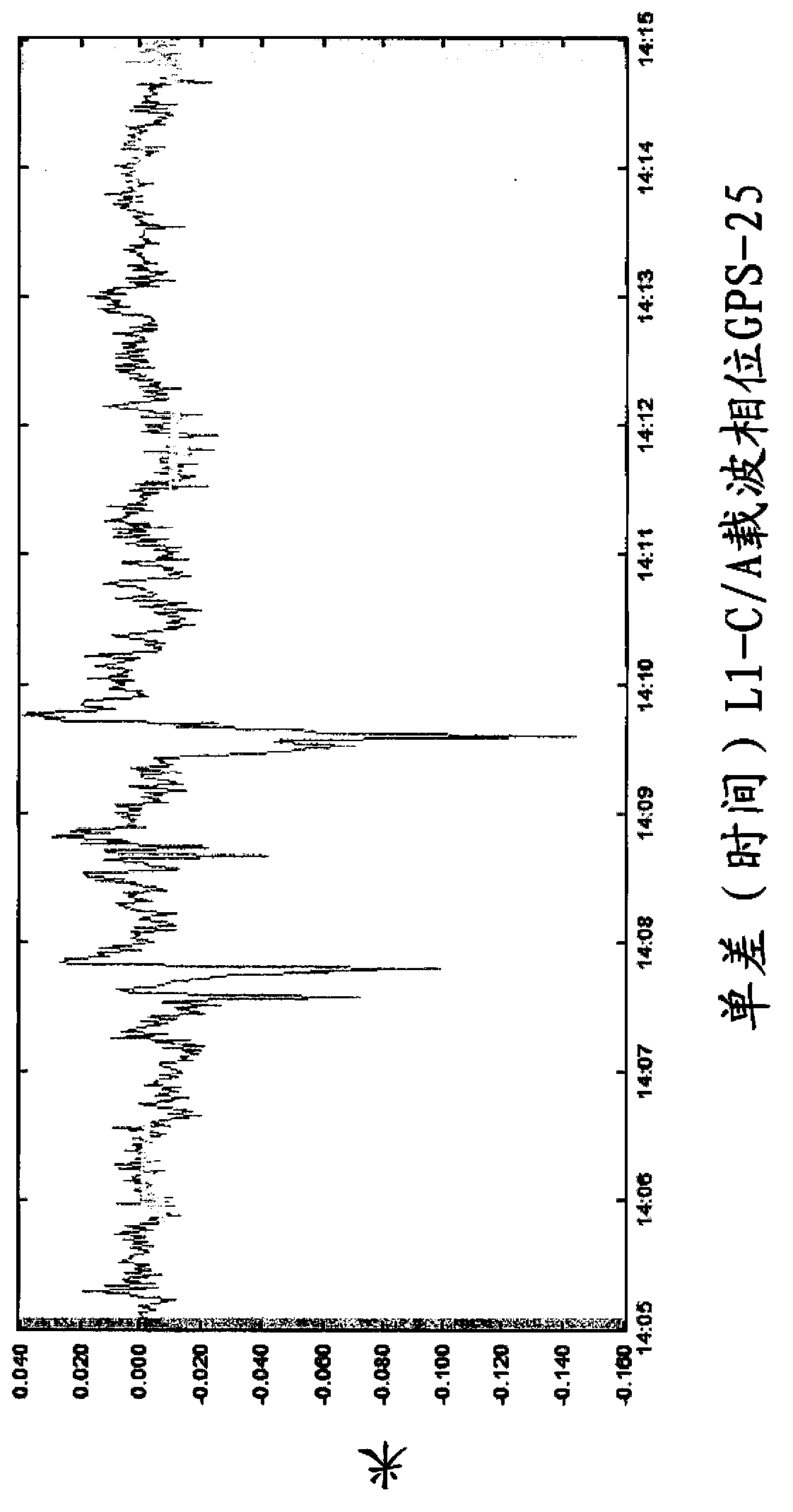
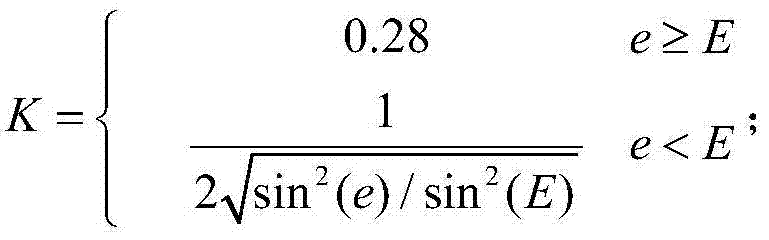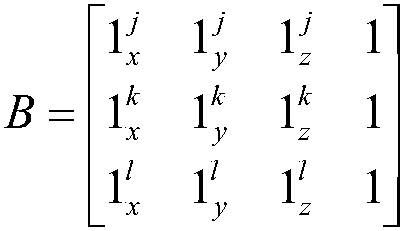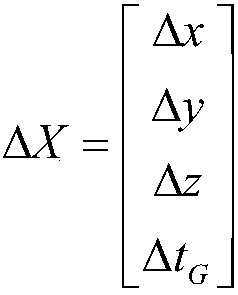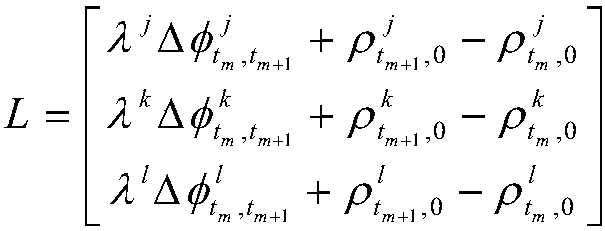Patents
Literature
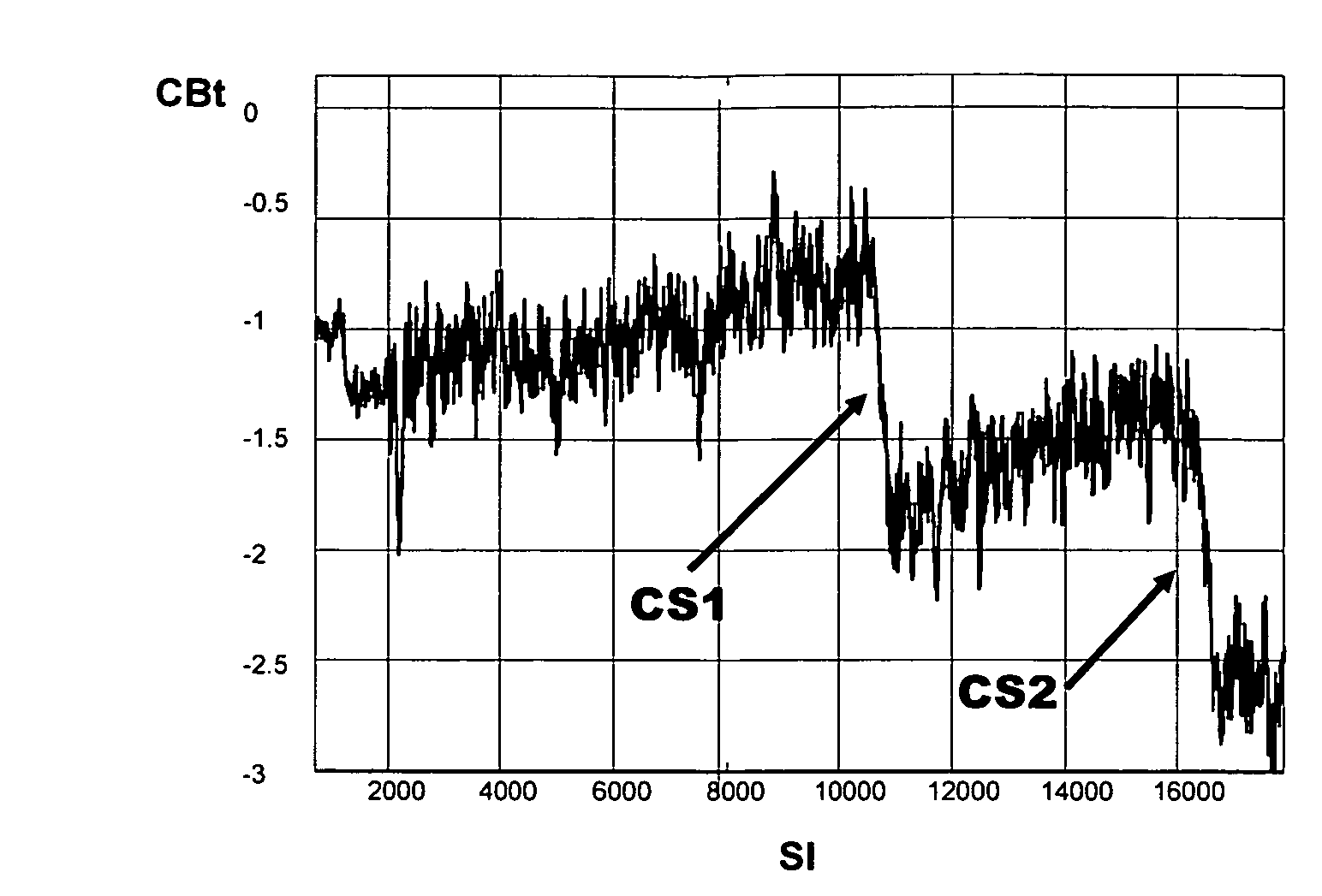
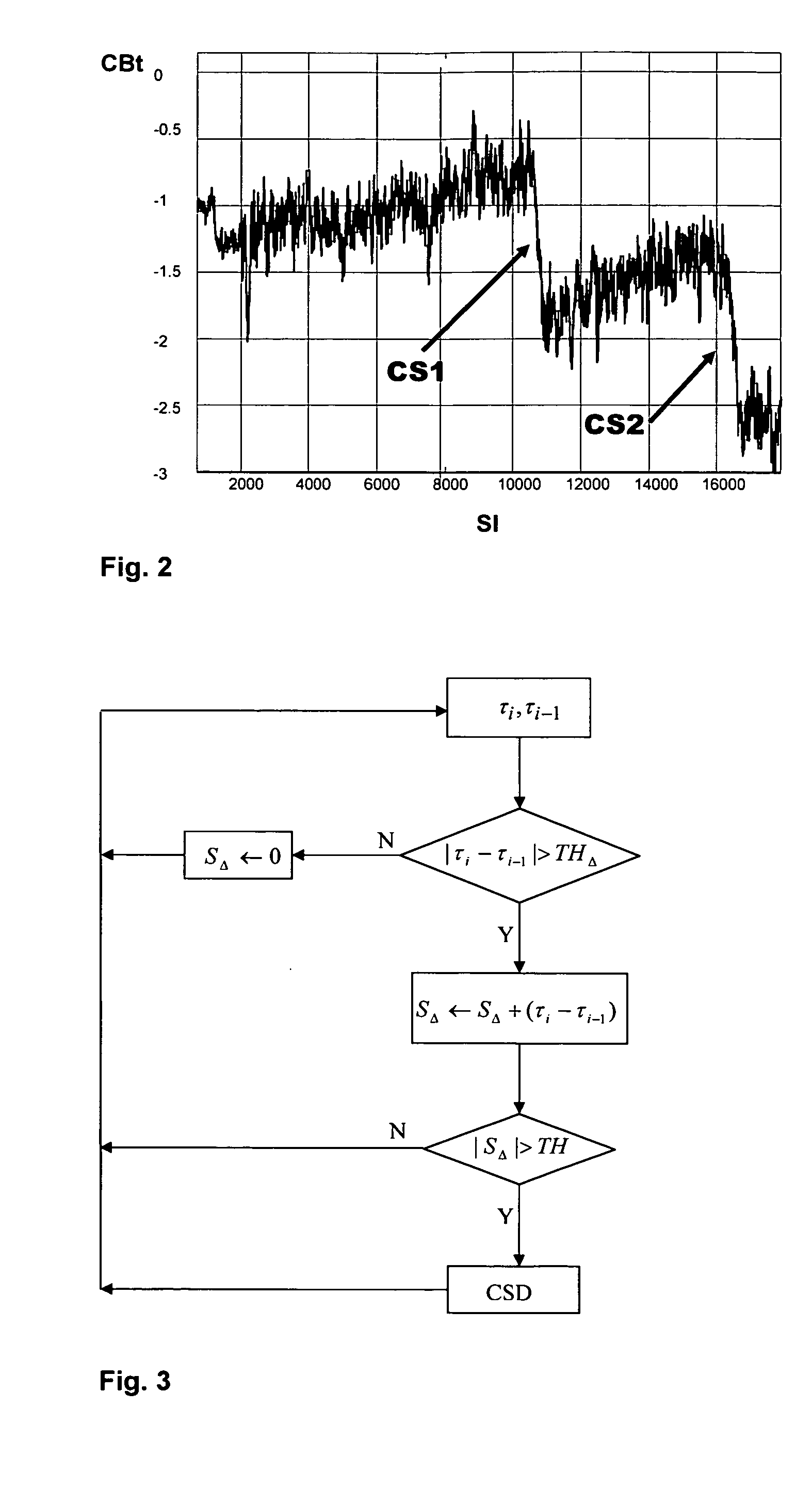
221 results about "Cycle slip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
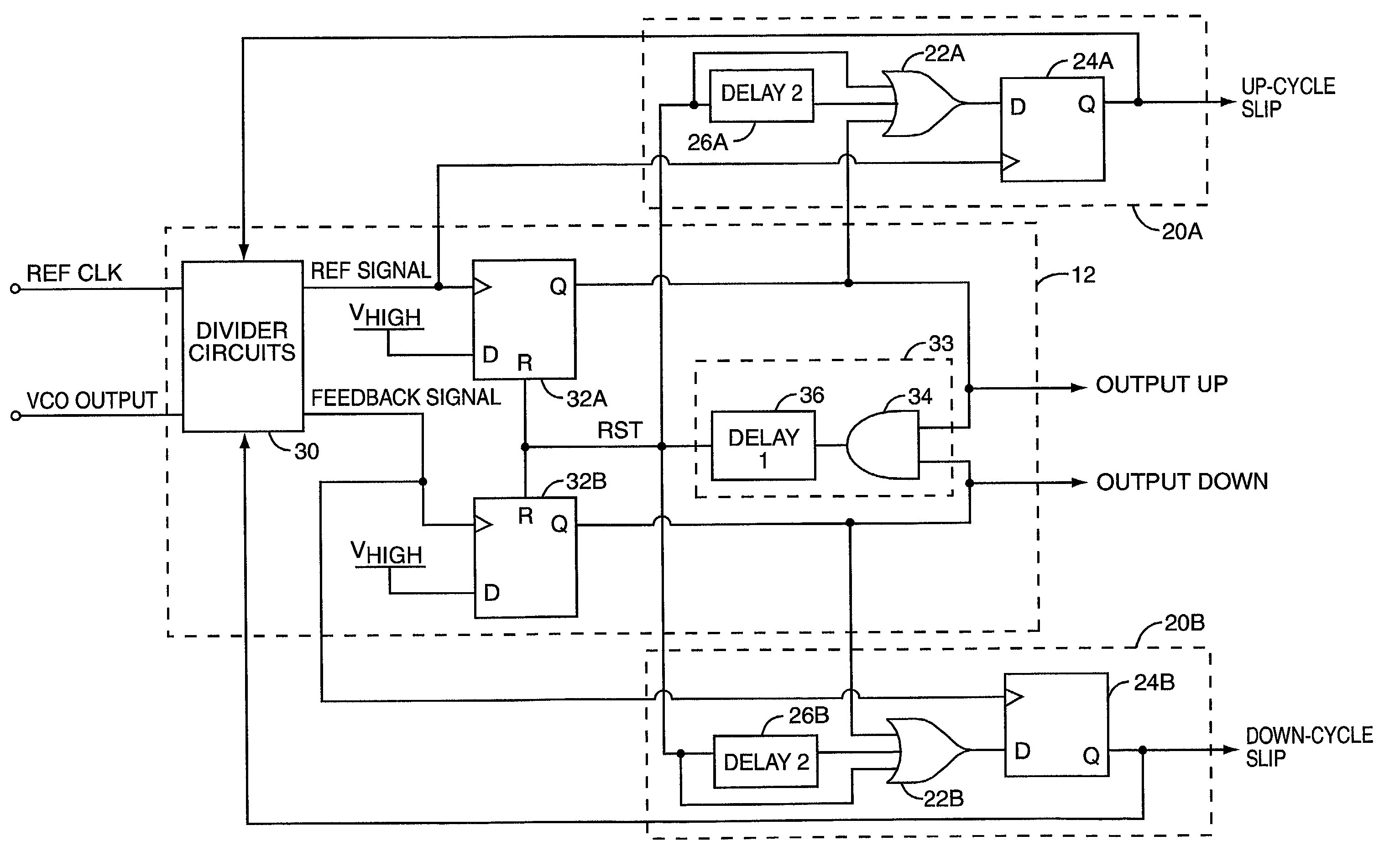
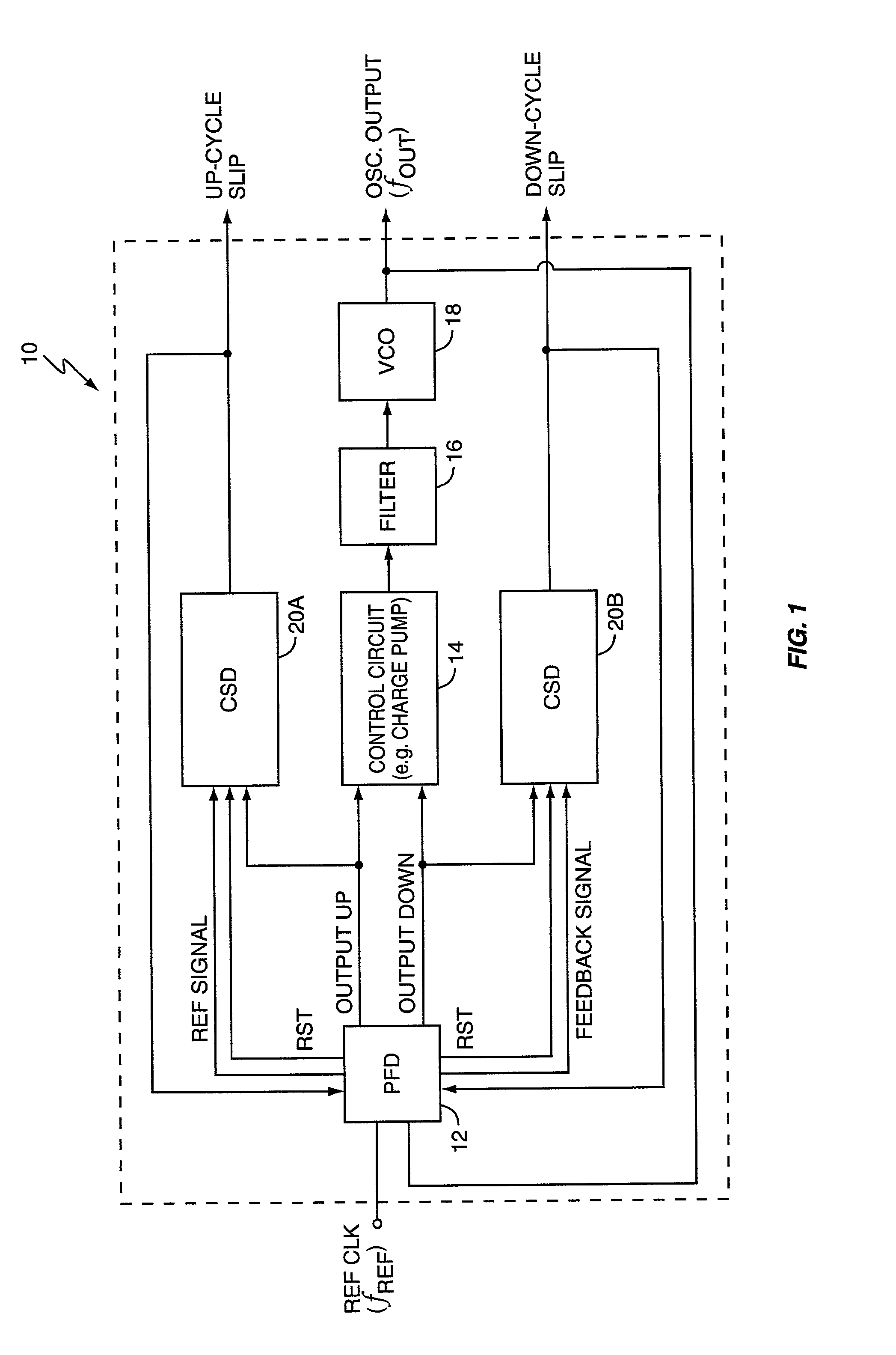
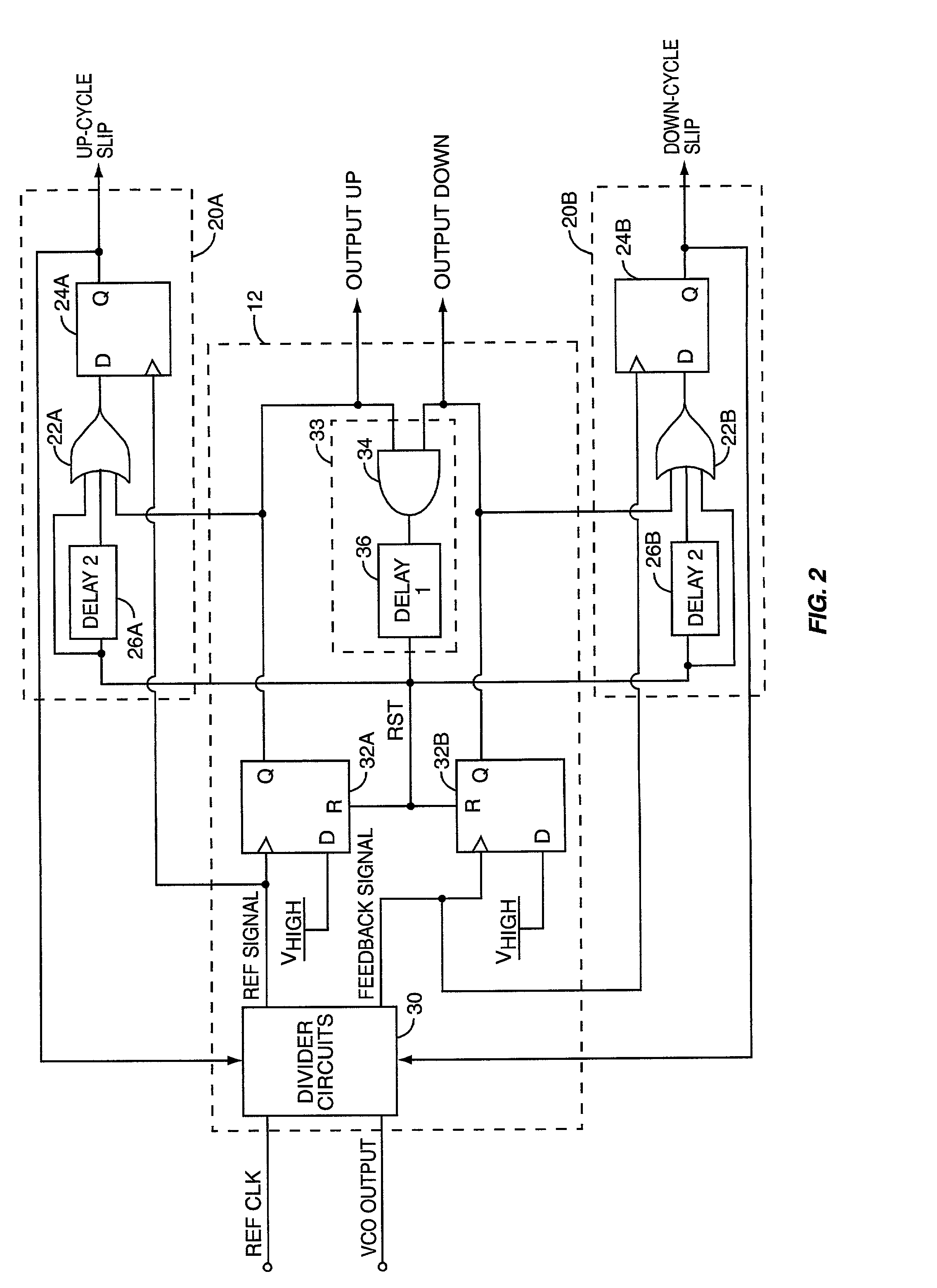
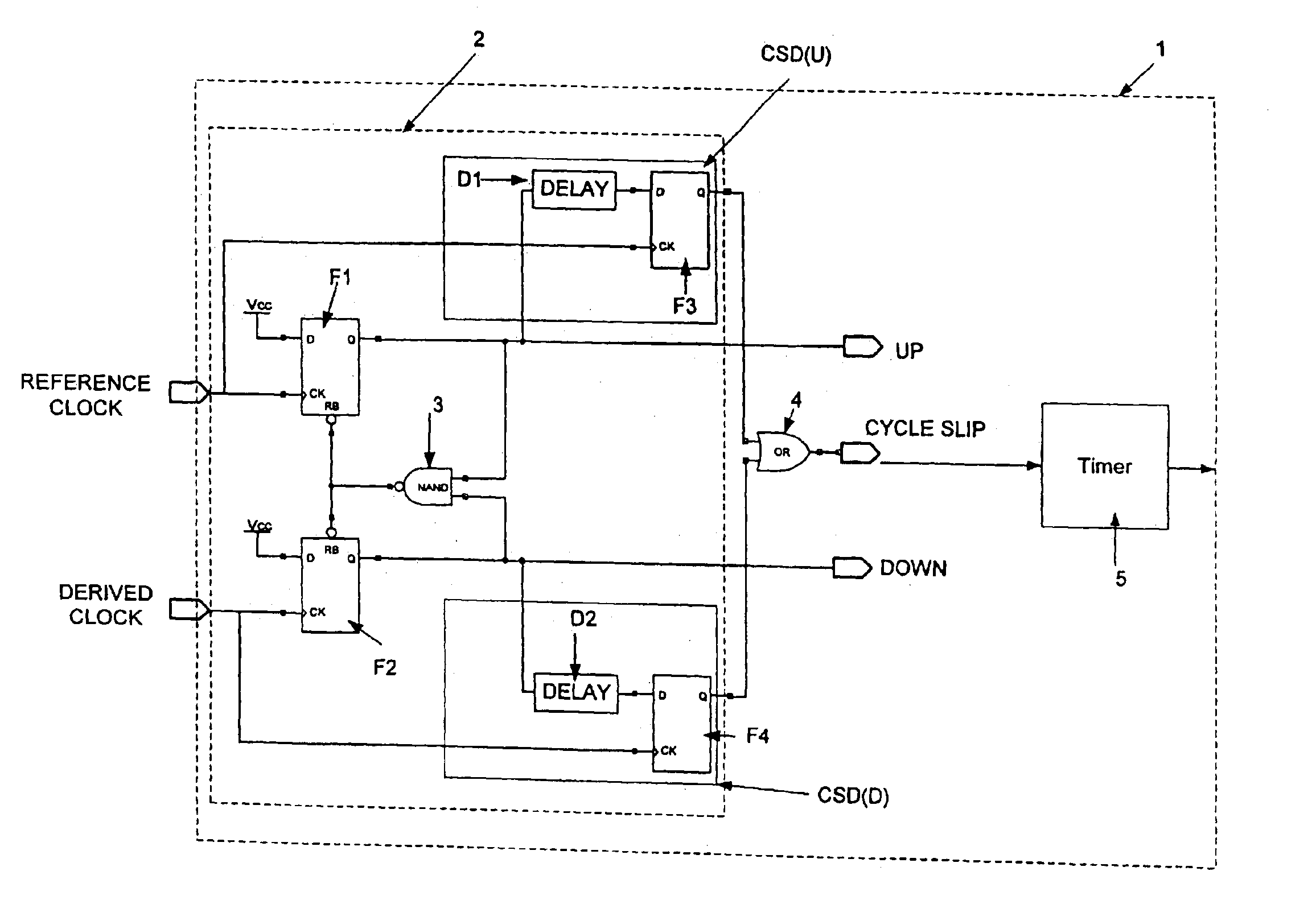
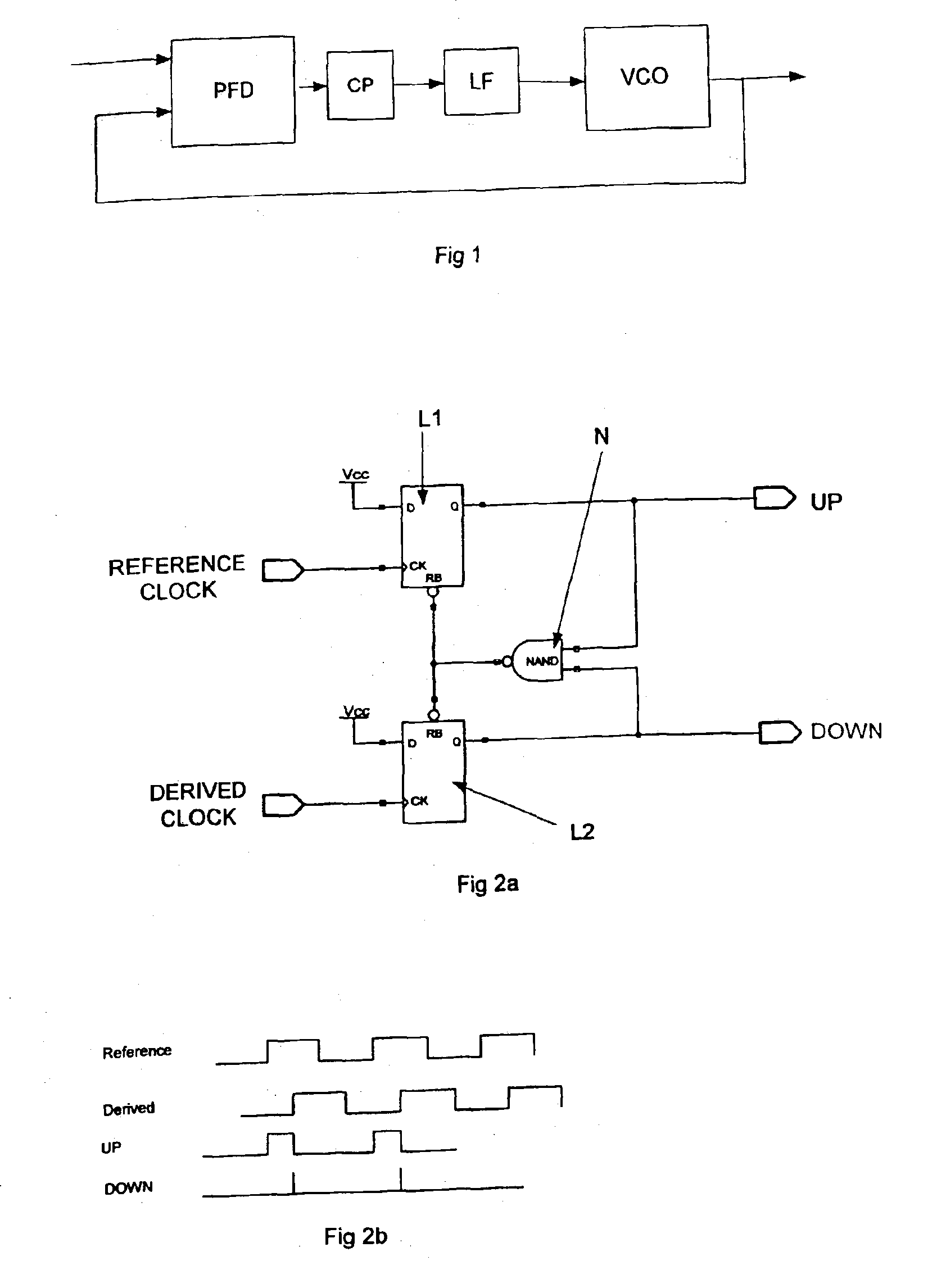
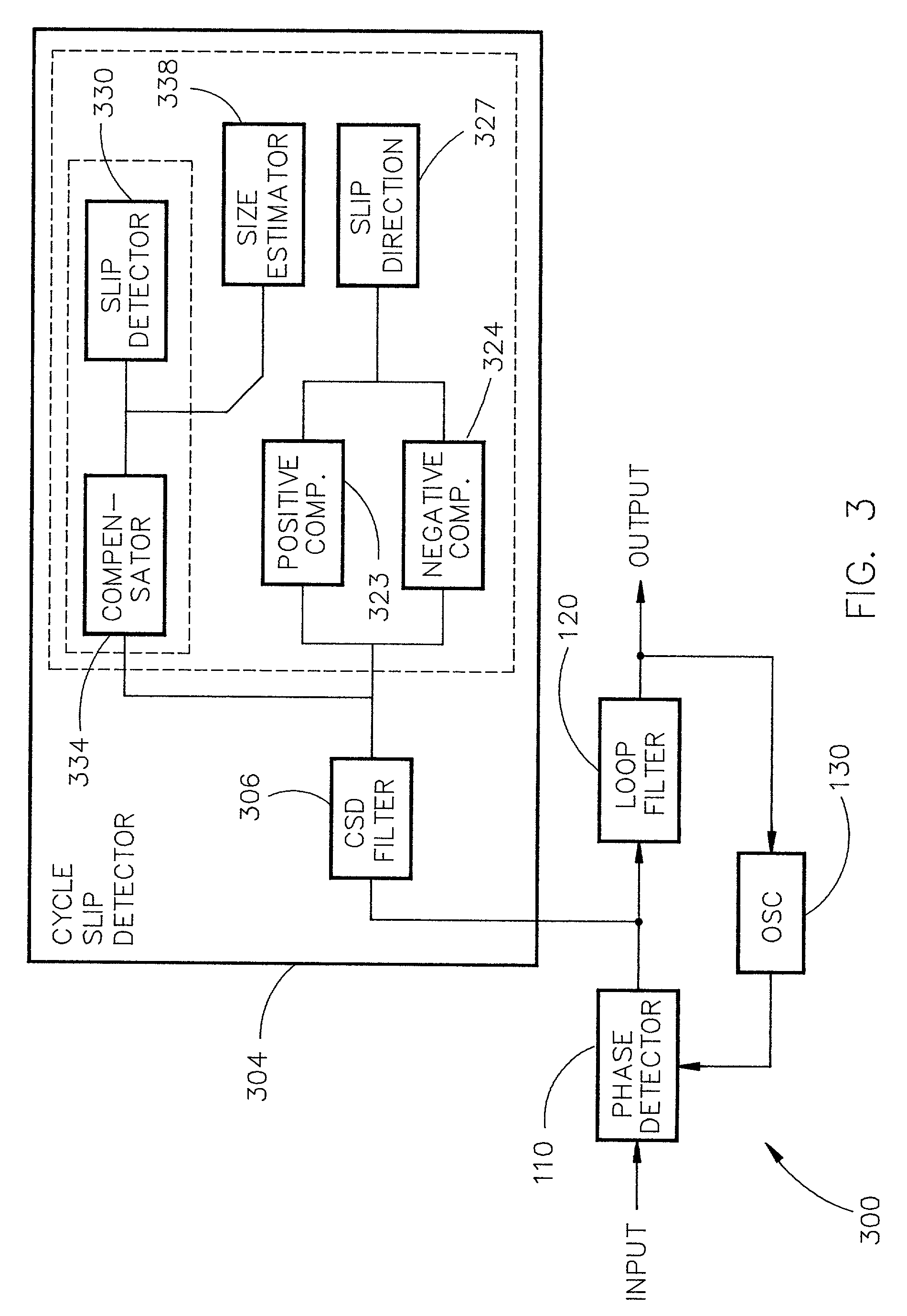
PLL cycle slip detection
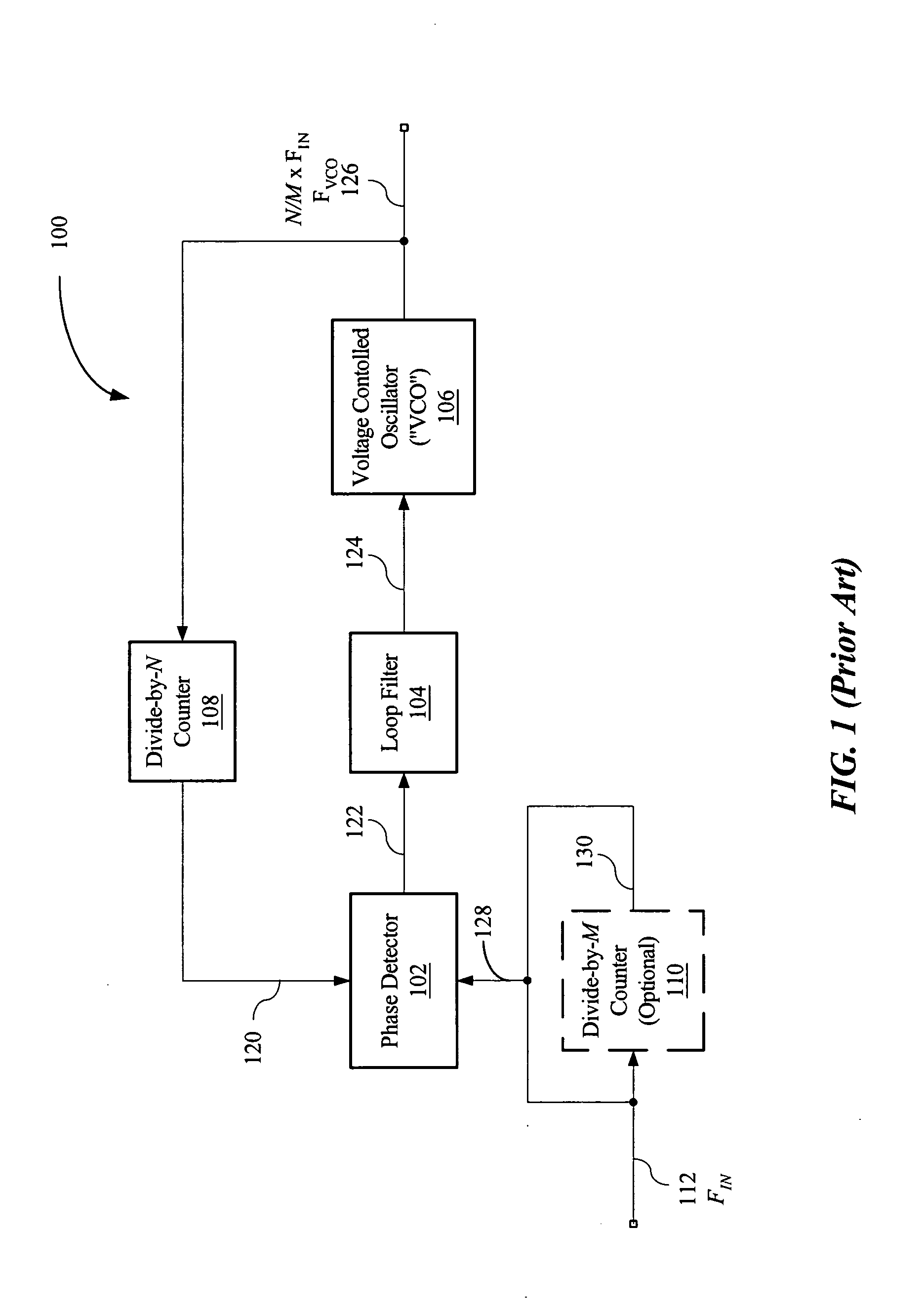
InactiveUS7003065B2Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleControl signalPhase locked loop circuit
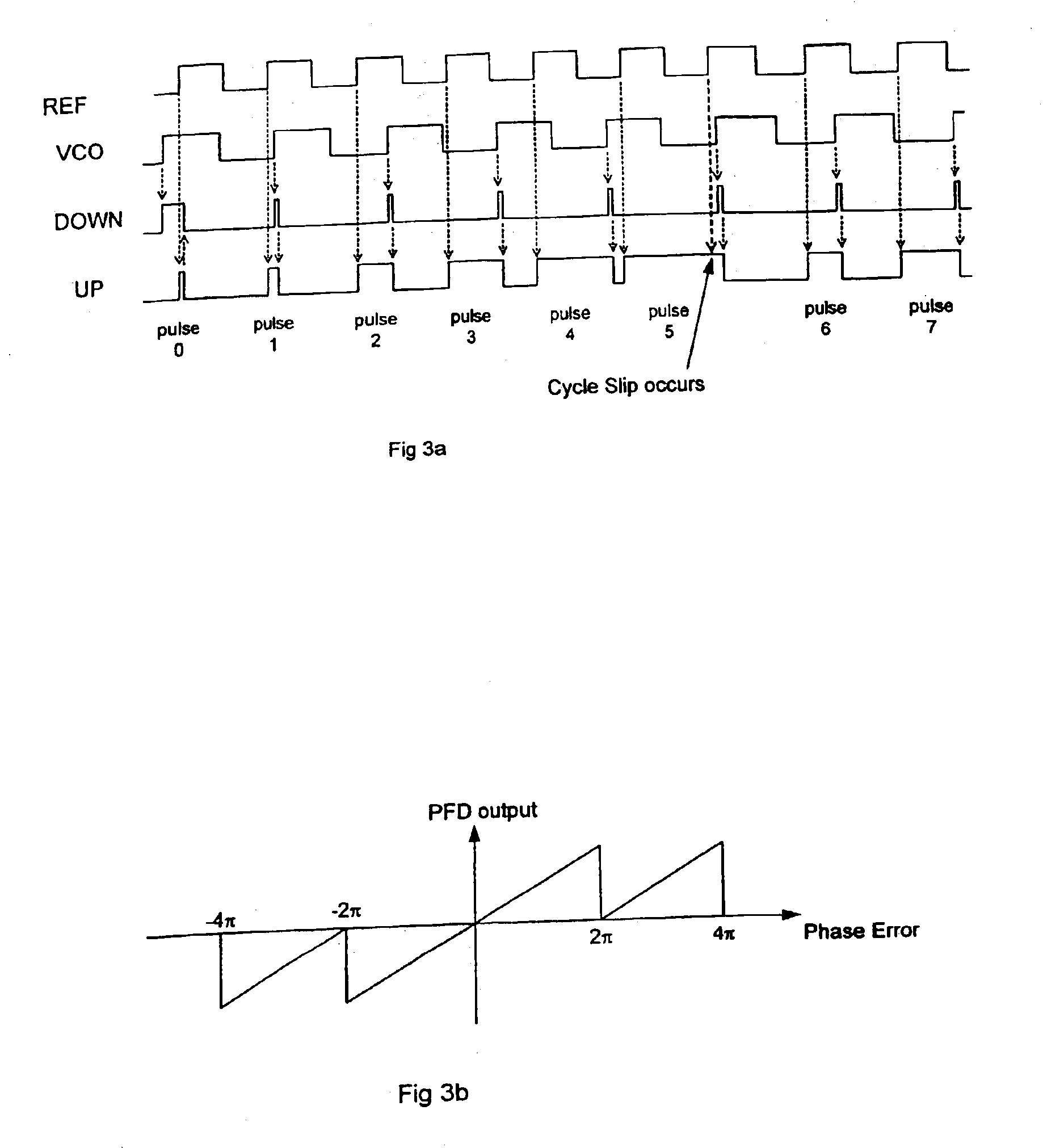
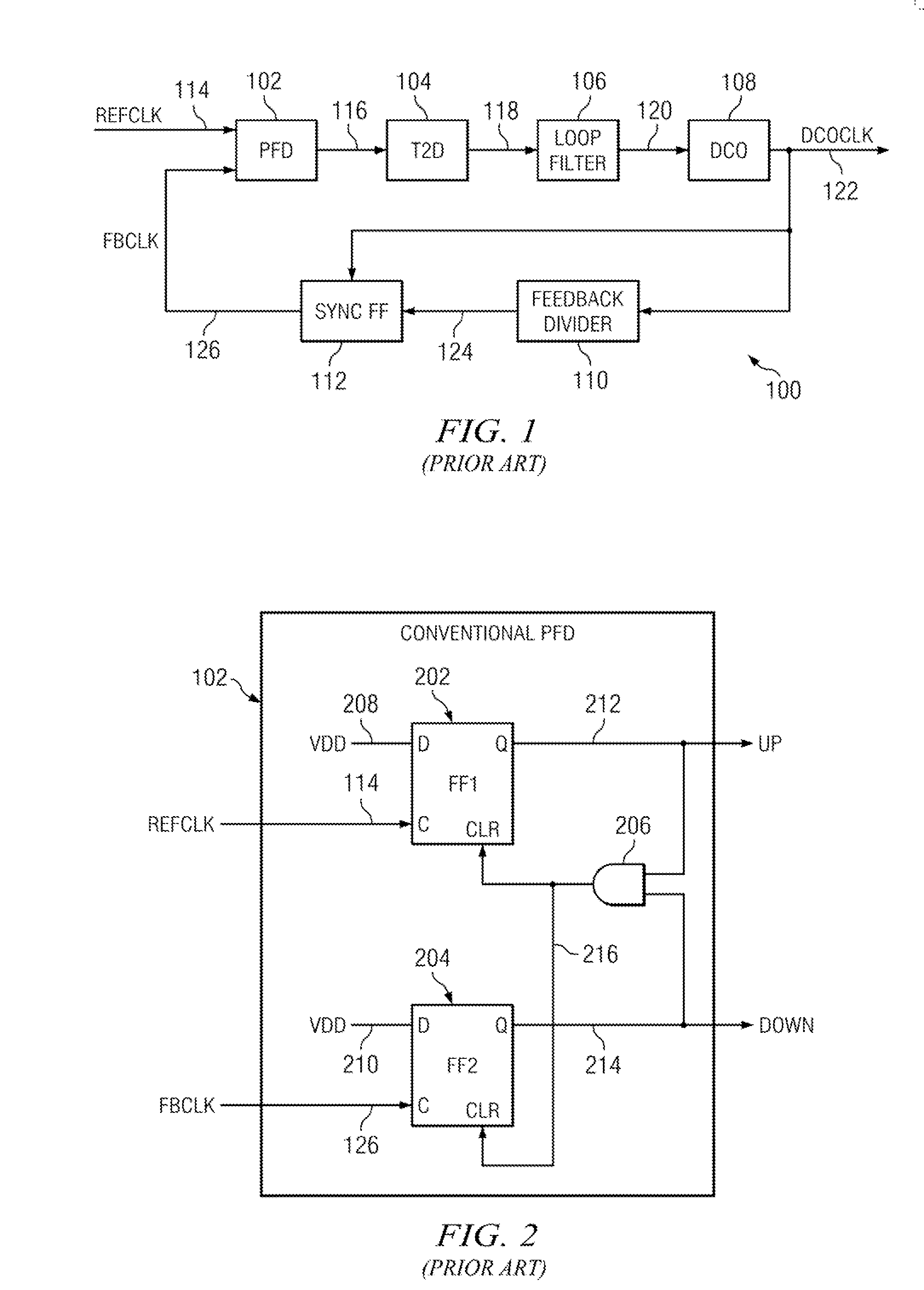
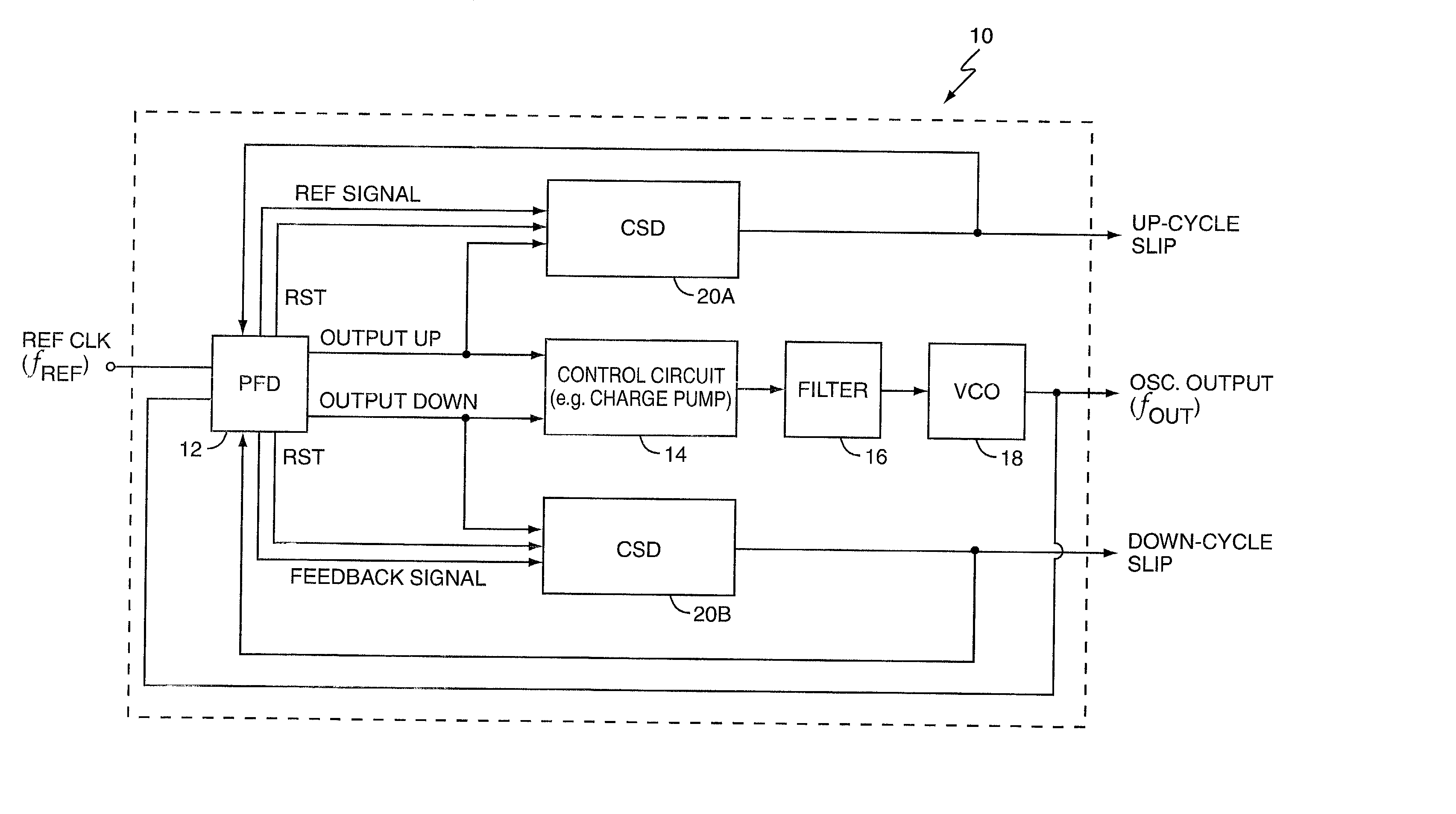
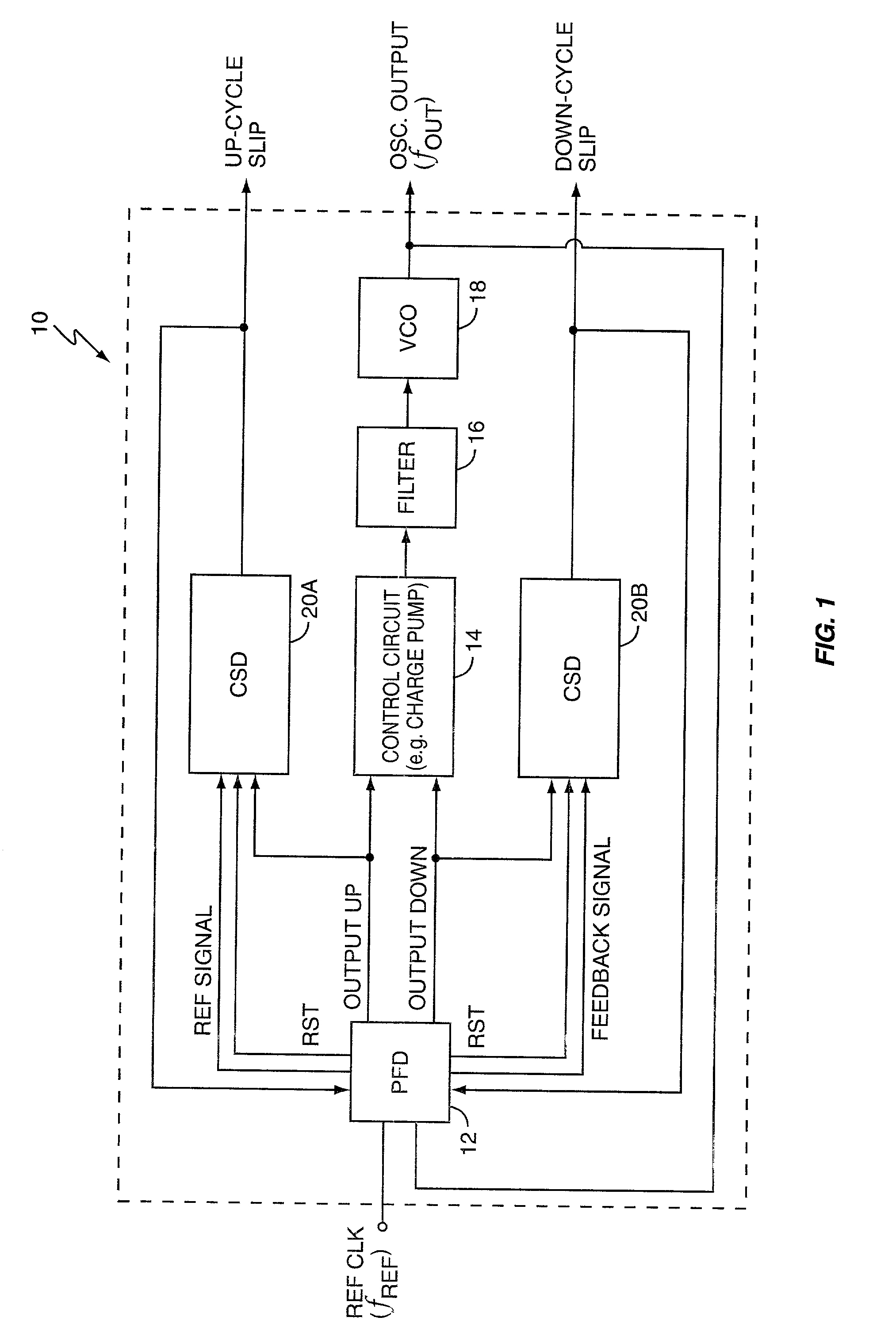
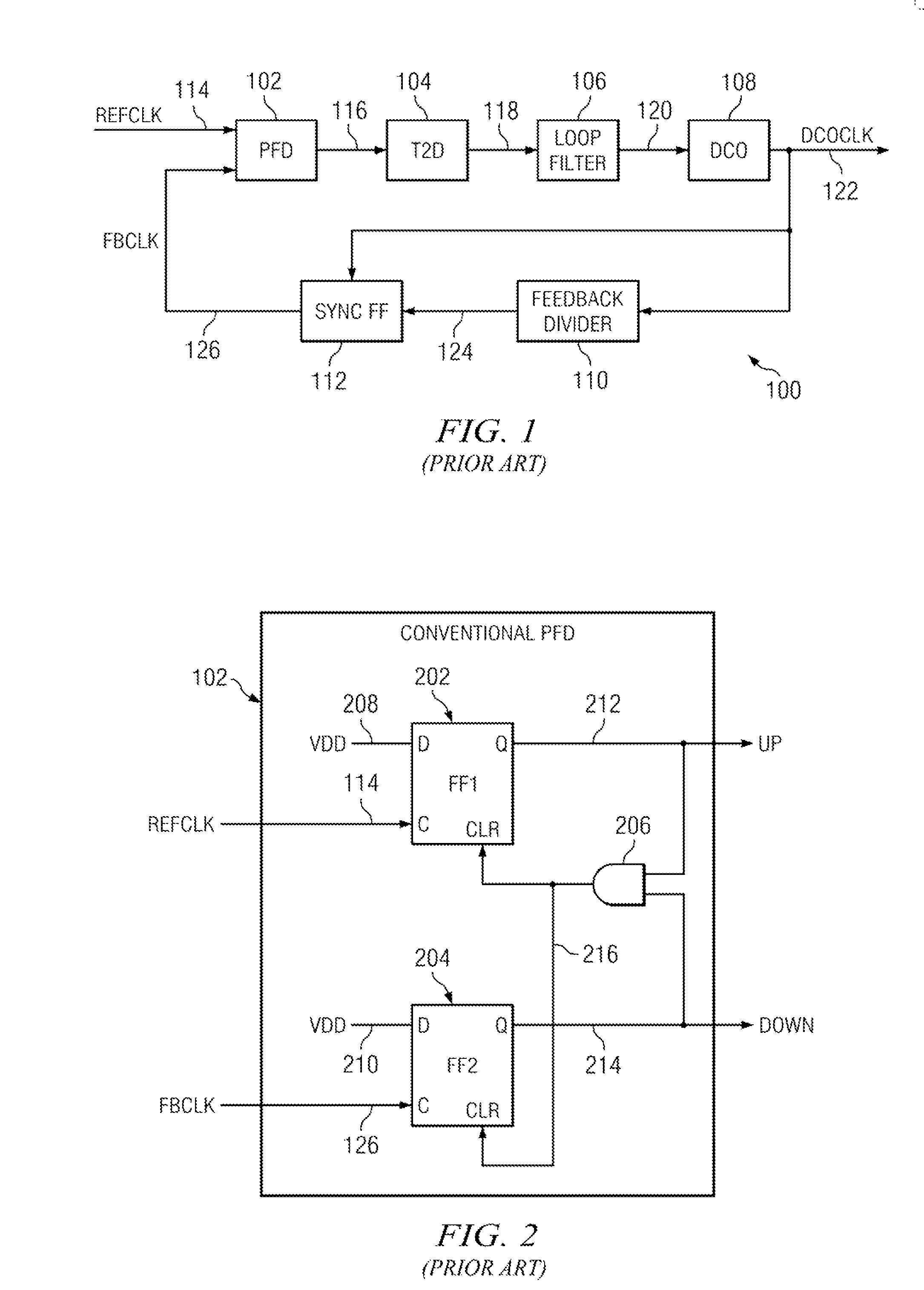
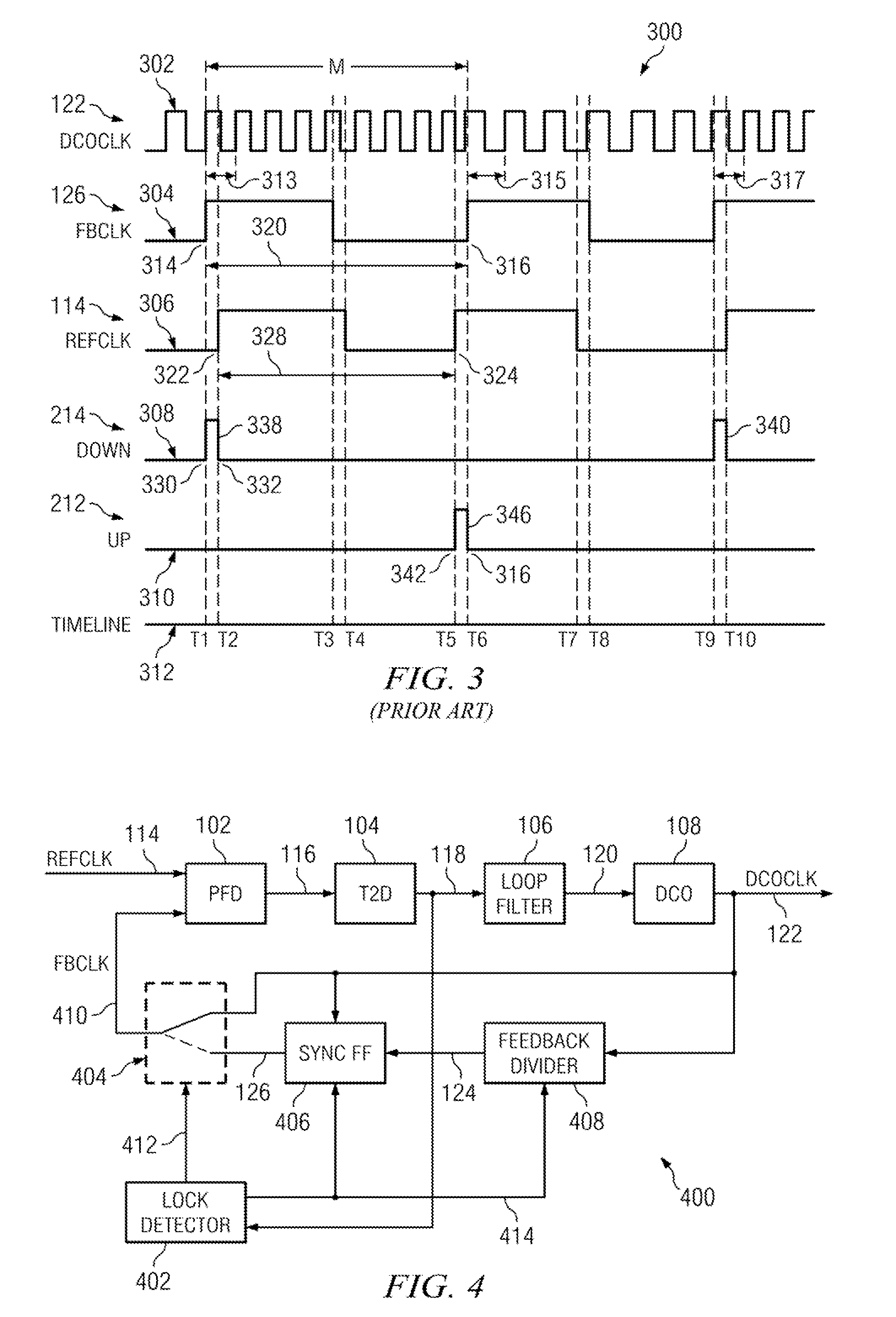
A cycle slip detector interfaces with a phase / frequency detector (PFD), such as might be used in a phase-locked loop circuit (PLL), and indicates when cycle slips occur in the PFD. Typically, the PFD generates output control signals as a function of the phase difference between first and second input signals, with the first input signal usually serving as a reference signal against which the PLL adjusts the second input signal. The PFD provides linear phase comparison between its input signals, provided their relative phase difference does not exceed ±2π radians. If one of the two signals leads or lags the other by more than that amount, a cycle slip occurs, and the PFD responds nonlinearly. The cycle slip detector provides logic for detecting and indicating leading and lagging cycle slips as they occur in the PDF, and is typically implemented as a minimal arrangement of logic gates and flip-flops.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
