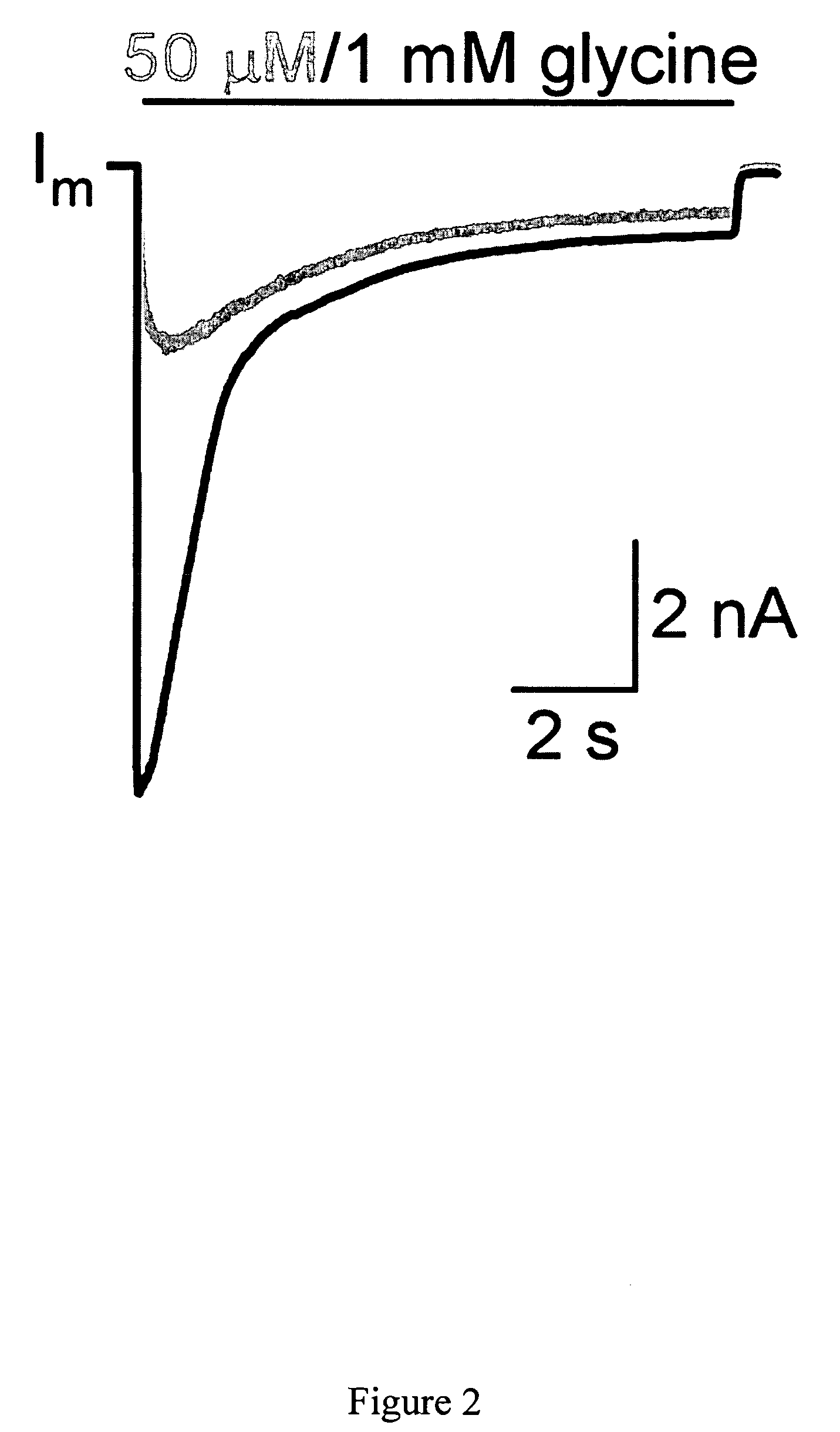Patents
Literature
55 results about "Excitable cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
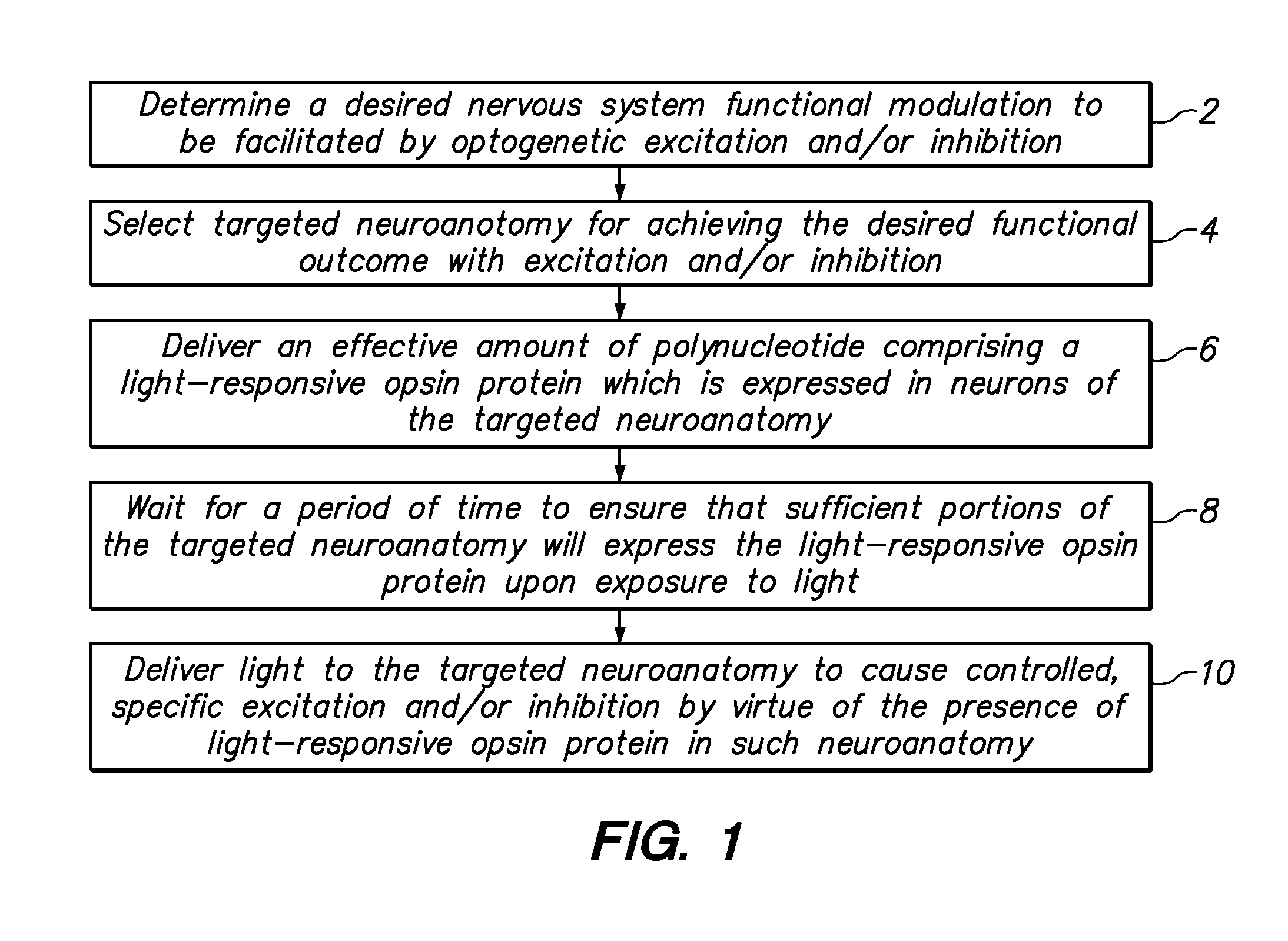
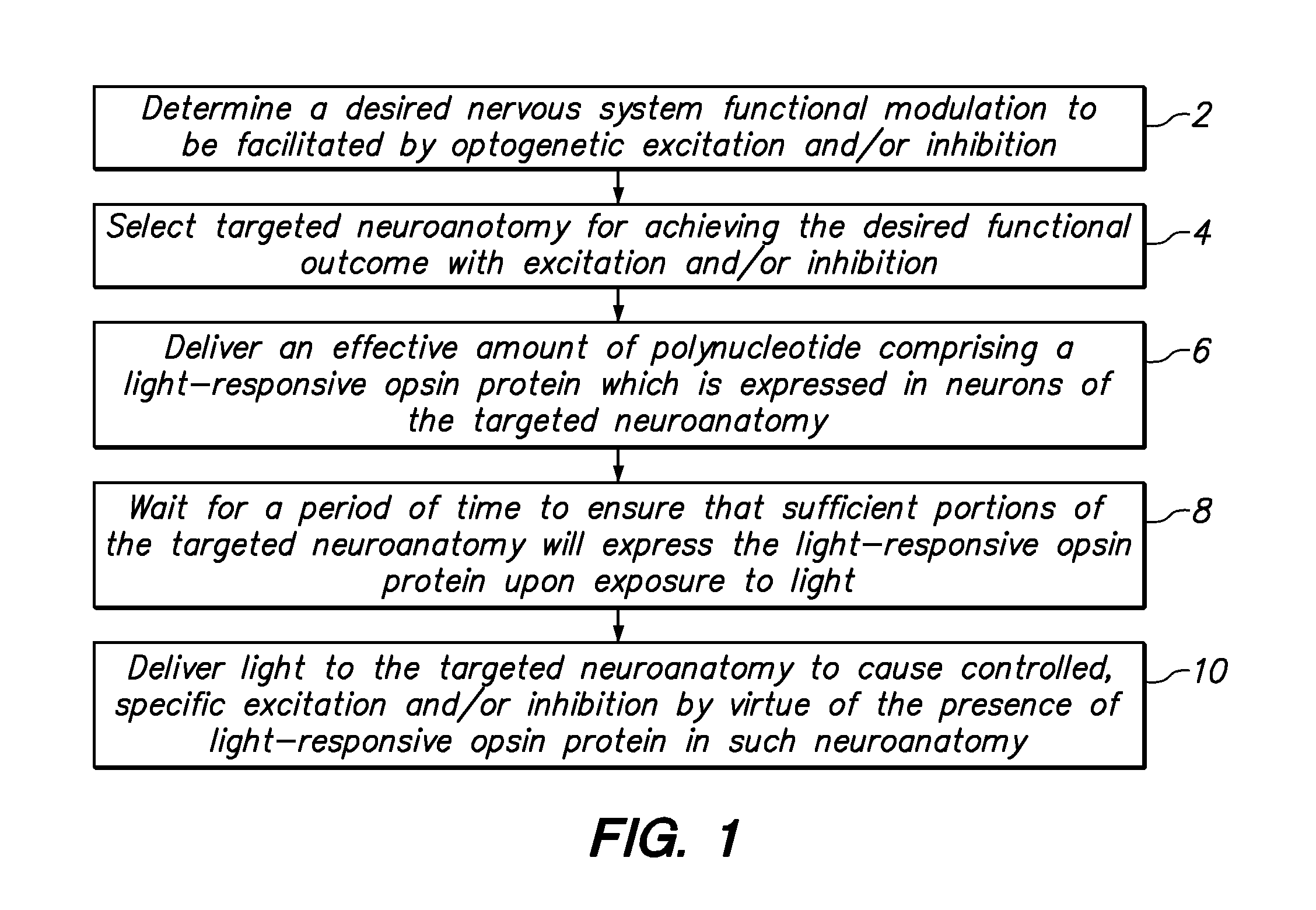
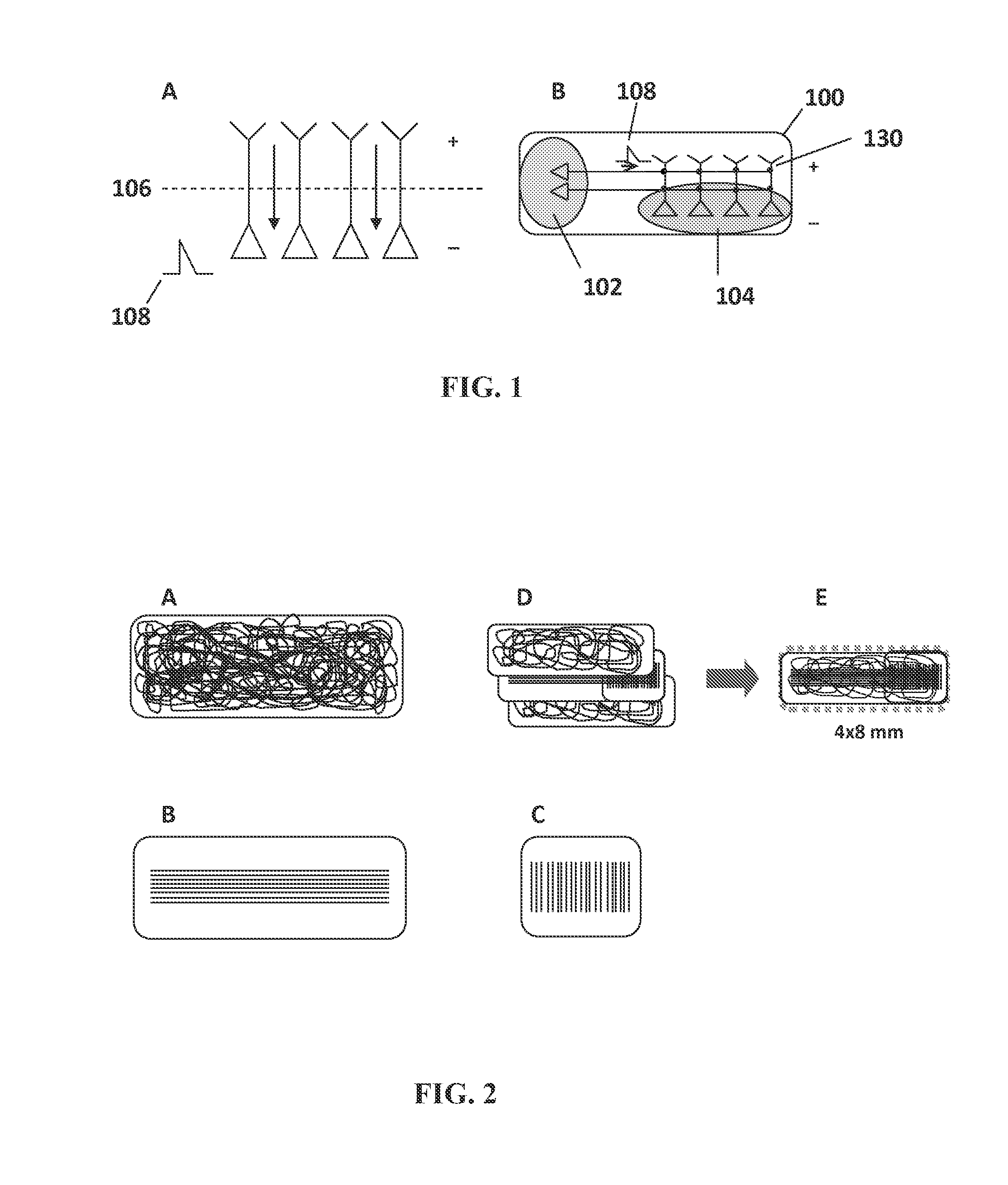
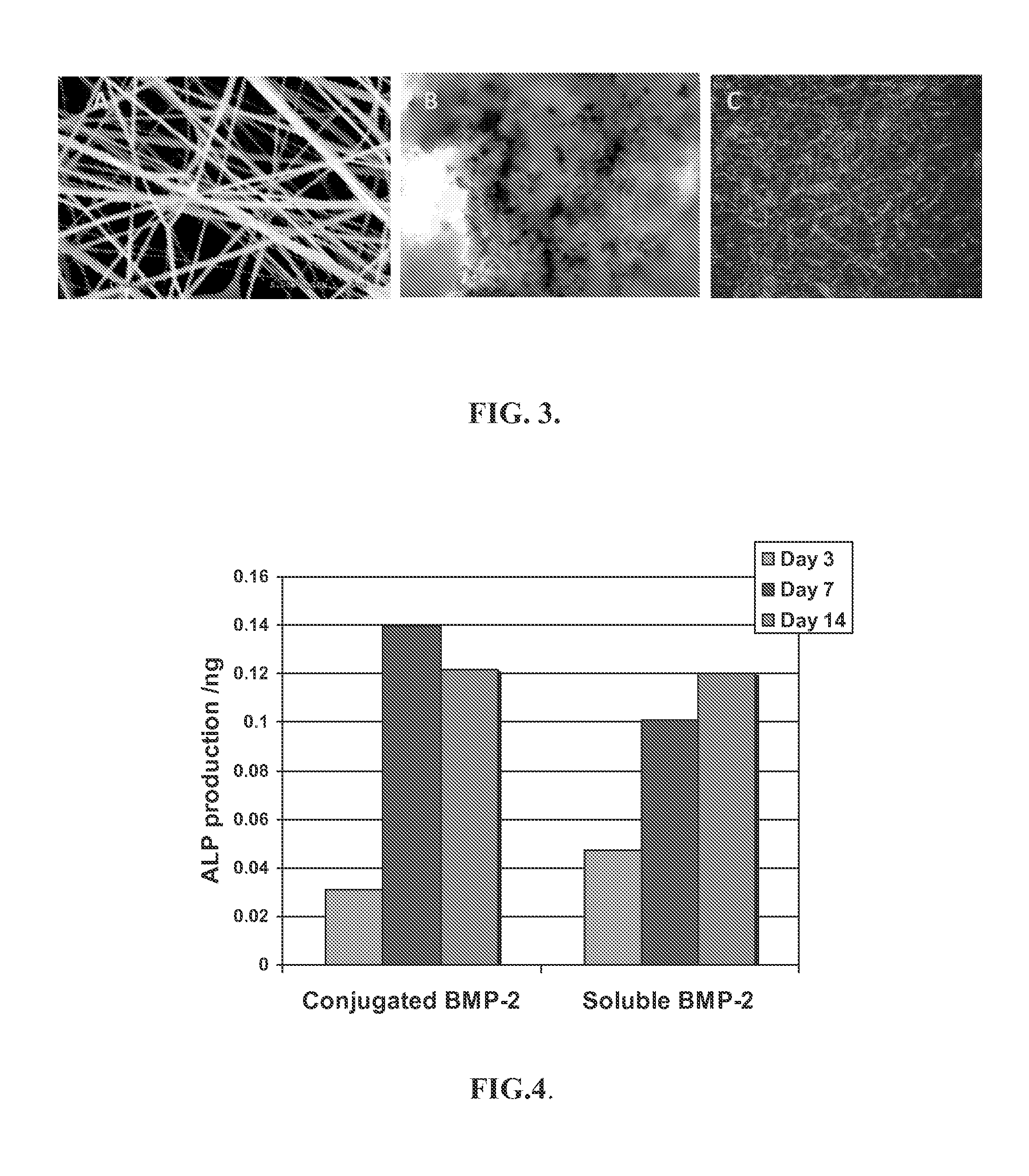
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070261127A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
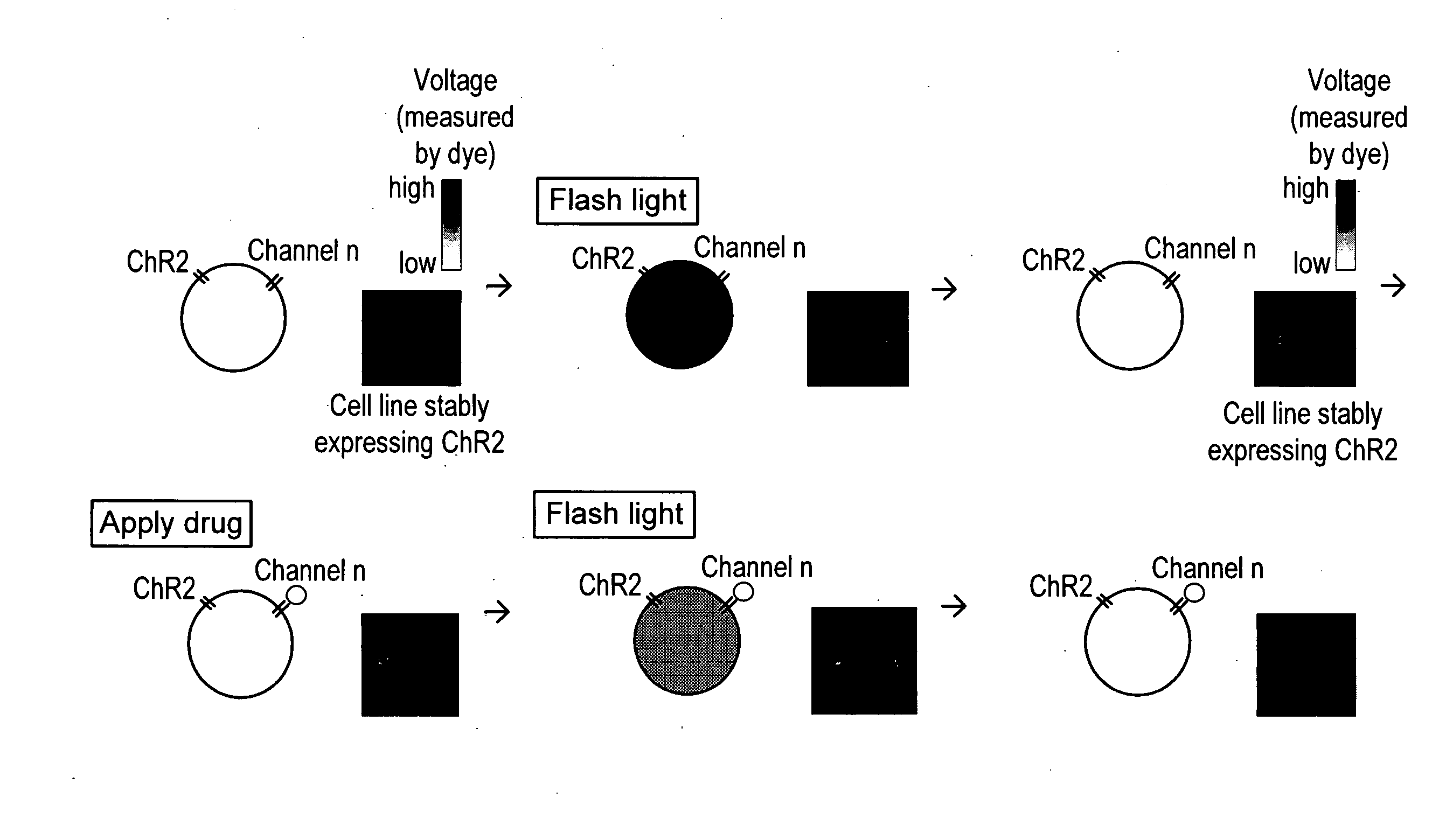
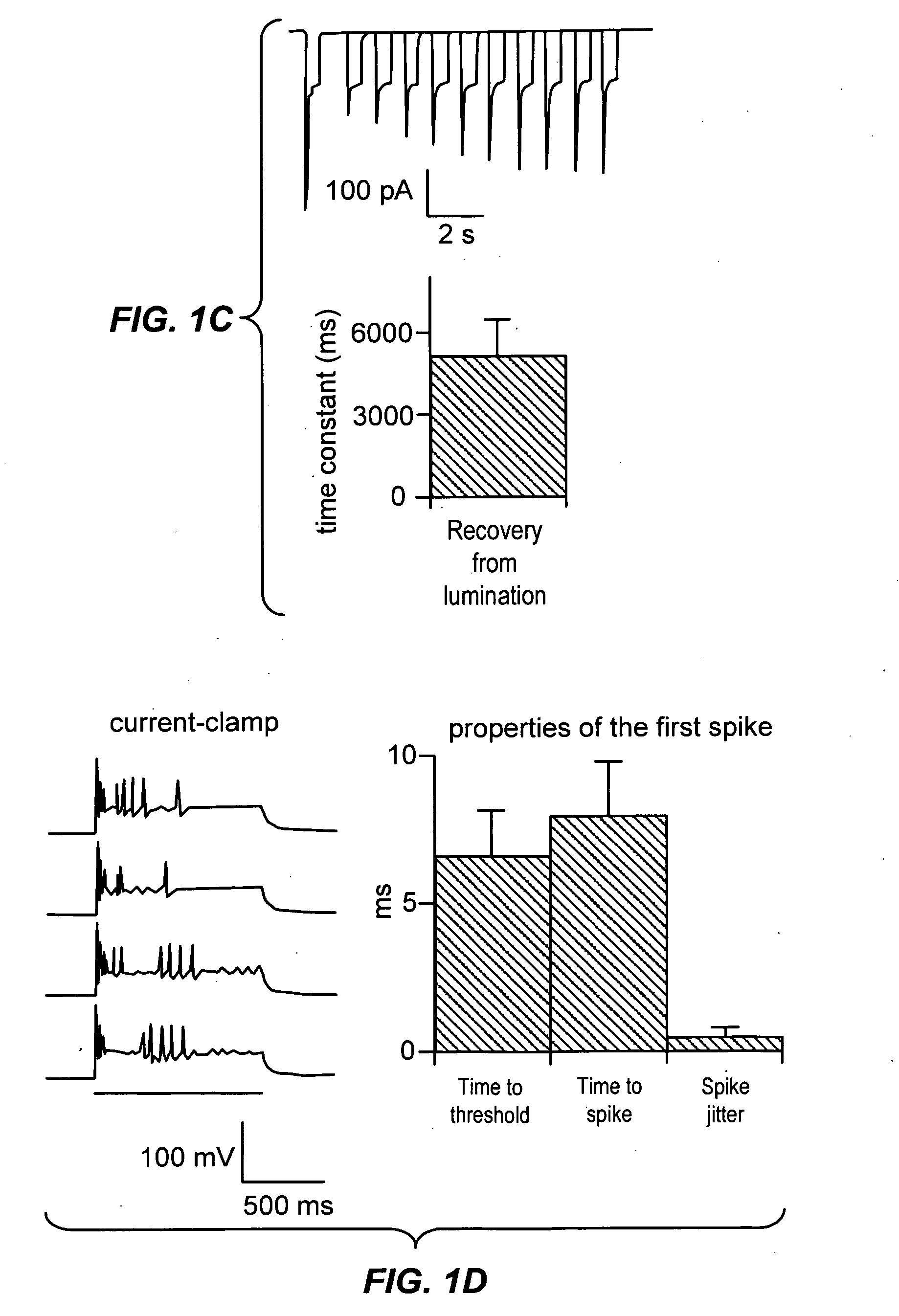
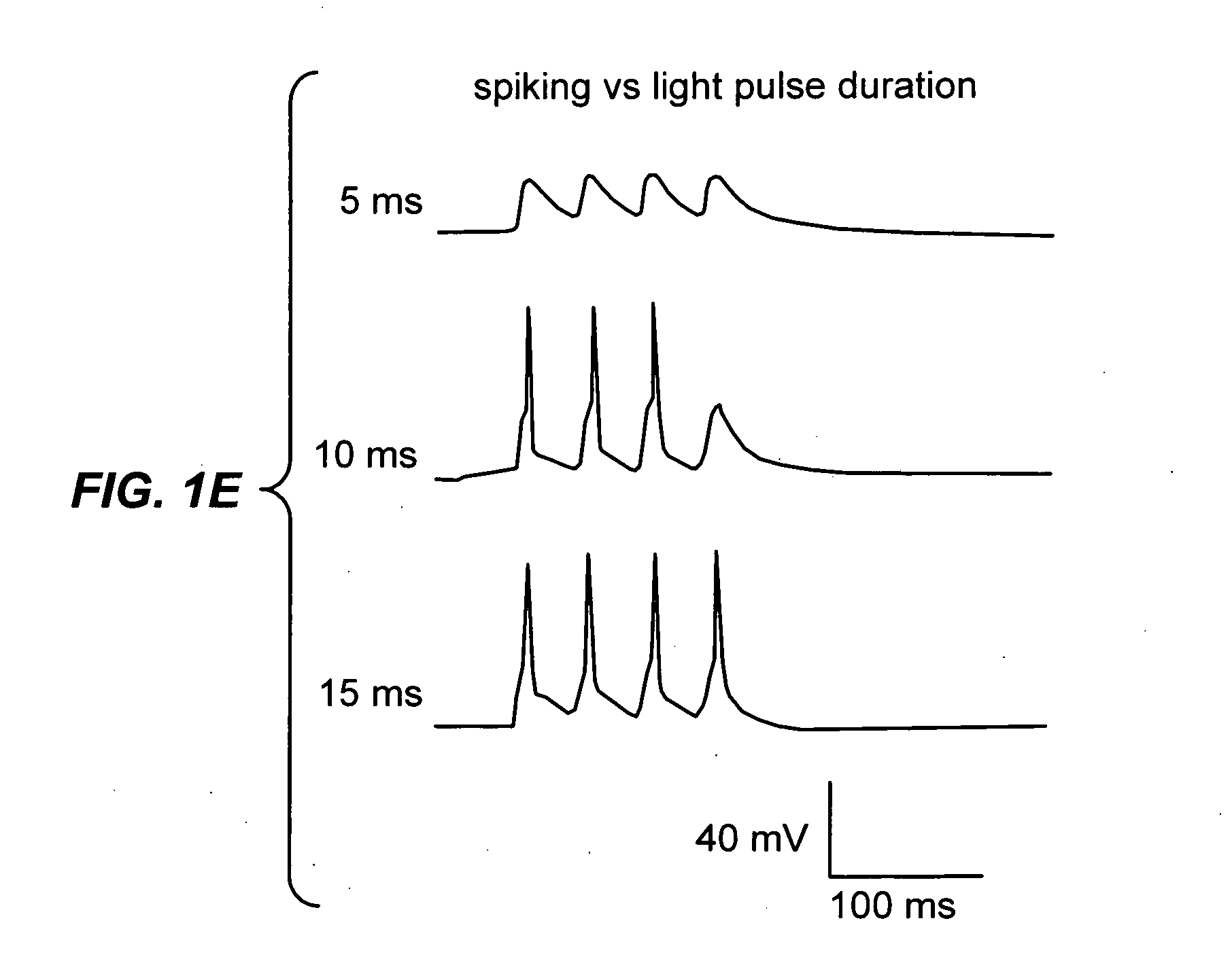
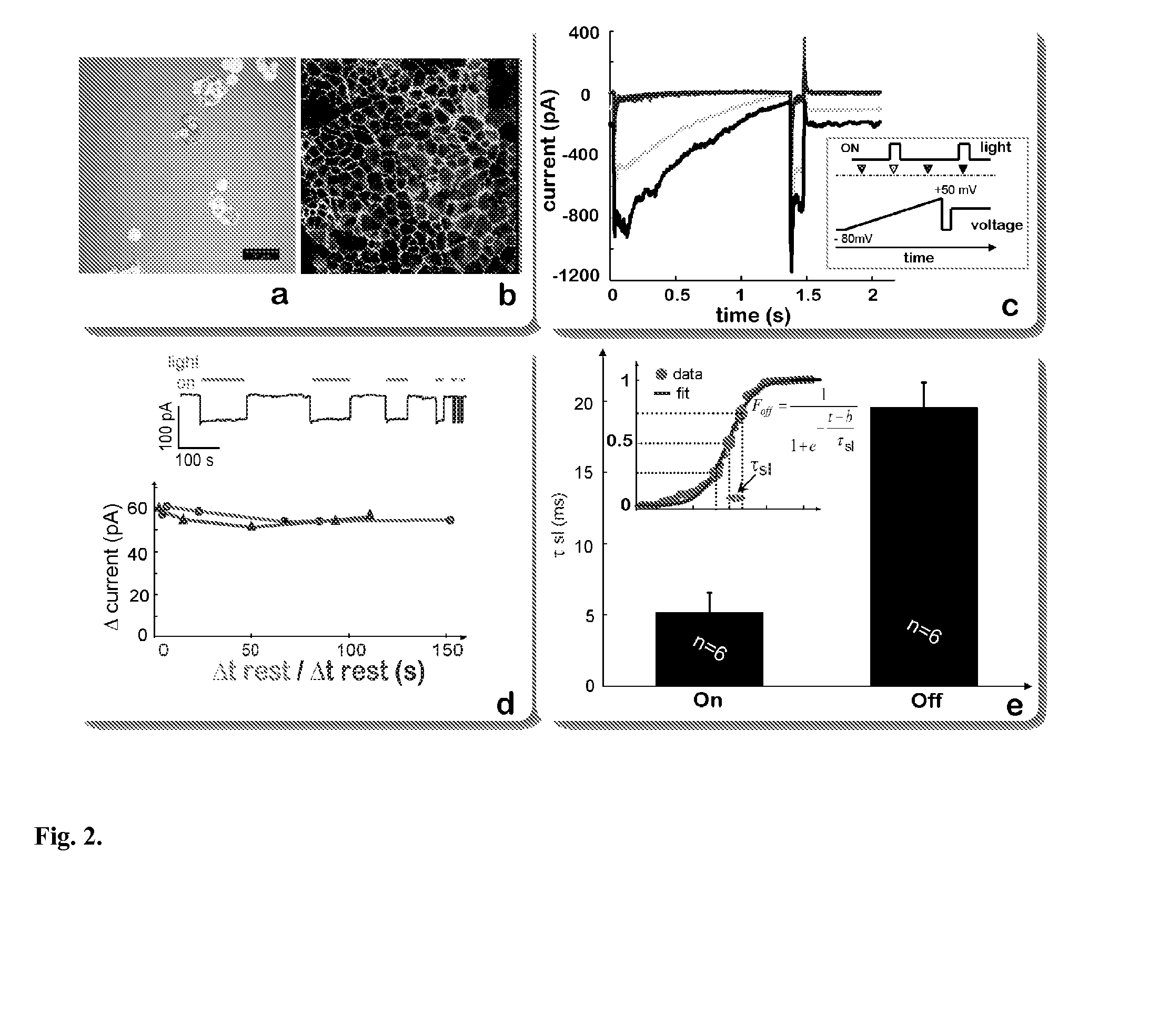
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Light-activated cation channel and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070054319A1Improve abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell membraneExcitable cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for light-activated cation channel proteins and their uses within cell membranes and subcellular regions. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-activated cation channels to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides millisecond-timescale temporal control of cation channels using moderate light intensities in cells, cell lines, transgenic animals, and humans. The invention provides for optically generating electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells useful for driving neuronal networks, drug screening, and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
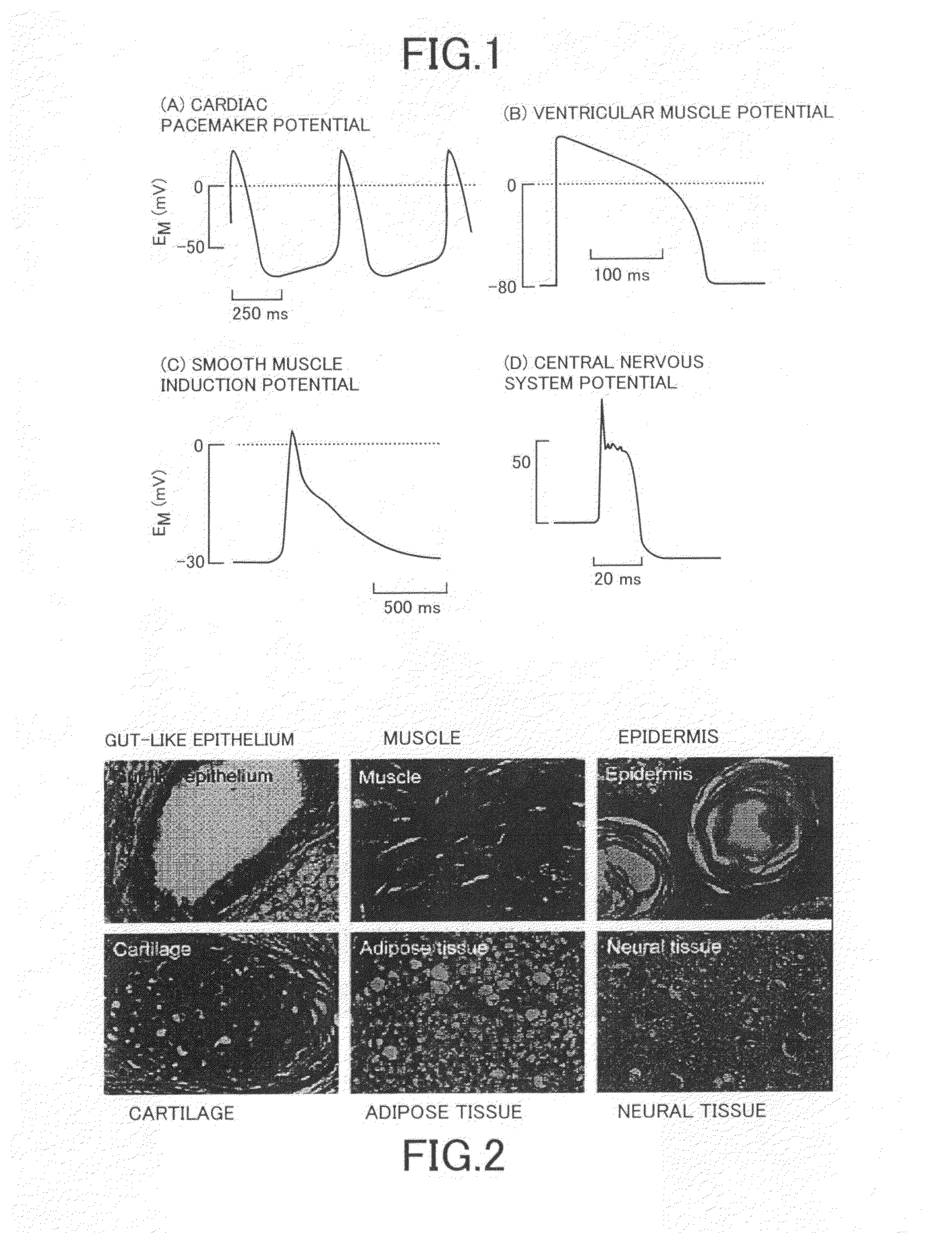
