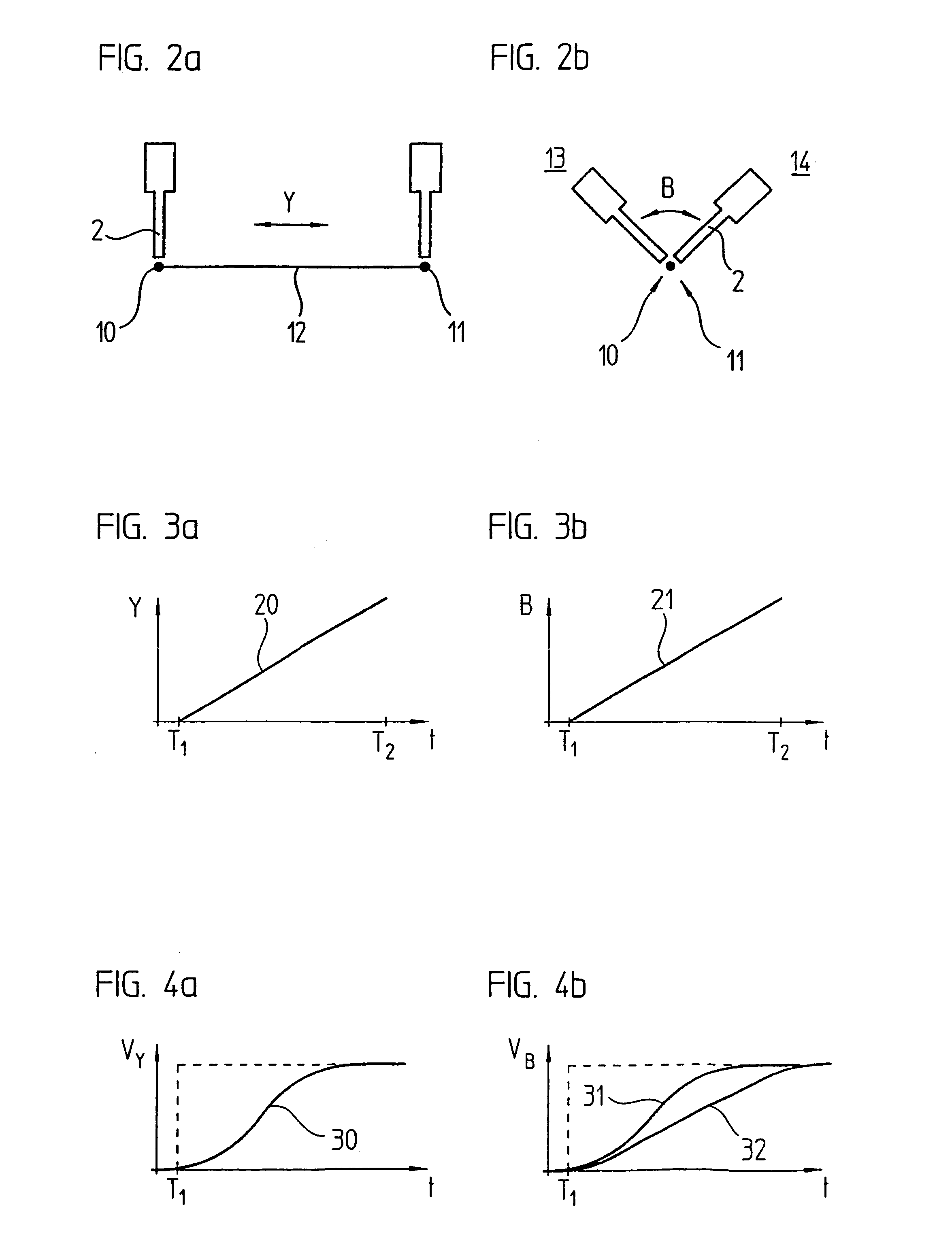
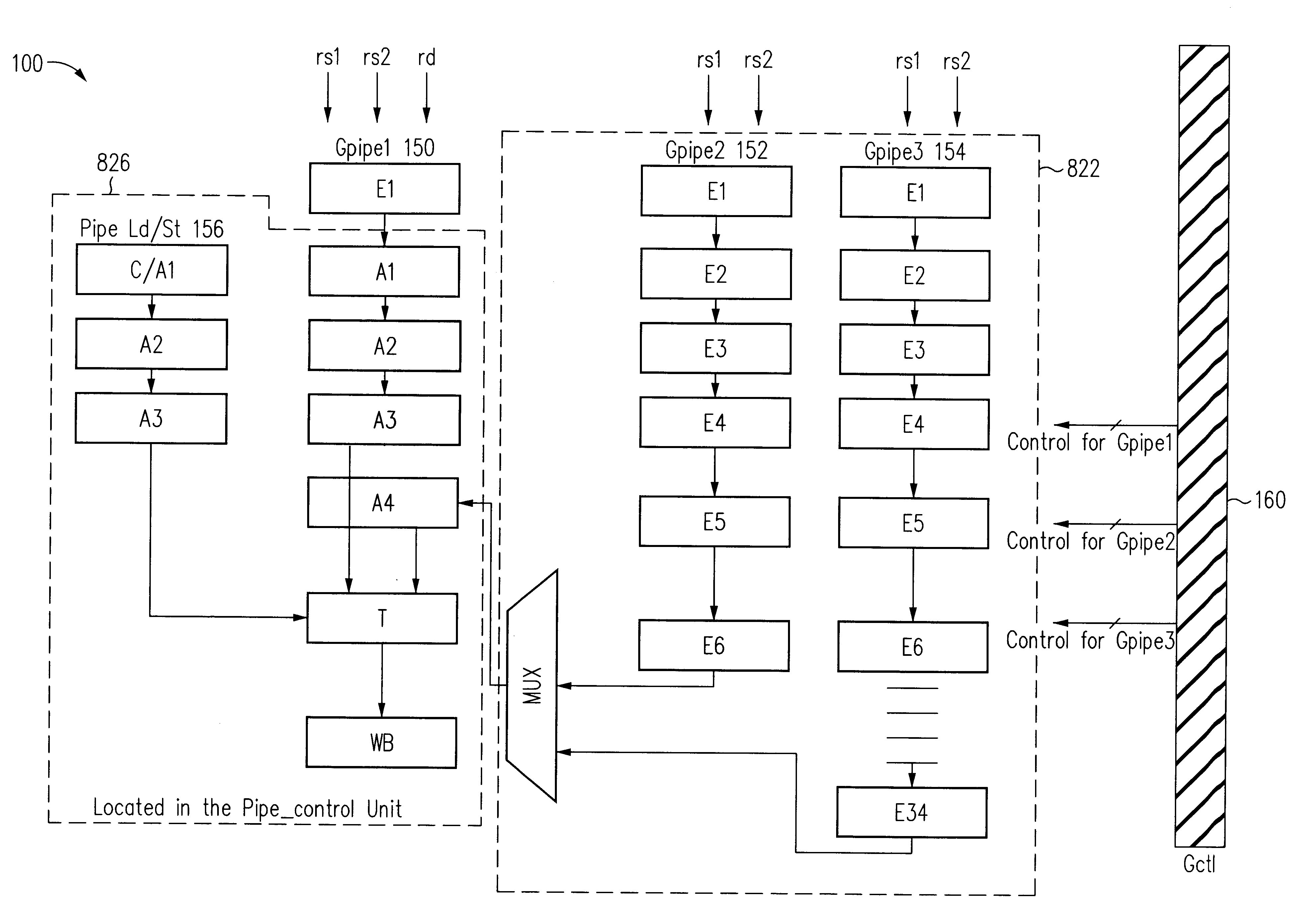
Patents
Literature
399 results about "Rounding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
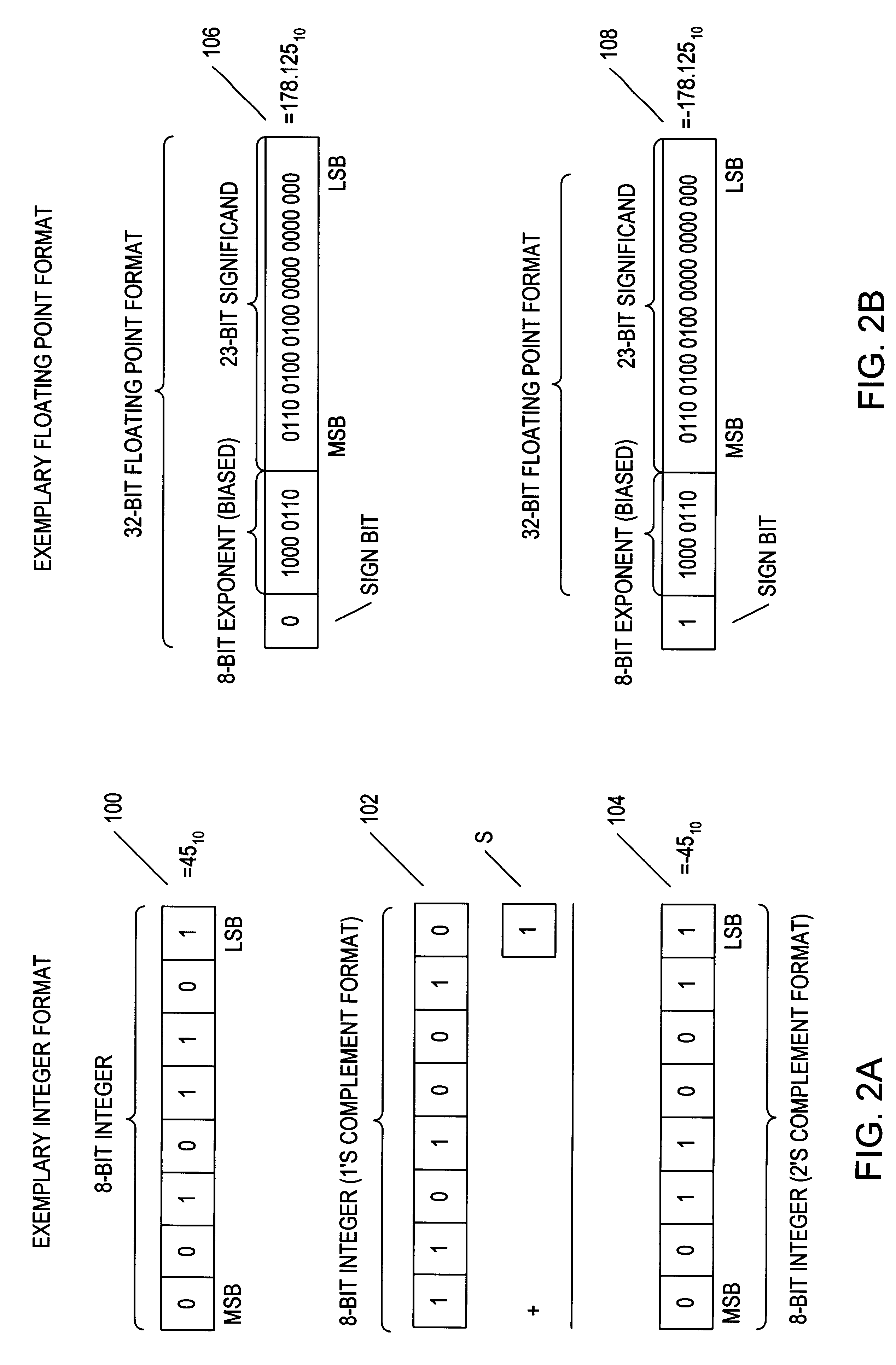
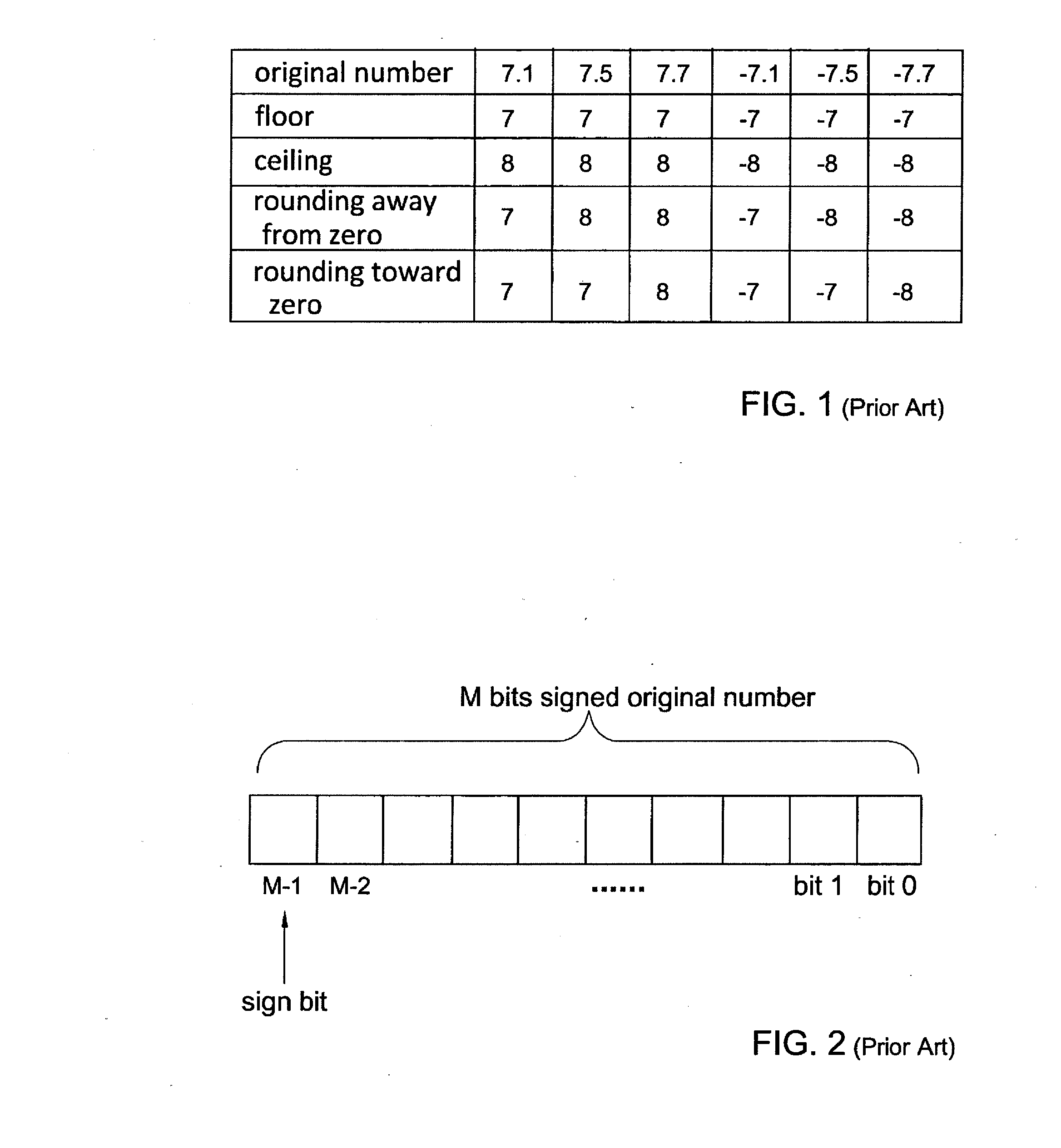
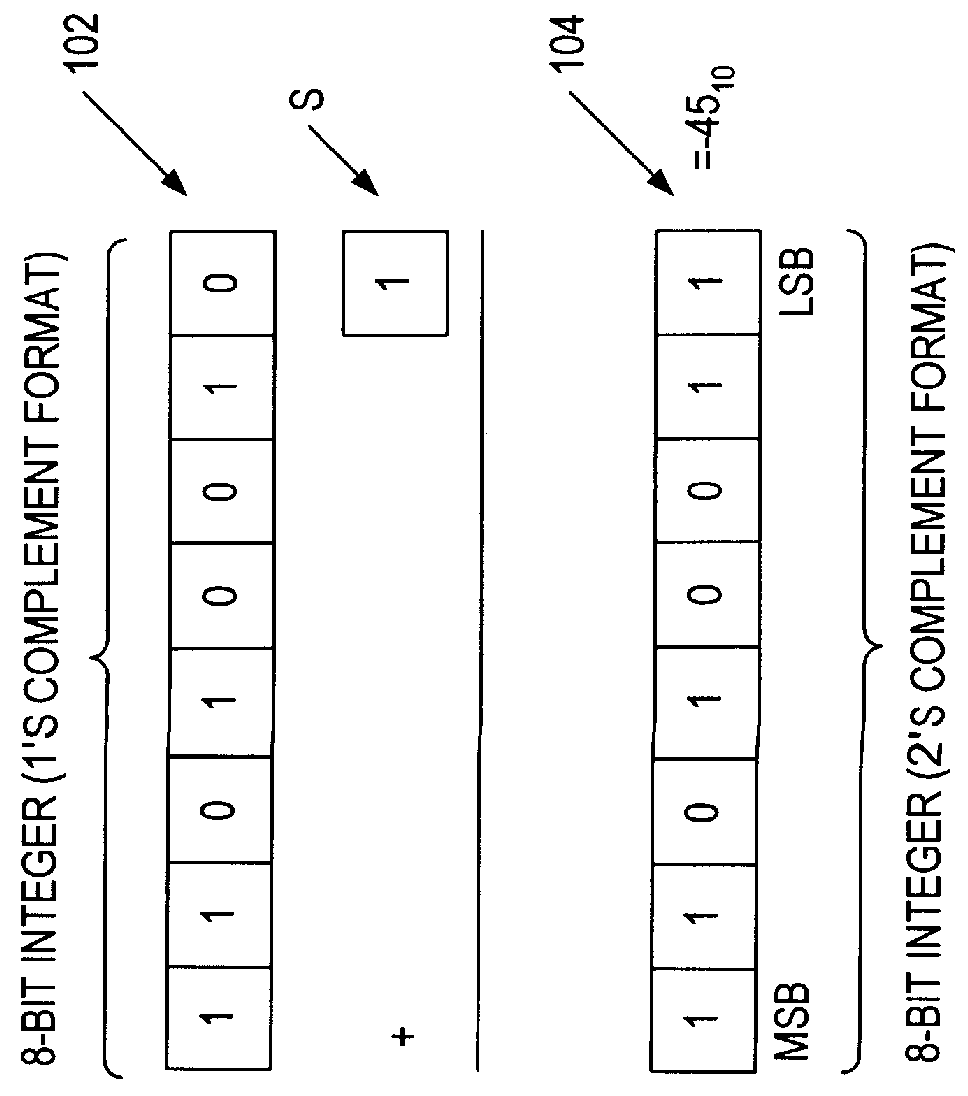
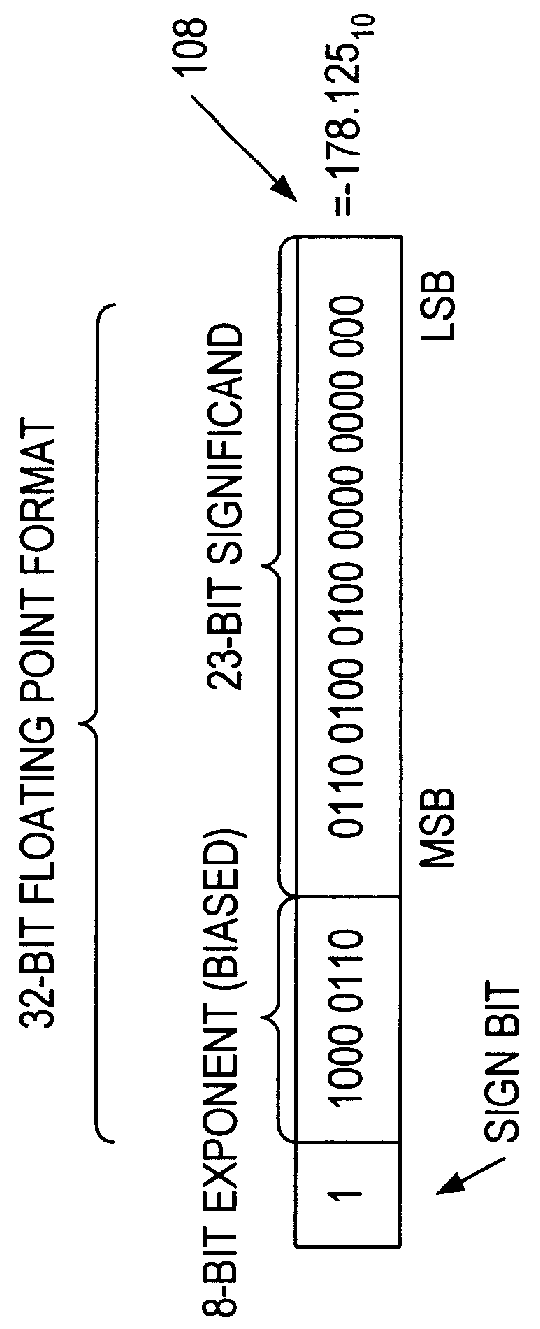
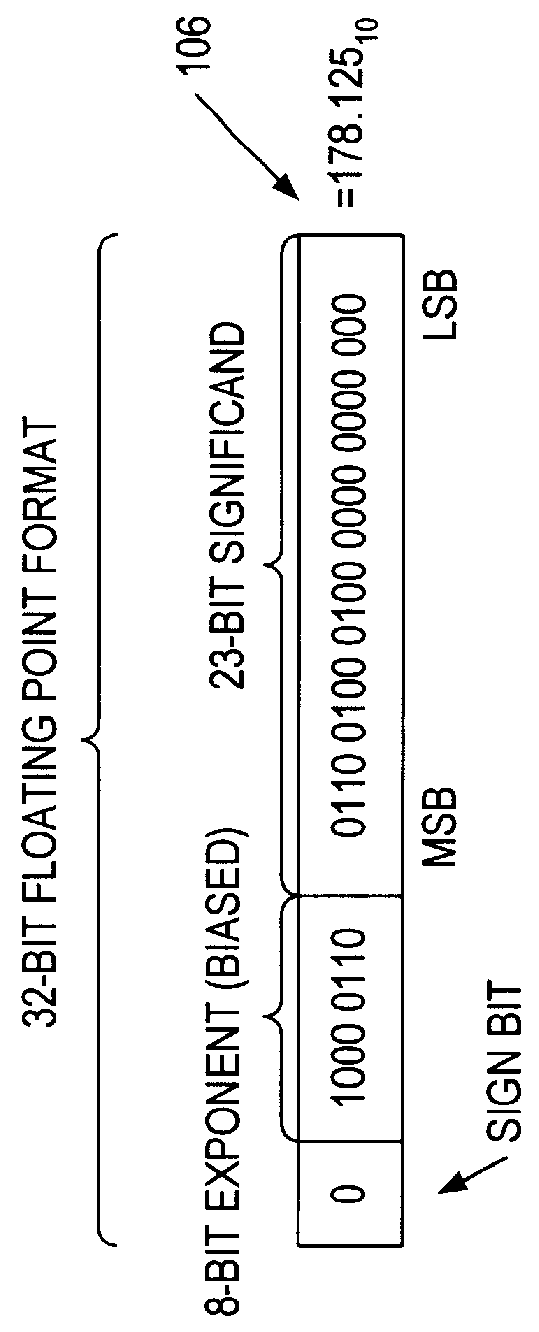
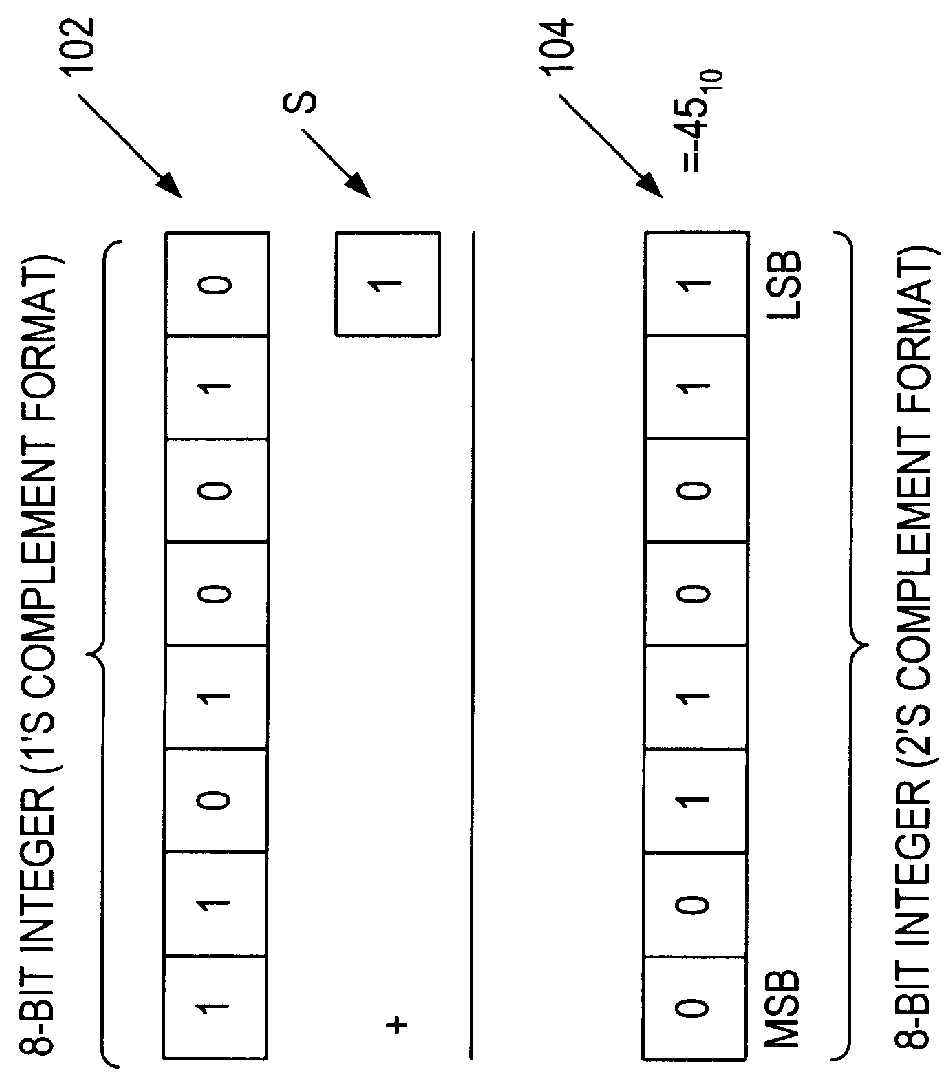
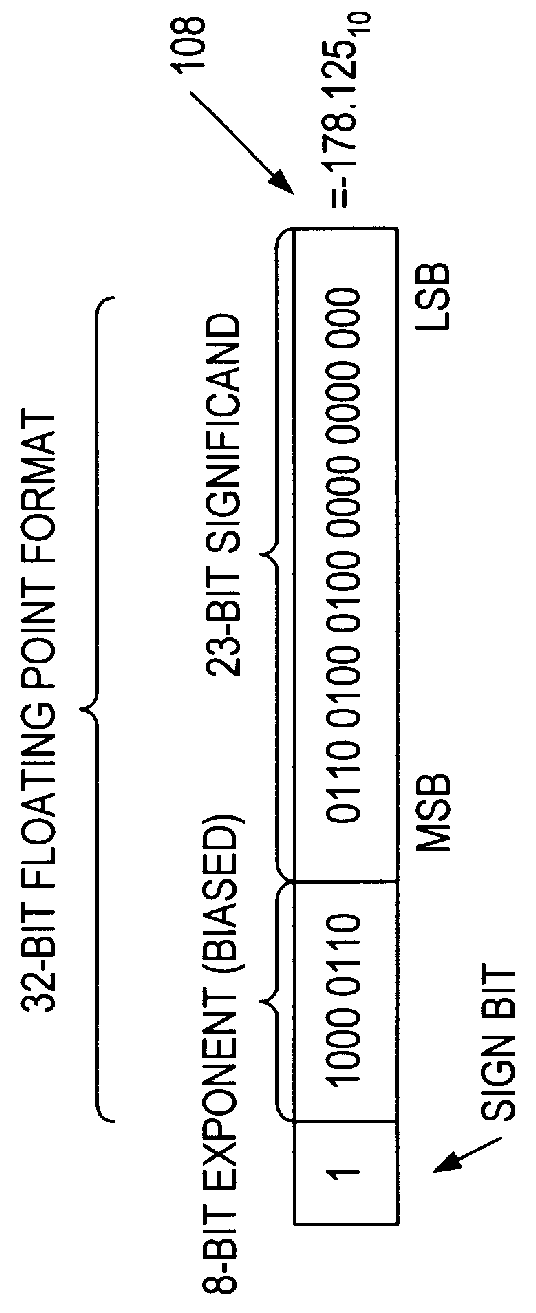
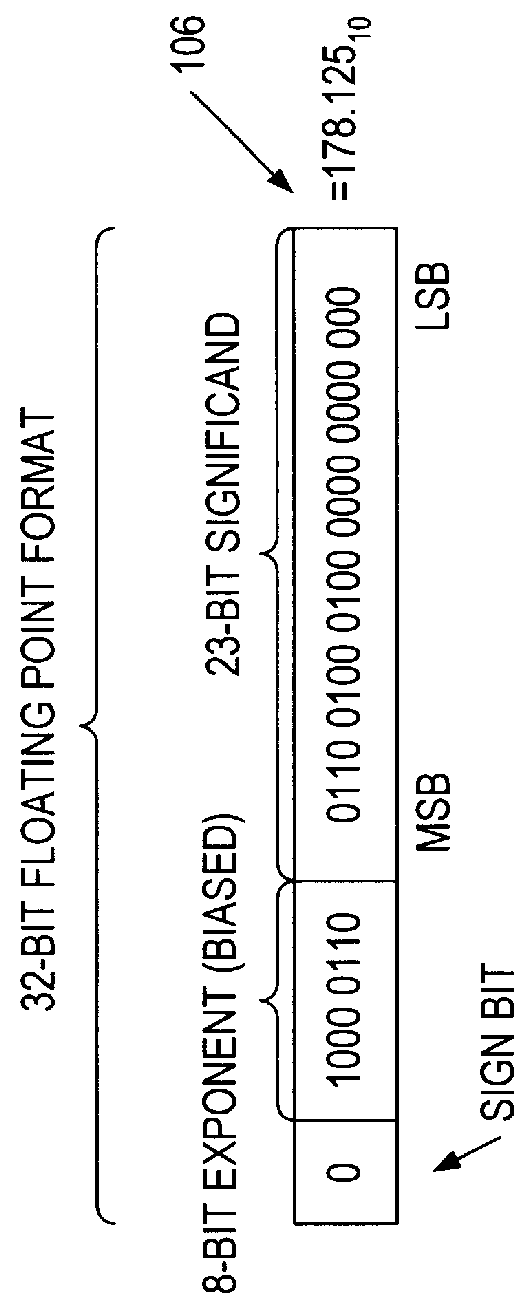
Rounding a number means replacing it with a different number that is approximately equal to the original, but has a shorter, simpler, or more explicit representation; for example, replacing $23.4476 with $23.45, or the fraction 312/937 with 1/3, or the expression √2 with 1.414.
