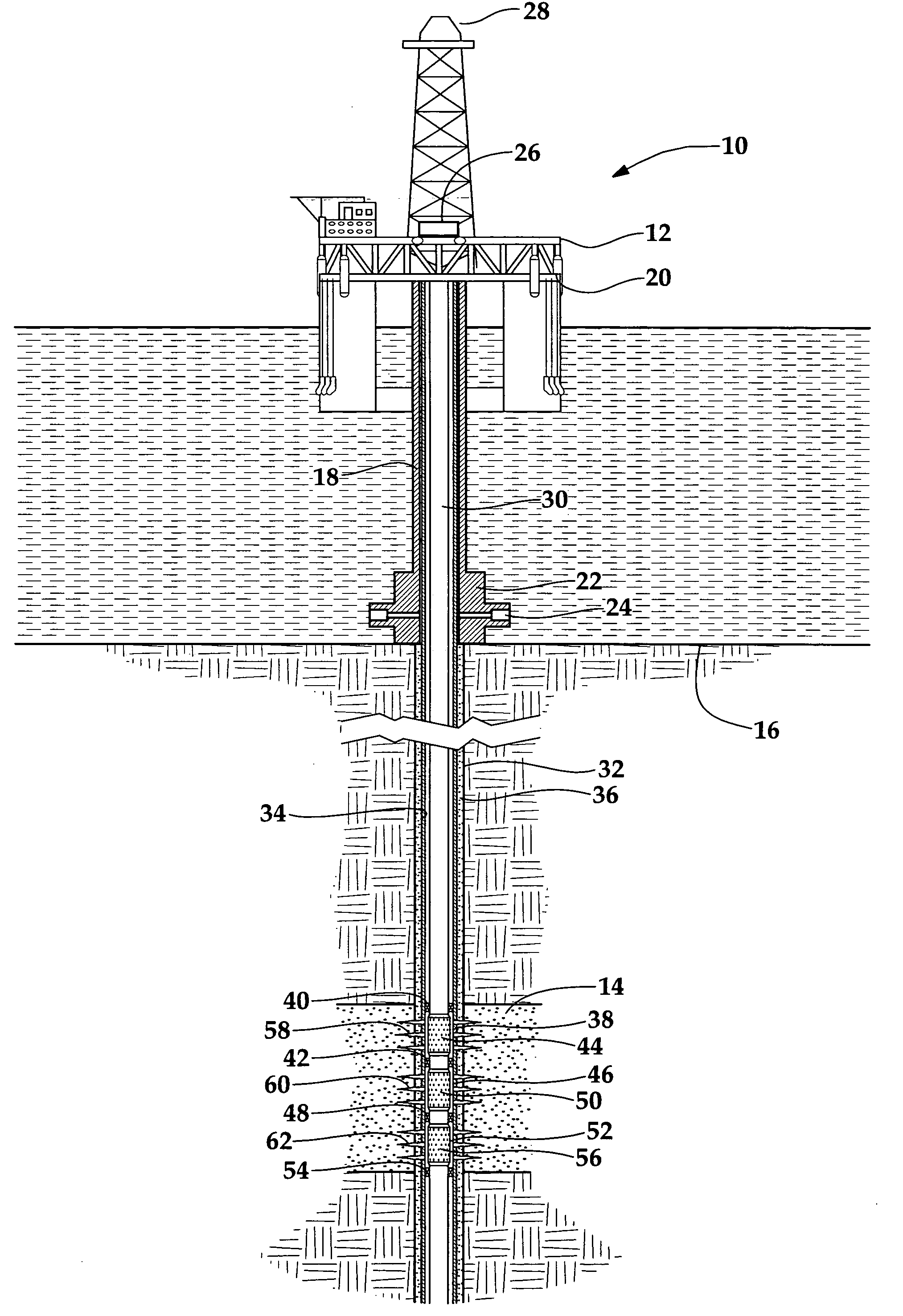
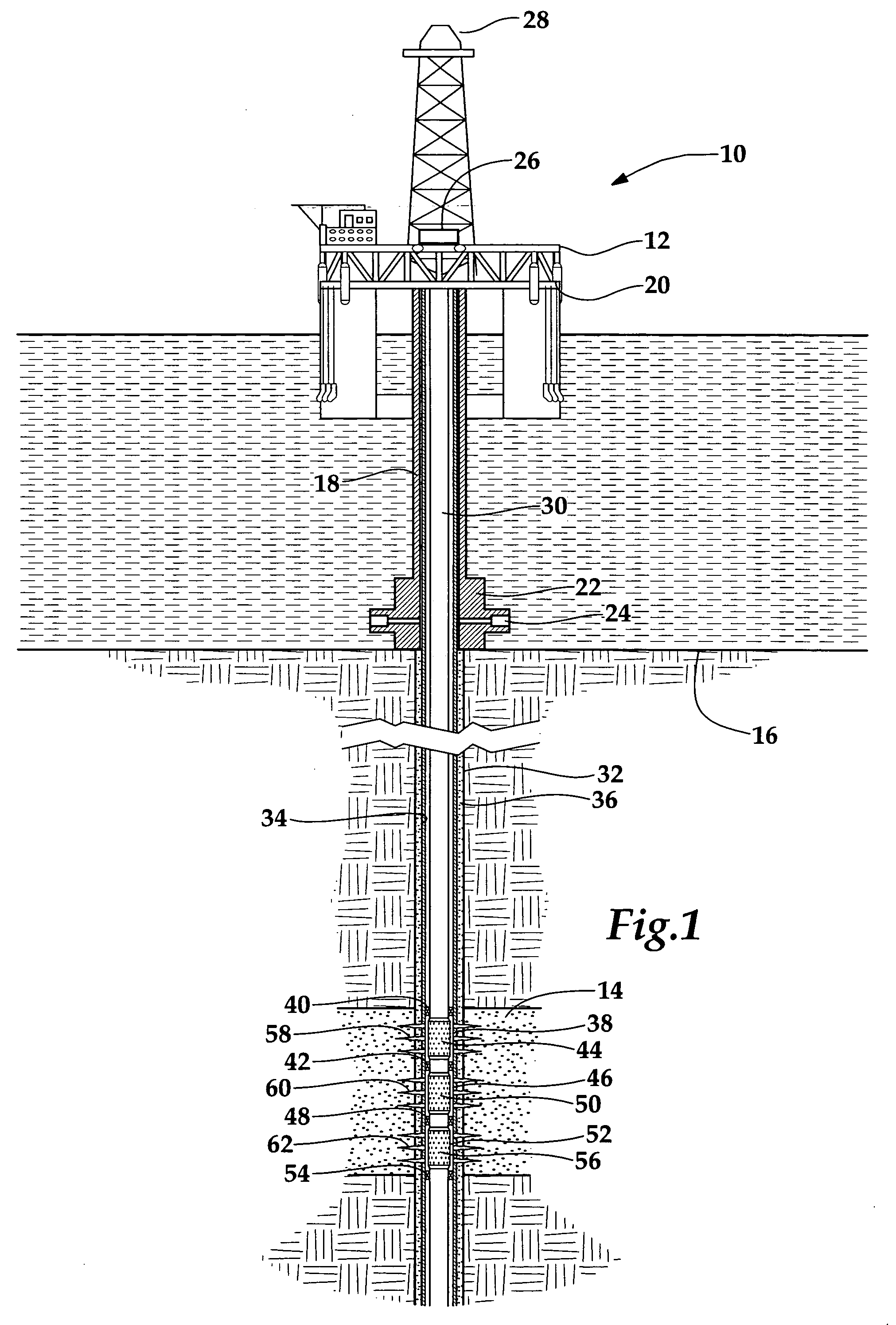
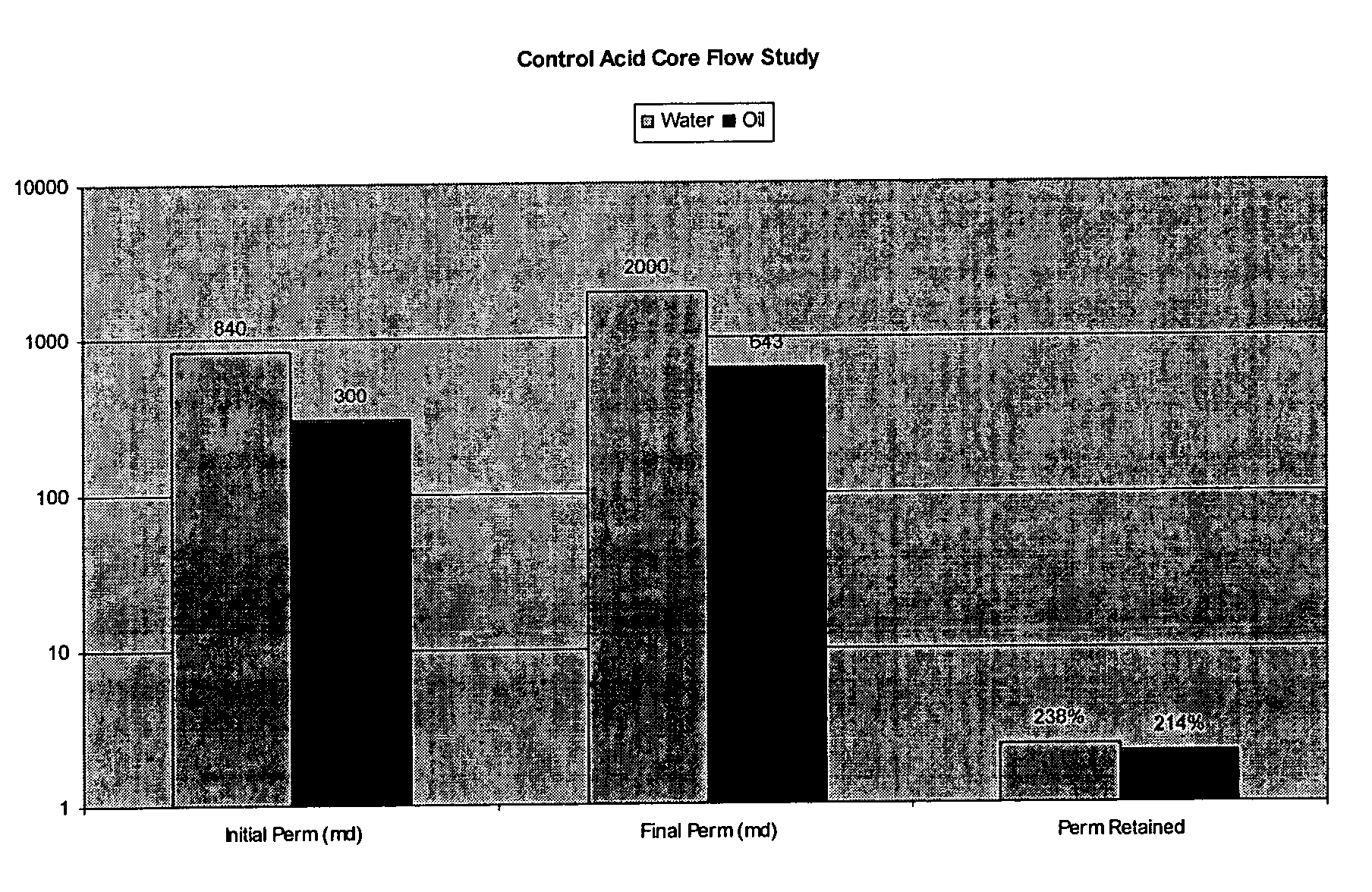
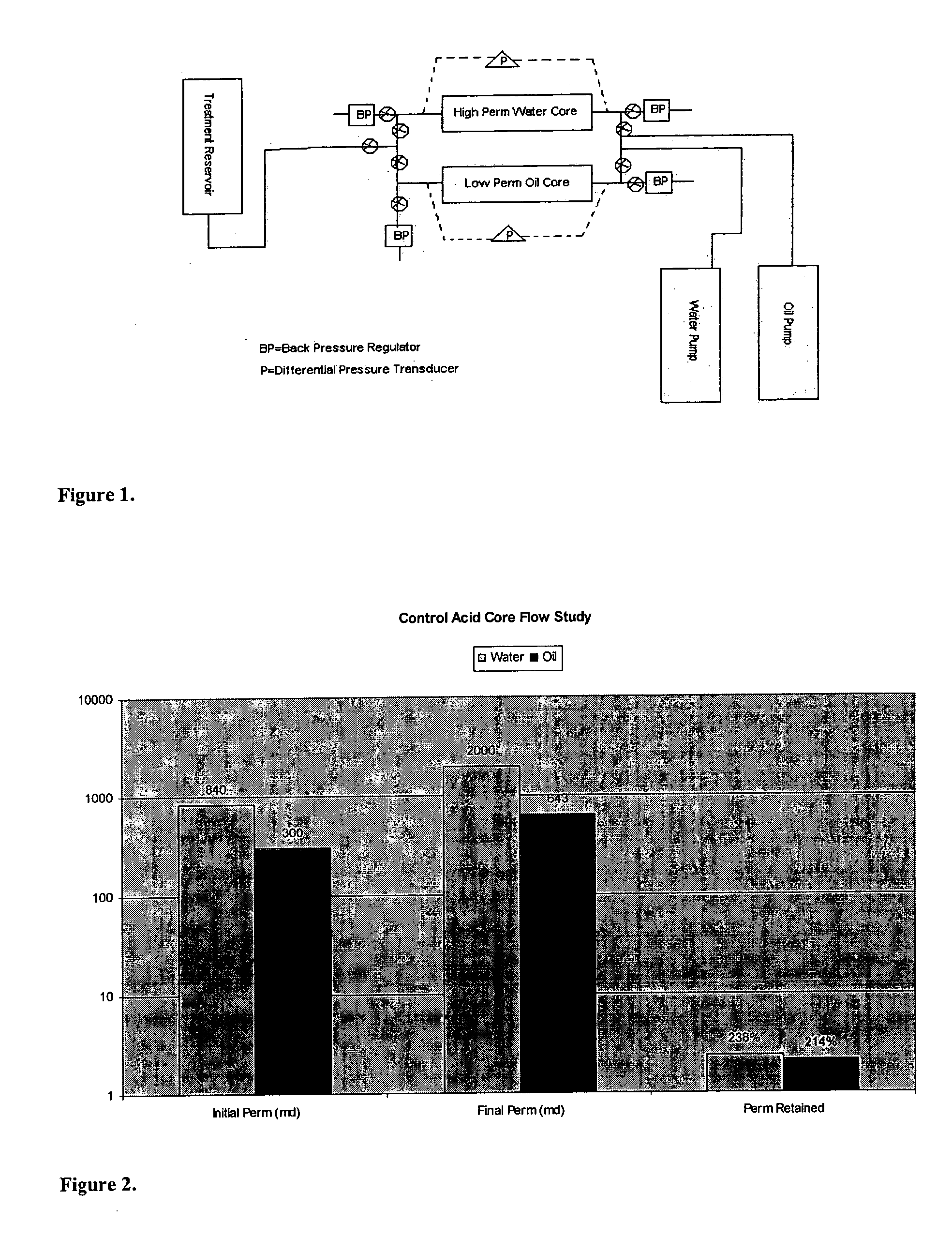
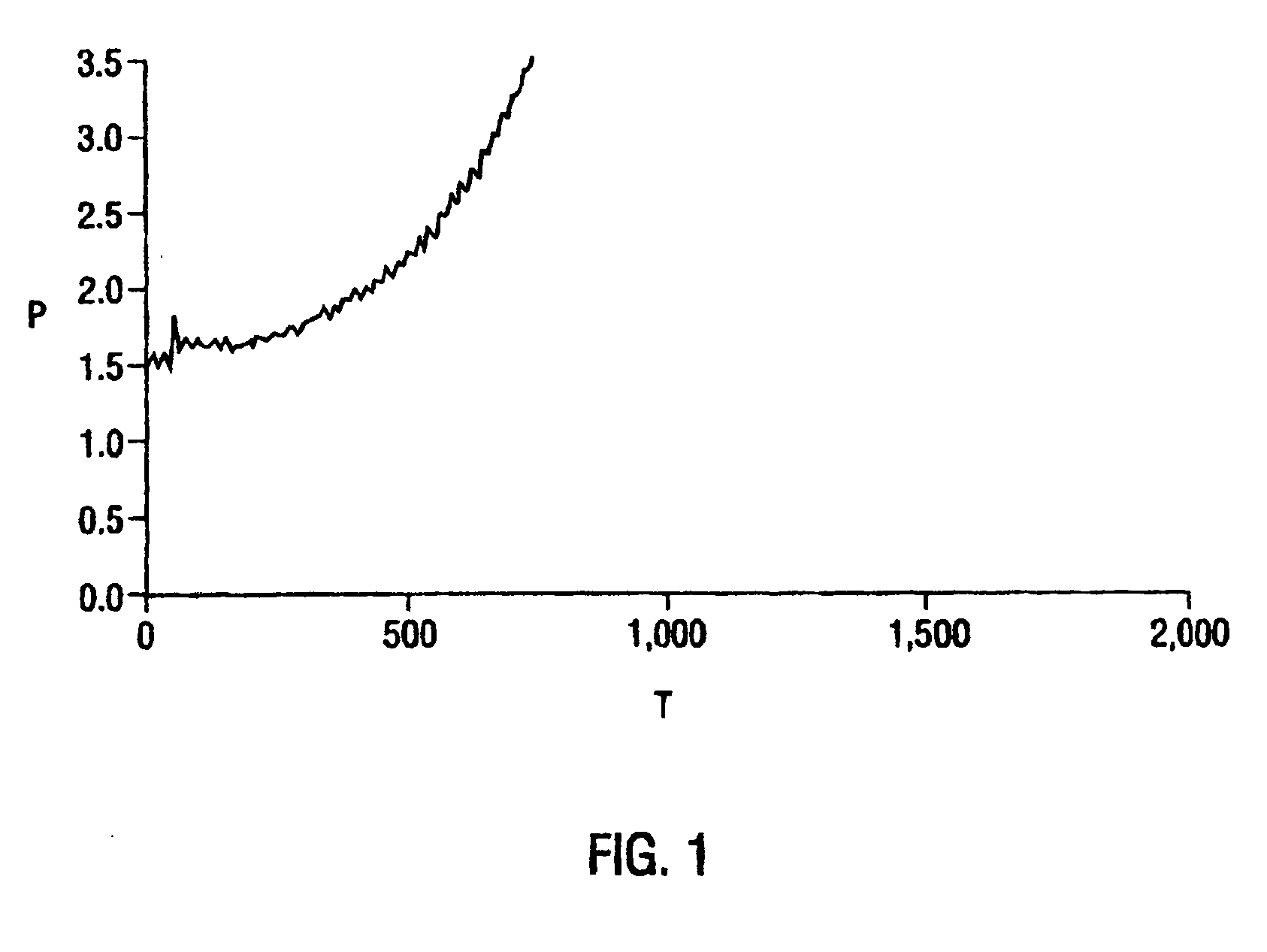
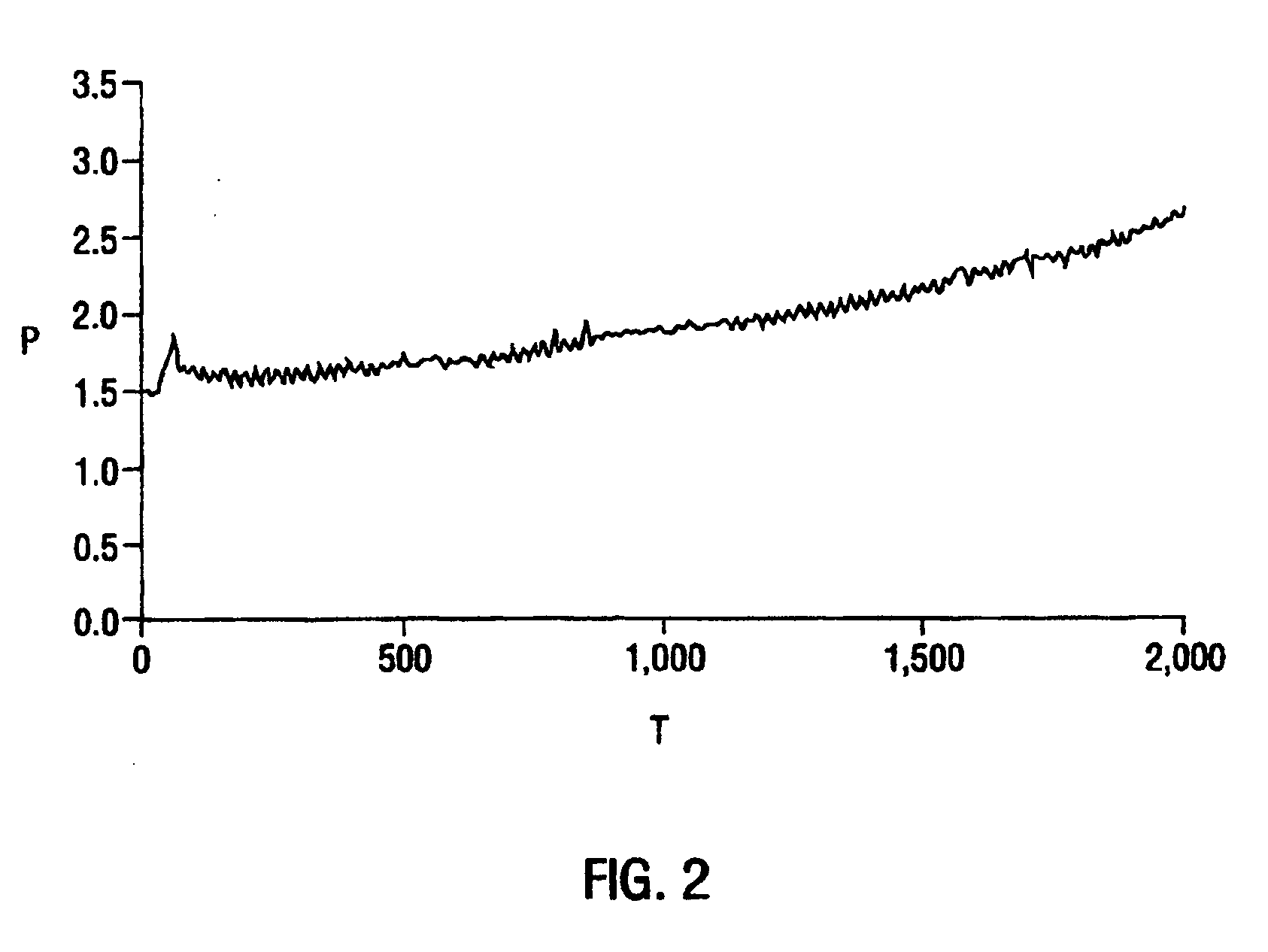
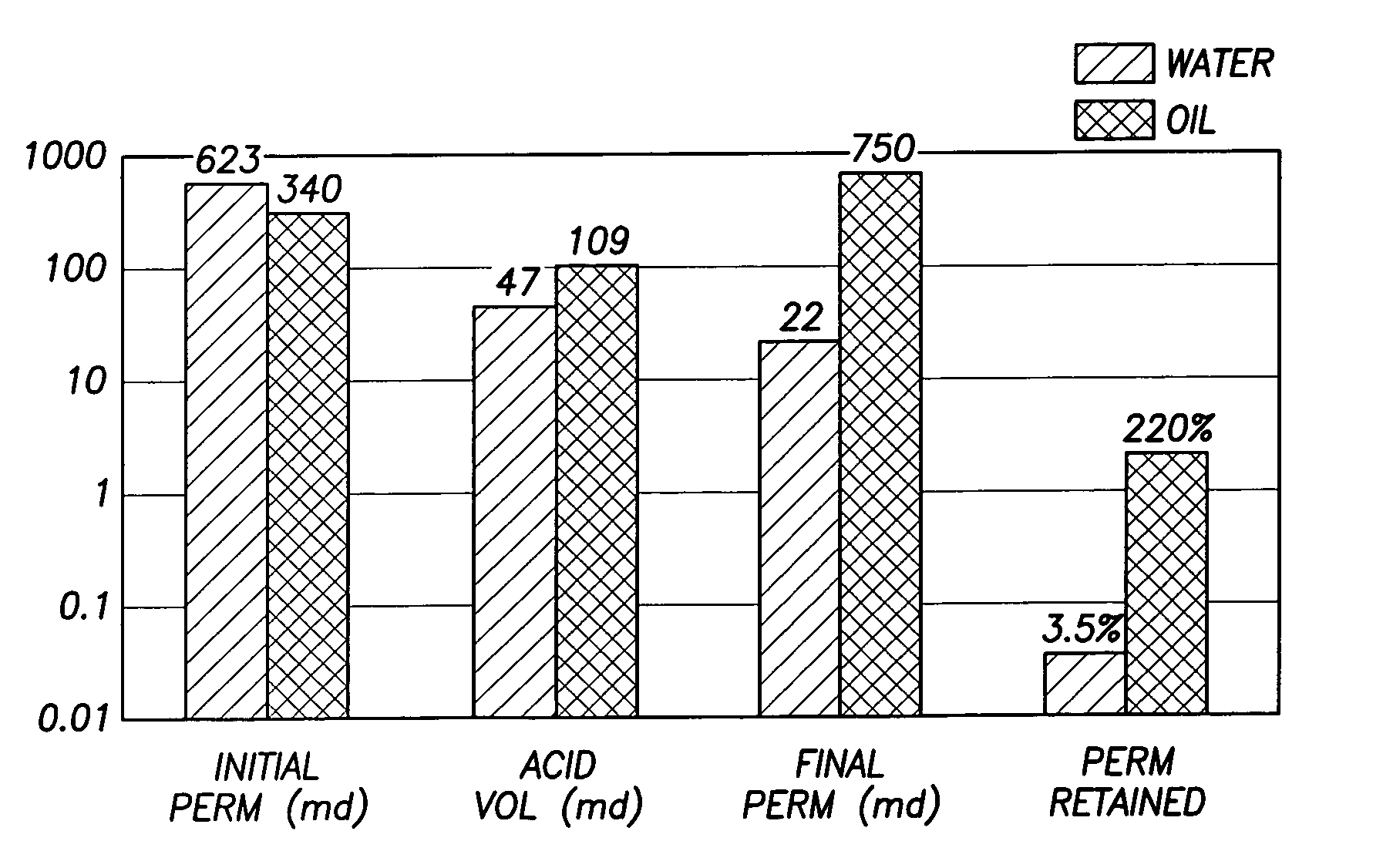
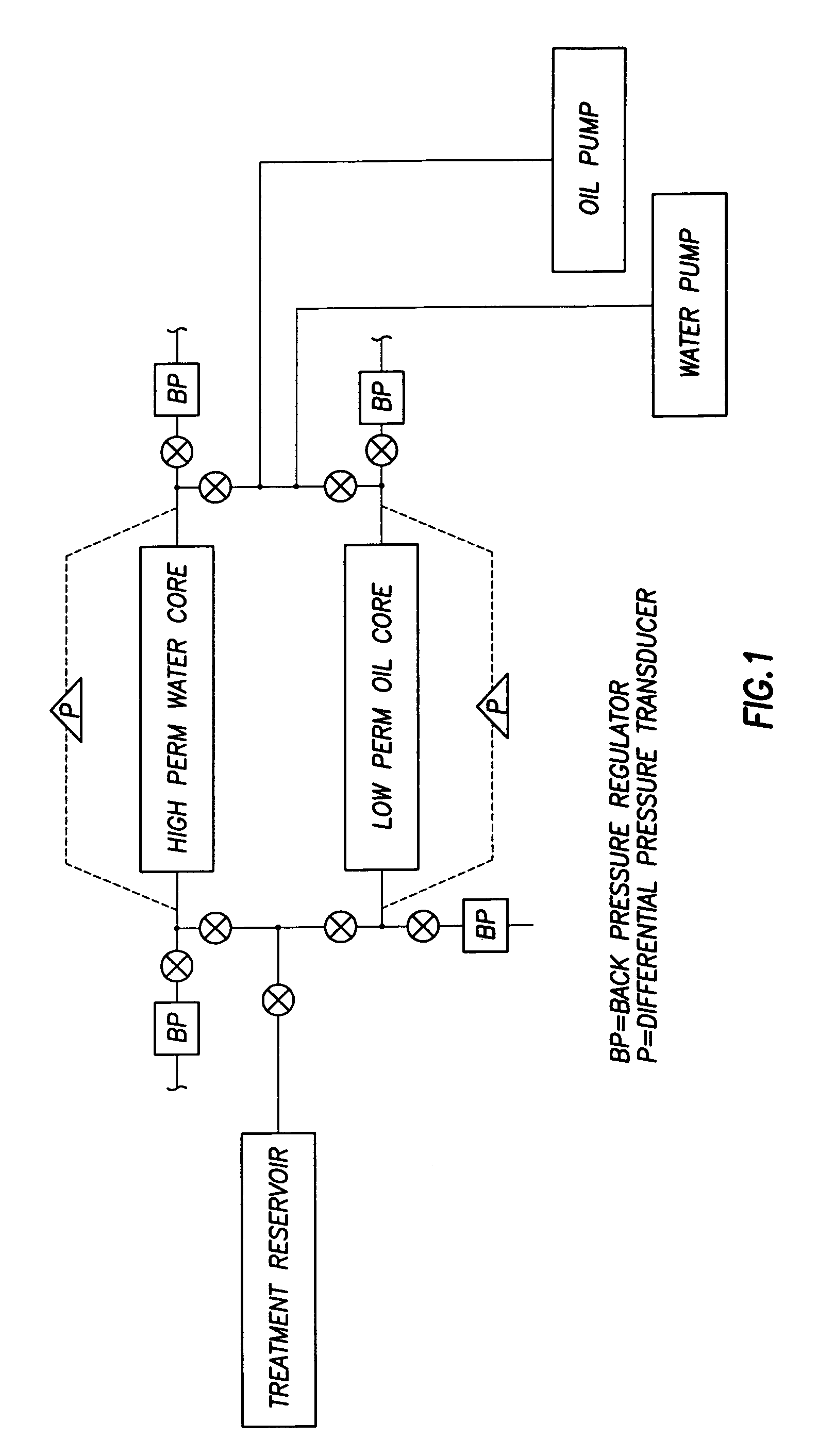
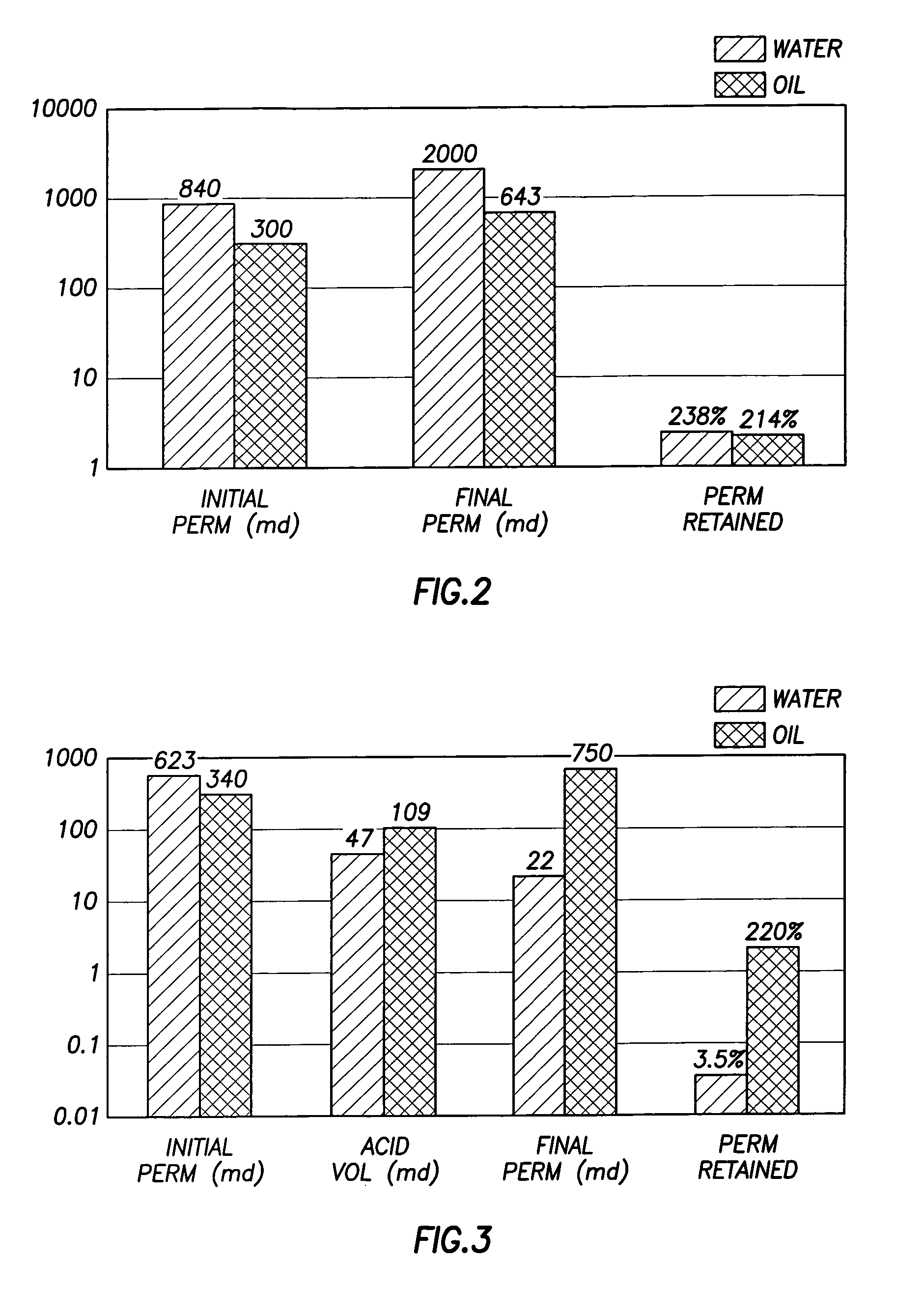
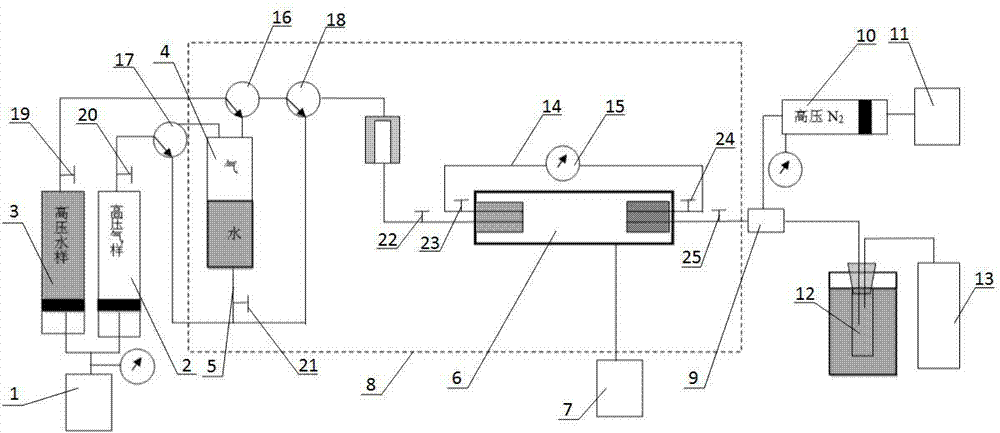
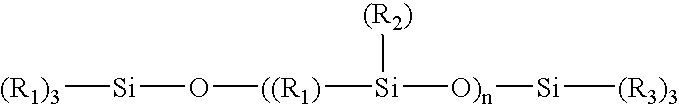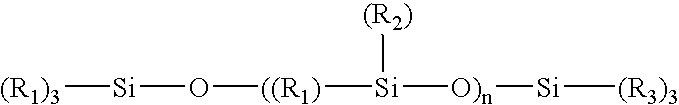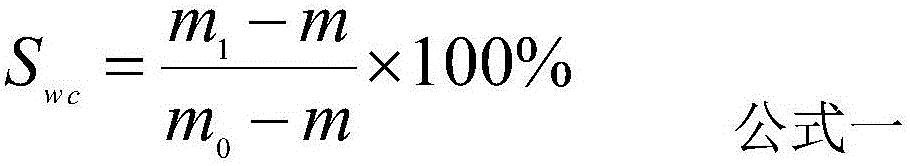Patents
Literature
