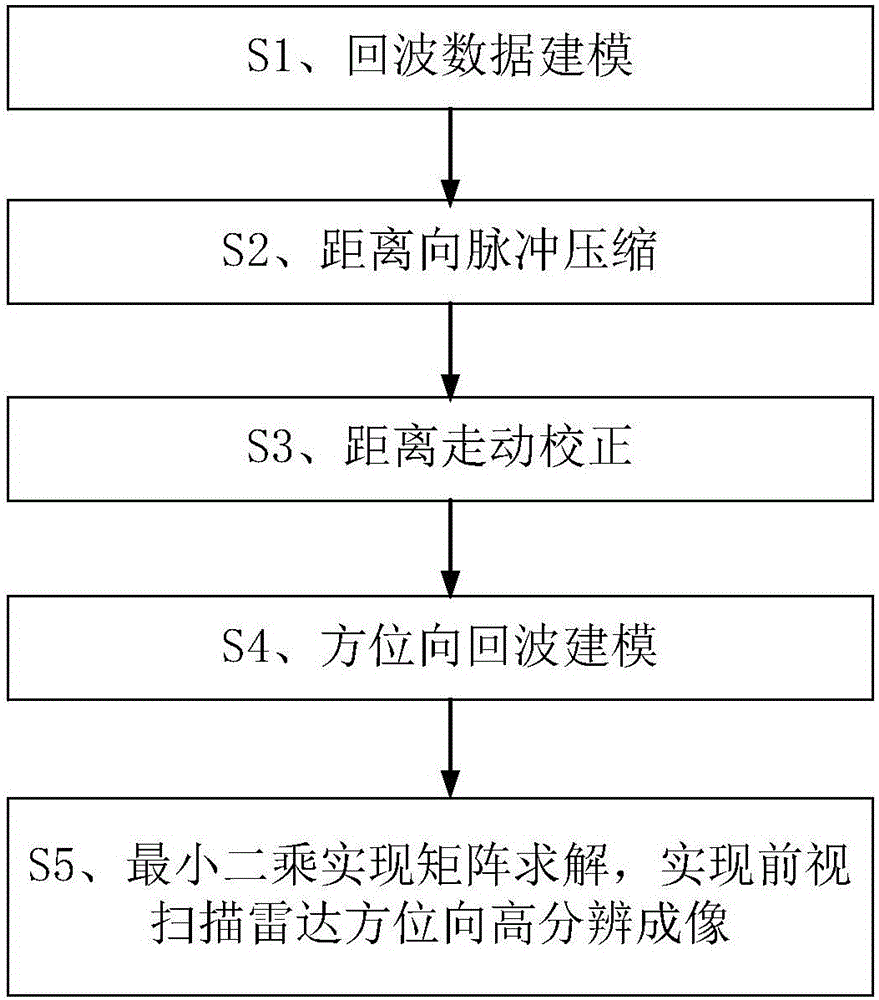
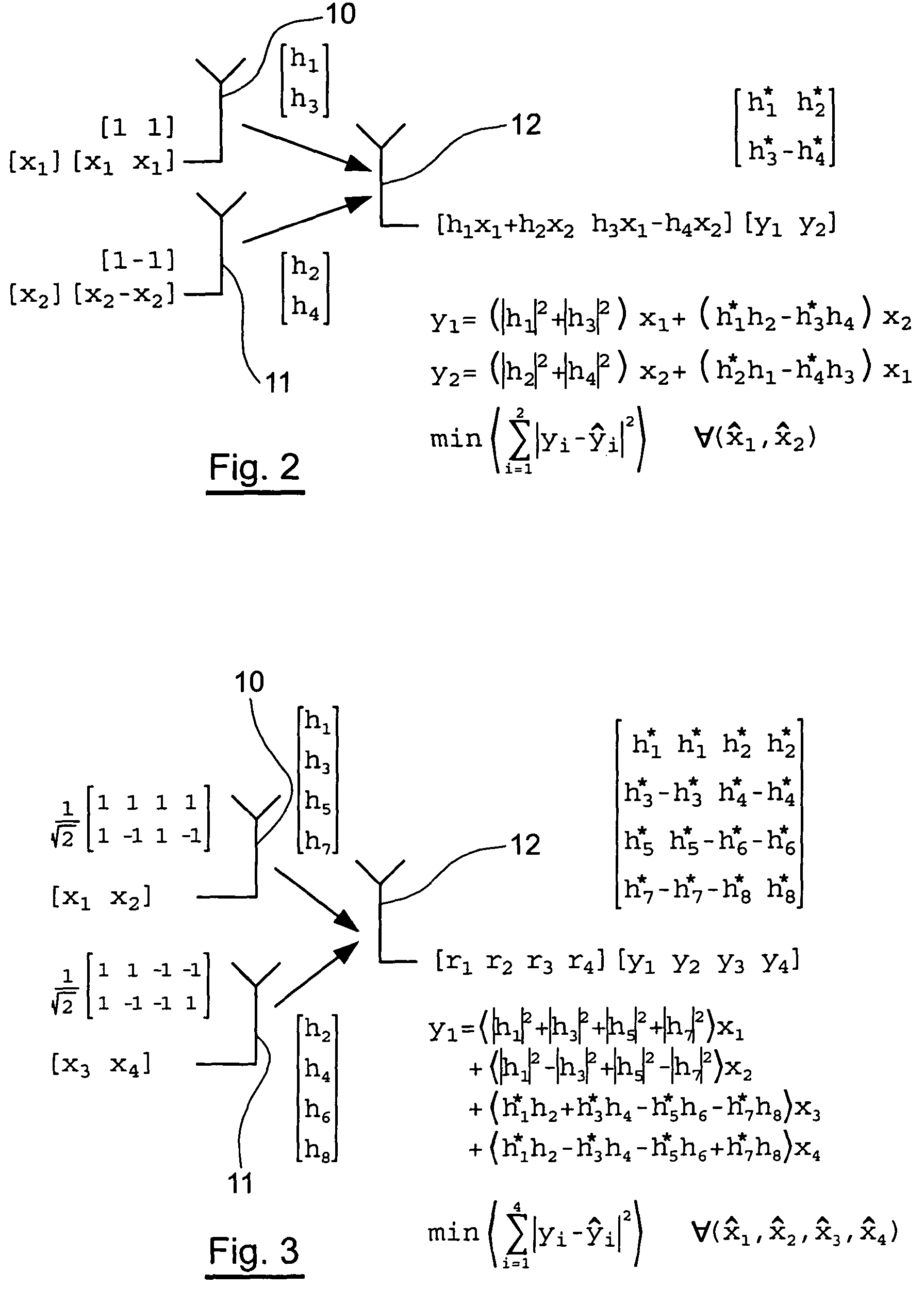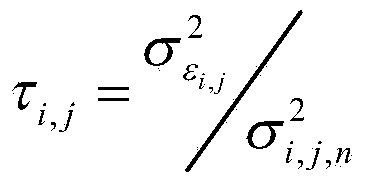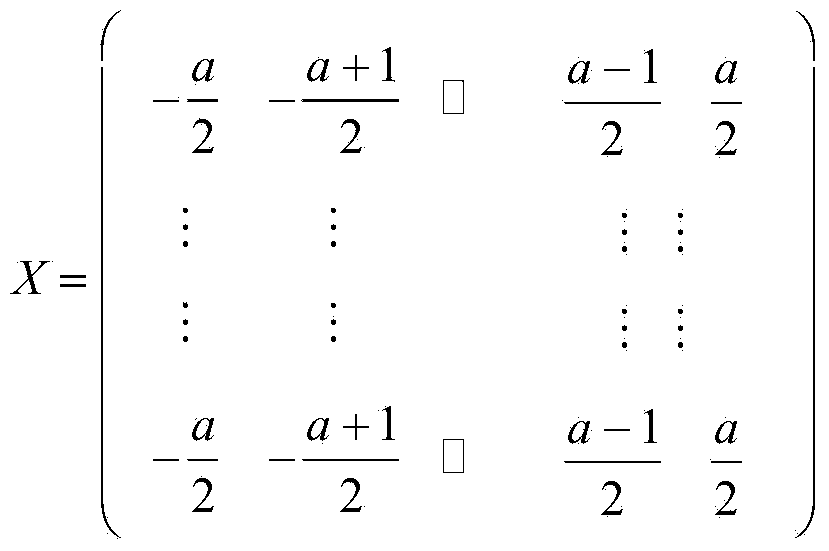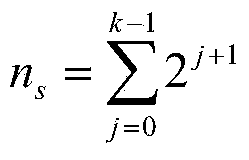Patents
Literature
405 results about "Square matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a square matrix is a matrix with the same number of rows and columns. An n-by-n matrix is known as a square matrix of order n. Any two square matrices of the same order can be added and multiplied. Square matrices are often used to represent simple linear transformations, such as shearing or rotation. For example, if R is a square matrix representing a rotation (rotation matrix) and v is a column vector describing the position of a point in space, the product Rv yields another column vector describing the position of that point after that rotation.
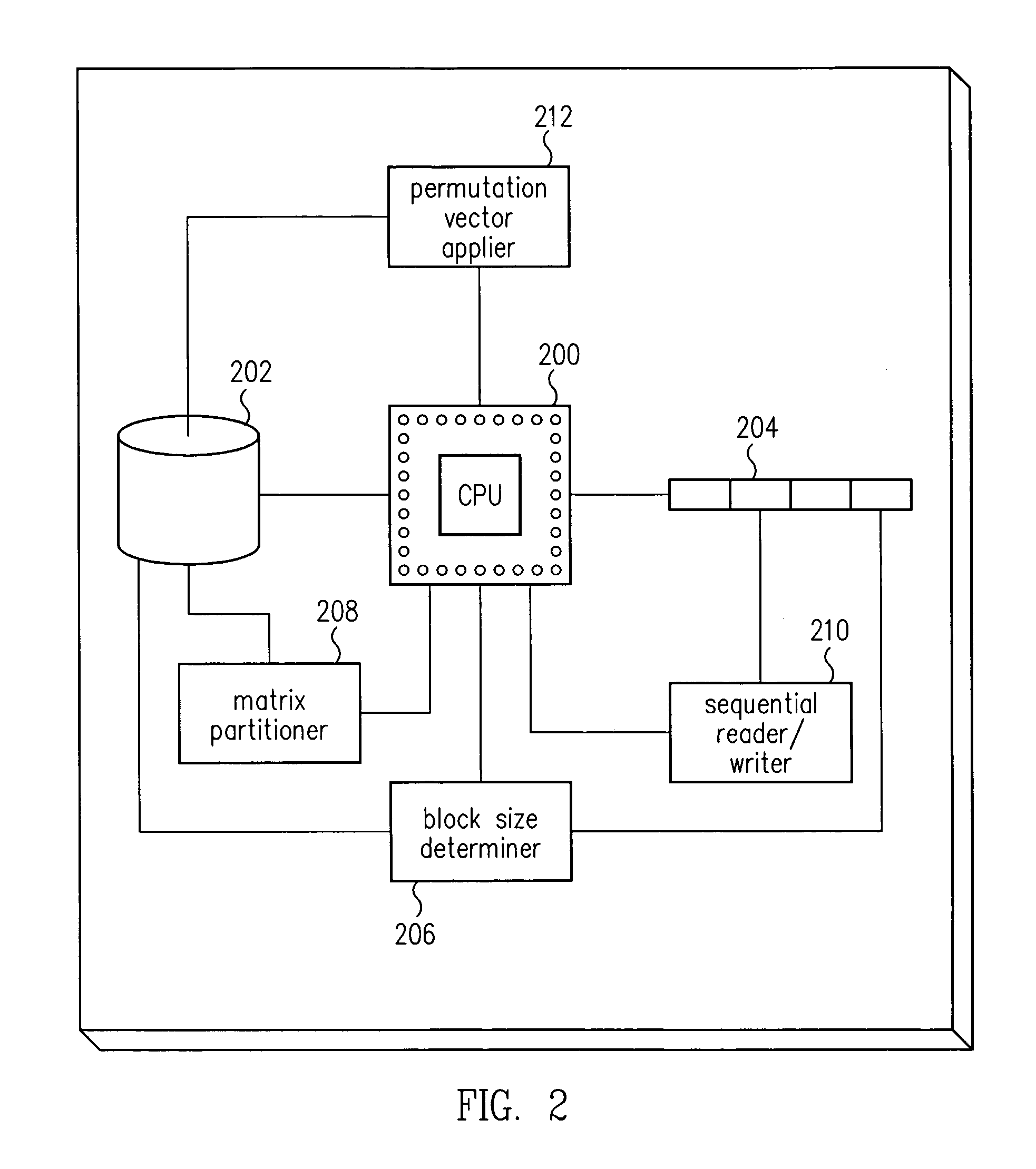
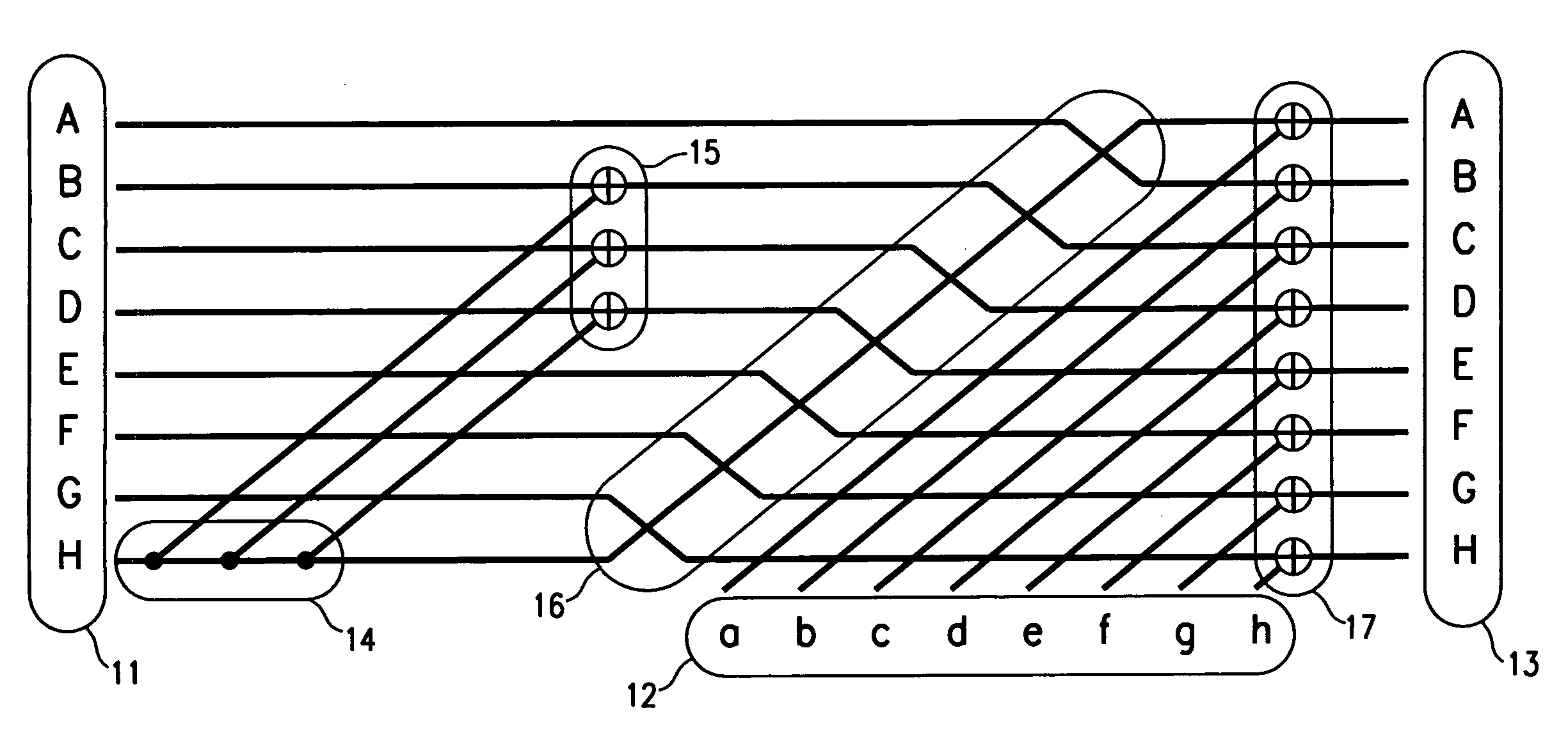
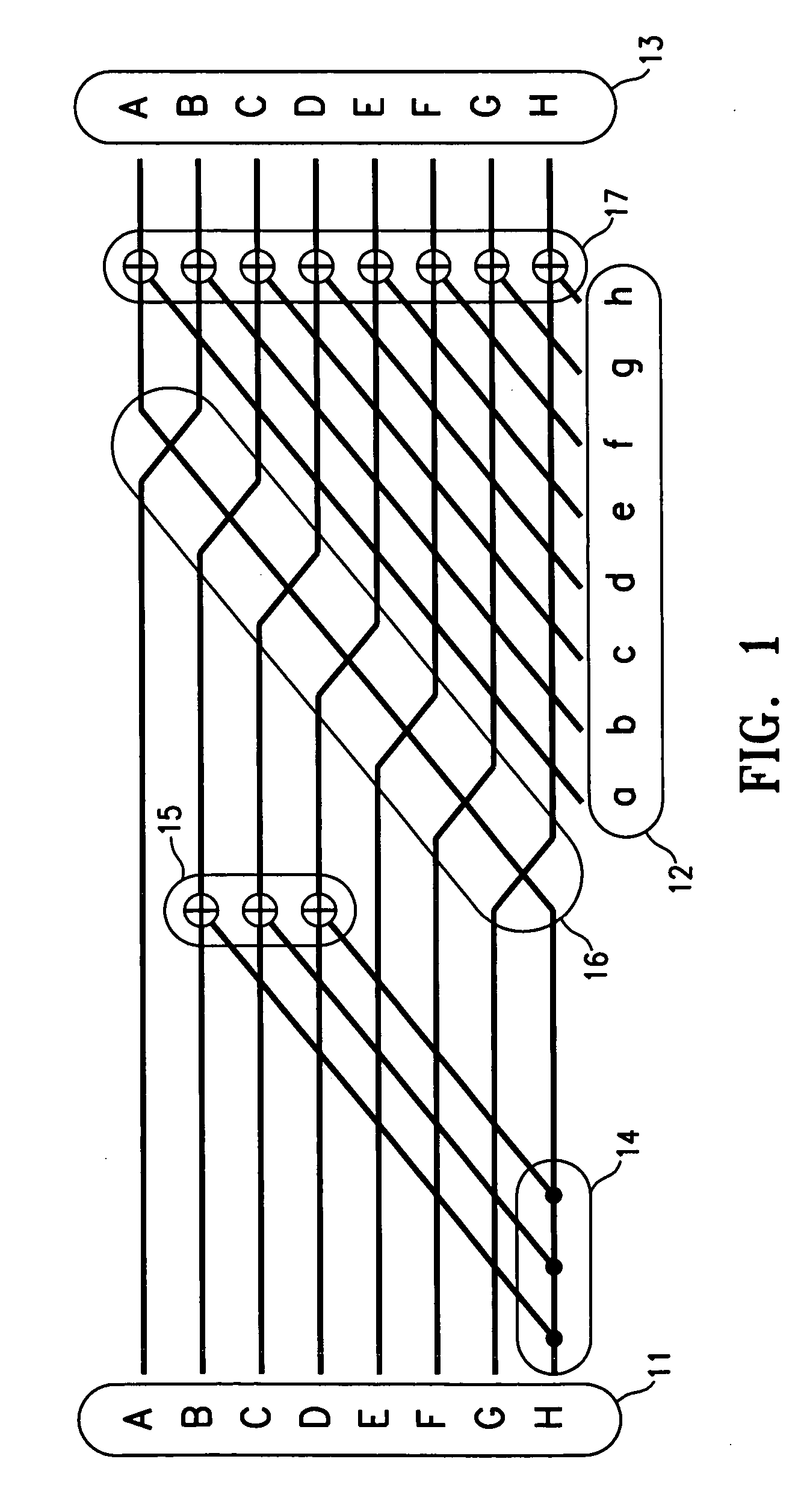
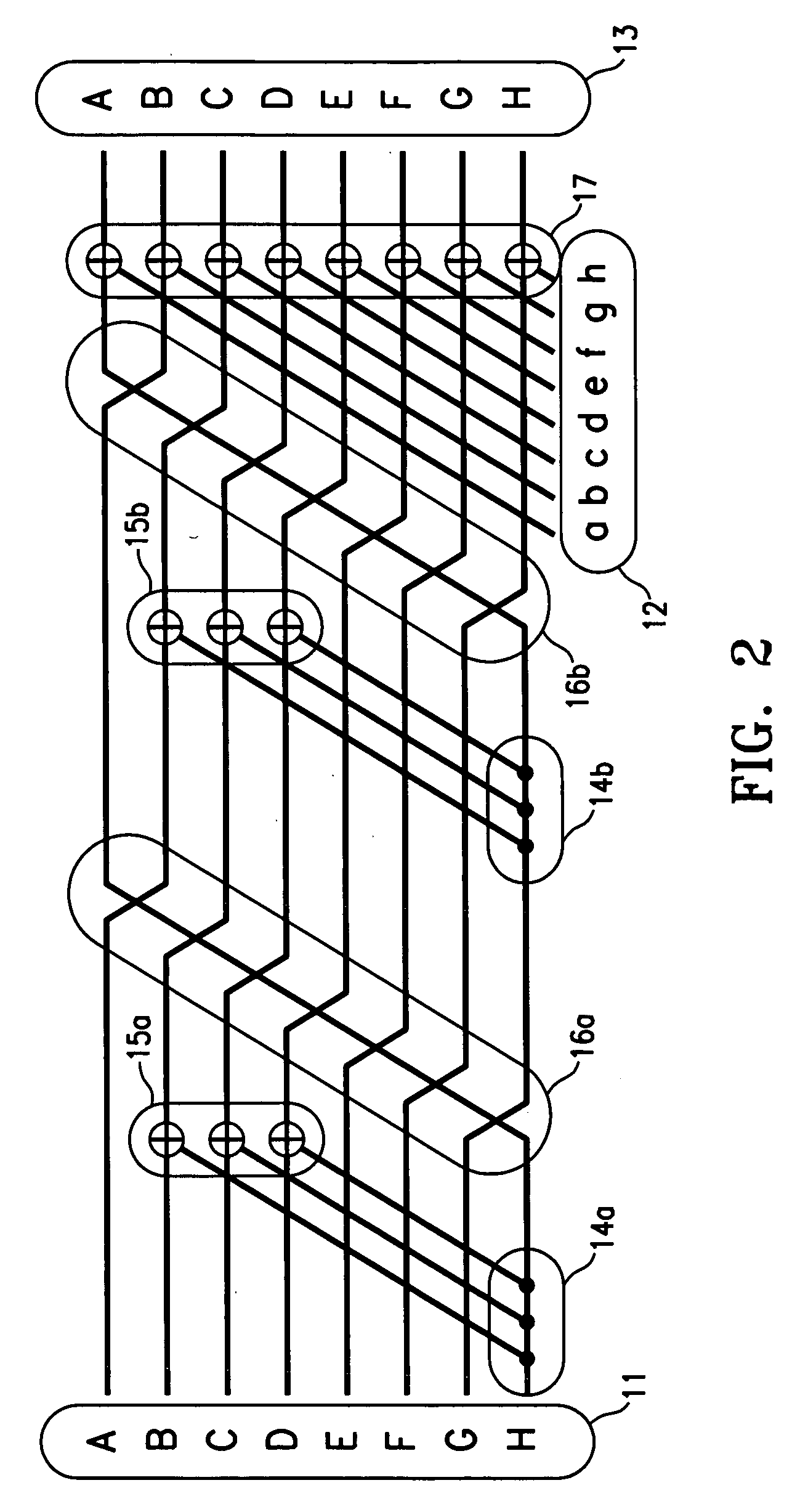
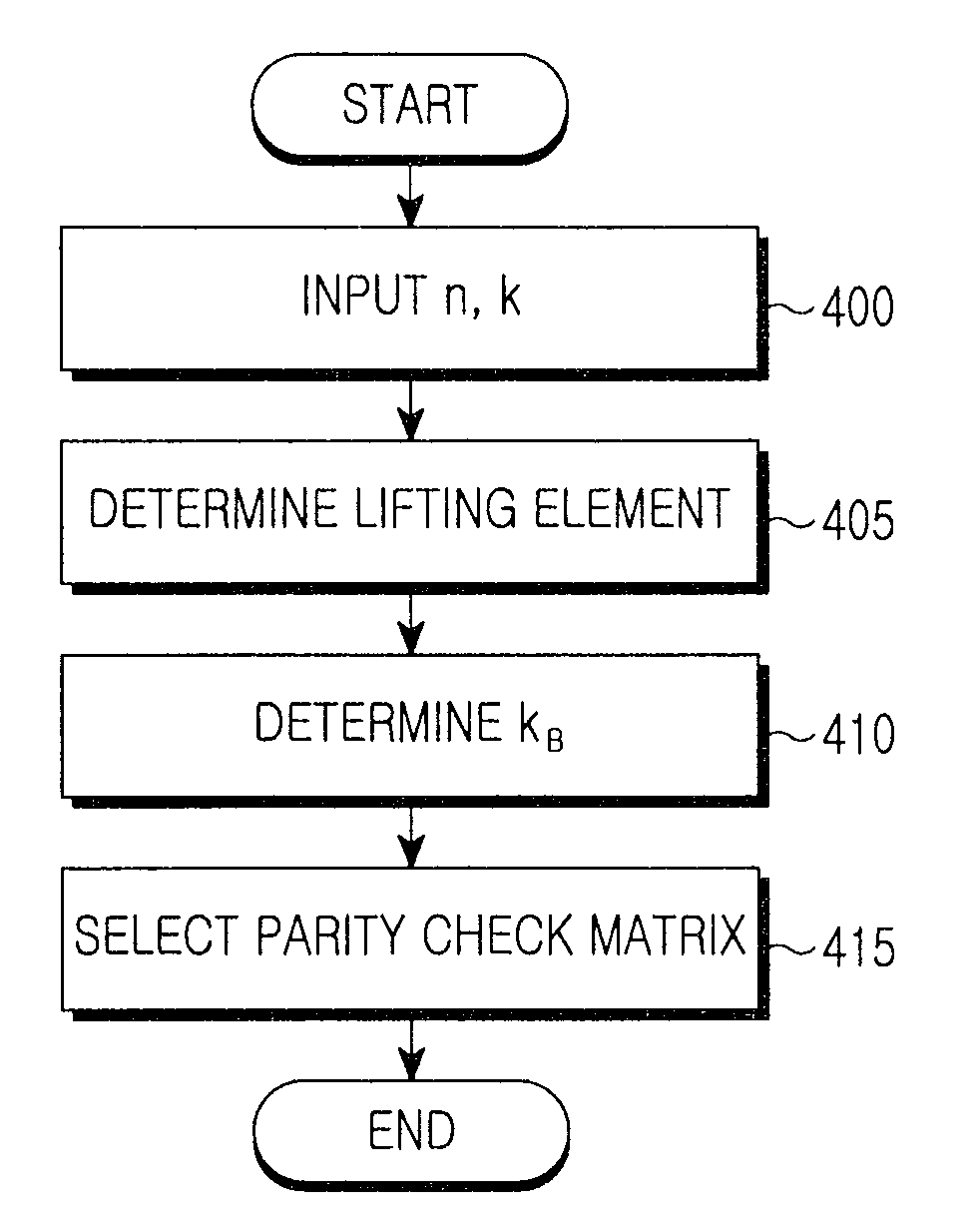
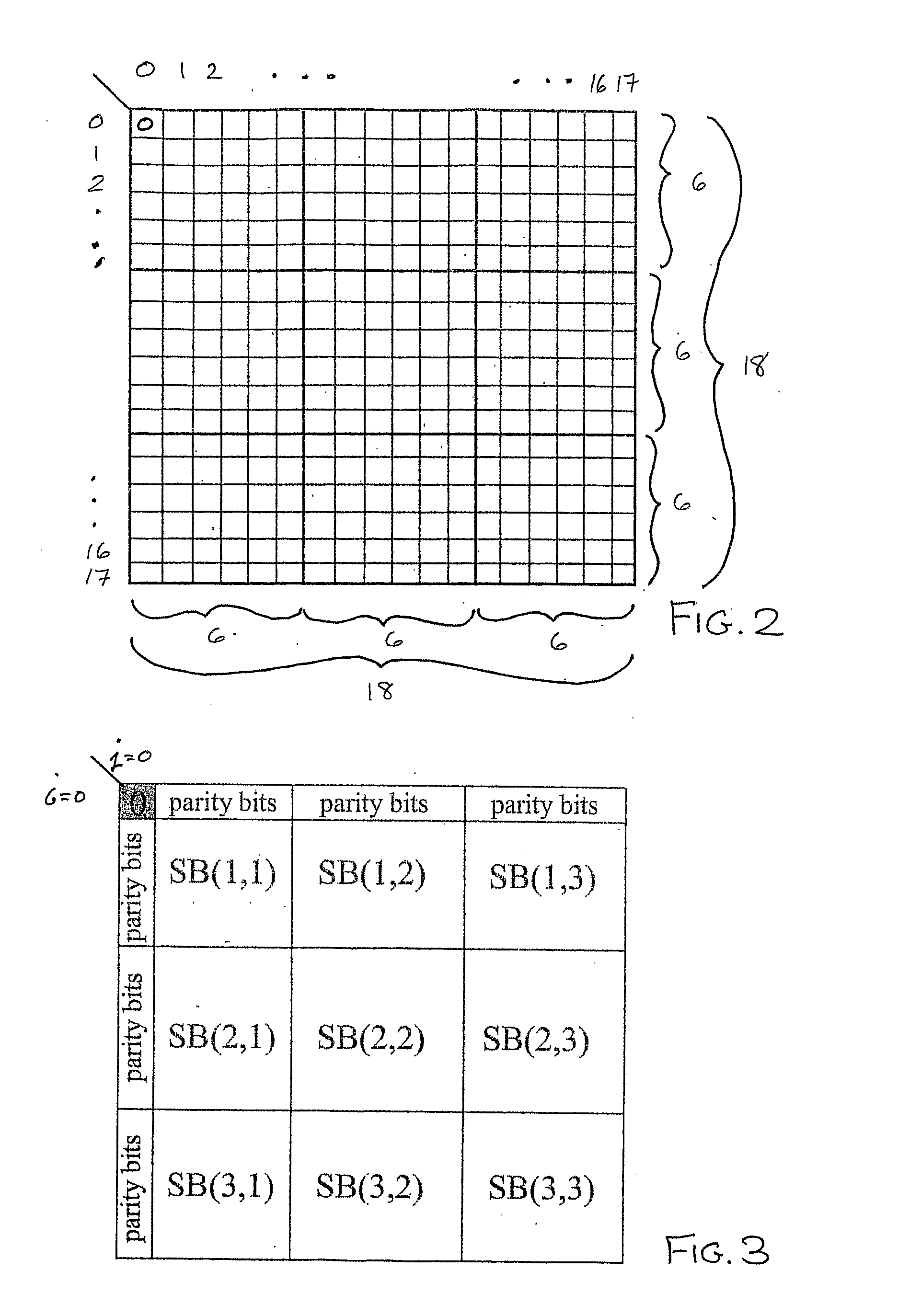
Apparatus and method for encoding a low density parity check code
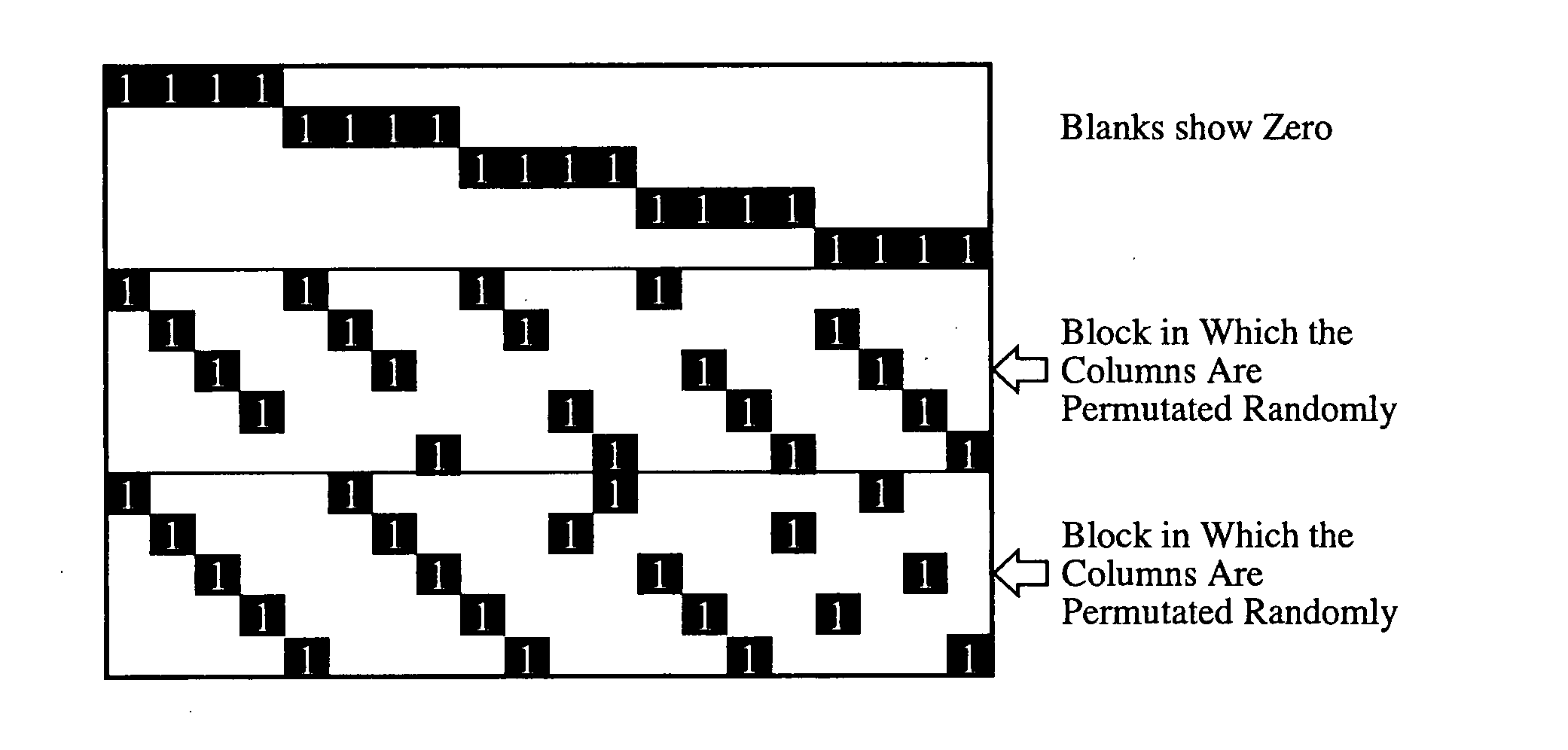
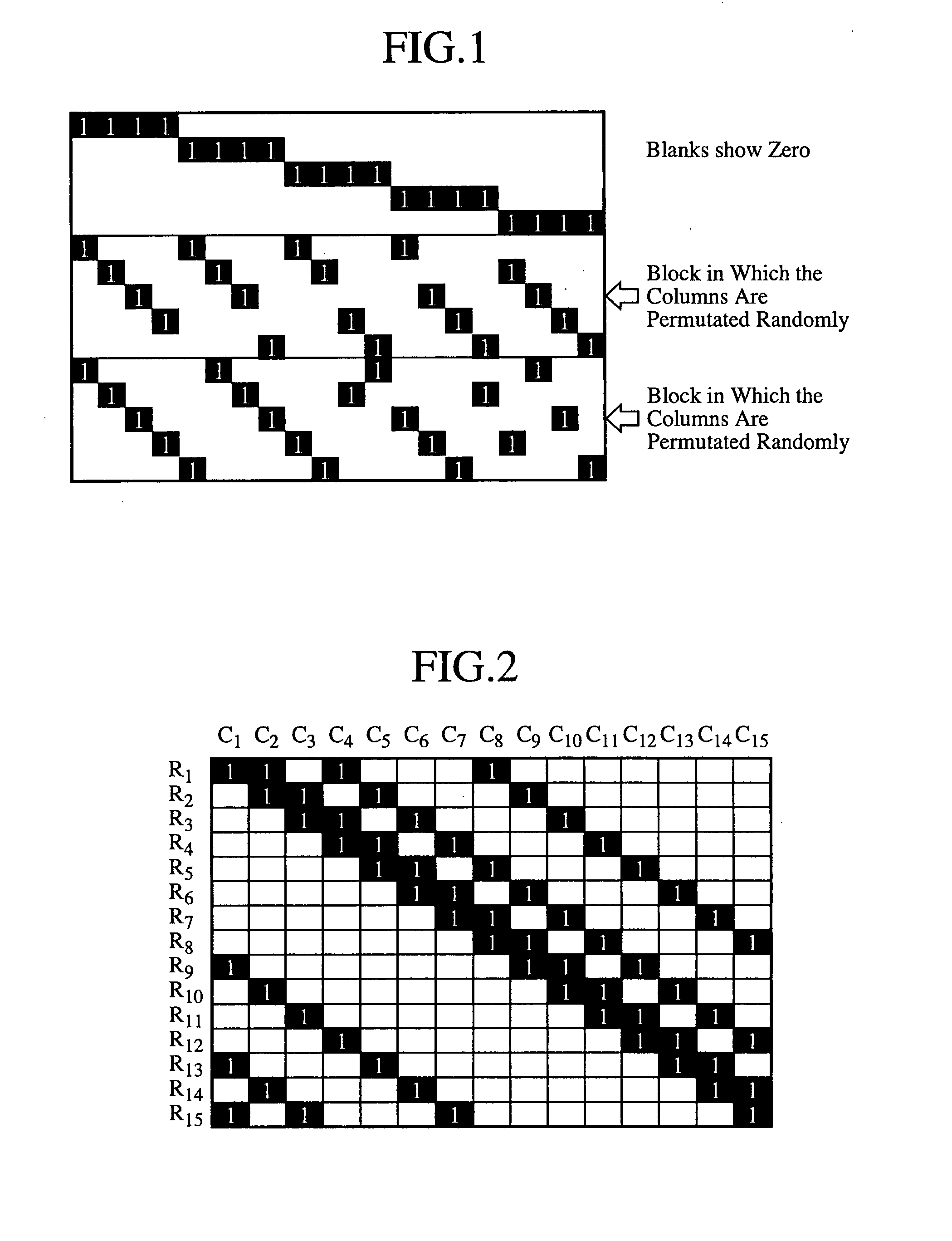
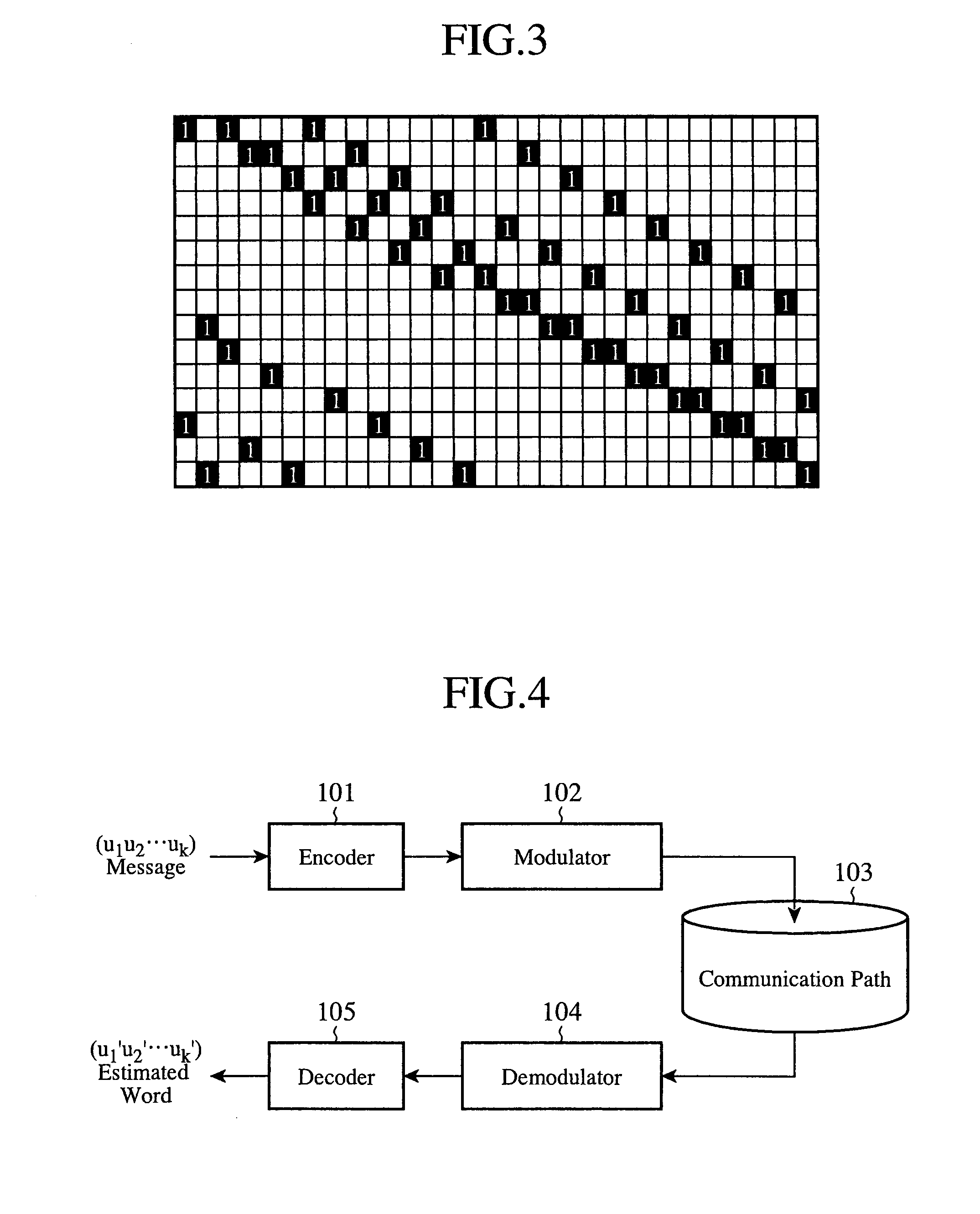
ActiveUS7178082B2Low Density Parity CheckEasy to calculateError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for generating an encoding matrix for a low density parity check (LDPC) code having a dual-diagonal matrix as a parity check matrix are disclosed. The apparatus and method construct an information sub-matrix of the encoding matrix with a predetermined number of square matrixes according to a predetermined code rate such that each of the square matrixes has columns and rows with a weight of 1 and has a different offset value, combine the square matrixes with the dual-diagonal matrix, and perform inter-row permutation on the information sub-matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiply redundant raid system and XOR-efficient method and apparatus for implementing the same
