Patents
Literature
394 results about "Neuron network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
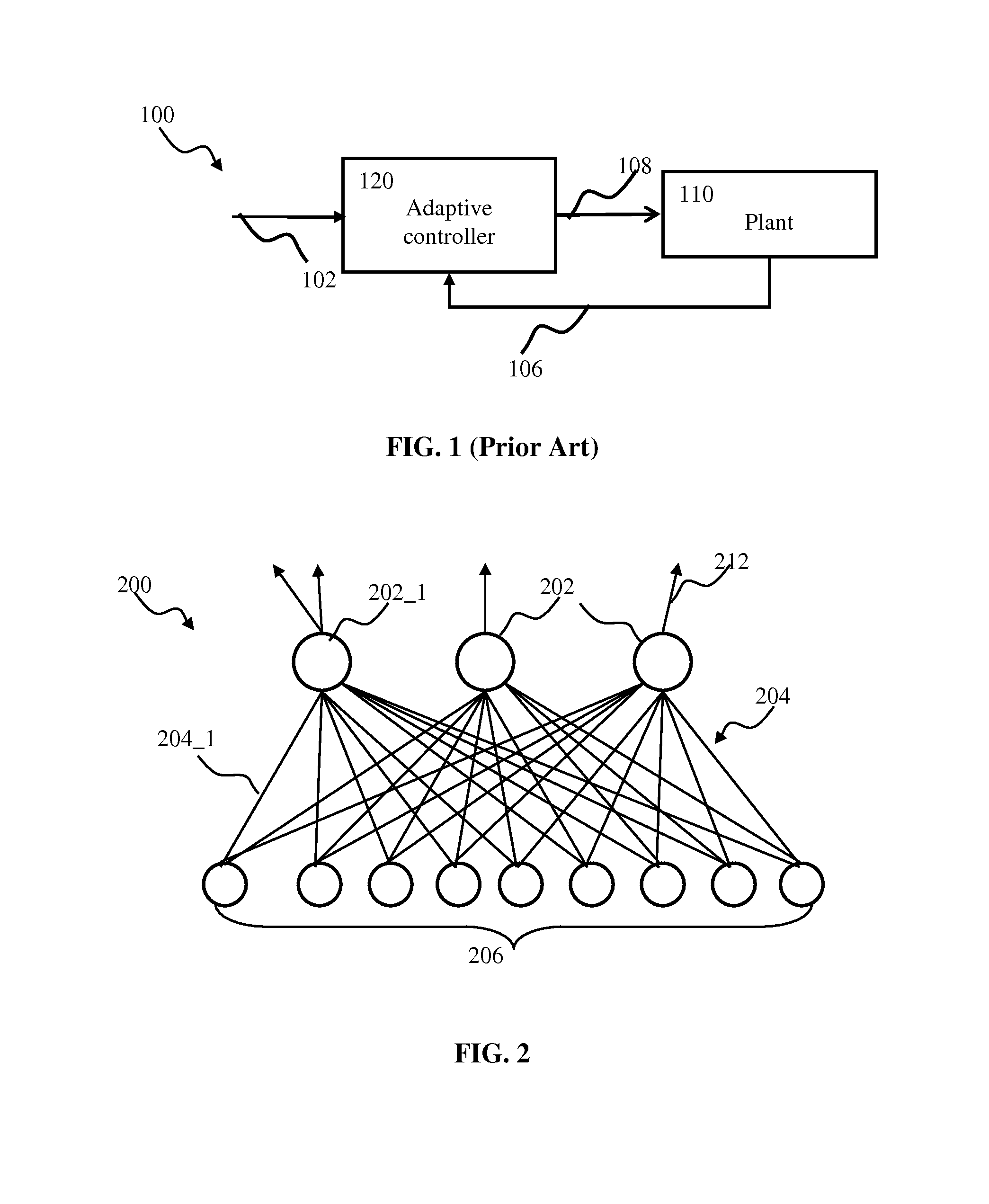
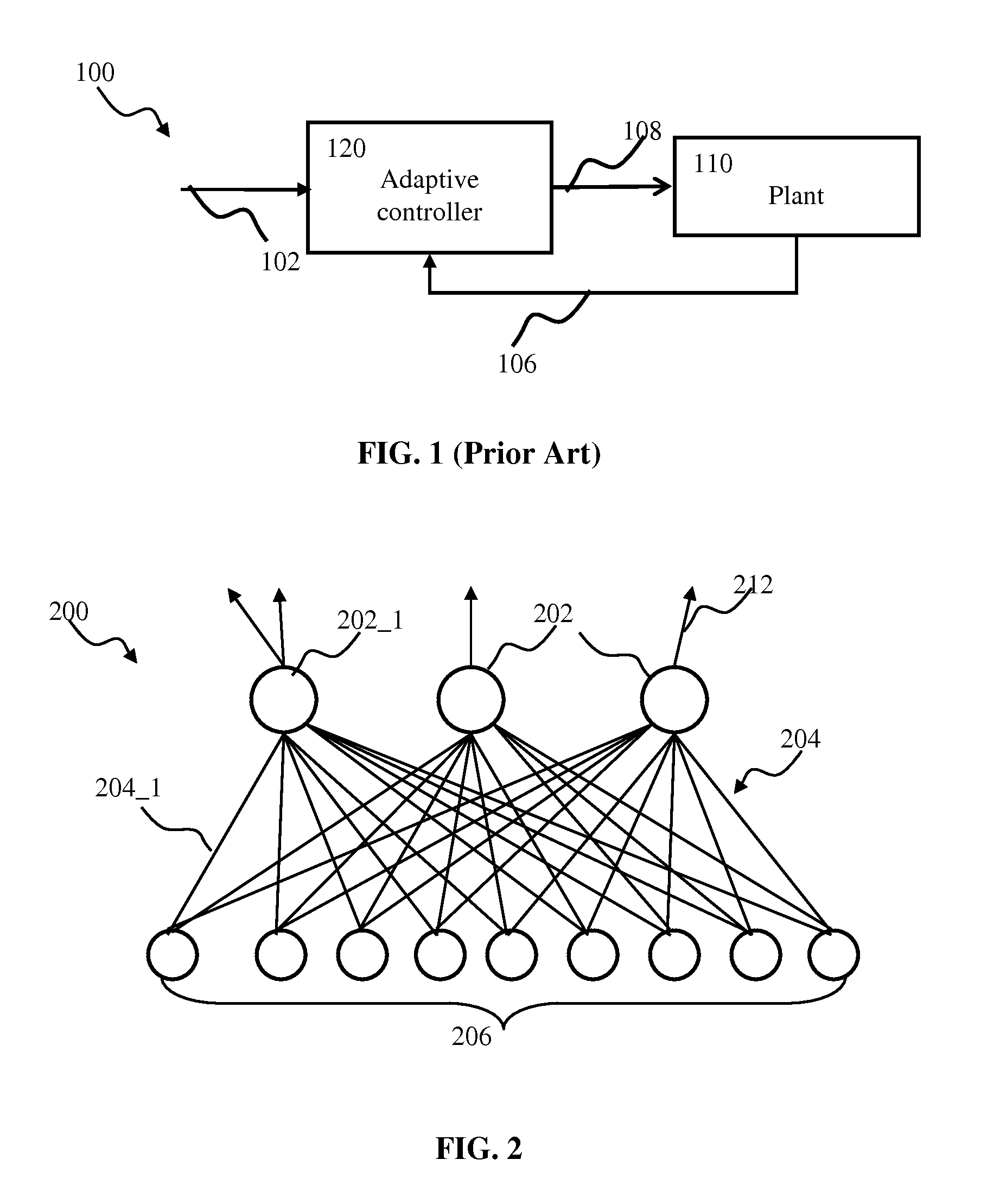
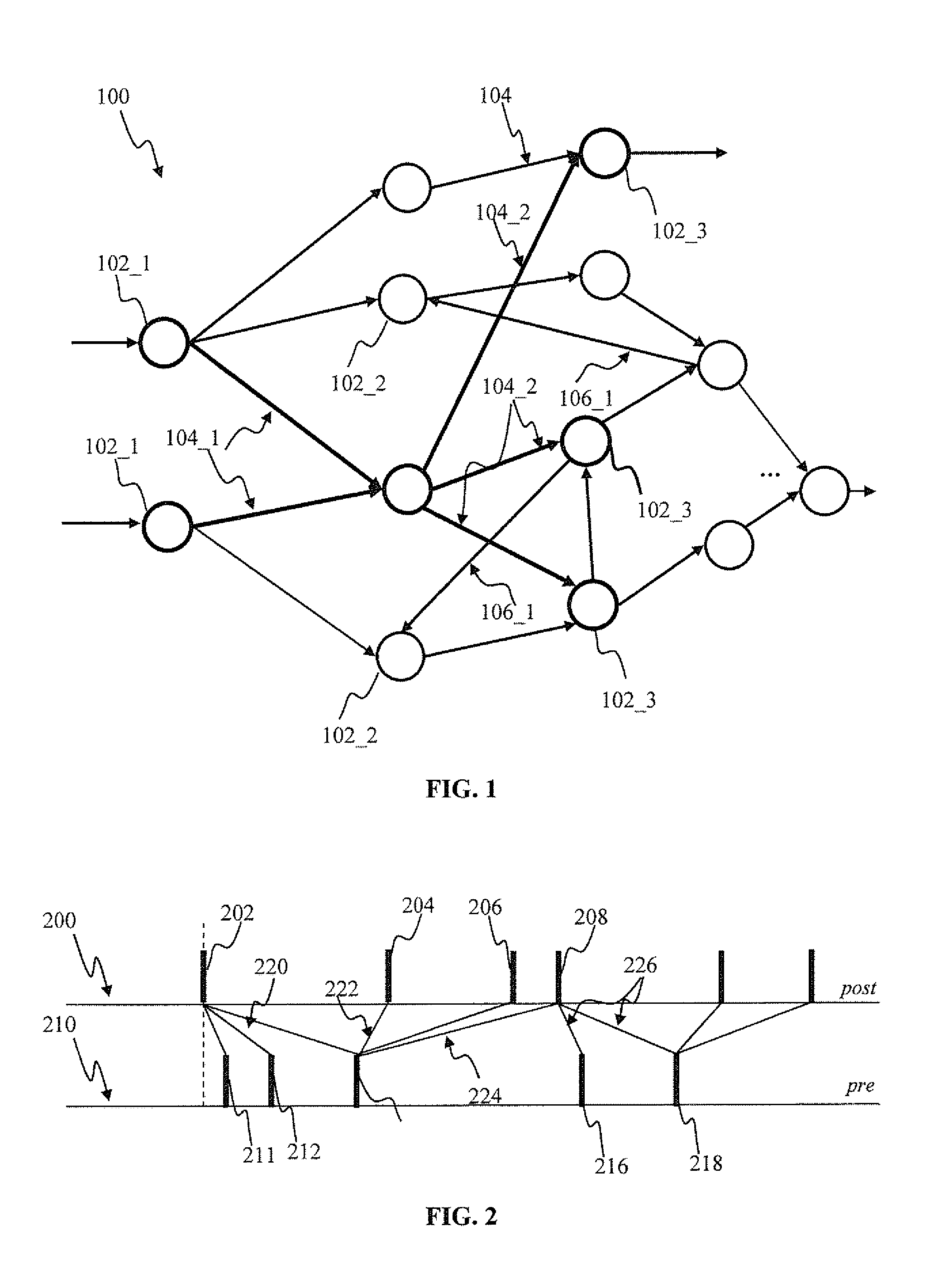
Neural network. A neural network is a computing paradigm that is loosely modeled after cortical structures of the brain. It consists of interconnected processing elements called neurons that work together to produce an output function. The output of a neural network relies on the cooperation of the individual neurons within the network to operate.
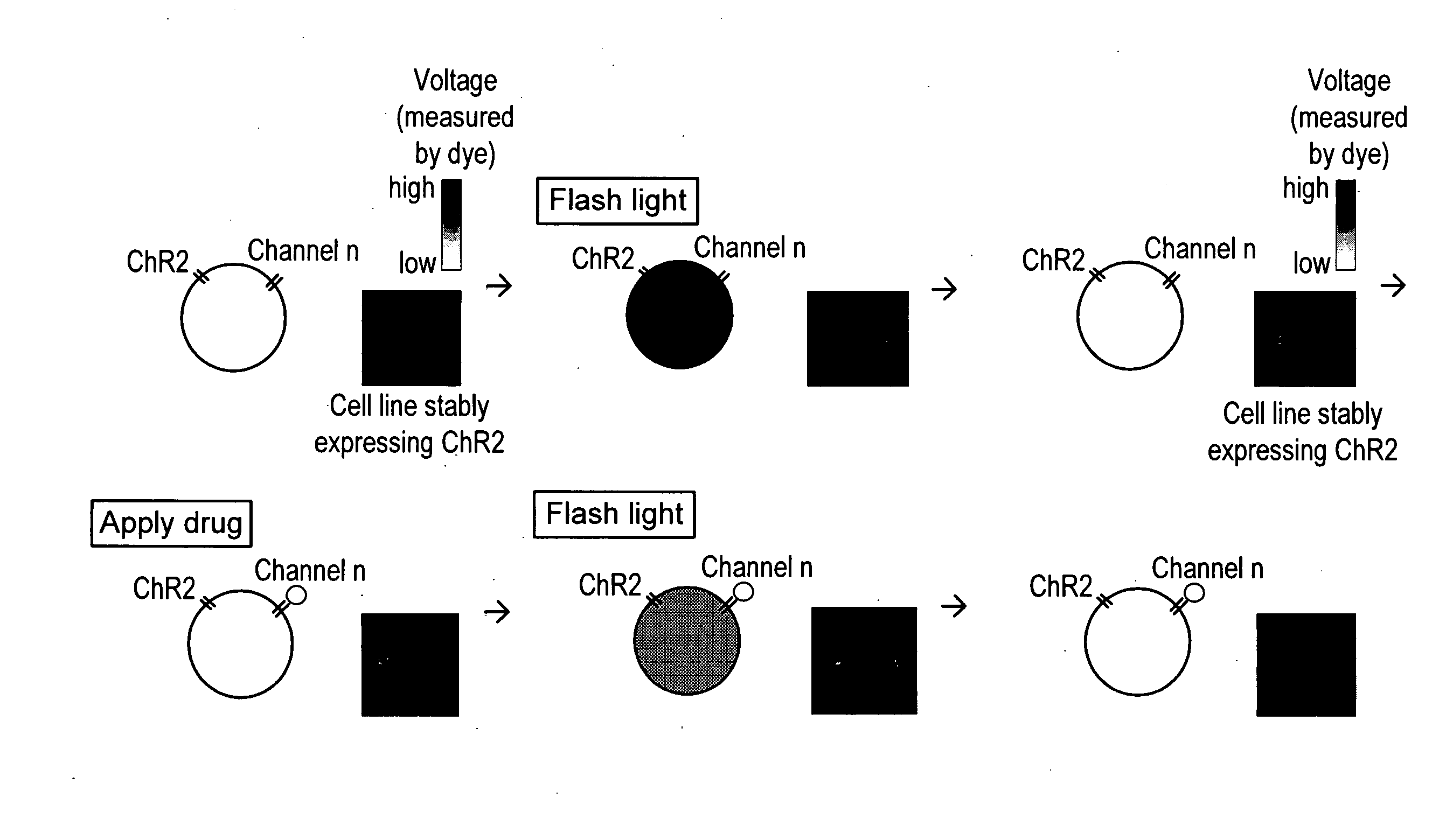
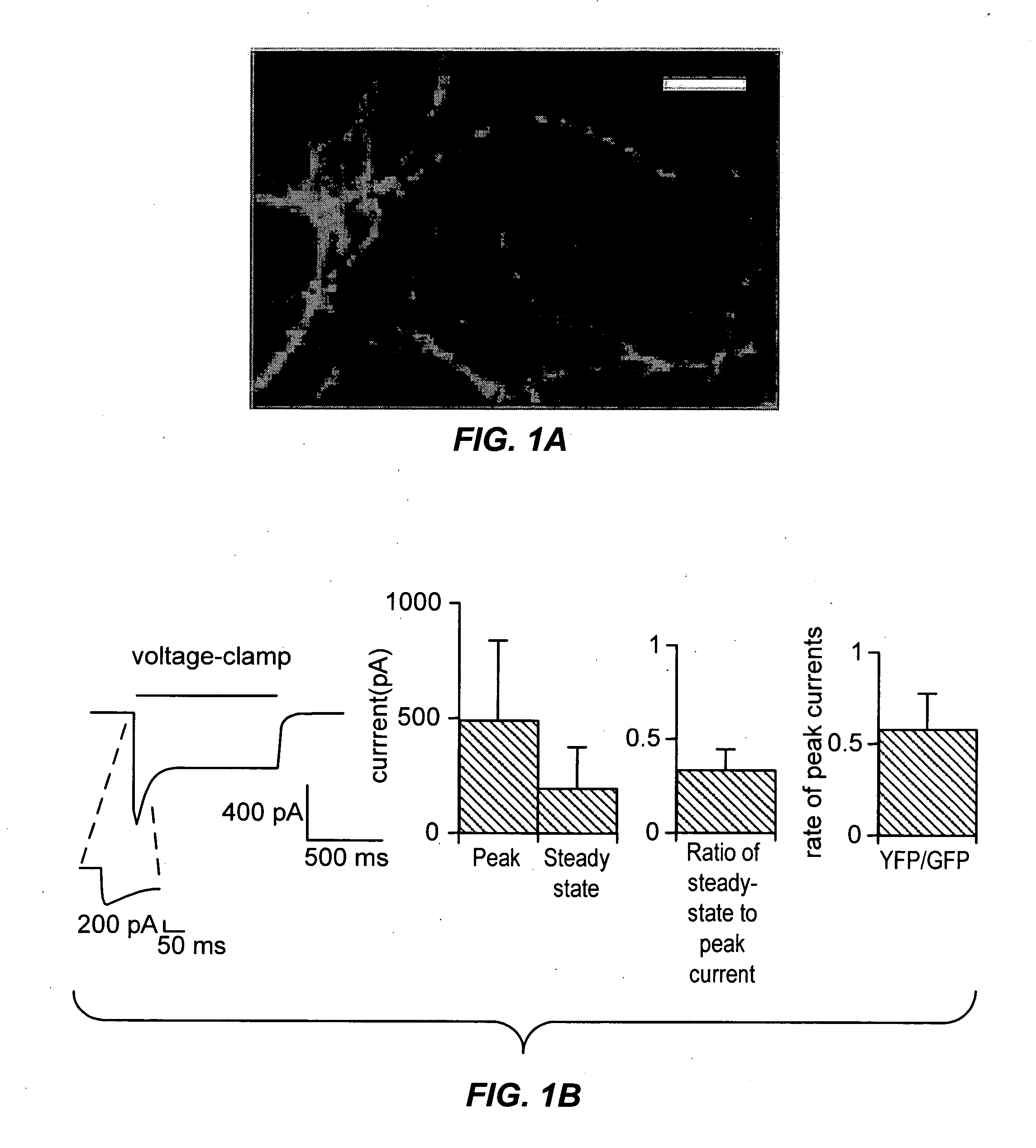
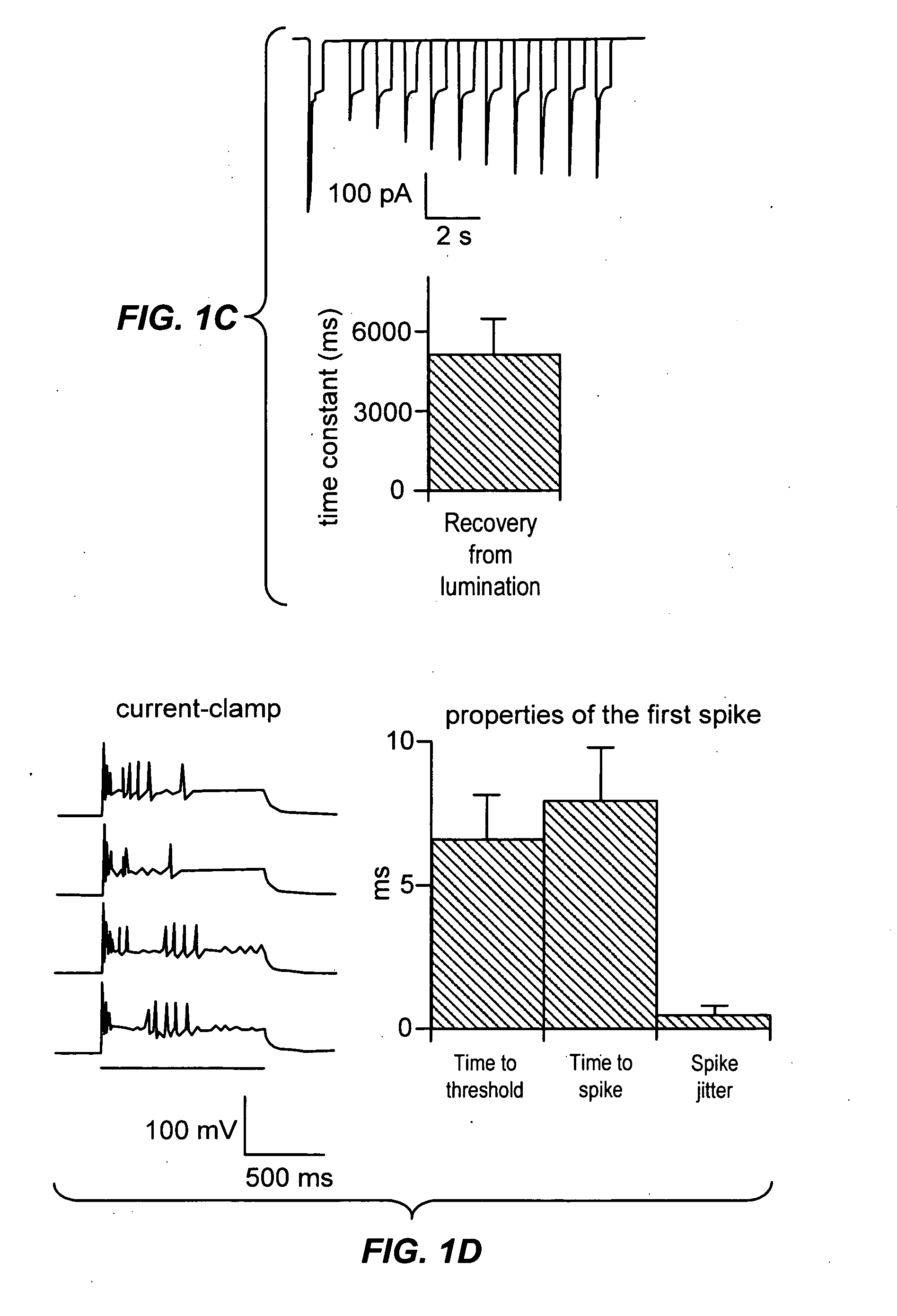
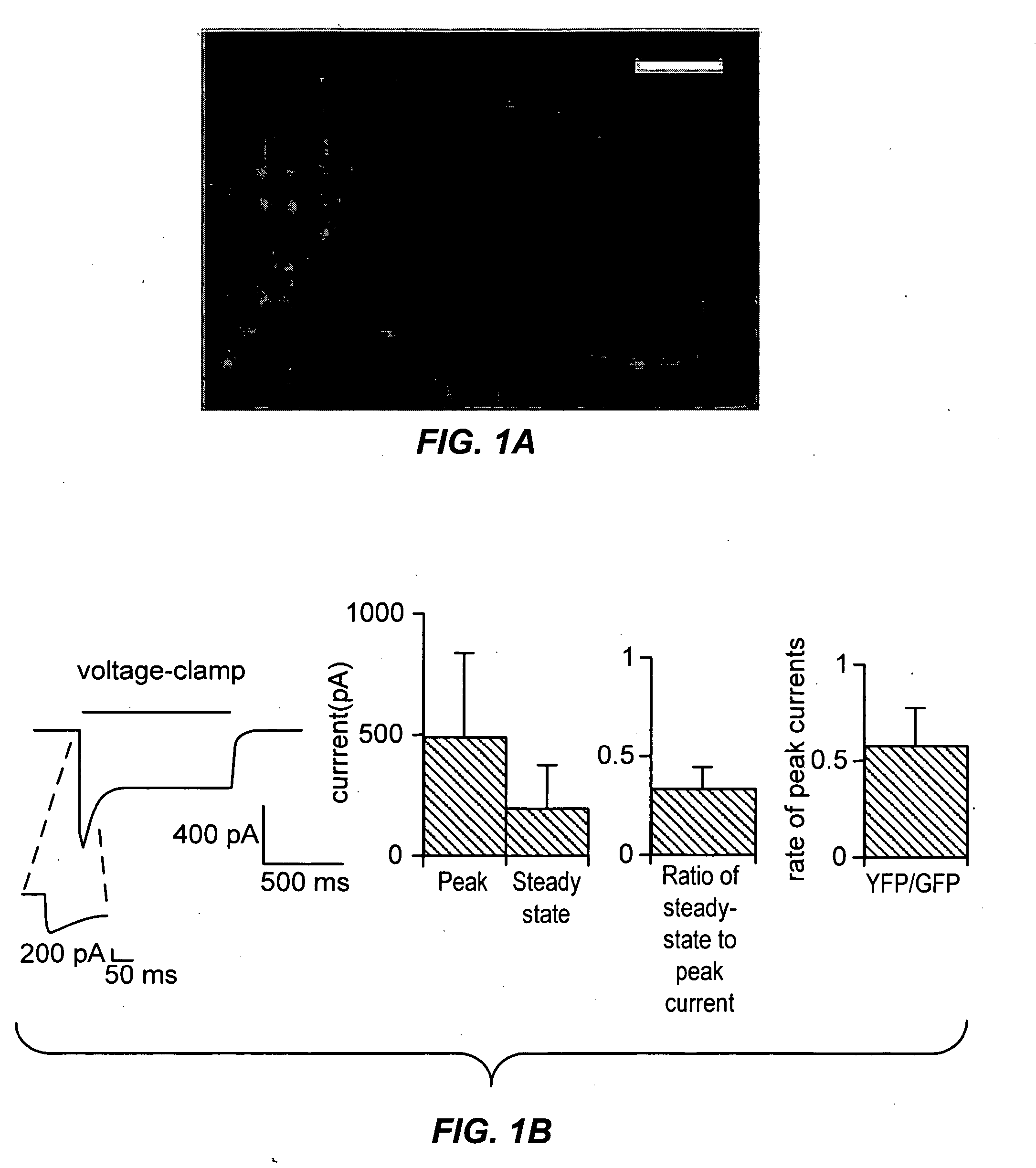
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
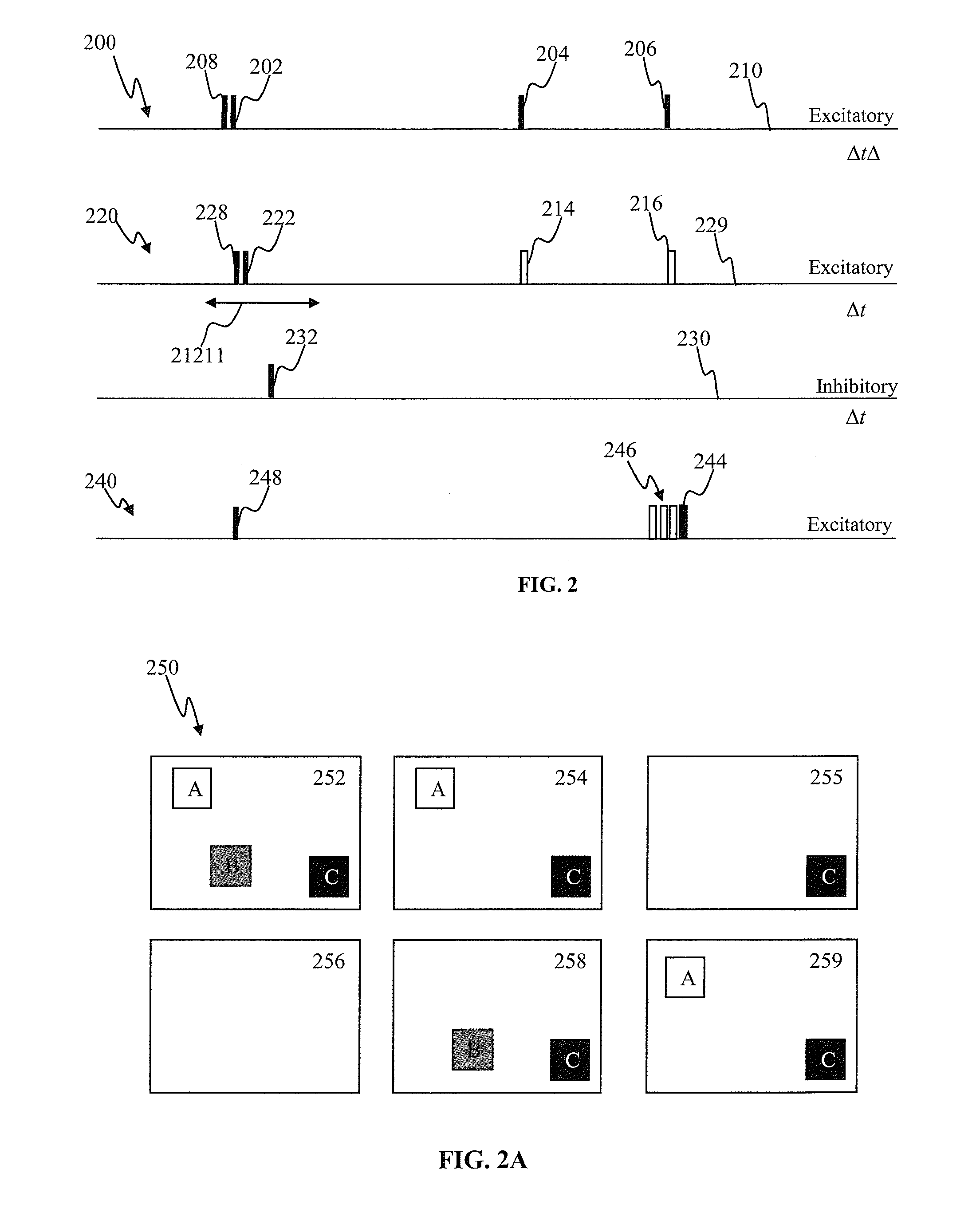
ActiveUS20070261127A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
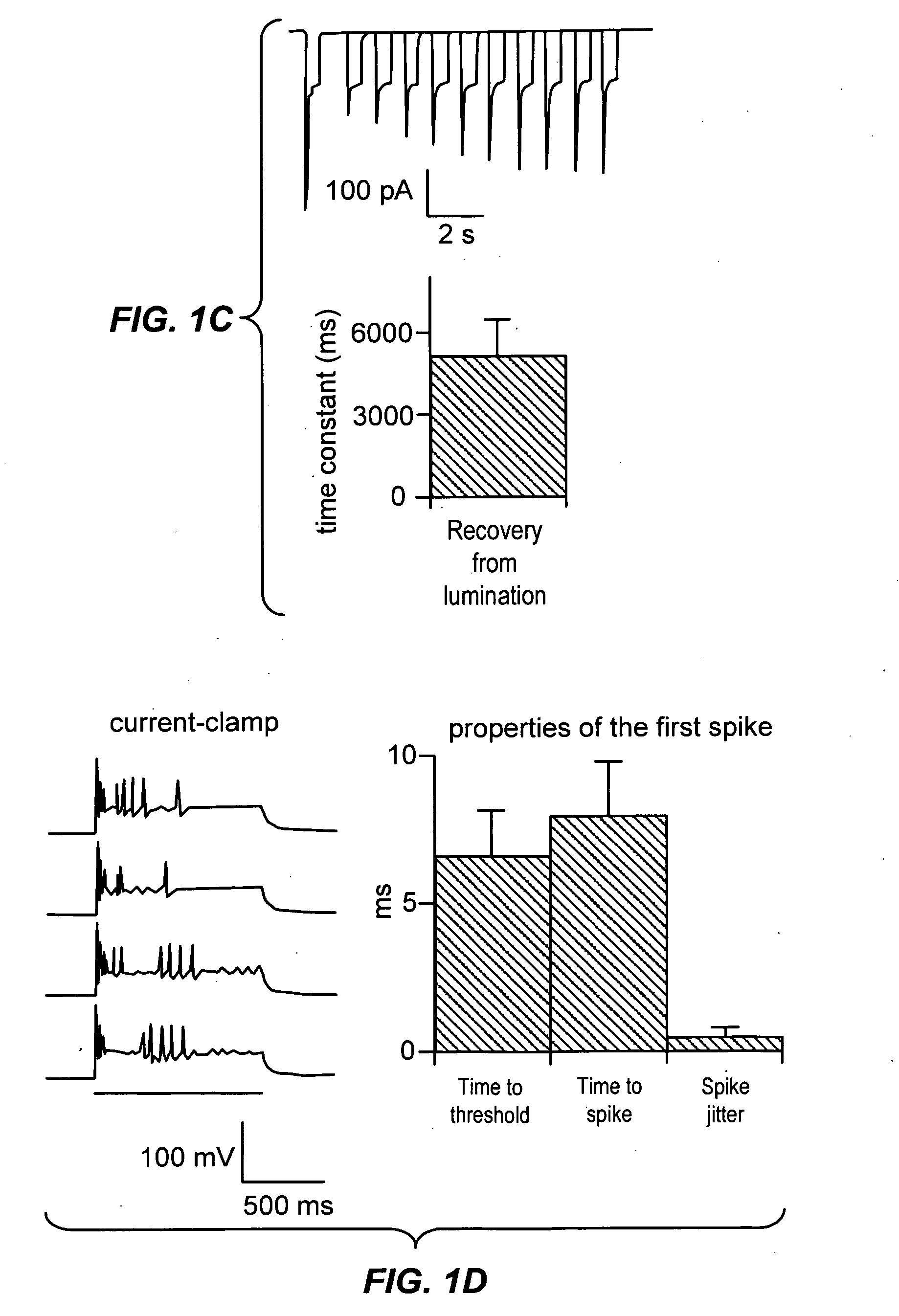
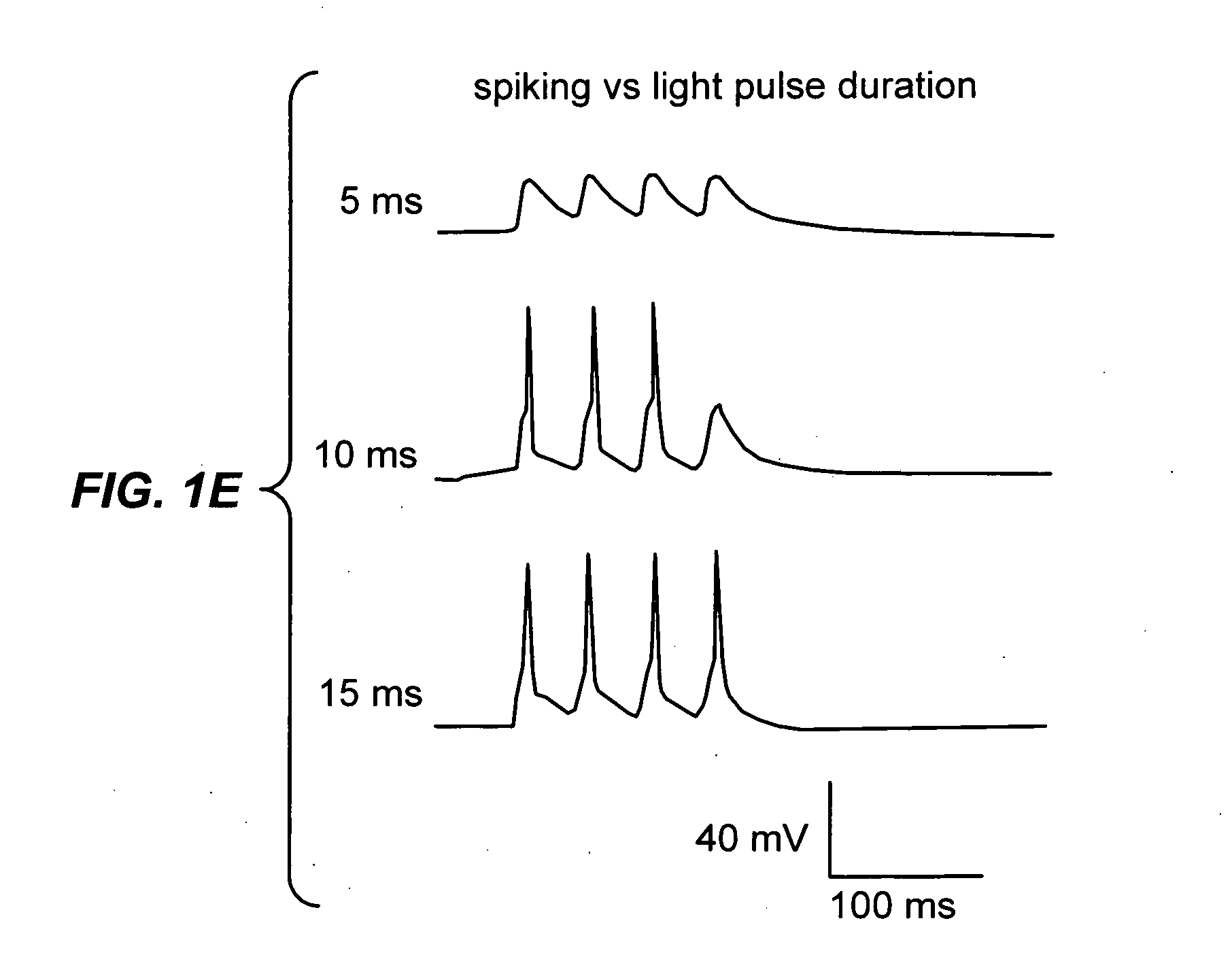
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070054319A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
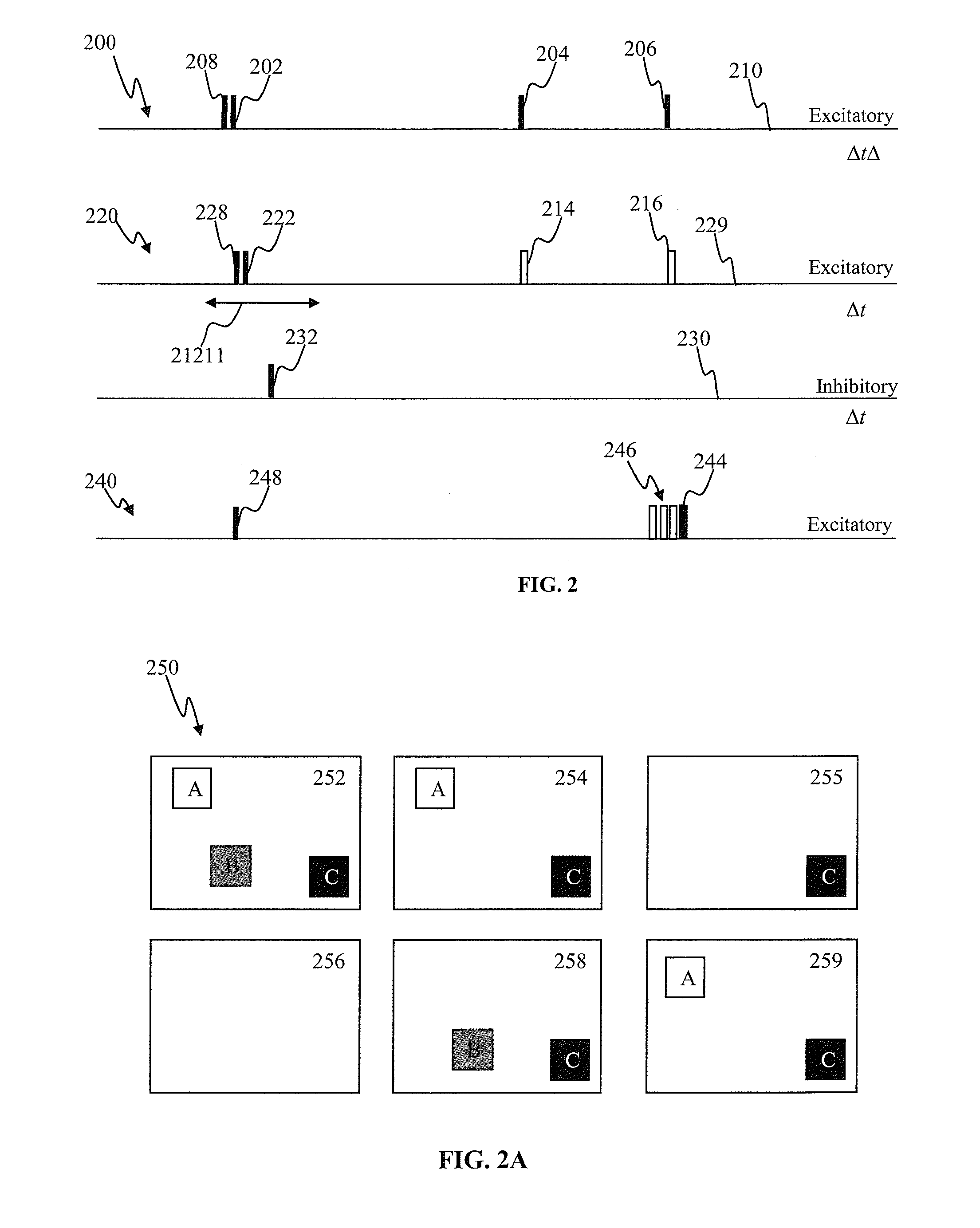
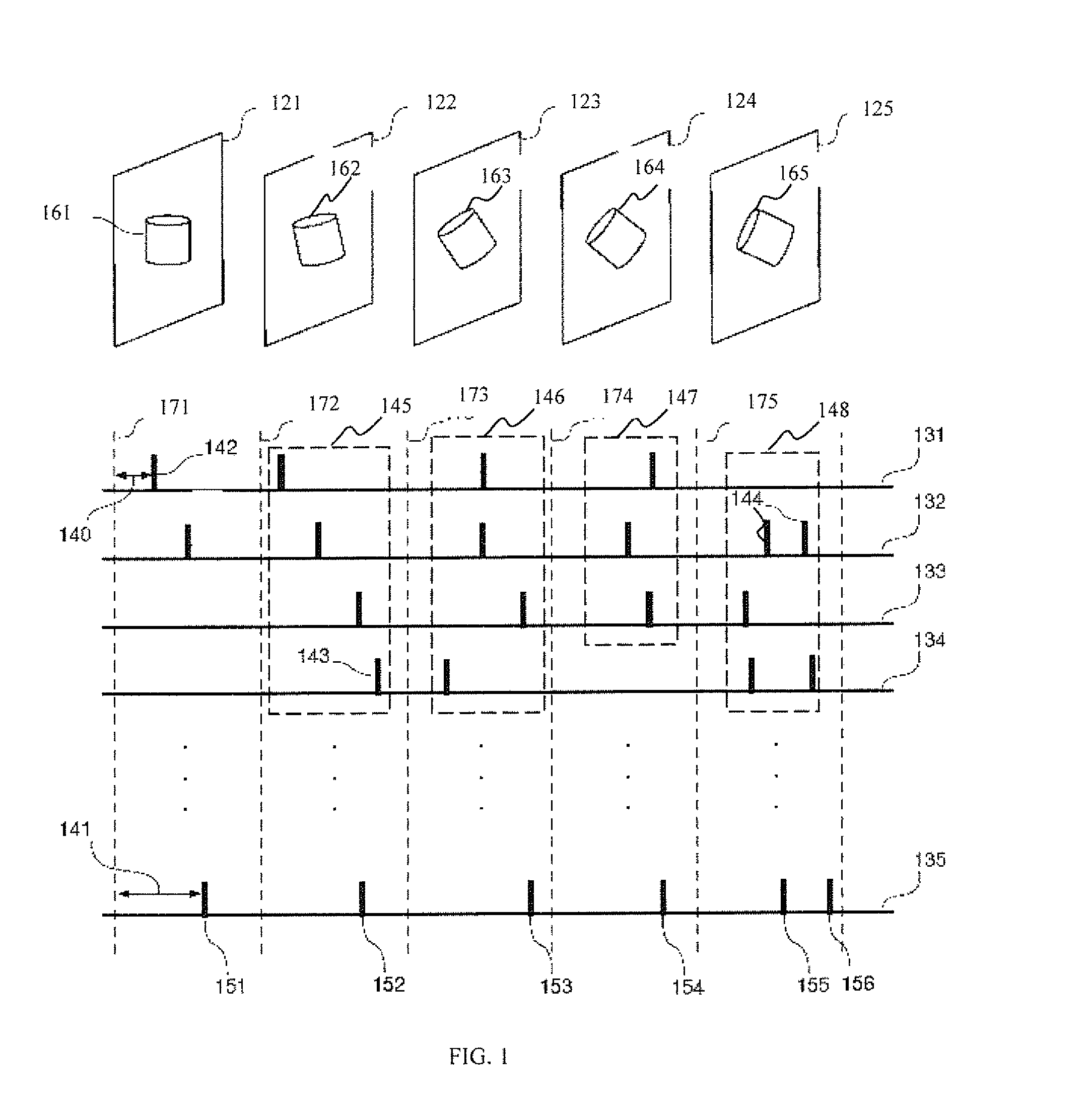
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140016858A1Reduce image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionNeuron network
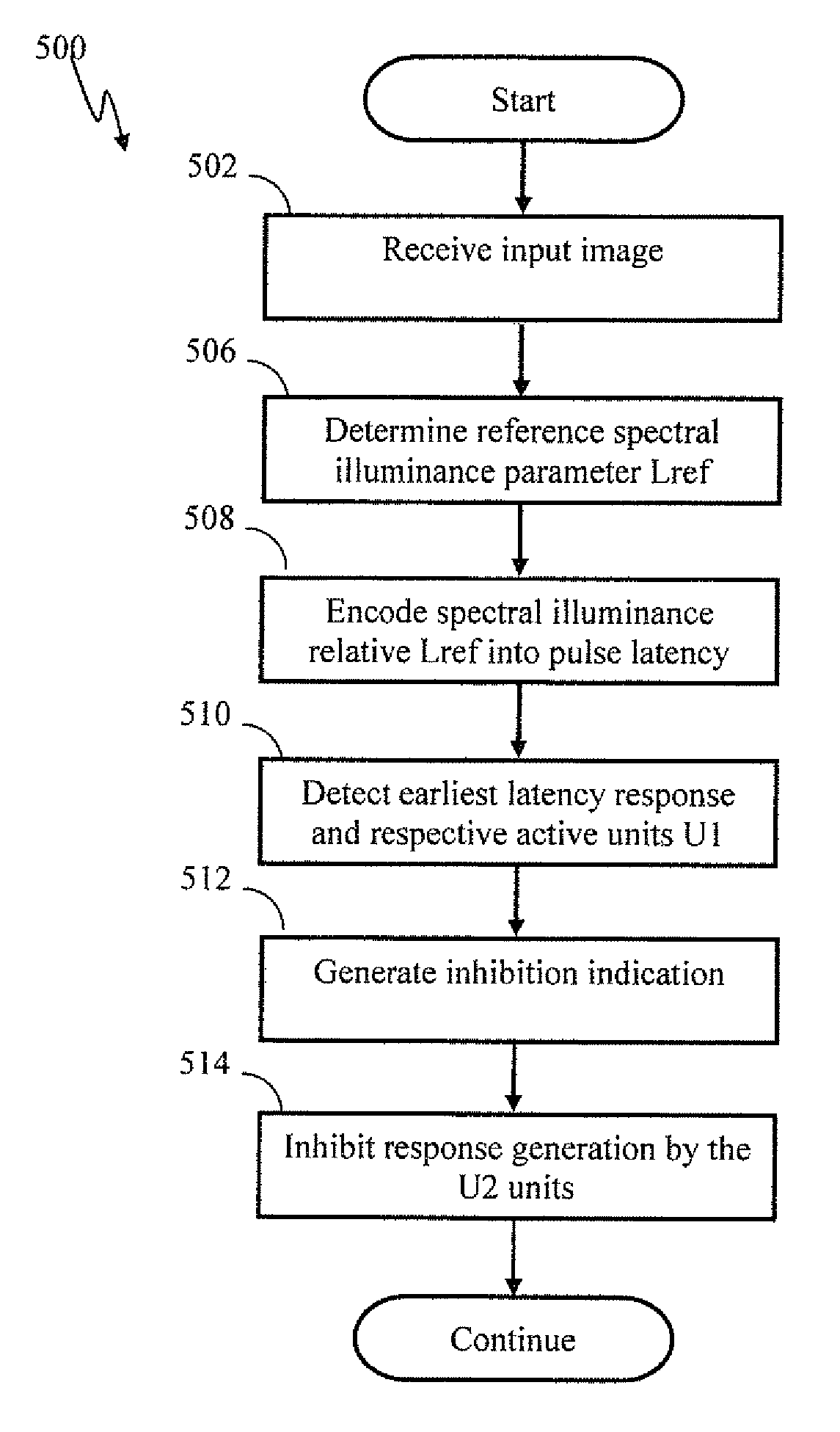
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
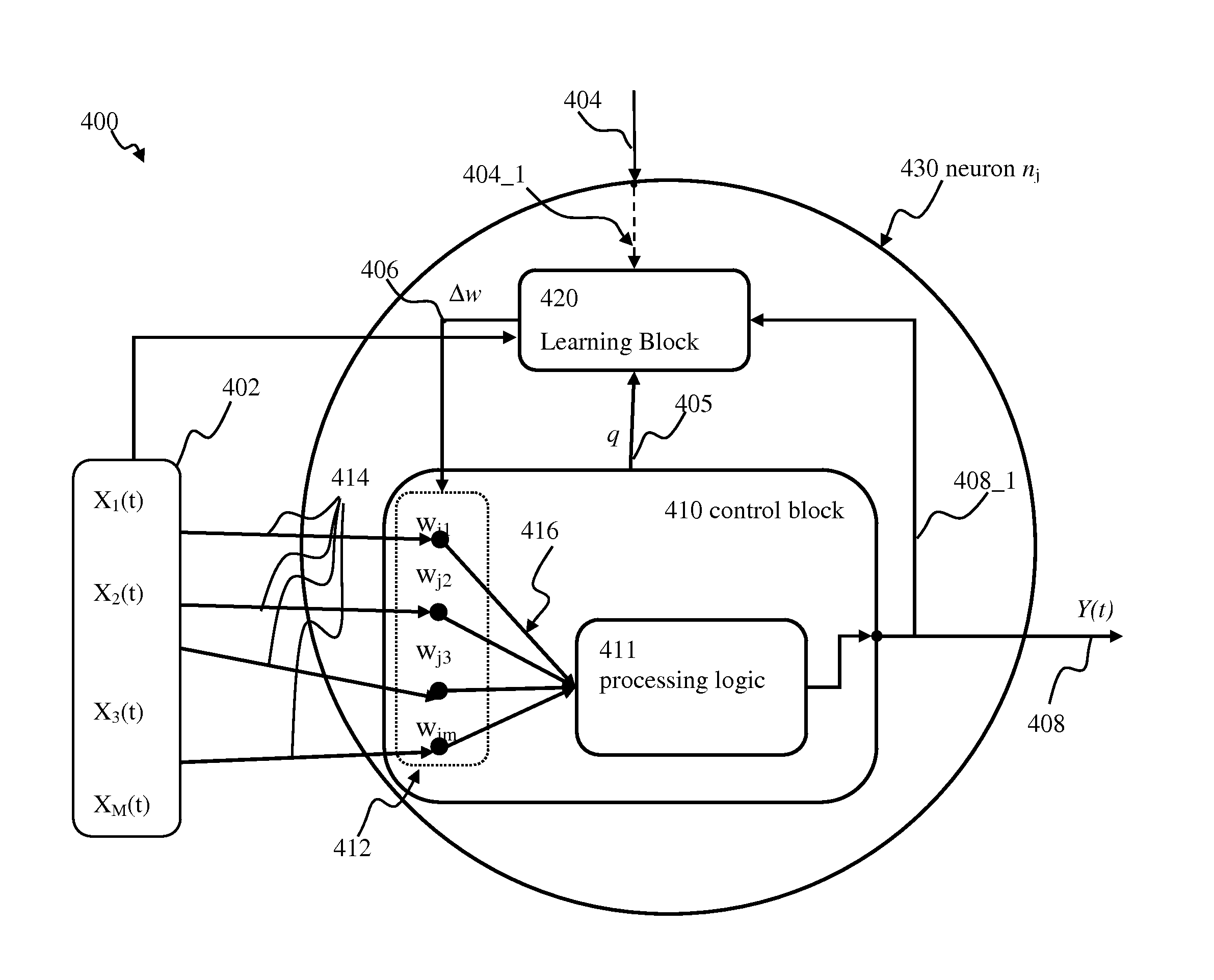
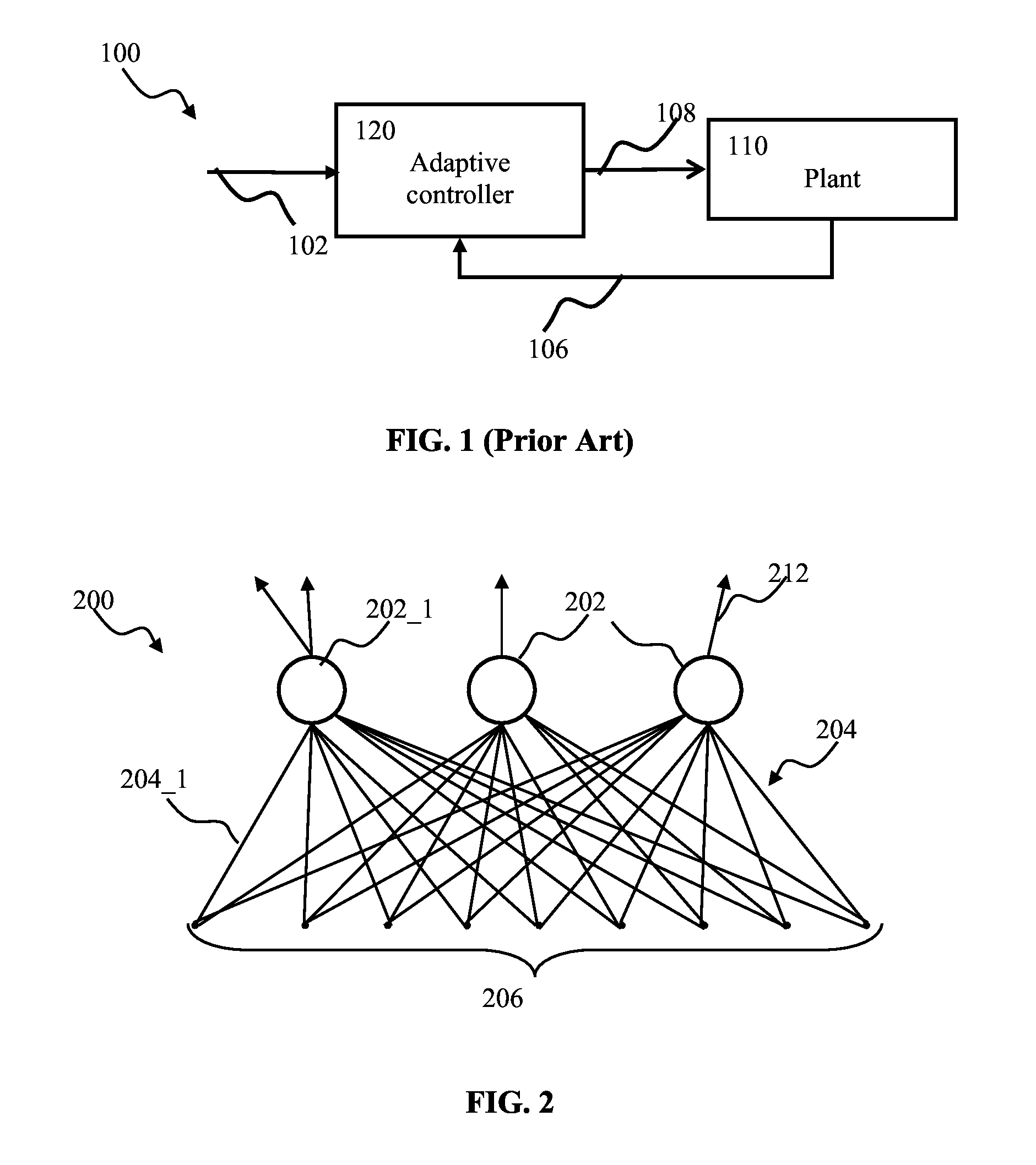
Spiking neuron network adaptive control apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140081895A1Minimizing distance measureSmooth connectionDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Adaptive controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block and a control block. The encoder may utilize basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. The relevant features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for efficient updates in spiking neuron network