680 results about "Relative permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
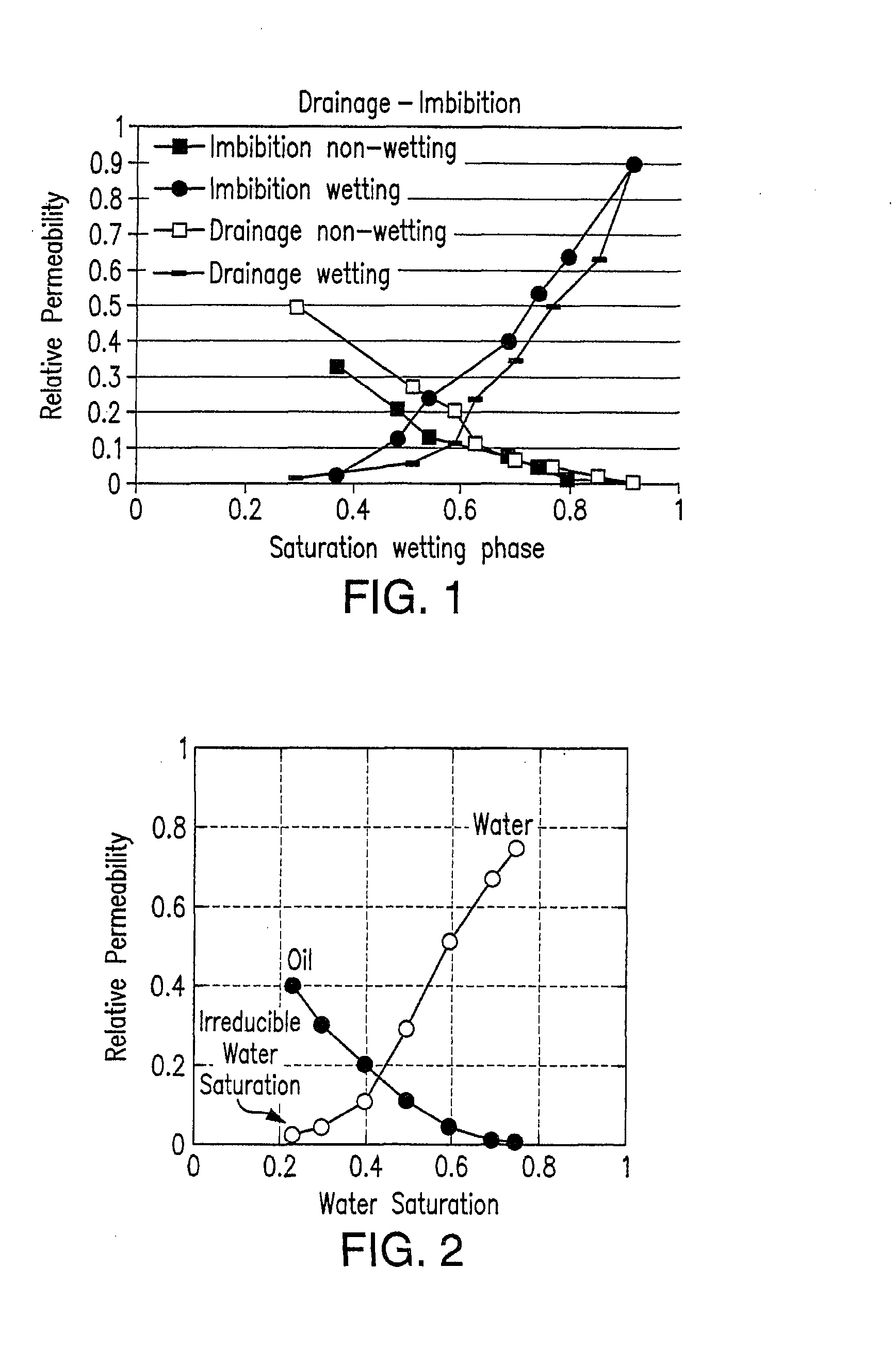
In multiphase flow in porous media, the relative permeability of a phase is a dimensionless measure of the effective permeability of that phase. It is the ratio of the effective permeability of that phase to the absolute permeability. It can be viewed as an adaptation of Darcy's law to multiphase flow. For two-phase flow in porous media given steady-state conditions, we can write qᵢ=-kᵢ/μᵢ∇Pᵢ for i=1,2 where qᵢ is the flux, ∇Pᵢ is the pressure drop, μᵢ is the viscosity.