InactiveUS7219289B2Efficient, high-redundancy erasure codeEasy to calculateCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesRAIDTheoretical computer science
Owner:TANDBERG DATA
Matrix transposition in a computer system
ActiveUS7031994B2Improves speed and parallelabilityEasy transpositionHandling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerAlgorithmComputerized system
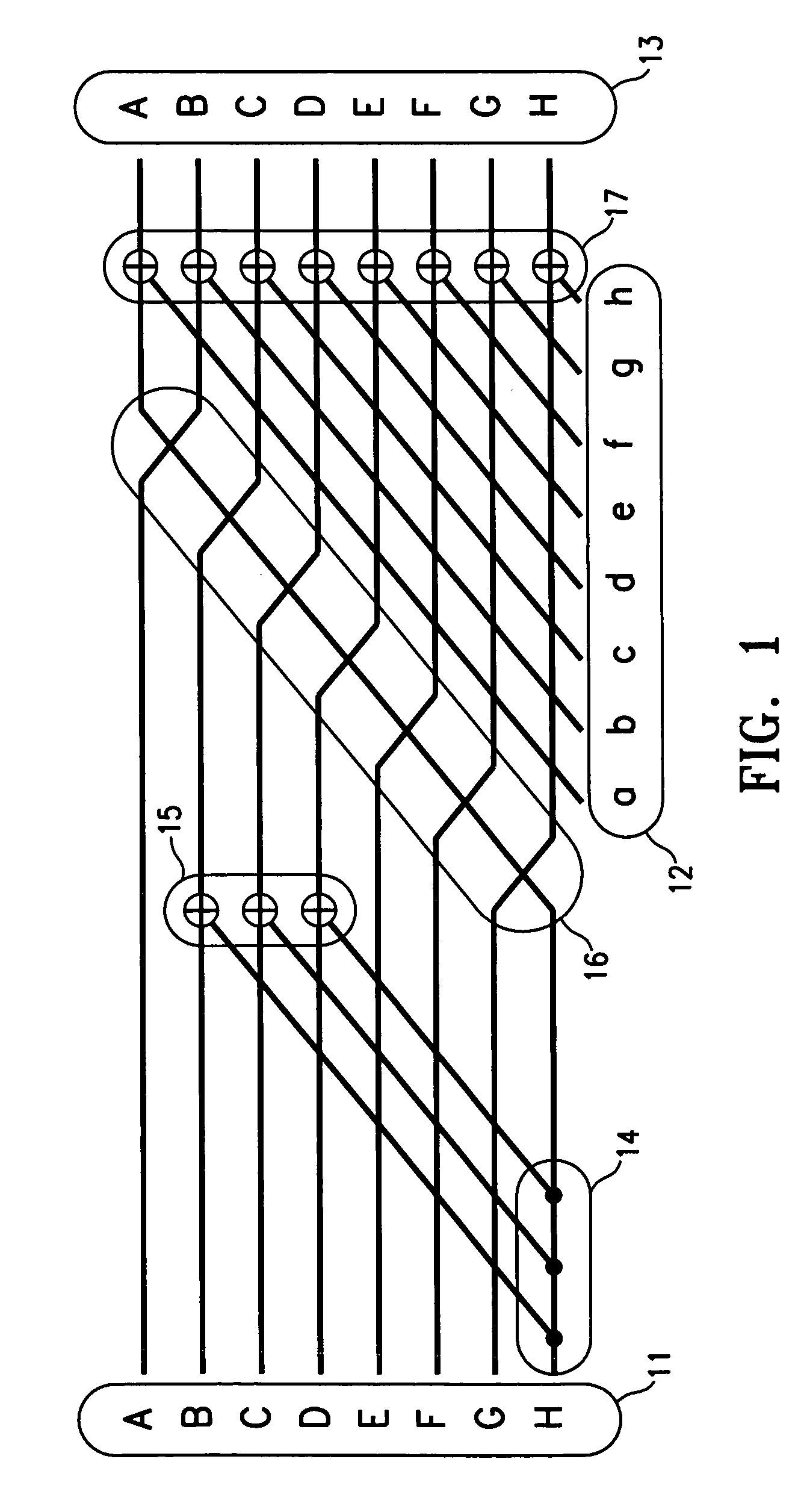
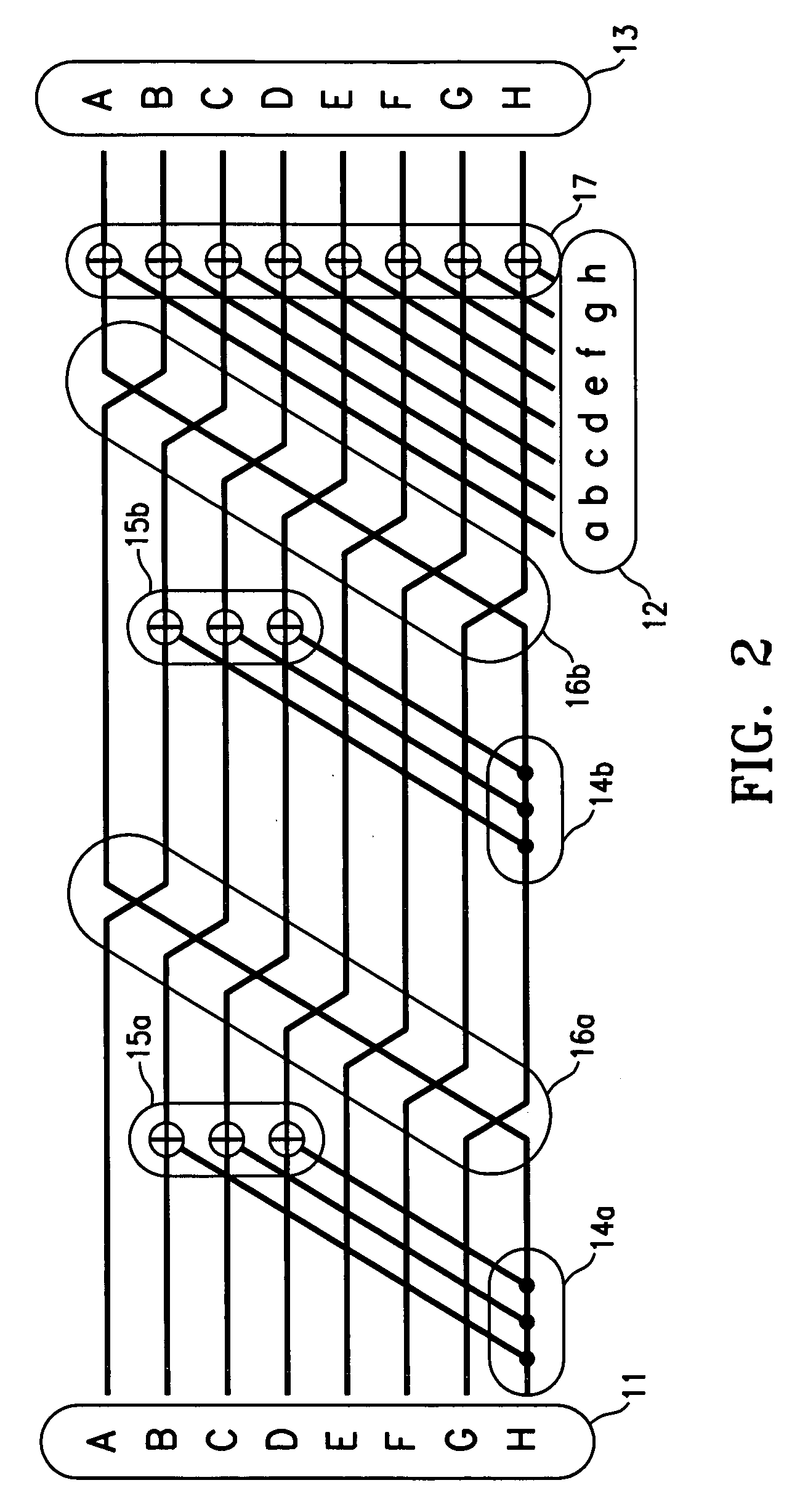
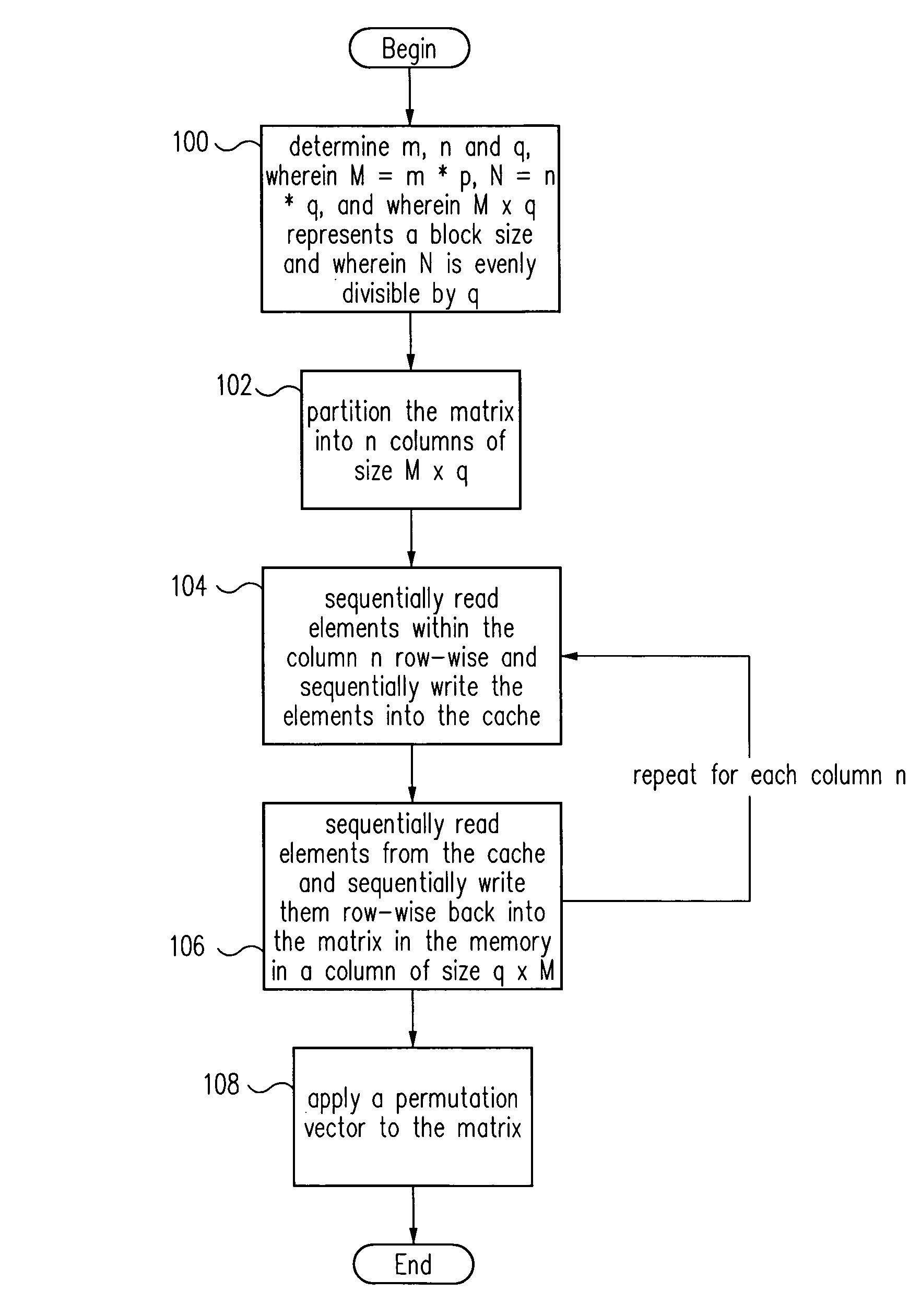
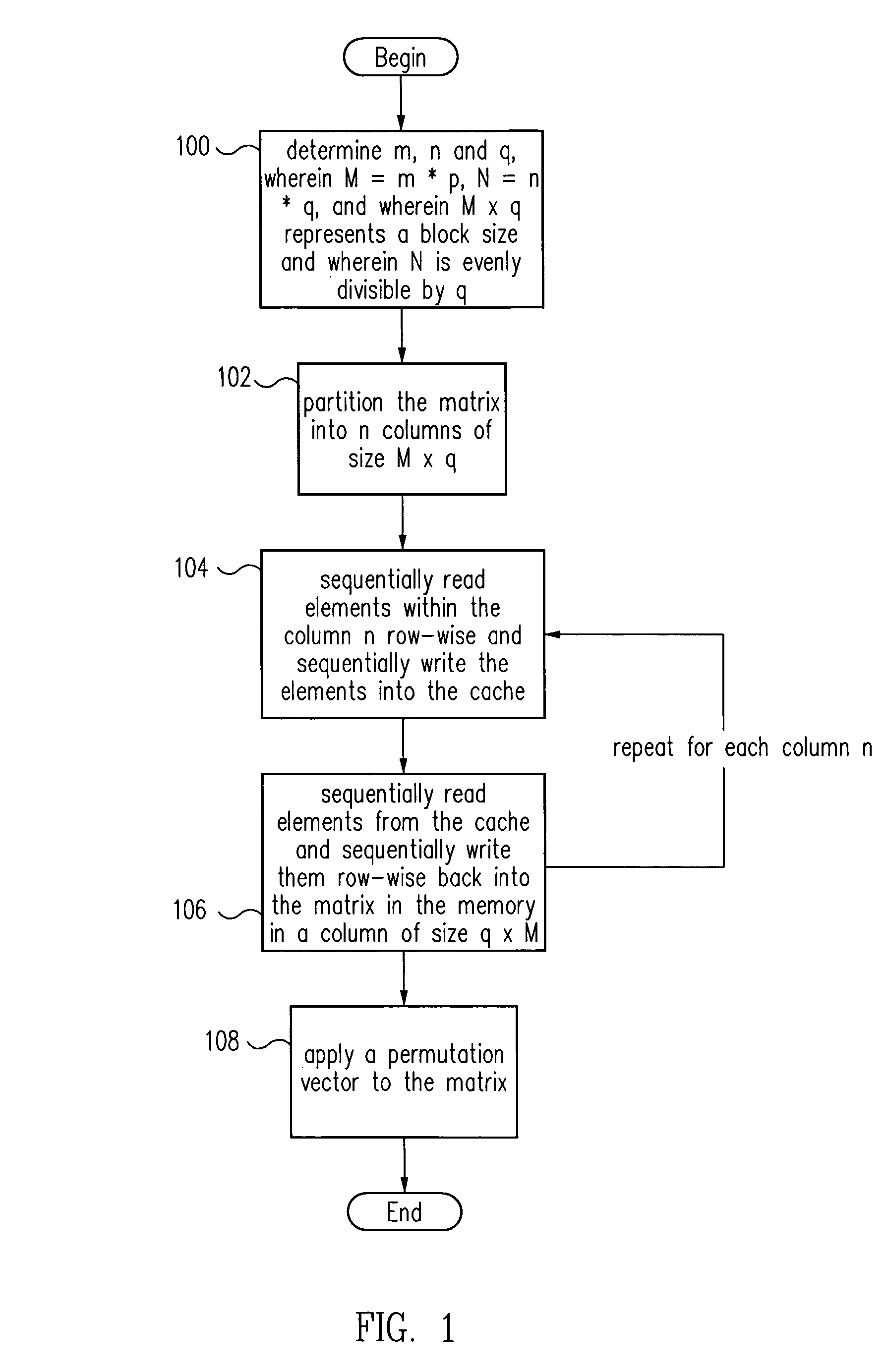
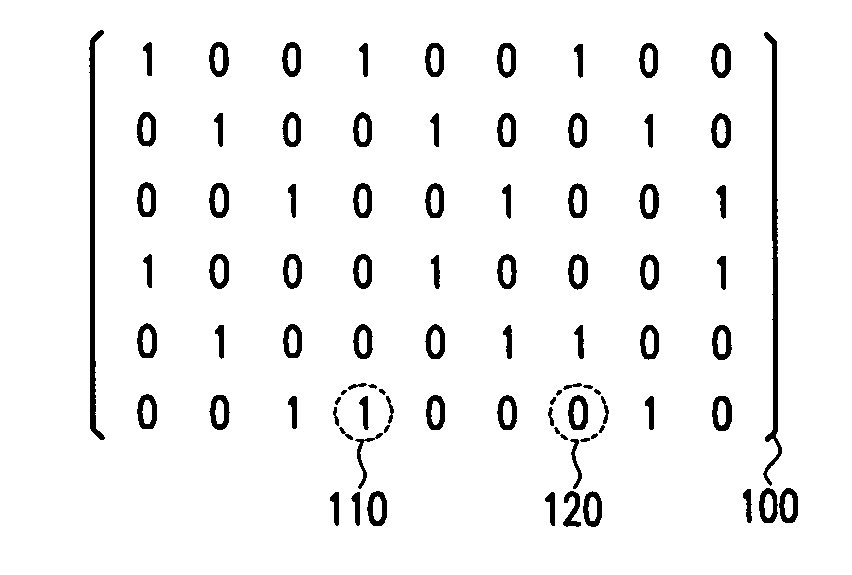
Improved transposition of a matrix in a computer system may be accomplished while utilizing at most a single permutation vector. This greatly improves the speed and parallelability of the transpose operation. For a standard rectangular matrix having M rows and N columns and a size M×N, first n and q are determined, wherein N=n*q, and wherein M×q represents a block size and wherein N is evenly divisible by p. Then, the matrix is partitioned into n columns of size M×q. Then for each column n, elements are sequentially read within the column row-wise and sequentially written into a cache, then sequentially read from the cache and sequentially written row-wise back into the matrix in a memory in a column of size q×M. A permutation vector may then be applied to the matrix to arrive at the transpose. This method may be modified for special cases, such as square matrices, to further improve efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
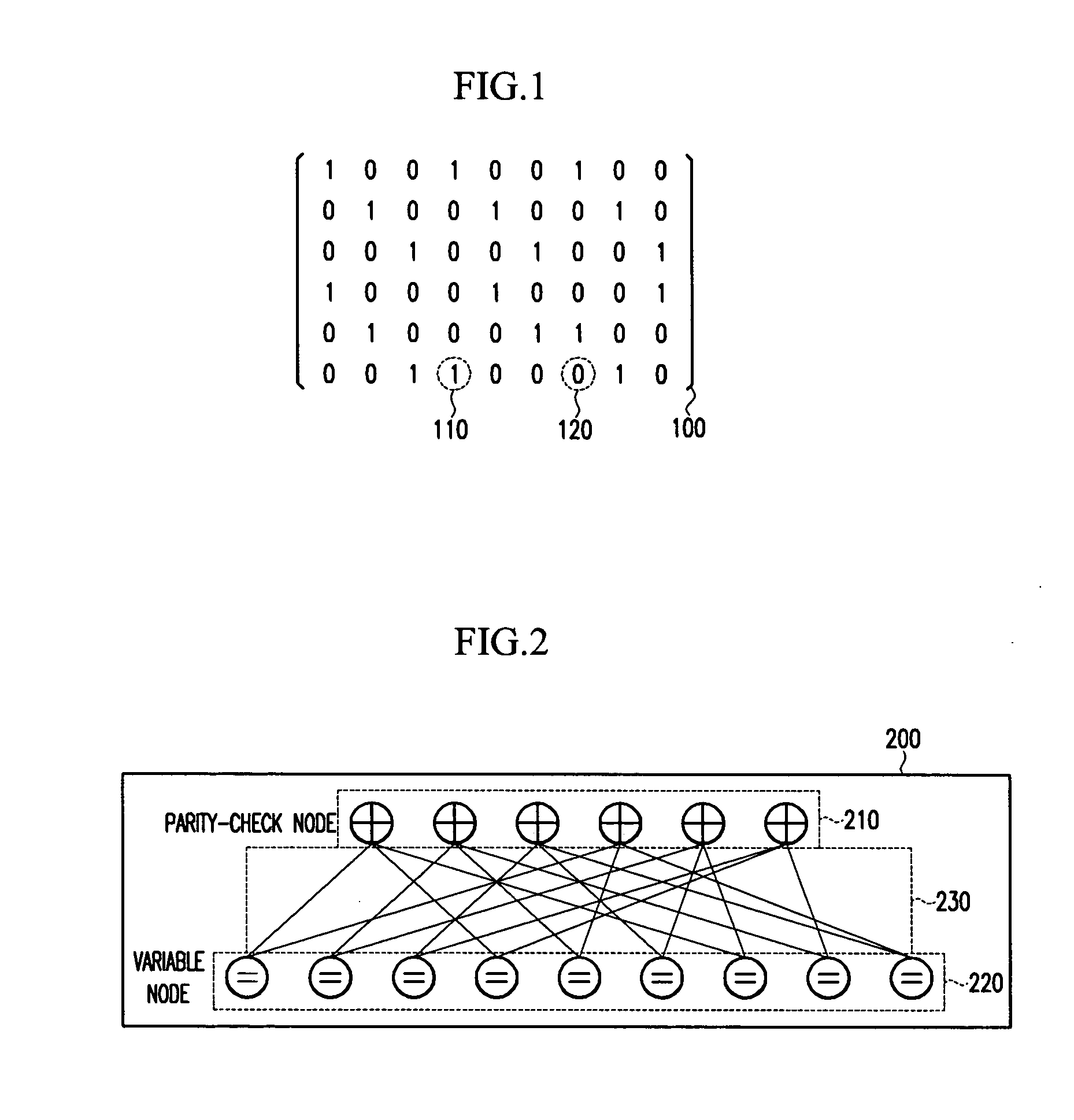
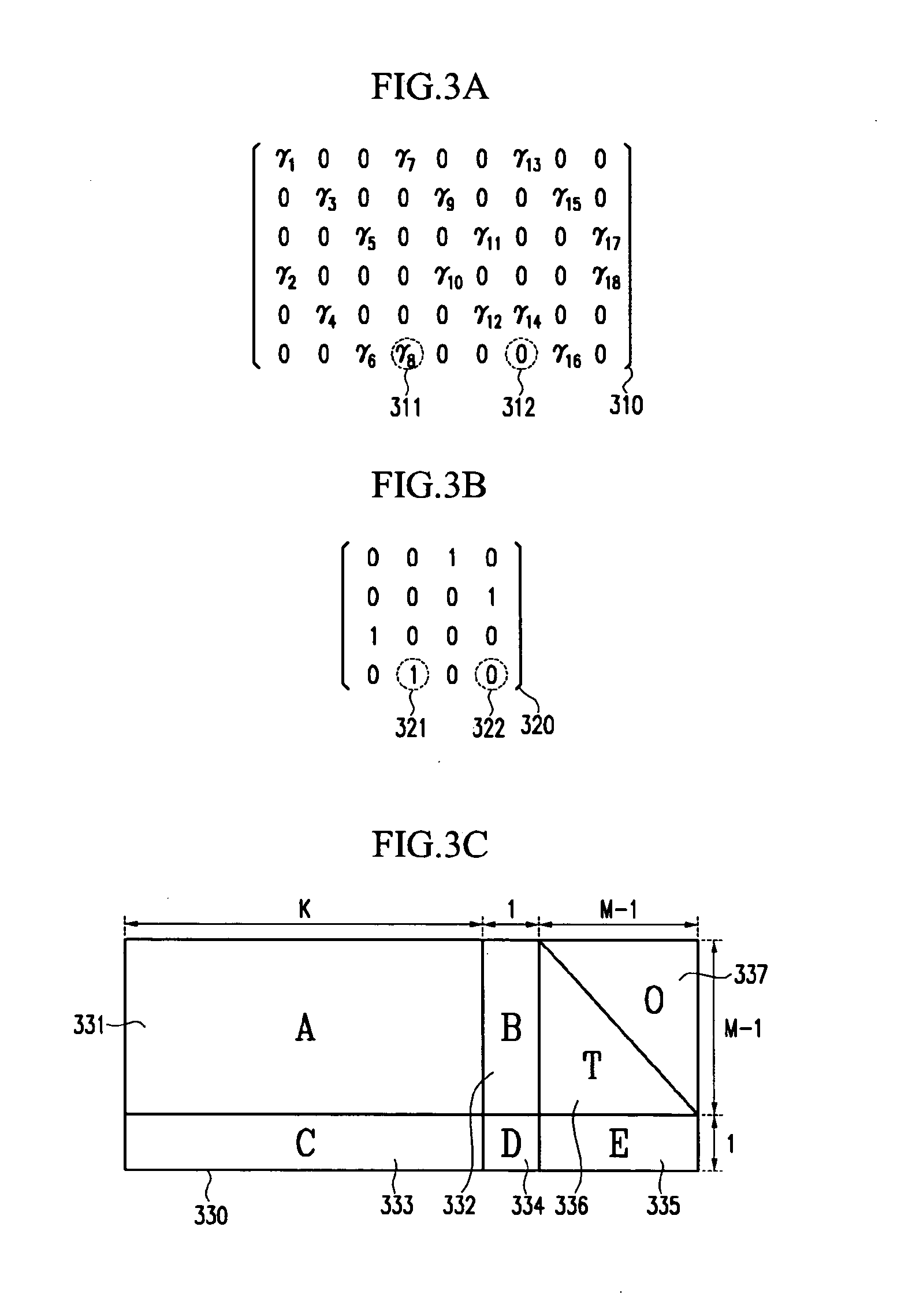
Apparatus for encoding and decoding of low-density parity-check codes, and method thereof
ActiveUS20050149840A1Reduce memory sizeHigh-speed and simple hardwareError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphAlgorithm
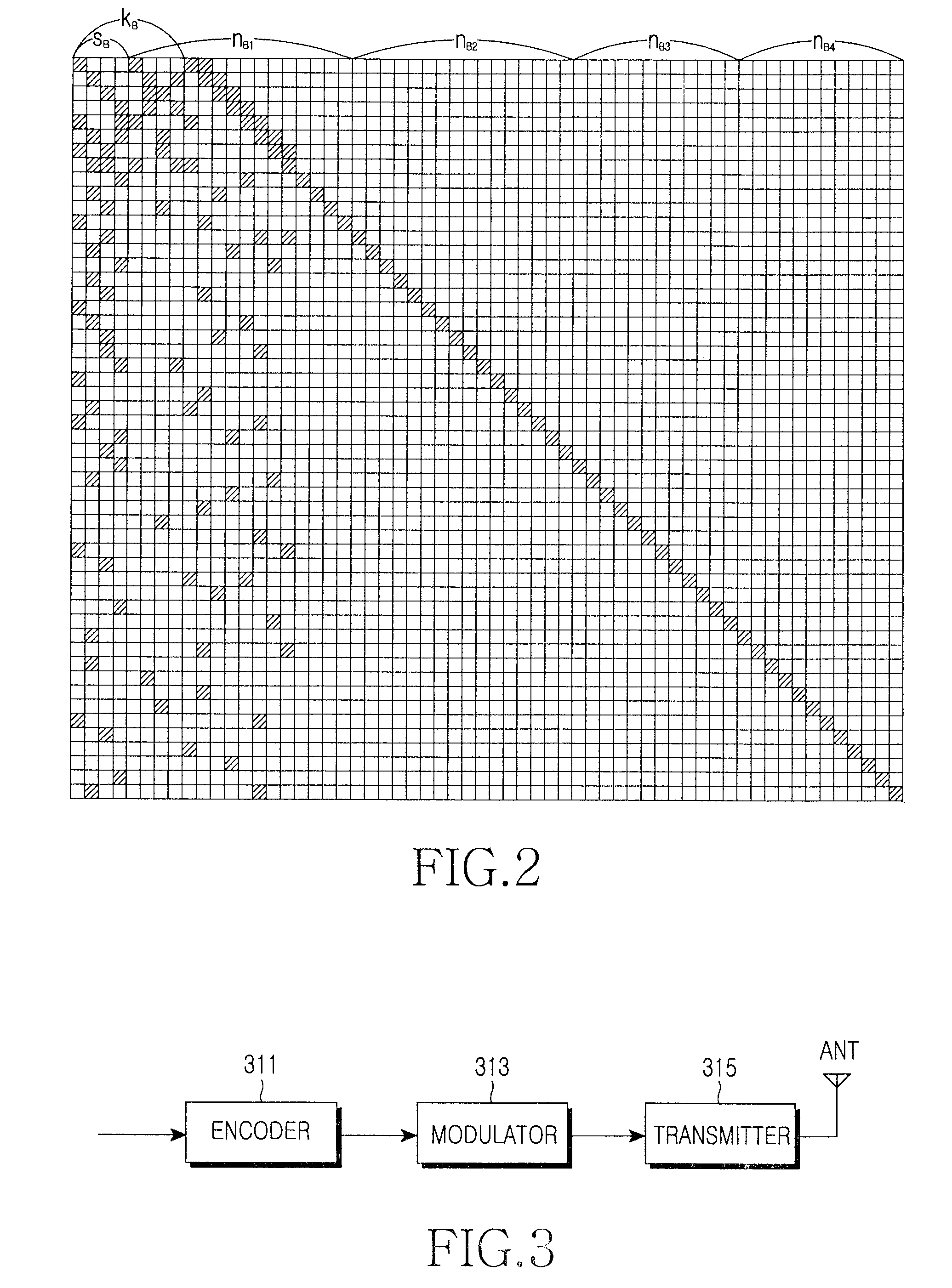
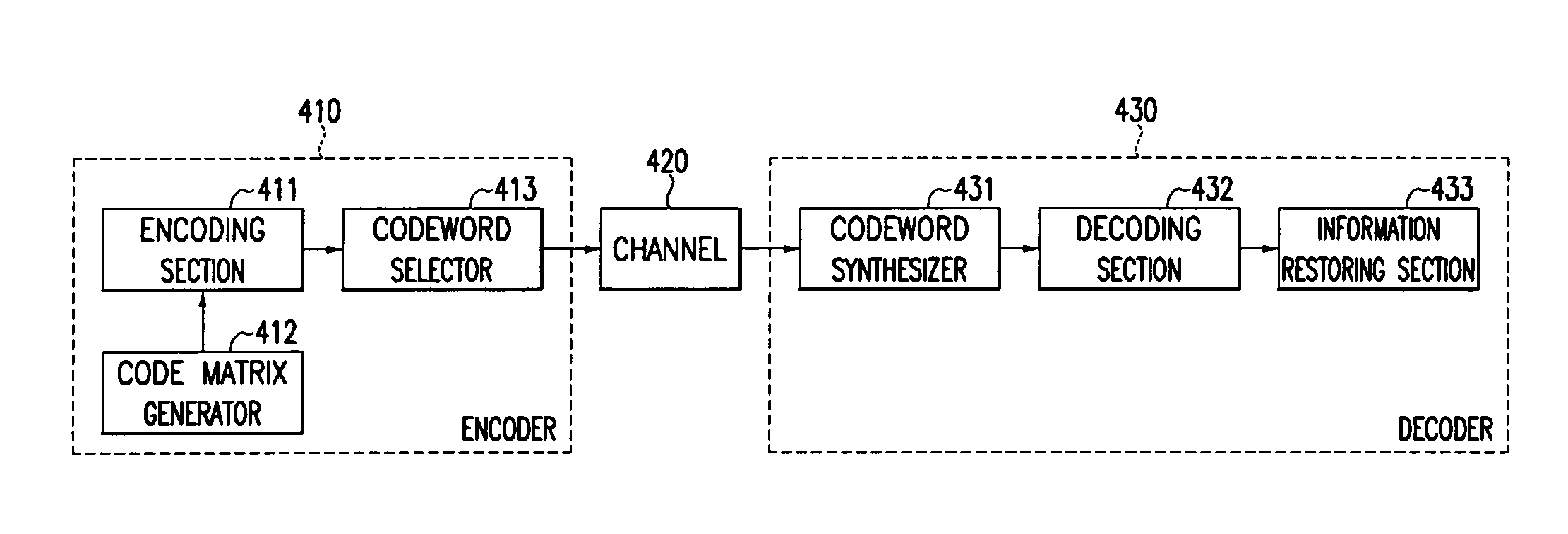
