Patents
Literature
308 results about "Spiking neural network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
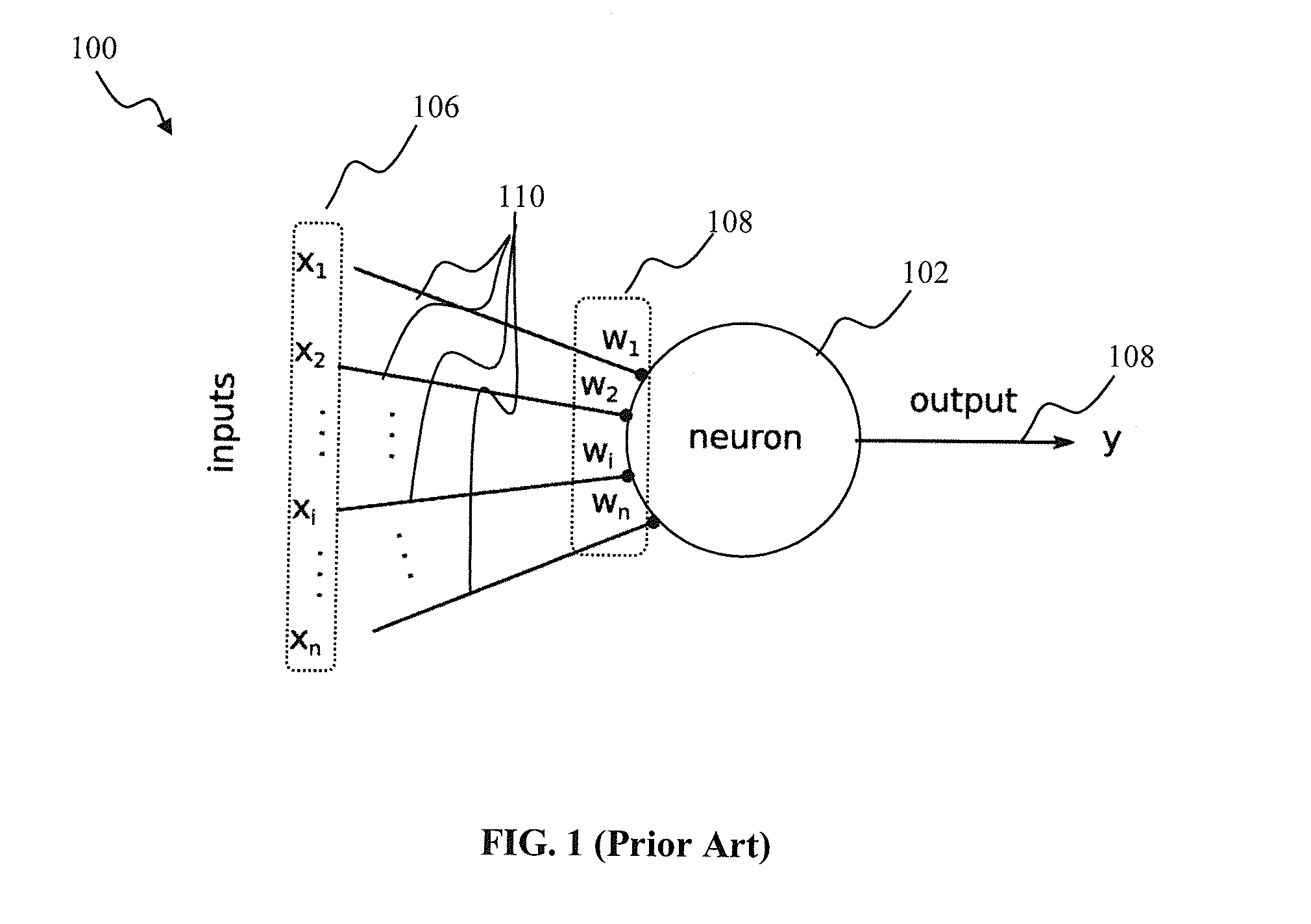
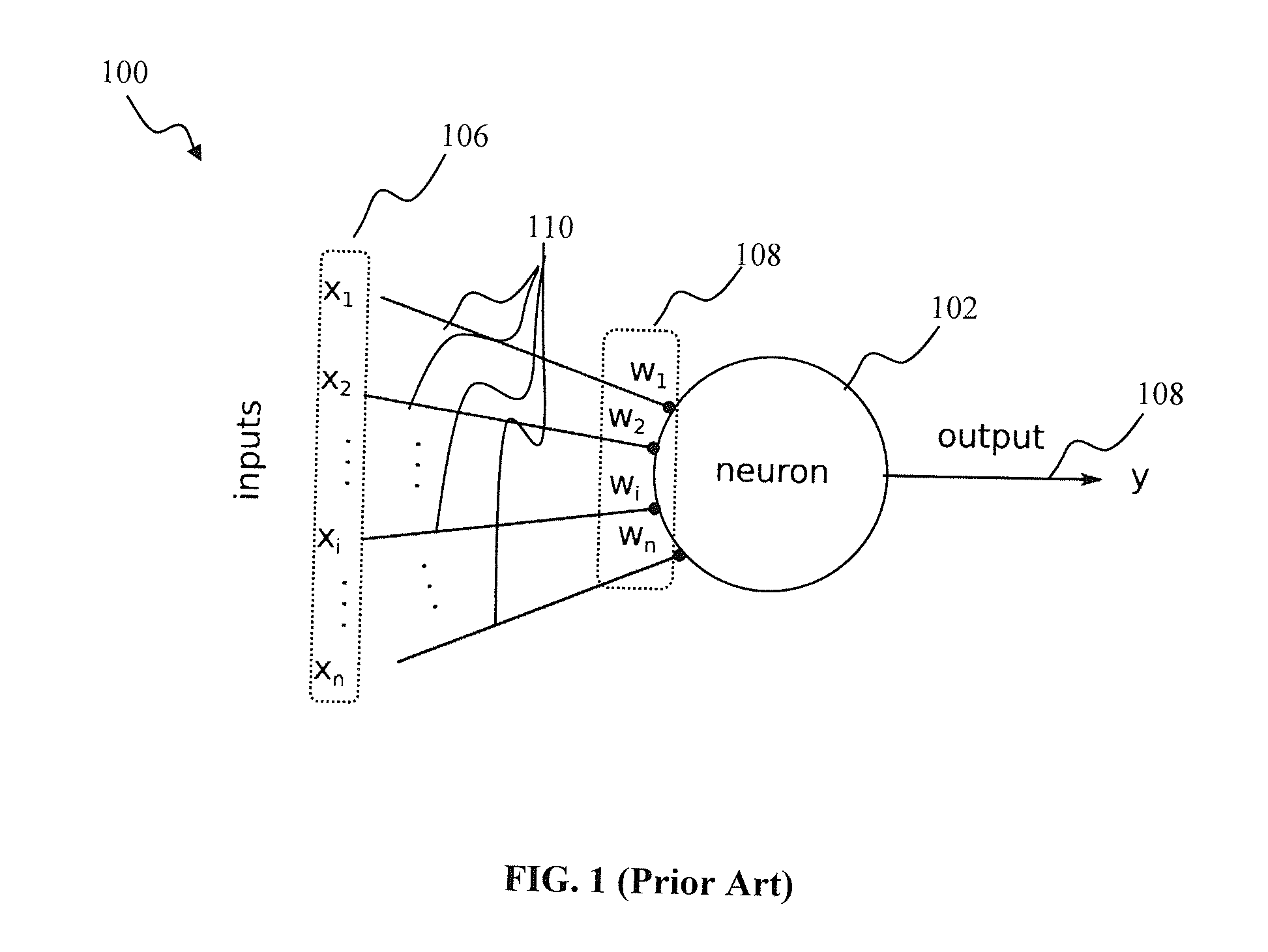
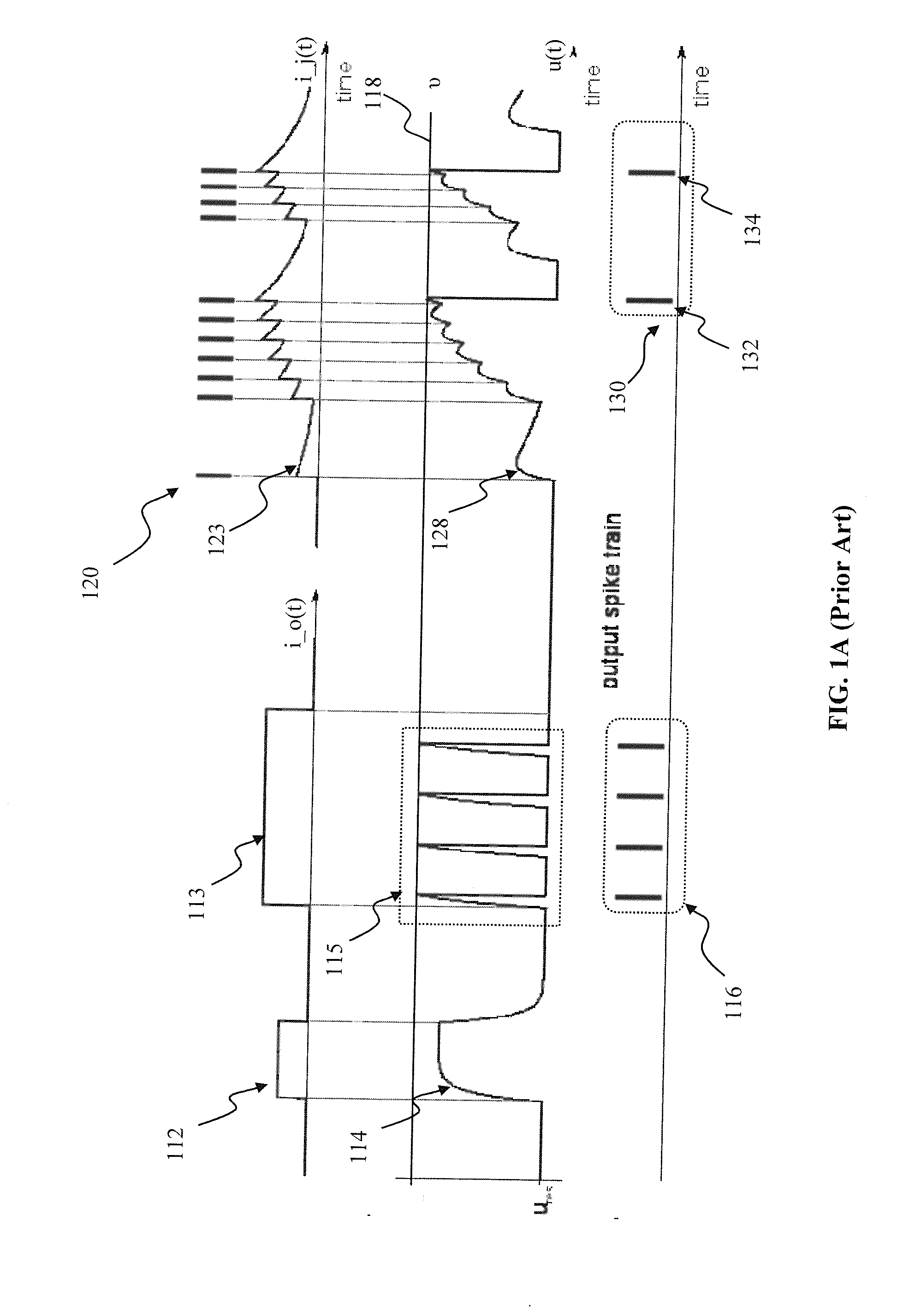
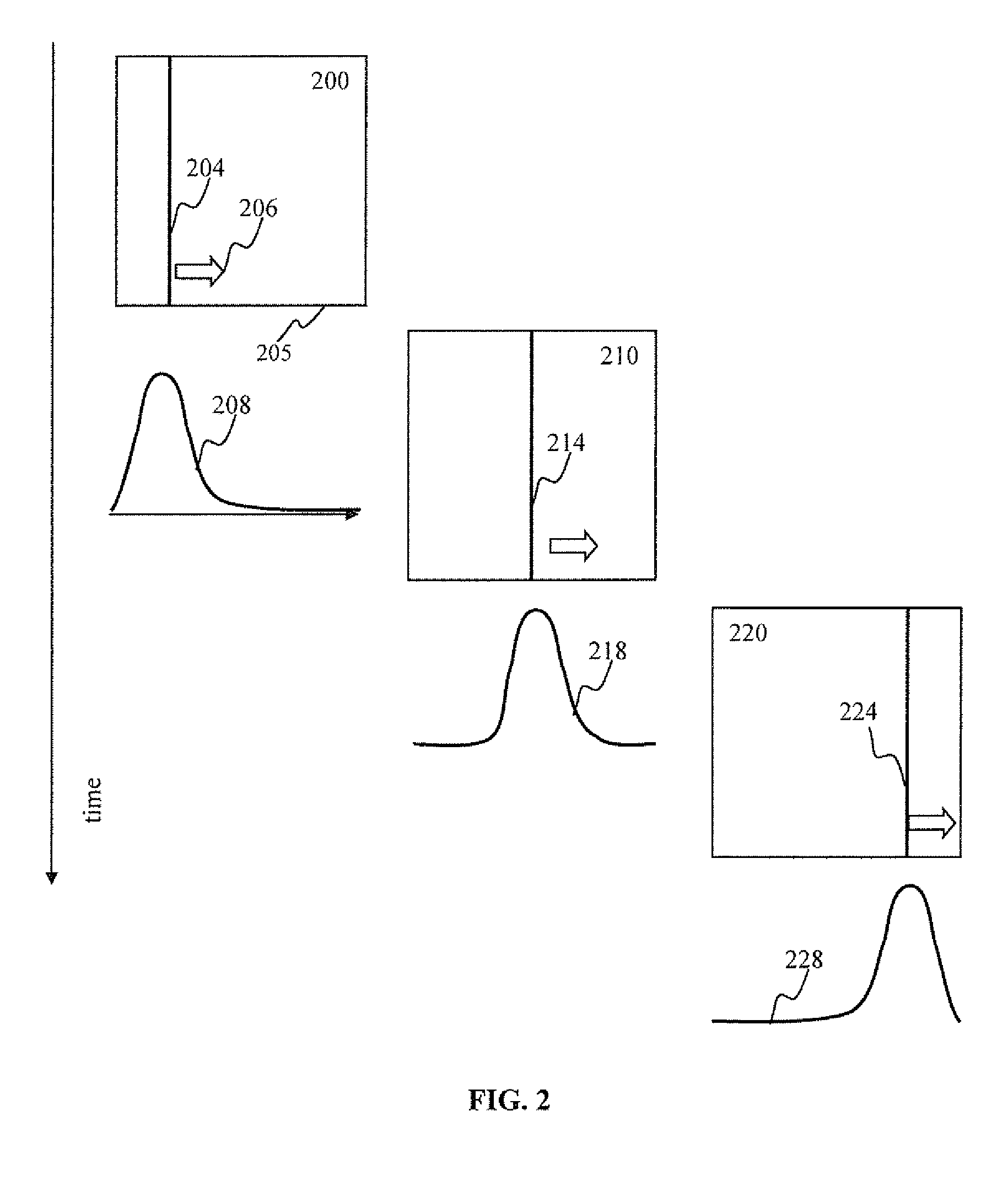
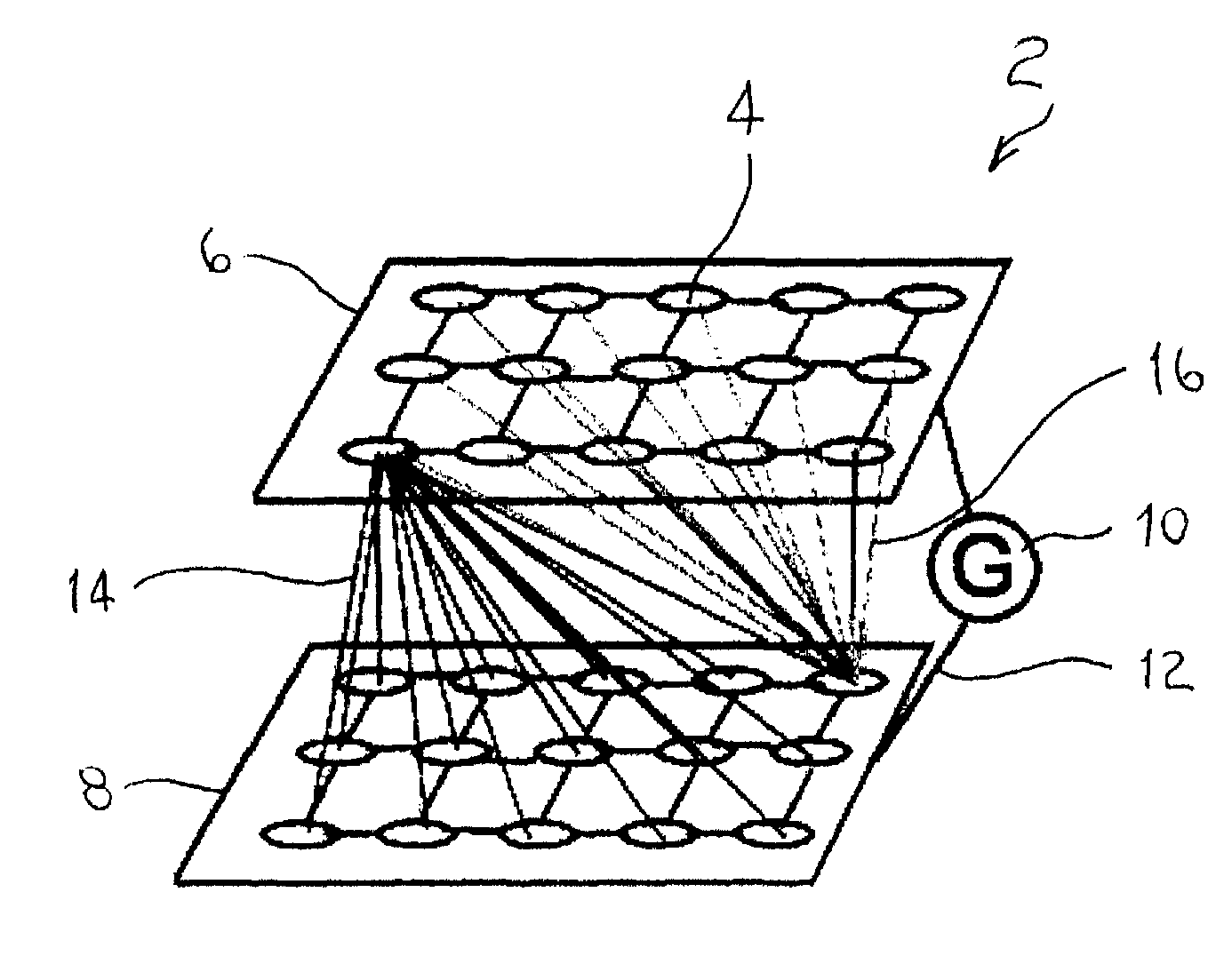
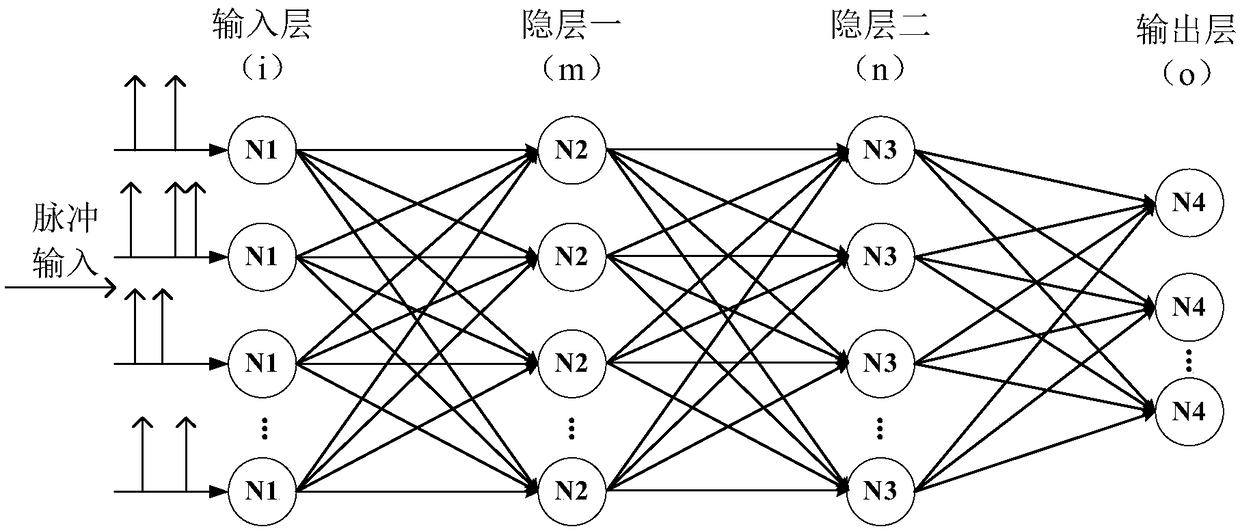
Spiking neural networks (SNNs) are artificial neural networks that more closely mimic natural neural networks. In addition to neuronal and synaptic state, SNNs incorporate the concept of time into their operating model. The idea is that neurons in the SNN do not fire at each propagation cycle (as it happens with typical multi-layer perceptron networks), but rather fire only when a membrane potential – an intrinsic quality of the neuron related to its membrane electrical charge – reaches a specific value. When a neuron fires, it generates a signal that travels to other neurons which, in turn, increase or decrease their potentials in accordance with this signal.
