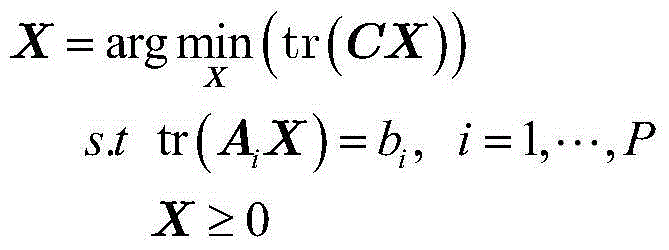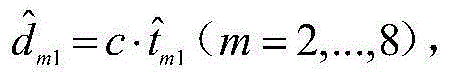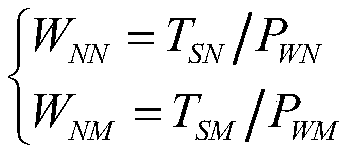Patents
Literature
104 results about "Product matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A customer/product matrix is a way of describing the relationships between customer types and product types/attributes. Example: Note: Please find some data quality related product descriptions in the post Data Quality and World Food. Filling out the matrix may be based on prejudices, gut feelings, assumptions, surveys, focus groups or data.
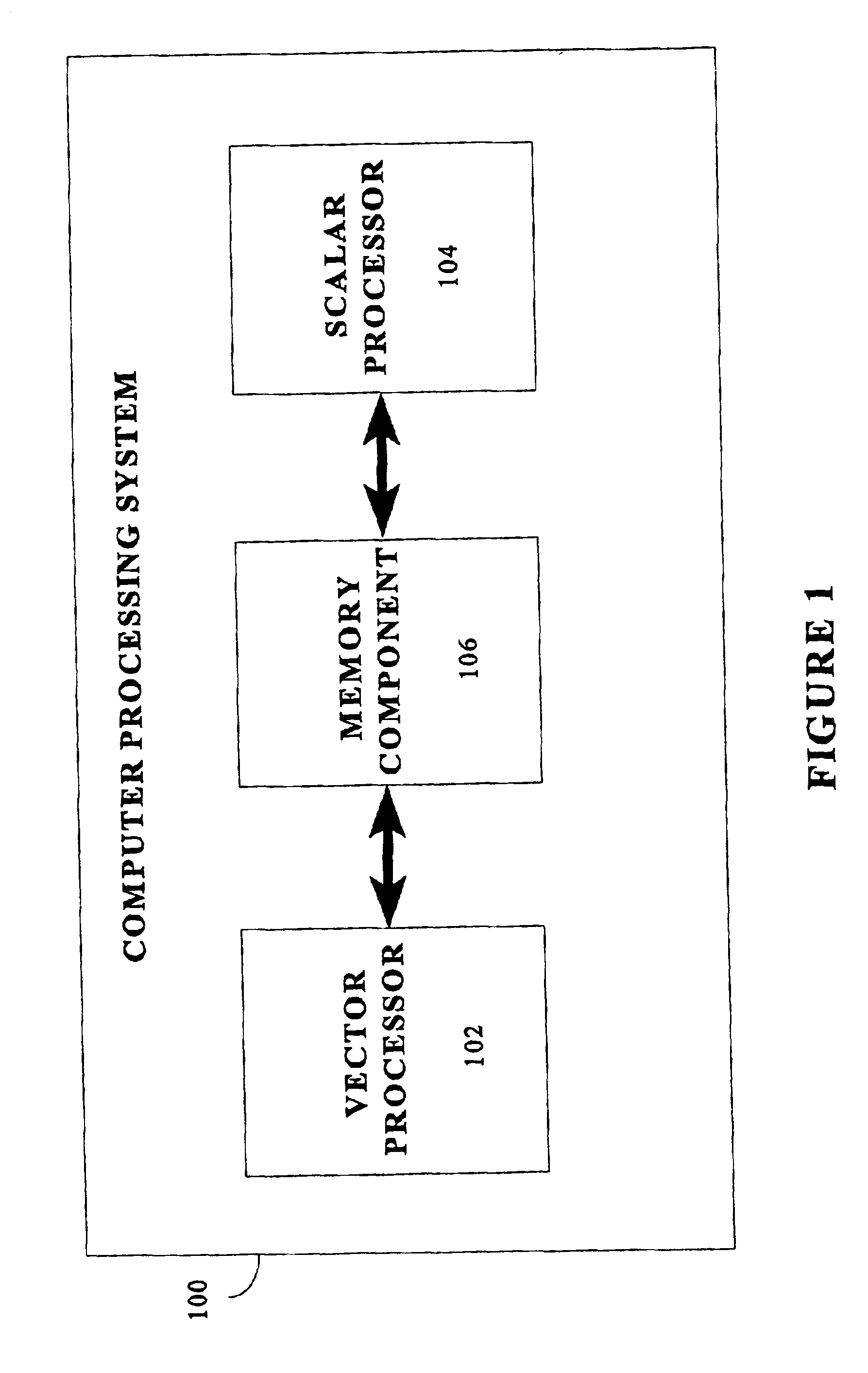
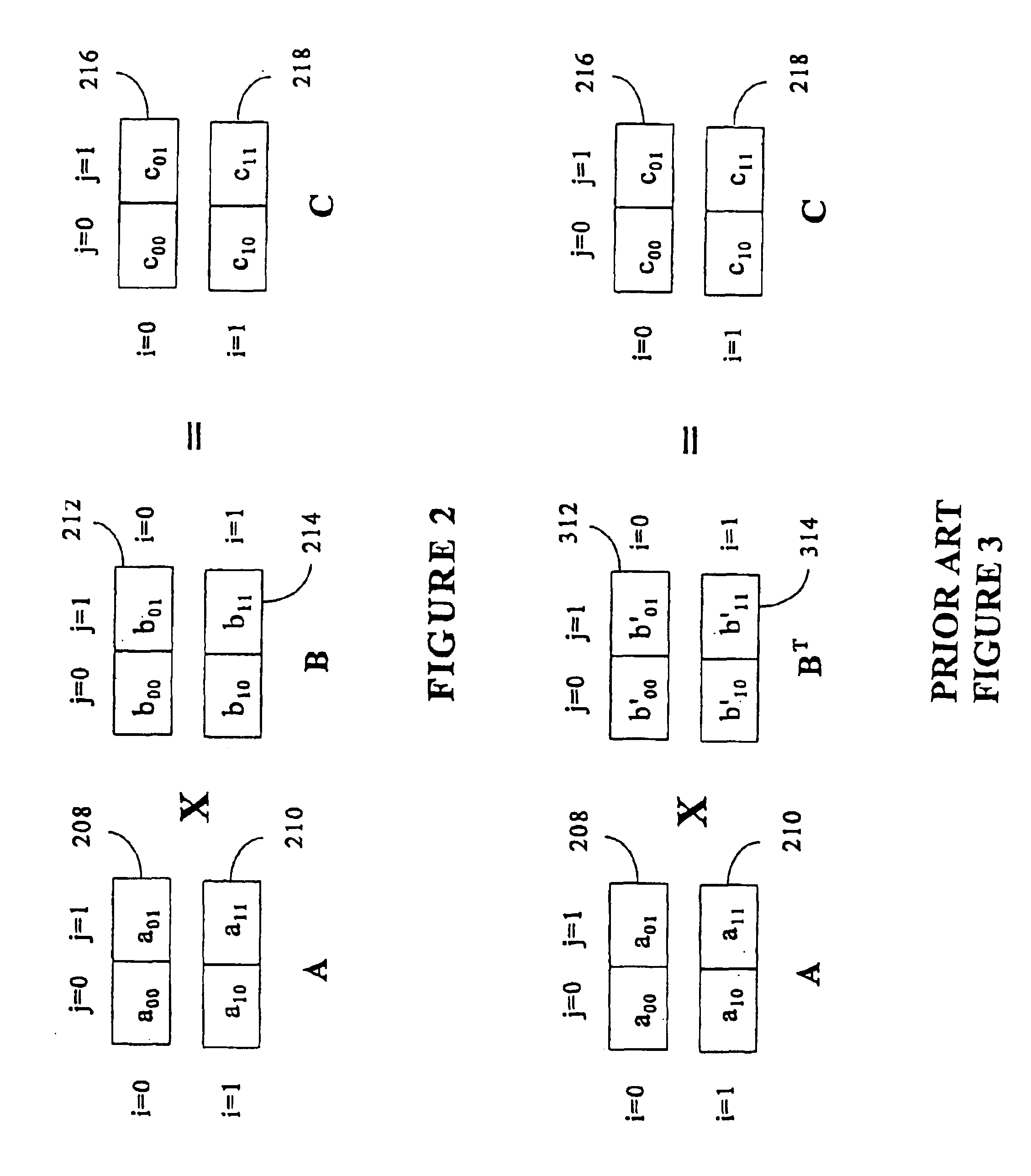
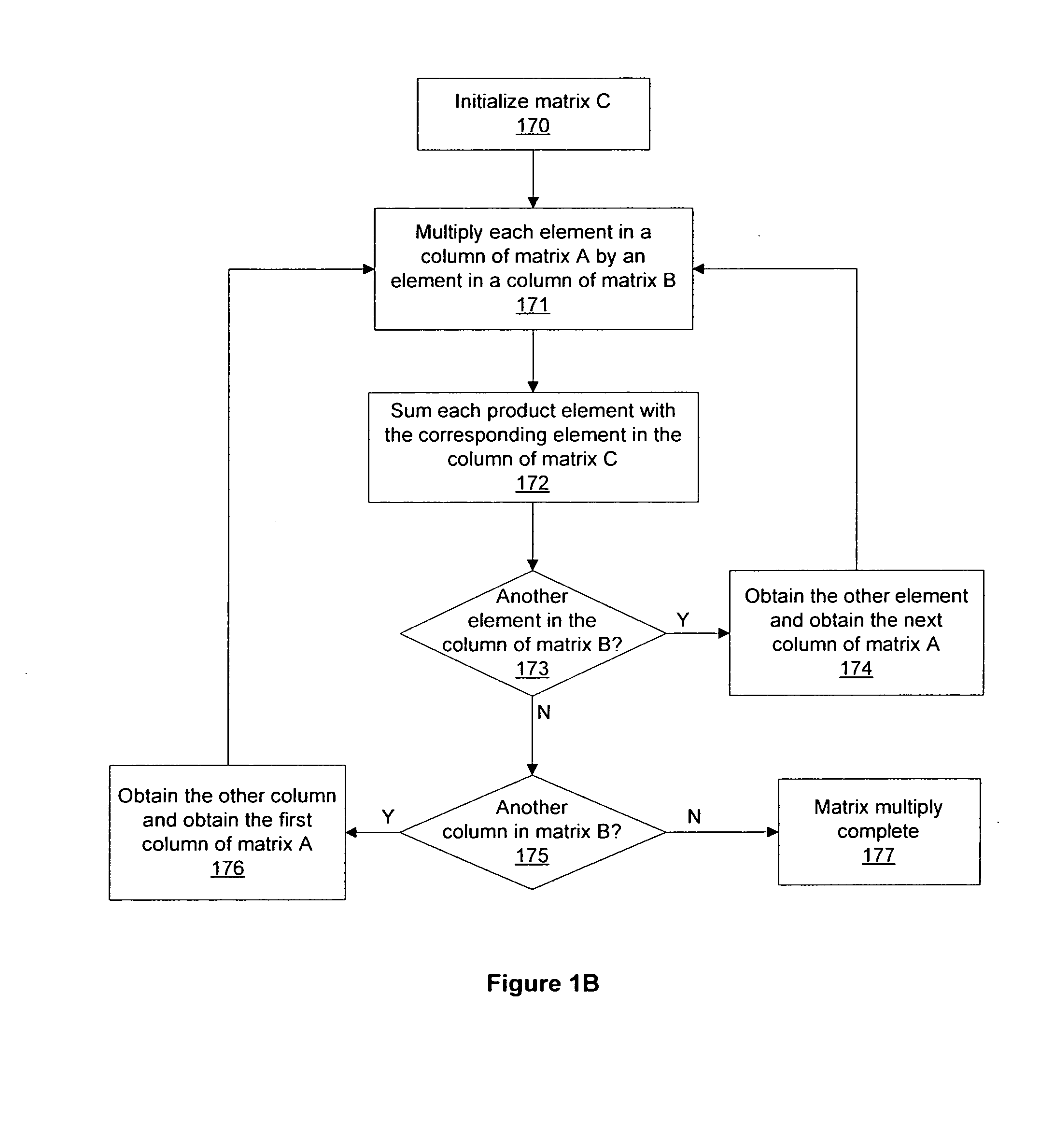
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS20050193050A1Efficient and rapid matrix multiplicationEfficient executionComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlAlgorithmProcessor register
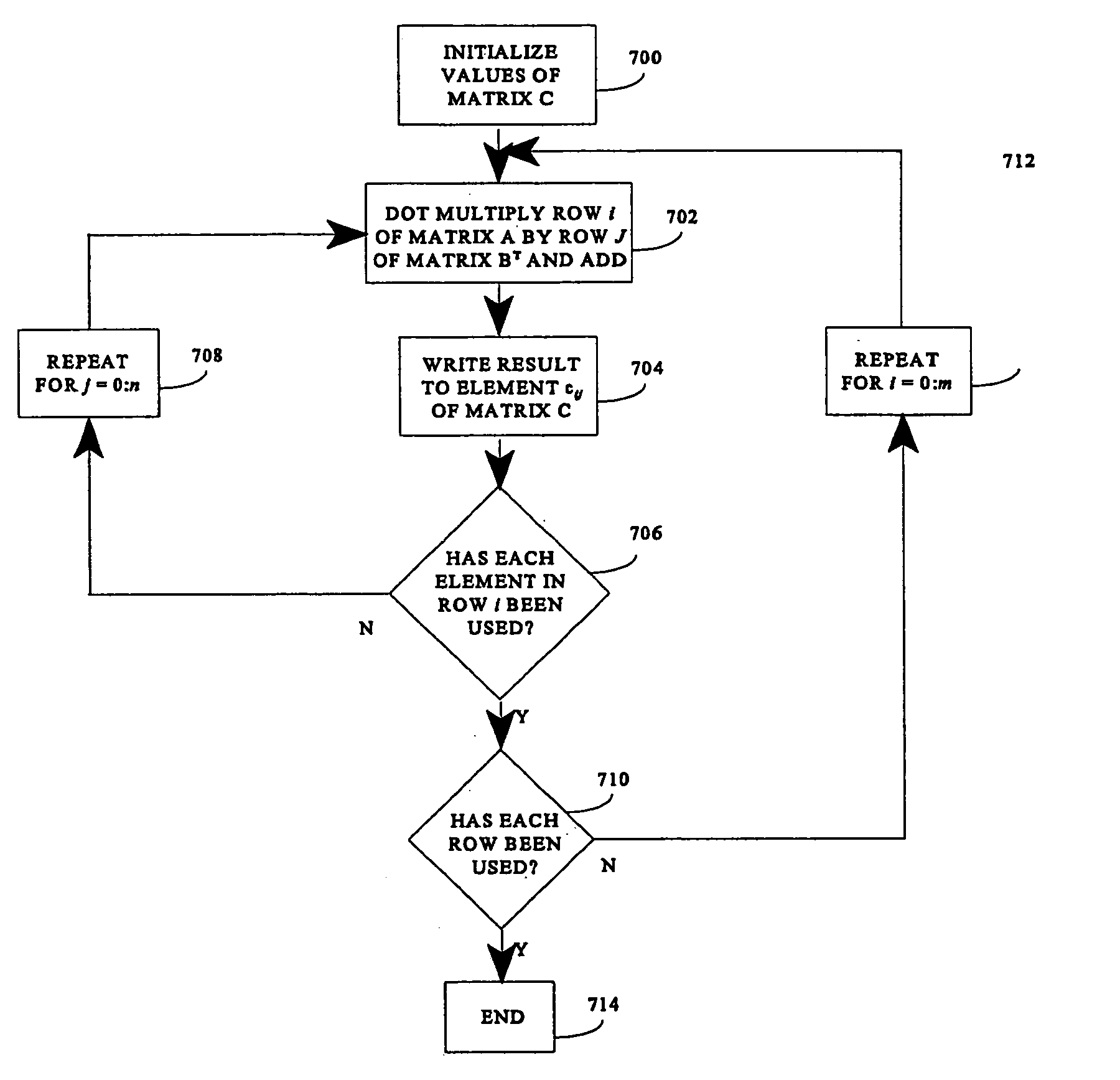
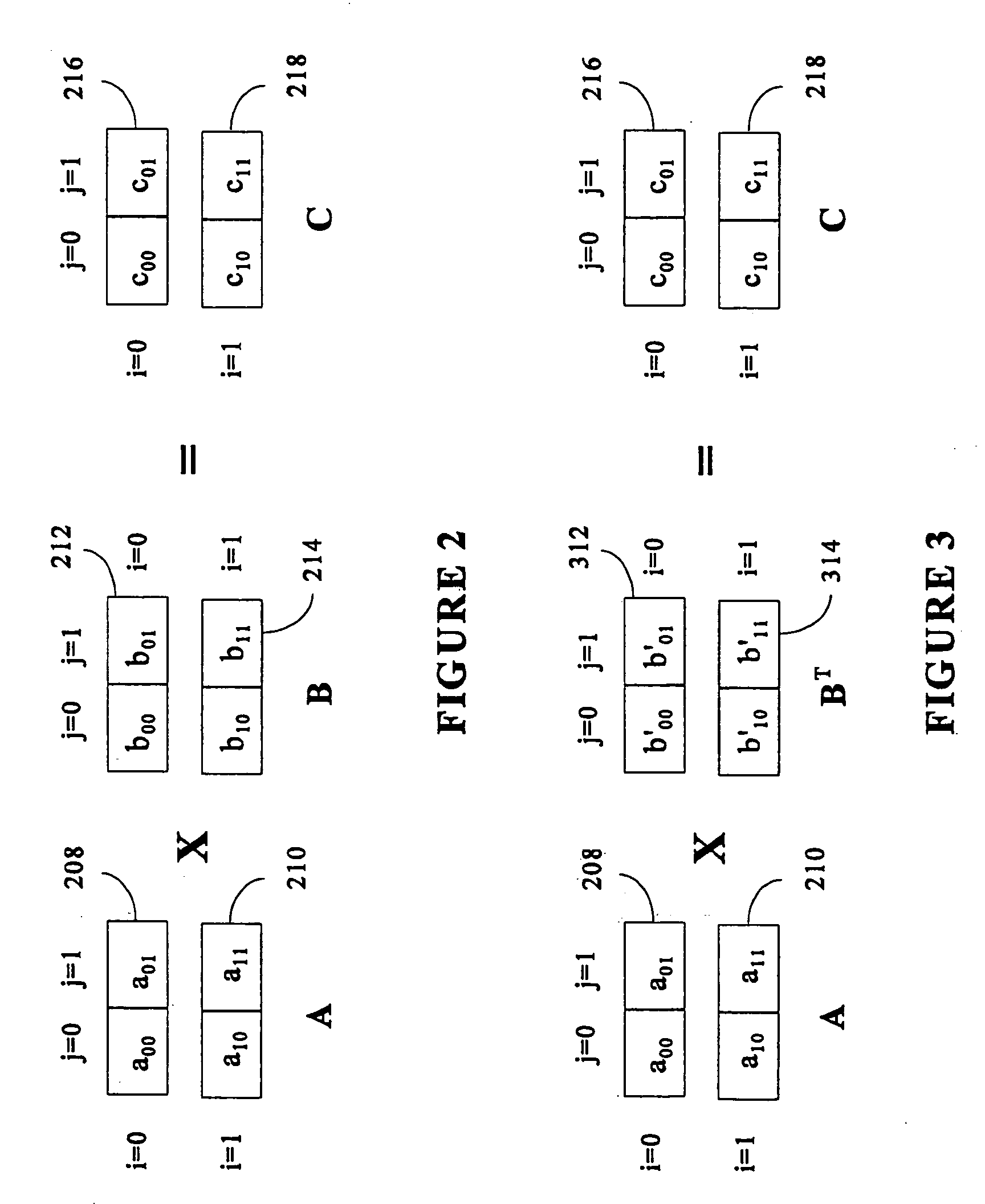
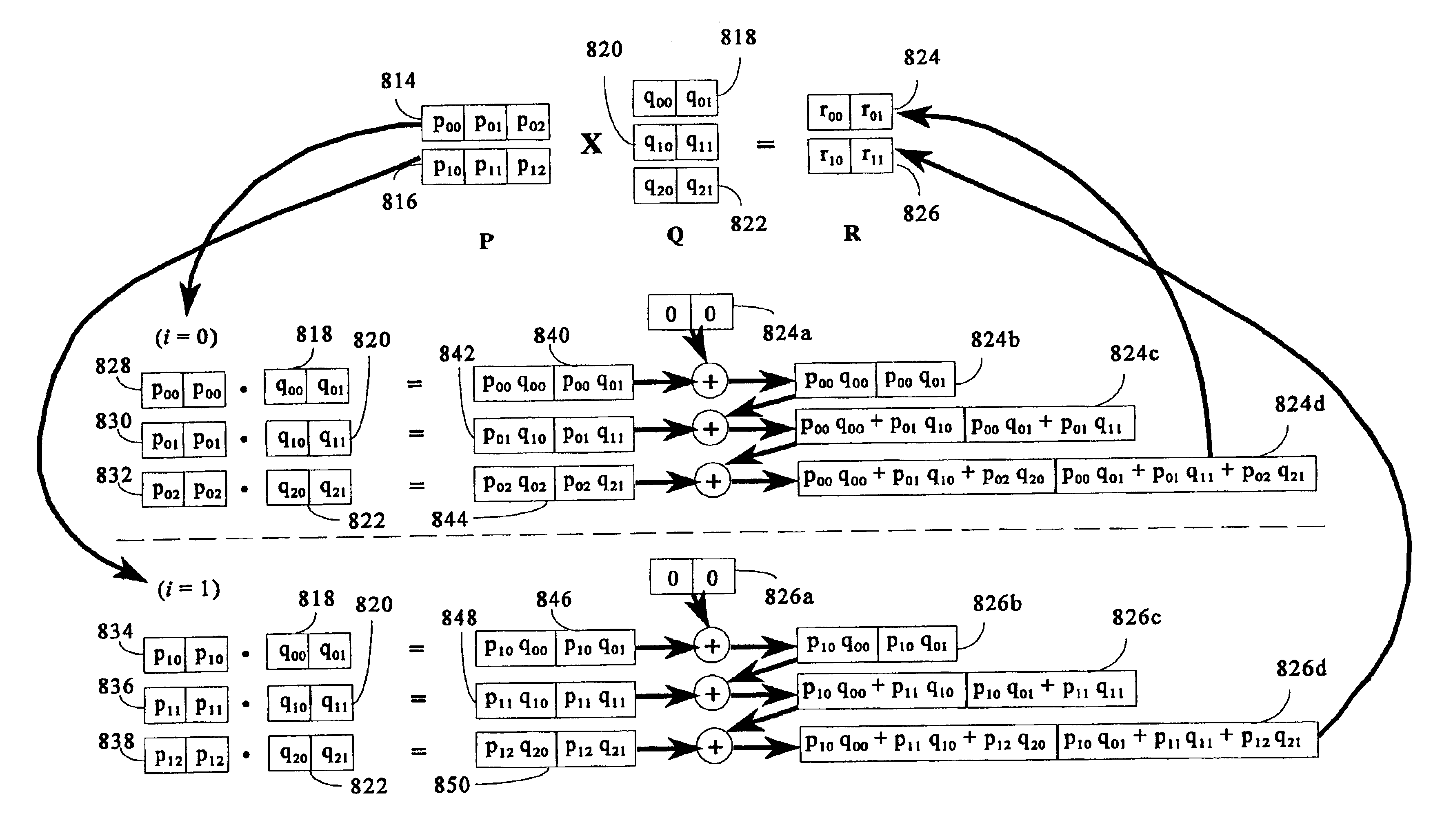
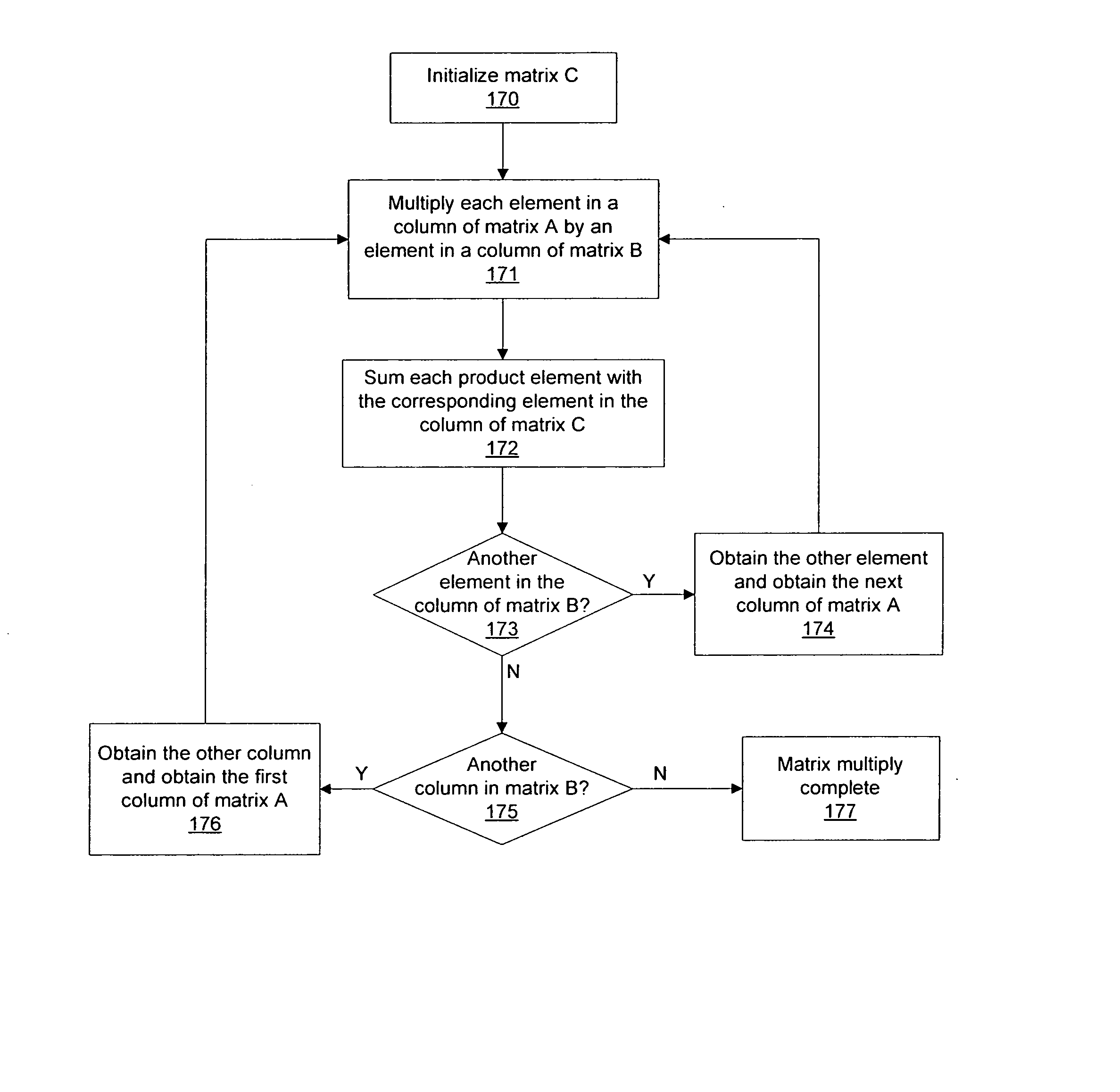
To perform multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system, partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which form a product matrix. Each matrix can be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
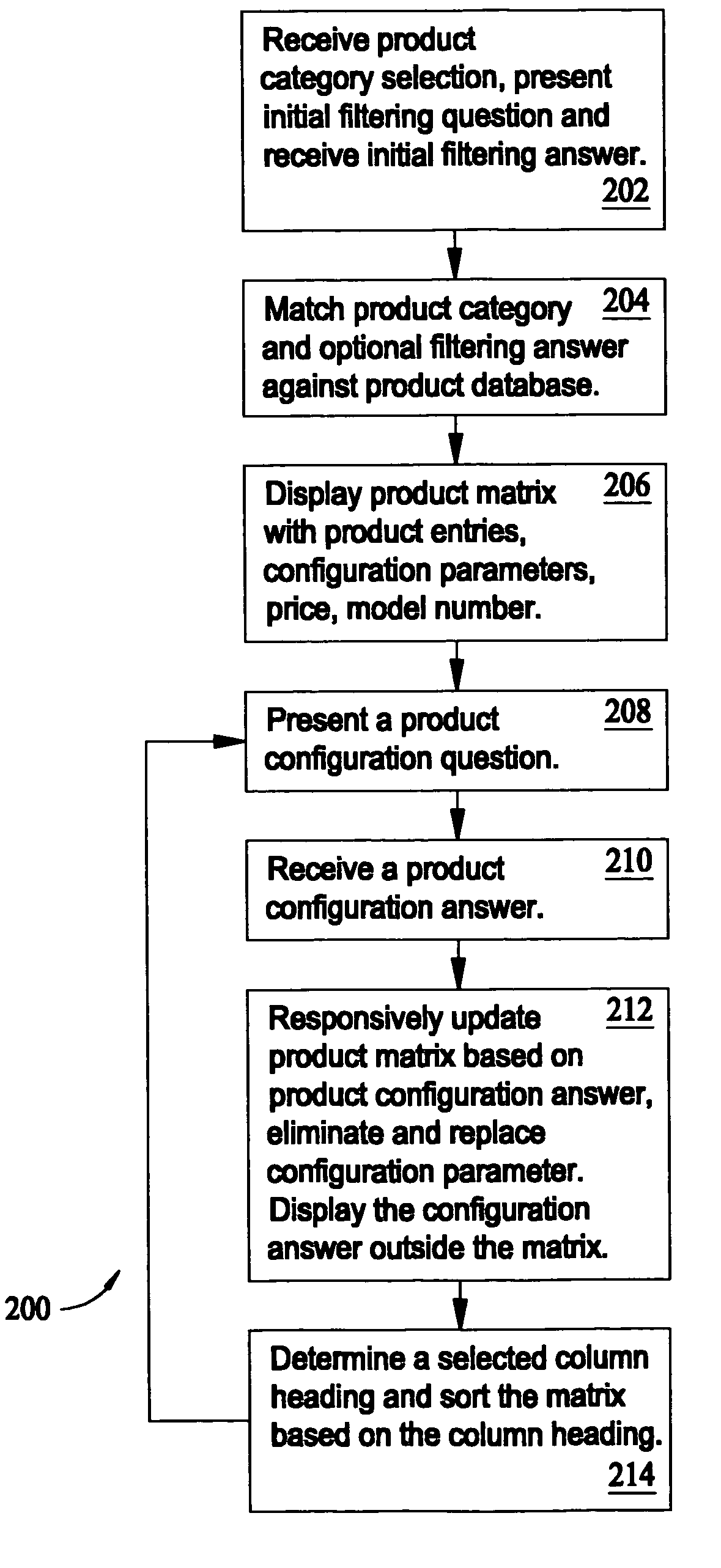
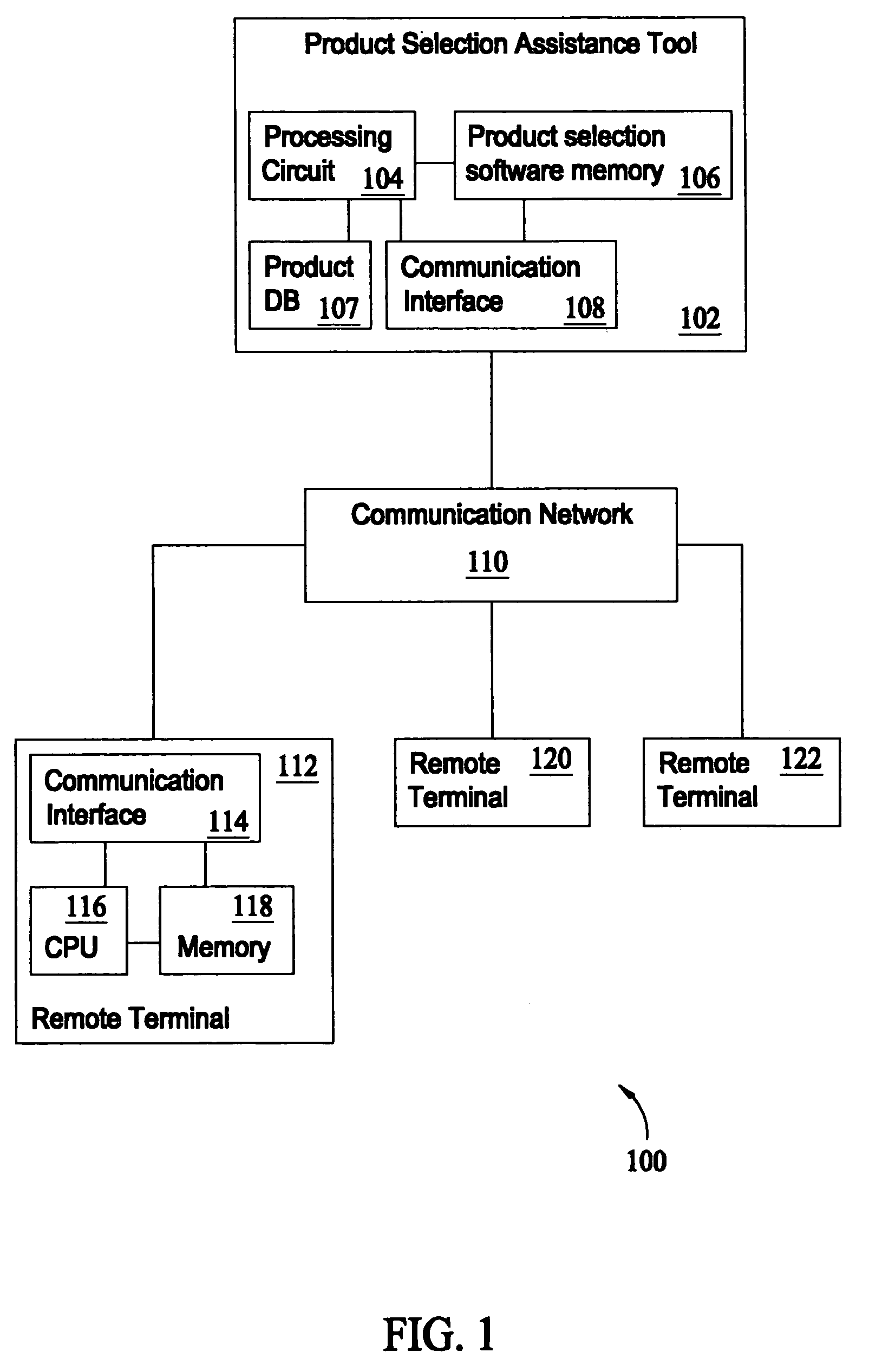
Method and apparatus for product selection assistance
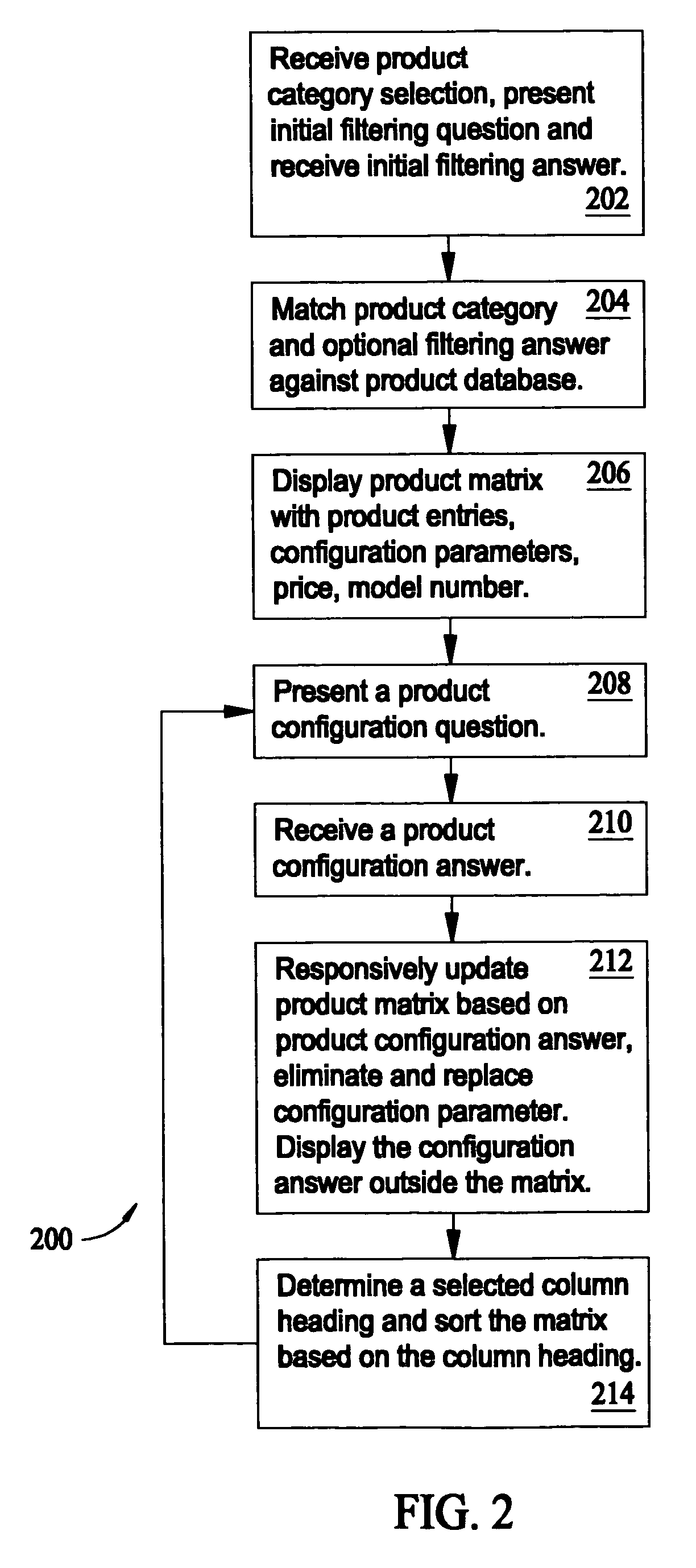
A method for product selection assistance includes receiving a product category selection, matching the product category selection against a product database to determine a plurality of matched products, and displaying a product matrix. The product matrix includes a product entry for each of the matched products. The product entries include a model identifier, a model price, and at least one product configuration parameter associated with the matched products. The method also includes presenting a product configuration question, receiving a product configuration answer, and responsively updating the product matrix based on the product configuration answer to eliminate at least one product entry in the product matrix.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for computing matrix transformations
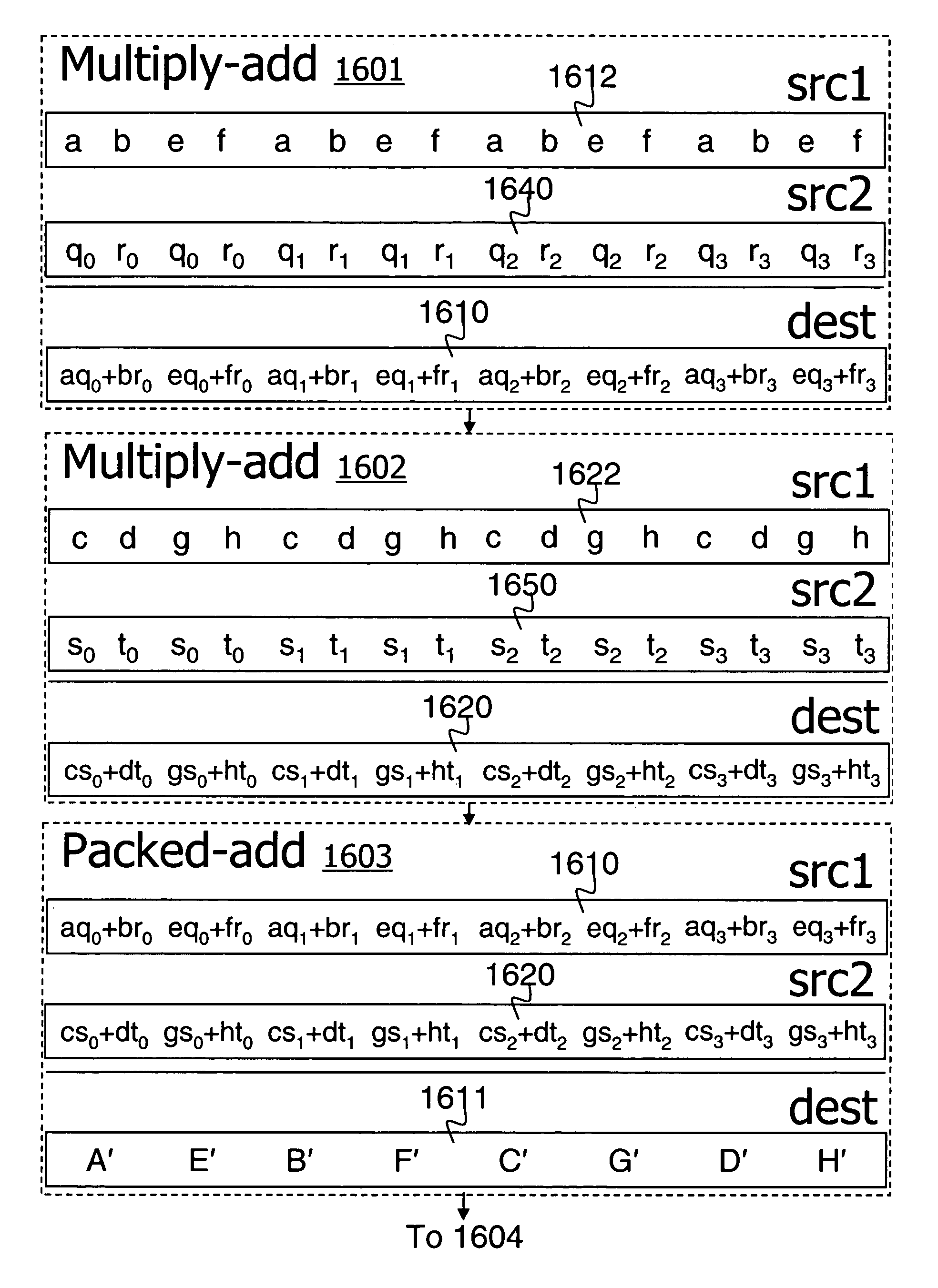
