are at virtual interfaces (VI) which are edge nodes in VRN. One of the virtual interfaces is selected as a master virtual interface and act as a collector and distributor of flow related information. In one aspect of the invention the VRN is used to provide, non-invasively, per-flow delay monitoring in a communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Resource allocation in virtual routers
InactiveUS20110016215A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksShared resourceResource allocation
A router system implements a plurality of virtual routers. Various combinations of resources may be shared by the router system when implementing the virtual routers. In one embodiment, the particular combination of resources to share when implementing the virtual router is user programmable.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
System and method for controlling routing in a virtual router system
ActiveUS7340535B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationPacket lossNetwork data
One or more functions are applied to network data packets in a virtual router. A packet comprising part of a packet flow is received, and the packet is evaluated to determine which of the one or more functions are to be applied to the flow. The results of the evaluation are stored in a record, and the functions indicated in the stored record are applied to subsequent packets in the packet flow.
Owner:FORTINET
Fully Distributed Routing over a User-Configured On-Demand Virtual Network for Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) on Hybrid Cloud Networks
A layer-3 virtual router connects two or more virtual networks. Virtual networks are overlaid upon physical networks. Each virtual network (VN) is a layer-2 network that appears to expand an organization's LAN using virtual MAC addresses. The network stack forms a virtual-network packet with a virtual gateway MAC address of the virtual router to reach a remote virtual network. A VN device driver shim intercepts packets and their virtual MAC and IP addresses and encapsulates them with physical packets sent over the Internet. A VN switch table is expanded to include entries for nodes on the remote virtual network so that all nodes on both virtual networks are accessible. A copy of the VN switch table is stored on each node by a virtual network management daemon on the node. A Time-To-Live field in the virtual-network packet is decremented for each virtual hop and a checksum recalculated.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
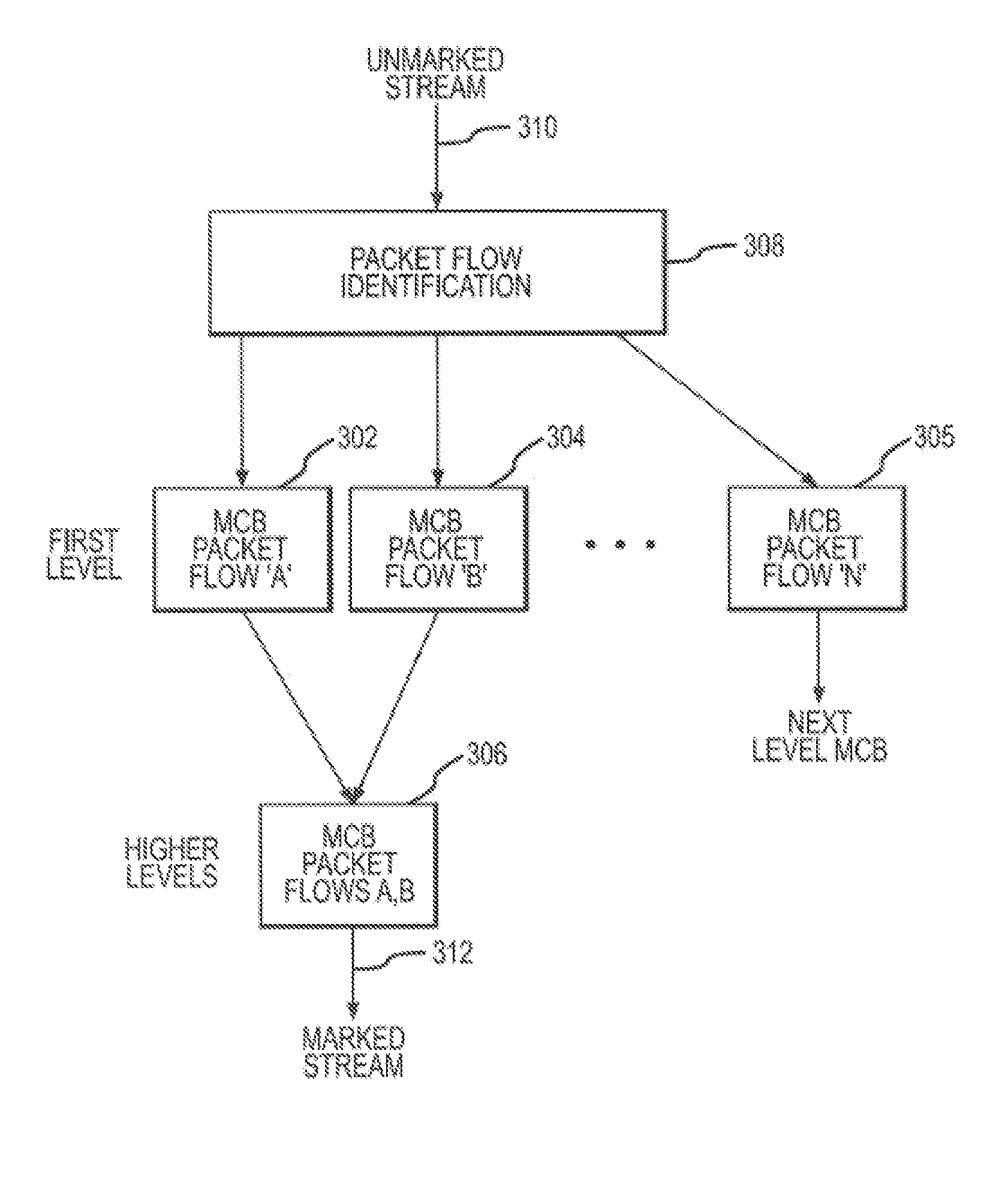
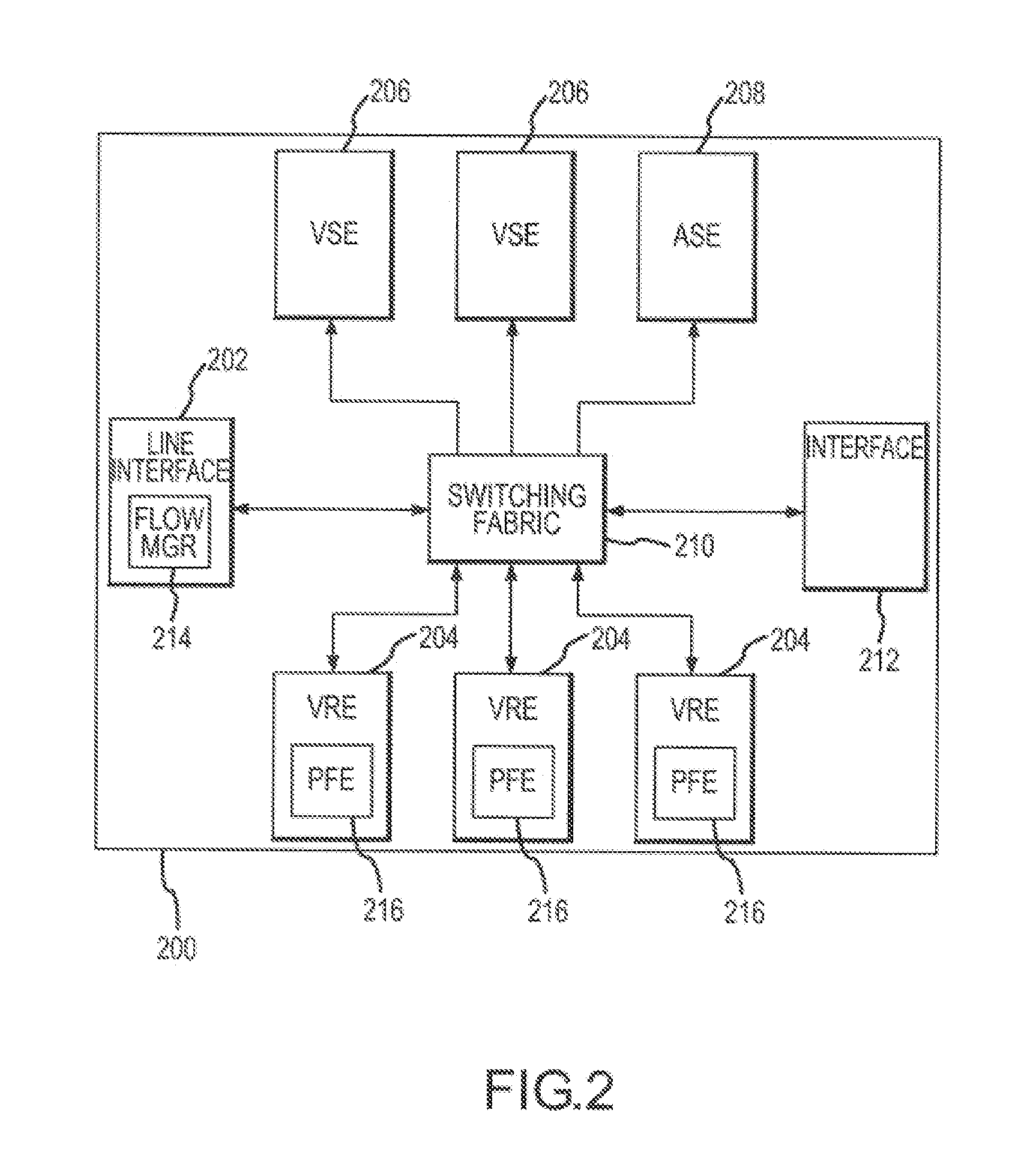
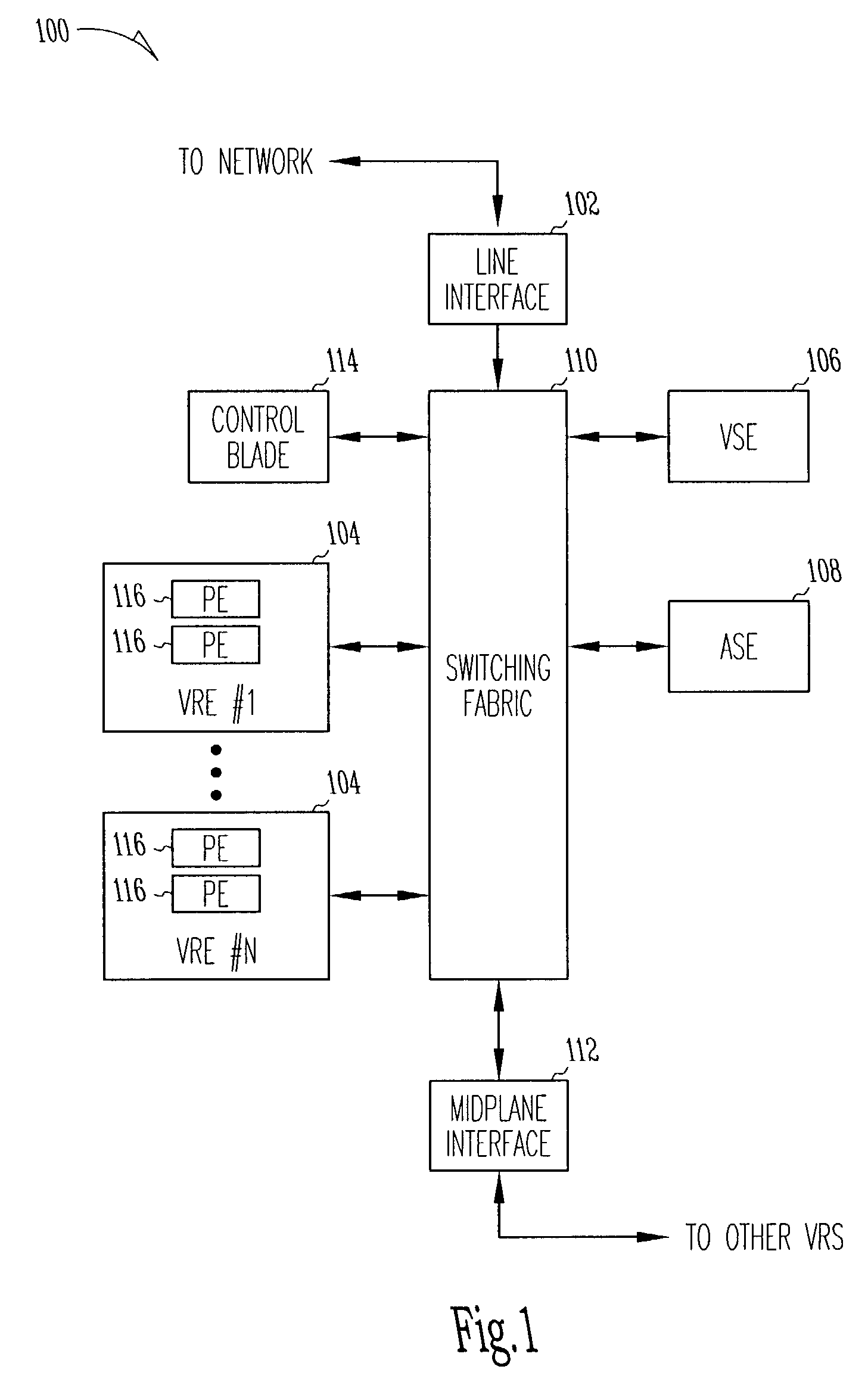
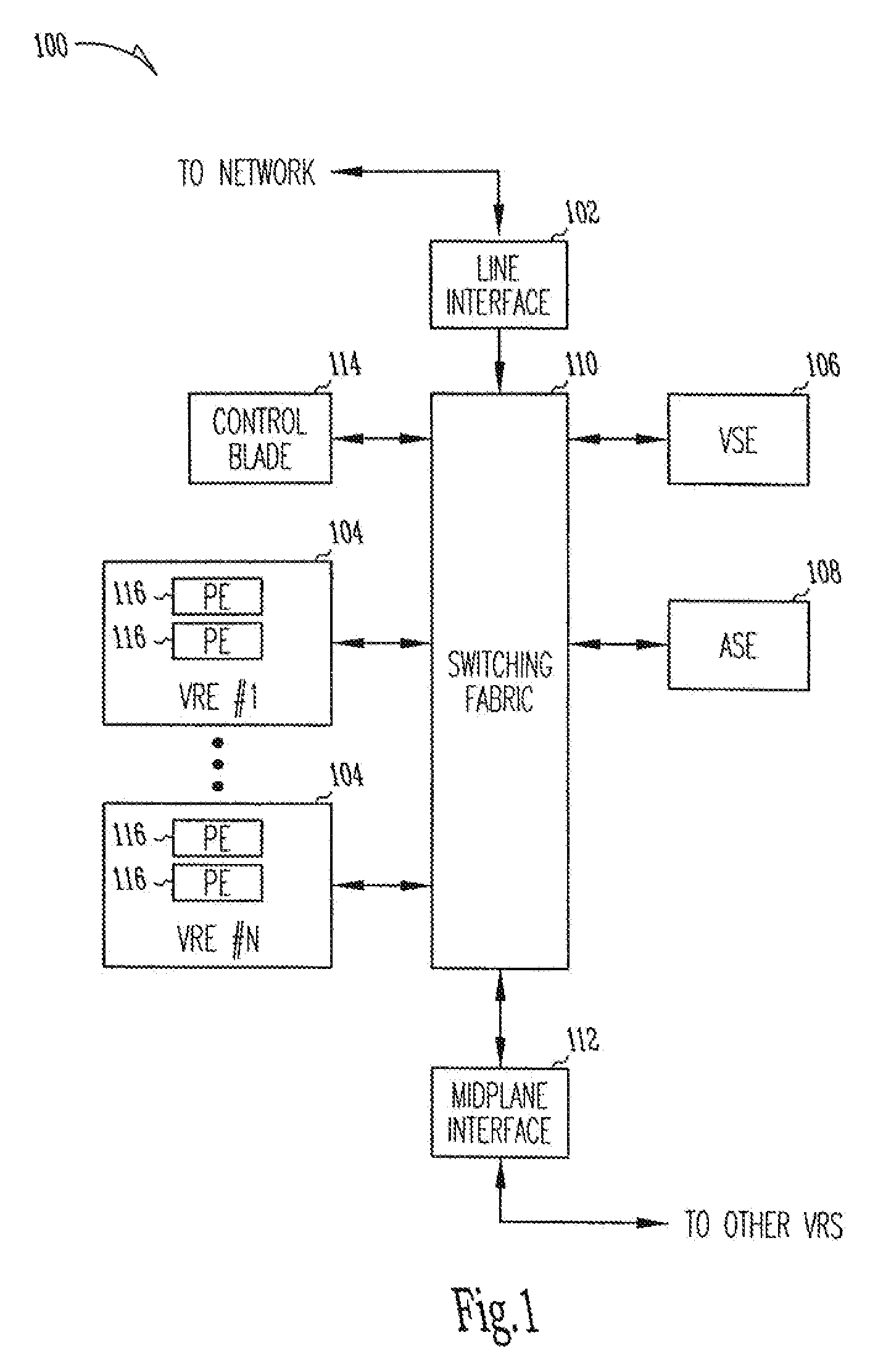
System and method for hierarchical metering in a virtual router based network switch
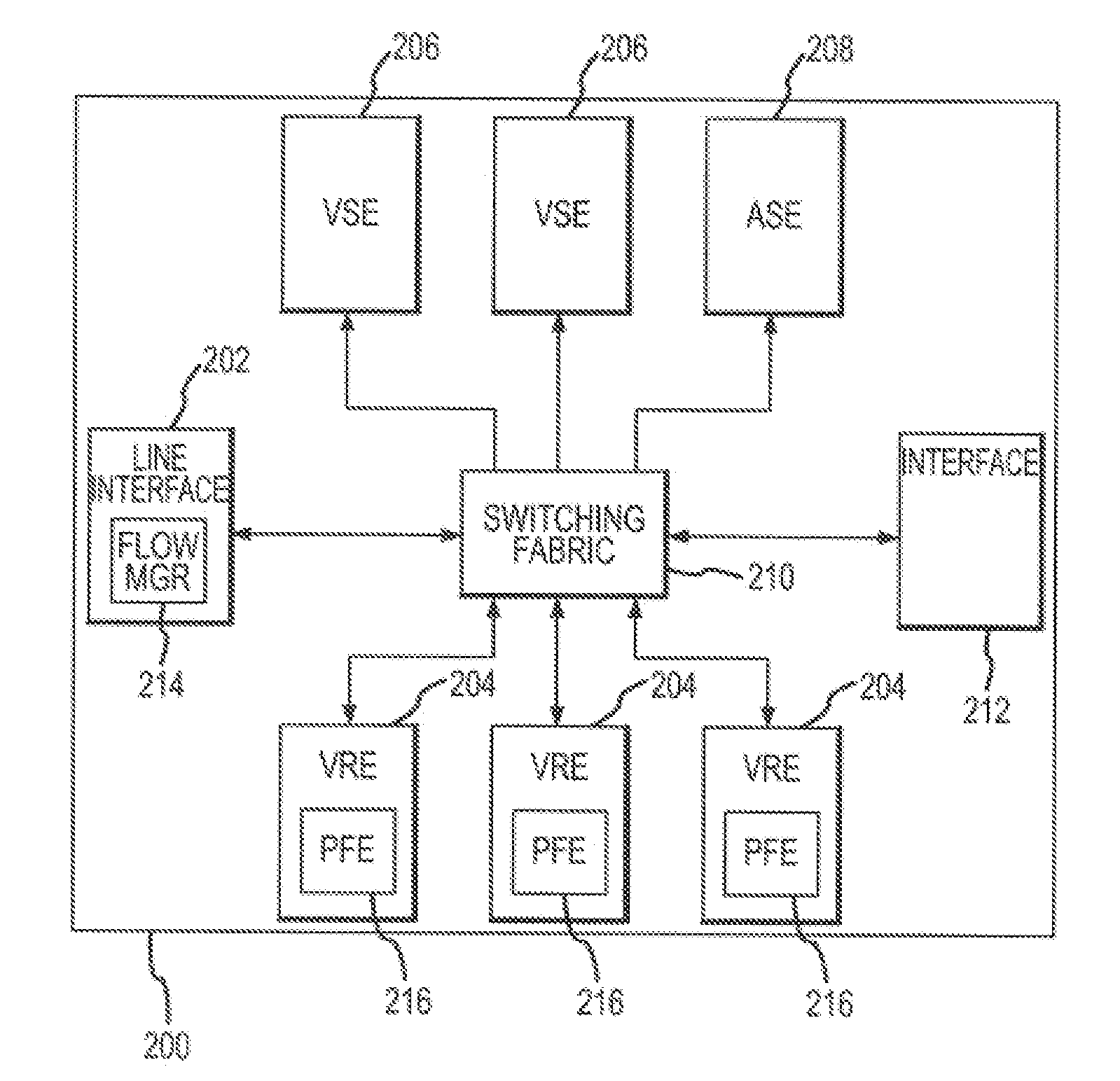
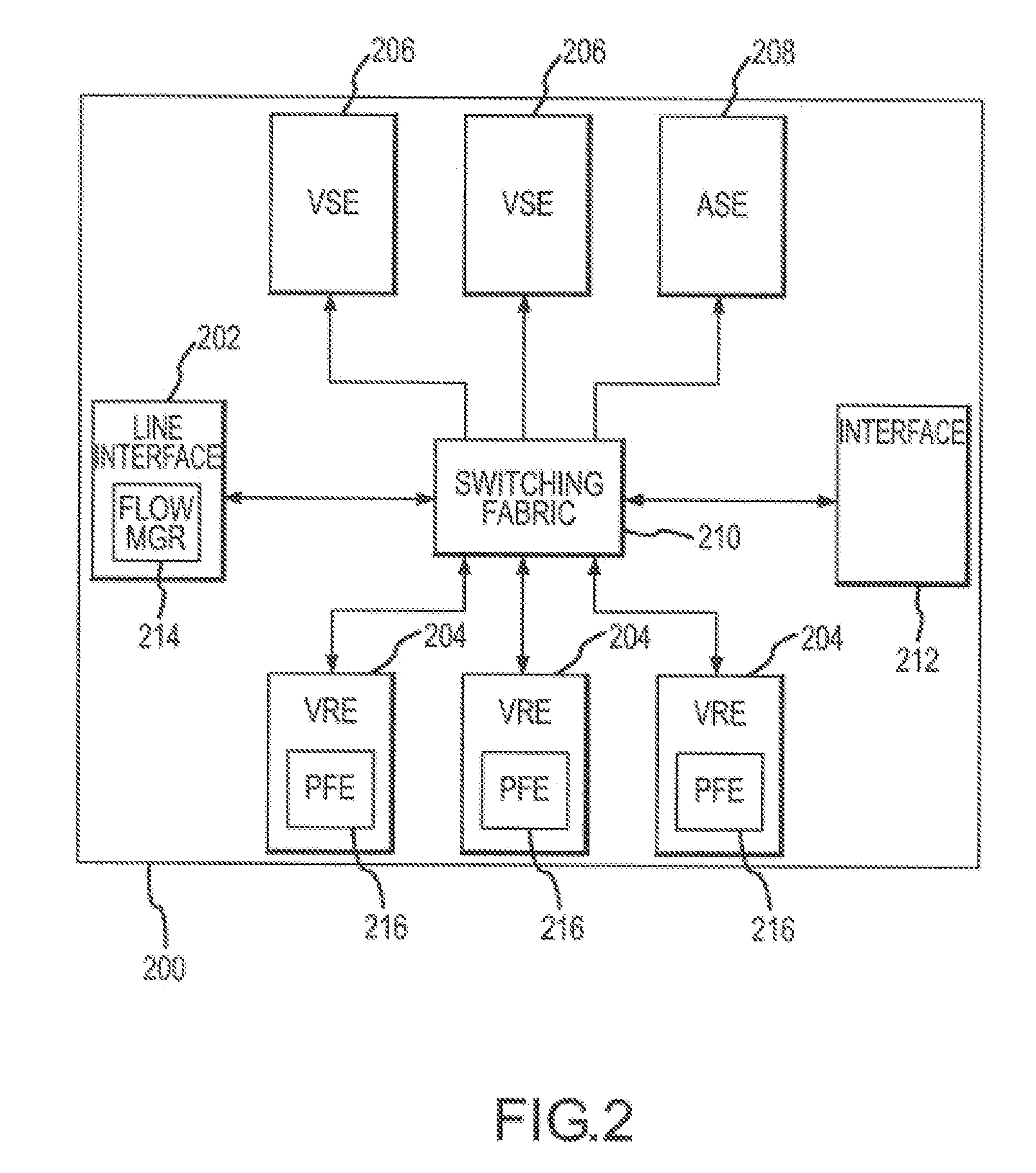
A virtual routing platform includes a line interface a plurality of virtual routing engines (VREs) to identify packets of different packet flows and perform a hierarchy of metering including at least first and second levels of metering on the packet flows. A first level of metering may be performed on packets of a first packet flow using a first metering control block (MCB). The first level of metering may be one level of metering in a hierarchy of metering levels. A second level of metering on the packets of the first packet flow and packets of a second flow using a second MCB. The second level of metering may be another level of metering in the hierarchy. A