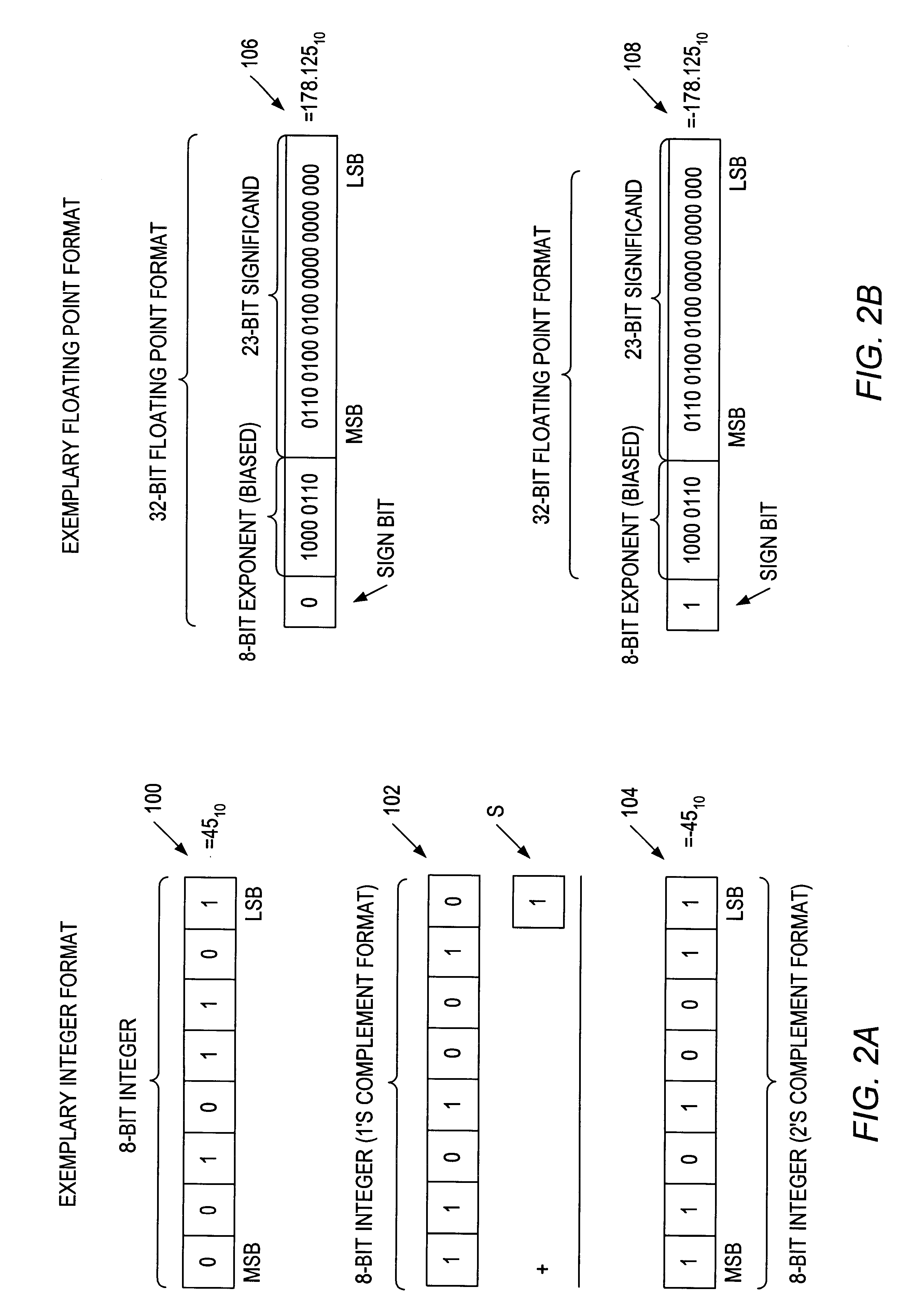
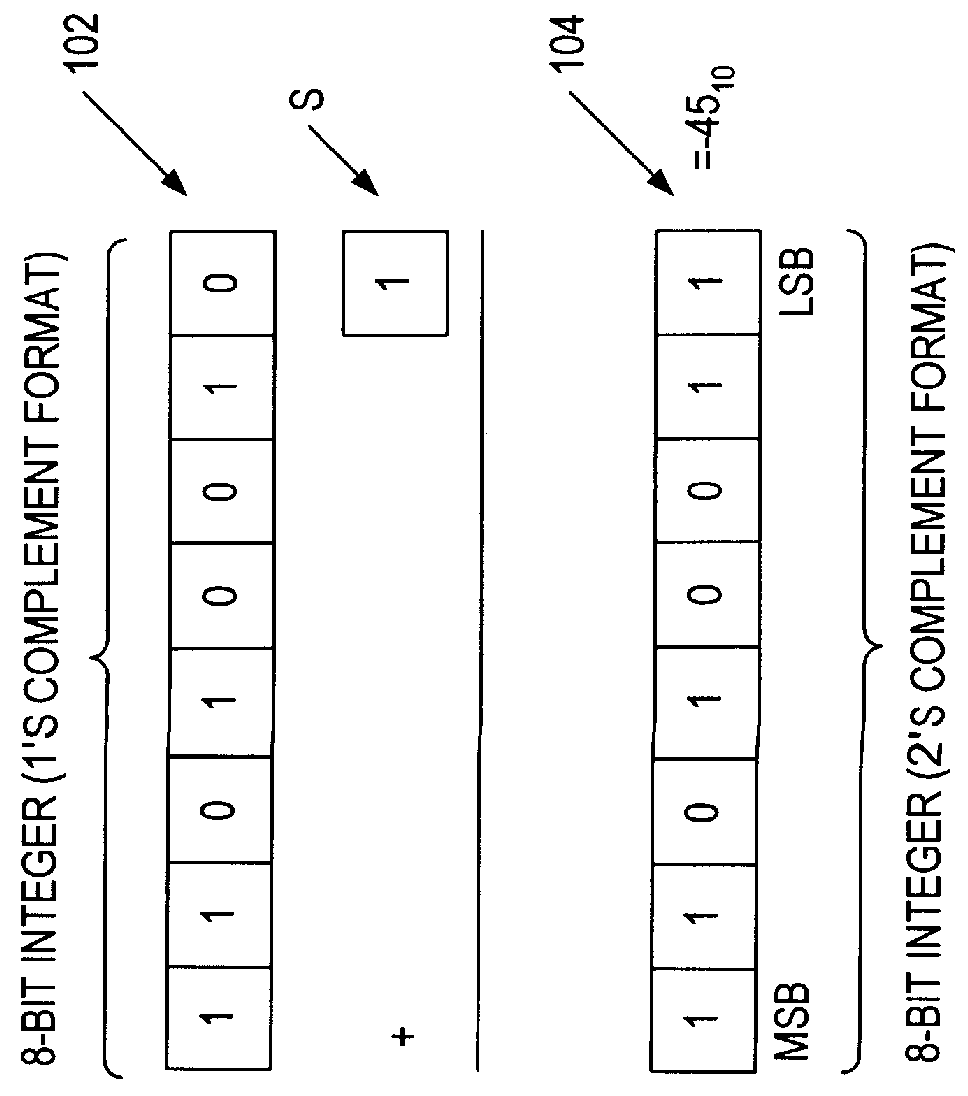
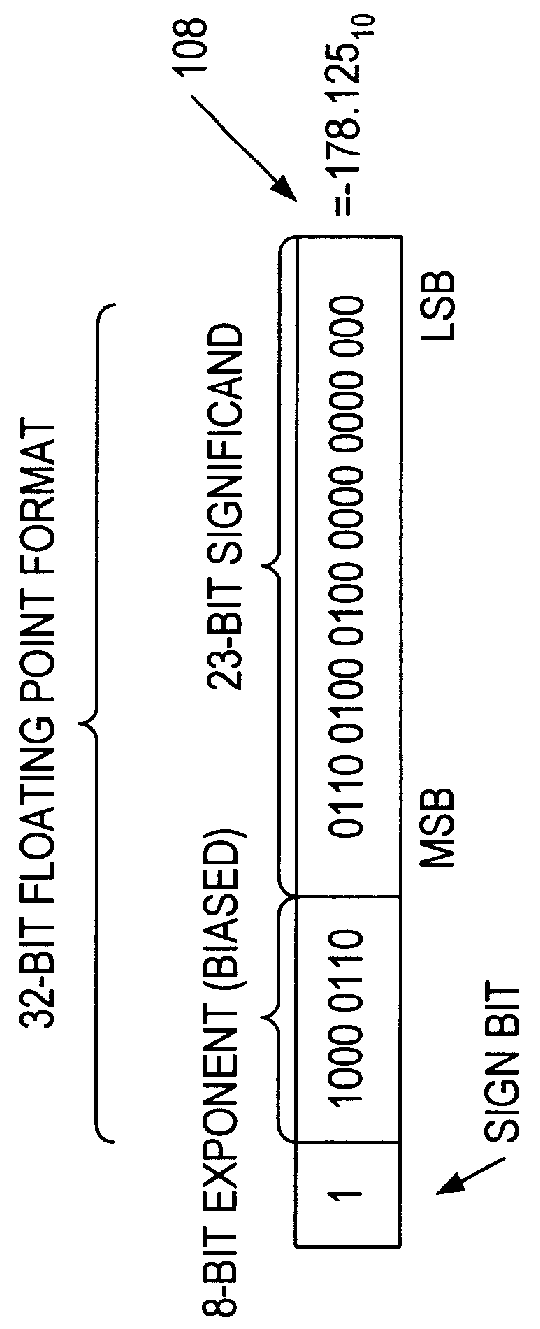
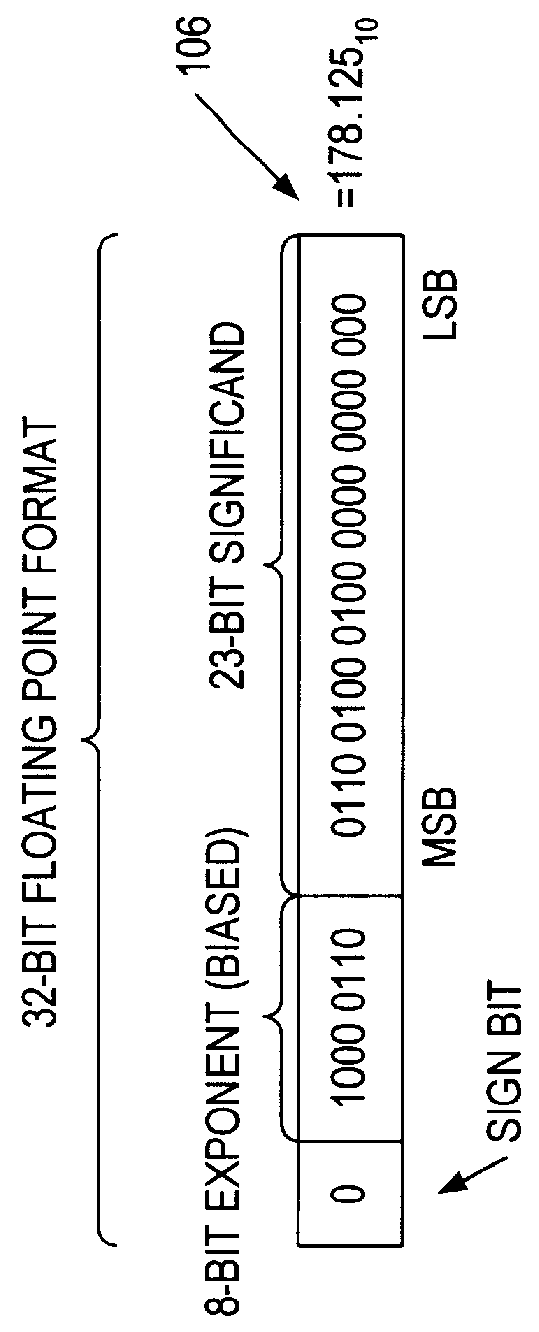
Patents
Literature
399 results about "Partial product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
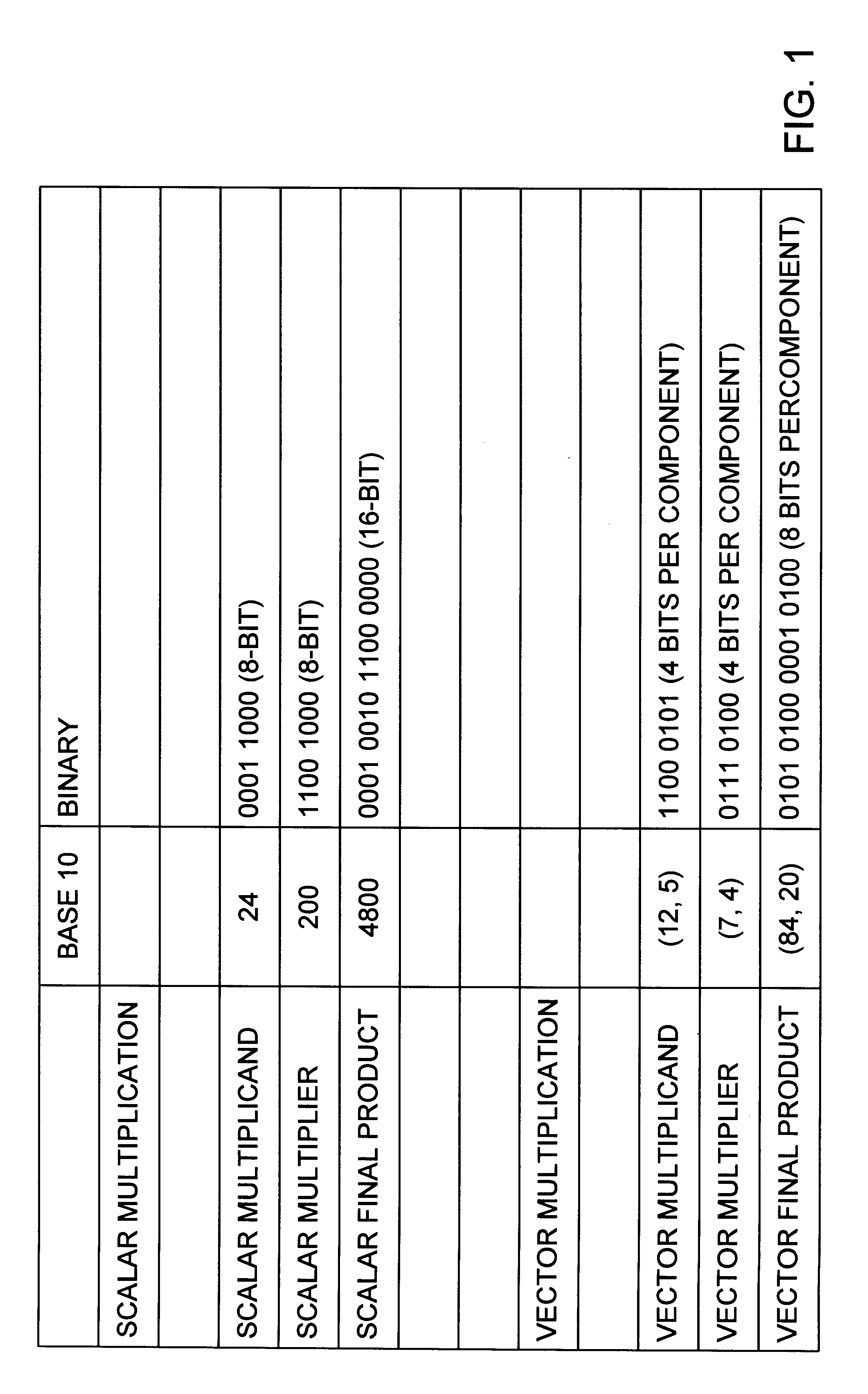
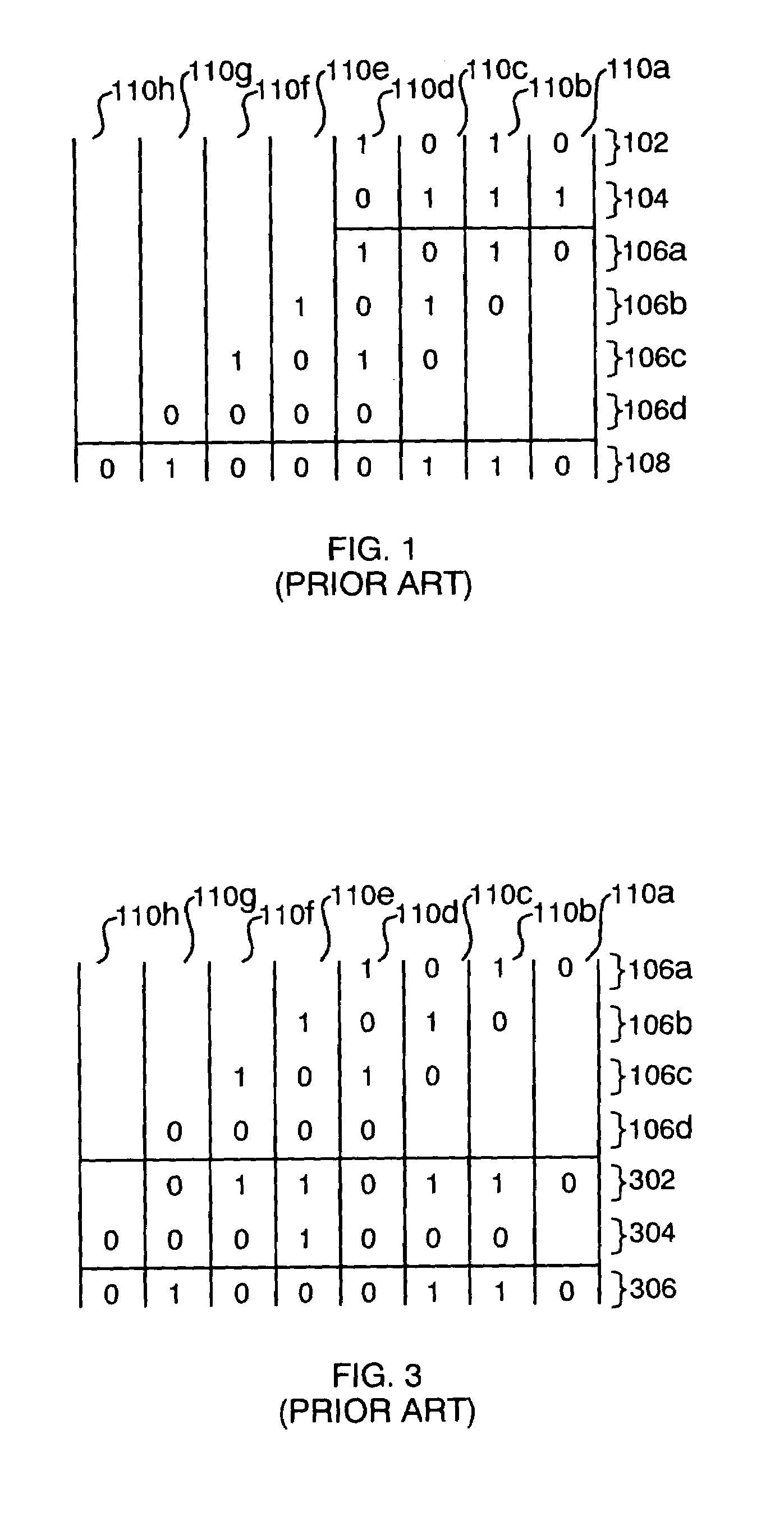
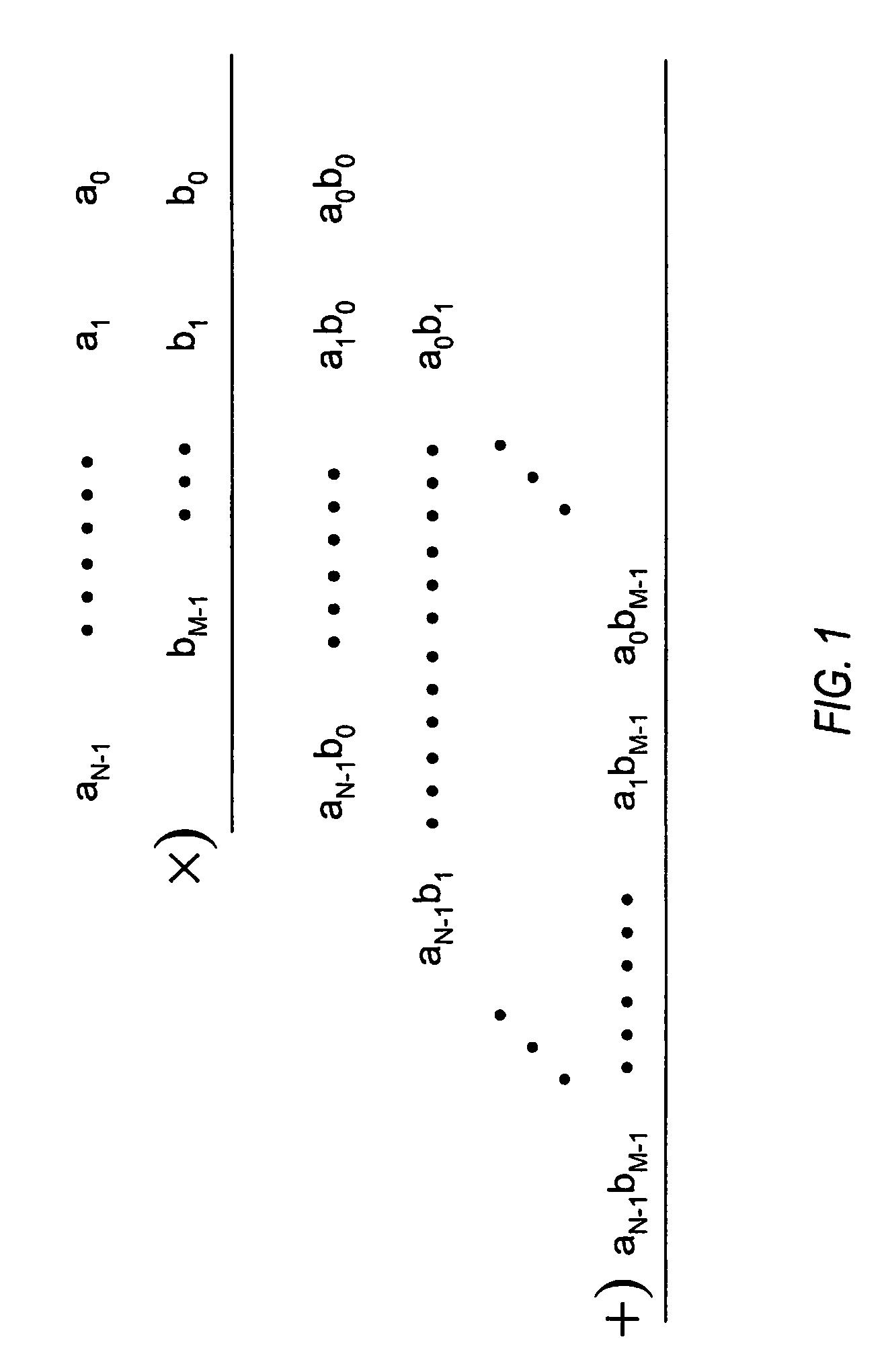
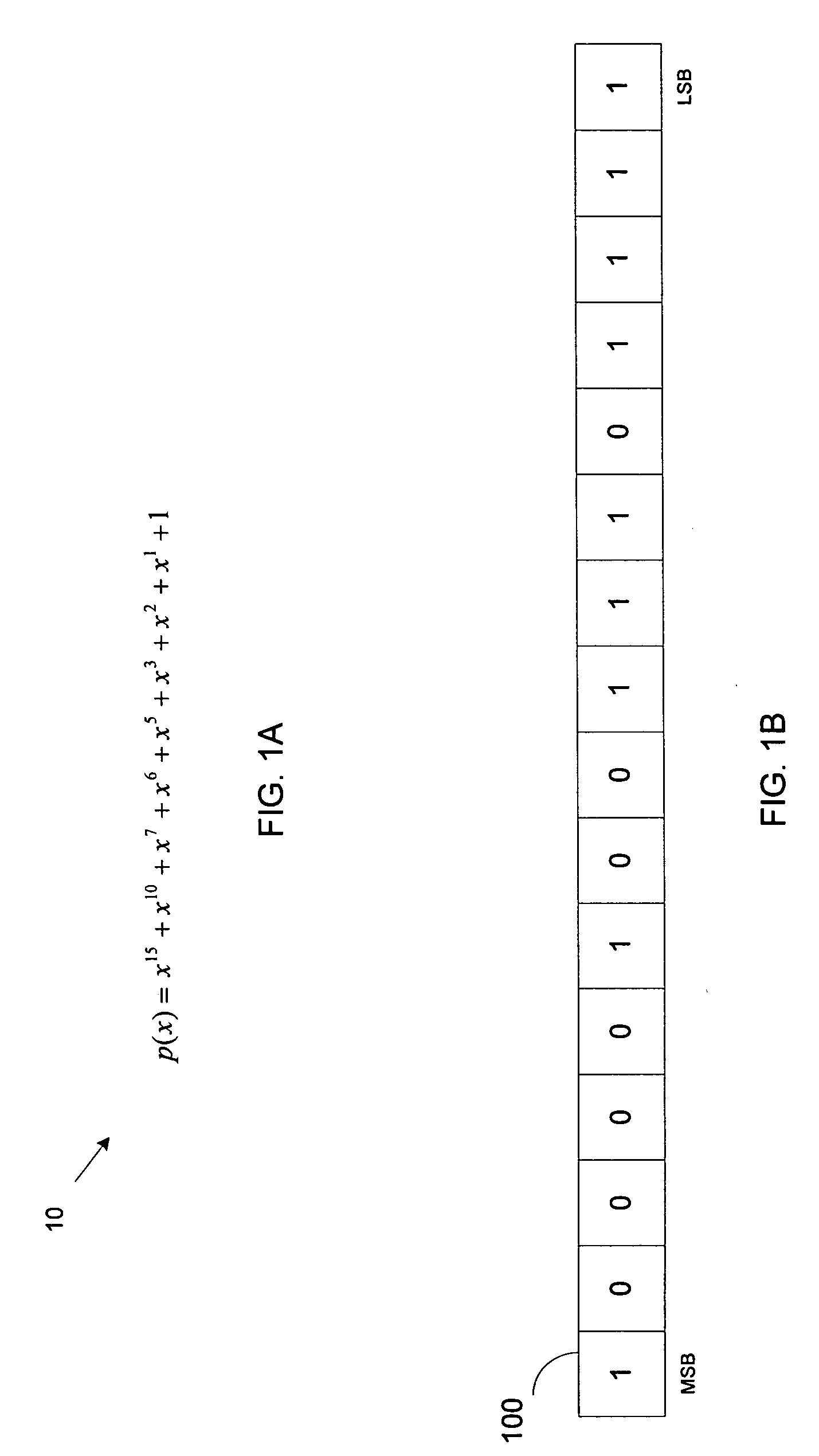
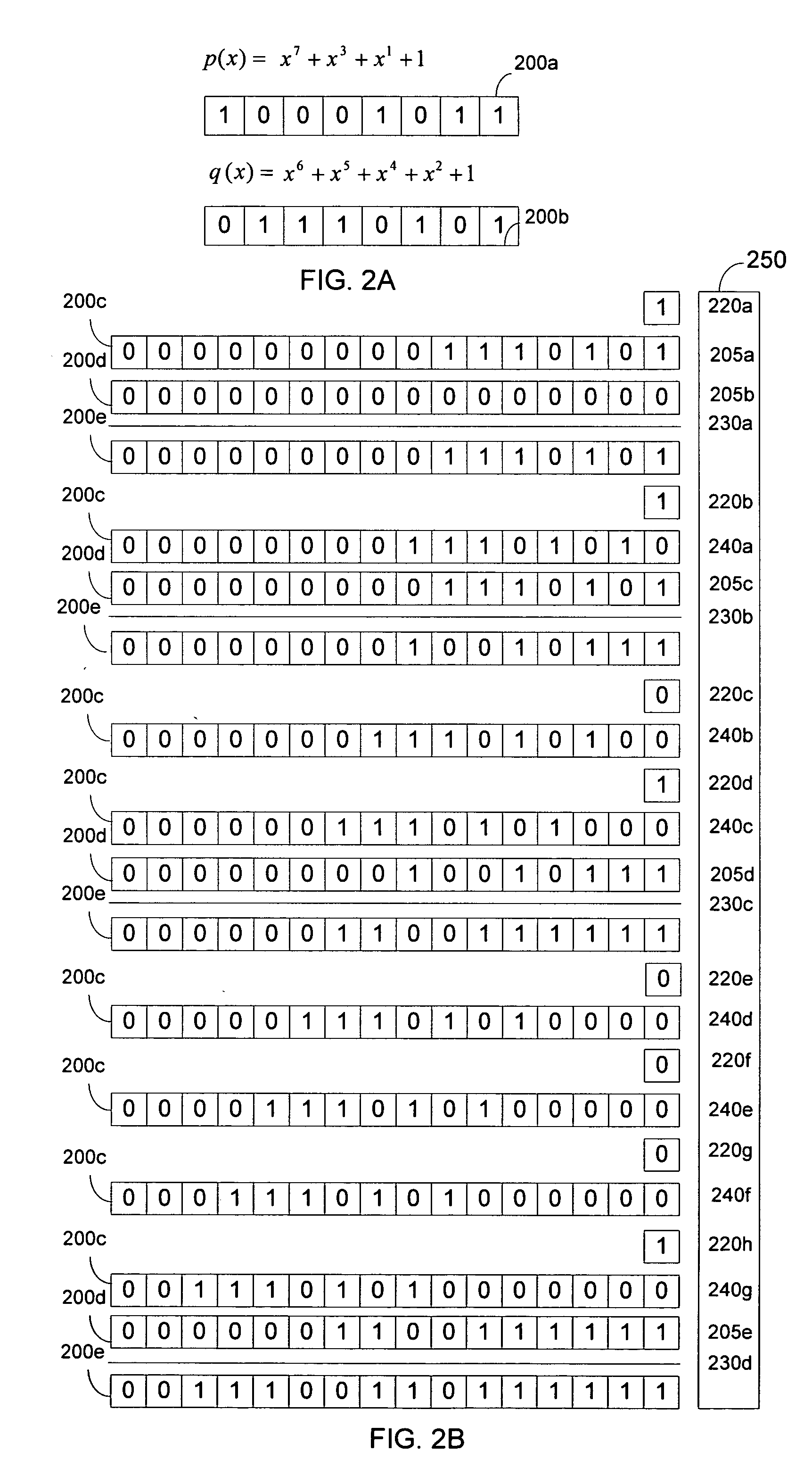
Partial product. A product formed by multiplying the multiplicand by one digit of the multiplier when the multiplier has more than one digit. Partial products are used as intermediate steps in calculating larger products. For example, the product of 67 and 12 can be calculated as the sum of two partial products, 134 (67 X 2) + 670 (67 X 10), or 804.
