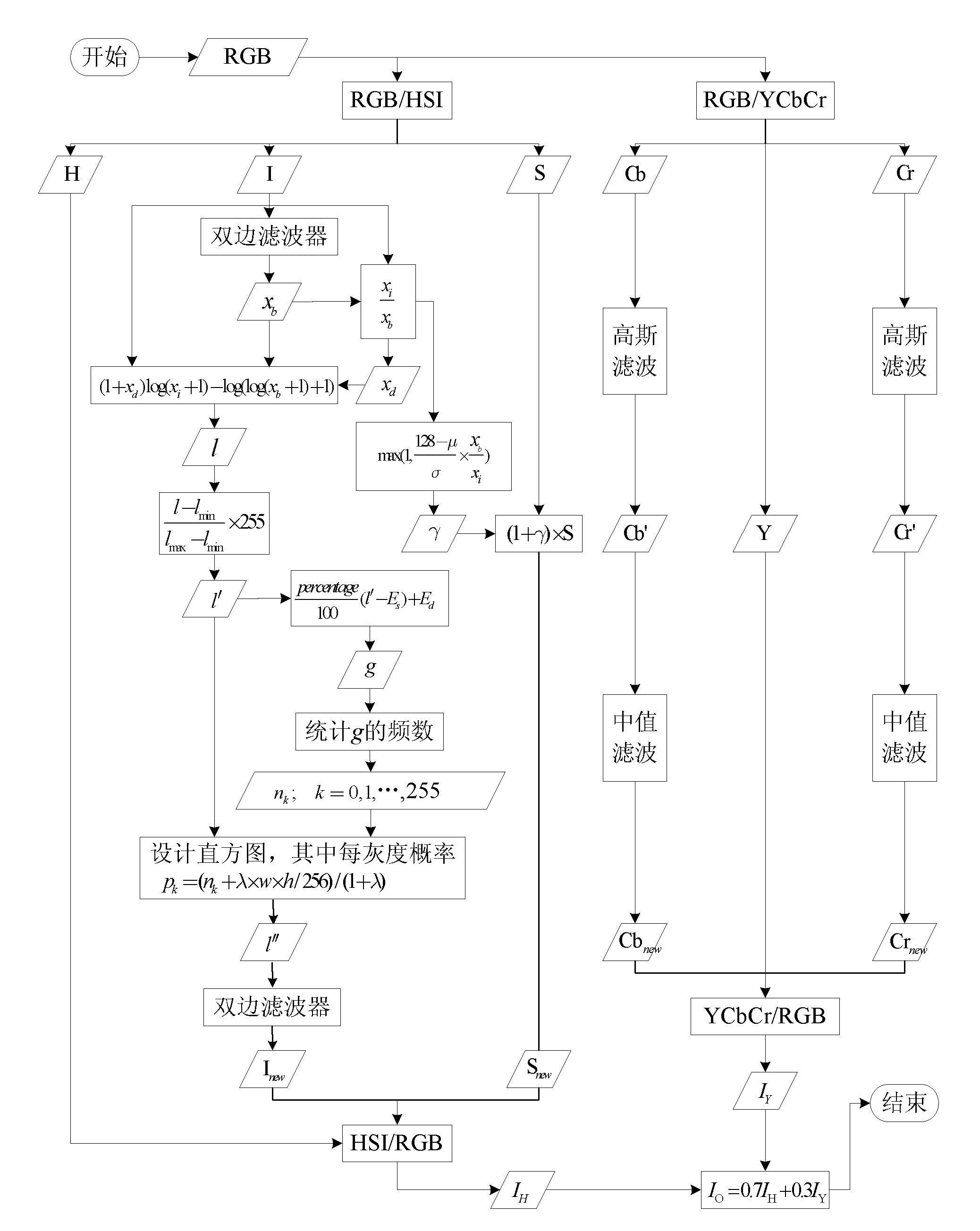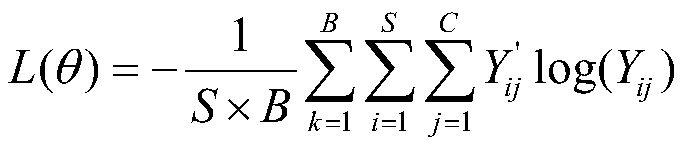Patents
Literature
1321 results about "Information loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Information loss. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article.
Method and Apparatus for On-Line Compressed Sensing
ActiveUS20090222226A1Improve system performanceAnalogue/digital conversionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsHigh rateDiscrete-time signal
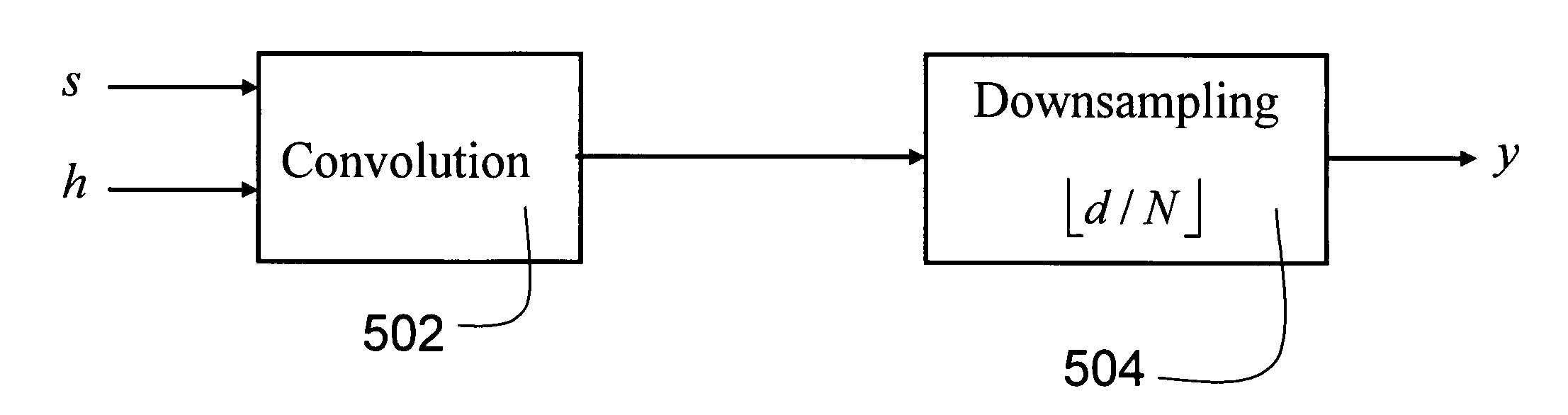
A typical data acquisition system takes periodic samples of a signal, image, or other data, often at the so-called Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate of two times the data bandwidth in order to ensure that no information is lost. In applications involving wideband signals, the Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate is very high, even though the signals may have a simple underlying structure. Recent developments in mathematics and signal processing have uncovered a solution to this Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate bottlenck for signals that are sparse or compressible in some representation. We demonstrate and reduce to practice methods to extract information directly from an analog or digital signal based on altering our notion of sampling to replace uniform time samples with more general linear functionals. One embodiment of our invention is a low-rate analog-to-information converter that can replace the high-rate analog-to-digital converter in certain applications involving wideband signals. Another embodiment is an encoding scheme for wideband discrete-time signals that condenses their information content.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Apparatus and methods for synaptic update in a pulse-coded network
InactiveUS20130073491A1Reducing memory bus overheadReduce overheadDigital computer detailsDigital dataSynapseSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for efficient synaptic update in a network such as a spiking neural network. In one embodiment, the post-synaptic updates, in response to generation of a post-synaptic pulse by a post-synaptic unit, are delayed until a subsequent pre-synaptic pulse is received by the unit. Pre-synaptic updates are performed first following by the post-synaptic update, thus ensuring synaptic connection status is up-to-date. The delay update mechanism is used in conjunction with system “flush” events in order to ensure accurate network operation, and prevent loss of information under a variety of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic unit firing rates. A large network partition mechanism is used in one variant with network processing apparatus in order to enable processing of network signals in a limited functionality embedded hardware environment.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
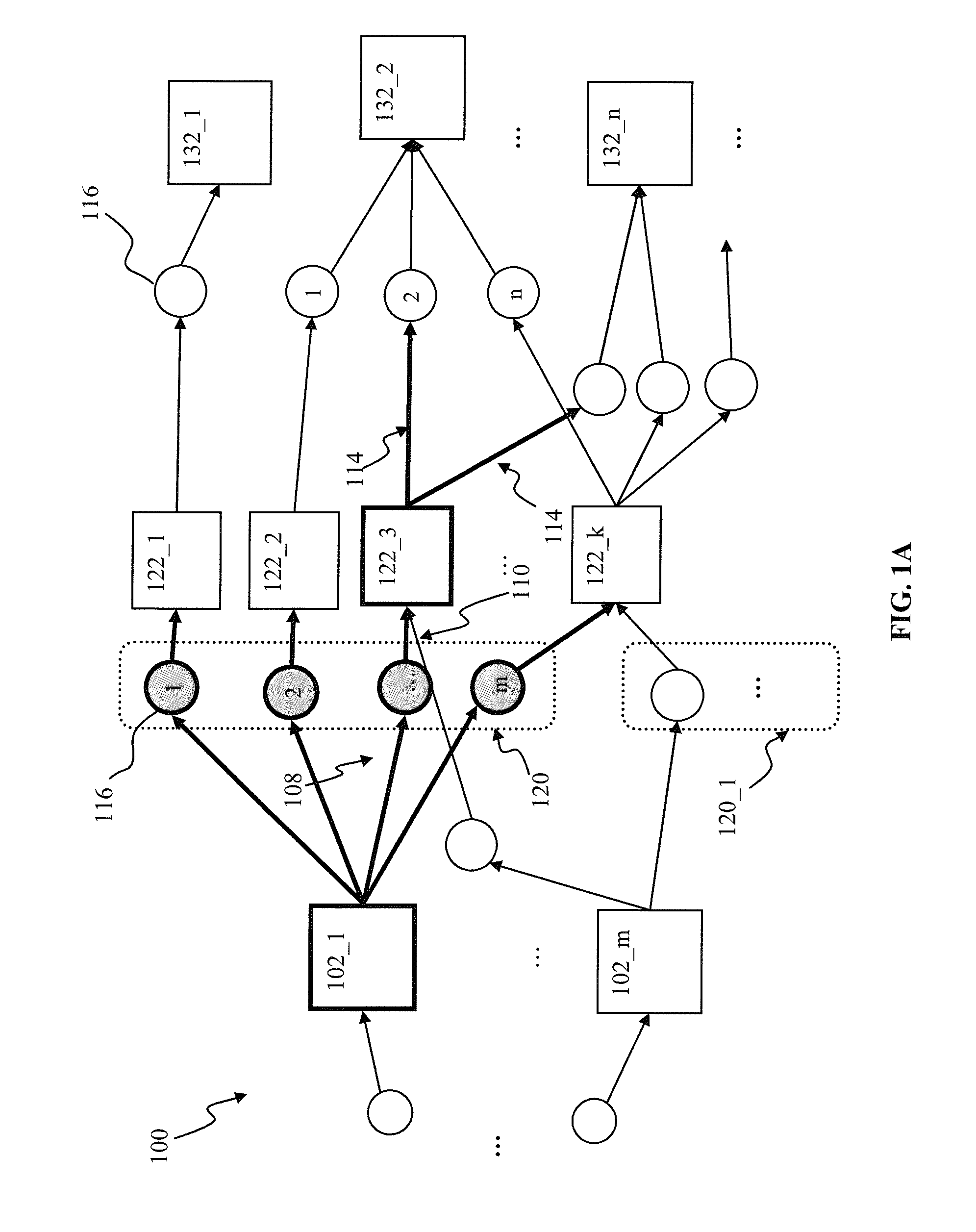
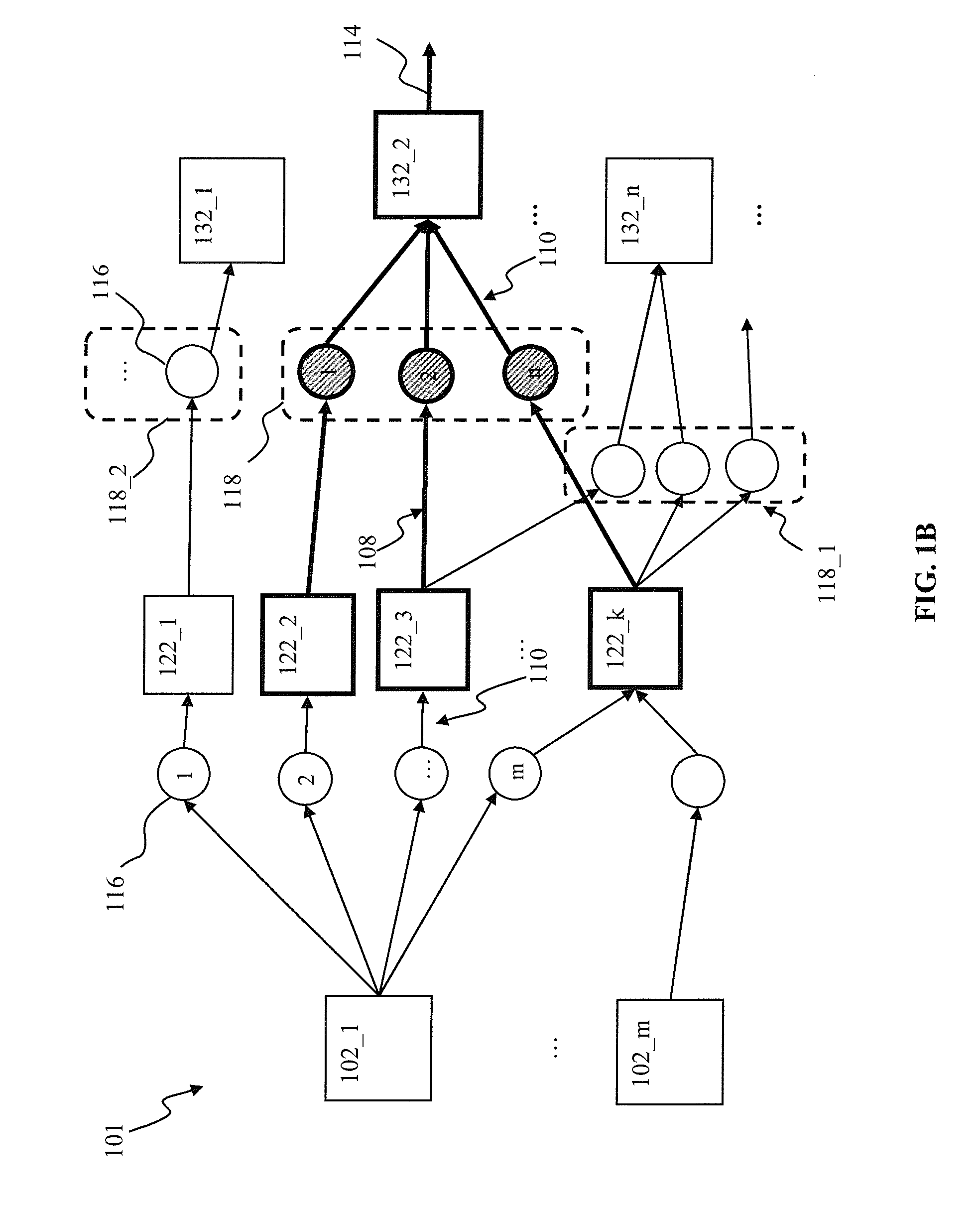
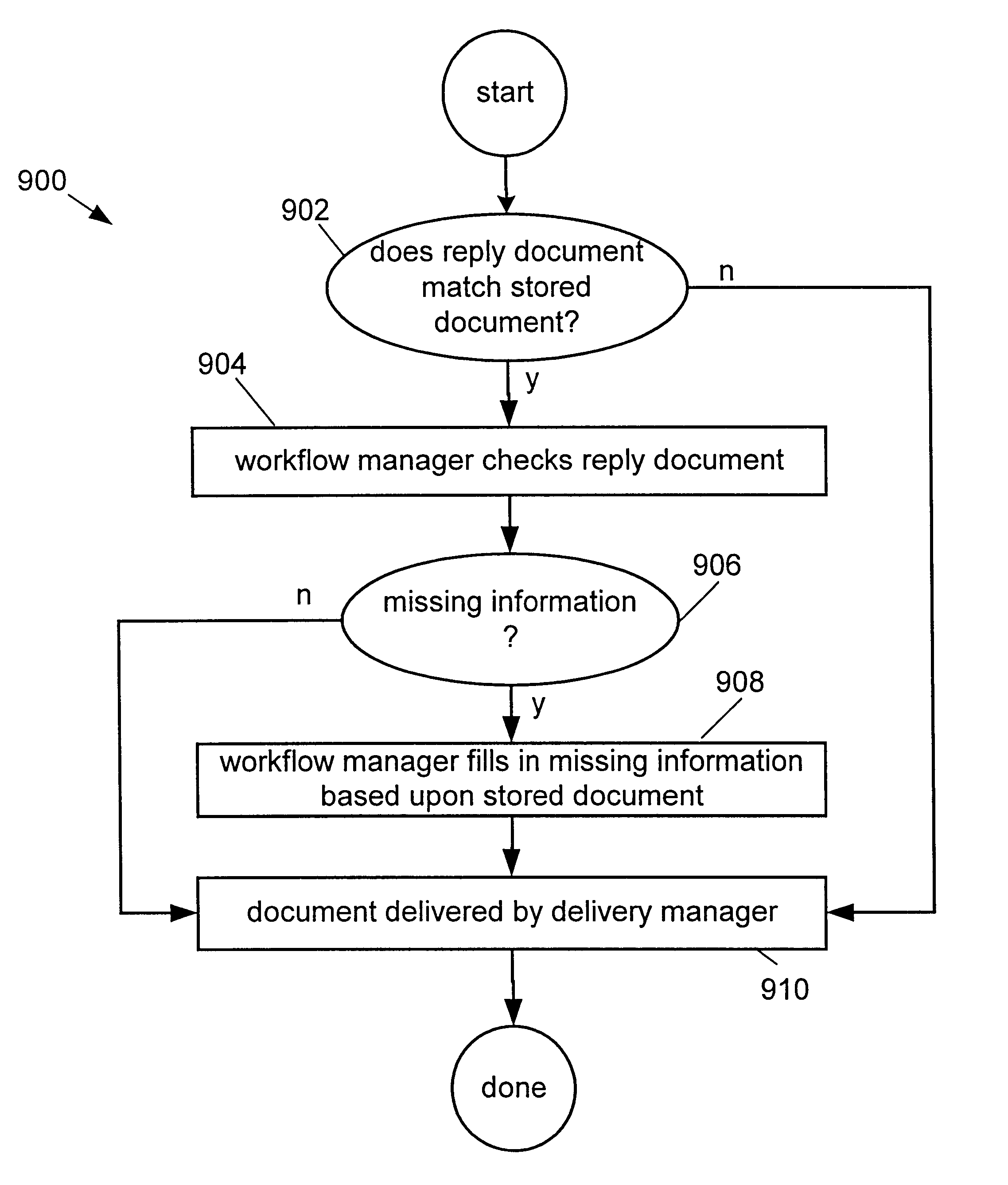
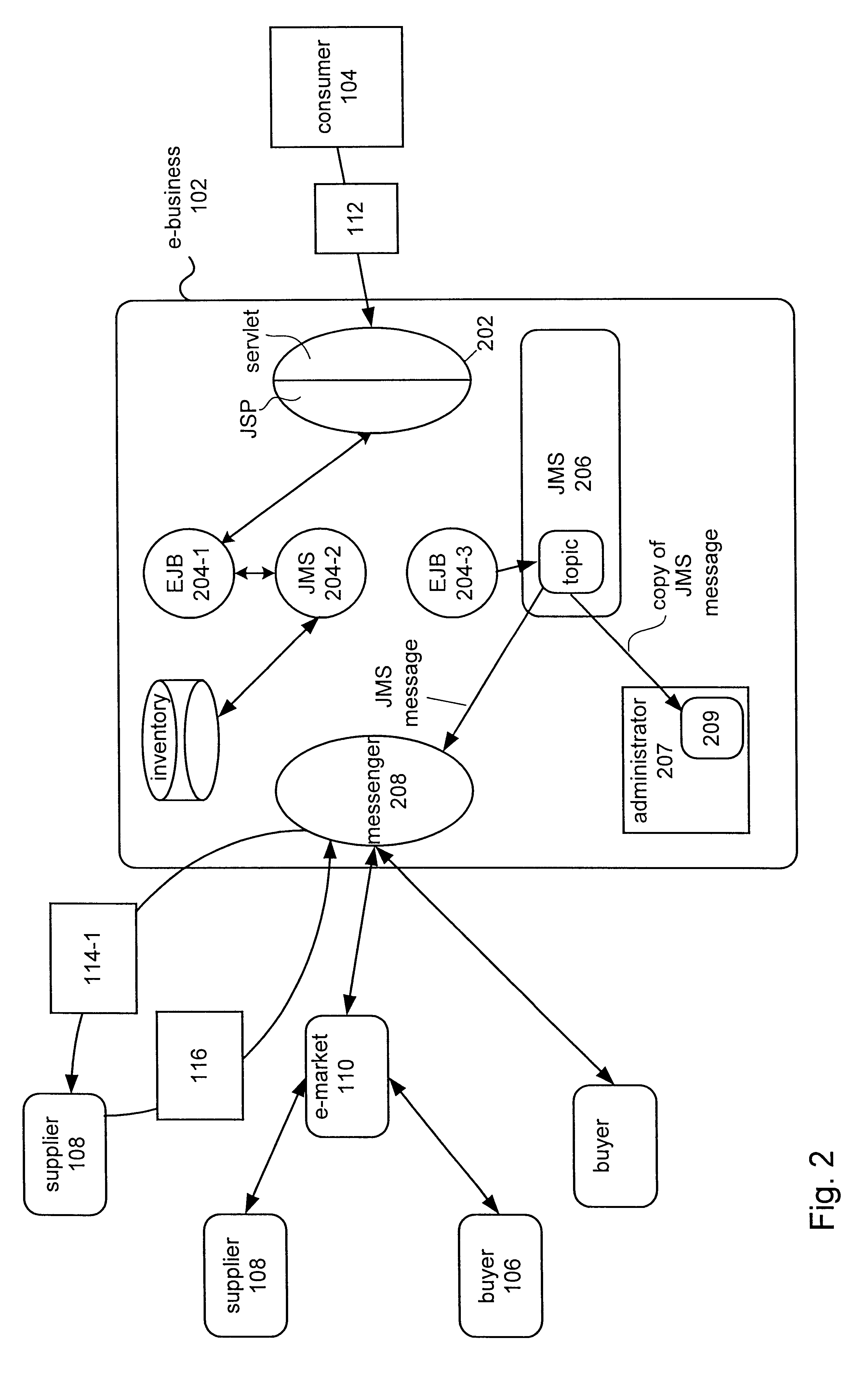
Techniques for preventing information loss in a business to business message in an enterprise computer system
InactiveUS6687848B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionBusiness-to-businessEnterprise computing
A method of maintaining informational integrity of a business to business (B2B) message in a distributed e-business environment is described. A sent message is stored a selected portion of which is flagged. A corresponding response message is then compared to the stored sent message. Based upon the comparing, when the response message matches the stored sent message, if a portion of the response message corresponding to the flagged portion is determined to be substantially missing, then the missing portion of the response message is replaced.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
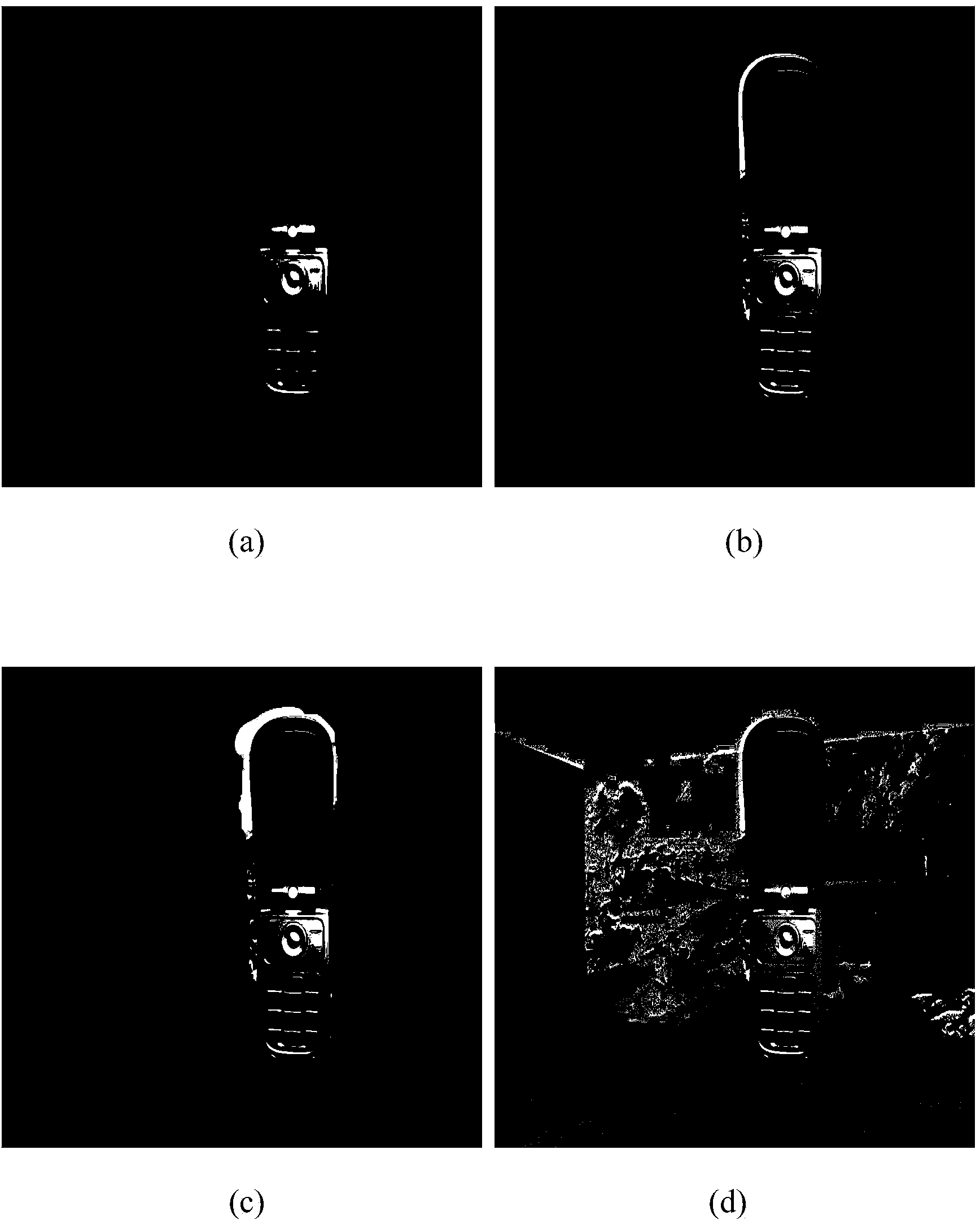
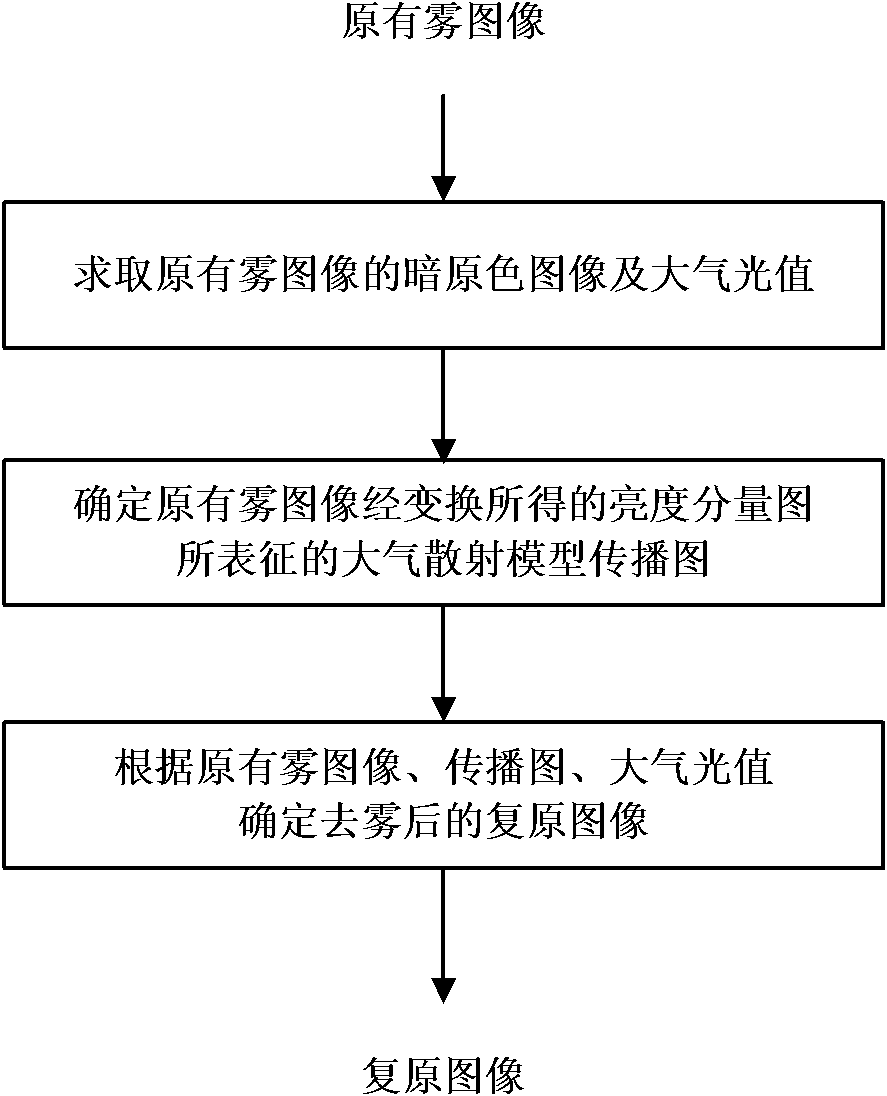
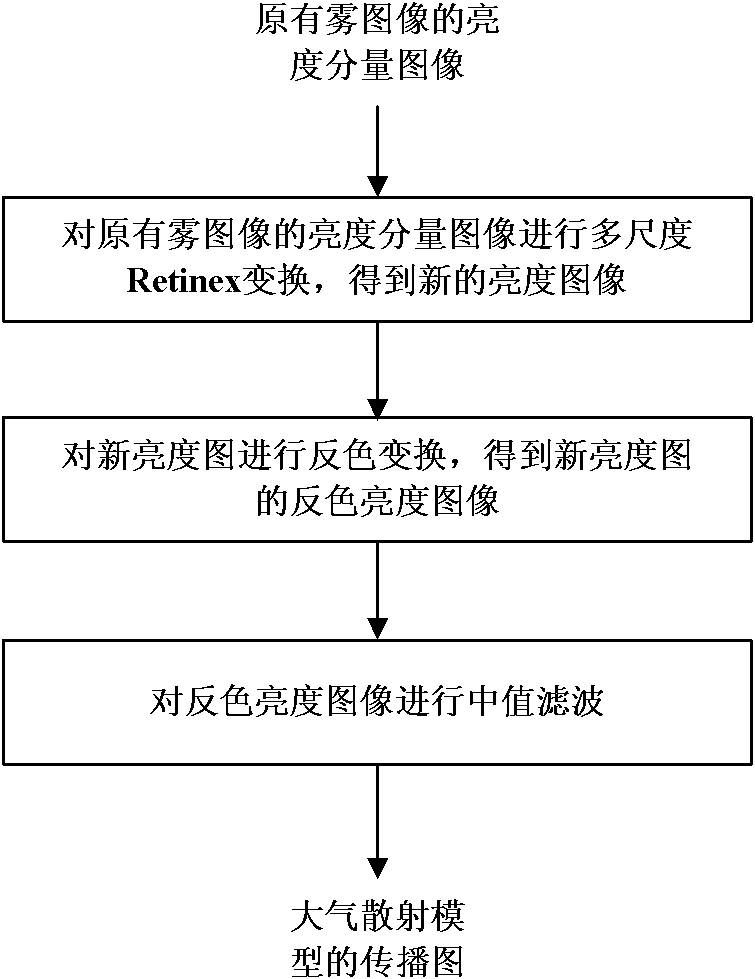
Automatic image defogging method based on dark primary colour
