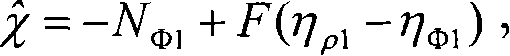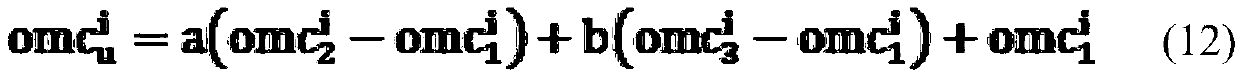Patents
Literature
700 results about "Ionosphere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ionosphere (/aɪˈɒnəˌsfɪər/) is the ionized part of Earth's upper atmosphere, from about 60 km (37 mi) to 1,000 km (620 mi) altitude, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on the Earth. The region below the ionosphere is called neutral atmosphere, or neutrosphere.
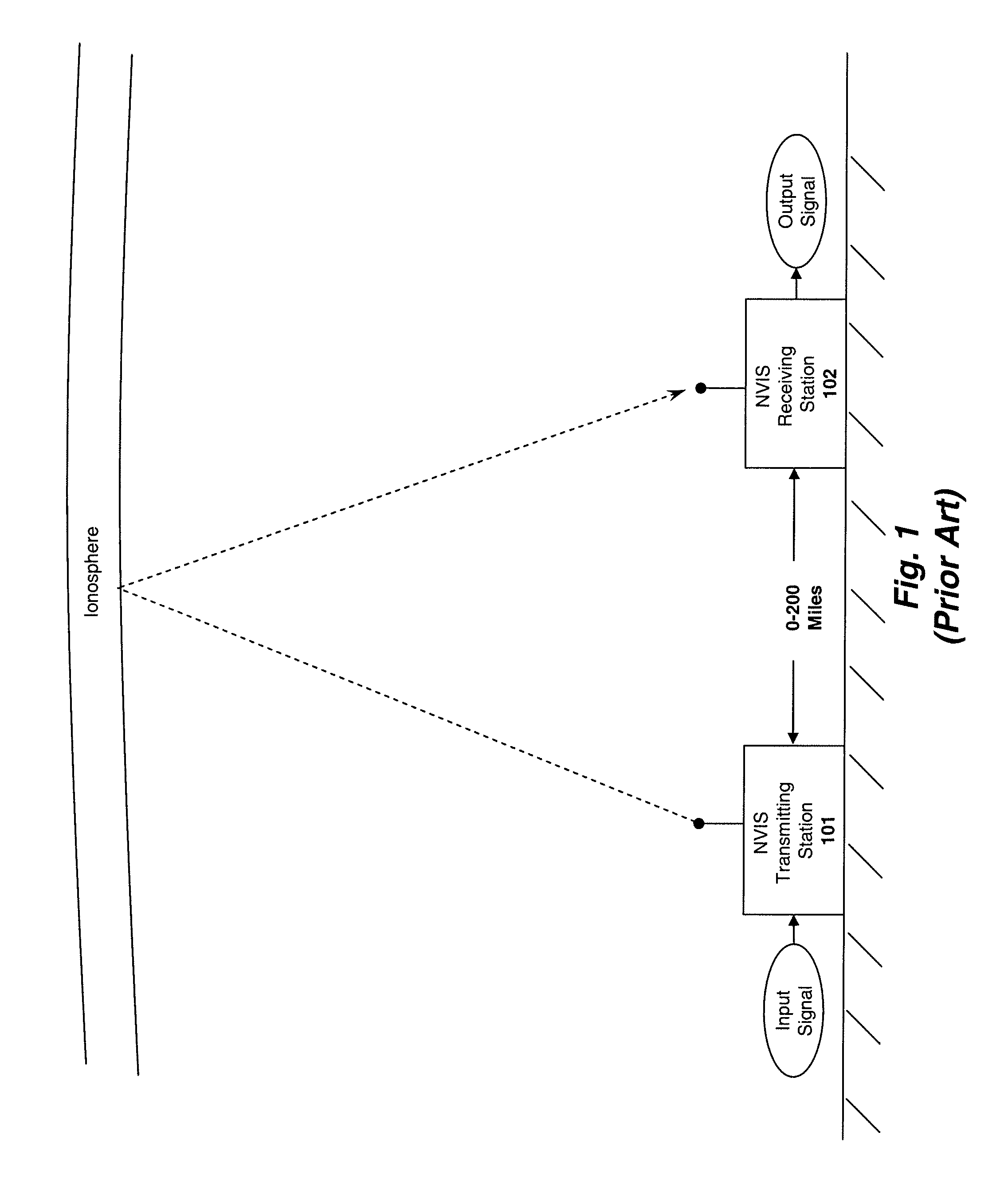
Method and apparatus for establishing low frequency/ultra low frequency and very low frequency communications
InactiveUS8299936B2Increase signal strengthShorten speedElectric signal transmission systemsDirection finders using radio wavesIonosphereElectromagnetic pulse
A method for generating electromagnetic waves in the ELF / ULF comprising the steps of using a ground-based Horizontal Electric Dipole (HED) antenna to send electromagnetic pulses upwardly in the E-region of the ionosphere to form an oscillatory or pulsed electric field; allowing said pulsed electric field to interact with magnetized plasma of the lower ionosphere to generate a pulsed horizontal and vertical current which have associated Horizontal and Vertical Electric Dipole moment; and allowing them to radiate.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Ionosphere modeling apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20090224969A1Fast convergenceImprove reliabilityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingIonosphereComputational physics
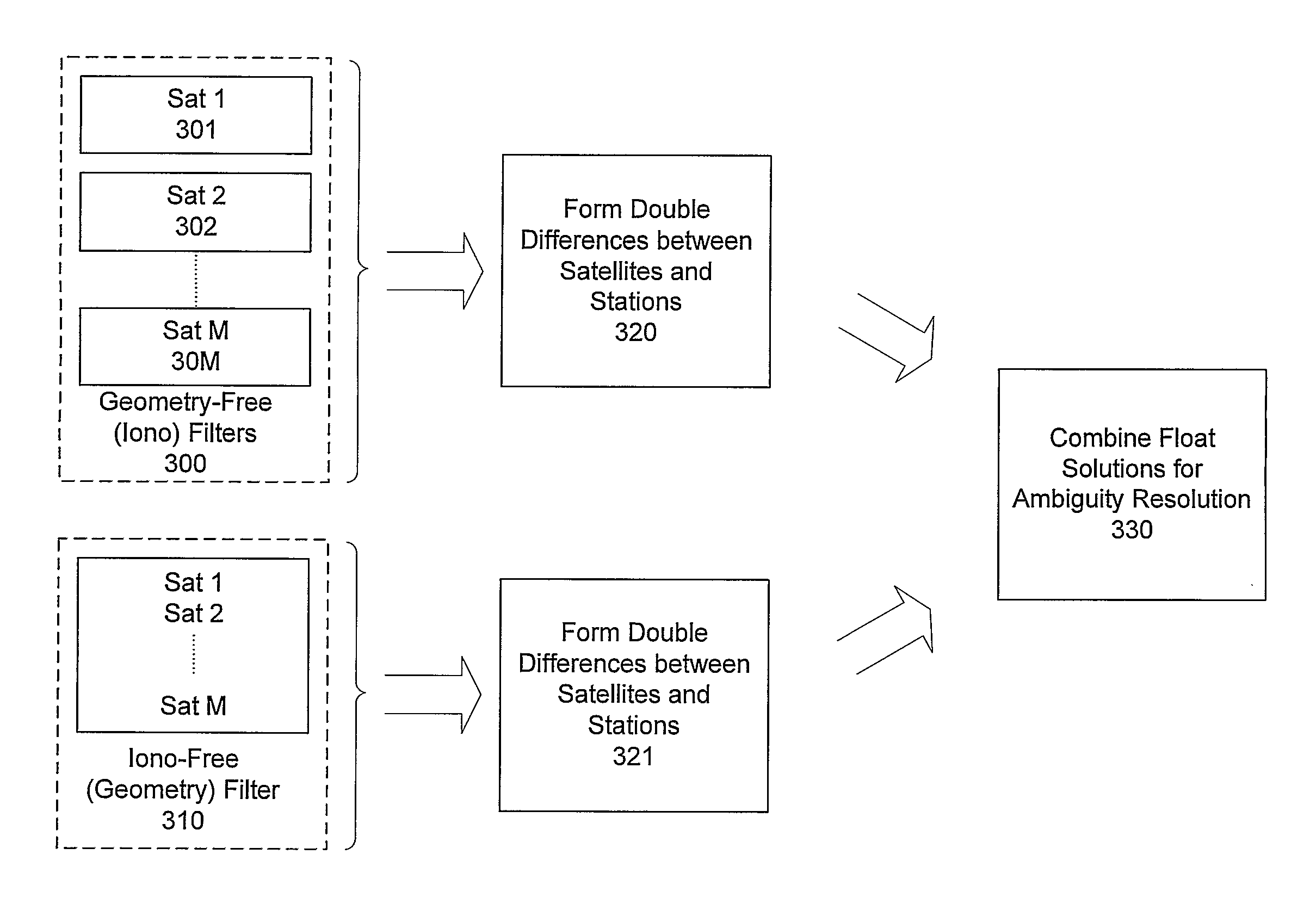
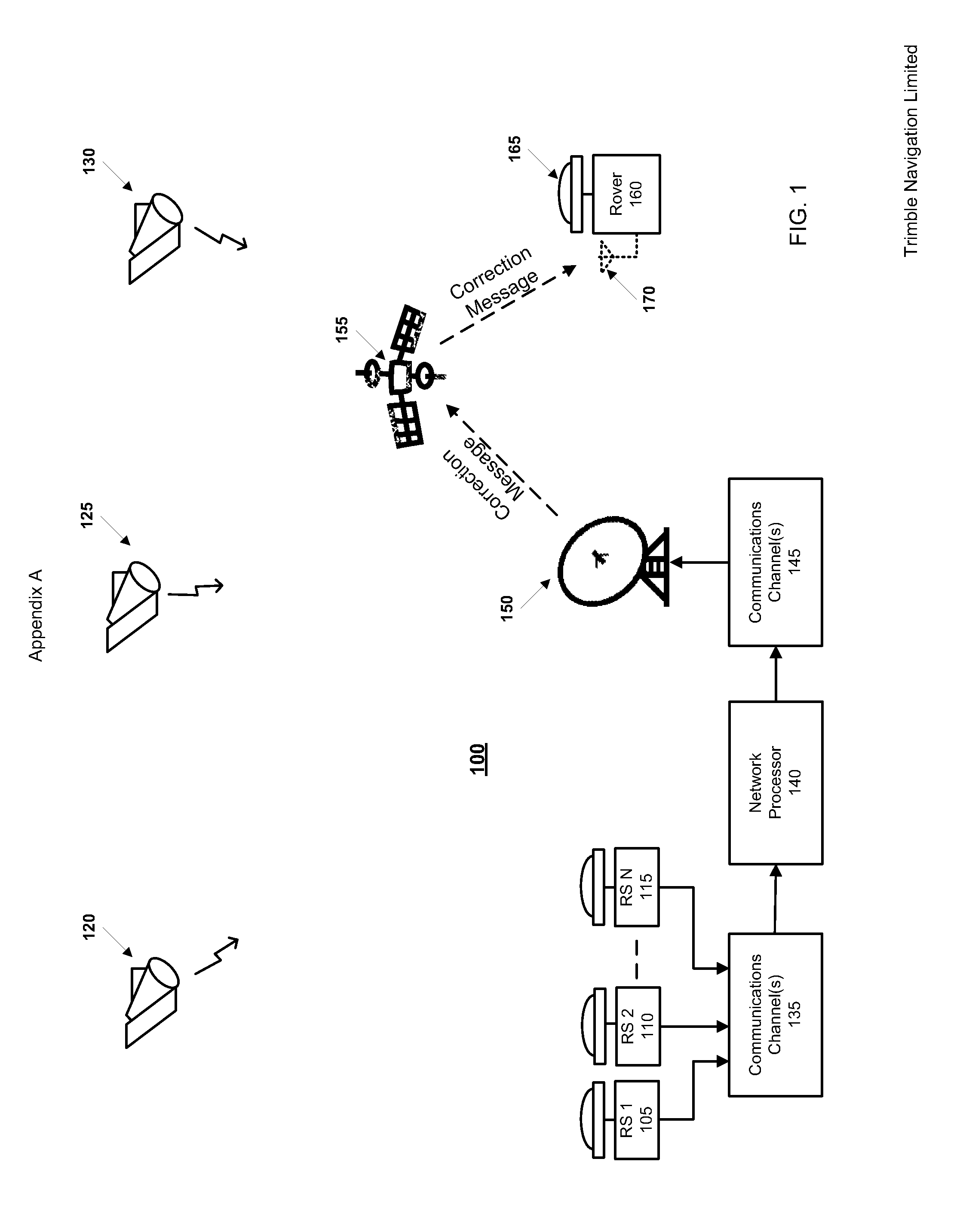
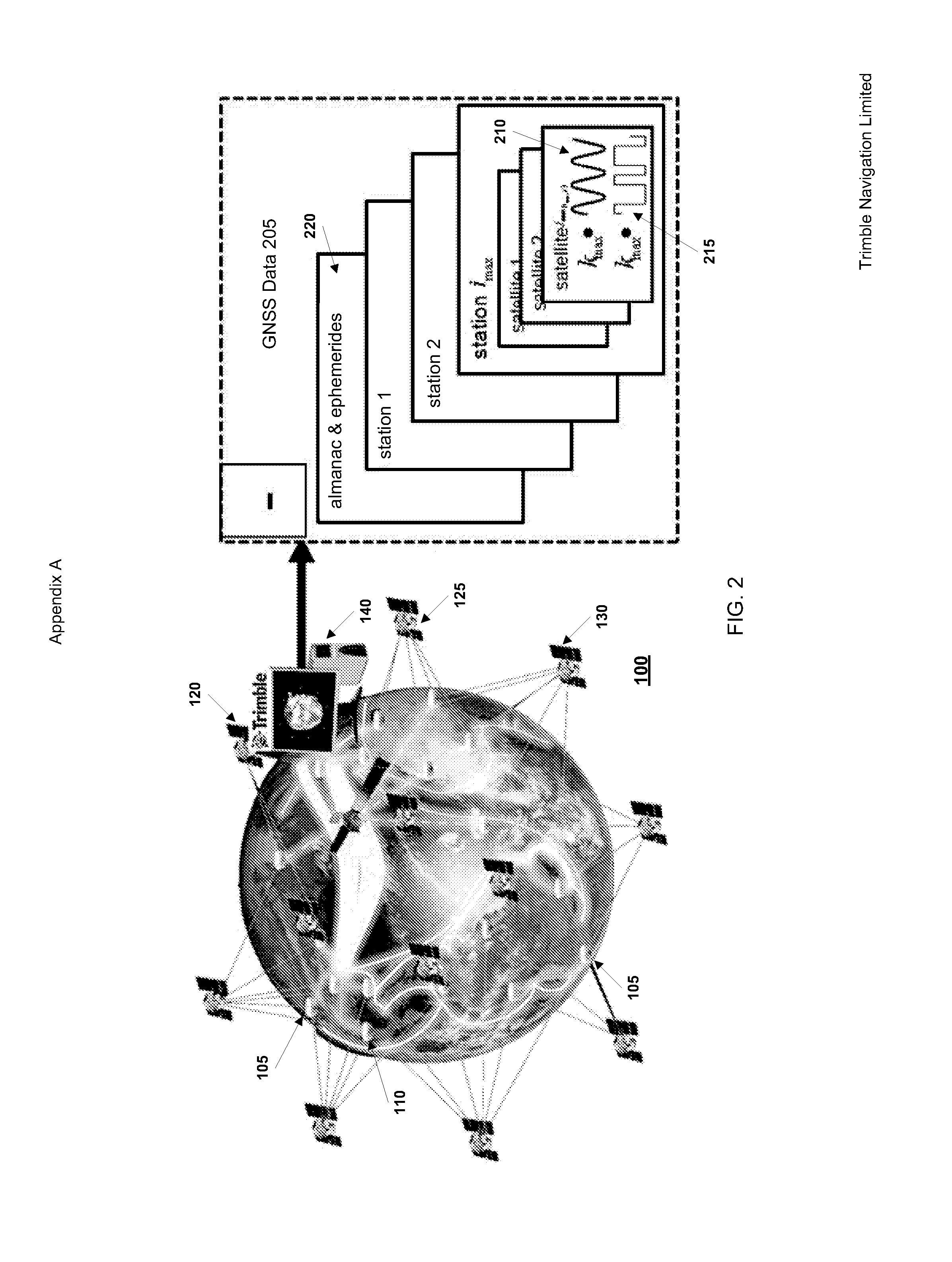
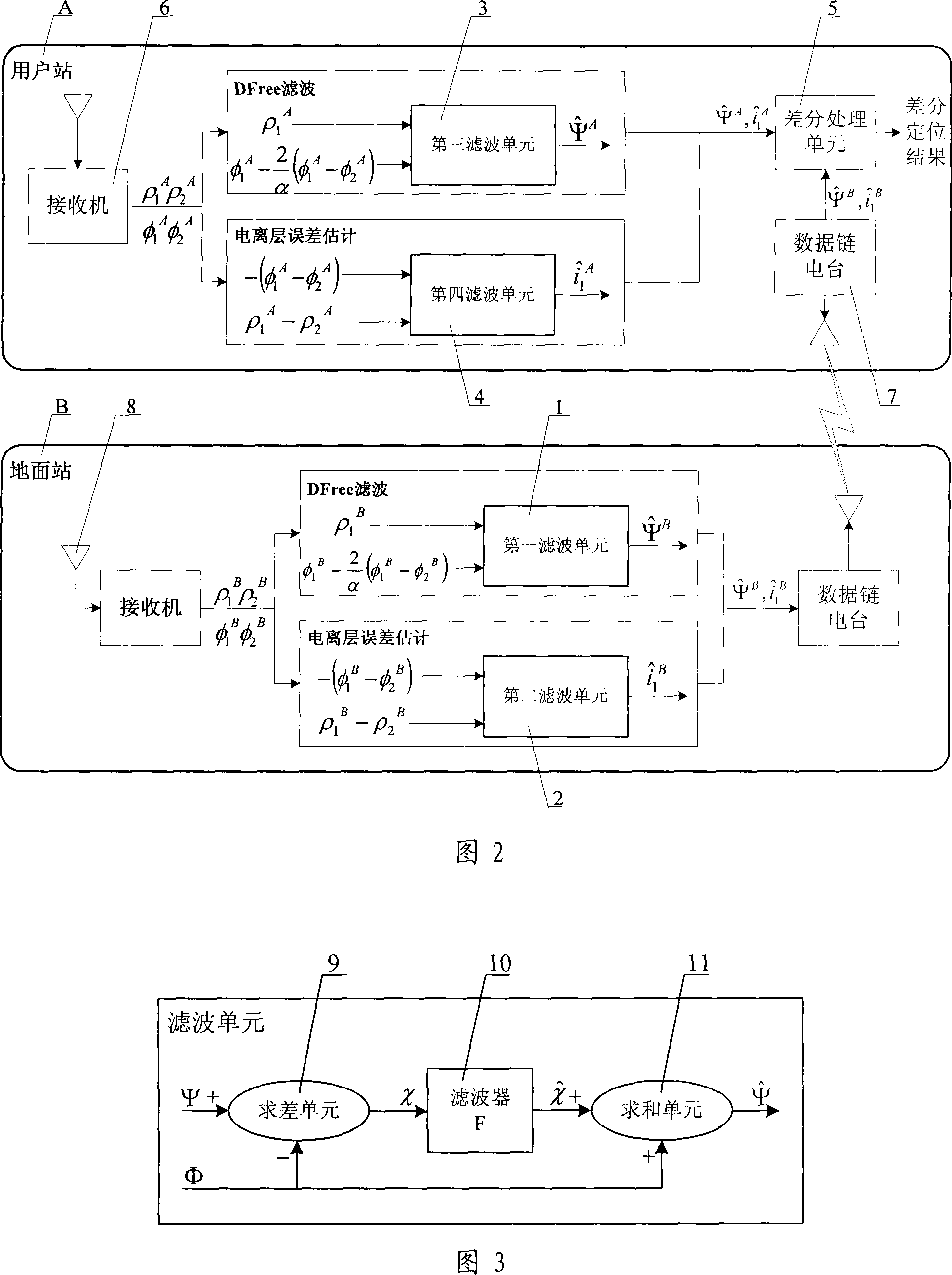
Methods and apparatus which characterize the ionospheric error across a network of GNSS reference stations are presented. The method relies on dual-frequency phase measurements in a geometry-free linear combination. The data are filtered for ambiguities and the characteristic parameters of the ionosphere. In combination with filter results from other combinations of phase measurements (ionosphere free combination), the physically-based model provides rapid and reliable ambiguity resolution.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
