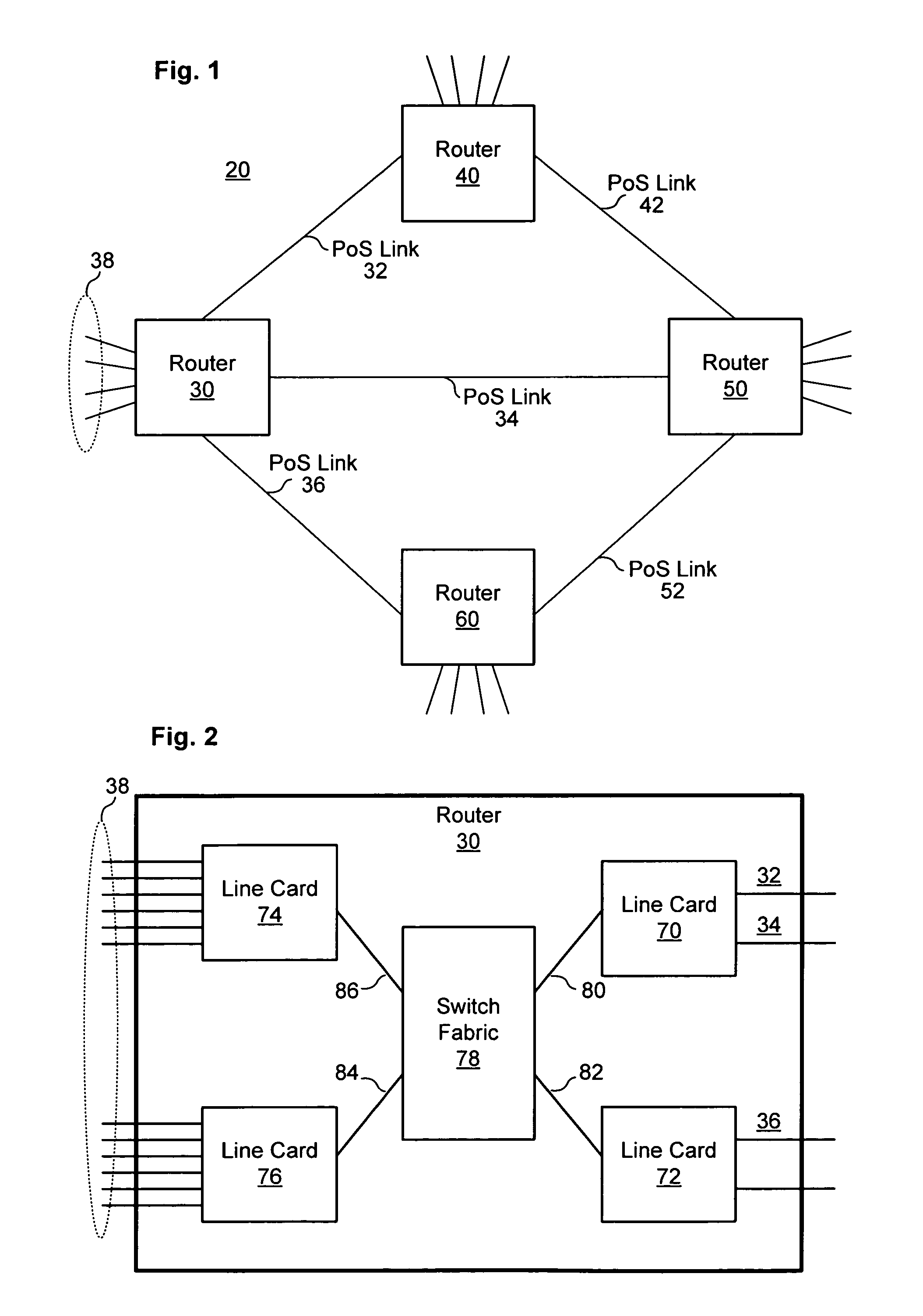
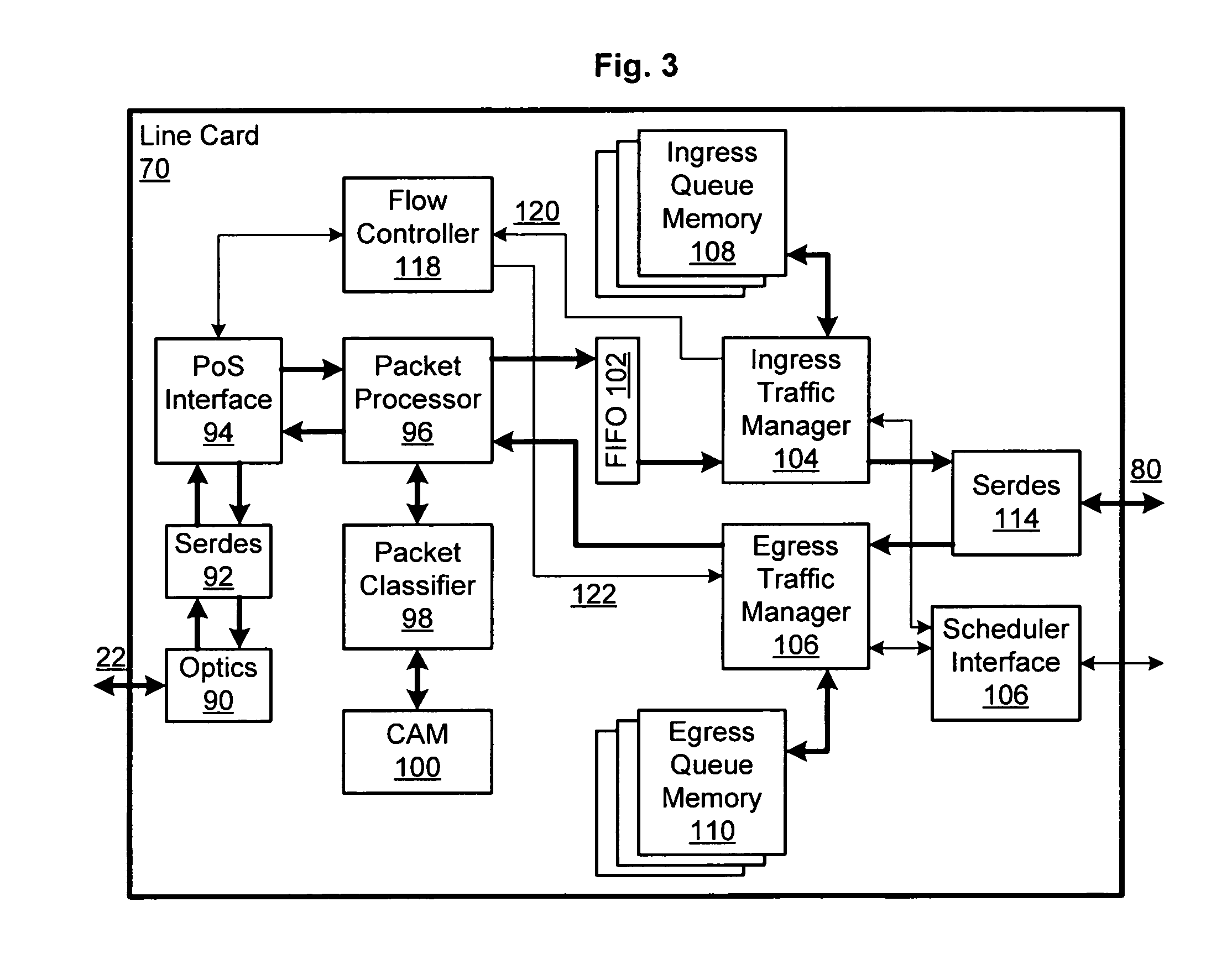
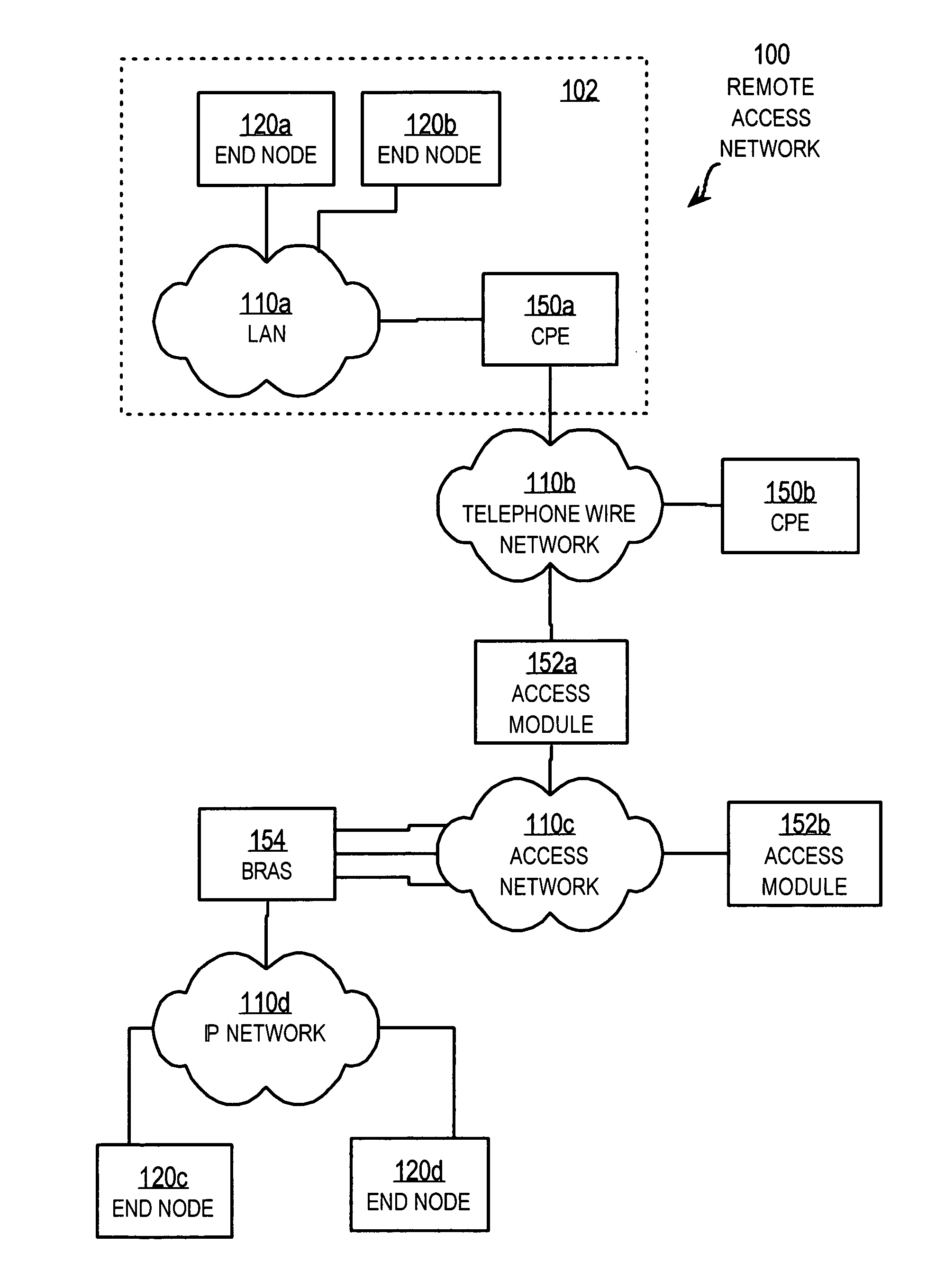
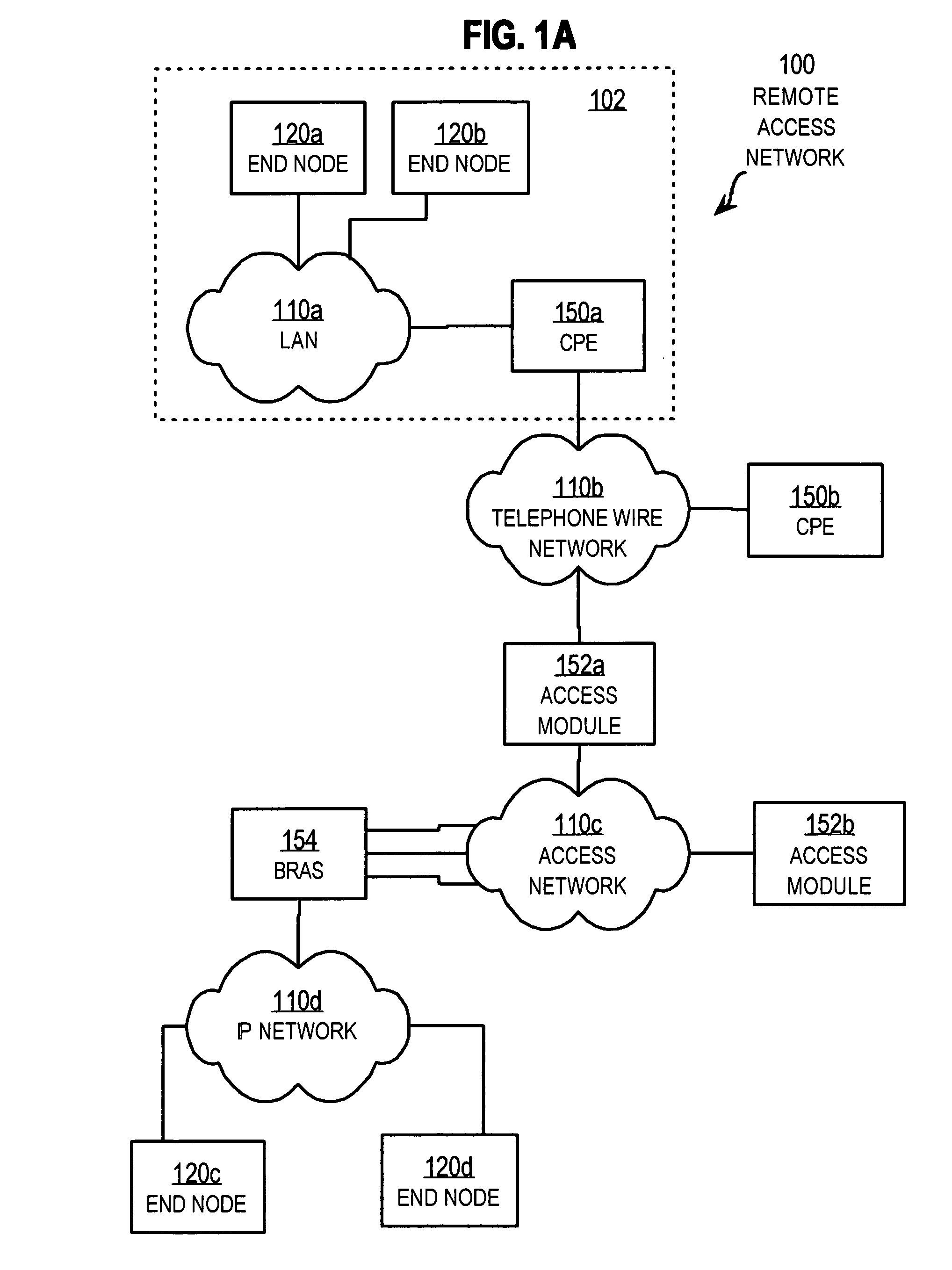
Patents
Literature
394 results about "Point-to-Point Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
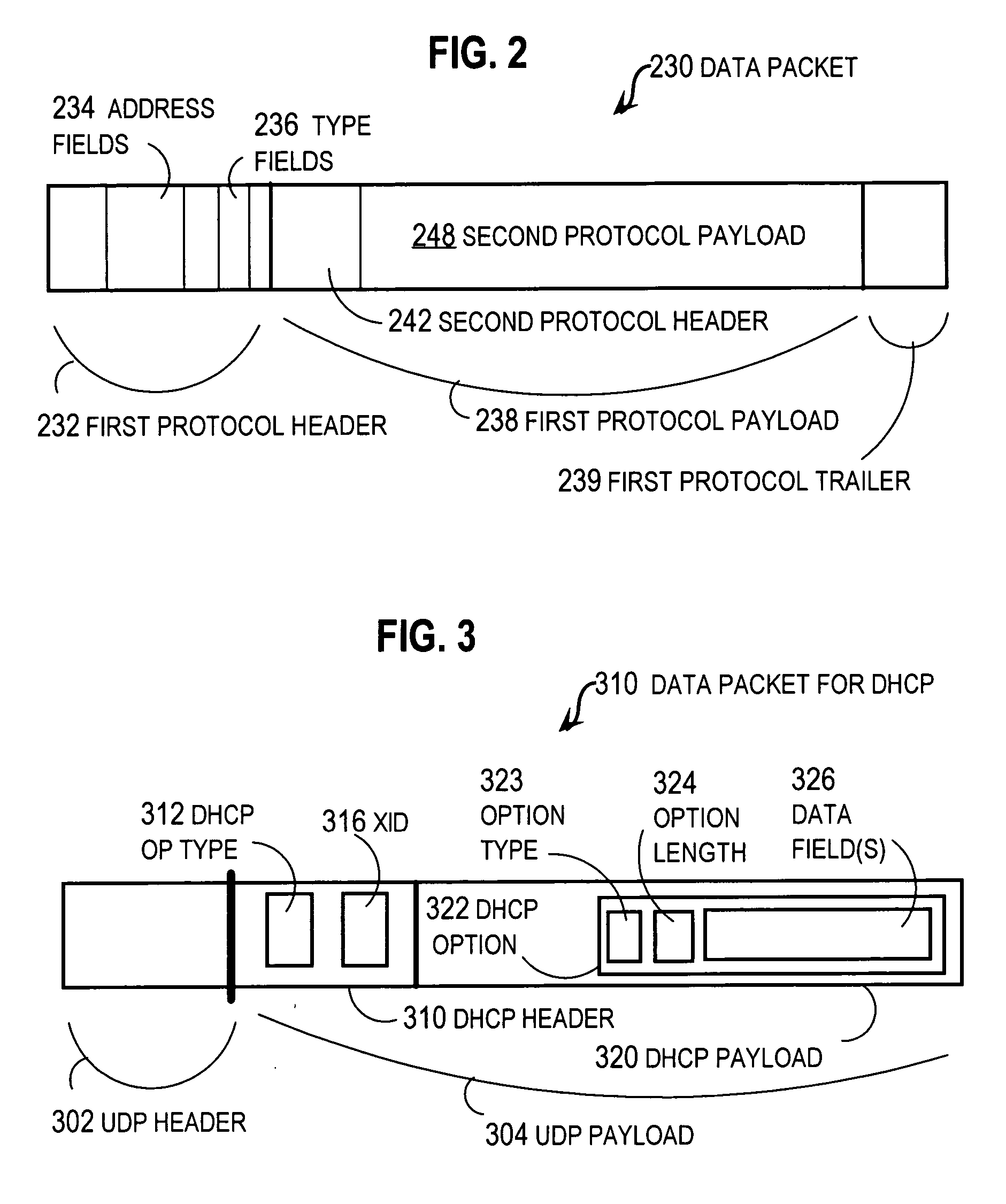
In computer networking, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer (layer 2) communications protocol between two routers directly without any host or any other networking in between. It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption, and compression.
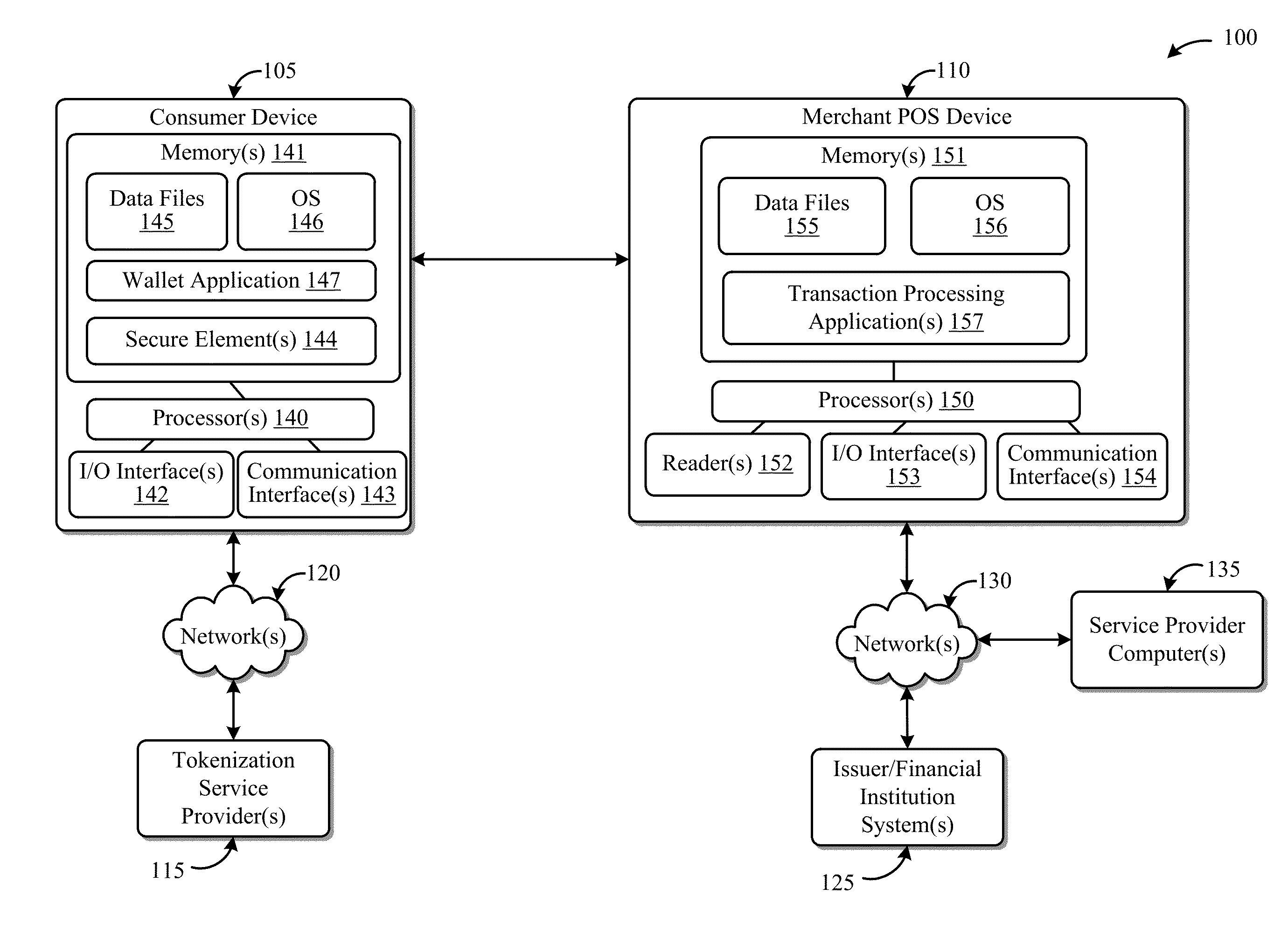
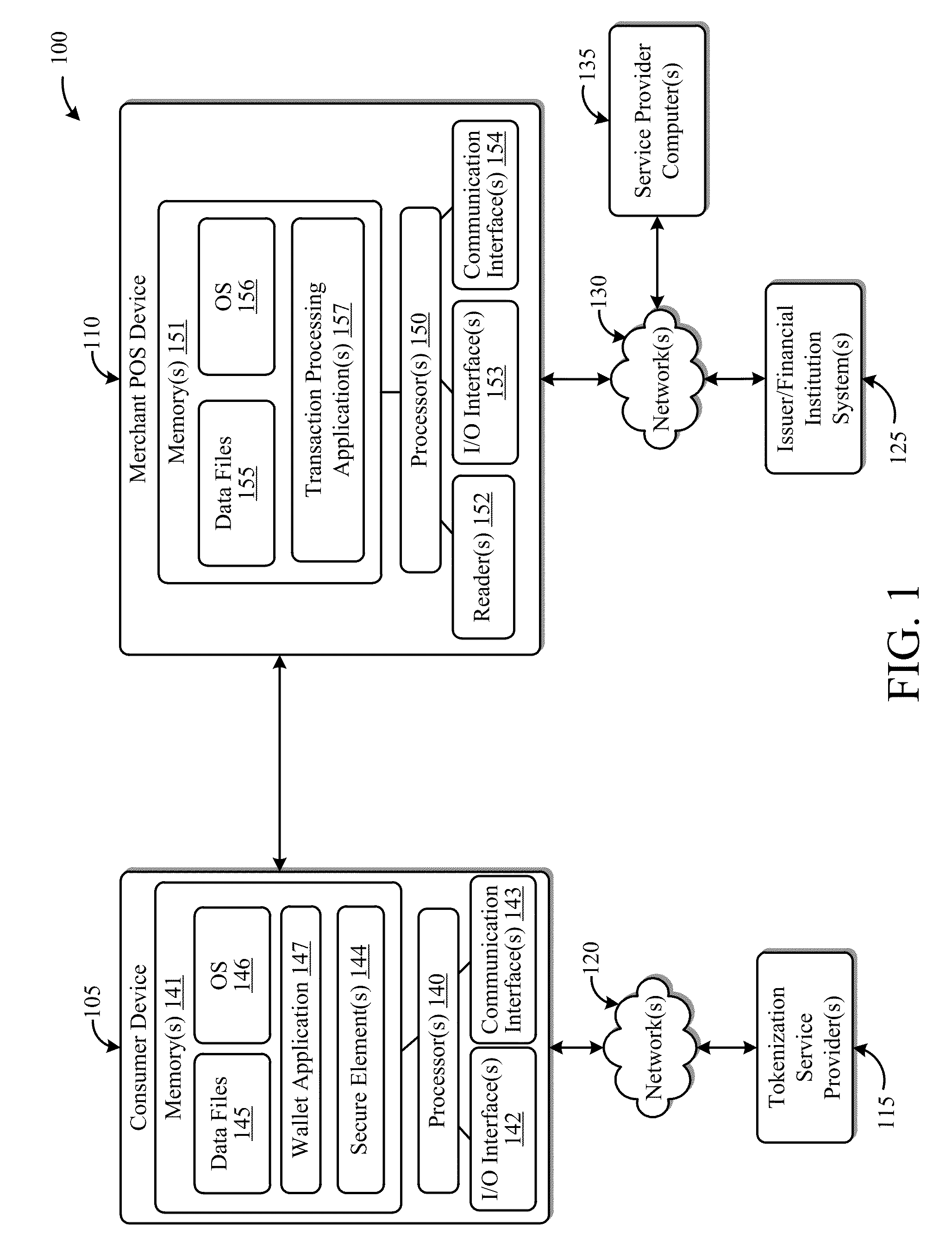
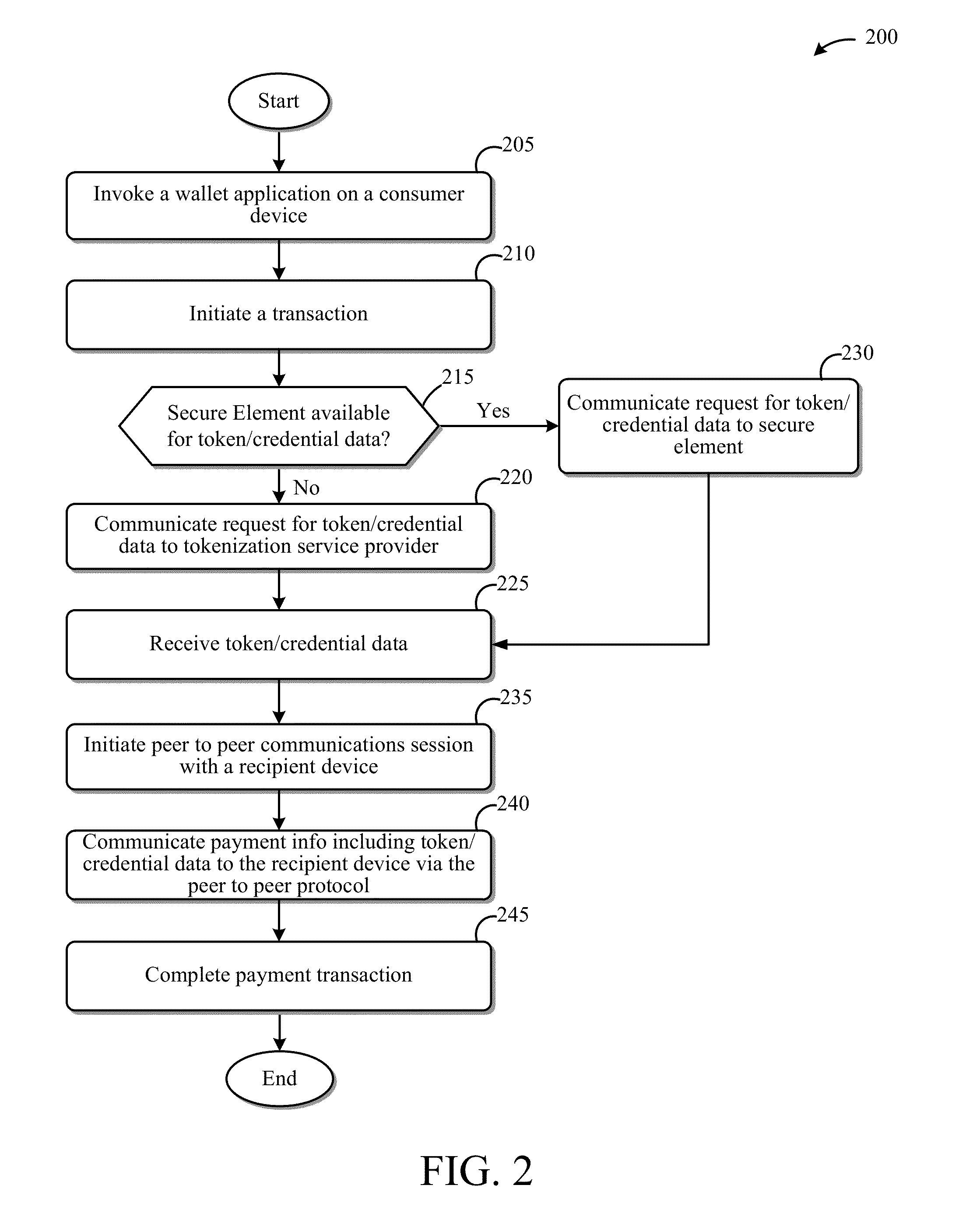
Systems and Methods for Facilitating Payments Via a Peer-to-Peer Protocol
ActiveUS20130254052A1Facilitate peer-to-peer communicationEasy to completeHand manipulated computer devicesFinancePoint-to-Point ProtocolPayment transaction
This disclosure describes systems and methods related to facilitating payments via a peer-to-peer protocol. Tokenized information associated with a payment transaction may be obtained. Establishment of a peer-to-peer communications session with a payment recipient device may be facilitated. The tokenized information to the recipient device via the established peer-to-peer communications session may be communicated in order to facilitate completion of the payment transaction.