A method and apparatus for performing matrix transformations including multiply-add operations and byte shuffle operations on packed data in a processor. In one embodiment, two rows of content byte elements are shuffled to generate a first and second packed data respectively including elements of a first two columns and of a second two columns. A third packed data including sums of products is generated from the first packed data and elements from two rows of a matrix by a multiply-add instruction. A fourth packed data including sums of products is generated from the second packed data and elements from two more rows of the matrix by another multiply-add instruction. Corresponding sums of products of the third and fourth packed data are then summed to generate two rows of a product matrix. Elements of the product matrix may be generated in an order that further facilitates a second matrix multiplication.
Owner:INTEL CORP
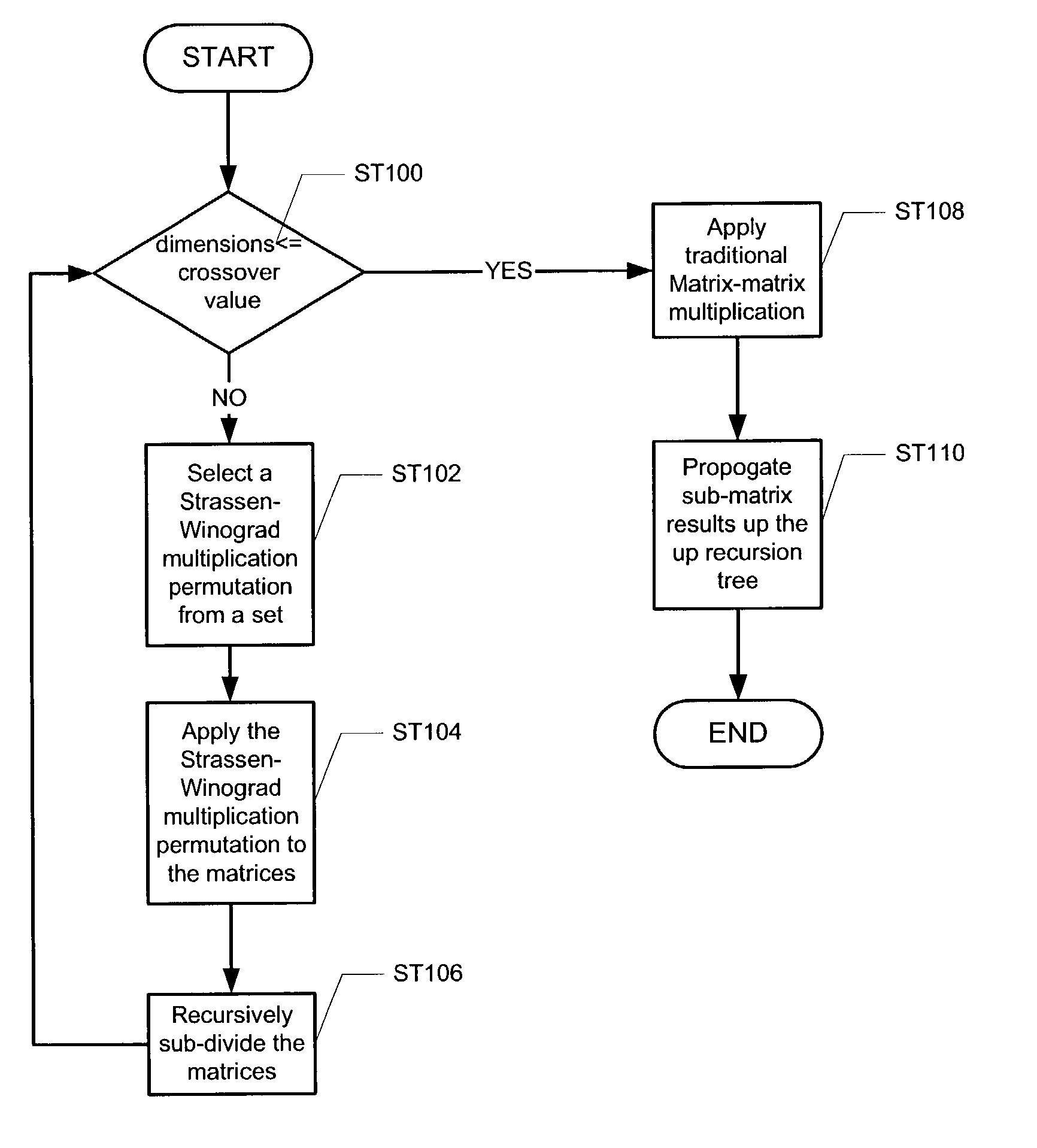
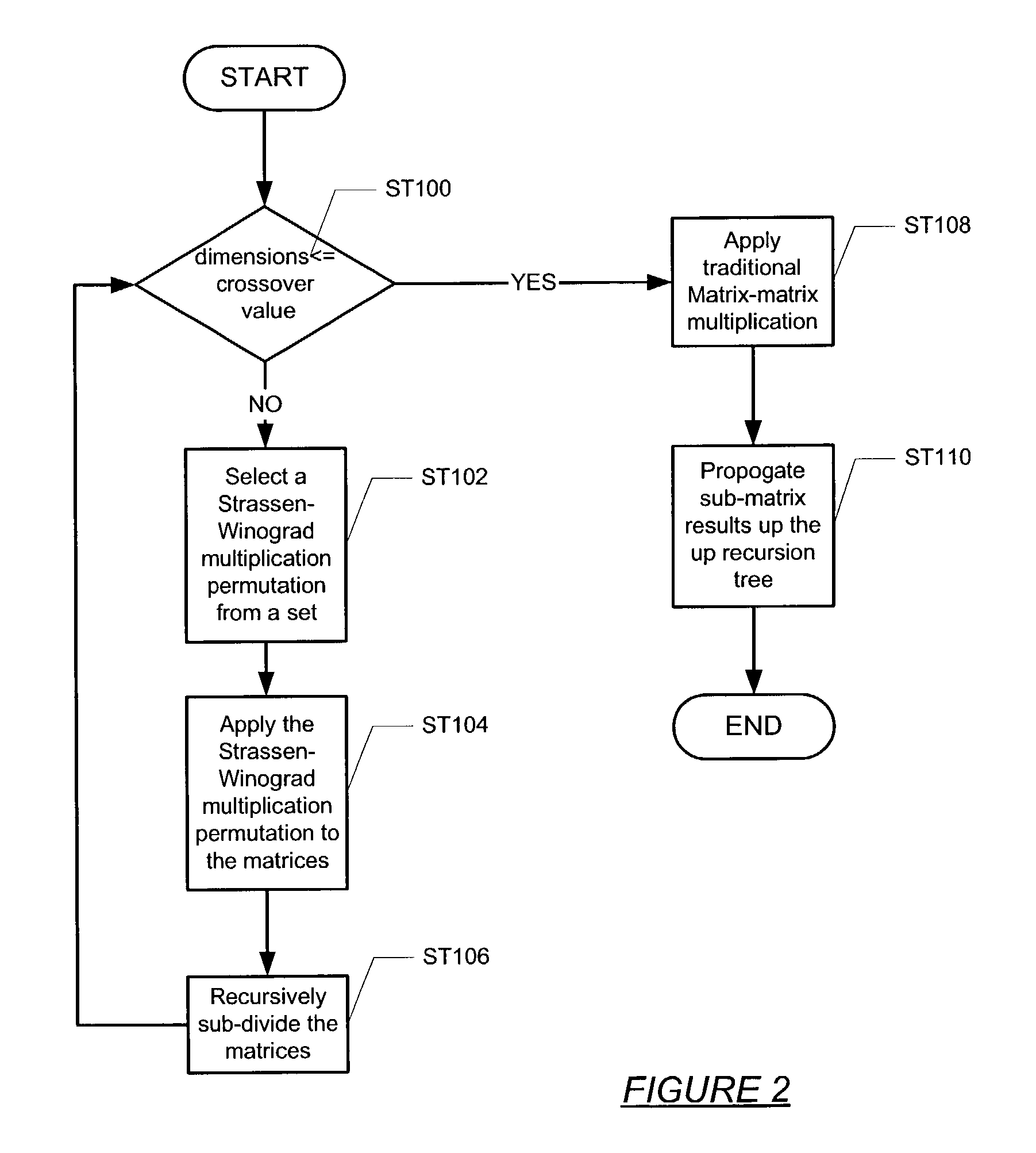
Precision improvement method for the Strassen/Winograd matrix multiplication method
ActiveUS7209939B2Reduce rounding errorsReduce errorsComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmComputerized system
A computer system for multiplying a first matrix and a second matrix that reduces rounding error, including a processor, a memory, a storage device, and software instructions stored in the memory for enabling the computer system, under the control of the processor, to perform obtaining a first set of dimension values for the first matrix and a second set of dimension values for the second matrix, selecting one of a plurality of multiplication permutations if the first set of dimension values and the second set of dimension values are greater than a crossover value, multiplying the first matrix by the second matrix using the multiplication permutation and a Strassen-Winograd method, recursively sub-dividing the first matrix and the second matrix producing a set of sub-matrix products and a recursion tree, and propagating the set of sub-matrix products up the recursion tree to produce a product matrix.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Management of compatibility of software products installed on a user's computing device
ActiveUS7984436B1Reduce in quantityVersion controlProgram loading/initiatingSoftware engineeringComputer compatibility
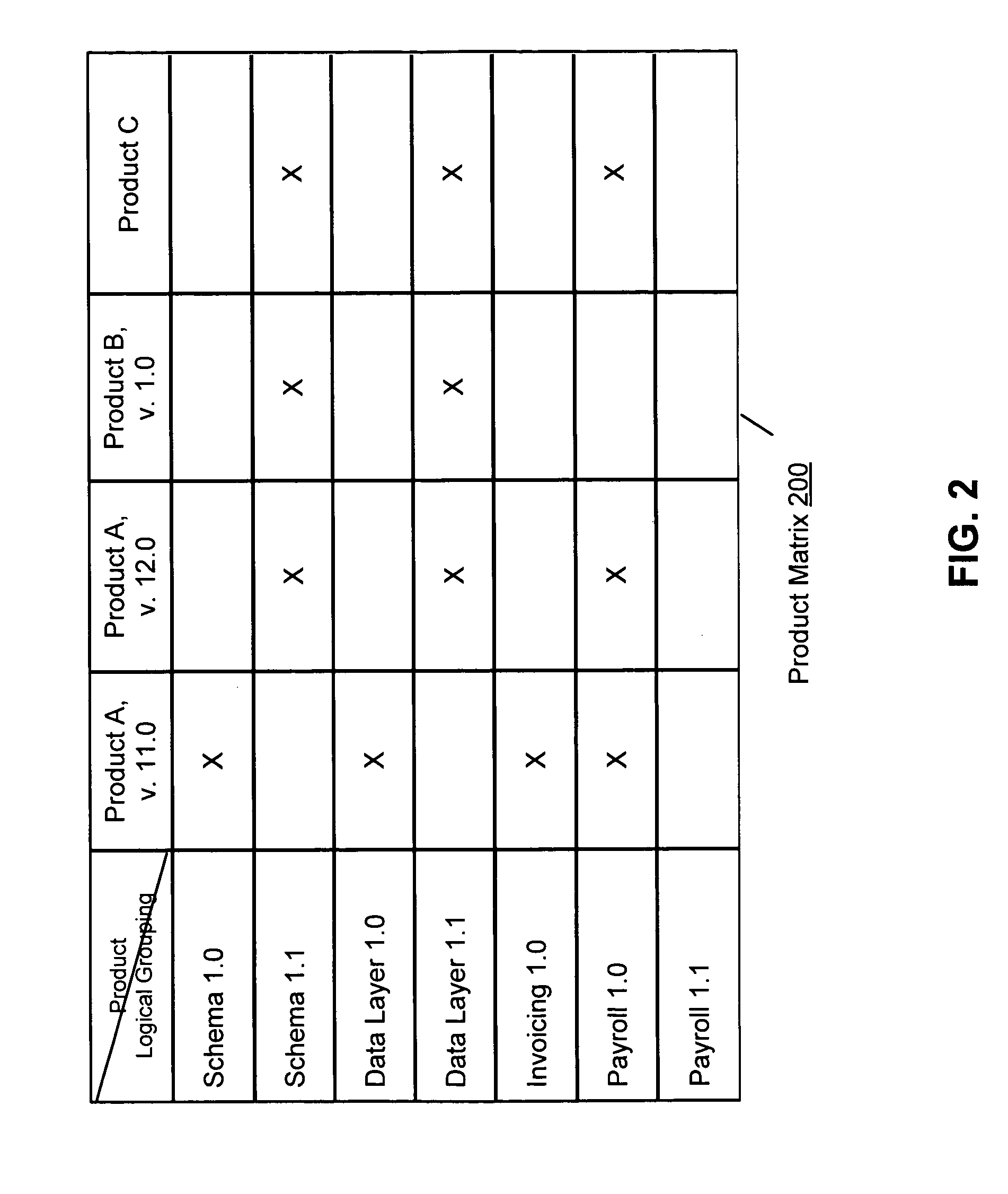
Physical components that share common attributes in a software product are combined into logical groupings. A product matrix also lists logical groupings that are included into each software product listed in the product matrix. A compatibility matrix indicates whether any two logical groupings listed in the product matrix are compatible. When a new product is provided for an installation, the compatibility matrix is consulted to determine whether any two logical groupings of the new product and installed product are compatible. An installation can proceed or be terminated based on the compatibility determination.
