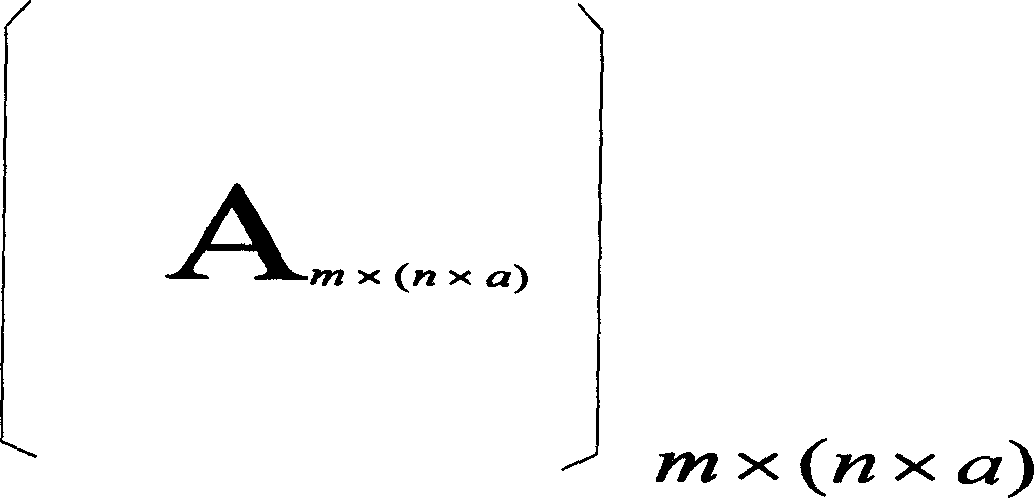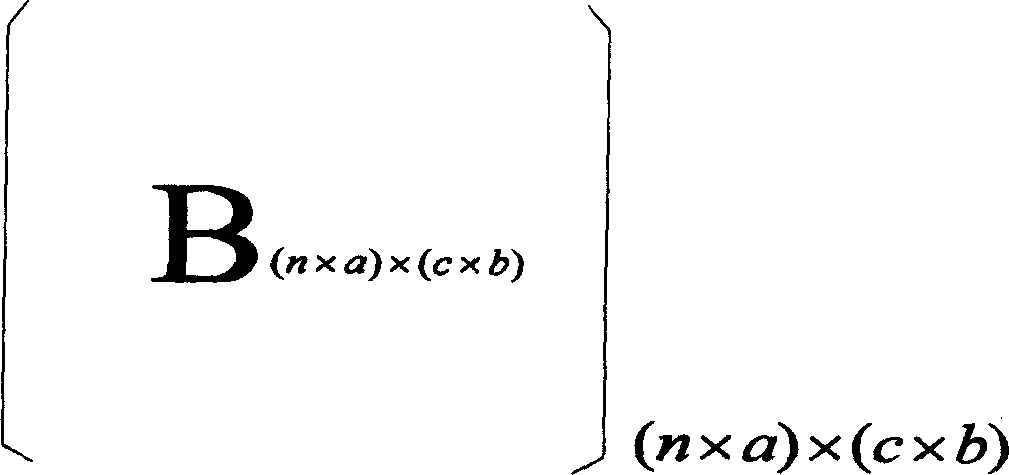Patents
Literature
117 results about "Large matrices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
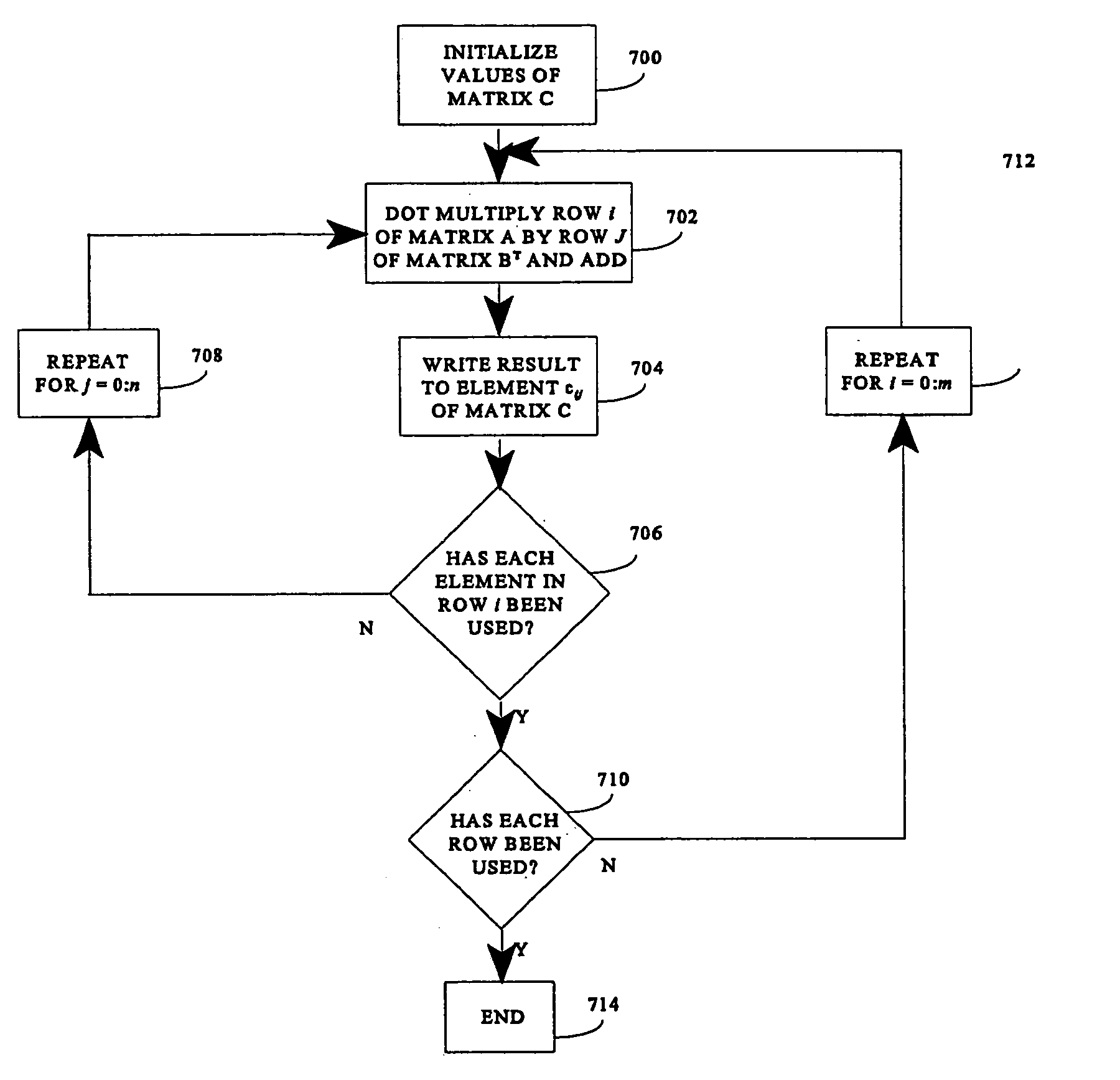
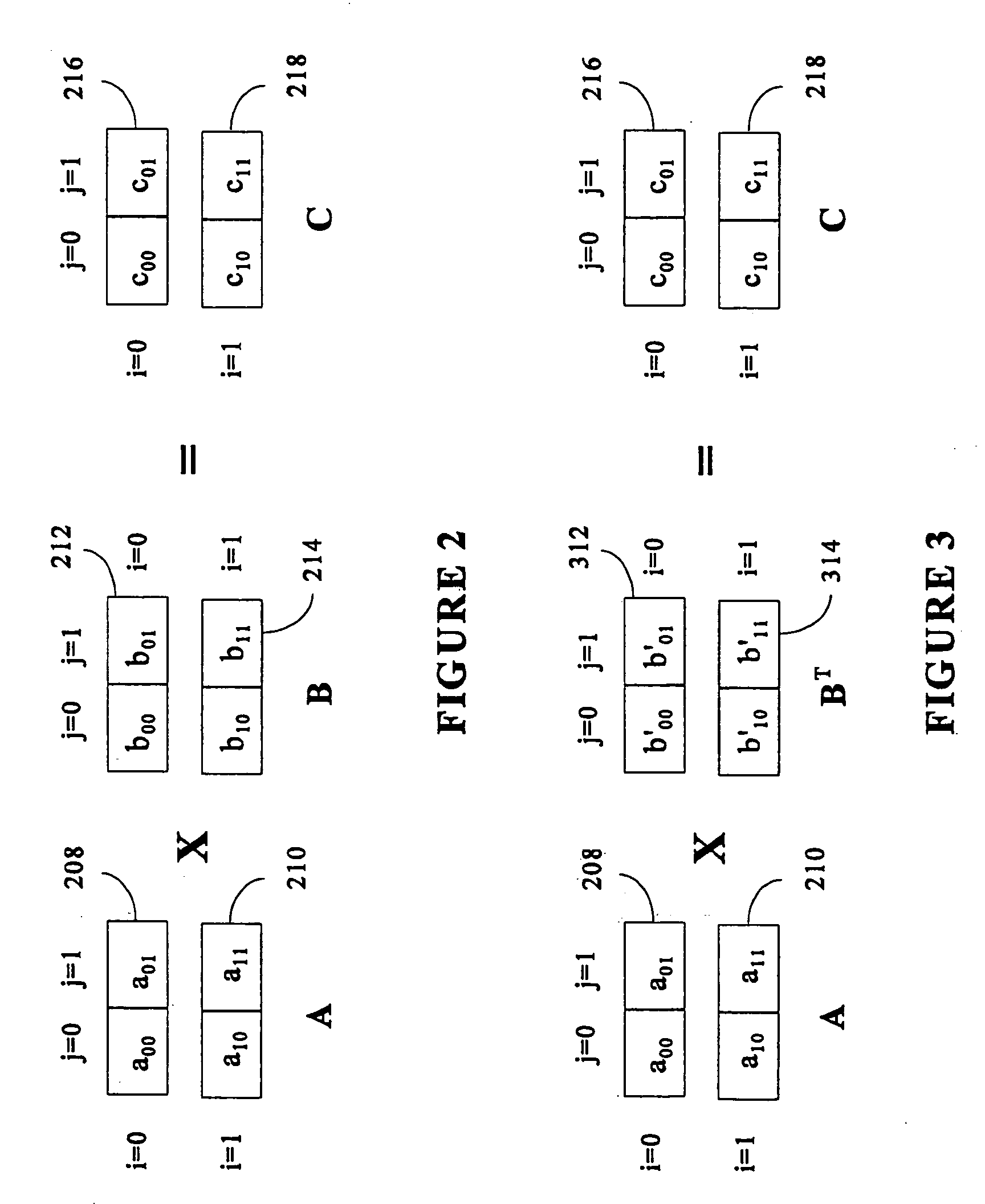
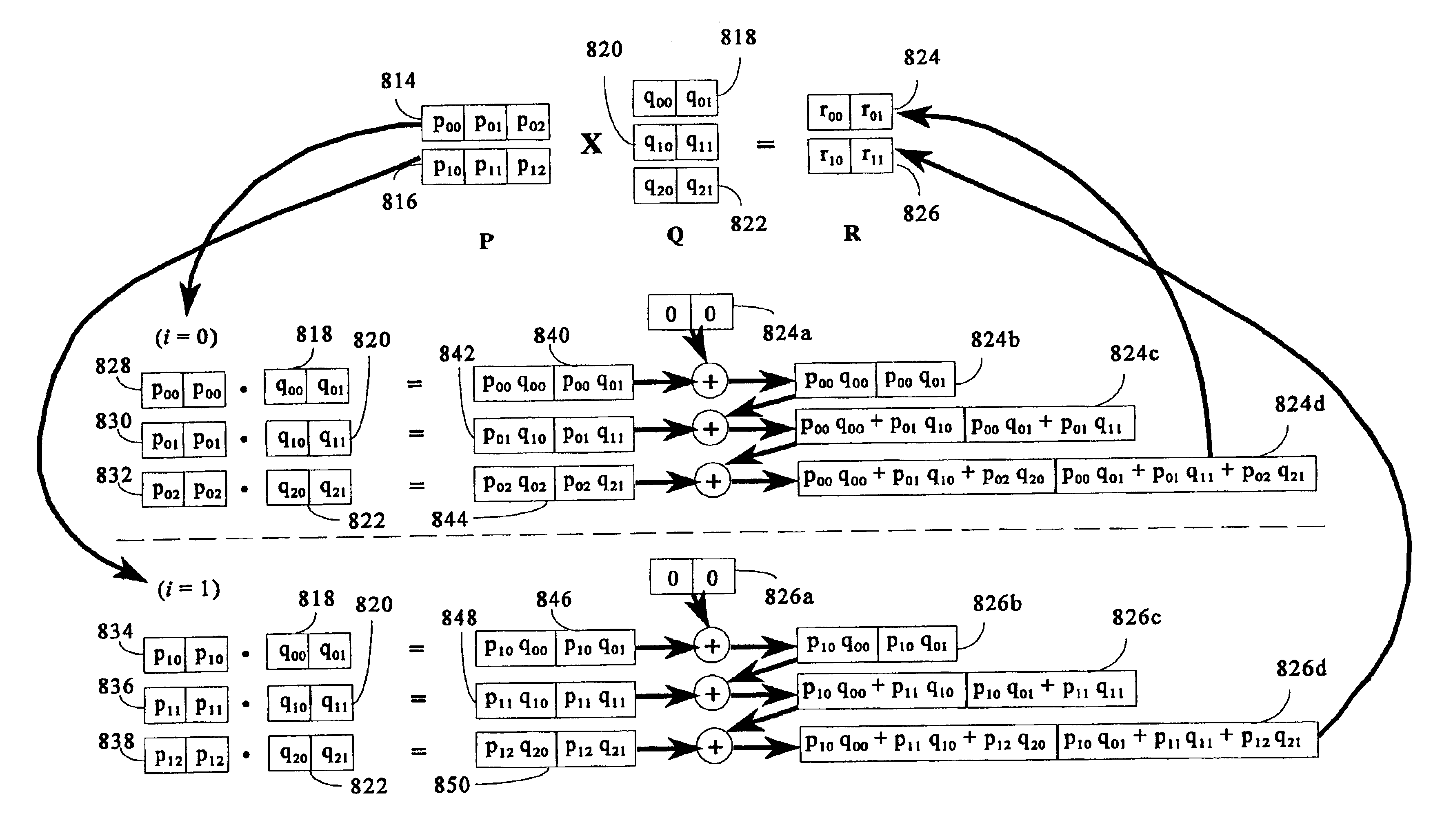
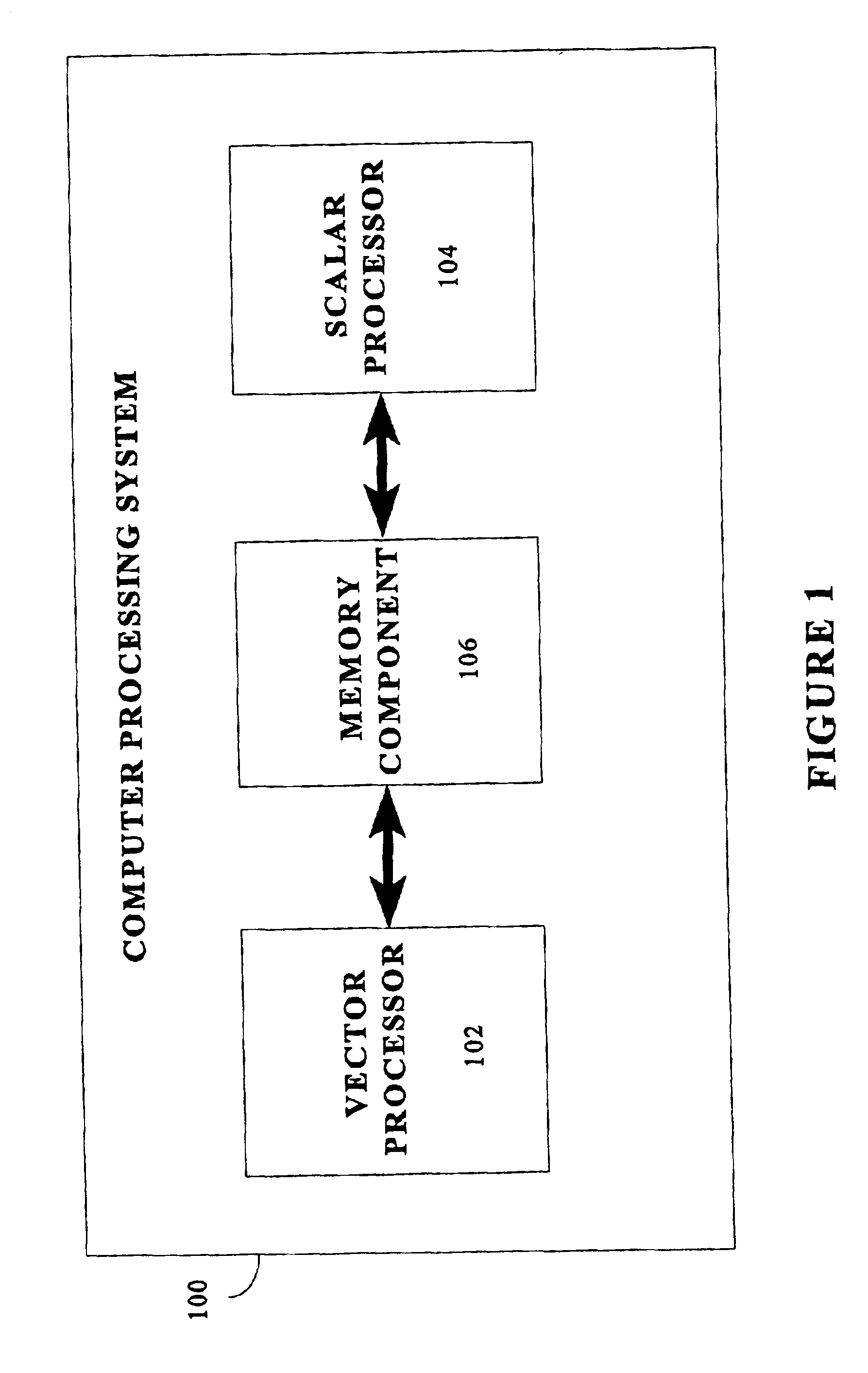
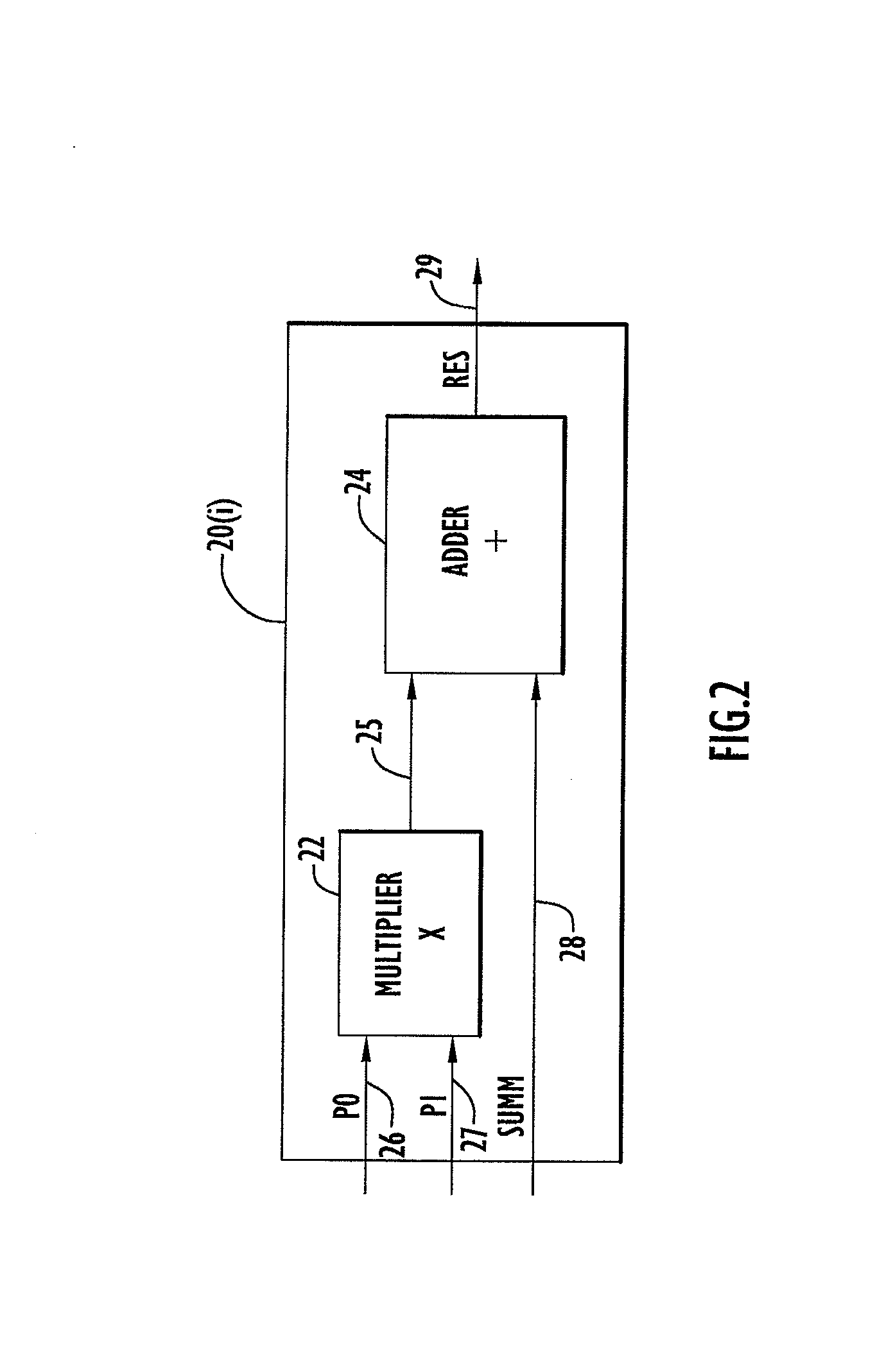
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS20050193050A1Efficient and rapid matrix multiplicationEfficient executionComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlAlgorithmProcessor register
To perform multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system, partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which form a product matrix. Each matrix can be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
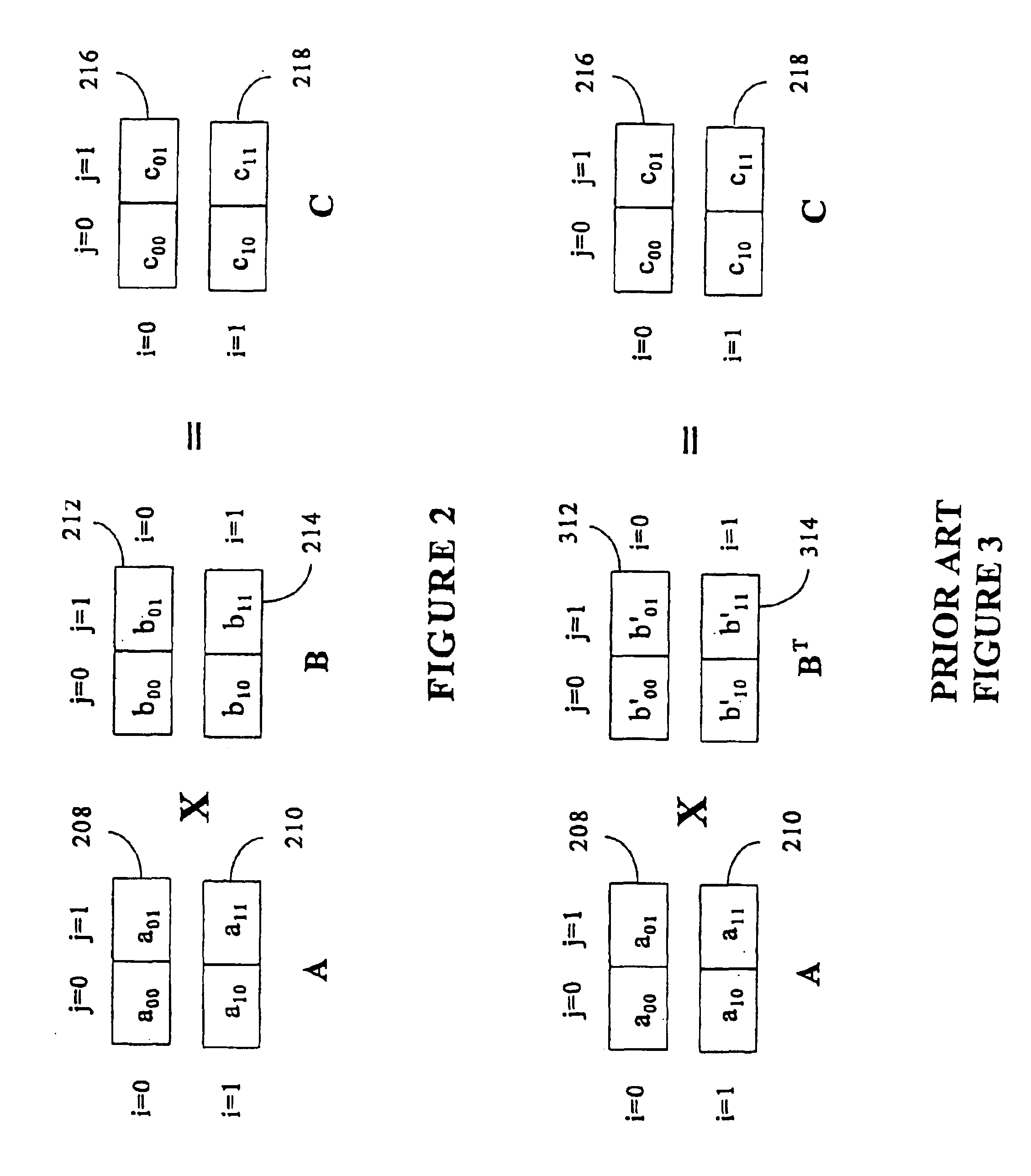
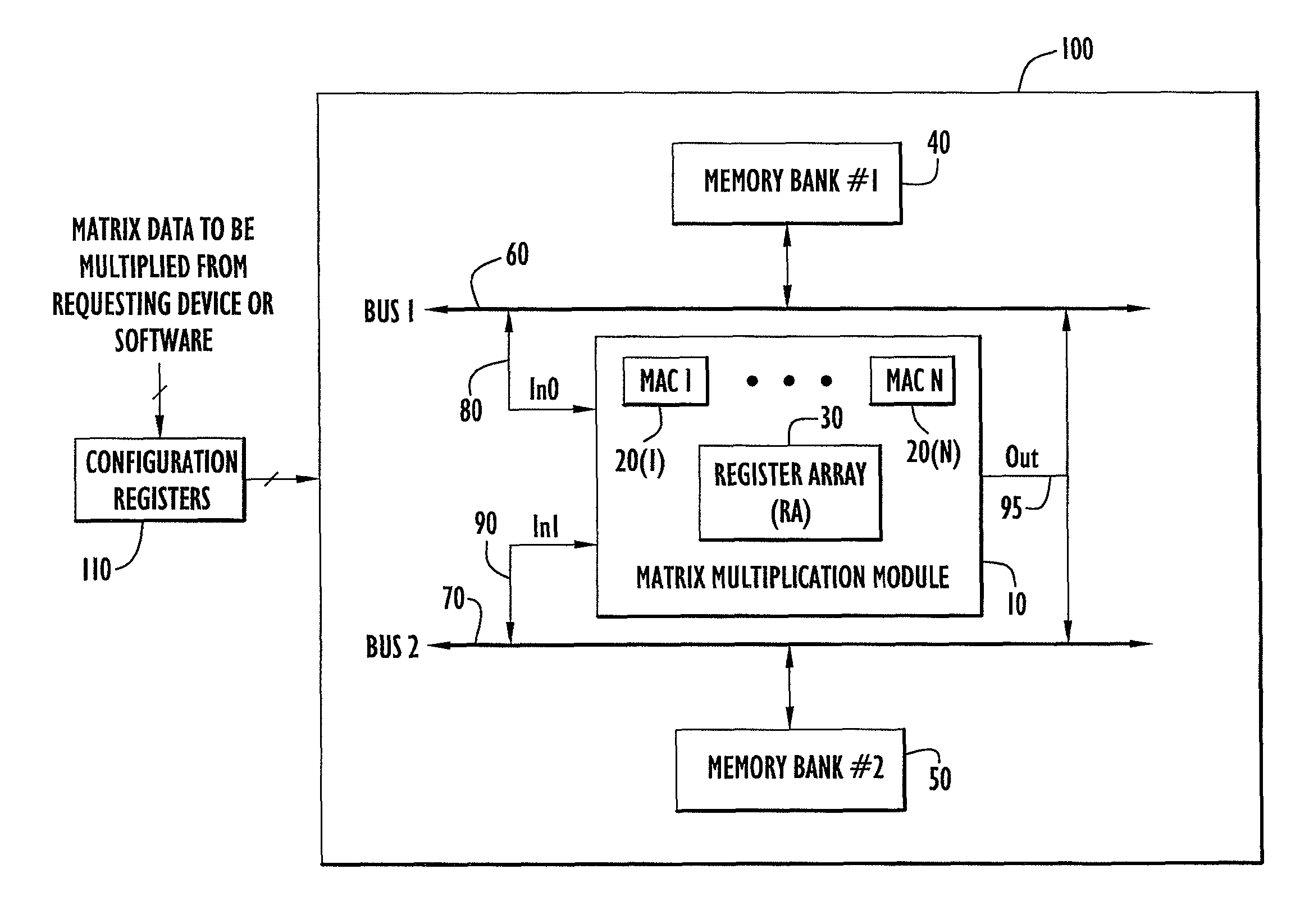
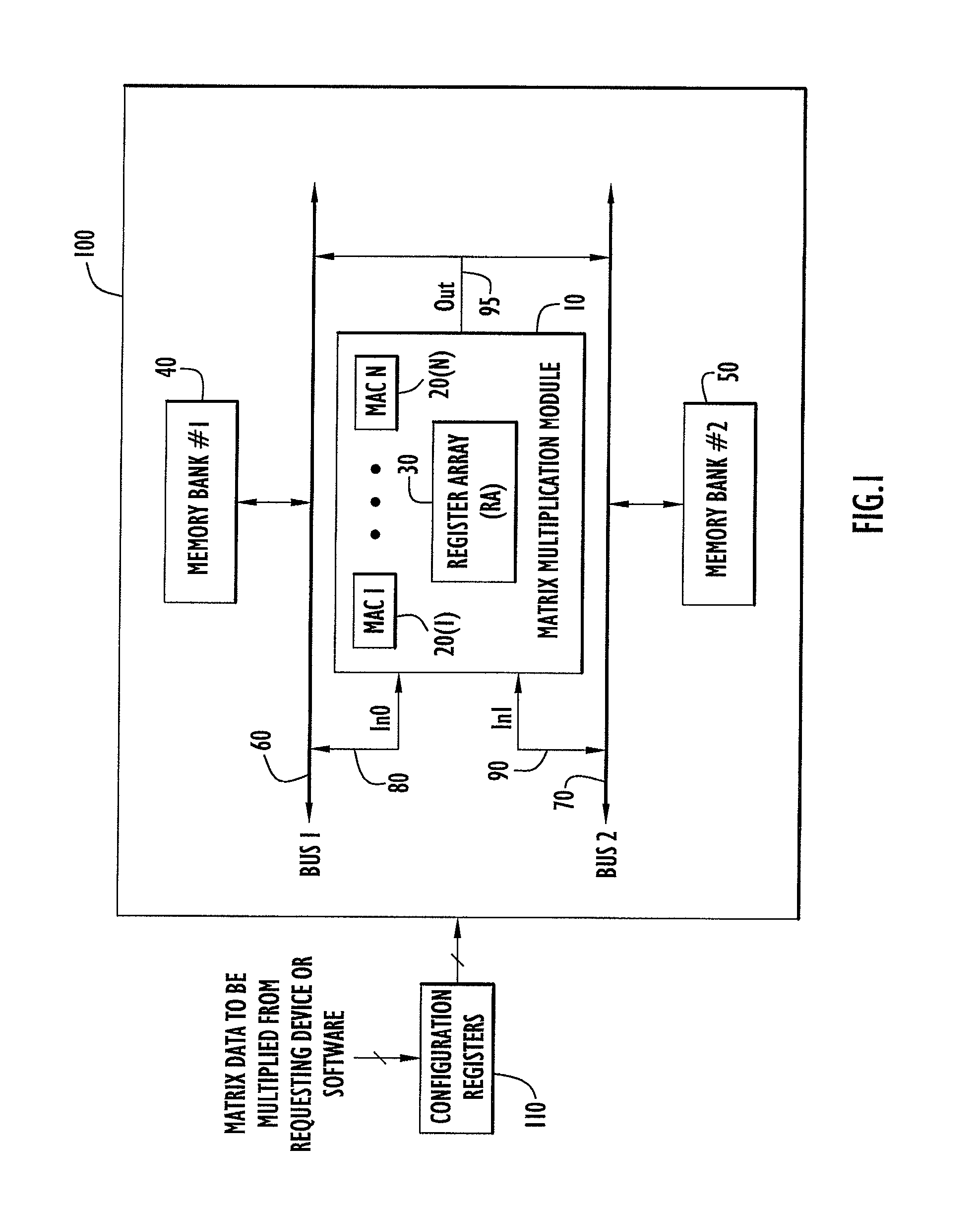
High speed and efficient matrix multiplication hardware module
ActiveUS8051124B2Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlClock rateComputer module
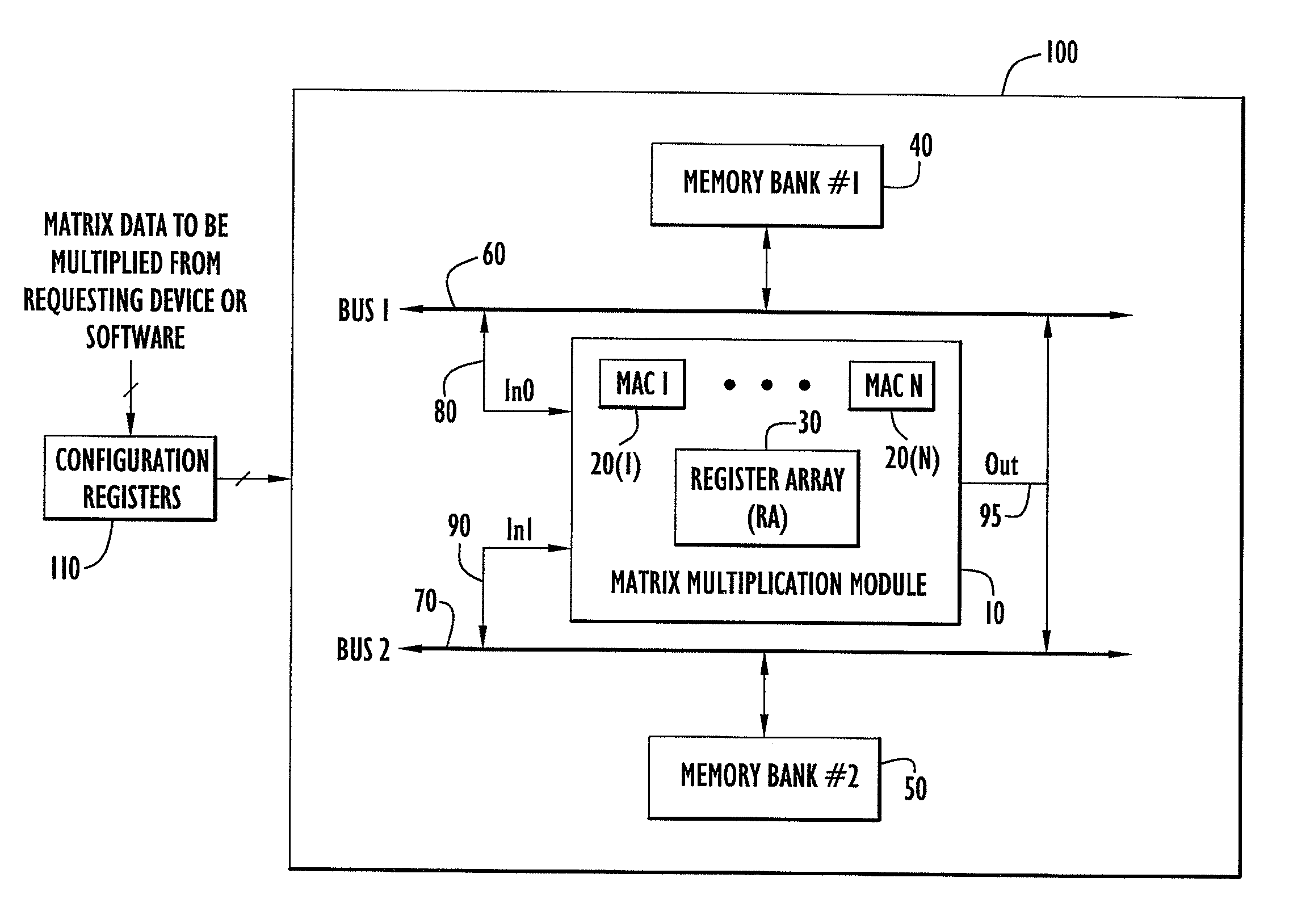
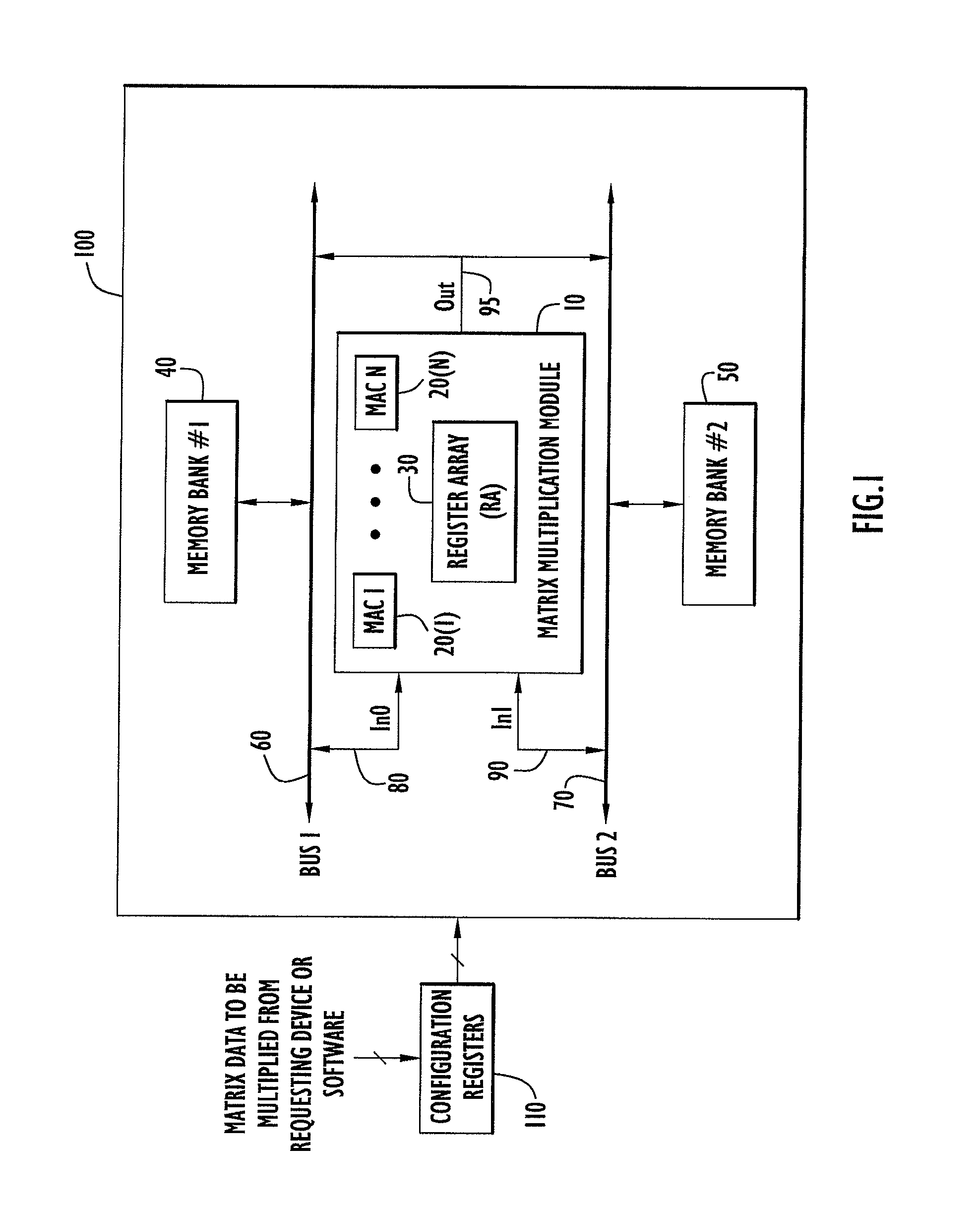
A matrix multiplication module and matrix multiplication method are provided that use a variable number of multiplier-accumulator units based on the amount of data elements of the matrices are available or needed for processing at a particular point or stage in the computation process. As more data elements become available or are needed, more multiplier-accumulator units are used to perform the necessary multiplication and addition operations. To multiply an N×M matrix by an M×N matrix, the total (maximum) number of used MAC units is “2*N−1”. The number of MAC units used starts with one (1) and increases by two at each computation stage, that is, at the beginning of reading of data elements for each new row of the first matrix. The sequence of the number of MAC units is {1, 3, 5, . . . , 2*N−1} for computation stages each of which corresponds to reading of data elements for each new row of the left hand matrix, also called the first matrix. For the multiplication of two 8×8 matrices, the performance is 16 floating point operations per clock cycle. For an FPGA running at 100 MHz, the performance is 1.6 Giga floating point operations per second. The performance increases with the increase of the clock frequency and the use of larger matrices when FPGA resources permit. Very large matrices are partitioned into smaller blocks to fit in the FPGA resources. Results from the multiplication of sub-matrices are combined to form the final result of the large matrices.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