Device and method for detecting analytes
InactiveUS6548311B1Influence is negligibleRelative density is smallBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityAnalyte
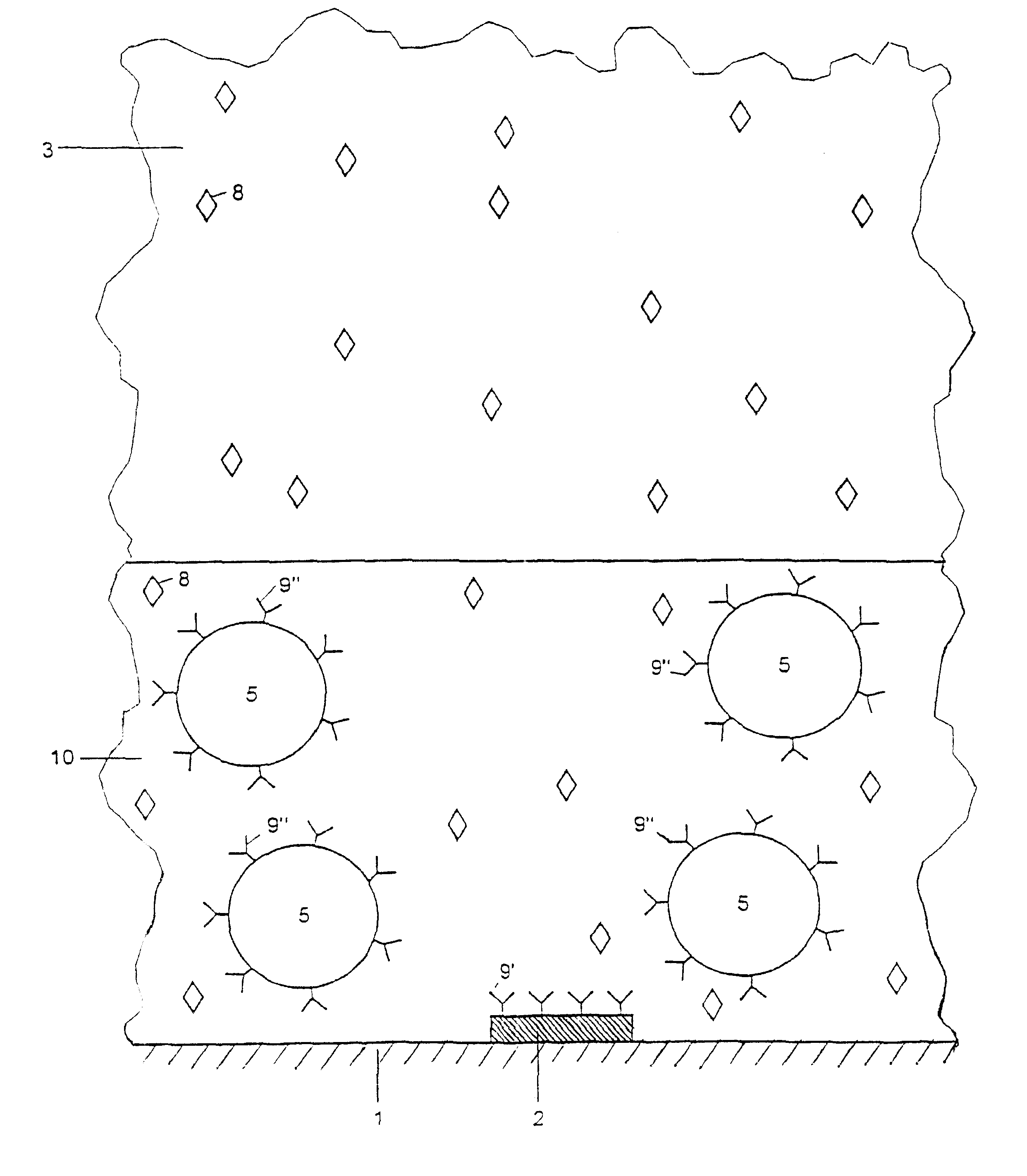
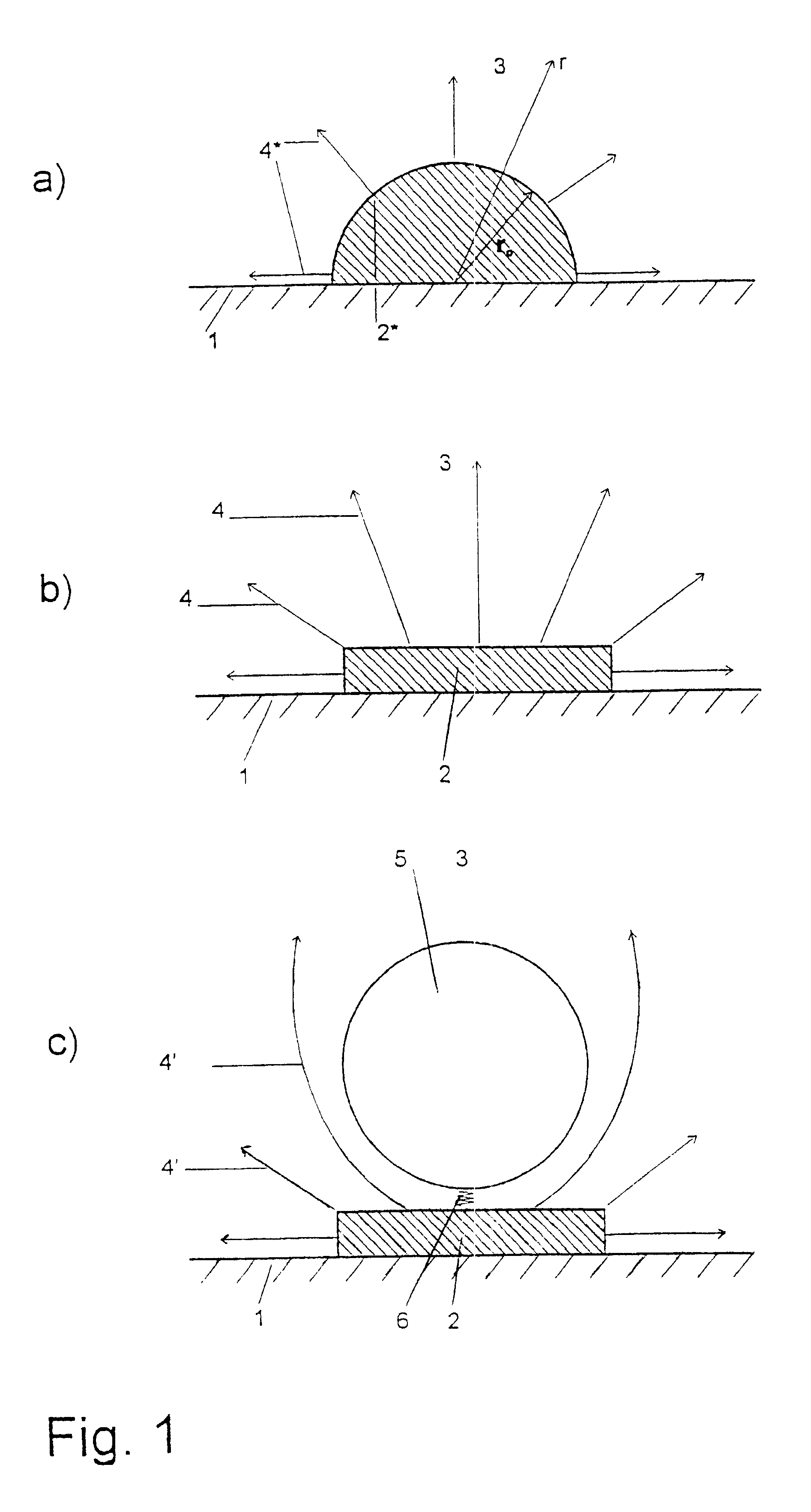
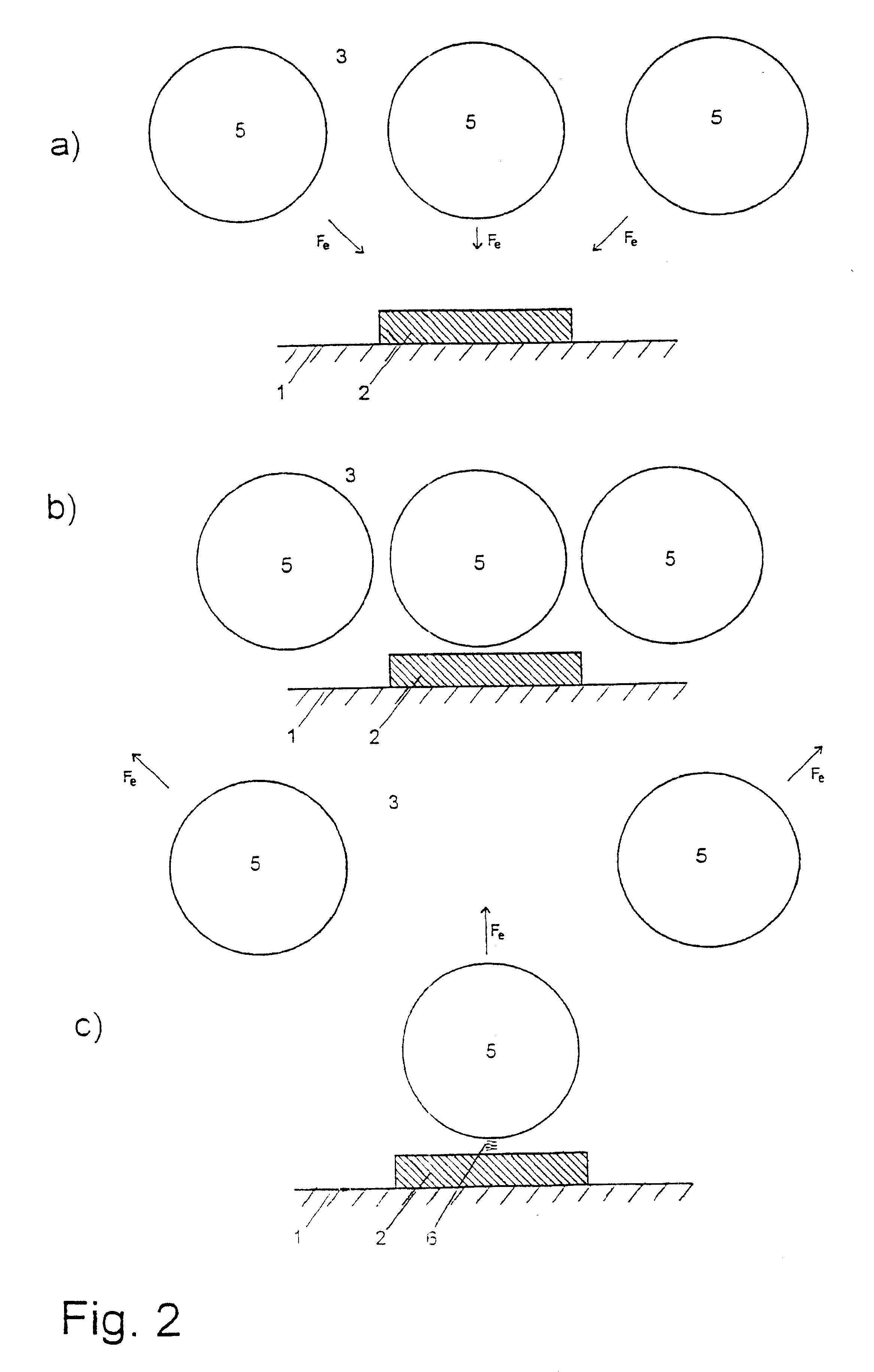
The invention relates to a method for detecting analytes and to a device for carrying out the method, for use for analysis or diagnosis in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry, molecular genetics, food chemistry, biotechnology, the environment and medicine. Marker particles (5) with different electrical properties or a different relative permeability to those of the measuring solution (3) surrounding them are used to detect the analytes (8). The marker particles (5) either bond specifically to the analytes (8) or to a base (2) in competition with the analyte. The analytes (8) are detected by the changes in an electrical field or an electrical current generated by electrodes (2) or in an electrical voltage applied to an electrode or in a magnetic field, said changes being caused by marker particles which have bonded with the analytes or by marker particles which have instead bonded to the base in an electrical field.
Owner:KNOLL MEINHARD
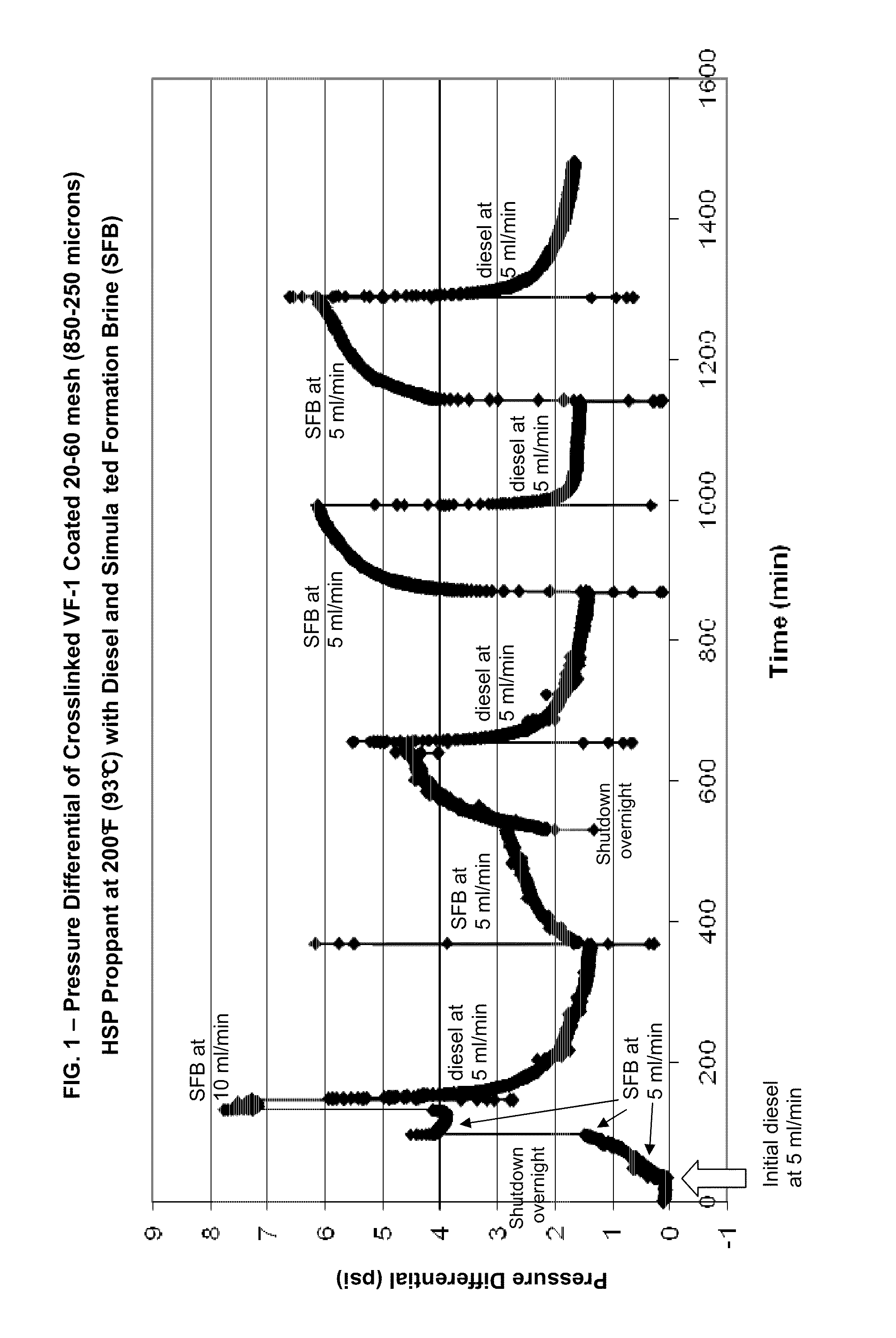
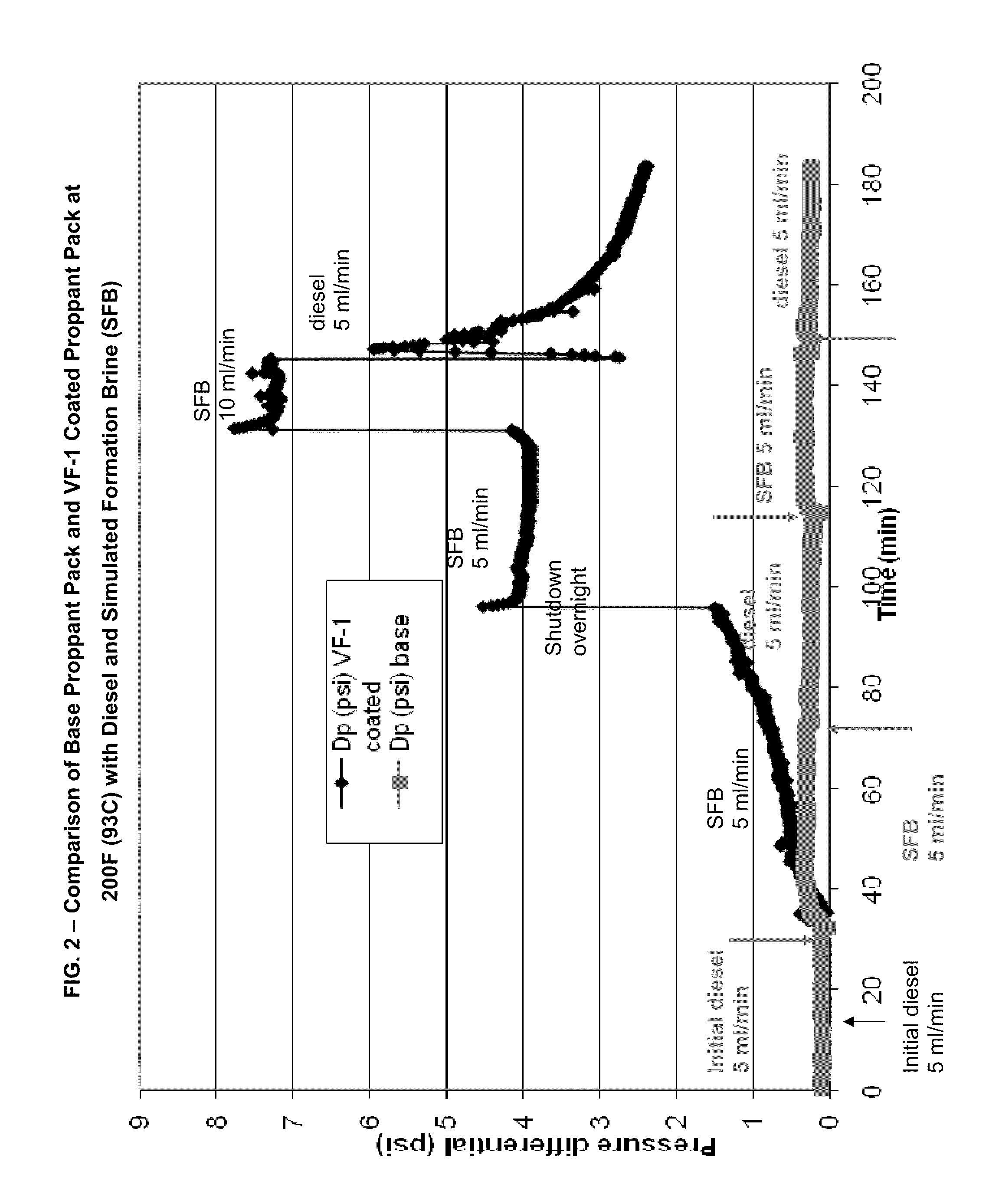
Coating and/or treating hydraulic fracturing proppants to improve wettability, proppant lubrication, and/or to reduce damage by fracturing fluids and reservoir fluids
InactiveUS20050244641A1Reduce conductivityEfficient arrangementSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsFracturing fluidCompound (substance)
Surface modified oil and gas well hydraulic fracturing proppants for improving wettability, altering chemical reactivity, altering surface topography, imparting lubricity or controlling relative permeability to flow of fluids of such proppants. The use and preparation of such coated proppants in hydraulic fracturing of subterranean formations is also described.
Owner:CARBO CERAMICS
Apparatus and method for reducing water production from a hydrocarbon producing well
InactiveUS20070012444A1Reduce water productionReduce penetrationFluid removalSealing/packingHydrophilic monomerWater production
A filtering apparatus for use in a hydrocarbon producing well for reducing water production therein includes a filtering medium treated with a relative permeability modifier such that the relative permeability modifier reduces the permeability of the filtering medium if the relative permeability modifier contacts water production. The relative permeability modifier may be used to treat a metal portion of the filtering medium in the case of a wire wrap screen or a wire mesh screen or may be use treat a metal portion or the prepacked component of a prepacked screen. The relative permeability modifier may be a polymer of at least one hydrophilic monomer and at least one hydrophobically modified hydrophilic monomer, a hydrophobically modified polymer, a hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymer, hydrophobically modified copolymers thereof or the like.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods of reducing water permeability for acidizing a subterranean formation
InactiveUS20050000694A1Reducing and precluding production of waterEliminate needFluid removalFlushingHydrophilic polymersHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The present invention provides a method of stimulating a subterranean formation penetrated by a well. The formation has a water-bearing section and a hydrocarbon-bearing section. The method includes the steps of: (a) introducing into the formation an aqueous treatment fluid containing a hydrophobically-modified relative permeability modifier, and (b) introducing an acidizing treatment fluid into the formation. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can be formed and introduced into the formation in several ways. For example, the hydrophobically-modified RPM can be the reaction product of a hydrophilic polymer and a hydrophobic compound that are capable of reacting with each other. The hydrophilic polymer is a polymer containing reactive amino groups in the polymer backbone or as pendant groups, which are capable of reacting with a hydrophobic alkyl halide compound. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can include, for example, a polymer of DMAEMA quaternized with an alkyl halide, wherein the alkyl halide has an alkyl chain length of 6 to 22 carbons.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Compositions containing water control treatments and formation damage control additives, and methods for their use