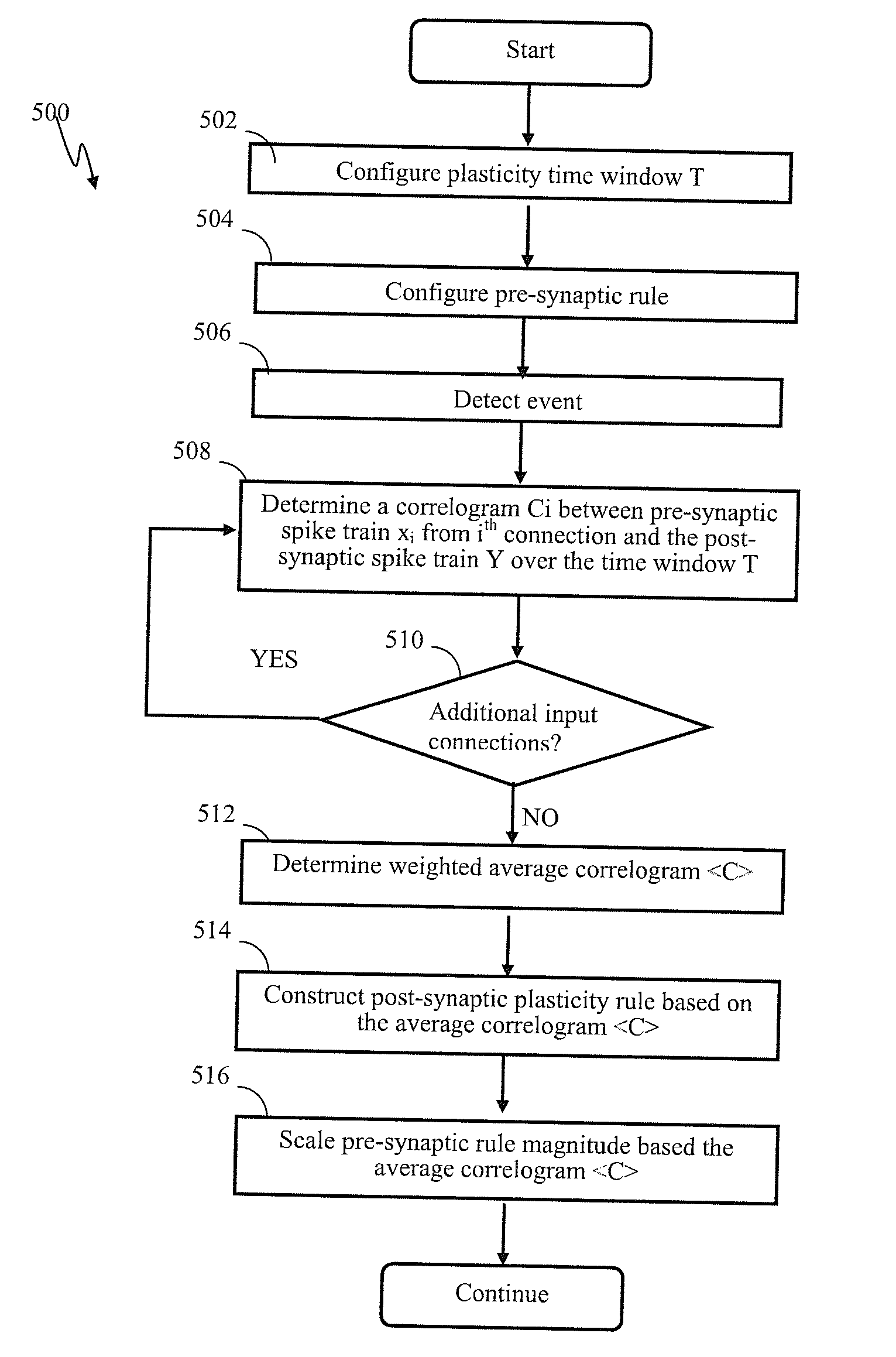
Efficient updates of connections in artificial neuron networks may be implemented. A framework may be used to describe the connections using a linear synaptic dynamic process, characterized by stable equilibrium. The state of neurons and synapses within the network may be updated, based on inputs and outputs to / from neurons. In some implementations, the updates may be implemented at regular time intervals. In one or more implementations, the updates may be implemented on-demand, based on the network activity (e.g., neuron output and / or input) so as to further reduce computational load associated with the synaptic updates. The connection updates may be decomposed into multiple event-dependent connection change components that may be used to describe connection plasticity change due to neuron input. Using event-dependent connection change components, connection updates may be executed on per neuron basis, as opposed to per-connection basis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
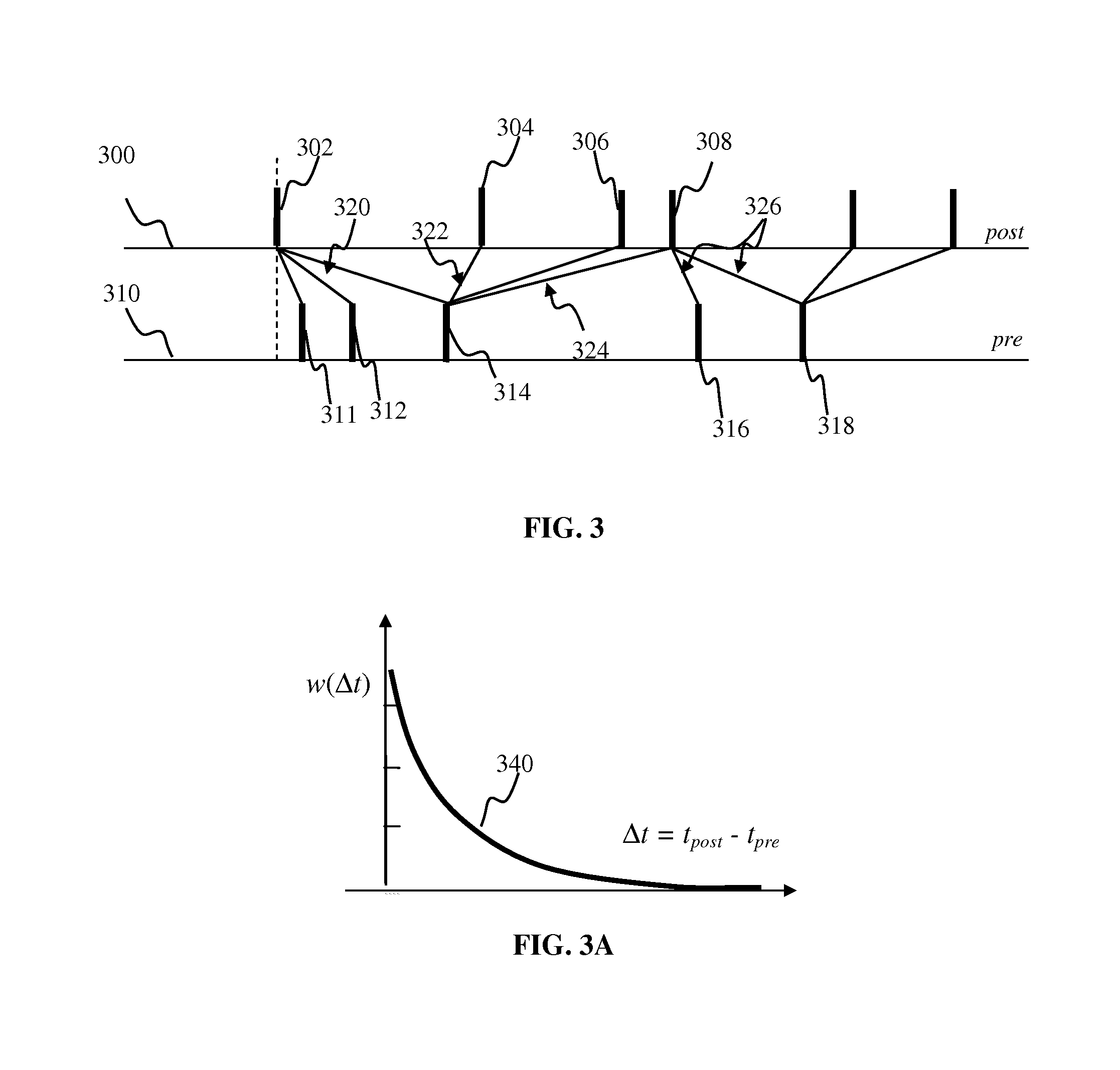
Conditional plasticity spiking neuron network apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140012788A1Improve performanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkNerve network
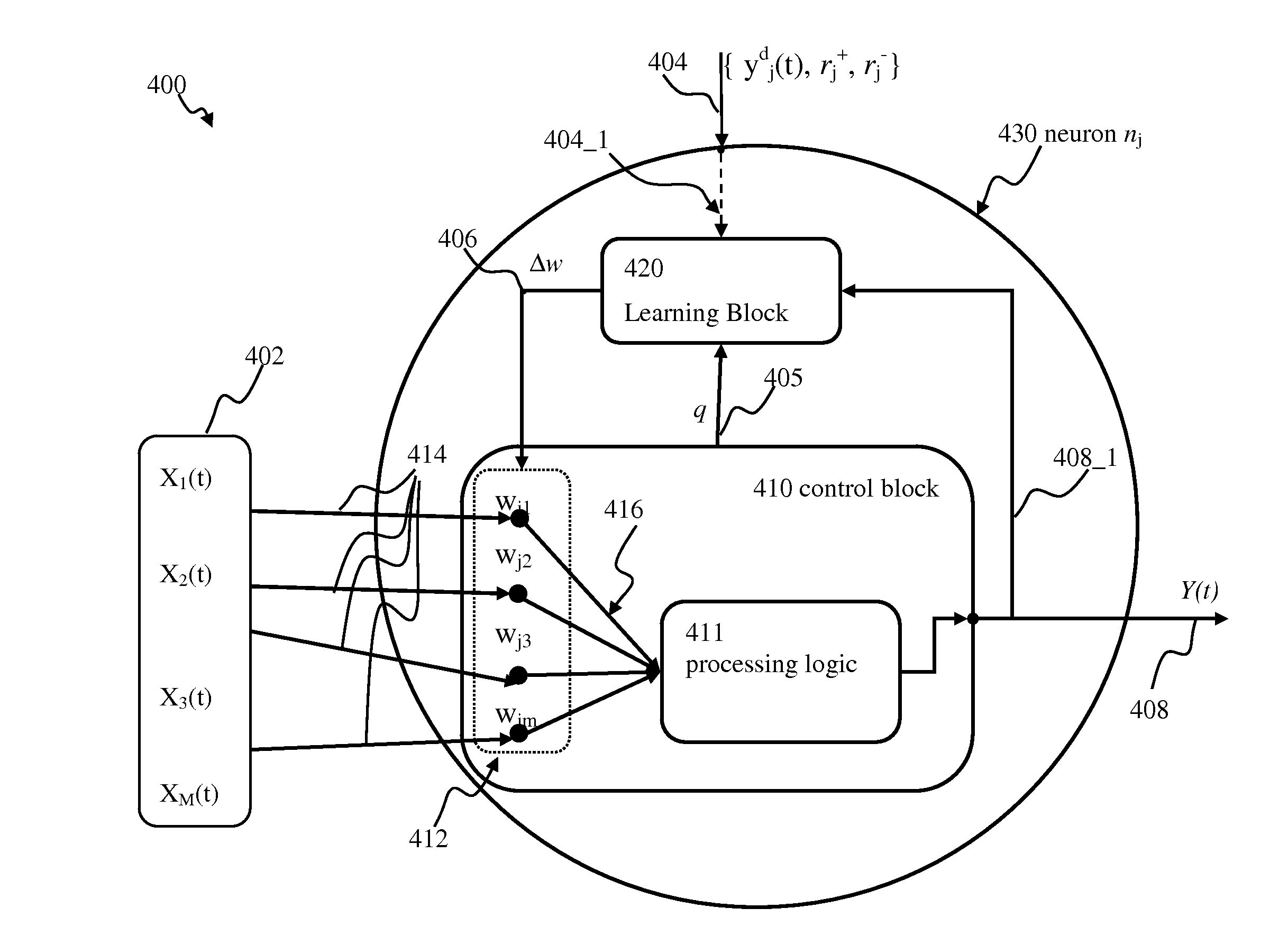
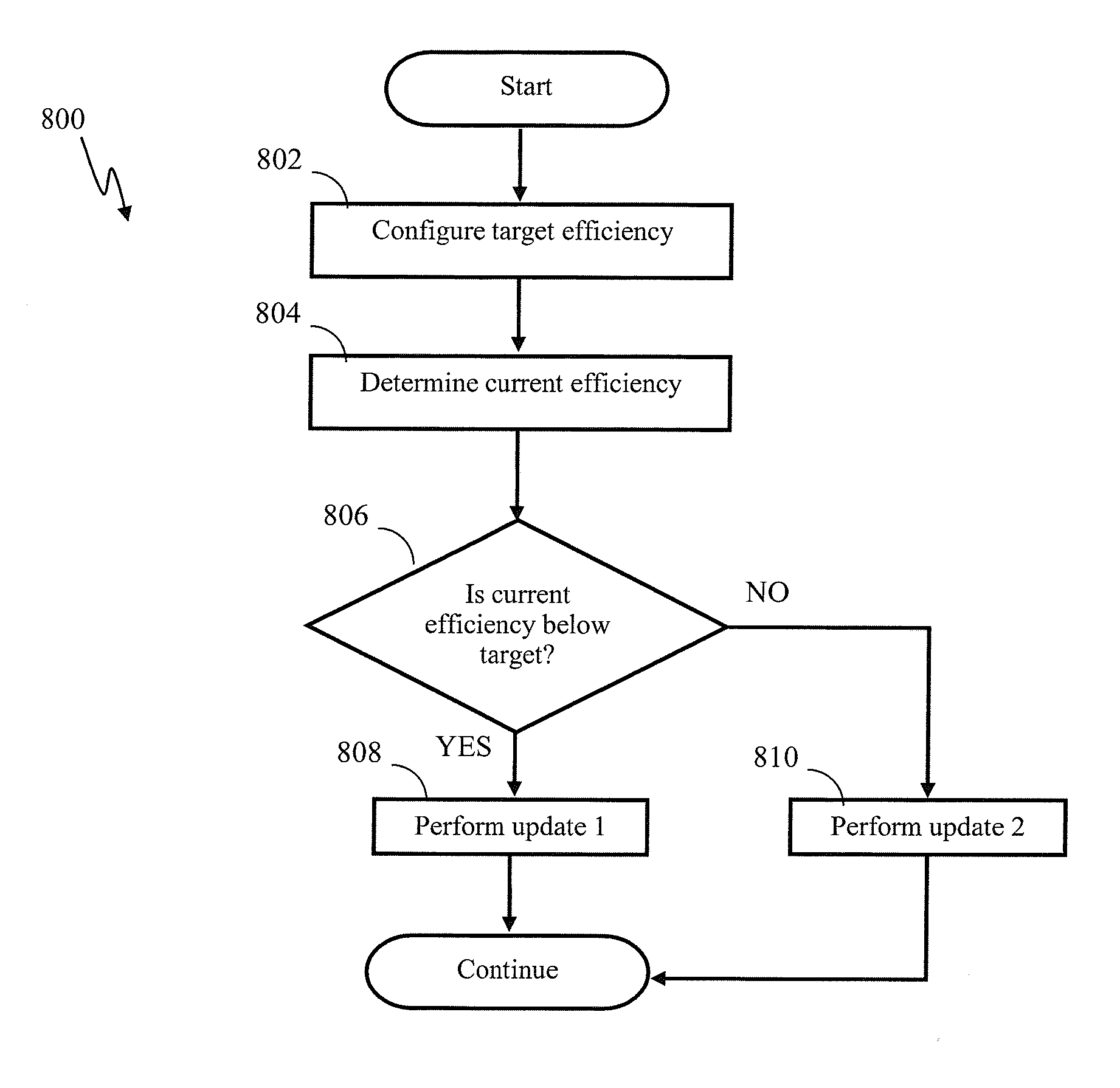
Apparatus and methods for conditional plasticity in a neural network. In one approach, conditional plasticity mechanism is configured to select alternate plasticity rules when performing connection updates. The selection mechanism is adapted based on a comparison of actual connection efficiency and target efficiency. For instance, when actual efficiency is below the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term potentiation. Similarly, when actual efficiency is above the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term connection depression. The conditional plasticity mechanism dynamically adjusts connection efficacy, and prevents uncontrolled increase of connection weights, thereby improving network operation when processing information of a varying nature.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for generalized state-dependent learning in spiking neuron networks