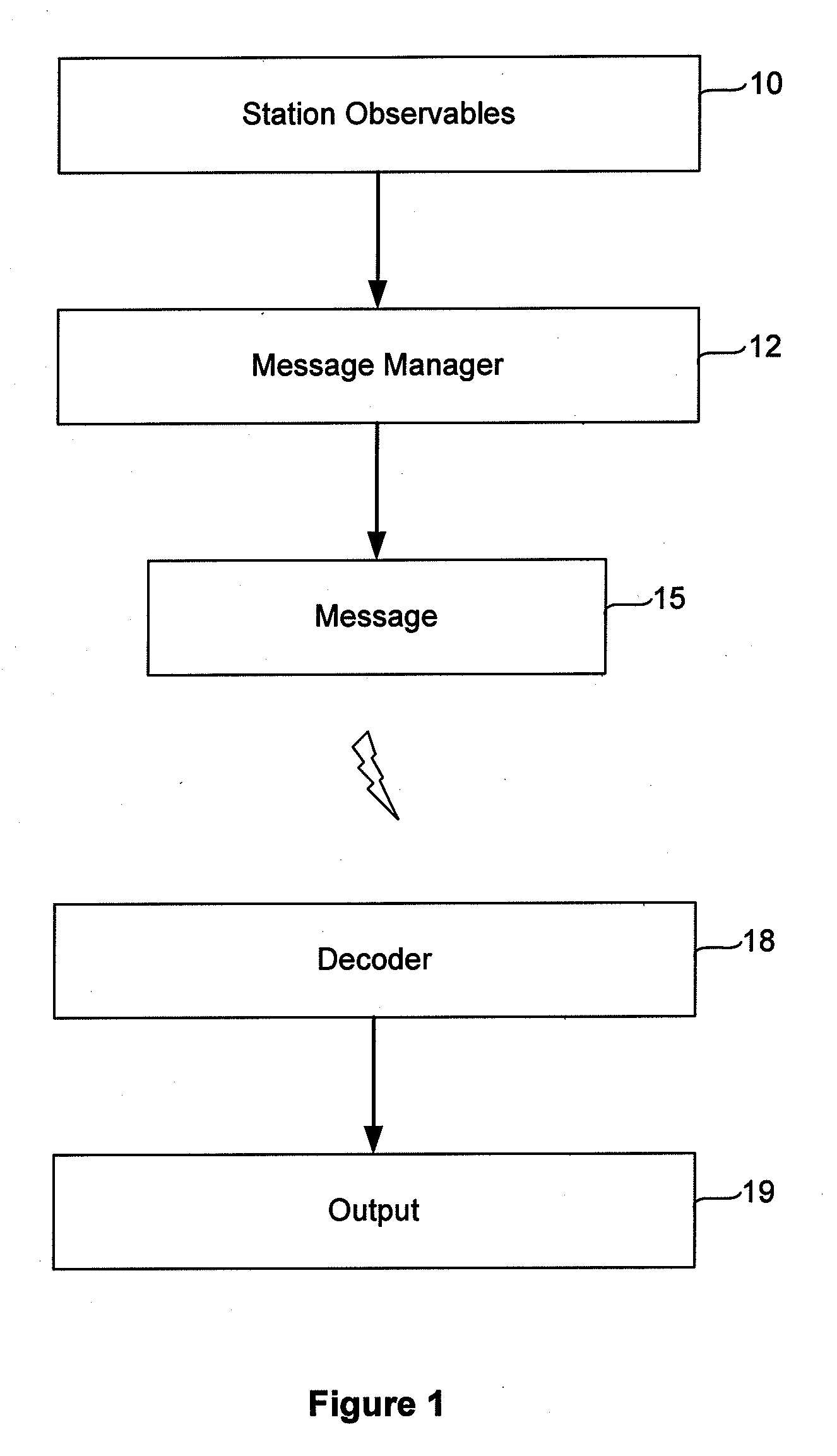
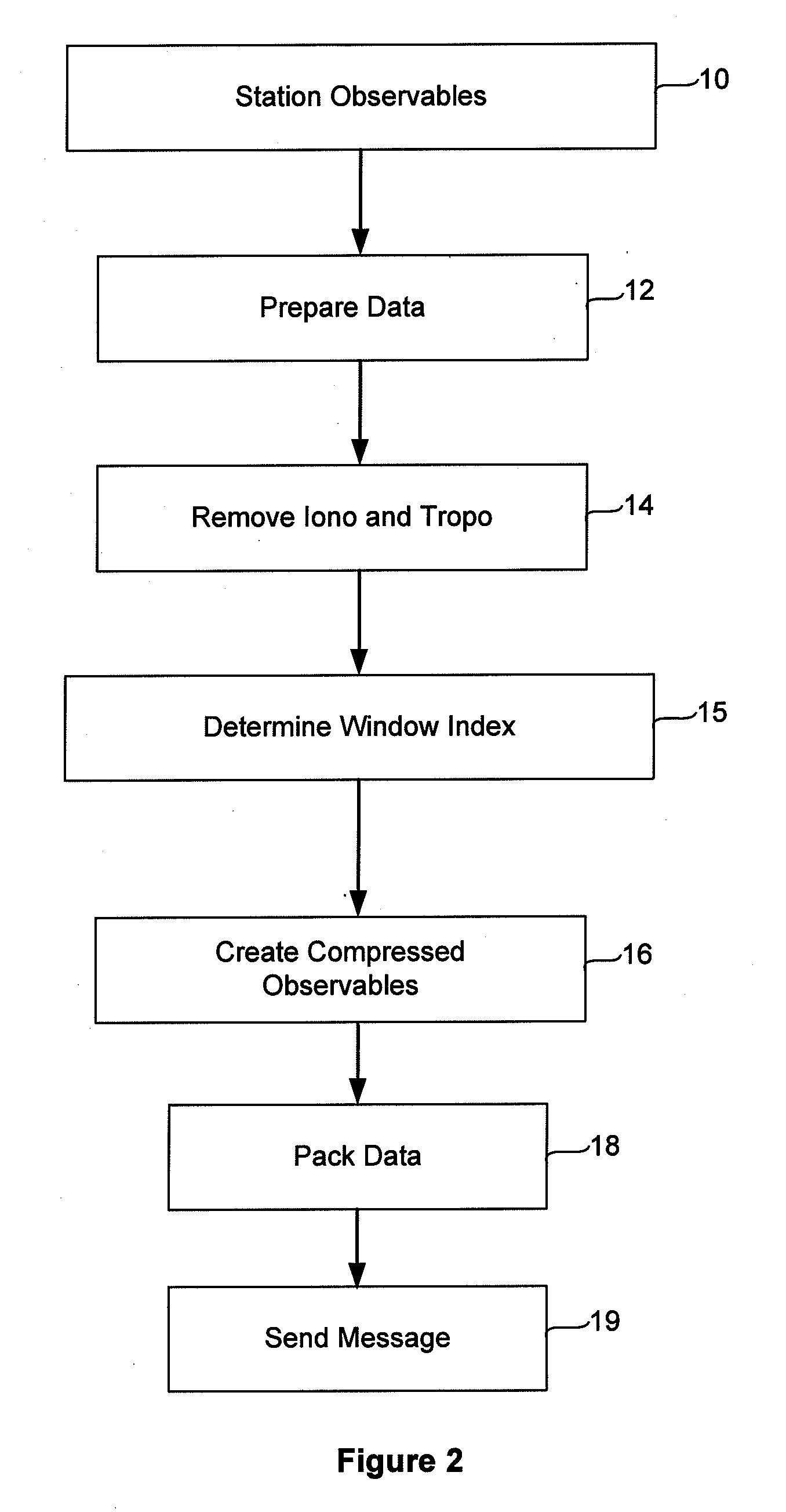
Continuous Tracking Counter for Enabling Cycle-slip Free Messages in a Network of Global Navigation System Satellite Receivers
ActiveUS20100085253A1Smooth bandwidth utilizationGuaranteed usageCode conversionSatellite radio beaconingHigh elevationSatellite tracking
A method of communicating satellite tracking information among a network of global navigation satellite system receivers is described. The method includes determining at a first GNSS receiver which satellites in a constellation of satellites have been continuously tracked over a preceding selected time period, and for each such satellite determining its elevation with respect to the zenith. Only the elevation value for the lowest satellite in the set of satellites for which all satellites of higher elevation values have been continuously tracked over the selected time period is then transmitted to the second GNSS receiver. That receiver can then reconstruct the set of satellites which have been continuously tracked.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Phase/frequency detector and phase lock loop circuit
ActiveUS6856202B2Avoid the needHigh frequencyPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleDetector circuitsControl signal
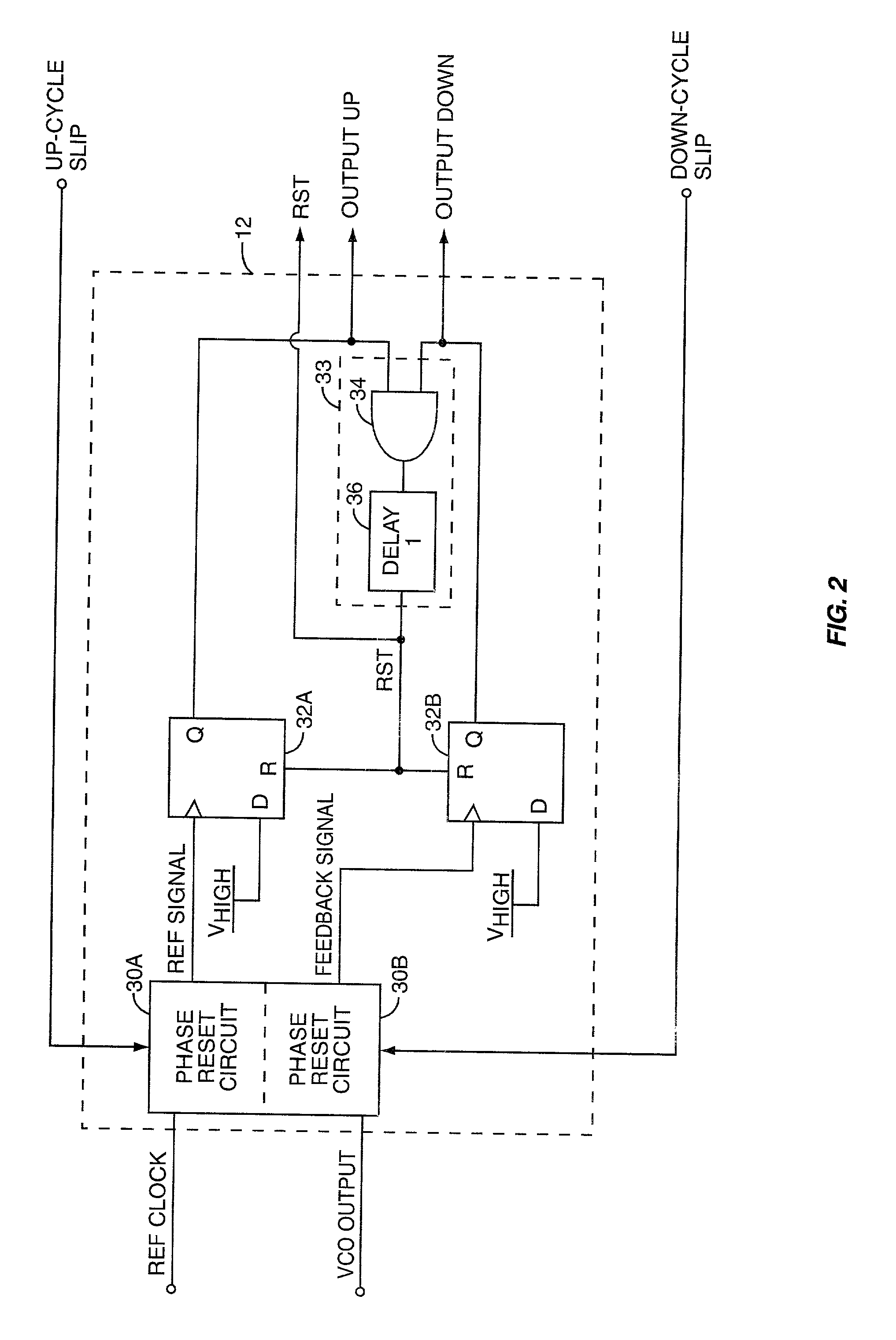