The invention discloses an automatic image defogging method based on dark primary color, which is used for solving the problem of information loss because the traditional defogging method highlights details by improving foggy day image contrast. The method provided by the invention comprises: A. calculating the dark primary color of the primary fog images and relevant atmosphere light value; B. according to the luminance component image of the original fog image, calculating a transmission image reflecting local fog concentration in an atmospheric scattering model; and C. determining the defogged primary image according to the fog image, the transmission image and the atmosphere light value in the atmospheric scattering model. Because of being built on the basis of a physical model, the invention can process various fog images in a self-adaption mode; and defogged images have favorable edge details and ideal contrast, and the clarifying effect is superior to the traditional defogging method based on image enhancement.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
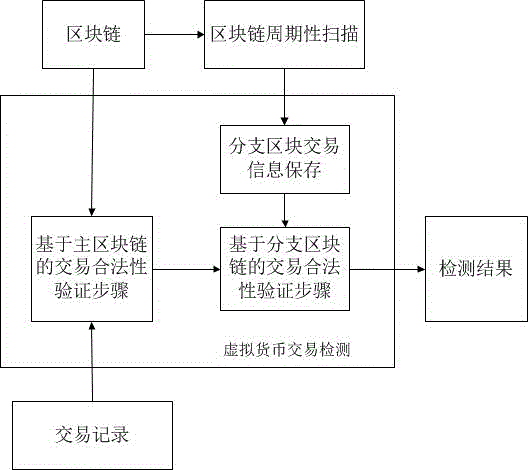
Virtual currency transaction validation method based on block chain multi-factor cross-validation
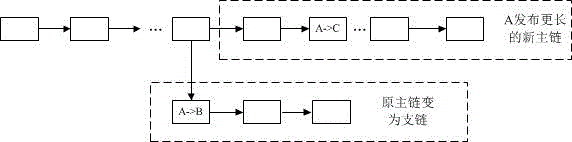
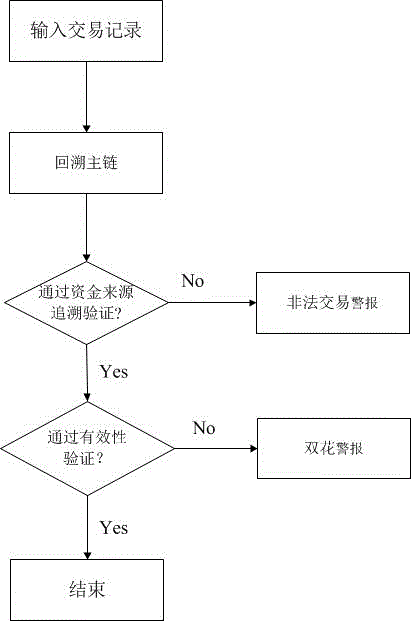
The invention provides a virtual currency transaction validation method based on block chain multi-factor cross-validation to solve the double-spending problem that virtual currency based on block chains are liable to 51% attacks and thus generates transactions. The method queries and backups a history block chain branch periodically, organizes confirmed transaction information into a hash chain list array which is easy for querying, and avoids branch transaction information losses induced by block chain evolution. During a virtual currency transaction, the method not only checks payer information, recipient information, a fund source, a currency transaction amount and the like recorded in a current main block chain, but also queries a backup branch block chain to check whether the current transaction and a history transaction on the branch block chain have the same fund source. If any transaction does not pass the check, a miner gives an alarm over the whole network about the transaction, so that the method can avoid the double-spending problem induced by illegal transactions.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Complex character recognition method based on deep learning
ActiveCN104966097AThe recognition result is accurateMeet the need for identificationNeural learning methodsCharacter recognitionNoise reductionOptical character recognition
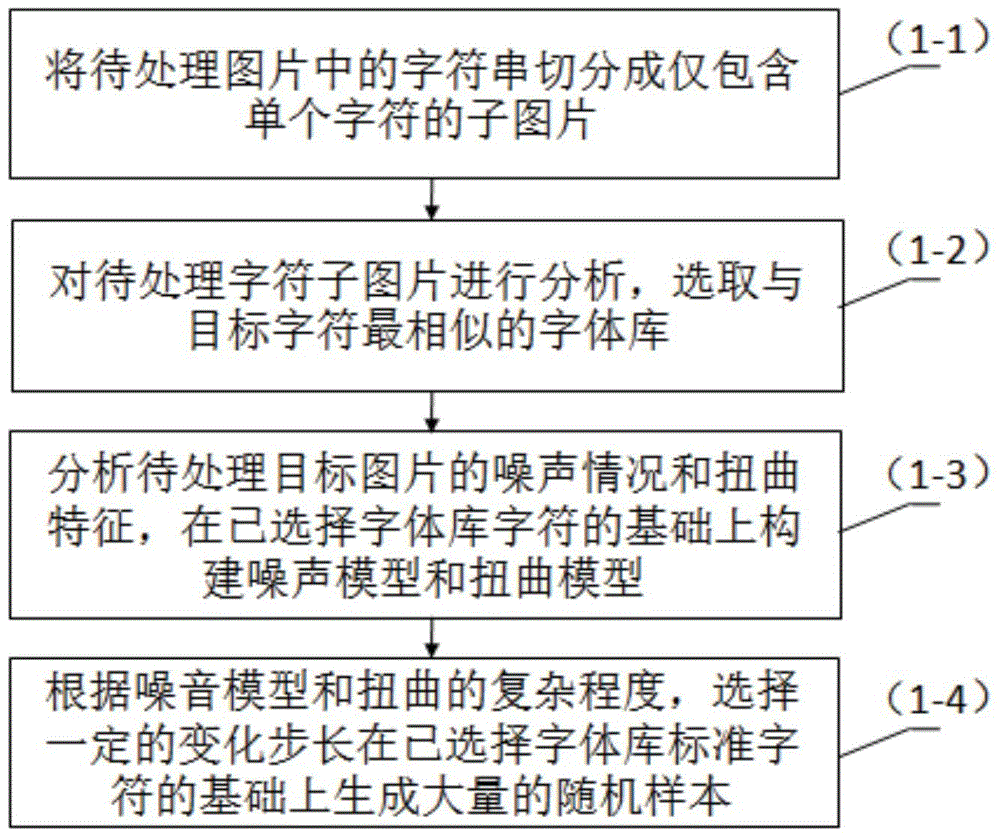
The invention relates to the field of image recognition, and especially relates to a complex character recognition method based on deep learning. Through the analysis of character complexity, a training sample, which contains a to-be-recognized image noise model and a distortion characteristic model, generated by a random sample generator is employed for the training of a deep neural network. The training sample comprises complex noise and distortion, and can meet the demands of the recognition of various types of complex characters. A few of manually annotated first training sample sets and a large amount of randomly generated second training sample sets are mixed and then inputted to the deep neural network, thereby solving a problem that a large number of manually annotated training samples are needed for character recognition through the deep neural network. Moreover, the most advanced deep neural network is employed for automatic learning under the condition that the noise and distortion of a to-be-recognized image are retained, thereby avoiding information loss caused by noise reduction in a conventional OCR method, and improving the recognition accuracy.
Owner:成都数联铭品科技有限公司
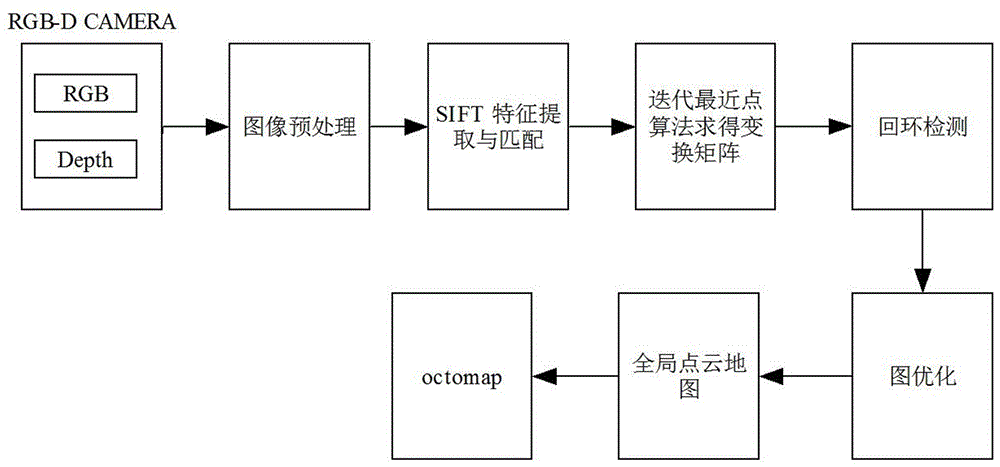
Map merging method of unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under city complex environment
InactiveCN106595659ASmall amount of calculationReduce the hidden danger of lossNavigational calculation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlWireless transmissionUncrewed vehicle
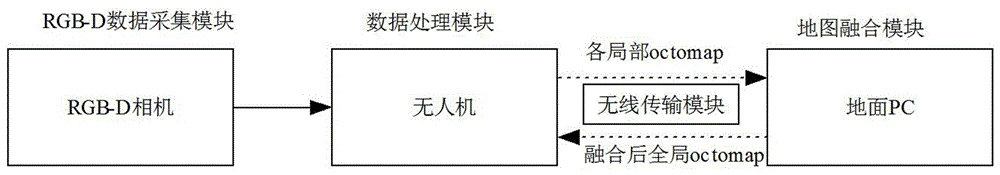