ActiveUS20140032459A1Easy to implementDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkArtificial intelligence
Generalized state-dependent learning framework in artificial neuron networks may be implemented. A framework may be used to describe plasticity updates of neuron connections based on connection state term and neuron state term. The state connections within the network may be updated based on inputs and outputs to / from neurons. The input connections of a neuron may be updated using connection traces comprising a time-history of inputs provided via the connections. Weights of the connections may be updated and connection state may be time varying. The updated weights may be determined using a rate of change of the trace and a term comprising a product of a per-neuron contribution and a per-connection contribution configured to account for the state time-dependency. Using event-dependent connection change components, connection updates may be executed on per neuron basis, as opposed to per-connection basis.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Modulated plasticity apparatus and methods for spiking neuron network
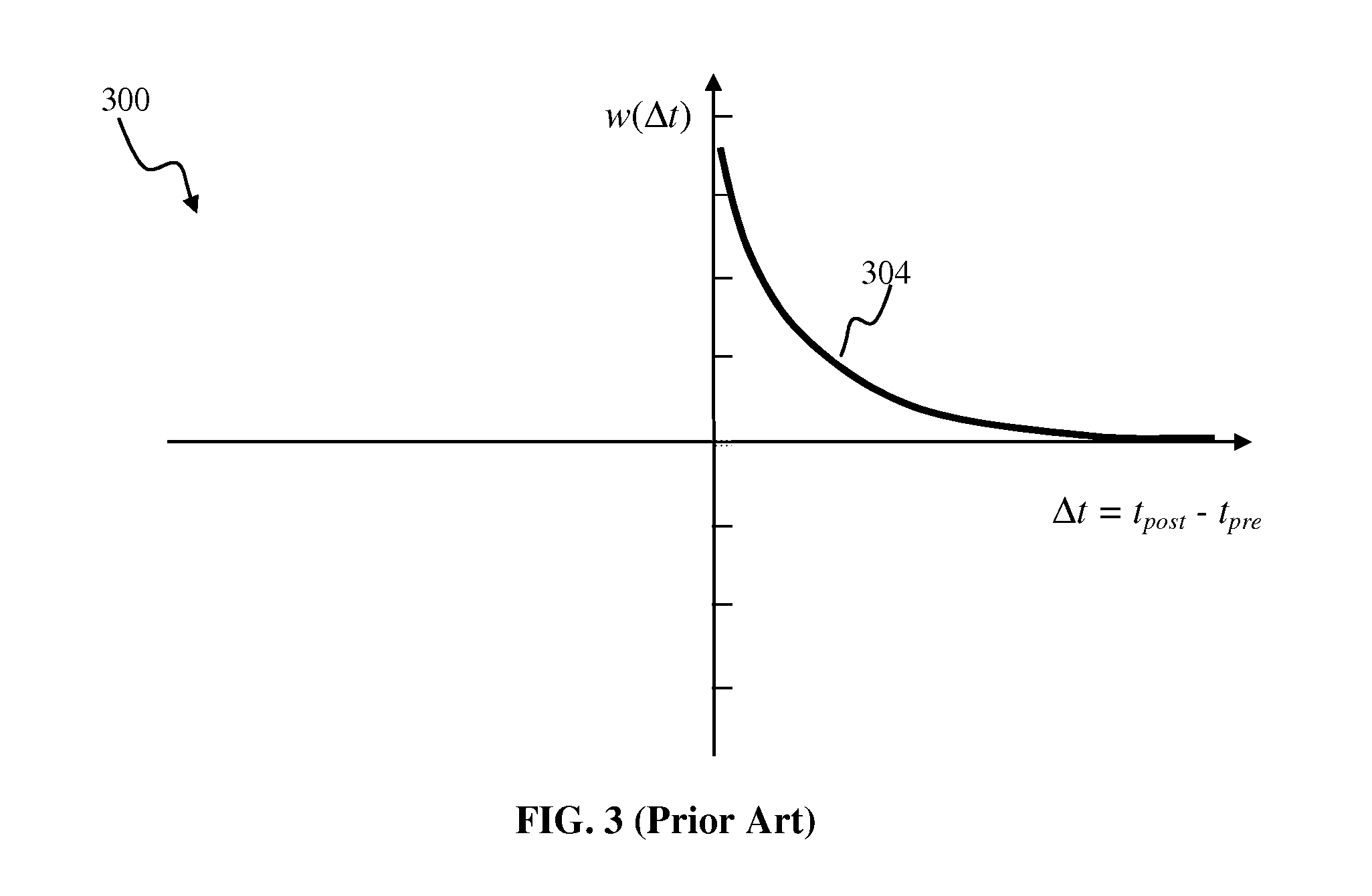
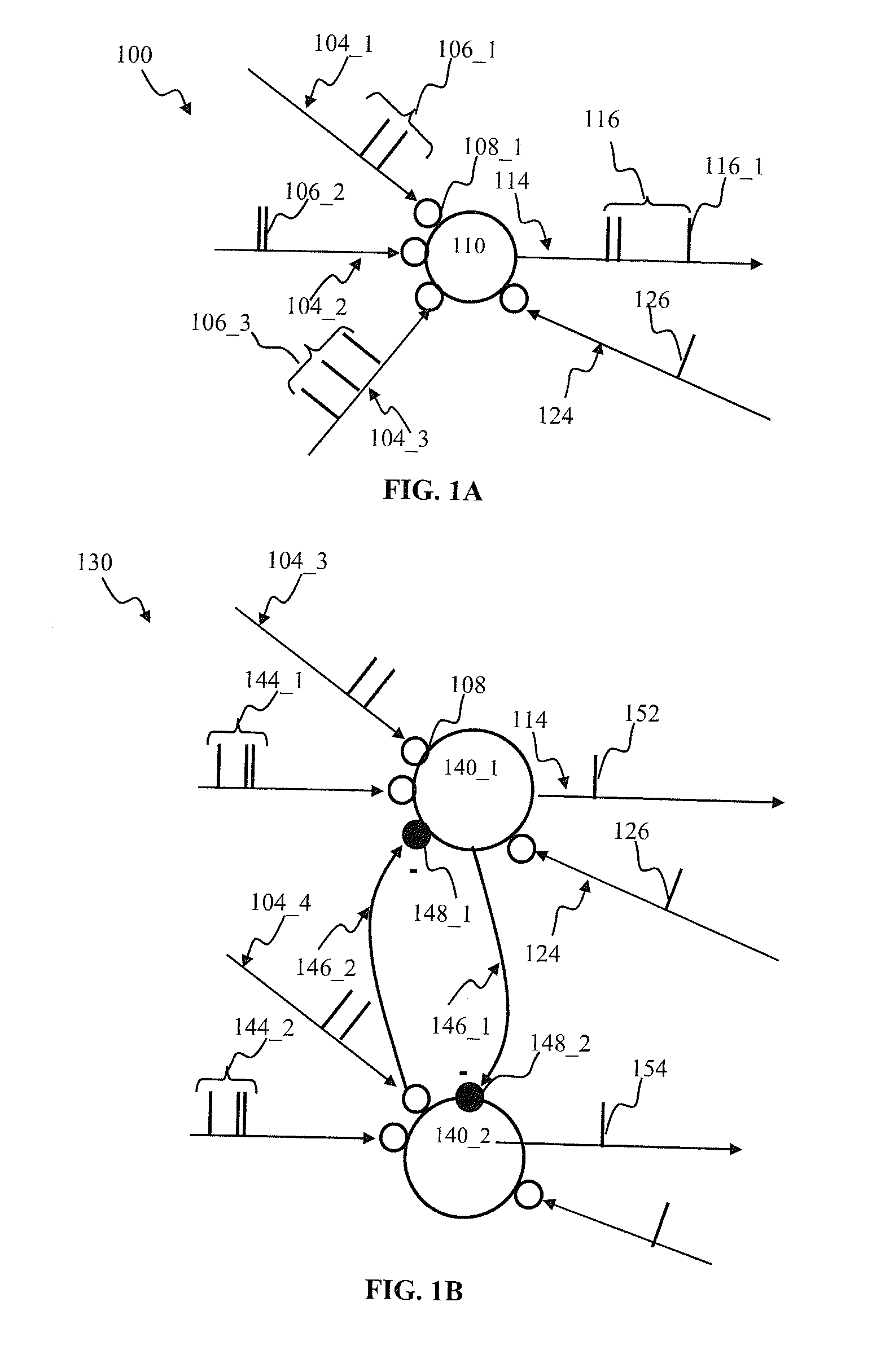
Apparatus and methods for modulated plasticity in a spiking neuron network. A plasticity mechanism may be configured for example based on a similarity measure between post-synaptic activities of two or more neurons that may be receiving the same feed-forward input. The similarity measure may comprise a dynamically determined cross-correlogram between the output spike trains of two neurons. An a priori configured similarity measure may be used during network operation in order to update efficacy of inhibitory connections between