The present invention relates to cycle slip detectors for phase and frequency detectors (PFD) and to lock detectors for phase lock loop (PLL) circuits. The present invention provides a cycle slip detector circuit for use with a phase and frequency detector circuit having first and second signal inputs, and arranged to provide first and second PLL control signal outputs responsive to clock edges in the first and second input signals respectively; the cycle slip detector circuit comprising: means for determining a cycle slip between said input signals by determining when a delayed output signal coincides with a respective input signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Accurate one-point positioning method for single-frequency GPS receiver
ActiveCN101403790AAchieve positioningEliminate the effects ofBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationGps receiverRatio method
The invention relates to a precise single point positioning method of a single-frequency GPS receiver, which comprises GPS data reading and pretreating steps, error correcting and resolving steps and a result output step, wherein the pretreating step comprises the cycle slip exploration and restoration which comprises the following steps: (1) m non-cycle-slip carrier phase observed values Phi are substituted into a formula and the polynomial fitting is then carried out; (2) a calculated polynomial coefficient is used for extrapolating a carrier phase observed value Phi of the next epoch which is then compared with the actual observed value Phi; (3) the carrier phase observed values of the first epoch and the i-1 epoch are utilized to obtain the variance ratio of the carrier phase observed values. The invention comprehensively utilizes the polynomial fitting method and the carrier phase variance ratio method to explore the cycle slip, combines the gross error correction to realize the precise single point positioning of a single-frequency GPS receiver, thereby effectively realizing the high-precision positioning and navigation of a GPS system.