High-precision matrix-vector multiplication on a charge-mode array with embedded dynamic memory and stochastic method thereof
InactiveUS20050125477A1Efficient multiplicationIncrease cell densityComputation using non-contact making devicesPhysical realisationRandom methodReal time signal processing
Analog computational arrays for matrix-vector multiplication offer very large integration density and throughput as, for instance, needed for real-time signal processing in video. Despite the success of adaptive algorithms and architectures in reducing the effect of analog component mismatch and noise on system performance, the precision and repeatability of analog VLSI computation under process and environmental variations is inadequate for some applications. Digital implementation offers absolute precision limited only by wordlength, but at the cost of significantly larger silicon area and power dissipation compared with dedicated, fine-grain parallel analog implementation. The present invention comprises a hybrid analog and digital technology for fast and accurate computing of a product of a long vector (thousands of dimensions) with a large matrix (thousands of rows and columns). At the core of the externally digital architecture is a high-density, low-power analog array performing binary-binary partial matrix-vector multiplication. Digital multiplication of variable resolution is obtained with bit-serial inputs and bit-parallel storage of matrix elements, by combining quantized outputs from one or more rows of cells over time. Full digital resolution is maintained even with low-resolution analog-to-digital conversion, owing to random statistics in the analog summation of binary products. A random modulation scheme produces near-Bernoulli statistics even for highly correlated inputs. The approach has been validated by electronic prototypes achieving computational efficiency (number of computations per unit time using unit power) and integration density (number of computations per unit time on a unit chip area) each a factor of 100 to 10,000 higher than that of existing signal processors making the invention highly suitable for inexpensive micropower implementations of high-data-rate real-time signal processors.