Owner:INTUIT INC
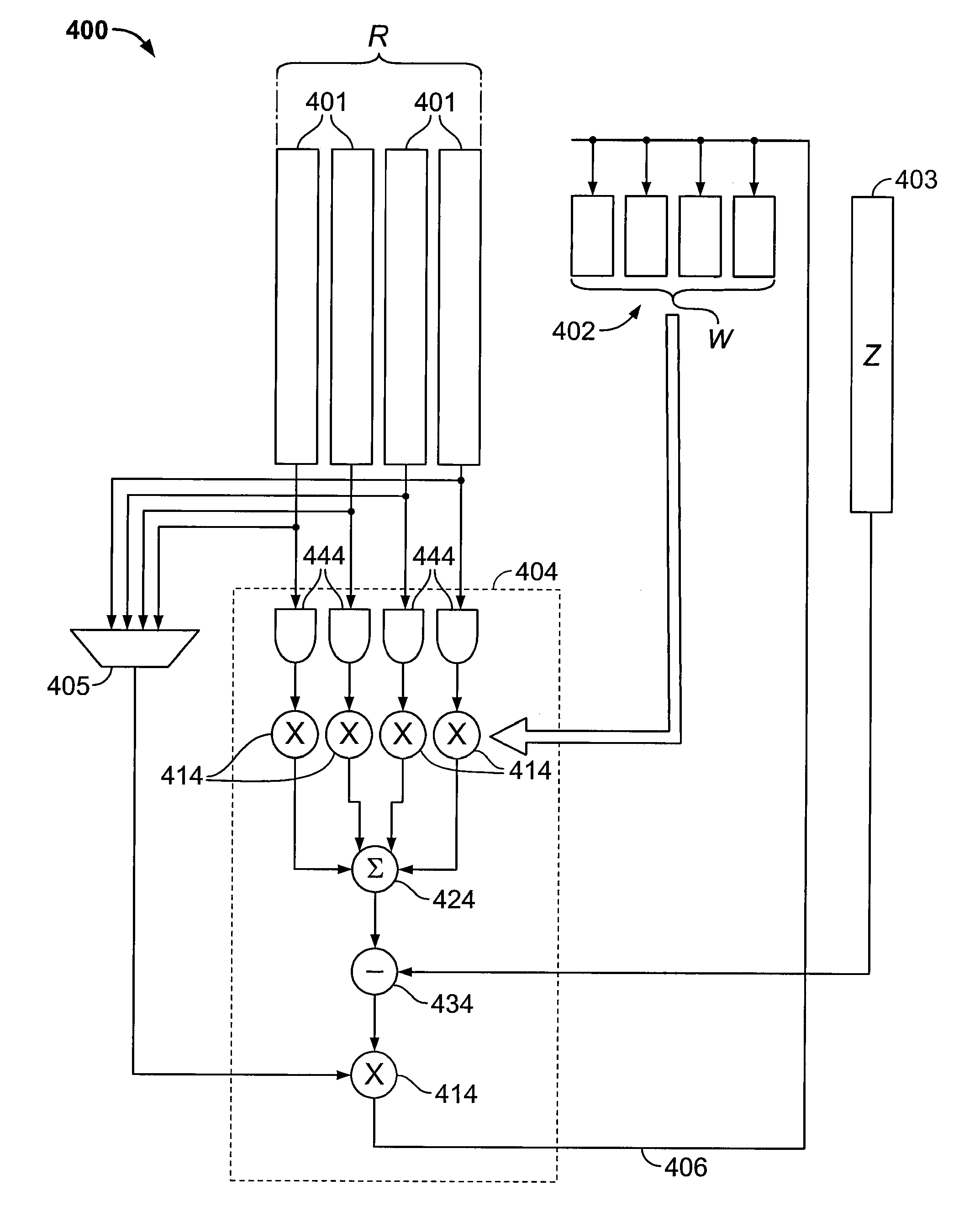
Matrix multiply with reduced bandwidth requirements
InactiveUS20070271325A1Reduce memory bandwidth requirementReduce memory bandwidthComputation using non-contact making devicesMultiprogramming arrangementsAlgorithmSingle element
Systems and methods for reducing the bandwidth needed to read the inputs to a matrix multiply operation may improve system performance. Rather than reading a row of a first input matrix and a column of a second input matrix to produce a column of a product matrix, a column of the first input matrix and a single element of the second input matrix are read to produce a column of partial dot products of the product matrix. Therefore, the number of input matrix elements read to produce each product matrix element is reduced from 2N to N+1, where N is the number of elements in a column of the product matrix.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Linear array SAR backward projection self-focusing imaging method based on positive semi-definite programming
The invention discloses a linear array SAR backward projection self-focusing imaging method based on positive semi-definite programming. A primary function matrix is accumulated through constructing a linear array SAR backward projection. A positive semi-definite programming method in a convex optimization theory is used for estimating a phase error matrix in linear array SAR echo data. A minimum rank of a product matrix between a backward projection accumulated primary function matrix and the phase error matrix is used. An optimal matrix under a constraining condition is solved for realizing phase error estimation of the linear array SAR and self-focusing imaging, thereby converting the linear array SAR backward projection algorithm imaging process to a form of multiplexing matrix with a vector, and obtaining a linear array SAR imaging result.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Solving linear matrices in an integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20110238720A1Eliminate needLower latencyComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationMatrix decompositionLinear matrix
Circuitry for solving linear matrix equations involving a resultant matrix, an unknown matrix and a product matrix that is a product of the resultant matrix and the unknown matrix includes matrix decomposition circuitry for triangulating an input matrix to create a resultant matrix having a plurality of resultant matrix elements on a diagonal, and having a further plurality of resultant matrix elements arranged in columns below the resultant matrix elements on the diagonal. The matrix decomposition circuitry includes an inverse square root multiplication path that computes diagonal elements of the resultant matrix having an inverse square root module, and the said inverse square root module computes inverses of the diagonal elements to be used in multiplication in place of division by a diagonal element. Latency is hidden by operating on each nth row of a plurality of matrices prior to any (n+1)th row.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
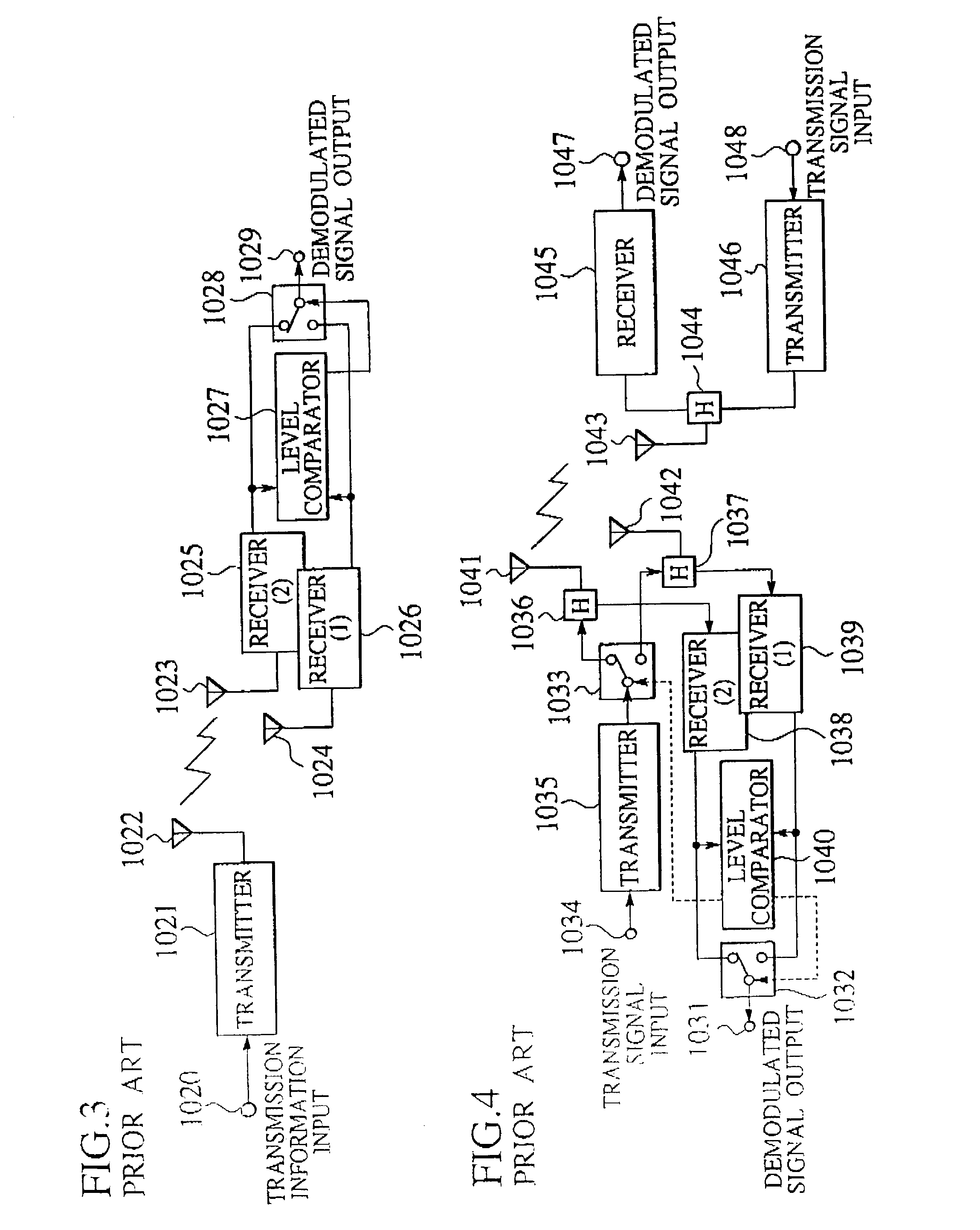
Communication method, communication system, transmitter, and receiver
InactiveUS20030152159A1Transmission control/equlisationSpatial transmit diversityAs elementCommunications system
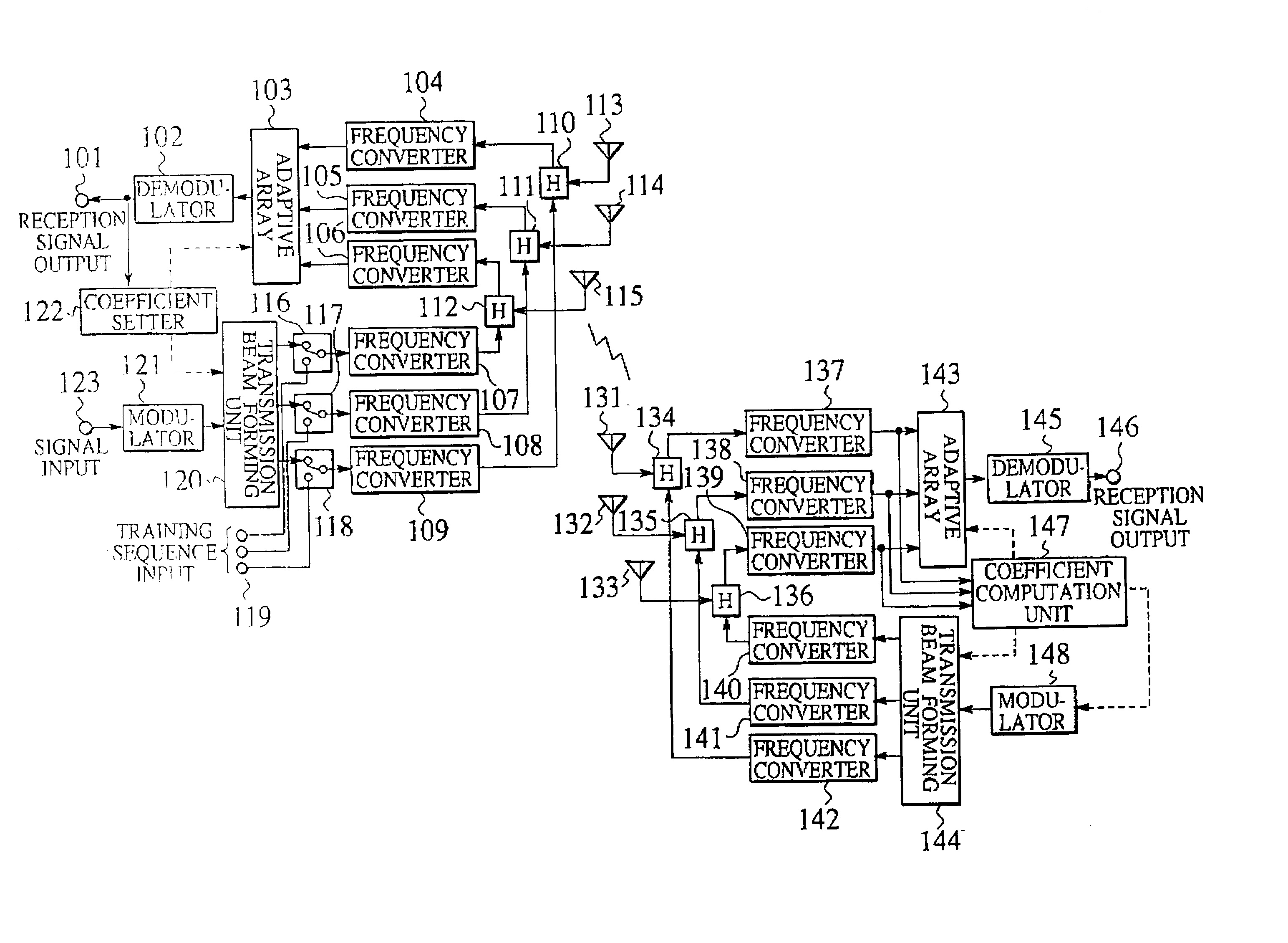
The communication system carries out signal processing adapted for transmission-channel characteristics. In the communication system, a right transmitter detects a transmission-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient sent from a left receiver and corrects, according to the transmission-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient, at least one of a transfer function and a spatial frequency characteristic of a transmission signal. The left receiver computes the transmission-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient and a reception-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient through the processes of detecting correlation of a reception signal, and carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on a product matrix obtained by multiplying a correlation matrix having the detected correlation as elements and a transported matrix of the correlation matrix together. According to the reception-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient, the left receiver corrects at least one of a frequency characteristic and a spatial frequency characteristic of the reception signal. The left receiver transmits the transmission-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient to the right transmitter, so that the right transmitter may correct at least one of a transfer function and a spatial frequency characteristics of a transmission signal according to the transmission-signal-characteristics-correcting coefficient.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
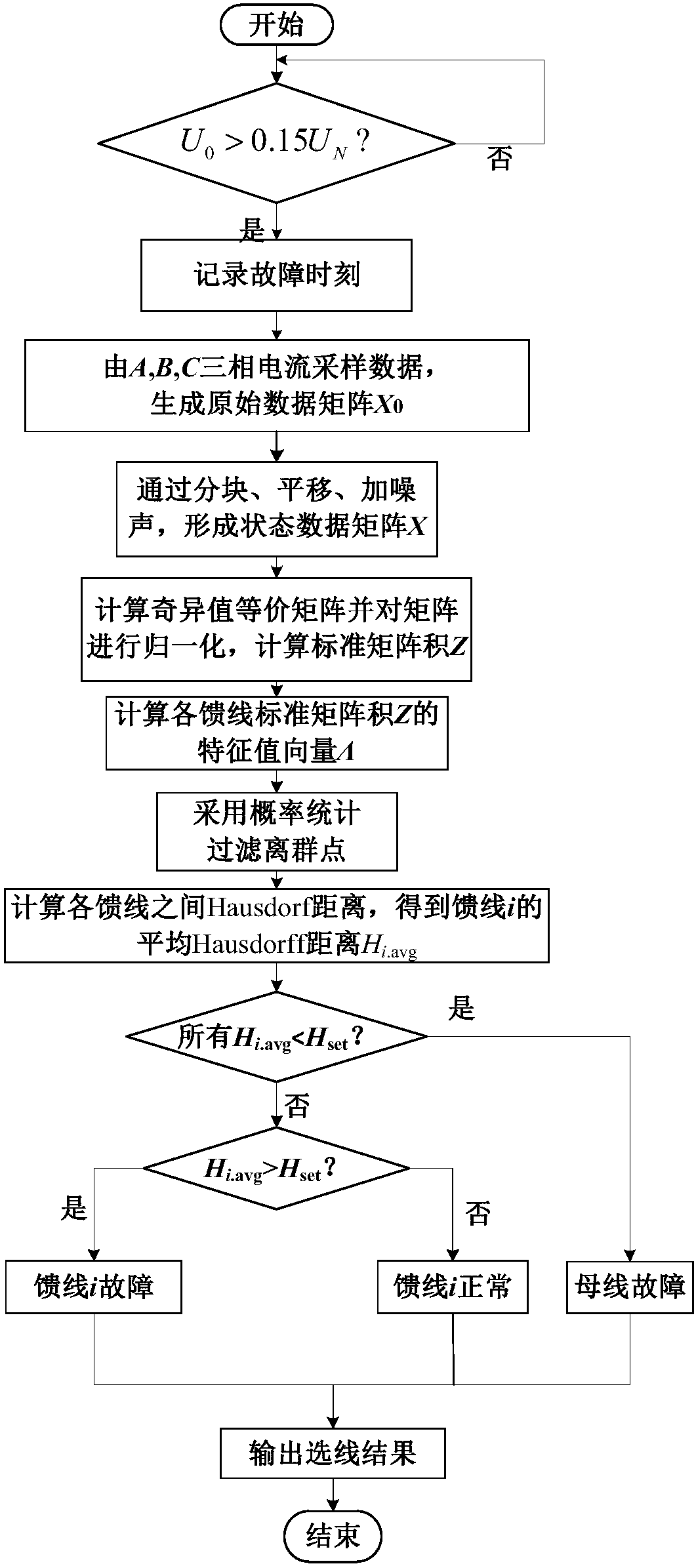
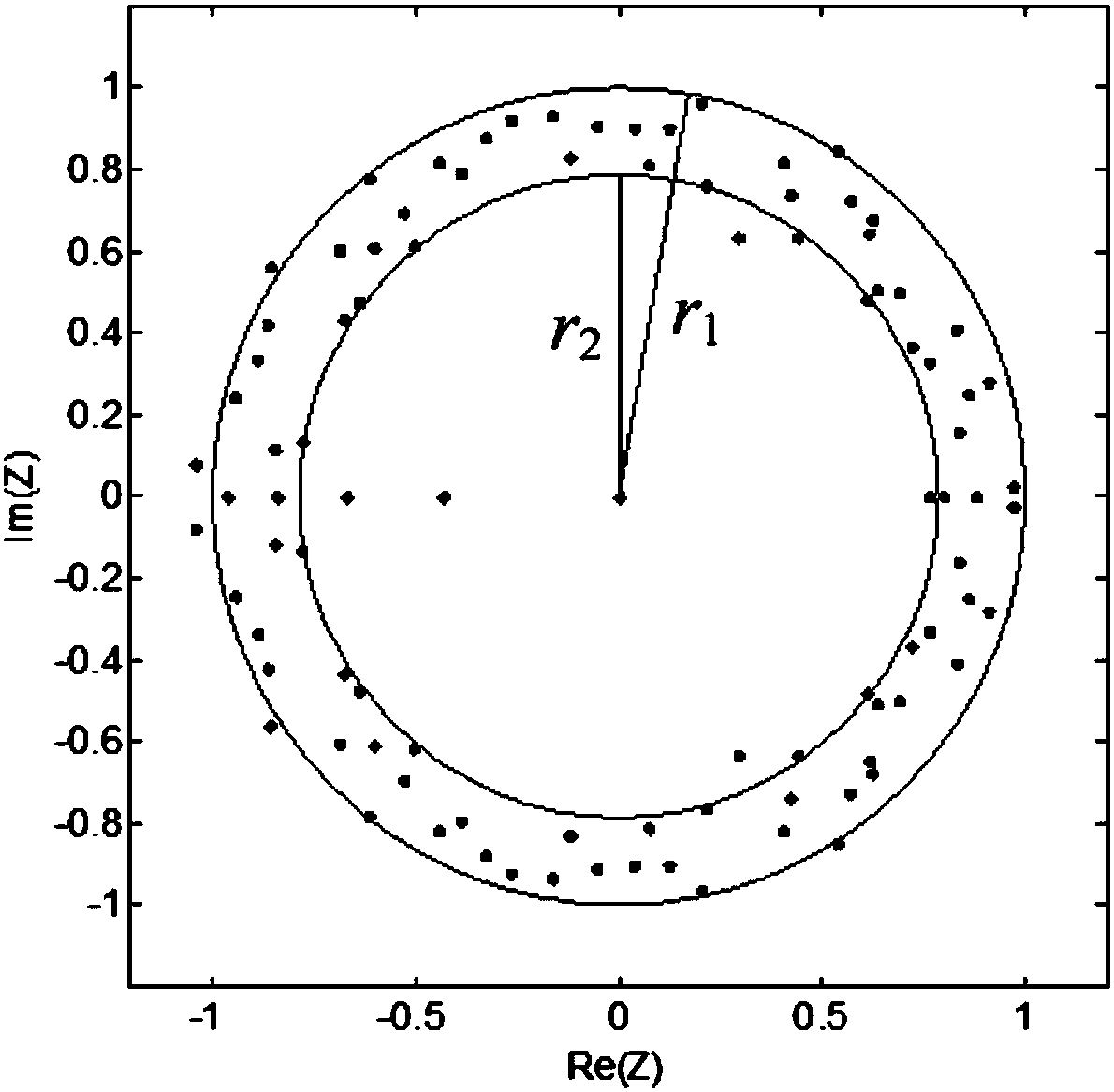
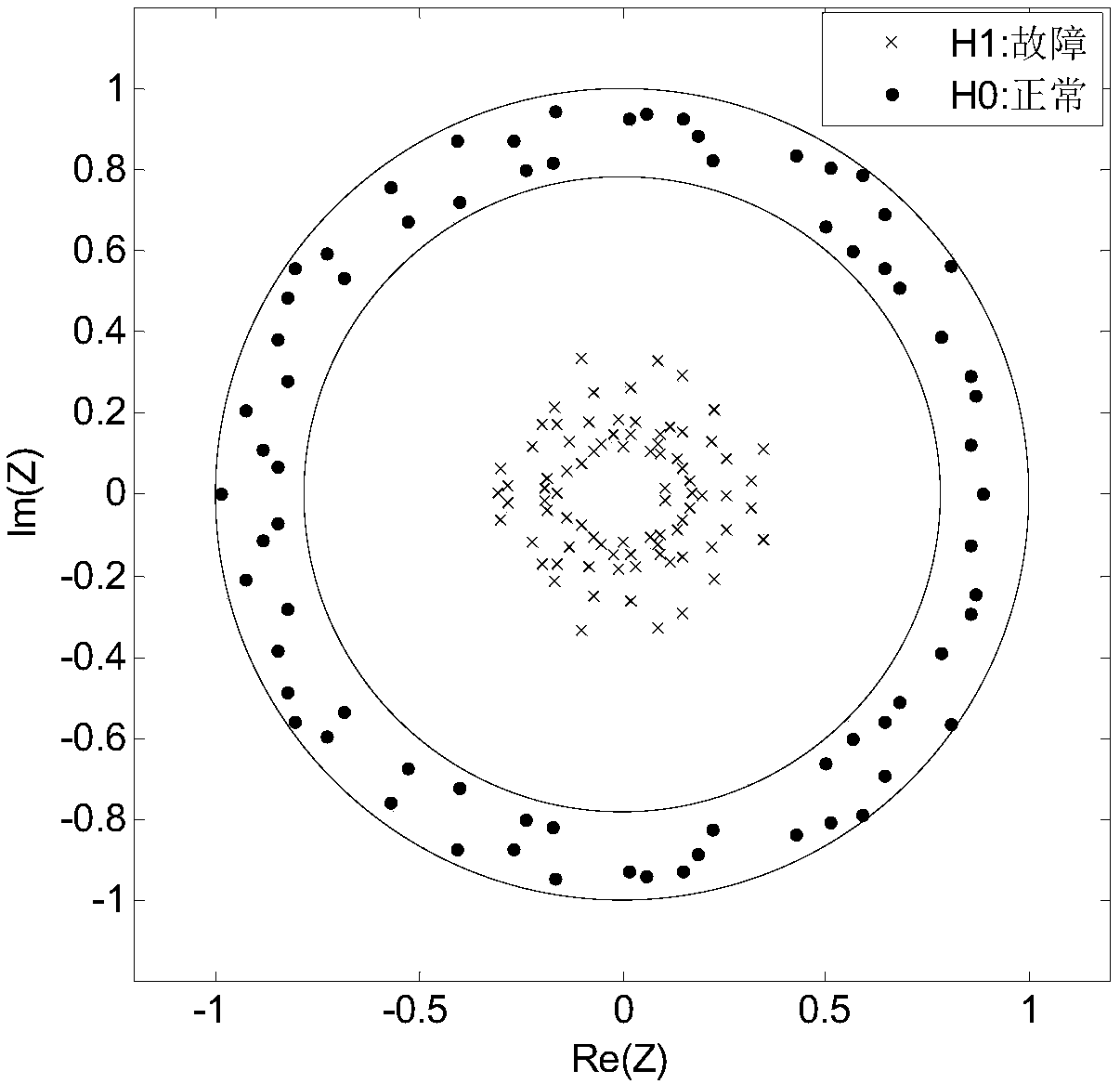
Distribution network fault line selection method based on random matrix and Hausdorff distance
ActiveCN108572303AThe fault line selection result is accurateImprove reliabilityFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemEuclidean vectorData Matrix