Owner:杭州亚龙智能科技有限公司
Low power digital phase lock loop circuit
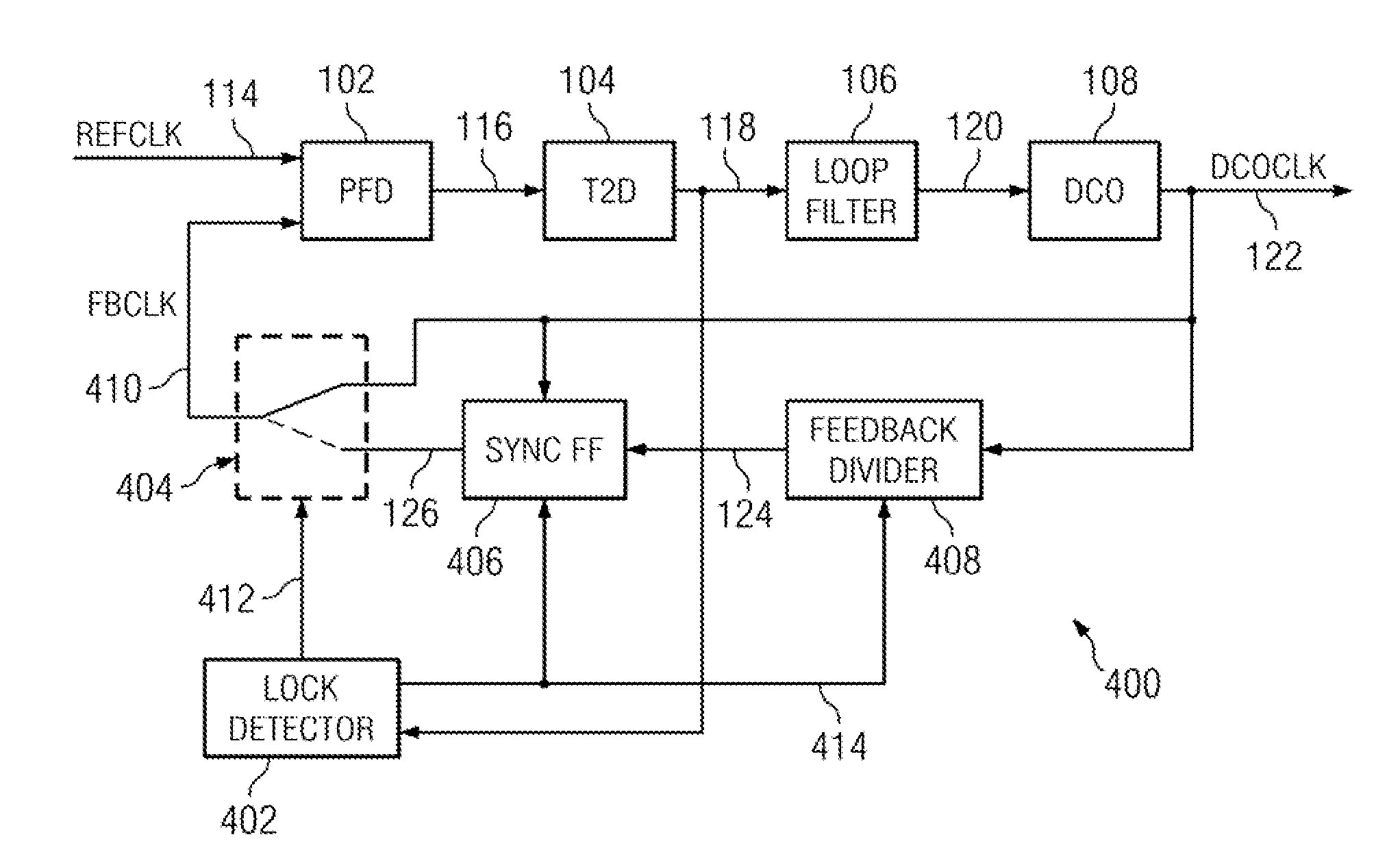
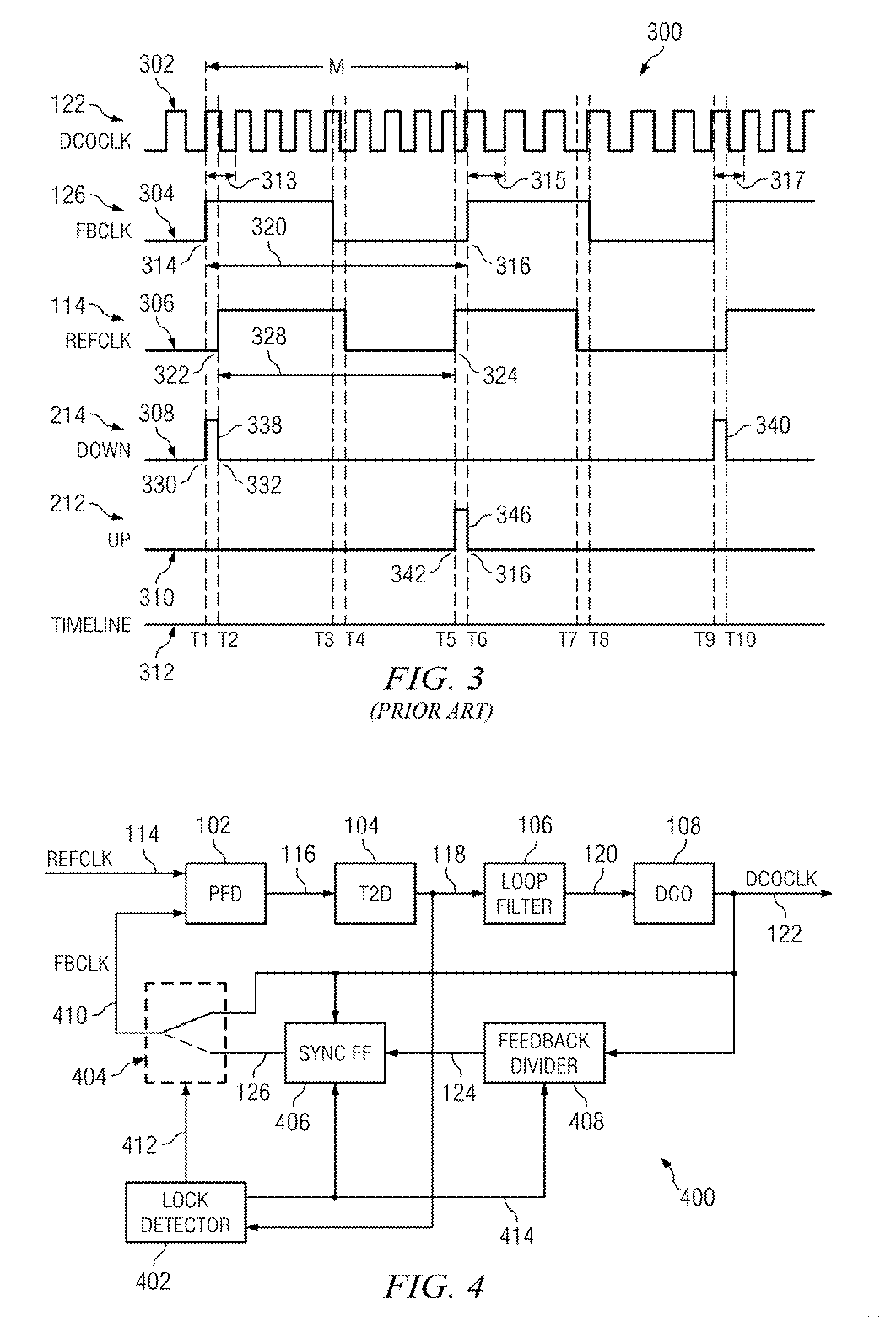
ActiveUS20110273210A1Increase power usageSufficient powerPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase locked loop circuitClock rate
A digital phase lock loop circuit, where under certain conditions the phase error is derived from phase comparison between a reference clock edge and the next oscillator clock edge rather than a feedback clock edge. This technique can be used to significantly reduce digital phase lock loop circuit power by disabling feedback divider and sync FF once initial frequency lock is established, provided phase jitter of digital phase lock loop circuit is low enough so that there is no cycle slip. This technique can also be used to multiply the effective reference clock frequency of digital phase lock loop circuits to increases the loop bandwidth, thus reducing the phase noise. Both the applications of this technique can be combined in some circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
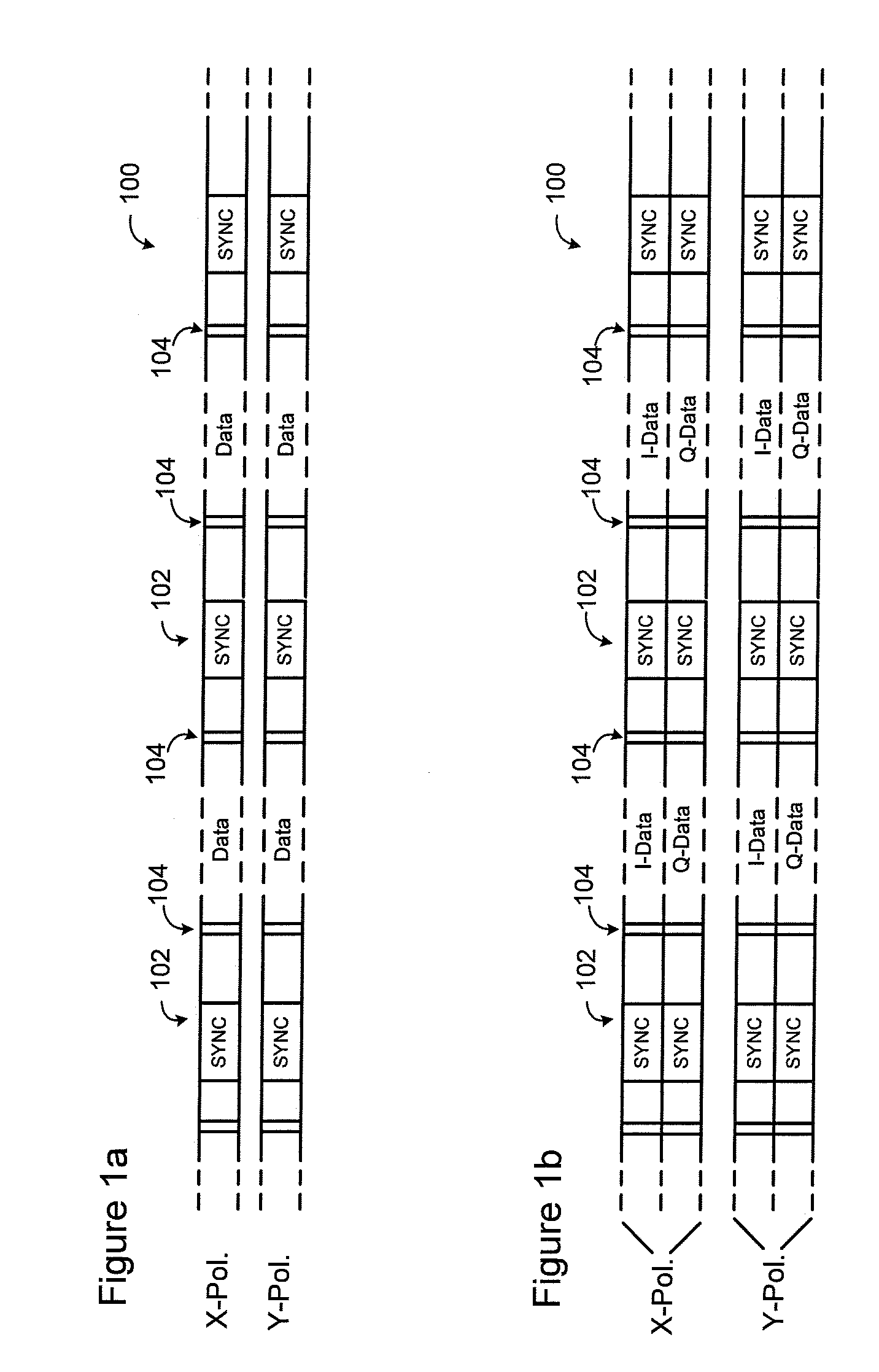
Cycle slip location and correction
Methods and techniques are disclosed for correcting the effect of cycle slips in a coherent communications system. A signal comprising SYNC bursts having a predetermined periodicity and a plurality of known symbols at predetermined locations between successive SYNC bursts is received. The received signal is partitioned into data blocks. Each data block encompasses at least data symbols and a set of check symbols corresponding to the plurality of known symbols at predetermined locations between a respective pair of successive SYNC bursts in the signal. Each data block is processed to detect a cycle slip. When a cycle slip is detected, the set of check symbols of the data block are examined to identify a first slipped check symbol, and a phase correction applied to data symbols of the data block lying between the first slipped check symbol and an end of the data block.
Owner:CIENA
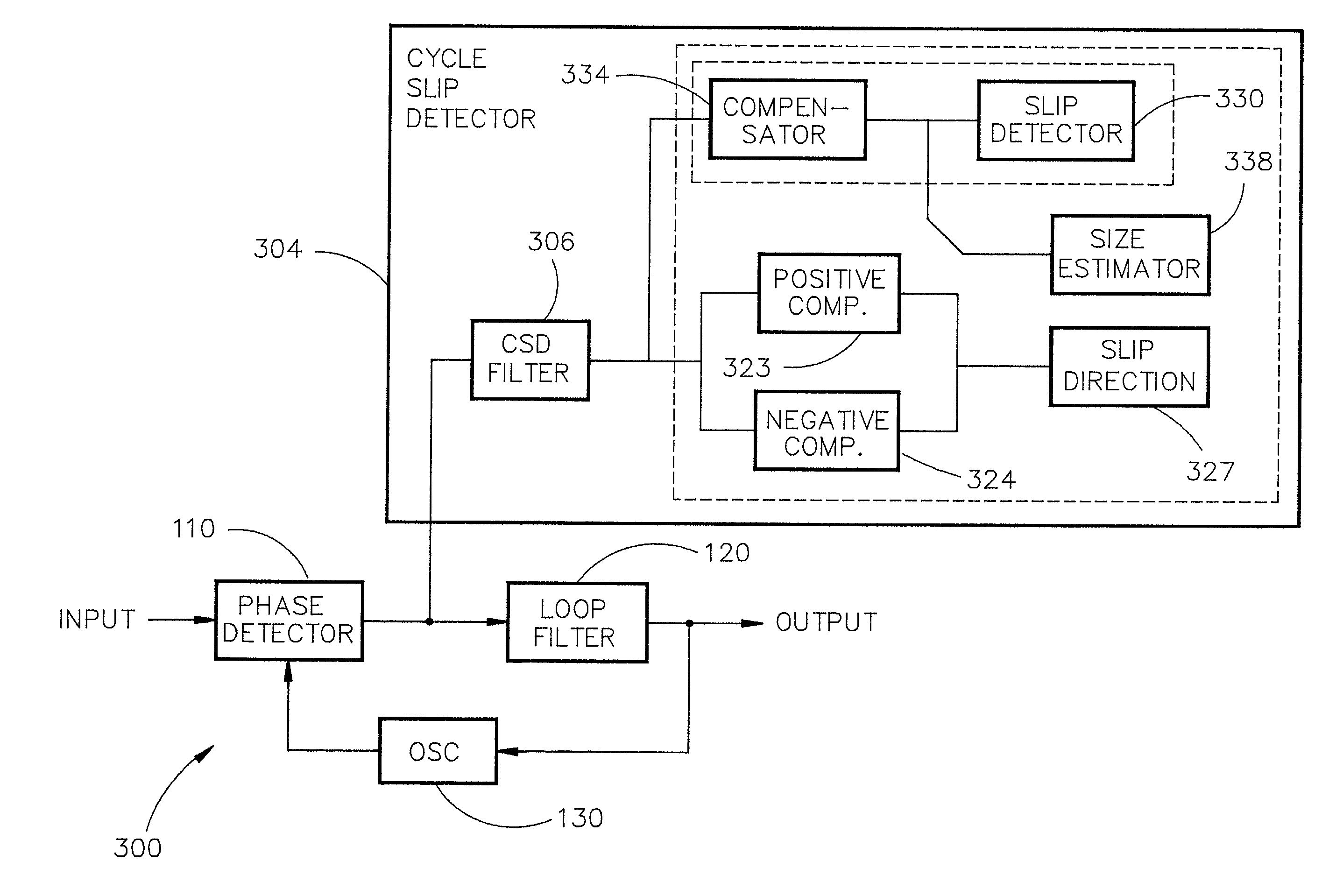
Cycle slip detection using low pass filtering
InactiveUS6973150B1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase differenceEngineering
A cycle slip detector and detection method for a phase comparison circuit are provided. The cycle slip detector includes a cycle slip detection filter possessing a predetermined filter bandwidth and a predetermined high frequency cut-off. The cycle slip detection filter receives a phase difference generated by the phase comparison circuit and transforms the phase difference into a filtered phase difference. The cycle slip detector further includes a compensator communicating with the cycle slip detection filter. The compensator compensates the magnitude based on a predetermined compensation response. The cycle slip detector further includes a cycle slip occurrence detector communicating with the compensator. The cycle slip occurrence detector compares a compensated magnitude of the filtered phase difference to a predetermined cycle slip threshold and generates a cycle slip output if the compensated magnitude exceeds the predetermined cycle slip threshold.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
A CORS base station cycle slip detection and repair method
InactiveCN102288978AEfficient repairAccurate detectionSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyObservation data
The invention discloses a continuous operational reference system (CORS) base station cycle slip detection and recovering method, which comprises the following steps that: firstly, an ionized layer residual method is used for carrying out cycle slip detection, a satellite with the cycle slip and the corresponding observation value are determined, then, a single-epoch dual-frequency observation equation is built according to the cycle slip detection results, the single-epoch dual-frequency observation equation is divided into two types, the first type is cycle-slip-free observation equations, the second type is cycle slip observation equations, the cycle slip generated by a non-reference satellite is used as a gross error, the cycle slip generated by a reference satellite is used as a system error, the first type observation equations are used for carrying out parameter estimation, the cycle slip of the reference satellite is determined, the estimated parameters are introduced into thesecond type observation equations, correction numbers are calculated, the cycle slip values of the reference satellite are obtained, and finally, the cycle slip base station observation data is recovered according to the relationship between the base lines in a CORS triangular net. Because the error time strong correlation of the precise coordinate, the dual-frequency convection layer, the ionized layer and the like is directly utilized, the cycle slip detection and recovery can be precisely carried out.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and Method for Recovering Carrier Phase in Optical Communications
ActiveUS20160065315A1Improve performanceError minimizationError preventionSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSkew angleHide markov model
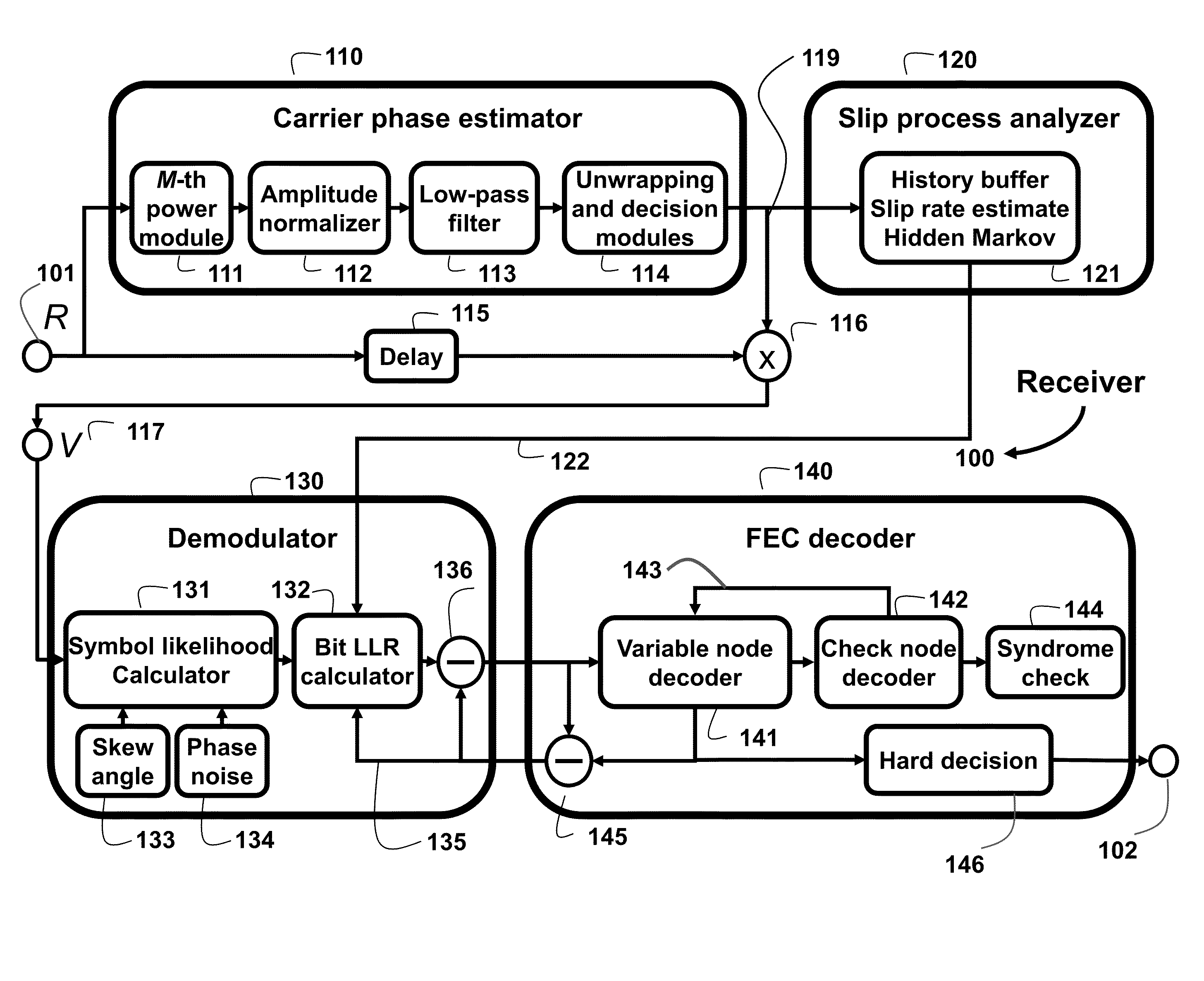
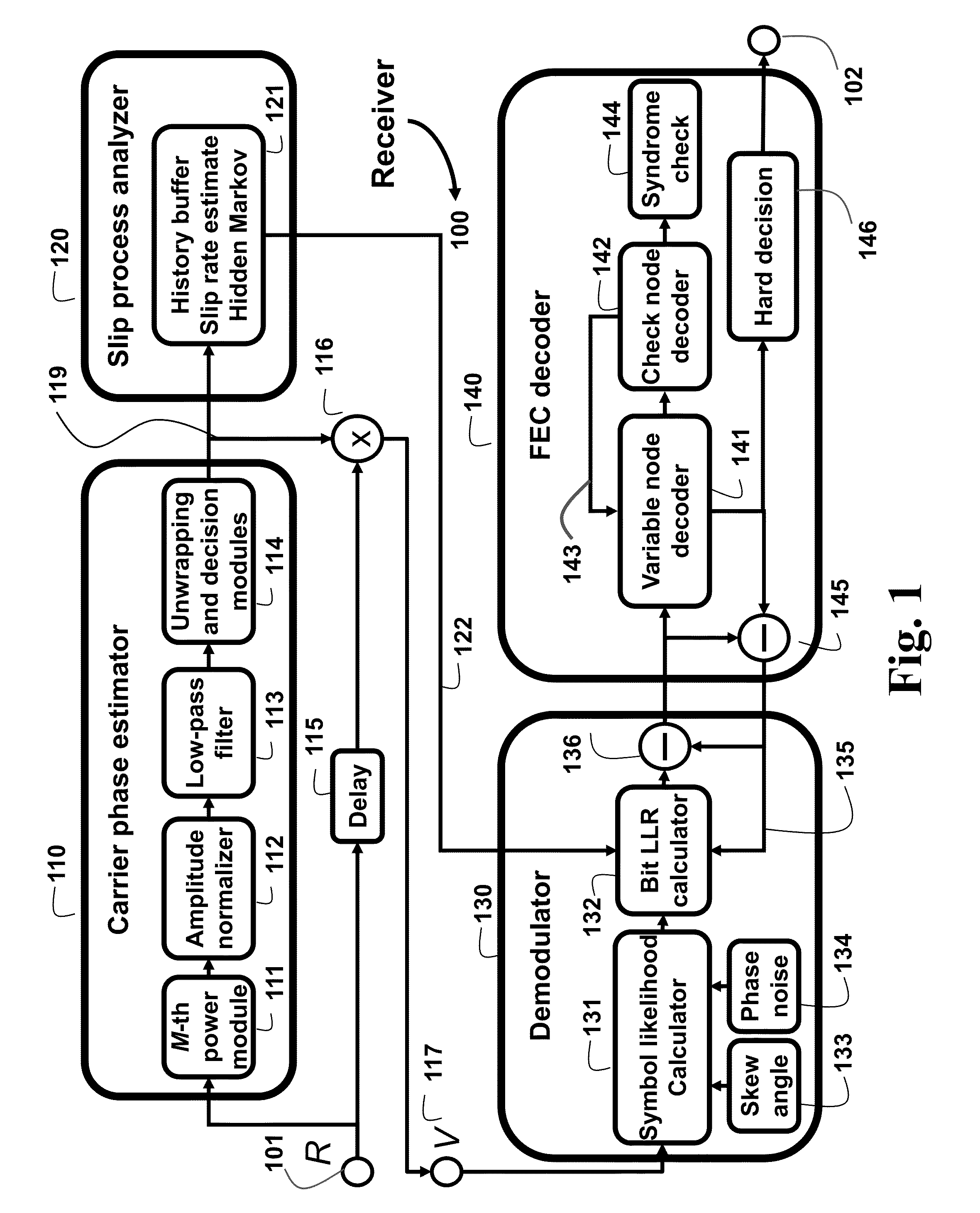
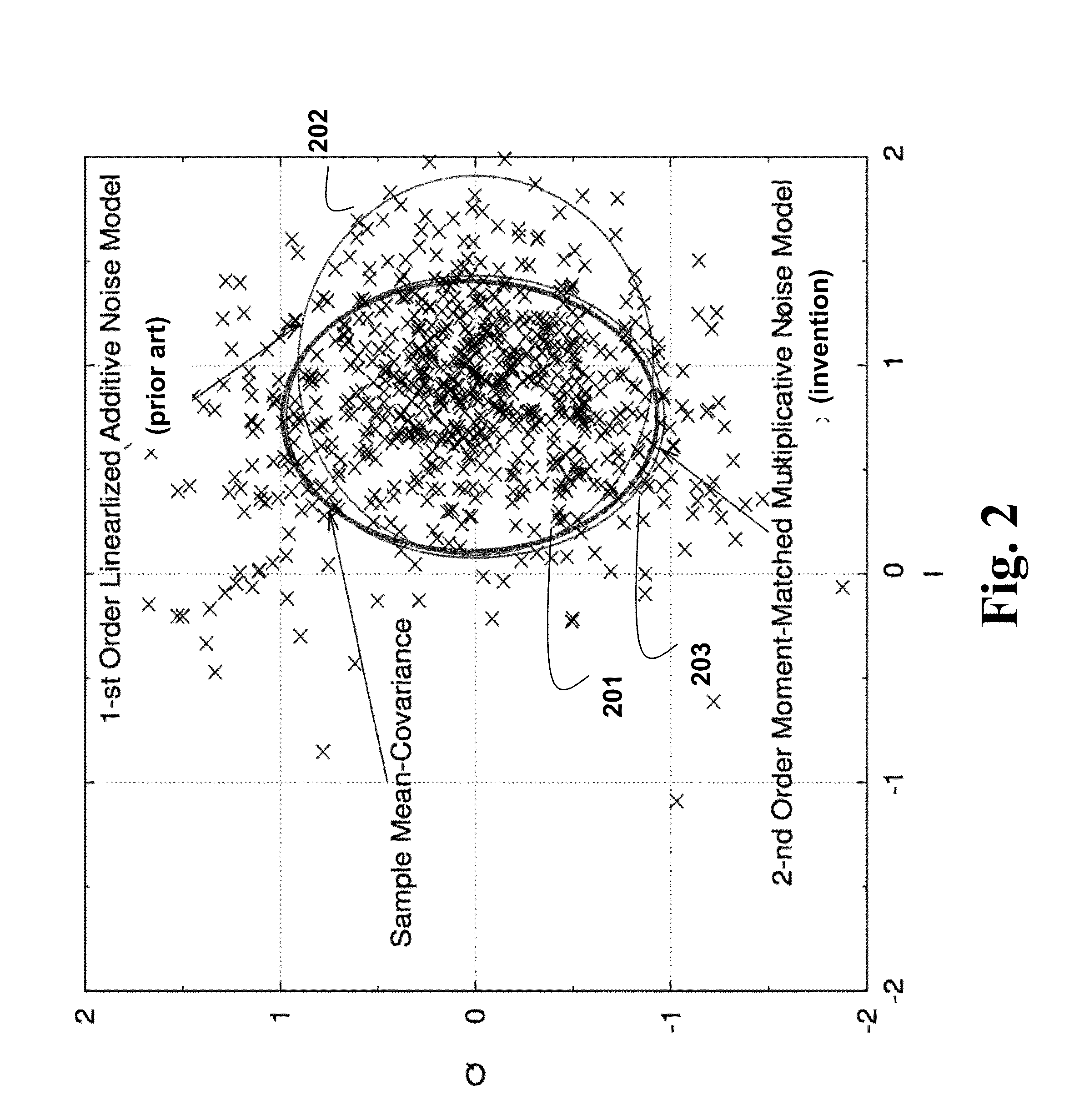
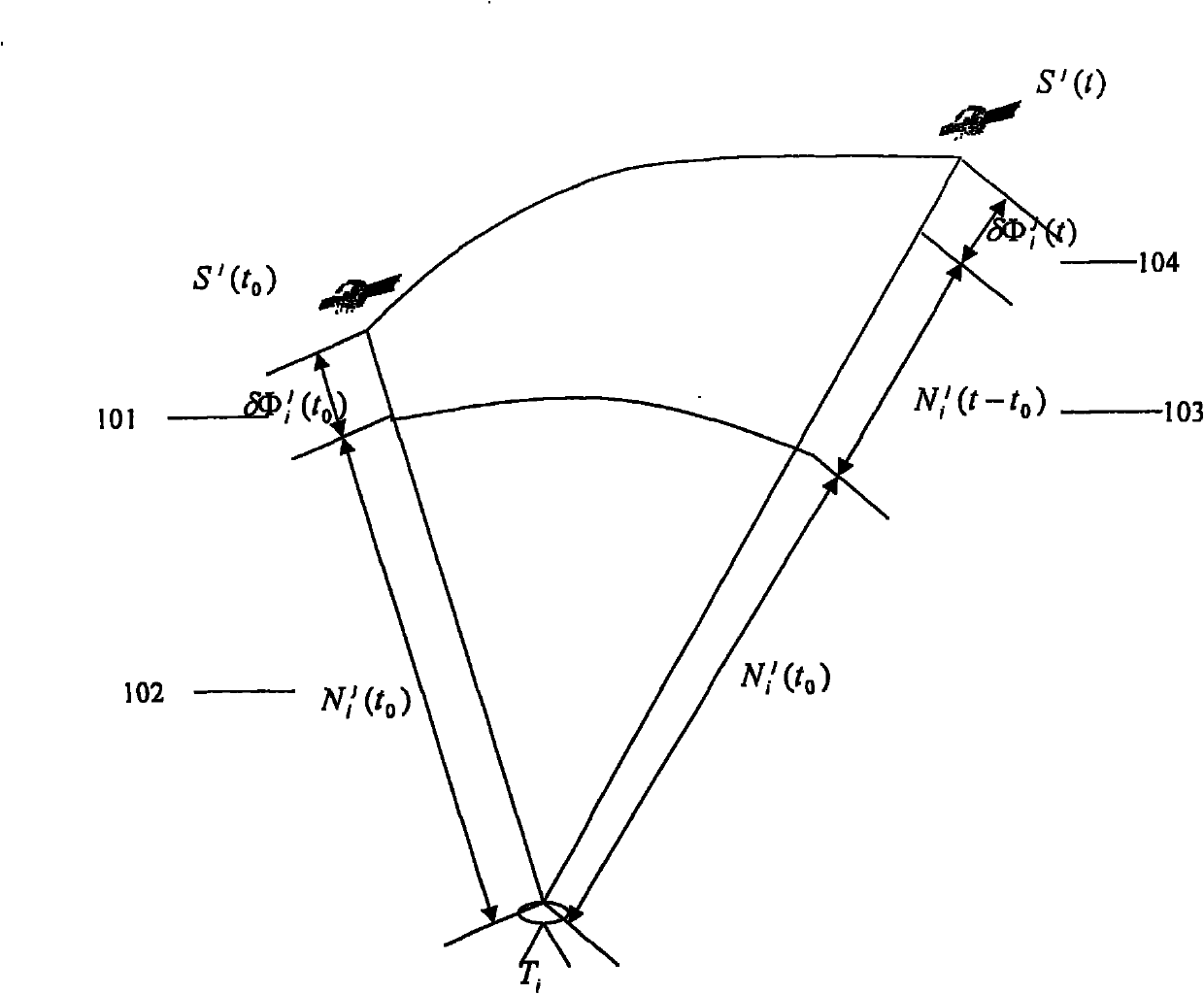