Owner:GENOV ROMAN A +1
Spatio-temporal speech enhancement technique based on generalized eigenvalue decomposition
InactiveUS20100076756A1Reduce computational complexityEliminate the effects ofSpeech recognitionEuclidean vectorSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
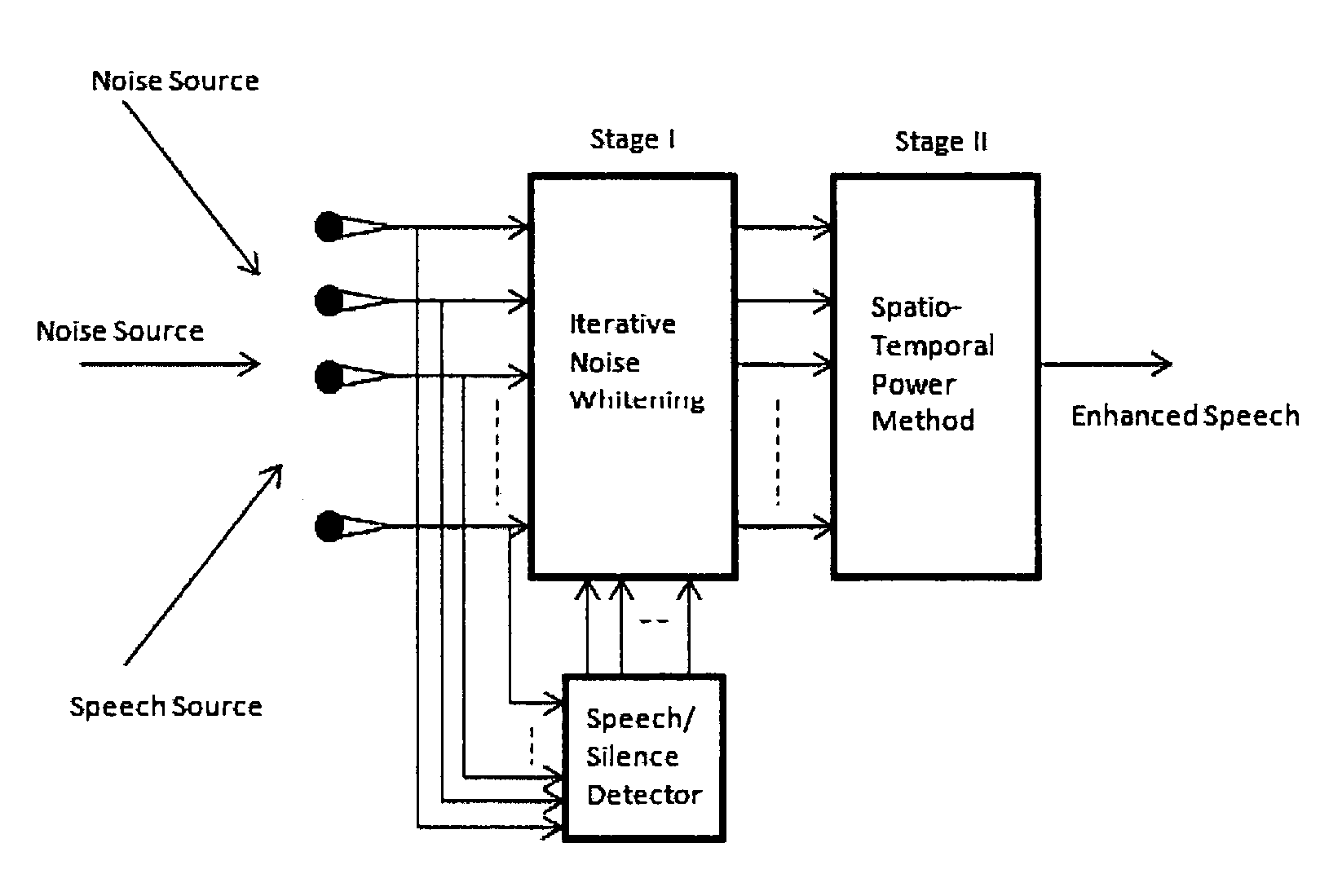
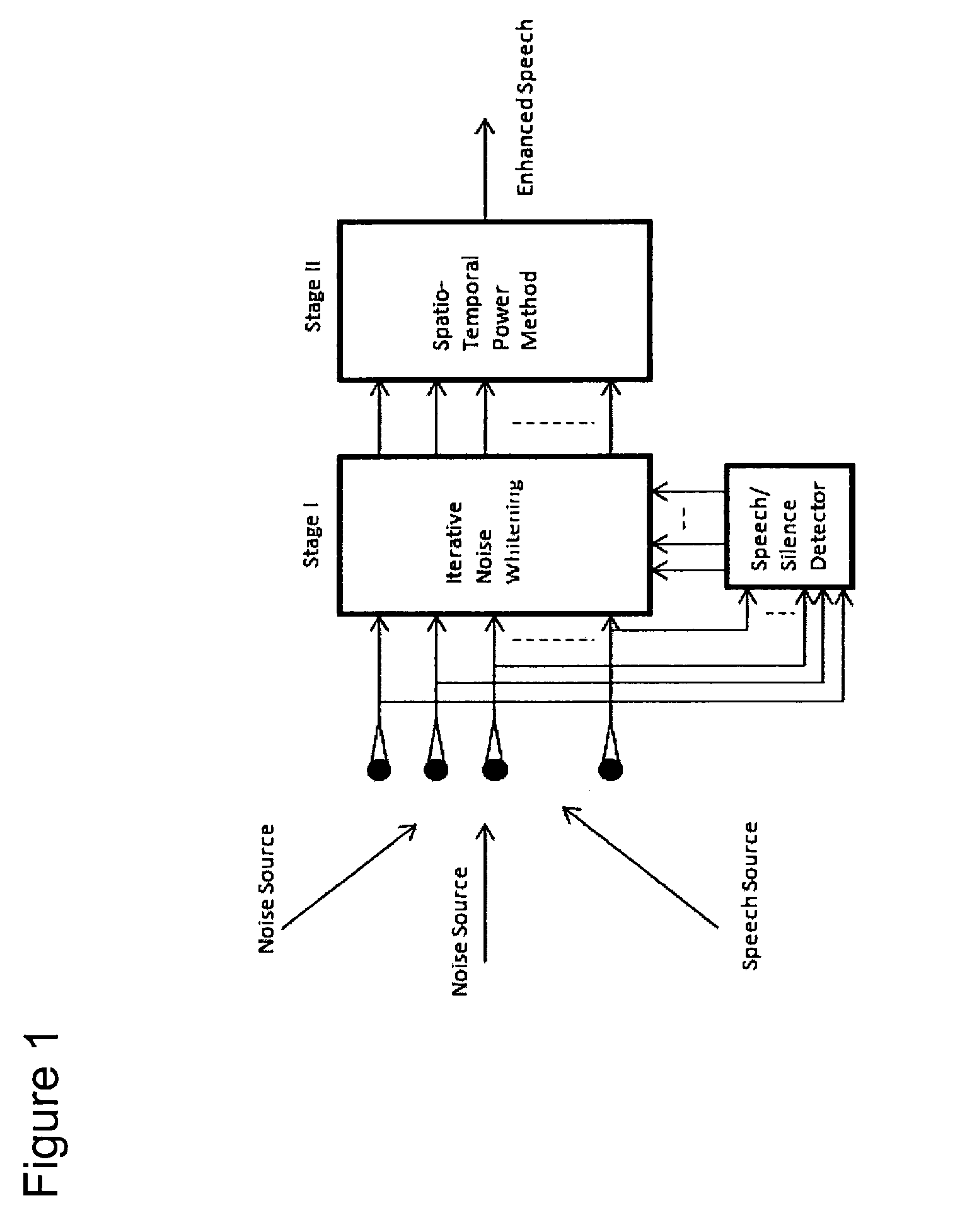
The present invention describes a speech enhancement method using microphone arrays and a new iterative technique for enhancing noisy speech signals under low signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) environments. A first embodiment involves the processing of the observed noisy speech both in the spatial- and the temporal-domains to enhance the desired signal component speech and an iterative technique to compute the generalized eigenvectors of the multichannel data derived from the microphone array. The entire processing is done on the spatio-temporal correlation coefficient sequence of the observed data in order to avoid large matrix-vector multiplications. A further embodiment relates to a speech enhancement system that is composed of two stages. In the first stage, the noise component of the observed signal is whitened, and in the second stage a spatio-temporal power method is used to extract the most dominant speech component. In both the stages, the filters are adapted using the multichannel spatio-temporal correlation coefficients of the data and hence avoid large matrix vector multiplications.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
High Speed and Efficient Matrix Multiplication Hardware Module
ActiveUS20090024685A1Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlClock rateParallel computing
A matrix multiplication module and matrix multiplication method are provided that use a variable number of multiplier-accumulator units based on the amount of data elements of the matrices are available or needed for processing at a particular point or stage in the computation process. As more data elements become available or are needed, more multiplier-accumulator units are used to perform the necessary multiplication and addition operations. To multiply an N×M matrix by an M×N matrix, the total (maximum) number of used MAC units is “2*N−1”. The number of MAC units used starts with one (1) and increases by two at each computation stage, that is, at the beginning of reading of data elements for each new row of the first matrix. The sequence of the number of MAC units is {1, 3, 5, . . . , 2*N−1} for computation stages each of which corresponds to reading of data elements for each new row of the left hand matrix, also called the first matrix. For the multiplication of two 8×8 matrices, the performance is 16 floating point operations per clock cycle. For an FPGA running at 100 MHz, the performance is 1.6 Giga floating point operations per second. The performance increases with the increase of the clock frequency and the use of larger matrices when FPGA resources permit. Very large matrices are partitioned into smaller blocks to fit in the FPGA resources. Results from the multiplication of sub-matrices are combined to form the final result of the large matrices.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
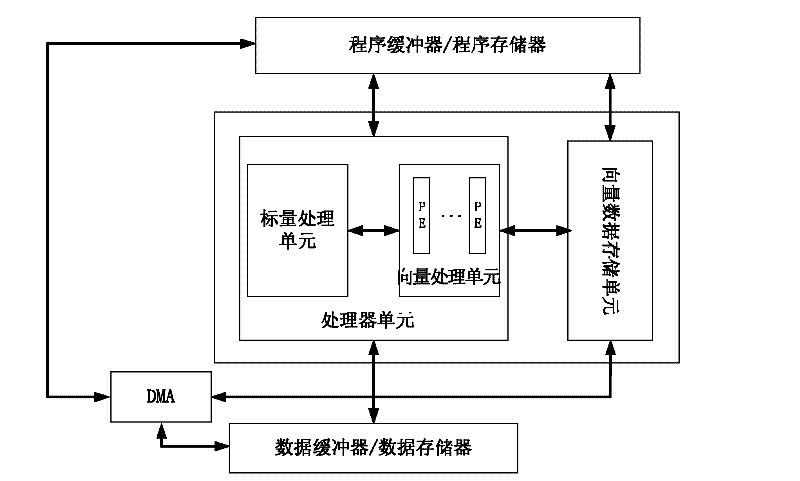
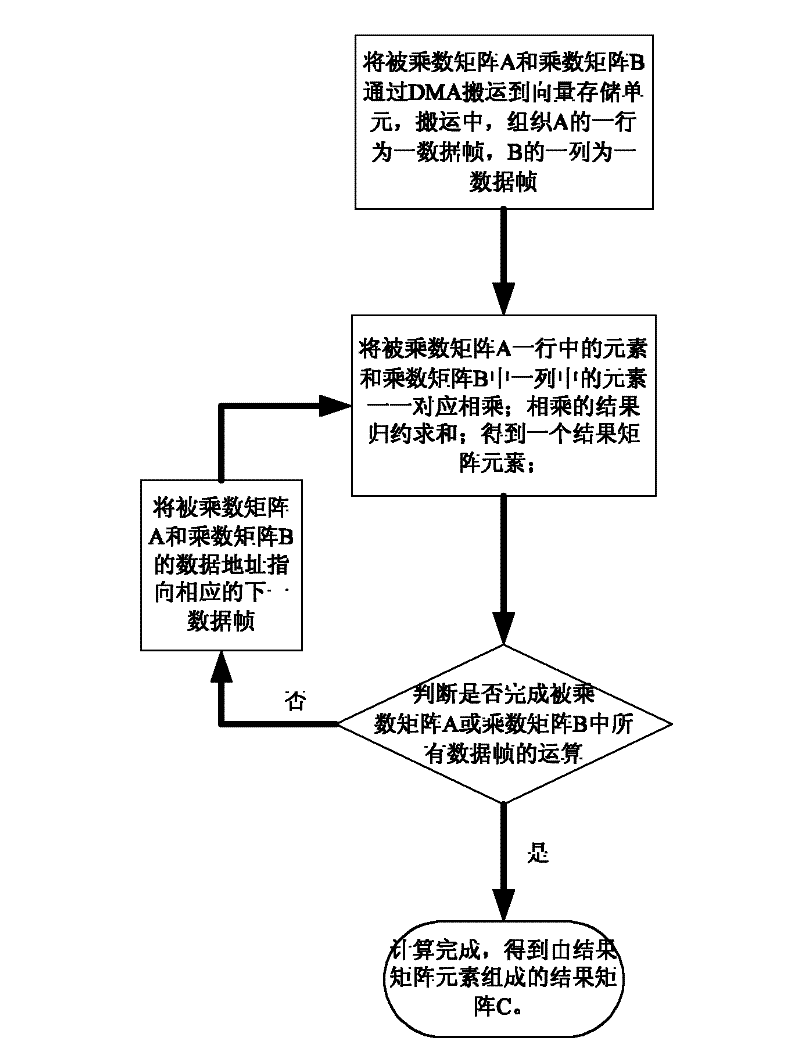
Vector processor oriented large matrix multiplied vectorization realizing method
ActiveCN102411558AImprove multiplication efficiencySimple stepsComplex mathematical operationsDirect memory accessEuclidean vector
The invention discloses a vector processor oriented large matrix multiplied vectorization realizing method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) inputting a multiplicand matrix A and a multiplier B; transporting the multiplicand matrix A and multiplier B to a vector storing unit by a DMA (direct memory access) controller; in transporting process, ordering the first to number n lines of the multiplier B into first to number n columns; (2) loading elements in one line of the multiplicand matrix A and in one column of the multiplier B to K parallel processing units and multiplying the elements in a one-to-one correspondence manner; reducing and summing the multiplied results in one pointed parallel processing unit; storing the summed result as a result matrix element in a vector storing unit; and (3) transferring to next line of the multiplicand matrix A and next column of the multiplier B; re-executing the step (2) until calculating all data frames and acquiring a result matrix C composed of matrix elements. The vectorization realizing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple principle, convenient operation and capability of improving calculating efficiency.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
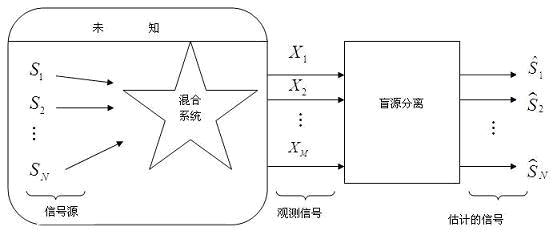
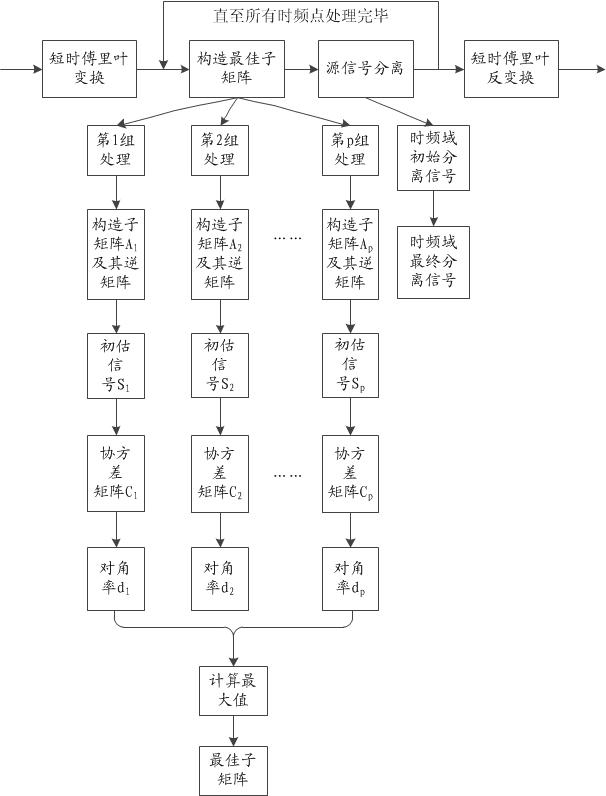
Underdetermined blind source separation (UBSS) method based on maximum matrix diagonal rate
The invention discloses an underdetermined blind source separation (UBSS) method based on a maximum matrix diagonal rate. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing inverse matrixes of C*M / N M*M-dimensional sub matrixes of a mixed matrix (wherein M and N are respectively the number of sensors and the number of source signals); multiplying the inverse matrixes by observation signal vectors to acquire initial estimation signal vectors; and sequentially calculating the covariance matrix, the solid matrix, the absolute value matrix and the diagonal rate of each initial estimation signal vector, selecting the initial estimation signal vector corresponding to the maximum diagonal rate as estimation of a source signal vector, and thus realizing underdetermined separation of sourcesignals. By the method, the requirement for source signal sparseness is reduced, aliasing of road source signals is allowed at each time frequency point at most, and the underdetermined separation problem of music signals and noise signals is solved. The requirement for the statistical property of the source signals is low, and the underdetermined separation problem of Gaussian signals and related signals is solved. In addition, by the method, processing of each time frequency point and each sub matrix can be executed in parallel, and hardware implementation is facilitated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
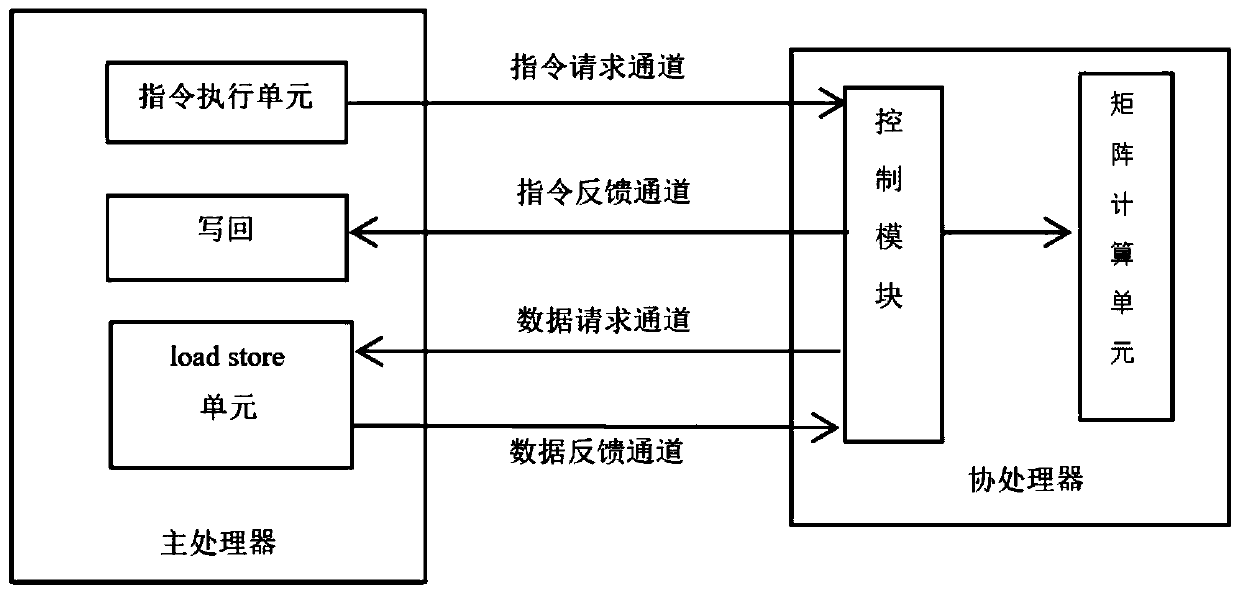
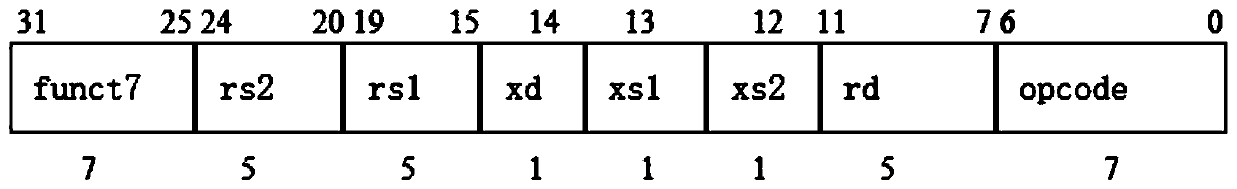
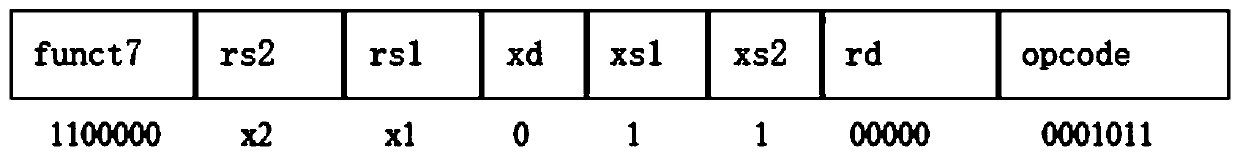
Matrix convolution calculation method, interface, coprocessor and system based on RISC-V architecture
ActiveCN109857460ACalculation speedReduce the number of memory accessesConcurrent instruction executionNeural architecturesExtensibilityProcessor design
The invention discloses a set based on RISC-. According to the method and system complete mechanism of the instruction, the interface and the coprocessor for matrix convolution calculation of the V instruction set architecture, traditional matrix convolution calculation is efficiently achieved in a software and hardware combined mode, and RISC-is utilized. Extensibility of V instruction sets, a small number of instructions and a special convolution calculation unit (namely a coprocessor) are designed; the memory access times and the execution period of a matrix convolution calculation instruction are reduced, the complexity of application layer software calculation is reduced, the efficiency of large matrix convolution calculation is improved, the calculation speed of matrix convolution isincreased, flexible calling of upper-layer developers is facilitated, and the coding design is simplified. Meanwhile, RISC-is utilized. The processor designed by the V instruction set also has greatadvantages in power consumption, size and flexibility compared with ARM, X86 and other architectures, can adapt to different application scenes, and has a wide prospect in the field of artificial intelligence.