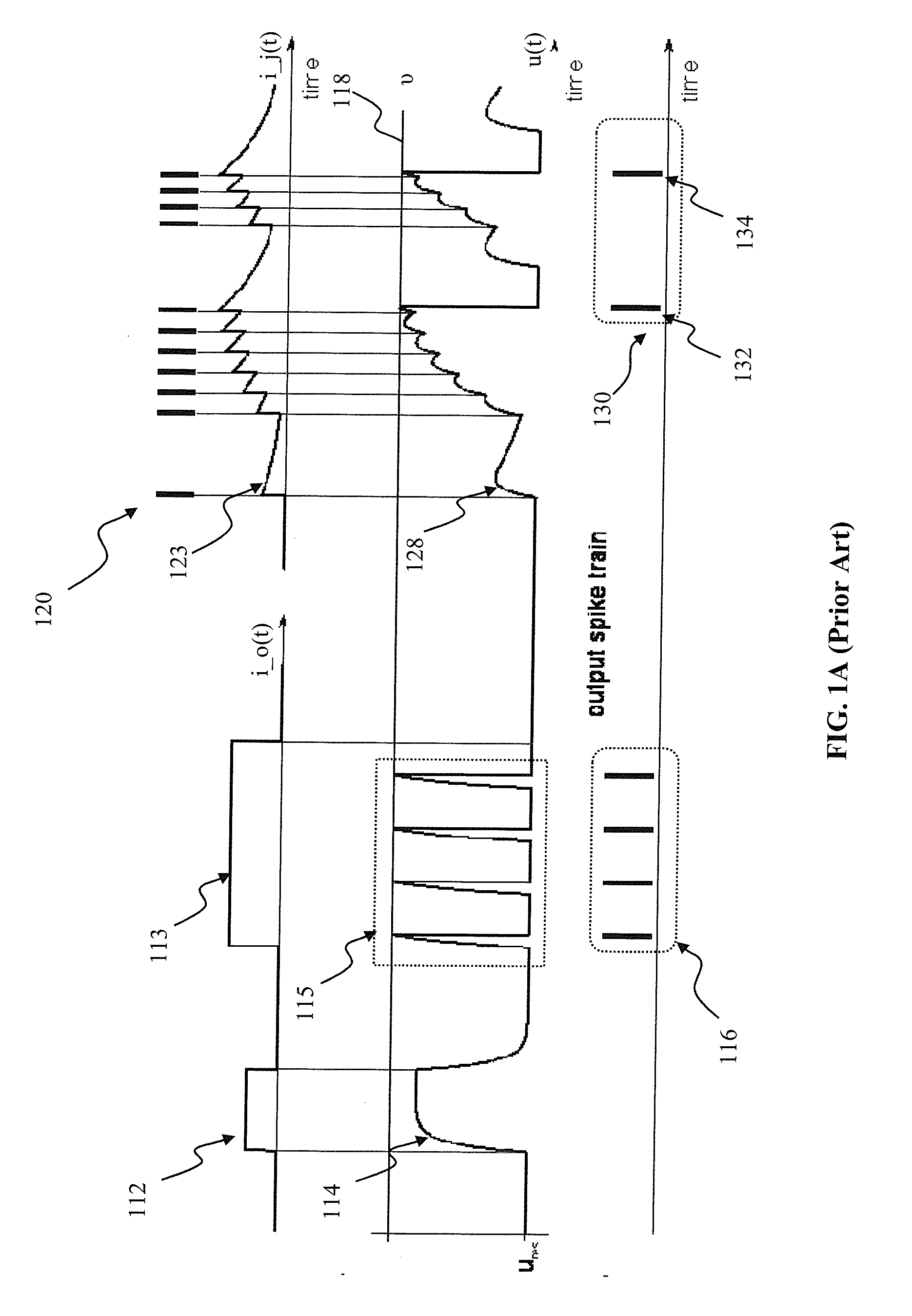
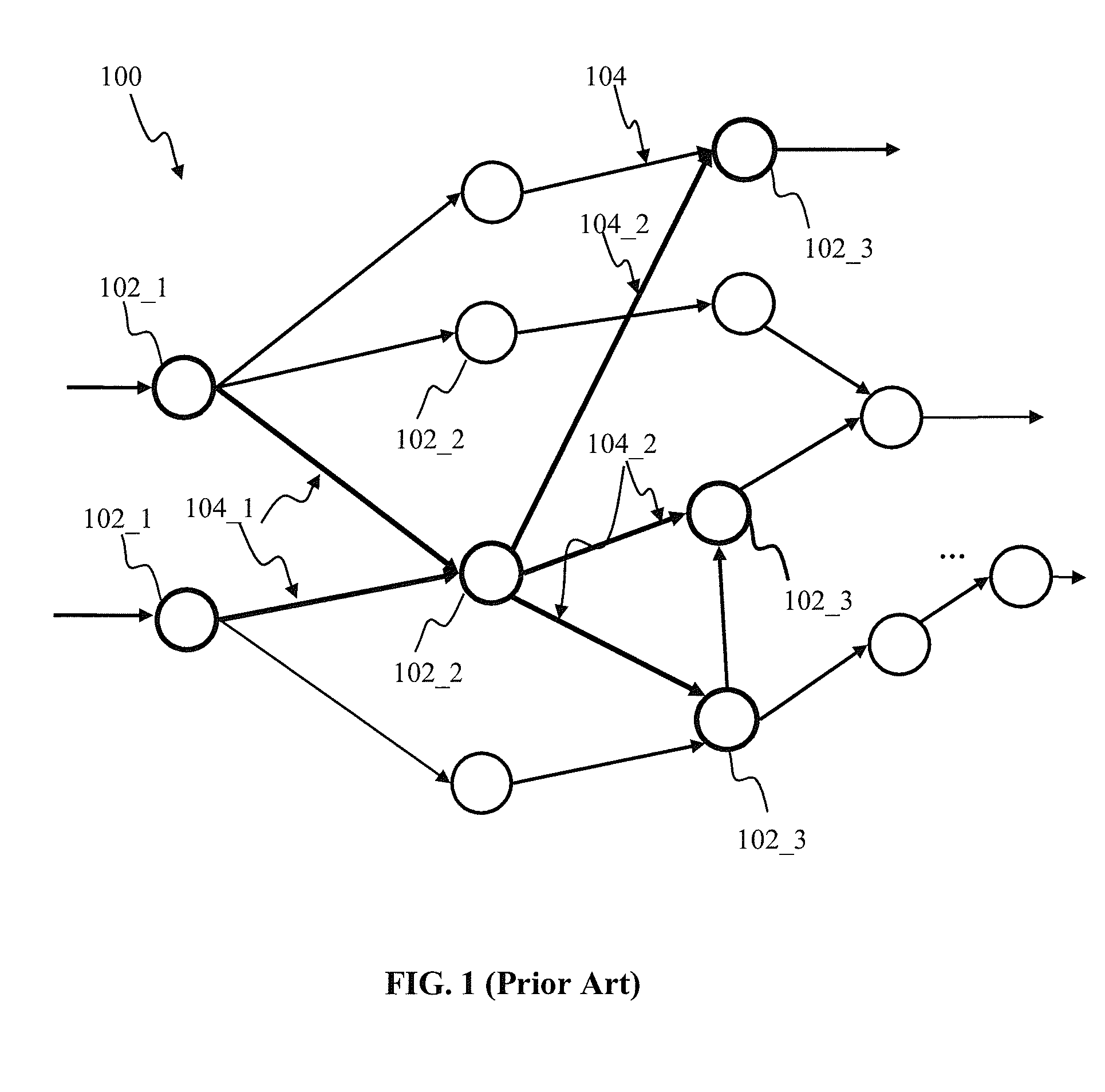
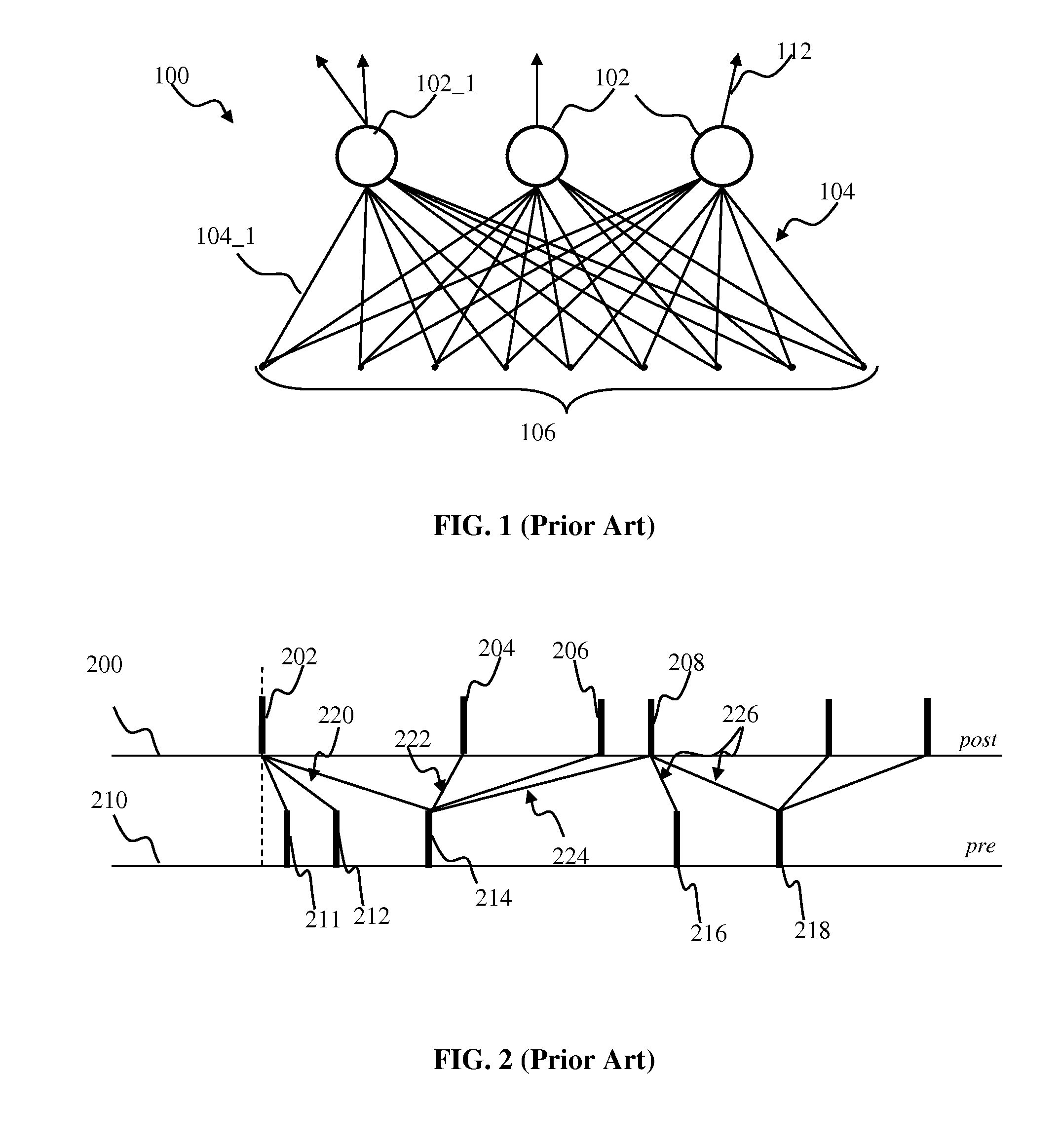
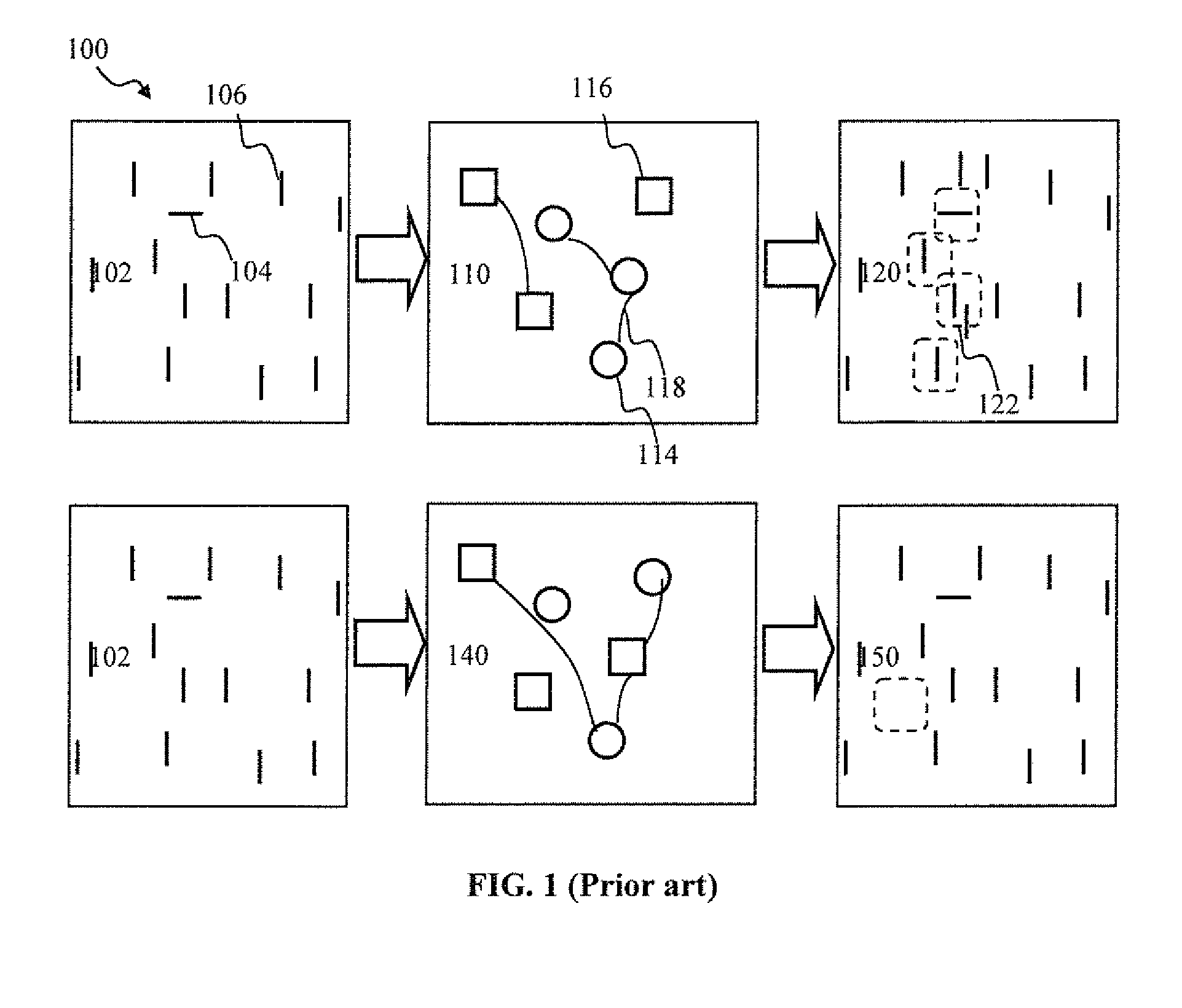
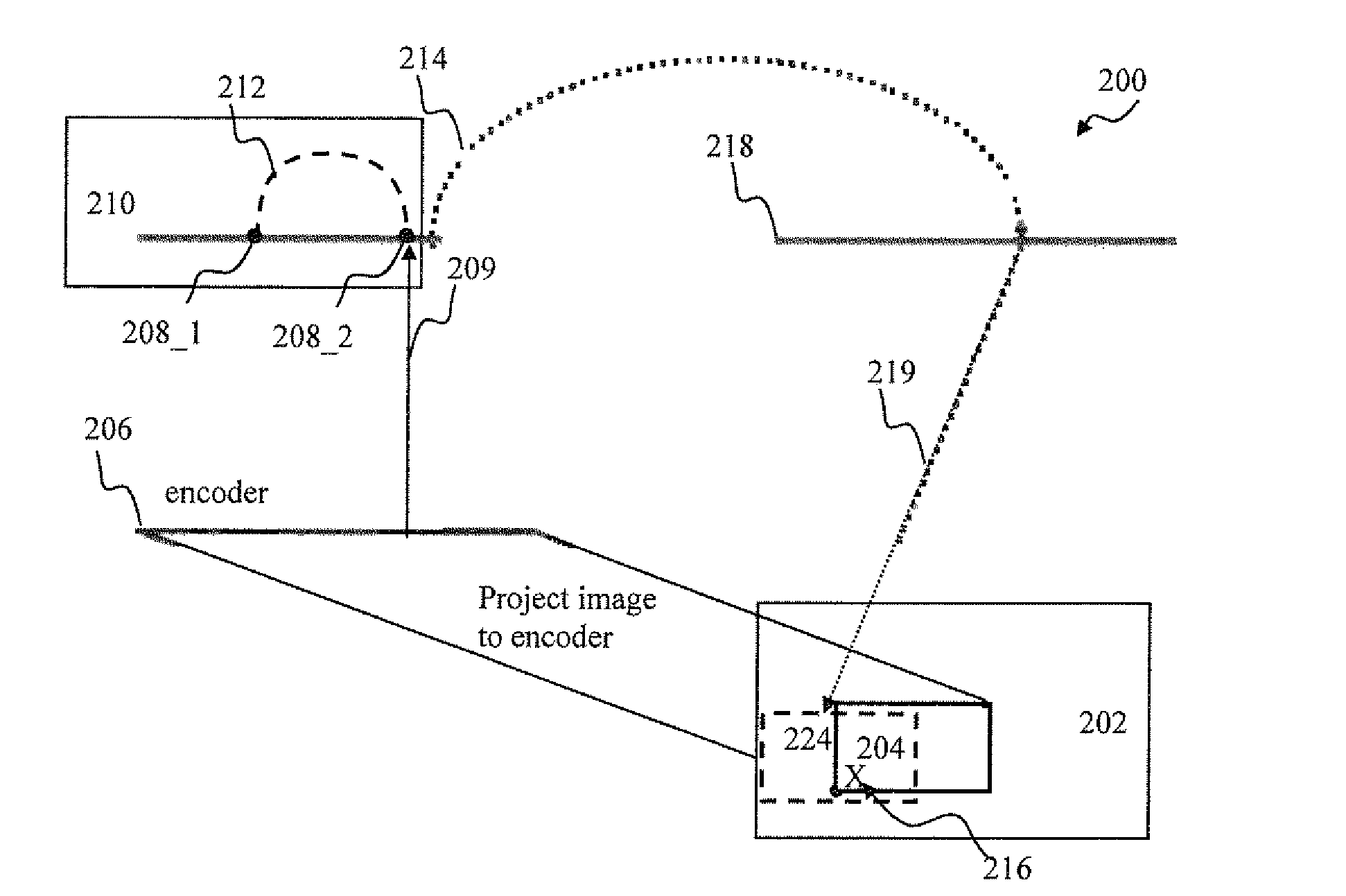
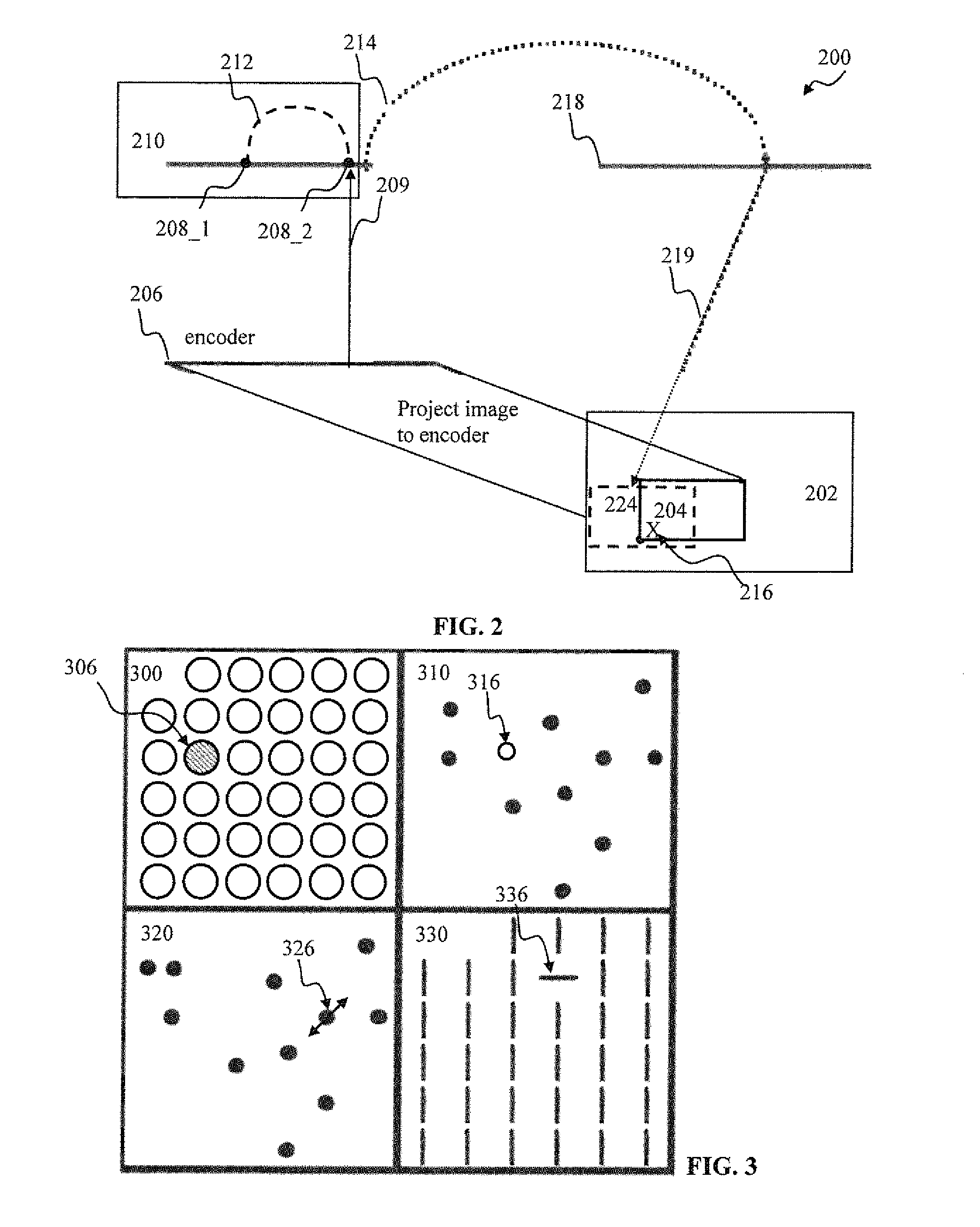
Spatio-temporal pattern recognition using a spiking neural network and processing thereof on a portable and/or distributed computer
ActiveUS20090287624A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpiking neural networkNeuron
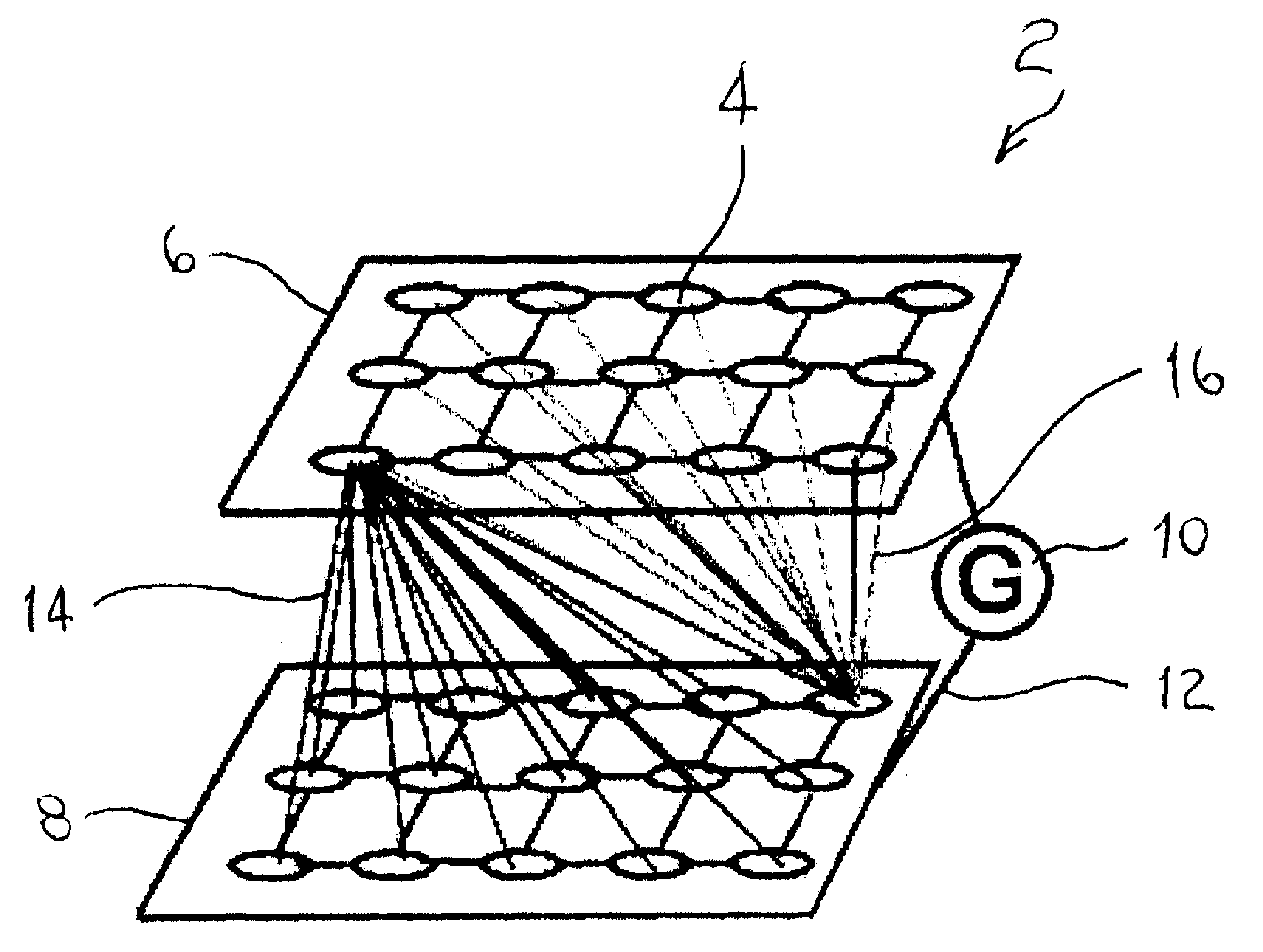
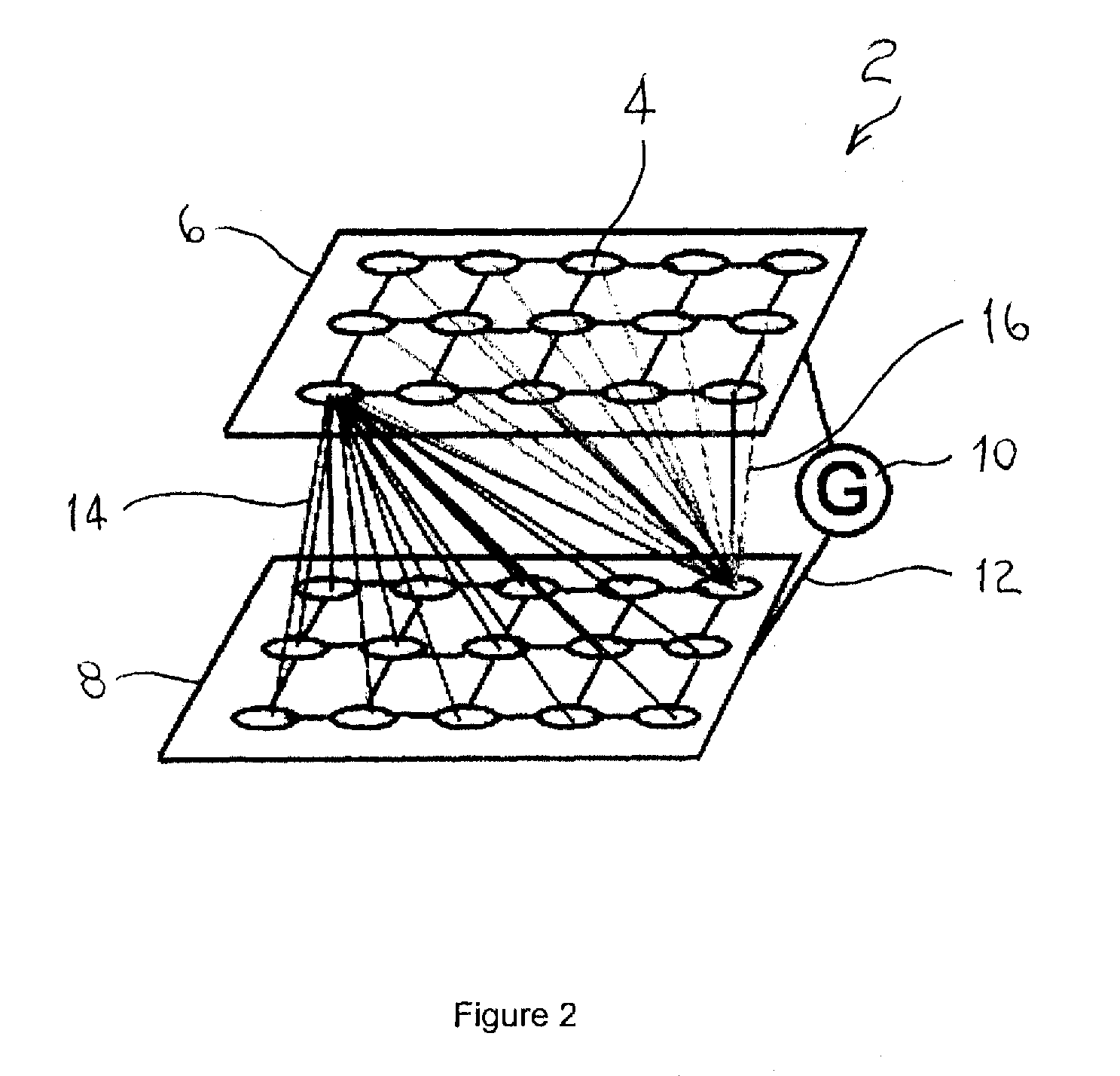
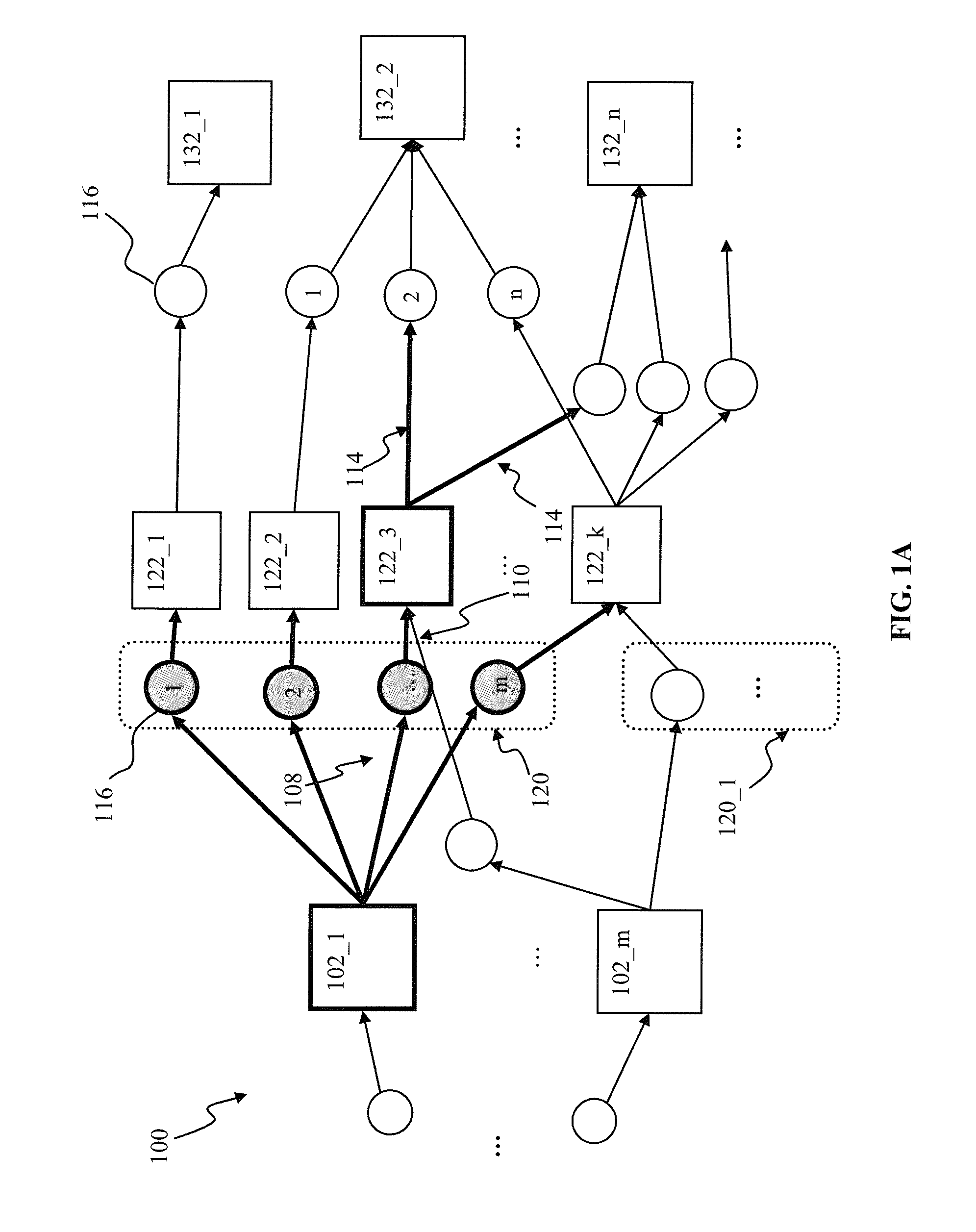
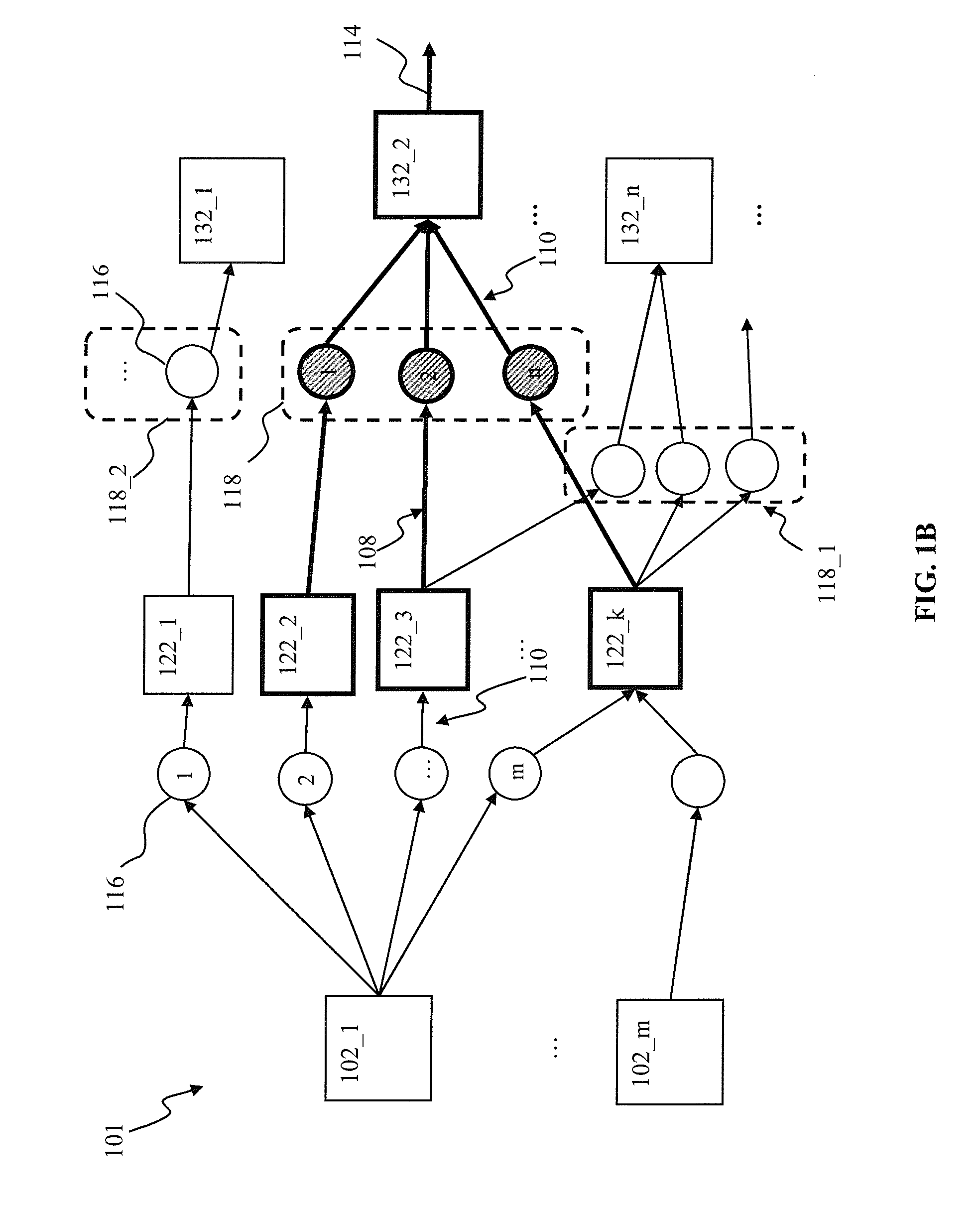
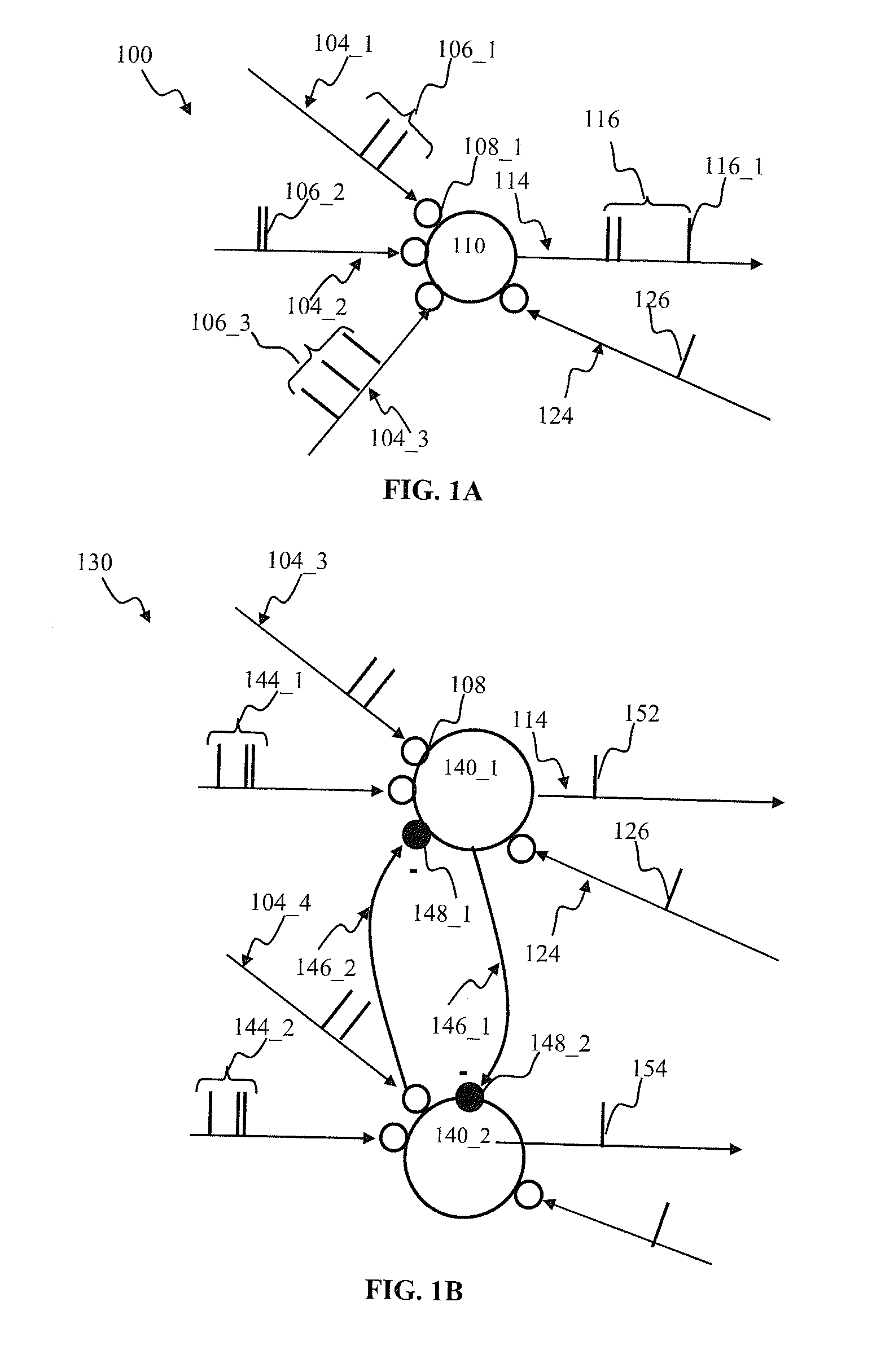
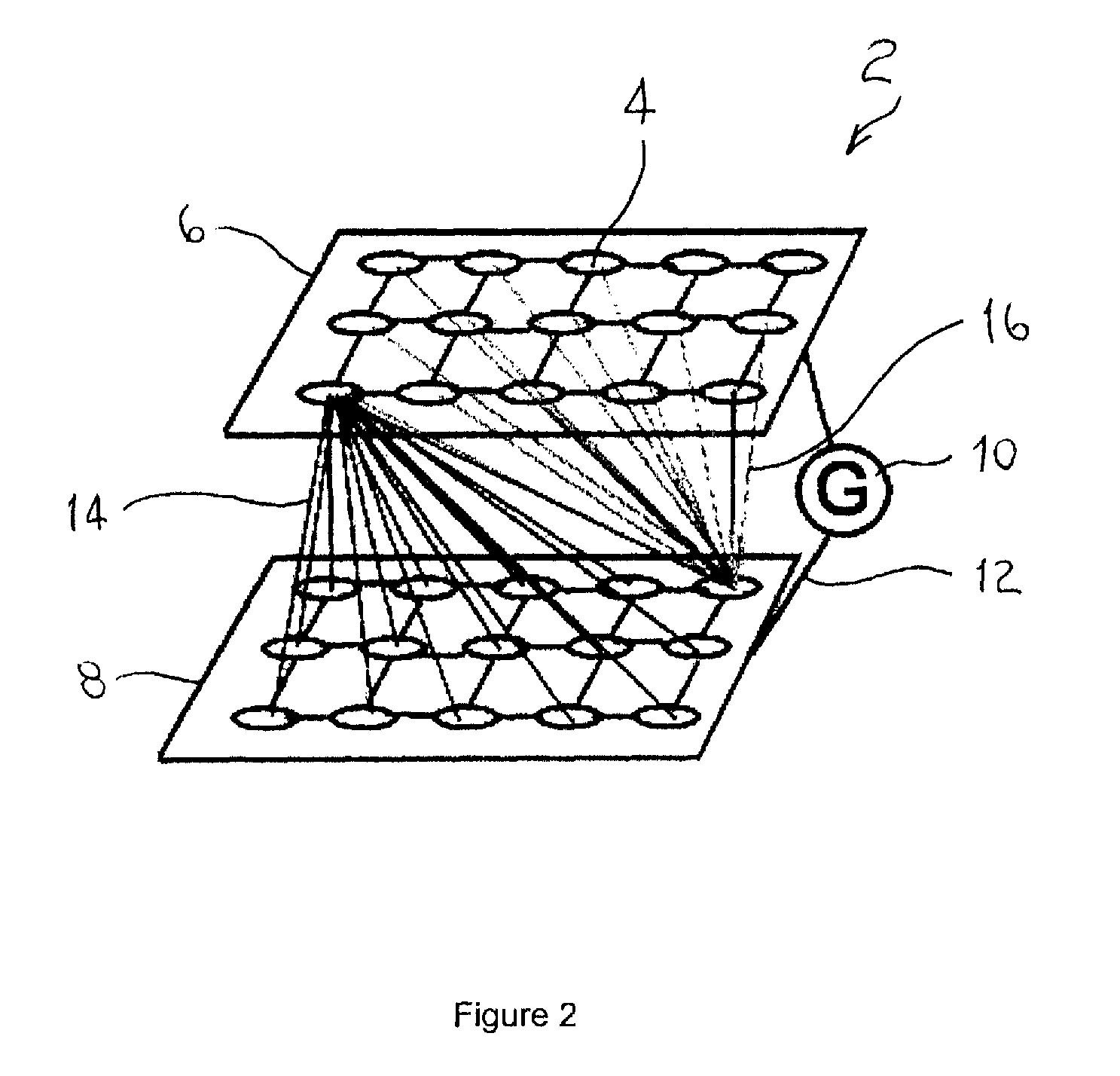
A system and method for characterizing a pattern, in which a spiking neural network having at least one layer of neurons is provided. The spiking neural network has a plurality of connected neurons for transmitting signals between the connected neurons. A model for inducing spiking in the neurons is specified. Each neuron is connected to a global regulating unit for transmitting signals between the neuron and the global regulating unit. Each neuron is connected to at least one other neuron for transmitting signals from this neuron to the at least one other neuron, this neuron and the at least one other neuron being on the same layer. Spiking of each neuron is synchronized according to a number of active neurons connected to the neuron. At least one pattern is submitted to the spiking neural network for generating sequences of spikes in the spiking neural network, the sequences of spikes (i) being modulated over time by the synchronization of the spiking and (ii) being regulated by the global regulating unit. The at least one pattern is characterized according to the sequences of spikes generated in the spiking neural network.
Owner:ROUAT JEAN +2
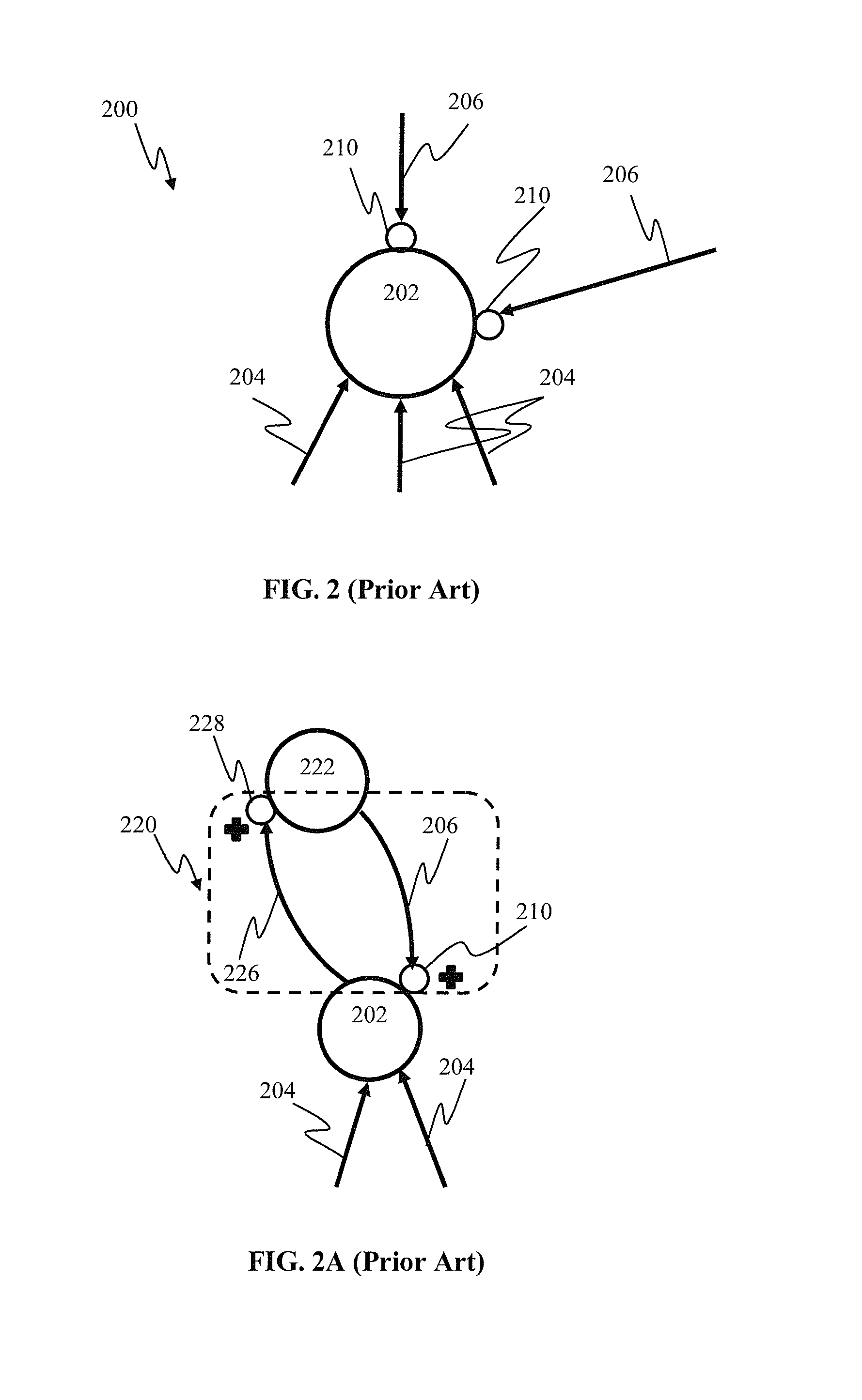
Apparatus and methods for synaptic update in a pulse-coded network
InactiveUS20130073491A1Reducing memory bus overheadReduce overheadDigital computer detailsDigital dataSynapseSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for efficient synaptic update in a network such as a spiking neural network. In one embodiment, the post-synaptic updates, in response to generation of a post-synaptic pulse by a post-synaptic unit, are delayed until a subsequent pre-synaptic pulse is received by the unit. Pre-synaptic updates are performed first following by the post-synaptic update, thus ensuring synaptic connection status is up-to-date. The delay update mechanism is used in conjunction with system “flush” events in order to ensure accurate network operation, and prevent loss of information under a variety of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic unit firing rates. A large network partition mechanism is used in one variant with network processing apparatus in order to enable processing of network signals in a limited functionality embedded hardware environment.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
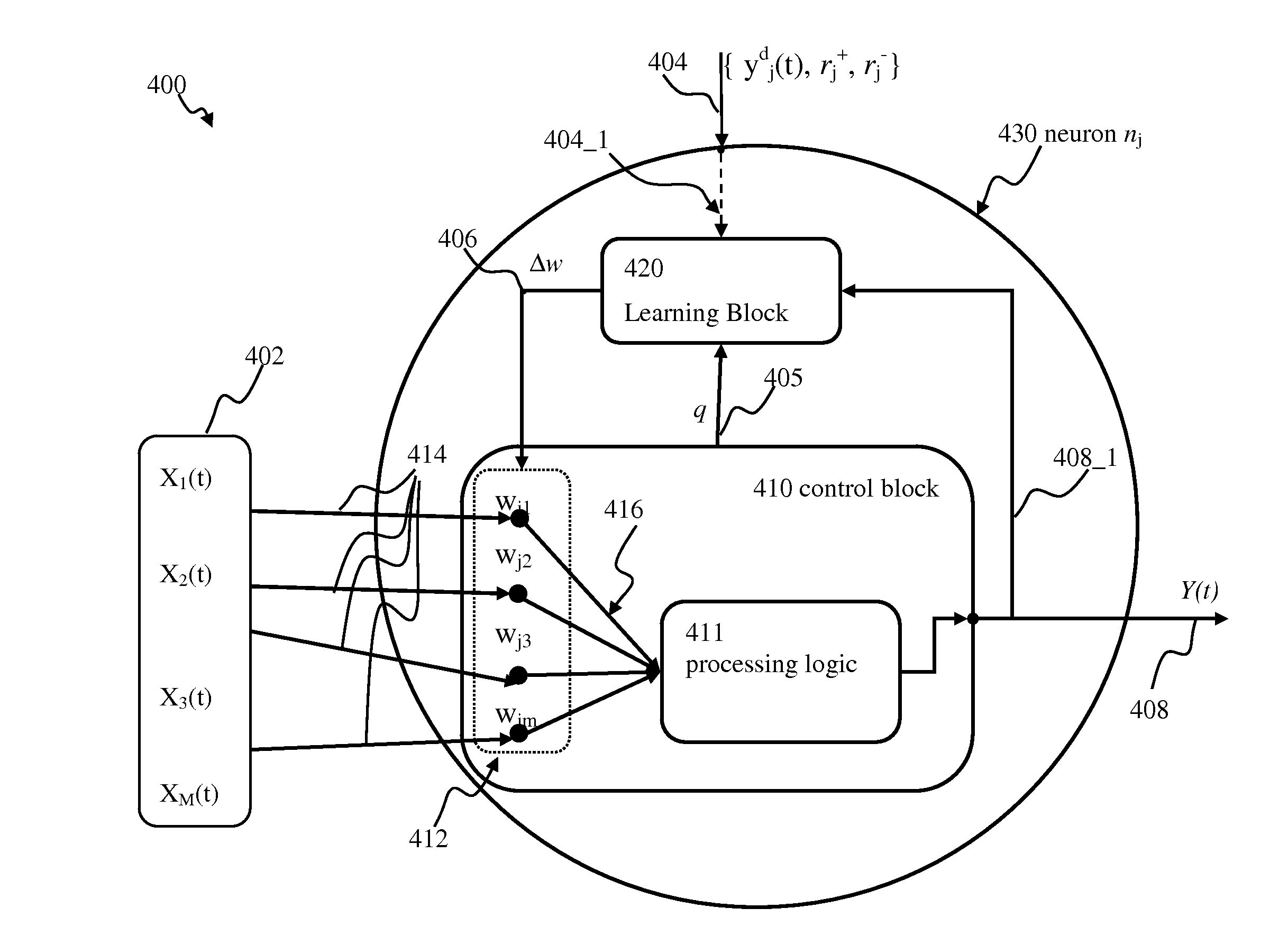