Application of electrical stimulation for functional tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS20050112759A1Highly integratedImprove functionalityMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processIt integrationCell survival
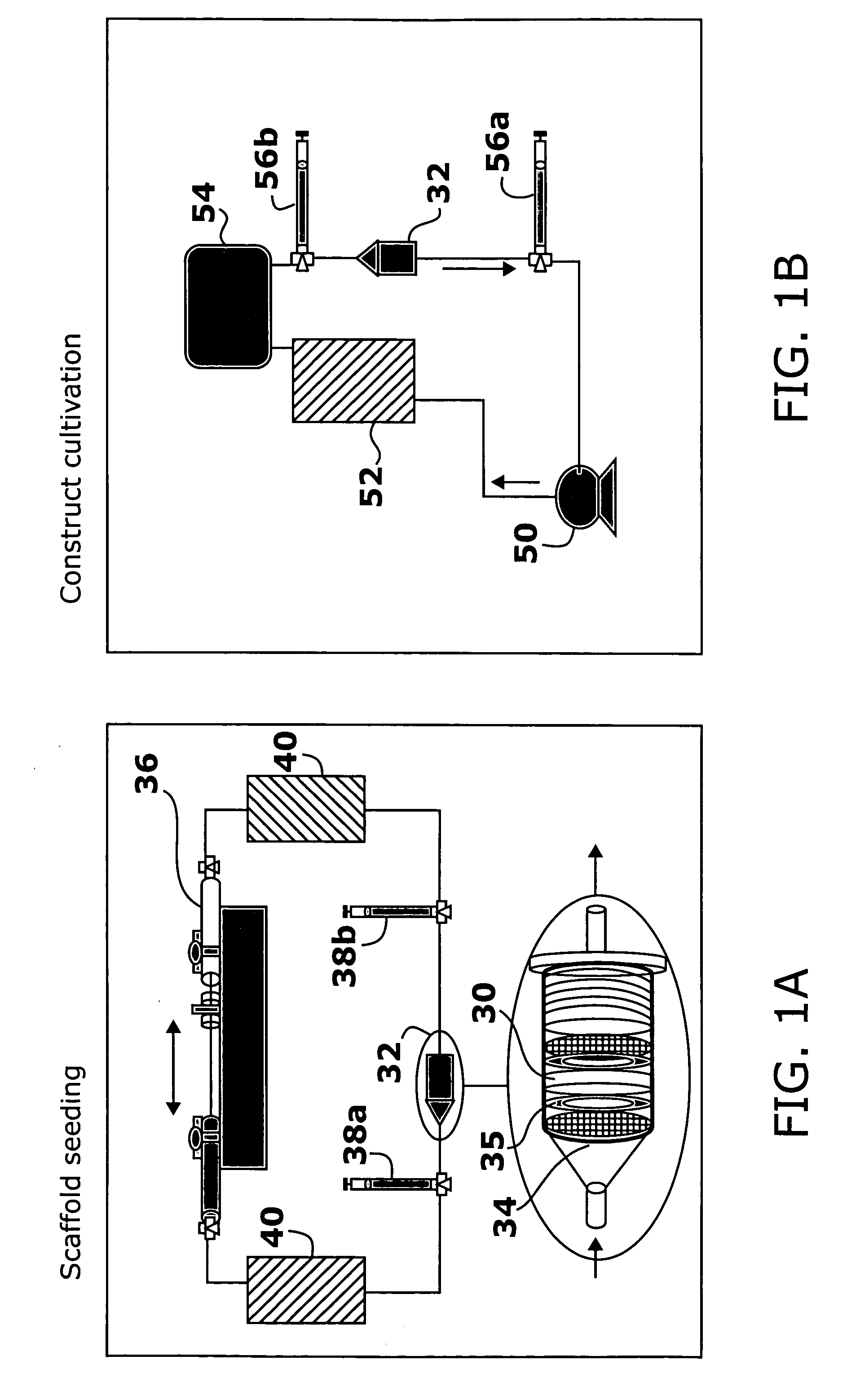
The present invention provides new methods for the in vitro preparation of bioartificial tissue equivalents and their enhanced integration after implantation in vivo. These methods include submitting a tissue construct to a biomimetic electrical stimulation during cultivation in vitro to improve its structural and functional properties, and / or in vivo, after implantation of the construct, to enhance its integration with host tissue and increase cell survival and functionality. The inventive methods are particularly useful for the production of bioartificial equivalents and / or the repair and replacement of native tissues that contain electrically excitable cells and are subject to electrical stimulation in vivo, such as, for example, cardiac muscle tissue, striated skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, bone, vasculature, and nerve tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
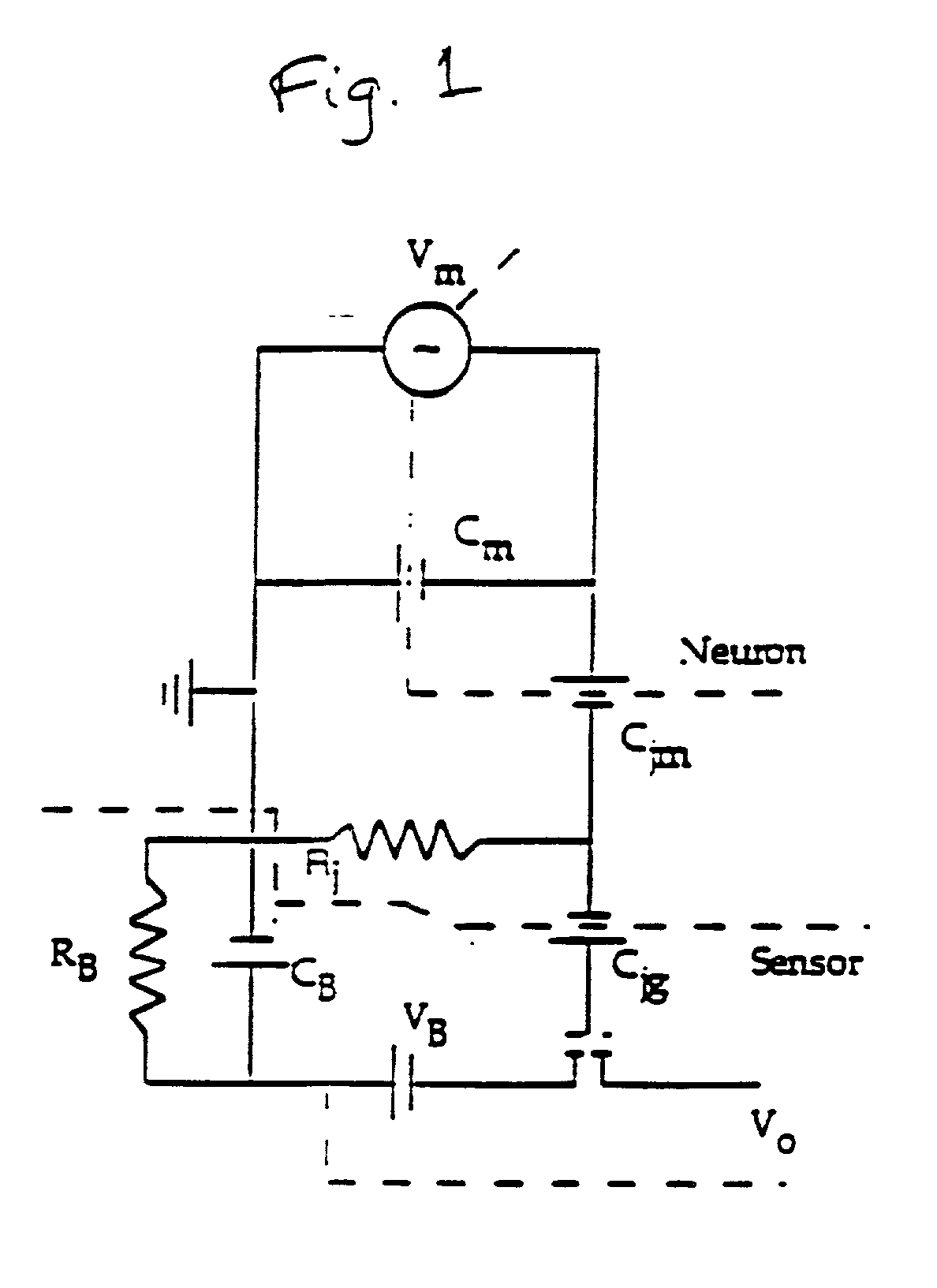
Biological membrane voltage estimator
InactiveUS6163719ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceExcitable cell
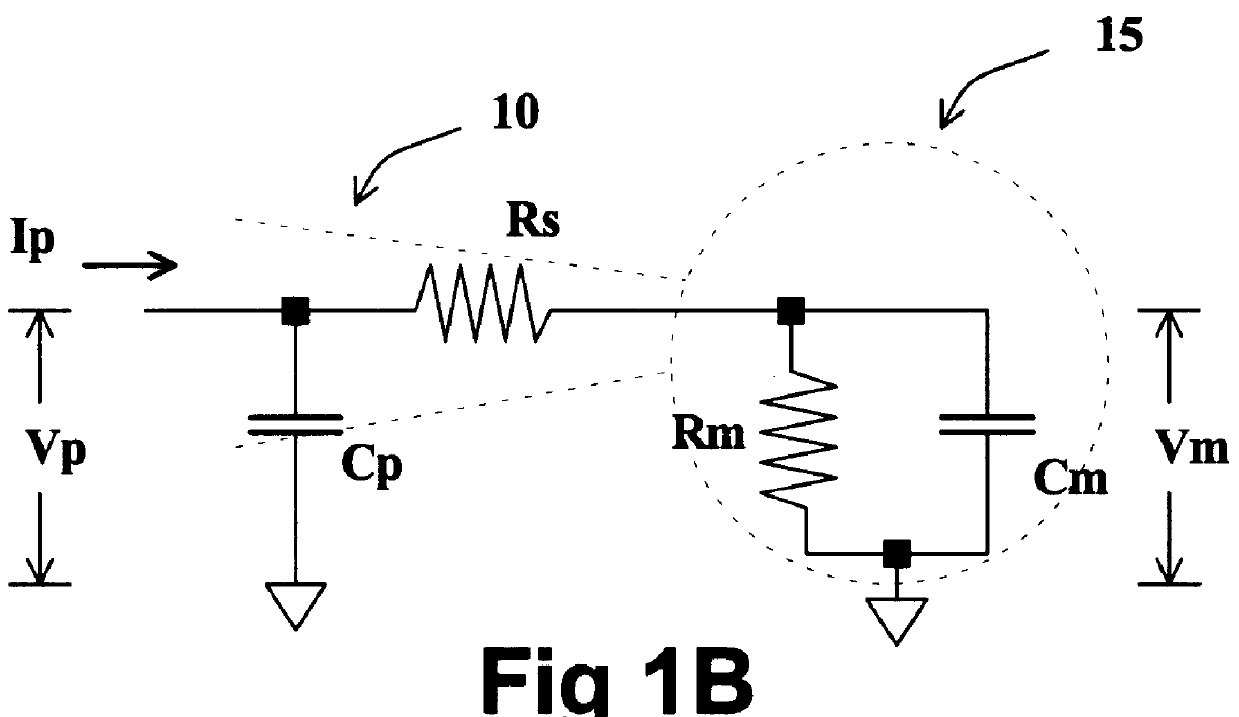
A method and apparatus for estimating the membrane voltage of a cell that is independent of cell conductance. This estimated voltage is used to implement stable, complete (100%) series resistance compensation for a single electrode voltage clamp amplifier, enabling the recording of rapid ionic currents in single, excitable cells.