An LDPC code encoding apparatus includes: a code matrix generator for generating and transmitting a parity-check matrix comprising a combination of square matrices having a unique value on each row and column thereof; an encoding means encoding block LDPC codes according to the parity-check matrix received from the code matrix generator; and a codeword selector for puncturing the encoded result of the encoding means to generate an LDPC codeword. The code matrix generator divides an information word to be encoded into block matrices having a predetermined length to generate a vector information word. The encoding means encodes the block LDPC codes using the parity-check matrix divided into the block matrices and a Tanner graph divided into smaller graphs in correspondence to the parity-check matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multiply redundant raid system and XOR-efficient method and apparatus for implementing the same
InactiveUS20060218470A1Efficient executionEffective calculationError detection/correctionCode conversionDecoding methodsRAID
An improved and extended Reed-Solomon-like method for providing a redundancy of m≧3 is disclosed. A general expression of the codes is described, as well as a systematic criterion for proving correctness and finding decoding algorithms for values of m>3. Examples of codes are given for m=3, 4, 5, based on primitive elements of a finite field of dimension N where N is 8, 16 or 32. A Horner's method and accumulator apparatus are described for XOR-efficient evaluation of polynomials with variable vector coefficients and constant sparse square matrix abscissa. A power balancing technique is described to further improve the XOR efficiency of the algorithms. XOR-efficient decoding methods are also described. A tower coordinate technique to efficiently carry out finite field multiplication or inversion for large dimension N forms a basis for one decoding method. Another decoding method uses a stored one-dimensional table of powers of α and Schur expressions to efficiently calculate the inverse of the square submatrices of the encoding matrix.