The invention discloses a map merging method of unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under city complex environment. The method comprises the steps of 1, collecting an image through an RGB-D camera installed on each unmanned aerial vehicle, utilizing the unmanned aerial vehicle to conduct pretreatment on the image, and then conducting image registration; 2, constructing a visual odometer, and achieving loop detection; 3, optimizing the posture of the unmanned aerial vehicle; 4, constructing an octomap map, and achieving real-time on-line SLAM; 5, transmitting the octomap into a ground computer, merging a local octomap into a global octomap, and then transmitting the merged all-region octomap to the unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the map merging method of the unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under the city complex environment, calculated quantity is reduced, real-time on-line SLAM can be achieved, and hidden danger of information losses brought by unstable wireless transmission is reduced; meanwhile, the task execution time is shortened, the task execution efficiency is improved, hidden danger brought by insufficient unmanned aerial vehicle cruising ability, finally more precise positioning can be obtained, and a more precise map can be established.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
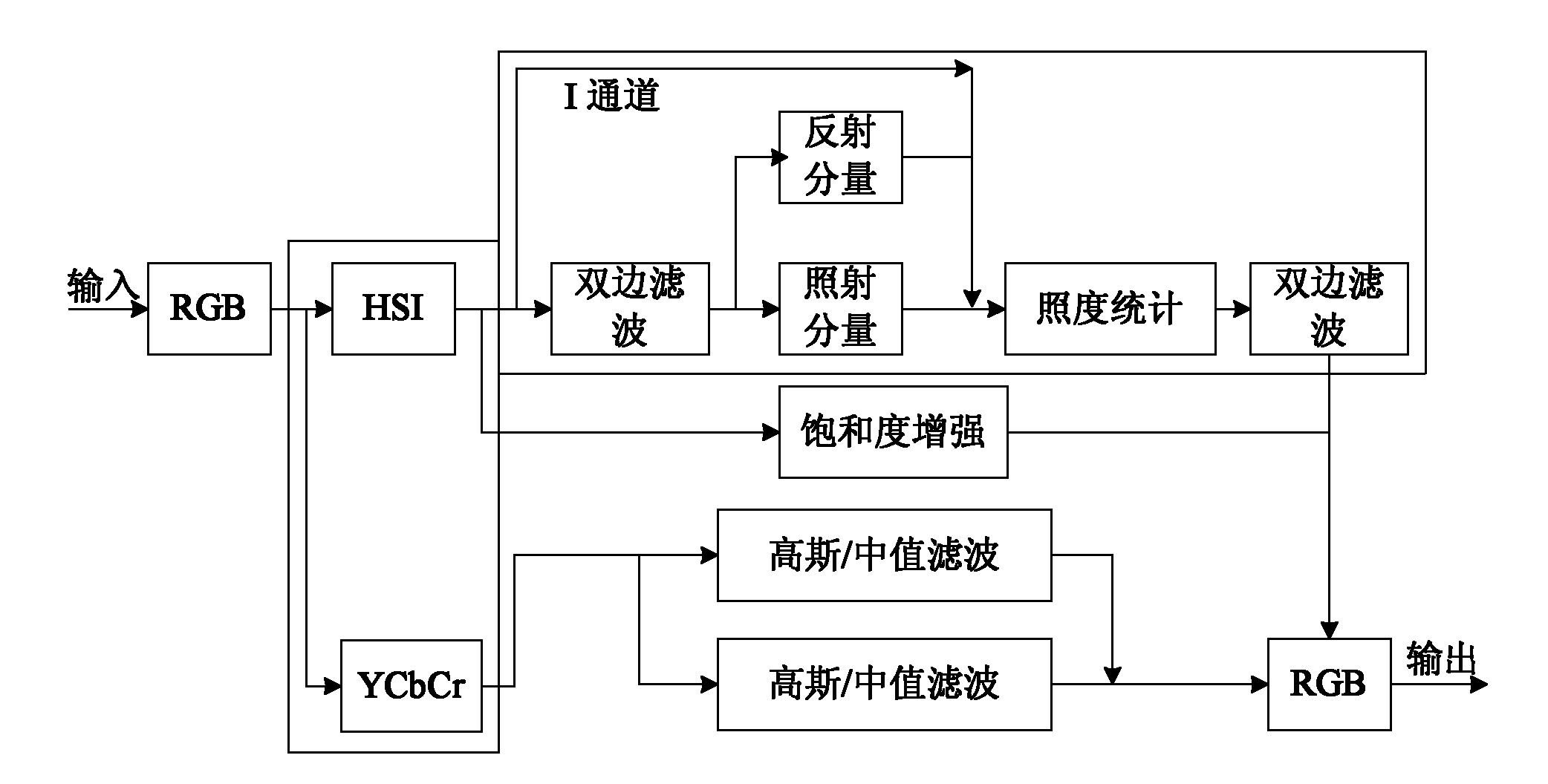
Color digital image enhancing and denoising method under random illumination
The invention discloses a color digital image enhancing and denoising method under random illumination. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, image denoising processing, namely converting an original image from an RGB space to a YCbCr space, removing a Gaussian noise by using a Gaussian filter and removing a salt and pepper noise by performing median filter; 2, image brightness / contract stretch processing, converting the image from the RGB space to an HSI space, decomposing the image by using a two-sided filter, processing by an improved Retinex model algorithm, and obtaining a new image saturation by performing saturation compensation; and 3, performing fusion display on the image acquired after denoising the YCbCr space and the image acquired by HSI space processing. By the method, the color constancy of the image can be kept, the dynamic range of the image can be improved well, and simultaneously noises of the image can be inhibited and removed with less texture and detail information loss.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method
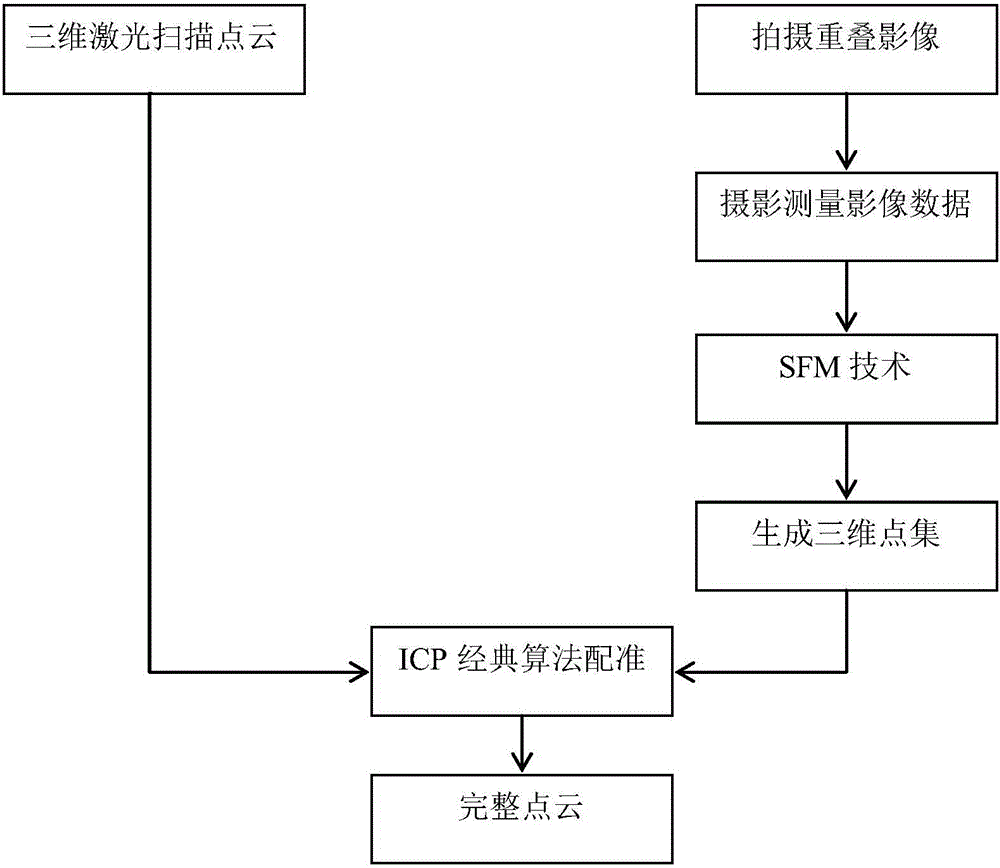
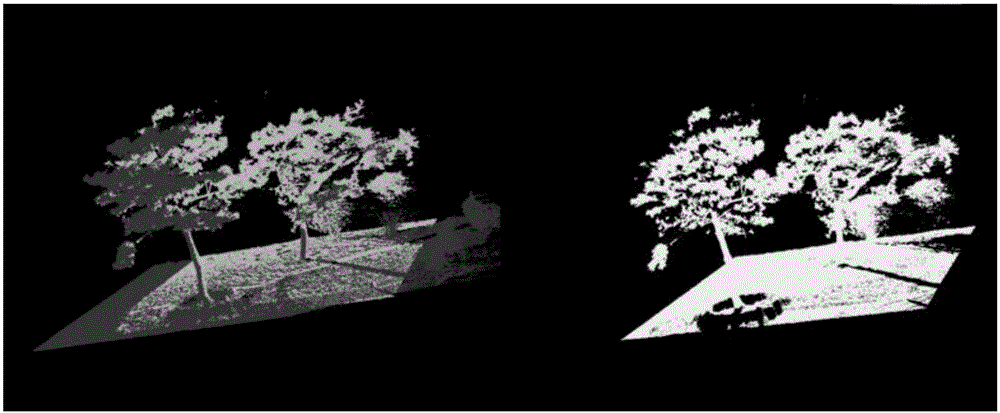
InactiveCN105931234AImprove noise immunityEnsuring rotation invarianceImage enhancementImage analysisLaser scanningImage fusion
The present invention provides a ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method, and the limitation of the scanning of the ground three-dimensional laser scanning technology is overcome. The point cloud data obtained by ground three-dimensional laser scanning often comprises various areas which can not be measured, point cloud holes are generated, and thus local area information of a scanned object is lost. The holes cause that a model can not realize visualization correctly, and model subsequent processing is influenced too. For the above problems, the invention aims to solve the problems through the following technical scheme that an SIFT image is used to carry out mosaic processing of collected image photos by means of an algorithm to obtain a panoramic image, the intensive reconstruction is carried out through the panoramic image to obtain the 3D point cloud data generated by the image photo, and an iterative closest point algorithm (ICP) is used to realize the registration working of laser scanning point cloud and image data generation point cloud.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
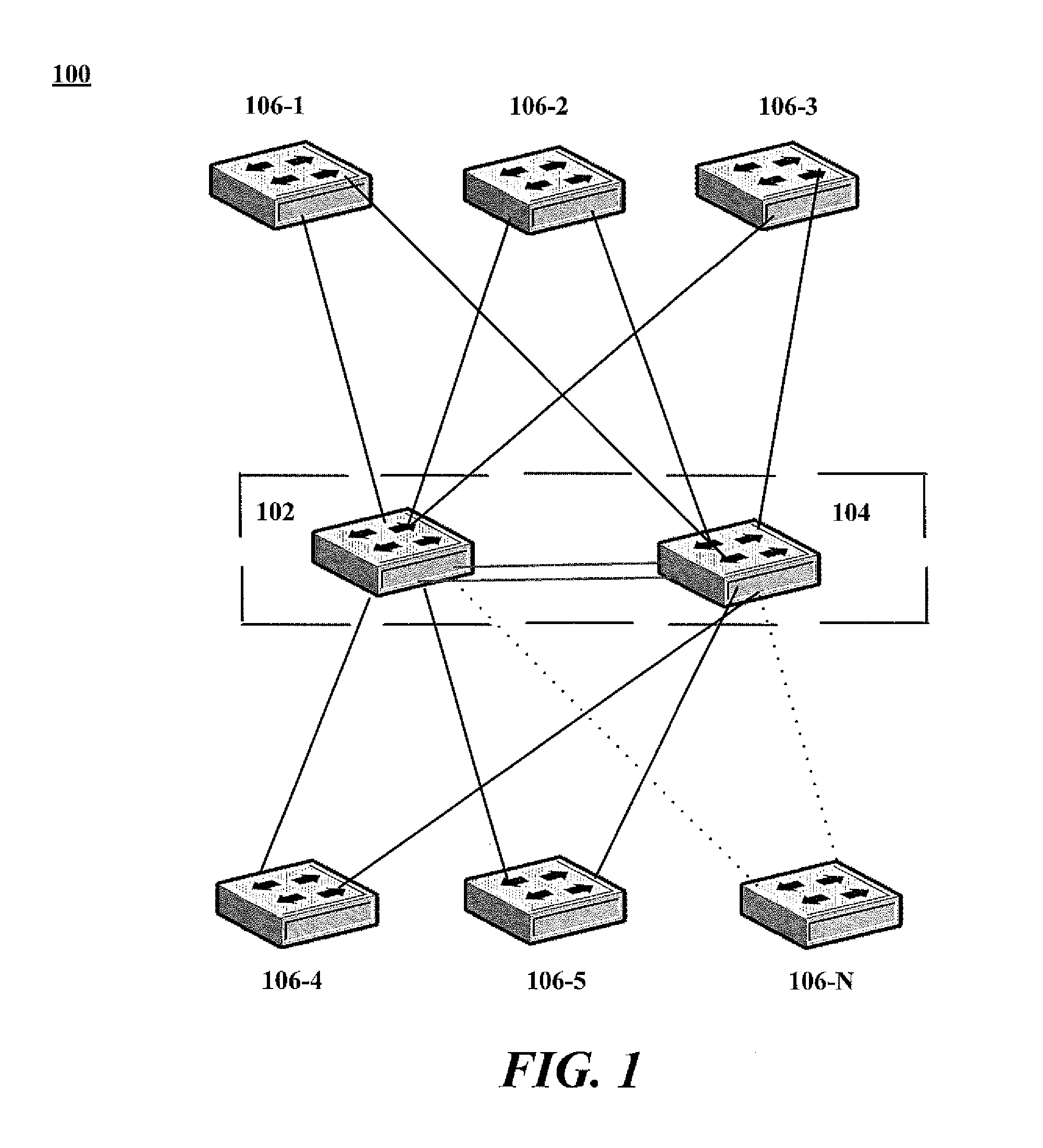
System and method for reducing information loss in an aggregated information handling system
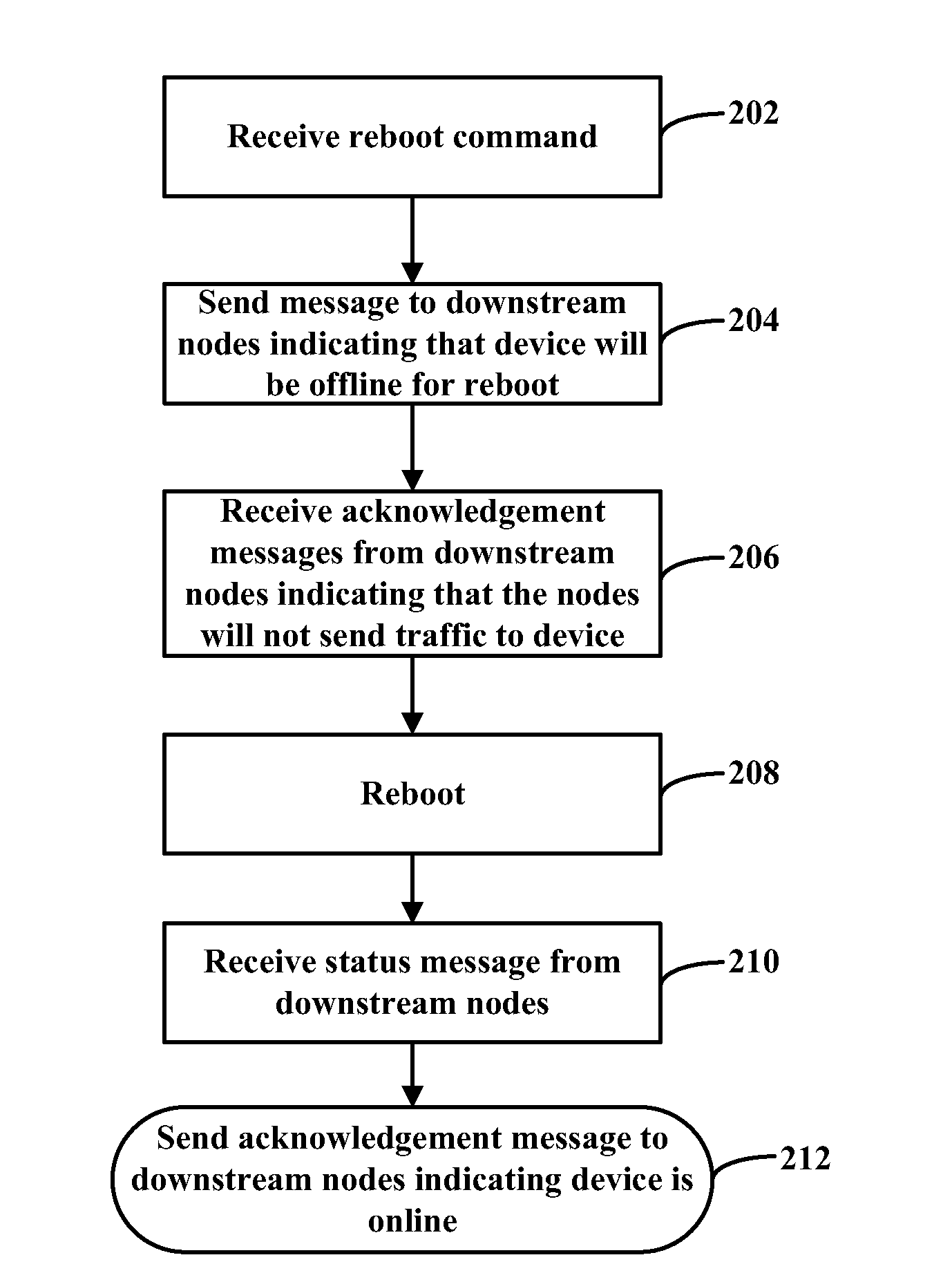
ActiveUS20130268590A1Energy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation handling systemInformation loss
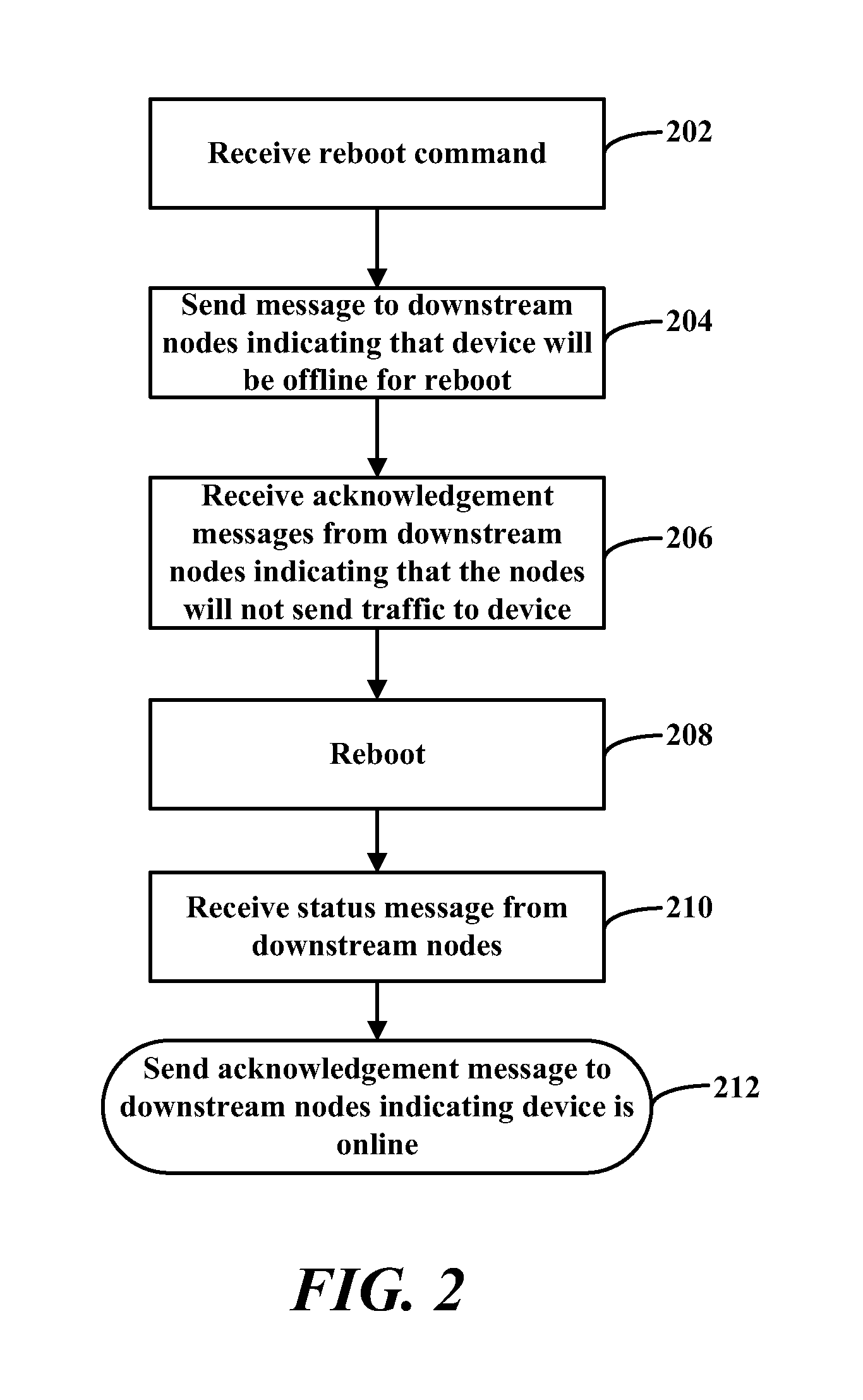