neighboring neurons. Correlated output activity may cause one neuron to inhibit output generation by another neuron thereby hindering responses by multiple neurons to the same input stimuli. The inhibition may be based on an increased efficacy of inhibitory lateral connection. The inhibition may comprise modulation of the pre synaptic portion the plasticity rule based on efficacies of feed-forward connection and inhibitory connections and a statistical parameter associated with the post-synaptic rule.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
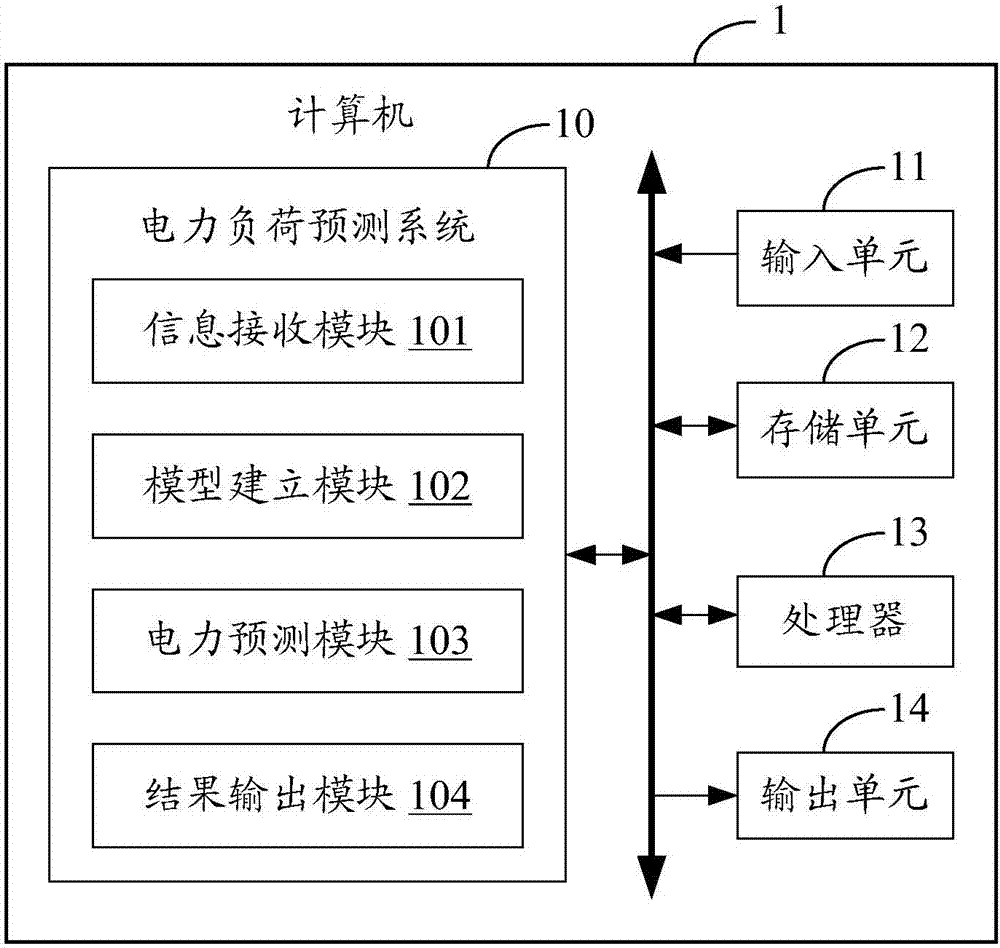
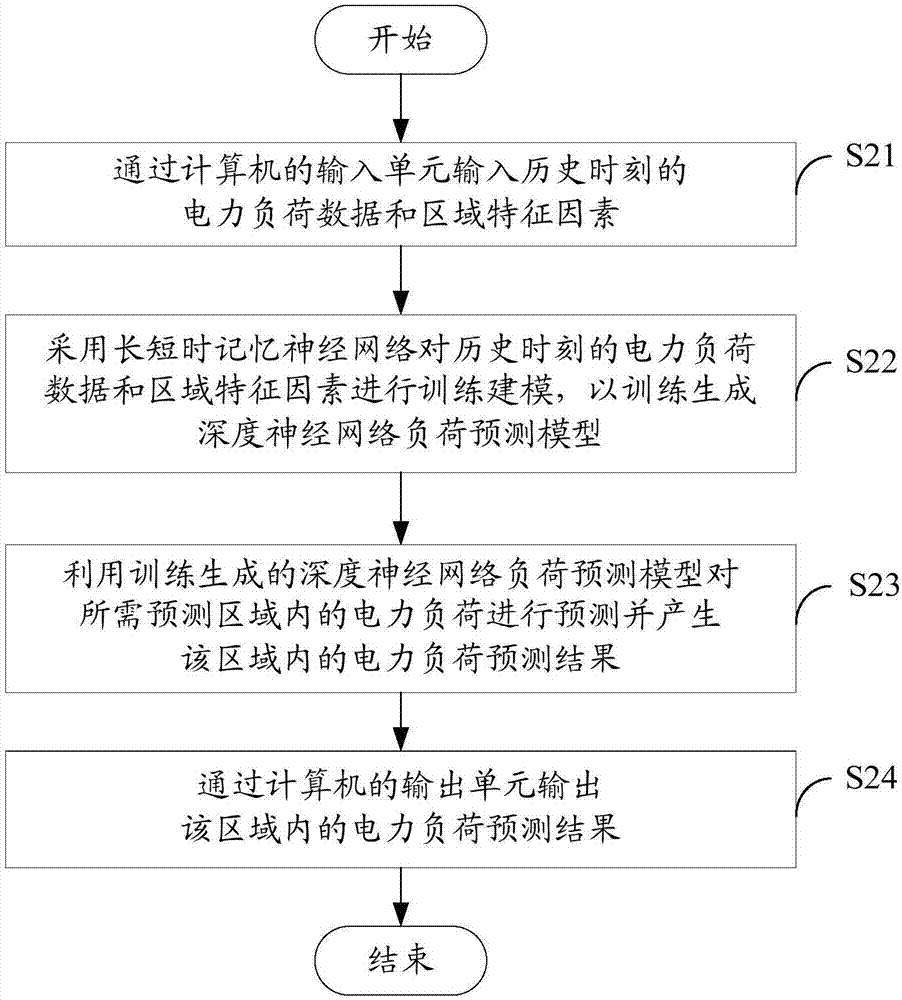
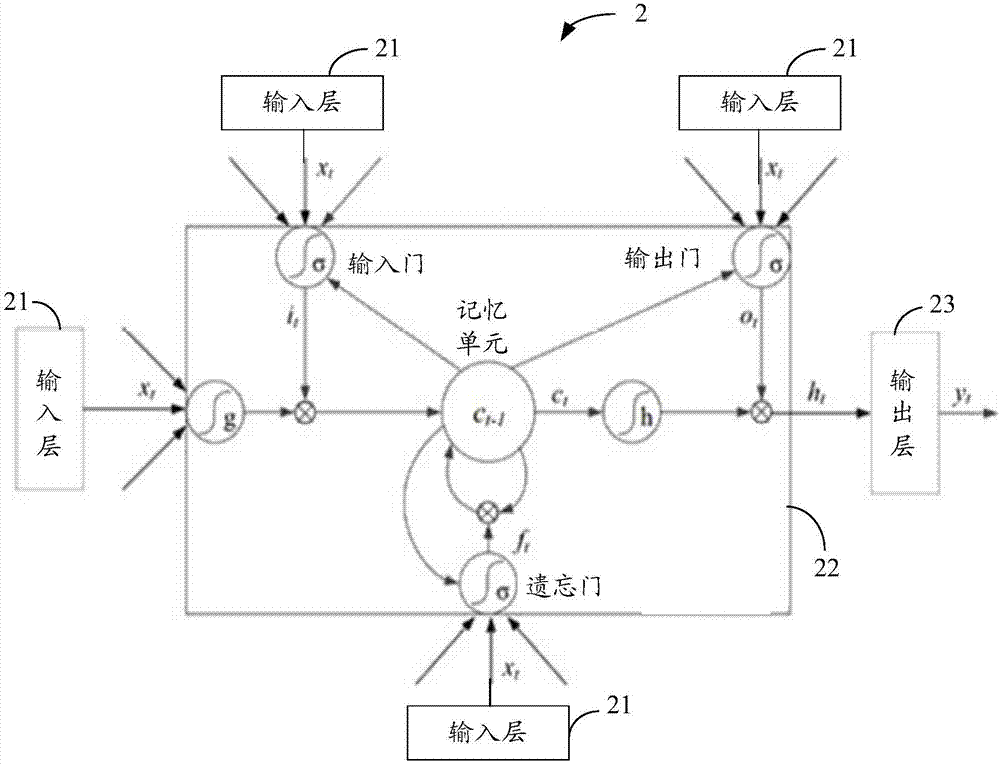
Power load forecasting method based on long short term memory neuron network
InactiveCN106960252AImprove predictive performancePrediction is accurateForecastingNeuron networkLoad forecasting
The invention discloses a power load forecasting method based on a long short term memory (LSTM) neuron network. The power load forecasting method comprises inputting power load data and a region feature factor at a historic moment through an input unit; carrying out training and modeling on the power load data and the region feature factor at the historic moment by means of an LSTM network in order to generate a deep neural network load forecasting model which is a single-layer multi-task deep neural network model or a double-layer multi-task deep neural network model used for power supply load forecasting; forecasting the power load in an area needing to be forecasted by means of the deep neural network load forecasting model, and generating a forecasting result of the power load in the area; and outputting the forecasting result of the power load in the area through an output unit. According to the invention, a multi-task learning power load forecasting model is constructed based on the LSTM network in the deep learning field, power consumption loads in multiple areas can be forecasted accurately, and the forecasting effect is improved.