cache-lock may be placed on the appropriate MCB prior to performing the level of metering. The first and second MCBs may be data structures stored in a shared memory of the virtual routing platform. The cache-lock may be released after performing the level of metering using the MCB. The cache-lock may comprise setting a lock-bit of a cache line index in a cache tag store, which may identify a MCB in the cache memory. The virtual routing platform may be a multiprocessor system utilizing a shared memory having a first and second processors to perform levels of metering in parallel. In one embodiment, a virtual routing engine may be shared by a plurality of virtual router contexts running in a memory system of a CPU of the virtual routing engine. In this embodiment, the first packet flow may be associated with one virtual router context and the second packet flow is associated with a second virtual router context. The first and second routing contexts may be of a plurality of virtual router contexts resident in the virtual routing engine.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
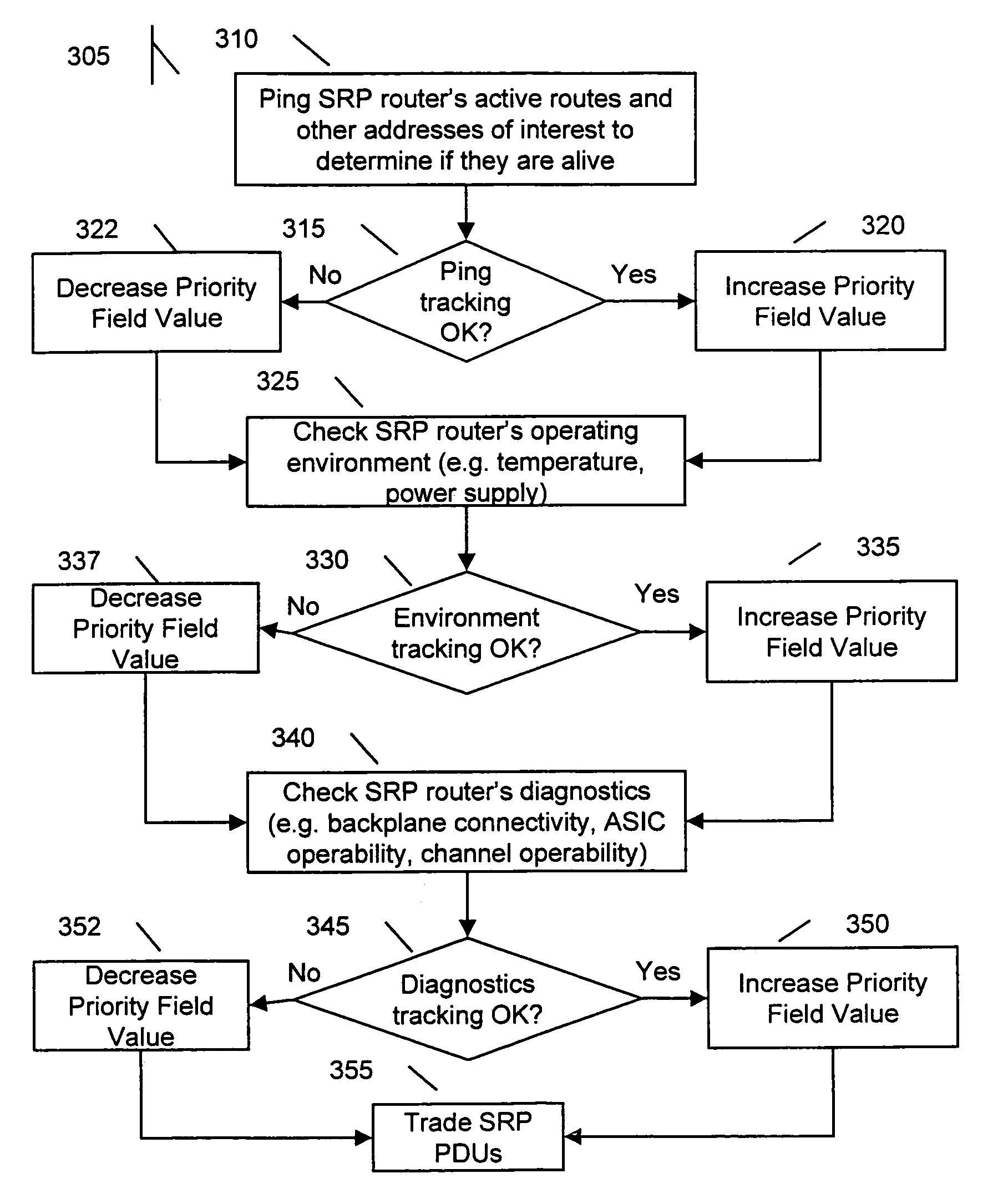
Method and apparatus for selecting redundant routers using tracking
A method for electing a master router in a virtual router network by obtaining a tracking parameter for each of the routers participating in a virtual router network. A priority value is assigned to each of the plurality of routers based on the tracking parameter and reported to each router at periodic intervals. The router with the highest priority value is elected, or re-elected, as the new master. The tracking parameters include a ping tracking parameter obtained by pinging the active routes listed in the routing table for each of the of routers participating in the virtual router network, an environmental tracking parameter obtained by inspecting the operating characteristics outside of the control of the router, including operating temperature and power supply status, and a diagnostic tracking parameter obtained by inspecting the diagnostic data representing operating characteristics within the control of the router, including an operability status of the router's circuitry and channels and a status of the packet-level connectivity to the physical layer backplane network.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system
The present application is directed towards systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system. In some embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing address resolution in IPv4 networks in a multi-core system. In other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing neighbor discovery in IPv6 networks in a multi-core system. In still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing network bridging in a multi-core system. In yet other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing link aggregation in a multi-core system. And in still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing virtual routers in a multi-core system.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
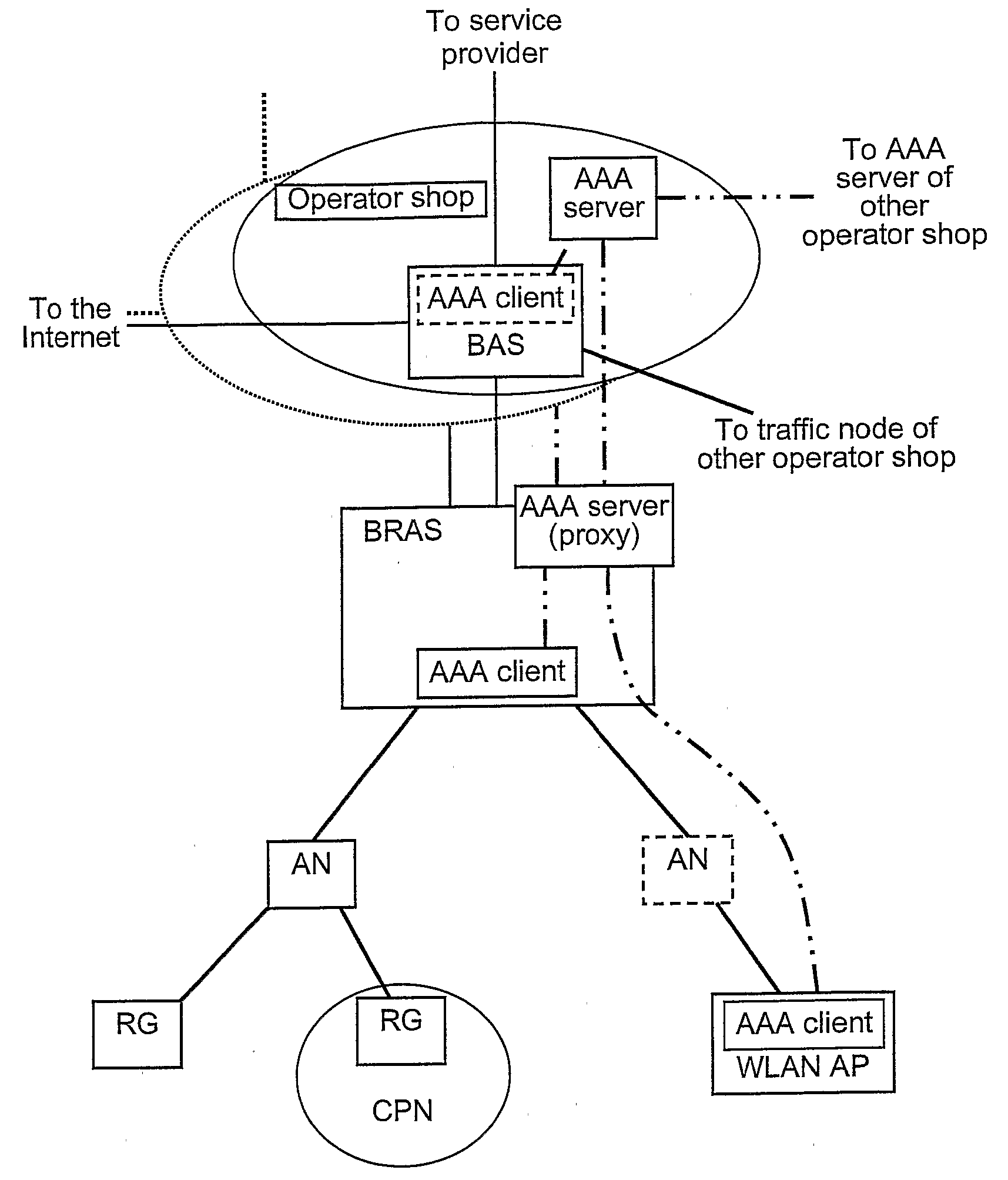
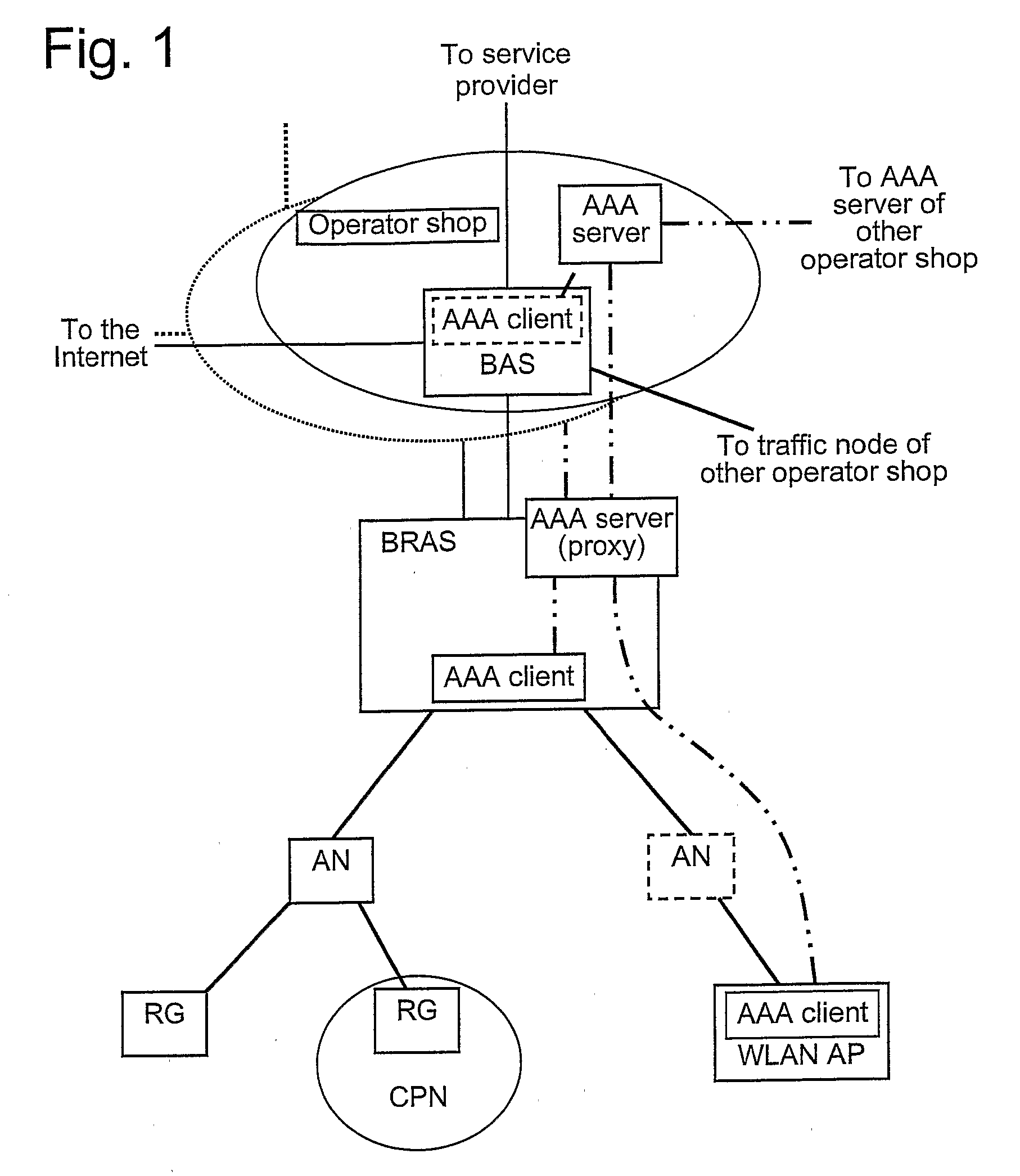
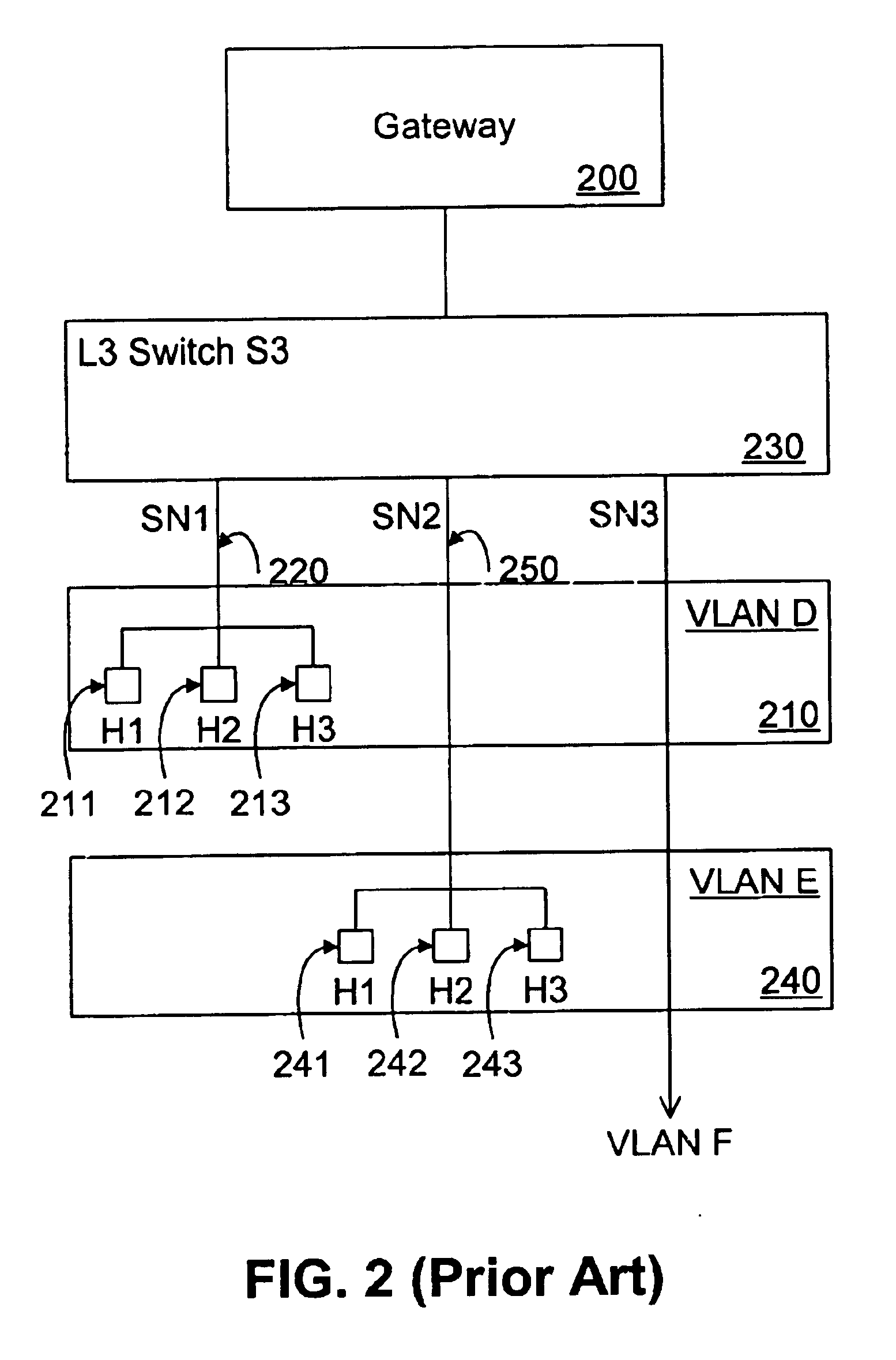
Operator Shop Selection