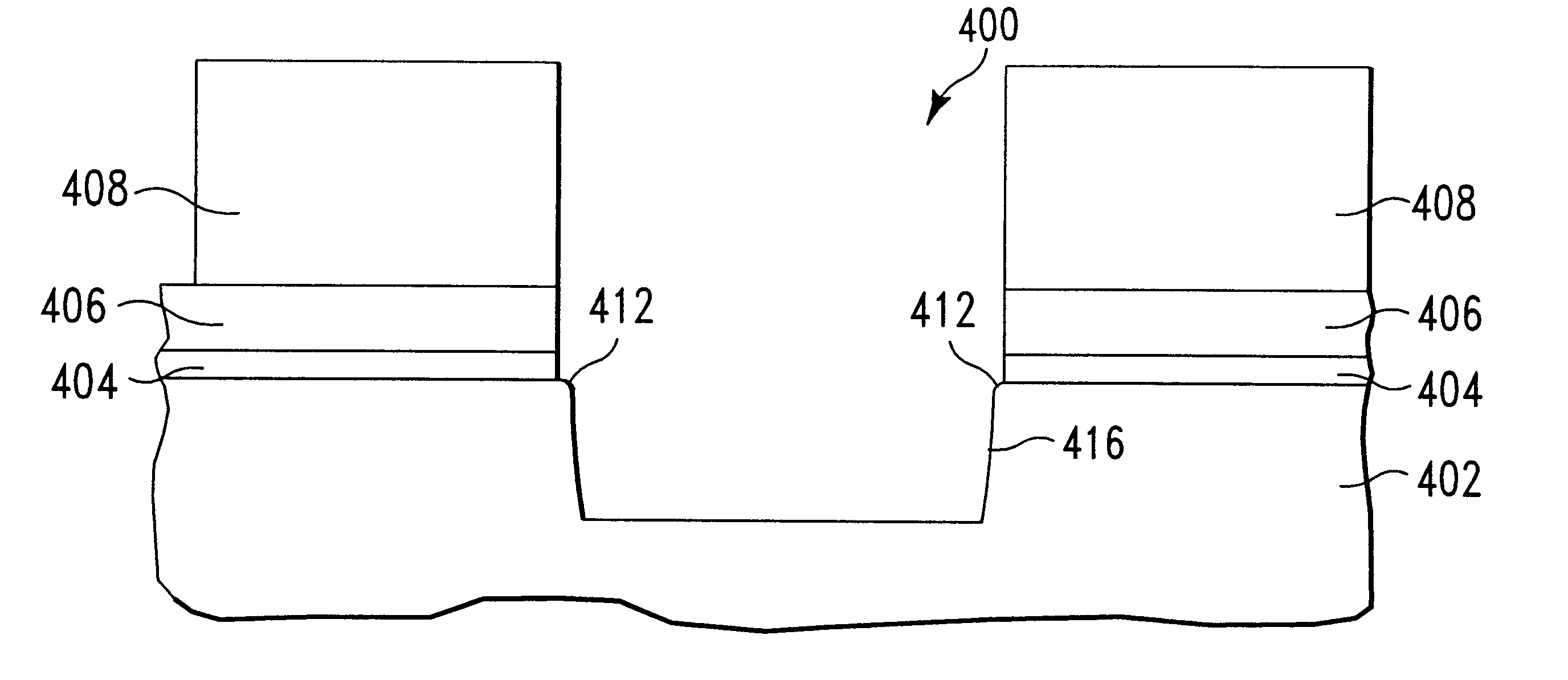
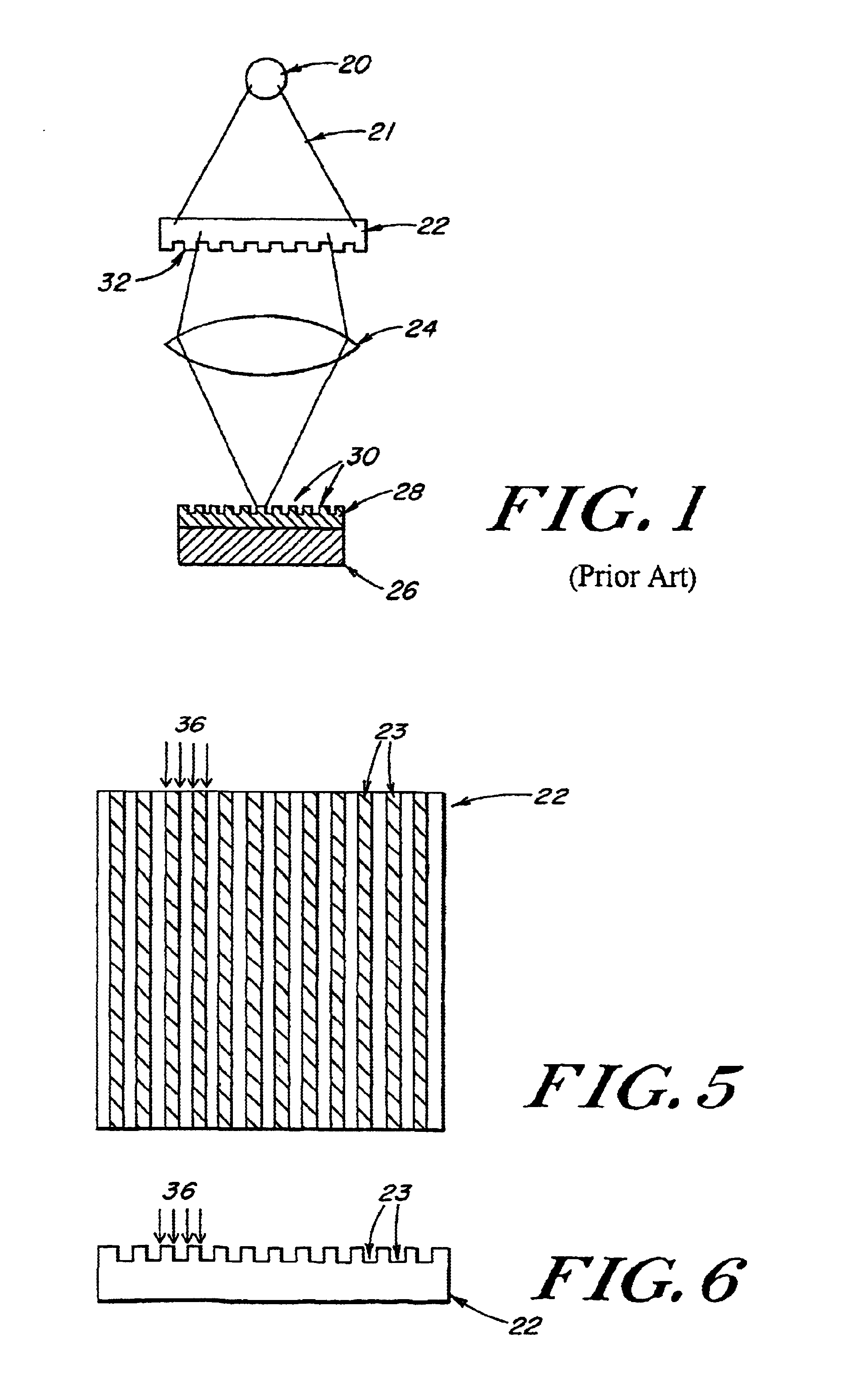
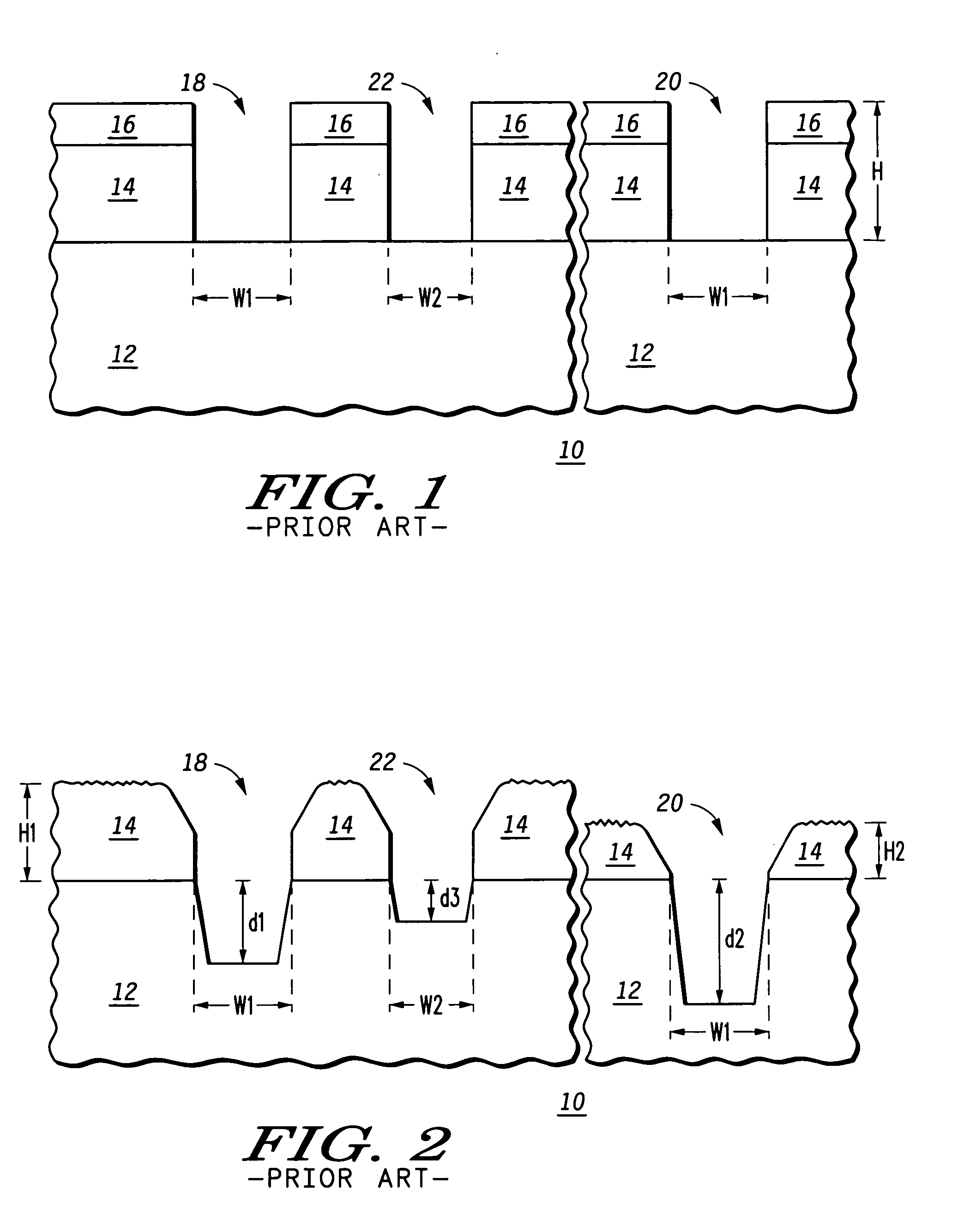
Method for etching a trench having rounded top and bottom corners in a silicon substrate
The present invention provides straight forward methods for plasma etching a trench having rounded top corners, or rounded bottom corners, or both in a silicon substrate. A first method for creating a rounded top corner on the etched silicon trench comprises etching both an overlying silicon oxide layer and an upper portion of the silicon substrate during a "break-through" step which immediately precedes the step in which the silicon trench is etched. The plasma feed gas for the break-through step comprises carbon and fluorine. In this method, the photoresist layer used to pattern the etch stack is preferably not removed prior to the break-through etching step. Subsequent to the break-through step, a trench is etched to a desired depth in the silicon substrate using a different plasma feed gas composition. A second method for creating a rounded top corner on the etched silicon trench comprises formation of a built-up extension on the sidewall of an overlying patterned silicon nitride hard mask during etch (break-through) of a silicon oxide adhesion layer which lies between the hard mask and a silicone substrate. The built-up extension upon the silicon nitride sidewall acts as a sacrificial masking material during etch of the silicon trench, delaying etching of the silicon at the outer edges of the top of the trench. This permits completion of trench etching with delayed etching of the top corner of the trench and provides a more gentle rounding (increased radius) at the top corners of the trench. During the etching of the silicon trench to its final dimensions, it is desirable to round the bottom corners of the finished silicon trench. We have discovered that a more rounded bottom trench corner is obtained using a two-step silicon etch process where the second step of the process is carried out at a higher process chamber pressure than the first step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
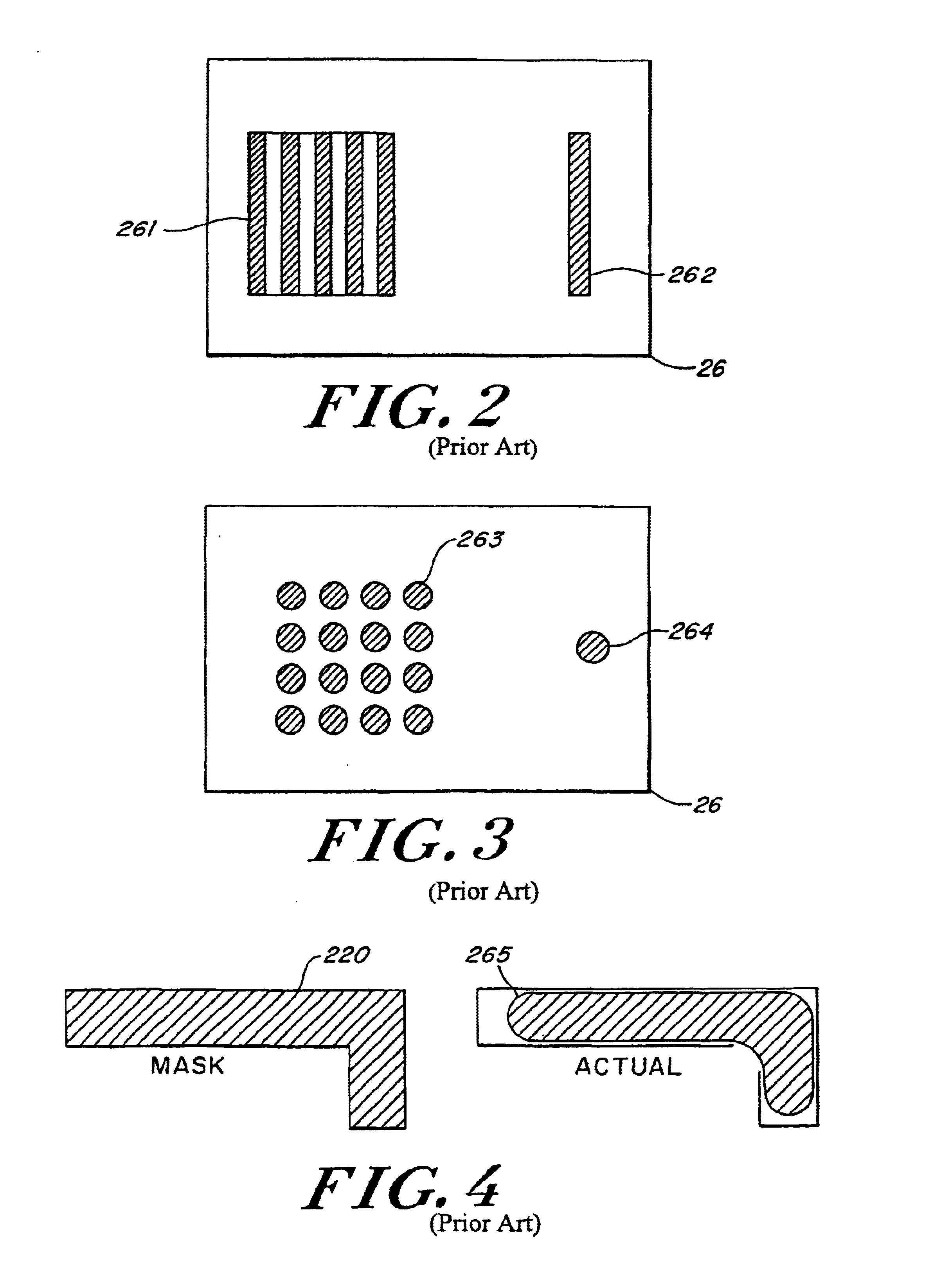
Method of design and fabrication of integrated circuits using regular arrays and gratings
InactiveUS6818389B2Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingRounding
A circuit fabrication and lithography process utilizes a mask including dense repetitive structures of features that result in a wide array of fine densely populated features on the exposed substrate film. Following this, a trimming procedure is performed to remove any unwanted fine patterned features providing multiple trimmed patterns on the substrate. An optional final step adds additional features as well as the interconnect features thus forming a circuit pattern. In this manner, all fine features may be generated using the exact same density of intensity patterns, and therefore, maximum consistency between features is established without the need for optical proximity correction. The secondary exposures are substantially independent from the initial dense-feature exposure in that the exposure of one set of features and the subsequent exposure of another set of features result in separate independent resist or masking layer reactions, thus minimizing corner rounding, line end shortening and other related spatial frequency effects and unwanted exposure memory effects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
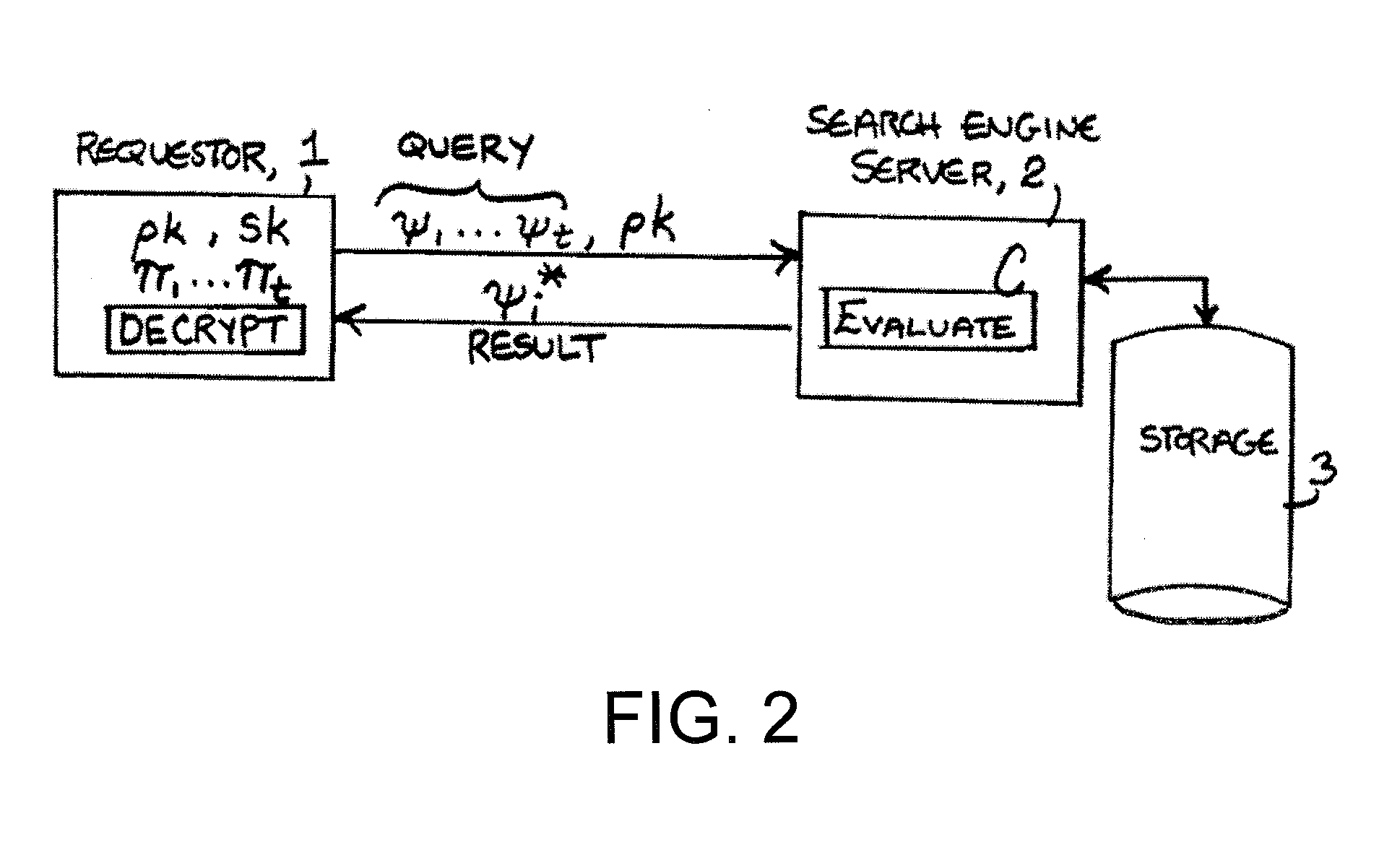
Fully Homomorphic Encryption
InactiveUS20130170640A1Reduce noise levelGrowth inhibitionPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationRoundingNoise level
In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a method and computer program include: receiving first and second ciphertexts having first and second data encrypted per an encryption scheme, the encryption scheme has public / secret keys and encryption, decryption, operation and refresh functions, the encryption function encrypts data, the decryption decrypts ciphertext, the operation receives ciphertexts and performs operation(s) on them, the refresh operates to prevent growth of the magnitude of noise for a ciphertext while reducing the modulus of the ciphertext without using the secret key, utilizing a modulus switching technique that involves transforming a first ciphertext c modulo q into a second ciphertext c′ modulo p while preserving correctness, the technique includes scaling by p / q and rounding, p<q; using the operation function(s), performing operation(s) on them to obtain a third ciphertext; and reducing a noise level of the third ciphertext using the refresh function.