Owner:FIRST DATA
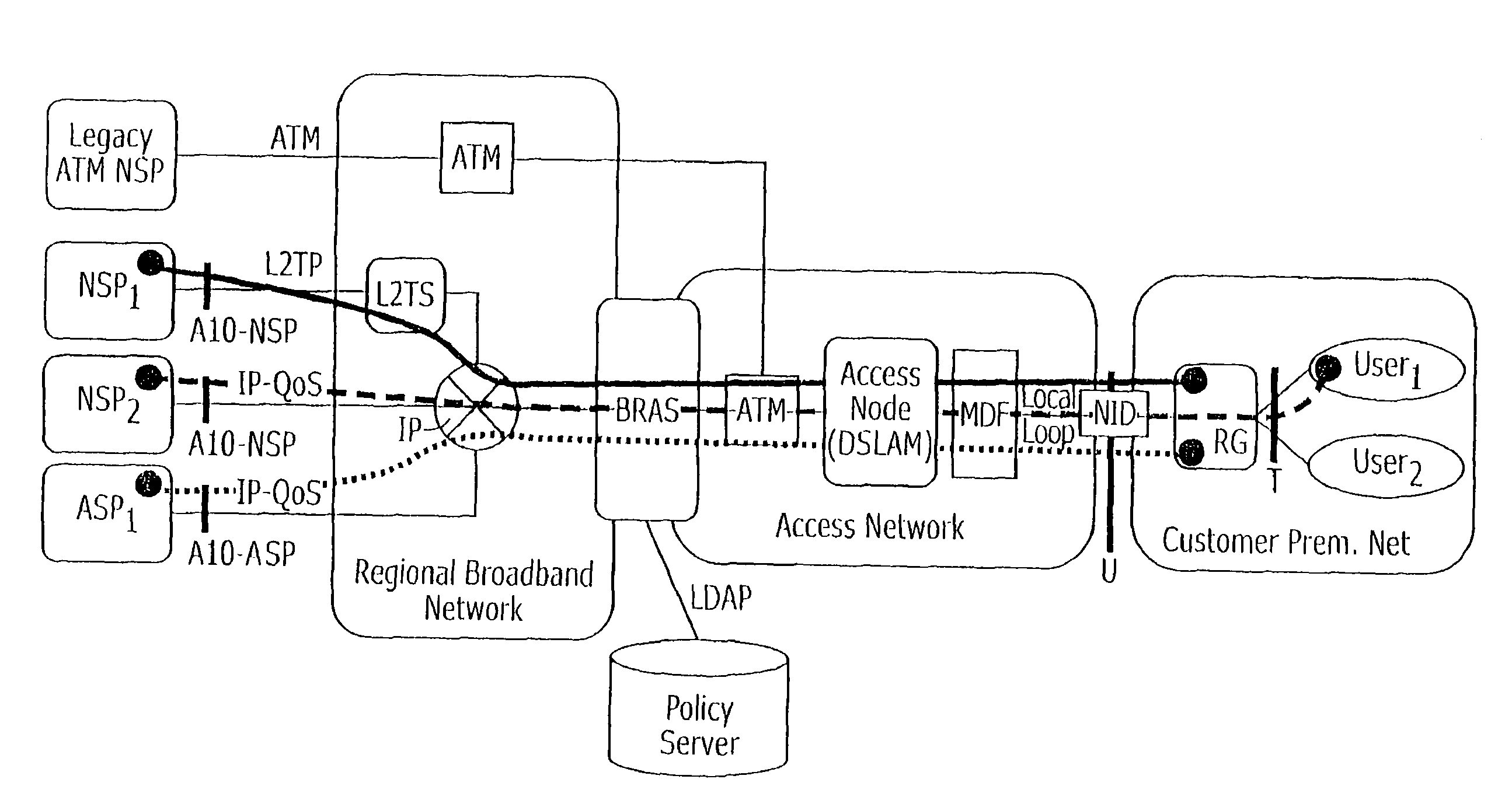
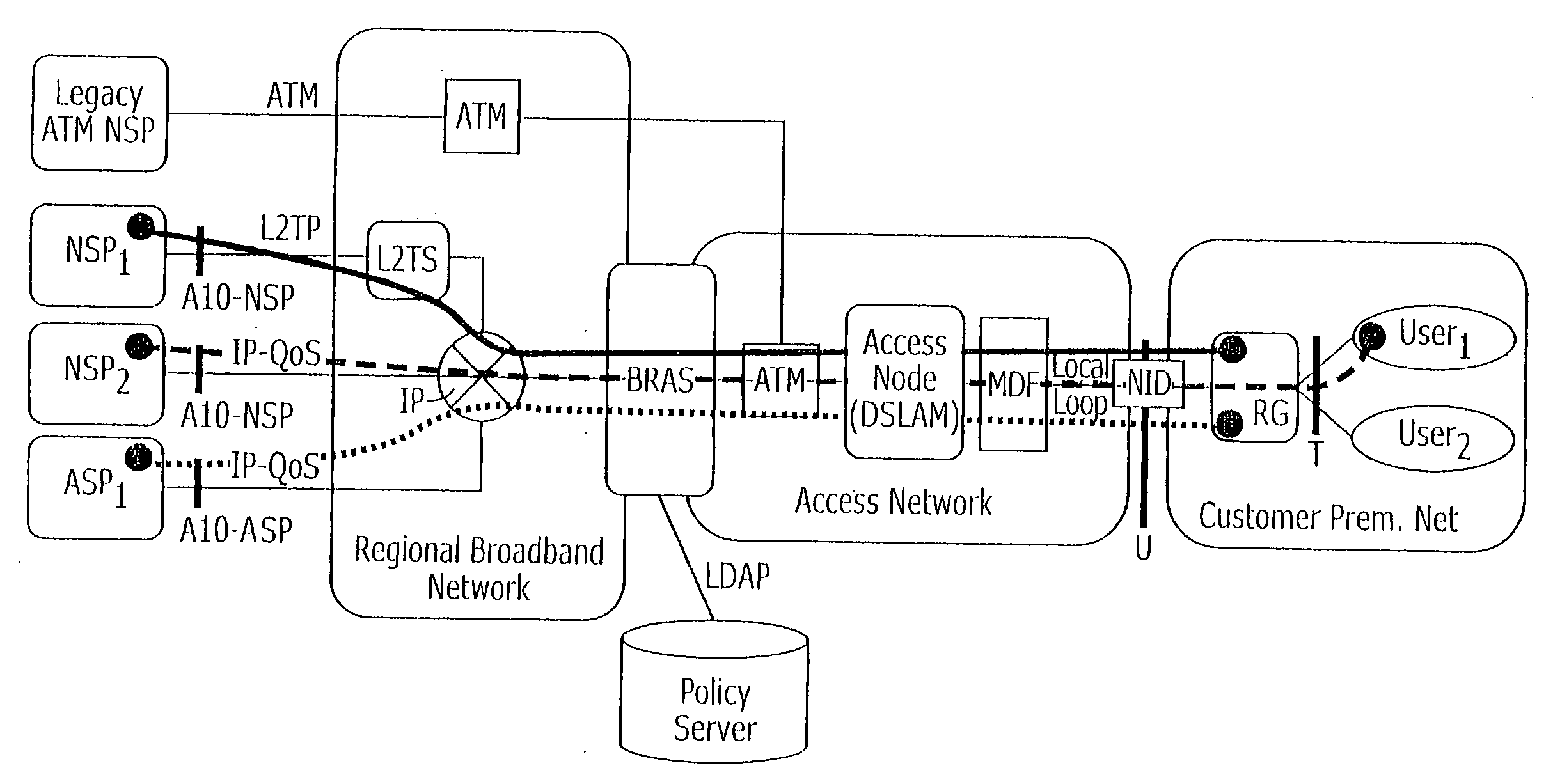
Methods of implementing dynamic QoS and/or bandwidth provisioning and related data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Techniques for replacing point to point protocol with dynamic host configuration protocol
ActiveUS20070203999A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPoint-to-Point ProtocolMessage type
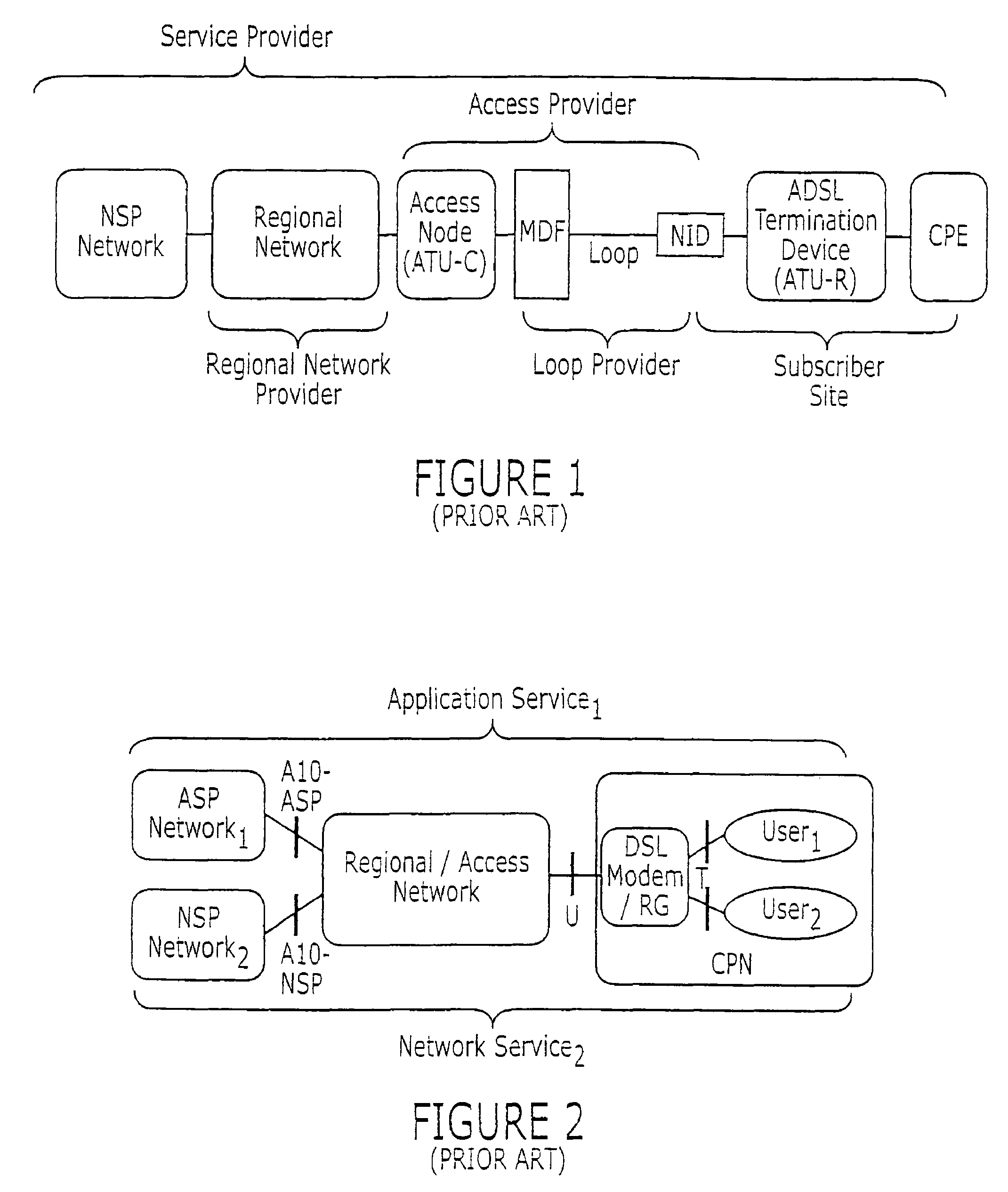
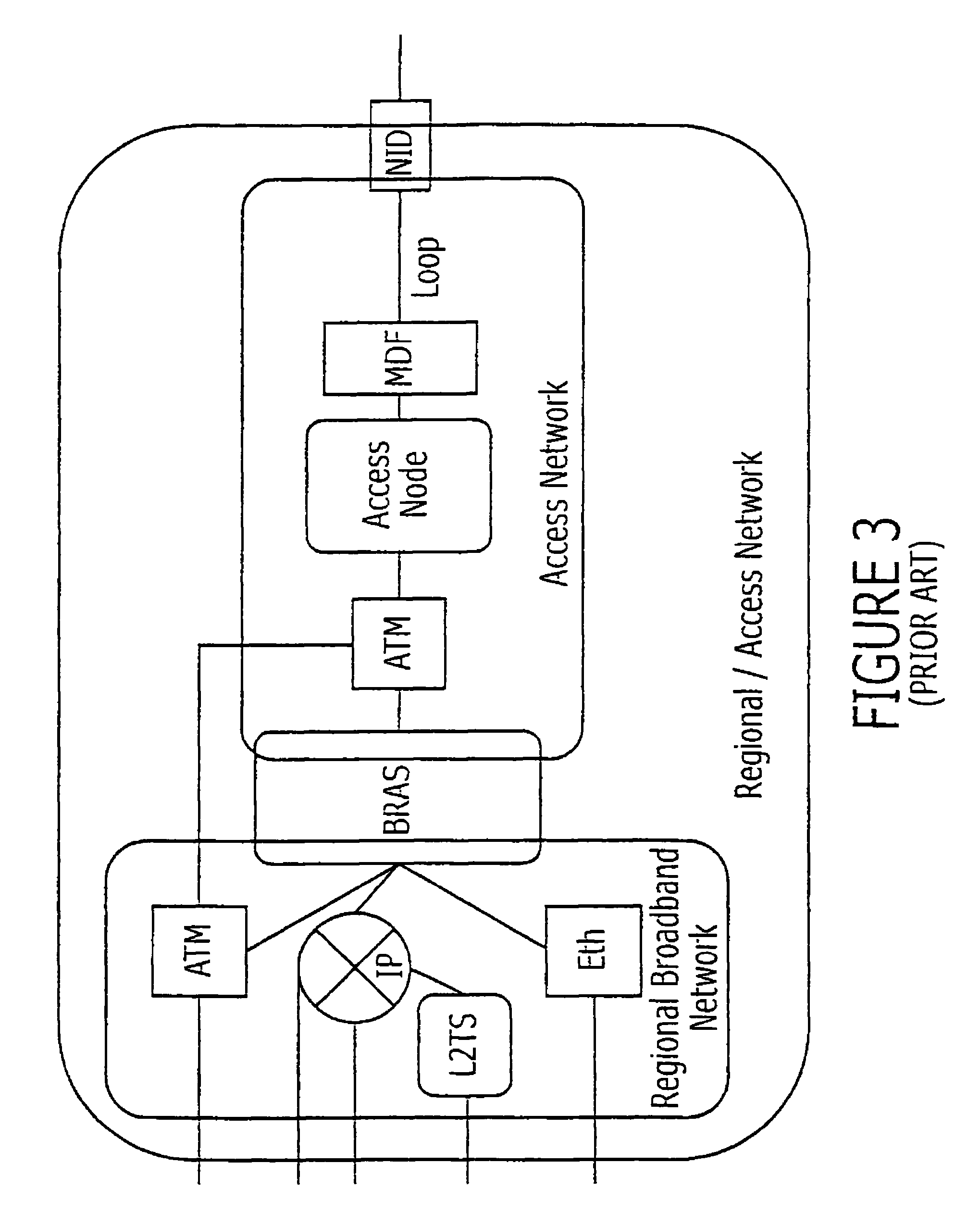
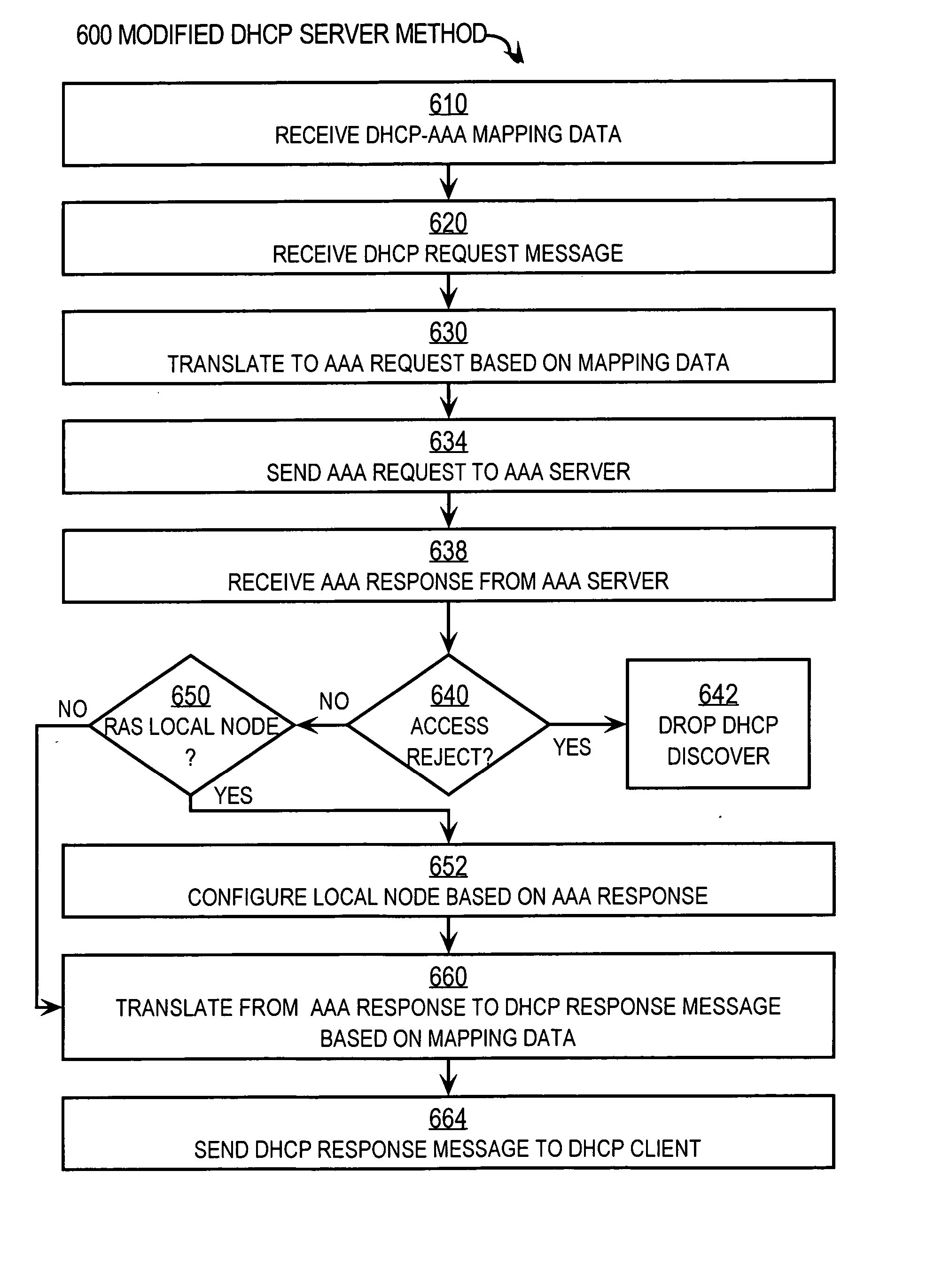
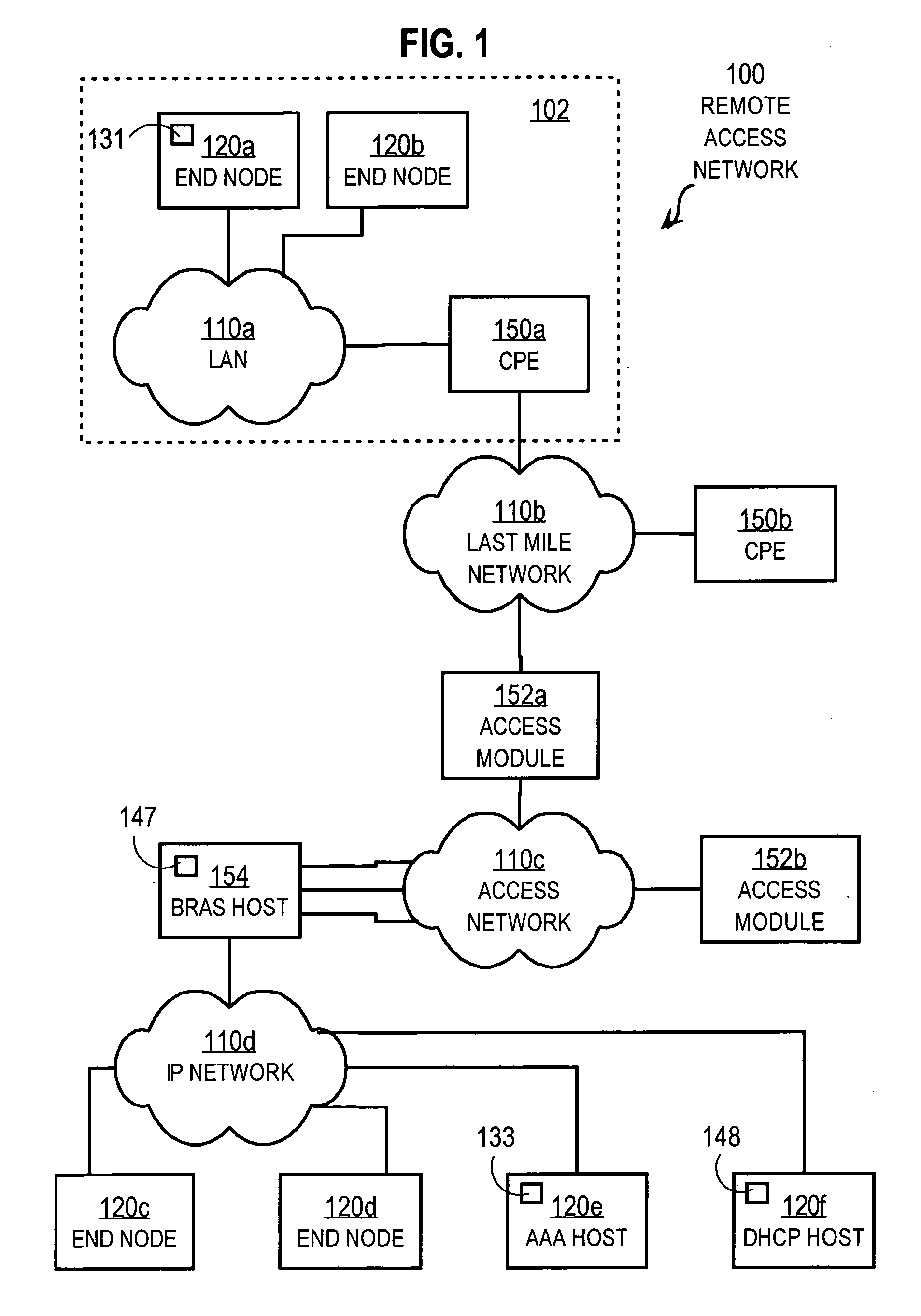
Techniques for providing remote access to a service provider network include exchanging multiple Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) formatted messages instead of any Point to Point Protocol (PPP) message to provide all PPP functions for accessing a service provider network from a customer node. The service provider network is on provider premises and the customer node is on customer premises different from the provider premises. The DHCP format is used to exchange authentication messages, user profile data on Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) servers, or session keep-alive echo messages, alone or in some combination. When all are message types are combined, these techniques provide a remote access server (RAS) with the capability to perform all functions presently provided by PPP processes. In some combinations, these techniques allow a modified DHCP server to replace a legacy AAA server.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods of implementing dynamic QoS and/or bandwidth provisioning and related data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products
A method of operating a data network may include establishing a data path through the data network between a routing gateway for a subscriber of the data network and a service provider providing a data service. Moreover, the data service may be provided for use at the routing gateway over the data path during a data session. A request may be received from the service provider wherein the request defines a data flow characteristic for the data path between the routing gateway and the service provider providing the data service during the data session. The data flow characteristic may then be transmitted to a node along the data path between the routing gateway and the service provider for enforcement of the data flow characteristic for the data path at the node. More particularly, the data session may be a point-to-point protocol data session. Related methods, data networks, data service providers, routing gateways, and computer program products are also discussed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
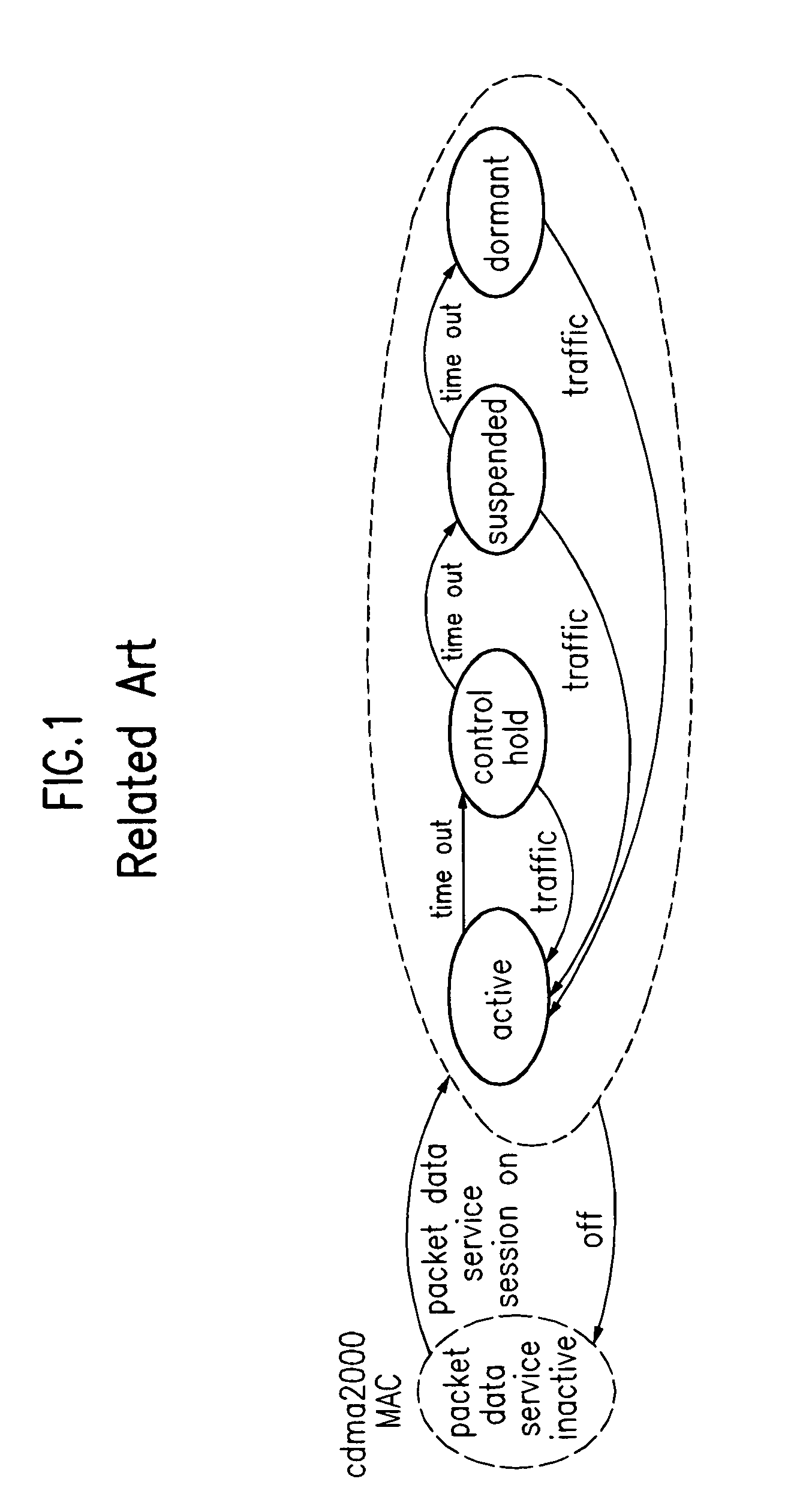
Instant activation of point-to point protocol (PPP) connection using existing PPP state
InactiveUS6628671B1Time-division multiplexWide area networksNetwork access serverPoint-to-Point Protocol
A network access server providing remote access to an IP network for a remote client initiates a PPP connection for a remote client quickly, and without requiring re-negotiation of Link Control Protocols and Network Control Protocols. The network access server has a PPP session with the remote client go dormant, for example when the user is a wireless user and goes out of range of a radio tower and associated base station. The network access server does not get rid of the PPP state for the dormant session, but rather switches that PPP state to a new session, such as when the client moves into range of a different radio tower and associated base station and initiates a new active session on the interface to the wireless network. The switching of PPP states may be within a single network access server, or from one network access server to another. This "context switching" of the active PPP session allows the mobile user to seamlessly move about the wireless network without having to re-negotiate Link Control Protocols and Network Control Protocols every time they move out of range of one radio tower and into range of another radio tower.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
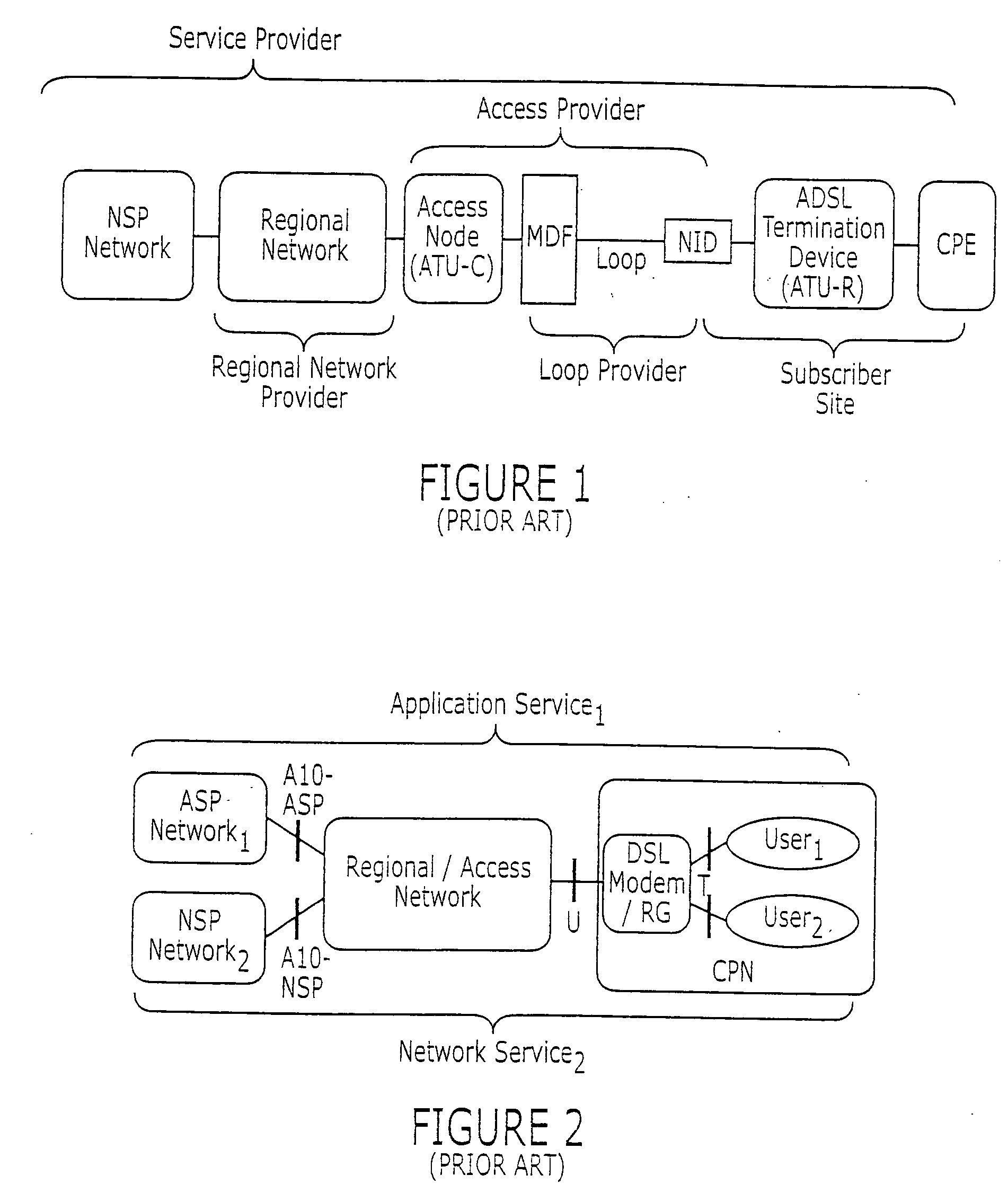
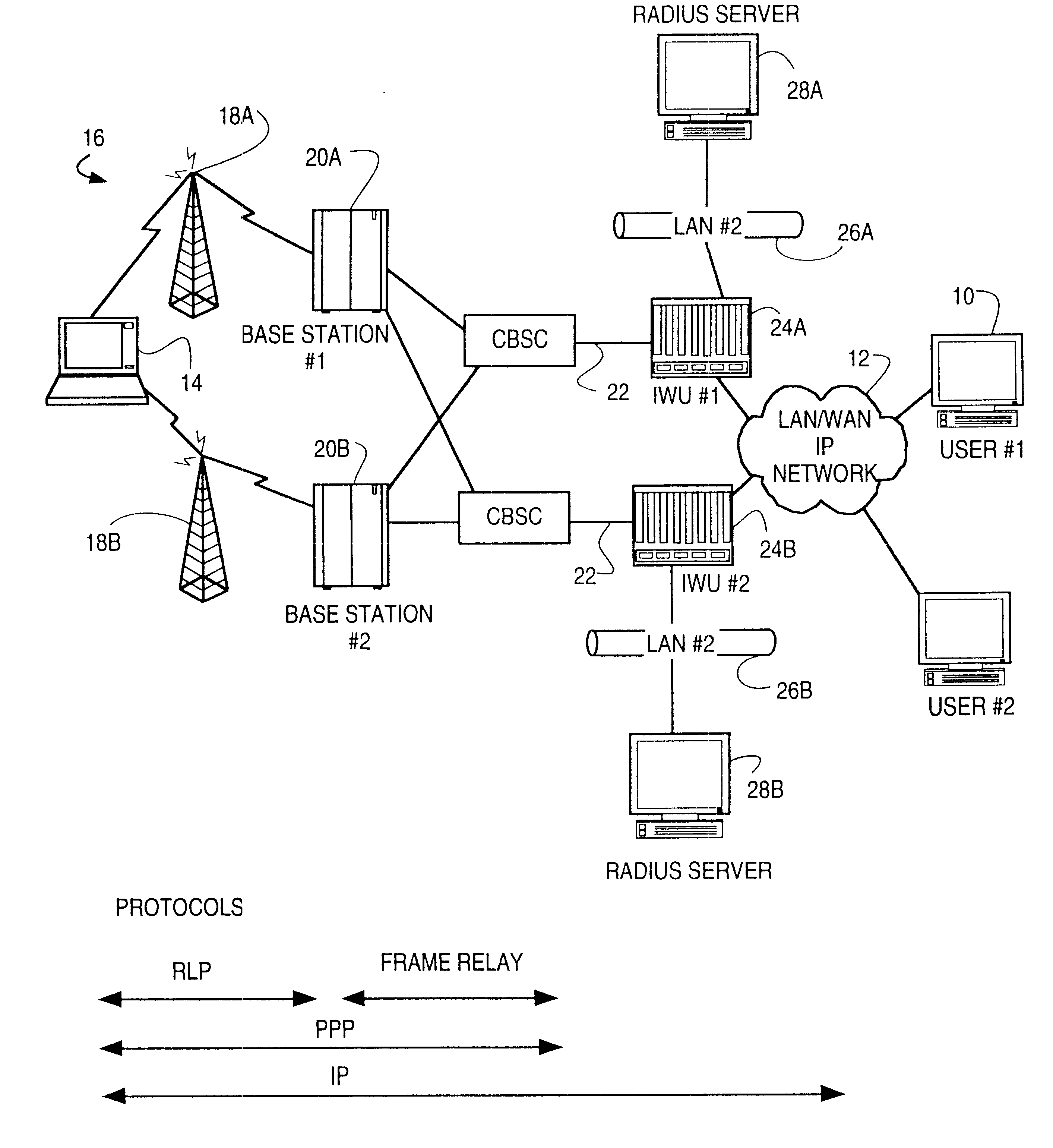
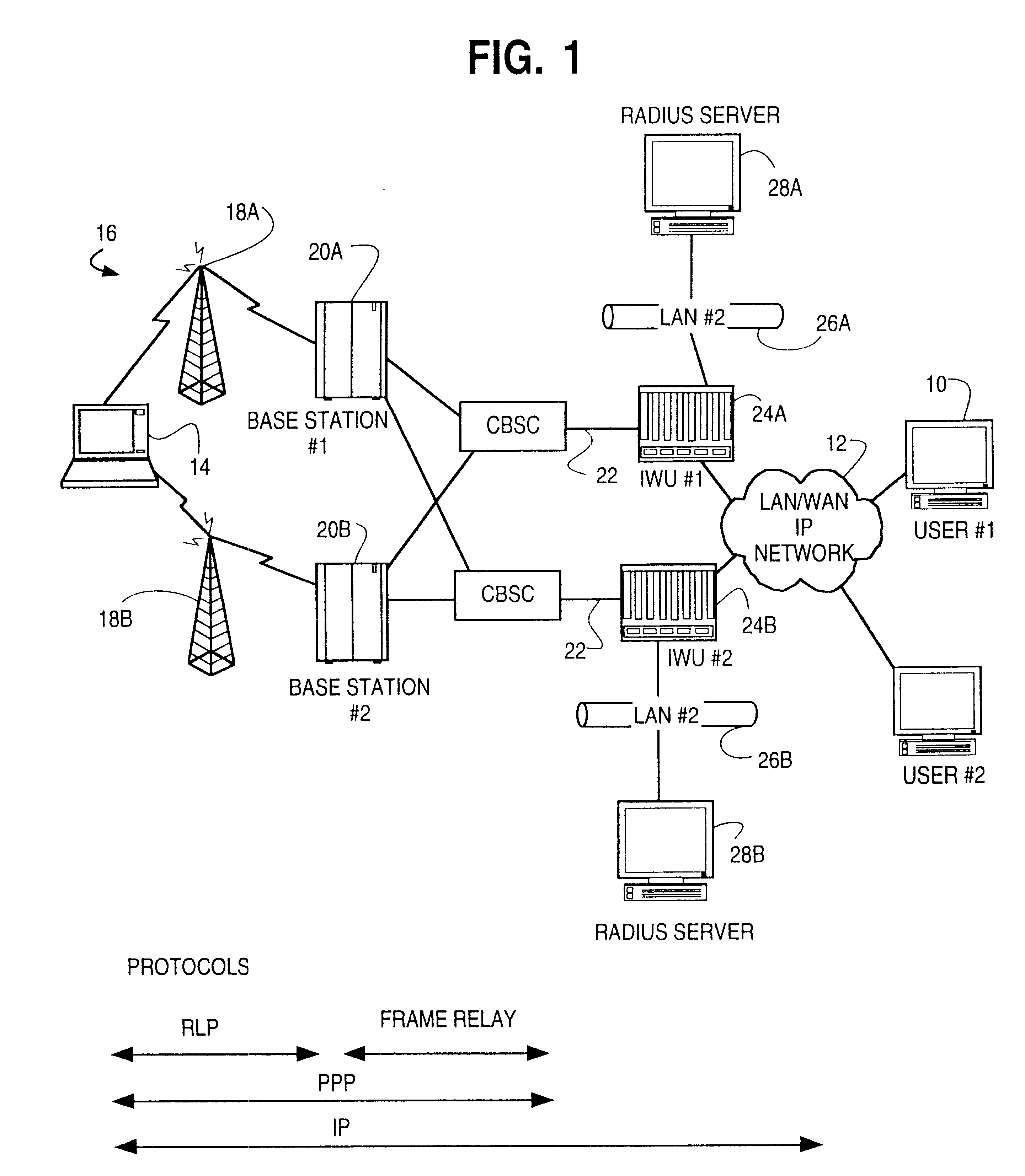
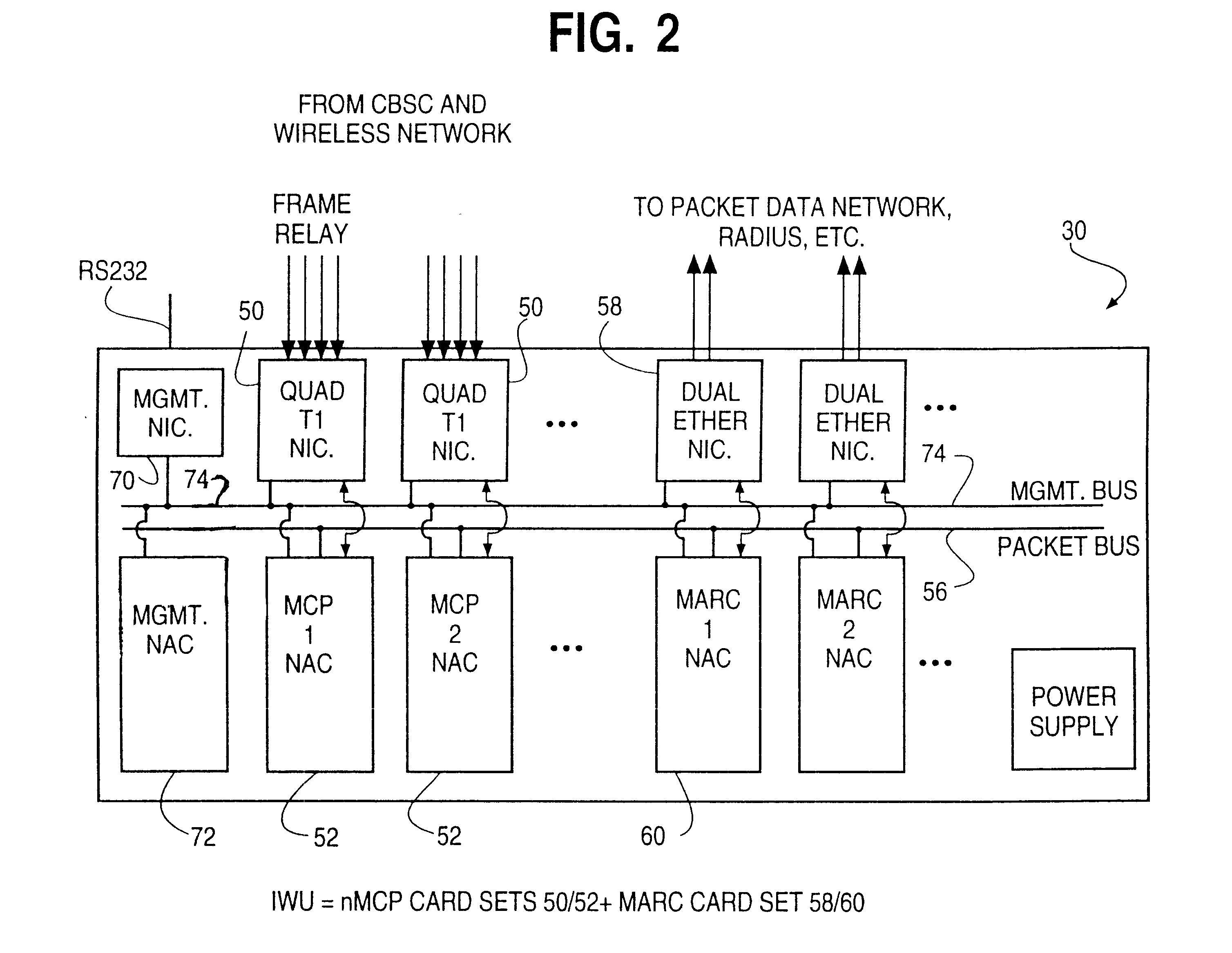
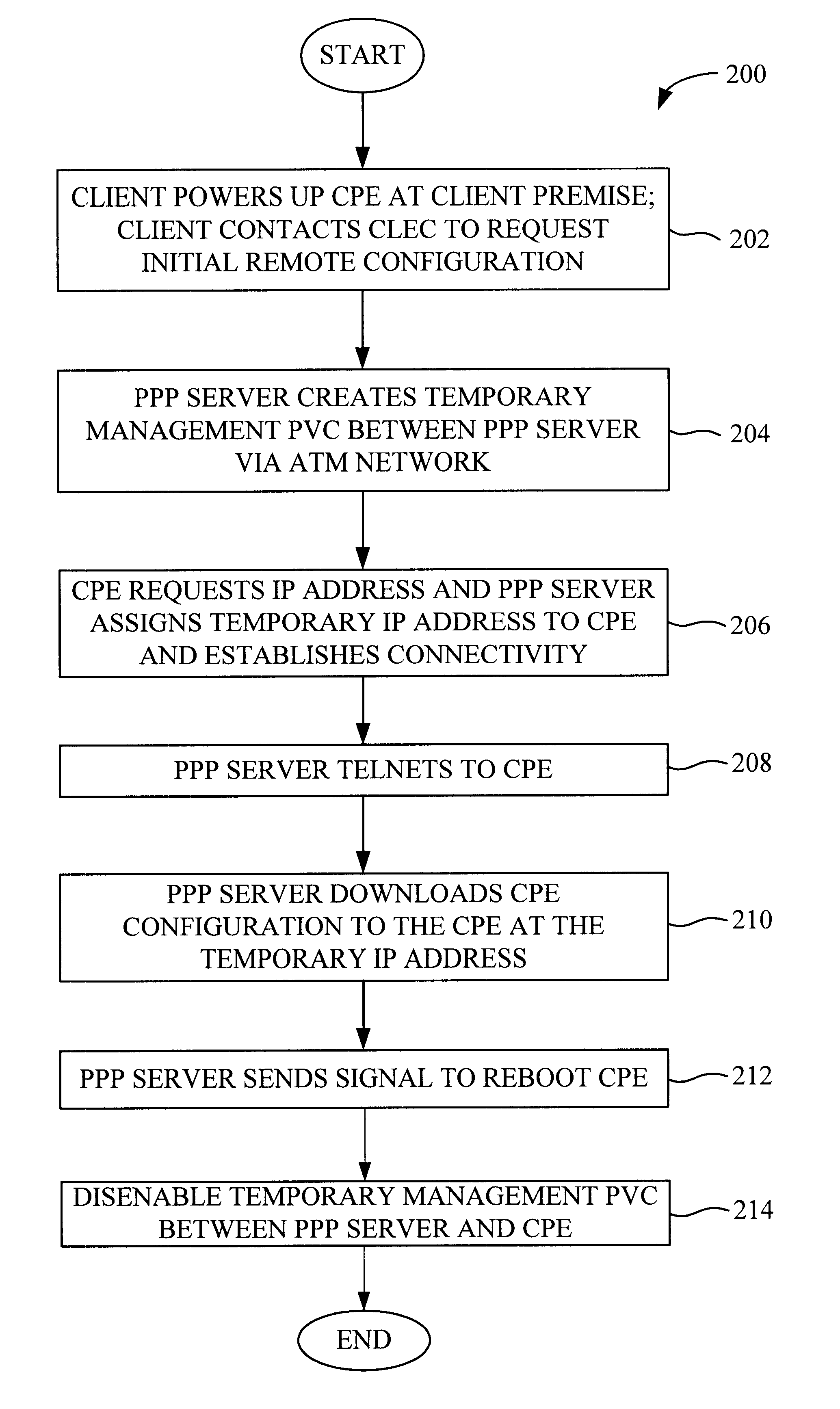
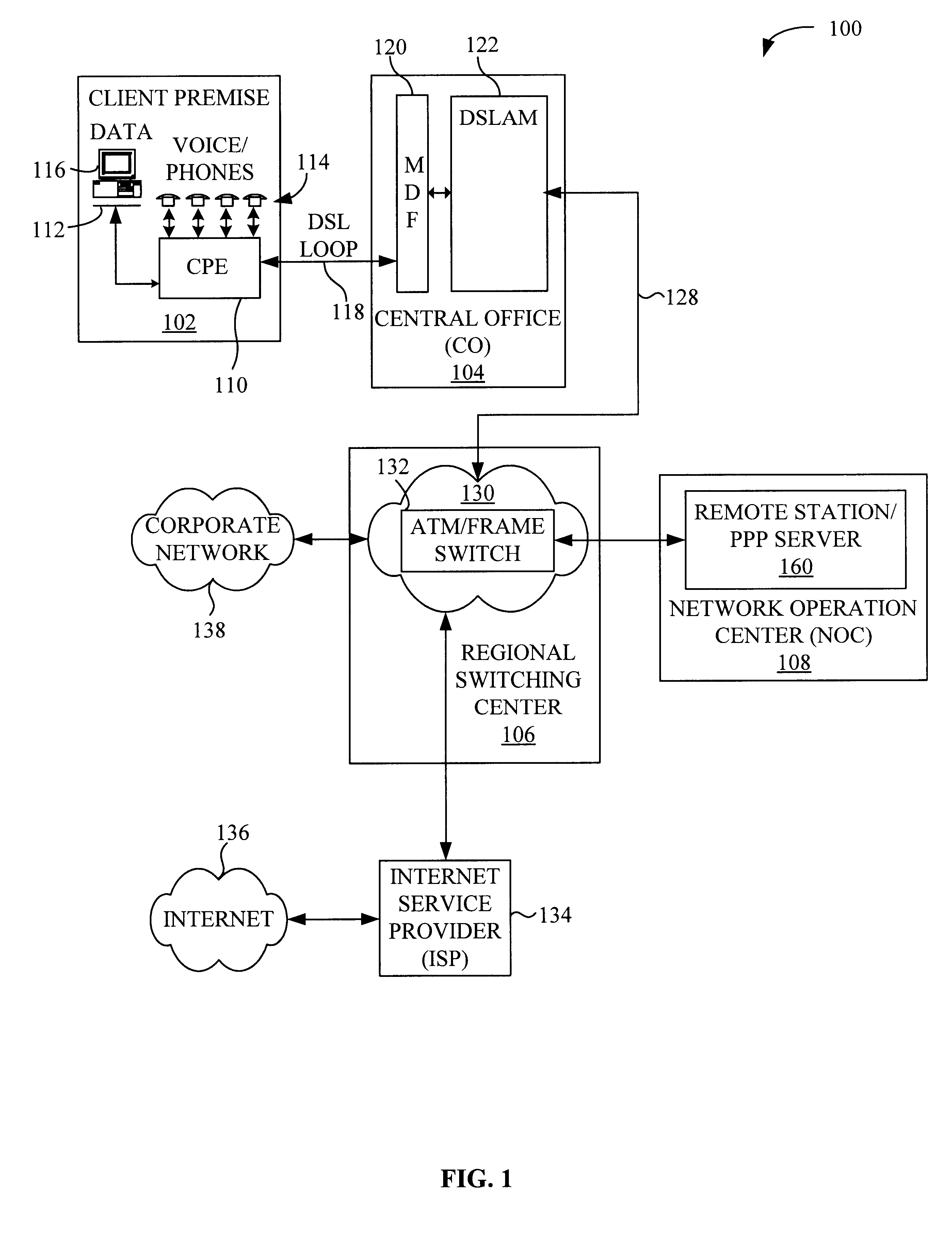
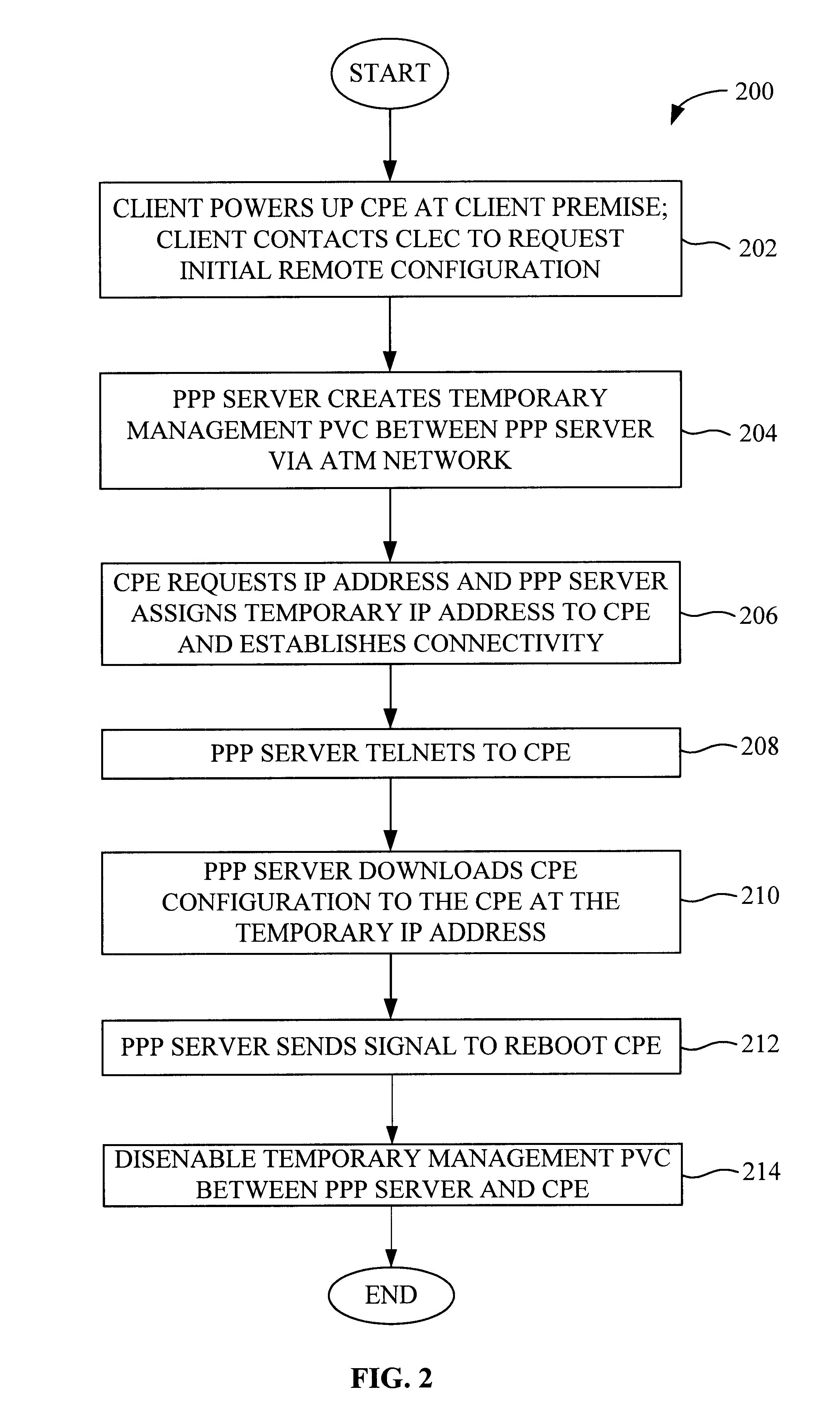
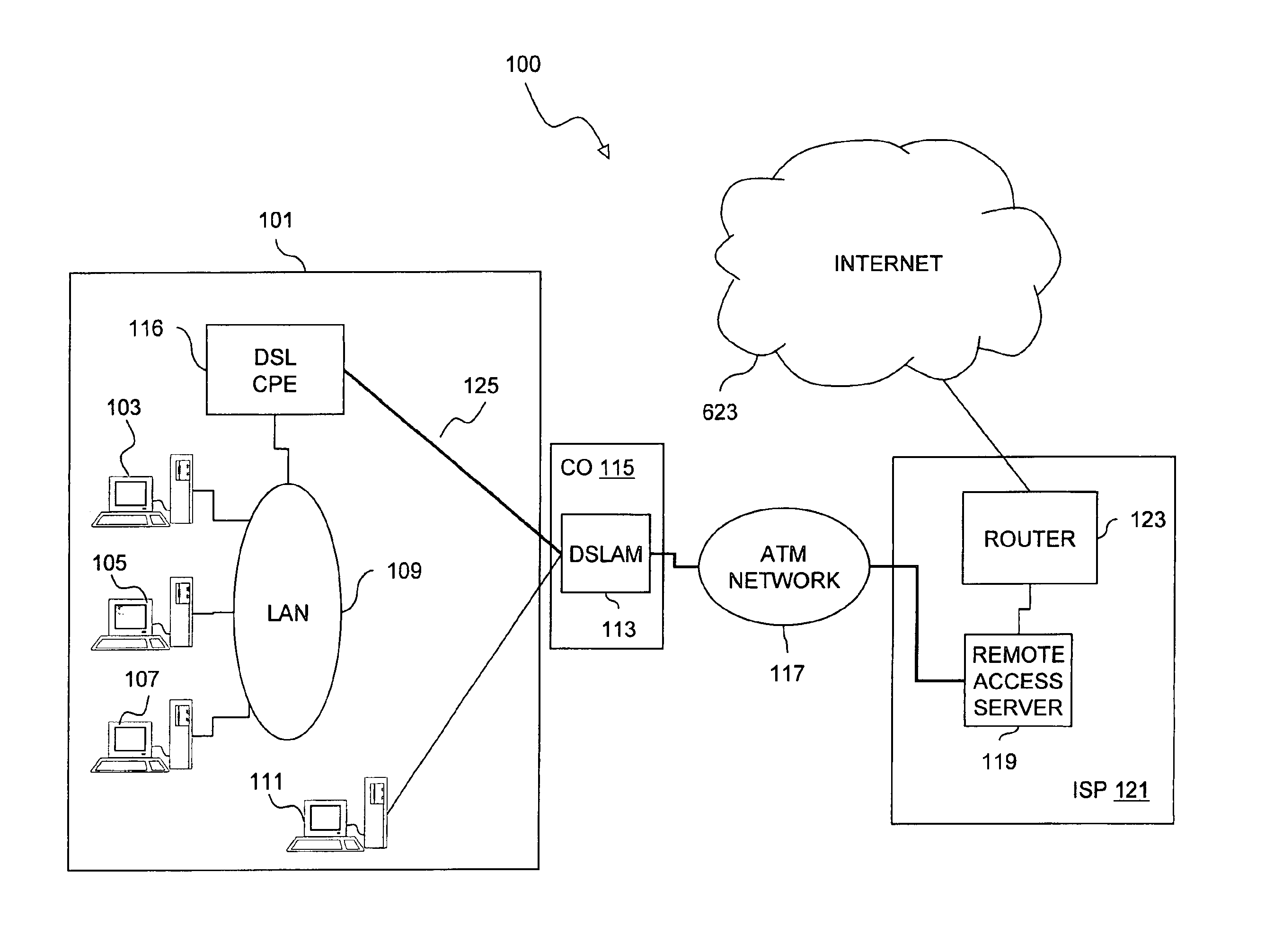
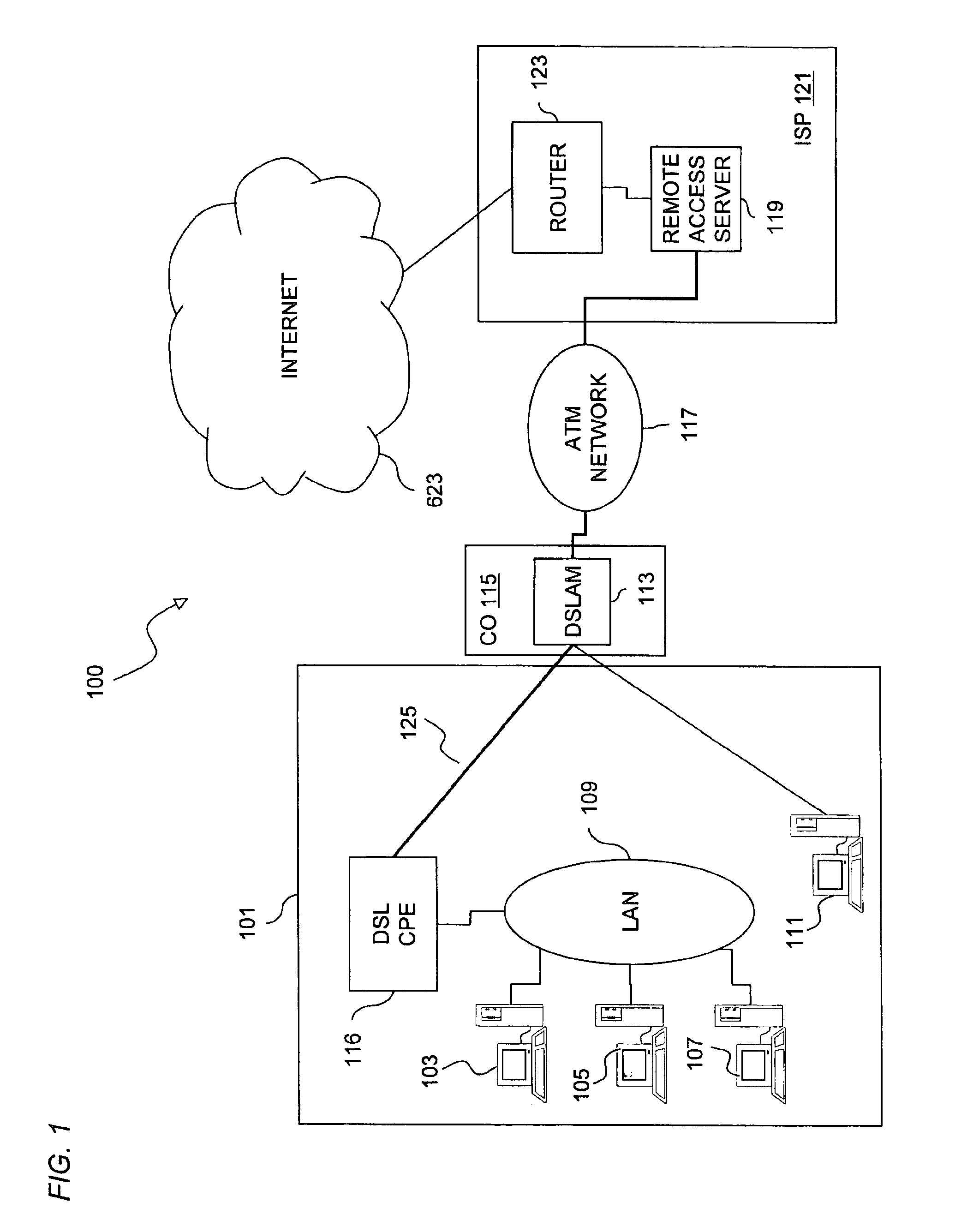