Owner:ALEMBIC INSTR
System and method for monitoring cardiomyocyte beating, viability and morphology and for screening for pharmacological agents which may induce cardiotoxicity or modulate cardiomyocyte function
ActiveUS20110039294A1Well representedImprove throughput efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell freePharmacological chaperone
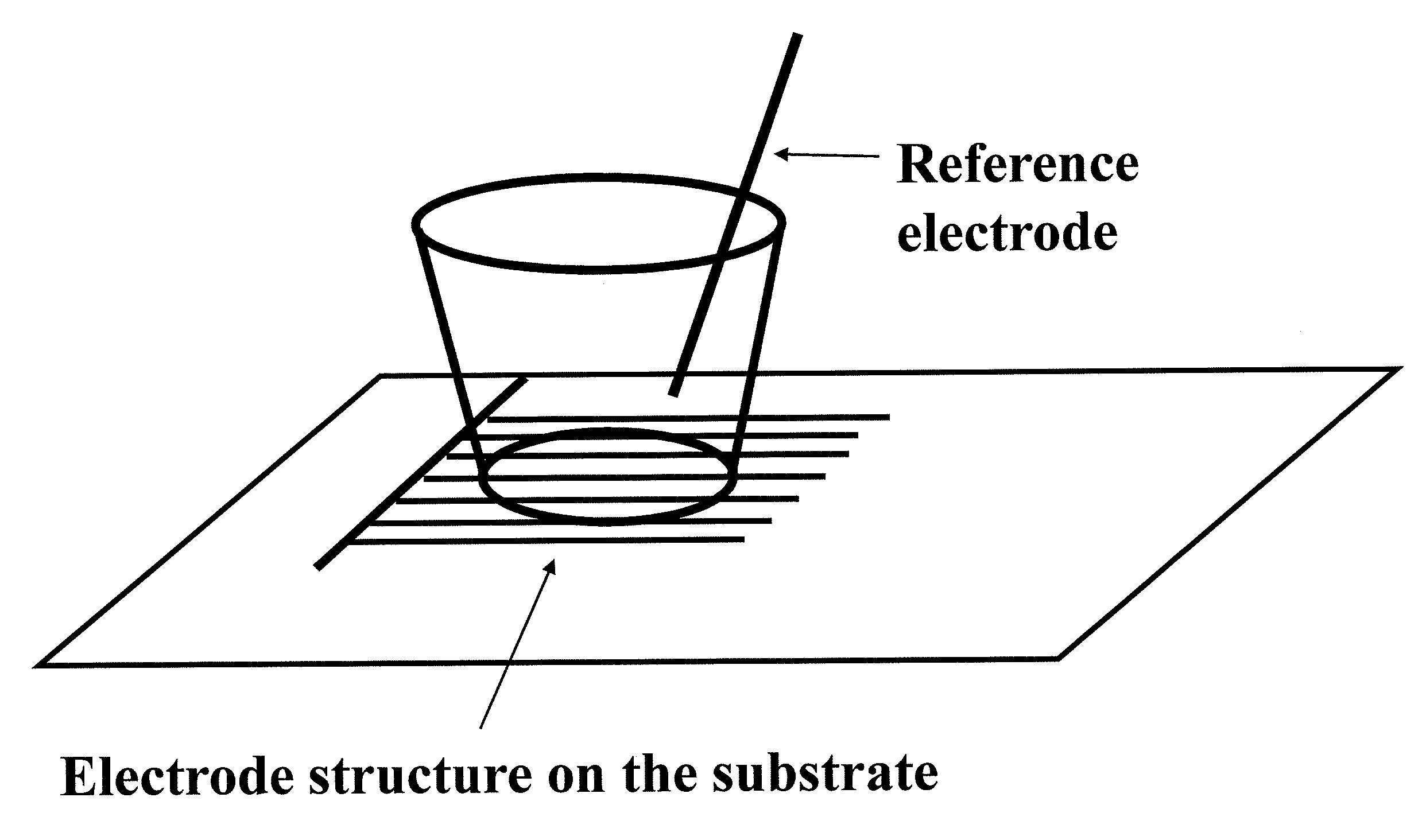
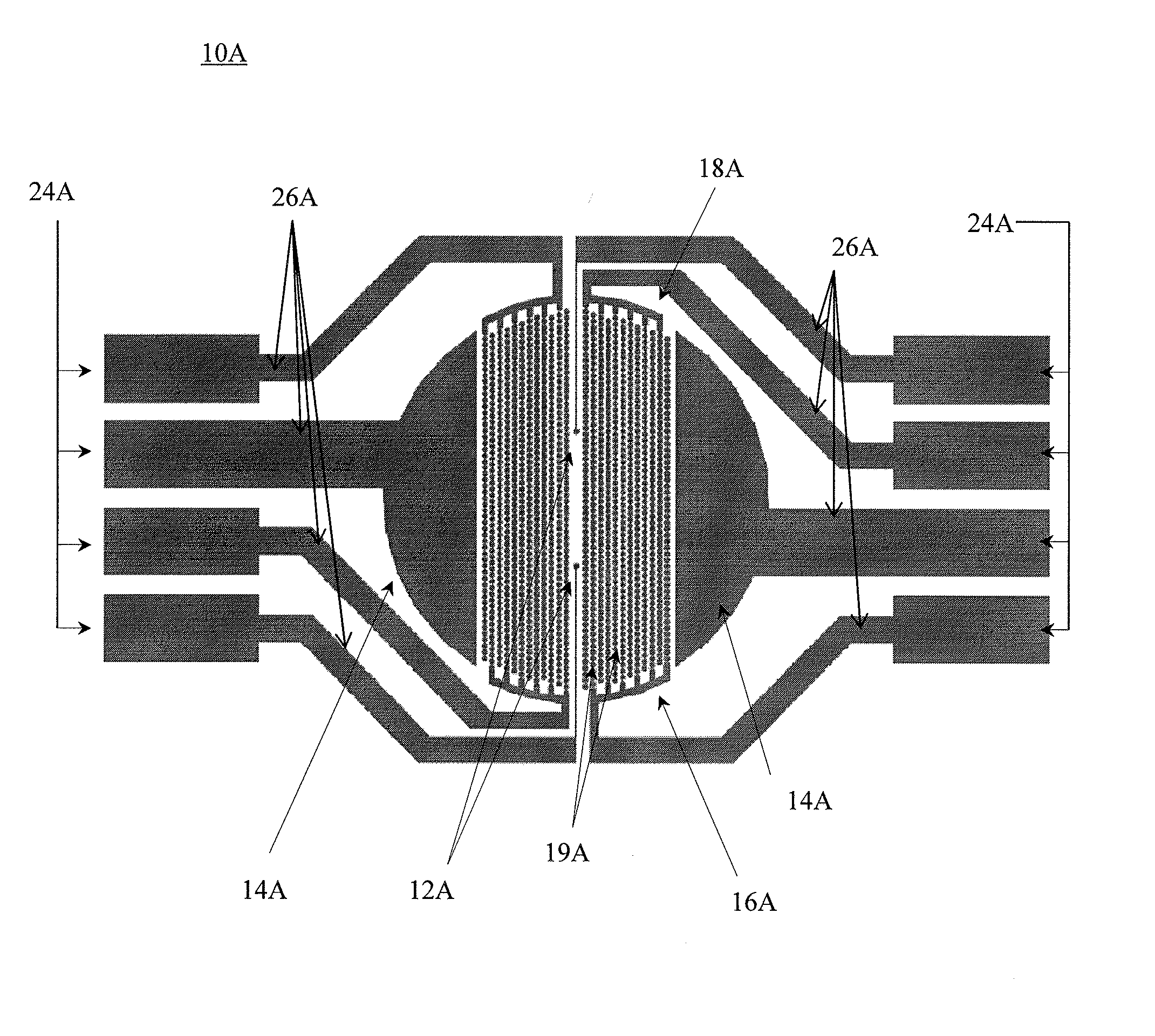
Devices and methods for performing extracellular recording of cells, such as excitable cells, cardiomyocytes, and cardiomyocyte precursor cells is provided. An exemplary device includes a nonconductive substrate forming or provided as a base of one or more wells; a recording electrode positioned on the substrate within the well, wherein the recording electrode is accessible to cells when a cell sample is added to the device; and a reference electrode positioned within the well in a cell-free zone, the cell-free zone characterized as free from contact with cells when the cell sample is added to the device, thereby preventing contact between cells and the reference electrode.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
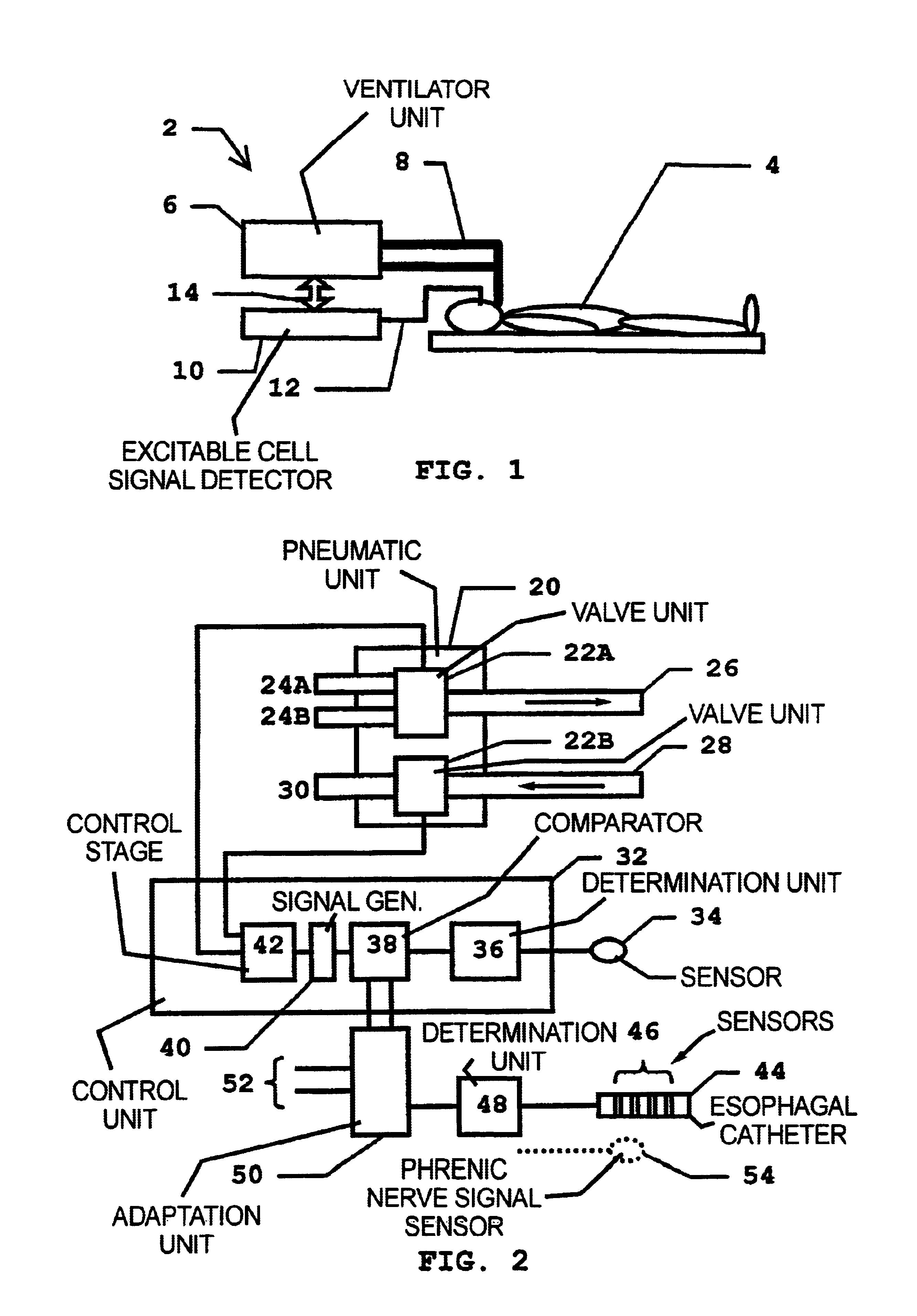
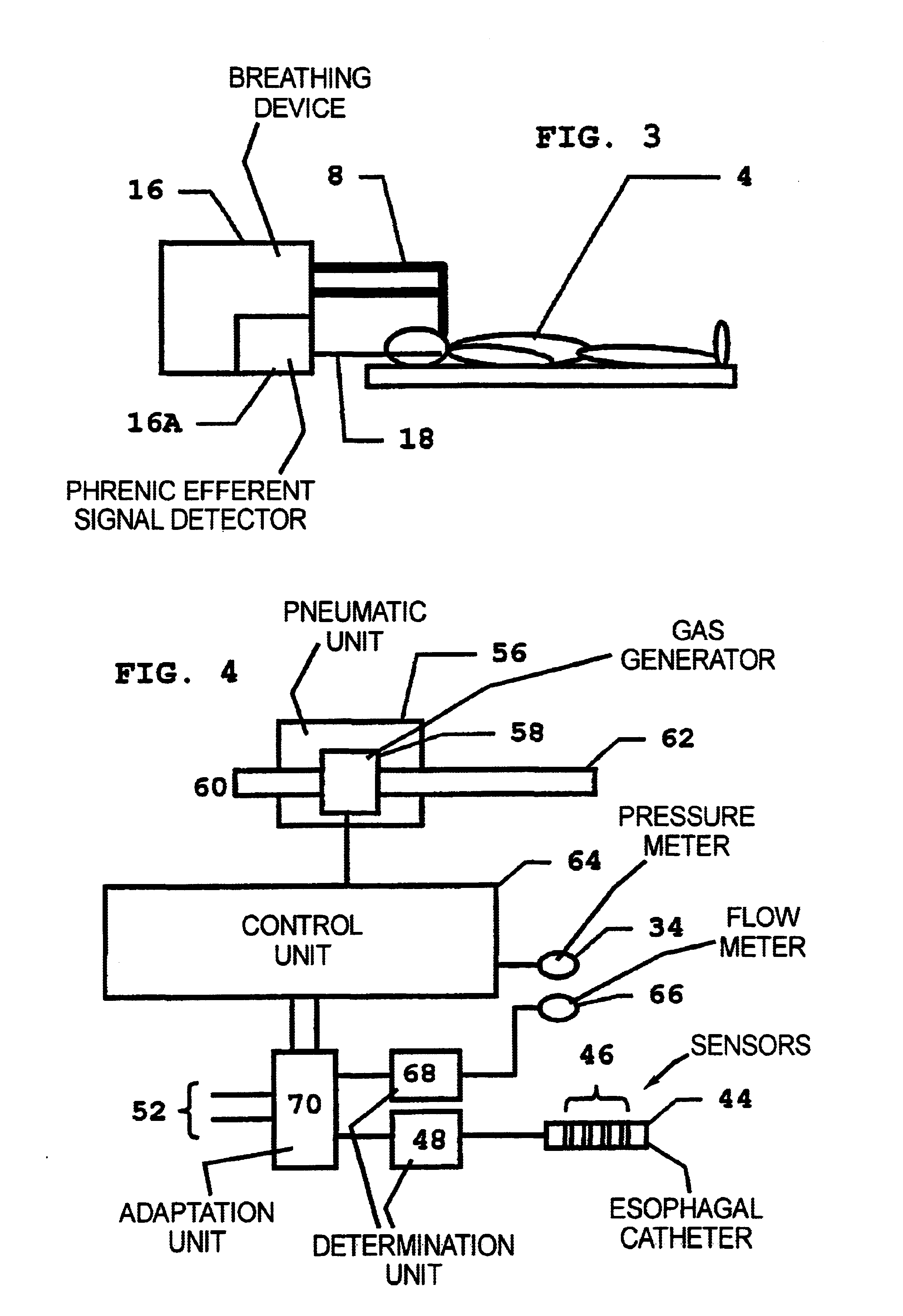
Method for adaptive triggering of a breathing device, and breathing device with adaptive triggering
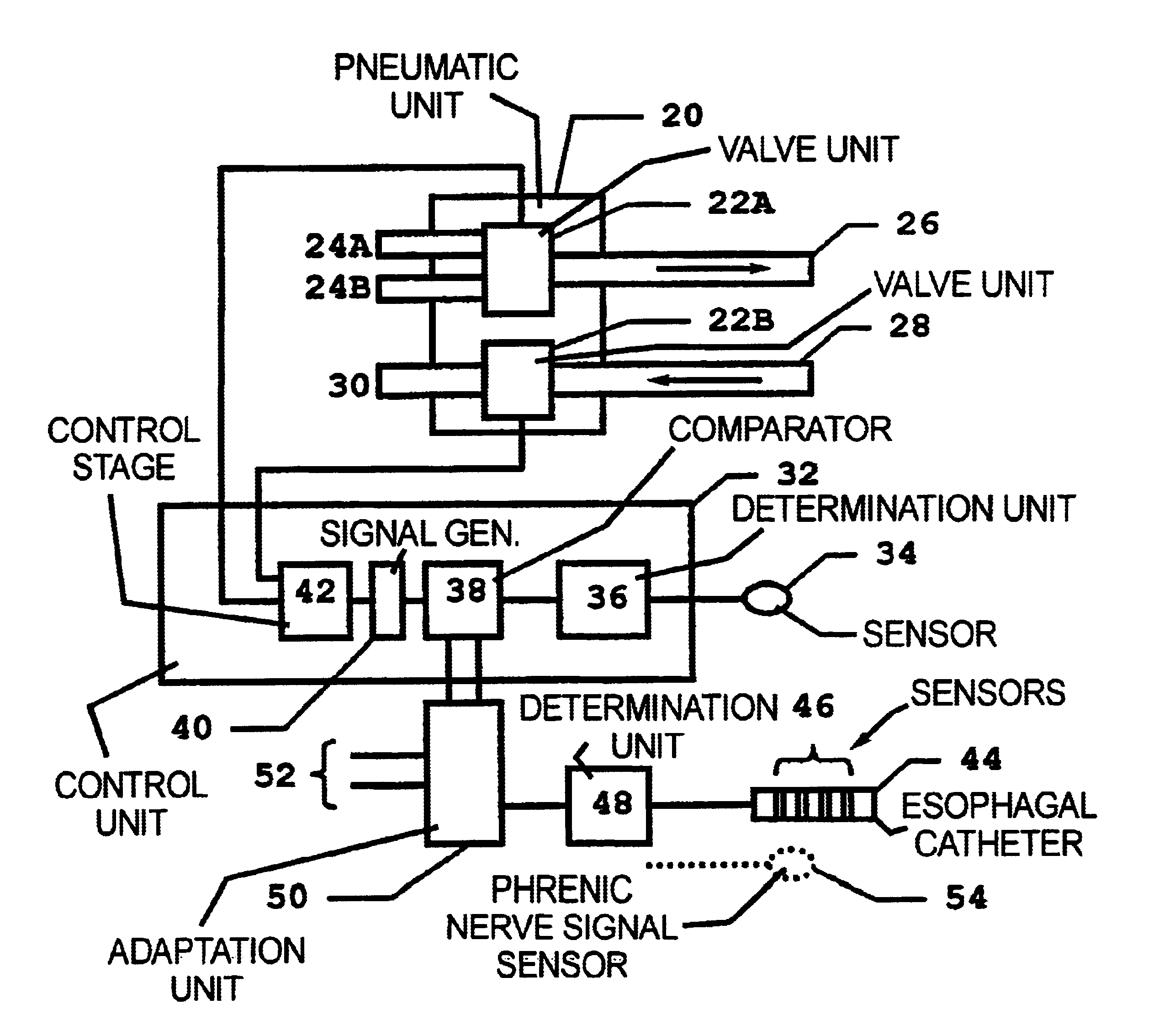
InactiveUS6837241B2Improves trigger methodRisk minimizationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phaseExcitable cell
In a method for adaptive triggering of respiratory phases in a breathing device, and a breathing device operating according to the method, first respiration indicator signal is determined based on at least one of the parameters flow and pressure, the respiration indicator signal is compared with a trigger requirement and a trigger signal is generated when the respiration indicator signal fulfils the trigger requirement. In order to shorten response times to respiration changes without losing stability, an excitable cell signal related to respiration is measured, and a second respiration indicator signal is determined based on the measured excitable cell signal, and the trigger requirement is adapted in relation to the second respiration indicator signal.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
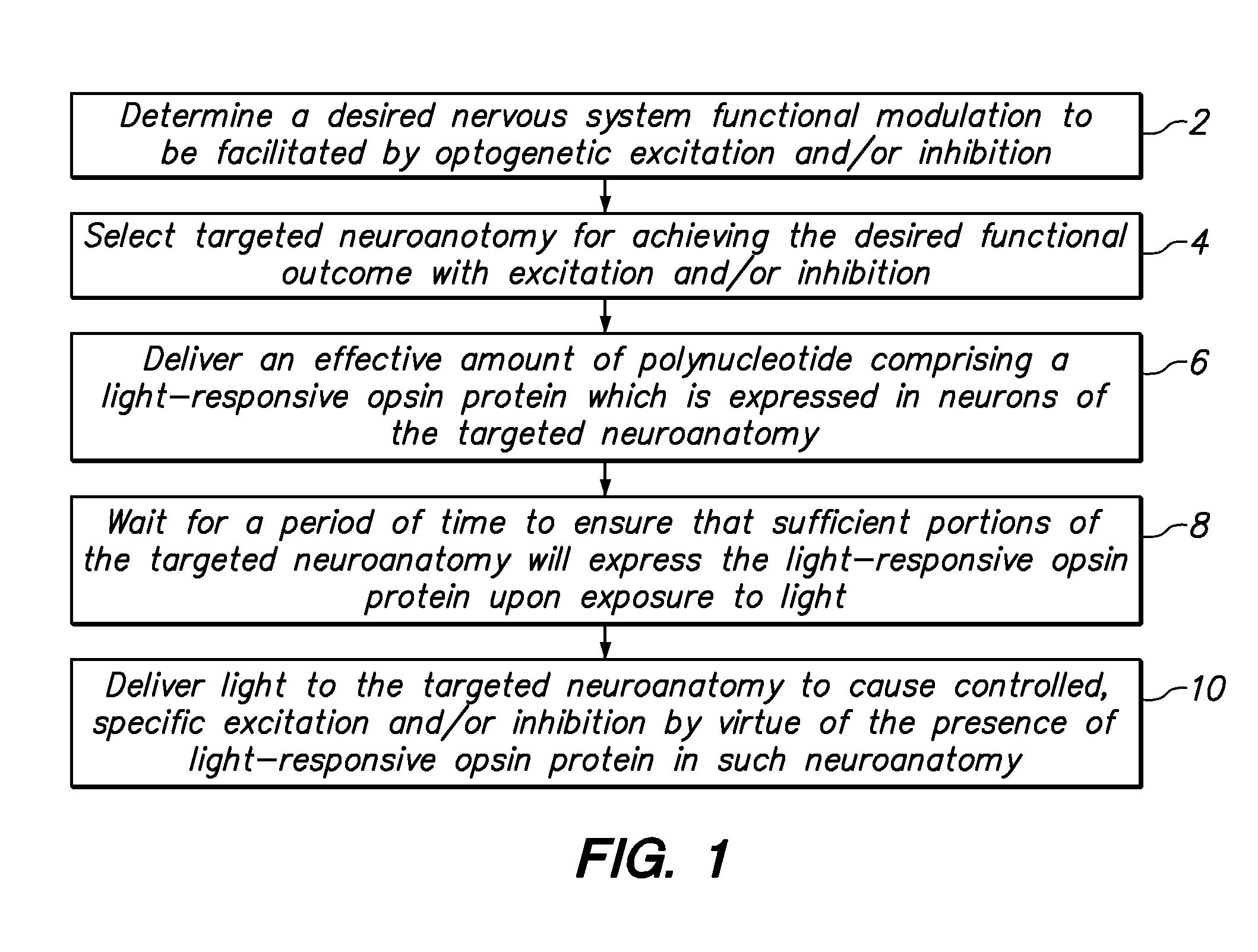
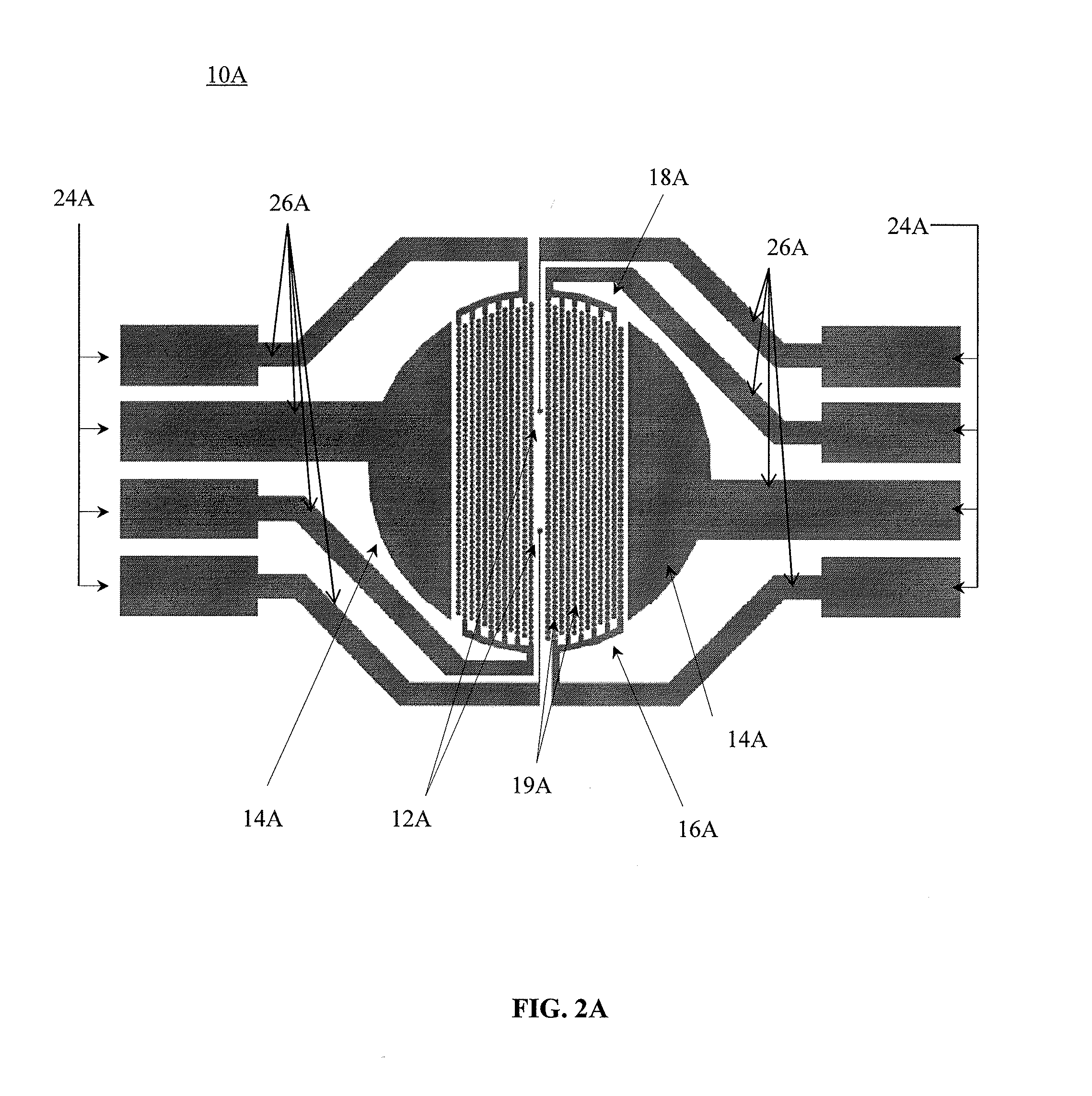
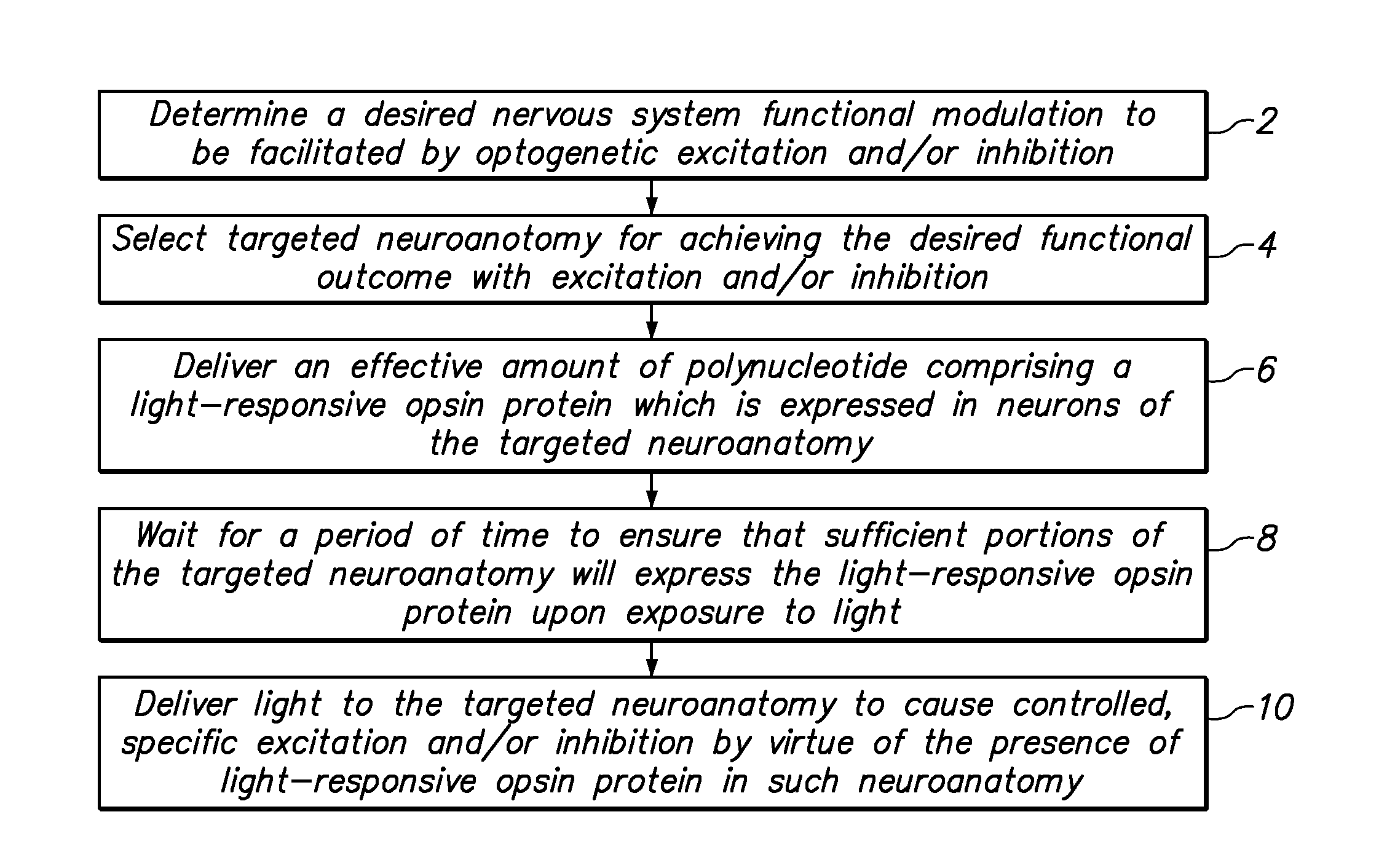
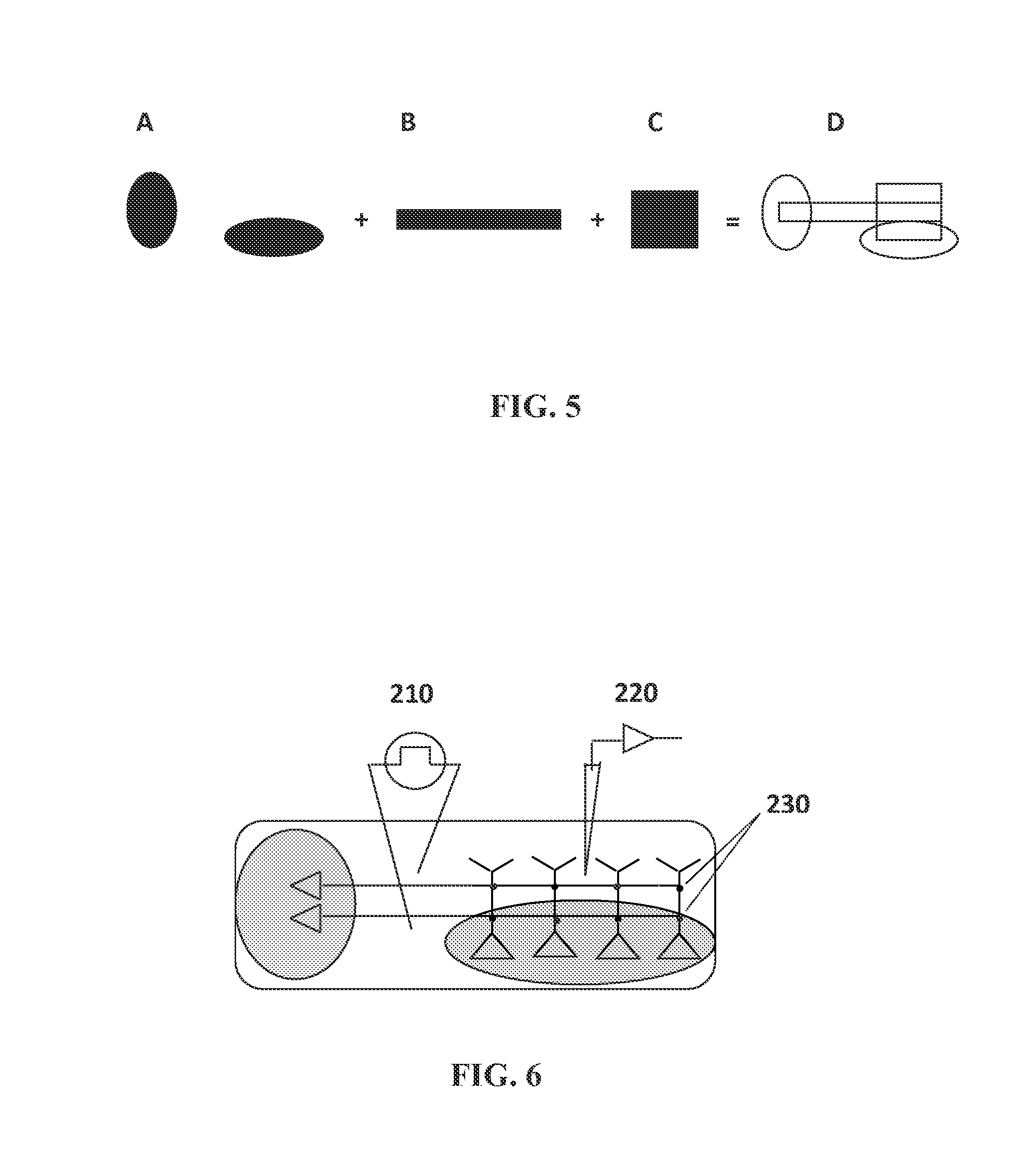
System and method for optogenetic therapy
Configurations are described for utilizing light-activated proteins within cell membranes and subcellular regions to assist with medical treatment paradigms, such as hypertension treatment via anatomically specific and temporally precise modulation of renal plexus activity. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-sensitive proteins to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides systems, devices, and methods for millisecond-timescale temporal control of certain cell activities using moderate light intensities, such as the generation or inhibition of electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS
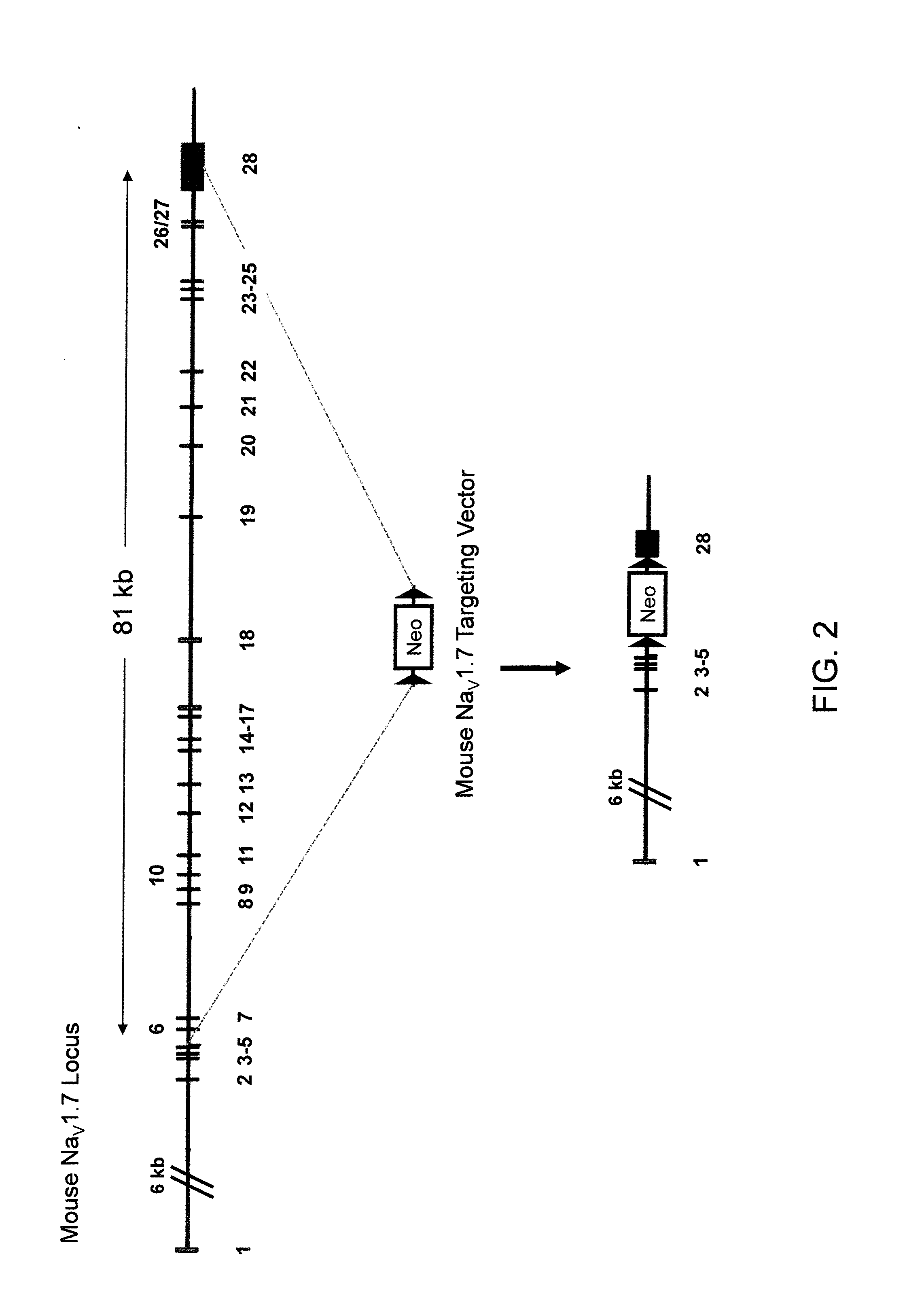
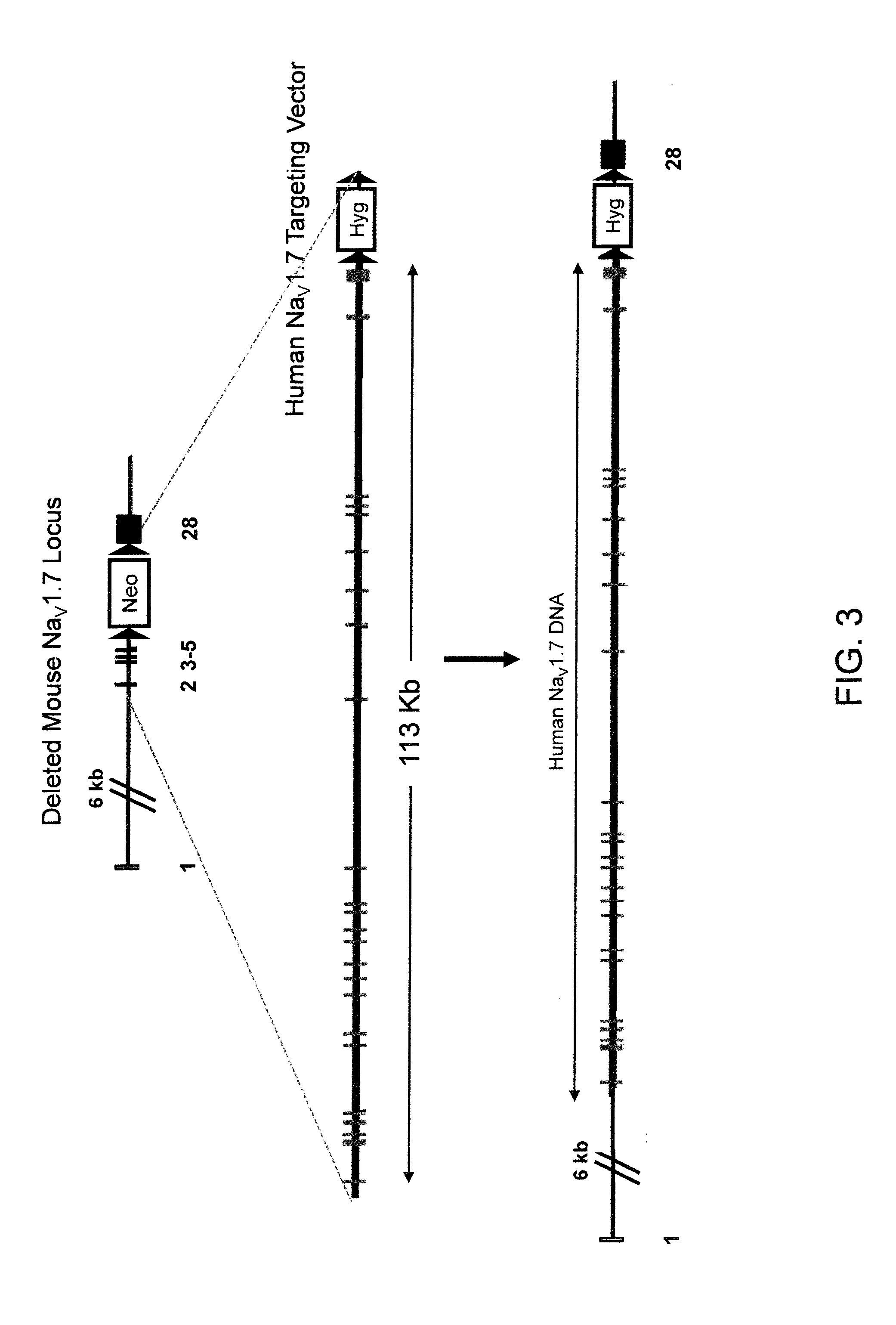
Mice Expressing Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels
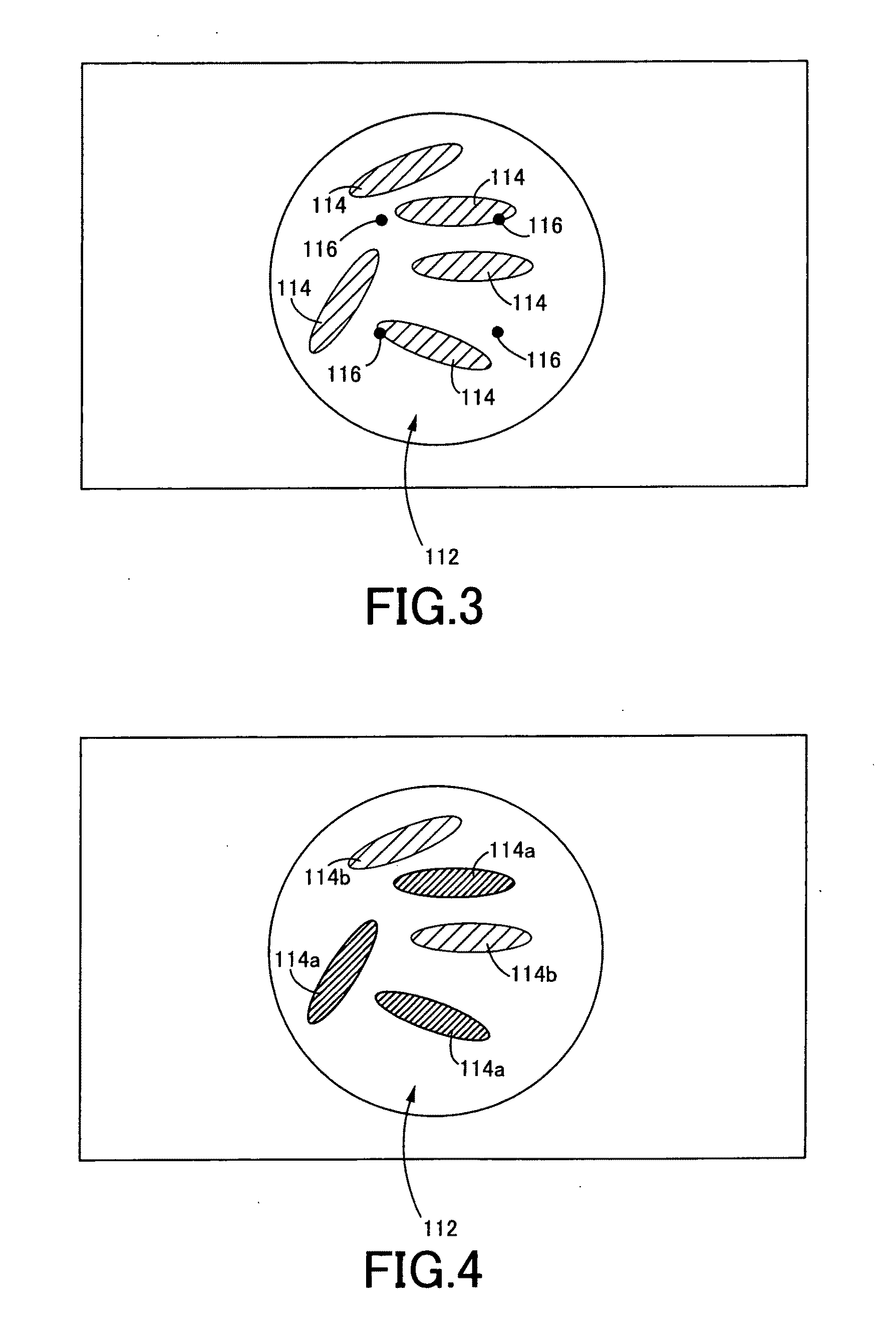
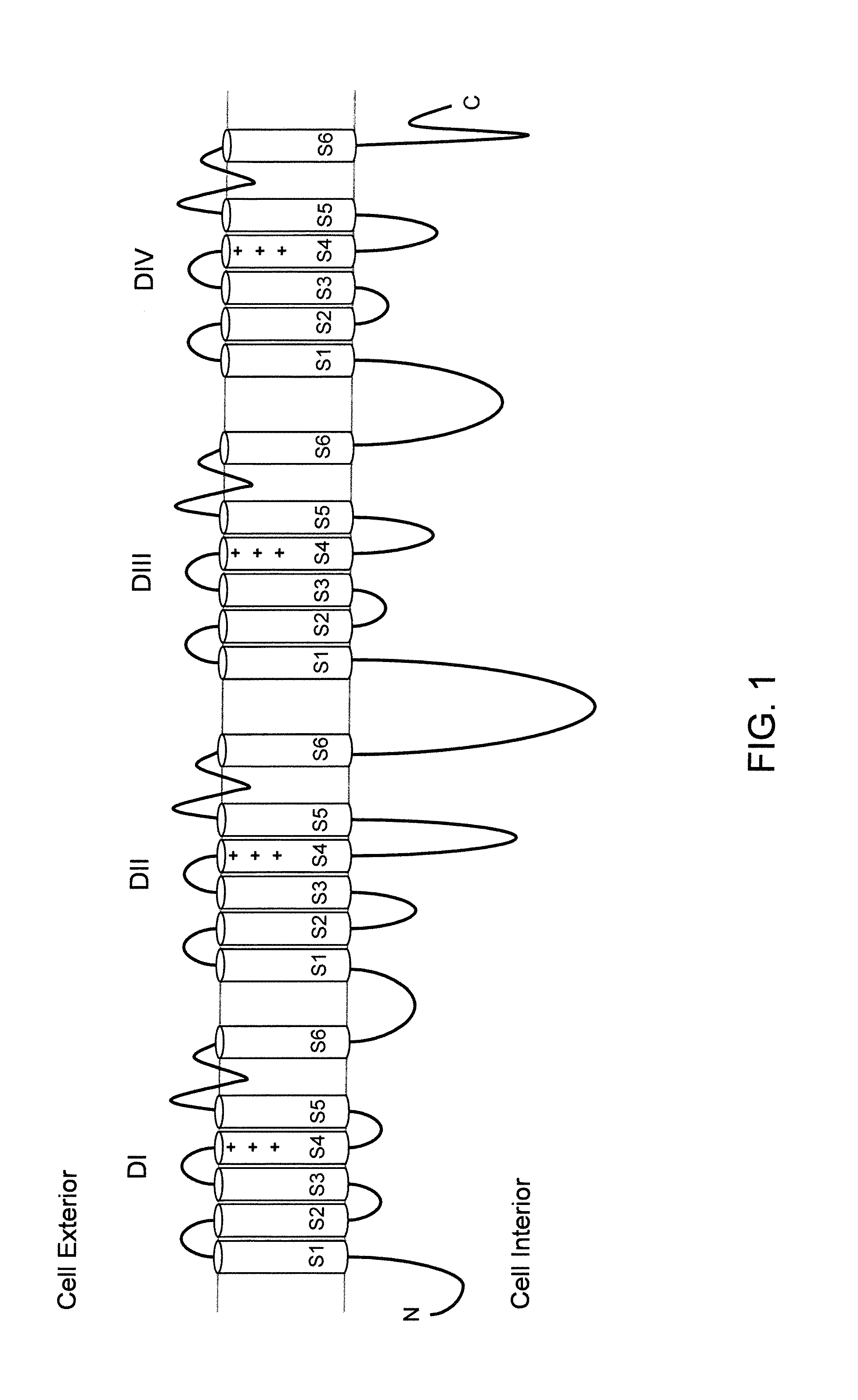
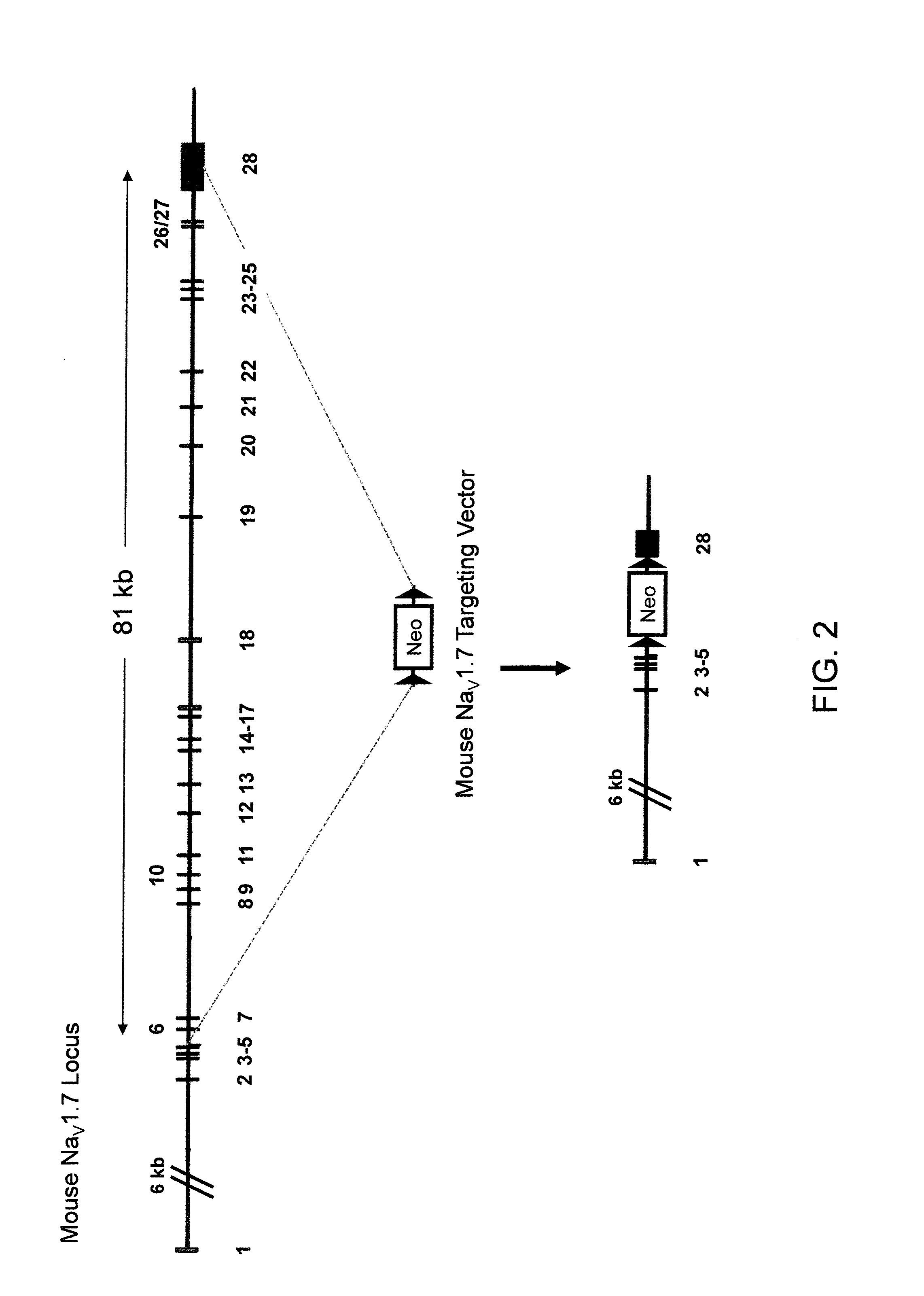
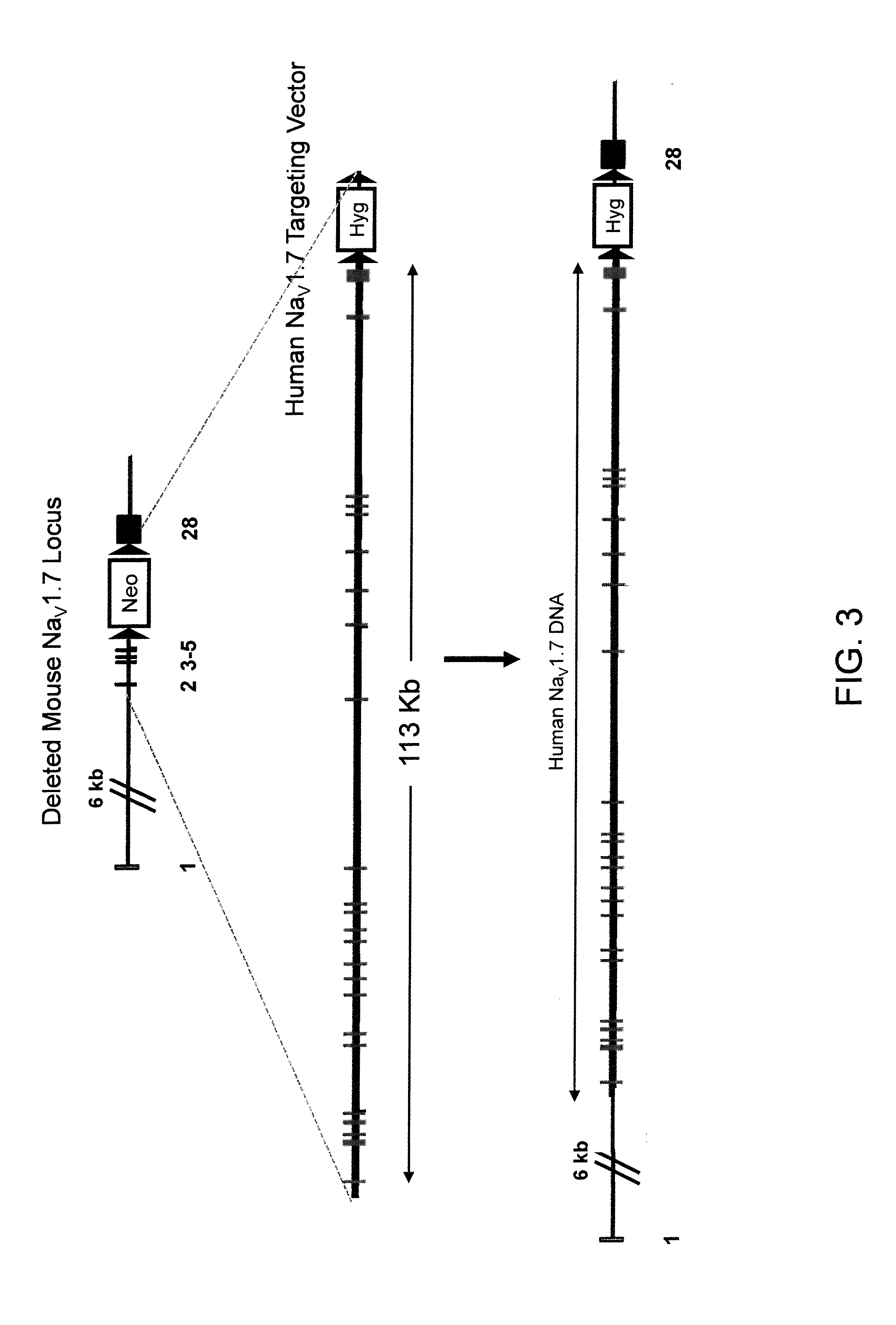