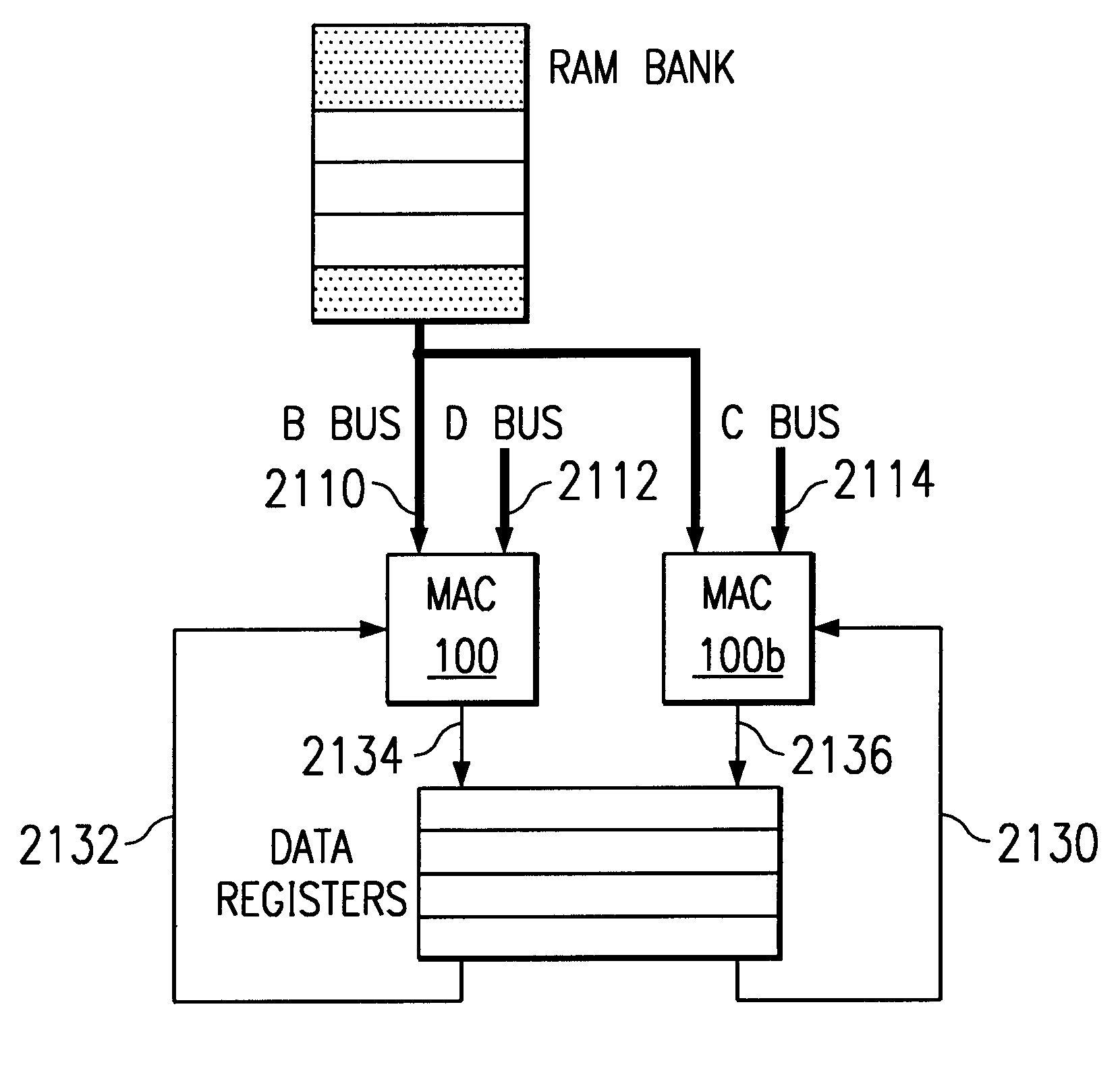
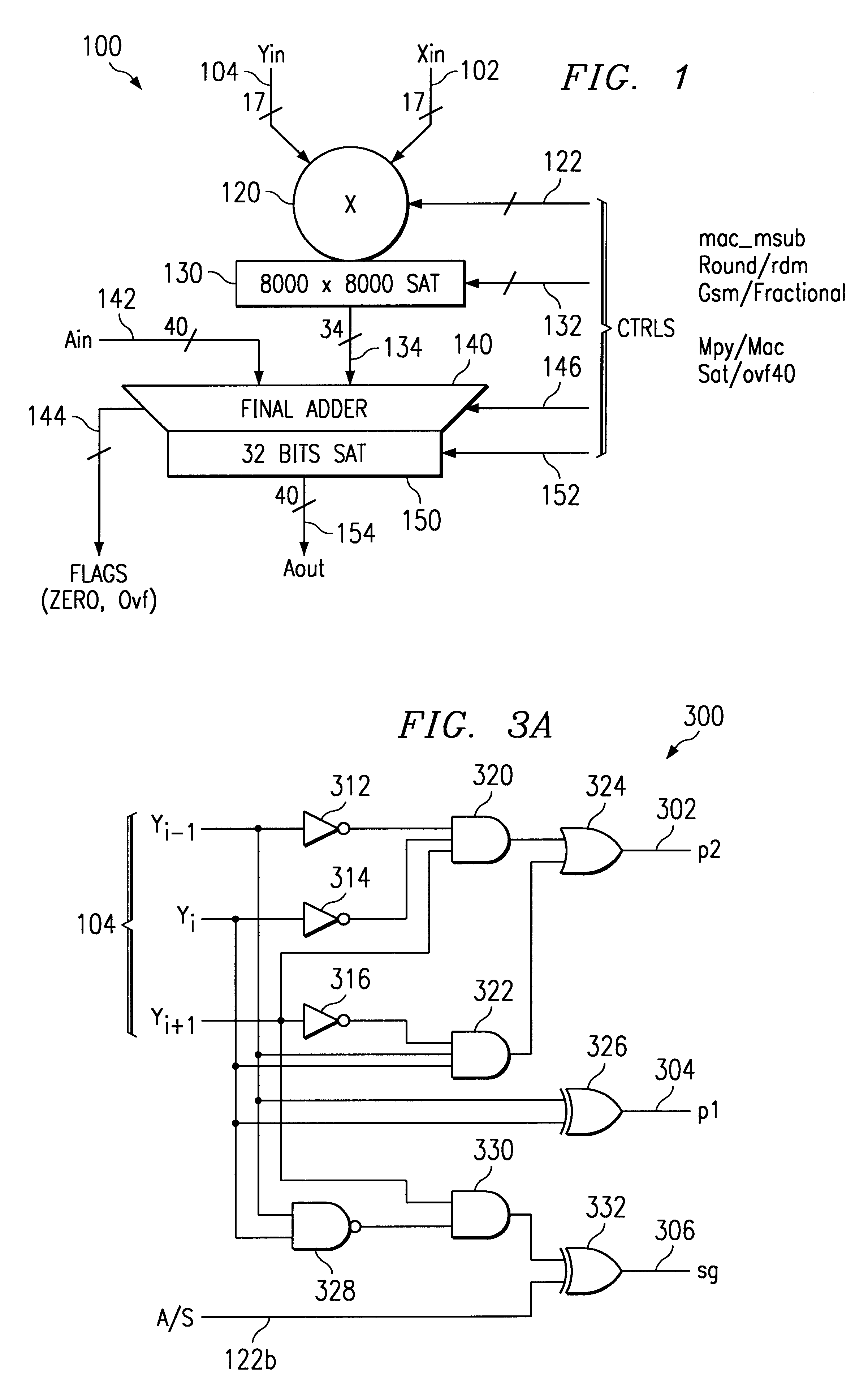
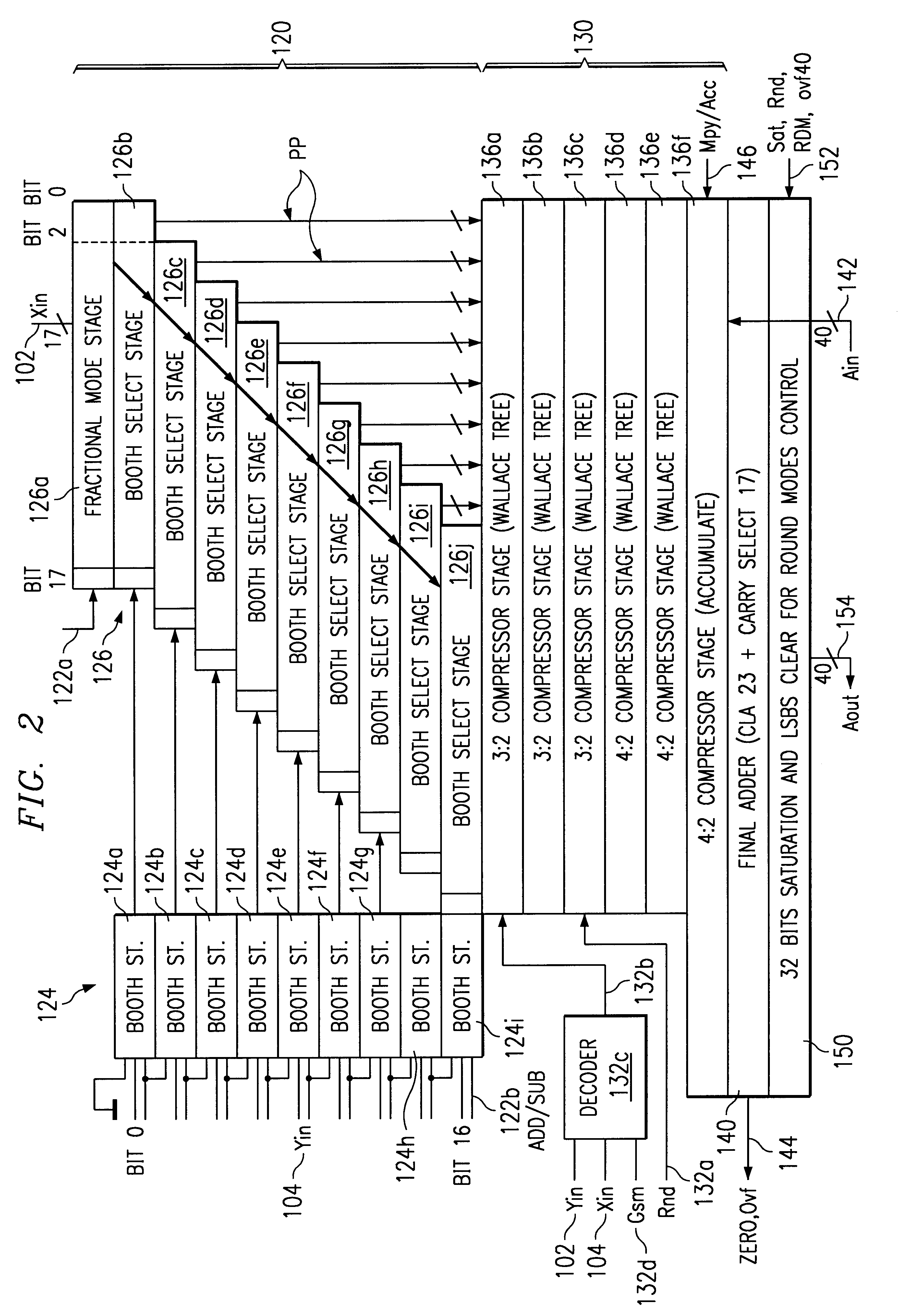
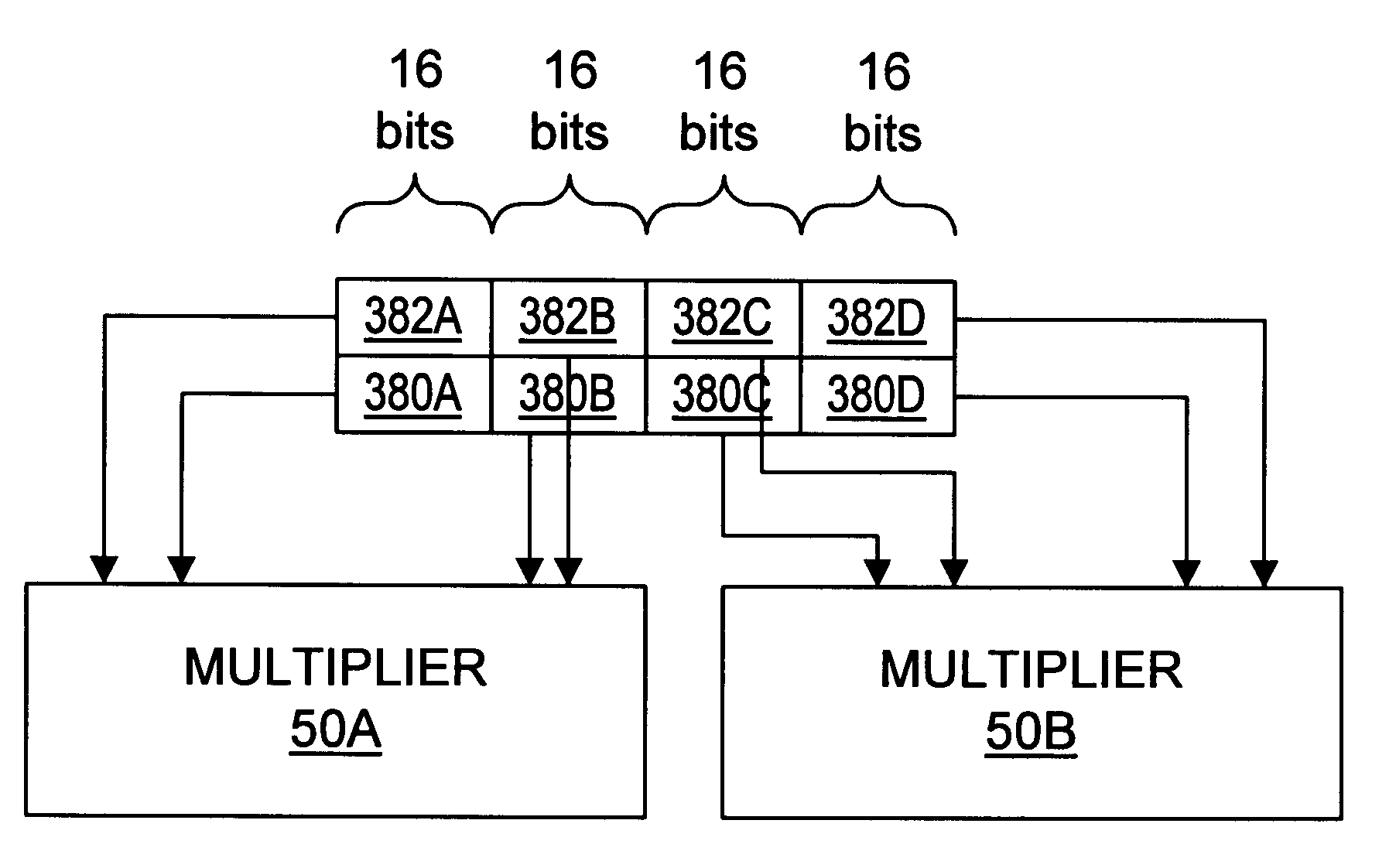
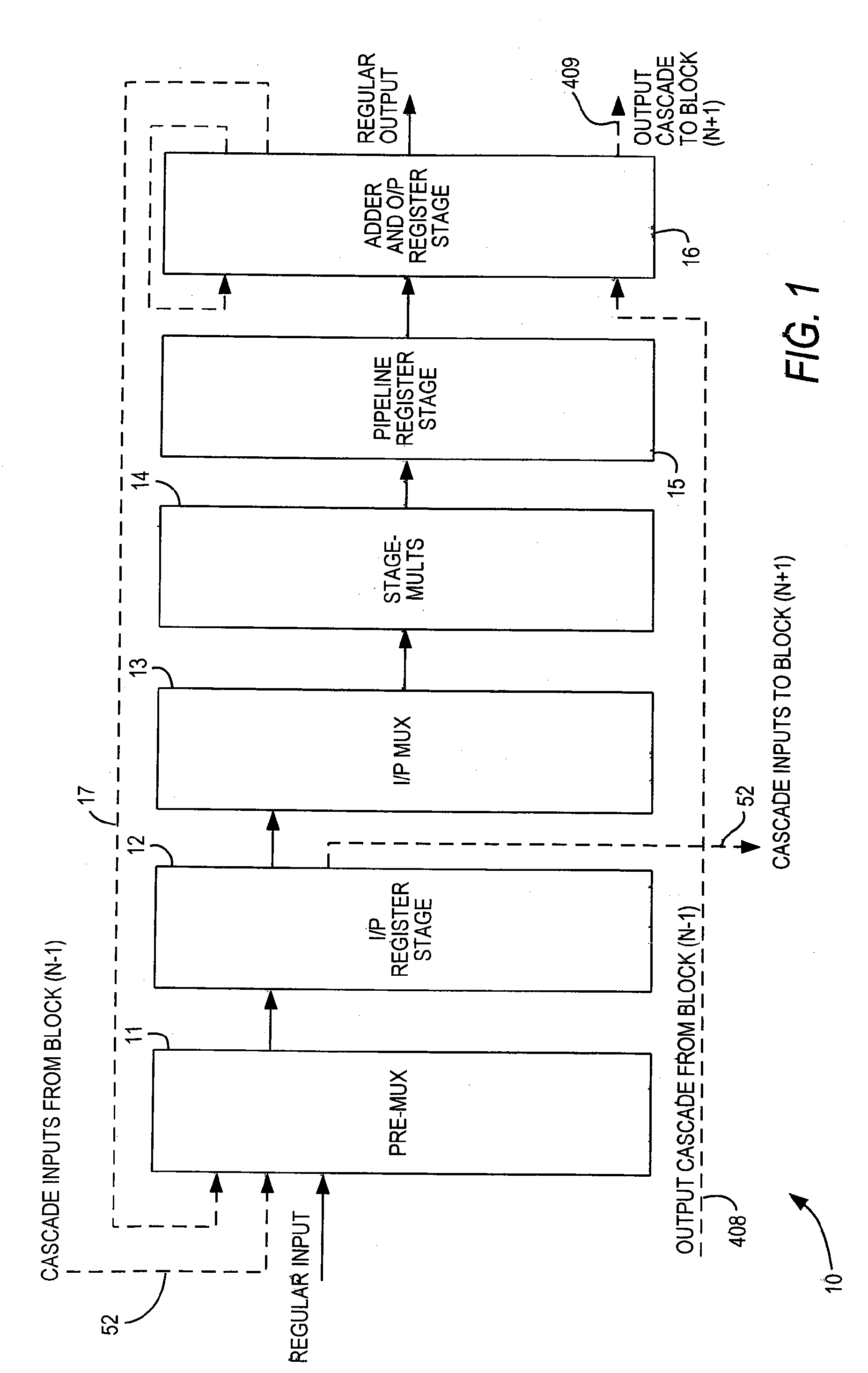
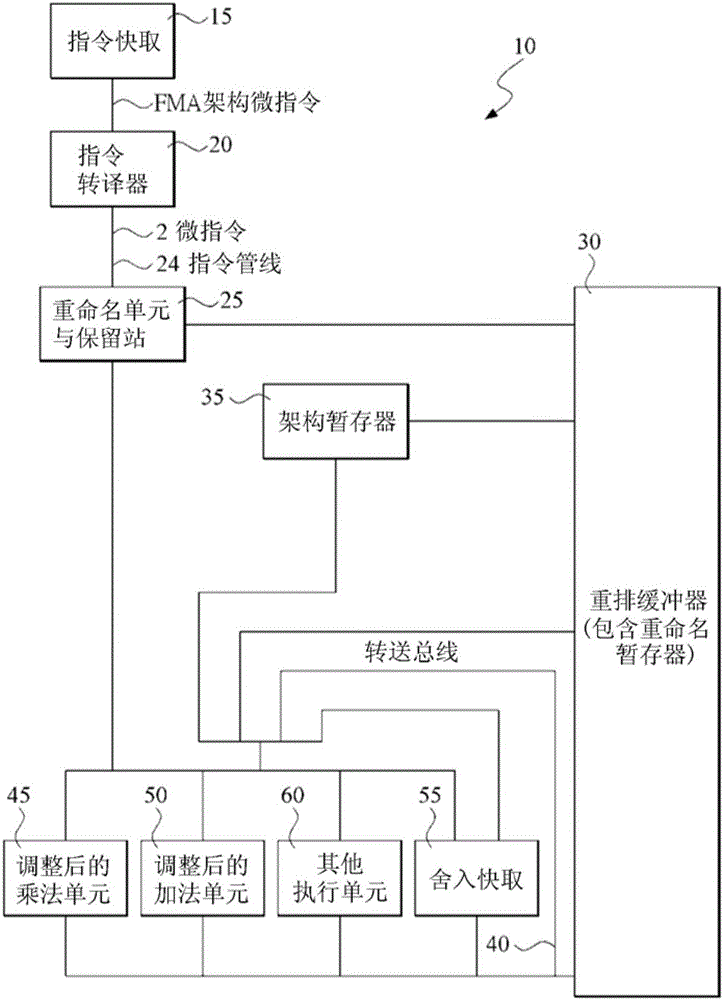
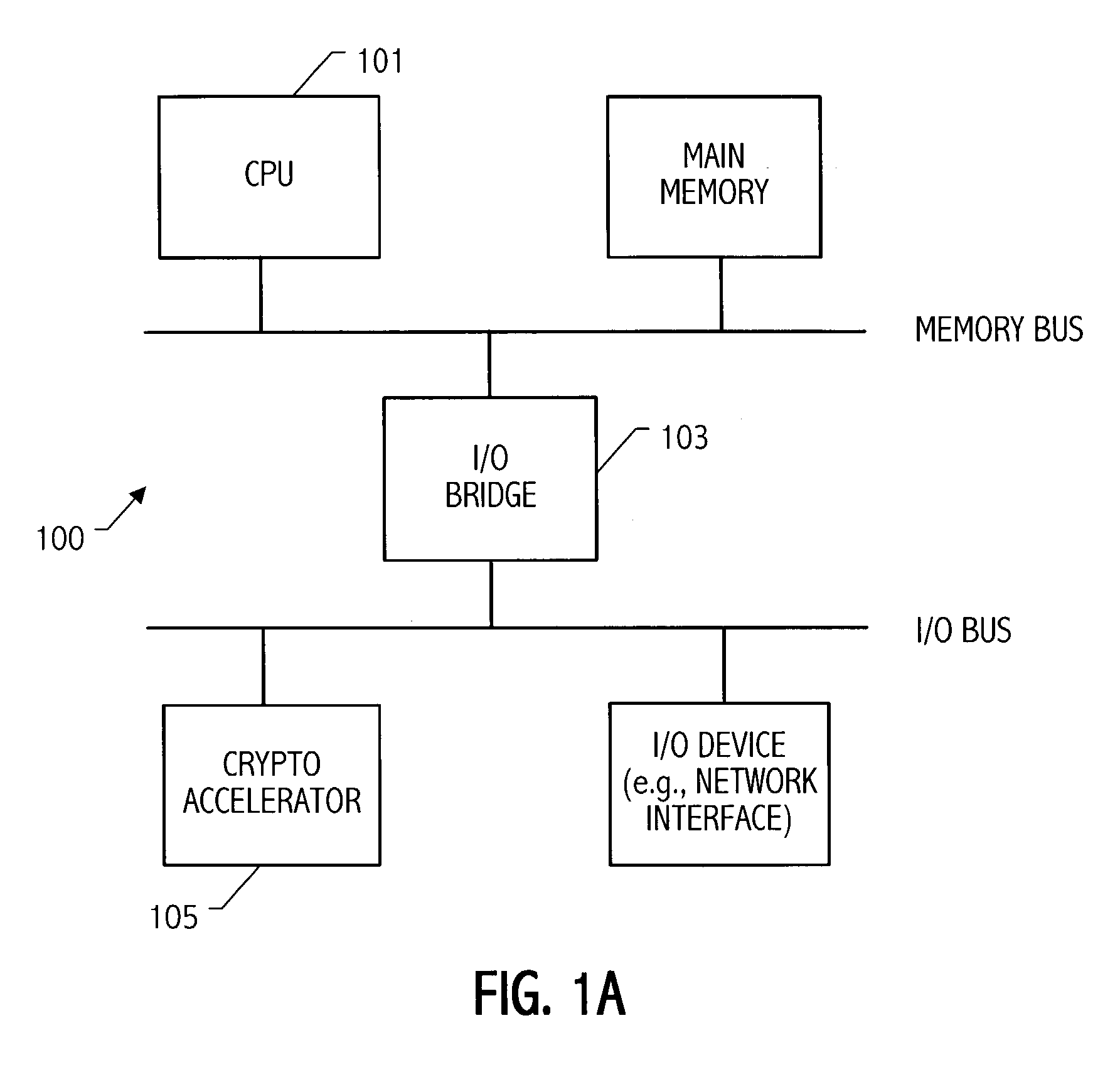
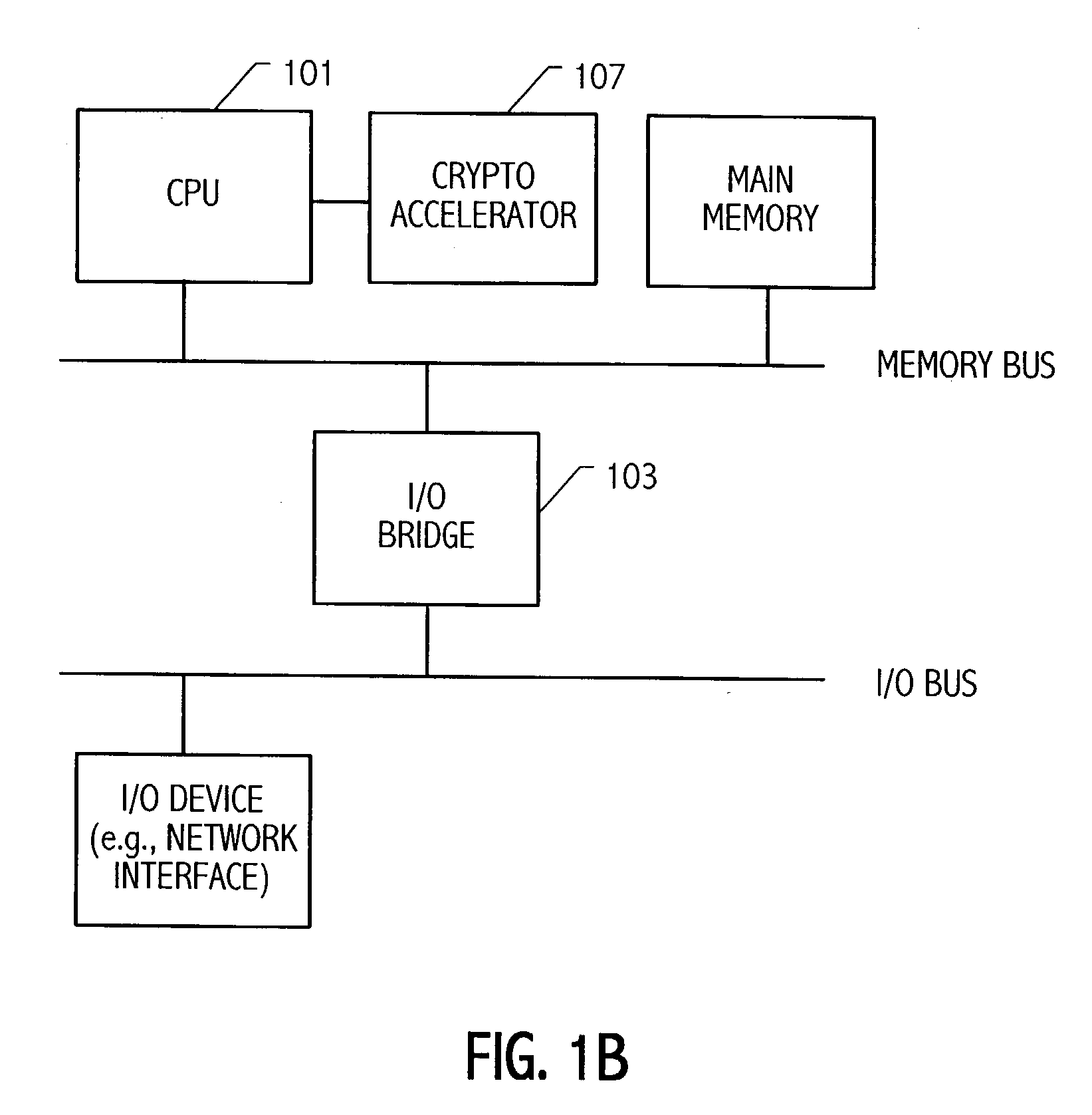
Multiplier accumulator circuits
A multiply-accumulate (MAC) unit, having a first binary operand X, a second binary operand Y, a third binary operand, Booth recode logic for generating a plurality of partial products from said first and second operands, a Wallace tree adder for reducing the partial products and for selectively arithmetically combining the reduced partial products with said third operand, a final adder for generating a final sum, and a saturation circuitry for selectively rounding or saturating said final sum is provided. A dual MAC unit is also provided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for multi-function arithmetic
InactiveUS6223198B1Runtime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesConstant powerRounding
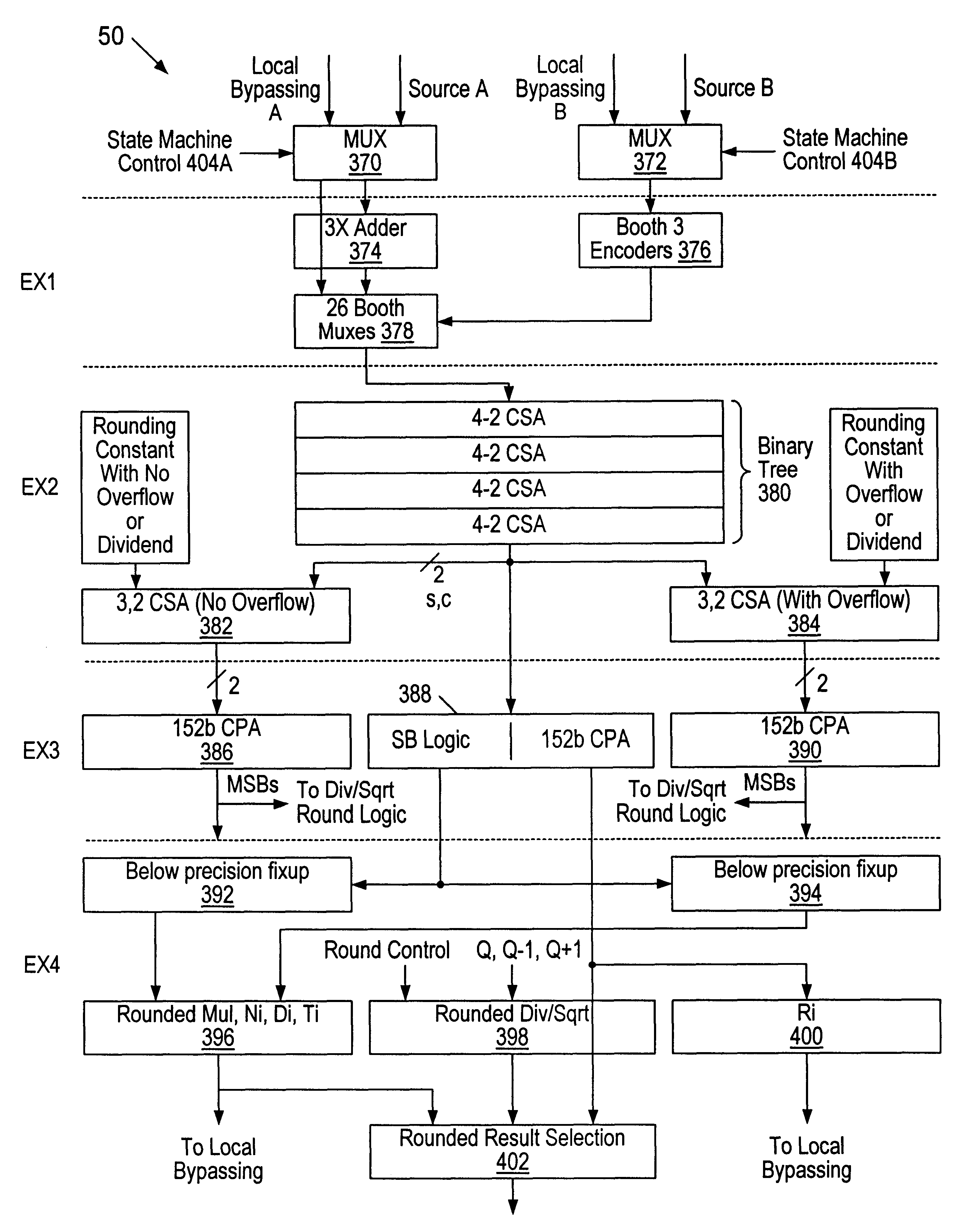
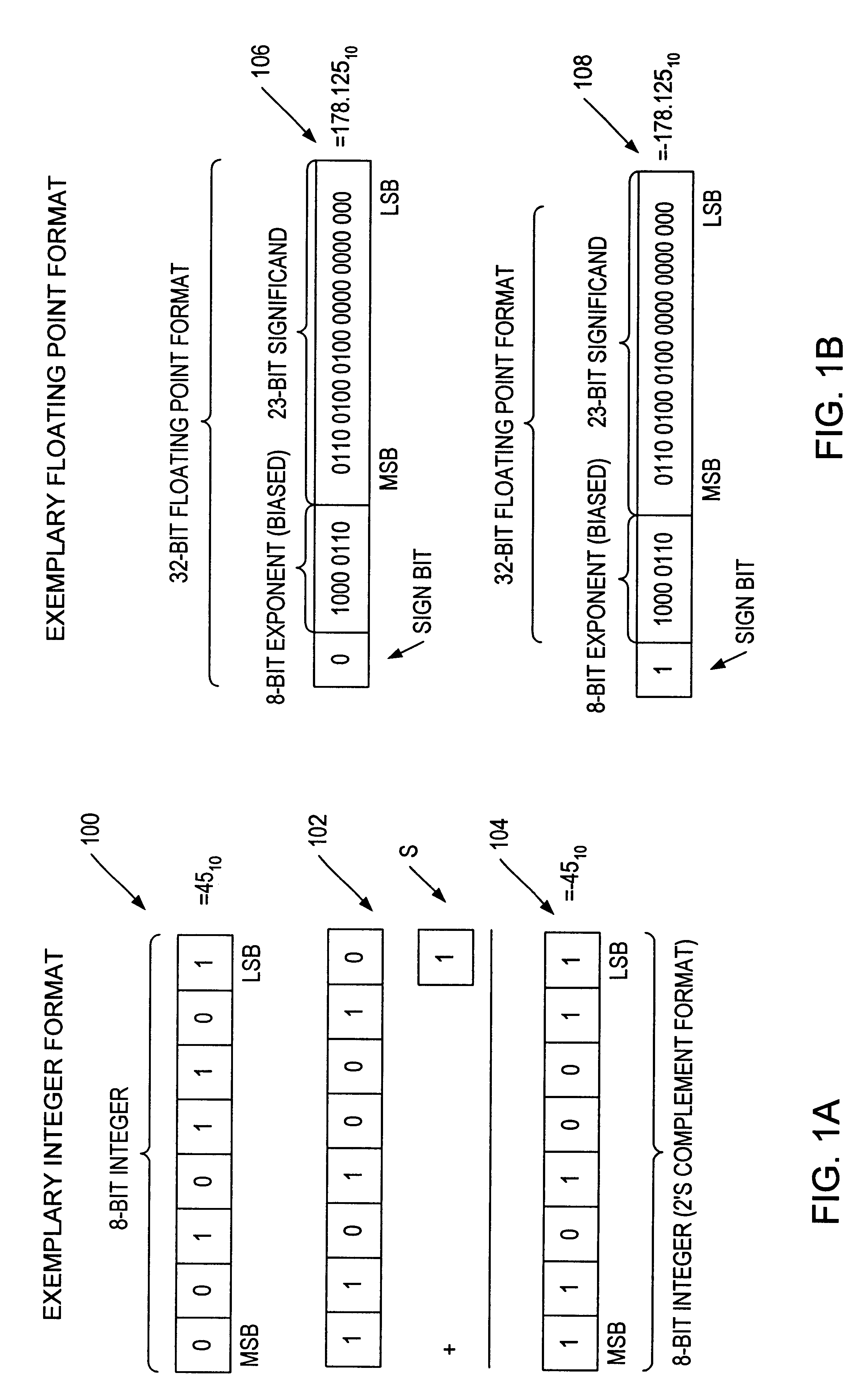
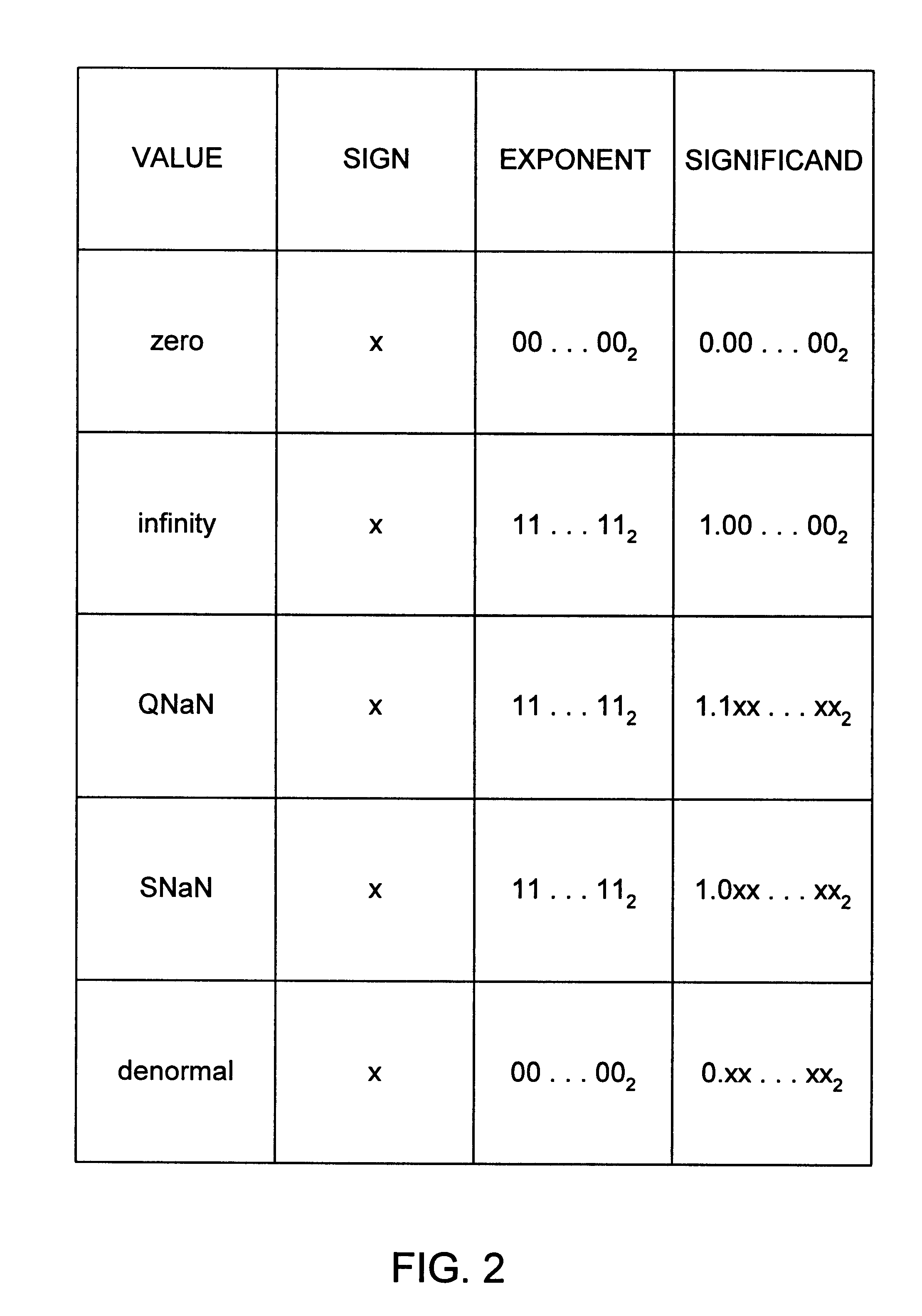
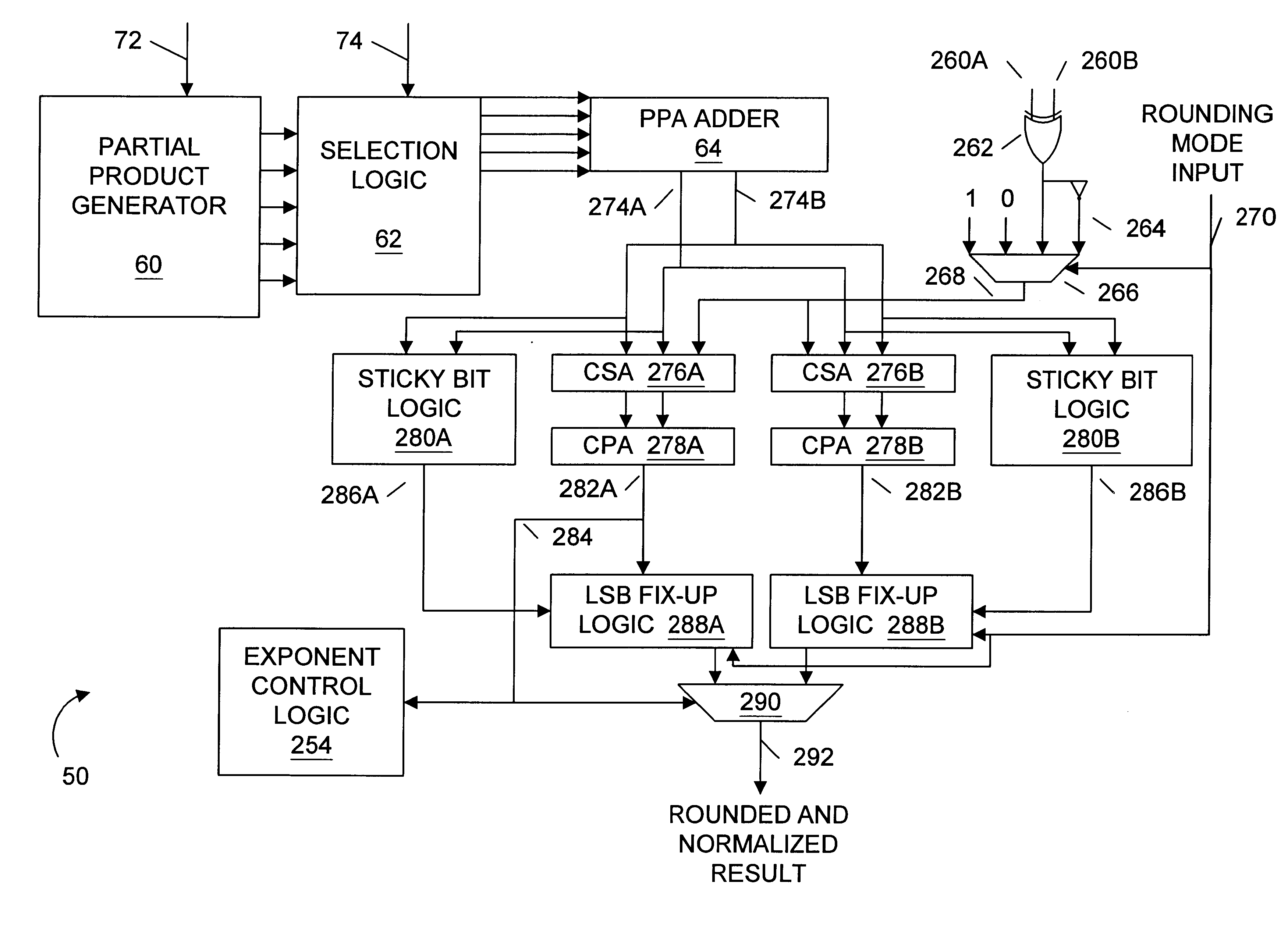
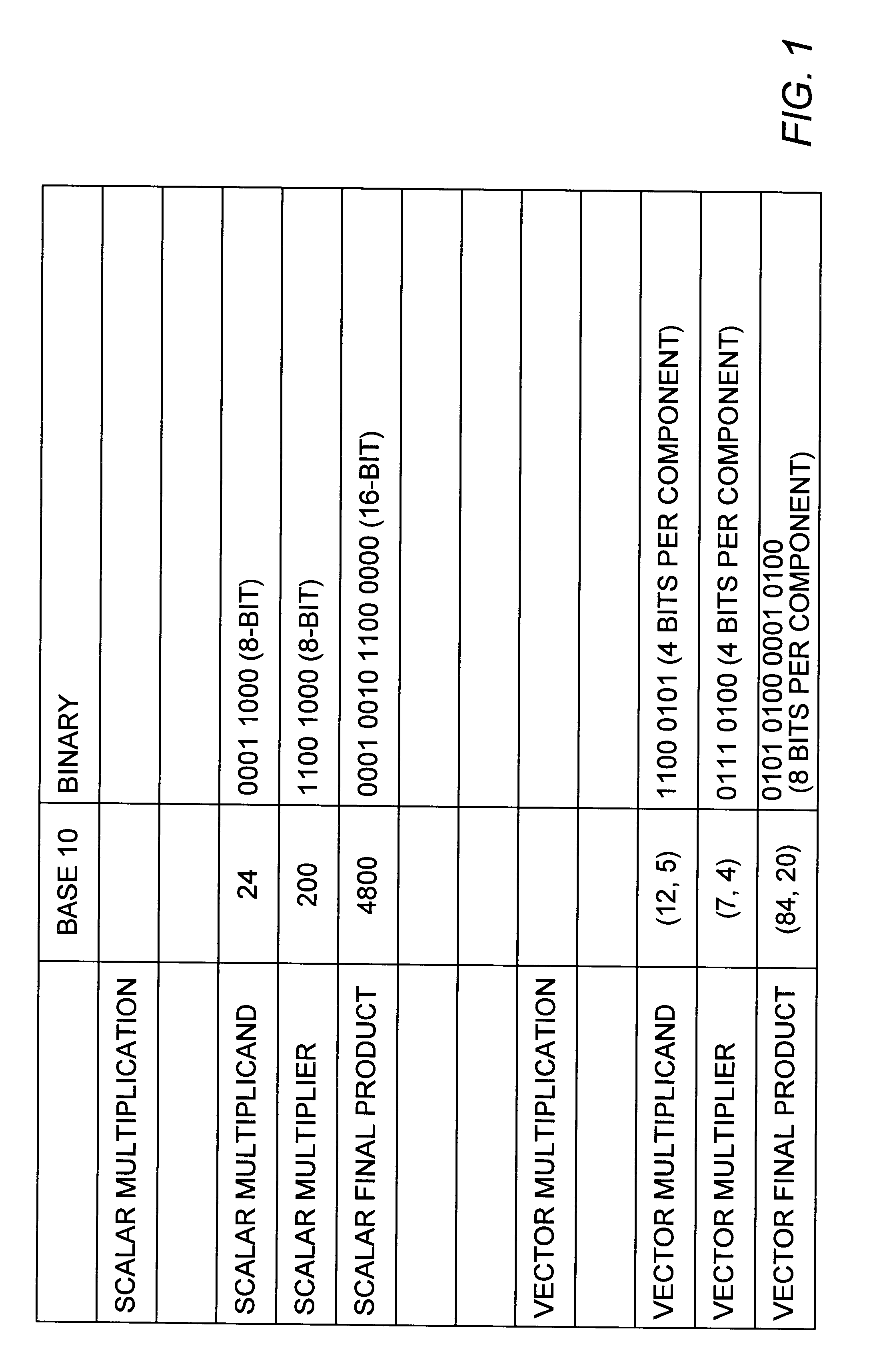
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated and used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative calculations to evaluate constant powers of an operand. Intermediate products that are formed may be rounded and normalized in two paths and then compressed and stored for use in the next iteration. An adjustment constant may also be added to increase the frequency of exactly rounded results.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
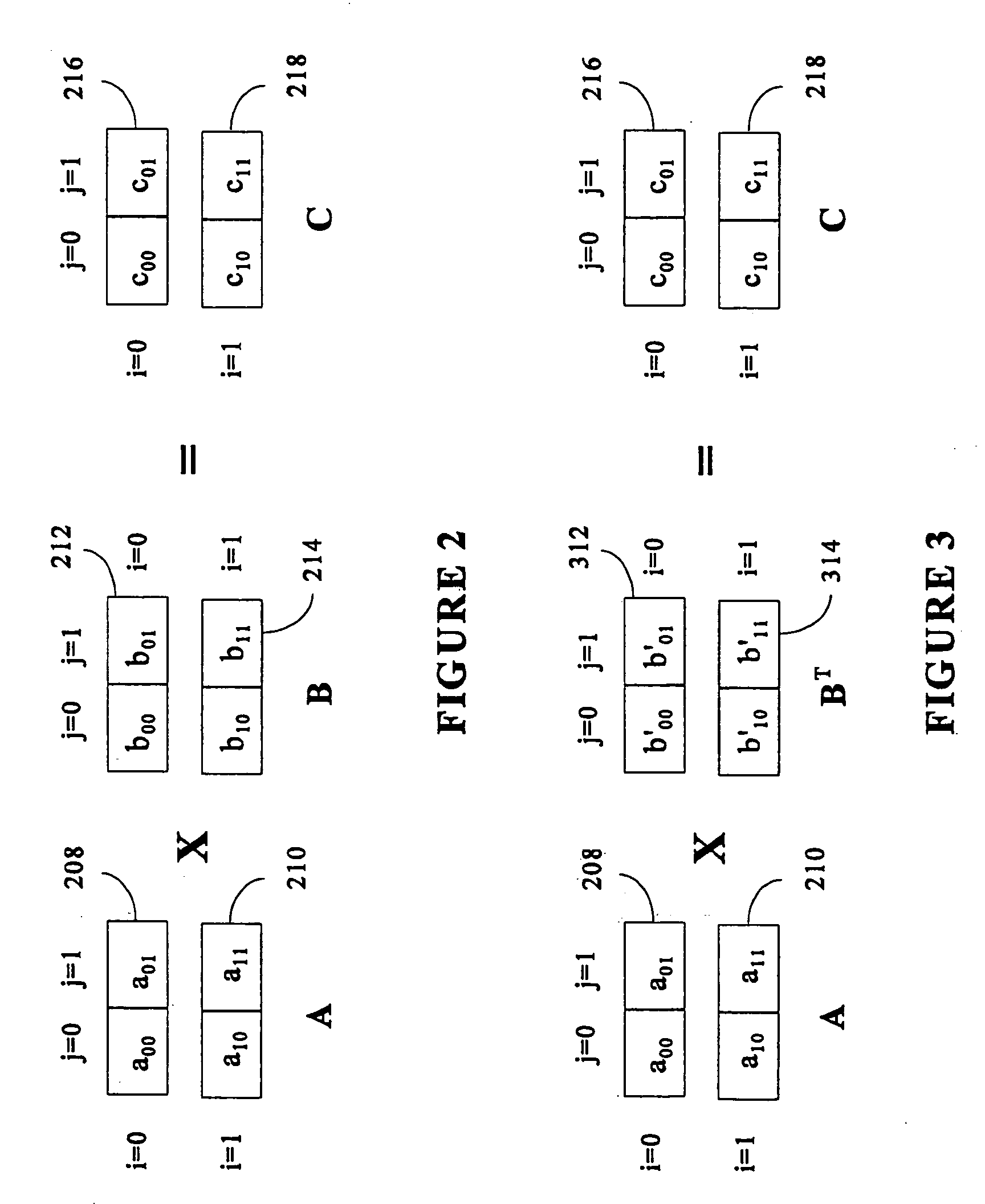
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
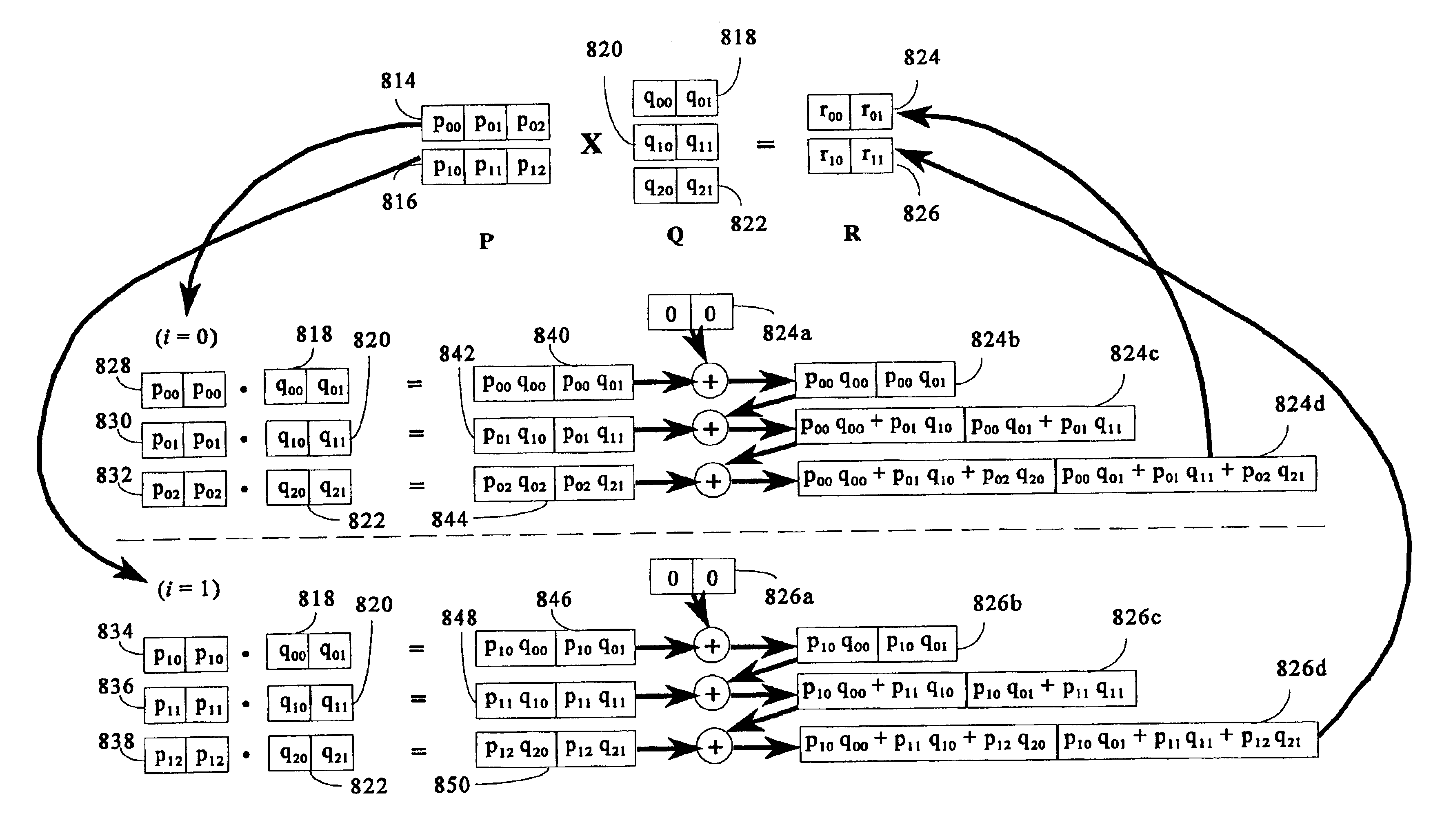
InactiveUS20050193050A1Efficient and rapid matrix multiplicationEfficient executionComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlAlgorithmProcessor register
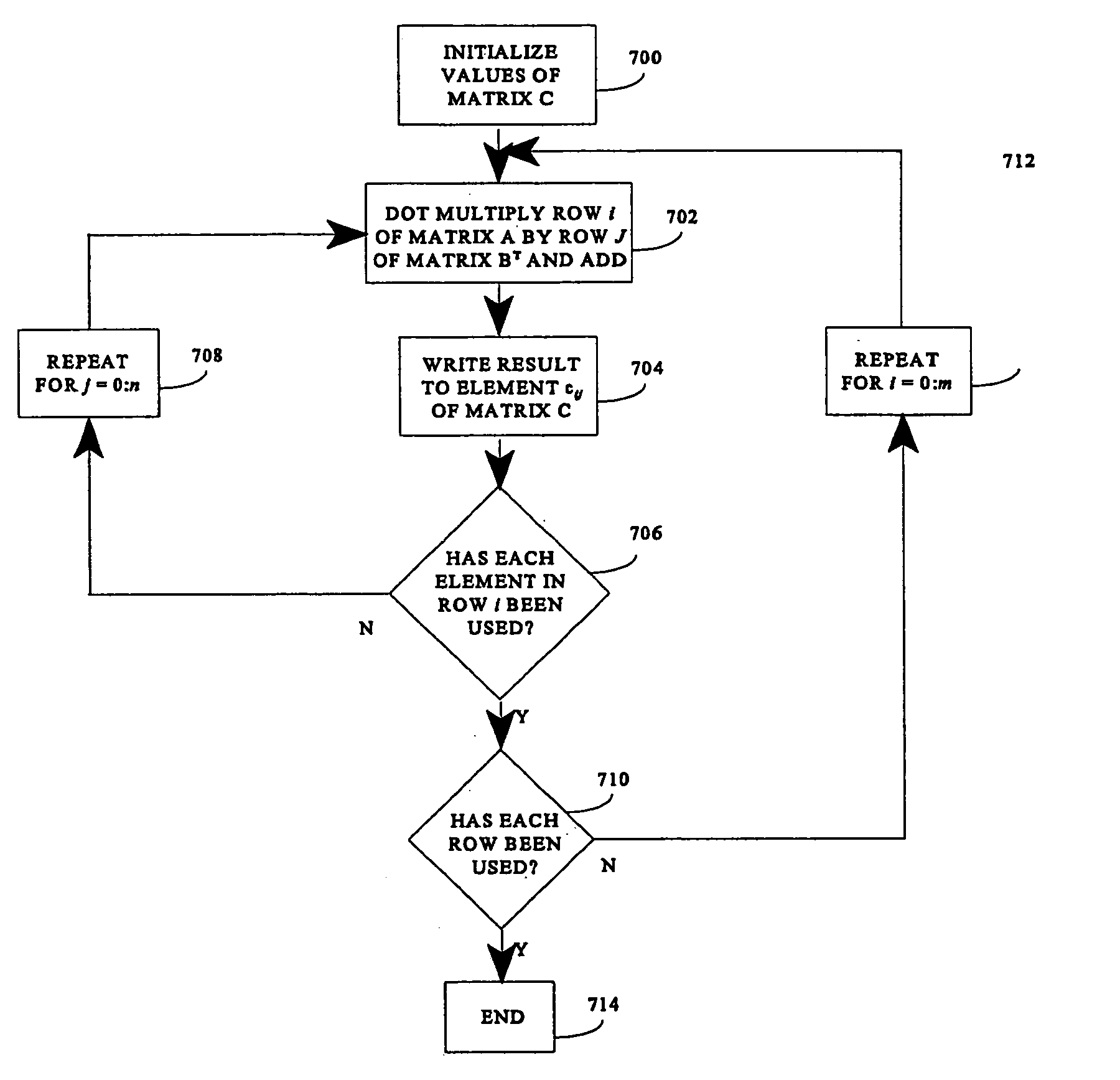
To perform multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system, partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which form a product matrix. Each matrix can be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for performing multiple types of multiplication including signed and unsigned multiplication
InactiveUS6144980ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesControl signalOperand
A multiplier capable of performing both signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured for use in a microprocessor and may include a partial product generator, a selection logic unit, and an adder. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. The multiplier is also configured to receive a first control signal indicative of whether signed or unsigned multiplication is to be performed and a second control signal indicative of whether vector multiplication is to be performed. The multiplier is configured to calculate an effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands based upon each operand's most significant bit and the control signal. The effective signs may then be used by the partial product generation unit and the selection logic to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, the adder is configured to sum them and output the results, which may be signed or unsigned. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier is configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method of high-speed monitoring based on the use of multivariate optical elements
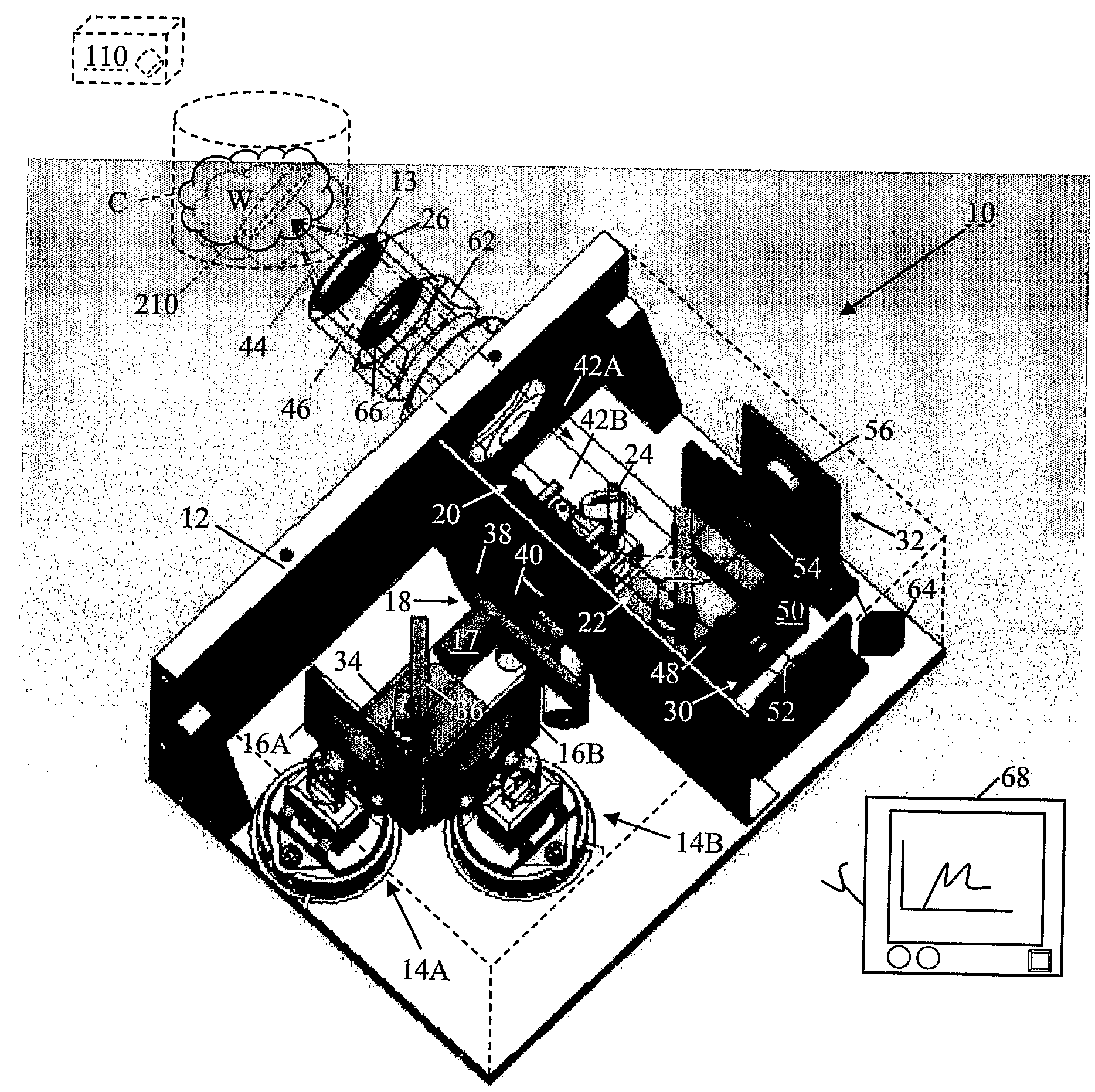
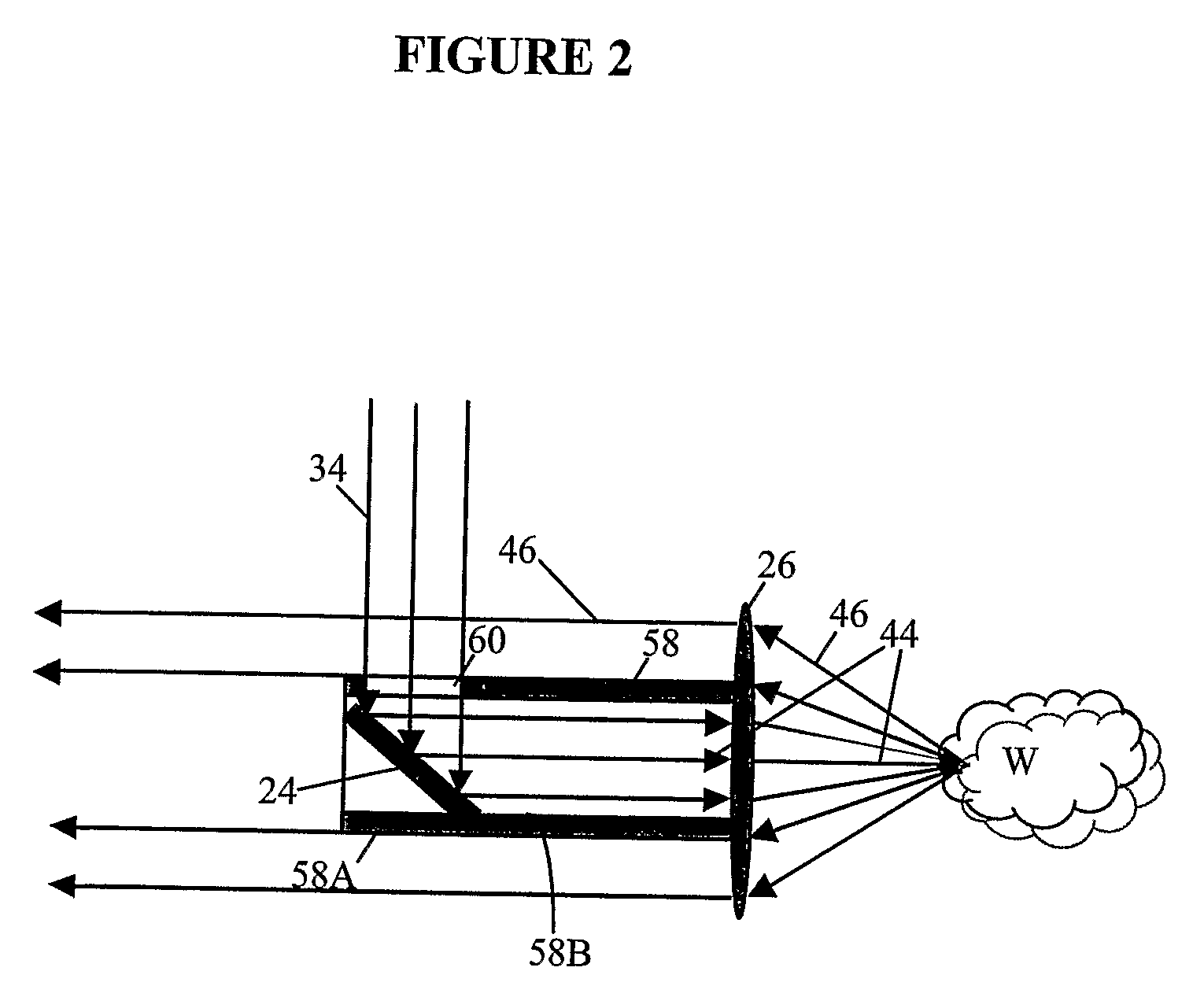
A method of high-speed processing and monitoring of a product, such as a pharmaceutical powder or tablet, comprises: moving the product (C) past an inspection station; illuminating at least a portion of the product with light; spectrally filtering a first portion of light carrying information about the product, o.g., transmitted or reflected light, by passing said first portion through at least one multivariate optical element (148) and detecting said filtered light with a first detector (152), —detecting a deflected second portion of said light with a second detector (156); and determining at least one selected property of the product based on the detector outputs.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Shared FP and SIMD 3D multiplier
