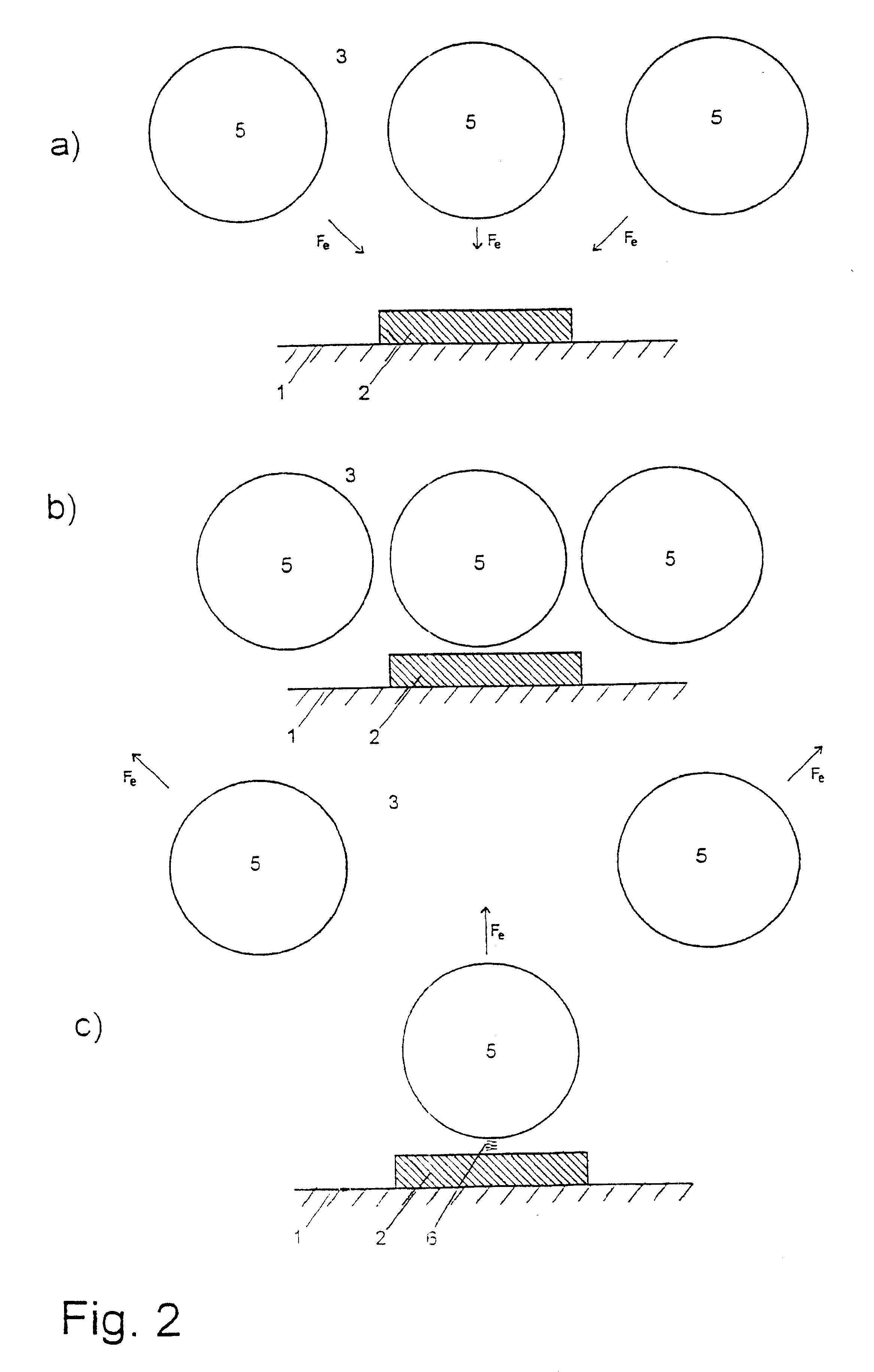
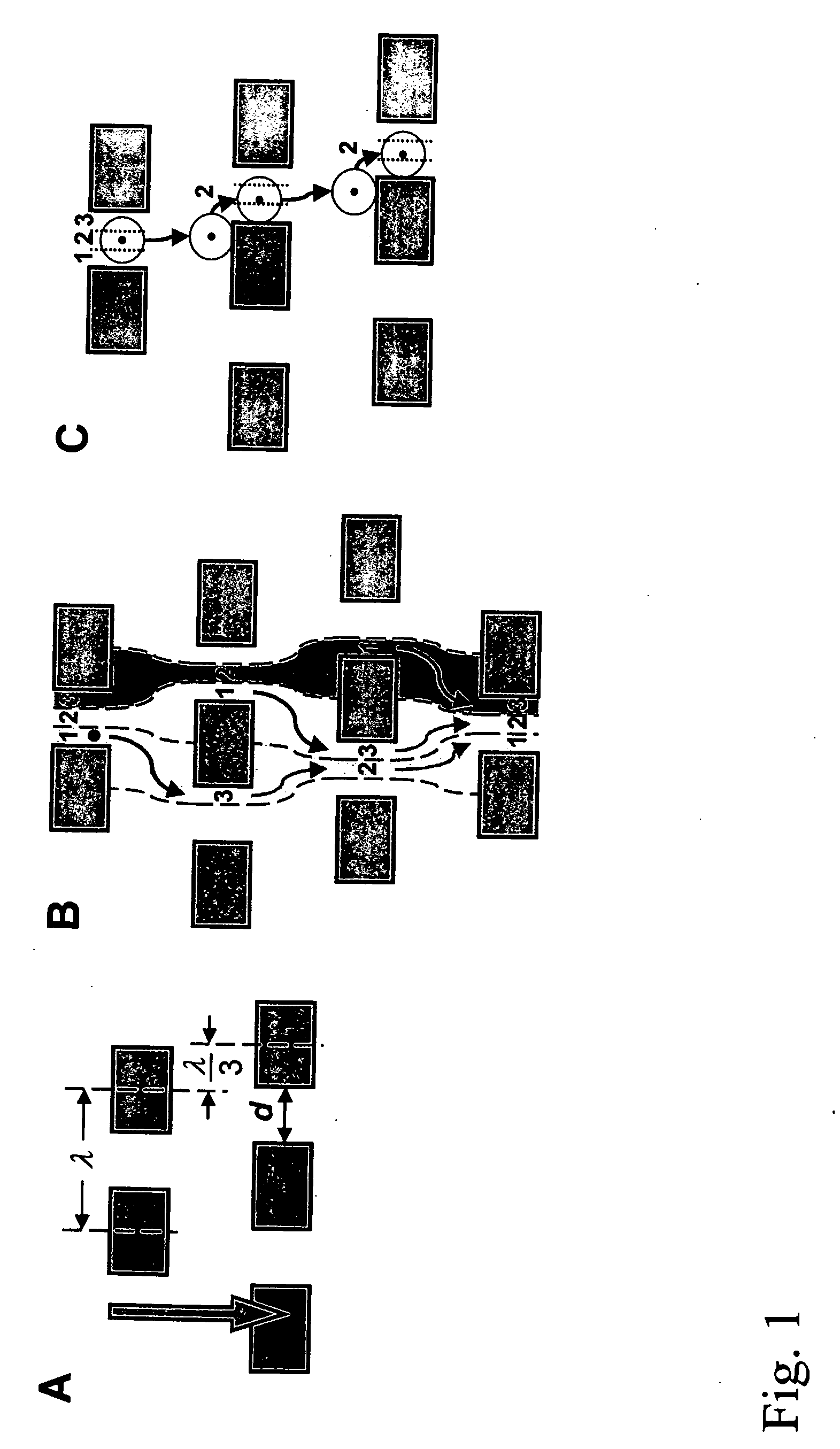
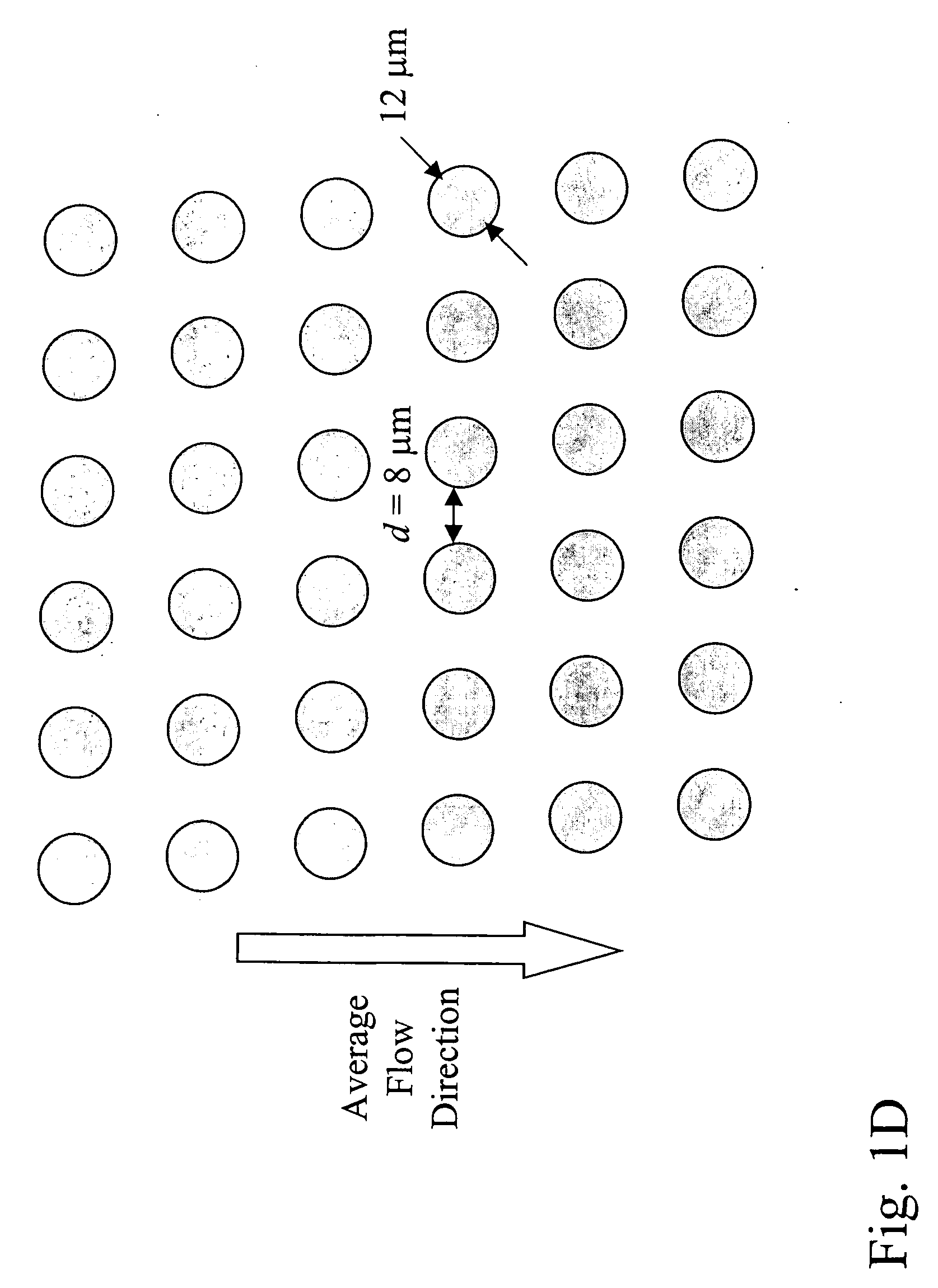
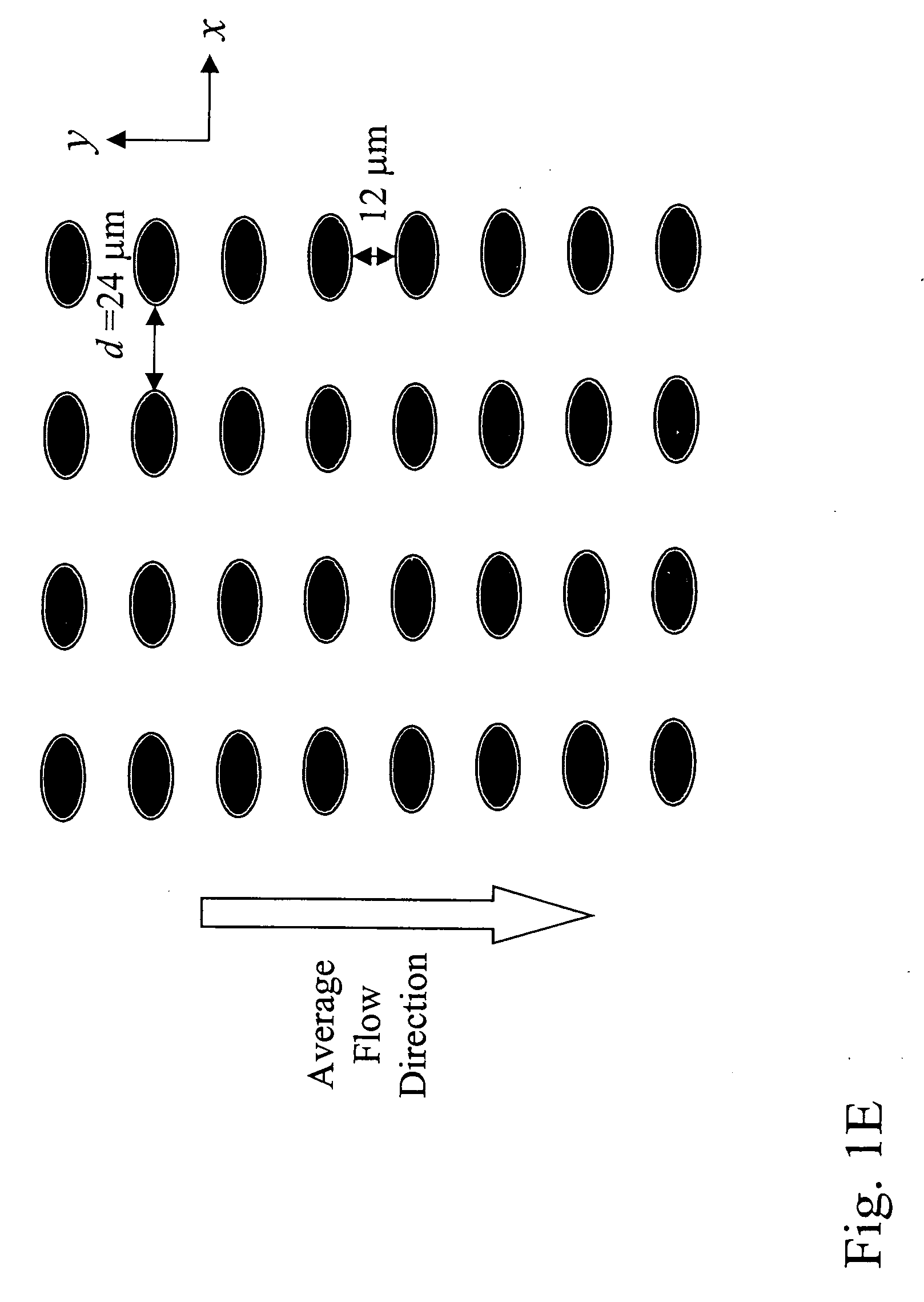
Patents
Literature
3743results about "Stress based microorganism growth stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
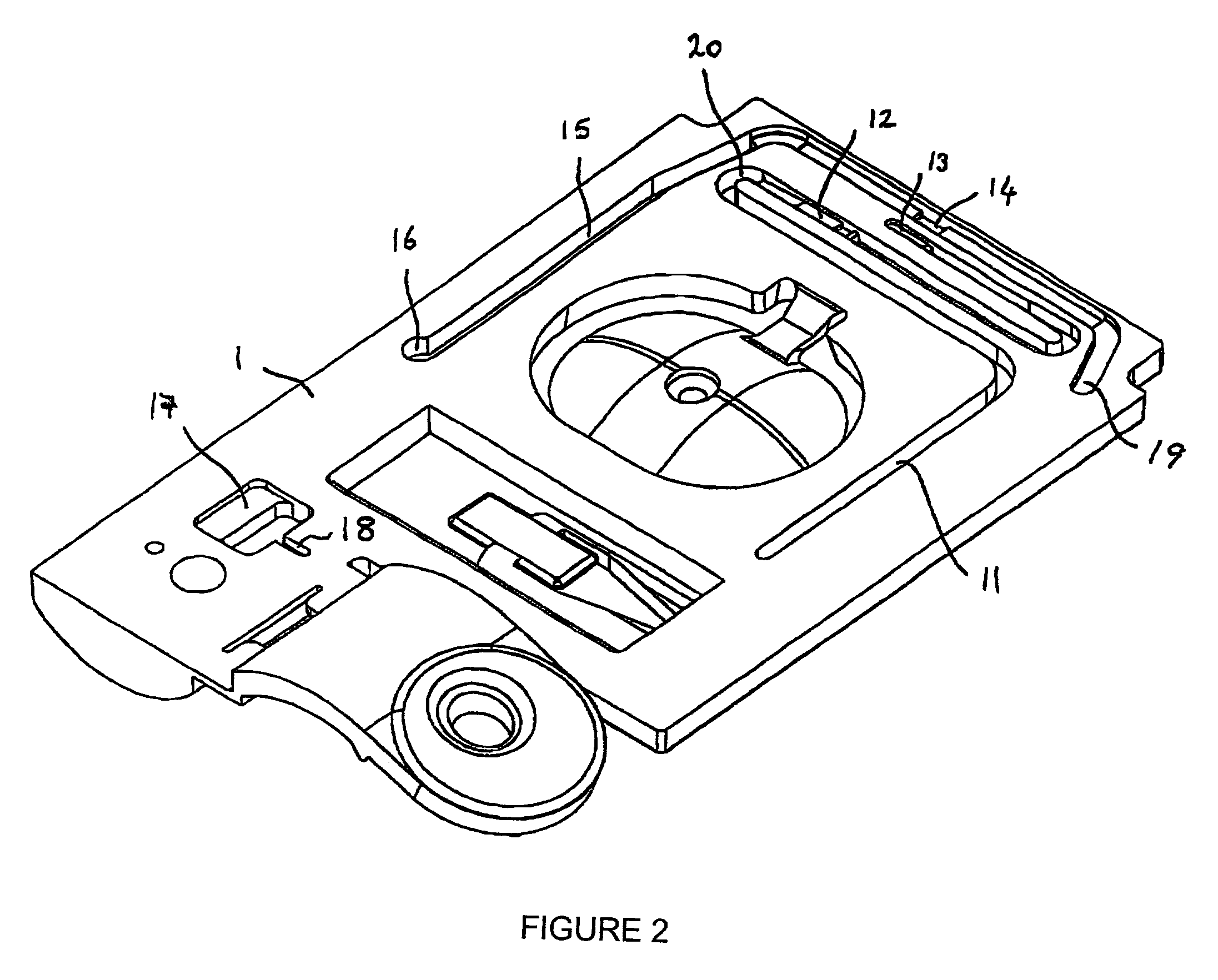
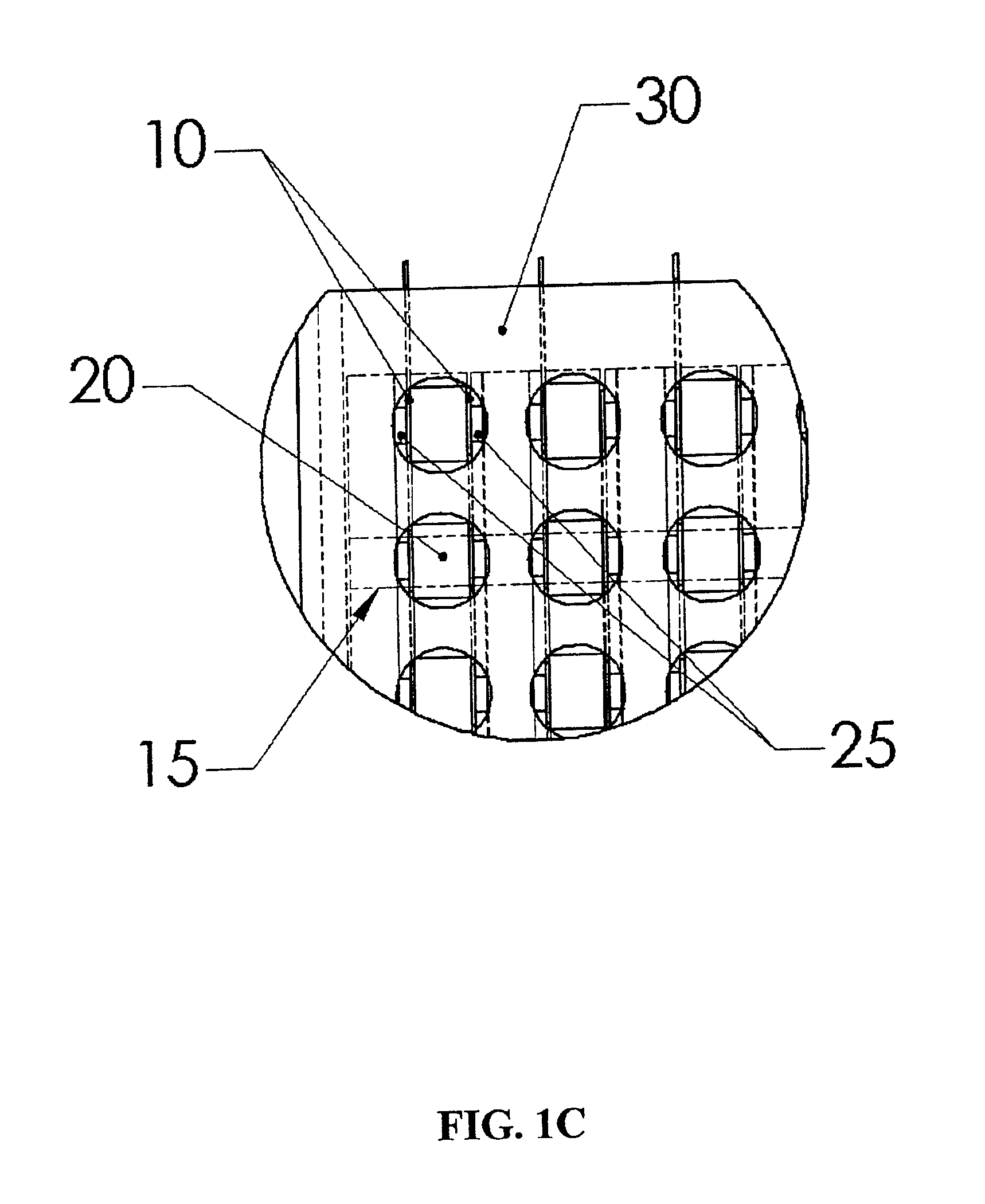
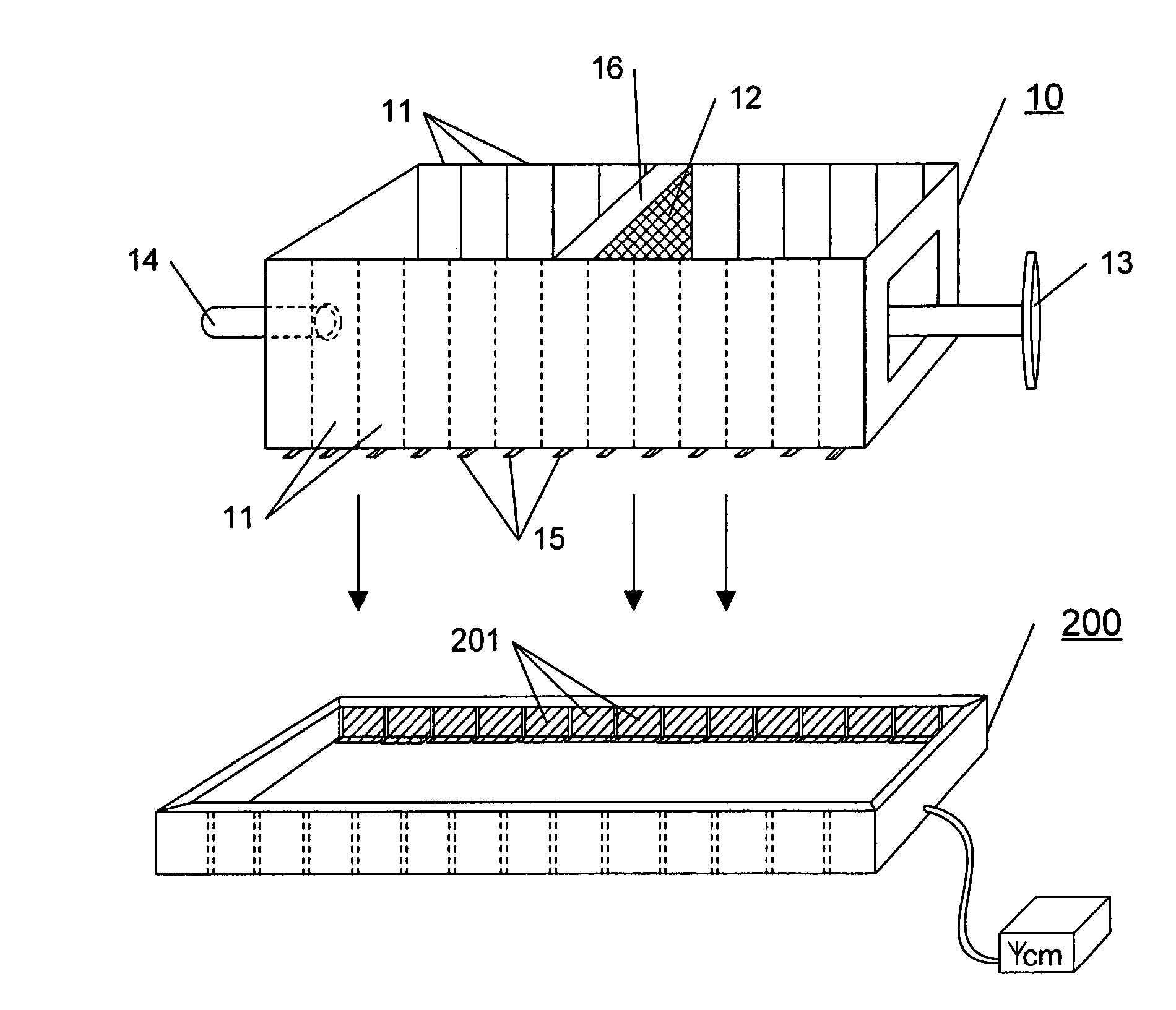
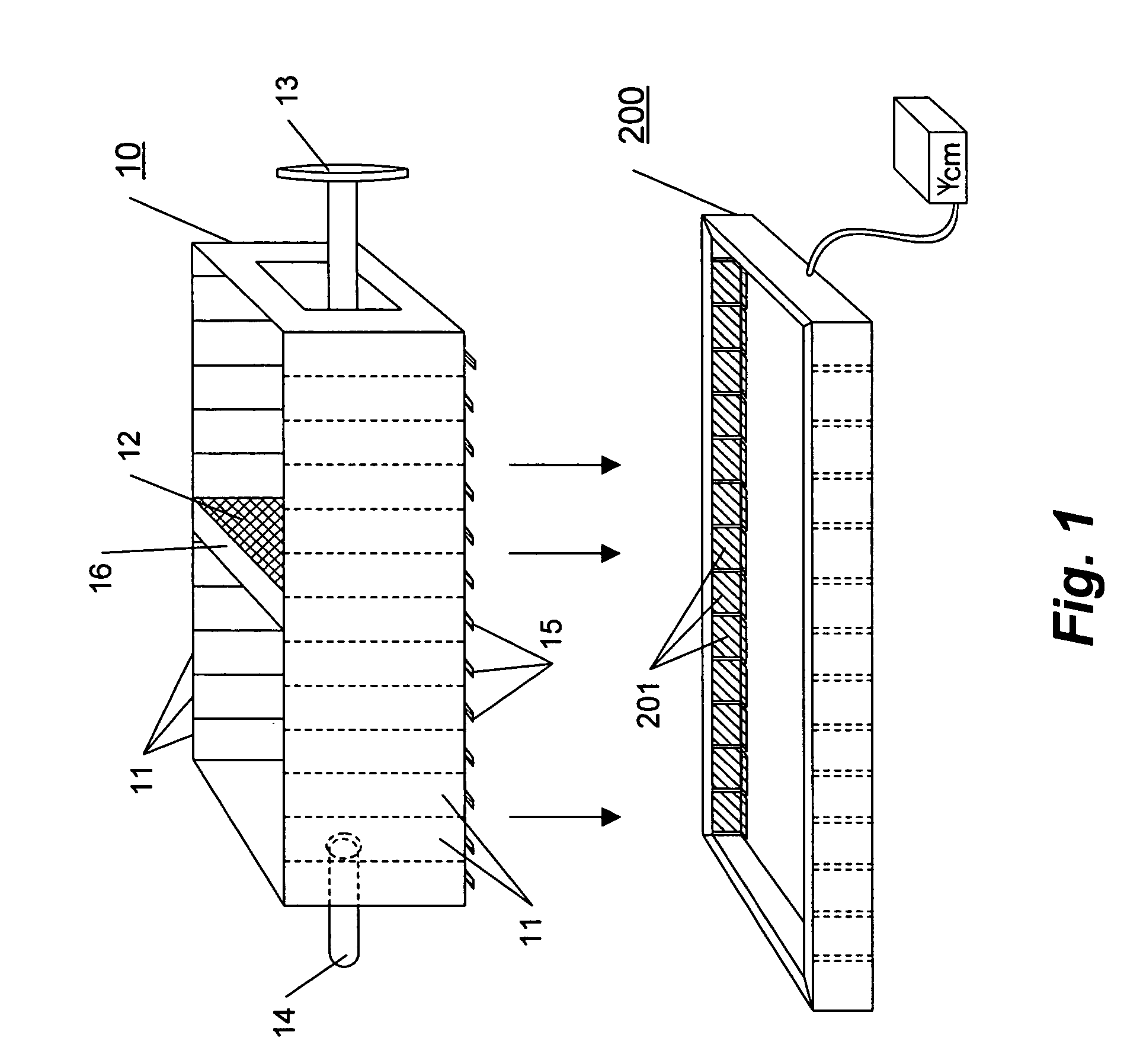
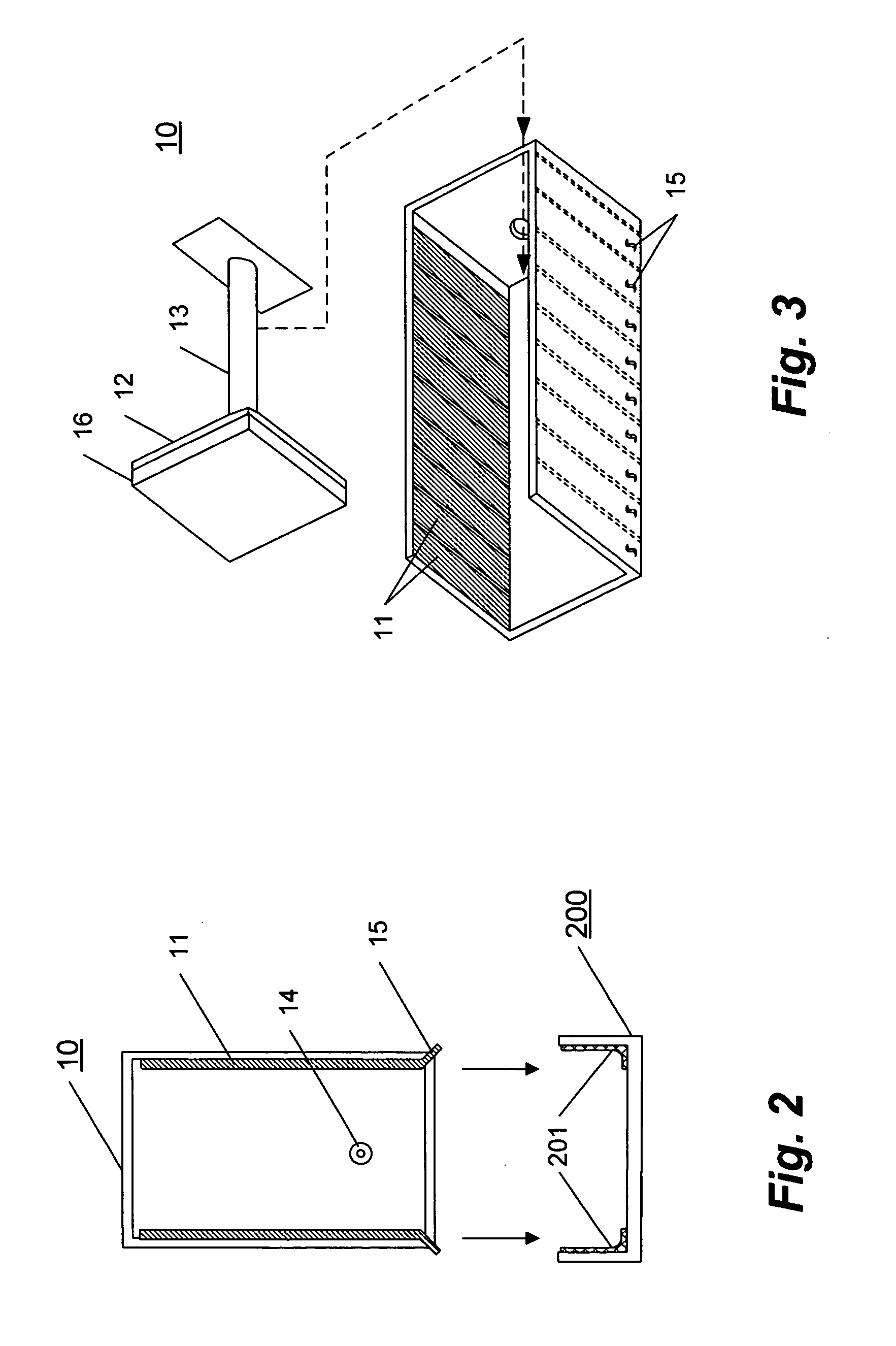
Drug delivery system and method
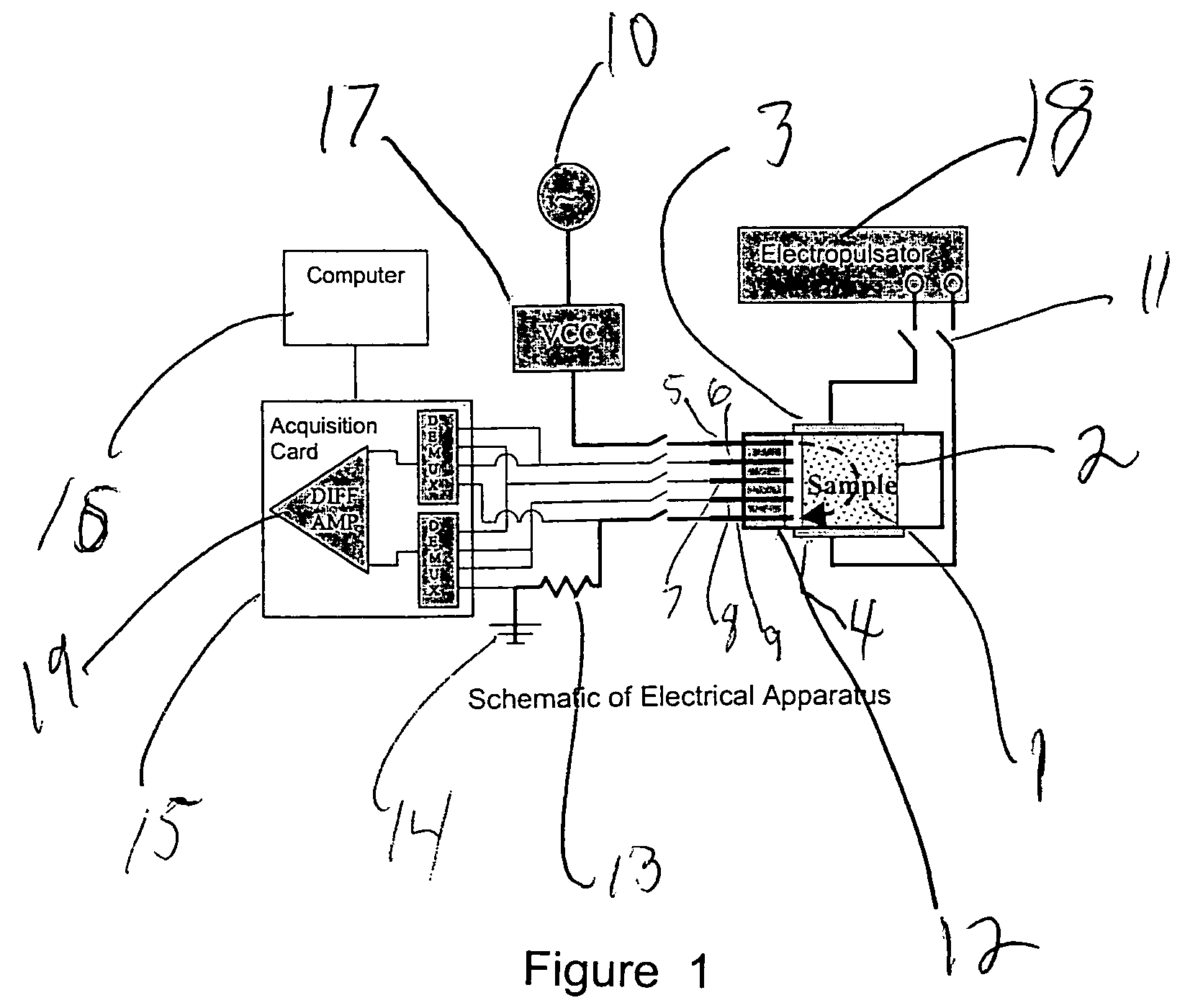
InactiveUS6041252AFacilitated releaseFast wayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyLiposomeBiomedical engineering
A method for delivering a therapeutic agent to a predetermined location in a host is disclosed, wherein a liposome-encapsulated therapeutic agent is administered to the host, and an electrical field which encompasses a predetermined region within the host is established, such that as the liposome-encapsulated agent is exposed to the electrical field the release of the agent from the liposome to the predetermined region is enhanced.