An access node for an Ethernet network is connected between an access point of user devices and a broadband remote access server for access to a plurality of service providing networks. It includes a VLAN handling unit having a memory for storing identifications of Ethernet frames transmitted in a first VLAN including the access node and a local virtual router function unit of the access server in a second VLANs. Each of the second VLANs including the access node, the local virtual router function unit and one of the virtual router function units of the access server for each of the virtual router function units. A control unit commands the handling unit to transmit frames from a new user device that has connected itself to the access point into the first virtual local area network. The control unit also receives information from the access server in respect of routing frames and its commands to the handling unit to transmit frames from user device which is connected to the access point and the frames from which are transmitted into the first VLAN to be instead transmitted into one of the second VLAN as given by the information received from the broadband remote access server, the frames thereby being transmitted to the server of the respective service providing network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
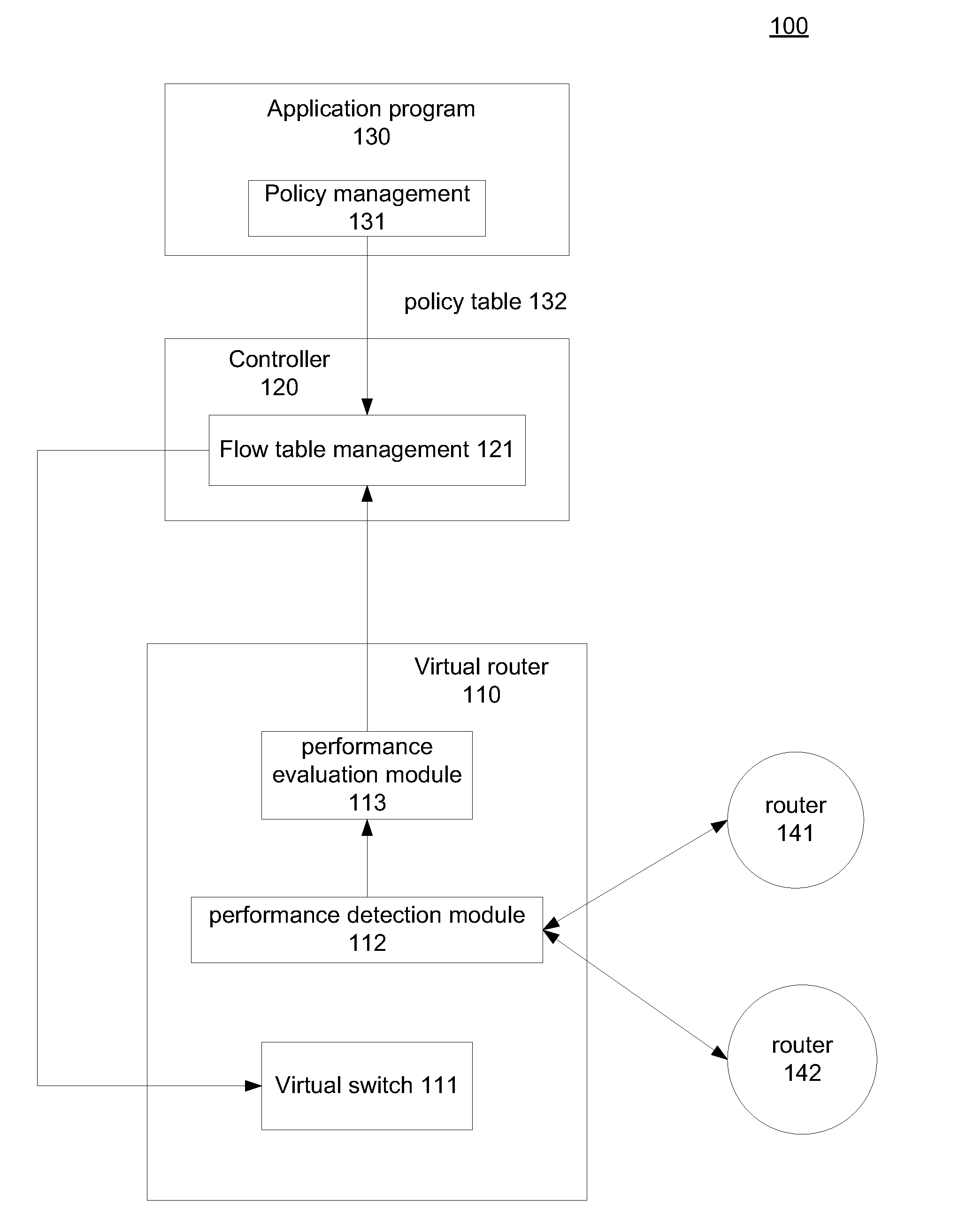
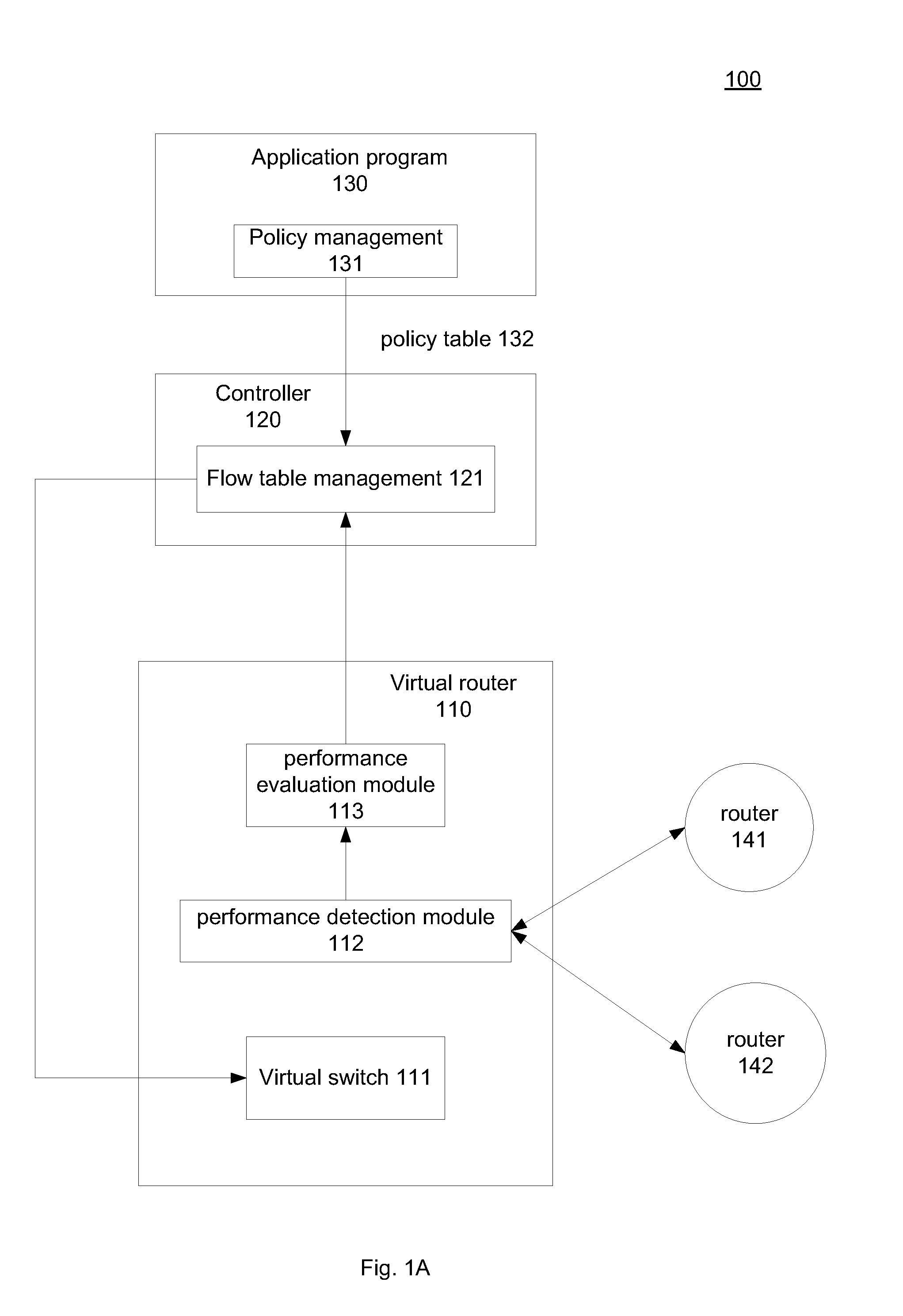
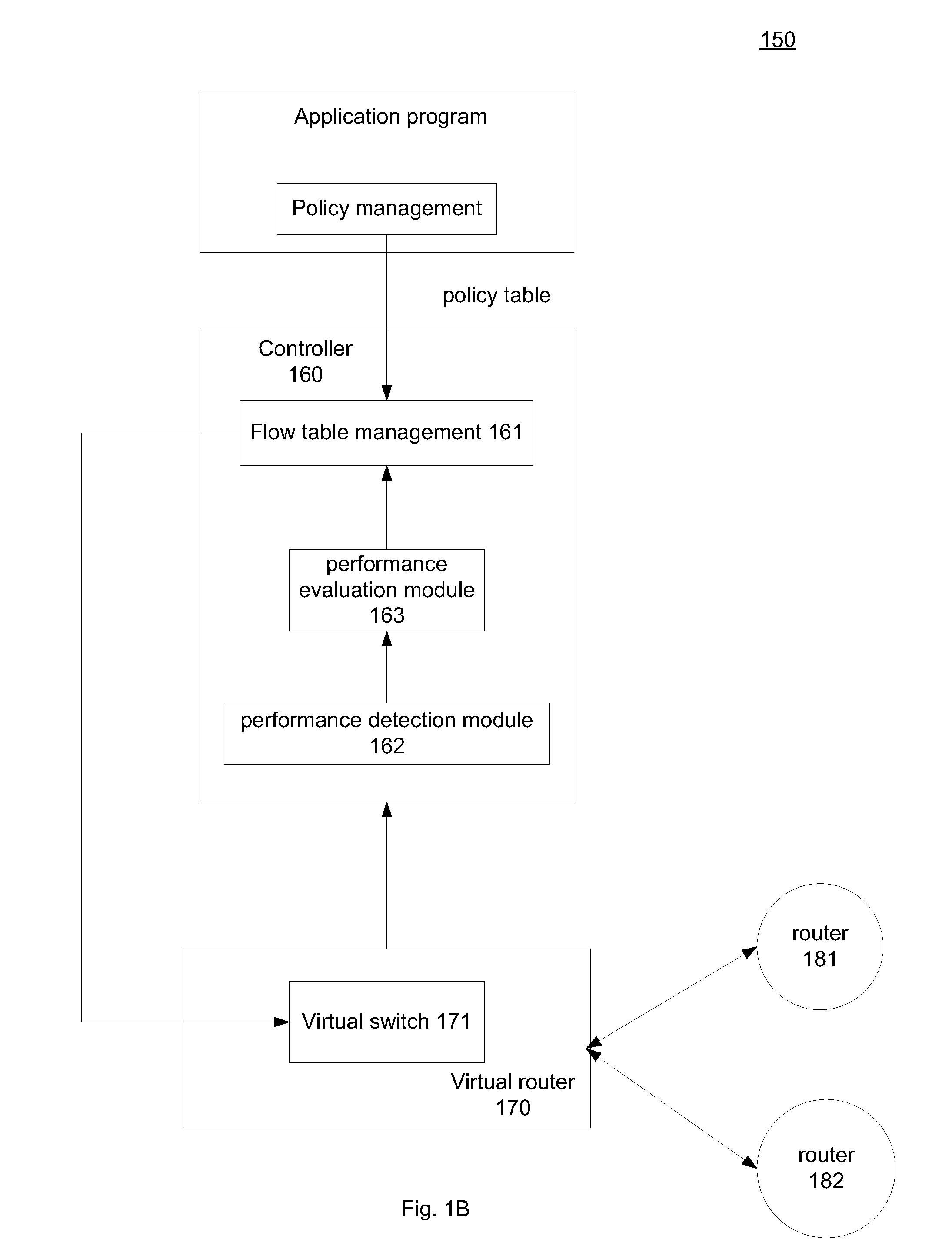
Performance-based routing in software-defined network (SDN)
System and method for performance-based routing in an SDN. An SDN controller is configured to adaptively determine data transmission routes based on real-time route performance evaluation provided by a virtual router. The virtual router includes a route detection component to attain route performance data and a performance evaluation component to evaluate the route performance based on predetermined criteria provided by the SDN controller. The evaluation result is sent to the SDN controller and used to intelligently determine a superior route selection and route usage for a specific application program. According to the determination, the SDN controller updates the flow table associated with the virtual router for subsequent data transmission.
Owner:ALGOBLU HLDG
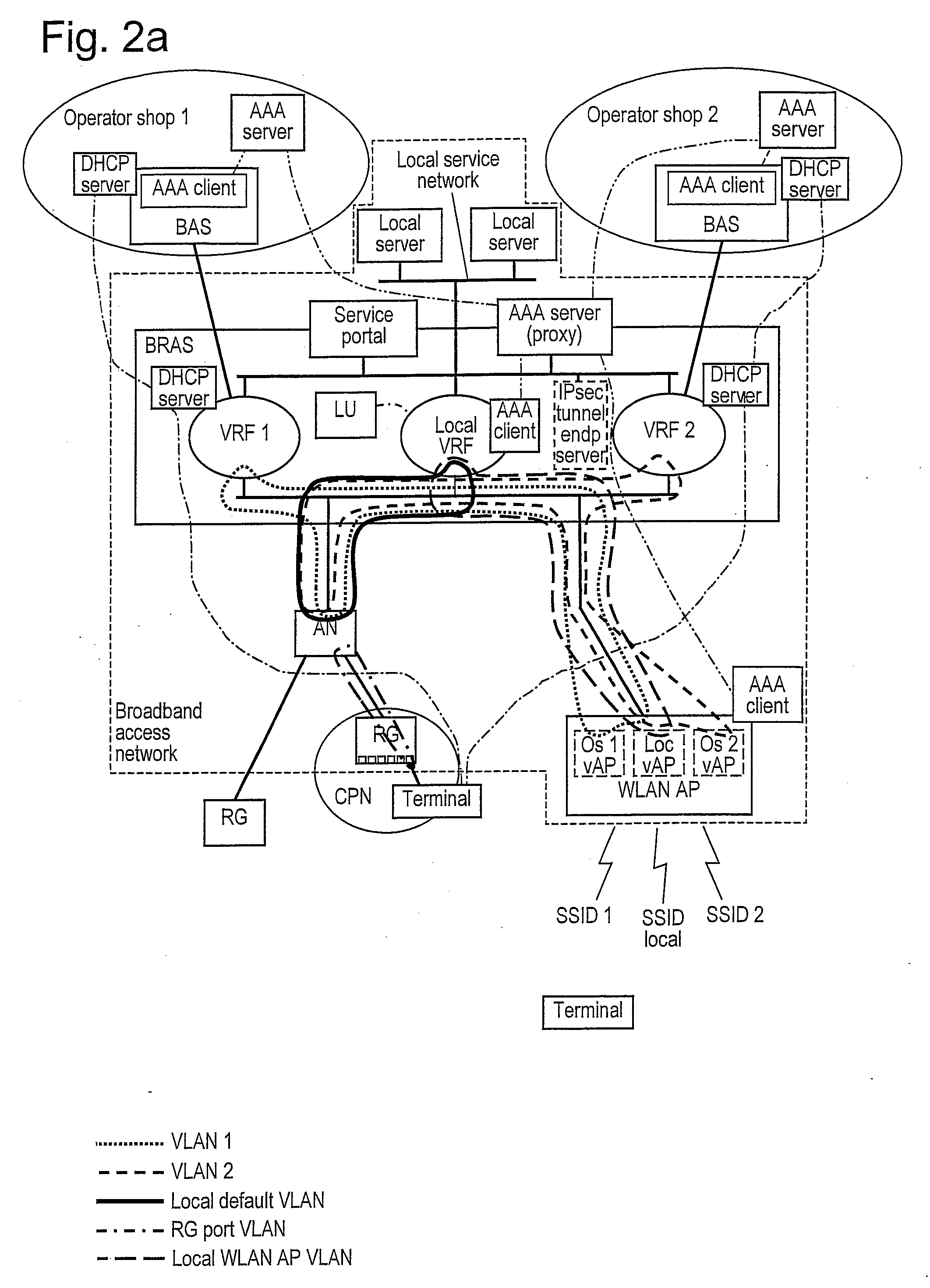
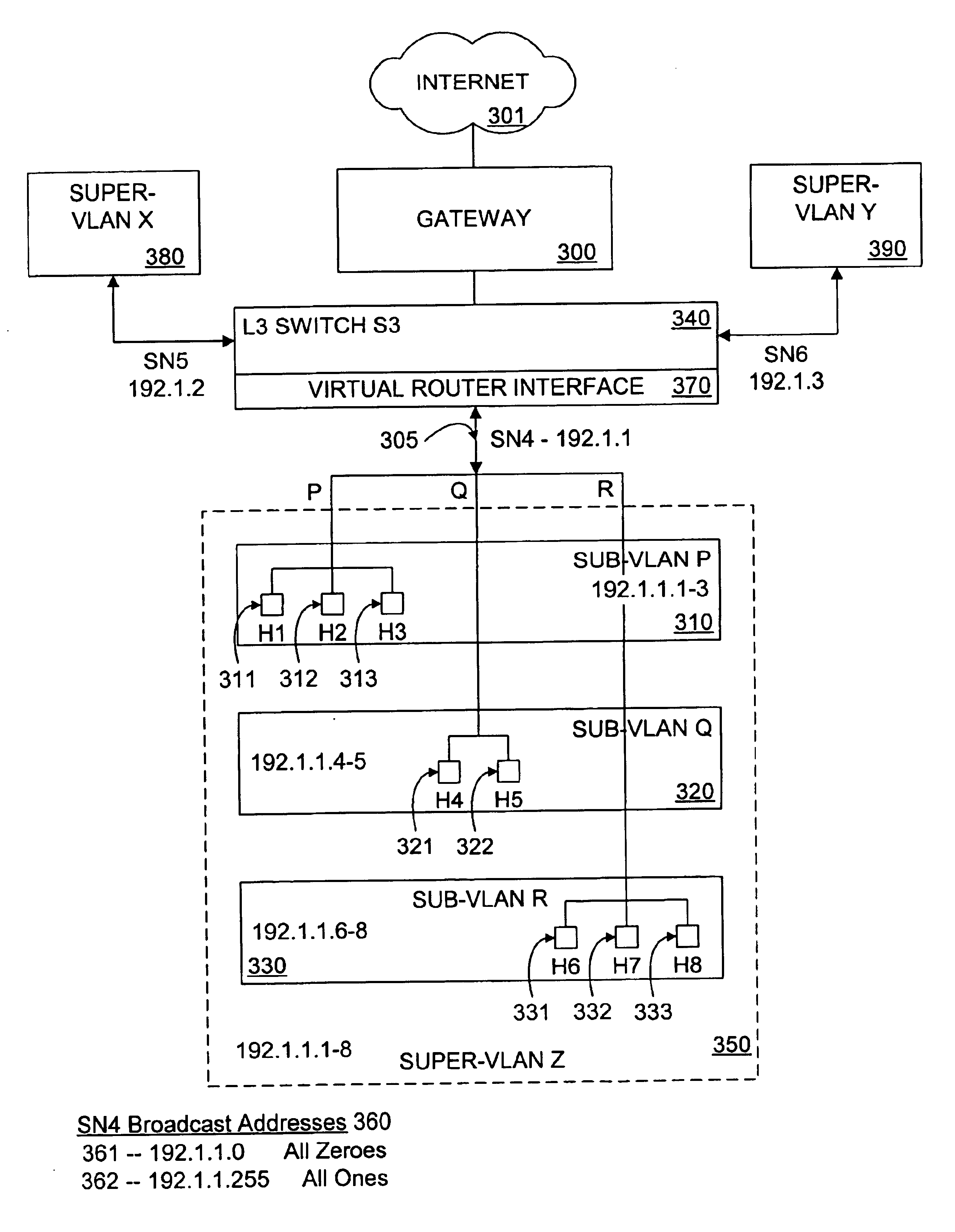
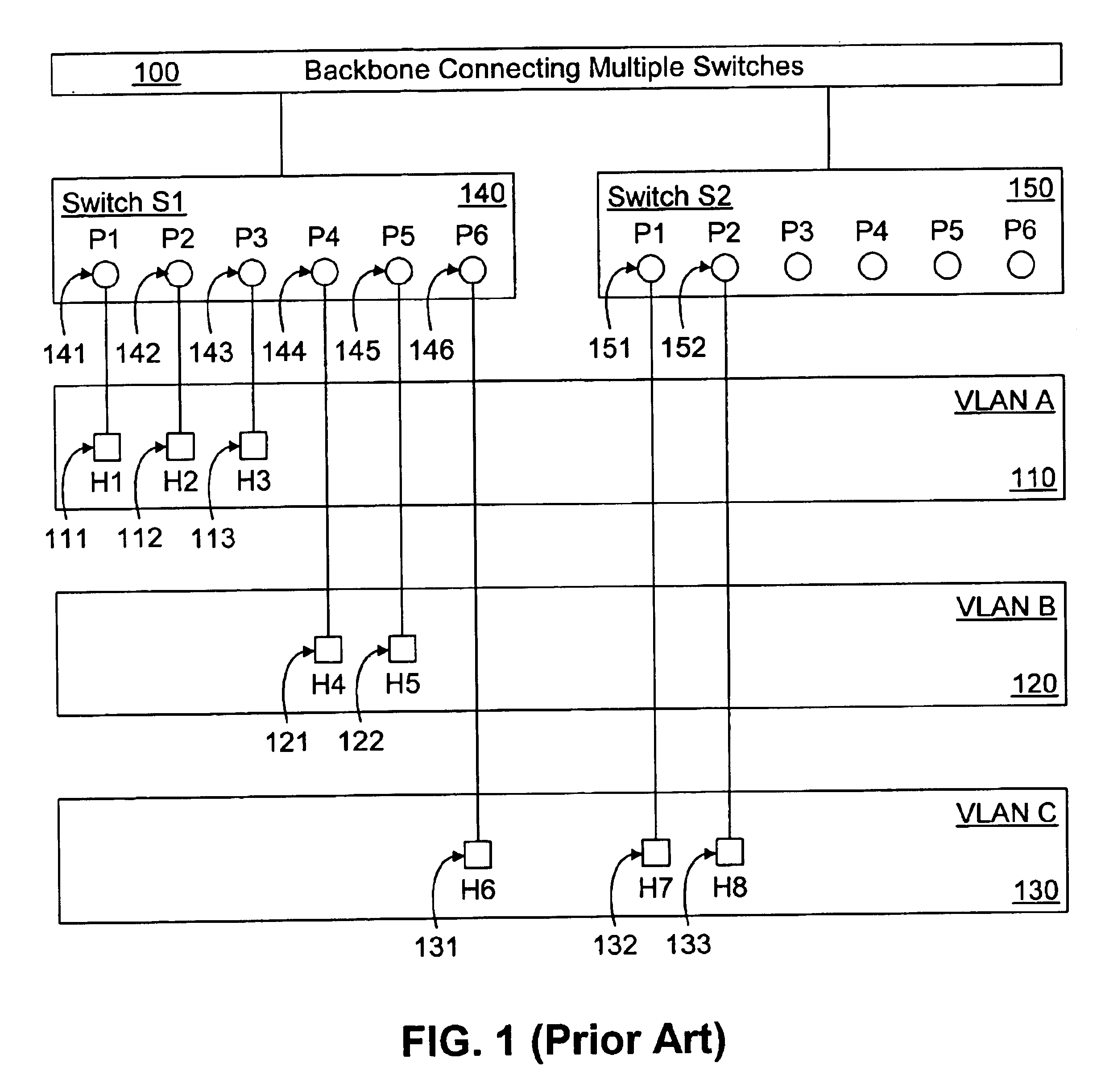
Method and system for VLAN aggregation
A method and system for an aggregated virtual local area network (VLAN) architecture in which several VLANs in a network share the same default router address and subnet mask, but remain isolated from one another's network traffic. Instead of the traditional method of assigning one subnet to a VLAN, each VLAN is assigned only a portion of a subnet's IP address space, and is further grouped into a super-VLAN uniquely associated with that subnet. Intra-VLAN traffic is forwarded only to host IP addresses assigned to that same VLAN according to a VLAN identifier carried in the data packet. Inter-VLAN traffic is processed by a virtual router interface which routes the data packet by applying the routing configuration for the subnet uniquely associated with the super-VLAN, according to a super-VLAN identifier carried in the data packet. The routing configuration used by the virtual router interface includes routing protocols, static routes, redundant router protocols and access-lists. Since each VLAN shares the same virtual router interlace, the traditional address overhead of a subnet is minimized, requiring only one default router and subnet mask, as well as only one pair of subnet broadcast addresses for all hosts on the subnet and the subnet itself. The aggregated VLAN architecture provides for the efficient use and management of a network's IP address space.
