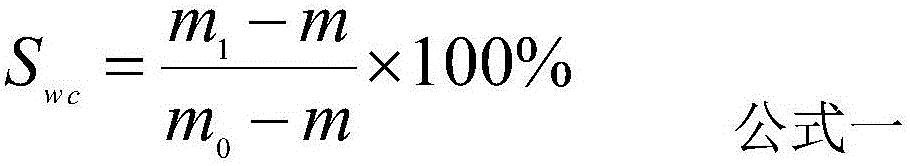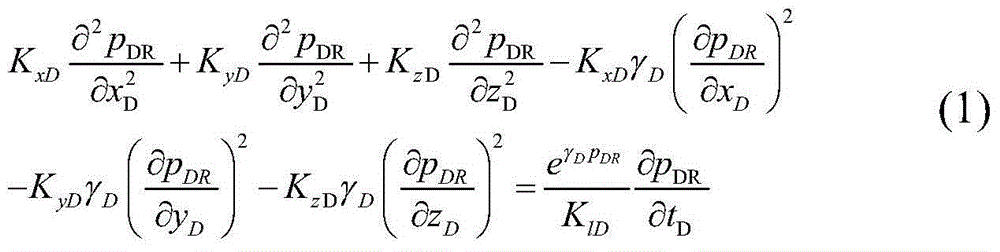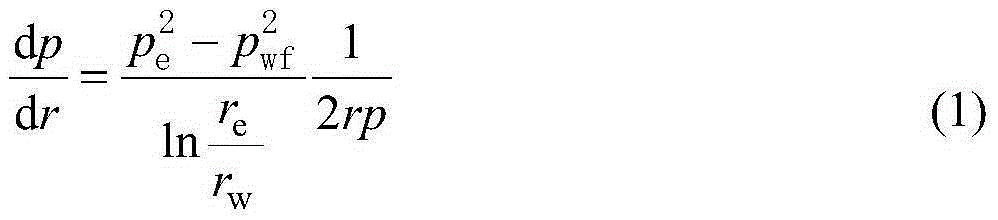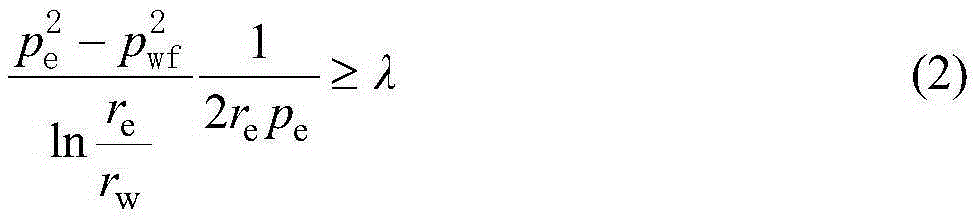Patents
Literature
199 results about "Tight gas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
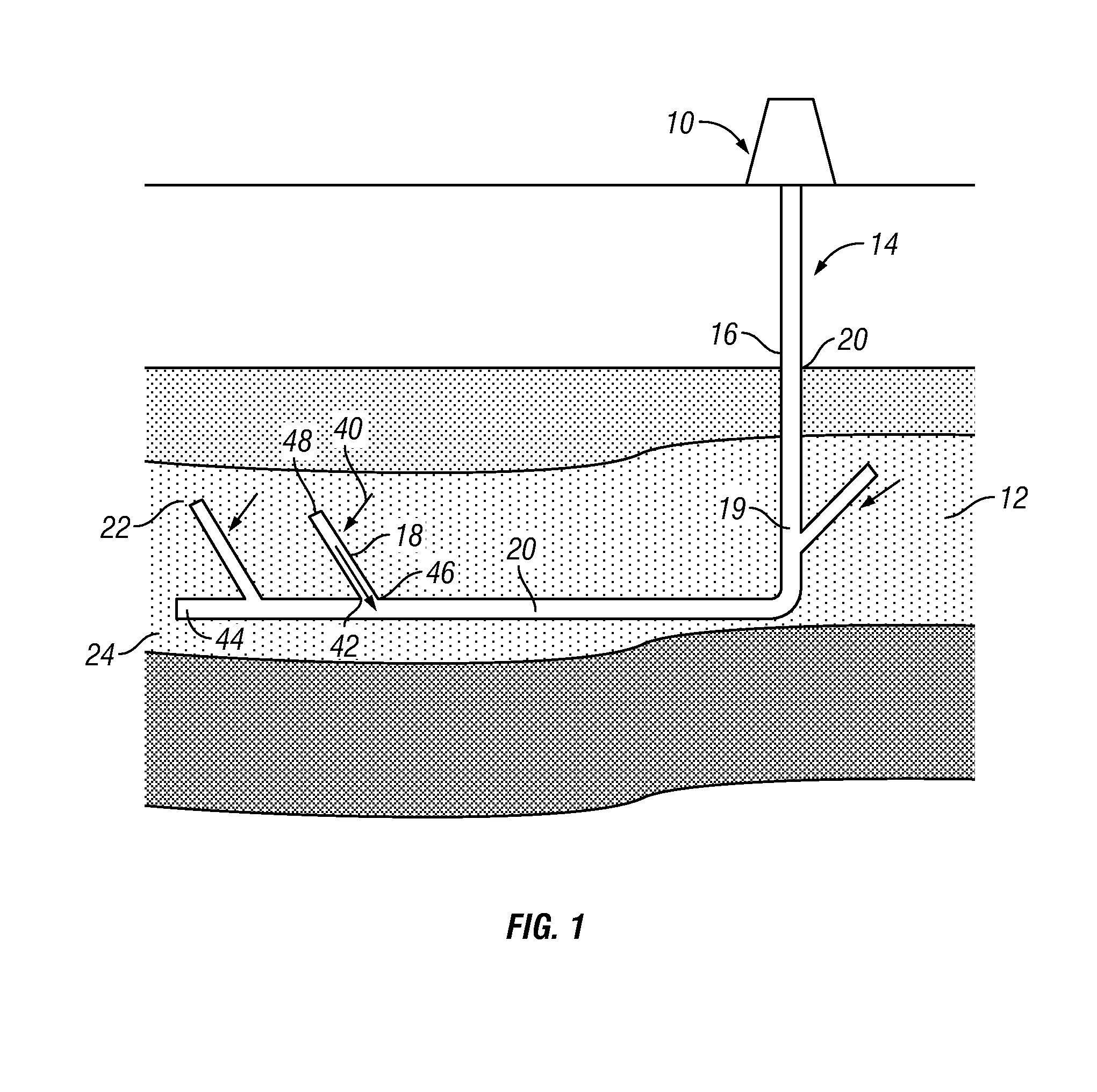
Tight gas is natural gas produced from reservoir rocks with such low permeability that massive hydraulic fracturing is necessary to produce the well at economic rates. Tight gas reservoirs are generally defined as having less than 0.1 millidarcy (mD) matrix permeability and less than ten percent matrix porosity. Although shales have low permeability and low effective porosity, shale gas is usually considered separate from tight gas, which is contained most commonly in sandstone, but sometimes in limestone. Tight gas is considered an unconventional source of natural gas.
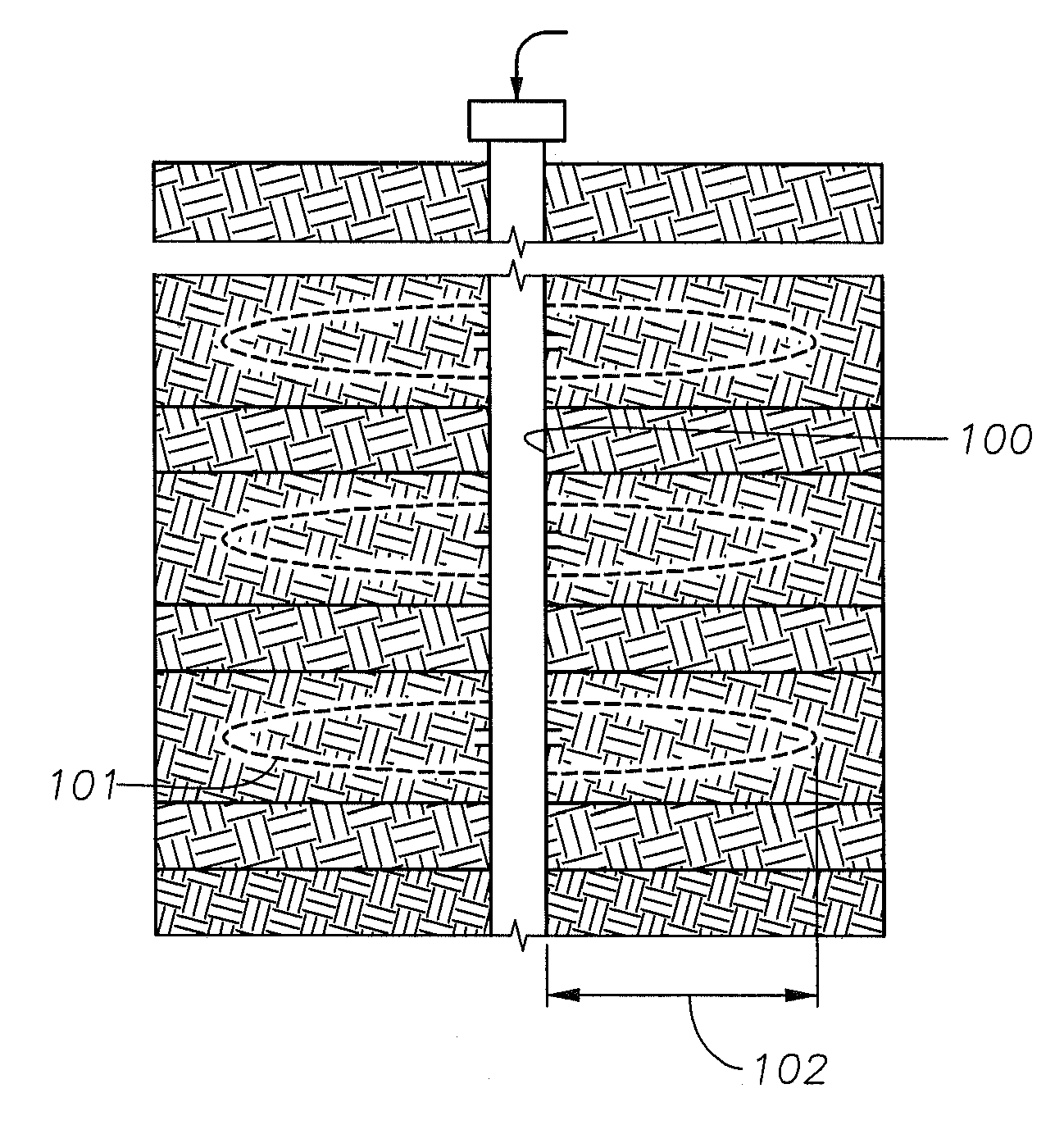
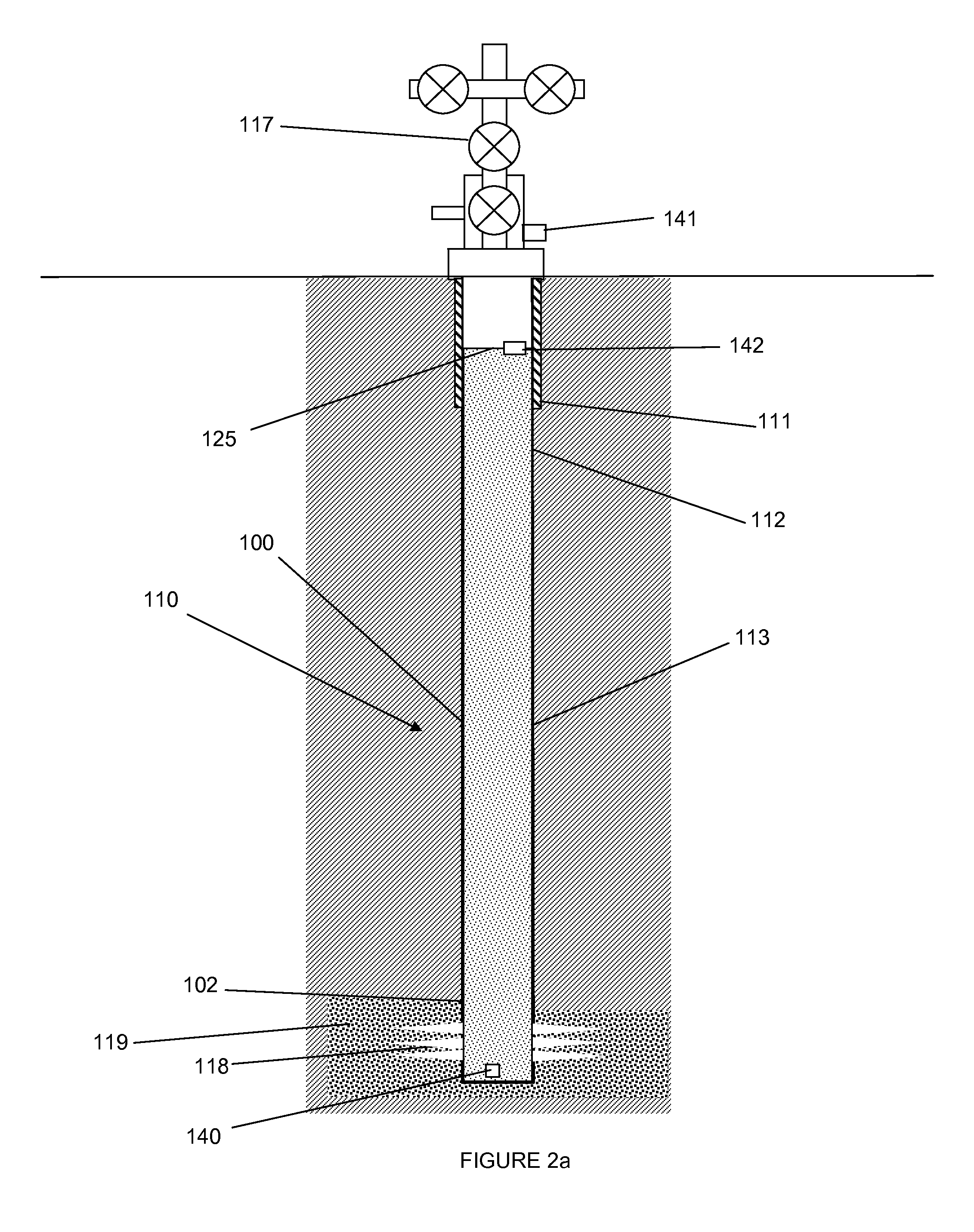
Tight Gas Stimulation by In-Situ Nitrogen Generation
InactiveUS20130126169A1Avoid reactionIncrease ratingsInsulationFluid removalHydrostatic pressureNitrogen
Provided is a method and composition for the in-situ generation of synthetic sweet spots in tight-gas formations. The composition can include nitrogen generating compounds, which upon activation, react to generate heat and nitrogen gas. The method of using the composition includes injecting the composition into a tight-gas formation such that upon activation, heat and nitrogen gas are generated. Upon the generation of nitrogen gas and heat within the formation, microfractures are produced within the formation and the hydrostatic pressure within the reservoir is reduced to less than the reservoir fluid pressure, such that the rate of production of hydrocarbons from the formation is increased.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
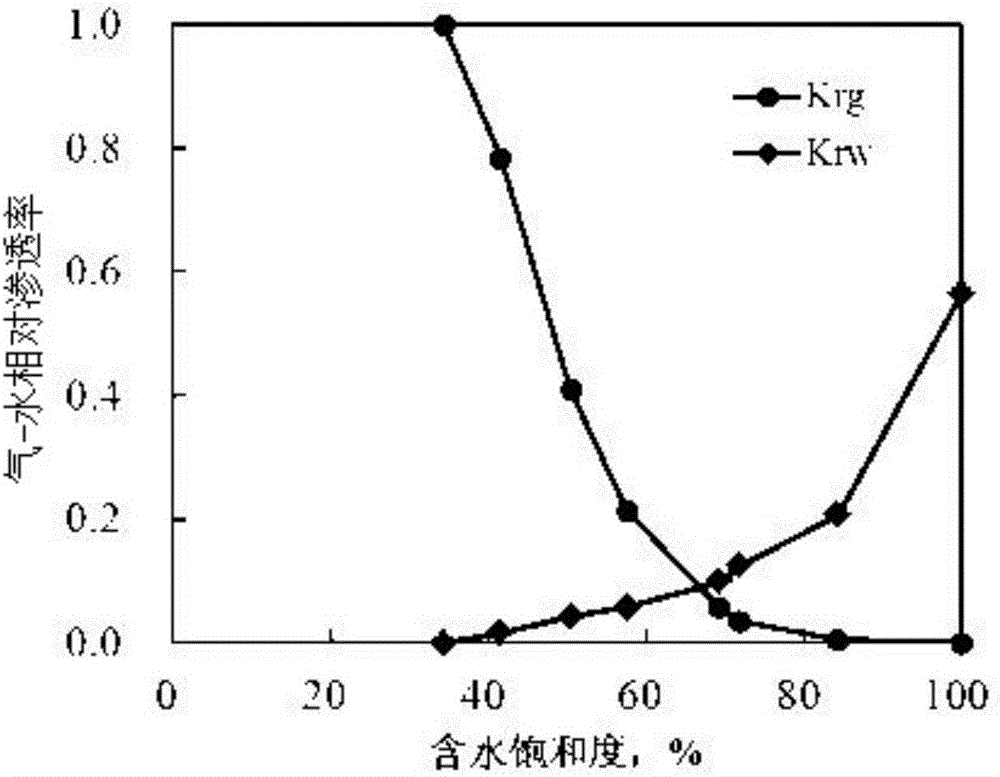
Method for testing gas-water relative permeability curve by using tight sandstone steady state method
ActiveCN106525690AIn line with the actual situationHigh reference valuePreparing sample for investigationPermeability/surface area analysisMeasurement pointDisplacement pressure
The invention provides a method for testing a gas-water relative permeability curve by using a tight sandstone steady state method. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a stone core; preparing simulation stratum water; vacuuming till the simulation stratum water is saturated; connecting an experiment device and heating to experiment temperature; putting the stone core into the experiment device, pressurizing, releasing the pressure, testing the mass and the liquid phase permeability of the stone core; establishing irreducible water saturation; controlling the flowing speed of gas, and injecting the simulation stratum water at a relatively slow flowing speed, after the gas flow at an outlet