InactiveUS6490607B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
A multiplier configured to perform multiplication of both scalar floating point values (XxY) and packed floating point values (i.e., X1xY1 and X2xY2). In addition, the multiplier may be configured to calculate XxY-Z. The multiplier comprises selection logic for selecting source operands, a partial product generator, an adder tree, and two or more adders configured to sum the results from the adder tree to achieve a final result. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative multiplication operations to implement such arithmetical operations such as division and square root. The multiplier may be configured to generate two versions of the final result, one assuming there is an overflow, and another assuming there is not an overflow. A computer system and method for performing multiplication are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Method and apparatus for rounding and normalizing results within a multiplier
InactiveUS6269384B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and calculating a rounded products
InactiveUS6038583ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
ActiveUS20070185952A1Reduce areaImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsLogic circuitsDigital signal processingBinary multiplier
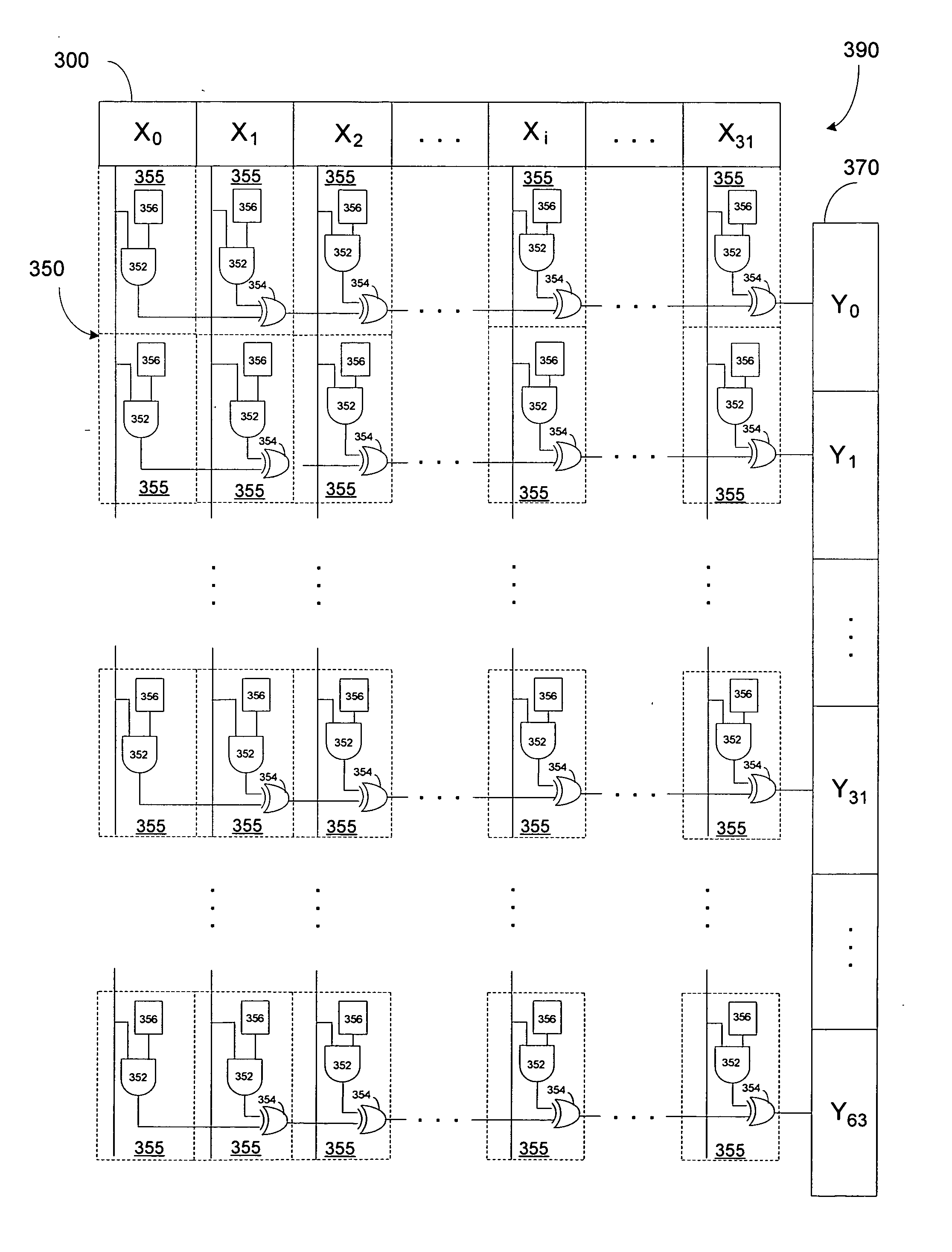
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device incorporates a fundamental processing unit that performs a sum of two multiplications, adding the partial products of both multiplications without computing the individual multiplications. Such fundamental processing units consume less area than conventional separate multipliers and adders. The specialized processing block further has input and output stages, as well as a loopback function, to allow the block to be configured for various digital signal processing operations.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
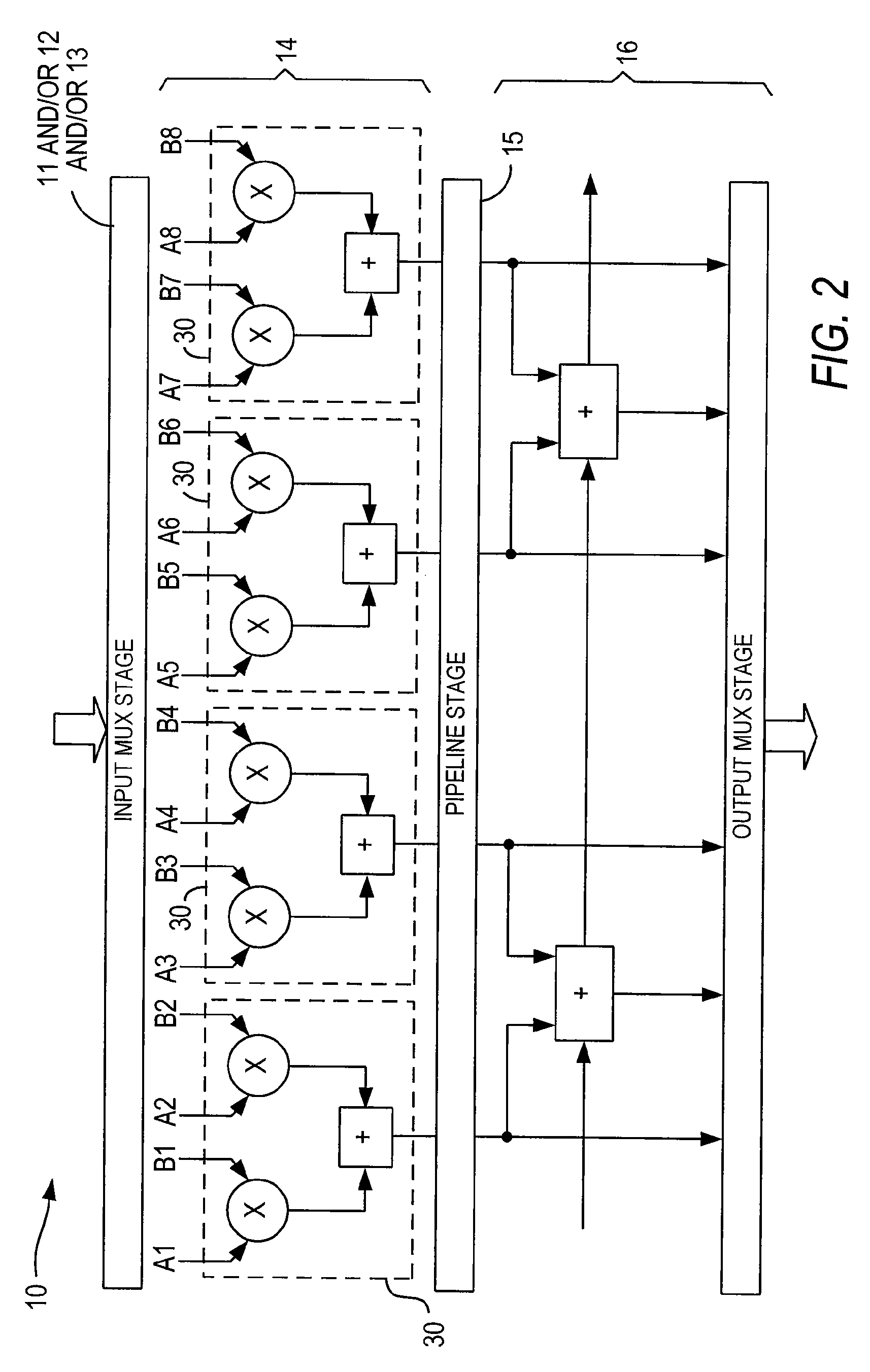
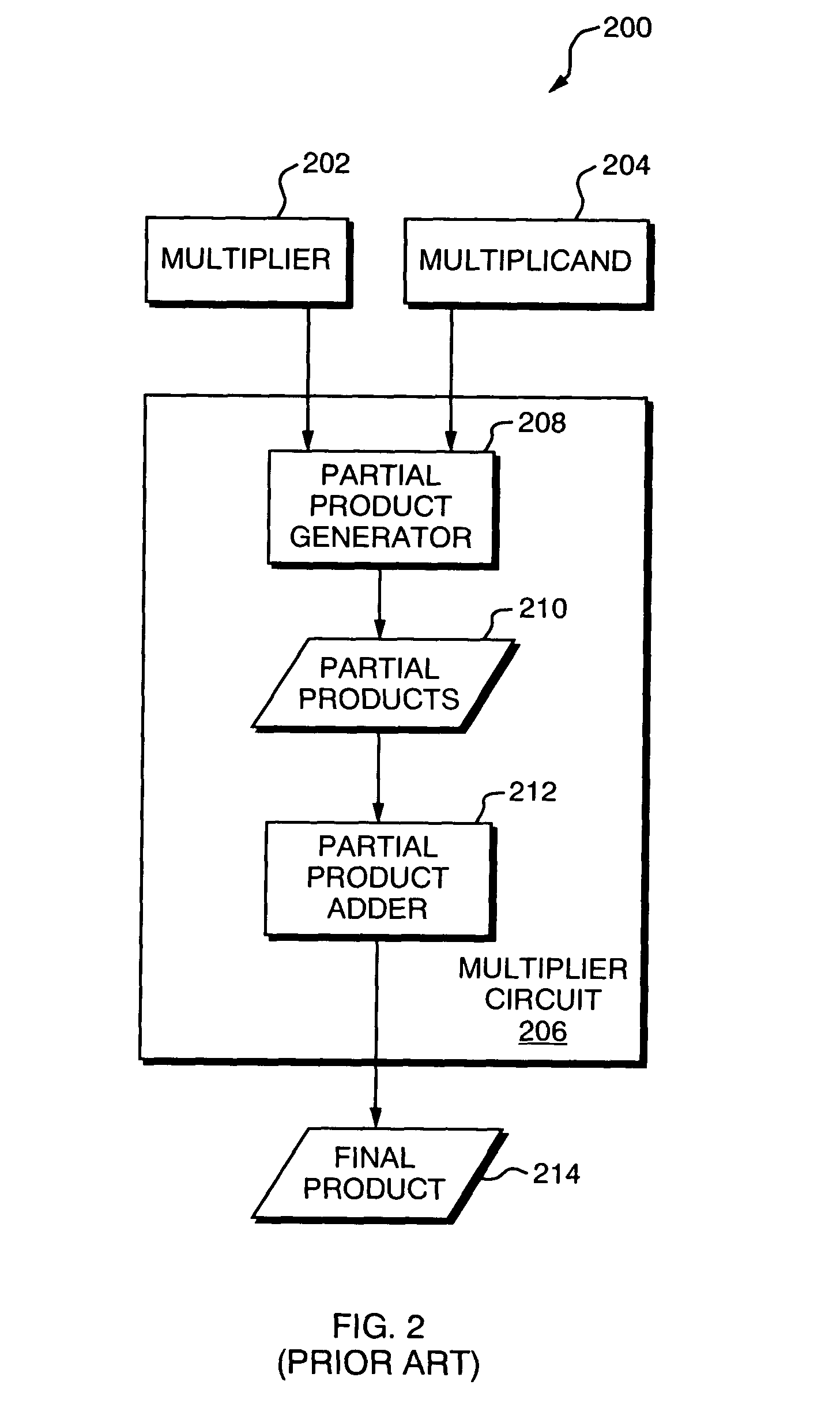
Multiplier circuit
A multiplier circuit is disclosed for multiplying a multiplicand by a multiplier. The multiplier circuit includes a partial product generator and a partial product adder. The partial product generator includes a first input to receive a multiplicand; a second input to receive a multiplier; partial product generation means for producing a plurality of partial products based on the multiplicand and the multiplier; and an output coupled to the partial product generation means to provide the plurality of partial products. The partial product adder includes an input coupled to the output of the partial product generator; a plurality of adders to add the plurality of partial products to produce a final product, the plurality of adders comprising a plurality of compressors having substantially the same width; and an output coupled to the plurality of adders to provide the final product.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
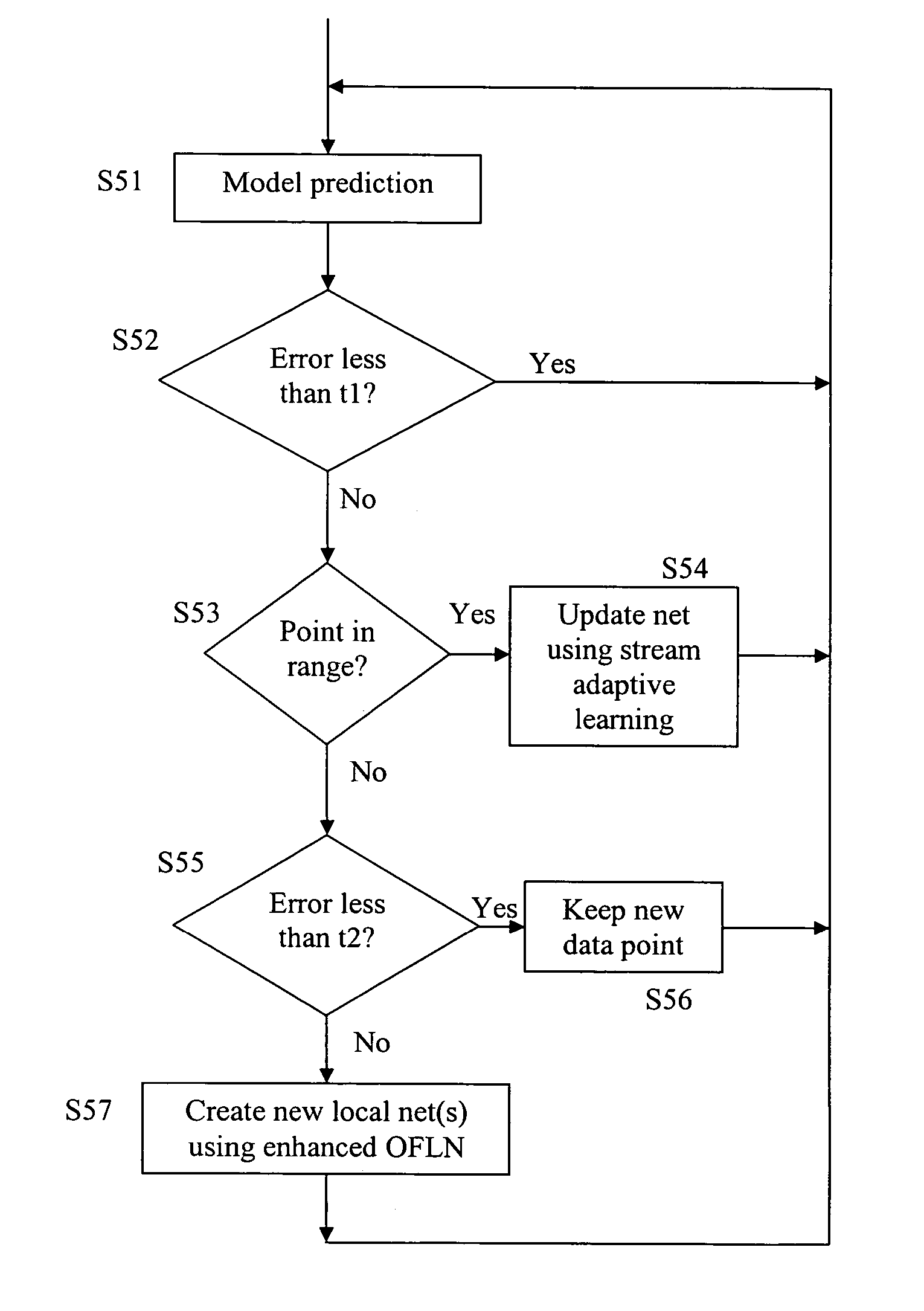
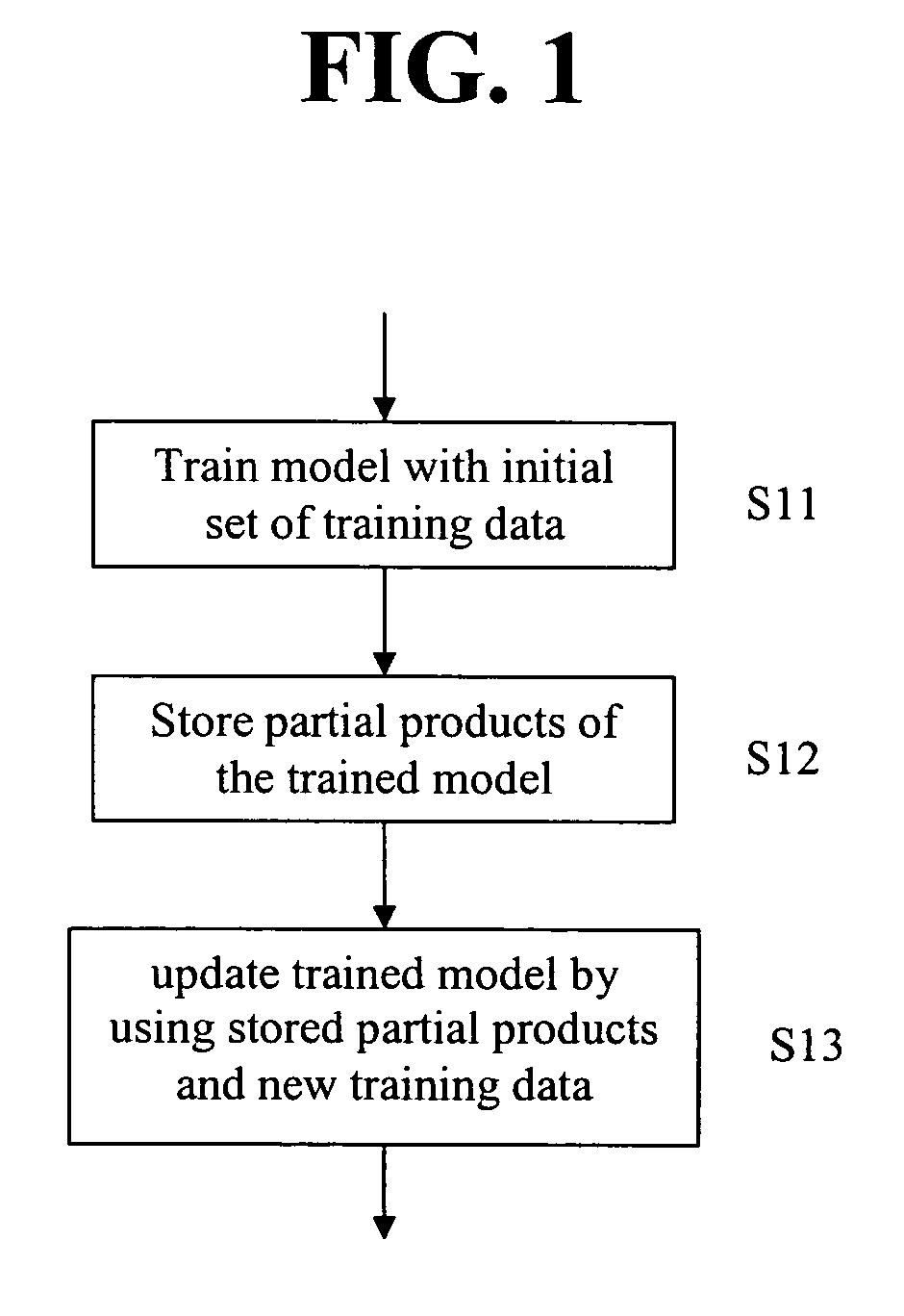
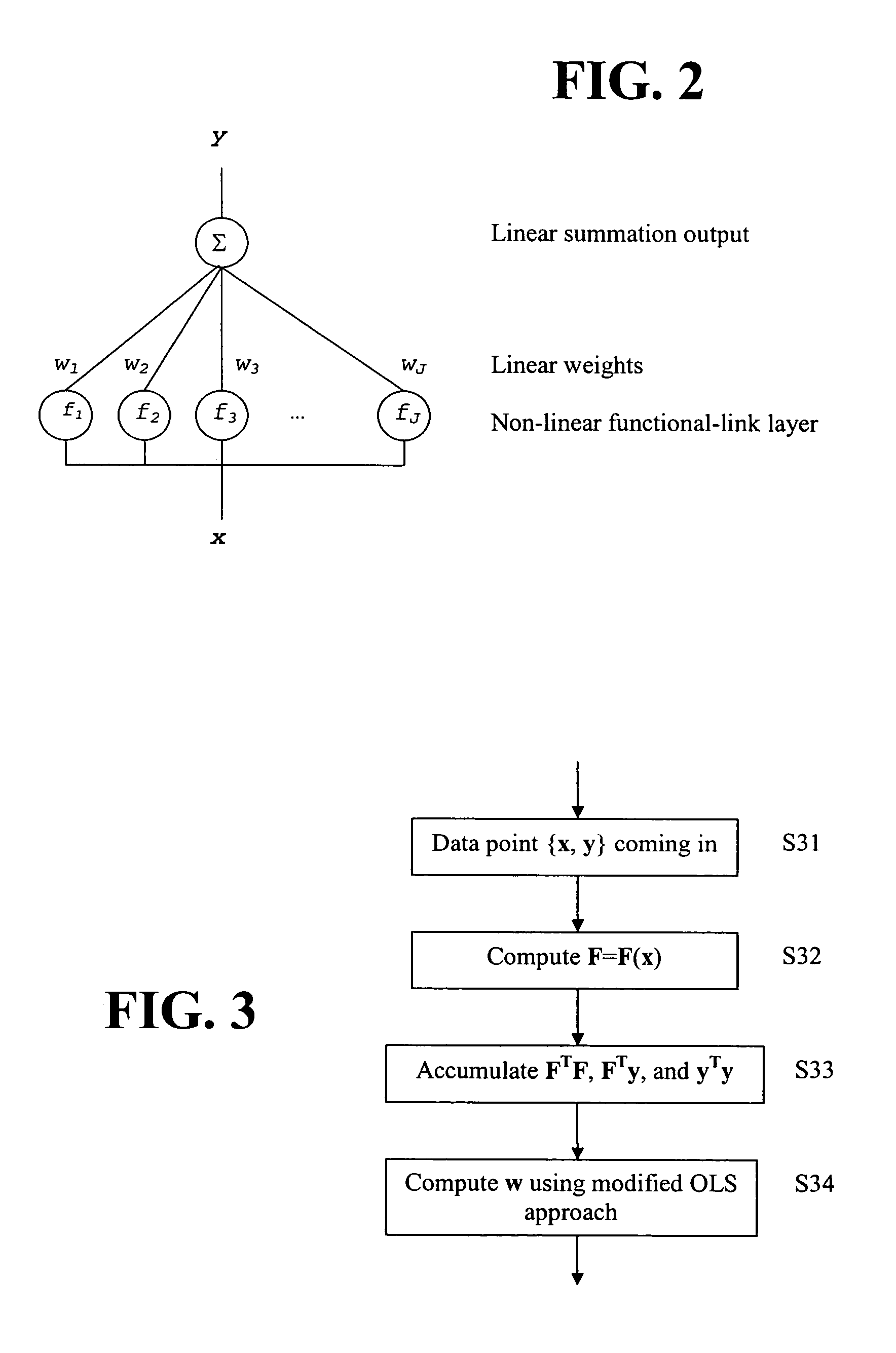
Adaptive learning enhancement to automated model maintenance
An adaptive learning method for automated maintenance of a neural net model is provided. The neural net model is trained with an initial set of training data. Partial products of the trained model are stored. When new training data are available, the trained model is updated by using the stored partial products and the new training data to compute weights for the updated model.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
Apparatus and method of multiplication using a plurality of identical partial multiplication modules
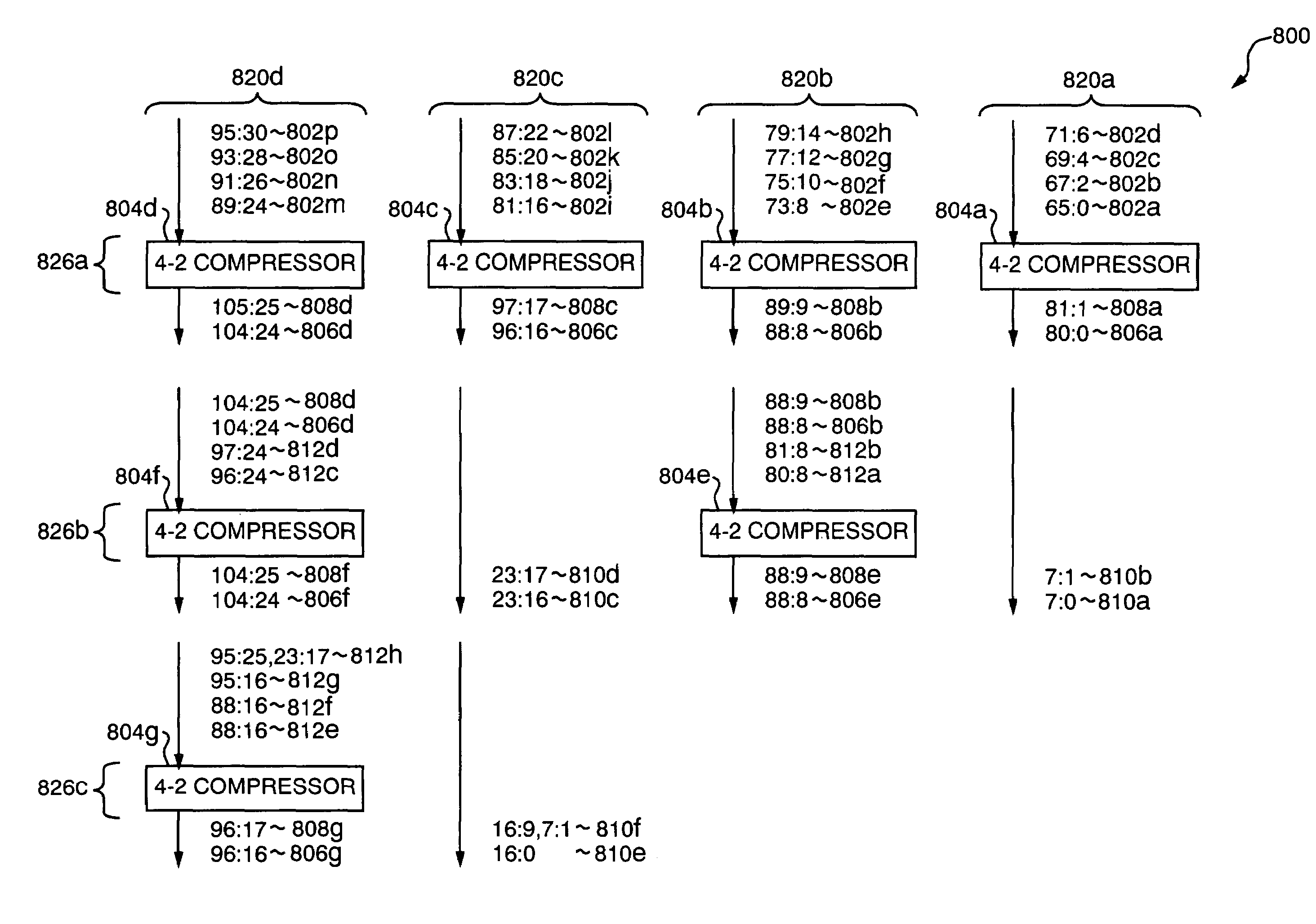
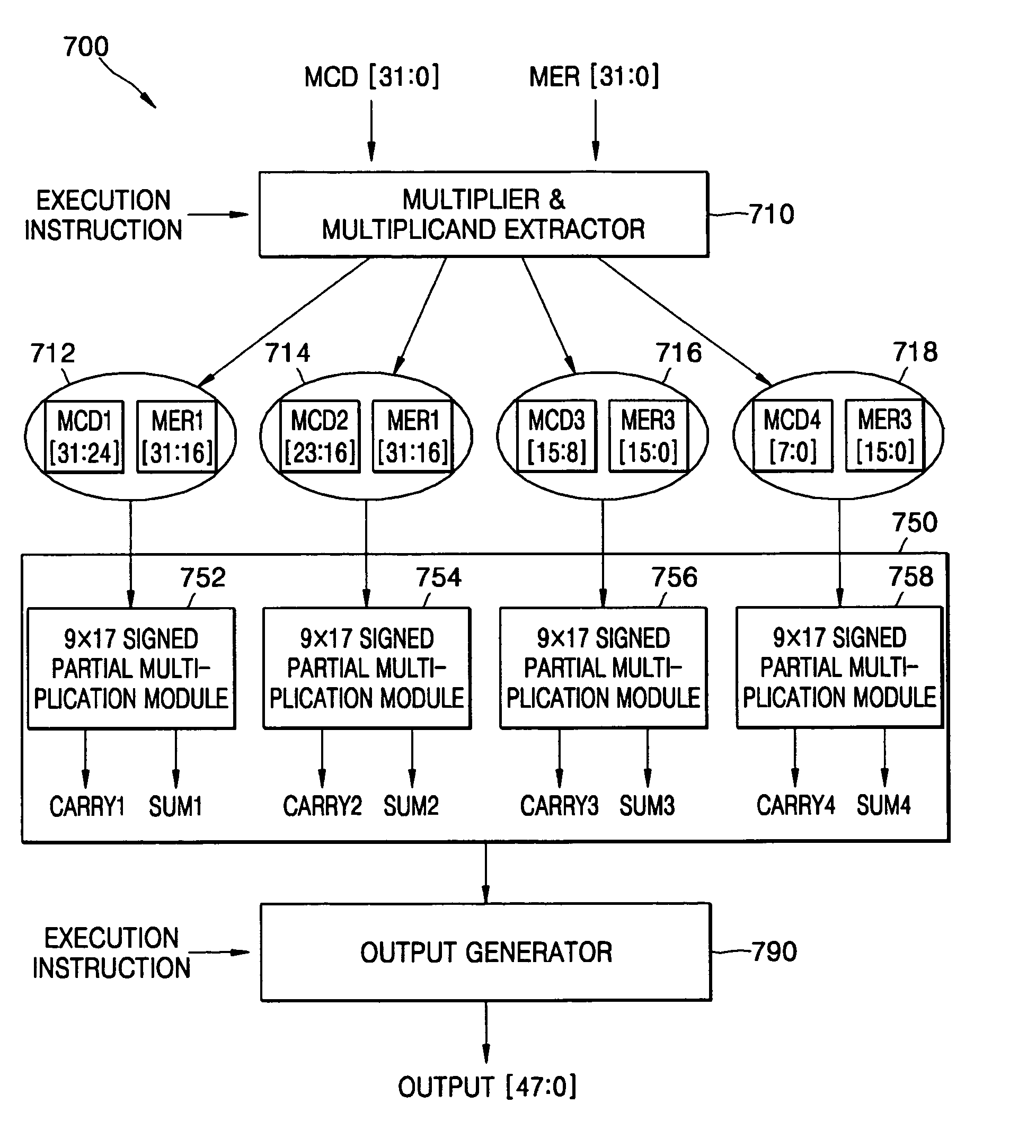