The invention discloses a distribution network fault line selection method based on a random matrix and a Hausdorff distance. Three-phase current sampling values of a feeder line before and after fault are selected, through blocking and translation processing, white Gaussian noise is added, a state data matrix is generated, a product matrix is obtained by using equivalent transformation of singular values of the random matrix, a standard matrix product is obtained by normalization, eigenvalue vectors are acquired, probability statistics is carried out, eigenvalue vectors with the probabilitiesP to be smaller than 10% are used as outliers to be filtered, a Hausdorff distance algorithm is adopted, the Hausdorff distances between the eigenvalue vector of a certain feeder line and the eigenvalue vectors of other feeder lines are calculated, the maximum value is removed, averaging is carried out to obtain an average Hausdorff distance of the feeder line, if the average distance is larger than a threshold, fault of the feeder line is judged, and if the average Hausdorff distance of each feeder line is smaller than the threshold, fault of a connected bus is judged. A fault feeder line and a fault bus can be judged accurately, the judgment does not rely on a distribution network model and is not influenced by a fault location, transition resistance, an initial phase angle and a line type, and the practicability is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
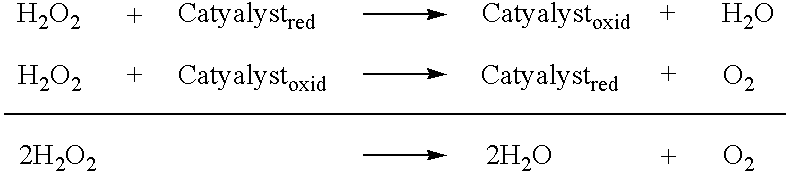
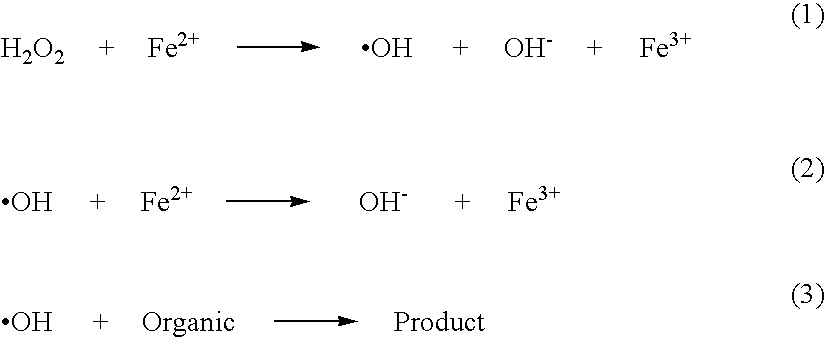
Stable peroxide containing personal care compositions
The present invention relates to stable personal care composition, including oral care compositions containing a peroxide source. The compositions are stabilized by eliminating or minimizing the presence in the composition of metals having radical forming potential with the peroxide. Preferably, the metals that are eliminated or reduced are cobalt, copper, palladium, nickel and iron. The compositions are further stabilized by the addition of agents having scavenging or quenching activity for free radicals. Reducing free radical activity in the product matrix prevents radical- mediated loss and degradation of peroxide and other ingredients, in particular organic compounds added as active or aesthetic agents, including flavors, perfumes, colorants and thickeners. Provided are peroxide containing oral care products with enhanced consumer appeal in terms of taste, mouthfeel and appearance, thereby encouraging compliance and regular use. Such attributes are important since use of these products may involve fairly long residence time in the mouth for efficacy.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Method to minimize compatibility error in hierarchical modulation using variable phase
ActiveUS20060276145A1Increase volumeIncrease the amount of dataRadio transmissionPhase-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataData stream
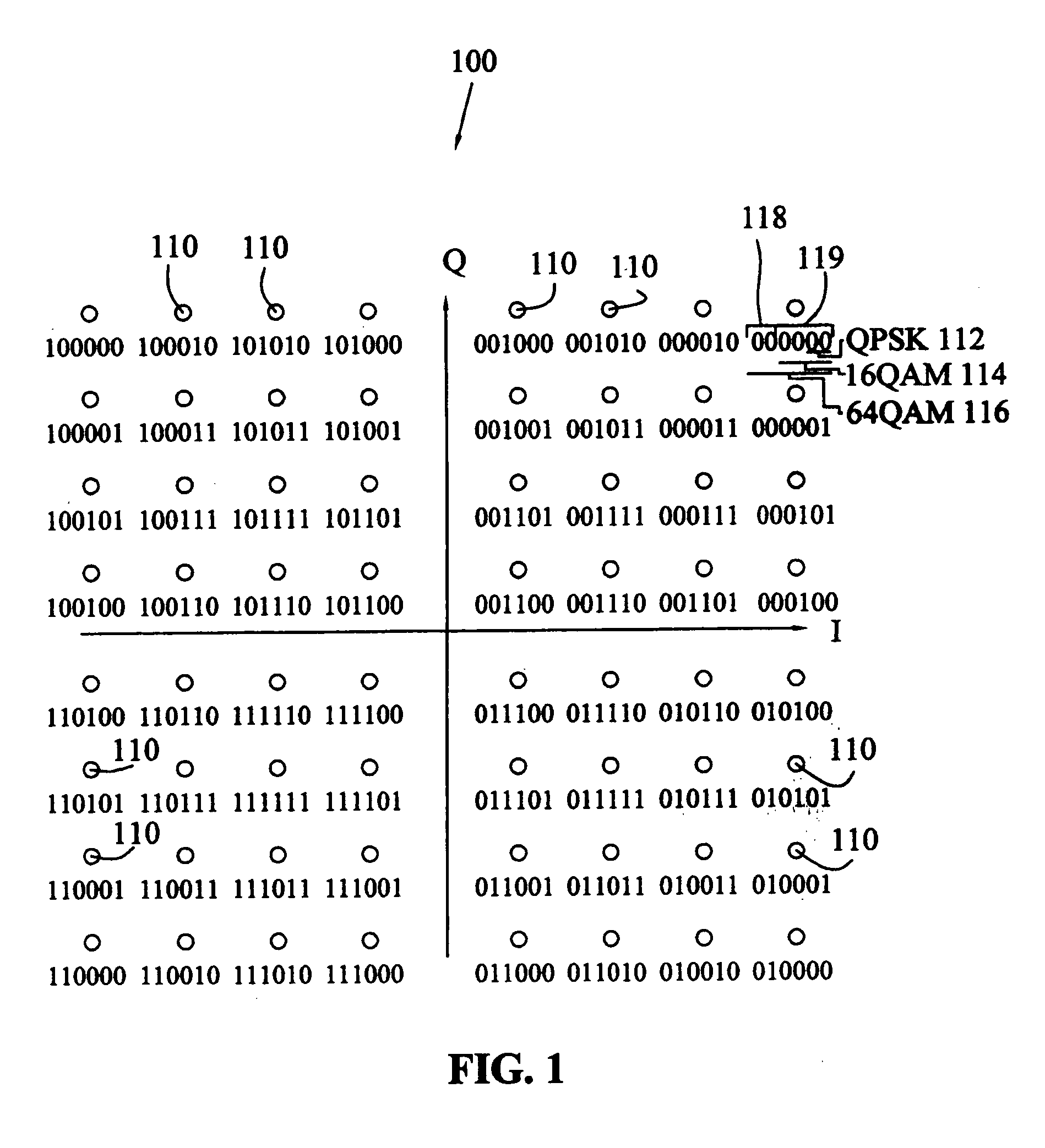
The present invention provides a method of hierarchically modulating first and second digital data streams in a broadcast system such as an SDAR system that is compatible with legacy receivers. The second digital data stream, but not the first, is provided with a non-binary pseudo-random encoding. A carrier is first modulated, e.g. QPSK, by the first digital data stream; and a second modulation is performed with the encoded second digital data stream. The encoding includes a multiplication of a matrix formed of 2, 3 or 4 consecutive bits of the secondary data stream by a matrix, e.g. a Hadamard matrix to form a product matrix having non-binary values that are used to modify consecutive symbols of the first modulation. The second modulation appears as Gaussian noise to legacy receivers over time.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
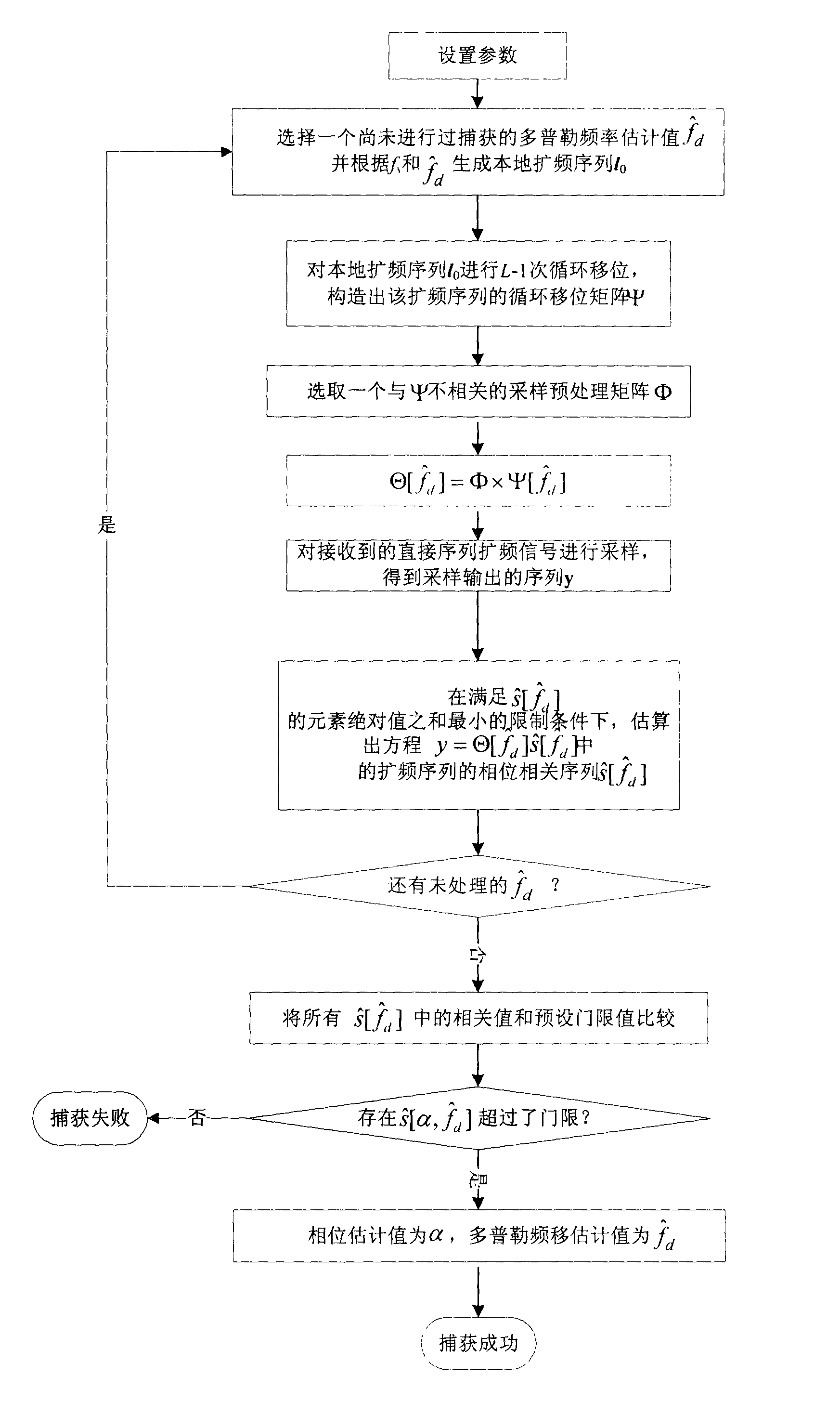
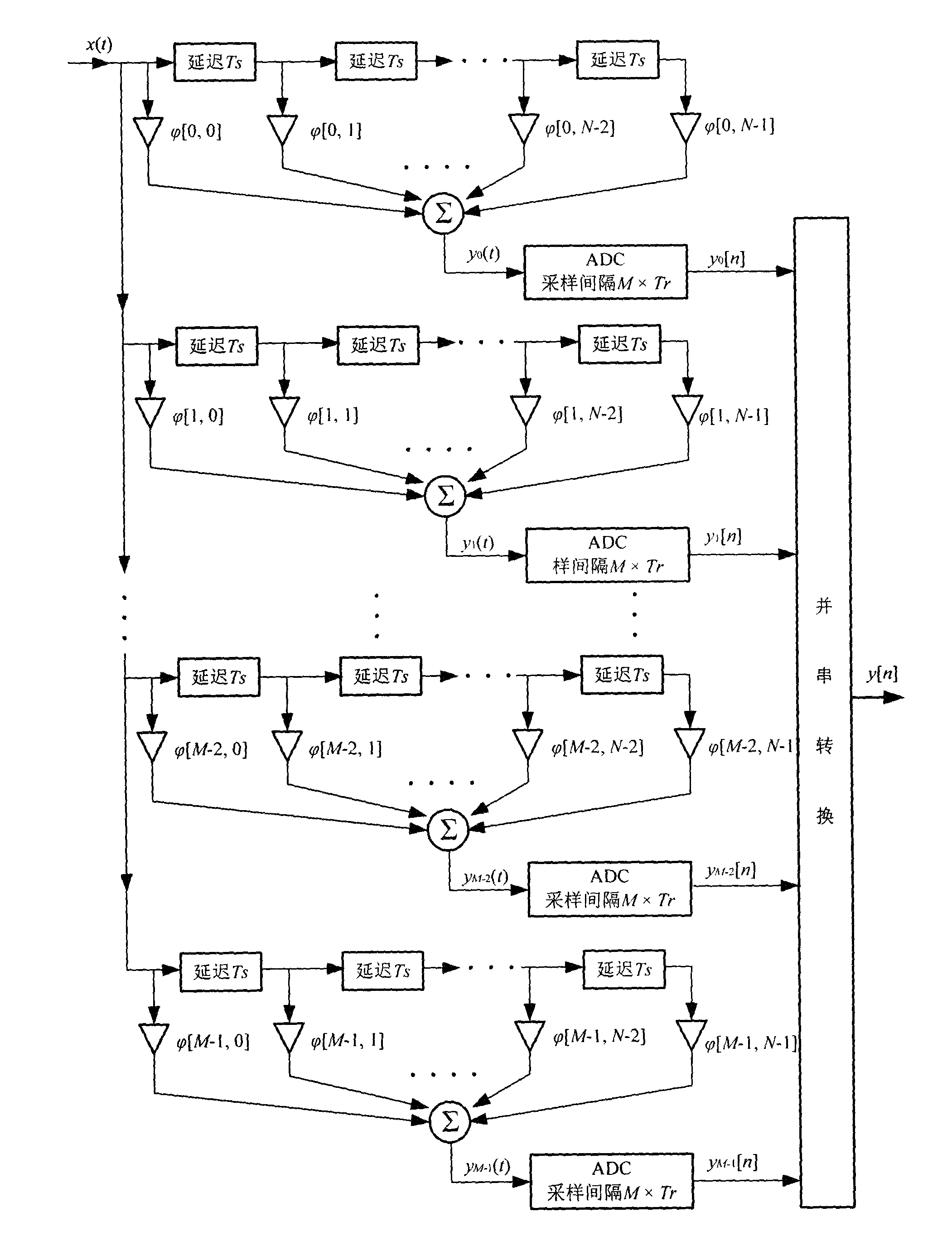
Novel direct sequence spread spectrum signal acquisition method
The invention relates to a novel direct sequence spread spectrum signal acquisition method in the direct sequence spread spectrum signal acquisition technology field. According to a technical scheme of the invention, obtained data is subjected to pretreatment, the data is sampled with a low sampling rate, and an observation signal is obtained. Through calculating projection value change of the observation signal on a product matrix of a pretreatment matrix and a cyclic shift matrix of a spread spectrum sequence, a phase value of a received spread spectrum signal is estimated. When employing the technical scheme to carry out spread spectrum signal acquisition, under a condition that a sampling rate is lower than Nyquist sampling law requirement, spread spectrum sequence acquisition is completed, thus cost of an acquisition system is substantially reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
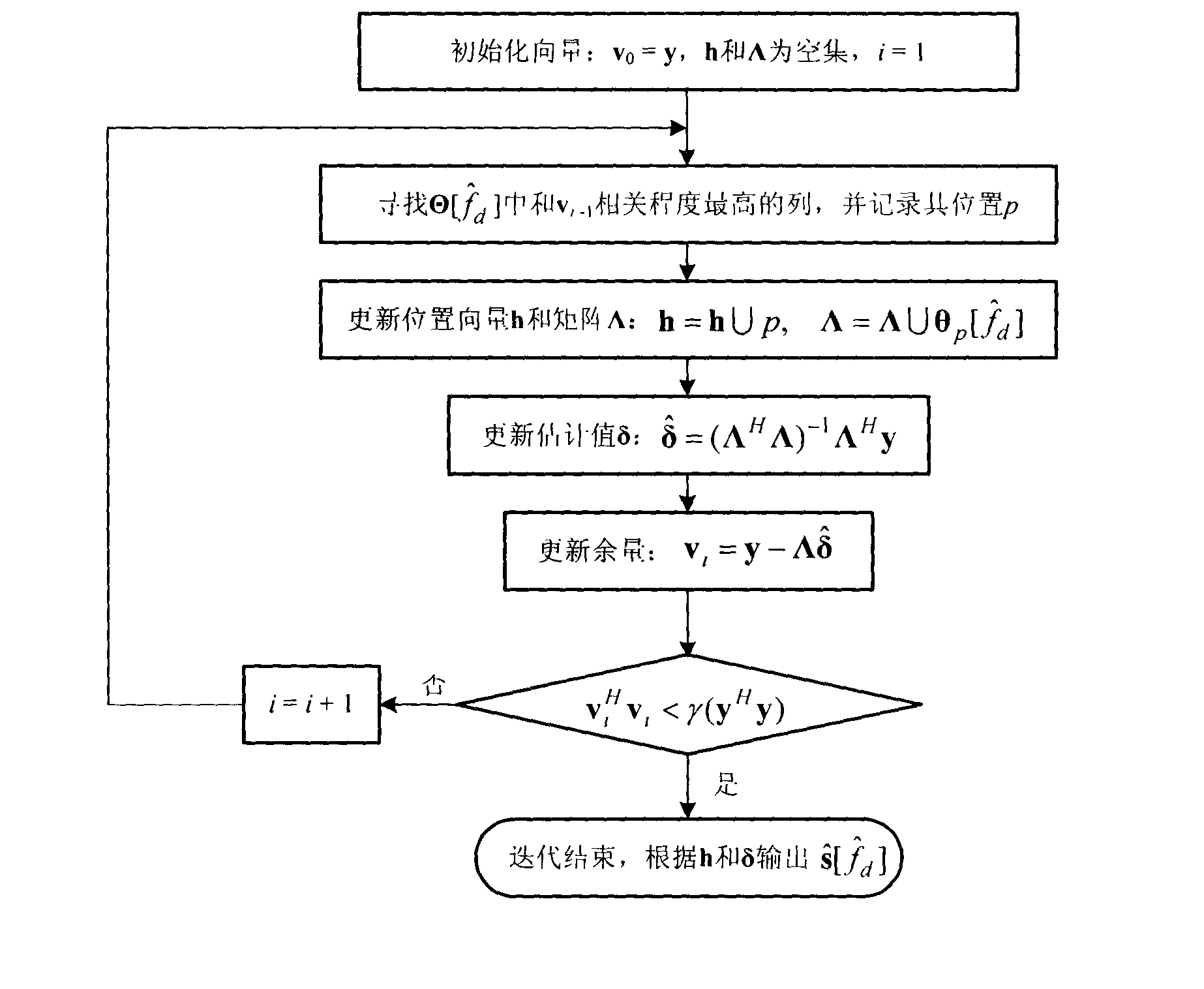
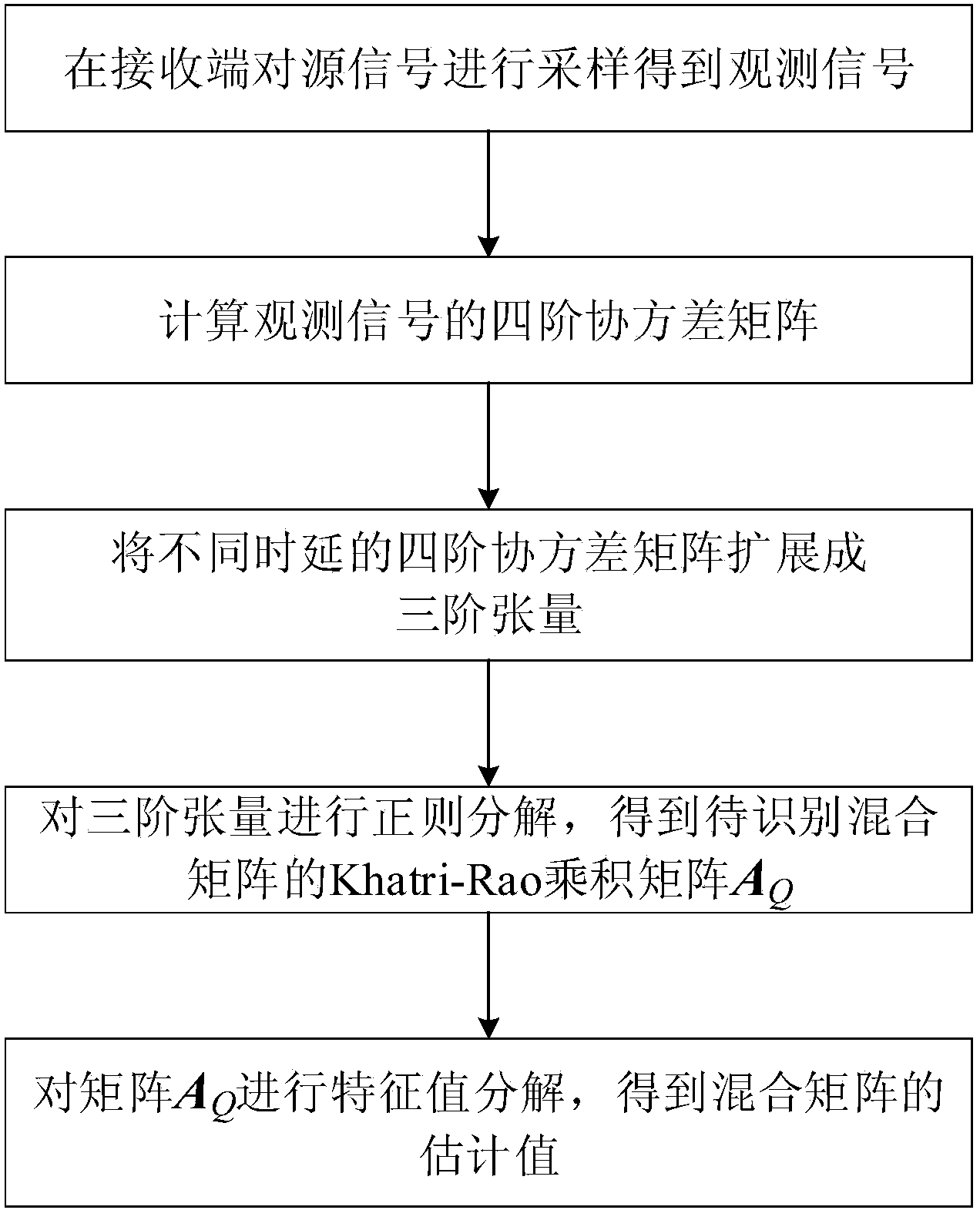
Hybrid matrix recognition method in underdetermined blind source separation based on tensor regular decomposition