A provided information handling system includes a plurality of aggregation devices configured to distribute information in a virtual link trunk and a plurality of nodes coupled to the aggregation devices. When an aggregation device receives a reboot command, that aggregation device is configured to transmit a first message to the nodes indicating that the aggregation device is rebooting, and receive a first acknowledgement message from the nodes indicating that they will not send any information to the rebooting aggregation device. The aggregation device is then configured to reboot, receive a second message from the nodes indicating the nodes are ready to receive information from the rebooted aggregation device, transmit a second acknowledgement message to the nodes indicating that the rebooted aggregation device has rebooted and is capable of receiving information, and receive information from one of the nodes for transmission to another node.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
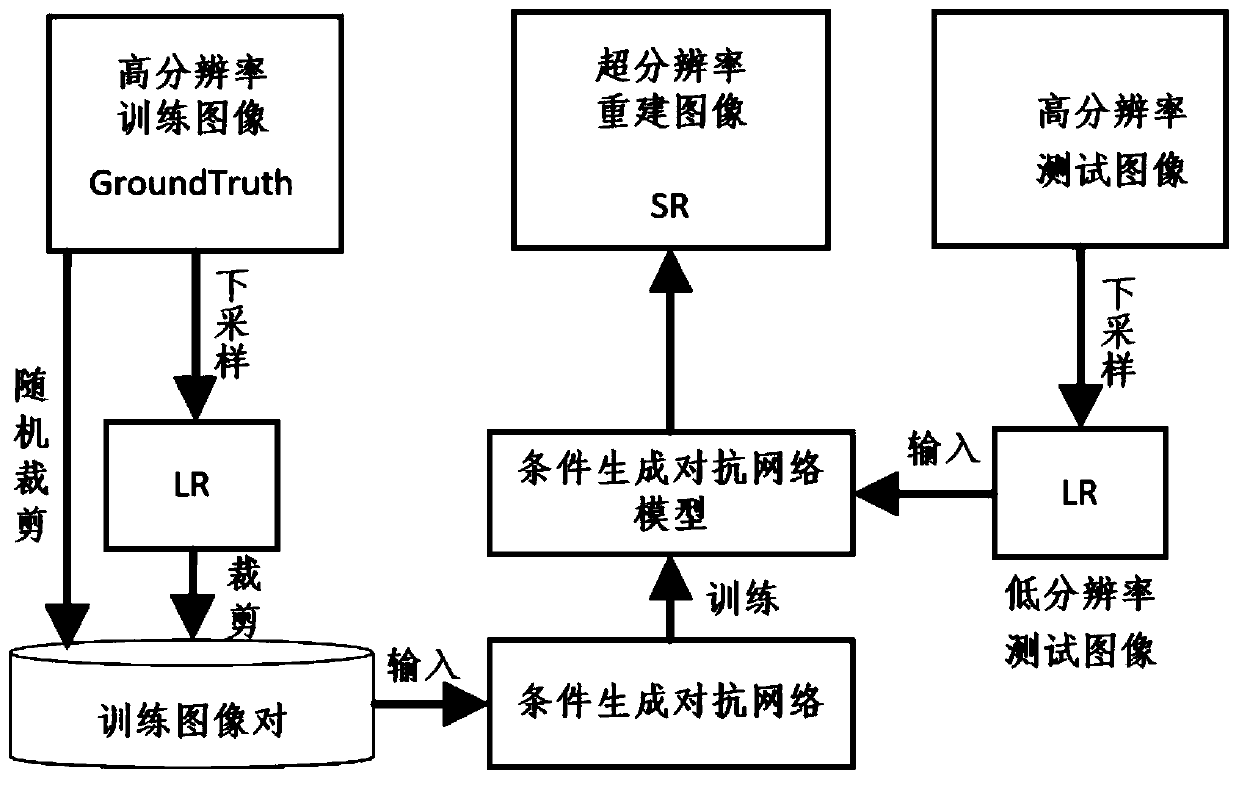
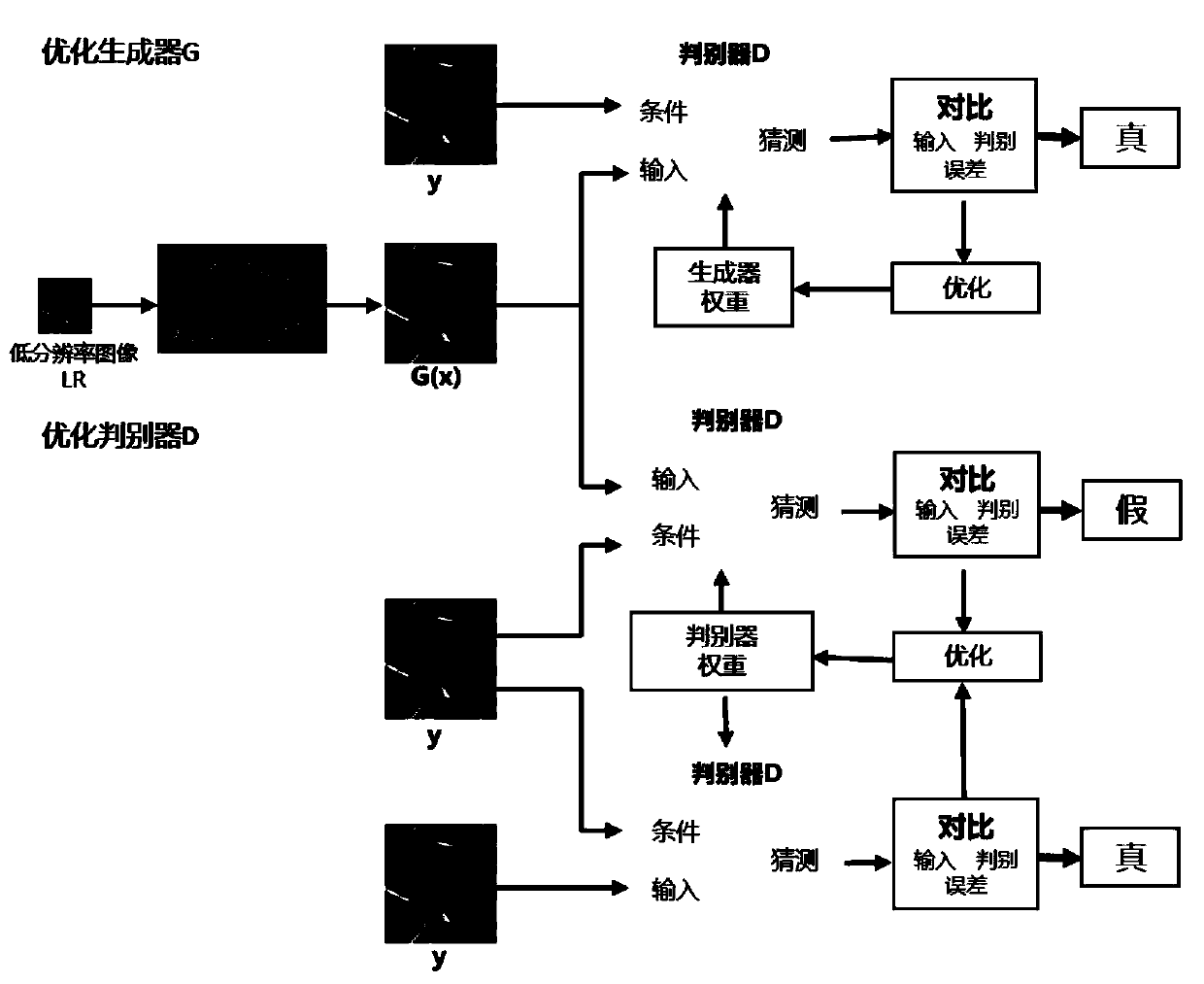
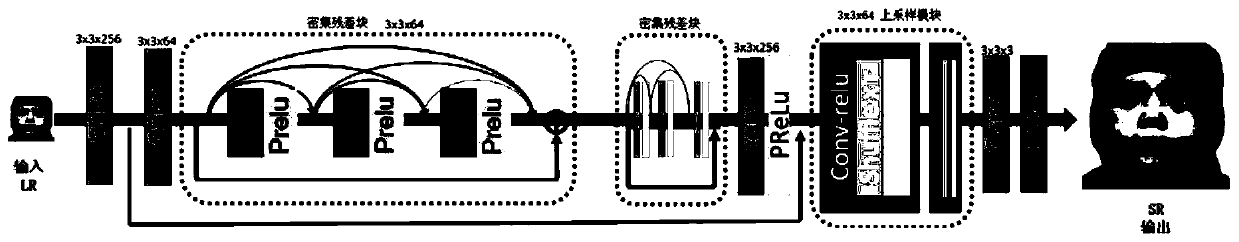
Super-resolution reconstruction method based on conditional generative adversarial network
ActiveCN109978762AImprove discrimination accuracySolve the problem of loss of high-frequency detailsGeometric image transformationInternal combustion piston enginesData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a super-resolution reconstruction method based on a conditional generative adversarial network, and the method specifically comprises the steps: making a low-resolution image and a corresponding high-resolution image training set by using a disclosed super-resolution image data set; constructing a conditional generative adversarial network model, using dense residual blocksin the generator network, and realizing super-resolution image reconstruction at the tail end of the generation network model by using a sub-pixel up-sampling method; inputting the training image setinto a conditional generative adversarial network for model training, and enabling a training model to converge through a perception loss function; carrying out down-sampling processing on the imagetest set to obtain a low-resolution test image; and inputting the low-resolution test image into the conditional adversarial network model to obtain a high-quality high-resolution image. The method can well solve the problems that a super-resolution image generated by a traditional generative adversarial network looks like clear, and evaluation indexes are extremely low, and meanwhile, the problems of gradient disappearance and high-frequency information loss are relieved through a dense residual network.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
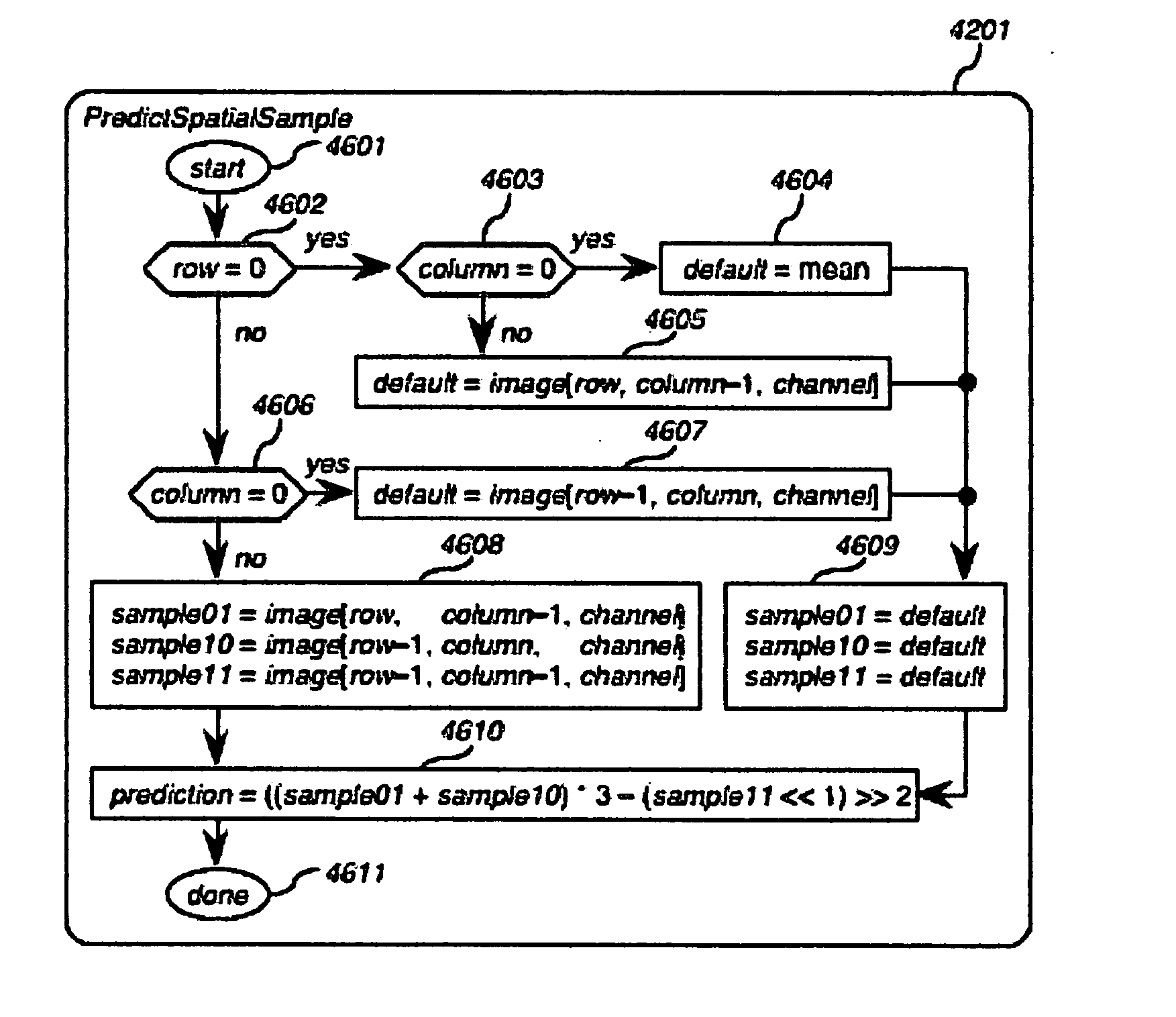
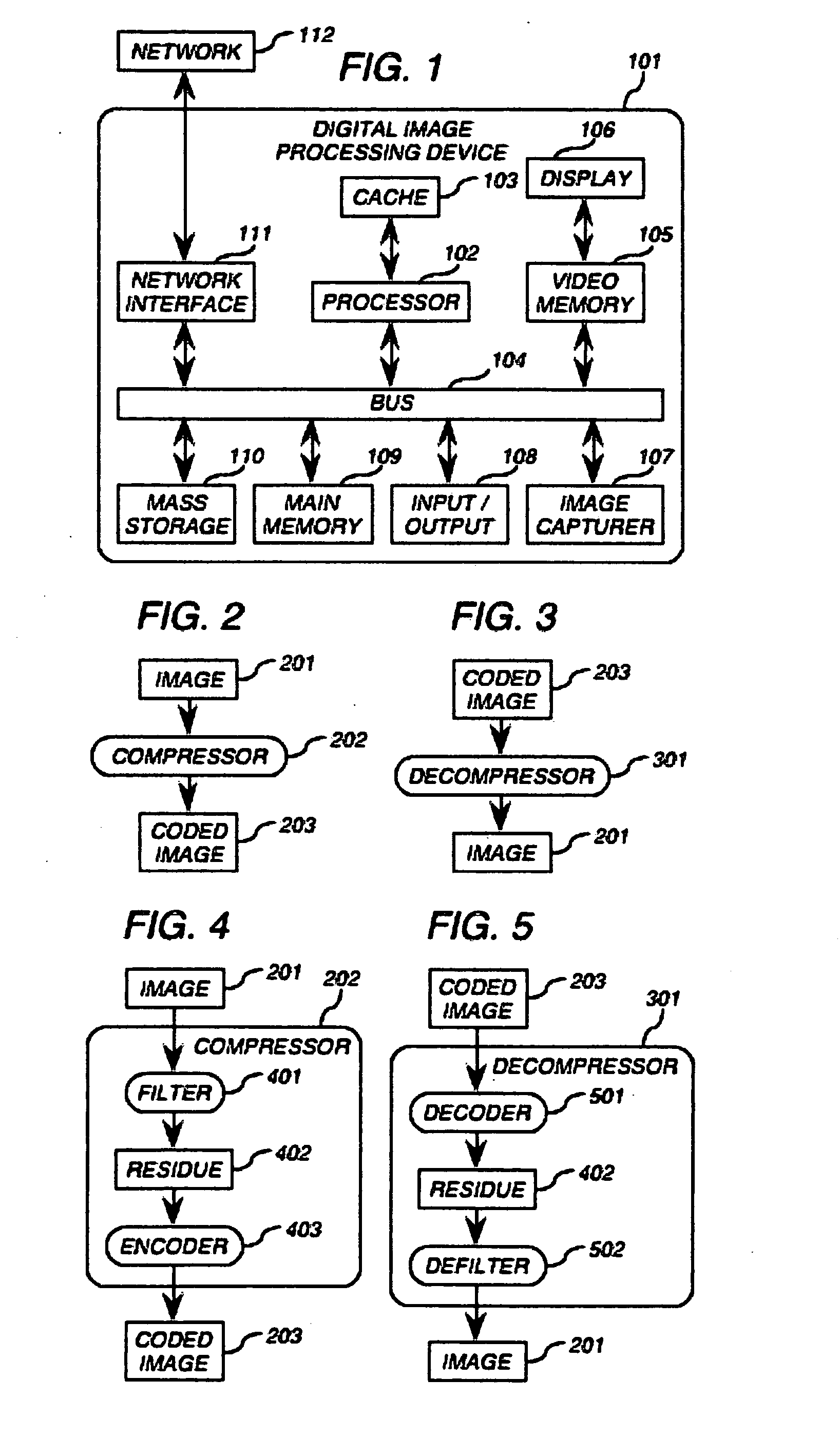
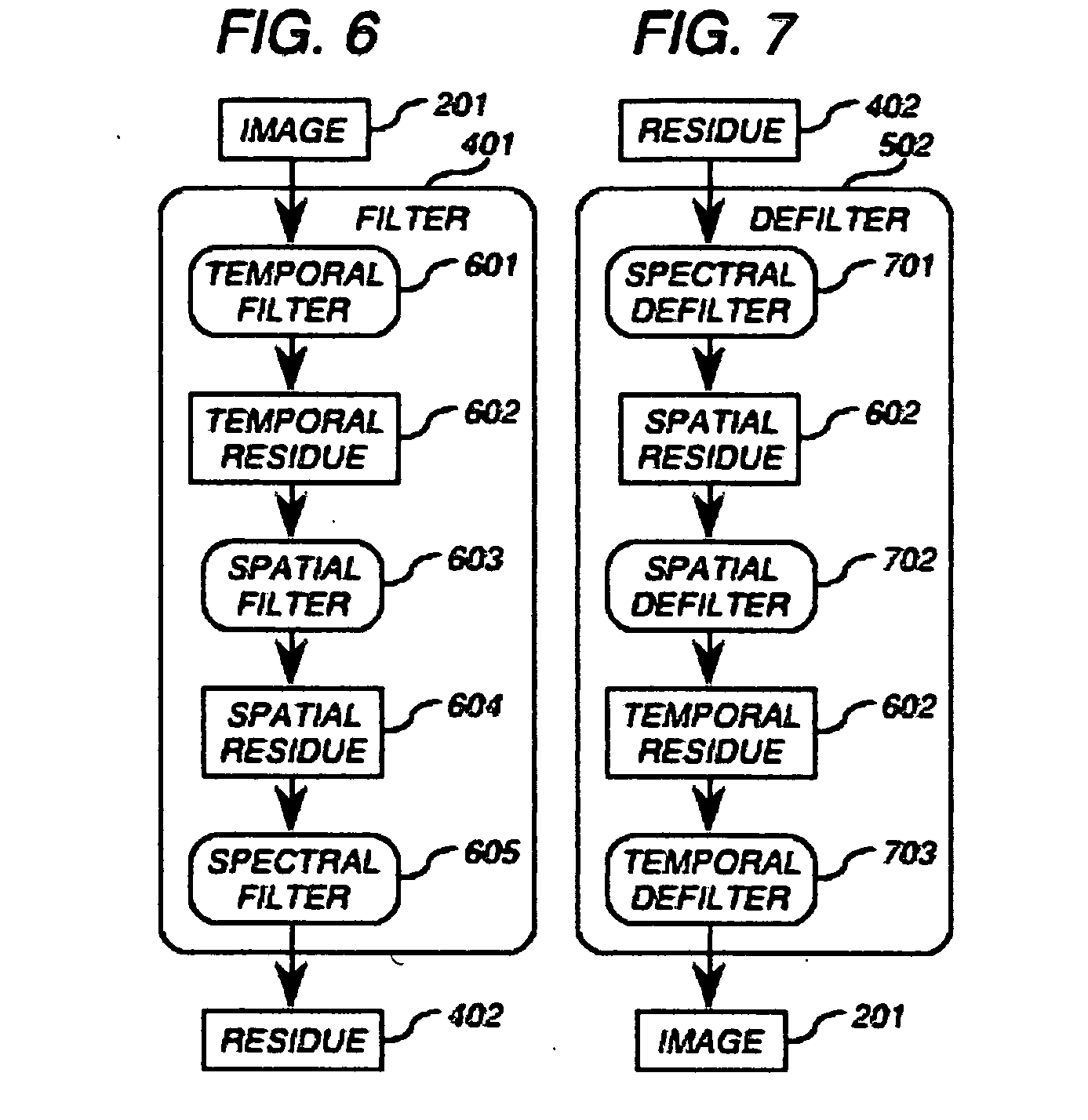
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
Electrocardiogram diagnosis method and system based on deep convolution neural network
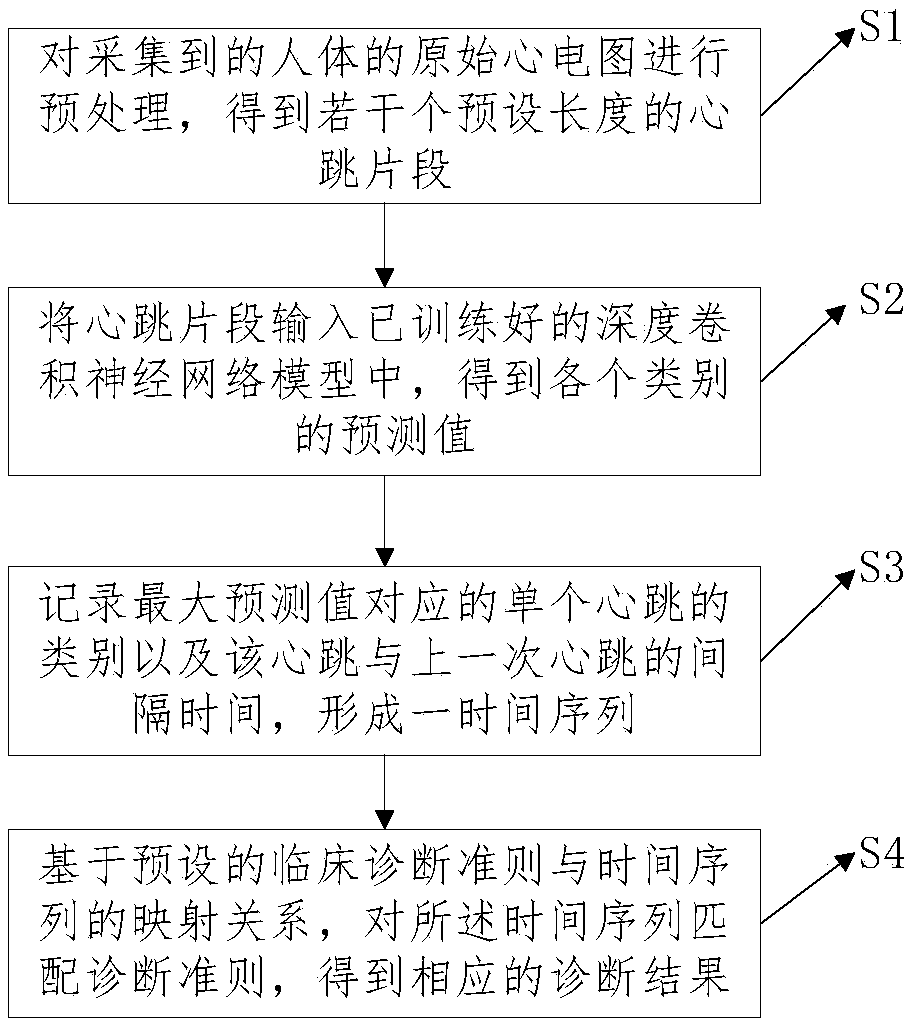
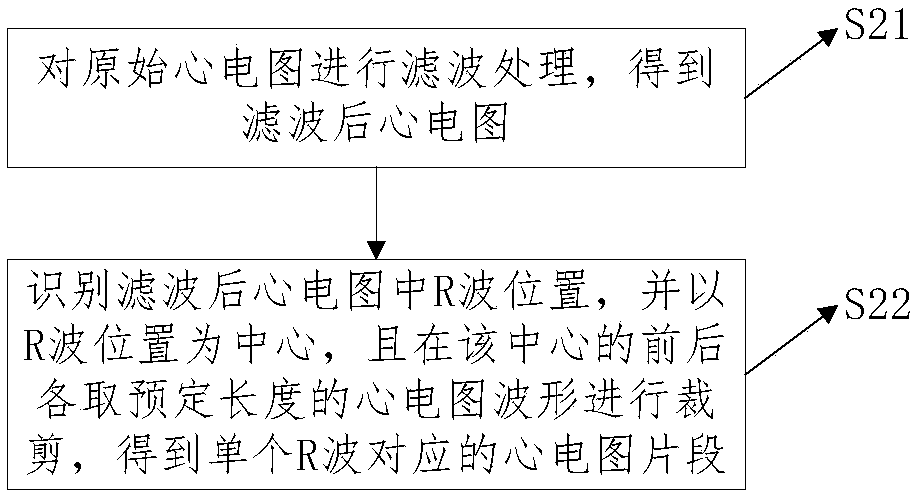
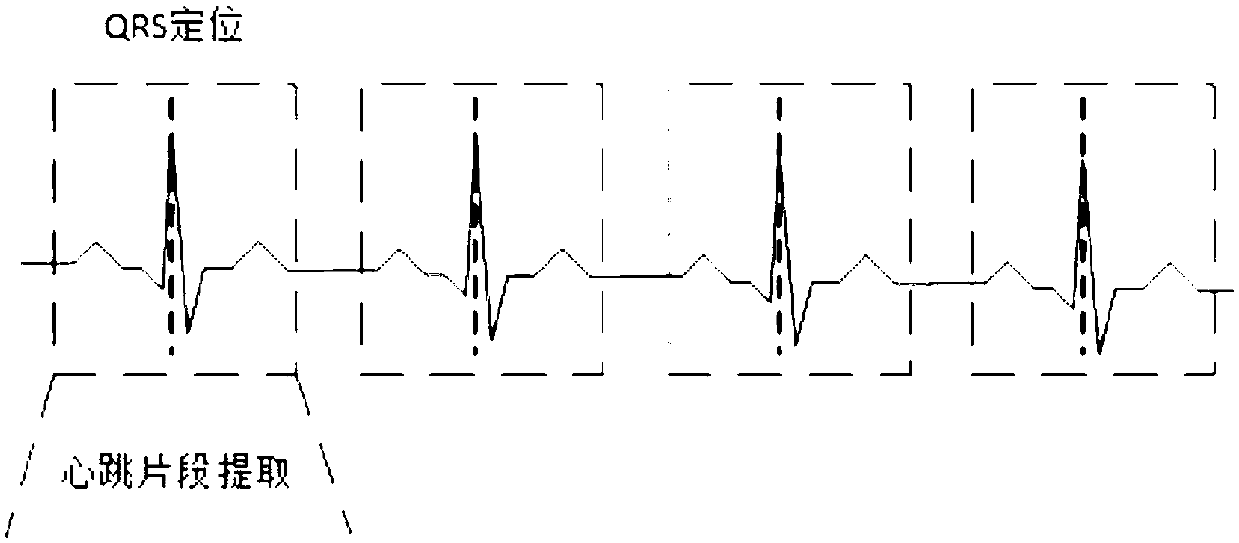
ActiveCN107822622ARealize automatic diagnosisAvoid problems such as introducingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNerve networkDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses an electrocardiogram diagnosis method and system based on a deep convolution neural network. The diagnosis method comprises the steps that a collected original electrocardiogram of the human body is preprocessed to obtain a plurality of heartbeat fragments with a preset length; the heartbeat fragments are input into a trained deep convolution neural network model, and a prediction value of each category is obtained; the category of a single heartbeat corresponding to the maximum prediction value and the time interval of the heartbeat and a previous heartbeat are recorded, and a time series is formed; on the basis of a preset mapping relation between a clinical diagnosis criterion and the time series, the time series is matched with the diagnosis criterion, and a corresponding diagnosis result is obtained. Any feature in the electrocardiogram is not required to be extracted, so that valid information loss, noise data introduction and other problems caused by manual screening and processing are avoided to the largest extent, and the influence of manual characteristic extraction on the diagnosis accuracy is reduced.