System and method for remote configuration and management of customer premise equipment over ATM
InactiveUS6584074B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPoint-to-Point ProtocolTTEthernet
Systems and methods for providing remote configuration and on-demand management of a CPE over DSL are disclosed. The method generally comprises creating a temporary management ATM virtual circuit between a remote Point-to-Point Protocol ("PPP") server and the CPE via an ATM network, assigning a temporary Internet Protocol ("IP") address to the CPE using PPP over ATM, telneting from the PPP server to the temporary IP address of the CPE, and downloading CPE configuration from the PPP server to the CPE. The creating, assigning, telneting, and downloading may be performed between the remote PPP server and a management port of the CPE. The system generally comprises a remote PPP server, a CPE including a management port adapted to send requests for connection to the PPP server and to receive data downloaded from the PPP server, and a temporary management ATM virtual circuit between the PPP server and the management port of the CPE.
Owner:GC PIVOTAL LLC
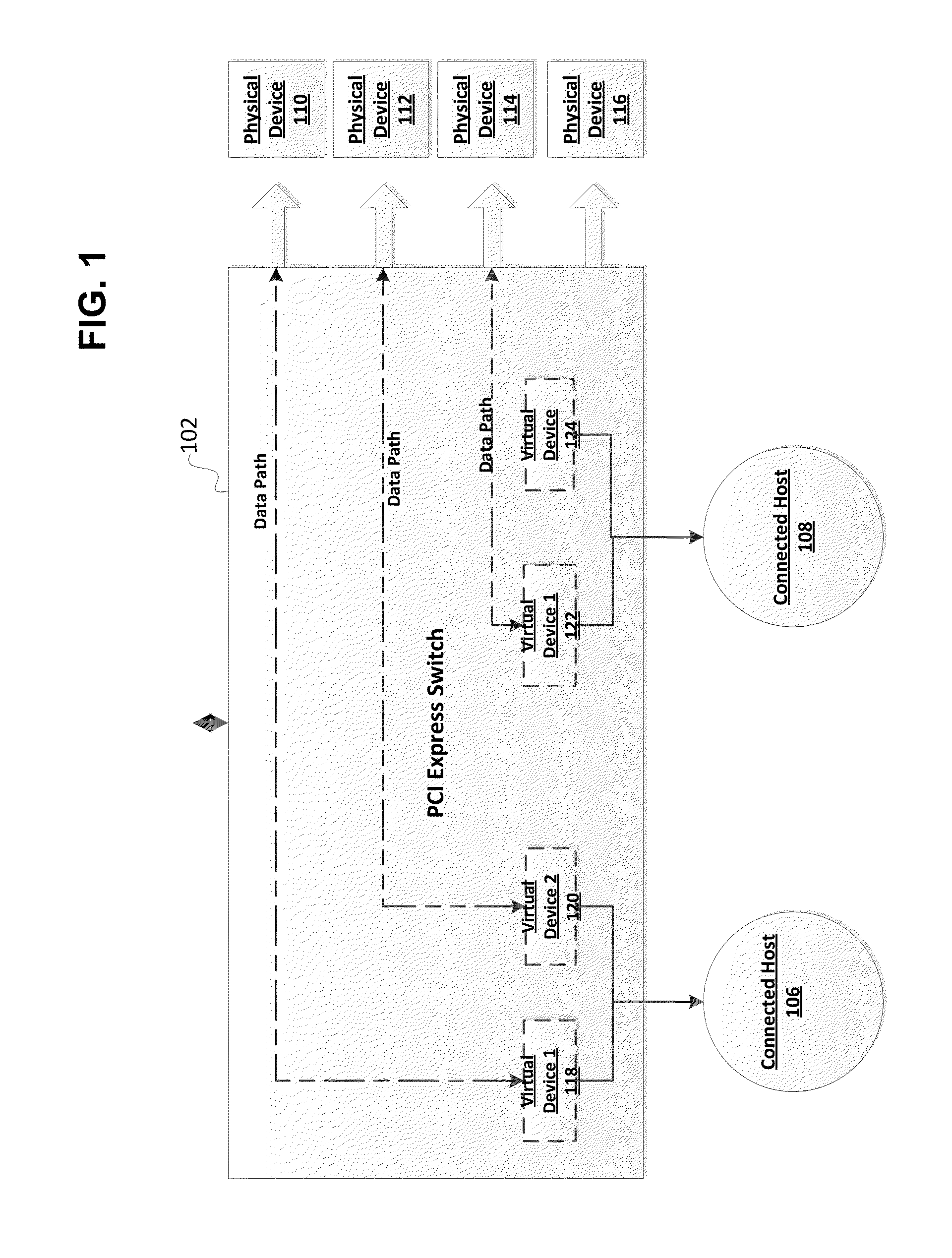
Multi-path id routing in a pcie express fabric environment
InactiveUS20140237156A1Internal/peripheral component protectionTransmissionPathPingPoint-to-Point Protocol
PCIe is a point-to-point protocol. A PCIe switch fabric has multi-path routing supported by adding an ID routing prefix to a packet entering the switch fabric. The routing is converted within the switch fabric from address routing to ID routing, where the ID is within a Global Space of the switch fabric. Rules are provided to select optimum routes for packets within the switch fabric, including rules for ordered traffic, unordered traffic, and for utilizing congestion feedback. In one implementation a destination lookup table is used to define the ID routing prefix for an incoming packet. The ID routing prefix may be removed at a destination host port of the switch fabric.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Mobile terminal and method of providing a network-to-network connection
InactiveUS6763012B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPoint-to-Point ProtocolNetwork connection
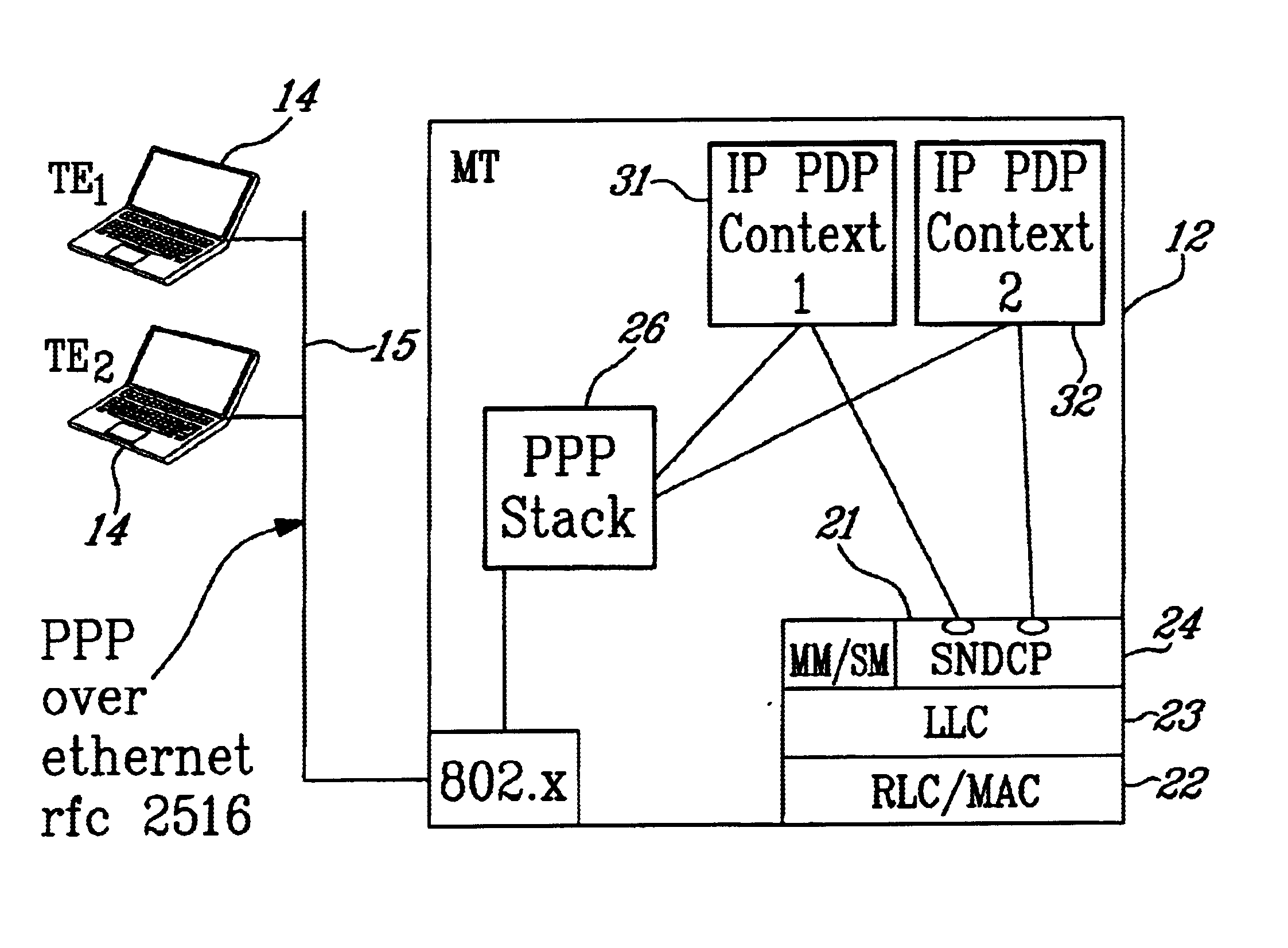
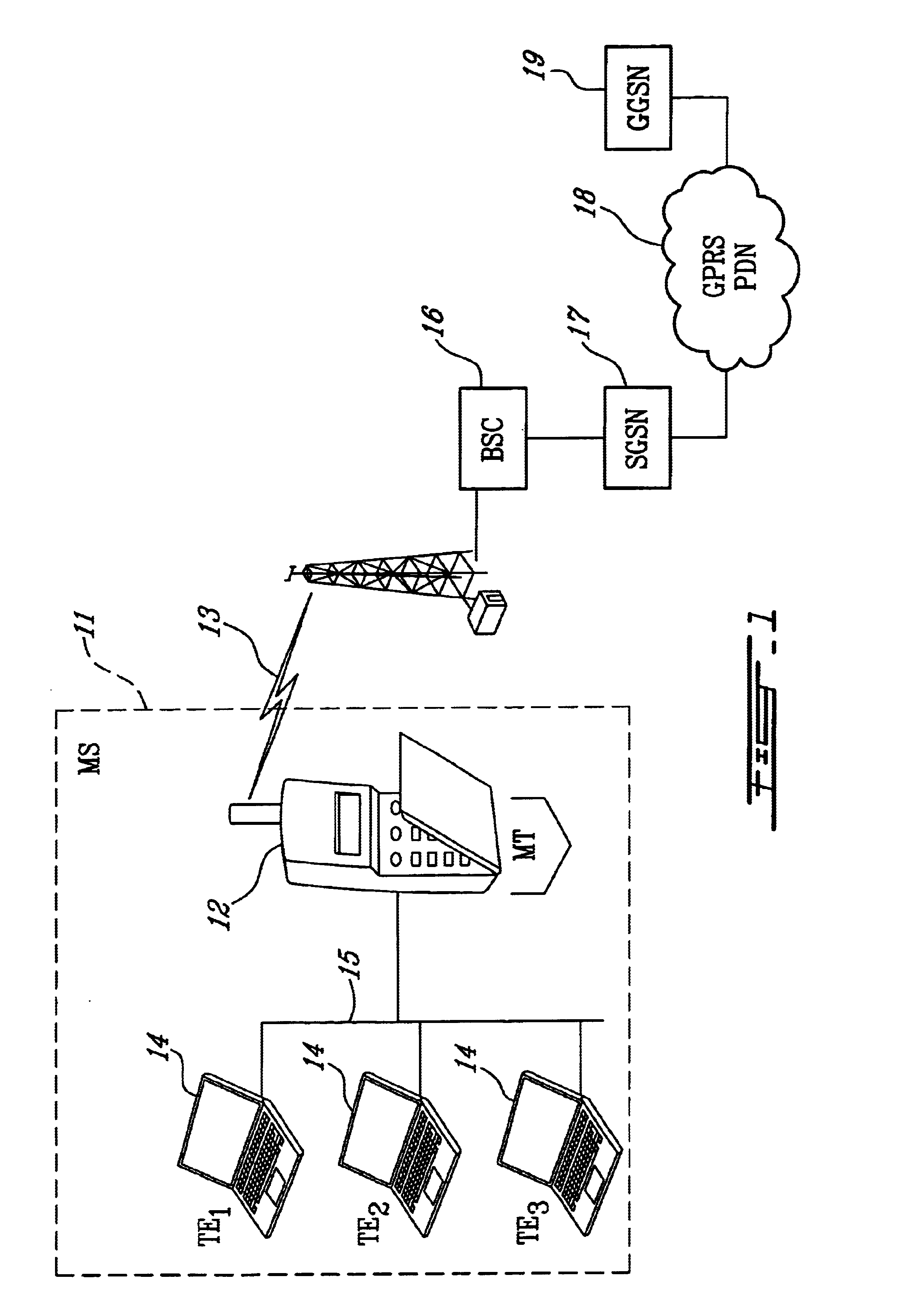
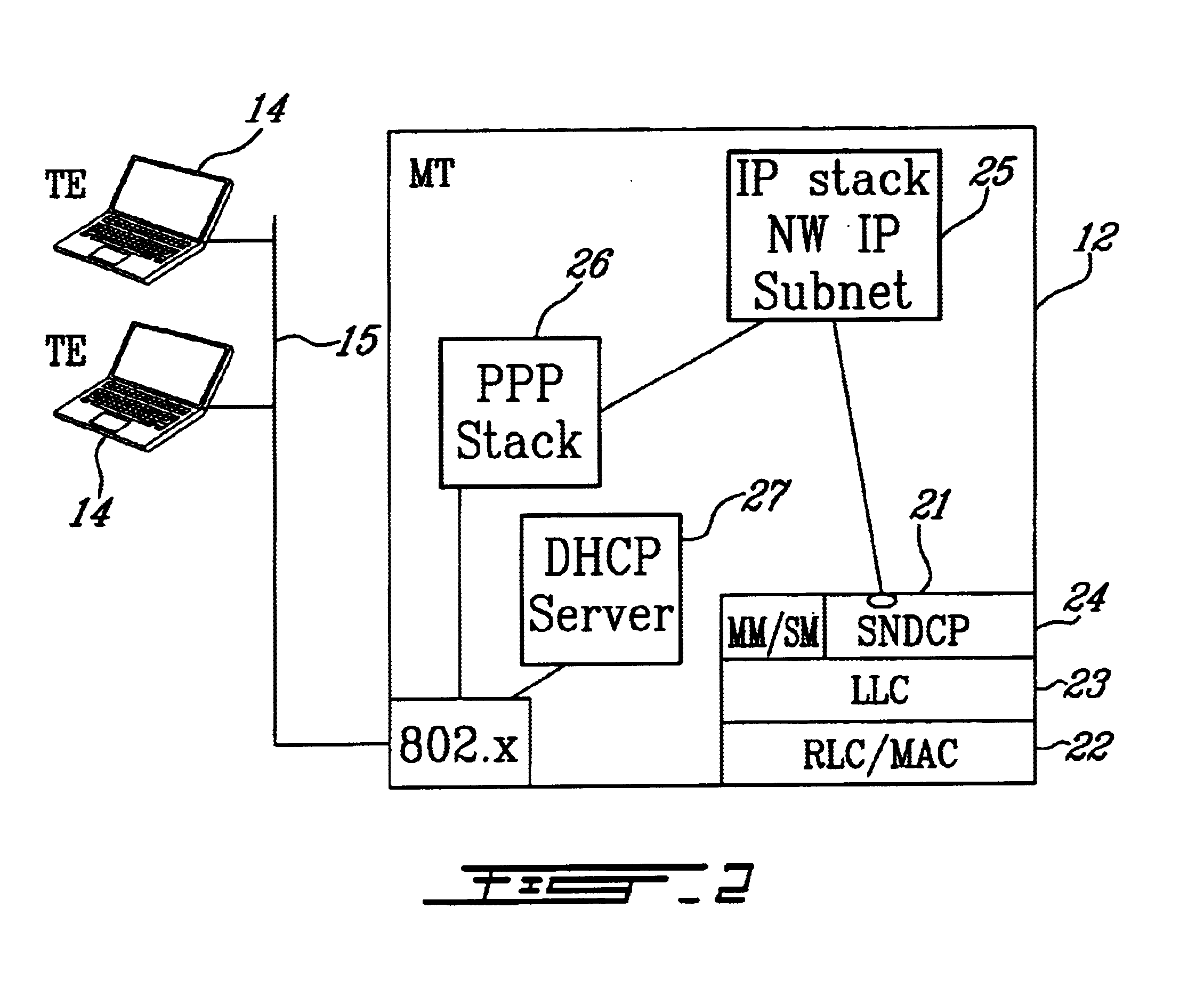
A mobile terminal (MT) and a method of connecting a plurality of devices on a computer network to a packet data network (PDN) over a single wireless link. In a first embodiment, the MT requests and receives from the PDN, a network IP address comprising a plurality of unique individual IP addresses. The number of IP addresses may be defined in a subscription agreement. The MT then utilizes a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server in the MT to distribute the plurality of unique individual IP addresses to the plurality of devices on the LAN. In a second embodiment, the MT requests a separate PDP Context for each device on the LAN requiring an IP address. The MT utilizes a Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) session between the devices on the LAN and the MT to virtually separate the physical network connection and distribute individual IP addresses to the plurality of devices on the LAN.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
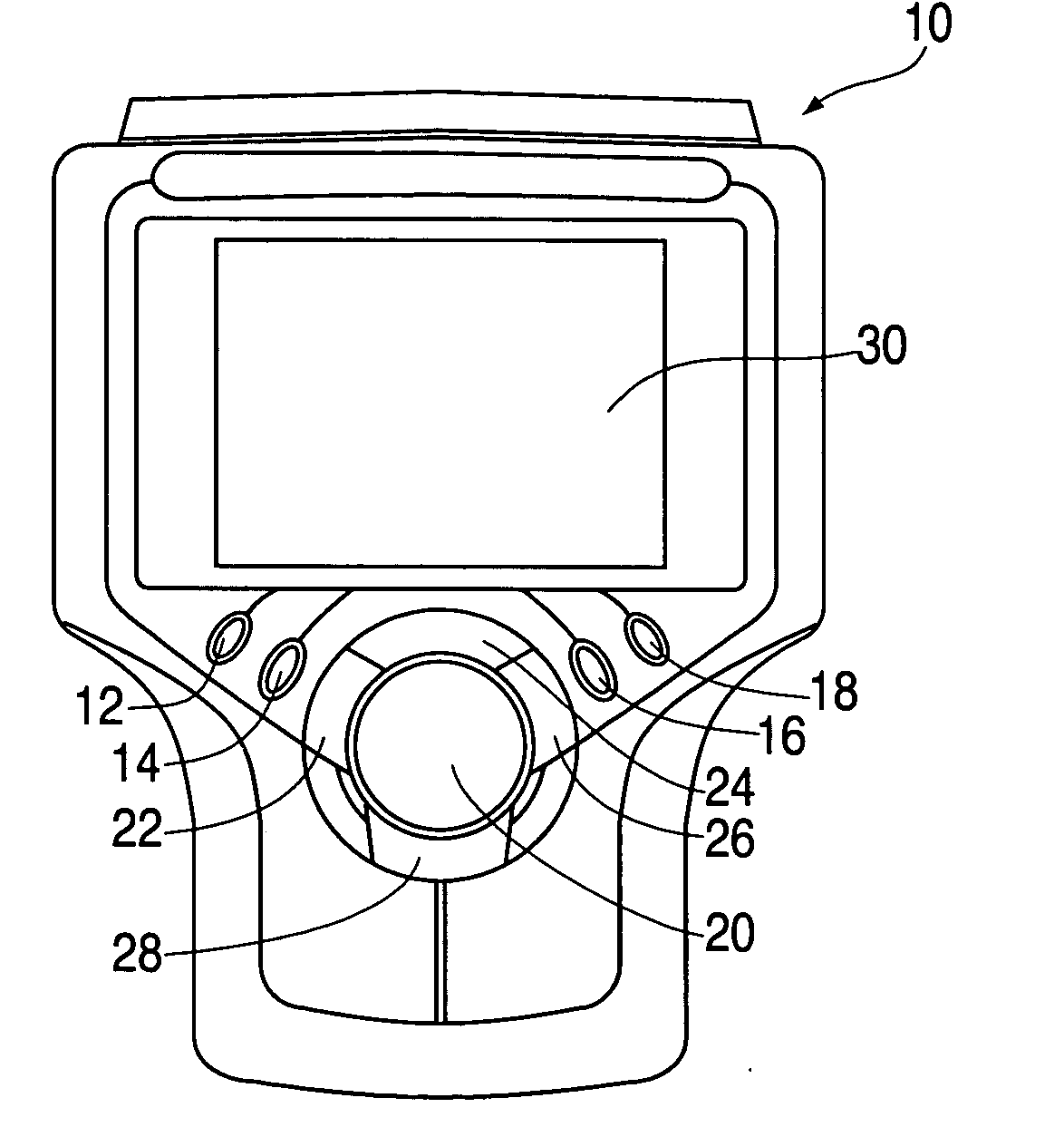
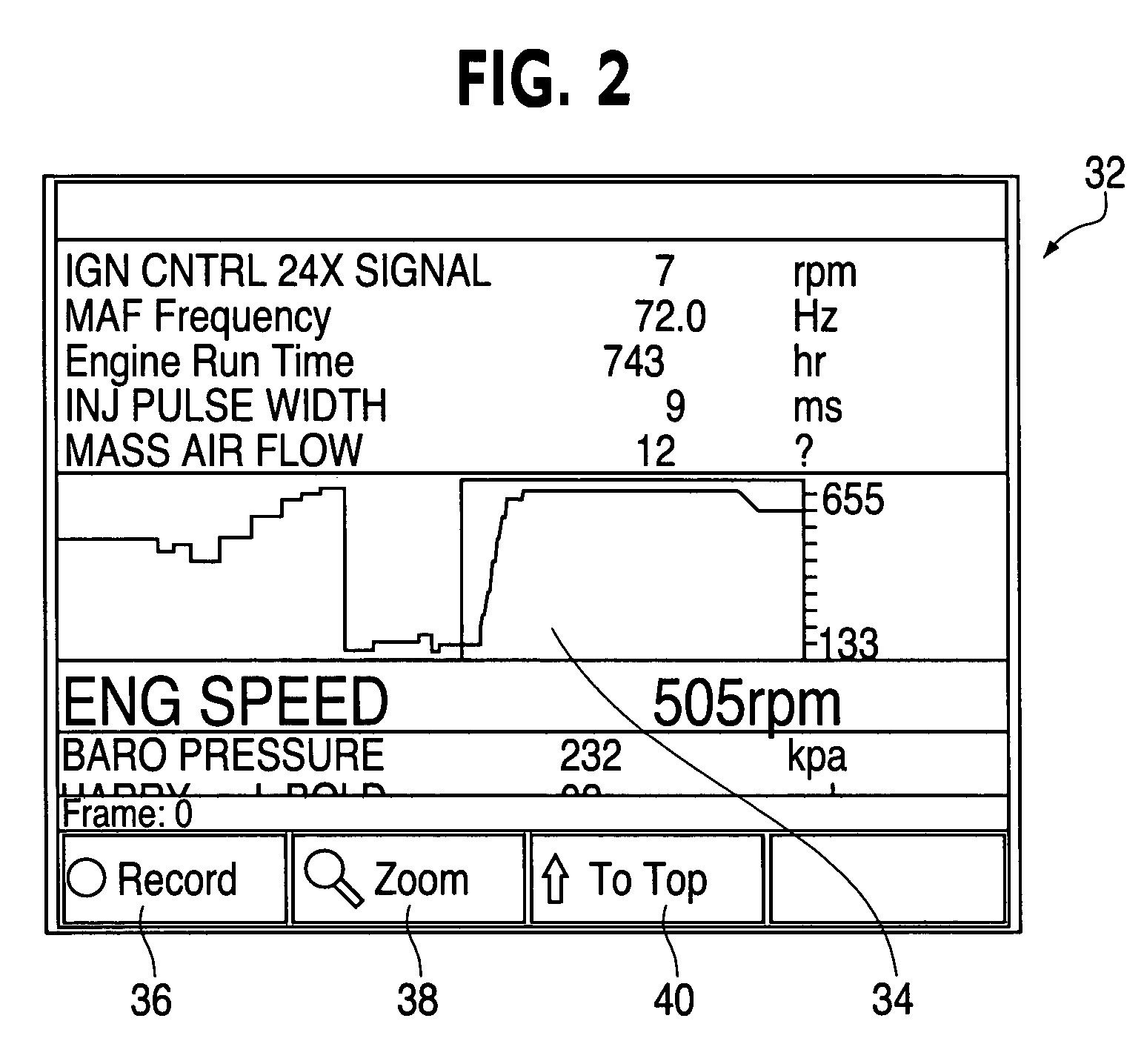
Connectivity between a scan tool and a remote device and method
InactiveUS20060101311A1Easy to upgradeEasy program upgrades/modificationsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesError detection/correctionModem deviceHand held
A hand-held diagnostic tool is designed to operate and easily upgrade software applications developed for automotive diagnostics. The diagnostic tool, which communicates with a plurality of motor vehicle control units, provides application upgrades and / or modifications and / or new algorithms that are developed / adapted via remote updating. The tool comprises full diagnostic capability capable of receiving diagnostic data from a motor vehicle for storage, analysis and / or further data transfer to a remote device. The tool may further comprise wireless capability to perform data transfer operations. Remote updating is accomplished through a number of external ports on the tool that facilitate modem, Ethernet and wireless communications, including point-to-point protocol connection to the Internet.