Neural network apparatus and methods for signal conversion
InactiveUS20130151450A1Digital computer detailsNeural architecturesNerve networkSpiking neural network
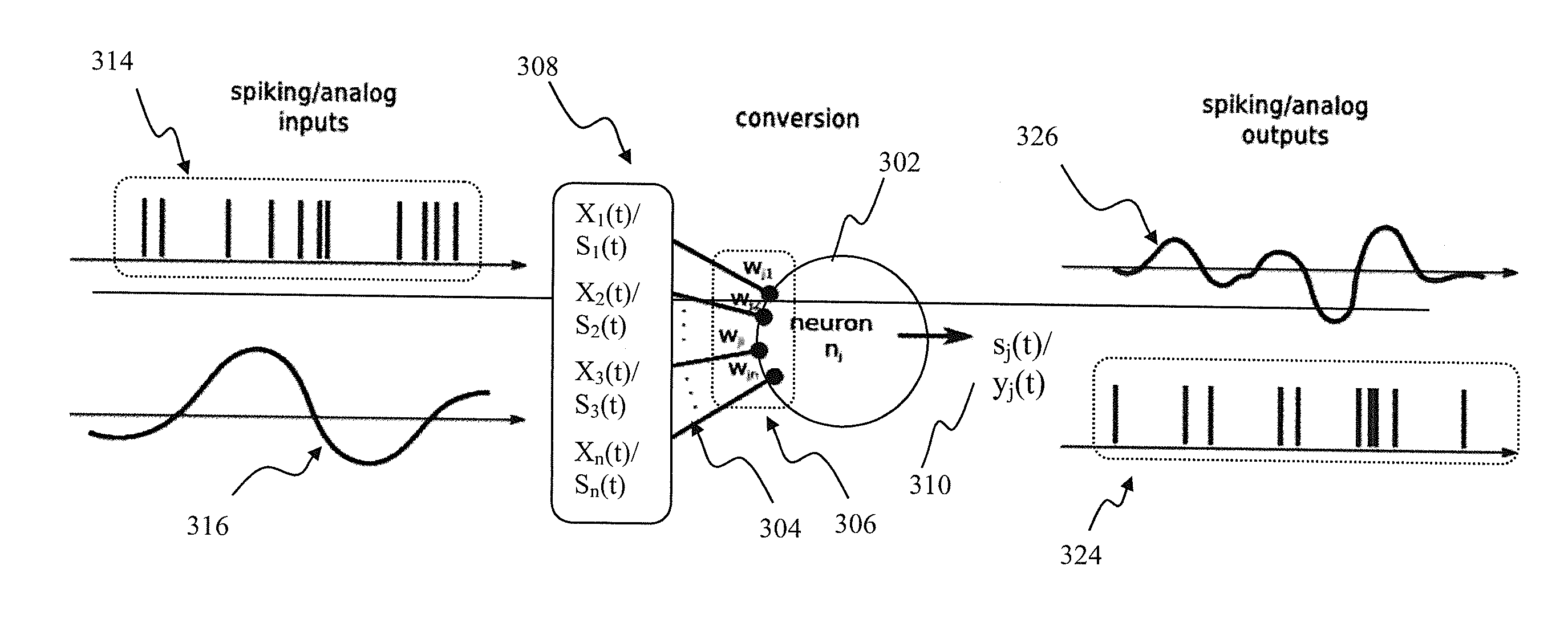
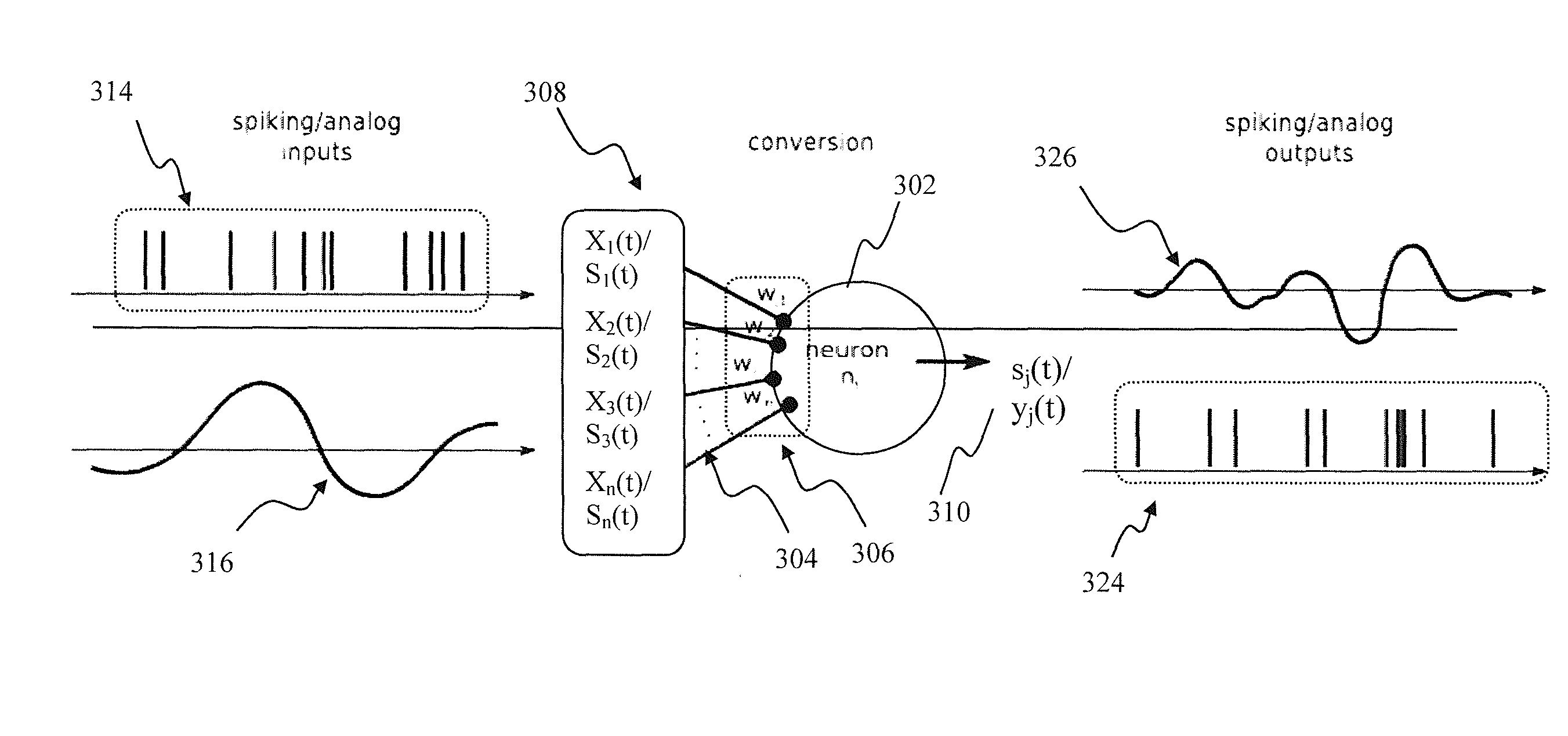
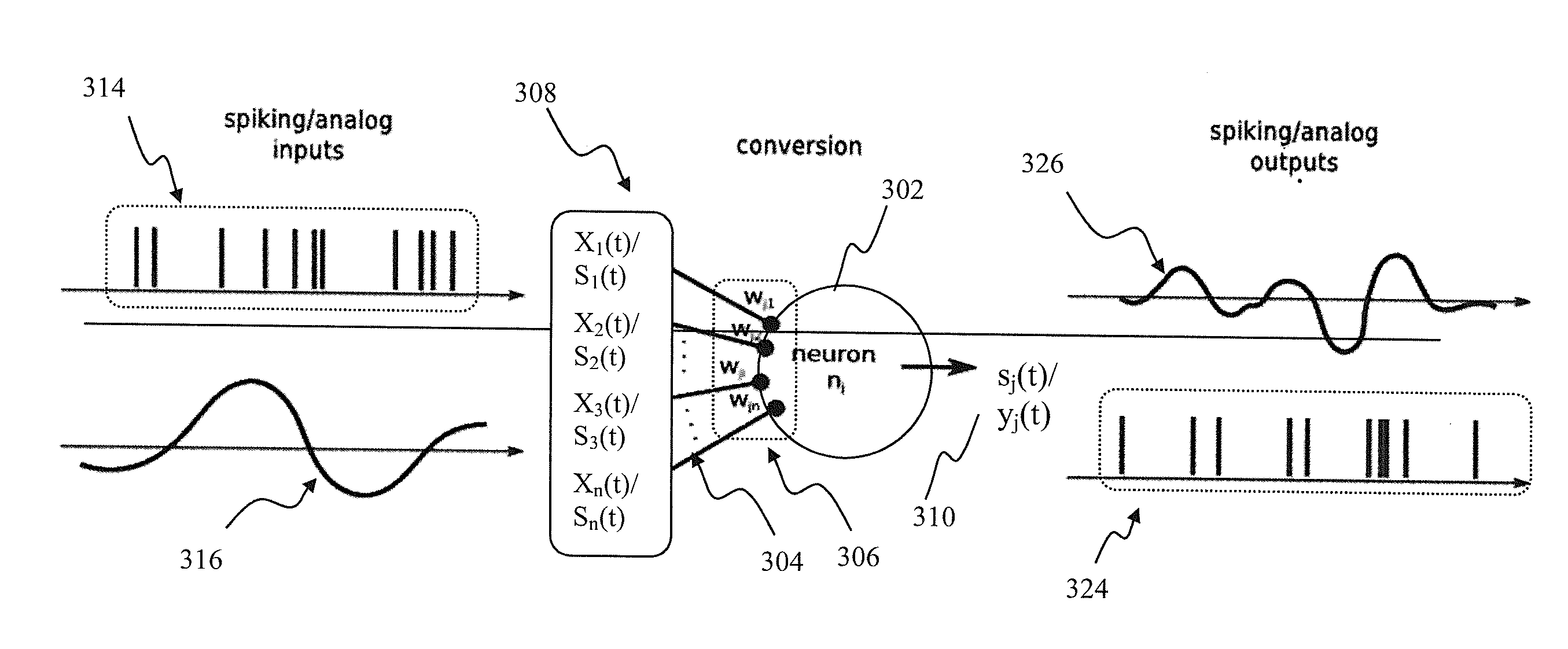
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:PONULAK FILIP
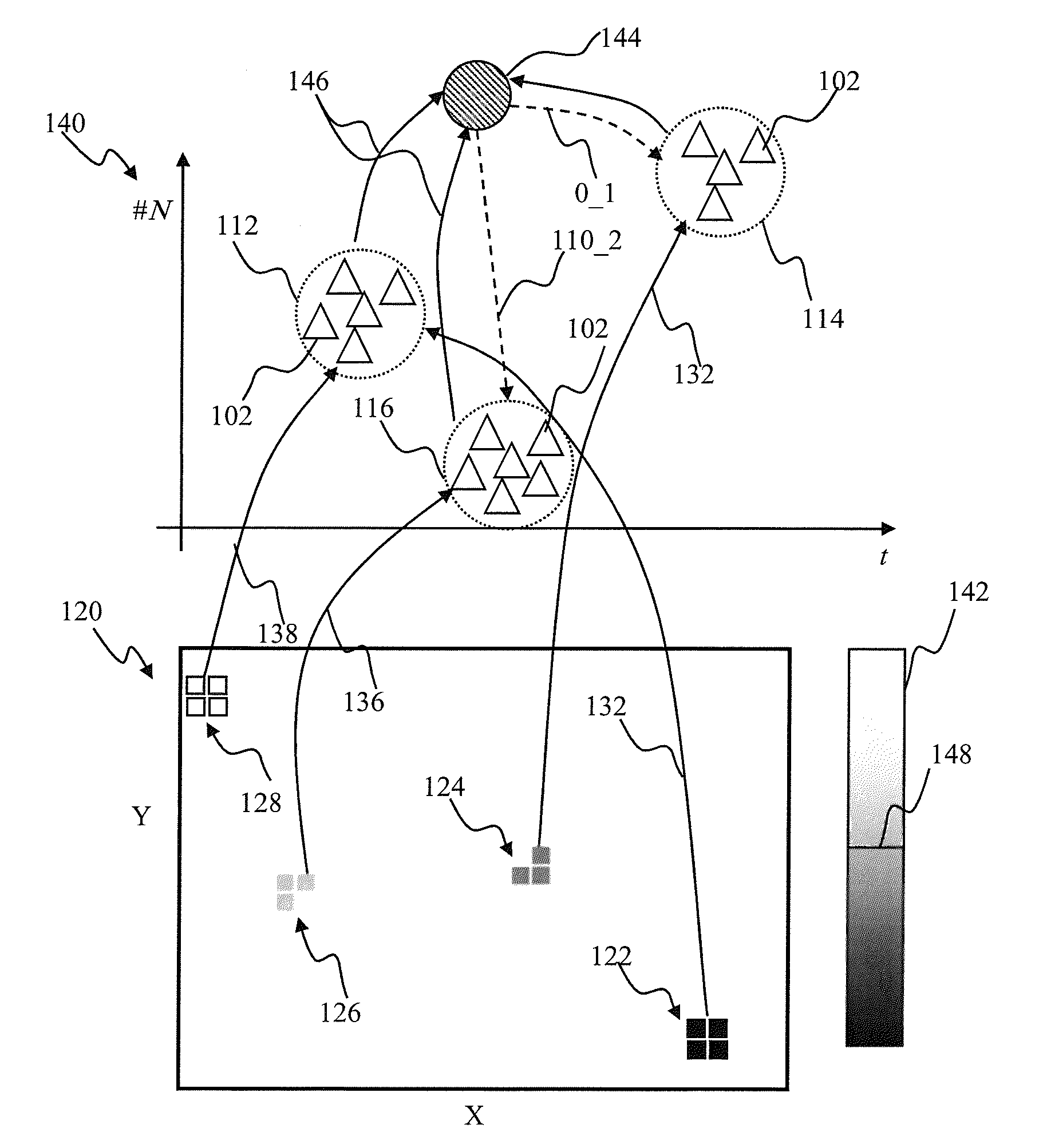
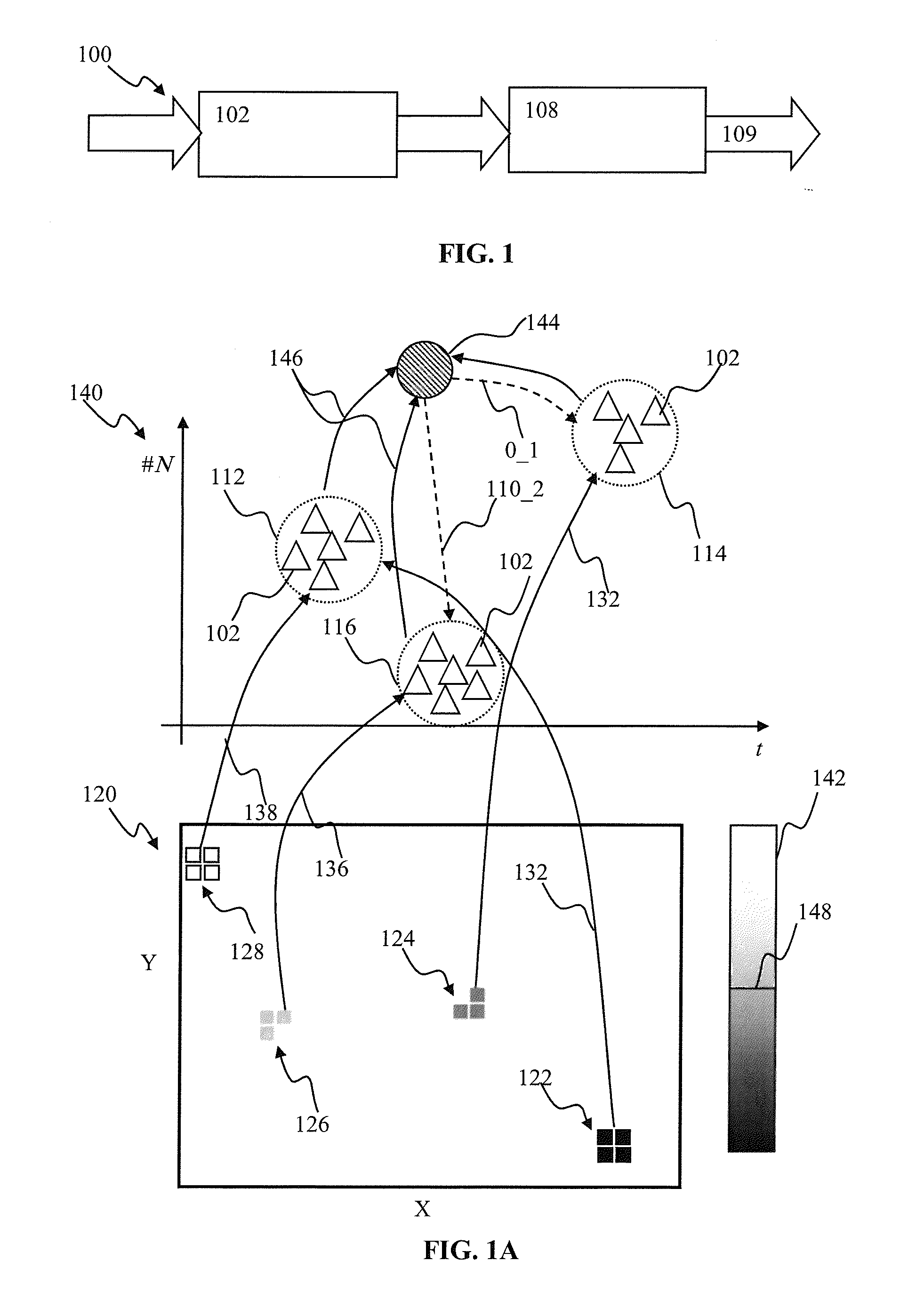
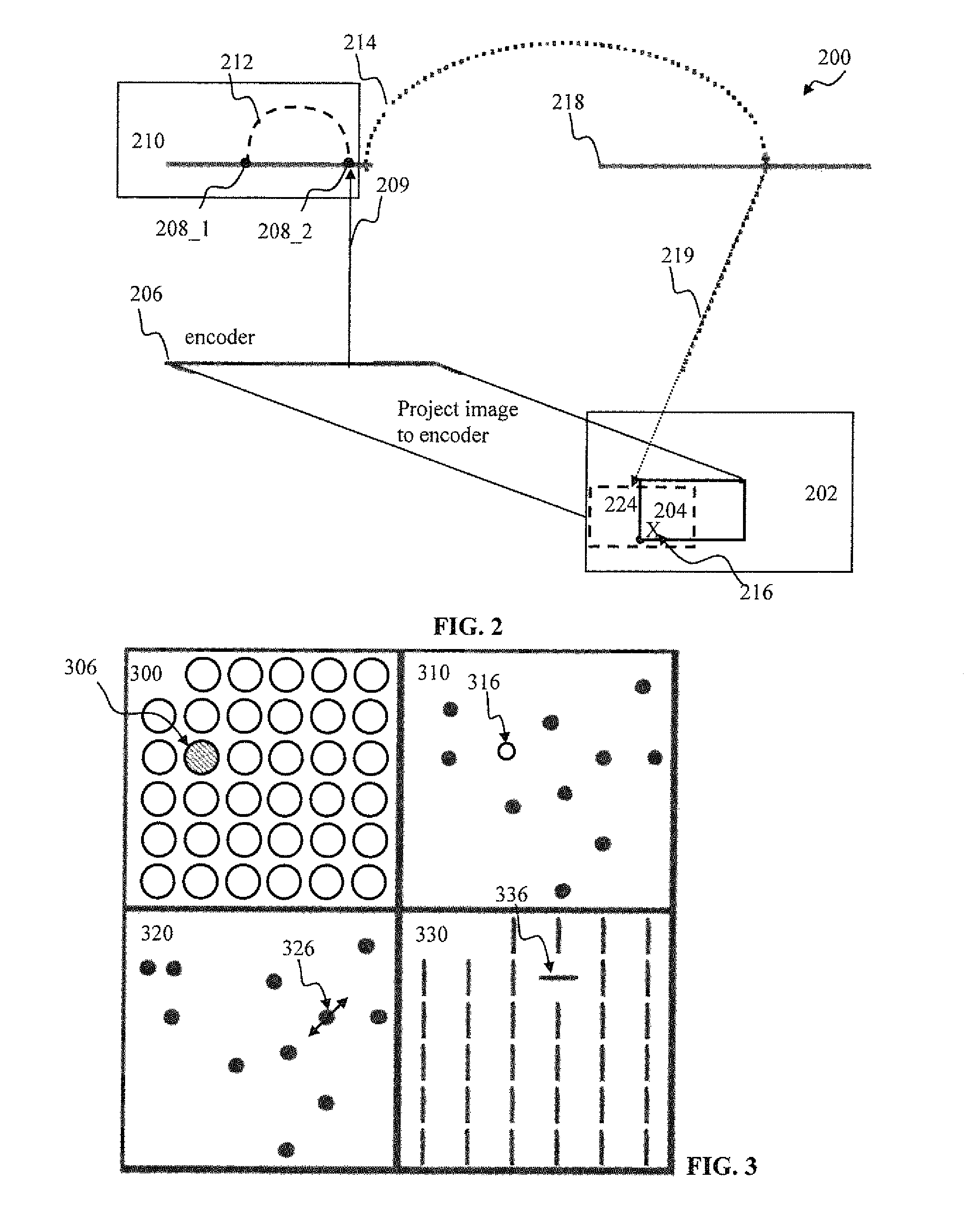
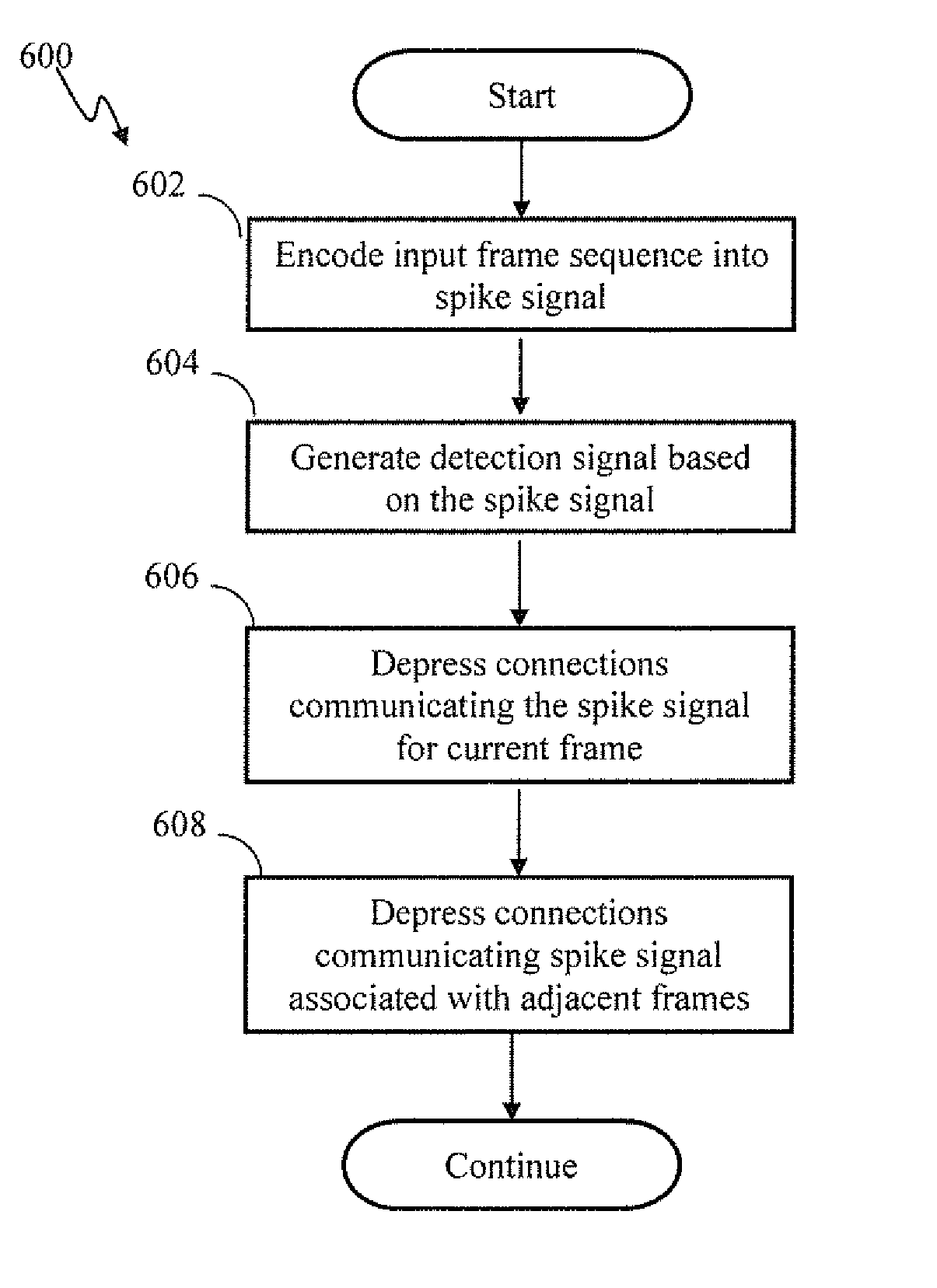
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140016858A1Reduce image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionNeuron network
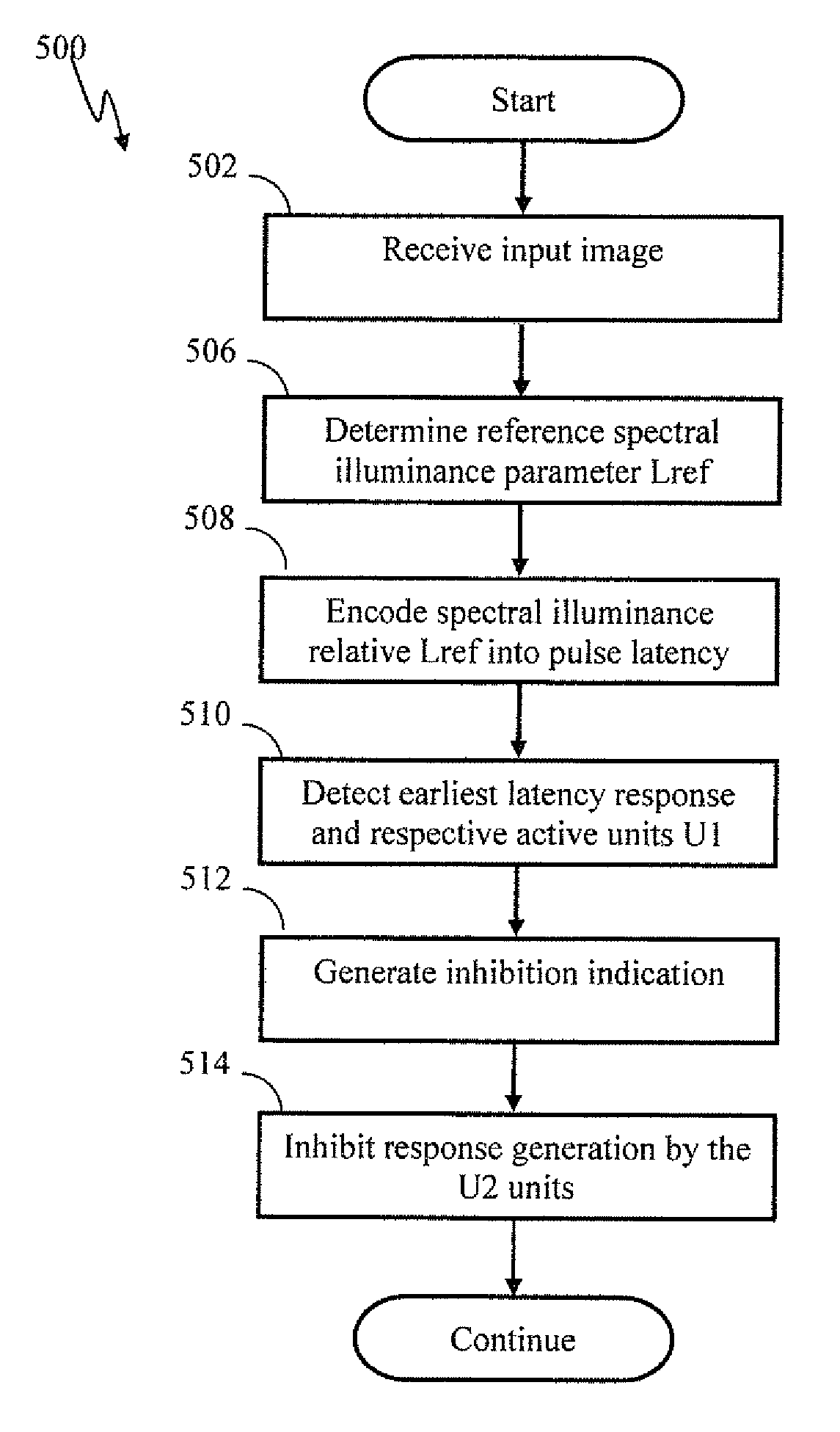
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
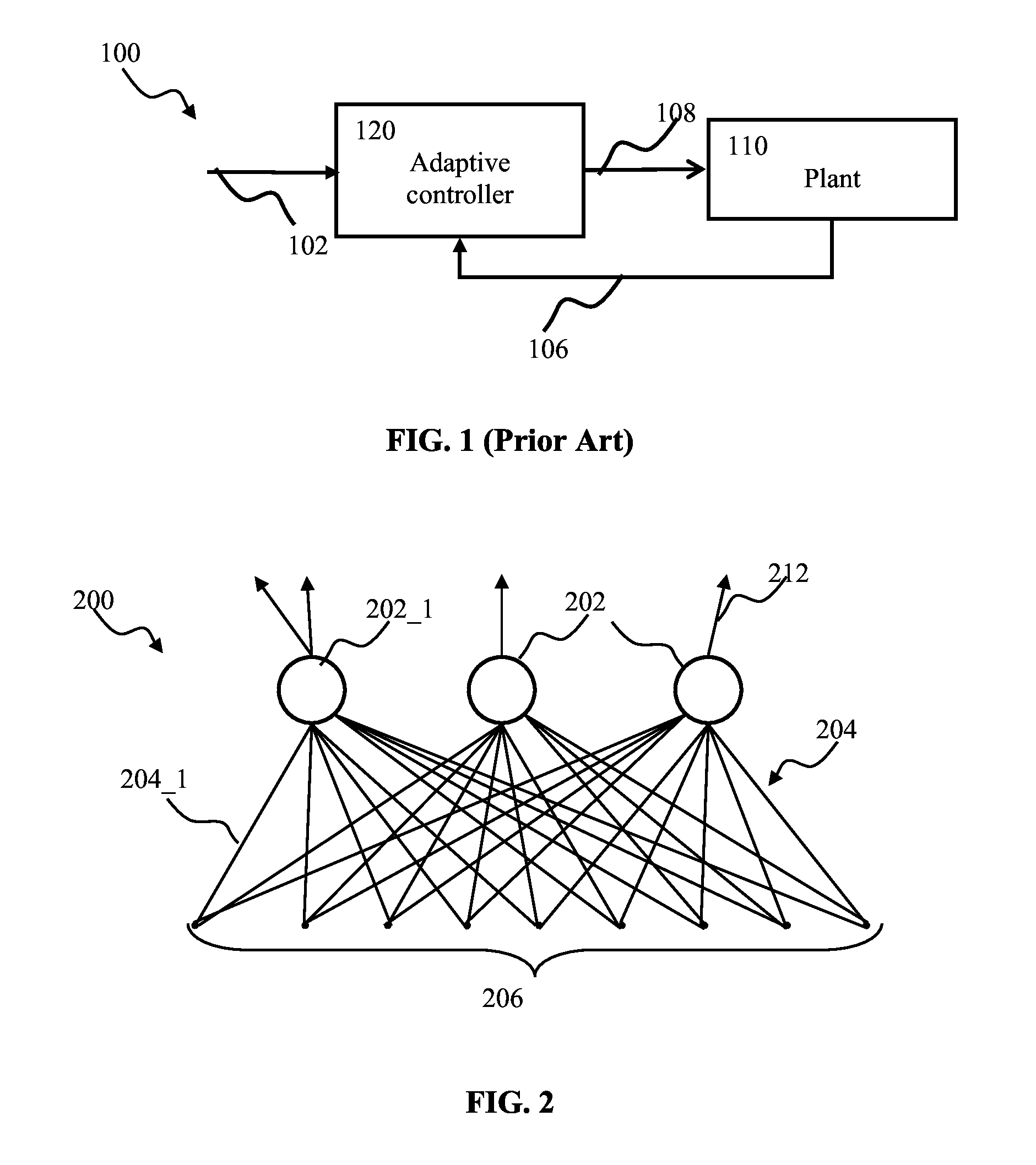
Spiking neuron network adaptive control apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140081895A1Minimizing distance measureSmooth connectionDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuron networkSpiking neural network
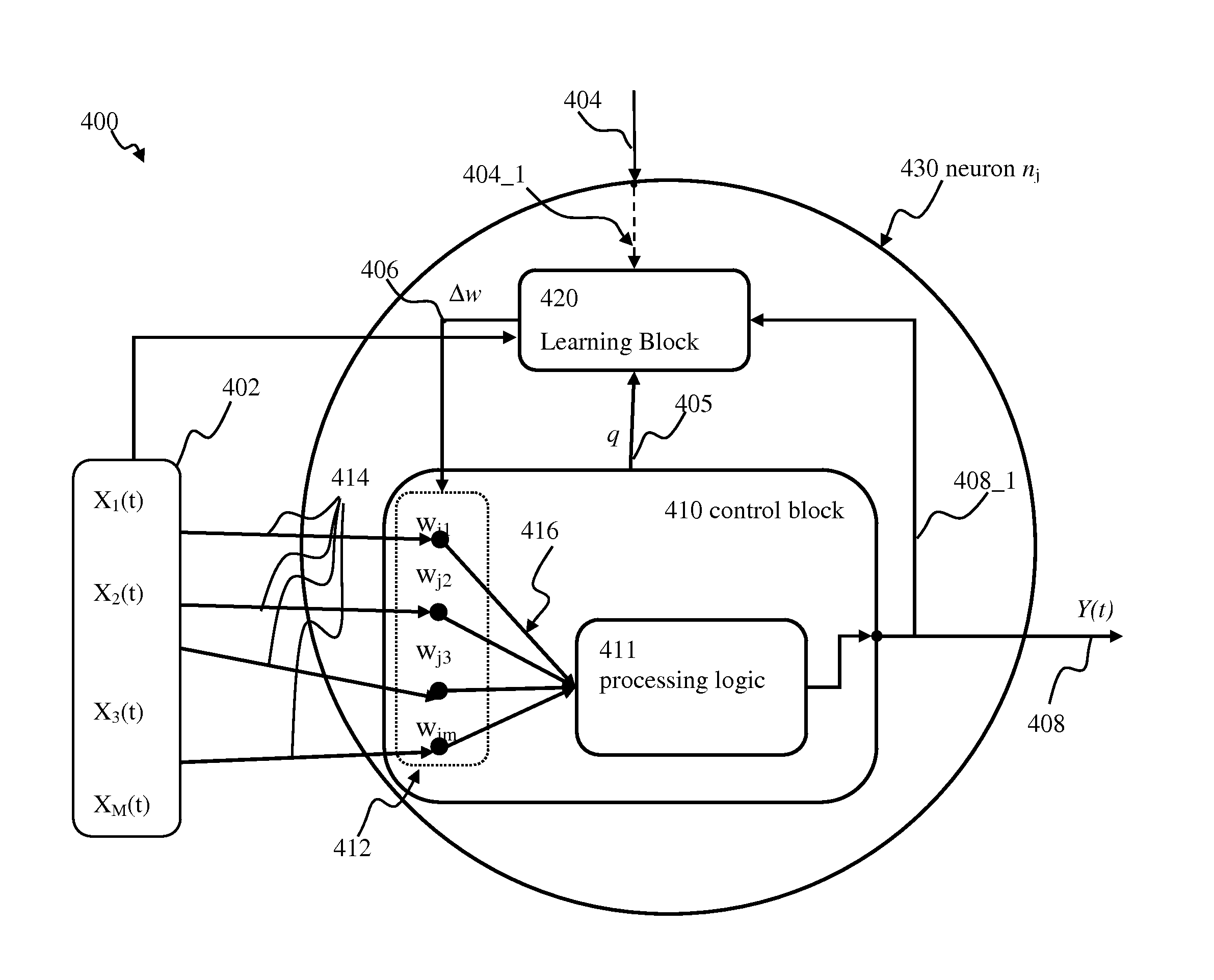
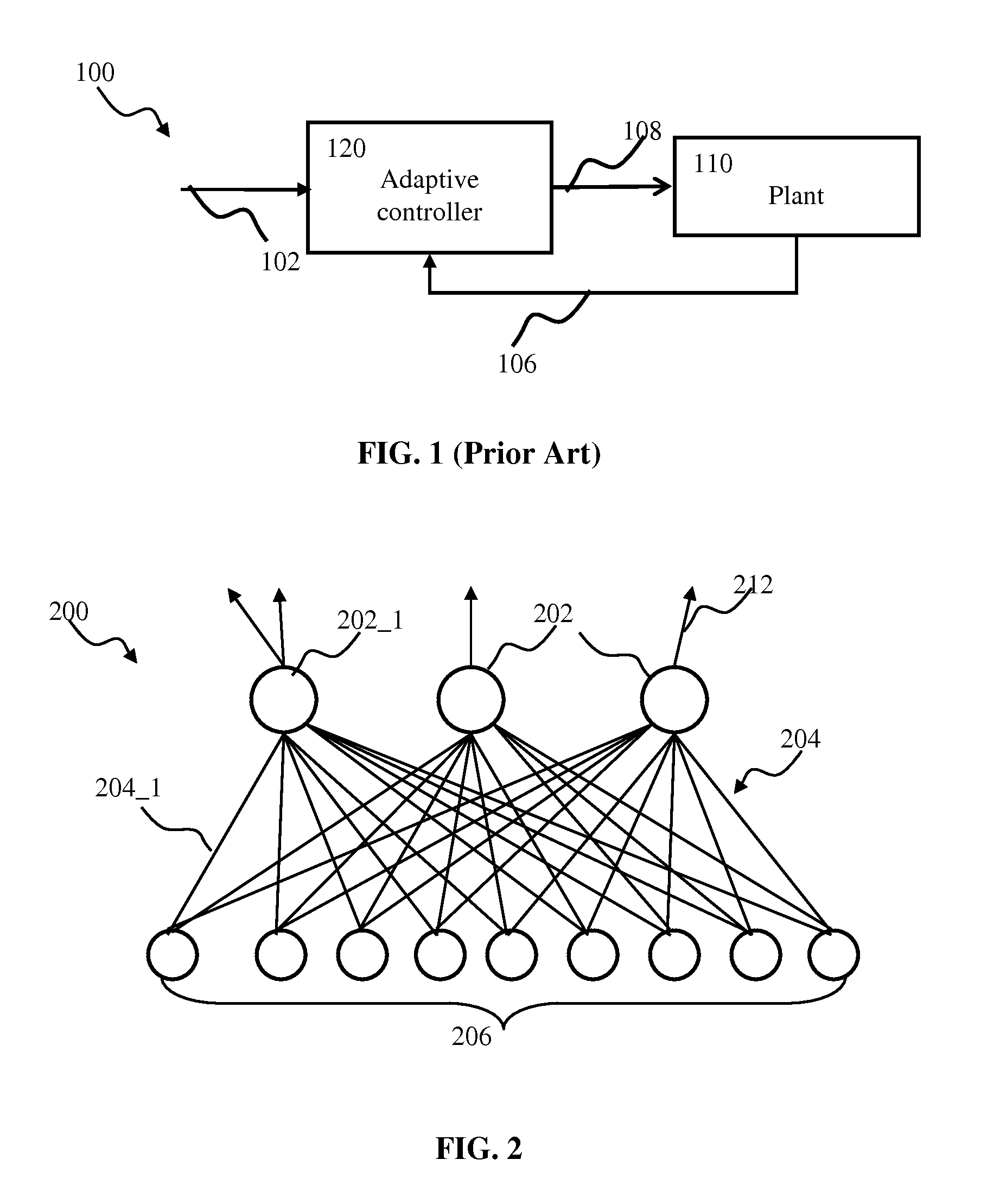
Adaptive controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block and a control block. The encoder may utilize basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. The relevant features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
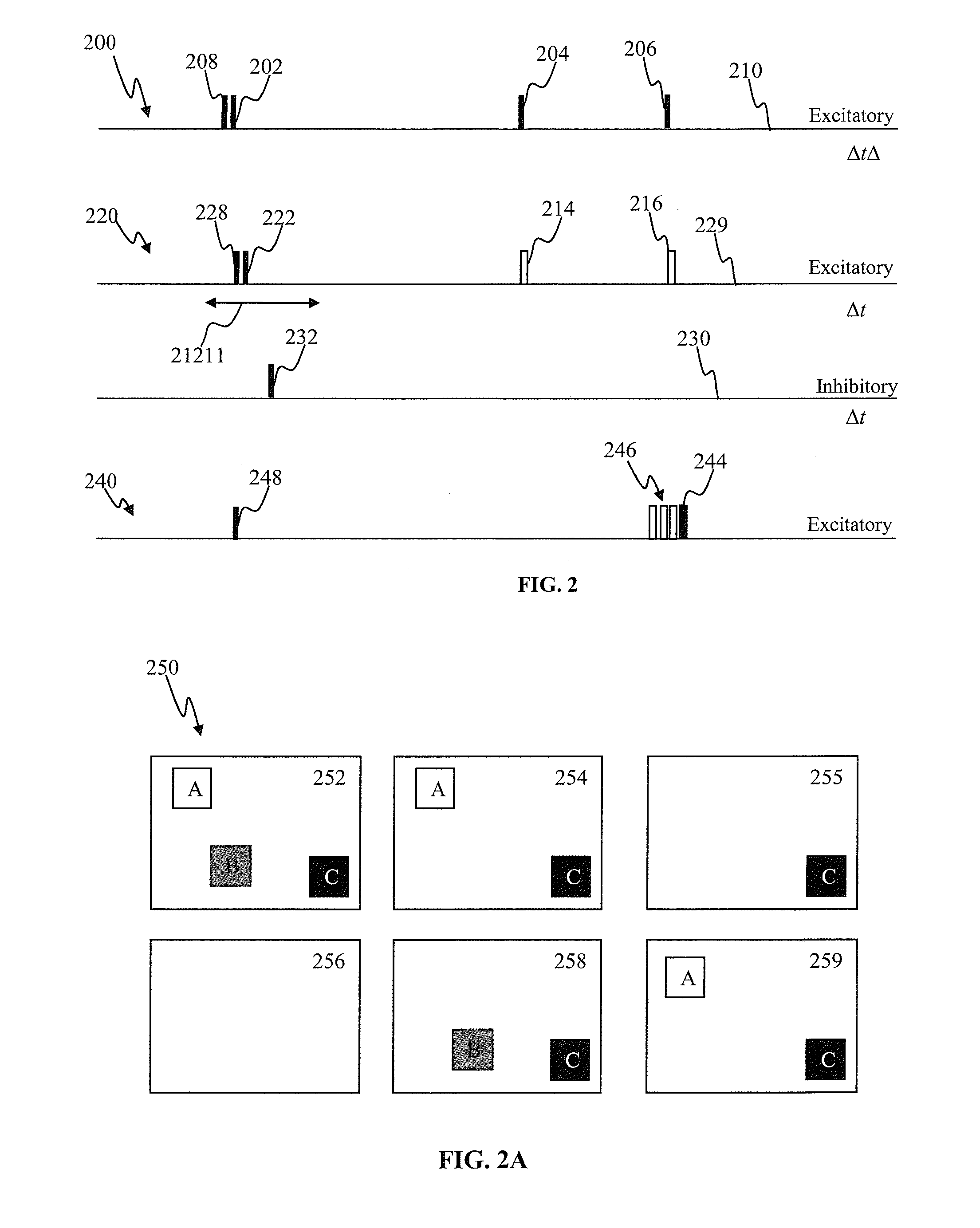
Spiking neural network feedback apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20130297541A1Low efficacyGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpiking neural networkArtificial intelligence
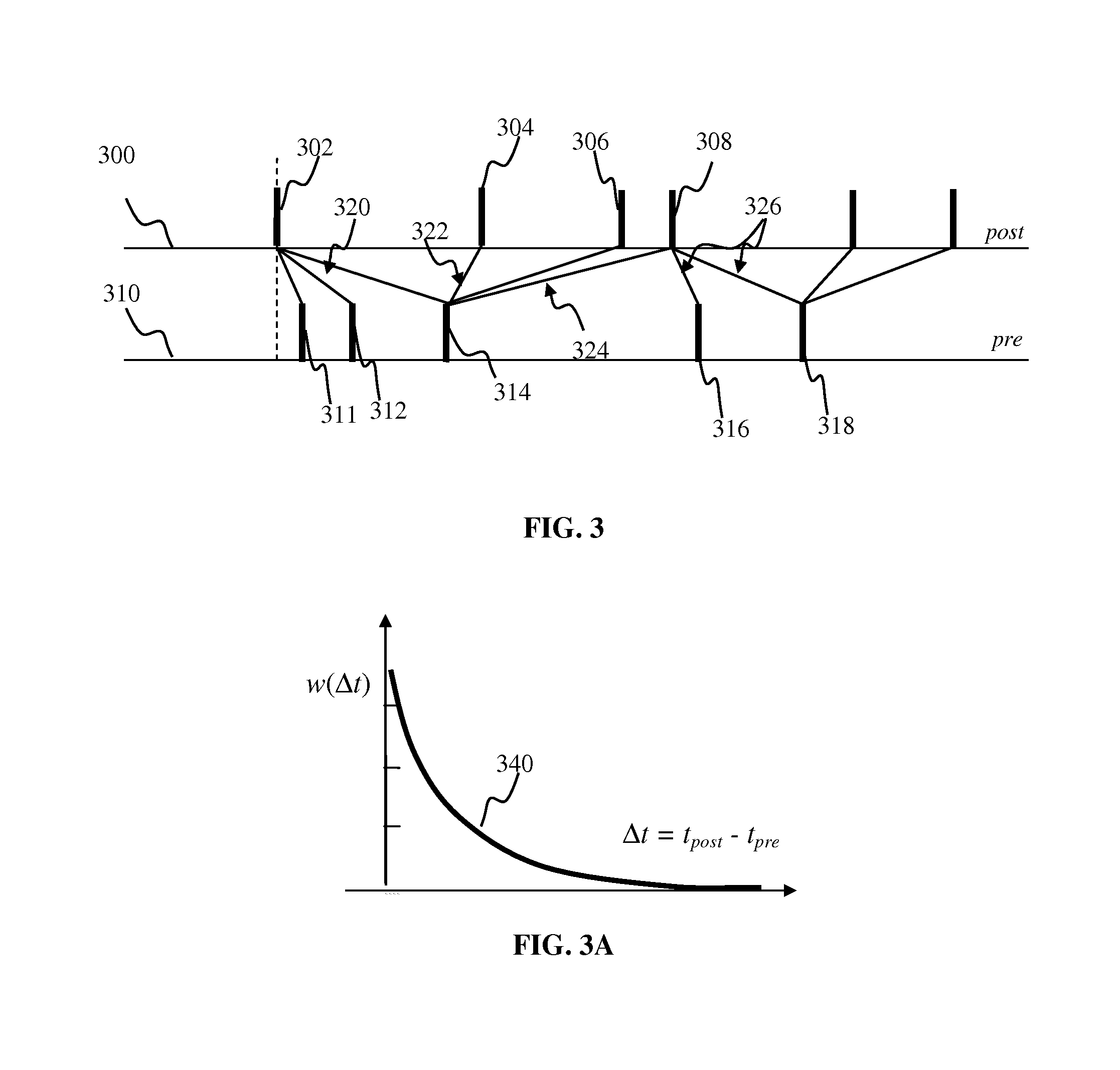
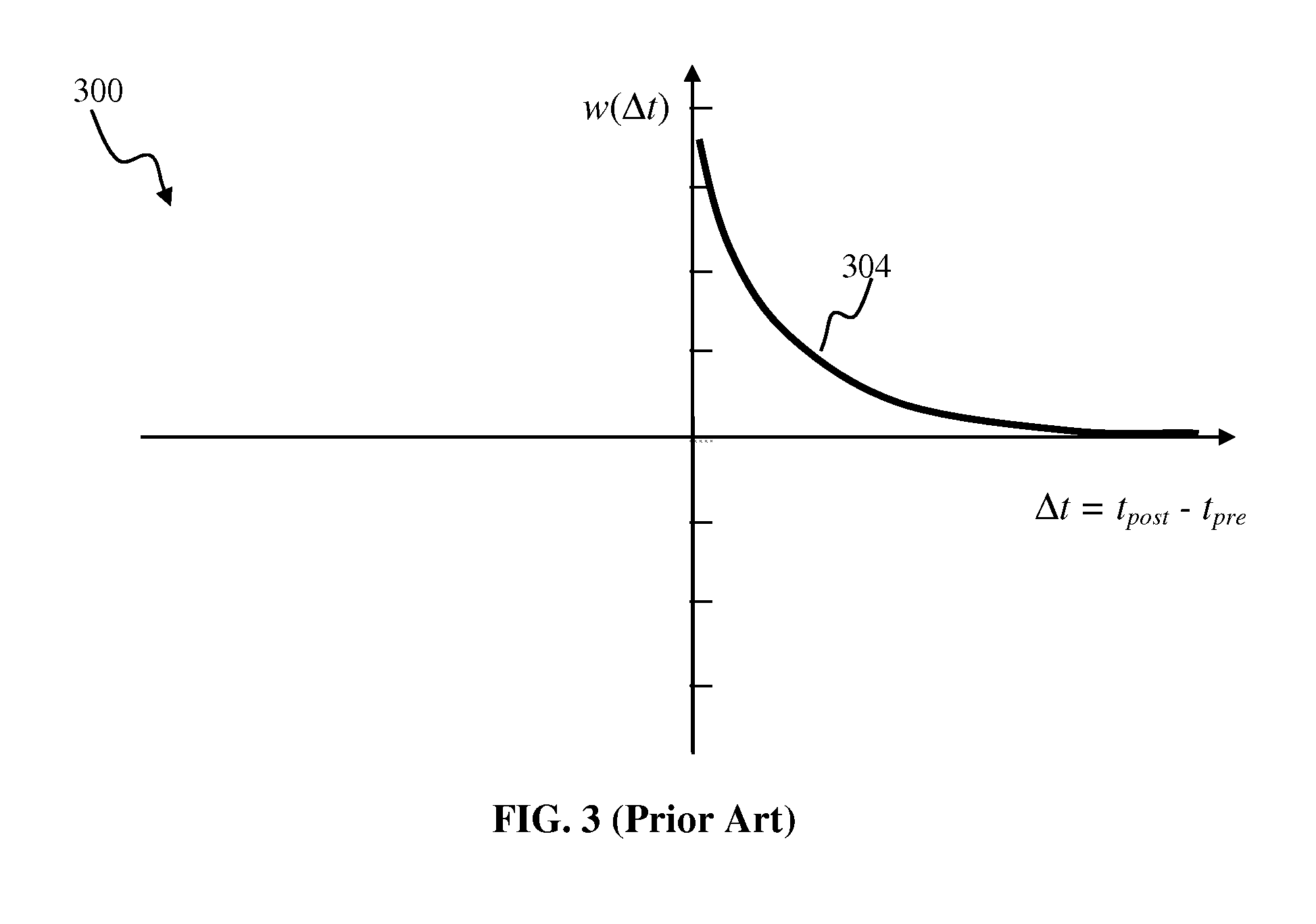
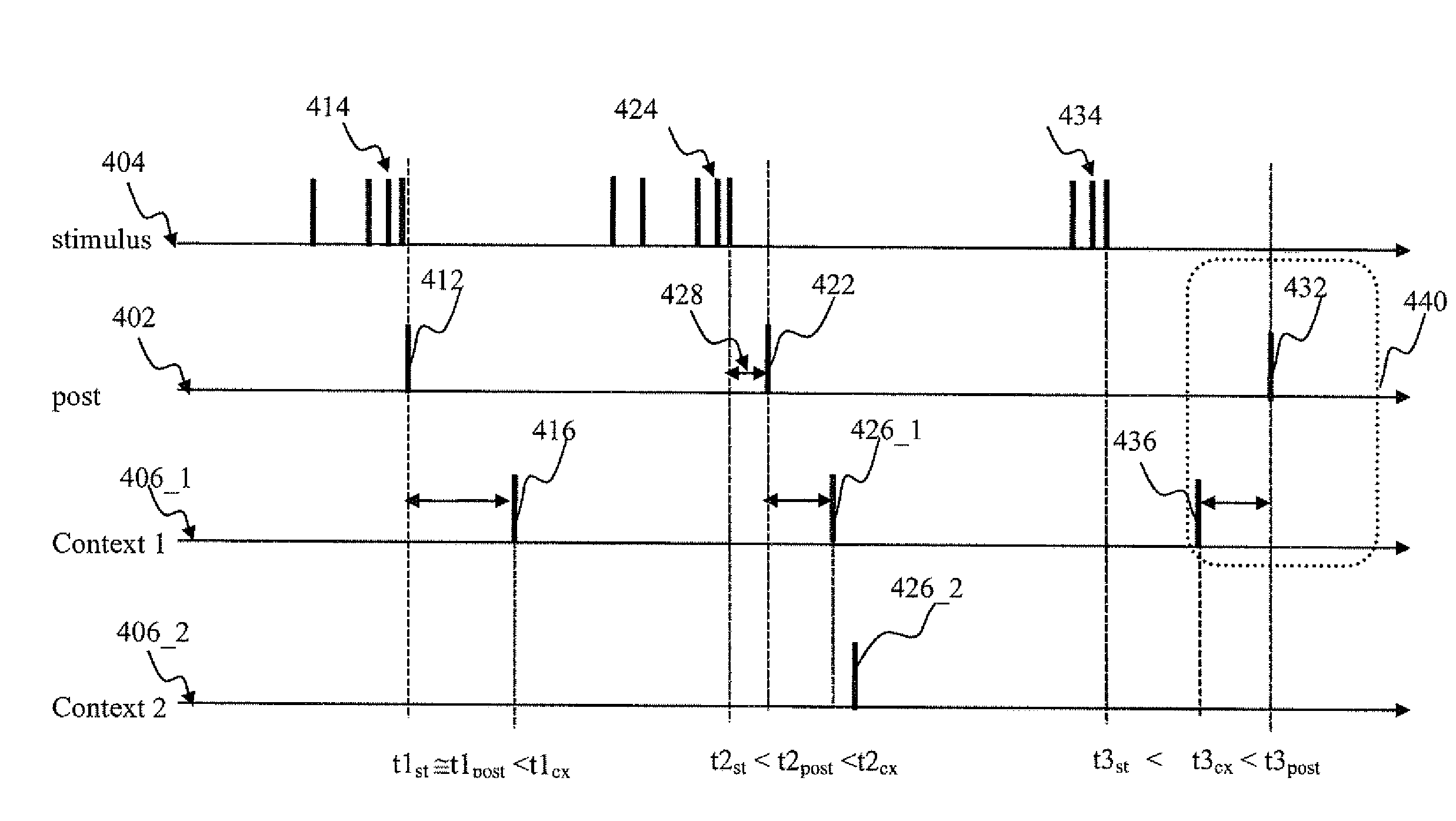
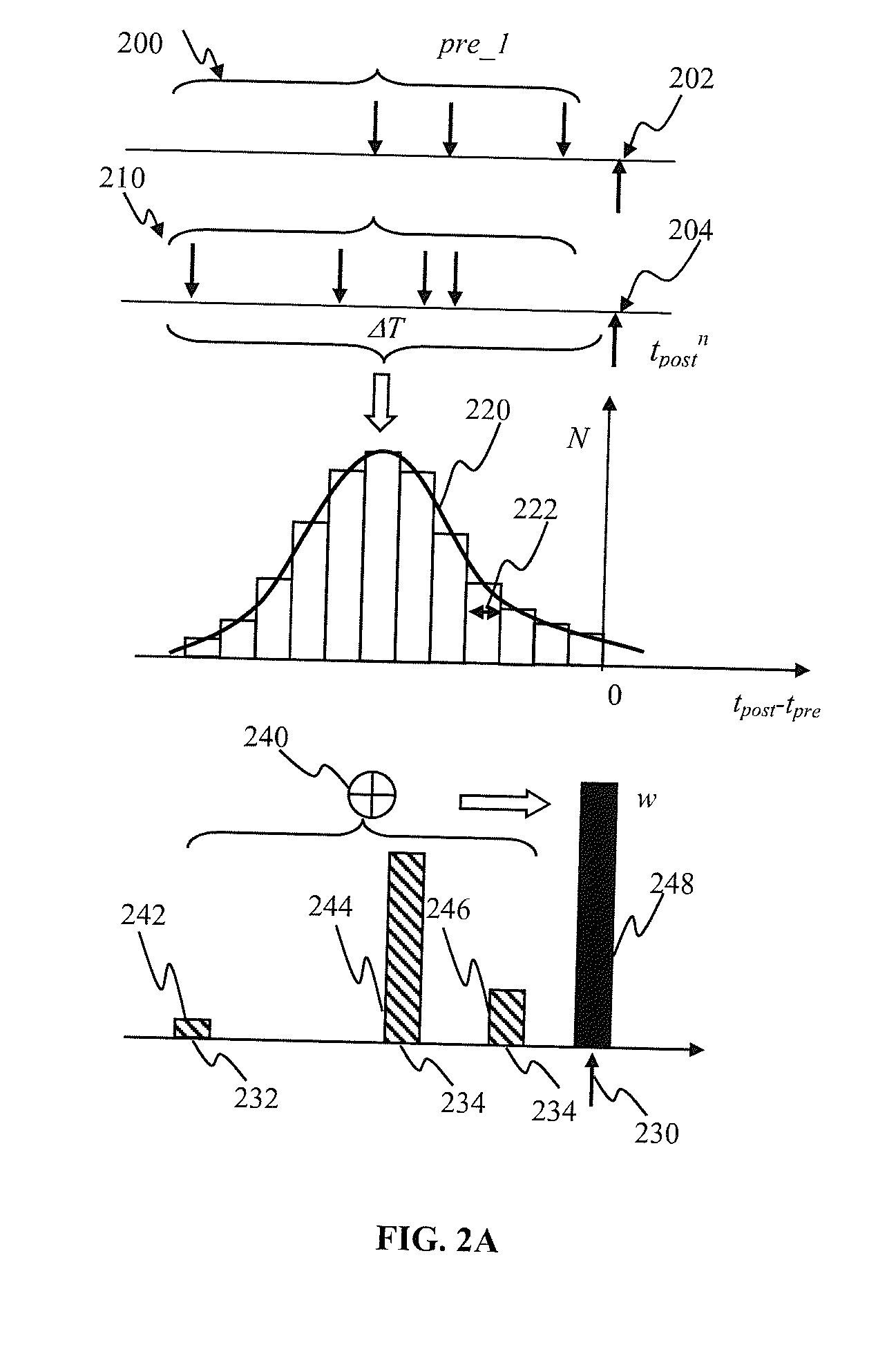
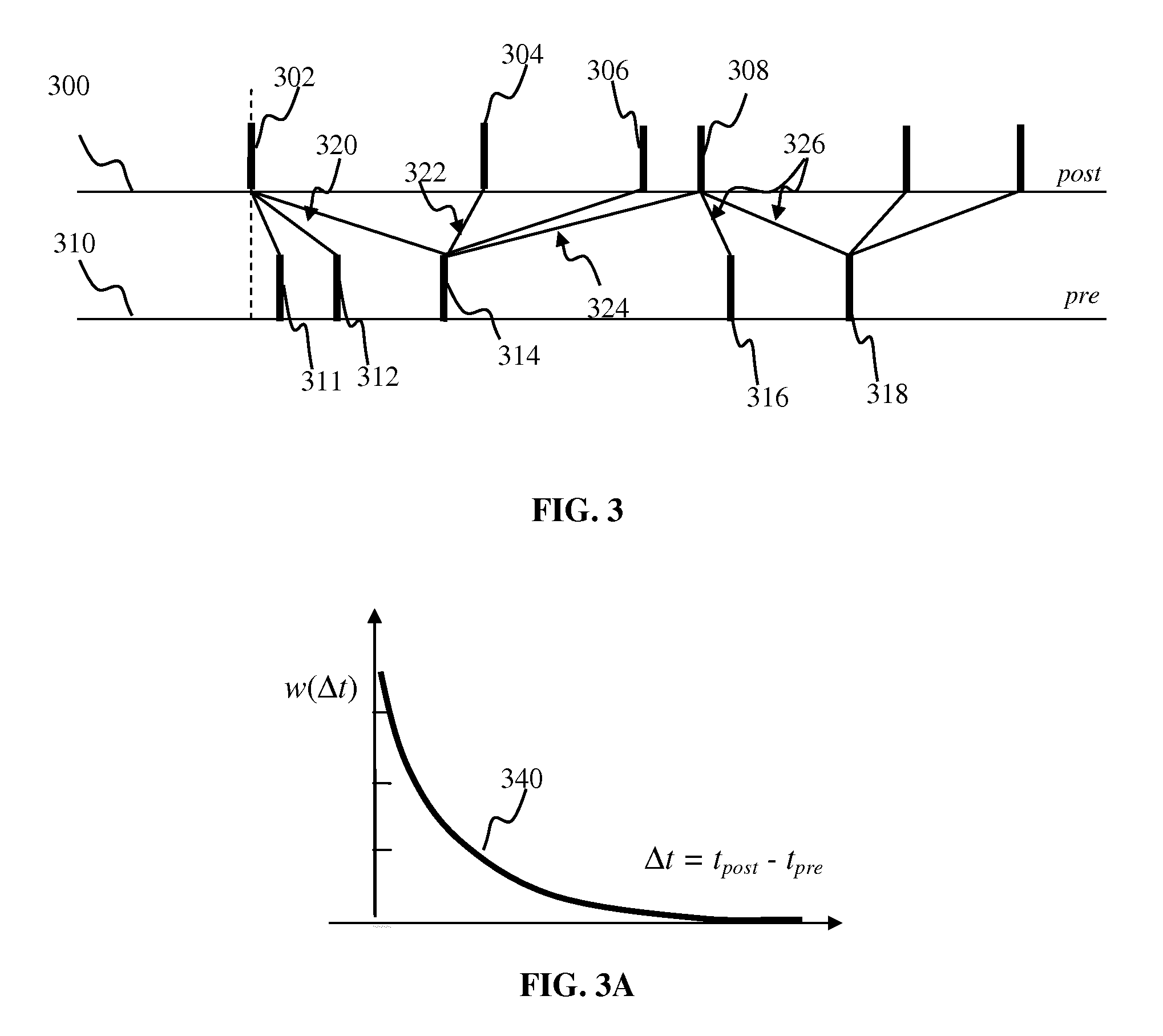
Apparatus and methods for feedback in a spiking neural network. In one approach, spiking neurons receive sensory stimulus and context signal that correspond to the same context. When the stimulus provides sufficient excitation, neurons generate response. Context connections are adjusted according to inverse spike-timing dependent plasticity. When the context signal precedes the post synaptic spike, context synaptic connections are depressed. Conversely, whenever the context signal follows the post synaptic spike, the connections are potentiated. The inverse STDP connection adjustment ensures precise control of feedback-induced firing, eliminates runaway positive feedback loops, enables self-stabilizing network operation. In another aspect of the invention, the connection adjustment methodology facilitates robust context switching when processing visual information. When a context (such an object) becomes intermittently absent, prior context connection potentiation enables firing for a period of time. If the object remains absent, the connection becomes depressed thereby preventing further firing.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for efficient updates in spiking neuron network