Owner:TANDBERG DATA
Method and apparatus for signal transmission/reception in a communication system using an HARQ scheme
ActiveUS20090204868A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionCommunications systemAlgorithm
An apparatus and method for transmitting a signal in a communication system using a Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) scheme are provided. The method includes generating a codeword vector by encoding an information vector by using a first parity check matrix of Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes, generating a transmission vector by processing the codeword vector, and transmitting the transmission vector. When the first parity check matrix includes a plurality of square matrix columns, each square matrix includes a size of L×L, the first parity check matrix is one of p parity check matrixes stored in the signal transmission apparatus, the p parity check matrixes support different numbers of information vector square matrix columns, and each of the numbers of information vector square matrix columns indicates the number of square matrix columns corresponding to the information vector from among the plurality of square matrix columns. The first parity check matrix is a parity check matrix supporting the number of information vector square matrix columns determined by using the length of the information vector and the value L from the p parity check matrixes, and the value L is determined by using p and the length of the information vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for encoding and decoding of low-density parity-check codes, and method thereof
ActiveUS7395494B2Reduce memory sizeHigh-speed and simple hardwareError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphParity-check matrix
An LDPC code encoding apparatus includes: a code matrix generator for generating and transmitting a parity-check matrix comprising a combination of square matrices having a unique value on each row and column thereof; an encoding means encoding block LDPC codes according to the parity-check matrix received from the code matrix generator; and a codeword selector for puncturing the encoded result of the encoding means to generate an LDPC codeword. The code matrix generator divides an information word to be encoded into block matrices having a predetermined length to generate a vector information word. The encoding means encodes the block LDPC codes using the parity-check matrix divided into the block matrices and a Tanner graph divided into smaller graphs in correspondence to the parity-check matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on the combination of six-layer convolutional neural network and spectral-space information
ActiveCN107292343ASolve the noise problemTo achieve the combinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti bandClassification methods
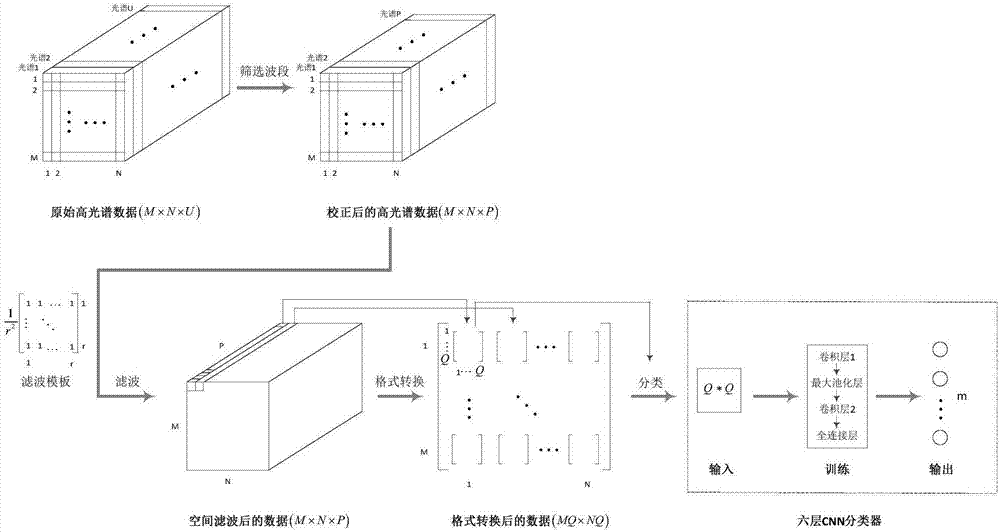
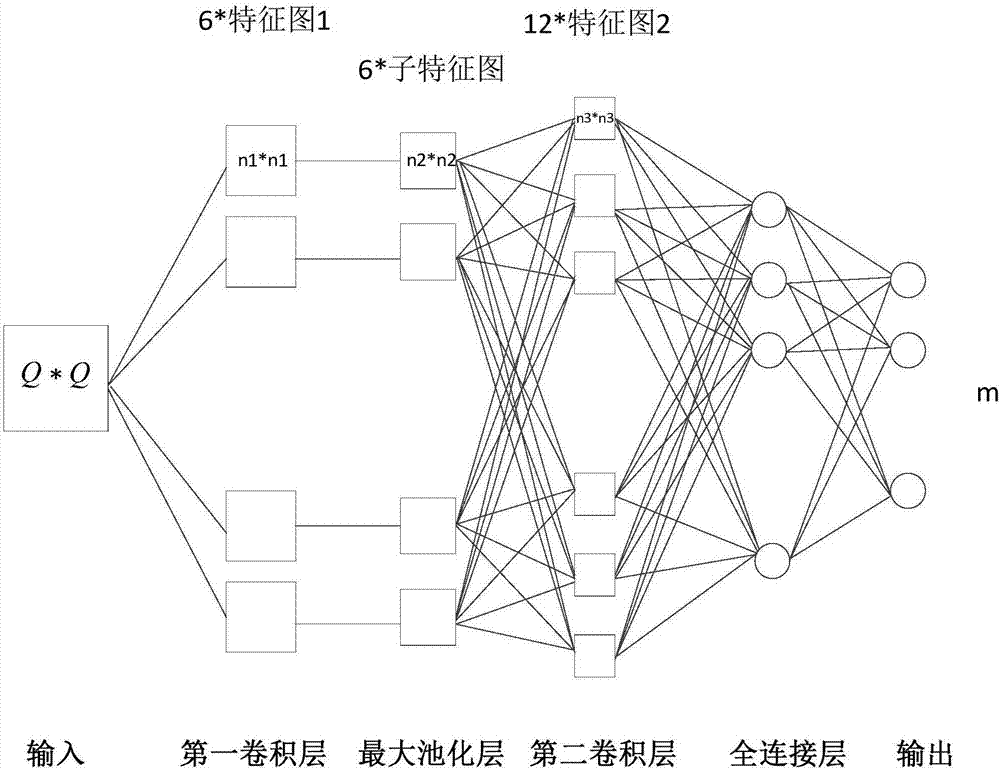
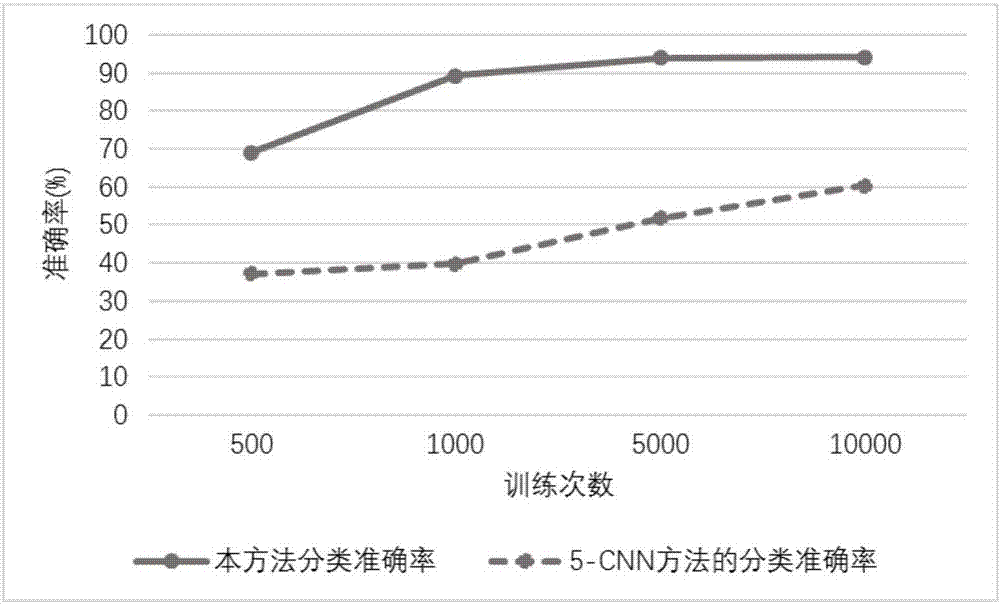
The present invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on the combination of six-layer convolutional neural network and spectral-space information. The method comprises: selecting the hyperspectral remote sensing image data of a certain number of bands; performing space mean-filtering on the two-dimensional image data of each selected band and then converting the format of the multi-band data corresponding to each pixel element; converting the one-dimensional vector into a square matrix, meaning that each pixel elements corresponds to a square matrix data; then, designing a six-layer classifier based on the deep learning template with an input layer, a first convolution layer, a largest pooling layer, a second convolution layer, a full connection layer and an output layer; extracting the square matrix data corresponding to several pixel elements as a training set to be inputted into the classifier and training the classifier; extracting the square matrix data corresponding to several pixel elements as a training set to be inputted into the trained classifier; observing the output classification result of the trained classifier; comparing with the real classification information; and verifying the performances of the trainer. With the method of the invention, higher classification accuracy can be obtained than from the currently available 5-CNN method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Transmitter having full-diversity and full-rate, a linear space-time code generating method for the transmitter, and a MIMO system using same
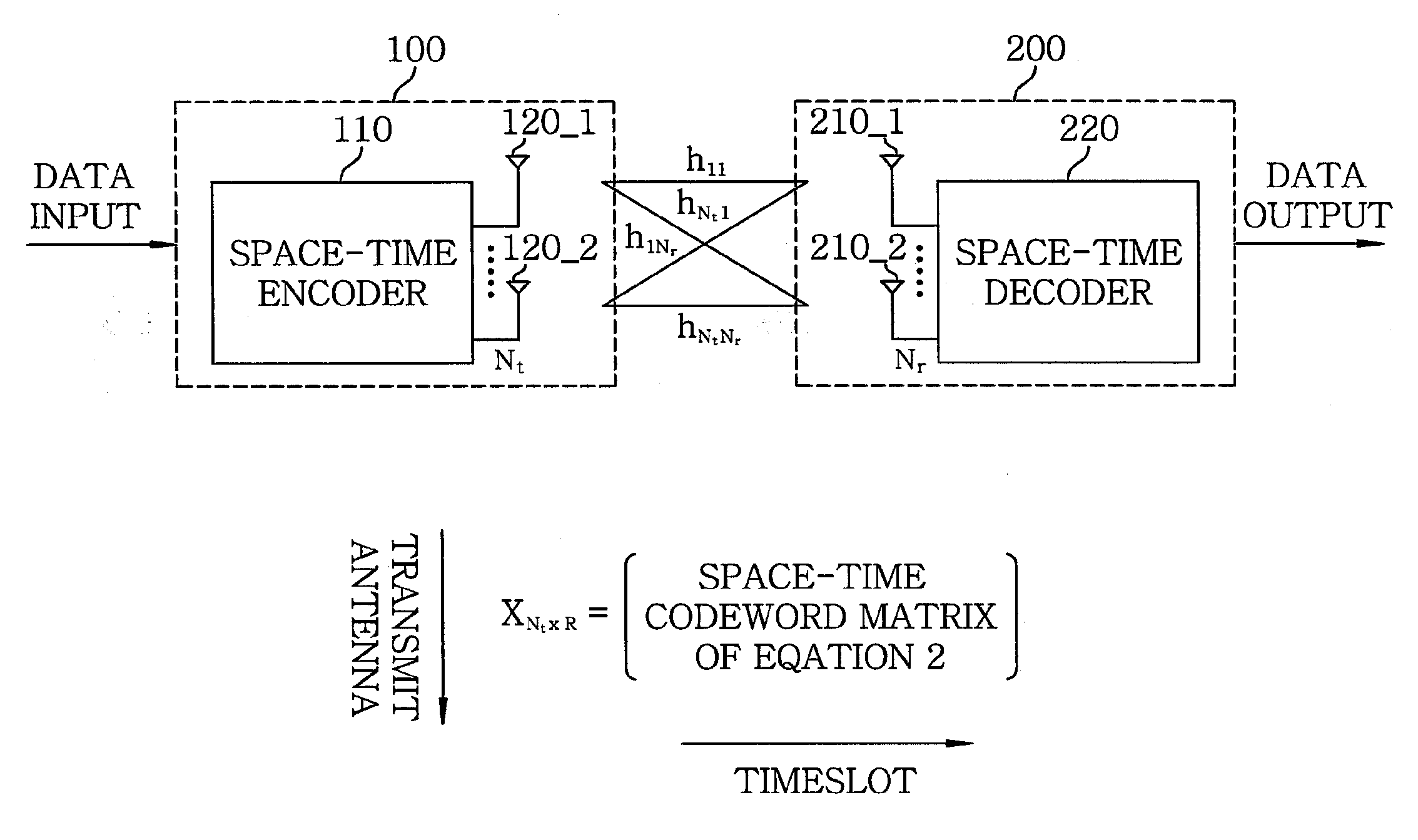
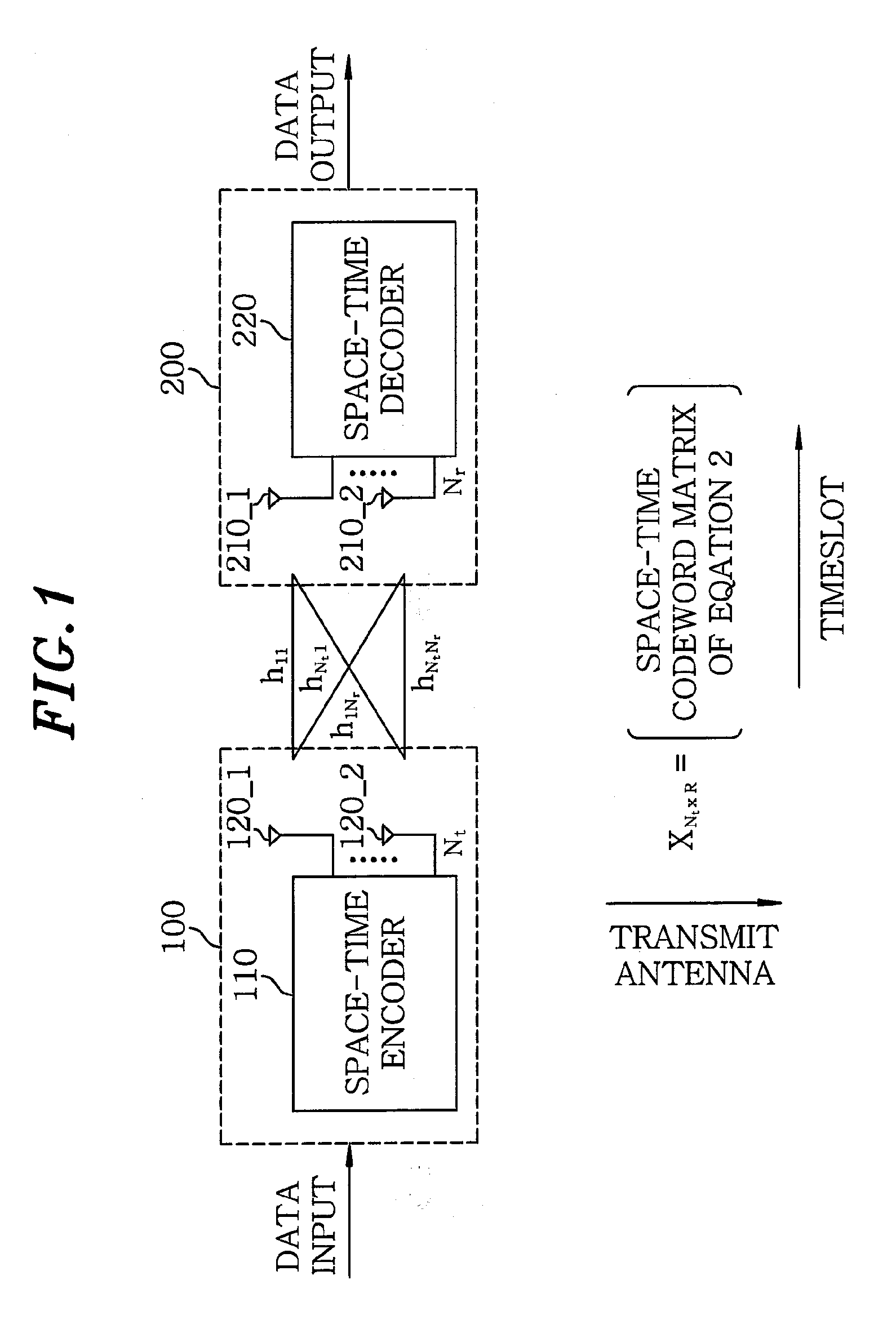
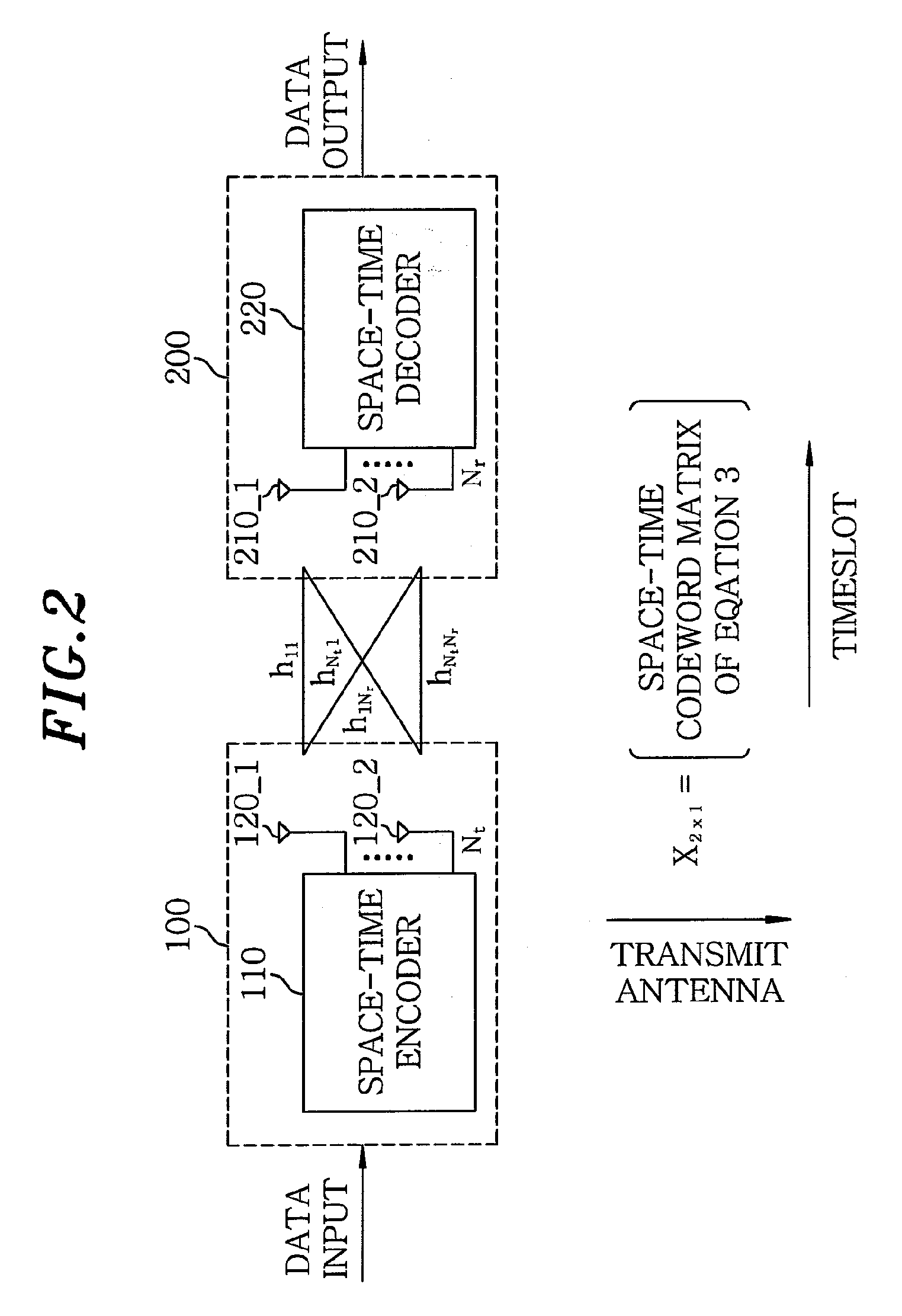
InactiveUS20090202015A1High gainMinimum delayDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFull RateTransmitter antenna
A space-time code has a codeword matrix. The codeword matrix is a square matrix with dimension equal to the number of the transmit antennas, wherein a row of the codeword matrix represents combined signals transmitted by each transmit antenna and a column of the codeword matrix represents timeslots of the number of the transmit antennas. Signals are transmitted through the rows of the number of spatial multiplexing rate, in each column of the matrix. Further, the symbols of the number of the transmit antennas are combined by way of utilizing complex weights, in each row of the matrix. With this space-time code, a delay is minimized, so that change of channels can be managed efficiently. Also, the space-time code has minimum number of data symbols, and thus its complexity is minimized.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
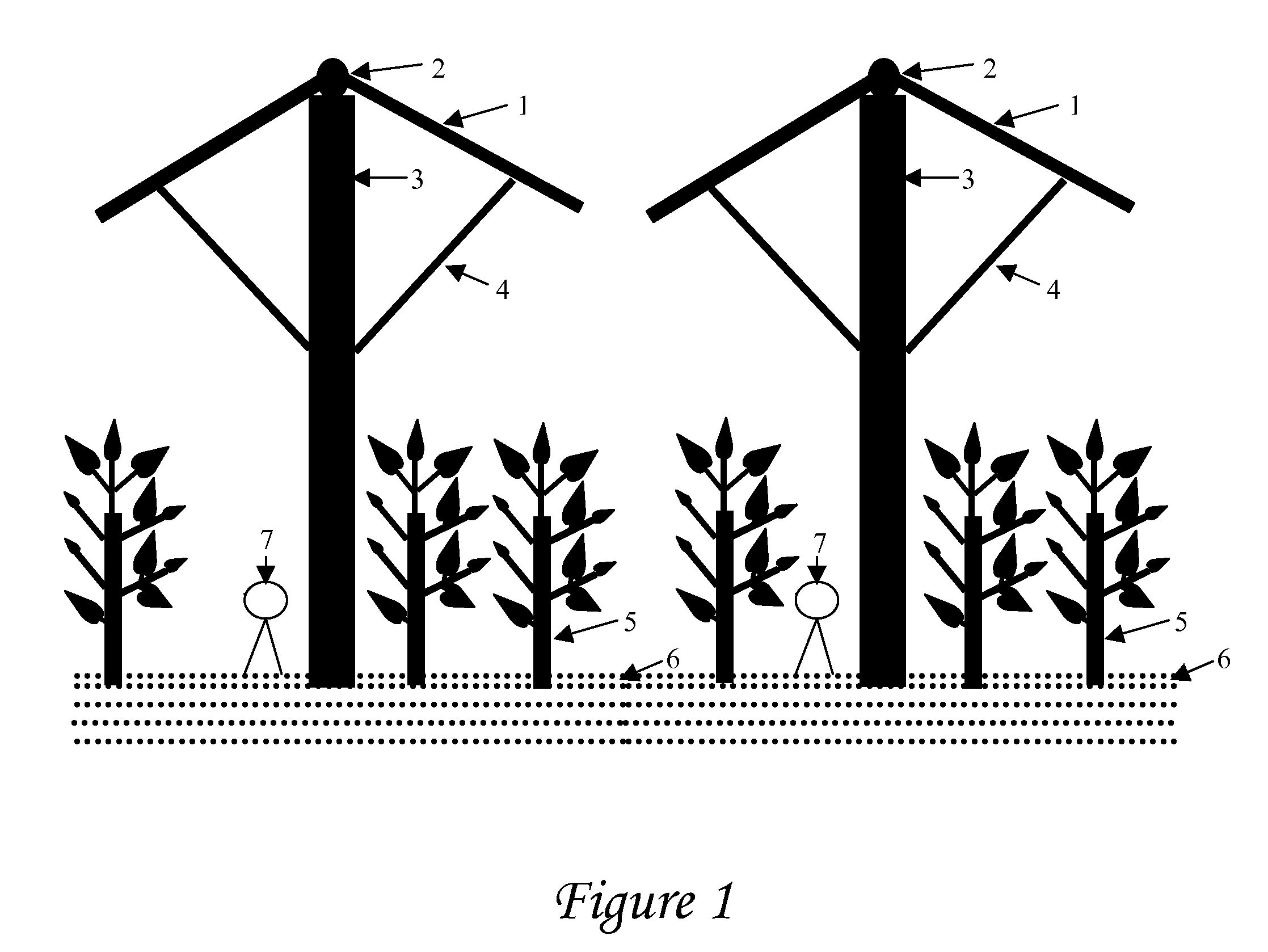
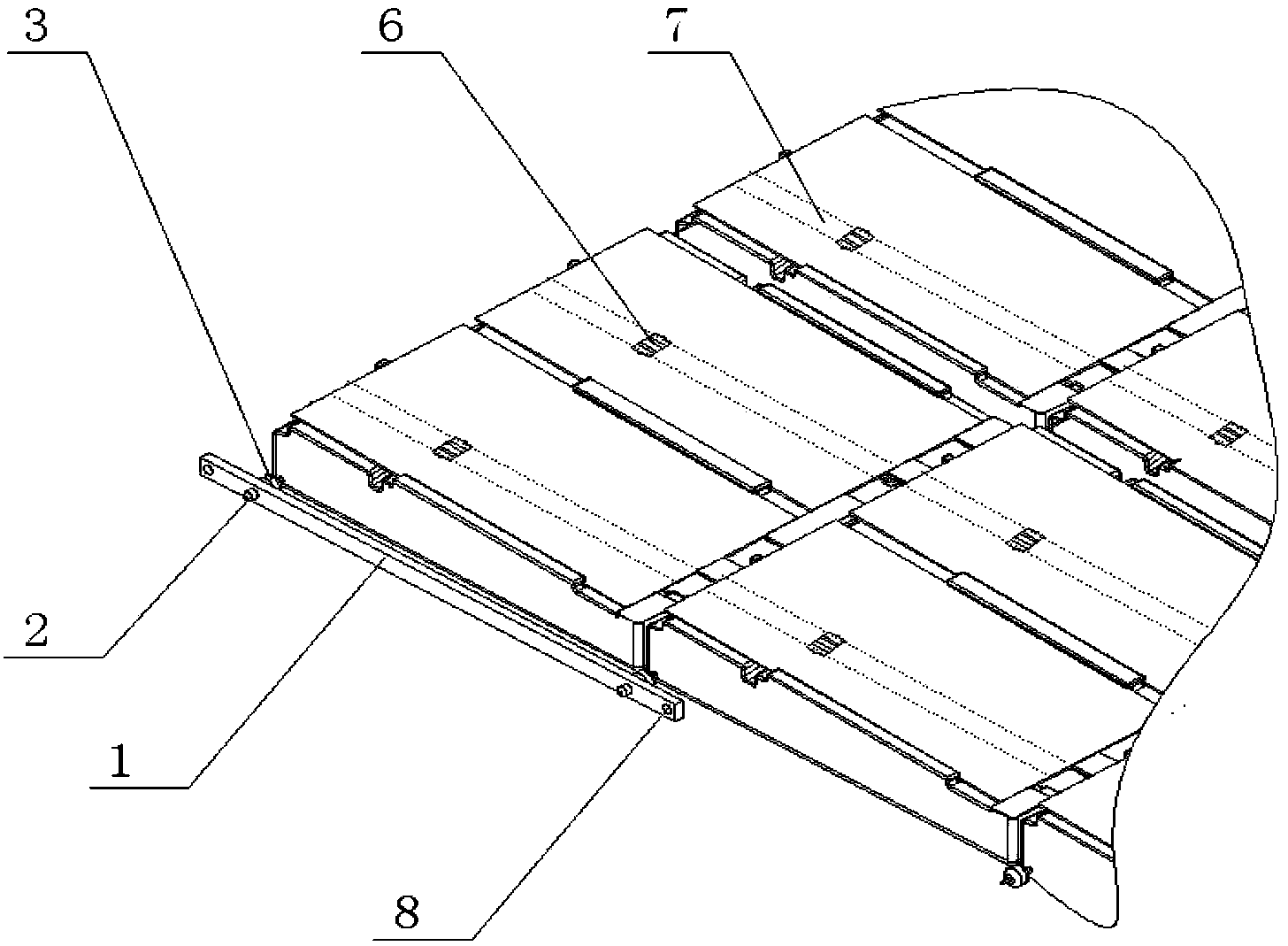
Apparatus and Method For Desert Environmental Control And For Promoting Desert Plants Growth
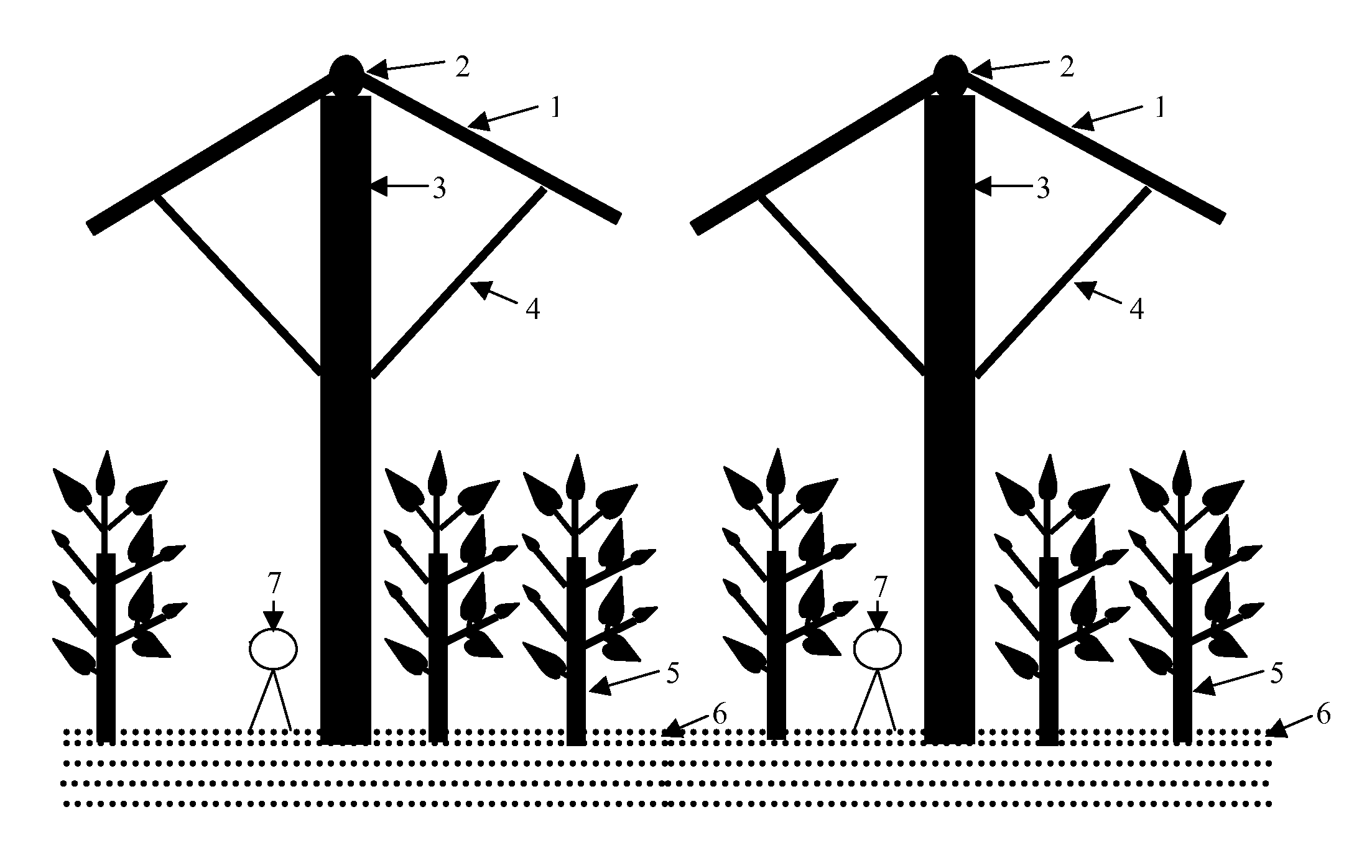
InactiveUS20080148631A1Efficient implementationReducing negative consequencePhotovoltaic supportsClimate change adaptationGrowth plantEngineering
A method of desert environmental control using the apparatus as disclosed herein that can be installed in huge expanse of desert area, evenly spaced in a square matrix type formation, forming a protective layer against sunlight, and turning the sun's natural energy into electrical power by the solar panel or photo-voltaic cells that can be placed upon the shade panel as disclosed herein, creating a friendly environment that promotes plants growth and thus turning arid desert land into human friendly land at a cost lower than other current systems.