Owner:IBM CORP
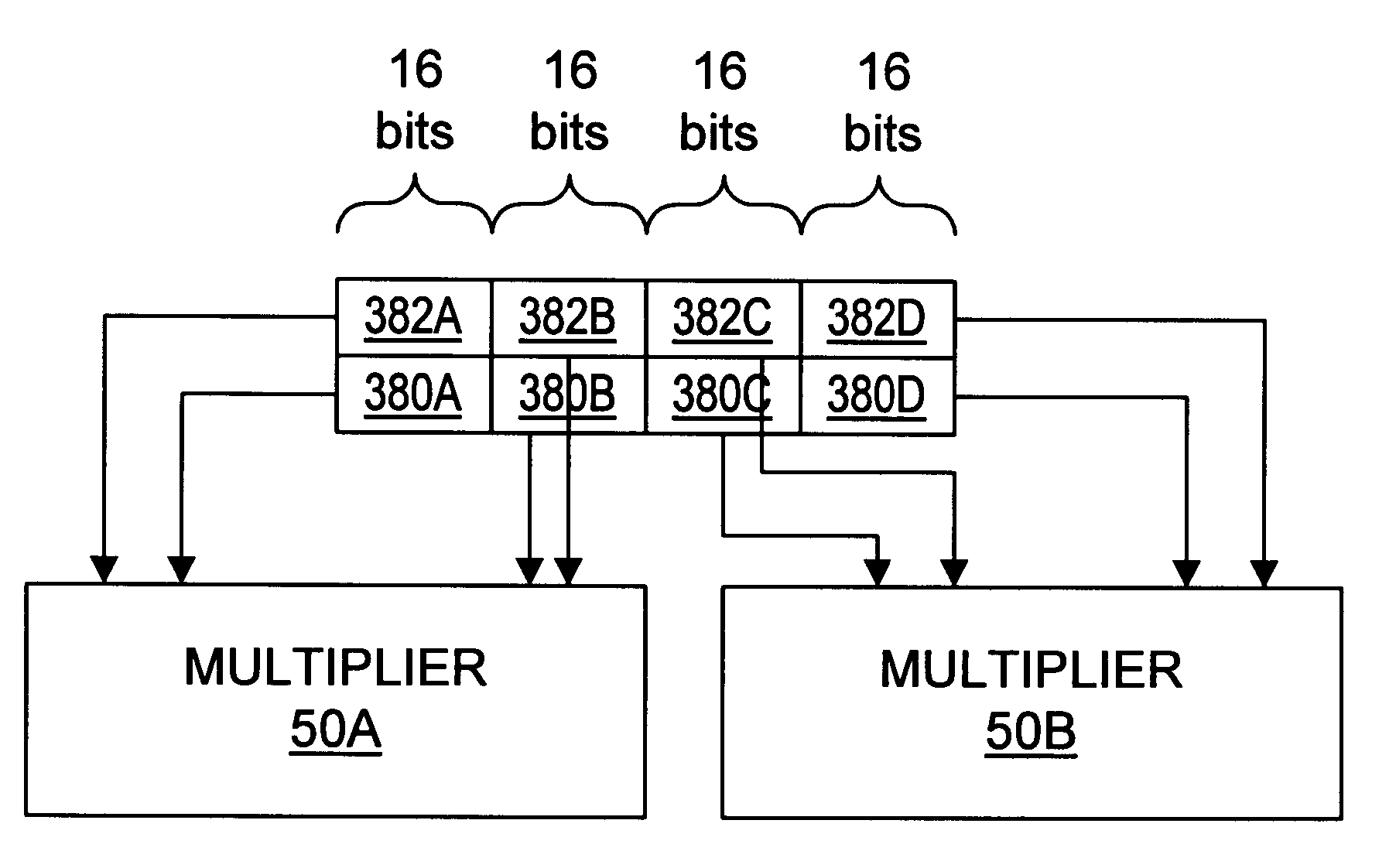
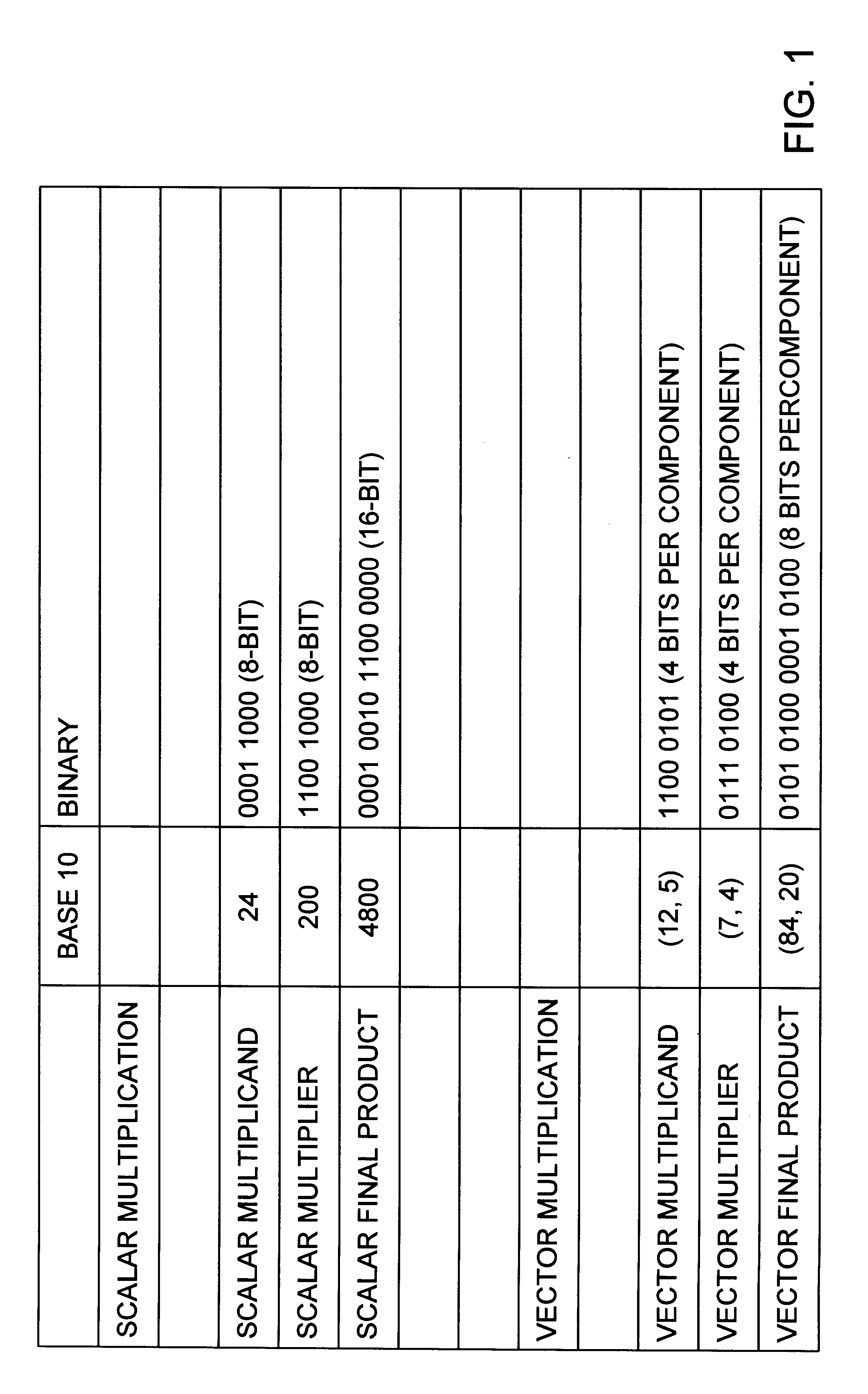
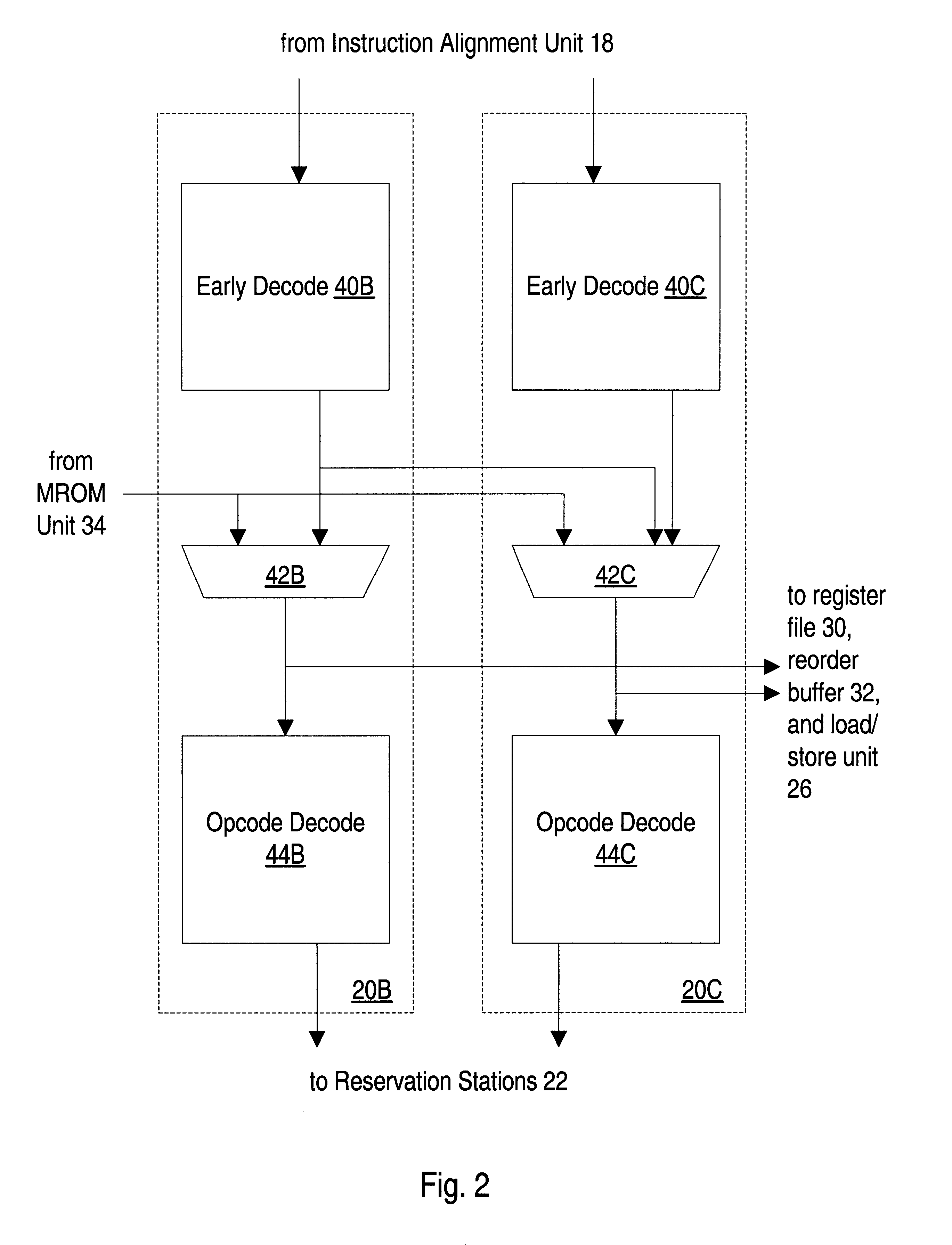
Method and apparatus for multi-function arithmetic
InactiveUS6223198B1Runtime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesConstant powerRounding
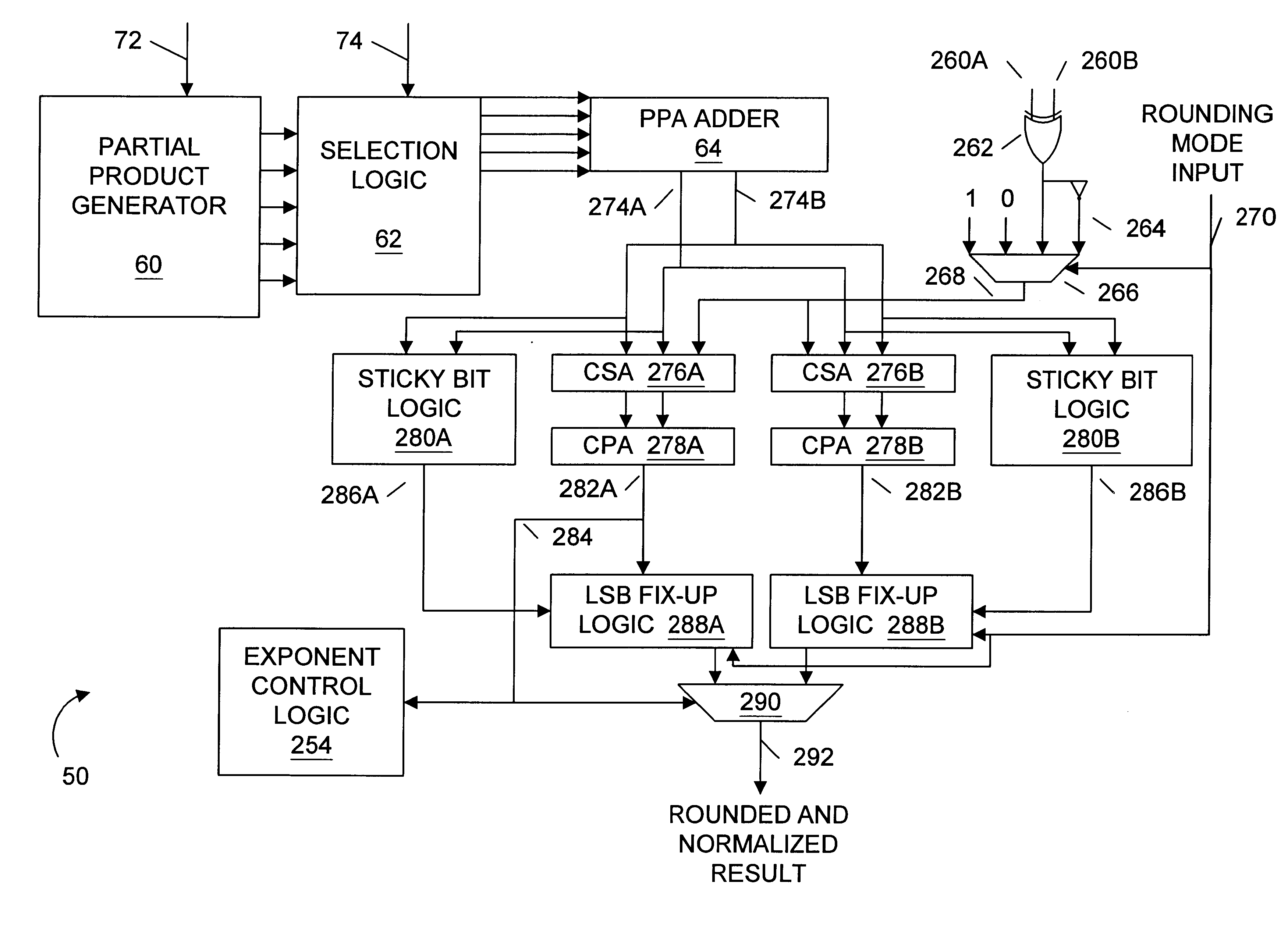
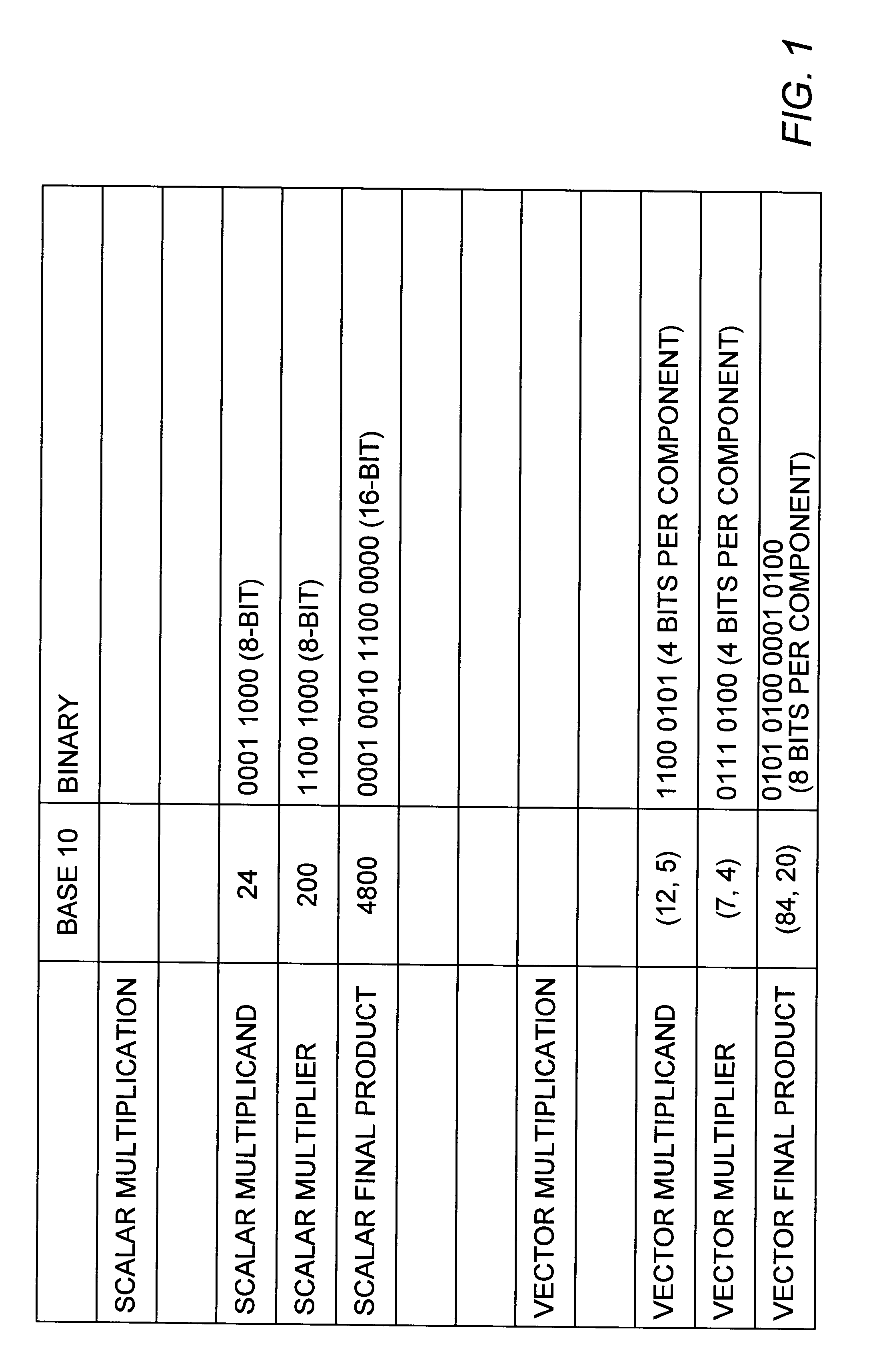
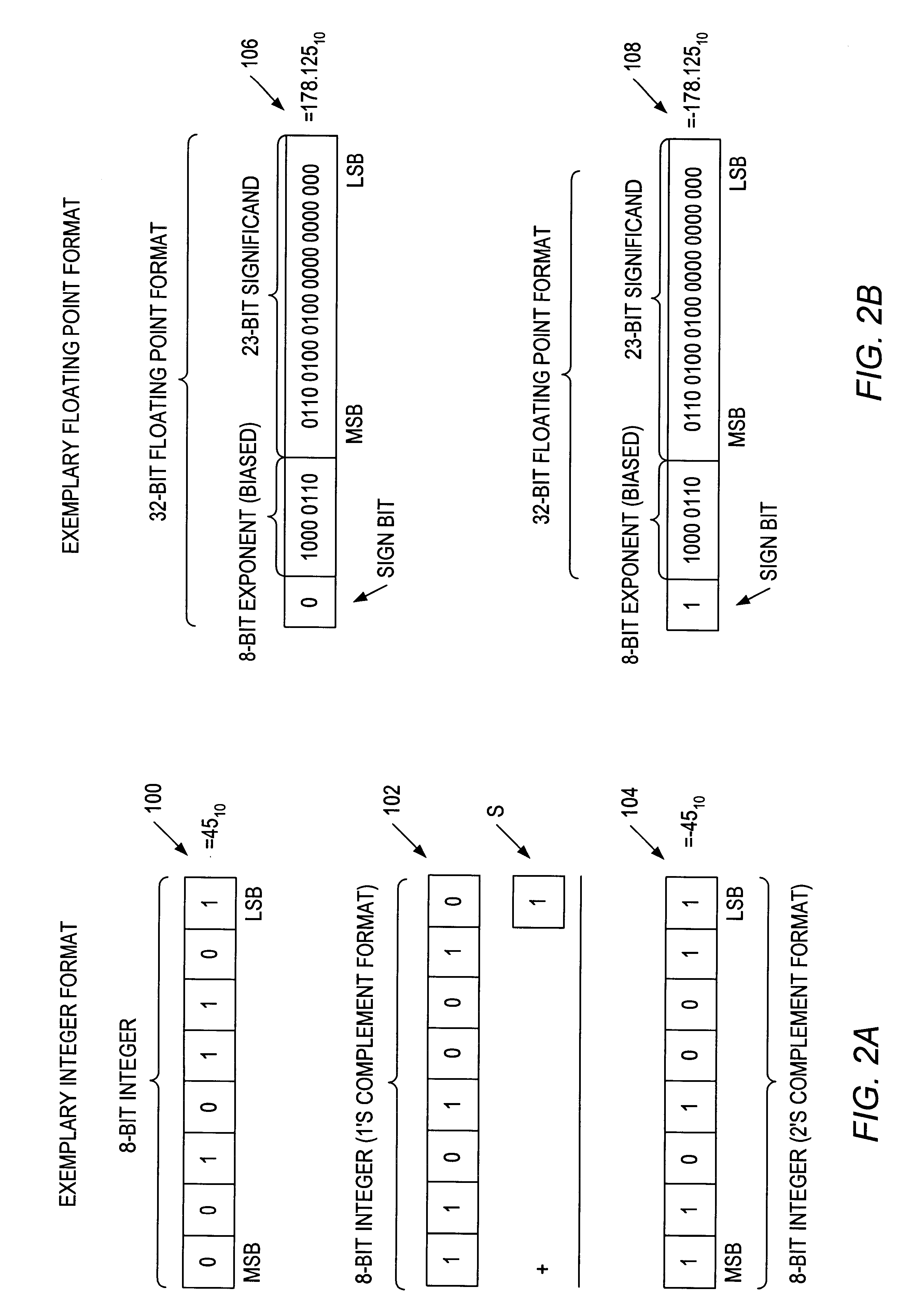
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated and used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative calculations to evaluate constant powers of an operand. Intermediate products that are formed may be rounded and normalized in two paths and then compressed and stored for use in the next iteration. An adjustment constant may also be added to increase the frequency of exactly rounded results.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Systems and methods for linking orders in electronic trading systems
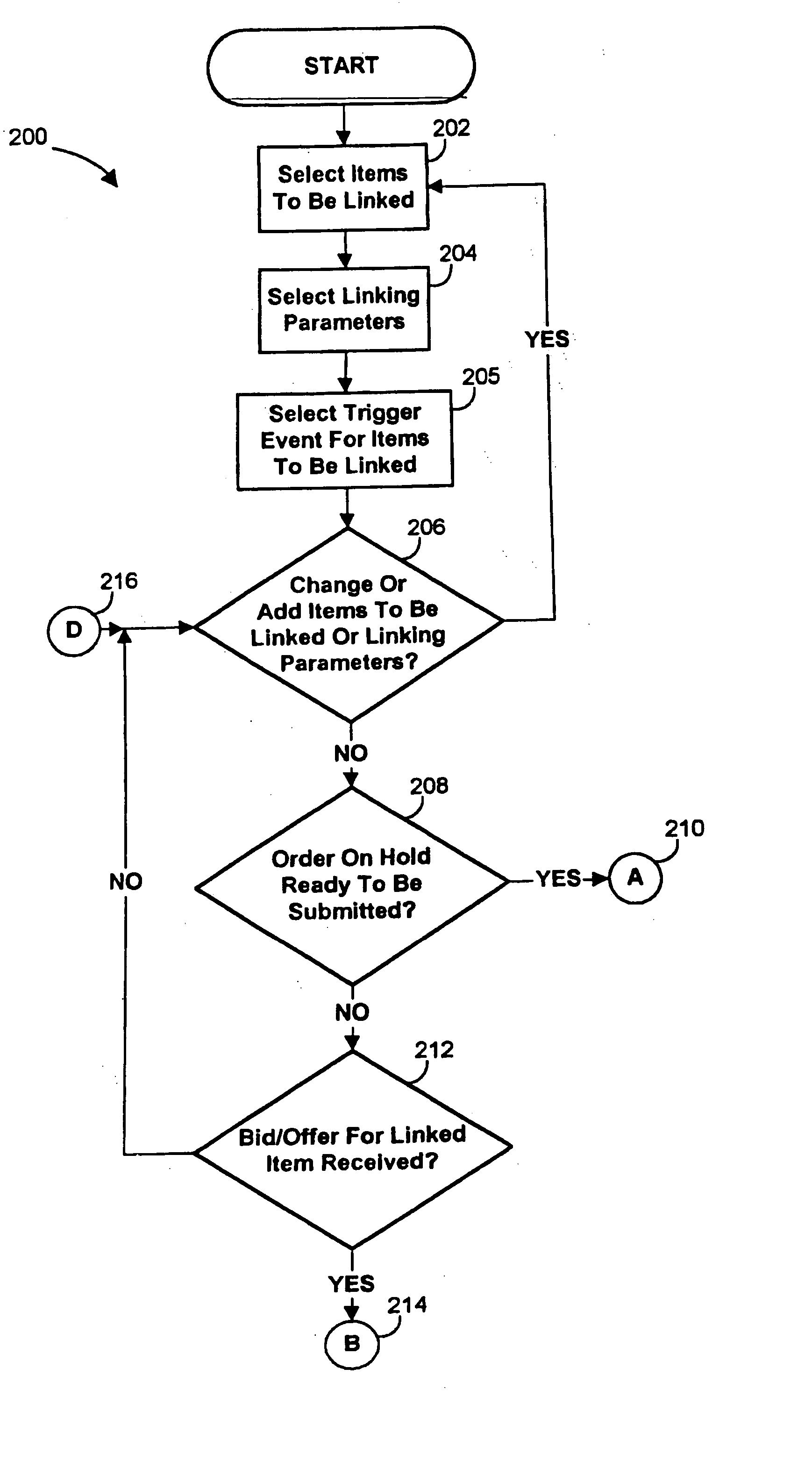
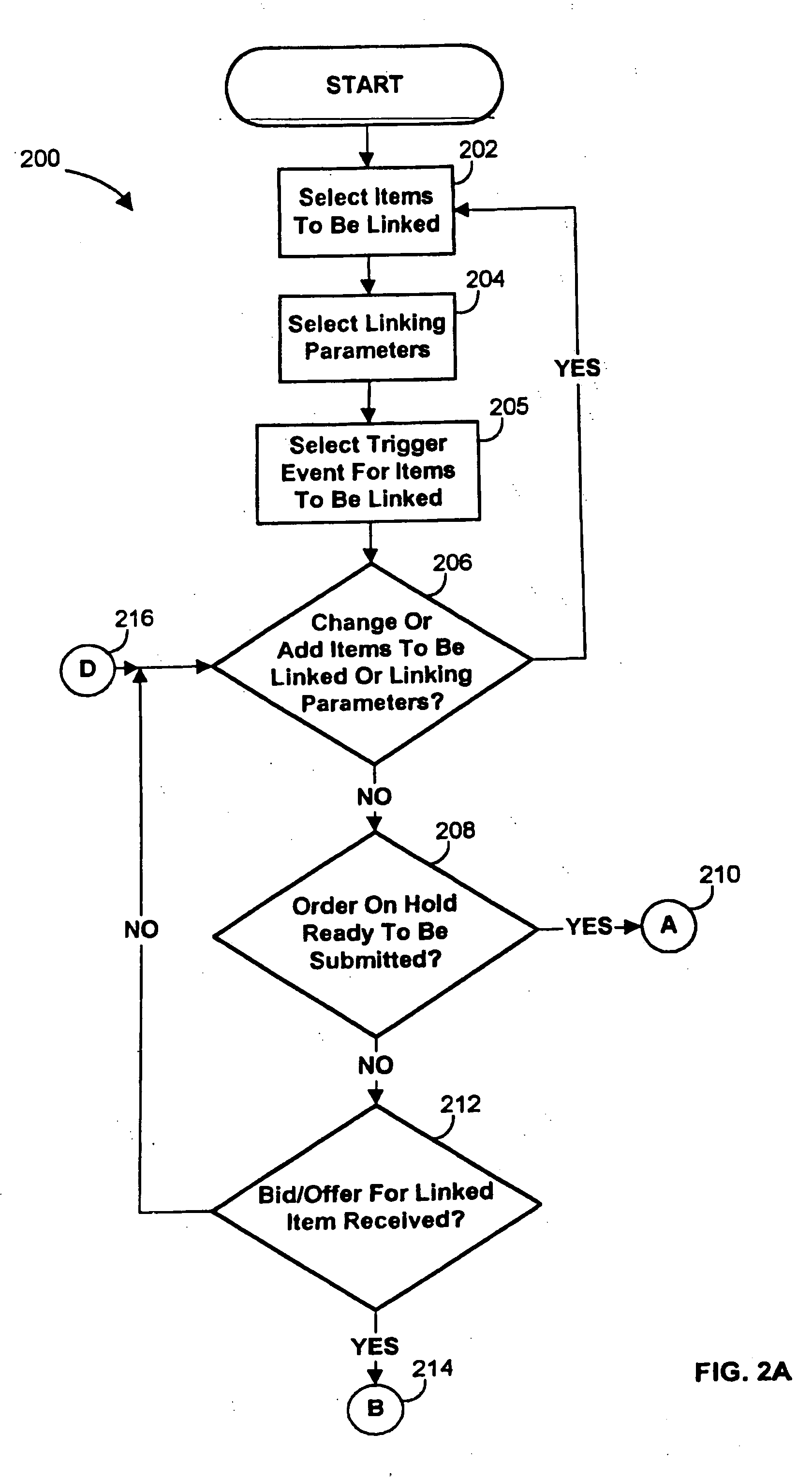
Systems and methods for linking orders in electronic trading systems are provided. These systems and methods enable a trader to select two or more items that are to be linked and specify linking parameters for those items. Any desired set of items may be linked, and the linking parameters may include price adjustments, order sequencing instructions, automatic / manual execution controls, execution delays commands, and update frequency limits. Upon detecting a bid or offer for a linked item, the systems and methods may then determine a size and a price for each linked item based upon the size and the price of the bid or offer for the first linked item. In this way, the sizes and the prices for the other linked items may be propagated from the size and the price for the first item. Once the size and the price for each item is determined, the systems and methods may submit orders for the items in accordance with the linking parameters. In the case where orders for linked items may only be submitted in designated lot sizes, the systems and methods may round the sizes of the orders to the designated lot sizes, and then submit remainder orders to make up for the rounding.