Efficient updates of connections in artificial neuron networks may be implemented. A framework may be used to describe the connections using a linear synaptic dynamic process, characterized by stable equilibrium. The state of neurons and synapses within the network may be updated, based on inputs and outputs to / from neurons. In some implementations, the updates may be implemented at regular time intervals. In one or more implementations, the updates may be implemented on-demand, based on the network activity (e.g., neuron output and / or input) so as to further reduce computational load associated with the synaptic updates. The connection updates may be decomposed into multiple event-dependent connection change components that may be used to describe connection plasticity change due to neuron input. Using event-dependent connection change components, connection updates may be executed on per neuron basis, as opposed to per-connection basis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Sensory input processing apparatus in a spiking neural network
ActiveUS20130297542A1Reduce formationDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpiking neural networkSpike-timing-dependent plasticity
Apparatus and methods for feedback in a spiking neural network. In one approach, spiking neurons receive sensory stimulus and context signal that correspond to the same context. When the stimulus provides sufficient excitation, neurons generate response. Context connections are adjusted according to inverse spike-timing dependent plasticity. When the context signal precedes the post synaptic spike, context synaptic connections are depressed. Conversely, whenever the context signal follows the post synaptic spike, the connections are potentiated. The inverse STDP connection adjustment ensures precise control of feedback-induced firing, eliminates runaway positive feedback loops, enables self-stabilizing network operation. In another aspect of the invention, the connection adjustment methodology facilitates robust context switching when processing visual information. When a context (such an object) becomes intermittently absent, prior context connection potentiation enables firing for a period of time. If the object remains absent, the connection becomes depressed thereby preventing further firing.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
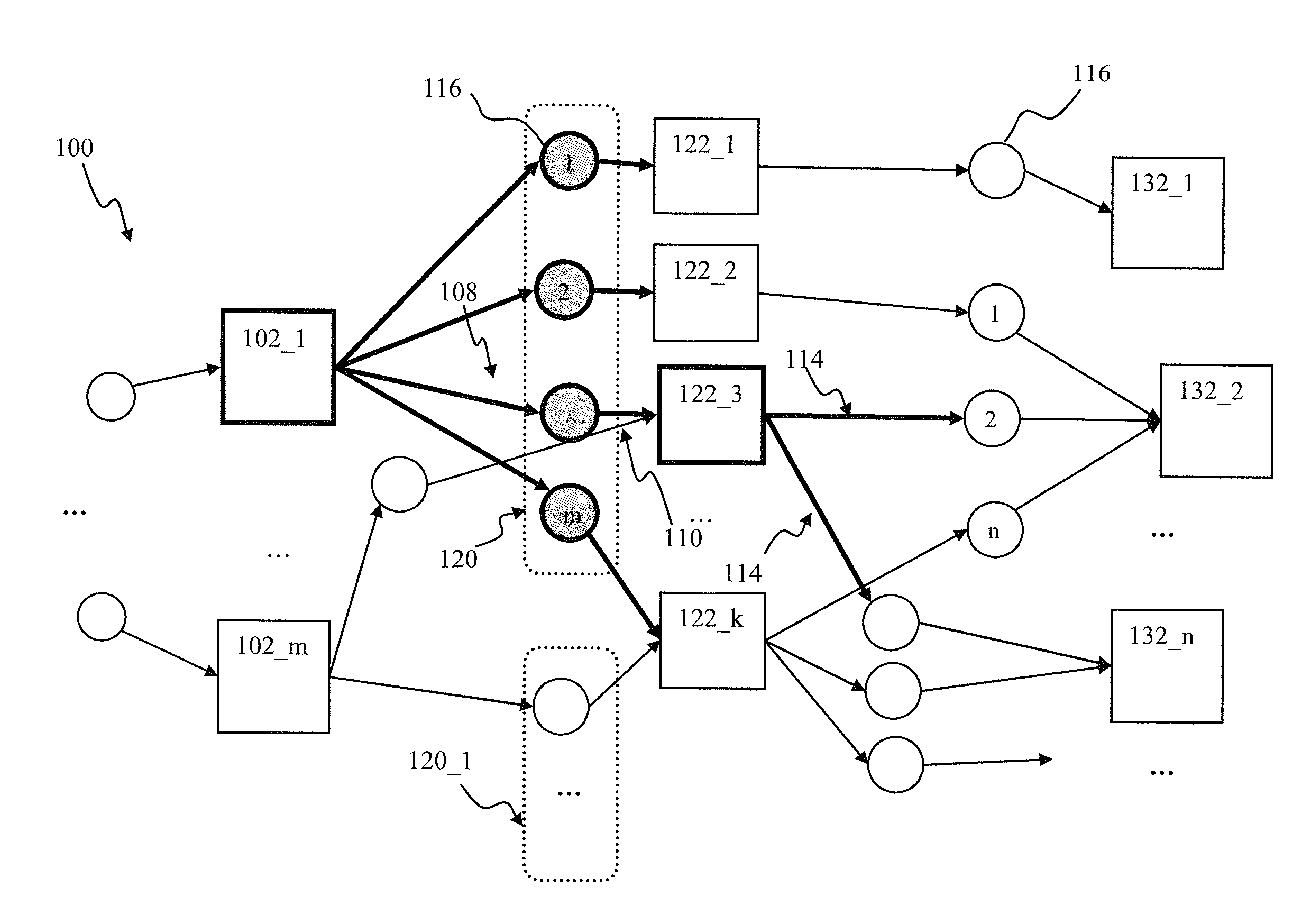
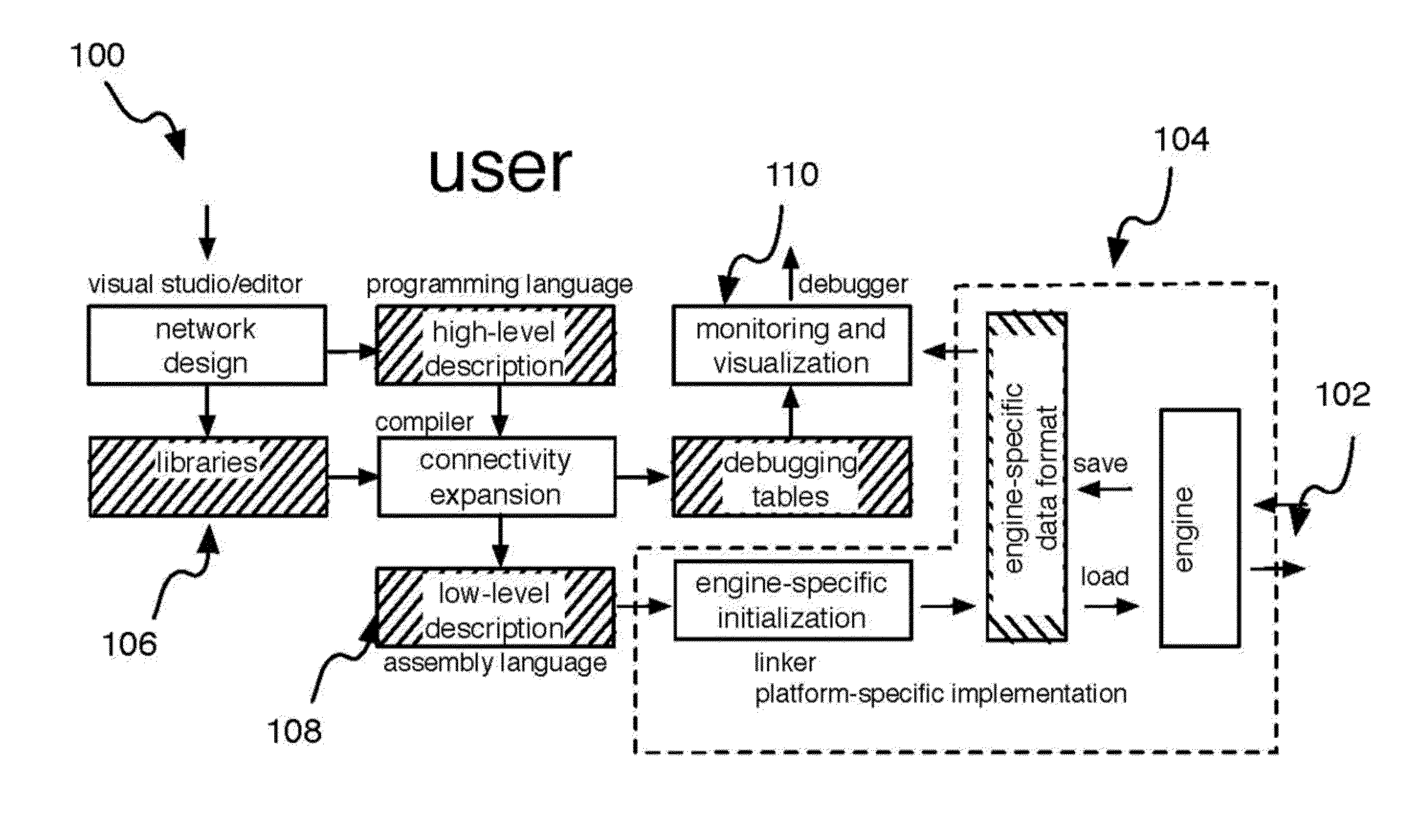
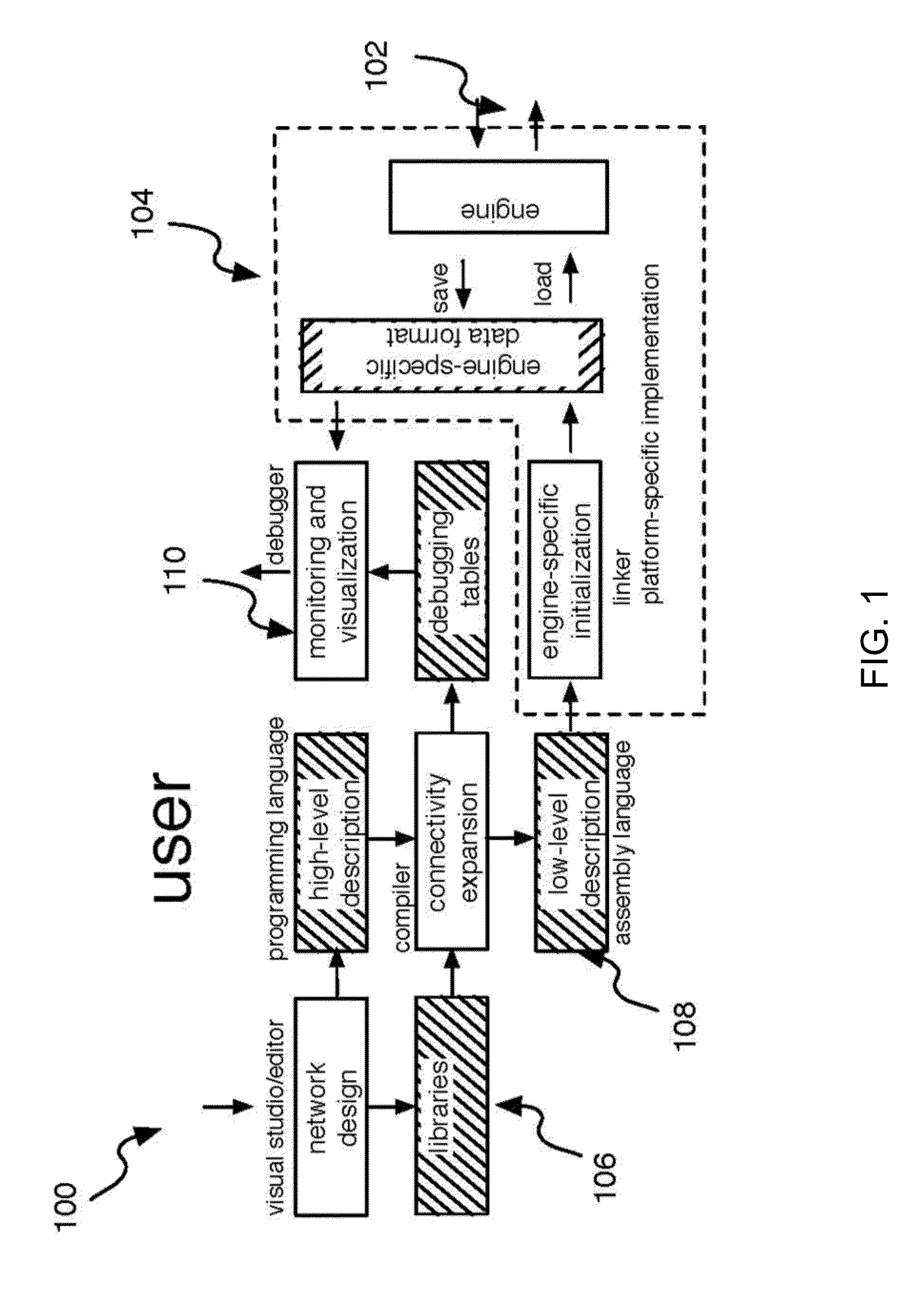
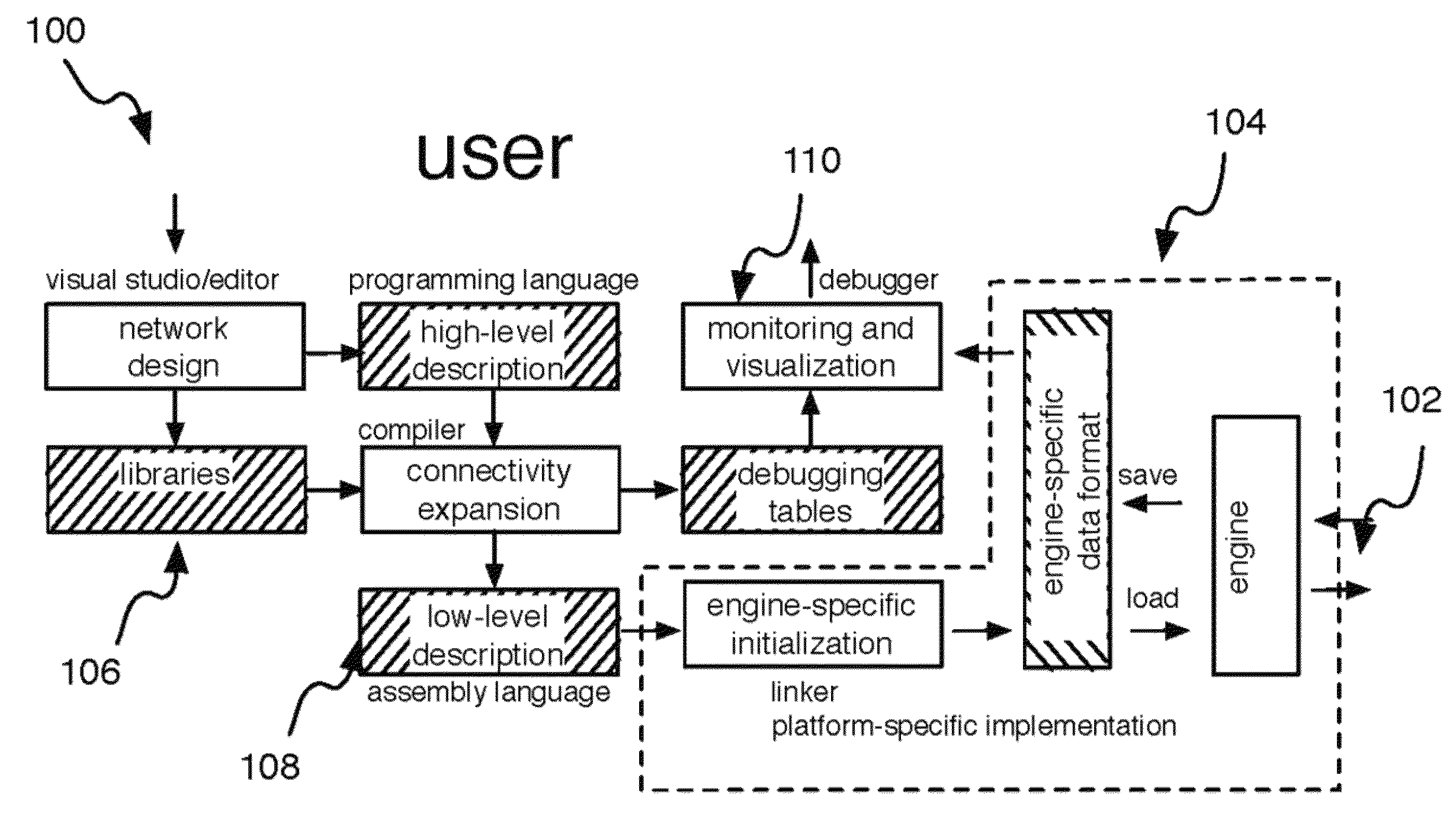
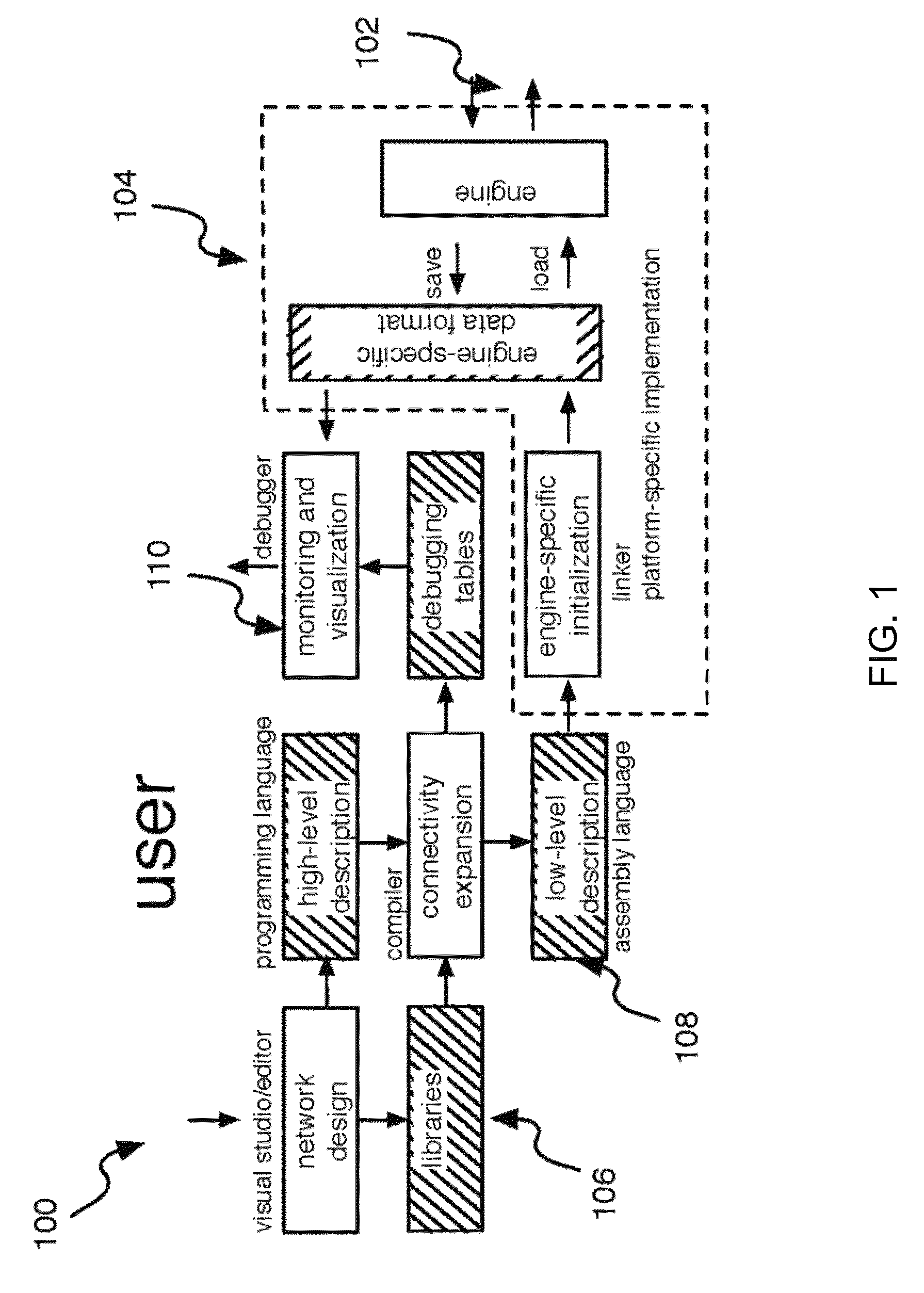
Elementary network description for efficient memory management in neuromorphic systems
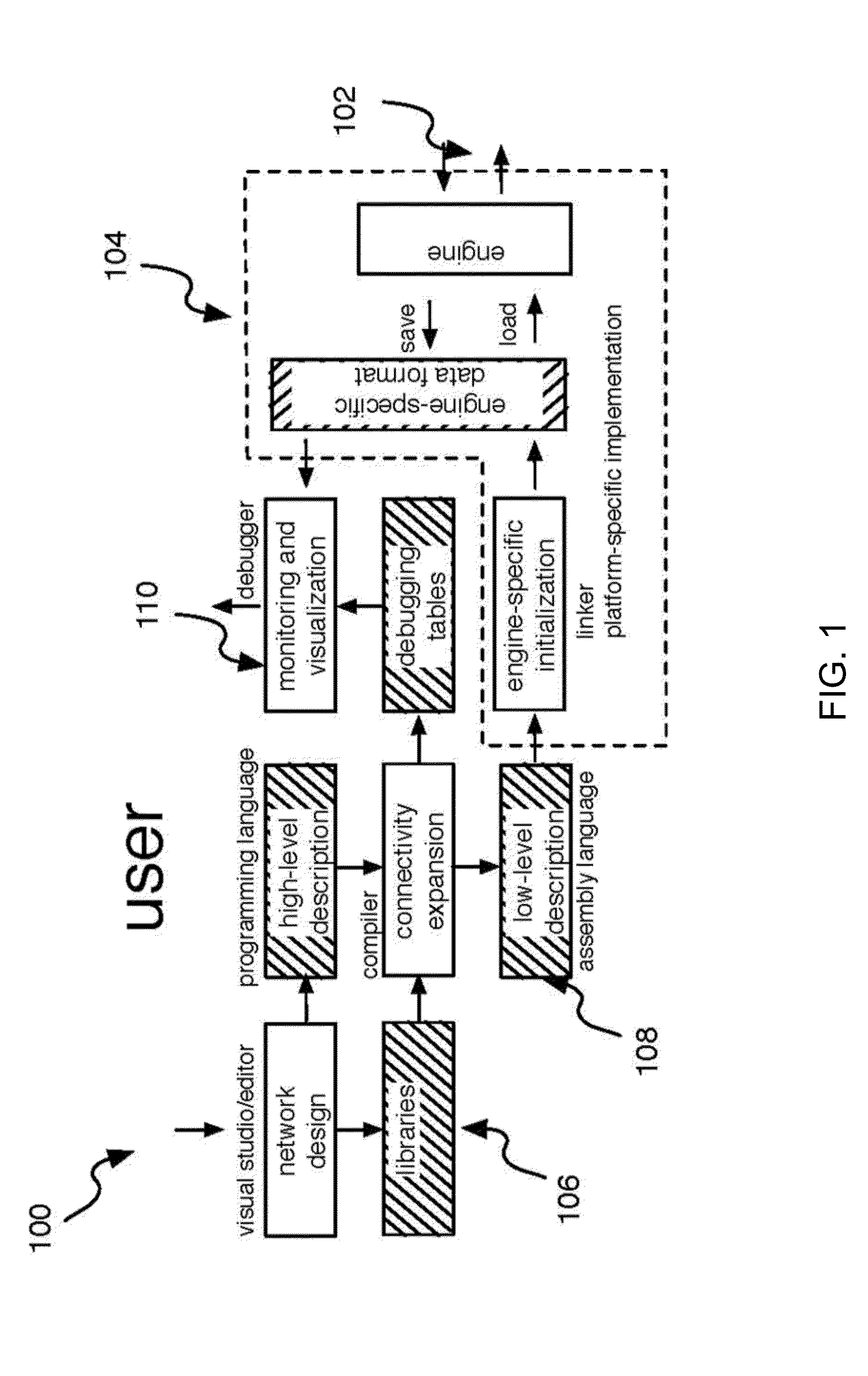
A simple format is disclosed and referred to as Elementary Network Description (END). The format can fully describe a large-scale neuronal model and embodiments of software or hardware engines to simulate such a model efficiently. The architecture of such neuromorphic engines is optimal for high-performance parallel processing of spiking networks with spike-timing dependent plasticity. Methods for managing memory in a processing system are described whereby memory can be allocated among a plurality of elements and rules configured for each element such that the parallel execution of the spiking networks is most optimal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Elementary network description for neuromorphic systems