ActiveUS20110307966A1High activityReduced activityAnimal cellsFermentationExcitable cellGenetically modified mouse
Genetically modified non-human animals and methods and compositions for making and using them are provided, wherein the genetic modification comprises a humanization of an extracellular loop of an endogenous NaV channel gene, in particular a humanization of the one or more extracellular pore loops of a NaV1.7 channel protein. Genetically modified non-human animals are also provided, wherein the genetic modification comprises replacement of an endogenous NaV channel gene, in particular a replacement of the endogenous NaV1.7 gene with a human NaV1.7 gene, and wherein the genetically modified non-human animals are capable of generating action potentials and communicating through the excitable cells of the genetically modified non-human animals via the expressed human or humanized NaV1.7 protein the surface of the excitable cells. Genetically modified mice are described, including mice that express the human or humanized NaV1.7 gene from the endogenous NaV1.7 locus, and wherein the mice comprise functional β-subunits.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
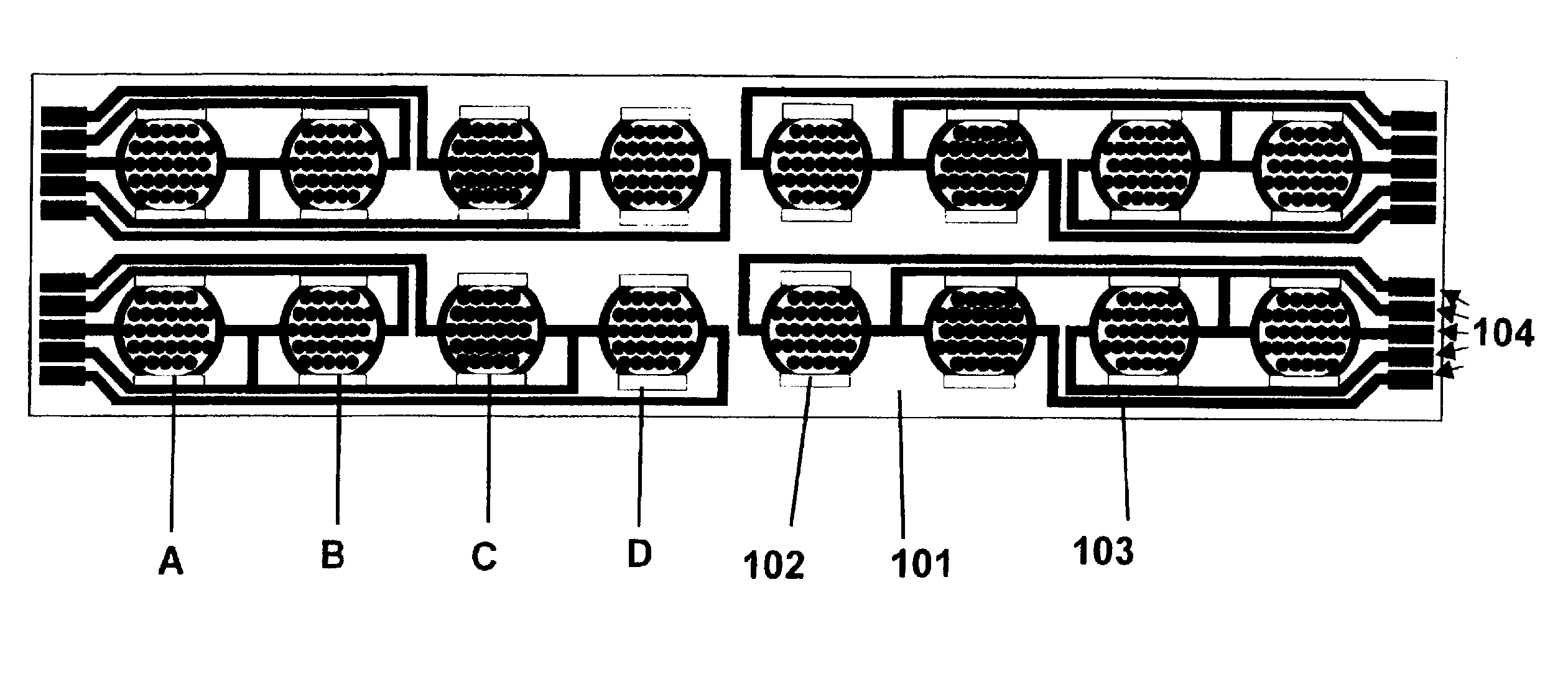
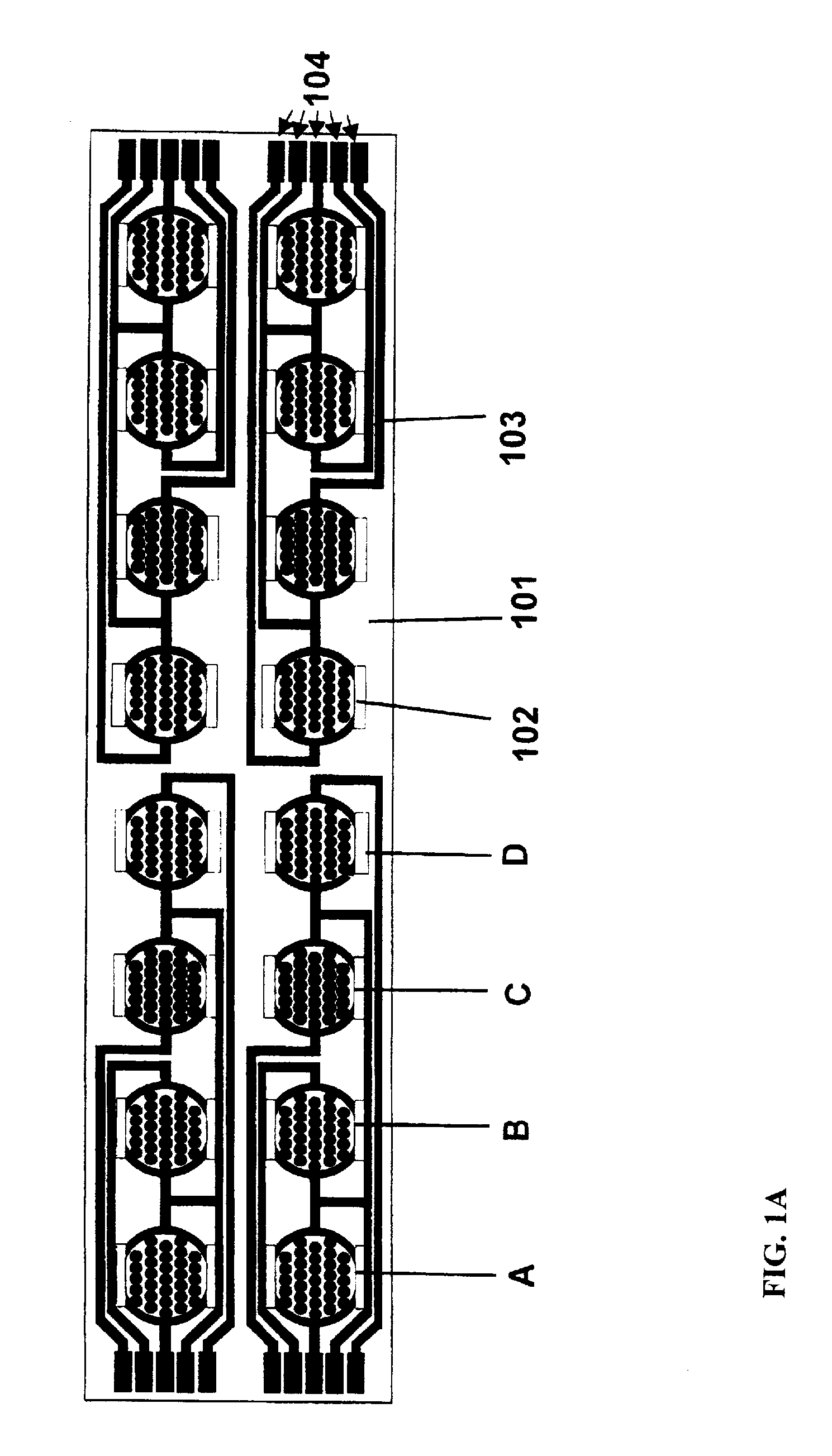
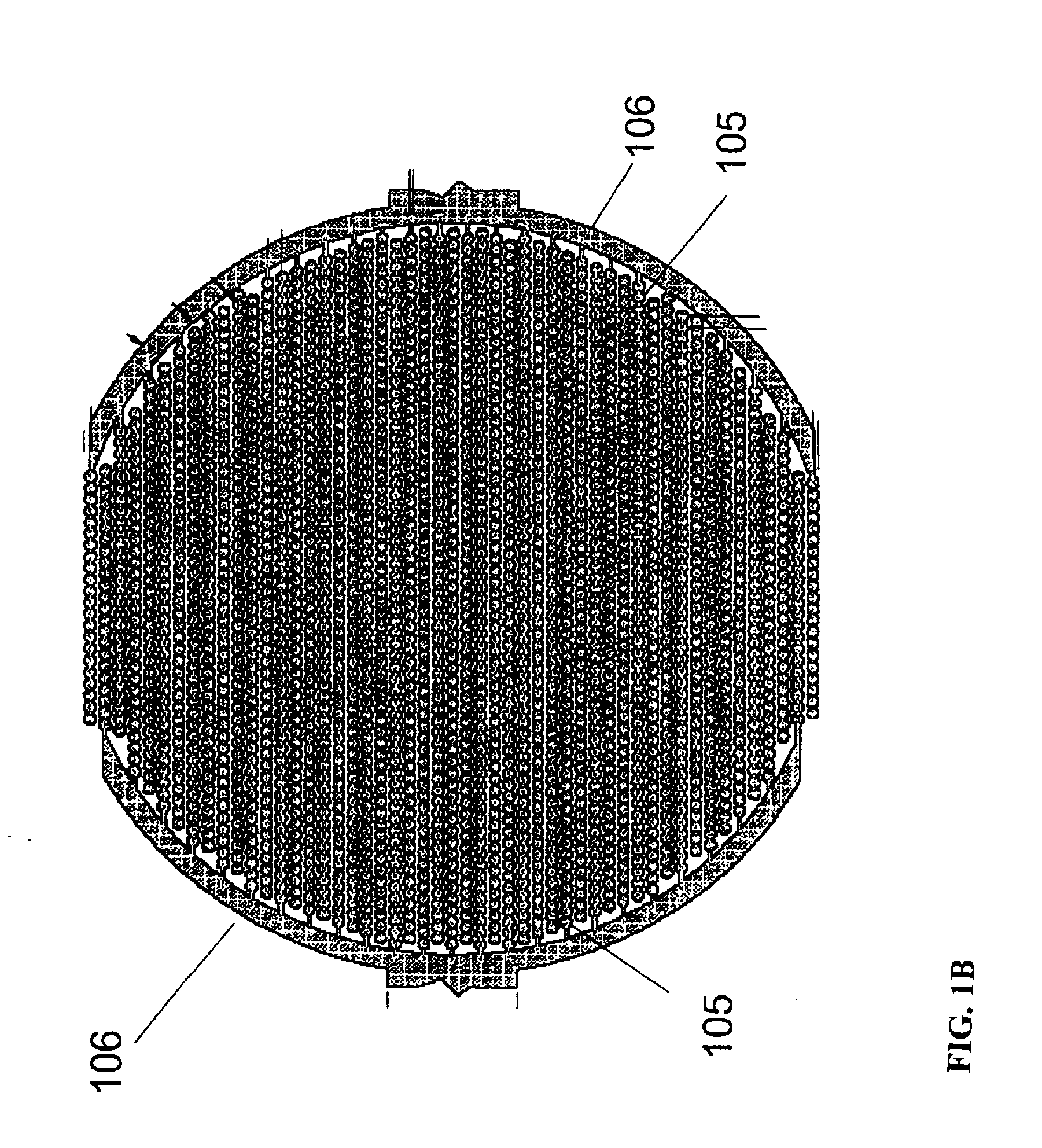
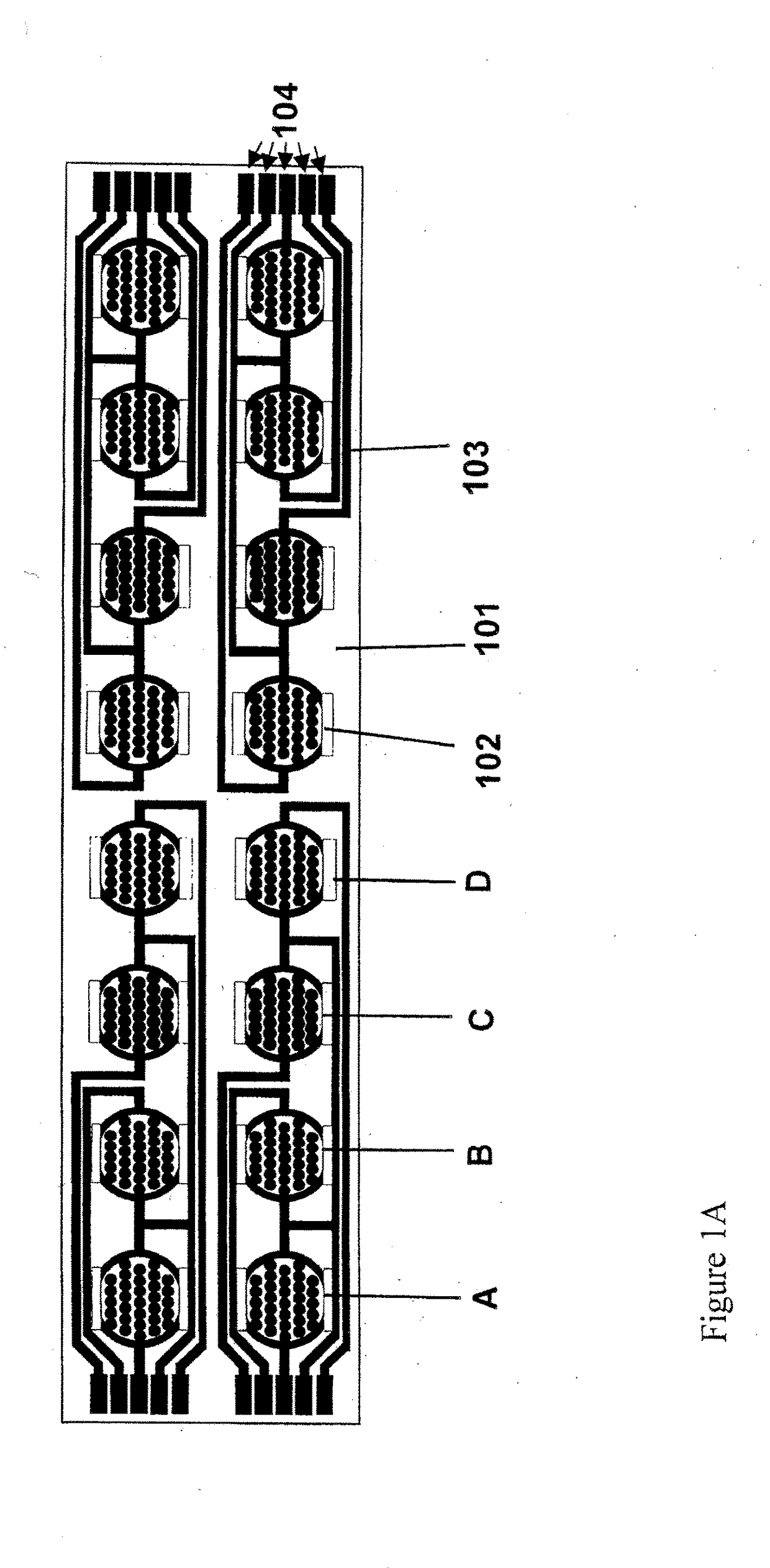
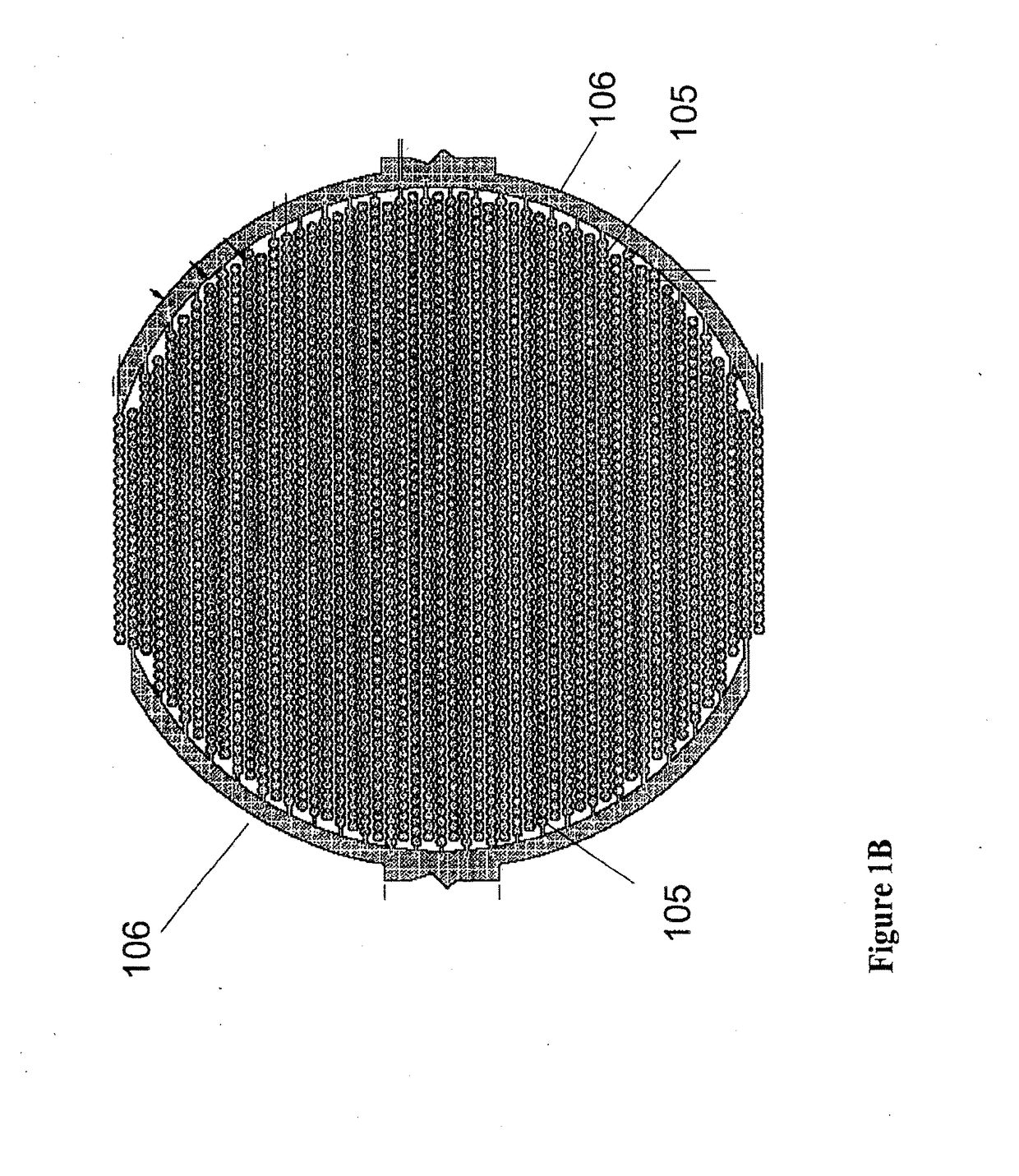
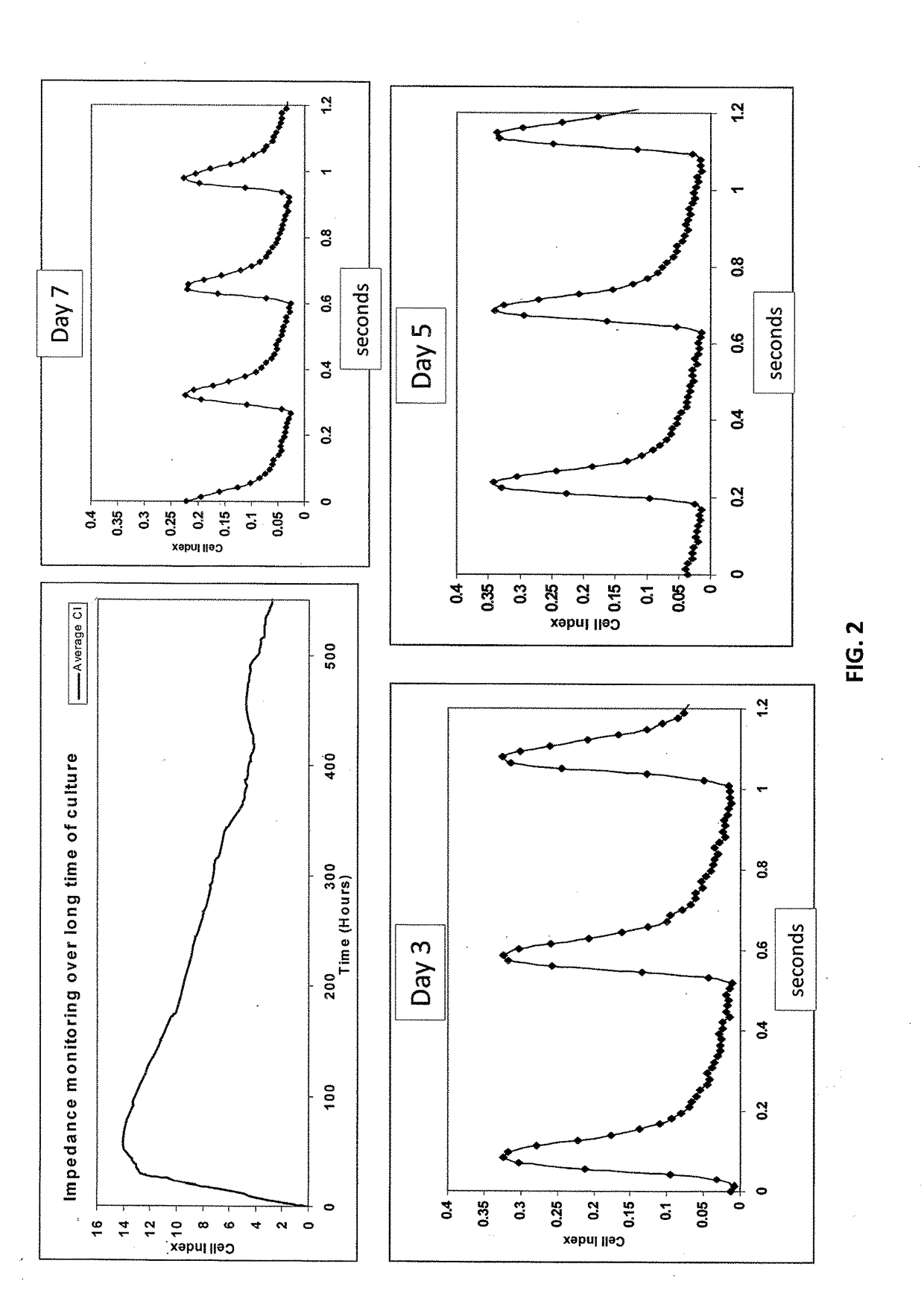
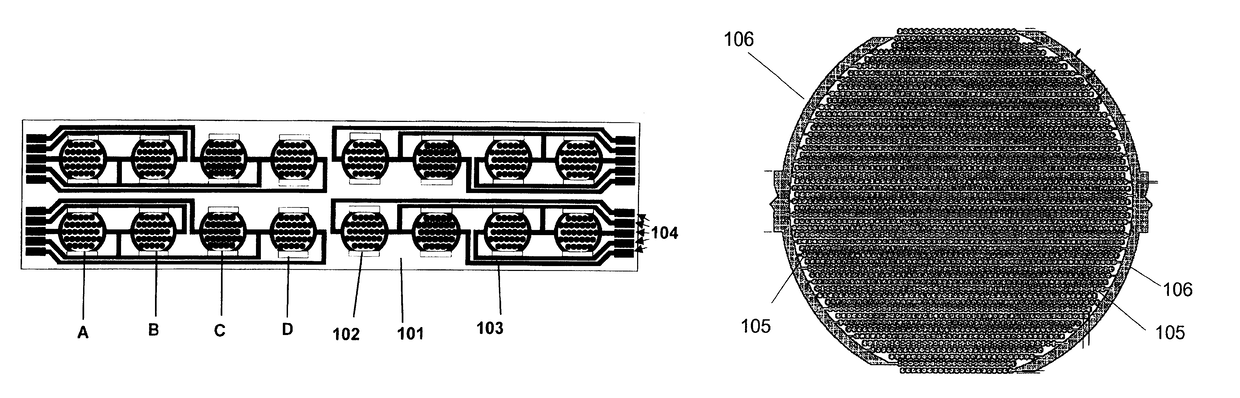
Label-Free Monitoring of Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Excitable Cells Using Impedance Based Systems with Millisecond Time Resolution
ActiveUS20100029506A1Easy to measureEffective monitoringLibrary screeningMaterial impedanceExcitable cellEngineering
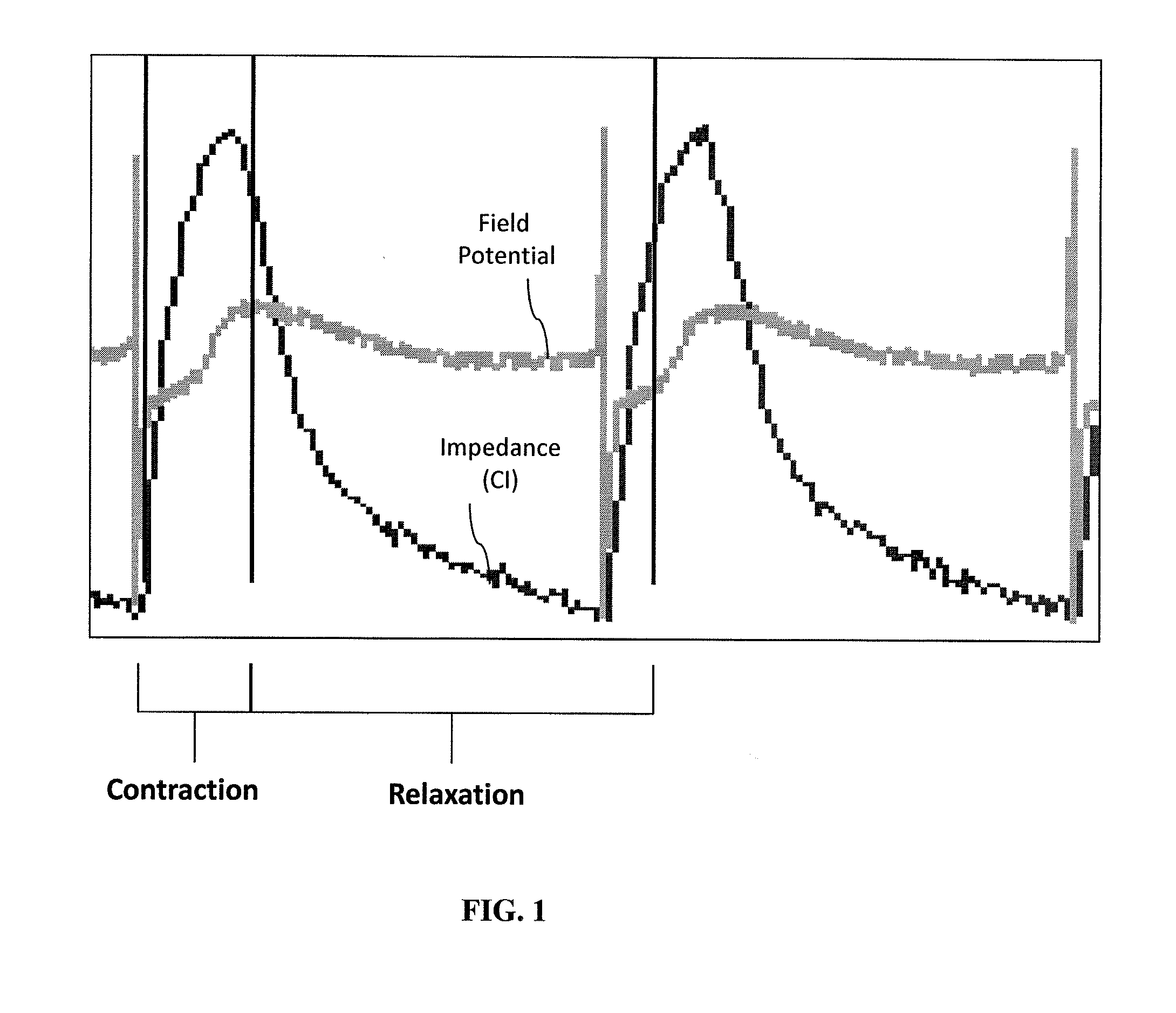
Systems and methods for improved monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells are provided, which provide millisecond time resolution. The system is capable of continuously monitoring excitation-contraction coupling in a relatively high-throughput manner. The system includes a device for monitoring cell-substrate impedance, an impedance analyzer capable of impedance measurements at millisecond time resolution, electronic circuitry that can engage the device and selectively connect two or more electrode arrays of the device to the impedance analyzer and a software program that controls the electronic circuitry and records and analyzes data obtained from the impedance analyzer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
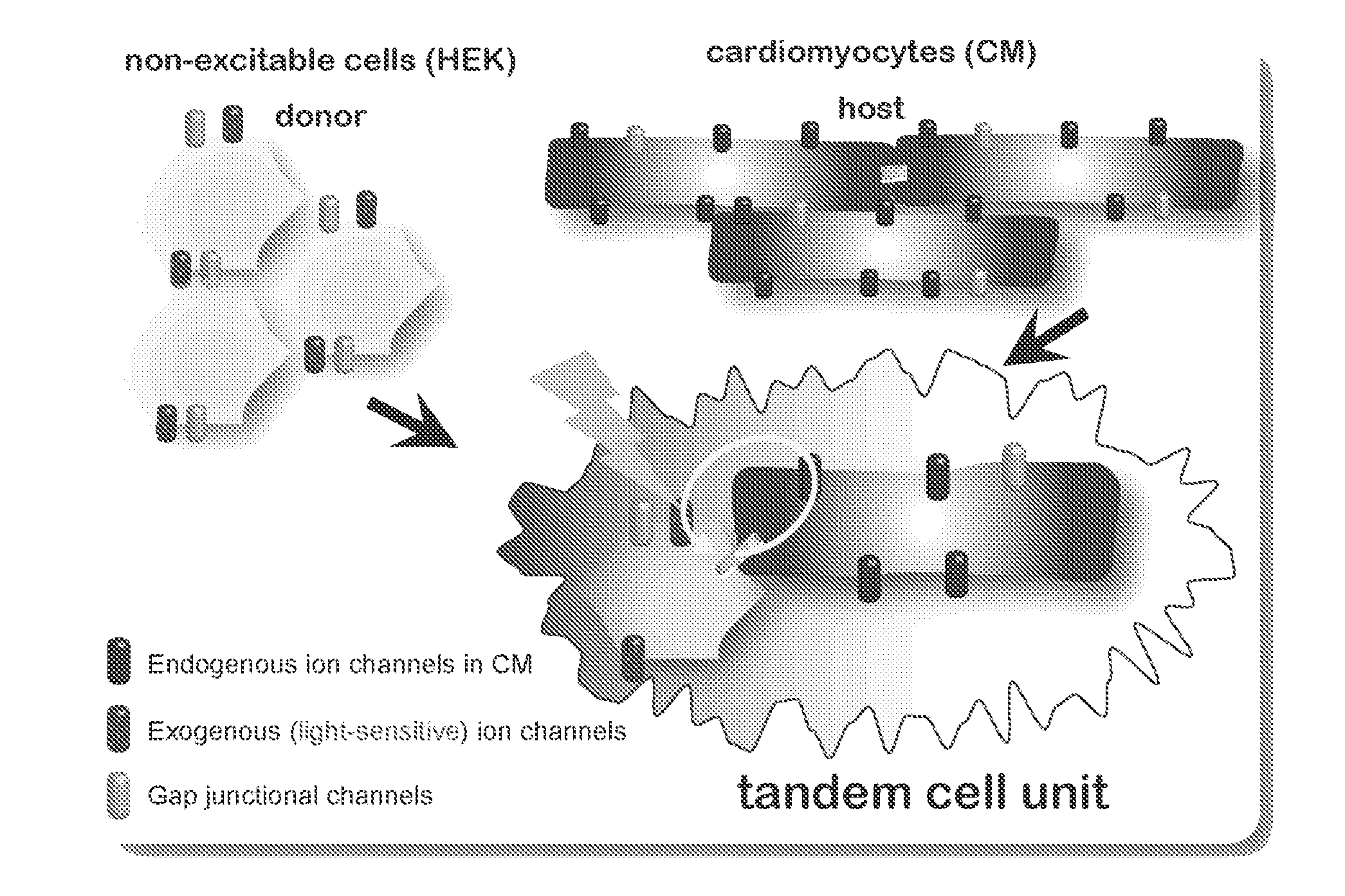
Optical control of cardiac function
InactiveUS20130274838A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImplantable neurostimulatorsIon Channel ProteinIonic Channels
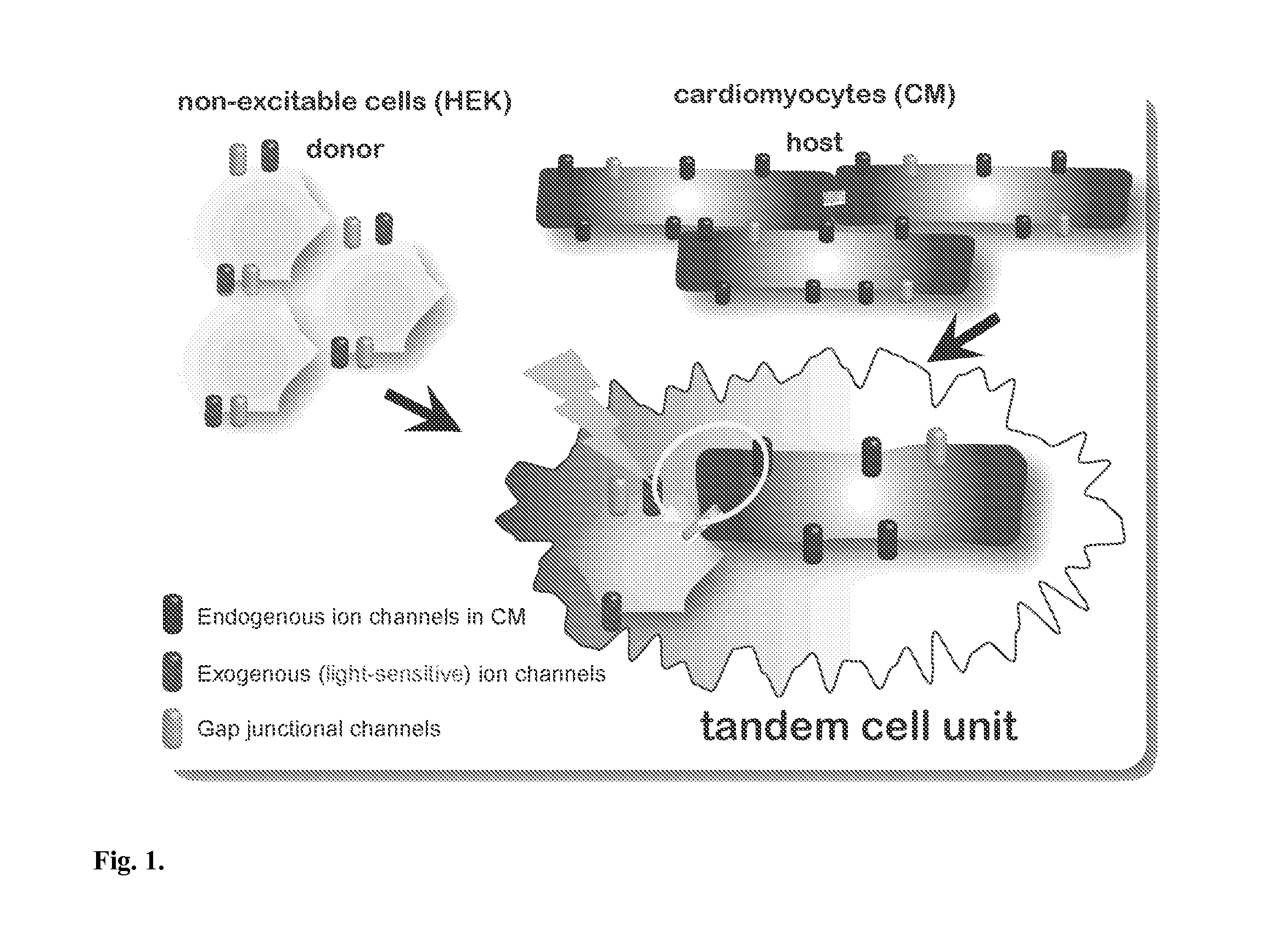
The invention features an optically-controlled biological device that includes a biological component comprising a non-excitable cell expressing a light-gated ion channel protein and capable of forming gap junction channels with a target cell, and an optical stimulation unit.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
System and method for monitoring cardiomyocyte beating, viability, morphology, and electrophysiological properties
InactiveUS20140203818A1Well representedImprove throughput efficiencyResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial impedanceElectro stimulationExcitable cell