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
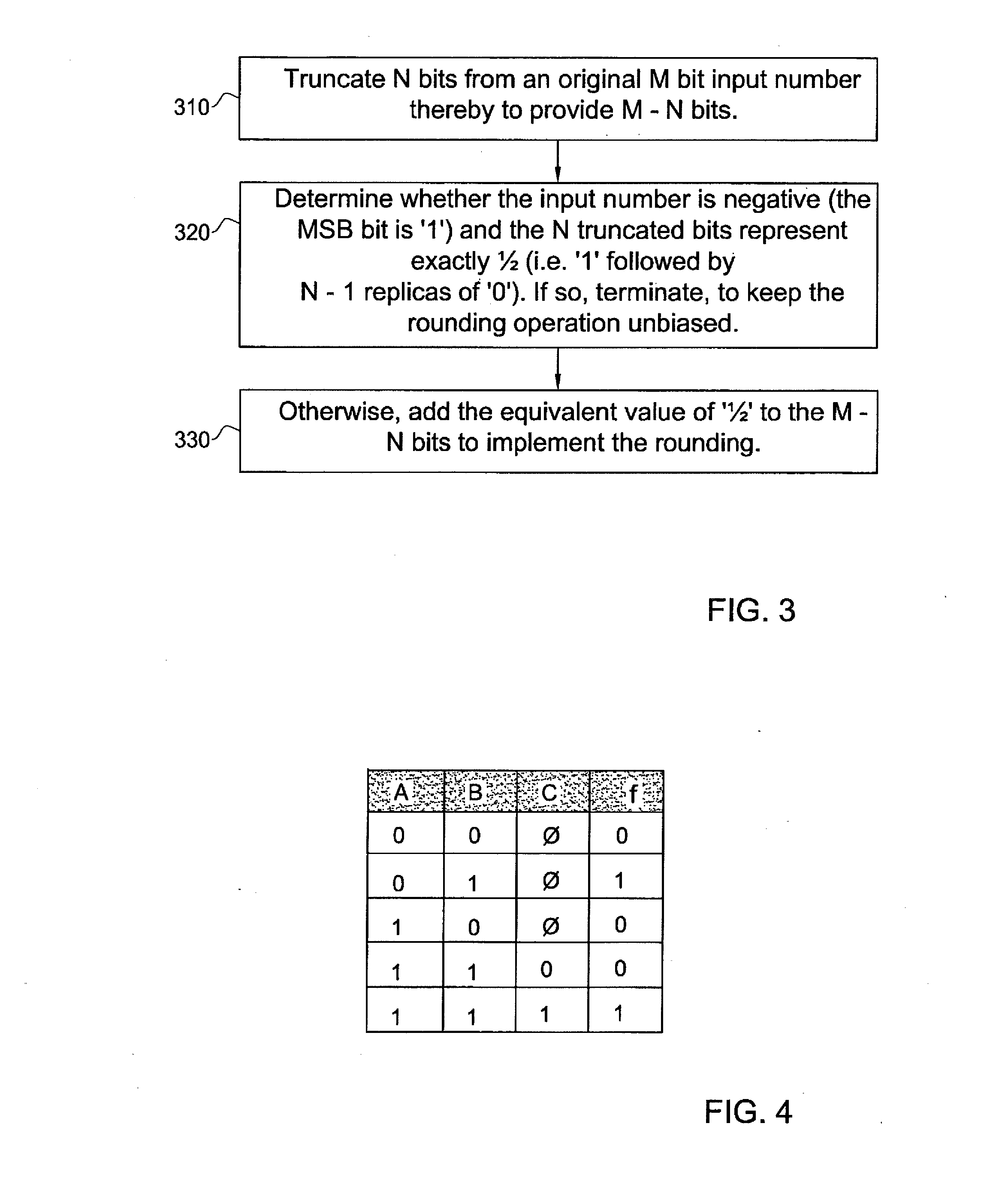
Apparatus and methods for hardware-efficient unbiased rounding
ActiveUS20100131580A1Low powerComputation using denominational number representationRoundingComputer science
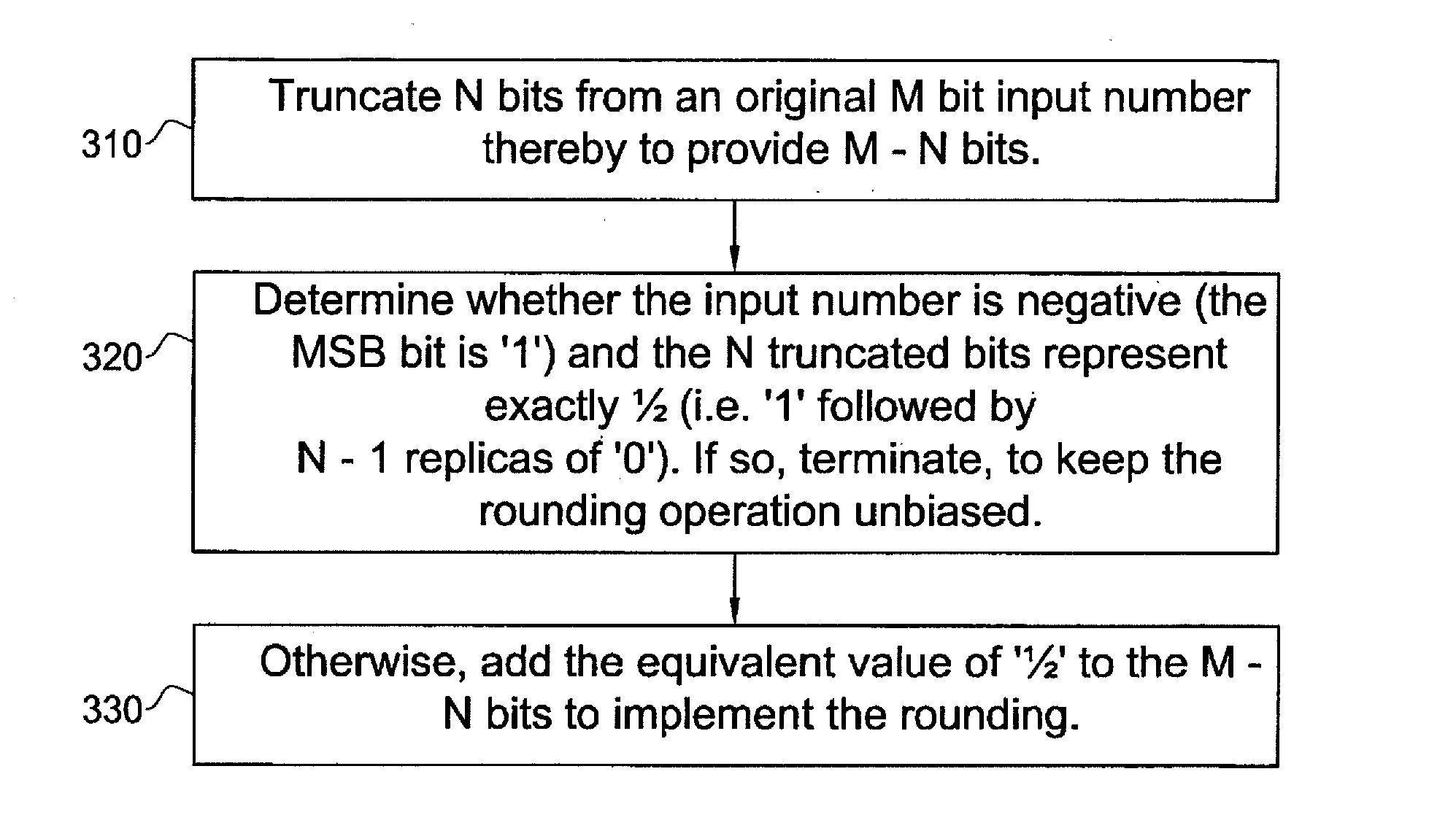
A system and method for unbiased rounding away from, or toward, zero comprising apparatus for truncating N bits from an original M bit input number thereby to provide a M−N bit number, and apparatus for adding the equivalent value of ‘½’ to the M−N bit number unless the input number is negative, or positive, respectively, and the N truncated bits represent exactly ½.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
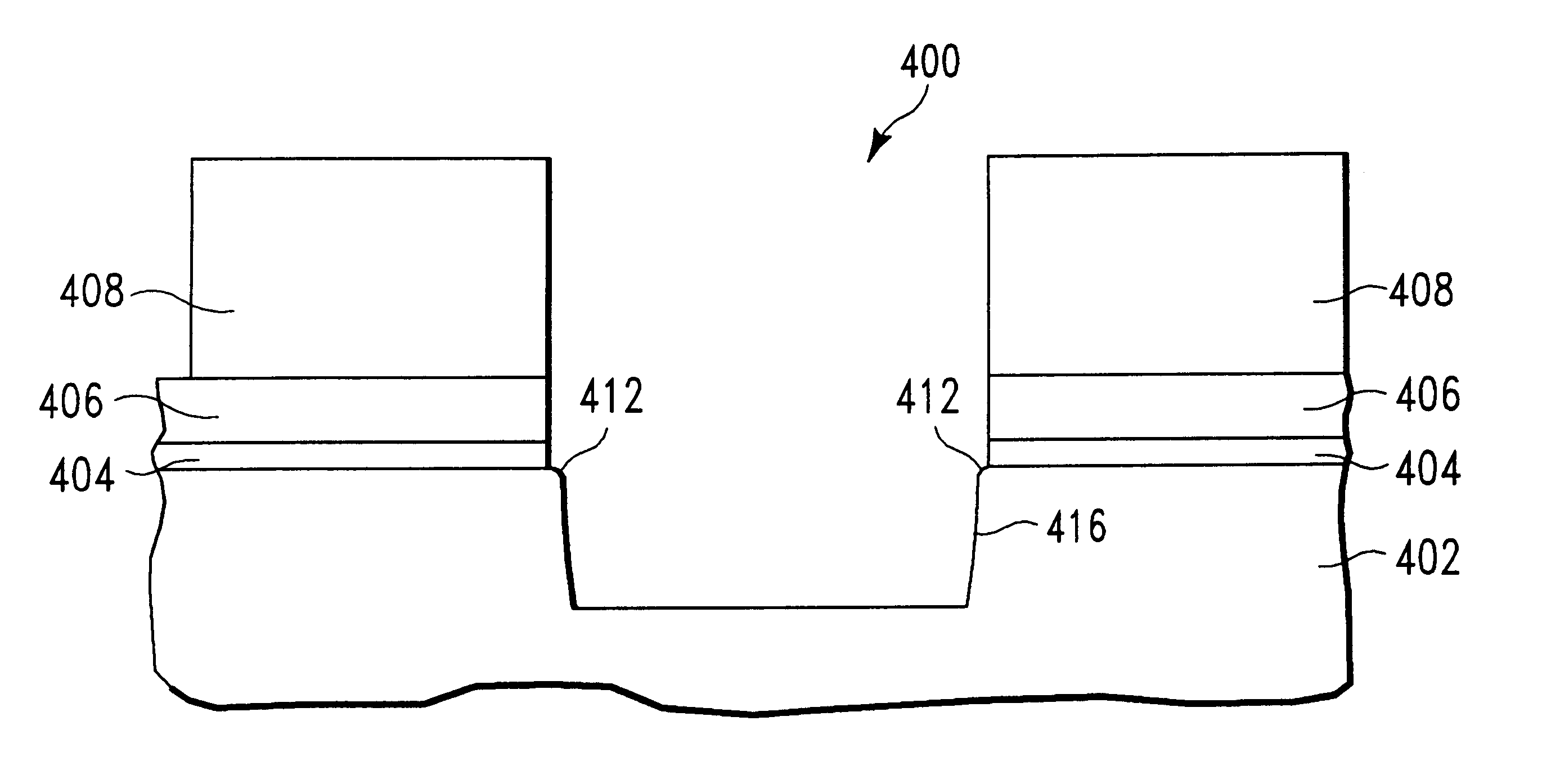
Metallization system of a semiconductor device comprising rounded interconnects formed by hard mask rounding
InactiveUS20110212616A1Increase widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoundingFilling materials
In sophisticated metallization systems, vertical contacts and metal lines may be formed on the basis of a dual inlaid strategy, wherein an edge rounding or corner rounding may be applied to the trench hard mask prior to forming the via openings on the basis of a self-aligned via trench concept. Consequently, self-aligned interconnect structures may be obtained, while at the same time providing superior fill conditions during the deposition of barrier materials and conductive fill materials.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
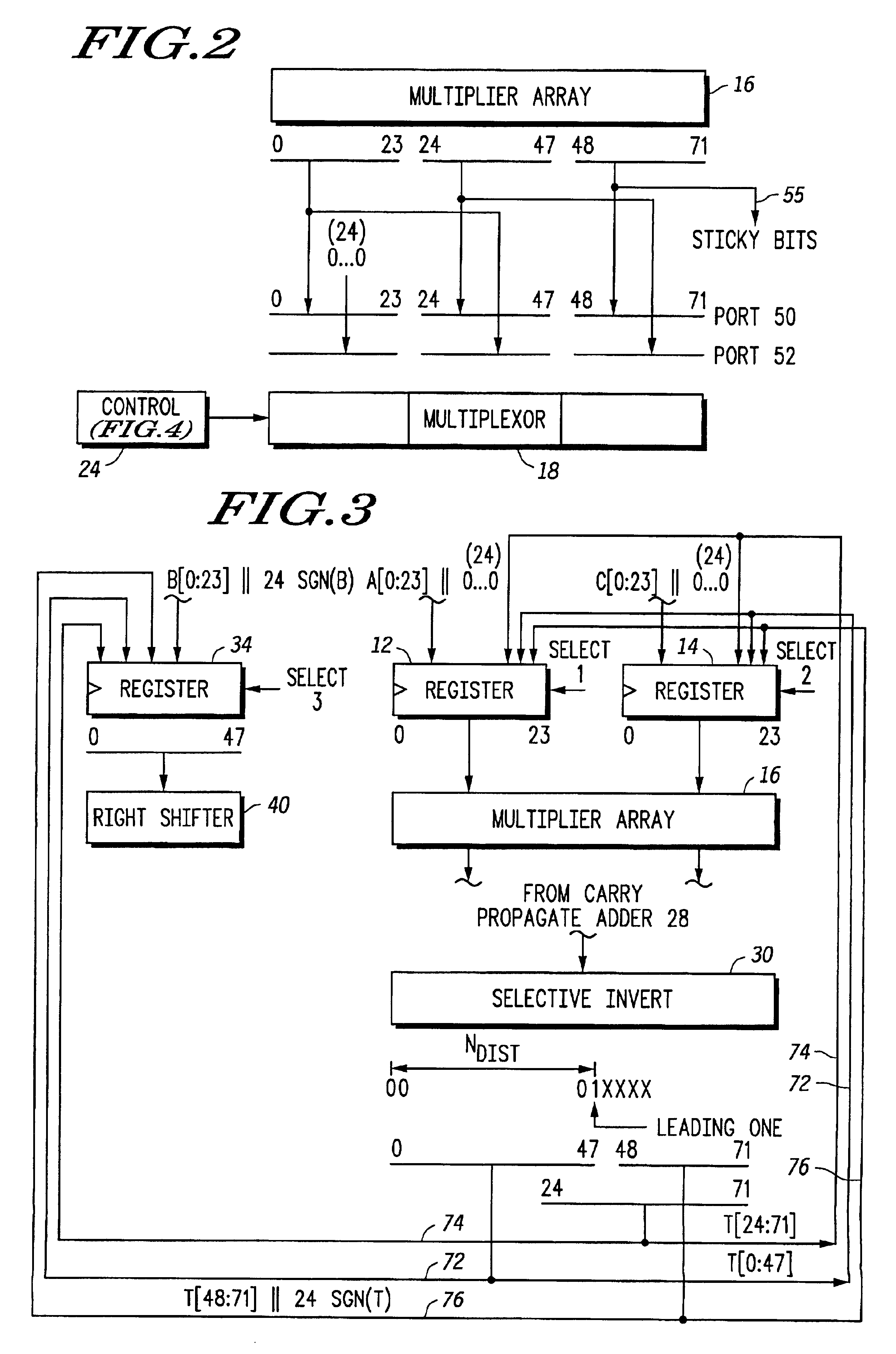
Method and apparatus for rounding and normalizing results within a multiplier
InactiveUS6269384B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and calculating a rounded products
InactiveUS6038583ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
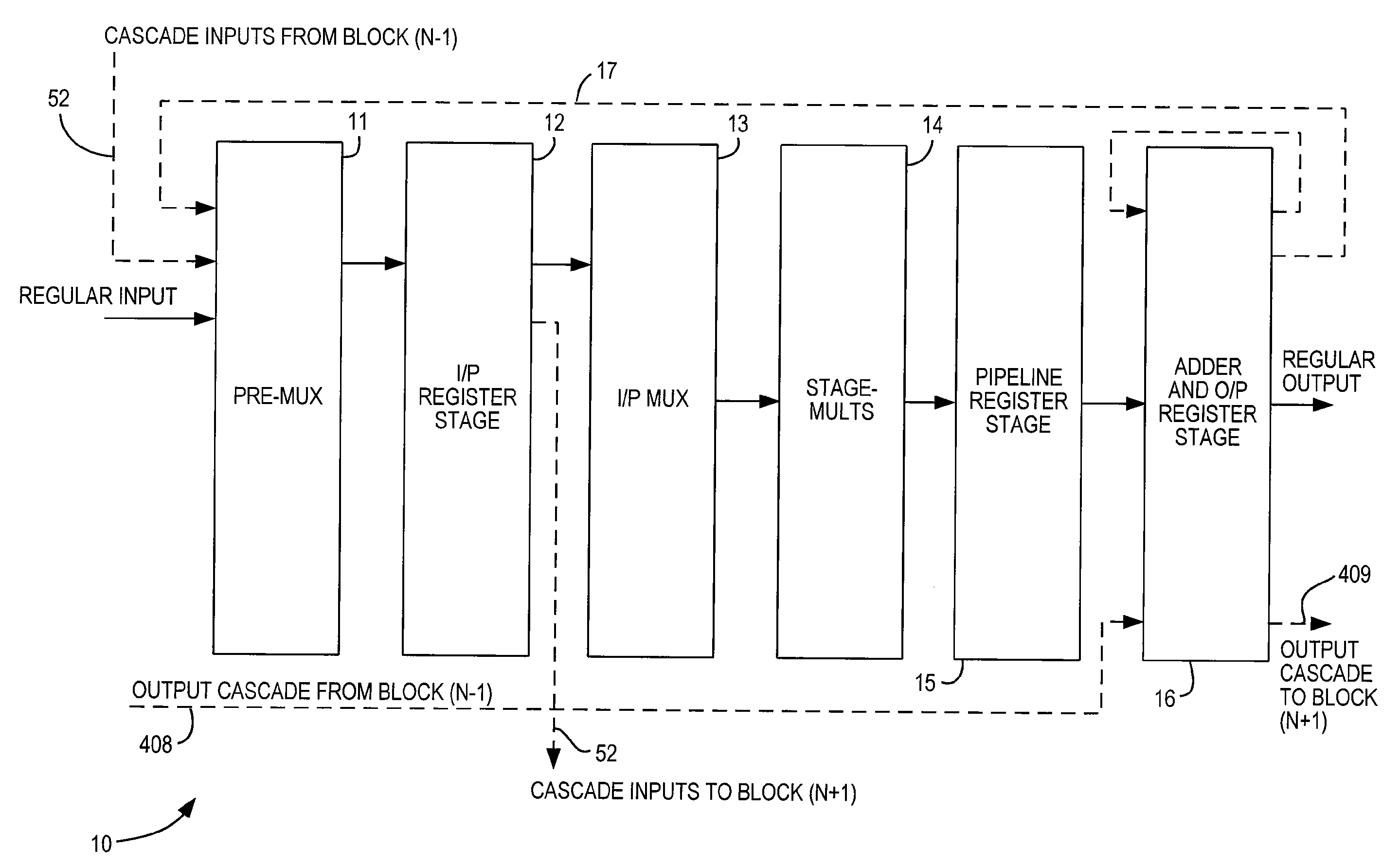
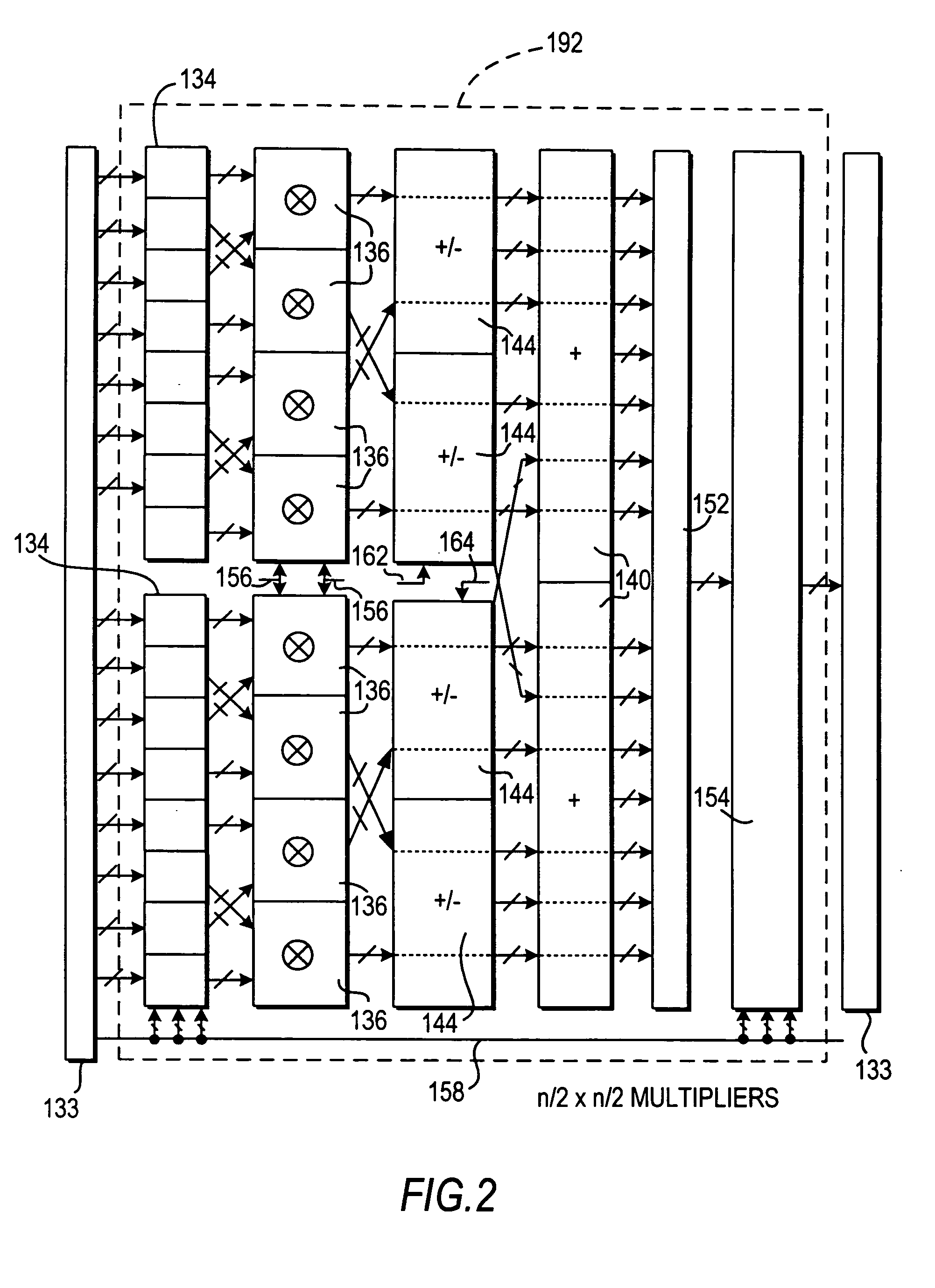
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
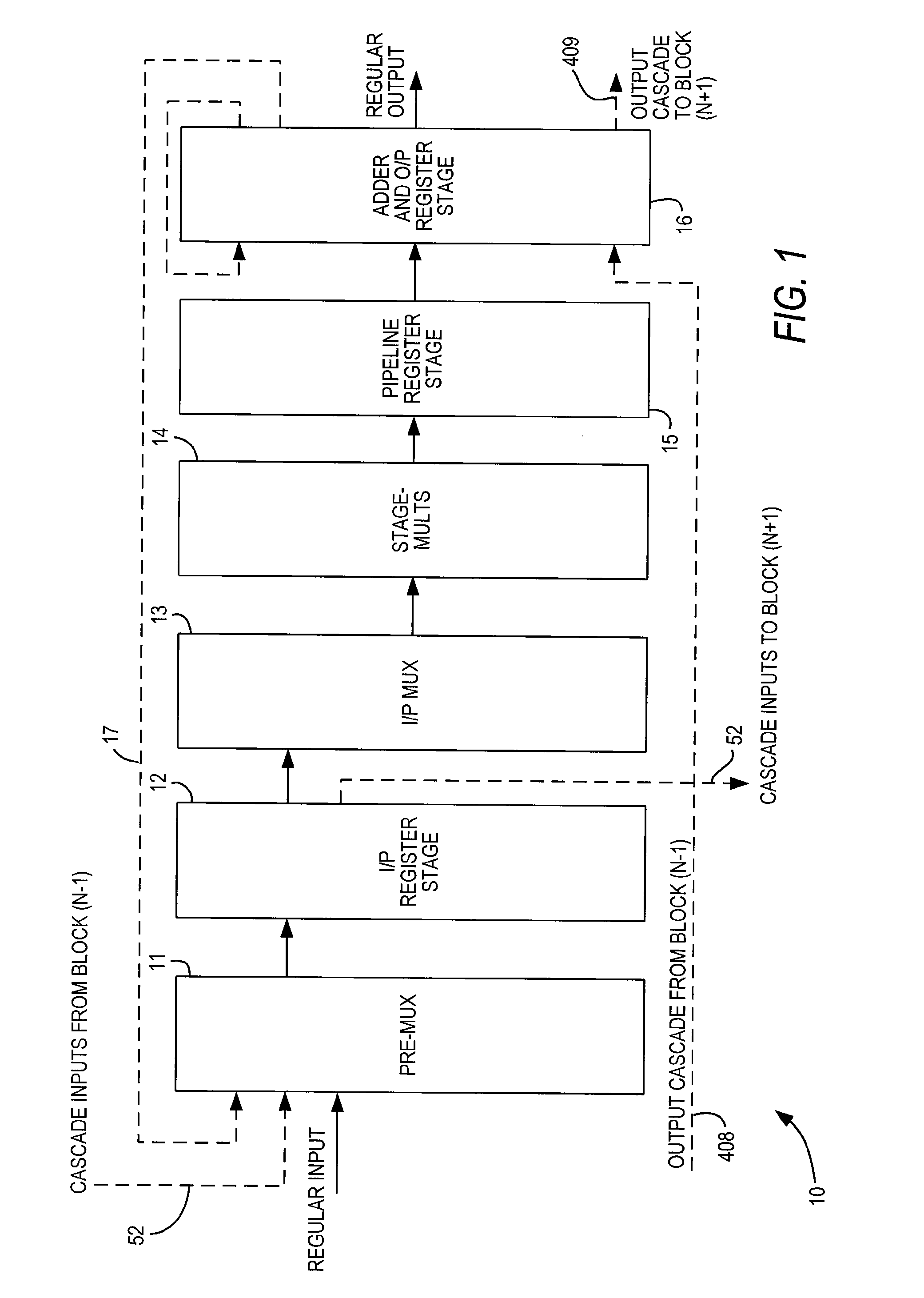
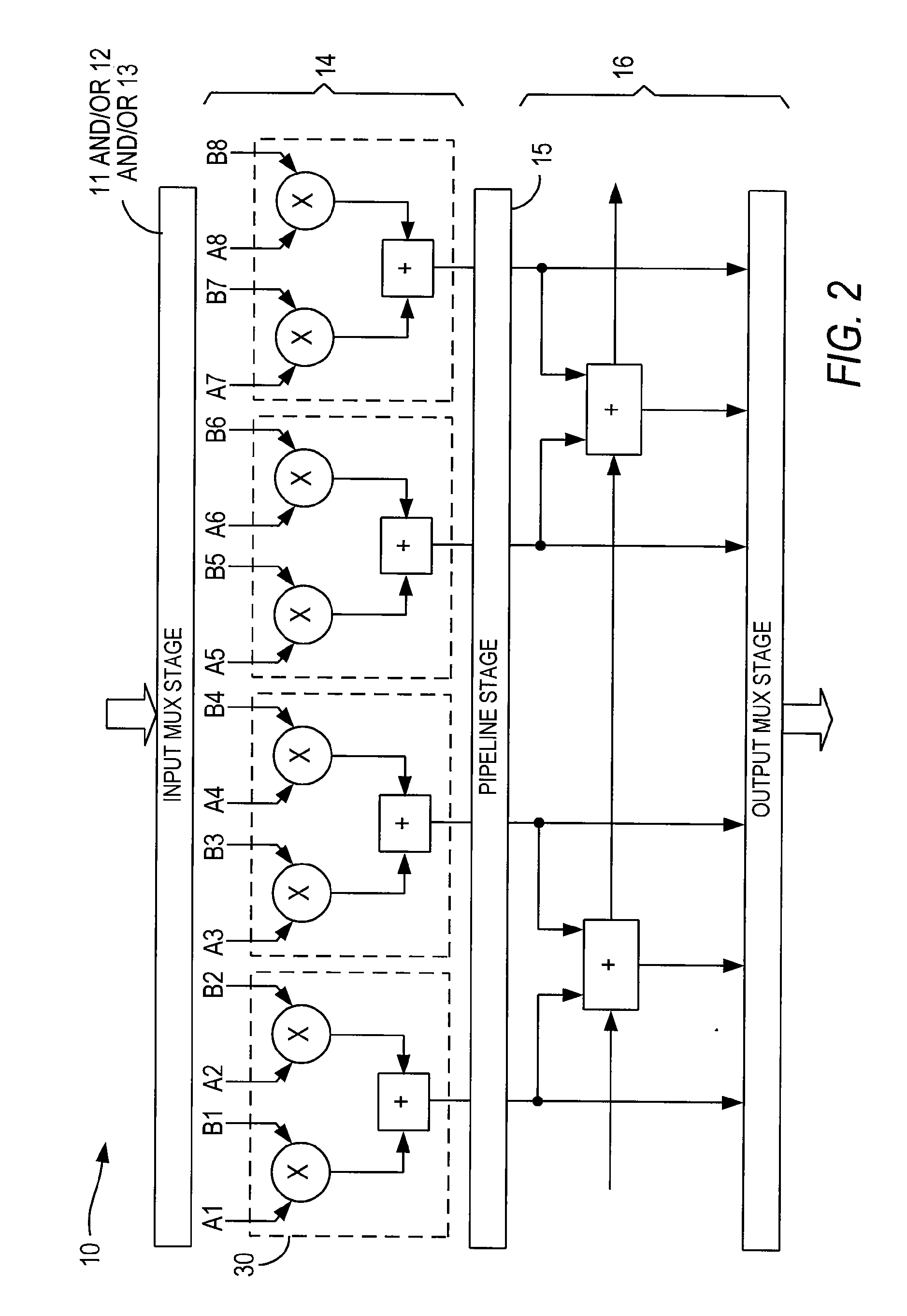
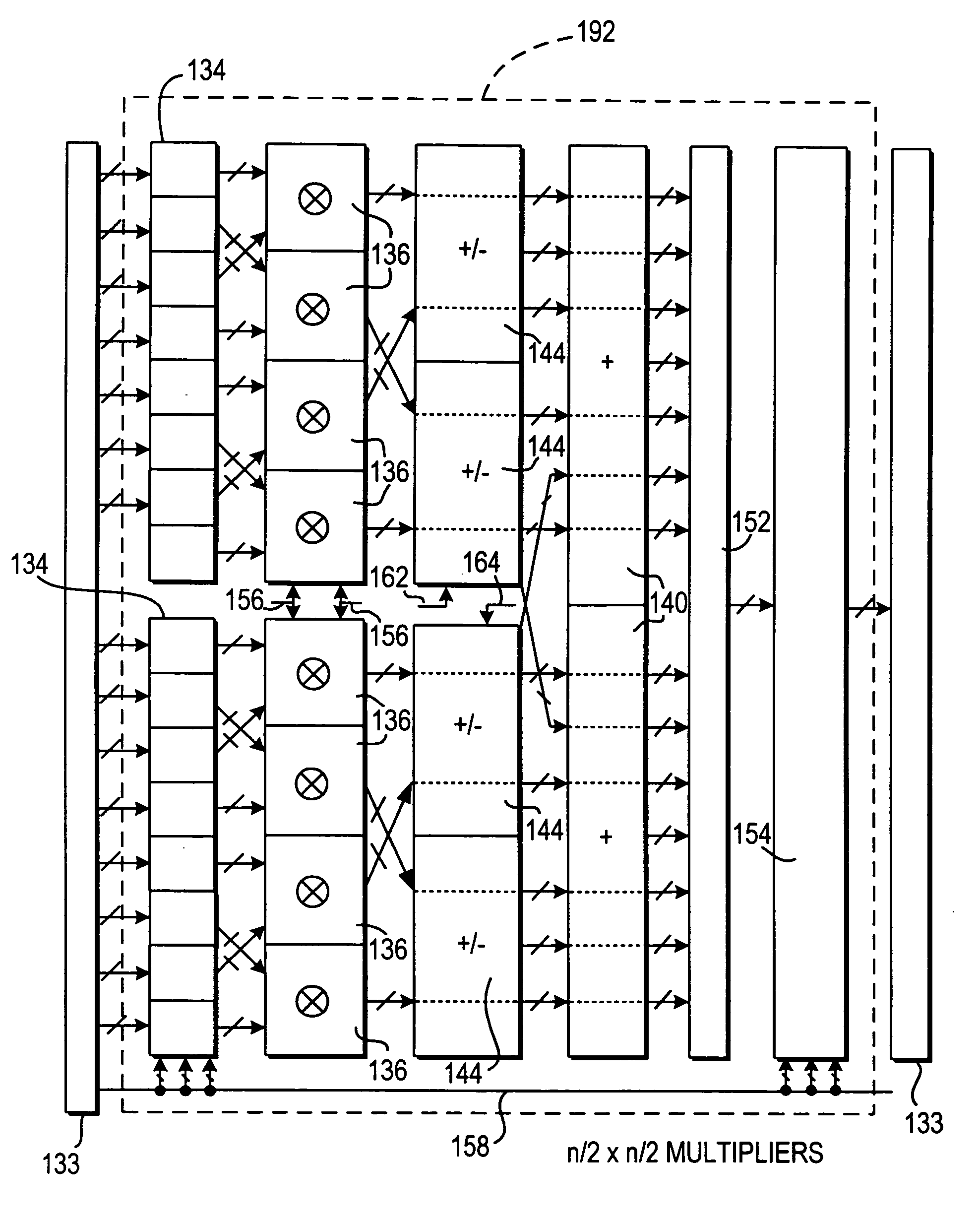
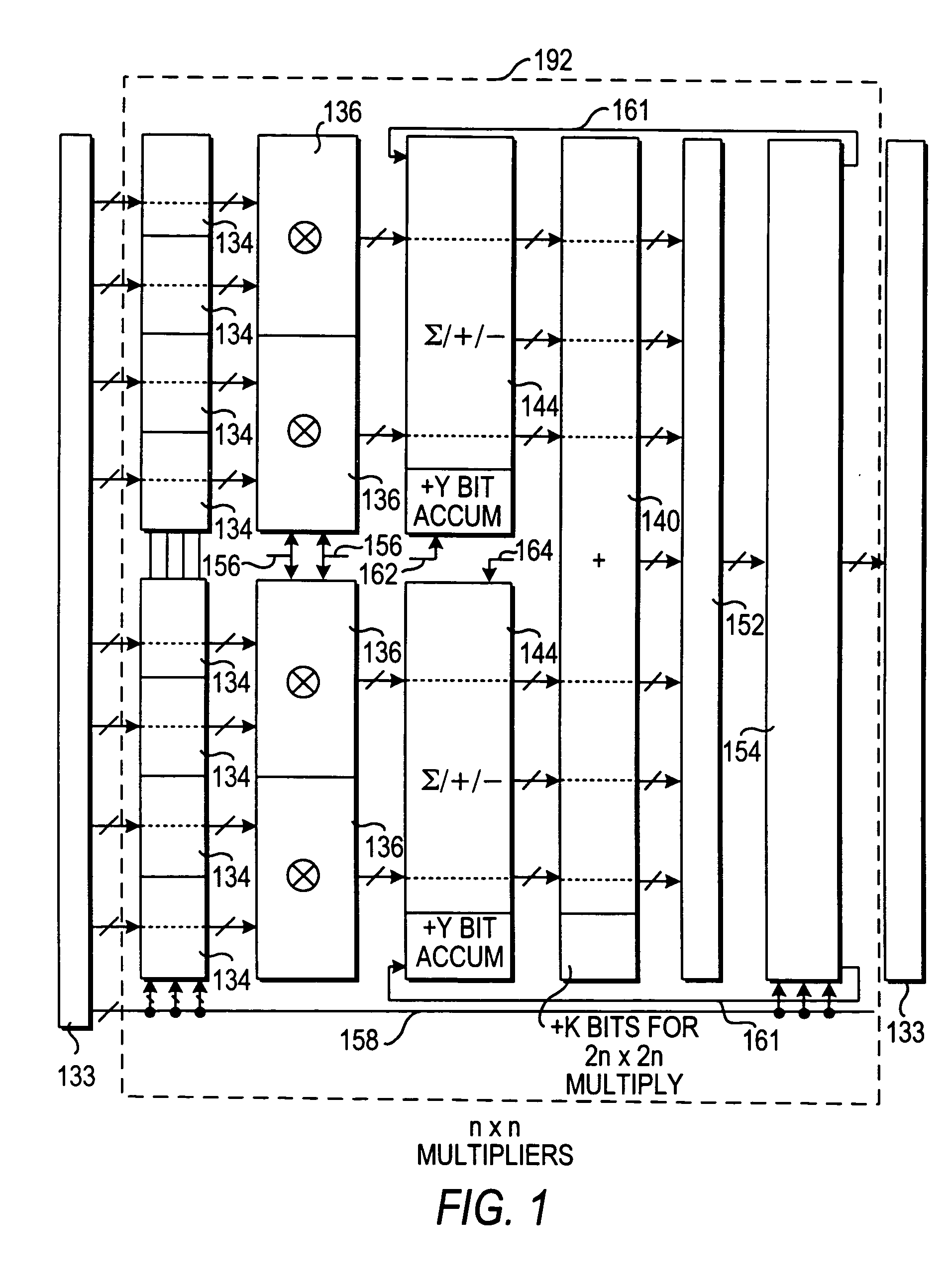
ActiveUS20070185951A1Improved roundingImproved rounding and saturationDigital computer detailsLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsRoundingProgrammable logic device
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device includes circuitry for performing multiplications and sums thereof, as well as circuitry for rounding the result. The rounding circuitry can selectably perform round-to-nearest and round-to-nearest-even operations. In addition, the bit position at which rounding occurs is preferably selectable. The specialized processing block preferably also includes saturation circuitry to prevent overflows and underflows, and the bit position at which saturation occurs also preferably is selectable. The selectability of both the rounding and saturation positions provides control of the output data word width. The rounding and saturation circuitry may be selectably located in different positions based on timing needs. Similarly, rounding may be speeded up using a look-ahead mode in which both rounded and unrounded results are computed in parallel, with the rounding logic selecting between those results.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Saturation and rounding in multiply-accumulate blocks
ActiveUS20050187999A1Provide capabilityEasy to useComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingBinary multiplier
Saturation and rounding capabilities are implemented in MAC blocks to provide rounded and saturated outputs of multipliers and of add-subtract-accumulate circuitrs implemented using DSP. These features support any suitable format of value representation, including the x.15 format. Circuitry within the multipliers and the add-subtract-accumulate circuits implement the rounding and saturation features of the present invention.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
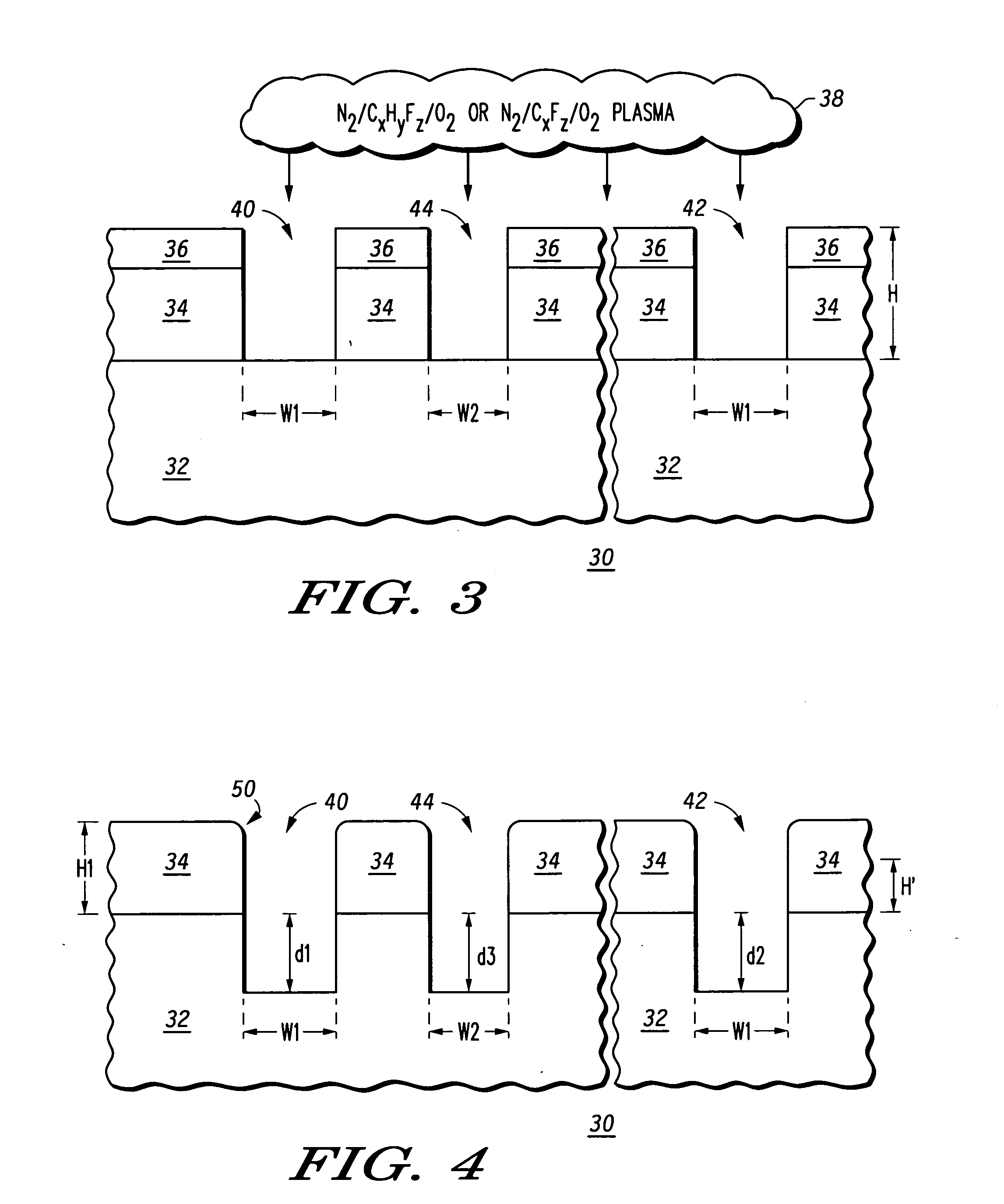
Method for etching a trench having rounded top corners in a silicon substrate
The present disclosure includes a method of plasma etching a trench having rounded top corners in a silicon substrate. One embodiment includes the following general steps: a) providing a semiconductor structure comprising a hard masking layer, overlying a silicon substrate; b) plasma etching through said hard masking layer and any additional underlying layers overlying said silicon substrate using at least one plasma feed gas which does not provide polymer deposition on surfaces of said semiconductor structure during etching; where said plasma etching exposes a face of said silicon substrate; and c) plasma etching at least a first portion of a trench into said silicon substrate using reactive species generated from a feed gas comprising a source of fluorine, a source of carbon, a source of hydrogen, and a source of high energy species which provide physical bombardment of said silicon substrate. Top corner rounding is effected by deposition of a thin layer of polymer on a top corner of the trench during etching of the first portion of the trench, resulting in the formation of a rounded "shoulder" at the top corner of the trench. Typically a layer of silicon oxide overlies at least a portion of the silicon substrate surface. The method described provides excellent critical dimension control over the active area of a transistor produced using the method and reduces the need to remove polymer from substrate and reactor surfaces after etching of the silicon trench.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