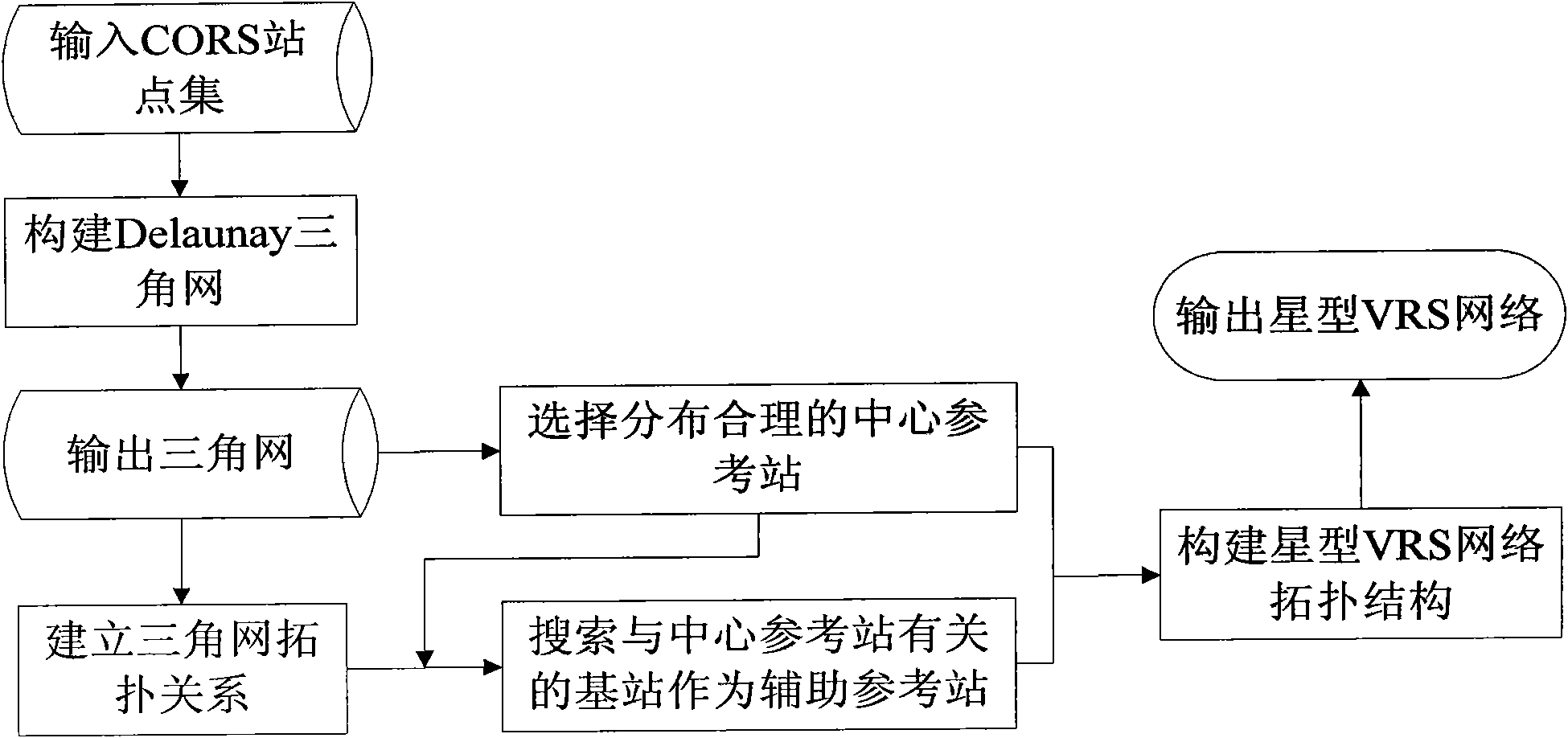
Method for positioning network RTK based on star-shaped virtual reference station
InactiveCN101943749AFixed fastHigh precisionPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereIonosphere
The invention discloses a method for positioning a network RTK based on a star-shaped virtual reference station, which comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing a star-shaped basic calculation unit, constructing a baseline calculation way for a star-shaped VRS network RTK and proposing an ambiguity calculation method suitable for the star-shaped VRS network RTK; and then studying the algorithm of the corrections of the ionosphere and the troposphere in the VRS network RTK aiming at the star shape. The method markedly increases the calculation speed on the network ambiguity by about 50% and has higher accuracy and reliability of the generated network correction.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
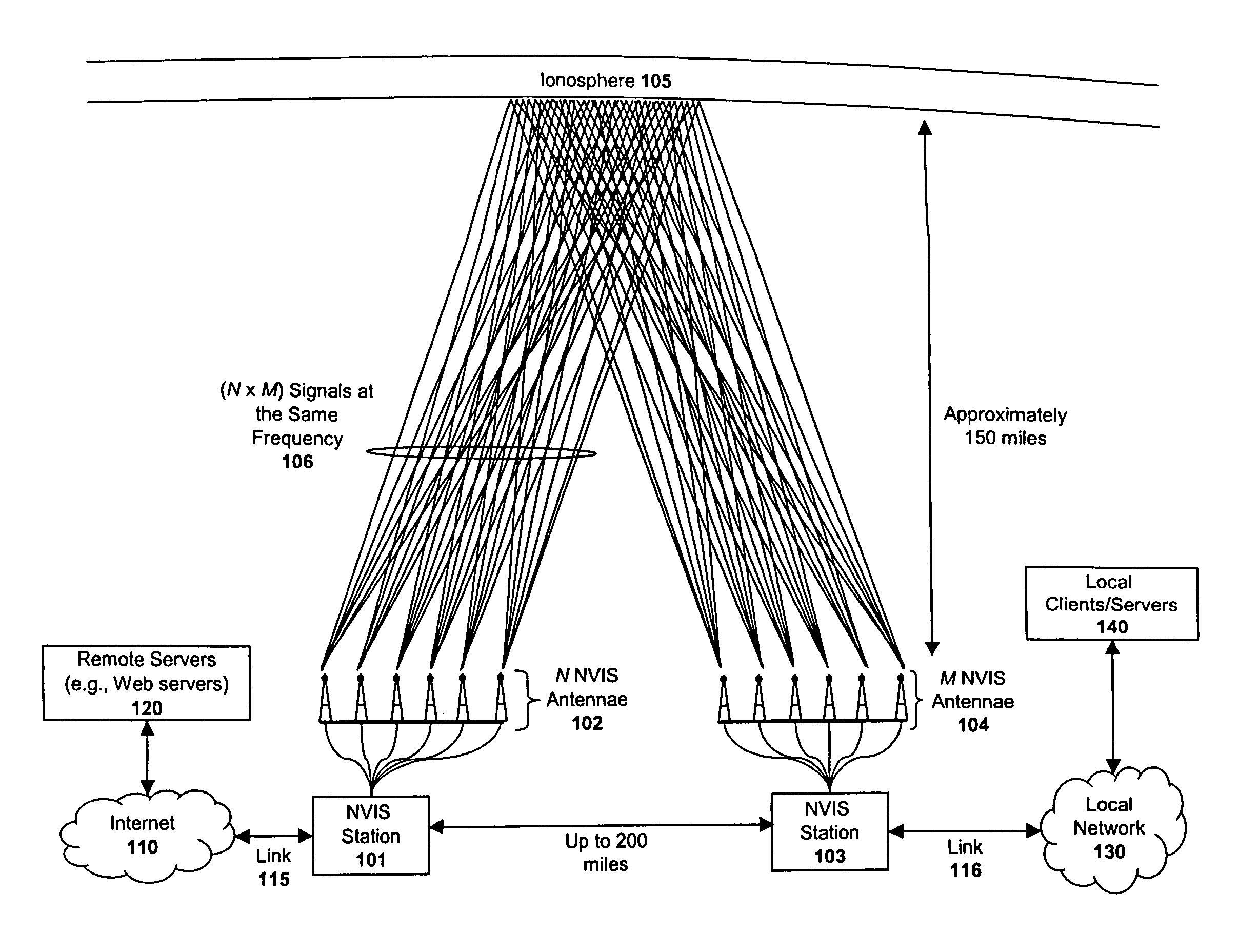
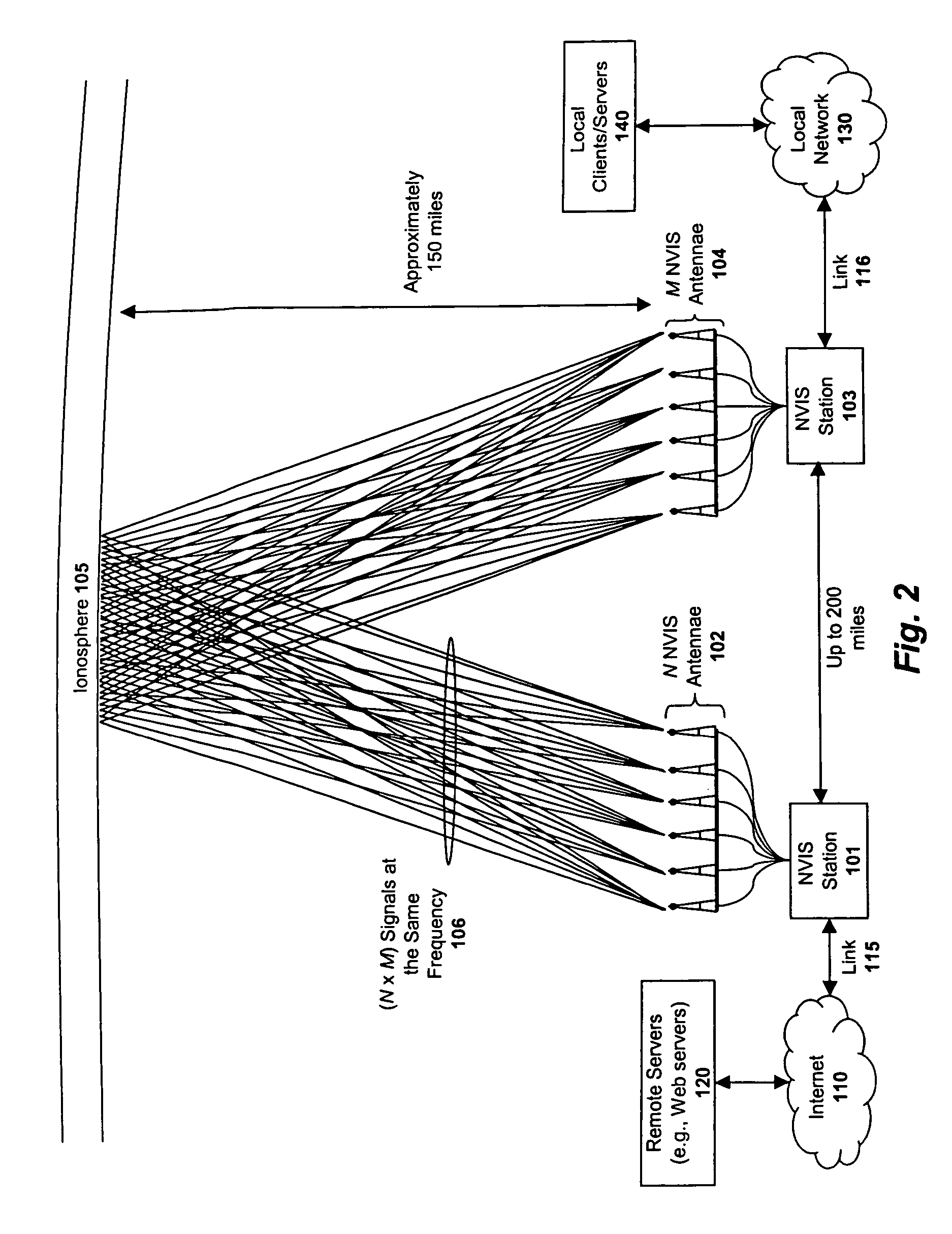
System and method for enhancing near vertical incidence skywave ("NVIS") communication using space-time coding
ActiveUS20050220207A1Polarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationCommunications systemData stream
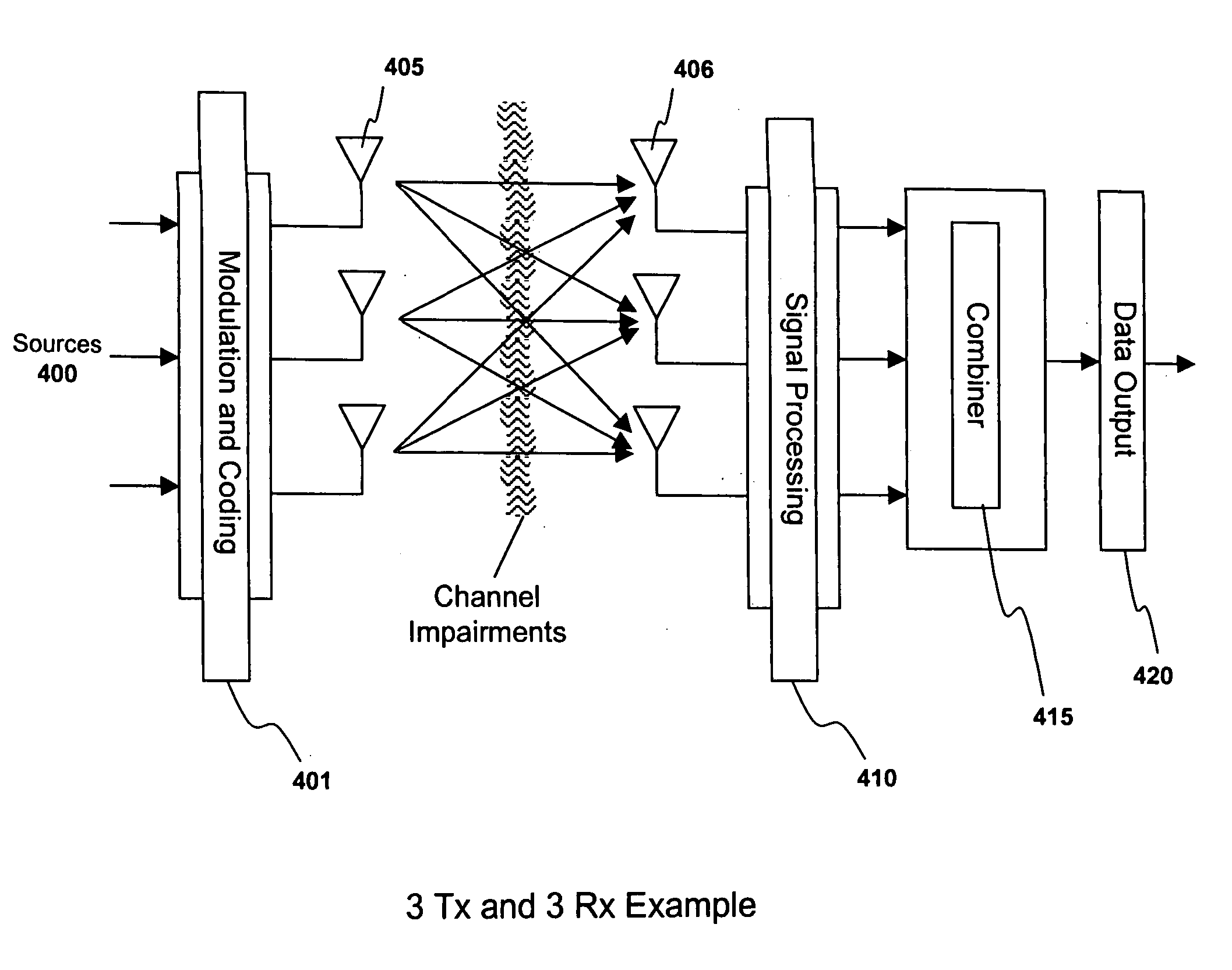
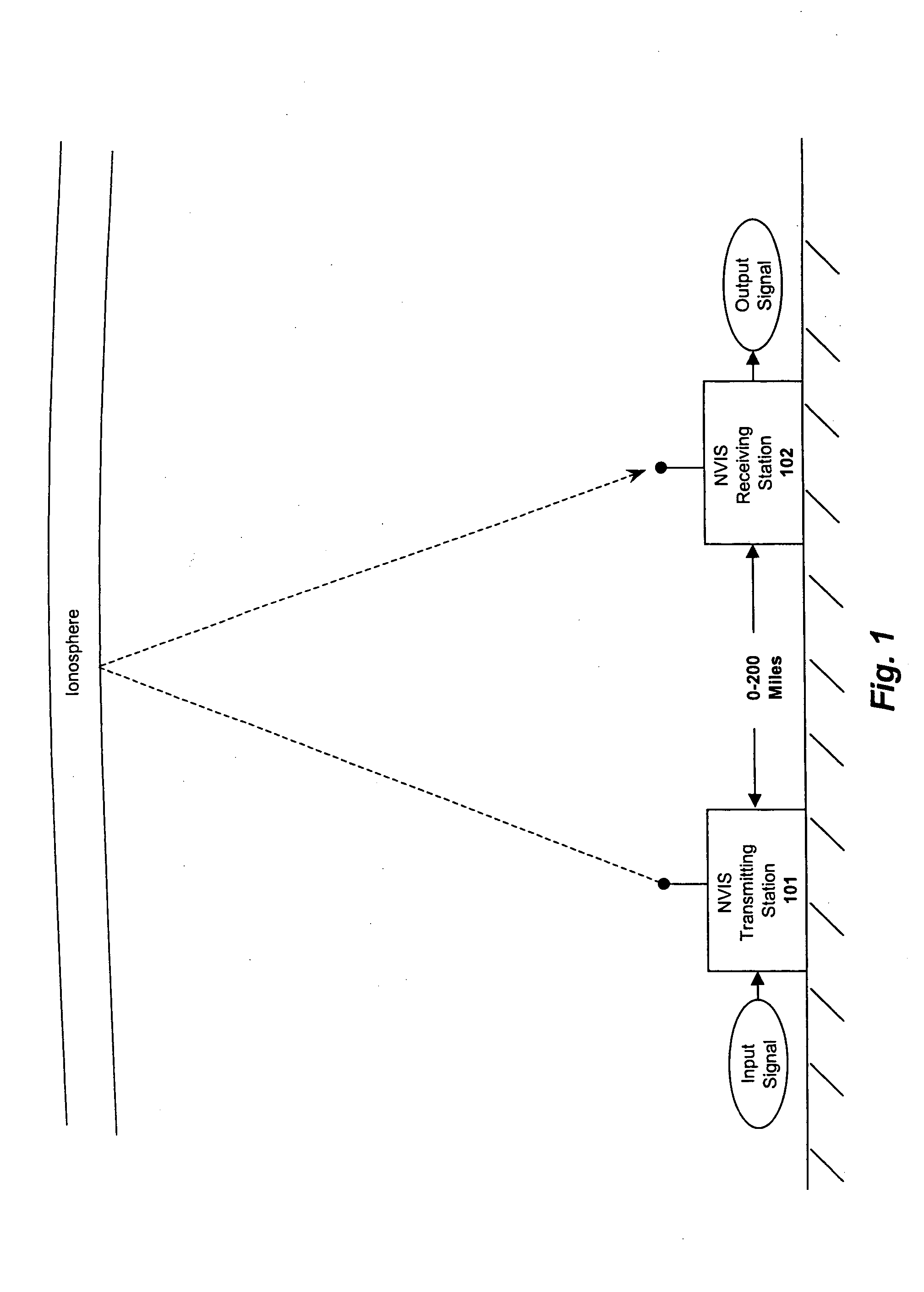
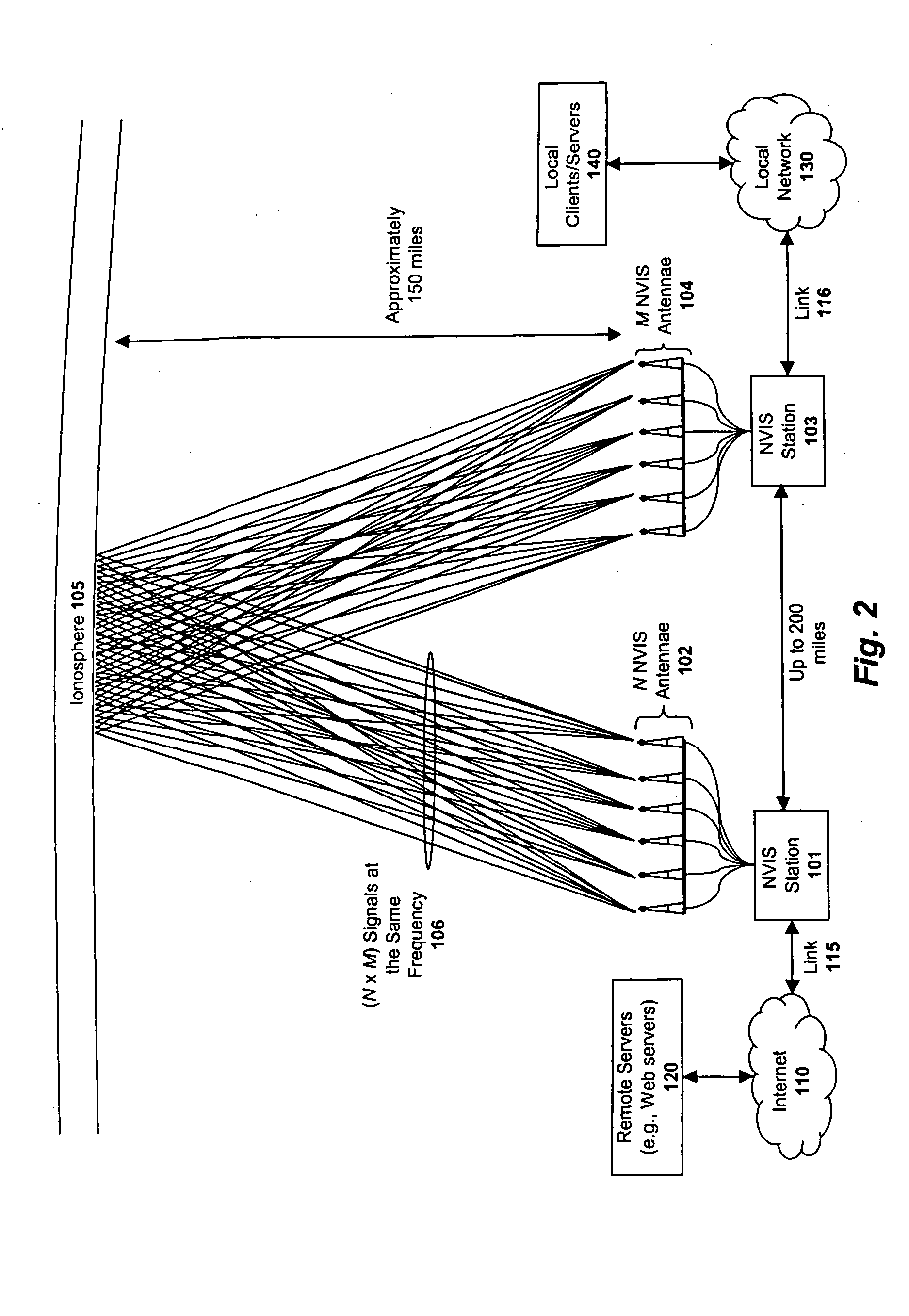
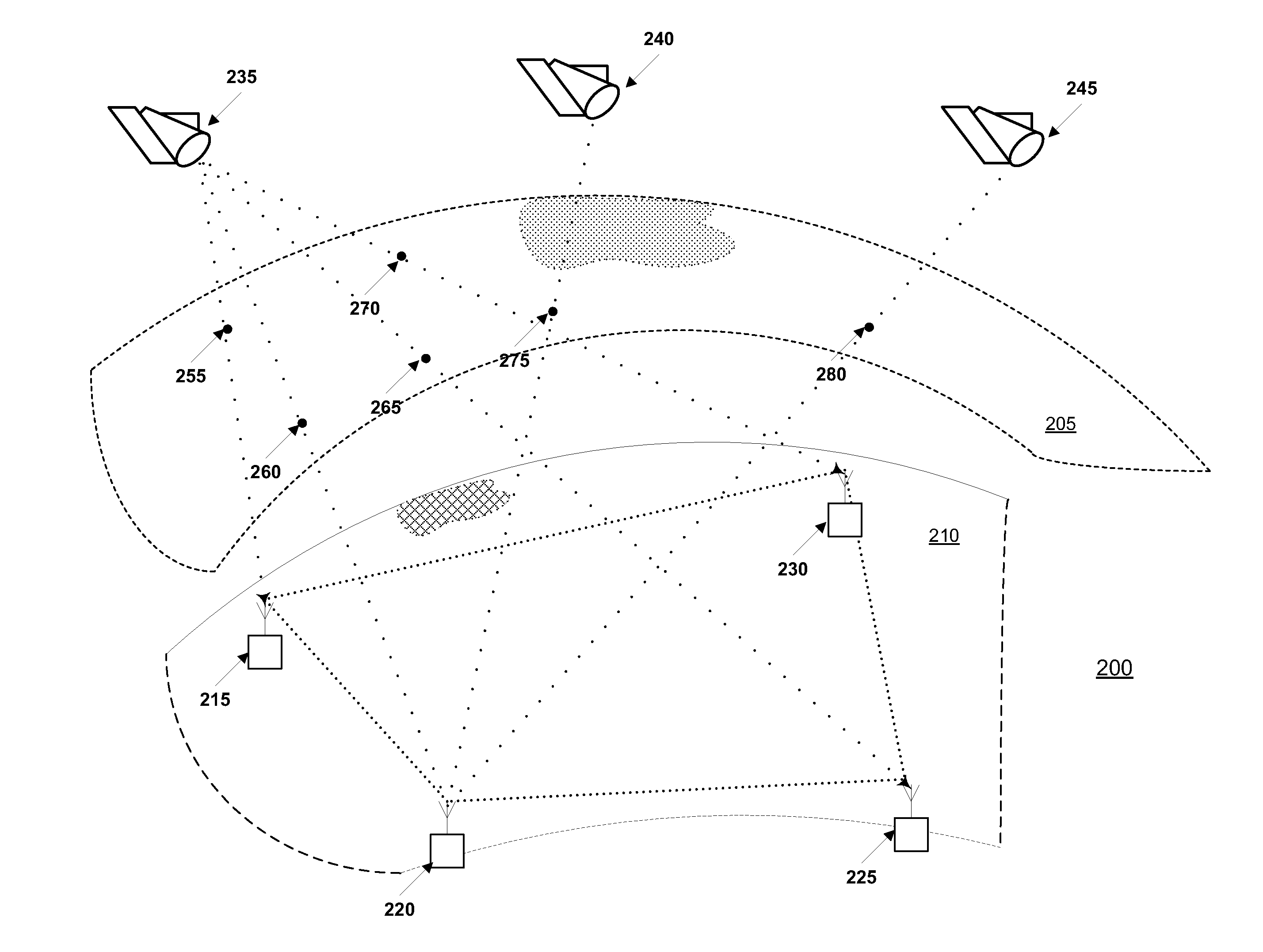
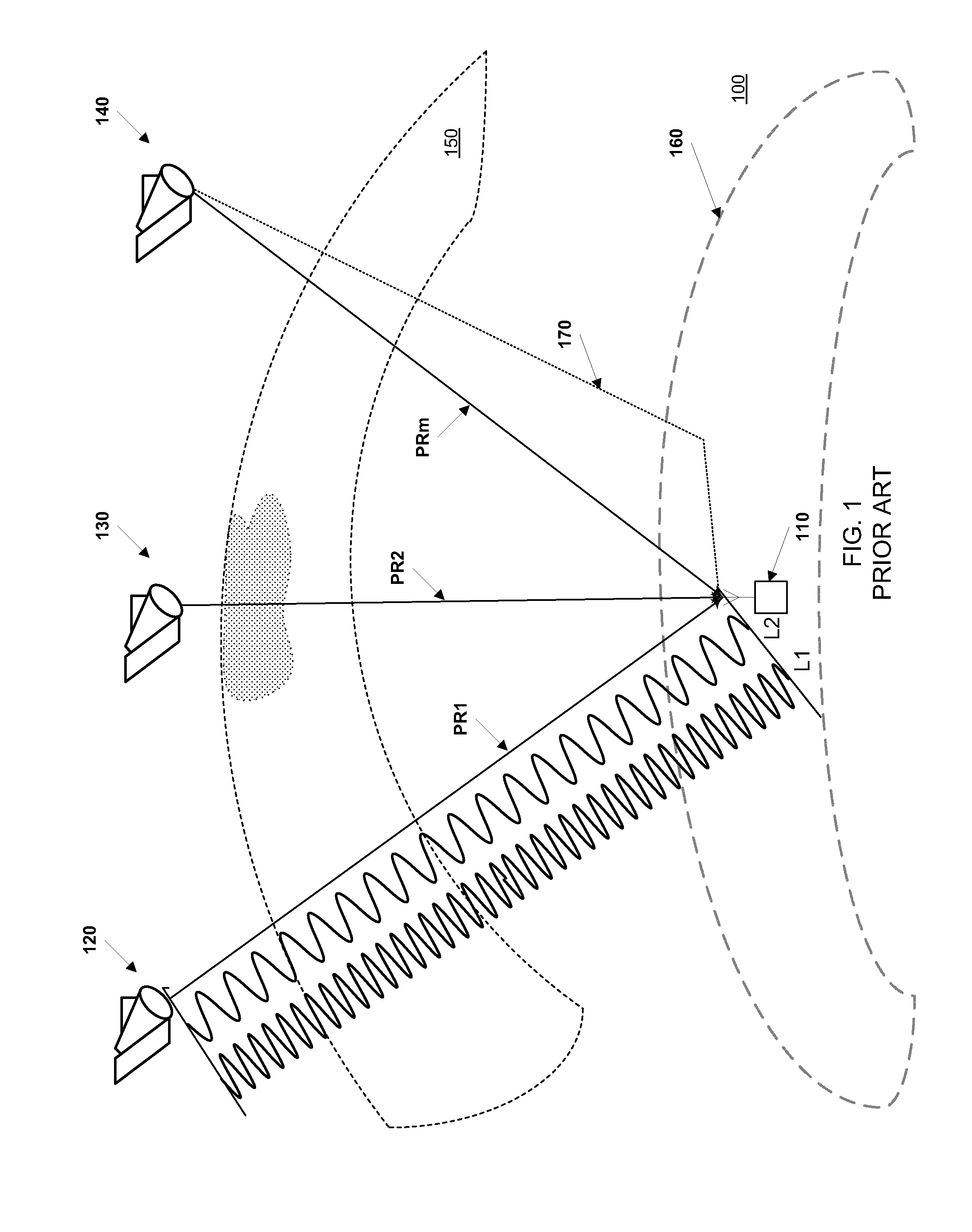
A system and method are described in which space-time coding techniques are used to transmit and receive multiple data streams within a near vertical incidence skywave (“NVIS”) communication system. Within the NVIS communication system, multiple independent data streams may be transmitted from a transmitting station at a high radiation angle, approaching or reaching 90 degrees. The data streams are reflected off of the ionosphere of the earth and received by one or more receiving stations. In one embodiment, the space-time coding techniques are multiple-input multiple-output (“MIMO”) signal communication techniques.