The embodiments of the invention provide methods to deal with problems of cycle slips, angular skew, and residual phase noise for high-speed optical communications employing any arbitrary high-order multi-dimensional modulation formats. The embodiments use a slip process analyzer, a skew angle estimator, and a phase noise variance estimator to provide feedforward soft-decision information of a carrier phase recovery (CPE) for more accurate likelihood calculation based on a high-order hidden Markov model (HMM). The log-likelihood calculation can be done jointly in dual polarization with joint Markov state transition. Some embodiments use a kernel filter or a particle filter for log-likelihood calculation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for detecting and restoring cycle slip of GPS (Global Positioning System) carrier phase under dynamic environment
InactiveCN102116867ASmall amount of calculationSimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceGps receiver
The invention discloses a method for detecting and restoring the cycle slip of a GPS (Global Positioning System) carrier phase under dynamic environment, comprising the steps of: carrying out difference kalman filtering calculation by utilizing a double-difference code pseudo-range observed quantity so as to obtain two epoch GPS receiver coordinates; constructing a carrier phase cycle slip detection equation by utilizing the two epoch GPS receiver coordinates and two epoch double-difference carrier phase observed quantities, calculating the equation and computing a residual error RMS (Root Mean Square) value; comparing the residual error RMS value with a set threshold, if the residual error RMS is greater than the set threshold, determining that the cycle slip occurs, selecting a satellite combination with the minimum residual error as a combination without the cycle slip by taking five satellites as a combination so as to restore the cycle slip, and then ending; if the residual error RMS value is less than or equal to the set threshold, comparing the result deltaX of the calculated cycle slip detection equation with the set threshold, if the result deltaX is less than the set threshold, determining that no cycle slip occurs and exiting the cycle slip detection process; and if the result deltaX is greater than the set threshold, determining that the cycle slip can not be detected and quitting from the cycle slip detection process.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
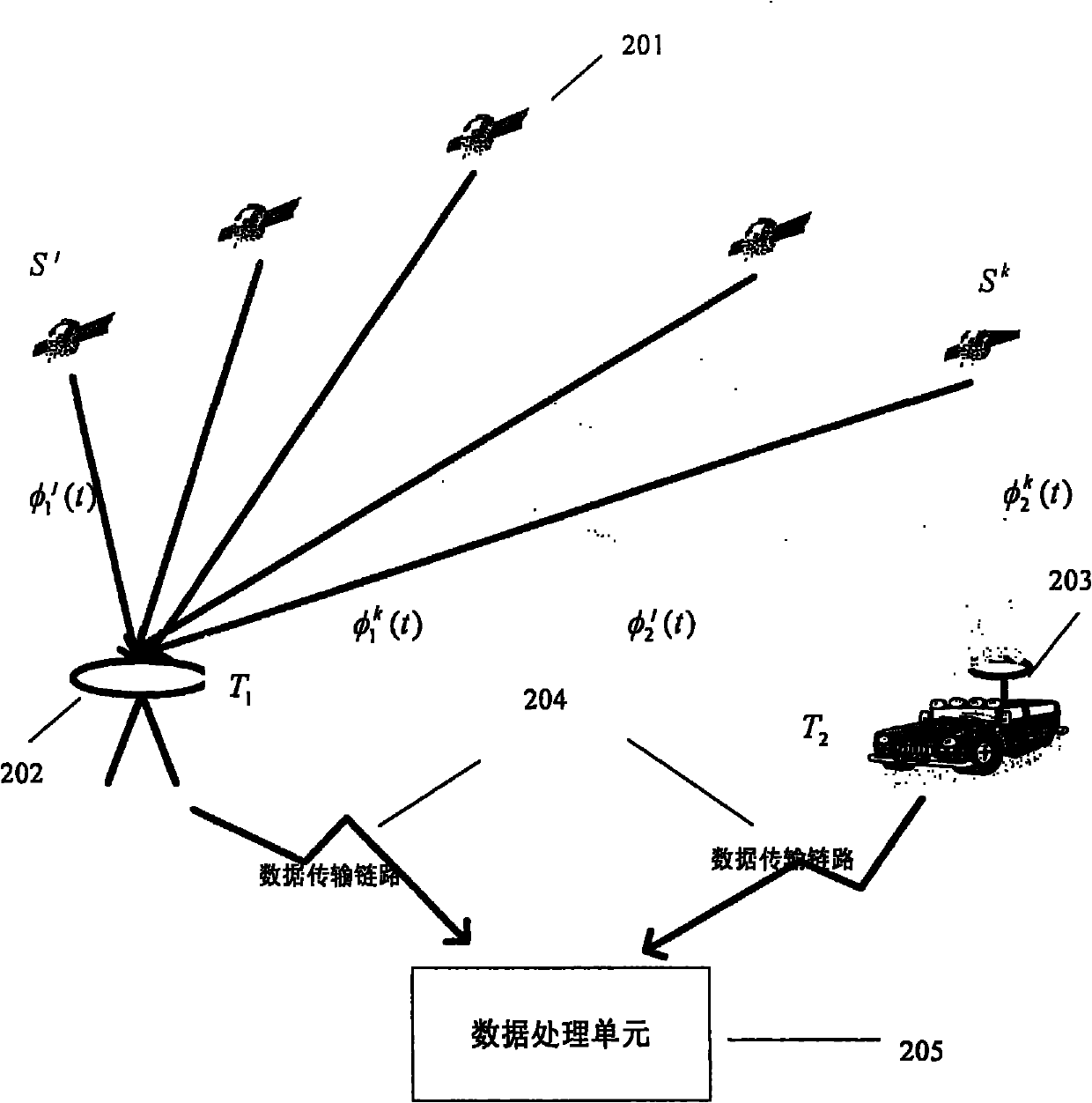
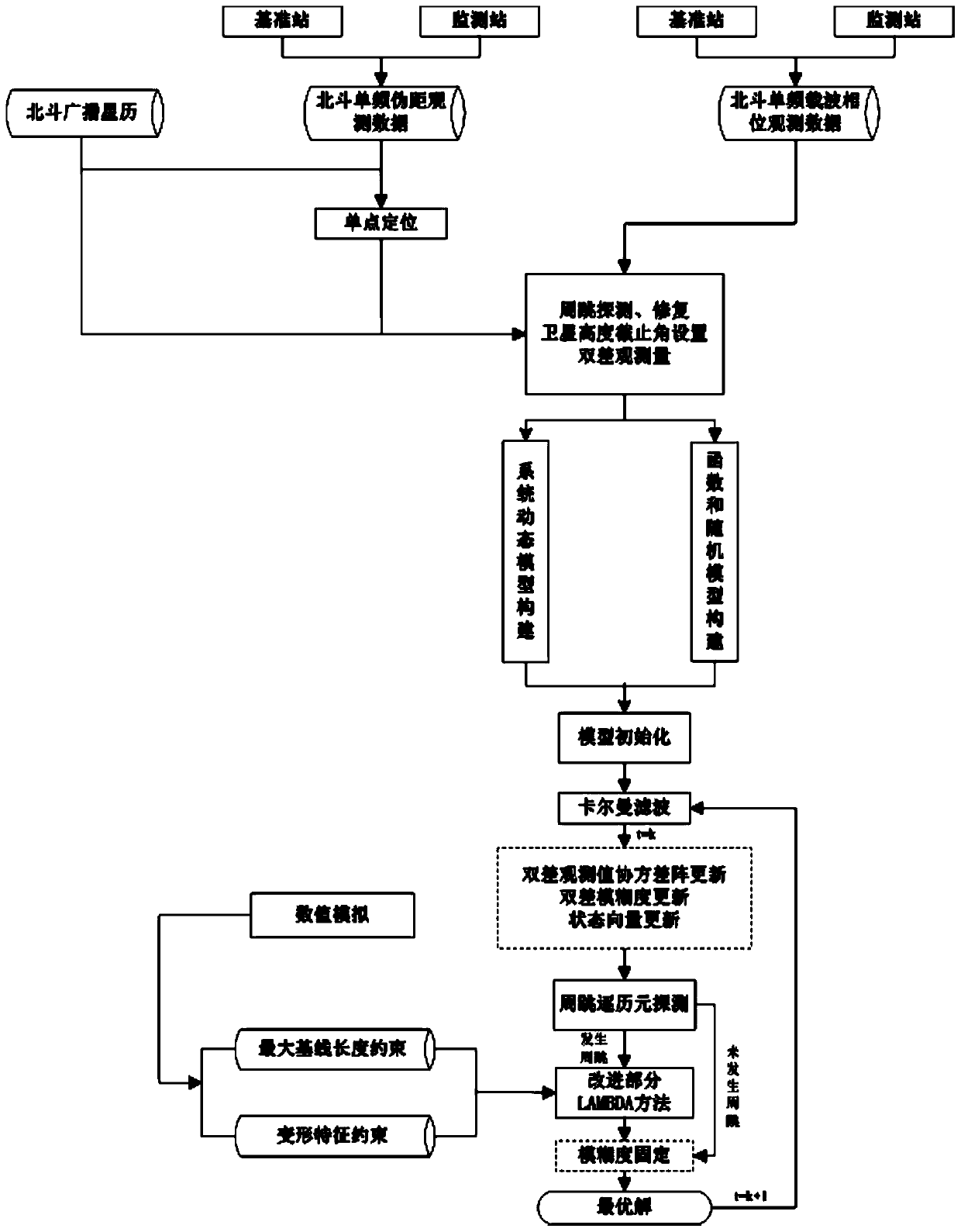
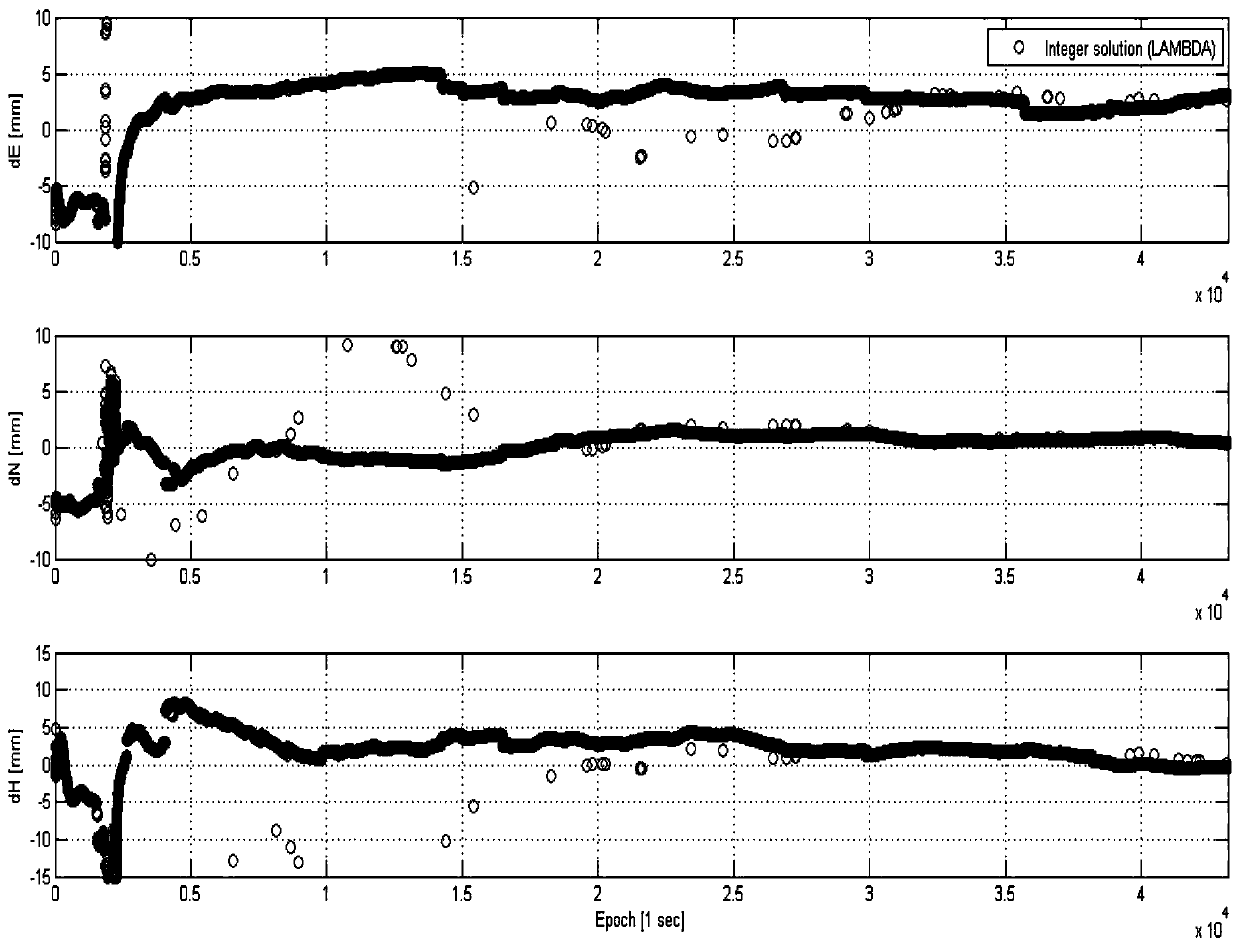
Positioning method for Beidou short baseline single frequency single epoch solution
ActiveCN109932735AGuaranteed monitoring accuracyReduce monitoring costsUsing electrical meansElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementDynamic modelsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a positioning method for Beidou short baseline single frequency single epoch solution. The method comprises steps of (1) Beidou single frequency pseudorange single point positioning, (2) data preprocessing, (3) establishment of a Kalman filter precision n-dimension dynamic model based on prior historical data and consideration of influences of a signal-to-noise ratio and asatellite elevation angle on an observation value, (4) model initialization, (5) Beidou single-frequency part ambiguity estimation to obtain a fixed value of each hierarchical ambiguity, (6) cycle-slip epoch-by-epoch detection in combination of the single-frequency ambiguity fixed value and an updating value, and (7) baseline vector calculation and coordinate covariance matrix updating based on the fixed ambiguity, and back substitution to a carrier phase observation equation after the ambiguity is fixed to obtain a baseline vector. The method can automatically eliminate the influences of tropospheric errors and multipath errors in real time, and realize accurate fixation of Beidou single frequency ambiguity. While the real-time performance and the precision of monitoring are ensured, themonitoring cost is greatly reduced, and promotion and application of the Beidou positioning technology is facilitated.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY DESIGN GRP CO LTD
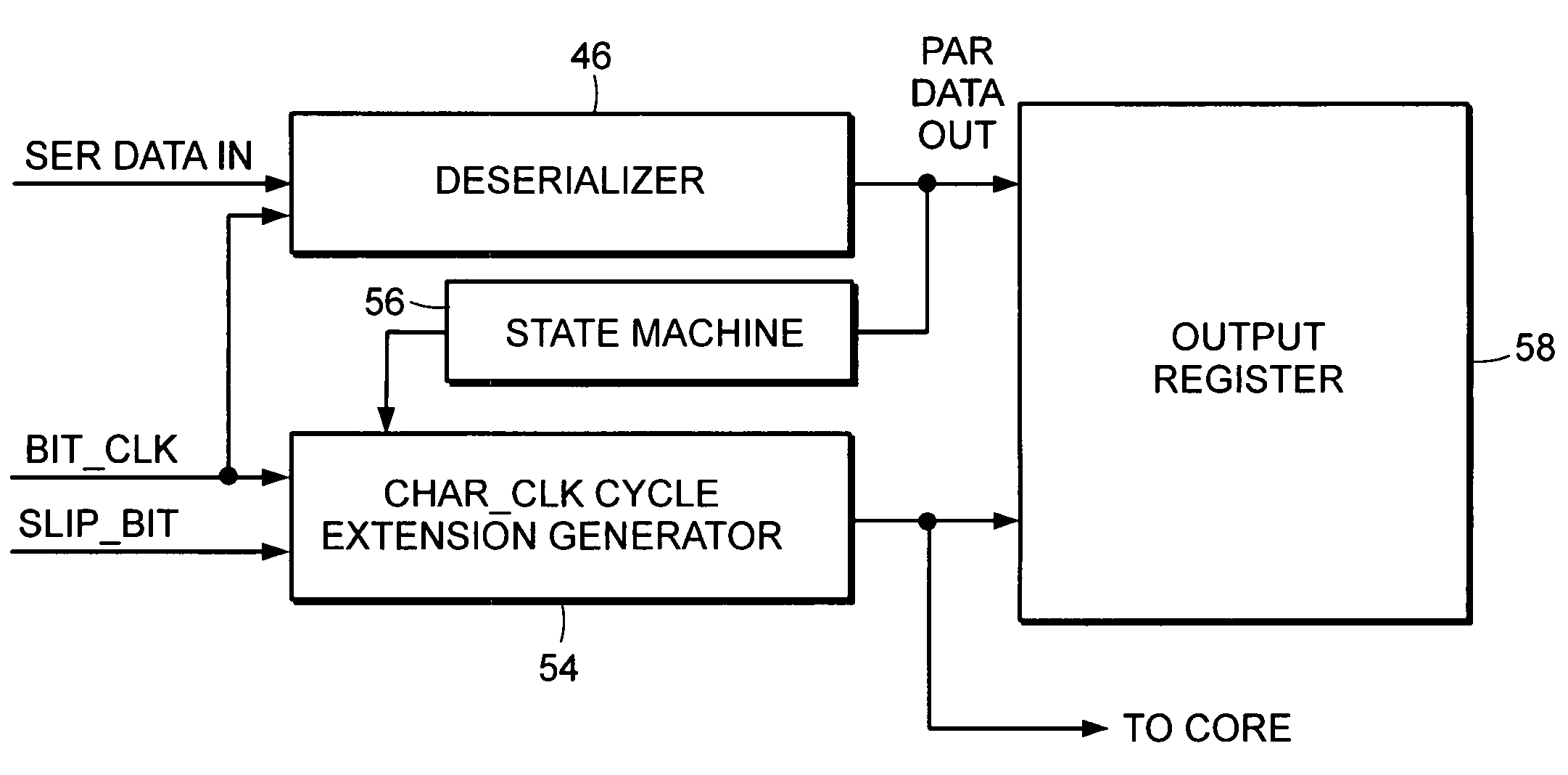
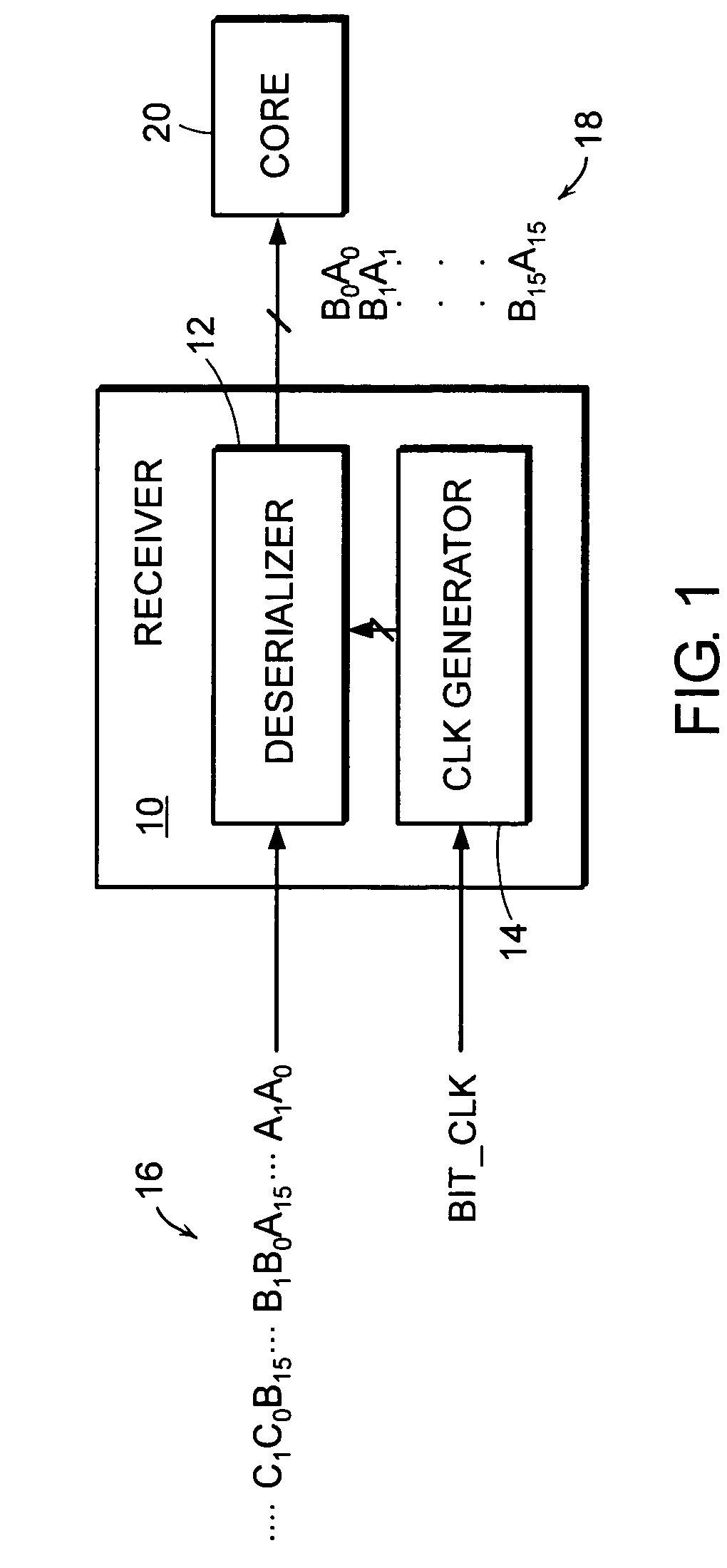
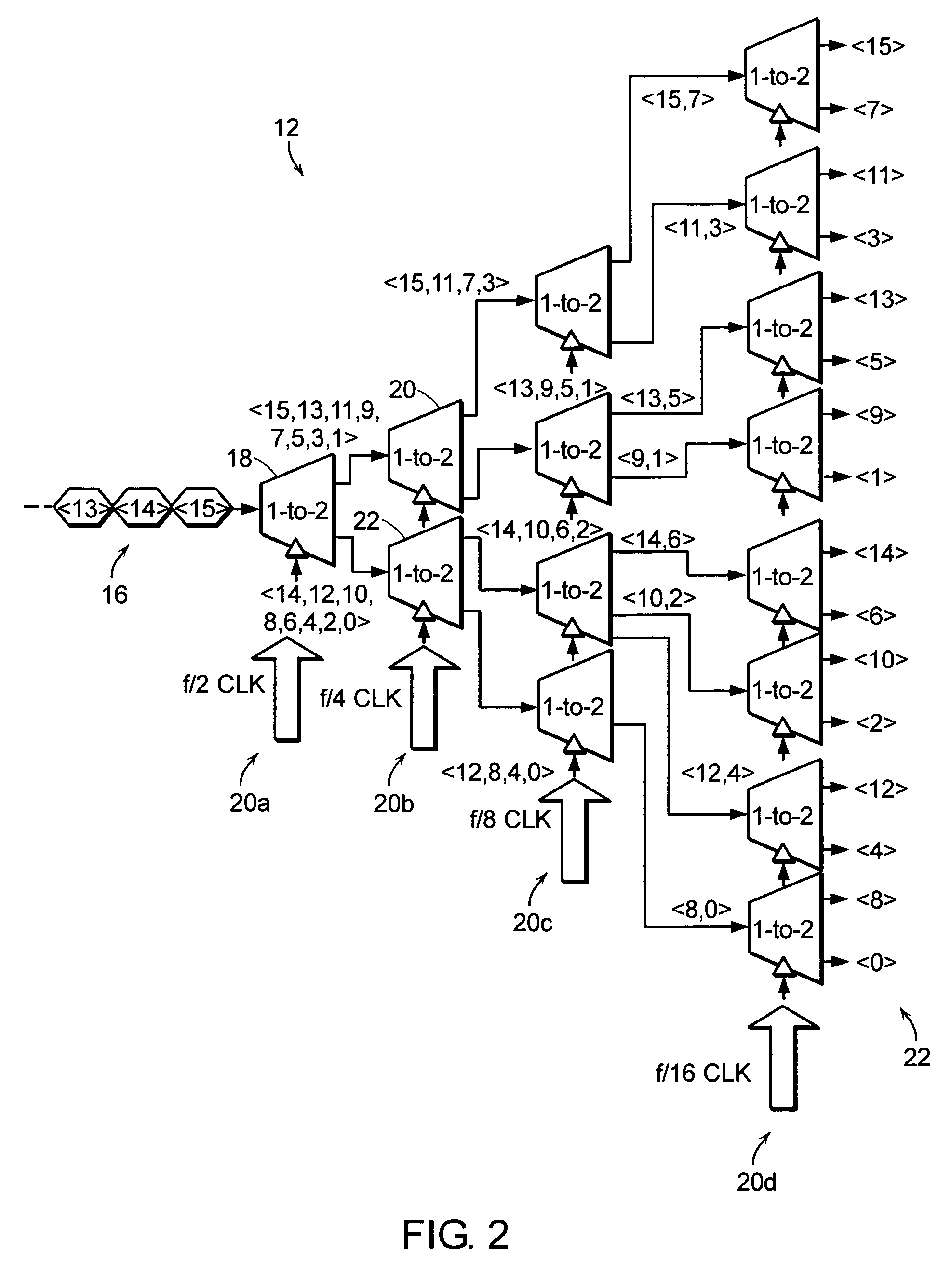
Cycle slip framing system and method for selectively increasing a frame clock cycle to maintain related bits within the same parallel-output frame of a deserializer
InactiveUS6970115B1Parallel/series conversionTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareClock generator
A system and method are provided for synchronizing a frame of related bits output from a deserializer to the related bits serially fed to the deserializer. Synchronization is achieved by overcoming a slip bit problem by selectively increasing the frame clock cycle during times in which the slip bit occurs. The deserializer is controlled by a clock generator that can include a counter which generates the frame clock. The counter can be asynchronously or synchronously reset, without any glitches occurring within the deserializer and, thus, avoiding any invalid bits output from the deserializer. The asynchronous reset forces the counter to a deterministic state, and the synchronous reset sets the counter to a valid state. In each instance, however, resets do not impart glitches to the deserializer and the deserializer output frame is maintained synchronous to related bits serially fed to the deserializer.