Devices, systems and methods for monitoring excitable cells, such as cardiomyocytes, on microelectrode arrays that couple the electro-stimulation of excitable cells to induce or regulate cardiomyocyte beating and the simultaneous measurement of impedance and extracellular recording to assess changes in cardiomyocyte beating, viability, morphology or electrophysical properties in response to a plurality of treatments.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for optogenetic therapy
Configurations are described for utilizing light-activated proteins within cell membranes and subcellular regions to assist with medical treatment paradigms, such as hypertension treatment via anatomically specific and temporally precise modulation of renal plexus activity. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-sensitive proteins to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides systems, devices, and methods for millisecond-timescale temporal control of certain cell activities using moderate light intensities, such as the generation or inhibition of electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS
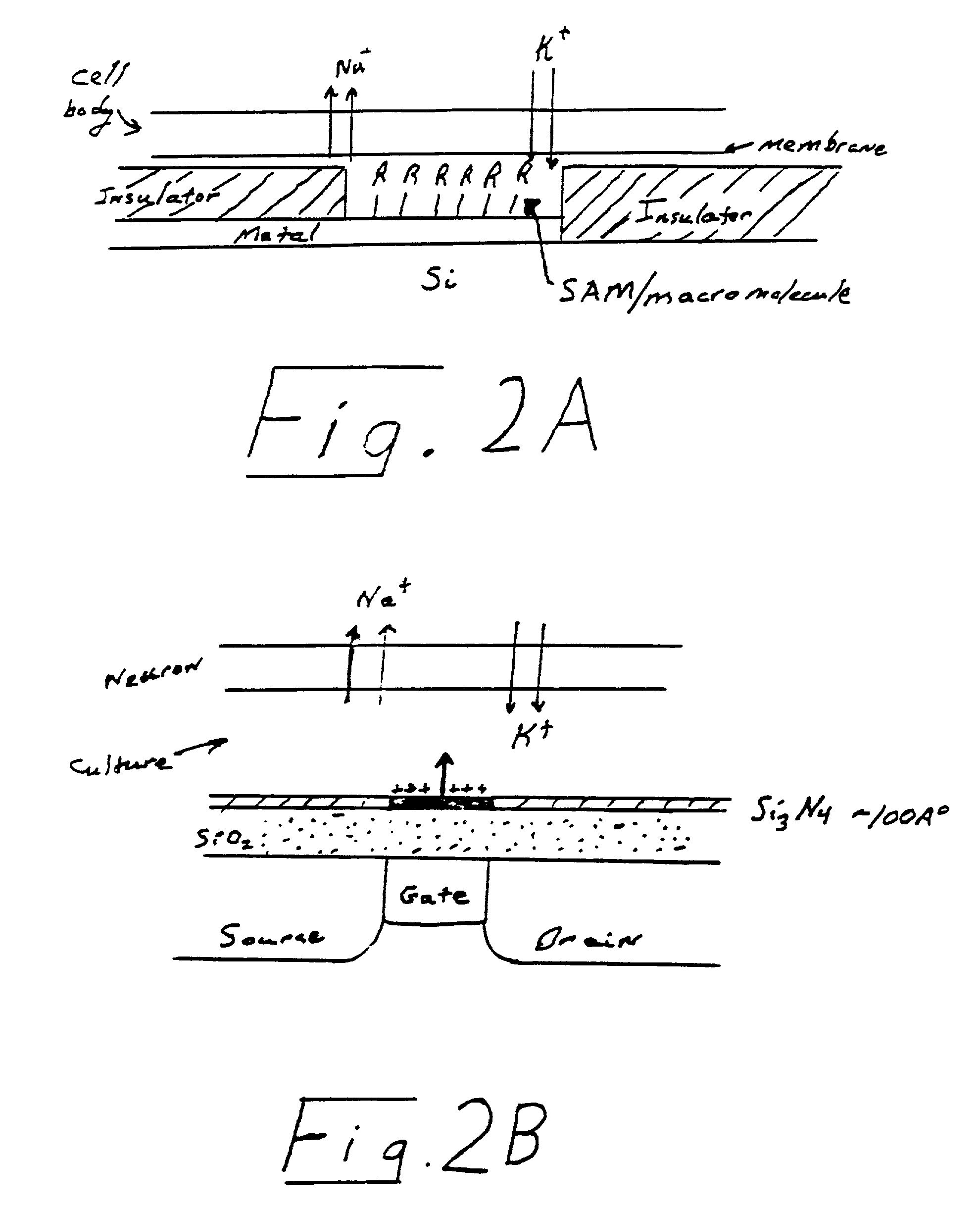
Biosensor for use in toxicity assessment and pharmacological screening
InactiveUS20030054333A1Prevents and impedes passageDirect contact guaranteeMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTest sampleTransducer
A biosensor for detecting a bioeffecting substance in a test sample includes a cell network of at least one electrically excitable cell provided on a substrate in a predetermined geometry with a predefined axonal / dendritic polarity. The at least one cell is capable of producing a signal in response to the presence of the bioeffecting substance. At least one signal transducer is provided with the substrate in a predetermined geometry and is capable of detecting the signal produced by the cell. A culture medium capable of supporting metabolism of the cell is also provided.
Owner:SCI APPL INT CORP
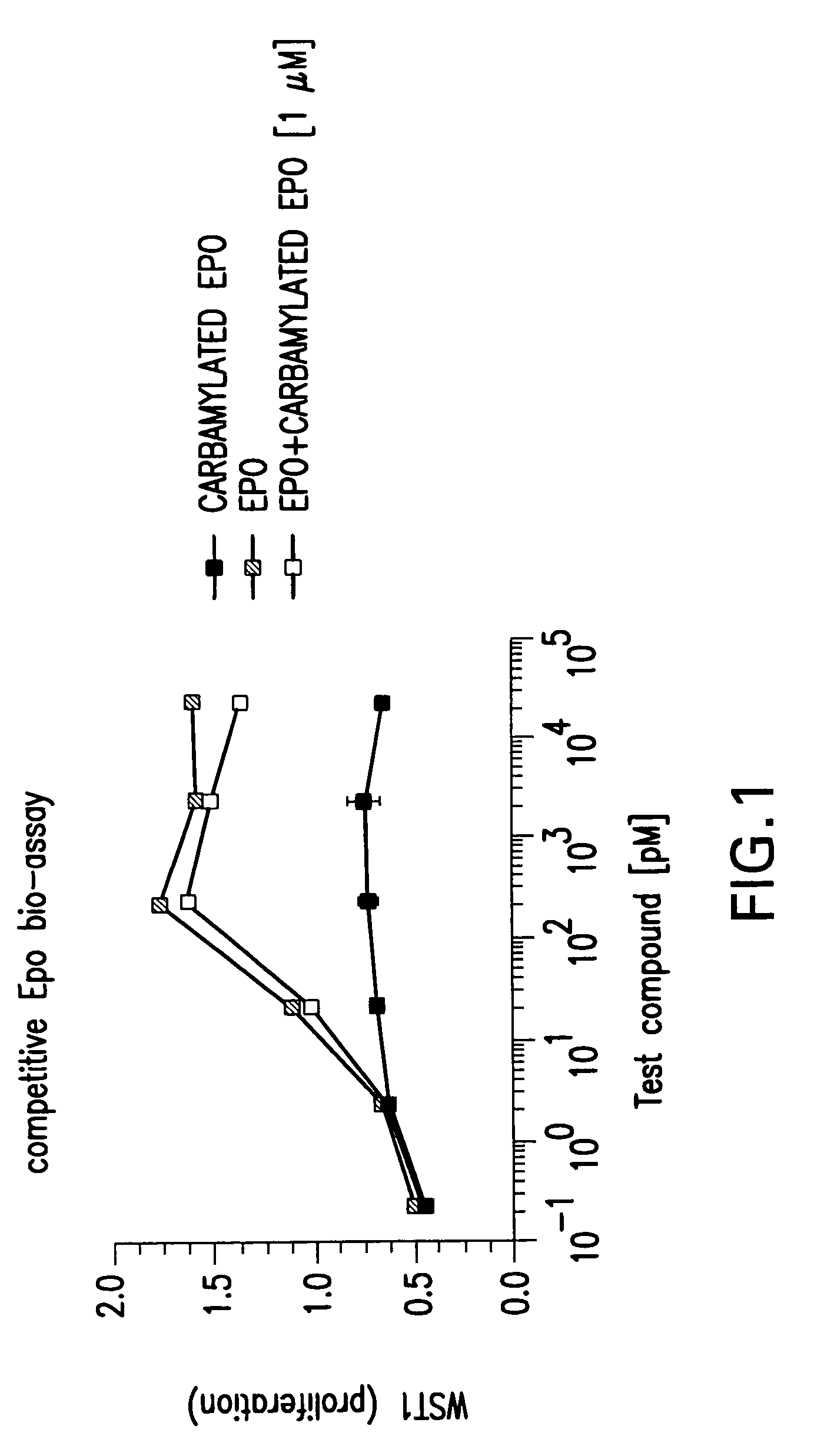
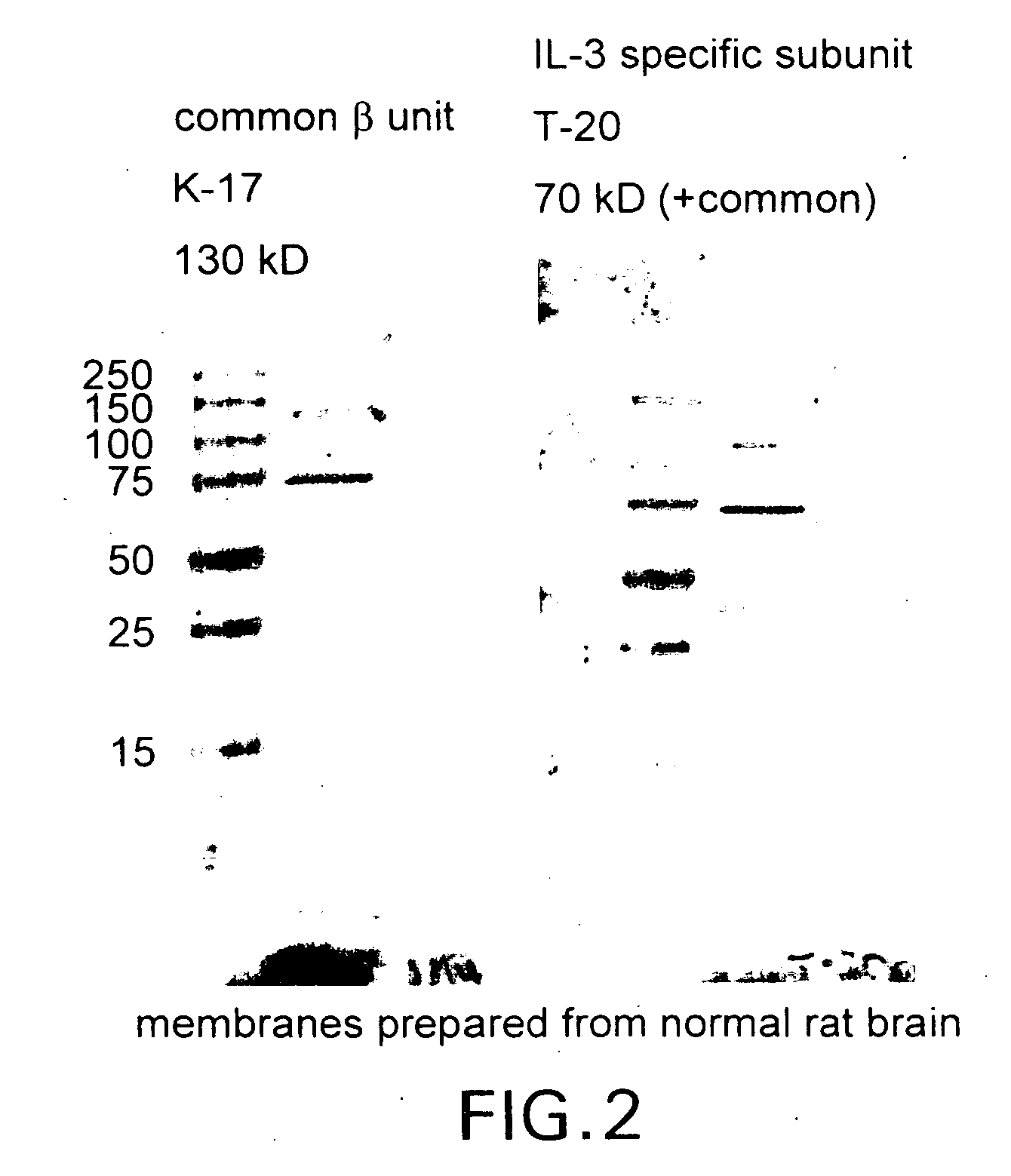
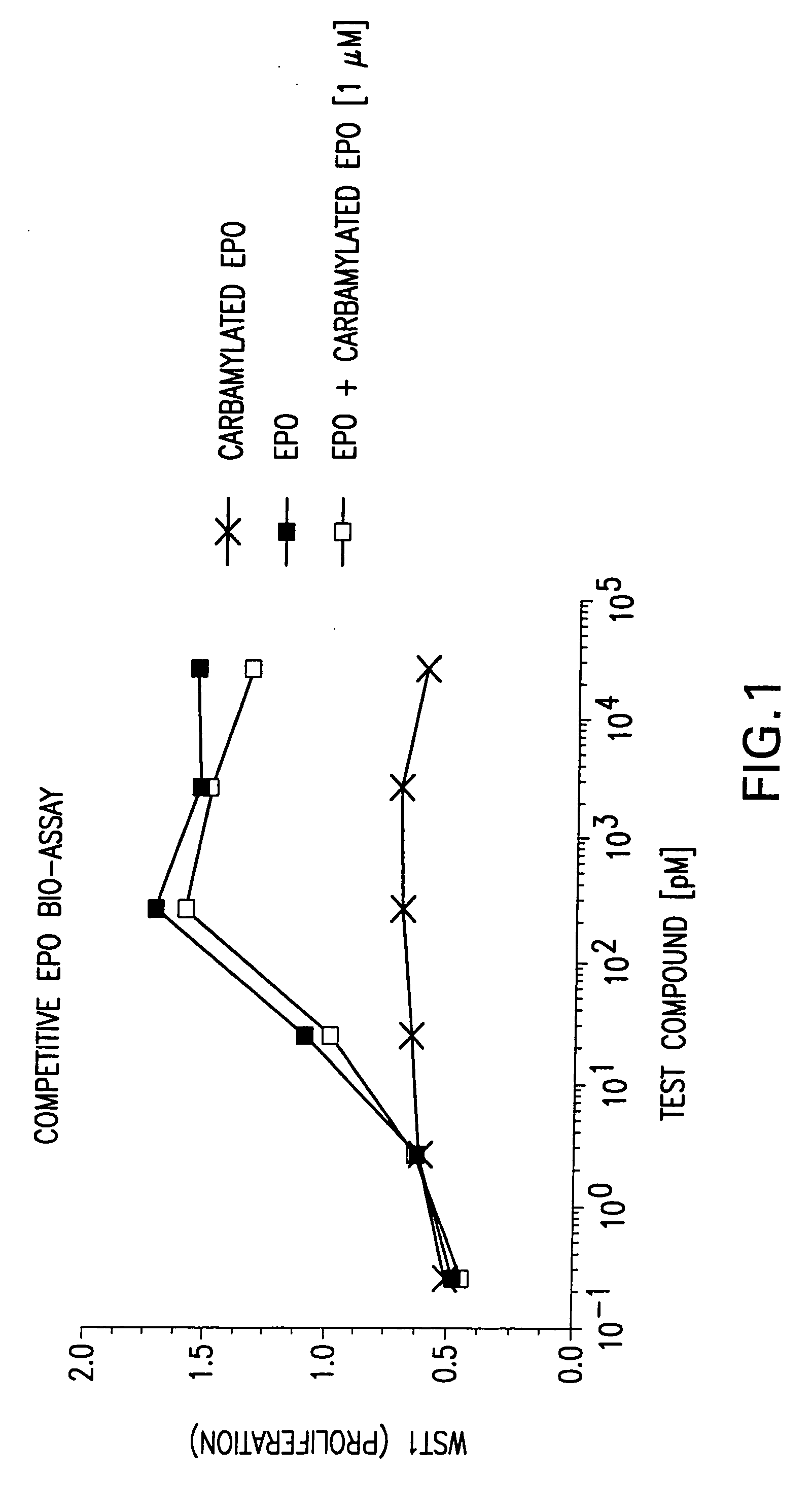
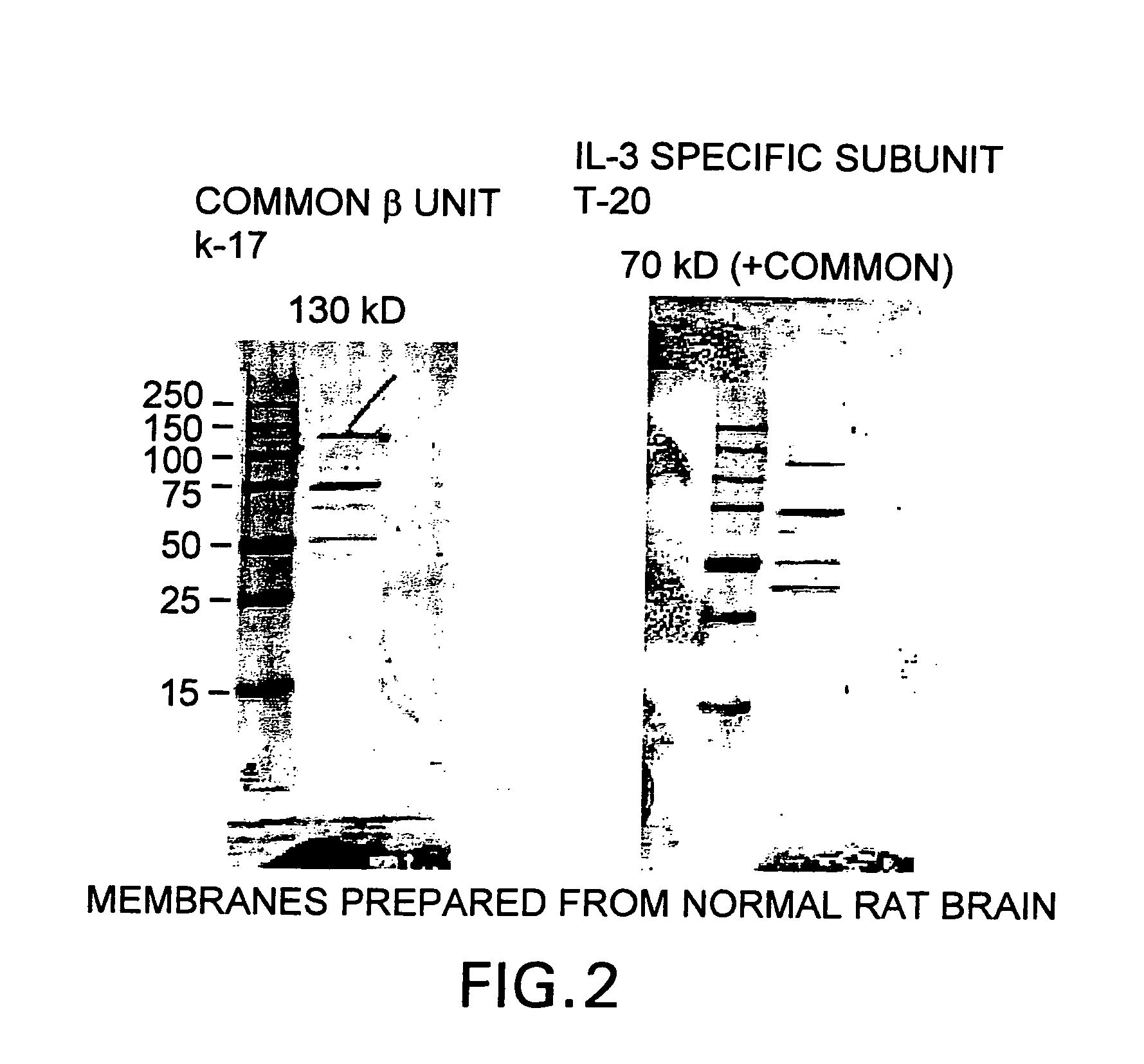
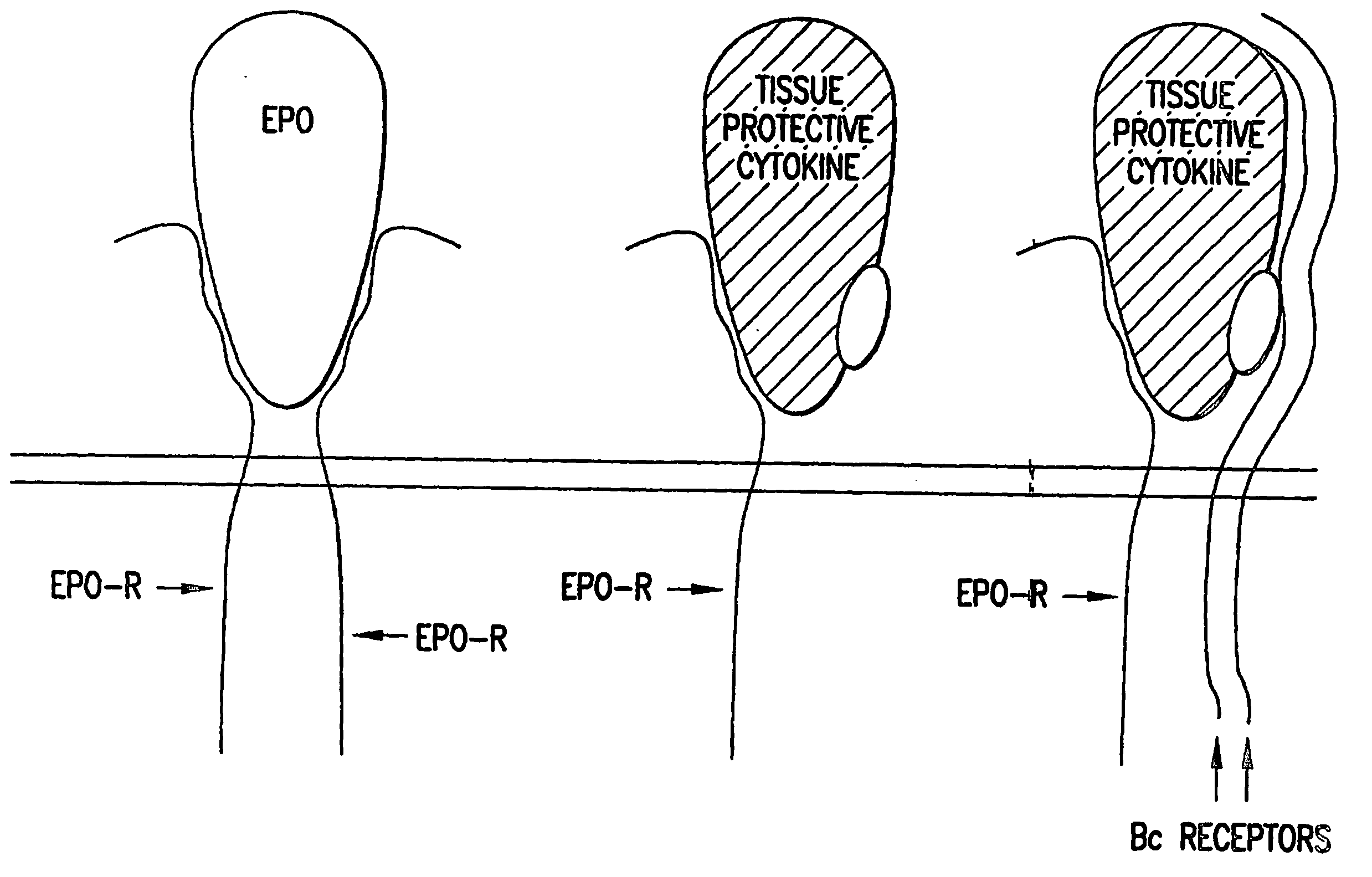
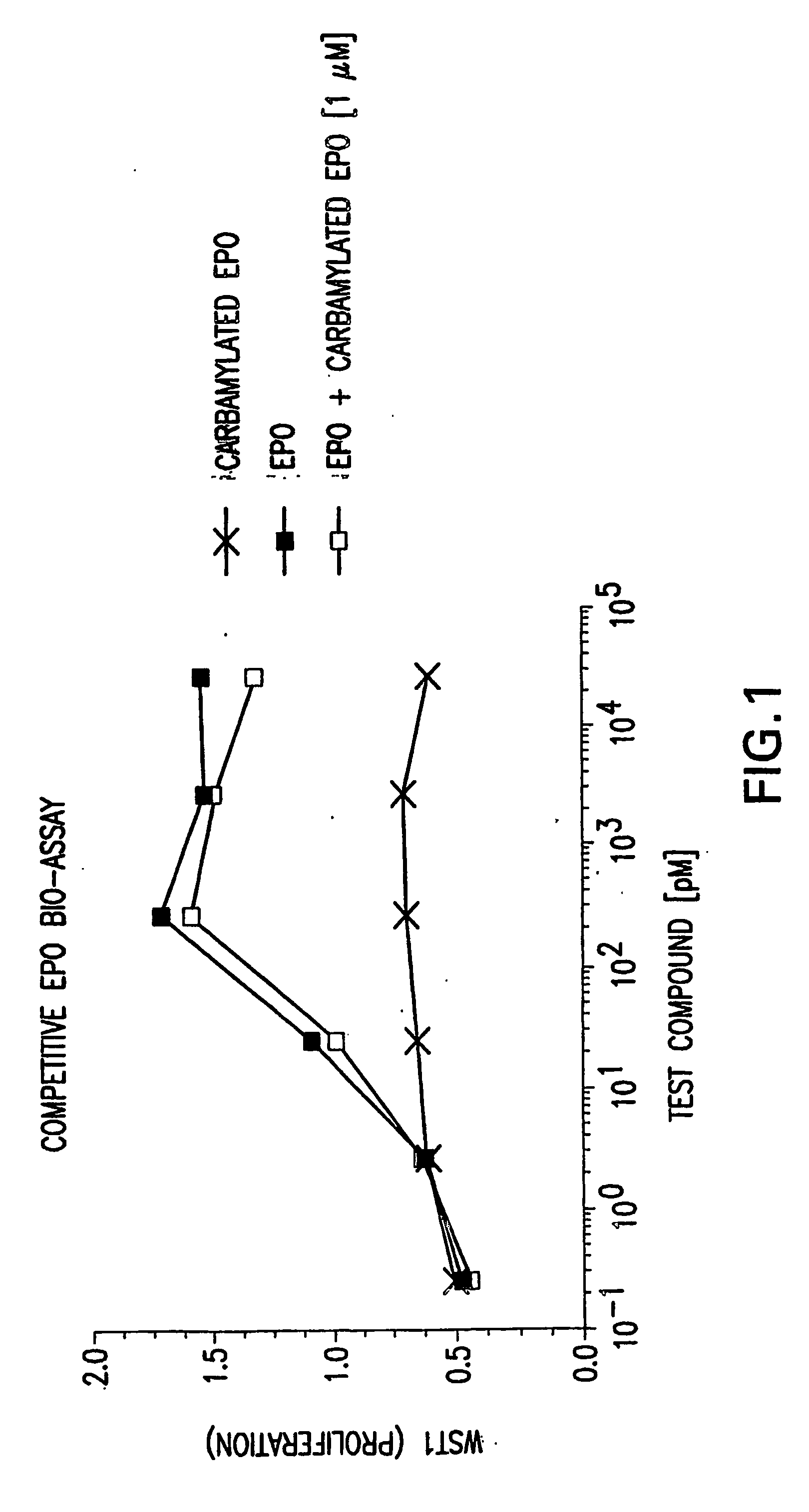
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex and assays for identifying tissue protective compounds
InactiveUS20040214236A1High activityEnhanced interactionSenses disorderNervous disorderNervous systemExcitable cell
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one betac Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat various conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +2
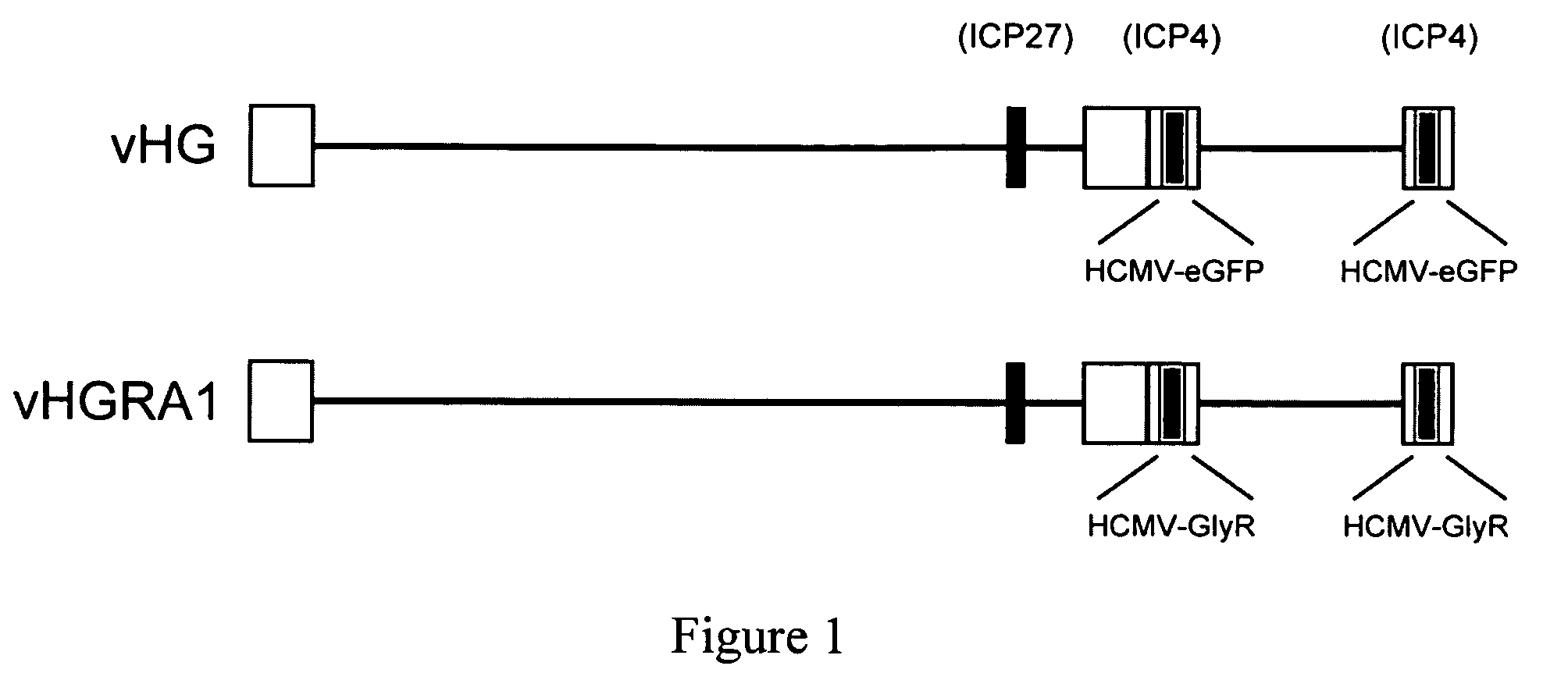
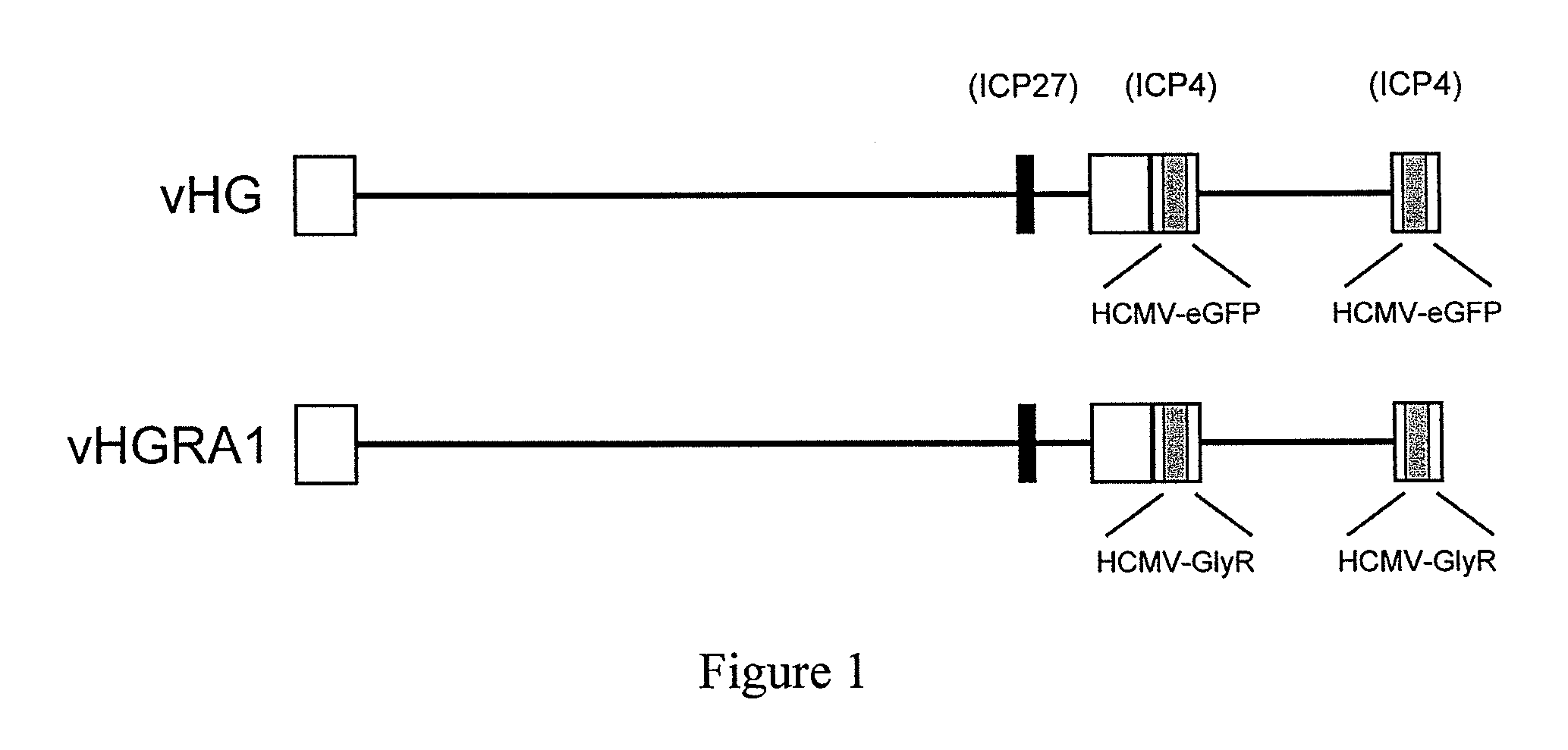
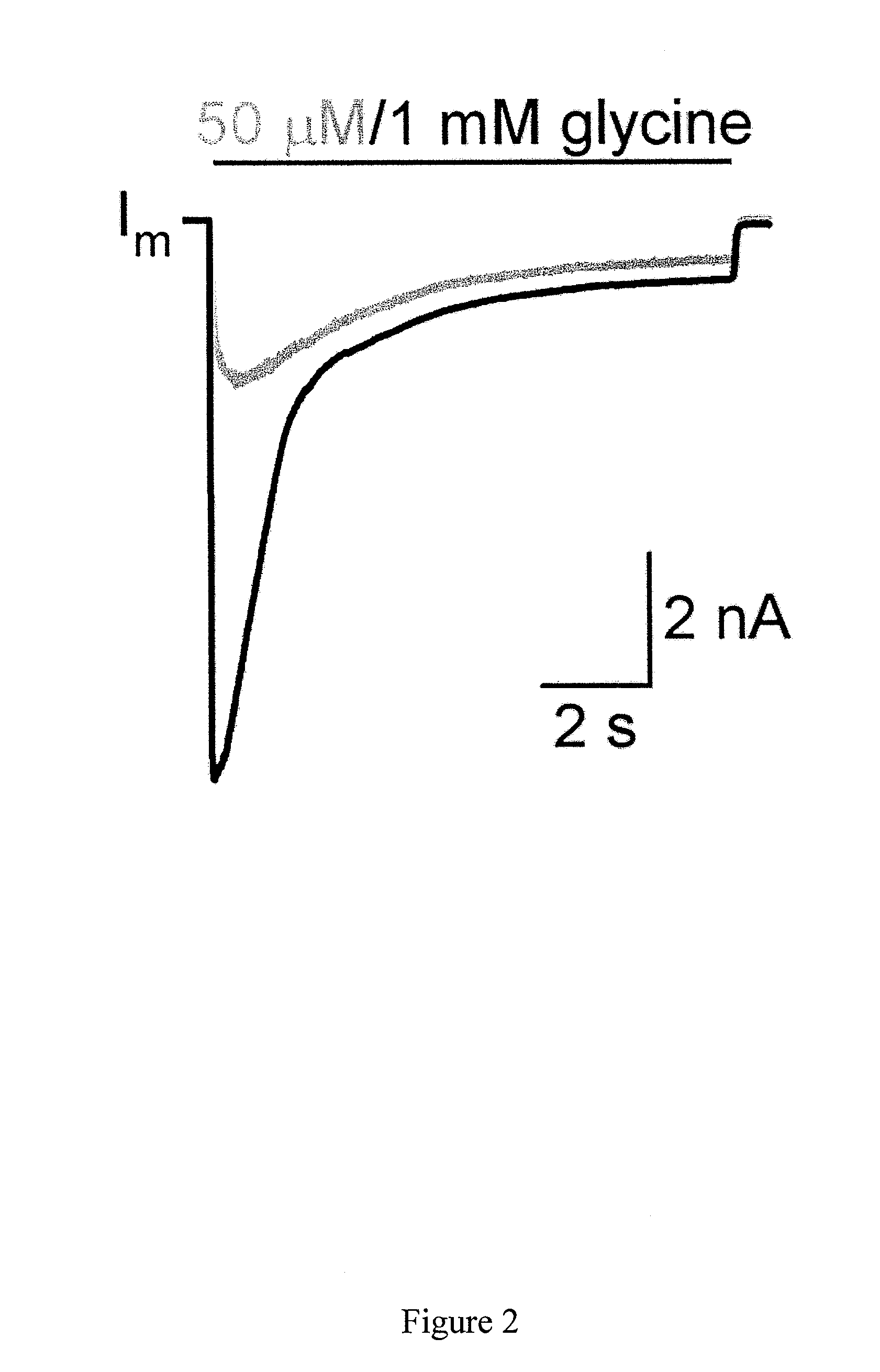
Targeted delivery of glycine receptors to excitable cells
InactiveUS20080289058A1Reduce decreaseReduces formalin-induced nociceptive behaviorOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlycine receptorAllosteric modulator
The invention provides a method of modulating electrophysiological activity of an excitable cell. The method involves causing exogenous expression of a glycine receptor (GlyR) protein in an excitable cell of a subject. Thereafter, the excitable cell is exposed to an allosteric modulator of the GlyR protein. Modulation of the exogenous GlyR protein (an ion channel) in response to the allosteric modulator modulates the electrophysiological activity of the excitable cell. The method can be used to control pain in a subject. The invention further provides a replication-defective HSV vector comprising an expression cassette encoding a GlyR protein, stocks and pharmaceutical compositions containing such vectors, and a transgenic animal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Targeted delivery of glycine receptors to excitable cells