Owner:REARDEN
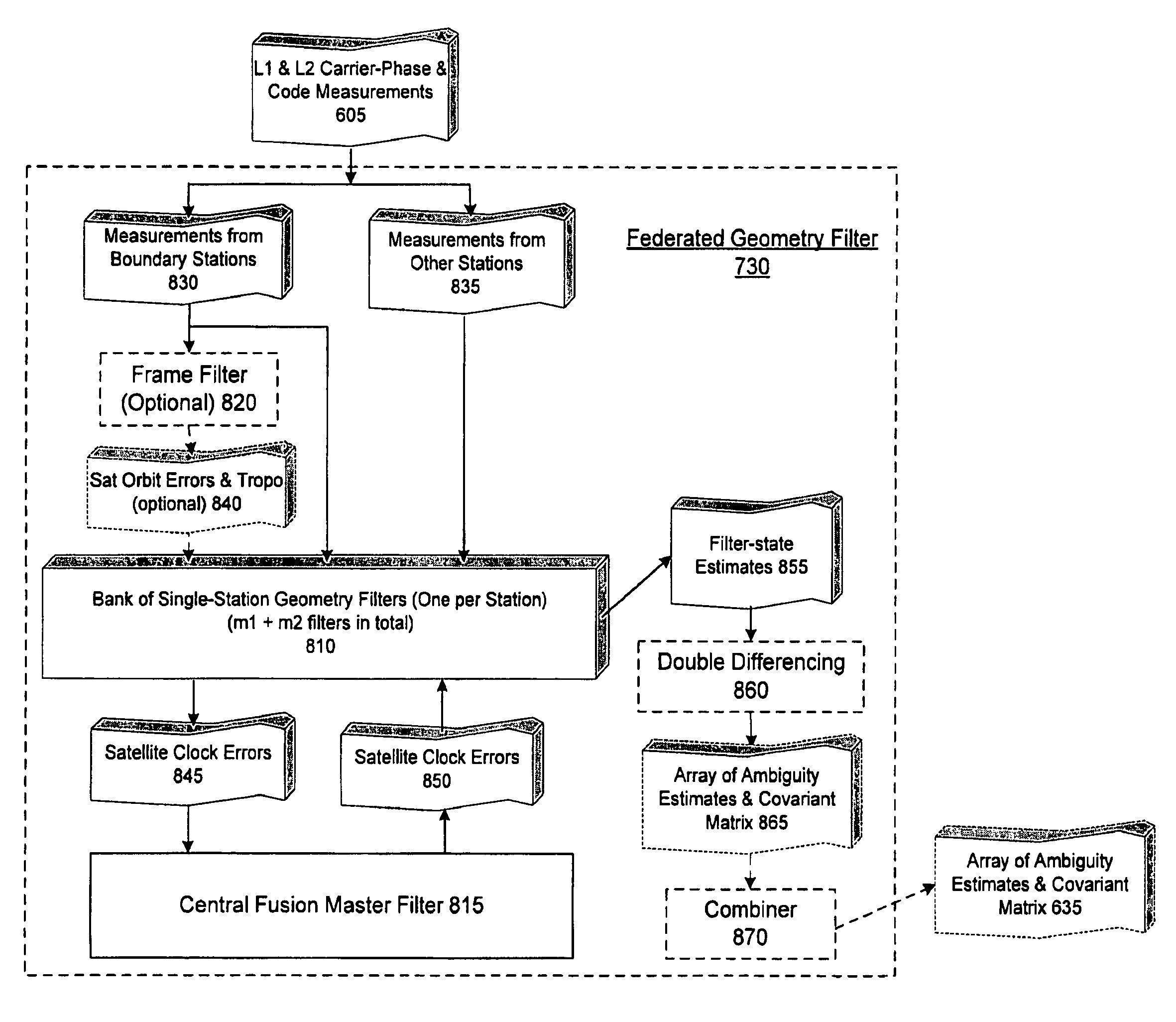
Gnss Signal Processing Methods and Apparatus
ActiveUS20090027264A1Reduce processing timePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingIonosphereComputer science
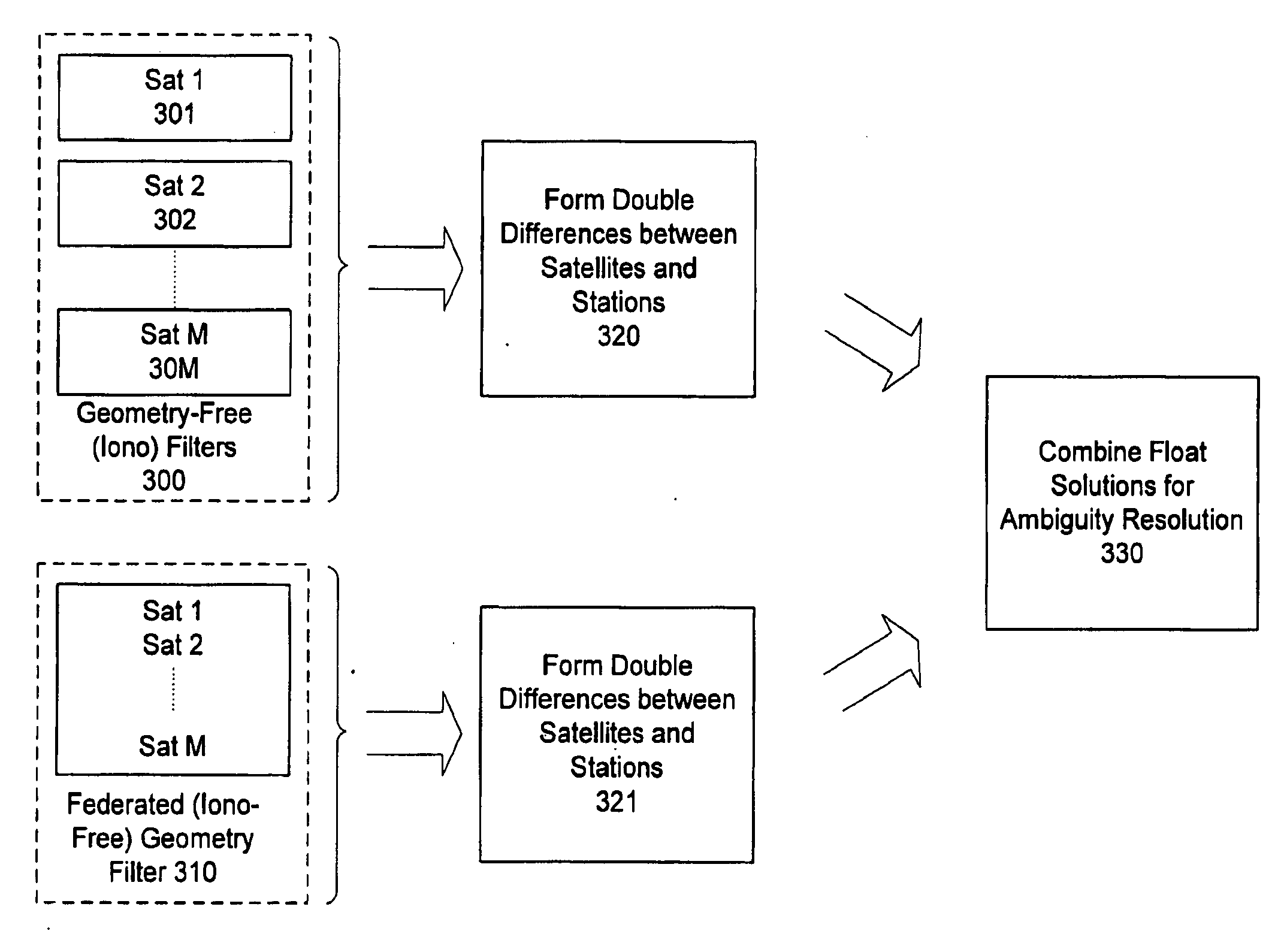
Methods and apparatus for processing of data from a network of GNSS reference stations are presented. An ionosphere-free, federated geometry filter is employed so that computation time increases only linearly with the increase in number of reference stations, significantly reducing processing time as compared to a centralized filter approach.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
GNSS Signal Processing with Ionospheric Bridging for Reconvergence
Methods and apparatus provide for positioning of a rover antenna from GNSS data derived from multi-frequency signals and correction data derived from a network of reference stations. Rover antenna position and multi-frequency ambiguities are estimated at each epoch. An ionospheric filter models variation in ionospheric bias per satellite. A set of ionospheric carrier-phase ambiguities is estimated at least when the multi-frequency ambiguities have attained a predetermined precision. The estimated ionospheric carrier-phase ambiguities are cached. After detecting interruption of signal at the rover antenna and determining reacquisition of signals at the rover antenna, an ionospheric bias per satellite over an interruption interval is predicted. For each satellite, a cached ionospheric carrier-phase ambiguity is combined with a predicted ionospheric bias to obtain a post-interruption ionospheric ambiguity estimate. The post-interruption ionospheric ambiguity estimates are used to aid estimation of rover antenna position after signal reacquisition.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
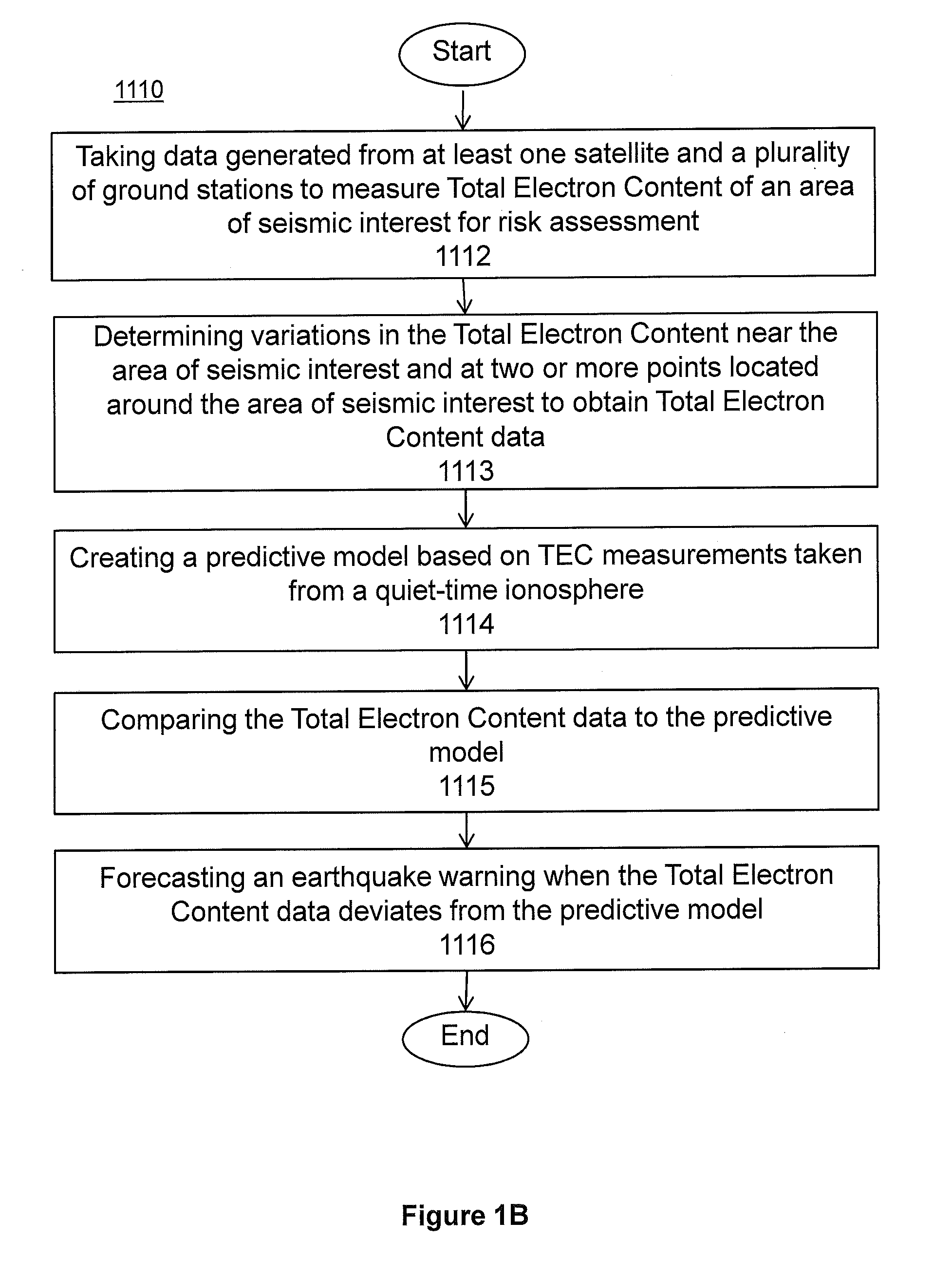
System and methods for risk prediction and assessment
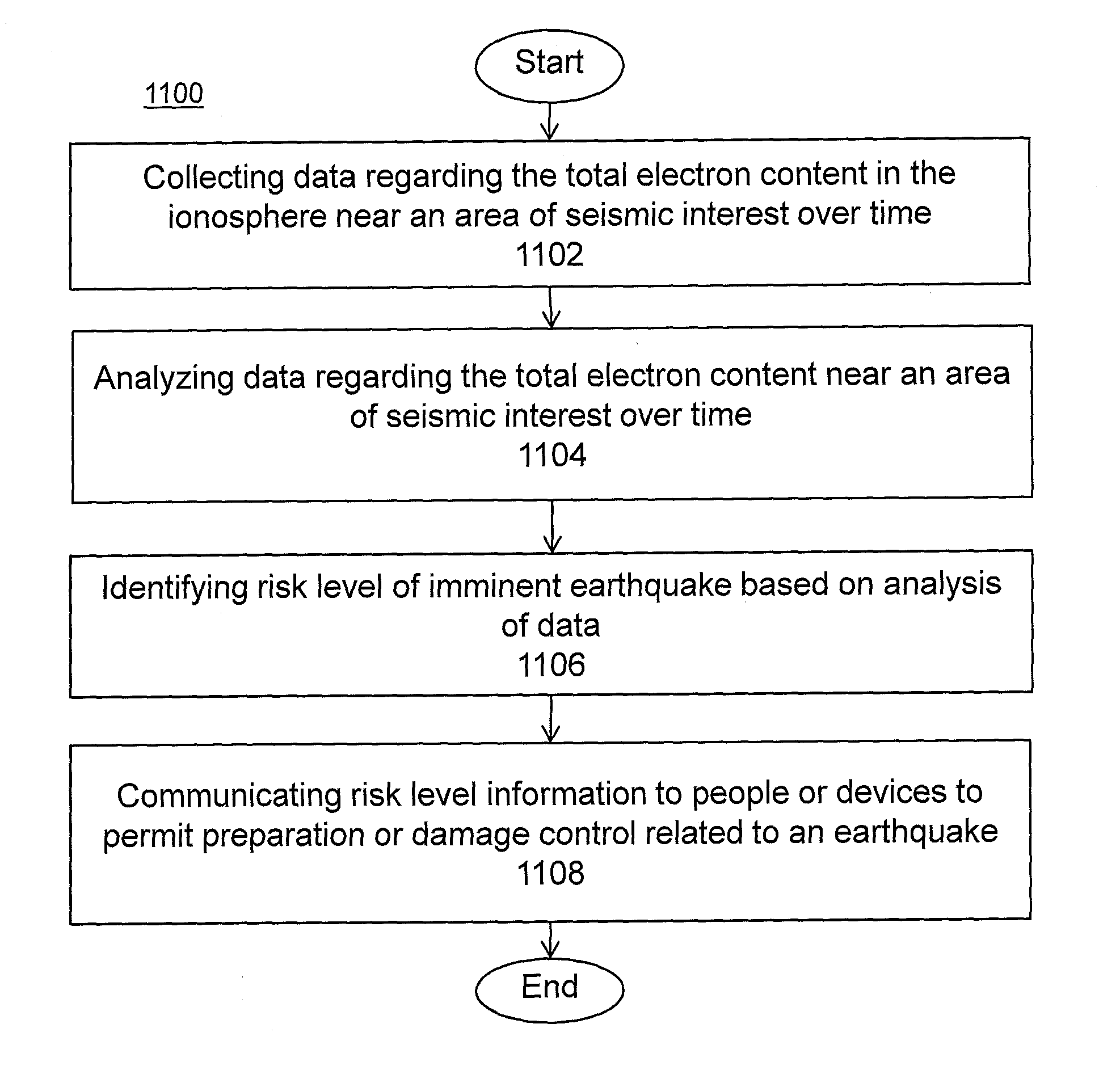
InactiveUS20150051837A1Weather condition predictionEarthquake measurementIonosphereTotal electron content
A system and methods for predicting and assessing risk before an event occurs. More particularly, the present invention predicts and assesses risk such as the occurrence of an earthquake prior to the event by collecting and analyzing changes in Total Electron Content (“TEC”) in the ionosphere.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COMMLIZATION CCTEC
GNSS signal processing methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7755542B2Reduce processing timeSatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionIonosphereComputer science
Methods and apparatus for processing of data from a network of GNSS reference stations are presented. An ionosphere-free, federated geometry filter is employed so that computation time increases only linearly with the increase in number of reference stations, significantly reducing processing time as compared to a centralized filter approach.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
System and method for enhancing near vertical incidence skywave (“NVIS”) communication using space-time coding
ActiveUS7885354B2Polarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationData streamCommunications system
A system and method are described in which space-time coding techniques are used to transmit and receive multiple data streams within a near vertical incidence skywave (“NVIS”) communication system. Within the NVIS communication system, multiple independent data streams may be transmitted from a transmitting station at a high radiation angle, approaching or reaching 90 degrees. The data streams are reflected off of the ionosphere of the earth and received by one or more receiving stations. In one embodiment, the space-time coding techniques are multiple-input multiple-output (“MIMO”) signal communication techniques.
Owner:REARDEN LLC
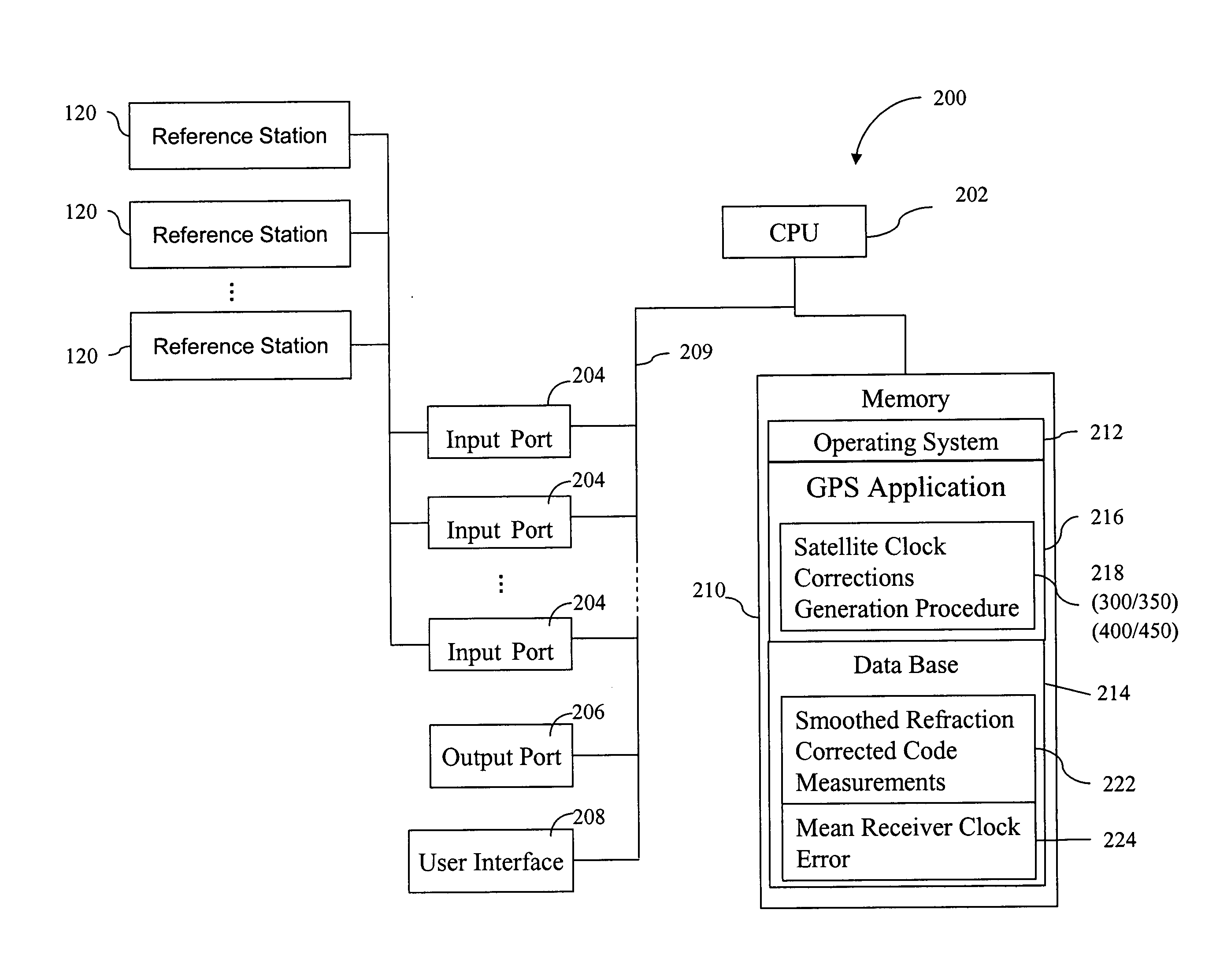
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS20050024263A1Easy accessCancel noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyGps measurement
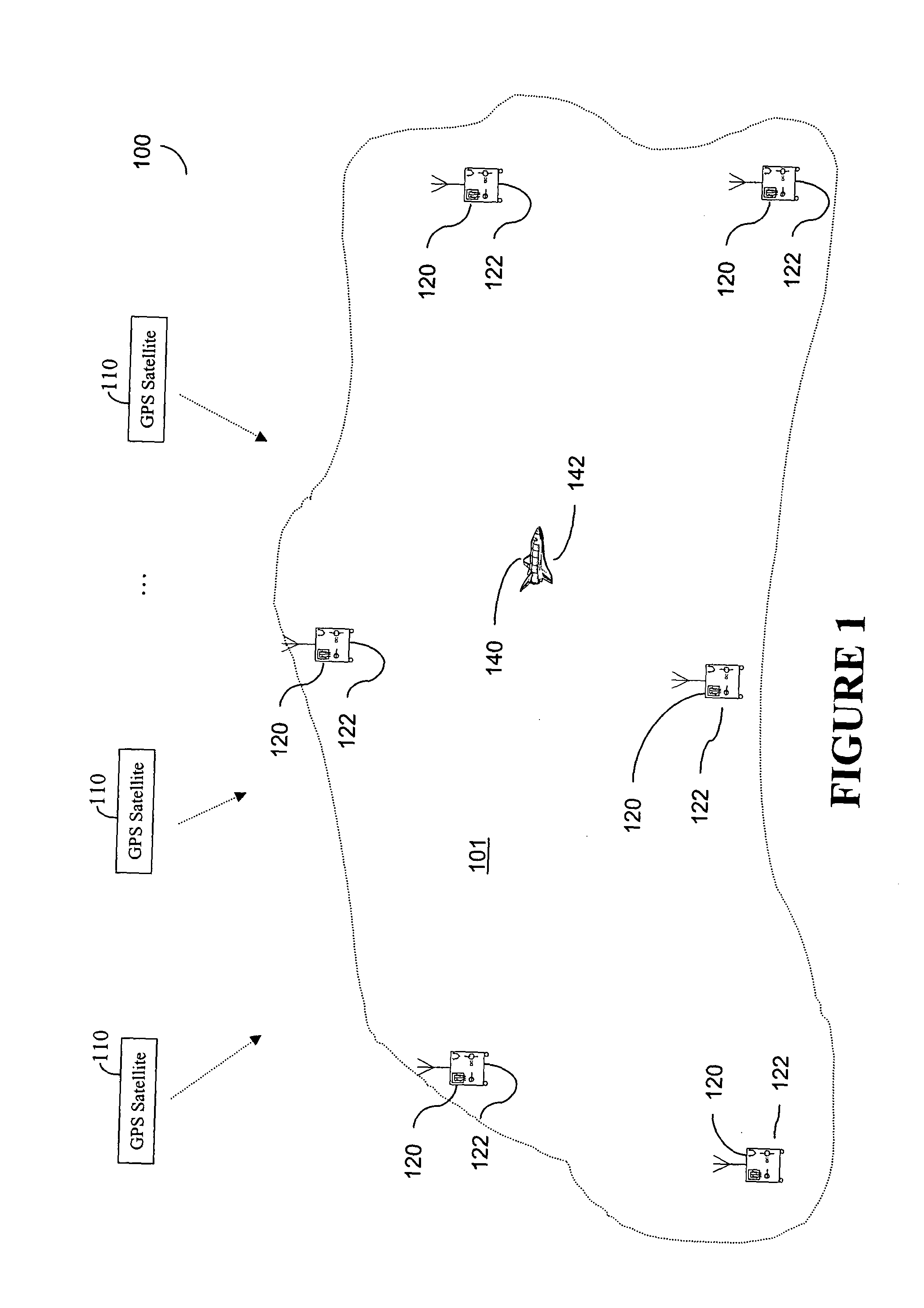
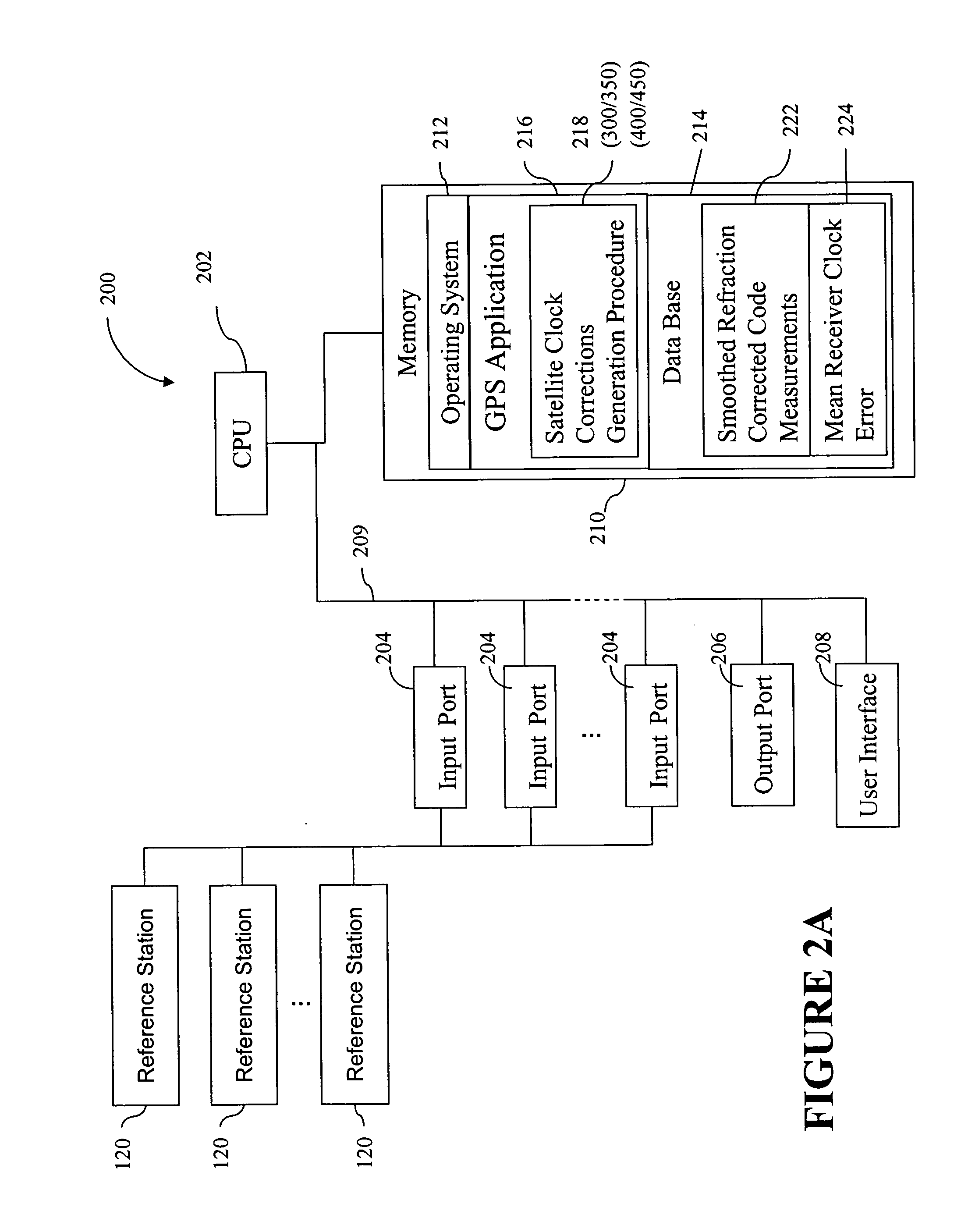
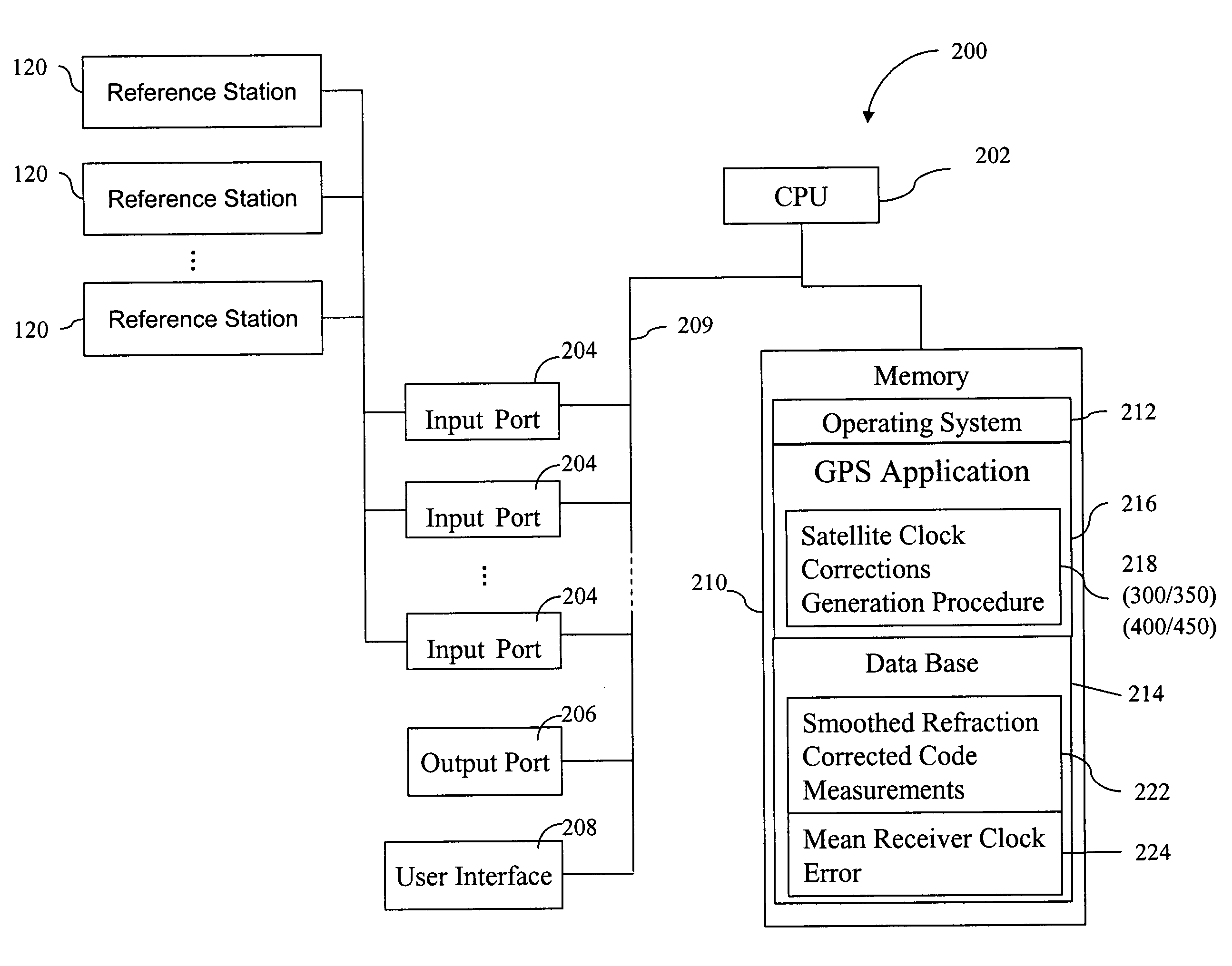
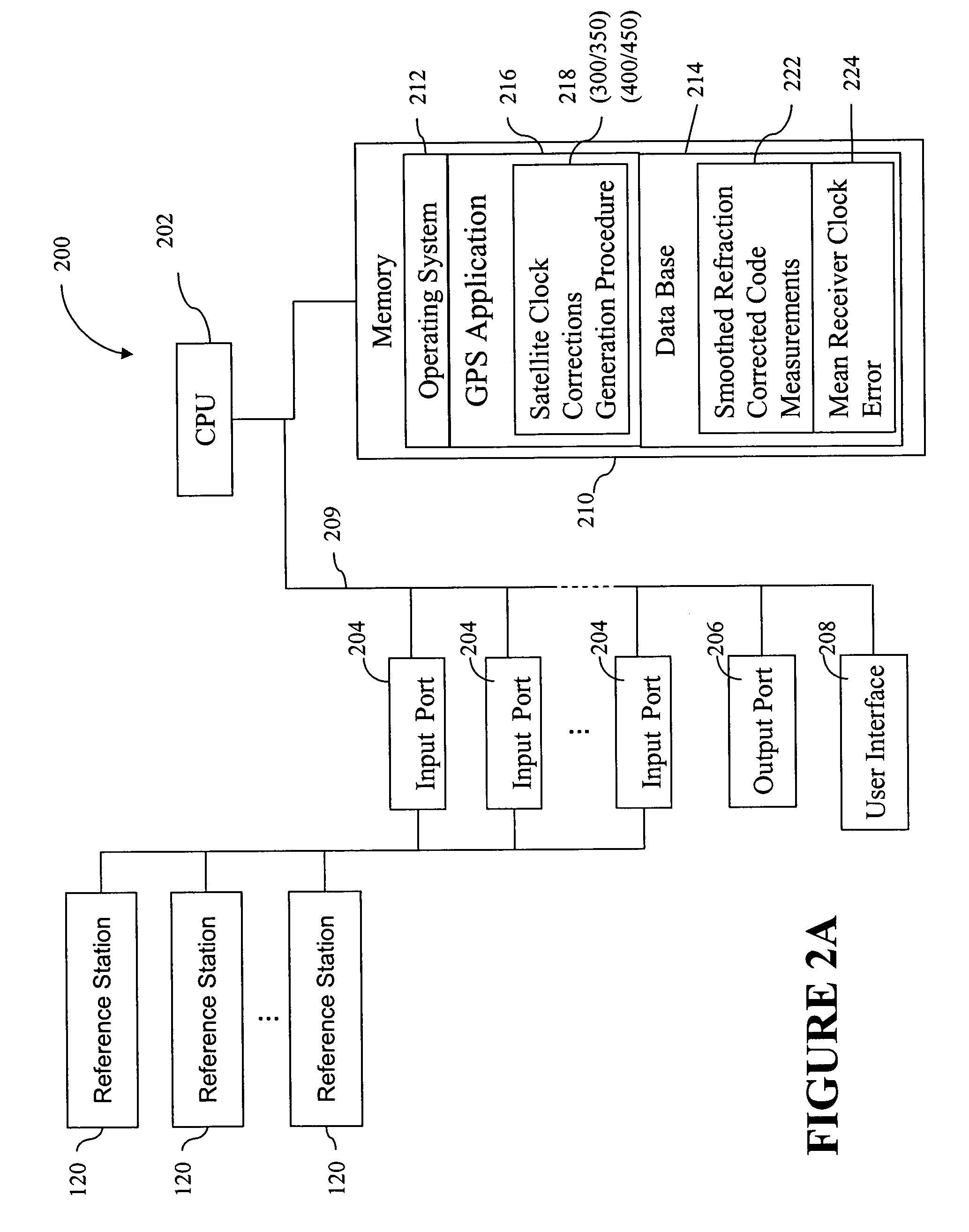
A method for generating satellite clock corrections for a WADGPS network computers satellite clock corrections after removing other substantial error components. Errors caused by the ionosphere refraction effects are removed from GPS measurements taken at reference stations using dual-frequency GPS measurements. The multipath noise are removed by smoothing of GPS pseudorange code measurements with carrier-phase measurements. The tropospheric refraction effect can be largely removed by modeling, and if desired, can be improved by the use of small stochastic adjustments included in the computation of the clock correction. After removing the above error factors, satellite clock corrections are computed for individual reference stations, and an average clock correction is formed for each of a plurality of satellites by taking an average or weighted average of the satellite clock corrections over reference stations to which the satellite is visible.