InactiveUS7769797B2Reduce hardware sizeMinimize power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierParallel computing
A multiplication apparatus including a multiplier and multiplicand extractor for dividing the multiplicand into partial multiplicands and dividing the multiplier into partial multipliers, and for generating partial input pairs by combining the partial multiplicands with the partial multipliers, and a multiplication executor including identical partial multiplication modules for receiving the partial input pairs and outputting partial carries and partial products. The apparatus further includes an output generator for combining the partial carries with the partial products according to the execution instruction to generate a final output. For simple multiplications, each of the partial multiplication modules can pass data to and from an adjacent partial multiplication module to calculate the partial carry and the partial product, and pass bits exceeding its own multiplication coverage.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Method for feedforward corrections for off-specification conditions
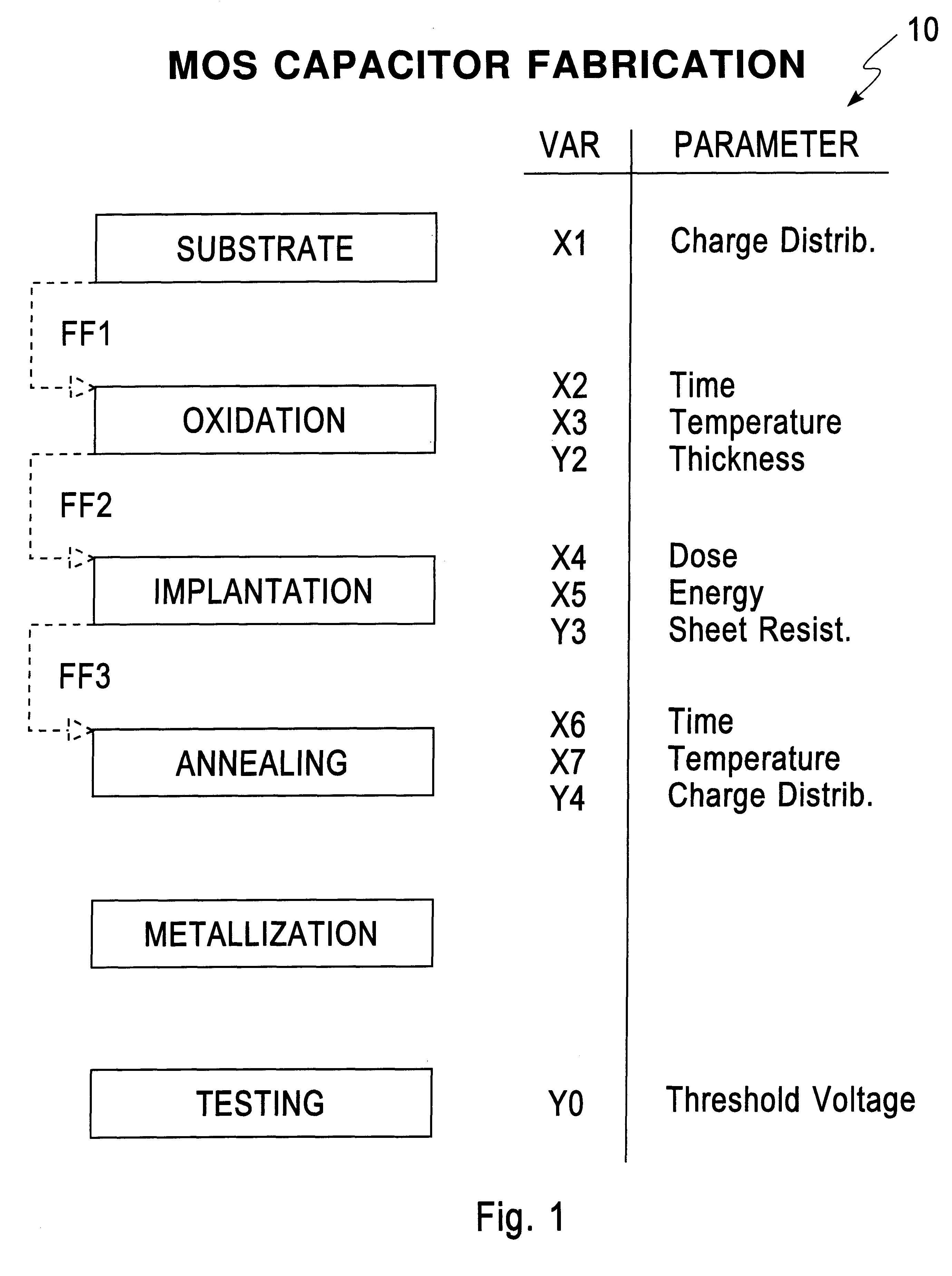
InactiveUS6240330B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringProcess conditions
In current manufacturing practices, if a process results in a partial product which is outside its specification, it is either sent back to be reworked, or is scrapped. This results in unacceptable waste. The present invention comprises a method for minimizing this wasted work and materials, by corrective actions by subsequent processes. This approach is general, and is capable of correcting the effects of out-of-specs manufacturing process conditions, including the salvaging of partial product, thereby obviating the need for rework or scrap.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low power array multiplier
InactiveUS7546331B2Lower latencyReduce power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesArray data structureBinary multiplier
An array multiplier comprises a partial product array including a plurality of array elements and a final carry propagate adder. Operands smaller than a corresponding dimension of the partial product array are shifted toward the most significant row or column of the array to reduce the number of array elements used to compute the product of the operands. Switching activity in the unused array elements may be reduced by turning off power to the array elements or by padding the shifted operands with zeros in the least significant bits. Additional power saving may be achieved by having bypass lines in the partial product array that bypasses non-essential array elements and by feeding partial sum and carry directly to the final carry propagate adder. Elements of the carry propagate adder may also be bypassed to achieve further power reduction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Structured mixed bit-width multiplying method and structured mixed bit-width multiplying device
InactiveCN102591615AReduce overheadIncrease profitDigital data processing detailsControl signalOperand
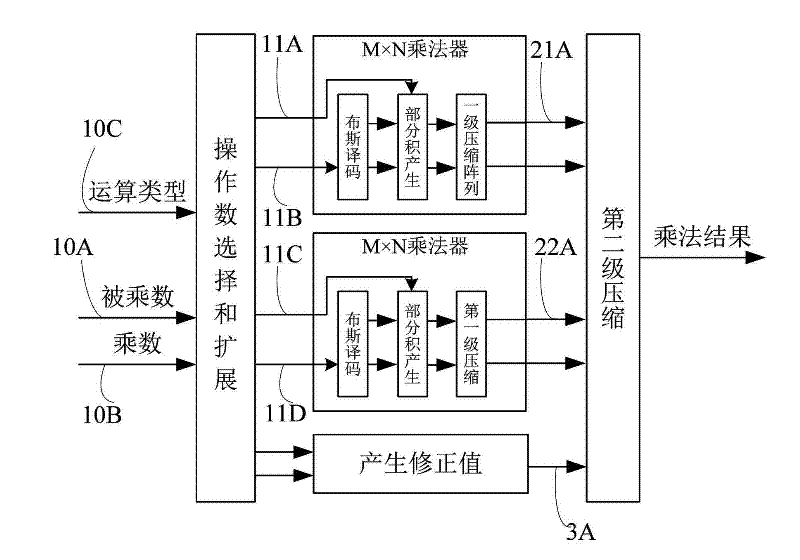
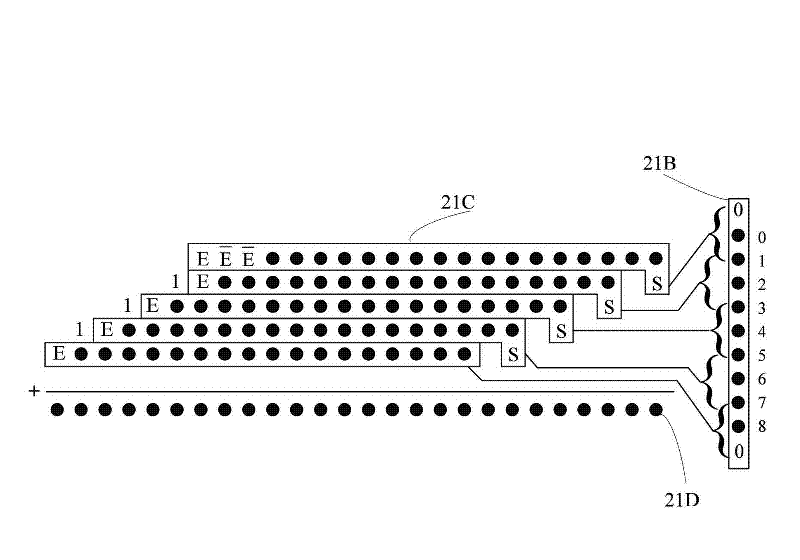
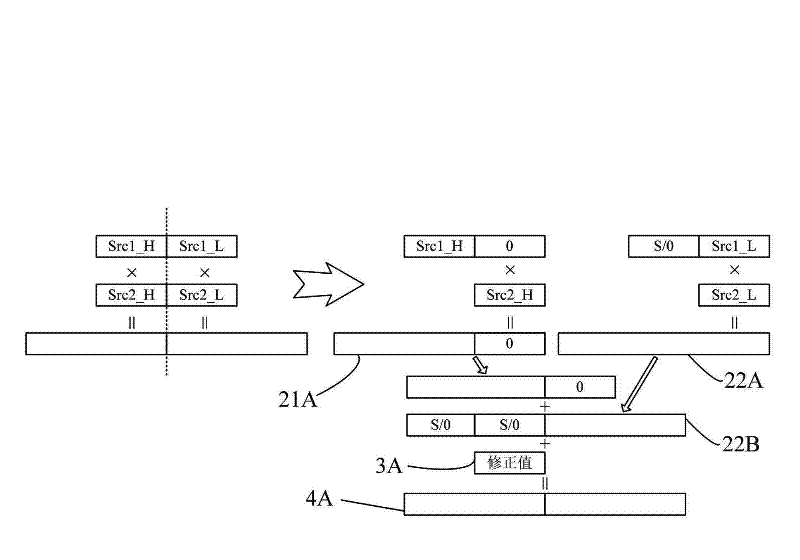
The invention discloses a structured mixed bit-width multiplying method and a structured mixed bit-width multiplying device. The method includes the steps: 1) inputting a multiplier, a multiplicand and a computing control signal; 2) splitting the multiplier and the multiplicand and performing sign bit expansion for the multiplier and the multiplicand; 3) importing the multiplier and the multiplicand to two MXN multiplying units for Booth decoding and generating partial products, and compressing the partial products; 4) generating a corrected value; and 5) compressing a compressed output result and the corrected value to obtain a multiplying result. The device comprises an operand selection and expansion unit, the first MXN multiplying unit, the second MXN multiplying unit, a correcting unit and a final product arithmetic element, wherein the operand selection and expansion unit is connected with the final product arithmetic element through the MXN multiplying unit, the second MXN multiplying unit and the correcting unit. The structured mixed bit-width multiplying device has the advantages of high hardware use ratio and area use ratio, high arithmetic speed, low hardware expenditure, simple structure and orderliness in obtained territory.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