ActiveCN104375976ASolving recognition problemsOvercome the disadvantages of difficulty in extracting self-sourced time-frequency pointsSpeech analysisComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a hybrid matrix recognition method in underdetermined blind source separation based on tensor regular decomposition. The method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, hybrid matrix estimation is limited by specific conditions. The method includes the implementation steps that (1), source signals are sampled and observation data are acquired; (2), four-order covariance matrixes in different time delays are calculated through four-order cumulants of the observation data; (3), the four-order covariance matrix in different time delays are expanded into a three-order tensor mode; (4), tensor regular decomposition is conducted on three-order tensors, and a Khatri-Rao product matrix of a hybrid matrix to be recognized is acquired; (5), the product matrix is processed through an eigenvalue decomposition method, and an estimated value of the hybrid matrix is acquired. The method has the advantage of being high in recognition accuracy and can be used in the fields of voice, communication, radar and biomedicine and used for underdetermined blind source separation under the time-frequency aliasing condition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Low-complexity underwater acoustic sparse time-varying channel estimation method based on compressed sensing
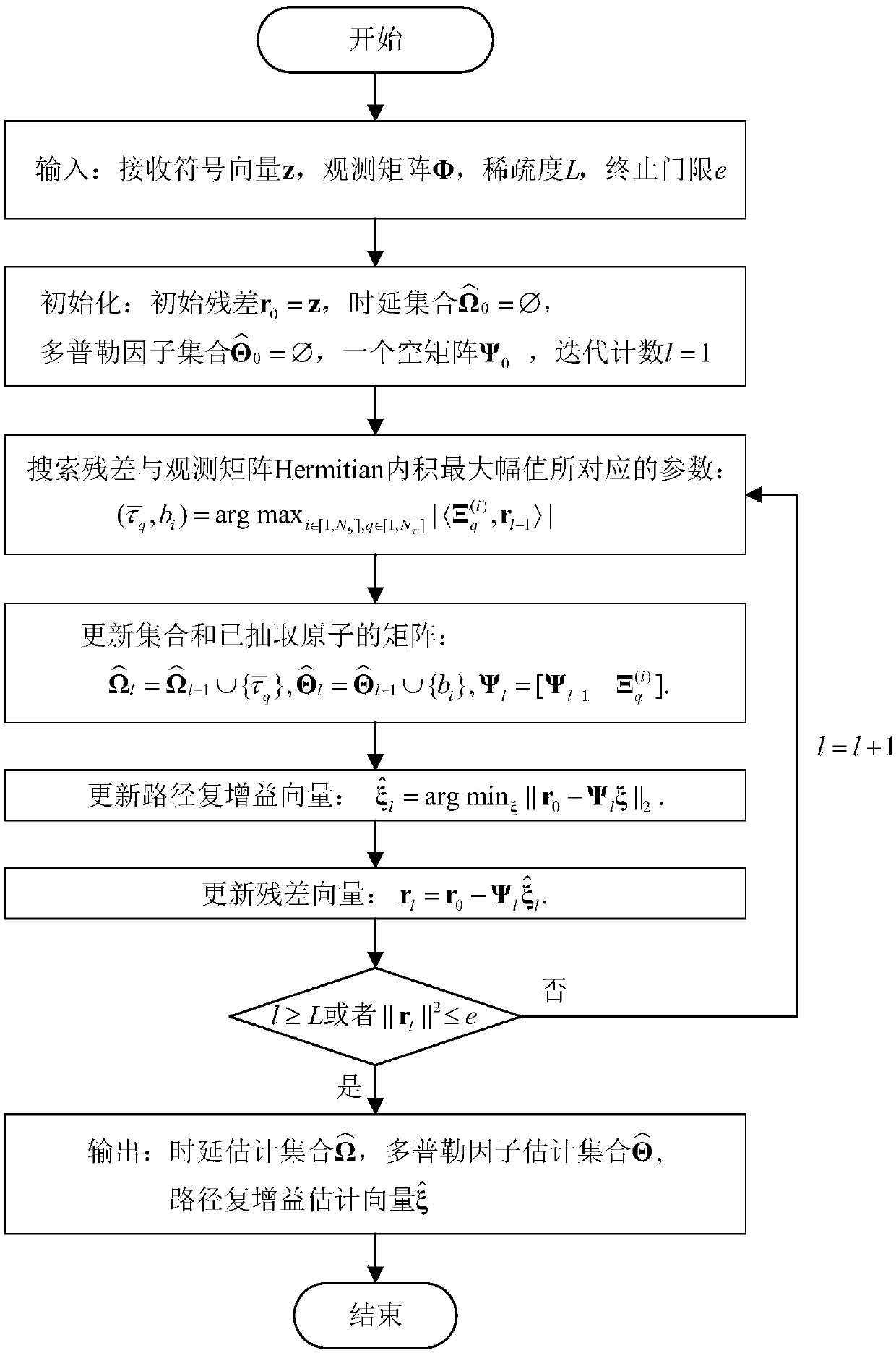
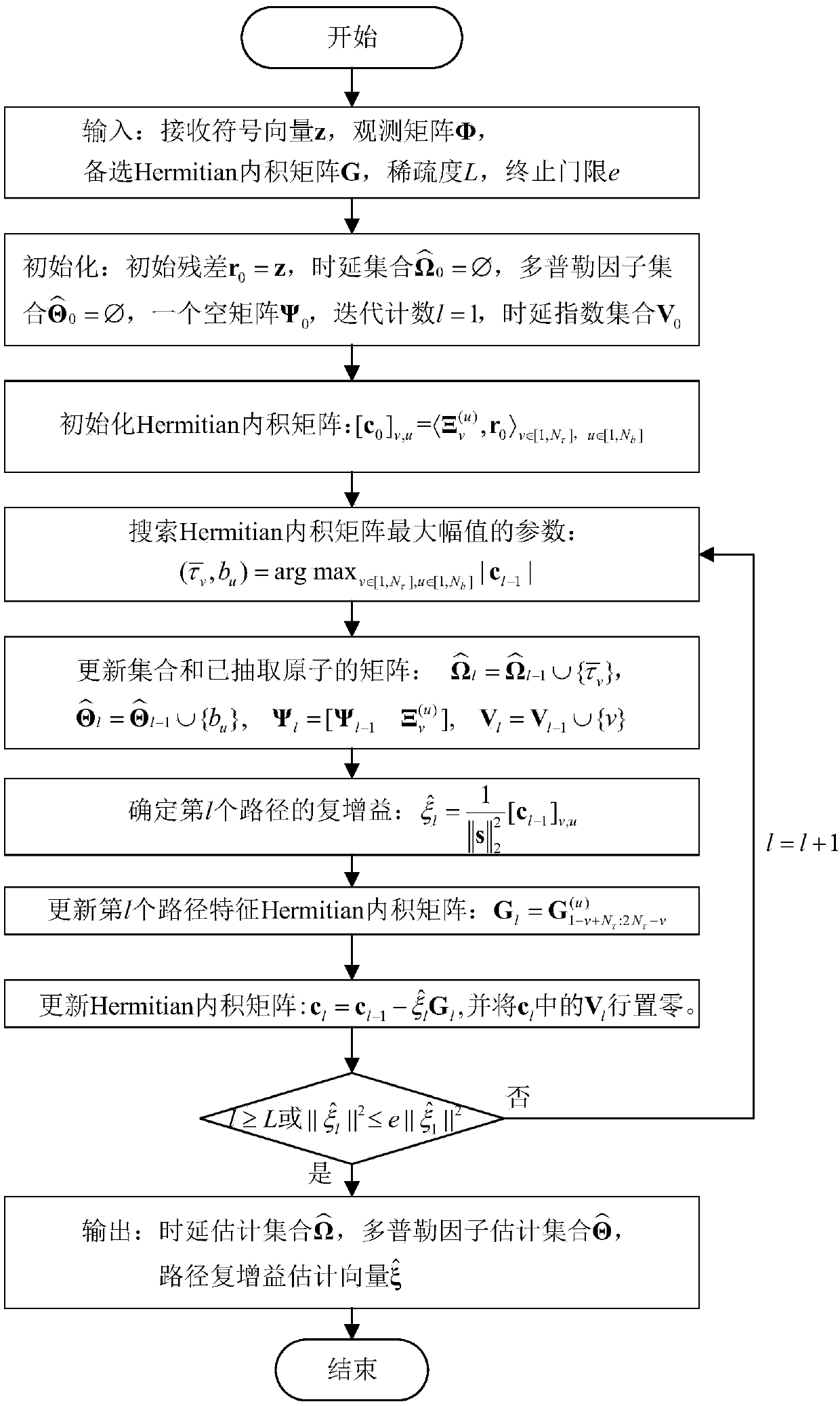
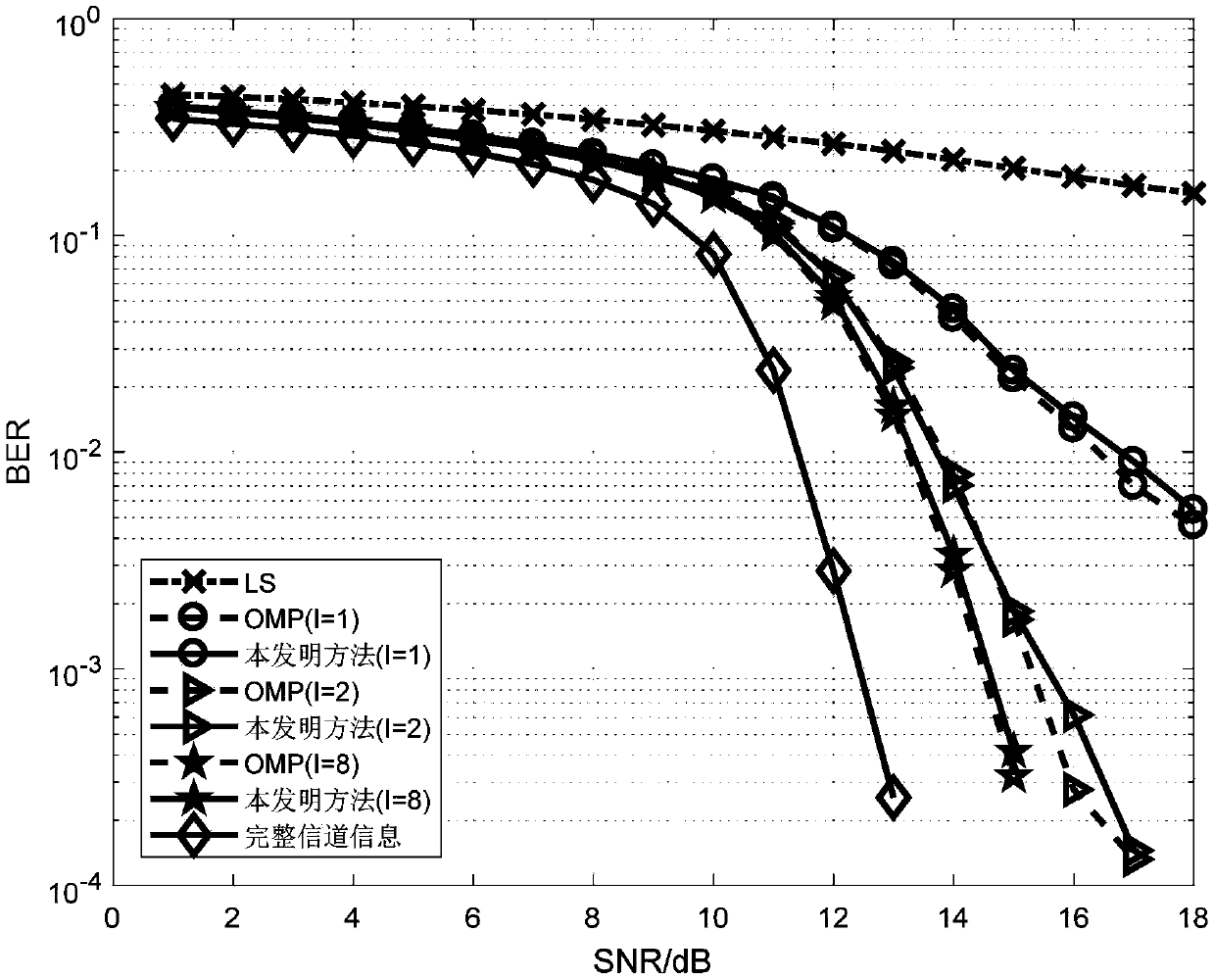
ActiveCN108848043AImprove estimation accuracyHigh computational complexityBaseband system detailsProduct matrixLow complexity
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Stable peroxide containing personal care compositions
InactiveUS20080175801A1Reduced activityReduce probabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPersonal careActive agent
The present invention relates to stable personal care composition, including oral care compositions containing a peroxide source. The compositions are stabilized by eliminating or minimizing the presence in the composition of metals having radical forming potential with the peroxide. Preferably, the metals that are eliminated or reduced are cobalt, copper, palladium, nickel and iron. The compositions are further stabilized by the addition of agents having scavenging or quenching activity for free radicals. Reducing free radical activity in the product matrix prevents radical-mediated loss and degradation of peroxide and other ingredients, in particular organic compounds added as active or aesthetic agents, including flavors, perfumes, colorants and thickeners. Provided are peroxide containing oral care products with enhanced consumer appeal in terms of taste, mouthfeel and appearance, thereby encouraging compliance and regular use. Such attributes are important since use of these products may involve fairly long residence time in the mouth for efficacy.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
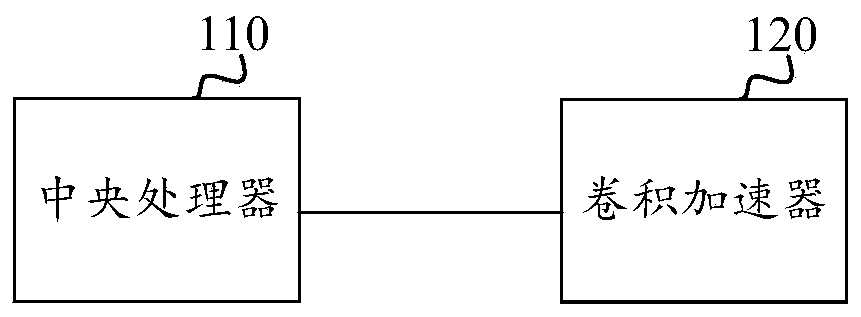
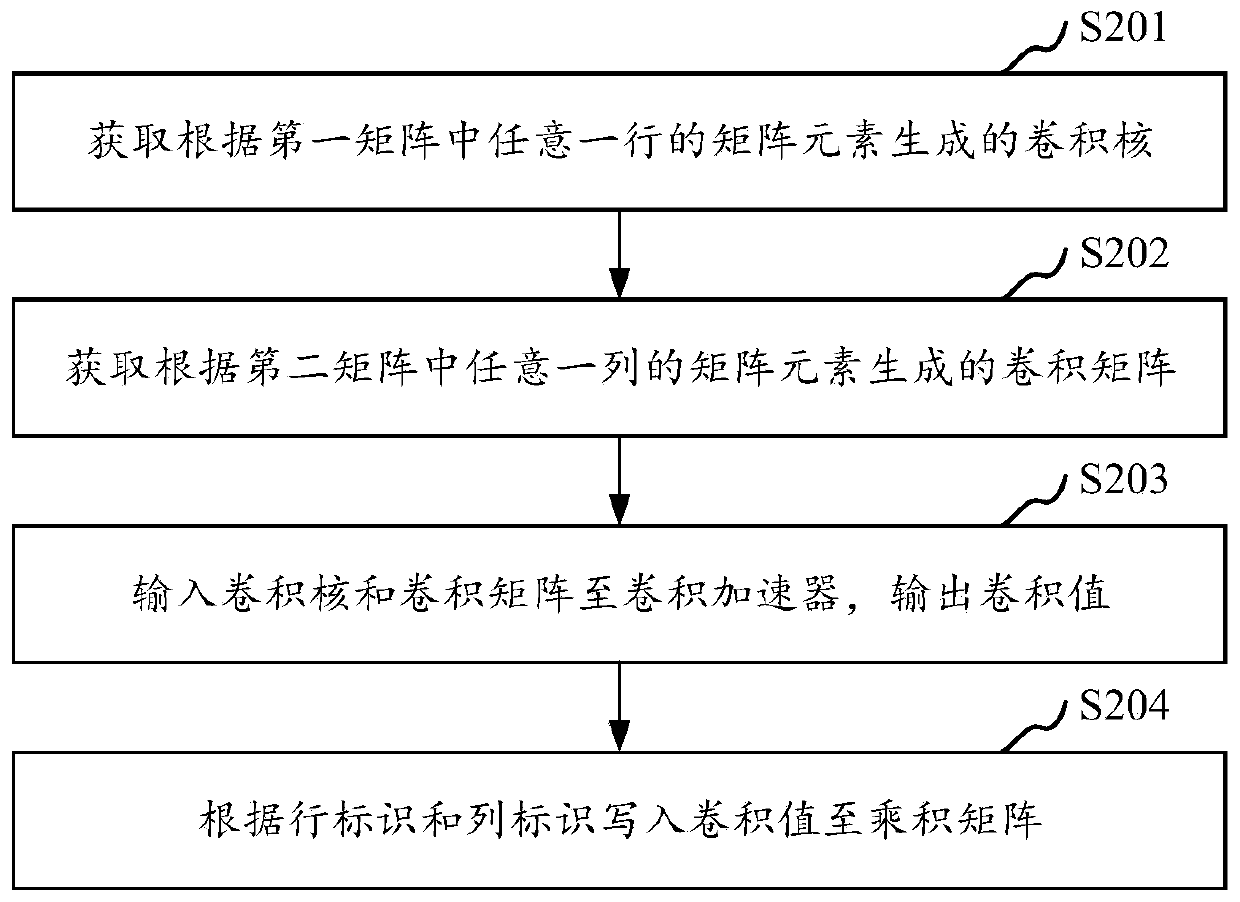
Matrix operation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110580324ALow costGuaranteed operation rateNeural architecturesComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmMatrix multiplication
The invention relates to a matrix operation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a convolution kernel generated according to matrix elements of any row in a first matrix, wherein the convolution kernel comprises a row identifier; obtaining a convolution matrix generated according to the matrix elements of any column in the second matrix, the convolution matrix comprising column identifiers, and the number of the matrix elements of each row of the first matrix being the same as the number of the matrix elements of each column ofthe second matrix; inputting the convolution kernel and the convolution matrix to a convolution accelerator, and outputting a convolution value; writing a convolution value into a product matrix according to the row identifier and the column identifier, wherein the product matrix is used for storing a product result of the first matrix and the second matrix. Matrix multiplication operation is converted into convolution operation, matrix product operation is achieved through a convolution accelerator, and the hardware cost is reduced while the operation rate is guaranteed.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Sparse matrix acceleration calculation method, device, equipment and system thereof
PendingCN109710213ACalculation speedReduce occupancyHandling data according to predetermined rulesAlgorithmMatrix multiplication
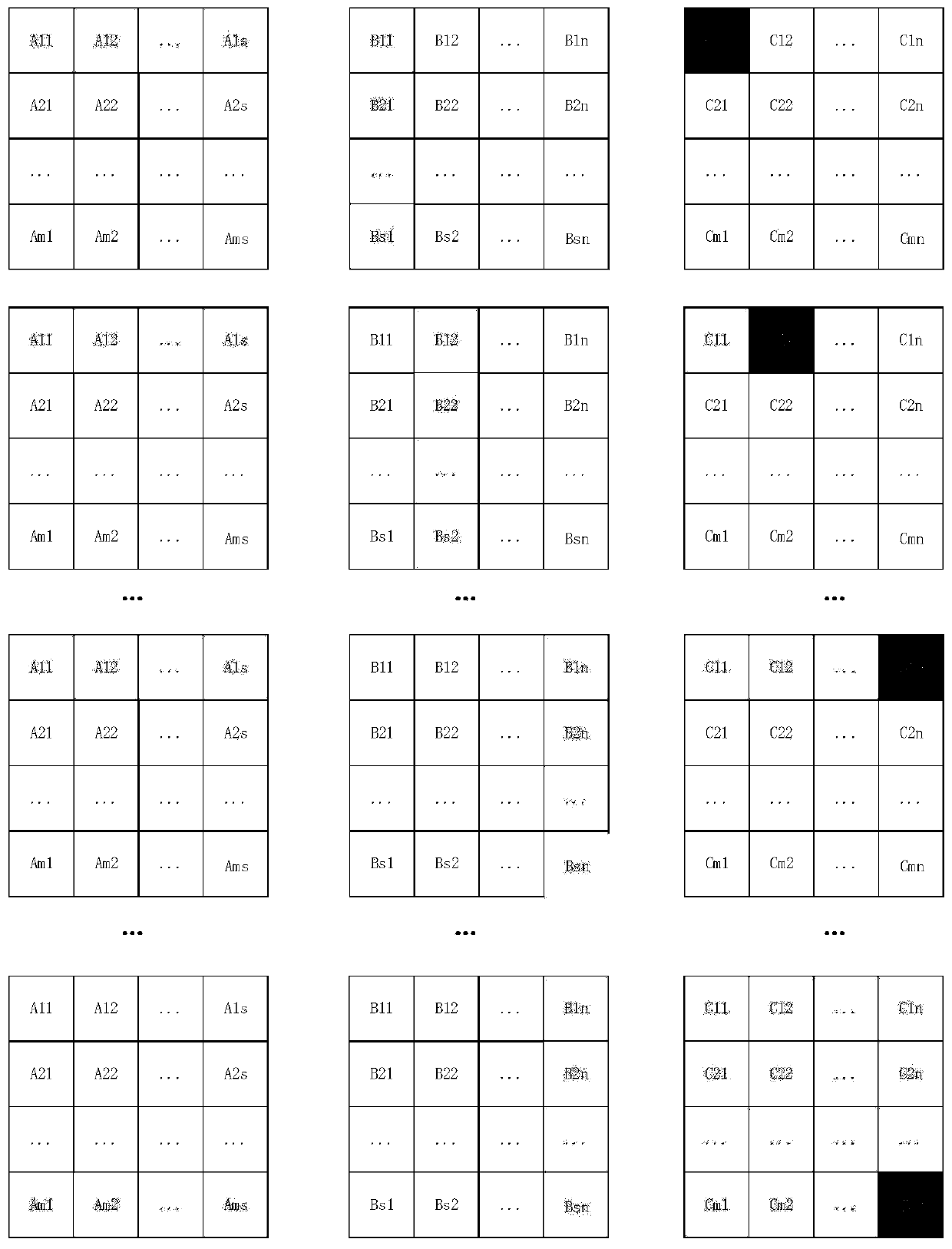
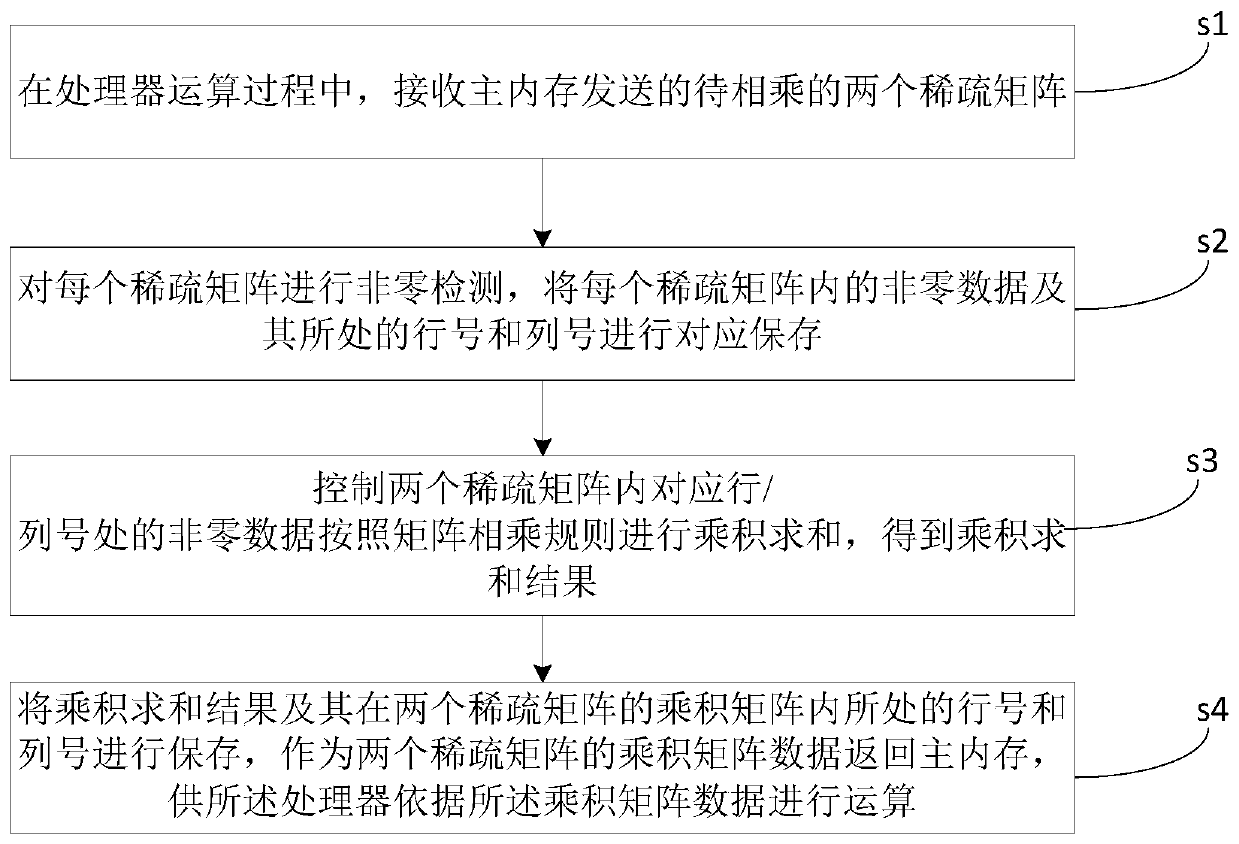
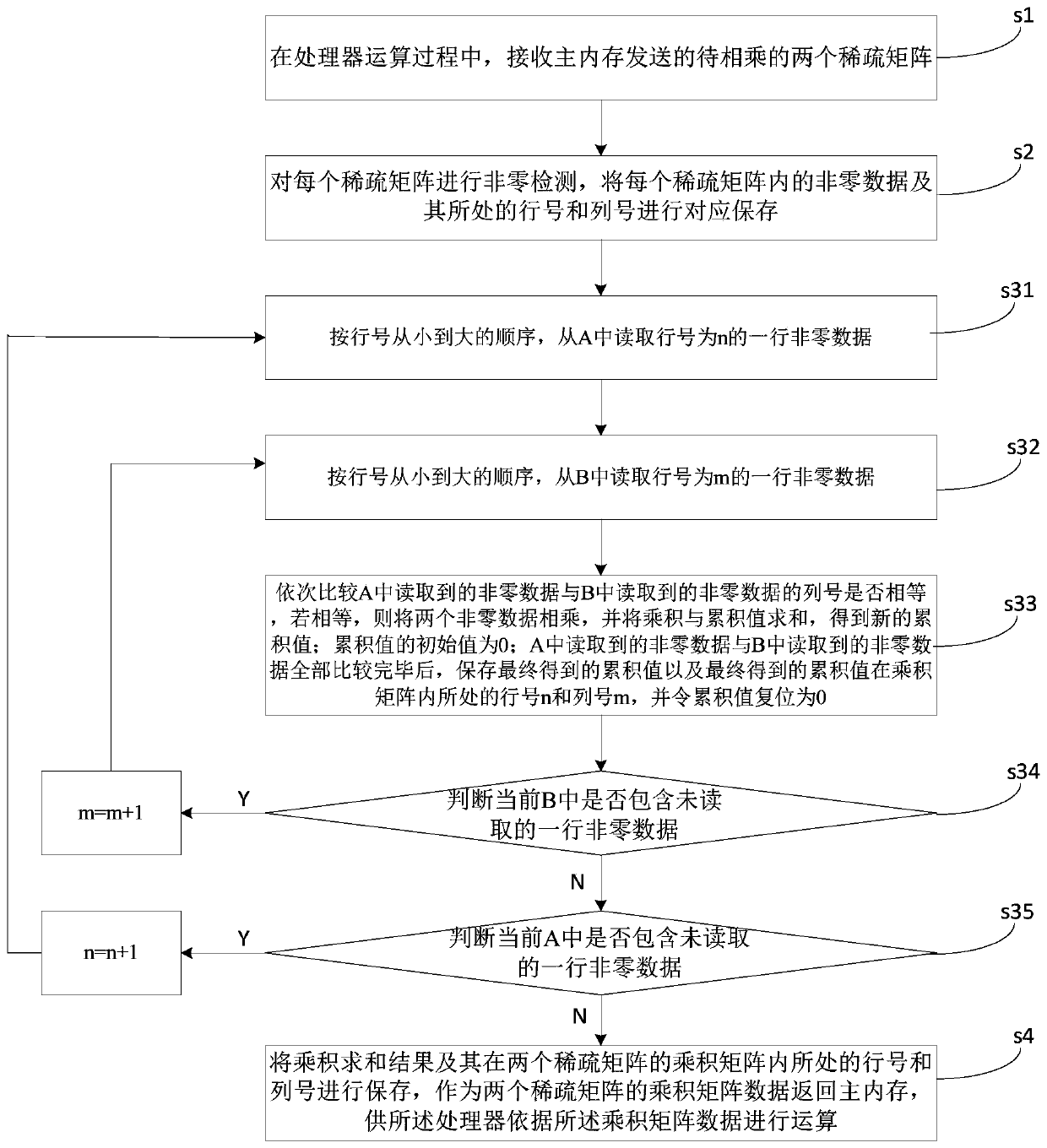
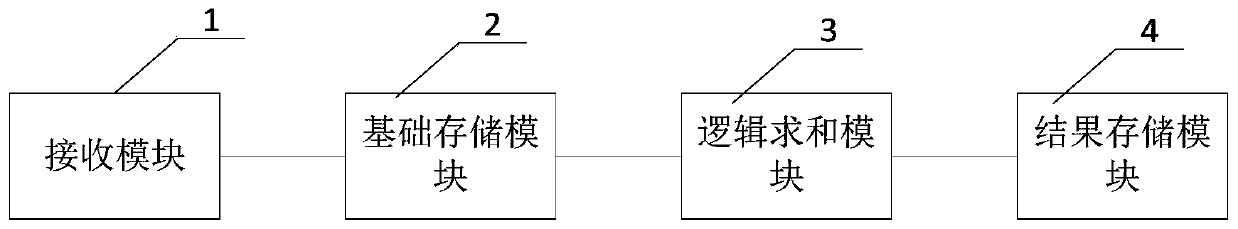