Owner:成都比特律动科技有限责任公司
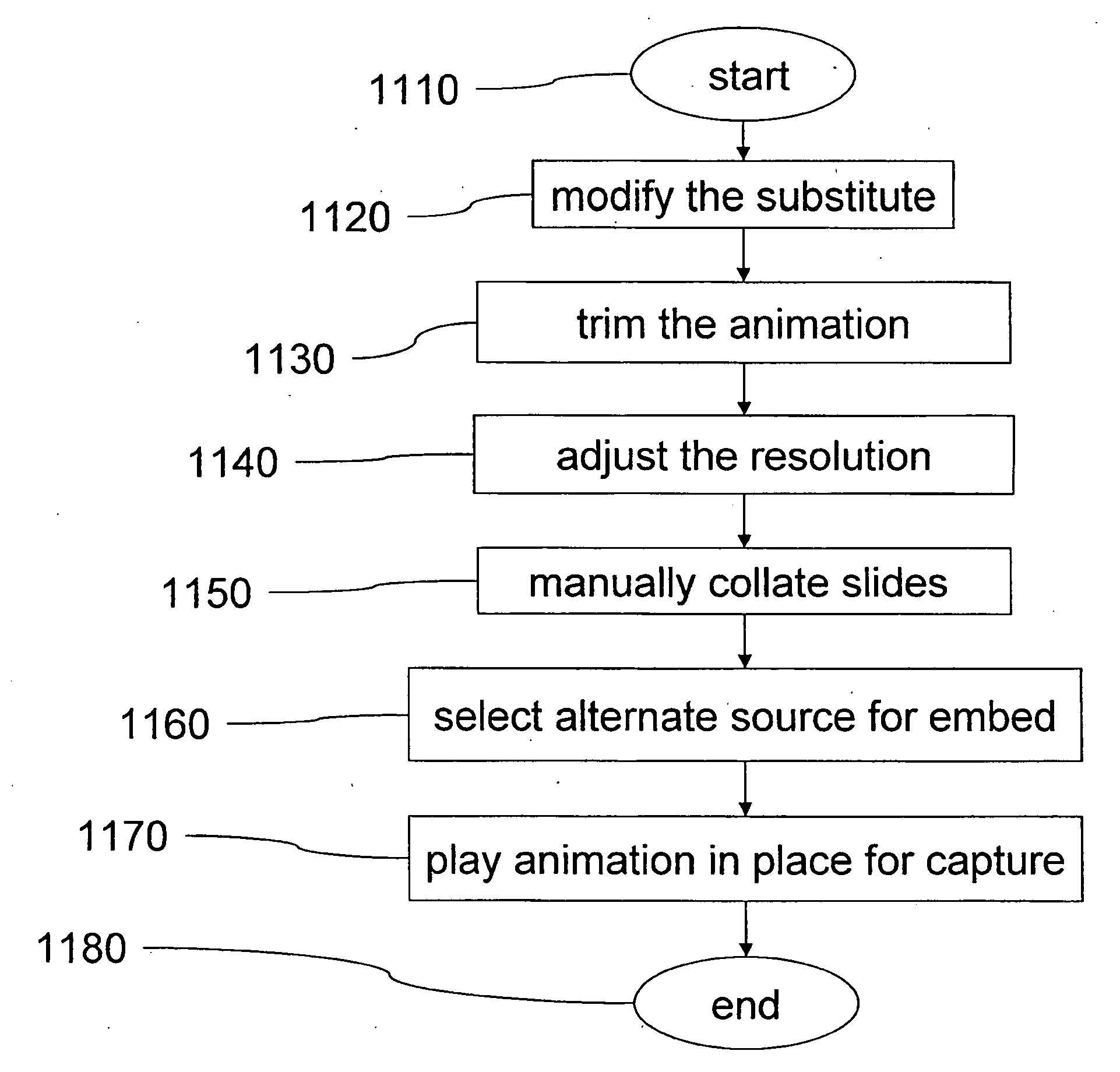
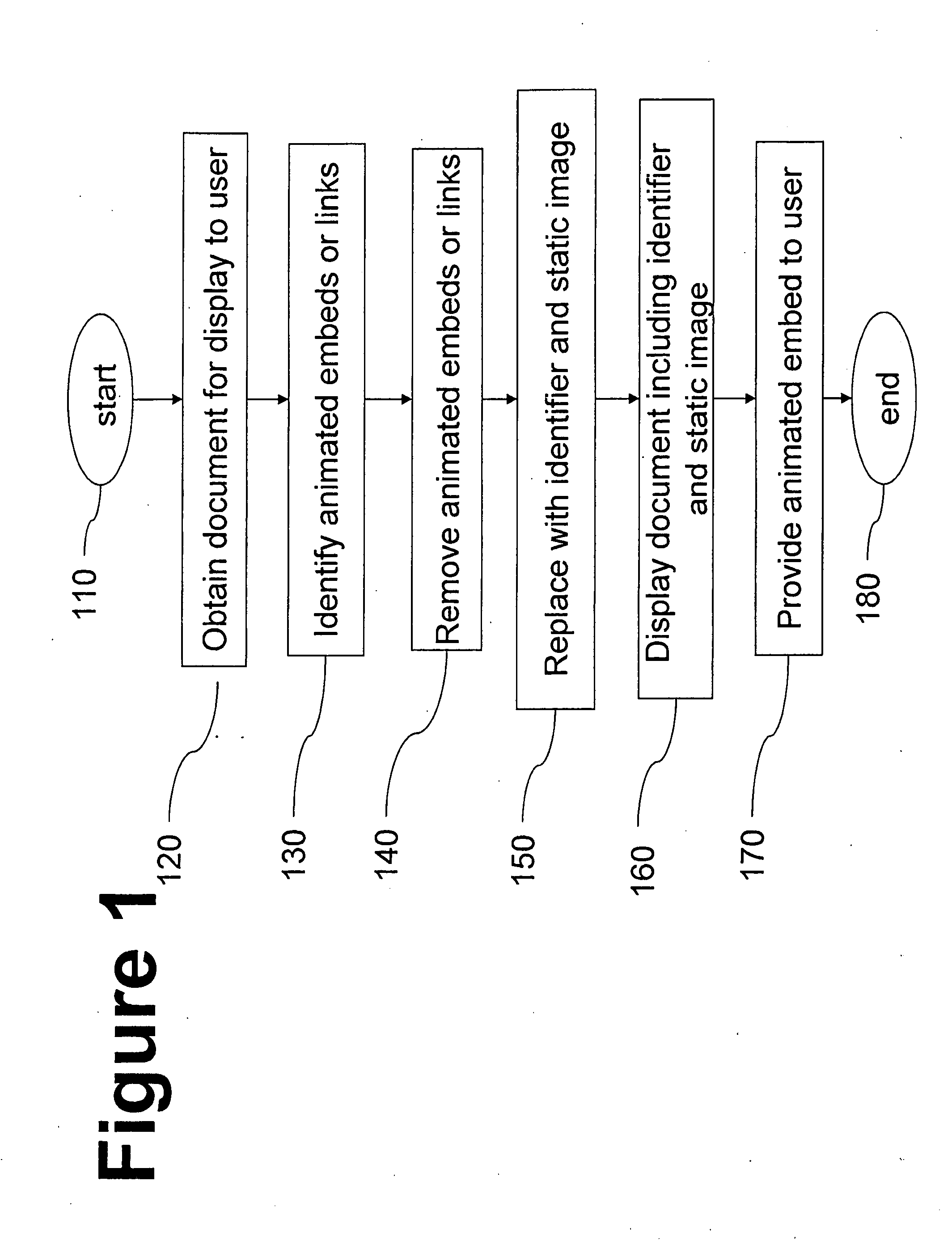
Systems and methods for viewing and printing documents including animated content
InactiveUS20100123908A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsWord processingAnimation
Most documents that are in use today embed or link to animated content. Presently, a large percentage of online content is hypertext markup language (HTML) and many HTML documents embed animations. The aforesaid online content is amenable to printing. However, embedding animated content in a document will lead to information loss when the document is printed. Users cannot print the animations or the videos embedded in documents. Therefore, there is provided a method and system for automatically finding animated content embedded in documents such as web pages, slide presentations, word processing documents, and PDF documents, that are being displayed to a user, replacing the animated content by a printable version, such as a keyframe, and a unique code, and assigning each animation a URL, to allow the users to retrieve the animations via a website on computer displays or mobile devices as they read the printed document.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
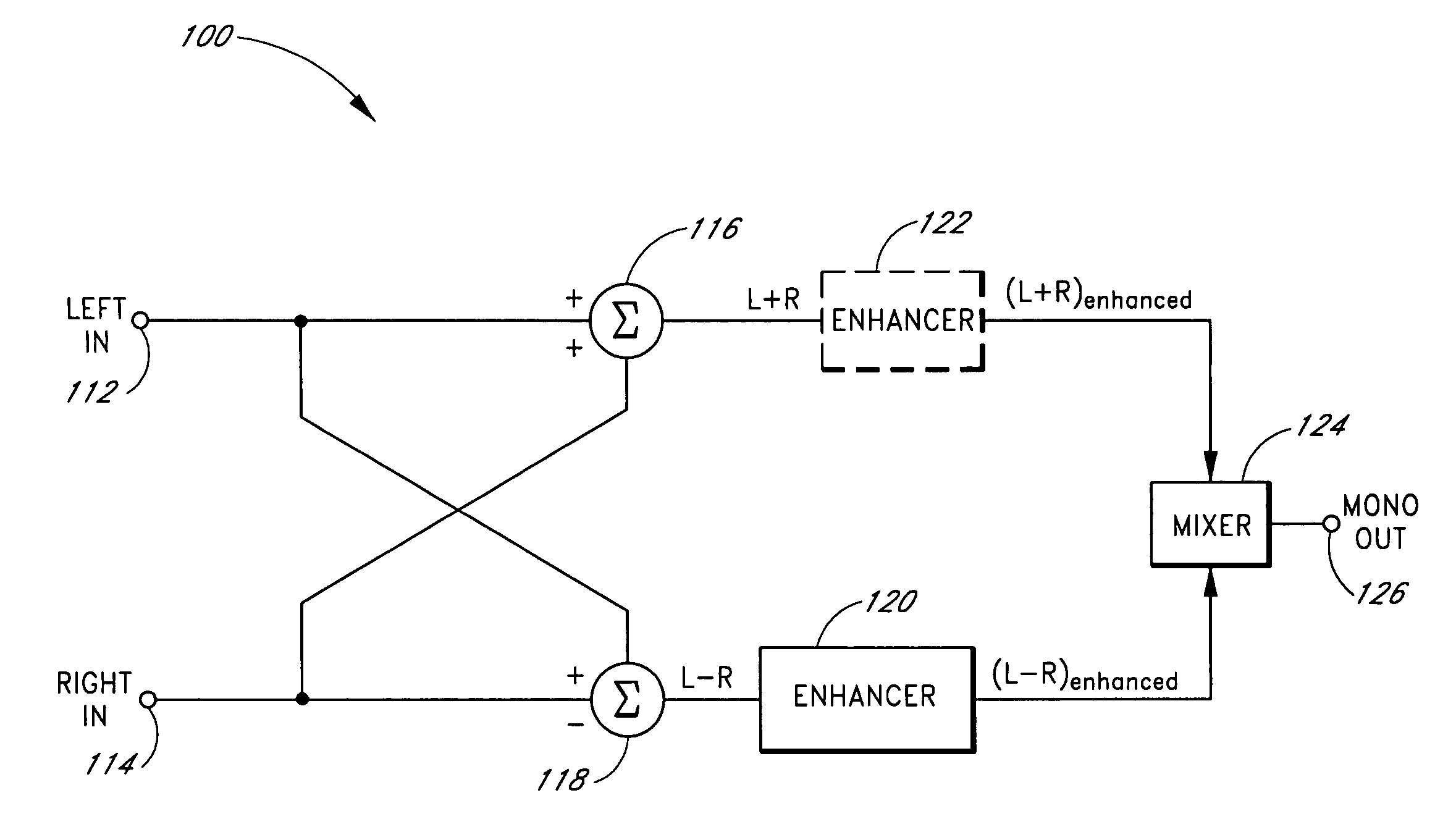
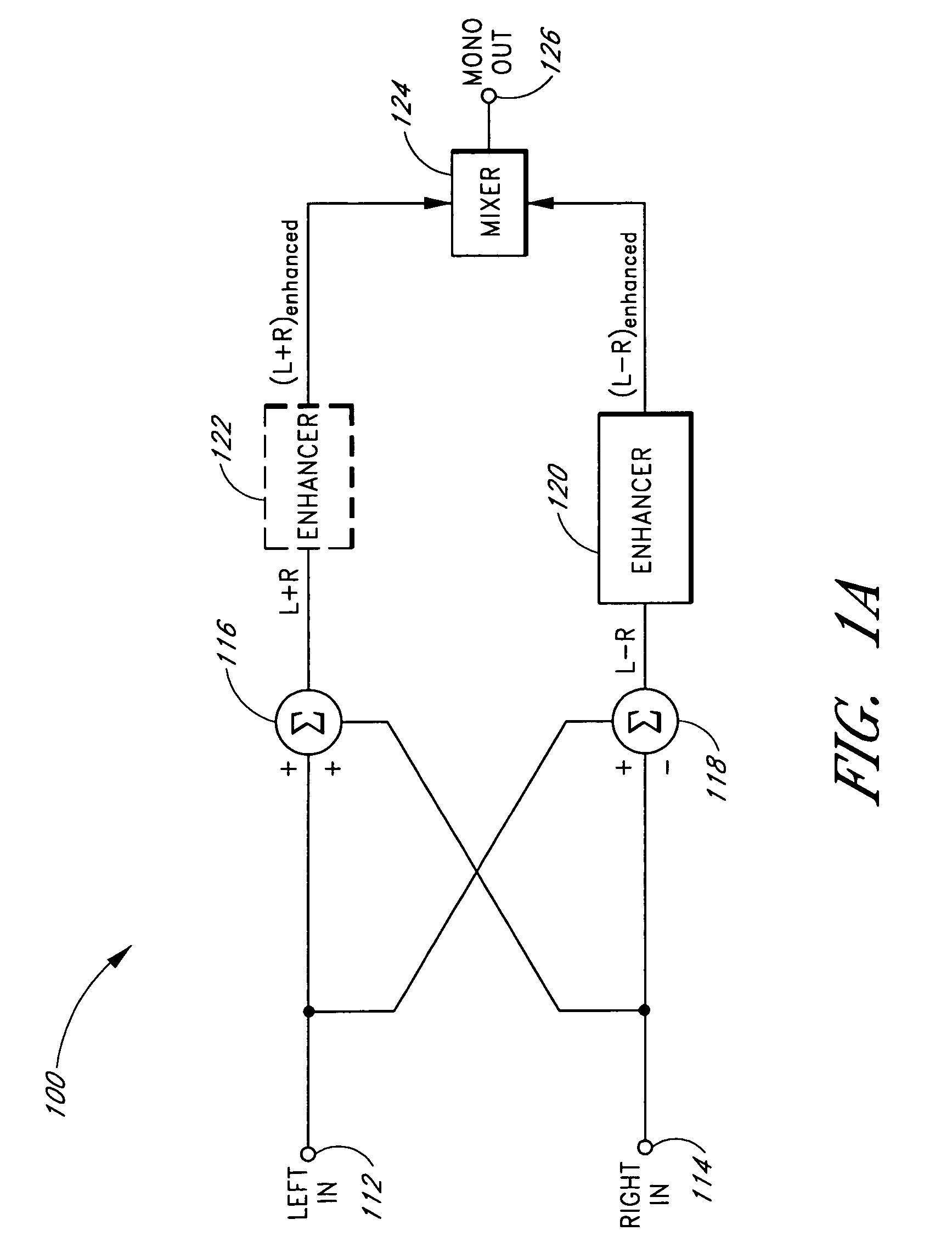
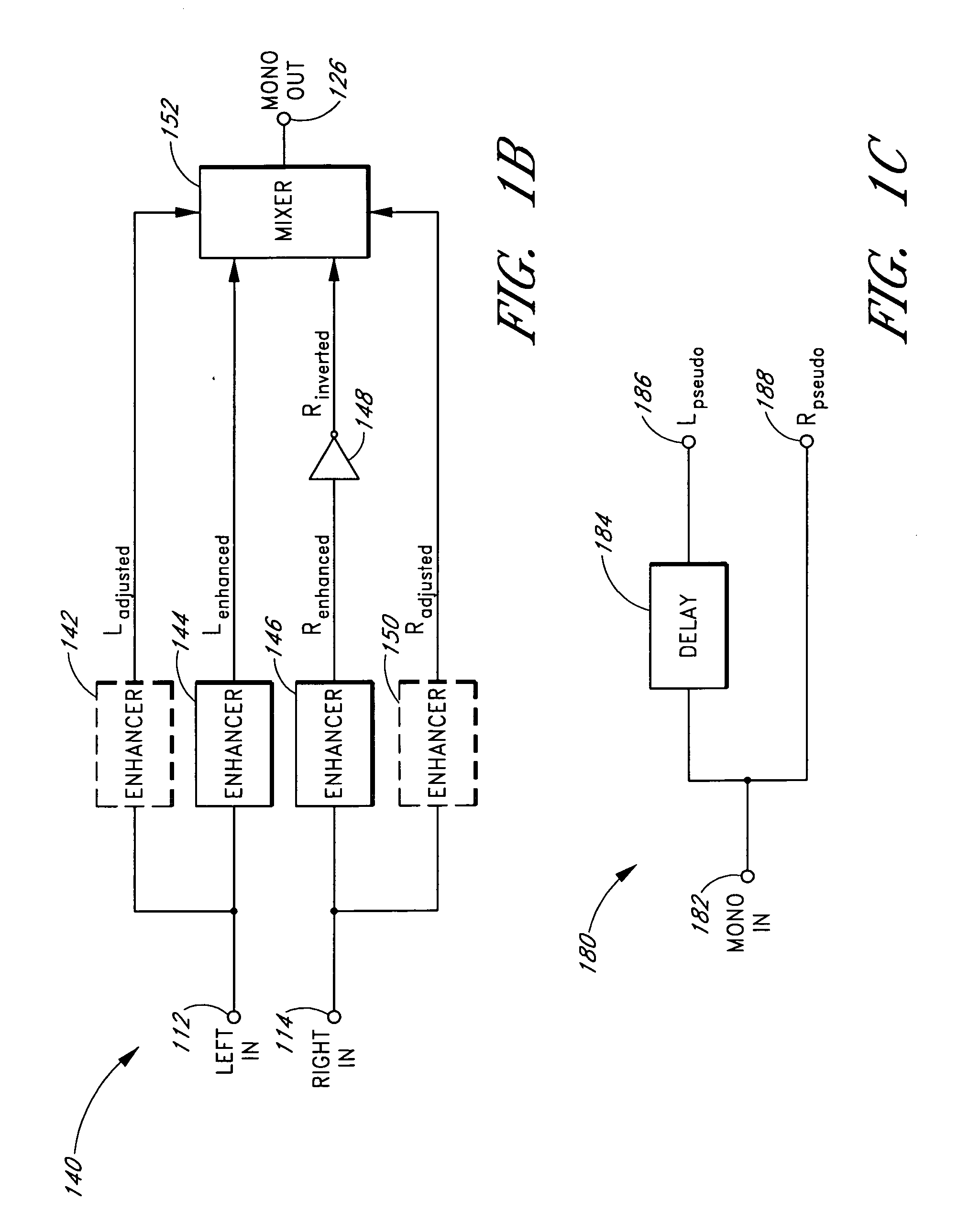
Systems and methods of spatial image enhancement of a sound source
ActiveUS20050129248A1Good audioAdditional componentBroadcast circuit arrangementsPseudo-stereo systemsSound sourcesVocal tract
Reproduction of stereophonic audio information over a single speaker requires summing multiple stereo channels. When signals having approximately equal magnitudes and approximately opposite phases at a frequency are added together, the audio information at the frequency is lost. To preserve areas of potential cancellation and potential audio information loss, the audio enhancement system adjusts the phase relationship between the stereophonic channels. To avoid the loss of the spatial content of the stereo signal, the audio enhancement system determines the difference information that exists between different stereophonic channels. The audio enhancement system enhances the difference information and mixes the enhanced difference information with the phase adjusted signals to generate an enhanced monophonic output.
Owner:DTS
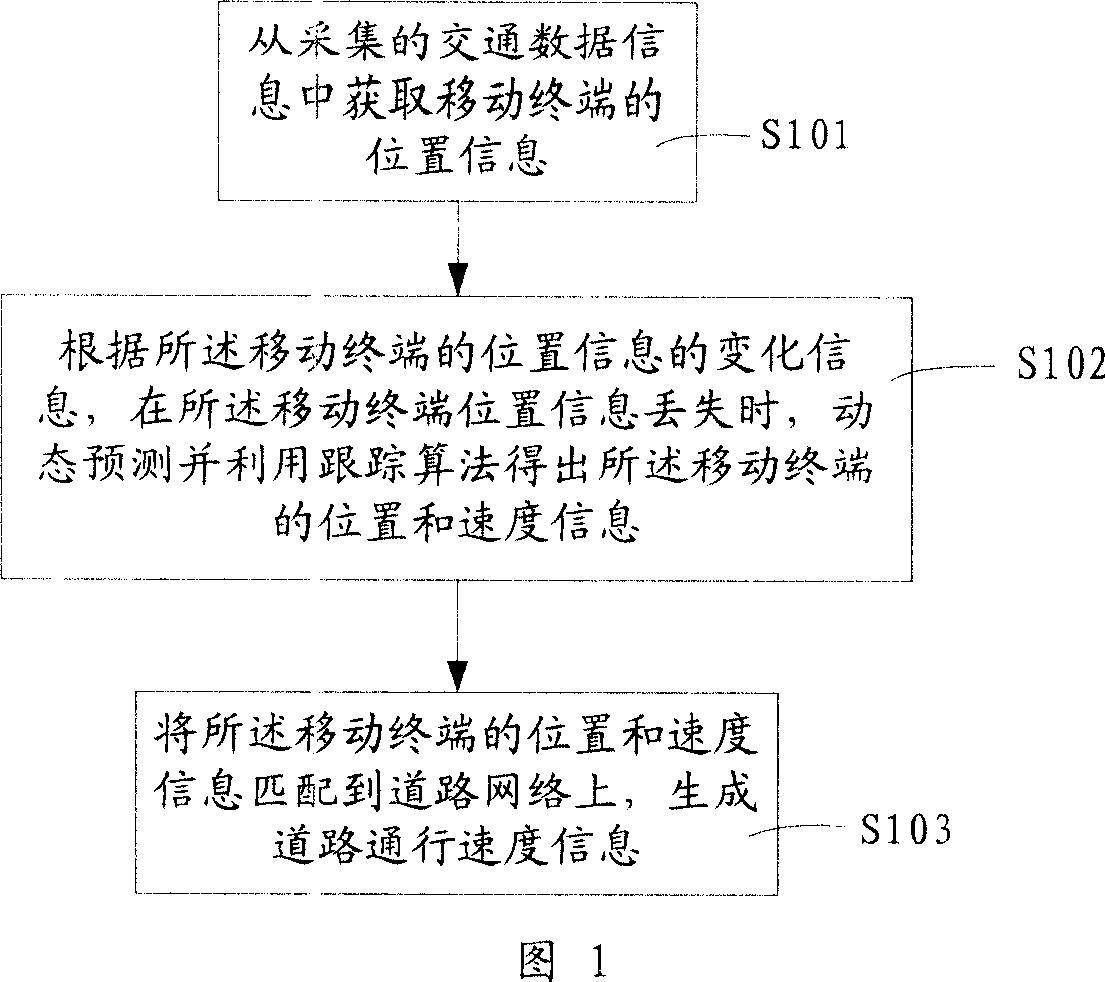
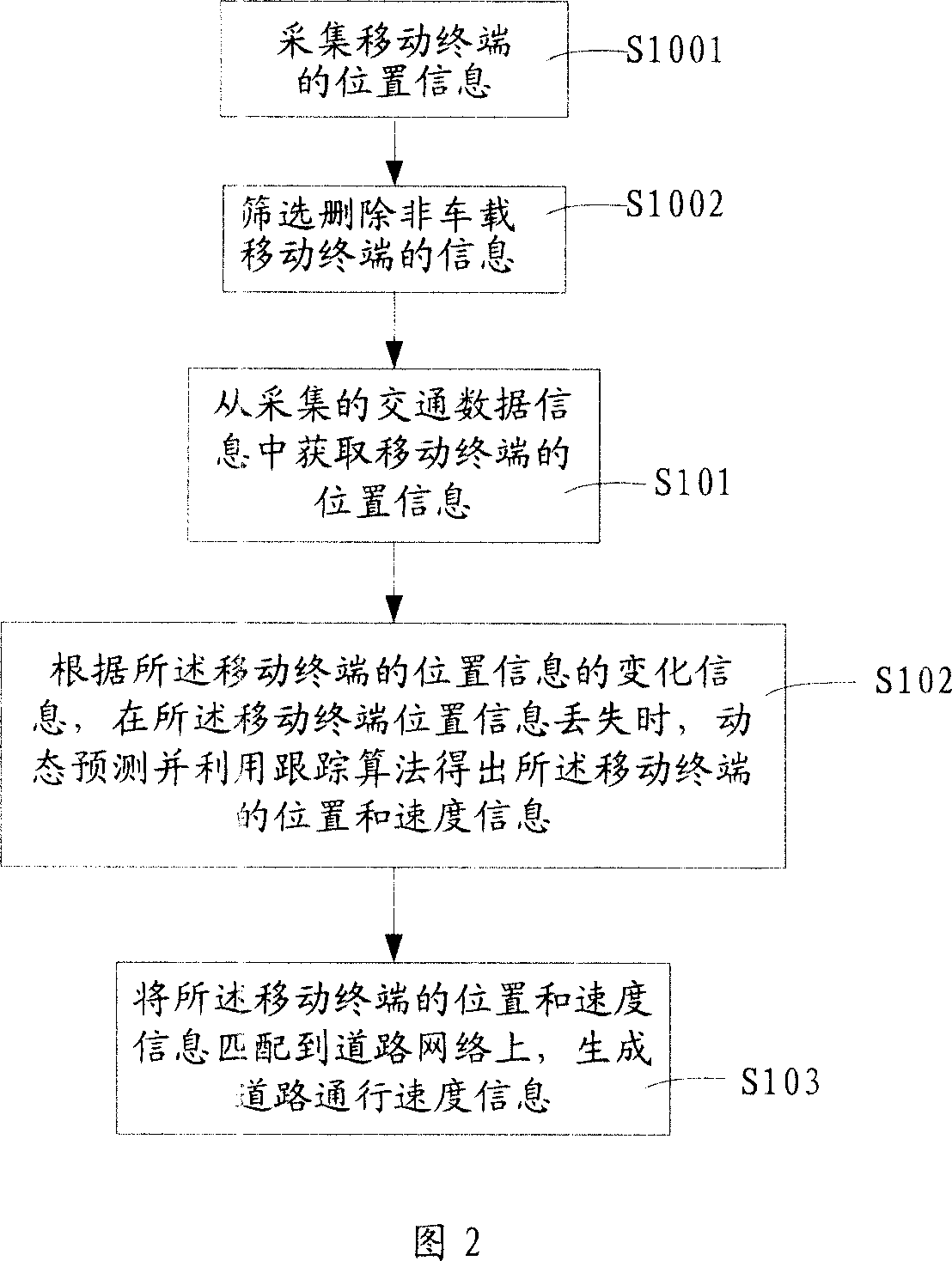
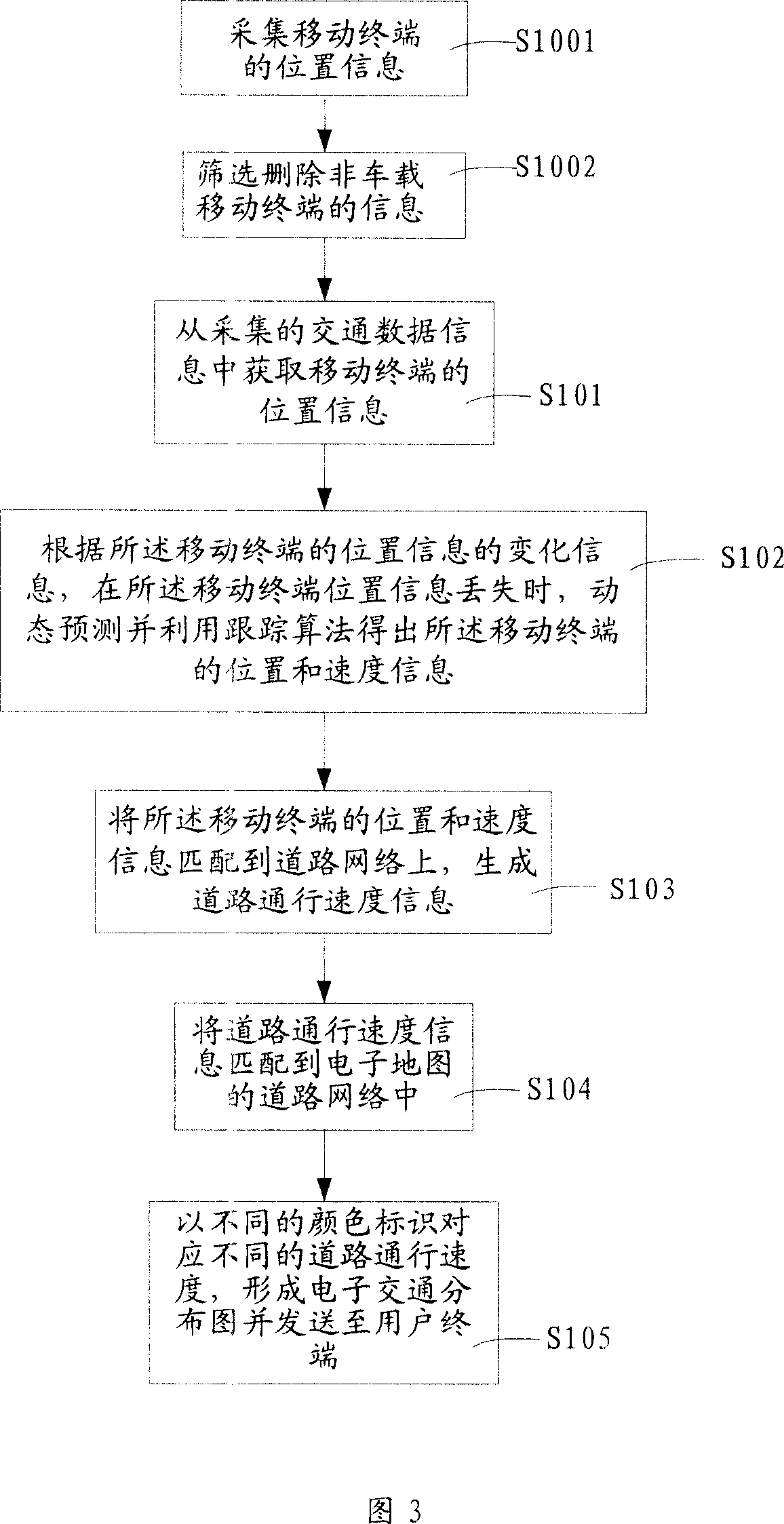
Roads traffic speed calculating and matching method and system
ActiveCN101136140AGuaranteed smoothnessIntegrity guaranteedDetection of traffic movementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData informationRoad networks
The traffic speed counting and matching method for road traffic includes: fetching position information of mobile terminals from collected traffic data information; when the position information of the mobile terminals is lost, according to the change information of the position information of the mobile terminals, dynamic predicting and obtaining the position and speed information of the mobile terminals by using follow-up arithmetic; matching the position and speed information of the mobile terminals onto a road network to generate road traffic speed information. The road traffic speed counting and matching system is also disclosed. The method and system can provide exact traffic condition information to traffic managers and going out people.