Owner:DEERE & CO
GNSS atmospheric estimation with federated ionospheric filter
ActiveUS20120092213A1Fast convergenceSatellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguityIonosphere
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers using sbas
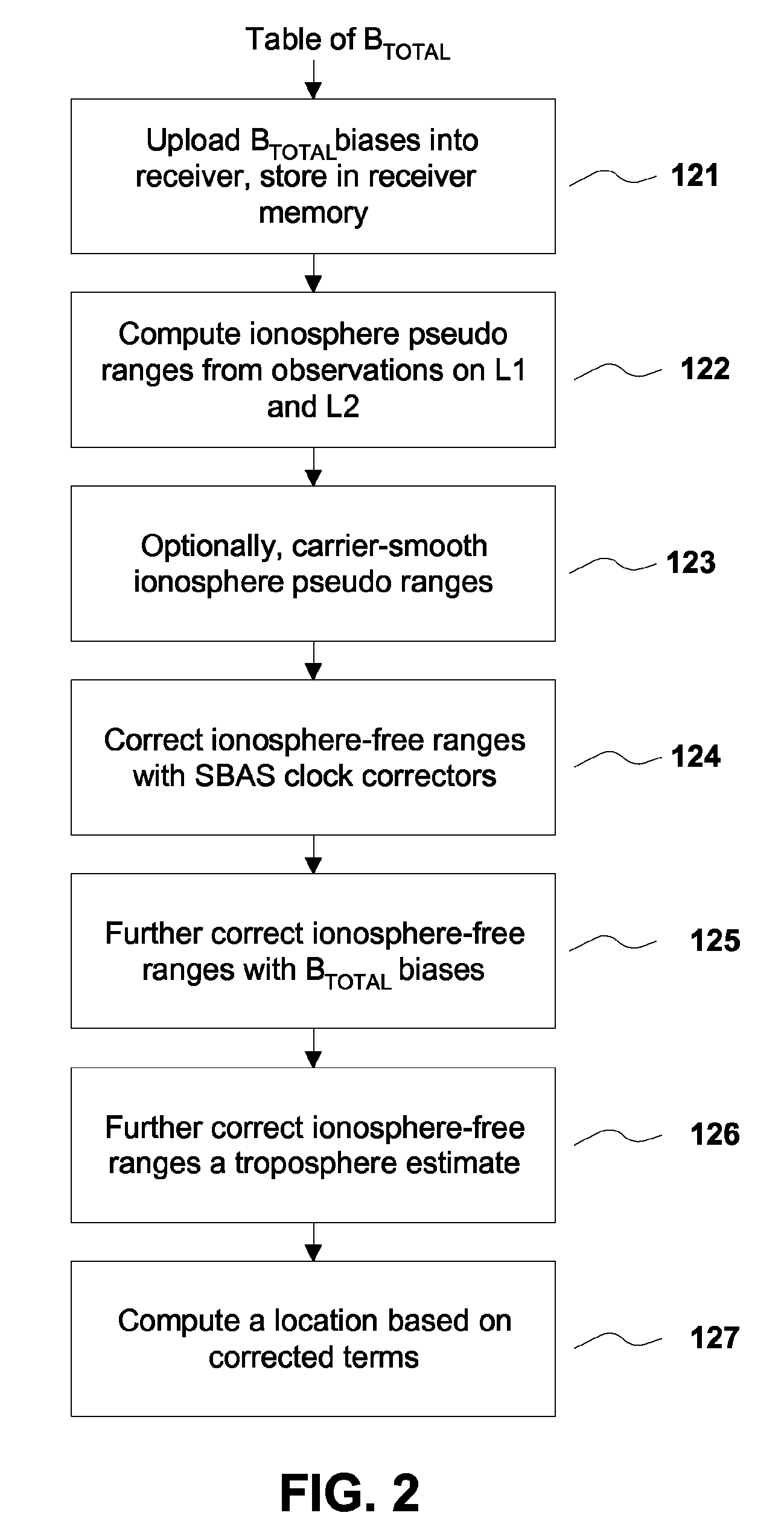
ActiveUS20100231443A1Improve performanceImprove navigation accuracySatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyIonosphere
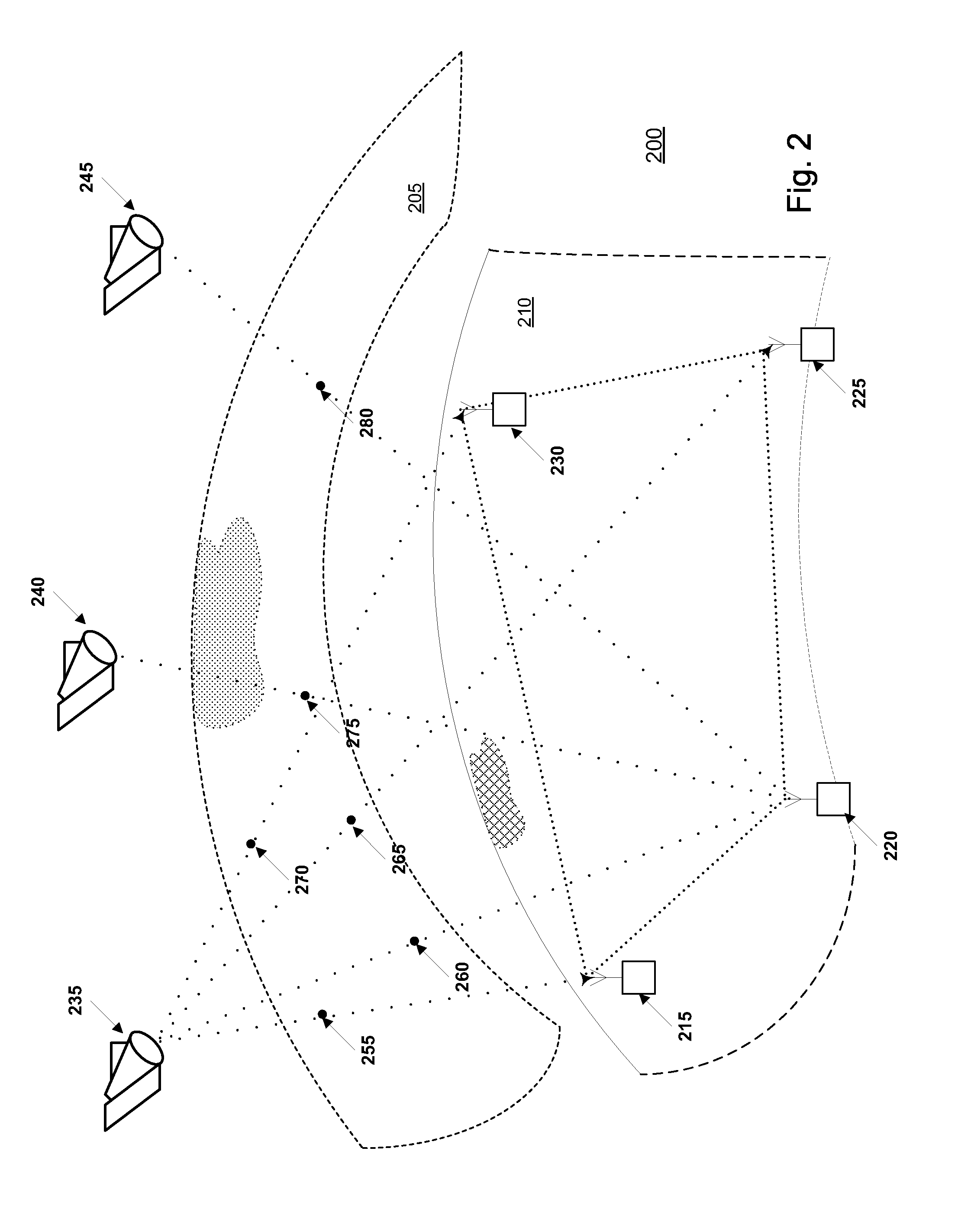
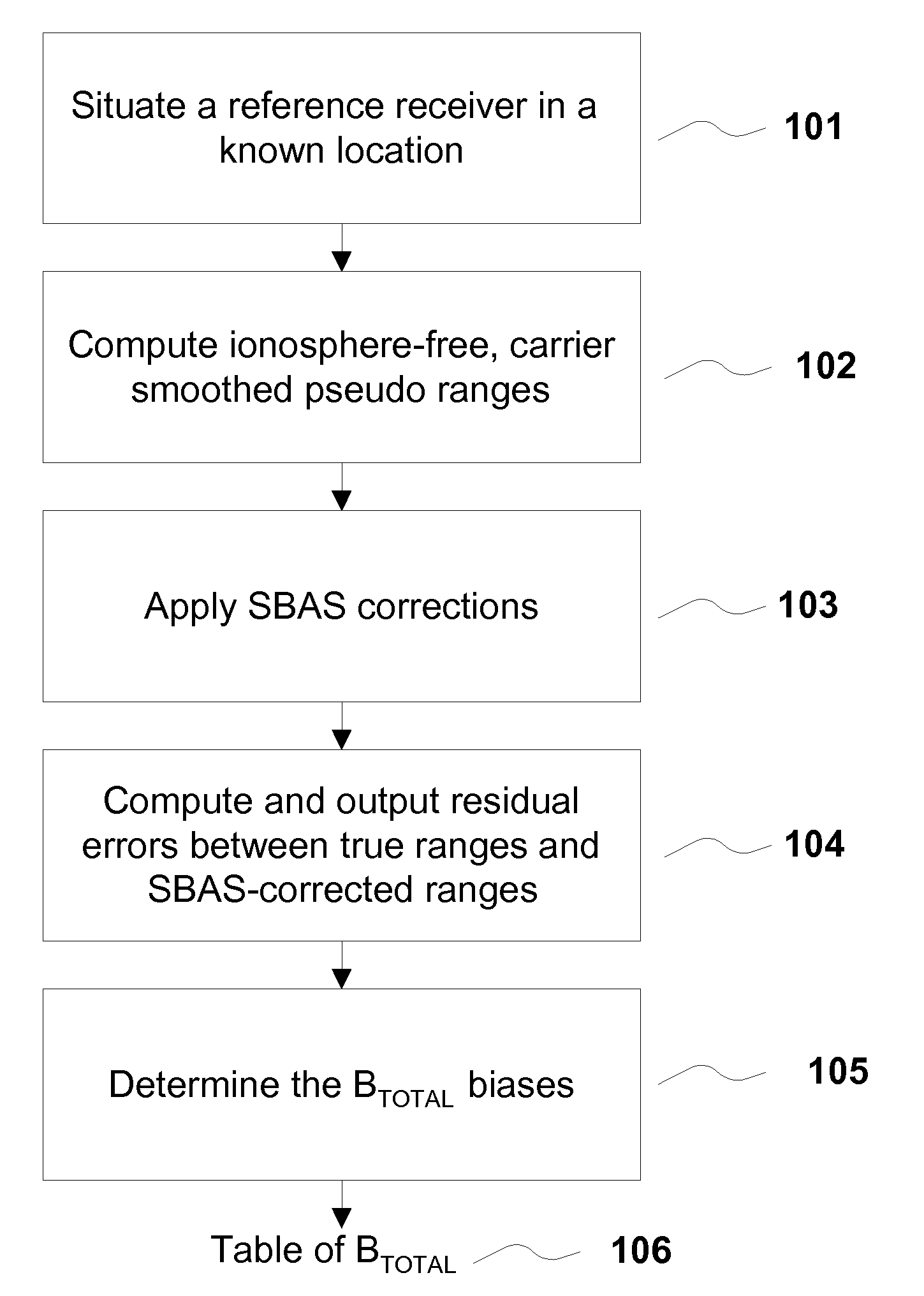
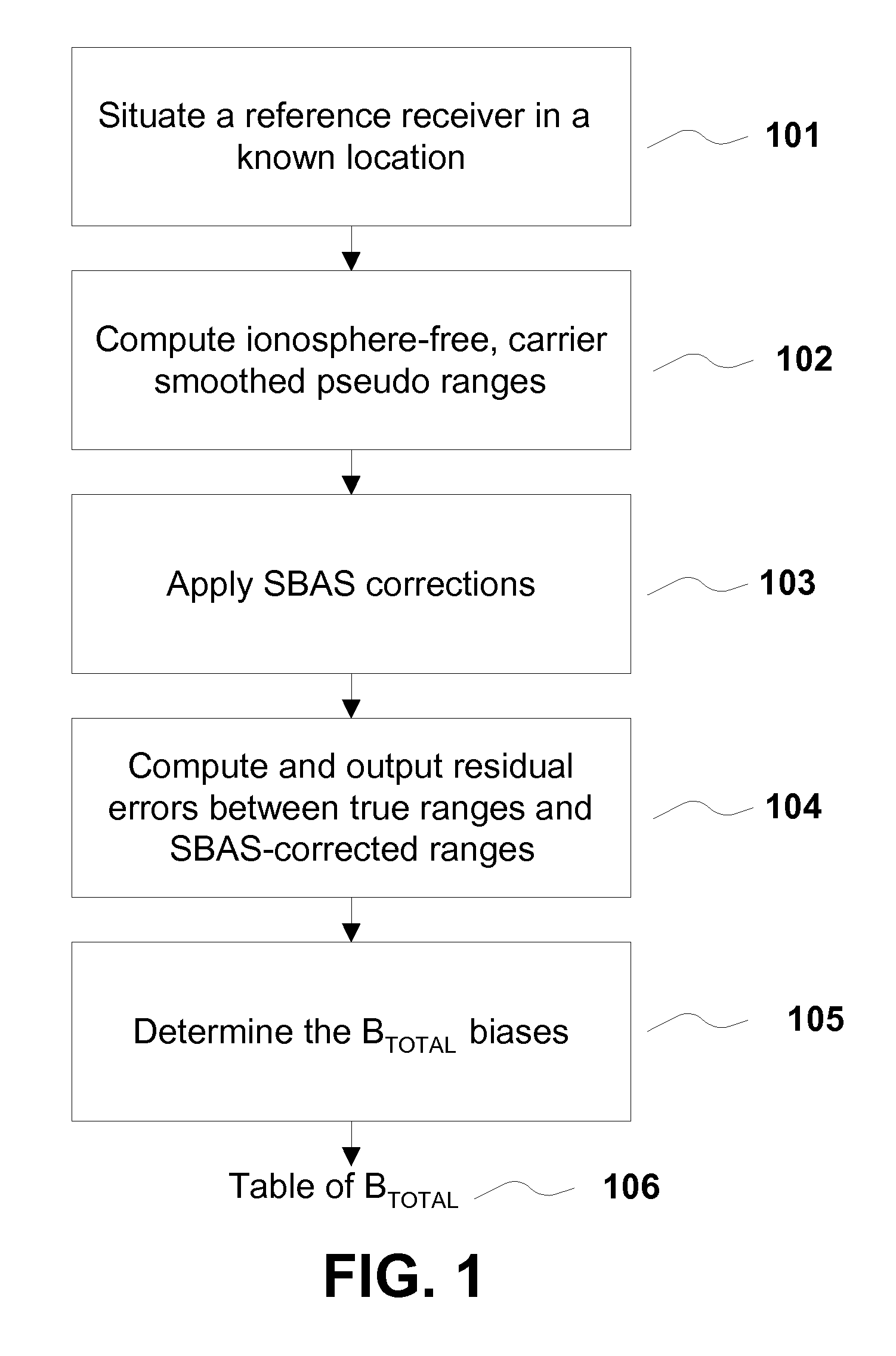
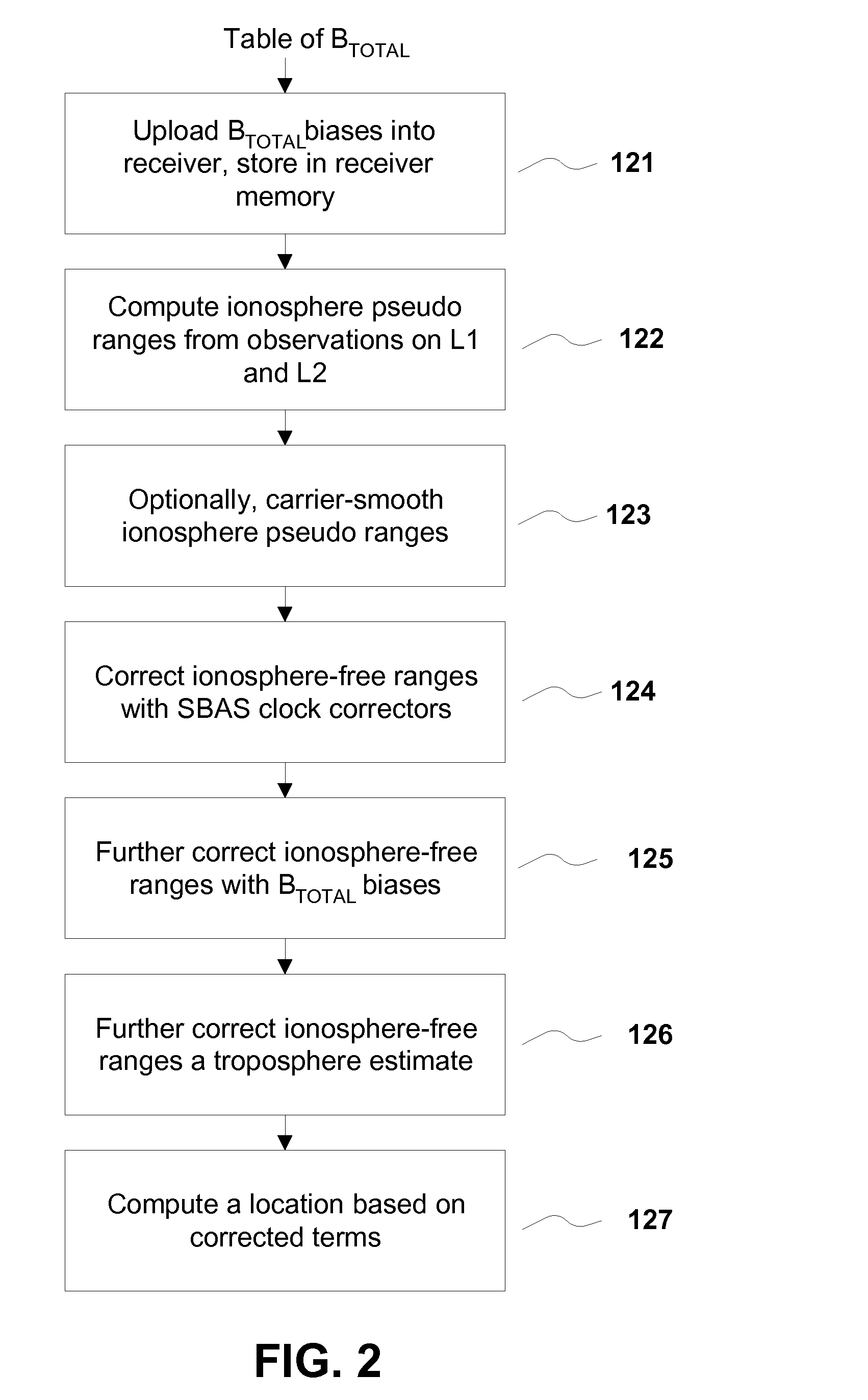
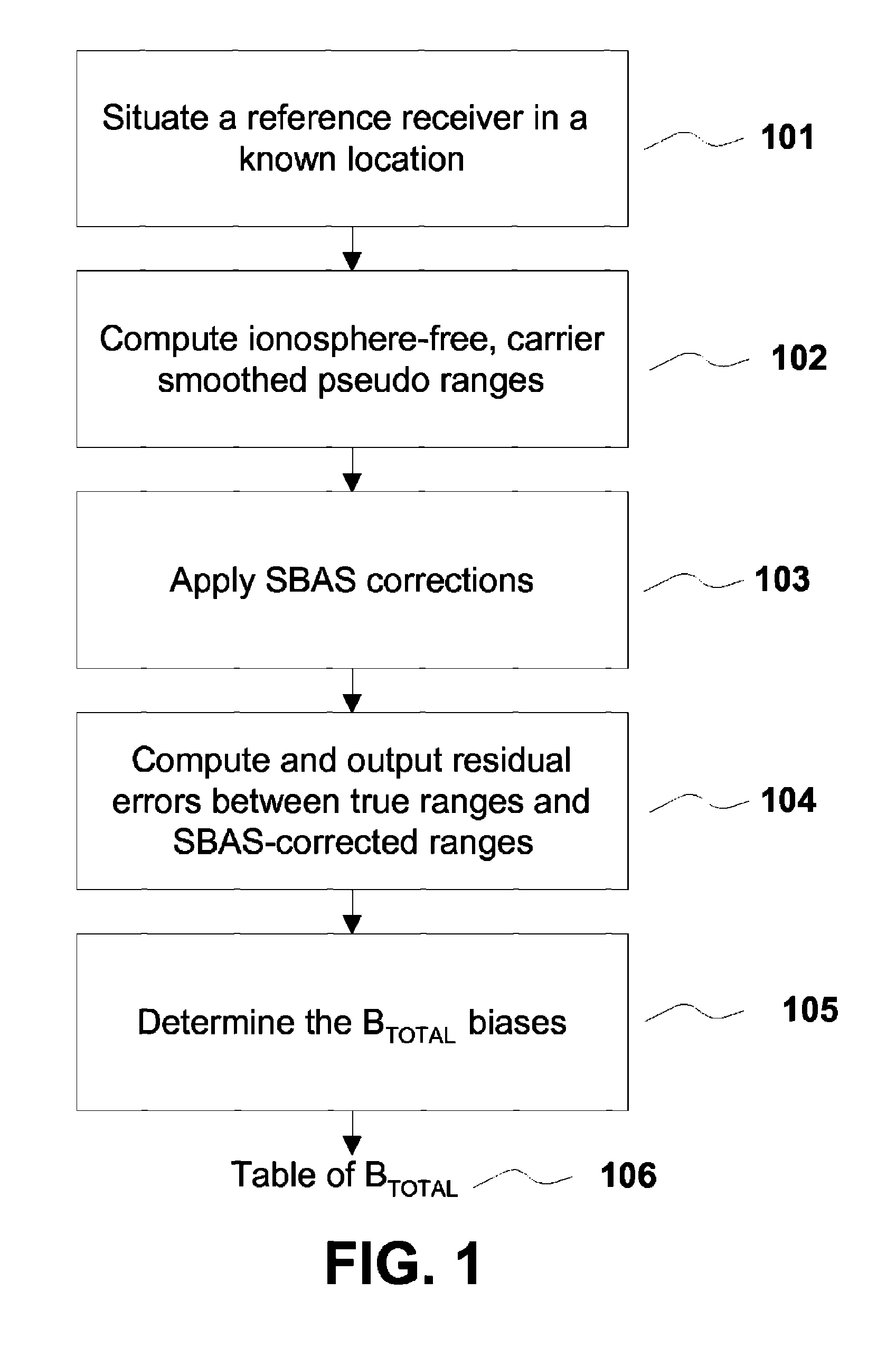
A method for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers circumvents the need for ionosphere corrections by using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A) to form ionosphere-free ranges. A table of biases is stored in microprocessor controller memory and utilized for computing a location using corrected ionosphere-free pseudo ranges. A system for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers includes a dual frequency GNSS receiver and a controller microprocessor adapted to store a table of bias values for correcting pseudo ranges determined using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A).