Owner:ICHOR MEDICAL SYST
Apparatus and methods for analyte measurement and immuno assay
ActiveUS20030170881A1Avoid disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careOrganism
The present invention relates to an apparatus for conducting a variety of assays for the determination of analytes in liquid samples, and relates to the methods for such assays. In particular, the invention relates to a single-use cartridge designed to be adaptable to a variety of real-time assay protocols, preferably assays for the determination of analytes in biological samples using immunosensors or other ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The cartridge provides novel features for processing a metered portion of a sample, for precise and flexible control of the movement of a sample or second fluid within the cartridge, for the amending of solutions with additional compounds during an assay, and for the construction of immunosensors capable of adaptation to diverse analyte measurements. The disclosed device and methods of use enjoy substantial benefits over the prior art, including simplicity of use by an operator, rapid in situ determinations of one or more analytes, and single-use methodology that minimizes the risk of contamination of both operator and patient. The disclosed invention is adaptable to the point-of-care clinical diagnostic field, including use in accident sites, emergency rooms, surgery, nursing homes, intensive care units, and non-medical environments.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Apparatus and methods for analyte measurement and immunoassay
ActiveUS7419821B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careEngineering
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Cell/tissue analysis via controlled electroporation
InactiveUS6482619B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyElectrical resistance and conductance
An electrical current is created across an electrically conductive medium comprising a cell which may be part of a tissue of a living organism. A first electrical parameter which may be current, voltage, or electrical impedance is measured. A second electrical parameter which may be current, voltage or a combination of both is then adjusted and / or analyzed. Adjustments are carried out to facilitate analysis and / or obtain a desired degree of electroporation. Analysis is carried out to determine characteristics of the cell membrane and / or tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
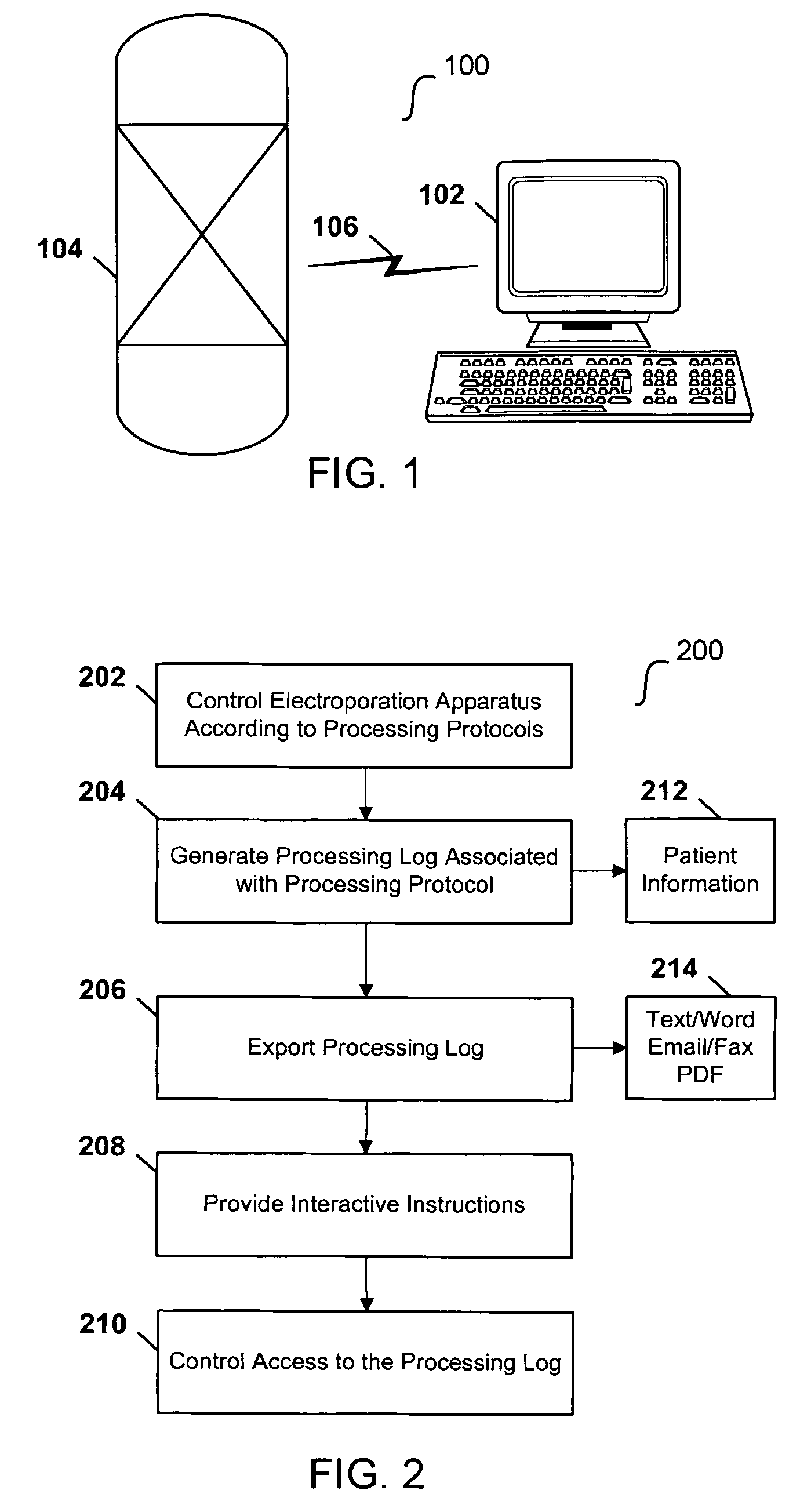
Computerized electroporation
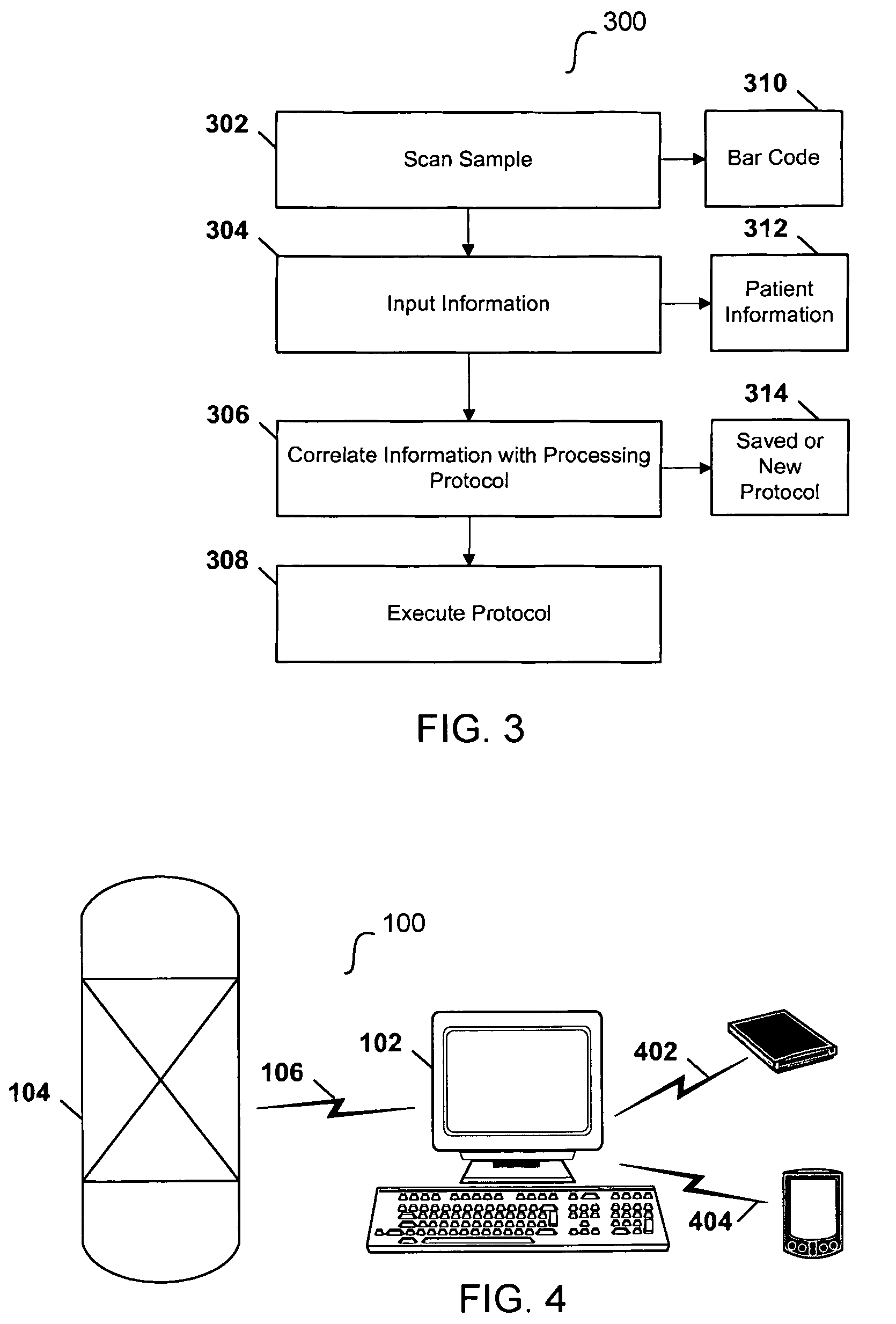
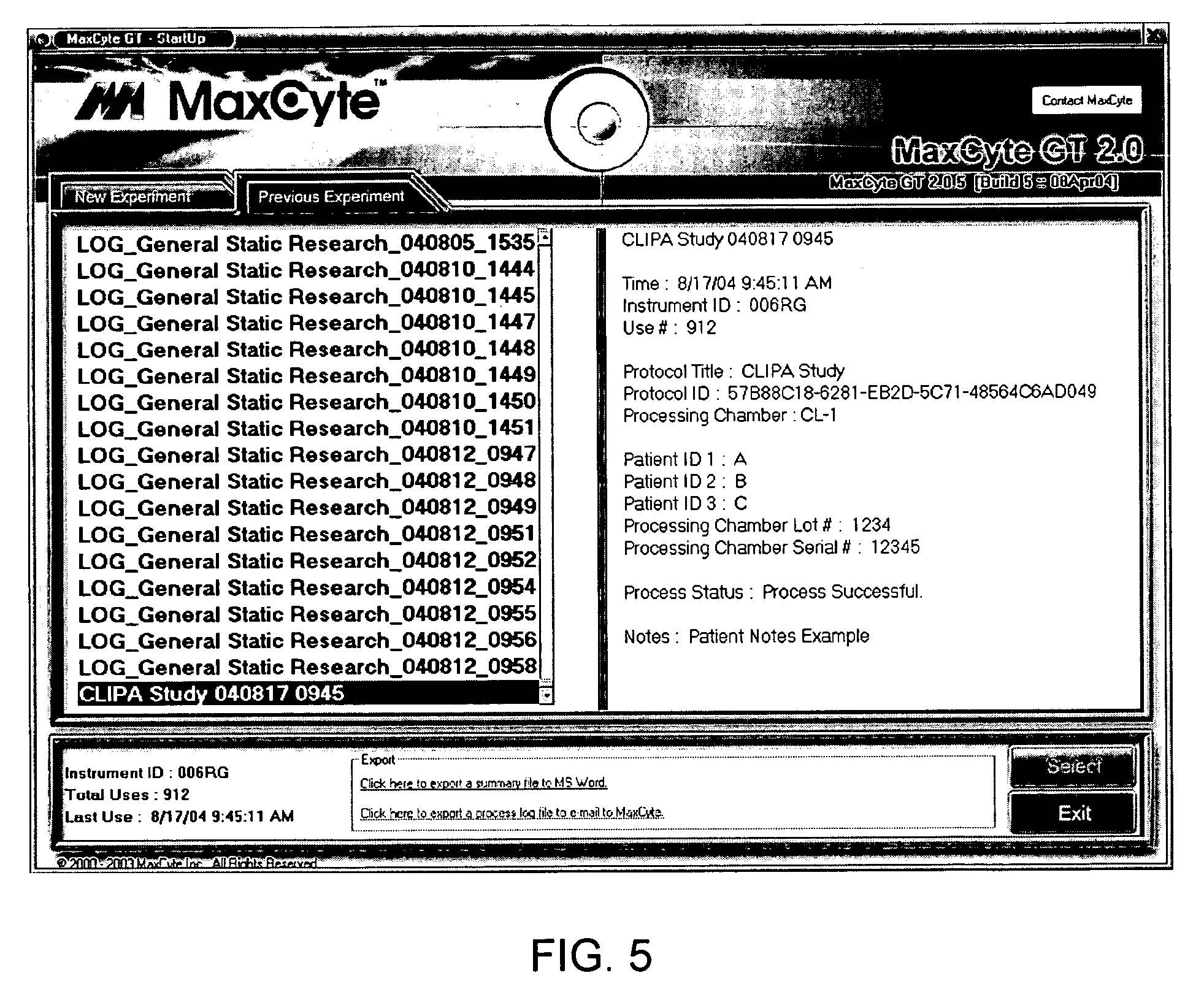
ActiveUS7991559B2General purpose stored program computerOther foreign material introduction processesInformation processingProcessing
Techniques for computerized electroporation. An electroporation apparatus may be controlled according to one of a plurality of previously-saved, user-defined processing protocols. A processing log associated with a processing protocol may be generated, and the processing log may include patient or sample specific information. The processing log or a summary of the processing log may be exported to a user. Interactive instructions may be provided to a user. Those instructions may correspond to one or more steps of a processing protocol.
Owner:MAXCYTE INC
Device and method for detecting analytes
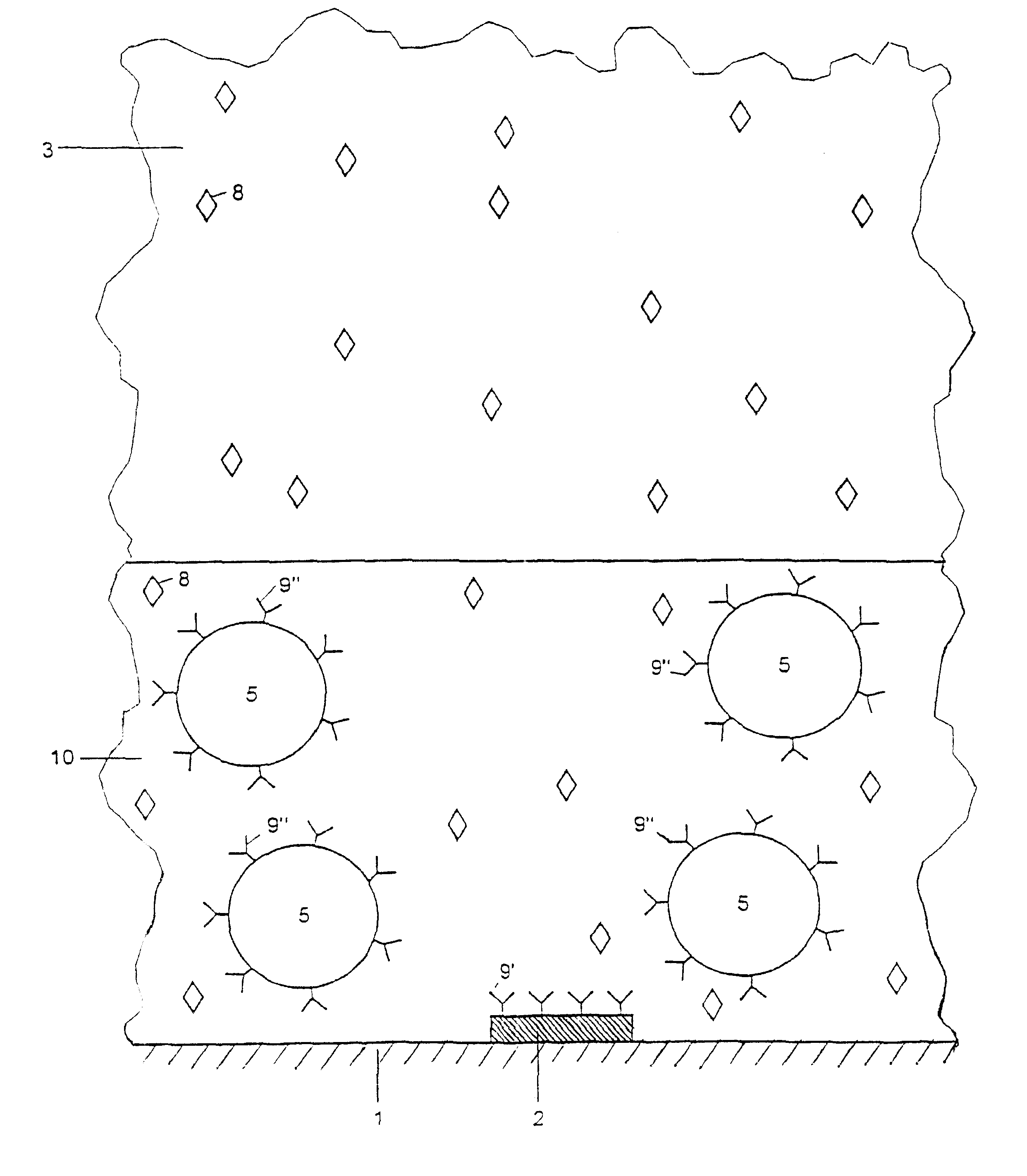
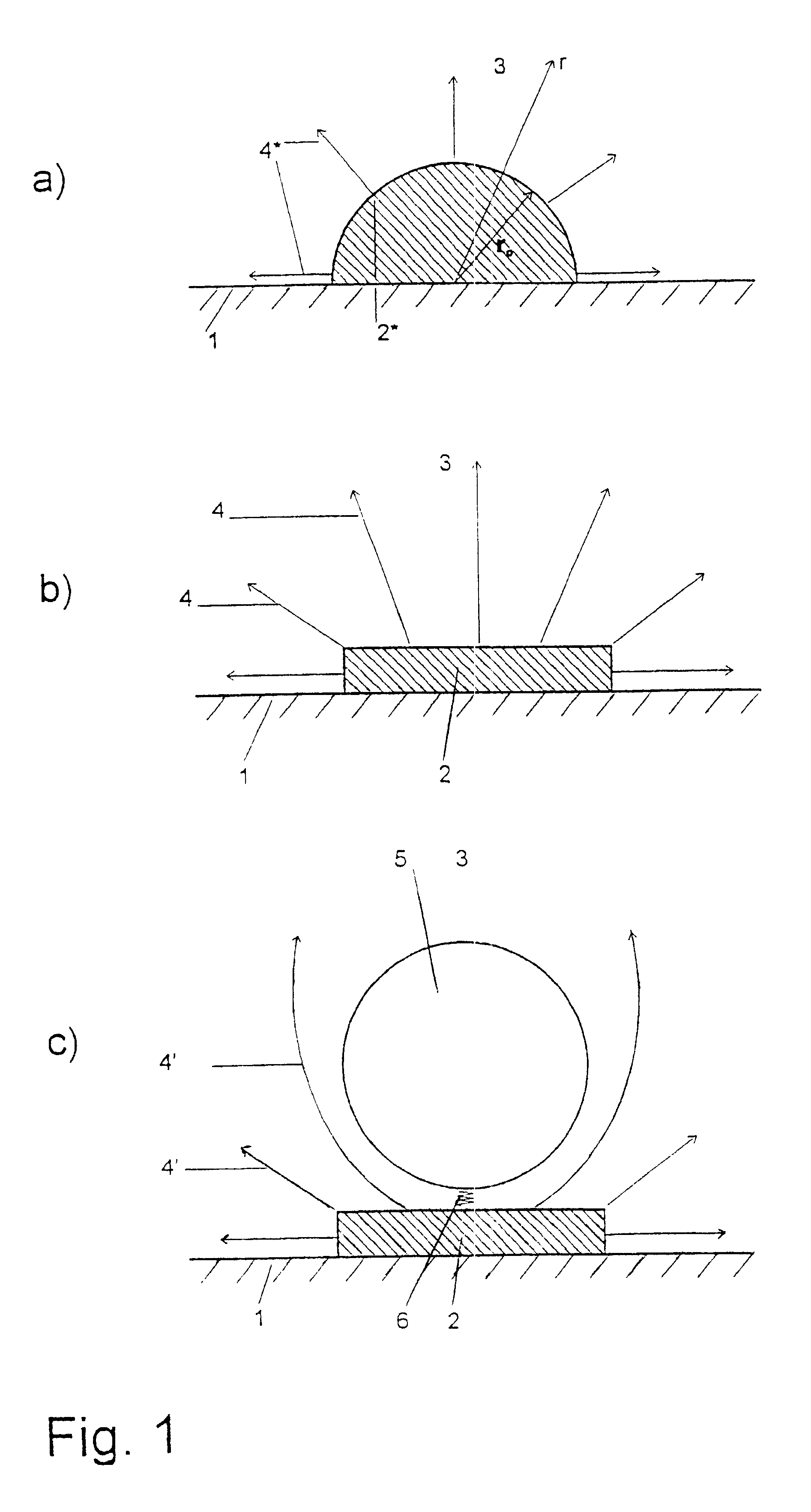
InactiveUS6548311B1Influence is negligibleRelative density is smallBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityAnalyte
The invention relates to a method for detecting analytes and to a device for carrying out the method, for use for analysis or diagnosis in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry, molecular genetics, food chemistry, biotechnology, the environment and medicine. Marker particles (5) with different electrical properties or a different relative permeability to those of the measuring solution (3) surrounding them are used to detect the analytes (8). The marker particles (5) either bond specifically to the analytes (8) or to a base (2) in competition with the analyte. The analytes (8) are detected by the changes in an electrical field or an electrical current generated by electrodes (2) or in an electrical voltage applied to an electrode or in a magnetic field, said changes being caused by marker particles which have bonded with the analytes or by marker particles which have instead bonded to the base in an electrical field.
Owner:KNOLL MEINHARD
Devices and methods for magnetic enrichment of cells and other particles
InactiveUS20060223178A1Small particle sizeLower the volumeArtificial cell constructsLaboratory glasswaresAnalyteMedicine
The invention features devices and methods for the enrichment of cells and other desired analytes by employing a magnetic field, alone or in conjunction with size-based separation. The devices and methods may be advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells or epithelial cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Bioreactors with substance injection capacity
InactiveUS20060154361A1Minimized pressure dropBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid mediumControl substances
A bioreactor with substance injection capability. In one embodiment, the bioreactor includes a first substrate having a first surface, an opposite second surface and edges. The bioreactor further includes a second substrate having a first surface and an opposite second surface, defining a cavity with a bottom surface, where the bottom surface is located therebetween the first surface and the second surface. The first surface of the first substrate is received by the second surface of the second substrate to cover the cavity so as to form a chamber for receiving cells and a liquid medium. A port is formed in the second substrate between the bottom surface and the first surface of the second substrate. As formed, the port is in fluid communication with the chamber to allow a stream of substance to be introduced into the chamber. The stream of substance is controlled so as to provide a gradient, or a concentration gradient of the substance, to the chamber. The stream of substance includes a substance affecting the growth of cells such as chemokine.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
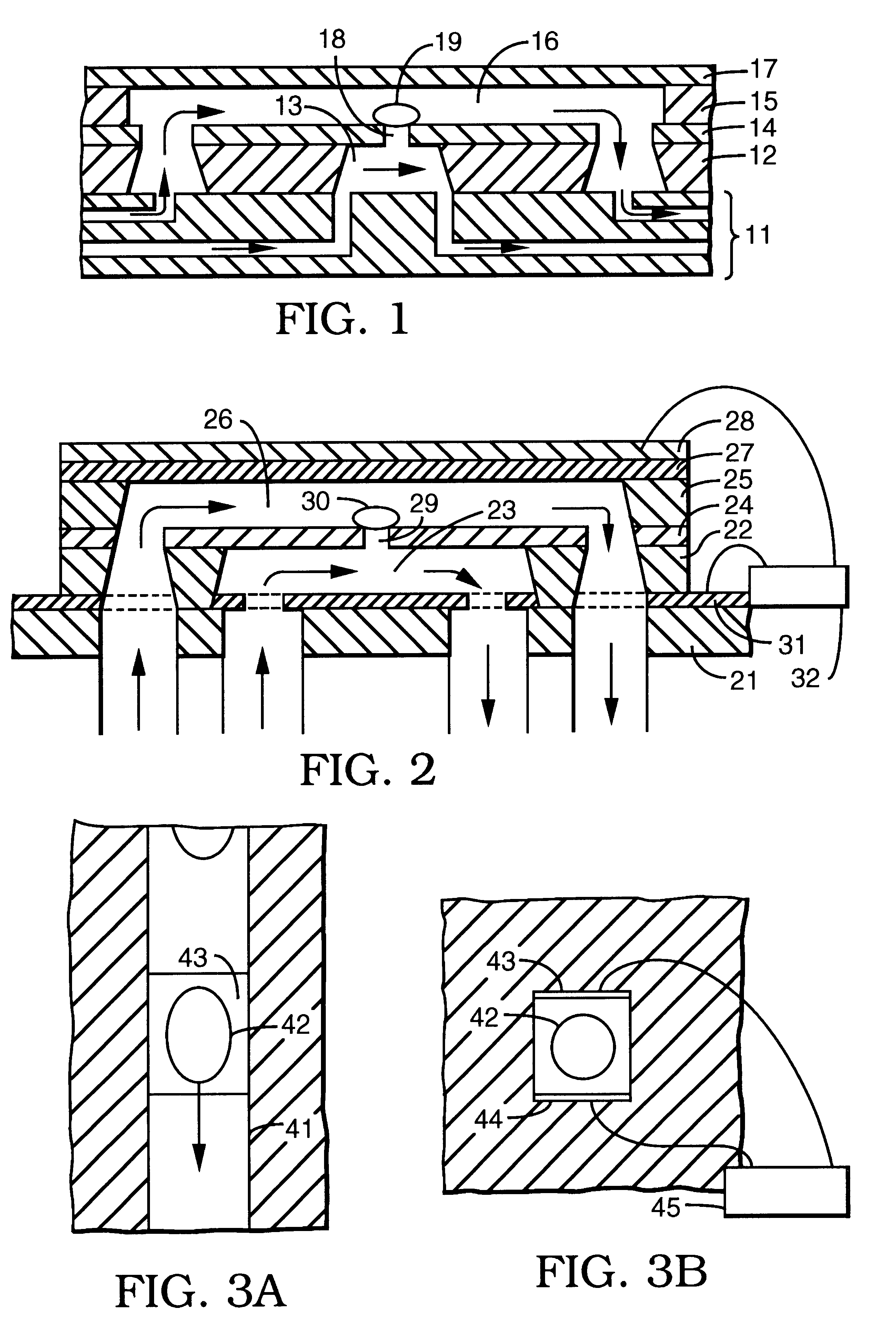
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS20060121610A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl mannerCell membrane
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrical impedance tomography to control electroporation
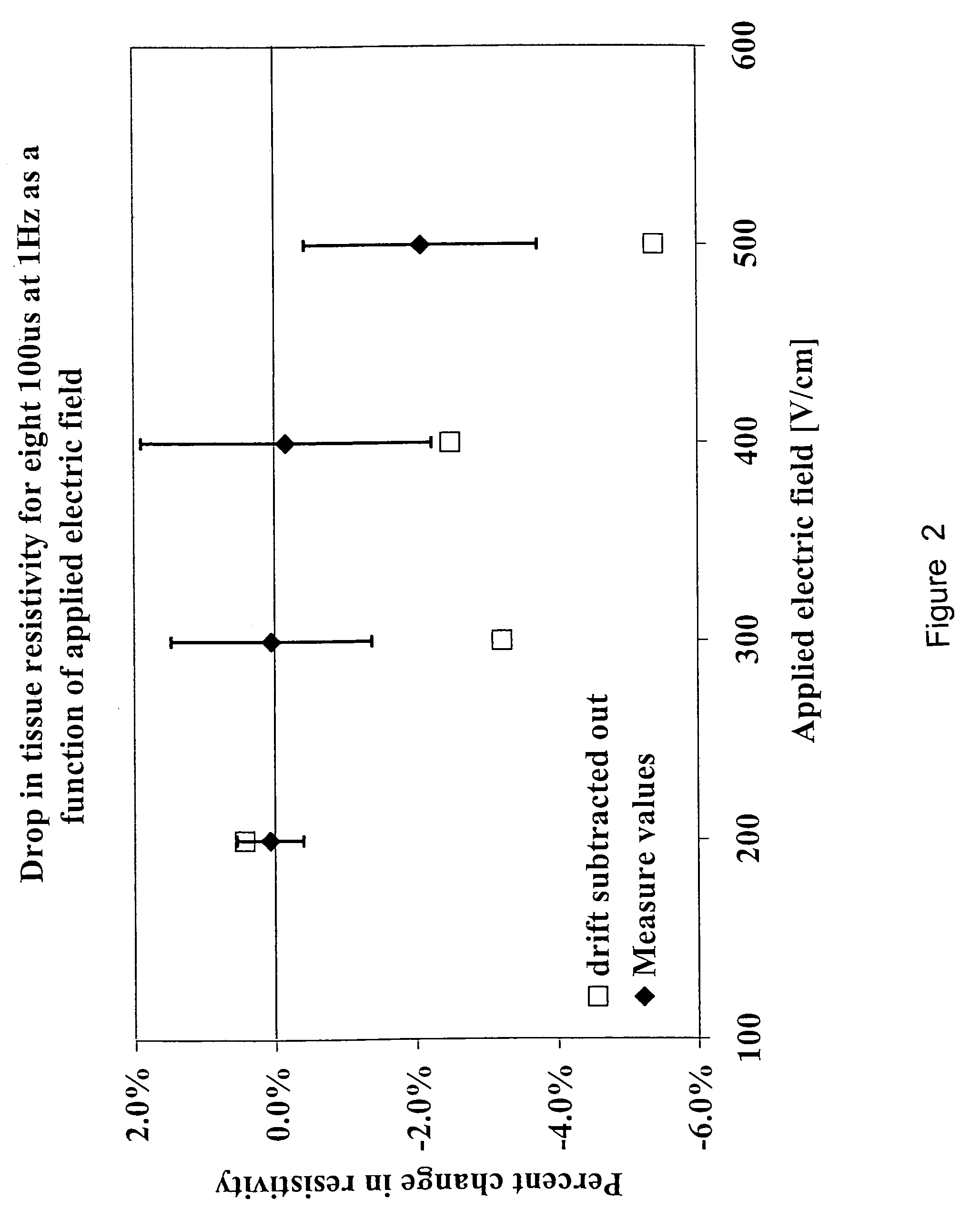
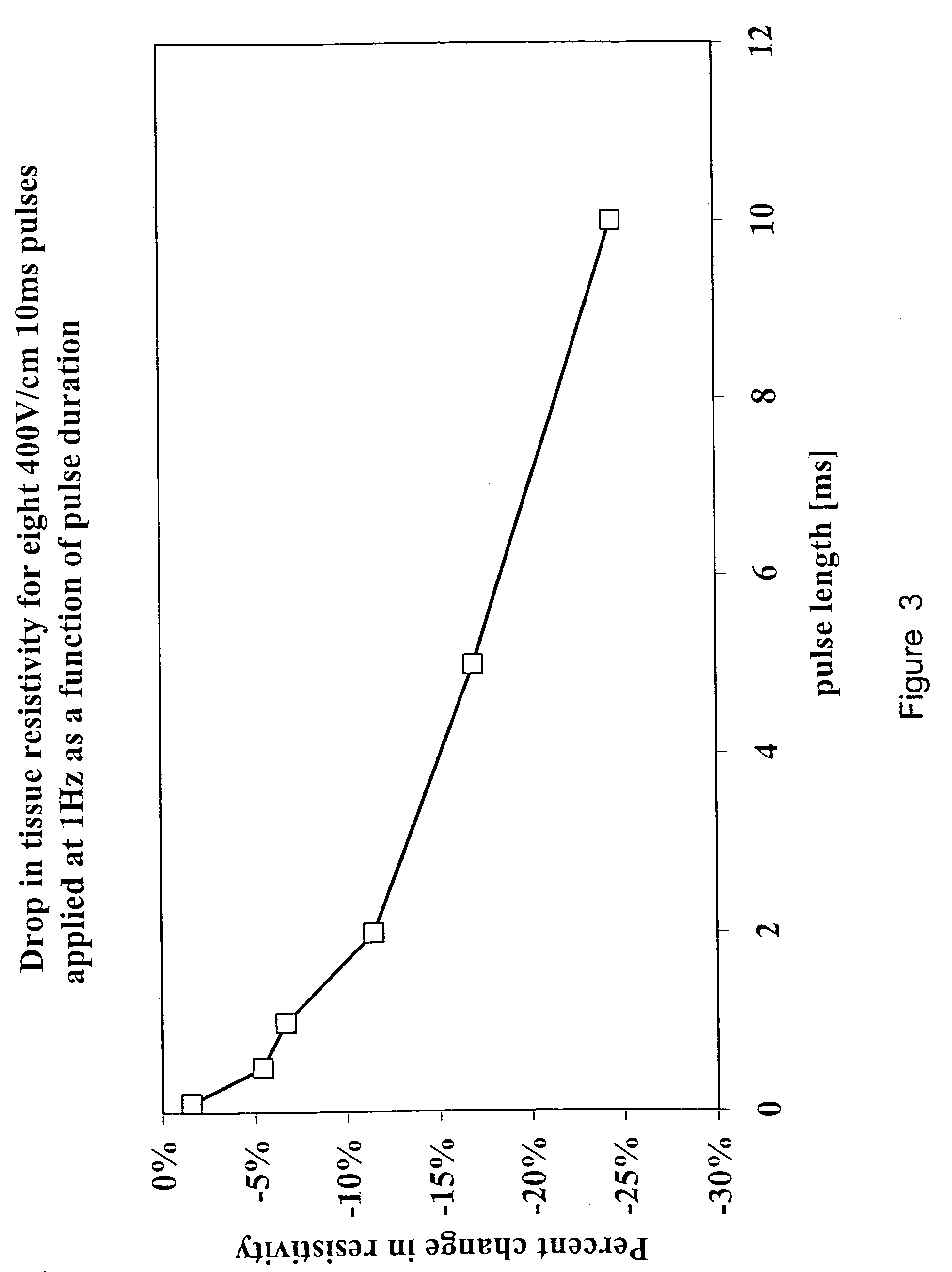
InactiveUS6387671B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Images created by electrical impedance tomography (EIT) are used to adjust one or more electrical parameters and obtain a desired degree of electroporation of cells in tissue. The parameters include current, voltage and a combination thereof. The cells are subjected to conditions such that they become permeabilized but are preferably not subjected to conditions which result in irreversible pore formation and cell death. The electroporation can analyze cell membranes, diagnose tissues and the patient as well as to move materials into and out of cells in a controlled manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of generating and recovering gas from subsurface formations of coal, carbonaceous shale and organic-rich shales
InactiveUS20040033557A1Maximizes bacterial degradationStable and economically favorable and environmentally cleanMicrobiological testing/measurementGas production bioreactorsOrganic compoundCoal
A method of generating and recovering gas from naturally existing subsurface formations Of coal, carbonaceous shale or organic-rich shales comprising the steps Of: injecting into fracture of the subsurface formation, under substantially anaerobic conditions, a consortia of selected anaerobic, biological microorganisms for in situ conversion of organic compounds in said formation into methane and other compounds; and producing methane through at least one well extending from said subsurface formation to the surfaces.