A simple format is disclosed and referred to as Elementary Network Description (END). The format can fully describe a large-scale neuronal model and embodiments of software or hardware engines to simulate such a model efficiently. The architecture of such neuromorphic engines is optimal for high-performance parallel processing of spiking networks with spike-timing dependent plasticity. Neuronal network and methods for operating neuronal networks comprise a plurality of units, where each unit has a memory and a plurality of doublets, each doublet being connected to a pair of the plurality of units. Execution of unit update rules for the plurality of units is order-independent and execution of doublet event rules for the plurality of doublets is order-independent.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Modulated plasticity apparatus and methods for spiking neuron network
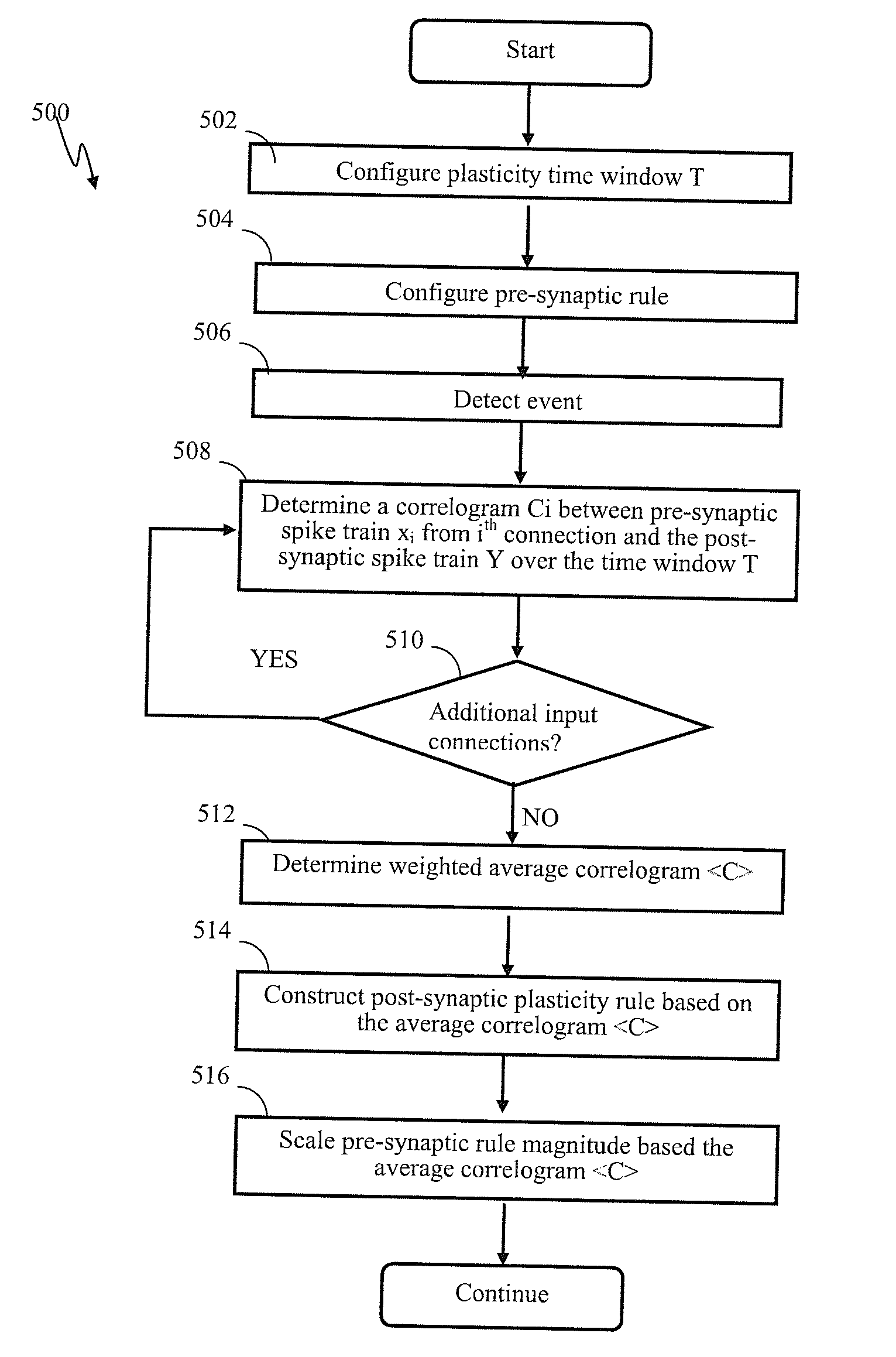
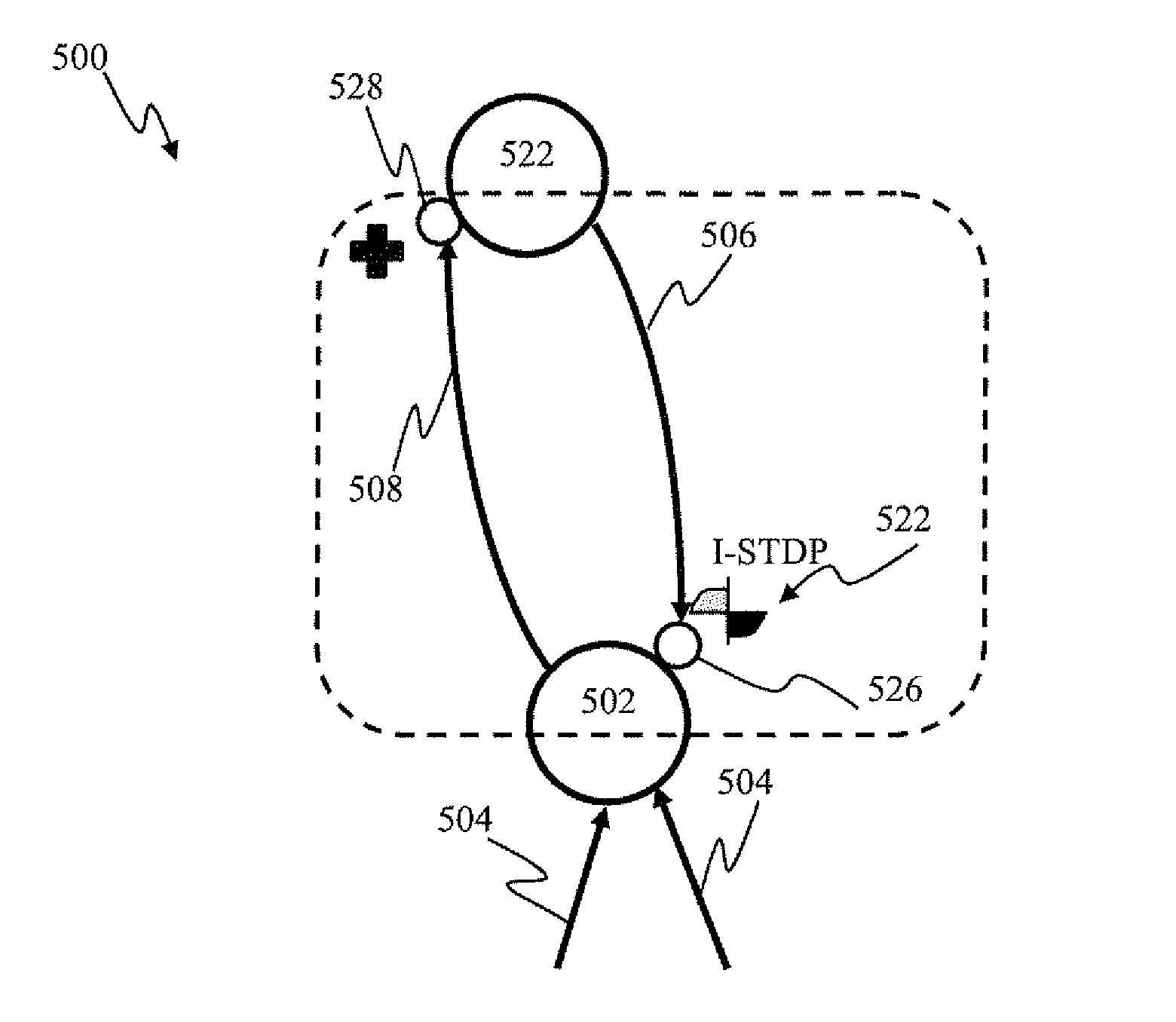
Apparatus and methods for modulated plasticity in a spiking neuron network. A plasticity mechanism may be configured for example based on a similarity measure between post-synaptic activities of two or more neurons that may be receiving the same feed-forward input. The similarity measure may comprise a dynamically determined cross-correlogram between the output spike trains of two neurons. An a priori configured similarity measure may be used during network operation in order to update efficacy of inhibitory connections between neighboring neurons. Correlated output activity may cause one neuron to inhibit output generation by another neuron thereby hindering responses by multiple neurons to the same input stimuli. The inhibition may be based on an increased efficacy of inhibitory lateral connection. The inhibition may comprise modulation of the pre synaptic portion the plasticity rule based on efficacies of feed-forward connection and inhibitory connections and a statistical parameter associated with the post-synaptic rule.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Spiking neural network object recognition apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20130297539A1Reduce probabilityDigital computer detailsDigital dataSynapseSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for feedback in a spiking neural network. In one approach, spiking neurons receive sensory stimulus and context signal that correspond to the same context. When the stimulus provides sufficient excitation, neurons generate response. Context connections are adjusted according to inverse spike-timing dependent plasticity. When the context signal precedes the post synaptic spike, context synaptic connections are depressed. Conversely, whenever the context signal follows the post synaptic spike, the connections are potentiated. The inverse STDP connection adjustment ensures precise control