Owner:BOCO INTER TELECOM
Binning predictors using per-predictor trees and MDL pruning
ActiveUS20070185896A1Reduce information lossReduces the introduction of false information artifactsDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMemory footprintData selection
Binning of predictor values used for generating a data mining model provides useful reduction in memory footprint and computation during the computationally dominant decision tree build phase, but reduces the information loss of the model and reduces the introduction of false information artifacts. A method of binning data in a database for data mining modeling in a database system, the data stored in a database table in the database system, the data mining modeling having selected at least one predictor and one target for the data, the data including a plurality of values of the predictor and a plurality of values of the target, the method comprises constructing a binary tree for the predictor that splits the values of the predictor into a plurality of portions, pruning the binary tree, and defining as bins of the predictor leaves of the tree that remain after pruning, each leaf of the tree representing a portion of the values of the predictor.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Behavior recognition method based on sparse spatial-temporal characteristics
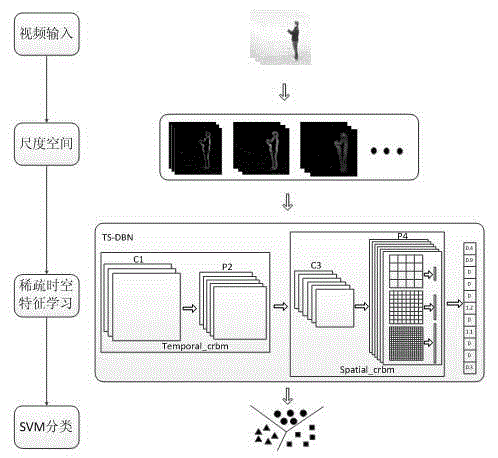
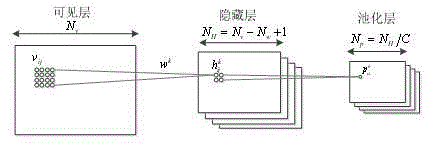
ActiveCN104933417AImprove performanceReduce feature dimensionCharacter and pattern recognitionDeep belief networkScale space
The invention discloses a behavior recognition method based on sparse spatial-temporal characteristics. The method comprises the steps as follows: step 1, convolving an input video with an original input video by using space-time Gabor to establish a scale space; step 2, using the expressions of different scales as values of different channels of a space-time depth belief network and associatively learning characteristics of multi-scale; step 3, recognizing and classifying the behavior characteristics. The behavior recognition method of the invention inputs depth network to associatively learn the characteristics of multi-scale by establishing the scale space to improve performance of behavior recognition. The behavior recognition method of the invention introduces the thought of spatial pyramid in terms of information loss problem of a pooling operation and performs multilevel expansion to pooling output, and combines with sparse coding to fuse pyramid multilevel characteristic, thereby improving characteristic dimension output by a pooling layer, further improving the performance of the original network and improving behavior recognition rate.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method of updating network information addresses
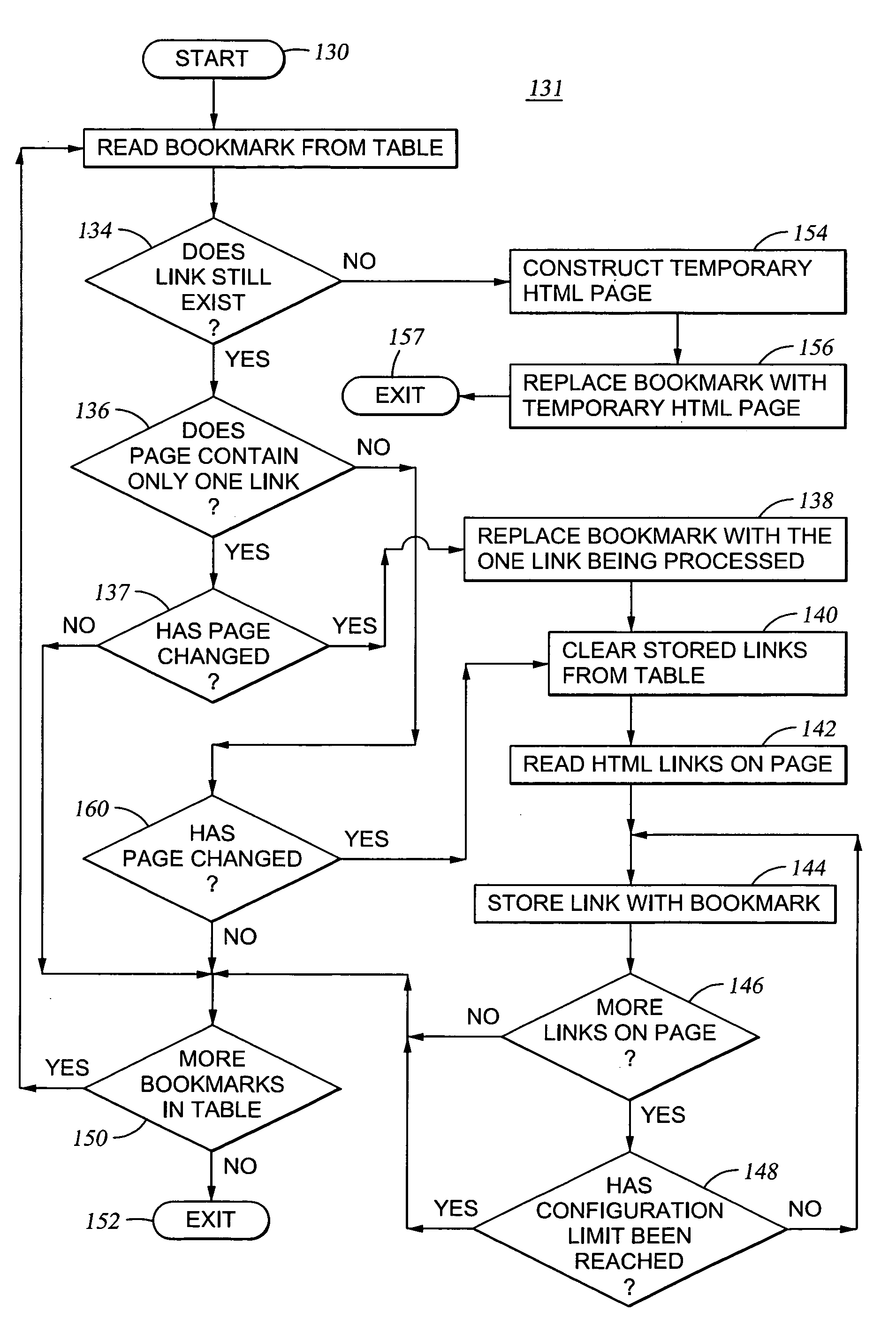
InactiveUS7028032B1Easy maintenanceAvoid lostDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsDocument preparationUniform resource locator
The present invention relates to a method and program product for facilitating the maintenance of current bookmarks and preventing the loss of information associated with a bookmark. In one aspect, the invention bookmarks a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) associated with one or more HTML documents at a user's request and creates a database table containing each bookmarked URL. The source code of the bookmarked URL is scanned for embedded links which are stored in the table according to the related bookmarked URL. To ensure that the bookmarks are current, a periodic verification of the status of a bookmarked URL is performed. A change in the location or / and contents of the one or more bookmarked HTML documents results in one or more actions to prevent the loss of data to the user. In one embodiment, the database table is refreshed to reflect any changes to the content of the HTML documents. In another embodiment, where a bookmarked HTML document has been moved to a new URL, the table is updated with a forwarding URL, i.e., the original URL is replaced with the new URL. Where a forwarding URL is not available, a backup document containing the stored embedded links related to the original URL is created.
Owner:TWITTER INC
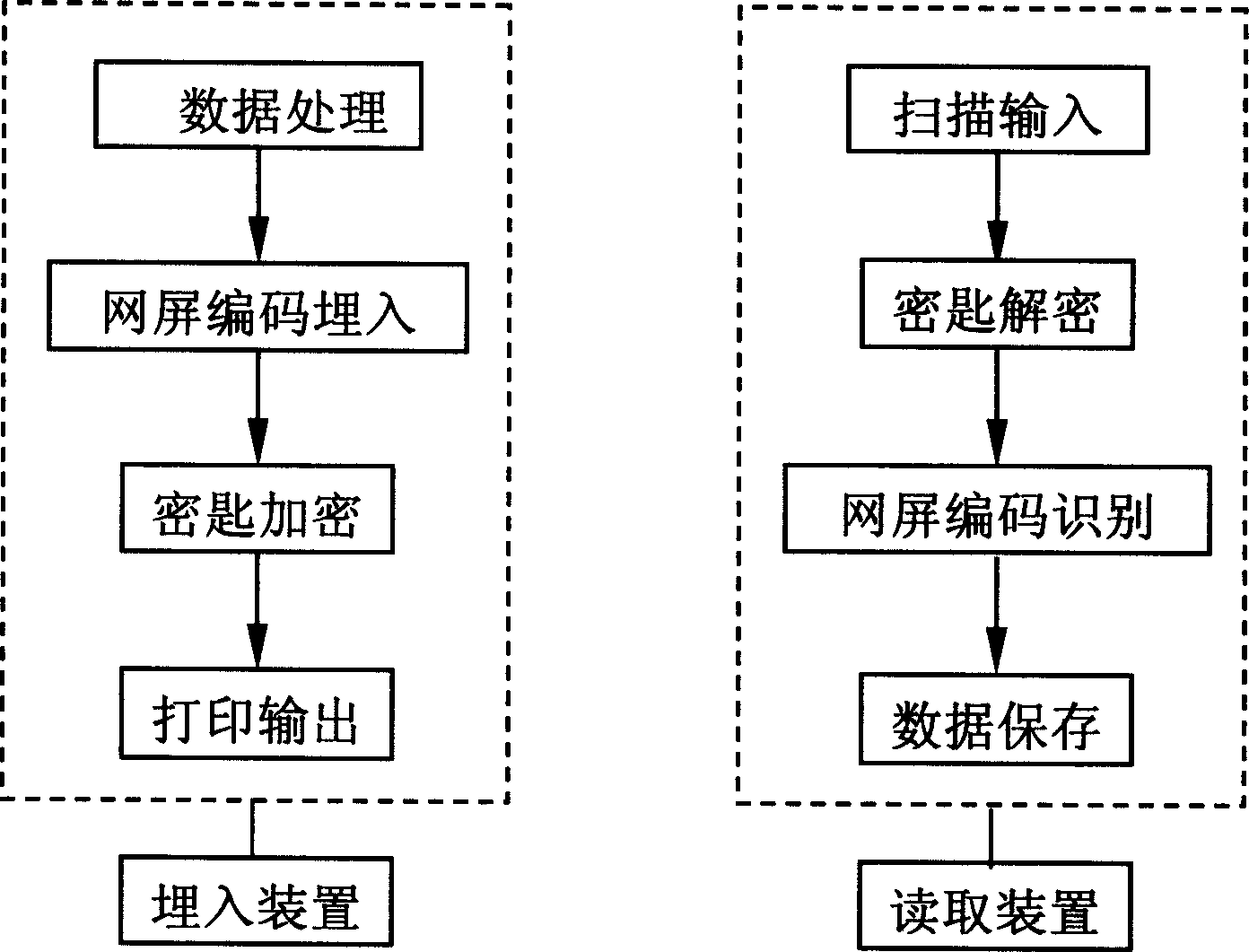
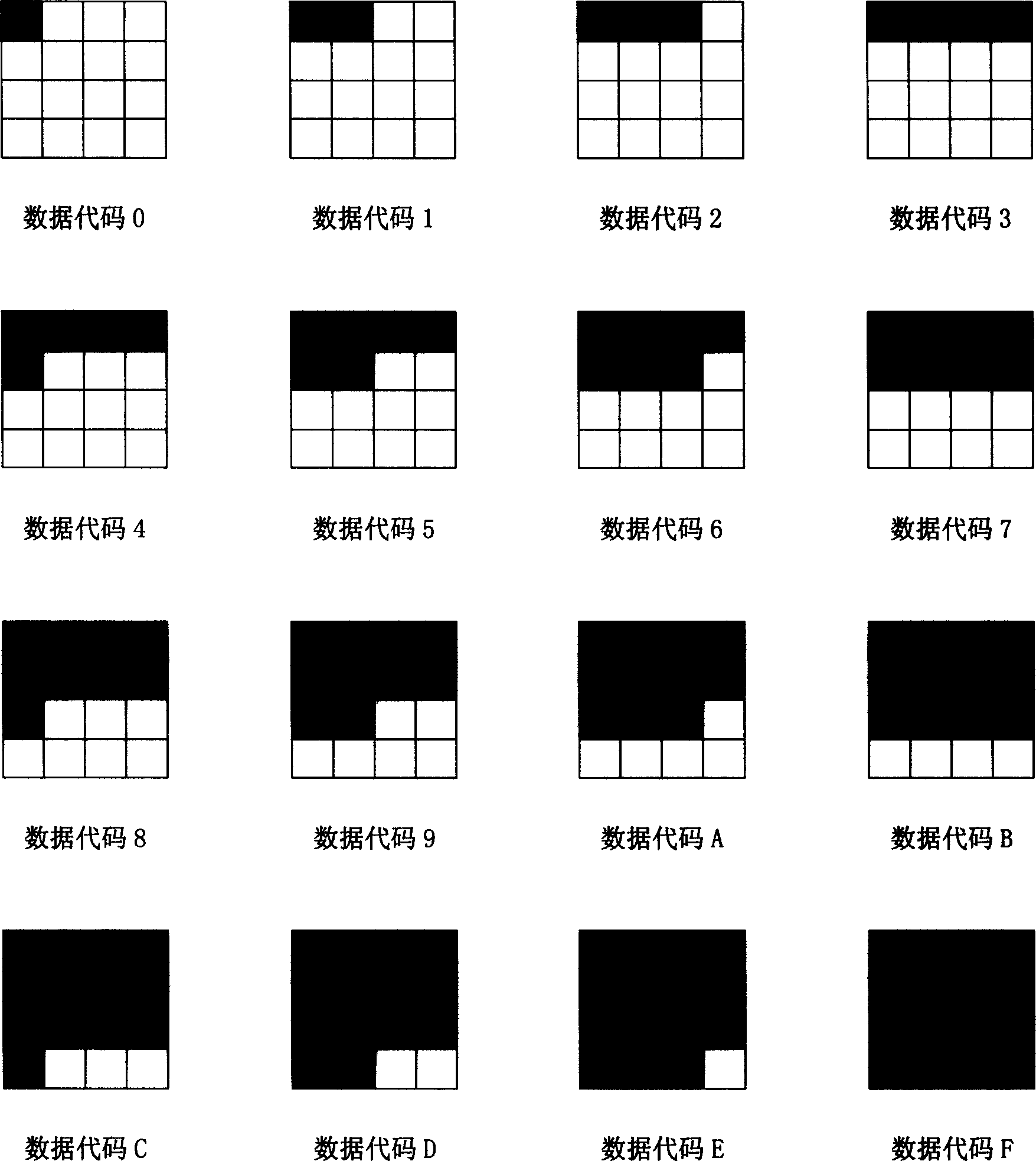
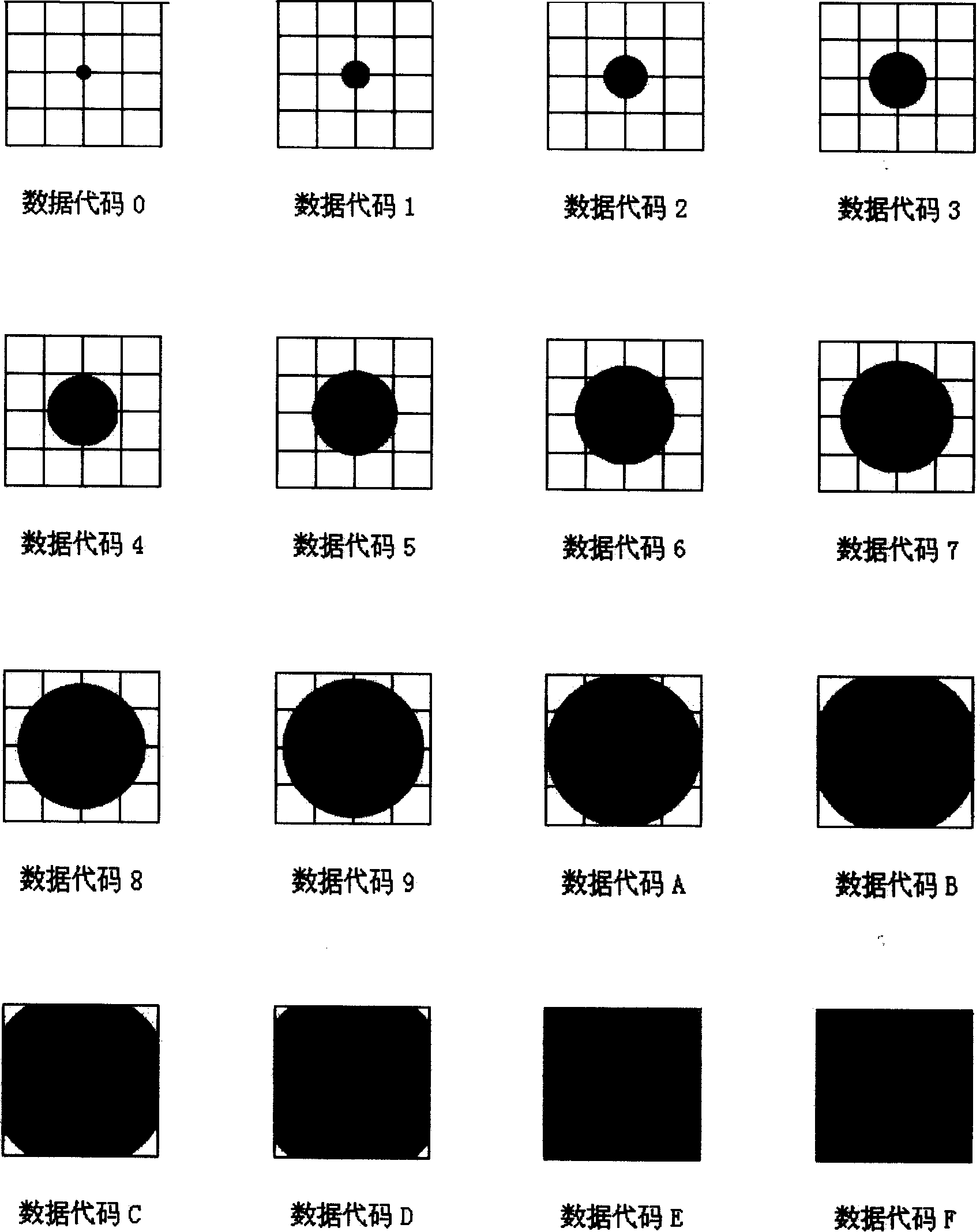
Network screen coding control method capable of recording mass data on paper
The invention relates to a net screen coding control method which can record plenty of data on paper. It includes net screen code embedding device which is composed by computer data process module, net screen code embedding module, key encryption module and printout module; net screen code reading device which is made up with scan input module, key decryption module, net screen code identification module and data storage module. The two devices make a system which can recode plenty of data on paper. Adopting the invention, plenty of data storage and net screen code which can recode plenty of data is realized through printing on paper or press. And confidential files' encryption and decryption is realized by using electronic files' method. Under condition of same area with two dimension bar code, the code method can record nearly ten times of information than two dimension bar and there is no limitation on occupied space and Chinese character record. It also resolves the problem of information loss because of local pollution. Data information can be embedded into image to resolve image quality destruction.