Owner:SCOTT ANDREW R +1
Electrochemical device for moving particles covered with protein
InactiveUS6972080B1Efficient disposalElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentBlood componentElectrolysis
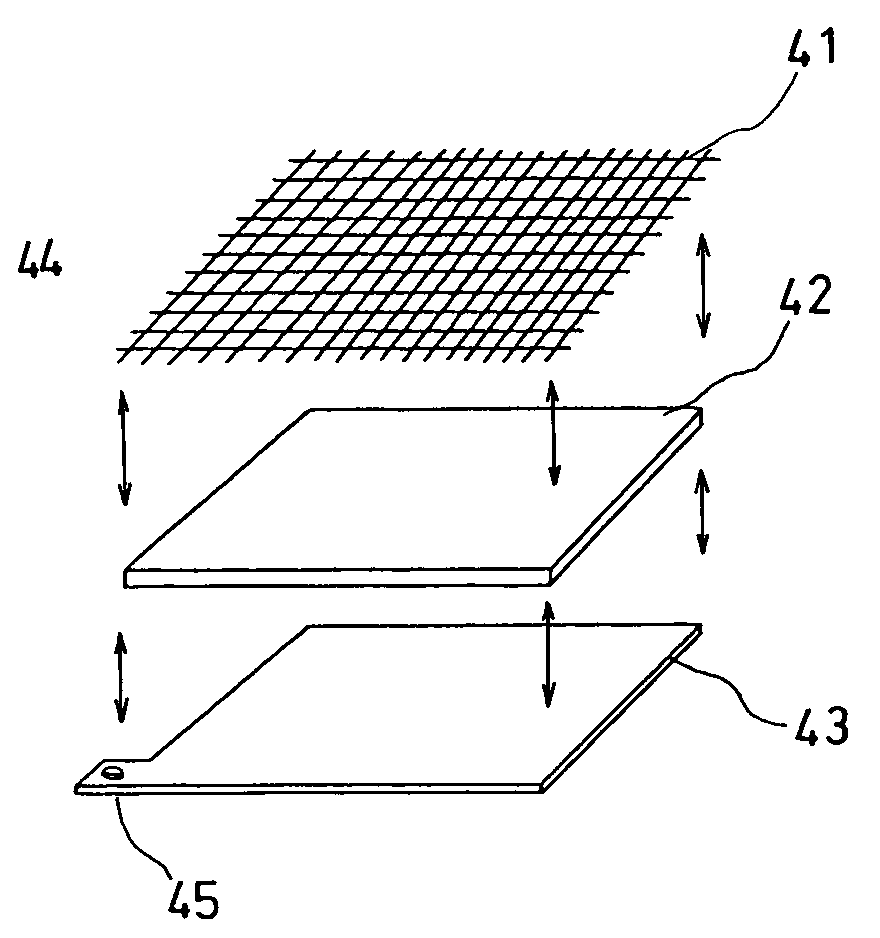
An electrochemical device for moving particles covered with a protein is provided. The device includes at least two electrodes that are in contact with a liquid containing the protein-covered particles and a circuit that generates a potential difference in a range that does not cause electrolysis of the liquid between the electrodes. The particles are moved by electrophoresis in the direction of the arrangement of the electrodes. The invention provided herein has numerous applications, including use in a microorganism concentration condensing device, a blood component induction device, and / or a blood component induction method, and / or an electric appliance that decreases the concentration of microorganisms present on the surface of a heat exchanger.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
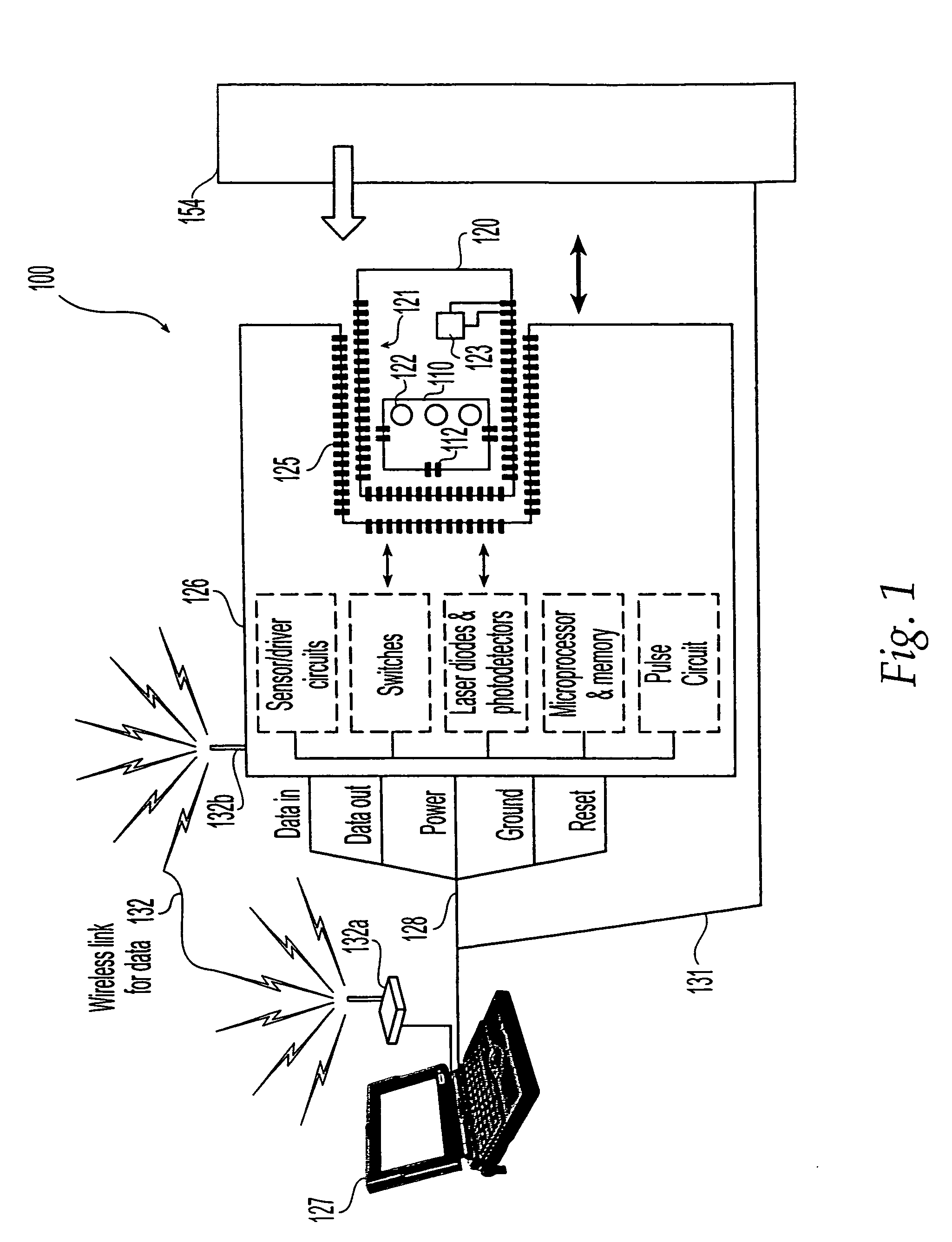
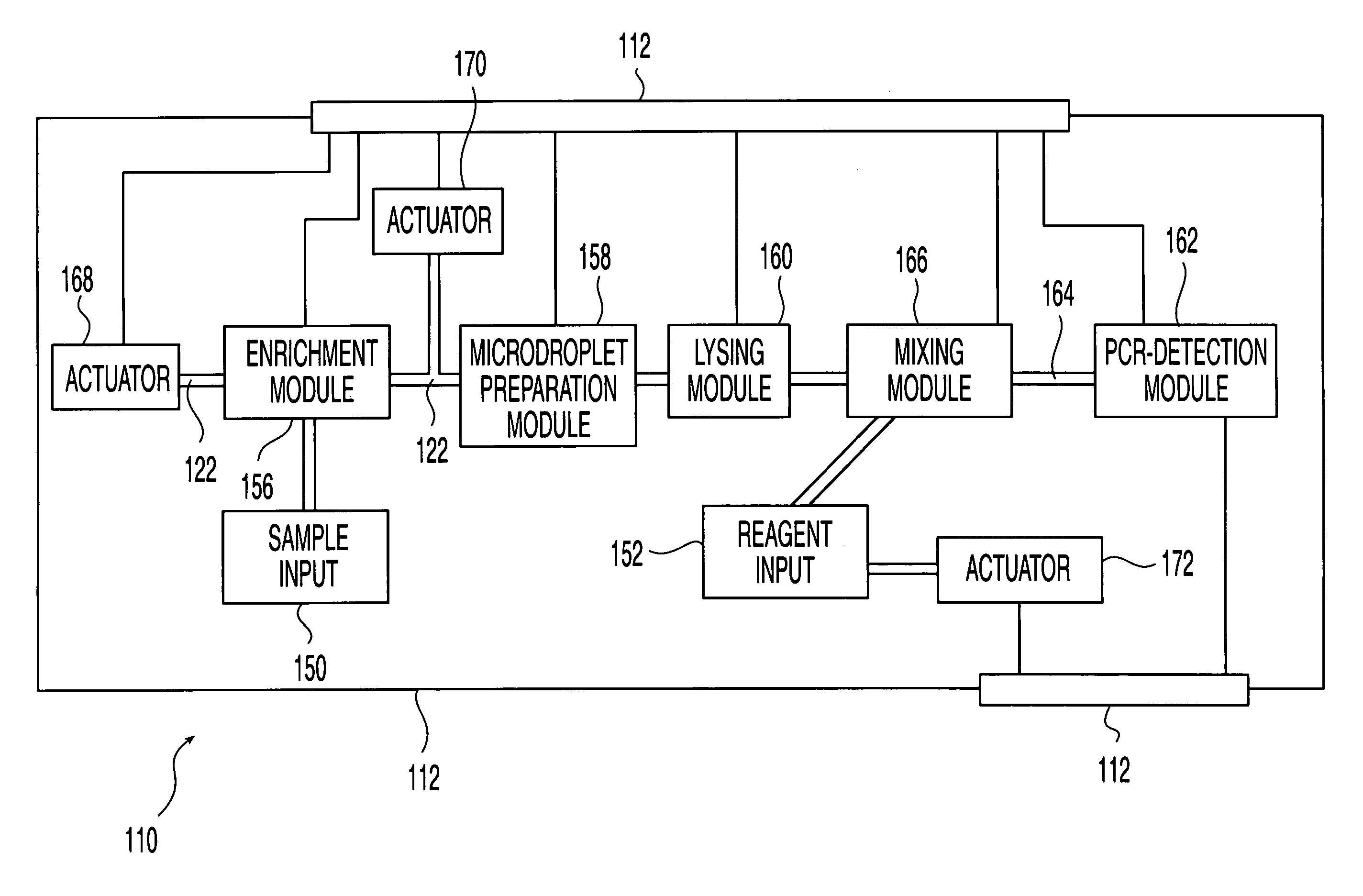
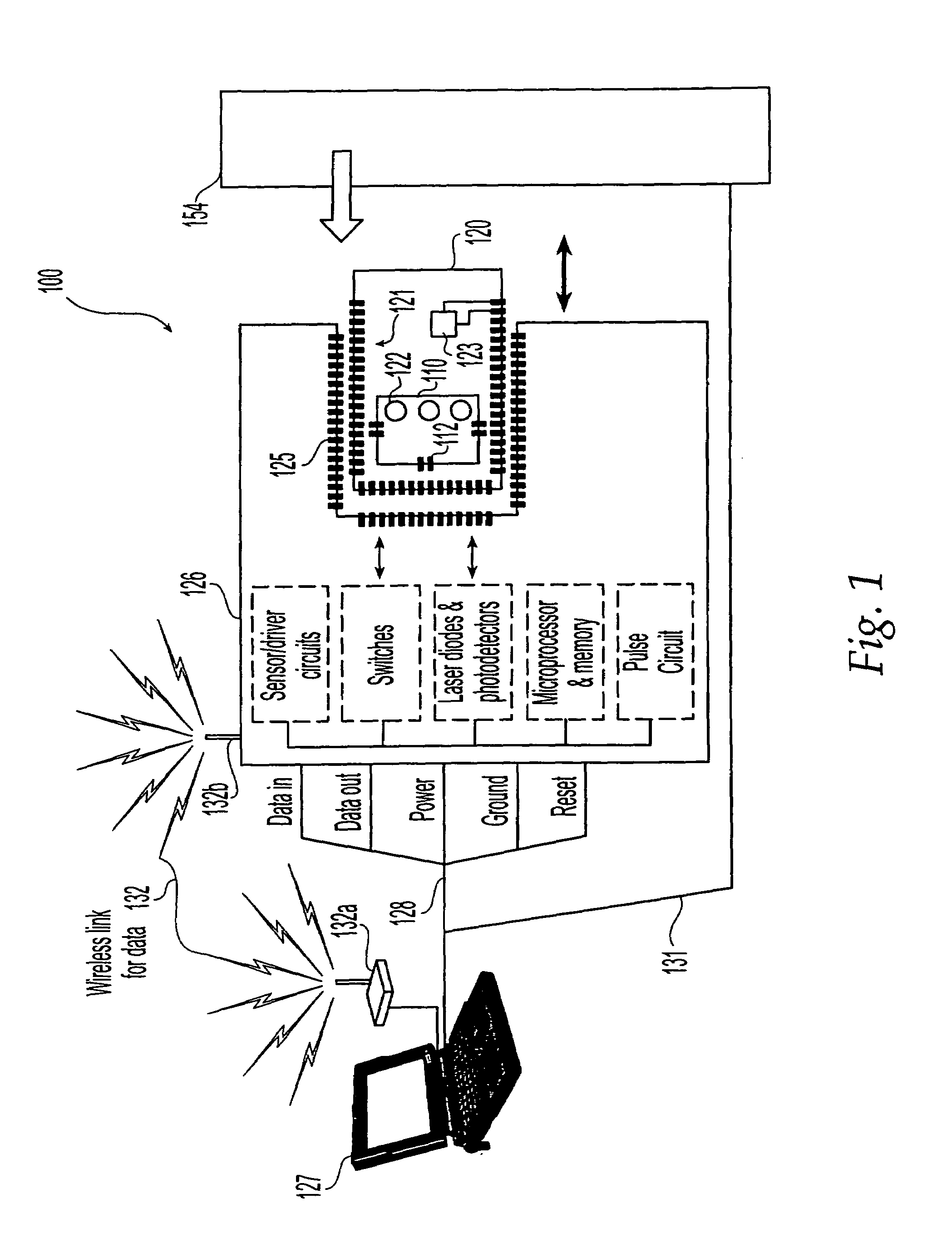
Methods and systems for releasing intracellular material from cells within microfluidic samples of fluids
InactiveUS7192557B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsFixed microstructural devicesSonificationCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to a microfluidic system for processing a cell-containing liquid. The system includes a lysing zone to receive the cell-containing sample and a positioning element to position the cell-containing sample in a lysing position in the vicinity of a lysing mechanism. The lysing mechanism releases intracellular material, such as DNA or RNA, from the cells. In one embodiment, the lysing mechanism includes electrodes for generating an electric field sufficient to release intracellular contents from the cells. Alternatively, the lysing mechanism may lyse the cells using chemical, heat and / or ultrasonic techniques or any combination of these techniques.
Owner:HANDLAB INC
Methods and systems for processing microfluidic samples of particle containing fluids
InactiveUS7270786B2Increase in sizeSmall sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFixed microstructural devicesProduct gasEngineering
The present invention relates to a microfluidic system for processing a cell-containing liquid. The system includes a microfabricated substrate having an enrichment channel to prepare an enriched cell sample from the cell-containing liquid. A flow through member is in liquid communication with the enrichment zone. The flow through member substantially prevents cells of the cell-containing fluid from exiting the enrichment zone while allowing liquid of the cell-containing liquid to exit the enrichment zone. A gas actuator associated with the enrichment zone provides a gas pressure sufficient to move the enriched cell sample from the enrichment zone.