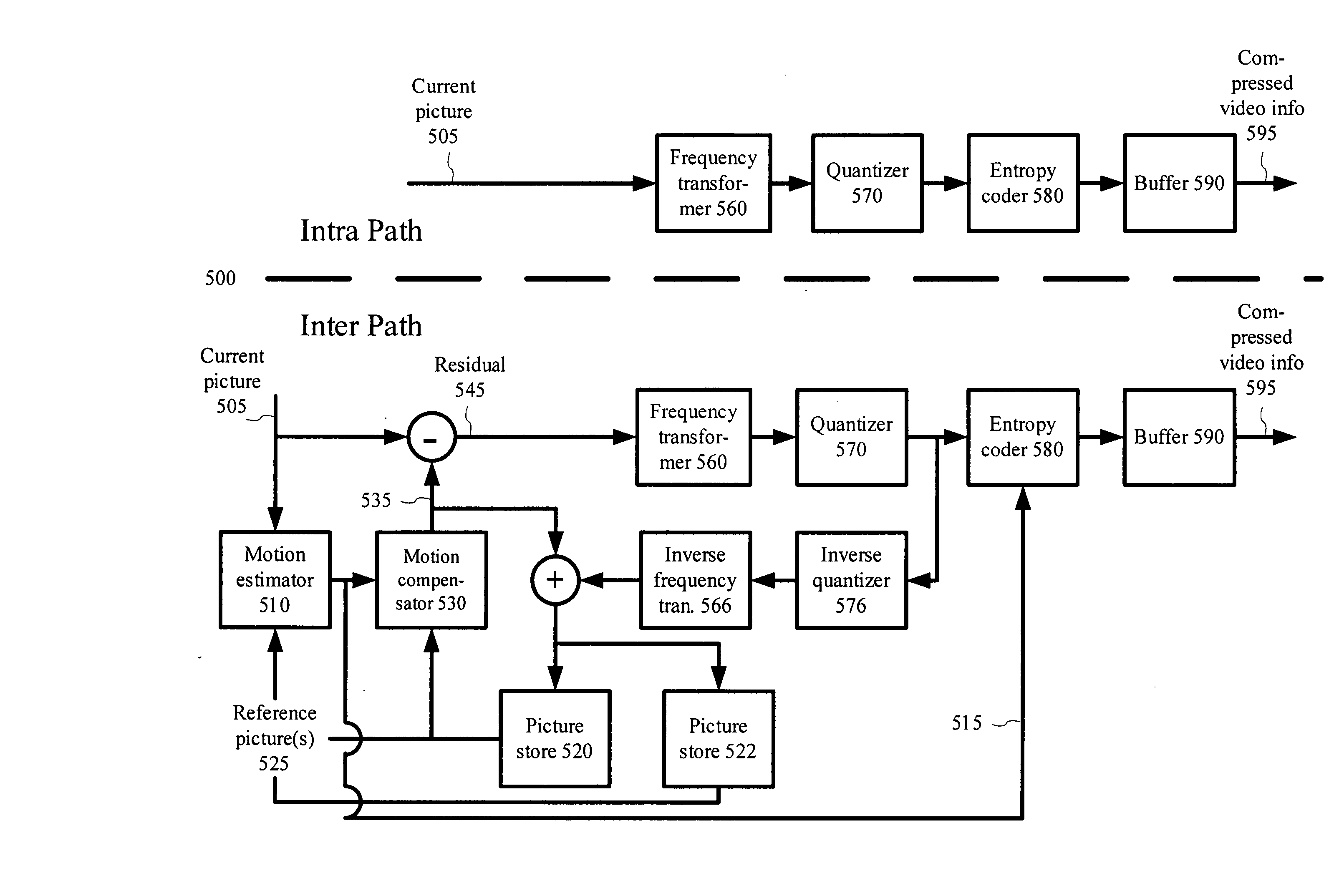
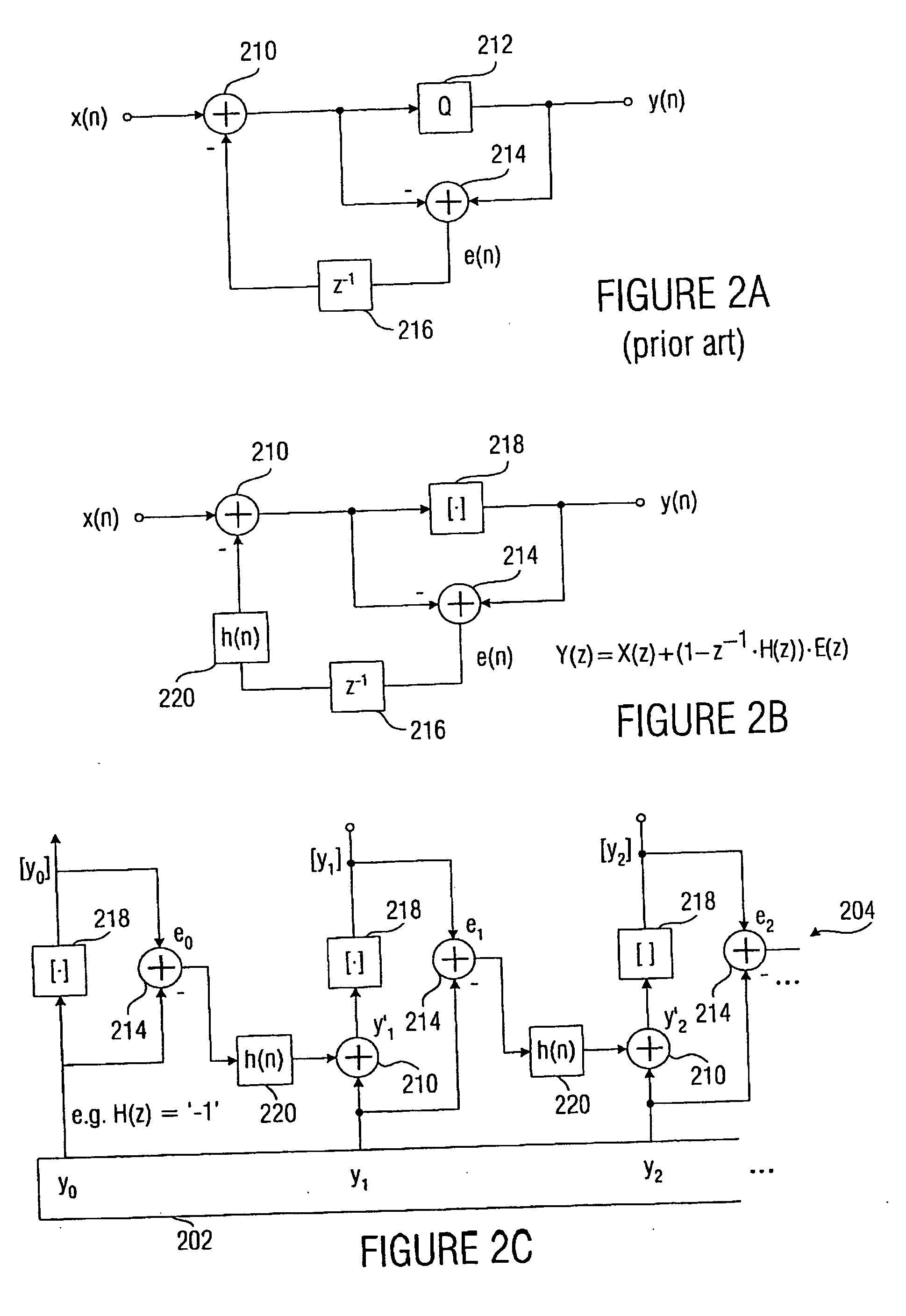
Estimating sample-domain distortion in the transform domain with rounding compensation
ActiveUS20070237236A1Improve accuracyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRoundingComputer vision
Techniques and tools are described for compensating for rounding when estimating sample-domain distortion in the transform domain. For example, a video encoder estimates pixel-domain distortion in the transform domain for a block of transform coefficients after compensating for rounding in the DC coefficient of the block. In this way, the video encoder improves the accuracy of pixel-domain distortion estimation but retains the computational advantages of performing the estimation in the transform domain. Rounding compensation includes, for example, looking up an index (from a de-quantized transform coefficient) in a rounding offset table to determine a rounding offset, then adjusting the coefficient by the offset. Other techniques and tools described herein are directed to creating rounding offset tables and encoders that make encoding decisions after considering rounding effects that occur after an inverse frequency transform on de-quantized transform coefficient values.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
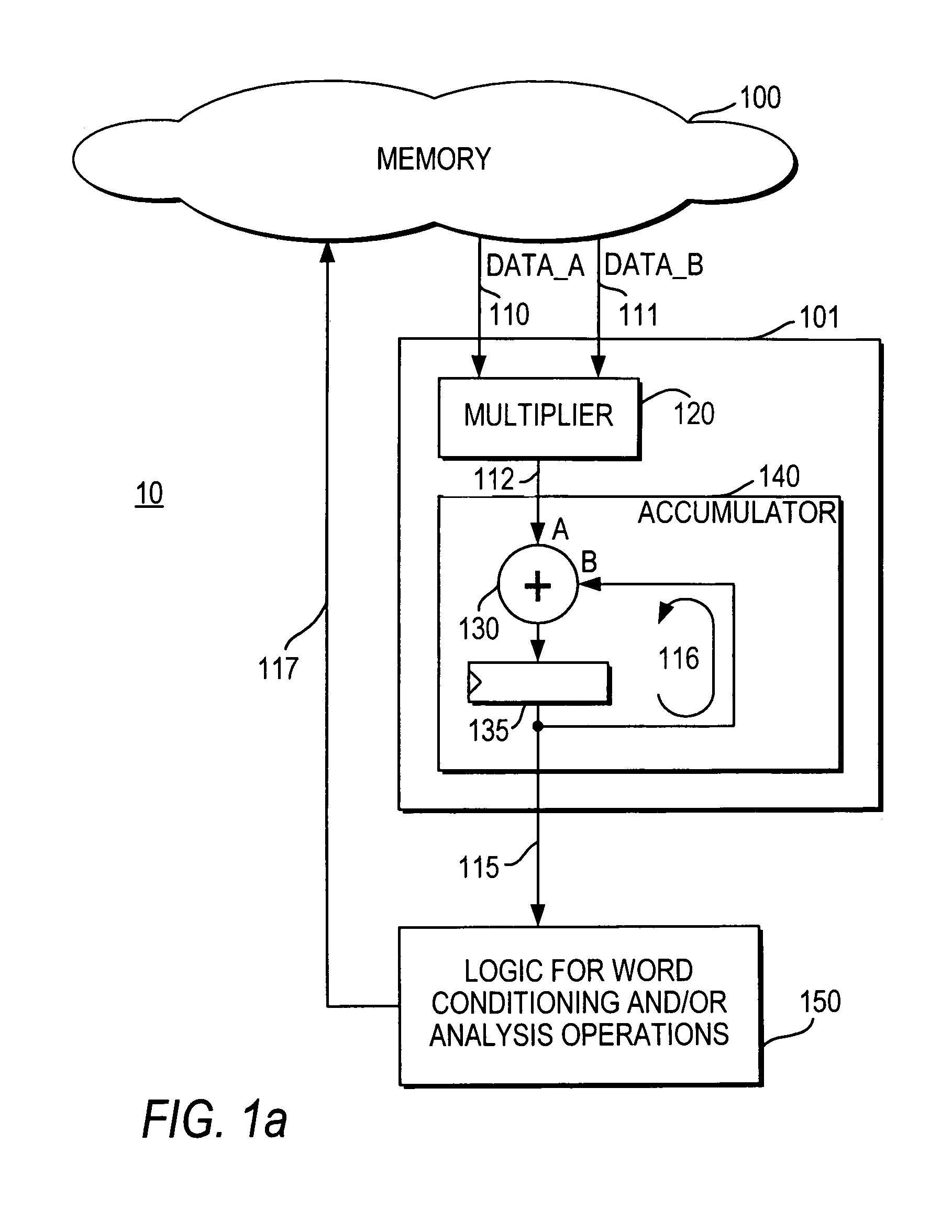
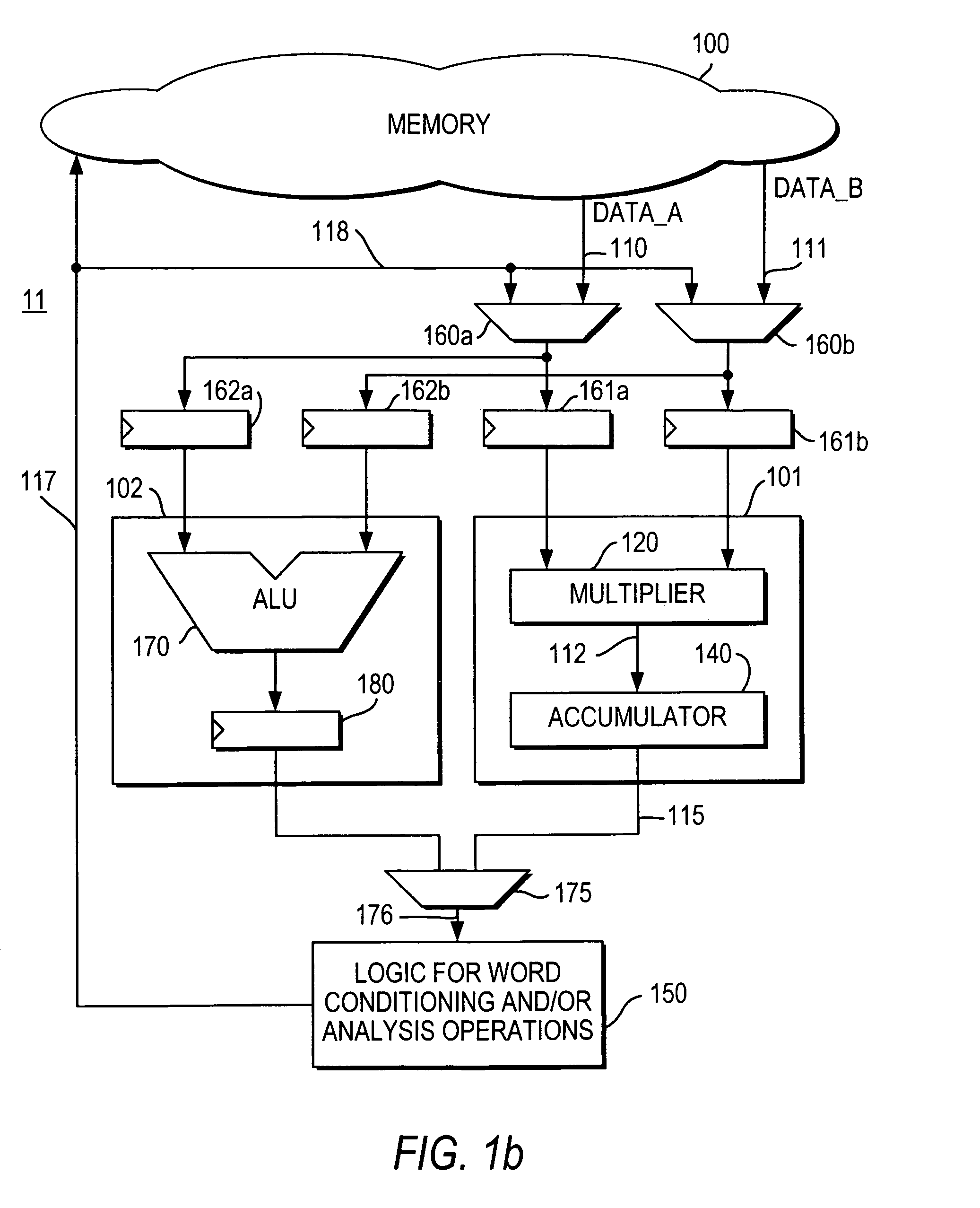
DSP processor architecture with write datapath word conditioning and analysis
InactiveUS6978287B1Improve throughputReduce delaysDigital computer detailsProgram controlRoundingBlock floating-point
Owner:ALTERA CORP
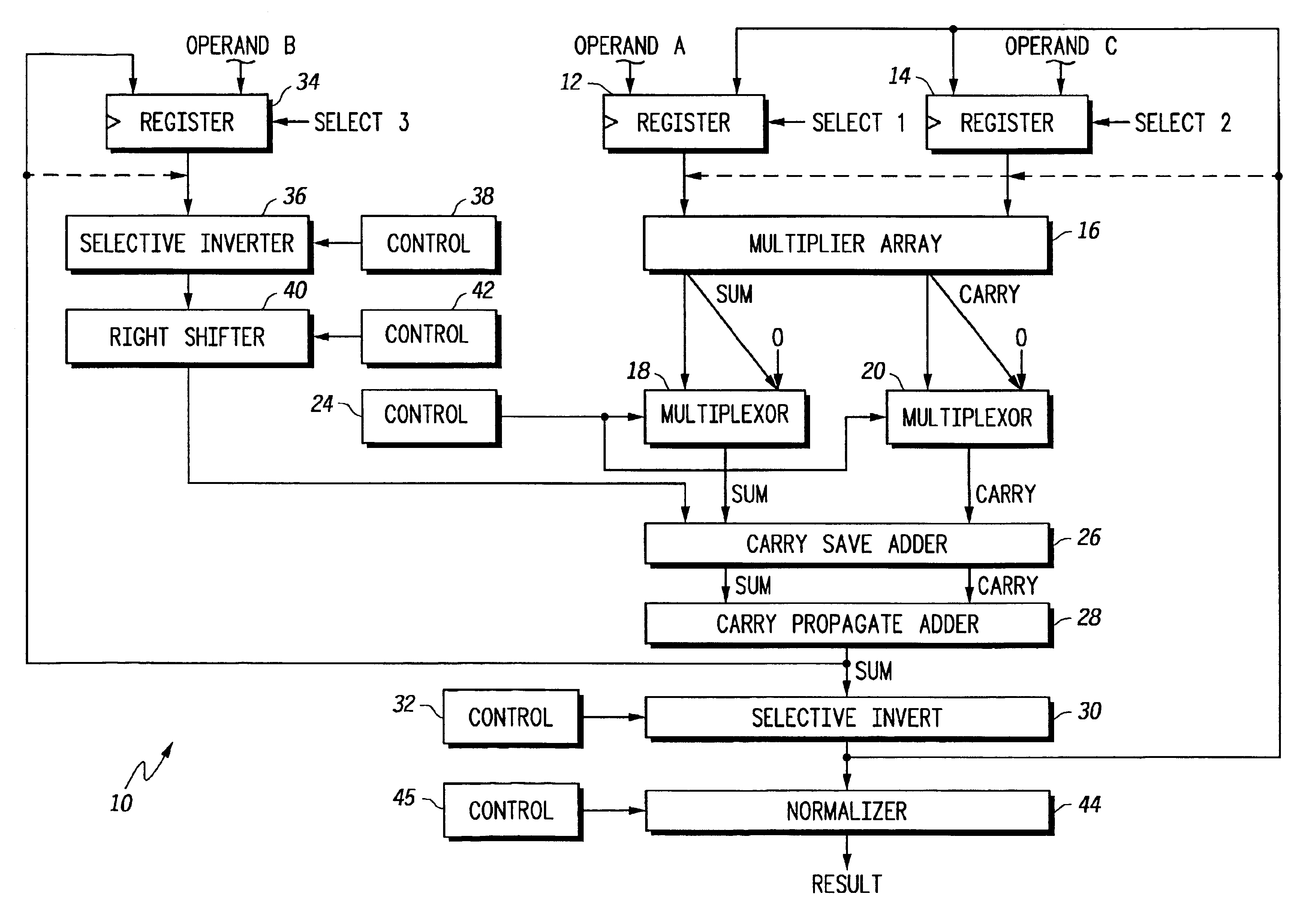
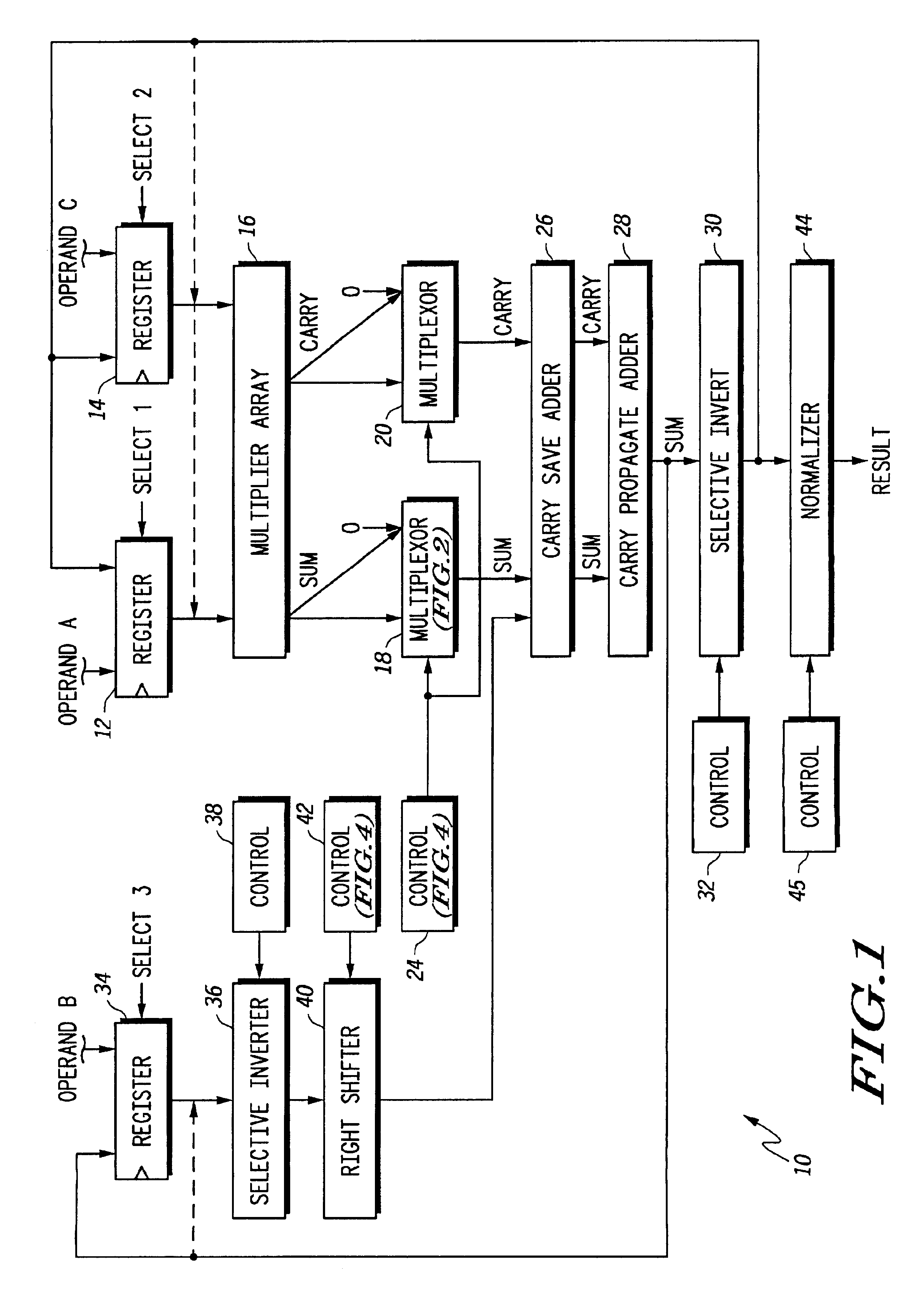
Floating point multiplier/accumulator with reduced latency and method thereof
A circuit (10) for multiplying two floating point operands (A and C) while adding or subtracting a third floating point operand (B) removes latency associated with normalization and rounding from a critical speed path for dependent calculations. An intermediate representation of a product and a third operand are selectively shifted to facilitate use of prior unnormalized dependent resultants. Logic circuitry (24, 42) implements a truth table for determining when and how much shifting should be made to intermediate values based upon a resultant of a previous calculation, upon exponents of current operands and an exponent of a previous resultant operand. Normalization and rounding may be subsequently implemented, but at a time when a new cycle operation is not dependent on such operations even if data dependencies exist.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
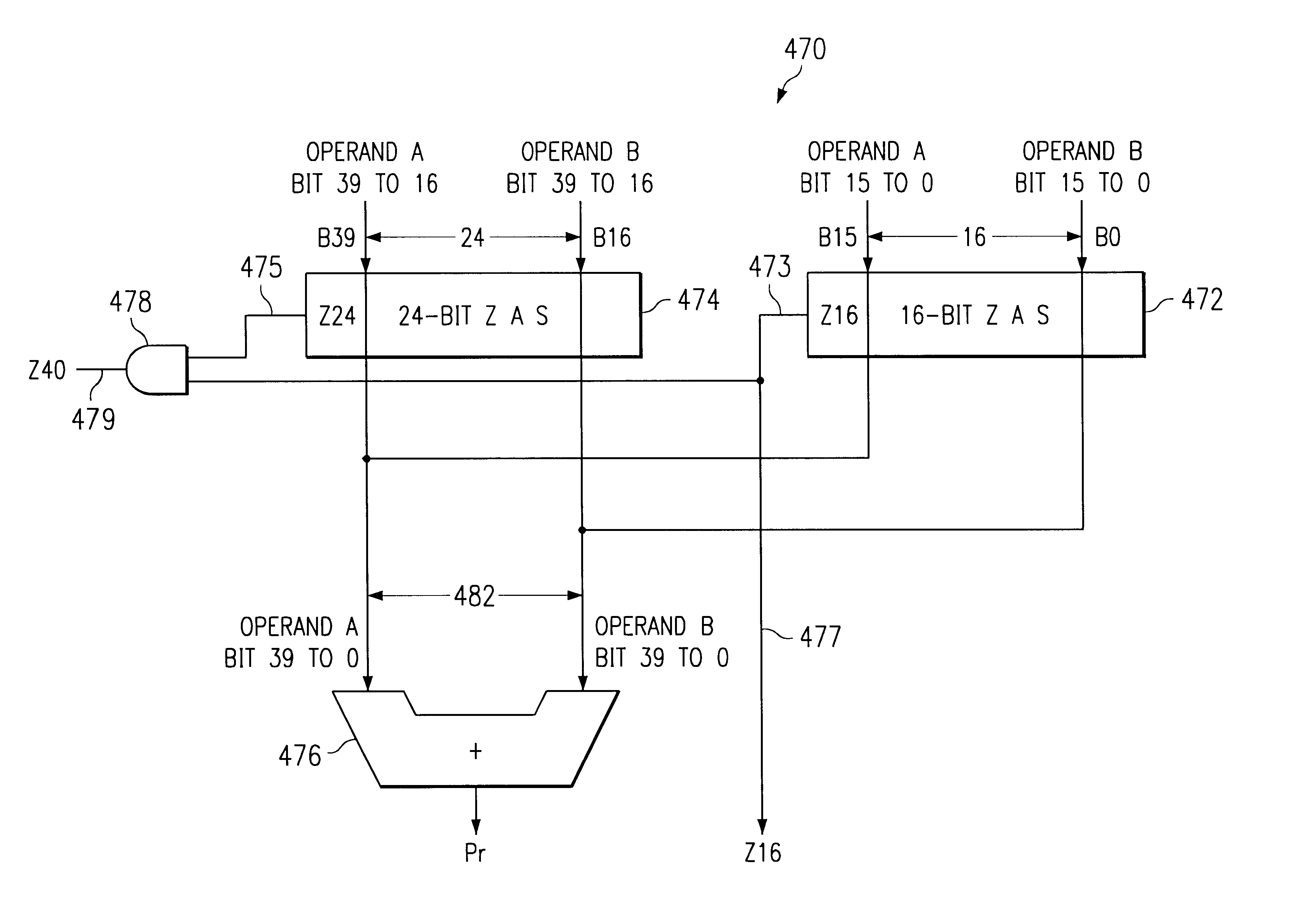
Rounding mechanisms in processors
InactiveUS7047272B2Efficient hardware implementationComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsRoundingAlgorithm
An arithmetic unit, for example a multiply and accumulate (MAC) unit 42, for a processing engine includes a partial product reduction tree 480. The partial product reduction tree will generate carry results and provides a final output to a final adder 470 connected to the partial production reduction tree. Unbiased rounding logic 476 is provided. A carry propagation tree is responsive to the carry results for anticipating a zero on each of N least significant bits of the final adder. When zero is anticipated on each of N least significant bits of the final adder, the carry propagation tree is operable to generate an output signal 477 which is used by the unbiased rounding stage to force the (N+1)th least significant bit of the final adder to zero. Through the use of a carry propagation tree to predict, or anticipate zeros on the N least significant bits, unbiased rounding can be effected without a time penalty in that a carry propagation tree can be configured to be at least a rapid as the carry propagation of the final adder. Where a zero anticipation function is provided, this can also be mapped onto the carry propagation tree, thus providing an efficient hardware implementation through sharing of that hardware between functions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Perpendicular head with trailing shield and rhodium gap process
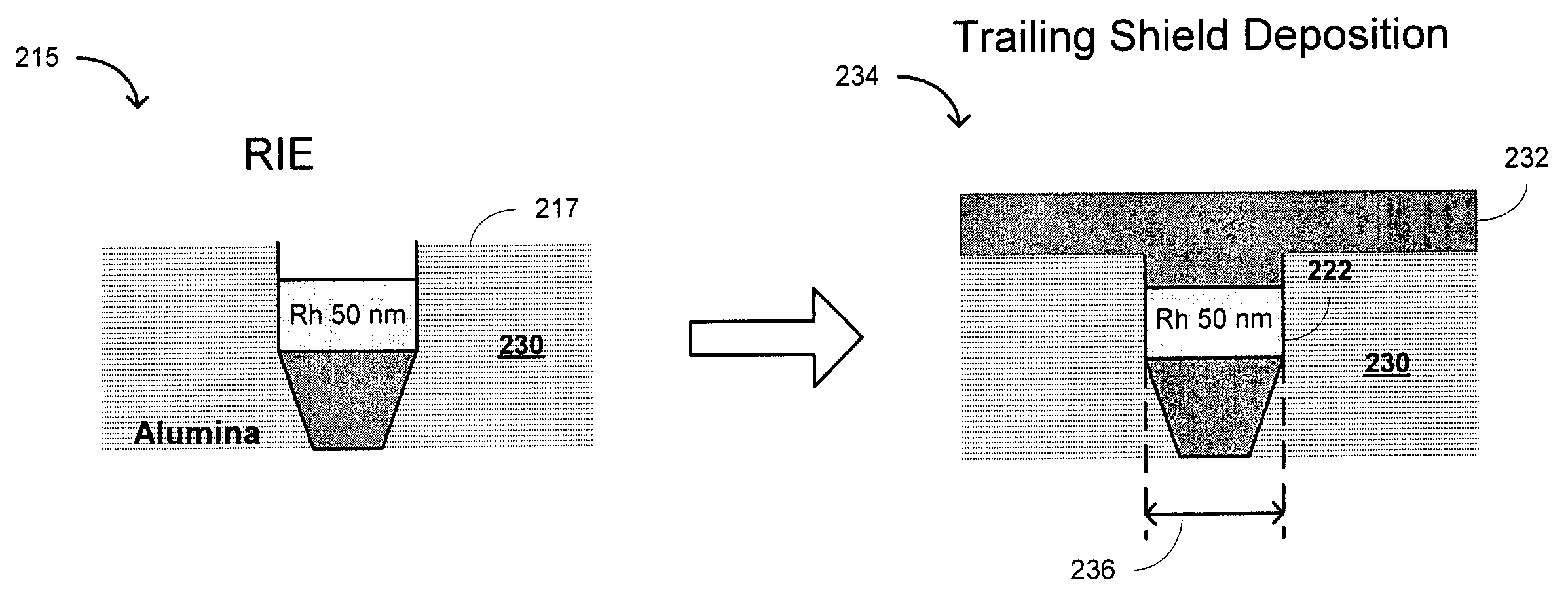
A perpendicular write head including a main pole and a trailing shield, the main pole being made of a diamond-like carbon (DLC) layer as hard mask and a rhodium (Rh) layer as shield gap, both DLC and Rh layers being CMP stop layers so as to avoid corner rounding and damage from chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process, the DLC layer being removed by reactive ion etching (RIE) to create a trench, the trailing shield being deposited into the trench for self alignment.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method for etching a quartz layer in a photoresistless semiconductor mask
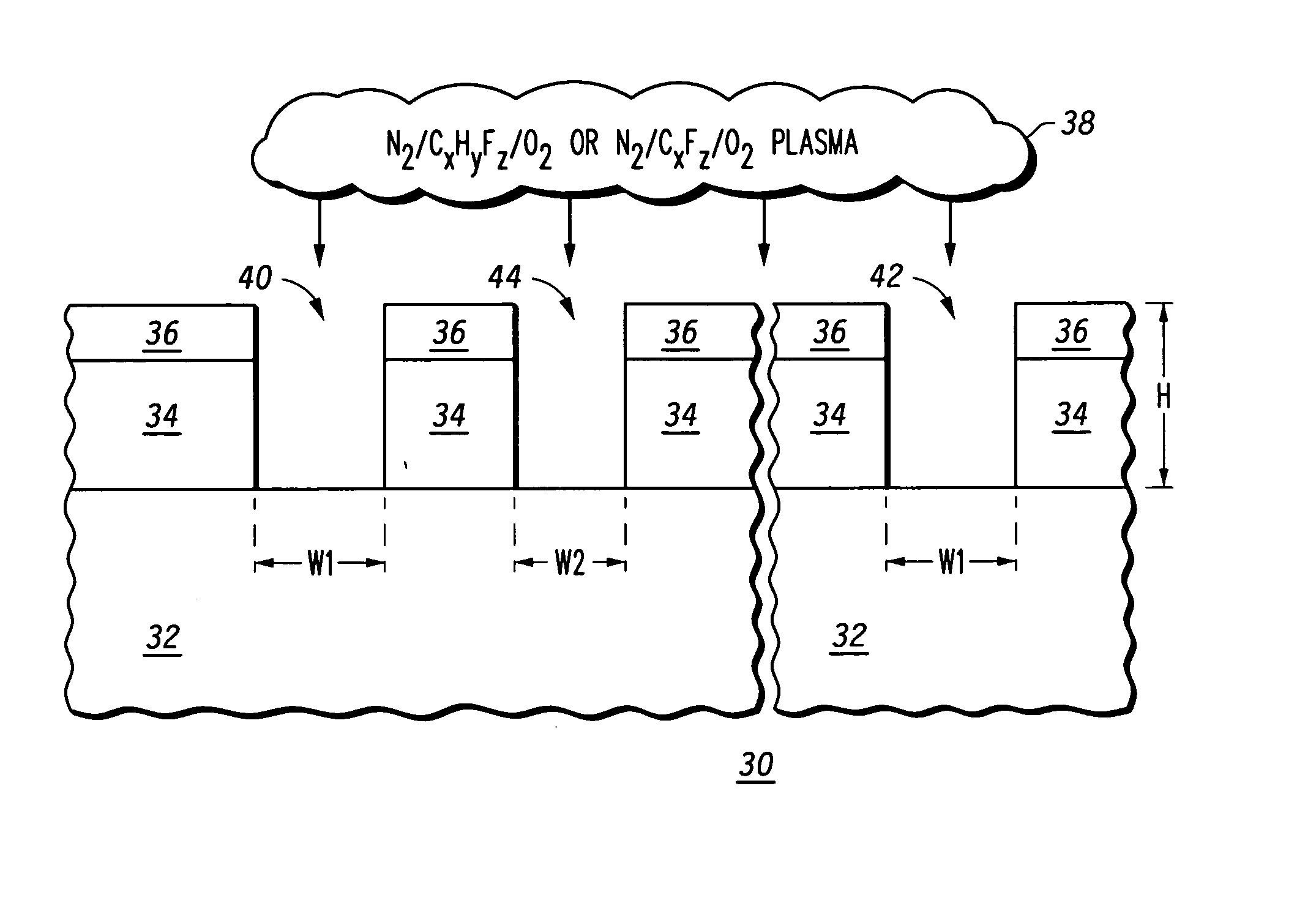