Owner:顾泽苍
Building area extraction method based on LiDAR data
The invention discloses a building area extraction method based on LiDAR data, which belongs to the field of extraction of building through the LiDAR data and includes early-age processing of the LiDAR data, resampling of original LiDAR data, reverse iteration mathematical morphological filtering and separation of building and dense trees. The building area extraction method directly processes three-dimensional (3D) point cloud data instead of converting the point cloud into depth images, avoids information loss and added calculation quantity in the conversion process, simultaneously utilizesdifferent windows to conduct mathematical morphological filtering operation through reverse gradual iteration, basically removes effects of terrain fluctuation on the building in the mathematical morphological filtering and obtains high extraction accuracy. The building area extraction method can quickly and accurately extract LiDAR points belonging to the building area from a large range of LiDAR points and is capable of providing reliable data support for urban three-dimensional modeling.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
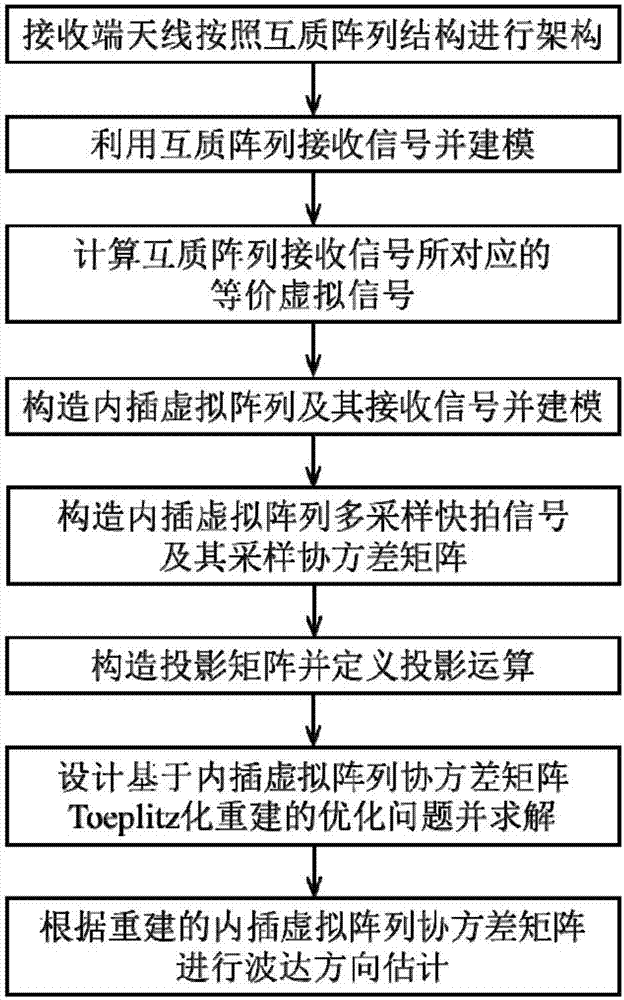
Co-prime array DOA (direction of arrival) estimation method based on interpolation virtual array covariance matrix Toeplitz reconstruction
ActiveCN107329108AIncrease freedomHigh resolutionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsHat matrixImage resolution
The invention discloses a co-prime array DOA (direction of arrival) estimation method based on interpolation virtual array covariance matrix Toeplitz reconstruction, and mainly solves a problem of information loss caused by the heterogeneity in a virtual array in the prior art. The method comprises the implementation steps: constructing a co-prime array at a receiving end; receiving an incident signal through the co-prime array, and carrying out the modeling; calculating an equivalent virtual signal corresponding to the signal received by the co-prime array; constructing an interpolation virtual array and carrying out the modeling; constructing a multi-sampling snapshot signals of the interpolation virtual array and a sampling covariance matrix; constructing a projection matrix, and defining projection calculation related with the projection matrix; constructing a reference covariance matrix according to all information in an original virtual array, designing an optimization problem based on the interpolation virtual array covariance matrix Toeplitz reconstruction, and solving the optimization problem; and carrying out the DOA estimation according to the reconstructed interpolation virtual array covariance matrix. The method improves the freedom degree and resolution of signal DOA estimation, and can be used for the passive positioning and target detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
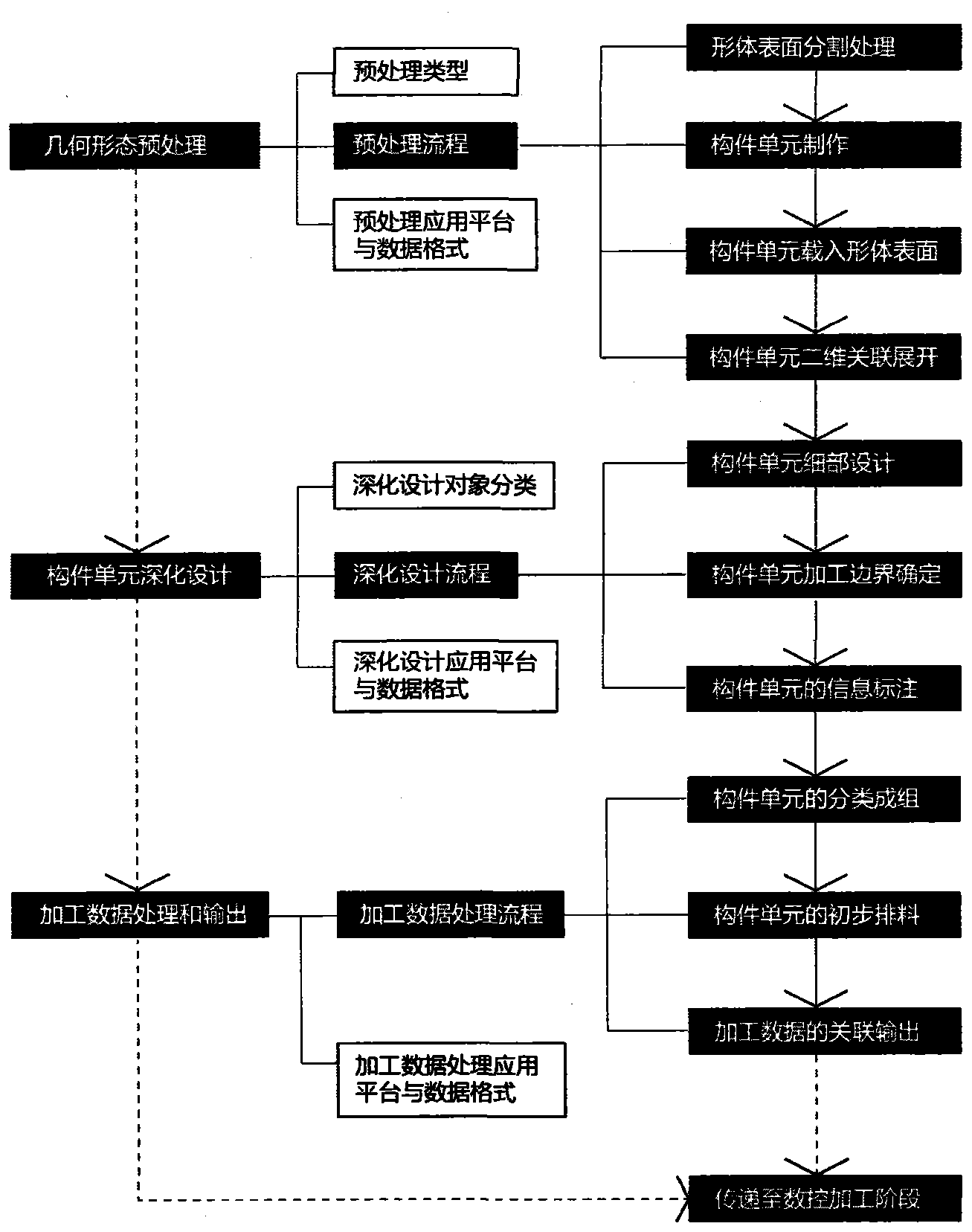
BIM (Building Information Modeling) platform-based numerical control machining pretreatment method of non-standard building enclosure component
ActiveCN104252558AAdaptive intelligenceReduce lossesSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlPretreatment method
The invention provides a BIM (Building Information Modeling) platform-based numerical control machining pretreatment method of a non-standard building enclosure component. The problem of information loss between every two sub-processes of a numerical control machining process of the non-standard building enclosure component and the problem of associated conversion of a two-dimensional detail and a three-dimensional model of the non-standard component are solved through the three steps of building geometric shape pretreatment, building component unit deep design and machining data processing and output.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
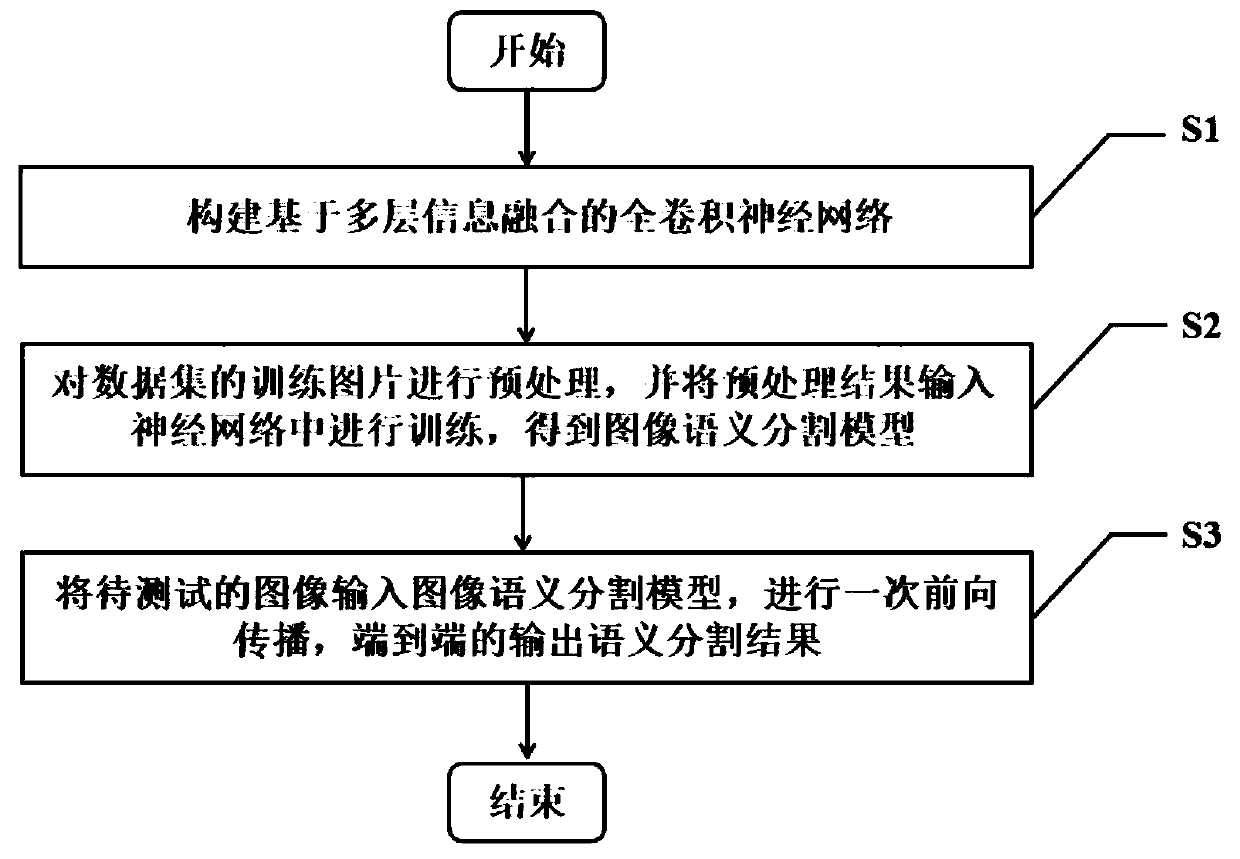
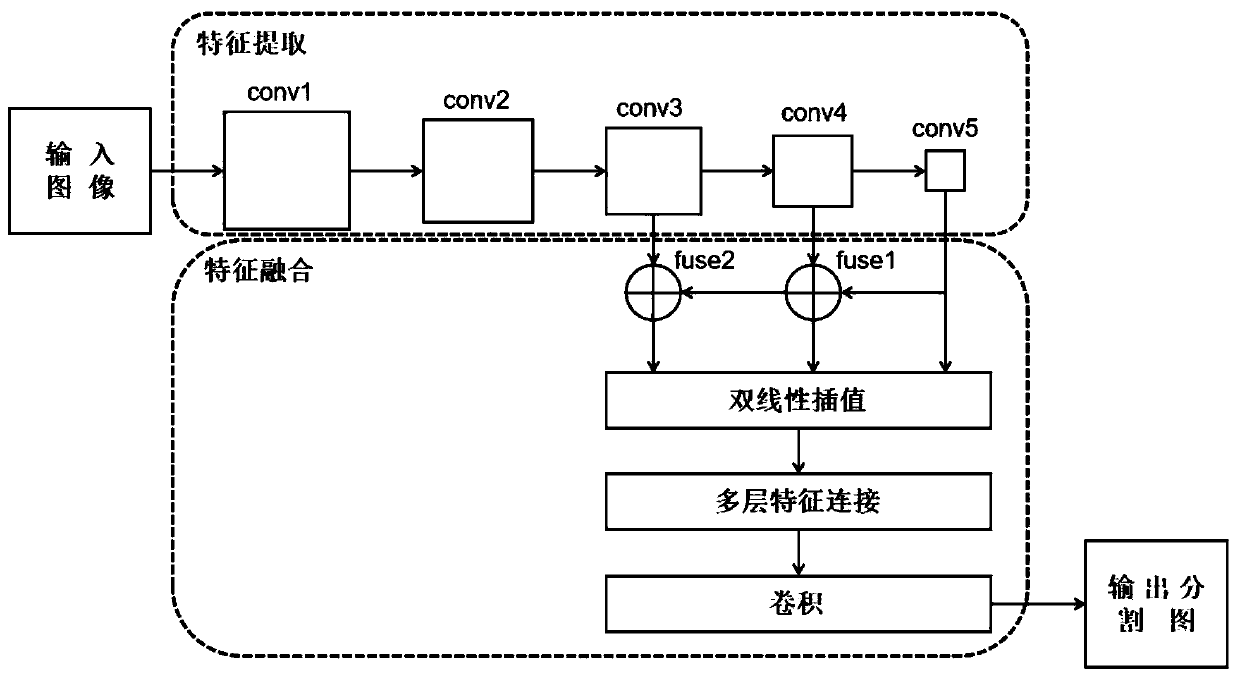
An image semantic segmentation method based on a multi-layer information fusion full convolutional neural network
InactiveCN109902748ASolve the lossImage semantic segmentation results are goodCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setForward propagation
The invention relates to an image semantic segmentation method based on a multi-layer information fusion full convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: constructing the multi-information fusion full convolutional neural network; Preprocessing the training picture of the data set, and inputting a preprocessing result into a neural network for training to obtain an image semantic segmentation model; Inputting the to-be-tested image into the image semantic segmentation model, performing one-time forward propagation, and outputting a semantic segmentation result in anend-to-end manner. Basic depth features of the image are extracted by using a convolutional neural network model; According to the method, the features are divided into the low-level features and thehigh-level features, and the low-level features and the high-level features are fused into the enhanced depth features, so that the problems of low image semantic segmentation accuracy and image spatial detail information loss can be effectively solved, and finally, a better image semantic segmentation result is obtained.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
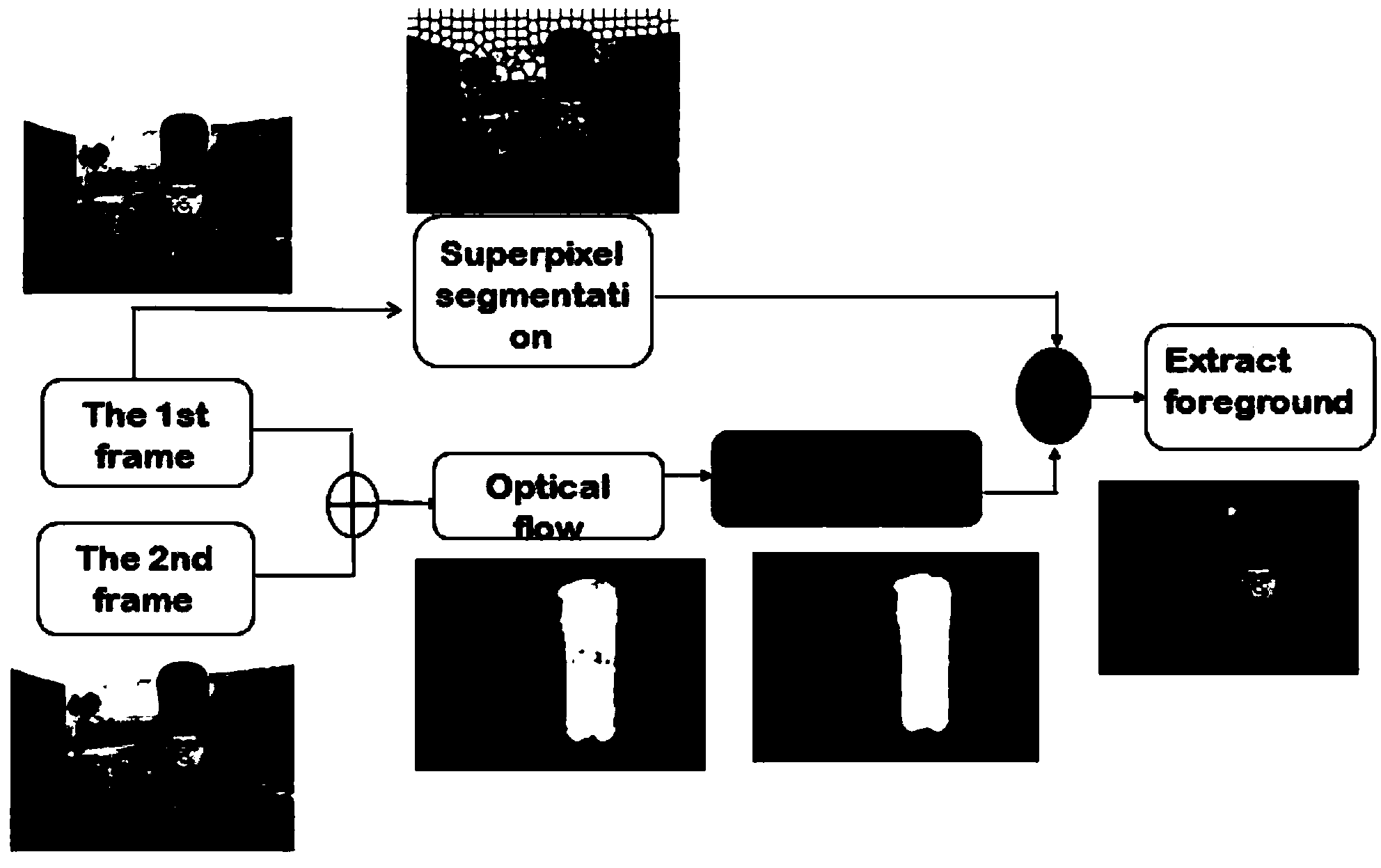
Moving object extraction method based on optical flow method and superpixel division
The invention discloses a moving object extraction method based on superpixel division and an optical flow method, and mainly solves the problems of more noises, high-frequency information loss, inaccurate boundary and the like of the existing moving object extraction method. The implementation steps of the method are as follows: (1), inputting an image, and pre-dividing the image into a superpixel set S to obtain a mark sheet I 2; (2), taking images of two adjacent frames in a video sequence and determining a rough position of a moving object by a Horn-Schunck optical flow method; (3), using the optical flow method to obtain the speed u in the horizontal direction and the speed v in the vertical direction, wherein V is speed amplitude of the optical flow method; (4) performing median filtering, Gauss filtering, binarization operation and morphology opening and closing operation on the optical flow result V to obtain V4; (5) using a superpixel division result to further correct the optical flow result, and extracting to obtain the accurate moving object. Superpixels belonging to a moving area are extracted accurately. Simulation experiments show that compared with the prior art, the moving object extraction method has the advantages of simple operation, small noise, clear boundary and the like, and can be used for extracting the moving object in the video sequence.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