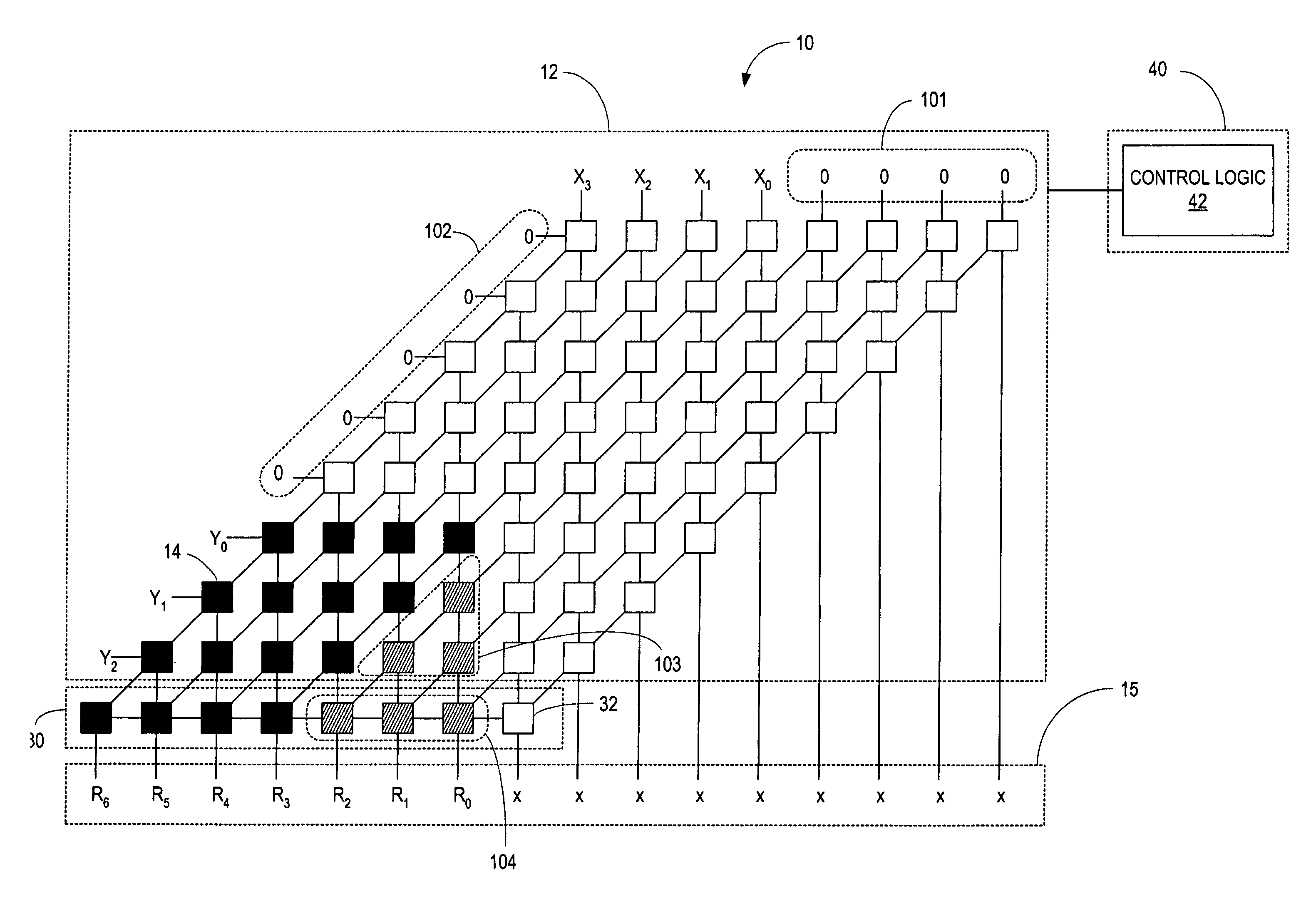
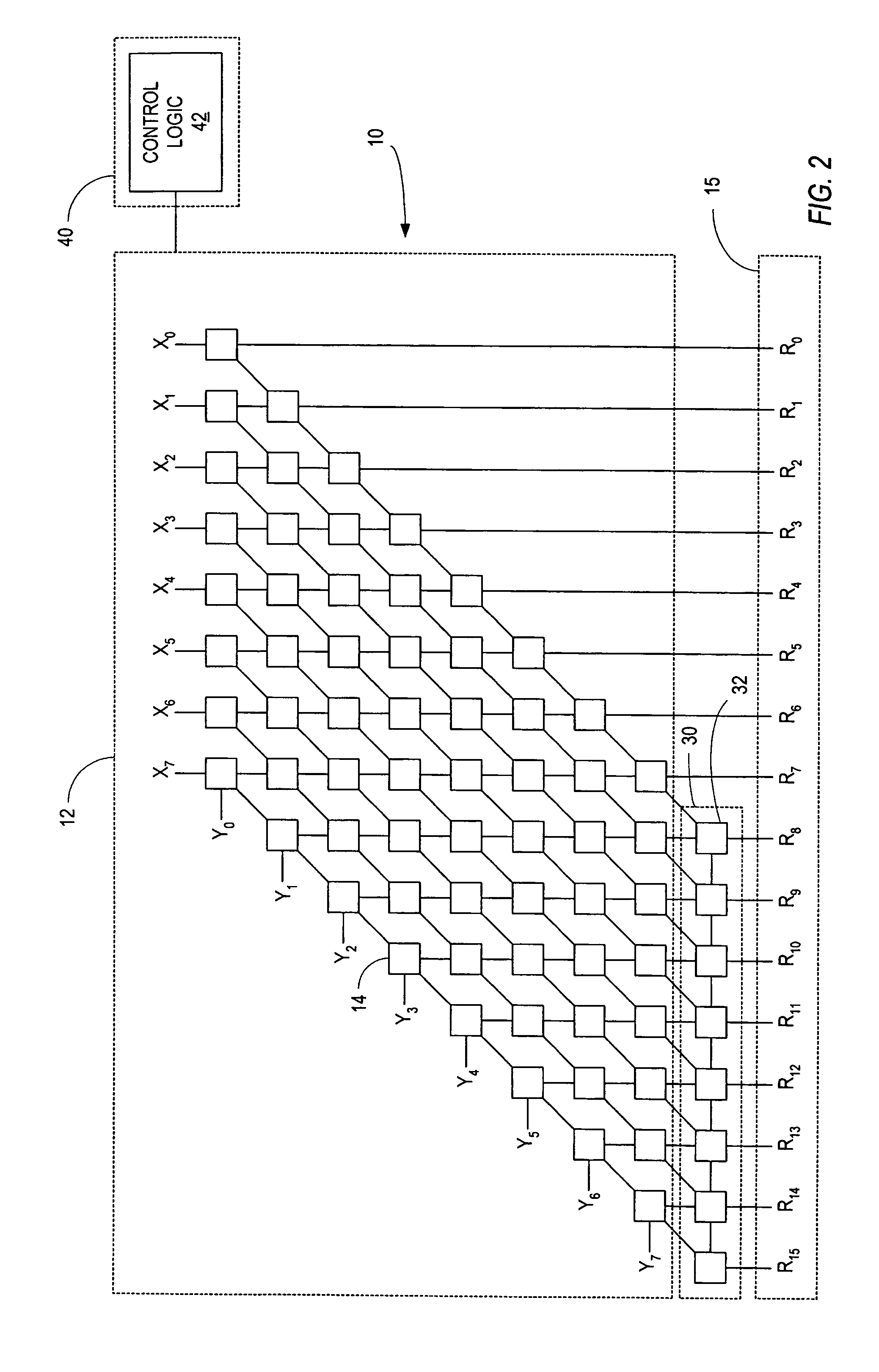
Galois field polynomial multiplication
In one aspect, a multiplier for performing multiplication of a first operand and a second operand is provided. The multiplier comprises a matrix having a plurality of matrix elements arranged in a plurality of columns, a first plurality of storage elements to store at least a portion of the first operand, the first plurality of storage elements connected diagonally to the matrix, and a second plurality of storage elements to store at least a portion of the second operand, the second plurality of storage elements connected vertically to the matrix. In another aspect, a multiplier for computing at least a partial product of a first operand having a first length and a second operand having a second length is provided. The multiplier comprises a first register to store at least a portion of the first operand, a second register to store at least a portion of the second operand, and a logic matrix formed from a plurality of matrix elements that together perform a multiplication operation, the logic matrix connected to the first register and the second register such that each matrix element receives at least one bit from the first register and at least one bit from the second register, wherein a number of the plurality of matrix elements does not exceed a product of the first length and the second length.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
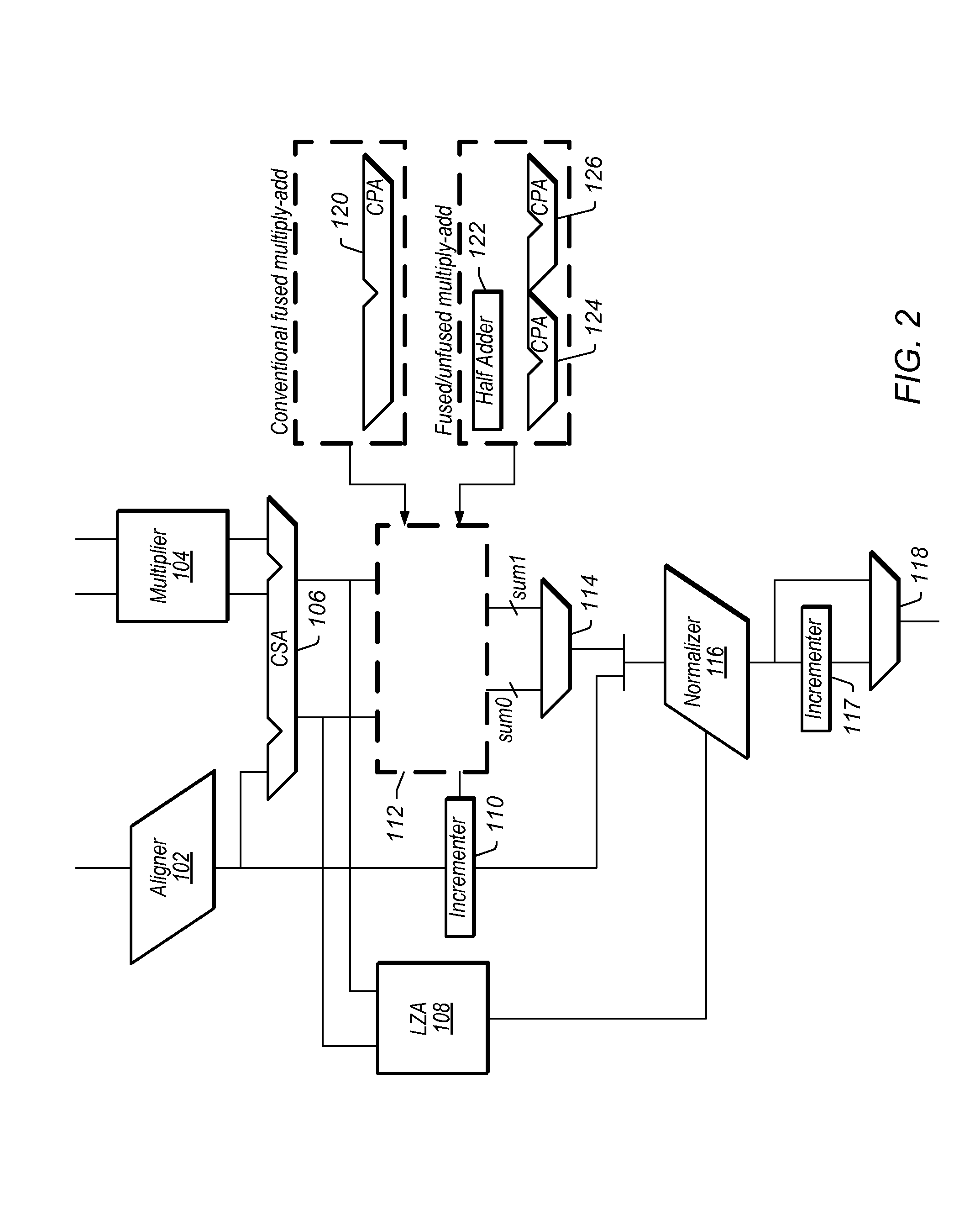
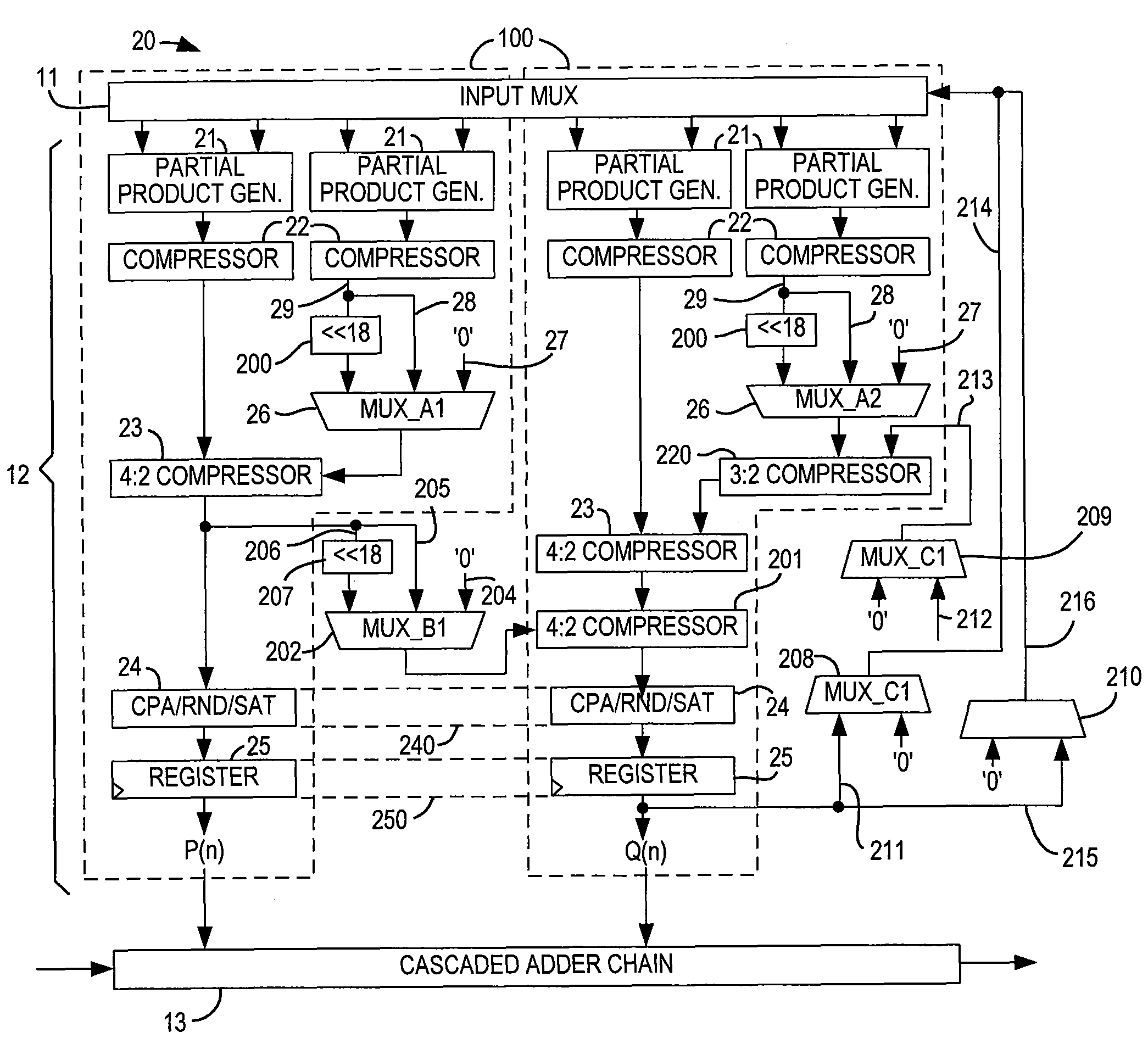
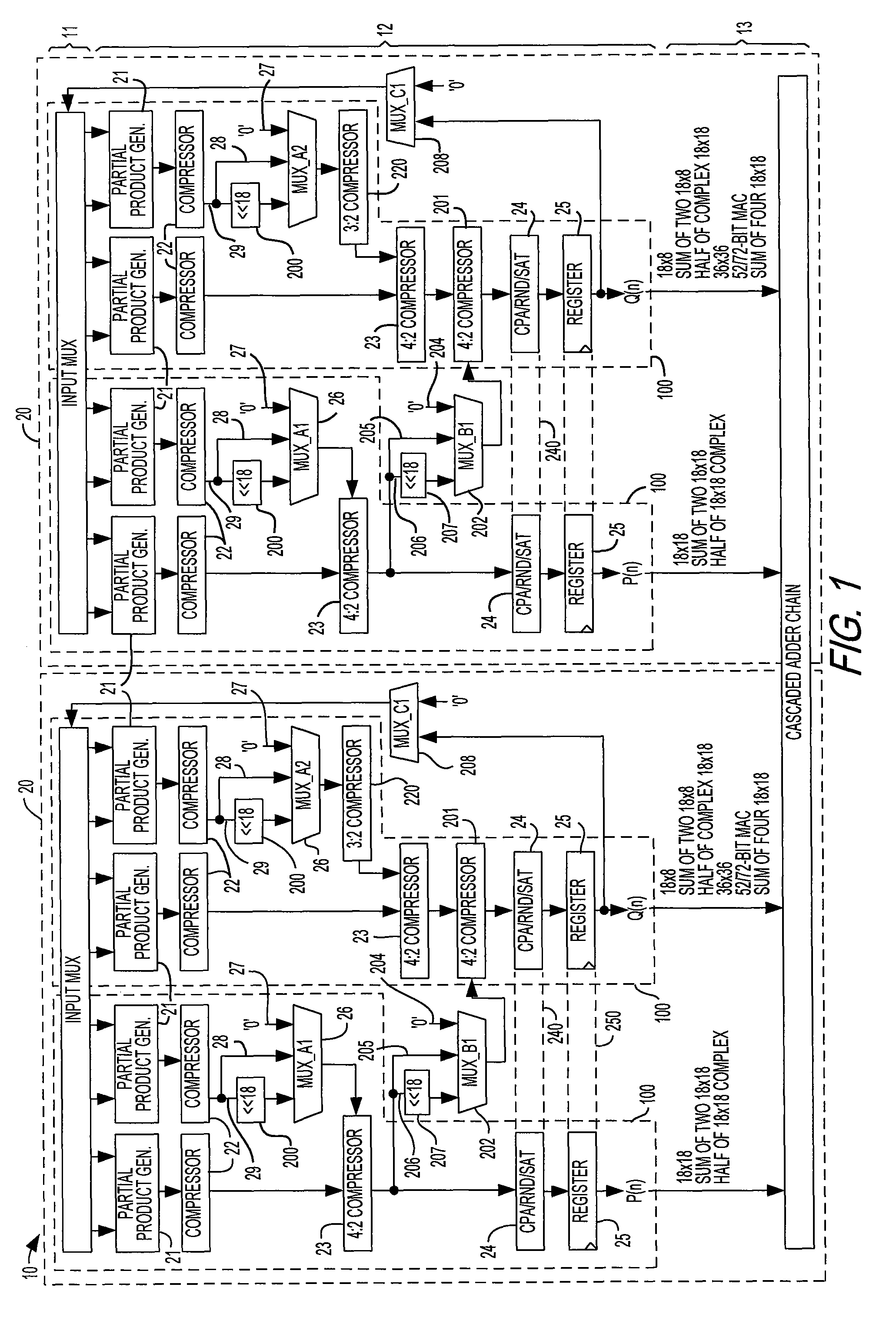
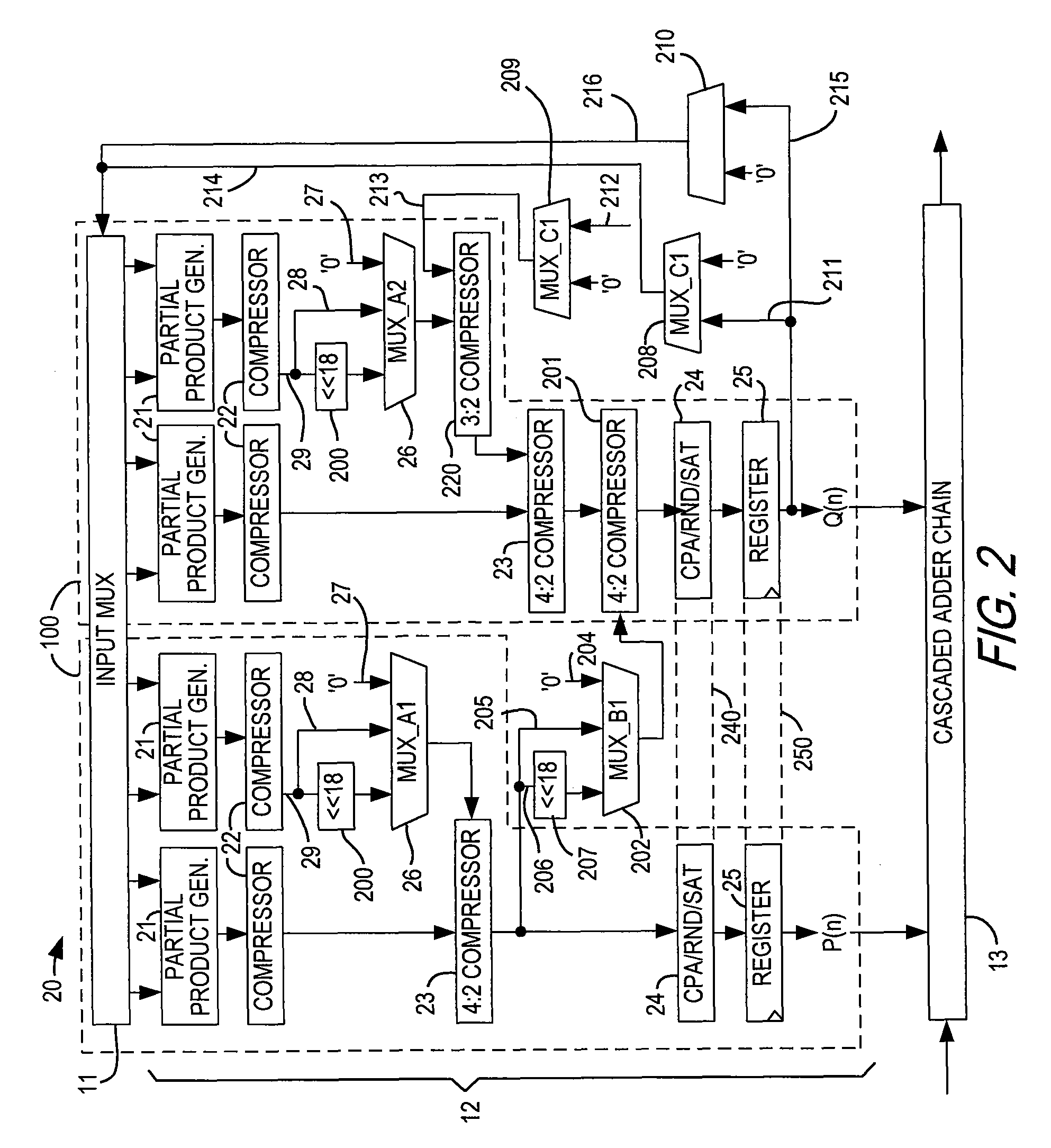
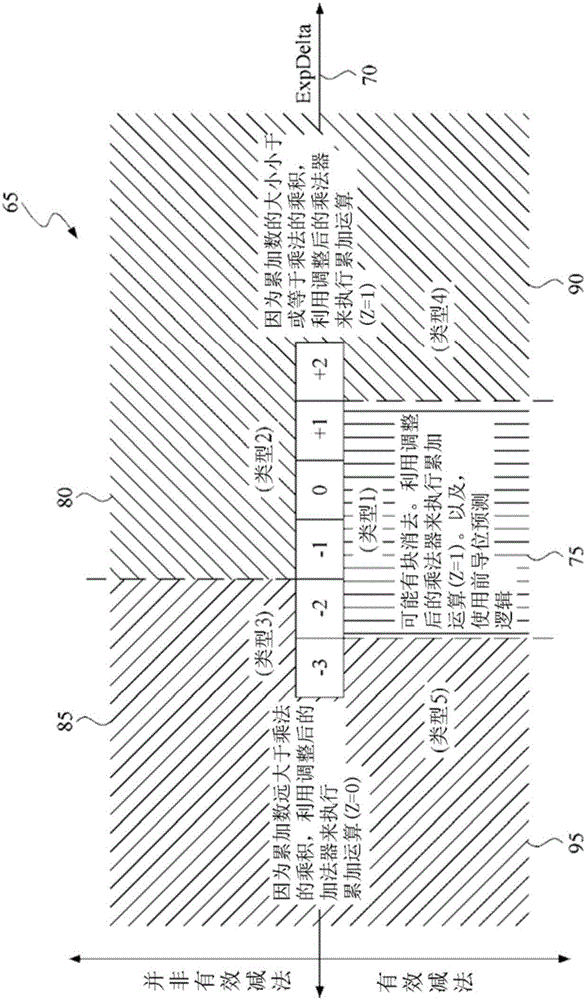
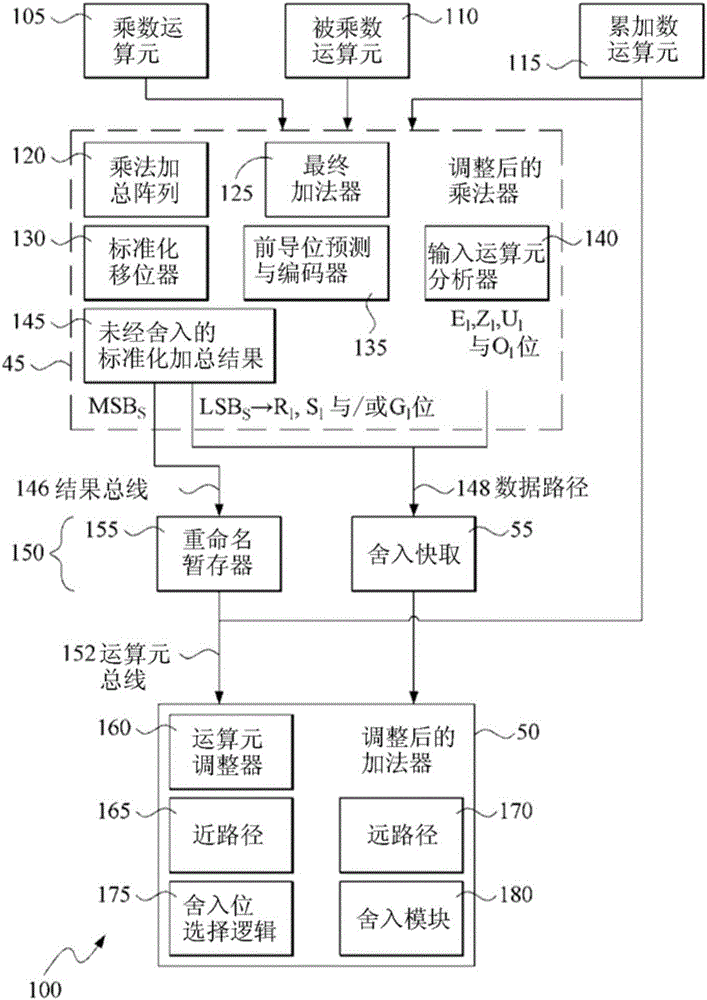
Processor which Implements Fused and Unfused Multiply-Add Instructions in a Pipelined Manner
ActiveUS20090248779A1Computations using contact-making devicesBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
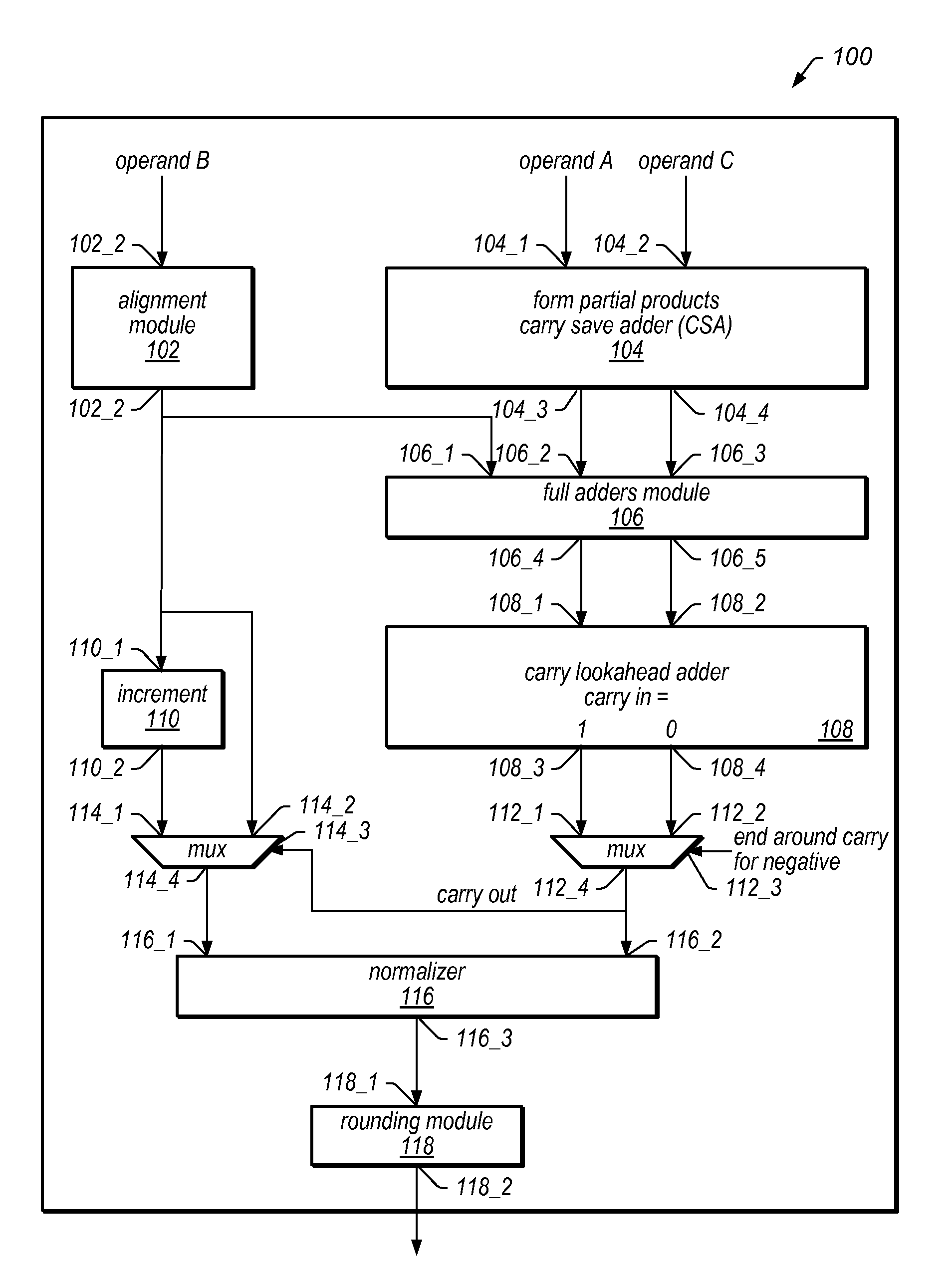
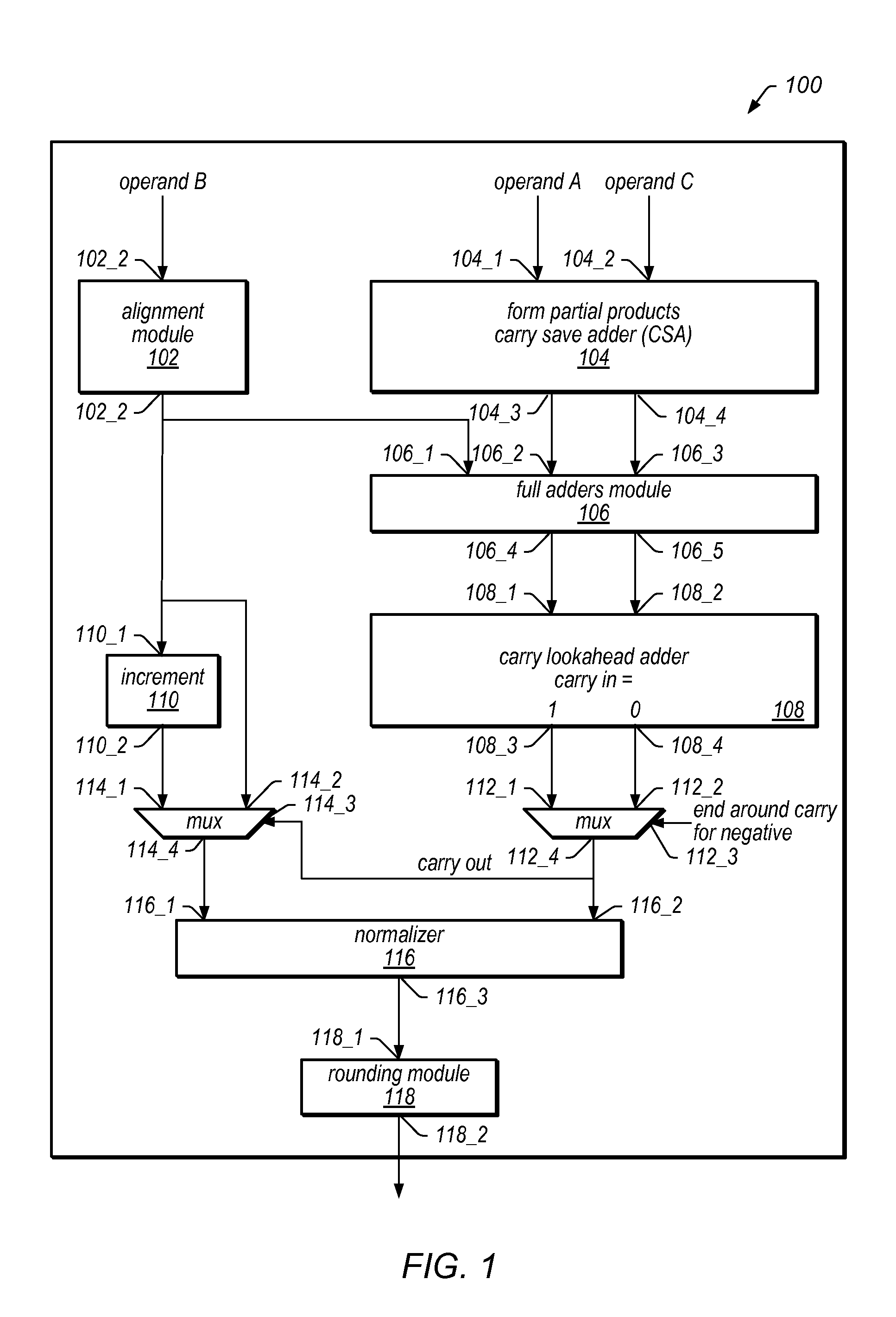
Implementing an unfused multiply-add instruction within a fused multiply-add pipeline. The system may include an aligner having an input for receiving an addition term, a multiplier tree having two inputs for receiving a first value and a second value for multiplication, and a first carry save adder (CSA), wherein the first CSA may receive partial products from the multiplier tree and an aligned addition term from the aligner. The system may include a fused / unfused multiply add (FUMA) block which may receive the first partial product, the second partial product, and the aligned addition term, wherein the first partial product and the second partial product are not truncated. The FUMA block may perform an unfused multiply add operation or a fused multiply add operation using the first partial product, the second partial product, and the aligned addition term, e.g., depending on an opcode or mode bit.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
InactiveUS7836117B1Reduce areaImprove efficiencyDigital technique networkDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingComputer architecture
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device incorporates a fundamental processing unit that performs a sum of two multiplications, adding the partial products of both multiplications without computing the individual multiplications. Such fundamental processing units consume less area than conventional separate multipliers and adders. The specialized processing block further has input and output stages, as well as a loopback function, to allow the block to be configured for various digital signal processing operations.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method and apparatus for simultaneously multiplying two or more independent pairs of operands and summing the products