InactiveUS20060065396A1Minimizes stepComparable and improved treatment resultConstructionsFluid removalControl treatmentRelative permeability
The present invention relates to compositions of aqueous compositions comprising relative permeability modifier (RPM) macromolecules and one or more formation damage control additives, for use in treating hydrocarbon-producing wells, formations, and equipment, as well as methods for the use of such compositions. Such compositions, comprising the RPM macromolecule and the one or more formation damage control additive, such as a scale control agent, can result in the formation of a composition wherein the components exhibit a “synergistic” effect, whereby the ability of the formation damage control additive to prevent formation damage is enhanced relative to the use of the same additive separately.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Methods and compositions for improving hydrocarbon recovery by water flood intervention
InactiveUS20070039732A1Increase productionIncrease oil productionFluid removalFlushingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCompound (substance)
Methods useful in improving hydrocarbon recovery from subterranean formations using relative permeability modifier (RPM) macromolecules are described. The RPMs are typically crosslinked RPMs having K-values from 250-300 which, when injected into an injector well associated with a producer well, redirect the production water so as to improve the injection profile of the well and simultaneously improve hydrocarbon recovery from the producer well.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Broad band antenna
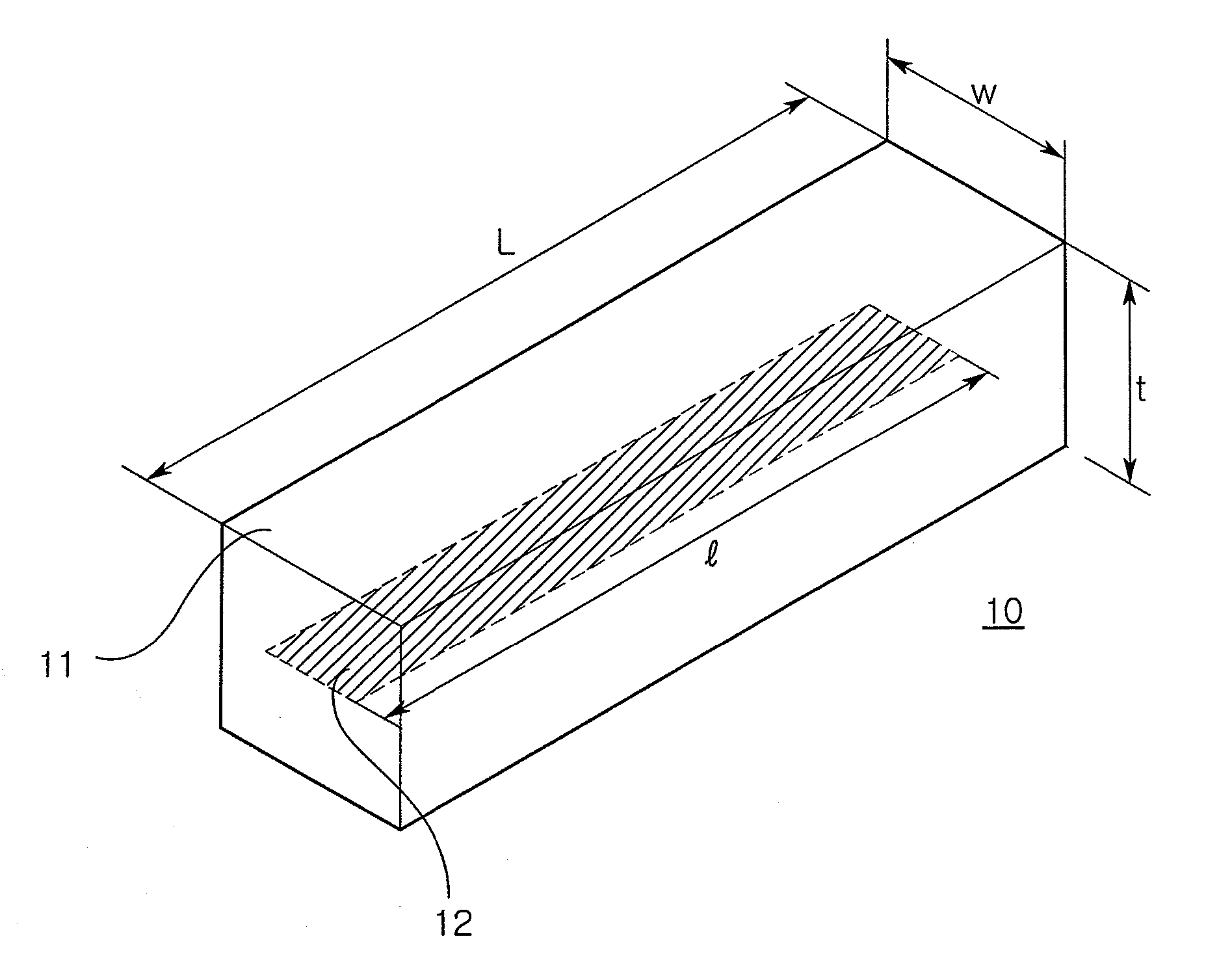
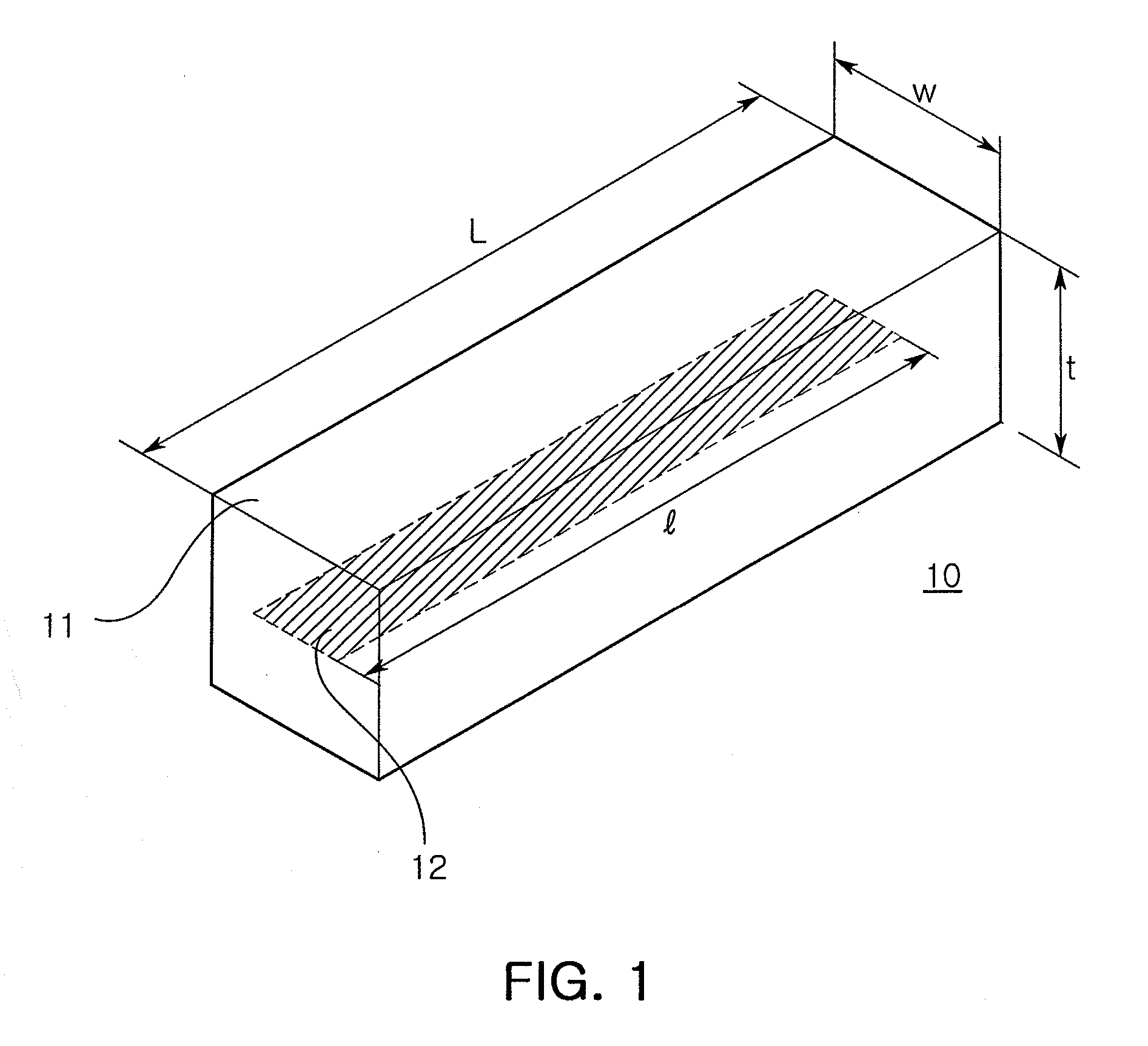
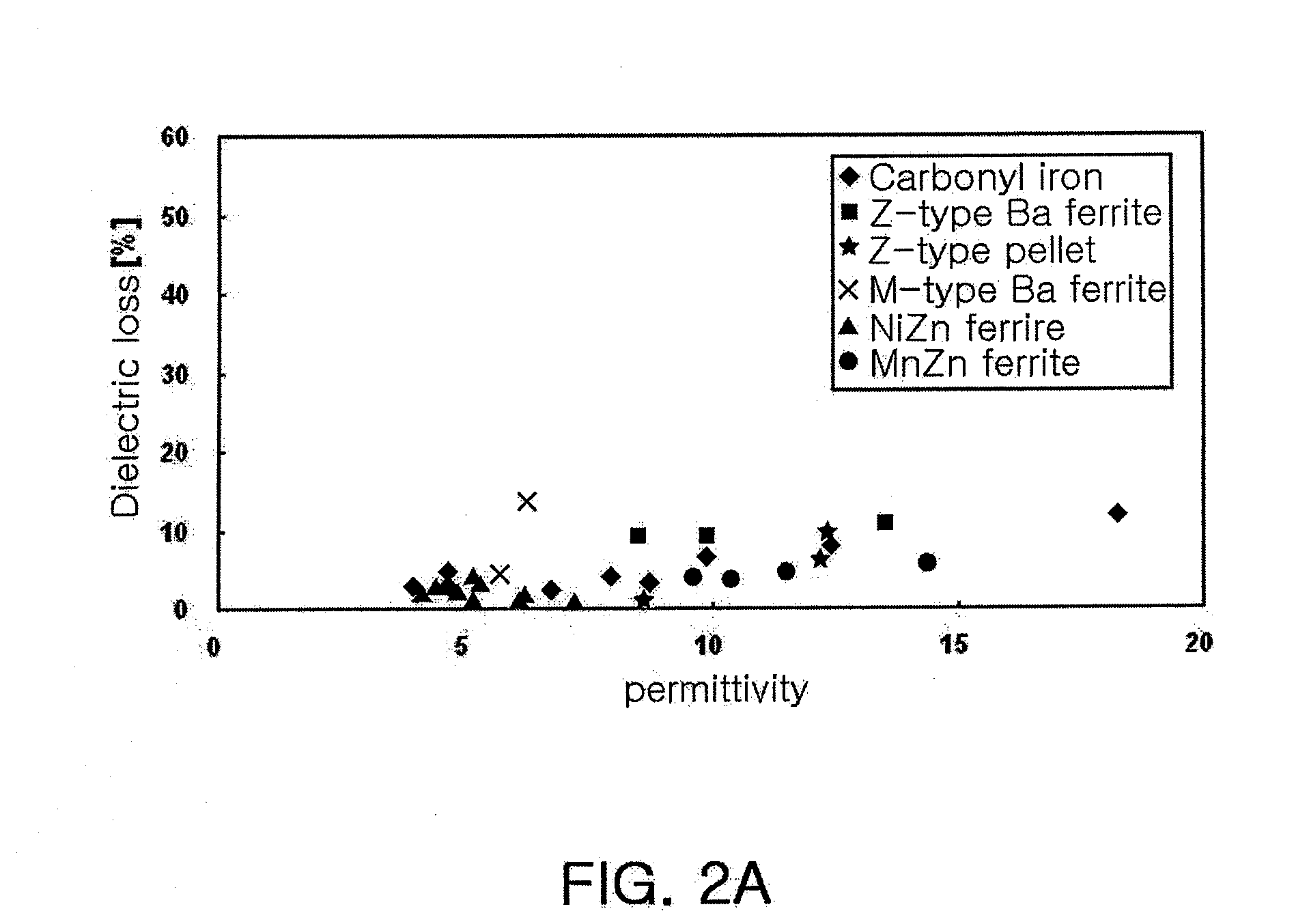
InactiveUS20080055178A1Big decrease in gainRadiating elements structural formsElongated active element feedPolymer resinBroadband
A broad band antenna including: a body formed of a material having a relative permittivity of 2 to 20, a relative permeability of 1 to 10, and a magnetic loss tangent of 0.001 to 0.2, at a usable frequency; and at least one radiator disposed on the body. The material forming the body may be a composite material formed of a polymer resin mixed with a magnetic powder. The composite material may contain the magnetic powder by 90 wt % with respect to a total weight.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
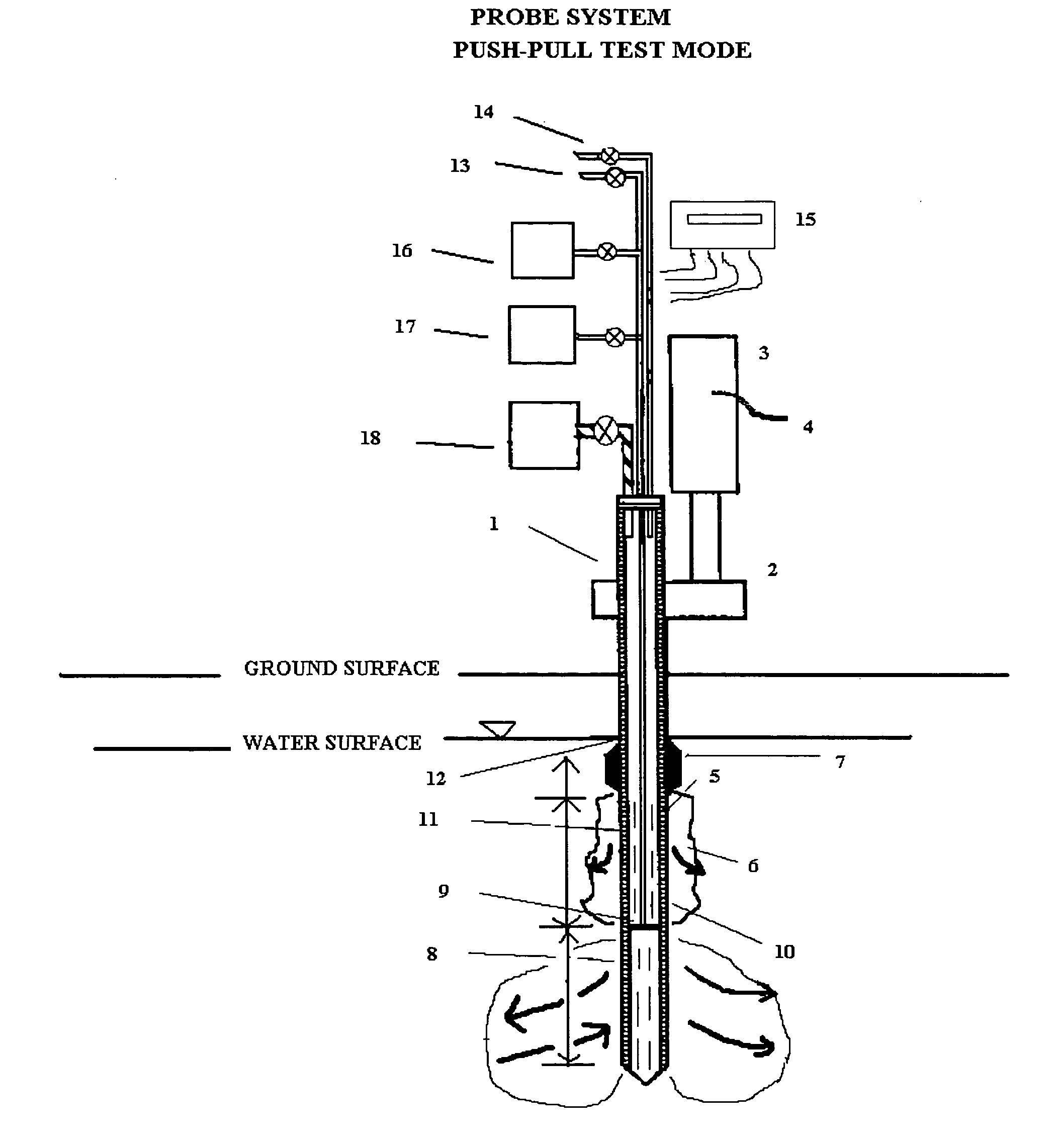
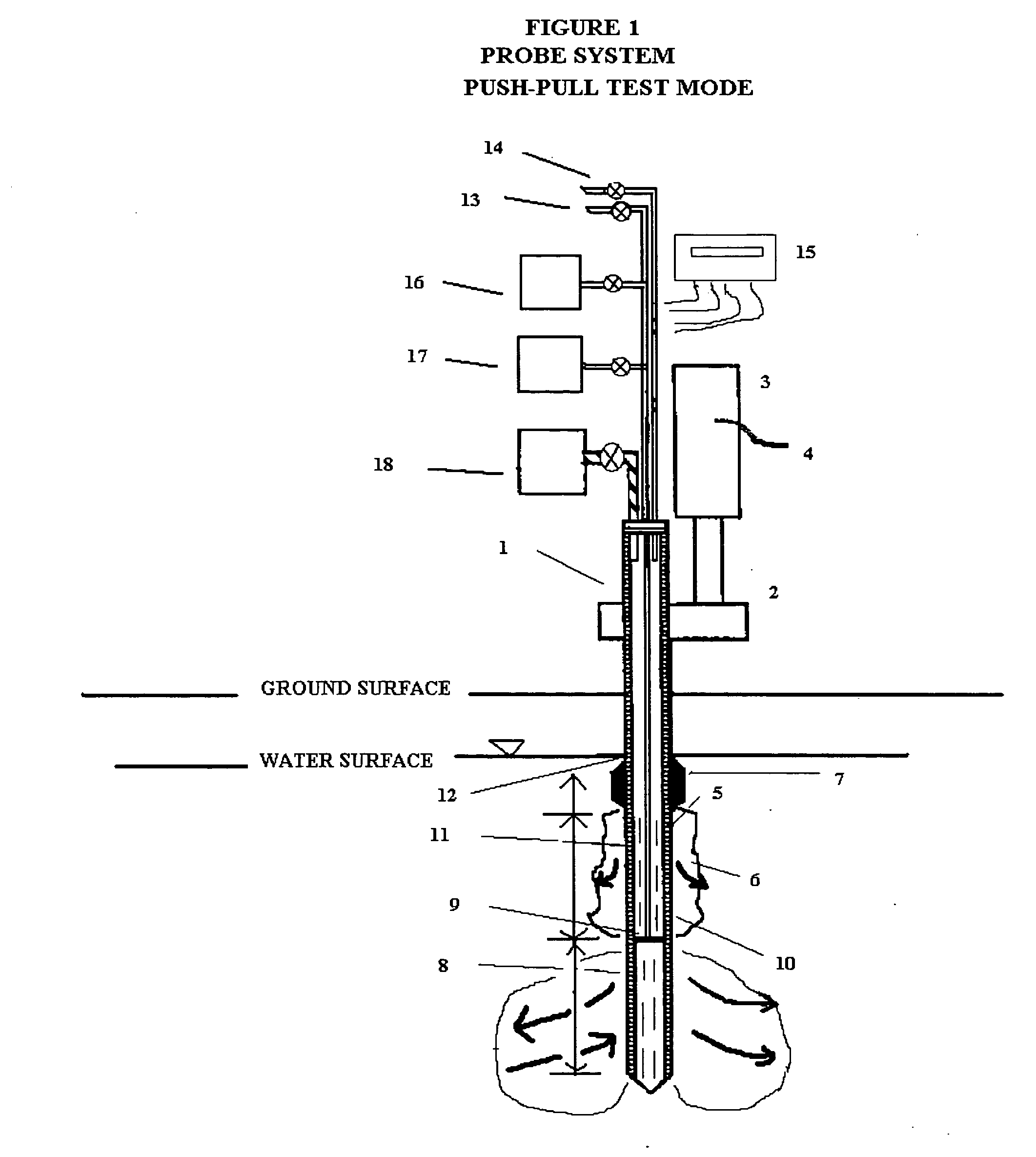
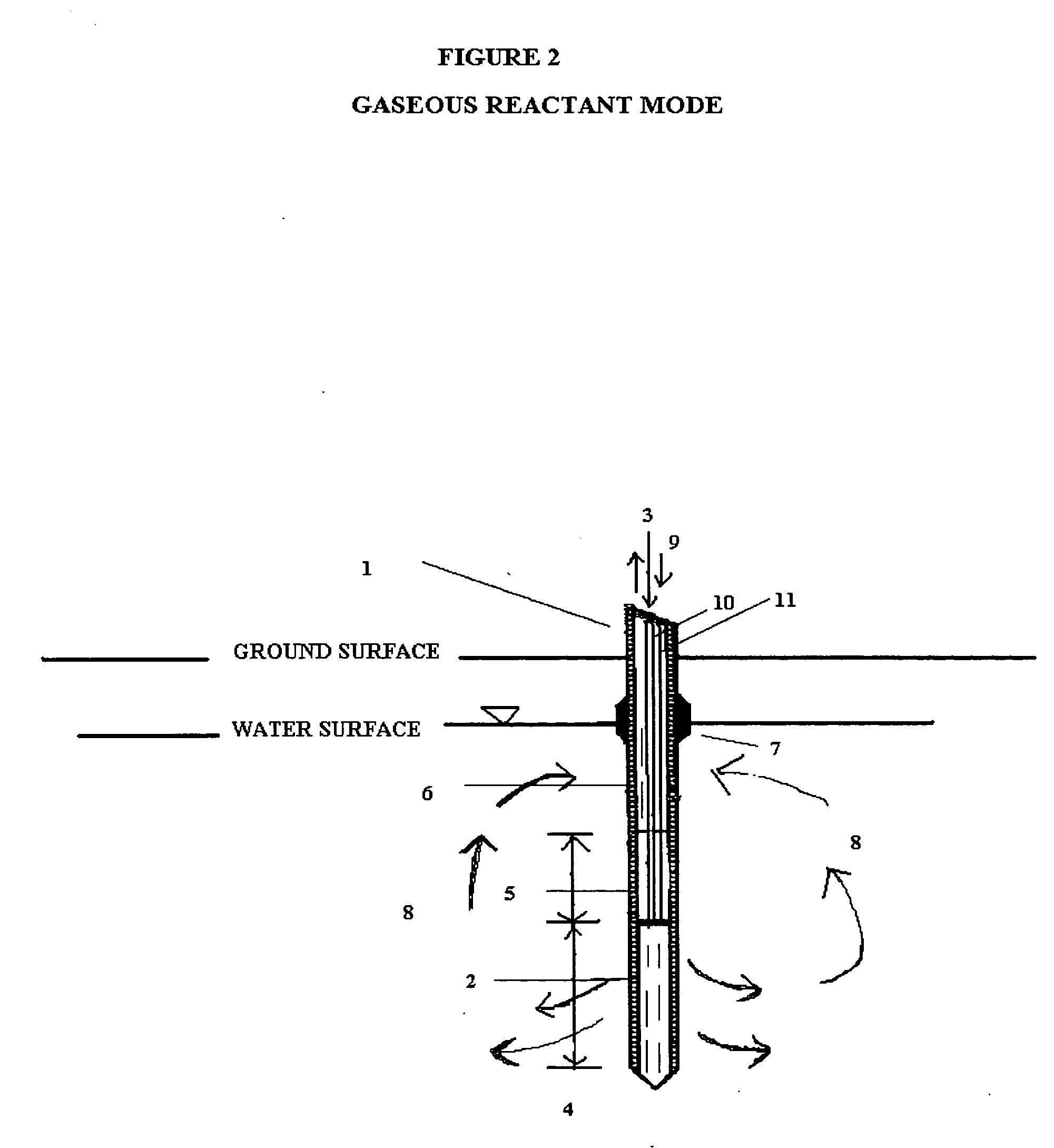
In situ remedial alternative and aquifer properties evaluation probe system
InactiveUS20060046297A1Prevent travelFaster and more easily automatedMicrobiological testing/measurementEarth material testingSoil gasPush technology
In general, the purpose of the probe system is to provide improved rapid field methods using re-designed direct push technology (DPT) and “push-pull testing” concepts to evaluate in situ chemical, biochemical, surfactant, adsorptive media, and leaching and fixation remediation technologies for hazardous subsurface contaminant(s). The probe system and methods described here when applied to a hazardous waste site being considered for in situ remediation of contaminants (organic or inorganic) by the listed treatment technologies will yield information that greatly reduces the uncertainty with regards to treatment effectiveness for the in situ soil, groundwater, and contaminant(s) conditions affecting dosage requirements and reaction rate(s) for various reactants. The probe system described here is multi-purpose in that it was designed: 1) to measure the relative permeability of the subsurface soil and groundwater to a liquid or gas ejectant, 2) to recover soil gas, soil, or groundwater samples for contaminant analyses, 3) to measure the chemical dosage and reaction, dissolution, adsorption, desorption, leaching, or fixation rate of a reactant such as a chemical or biochemical oxidant, metallic or bimetallic dehalogenating agent, surfactant or emulsifier solution, adsorbent media regenerant, leaching or fixation reagent that is injected into the matrix and withdrawn during a push-pull test, 4) to perform combinations of the above, 5) to measure the in situ adsorption capacity of adsorbent media and subsequently measure the effectiveness of regenerant(s) for the adsorbent media, and (6) to measure the effectiveness of a treated soil column for inorganic contaminant(s) leaching or fixation. In addition to being an in situ remedial alternatives evaluation tool, the probe system can be used as a reactant(s) delivery device after the specific remedial technology has been selected.