of feedback-induced firing, eliminates runaway positive feedback loops, enables self-stabilizing network operation. In another aspect of the invention, the connection adjustment methodology facilitates robust context switching when processing visual information. When a context (such an object) becomes intermittently absent, prior context connection potentiation enables firing for a period of time. If the object remains absent, the connection becomes depressed thereby preventing further firing.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
ActiveUS8972315B2Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
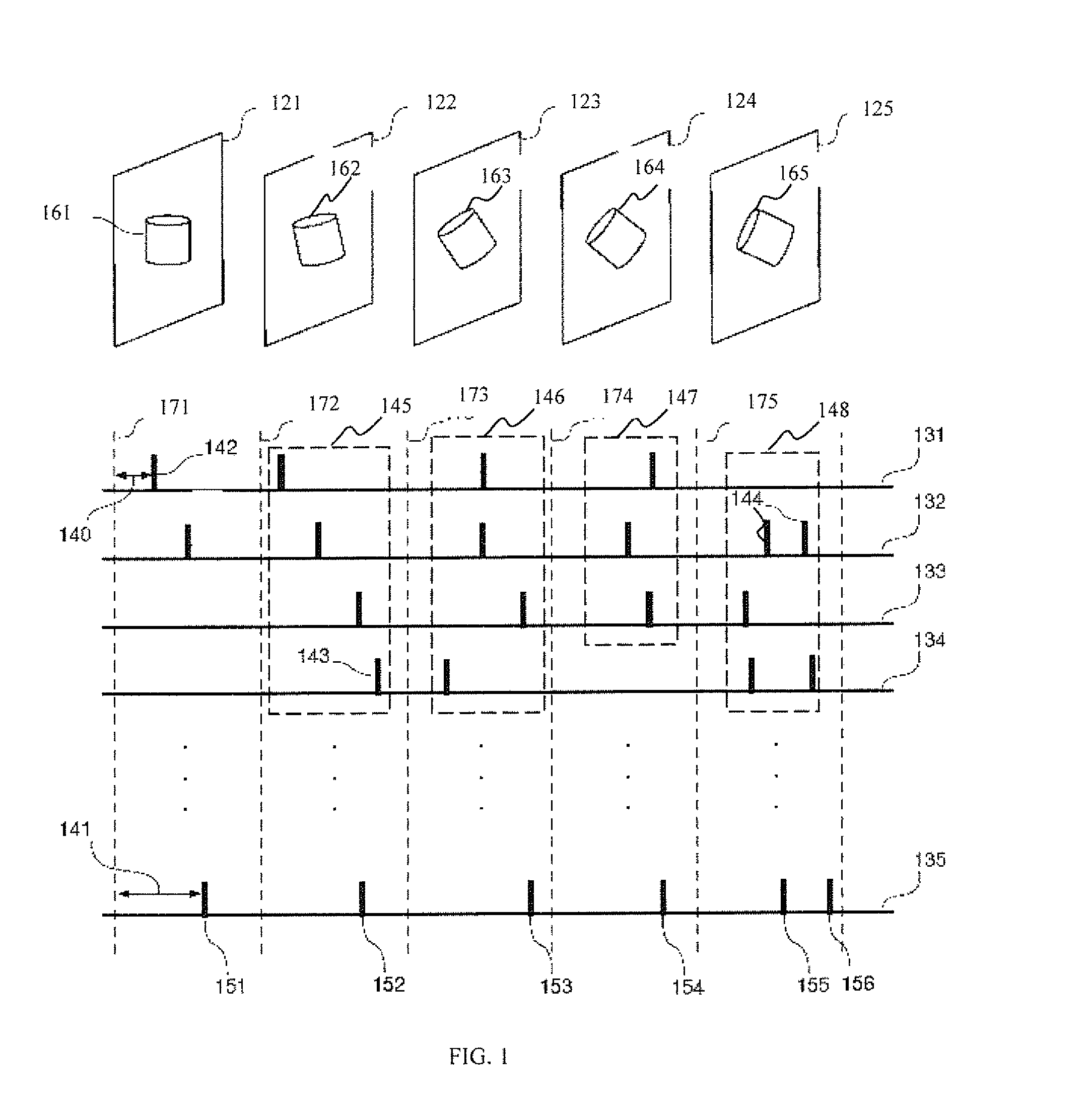
Spiking network apparatus and method with bimodal spike-timing dependent plasticity
ActiveUS20140229411A1Facilitate network normalizationPreventing feedback loopImage enhancementImage analysisNeuron networkBi modal
Apparatus and methods for learning in response to temporally-proximate features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes bi-modal spike timing dependent plasticity in a spiking neuron network. Based on a response by the neuron to a frame of input, the bi-modal plasticity mechanism is used to depress synaptic connections delivering the present input frame and to potentiate synaptic connections delivering previous and / or subsequent frames of input. The depression of near-contemporaneous input prevents the creation of a positive feedback loop and provides a mechanism for network response normalization.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Modulated stochasticity spiking neuron network controller apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9189730B1Lower Level RequirementsDiminished rate of learningNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNeuron networkNeural network controller
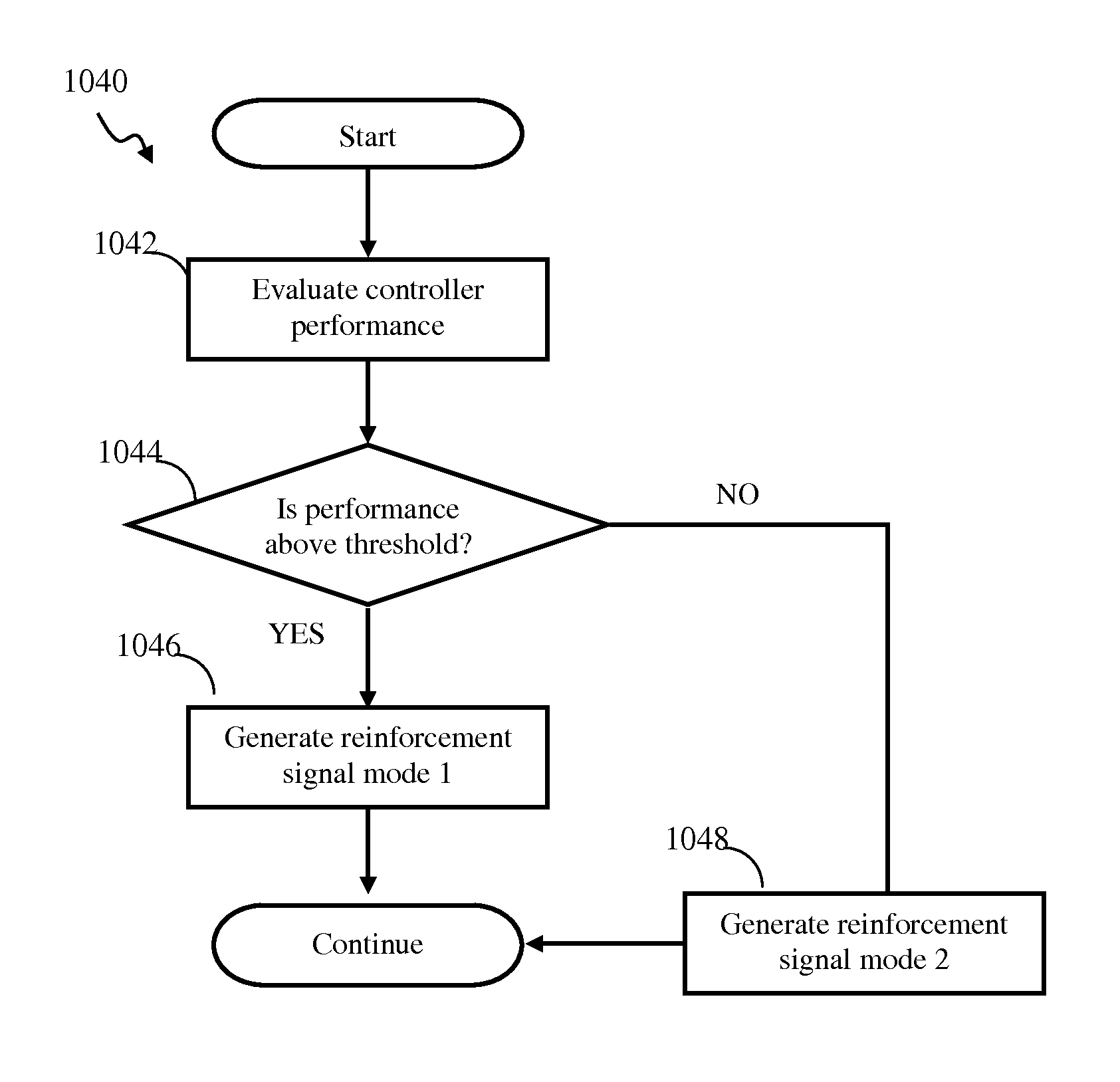
Adaptive controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block and a control block. The encoder may utilize basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. The relevant features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome. The stochasticity of the learning process may be modulated. Stochasticity may be increased during initial stage of learning in order to encourage exploration. During subsequent controller operation, stochasticity may be reduced to reduce energy use by the controller.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Contrast enhancement spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140193066A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Temporal winner takes all spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9070039B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. An inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Intelligent modular robotic apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140019392A1Increased compact structureHigh densityDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNegative feedbackBiological body