is stable, increasing the flowing speed of liquid, and measuring a next point till displacement pressure meets the maximum set value and the flowing speed of the gas at the outlet is reduced to 0.1mL / minute, and terminating the experiment; according to improved phase permeability equations, calculating water saturation and relative permeability of different points. By adopting the method, two-phase permeation characteristics in the tight gas reservoir production process under stratum conditions can be simulated, the influence of the temperature on gas-water viscosity is taken into account, the influence of pressurization on the water content of the stone core is also taken into account, the irreducible water saturation and the relative permeability curve can be relatively accurate and reliable, and high-value data can be provided for gas reservoir production evaluation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
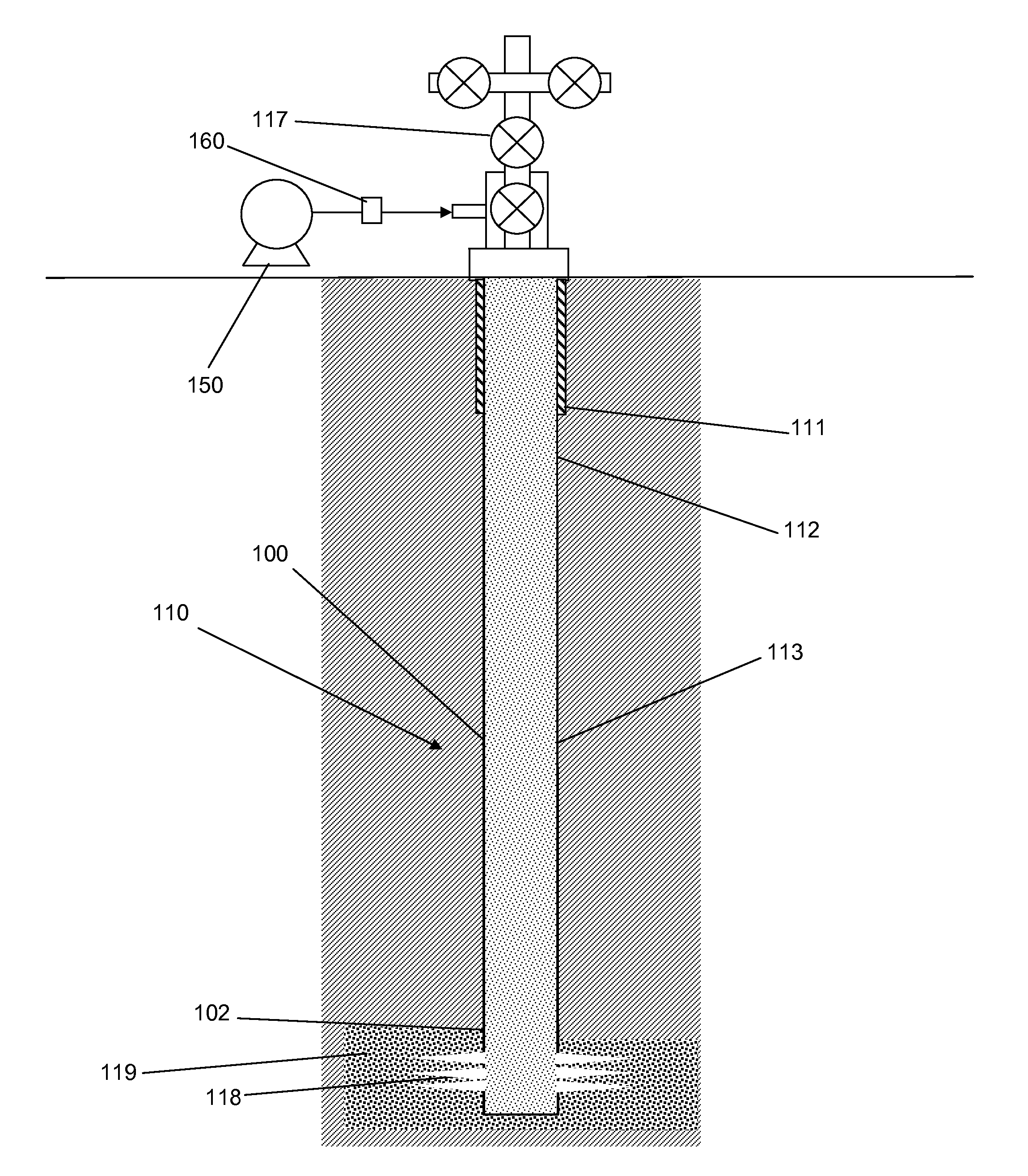
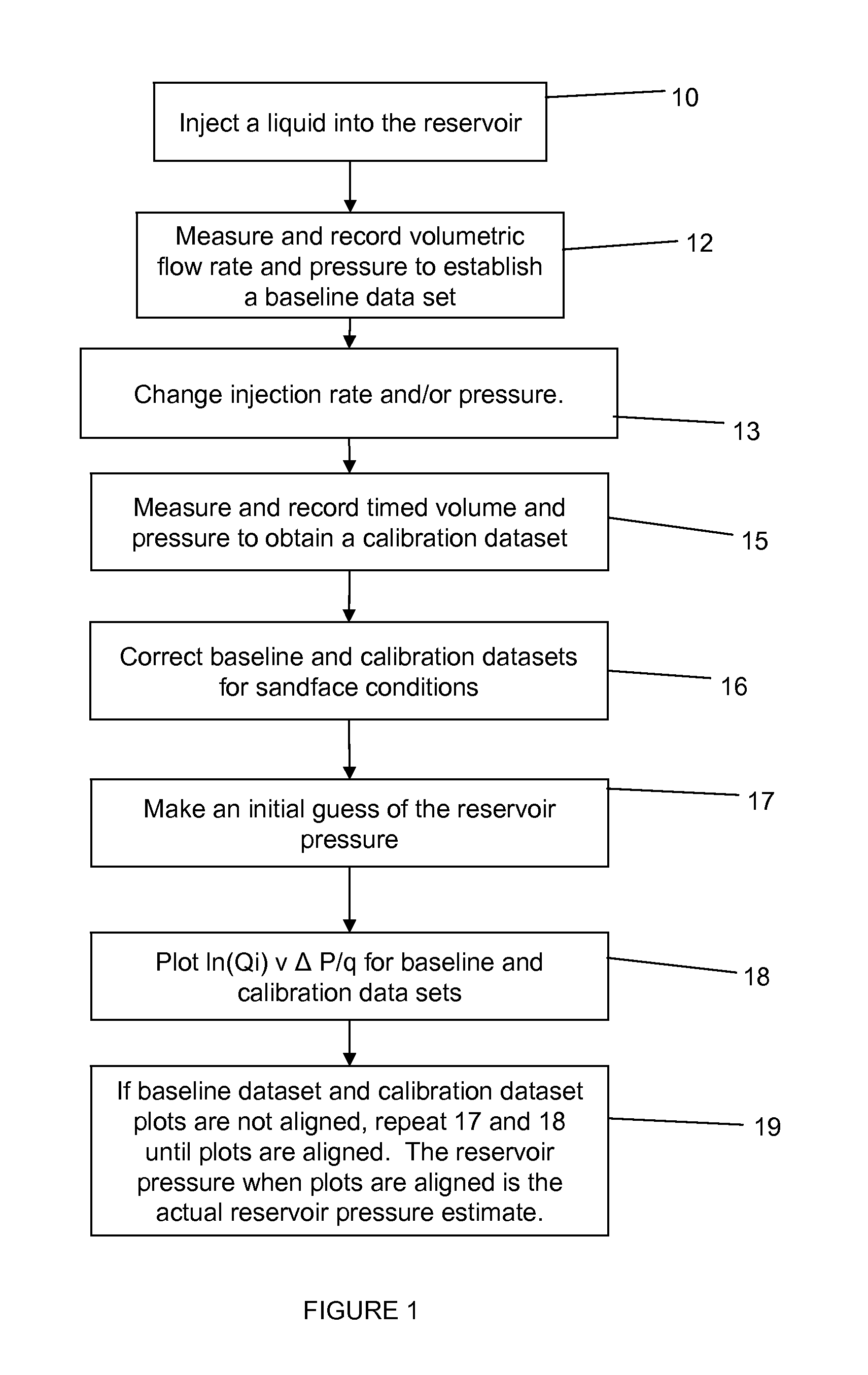
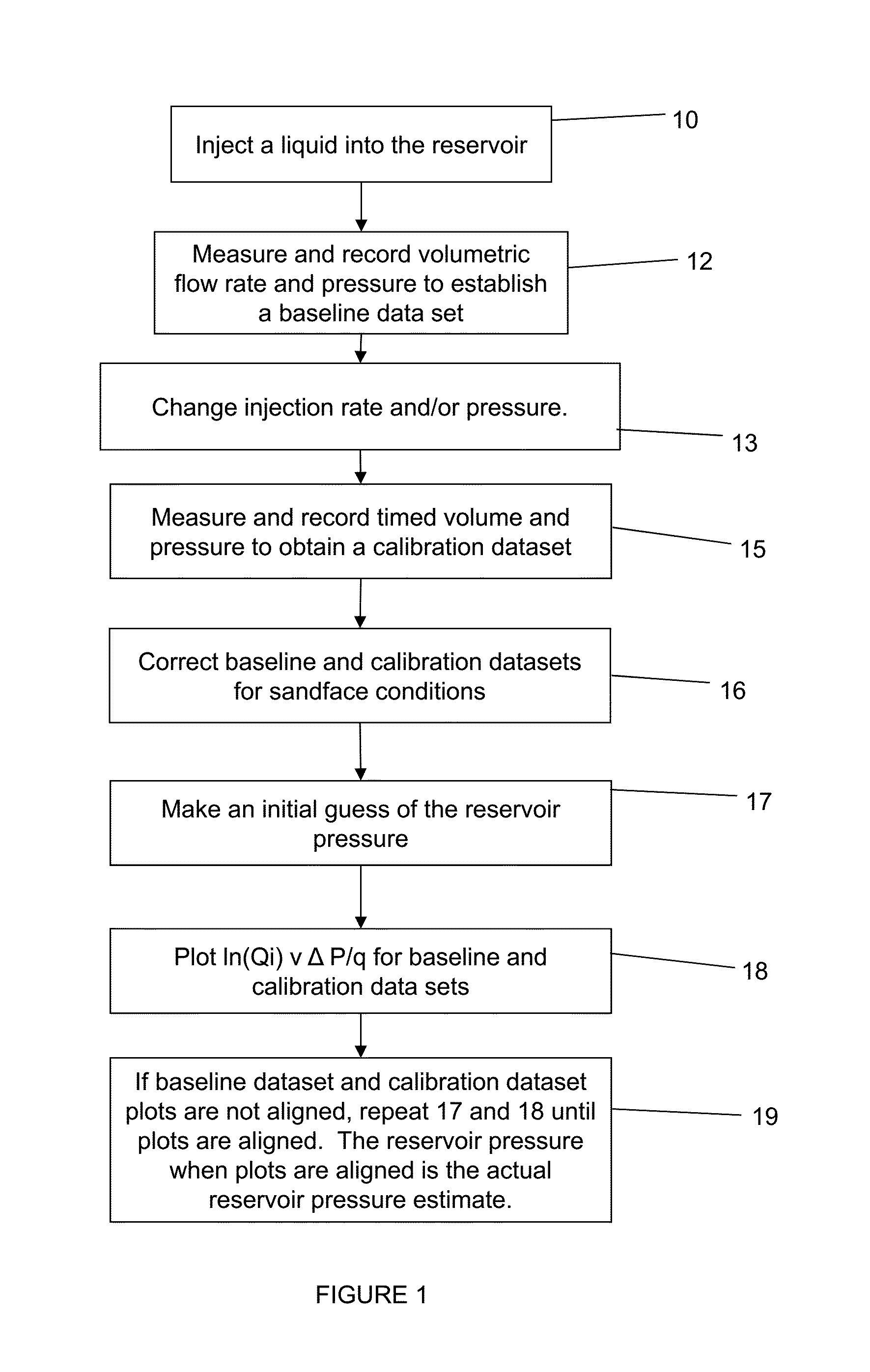
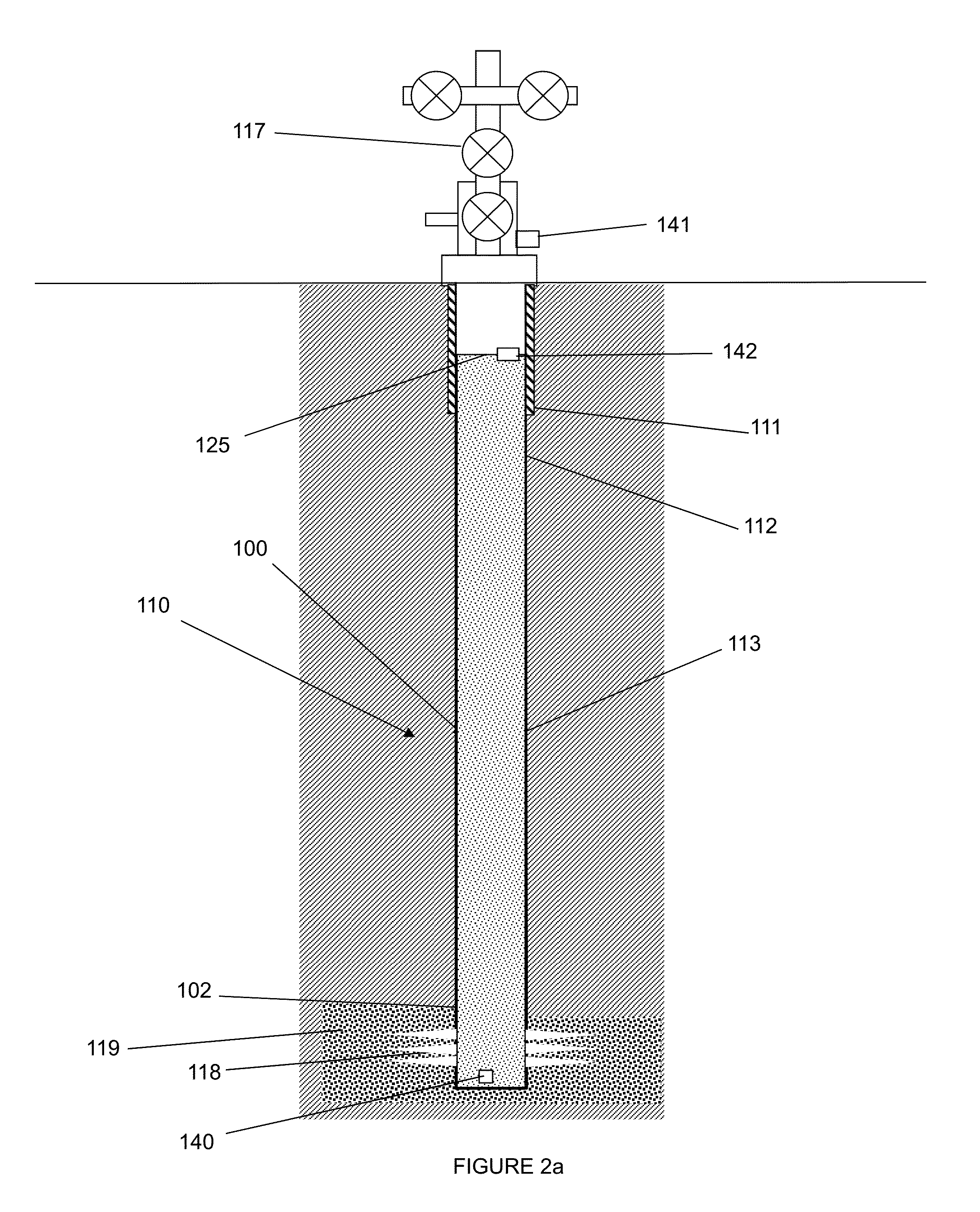
Method of determining reservoir pressure
ActiveUS20120158310A1Reduce penetrationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBaseline dataInjection pressure
A new approach is disclosed for measuring the pressure of tight gas reservoirs, using information obtain from continuous injection prior to hydraulic fracture stimulation. The technique can be obtained utilizing either bottom-hole or surface pressure gauges and properly instrumented surface injection pumps. The analysis is completed by plotting injection and rate data in a specialized form from terms arranged in Darcy's radial flow equation to obtain a curve or trend. The key component to proper application of this technique is to obtain both baseline and one or more calibration data sets. These calibration data sets are obtained by either increasing or decreasing the injection pressure and / or rate from the baseline data. Initial reservoir pressure is assumed, but the calibration data indicates if the guess was too high or low. Accurate estimates of reservoir pressure may be obtained in a few iterations.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Non-Acidic Exothermic Sandstone Stimulation Fluids
Provided is a method and composition for the in-situ generation of synthetic sweet spots in tight-gas formations. The composition can include nitrogen generating compounds, which upon activation, react to generate heat and nitrogen gas. The method of using the composition includes injecting the composition into a tight-gas formation such that upon activation, the heat and nitrogen gas generated
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
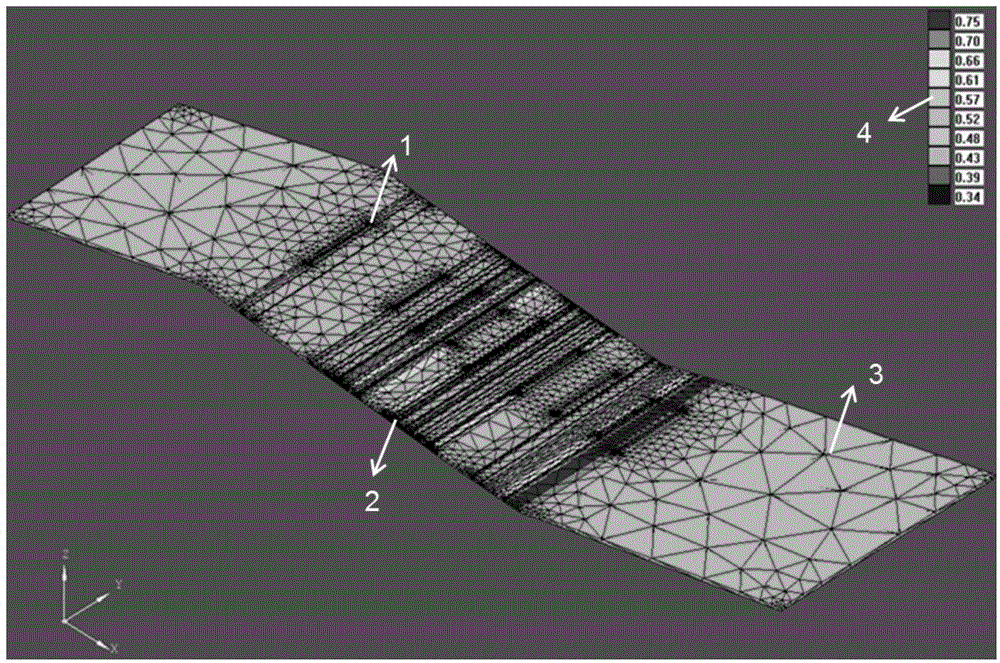
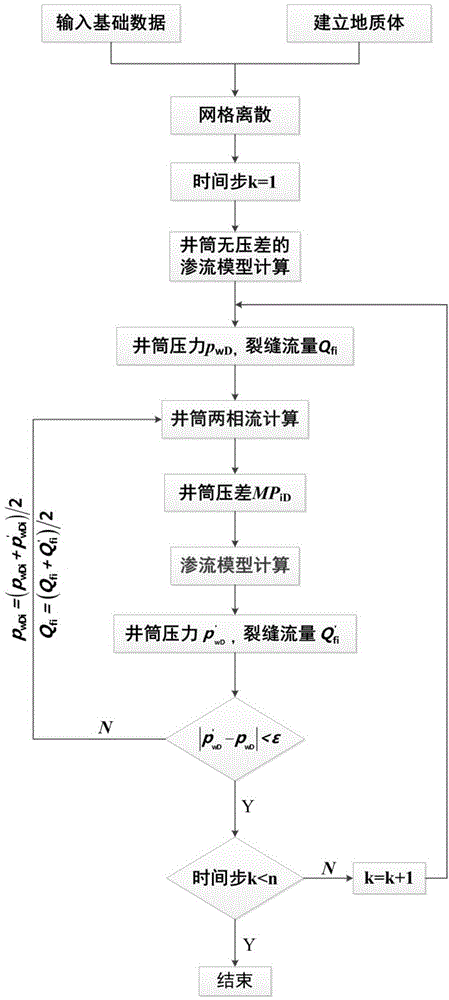
Tight gas fracturing horizontal well numerical value well testing model building and solving method