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
Method for estimating phase deviation in precise single-point positioning technology
InactiveCN102353969AImprove robustnessGuaranteed sizeSatellite radio beaconingPoint-to-Point ProtocolIonosphere
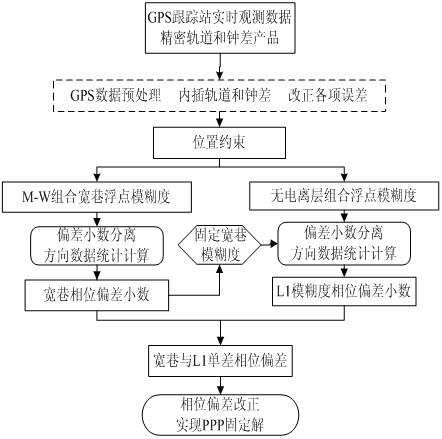
The invention discloses a method for estimating a phase deviation in a precise single-point positioning technology, which comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out parameter estimation on single-difference non-ionized layer combined ambiguity by using a position as a restraint condition according to data of a reference station in a tracking network; secondly, carrying out parameter estimationon single-difference wide-lane ambiguity by adopting an M-W combination, separating out a decimal part of the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity, and carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using a directional data statistic theory, modifying and fixing the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity as an integer; thirdly, resolving a single-difference L1 ambiguity floating point solution according to a single-difference non-ionized layer ambiguity estimation value and a single-difference wide-lane ambiguity integer solution, separating the decimal part, carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using the direction data statistic theory; and finally, broadcasting the wide-lane and the L1 phase deviation decimal part to a user of a roving station so as to be used for fixing the single-difference integral ambiguity solution of the wide lane and the L1 and further obtaining a PPP (Point to Point Protocol) static solution.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ionosphere modeling apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7868820B2Improve efficiencyGood knowledgePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyImage resolution
Methods and apparatus which characterize the ionospheric error across a network of GNSS reference stations are presented. The method relies on dual-frequency phase measurements in a geometry-free linear combination. The data are filtered for ambiguities and the characteristic parameters of the ionosphere. In combination with filter results from other combinations of phase measurements (ionosphere free combination), the physically-based model provides rapid and reliable ambiguity resolution.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Locating method for satellite navigation reinforcing system
InactiveCN101109805AOvercome precisionOvercome distancePosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTroposphereIonosphere
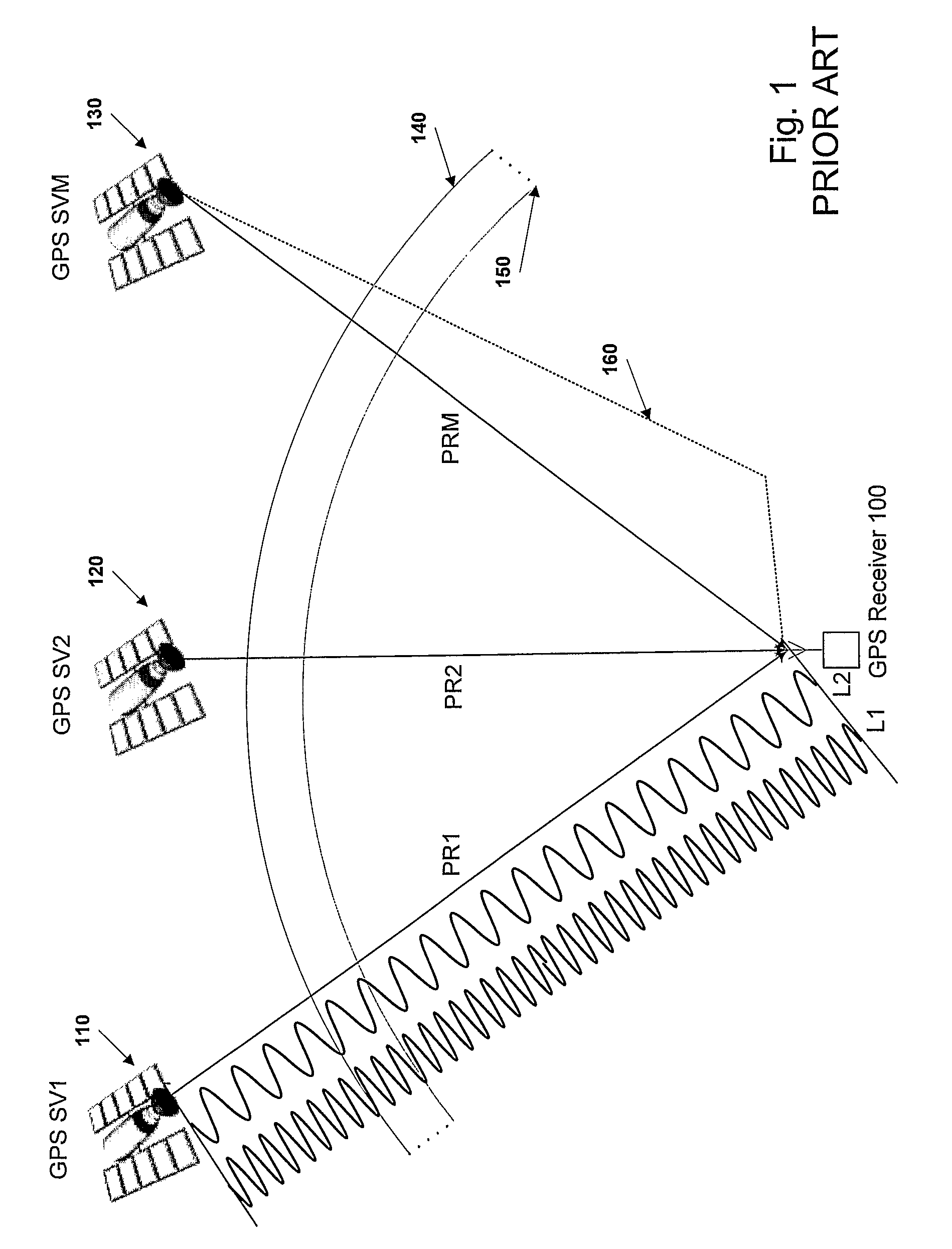
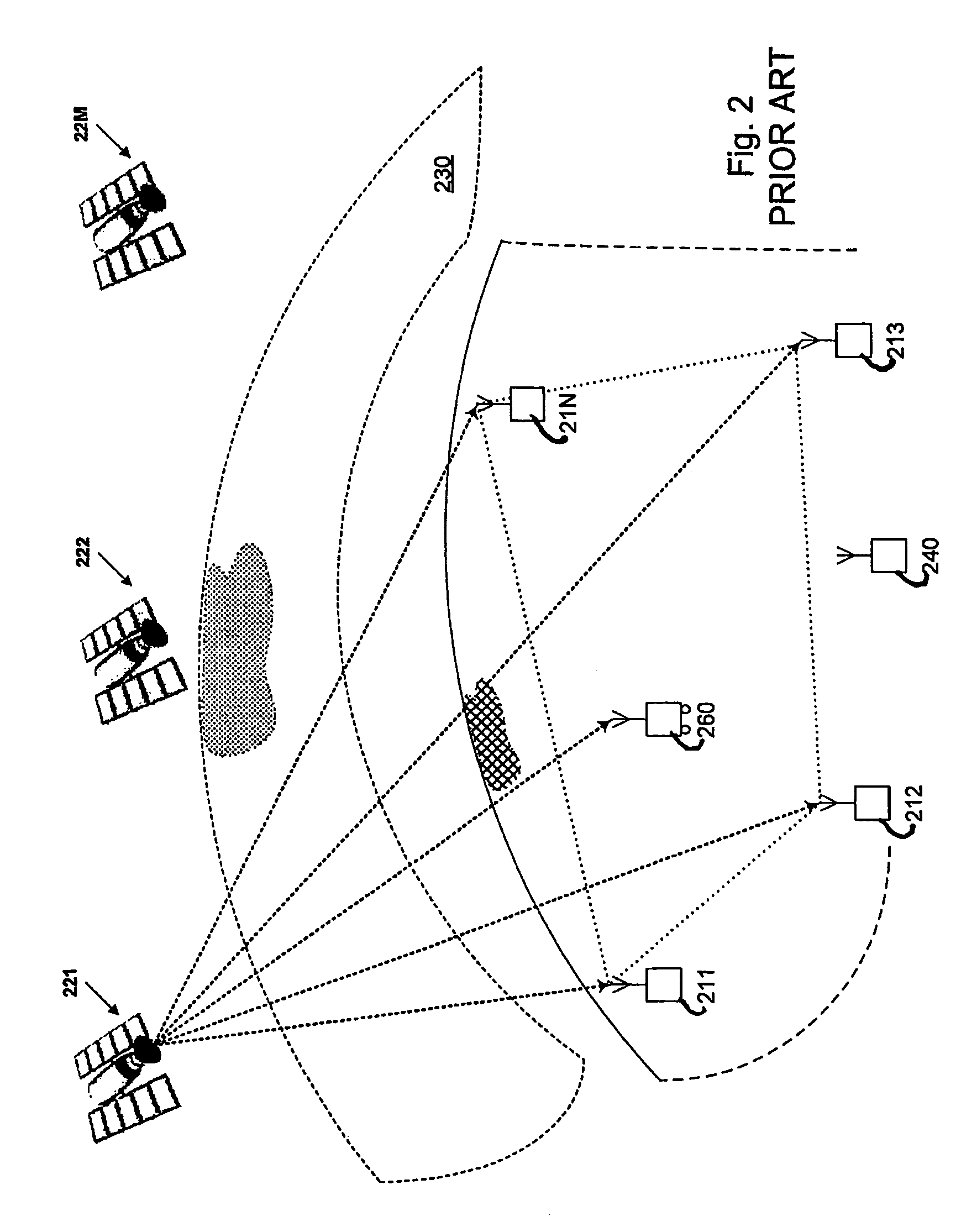
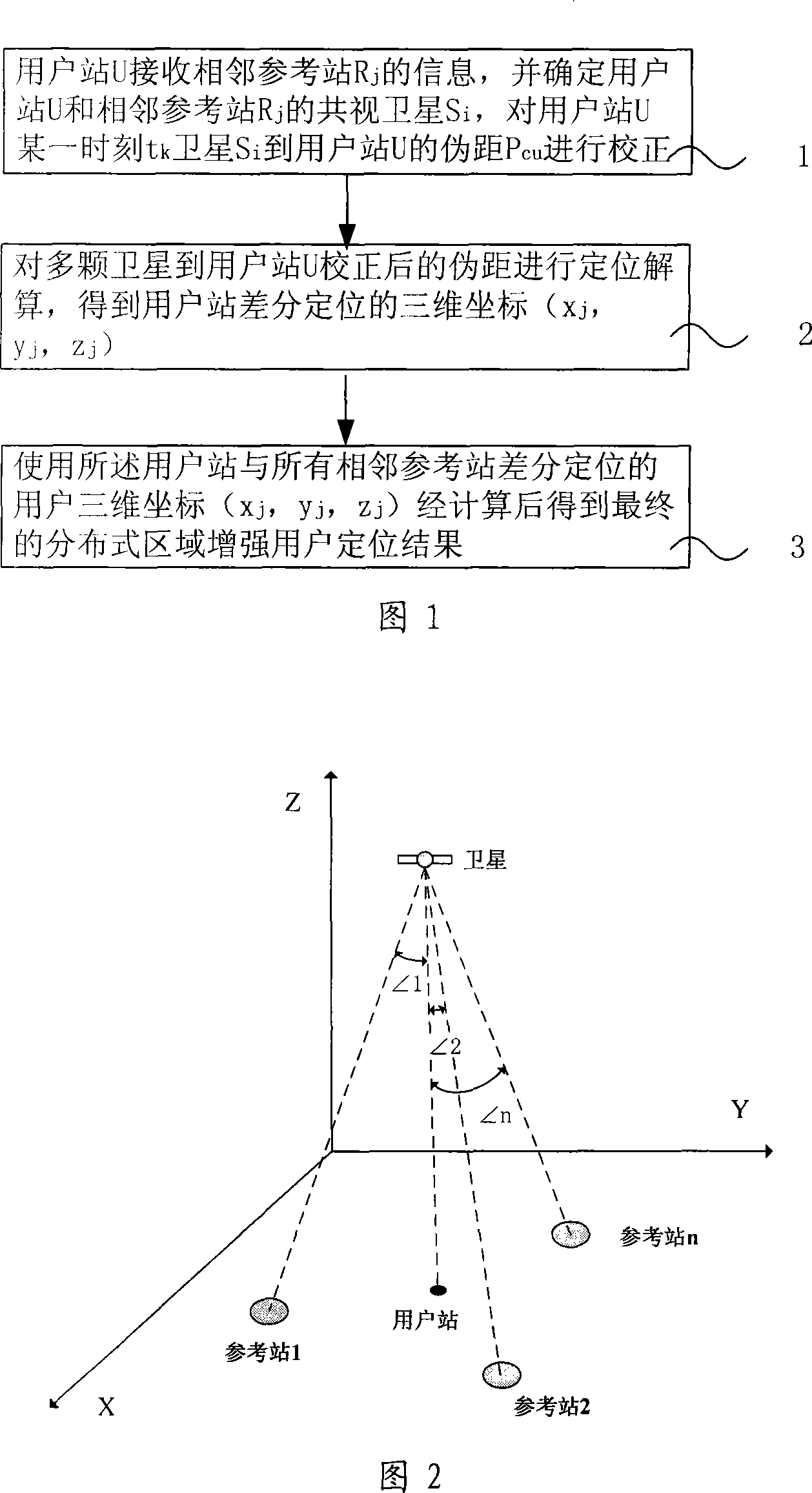
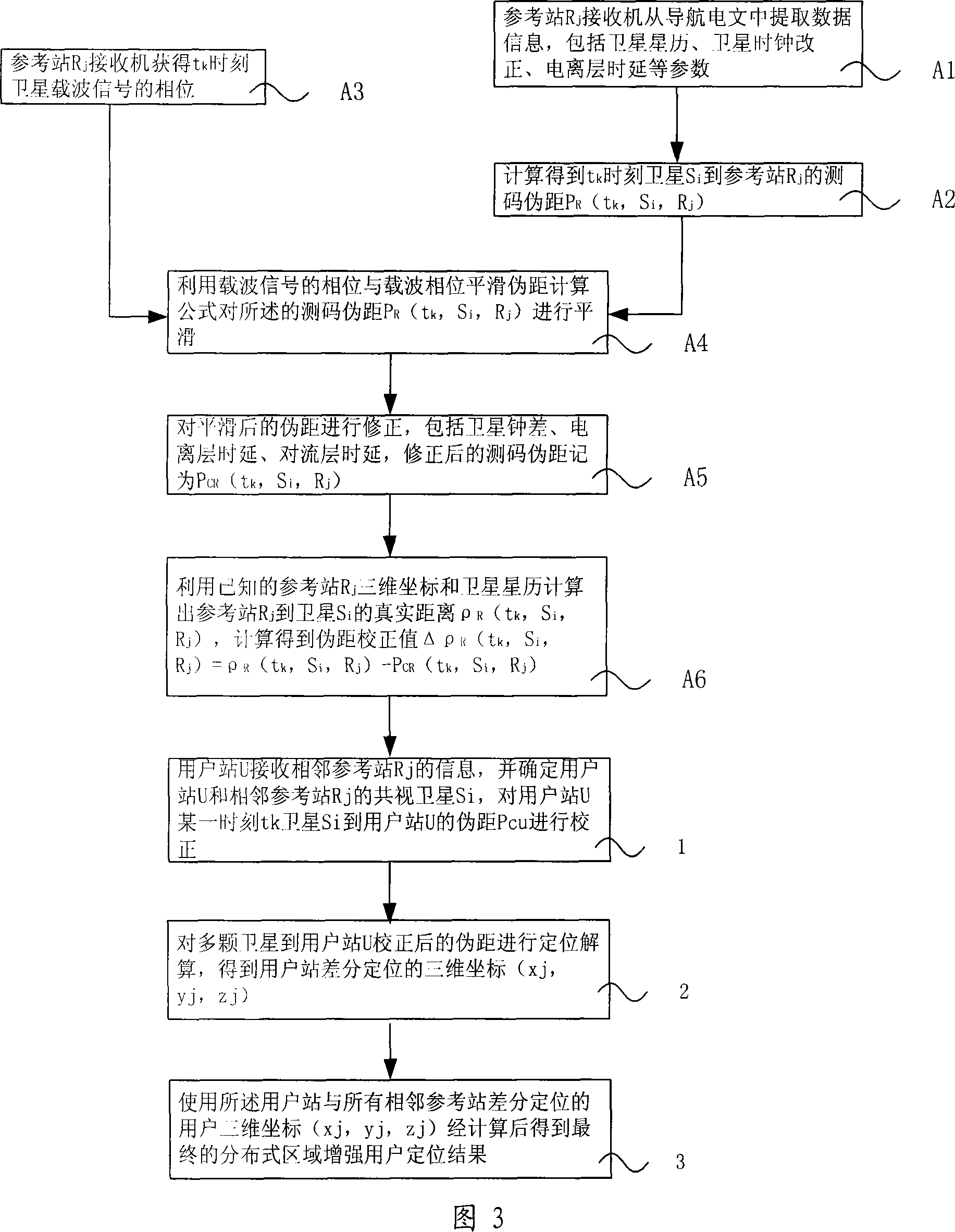
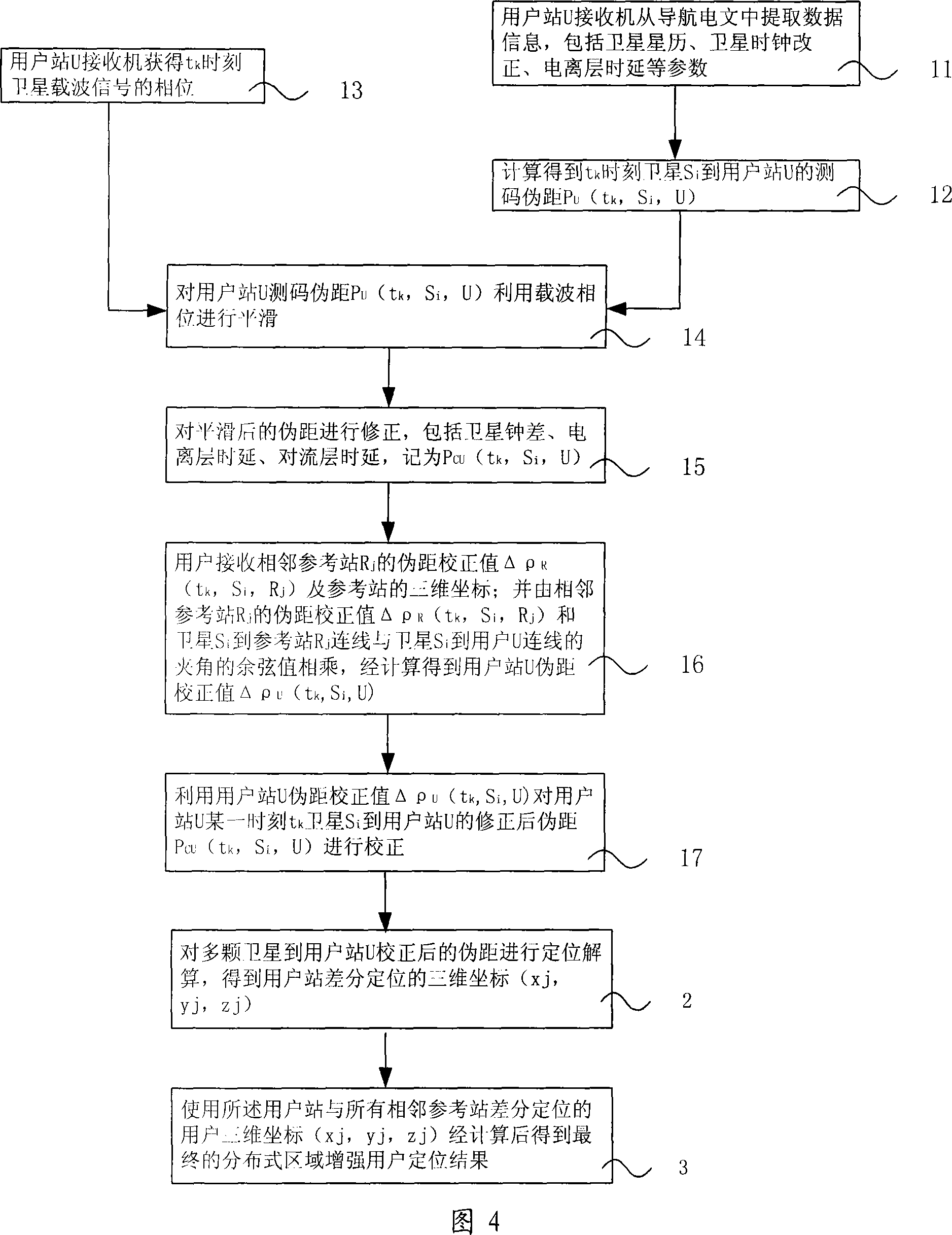
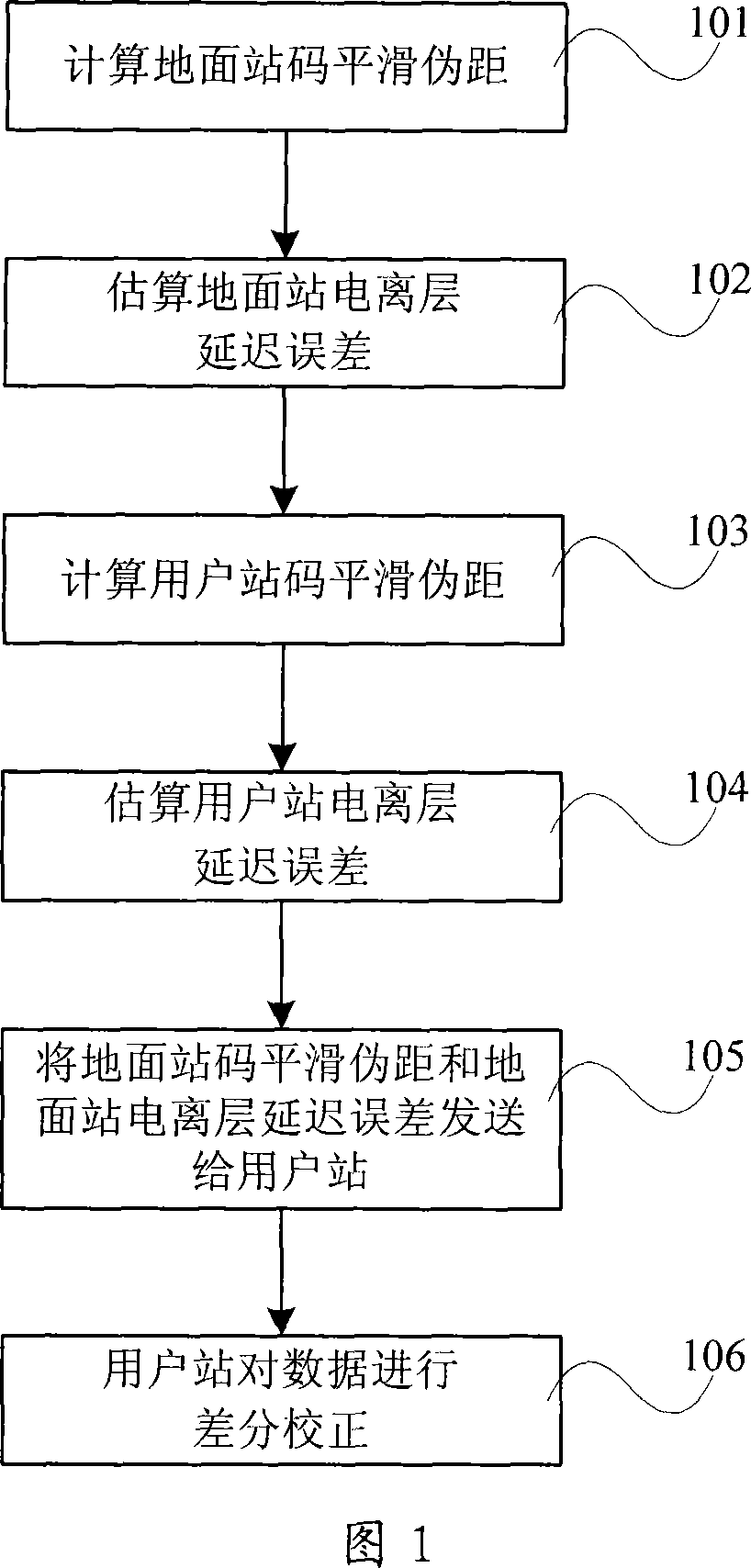
The invention relates to a positioning method for a satellite navigation enhancing system comprising such procedures as, a user station receives info from an adjacent reference station, and determines the mutually-visual satellite of the user station and the adjacent reference station, and calibrates the pseudo distance from a satellite to the user station in a time period; a reference station adjacent to the user station is used to carry out positioning resolution of the calculated pseudo distance from a plurality of satellites to the user station, so as to get the 3D coordinates of the differential positioning of the user station; the positioning result of the user is enhanced by using the final distributed area got by weighted average calculation of 3D coordinates of differential positioning of the user station and all adjacent reference stations. The invention enhances the positioning accuracy for a user by using the enhancing info from a plurality of local areas in a foundation enhancement covered area in respect to the shortcoming that the positioning accuracy is greatly reduced when the user is far from the ground station and a big difference exists between the delay error of the ground station and that of the ionized stratum and the troposphere of the user.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS7117417B2Easy accessCancel noiseInstruments for road network navigationError preventionWide areaDual frequency
Owner:DEERE & CO
System and method for precision acoustic event detection
ActiveUS20060161339A1High precisionImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayClock drift
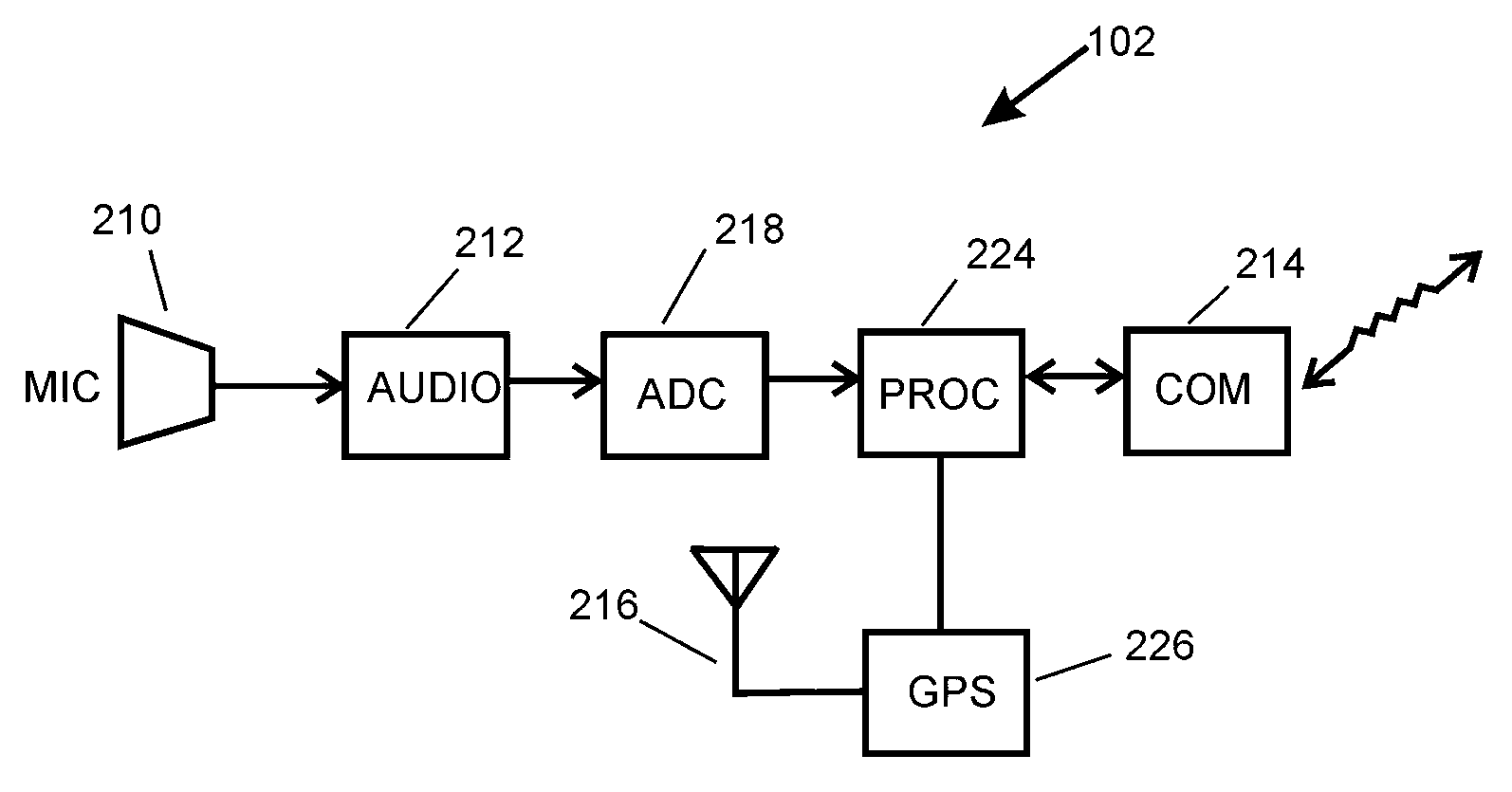
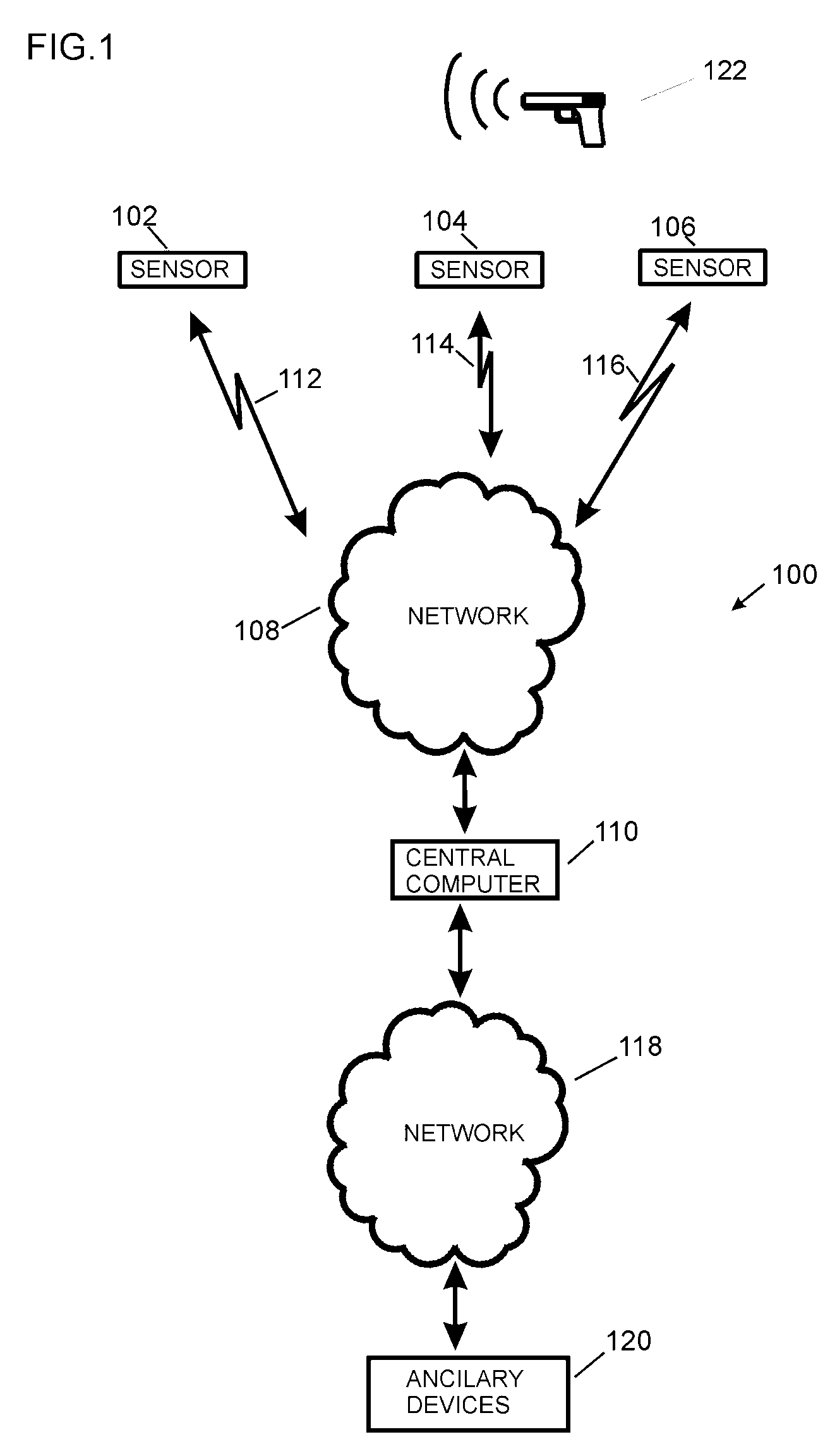