InactiveUS6085213ARuntime instruction translationComputation using non-contact making devicesRoundingControl signal
A multiplier capable of performing signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. An effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands may be calculated based upon each operand's most significant bit and a control signal. The effective signs may then be used to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, they may be summed and the results may be output. The results may be signed or unsigned, and may represent vector or scalar quantities. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier may be configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components. The multiplier may also be configured to sum the products of the vector components to form the vector dot product. The final product may be output in segments so as to require fewer bus lines. The segments may be rounded by adding a rounding constant. Rounding and normalization may be performed in two paths, one assuming an overflow will occur, the other assuming no overflow will occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
ActiveUS8041759B1Reduce areaImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsDigital signal processingIir filtering
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device incorporates a fundamental processing unit that performs a sum of two multiplications, adding the partial products of both multiplications without computing the individual multiplications. Such fundamental processing units consume less area than conventional separate multipliers and adders. The specialized processing block further has input and output stages, as well as a loopback function, to allow the block to be configured for various digital signal processing operations, including finite impulse response (FIR) filters and infinite impulse response (IIR) filters. By using the programmable connections, and in some cases the programmable resources of the programmable logic device, and by running portions of the specialized processing block at higher clock speeds than the remainder of the programmable logic device, more complex FIR and IIR filters can be implemented.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Division unit in a processor using a piece-wise quadratic approximation technique
InactiveUS6351760B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesComputational logicRounding
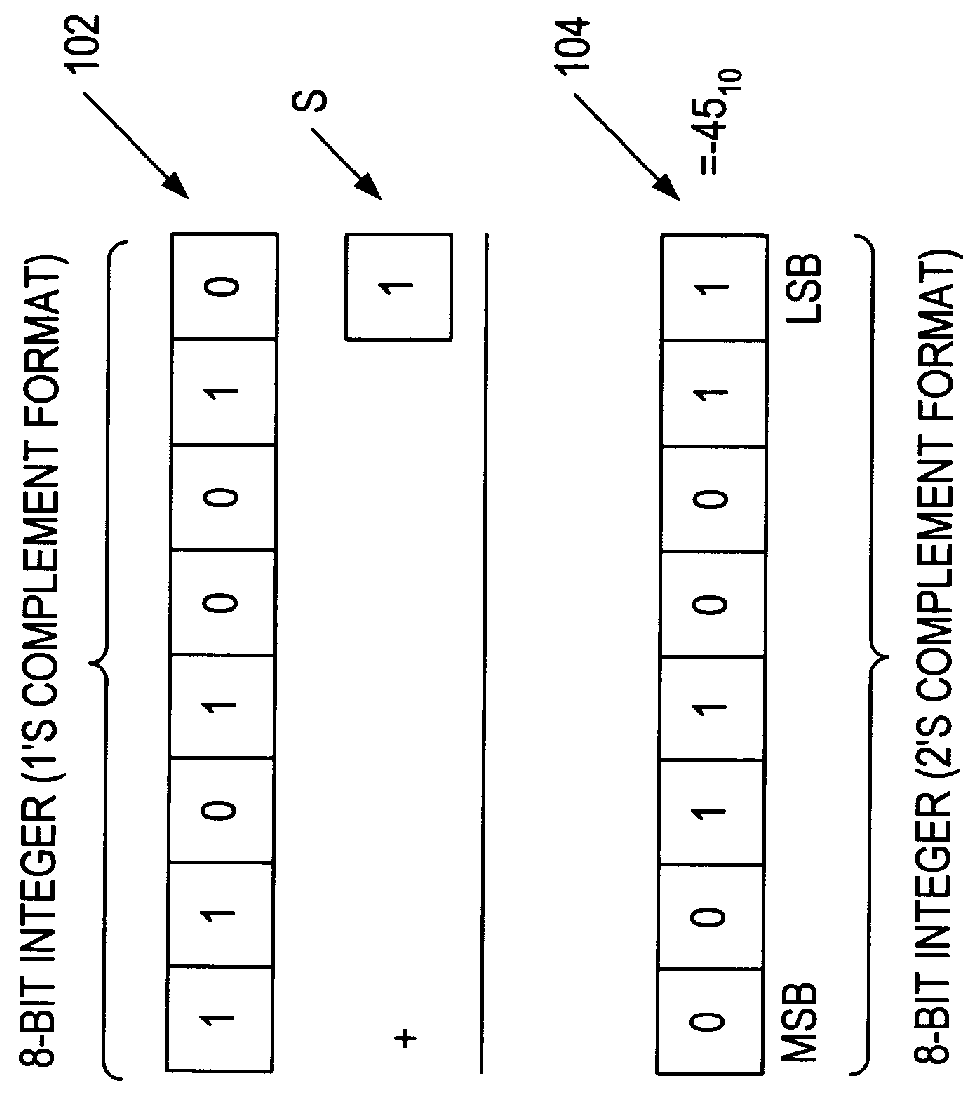
A computation unit computes a division operation Y / X by determining the value of a divisor reciprocal 1 / X and multiplying the reciprocal by a numerator Y. The reciprocal 1 / X value is determined using a quadratic approximation having a form:where coefficients A, B, and C are constants that are stored in a storage or memory such as a read-only memory (ROM). The bit length of the coefficients determines the error in a final result. Storage size is reduced through use of "least mean square error"techniques in the determination of the coefficients that are stored in the coefficient storage. During the generation of partial products x2, Ax2, and Bx, the process of rounding is eliminated, thereby reducing the computational logic to implement the division functionality.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Process for transferring product information utilizing barcode reader into permanent memory for an implanted medical device
A barcode having product information is paired with an implantable medical device or component. The barcode is optically read and at least a portion of the product information is stored into a temporary memory. At least a portion of the product information stored in the temporary memory is electronically written to permanent memory of an RFID chip associated with the implanted medical device or component.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
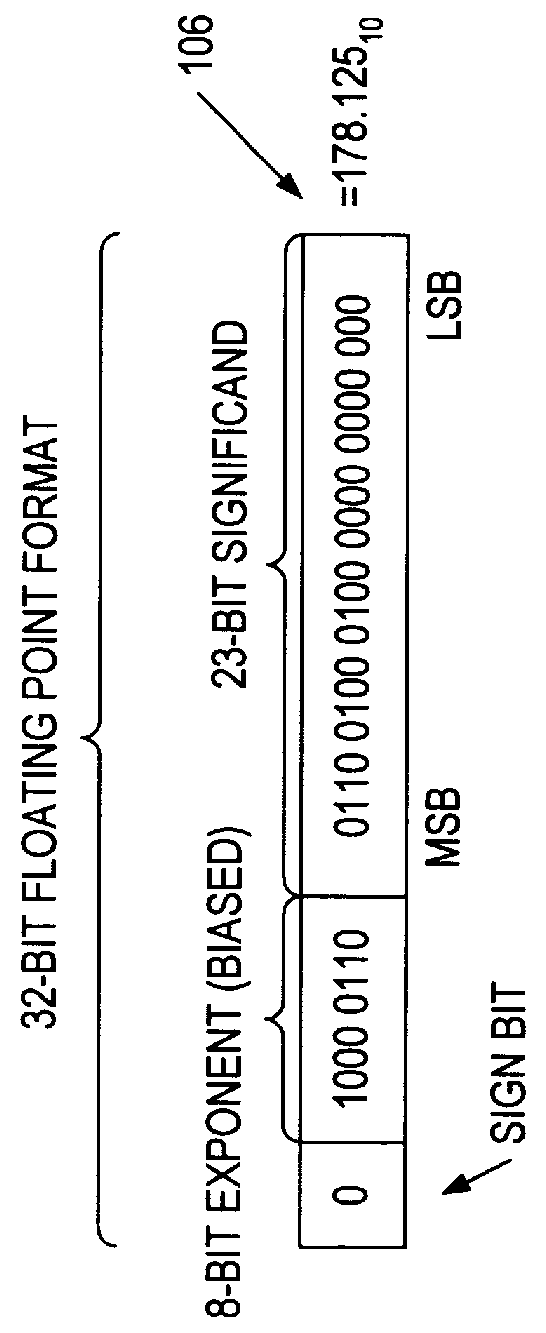
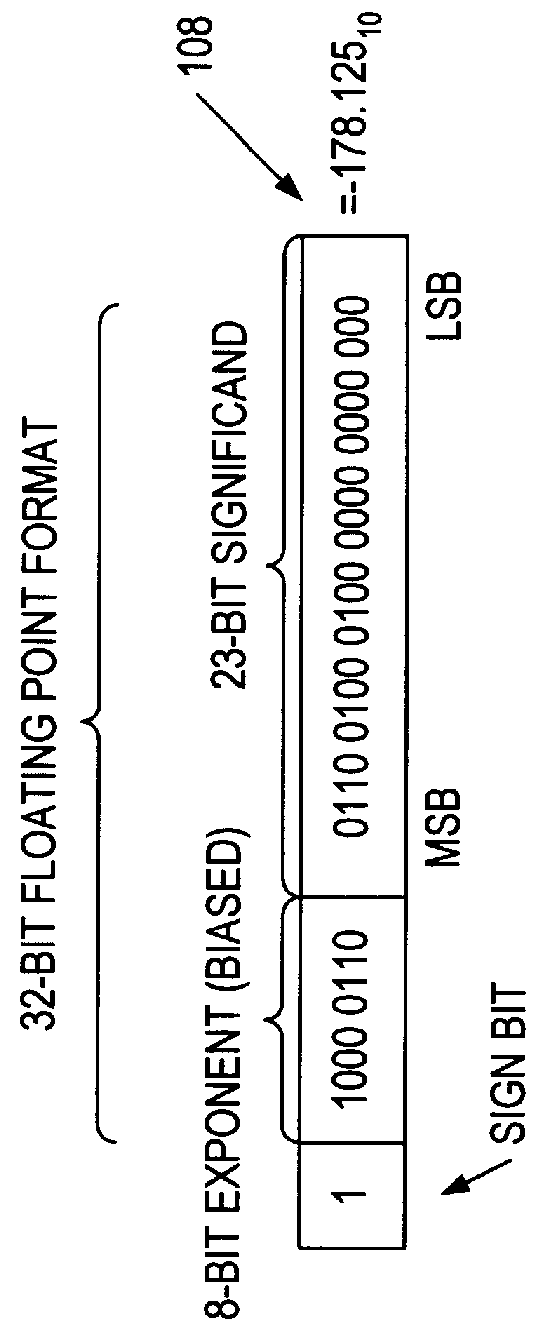
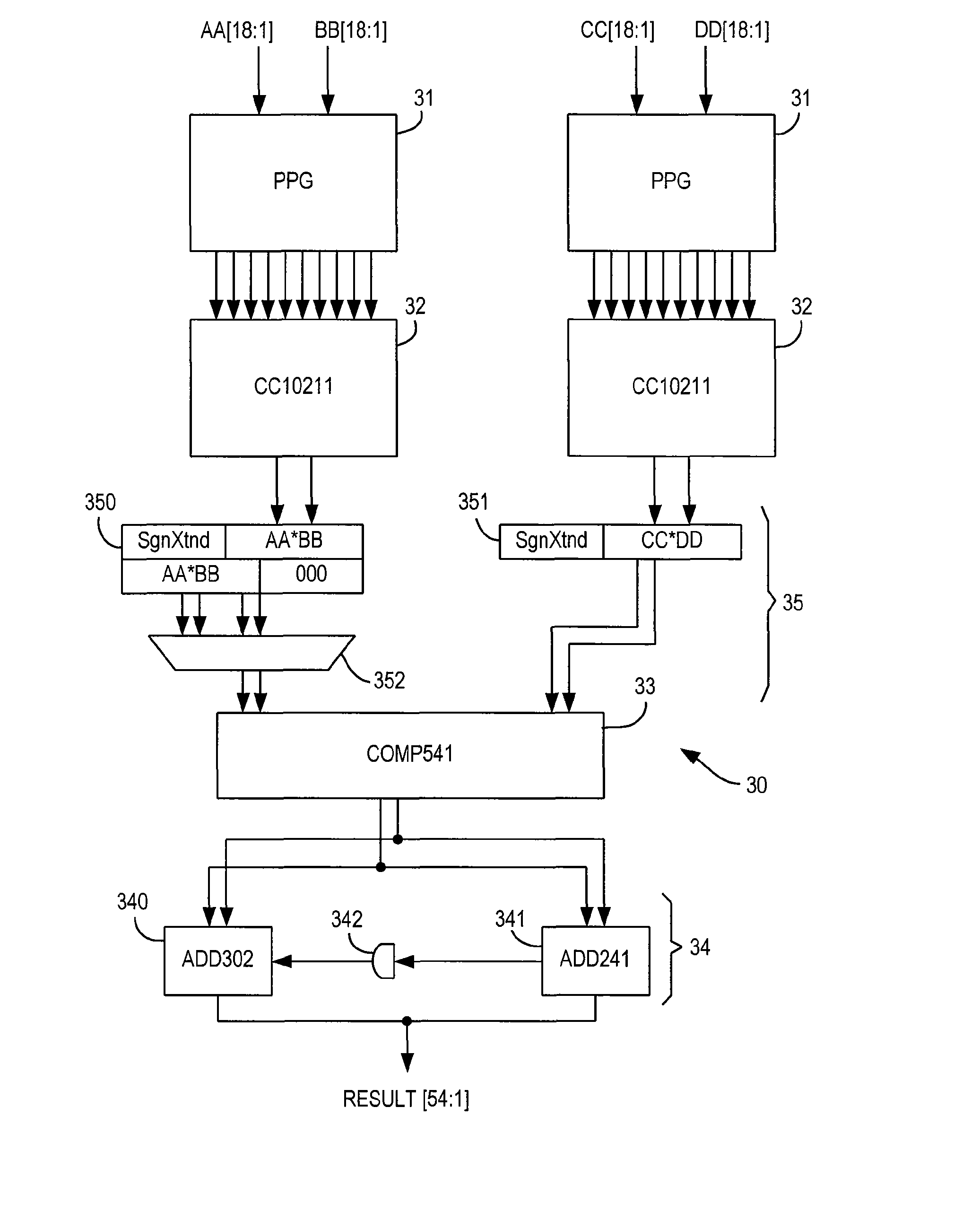
Floating point multiplier with partial product shifting circuitry for result alignment