Owner:SPX CORP
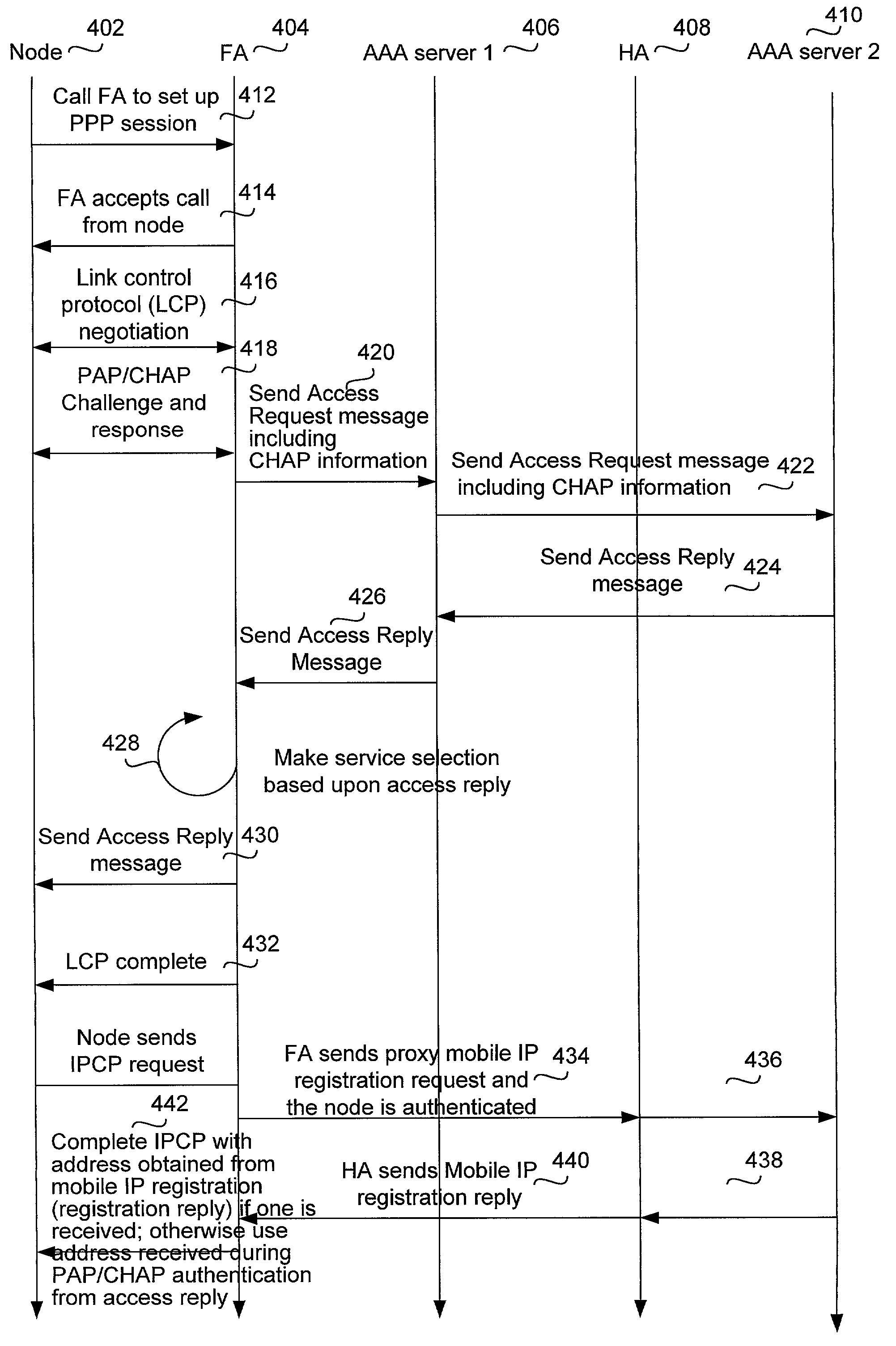
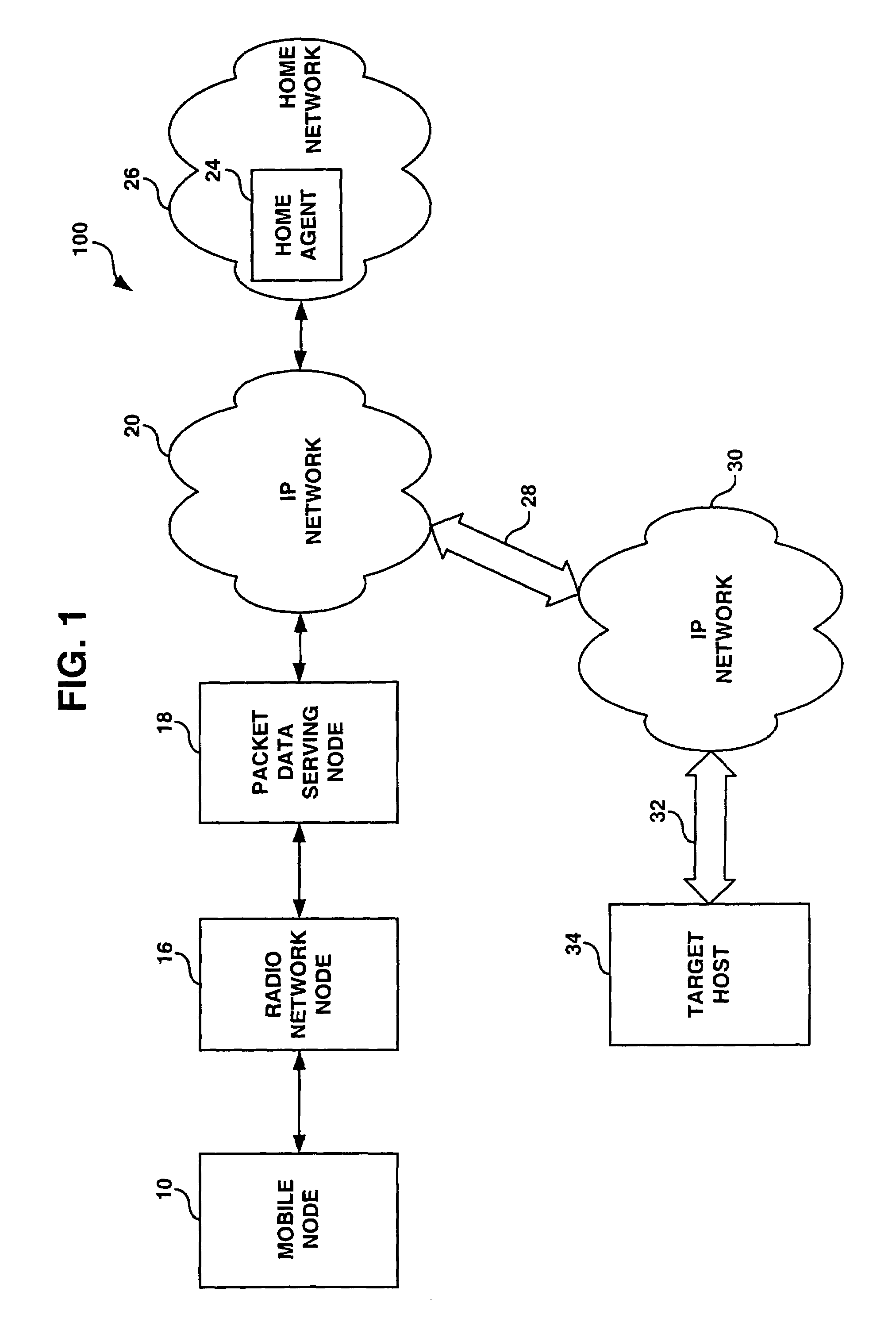
Enabling mobility for point to point protocol (PPP) users using a node that does not support mobility
InactiveUS7152238B1Digital data processing detailsWireless network protocolsComputer networkPoint-to-Point Protocol
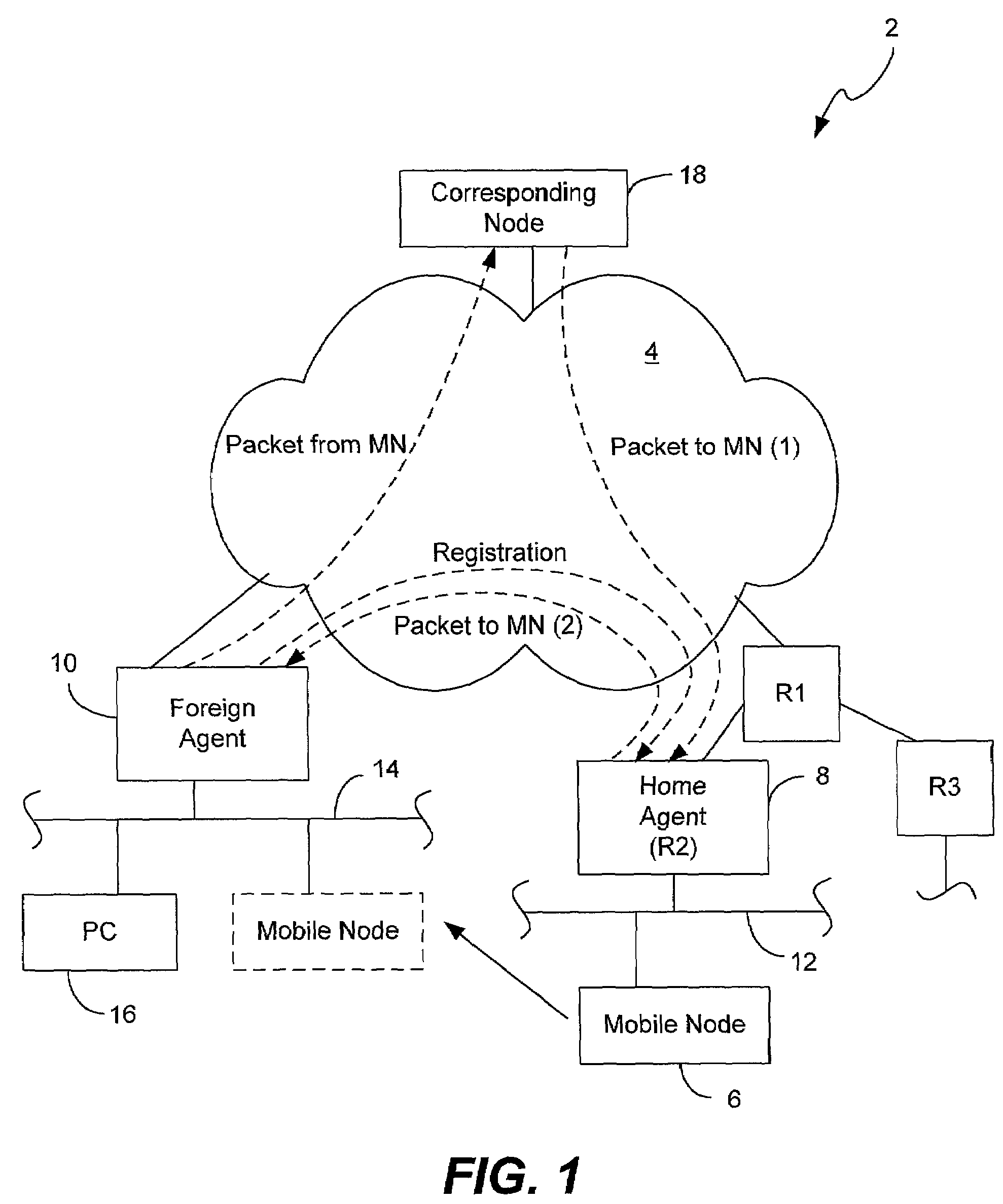
Methods and apparatus for sending a registration request packet on behalf of a node that supports PPP but does not support Mobile IP is implemented in a Foreign Agent. The method comprises accepting a call from the node and receiving authentication information associated with a PPP authentication protocol from the node, the authentication information enabling a PPP node to be authenticated. From this authentication information, a PPP node profile is obtained. The PPP node profile includes registration information associated with the node that enables proxy registration to be performed by the Foreign Agent on behalf of the node, where the registration information associated with the node identifies a Home Agent associated with the node. The registration information may also include other information that may be pertinent to the composition of a registration request packet. A registration request packet including the registration information associated with the node is then composed and sent to the Home Agent on behalf of the node. The registration request packet that is sent by the Foreign Agent also may include a registration indicator indicating whether registration being performed by the Foreign Agent on behalf of the node is a re-registration by the Foreign Agent or an initial registration by the Foreign Agent. More particularly, in accordance with one embodiment, the registration request packet includes a sequence number indicating an order within a sequence of one or more registrations performed by one or more Foreign Agents on behalf of the node. From the sequence number, a Home Agent receiving the registration request packet may determine whether the Foreign Agent is performing a re-registration or an initial registration on behalf of the node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-link PPP over heterogeneous single path access networks
InactiveUS20060062206A1Guaranteed to continue to useTime-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesAccess networkPoint-to-Point Protocol
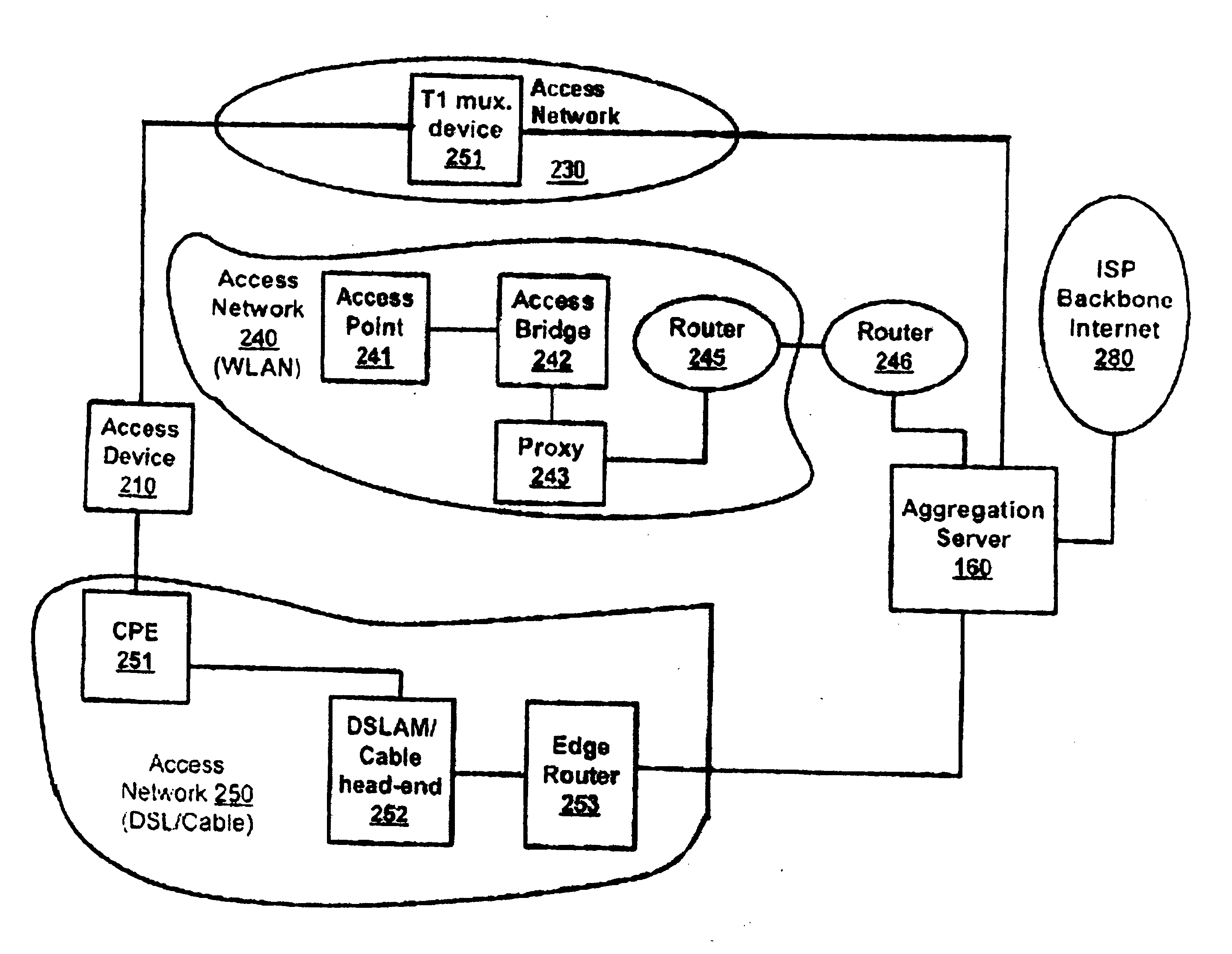
Methods and apparatuses enabling secure multi-link point to point protocol over connected heterogeneous single path access networks are described. In one embodiment, a method of an access device includes associating the access device with a single-path network and at least one other network, and accessing a data of a service provider through an aggregation server connected to the single-path network and the other network. In one embodiment, the aggregation server transfers the data to the access device at a combined throughput speed of the single-path network and the at least one other network. The method may include maintaining a connection between the access device and the aggregation server even when any one or more of the single-path network and the at least one other network disconnect.
Owner:KRISHNASWAMY VIJAYARAGHAVAN
Fault tolerant automatic protection switching for distributed routers
InactiveUS6956816B1Providing fault toleranceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolAutomatic protection switching
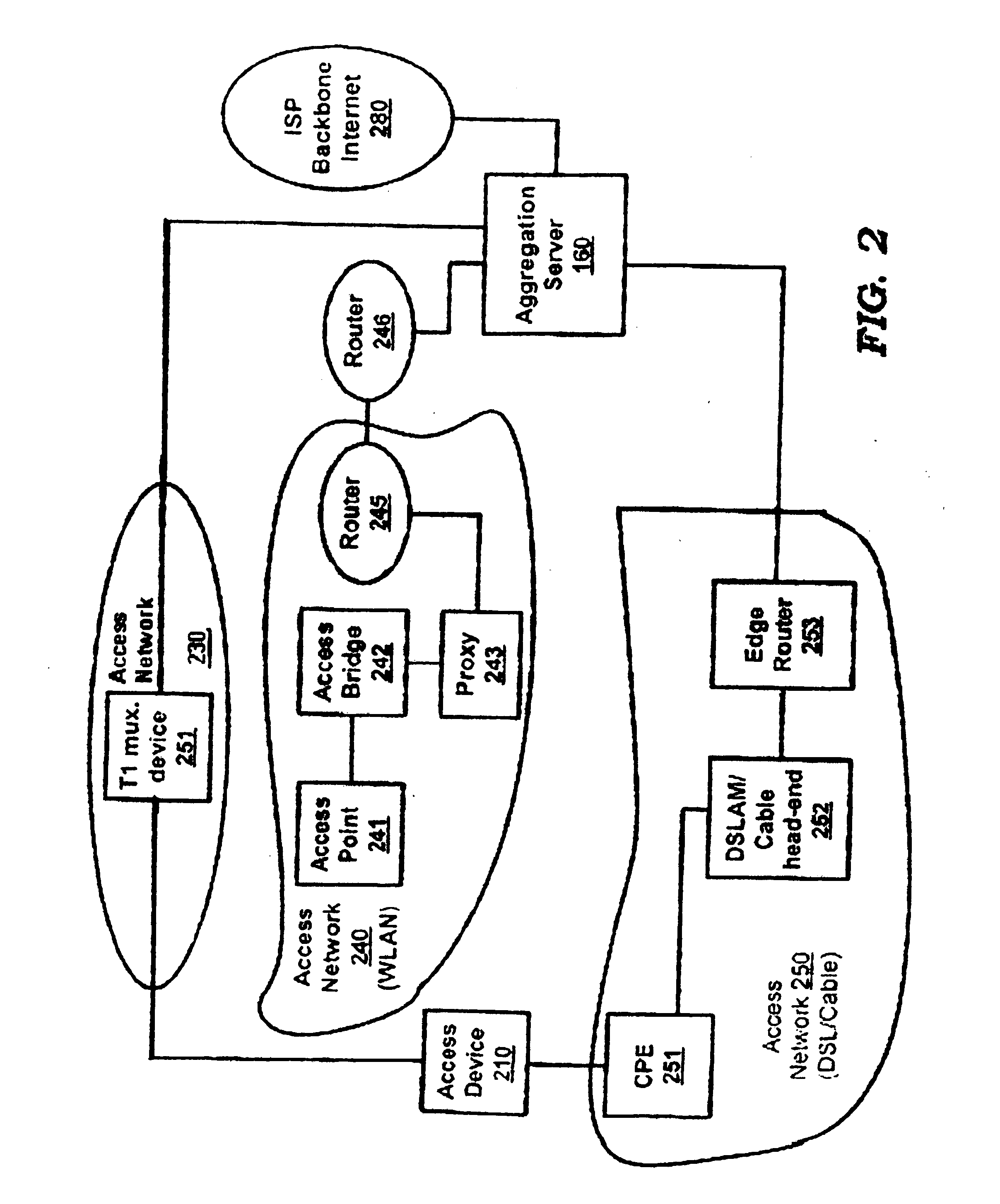
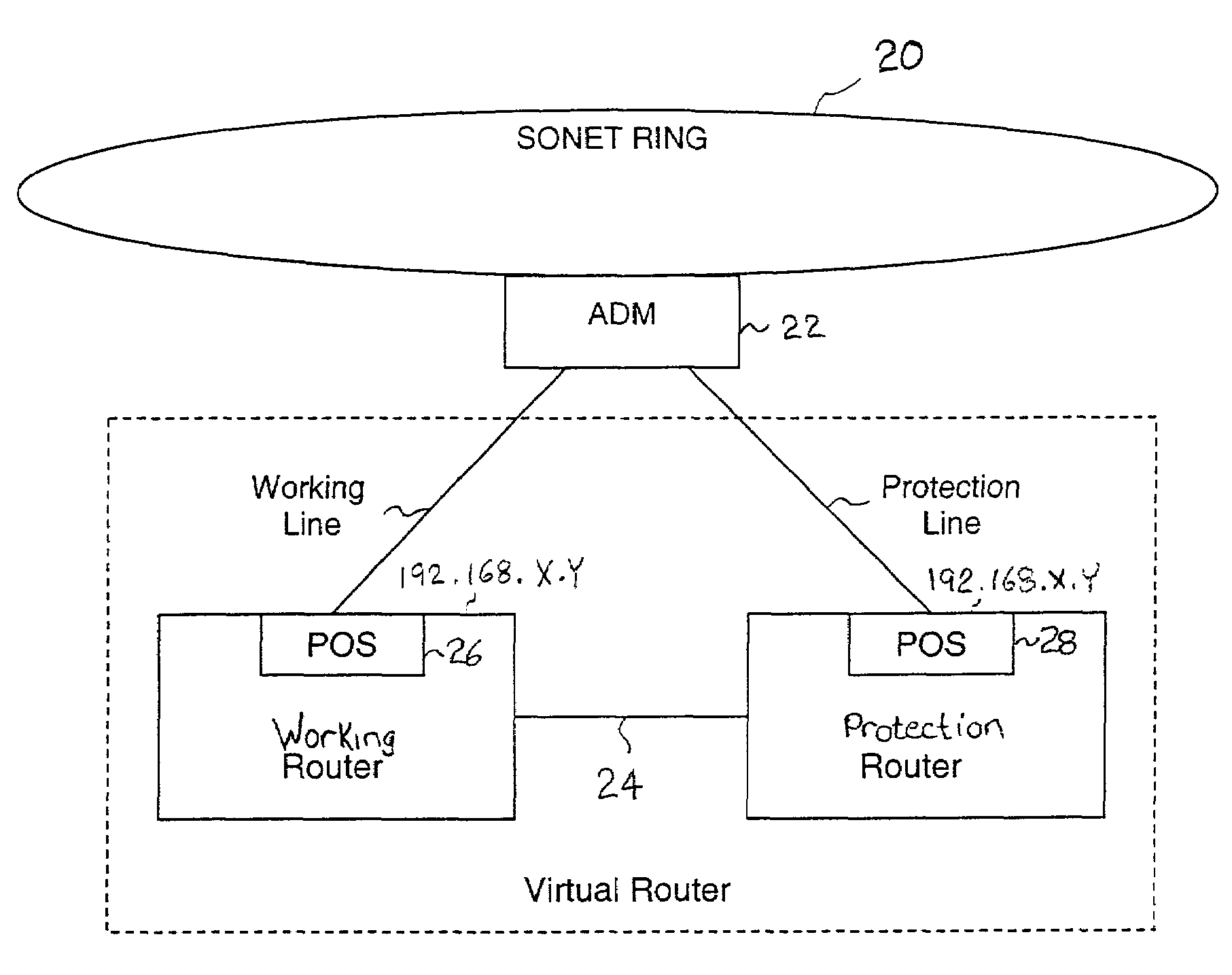
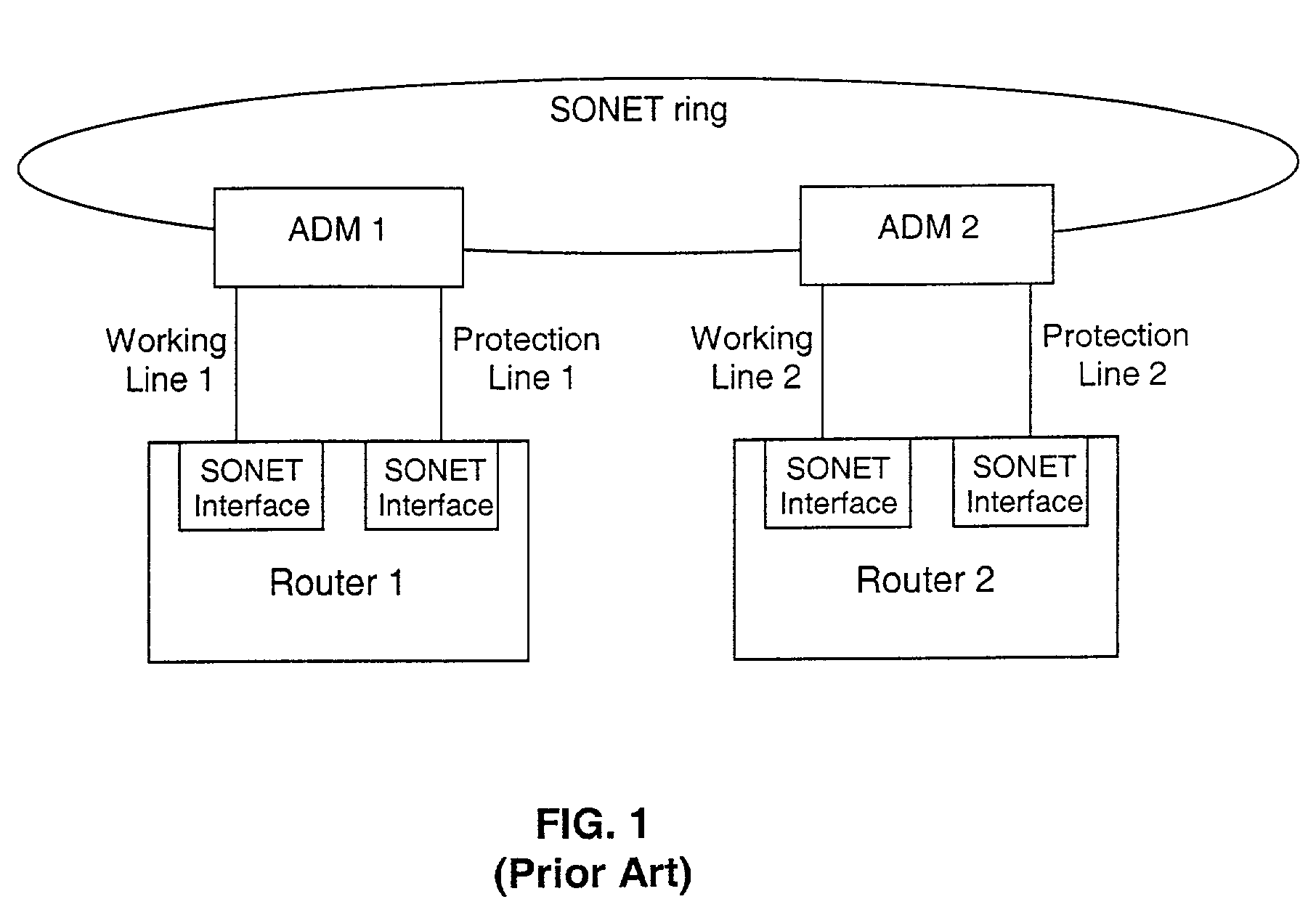
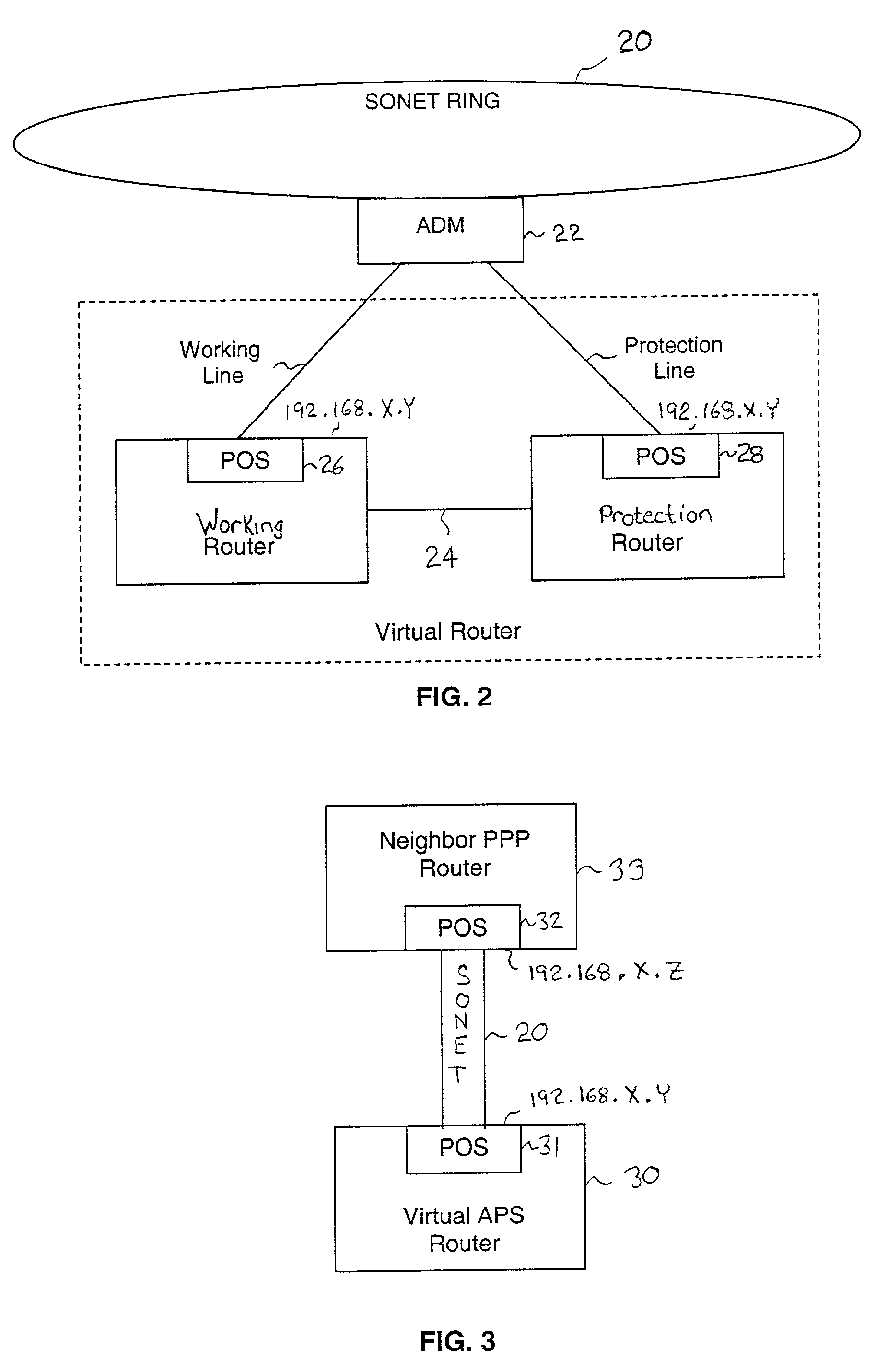
A working router is coupled to a SONET add-drop multiplexor (ADM) through a working line and a protection router is coupled to the ADM through a protection line. The routers are coupled to each other by a separate side-band connection and comprise a virtual router from the perspective of the neighboring router, which communicates with the virtual router over the SONET network using the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). The protection router transmits a heartbeat message to the working router over the side-band connection. If the protection router does not receive a response thereto, it initiates a line switch within the add-drop multiplexor. Once the line switch is complete, the protection router exchanges datagrams with the neighboring router, via the ADM and SONET ring to which the ADM is coupled. The protection router establishes a PPP connection between itself and the neighboring router device coupled to the SONET ring, utilizing the Link Control Protocol (LCP). The protection router includes a predetermined identifier value that identifies the originator of the request, in the LCP Identifier field of LCP request datagrams. The neighboring router includes the Identifier value received in a request datagram in the corresponding response datagram transmitted over the SONET ring to the ADM. Because datagrams received by the ADM from the SONET link are transmitted over both the working and the protect lines, the working router receives the same response as the protection router. Thus, by examining the identifier field, and recognizing the identifier value as that assigned to the protection router, the working router determines that the line switch to the protection router has occurred.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
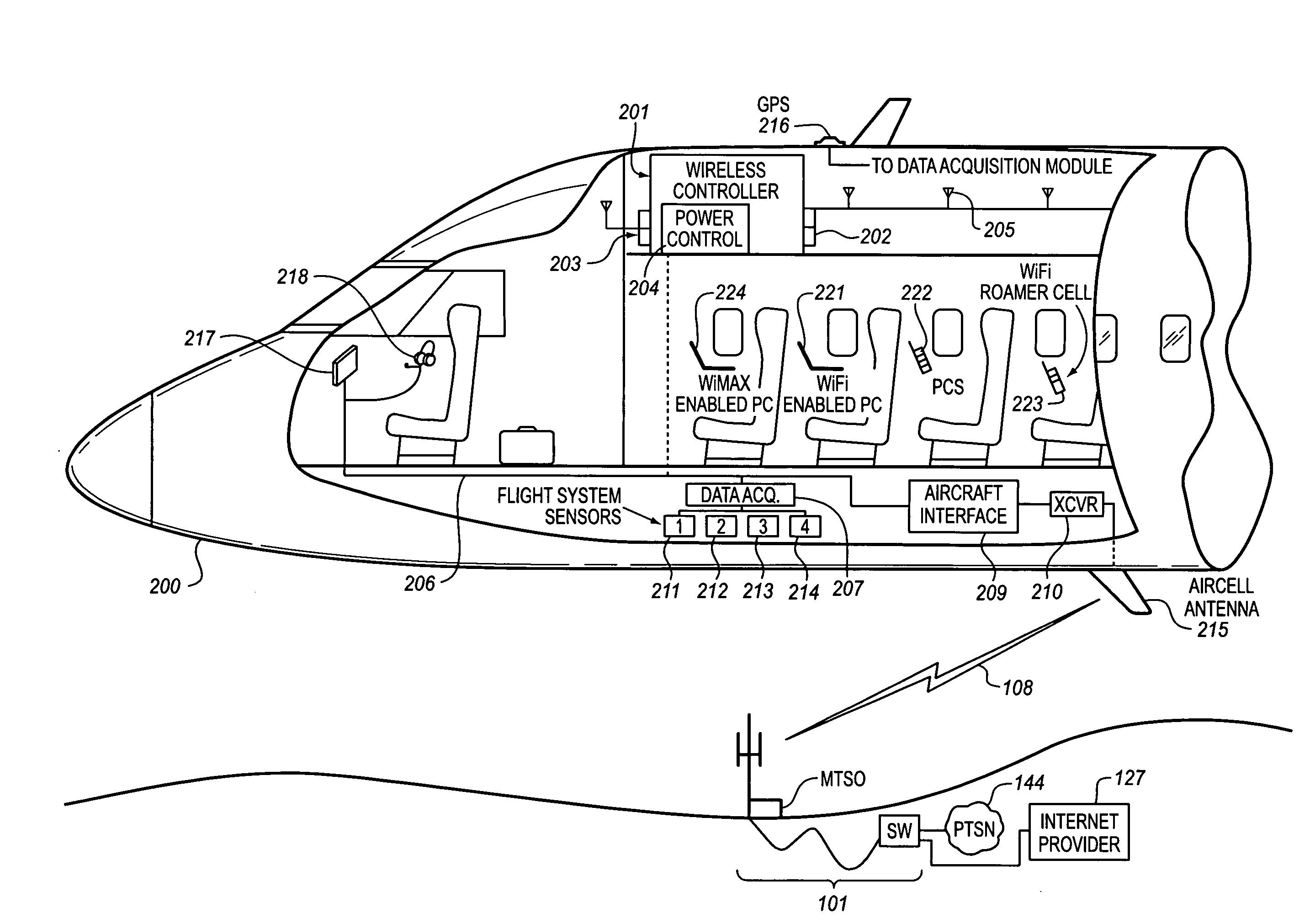