ActiveCN104895550AFit closelyCalculation speedSurveySpecial data processing applicationsCouplingCurve fitting
The invention provides a tight gas fracturing horizontal well numerical value well testing model building and solving method. The method includes the following steps: step one, generating two-dimensional geologic body and a three-dimensional geologic body of a tight gas reservoir fracturing horizontal well; step two, performing grid discretization on the generated two-dimensional geologic body and the generate three-dimensional geologic body of the tight gas reservoir fracturing horizontal well; step three, calculating a pressure-difference-free seepage model of a horizontal well shaft; step four, building a coupling model, solving the built coupling model, and enabling acquired solutions to generate a well testing theoretical curve; step five, fitting the theoretical curve acquired in step four with a measured curve to acquire parameters of well testing explanation. The method has the advantages of high calculation speed, good curve fitting effect and accurate explanation result.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
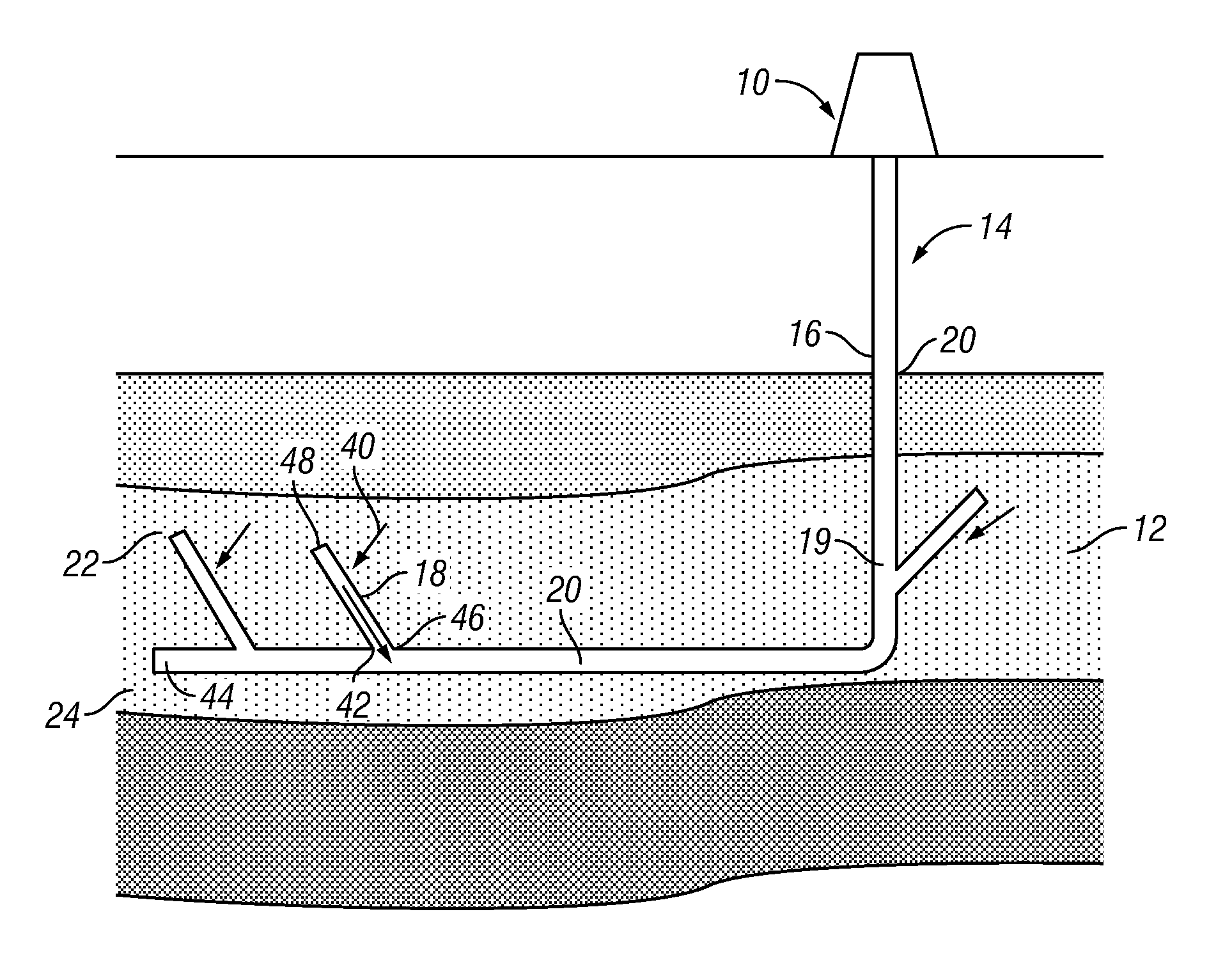
Upgoing drainholes for reducing liquid-loading in gas wells
ActiveUS20120048568A1High depthFluid removalDrinking water installationEnvironmental geologyGas formation
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Pressure muscular strength enhancing system and controller, and method being carried out by controller
ActiveUS20060128538A1Simple methodIncrease pressureVibration massageGenitals massageAutomatic controlMuscle strength
To provide a pressure muscle strength increasing apparatus that allows accurate adjustment of the degree of blood flow restriction when a pressure muscle strength increasing method is carried out. The pressure muscle strength increasing apparatus is comprised of a tight fitting device 100, a pressure setting segment 200, quantification segments 300, and a control segment 400. The tight fitting device 100 is wrapped around a predetermined range on a limb. The tight fitting device 100 has an air-tight gas bag. The compression force applied to the limb can be varied by supplying the air to and removing the air from the gas bag. The pressure setting segment 200 controls the supply and removal of the air into and from the gas bag. The quantification segment 300 is intended to be rest on the limb which the tight fitting device 100 is wrapped around on the distal side thereof to quantify a quantification target that varies depending on the increase and decrease of the compression force. The control segment 400 controls the pressure setting segment 200 based on the quantification target. As described above, the pressure muscle strength increasing apparatus automatically controls the compression force based on the quantification target.