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
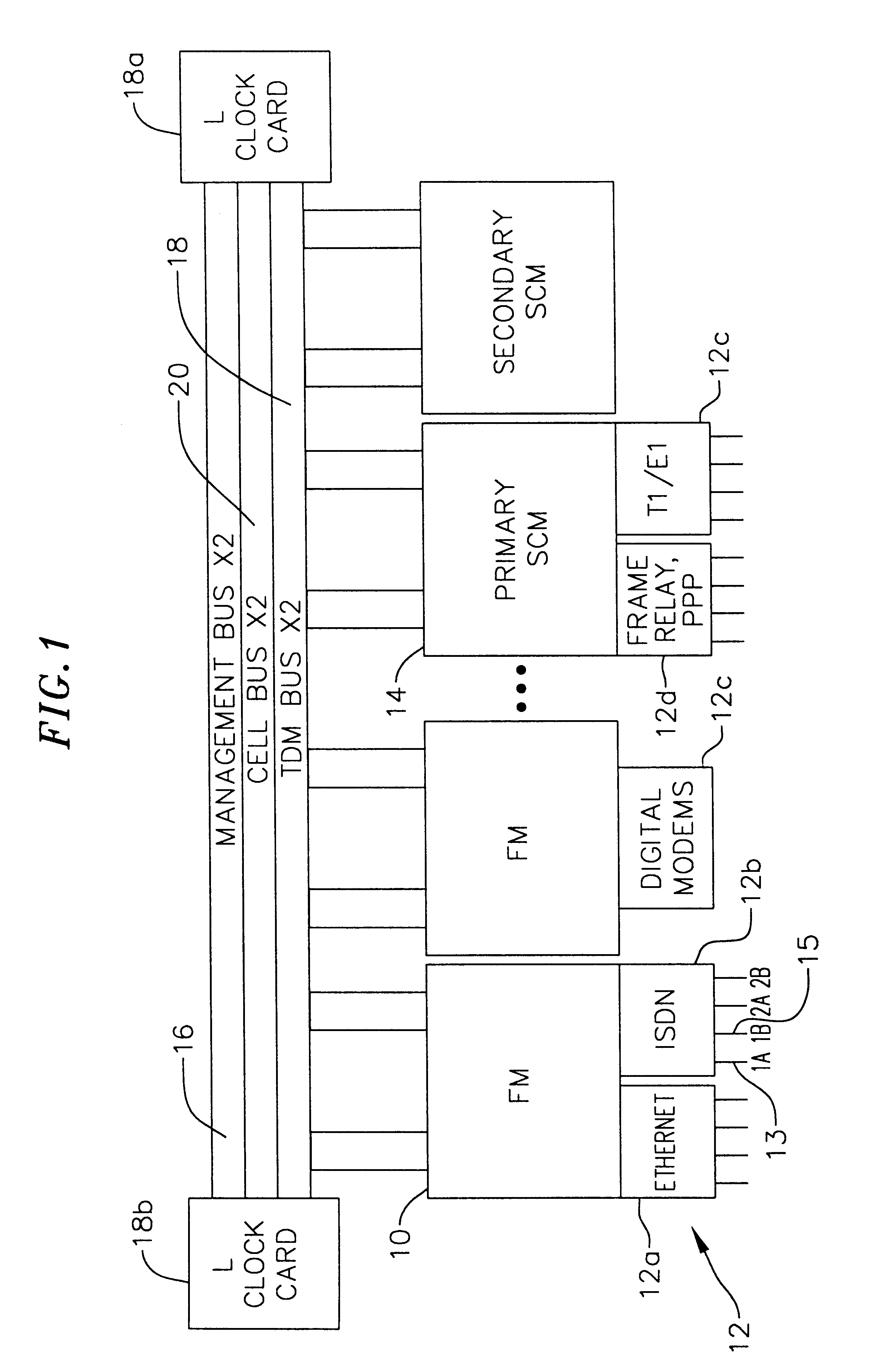
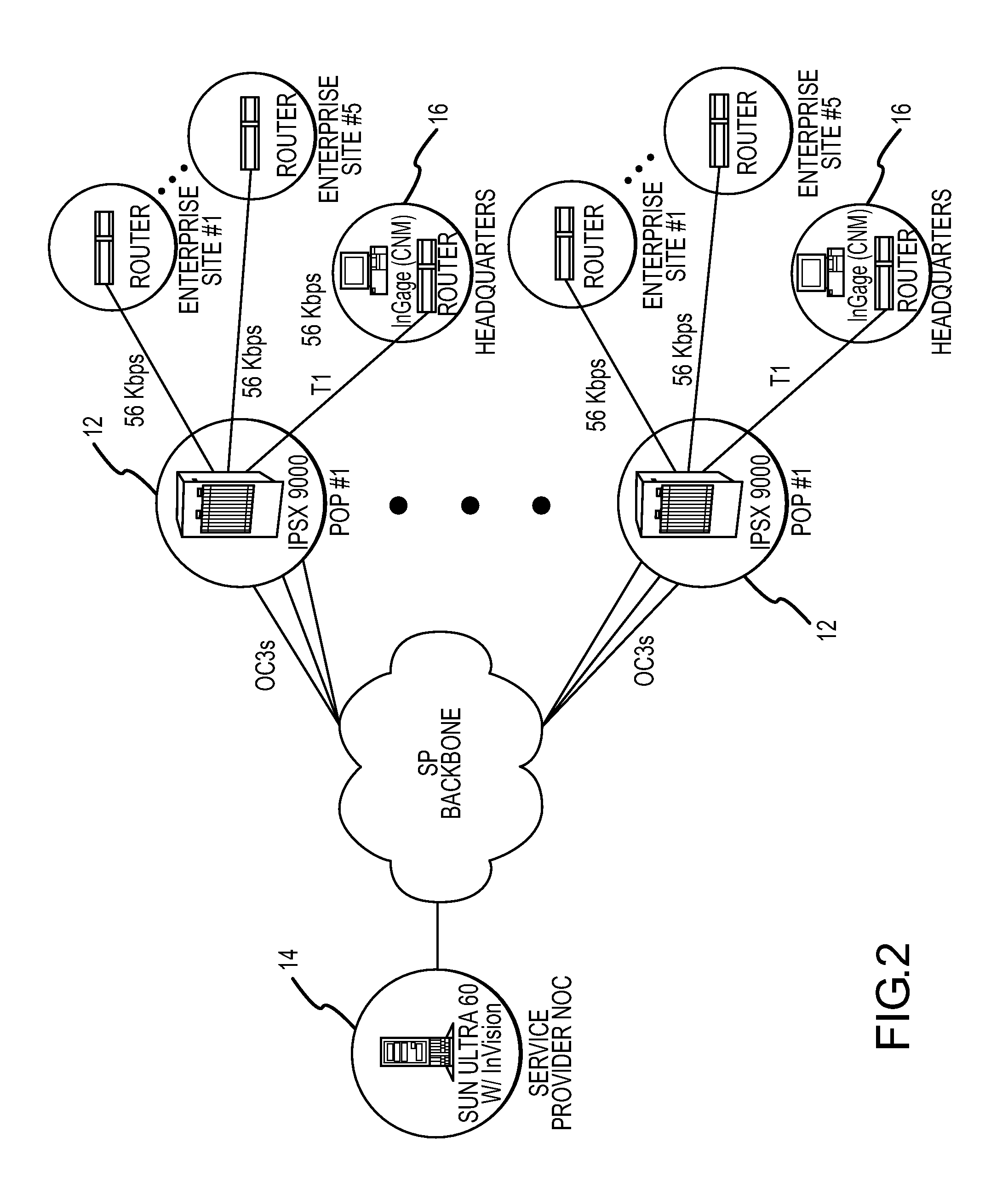
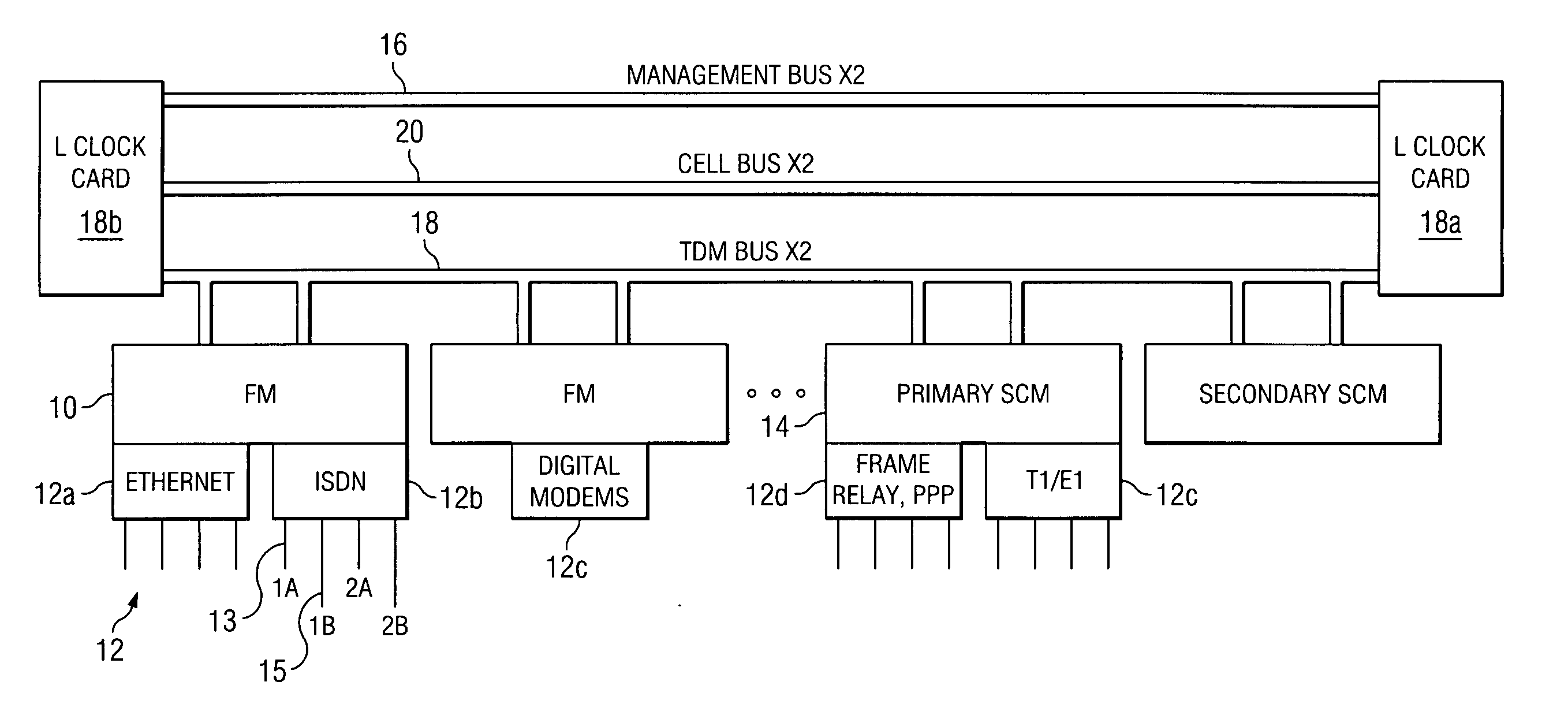
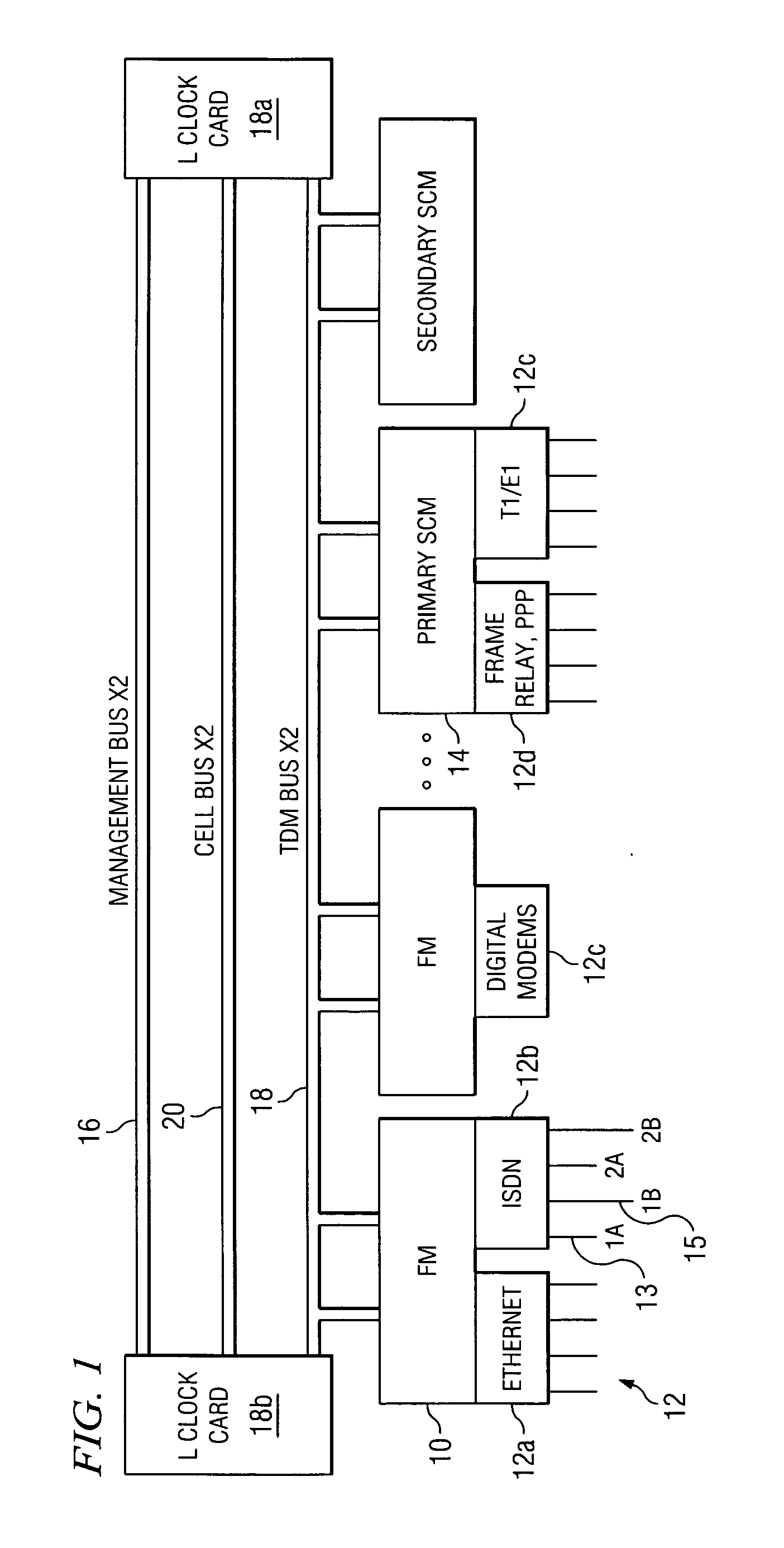
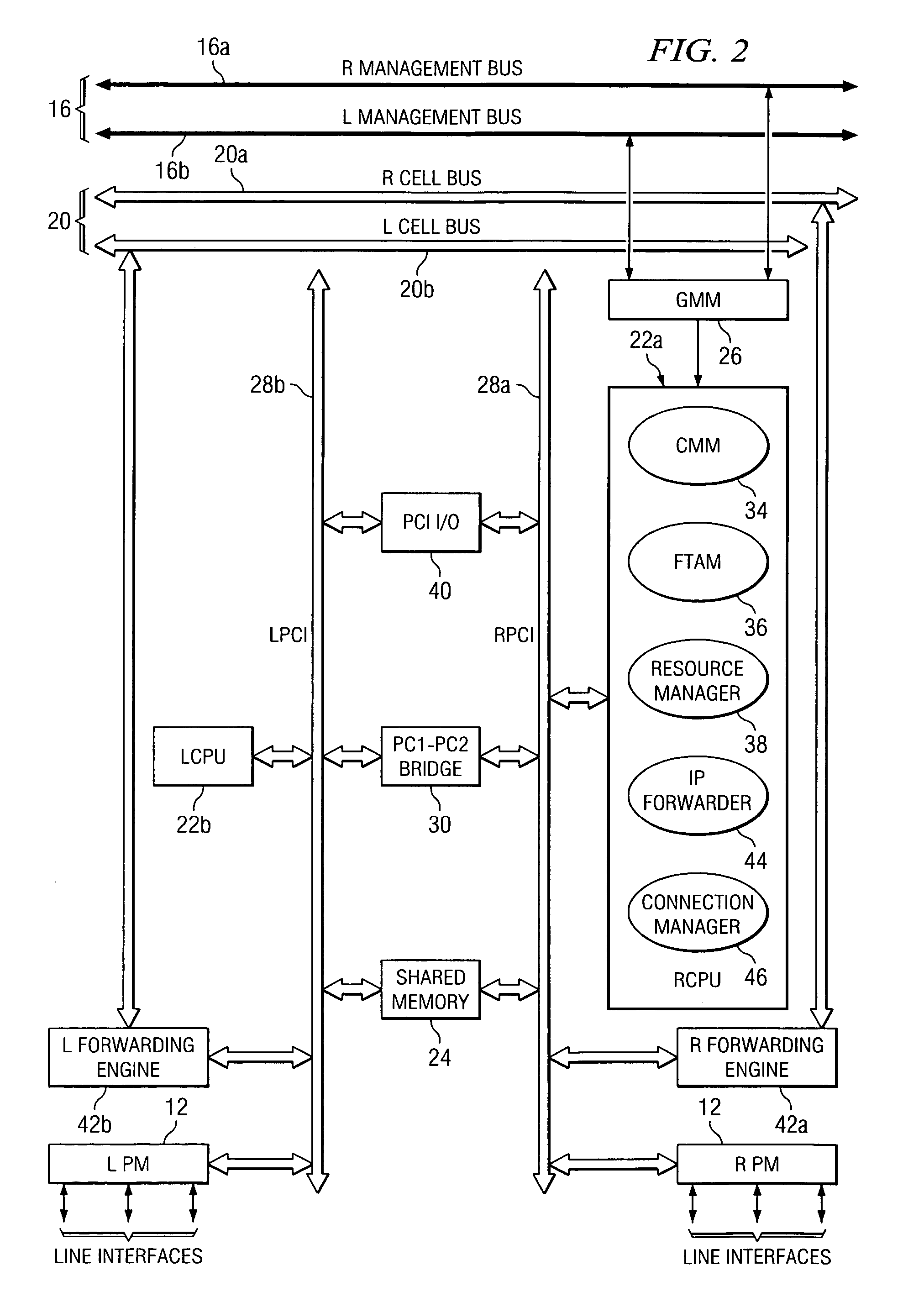
Multi-service network switch
InactiveUS6850531B1Raise priorityReduce dependenceData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDomain nameModem device
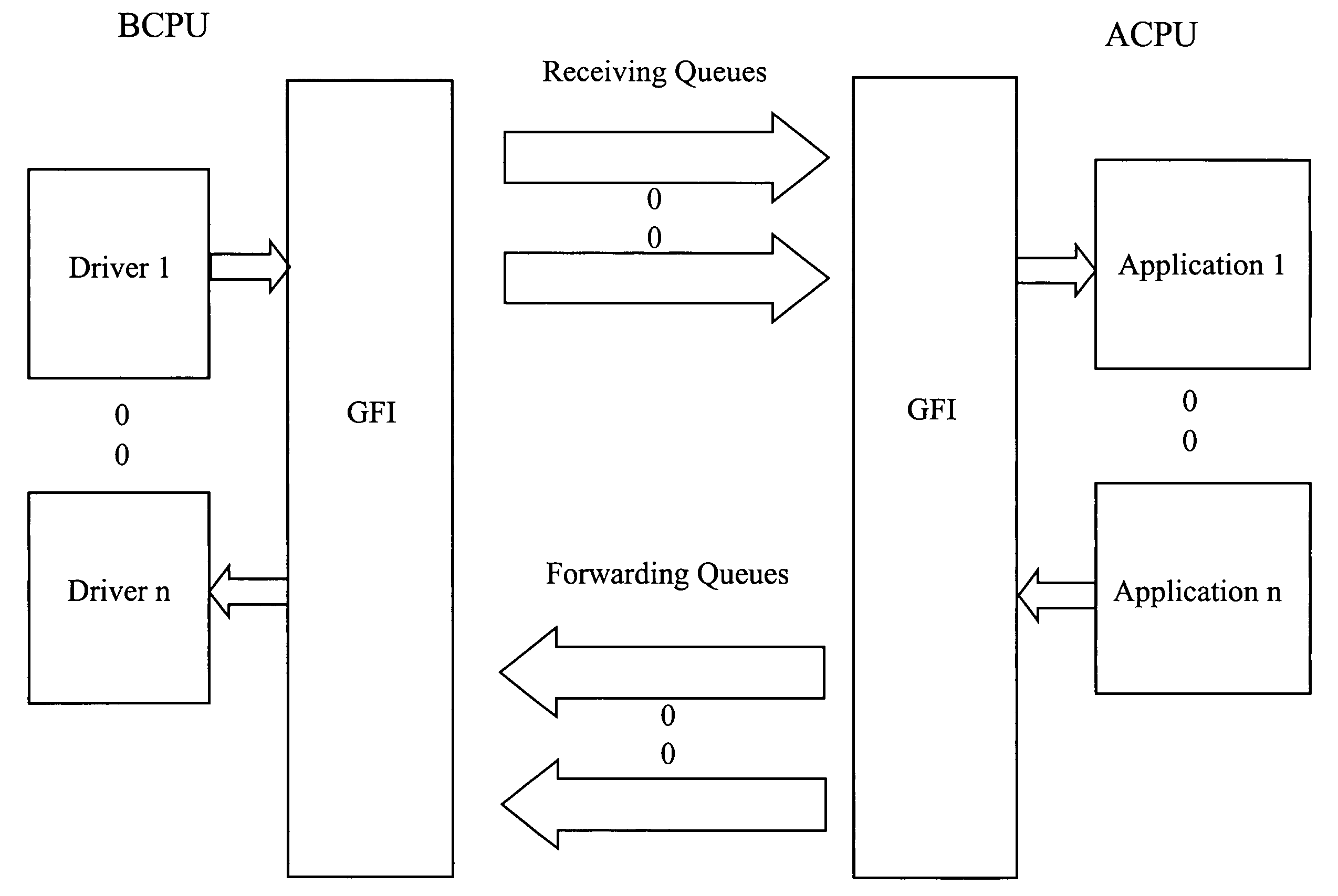
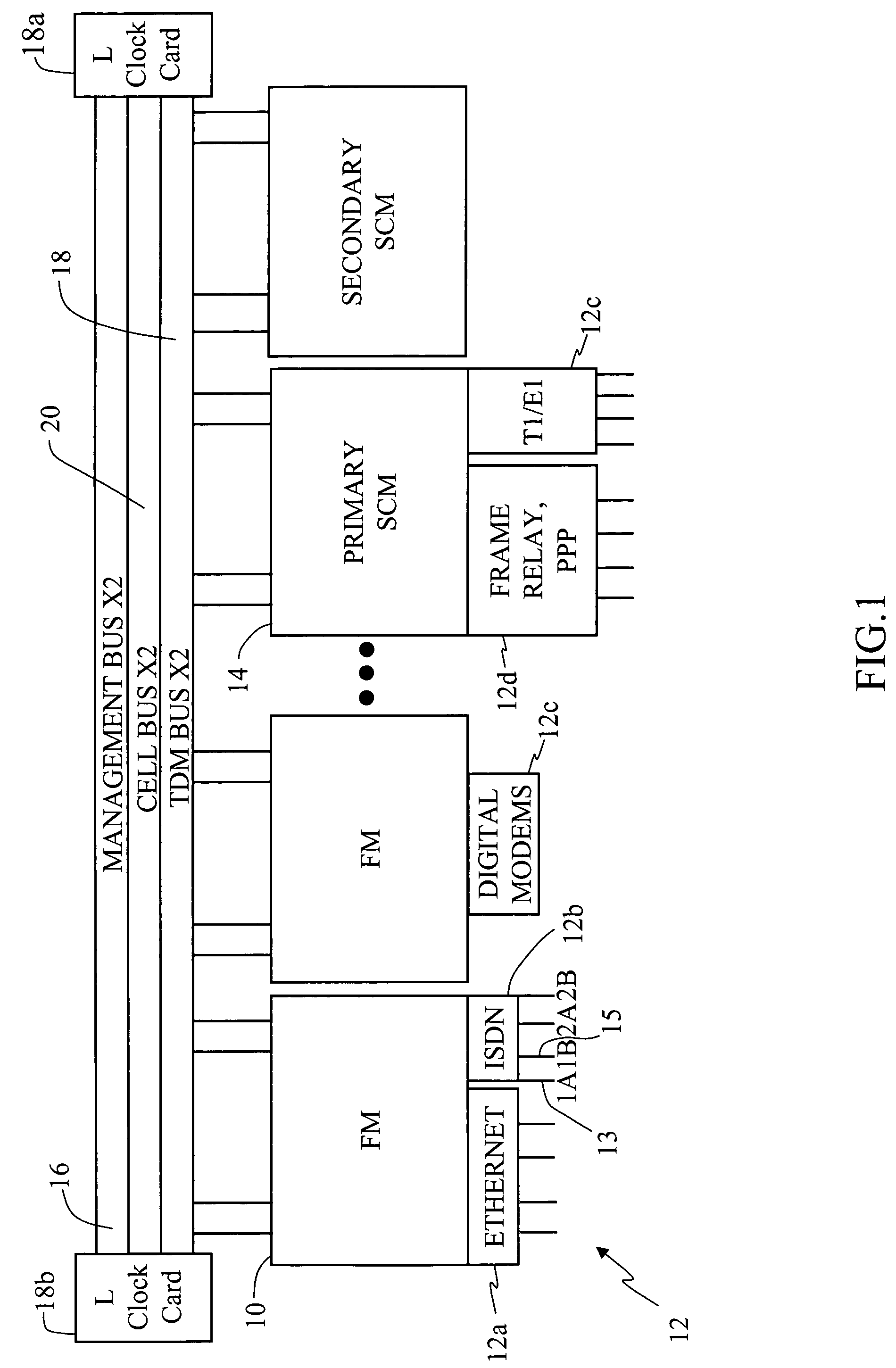
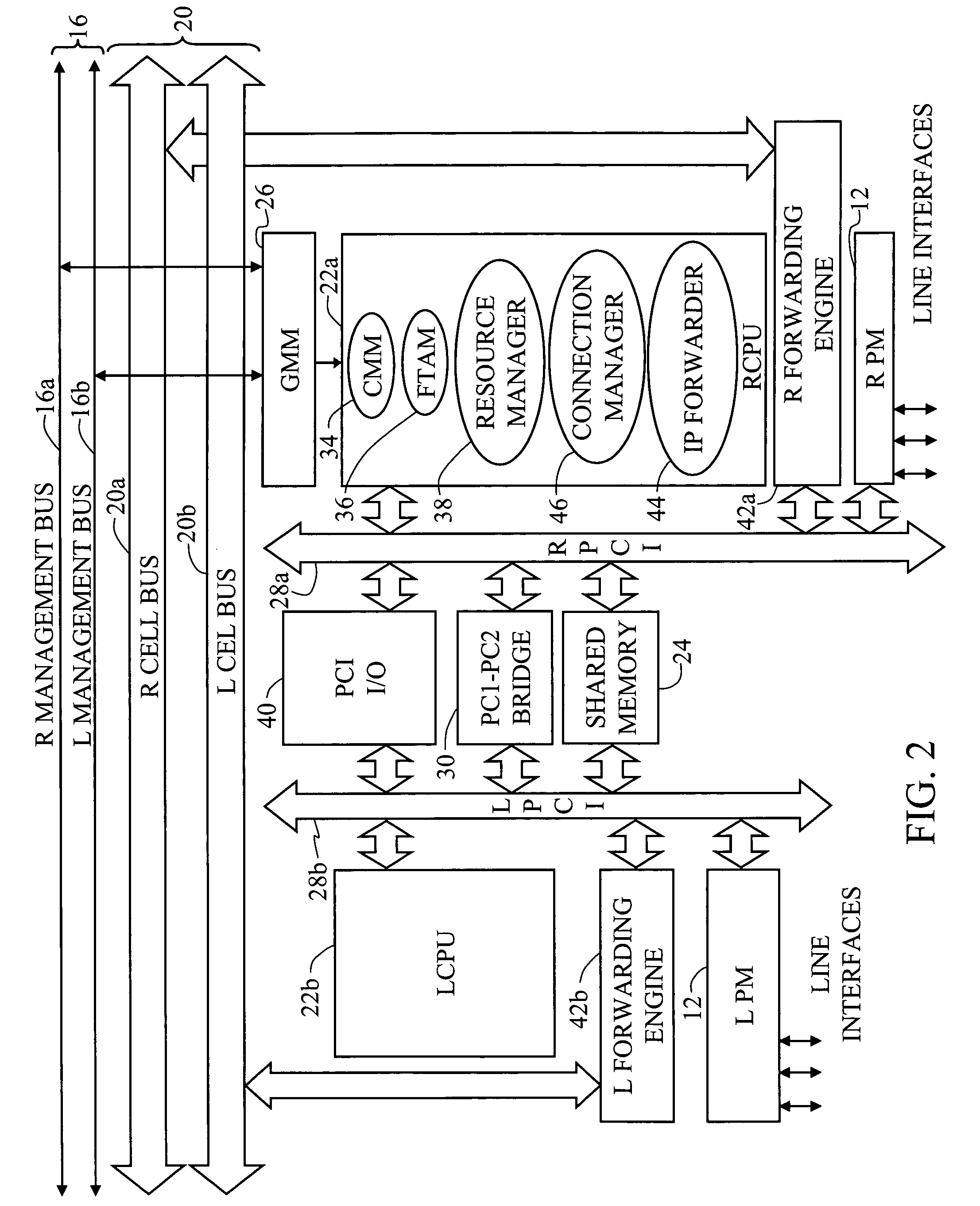
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Hierarchical metering in a virtual router-based network switch
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Resource allocation in virtual routers
ActiveUS20030169747A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationShared resourceResource allocation
A router system implements a plurality of virtual routers. Various combinations of resources may be shared by the router system when implementing the virtual routers. In one embodiment, the particular combination of resources to share when implementing the virtual router is user programmable.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
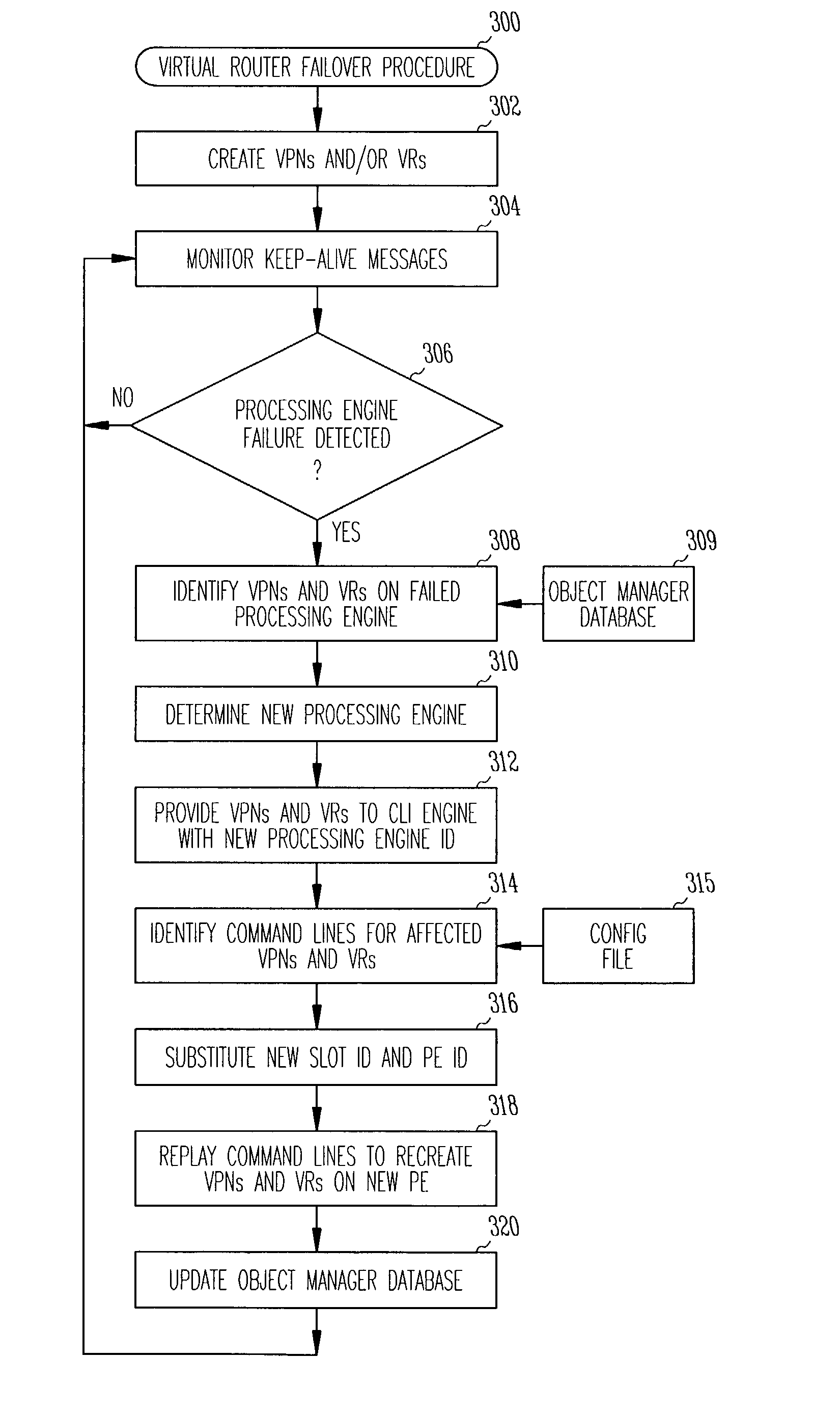
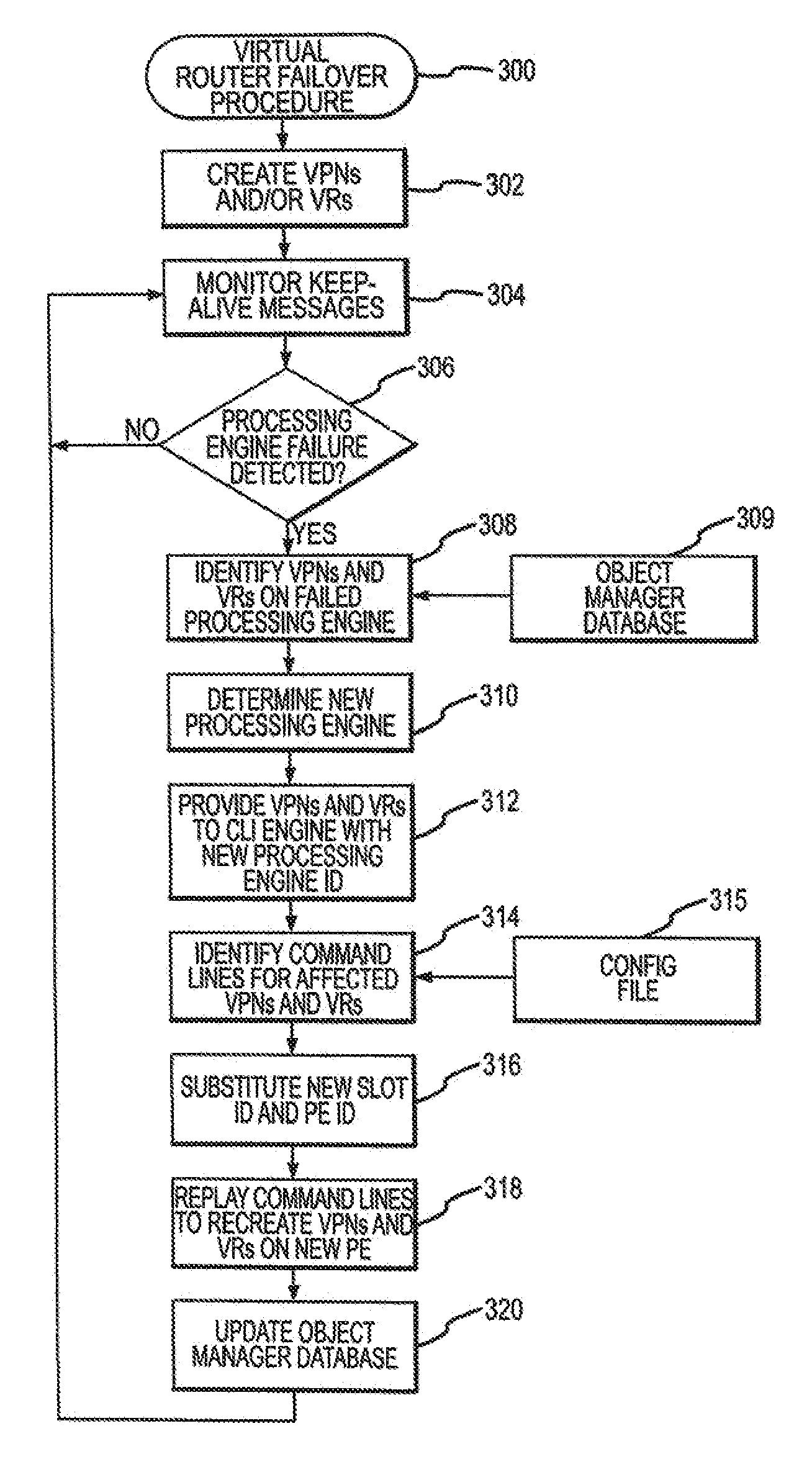
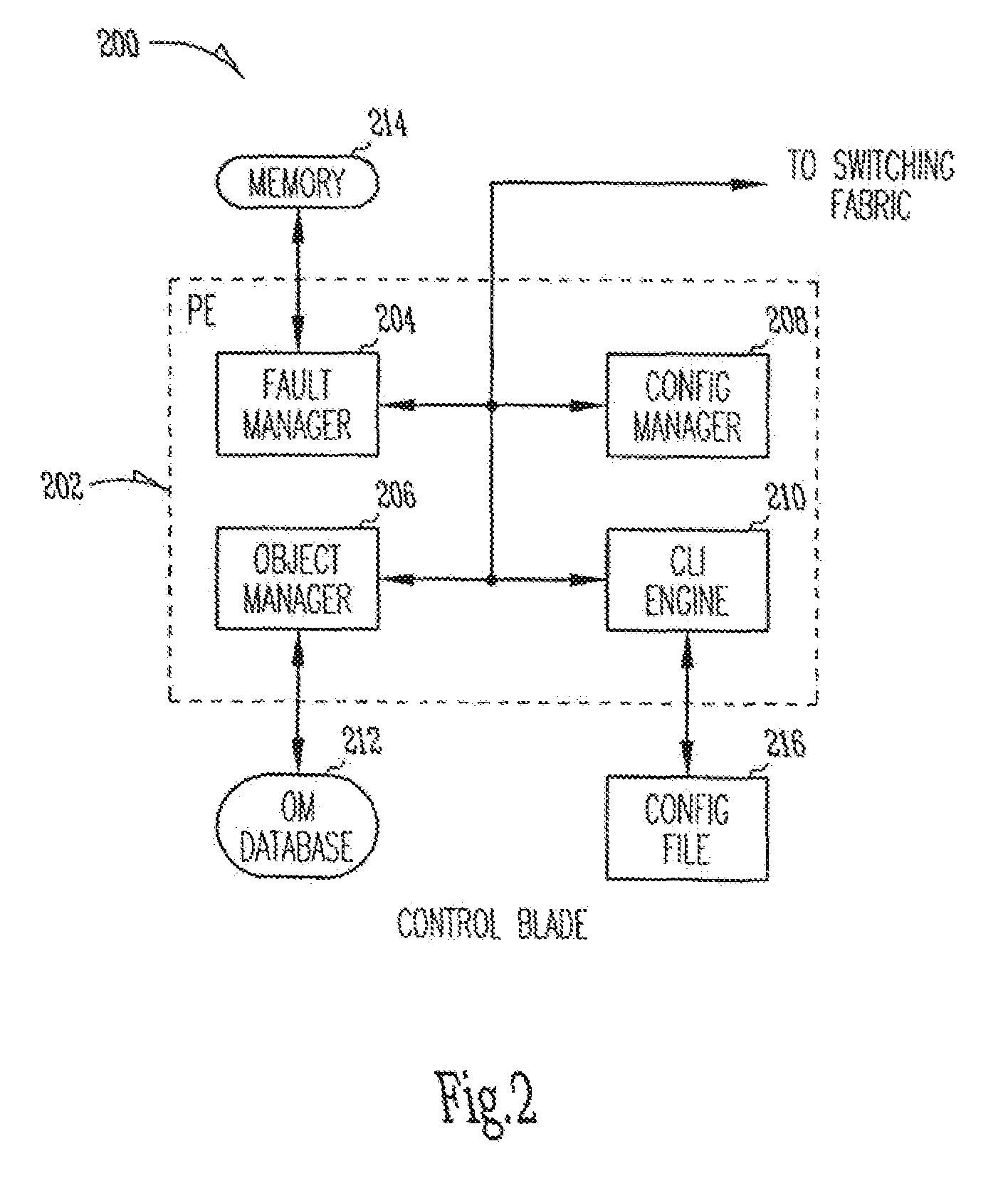
System and method for virtual router failover in a network routing system