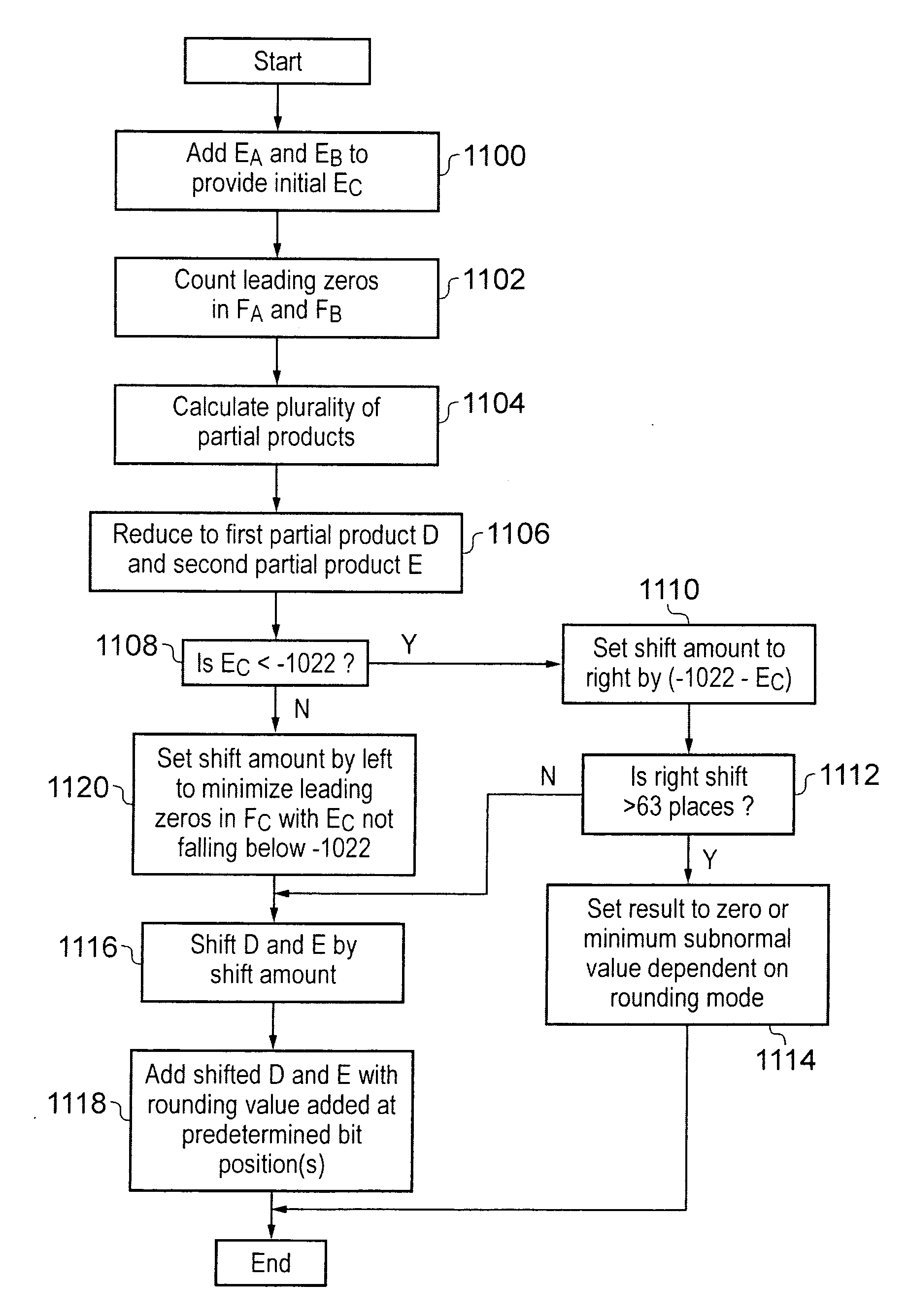
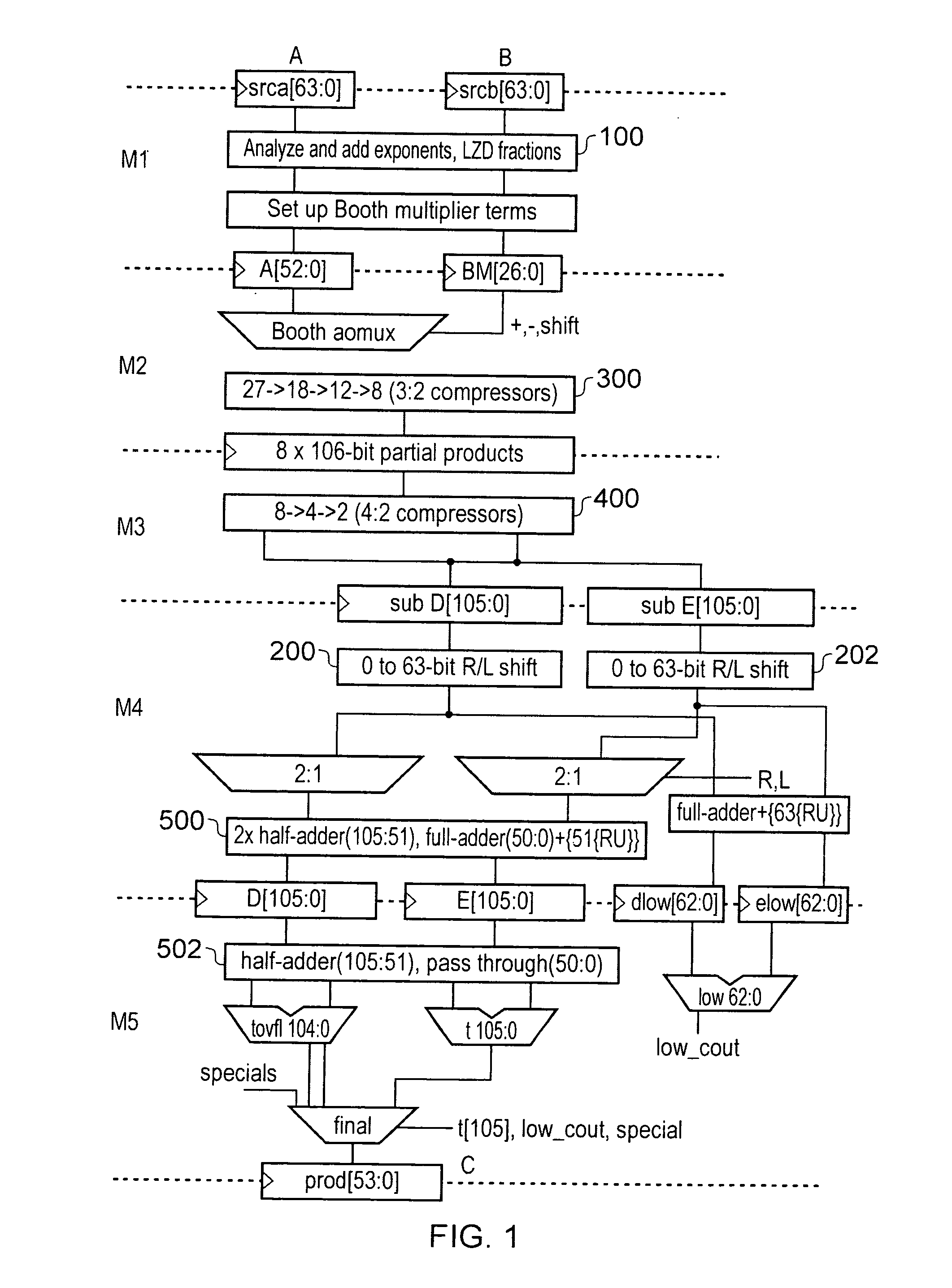
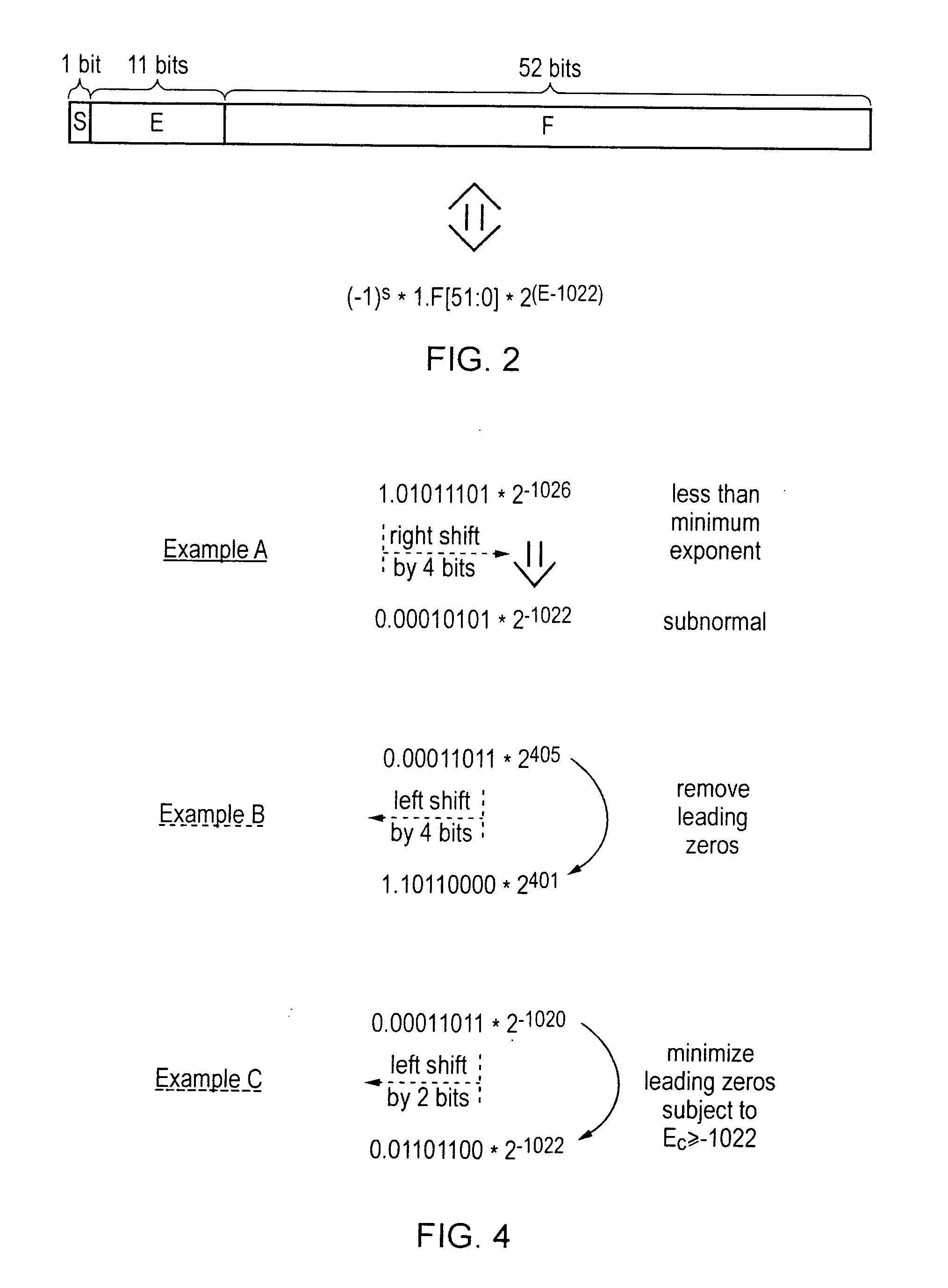
ActiveUS20110106868A1Minimize the numberReduce delaysDigital computer detailsData conversionRight shiftOperand
A floating point multiplier includes a data path in which a plurality of partial products are calculated and then reduced to a first partial product and a second partial product. Shift amount determining circuitry 100 analyses the exponents of the input operands A and B as well as counting the leading zeros in the fractional portions of these operands to determine an amount of left shift or right shift to be applied by shifting circuitry 200, 202 within the multiplier data path. This shift amount is applied so as to align the partial products so that when they are added they will produce the result C without requiring this to be further shifted. Furthermore, shifting the partial products to the correct alignment in this way in advance of adding these partial products permits injection rounding combined with the adding of the partial products to be employed for cases including subnormal values.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method and apparatus for simultaneously performing arithmetic on two or more pairs of operands
InactiveUS6026483AComputations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationControl signalOperand
A multiplier capable of performing both signed and unsigned scalar and vector multiplication is disclosed. The multiplier is configured for use in a microprocessor and comprises a partial product generator, a selection logic unit, and an adder. The multiplier is configured to receive signed or unsigned multiplier and multiplicand operands in scalar or packed vector form. The multiplier is also configured to receive a first control signal indicative of whether signed or unsigned multiplication is to be performed and a second control signal indicative of whether vector multiplication is to be performed. The multiplier is configured to calculate an effective sign for the multiplier and multiplicand operands based upon each operand's most significant bit and the control signal. The effective signs may then be used by the partial product generation unit and the selection logic to create and select a number of partial products according to Booth's algorithm. Once the partial products have been created and selected, the adder is configured to sum them and output the results, which may be signed or unsigned. When a vector multiplication is performed, the multiplier is configured to generate and select partial products so as to effectively isolate the multiplication process for each pair of vector components.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
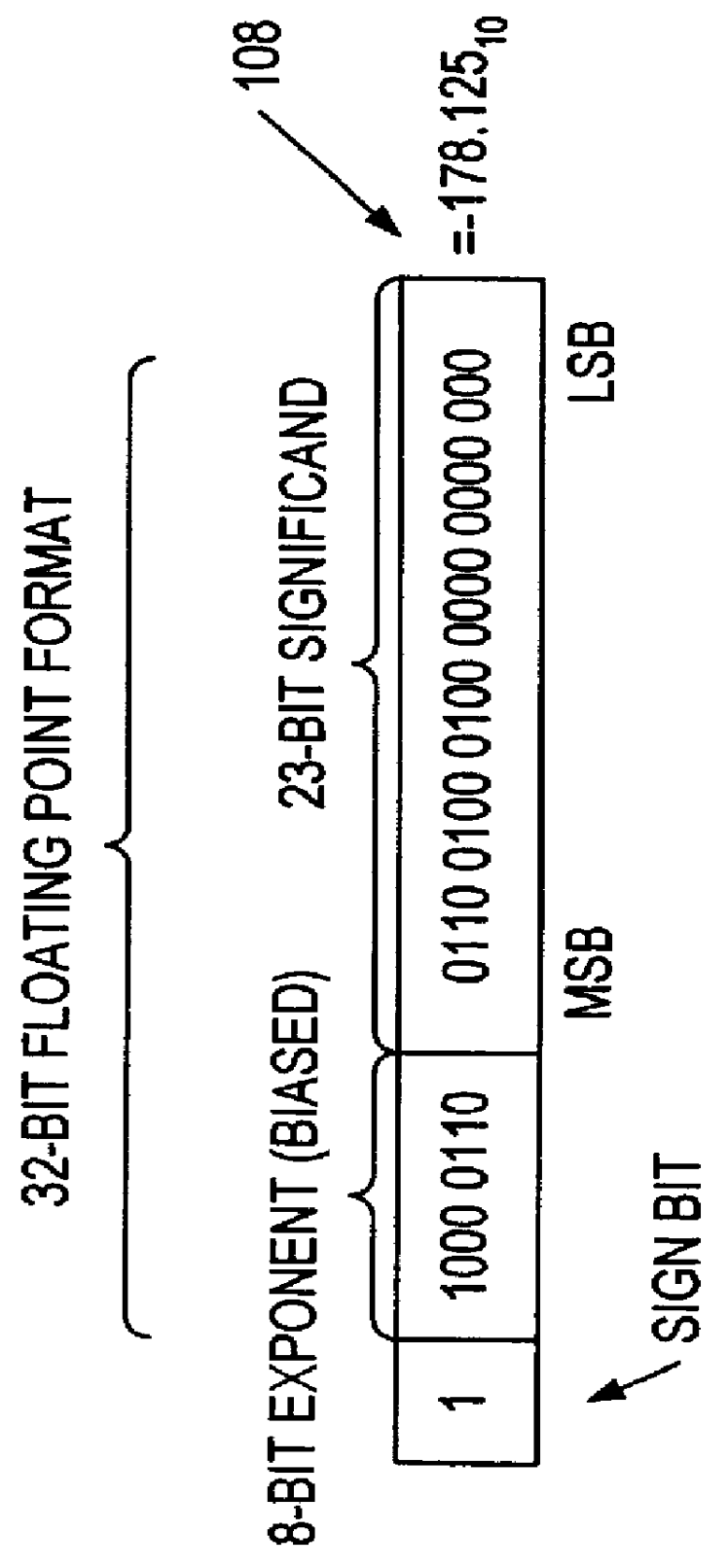
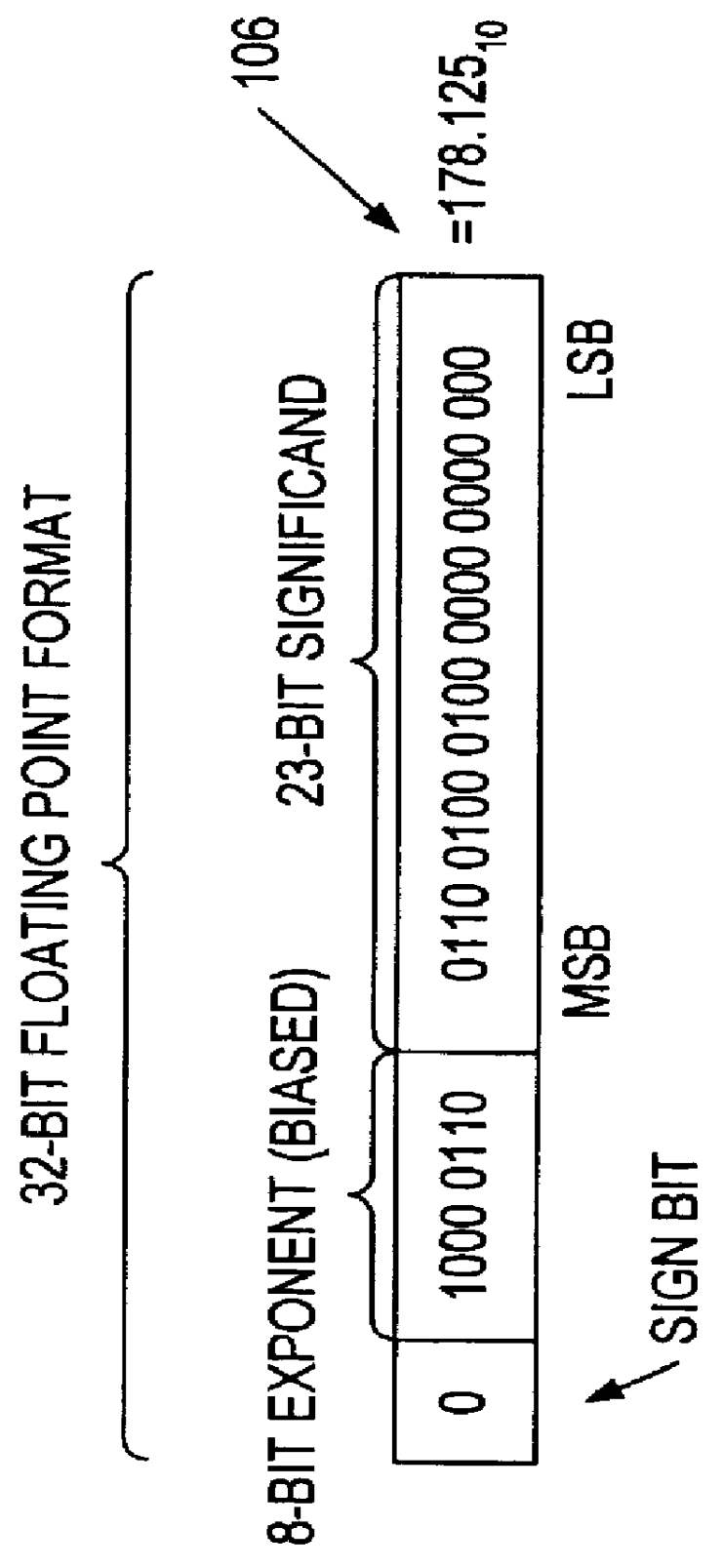
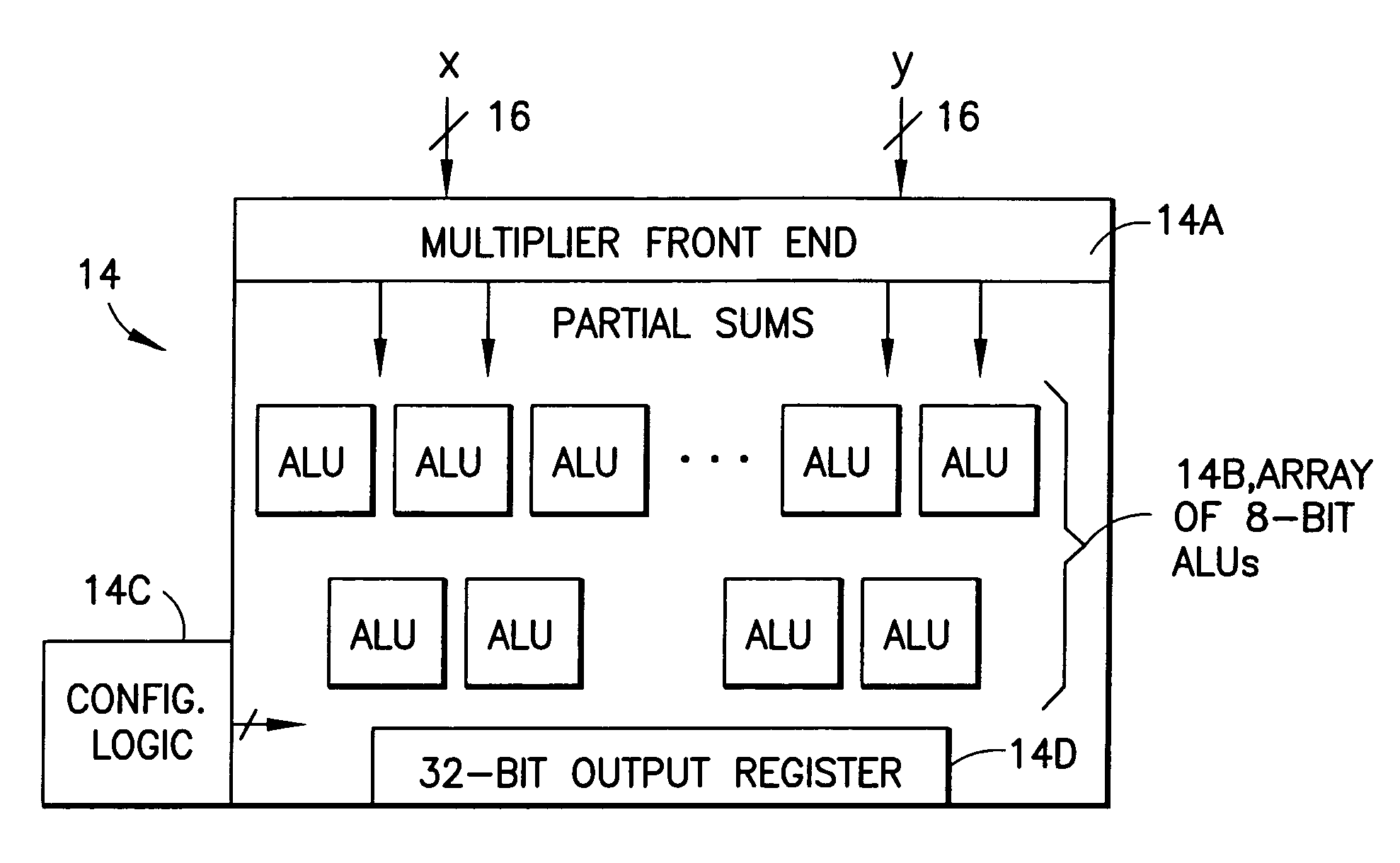
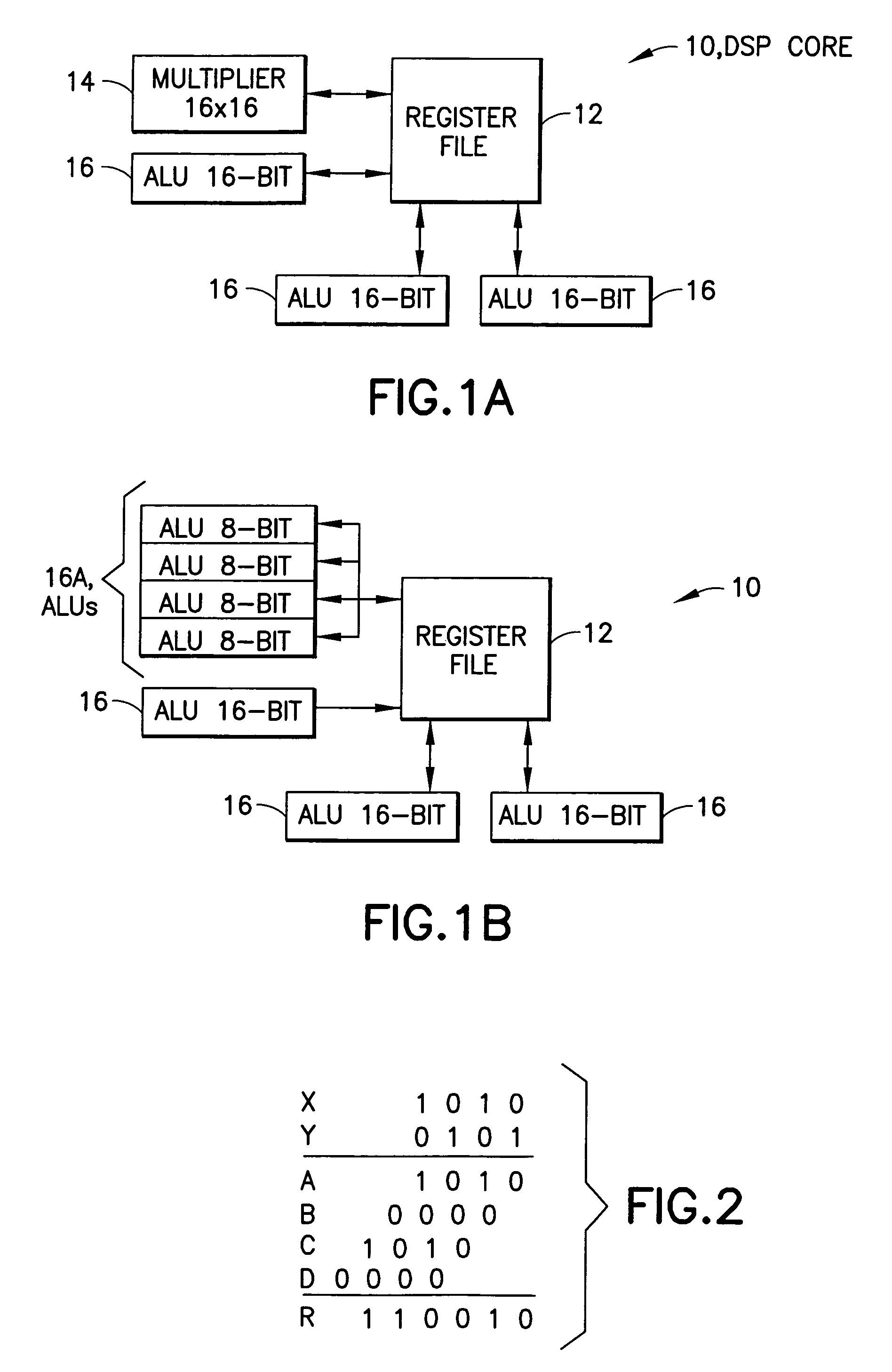
Dynamically configurable processor
InactiveUS6959316B2Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlBinary multiplierData source
A data processor, such as a DSP, includes a multiplier block having a multiplier front end for generating partial products from input operands, and further includes a plurality of ALUs having inputs that are switchably or programmably coupled, in a first mode of operation, to first data sources representing outputs of the multiplier front end. In the first mode of operation the ALUs add together partial products received from the multiplier front end to arrive at a multiplication result. In a second mode of operation the inputs of the plurality of ALUs are switchably or programmably coupled to second data sources for performing at least one of arithmetic and logical operations on data received from the second data sources.
Owner:HTC CORP
Apparatus and method for multiple pass extended precision floating point multiplication
InactiveUS8019805B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesComputational scienceCarry-save adder