Owner:HANDYLAB
System for identifying and sorting living cells
ActiveUS20120122084A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow cellIr absorption
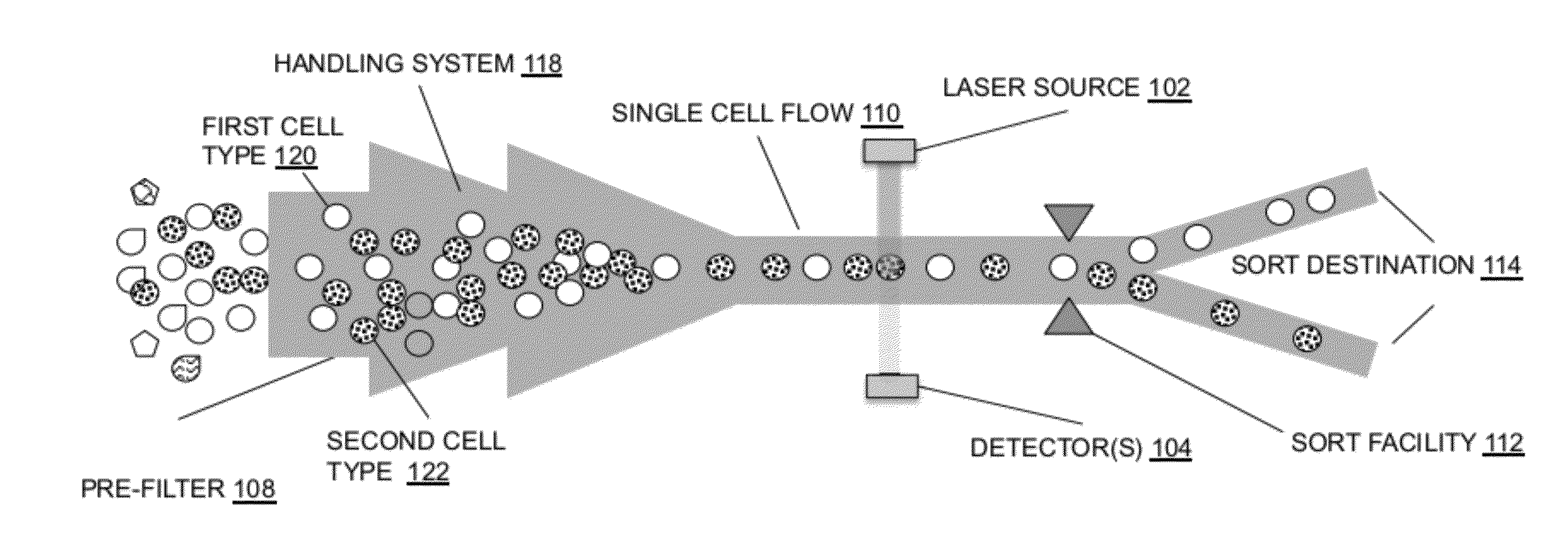
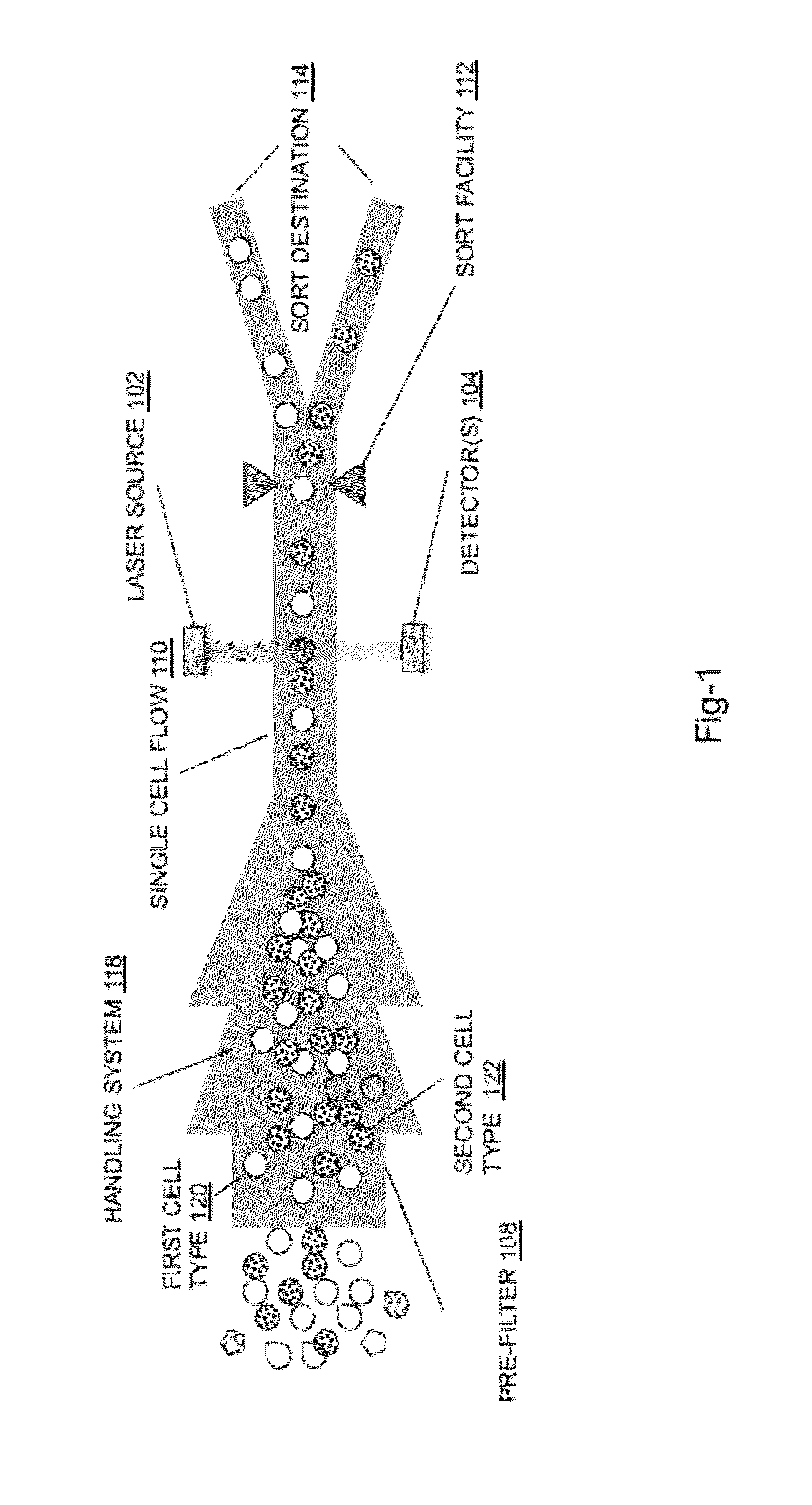
In embodiments of the present invention, a system and method of cytometry may include presenting a single sperm cell to at least one laser source configured to deliver light to the sperm cell in order to induce bond vibrations in the sperm cell DNA, and detecting the signature of the bond vibrations. The bond vibration signature is used to calculate a DNA content carried by the sperm cell which is used to identify the sperm cell as carrying an X-chromosome or Y-chromosome. Another system and method may include flowing cells past at least one QCL source one-by-one using a fluid handling system, delivering QCL light to a single cell to induce resonant mid-IR absorption by one or more analytes of the cell, and detecting, using a mid-infrared detection facility, the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light is used to identify a cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
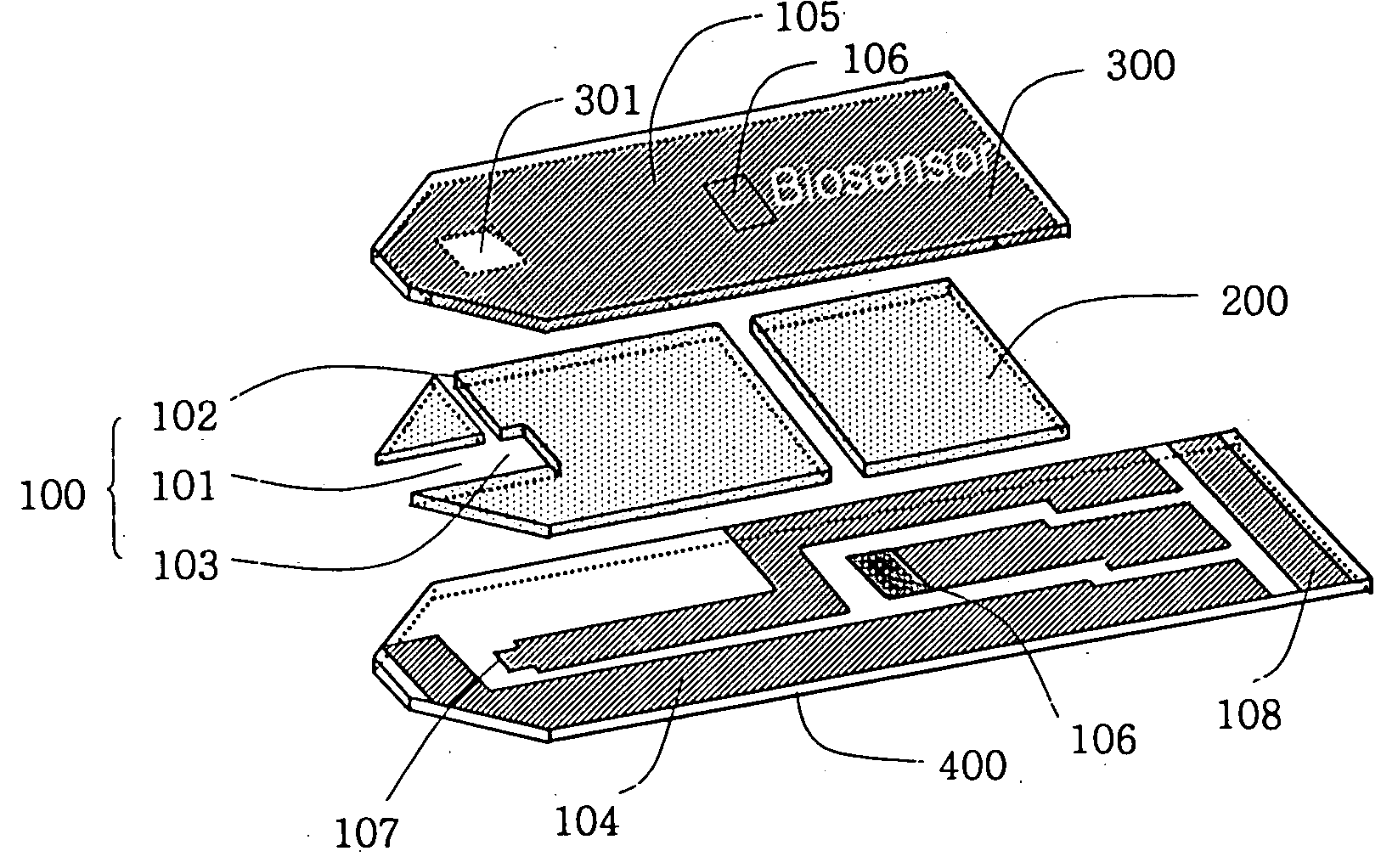
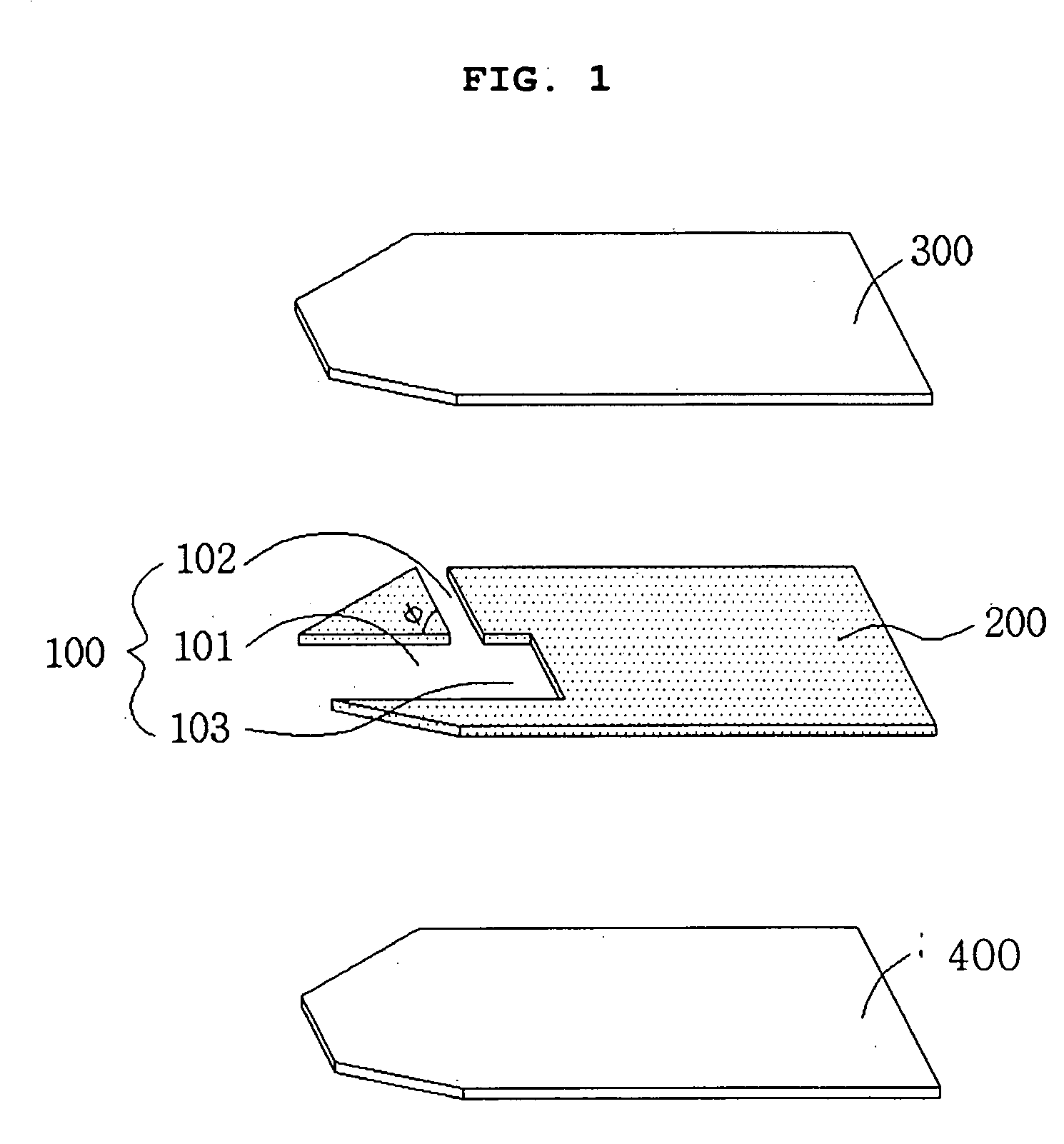
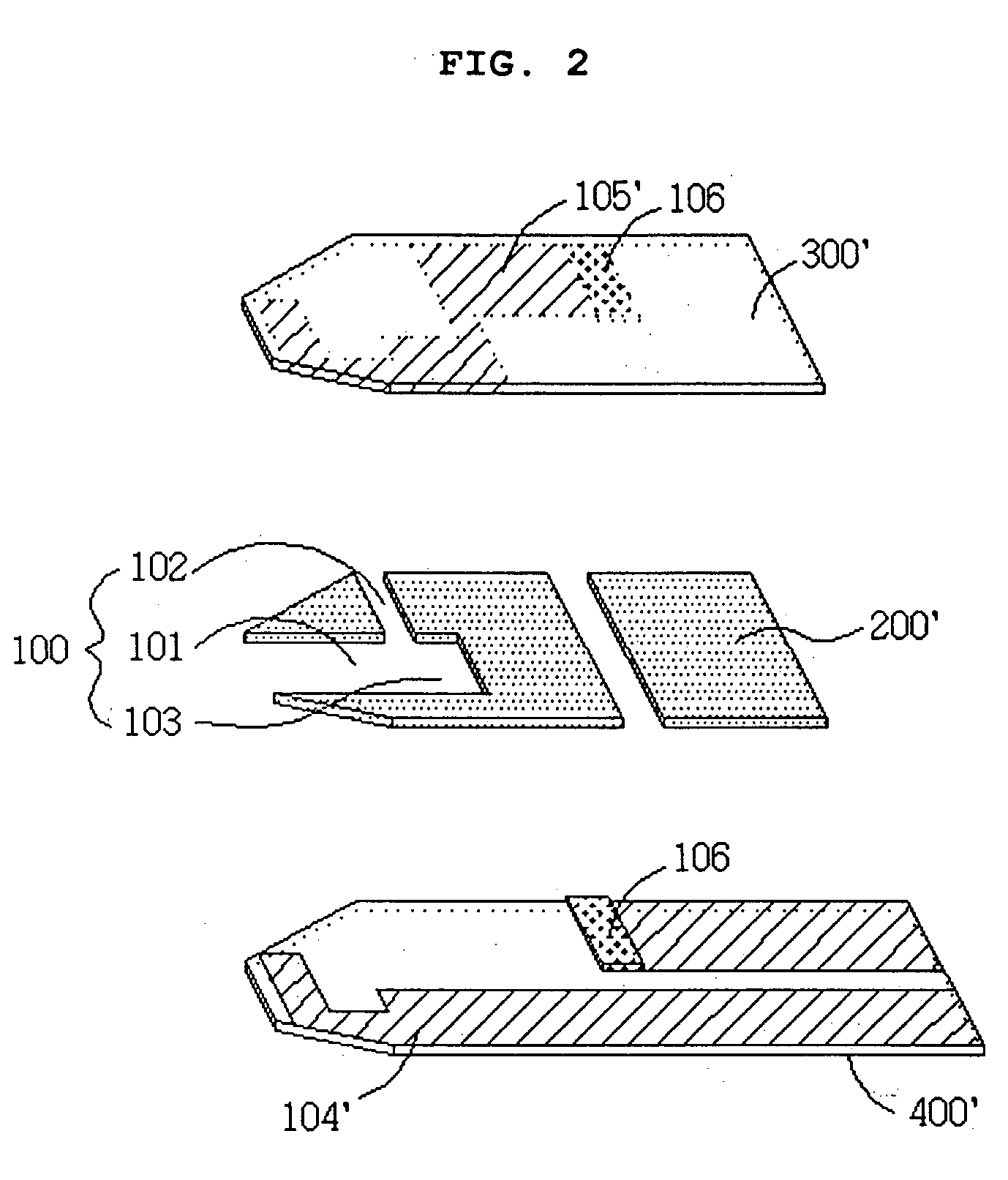
Electrochemical biosensor
ActiveUS20050000808A1Reduced hematocrit level-dependent biasImprove manufacturabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectron transfer mediatorElectrochemical biosensor
There is provided the reagent layer composition that can substantially reduce the measurement bias arising from hematocrits. The addition of fatty acid (4-20 carbons) and quaternary ammonium salt to a commonly used reagent layer composition composed of an enzyme, an electron transfer mediator, and several water soluble polymers not only reduce the hematocrit level-dependent bias but also provide very stable performance for an extended period of time. Disclosed are also various types of sub microliter sample volume electrochemical biosensors that are suitable to use with the reagent layer composition of present invention.