In a network routing system, a control blade provides for redundancy and failover of virtual routers (VRs) instantiated by objects running on processing engines of the several virtual routing engines (VREs). When the control blade detects a failure of one processing engines, it may identify the virtual private networks (VPNs) and / or VRs operating on the failed processing engine. The control blade identifies a set of command lines corresponding with the identified VPNs and VRs, and replays the set of command lines with an identity of a new processing engine to recreate the identified VPNs and VRs on the new processing engine.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Autonomic network node system
InactiveUS8320388B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationAutonomic controlDistributed computing
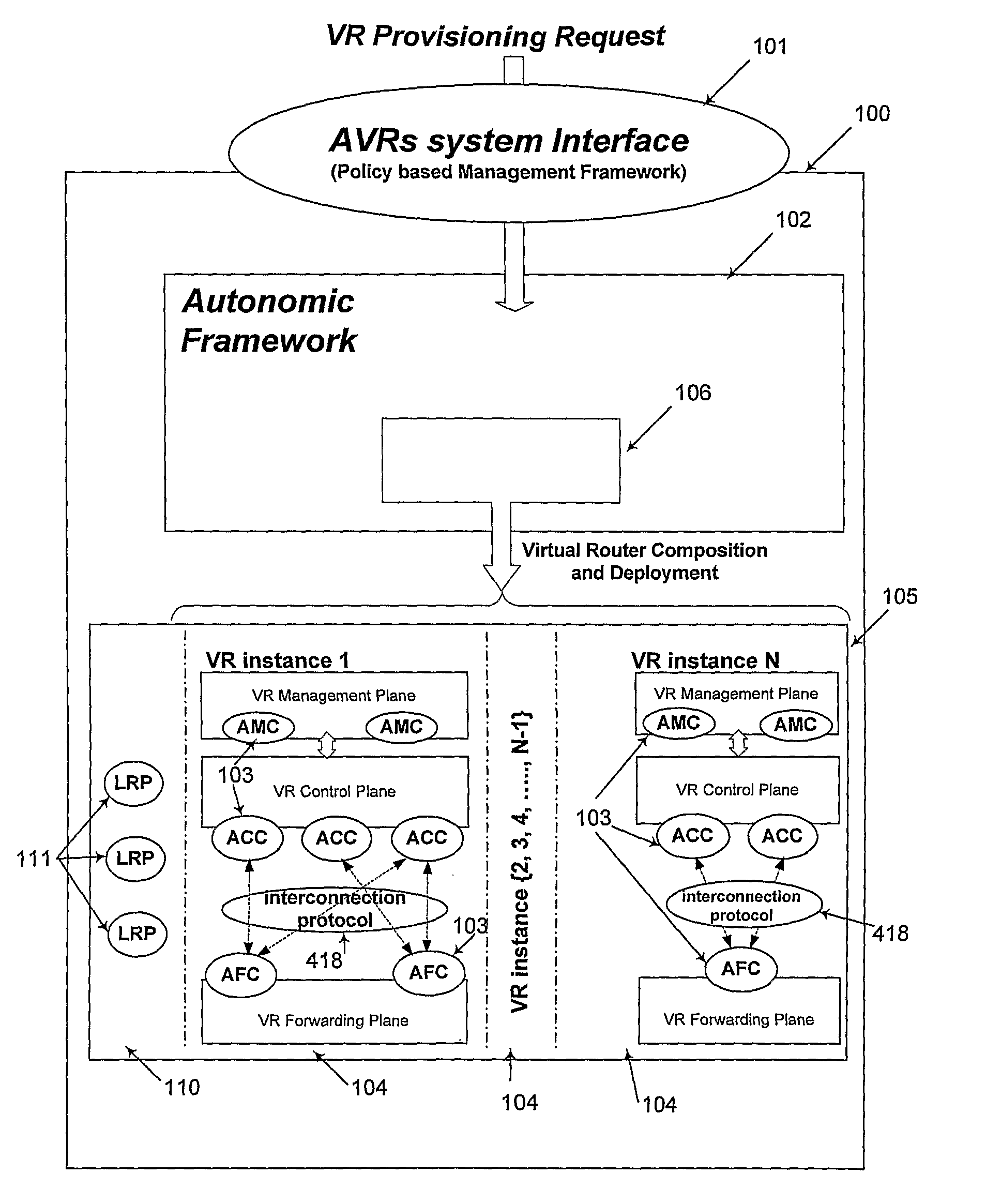
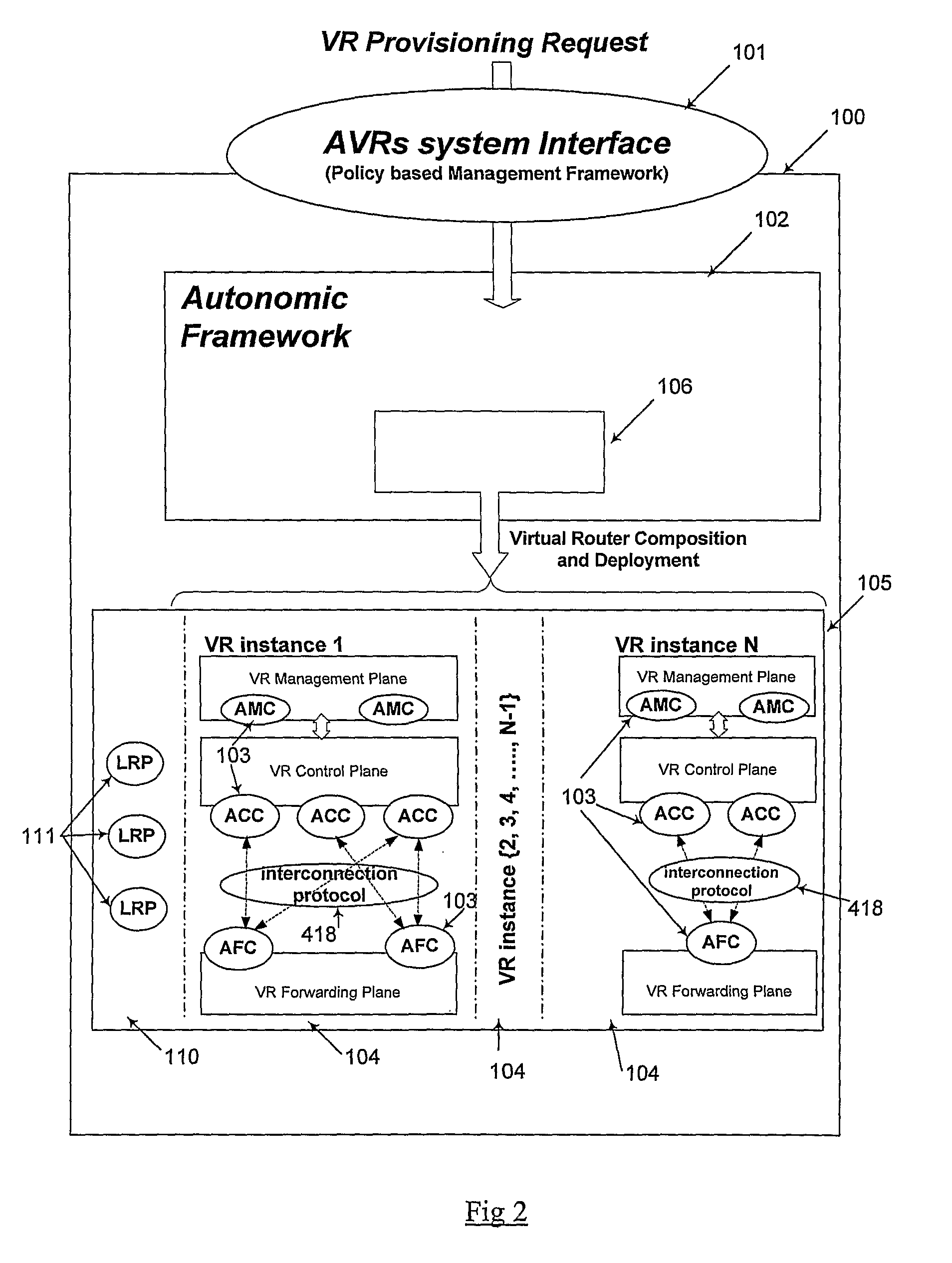
An autonomic network node system for providing at least one virtual router (VR) for providing on demand virtual routing service, the autonomic network node system includes a plurality of autonomic router components (ARCs) comprising at least one autonomic control component (ACC) and at least one autonomic forwarding component (AFC), physical resources comprising a plurality of logical resource partitions (LRPs), at least one database for storing information relating to the plurality of ARCs and LRPs, and a autonomic framework configured for receiving at least one request of on demand virtual routing service, accessing at the at least one database, allocating at least one LRP to perform at least one ARC to be installed in the autonomic network node system, installing the at least one ARC in the autonomic network node system, allocating the installed ARC and, updating the at least one database.