Owner:NANJING HUAJIE IMI TECH CO LTD
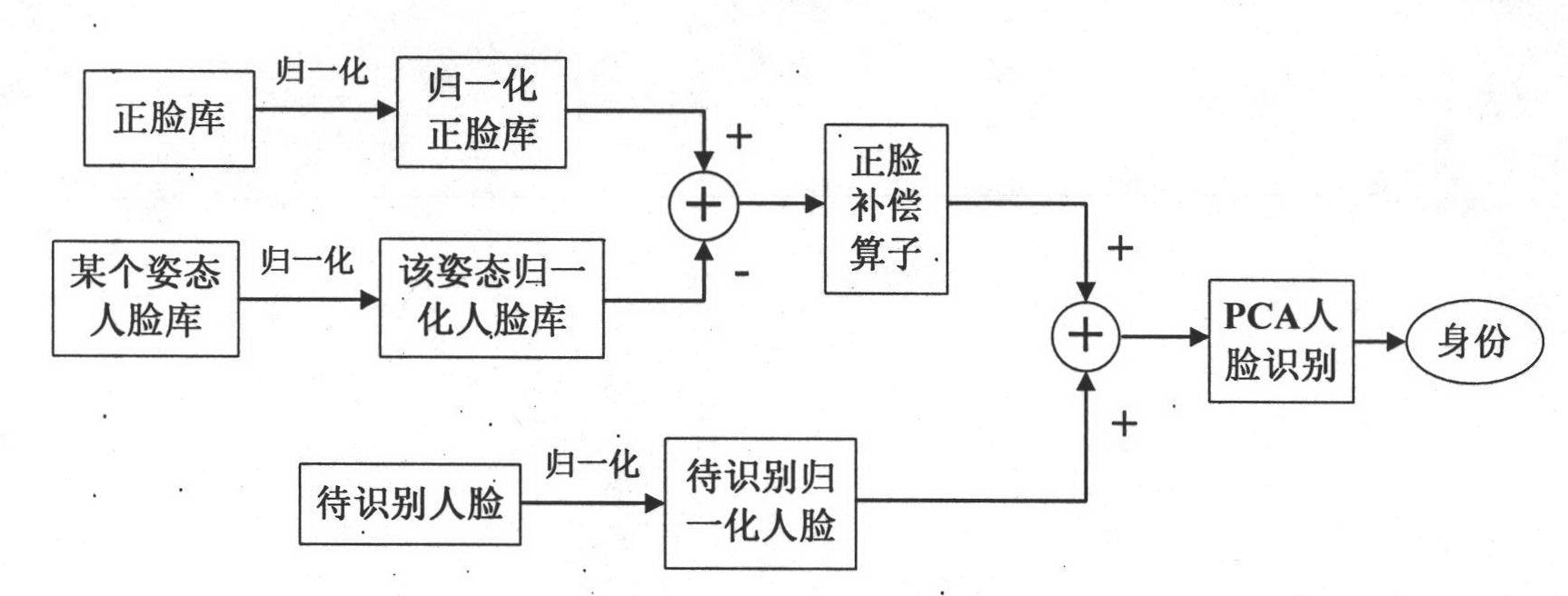
Front-face-compensation-operator-based multi-pose human face recognition method
InactiveCN102013011ASmall amount of calculationCalculation speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisLarge matrices
The invention discloses a simple and effective principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm-based multi-pose human face recognition technique, which compensating a multi-pose human face by using a front face compensation operator and using the compensated human face for multi-pose human face recognition. The attached figure in the abstract of the description is the whole multi-pose human face recognition flow chart. In the invention, when the PCA algorithm is used for human face recognition, the front face compensation operator compensates for front face profile information, namely feature face information corresponding to the large feature value resolved by the PCA algorithm, lacking in a multi-pose human face to be recognized, and reduces part of multi-pose human face information interfering with the PCA algorithm. A multi-pose human face usually lacks a front face profile which is more important information for PCA algorithm. Compared with the prior art, the technique has the advantages that: calculating by using an average face and avoiding using the method for training by forming a large matrix with human faces from a human face library, the calculation amount is reduced; thehuman face normalization requirement is low; it is easy to choose a human face library; and fewer faces are required to be trained. In addition, the algorithm used by the technique is simple, a good recognition effect can be achieved by simple addition and subtraction operation, and the technique can be used for recognizing human faces in all poses. In the invention, the method for compensating the multi-pose human face by using the front face compensation operator provides a new way for improving multi-pose human face recognition rate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
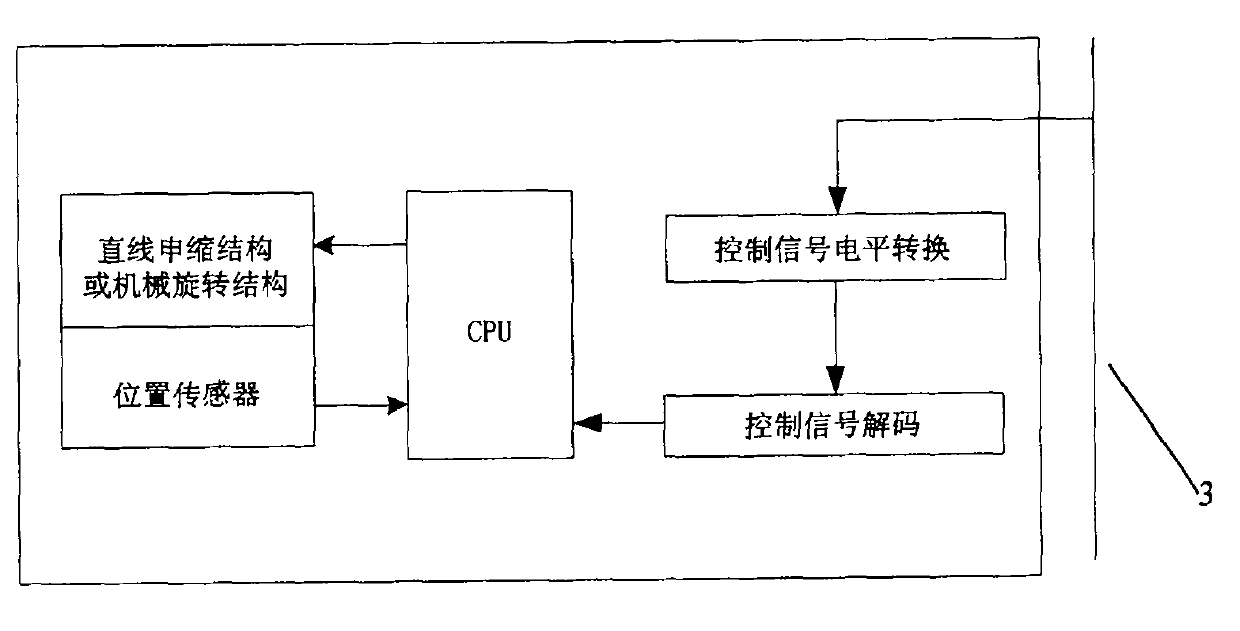
Flexible rotation display matrix
The invention relates to the technologies of electronic communication, mechanical control and image processing, and is manly applied to the exhibition and display industry. A flexible rotation display matrix comprises an electric flexible unit with a position sensing function, an electric rotation unit with the position sensing function, a flexible rotation unit control circuit and a total control circuit, wherein the electric unit can be spliced into a matrix module; the matrix module can be further spliced into a large matrix display screen; each unit is uniformly controlled by the total control circuit; display content sent from a PC (personal computer) machine is formed into one frame of stereo dynamic image according to different flexible positions or rotation angles of each unit; and the equipment can be cooperated with other sound, light and electricity equipment through cooperative control lines to achieve the shocked display effect.
Owner:ANHUI LONG VOLT ENERGY CO LTD
Peak-to-average power ratio reduction method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing systems based on path finding
InactiveUS20110274186A1Reduce probabilityComputation is complicatedSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityComputer science
In a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) reduction method for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system based on path finding, the method applied to the OFDM system uses an ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm and a PTS to reduce a PAPR value, and an area of a computing circuit. In a simulated result, the method can reduce the PAPR effectively, and can be executed by a lower level of complexity of the computation. To solve a large matrix of the PTS, an ant colony optimization algorithm is used for calculating phase rotation vectors of a better quality effectively to achieve the effects of improving the performance, overcoming the high level of complexity of the computing circuit, and reducing the large area of the computing circuit.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Three-phase decoupling load flow calculation method of power distribution network based on path matrix
ActiveCN102842907AAvoid calculationSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsComponent LoadLoop analysis
The invention discloses a three-phase decoupling load flow calculation method of a power distribution network based on a path matrix. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting a symmetrical component method to perform sequence component decoupling on a three-phase unbalanced power distribution network to obtain zero sequence, a power distribution sequence network with positive sequence and negative sequence, and adopting a loop-analysis method based on the path matrix to perform one-phase-sequence component load flow calculation to obtain load flows of the three-sequence networks; and secondly, transforming sequence network load flows in a phase component mode by an inverse transformation principle of the symmetrical component method to obtain three-phase load flows. By using the method, a three-phase unbalanced power distribution network system is decoupled into zero sequence, positive sequence and negative sequence networks, so that large matrix manipulation in the three-phase load flow calculation is avoided, the calculated amount is decreased, and the calculation efficiency is improved. The method has the advantages of clear calculation process, simple programming and fast calculation speed. Finally, a 6-busbar test example verifies the correctness and good convergence; and the method is good in generality and practical applicability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Cell tray
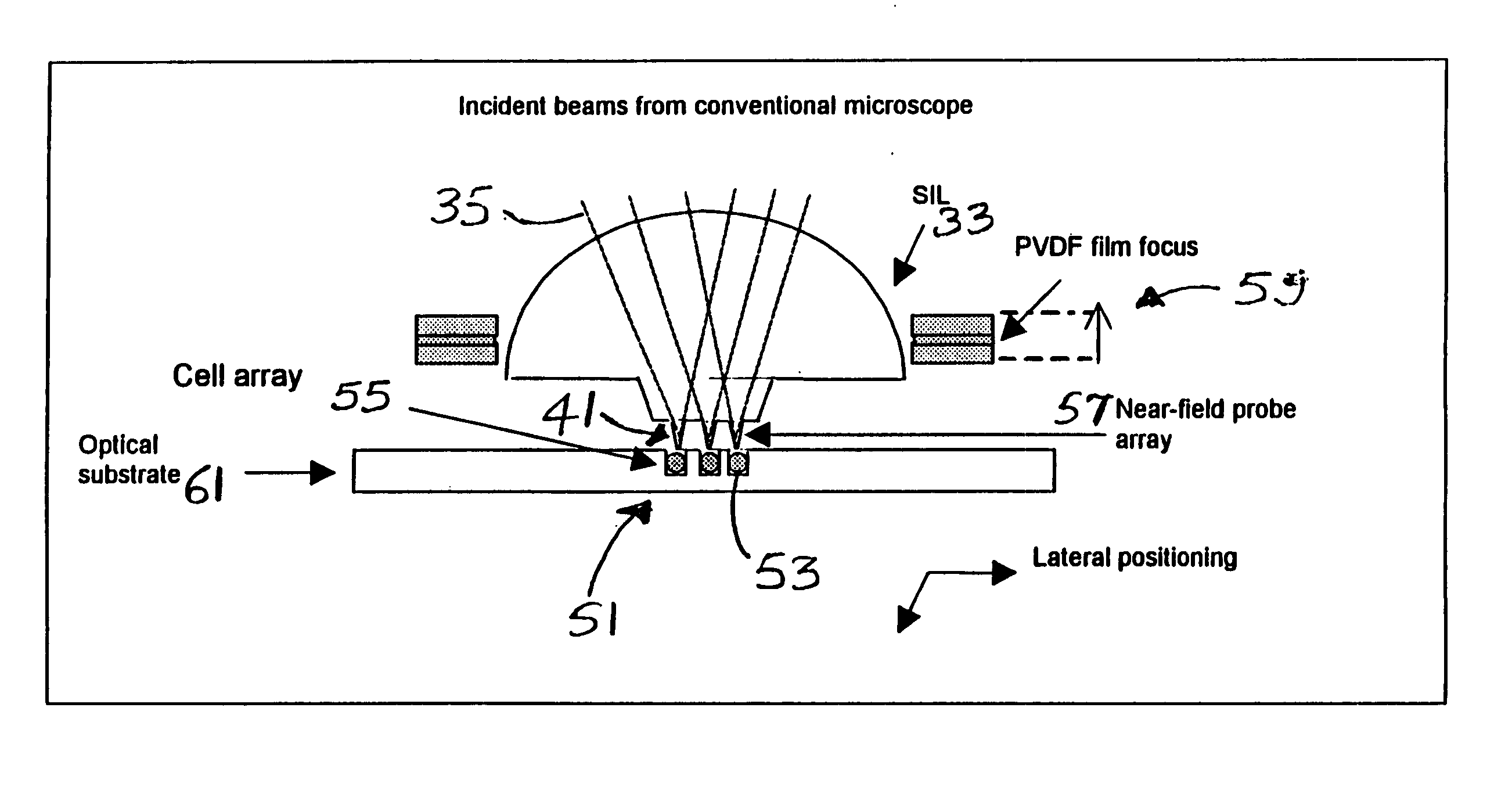
ActiveUS20060119843A1Mass productionIncrease pointsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscope slideMulti dimensional
A cell tray has a multi-dimensional array of cells in precise, equally spaced wells (cubicles or silos) containing medium of interest. The ordered cell array enables automated processing as well as simultaneous monitoring and analyzing of a large matrix of cells, biological fluids, chemicals and / or solid samples. The invention is an integrated device and is fabricated into substrates similar to microscope slides. The ordered array of cells in precise locations helps in parallel analysis and processing of cells simultaneously. Each cell cubicle or silo in the array is located equidistant from its nearest neighbors in an orthogonal direction. The location of each well can be precisely measured and recorded in an automated processing system. Included in the bottom of each cell well is an optional micro-lens. An array of probes provides parallel cell processing and monitoring capabilities, including microinjection and microscope analysis. The cell tray when integrated with the Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT or NANOPOINT) device results in sub-wavelength high-resolution imaging with a nanosensor array capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment.
Owner:NANOPOINT
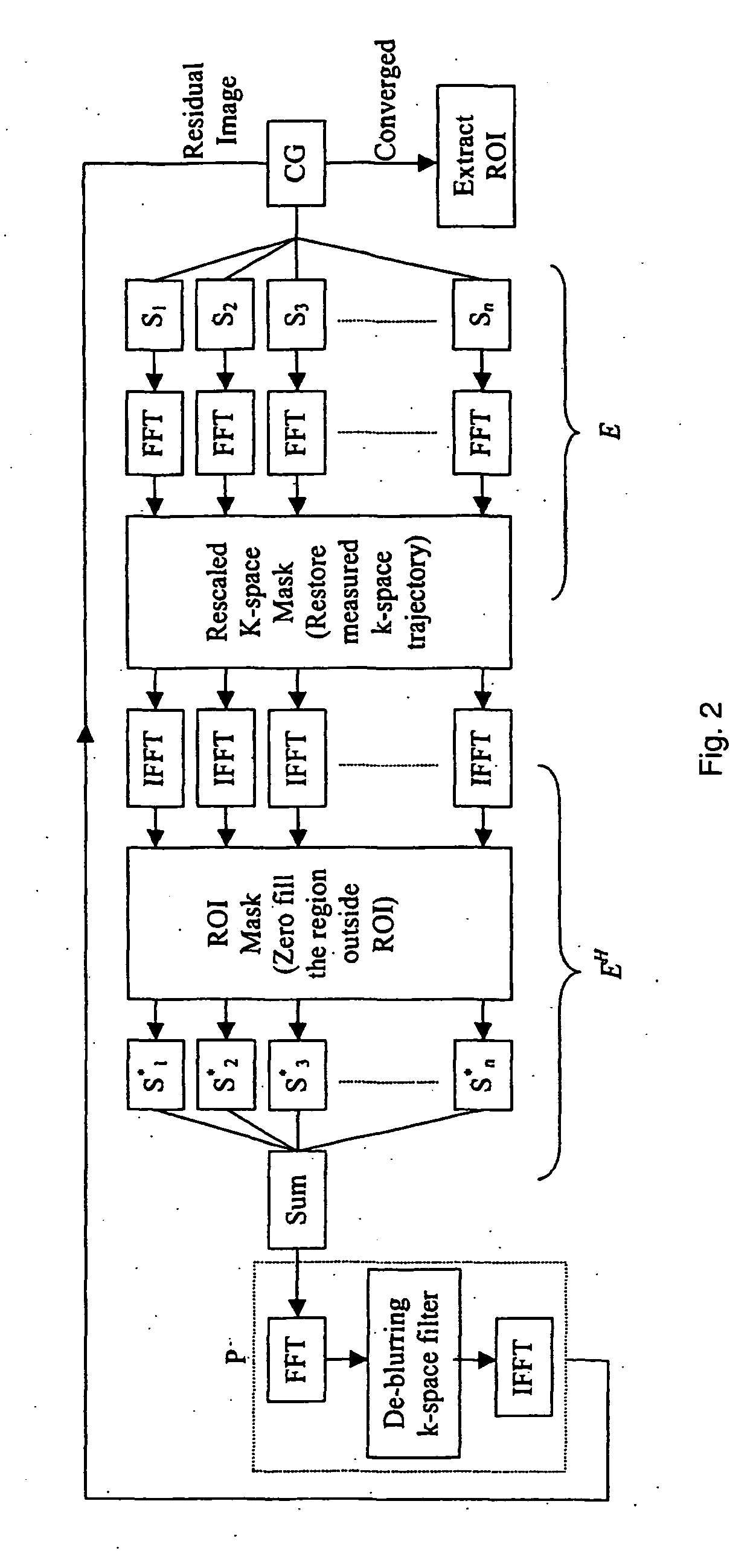
Fast self-calibrating radial sensitivity encoded image reconstruction using rescaling and preconditioning
InactiveUS20080144900A1Remove complexityFast convergenceMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmReduction factor
In a magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus, sensitivity encoding (SENSE) with radial sampling trajectories combines the gridding principle with conjugate-gradient least-squares (CGLS) iterative reconstruction. Radial k-space is mapped to a larger matrix by a resealing factor to eliminate the computational complexity of conventional gridding and density compensation. To improve convergence rate of high spatial frequency signals in CGLS iteration, a spatially invariant de-blurring k-space filter uses the impulse response of the system. This filter is incorporated into the SENSE reconstruction as preconditioning. The optimal number of iterations represents a tradeoff between image accuracy and noise over several reduction factors.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
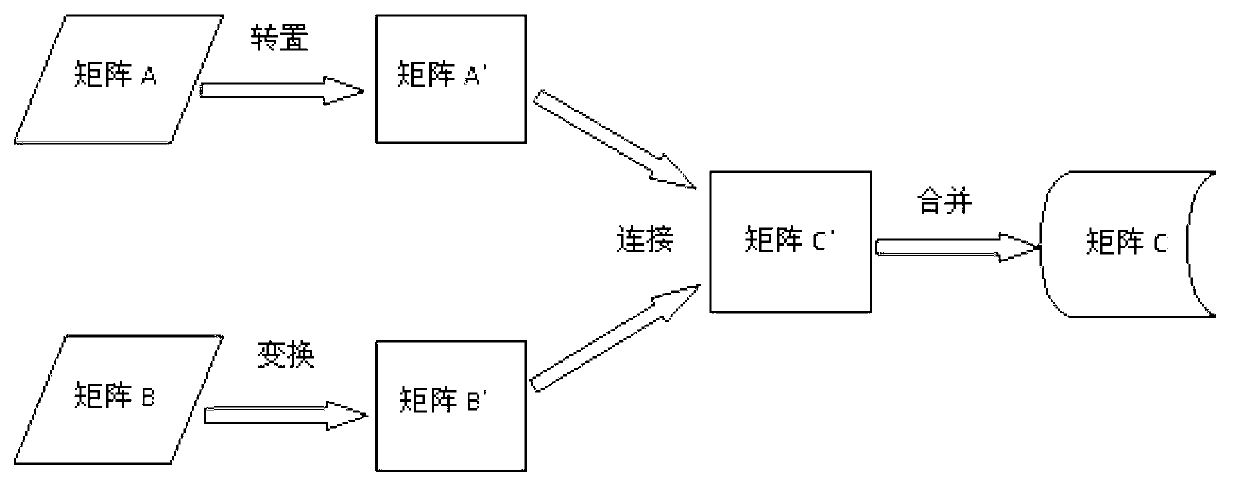
Large-scale sparse matrix multiplication method based on mapreduce
InactiveCN103106183AReduce restrictionsCalculation speedDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmSparse matrix multiplication
The invention provides a large-scale sparse matrix multiplication method based on mapreduce. Suppose that the large-scale sparse matrixes are A and B, and a multiplication matrix of A and B is C. The method includes the following steps: step 10, a mapreduce Job finishes transposing of the matrix A and outputting of a matrix A'; step 20, a transformational matrix B converts a storage mode using the matrix B as a coordinate point into a storage mode of sparse vector, and outputs a matrix B'; step 30, connecting the matrix A' and the matrix B', calculating a product component, obtaining the product component of a column number K on the matrix A and column number K on the matrix B of Cij; step 40, merging the product components, calculating Cij through accumulation of the product components Cij_k. The large-scale sparse matrix multiplication is converted into basic operations of transposition and transformation, connection and merging and the like which are suitable for mapreduce calculation, and the problem of resource limit of a single machine large-scale sparse matrix multiplication is solved.