Owner:OXYTEC LLC
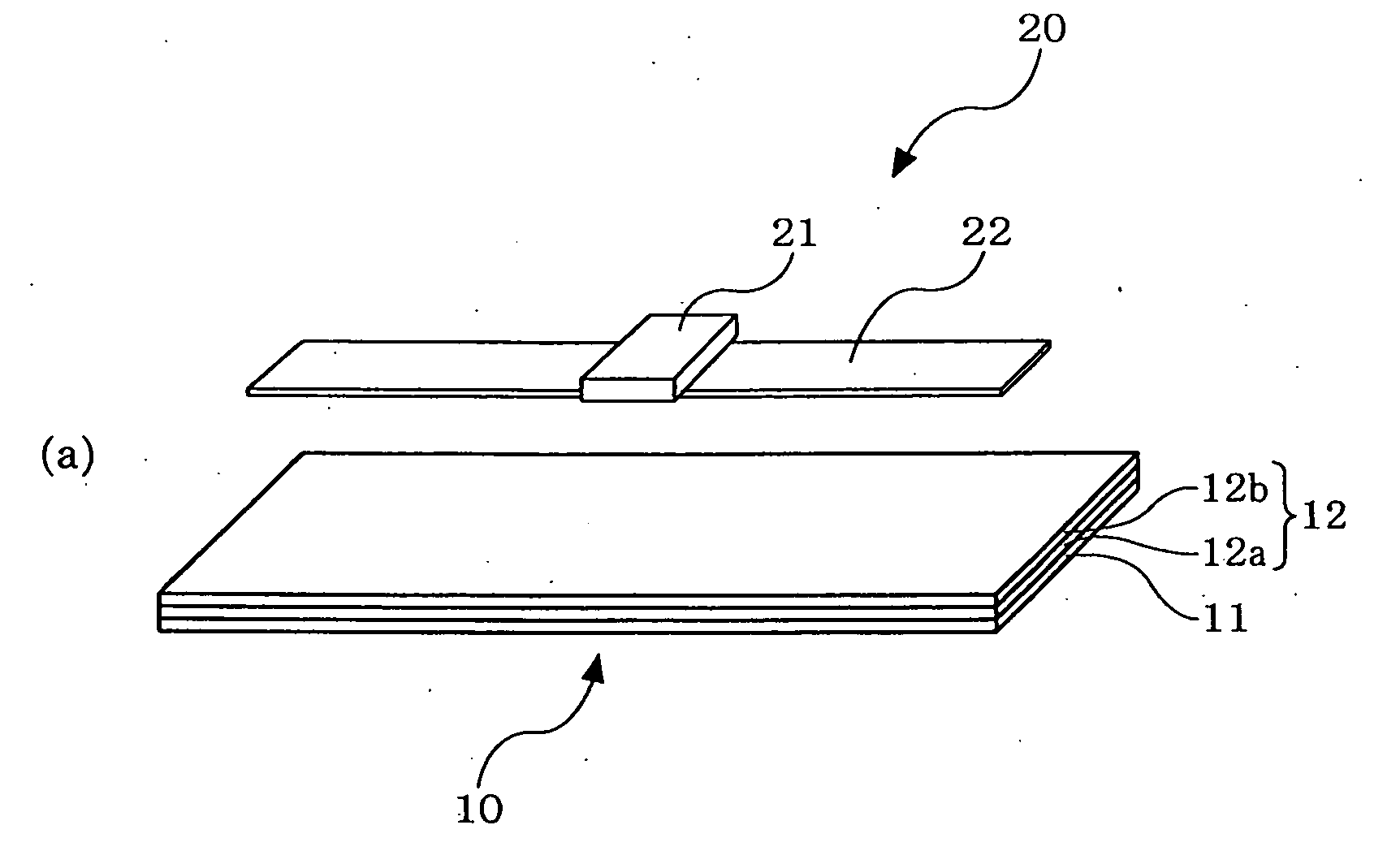
Rfid Tag Substrate For Metal Component
InactiveUS20100219252A1Small sizeConvenient wireless communicationContainer decorationsLevel indicationsDielectricGeneral purpose
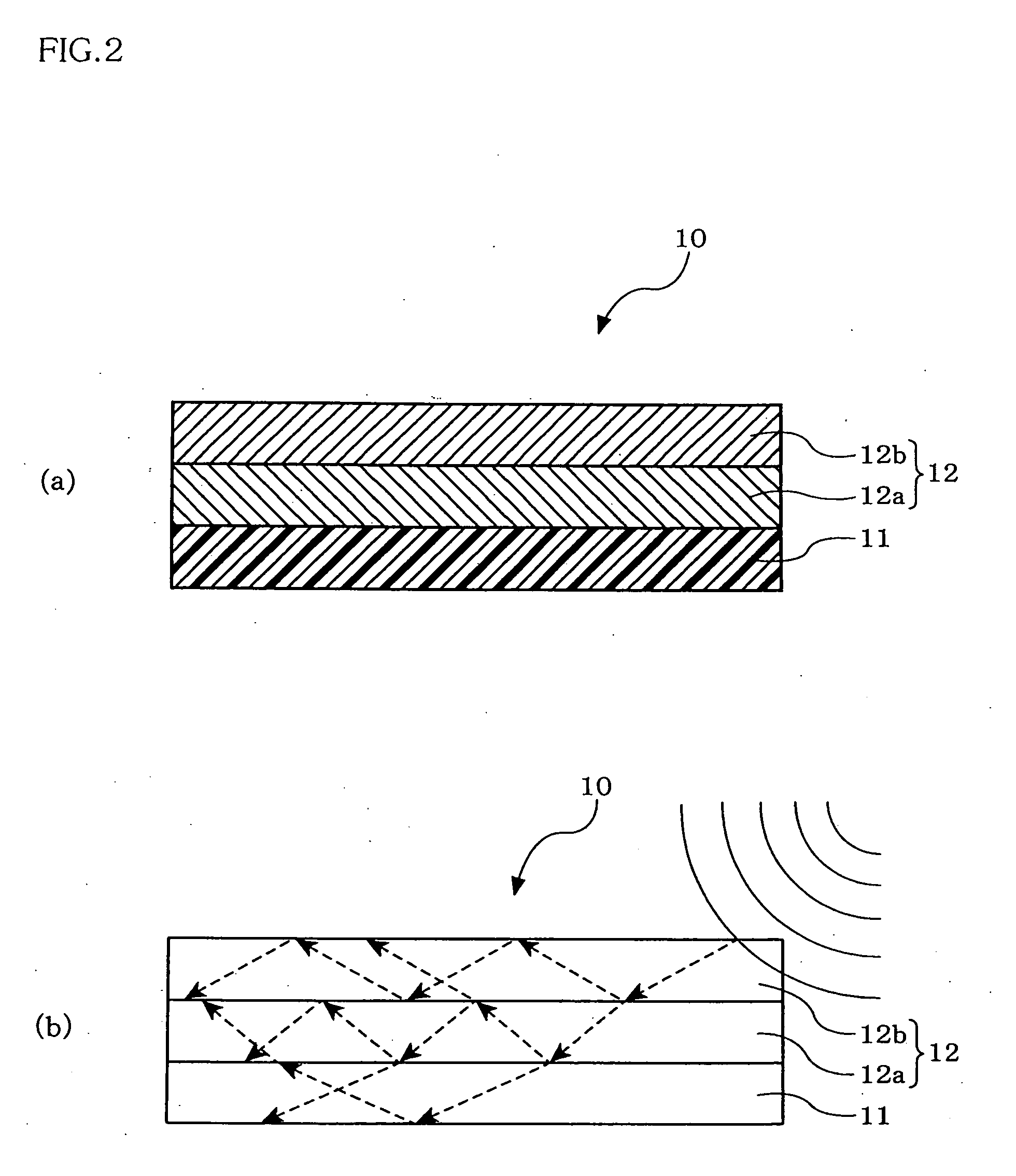
The present invention provides an RFID tag substrate in which communication characteristics of an RFID tag do not vary by an influence of contents in a container, the communication characteristics of the RFID tag are not deteriorated even if a metal container is used, the communication characteristics of the RFID tag can be excellently maintained irrespective of a material or contents of a container, and the tag can be reduced in thickness / size, and which can use a general-purpose RFID tag as it is and is suitable for a microwave type RFID tag that uses a UHF band or a frequency band of, e.g., 2.45 GHz in particular.There is provided an RFID tag substrate 10 on which an RFID tag 20 that performs wireless communication with a reader / writer is disposed, comprising: a substrate layer 11; and a functional layer 12 formed of a high-dielectric-constant layer 12a and a high-permeable layer 12b having different characteristics, wherein the functional layer having predetermined relative dielectric constant and relative permeability is provided, and a product of the relative dielectric constant and the relative permeability is not smaller than 250.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
Method and system for integrating logging tool data and digital rock physics to estimate rock formation properties
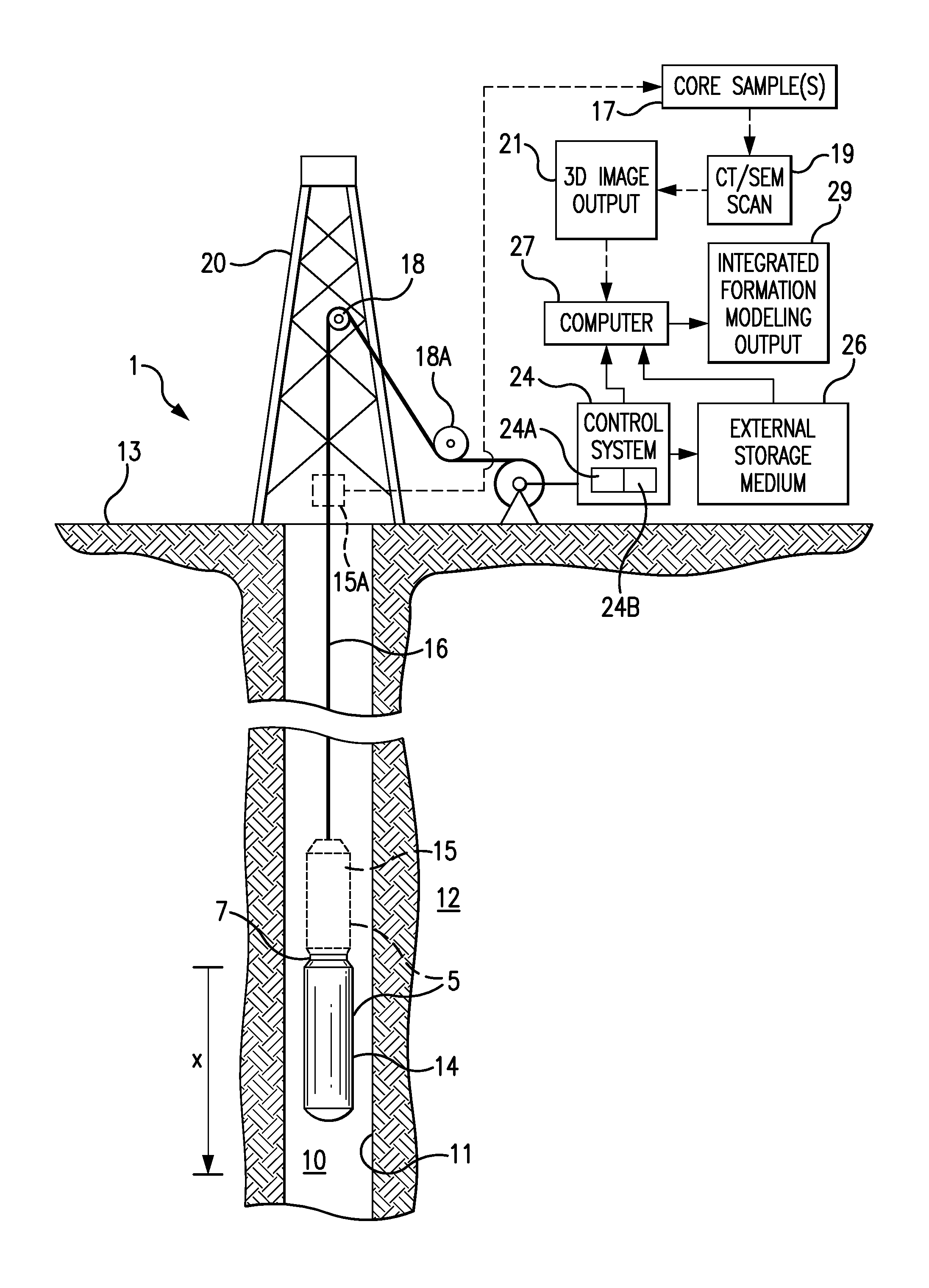
ActiveUS9507047B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationNuclear radiation detectionPorosityCt scanners
The present invention relates to a method and system for integrating logging tool data and digital rock physics to estimate rock formation properties. A rock sample from a logging tool such as a sidewall plug or large enough cutting can be extracted by the logging tool at approximately the same well bore location that the logging tool measures fluid properties. The rock samples thus obtained is scanned using a CT scanner, scanning electron microscope or other suitable scanning device. The resulting scanned rock image can be segmented and rock properties comprising porosity, absolute permeability, relative permeability, capillary pressure and other relevant rock properties are calculated. The resulting digital calculations are integrated with logging tool data and rock property estimates to improve the accuracy and timeliness of the logging tool data.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods of reducing water permeability for acidizing a subterranean formation
InactiveUS7182136B2Reducing and precluding production of waterEliminate needFluid removalFlushingHydrophilic polymersChain length
The present invention provides a method of stimulating a subterranean formation penetrated by a well. The formation has a water-bearing section and a hydrocarbon-bearing section. The method includes the steps of: (a) introducing into the formation an aqueous treatment fluid containing a hydrophobically-modified relative permeability modifier, and (b) introducing an acidizing treatment fluid into the formation. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can be formed and introduced into the formation in several ways. For example, the hydrophobically-modified RPM can be the reaction product of a hydrophilic polymer and a hydrophobic compound that are capable of reacting with each other. The hydrophilic polymer is a polymer containing reactive amino groups in the polymer backbone or as pendant groups, which are capable of reacting with a hydrophobic alkyl halide compound. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can include, for example, a polymer of DMAEMA quaternized with an alkyl halide, wherein the alkyl halide has an alkyl chain length of 6 to 22 carbons.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
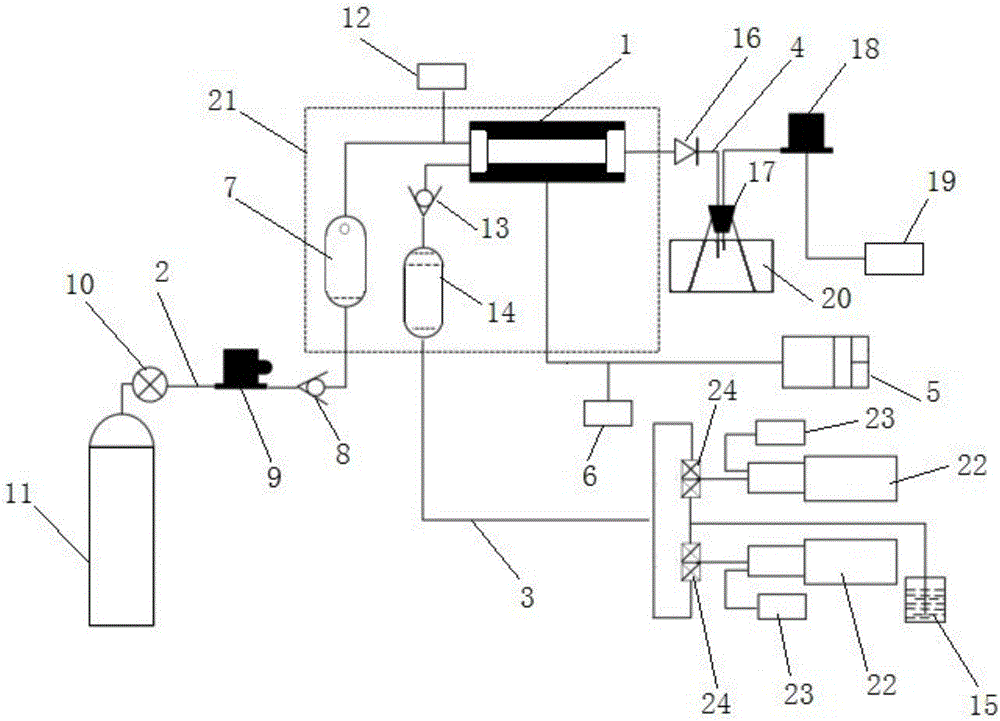
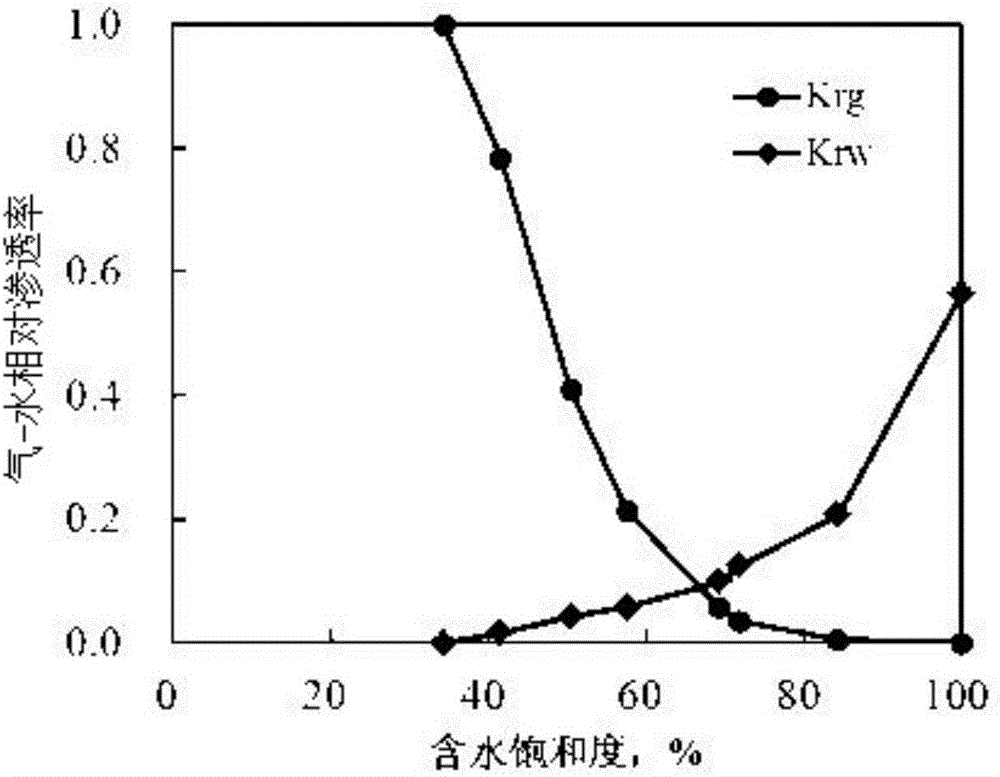
Determining method for stratum high-temperature high-pressure gas-phase and water-phase relative permeability curve
ActiveCN103645126AHigh value availableHigh precisionPermeability/surface area analysisRock coreGas phase
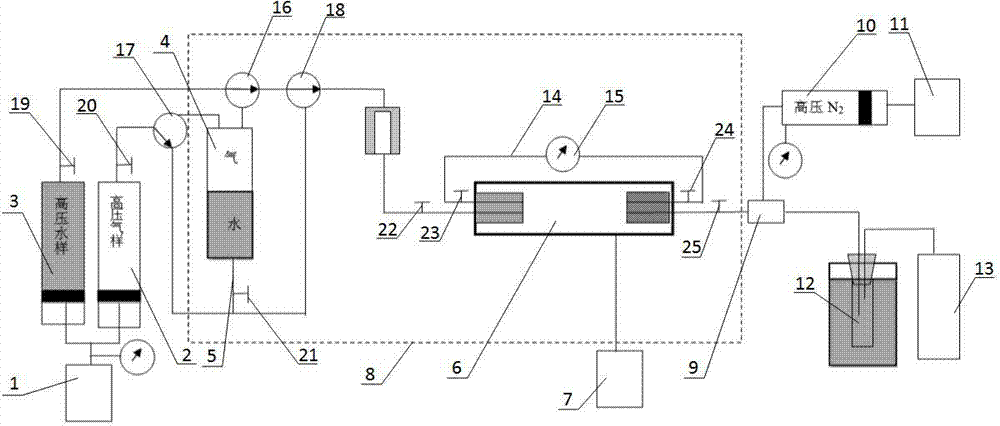
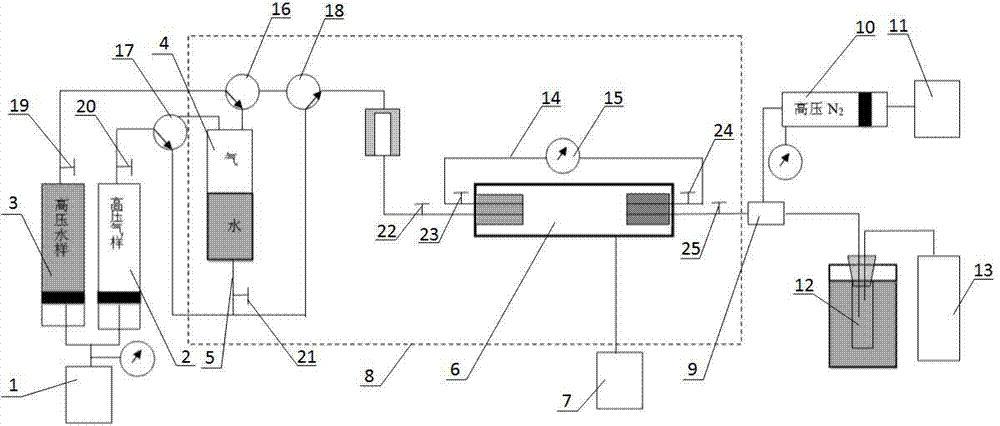
The invention discloses a determining method for a stratum high-temperature high-pressure gas-phase and water-phase relative permeability curve. The determining method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a rock core; S2, preparing fluid; S3, carrying out a single separation test on balance gas and balance stratum water; S4, saturating the rock core with water; S5, carrying out a connecting flow and raising the temperature to generate a pressure; S6, carrying out a balance water-phase permeability Kw test; S7, carrying out a gas-driving-water process relative permeability test; S8, correcting an accumulated water yield amount W(t) and an accumulated gas yield amount G(t); converting a value recorded under a ground condition to a stratum condition; and S9, calculating a water-phase relative permeability rate Krw and a gas-phase relative permeability rate Krg at each moment, and a gas-containing saturation degree (Sge) of a rock sample outlet end face. The determining method for the stratum high-temperature high-pressure gas-phase and water-phase relative permeability curve has the beneficial effects that high-temperature and high-pressure conditions of a real gas deposit stratum are effectively simulated and the influences on rocks and the fluid by the high-temperature and high-pressure conditions of the stratum are sufficiently considered; a determined result meets the actual production and the usable value of experimental data is high; the disadvantages in an existing determining method are overcome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