Owner:GROUPE DES ECOLES DES TELECOMM GET
Multi-service network switch with a generic forwarding interface
InactiveUS7116679B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameModem device
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
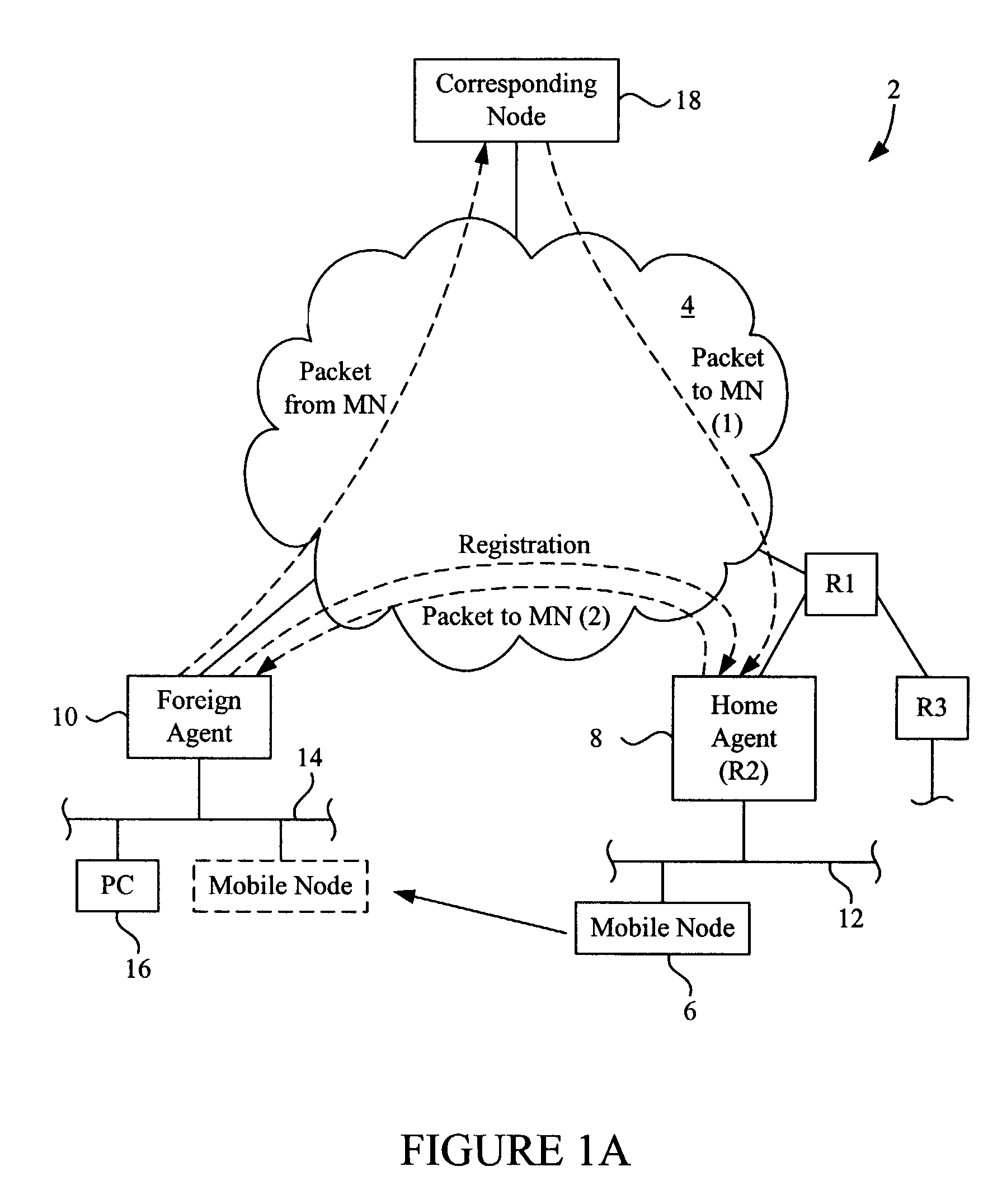
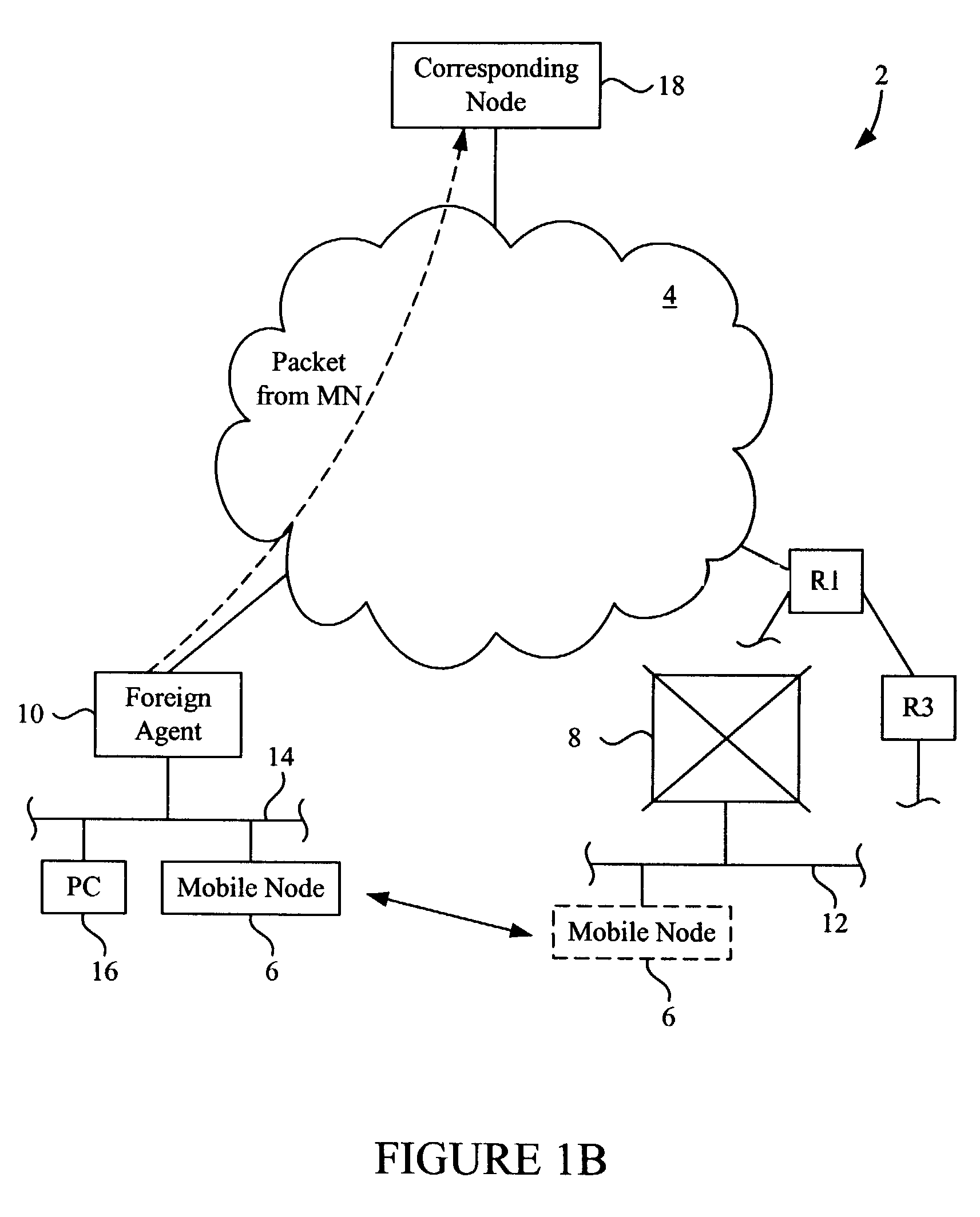
Methods and apparatus for implementing home agent redundancy
InactiveUS7227863B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkMobile IP
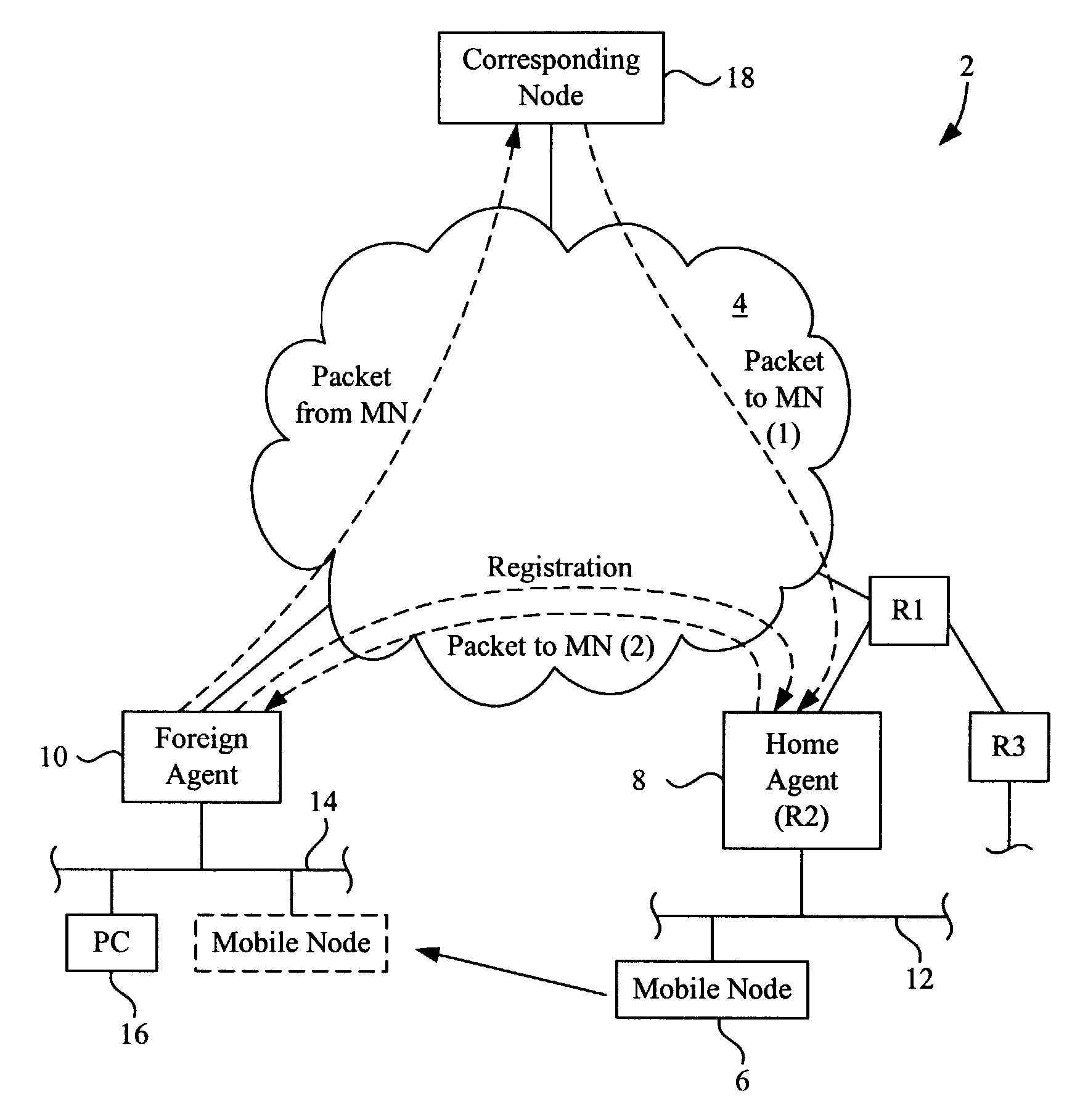
Methods and apparatus for maintaining Mobile IP operation in a Home Agent are disclosed. In a Home Agent, a Mobile Node is registered and a registration entry is created in a mobility binding table for the Mobile Node. A multicast message is then sent to a virtual router group to which the Home Agent belongs and with which the Home Agent shares a virtual IP address. The multicast message notifies the virtual router group of the registration. A similar process may be performed when a Mobile Node is de-registered. When an active or non-active Home Agent is initialized, it sends a multicast mobility binding table request to the redundancy group indicating that bindings are requested. The Home Agent may then receive bindings in response to the request and update its mobility binding table with the received bindings.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
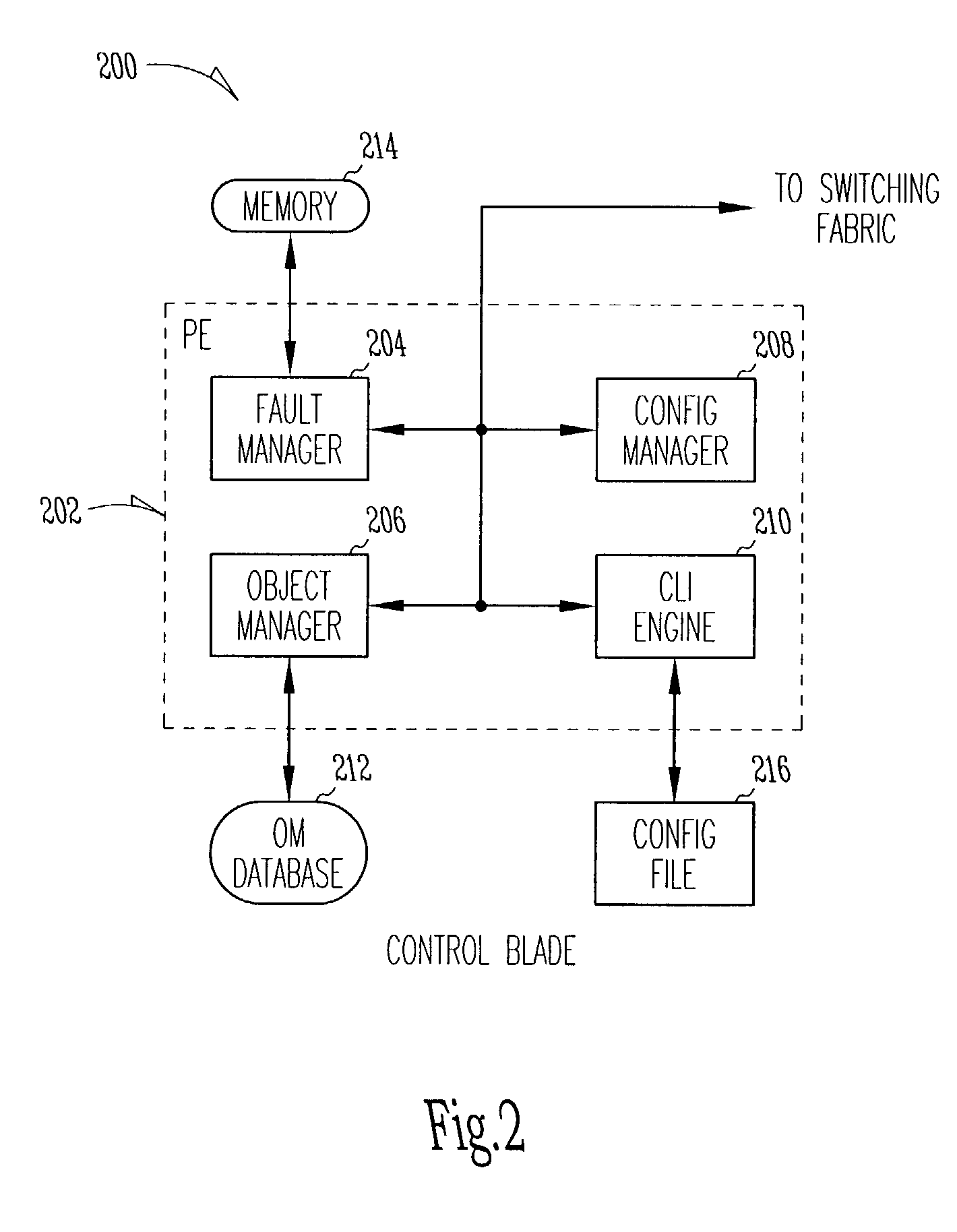
Switch management system and method
ActiveUS20070083528A1TransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemProcessor element
A system and method of managing a switch includes installing a switch having a plurality of processor elements, installing an operating system on each processor element, creating a system virtual router and configuring the processor elements from the system virtual router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-service network switch with independent protocol stack architecture
InactiveUS20050180429A1Reduce bottlenecksImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDomain nameRouting table
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
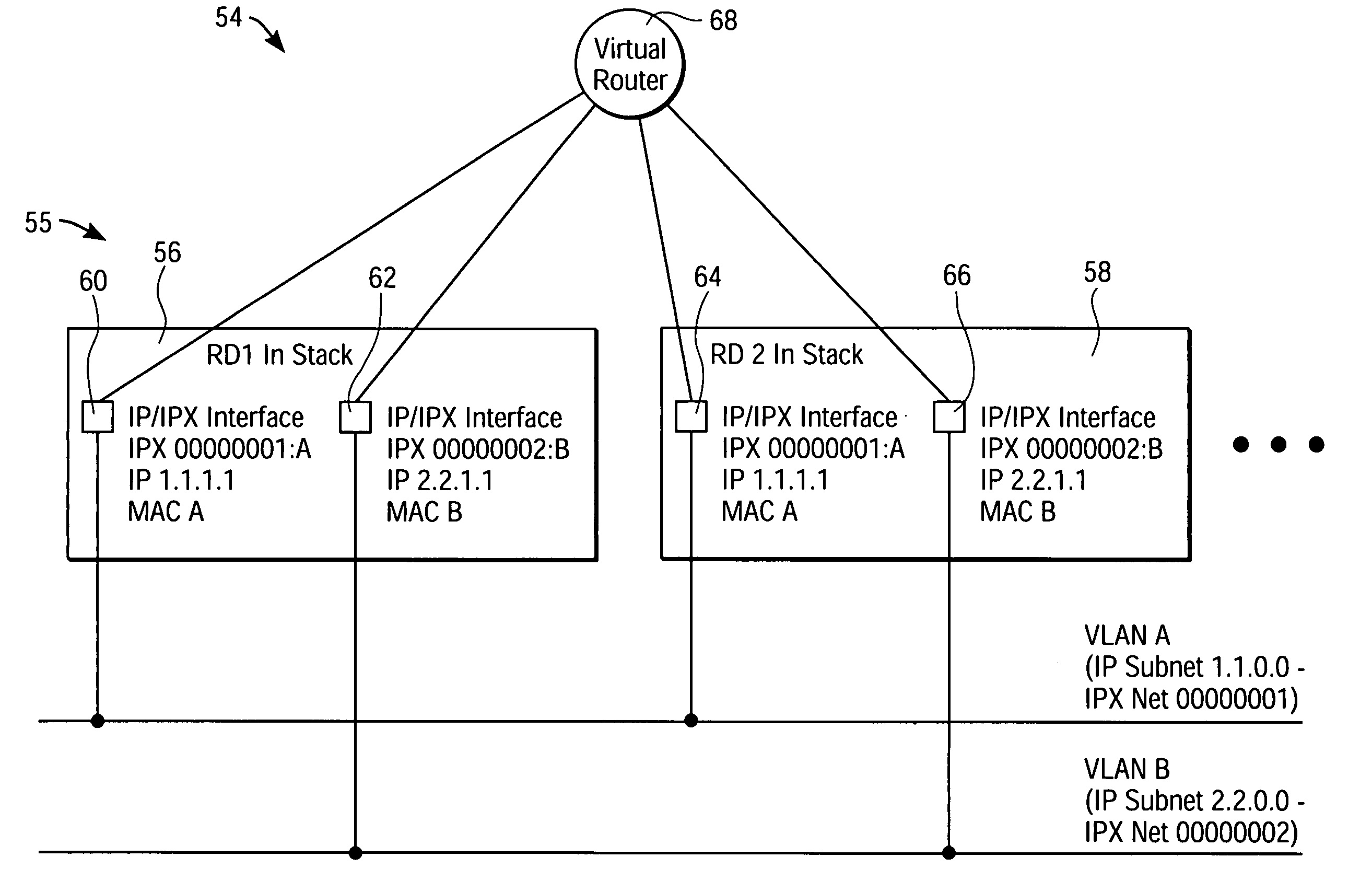
Method and system for emulating a single router in a switch stack
A system and method for emulating a single router in a switch stack is described. The switch stack is connected to virtual local area networks (VLANs) and comprises a number of stack devices that can include routing devices (RDs) having interfaces to the VLANs and non-routing devices (NRDs). All of the interfaces of the RDs share the same router and VLAN configuration addresses, including router Media Access Control addresses. One RD is appointed as a master in the switch stack and all other RDs use the configuration addresses of the master. Each NRD is owned by a corresponding routing device according to an ownership algorithm. The shared configuration addresses allow the switch stack to appear as a “virtual router” to nodes belonging to VLANs connected to the switch stack.