Owner:I SENS INC
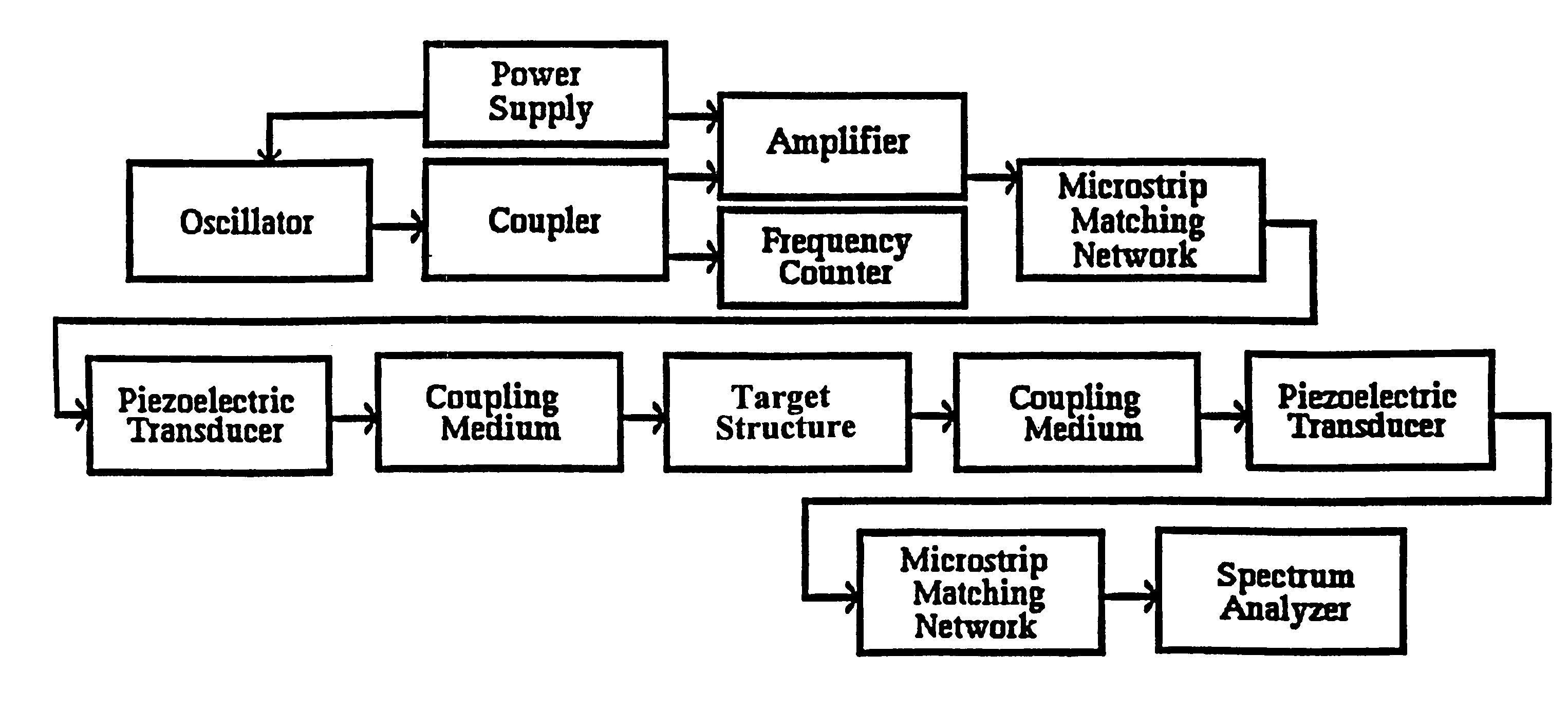
Methods for using resonant acoustic and/or resonant acousto-EM energy to detect and/or effect structures
InactiveUS7165451B1Avoid damageAccurate detectionVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
Methods and Apparatus for the Manipulation of Particle Suspensions and Testing Thereof
InactiveUS20070243523A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophysiology studyElectroporation
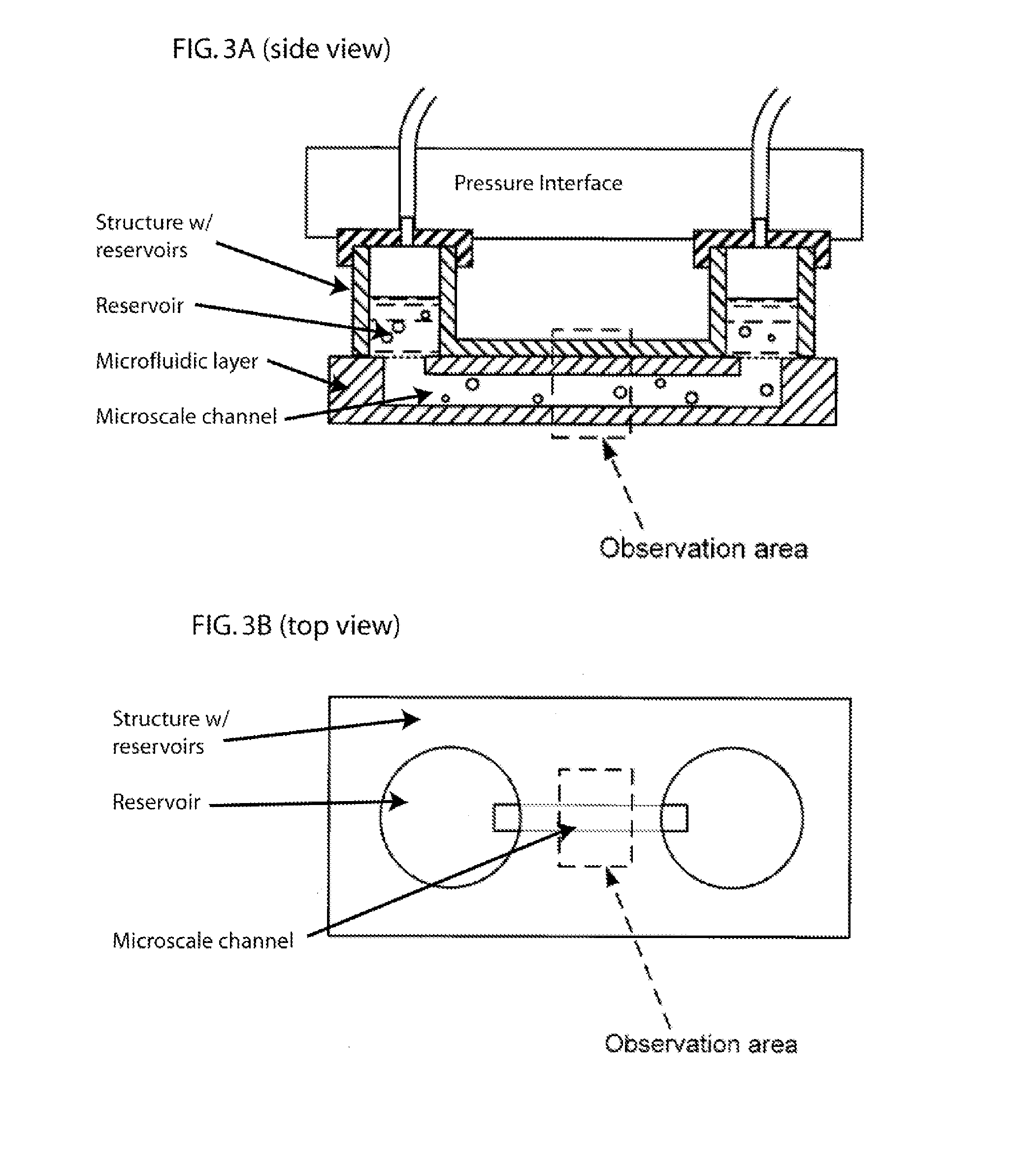
Apparatus and methods are provided for analysis of individual particles in a microfluidic device. The methods involve the immobilization of an array of particles in suspension and the application of experimental compounds. Such methods can also include electrophysiology studies including patch clamp recording, electroporation, or both in the same microfluidic device. The apparatus provided includes a microfluidic device coupled to a multi-well structure and an interface for controlling the flow of media within the microchannel device.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS6428959B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
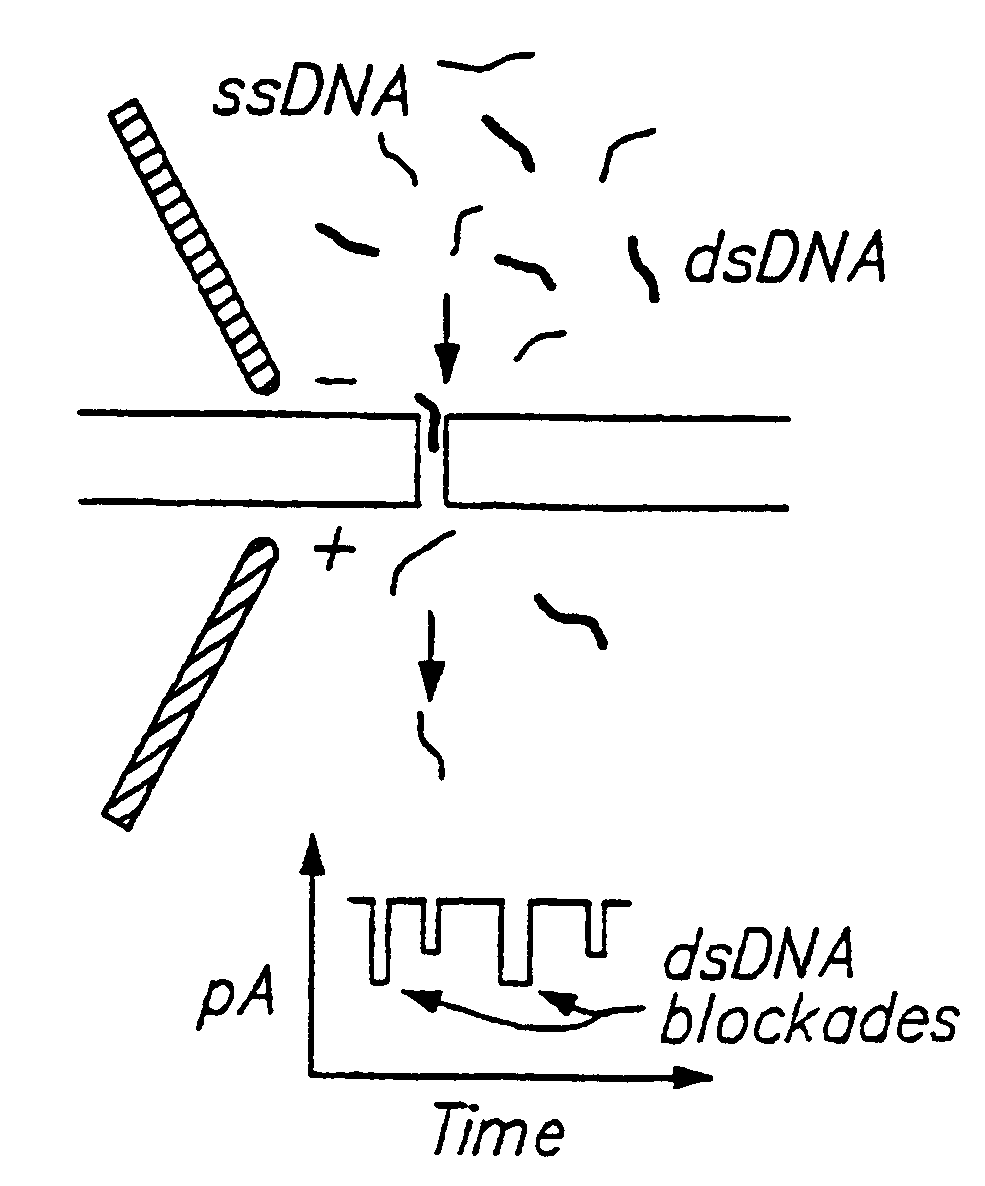
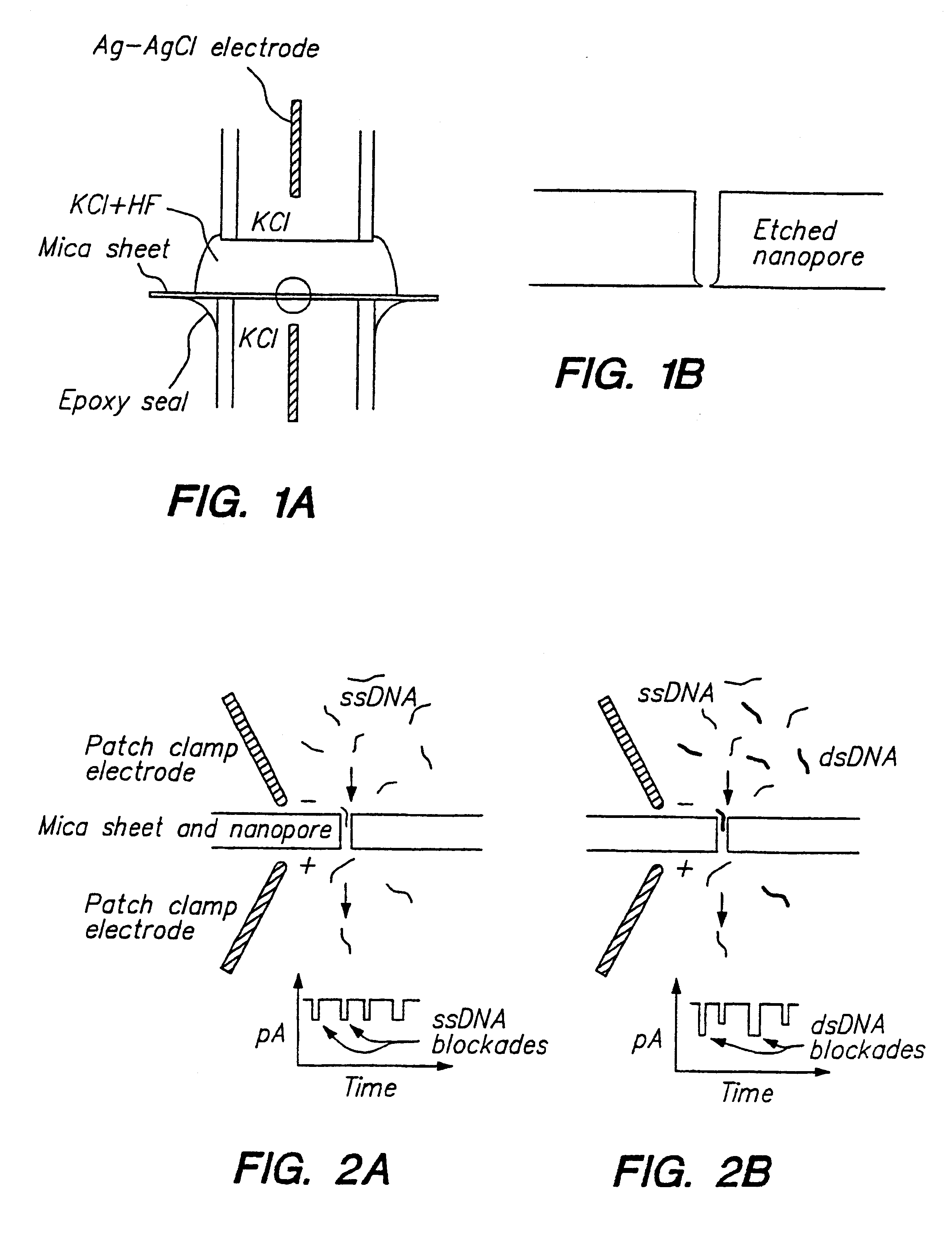
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes in tissue
InactiveUS20050282284A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyBiological cellElectricity
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in individual and multiple biological cells present in biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Droplet actuation system and method
InactiveUS7816121B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentTemperature controlElectrical and Electronics engineering
A droplet actuation system is provided including a droplet actuation device including a substrate that includes electrodes for conducting droplet operations; temperature control means for heating and / or cooling a region of the droplet actuation device and arranged such that a droplet can be transported on the electrodes to a region for heating; and a means for effecting a magnetic field in proximity to one or more of the electrodes sufficient to immobilize magnetically responsive beads in a droplet on the substrate during droplet operations. The system further includes a processor for controlling the electrodes and temperature control means, wherein the processor is programmed, and electrodes and magnetic field are arranged, to cause the electrodes to split a droplet including the magnetically responsive beads yielding a first daughter droplet which includes the magnetically responsive beads and a second daughter droplet without a substantial amount of the magnetically responsive beads.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS6403348B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyControl mannerCell membrane
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sonoporation systems and methods
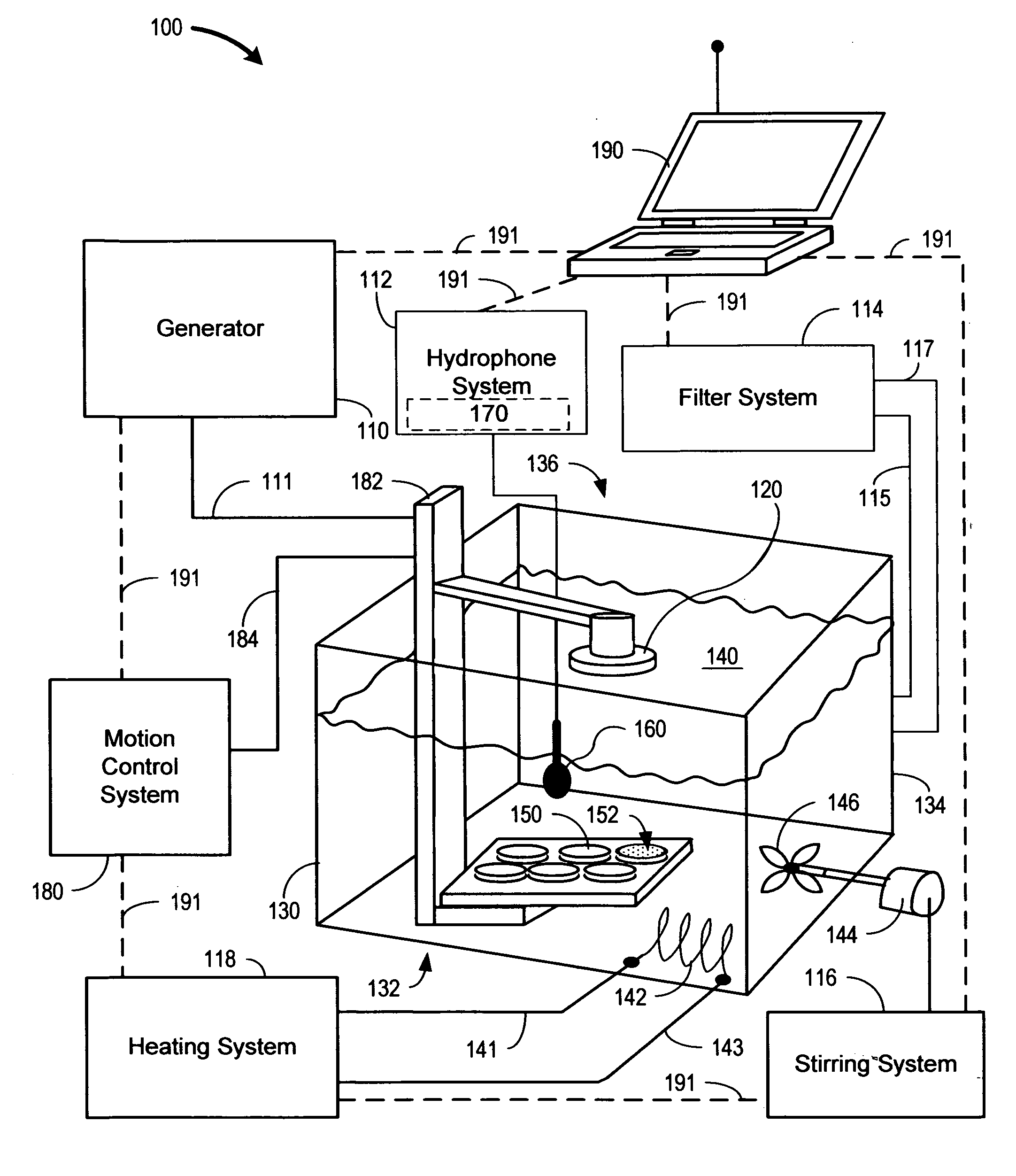
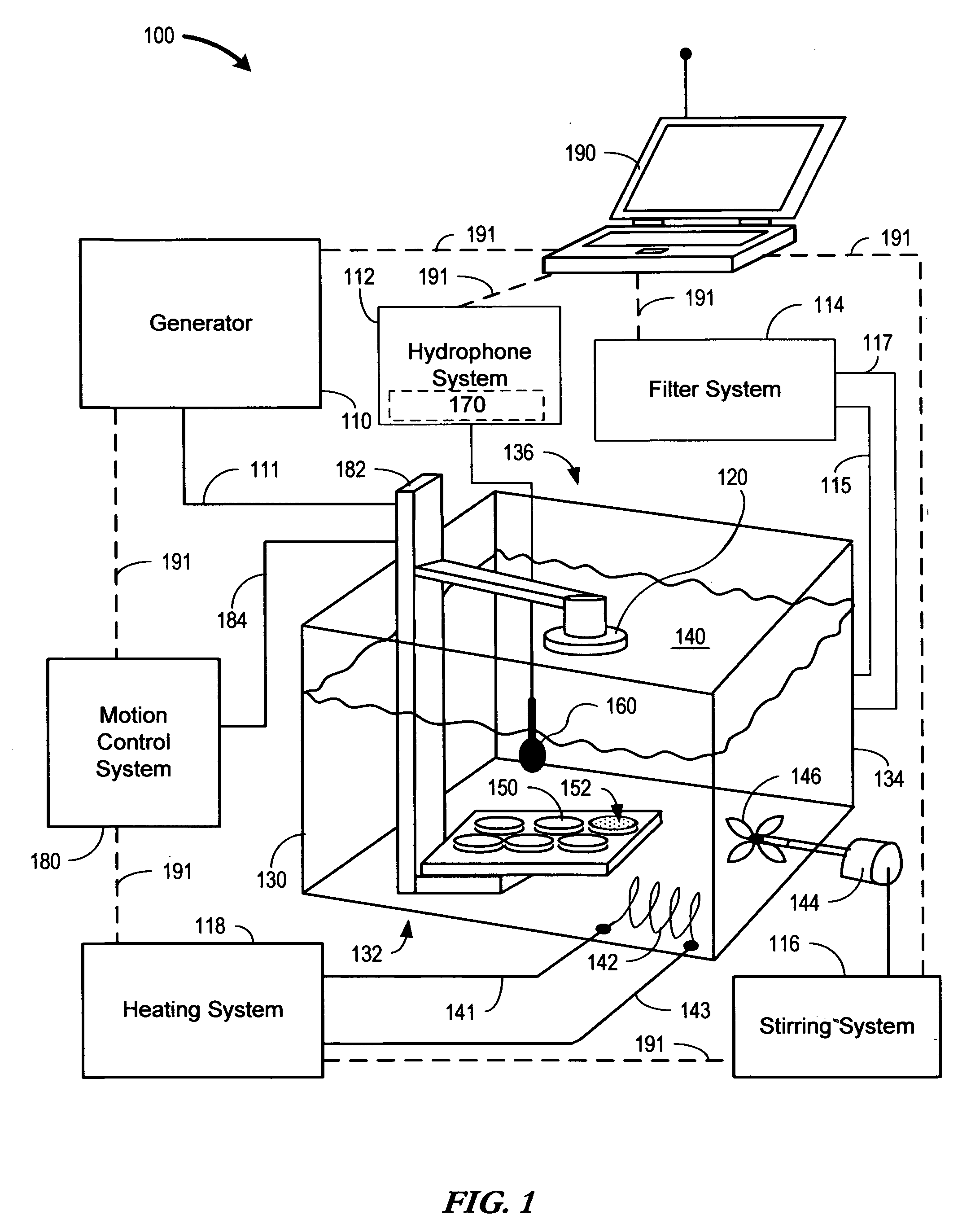
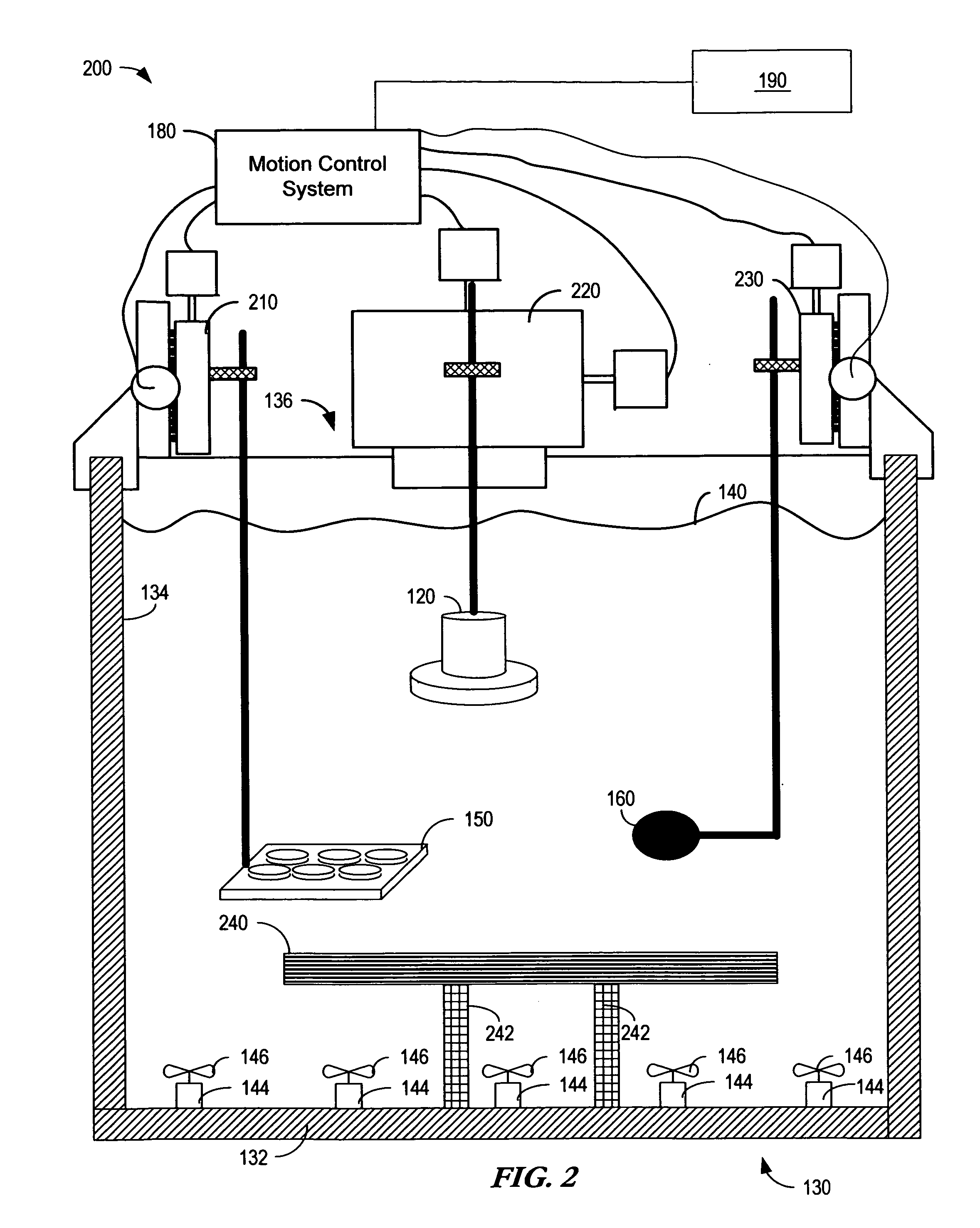
InactiveUS20100009424A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrophone
The present invention is directed to devices and methods that apply ultrasonic energy for the purpose of inducing transfection and cell transformation. A sonoporation system in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes an ultrasonic electrical energy generator connected to an ultrasonic transducer producing stress waves. The ultrasonic transducer is connected to a fluid containment tank configured to accept at least a portion of the ultrasonic transducer whereby the ultrasonic stress waves may be delivered into the fluid medium. A cell holder is configured to hold one or more cells desirable for transfection. A hydrophone may be electrically connected to an acoustic stress wave intensity detection circuit. A motion control system having an arm configured to receive one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone is configured to provide motion of one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone within the fluid medium.