Owner:FUJIAN TQ DIGITAL
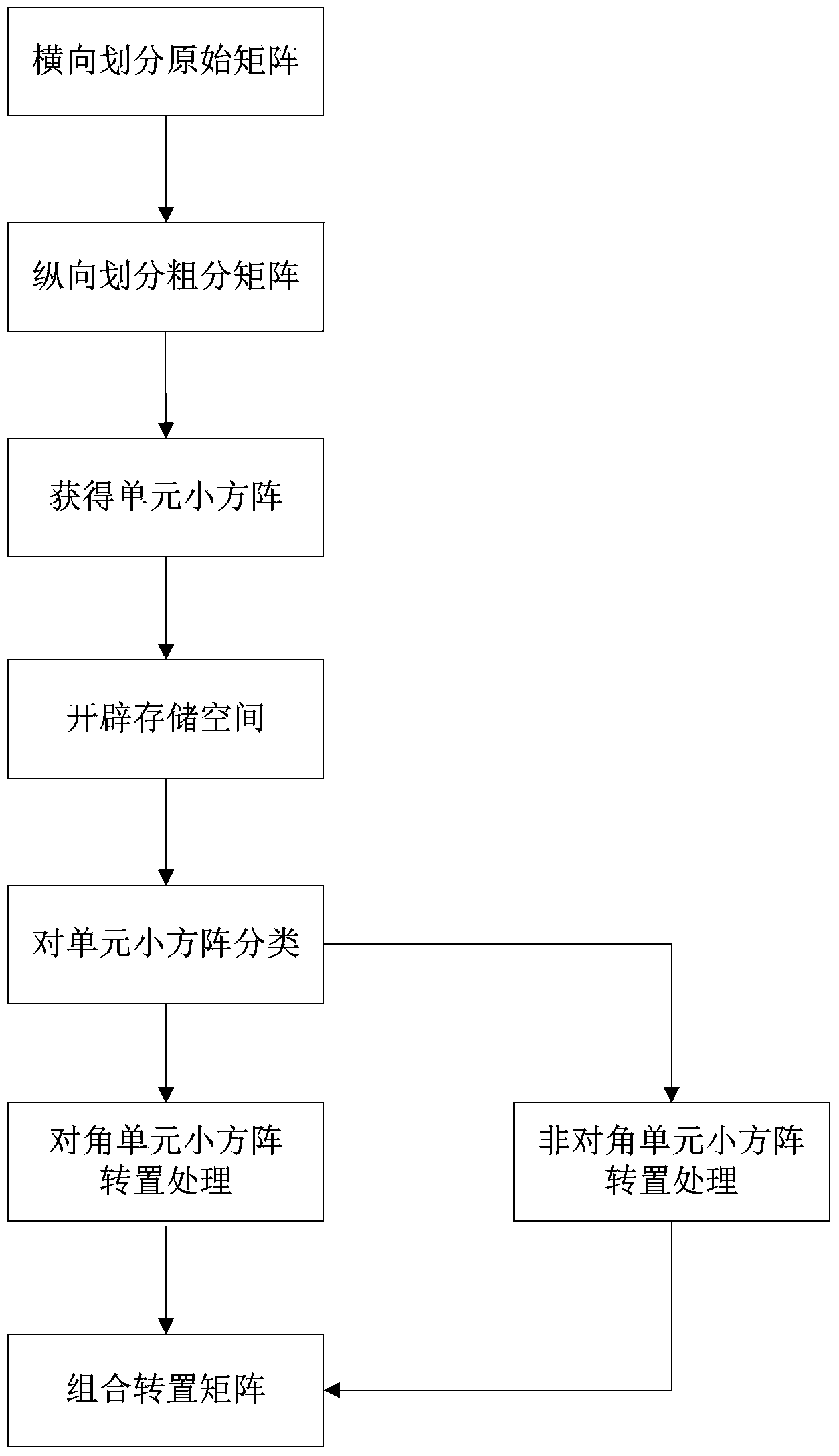
Matrix transposition method in SAR imaging system based on DSP chip
InactiveCN103412284ASave storage spaceOvercome the disadvantage of taking a lot of time to moveRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarAlgorithm
The invention discloses a matrix transposition method in an SAR imaging system based on a DSP chip. The problems that radar real-time imaging storage space is small, and the requirement for real-time performance is high are mainly solved. The implementation process of the matrix transposition method comprises the steps that (1) an original matrix is transversely divided; (2) a rough classification matrix is longitudinally divided; (3) small unit matrixes are obtained; (4) storage space is created; (5) the small unit matrixes are classified; (6) transposition is carried out on the small diagonal unit matrixes; (7) transposition is carried out on the small non-diagonal unit matrixes; (8) the transpositioned matrixes are combined. The matrix transposition method aims at the transposition operation of a large-scale radar return original data matrix, the large matrix is roughly and finely divided into two classes of small unit matrixes, different transposition methods are applied to processing the matrixes, a large amount of storage space is saved, and operation efficiency is improved. The matrix transposition method is simple, easy to implement and suitable for the transposition operation of various radar real-time imaging systems and other systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-speed coding method of low density check code
InactiveCN1862971AGood application effectAvoid simultaneous calculationsError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer architectureLow-density parity-check code
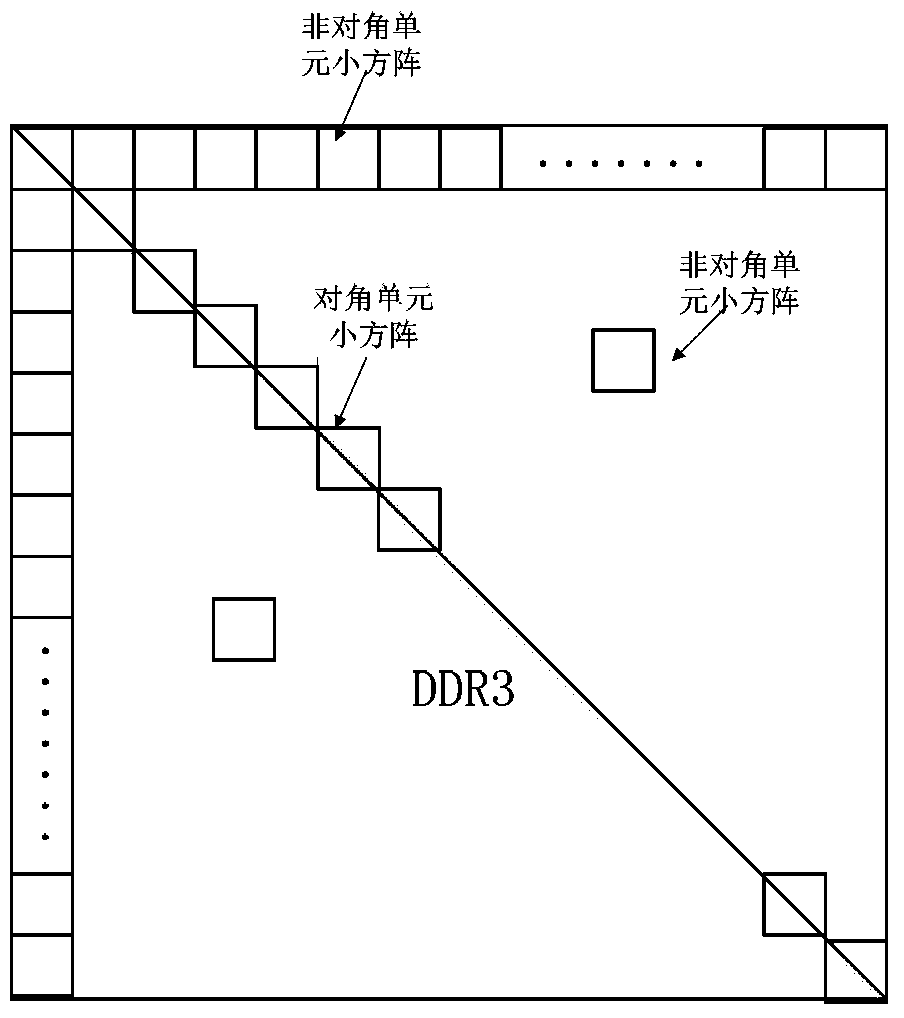
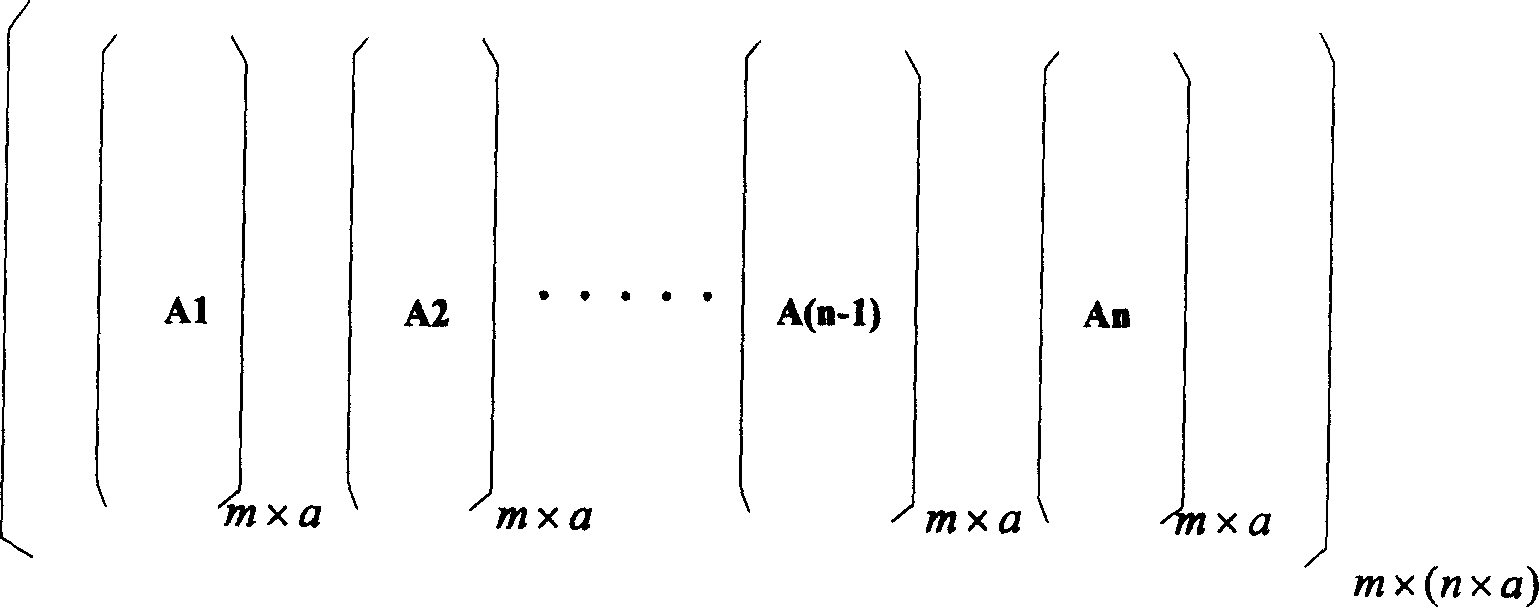
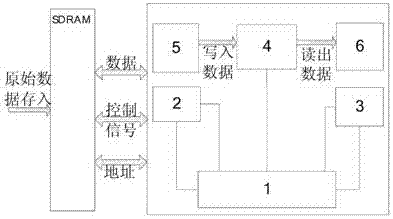
The invention discloses the low dense checkout code high speed coding method, by the partition of the date source matrix and the building matrix, the multiplication operation between the date source matrix A and the building matrix B can be transformed into the multiplication operation between the n son matrix with the (m*a) dimensions of the matrix A and the nxc son matrix with the (axb) dimensions of the matrix B. The invention relates to the LDPC coding method, the LDPC coding setting can be realized cooperated with the FPGA by using the memorizer saving data source matrix and the building matrix such as the SDRAM. The realized LDPC coding setting has many merits such as the high operating speed, the low spending of the system and the good ability. Compared with the conventional LDPC coding method, the invention has the better project realizing ability and the quicker coding speed. The invention can avoids the speed bottleneck problem of the storage to improve the realizing ability of the LDPC coding setting when the large matrix multiplying.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Completion type in-place matrix transposition method
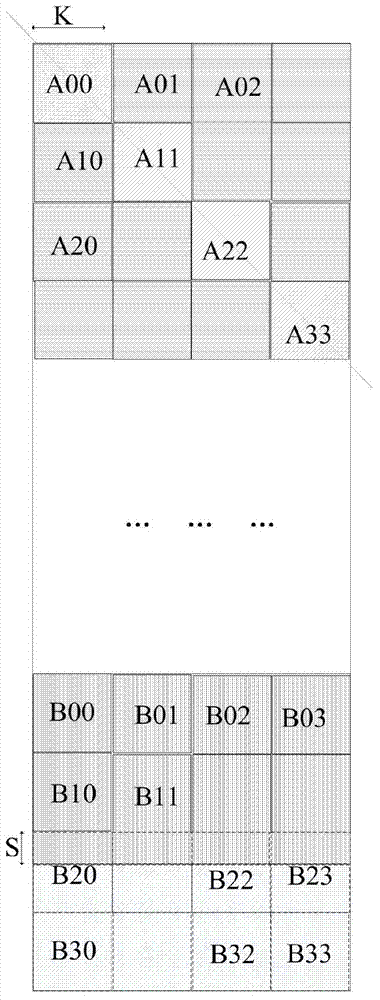
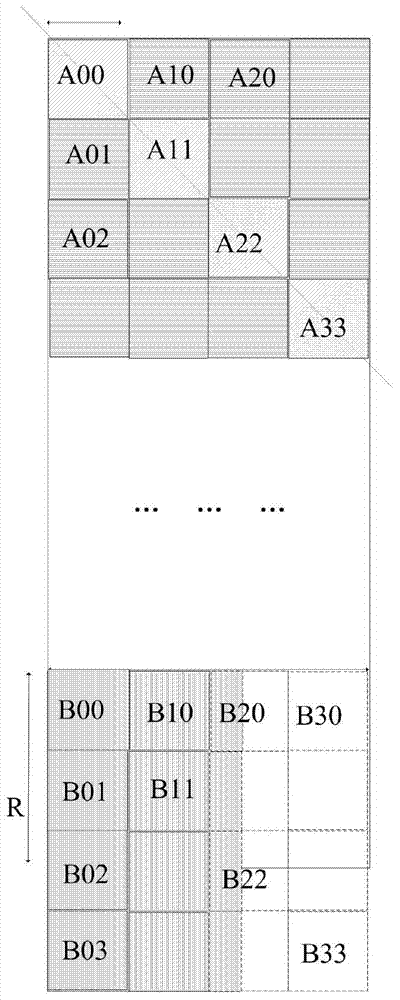
ActiveCN103760525AImprove utilization efficiencyEasy to handleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDiagonalComputer science
The invention discloses a completion type in-place matrix transposition method. A two-dimensional matrix A is divided into multiple square matrixes using the part with smaller line number and smaller column number as side length, the part which is insufficient for being divided into square matrixes is completed to form a square matrix, and the completion part does not contain data. Resegmentation is carried out on the square matrixes by using K*K matrixes, all the K*K matrixes along diagonal lines or off-diagonal lines are read into an RAM module to carry out transposition processing, the two-dimensional matrixes obtained through the transposition processing is read from an SARAM and output in sequence, and a matrix after final transposition is obtained. The completion type in-place matrix transposition method has the advantages that the method is suitable for the transposition of the matrixes with the smaller one of the line number and the column number of the matrixes is positive integral multiples of power of two, the utilizing efficiency of SDRAM type memorizers can be improved effectively, and the processing performance of large matrix type transposition type digital signals can be improved.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
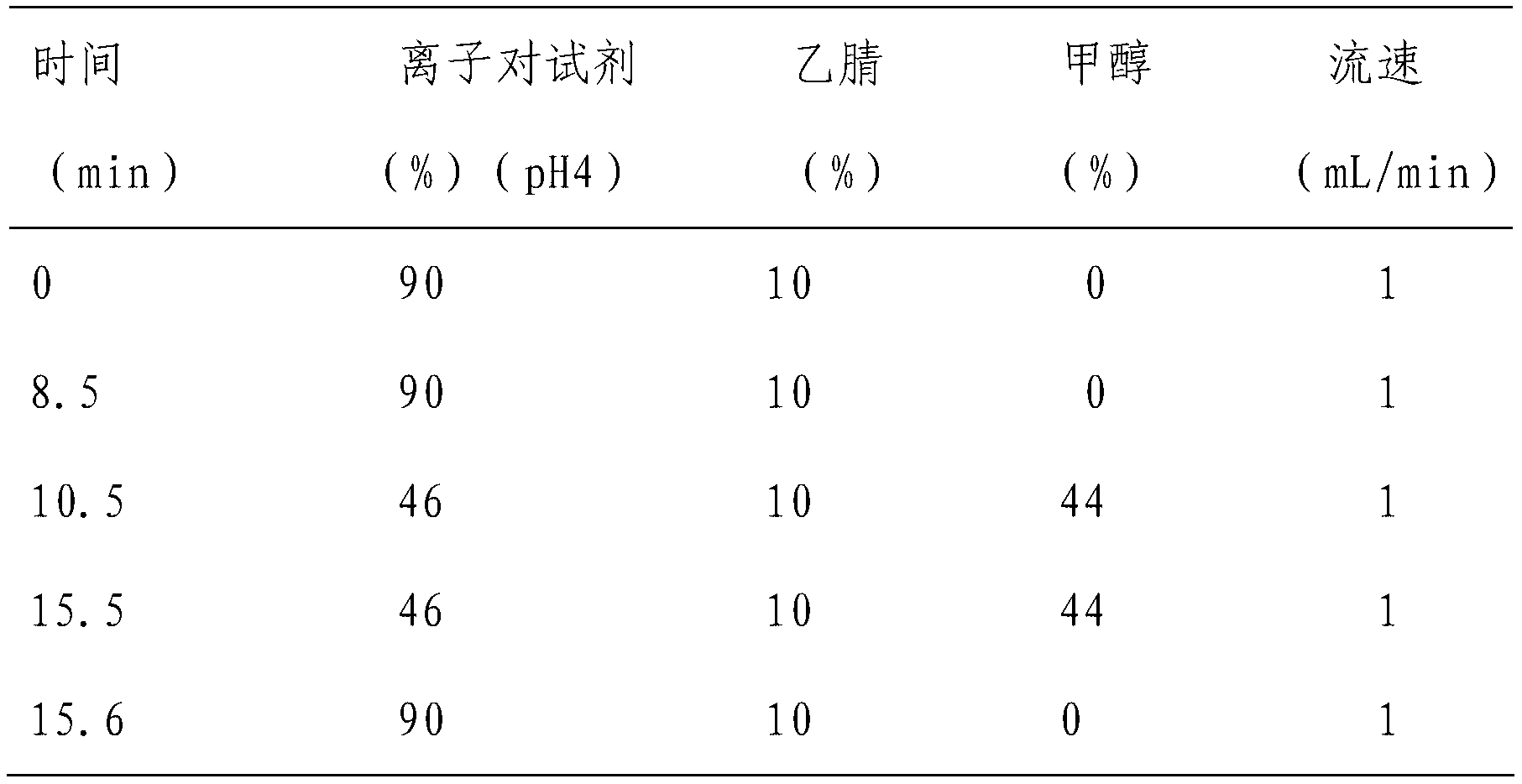
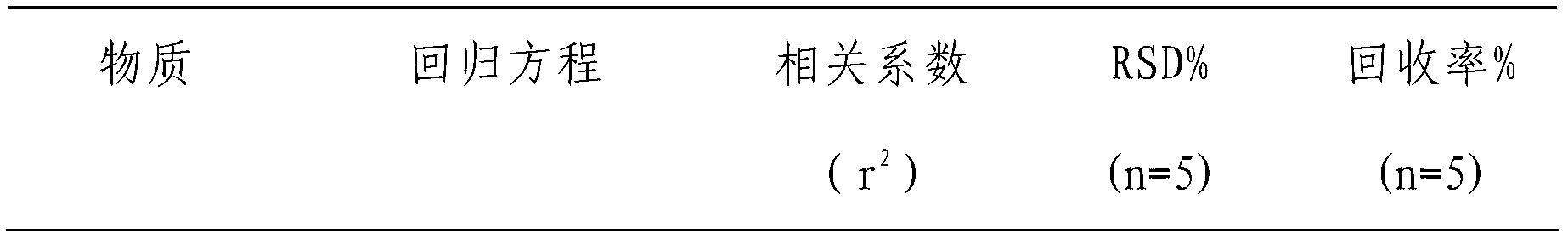
Detection method of nitrate and nitrite in blood, urine and tissue
The invention discloses a detection method of nitrate and nitrite in blood, urine and tissue. In the weak acidic condition, nitrate ions and an ion pair reagent form an ion pair, and nitrite and a Griess reagent are reacted for a diazotization coupling reaction for forming an azo compound, thereby nitrate and nitrite which can not be retained on the chromatographic column without UV absorption can be analyzed by liquid chromatogram at different wavelengths, and mutual interferences are eliminated. The nitrate and nitrite detection in blood, urine and tissue which have large matrix interferences and low contents have larger applicability, and the detection limit of nitrate and nitrite are 0.2 mu g / mL and 0.05 mu g / mL respectively. The invention has the characteristics of simple operation, rapid determination, efficiency, accuracy, etc.