Owner:X TRIP INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
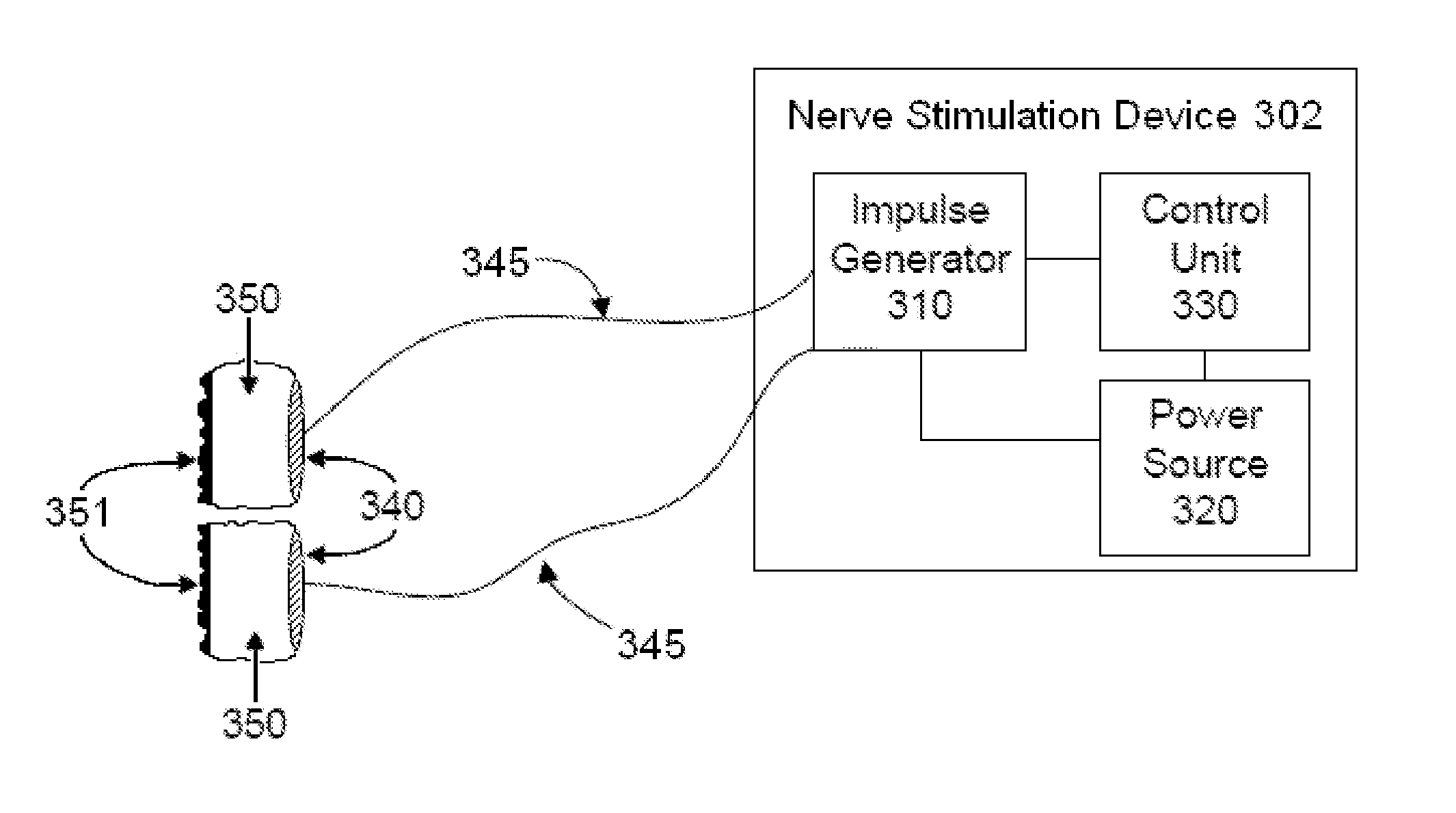
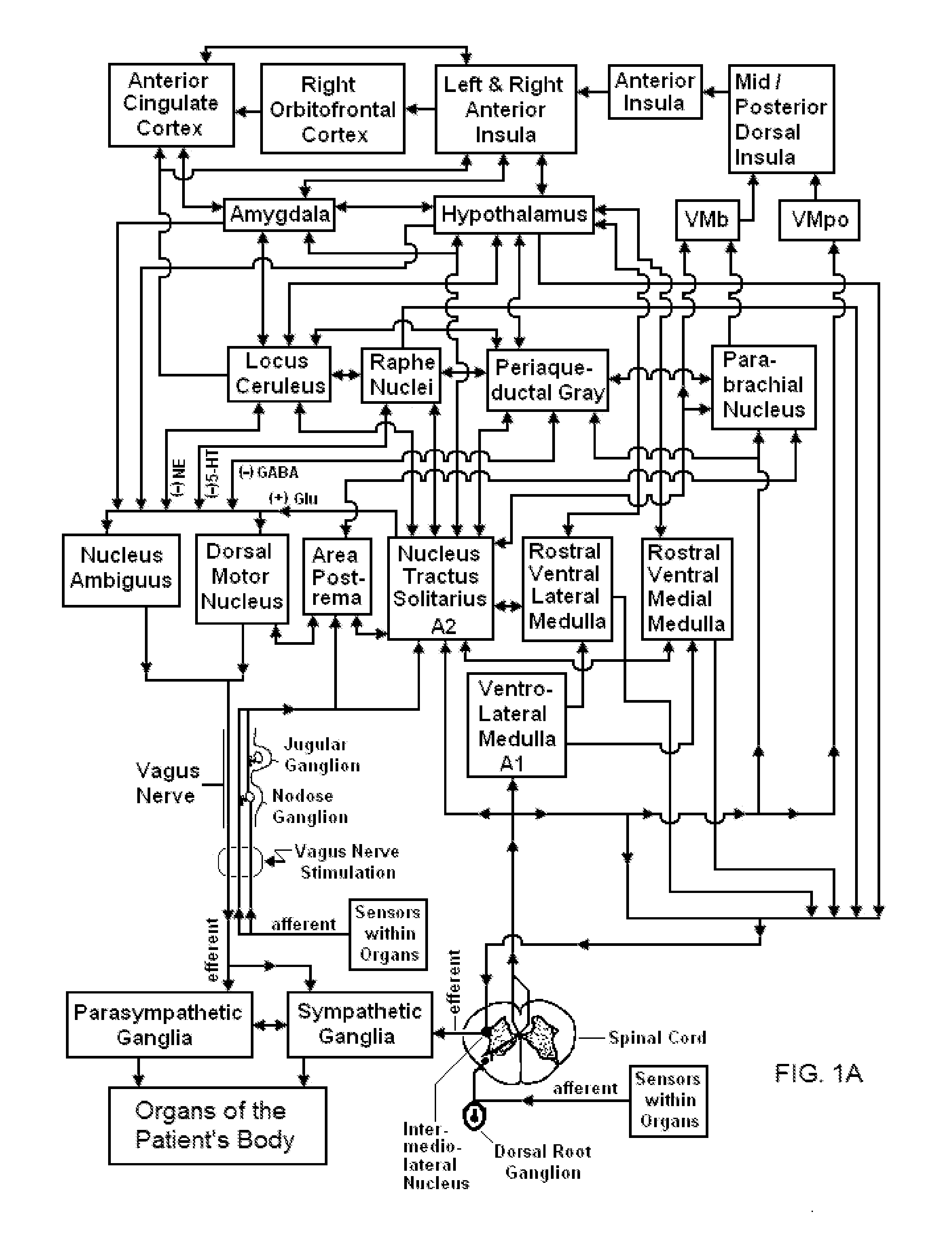
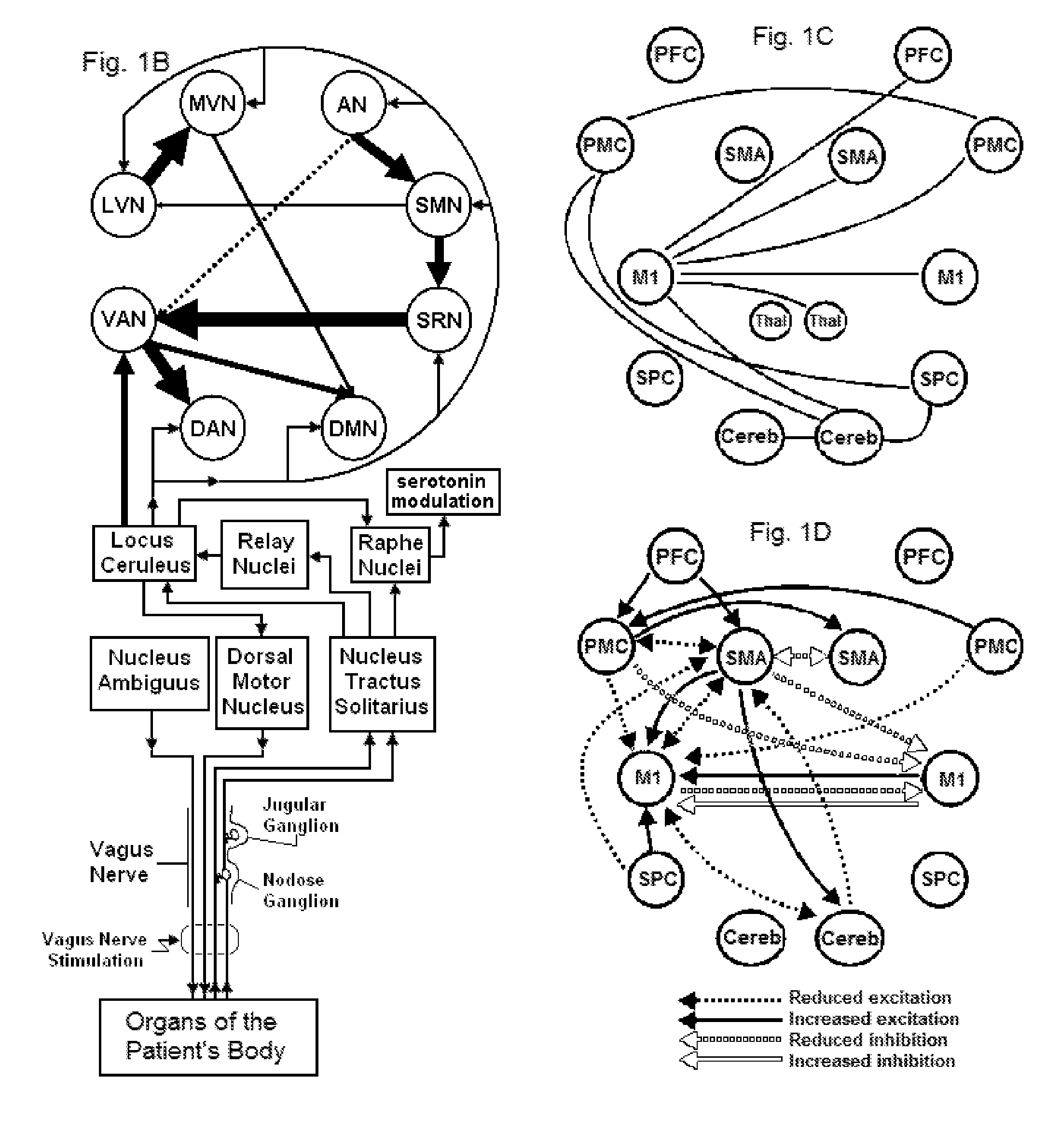
Vagal nerve stimulation to avert or treat stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS20130317580A1Improve the level ofInhibition of excitementSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSerotoninRisk stroke
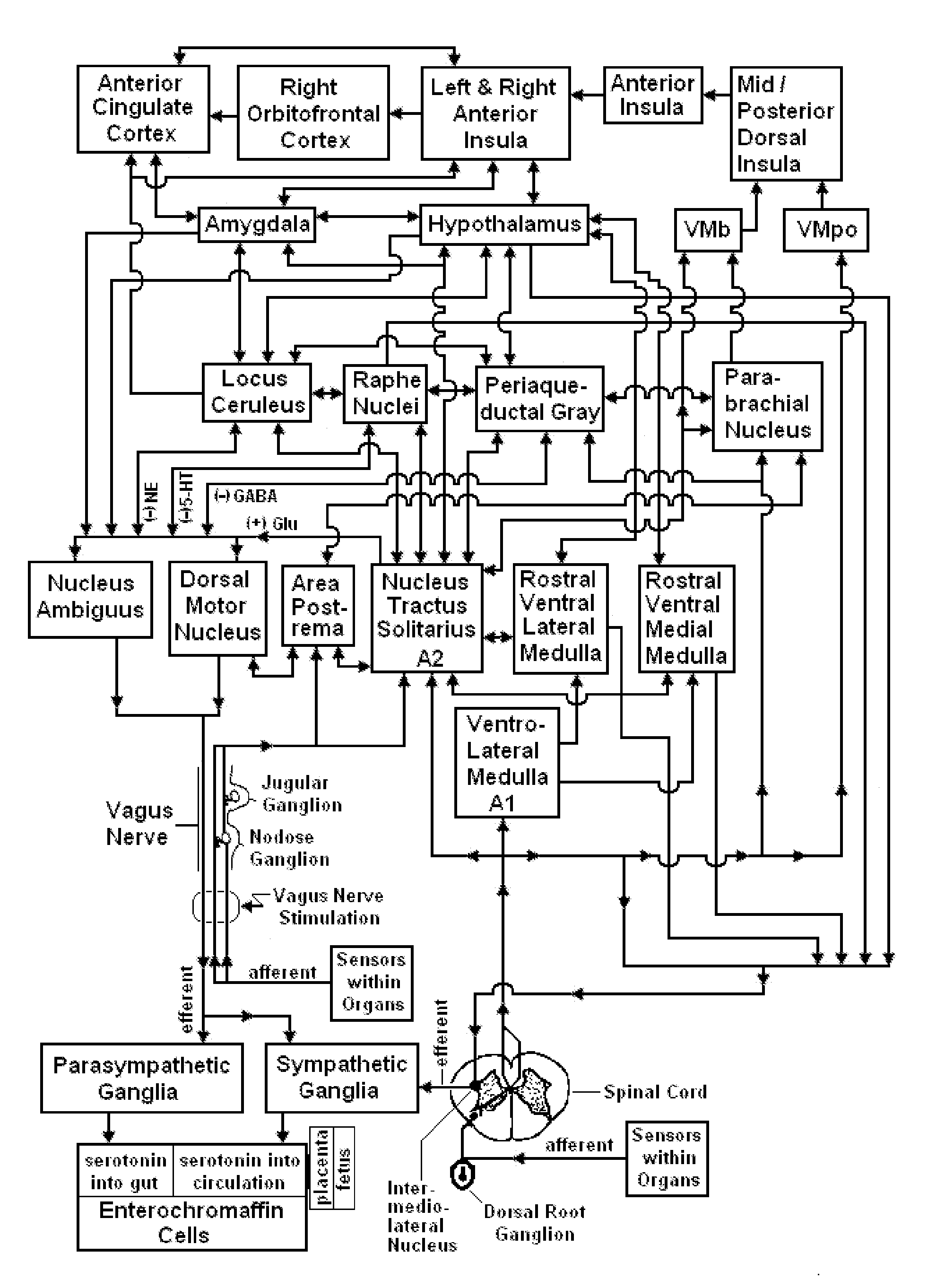
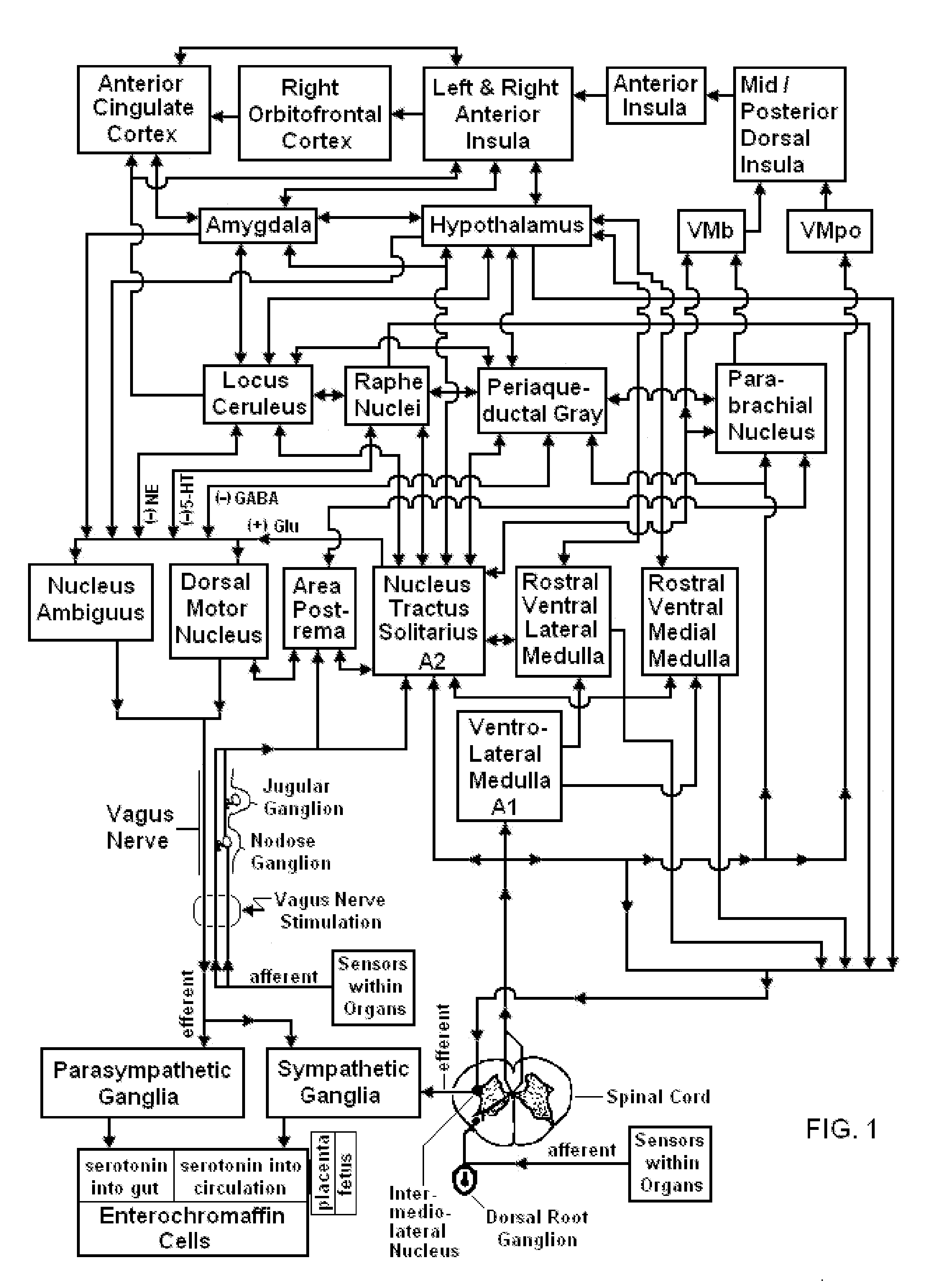
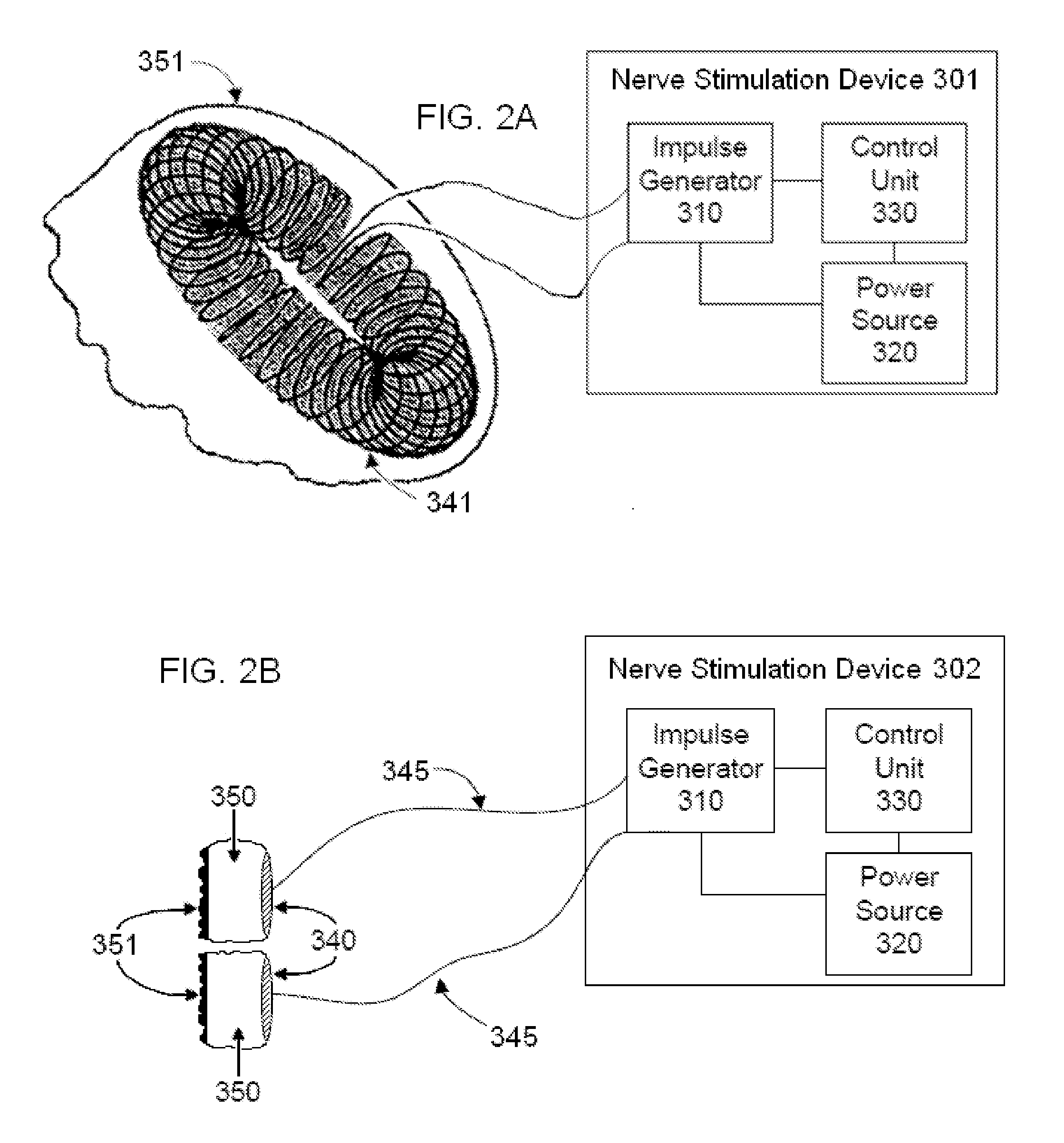
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing a stroke and / or a transient ischemic attack in a patient. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. Vagus nerve stimulation is used to modulate the release of GABA, norepinephrine, and / or serotonin, thereby providing neuroprotection to the patient; to modulate the activity of resting state neuronal networks, particularly the sensory-motor network or resting state networks containing the insula; and to avert a stroke or transient ischemic attack that has been forecasted.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Apparatus and methods for state-dependent learning in spiking neuron networks
State-dependent supervised learning framework in artificial neuron networks may be implemented. A framework may be used to describe plasticity updates of neuron connections based on a connection state term and a neuron state term. Connection states may be updated based on inputs and outputs to and / or from neurons. The input connections of a neuron may be updated using input traces comprising a time-history of inputs provided via the connection. Weight of the connection may be updated and connection state may be time varying. The updated weights may be determined using a rate of change of the input trace and a term comprising a product of a per-neuron contribution and a per-connection contribution configured to account for the state time-dependency. Using event-dependent connection change components, connection updates may be executed on a per neuron basis, as opposed to a per-connection basis.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
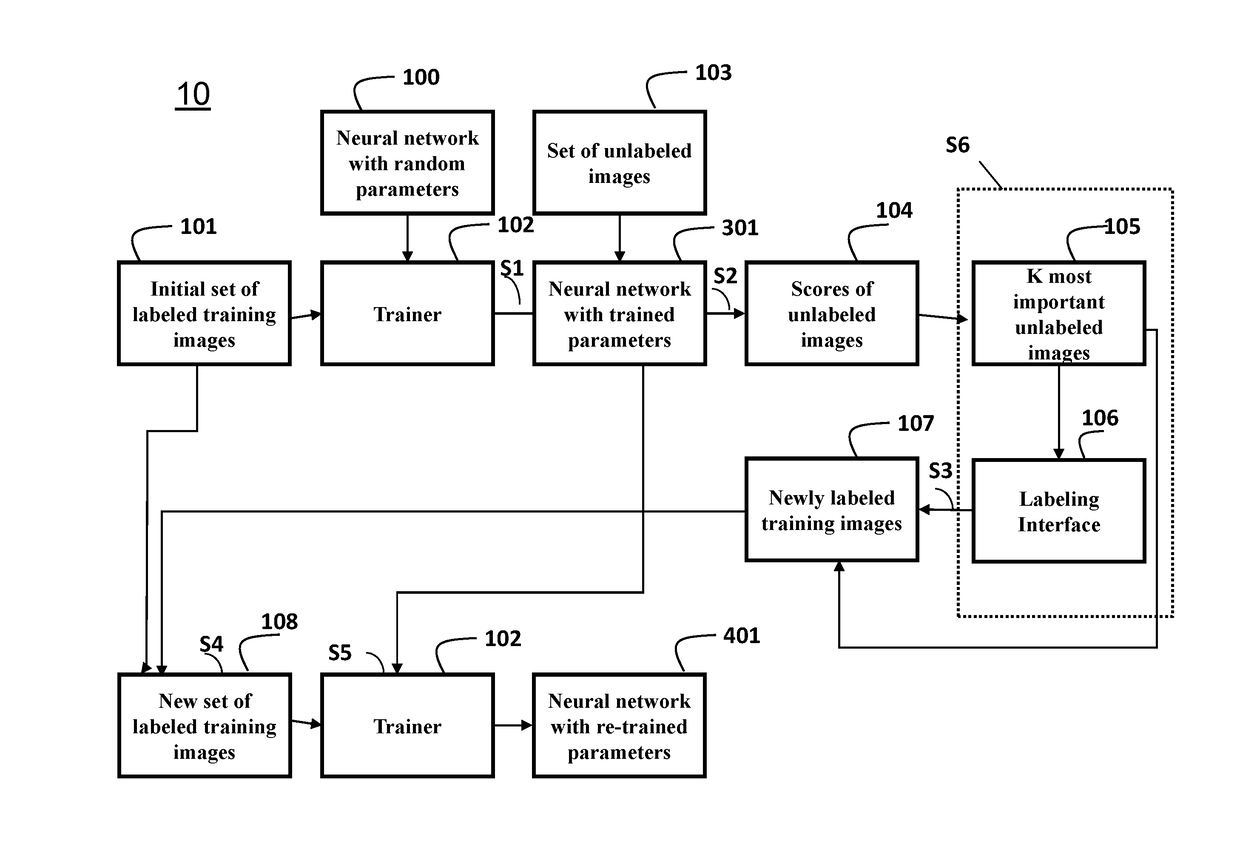
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
ActiveUS8972315B2Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
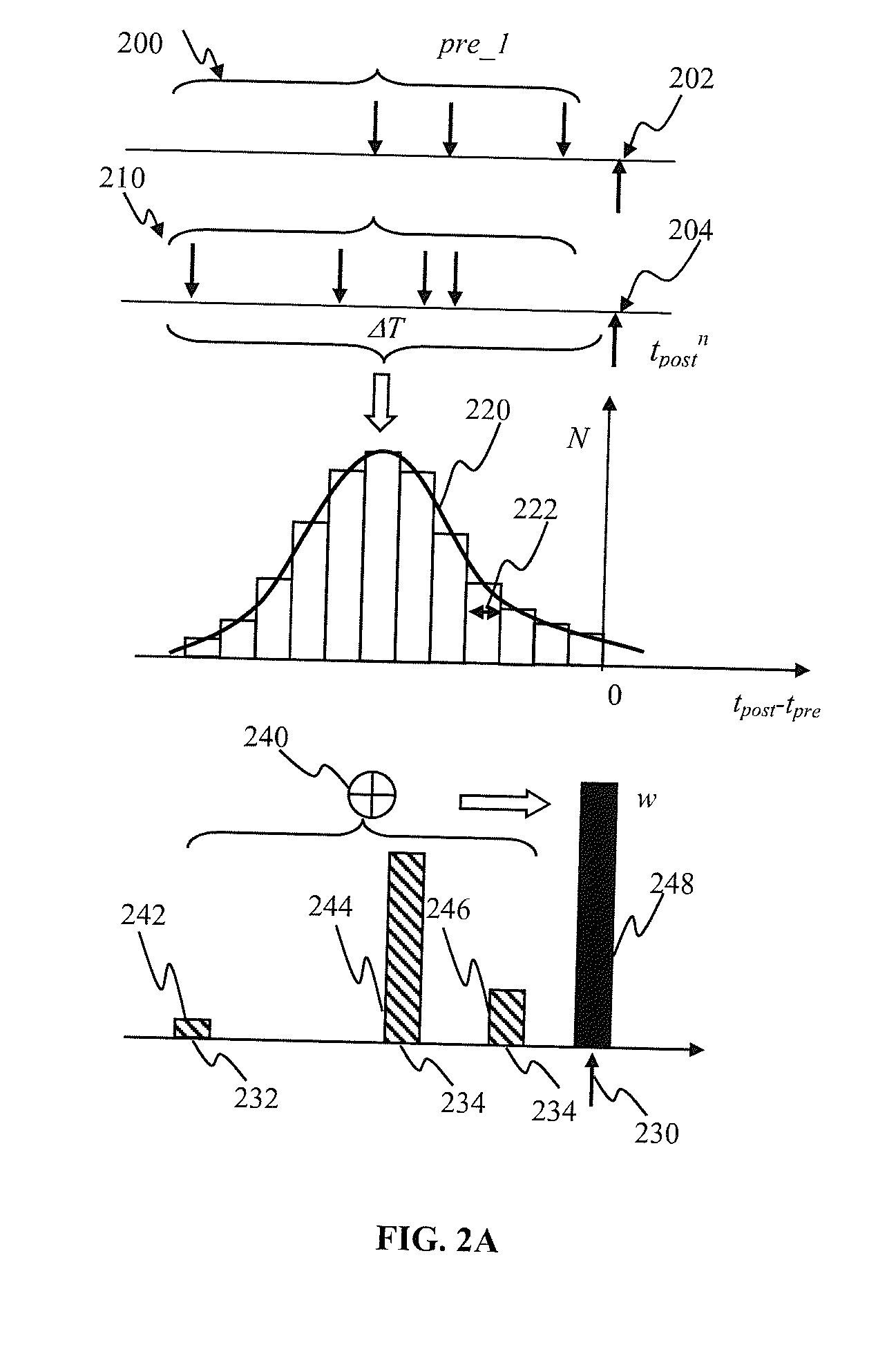
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
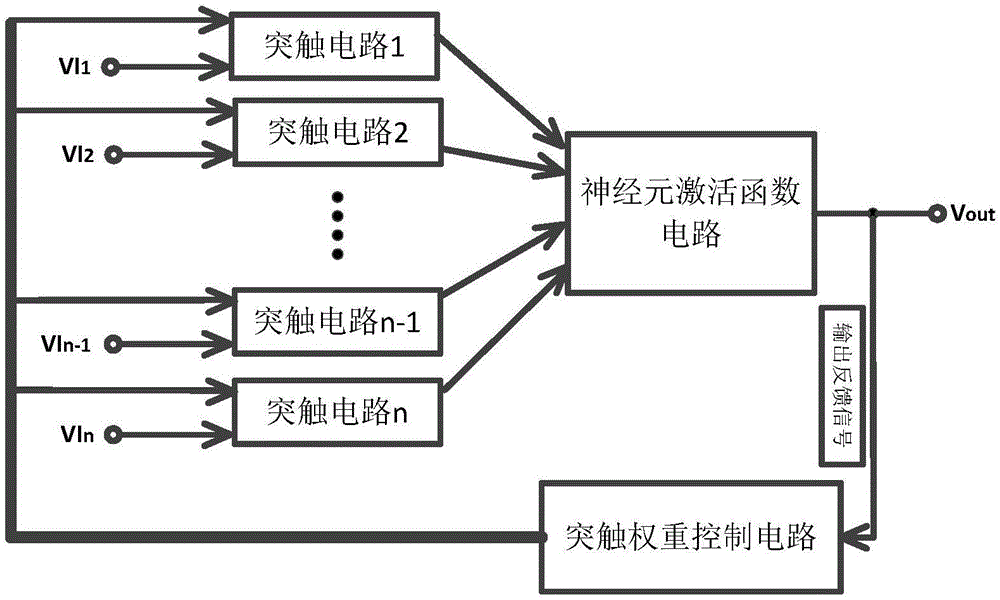
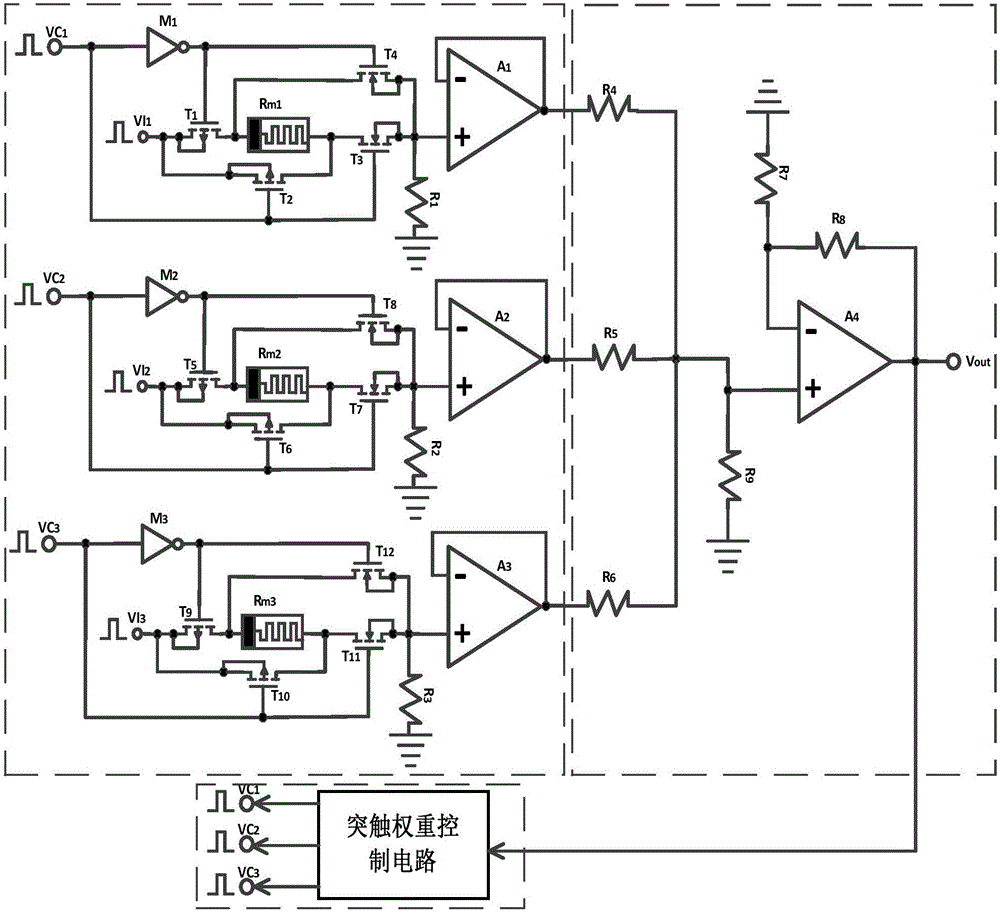
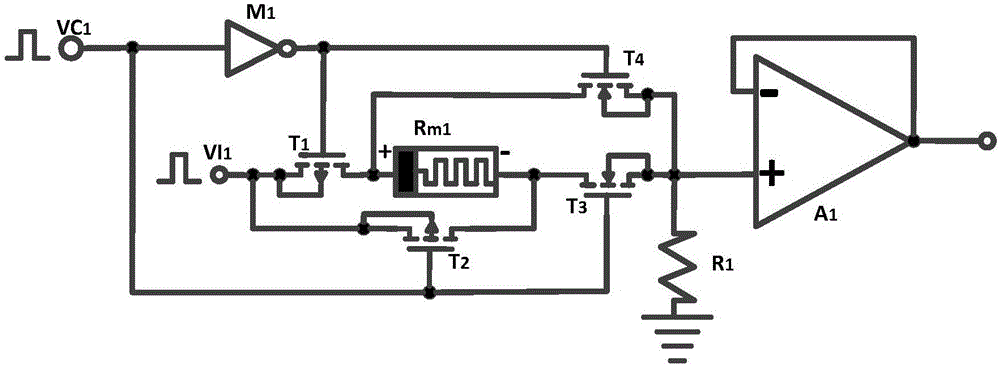
Memristor-based neuron circuit
ActiveCN106815636AGood effectEasy compositionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationActivation functionNerve network
The invention discloses a memristor-based neuron circuit, comprising a synaptic circuit, a neuron activation function circuit and a synaptic weight control circuit. In the synaptic circuit, a memristor, under the control of four MOS tubes, changes the memristor value to simulate the change of the synaptic weight in the neuron network. The designed neuron synaptic circuit is capable of being directly connected with a digital logic electrical level so as to achieve convenient and real-time adjustment to the synaptic weight and through the use of the feature that the output voltage of an operational amplifier is restricted by the power supply voltage, the neuron circuit activation function can be realized as a saturated linear function. The neuron synaptic weight change circuit can utilize the existing CMOS micro-controller and at the same time, the micro-controller can be loaded by the neuron network algorithm to change the synaptic weight to realize corresponding functions. According to the invention, a plurality of neuron circuits could be connected into a large-scale neuron network for complicated functions such as mode identification, signal processing, associated memory and non-linear mapping, etc.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