Owner:RPX CORP
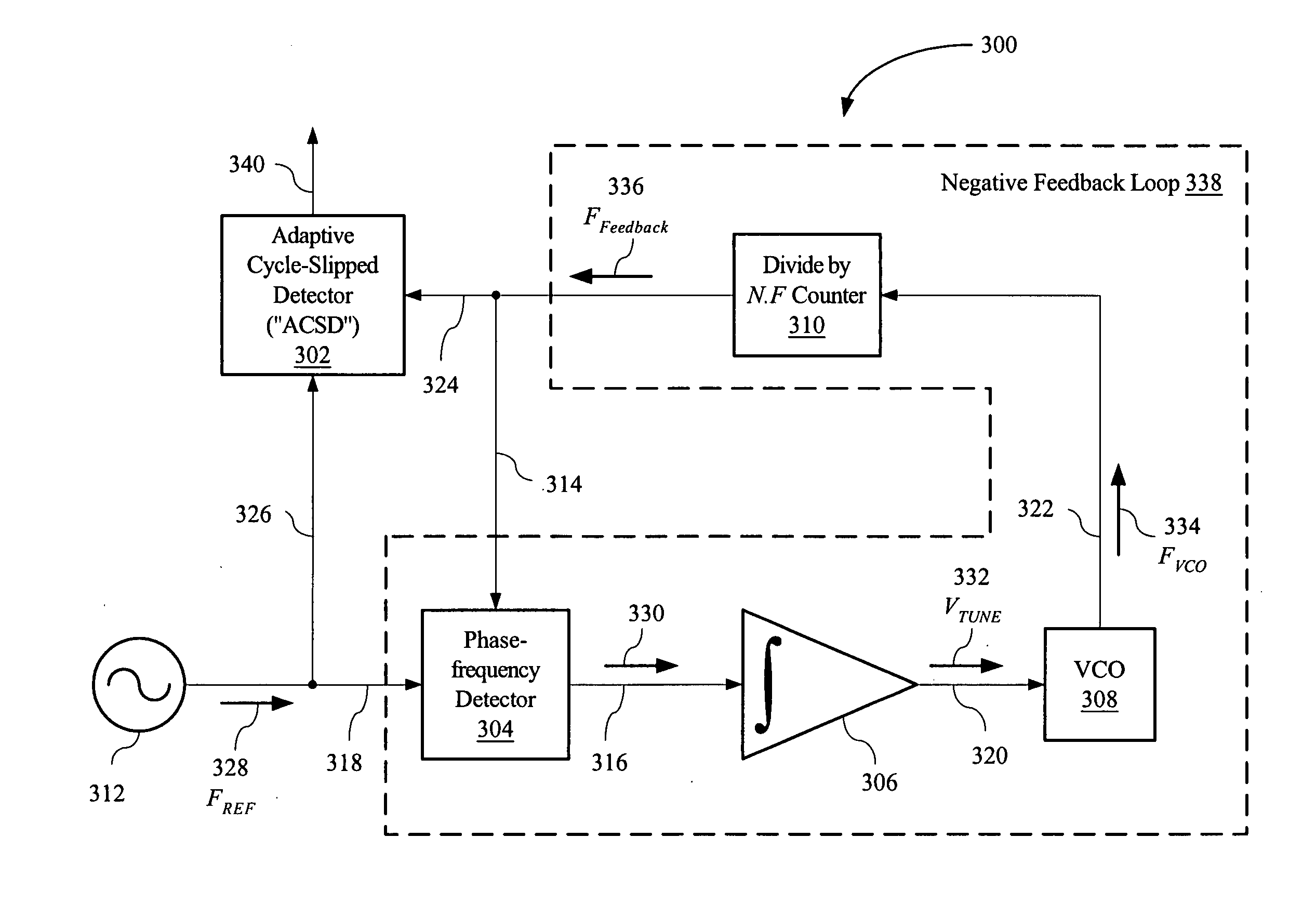
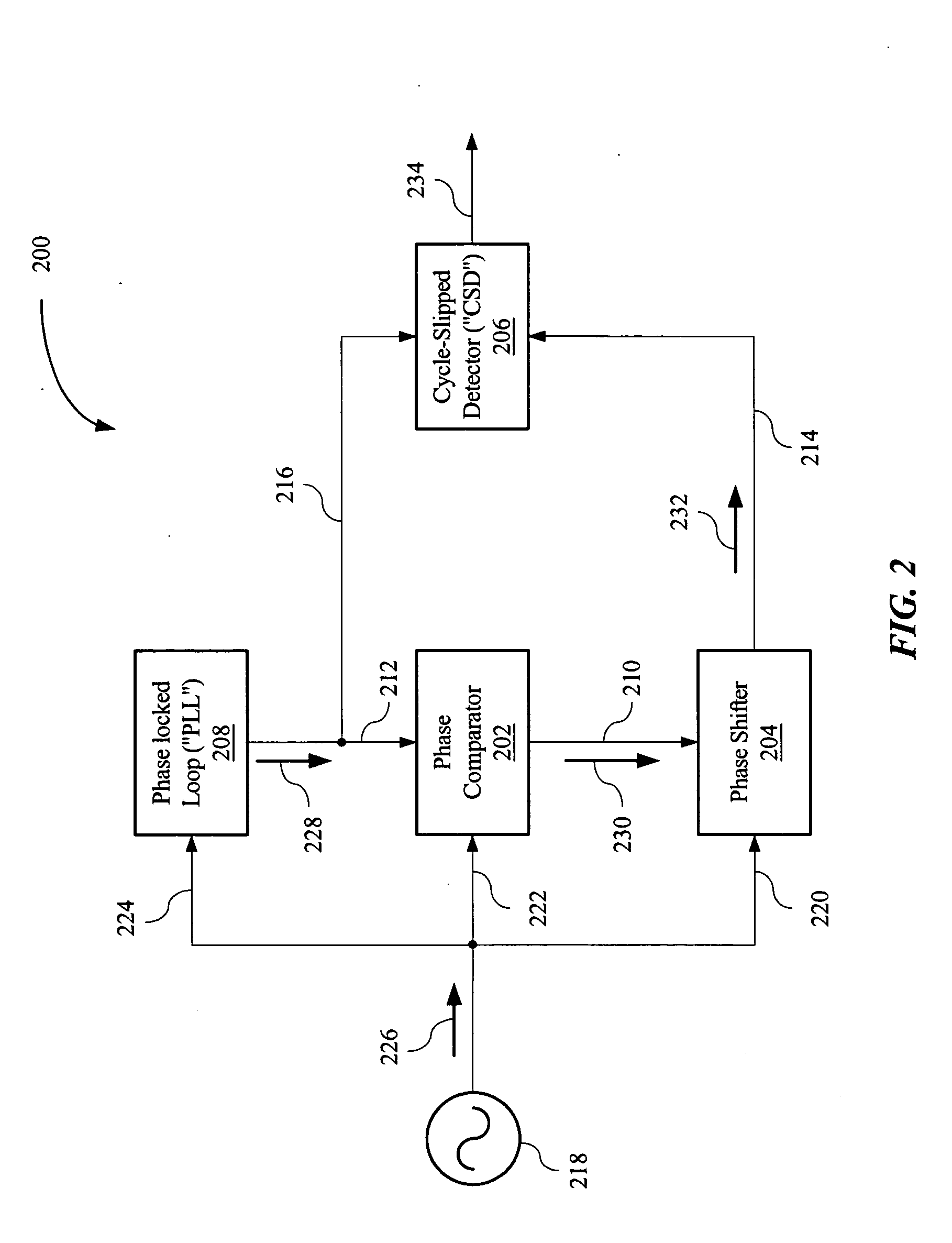
Adaptive cycle-slipped detector for unlock detection in phase-locked loop applications
An adaptive cycle-slipped detector (“ACSD”) for use in a Phase-Locked Loop (“PLL”) circuit. The ACSD may include a phase comparator, a phase shifter in signal communication with the phase comparator, and a cycle-slipped detector (“CSD”) in signal communication with the phase shifter.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Advanced global navigation satellite systems (gnss) positioning using precise satellite information
A method is provided for estimating parameters useful to determine the position of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver or a change in the position thereof. The method includes the steps of: obtaining at least one GNSS signal received at the GNSS receiver from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites; obtaining, from at least one network node, precise satellite information on: (i) the orbit or position of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites, and (ii) a clock offset of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites; identifying, among the obtained GNSS signals, a subset of at least one GNSS signal possibly affected by a cycle slip, the identified subset being hereinafter referred to as cycle-slip affected subset; and estimating parameters useful to determine the position of the GNSS receiver or a change in the position of the GNSS receiver using at least some of the obtained GNSS signals which are not in the cycle-slip affected subset, and the precise satellite information.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Airborne laser scanning system error calibration method
ActiveCN109917356AImprove automationImprove work efficiencyUsing optical meansSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention belongs to the technical field of airborne laser scanning geometric positioning, and particularly discloses an airborne laser scanning system error calibration method. The method in thescheme comprises steps: error calibration is carried out, cycle slip detection and repair of GNSS data are carried out, the GNSS data comprise airborne data and ground reference station data, and theintegrity of the data is ensured; a ambiguity-assisted bridging method is adopted for cycle slip detection and repair, assuming that the previous epoch ambiguity makes the positioning reach a smallervariance, the ambiguity of the group also meets a latter epoch, the cycle slip is judged according to whether the next epoch positioning variance is close to zero, the GNSS data are differentially processed, GNSS double-difference observation equation integer ambiguity is determined, and a calibration mathematical model is established. Independent control field layout is not needed, the method issimple and easy to operate, the automation of system error calibration can be improved, the working time is reduced, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:WUHAN GEOSUN NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
GPS (global positioning system) dual-frequency non-difference cycle slip detecting and restoring method and device
InactiveCN104749594AMeet the needs of high-precision positioningImprove the success rate of cycle slip detectionSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencySlide window
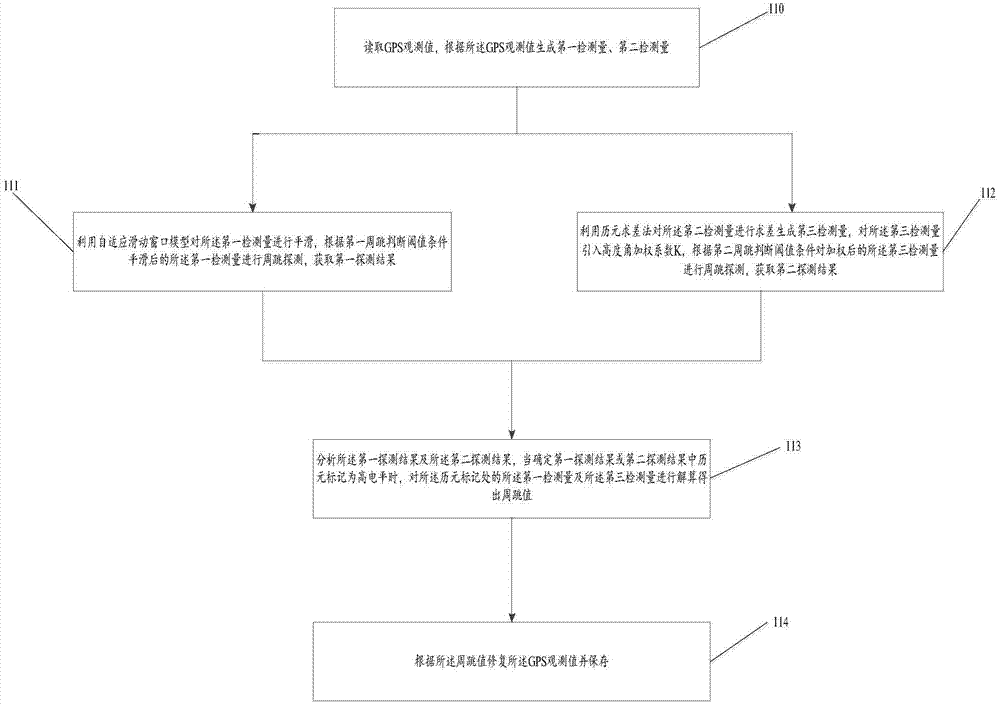
The invention discloses a GPS (global positioning system) dual-frequency non-difference cycle slip detecting and restoring method and device. The method includes: reading a GPS observing value, and generating first detection quantity and second detection quantity according to the GPS observing value; utilizing a self-adaptive sliding window model to smooth the first detection quantity, adjusting the first detection quantity after being smoothed according to a first cycle slip judgment threshold value for cycle slip detection to acquire a first detection result; utilizing a epoch difference-solving method for difference solving of the second detection quantity to generate third detection quantity, and performing cycle slip detection on the third detection quantity to acquire a second detection result; analyzing the first detection result and the second detection result, and calculating the first detection quantity and the second detection quantity at a cycle slip epoch to acquire a first cycle slip value and a second cycle slip value; restoring the GPS observing value according to the cycle slip values. By the GPS dual-frequency non-difference cycle slip detecting and restoring method and device, cycle slip detection success rate and cycle slip restoring accuracy can be improved, so that needs on high-accuracy positioning of GPS navigation can be met, and small cycle slip, big cycle slip, special cycle slip and continuous cycle slip can be detected and restored.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
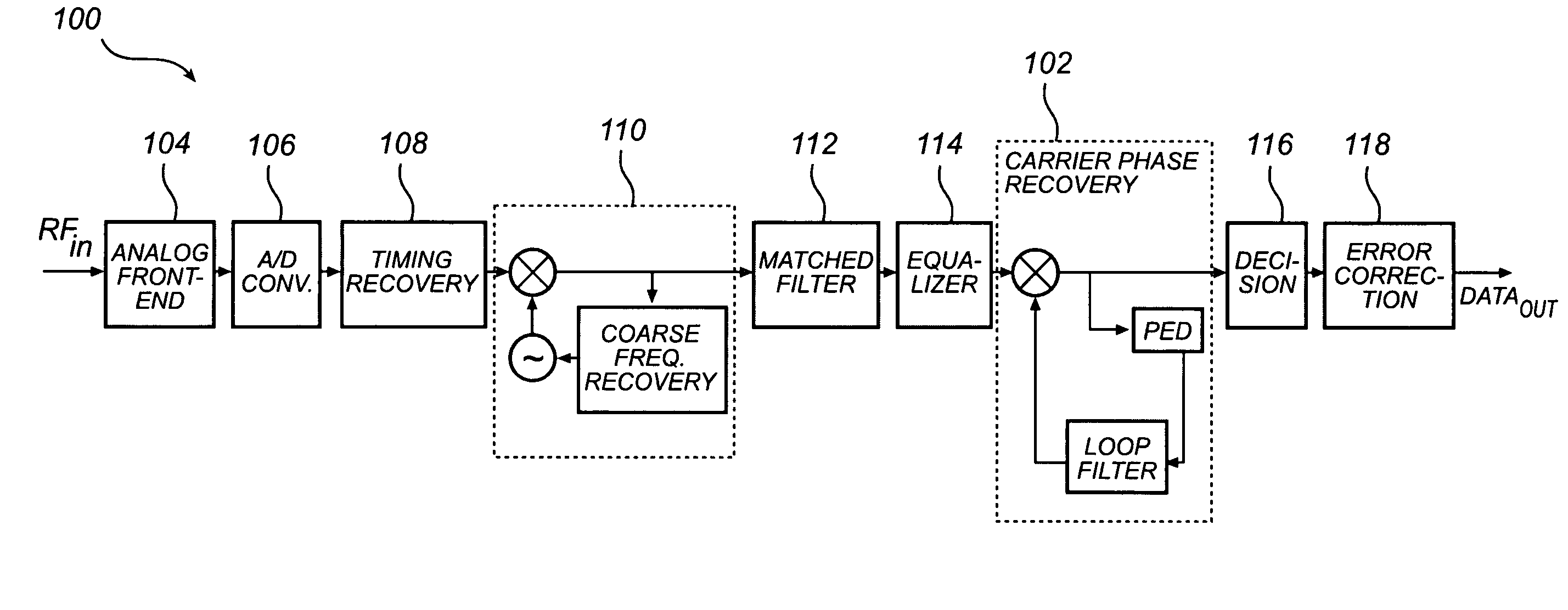
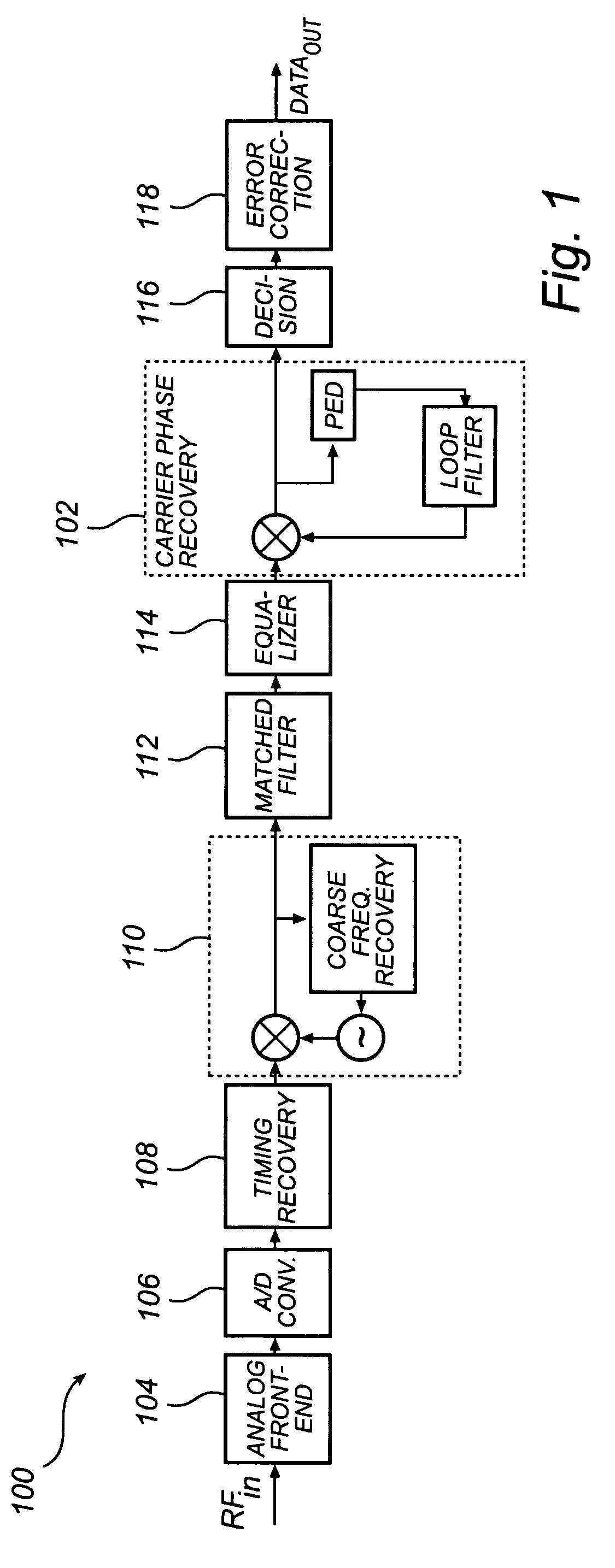
Cycle slip detection for timing recovery
InactiveUS20090268857A1Improve cycle slip detectionLow signal noiseNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPulse automatic controlDigital dataSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and an arrangement for cycle slip detection for timing recovery of a received analog signal comprising asynchronously sampled digital data are recommended. More specifically a fully digital implementation of a timing recovery control loop using a technique known as interpolated timing recovery and improved cycle slip detection as well as improved cycle slip correction based on said cycle slip detection are recommended. The method comprises the steps of using an output signal of the loop filter in the control loop for timing recovery, generating averaged timing error values from said filtered timing error signal and accumulating changes of the averaged timing error values in adjacent blocks of samples which exceed a first threshold. Accumulated averaged timing error changes of adjacent blocks which exceed a second threshold are then declared as cycle slip and the number of cycle slips is determined by a third threshold being a tolerance threshold. Furthermore, a first-in, first-out memory is provided for sample insertion or deletion, which means that a sample insertion or sample deletion takes place in the sample domain with increased reliability and an improved method for cycle slip detection is recommended due to increased robustness against noise and inappropriately chosen timing loop parameters, which is also applicability for systems with frequency-offsets. The method and a corresponding arrangement are applicable for timing recovery of signals having high intersymbol interference, low signal to noise ratio and frequency offset as e.g. provided by reading a high-density data storage medium or received by mobile phone.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
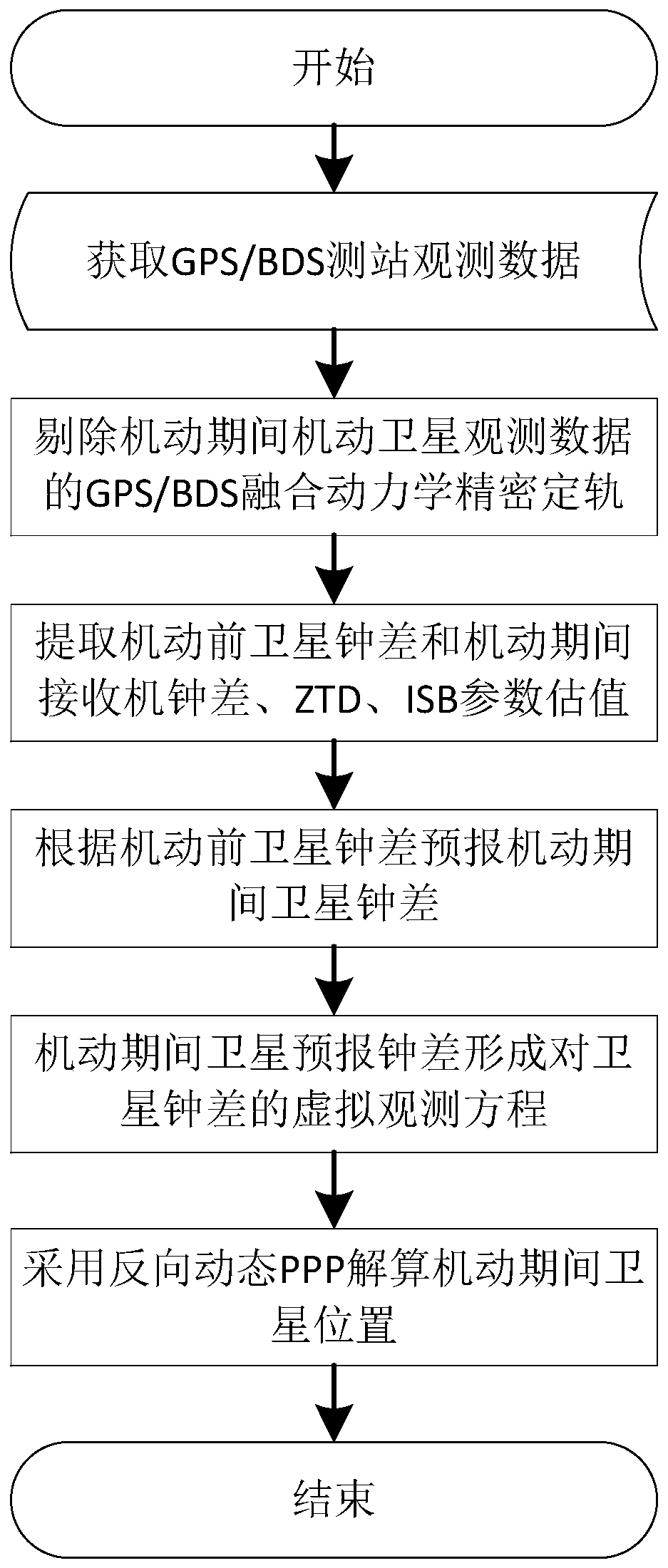
GNSS maneuvering satellite orbit determination method with additional clock error model constraint
ActiveCN110231037AAvoid certain effectsImproving the Accuracy of Track Radial Orbit DeterminationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataAmbiguity
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) maneuvering satellite orbit determination method with additional clock error model constraint, comprising the steps of: acquiring observation data of an observation station; 2) eliminating observation data after maneuvering, and performing dynamic precision orbit determination calculation on arc sections before and during maneuvering; 3) extracting estimation values of a satellite clock error before maneuvering, an ambiguity, a receiver clock error during maneuvering, a ZTD (Zenith Tropospheric Delay) and an ISB (Inter-SystemBias) parameter; 4) establishing a clock error forecasting model based on the estimation value of the satellite clock error before maneuvering; 5) fixing the receiver clock error, the ambiguity without cycle slip, the ZTD and the ISB parameter, adding constraint of the clock error forecasting model, and performing orbit determination calculation on a satellite orbit during maneuvering by adoptinga reverse dynamic precision single-point positioning method; and 6) iteratively solving position parameters of the maneuvering satellite at the current epoch until the position parameters are converged, and performing solving at the next epoch. According to the GNSS maneuvering satellite orbit determination method of the invention, through introduction of the satellite clock error forecasting model constraint, the correlation between satellite orbit radial direction and the satellite clock error can be greatly weakened, and the orbit radial direction orbit determination precision of the maneuvering satellite is effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
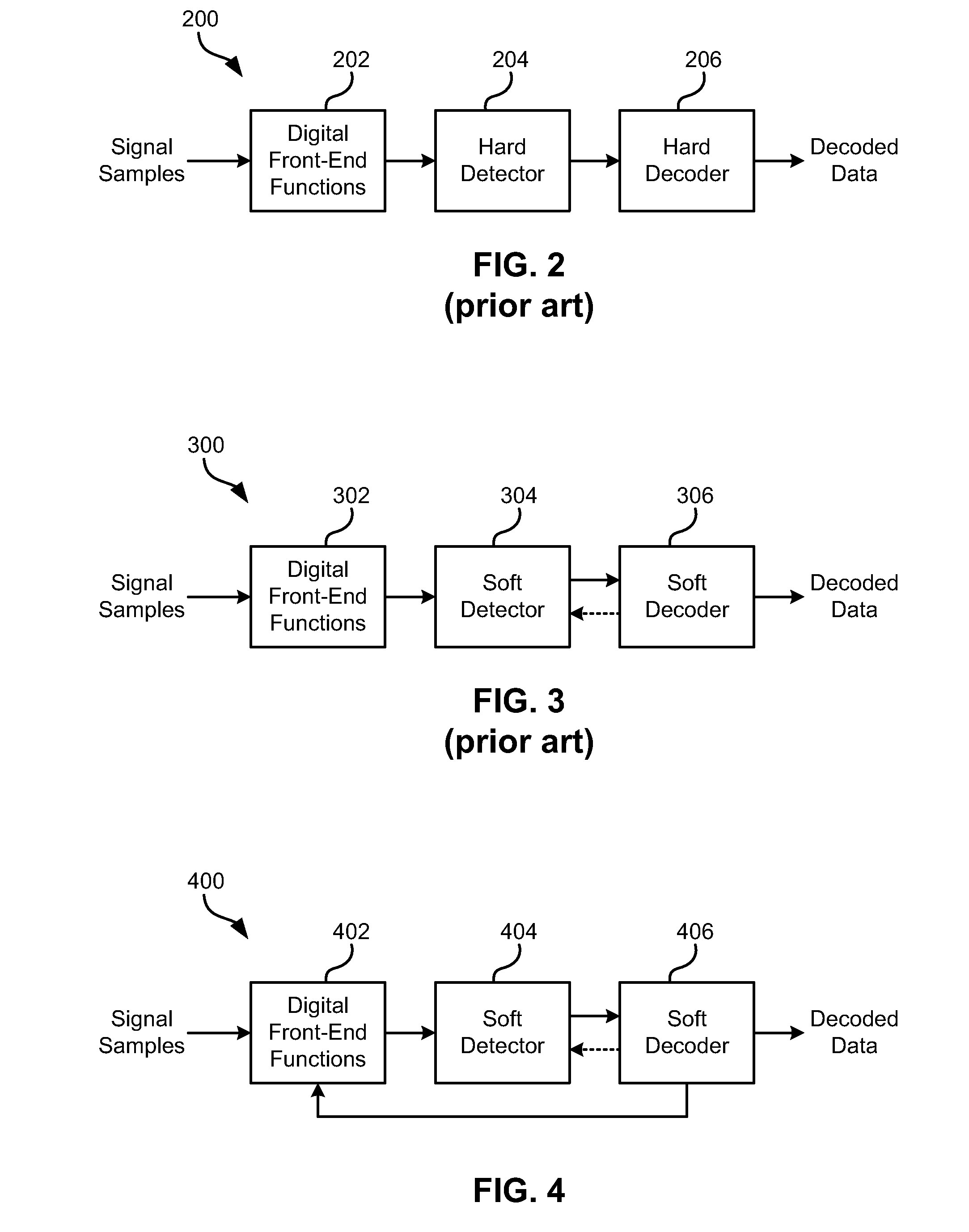
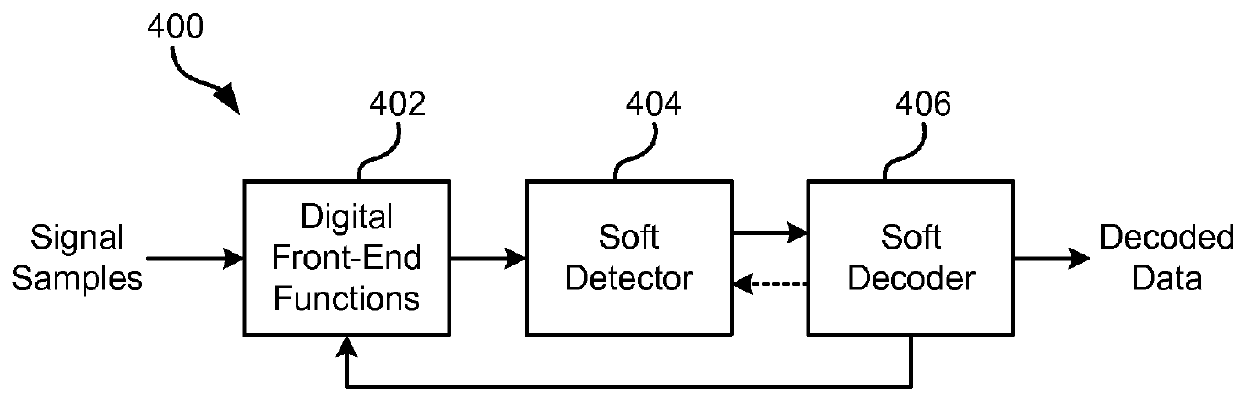
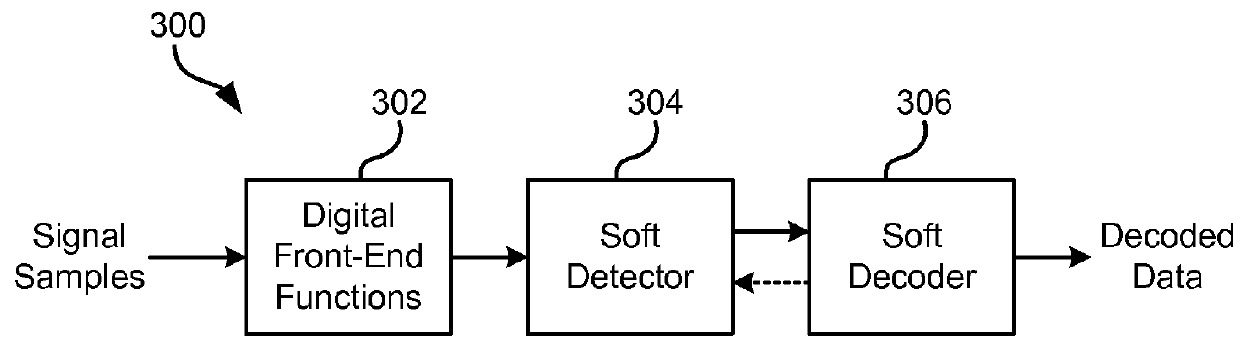
Cycle-slip resilient iterative data storage read channel architecture
InactiveUS20140355147A1Modification of read/write signalsAnalogue recording/reproducingCycle slipPerformance improvement
According to one embodiment, a magnetic medium's readback signal samples are processed iteratively to provide a slip-resistant read channel by feeding the decoder output decisions back to the read channel front end where they are used to drive the decision-aided digital signal processing functions and control loops. Since data decisions provided by the decoder are typically more reliable than those provided by the detector, a significant performance improvement is obtained. A more reliable operation of the digital front-end signal processing functions in turn allows improvements to the reliability of the decoded data. Usage of Error Correcting Code (ECC) schemes that are soft decodable makes the read channel technique, described according to various embodiments herein, particularly efficient.