A floating point multiplier circuit includes partial product generation logic configured to generate a plurality of partial products from multiplicand and multiplier values. The plurality of partial products corresponds to a first and second portion of the multiplier value during respective first and second partial product execution phases. The multiplier also includes a plurality of carry save adders configured to accumulate the plurality of partial products generated during the first and second partial product execution phases into a redundant product during respective first and second carry save adder execution phases. The multiplier further includes a first carry propagate adder coupled to the plurality of carry save adders and configured to reduce a first and second portion of the redundant product to a multiplicative product during respective first and second carry propagate adder phases. The first carry propagate adder phase begins after the second carry save adder execution phase completes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Split-path fused multiply-accumulate operation using first and second sub-operations
ActiveCN105849690AReduce cumulative power consumptionRound cache avoidanceDigital data processing detailsInstruction analysisMultiply–accumulate operationParallel computing
A microprocessor executes a fused multiply-accumulate operation of a form +-A * B +- C by dividing the operation in first and second suboperations. The first suboperation selectively accumulates the partial products of A and B with or without C and generates an intermediate result vector and a plurality of calculation control indicators. The calculation control indicators indicate how subsequent calculations to generate a final result from the intermediate result vector should proceed. The intermediate result vector, in combination with the plurality of calculation control indicators, provides sufficient information to generate a result indistinguishable from an infinitely precise calculation of the compound arithmetic operation whose result is reduced in significance to a target data size.
Owner:上海兆芯集成电路股份有限公司
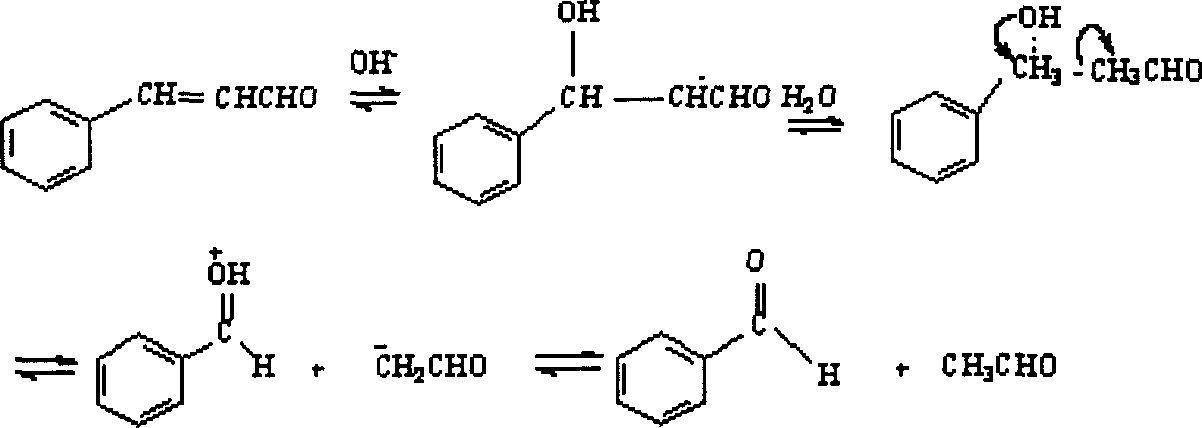
Preparation method of natural benzaldehyde
InactiveCN1911891ANot easy to polycondensateIncrease concentrationOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationBenzaldehydeProduct gas
The natural benzaldehyde preparing process includes the following steps: the heated reaction between natural cinnamic aldehyde and water solution of alkaline matter in a reactor to produce natural benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde; rectification in a rectifier in the upper part of the reactor to produce gaseous natural benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde in the top of the rectifier; condensing the gaseous natural benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde; and conveying partial product to post section. The process has continuous elimination of the produced natural benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde, high material concentration, high reaction efficiency, low production cost and high product quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUASHENG FLAVORING
Generic modular multiplier using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030206628A1Public key for secure communicationDigital computer detailsBinary multiplierParallel computing
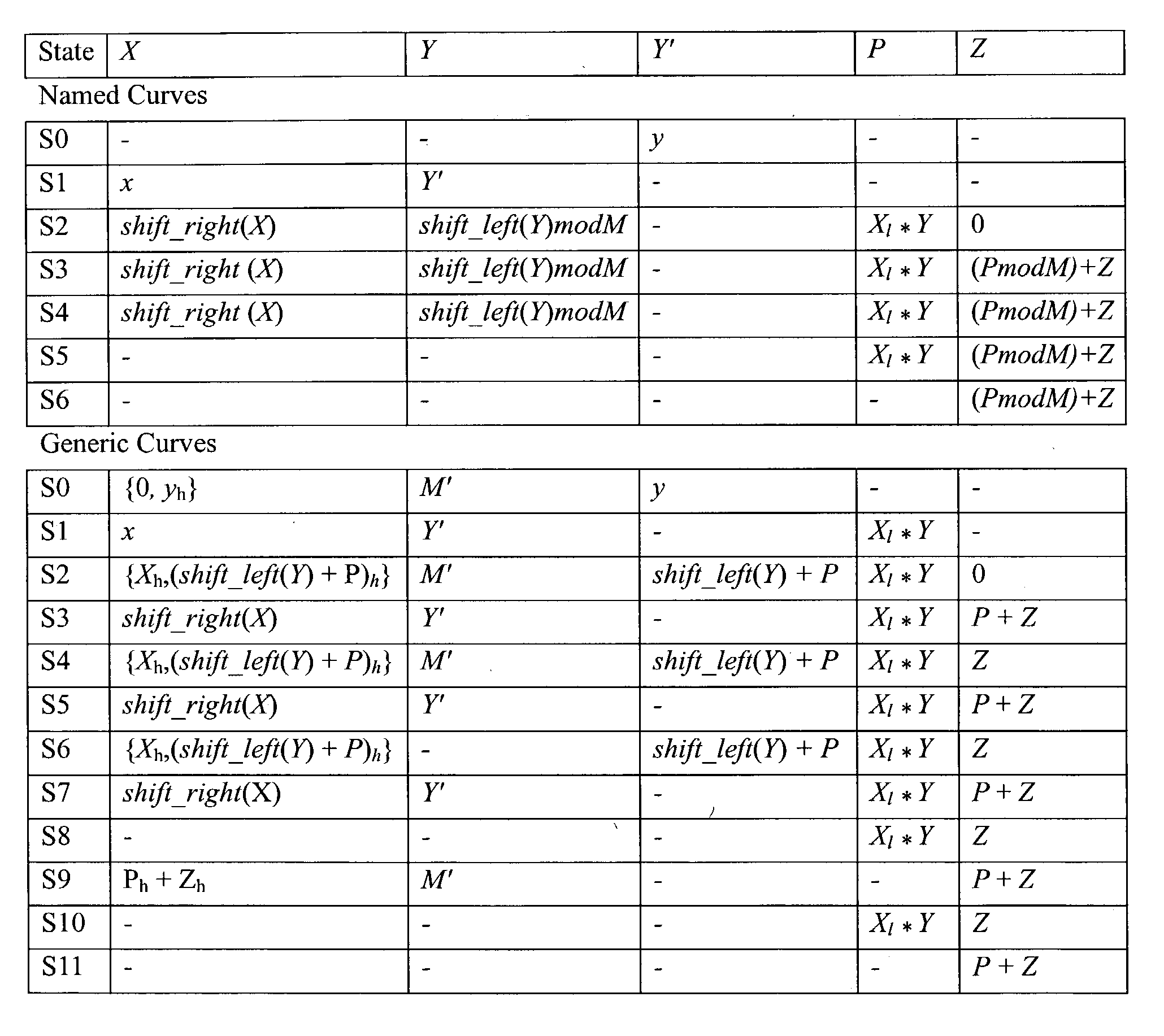
An apparatus multiplies a first and a second binary polynomial X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, and where the coefficients ai are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The degree of X(t)<n, and the degree of Y(t)<n, and m<=n. The apparatus includes a digit serial modular multiplier circuit coupled to supply a multiplication result of degree >=m of a multiplication of the first and second binary polynomials. The digit serial modular multiplier circuit includes a first and second register, each being <=n bits. A partial product generator circuit multiplies a portion of digit size d of contents of the first register and contents of the second register. The partial product generator is also utilized as part of a reduction operation for at least one generic curve.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com