ActiveUS20050164514A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoundingLithographic artist
A chromeless phase lithography mask (30) that does not require photoresist to manufacture has a quartz substrate (32) is etched by using a plasma (38) containing one of a nitrogen augmented hydro-fluorocarbon oxygen mixture and a nitrogen augmented fluorocarbon oxygen mixture. Various hydro-fluorocarbons or fluorocarbons may be used. The nitrogen addition results in etched openings in the quartz substrate that have substantially vertical sidewalls in a uniform manner across the substrate. Surface roughness is minimized and edges of the openings are well-defined with minimal rounding. The etch rate is rendered controllable by reducing bias power without degrading a desired vertical sidewall profile.
Owner:NXP USA INC
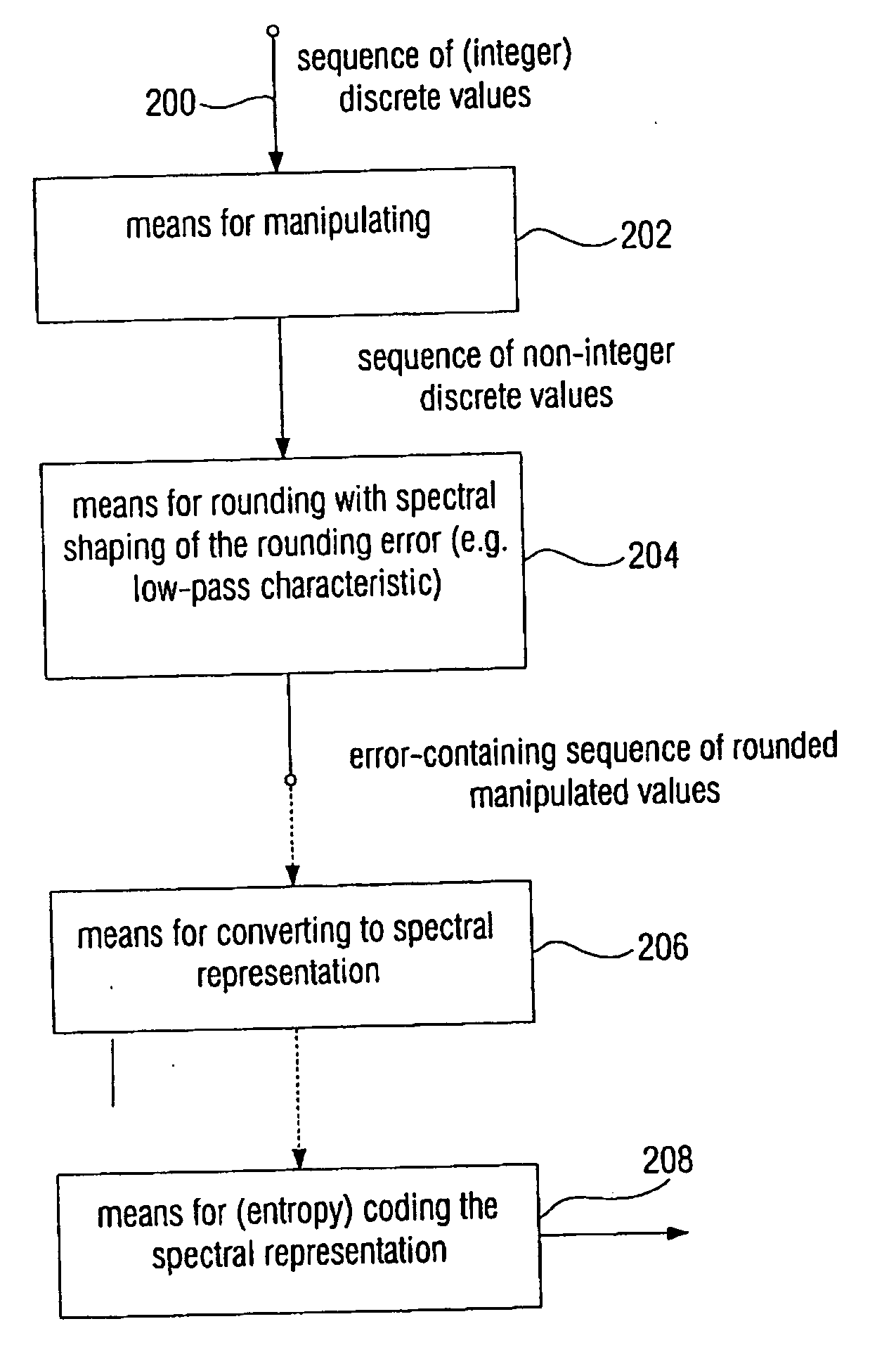
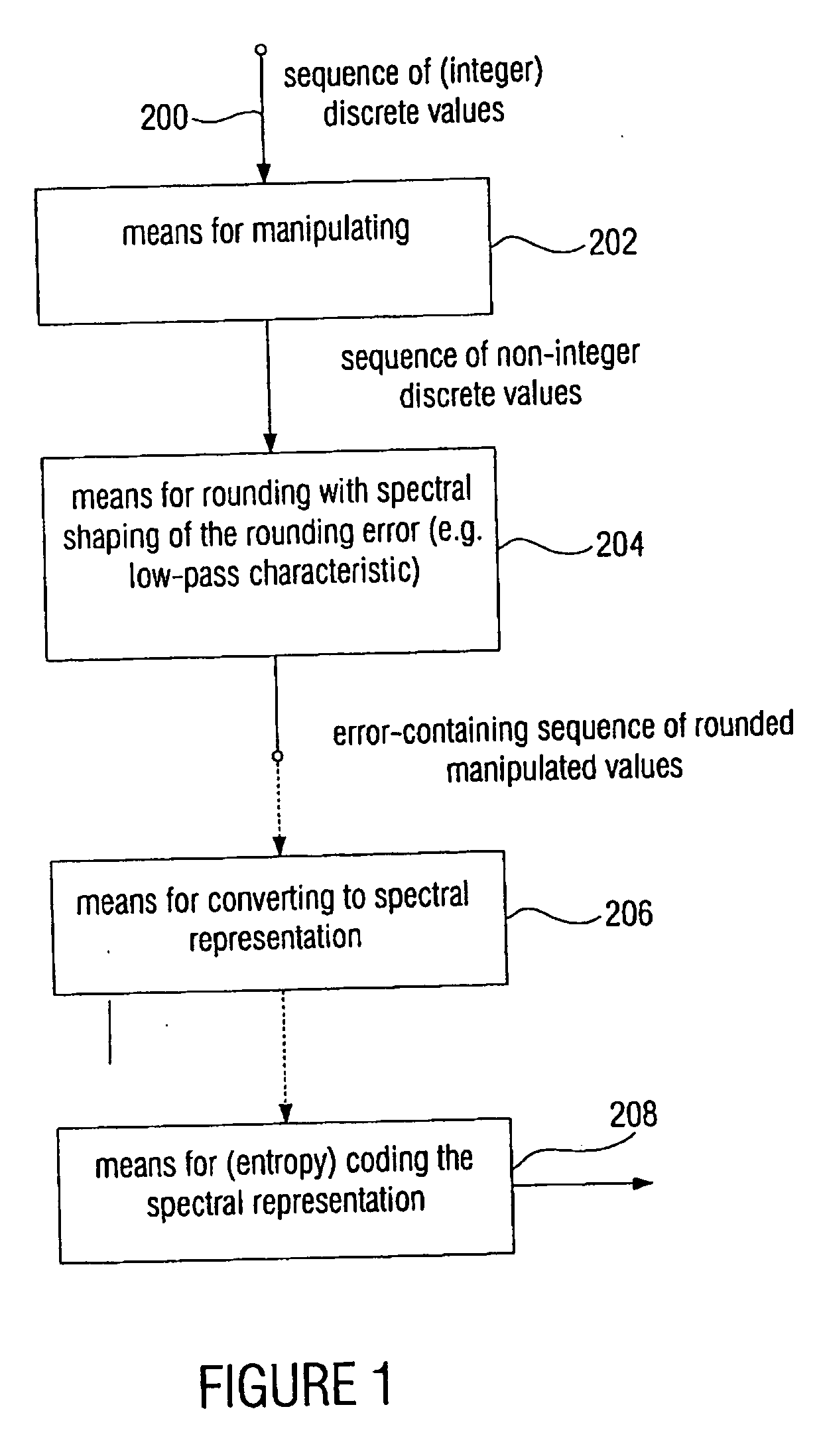
Device and method for processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values
ActiveUS20060210180A1Few rounding errorIncrease the number ofSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLossless codingFrequency spectrum
When processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values, wherein there is a first frequency range, in which the signal has a high energy, and wherein there is a second frequency range, in which the signal has a low energy, the sequence of discrete values is first manipulated to obtain a sequence of manipulated values, so that at least one of the manipulated values is non-integer. Then the sequence of manipulated values is rounded to obtain a sequence of manipulated values. The rounding is formed to effect a spectral shaping of a generated rounding error so that a spectrally shaped rounding error has a higher energy in the first frequency range than in the second frequency range. By spectrally shaping the rounding error so that the rounding error does not have any energy either in the storage areas where there is no signal energy, an especially efficient coding is obtained particularly in connection with a lossless coding context.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
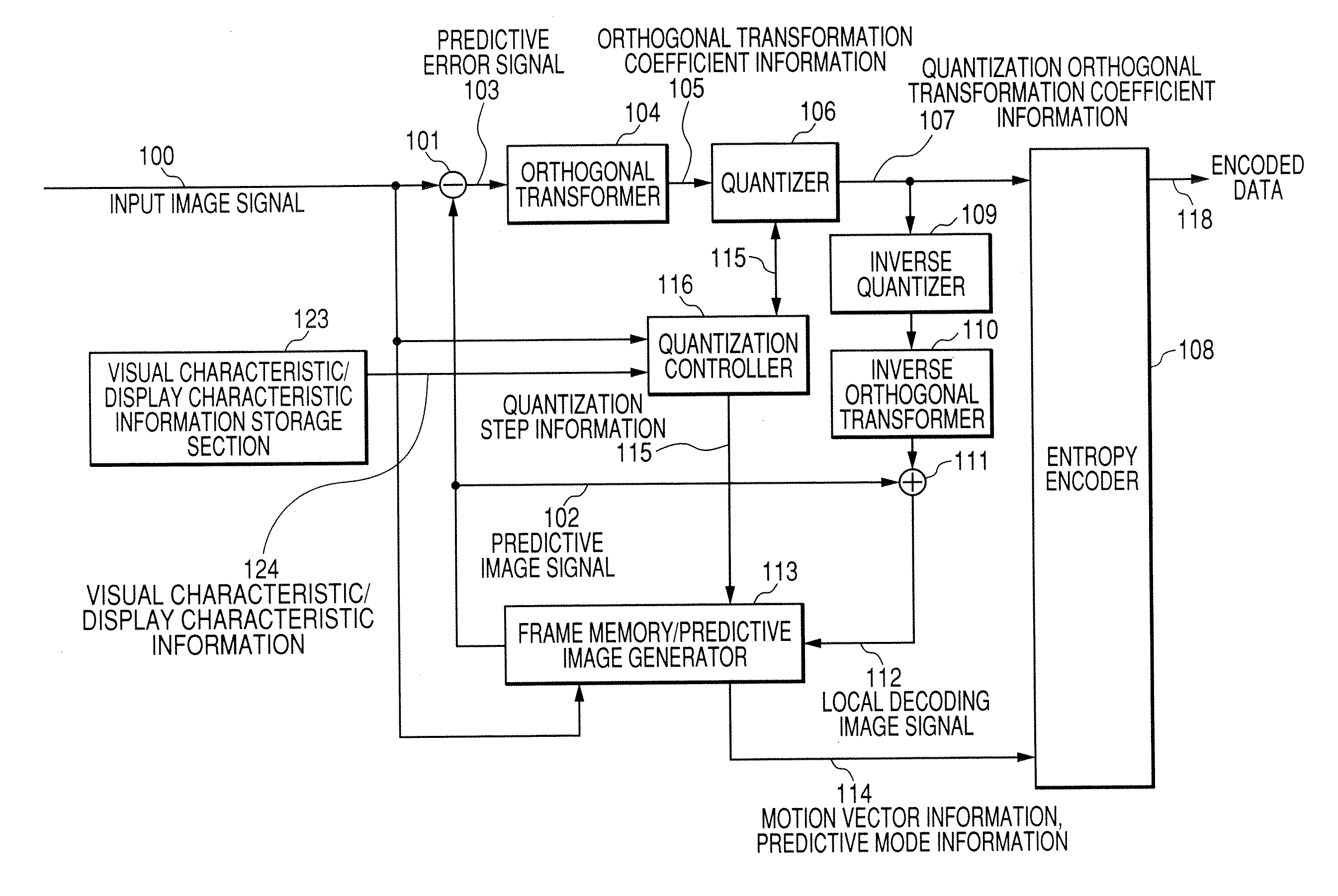
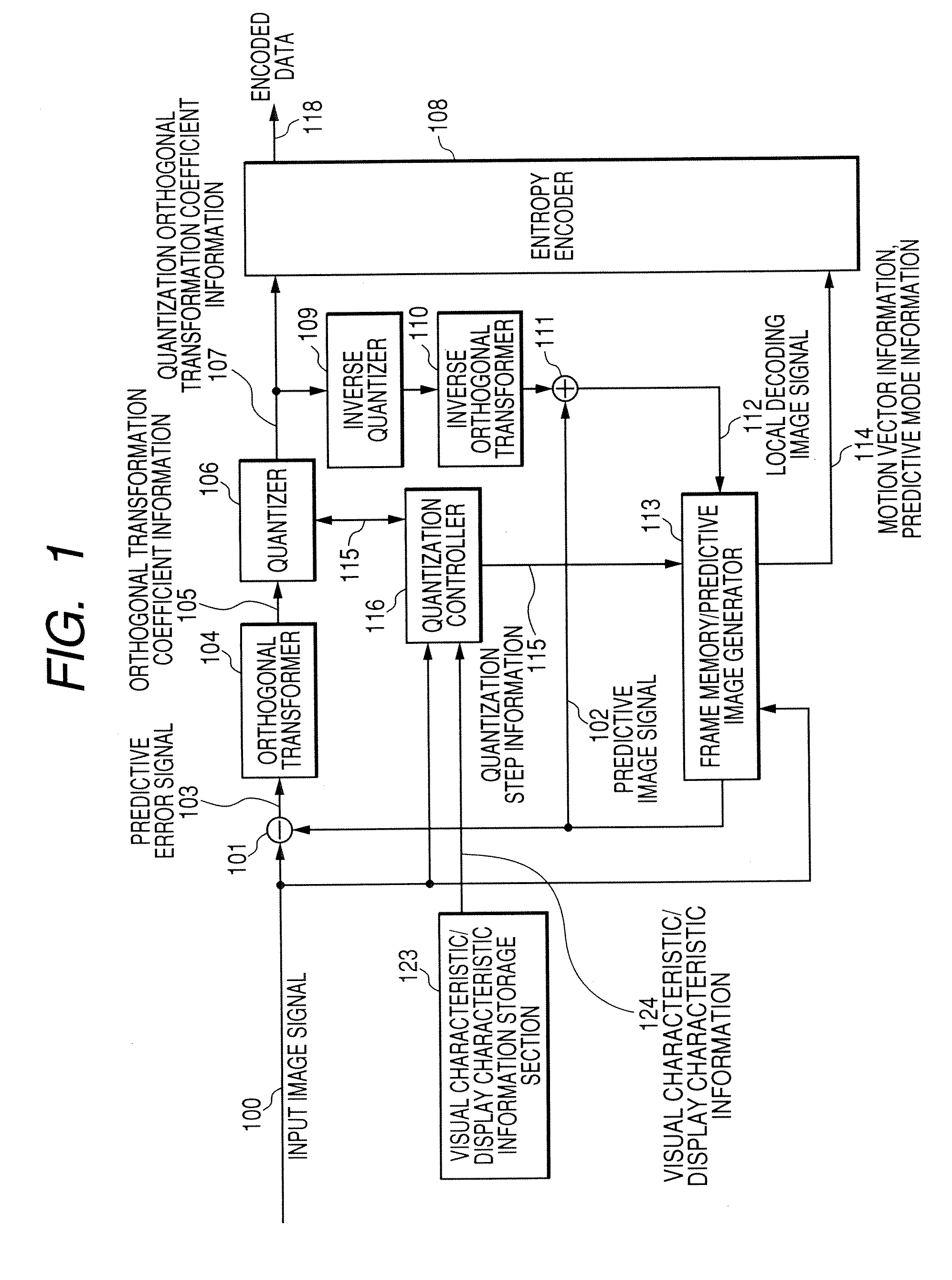
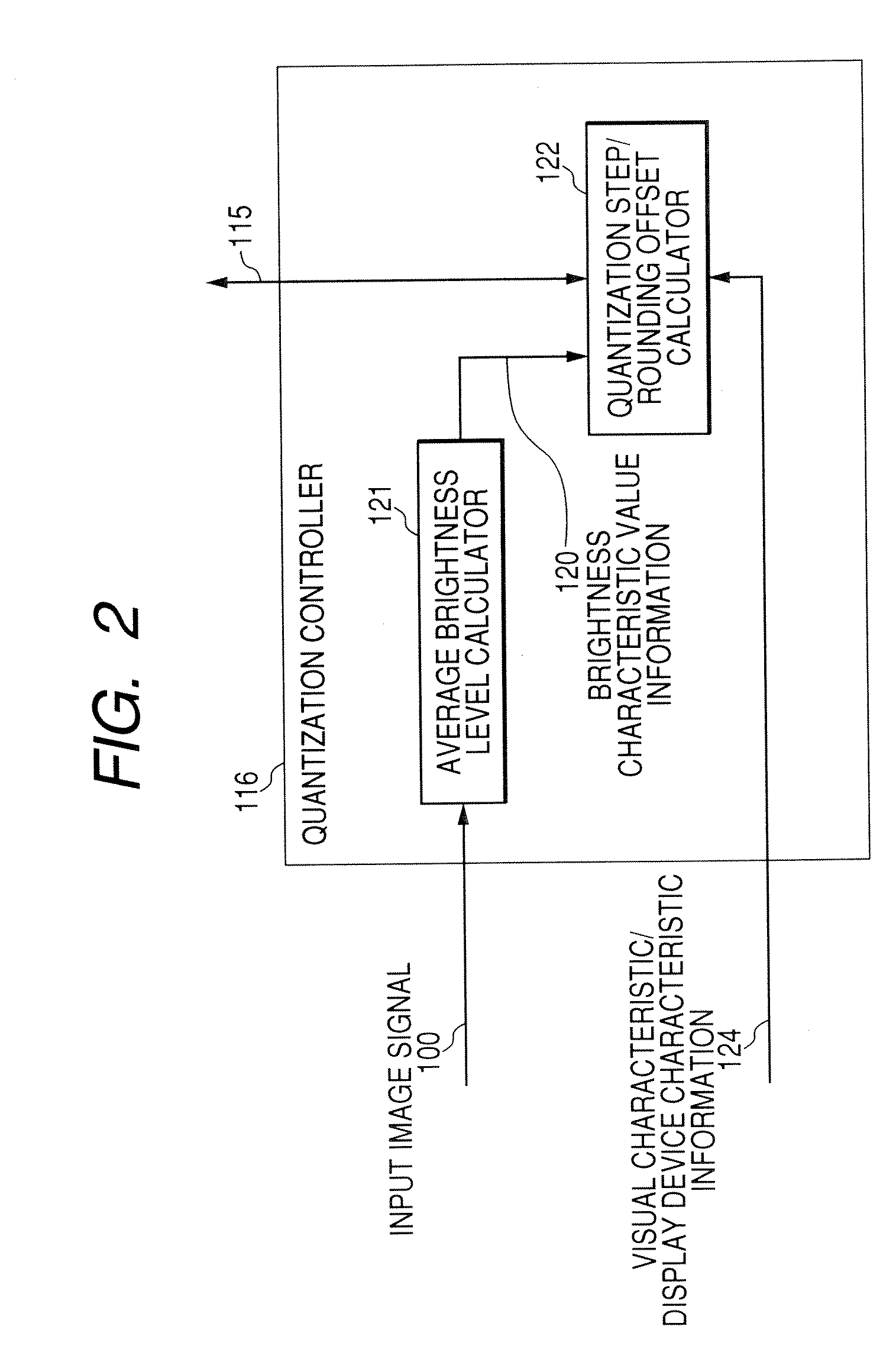
Image encoding apparatus and image encoding method
InactiveUS20070058714A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRoundingComputer science
An image encoder includes: an image encoder that performs encoding of an image; and a setting unit that sets a quantization parameter for each of encoding units arbitrary defined in the image, the quantization parameter including a rounding offset that is used in the encoding performed by the image encoder. The setting unit changes the rounding offset initially set into a larger rounding offset when brightness information of the encoding unit subjected to the encoding becomes smaller than or equal to a threshold value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and summing the products
InactiveUS6085213ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Powerline data communication
InactiveUS6956906B2Easy to useAccurate dataSystems with measurements/testing channelsError preventionTelecommunicationsRounding
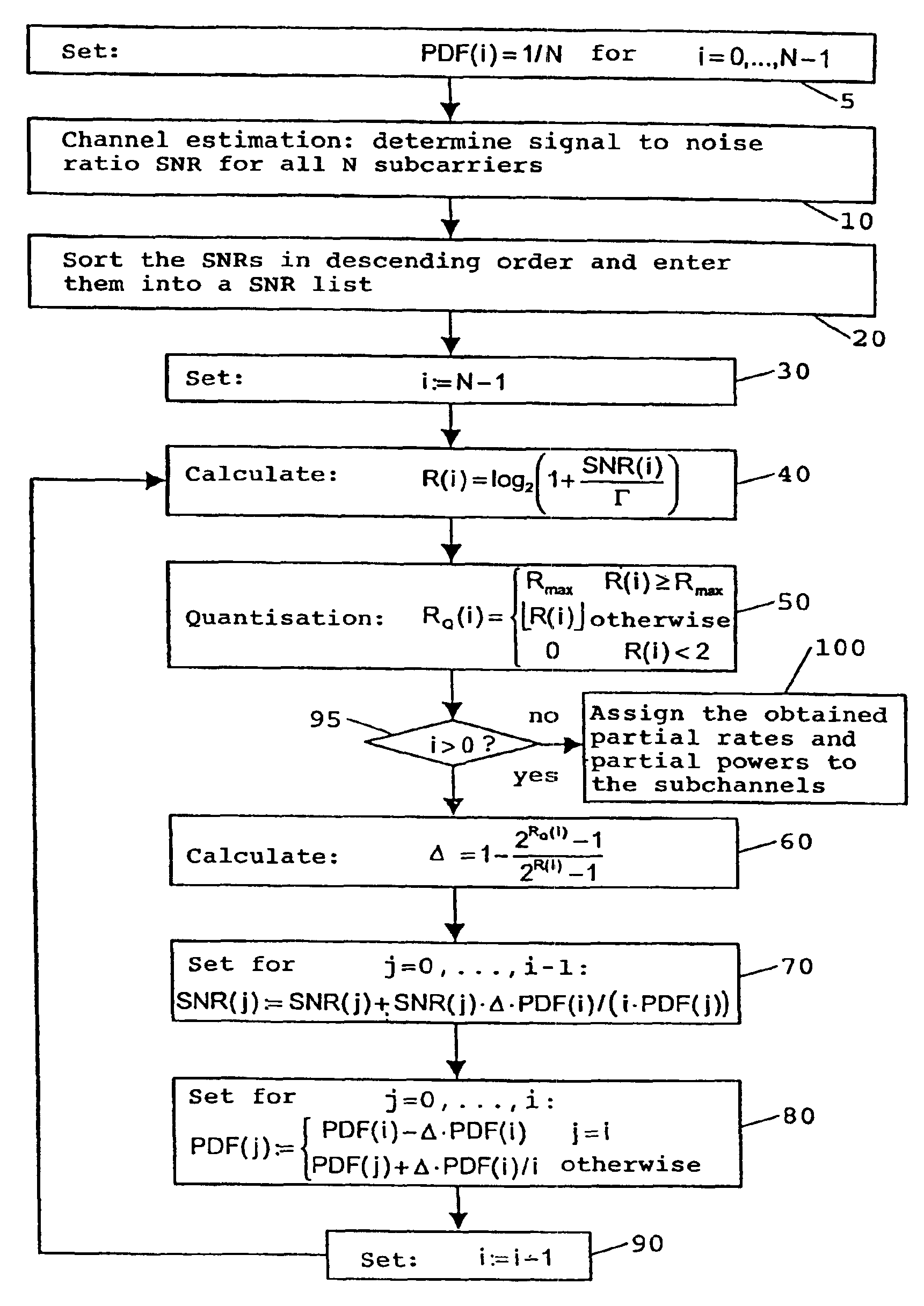
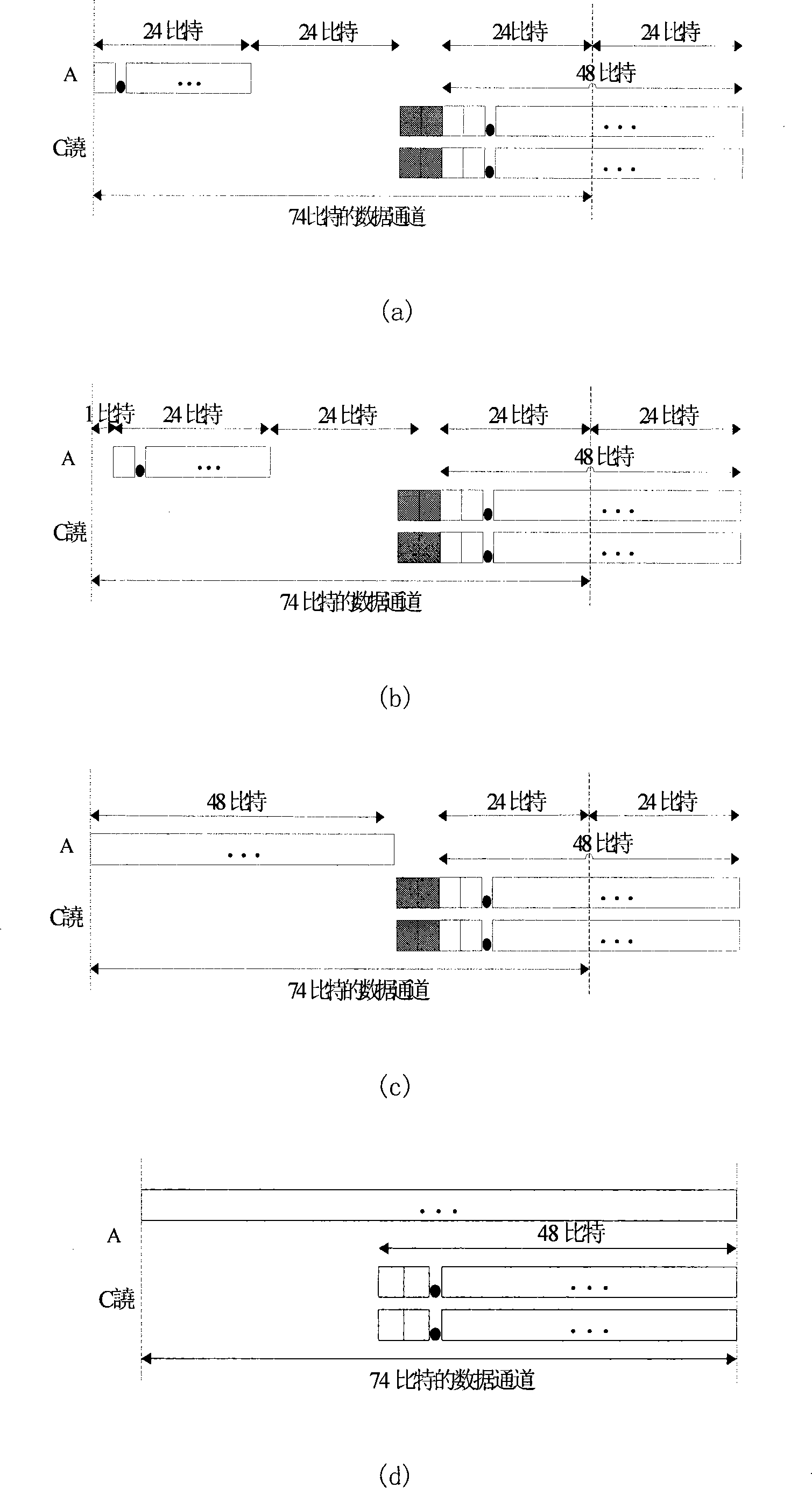
Data communication between two devices (11, 12) over the public powerline network (13) uses a multi carrier technology wherein a communication channel is divided into a plurality of subchannels by frequency division multiplexing. A partial power as part of the total transmission power and a partial rate as a fraction of the total data rate are assigned to each subchannel as follows:Initially, the same partial power is assigned to each subchannel and the S / N ratio of each subchannel is obtained. Starting with the subchannel of the lowest S / N ratio and proceeding to that of the highest S / N ratio, the following steps are performed for each subchannel:Firstly, the partial rate is assigned in accordance with the respective S / N ratio such as to result in a predetermined transmission error rate. The assigned partial rate is then quantised to an integral value. If the quantising corresponds to a rounding down, the initially assigned partial power is reduced such that the transmission error rate remains the same as before quantisation. Further, the partial power of other subchannels with higher S / N ratio is increased such that the sum of all partial powers remains constant. Eventually, the increased S / N ratio resulting from increasing the partial power for these subchannels is calculated so that, when the present steps are conducted for them, an optimum partial rate can be assigned to them.This method maximises the total data rate of the entire communication channel while the error rate of each subchannel and the sum of all partial powers remain constant.
Owner:POLYTRAX INFORMATION TECH
Method for continuous-path control
InactiveUS7012395B2Improve surface qualityMachine becomes highComputer controlSimulator controlNumerical controlRounding