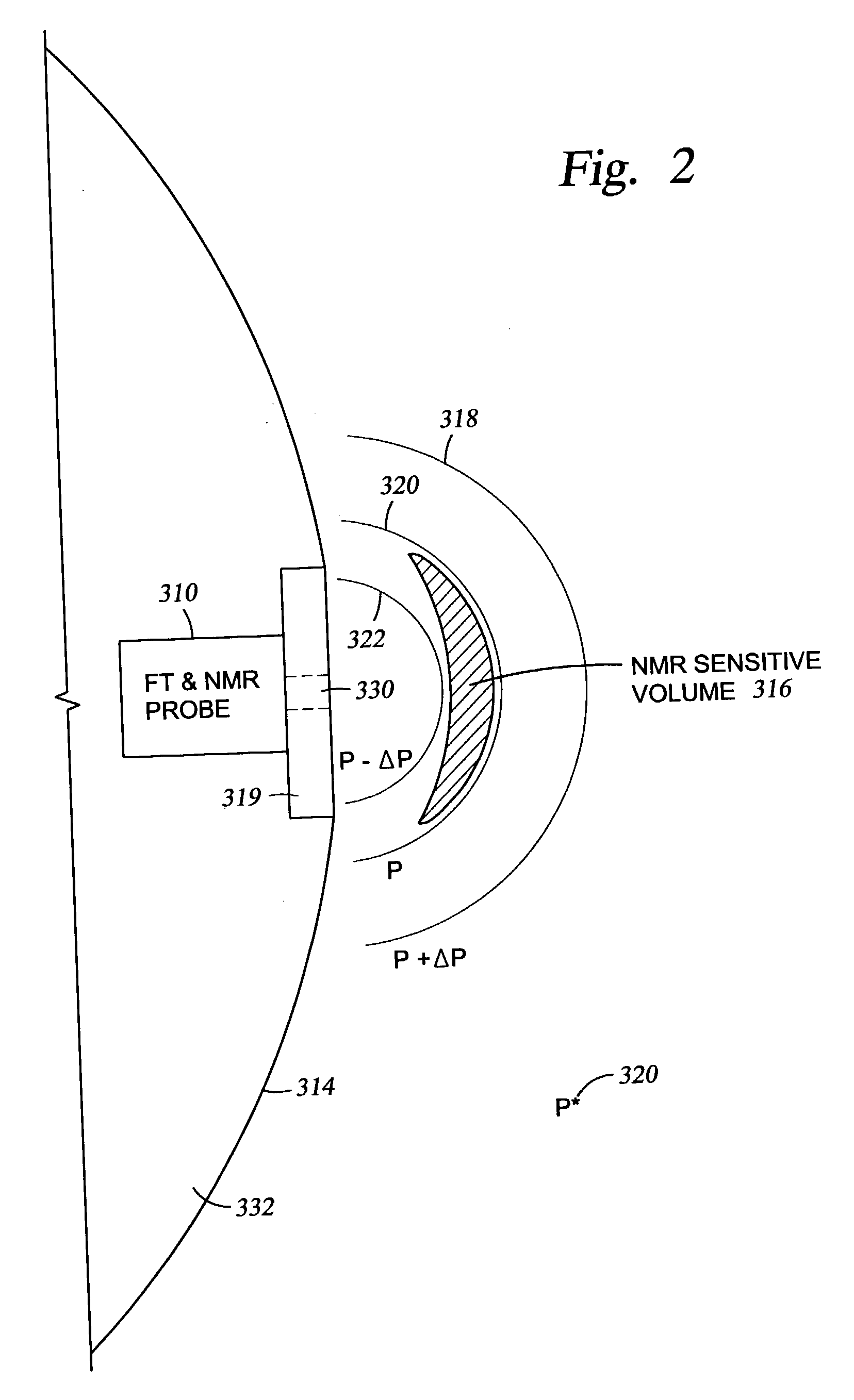
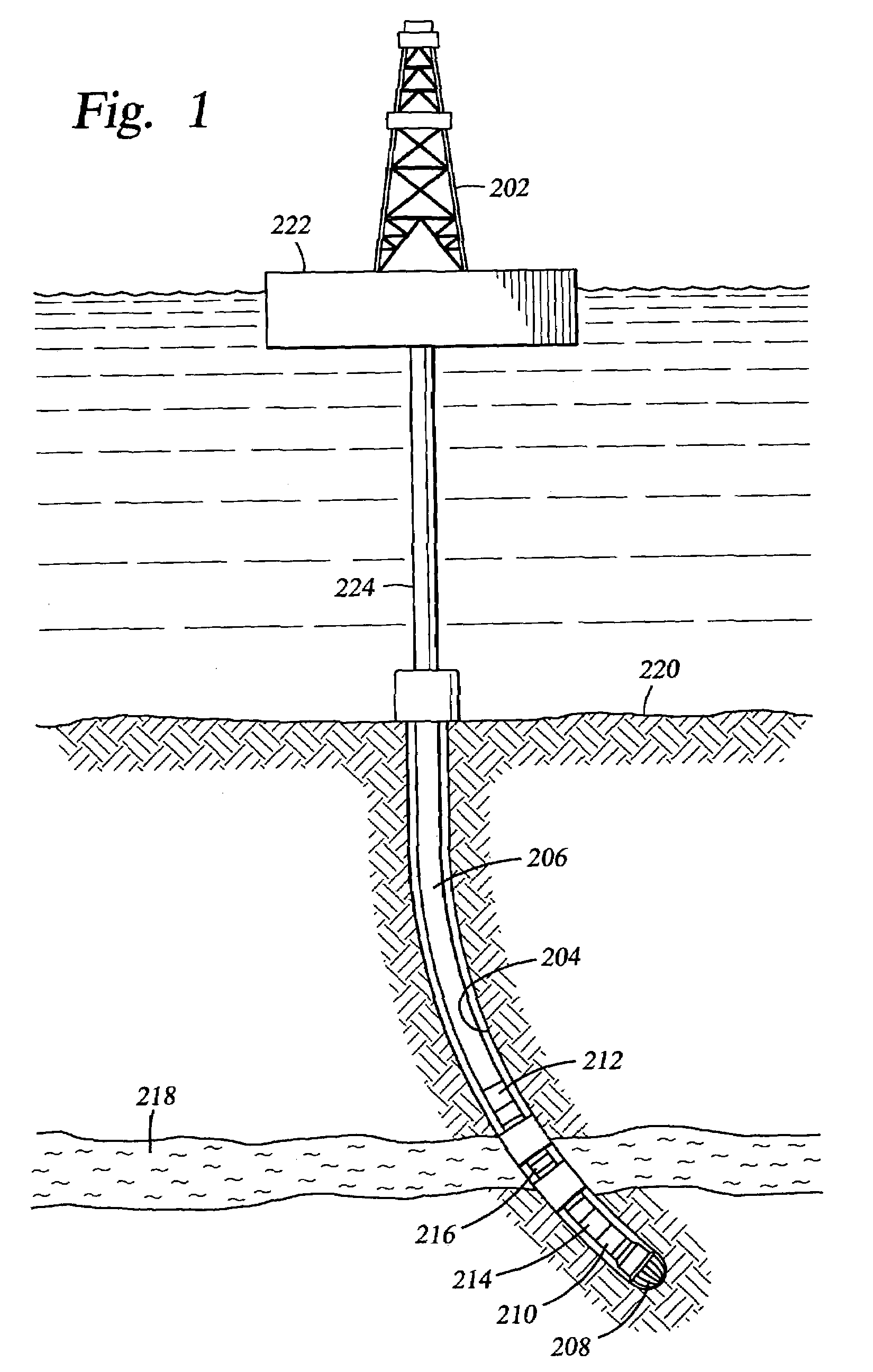
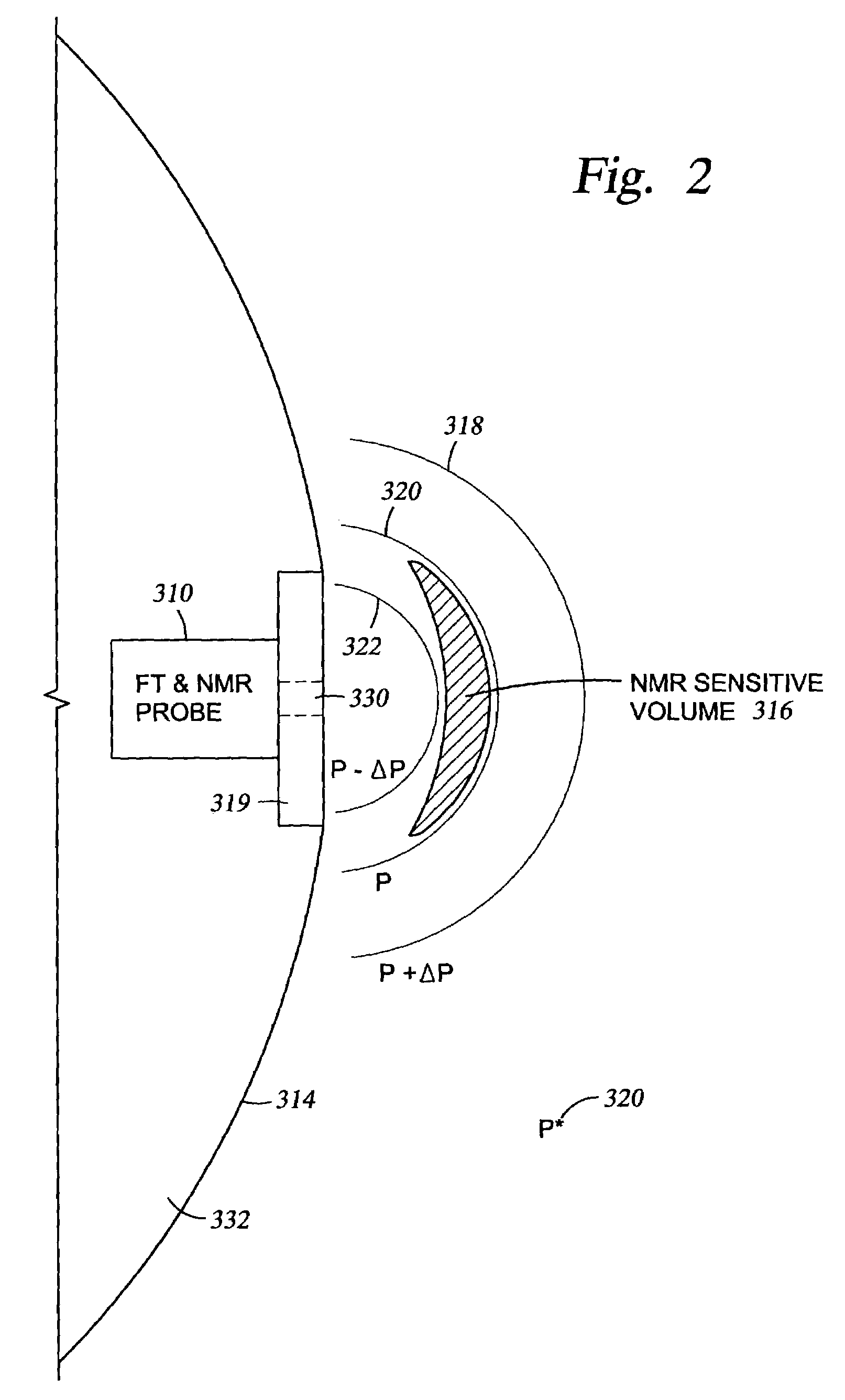
Method and apparatus for combined NMR and formation testing for assessing relative permeability with formation testing and nuclear magnetic resonance testing
InactiveUS20040055745A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Formation testing, resistivity and NMR measurements are used concurrently to determine a relative permeability representative of a formation surrounding the borehole. A method and apparatus is provided for accurate determination of the relative permeability for a formation by measuring saturation levels in a region of interest determined from resistivity or NMR readings versus time during formation draw down pressure testing. The method and apparatus determines and effective permeability over time for various saturation levels to determine the relative permeability for the formation at each saturation level and also enables determination of the efficacy of utilizing completion fluids in the formation to increase formation productivity. The method and apparatus enables more accurate determination of effective permeability and the irreducible saturation level. The method and apparatus also provides for determination of whether a pad is sealed properly against a borehole wall and determines if a probe is clogged.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Permeability-modifying drilling fluids and methods of use
InactiveUS20050155796A1Reduce penetrationLiquid/gas jet drillingFluid removalWater solubleRelative permeability
The present invention provides drilling fluids that comprise a base fluid and a water-soluble relative permeability modifier. In addition, the present invention provides methods of reducing the permeability of a subterranean formation to aqueous-based fluids during the drilling phase that comprises providing a water-soluble relative permeability modifier; and placing the water-soluble relative permeability modifier into the subterranean formation during the drilling phase. The present invention provides methods of drilling a well bore in a subterranean formation comprising providing a drilling fluid that comprises a base fluid and a water-soluble relative permeability modifier, and placing the drilling fluid in the subterranean formation. The water-soluble relative permeability modifiers of the present invention generally may comprise hydrophilically modified polymers, hydrophobically modified polymers, or water-soluble polymers without hydrophobic or hydrophilic modification.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Drill-in fluids and associated methods
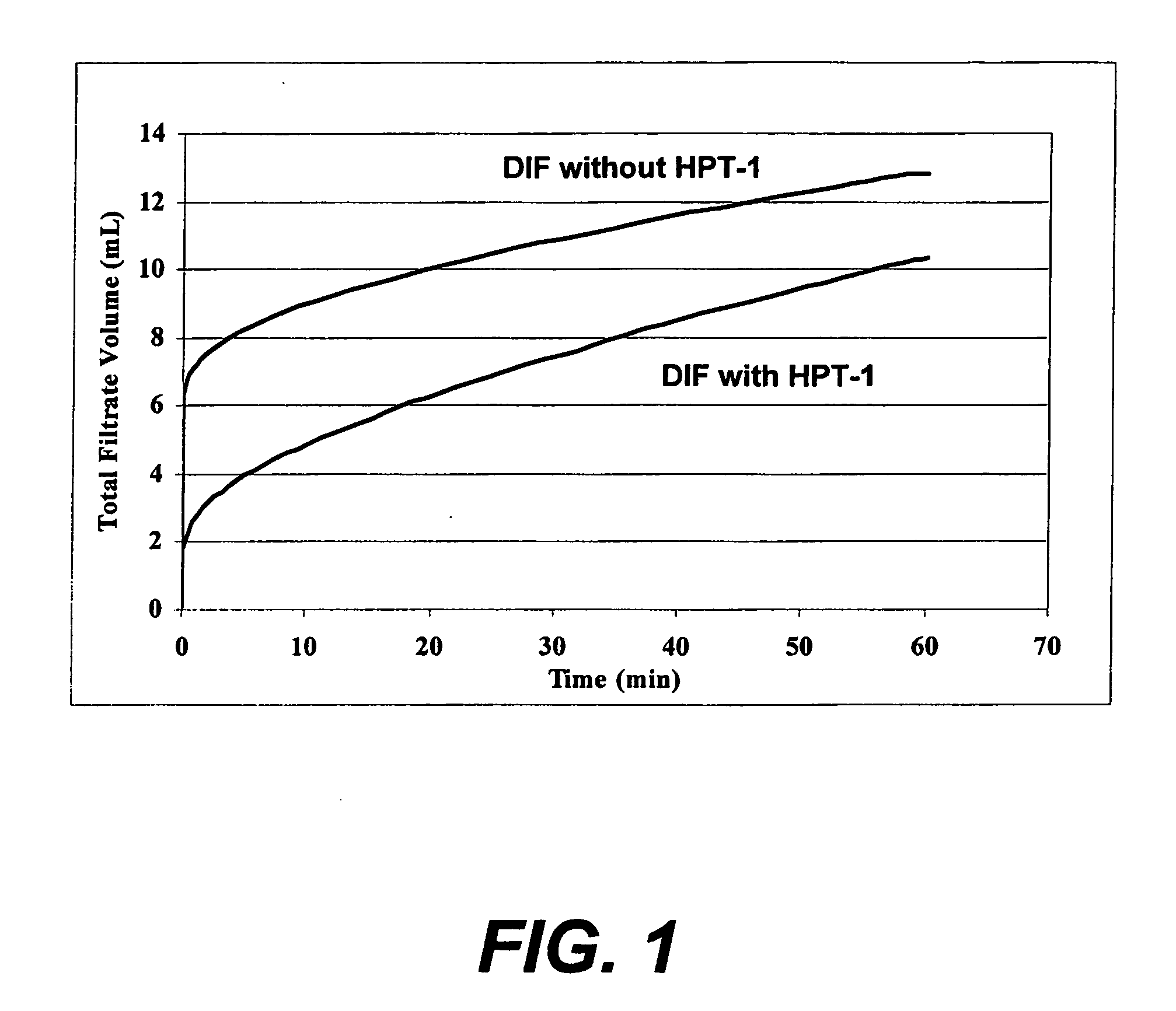
InactiveUS20080070807A1Fluid loss through the self-degrading filter cake is reducedLiquid/gas jet drillingFluid removalRelative permeabilityDrill
Of the many methods provided, in one embodiment, the present invention provides a method comprising: placing a drill-in fluid in a subterranean formation, the drill-in fluid comprising an aqueous base fluid, a viscosifier, a relative permeability modifier fluid loss control additive, and a degradable bridging agent comprising a degradable material capable of undergoing an irreversible degradation downhole; and forming a self-degrading filter cake comprising the bridging agent upon a surface within the formation whereby fluid loss through the self-degrading filter cake is reduced.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
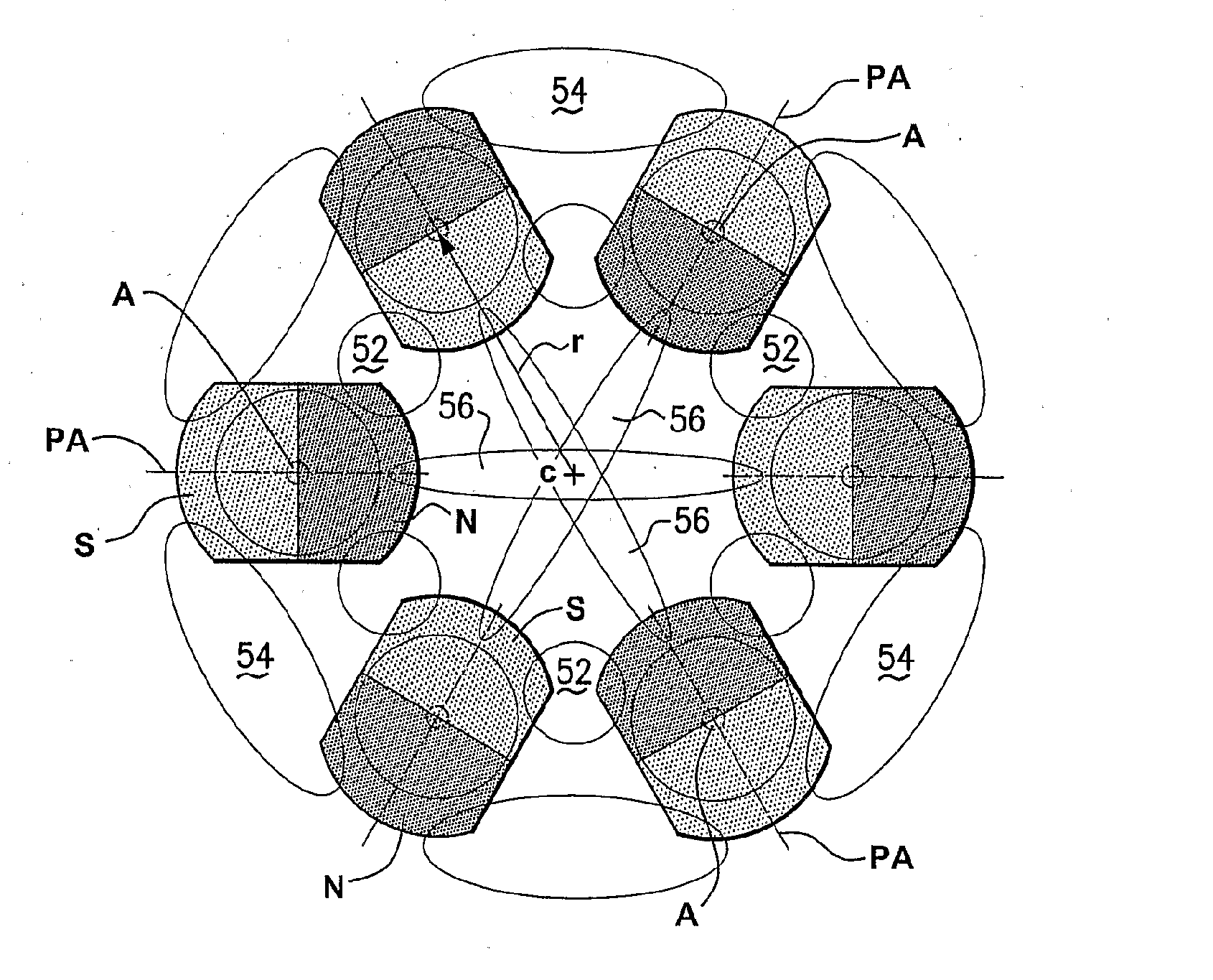
Magnet Arrays
InactiveUS20090027149A1Expand the field of viewDoubling numberElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic reluctancePole piece
Method and device for self-regulated flux transfer from a source of magnetic energy into one or more ferromagnetic work pieces, wherein a plurality of magnets, each having at least one N-S pole pair defining a magnetization axis, are disposed in a medium having a first relative permeability, the magnets being arranged in an array in which gaps of predetermined distance are maintained between neighboring magnets in the array and in which the magnetization axes of the magnets are oriented such that immediately neighboring magnets face one another with opposite polarities, such arrangement representing a magnetic tank circuit in which internal flux paths through the medium exist between neighboring magnets and magnetic flux access portals are defined between oppositely polarized pole pieces of such neighboring magnets, and wherein at least one working circuit is created which has a reluctance that is lower than that of the magnetic tank circuit by bringing one or more of the magnetic flux access portals into close vicinity to or contact with a surface of a ferromagnetic body having a second relative permeability that is higher than the first relative permeability, whereby a limit of effective flux transfer from the magnetic tank circuit into the working circuit will be reached when the work piece approaches magnetic saturation and the reluctance of the work circuit substantially equals the reluctance of the tank circuit.