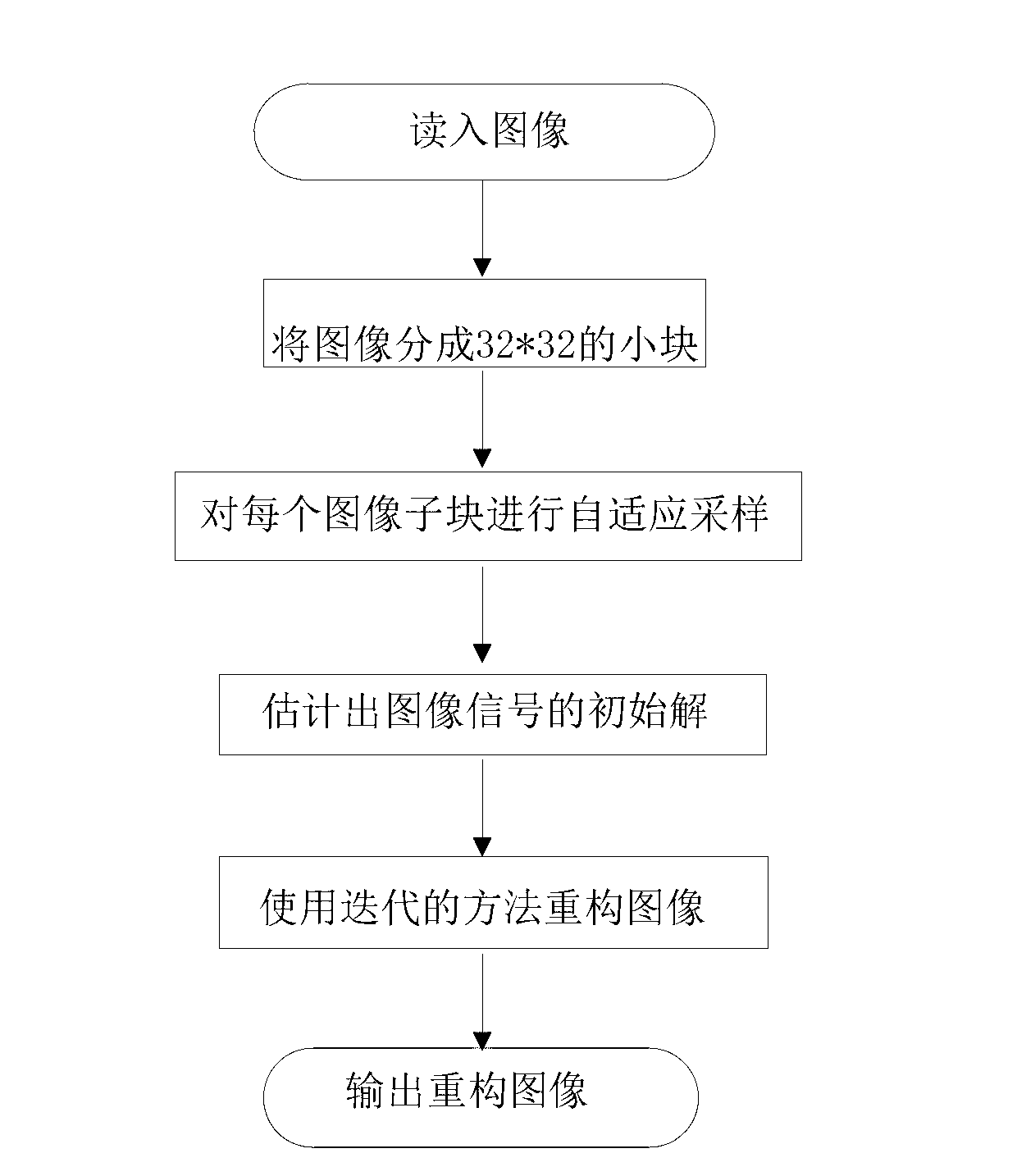
Adaptive compressed sensing-based non-local reconstruction method for natural image
InactiveCN102722896AValid reservationKeep information2D-image generationPattern recognitionAdaptive compression
The invention discloses an adaptive compressed sensing-based non-local reconstruction method for a natural image. The problems of serious reconstructed image information loss and the like in the prior art are mainly solved. The method is implemented by the steps of: (1) dividing an image into N 32*32 sub-blocks, obtaining a basic sensing matrix Phi' according to a basic sampling rate b and a sensing matrix Phi, and sampling a signal by utilizing Phi' to obtain a basic observation vector; (2) estimating a standard deviation sequence {d1, d2, ..., and dN} of the image according to the basic observation vector; (3) adaptively allocating a sampling rate ai for each sub-block according to the standard deviation sequence {d1, d2, ..., and dN}, and constructing an adaptive sensing matrix, and sampling the signal by utilizing the adaptive sensing matrix to obtain an adaptive observation vector; (4) forming an observation vector of each sub-block by using the basic observation vector and the adaptive observation vector; (5) obtaining an initial solution x0 of the image according to the observation vector; and (6) performing iteration by using x0, and reconstructing the original image until consistency with a finishing condition is achieved to obtain a reconstructed image x'. The method has the advantages of high image reconstruction quality, clear principle and operational simplicity, and is applied to the sampling and reconstruction of the natural image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
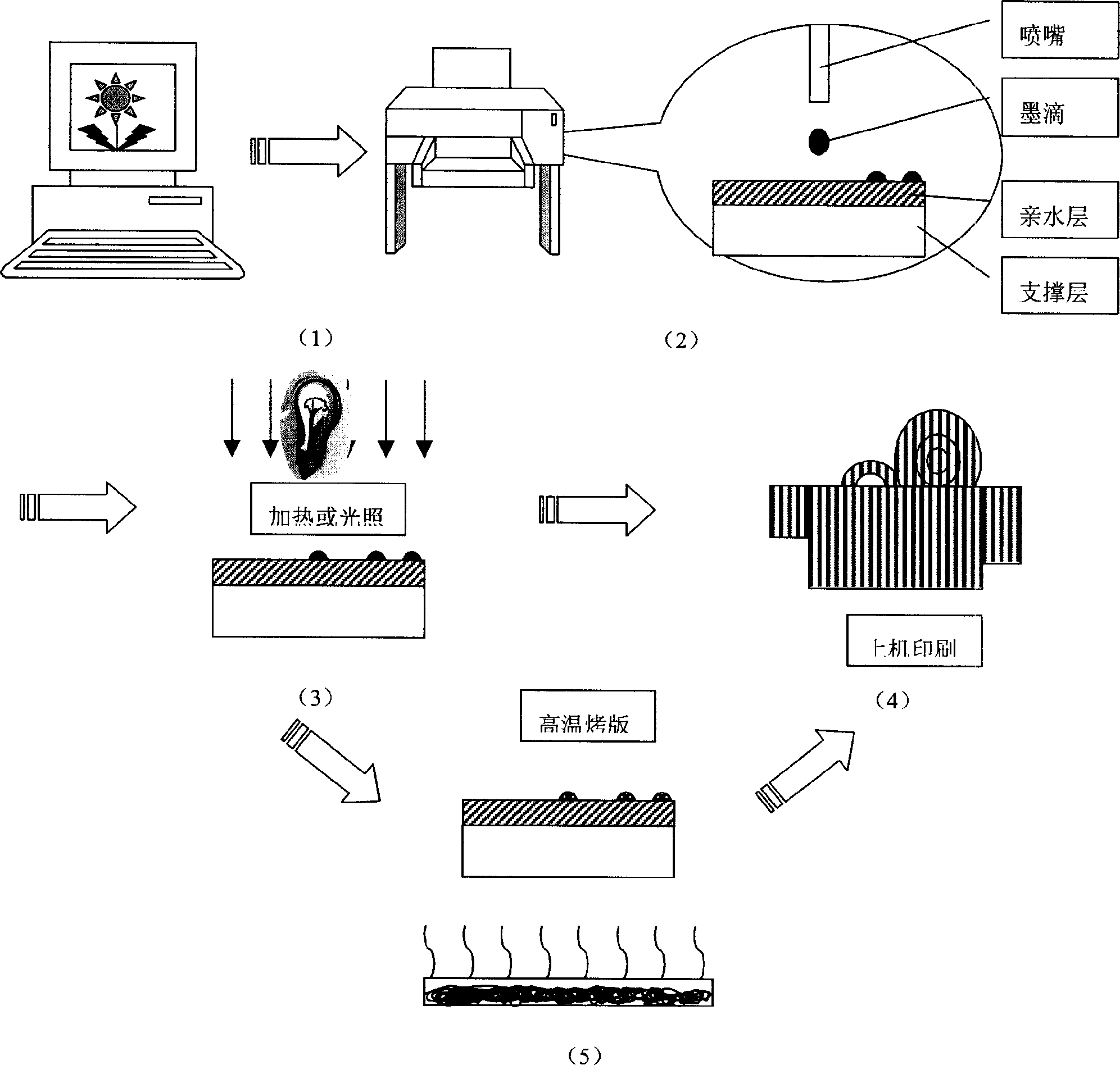
CTP plate making method and apparatus by using ink jet imaging principle
InactiveCN1800982AEliminate cumbersome operationsLow costPlate printingFoil printingInkjet printingInformation loss
The invention discloses a CTP direct platemaking method and equipment, which is characterized by the following: adapting ink-jet image-forming elementary to spray the ink-wet on the hydrophilic plate surface to form the ink-wet information record area; fixing the printed information on the printing surface through optical solidification or heat solidification. The invention reduces the information loss and simplifies the developing course, which saves the film and subsequent developing craft.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKE NANO THINK PRINT TECH
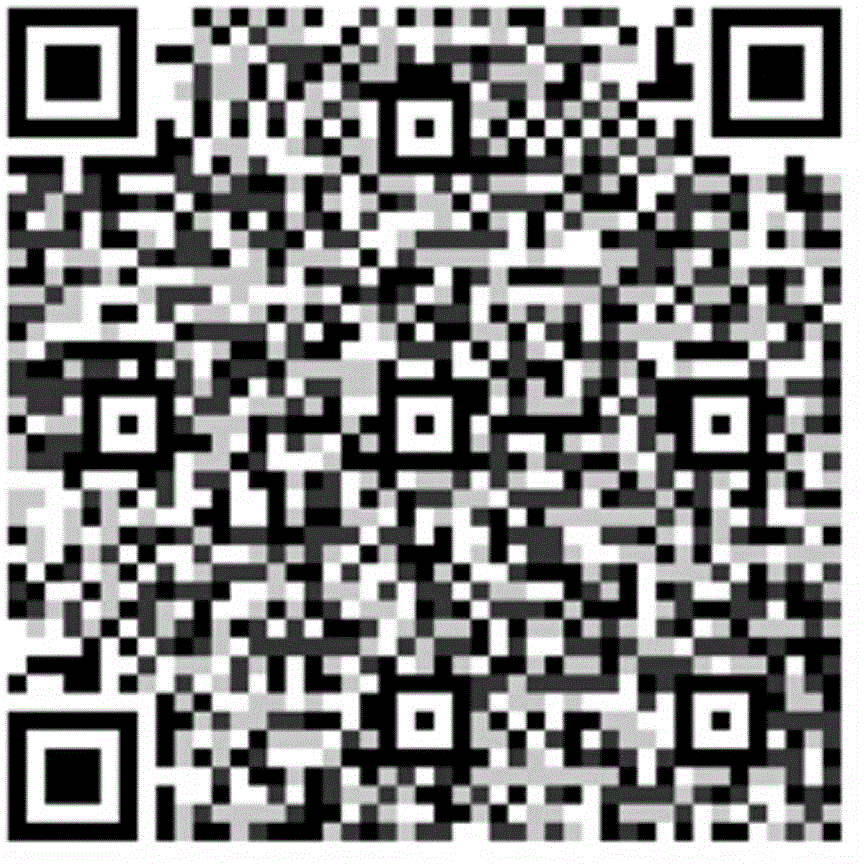
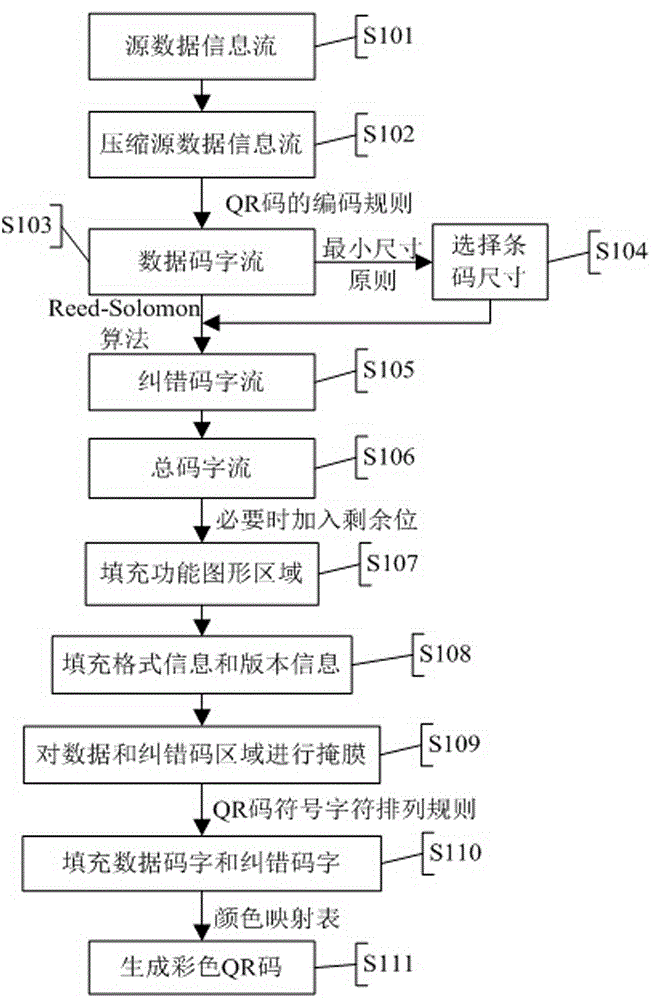
Method of encoding/decoding color QR code
ActiveCN104899630AIncrease capacityIncrease data capacityRecord carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationPattern recognitionData capacity
This invitation discloses a method of encoding / decoding a color QR (Quick Response) code. The method maintains the reliability and robustness of a standard black and white QR code, and employs a lossless compression algorithm to make the data capacity of a color QR code much larger than the data capacity of other colored two-dimensional code of a same kind. In addition, encoding colors are not required to be the most distant from each other in an RGB color space in order to enhance color resolution. A process of encoding / decoding a color QR code does not require color space transfer, i.e., color information loss can be avoided. Color QR cod decoding has no special requirements for ambient lighting, and does not need to utilize reference colors as a palette, thereby greatly reducing computational complexity, and obtaining 100% decoding accuracy.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
System for monitoring building safety by wireless radio frequency discrimination RFID
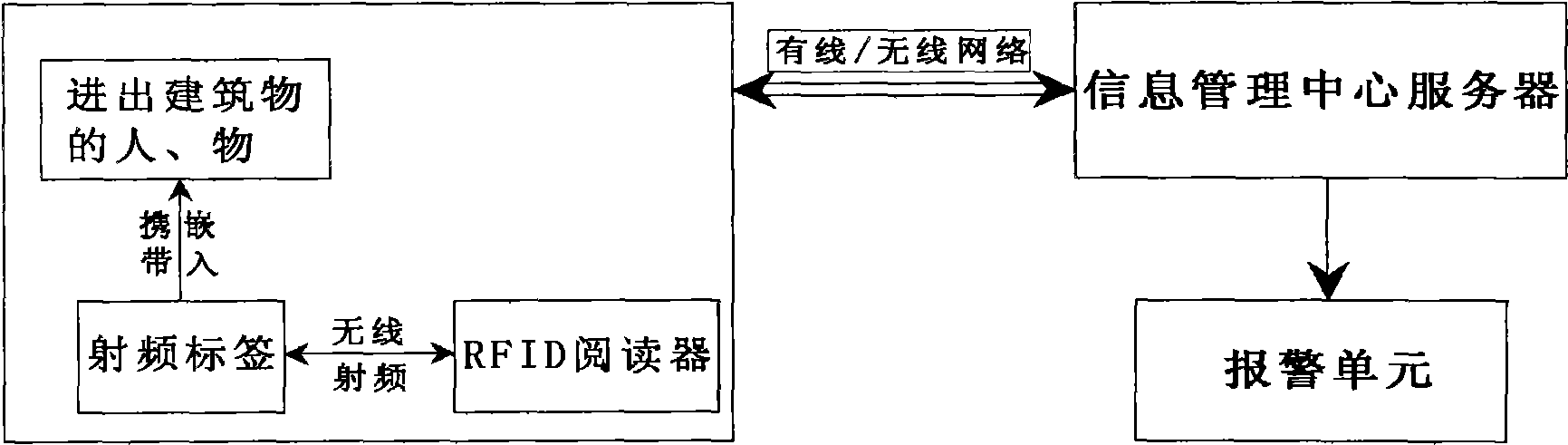
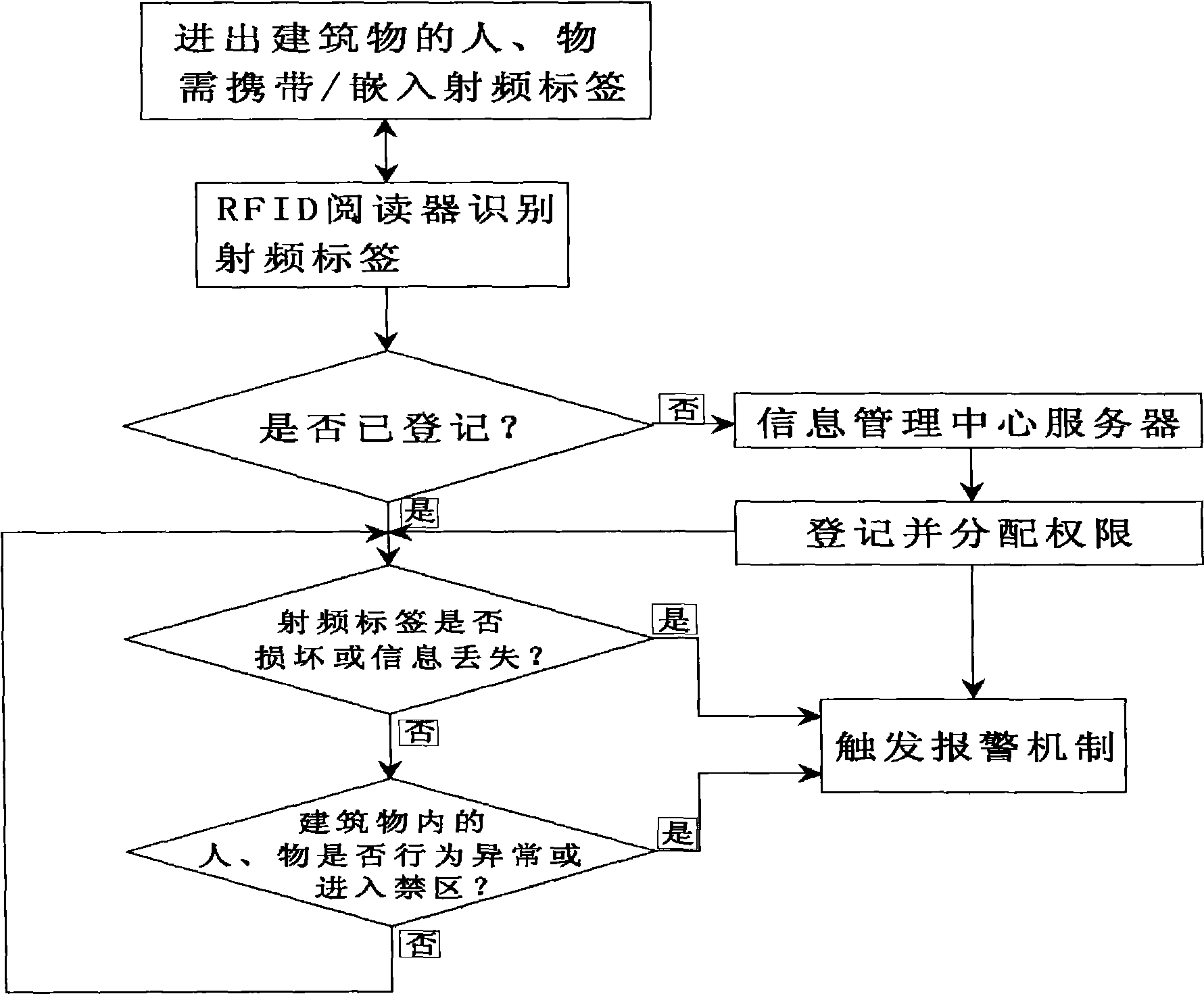
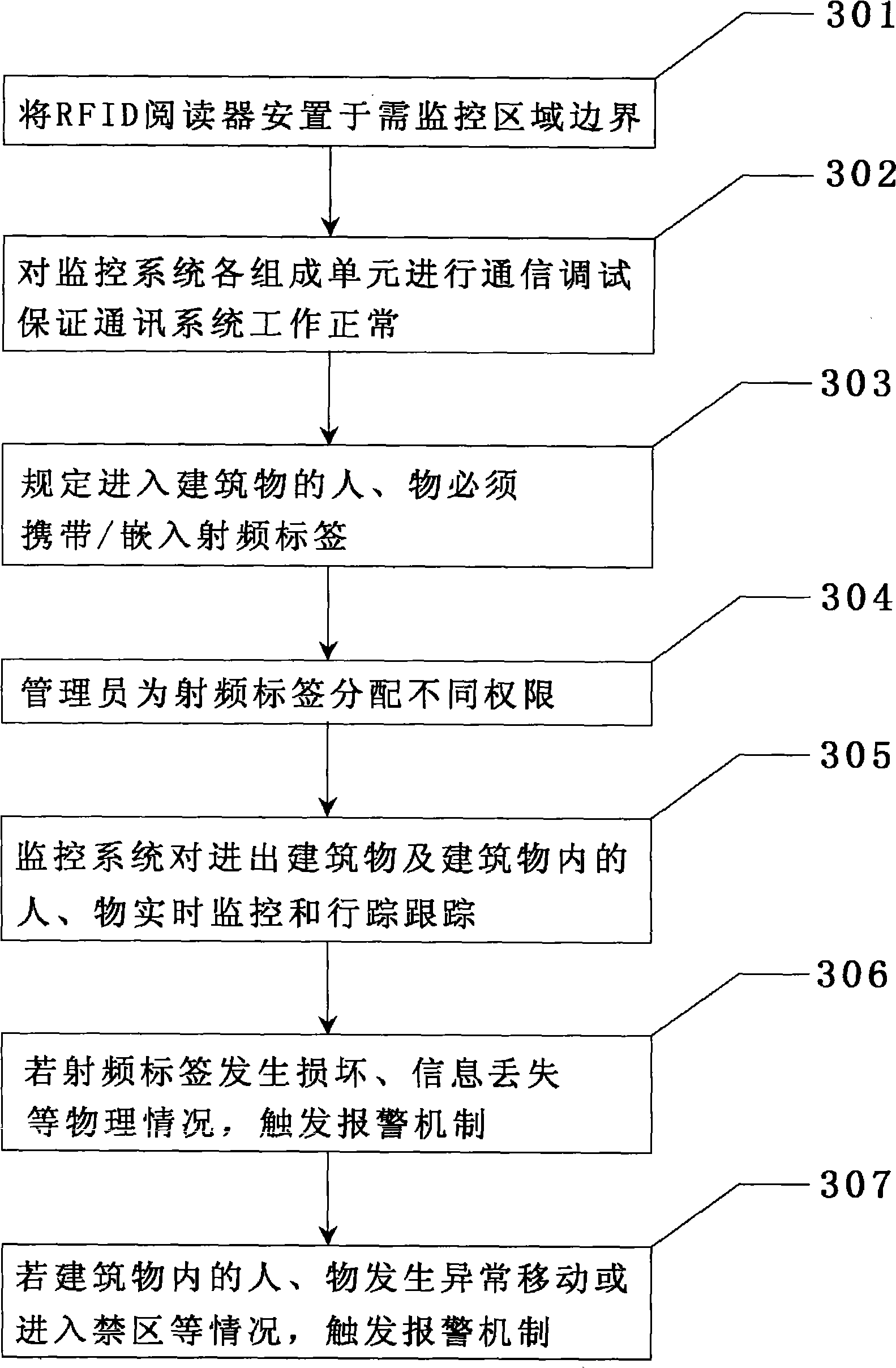
InactiveCN101510324AReal-time monitoring in and outReal-time track and traceCo-operative working arrangementsIndividual entry/exit registersComing outEngineering
A building safety monitoring system by using radio frequency identification (RFID) comprises a monitoring unit, an information management center server and an alarm unit. The monitoring unit comprises an RFID reader and a radio frequency label; the RFID reader is arranged at the boundary of an area to be monitored to detect the radio frequency label information from personnel or objects with the radio frequency label entering the monitored area and to send the detected radio frequency label information to the information management center server through a wire / wireless network; the information management center server stores the radio frequency label information, makes real-time processing to the monitored data according to a predetermined mechanism and generates alarm through the alarm unit if the radio frequency label is damaged, has the situation of information loss, abnormal movement or entering the restricted area, and the like. The building safety monitoring system has the characteristics that the information management center server can monitor the situations that the personal and the objects with the radio frequency label come in / come out of the building in real time, thus realizing the real-time safety monitoring of the building.
Owner:黄以华
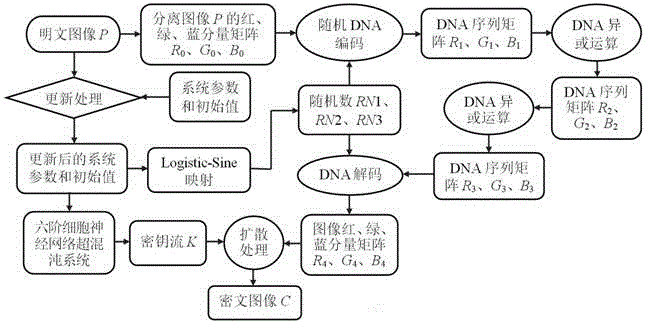
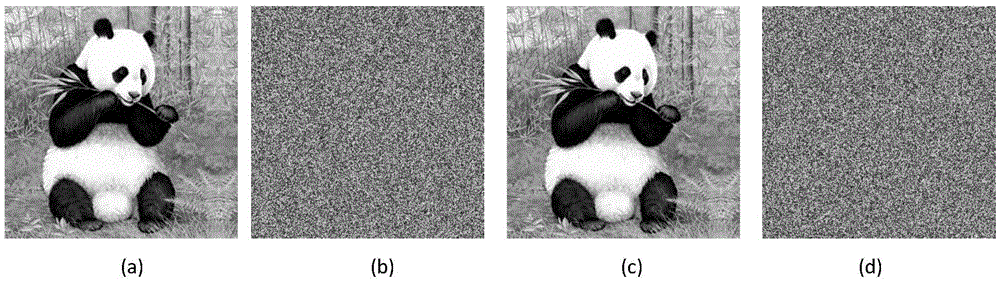
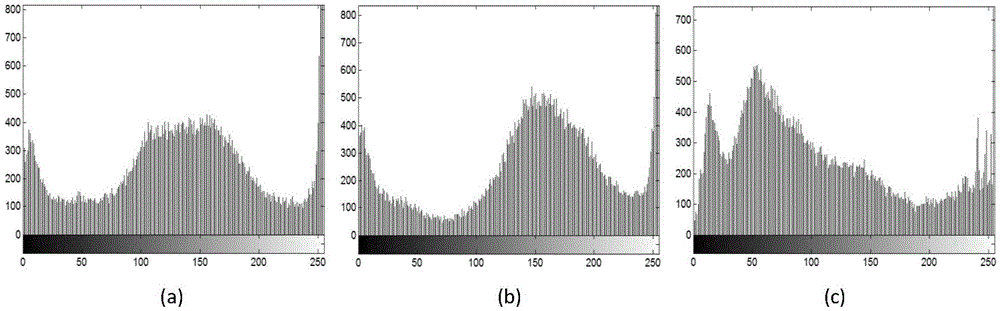
Color image encryption method based on cellular neural network hyperchaos and DNA sequence
The invention belongs to the technical field of information security, and particularly relates to a color image encryption method based on cellular neural network hyperchaos and a DNA sequence. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of separating red, green and blue three primary color components of a color plaintext image; updating and generating parameters and initial values of a six-order cellular neural network hyperchaotic system and a Logistic-Sine mapping system through the plaintext image, respectively carrying out iterative operation on the two chaotic systems, and obtaining red, green and blue components of an encrypted image according to a DNA encoding rule and a DNA decoding rule; and finally, changing the pixel values of the encrypted image through key stream and a bitwise XOR operation to obtain a final ciphertext image. The decryption is a reverse operation of the encryption process. Compared with the existing image encryption method, the color image encryption method provided by the invention has the advantages of high security, good encryption effect, strong robustness, no information loss and the like, and thus being capable of being widely used in military, remote sensing, remote medical treatment, commerce and other fields.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com