In a method for continuous-path control in at least two linear axes and at least one angle axis, the movement of a tool relative to a workpiece is predefined by a parts program for a numerical control. The velocity control in the numerical control is performed separately for the linear axes and the angle axes. Deviations in the movement between the tool and the workpiece resulting due to the separate velocity control may be corrected by compensation movements of the linear axes. The separate velocity control for the linear axes and the angle axes may be achieved by rounding the velocity profiles in the angle axes more significantly than the velocity profiles in the linear axes. A measure for the rounding for velocity profiles may be predefined separately for the angle axes and the linear axes.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Model area change rate-based adaptive hierarchical processing method
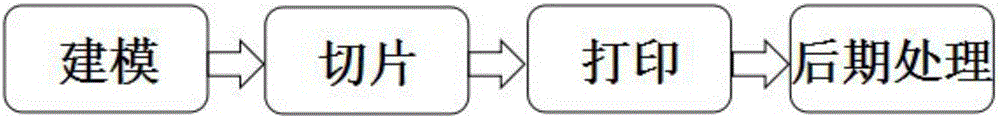
InactiveCN106202687ASolve molding accuracySolve molding speedGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusRoundingLayer thickness
The invention discloses a model area change rate-based adaptive hierarchical processing method. The method comprises the following steps of importing an STL model and establishing a model topological structure; performing uniform hierarchical slicing on the model with the highest precision, obtaining a two-dimensional polygon contour layer and calculating an area of each layer of a polygon after slicing; performing derivation on the area of each layer of the polygon to obtain an area change rate of the model; comparing the calculated area change rate with a threshold according to a relationship between the area change rate of the model and the printing precision, and obtaining a printing precision distribution situation of the model in a printing direction; calculating hierarchical layer thickness data required for model printing, and performing processing by using a rounding-off method to generate adaptive hierarchical layer thickness data; and reading the hierarchical layer thickness data by a slicing engine, and performing adaptive layer thickness slicing on the model to obtain a gcode file required for printing. According to the method, while the detail characteristics of the model are ensured, the forming speed of the model is increased, and the printing time is effectively shortened.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Division unit in a processor using a piece-wise quadratic approximation technique
InactiveUS6351760B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesComputational logicRounding
A computation unit computes a division operation Y / X by determining the value of a divisor reciprocal 1 / X and multiplying the reciprocal by a numerator Y. The reciprocal 1 / X value is determined using a quadratic approximation having a form:where coefficients A, B, and C are constants that are stored in a storage or memory such as a read-only memory (ROM). The bit length of the coefficients determines the error in a final result. Storage size is reduced through use of "least mean square error"techniques in the determination of the coefficients that are stored in the coefficient storage. During the generation of partial products x2, Ax2, and Bx, the process of rounding is eliminated, thereby reducing the computational logic to implement the division functionality.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Paralleling floating point multiplication addition unit
ActiveCN101178645AAchieving Instruction Level ParallelismDigital data processing detailsConcurrent instruction executionProduction lineRounding
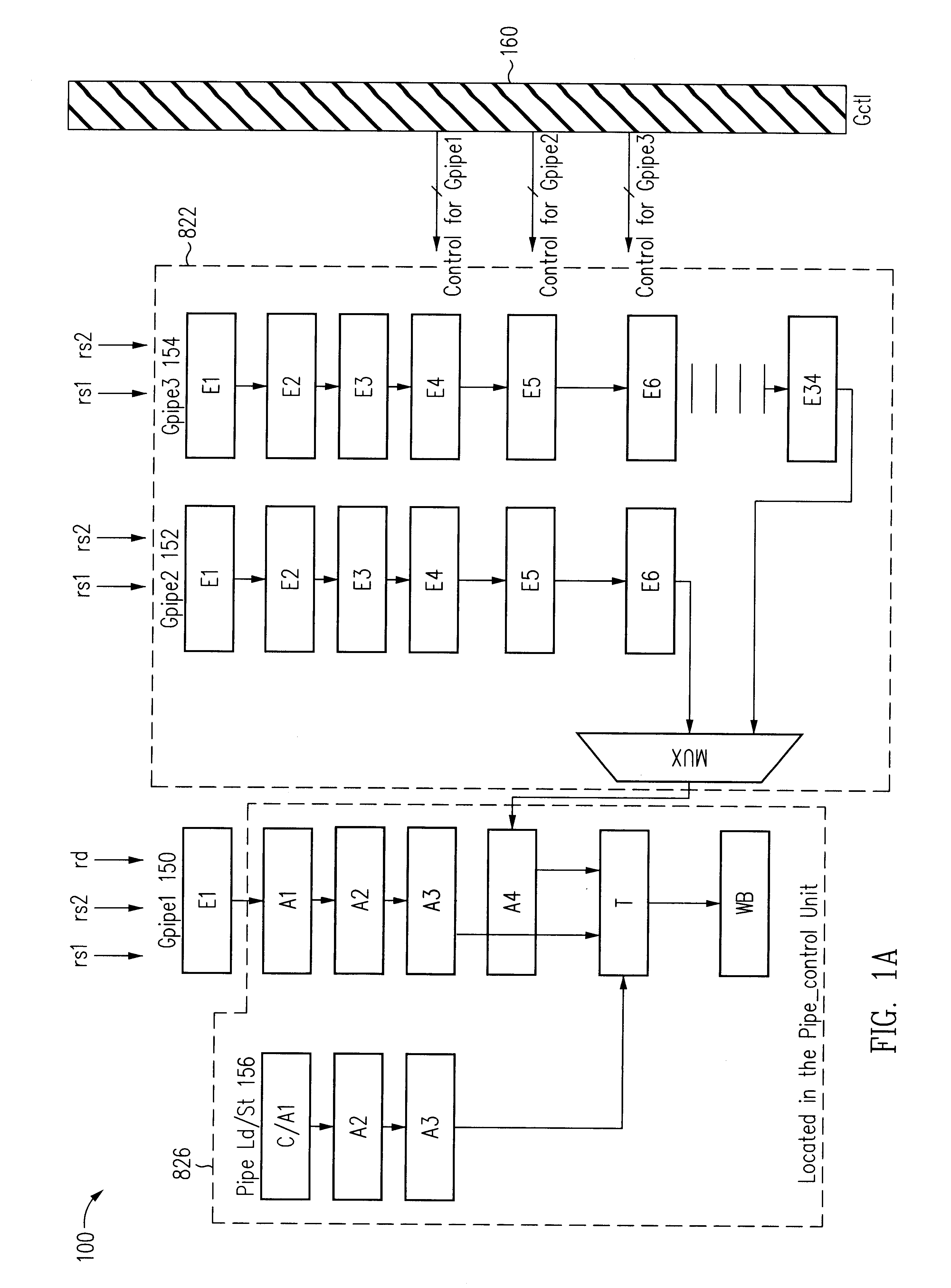
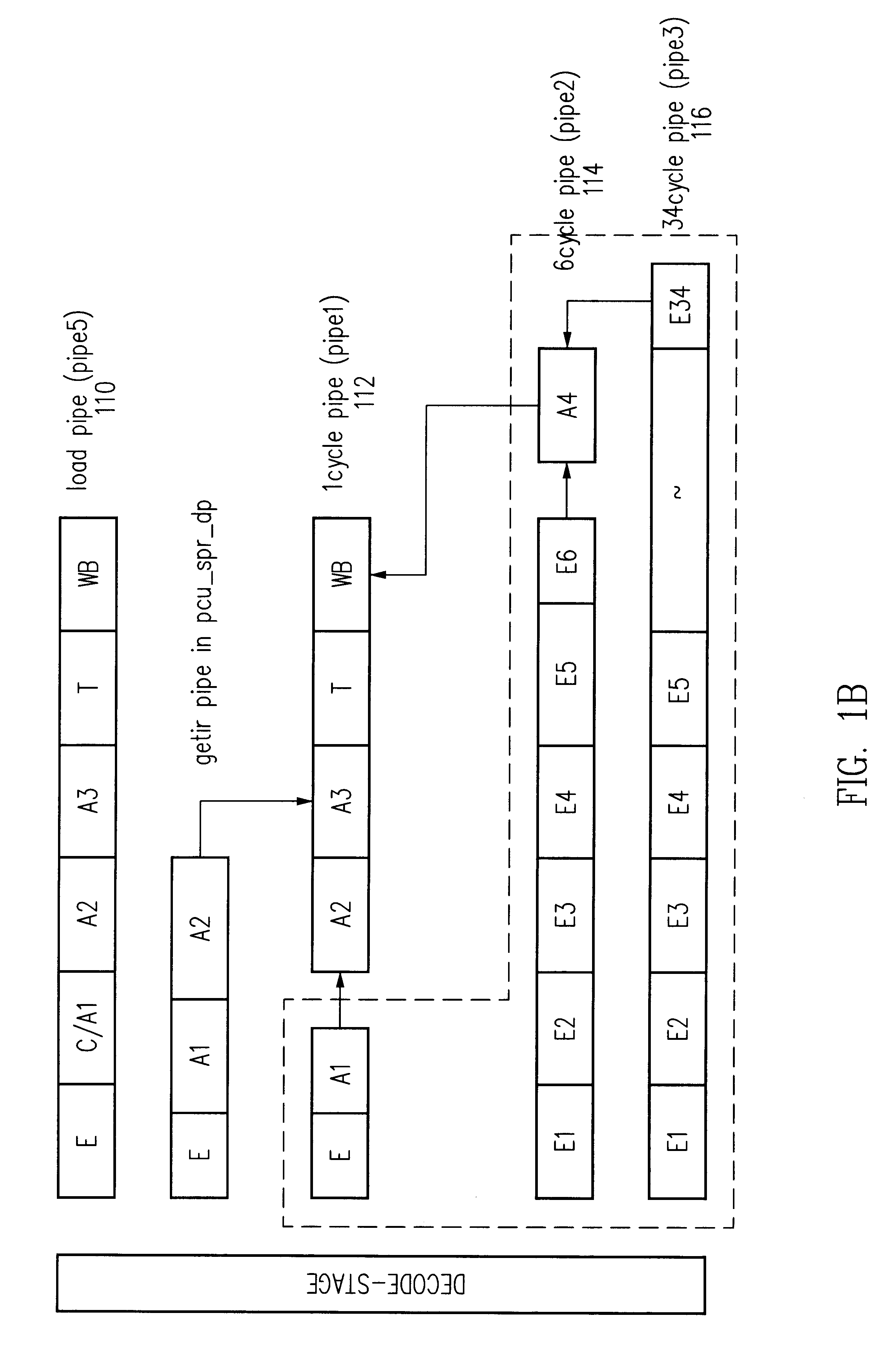
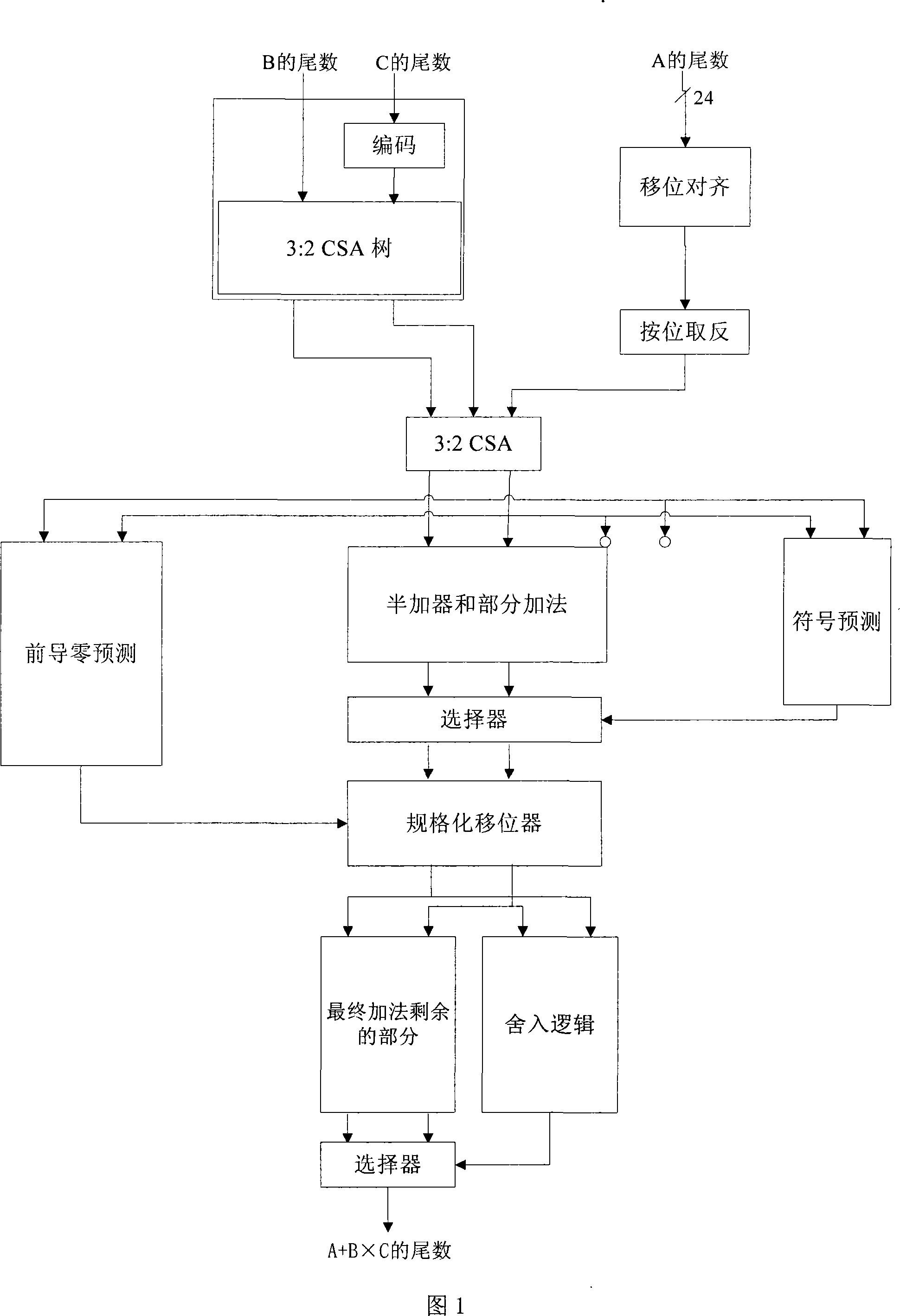
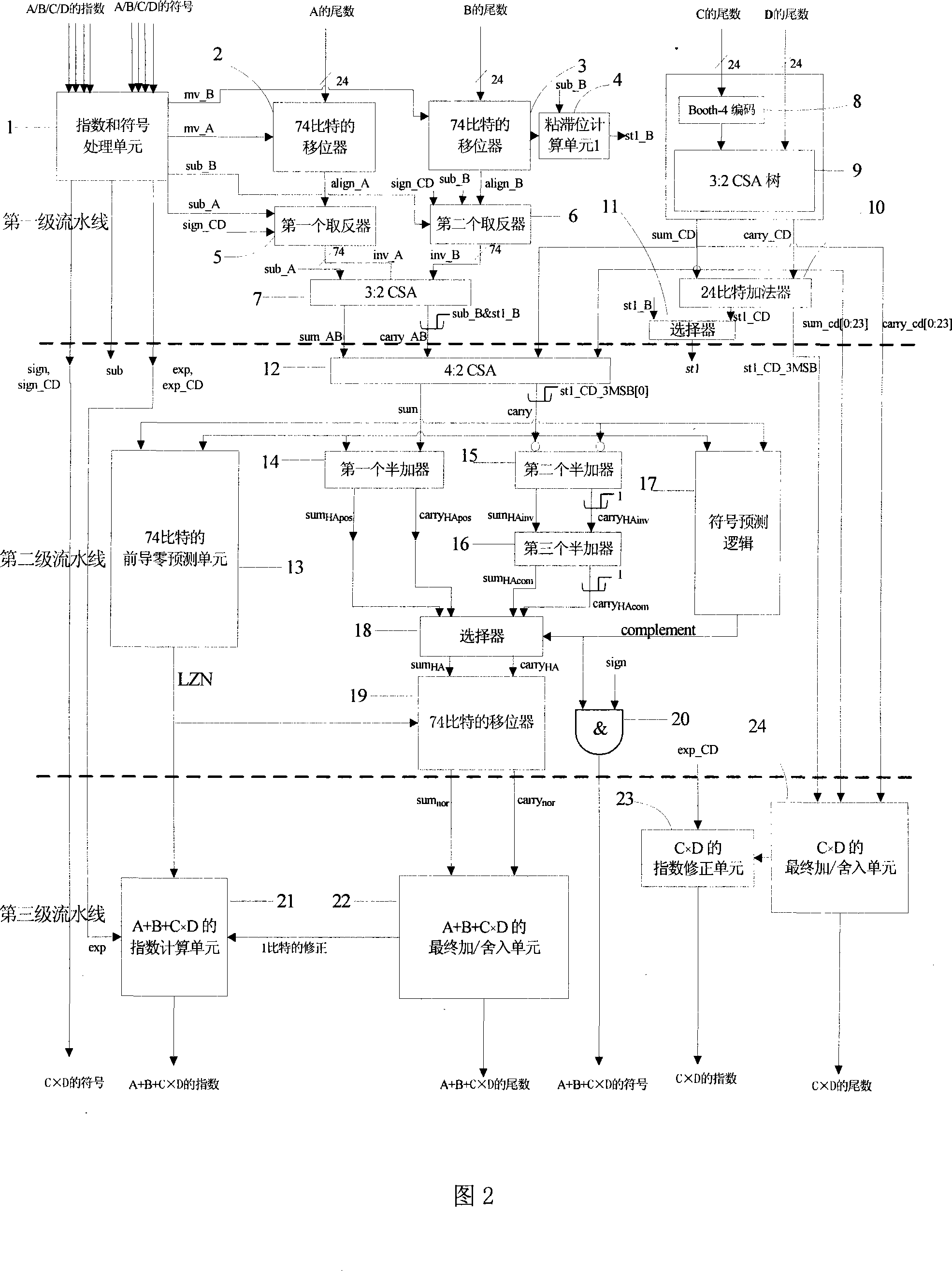
The invention relates to a parallel floating-point fused multiply-add unit which simplifies similar technique and achieves the multiply-add operation of A+B+C*D (A is equal to or greater than B) and acquires the result of C*D, so as to achieve three classes production line: in the first production line, A and B are displaced and snapped, and the C*D is coded and part of C*D is compressed; in the second production line, the displacement and snapped result of A and B and the result of partial compressed C*D are compressed in 4:2CSA, and then front zero guide prediction, character prediction, half-add operation and normalized displacement are accomplished; in the third production line, the final add operation and rounding of A+B+C*D are accomplished and the index is counted, and the mantissa and the index of C*D are counted according to the output of the first production line. The invention has the advantages of achieving the parallel of instruction grade; accomplishes an add instruction and a multiply instruction at the same time; and also can accelerate two continuous instructions with correlative data.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fully homomorphic encryption
InactiveUS9083526B2Reduce noise levelGrowth inhibitionPublic key for secure communicationHardware monitoringRoundingCiphertext