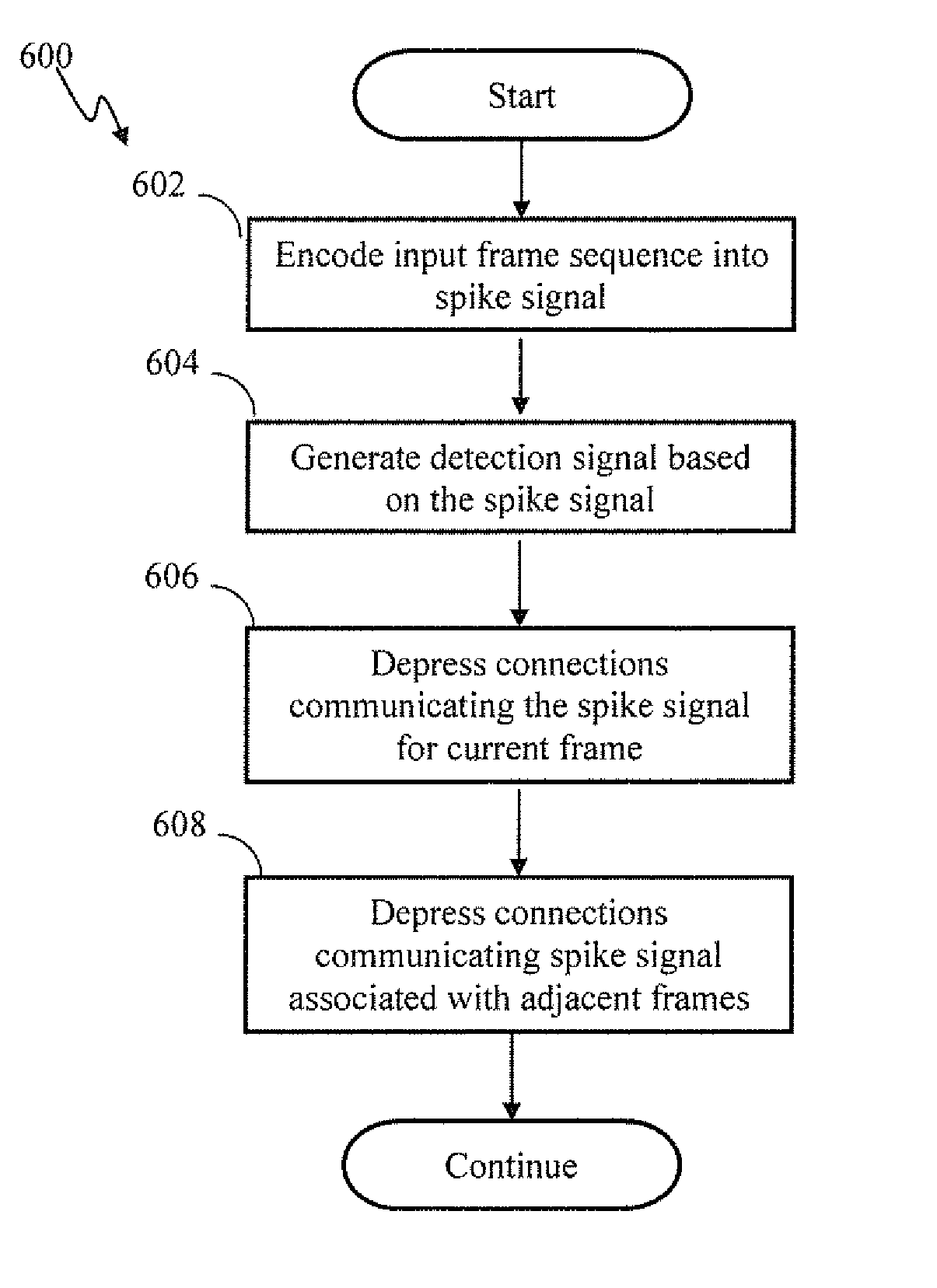
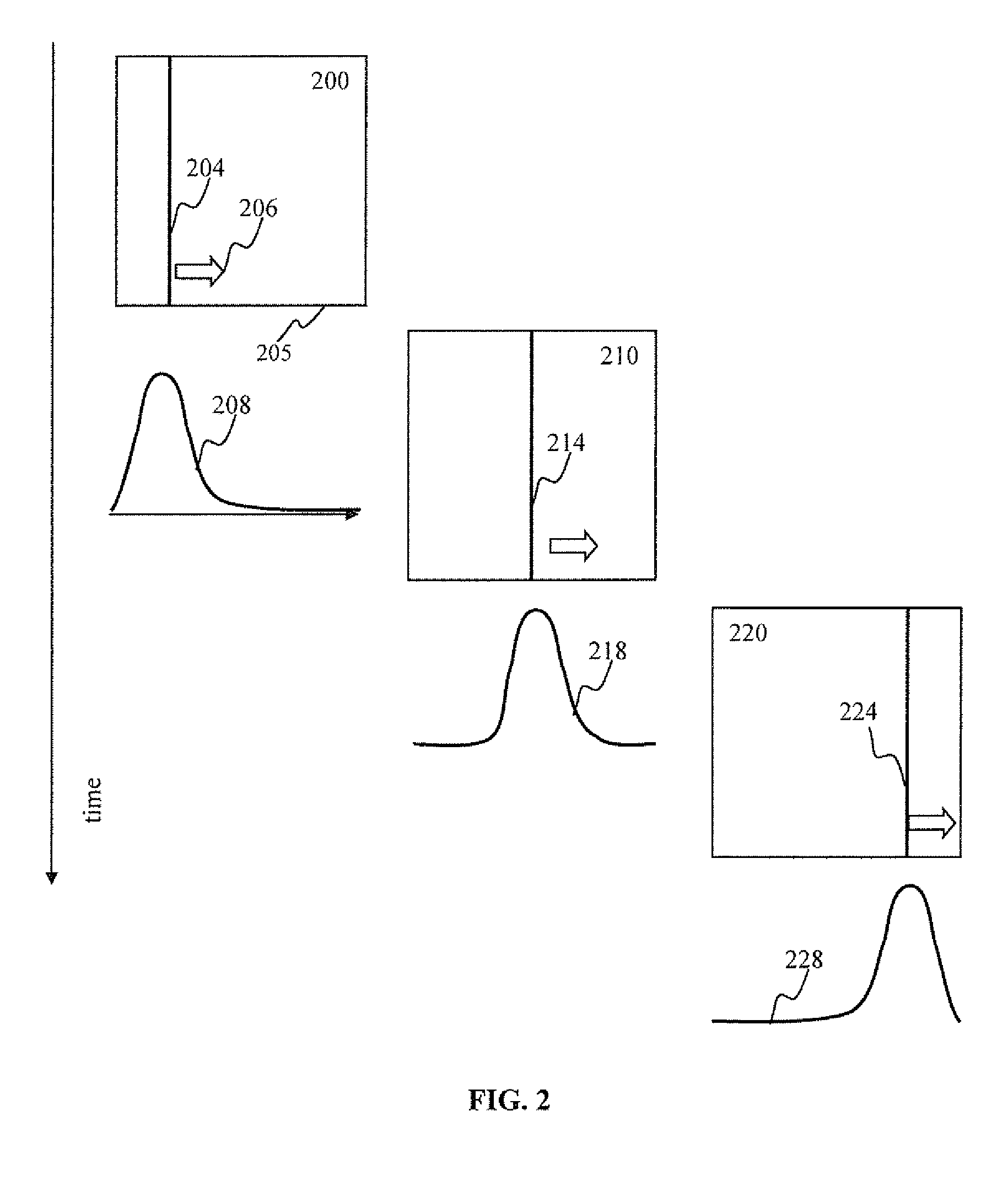
Spiking network apparatus and method with bimodal spike-timing dependent plasticity
ActiveUS20140229411A1Facilitate network normalizationPreventing feedback loopImage enhancementImage analysisNeuron networkBi modal
Apparatus and methods for learning in response to temporally-proximate features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes bi-modal spike timing dependent plasticity in a spiking neuron network. Based on a response by the neuron to a frame of input, the bi-modal plasticity mechanism is used to depress synaptic connections delivering the present input frame and to potentiate synaptic connections delivering previous and / or subsequent frames of input. The depression of near-contemporaneous input prevents the creation of a positive feedback loop and provides a mechanism for network response normalization.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
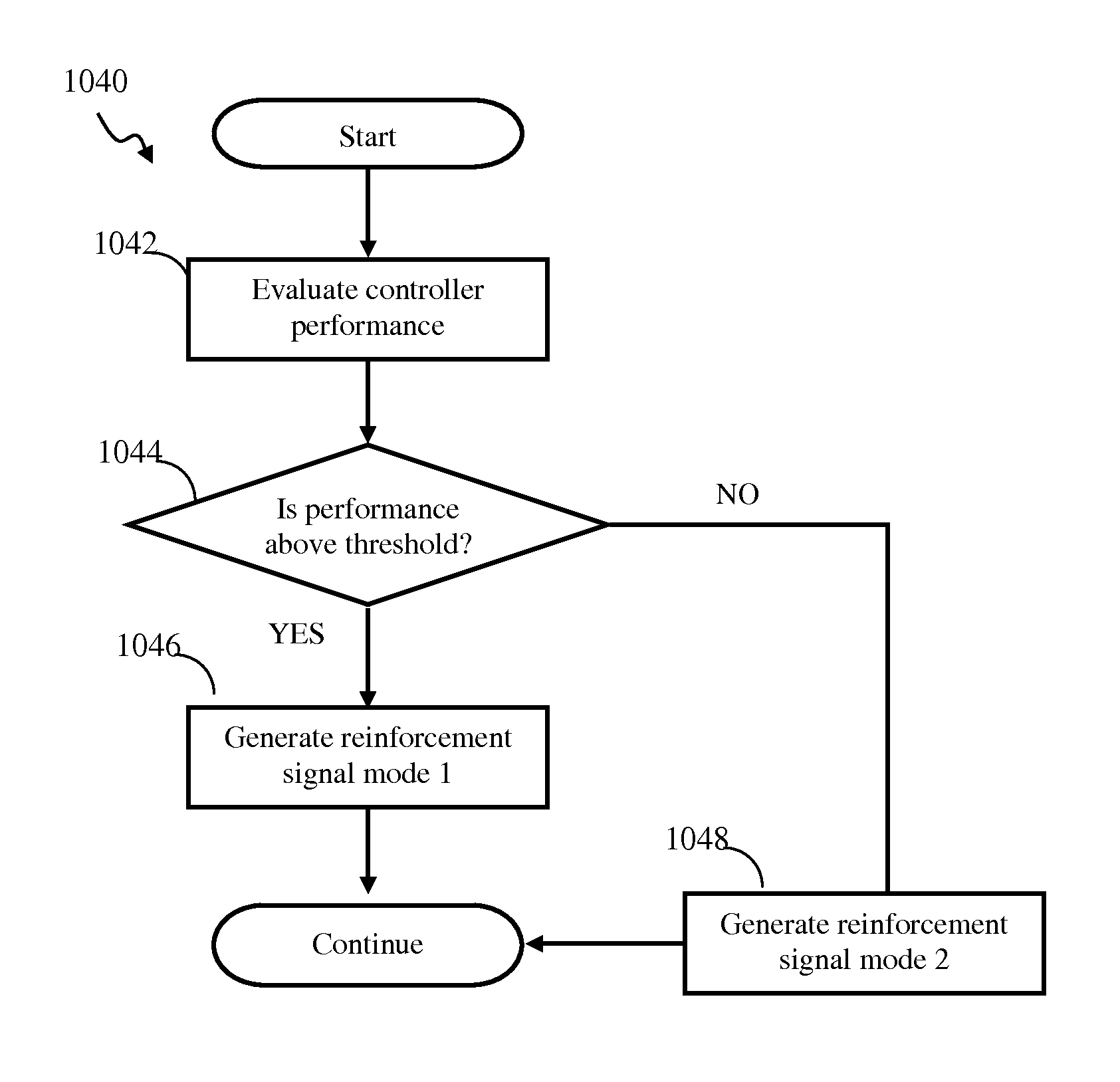
Modulated stochasticity spiking neuron network controller apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9189730B1Lower Level RequirementsDiminished rate of learningNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNeuron networkNeural network controller
Adaptive controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block and a control block. The encoder may utilize basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. The relevant features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome. The stochasticity of the learning process may be modulated. Stochasticity may be increased during initial stage of learning in order to encourage exploration. During subsequent controller operation, stochasticity may be reduced to reduce energy use by the controller.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Contrast enhancement spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140193066A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Temporal winner takes all spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9070039B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. An inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Intelligent modular robotic apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140019392A1Increased compact structureHigh densityDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNegative feedbackBiological body
Apparatus and methods for an extensible robotic device with artificial intelligence and receptive to training controls. In one implementation, a modular robotic system that allows a user to fully select the architecture and capability set of their robotic device is disclosed. The user may add / remove modules as their respective functions are required / obviated. In addition, the artificial intelligence is based on a neuronal network (e.g., spiking neural network), and a behavioral control structure that allows a user to train a robotic device in manner conceptually similar to the mode in which one goes about training a domesticated animal such as a dog or cat (e.g., a positive / negative feedback training paradigm) is used. The trainable behavior control structure is based on the artificial neural network, which simulates the neural / synaptic activity of the brain of a living organism.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for predicting user behavior in wireless Internet
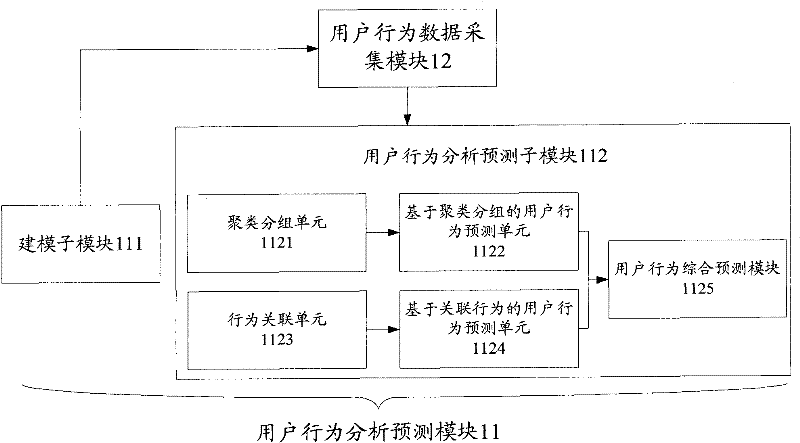
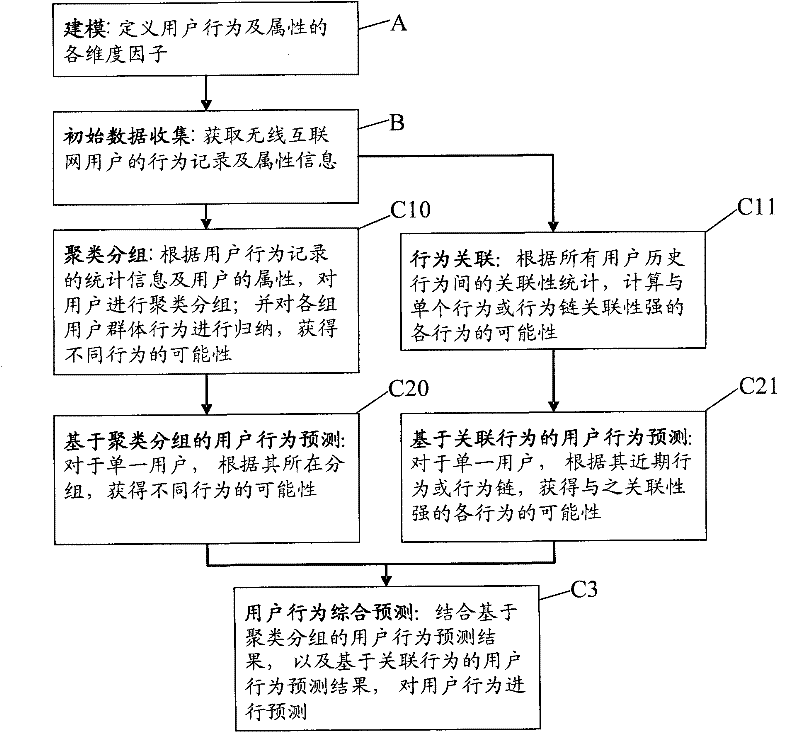
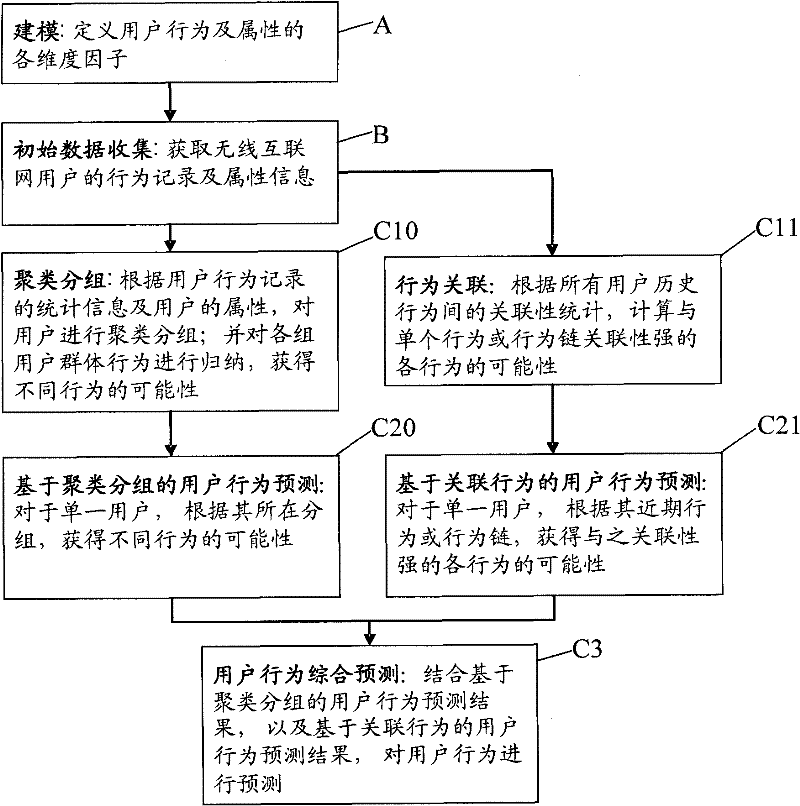
InactiveCN102238045AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed validityGenetic modelsData switching networksNeuron networkBehavioral analytics