Owner:IBM CORP
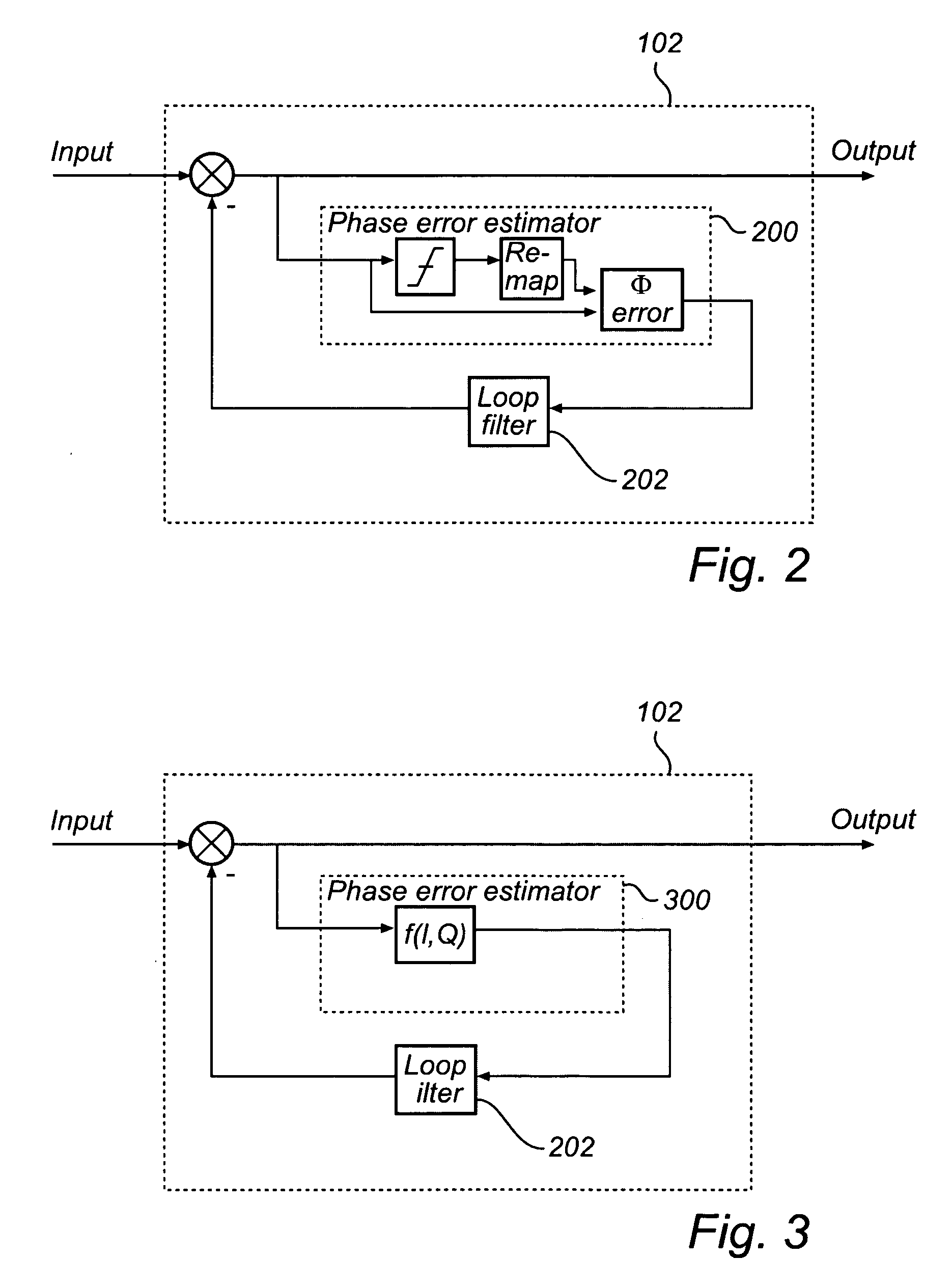
QAM phase error detector
InactiveUS20090147839A1Reducing cycle slipImprove transfer rateCarrier regulationPulse modulationLoop filterPhase detector
The present invention relates to a method for reducing cycle slips in a carrier recovery loop for a phase detector, the method comprising the steps of receiving an input signal consisting of samples, each received sample having an in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) component, providing the input signal to a phase error estimator adapted to determine a phase error estimate, providing the phase error estimate to a loop filter, and forming an output signal from the carrier recovery loop by subtracting an output from the loop filter from the input signal, wherein the phase error estimate is determined based on a combination of the amplitude and phase of the samples and a probability measure for a specifically transmitted symbol, thereby improving phase tracking performance of the carrier recovery loop.Advantages with the present invention includes reduction of cycle slips without using a high performance, and expensive, hardware solution, at the same time as it is possible to suppress the effects of decision errors which enables higher gain, thereby giving an improvement in Bit Error Rate (BER) in low SNR conditions.The present invention also relates to a corresponding phase detector
Owner:ADVANTECH WIRELESS TECH USA INC
Satellite navigation positioning carrier phase cycle slip rehabilitation method
InactiveCN101334458AGreat practicabilityFix fast and preciseBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationGeomorphologyCycle slip
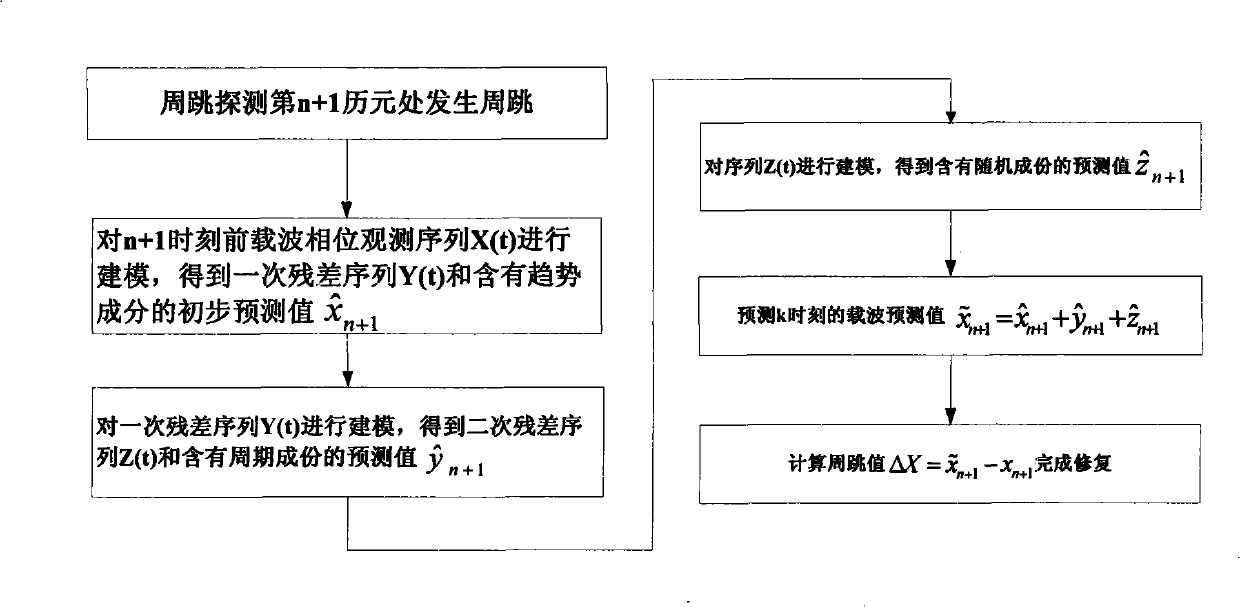
The invention discloses a cycle slip repair method of carrier phase in the satellite navigation positioning, belonging to the technical field of satellite navigation positioning and relating to the cycle slip repair method of a positioning receiver based on the carrier phase positioning process. The phase observation values of n epochs of carriers before the occurrence of the cycle-slip are selected to constitute a sequence (Xt), the (Xt) is firstly carried out with the modeling to obtain a forecast value x n plus 1 of the trend component and a first residual sequence (Yt); the first residual sequence (Yt) is then carried out with the modeling to obtain the forecast value y n plus 1 of the periodic component and a second residual sequence (Zt); then the second residual sequence (Zt) is carried out with the modeling to obtain the forecast value z n plus 1 containing the random component; the corresponding inverse transformation is finally carried out according to the forecast values obtained by various models, thereby obtaining the forecast value x n plus 1 of the carrier phase of the n plus 1st epoch at the occurrence of the cycle-slip and further completing the repair of the cycle-slip. The cycle slip repair method does not need the additional auxiliary information and can rapidly and accurately complete the cycle slip repair. The cycle slip repair method can rapidly, conveniently and reliably realize the high-precision positioning of the carrier phase measurement and can be widely applied in a high-precision navigation positioning system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION ENG IN
Multi-mode GNSS single-frequency cycle slip detecting and repairing method supporting RTPPP and RTK
ActiveCN108169774AReduce the numberReduce false positive rateSatellite radio beaconingClock correctionBack calculation
The invention provides a multi-mode GNSS single-frequency cycle slip detecting and repairing method supporting RTPPP and RTK. The method comprises: an inter-epoch difference is constructed; a time-dependent ionized layer error, a tropospheric error and clock correction delay errors between different systems are eliminated; overall least squares estimation is carried out; if a position correction number covariance DX^X^ is larger than or equal to threshold 1, five satellites are selected circularly and a cycle-slip-free combination with the highest reliability is found out to obtain position and clock difference drift correction number; a new residual vector is obtained by back calculation, wherein the residual vector is an inter-epoch cycle slip floating point solution; and the cycle slipfloating point solution is processed by rounding off in an acceptable range to determine whether the cycle slip can be restored or be a gross error. According to the invention, three different empirical thresholds are set based on different detection quantity meanings, so that the probability of missed determination and false determination during the cycle slip restoring process can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING NORTH OPTICAL ELECTRONICS
Pll cycle slip compensation
InactiveUS20020125961A1Reduce control signalingImprove performancePulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase anglePhase differenceControl signal
Phase-reset circuits provide first and second frequency-divided input signals to a phase / frequency detector (PFD) used in a phase-locked loop (PLL). The phase-reset circuits receive first and second input signals, with the first input signal usually serving as a reference signal against which the PLL adjusts the second input signal. The PFD generates control signals based on the phase difference between the frequency-divided input signals. Normally, the phase-reset circuits frequency divide the first and second input signals using divisors N and M, respectively. If other circuitry detects that the PFD has missed a clock cycle in the first or second clock-divided input signals, the corresponding phase-reset circuit alters its divider so that the next clock edge on the corresponding input signal clocks through to the PFD. This causes the PFD to quickly set its affected control signal to what it would have been had the clock cycle not been missed.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
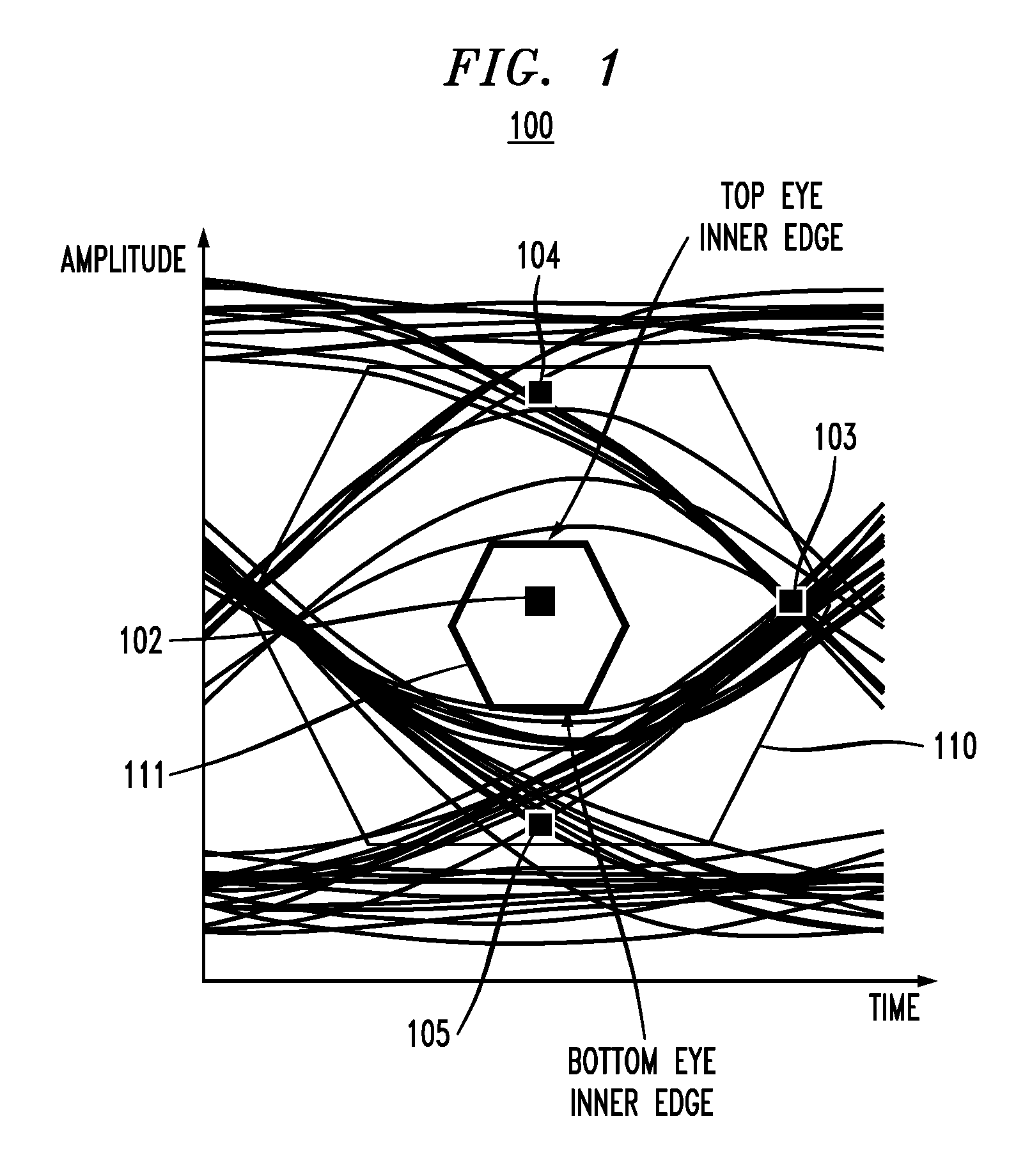
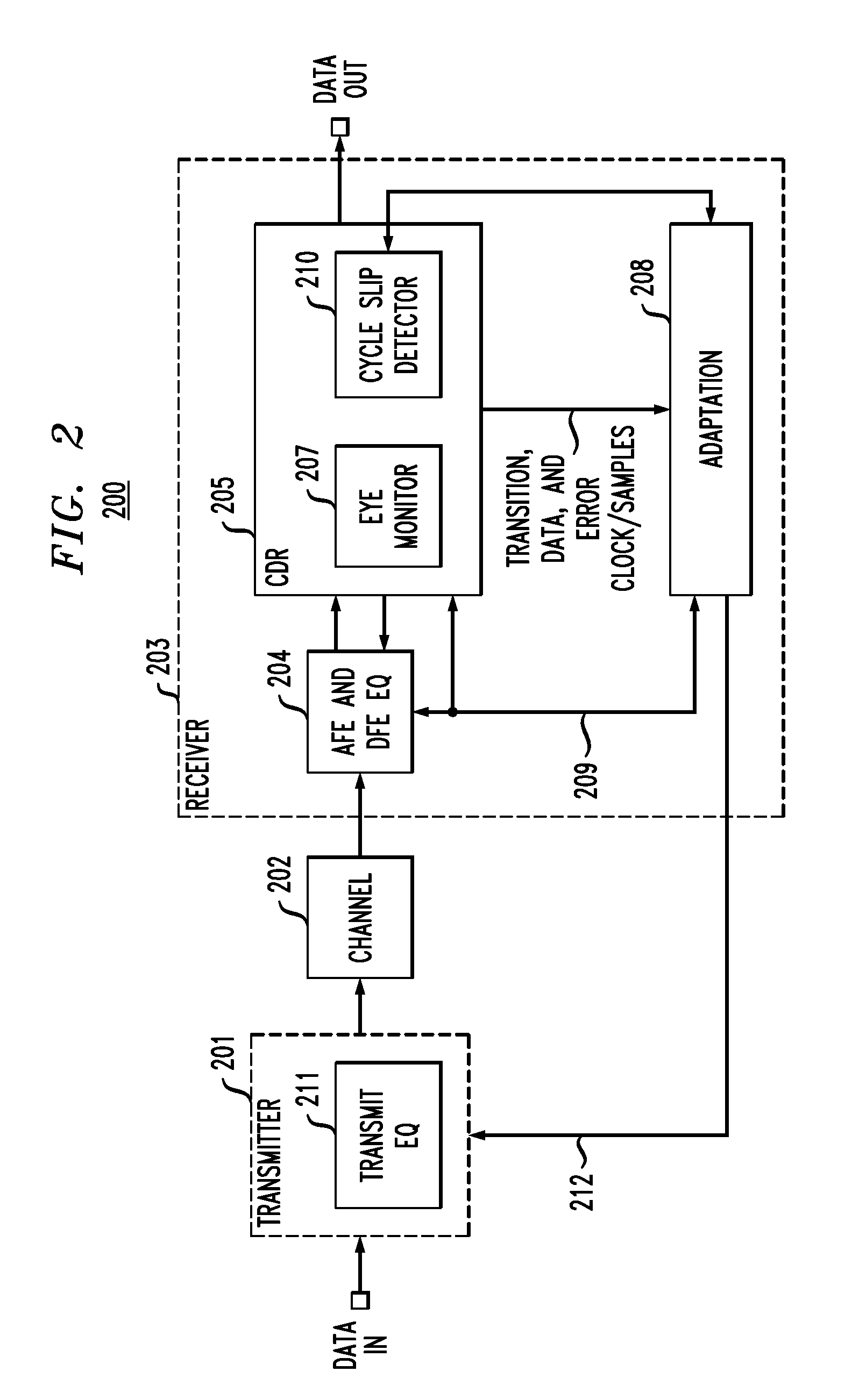
Receiver training with cycle slip detection and correction
ActiveUS20120230454A1Well formedMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsTransceiverCheck point
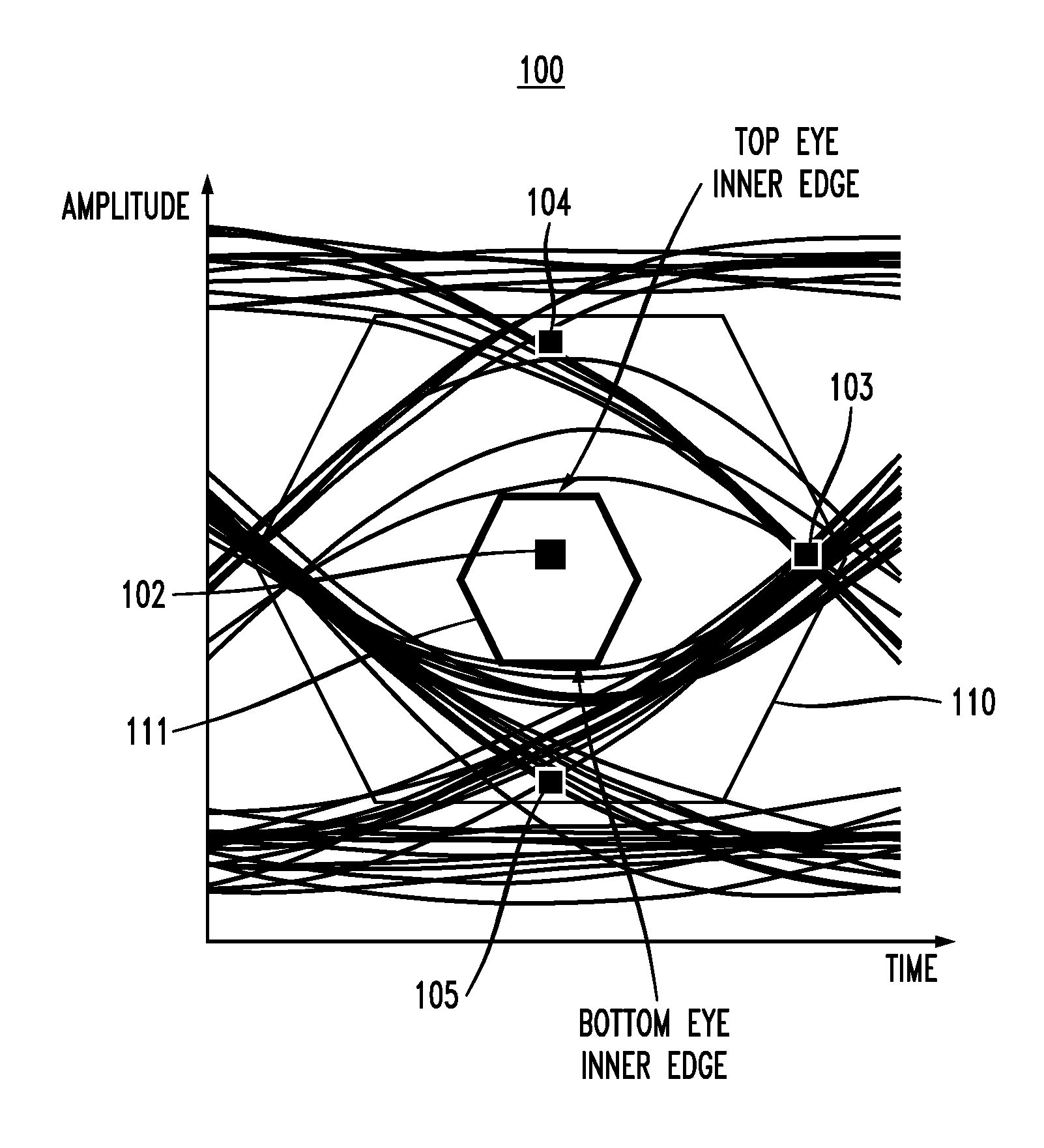
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes a clock and data recovery module (CDR) with an eye monitor and a cycle slip monitor. The cycle slip detector monitors a CDR lock condition, which might be through detection of slips in sampling and / or transition timing detection. The cycle slip detector provides a check point to sense system divergence, allowing for a mechanism to recover CDR lock. In addition, when the CDR is out-of-lock, the various parameters that are adaptively set (e.g., equalizer parameters) might be invalid during system divergence. Consequently, these parameters might be declared invalid by the system and not used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Cycle-slip resilient iterative data storage read channel architecture
InactiveUS20160055882A1Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageDecision takingCycle slip
In one embodiment, a system for cycle-slip resilient iterative read channel operation includes a processor and logic integrated with and / or executable by the processor. The logic is configured to, in an iterative process until a maximum number of iterations has been reached or a valid codeword is produced, execute cycle-slip detection on signal samples to detect one or more cycle-slip events. Also, the logic is configured to selectively alter a timing estimate driving a phase-locked loop (PLL) during any time interval determined to experience a cycle slip in a first pass as indicated by one or more cycle-slip pointers. Additionally, the logic is configured to generate a set of decisions provided by a detector and generate a set of decisions provided by a decoder. Moreover, the logic is configured to output decoding information relating to the signal samples in response to a decoding algorithm producing a valid codeword.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
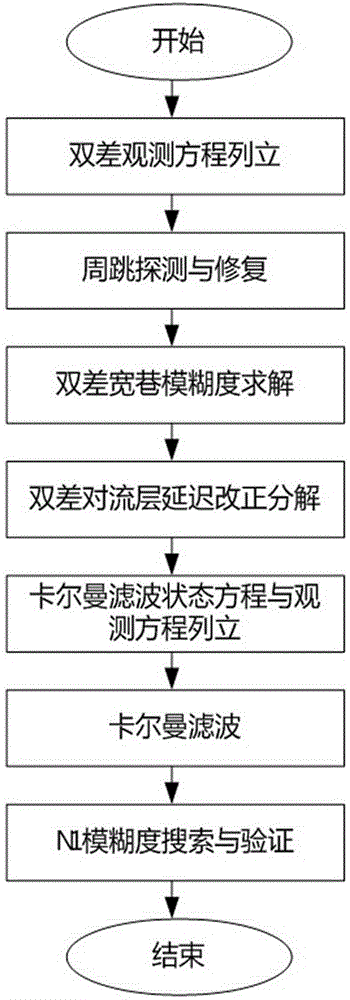
CORS reference station network baseline ambiguity resolving method considering troposphere influence
ActiveCN105842719AHigh precisionImprove search efficiencySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention discloses a CORS reference station network baseline ambiguity resolving method considering a troposphere influence. The method is characterized by through dual-frequency data collected by a geodesic receiver, establishing a GNSS double difference observation equation; using a real distance from a satellite to the receiver to carry out detection and repairing of cycle slip; through using a MW combination observation value, carrying out solving and verification of wide-lane ambiguity; through writing troposphere delay errors of two ends of a baseline into a product of a projection function and site zenith troposphere delay, establishing a Kalman filtering observation equation and establishing a Kalman filtering state equation; through smoothing a Kalman filter, filtering a floating point value of L1 integer cycle ambiguity; searching the L1 integer cycle ambiguity floating point value acquired through the Kalman filtering; and verifying the searched L1 integer cycle ambiguity. In the invention, a characteristic that a base station coordinate in a network RTK is accurate and known is fully used, high precision is possessed and small cycle slip can be detected and repaired.