Owner:云南健牛环境监测有限公司
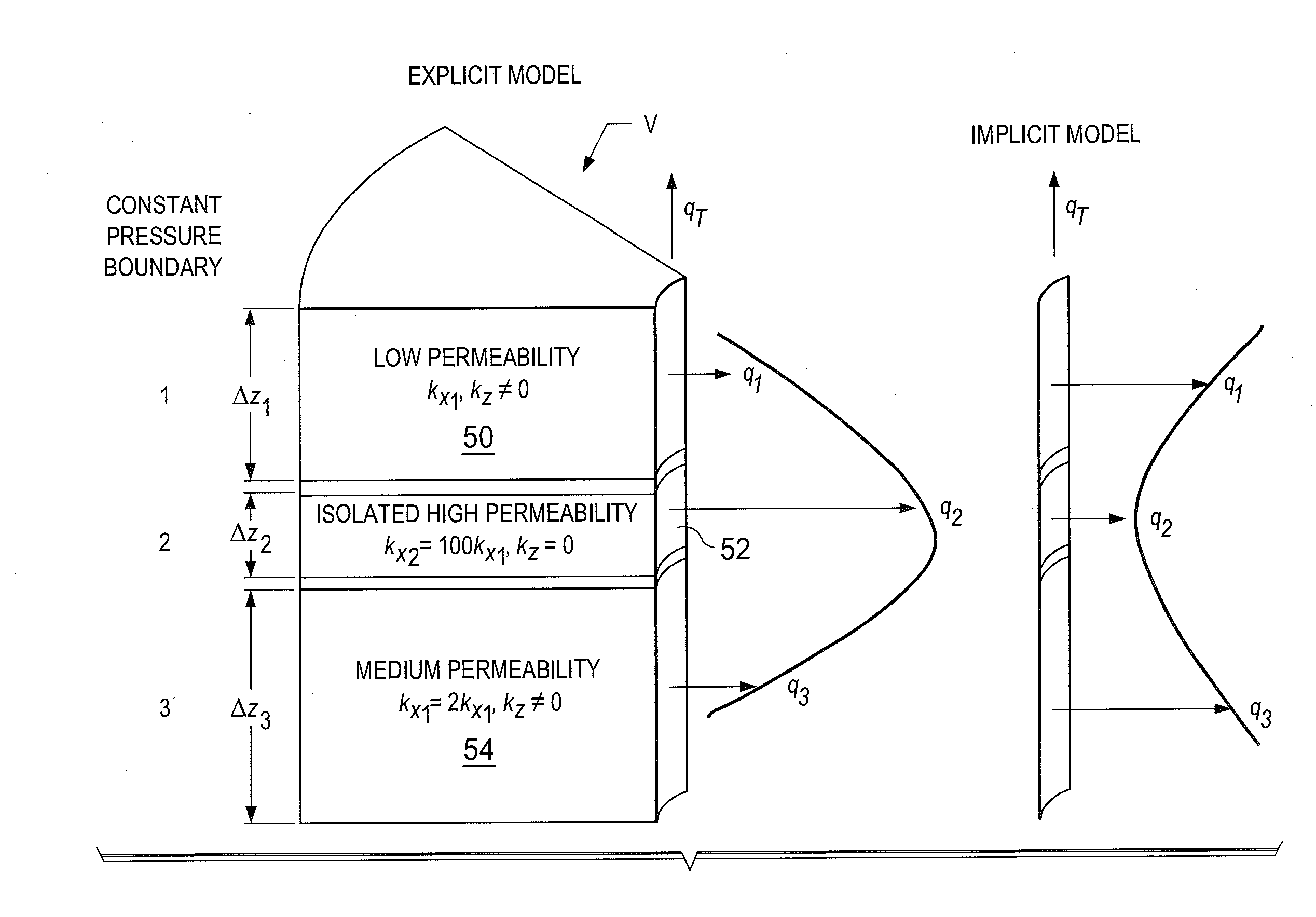
Sequential fully implicit well model for reservoir simulation
A subsurface hydrocarbon reservoir with wells is simulated by sequential solution of reservoir and well equations to simulate fluid flow inside the reservoir and well production rates. Sequential solution of reservoir and well equations treats wells as specified bottom hole pressure wells. This avoids solving large matrices resulting from the simultaneous solution of the reservoir and well equations which can be computationally very expensive for large number of unknowns and require special sparse matrix solvers. Such sequential solution involves regular reservoir system solvers complemented by a small matrix for the numerical solution of the well bottom hole pressures.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Image denoising method based on high-order overlapping group sparse total variation
InactiveCN110084756AIncrease differentiationImprove protectionImage enhancementFast Fourier transformImage denoising
The invention provides an image denoising method based on high-order overlapping group sparse total variation, and provides an overlapping group sparse total variation image recovery method based on high-order regularization term constraint on the basis of a traditional first-order overlapping group sparse total variation technology. According to the first-order overlapping combination technology,a total variation gradient of each conventional pixel is popularized into a combination gradient, so that the difference between a smooth region and an edge region is improved, and a high-order regular term can more effectively alleviate a'step effect 'from second-order or higher-order gradient information, so that the protection on the edge of the image is improved. In order to improve the operation speed of image restoration, transverse and longitudinal differential matrix operation of an image is modeled as convolution operation, periodic boundary conditions are combined, so that two-dimensional fast Fourier transform is skillfully applied to an image restoration problem, and point multiplication operation on a frequency domain is used for replacing large matrix operation on an airspace.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
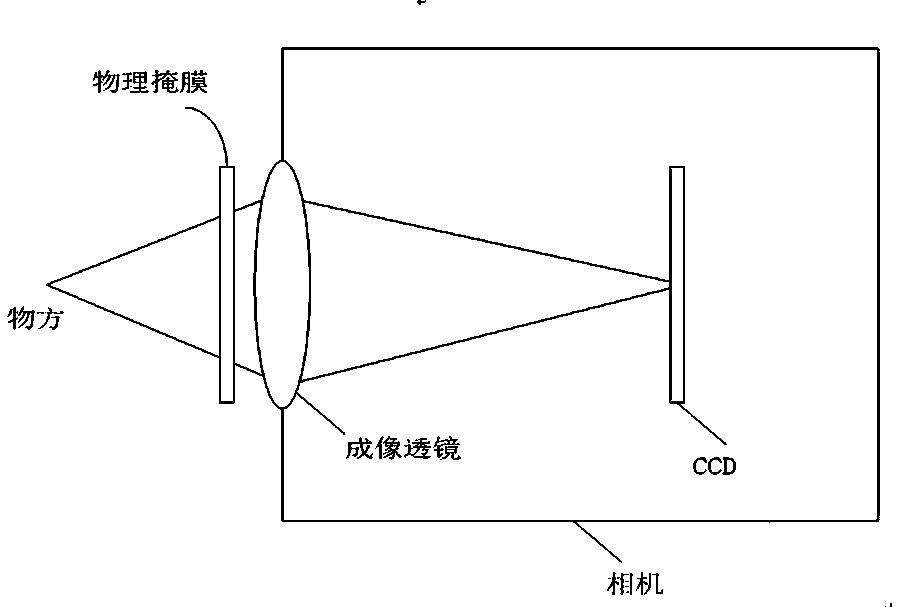
Squeezed light field physical reconstruction method
ActiveCN107622515AAchieve reconstructionImprove convenience2D-image generationCode conversionCamera lensHat matrix
The invention provides a squeezed light field physical reconstruction method. The method comprises steps: (1) multiple random matrixes are generated through a computer, the random matrixes form a large matrix, the large matrix is printed on a film, and a physical mask is generated; (2) the physical mask is used as an acquisition object, a mask image is acquired through moving an aperture arrangedin front of a camera, each mask image is a projection matrix pi, and a measurement matrix phi is acquired through the acquired projection matrix pi; (3) the physical mask is placed before an imaging lens of the camera to form a mask camera, and the mask camera is used to photograph a coded image to be used as a measurement value y; (4) a sparse matrix psi and a sparse vector alpha are acquired; and (5) reconstruction of original signals f is carried out through compressed sensing. The mask is placed before a common industrial camera lens, and through one-time photographing, multi-angle of viewlight field reconstruction can be realized. In comparison with a mode of placing the mask between the camera lens and a CCD, the method of the invention is better in convenience, and the mask camerais realized more easily.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
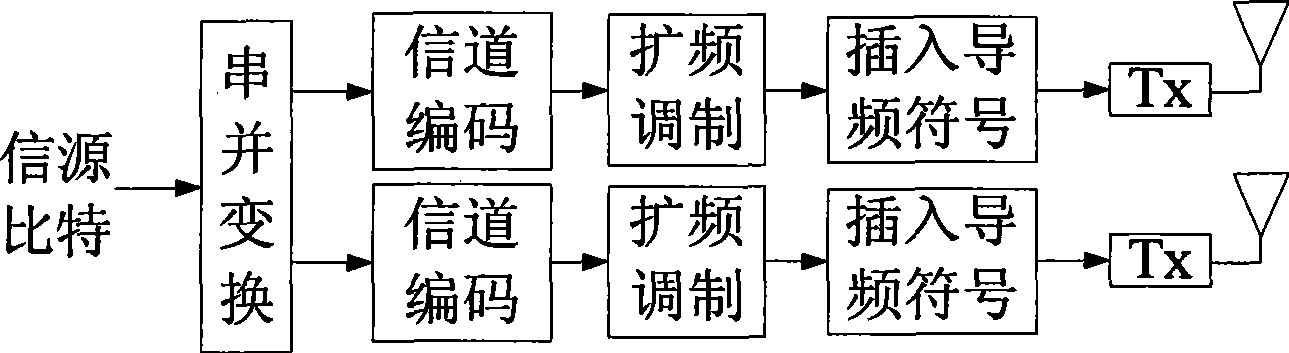
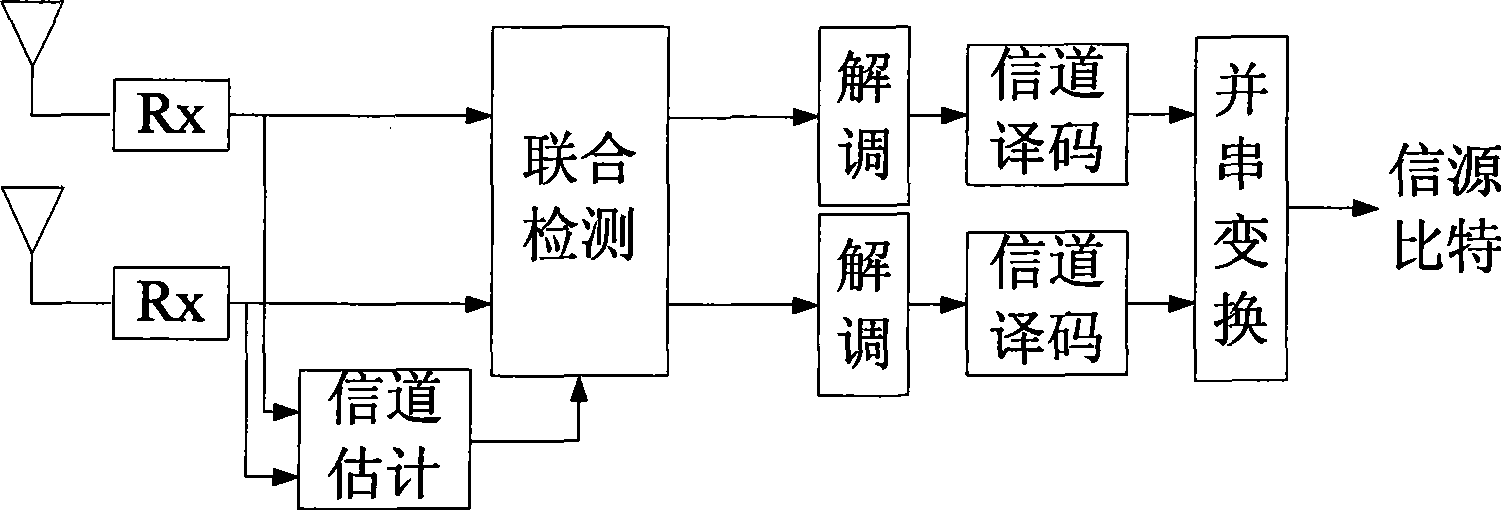
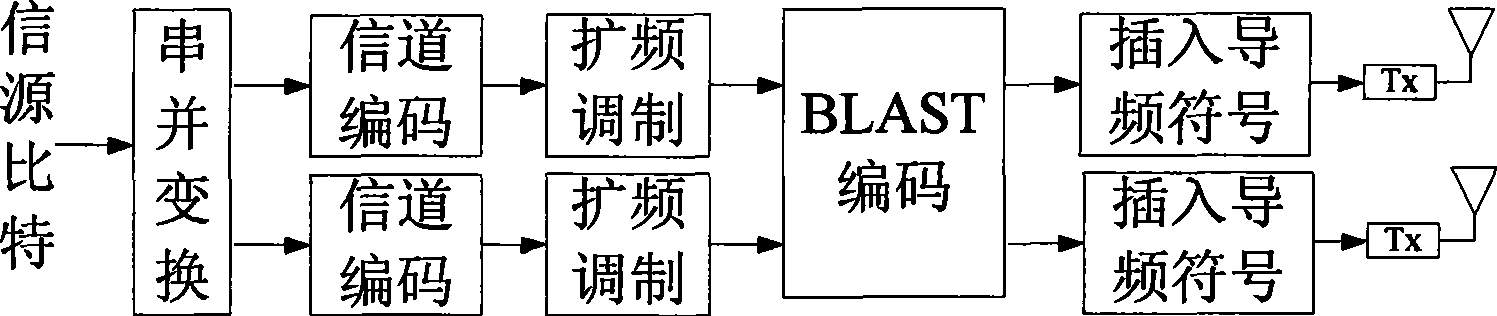
Space multiplexing method and apparatus in TD-SCDMA system
InactiveCN101488775AIncrease data transfer rateImprove spectrum utilizationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMultiplexingTD-SCDMA
The invention relates to a space reuse method in a TD-SCDMA system. The method is as follows: a high-speed data stream is converted into a plurality of paralleling low speed data streams at a transmitting terminal by serial-parallel conversion; after channel coding, spread spectrum and modulation, the layered space-time code is carried out on the low speed data streams, and then the treated low speed data streams are simultaneously transmitted on a plurality of sending antennas; correspondingly, the layered space-time decoding is carried out on receiving signals at a receiving end according to the estimation value of channels. The invention further provides a device for realizing the method. Compared with prior art, the invention not only effectively increases the data rate of a TD-SCDMA system, avoids the inversion process of a large matrix needing to be carried out when the joint detection is directly carried out, reduces the complexity and effectively increases the data transmission rate and frequency spectrum utilization.
Owner:ZTE CORP
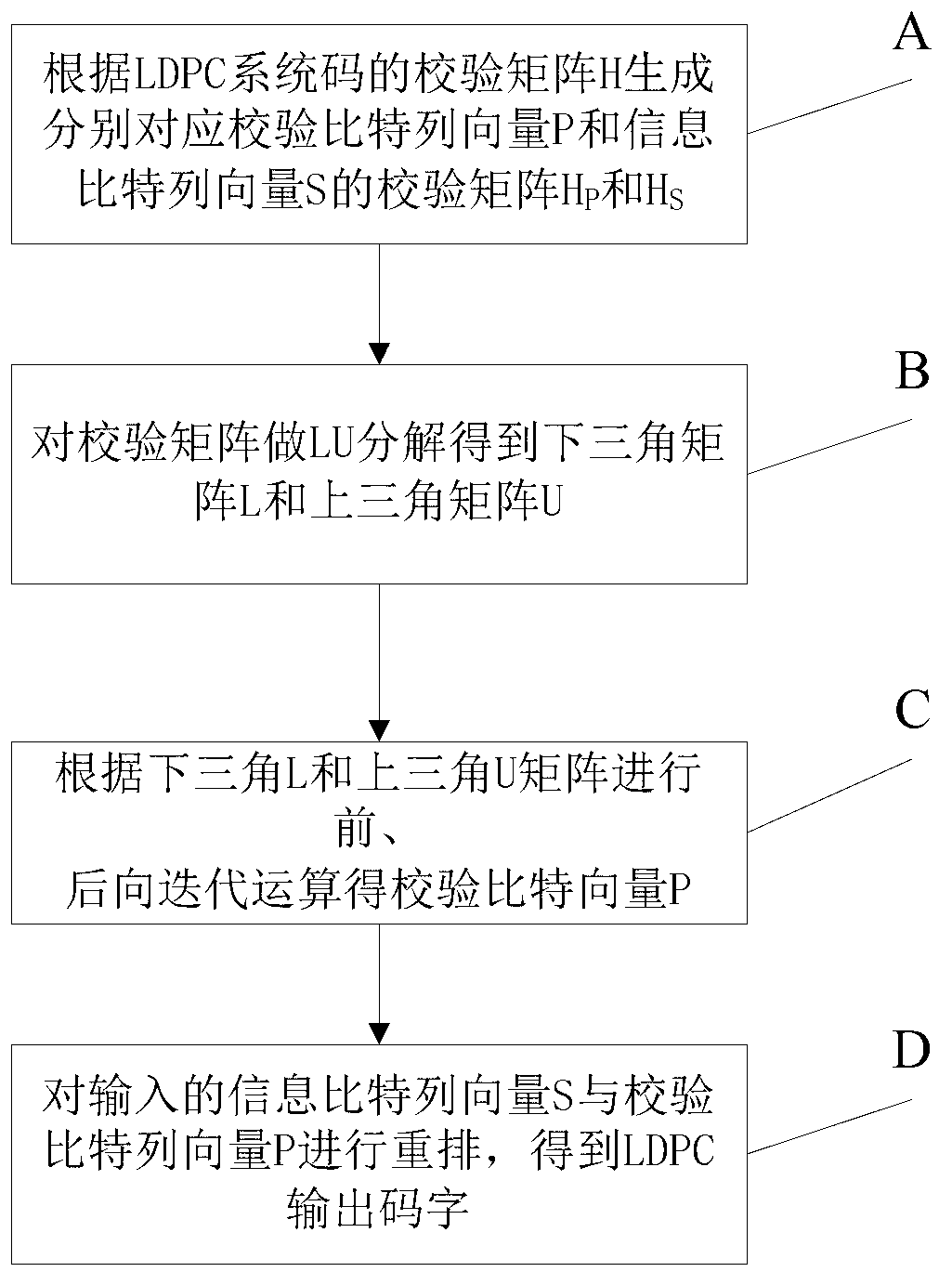
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) encoding method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) and used in CMMB (China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting) exciter
InactiveCN102739259AAvoid the problem of large storage resource requirementsReduce computational complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer architectureDecomposition
The invention discloses an LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) encoding method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) and used in CMMB (China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting) exciter. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing a verification matrix H of an LDPC system code on an MATLAB (Matrix Laboratory) platform, so as to generate verification matrixes Hp and Hs which correspond to a verification bit column vector P and an information bit column vector S; carrying out LU (Logical Unit) decomposition to the verification matrixes so as to obtain a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U; and realizing the LDPC encoding on the FPGA platform, which mainly involves the storage of a large matrix, matrix multiplication, forward iteration and backward iteration. According to the encoding method, an encoding mode based on a LU decomposition verification matrix is adopted; the logic calculation that large matrixes are multiplied is avoided; and the problem of large requirement on FPGA internal storage resource caused by large data quantity storage is solved, thereby simplifying the logic calculation operation, saving the storage space, and being beneficial for the realization of the LDPC encoding of the CMMB system.