Owner:INTEL CORP
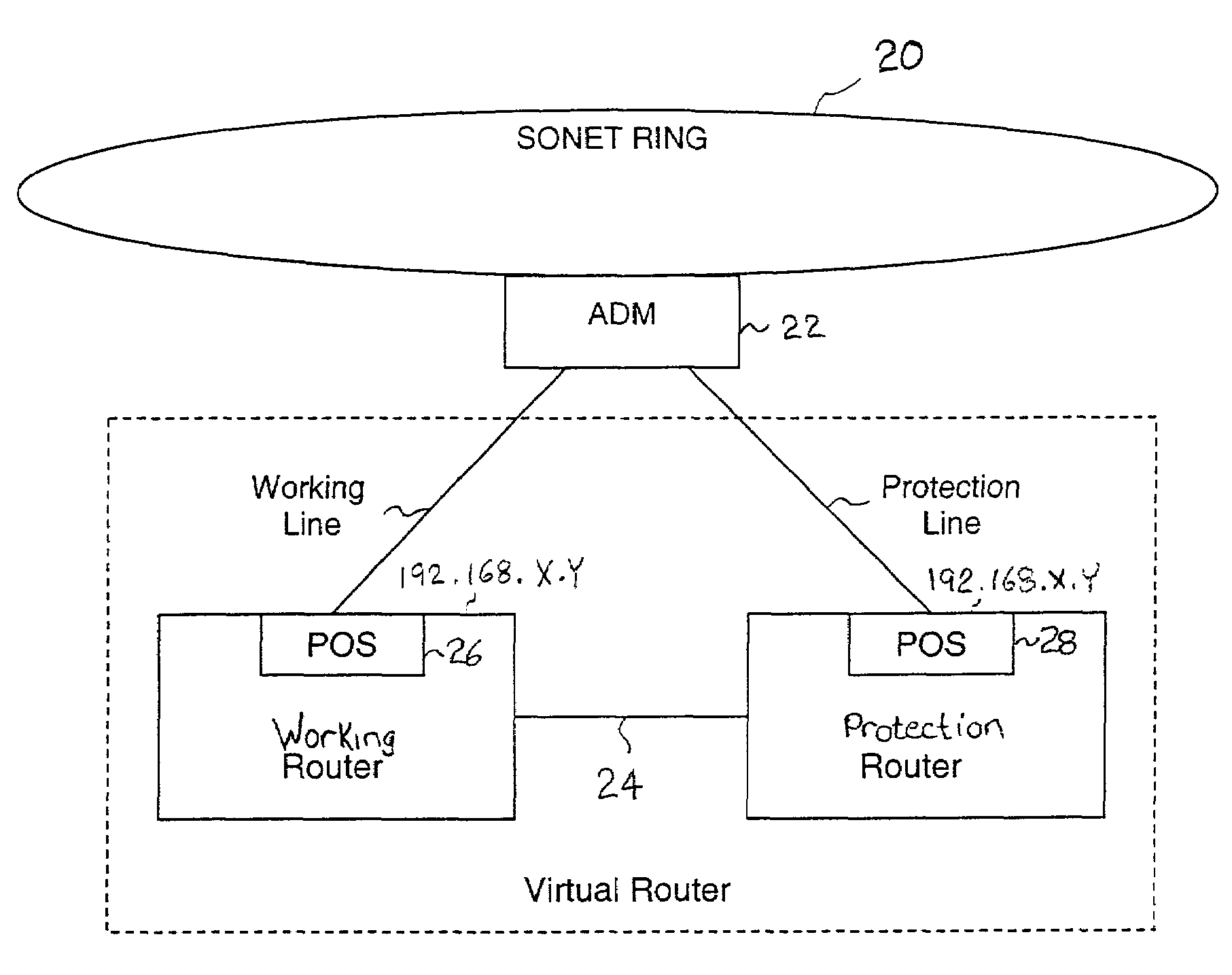
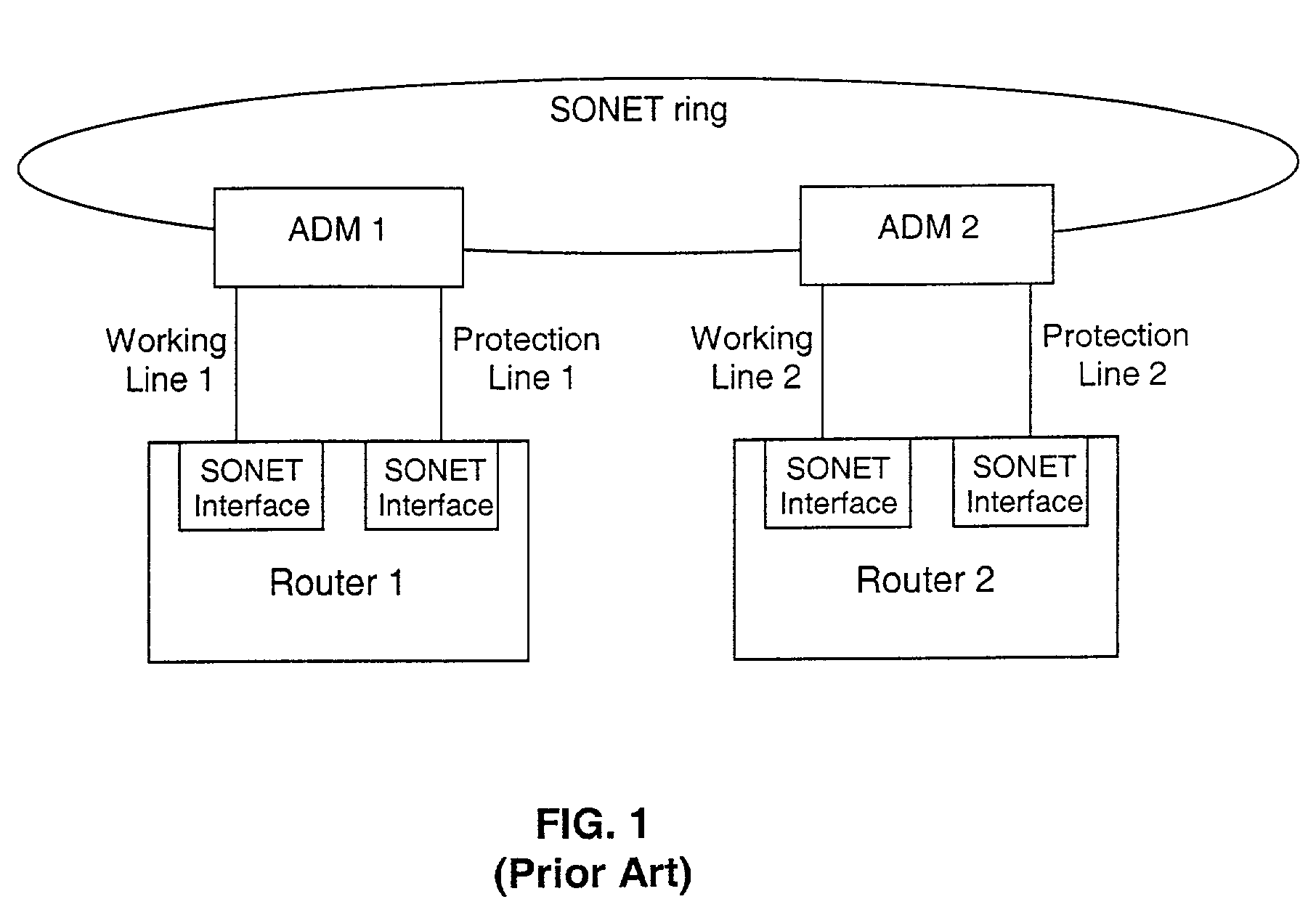
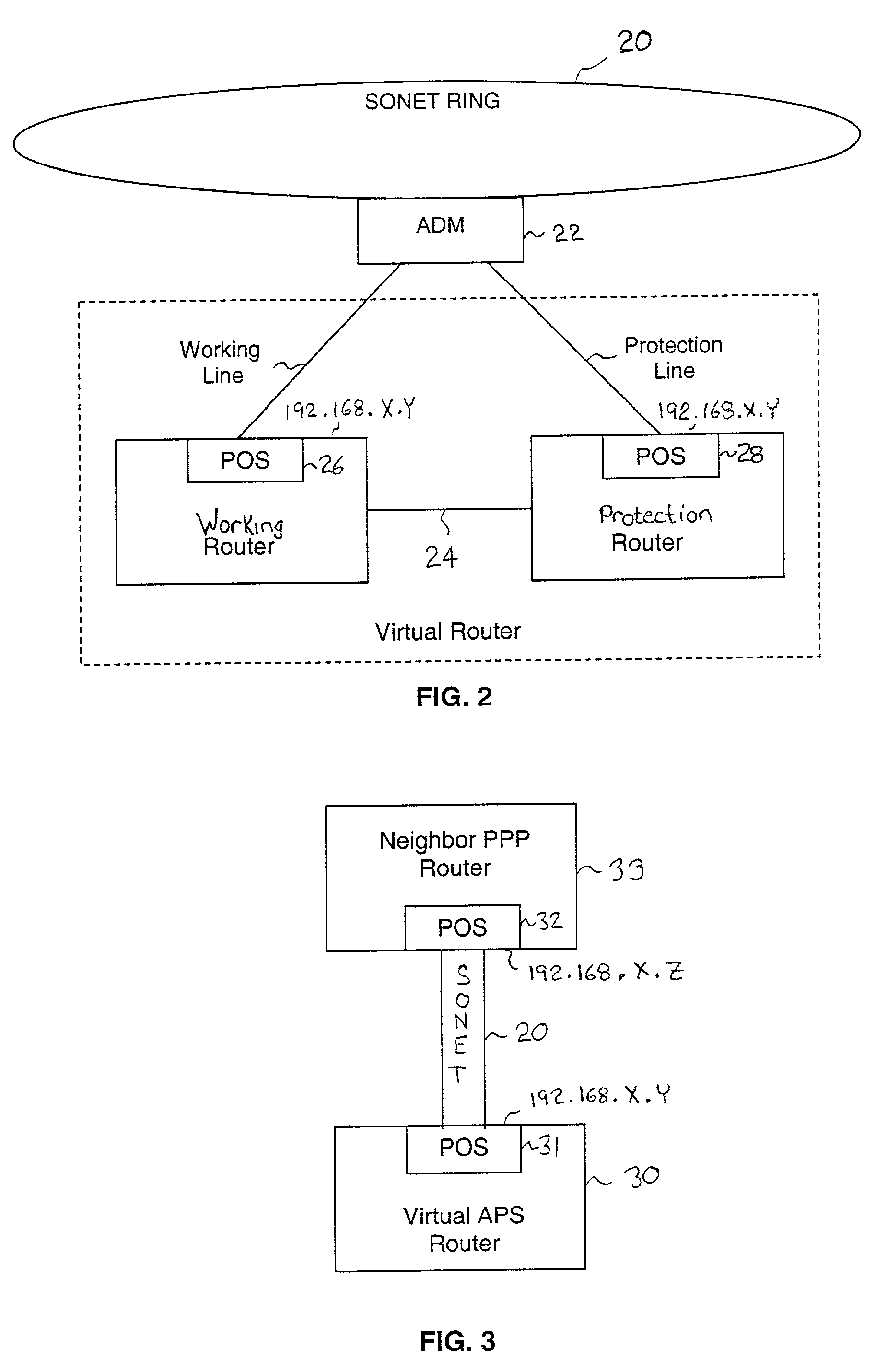
Fault tolerant automatic protection switching for distributed routers
InactiveUS6956816B1Providing fault toleranceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolAutomatic protection switching
A working router is coupled to a SONET add-drop multiplexor (ADM) through a working line and a protection router is coupled to the ADM through a protection line. The routers are coupled to each other by a separate side-band connection and comprise a virtual router from the perspective of the neighboring router, which communicates with the virtual router over the SONET network using the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). The protection router transmits a heartbeat message to the working router over the side-band connection. If the protection router does not receive a response thereto, it initiates a line switch within the add-drop multiplexor. Once the line switch is complete, the protection router exchanges datagrams with the neighboring router, via the ADM and SONET ring to which the ADM is coupled. The protection router establishes a PPP connection between itself and the neighboring router device coupled to the SONET ring, utilizing the Link Control Protocol (LCP). The protection router includes a predetermined identifier value that identifies the originator of the request, in the LCP Identifier field of LCP request datagrams. The neighboring router includes the Identifier value received in a request datagram in the corresponding response datagram transmitted over the SONET ring to the ADM. Because datagrams received by the ADM from the SONET link are transmitted over both the working and the protect lines, the working router receives the same response as the protection router. Thus, by examining the identifier field, and recognizing the identifier value as that assigned to the protection router, the working router determines that the line switch to the protection router has occurred.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
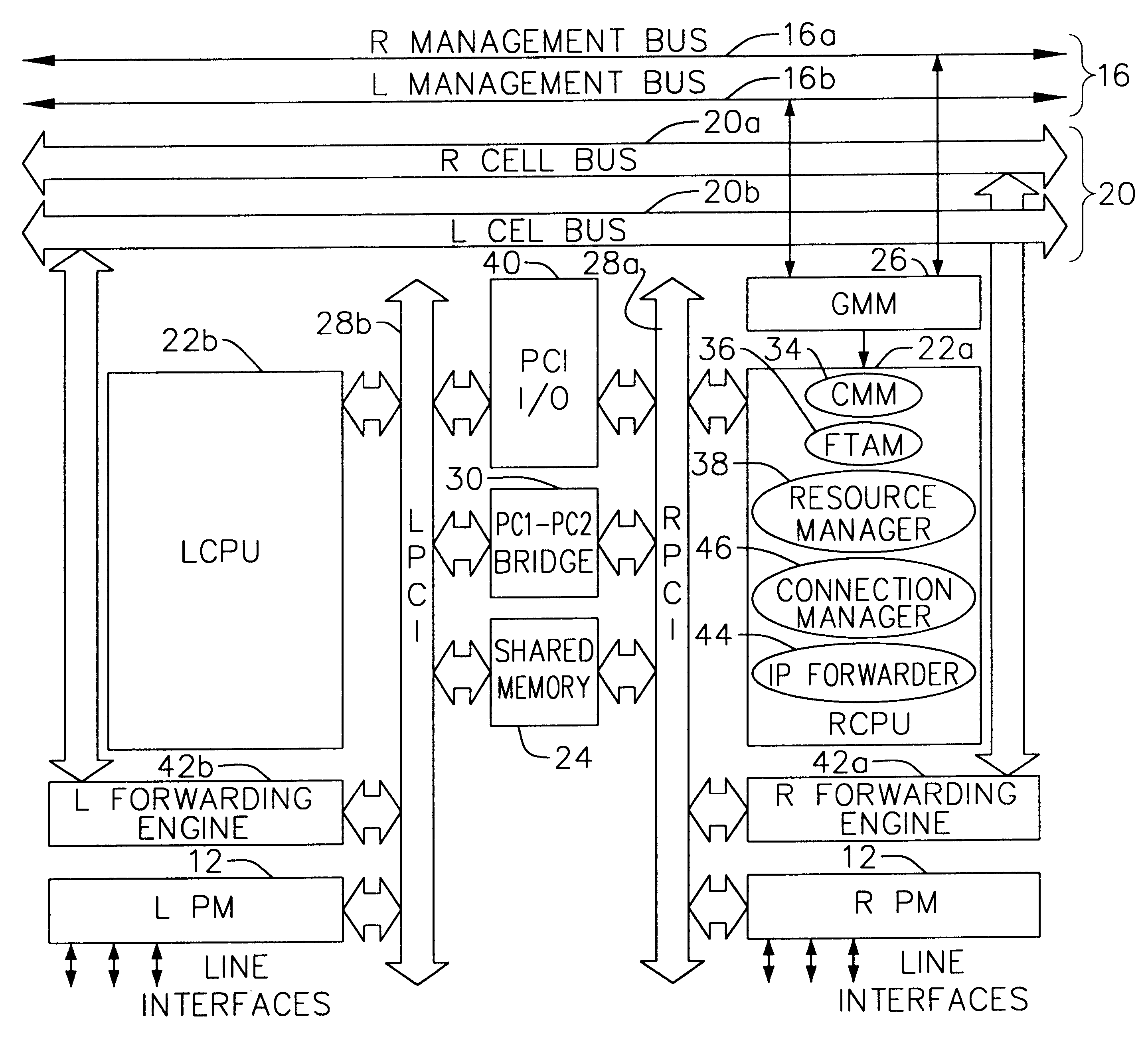
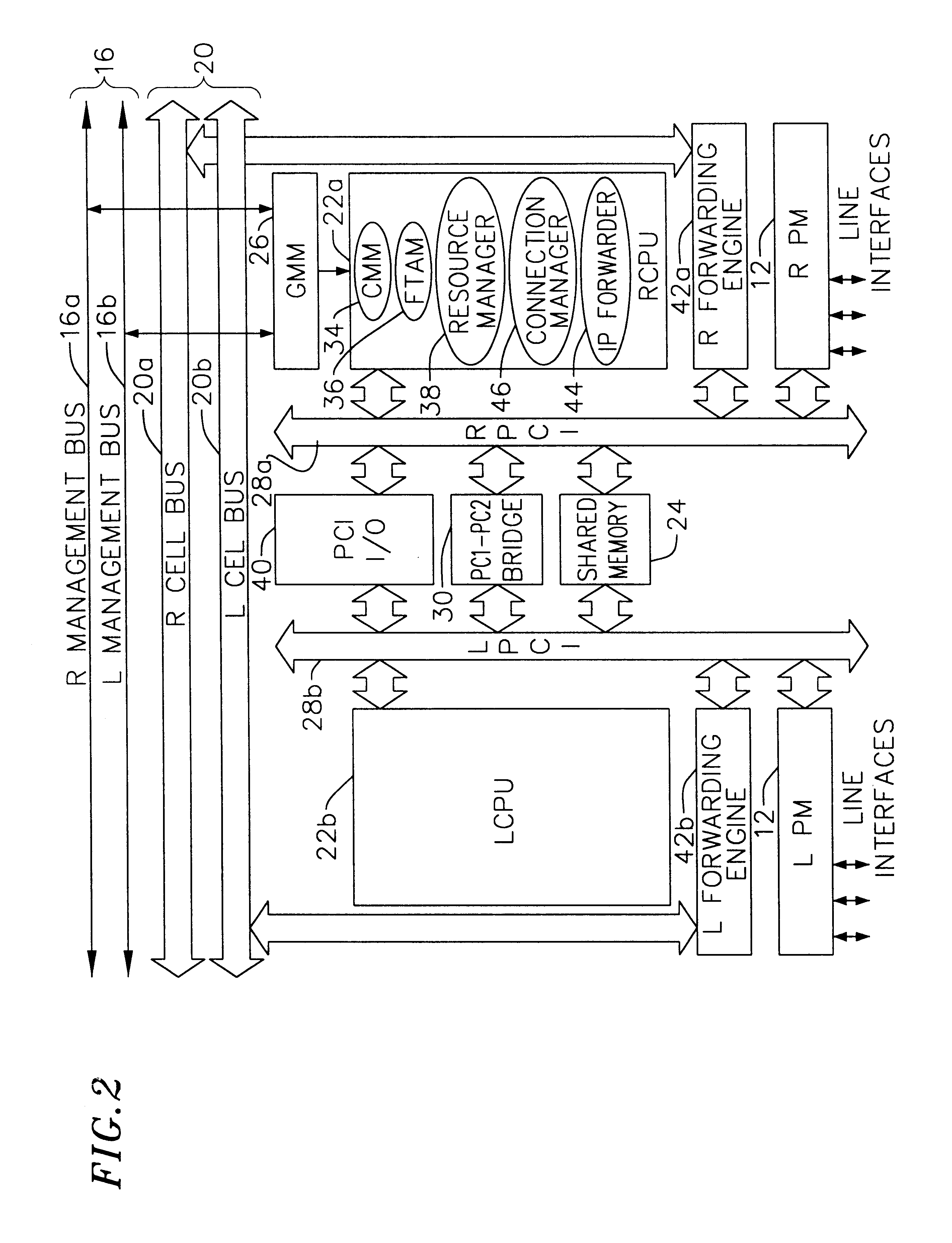
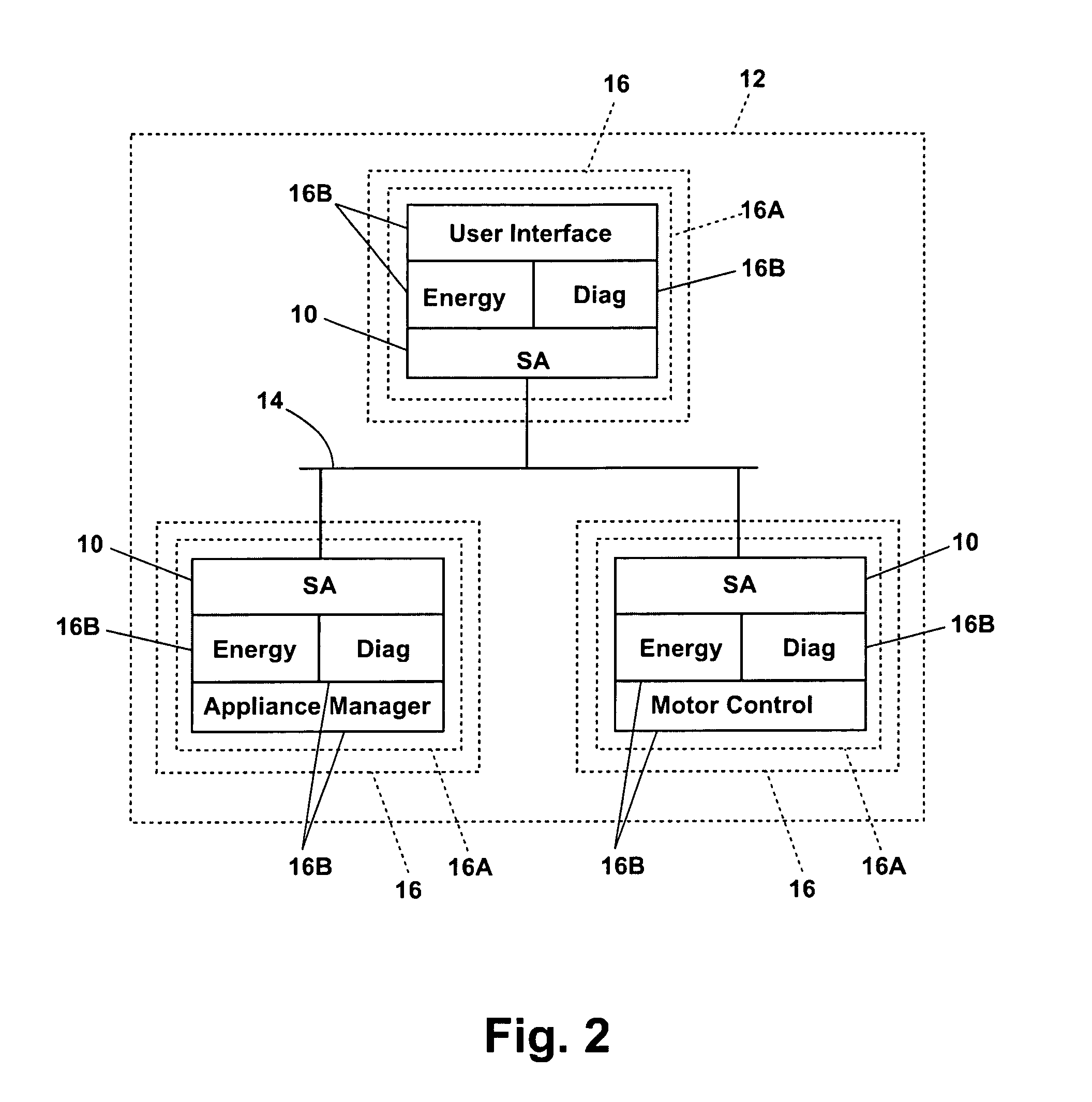
Software architecture system with embedded virtual router
ActiveUS20080104212A1Facilitate communicationEnergy efficient ICTWashing controlling processesSoftware architectureAppliance component
The invention relates to a network system of at least two appliances, each appliance configured to perform a cycle of operation on an article, and each appliance having its own software architecture. An embedded virtual router enables communication among appliance components independent of the architecture of the software.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
System and method for virtual router failover in a network routing system