ActiveUS20110213017A1Nervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGlycine receptorAllosteric modulator
The invention provides a method of modulating electrophysiological activity of an excitable cell. The method involves causing exogenous expression of a glycine receptor (GlyR) protein in an excitable cell of a subject. Thereafter, the excitable cell is exposed to an allosteric modulator of the GlyR protein. Modulation of the exogenous GlyR protein (an ion channel) in response to the allosteric modulator modulates the electrophysiological activity of the excitable cell. The method can be used to control pain in a subject. The invention further provides a replication-defective HSV vector comprising an expression cassette encoding a GlyR protein, stocks and pharmaceutical compositions containing such vectors, and a transgenic animal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex, assays for identifying tissue protective compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060216757A1Reduce apoptosisPromote recoveryCompound screeningPeptide librariesNervous systemExcitable cell
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one βc Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat or prevent various diseases, disorders, or conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:THE KENNETH S WARREN INST
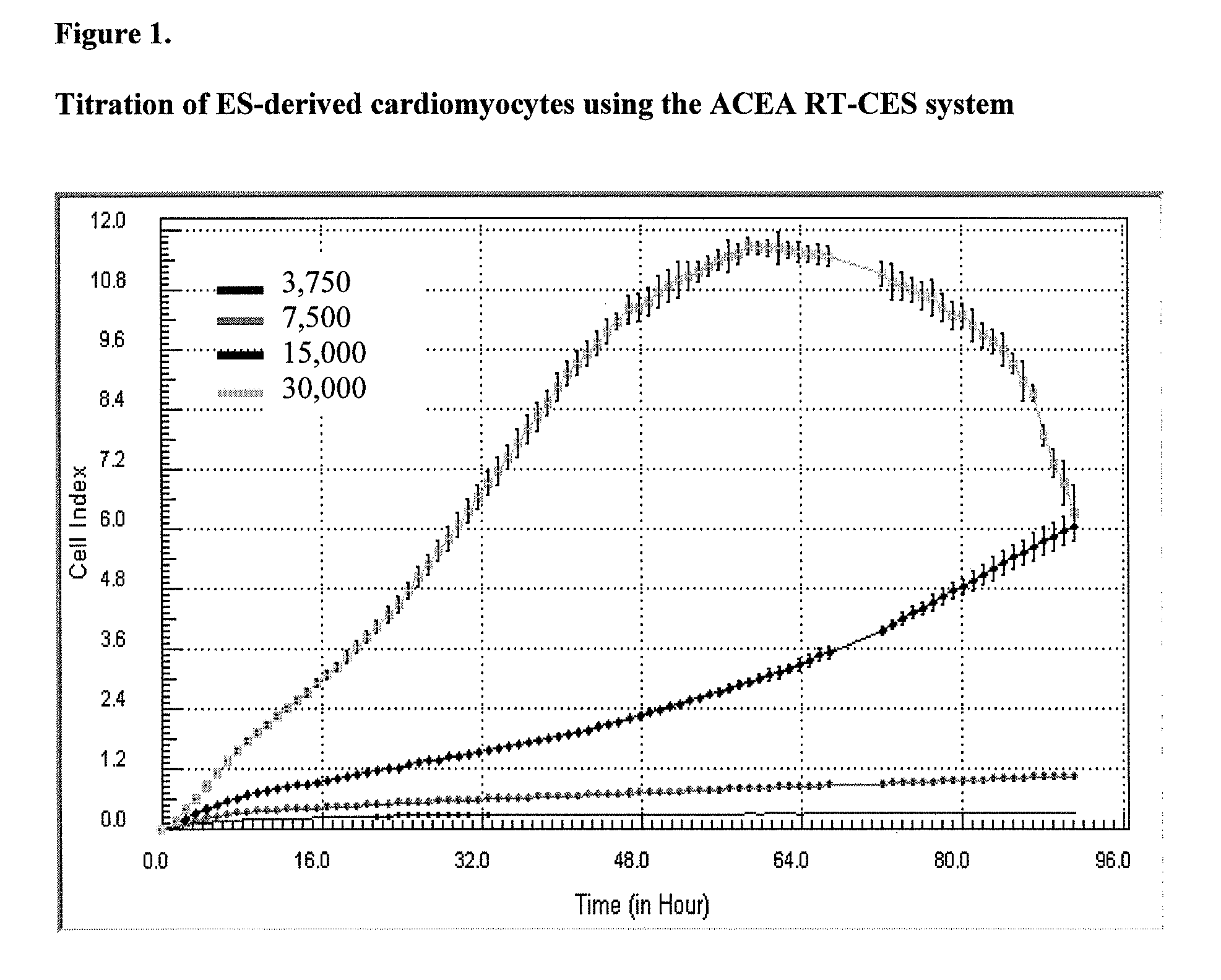
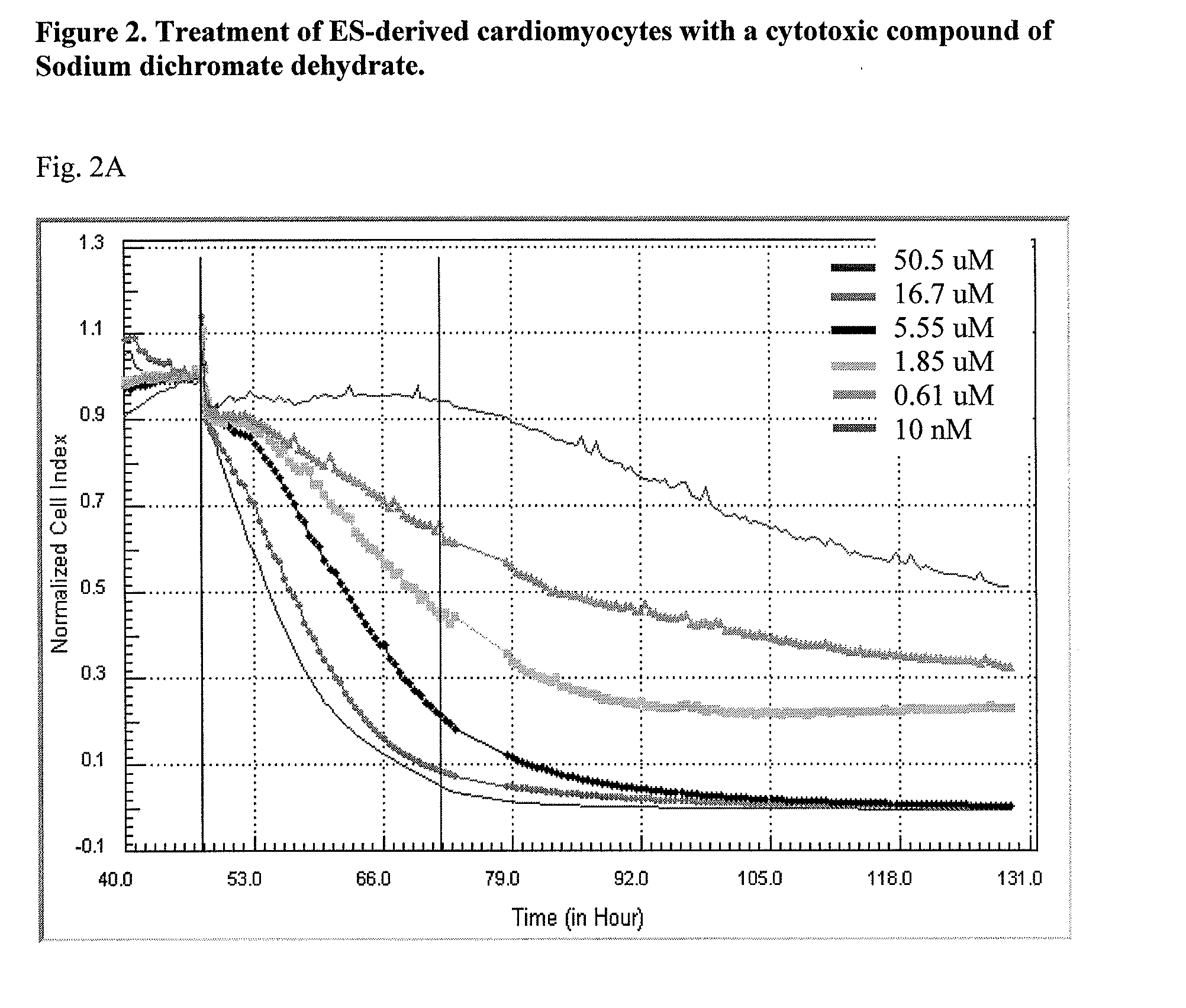
Data analysis of cells undergoing excitation contraction coupling as detected on real-time cell analysis (RTCA) instruments
A method of determining a beating parameter of cells that undergo excitation contraction coupling, the method including providing a cell analysis device having a substrate and a sensor that measures cell adhesion or attachment to the substrate in millisecond time resolution; adding excitable cells capable of undergoing excitation contraction coupling to the substrate; monitoring cell adhesion or attachment of the excitable cells to the substrate in millisecond time resolution; and calculating one or more beating parameters from the monitored adhesion.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Label-free monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells using impedance based systems with millisecond time resolution
ActiveUS9709548B2Easy to measureEffective monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningImage resolutionExcitation–contraction coupling
Systems and methods for improved monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells are provided, which provide millisecond time resolution. The system is capable of continuously monitoring excitation-contraction coupling in a relatively high-throughput manner. The system includes a device for monitoring cell-substrate impedance, an impedance analyzer capable of impedance measurements at millisecond time resolution, electronic circuitry that can engage the device and selectively connect two or more electrode arrays of the device to the impedance analyzer and a software program that controls the electronic circuitry and records and analyzes data obtained from the impedance analyzer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
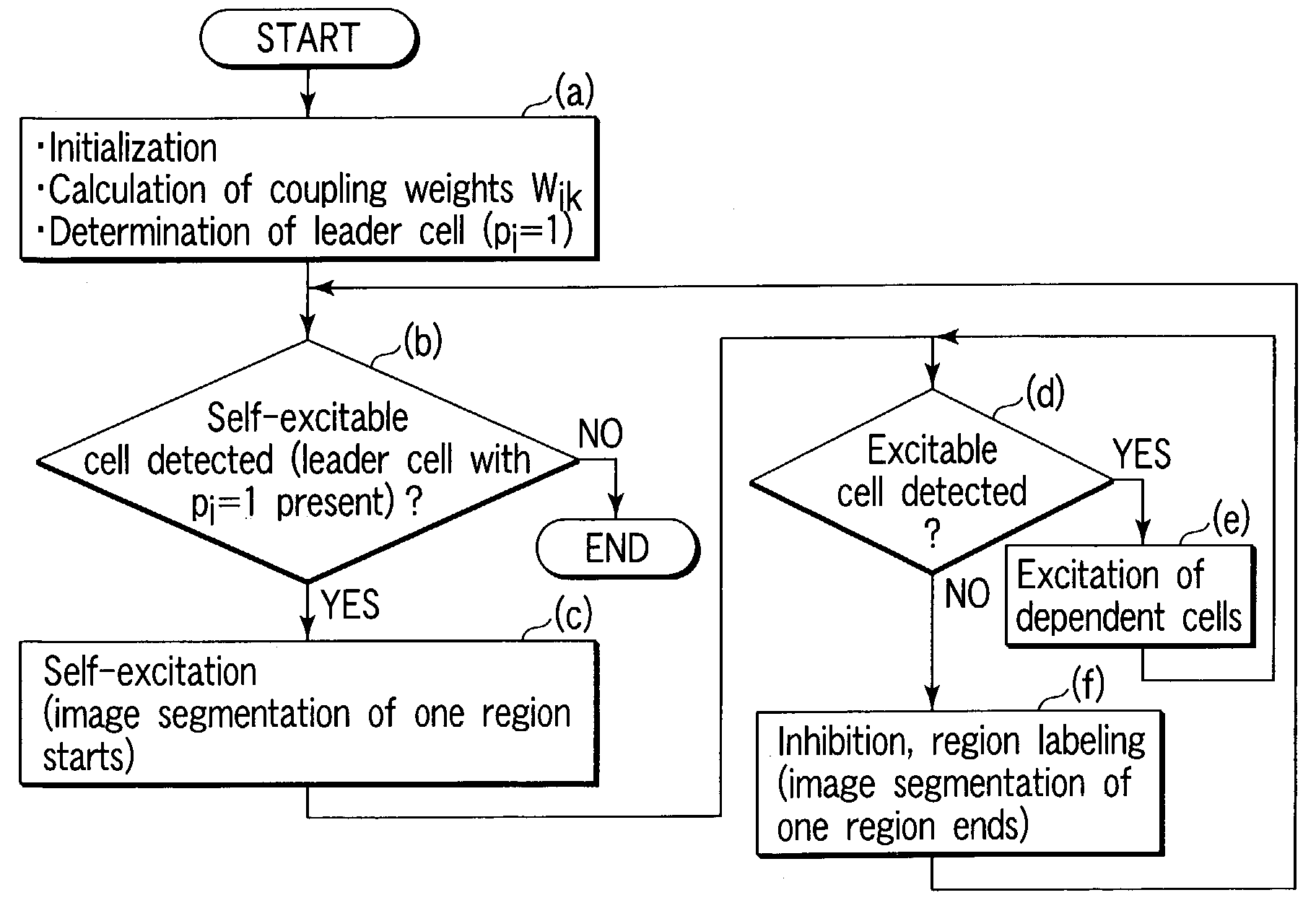