The invention discloses a system and method for predicting user behavior in wireless Internet. The system comprises a user behavior data acquisition module which is positioned on a client and is used for acquiring user behavior data within user running time and transmitting the user behavior data to a server, and a user behavior analyzing and predicting module which is positioned on a server side and is used for establishing a user behavior model and analyzing and predicting user behavior according to user behavior data acquired by the user behavior data acquisition module positioned on the client. The method comprises the following steps of: A, establishing a user behavior model; B, acquiring user behavior data within user running time; and C, and analyzing and predicting user behavior according to the acquired user behavior data. According to the technical scheme of invention, the integrity and effectiveness of data can be ensured; and behavior prediction is partitioned into group long-term behavior prediction and individual short-term behavior prediction, so that the correlation between user property and user behavior is fully mined. Comprehensive behavior prediction is performed by using a neural network, so that a prediction result is perfected and made accurate continuously.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MAILIAN COMP TECH
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
ActiveUS20140122399A1Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
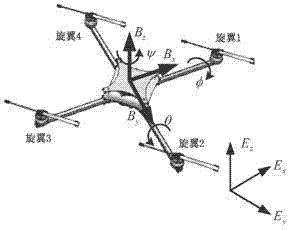
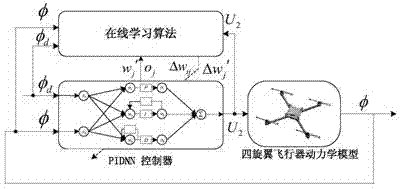
Four-rotor aircraft control method based on PID neural network (PIDNN) control
InactiveCN104765272AZero errorGuaranteed stabilityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsDynamic equationInner loop
The invention discloses a four-rotor aircraft control method based on PID neural network (PIDNN) control. First, dynamic equations of a four-rotor aircraft are established based on the Newton-Euler equations, and then, a nested controller is proposed. An inner loop decentralized controller is designed based on a PIDNN method to realize attitude control, and the outer loop adopts a classical PID control method. Next, online learning of a PIDNN controller is realized by an error back propagation method, the connection initial weight of PIDNN is determined based on the principle of PID control, and an appropriate learning step is selected according to the discrete Lyapunov theory to guarantee the convergence of the controller. Thus, the control problem of a four-rotor aircraft caused by high degree of nonlinearity, strong coupling and under-actuating capability, disturbance from the external environment in the process of flight and other factors can be effectively solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
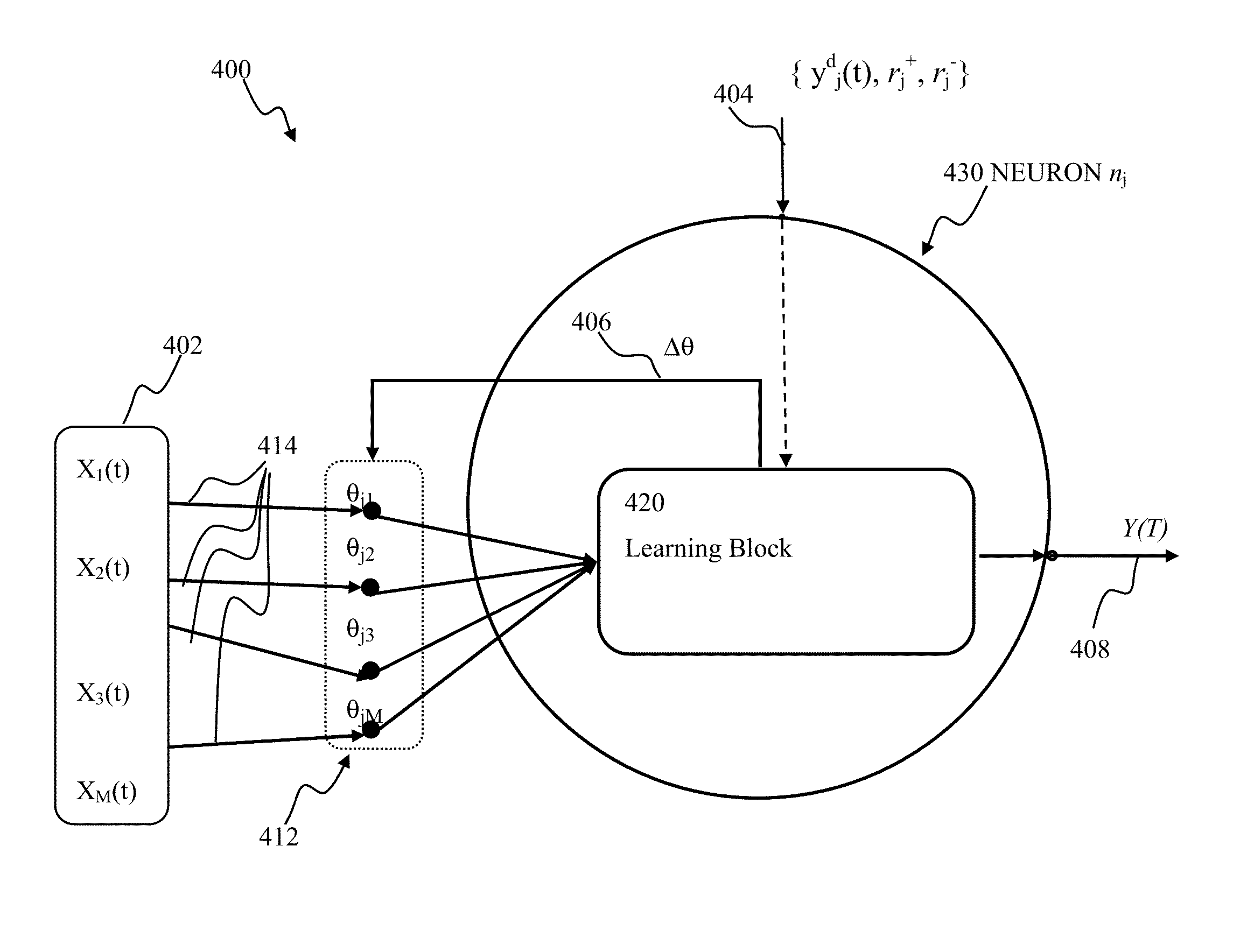
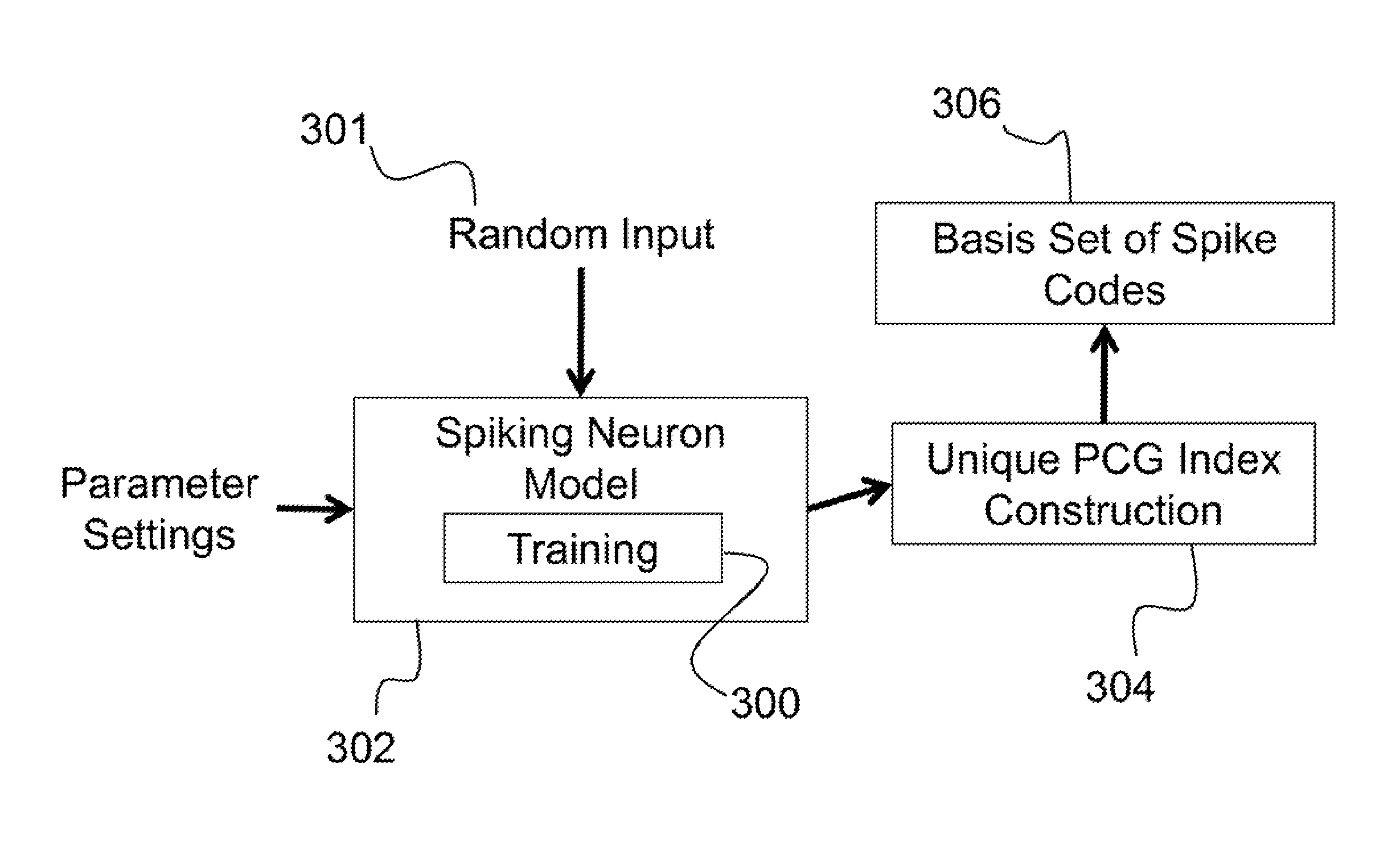
System for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal
Described is a system for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal. The system constructs an index of unique polychronous groups (PCGs) from a spiking neuron network. Thereafter, a basis set of spike codes is generated from the unique PCGs. An input signal can then be received, with the input signal being spike encoded using the basis set of spike codes from the unique PCGs. The input signal can then be reconstructed by looking up in a reconstruction table, for each unique PCG in the basis set in temporal order according to firing times, anchor neurons. Using a neuron assignment table, an output location can be looked up for each anchor neuron to place a value based on the firing times of each unique PCG. Finally, the output locations of the anchor neurons can be compiled to reconstruct the input signal.