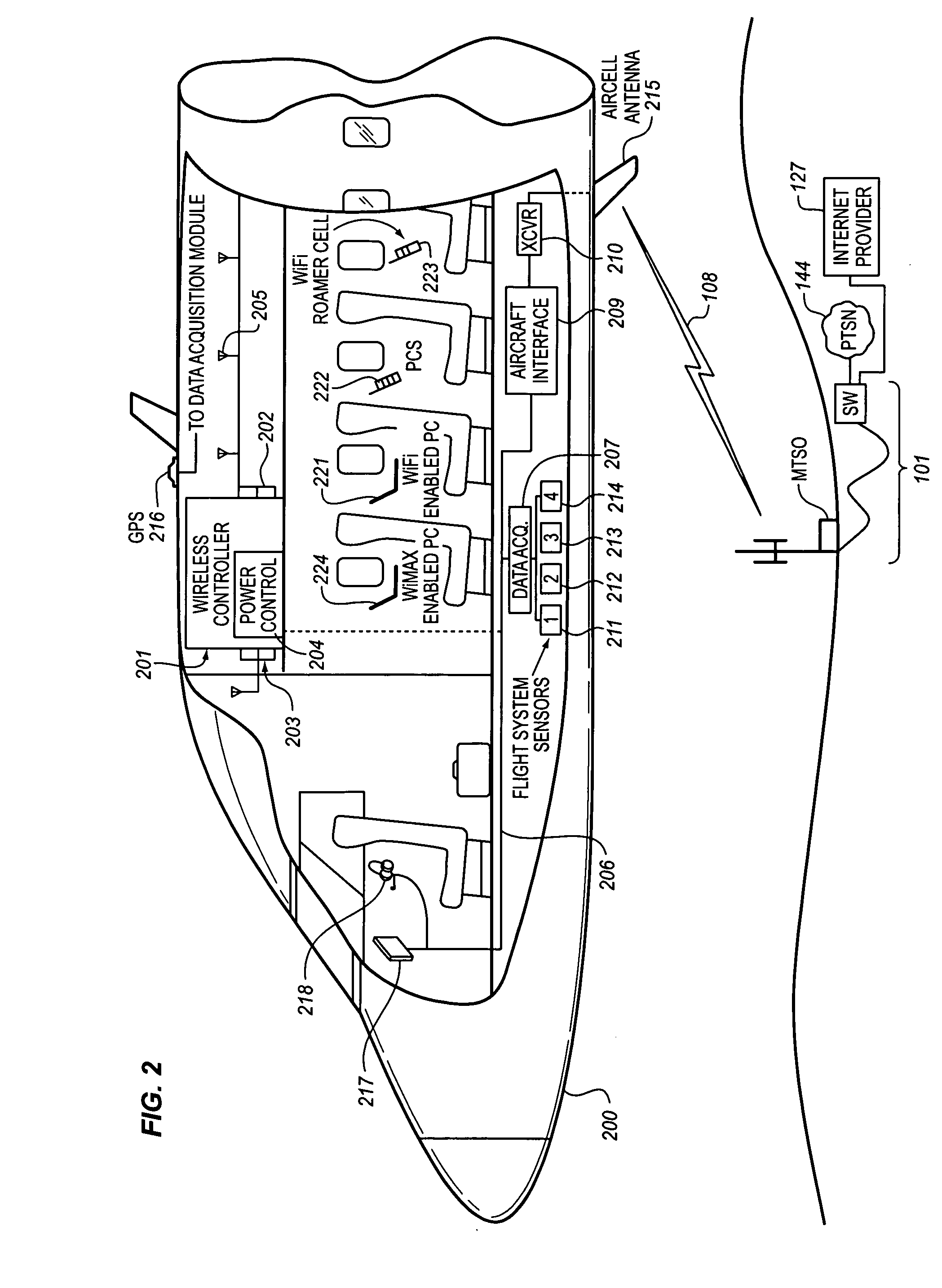
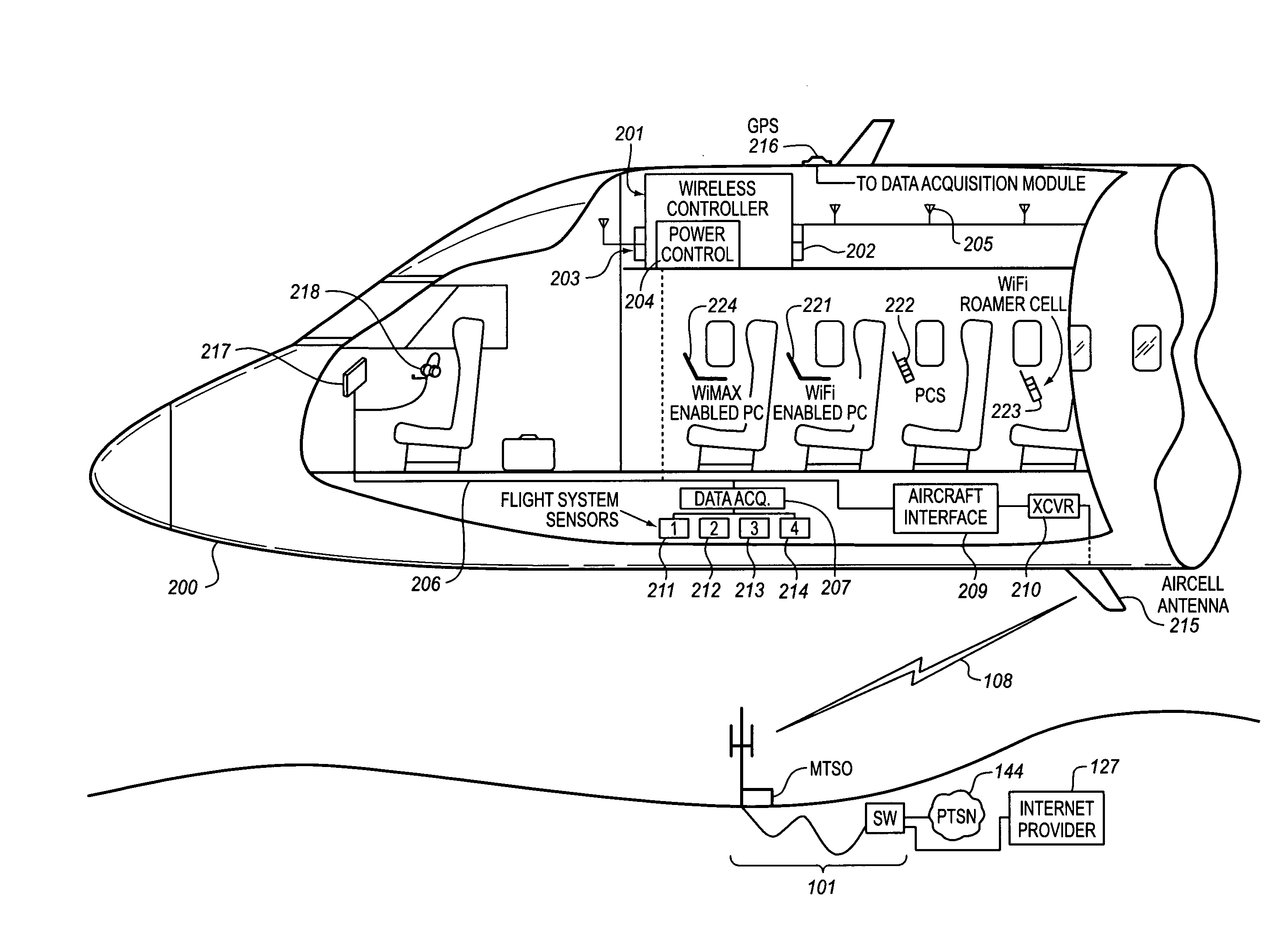
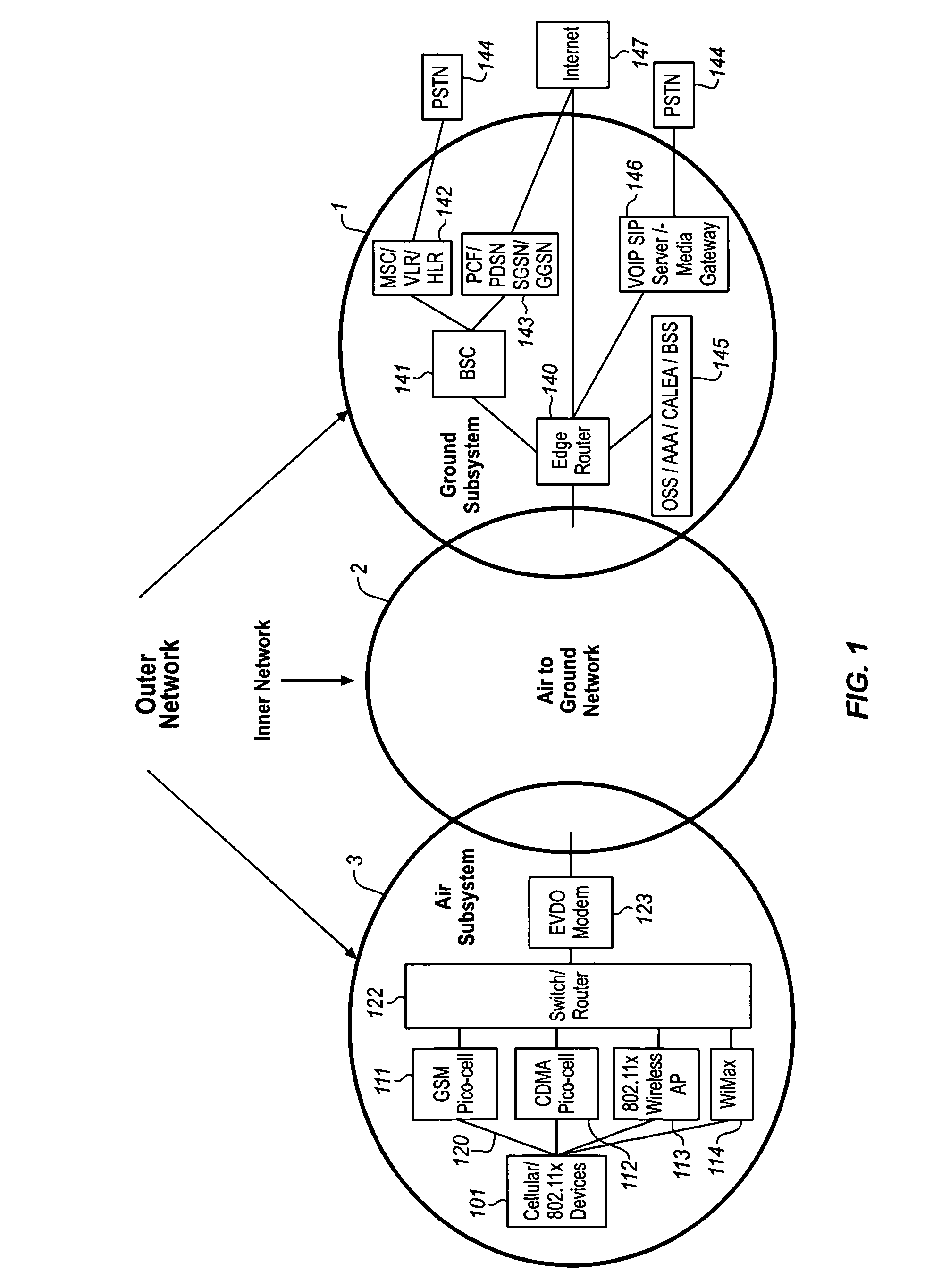
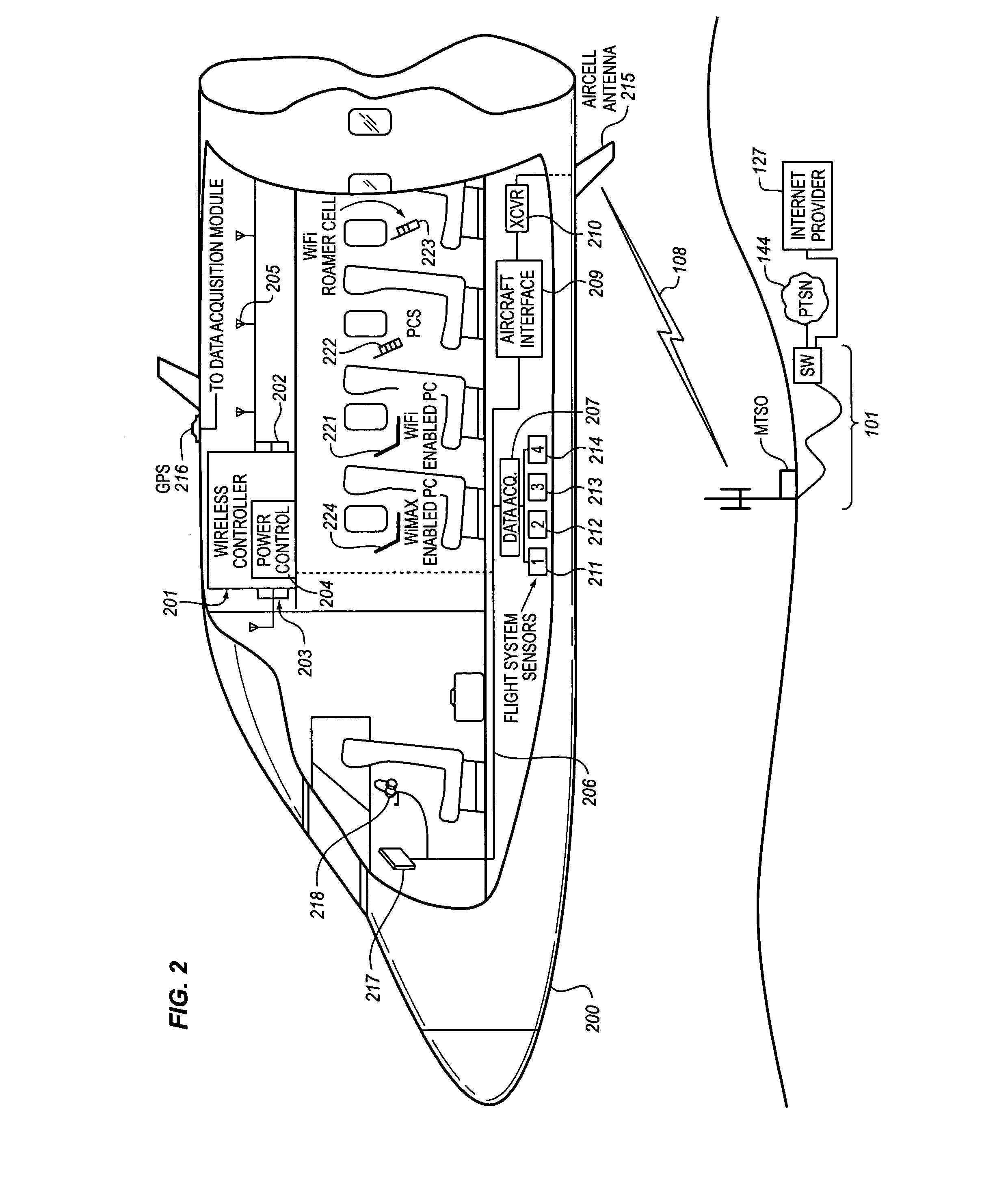
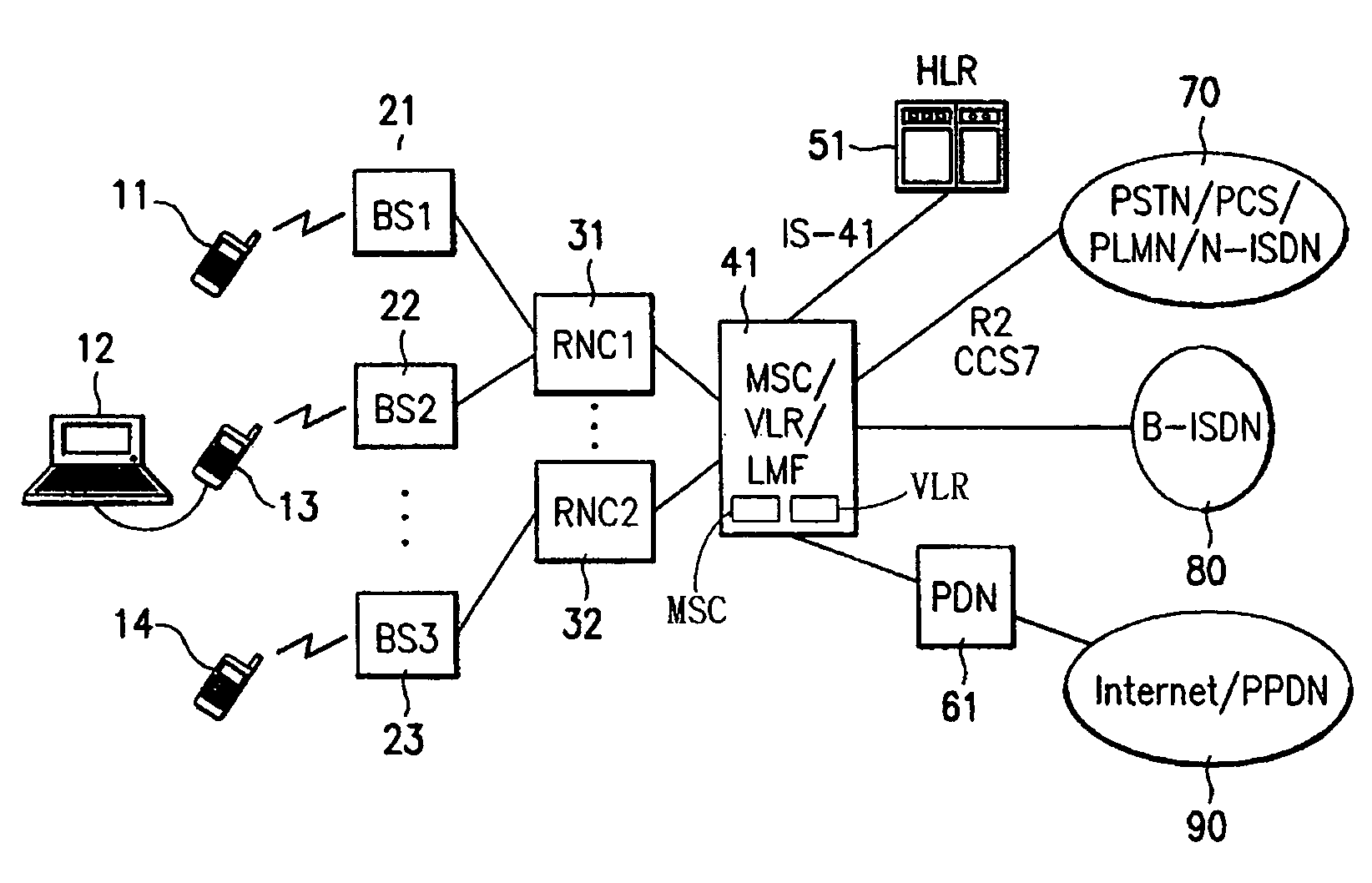
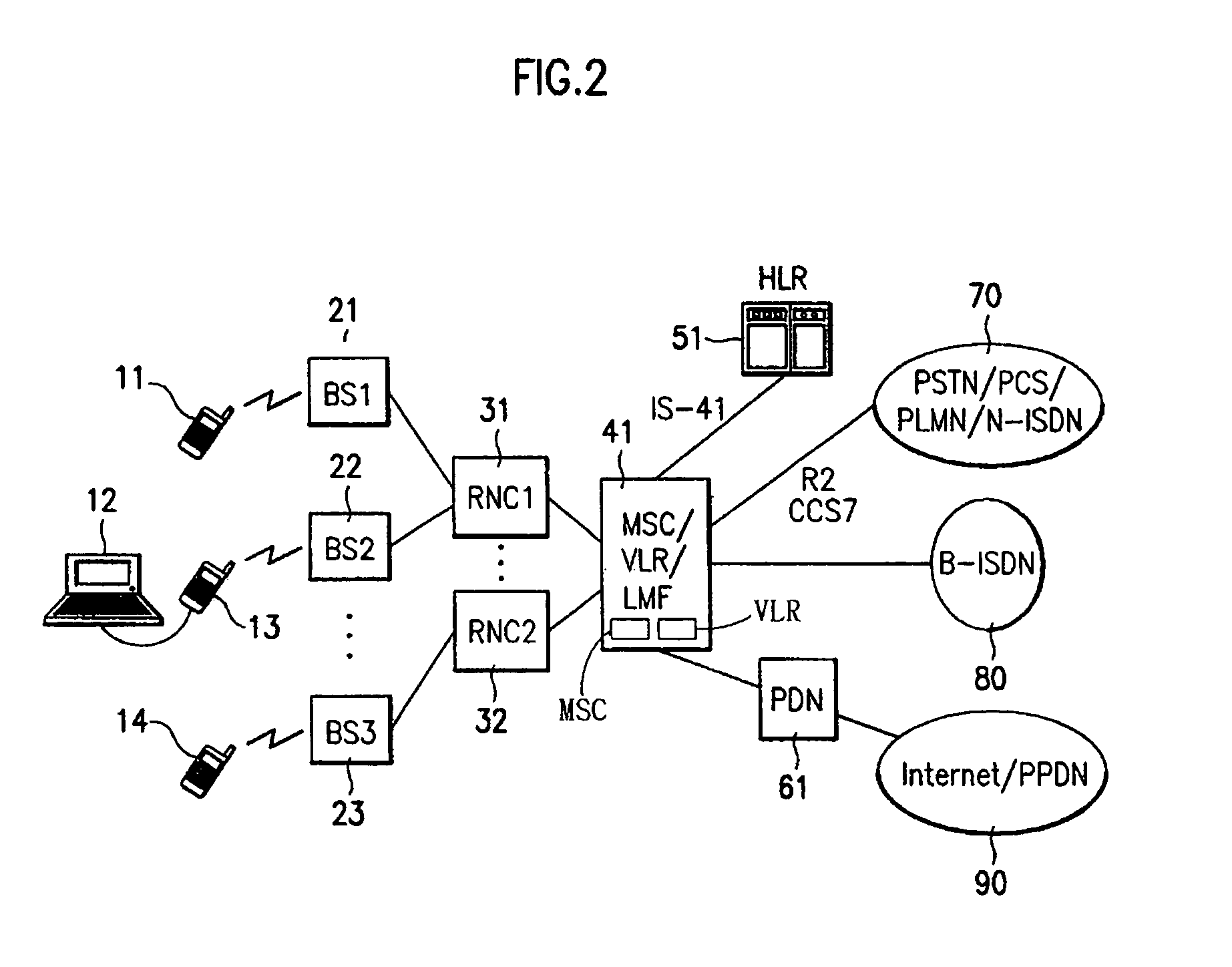
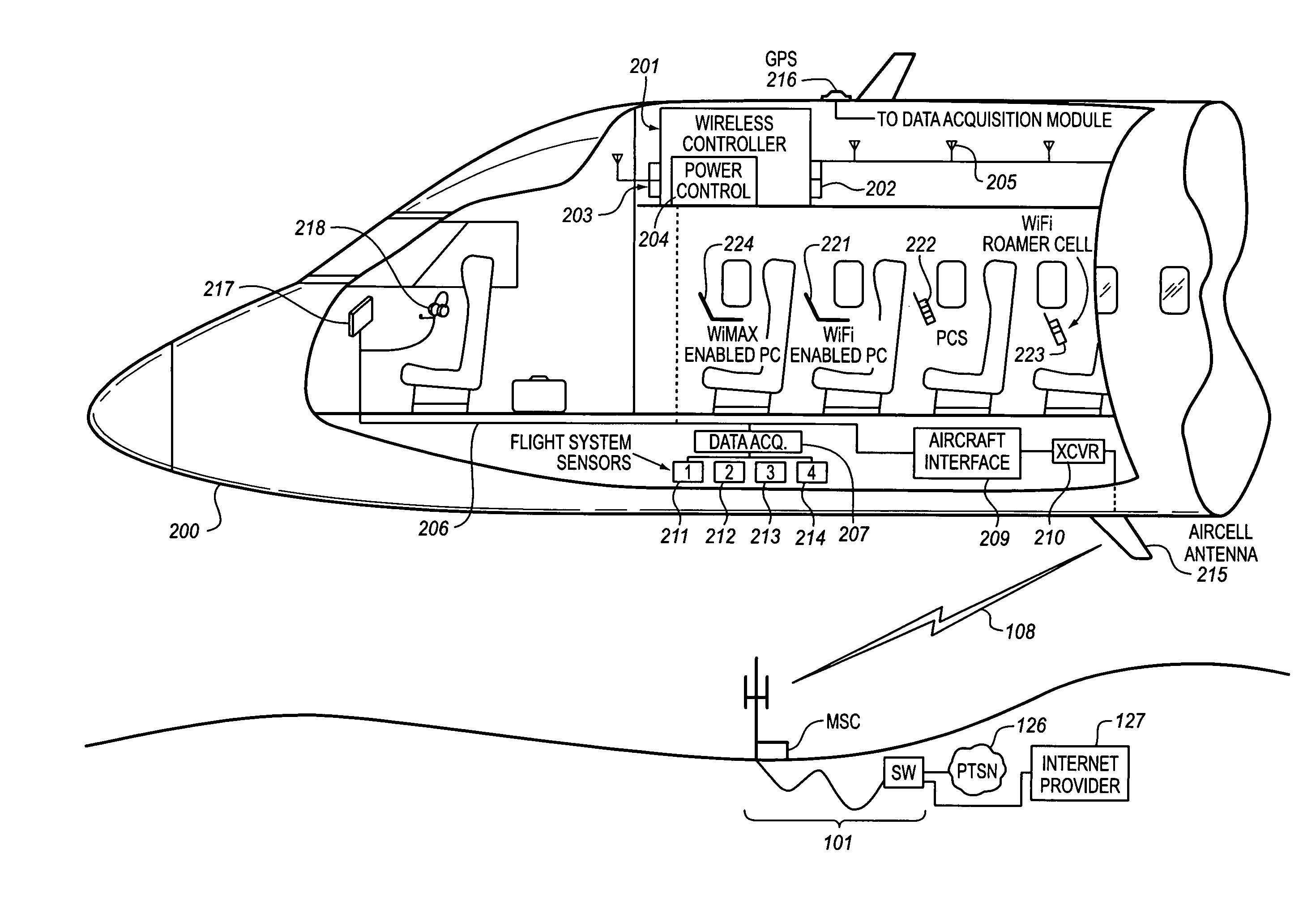
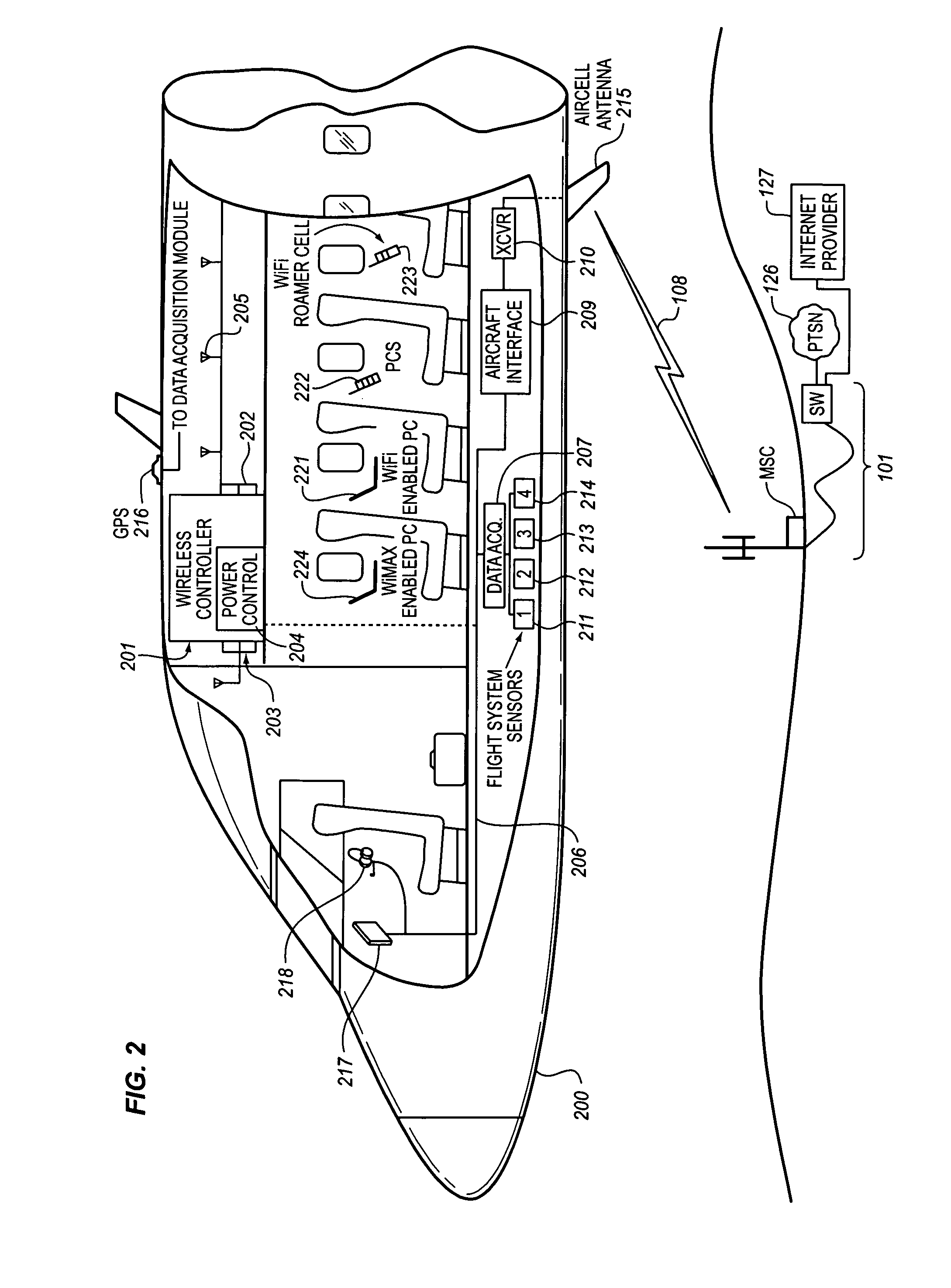
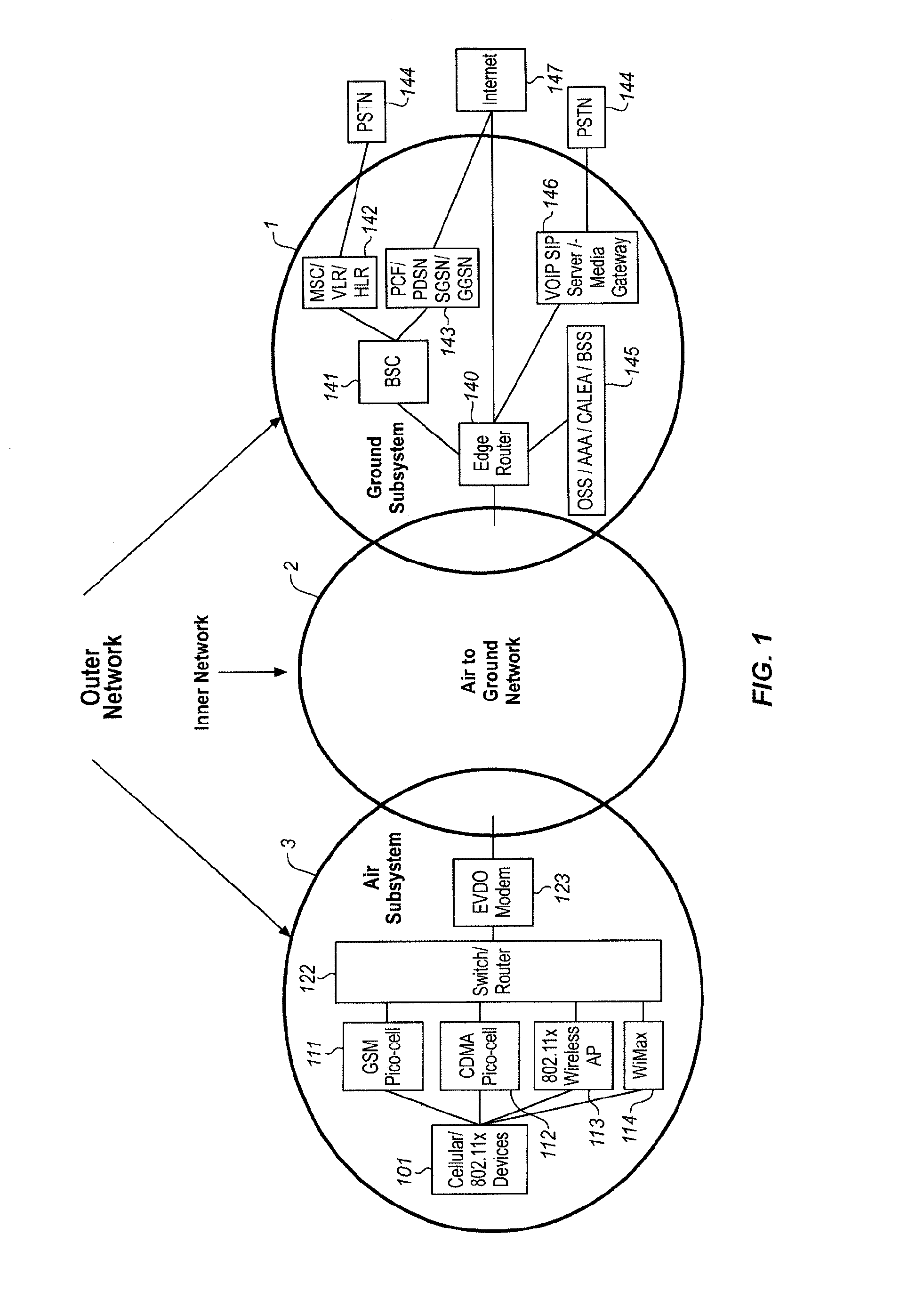
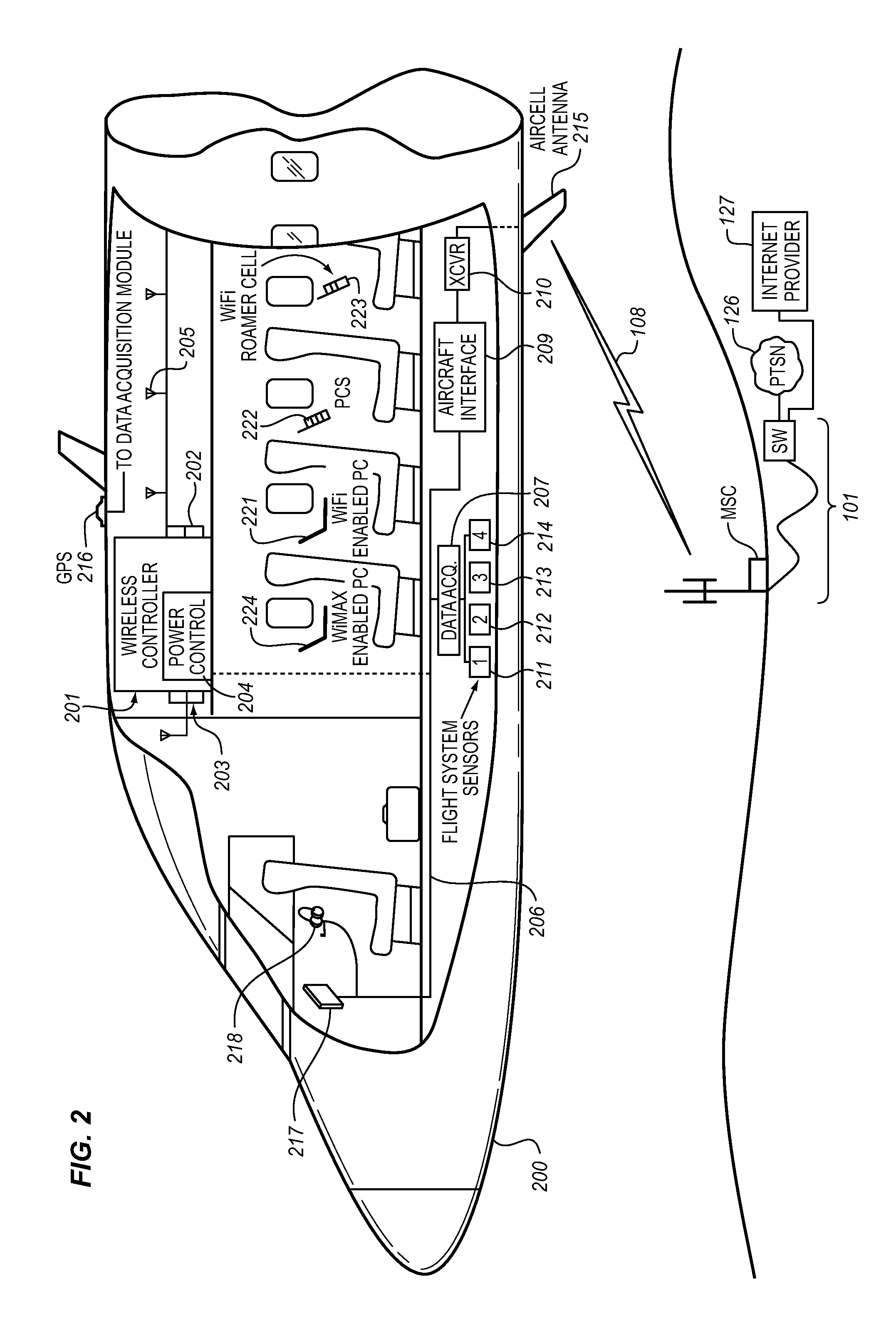
System for managing mobile internet protocol addresses in an airborne wireless cellular network
InactiveUS20080182573A1Improve travel experienceSimplifies provision of serviceNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPoint-to-Point ProtocolTTEthernet
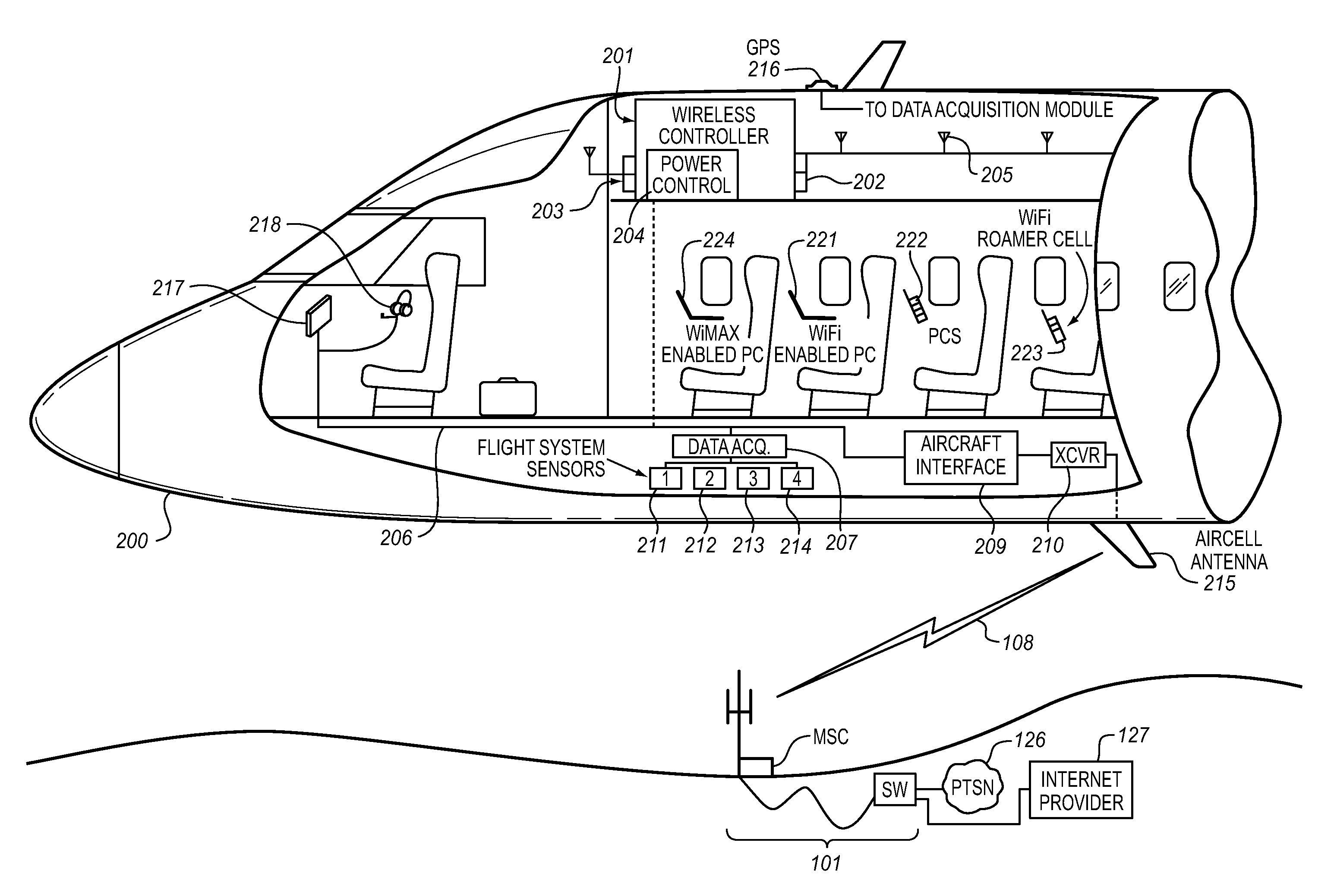
The Aircraft Mobile IP Address System provides wireless communication services to passengers who are located onboard an aircraft by storing data indicative of the individually identified wireless devices located onboard the aircraft. The System assigns a single IP address to each Point-to-Point Protocol link which connects the aircraft network to the ground-based communication network but also creates an IP subnet onboard the aircraft. The IP subnet utilizes a plurality of IP addresses for each Point-to-Point link thereby to enable each passenger wireless device to be uniquely identified with their own IP address. This is enabled since both Point-to-Point Protocol IPCP endpoints have pre-defined IP address pools and / or topology configured; each Point-to-Point Protocol endpoint can utilize a greater number of IP addresses than one per link. Such an approach does not change IPCP or other EVDO protocols / messaging but does allow this address to be directly visible to the ground-based communication network.
Owner:GOGO LLC
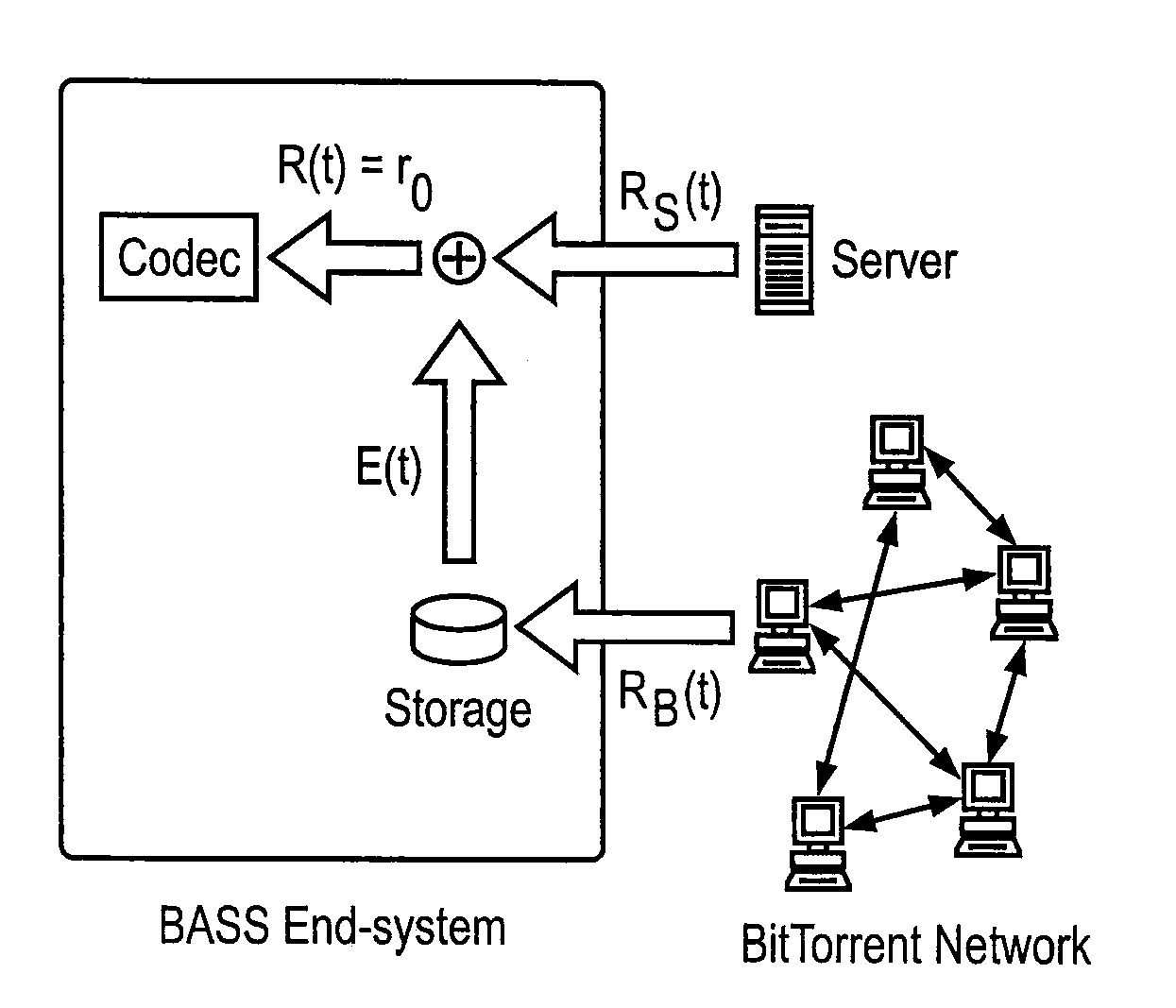
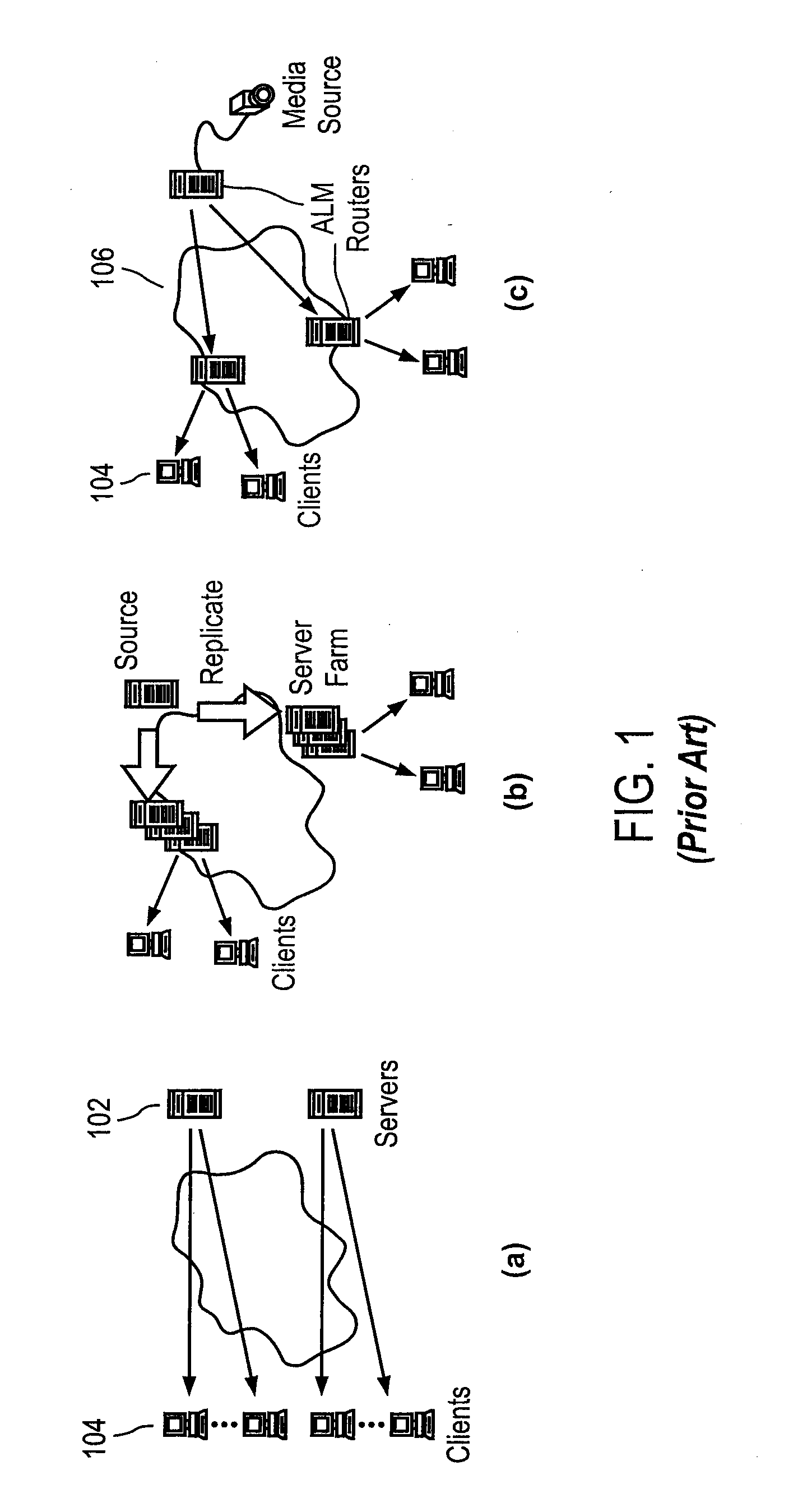
Peer-to-Peer Streaming Of Non-Live Content
ActiveUS20080140853A1Minimal impactEasy to scaleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPoint-to-Point ProtocolEnd system
A Peer-to-Peer protocol such as BitTorrent is used to assist streaming. Peers download streaming content from the P2P network while simultaneously playing the downloaded content. As the stream plays, an end system downloads any missing pieces directly from a server or other infrastructure node. This method roughly squares server capacity and can be refined to require on average 0(1) servers regardless of the number of concurrent users. Thus BitTorrent assisted streaming scales better than traditional server-client and other infrastructure-only solutions, each of which requires a number of infrastructure nodes that scale linearly as a function of the number of users. Unlike End-System-Multicast, BitTorrent assisted streaming does not subject users to the vagaries of intermediate unreliable, potentially bandwidth-constrained end-systems; the departure of any single end-system has minimal impact on overall performance; and BitTorrent has a well-crafted incentive mechanism for encouraging users to contribute their upstream capacity.
Owner:BITTORRENT
Remote updating method and apparatus
InactiveUS6874680B1Easy to upgradeEasy program upgrades/modificationsDigital data processing detailsSensing record carriersModem devicePoint-to-Point Protocol
A hand-held diagnostic tool designed to operate and easily upgrade software applications developed for automotive diagnostics, is disclosed. The diagnostic tool, which communicates with a plurality of motor vehicle control units, provides application upgrades and / or modifications and / or new algorithms that are developed / adapted via remote updating. Remote updating is accomplished through a number of external ports on the tool that facilitate modem, Ethernet and wireless communications, including point-to-point protocol connection to the Internet.
Owner:SPX CORP
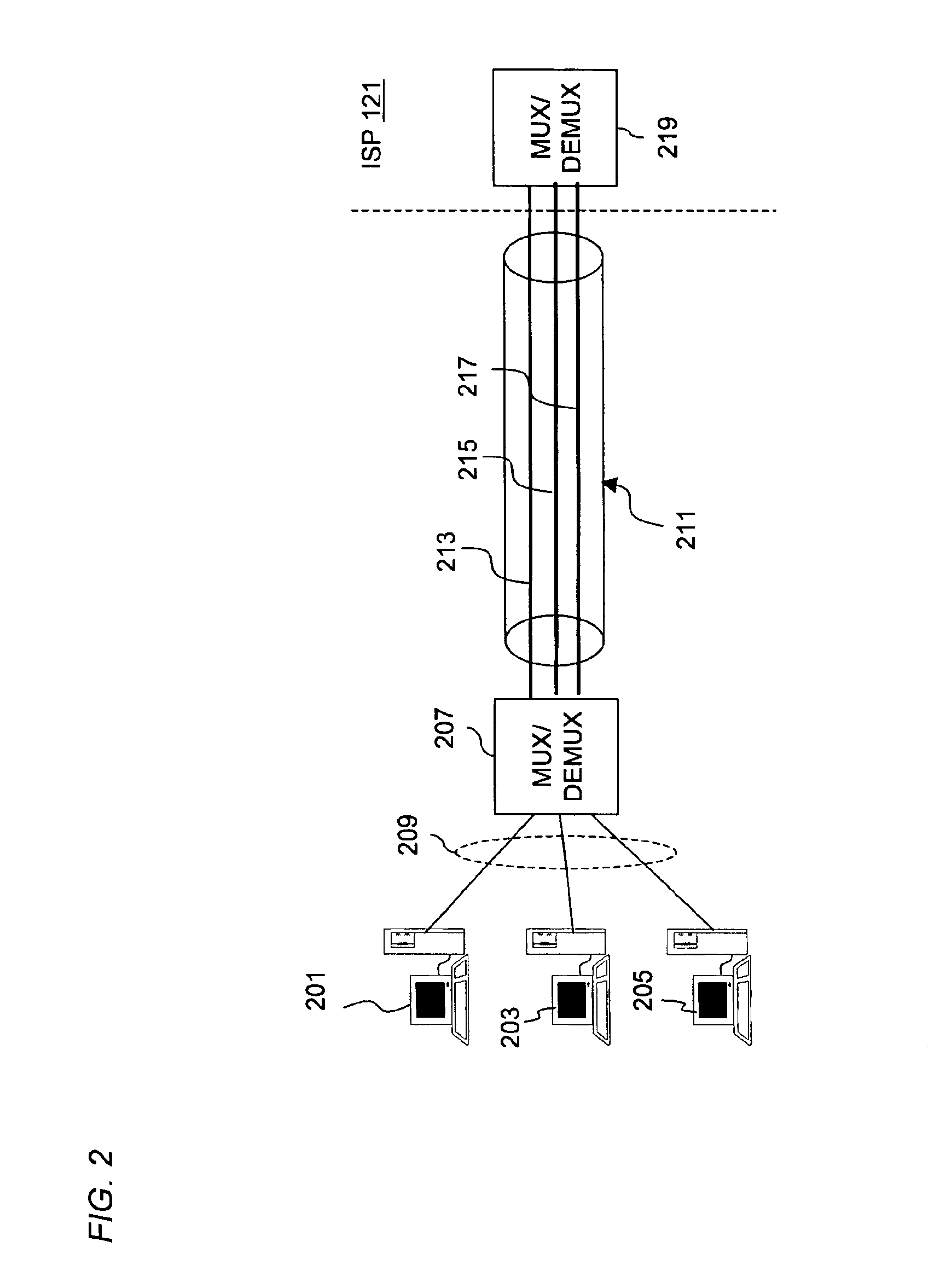
Method and system of providing multi-user access to a packet switched network
InactiveUS6891825B1Low costSimple configurationTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexCommunications softwareNetwork Communication Protocols
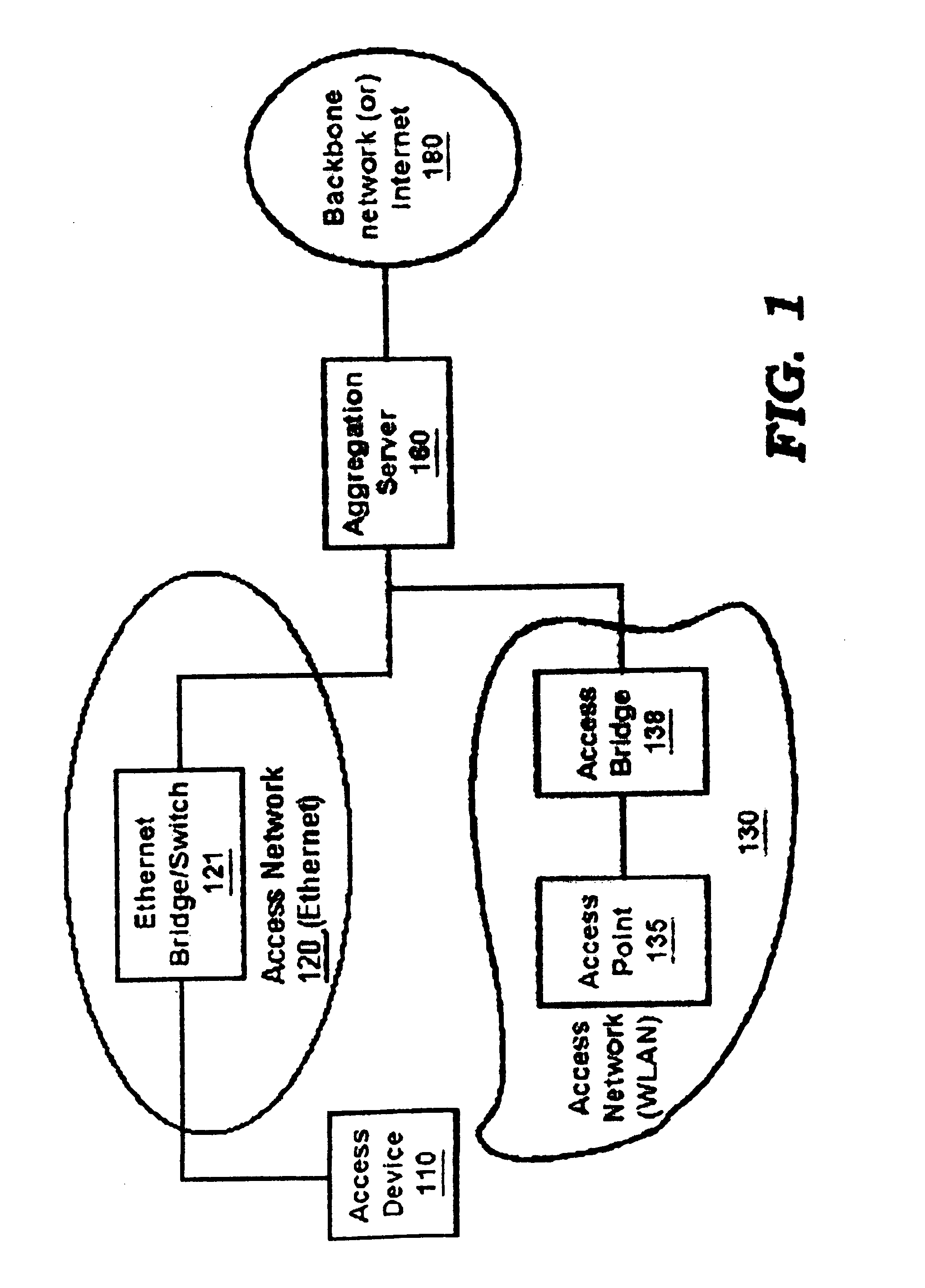
An approach for providing multi-user access to a packet switched network via a shared Ethernet-based local area network (LAN) is disclosed. Multiple end user stations are connected to the LAN, in which each of end user stations executes a communication software. The communication software is based upon a communication protocol (e.g., Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)) that establishes a point-to-point communication session. The end user stations generate packets based upon the communication protocol. In addition, each of the end user stations selectively encapsulates the communication protocol packets using the Ethernet-based LAN protocol. Further, attached to the LAN is a customer premise equipment (CPE), which transmits the encapsulated packets to a line terminating equipment, which according to one embodiment is a digital subscriber line (DSL) access multiplexer that is located in a central office. The line terminating equipment transports the multiple PPP sessions to a multiplexer / demultiplexer, which is located within a regional carrier's network. In one embodiment, the multiplexer / demultiplexer is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switch, which simultaneously transports the multiple PPP sessions over a single permanent virtual circuit (PVC); VPI / VCIs (Virtual Path Identifier / Virtual Connection Identifier) are mapped to the multiple PPP sessions. The multiple PPP sessions are terminated at a remote access server, which recovers and forwards the packets to a backbone router. Thereafter, the backbone router forwards the packets to the packet switched network.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