Apparatus and methods for an extensible robotic device with artificial intelligence and receptive to training controls. In one implementation, a modular robotic system that allows a user to fully select the architecture and capability set of their robotic device is disclosed. The user may add / remove modules as their respective functions are required / obviated. In addition, the artificial intelligence is based on a neuronal network (e.g., spiking neural network), and a behavioral control structure that allows a user to train a robotic device in manner conceptually similar to the mode in which one goes about training a domesticated animal such as a dog or cat (e.g., a positive / negative feedback training paradigm) is used. The trainable behavior control structure is based on the artificial neural network, which simulates the neural / synaptic activity of the brain of a living organism.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:PONULAK FILIP
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
ActiveUS20140122399A1Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Spatio-temporal pattern recognition using a spiking neural network and processing thereof on a portable and/or distributed computer
ActiveUS8346692B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSynaptic weightSpiking neural network
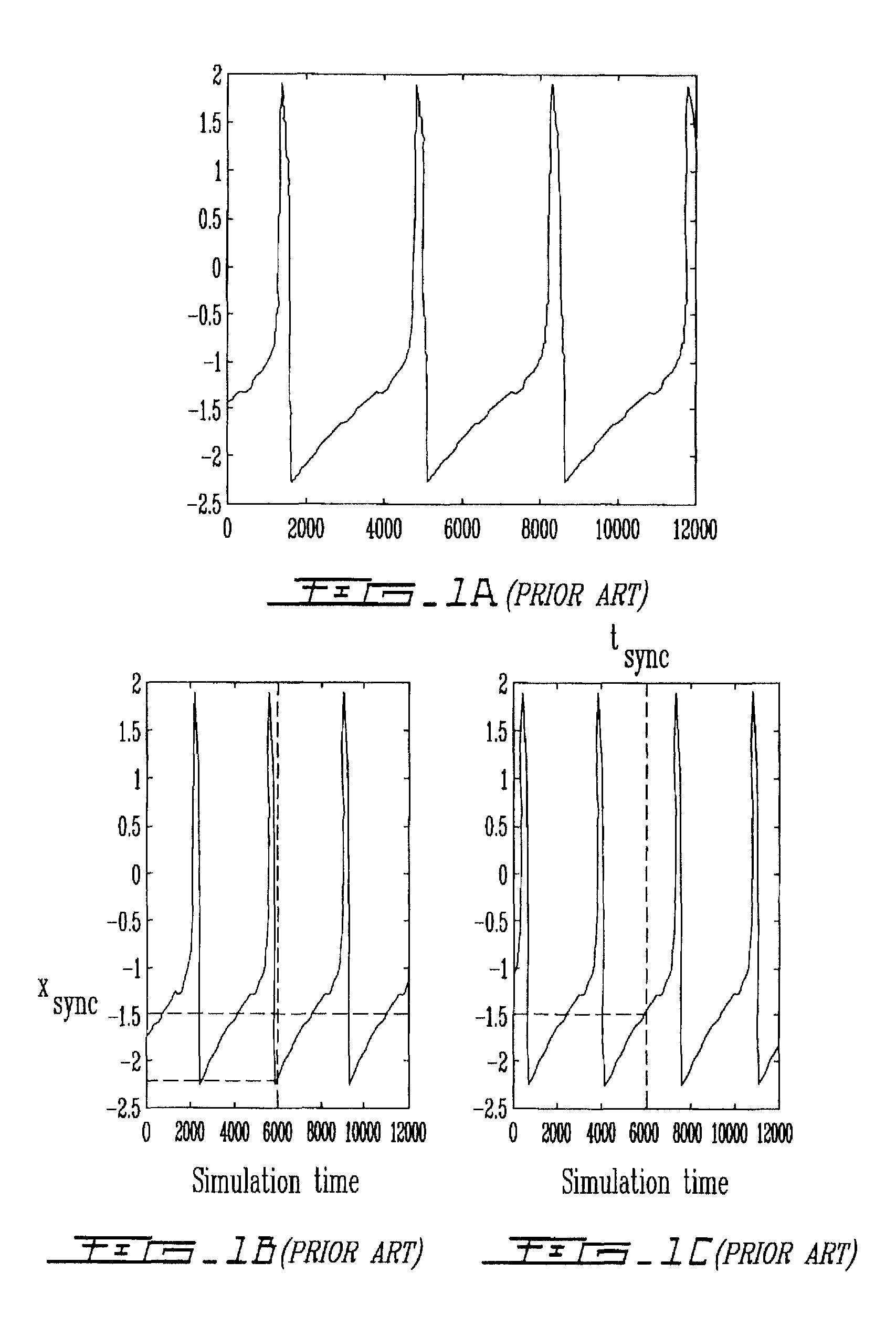
A spiking neural network has a layer of connected neurons exchanging signals. Each neuron is connected to at least one other neuron. A neuron is active if it spikes at least once during a time interval. Time-varying synaptic weights are computed between each neuron and at least one other neuron connected thereto. These weights are computed according to a number of active neurons that are connected to the neuron. The weights are also computed according to an activity of the spiking neural network during the time interval. Spiking of each neuron is synchronized according to a number of active neurons connected to the neuron and according to the weights. A pattern is submitted to the spiking neural network for generating sequences of spikes, which are modulated over time by the spiking synchronization. The pattern is characterized according to the sequences of spikes generated in the spiking neural network.
Owner:ROUAT JEAN +2
System for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal
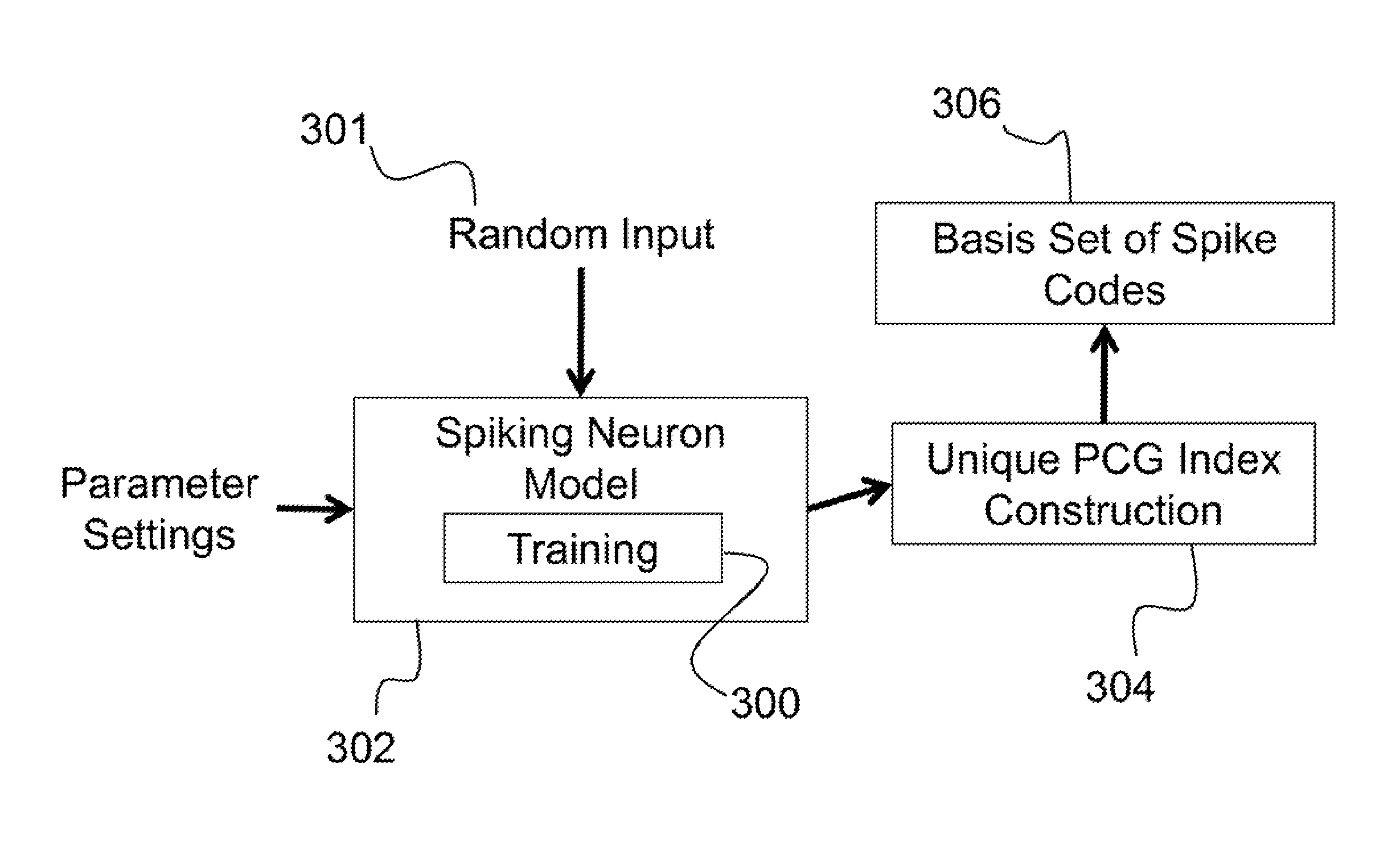
Described is a system for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal. The system constructs an index of unique polychronous groups (PCGs) from a spiking neuron network. Thereafter, a basis set of spike codes is generated from the unique PCGs. An input signal can then be received, with the input signal being spike encoded using the basis set of spike codes from the unique PCGs. The input signal can then be reconstructed by looking up in a reconstruction table, for each unique PCG in the basis set in temporal order according to firing times, anchor neurons. Using a neuron assignment table, an output location can be looked up for each anchor neuron to place a value based on the firing times of each unique PCG. Finally, the output locations of the anchor neurons can be compiled to reconstruct the input signal.