A system and method for providing precision locations for sensors which make up an array of sensors in a gunshot detection system. In a preferred embodiment sensors employ a commercial GPS which reports a sensor position or a group of pseudoranges to GPS satellites. A server collects differential information from a differential node and, in one preferred embodiment, calculates a precision position for each sensor by adjusting the reported position or pseudoranges with the differential information. In another preferred embodiment differential information is sent from the host to individual sensors which calculate their own precision positions. Differential information may be latitude and longitude corrections, pseudorange corrections, ionospheric delay, GPS satellite clock drift, or other corrective term which will improve the accuracy of a sensor position.
Owner:SHOTSPOTTER
Gridding real-time monitoring method for total electron content of ionized layer
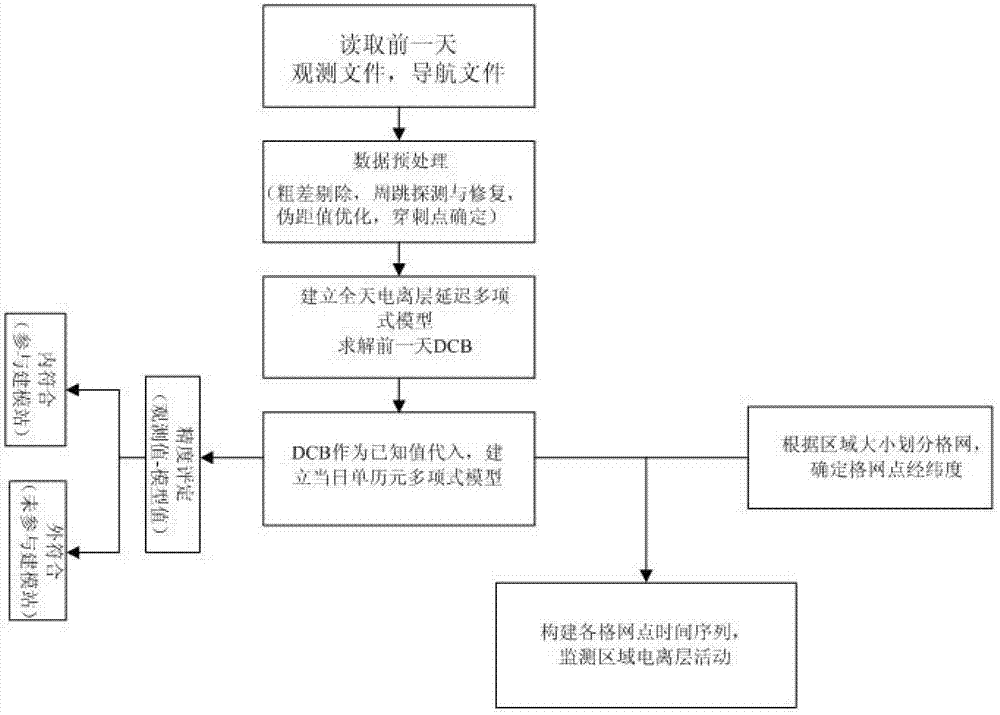
InactiveCN103197340AMonitoring changes in total electron contentExcellent internal coincidence accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentIonosphereIonospheric total electron content
The invention discloses a gridding real-time monitoring method for total electron content of an ionized layer. The gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer comprises the steps of firstly using data of a plurality of reference stations in a continuous operation reference station network to build a whole day ionized layer delay polynomial model, and resolving a receiver hardware delay of the day before and a satellite hardware delay of the day before; and then using the receiver hardware delay of the day before and the satellite hardware delay of the day before to correct the total content of electron concentration of the ionized layer on a satellite propagation path on the day of monitoring according to a characteristic that the receiver hardware delay and the satellite hardware delay are stable, and building a single epoch multi-station polynomial model to monitor changes of the total electron content of the ionized layer in the zenith direction of a grid point after gridding in real time. Experiment results of all epochs in a whole day indicate that inner coincidence precision of the gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer is averagely superior to 1TECU, and outer coincidence precision of the gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer is averagely 1TECU.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
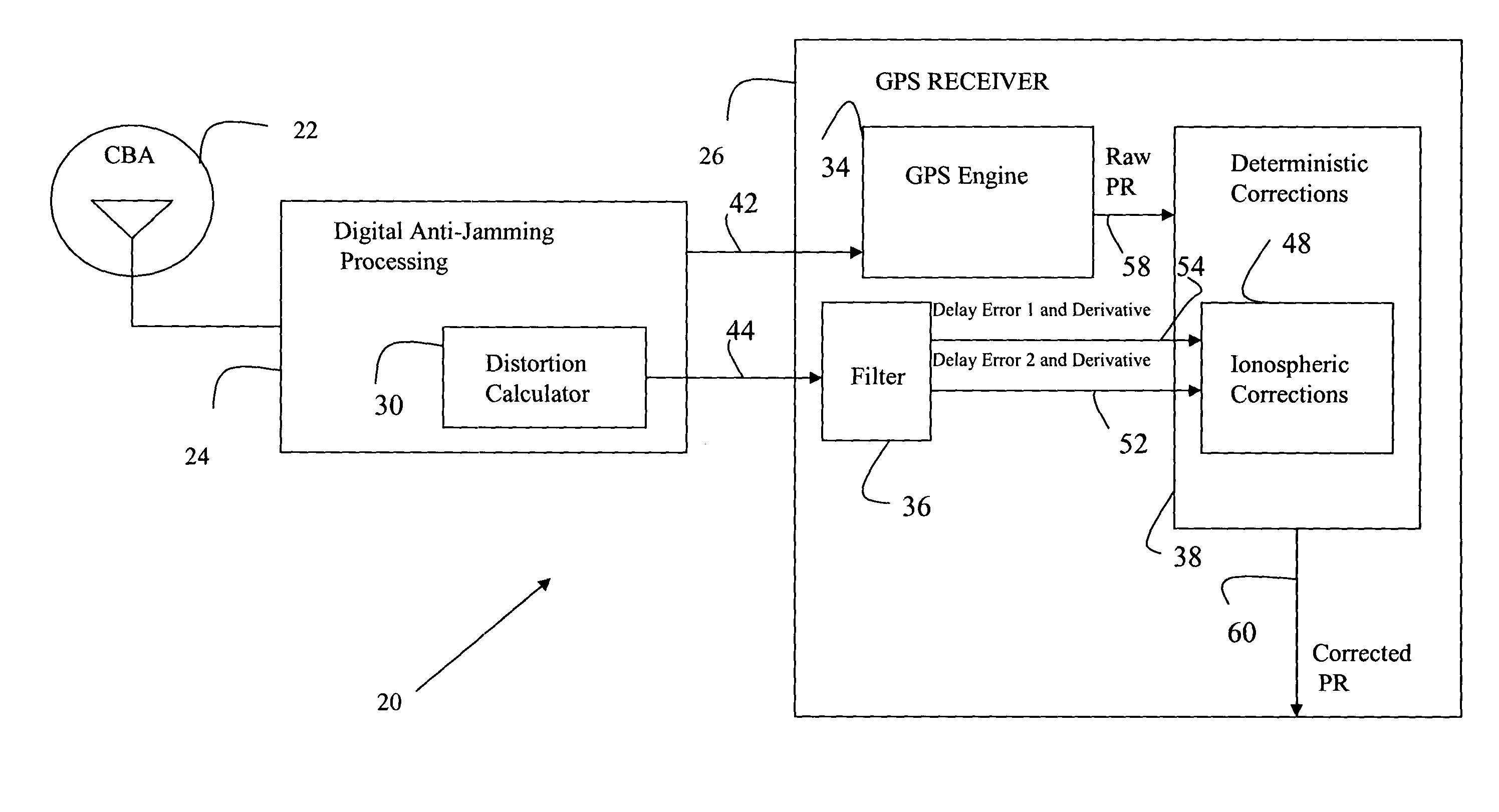
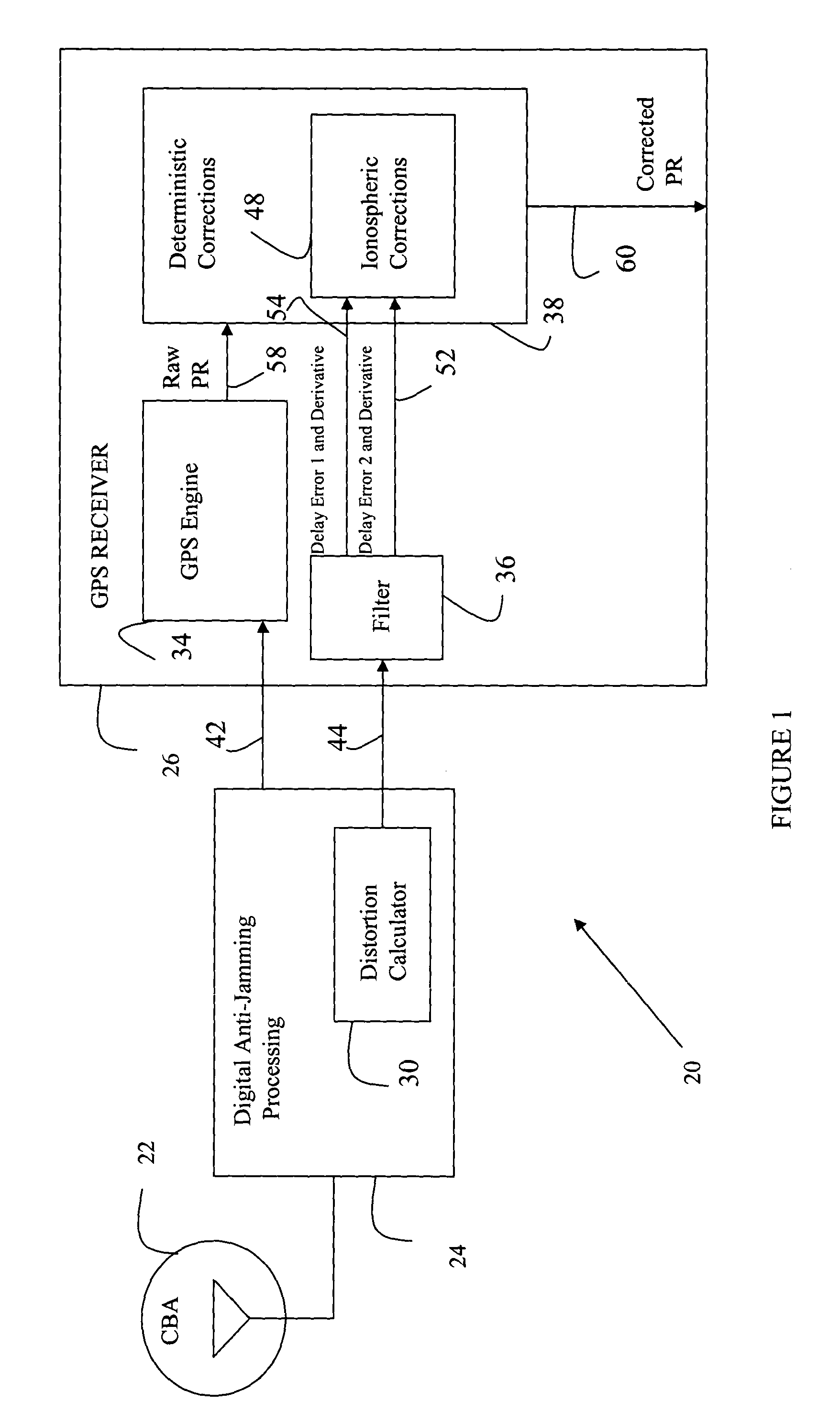
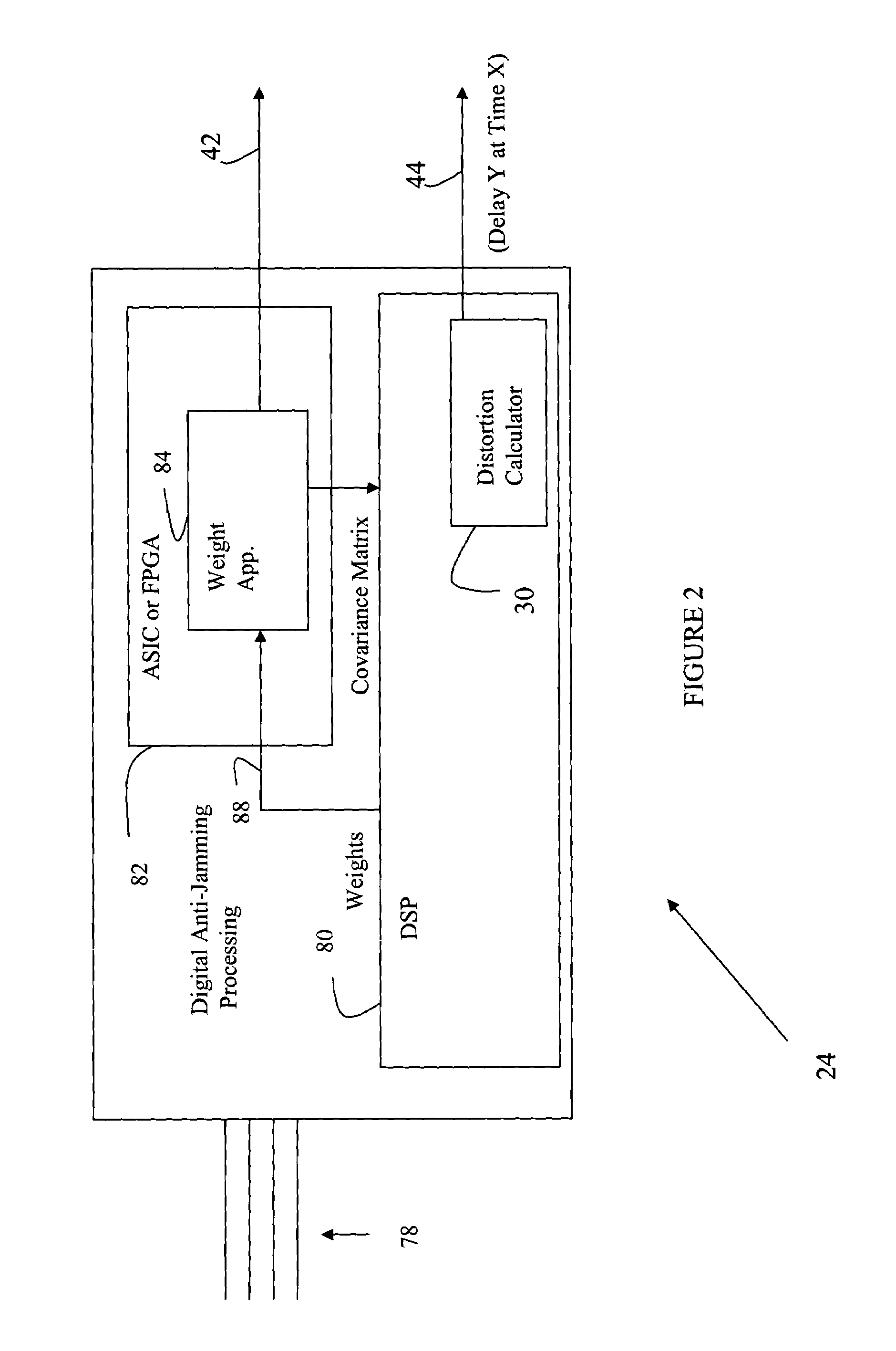
Accommodation of anti-jamming delays in GNSS receivers
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
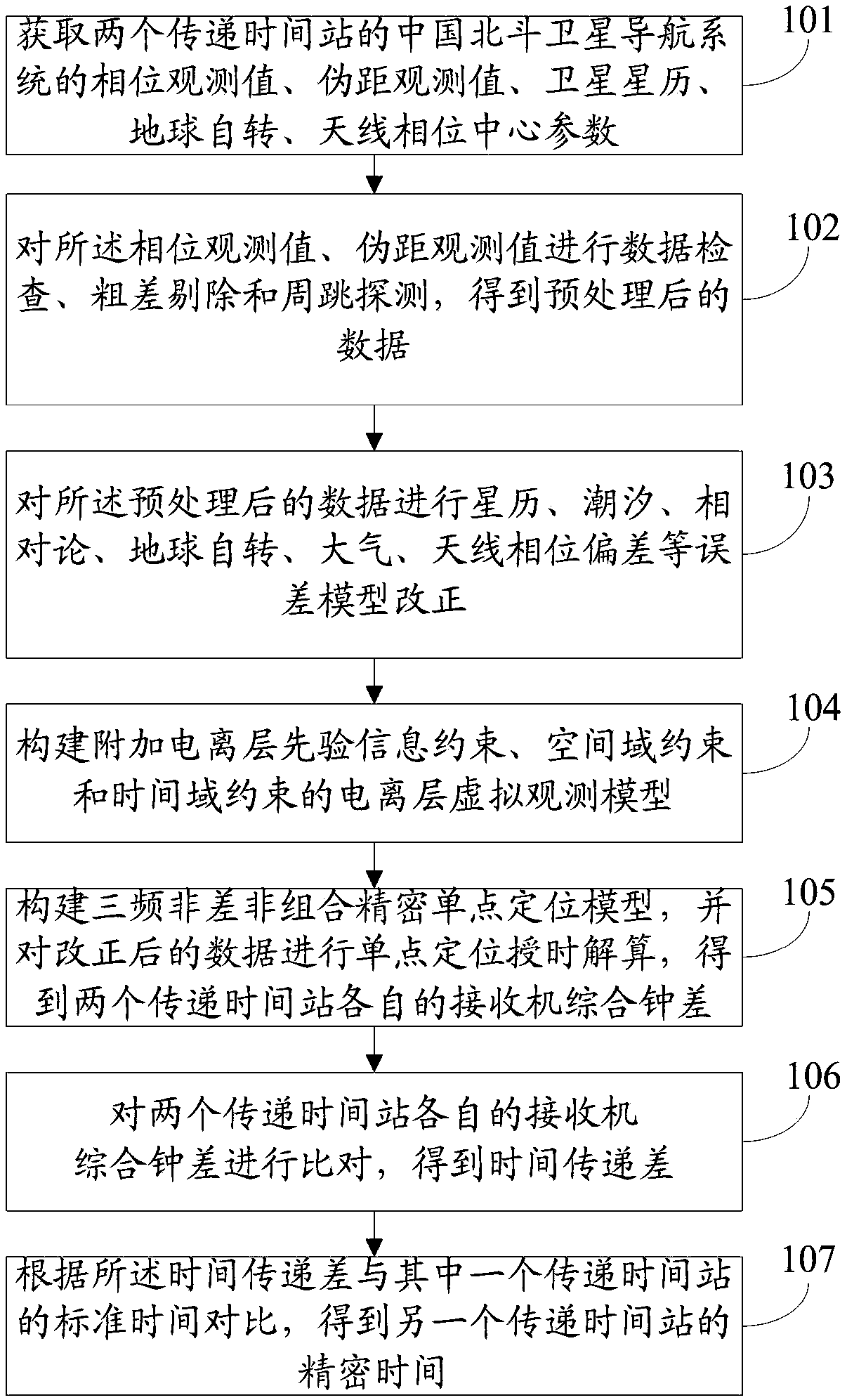
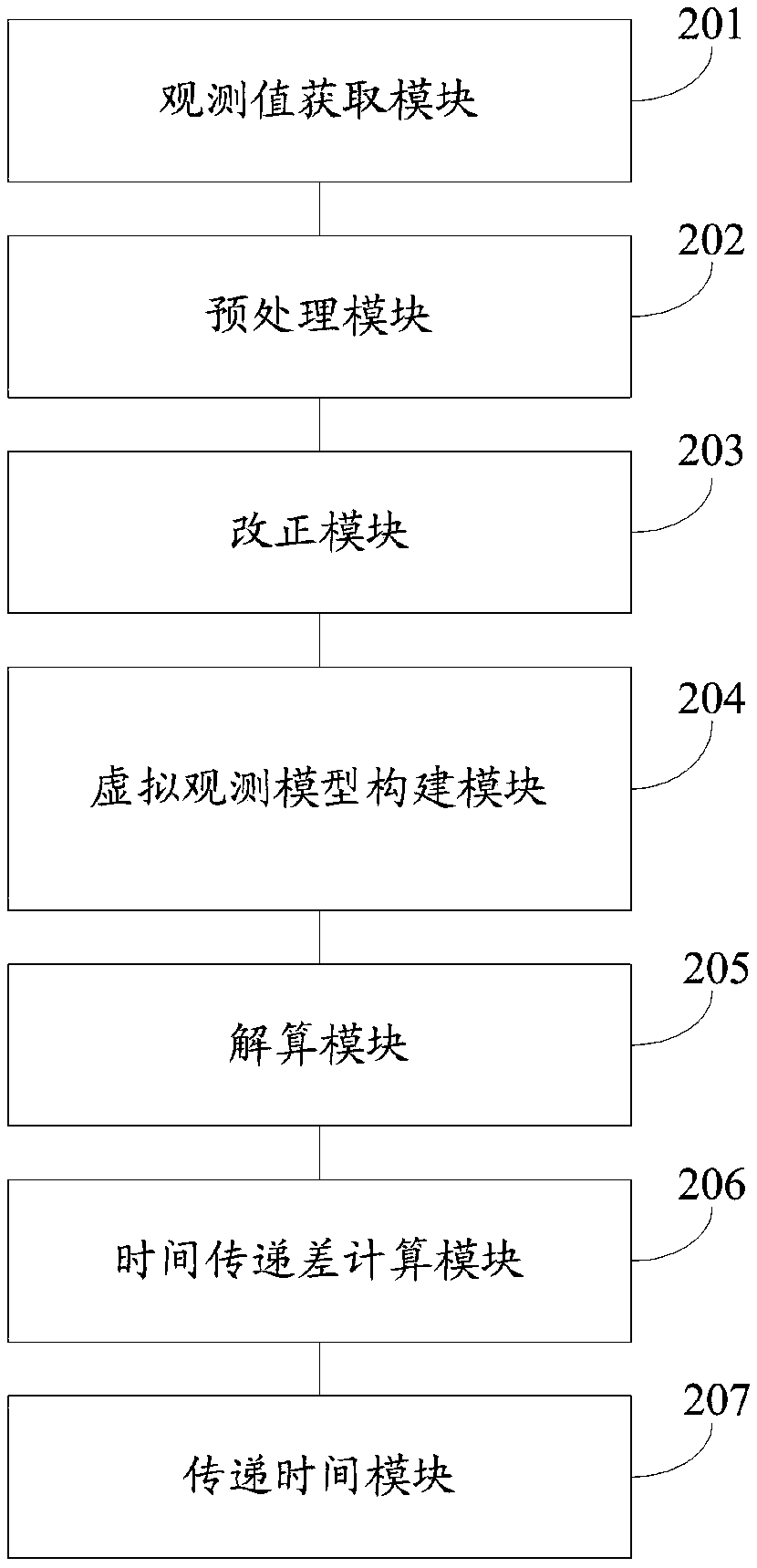
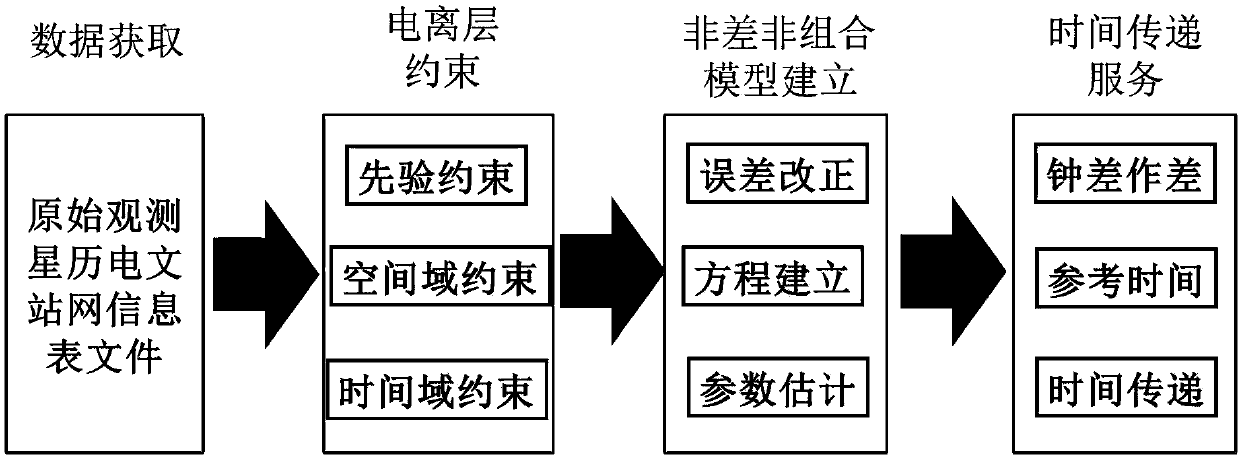
Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method
ActiveCN108919634AReduce observation noiseImprove time transfer accuracyRadio-controlled time-piecesEarth's rotationClock correction
The invention discloses a Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method. The method includes the steps that phase observation value, pseudo-range observation value, satellite ephemeris, earth rotation, antenna phase center and other parameters of China Beidou satellite navigation systems at two time transmission stations are obtained; data check, gross error reject and cycle slip detection are carried out, error models of ephemeris, tide, relativity, the earth rotation, atmosphere and antenna phase deviation are corrected; an ionospheric virtual observation model with additional ionospheric prior information constraints, spatial domain constraints and time domain constraints is constructed; and a three-frequency non-differentialnon-combinatorial precise single-point positioning model is constructed, a single-point positioning timing solution is carried out on corrected data, and comprehensive clock corrections of receivers of the two transmission time stations are obtained and compared to obtain a time transmission difference; and compared with standard time of one of the two transmission time stations, precise time of the other one of the two transmission time stations is obtained. According to the Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method, the observation noise can be reduced, and the accuracy and reliability of time transmission are improved.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Error separation method based on foundation strength system and foundation strength system
InactiveCN101089650AEliminate the effects of spatial gradientsReduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingIonosphereGround station
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers using SBAS
ActiveUS8085196B2Improve performanceImprove navigation accuracySatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyIonosphere
A method for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers circumvents the need for ionosphere corrections by using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A) to form ionosphere-free ranges. A table of biases is stored in microprocessor controller memory and utilized for computing a location using corrected ionosphere-free pseudo ranges. A system for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers includes a dual frequency GNSS receiver and a controller microprocessor adapted to store a table of bias values for correcting pseudo ranges determined using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A).
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
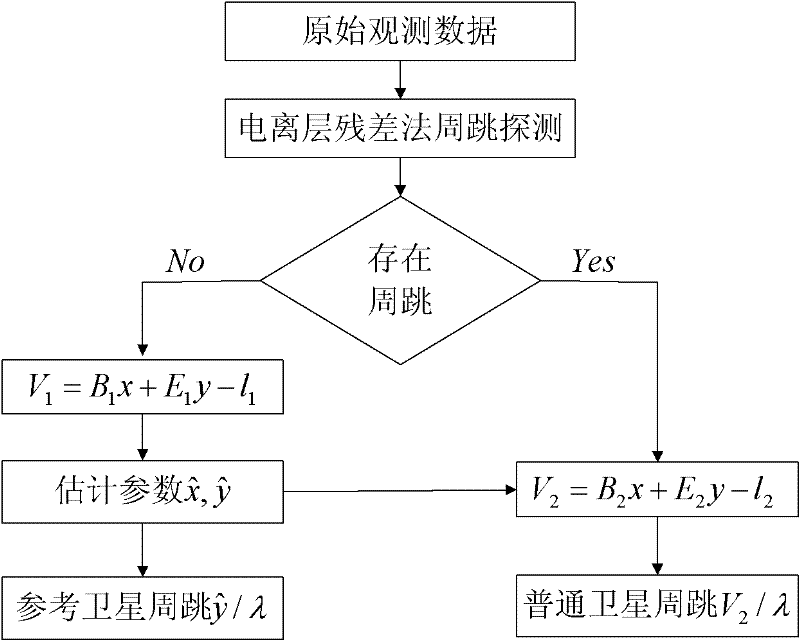
A CORS base station cycle slip detection and repair method
InactiveCN102288978AEfficient repairAccurate detectionSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyObservation data
The invention discloses a continuous operational reference system (CORS) base station cycle slip detection and recovering method, which comprises the following steps that: firstly, an ionized layer residual method is used for carrying out cycle slip detection, a satellite with the cycle slip and the corresponding observation value are determined, then, a single-epoch dual-frequency observation equation is built according to the cycle slip detection results, the single-epoch dual-frequency observation equation is divided into two types, the first type is cycle-slip-free observation equations, the second type is cycle slip observation equations, the cycle slip generated by a non-reference satellite is used as a gross error, the cycle slip generated by a reference satellite is used as a system error, the first type observation equations are used for carrying out parameter estimation, the cycle slip of the reference satellite is determined, the estimated parameters are introduced into thesecond type observation equations, correction numbers are calculated, the cycle slip values of the reference satellite are obtained, and finally, the cycle slip base station observation data is recovered according to the relationship between the base lines in a CORS triangular net. Because the error time strong correlation of the precise coordinate, the dual-frequency convection layer, the ionized layer and the like is directly utilized, the cycle slip detection and recovery can be precisely carried out.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
GNSS Signal Processing Methods and Apparatus with Geometric Filter
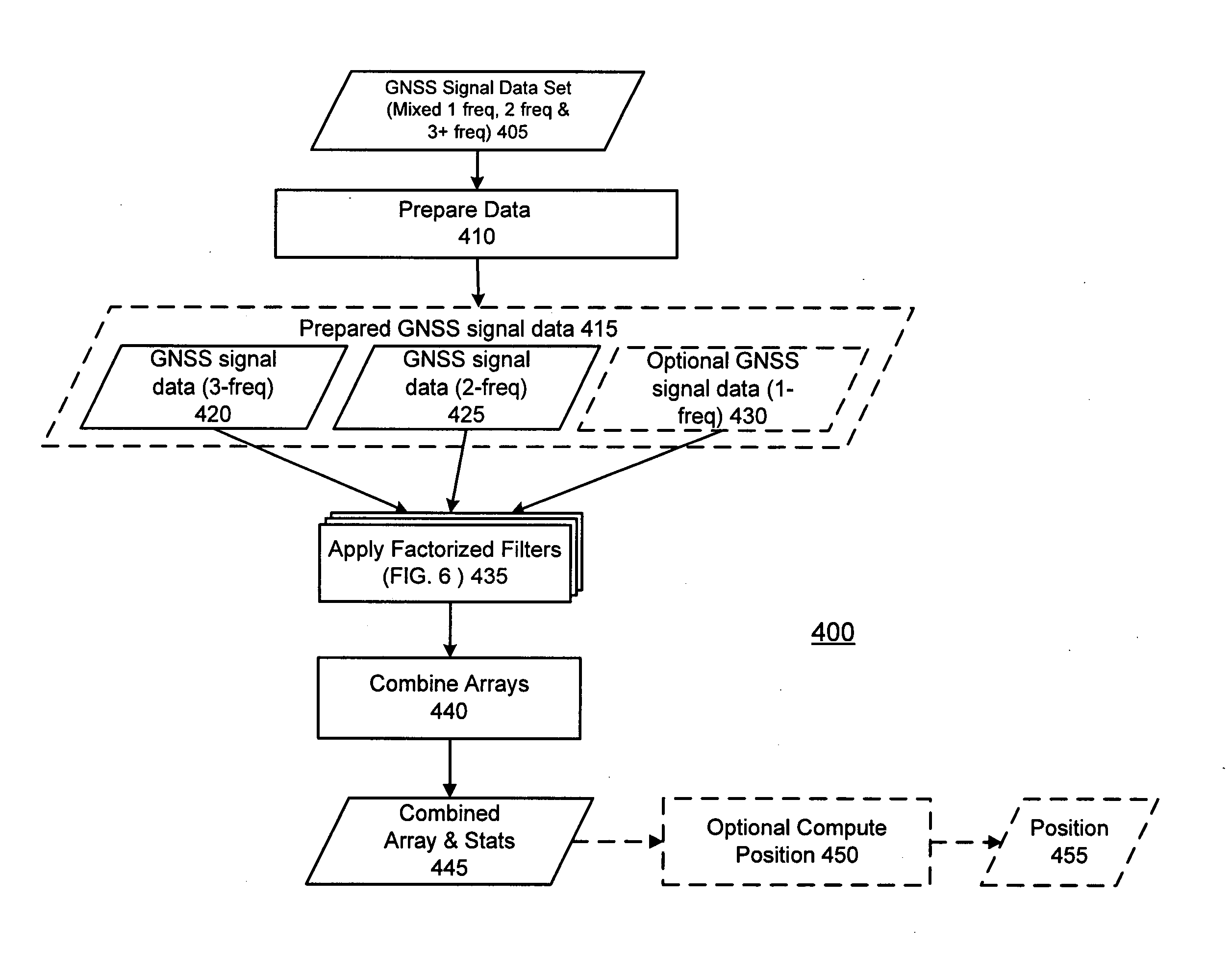
ActiveUS20110267228A1Speed up the processGood estimateSatellite radio beaconingFilter (signal processing)Carrier signal
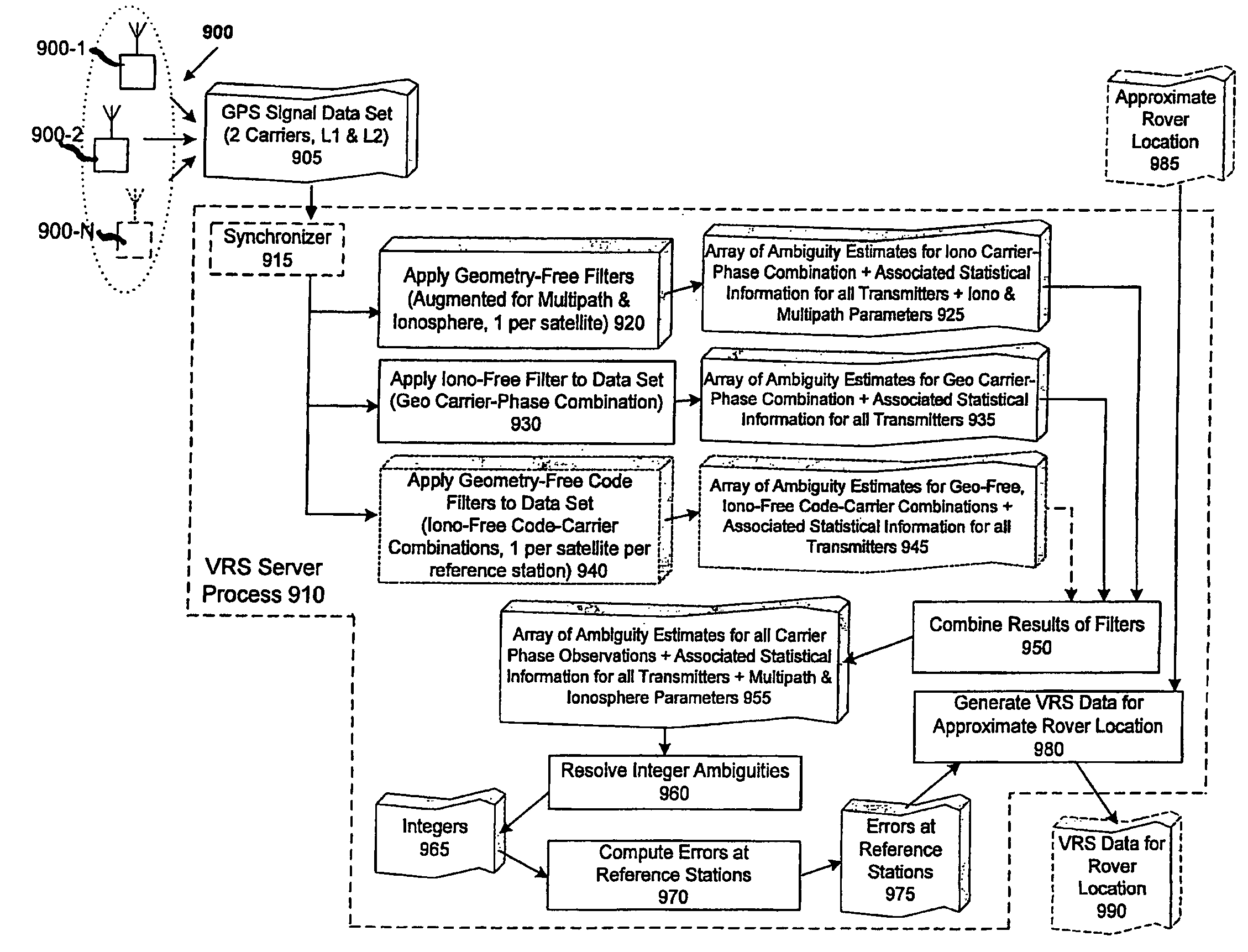
Methods and apparatus are provided for processing a set of GNSS signal data derived from signals of a first set of satellites having at least three carriers and signals of a second set of satellites having two carriers. A geometry filter uses a geometry filter combination to obtain an array of geometry-filter ambiguity estimates for the geometry filter combination and associated statistical information. Ionosphere filters use a two-frequency ionospheric combination to obtain an array of ionosphere-filter ambiguity estimates for the two-frequency ionospheric combinations and associated statistical information. Each two-frequency ionospheric combination comprises a geometry-free two-frequency ionospheric residual carrier-phase combination of observations of a first frequency and observations of a second frequency. Auxiliary ionosphere filters use an auxiliary ionospheric combination to obtain an array of auxiliary-ionosphere-filter ambiguity estimates for the auxiliary ionospheric combinations and associated statistical information. Each auxiliary ionospheric combination uses carrier-phase observations of a third frequency and carrier-phase observations of at least one of the first frequency and the second frequency. A combined array of ambiguity estimates is prepared for all carrier phase observations and associated statistical information by combining the arrays of the geometry filter and the ionosphere filters and the auxiliary ionosphere filters.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
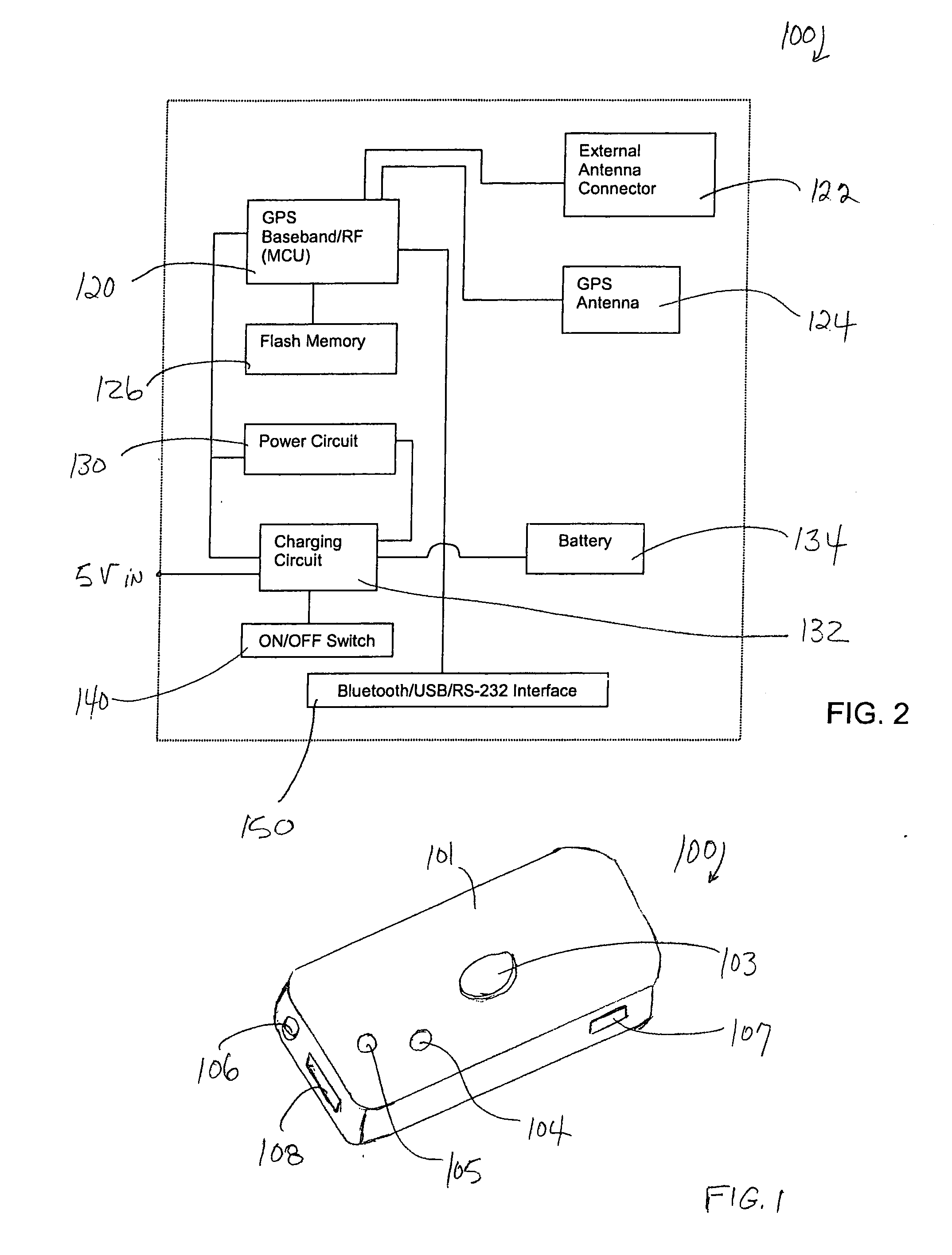
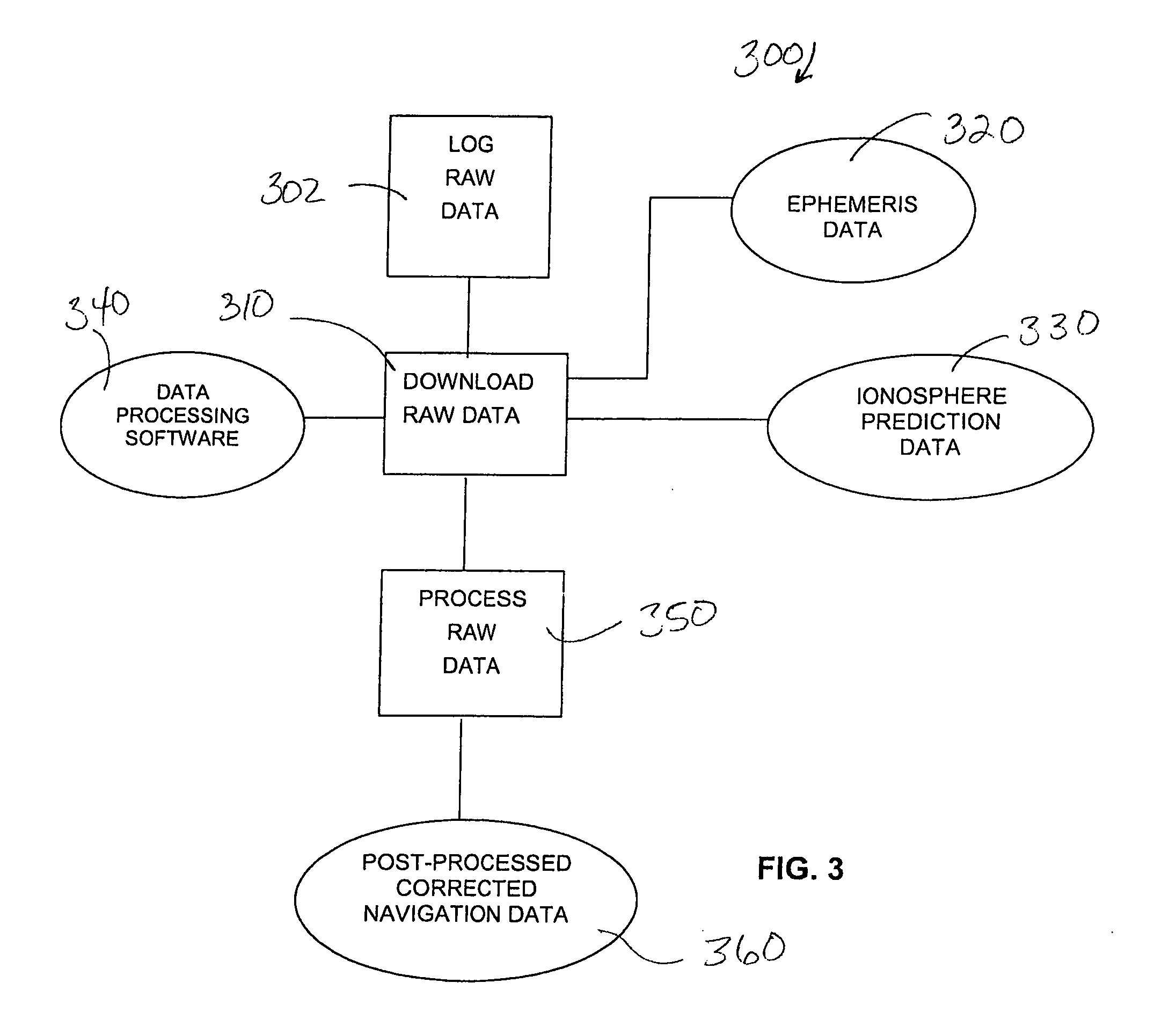
Method and device for processing raw GPS data
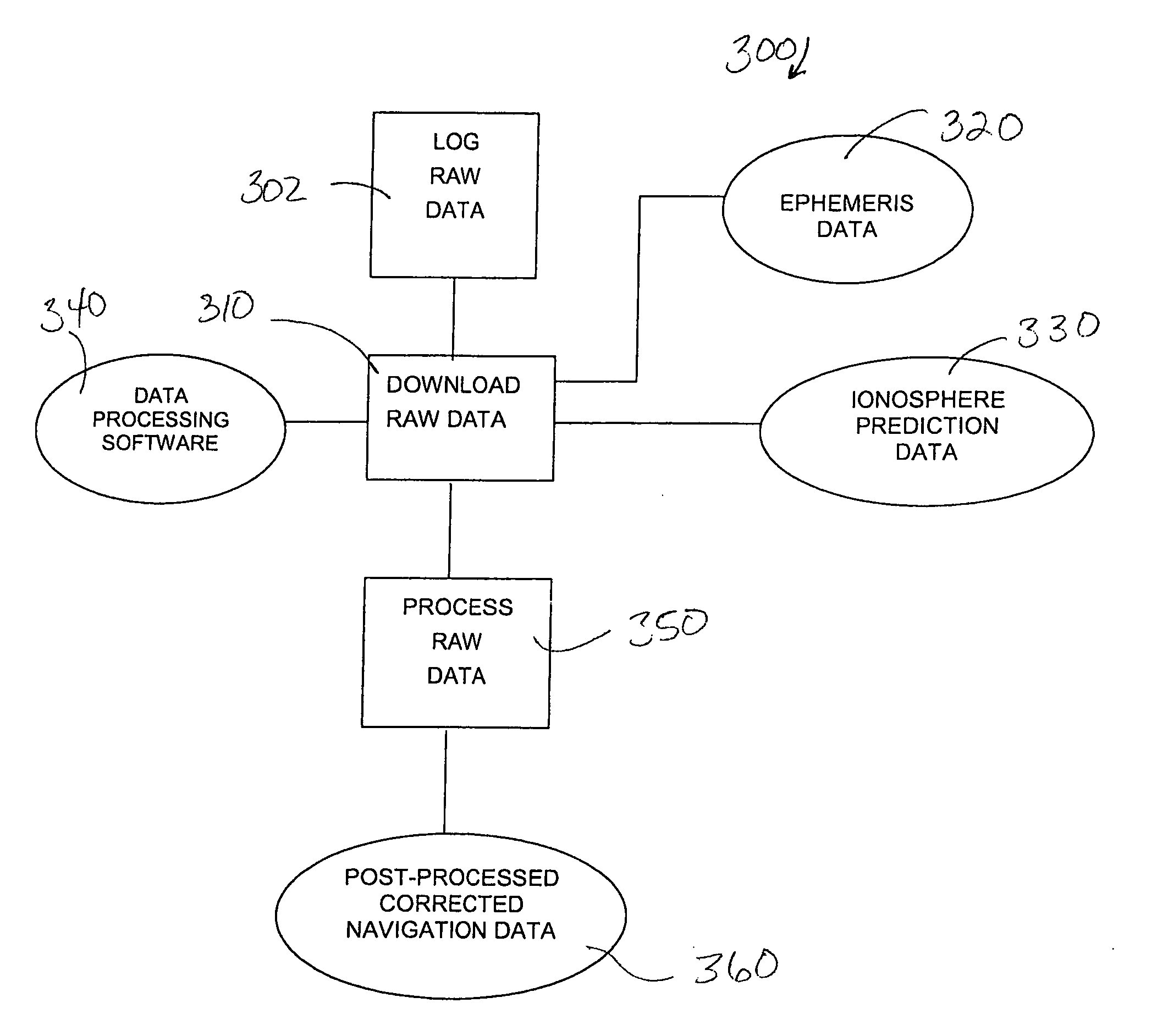
InactiveUS20050162312A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingProgram instructionGps receiver
Method and device for processing raw GPS data to obtain extremely accurate corrected navigation data. The device is a stand-alone, puck-like GPS receiver / data logger that records raw data according to pre-programmed instructions. Ephemeris data and / or ionosphere prediction data that provide high accuracy for the time and location of data logging are uploaded into data processing software for processing the raw GPS data received via satellite signal. The raw GPS data may be post-processed on an external computing device or processed in realtime in the GPS receiver / data logger. The corrected navigation data thus obtained provides navigation data with submeter accuracy.