Owner:HRL LAB
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS8977582B2Reduce image dataDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContent distributionNeuron network
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
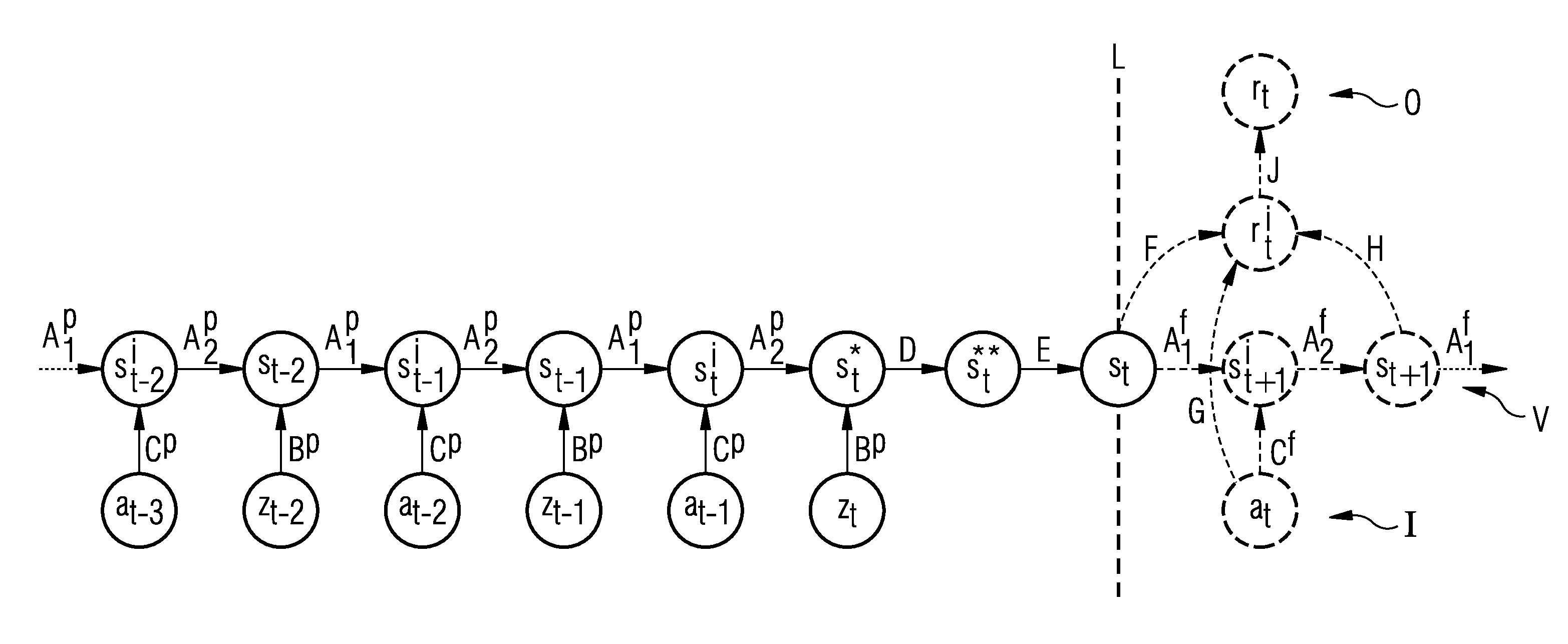
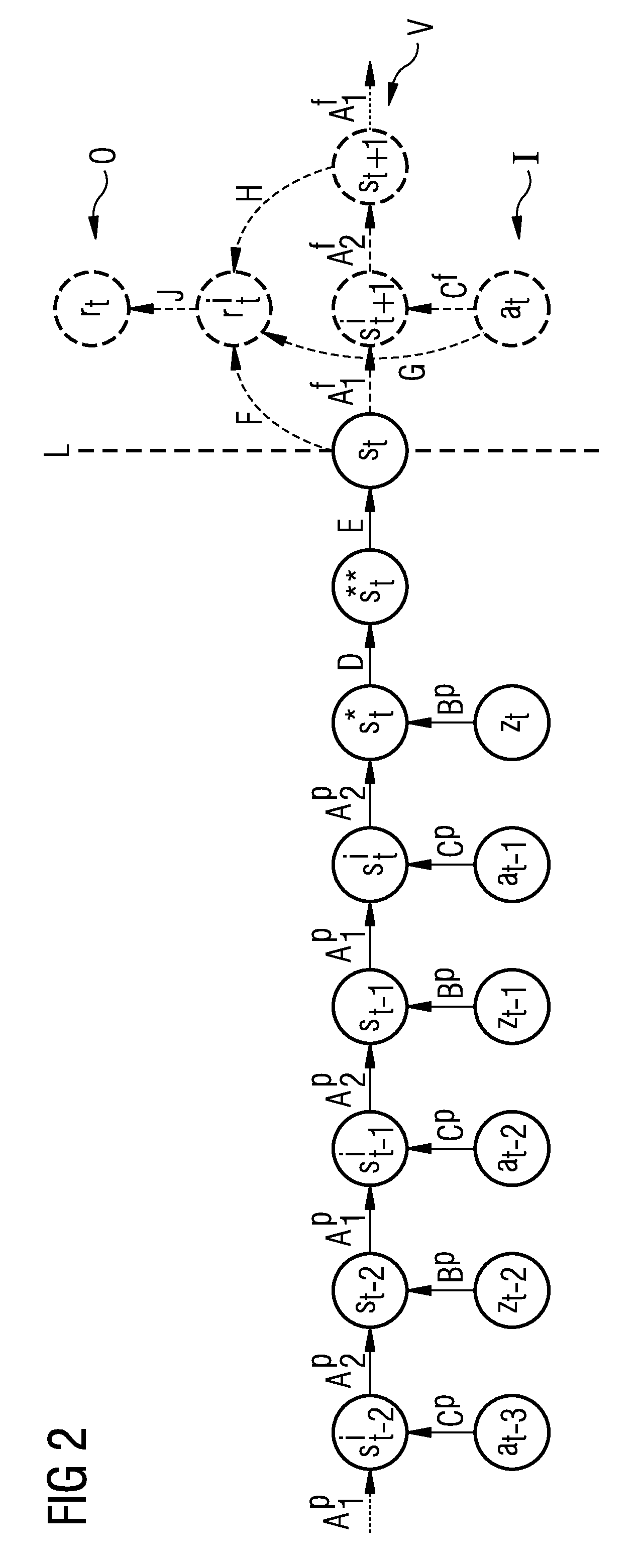
Method for the computer-aided control of a technical system
InactiveUS20130013543A1Improve accuracyImprove computing efficiencyDigital computer detailsNeural learning methodsHidden layerComputer-aided
A method for the computer-aided control of a technical system is provided. A recurrent neuronal network is used for modeling the dynamic behaviour of the technical system, the input layer of which contains states of the technical system and actions carried out on the technical system, which are supplied to a recurrent hidden layer. The output layer of the recurrent neuronal network is represented by an evaluation signal which reproduces the dynamics of technical system. The hidden states generated using the recurrent neural network are used to control the technical system on the basis of a learning and / or optimization method.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat or prevent autism spectrum disorders and other disorders of psychological development
ActiveUS20130184792A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsExternal electrodesPervasive developmental disorderArrhythmia sinus
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing an autism spectrum disorder, a pervasive developmental disorder, or a disorder of psychological development. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. The nerve stimulation may be used as a behavior conditioning tool, by producing euphoria in an autistic individual. Vagus nerve stimulation is also used to modulate circulating serotonin levels in a pregnant woman so as to reduce the risk of having an autistic child; modulate the levels of growth factors within a child; promote balance of neuronal excitation / inhibition; modulate the activity of abnormal resting state neuronal networks; increase respiratory sinus arrhythmia; and avert episodes of motor stereotypies with the aid of forecasting methods.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC +1
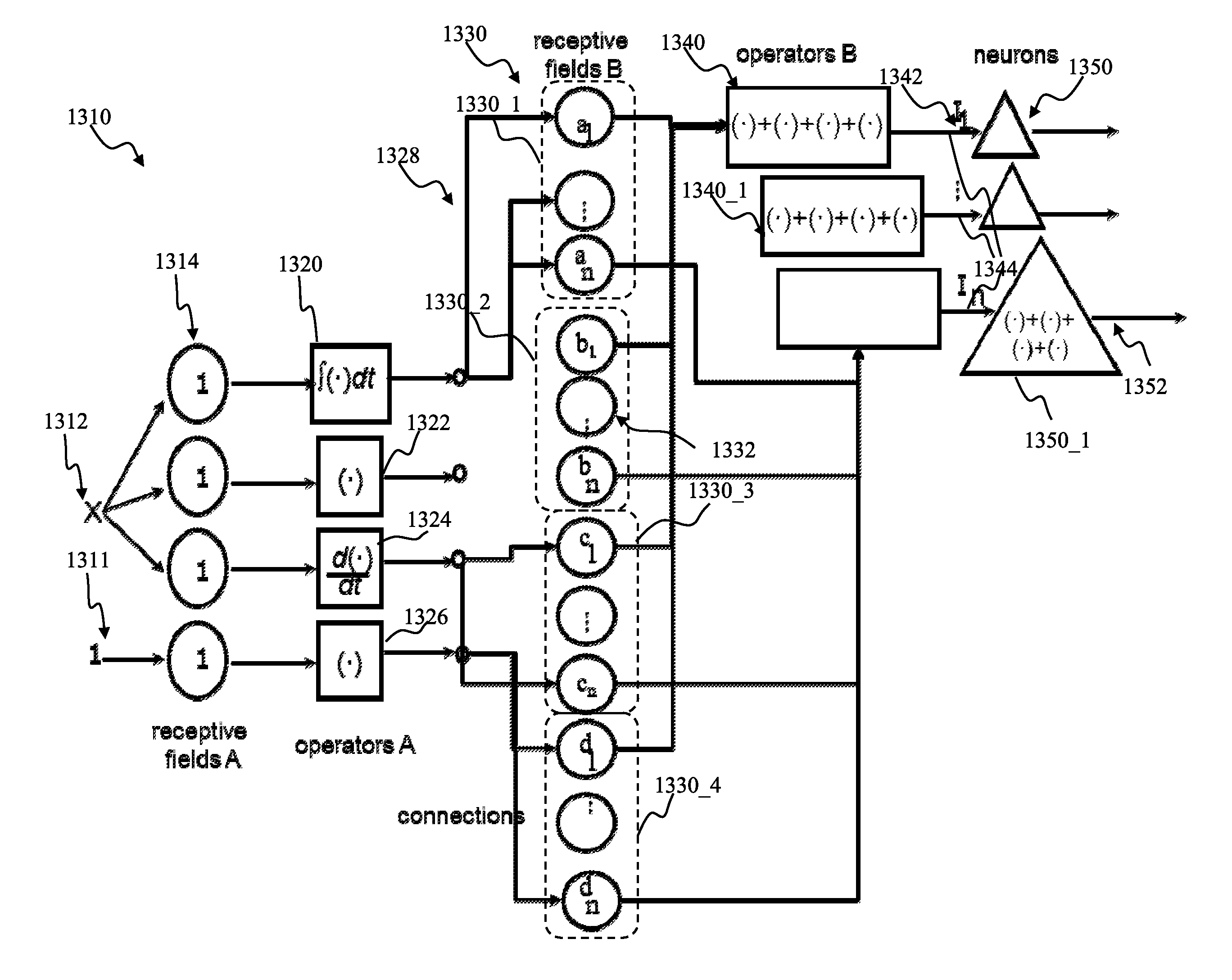
Proportional-integral-derivative controller effecting expansion kernels comprising a plurality of spiking neurons associated with a plurality of receptive fields
ActiveUS9082079B1Improve connection efficiencyEasy to measureDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuron networkControl engineering
Adaptive proportional-integral-derivative controller apparatus of a plant may be implemented. The controller may comprise an encoder block utilizing basis function kernel expansion technique to encode an arbitrary combination of inputs into spike output. The basis function kernel may comprise one or more operators configured to manipulate basis components. The controller may comprise spiking neuron network operable according to reinforcement learning process. The network may receive the encoder output via a plurality of plastic connections. The process may be configured to adaptively modify connection weights in order to maximize process performance, associated with a target outcome. Features of the input may be identified and used for enabling the controlled plant to achieve the target outcome.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
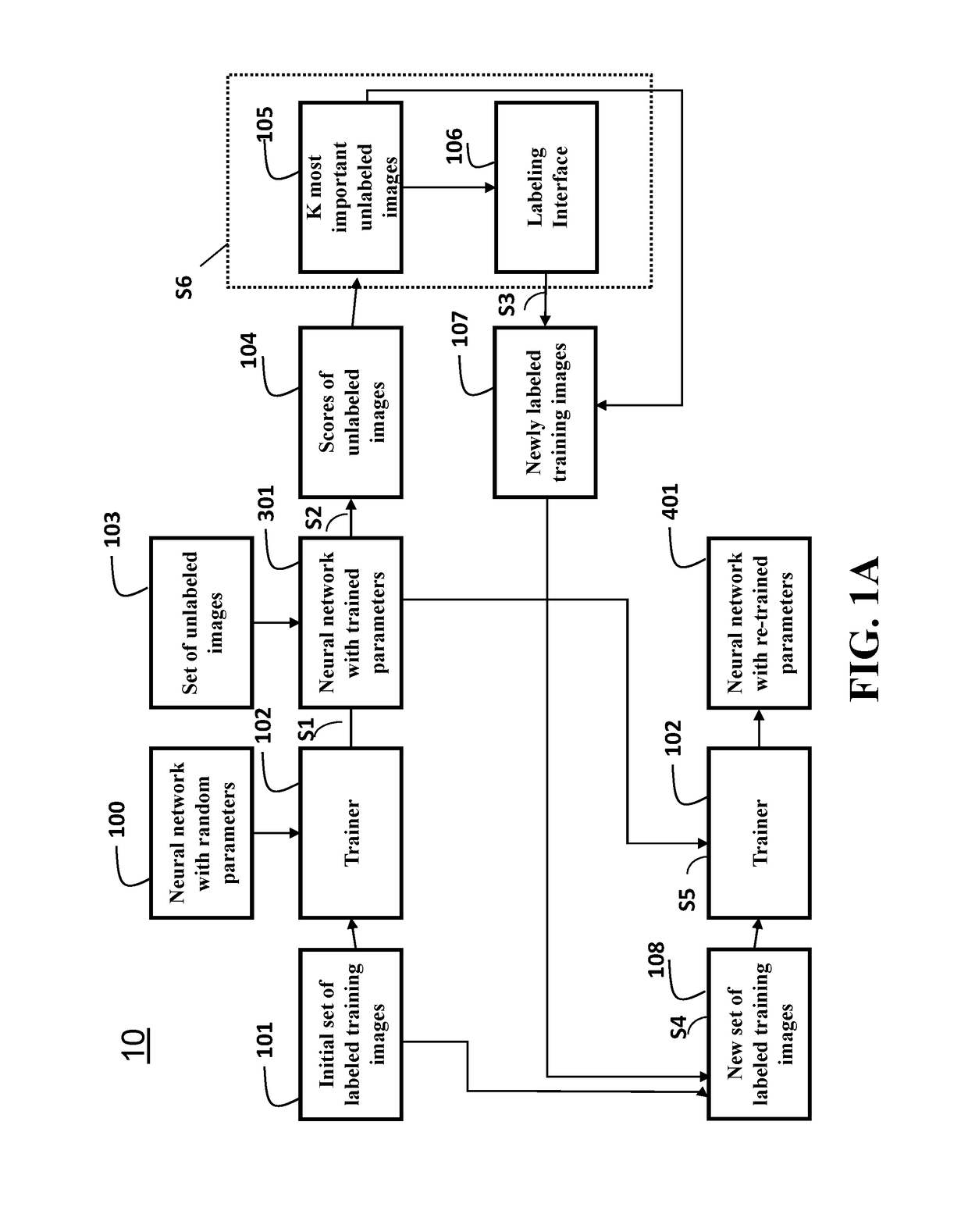
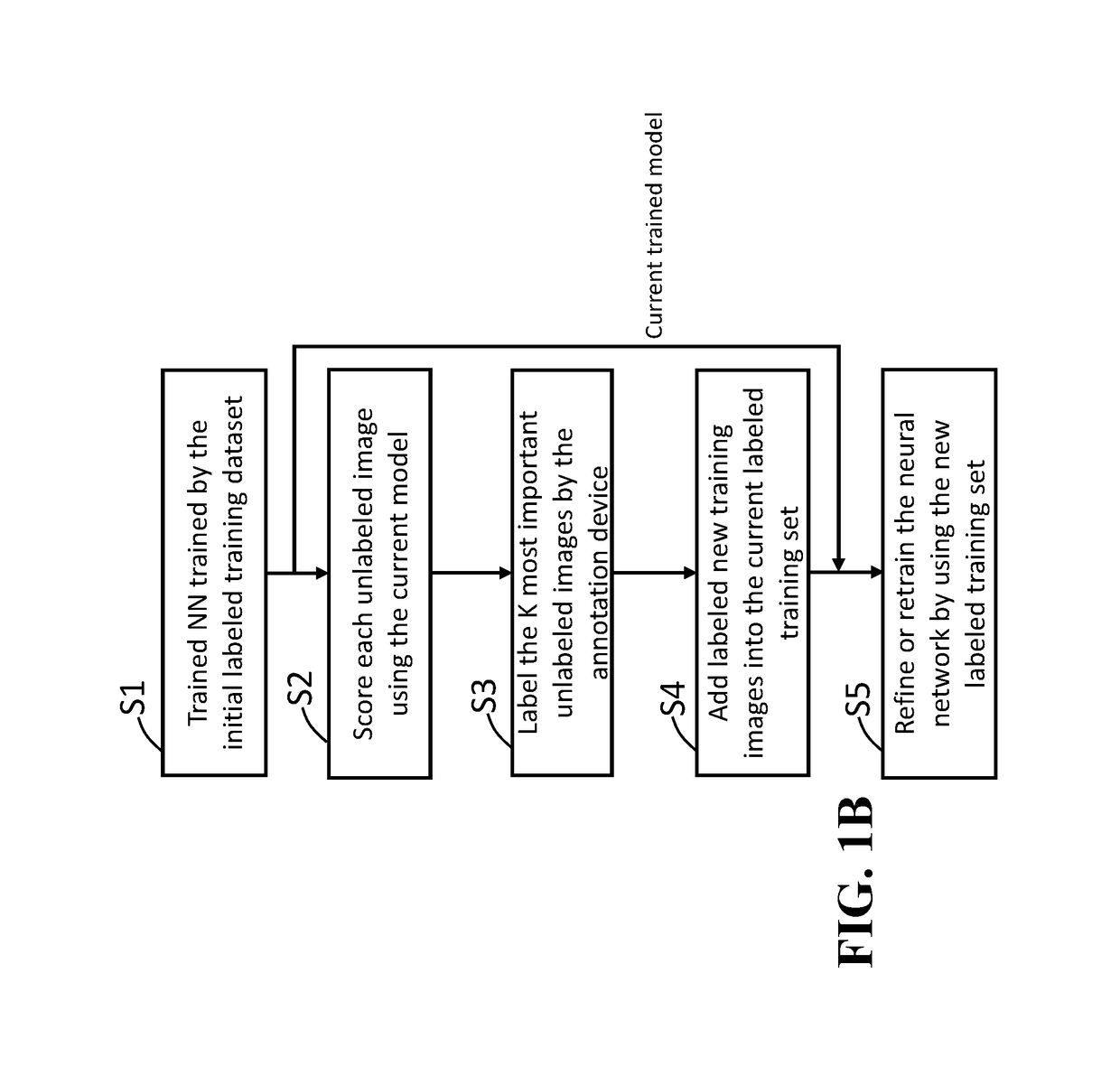
Active Learning Method for Training Artificial Neural Networks
InactiveUS20180144241A1Improve accuracyFunction increaseNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNeuron networkProactive learning
A method for training a neuron network using a processor in communication with a memory includes determining features of a signal using the neuron network, determining an uncertainty measure of the features for classifying the signal, reconstructing the signal from the features using a decoder neuron network to produce a reconstructed signal, comparing the reconstructed signal with the signal to produce a reconstruction error, combining the uncertainty measure with the reconstruction error to produce a rank of the signal for a necessity of a manual labeling, labeling the signal according to the rank to produce the labeled signal; and training the neuron network and the decoder neuron network using the labeled signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Temporal winner takes all spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140219497A1Suppress generationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionImage compression
Apparatus and methods for contrast enhancement and feature identification. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. An inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the other neurons within an area of influence of the inhibitory neuron. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the other neurons to stimulus that is proximate to the feature thereby increasing contrast within the encoded data. The contrast enhancement may facilitate feature identification within the image. Feature detection may be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Portable intelligent electronic nose and its preparing process
InactiveCN1381721AWith quantitative functionEasy to measureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayNeuron network
A portable intelligent electronic nose for recognizing gas and its preparing method feature use of 4-8 sensor arrays whose signal output is serially sent to a regulator circuit, a pattern recognizer and a computer. The pattern recognition and non-linear fitting of nerve cell network, the artificial nerve network model with forward transfer, and the training algorithm with backward transfer of error are used. The electronic nose can detect one or several gases in the range of selected sensors and further possess the function of quantitative analysis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Izhikevich neural network synchronous discharging simulation platform based on FPGA
InactiveCN104615909AIncrease flexibilityEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsControl signalNetwork model
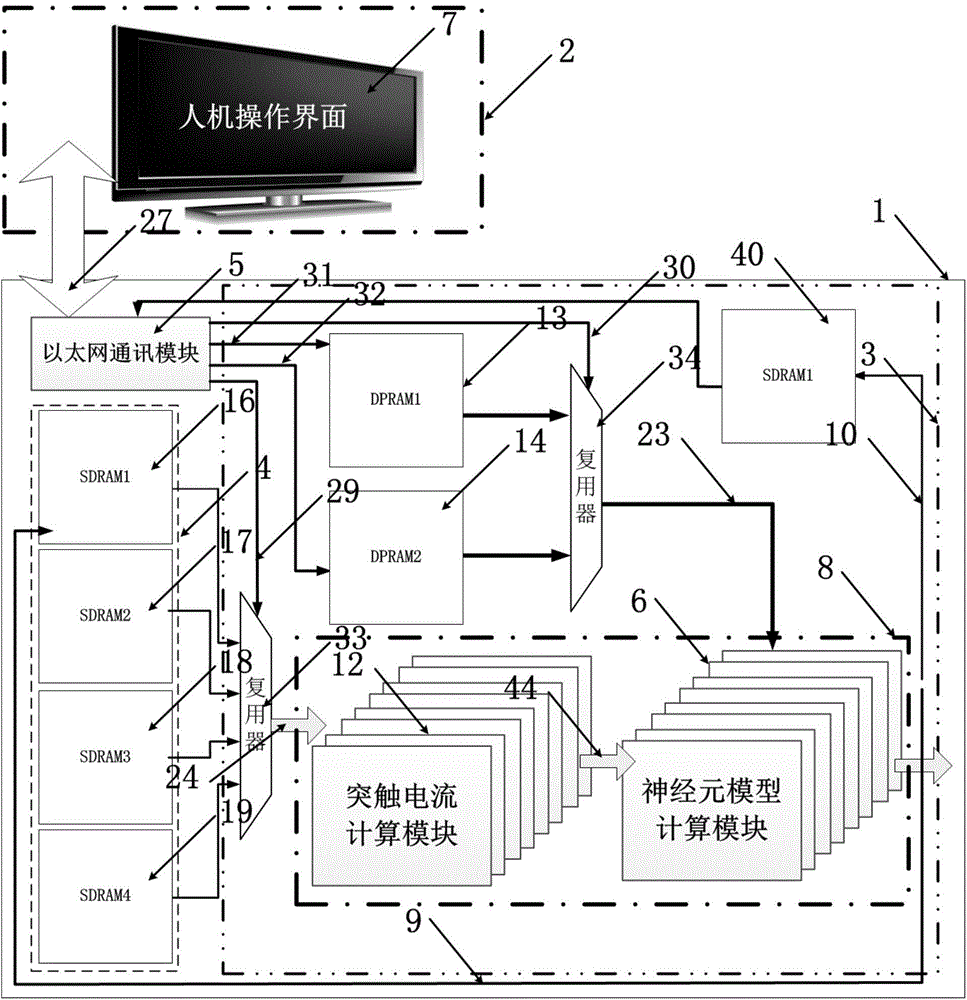
The invention provides an Izhikevich neural network synchronous discharging simulation platform based on an FPGA. The simulation platform comprises an FPGA neural network computing processor and an upper computer which are connected with each other. The FPGA neural network computing processor comprises an FPGA chip, an off-chip memorizer array and an Ethernet communication module, wherein the FPGA chip receives an upper computer control signal output by the off-chip memorizer array, and receives a presynaptic membrane potential signal output by the off-chip memorizer array. The upper computer is in communication with the FPGA chip and the off-chip memorizer array through a VB programming realization man-machine operating interface and the Ethernet communication module, and a neural network model is established on the FPGA chip through Verilog HDL language programming. The Izhikevich neural network synchronous discharging simulation platform has the advantages that the hardware modeling of the phenotype and physiological type neural network model is achieved through an animal-free experiment serving as a biological neural network on the basis of an FPGA neural network experiment platform conducting computation at a high speed, and the consistency with true biological nerve cells on the time scale can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com