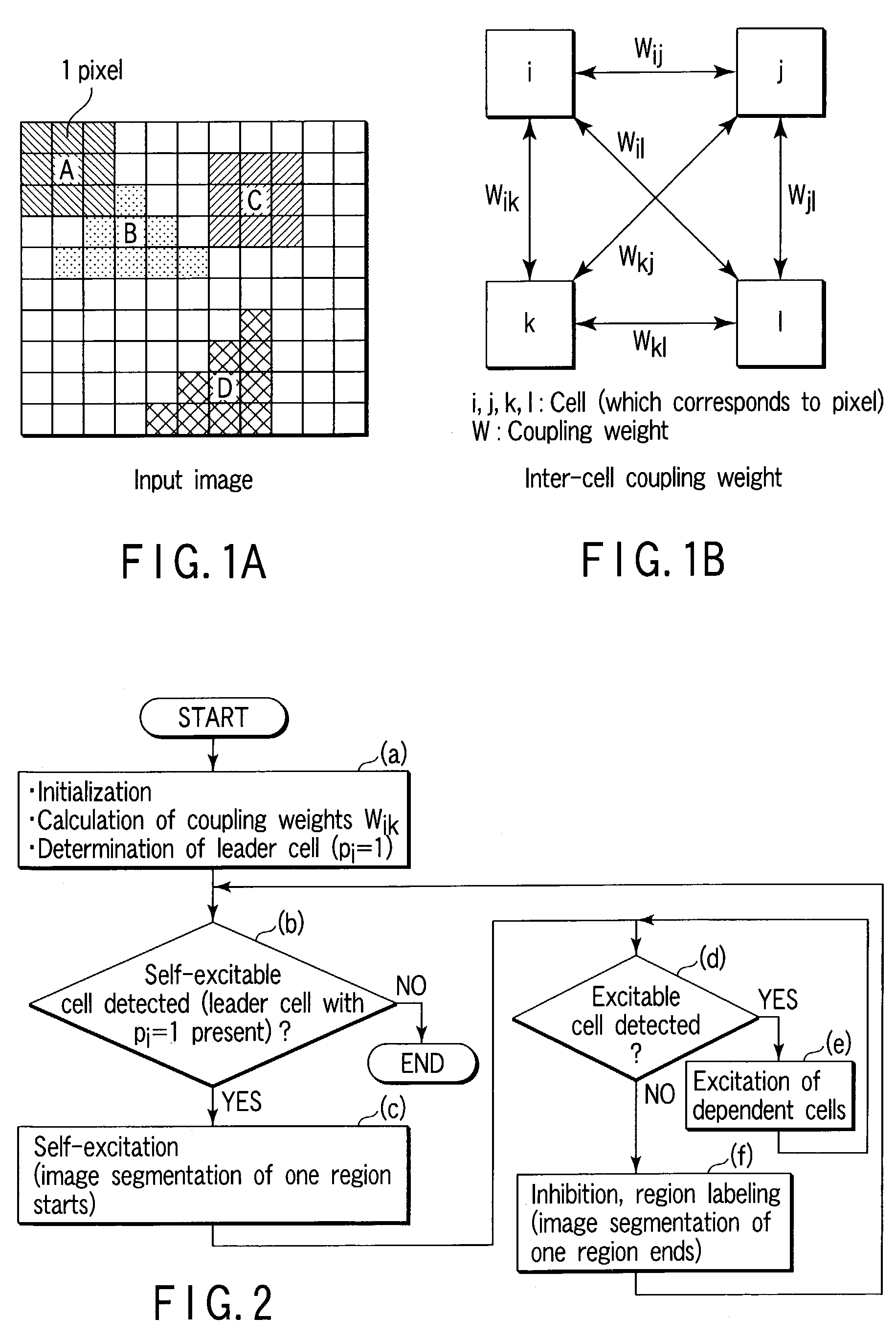
Image segmentation method, image segmentation apparatus, image processing method, and image processing apparatus
ActiveUS7298899B2Increase speedIncrease application speedImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiology
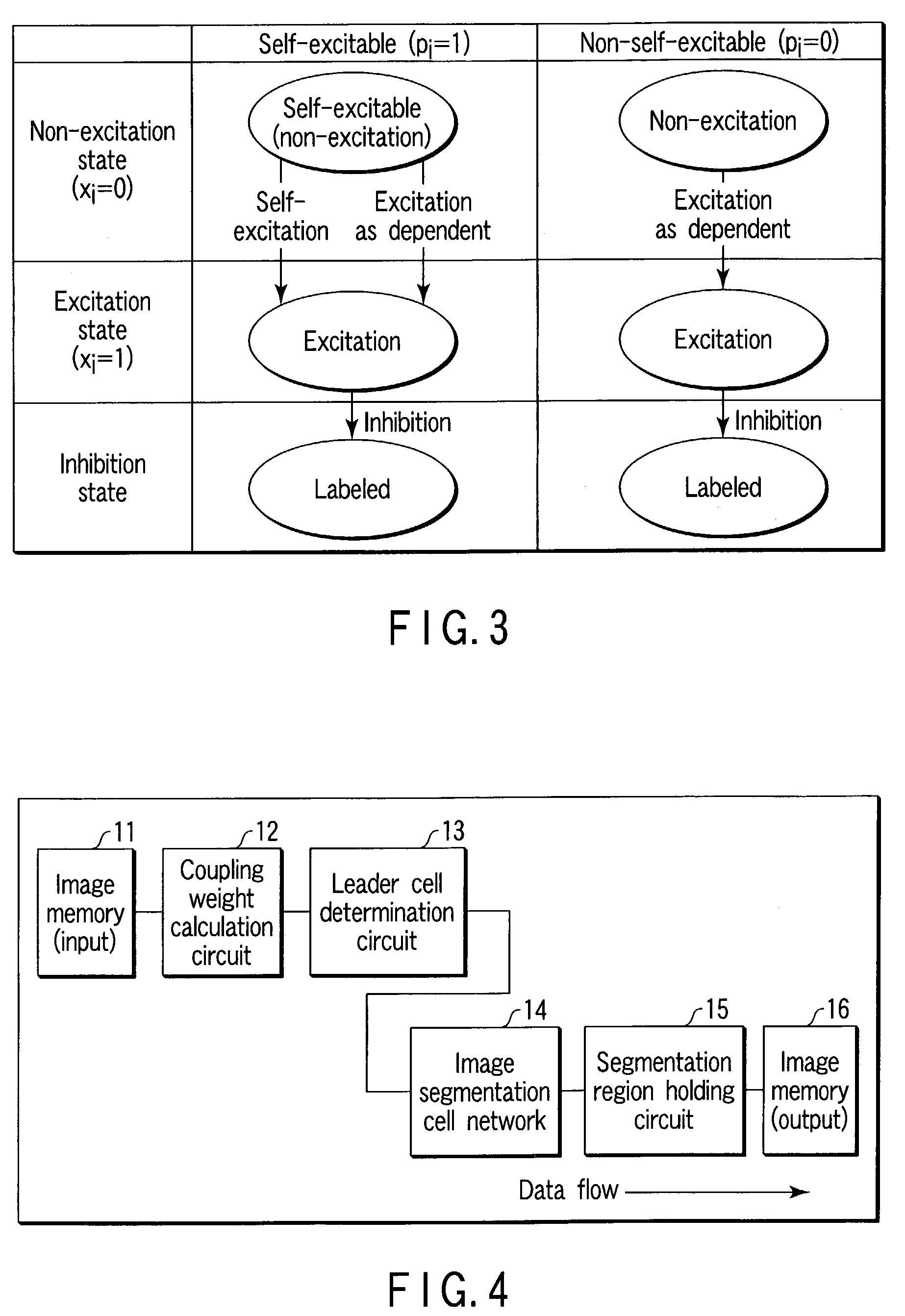
Cells i corresponding to pixels are initialized into a non-excitation state, to calculate coupling weights Wik between the eight cells k adjacent to the cells i, thereby determining leader cells pi=1 based on calculation results. Next, one leader cell yet to be excited is selected as a self-excitable cell. The selected cell is put into the excitation state, the excitable cells are selected based on the coupling weights between the adjacent cells, and the selected cells are put into the excitation state. These operations are repeated until no excitable cell is detected any more and, if there no excitable cell is detected any more, inhibition processing is performed, thereby completing image segmentation of one region. These operations are repeated until there is no non-excited and non-inhibited leader cell any more, thereby pinpointing regions belonging to the same category from an input image and identifying them as an image segmentation regions.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Application of electrical stimulation for functional tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS8367410B2Highly integratedImprove functionalityMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processExcitable cellIt integration
The present invention provides new methods for the in vitro preparation of bioartificial tissue equivalents and their enhanced integration after implantation in vivo. These methods include submitting a tissue construct to a biomimetic electrical stimulation during cultivation in vitro to improve its structural and functional properties, and / or in vivo, after implantation of the construct, to enhance its integration with host tissue and increase cell survival and functionality. The inventive methods are particularly useful for the production of bioartificial equivalents and / or the repair and replacement of native tissues that contain electrically excitable cells and are subject to electrical stimulation in vivo, such as, for example, cardiac muscle tissue, striated skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, bone, vasculature, and nerve tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tissue Protective Cytokine Receptor Complex, Assays for Identifying Tissue Protective Compounds and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090136519A1Easy to measureFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNervous systemExcitable cell
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +1
System and method for optogenetic therapy
Configurations are described for utilizing light-activated proteins within cell membranes and subcellular regions to assist with medical treatment paradigms, such as hypertension treatment via anatomically specific and temporally precise modulation of renal plexus activity. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-sensitive proteins to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides systems, devices, and methods for millisecond-timescale temporal control of certain cell activities using moderate light intensities, such as the generation or inhibition of electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS
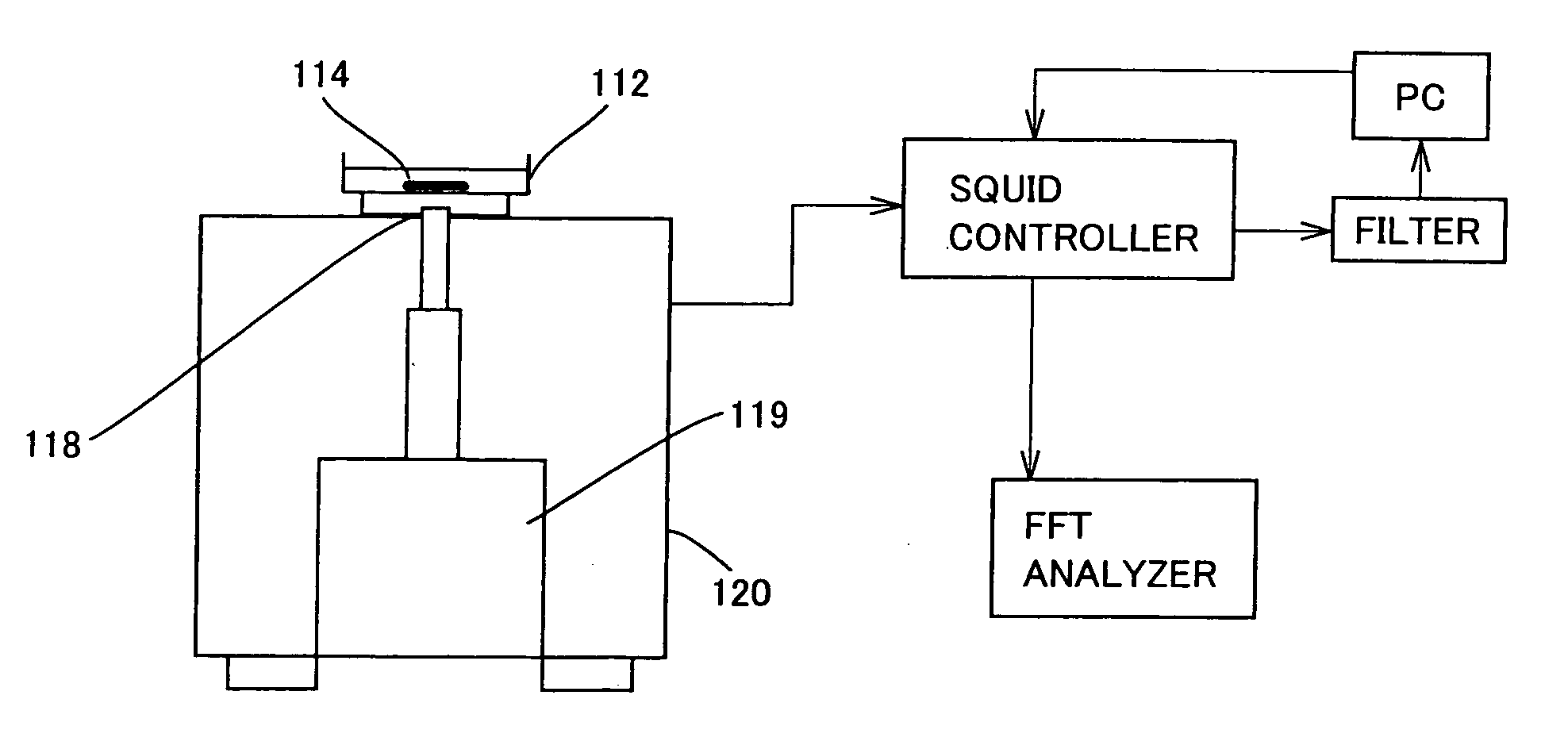
Cellular tissue magnetic signal detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20110163744A1High precisionExclude influenceMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMaterial analysisElectricityNoise level
A cellular tissue magnetic signal detecting device for detecting a magnetic signal locally generated in a cellular tissue including an excitable cell generating an electrical excitation, the cellular tissue magnetic signal detecting device includes: a magnetic sensor head operative to approach the cellular tissue within 1000 μm; and a magnetic detecting section detecting the magnetic signal with a resolution of 1000 μm or less at a noise level of 1 nT or less, and a response speed of 1 ms or less based on an output signal from the magnetic sensor head; the magnetic sensor head including magneto impedance sensor.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Mice expressing human voltage-gated sodium channels
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
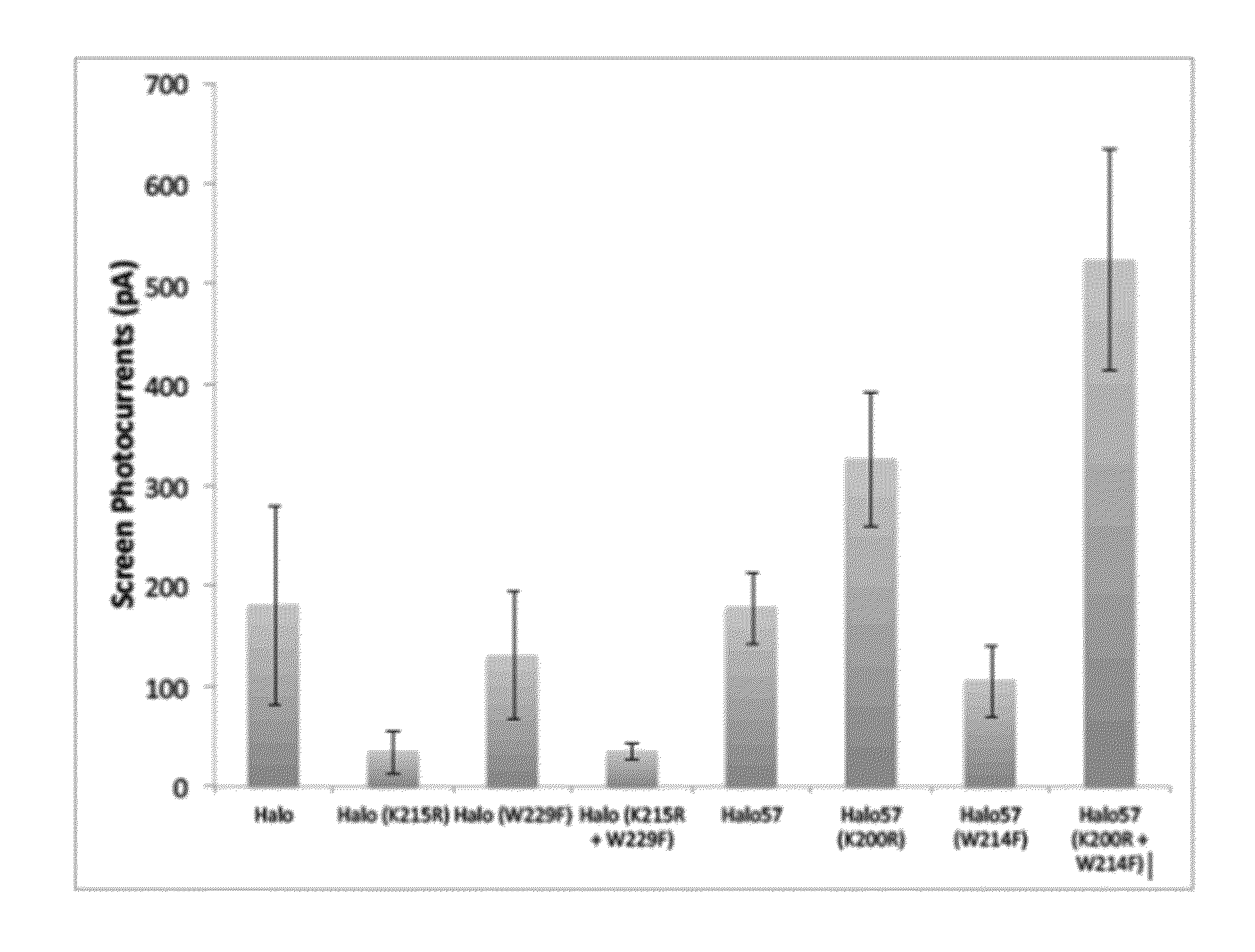
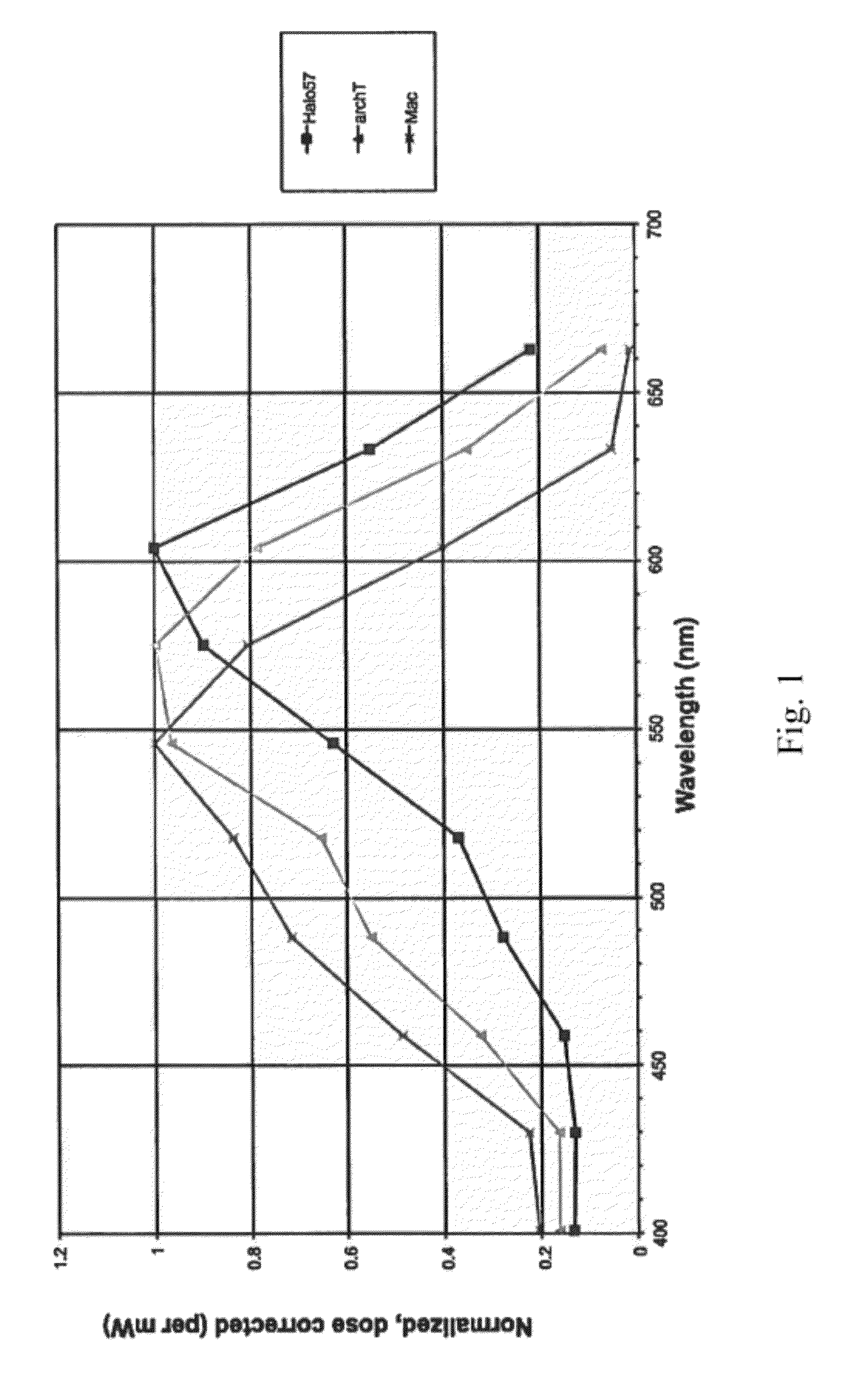
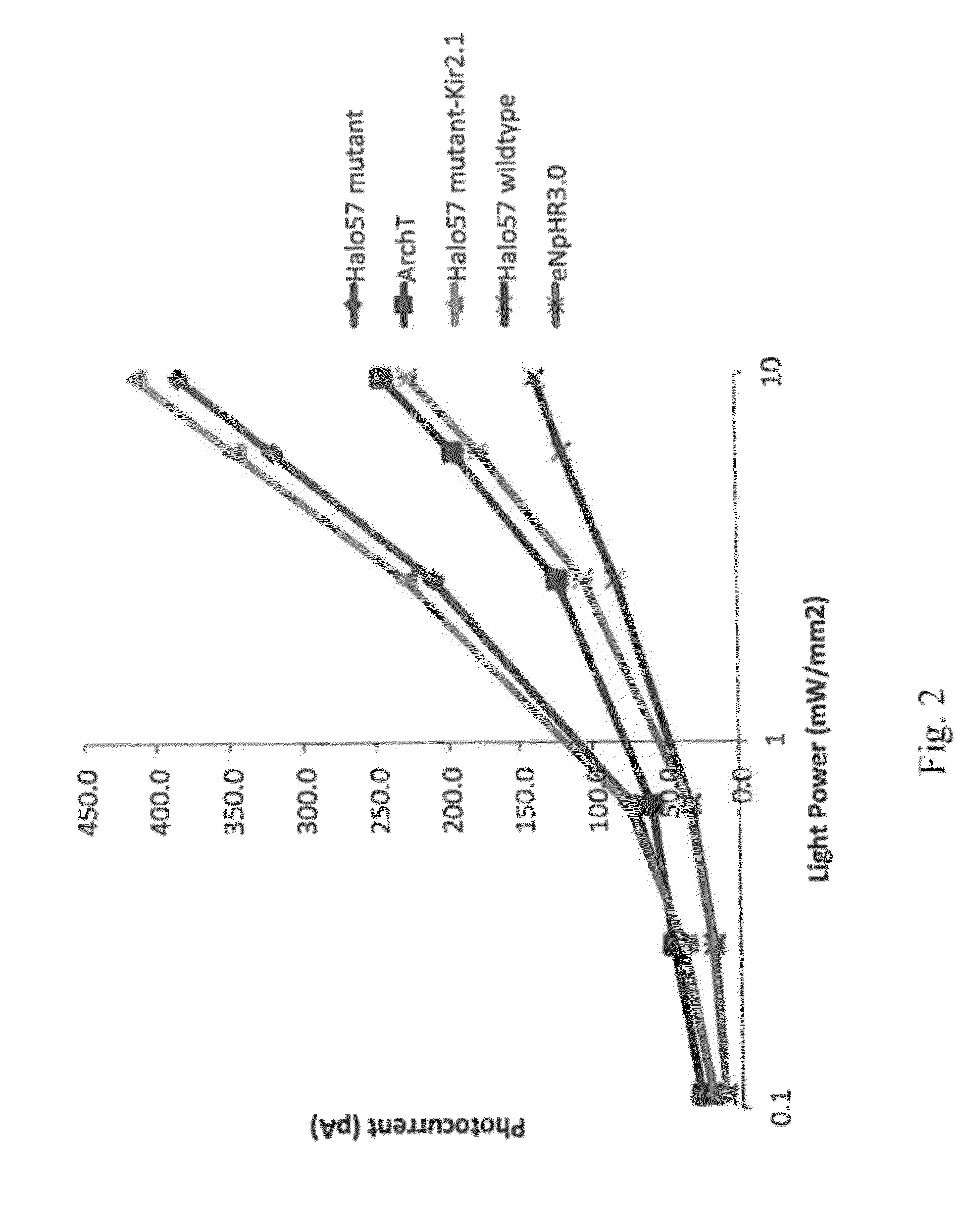
Red-shifted opsin molecules and uses thereof
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tissue scaffolds for electrically excitable cells
InactiveUS20160251646A1Superior predictive powerLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanofibrous scaffoldNanofiber
Inventive concepts relate generally to nanofibrous scaffolds useful for electrophysiological assays. Scaffolds include polymeric nanofibrous components and electrically excitable cells immobilized at a distinct cell seeding domains on the scaffold. Methods and kits including the scaffolds are also described.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SURFACE TECHNOLOGIES LLC
System and method for optogenetic therapy
Configurations are described for utilizing light-activated proteins within cell membranes and subcellular regions to assist with medical treatment paradigms, such as hypertension treatment via anatomically specific and temporally precise modulation of renal plexus activity. The invention provides for proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and methods for genetically targeted expression of light-sensitive proteins to specific cells or defined cell populations. In particular the invention provides systems, devices, and methods for millisecond-timescale temporal control of certain cell activities using moderate light intensities, such as the generation or inhibition of electrical spikes in nerve cells and other excitable cells.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS
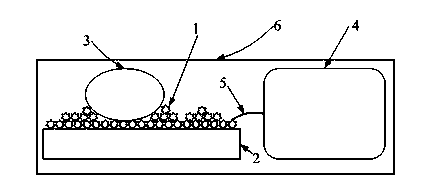
Electric excitation cell culture method
InactiveCN103849566AQuality improvementSimple structureTissue/virus culture apparatusStress based microorganism growth stimulationPetri dishExcitable cell
The present invention discloses an electric excitation cell culture method, wherein an electrostatic spinning electrode 1, a culture dish substrate 2, electric excitation cells 3, an electric stimulation module 4, and an electrode connection wire 5 are adopted. According to the present invention the structure is simple, and electric stimulation can be added based on three dimensional culture of the skeleton so as to improve culture quality of the electrically excitable cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUDONG INTPROP PROTECTION ASSOC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com