Owner:WAN YOU BAO
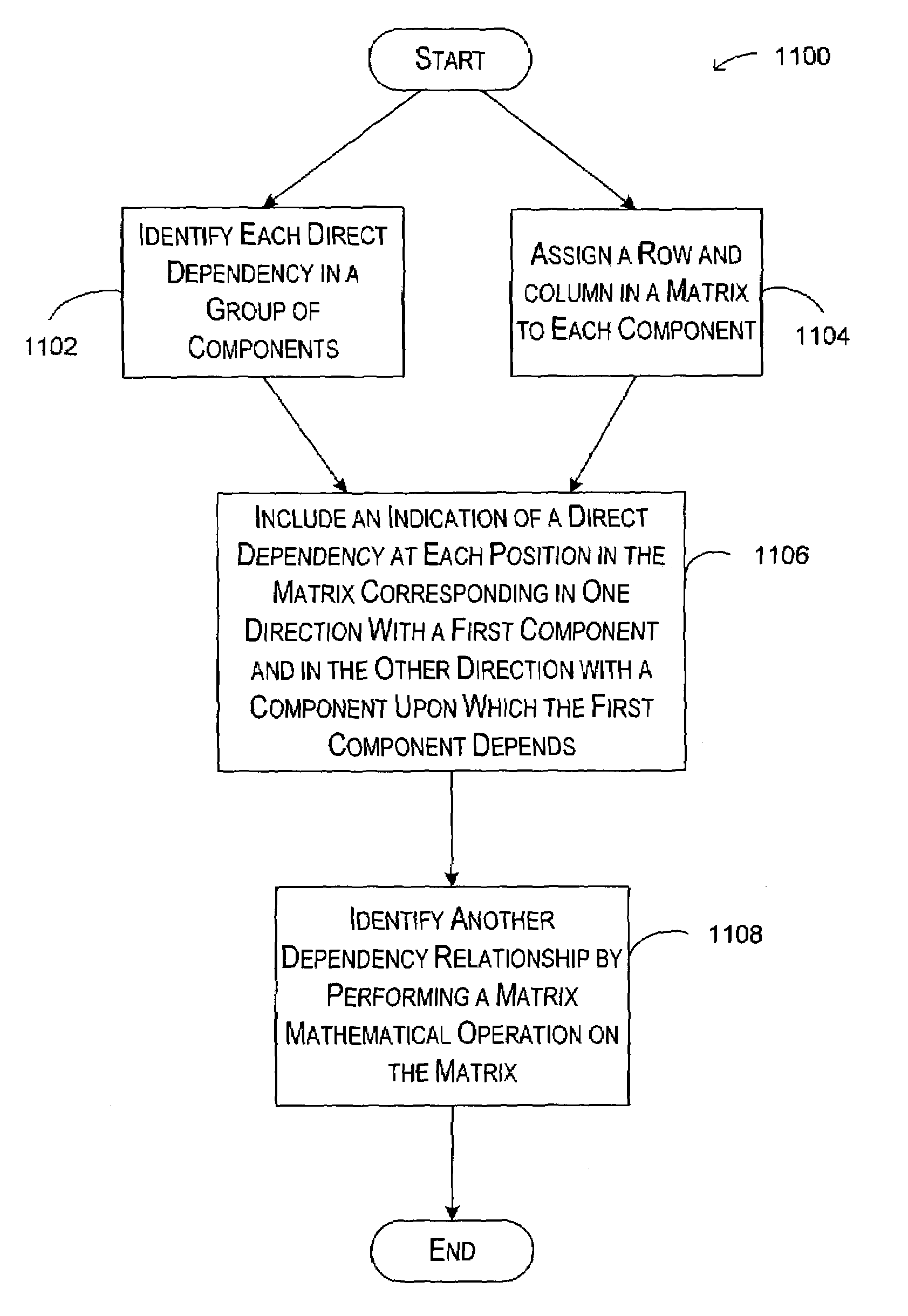
Component dependency matrices
InactiveUS7174540B2Version controlSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingDependency relation
Described is a system and method for identifying dependency relationships between components in a group of software components. Given a group of software components, a set of direct dependencies between each of the components and any other component is identified. The direct dependencies are indicated in a square matrix where each component in the group of components has a corresponding row and column. A particular component has the same row number as column number in the matrix. Multiplying that the matrix by itself identifies second-order dependencies. Higher order dependencies are identified by repeating the multiplication of the resultant matrix by the first-order dependency matrix. In other words, multiplying the third-order matrix by the first-order matrix achieves the fourth-order matrix, and so on.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for calibrating three-dimensional imaging system
InactiveCN101949693AEasy CalibrationEasy Calibration TasksUsing optical meansSinusoidal gratingDiffuse reflection
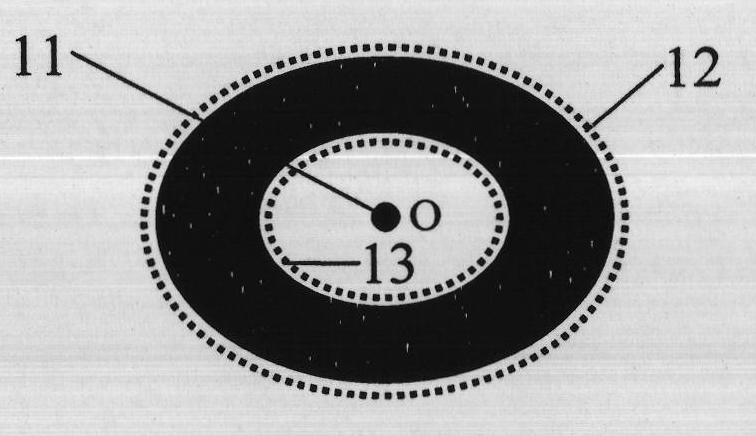
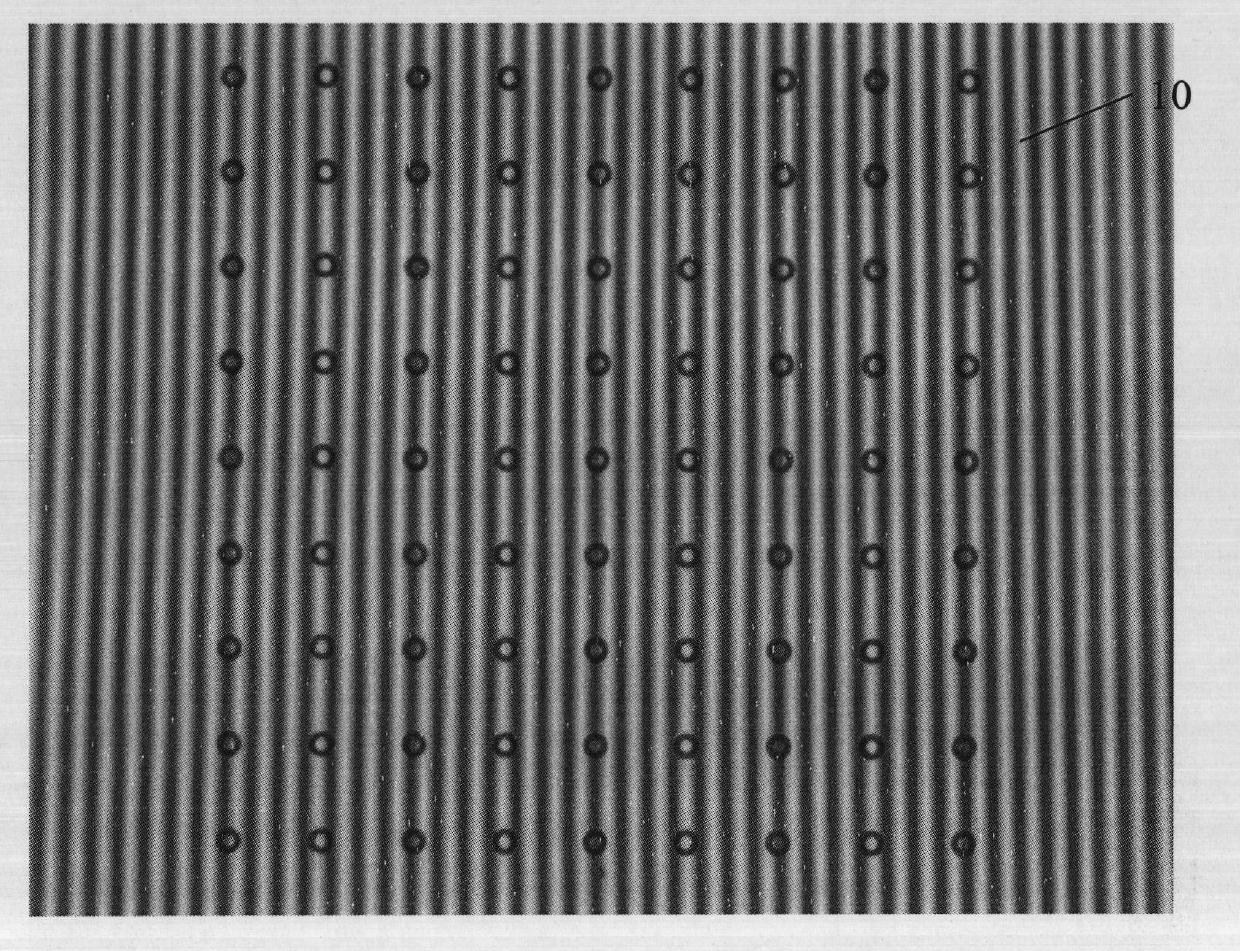
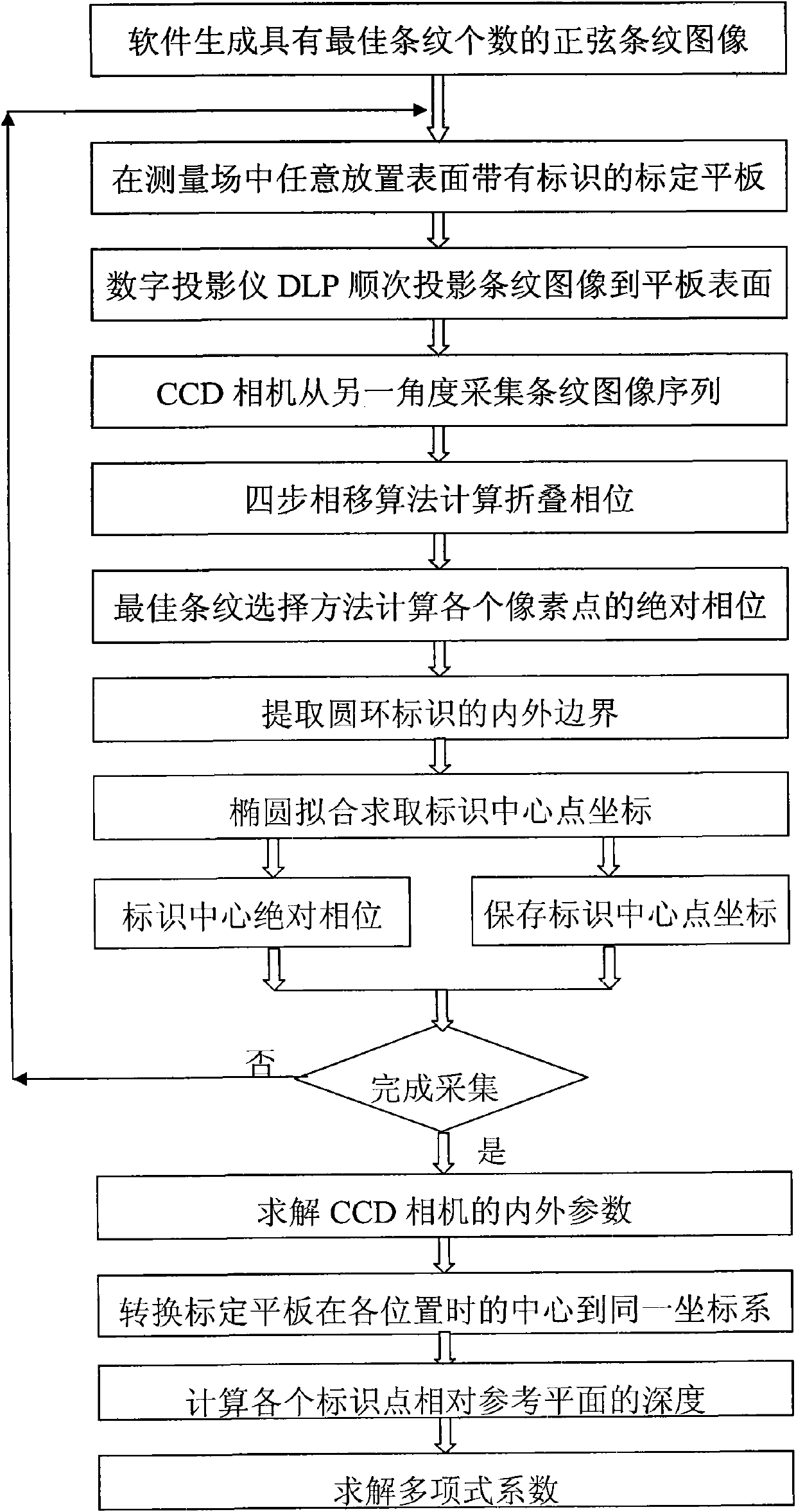
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a three-dimensional imaging system, which comprises the following steps of: 1, designing a calibration flat plate to be white and have a diffuse reflection surface and designing black annular identifiers in a square matrix arrangement mode on the calibration flat plate simultaneously, wherein the center distance between adjacent identifiers is equal; 2, placing the calibration flat plate at different positions in a measurement field, projecting non-uniform sinusoidal grating stripes with the optimal number of stripes at each placement position onto the surface of the calibration flat plate, and acquiring and calculating the absolute phase of each white pixel point inside the black annular identifiers; 3, extracting the central point position of each identifier from a corresponding absolute phase diagram to solve the relative depths of the identifiers when the calibration flat plate is at each placement position; 4, establishing a high-order polynomial (A) to express the relationship between the absolute phases and the relative depths; and 5, converting the absolute phases into actual depth data by using the calibrated polynomial coefficients so as to finish the calibration of the three-dimensional imaging system.
Owner:众趣(北京)科技有限公司
Method for eliminating noise from image generated by image sensor
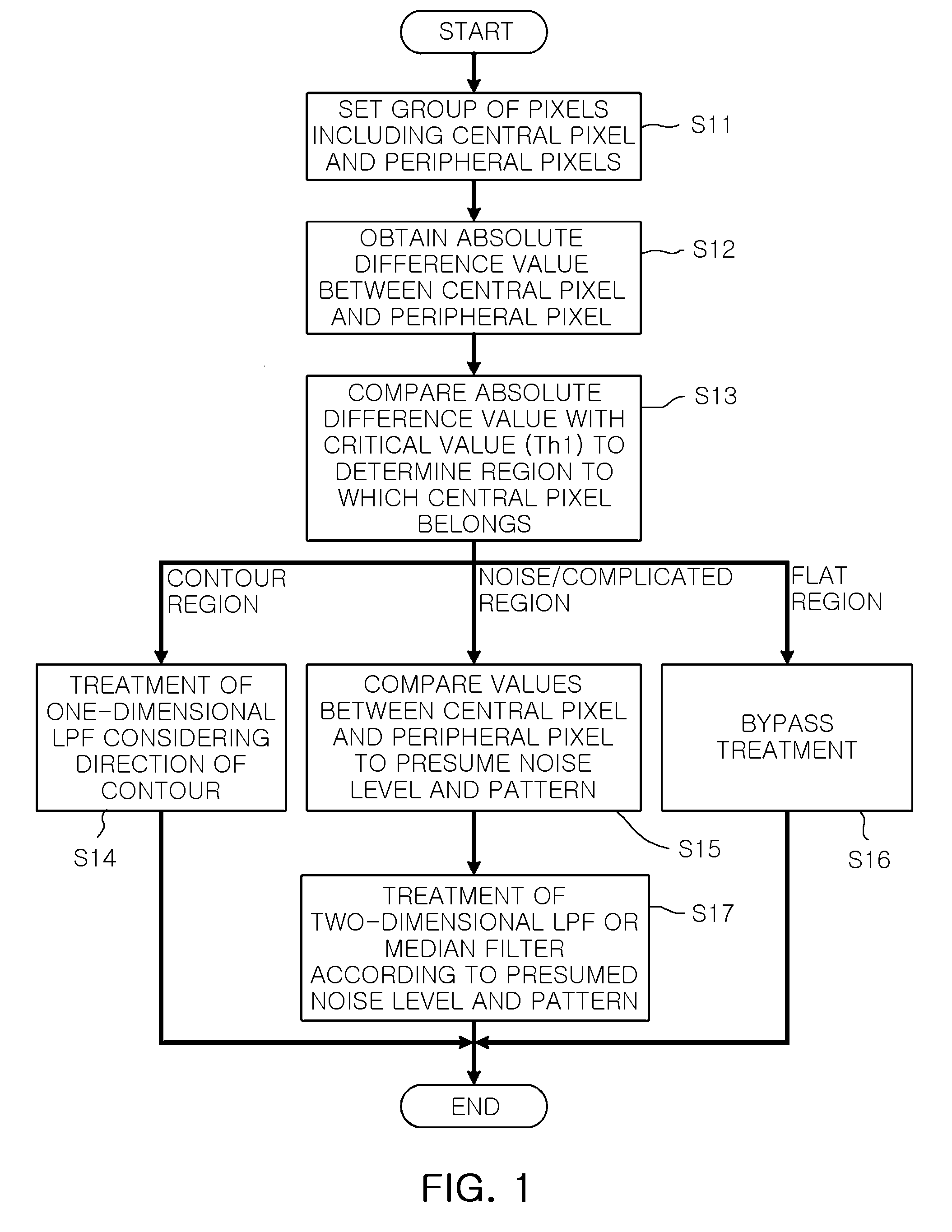
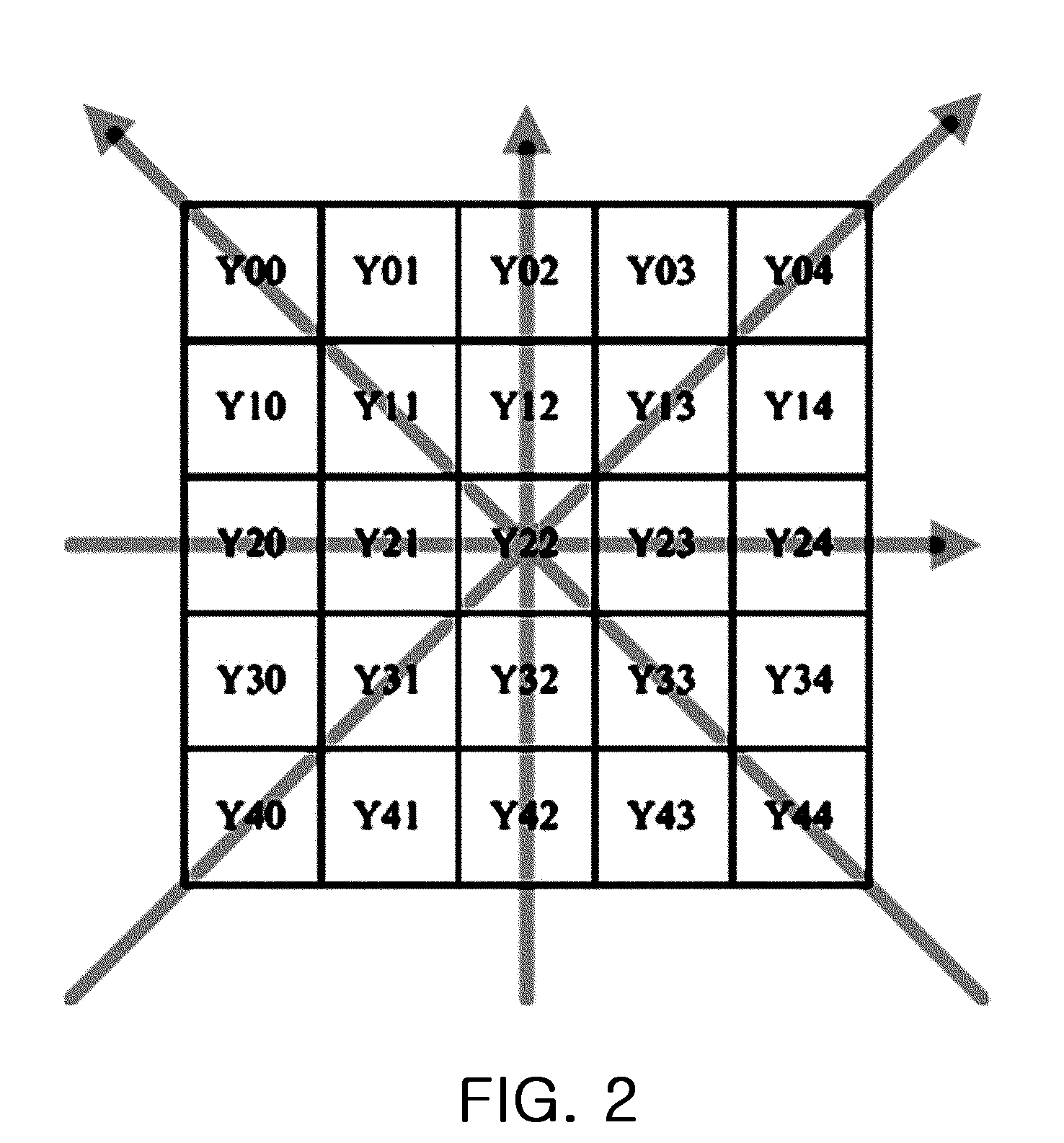
ActiveUS20090052798A1Cancel noiseImprove the level ofImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNoise levelAbsolute difference
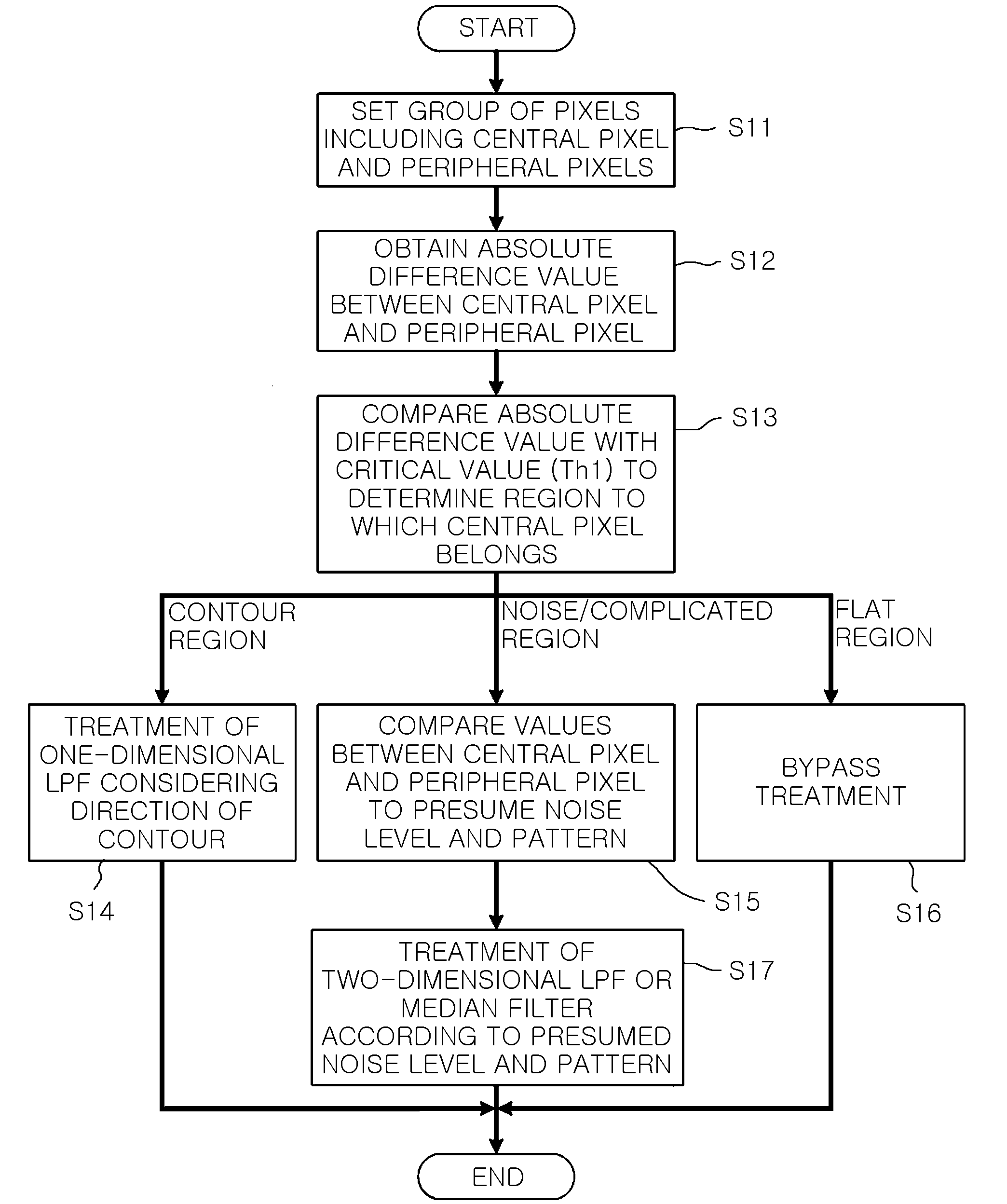
A method for eliminating noise from an image generated by an image sensor, includes: setting a group of pixels arranged in a square matrix and including a central pixel intended to eliminate the noise in the image and peripheral pixels arranged around the central pixel; obtaining absolute difference values between a luminance value of the central pixel and a luminance value of the peripheral pixels according to directionalities of the peripheral pixels about the central pixel; comparing the obtained absolute difference values with first critical values to determine a region to which the central pixel belongs; when the determined region is the contour region, eliminating noise of the group of the pixels according to directionality of the contour; and when the determined region is the noise region, eliminating the noise of the group of the pixels according to a noise level of the group of the pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
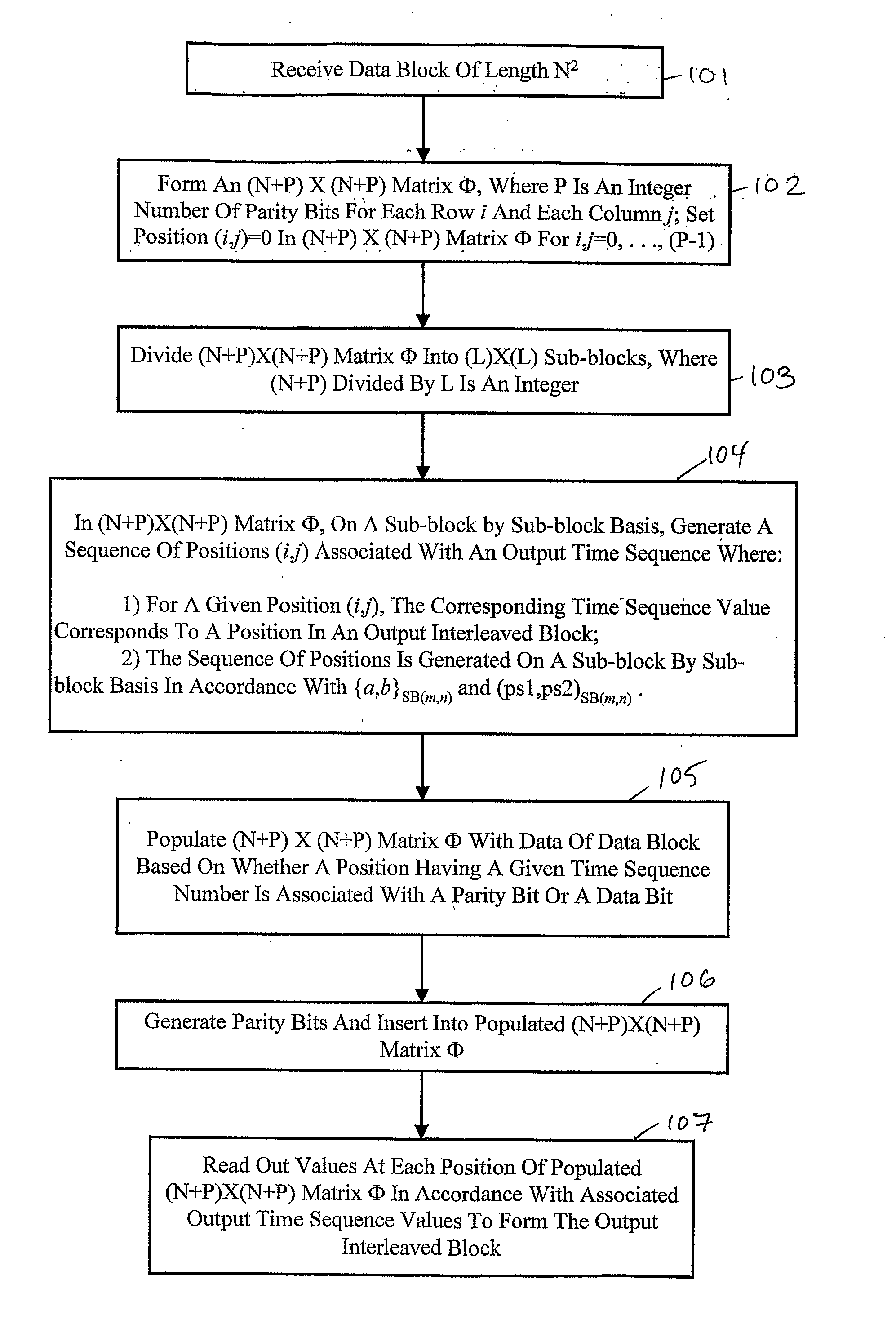
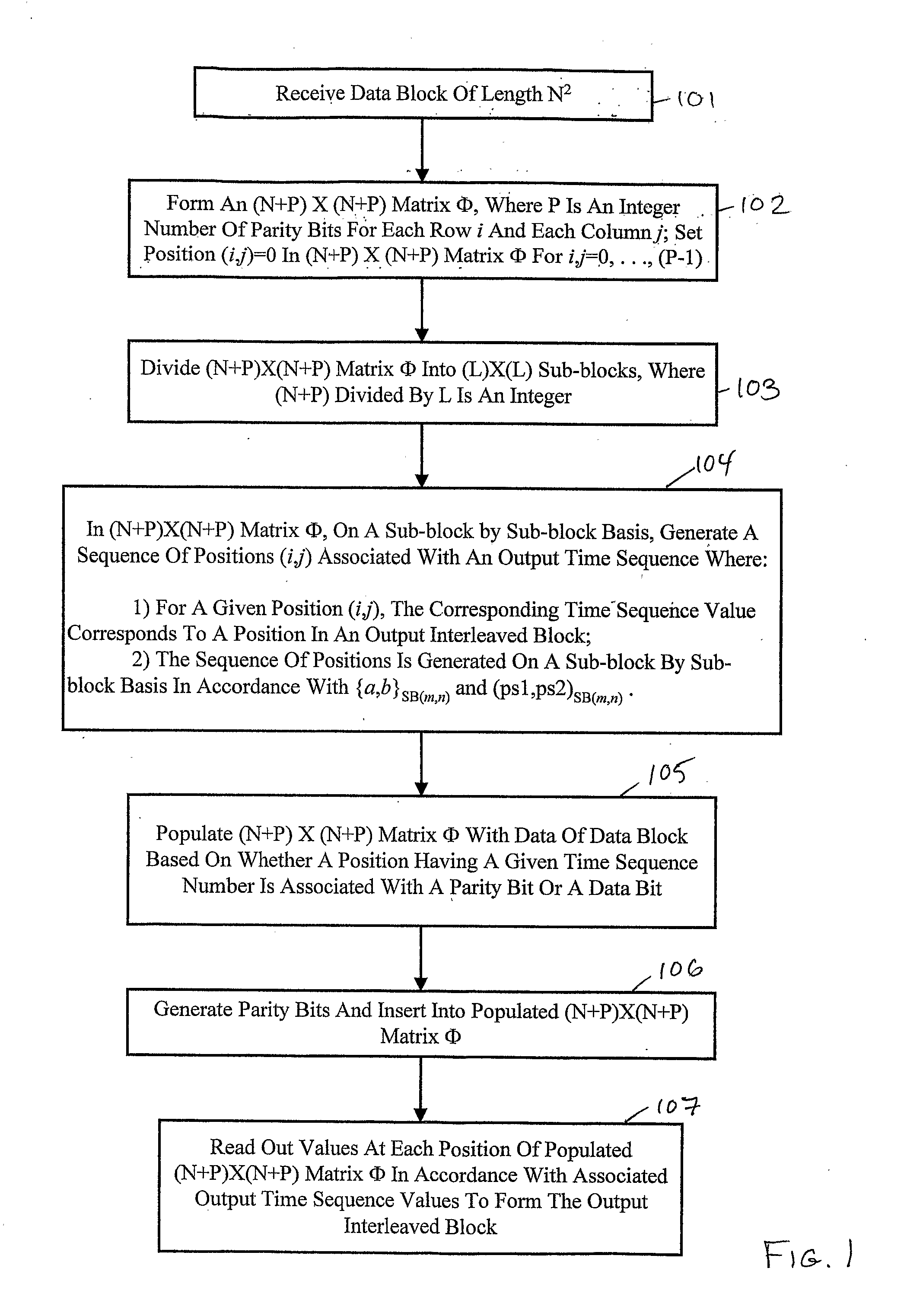
Interleaver and De-Interleaver
An interleaver employs a generalized method of generating a mapping. The mapping is generated for interleaving bits of a data block and associated error detection / correction information. The data block is of length N, and the length of the error detection / correction information is P. An (N+P)×(N+P) square matrix is formed and divided into sub-blocks, where one portion of the matrix is associated with error detection / correction information and another portion is associated with data of the data block. New positions in the matrix are generated in a time sequence on a sub-block by sub-block basis based on a generator seed pair and an original position seed pair. The time sequence also corresponds to positions in an output interleaved block. Once the new position sequence is generated, the matrix is populated with data and error detection / correction information based on the corresponding time sequence. A de-interleaver performs the inverse mapping of the interleaver.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
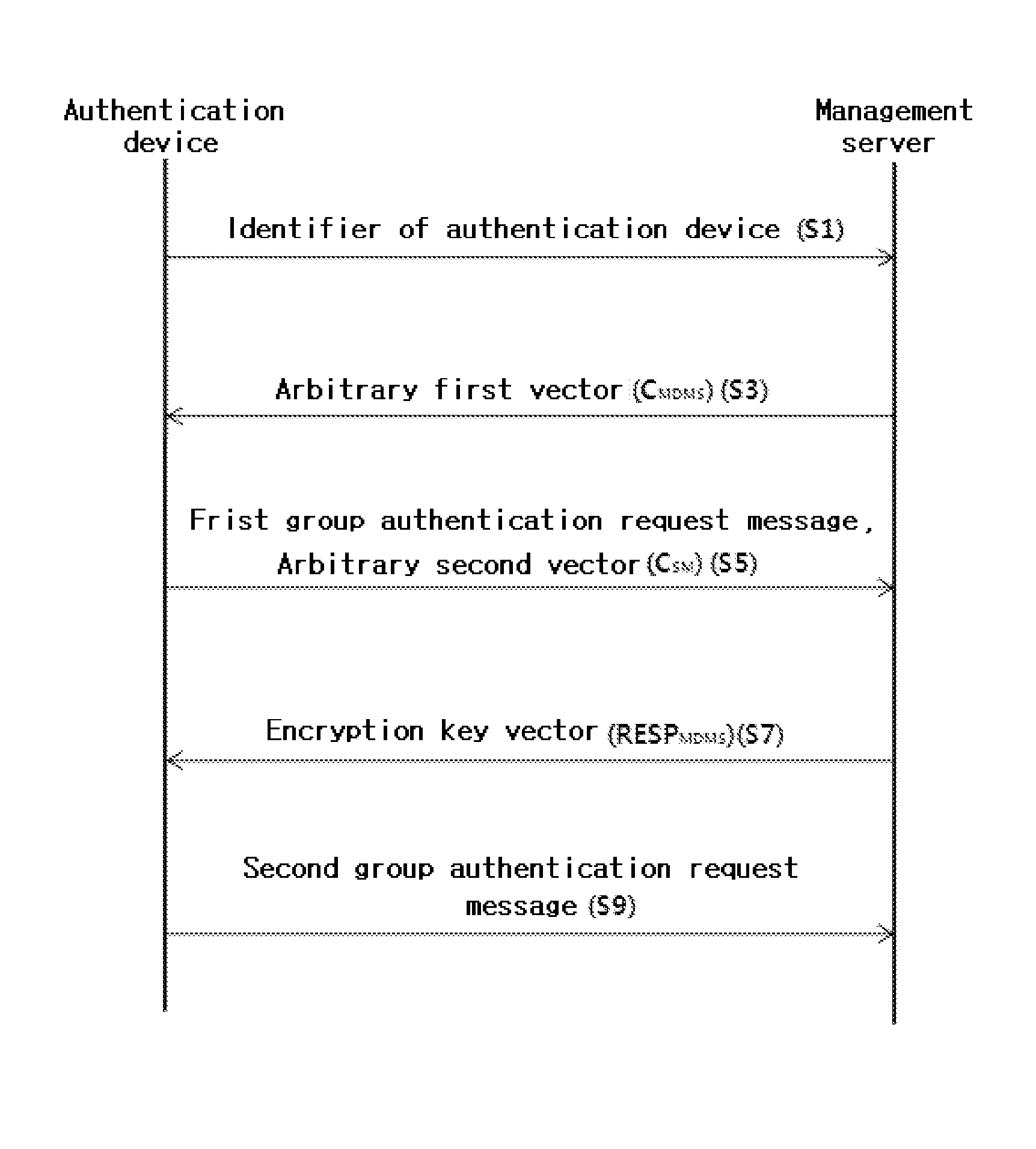
Method for authenticating low performance device
ActiveUS20130346741A1Reduce performanceMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash function
The present invention relate to a method for authenticating a low performance device, and more particularly, to a device authenticating method, in which a low performance device such as a smart meter of a smart grid is authenticated in a matrix operation instead of an exponential operation through a homomorphic hash function (HHF) of a non-square matrix M, so that the amount of operations required for authenticating the device can be reduced and the device can be safely authenticated even without a separate certificate authority.