System for creating an air-to-ground IP tunnel in an airborne wireless cellular network to differentiate individual passengers
InactiveUS20090010200A1Improve travel experienceSimplifies provision of serviceNetwork topologiesConnection managementPoint-to-Point ProtocolIp address
The Aircraft Air-To-Ground IP Tunnel System provides wireless communication services to passengers located onboard an aircraft by storing data indicative of the individually identified passenger wireless devices located onboard the aircraft. The Aircraft Air-To-Ground IP Tunnel System assigns a single IP address to each Point-to-Point Protocol link connecting the aircraft network to the ground-based communication network and creates an IP subnet onboard the aircraft. The IP subnet utilizes a plurality of IP addresses for each Point-to-Point link, enabling each passenger wireless device to be uniquely identified with their own IP address. This is enabled since both Point-to-Point Protocol IPCP endpoints have pre-defined IP address pools and / or topology configured, so each Point-to-Point Protocol endpoint can utilize a greater number of IP addresses than one per link. Such an approach does not change IPCP or other EVDO protocols / messaging but allows this address to be directly visible to the ground-based communication network.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
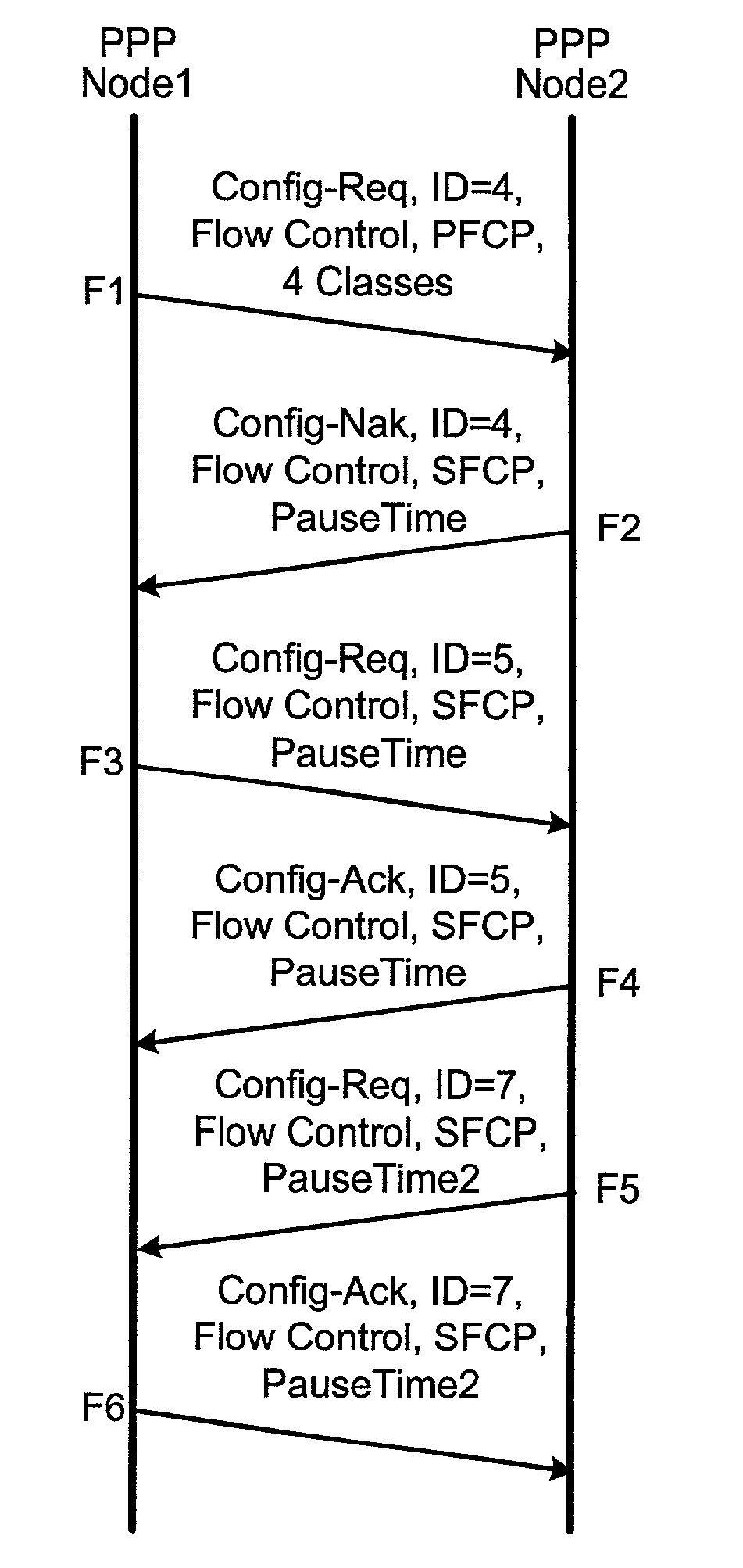
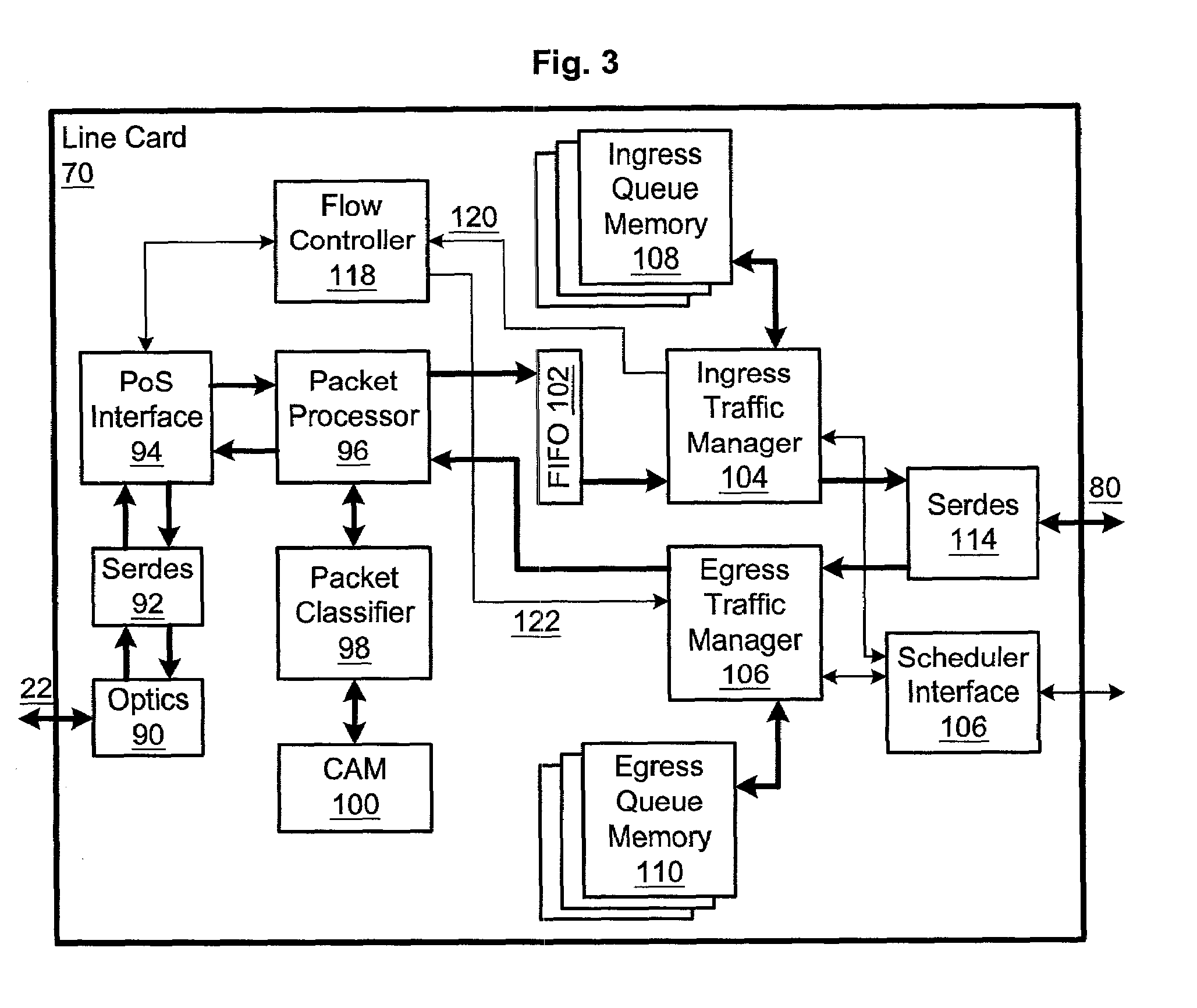
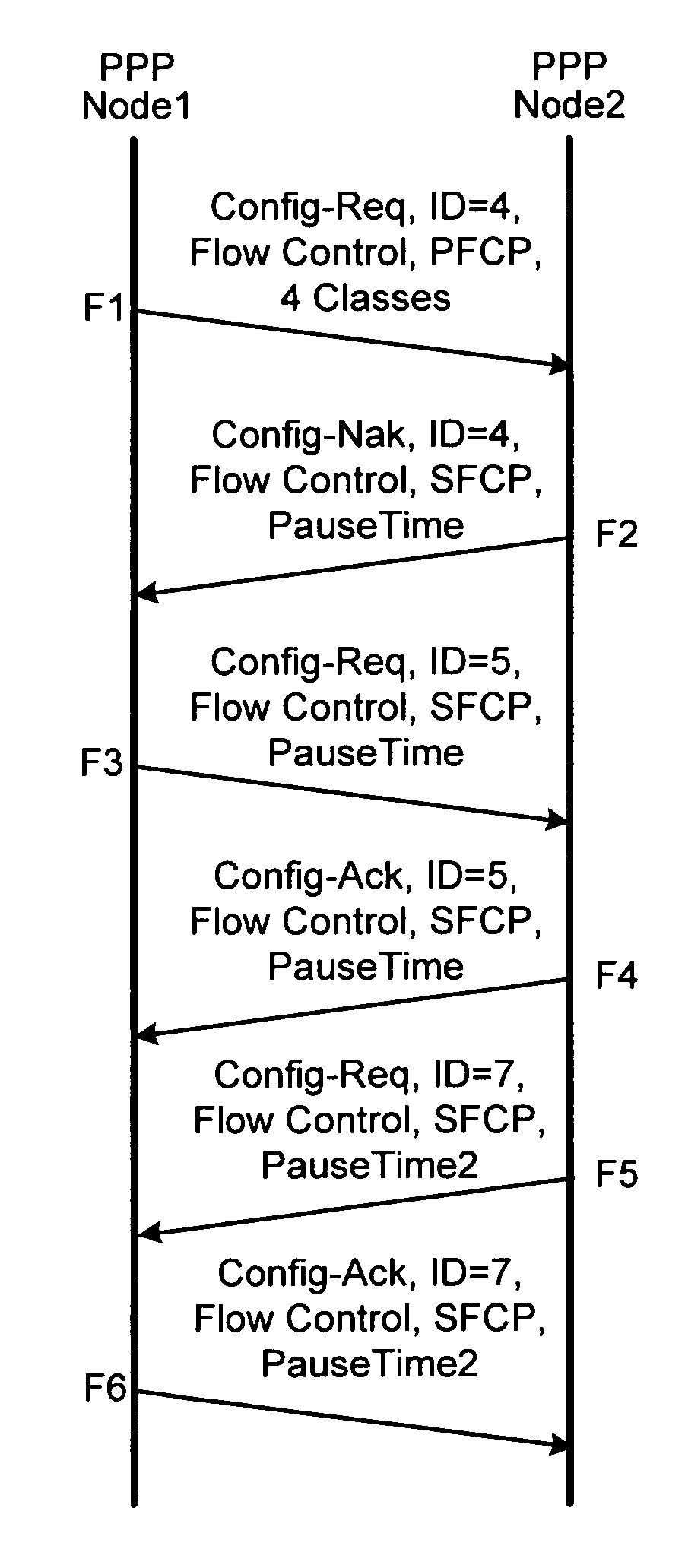
Point-to-point protocol flow control extension
ActiveUS7062568B1Less disruptiveEnergy efficient ICTError preventionPoint-to-Point ProtocolDistributed computing
Method and apparatus are disclosed for flow control over Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) data links. A method of negotiating such flow control between two PPP peers is disclosed, along with methods for operating flow control across a PPP link. In one embodiment, flow control frames carry an IEEE802.3x MAC control frame payload—the PPP implementation repackages such frames as MAC control frames and passes them to a MAC, which performs flow control. In another embodiment, flow control frames allow flow control commands to be applied differently to different service classes such that PPP flow can be controlled on a per-class basis.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
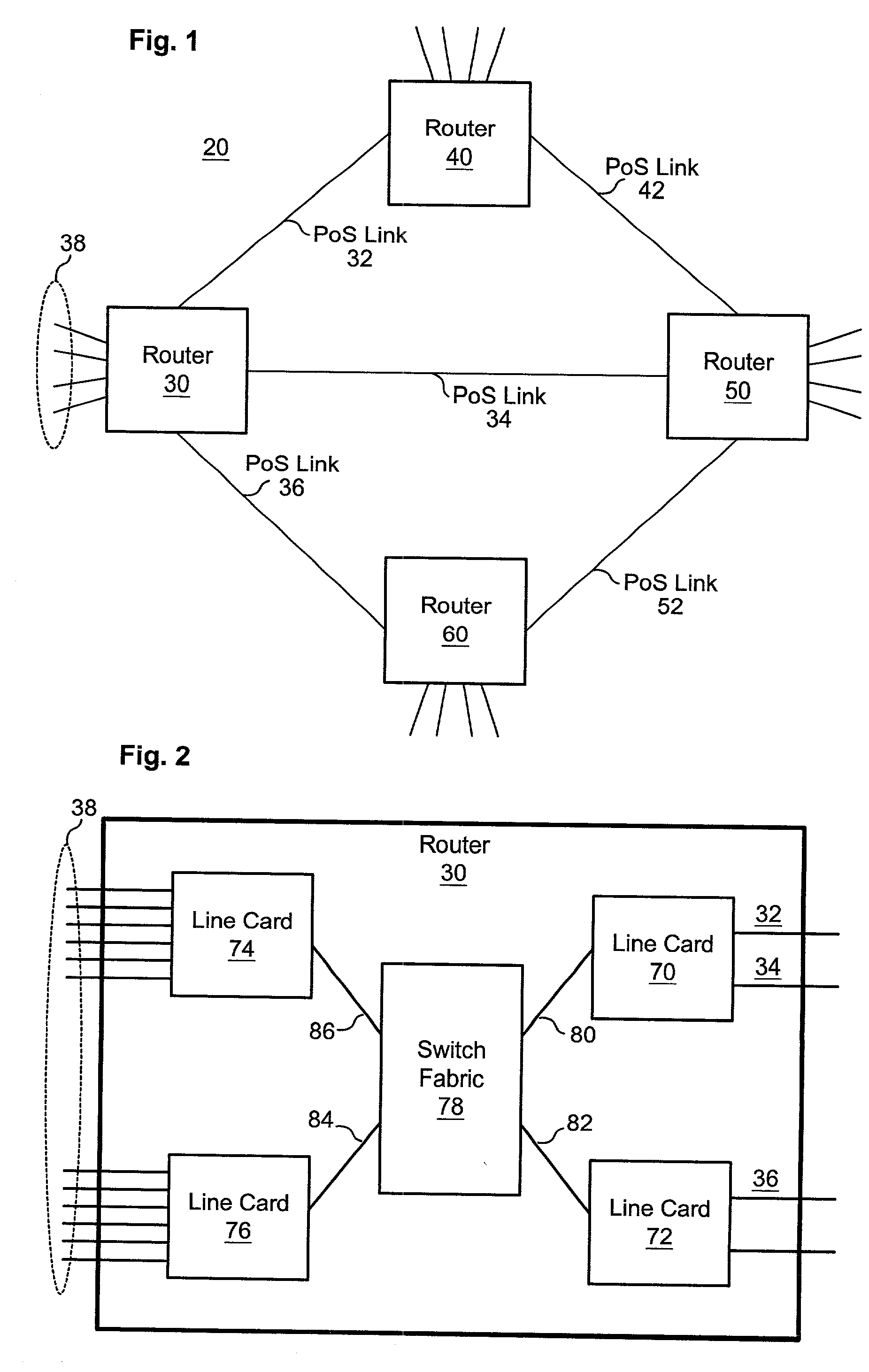
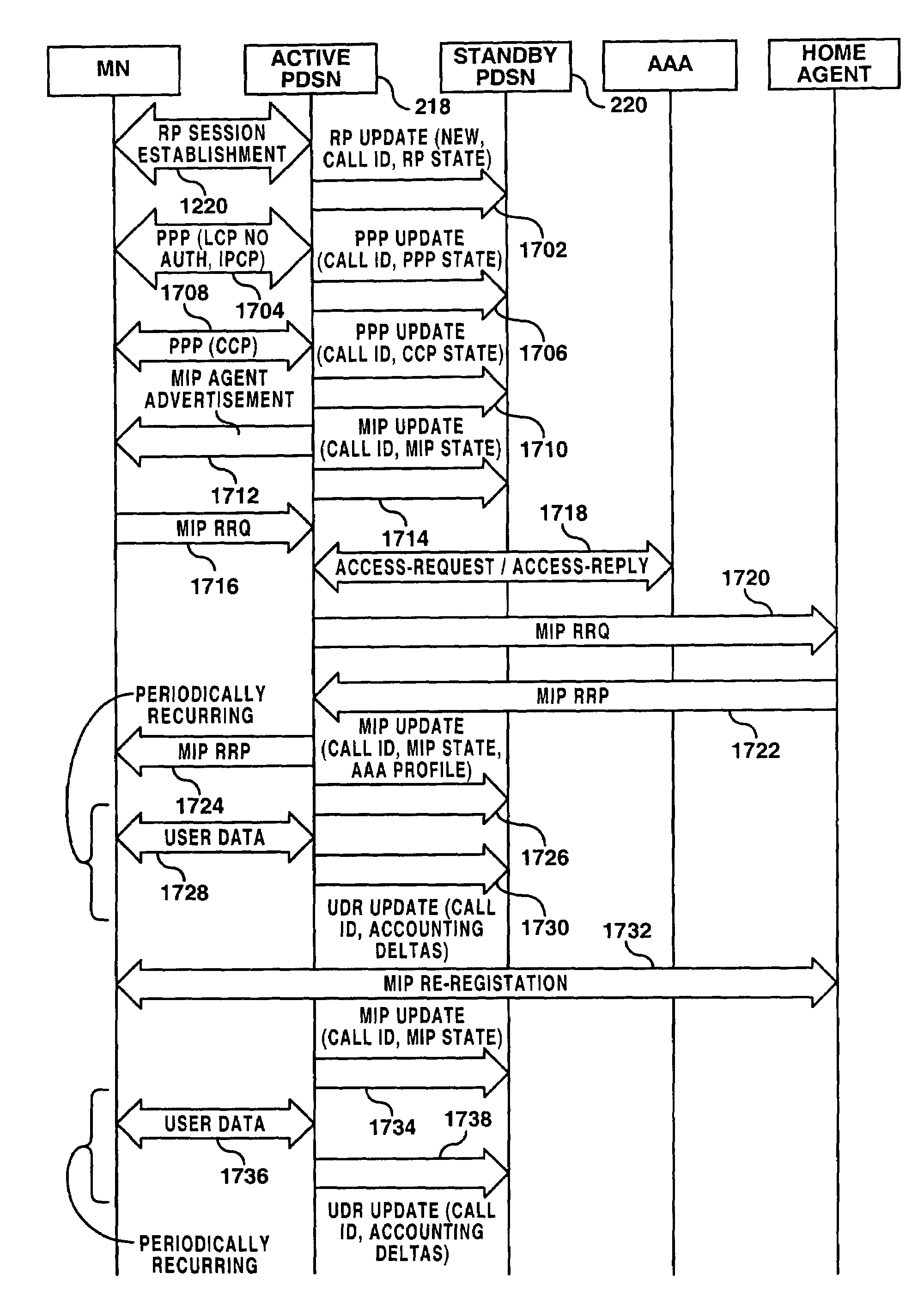
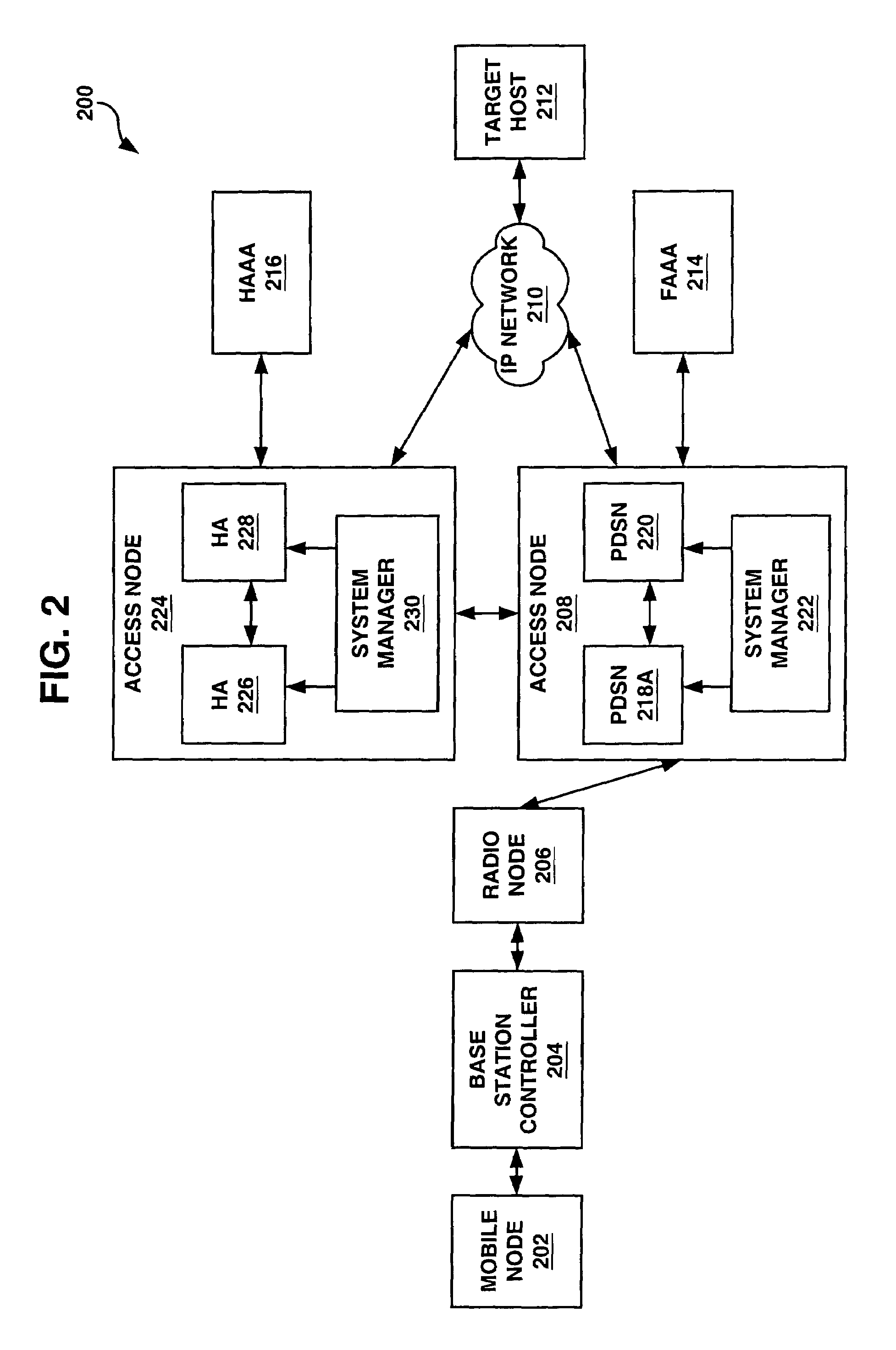
System and method for point-to-point protocol device redundancey
InactiveUS7082130B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket data serving nodePoint-to-Point Protocol
A system and methods are shown for providing packet data serving node (PDSN) redundancy. One exemplary method includes providing an access node with a plurality of packet data serving nodes and at least one system manager, establishing an N to 1 redundancy of active to standby PDSNs. Upon establishing a communications session with a mobile node, each active PDSN provides state updates to the standby PDSN including only non-recoverable data. Upon failure of any active PDSN, the standby PDSN reassigned as an active PDSN replacing the failed unit and assuming the communications session with the mobile node. The remaining active PDSNs are notified of the reassignment and transmission of updated state data is discontinued.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
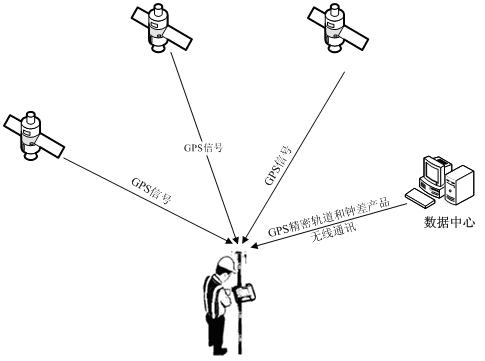
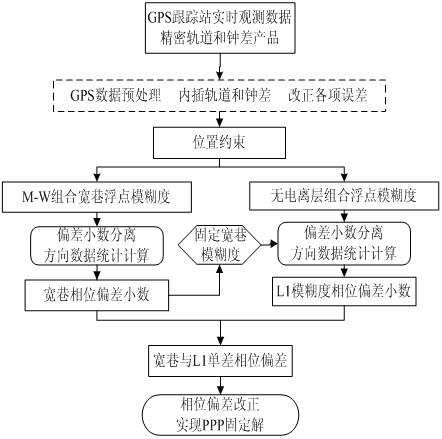
Method for estimating phase deviation in precise single-point positioning technology
InactiveCN102353969AImprove robustnessGuaranteed sizeSatellite radio beaconingPoint-to-Point ProtocolIonosphere
The invention discloses a method for estimating a phase deviation in a precise single-point positioning technology, which comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out parameter estimation on single-difference non-ionized layer combined ambiguity by using a position as a restraint condition according to data of a reference station in a tracking network; secondly, carrying out parameter estimationon single-difference wide-lane ambiguity by adopting an M-W combination, separating out a decimal part of the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity, and carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using a directional data statistic theory, modifying and fixing the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity as an integer; thirdly, resolving a single-difference L1 ambiguity floating point solution according to a single-difference non-ionized layer ambiguity estimation value and a single-difference wide-lane ambiguity integer solution, separating the decimal part, carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using the direction data statistic theory; and finally, broadcasting the wide-lane and the L1 phase deviation decimal part to a user of a roving station so as to be used for fixing the single-difference integral ambiguity solution of the wide lane and the L1 and further obtaining a PPP (Point to Point Protocol) static solution.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