Owner:ALLWIN TELECOMM
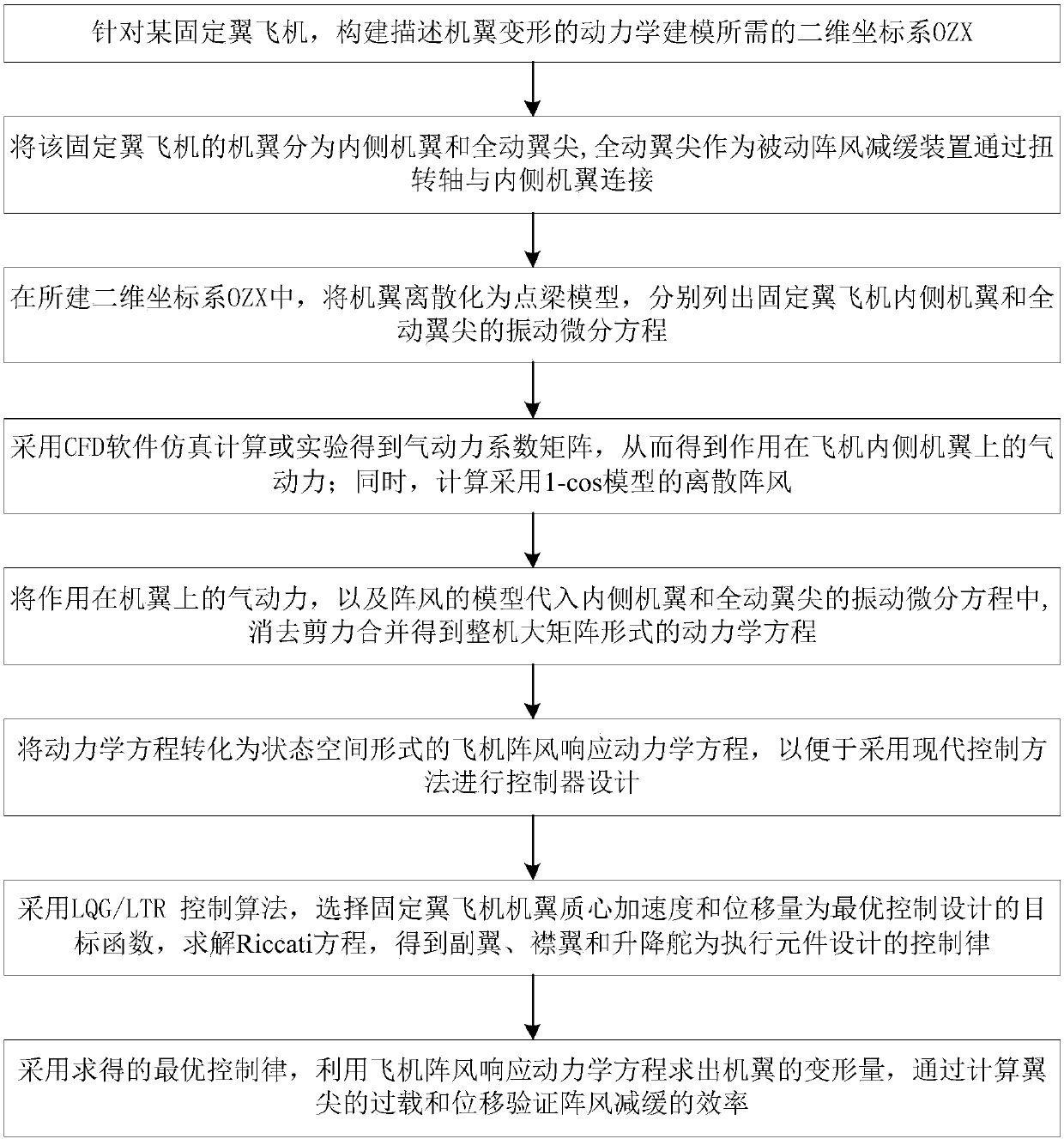
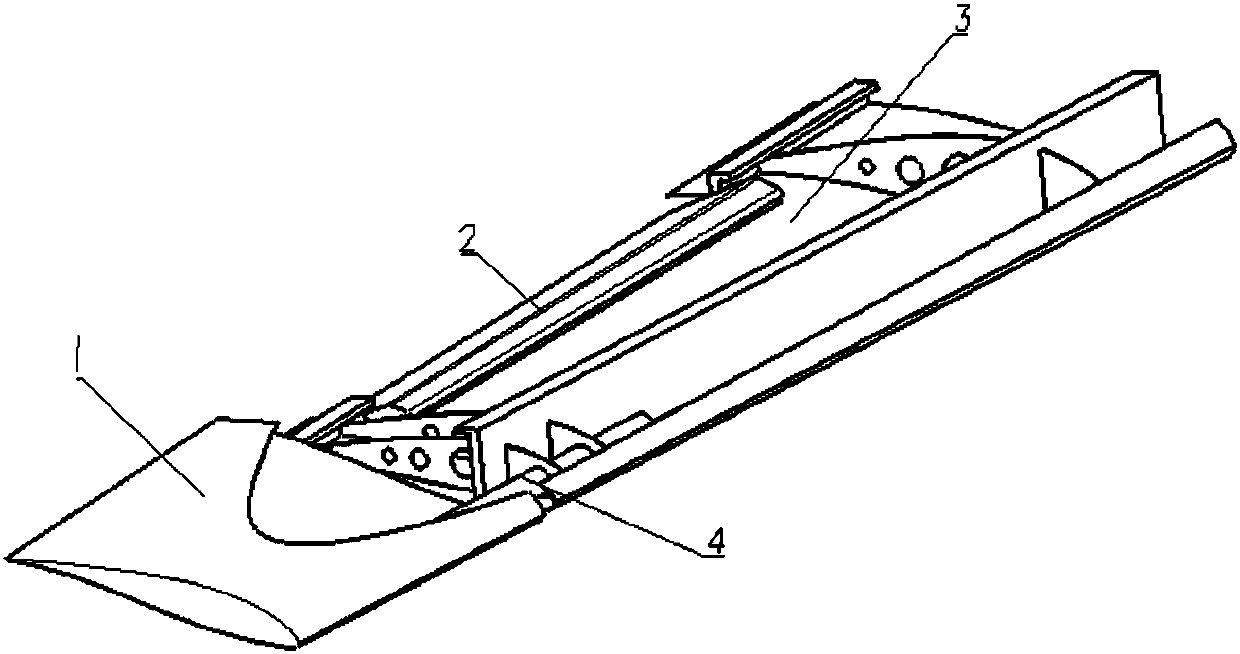
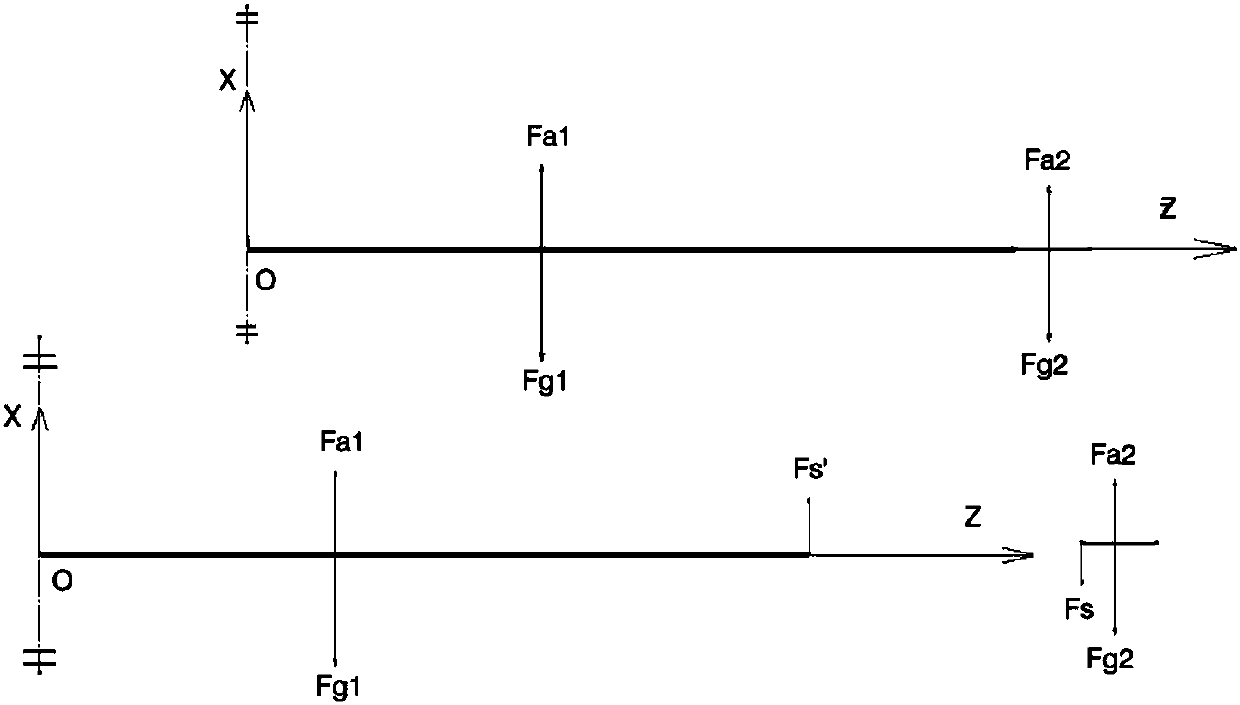
Active and passive combined fixed-wing aircraft gust alleviation control method
ActiveCN108516101AIncrease the efficiency of mitigationGood attenuationHeat reducing structuresGround installationsDynamic equationFixed wing
The invention discloses an active and passive combined fixed-wing aircraft gust alleviation control method, and belongs to the technical field of aircraft control. Firstly, a two-dimensional coordinate system OZX is constructed, a wing comprises an inner side wing body and a full-moving wing tip, the wing is discretized in the OZX, and a vibration differential equation of the inner side wing bodyand the all-moving wing tip is listed; aerodynamic force acting on the inner side wing body is obtained through an aerodynamic force coefficient matrix, and discrete gust is calculated; the aerodynamic force and a model of the gust are substituted into the vibration differential equation, shear force merging is eliminated to obtain a kinetic equation in a complete machine large matrix form, and the kinetic equation is converted into an aircraft gust response dynamics equation; the acceleration and displacement of the wing mass center of a fixed-wing aircraft are selected as an objective function of the optimal control design, the deformation of the wing is worked out, and the efficiency of gust alleviation is verified. According to the method, under the same gust intensity and overload requirements, a required rudder deflection angle is reduced, the efficiency of the gust alleviation is improved, and a good weakening effect on the overload and deformation of the wing tip is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
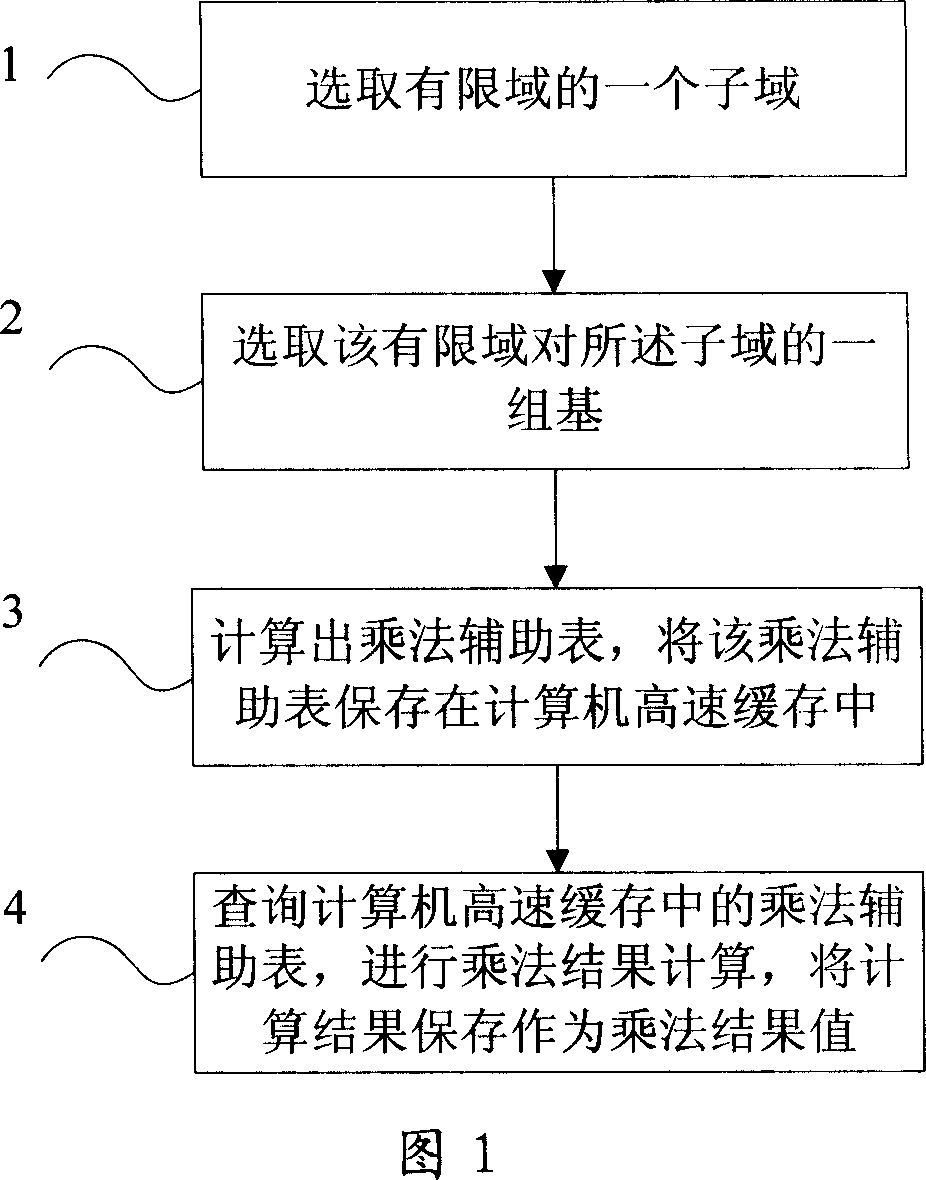
Computer implementation method of multiplier over finite field and computer implementation method of large matrix element elimination
InactiveCN101008937AFast implementationShorten the timeDigital function generatorsComplex mathematical operationsAs elementByte
This invention relates to one computer realization method for limit area multiplication, which comprises the following steps: selecting one sub zone according the following conditions as element number, bit number in zone and limit zone expansion product less than computer high speed buffer capacity; b, selecting limit zone set base; c, according to the base and multiplication aid list storing the aid list into computer high speed buffer; d, indexing computer high speed buffer product aid list to compute result as results value.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
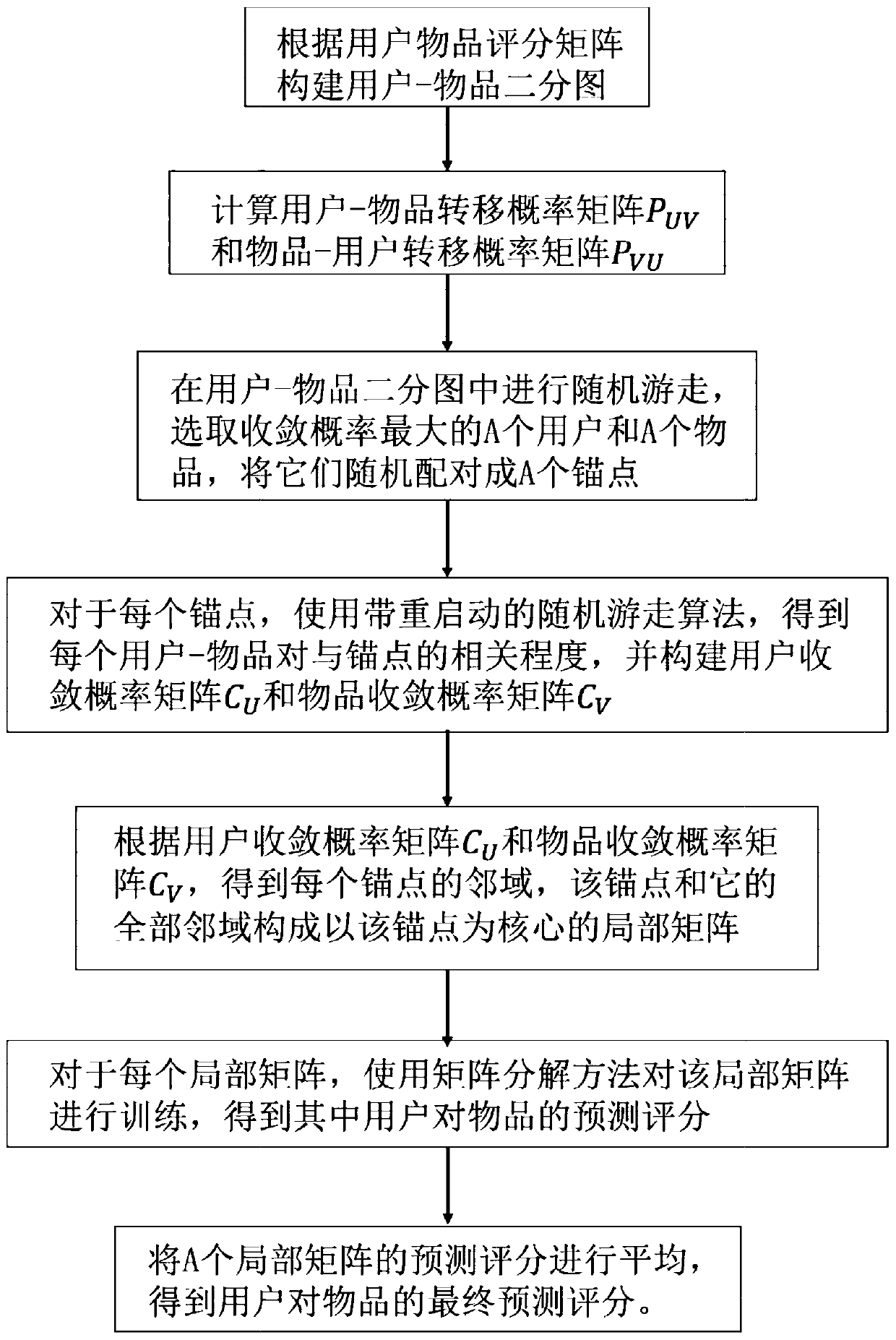
Score prediction method for constructing local matrix based on graph random walk
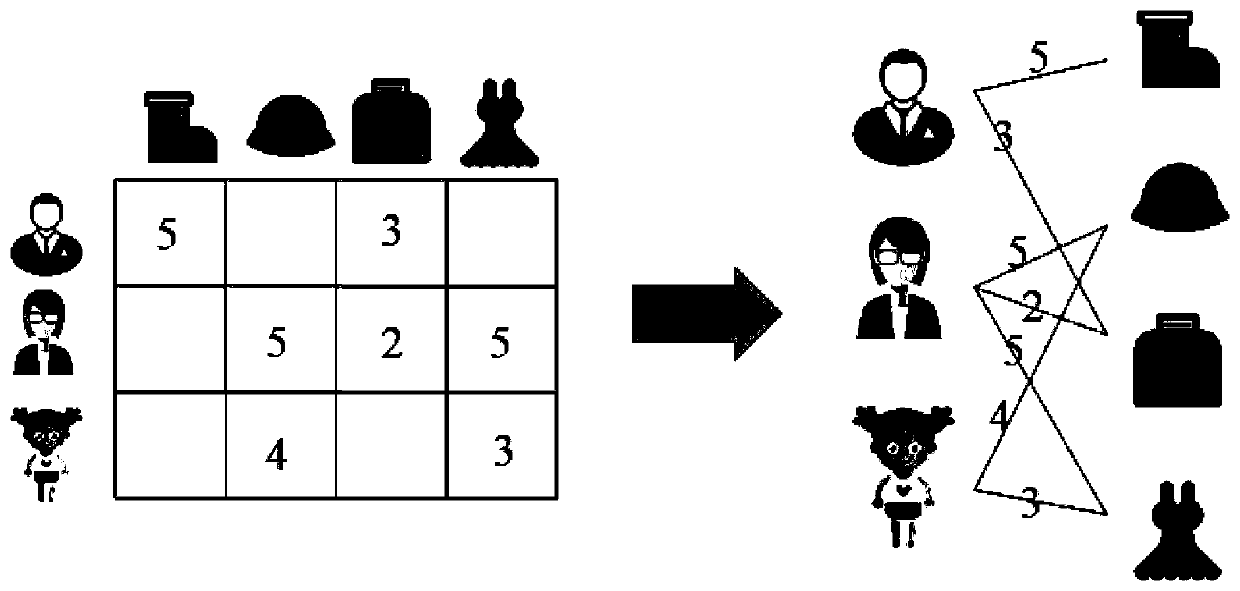
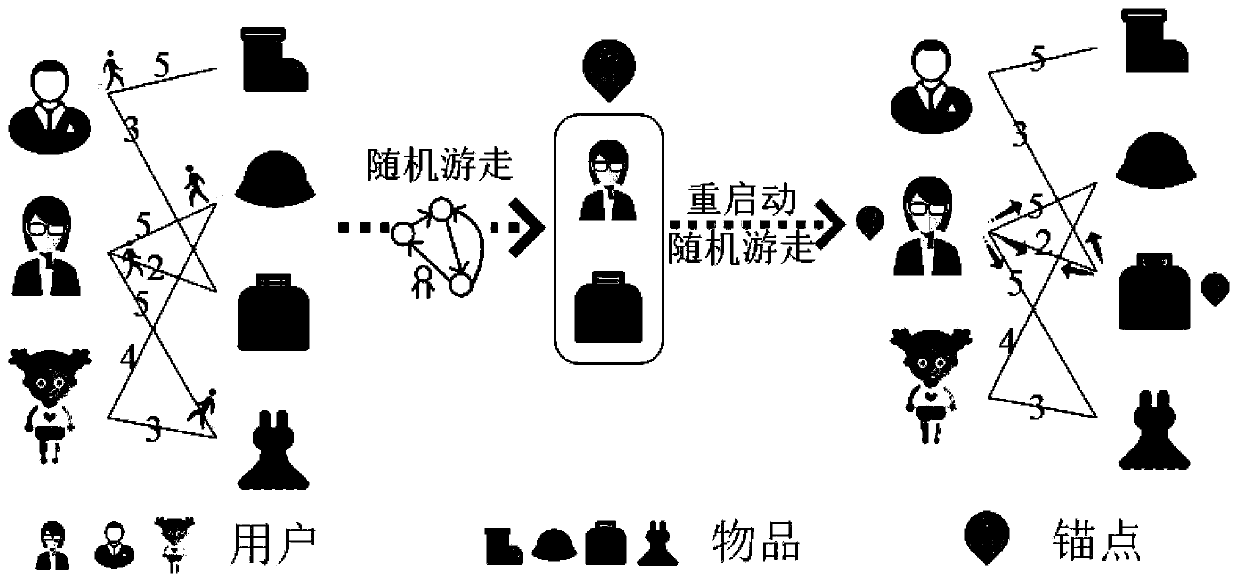
ActiveCN110322053AImprove forecast accuracyAvoid lostForecastingBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPersonalizationNODAL
The invention discloses a score prediction method for constructing a local matrix based on graph random walk, and belongs to the field of personalized recommendation. Depending on user-article scoringmatrix, a user-article bipartite graph is constructed, random walk is carried out on the bipartite graph, and A users with the maximum node convergence probability after walk and articles are selected to form A anchor points; and for each anchor point, a random walk algorithm with restart is adopted to obtain a correlation between each node and the anchor point so as to distribute each node intoa corresponding anchor point neighborhood. Each anchor point and the neighborhood thereof form a local matrix, and score prediction is carried out in each local matrix by using a matrix decompositionmethod. The prediction scores of the A local matrixes are averaged to obtain a final prediction result. According to the method, anchor points are selected and neighborhoods of the anchor points are constructed based on graph random walk, so that errors caused by a traditional distance calculation process are avoided; starting from nodes, the nodes are distributed to different anchor point neighborhoods, and complete coverage of a large matrix can be achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Matrix preprocessing method and device, terminal and readable storage medium
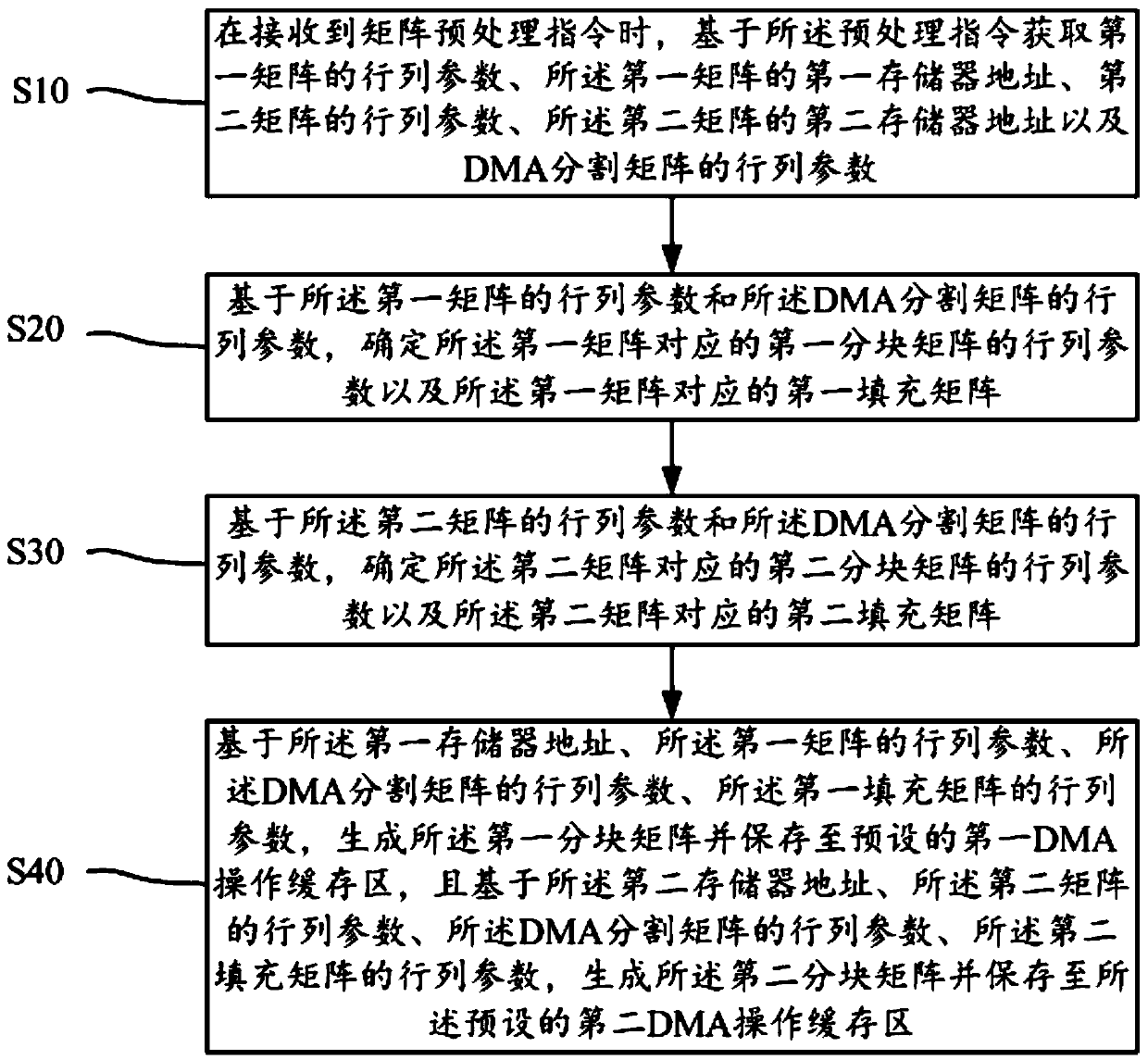
PendingCN110390075AGuaranteed efficiencyGuaranteed operating efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionProcessing InstructionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a matrix preprocessing method. The method comprises the following steps: when receiving a matrix preprocessing instruction, acquiring parameters of a first matrix, parameters of a second matrix and parameters of a DMA segmentation matrix based on the preprocessing instruction, generating the first block matrix and the second block matrix based on the parameters of the firstmatrix and the parameters of the DMA segmentation matrix, and storing the first block matrix and the second block matrix in the preset DMA operation cache region. The invention further discloses a device, a terminal and a readable storage medium. An existing matrix operation unit can be flexibly used as a matrix basic operation resource, operation functions such as multiplication, addition or transposition of a large matrix can be efficiently, conveniently and rapidly achieved, and the problems of flexibility, universality, expandability and reusability of matrix operation processing are solved while the processing performance and the operation efficiency of matrix operation are guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGDONG COMM & NETWORKS INST
Smart antenna, method and apparatus for adaptive beam forming
InactiveUS20060114154A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityTime delaysSmart antenna
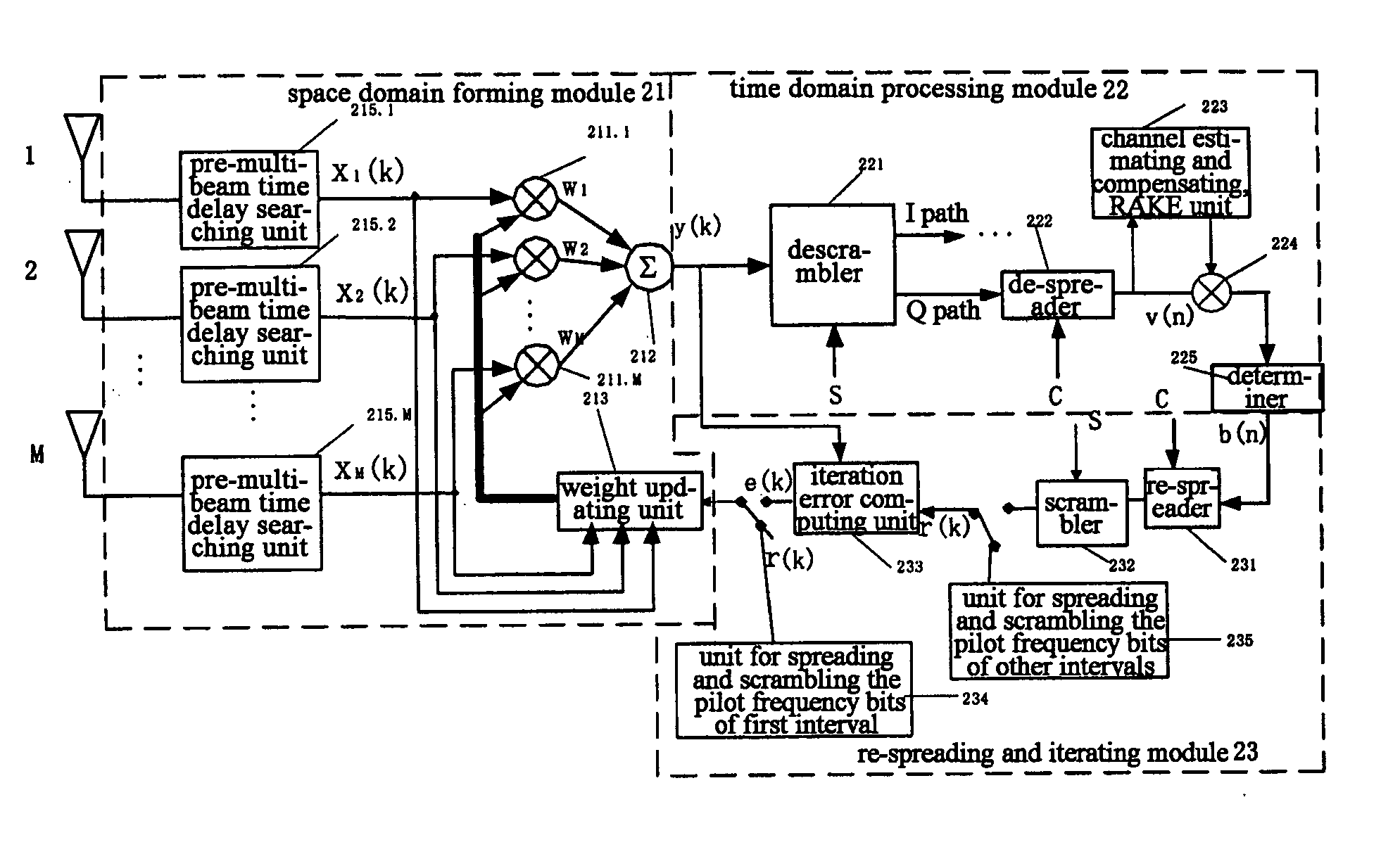
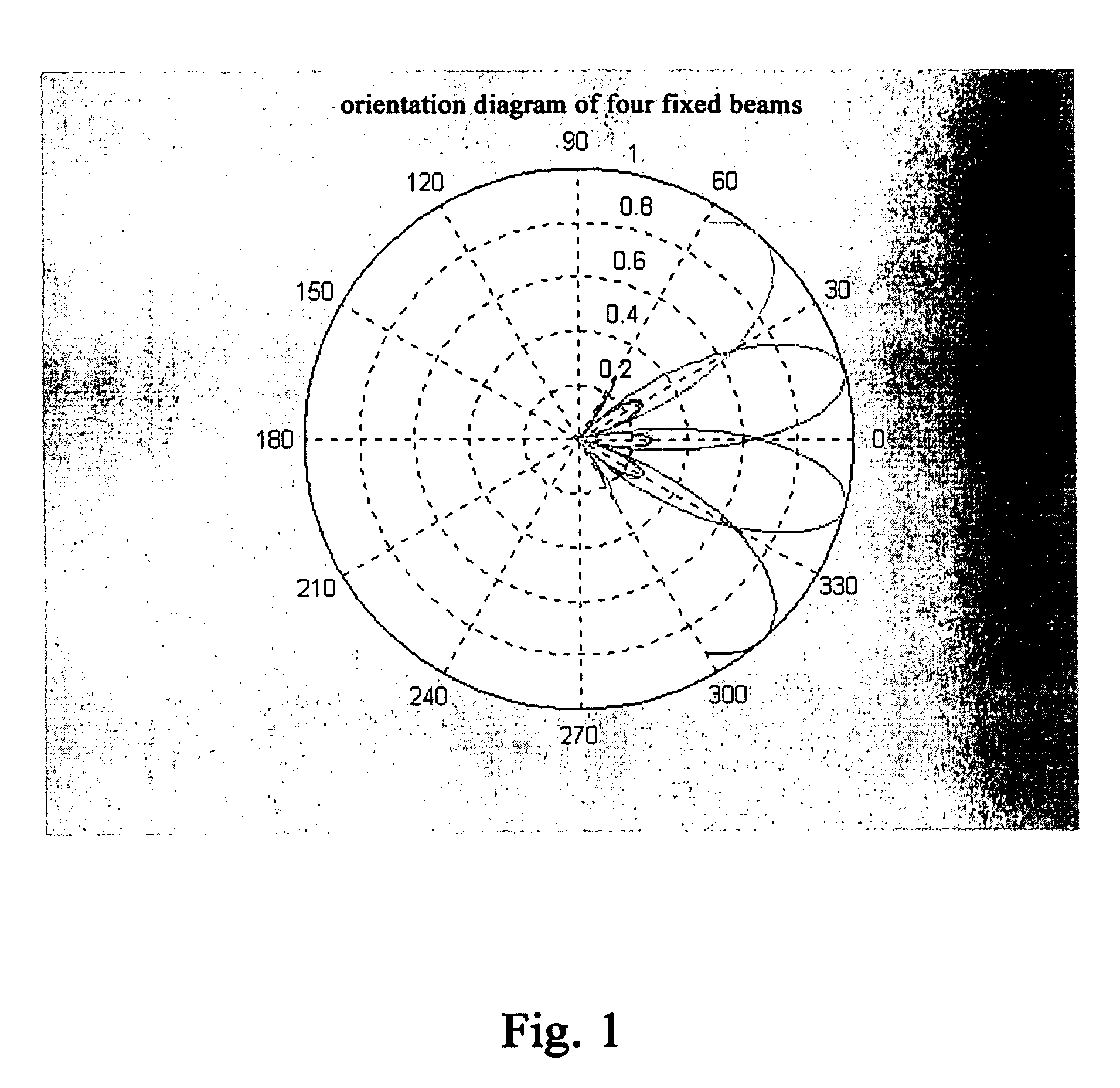
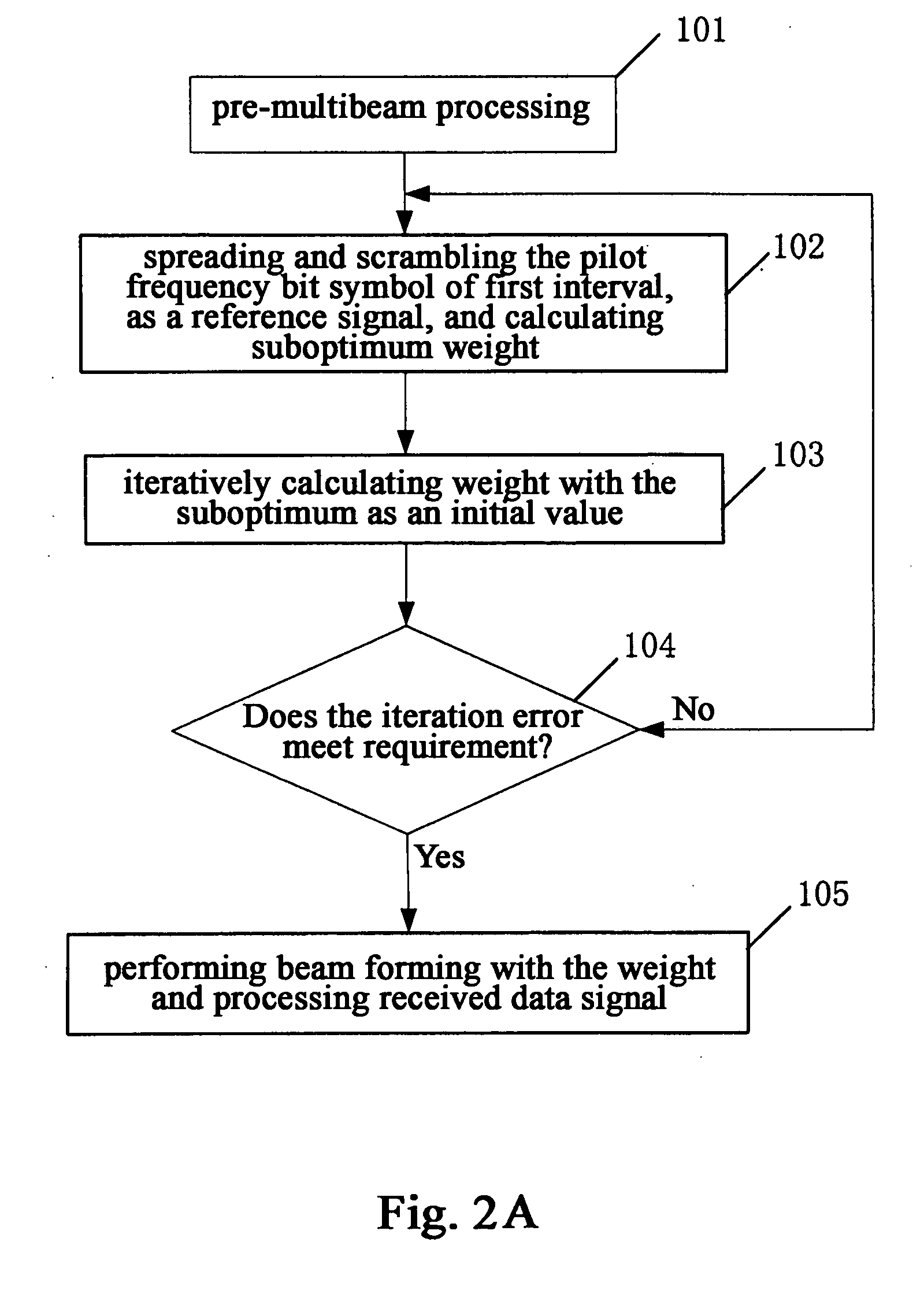
The present invention discloses a beam forming method for a smart antenna and a beam forming apparatus for a smart antenna. Said method comprises: implementing pre-multibeam processing and time delay aligning to array signals; calculating a suboptimum weight by means of a pilot frequency symbol; iteratively calculating an optimum weight with said suboptimum weight as an initial value; forming beams by means of said optimum weight. To use the beam forming method and apparatus of the present invention, it can reduce the bit error ratio for receiving and outputting greatly and avoid the multiplication between large matrixes and matrix inversion and then replace them by simple addition and multiplication, so as to reduce the difficulty for hardware implement and make it easier to be performed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com