Owner:INST FOR BASIC SCI
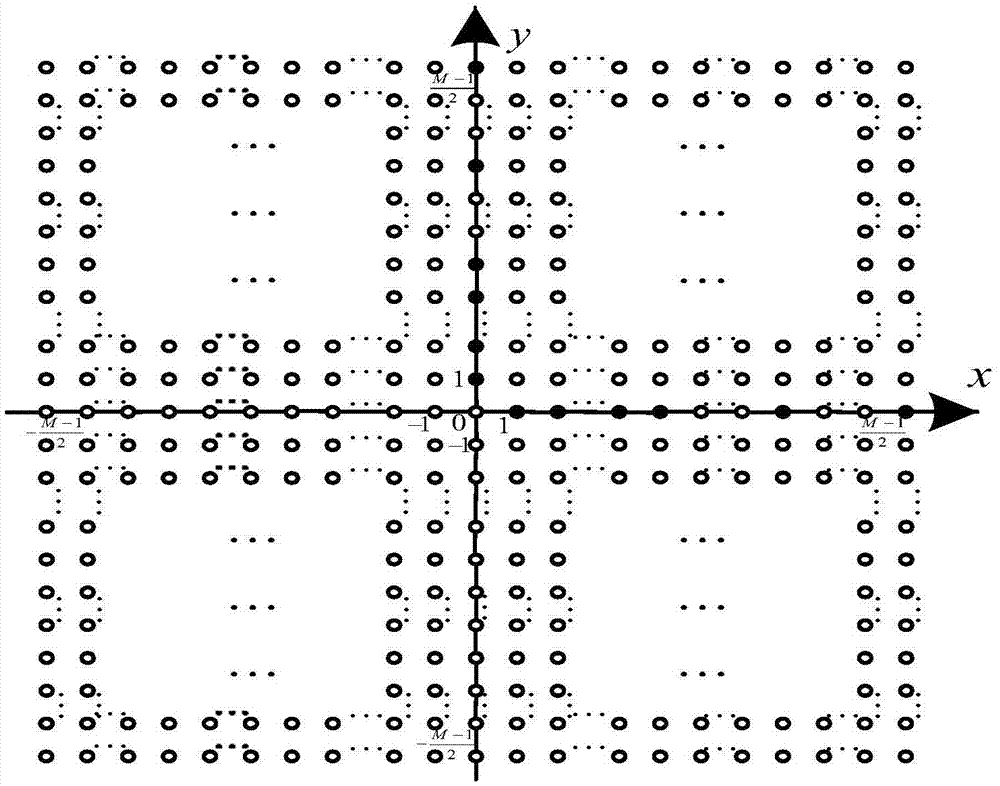
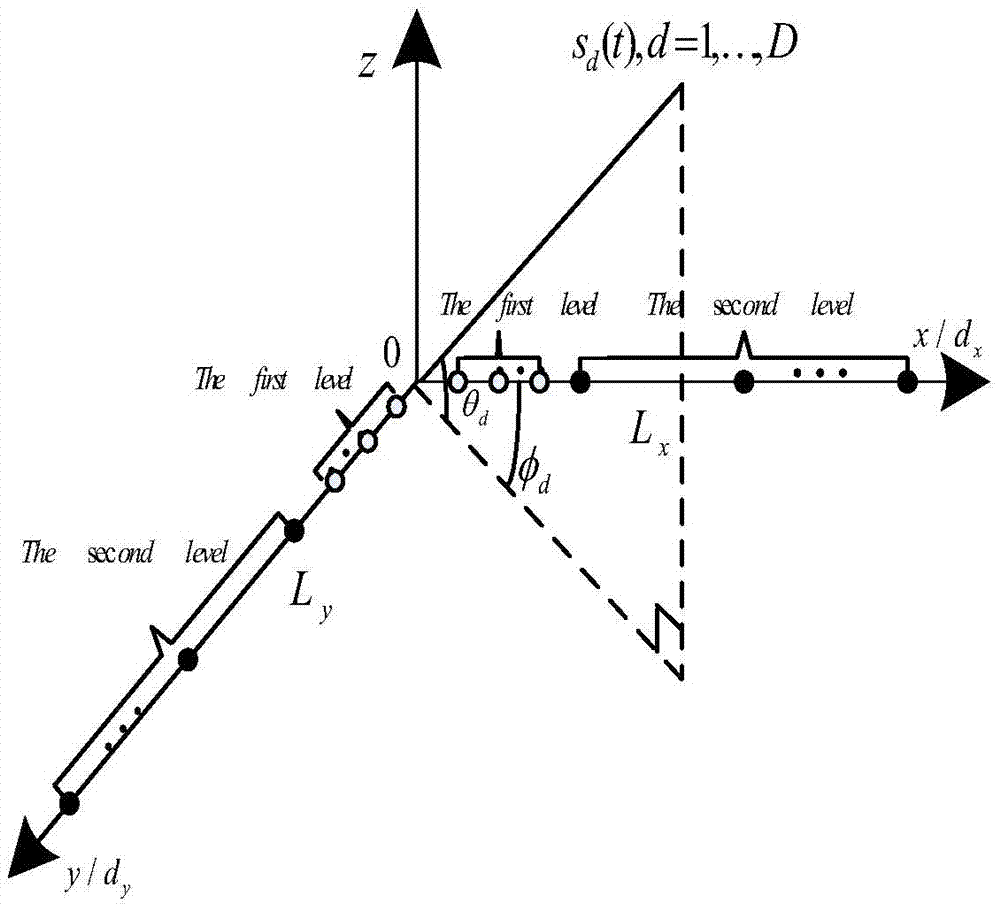
Nested L-shaped antenna array structure and direction of arrival estimation method thereof
InactiveCN105445696ASimple structureEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFeature vectorDecomposition
The invention relates to a nested L-shaped antenna array structure and a direction of arrival estimation method thereof. The direction of arrival estimation method includes the following steps that: a nested L-shaped antenna array structure is constructed, and the received signals of a physical array antenna structure is determined based on the nested L-shaped antenna array structure; the high-order cumulant matrix of the received signals of the physical array antenna structure is obtained through using a high-order cumulant DOA algorithm; vectorization calculation is performed on the high-order cumulant matrix, so that a vectorized high-order cumulant matrix can be obtained, and the information of maximum continuous virtual square matrixes is extracted, and equivalent received signals can be obtained; two-dimensional spatial smoothing processing is performed on the equivalent received signals, so that an equivalent autocorrelation matrix can be obtained, eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the equivalent autocorrelation matrix, so that a signal feature vector matrix and a noise feature vector matrix can be obtained; and the signal feature vector matrix and the noise feature vector matrix are utilized to construct a spectral peak searching relational expression, and direction of arrival estimation is carried out, and the estimated value of the direction of arrival of the received signals is obtained. According to the nested L-shaped antenna array structure and the direction of arrival estimation method thereof adopted, a larger effective aperture can be realized when few array elements are adopted, and direction of arrival estimation precision can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Determining method and device of optimal installing inclination angle of photovoltaic module
InactiveCN106372346AAccurate calculationLow investment costData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationOptical transmittanceDirect radiation
The invention discloses a determining method and device of the optimal installing inclination angle of a photovoltaic module, and relates to a photovoltaic equipment arrangement technology. The method comprises the steps of determining the light transmittance of photovoltaic module square matrix surfaces corresponding to light ray incidence angles at different moments in the set time period; calculating the direct radiation quantity of the inclination area of the photovoltaic module according to the light transmittance; determining the total daily radiation quantity of the photovoltaic module in the daily set time period according to the direct radiation quantity, the scattering radiation quantity and the reflecting radiation quantity of the inclination area of the photovoltaic module; determining the total power generation quantity of a photovoltaic system in one period according to the total daily radiation quantity and the installed capacity on the set land area; determining the cost per kilowatt hour of electricity in unit area according to the total power generation quantity and the static investment cost of the photovoltaic system; determining the inclination angle corresponding to the minimum value of the cost per kilowatt hour of electricity as the optimal installing inclination angle of the photovoltaic module. The problem that a traditional optimal inclination angle calculation method does not consider the growing economy is solved; the effect that the cost per kilowatt hour of electricity is the lowest is achieved.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
Accuracy correcting method of laser marking machine
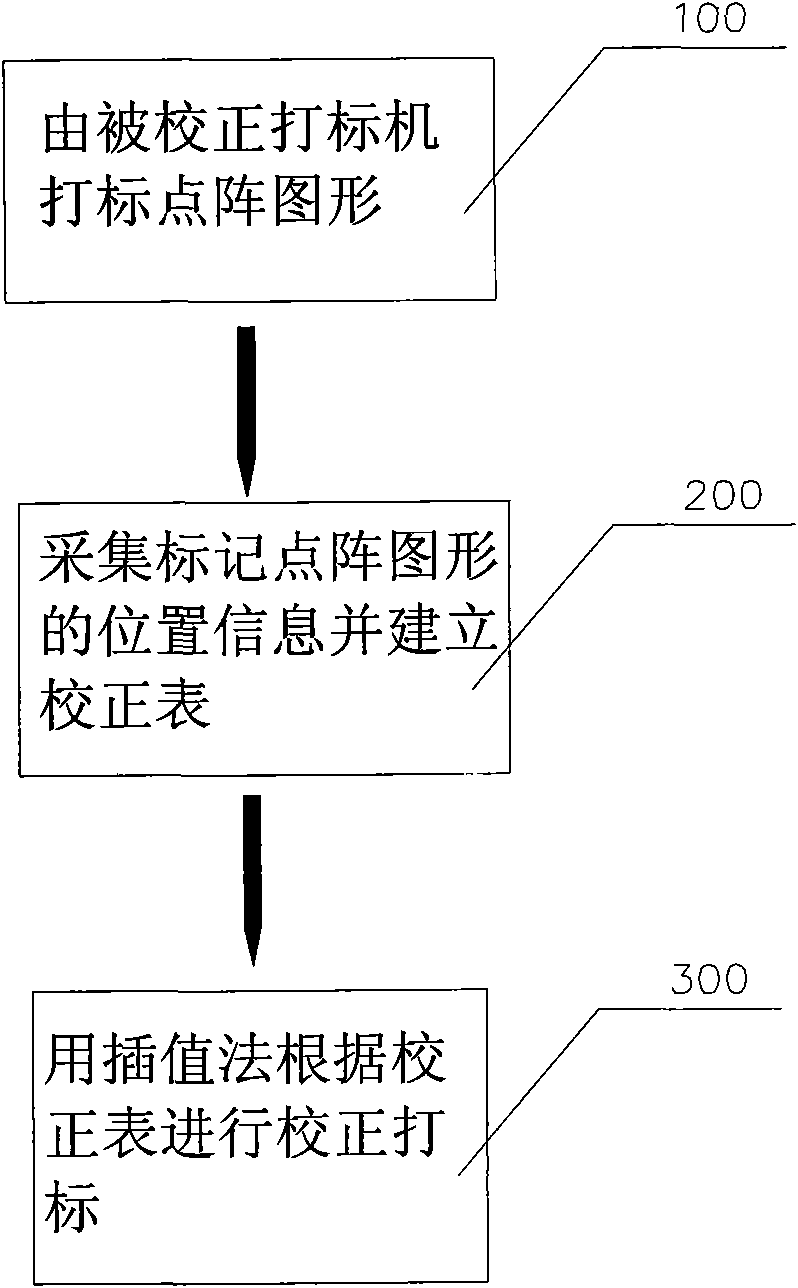
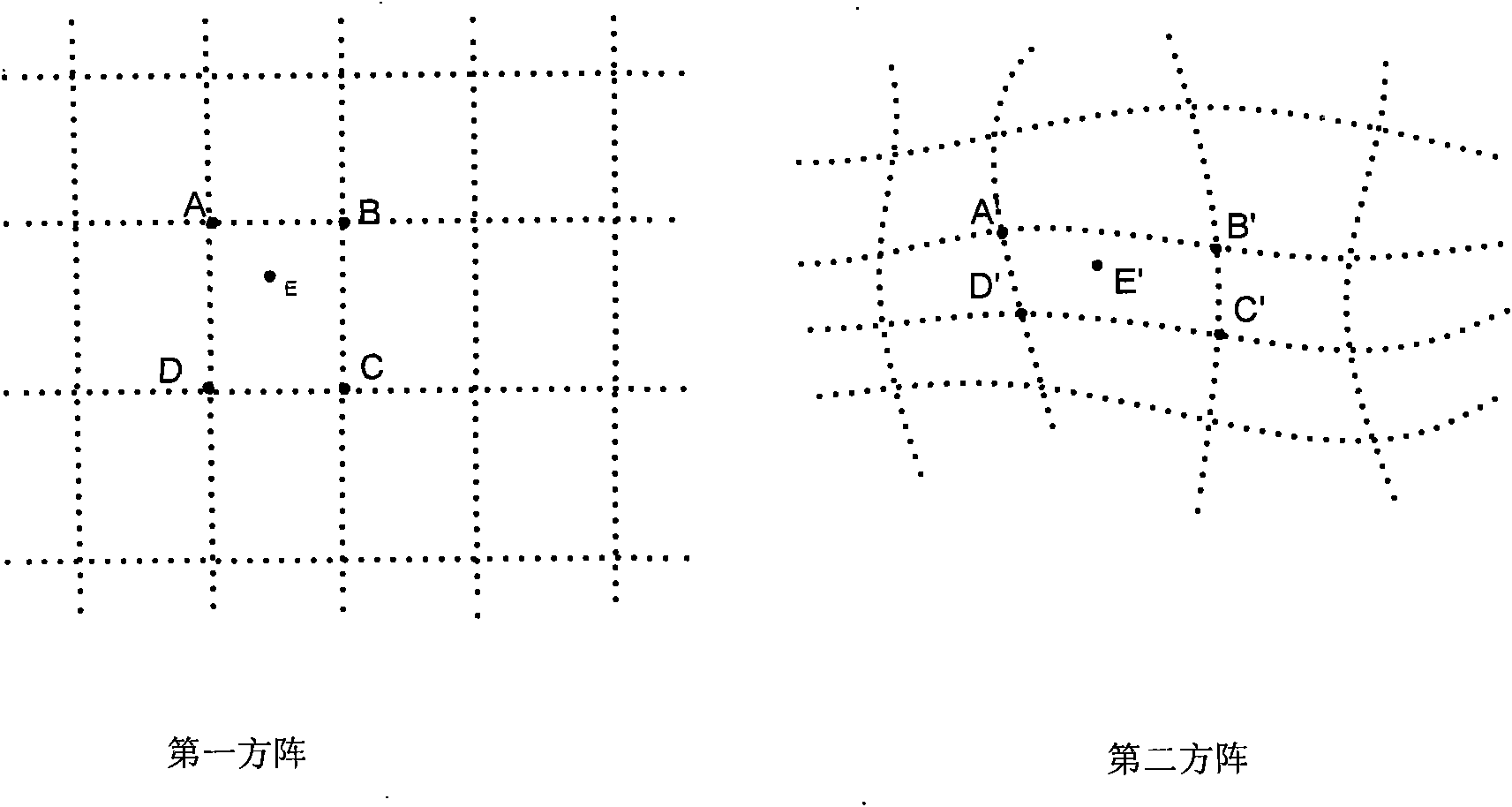
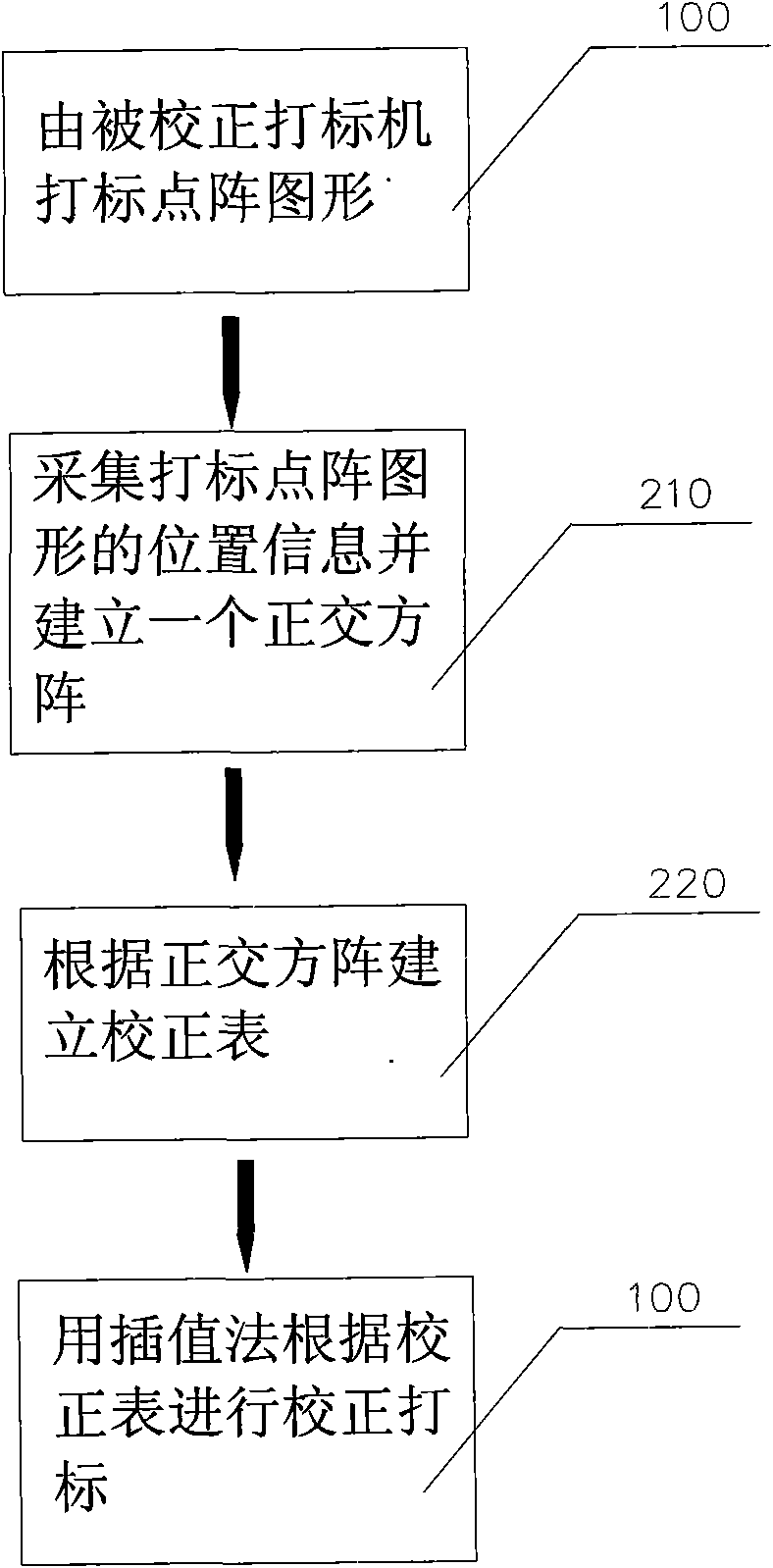
ActiveCN101685488AImprove calibration accuracyHigh precisionDigitally marking record carriersPrintingDot matrixAlgorithm
The invention provides an accuracy correcting method of a laser marking machine, which comprises the following steps: collecting the position information of dots in a marking dot matrix of the laser marking machine, establishing a correction table by the collected position information of the dot matrix and the dot matrix in the system, and correcting marks by adopting an interpolation method. Simultaneously, in order to simplify the algorithm and reduce the implementation cost, methods of taking an orthogonal square matrix and correcting and marking an image collecting device are also adopted.The accuracy correcting method has high correcting accuracy, simple and convenient calculation and low implementation cost.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
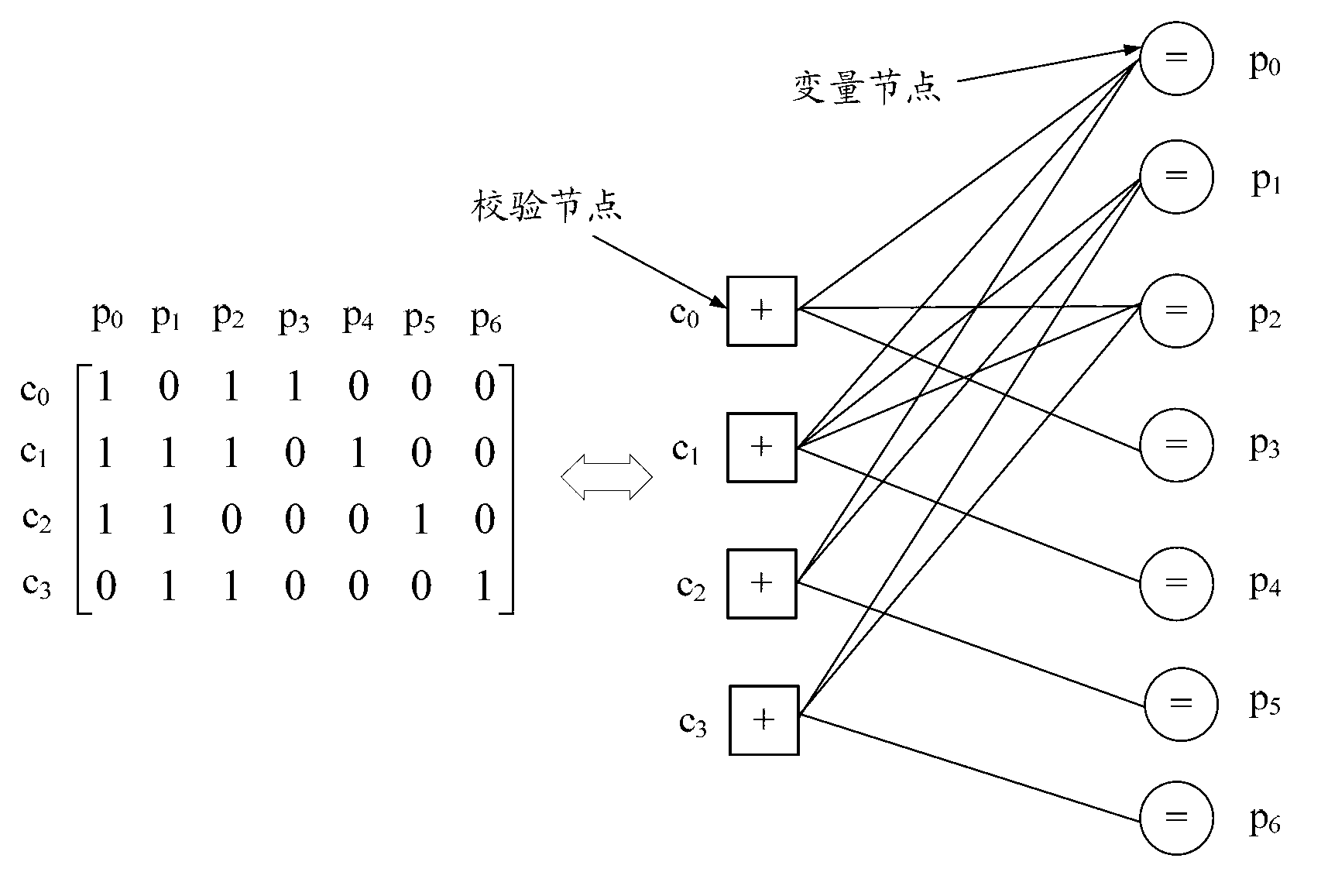
Check Matrix Generating Apparatus and Communication Apparatus
InactiveUS20080184084A1Promote generationStable characteristicsElectronic circuit testingChecking code calculationsAlgorithmLow-density parity-check code
A check matrix generating apparatus calculates a parameter for pseudo-random-number permutation matrices using a predetermined information length, a coding rate, and a maximum column degree, generates the pseudo-random-number permutation matrices from the calculated parameter for the pseudo-random-number permutation matrices by using a pseudo-random-number sequence and a Latin square matrix, determines, as a parameter, a combination of degree distributions which can be adopted for optimization of a degree distribution of generation of a check matrix which can be formed with the pseudo-random-number permutation matrices, using the predetermined information length, coding rate, and maximum column degree, optimizes the degree distribution of generation of a check matrix under a restriction condition based on the determined combination of degree distributions which can be adopted, and arranges the generated pseudo-random-number permutation matrices according to the optimized degree distribution of generation of the check matrix so as to generate the check matrix for low-density parity-check codes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
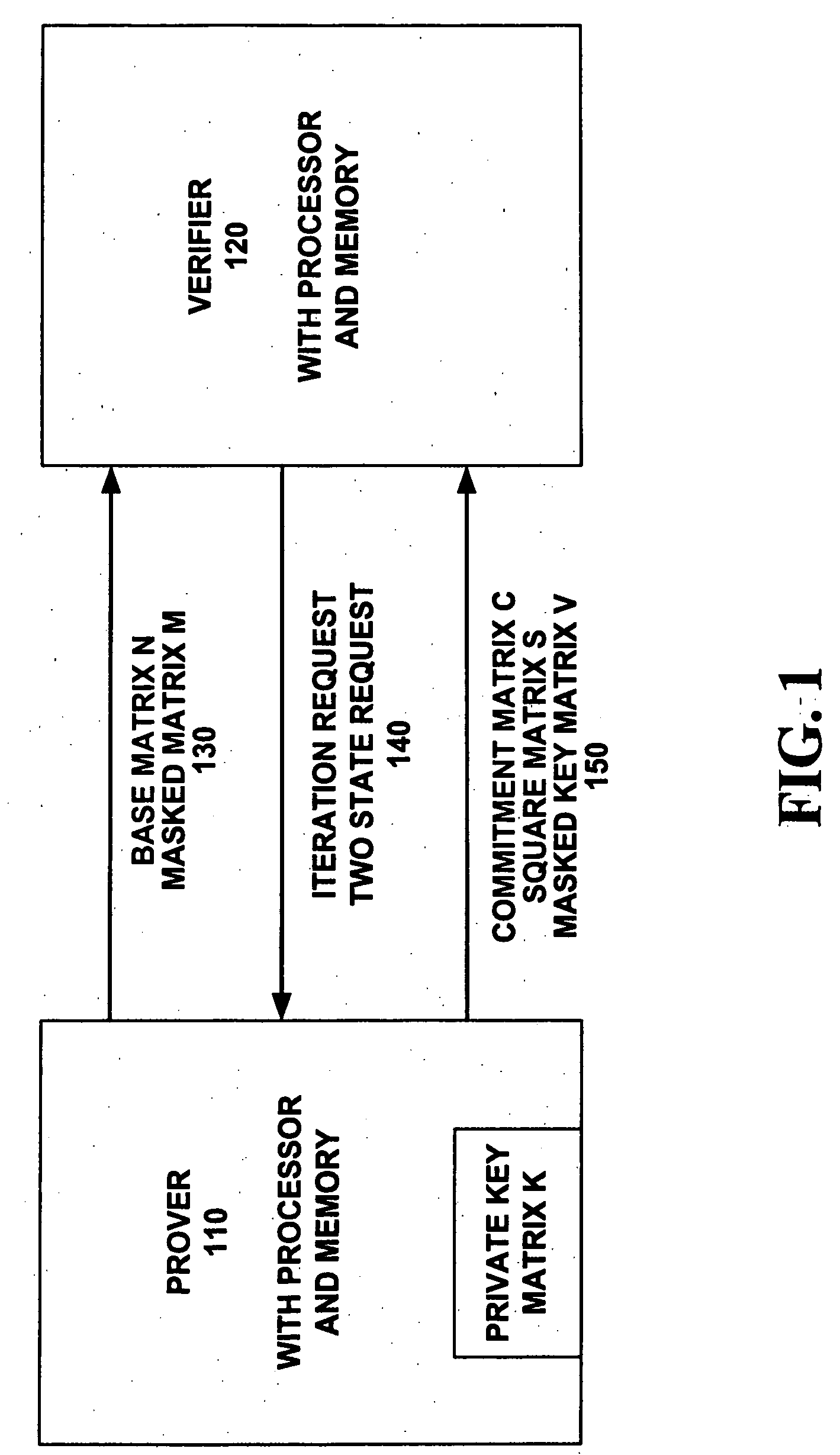
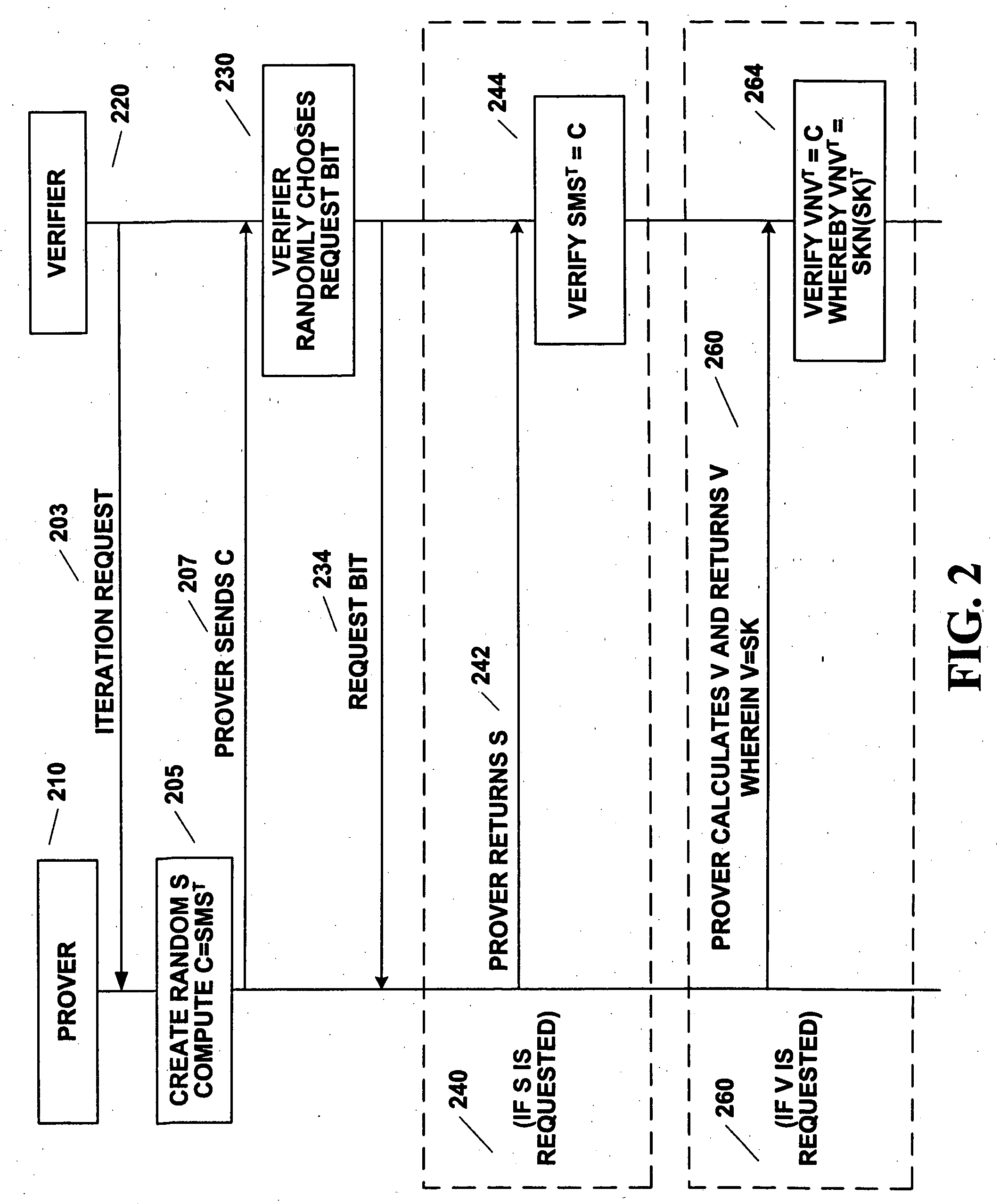
Method for zero-knowledge authentication of a prover by a verifier providing a user-selectable confidence level and associated application devices
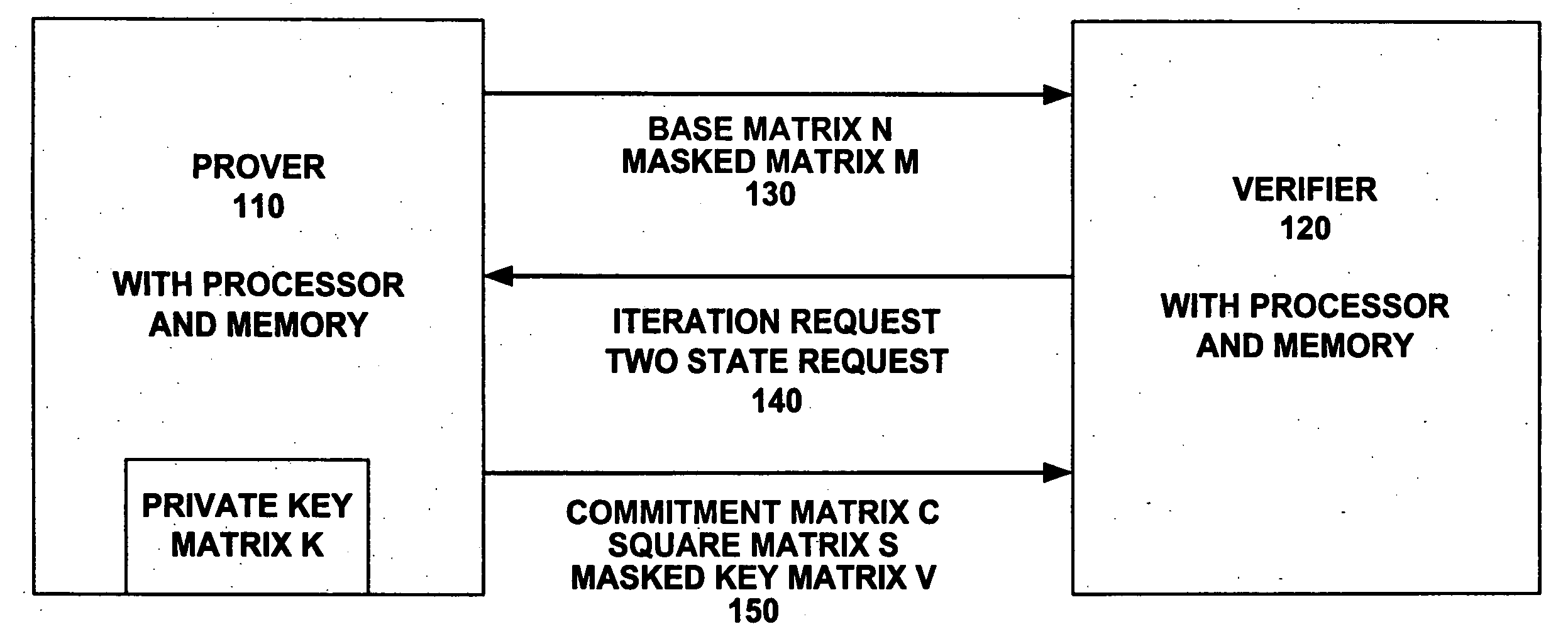
InactiveUS20060195692A1Improve trustComputationally efficientPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Authentication is performed to a confidence level (CL) desired by a verifier (220). A prover (210) picks and sends certain same size, square matrices to the verifier (220). A random request bit is sent (234) from the verifier (220) to the prover (210) after the receipt of a certain square matrix. Depending on the request bit, calculations are made (244, 264) by the verifier (220) to determine if the matrices sent from the prover are verifiable. The prover (210) is iteratively authenticated by the verifier (220). Iterations are continued until (320) a count of the iterations (IL) reaches a number sufficient to achieve the desired confidence level (CL). After a delay, more iterations can achieve a higher confidence level by building on previous result of authentication without having to begin at zero. During this delay, the verifier (220) can perform tasks in reliance on the result of authentication. Digital logic can perform the authentication.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