The invention discloses a sparse matrix acceleration calculation method, which comprises the following steps: in the operation process of a processor, receiving two sparse matrixes to be multiplied sent by a main memory; performing non-zero detection on each sparse matrix, and correspondingly storing the non-zero data in each sparse matrix and the row number and the column number where the non-zero data are located; Controlling non-zero data at corresponding row / column numbers in the two sparse matrixes to carry out product summation according to a matrix multiplication rule to obtain a product summation result; and storing the product summation result and the row number and the column number of the product summation result in the product matrix of the two sparse matrixes, returning the product summation result as product matrix data of the two sparse matrixes to the main memory, and enabling the processor to perform operation according to the product matrix data. When the sparse matrix is multiplied, only the non-zero data is calculated and stored, so that the occupation of the storage space is reduced, and the calculation speed is increased. The invention further discloses a device, equipment and a system based on the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG INSPUR BIG DATA RES CO LTD
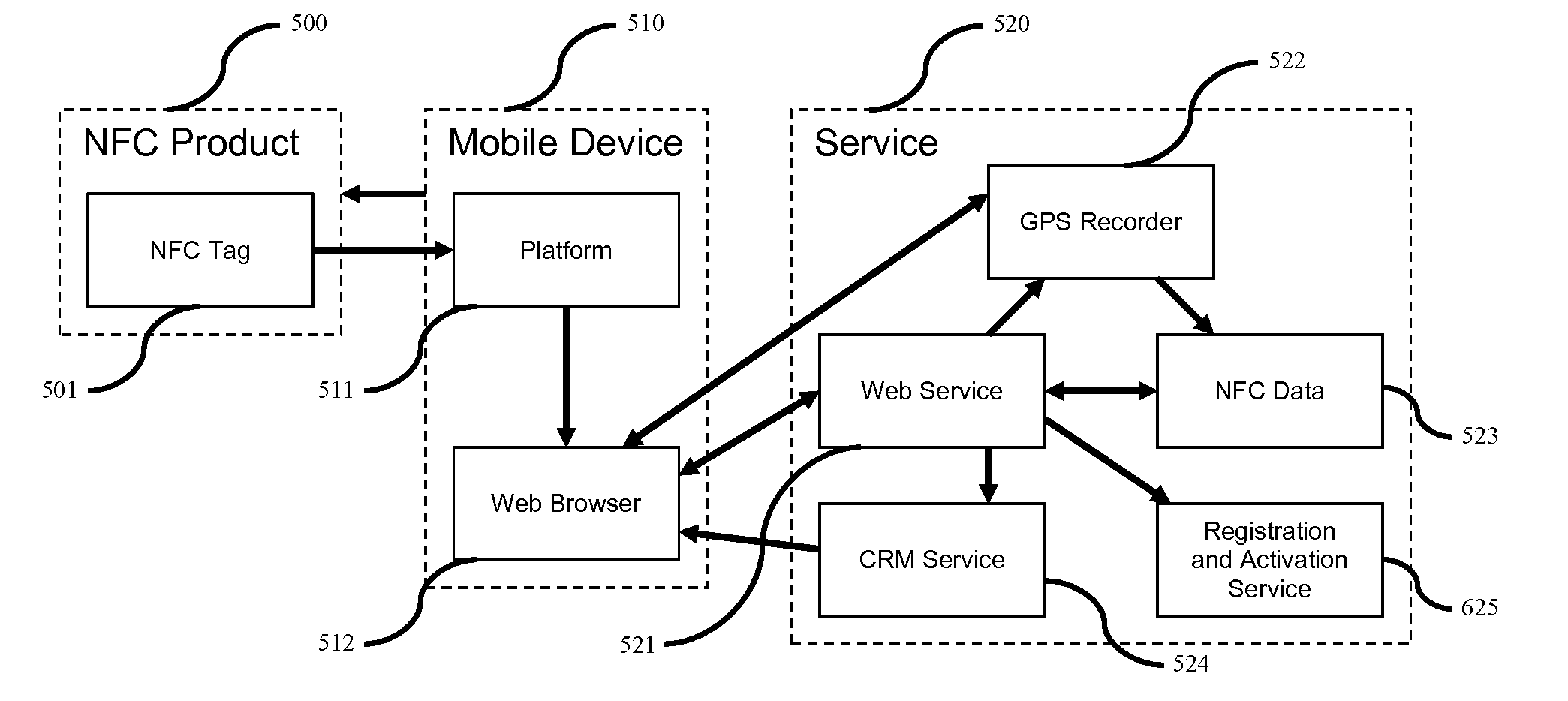
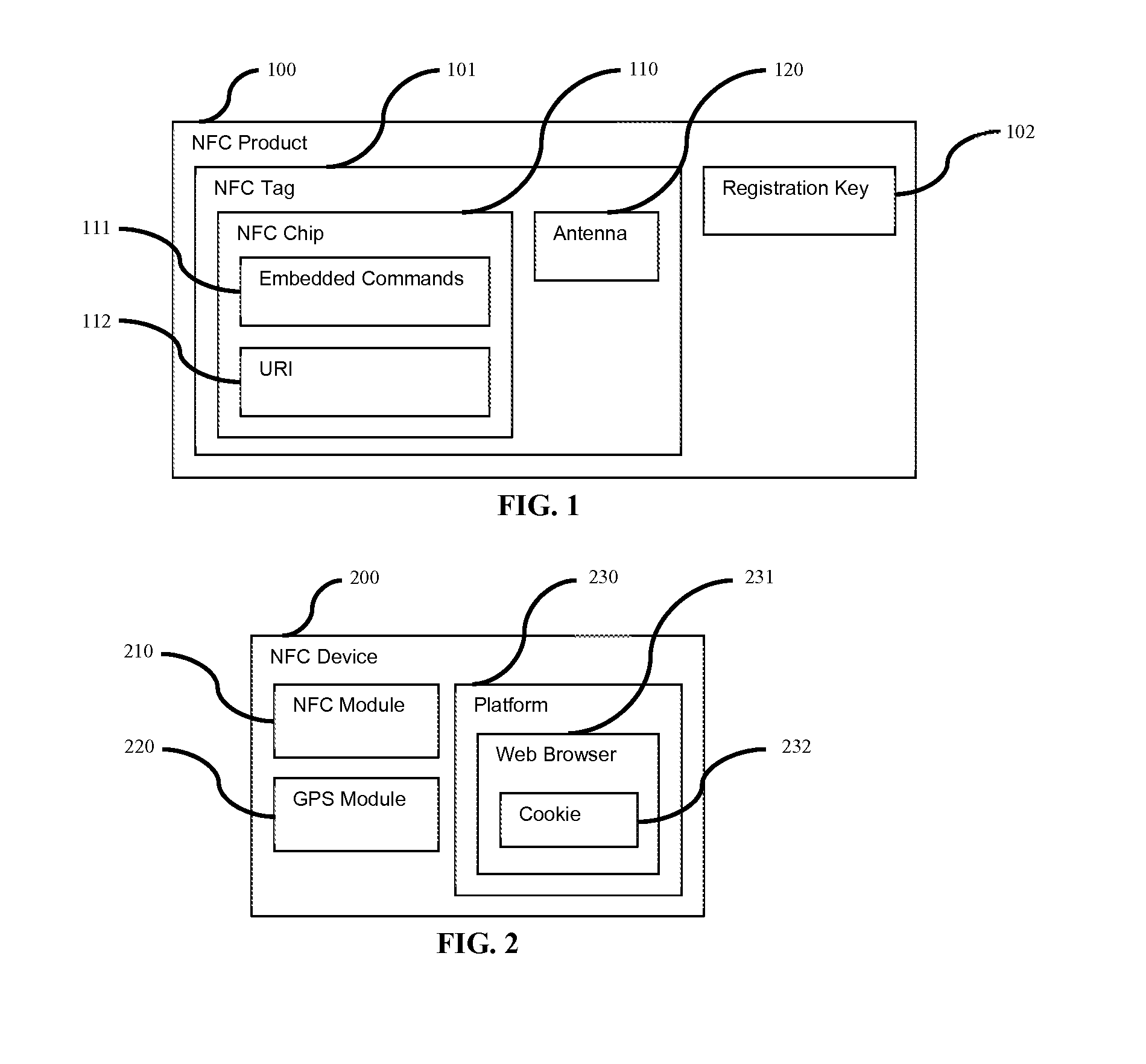
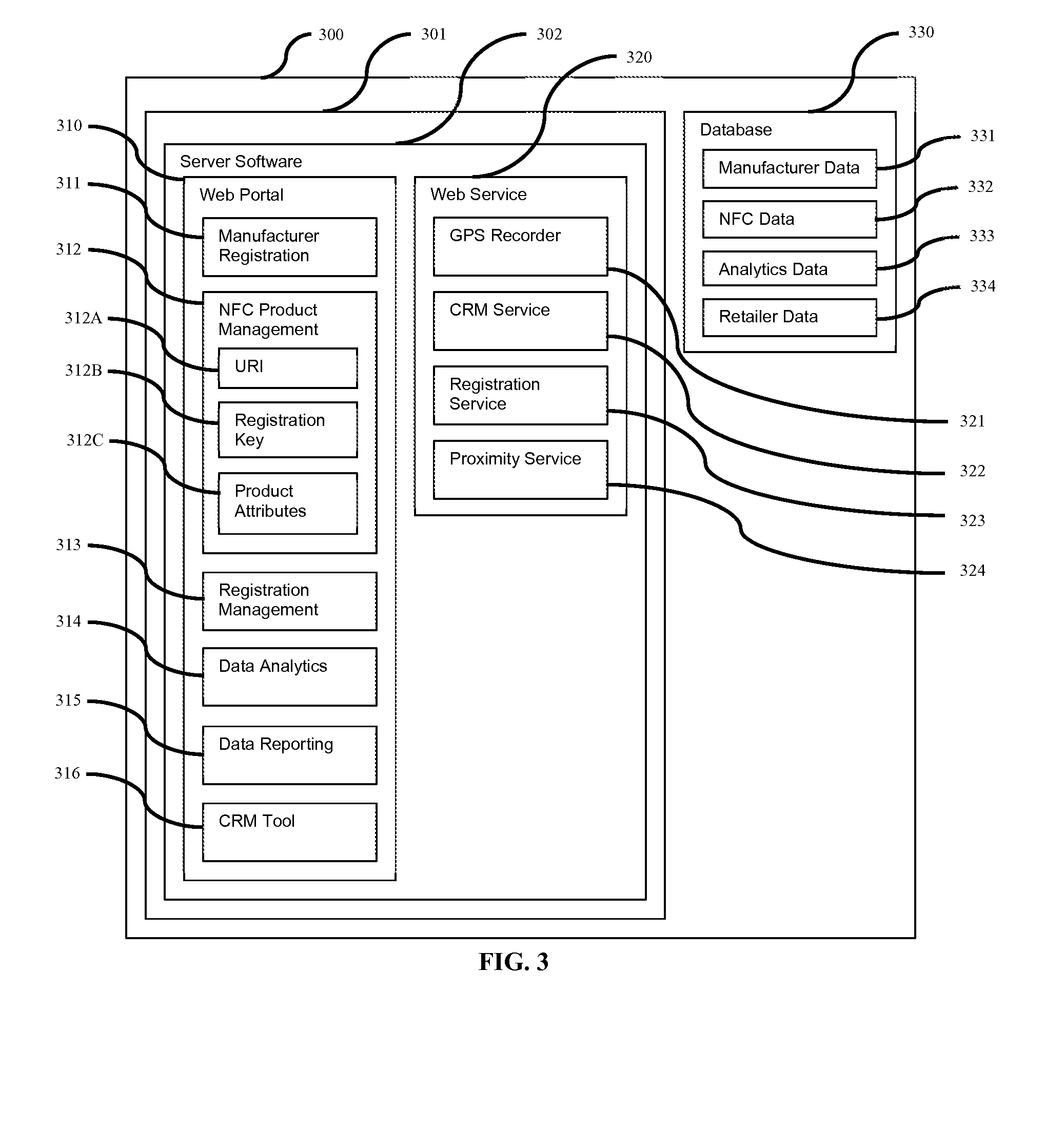
System and Method for Near Field Communication (NFC) Crowdsource Product Matrix
A method and system for managing product information is provided, the method comprising: establishing an NFC communication between an NFC chip imbedded in an NFC product and an NFC device; receiving a unique reference identification (URI) for the NFC product from the NFC chip; collecting location data of the NFC device; associating the URI with the location data; and transmitting the URI and the associated location data to a cloud infrastructure.
Owner:CHEIN JASON SHIH SHEN
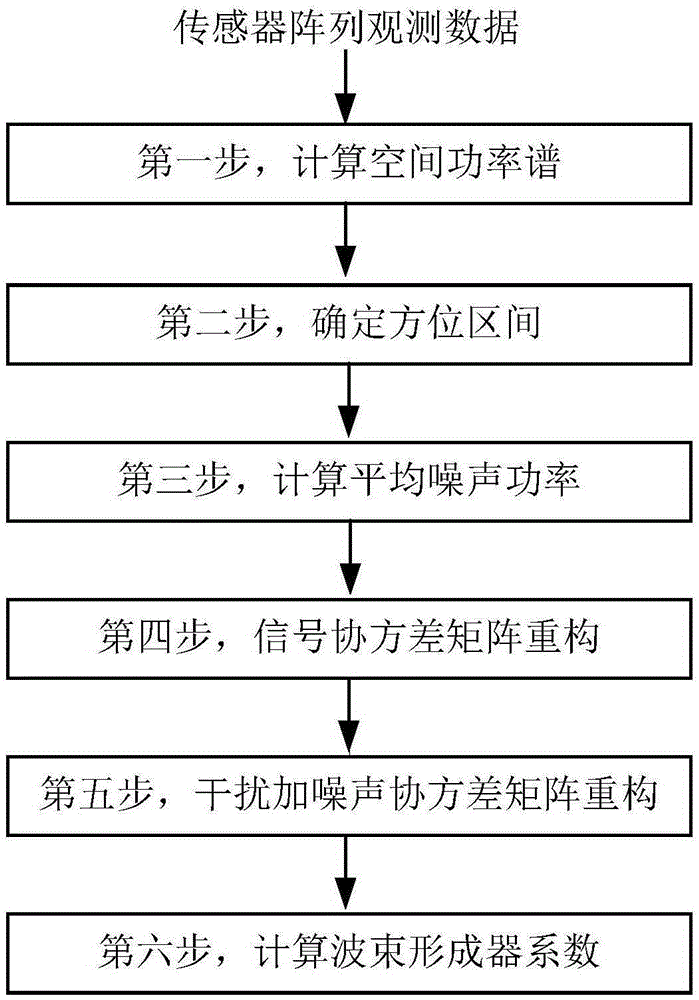
Sensor array steady adaptive beamforming method
ActiveCN105335336AFix performance issuesSolve the real problemComplex mathematical operationsSensor arrayFeature vector
The invention provides a sensor array steady adaptive beamforming method comprising the following steps: using array observation data covariance matrix to calculate orientation vector; calculating array observation data space power spectrum according a sample covariance matrix and the orientation vector; determining an orientation section of desired signals and interference signals according to a spectrum peak position of the space power spectrum; averaging space power spectrums outside the orientation section, and calculating an average noise power; using a convex optimization method to obtain reconstructed a signal covariance matrix and an interference plus noise covariance matrix; calculating a product matrix of the said two matrixes, and using the feature vectors corresponding to the maximum feature value to obtain beamforming device factors. The method can effectively solve the performance saturation problems in the adaptive beamforming process, so the adaptive beamforming is high in stability, and easy to be applied.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
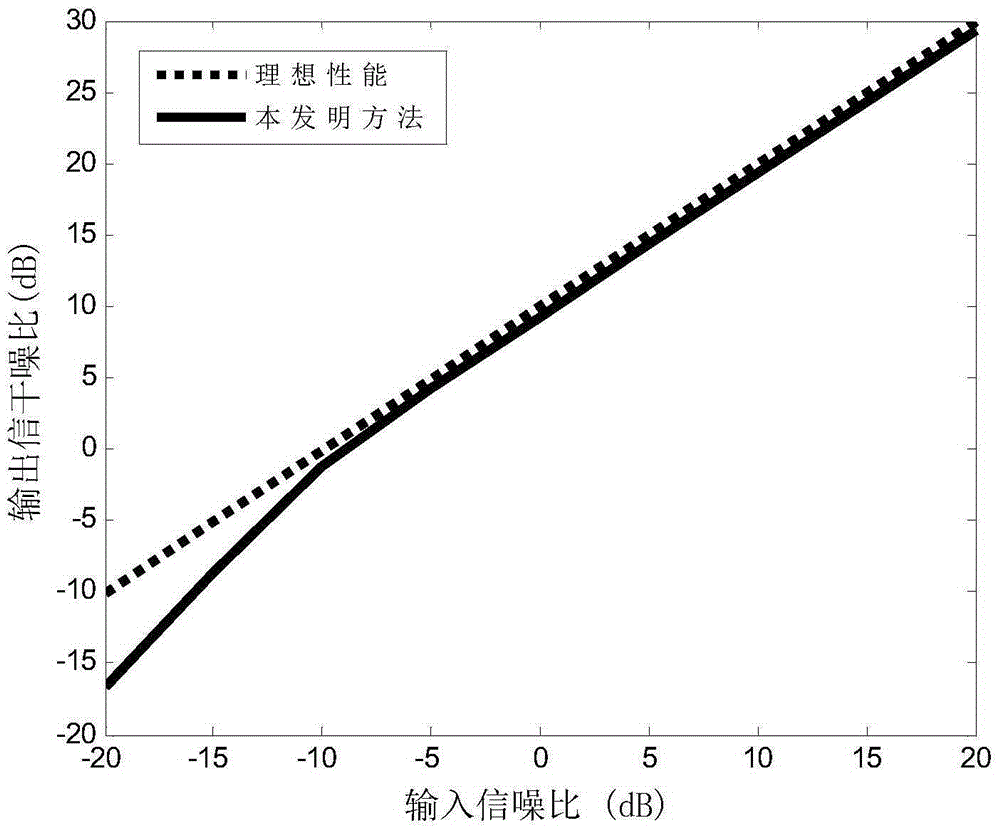
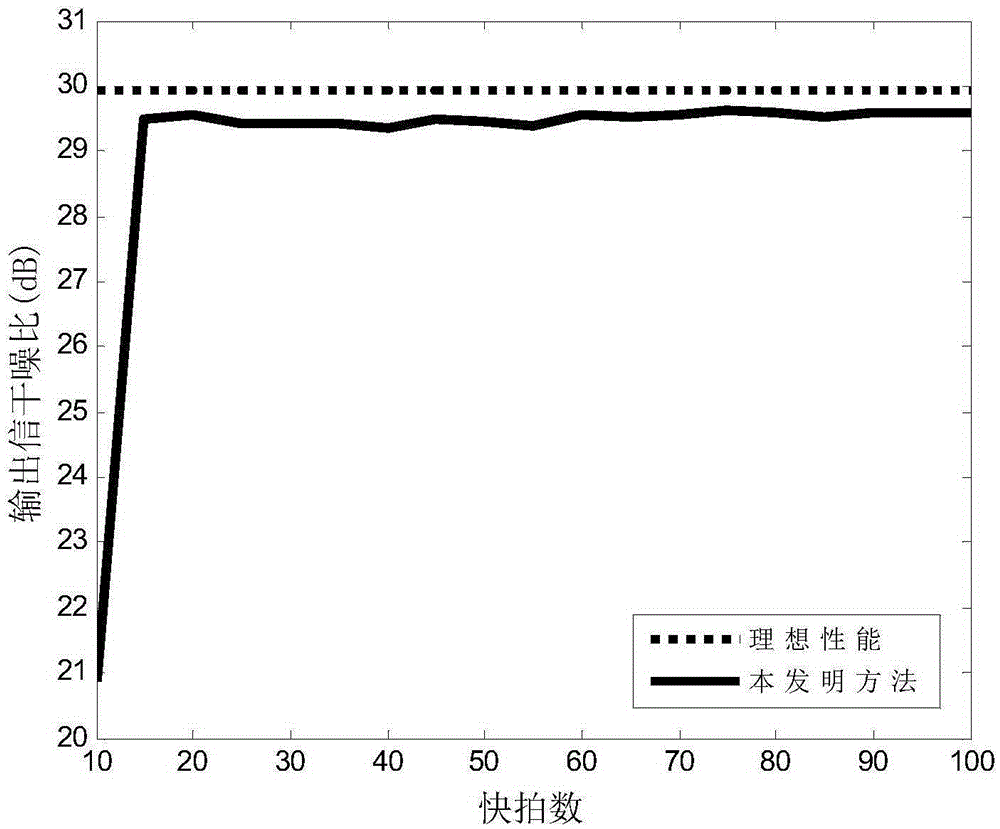
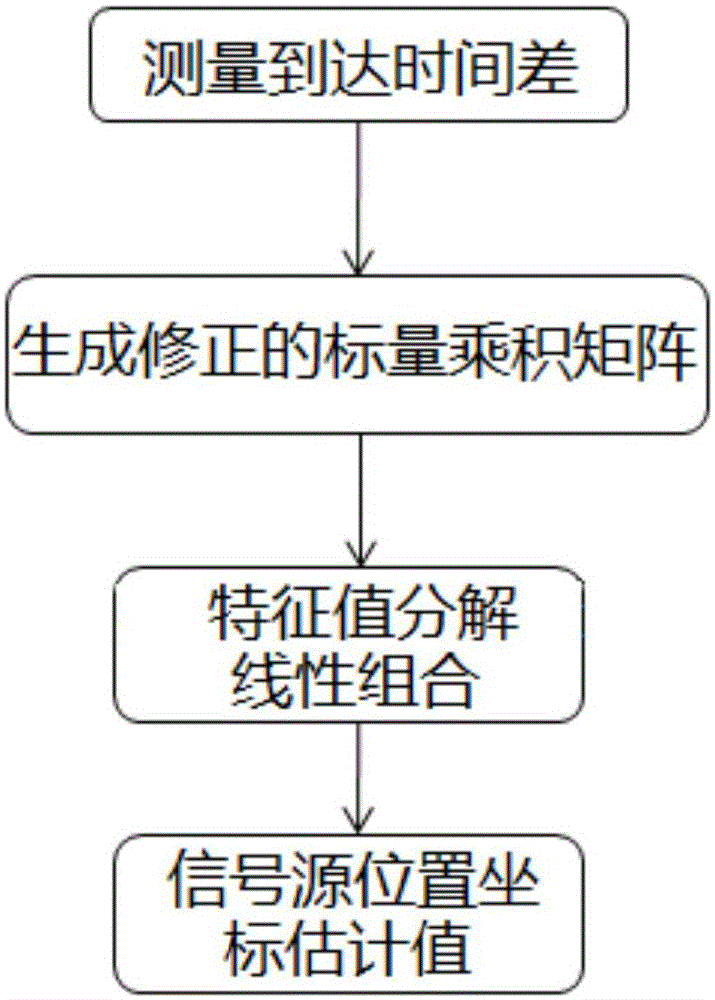
TDOA positioning method based on fourth and fifth characteristic vectors of MDS subspace
The invention relates to a TDOA positioning method based on the fourth and fifth characteristic vectors of an MDS subspace. Position coordinates of sensors distributed in a plane are collected to measure the time difference between that a signal source arrives at the sensors and that the signal source arrives at a reference sensor, and corresponding distance difference of arrival is calculated; a scalar product matrix is generated on the basis of the distance difference of arrival, the subspace is analyzed, obtained characteristic values are arranged in the descending order of the absolute values, and the fourth and fifth characteristic vectors are extracted and superposed linearly; and the vectors after linear superposition serve as a combined coefficient, and column vectors in a position coordinate matrix are combined linearly to obtain an estimated value of the position coordinate of the signal source. Through a multidimensional scaling method, the position coordinate of the signal source of low error is estimated according to the measured TDOA.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Product counseling system, product development program, and machine-readable recording medium
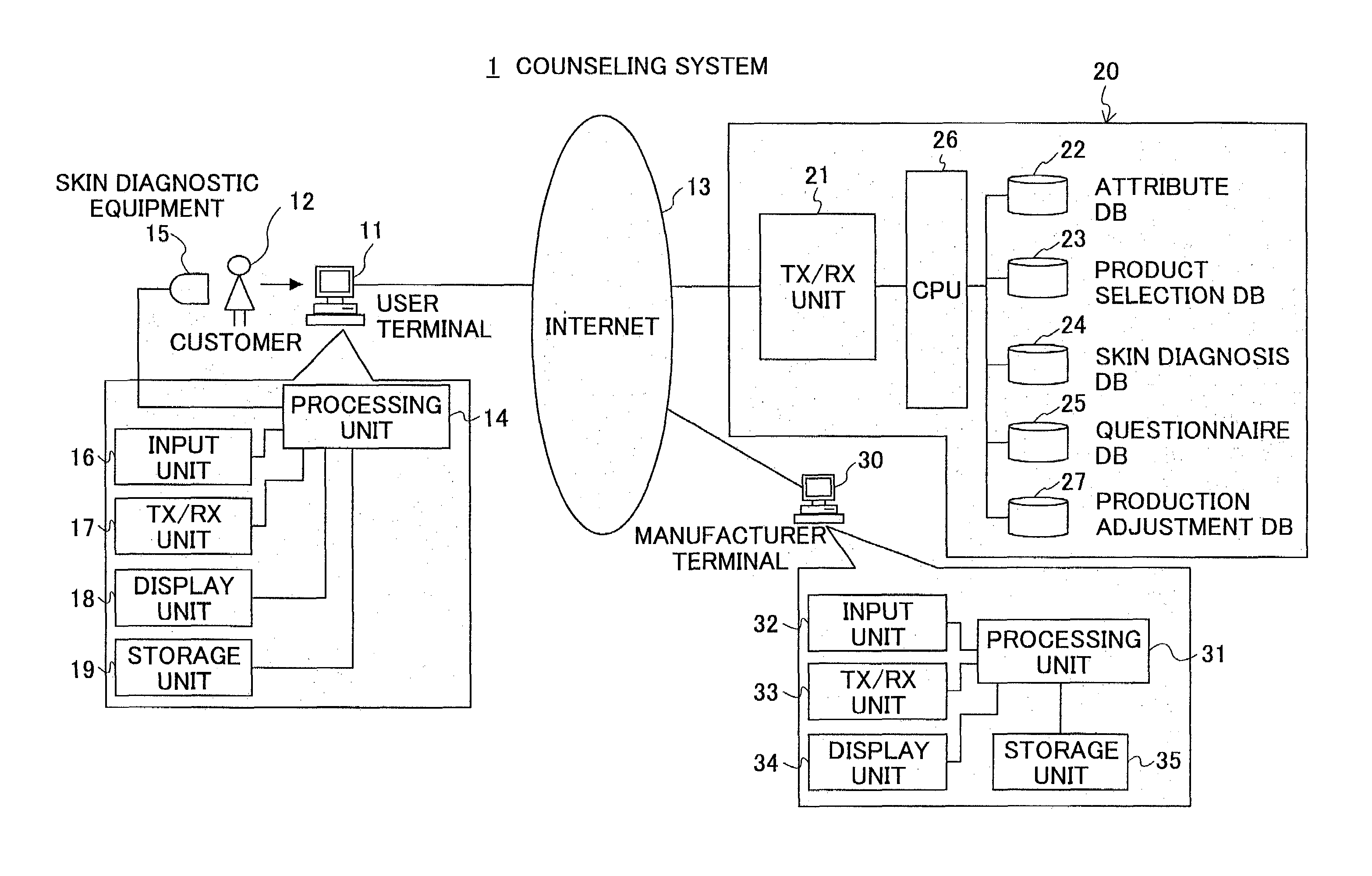
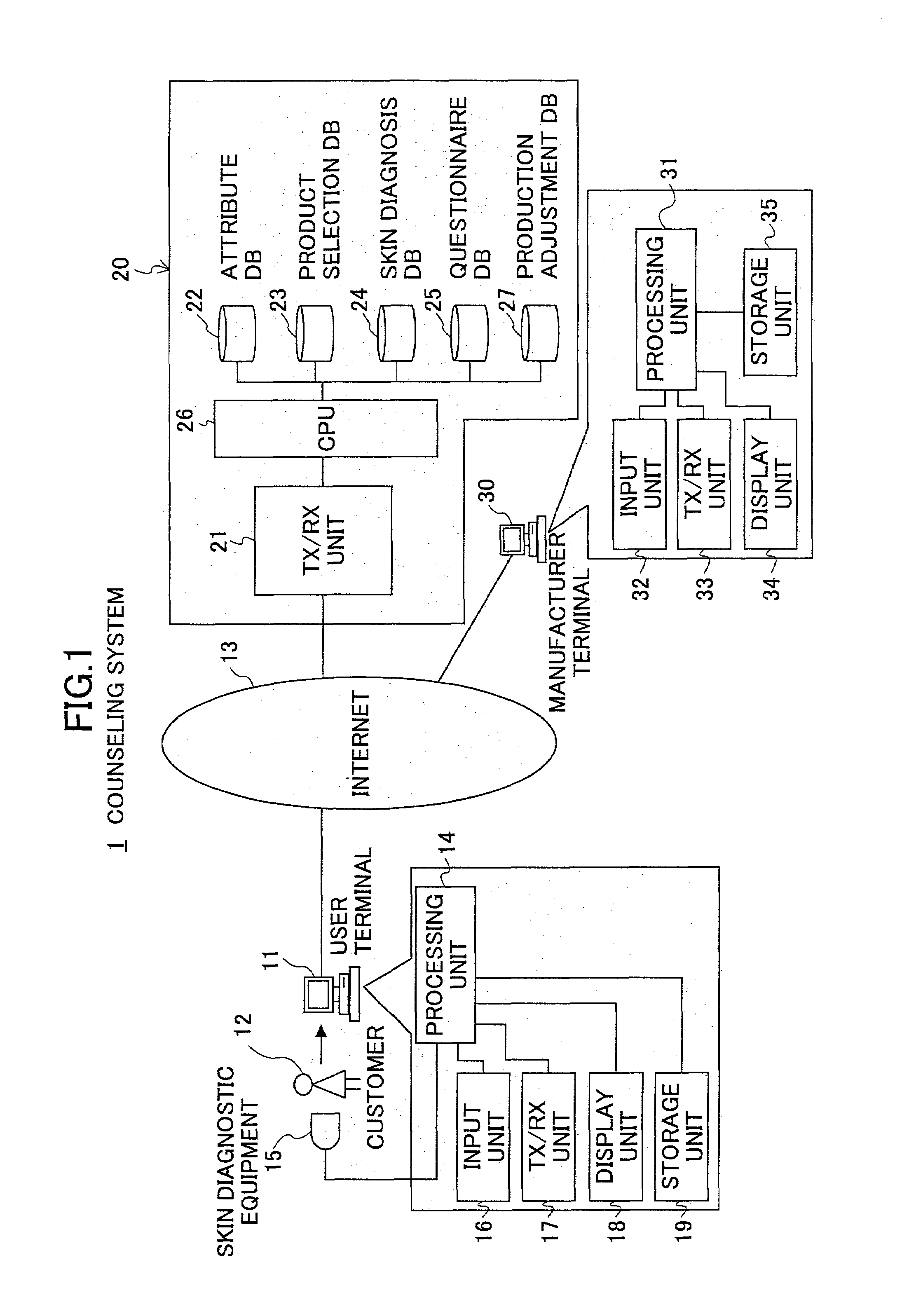
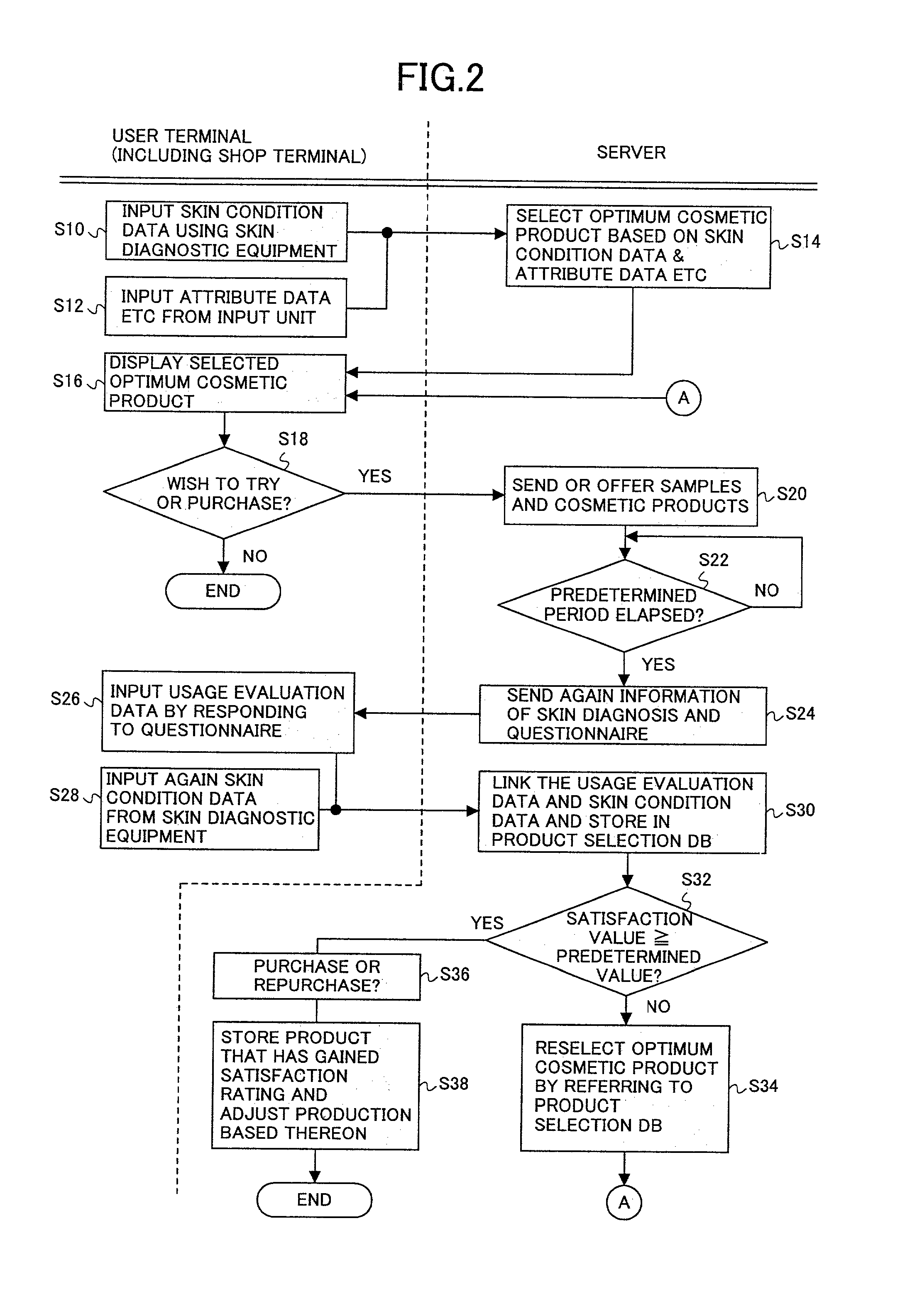
ActiveUS7634538B2Efficient supplyOptimization of inventory adjustmentMultiple digital computer combinationsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProduct selectionComputer terminal
The present invention is a cosmetic product counseling system in which a user terminal is provided with skin diagnostic equipment for measurement of the skin of customers. Cosmetic products suited for the customers are selected based on skin condition data obtained from the skin diagnostic equipment before selecting a cosmetic product and attribute data entered from the user terminal which are in the server. A product selection DB is provided in which product matrices linking each item contained in the skin condition data and product characteristics of the cosmetics are stored. Then, based on result skin condition data indicating skin condition of the customer after using the selected cosmetic product and usage evaluation data entered by the customer responding to a questionnaire, the cosmetic product is reselected until a predetermined satisfaction rating is obtained from the customer.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Convolutional neural network parallel processing method based on OpenCL