In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a method and computer program include: receiving first and second ciphertexts having first and second data encrypted per an encryption scheme, the encryption scheme has public / secret keys and encryption, decryption, operation and refresh functions, the encryption function encrypts data, the decryption decrypts ciphertext, the operation receives ciphertexts and performs operation(s) on them, the refresh operates to prevent growth of the magnitude of noise for a ciphertext while reducing the modulus of the ciphertext without using the secret key, utilizing a modulus switching technique that involves transforming a first ciphertext c modulo q into a second ciphertext c′ modulo p while preserving correctness, the technique includes scaling by p / q and rounding, p<q; using the operation function(s), performing operation(s) on them to obtain a third ciphertext; and reducing a noise level of the third ciphertext using the refresh function.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Flow chamber
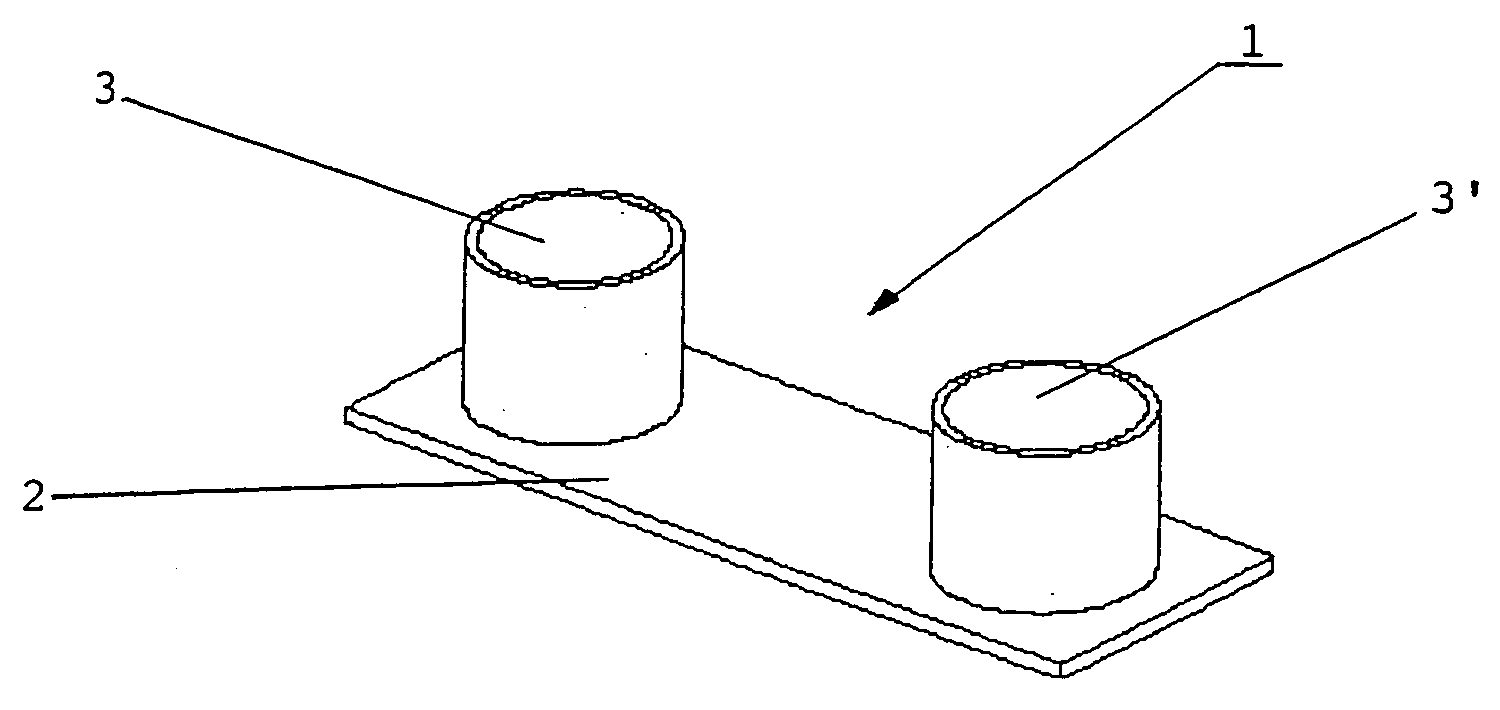
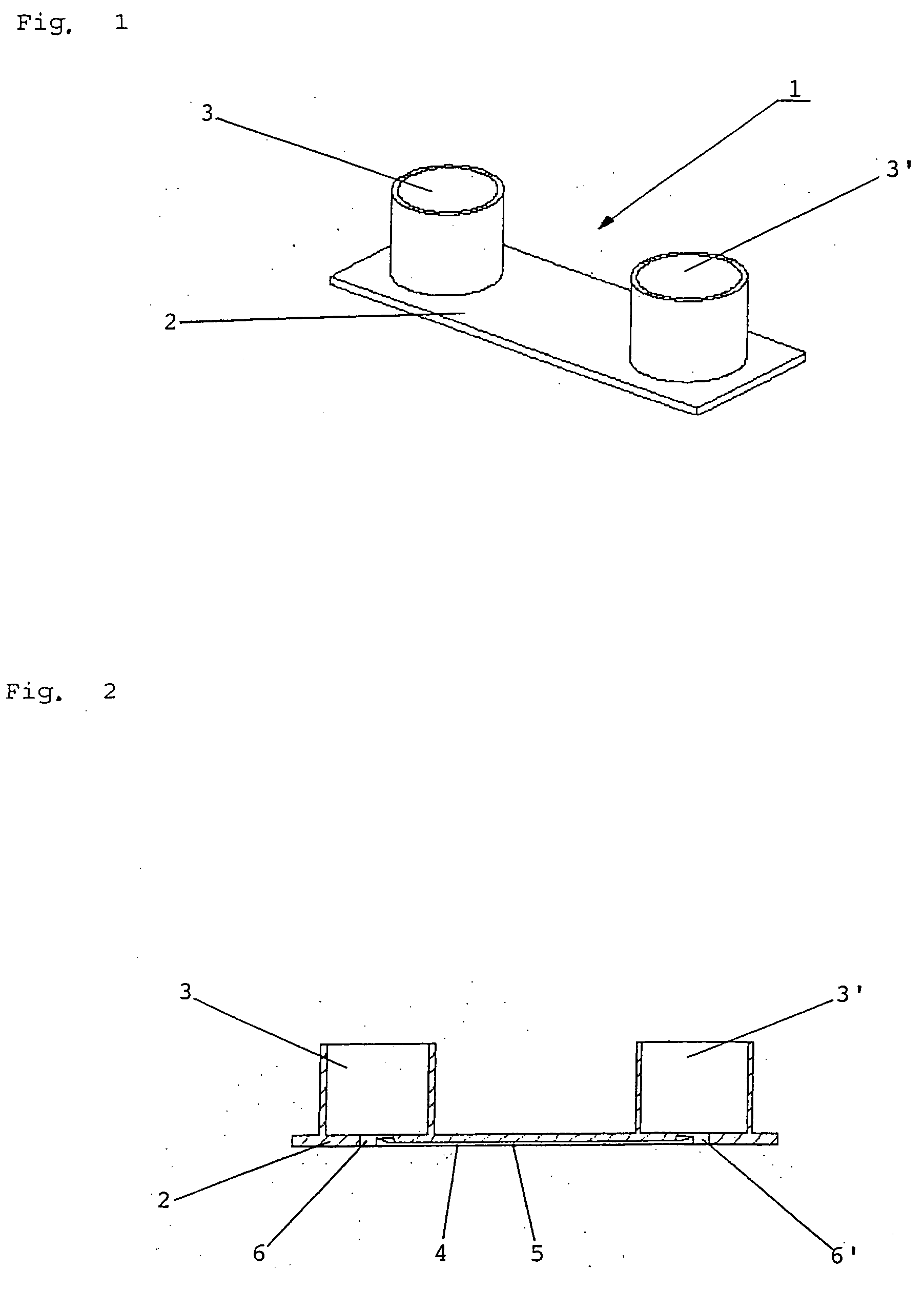
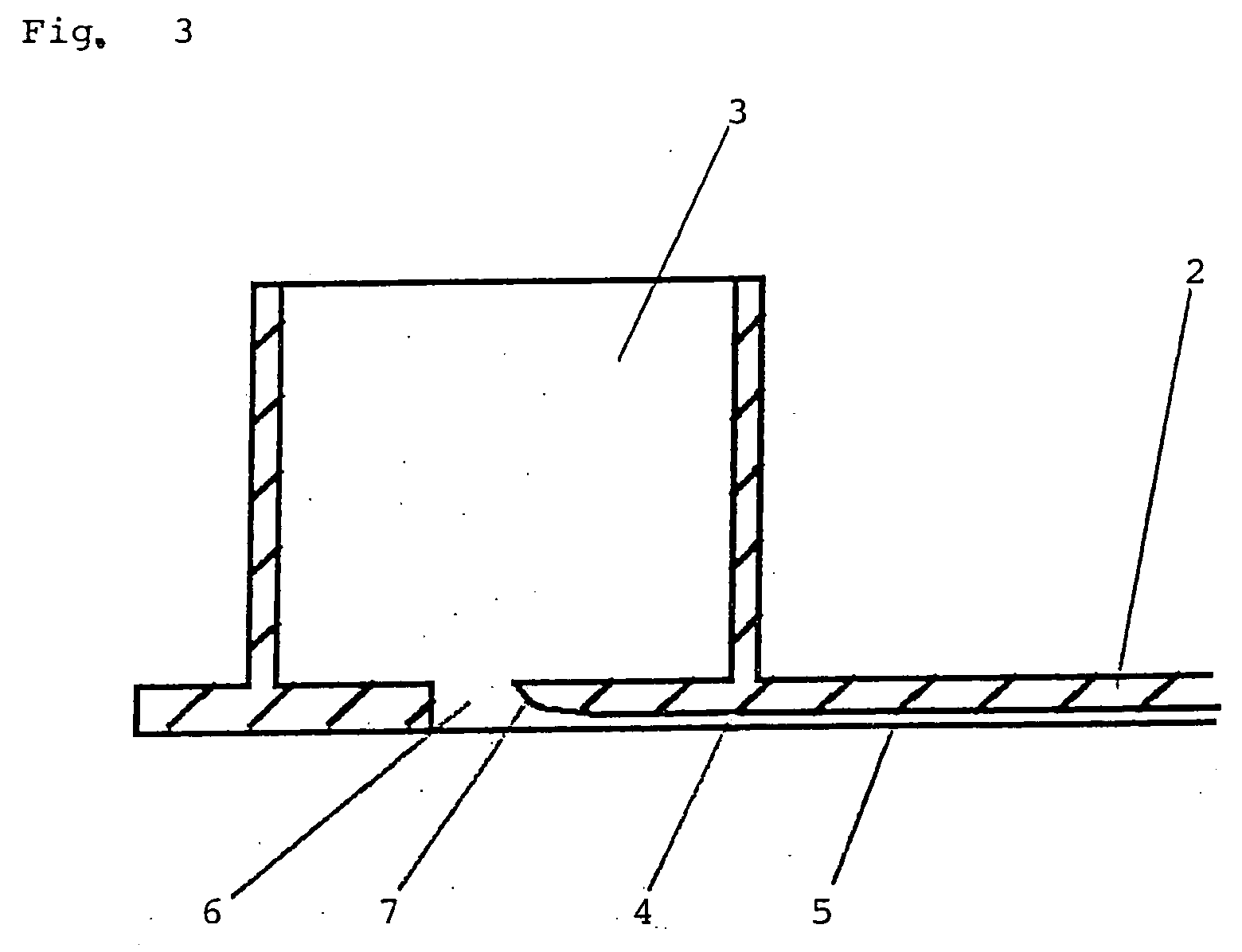
ActiveUS20050019231A1Simple and inexpensive manufacturing modeMechanical stabilitySamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansRoundingPlastic materials
A flow chamber (1) made of plastics as an object carrier for light-microscopic examinations comprised at least one channel (4) in a base plate (2), said channel having a width of 0.01 to 20 mm and a height of 0.01 to 5 mm. One liquid reservoir (3, 3′) each is connected to the inlet and outlet opening (6, 6′) of the channel, whereby a communicating system is generated. The bottom and / or the cover of this chamber is made of a high-class plastic material and may be functionalized. The inlet and outlet portions of the channel may be formed by a rounding (7) of the channel edges or by a surface treatment in a manner that drop formation is prevented and the flow is therefore not obstructed. In a method of sample preparation for light-optical microscopic examinations, a sample flow is generated by a system of communicating pipes, in that a reservoir of a solution with the sample is connected via a third channel with at least one further reservoir and the filling level of the reservoirs differs at the beginning of the examination.
Owner:IBIDI
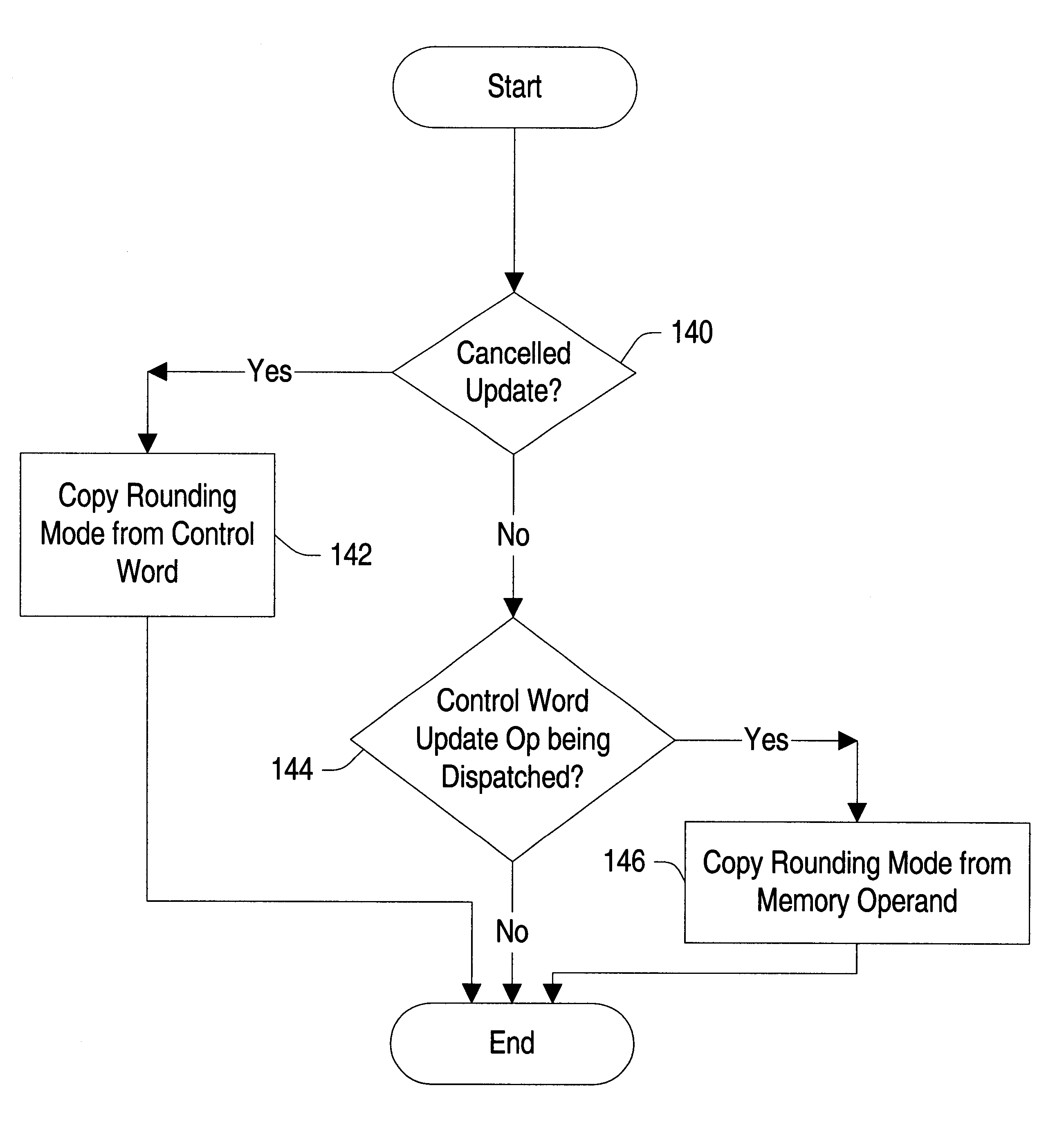
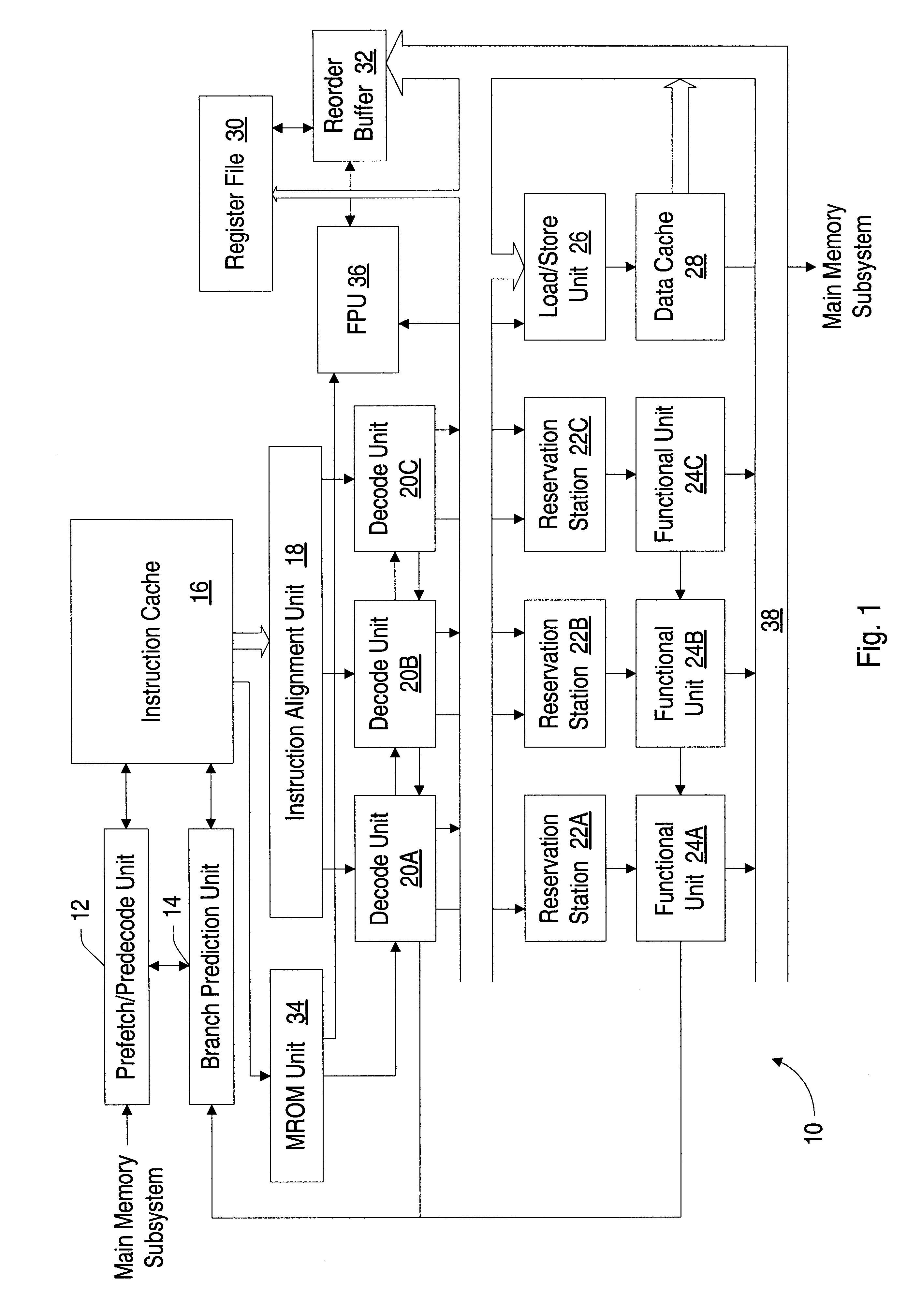
Piping rounding mode bits with floating point instructions to eliminate serialization
InactiveUS6233672B1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsRoundingProcessor register
A floating point unit is provided which conveys the rounding mode in effect upon dispatch of a particular instruction with that particular instruction into the execution pipeline of the floating point unit. Upon dispatch of a control word update instruction into the execution pipeline, the rounding mode is updated according to the updated control word provided for the control word update instruction. Instructions subsequent to the control word update instruction thereby receive the updated rounding mode as those instructions are dispatched. The updated rounding mode is available to the subsequent instructions prior to retiring the control word update instruction. The rounding mode is therefore updated without serializing the update. If the control word update instruction modifies the value in a field other than the rounding mode, the instructions subsequent to the control word update instruction may be discarded and re-executed subsequent to updating the control word register with the updated control word. In this manner, the control word update is effectively serialized for cases in which a field other than the rounding mode is updated.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
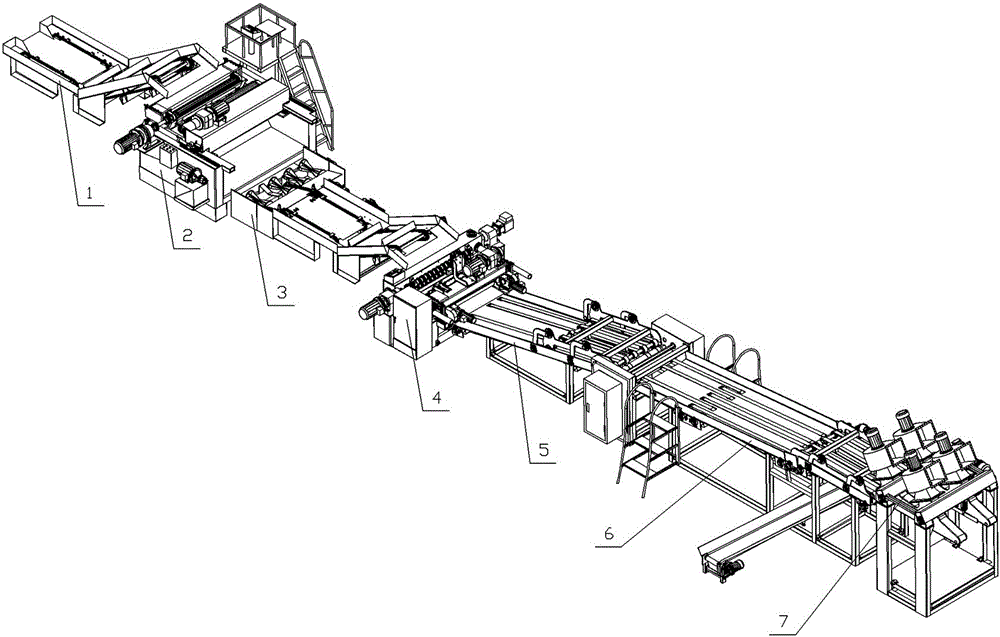
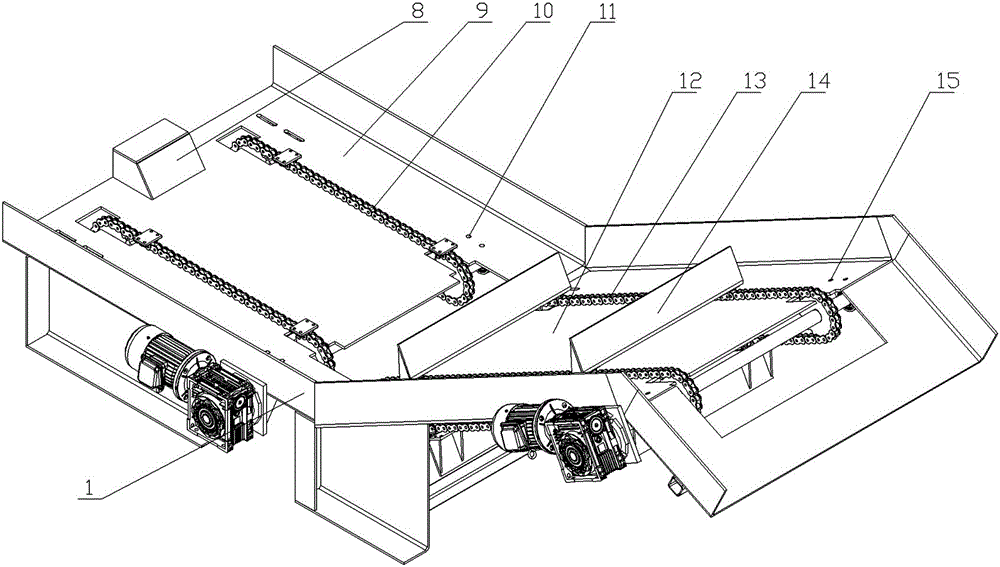
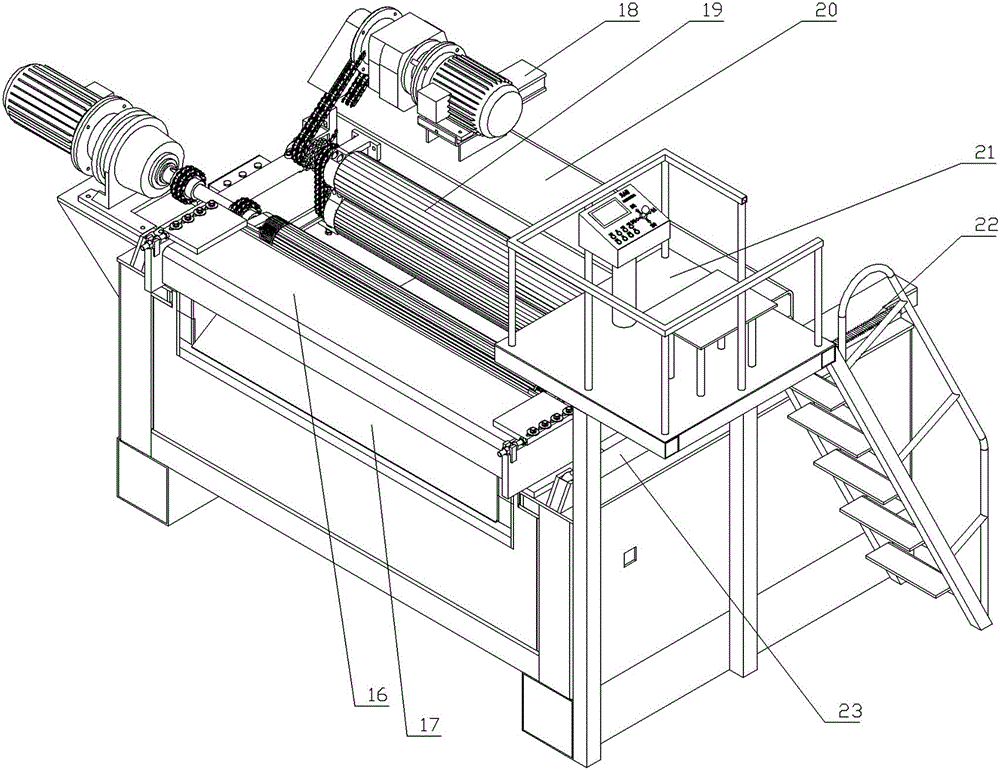
Panel feeding, rotary-cutting and stacking integrated device
ActiveCN105084055ARealize fully automatic flow operationVeneer manufactureArticle feedersRoundingEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of rotary-cutting of timber and discloses a panel feeding, rotary-cutting and stacking integrated device. The panel feeding, rotary-cutting and stacking integrated device comprises a rounding machine and a rotary-cutting machine. The panel feeding, rotary-cutting and stacking integrated device is characterized in that a feeding device is arranged at the feeding end of the rounding machine, and a timber collator is arranged at the discharging end of the rounding machine; the back side of the collator is connected with the rotary-cutting machine through the feeding device; a conveying rack is arranged at the discharging end of the rotary-cutting machine and is connected with a vacuum adsorption automatic panel collector through a screening device. According to the panel feeding, rotary-cutting and stacking integrated device, rounding, rotary-cutting and stacking of timber are integrated, the feeding device, the collator and the screening device are additionally arranged, fully-automatic streamlined production is achieved, and the technical problems that in the prior art, dangerousness is high, time consumption and labor consumption are high, occupied space is large, and working efficiency is low are effectively solved.
Owner:SHANDONG XUANJIN MACHINERY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com