Owner:KAATSU JAPAN
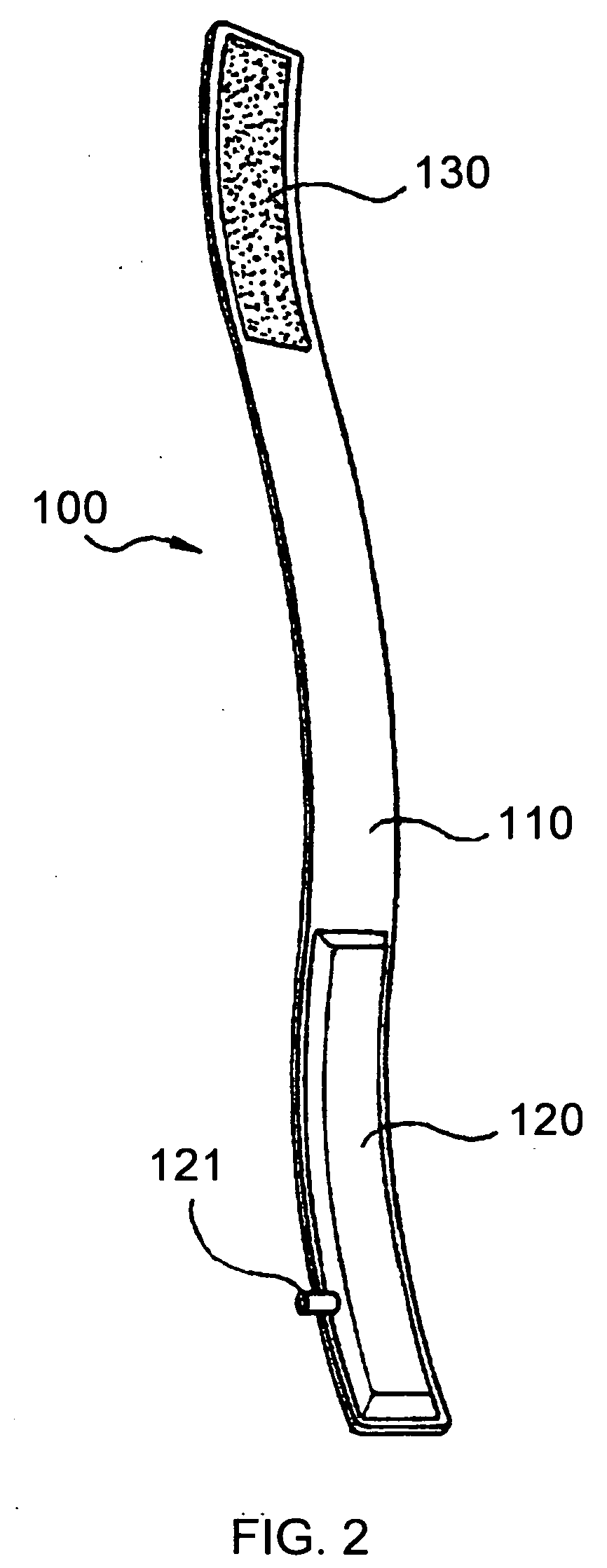
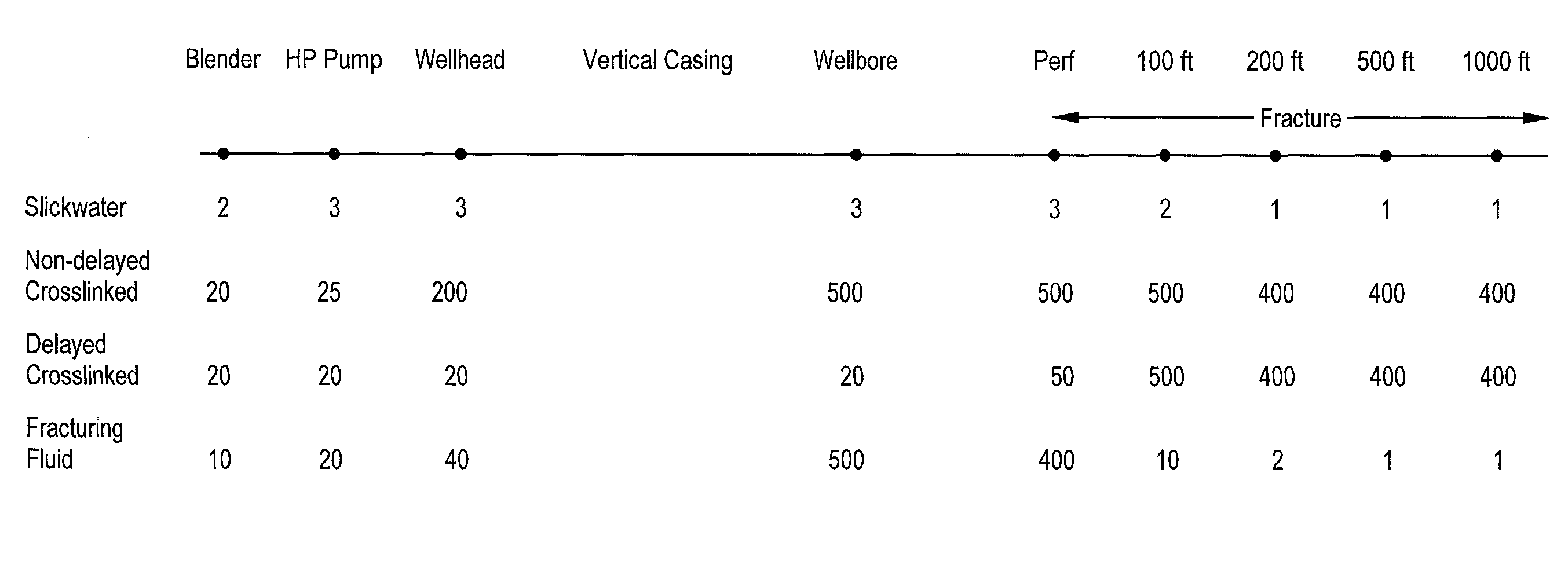
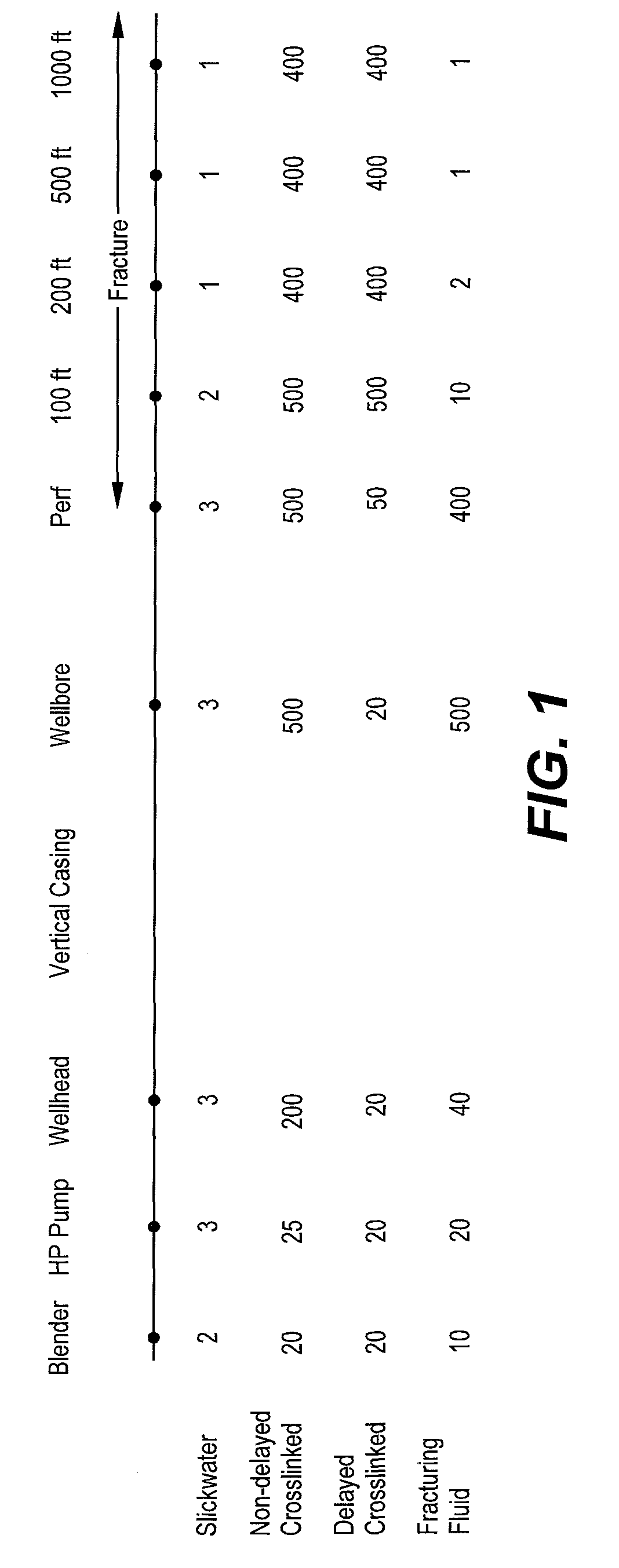
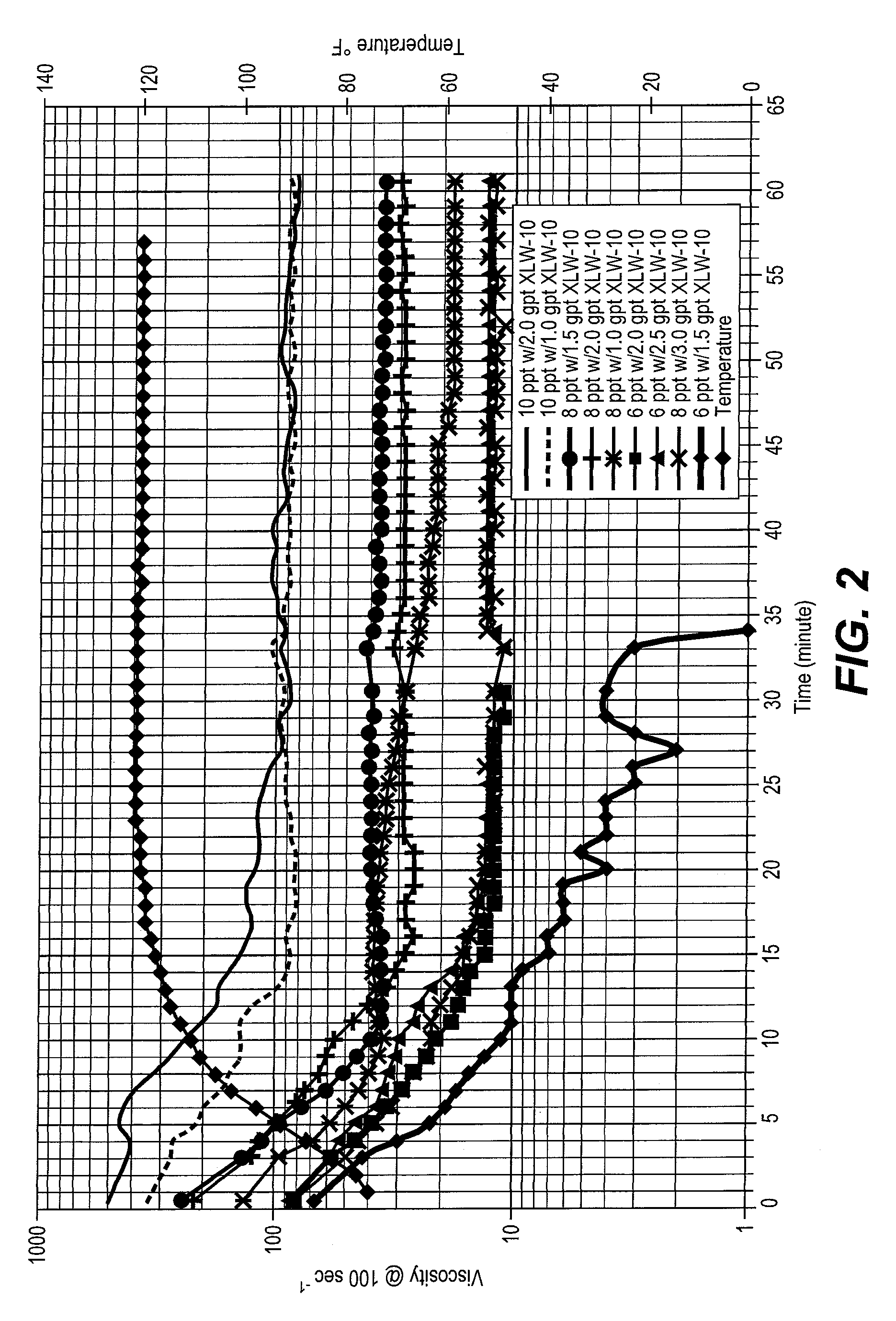
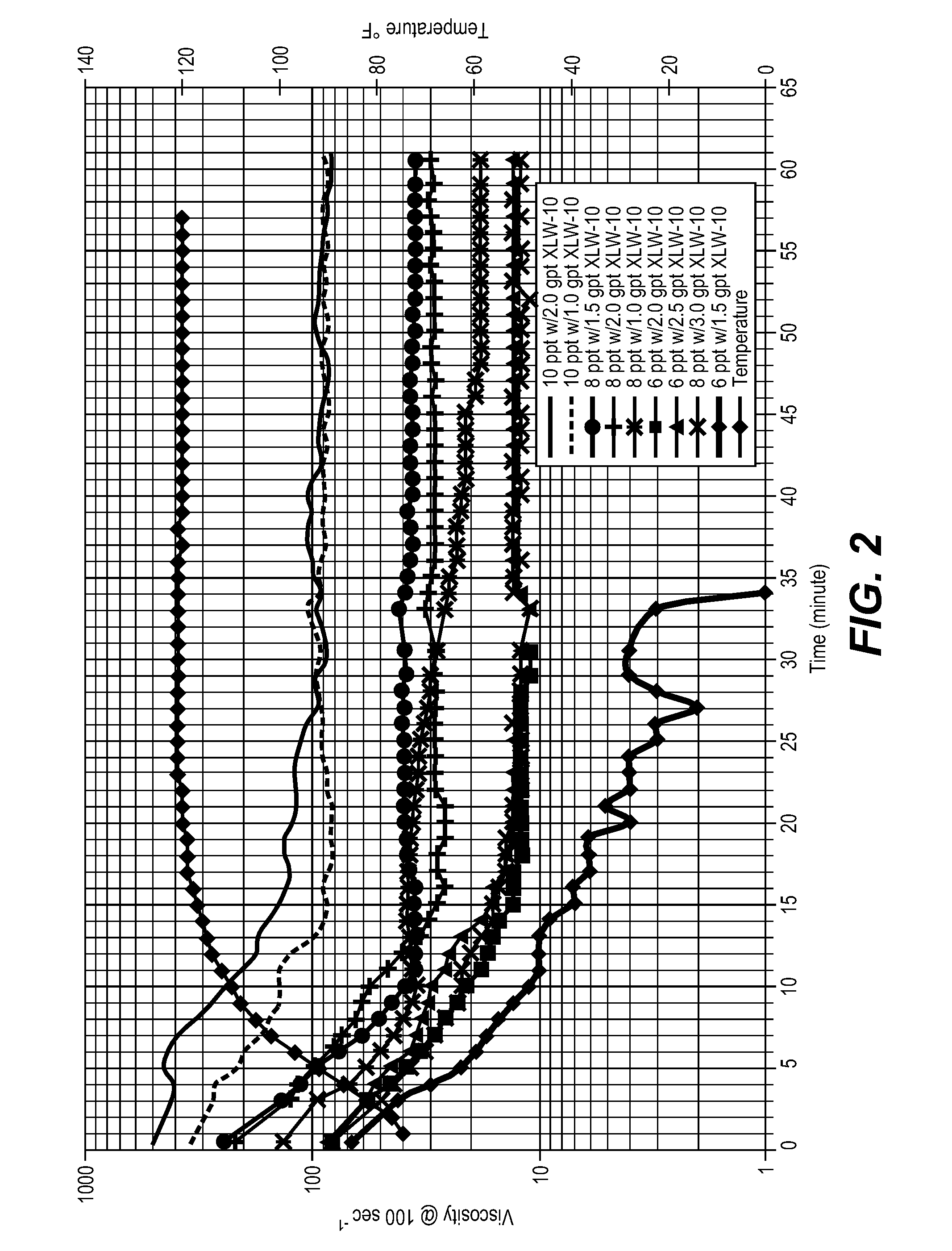
Method of fracturing subterranean formations with crosslinked fluid
ActiveUS8371383B2Particular applicabilityHigh viscosityFluid removalDrilling compositionApparent viscosityFracturing fluid
Subterranean formations, such as tight gas formations, may be subjected to hydraulic fracturing by introducing into the formation a fracturing fluid of an aqueous fluid, a hydratable polymer, a crosslinking agent and proppant. The fracturing fluid is prepared in a blender and then pumped from the blender into the wellbore which penetrates the formation. The fluid enters the reservoir through an entrance site. The apparent viscosity of the fluid decreases distally from the entrance site such that at least one of the following conditions prevails at in situ conditions:(a) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid 100 feet from the entrance site is less than 10 percent of the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid at the entrance site;(b) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid 15 minutes after introduction into the entrance site is less than 15% of the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid at the entrance site; or(c) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid is less than 10 cP within 15 minutes after being introduced through the entrance site.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for analyzing and evaluating tight sandstone reservoir diagenetic facies based on porosity evolution
InactiveCN103308433AImprove the accuracy of evaluation and recognitionEasy to operatePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityOperability
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and evaluating tight sandstone reservoir diagenetic facies based on porosity evolution. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the physical property of a block objective interval sample, analyzing and judging sheet information, dividing a diagenetic facies reservoir and a porosity evolution model of the diagenetic facies reservoir, calculating porosity evolution characteristic parameters of diagenetic stages of the block objective interval sample, establishing a diagenetic reservoir facies classification evaluation index system, and evaluating the tight sandstone reservoir diagenetic facies by adopting grey theory integration according to the diagenetic reservoir facies classification evaluation index system. In practical