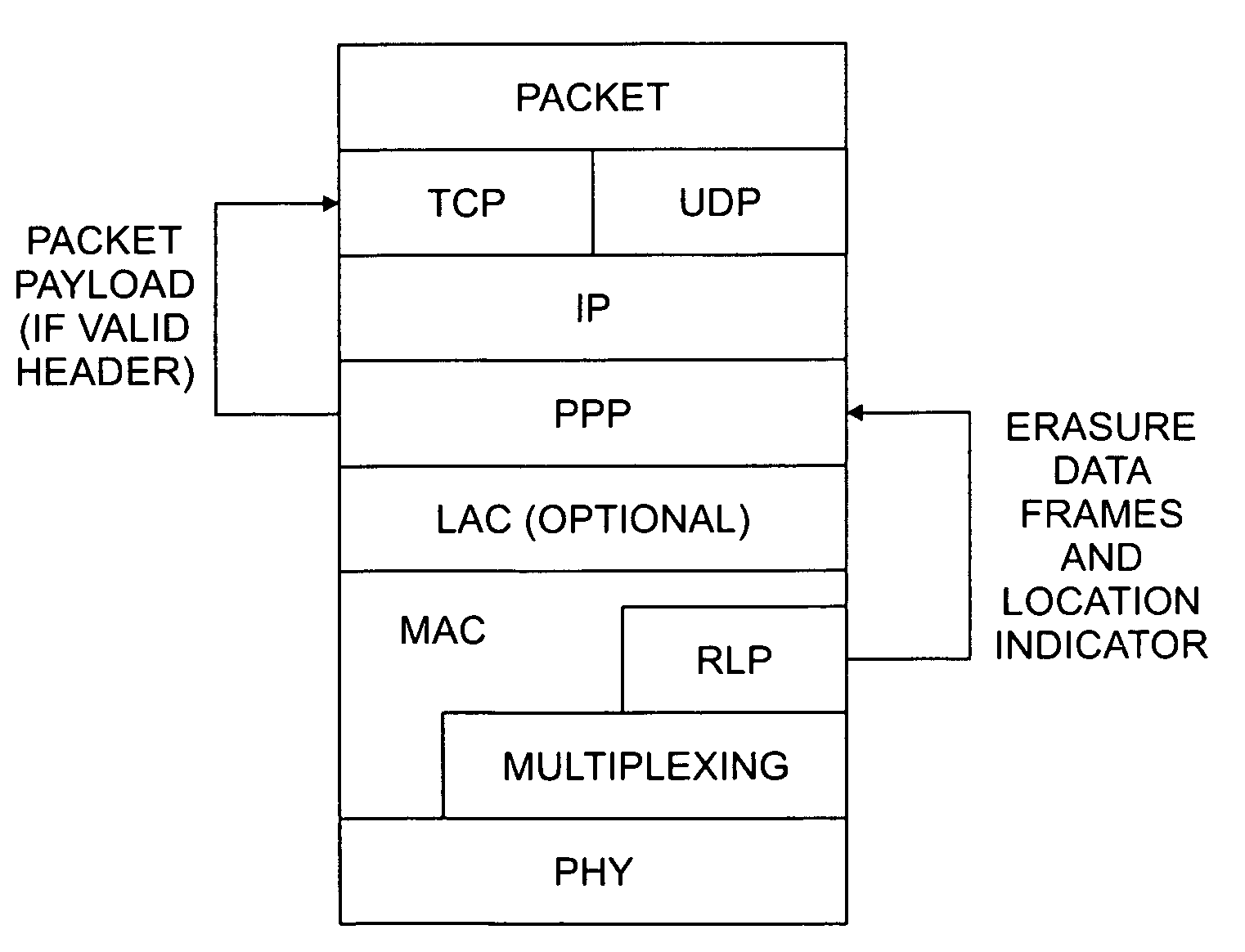
Radio link protocol (RLP)/point-to-point protocol (PPP) design that passes corrupted data and error location information among layers in a wireless data transmission protocol
InactiveUS7031257B1Reduces or avoids unnecessary packet discardingImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolError location
A radio link protocol (RLP) / point-to-point protocol (PPP) design is disclosed for wireless multimedia packet networks that passes corrupted packet data and error location information among OSI layers. The RLP layer provides erasure data frames and optionally error location indicators to the PPP layer. When the PPP layer has access to the erasure data frames, the data frames can be padded with a predefined value, such as all zeroes “0” to prevent error propagation from one data frame (or octet) to the following data frames (or octets). When the PPP layer has access to the error location information, the PPP layer can detect if the PPP packet header is corrupted. When a valid header is detected, the PPP layer forwards the packet payload to the higher layers (TCP, UDP) whether or not the payload is properly received. Thus, the application has access to all the usable information, so the application can determine whether and how to utilize the information. The RLP / PPP design of the present invention allows packets with partially corrupted payloads to still be forwarded to the UDP layer and then to the application layer.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
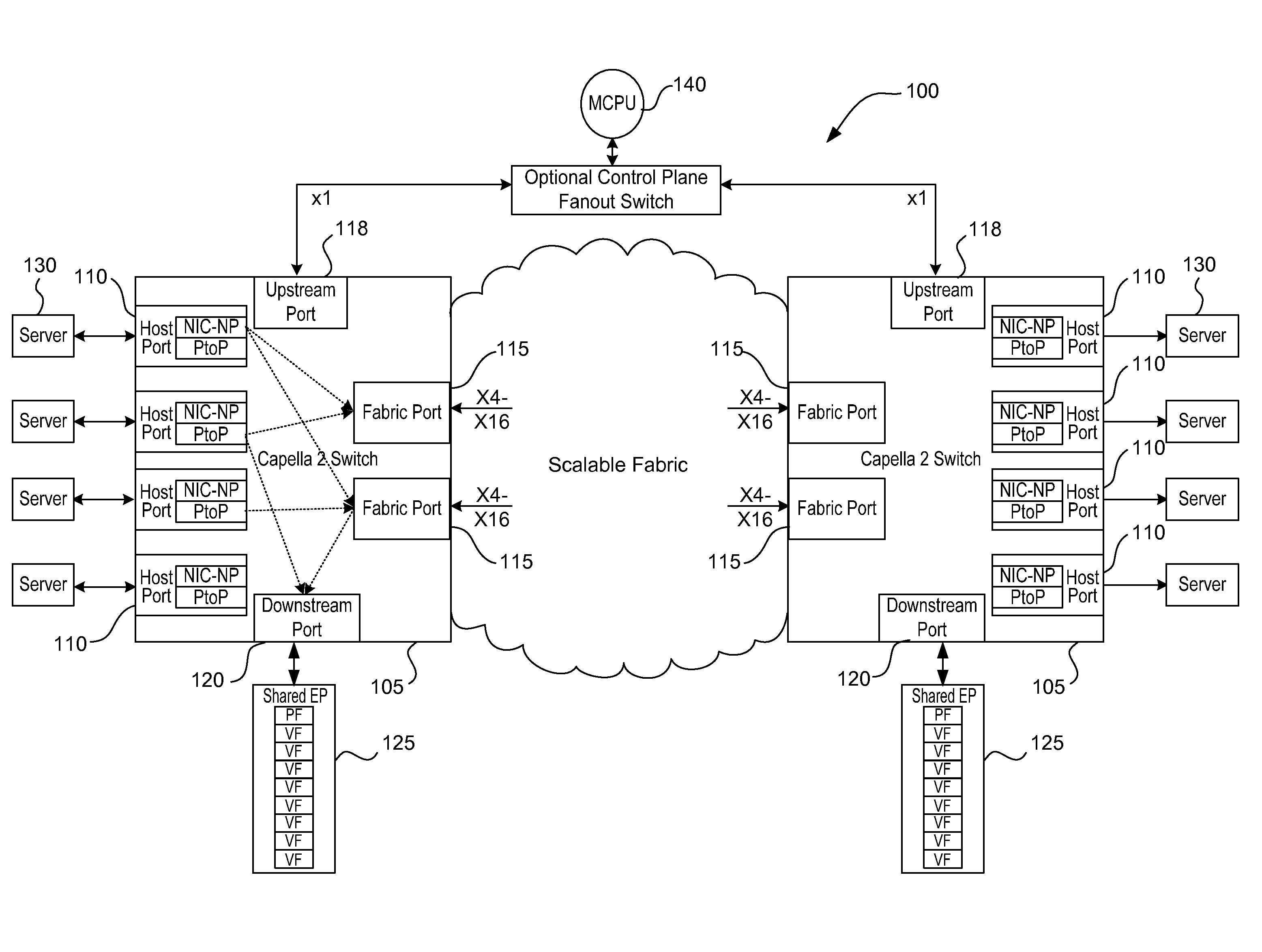
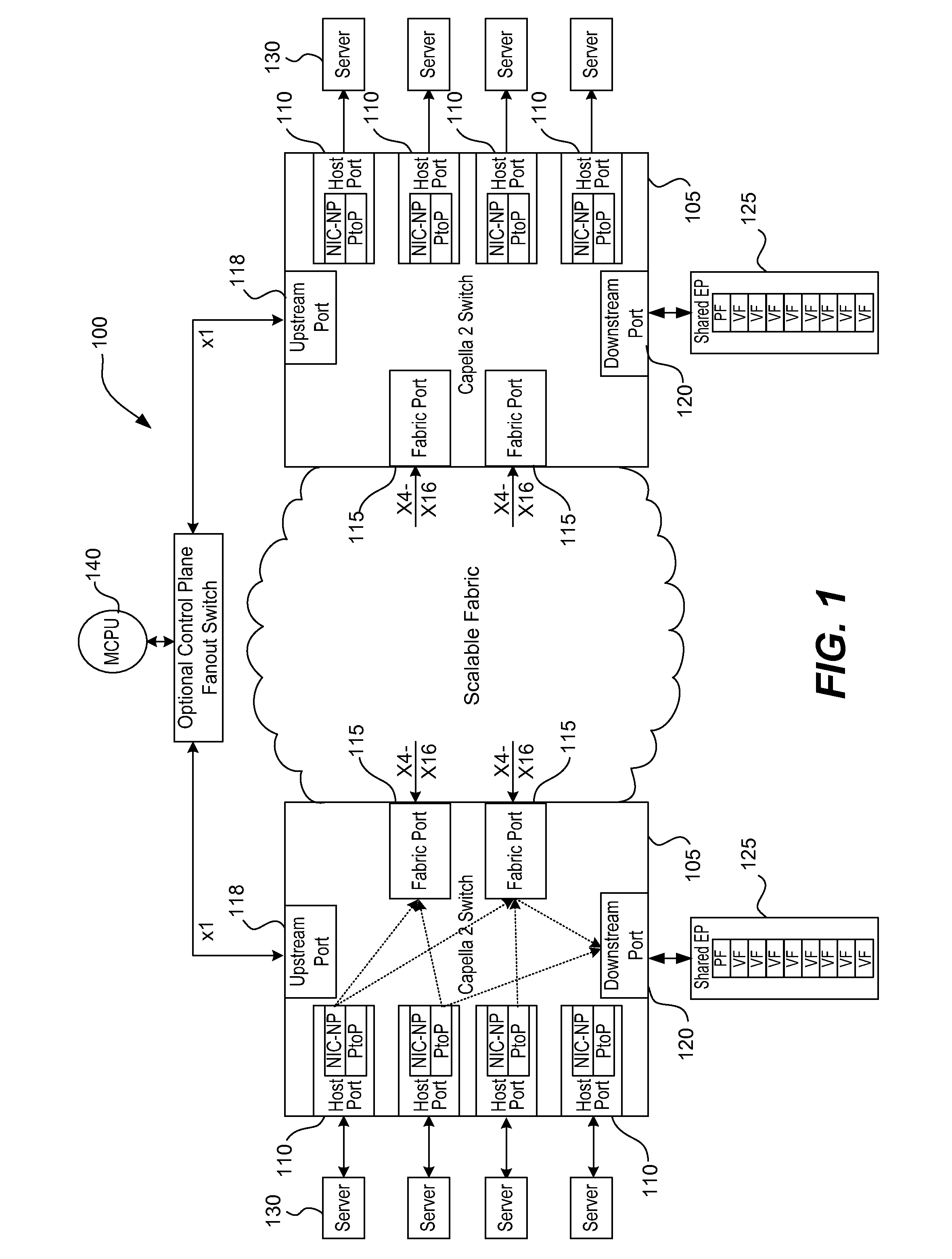
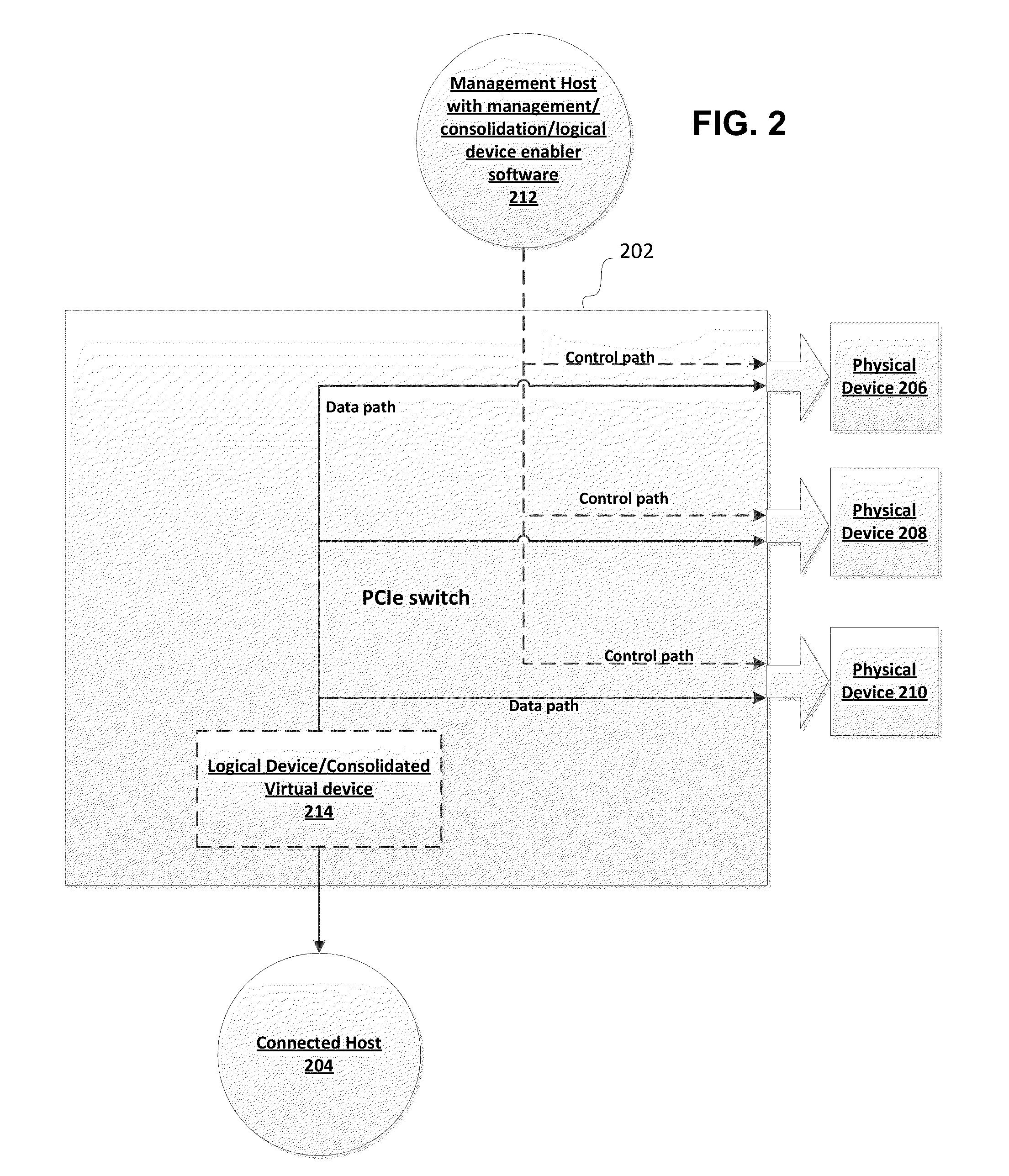
Method and apparatus for securing and segregating host to host messaging on PCIe fabric
ActiveUS8880771B2Improve functionalityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolStructure of Management Information
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
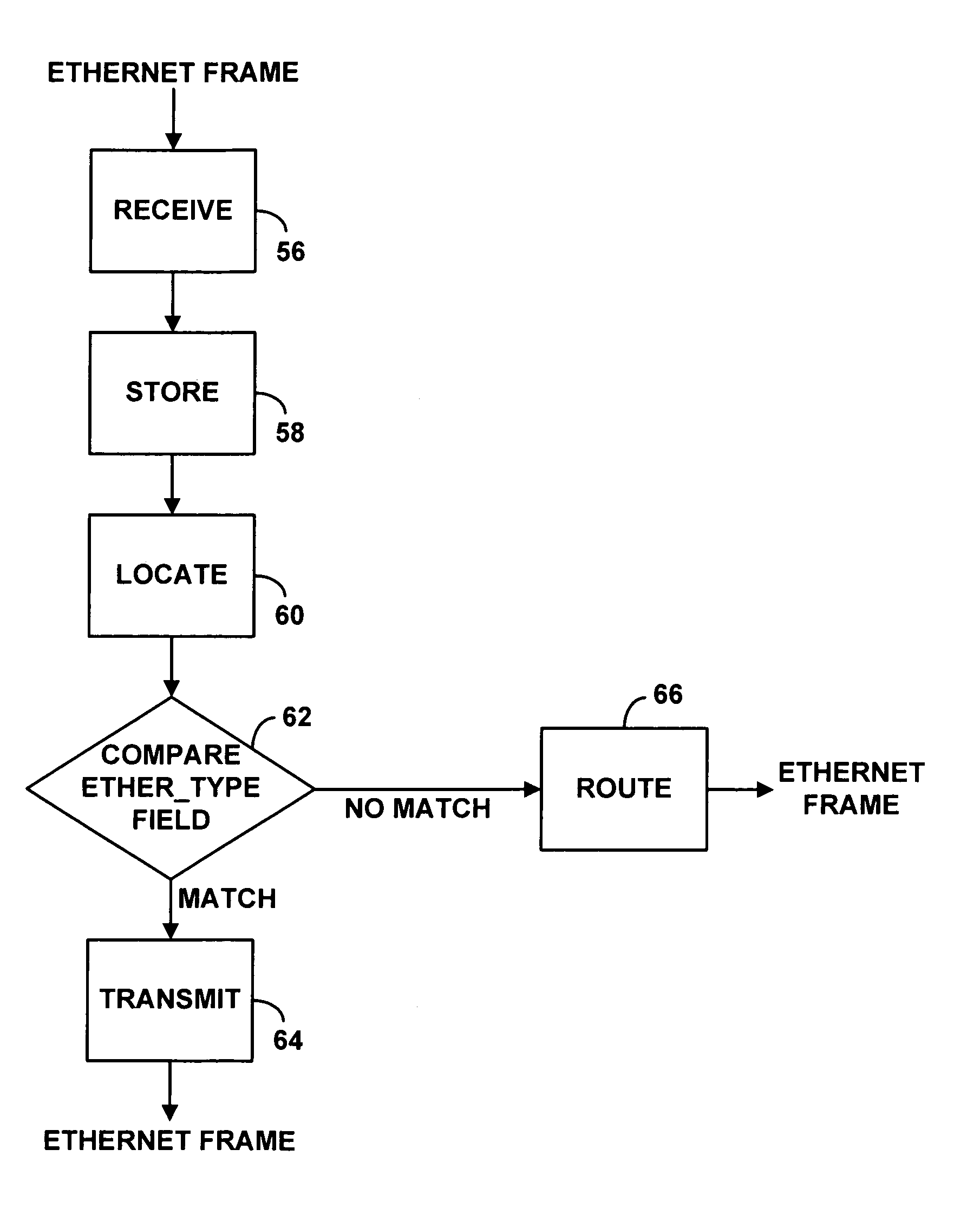
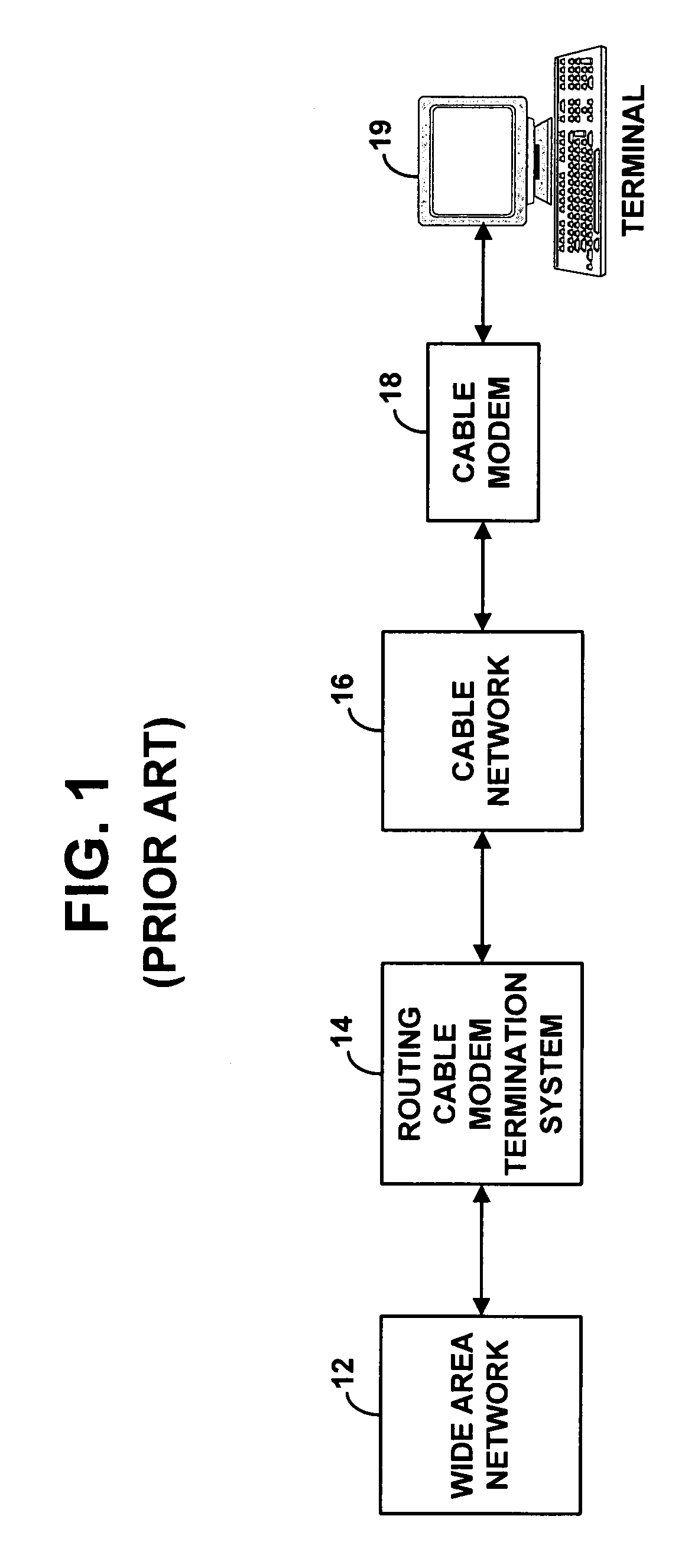
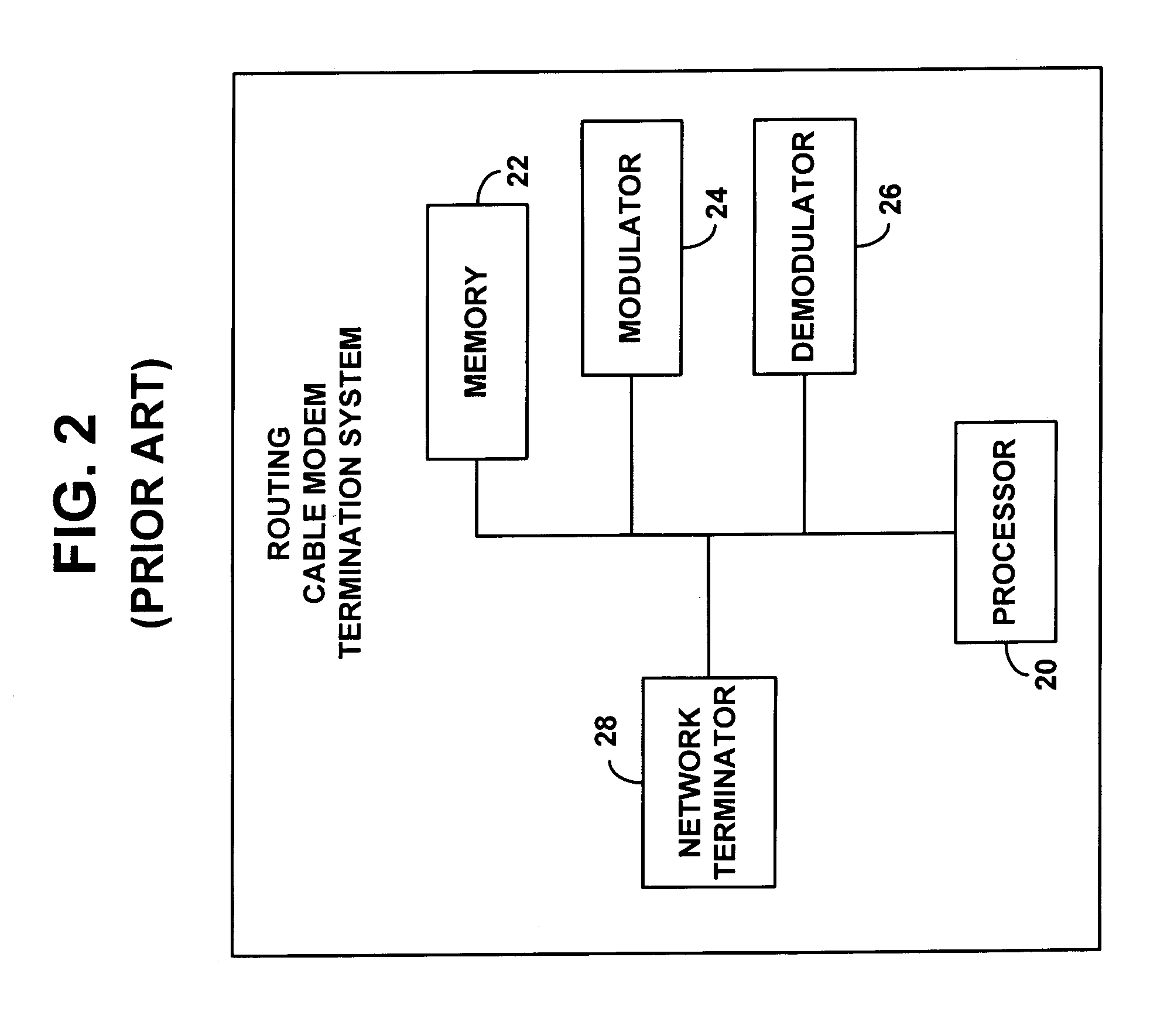
Method and apparatus for PPPoE bridging in a routing CMTS
InactiveUS7039049B1Reserved functionPrevent spoofing attacksBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexPoint-to-Point ProtocolModem device
A routing Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) configured to enable Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE). The routing CMTS may bridge Ethernet frames related to a PPPoE connection from a first network to a second network. Bridging Ethernet frames allows terminals in different networks to establish a PPPoE connection. A routing CMTS may also collect state information regarding PPPoE connections. The routing CMTS may use the state information to only bridge Ethernet frames related to valid PPPoE connections. It may act as a firewall to prevent spoofing attacks.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
System and method for controlling packet data service in mobile communication network
InactiveUS7035636B1Eliminate the problemRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionRadio networksPoint-to-Point Protocol
A system and method is provided for controlling a packet data service in a mobile communication network, in which, when a packet data service active terminal moves from an area of an old radio network controller to an area of a new radio network controller in either a suspended state or a dormant state, the same medium access control state information and the same radio resource control information are applied between the new radio network controller and the active terminal. Therefore, the packet data service can rapidly be resumed on the basis of an initially established point-to-point protocol link. If the active terminal moves from the old radio network controller to the new radio network controller under the condition that only a point-to-point protocol state is maintained between the active terminal and a packet data node, the active terminal detects a received pilot signal and checks a system overhead message. If the active terminal should perform a handoff operation in the suspended state, the active terminal requests the old radio network controller to permit its change to the dormant state or an active state.
Owner:SISVEL INT
System for creating an aircraft-based internet protocol subnet in an airborne wireless cellular network
InactiveUS20080181169A1Improve travel experienceSimplifies provision of serviceNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionInternet protocol suitePoint-to-Point Protocol
The Aircraft IP Subnet System provides wireless communication services to passengers located onboard an aircraft by storing data indicative of individually identified wireless devices that are located onboard the aircraft. The Aircraft IP Subnet System assigns a single IP address to each Point-to-Point Protocol link connecting the aircraft network to the ground-based communication network and creates an IP subnet onboard the aircraft. The IP subnet utilizes a plurality of IP addresses for each Point-to-Point link, thereby to enable each passenger wireless device to be uniquely identified with their own IP address. This is enabled since both Point-to-Point Protocol IPCP endpoints have pre-defined IP address pools and / or topology configured, so each Point-to-Point Protocol endpoint can utilize a greater number of IP addresses than one per link. Such an approach does not change IPCP or other EVDO protocols / messaging but allows this address to be directly visible to the ground-based communication network.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