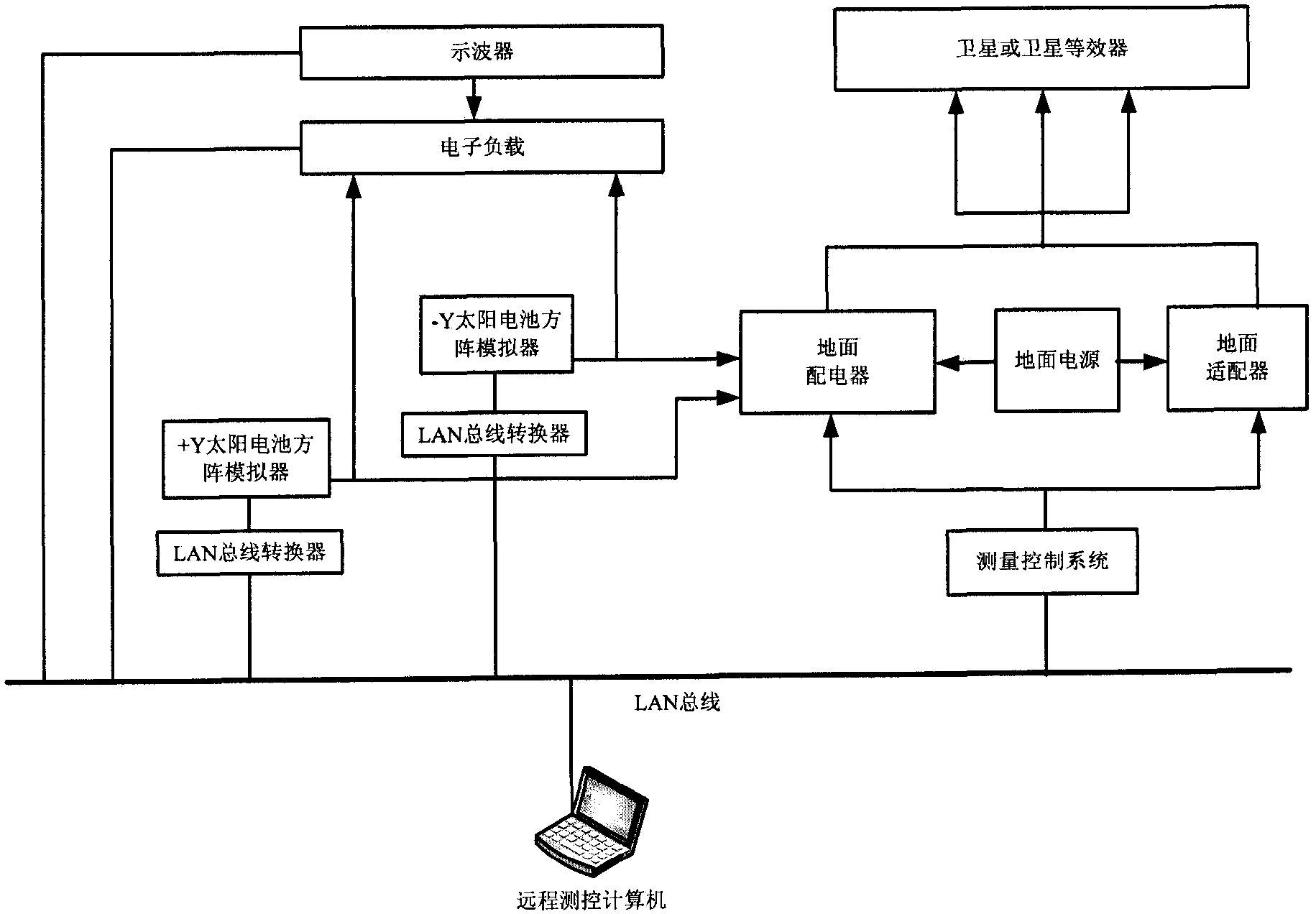
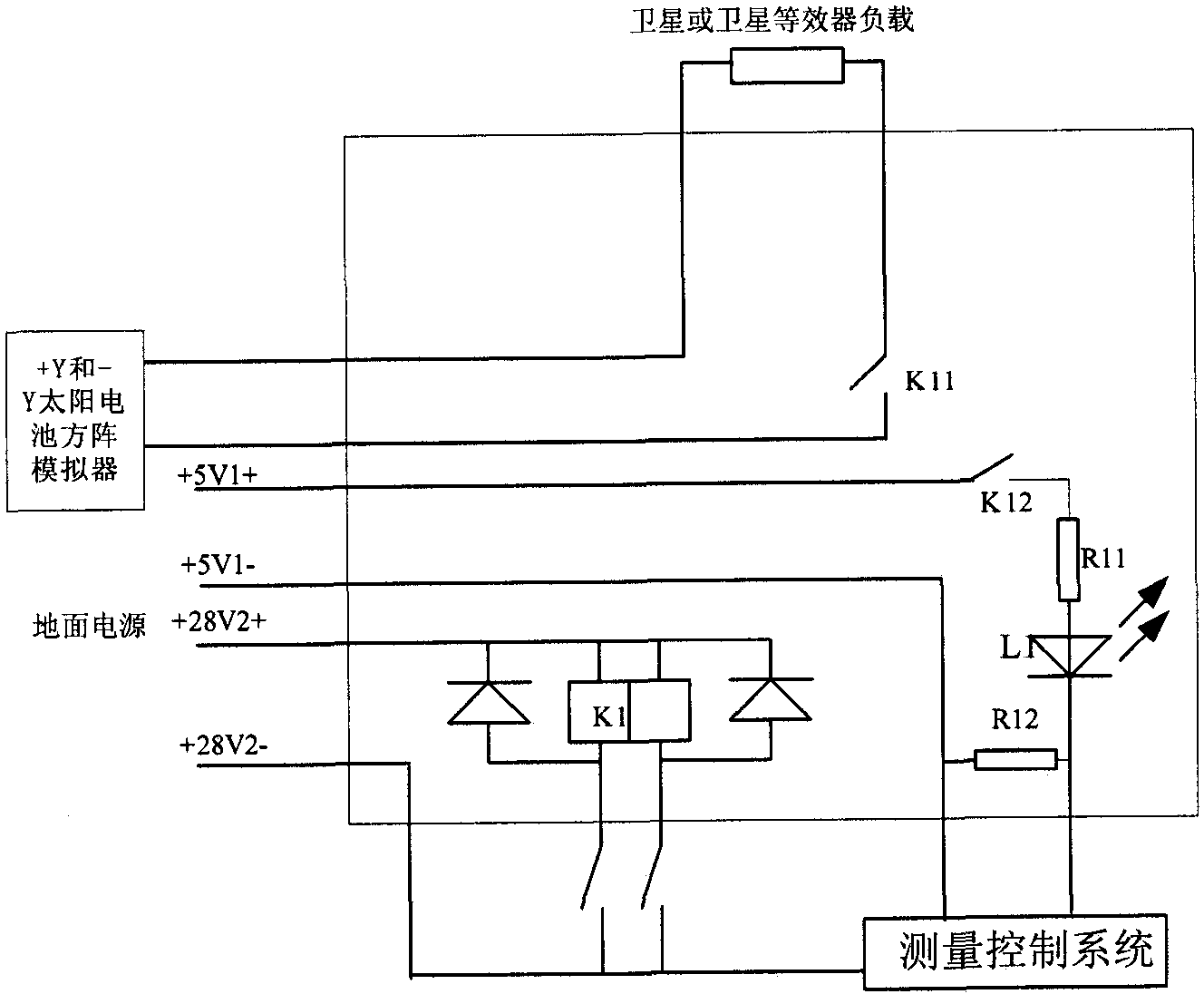
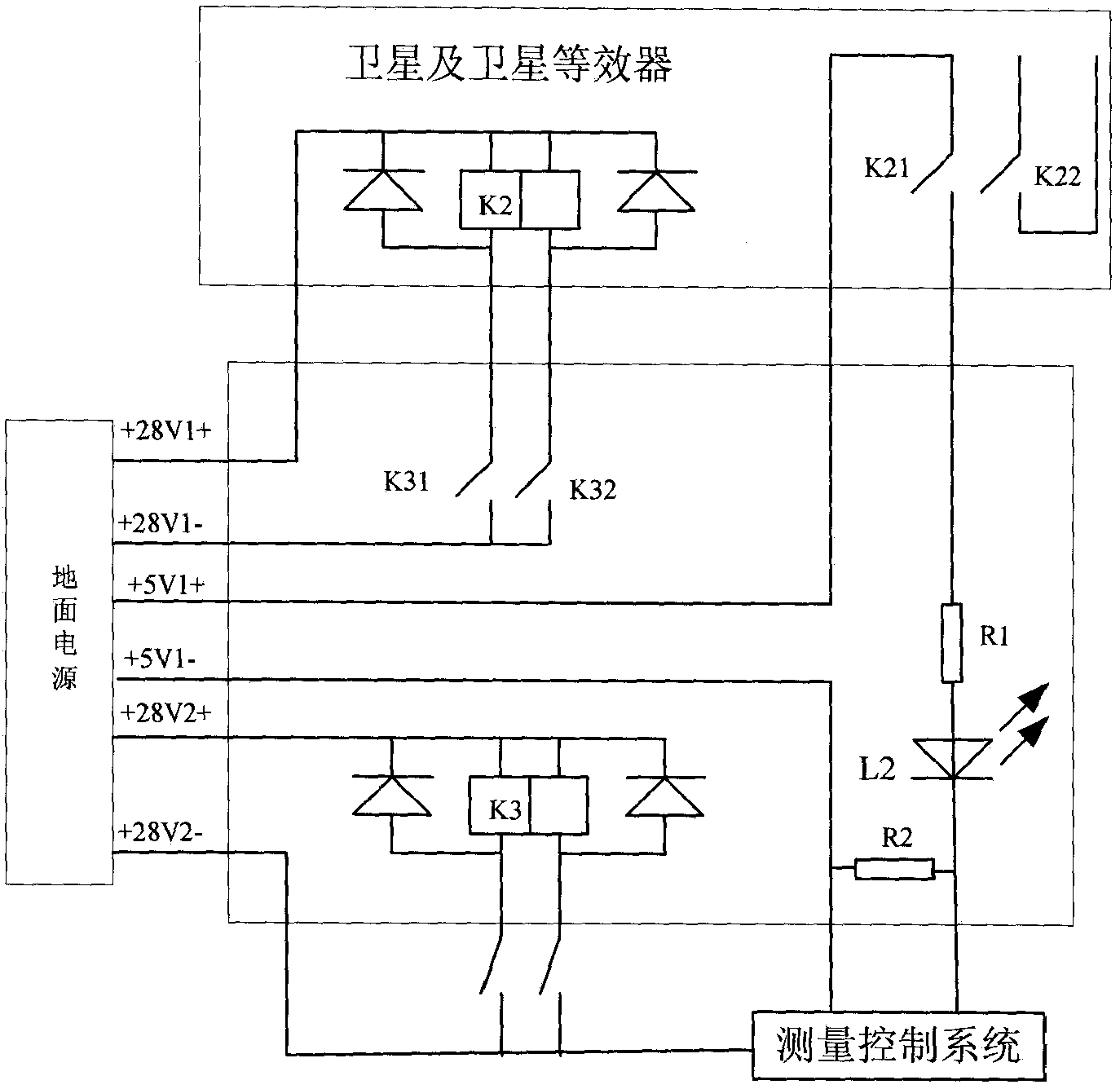
A satellite power supply and distribution test system based on lan bus
A satellite power supply and distribution test system based on LAN bus, including remote measurement and control computer, measurement control system, ground power supply, ground adapter, ground power distributor, +Y solar battery array simulator, -Y solar battery array simulator, LAN bus converters, electronic loads and oscilloscopes. The present invention uses the solar array simulator to simulate the output characteristics of satellite solar cells, and realizes the test control function and simulation of satellite power supply and distribution signals through ground distributors, ground adapters and satellite equivalents. The test equipment is connected together through the LAN bus, the test layout is flexible, and the test system can be remotely controlled without being affected by the test environment. The system structure is simple and the development cycle is short.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
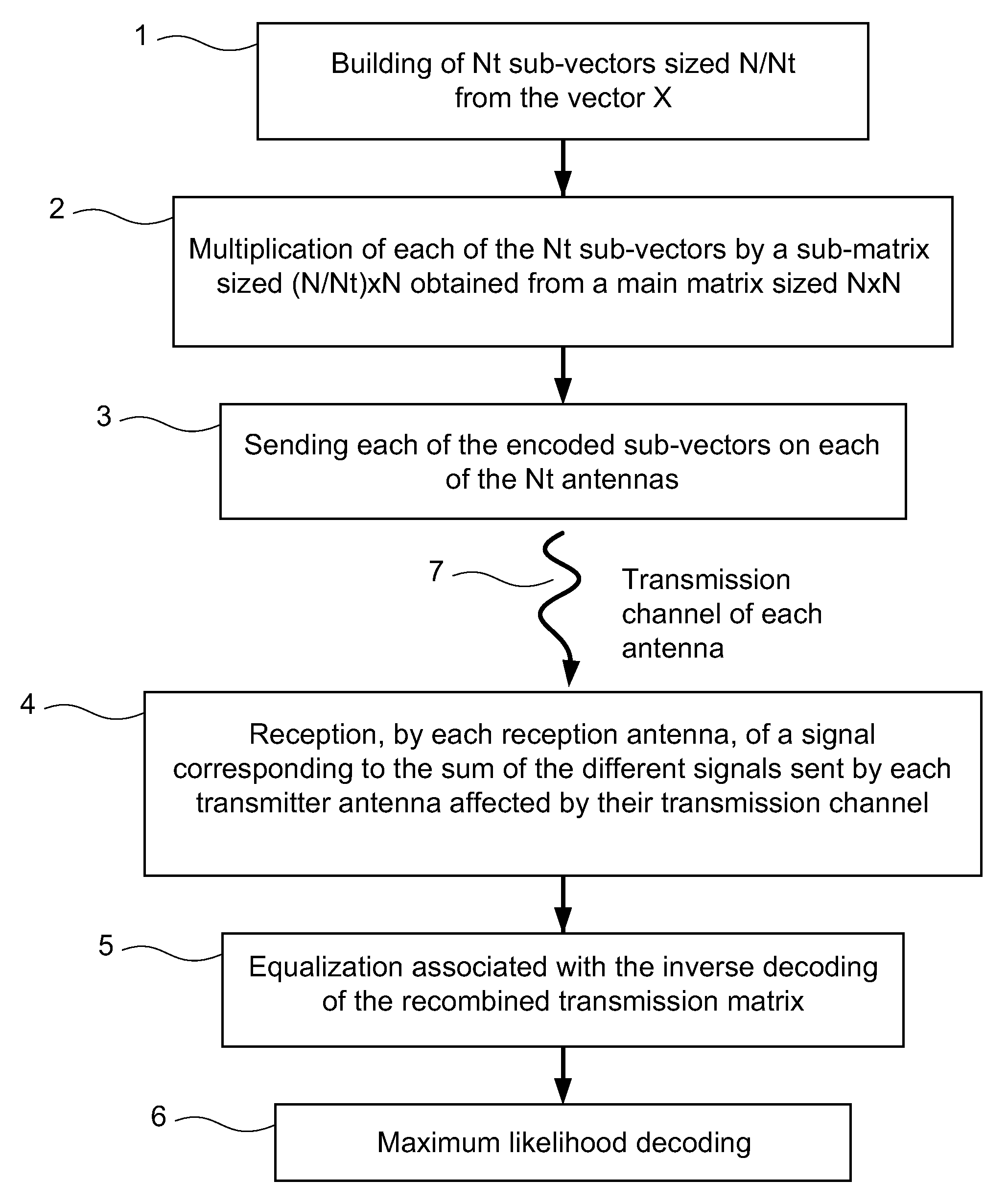
Method for the multiple-antenna transmission of a signal by space-time block codes, corresponding reception method and signal
ActiveUS7920638B2Improve performanceEasy to adaptSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityAntenna correlationUnitary matrix
An embodiment of the invention relates to a method for sending a signal formed by successive vectors each comprising N symbols to be sent, and implementing at least two transmitter antennas. A distinct sub-matrix is associated with each of said antennas, said sub-matrices being obtained by subdivision of a unitary square matrix, and each of said antennas sends sub-vectors, obtained by subdivision of said vectors, respectively multiplied by said sub-matrices so as to form, as seen from a receiver, a single combined signal representing the multiplication of said vectors by said unitary matrix.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
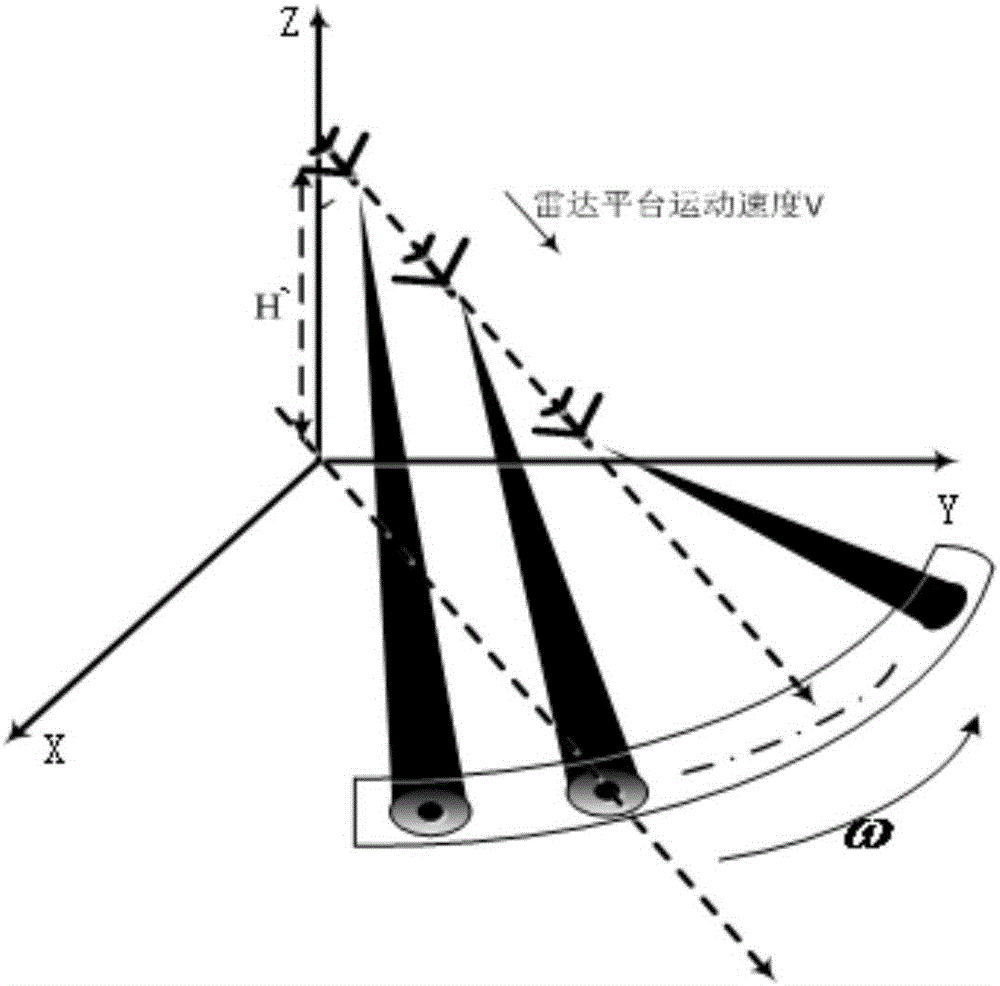
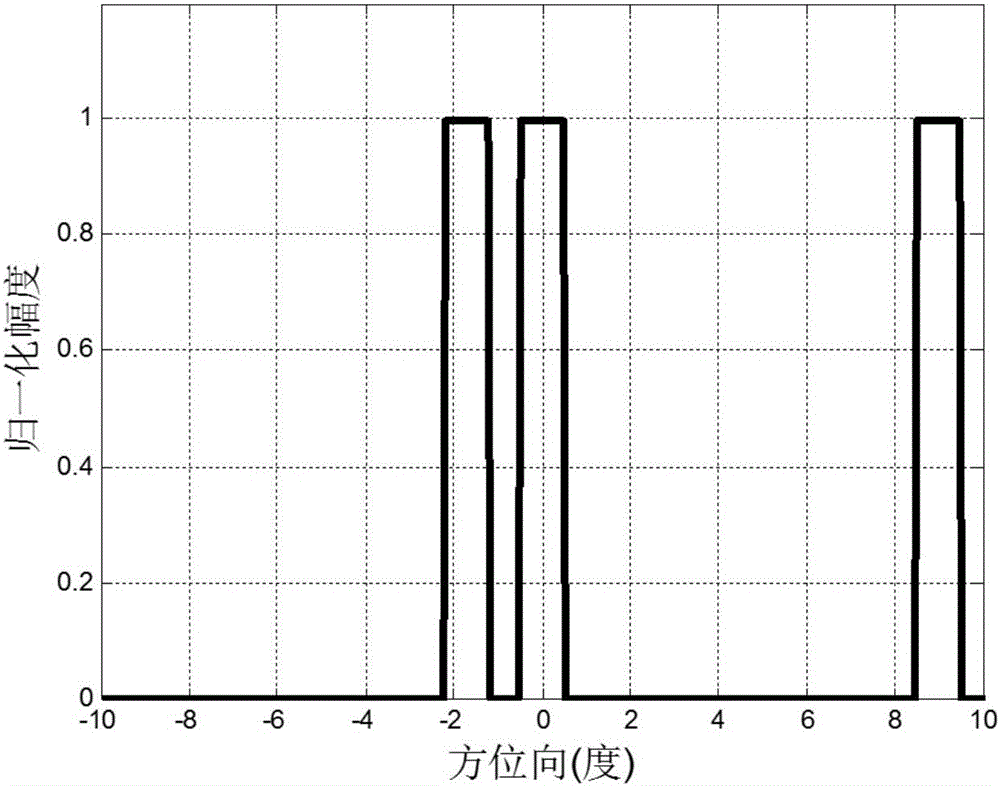
Method of realizing high-resolution imaging of forwarding looking radar
ActiveCN106680817ASolving non-square matrix problemsAchieve resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingScattering function
The invention discloses a method of realizing high-resolution imaging of a forwarding looking radar. The method uses the least squares to address the problem that a matrix is not a square matrix of a radiation pattern, uses the truncated singular value decomposition method to suppress amplification of noise, resolves the estimation amount of an object scattering function, and realizes high-resolution imaging of forward looking scanning radar direction. According to the application, the method is fully aware of the problem of possible information loss in the presence of an object on an edge in traditional tsvd processing method which decomposes on the basis of a matrix truncated singular value and then resolves an inversion. According to the application, the method addresses the problem that a matrix is not a square matrix of a radiation pattern, and by using least squares, obviates the need for processing an original matrix, resolves an error minimum resolution by 2-nom minimization, saves edge information, and resolves the estimation amount of the object scattering function; the method analyzes and solves too loud noise in the process of resolving the estimation amount, and uses the truncated singular value decomposition method to suppress the amplification of the noise, such that the method realizes high-resolution imaging of the forward looking scanning radar.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sudoku playing board, system and method
The present invention is concerned with a game board and system for playing multiple Sudoku type problem-solving games. The system comprises a three-dimensional board having a first array of n2 identical cavities arranged in a square matrix and at least one second array totaling at least n2 identical cavities arranged in at least n series of n cavities, at least n identical series of n pegs adapted to fit in said cavities in a plurality of definite angular positions, each peg defining a body having opposite first and second end faces, each peg in a series having its first face bearing one of a series of n different indicia. The body preferably has a polygonal cross-section and the system may further comprise a plurality of rings adapted to slide about the perimeter of said body. A method of playing Sudoku type problem-solving games using the system is further provided.
Owner:OUELLET DENIS
Construction method of low bit-rate quasi-cyclic accumulative repeat accumulate codes
InactiveCN102843145AModerate complexityImprove performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMultiple edgesRound complexity
The invention provides a construction method of low bit-rate quasi-cyclic accumulative repeat accumulate codes, wherein an accumulative repeat accumulate code protograph, a check node expanding by a linear block code check matrix, a basic check matrix corresponding to a basic bipartite graph and a cyclic offset searching method of quasi-cyclic approximate cycle extrinsic message degree are comprised. The construction method comprises the following steps of: constructing a basic accumulative repeat accumulate code protograph; expanding the check node of the accumulative repeat accumulate code protograph by using the linear block code check matrix; carrying out copying and repeating processing for eliminating multiple edges to obtain the basic bipartite graph; converting the basic bipartite graph into a matrix, and carrying out square matrix expansion on data in the matrix to obtain a quasi-cyclic matrix; and carrying out optimized searching on cyclic offset of a non-zero cyclic square matrix by using a quasi-cyclic approximate cycle extrinsic message degree method and finishing encoding. The low bit-rate quasi-cyclic accumulative repeat accumulate codes constructed by the construction method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of high performance, moderate complexity, simple encoding and decoding structure and the like and can be applied to a channel encoding occasion in the digital communication field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Distributed wireless LED display system