Owner:WUHAN GEOSUN NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
Cycle slip detection
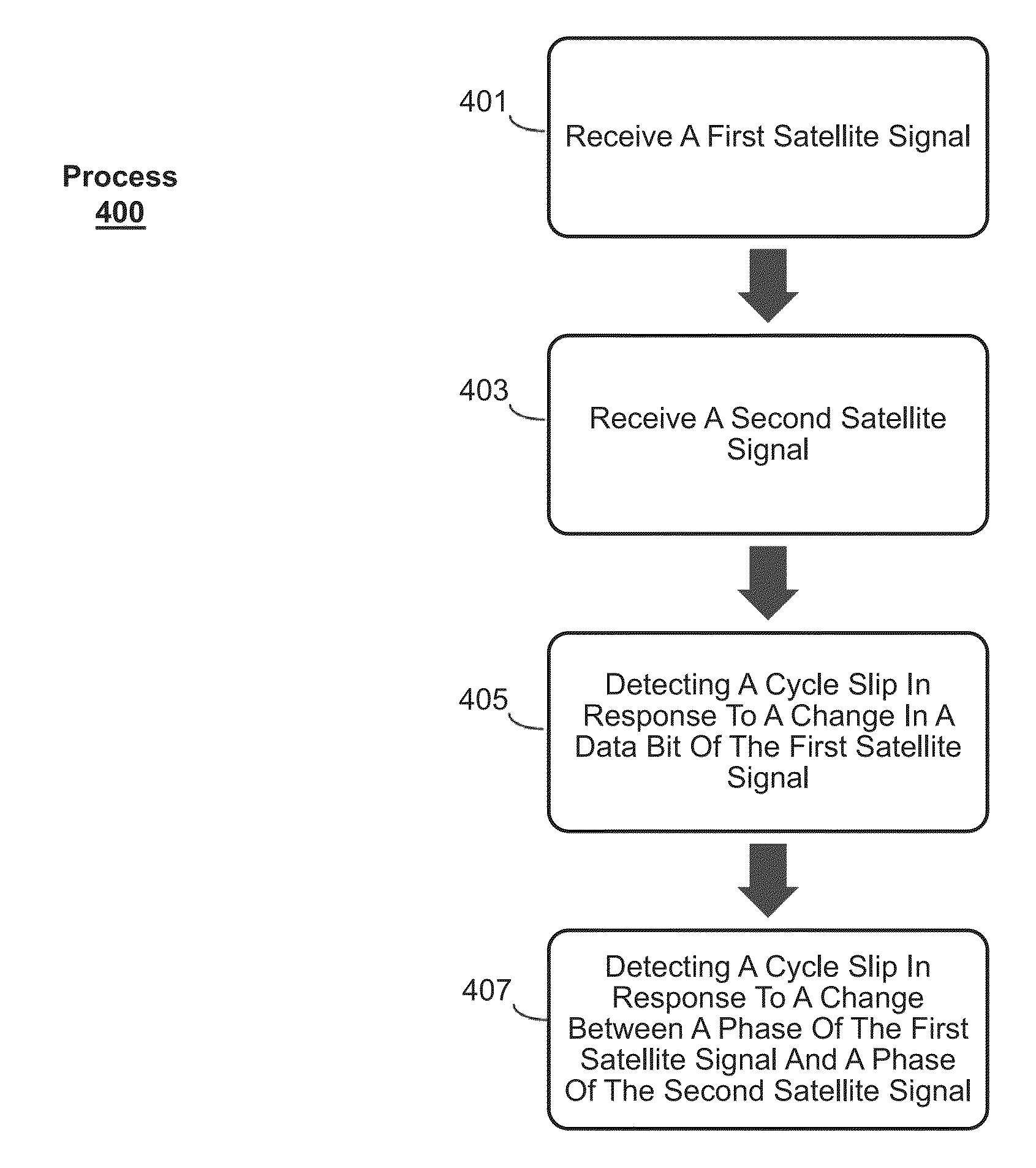
Systems and methods for detecting and displaying cycle slips are provided. In one example method, a first L1 signal and a second L2 signal may be received. The coarse / acquisition code from the L1 signal may be extracted and may be monitored to detect a phase shift in the code. In response to detecting a phase shift in the code, a data bit of the L1 signal may be monitored for a predetermined length of time to detect a change in the data bit. A cycle slip may be detected in response to detecting a change in the data bit during the predetermined length of time. In another example, a cycle slip may be detected in response to detecting a change between a phase of the L1 signal and a phase of the L2 signal.
Owner:JAVAD GNSS
Low power digital phase lock loop circuit
ActiveUS8222933B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase locked loop circuitClock rate
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Imported Doppler observation value construction method in consideration of clock jumps of GNSS receiver
PendingCN106772472AImprove execution efficiencyImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingTime markDependability
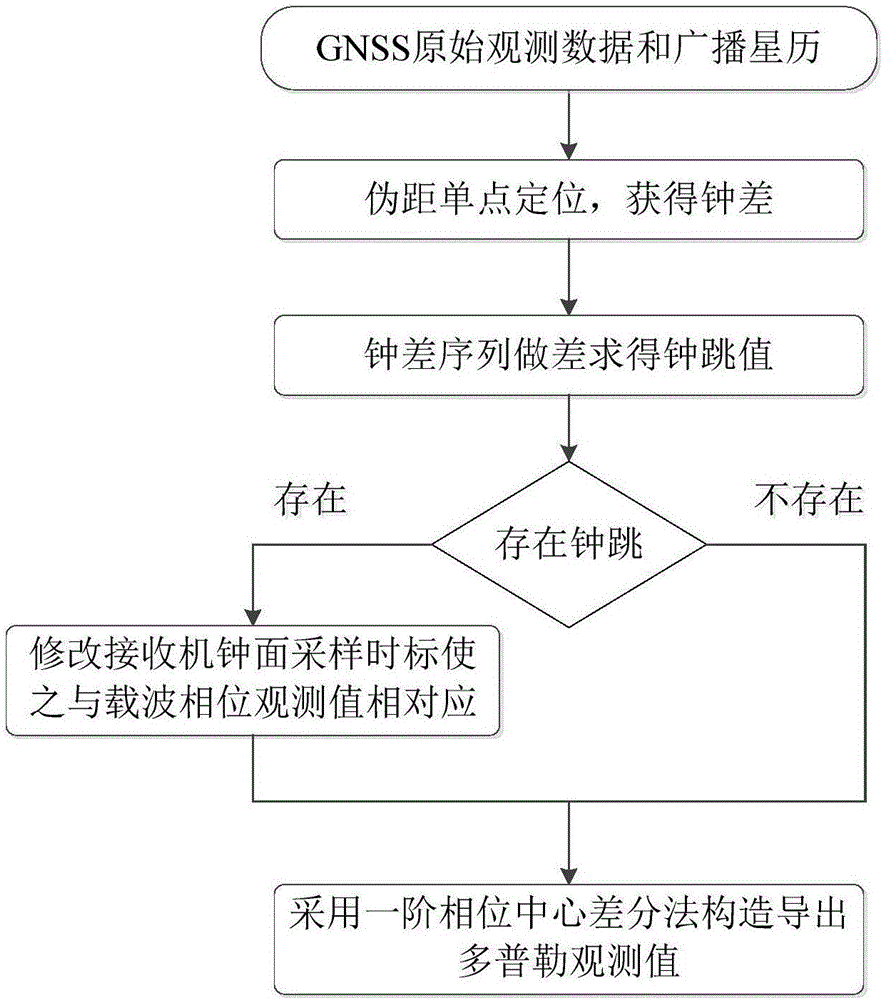
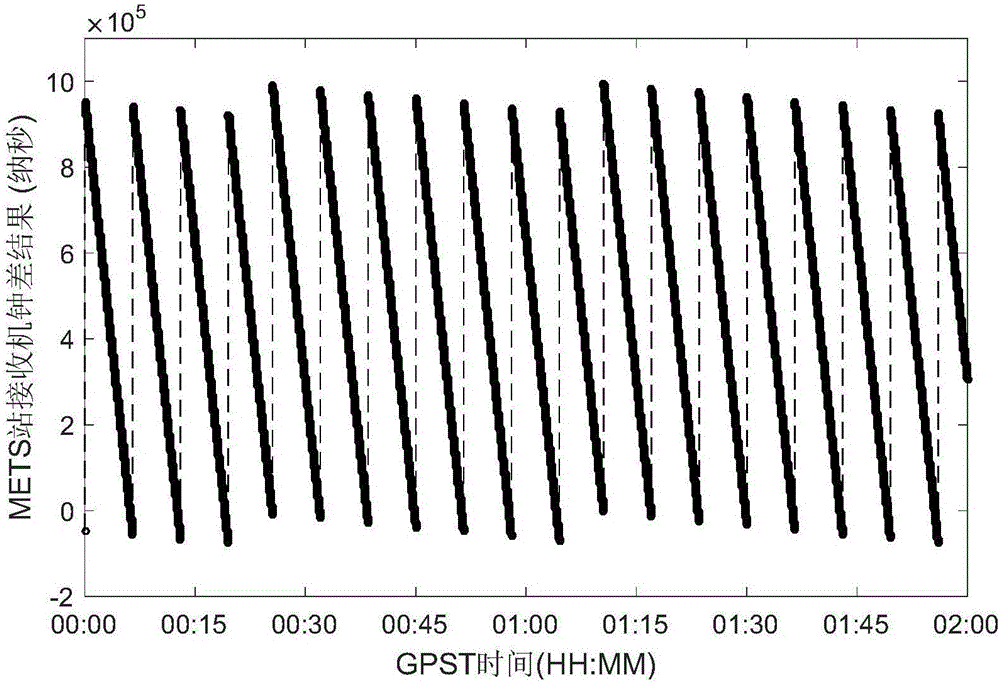
The invention discloses an imported Doppler observation value construction method in consideration of clock jumps of a GNSS receiver. Firstly a clock difference of the receiver is calculated by means of pseudo range single-point positioning. Then a clock difference sequence is utilized for constructing a clock jump inspection amount and clock jump judgment is performed. If the clock jumps exist, a clock surface sampling time mark of the receiver is modified for being corresponding with an observed value of a carrier phase. Finally a one-order phase central difference method is utilized for constructing a Doppler observation value. According to the imported Doppler observation value construction method, in a manner of modifying the sampling time mark instead of the carrier phase observation value, the carrier phase observation value corresponds with a true sampling time mark, thereby effectively preventing many unnecessary cycle slip detecting and restoring processes, remarkably improving execution efficiency, accuracy and reliability in construction and importing of the Doppler observation value.
Owner:THE FIRST MONITORING CENT OF CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTATION +1
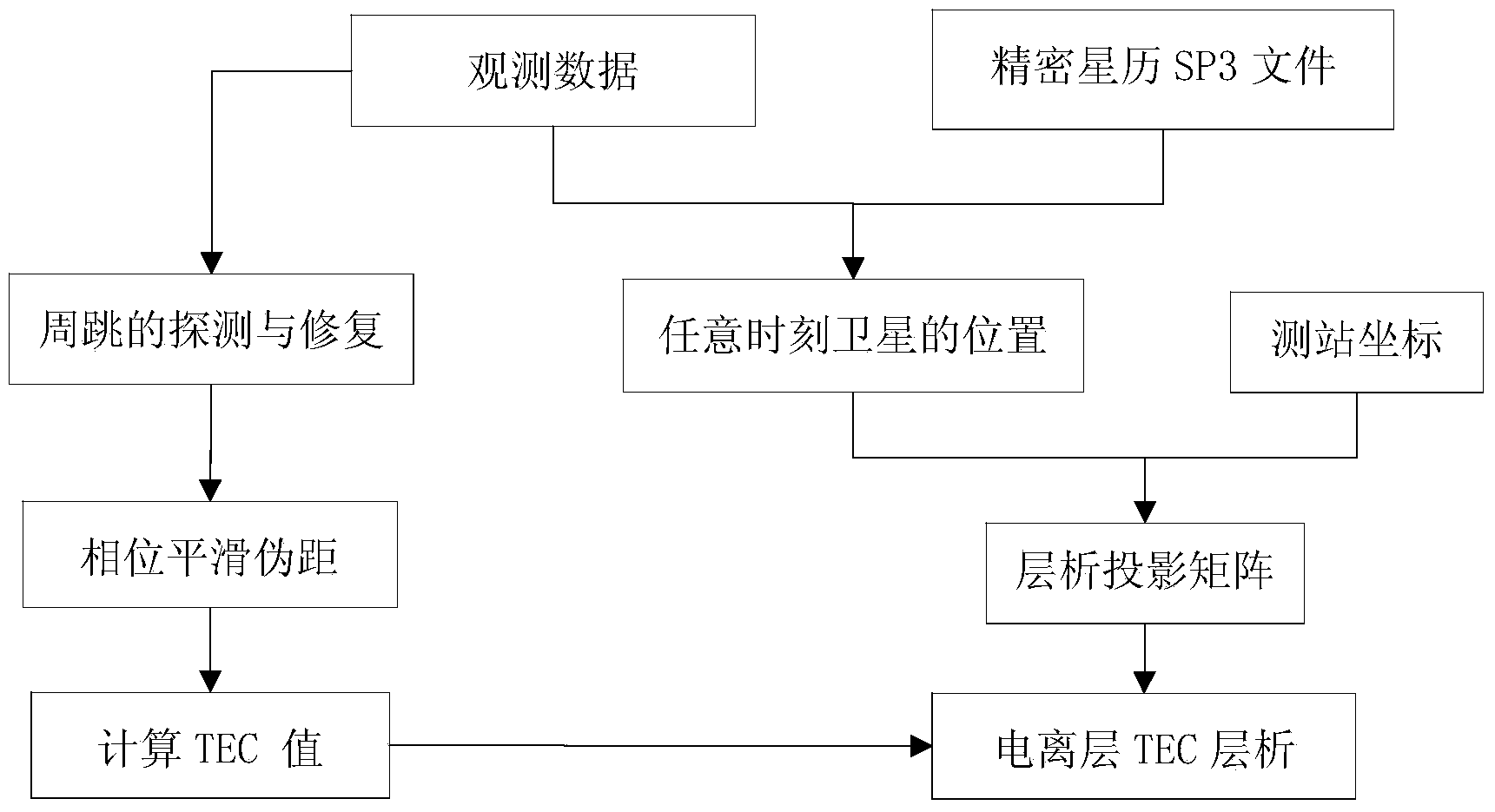
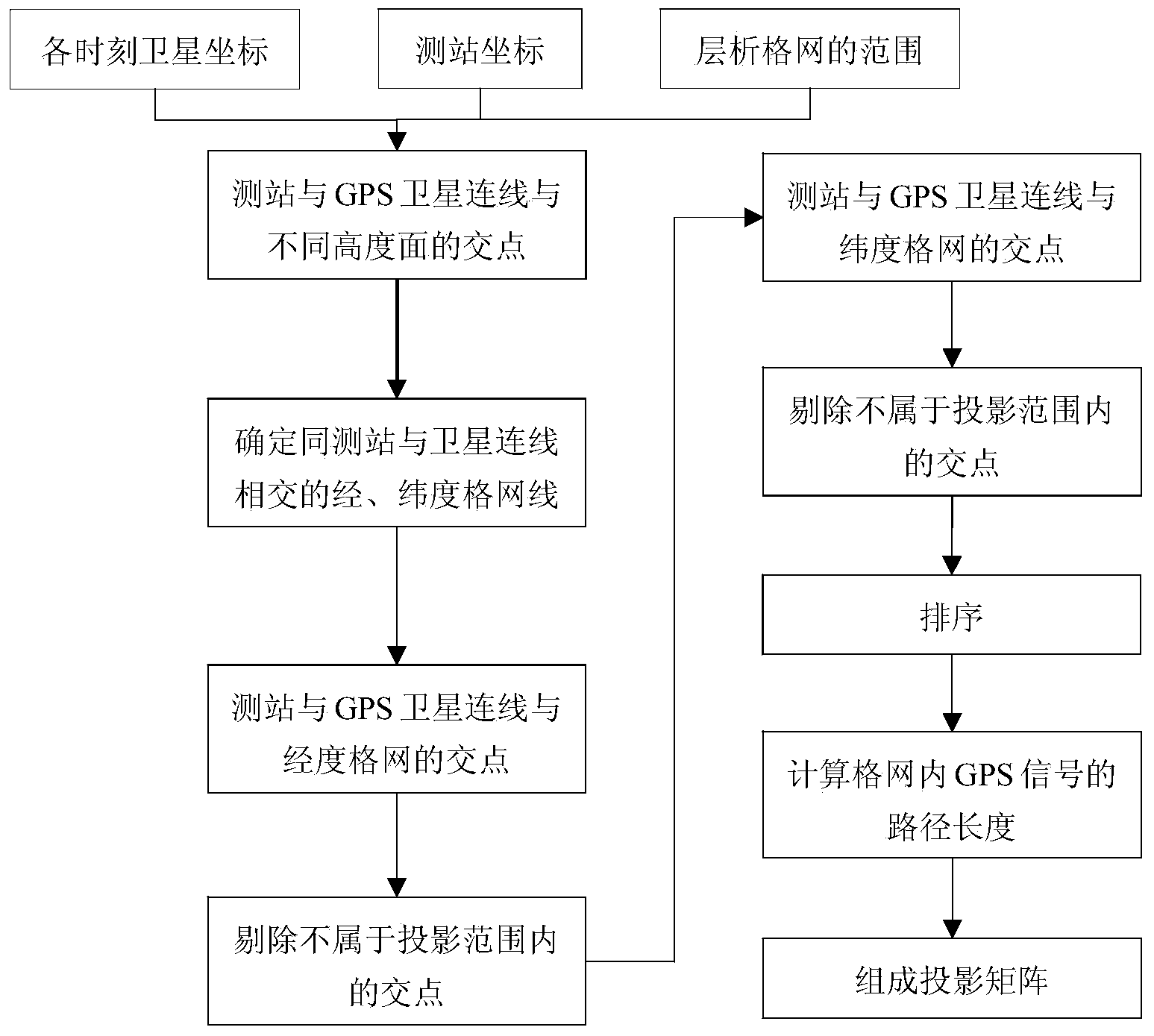
GPS ionized layer TEC chromatographic method
The invention provides a GPS ionized layer TEC chromatographic method. According to the method, GPS observation data are obtained, the coordinate of a satellite at any moment is interpolated in the Lagrange interpolation method in comparison with a GPS precise ephemeris, the GPS cycle slip is detected and repaired, the GPS phase position smooth pseudo-range, a TEC value and a chromatographic projection matrix are calculated, and finally ionized layer TEC chromatography is performed. The GPS ionized layer TEC chromatographic method is a chromatographic projection matrix solving method based on the GPS observation data, and ionized layer TEC chromatography calculation is realized conveniently, rapidly and efficiently.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com