Owner:ARTISON
Impedance based devices and methods for use in assays
ActiveUS7470533B2Easy to adaptNoise minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityConductive materials
A device for detecting cells and / or molecules on an electrode surface is disclosed. The device detects cells and / or molecules through measurement of impedence changes resulting from the cells and / or molecules. A disclosed embodiment of the device includes a substrate having two opposing ends along a longitudinal axis. A plurality of electrode arrays are positioned on the substrate. Each electrode array includes at least two electrodes, and each electrode is separated from at least one adjacent electrode in the electrode array by an expanse of non-conductive material. The electrode has a width at its widest point of more than about 1.5 and less than about 10 times the width of the expanse of non-conductive material. The device also includes electrically conductive traces extending substantially longitudinally to one of the two opposing ends of the substrate without intersecting another trace. Each trace is in electrical communication with at least one of the electrode arrays.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
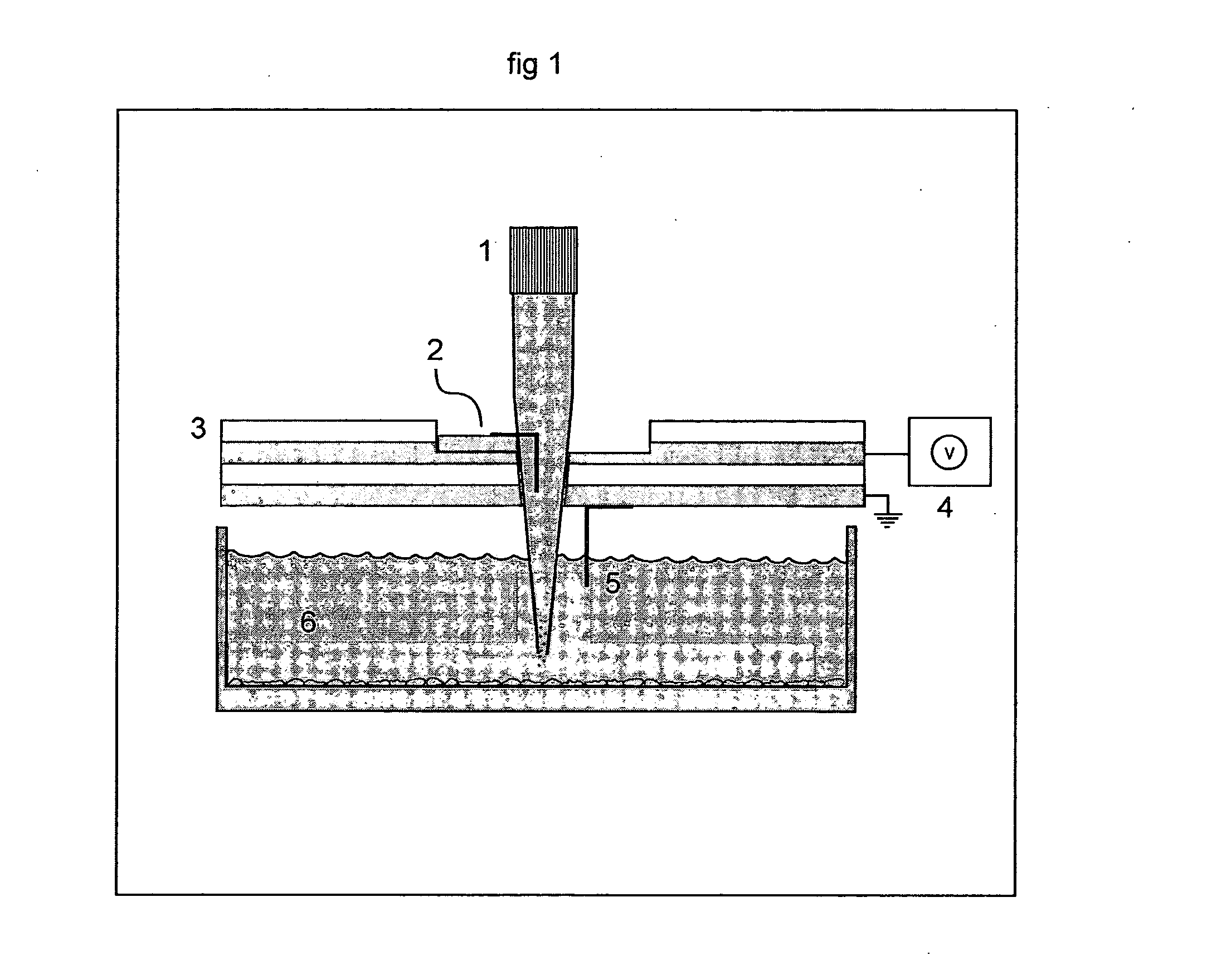
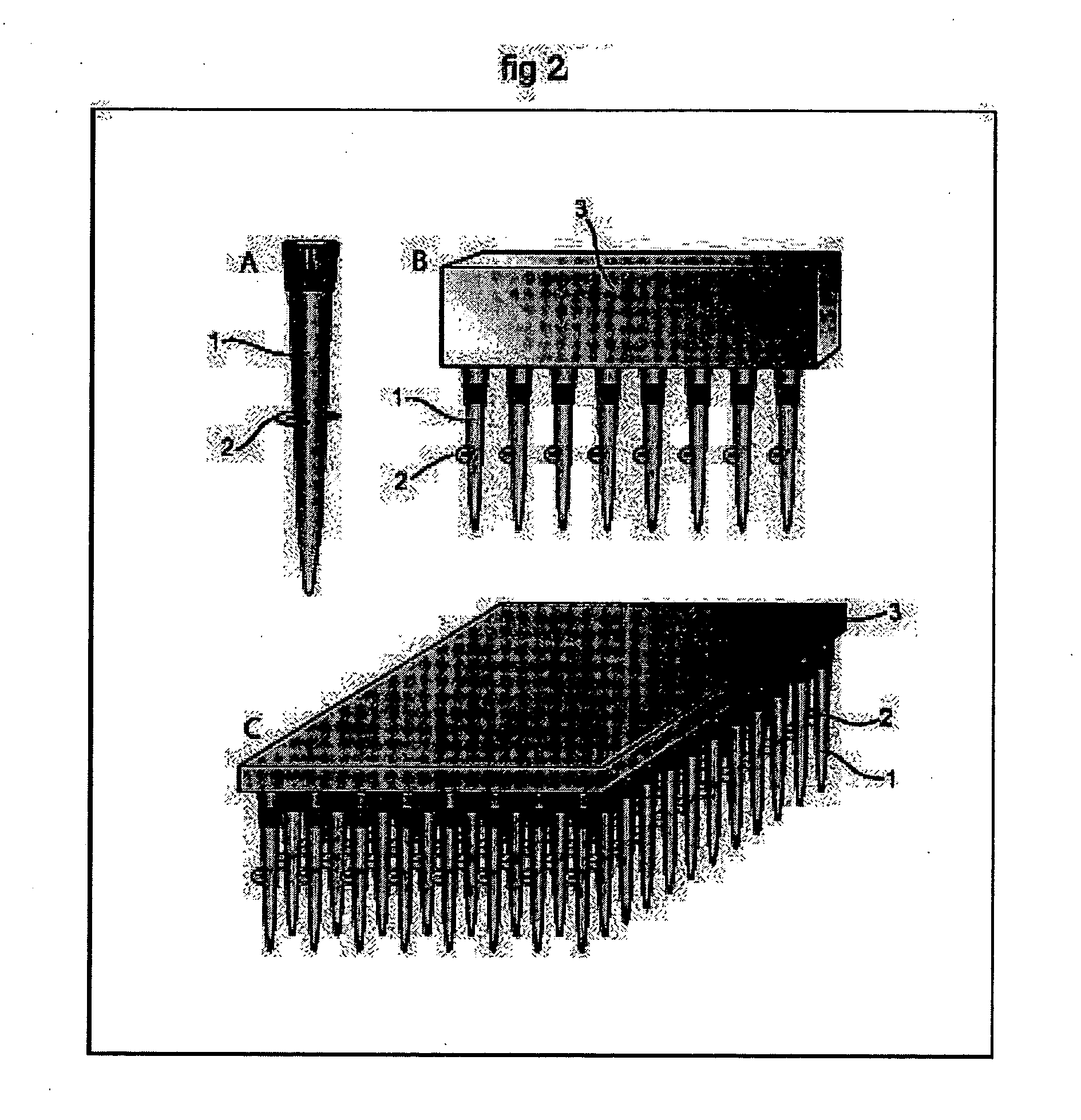
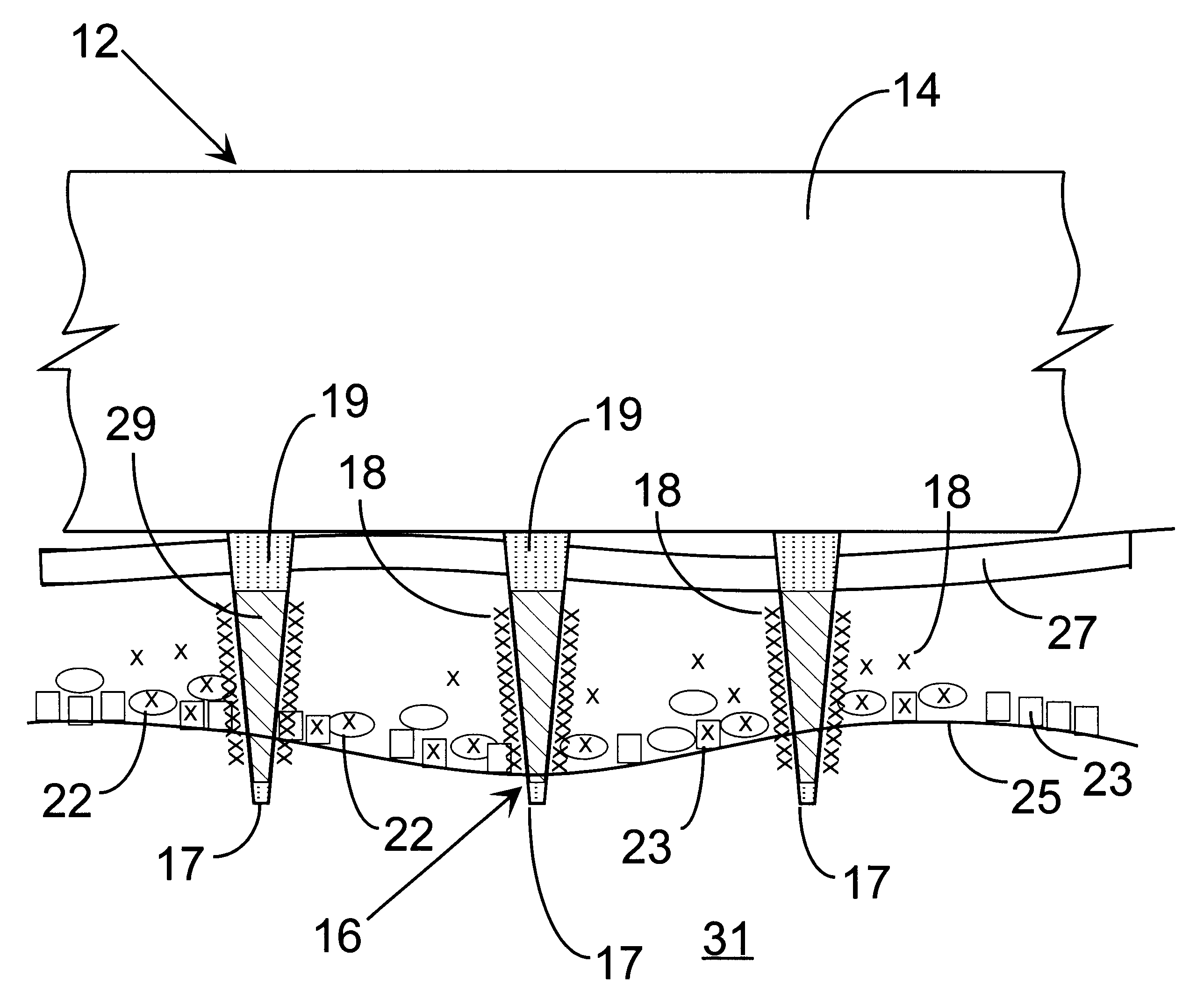
Method and apparatus for spatially confined electroporation
InactiveUS20050048651A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyBiological targetElectroporation
The invention provides hollow-tip-electrodes for spatially localized delivery of substances to one or more biological targets present in a population comprising target and non-target molecules, macromolecules, and / or cells. The invention also provides electrode plates for receiving one or more of such tips, tip-electrode plates comprising electrode plates comprising one or more electrode tips, and systems comprising tip-electrodes and containers for containing one or more biological targets, e.g., such as molecules, macromolecules, and / or cells. The invention further provides methods for using such systems and components thereof. In one preferred aspect, the systems are used for spatially confined electroporation of cells and cell structures. The invention facilitates high throughput screening of agents (e.g., such as drugs) that act on intracellular targets.