The invention belongs to the wireless transmission and LED display control technology field, in particular to a distributed type wireless LED display system. The display system is composed of a wireless controller and a plurality of wireless display boards. The wireless display boards preset pre-displayed picture information before being used, each wireless display board displays a pixel point of a whole picture, and a complete picture is formed by all the wireless display boards together. When the invention is used, synchronous control signals transmitted through the wireless controller are received, a pre-displayed picture is started, and thereby the effect that each wireless display board synchronously displays the pre-stored pictures is achieved. The system adopts the distributed type design and the centralized wireless control, the application field is extremely wide, such as the auditorium dynamic picture displaying and the athlete square matrix dynamic showing of large-scale sport meetings and concerts, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Denoising method for seismic signal based on Shearlet transform
InactiveCN103399348AImprove denoising effectGood practical valueSeismic signal processingComputer scienceFilter bank
The invention discloses a denoising method for a seismic signal based on the Shearlet transform, which comprises the following steps: 1, two-dimensional seismic section data is read; 2, the two-dimensional seismic section data S is expanded into a square matrix S1 of which the length and the width are odd; 3, a frequency domain orientation filter set is built; 4, multiplying operation is performed on all the transform matrixes and a signal vector respectively, and two-dimensional Fourier inverse transform is performed, so that Shearlet coefficients C<i,j> in various directions and dimensions are obtained; 5, threshold value processing is performed; 6, Shearlet inverse transform is performed on the Shearlet transform coefficients subjected to threshold value processing to obtain the denoised signal. According to the denoising method, the Laplace decomposition is performed on the seismic signal with noise, and then filtering processing is performed by utilizing a Shearlet function to obtain the corresponding Shearlet coefficient; the noise signal is filtered through threshold value processing, and the denoised signal is recovered through sampling Shearlet transform under the inverse condition, so that the better denoising effect is obtained, and the method has an excellent practical value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix and power generation system using overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix
ActiveCN103986406ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyFloating platformPhotovoltaic power generation
The invention discloses an overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix and a power generation system using the overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix. The overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix includes a square matrix formed through mutual cooperation of floating platforms. In the square matrix, cooperation parts of adjacent two columns of floating platforms are in through connection through steel cables. The steel cables are fixed by fixing edgings installed at side edges of the matrix. A plurality of the overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrixes are spliced and used as a carrier of a photovoltaic assembly in a photovoltaic power generation system and thus it is realized that overwater solar energy is utilized through the photovoltaic power generation system. The overwater photovoltaic assembly bearing unit square matrix has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in cost, convenient to build up and high in environment adaptability and the like and is wide in application prospect.
Owner:北京大昱光伏科技有限公司
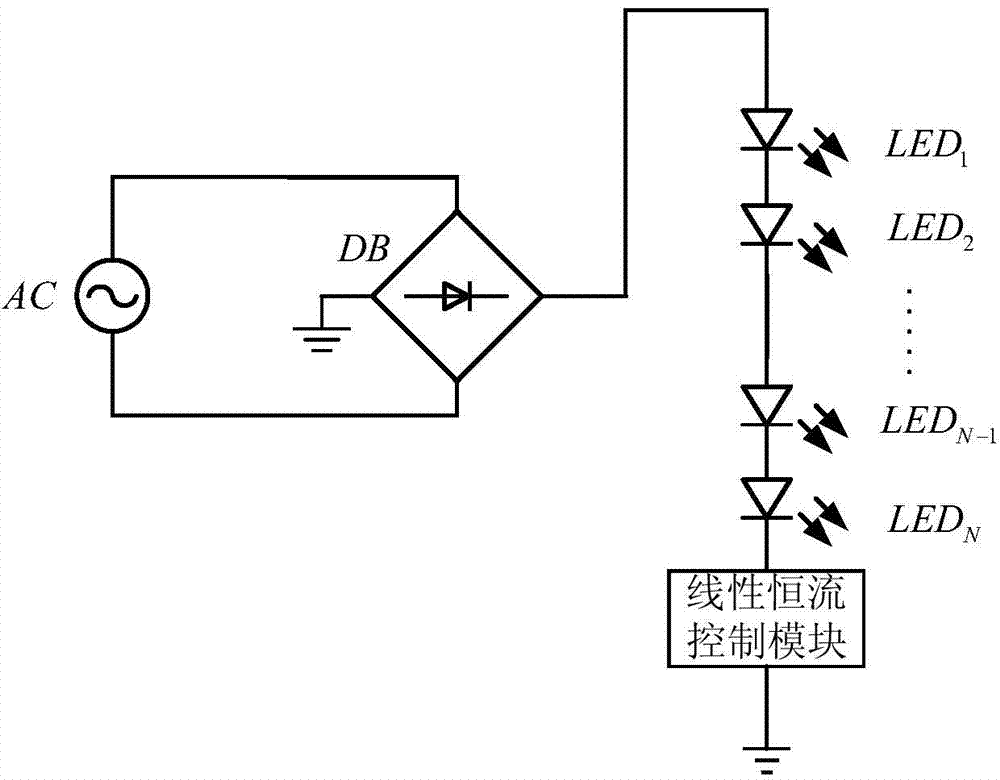
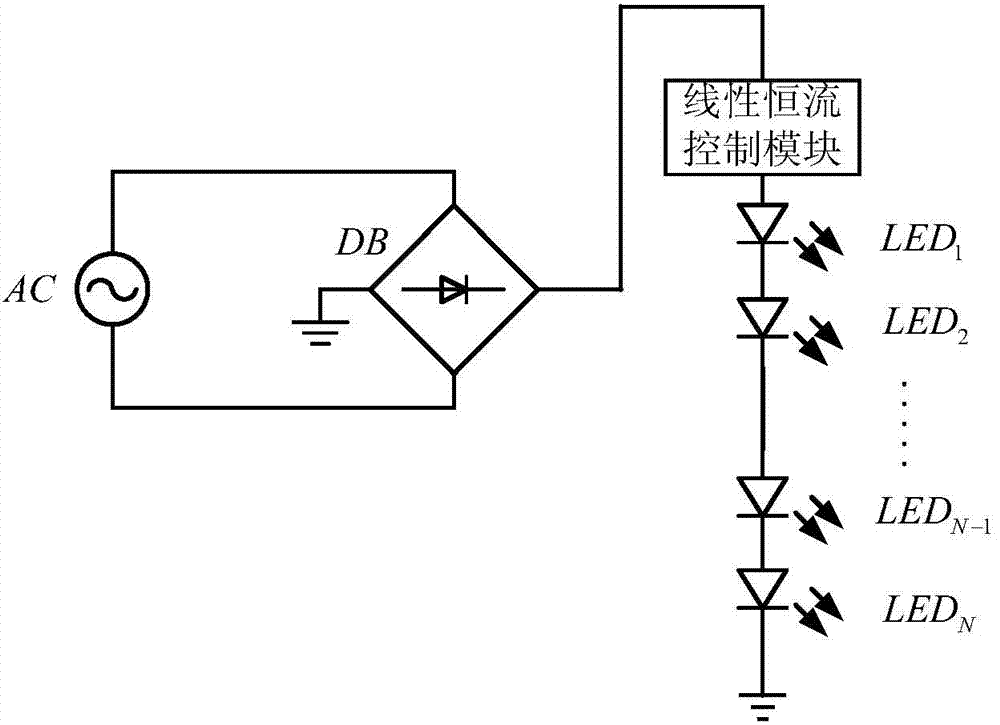
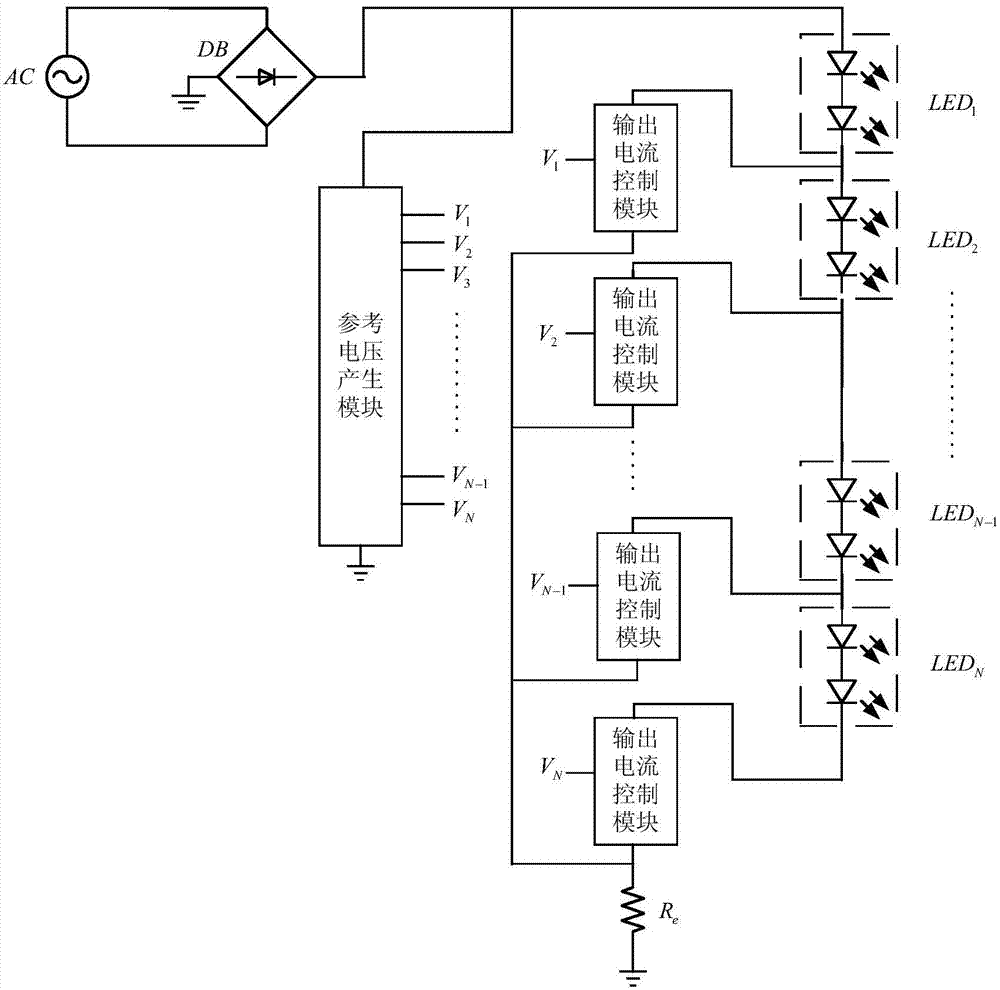
LED driving circuit
ActiveCN103596328AReduce power consumptionReduce usageElectric light circuit arrangementPower factorLed array
The invention discloses an LED driving circuit. The LED driving circuit is connected with an LED array, wherein the LED array is an N-dimensional square matrix, and the N is a natural number which is larger than one. The LED driving circuit comprises a current source module, a bleeder circuit module, a comparator circuit module, a logic control module and a switch module, wherein the current source module is used for providing a constant-current power source for the LED array, the bleeder circuit module is used for carrying out voltage division sampling on input voltage, and outputting a plurality of sets of sampled voltage, the comparator circuit module is used for comparing reference voltage with the sampled voltage, and outputting a plurality of sets of comparison signals correspondingly, the logic control module is used for carrying out logical operation on the basis of the comparison signals, and outputting a logic voltage sequence, and the switch module is used for having on-off control over the LED array according to the logic voltage sequence. According to the LED driving circuit, when a switching tube is connected, the switching tube works in a linear zone, power consumption of the switching tube is reduced, and conversion efficiency is improved; according to a simulation result, the power factor of the LED driving circuit can be more than 99%, and the conversion efficiency of the LED driving circuit is about 90%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ultra-high brightness LED matrix straight-downward backlight module applied to large-scale LCD
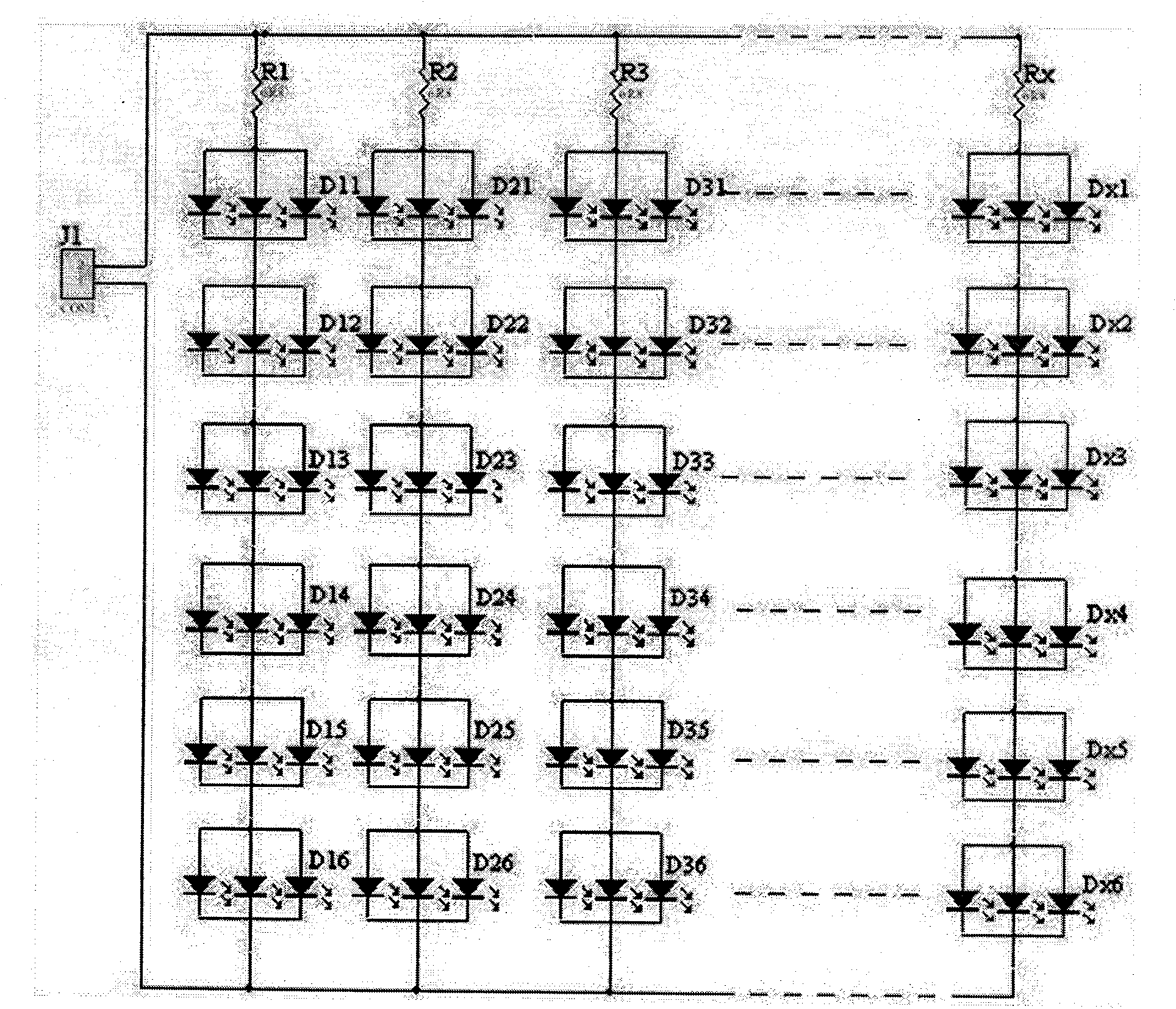
ActiveCN101634777AImprove modular expansion packageConvenient modular expansion packagePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses an ultra-high brightness LED matrix straight-downward backlight module applied to a large-scale LCD which has a size of more than 32 inchs. In an LED matrix module six LEDs are connected in series into a straight row, and LED are arranged longitudinally and transversally to form a square matrix; the length and the row number of a printed circuit board (PCB) extends all along to both sides of a screen visible area of the LCD in the arrangement and combination mode and correspondingly adjusts according to the size of the screen so that the arrangement area of an LED matrix is consistent with a display area of the LCD; LEDs the surfaces of which are welded and packaged with 5.0*5.0mm or 3.5*2.8mm three-core gold-white high-brightness overhead light are selected, color coordinate values are: X: 0.303 and Y:0.293 and a brightness value is more than 7000 mcd and is graded by 0.1V to ensure the consistency of low-brightness work; and a distance between two LEDs is 15.6-16.5mm, every six LEDs are connected in series into a straight row, and a distance between two straight rows is 15.6-16.5mm. The straight-downward ultra-high backlight module manufactured by applying an LED matrix improves the brightness higher than 1200 LUH, not only satisfies the requirement for visual brightness under outside sunshine, but also solves the problems of overlarge power and overheating, and the LED matrix has brightness with a large controllable range and is energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:超亮商显传媒(深圳)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com