applications, the method improves the evaluation recognition accuracy of the tight gas reservoir; in rapid and high-efficiency development evaluation of the tight gas reservoir, the method provides a favorable diagenetic reservoir facies tract, a gas bearing enrichment target of the facies tract and a well area for a gas field block, and provides criteria for a gas deposit block allocation rolling development well and a development preparation well; and in addition, the method has the characteristics of simplicity, practicality and high operability.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
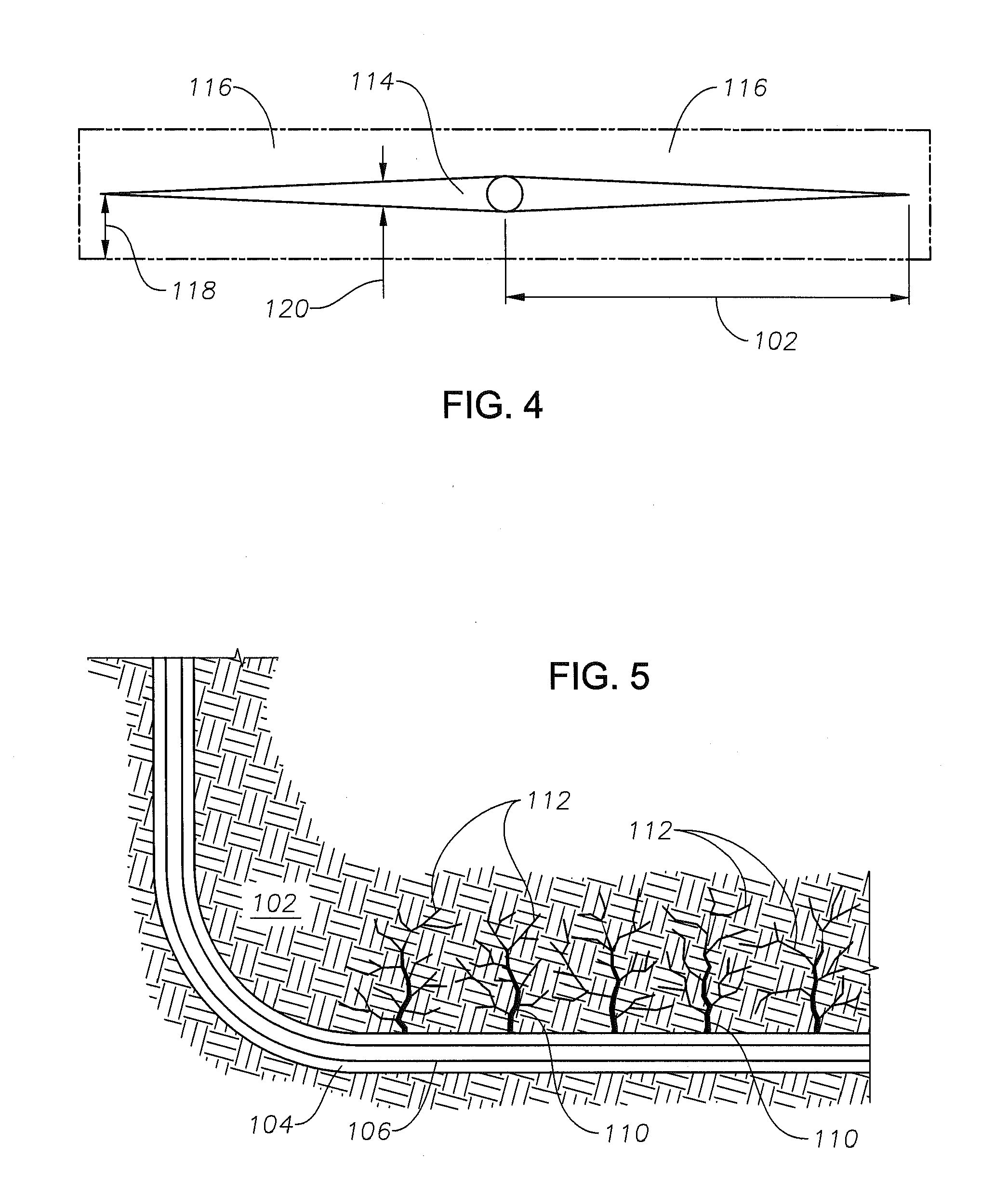
Synthetic Sweet Spots in Tight Formations by Injection of Nano Encapsulated Reactants
InactiveUS20130126175A1Increase productionEasy to produceFluid removalFlushingProduct gasBiological activation
Provided is a method and composition for the in-situ generation of synthetic sweet spots in tight-gas formations. The composition can include gas generating compounds, which upon activation, exothermically react to generate heat and gas. The method of using the composition includes injecting the composition into a tight-gas formation such that upon activation, the heat and gas are generated, resulting in the formation of fractures and microfractures within the formation.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
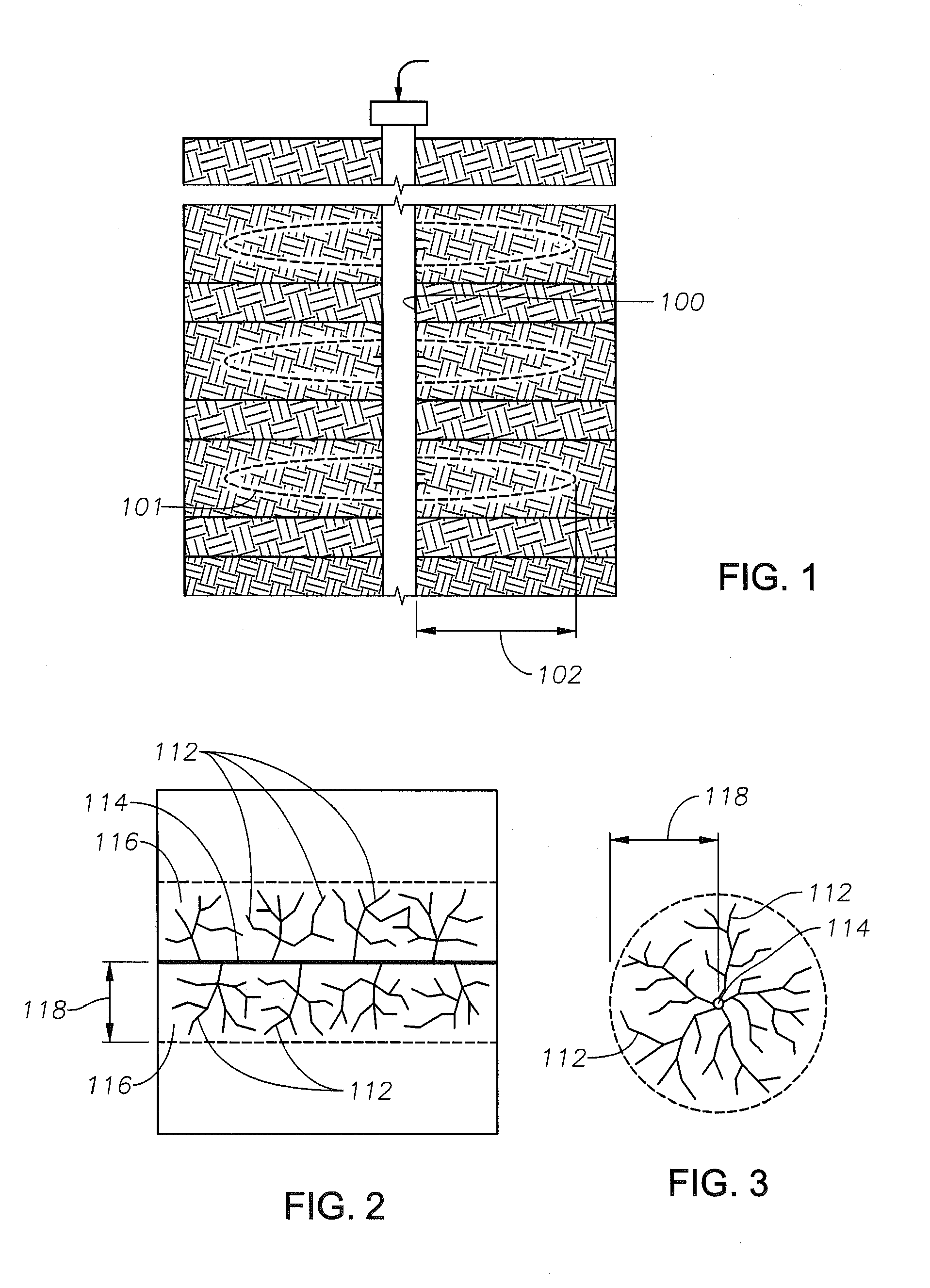
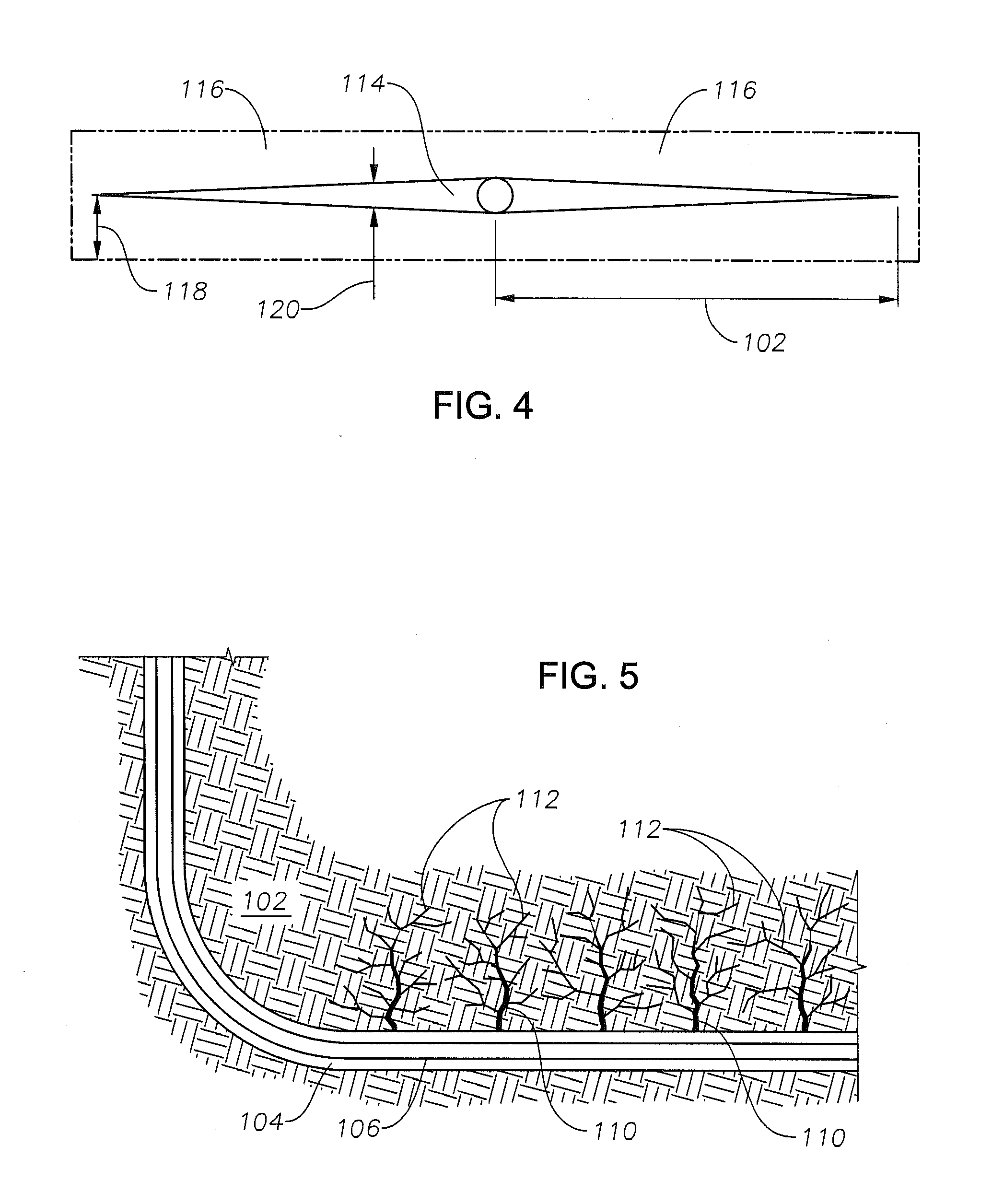
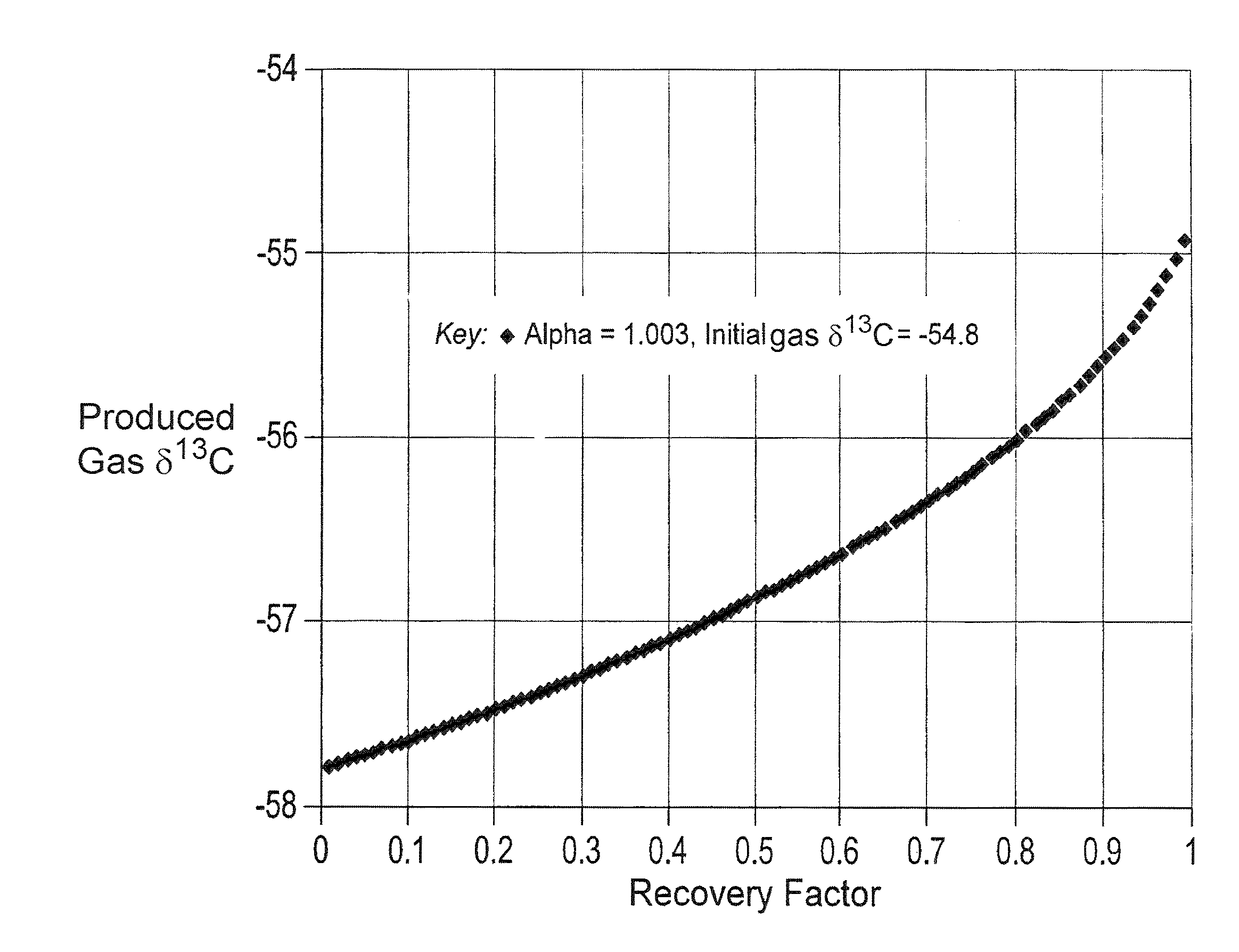
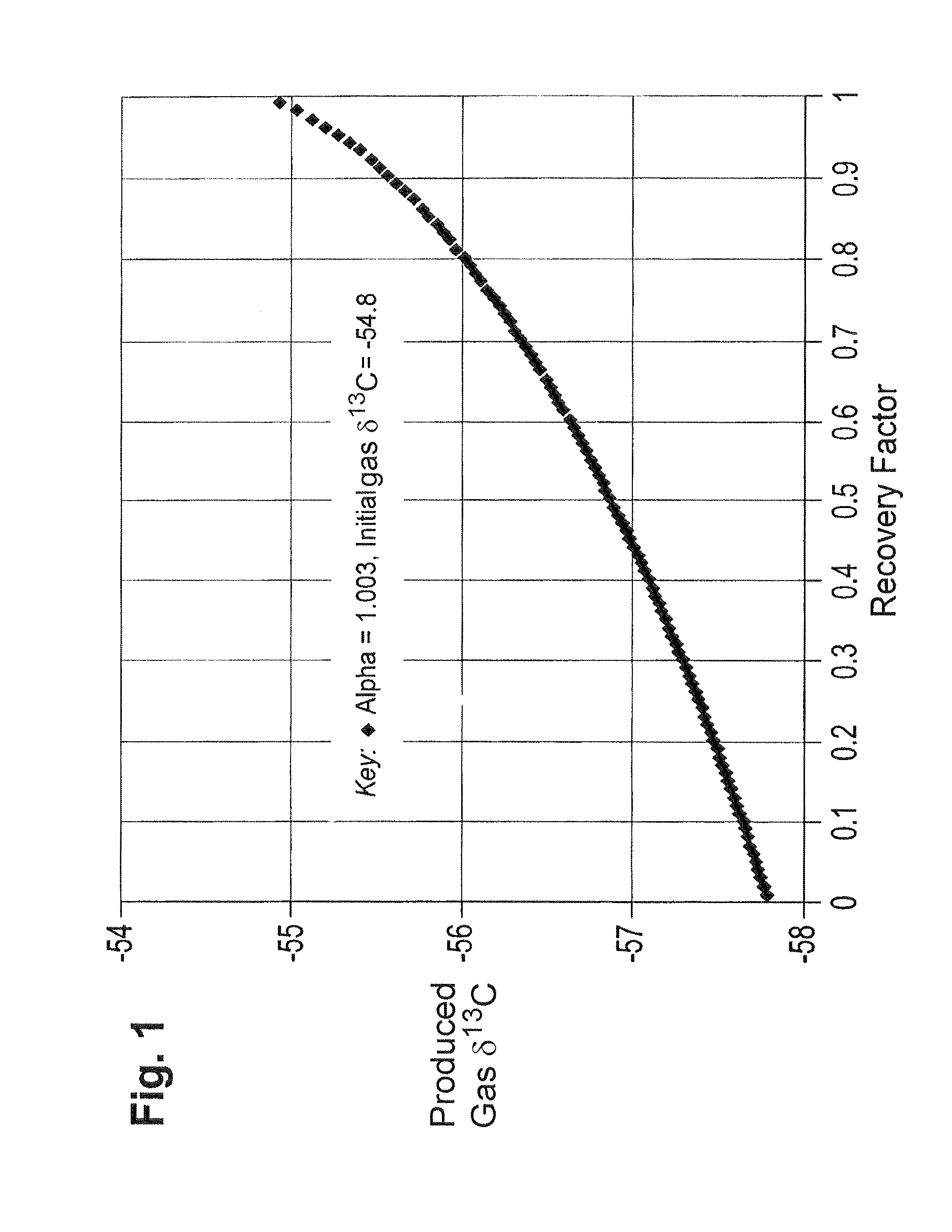
Geochemical surveillance of gas production from tight gas fields
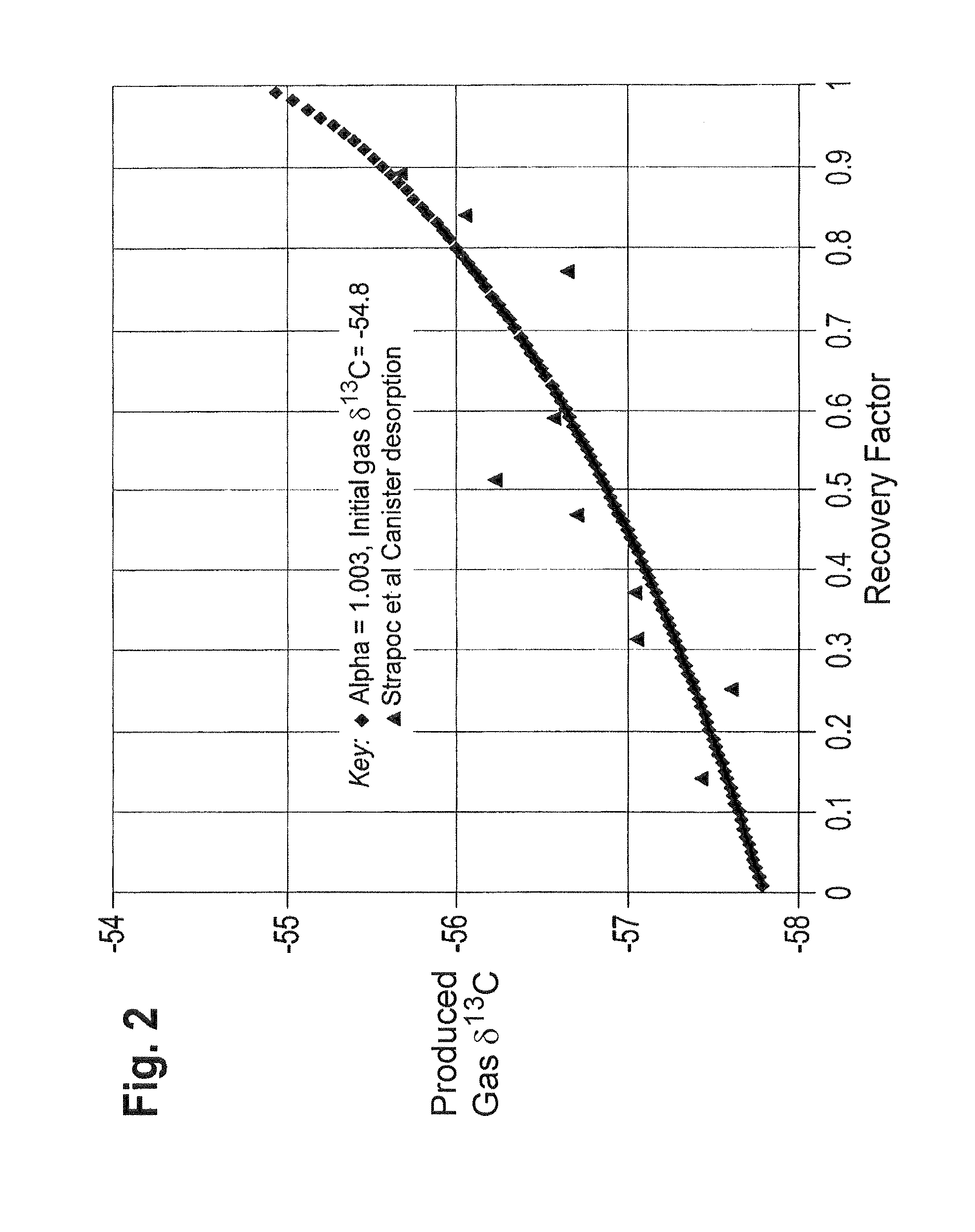
InactiveUS8505375B2Easy to managePromote recoverySurveyConstructionsField methodsIsotopic composition
Owner:BP EXPLORATION OPERATING CO LTD
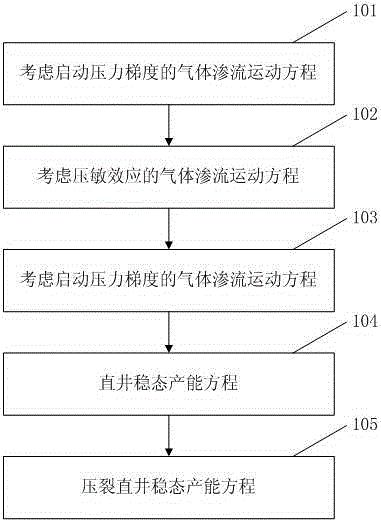
Productivity calculation method with tight gas reservoir percolation mechanism taken into consideration
InactiveCN106545336AEfficient scale developmentEfficient developmentFluid removalPressure sensitivityCalculation methods
The invention provides a productivity calculation method with the tight gas reservoir percolation mechanism taken into consideration. The method comprises the steps of 1, establishing a gas percolation motion equation with the starting pressure gradient taken into consideration; 2, establishing a gas percolation motion equation with the pressure-sensitivity effect taken into consideration; 3, establishing a percolation with the pressure-sensitivity effect and the starting pressure gradient taken into consideration; 4, describing percolation, in a gas reservoir, of fluid through the percolation