Owner:MAGSWITCH TECH WORLDWIDE PTY LTD
Method of Controlling Water Production Through Treating Proppants With RPMS
ActiveUS20110098377A1Prevent water flowFluid removalDrilling compositionWater productionRelative permeability
Water production from a subterranean formation is inhibited or controlled by pumping a fluid containing coated particles through a wellbore into the formation. The particles have been previously coated with a relative permeability modifier (RPM). Upon contact with water, the RPM coating expands or swells and inhibits and controls the production of water. The RPM may be a water hydrolyzable polymer having a weight average molecular weight greater than 100,000. The particles may be conventional proppants or gravel.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method For Simulating Fractional Multi-Phase/Multi-Component Flow Through Porous Media
ActiveUS20130018641A1Ease of evaluationAccurate representationVolume/mass flow measurementGeomodellingPorous mediumComputerized system
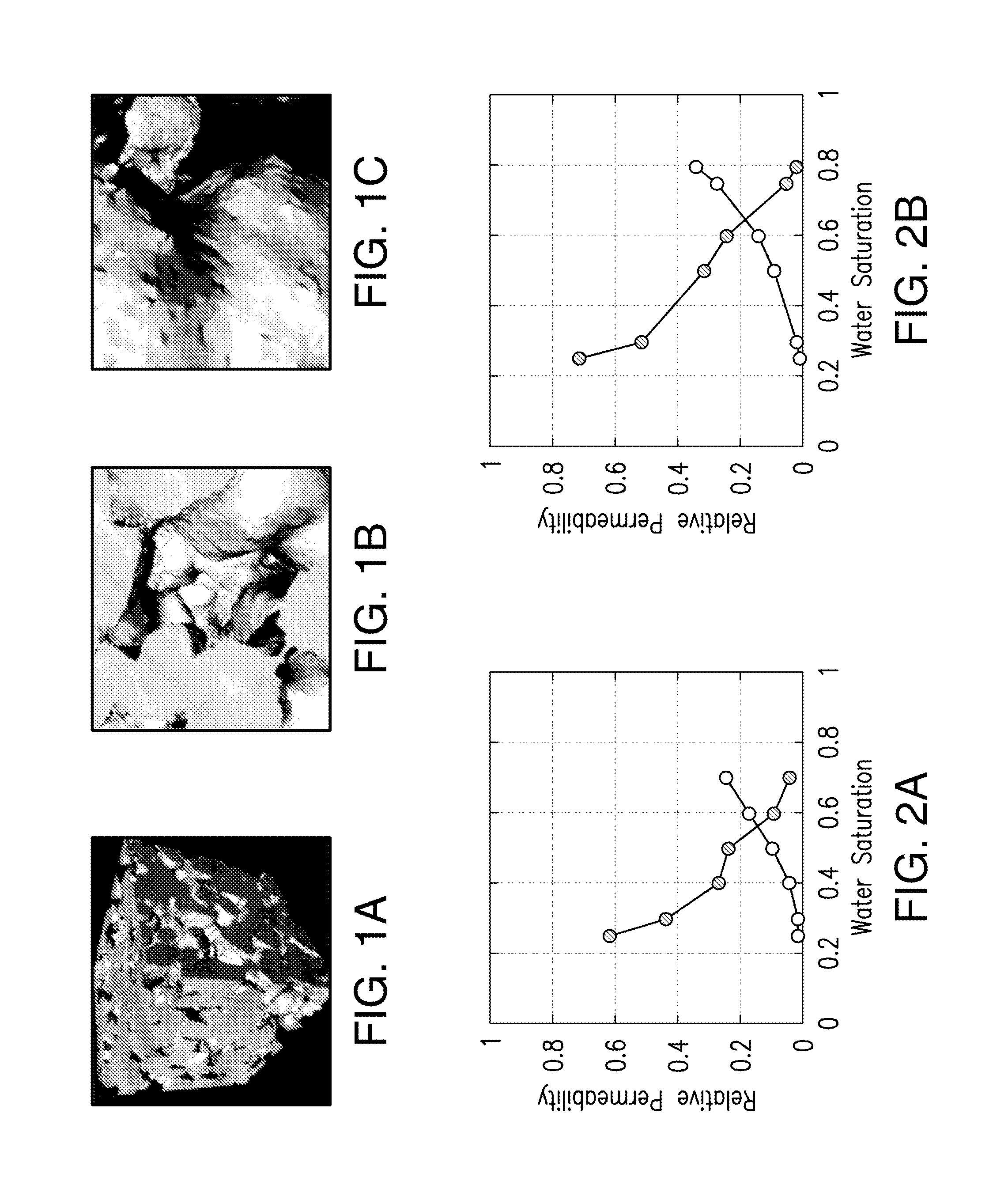
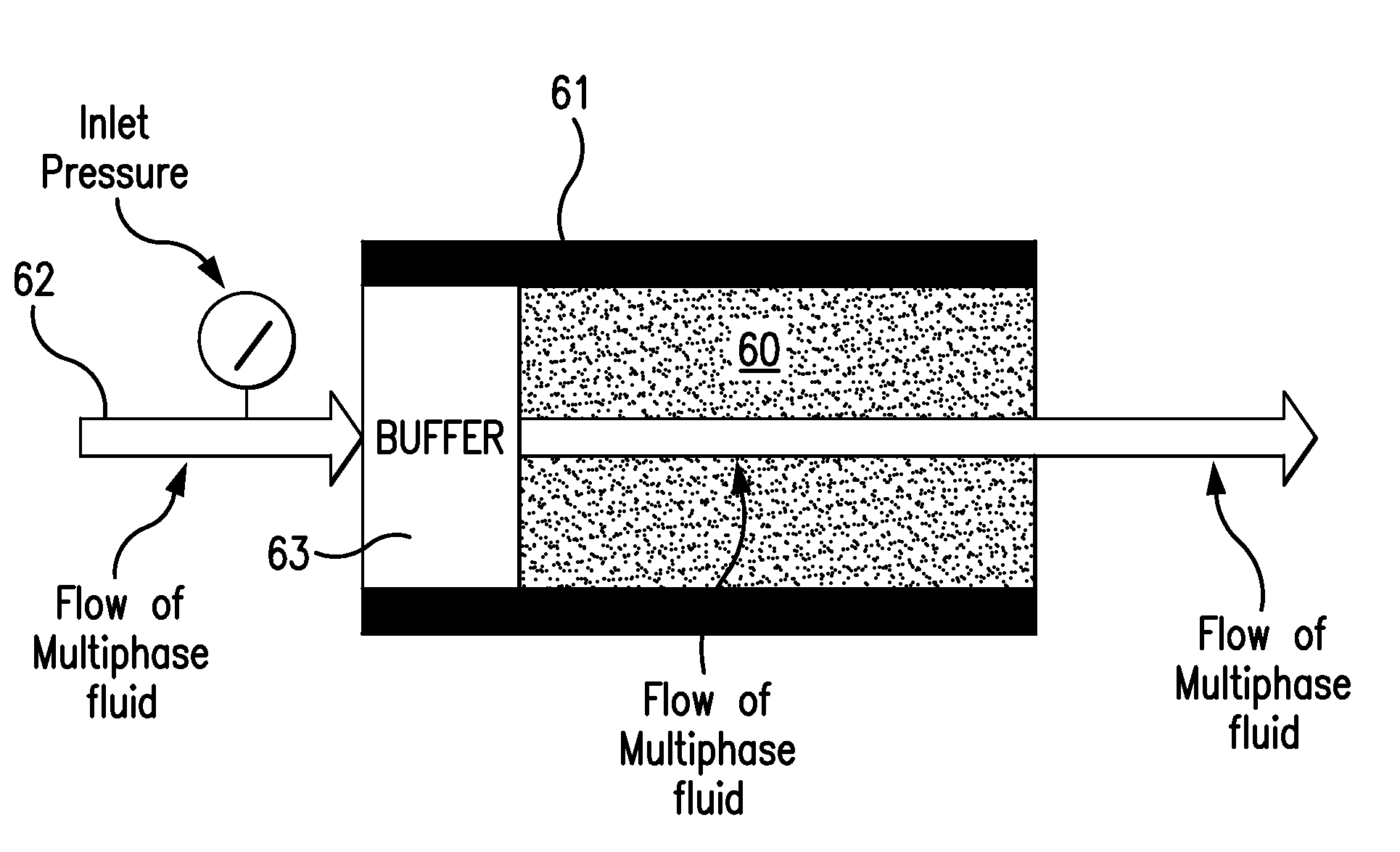
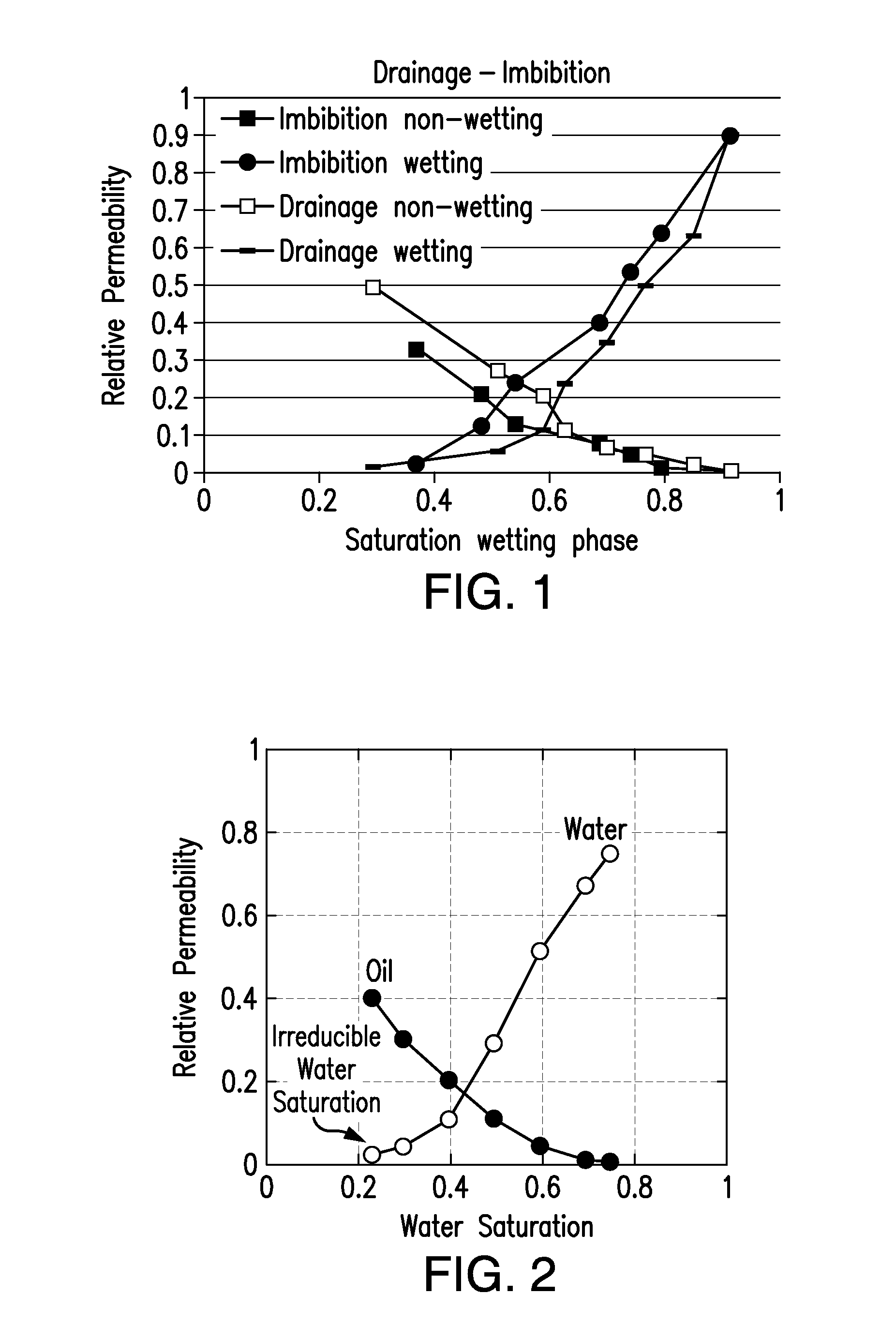
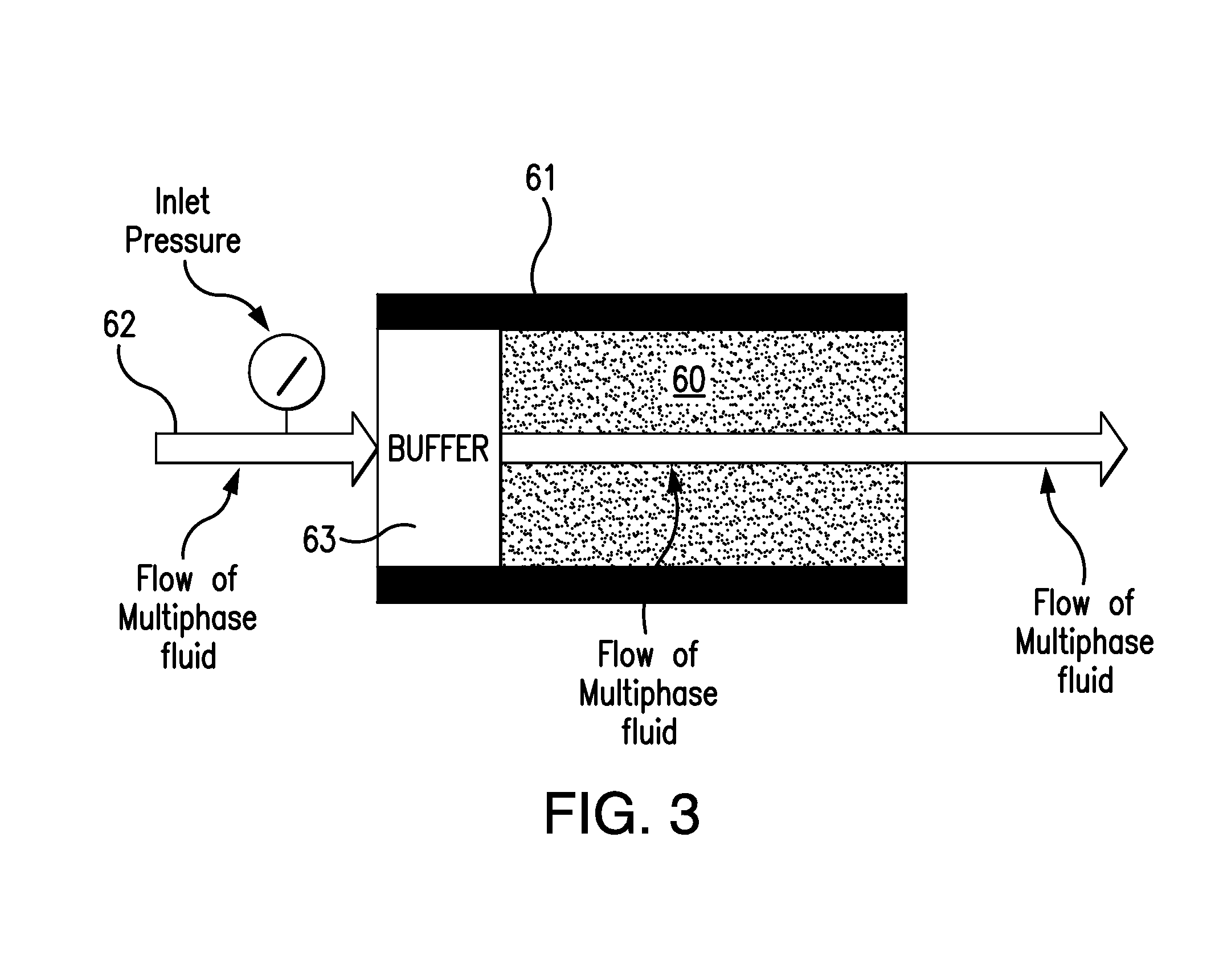
A method for computing or estimating fractional, multi-phase / multi-component flow through a porous medium employing a 3D digital representation of a porous medium and a computational fluid dynamics method to calculate flow rates, pressures, saturations, internal velocity vectors and other flow parameters is described. The method employs a unique method of introducing non-wetting and wetting fluids into the pores at the inlet face of the 3D digital representation of a porous medium and a novel process control application to achieve quasi-steady state flow at low inlet concentrations of non-wetting fluid. In addition, the method of the present invention reduces the time required to simulate to complete the fluid dynamic calculations. The resulting values of flow of non-wetting fluid, wetting fluid, saturation, and other parameters are used to generate plots of relative permeability imbibition and drainage curves. Computerized systems and programs for performing the method are also provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods for controlling water and sand production in subterranean wells
Methods comprising introducing a relative permeability modifier fluid into at least a portion of a subterranean formation to form a treated portion of the subterranean formation; and introducing a consolidating agent into the treated portion of the subterranean formation so as to transform at least a section of the treated portion of the subterranean formation into a consolidated region. In some embodiments, the subterranean formation may have been previously hydraulically fracture-stimulated.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Metal polyporous material with gradient pore structure and preparation thereof
The invention provides a metal porous material with a gradient pore structure, which is formed by at least two porous layers with different pore diameter. The pore diameter of the metal porous material gradually decreases or gradually increases with the thickness direction of the material; a bottom layer of the porous layers is a macropore layer used as a support body; a surface layer of the porous layers is a pore layer used as a filtering precision control layer; the material of the macropore layer is a composite wire gauze, a metal fiber felt or a powder sintered metal porous material; and the material of the pore layer is superfine metal powder or superfine metal fiber. A method for preparing the metal porous material comprises a step of using spraying, dipping or centrifugal coating method to manufacture at least one pore layer on the surface of the support body. Compared with the prior metal porous material in the same grade, the metal porous material with the gradient pore structure has the advantages of obviously raising permeability coefficient, well solving the contradiction between the pore diameter and relative permeability coefficient of the metal porous material and having a simple process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Drill-in fluids and associated methods
Of the many compositions provided herein, in one embodiment, the present invention provides a drill-in fluid comprising an aqueous base fluid, a viscosifier, a relative permeability modifier fluid loss control additive, and a degradable bridging agent comprising a degradable material capable of undergoing an irreversible degradation downhole.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Magnetic core and coil component using the same
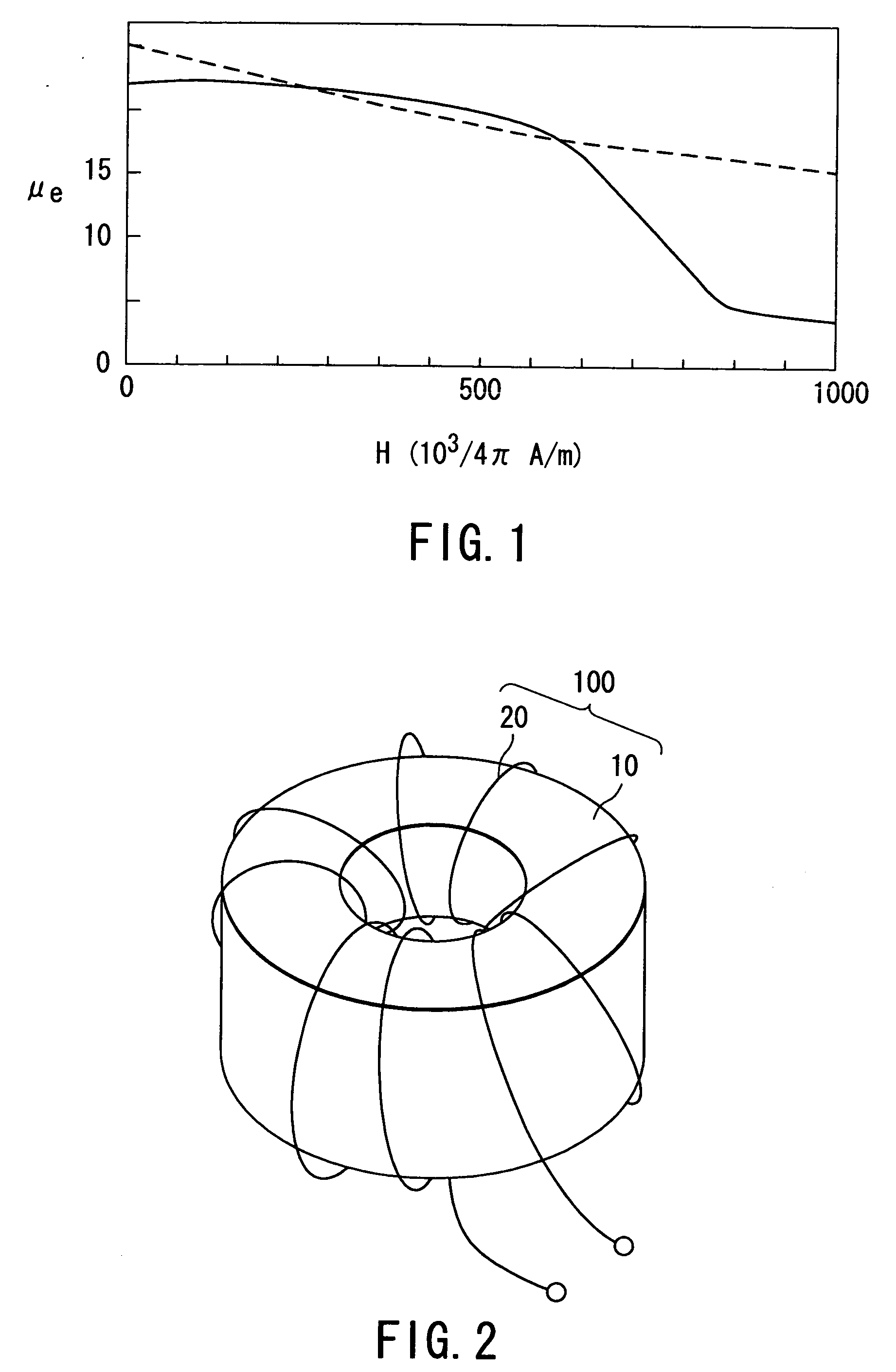
InactiveUS20050007232A1Inorganic material magnetismTransformers/inductances magnetic coresRelative permeabilityMaterials science
A magnetic core is obtained by hardening or curing a mixture of magnetic powder and resin. The magnetic core shows a superior DC bias characteristic which does not become drastically saturated but is gently saturated even beyond 1000*103 / 4π [A / m]. Therefore, the magnetic core has sufficient relative permeability more than ten.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
Methods and compositions for reducing the production of water and stimulating hydrocarbon production from a subterranean formation
InactiveUS20060234874A1Reduce water productionPromote productionFluid removalFlushingRelative permeabilityHydrocarbon
The present invention relates to subterranean treatment fluids, and more particularly, the present invention relates to subterranean treatment fluids comprising relative permeability modifiers and methods for using such subterranean treatment fluids in subterranean operations to reduce the production of water from and stimulate hydrocarbon production in a subterranean formation. In certain embodiments, the methods of the present invention generally comprise the steps of providing a permeability-modifying aqueous treatment fluid comprising a relative permeability modifier and contacting a subterranean formation with the permeability-modifying aqueous treatment fluid. Optionally, the permeability-modifying aqueous treatment fluid may be injected in the subterranean formation at a pressure sufficient to create or enhance at least one fracture therein. In another embodiment, the relative permeability modifier may be provided by appropriate reaction in situ.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Small low profile antennas using high impedance surfaces and high permeability, high permittivity materials
InactiveUS6967621B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateGround plane
A low profile antenna includes an antenna and a ground plane structure operatively associated with the antenna. The ground plane structure has a generally planar surface, at least one protrusion extending from the planar surface and a dielectric substrate supported by the planar surface. The dielectric substrate includes a relative permeability (μ) of greater than or equal to about one and a relative permittivity (ε) of greater than or equal to about one.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Method for testing gas-water relative permeability curve by using tight sandstone steady state method
ActiveCN106525690AIn line with the actual situationHigh reference valuePreparing sample for investigationPermeability/surface area analysisMeasurement pointDisplacement pressure