ActiveCN110110844AEasy to handleOvercome the complex structureNeural architecturesParallel processingMatrix multiplication
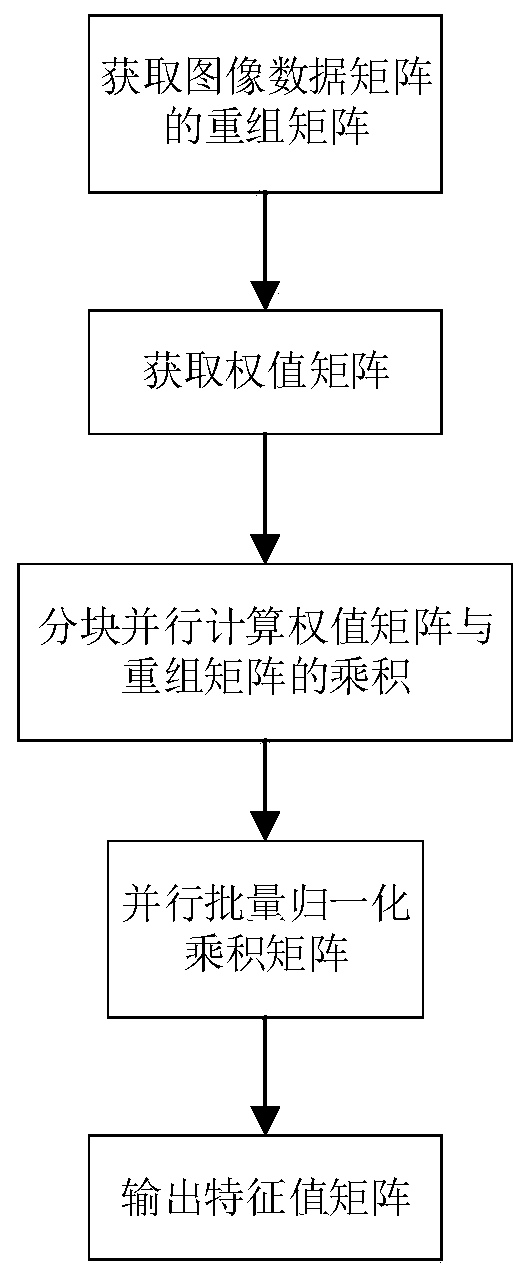
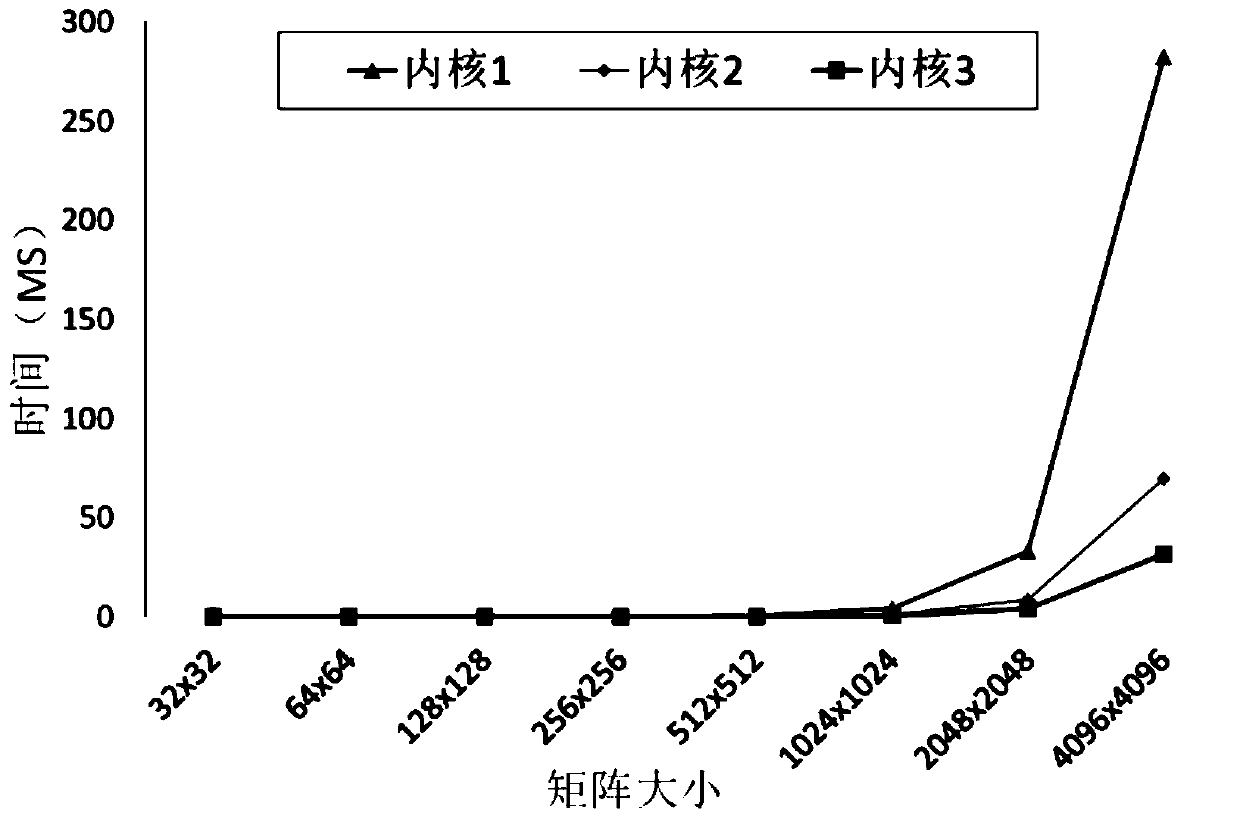
The invention provides a convolutional neural network parallel processing method based on an OpenCL, and mainly solves the problems of high model complexity and slow operation speed in the existing convolutional neural network parallel processing. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a recombination matrix of an image data matrix; obtaining a weight matrix; carrying out parallel computing on the product of the weight matrix and the recombination matrix in a blocking manner; performing parallel batch normalization on the product matrix; and outputting a characteristic value matrix. According to the invention, a large number of parallel computing units in a computer graphics processing unit (GPU) are utilized to convert the convolution process of the convolutional neural network intolarge-scale matrix multiplication, the product of the weight matrix and the recombination matrix is subjected to block parallel computing, the processing process of convolution layer data is simplified, the access mode of the data is optimized, the reuse rate of the data is improved, and the operation speed of the convolutional neural network is greatly improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
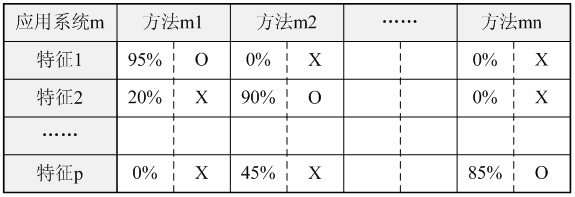
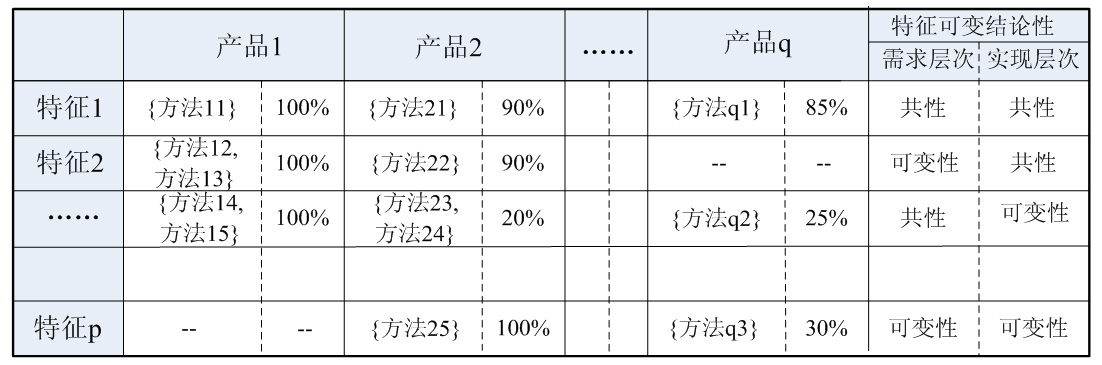
Reverse engineering analysis method of feature variability in software product line development
InactiveCN101894038AAccurate Requirements Variability KnowledgeComprehensive demand variability knowledgeProgram controlMemory systemsProduction lineReverse analysis
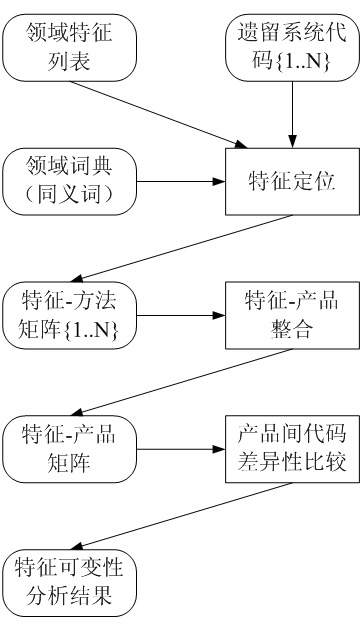
The invention belongs to the software development technical field, in particular relating to a reverse engineering analysis method of feature variability in software product line development. In the method, legacy system codes and a domain feature list are taken as input, and a variability analysis result for domain features is acquired through reverse analysis to show variability description on a demand layer and an implementation layer. The reverse engineering analysis method comprises the following steps: establishing a feature-classification matrix set by adopting a feature localization technology; carrying out feature-product integration, and establishing a feature-product matrix to obtain the variability on the demand layer; and comparing the difference of the legacy codes for each feature to obtain the variability on the implementation layer. The reverse engineering analysis method combines domain knowledge in the codes with knowledge in the forward process together to obtain more accurate and comprehensive variability conclusions; and meanwhile variability analysis on the feature implementation layer brings benefits for design and implementation activities of a product line.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
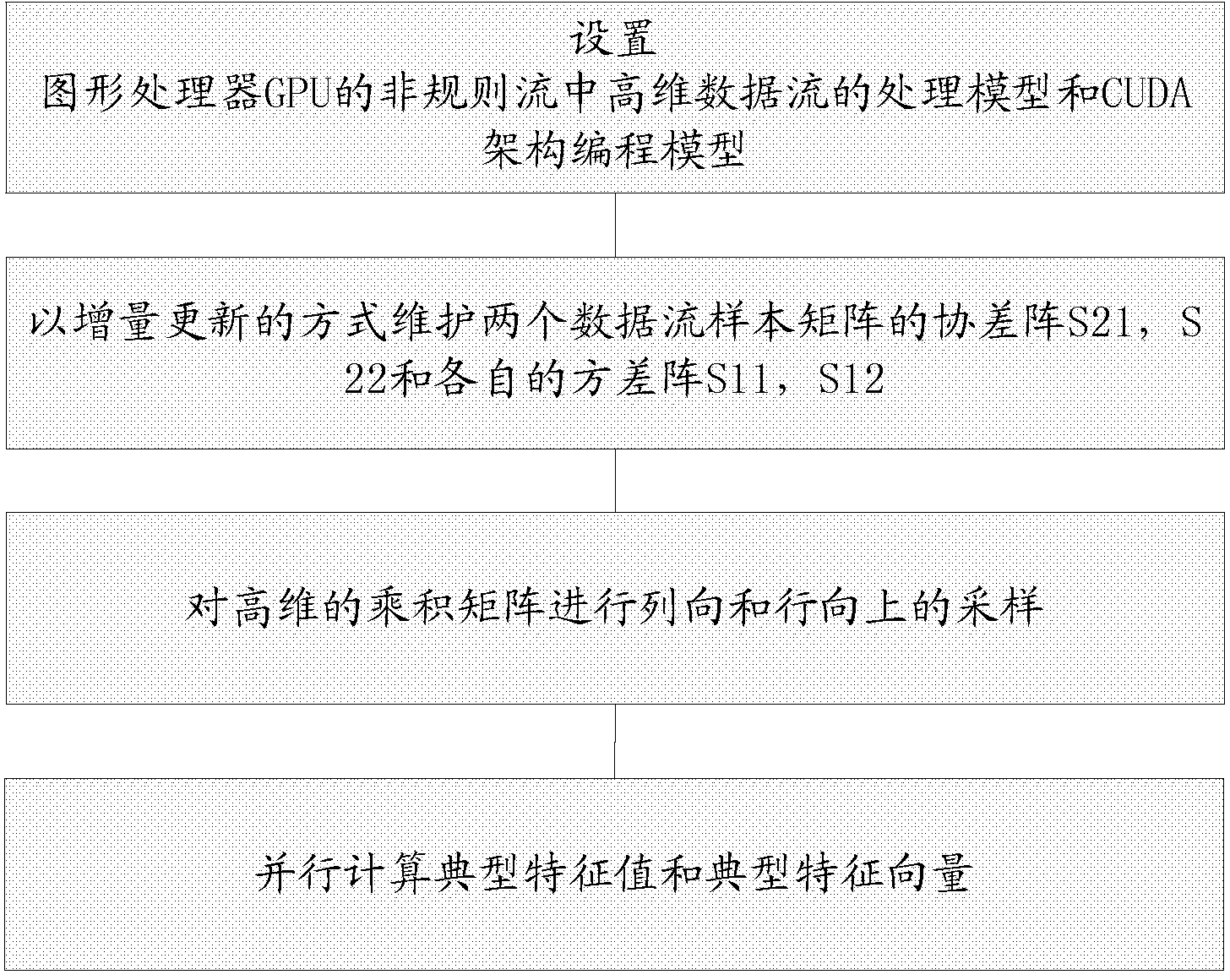
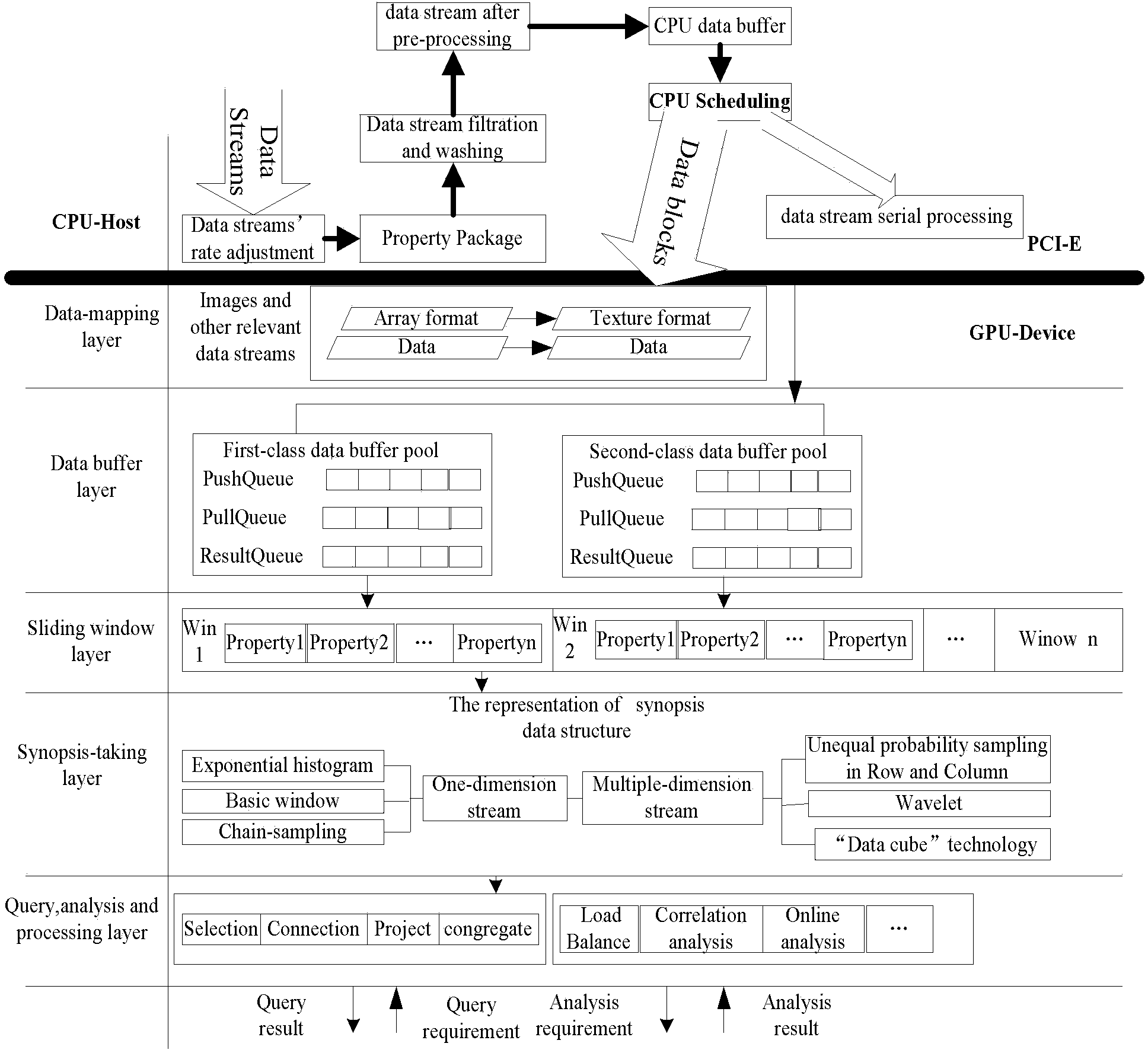
High-dimensional data stream canonical correlation parallel computation method and high-dimensional data stream canonical correlation parallel computation device in irregular steam
InactiveCN104102476AImprove real-time performanceDimensionality reductionConcurrent instruction executionData streamCorrelation analysis
Based on a CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) and a processing model of high-dimensional data steam in irregular steam of a GPU (Graphic Processing Unit), the invention provides a high-dimensional data stream canonical correlation parallel computation method in the irregular steam. According to the method, on the processing model of the high-dimensional data steam, a CUDA programming model of the GPU and a sliding window data steam mode are adopted for maintaining covariance matrixes S21 and S22 and respective variance matrixes S11 and S12 of two data steam sample matrixes in an incremental updating mode; then, a synopsis data structure is generated; high-dimensional product matrixes are subjected to sampling in the row direction and the line direction for realizing dimensionality reduction; canonical feature values and canonical feature vectors are subjected to parallel computation according to matrixes obtained through sampling; the cost for generating the canonical correlation coefficient is reduced; and the real-time performance of high-dimensional data stream correlation analysis is obviously improved.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
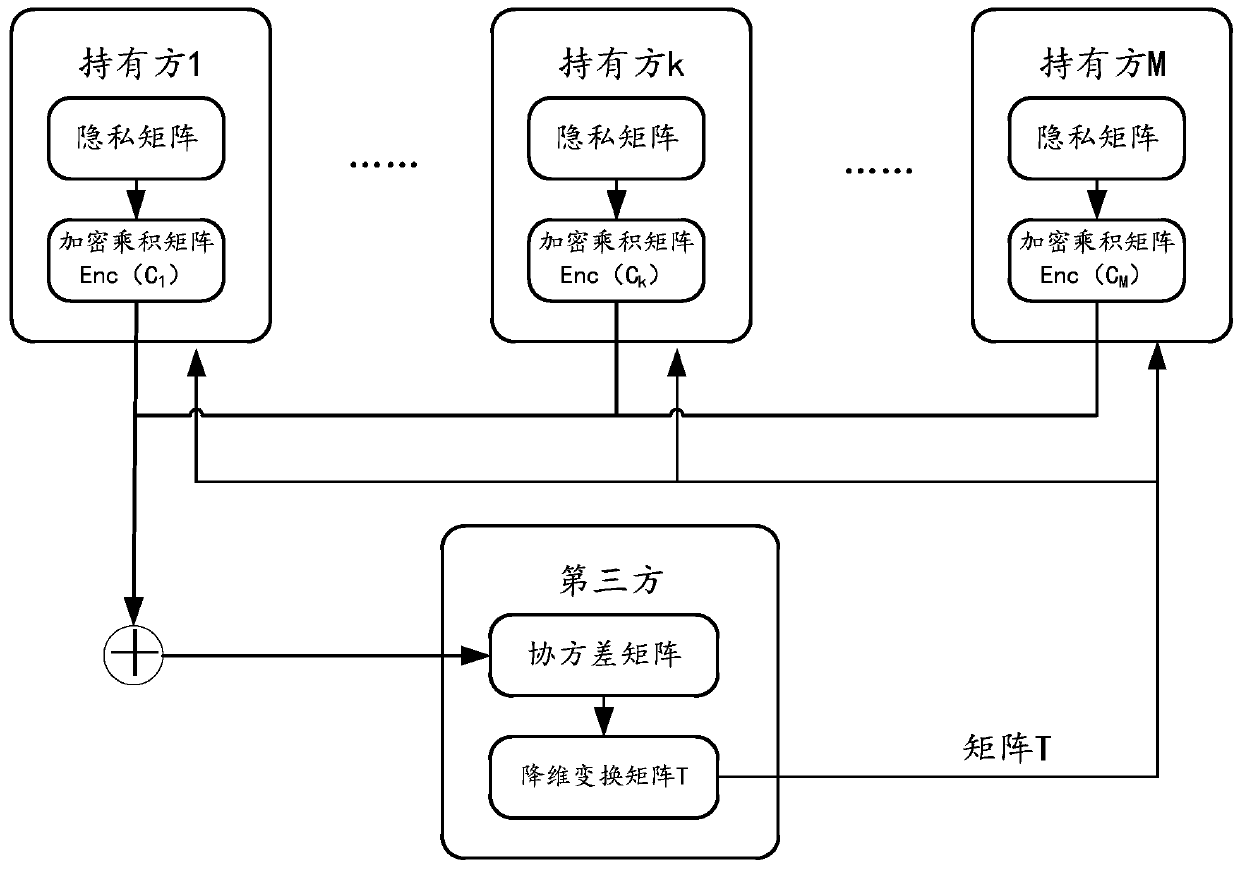
Method and device for performing multi-party joint dimension reduction processing on private data
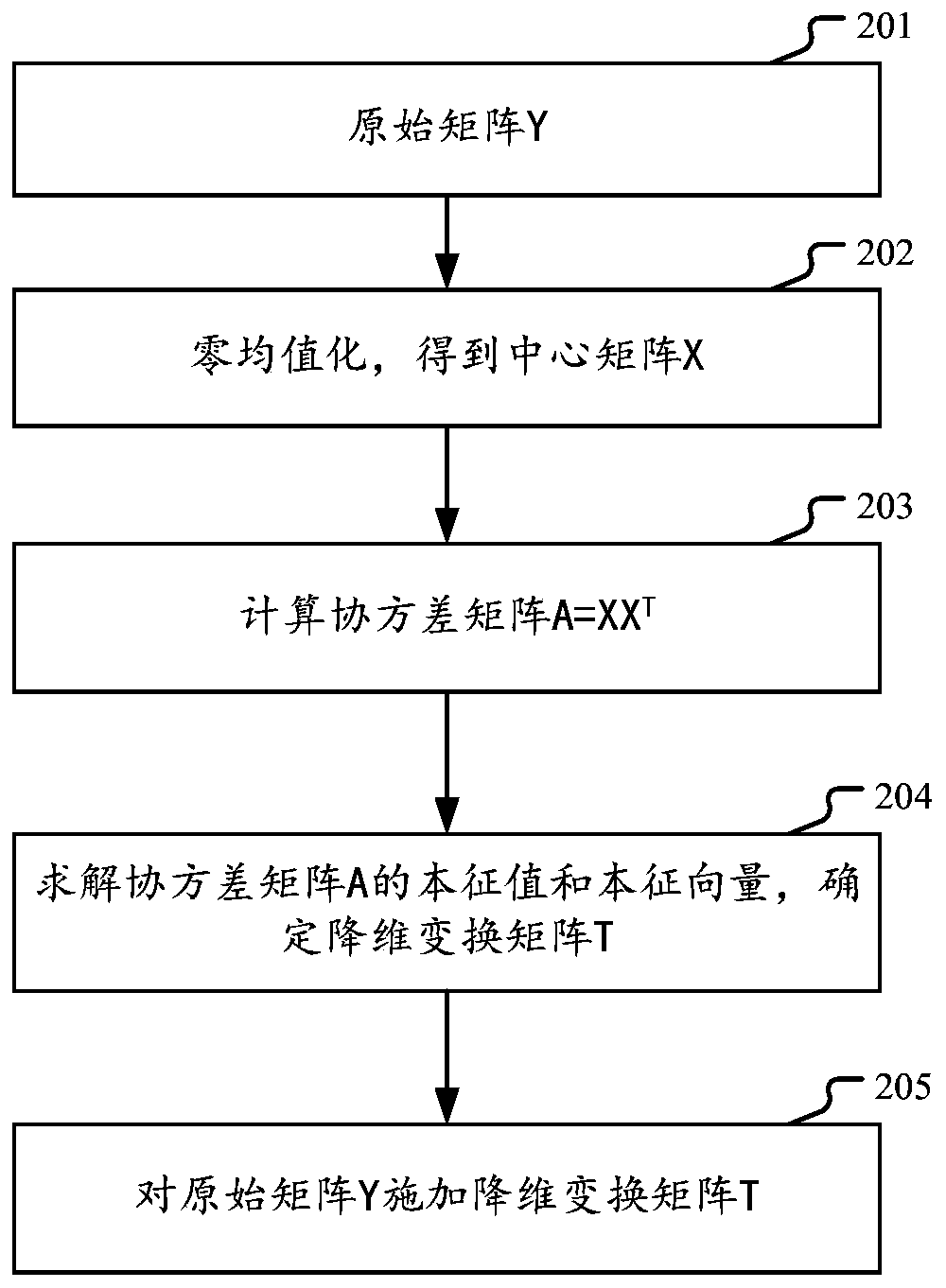
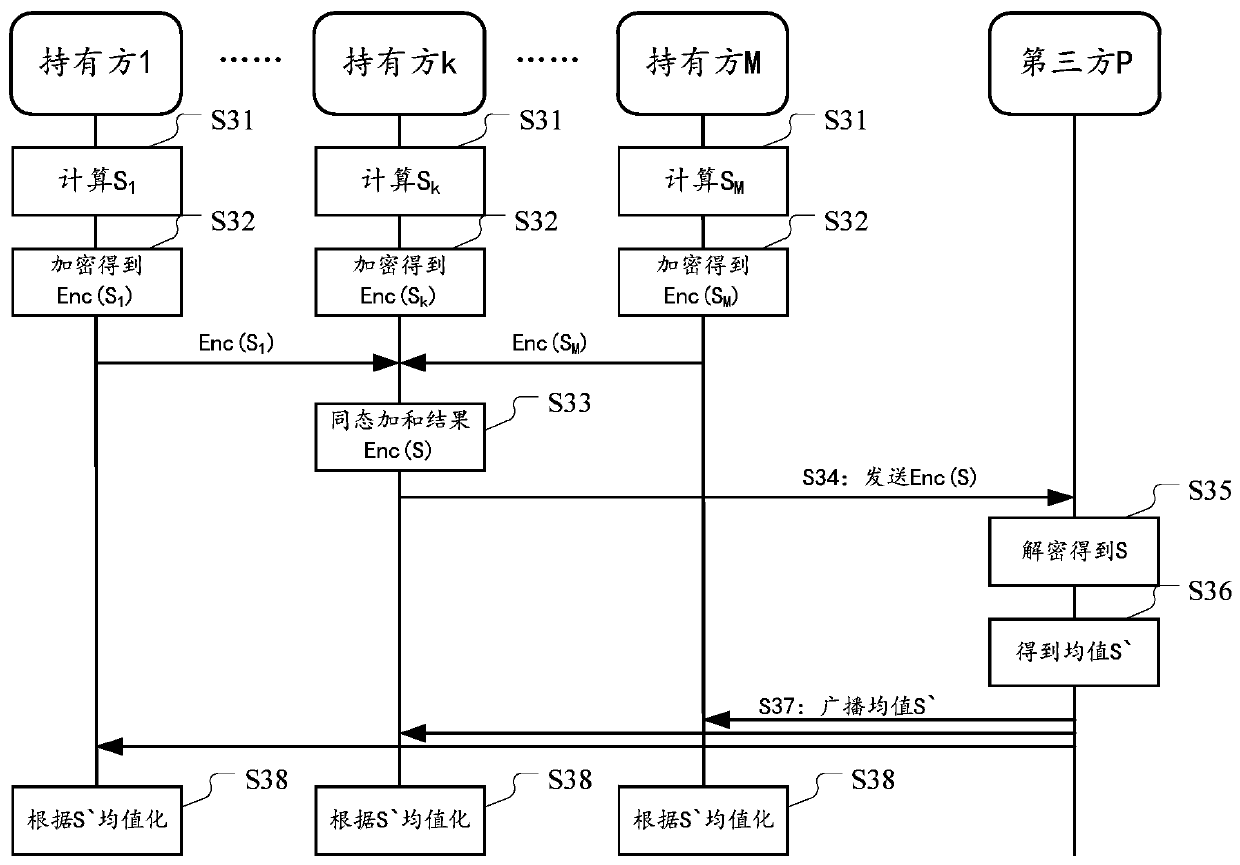