Owner:DELORME PUBLISHING
Unified model-based Beidou undifferenced and uncombined PPP (precise point positioning)-RTK (real-time kinematic) positioning method
InactiveCN107561568AImprove unityRealize seamless linkSatellite radio beaconingAlgorithmReal Time Kinematic
The present invention provides a unified model-based Beidou undifferenced and uncombined PPP (precise point positioning)-RTK (real-time kinematic) positioning method. According to the method, as for users on the globe, real-time orbits and clock error corrections are received, so that undifferenced and uncombined PPP calculation is performed; initialization is performed, so that decimeter-centimeter-level precision positioning is realized; for users in regions, integrated error corrections of the regions are received, undifferenced network RTK calculation is performed; and initialization is performed, so that centimeter-level precision positioning is realized. With the method of the invention adopted, the seamless linking of undifferenced PPP data processing and undifferenced network RTK data processing can be realized, fast and high-precision positioning services can be provided, and the total electron content of an ionized layer and the differential code deviation information of a receiver can be obtained.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
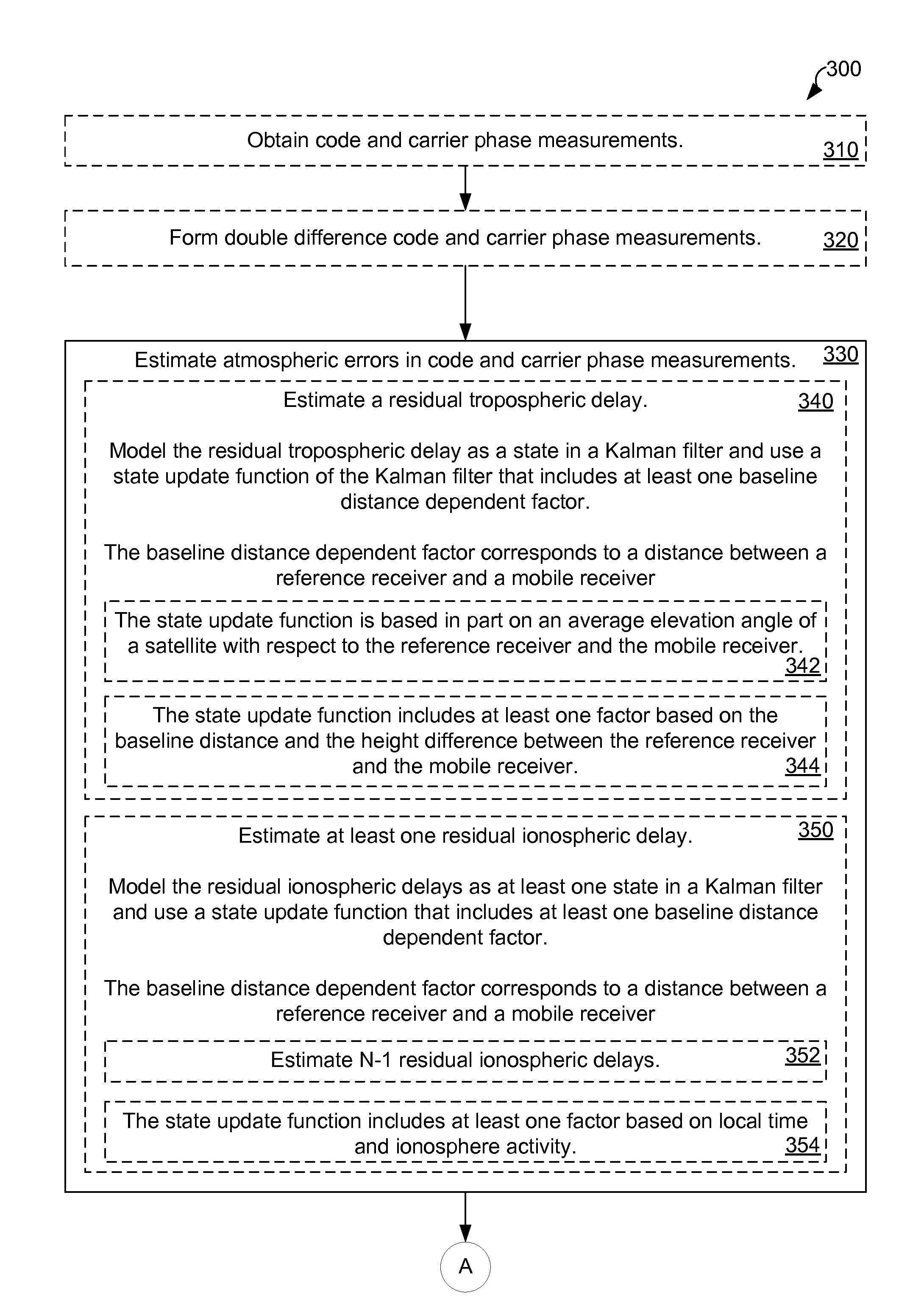
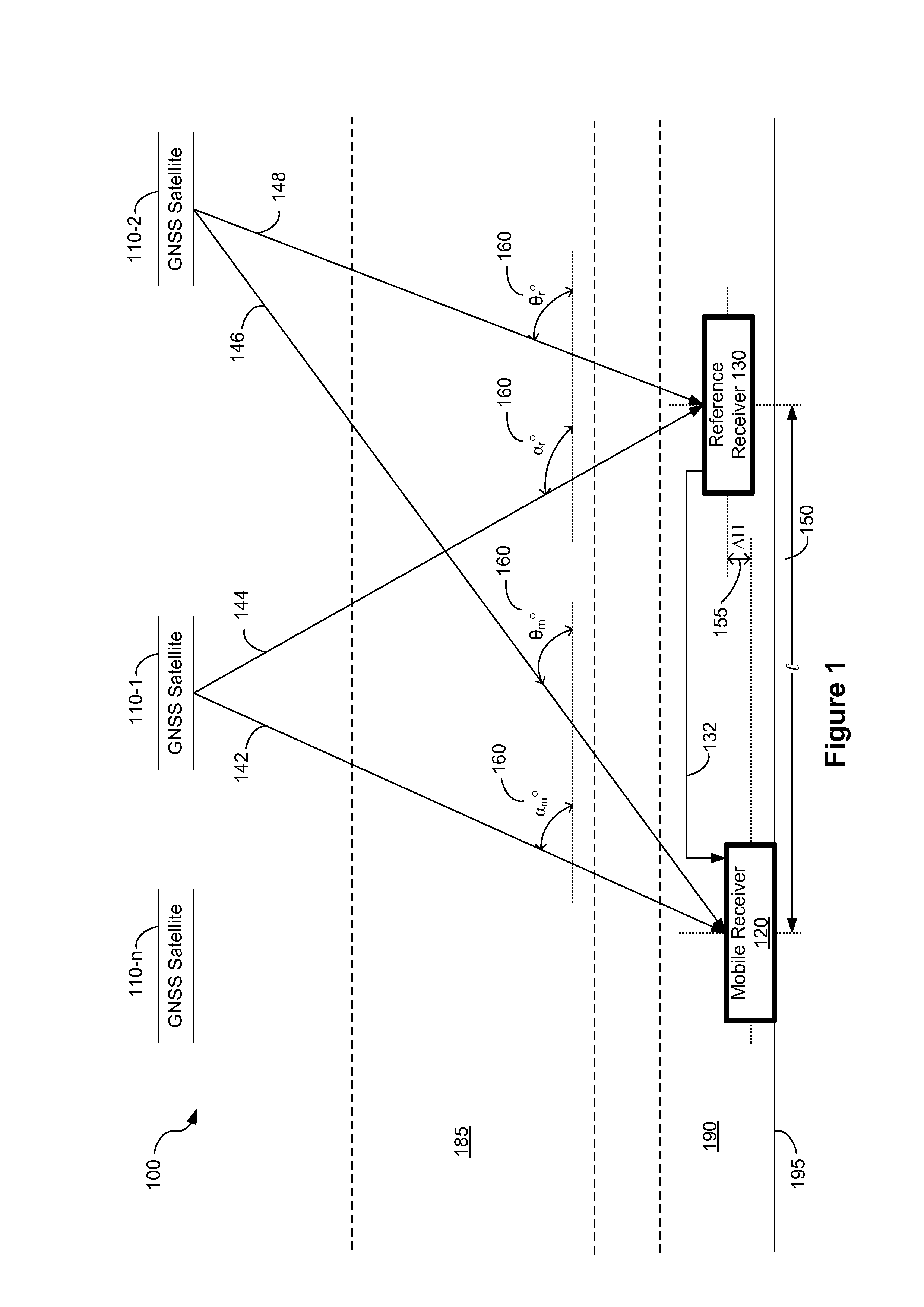
Distance dependent error mitigation in real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning
ActiveUS8242953B2Distance can be inaccuratePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterDynamic noise
A method for mitigating atmospheric errors in code and carrier phase measurements based on signals received from a plurality of satellites in a global navigation satellite system is disclosed. A residual tropospheric delay and a plurality of residual ionospheric delays are modeled as states in a Kalman filter. The state update functions of the Kalman filter include at least one baseline distance dependant factor, wherein the baseline distance is the distance between a reference receiver and a mobile receiver. A plurality of ambiguity values are modeled as states in the Kalman filter. The state update function of the Kalman filter for the ambiguity states includes a dynamic noise factor. An estimated position of mobile receiver is updated in accordance with the residual tropospheric delay, the plurality of residual ionospheric delays and / or the plurality of ambiguity values.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Precise GNSS positioning system with improved ambiguity estimation
Method for precise GNSS positioning system with improved ambiguity estimation. The method is based on the realization that, especially during convergence, the estimated float ambiguities are biased when estimated simultaneously with the ionosphere parameters. The “ionosphere-like” biases can be separated from the actual float ambiguities by using the fixed wide-lane (or extra wide-lane) integer ambiguities. The original real-valued ambiguities (e.g., one of L1, L2 and L5 in the GPS case) are corrected using the corresponding biases, resulting in reliable float ambiguities that are taken as input in the next processing step.
Owner:FUGRO
Long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing
ActiveCN105372691AHigh precisionOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
A long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing is provided in order to improve the success rate of ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of relative positioning results. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: first, collecting and pre-processing input data, and determining the absolute general orbit of a formation satellite; then, eliminating the geometric distance and clock error in differential observation data, estimating a single-difference phase ambiguity float solution and a single-difference ionosphere delay parameter, carrying out double-difference transform to get a double-difference wide-lane ambiguity float solution and a covariance matrix, and fixing the double-difference wide-lane integer ambiguity and the double-difference narrow-lane integer ambiguity; and finally, outputting the relative positioning result of ambiguity fixing. By adopting the method of the invention, the problem that ambiguity fixing strongly depends on a pseudo code with low observation precision due to equally-weighted pseudo code and phase processing in M-W combination in the traditional method is avoided, the success rate of long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of final relative positioning results are improved, calculation is stable, and the reliability of relative positioning results is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
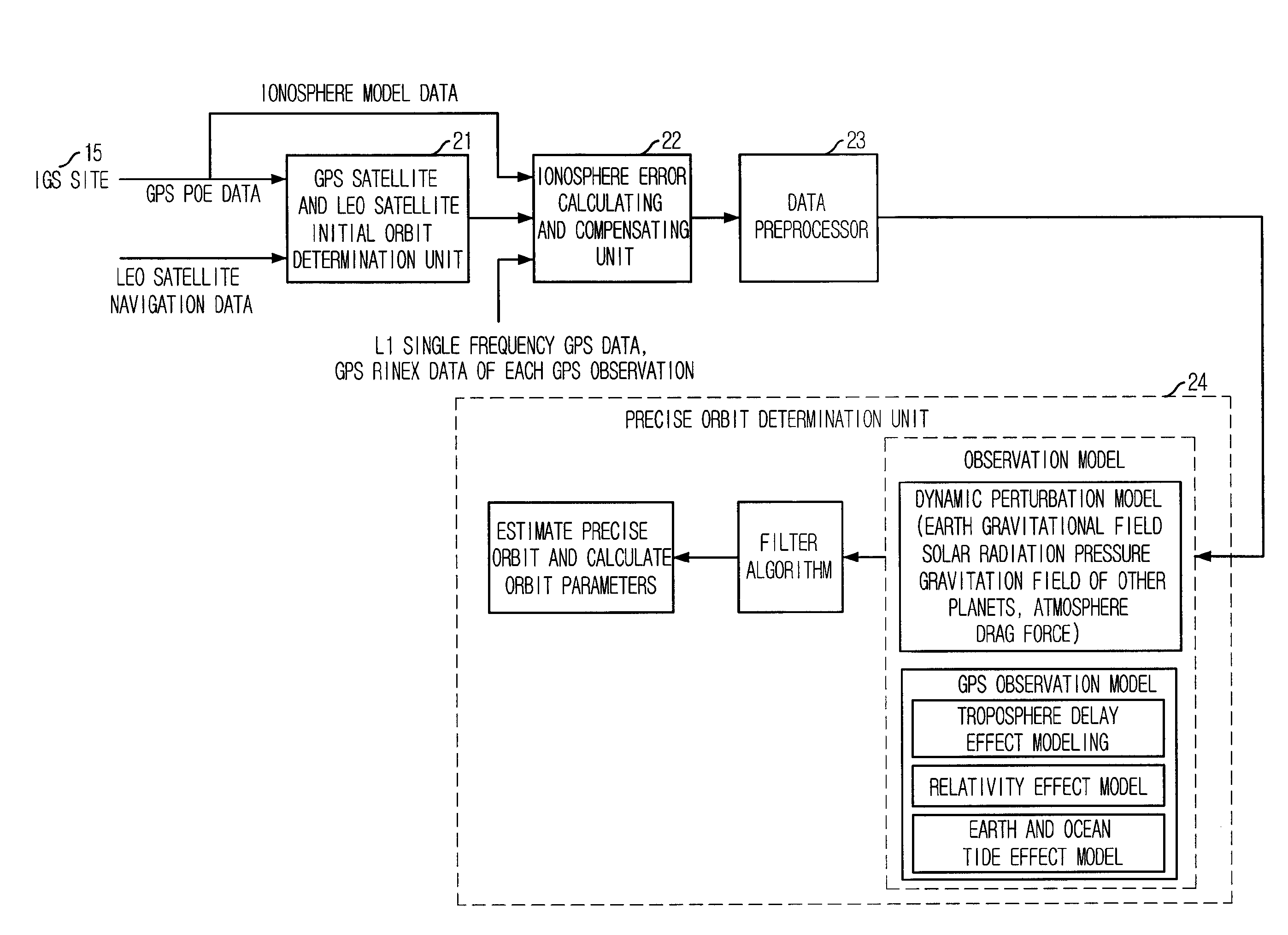
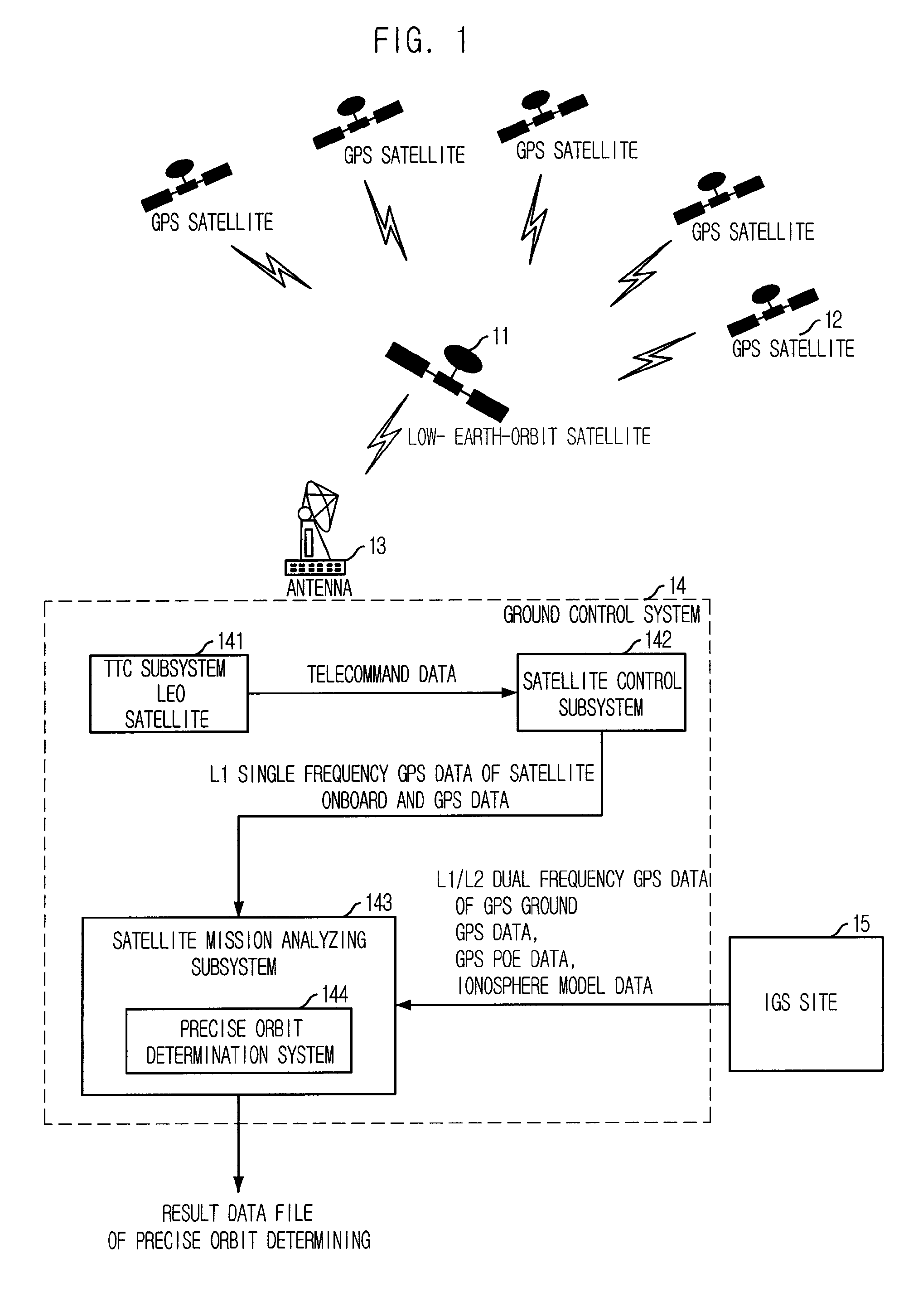
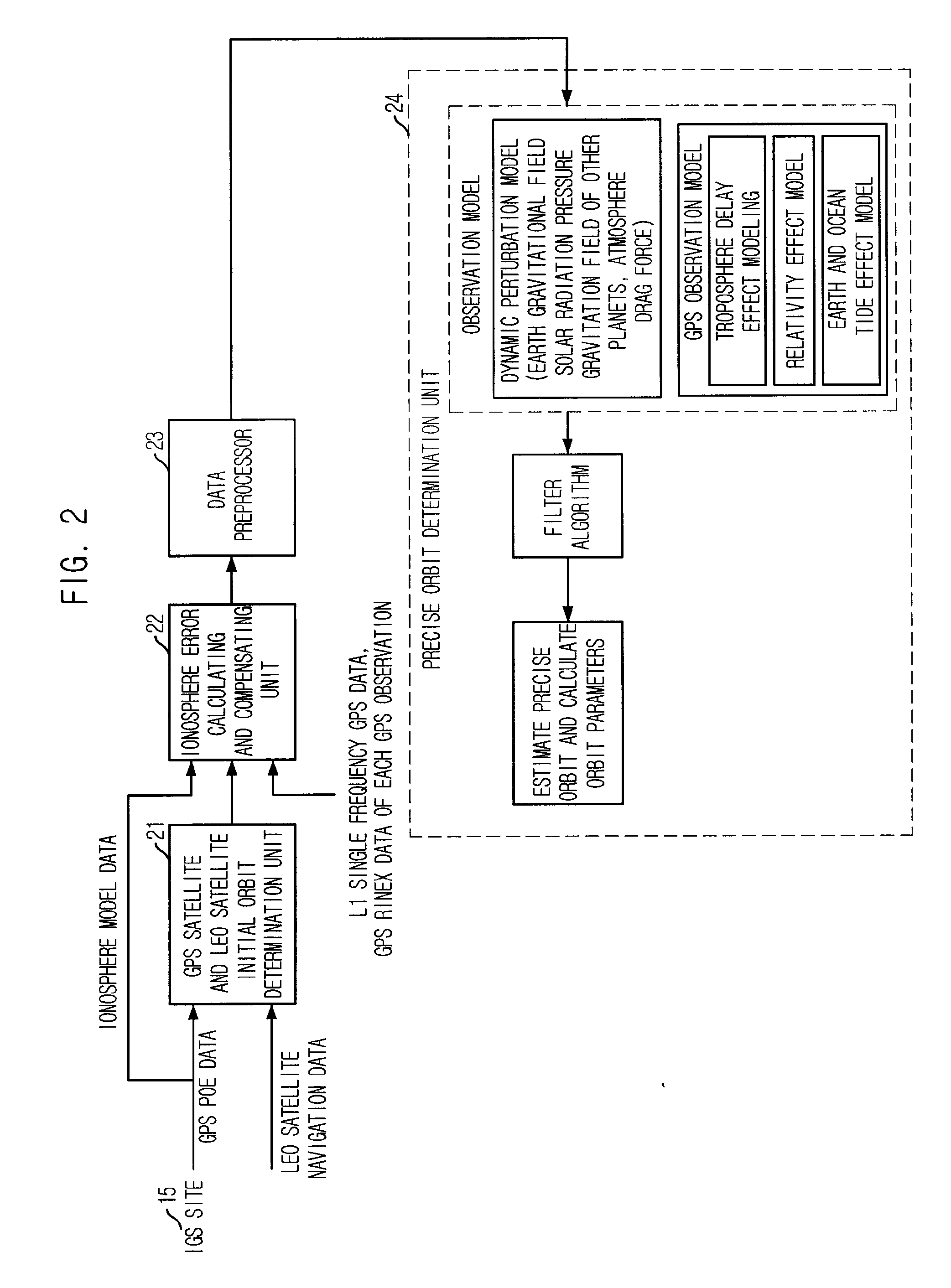
Method for correcting ionosphere error, and system and method for determining precision orbit using the same
InactiveUS20090091493A1Eliminate errorsAccurately determinePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingHigh elevationOne pass
Provided is a method of correcting an ionosphere error, a system of a precise orbit determination using the same and a method thereof. The method includes the steps of: a) determining a time of a highest elevation angle of a GPS satellite per one pass of each GPS satellite received at a LEO satellite or a receiver on a ground; b) determining a minimum total electron content found from an ionosphere model of the determined time per one pass of each GPS satellite; c) determining a total electron content directly calculated from the LEO satellite or a single frequency GPS data; d) determining an ionosphere error value of a single frequency GPS data by combining the minimum total electron content and the directly calculated total electron content; and e) correcting pseudorange data or carrier phase data based on the determined ionosphere error value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com