Owner:HRL LAB
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS8977582B2Reduce image dataDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionNeuron network
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
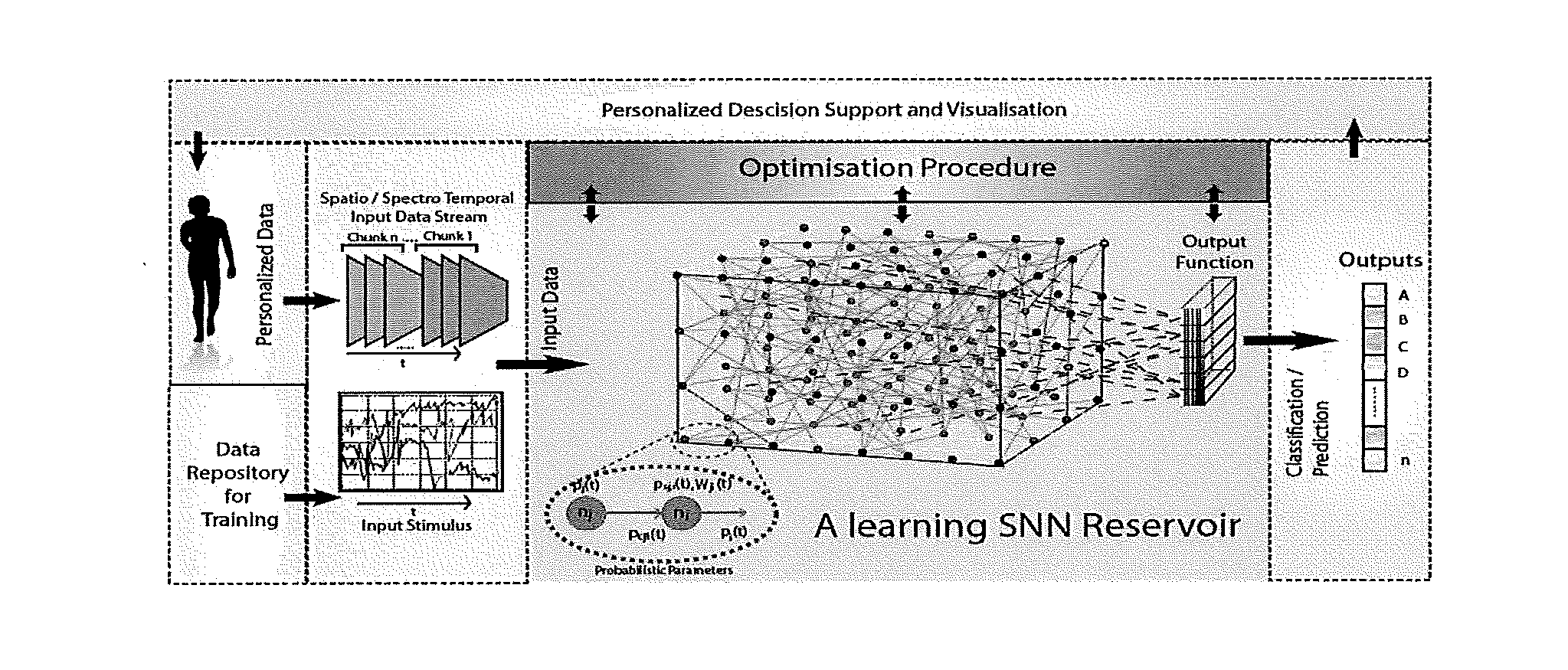
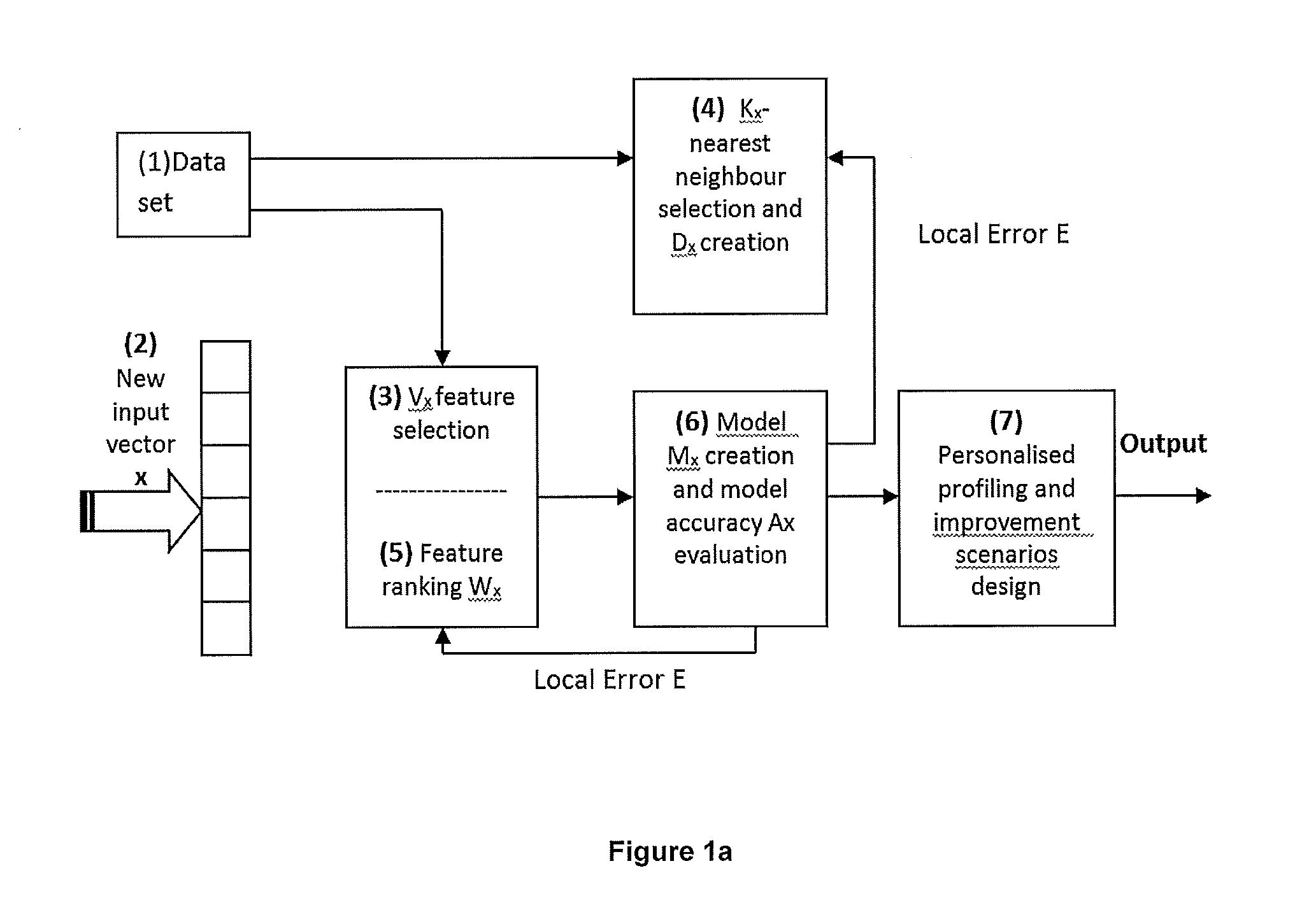
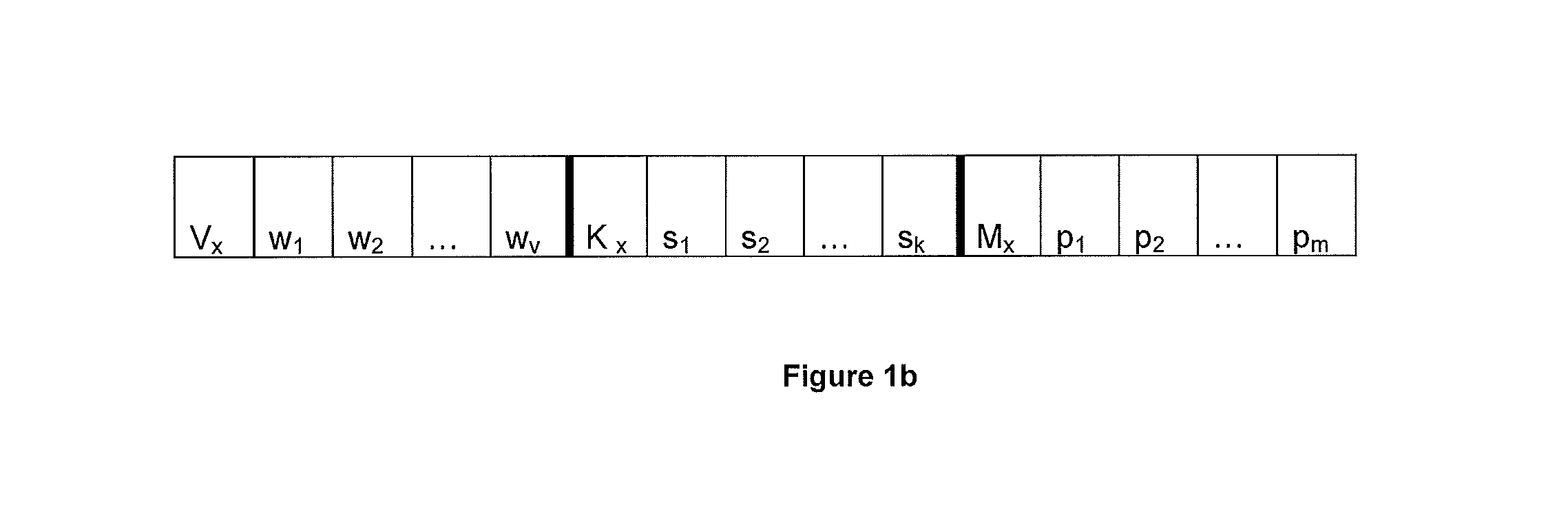
Improved Method And System For Predicting Outcomes Based On Spatio/Spectro-Temporal Data
ActiveUS20160210552A1Improve accuracyShorten the timeDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpike trainSpatiotemporal pattern
This invention involves use of temporal or spatio / spector-temporal data (SSTD) for early classification of outputs that are results of spatio-temporal patterns of data. Classification models are based on spiking neural networks (SNN) suitable to learn and classify SSTD. The invention may predict early events in many applications, i.e. engineering, bioinformatics, neuroinformatics, predicting response to treatment of neurological and brain disease, ecology, environment, medicine, and economics, among others. The invention involves a method and system for personalized modelling of SSTD and early prediction of events based on evolving spiking neural network reservoir architecture (eSNNr). The system includes a spike-time encoding module to encode continuous value input information into spike trains, a recurrent 3D SNNr and an eSSN as an output classification module.
Owner:AUT VENTURES LTD
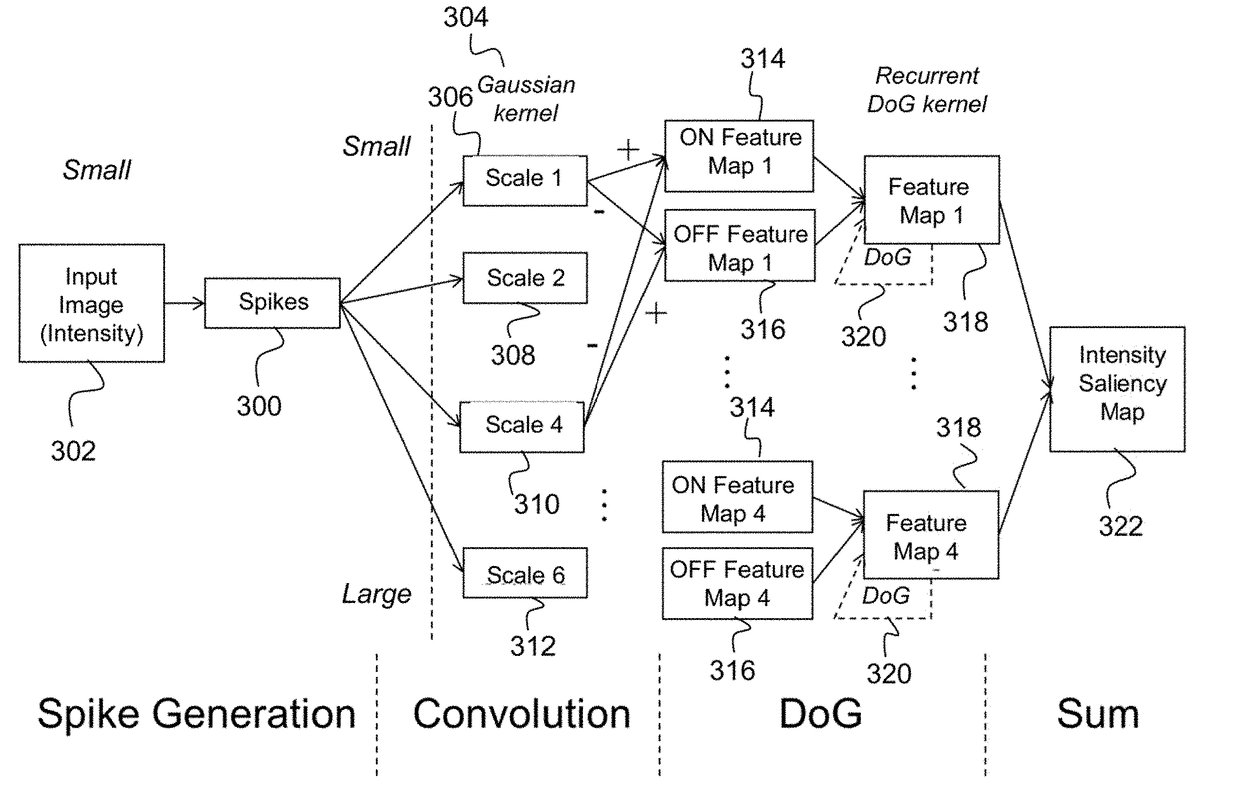
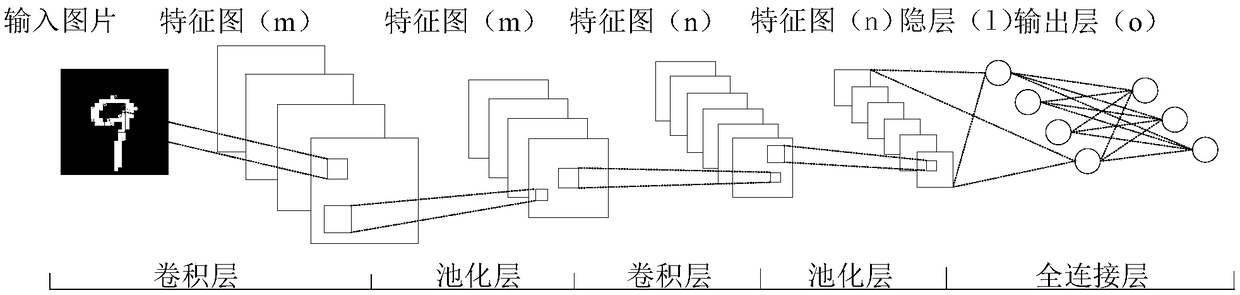
Method for object detection in digital image and video using spiking neural networks
ActiveUS20170300788A1Increasing spike activityReducing spike activityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSaliency mapSpiking neural network
Described is a system for object detection in images or videos using spiking neural networks. An intensity saliency map is generated from an intensity of an input image having color components using a spiking neural network. Additionally, a color saliency map is generated from a plurality of colors in the input image using a spiking neural network. An object detection model is generated by combining the intensity saliency map and multiple color saliency maps. The object detection model is used to detect multiple objects of interest in the input image.
Owner:HRL LAB
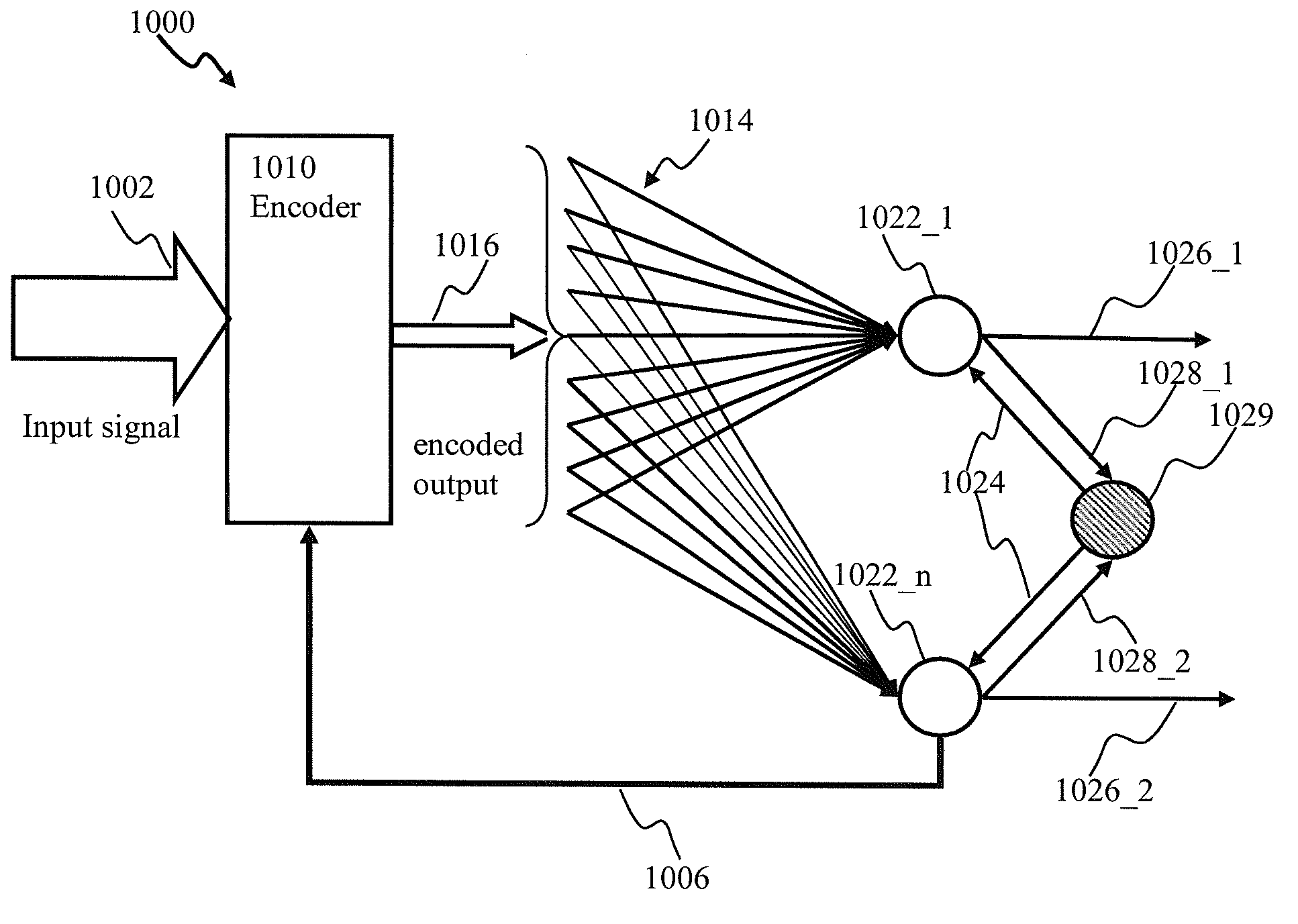
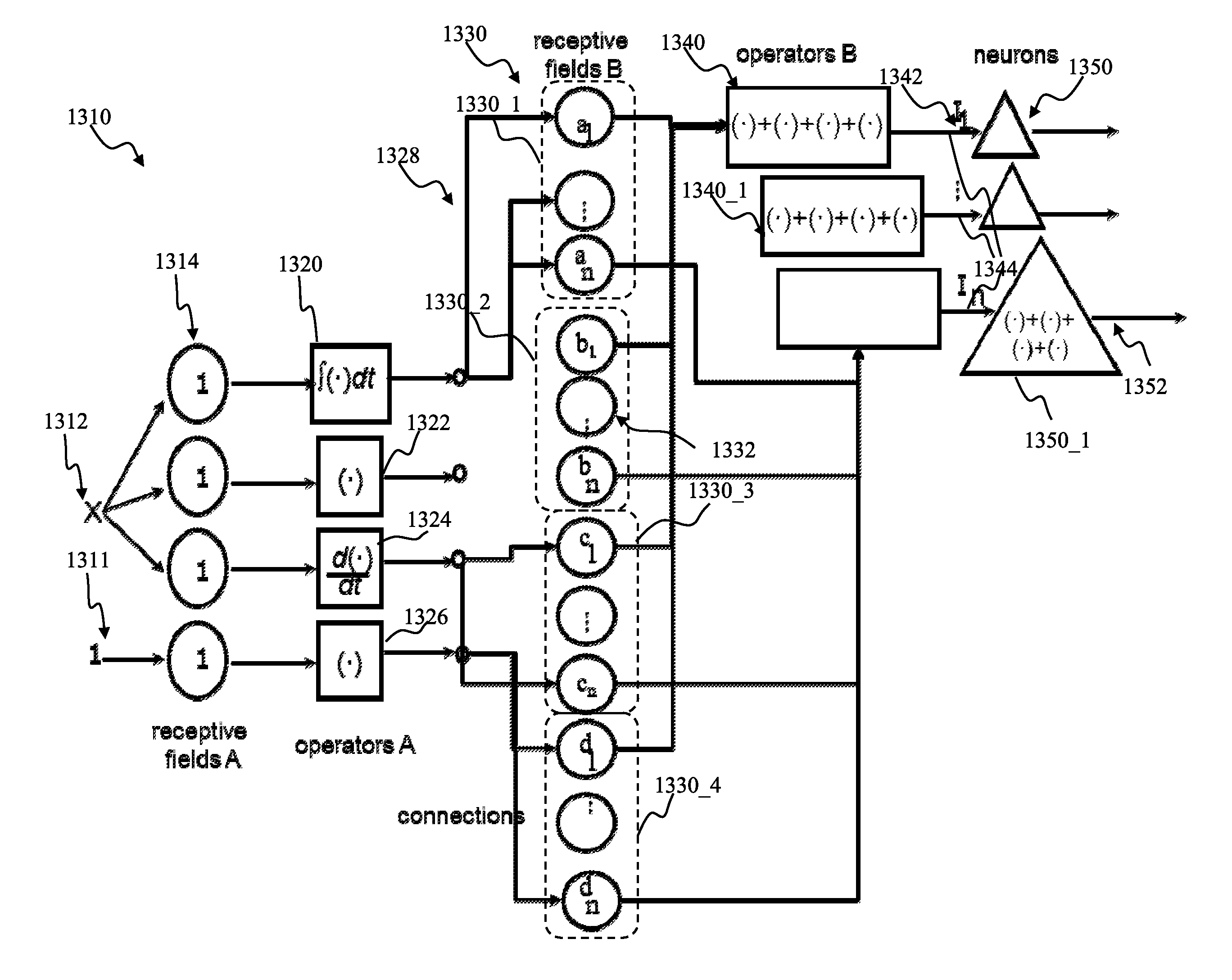
Proportional-integral-derivative controller effecting expansion kernels comprising a plurality of spiking neurons associated with a plurality of receptive fields
ActiveUS9082079B1Improve connection efficiencyEasy to measureDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuron networkControl engineering
Adaptive proportional-integral-derivative controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block utilizing basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The basis function kernel may comprise one or more operators configured to manipulate basis components. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. Features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Temporal winner takes all spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140219497A1Suppress generationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. An inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Elementary network description for efficient memory management in neuromorphic systems
A simple format is disclosed and referred to as Elementary Network Description (END). The format can fully describe a large-scale neuronal model and embodiments of software or hardware engines to simulate such a model efficiently. The architecture of such neuromorphic engines is optimal for high-performance parallel processing of spiking networks with spike-timing dependent plasticity. Methods for managing memory in a processing system are described whereby memory can be allocated among a plurality of elements and rules configured for each element such that the parallel execution of the spiking networks is most optimal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
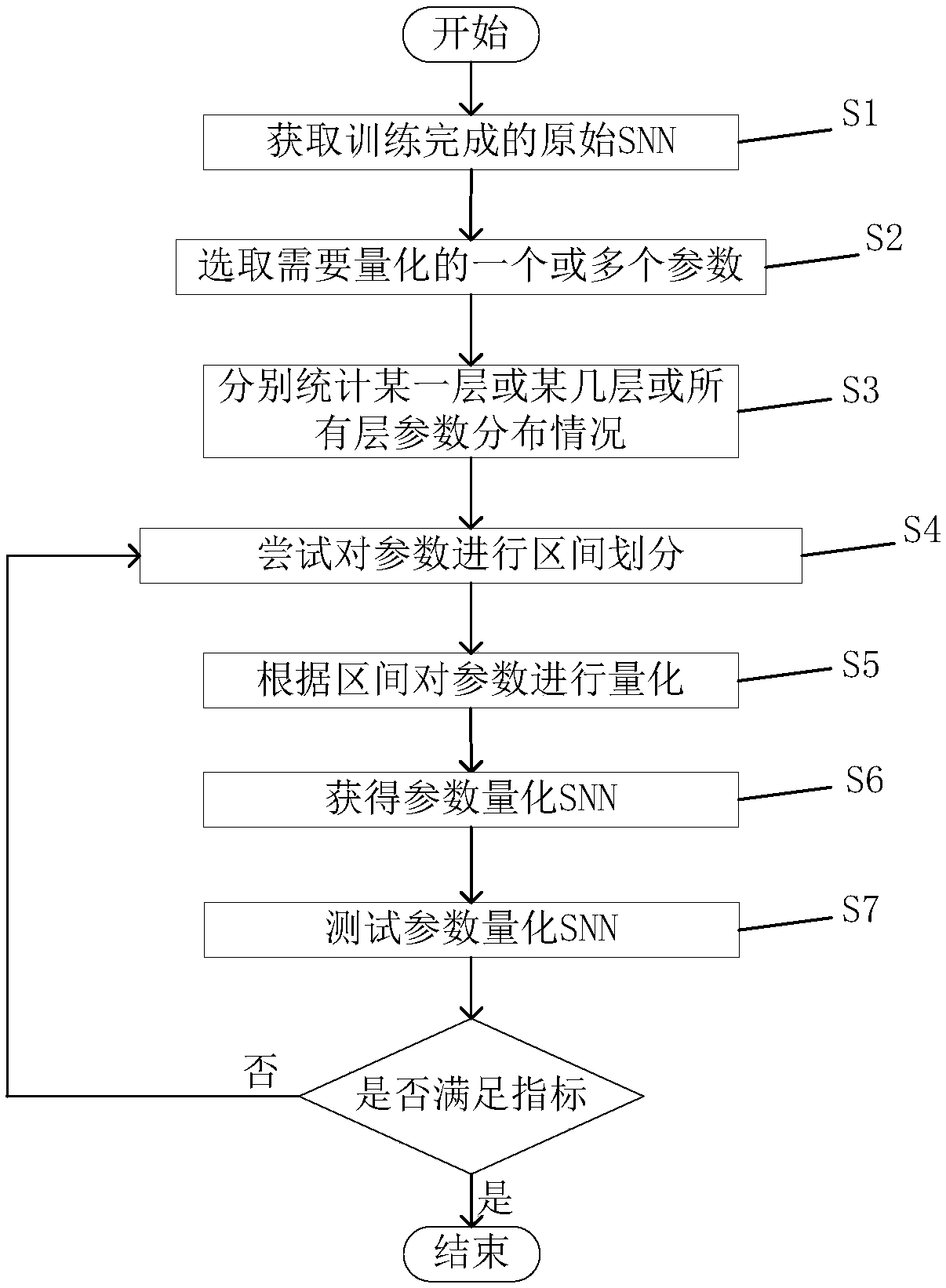
Parameter quantization method of spiking neural network (SNN)
InactiveCN108717570ARealize parameter quantizationPerformance is not affectedPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionNerve network
The invention relates to the field of neural network technology, and particularly to a parameter quantization method of a spiking neural network (SNN). According to the method of the invention, the original spiking neural network of which training is completed is obtained through offline mapping or online training, parameters of weights, thresholds, leakage constants, set voltage, refractory periods, synaptic delay and the like of the spiking neural network of which training is completed are quantified, and all layers of the neural network can share the same set of quantified parameters or each layer respectively has one set of quantified parameters. The spiking neural network after parameter quantization requires only a small number of parameters for realizing high-precision spiking-neural-network functions. According to the method, parameter storage space of the spiking neural network is effectively saved while high precision is maintained, operation speed is improved, and operationpower consumption is lowered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com