Point-to-point protocol flow control extension
InactiveUS7558872B1Less disruptiveEnergy efficient ICTError preventionPoint-to-Point ProtocolDistributed computing
Method and apparatus are disclosed for flow control over Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) data links. A method of negotiating such flow control between two PPP peers is disclosed, along with methods for operating flow control across a PPP link. In one embodiment, flow control frames carry an IEEE802.3x MAC control frame payload—the PPP implementation repackages such frames as MAC control frames and passes them to a MAC, which performs flow control. In another embodiment, flow control frames allow flow control commands to be applied differently to different service classes such that PPP flow can be controlled on a per-class basis.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
Techniques for migrating a point to point protocol to a protocol for an access network
InactiveUS20060168270A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionAccess networkPoint-to-Point Protocol
Techniques for exchanging point to point protocol (PPP) information among network nodes using an arbitrary network protocol include determining whether a PPP payload includes PPP control data. If so, then an outbound protocol frame is generated with the PPP control data in a payload and with an outbound protocol type field that indicates PPP control data. The outbound protocol frame is sent to a server which uses the PPP control data. The outbound protocol is different from PPP and from PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) and from PPP over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) protocol (PPPoA). The outbound protocol may be Ethernet or ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) or some other protocol. These techniques allow PPP control plane functionality while utilizing IP over Ethernet for the data plane.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mobile IP registration in selected inter-PDSN dormant hand-off cases in a CDMA2000-based cellular telecommunications network
InactiveUS6907016B2Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications network
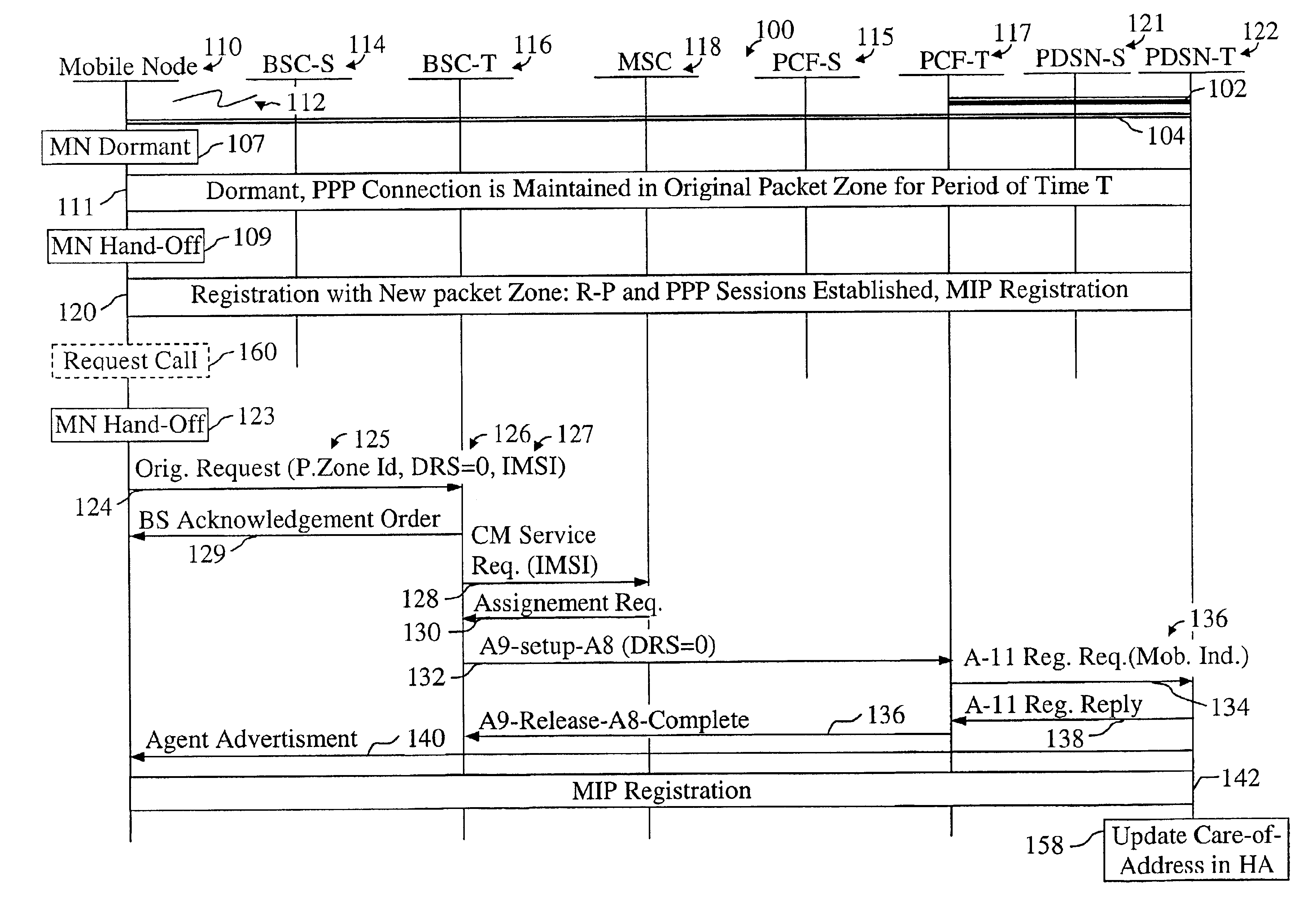
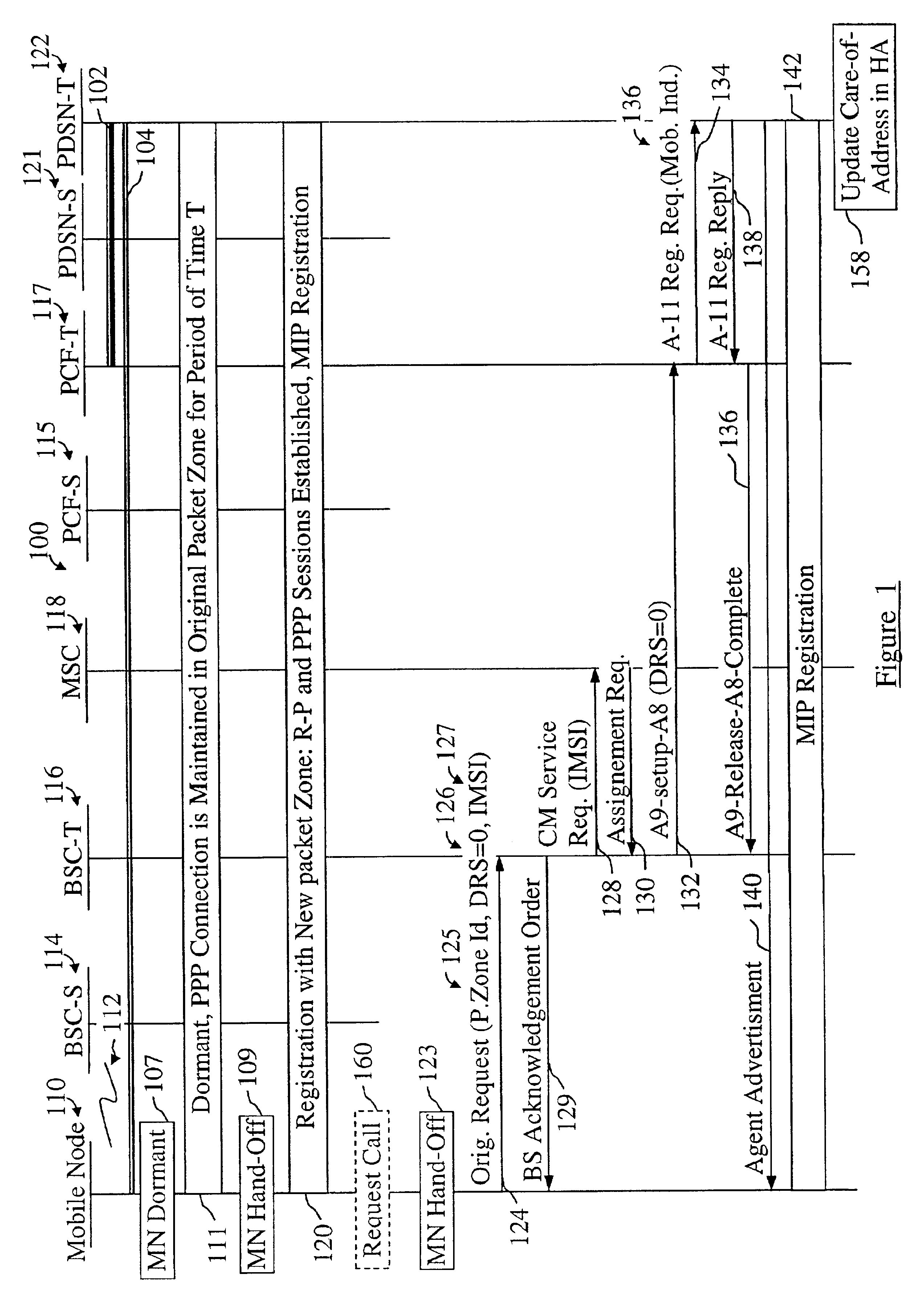
In a cellular telecommunications network, a method and system for performing dormant hand-off for a dormant Mobile Node (MN) between a source packet zone an a target packet zone, when the MN still has an active A10 and Point-to Point Protocol (PPP) connection in the target packet zone. According to the method, when handed-off, the MN issues an origination request with a Data Ready to Sent (DRS) parameter set to zero for the target Base Station Controller (BSC-T) which responsive to the request further sends an A9-setup-A8 registration request to a target Packet Control Function (PCF-T). The PCF-T then sends an A-11 Registration Request message to a Packet Data Service Node (PDSN-T) of the target packet zone. Responsive to the receipt of the Registration request, the PDSN-T sends an agent advertisement message to the MN and initiates the Mobile IP (MIP) registration procedure, and the MN can register the care-of-address information relating to the new serving PDSN, the PDSN-T, with its Home Agent (HA). According to another embodiment, the same method is to be used for performing a hand-off of the dormant MN to the target packet zone, when the MN, before issuing the origination request, demands the activation of a packet data session.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System for creating an aircraft-based internet protocol subnet in an airborne wireless cellular network
InactiveUS8081969B2Simplifies provision of serviceImprove travel experienceNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
The Aircraft IP Subnet System provides wireless communication services to passengers located onboard an aircraft by storing data indicative of individually identified wireless devices that are located onboard the aircraft. The Aircraft IP Subnet System assigns a single IP address to each Point-to-Point Protocol link connecting the aircraft network to the ground-based communication network and creates an IP subnet onboard the aircraft. The IP subnet utilizes a plurality of IP addresses for each Point-to-Point link, thereby to enable each passenger wireless device to be uniquely identified with their own IP address. This is enabled since both Point-to-Point Protocol IPCP endpoints have pre-defined IP address pools and / or topology configured, so each Point-to-Point Protocol endpoint can utilize a greater number of IP addresses than one per link. Such an approach does not change IPCP or other EVDO protocols / messaging but allows this address to be directly visible to the ground-based communication network.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
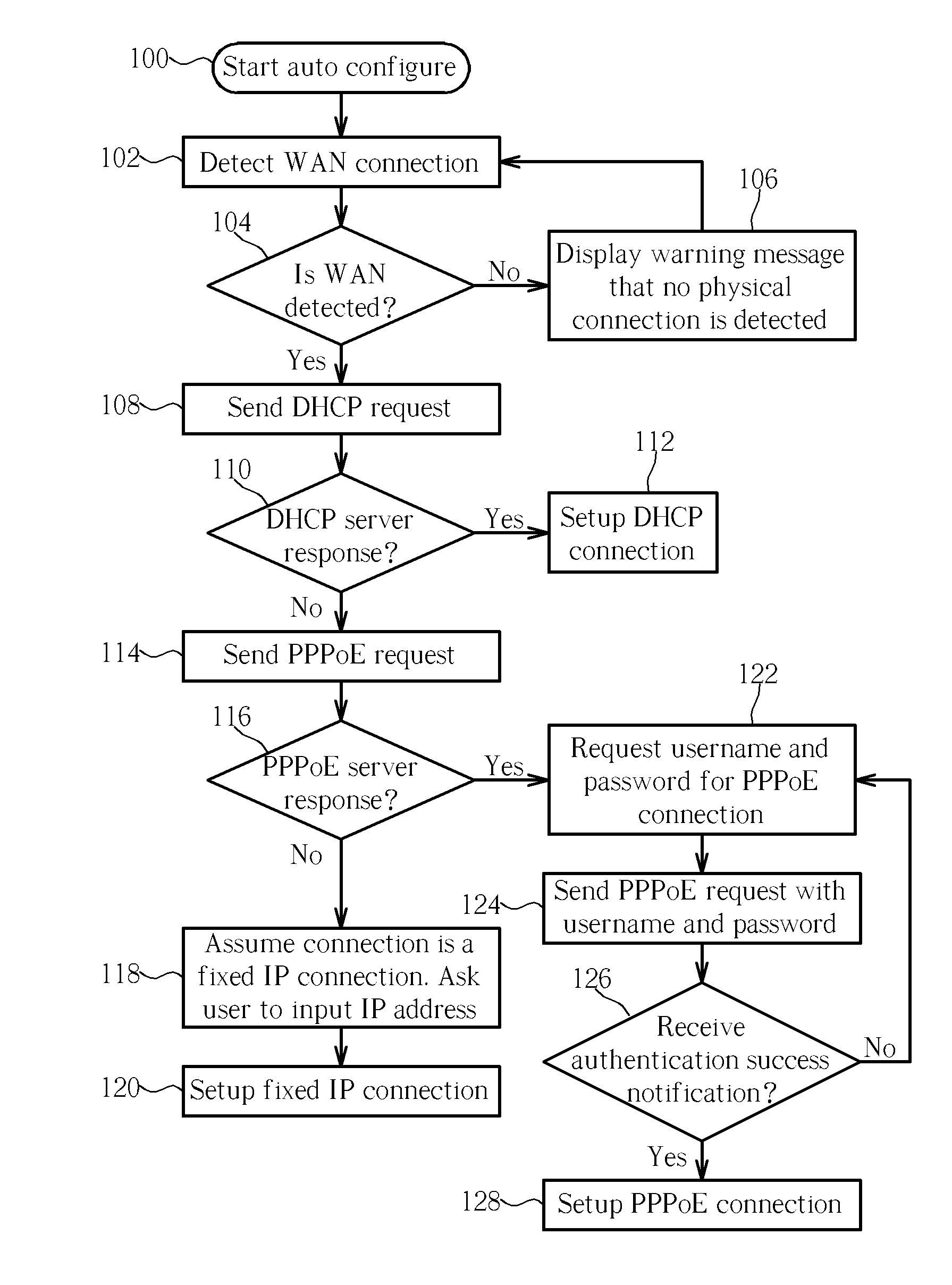
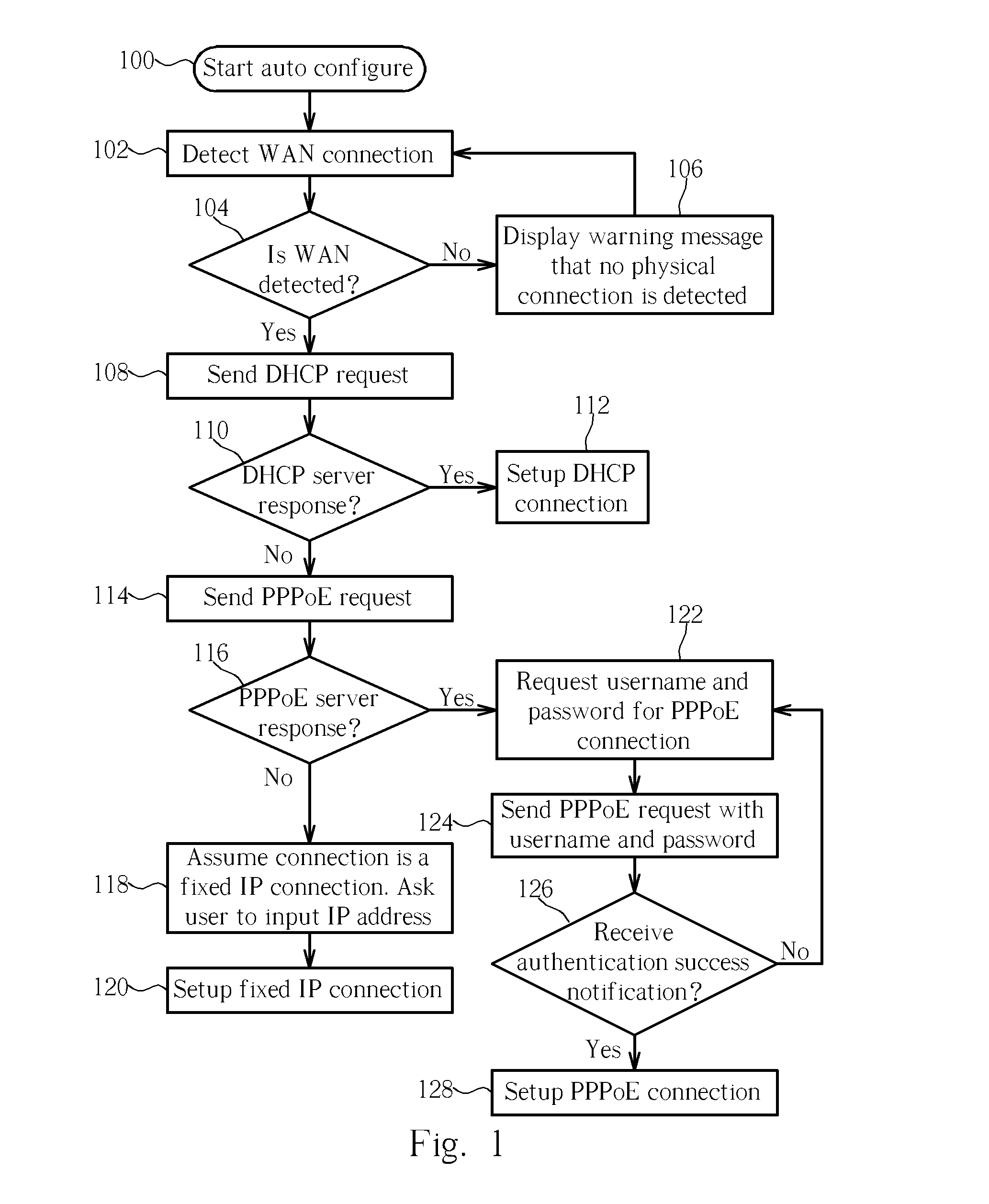
Method of setting up a wireless router
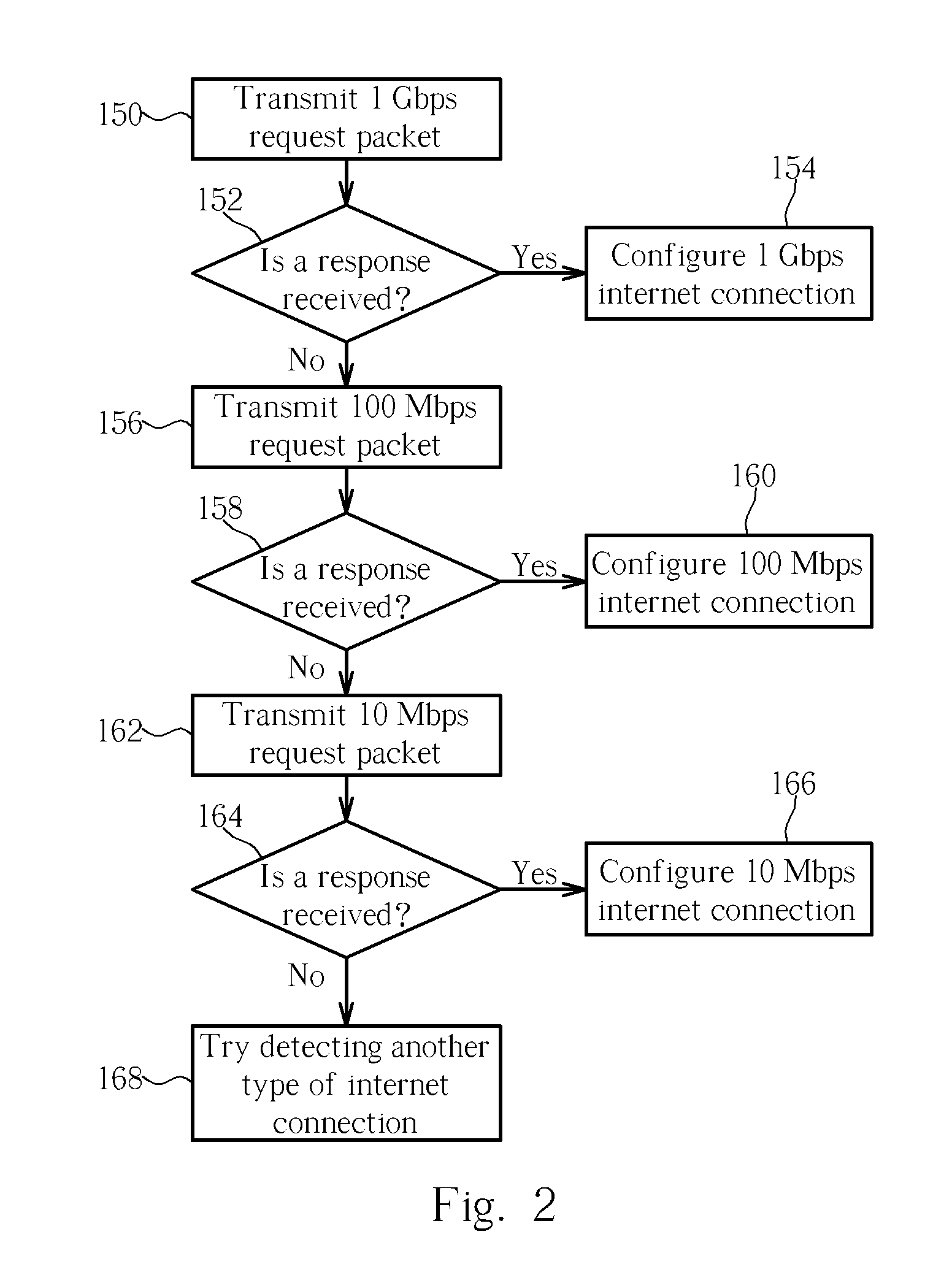
InactiveUS20070058538A1Quick Auto DetectError preventionTransmission systemsWireless routerPoint-to-Point Protocol
Owner:UNICATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com