equation established in step 3, and establishing a vertical shaft steady state productivity equation; and 5, describing percolation, in a stratum, of gas through the percolation equation established in step 1 according to formed infinite flow-guiding vertical cracks, and establishing a fracturing vertical shaft steady state productivity equation. By means of the productivity calculation method with the tight gas reservoir percolation mechanism taken into consideration, theoretical productivity of a gas well can be determined in the tight gas reservoir development process; production allocation of the gas well can be instructed; influence of the starting pressure gradient and the pressure-sensitivity effect on productivity can be determined quantitatively; and a great significance is achieved for studying the tight low-percolation gas reservoir.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
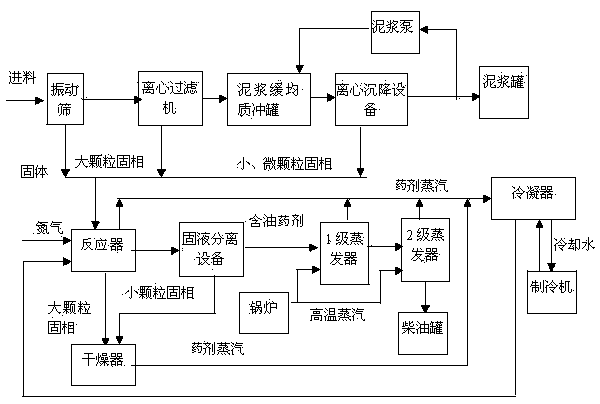
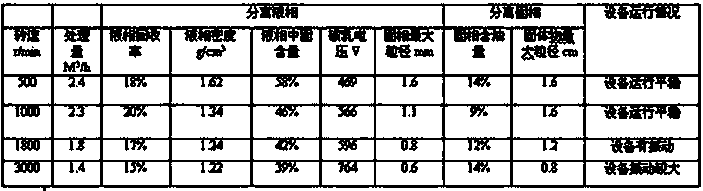
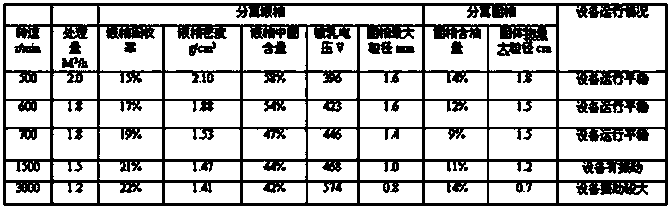
Process for recycling oil-based mud and oil bases from oil-based mud drilling wastes
The invention belongs to the treatment field of oil-based mud or oil-based drilling cuttings in the well drilling of shale gas, tight gas and conventional oil gas fields, and in particular relates to a treatment recycling process for synchronously recycling the oil-based mud and oil bases from oil-based mud drilling wastes. The treatment recycling process is characterized by comprising the following steps: performing centrifugal separation on the oil-based mud; recycling the oil-based mud in a deep desorption manner via reagents at a normal temperature; and performing mixed distillation on the reagents containing oil and recycling the condensed reagents. According to the reaction process, the harmless treatment of the oil-based mud or the oil-based drilling cuttings can be realized, wherein the content of the oil in a final solid-phase product is less than 1%; the majority of oil ingredients in the oil-based mud or the oil-based drilling cuttings can be recycled, wherein the recycling rate of the oil bases is greater than 90%. The adopted reaction reagents can be almost recycled for reutilization, wherein the loss of the reagents is less than 2%. In addition, the treatment procedures are all performed under a normal temperature and a normal pressure, so that the treatment time is short; the secondary pollution is nearly avoided. The treatment recycling process is low in equipment investment and operation cost. Thus, the treatment recycling process is obvious in environmental, social and economic benefits.