In a network routing system,a control blade provides for redundancy and failover of virtual routers (VRs) instantiated by objects running on processing engines of the several virtual routing engines (VREs). When the control blade detects a failure of one processing engines, it may identify the virtual private networks (VPNs) and / or VRs operating on the failed processing engine. The control blade identifies a set of command lines corresponding with the identified VPNs and VRs, and replays the set of command lines with an identity of a new processing engine to recreate the identified VPNs and VRs on the new processing engine.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
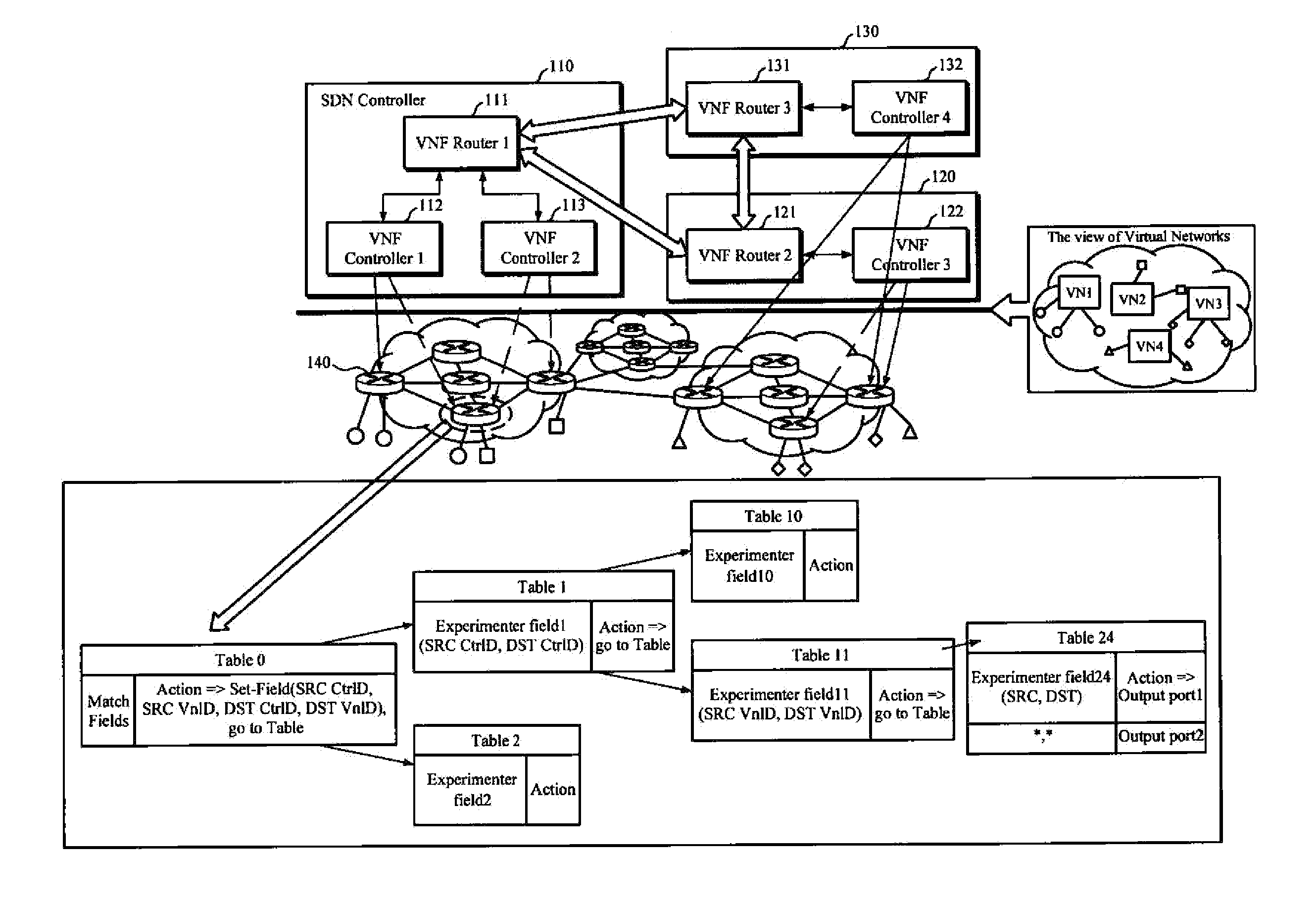
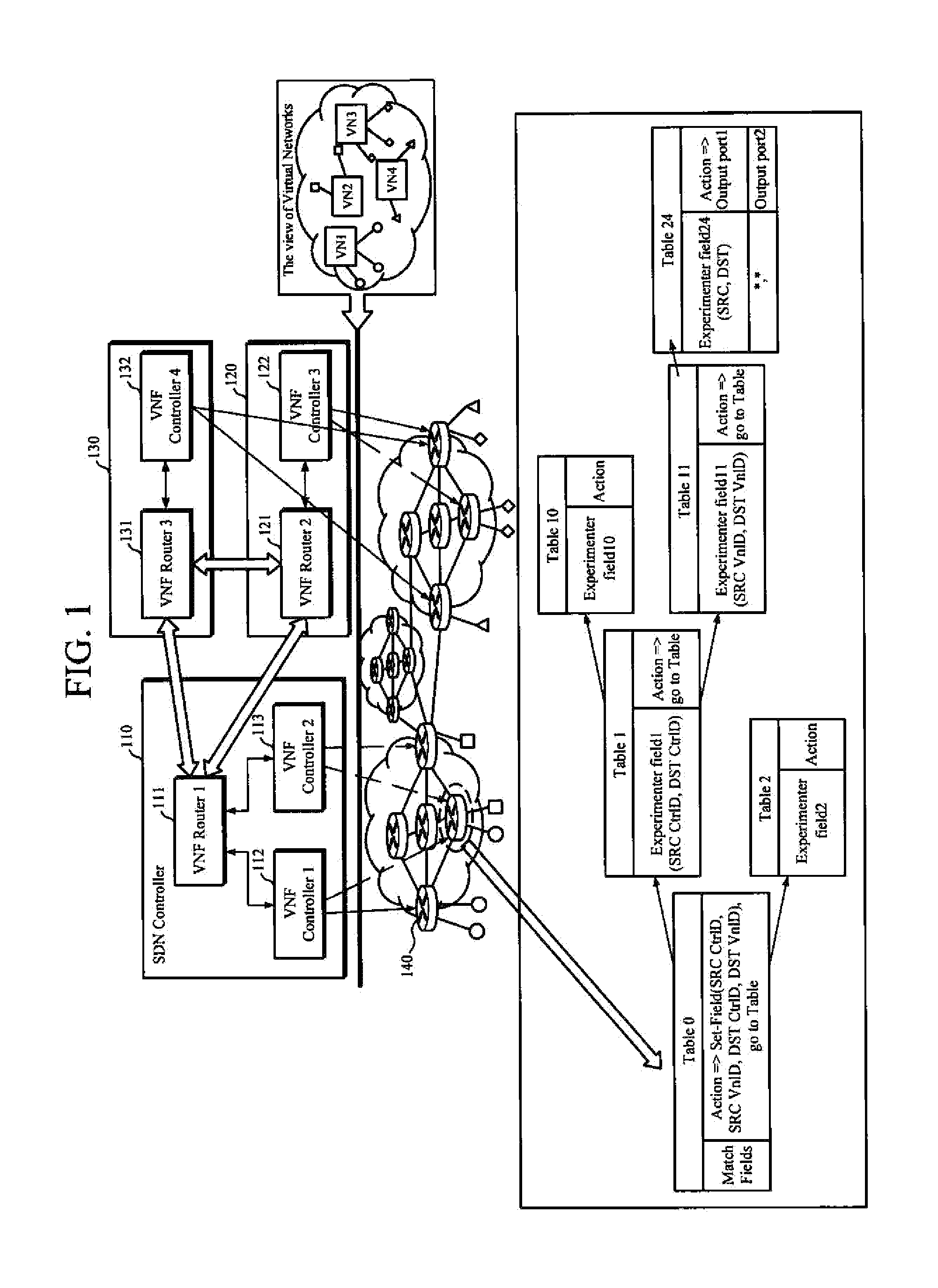
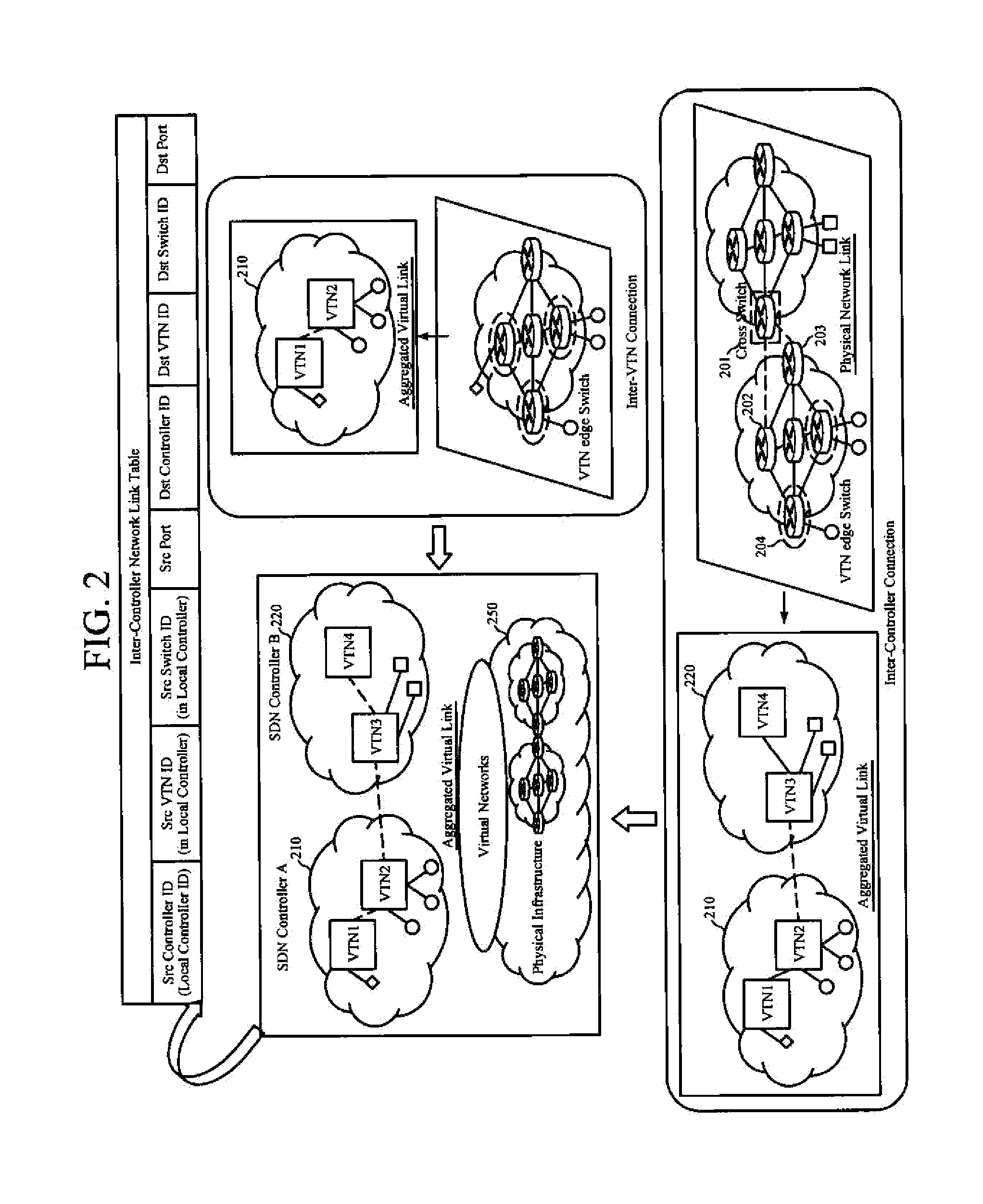
System and method for virtual network-based distributed multi-domain routing control
InactiveUS20160134527A1Efficient routingNetwork connectionsHigh level techniquesTopology informationExchange network
A system for distributed multi-domain routing control includes two or more software-defined network (SDN) controllers and virtual routers. The two or more SDN controllers create virtual topology information by collecting information about switches under the control thereof, exchange network information about a different virtual network, as well as create a routing path from a source terminal to a destination cross switch or a routing path from the destination cross switch to a destination terminal based on location identification information of the destination terminal and / or the virtual topology information. Then, the virtual routers manage communication between the different virtual tenant networks or communication between each virtual tenant network and an external network.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
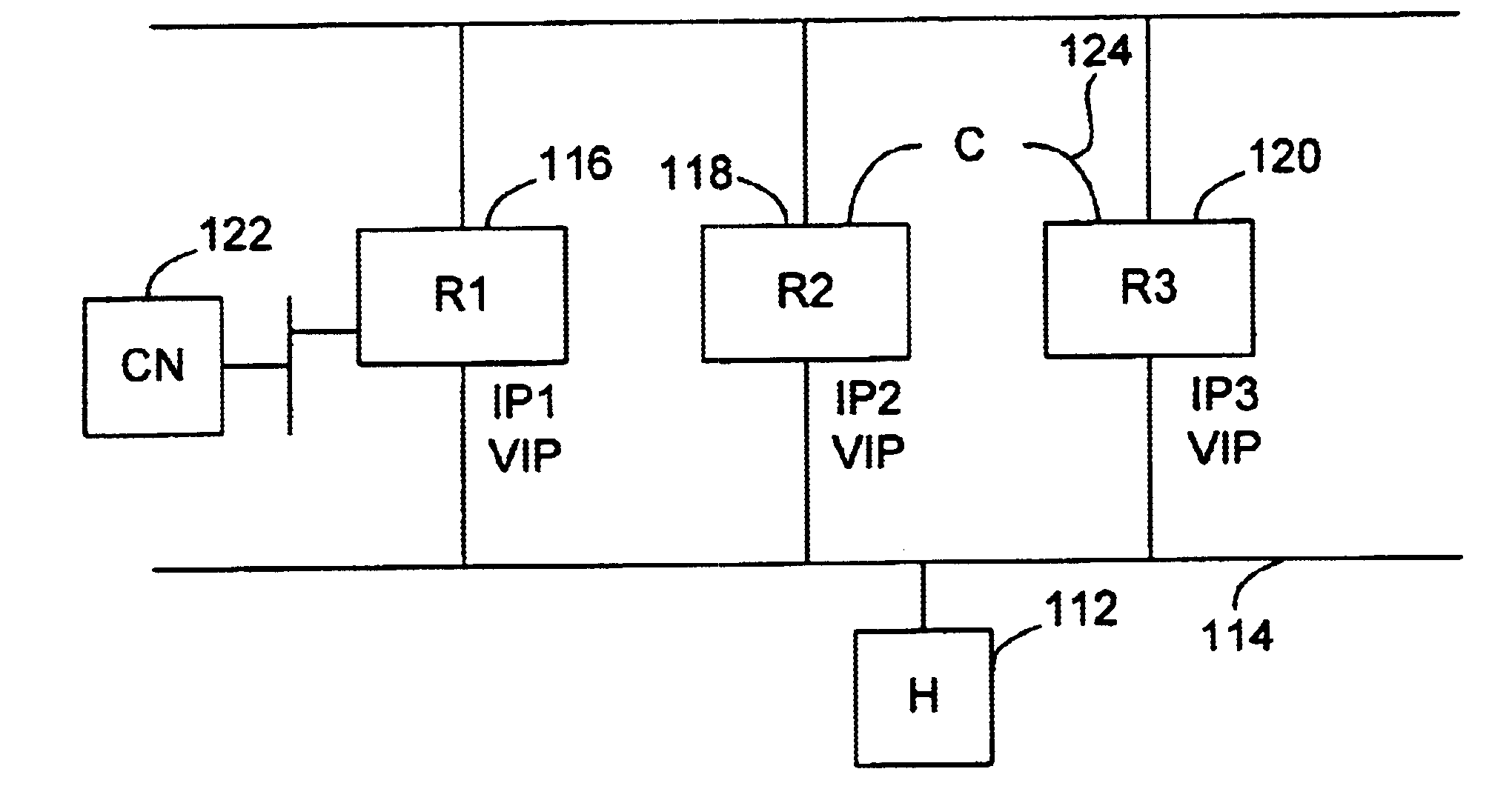
Redirection to a virtual router
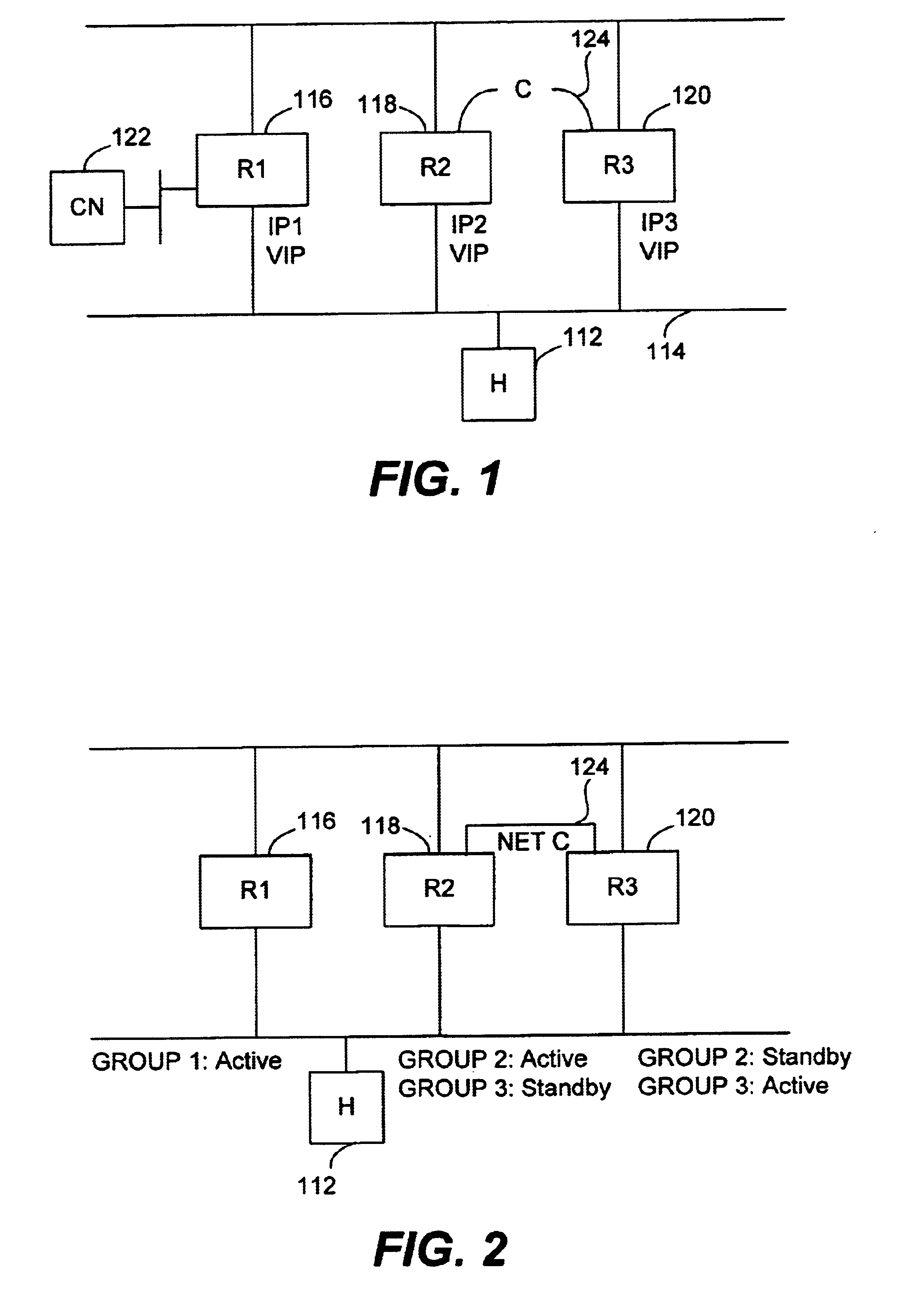
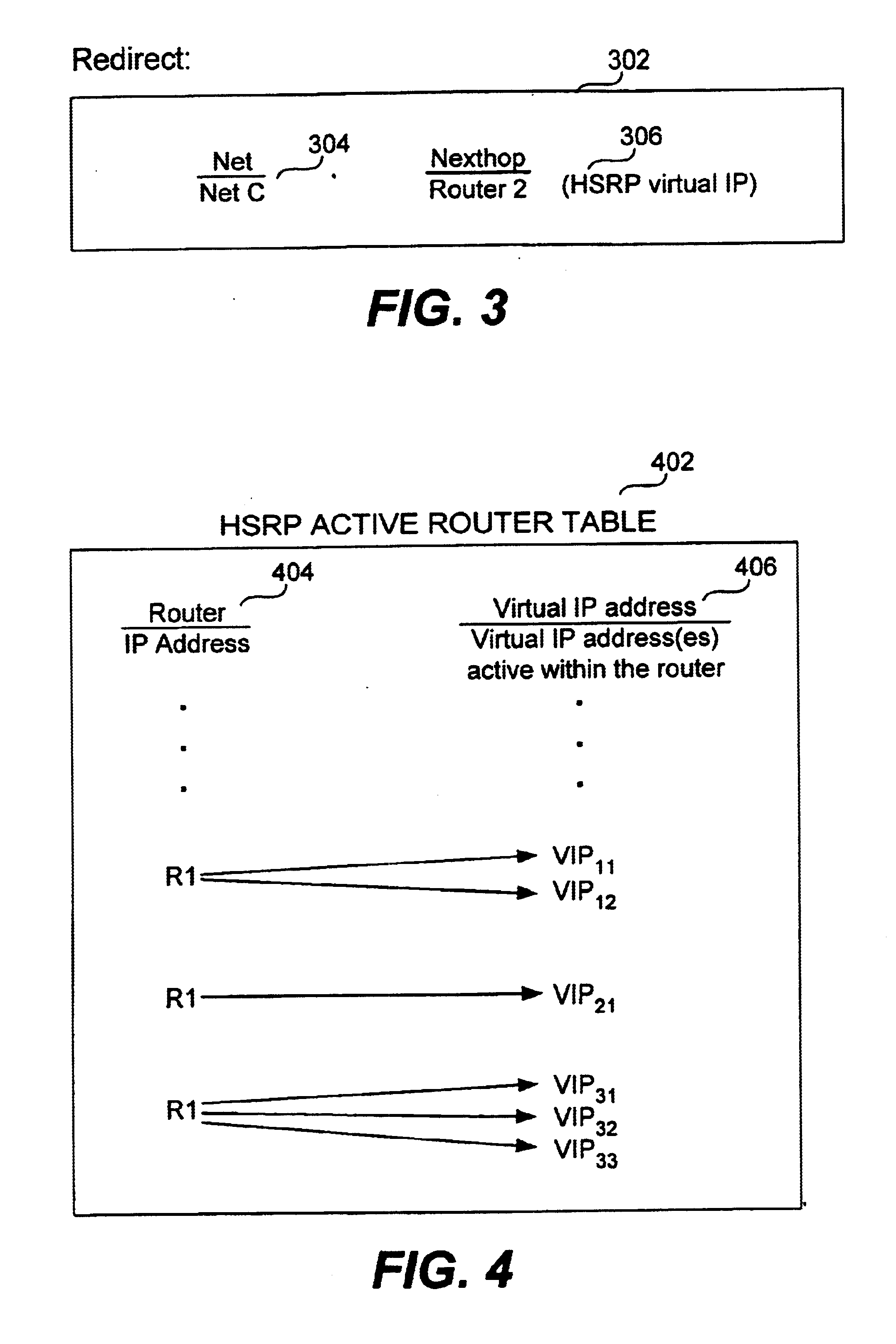
InactiveUS6885667B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableComputer science
Methods and apparatus for sending a redirect packet to a host by a first router that supports a virtual router protocol are disclosed. Specifically, the redirect packet notifies the host that specific packets are to be redirected to a second router. First, the first router receives a packet from a host, where the packet includes a source address identifying the host and a destination address identifying a destination network. The first router ascertains the destination network of the packet from the destination address and obtains from a routing table an address of a next router that is coupled to the packet's destination network. The first router then determines whether to send a redirect packet to the host. In accordance with one embodiment, this is performed by determining whether the next router and the host identified by the source address of the packet are on the same network. When it is determined that the next router and the host are on the same network, the first router composes and sends the redirect packet to the host. The redirect packet serves to notify the host that packets addressed to the destination network are to be redirected to a virtual address of the next router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com