Owner:CELLECTRICON
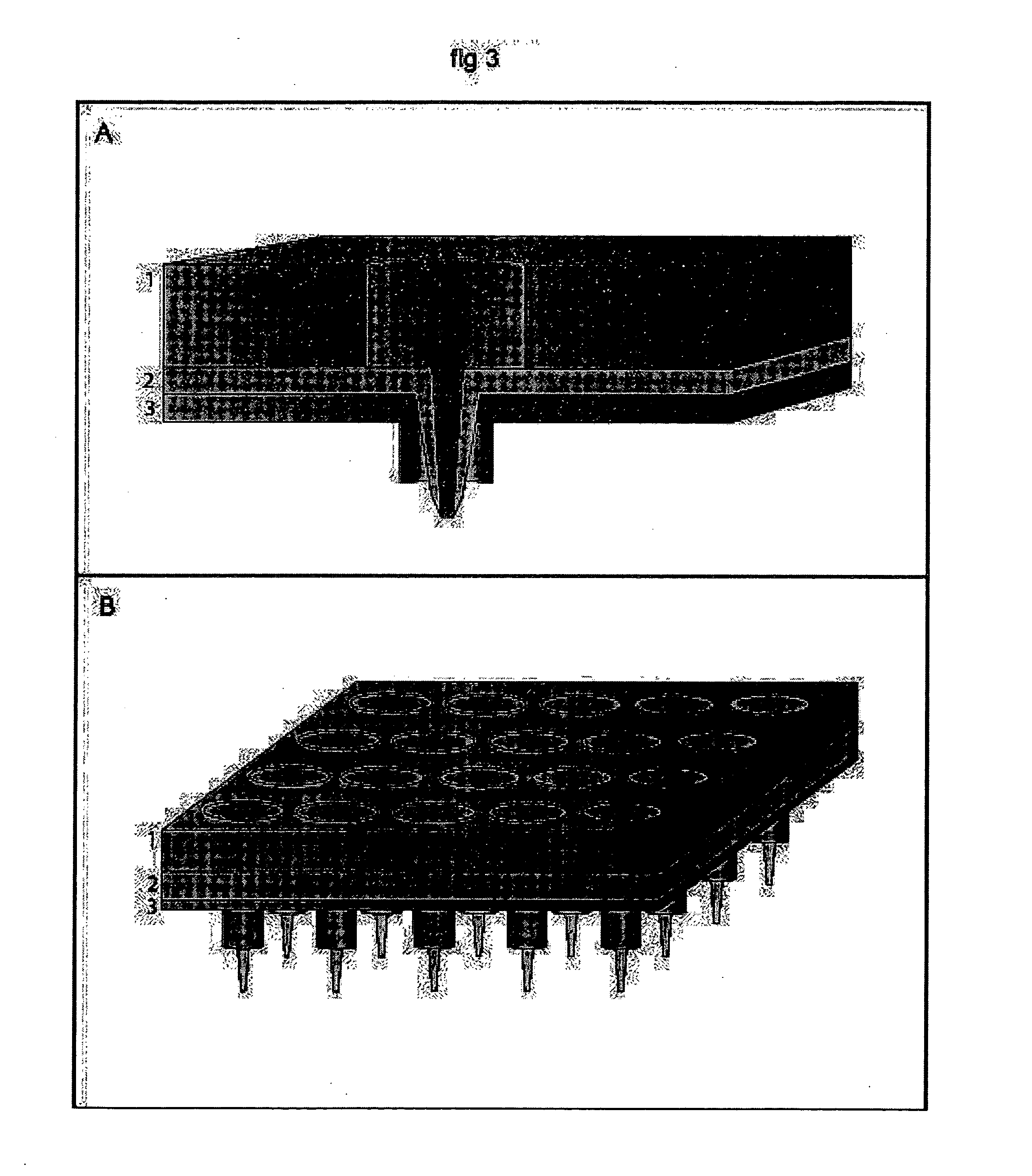
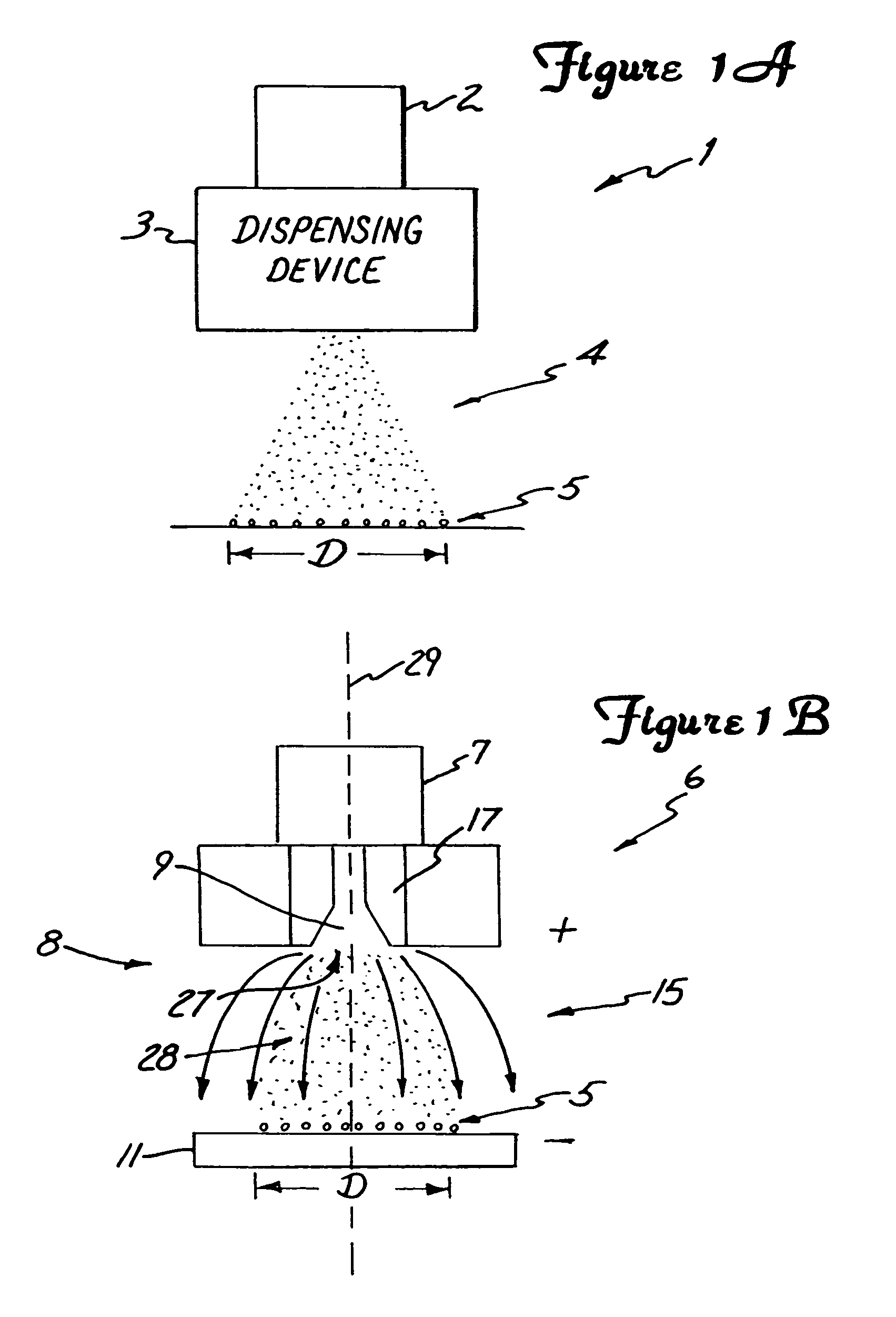
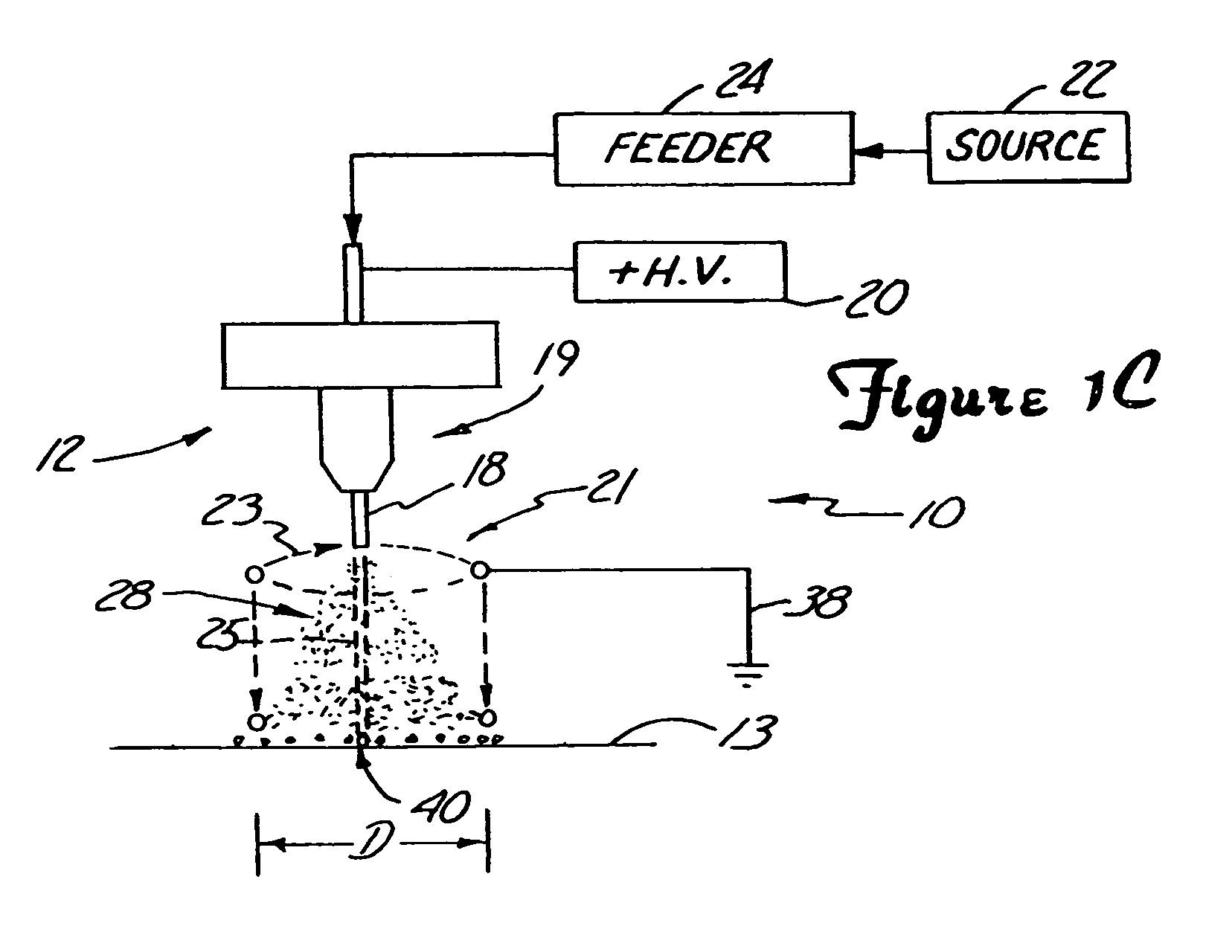
Electrospraying apparatus and method for coating particles
An electrospraying apparatus and / or method is used to coat particles. For example, a flow including at least one liquid suspension may be provided through at least one opening at a spray dispenser end. The flow includes at least particles and a coating material. A spray of microdroplets suspending at least the particles is established forward of the spray dispenser end by creating a nonuniform electrical field between the spray dispenser end and an electrode electrically isolated therefrom. The particles are coated with at least a portion of the coating material as the microdroplet evaporates. For example, the suspension may include biological material particles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes in tissue
InactiveUS7053063B2High levelImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceBiological cell
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in individual and multiple biological cells present in biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Delivery of macromolecules into cells
InactiveUS6603998B1Raise the threshold voltageReducing pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyLangerhan cellA-DNA
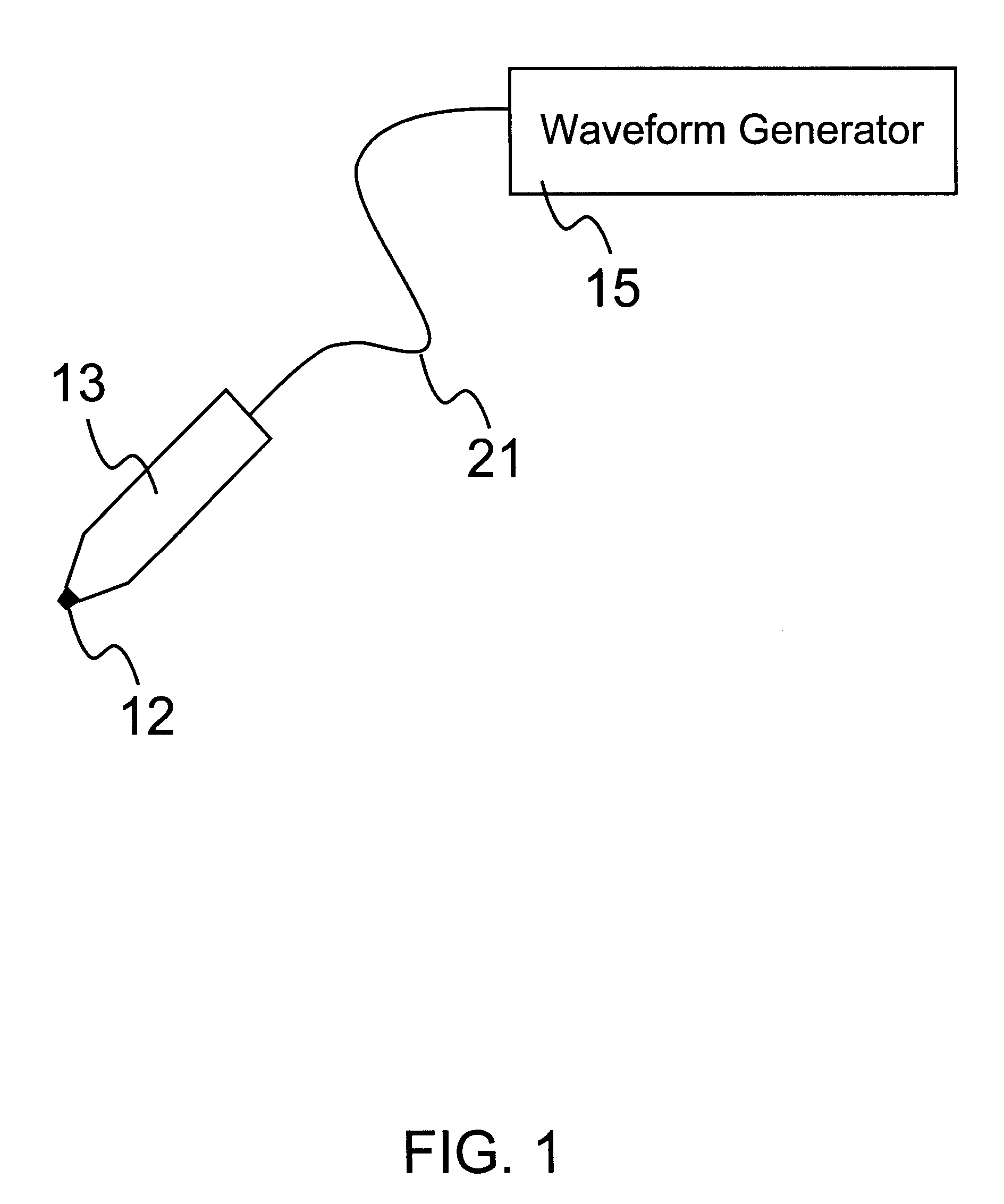
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells, such as Langerhans cells (22) in the epidermis (20) of a patient, which includes the steps of coating electodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12) with solid phase macromolecules to be delivered, such as a DNA, and / or RNA vaccine or a protein-based vaccine, attaching the electrode assembly (12) having the coated electrodes (16) to an electrode assembly holder (13), providing a waveform generator (15), establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16), and the waveform generator (15), locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, such as by penetrating the needle electrode (16) into the epidermis (20) above the epidermal basal lamina, and providing pulse waveform from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that macromolecule on the electrodes (16) is driven off of the electrodes (16), and delivered into the biological cells, such as the Langerhans cells (22).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
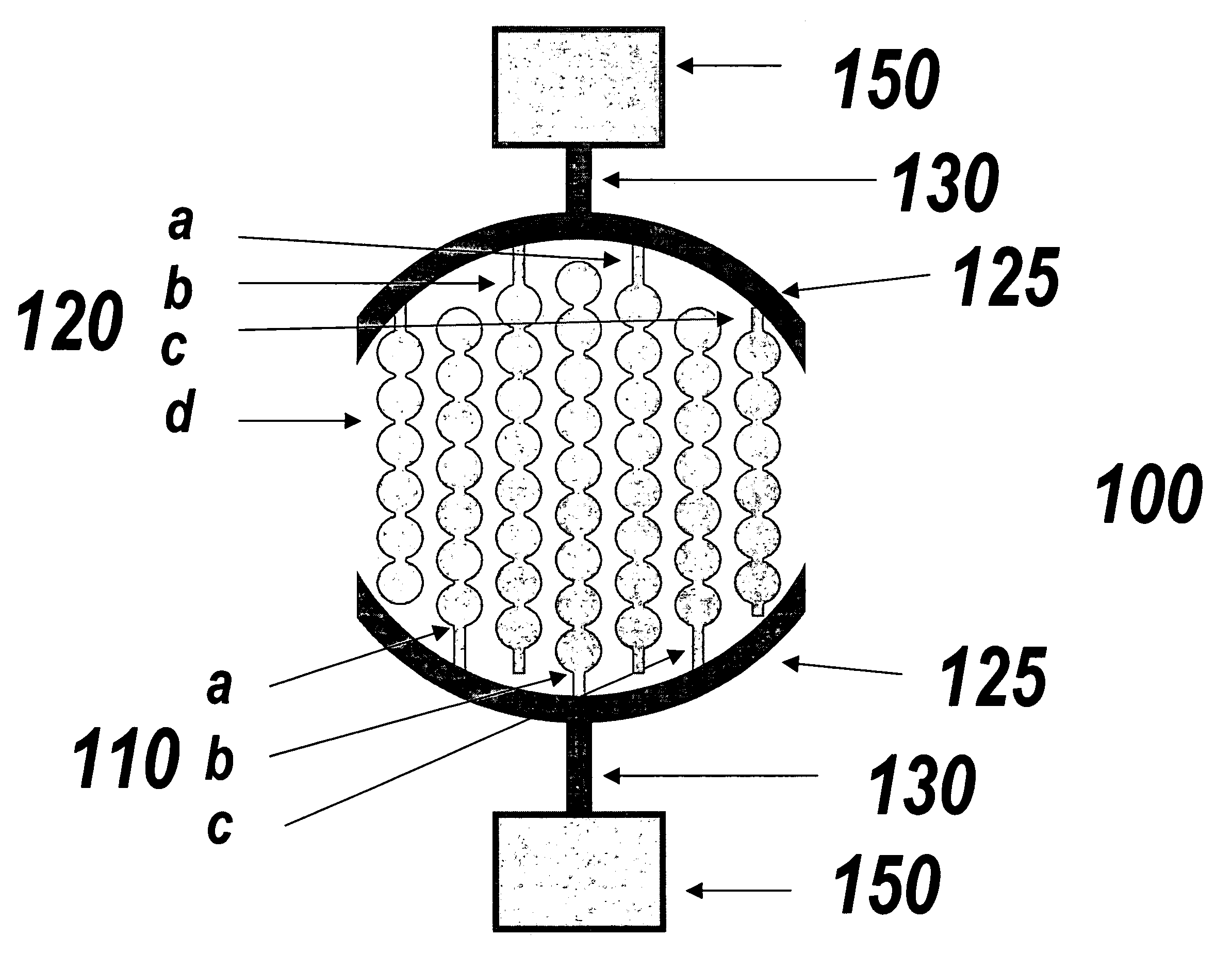
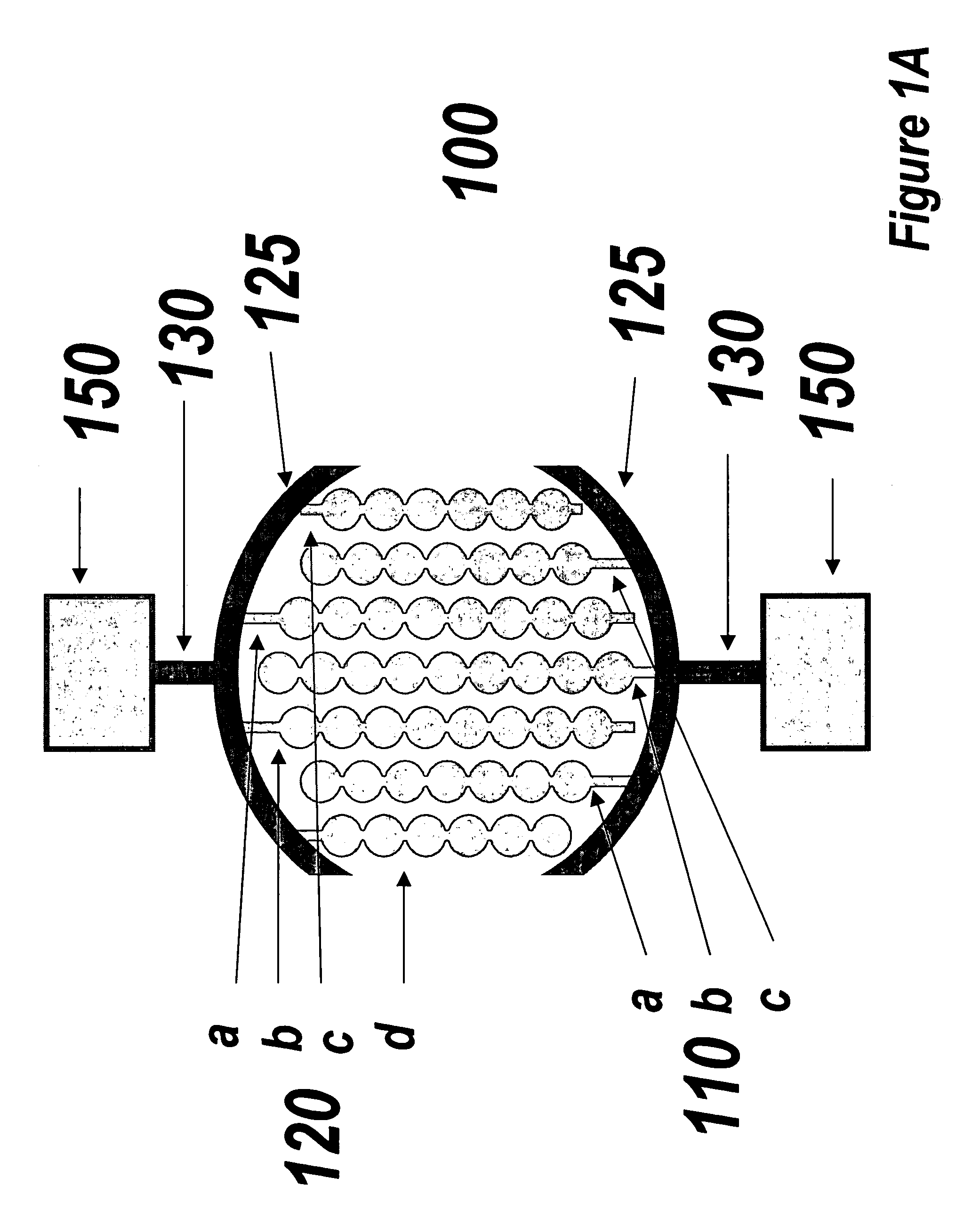
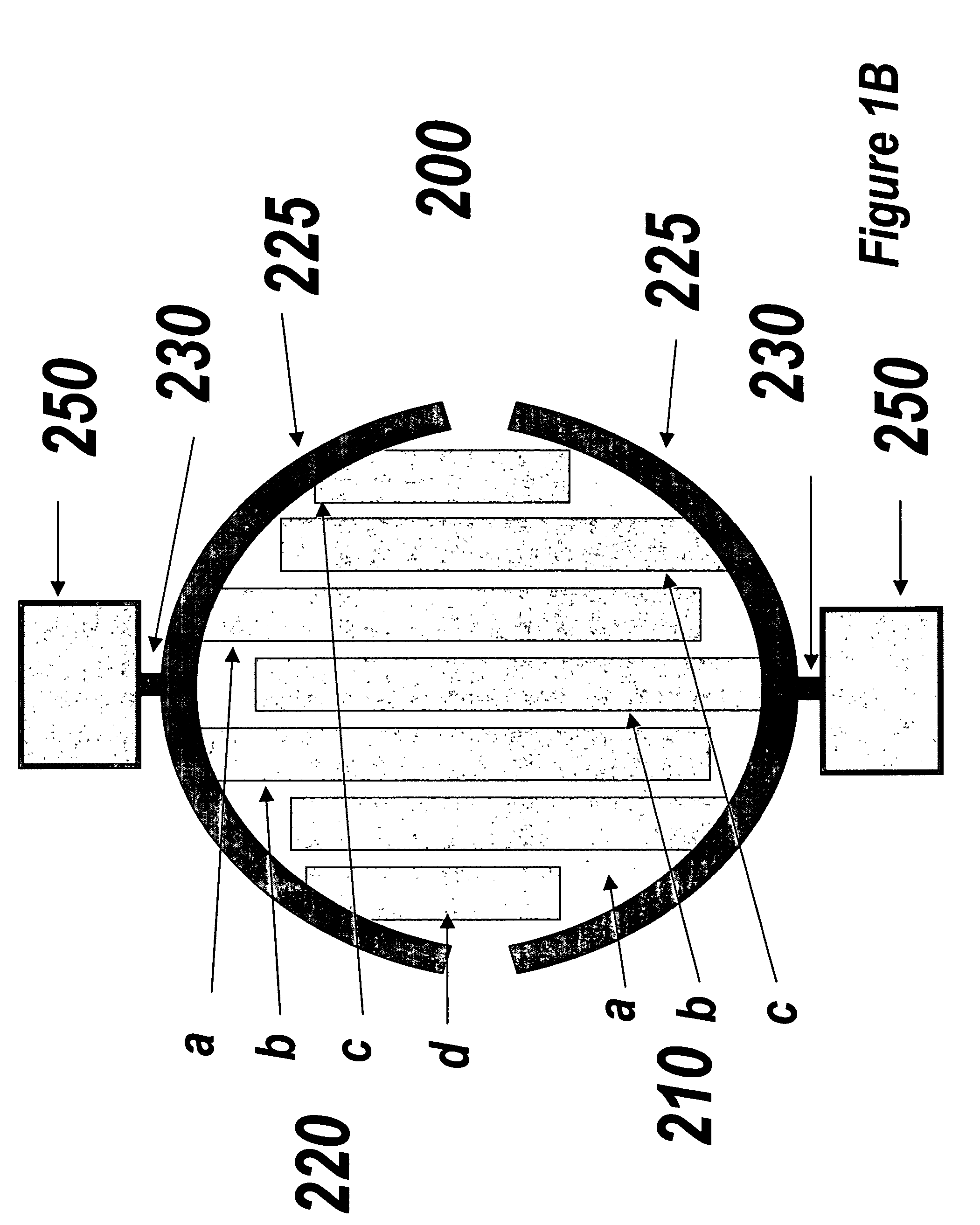
Multi-well plate and electrode assemblies for ion channel assays
InactiveUS6969449B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical field strengthEngineering
Plate and electrode assemblies include configurations allowing for relatively uniform electric field production. The electrodes may comprise strips of conductive material plated onto the bottom surface of sample wells or they may comprise plate electrodes extending down into the well. In some embodiments, the electric field strength varies by less than about 10% from a mean field intensity over at least about 20% of the surface area of the bottom surface of a sample well.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA SAN DIEGO LLC
Variable volume electroporation chamber and methods therefore
InactiveUS20070128708A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellEngineering
Disclosed is a chamber apparatus for electroporating in vitro relatively large volumes of a fluid medium carrying biological-cells-or-vesicles wherein-a reservoir for carrying said cells and vesicles is variable in its volume on demand and wherein the volume chosen is directly related to the volume of the sample to be electroporated. The apparatus has further embodiments wherein the chamber is disposable and can be operated either in isolation from a patient or connected thereto.
Owner:GENETRONICS INC
Popular searches
Biochemistry cleaning apparatus Biomass after-treatment Electrical/wave energy microorganism treatment Enzymology/microbiology apparatus Tissue/virus culture apparatus Liposomal delivery Stress based microorganism growth stimulation Electrical/wave energy enzyme treatment Specific use bioreactors/fermenters Material analysis by optical means
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com