Owner:四川博盛永业工程技术有限公司
Multifunctional multi-field coupled seepage experiment device and testing method
ActiveCN107462508AMeet the needs of low temperatureMeet the needs of high temperaturePermeability/surface area analysisBorehole/well accessoriesMulti fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional multi-field coupled seepage experiment device. The multifunctional multi-field coupled seepage experiment device comprises a device body, a stress field control system, a temperature field control system, a fluid loading control system and a fluid seepage measurement system. The invention further discloses seepage experiments performed on tight gas, shale gas, tight oil, shale oil, natural gas hydrate and geothermal heat in a multi-field coupled state of a temperature field, a stress field, a pore pressure field and a seepage field. The invention has the beneficial effects: the temperature and pressure needs of the tight gas, the shale gas, the tight oil and the shale oil are met, and more importantly, it meets the high temperature need of geothermal heat exploitation can be met while the low temperature need of a natural gas hydrate flow test is met; a real stratum environment is simulated, and the exploitation seepage experiments of unconventional energy resources such as the tight gas, the shale gas, the tight oil, the shale oil, the natural gas hydrate, a dry hot rock and the like can be completed respectively by using the same equipment.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
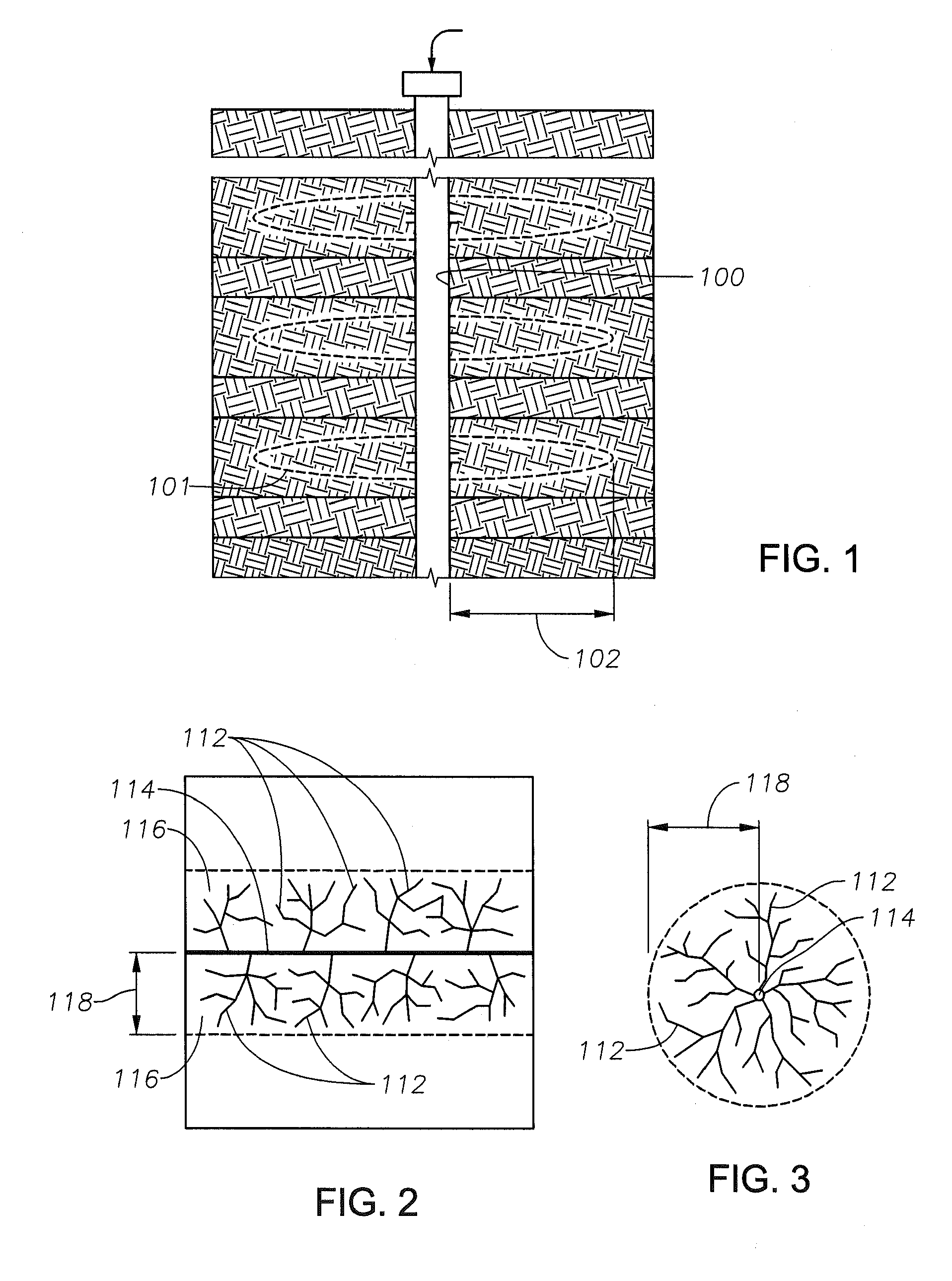
Tight gas stimulation by in-situ nitrogen generation
ActiveUS20150175879A1Increase ratingsImprove productivityInsulationFluid removalHydrocotyle bowlesioidesEngineering
Provided is a method and composition for the in-situ generation of synthetic sweet spots in tight-gas formations. The composition can include nitrogen generating compounds, which upon activation, react to generate heat and nitrogen gas. The method of using the composition includes injecting the composition into a tight-gas formation such that upon activation, heat and nitrogen gas are generated. Upon the generation of nitrogen gas and heat within the formation, microfractures are produced within the formation and the hydrostatic pressure within the reservoir is reduced to less than the reservoir fluid pressure, such that the rate of production of hydrocarbons from the formation is increased.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
A numerical analysis method for multi-section volume fracturing horizontal well of tight gas
ActiveCN109522634AImprove interpretation accuracyFit closelyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelHorizontal wells
The invention relates to a numerical analysis method for dense gas multi-section volume fracturing horizontal well, comprising the following steps: step 1, establishing a geological structure model ofthe network fracture of the multi-section volume fracturing horizontal well; 2, establishing a heterogeneous geological body of fractured horizontal well network fracture; 3, establish a well test mathematical model of a compact gas multi-stage fracturing horizontal well base on that fracture network form; 4, carrying out numerical solution on a network fractured horizontal well test model by using a mixed element finite element method; 5, generating a multi-section volume fracturing horizontal well actual t well curve according to that well test data, and fitting the theoretical curve solvedby the model in the step 4 with the actual measurement curve to obtain the well test interpretation parameters. This method is of great significance to improve the interpretation accuracy of volume fracturing horizontal wells, to obtain the parameters of volume fracturing network and to evaluate the effect of volume fracturing. The invention has the characteristics of good well test curve fitting, accurate interpretation result, strong practicability and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid for tight gas reservation well and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid for a tight gas reservation well and a preparation method of the nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid. The nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid is prepared by 0.3-0.5 part of amino silicon oil nanometer emulsion and 100 parts of water by weight. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding an emulsifying agent and a low-molecule alcohol into the amino silicon oil; uniformly mixing the emulsifying agent, the low-molecule alcohol and the amino silicon oil; adding an organic acid and some water; continuously stirring, then adding an electrolyte and the rest water, stirring until the phase is homogeneous, and then obtaining amino silicon oil nanometer emulsion. The preparation process mentioned in the invention is simple, the process is easy to control, and the nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid obtained has hydrophobicity, obvious water control effect, low viscosity, small grain size, low surface tension and stable performance, so the nanometer emulsion type water control fracturing fluid is suitable for water control fracturing improvement of a near-water or high-water content tight gas reservation well.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
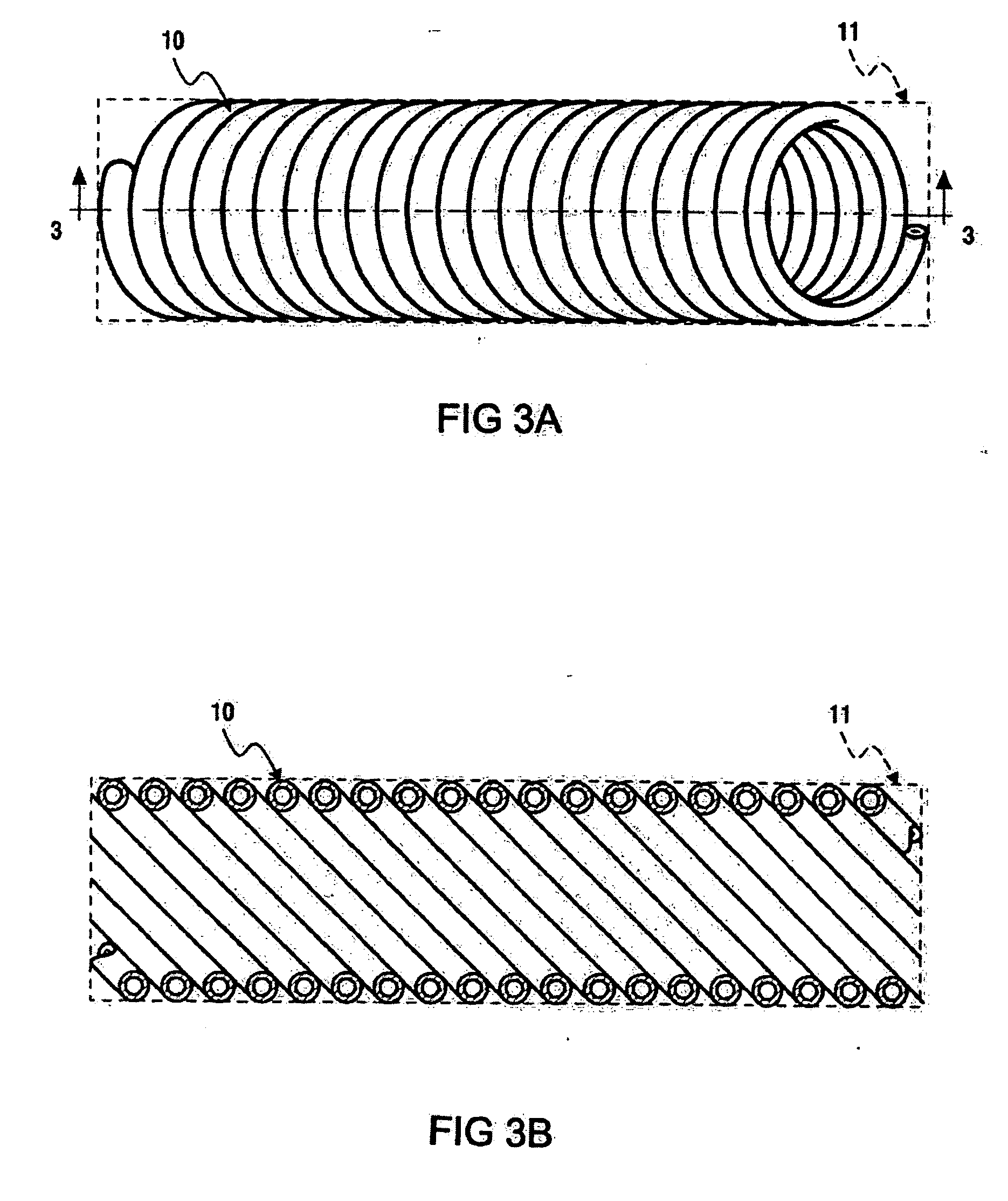
Tube shaped high pressure storage tank
InactiveUS20070075085A1Easy to placeContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsHigh pressureMechanical engineering