ActiveCN111400766AEnsure safetyDigital data protectionCommunication with homomorphic encryptionThird partyAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for performing multi-party joint dimension reduction processing on private data. The method comprises the steps: enabling each data holderin multiple parties to perform transposed multiplication operation on a locally owned private data matrix to obtain a product matrix; employing a public key of a third party to perform homomorphic encryption on the product matrix, and then summarizing the product matrix into a certain operation platform to perform homomorphic addition operation, and sending a homomorphic addition result to the third party; enabling the third party to decrypt the homomorphic addition result to obtain a covariance matrix required by principal component analysis so as to determine a dimensionality reduction transformation matrix, and broadcasting the dimensionality reduction transformation matrix to each holder. Therefore, each holder can use the dimension reduction transformation matrix to carry out dimension reduction processing. In this way, the security of private data in each holder is ensured.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Multi-label cooperative positioning method based on weighted MDS
InactiveCN108732534AParticular environment based servicesPosition fixationMultidimensional scalingAlgorithm
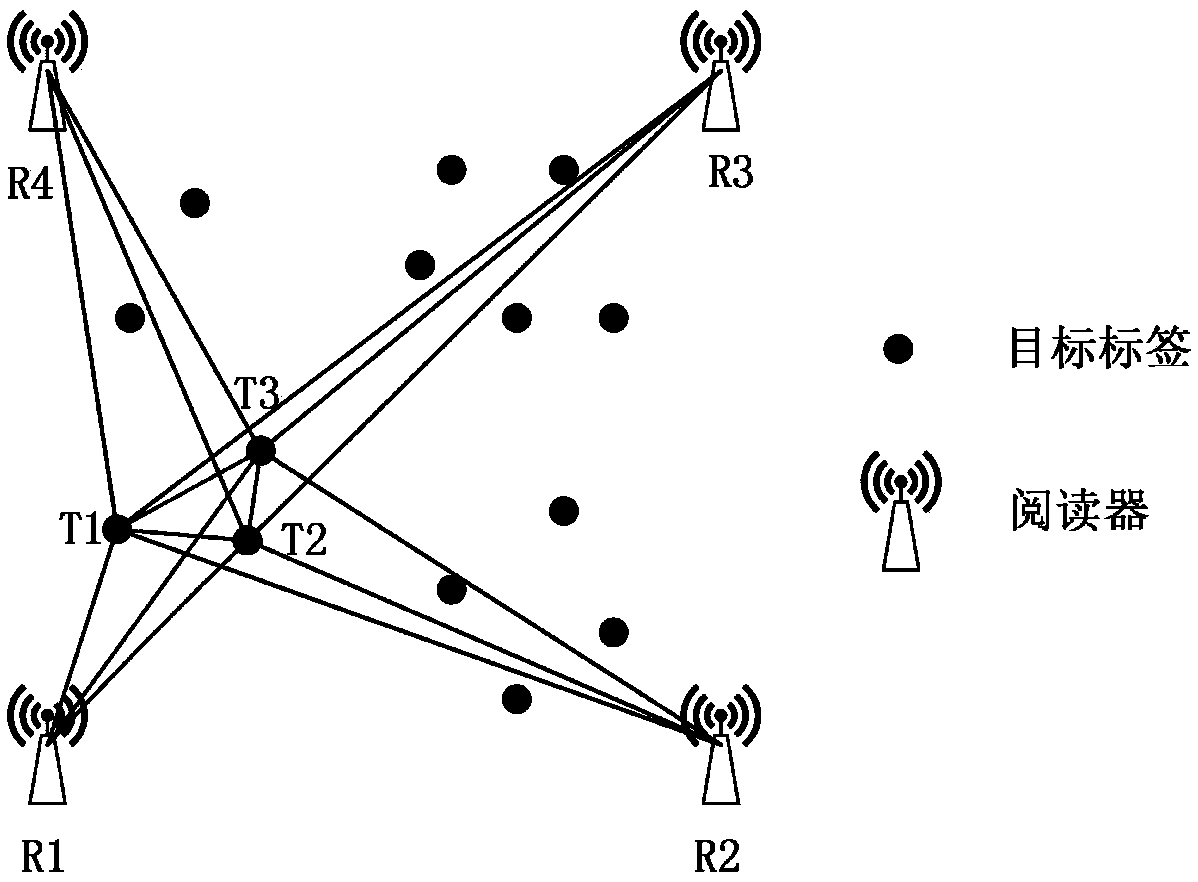
The invention relates to a multi-label cooperative positioning method based on weighted MDS. The multi-label cooperative positioning method comprises the steps of: placing target tags in an indoor scene, and estimating a region range in which the target tags are located according to distances from the target tags to readers; establishing an Euclidean distance matrix D<^>; calculating to obtain a scalar product matrix Bs<^> according to a relationship between a scalar product matrix and the Euclidean distance matrix; and adopting a weighted MDS algorithm for positioning the target tags, whereinthe positioning is implemented by regarding a unit matrix I<M+N> as the weight of the algorithm at first to obtain positions of the target tags, regarding the positions as initial estimated positionsof the target tags in the following iterative calculation, utilizing the obtained estimated positions of the target tags, adopting residual vector variance as the new weight W of the algorithm, acquiring new estimated positions of the target tags again until the positioning precision meets the requirement, and outputting the finally-obtained estimated positions X0<^> of the target tags.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for synthesizing high-purity aluminum silicon carbon superfine powder
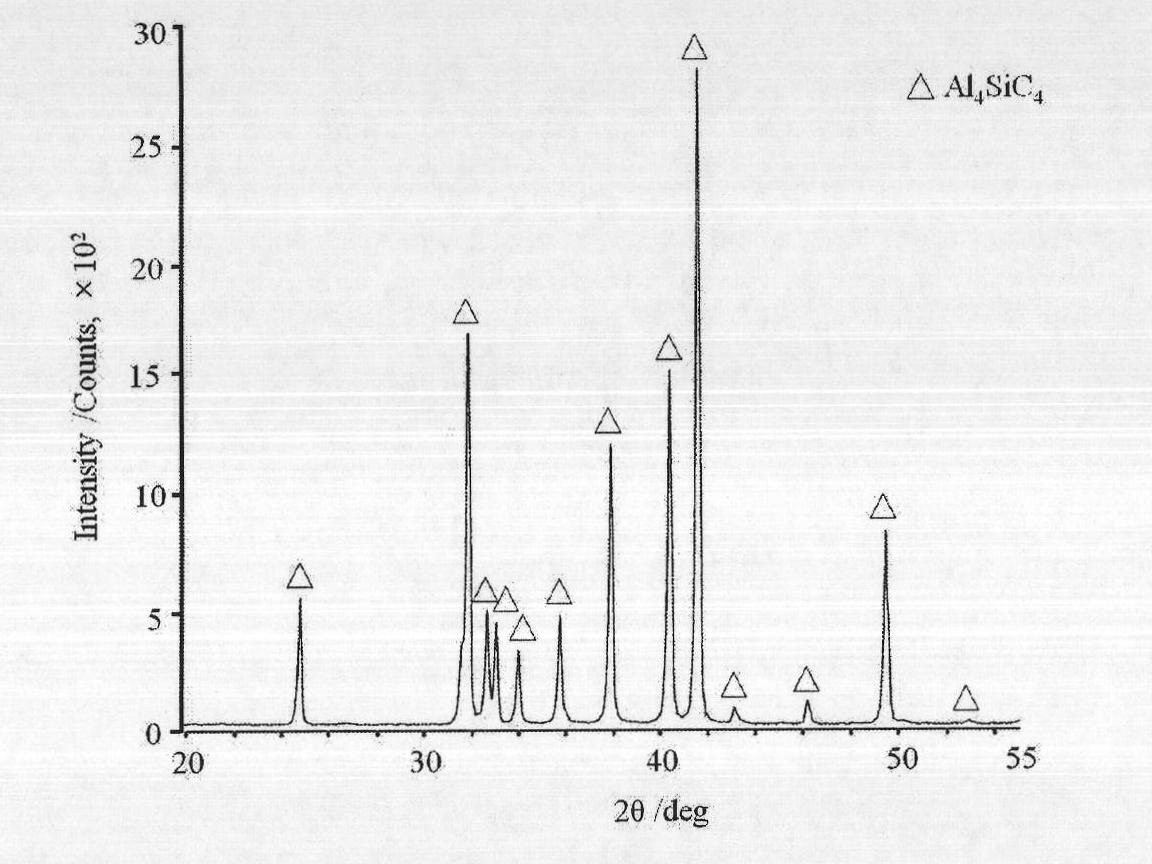
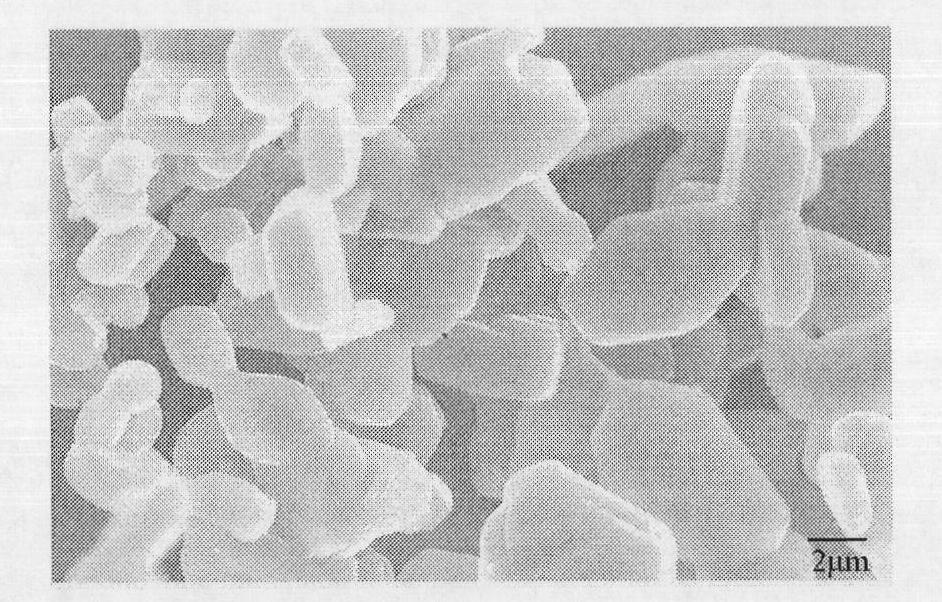
The invention discloses a method for preparing aluminum silicon carbon superfine powder. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) weighing the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 20 to 30 percent of kaolin, 40 to 50 percent of Al2O3 raw material and 20 to 30 percent of carbon raw material; stirring and mixing the raw materials to obtain a mixture; and 2) heating the mixture in vacuum or argon atmosphere at the temperature of between 1,600 and 1,700 DEG C, preserving the heat for 8 to 10 hours, cooling, and removing the impurity layer on the surface of the product to obtain the aluminum silicon carbon superfine powder. The average granularity of the prepared aluminum silicon carbon superfine powder is 2 to 5 microns, and the mass percentage content of Al4SiC4 is over 99 percent. The aluminum silicon carbon superfine powder can be directly used as a ceramic product matrix component; and a blocky aluminum silicon carbon material does not need to be synthesized and crushed into superfine powder, so that energy is saved. The method is simple, convenient, feasible and efficient; and the obtained product has high yield and purity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
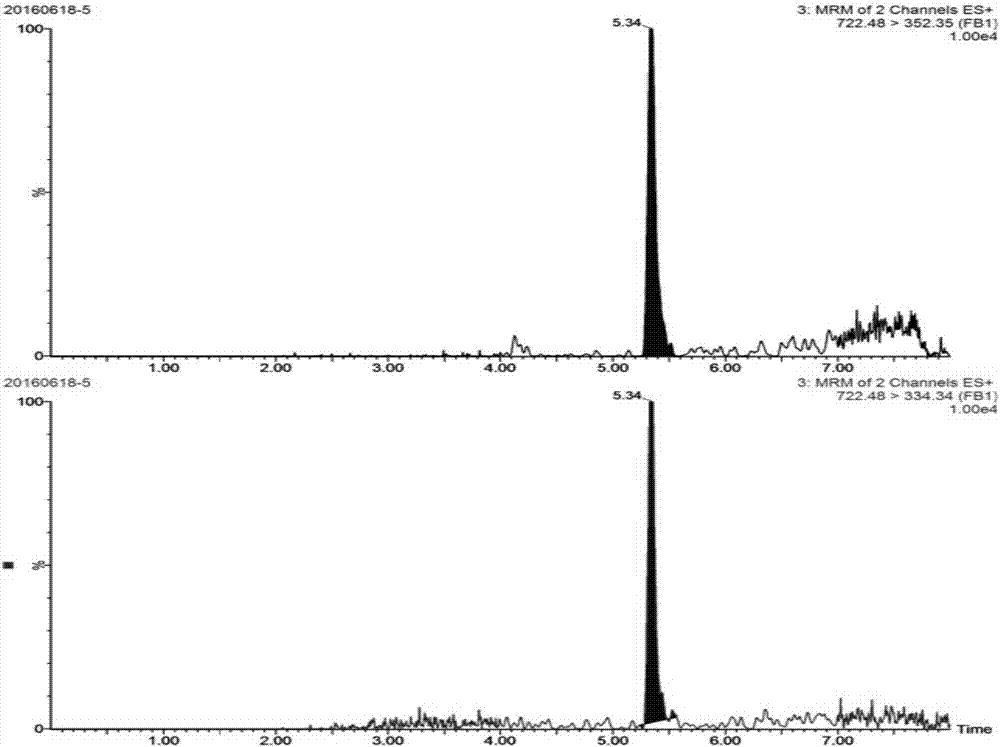
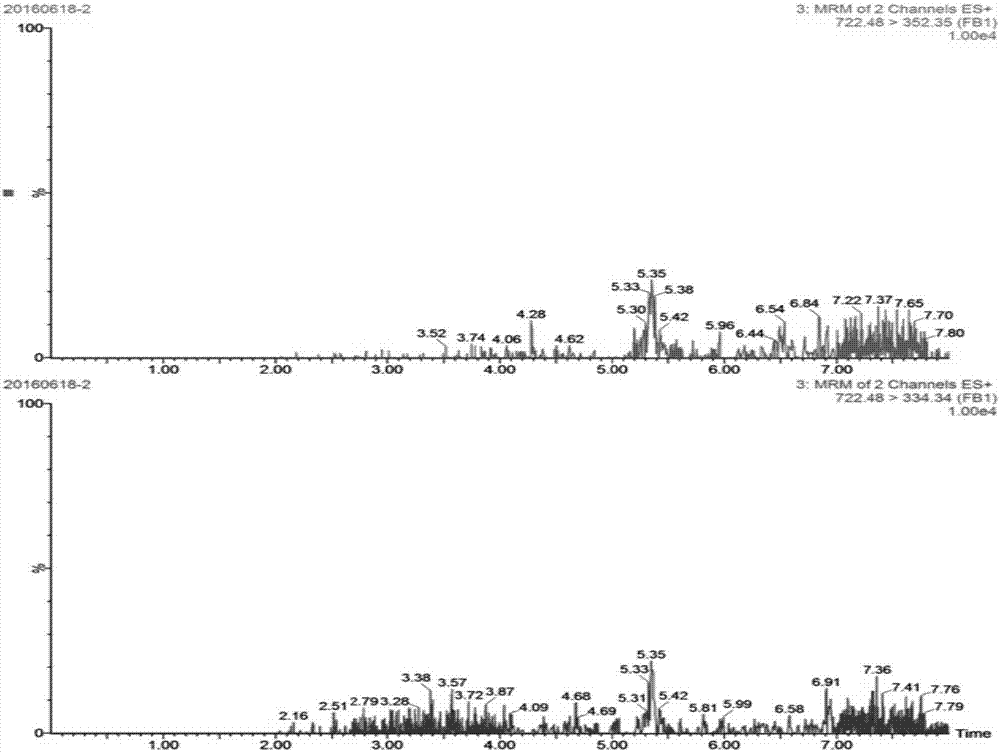
FB1(fumonisin B1) matrix standard substance and preparation method thereof
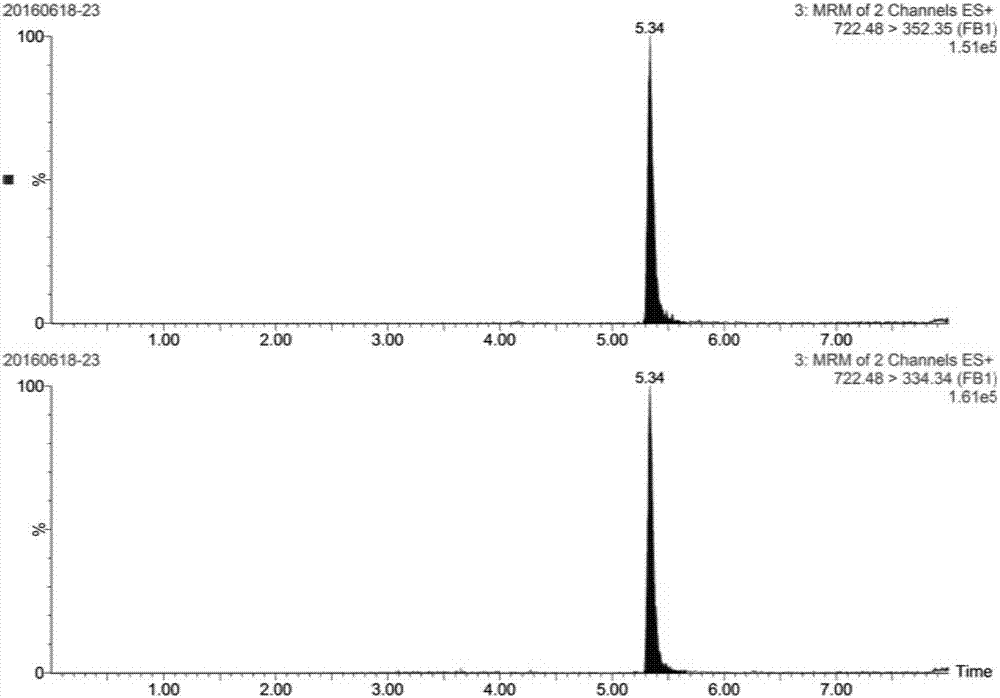
InactiveCN107478478AGuaranteed monitoringAvoid inaccurate test resultsPreparing sample for investigationFreeze-dryingFumonisin B1
The invention provides a preparation method of an FB1(fumonisin B1) matrix standard substance. The method comprises steps as follows: toxigenic fungus strains of FB1 are inoculated to a culture medium of edible agricultural products and cultured for toxin production, and the highly toxigenic culture medium is lyophilized by a lyophilizer, smashed and screened; blank edible agricultural product powder is added according to the principle of geometric-proportion dilution, FB1 is enabled to reach the quantity level, the materials are mixed uniformly, and the edible agricultural product matrix standard substance of FB1 is obtained. According to the prepared edible agricultural product matrix standard substance of FB1, a value traceability substance is provided for daily FB1 residue detection, the problem of inaccurate detection results caused by matrix difference is solved, and monitoring for FB1 in the agricultural products such as corn, wheat, rice and the like is accurately guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com