The invention provides a method for testing a gas-water relative permeability curve by using a tight sandstone steady state method. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a stone core; preparing simulation stratum water; vacuuming till the simulation stratum water is saturated; connecting an experiment device and heating to experiment temperature; putting the stone core into the experiment device, pressurizing, releasing the pressure, testing the mass and the liquid phase permeability of the stone core; establishing irreducible water saturation; controlling the flowing speed of gas, and injecting the simulation stratum water at a relatively slow flowing speed, after the gas flow at an outlet is stable, increasing the flowing speed of liquid, and measuring a next point till displacement pressure meets the maximum set value and the flowing speed of the gas at the outlet is reduced to 0.1mL / minute, and terminating the experiment; according to improved phase permeability equations, calculating water saturation and relative permeability of different points. By adopting the method, two-phase permeation characteristics in the tight gas reservoir production process under stratum conditions can be simulated, the influence of the temperature on gas-water viscosity is taken into account, the influence of pressurization on the water content of the stone core is also taken into account, the irreducible water saturation and the relative permeability curve can be relatively accurate and reliable, and high-value data can be provided for gas reservoir production evaluation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and apparatus for combined NMR and formation testing for assessing relative permeability with formation testing and nuclear magnetic resonance testing
InactiveUS7032661B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Formation testing, resistivity and NMR measurements are used concurrently to determine a relative permeability representative of a formation surrounding the borehole. A method and apparatus is provided for accurate determination of the relative permeability for a formation by measuring saturation levels in a region of interest determined from resistivity or NMR readings versus time during formation draw down pressure testing. The method and apparatus determines and effective permeability over time for various saturation levels to determine the relative permeability for the formation at each saturation level and also enables determination of the efficacy of utilizing completion fluids in the formation to increase formation productivity. The method and apparatus enables more accurate determination of effective permeability and the irreducible saturation level. The method and apparatus also provides for determination of whether a pad is sealed properly against a borehole wall and determines if a probe is clogged.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
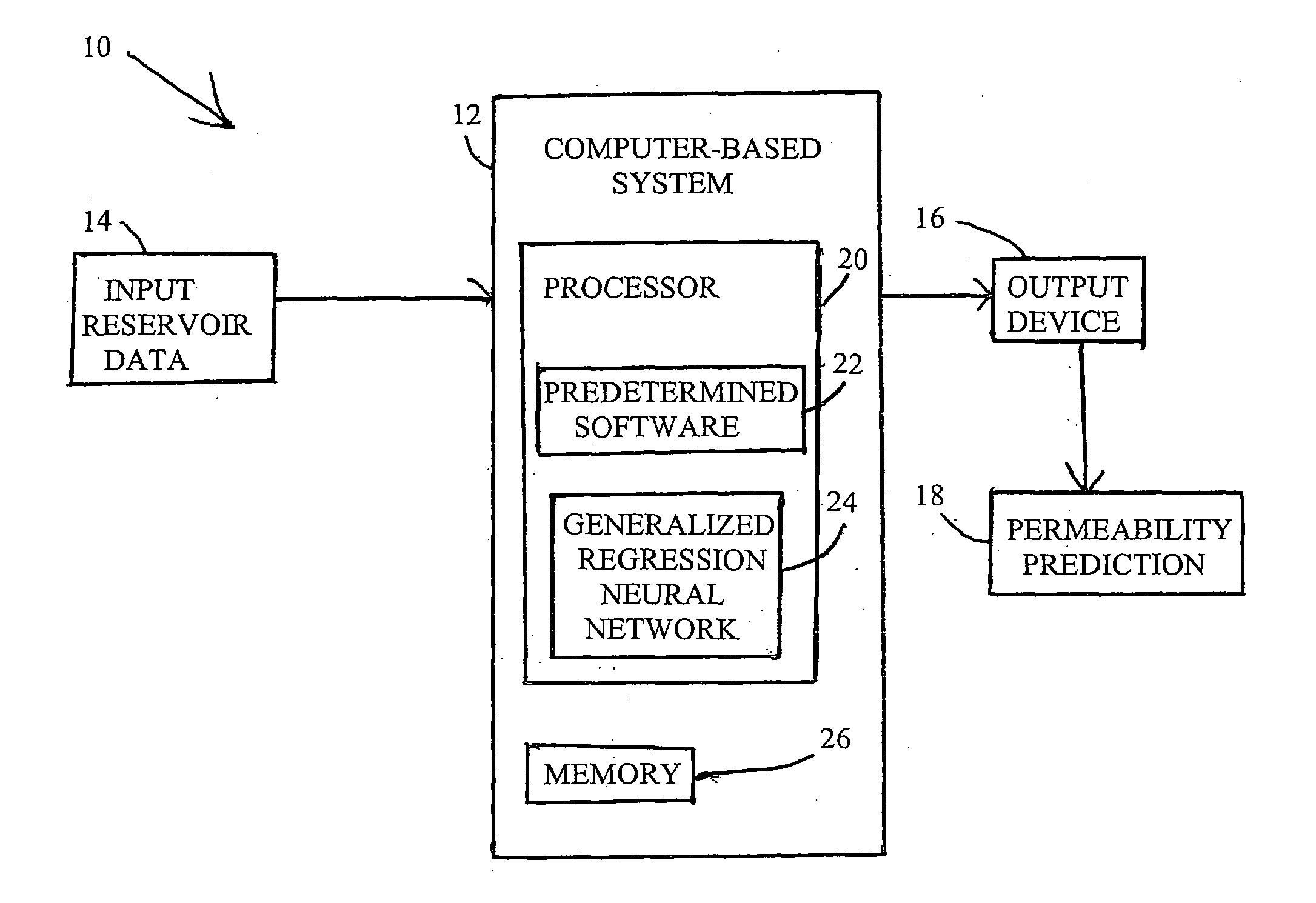
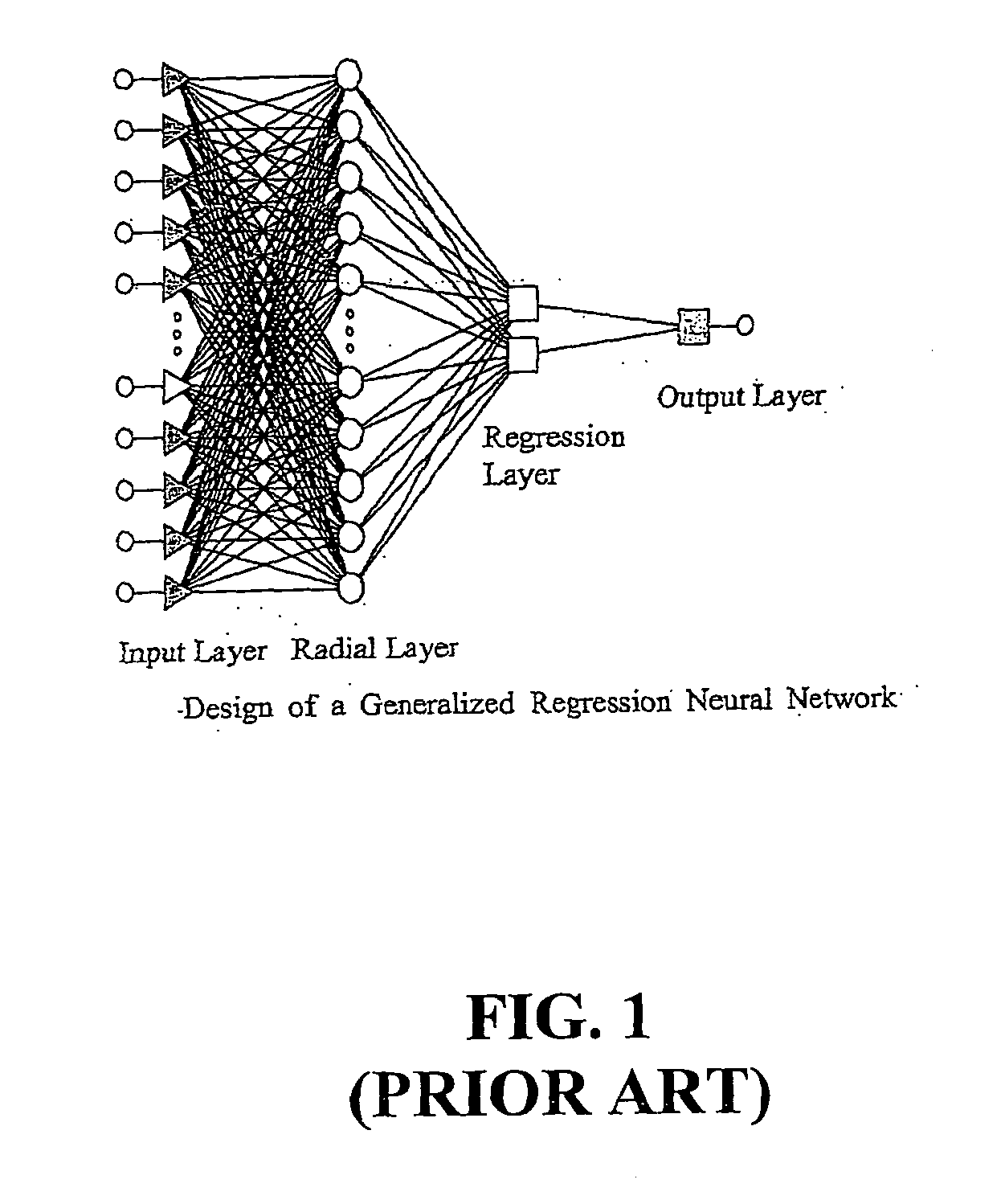
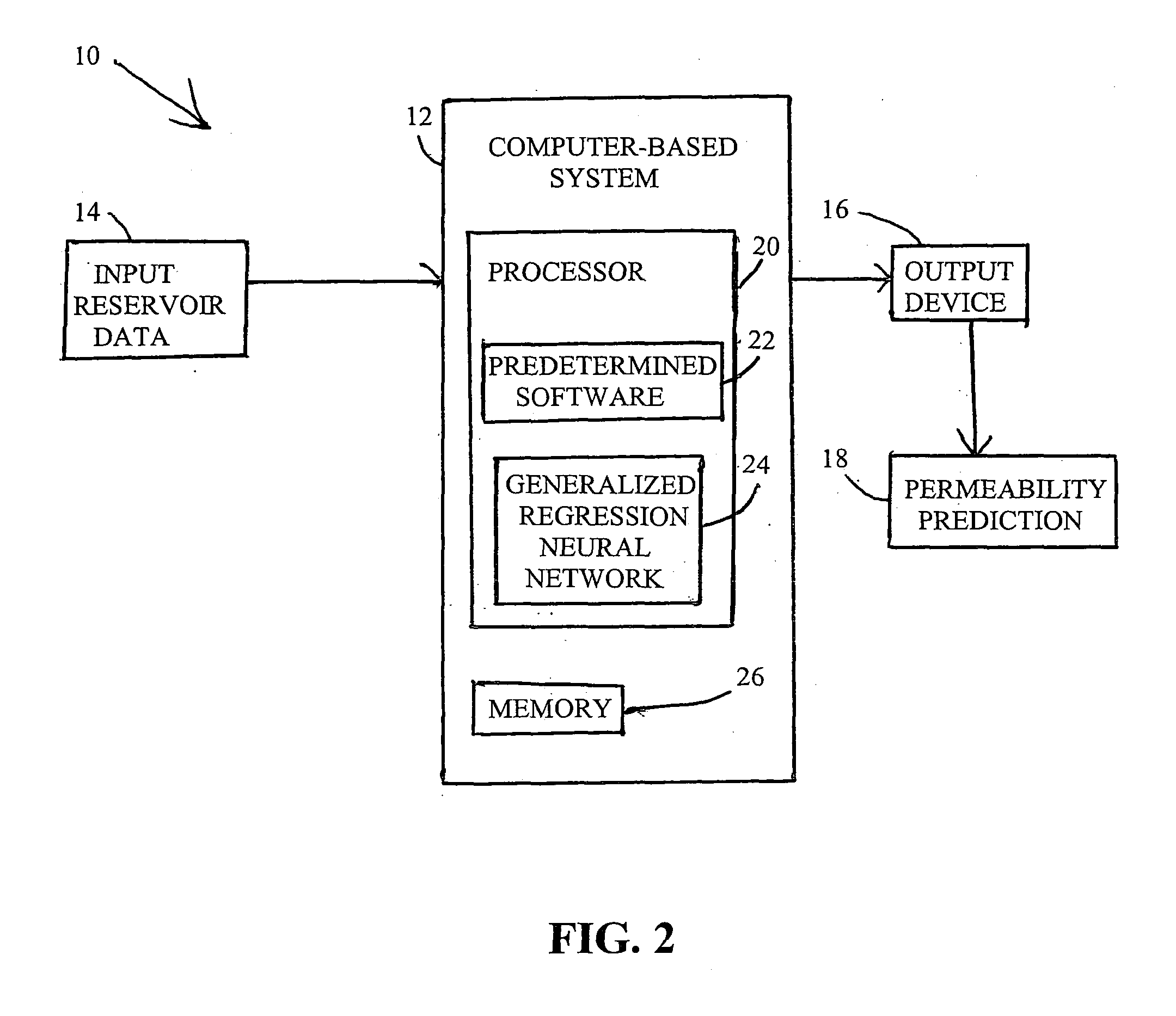
Artificial neural net work models for determining relative permeability of hydrocarbon reservoirs
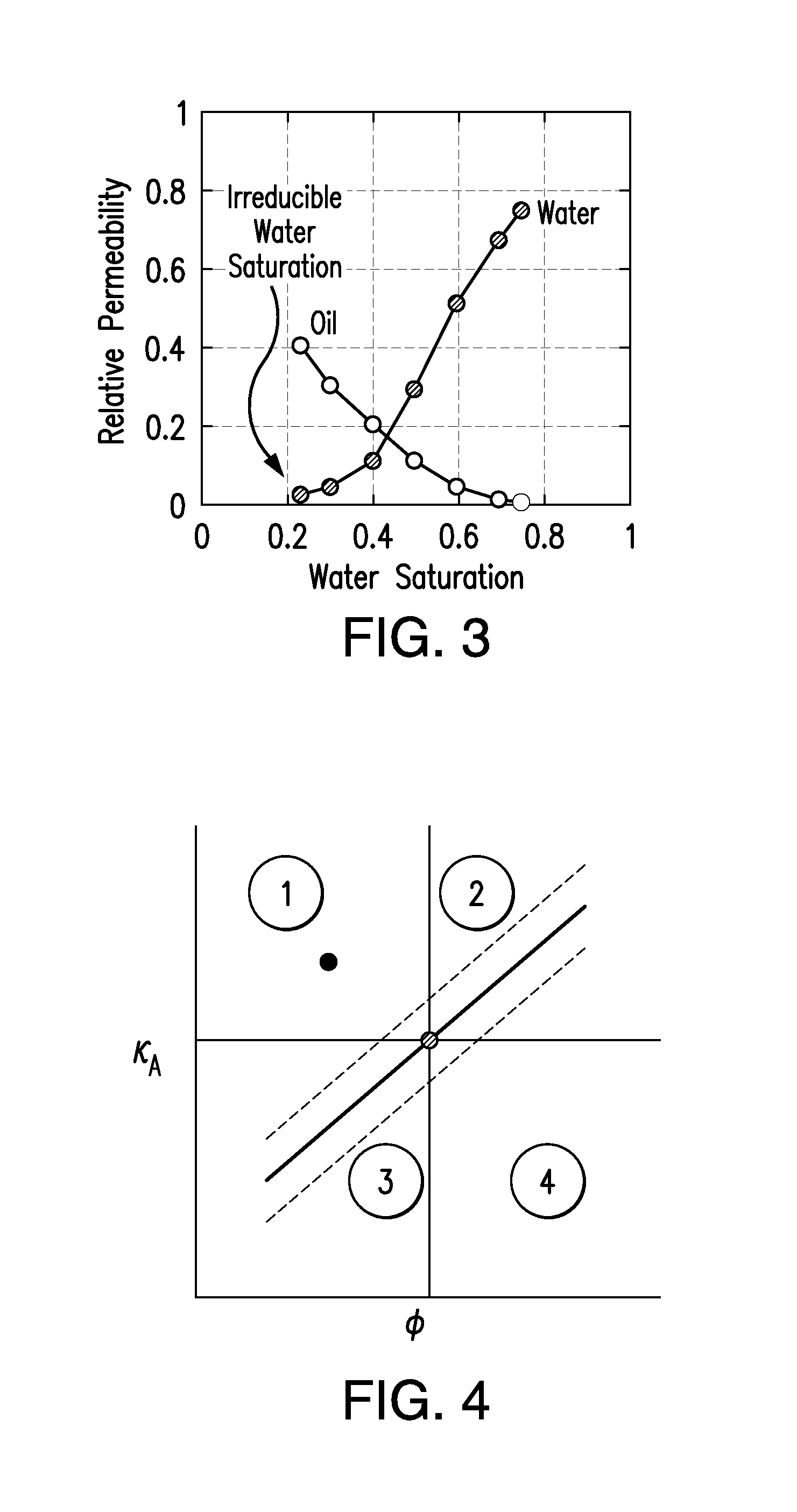
A system and method for modeling technology to predict accurately water-oil relative permeability uses a type of artificial neural network (ANN) known as a Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN) The ANN models of relative permeability are developed using experimental data from waterflood core test samples collected from carbonate reservoirs of Arabian oil fields Three groups of data sets are used for training, verification, and testing the ANN models Analysis of the results of the testing data set show excellent correlation with the experimental data of relative permeability, and error analyses show these ANN models outperform all published correlations
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Methods and compositions for the diversion of aqueous injection fluids in injection operations
An exemplary method of the present invention for performing an injection operation includes providing a water-soluble relative permeability modifier, introducing the water-soluble relative permeability modifier into a subterranean formation; and injecting an aqueous injection fluid into the subterranean formation after introducing the water-soluble relative permeability modifier. An exemplary permeability-modifying injection fluid of the present invention contains water-soluble relative permeability modifier. The water-soluble relative permeability modifiers of the present invention include hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymers, hydrophilically modified water-soluble polymers, and water-soluble polymers without hydrophobic or hydrophilic modification.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Device and method for testing gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation curve of high-temperature high-pressure high-sulfur-content gas reservoir
ActiveCN104568678ARapid determinationAccurate measurementSurface/boundary effectPermeability/surface area analysisGas phaseData acquisition
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing a gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation curve of a high-temperature high-pressure high-sulfur-content gas reservoir. The testing device comprises a displacement system, a stratum condition simulation system, a back-pressure system, a data testing system and a data acquisition system. The testing method comprises the following steps: selecting and treating a rock core; preparing rock core saturated stratum water and liquid sulfur; simulating a high-temperature and high-pressure environment of the stratum; determining the condition of liquid sulfur phase permeability under irreducible water saturation; performing a phase permeation test on filling of gas-liquid sulfur according to a set ratio; recording the amount VSi of liquid sulfur and the gas amount Vgi generated totally; correcting the stratum condition; calculating the relative permeability Krs of the liquid sulfur phase, the relative permeability Krg of the gas phase and the gas saturation Sg of a rock sample at each moment and the like. The device and the method disclosed by the invention can be used for safely, conveniently, rapidly, accurately and efficiently measuring the high-temperature high-pressure gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation data and providing scientific data support for making a reasonable development scheme for the high-sulfur-content gas reservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method For Evaluating Relative Permeability For Fractional Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Fluid Flow Through Porous Media
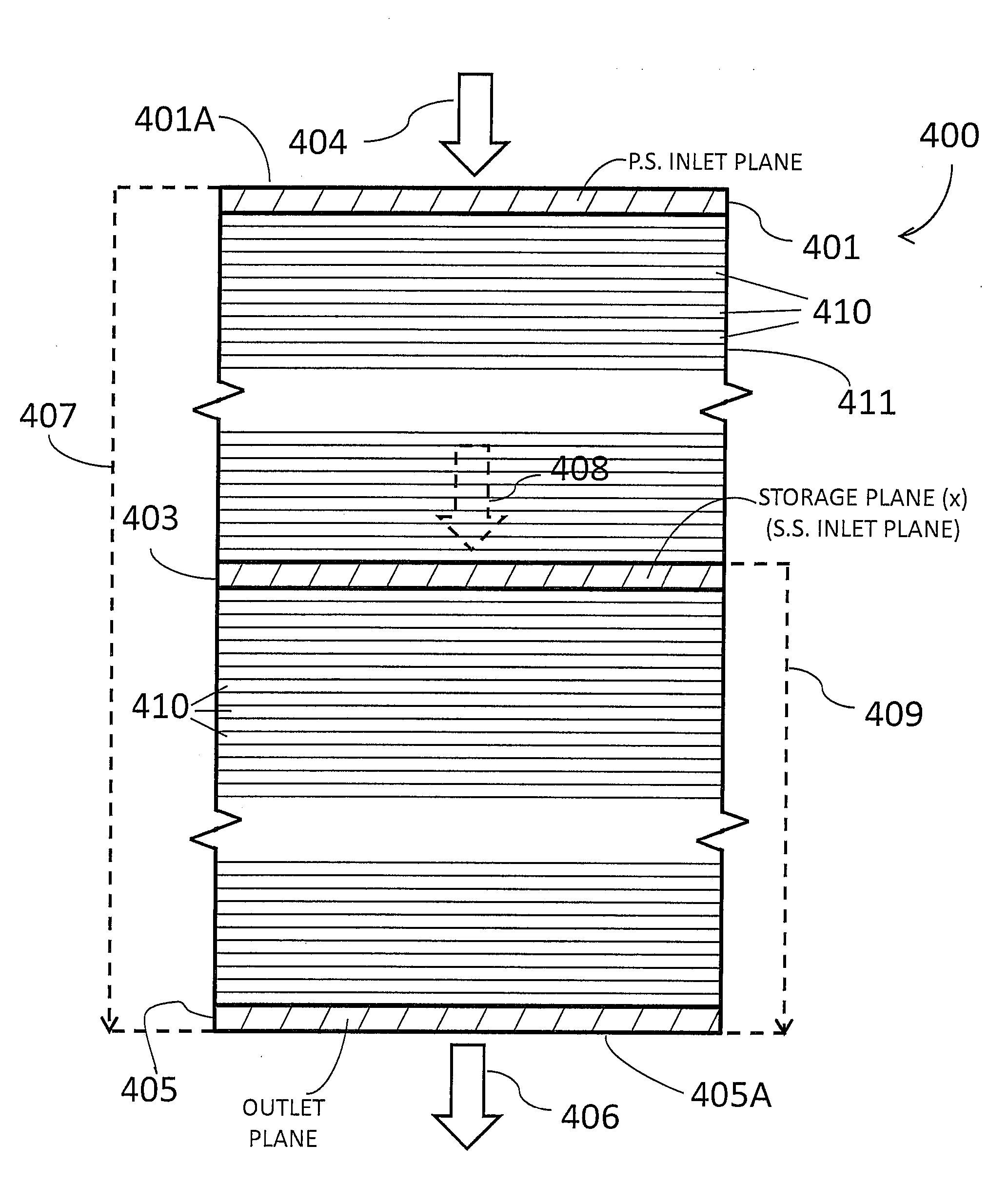
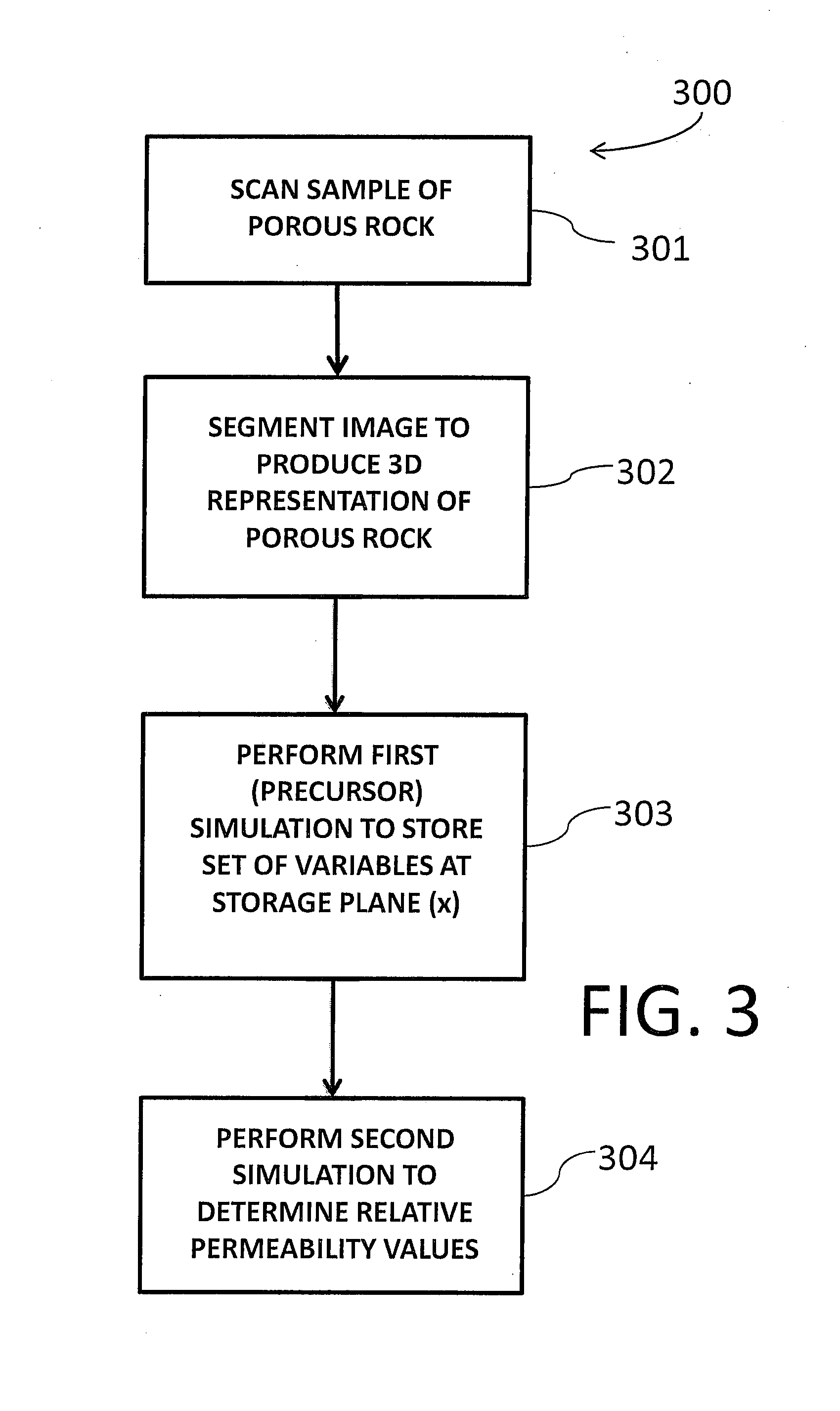
ActiveUS20140019053A1Improved evaluation and estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDesign optimisation/simulationDynamic methodFluid transport
A method for computing or estimating relative permeability for fractional multi-phase, multi-component fluid flow through a porous medium, which employs a 3D digital representation of a porous medium and a computational fluid dynamics method to calculate flow rates, pressures, saturations, velocities and other flow parameters, is described. The method employs a unique method which integrates a precursor simulation used to generate a set of variables like pressure, saturation and velocity distribution associated with a selected storage plane in the 3D digital representation of a porous medium, which variables are used as inlet condition in the workflow of a second simulation that can generate values of fractional flow rates, pressures, saturations, velocities, or other parameters of wetting and non-wetting phases, which can be used to compute or estimate relative permeability values or other fluid transport properties of the porous medium. Computerized systems and programs for performing the method are also provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com