A flexible, high pressure, tubular storage vessel for storing and dispensing a compressed gas. The vessel has a gas impermeable inner core member comprising a flexible material and defining an inner diameter of a fluid-carrying channel adapted to store the compressed gas. A flexible reinforcing material is circumferentially disposed about the inner core member. The flexible reinforcing material is surrounded by an air-tight gas barrier wrapping defining an outer diameter. The vessel is configured to be coiled or shaped having a plurality of bends. The bend areas may have a variable inner diameter and are preferably provided with additional reinforcing material.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
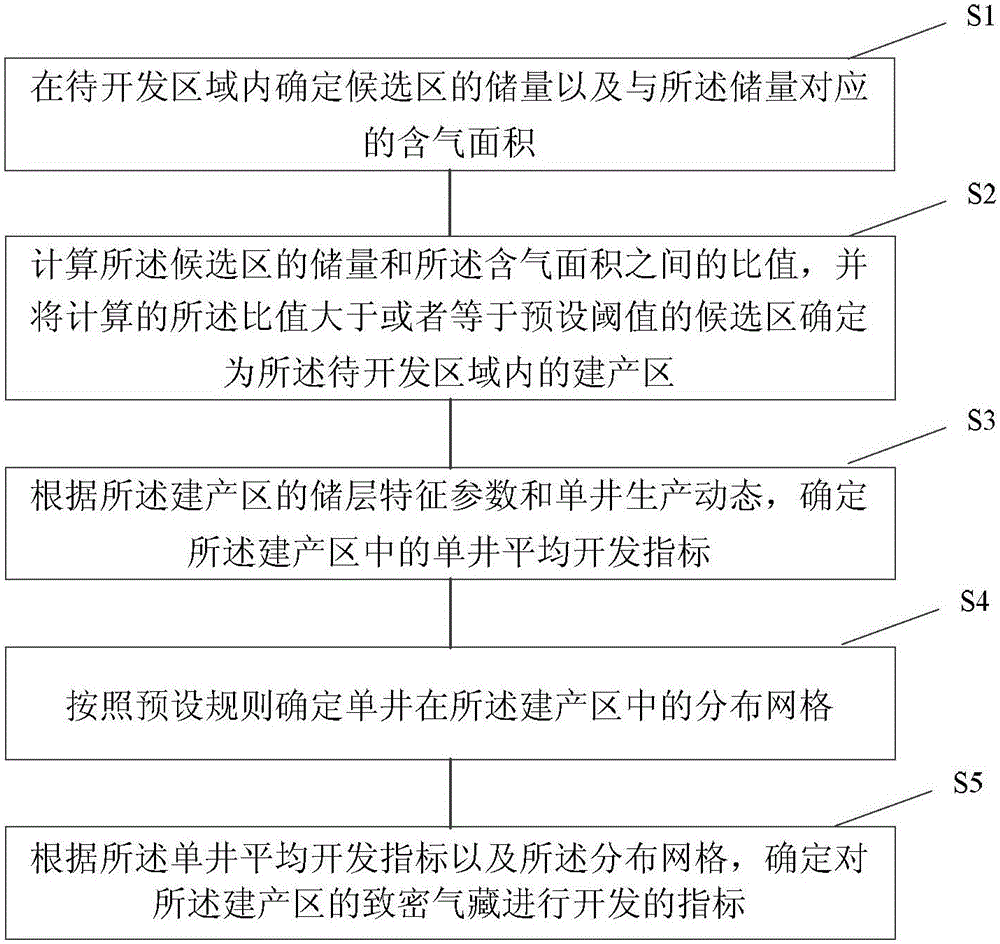
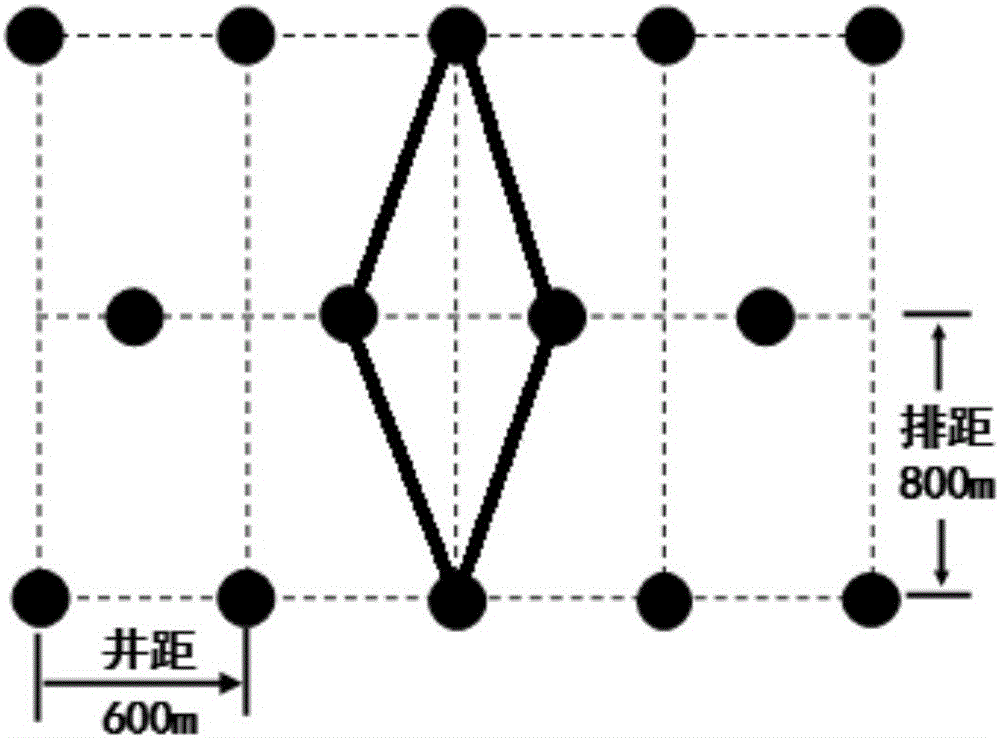
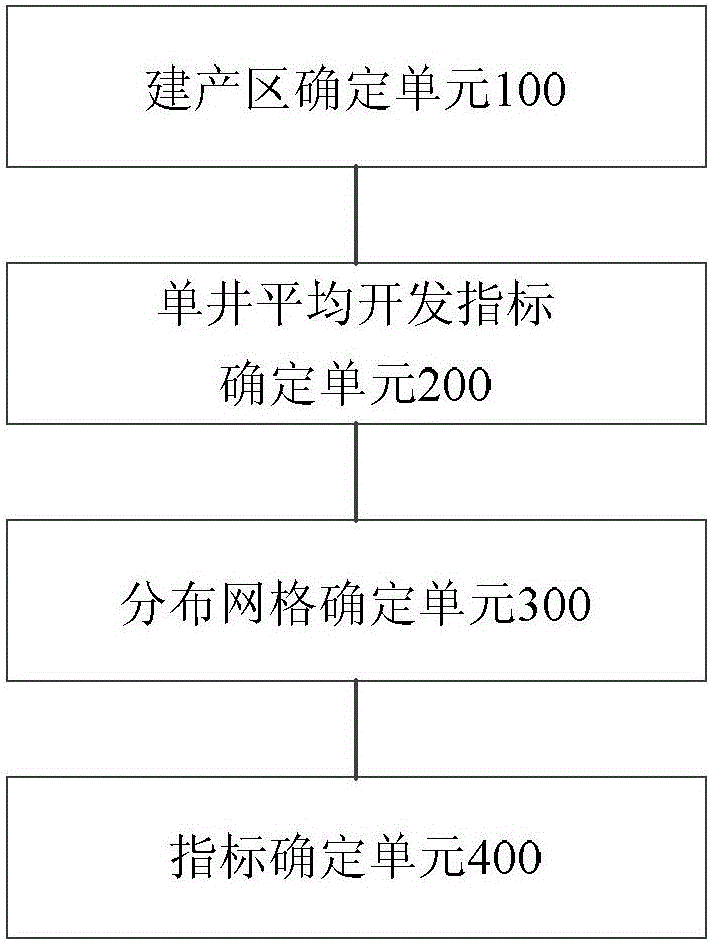
Method for determining tight gas reservoir development index and device thereof
ActiveCN105913332ADetermine development metricsData processing applicationsEnvironmental geologyTight gas
The application provides a method for determining a tight gas reservoir development index and a device thereof. The method comprises the steps that a production region is determined in a region to be developed; the single well average development index of the production region is determined according to the reservoir characteristic parameters and the single well dynamic production state of the production region; the distributed grids of a single well in the production region are determined according to the preset rules; and the tight gas reservoir development index of the production region is determined according to the single well average development index and the distributed grids. According to the method for determining the tight gas reservoir development index and the device thereof, the tight gas reservoir development index can be determined according to the intrinsic characteristics of the tight gas reservoir.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
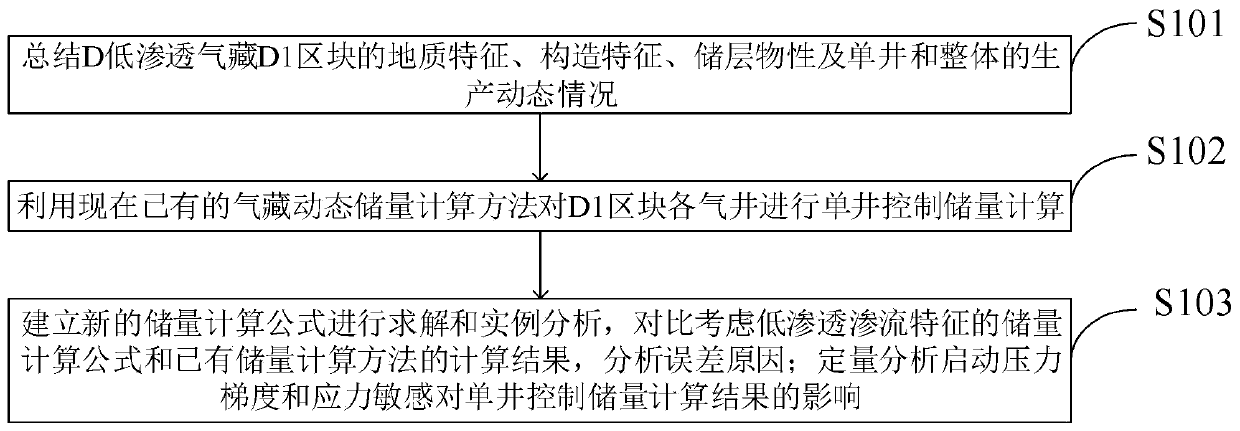
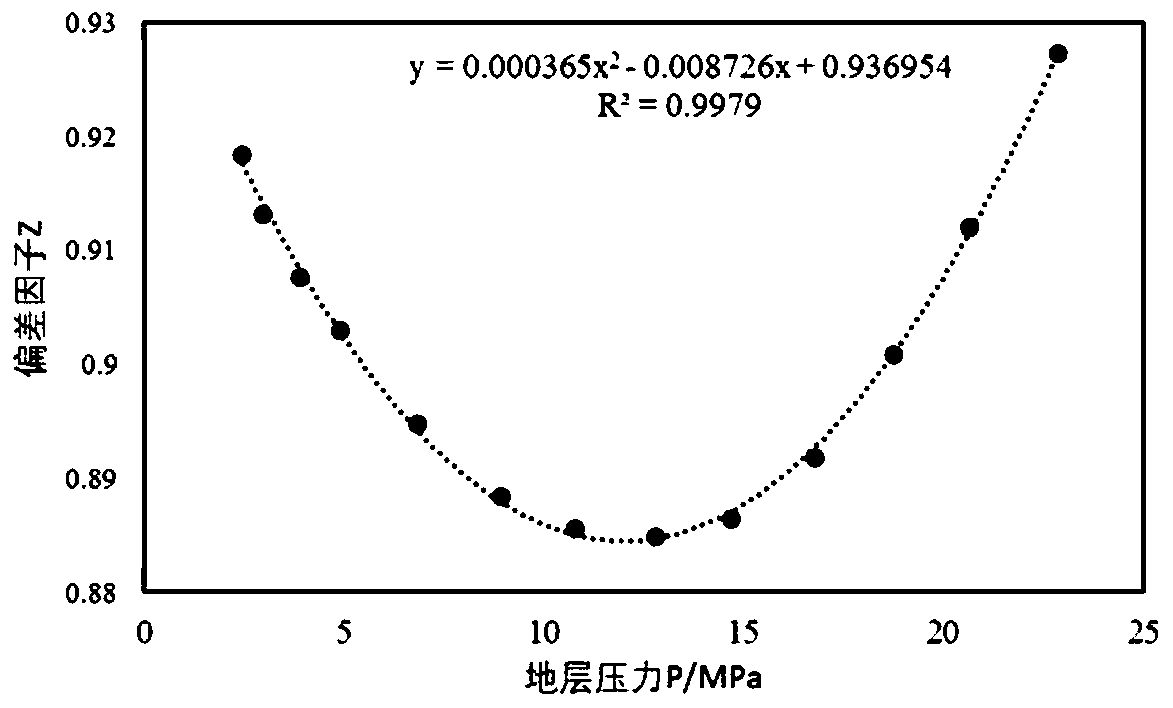
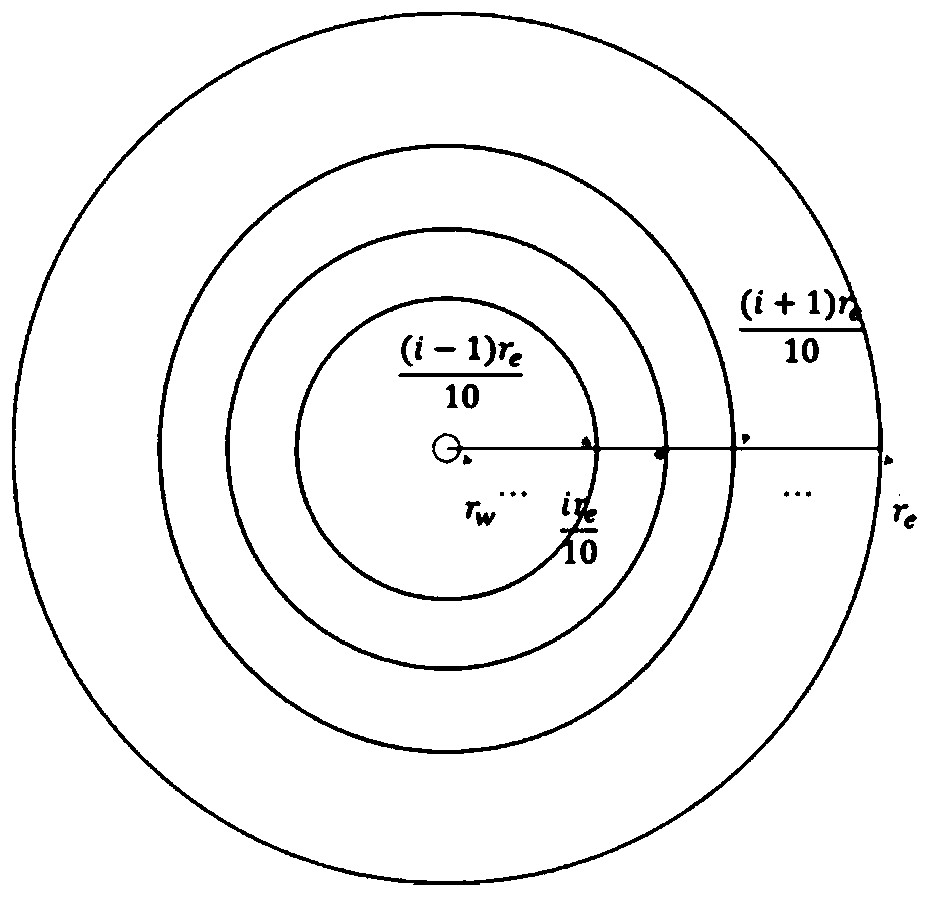
Single-well control reserve calculation and residual gas analysis method for low-permeability tight gas reservoir
ActiveCN110334431ACalculations are smallReduced stress sensitivitySurveyFluid removalGas analysisAnalysis method
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil and gas field development, and discloses a single-well control reserve calculation and residual gas analysis method for a low-permeability tight gasreservoir, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the single-well control reserve calculation of each gas well of a block through a gas reservoir dynamic reserve calculation method; establishing a new reserve calculation formula for solution and instance comparative analysis; quantitatively analyzing the influence of the starting pressure gradient and the stress sensitivity on the single-well control reserve calculation result; after analysis of influence factors of the reserve calculation result, obtaing a result that when the starting pressure gradient reaches 0.02 MPa / m, the reserve calculation result is significantly reduced compared with a conventional method, but after the starting pressure gradient is greater than 0.1 MPa / m, the influence degree gradually tends to be stable; the stronger the reservoir stress sensitivity is, the smaller the reserve calculation result is. The embodiment of the invention shows that the method has good theoretical and practical application values for accurately determining the single-well control dynamic reserves of the low-permeability tight gas reservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
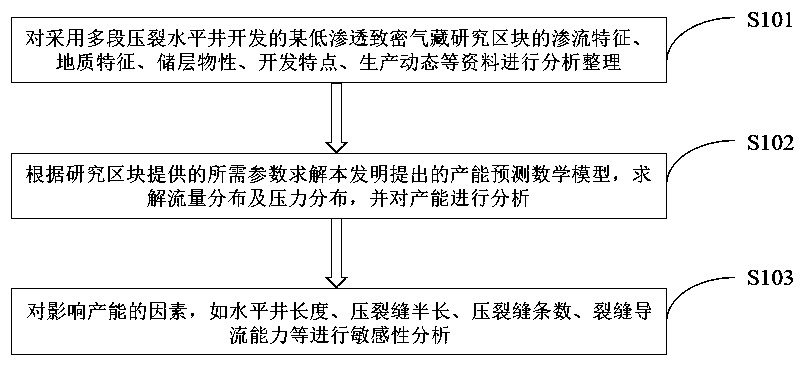
Productivity prediction model and productivity sensitivity analysis method for multi-section fractured horizontal well in low-permeability tight gas reservoir
The invention belongs to the field of tight sandstone gas reservoir development, and discloses a productivity prediction model and productivity sensitivity analysis method for a multi-section fractured horizontal well in a low-permeability tight gas reservoir. The model and method are characterized in that after a variety of factors, such as high-speed non-darcy effect, stress sensitivity, slippage effect, stratum pressure drop, in-fracture linear flow and in-fracture radial flow and shaft pressure drop are comprehensively considered, a steady-state seepage low model of the fractured horizontal well is provided; the influence of the various factors on a productivity calculation result is quantitatively analyzed; through example verification, for the multi-section fractured horizontal wellin the tight gas reservoir, the model can accurately predict the productivity; and a productivity sensitivity analysis result shows that the influences of horizontal well length, fracture half length,fracture number and fracture flow conductivity on the productivity have obvious limits, and a reasonable value should be selected from the perspective of economic development. The model and method have extremely high theoretical and application values for productivity prediction and productivity sensitivity analysis for the multi-section fractured horizontal well in the low-permeability tight gasreservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
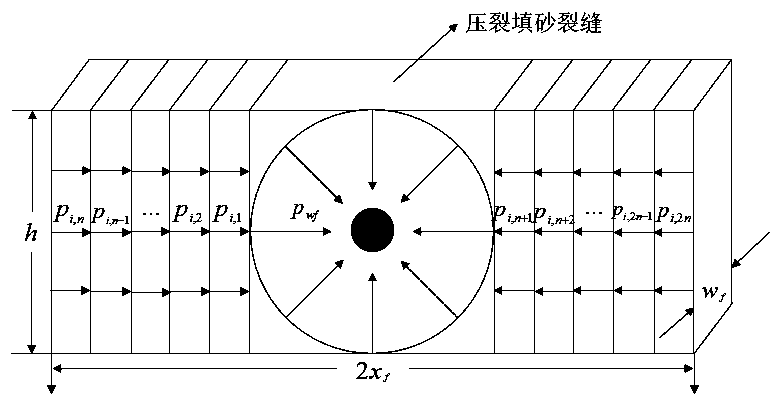
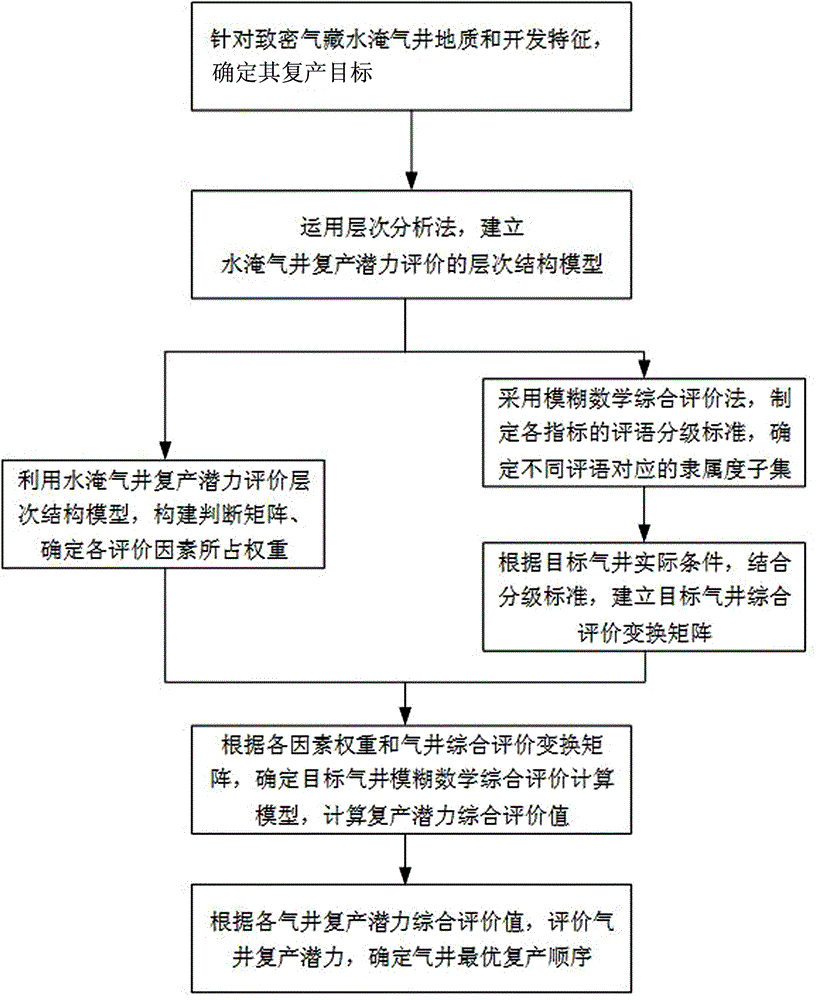
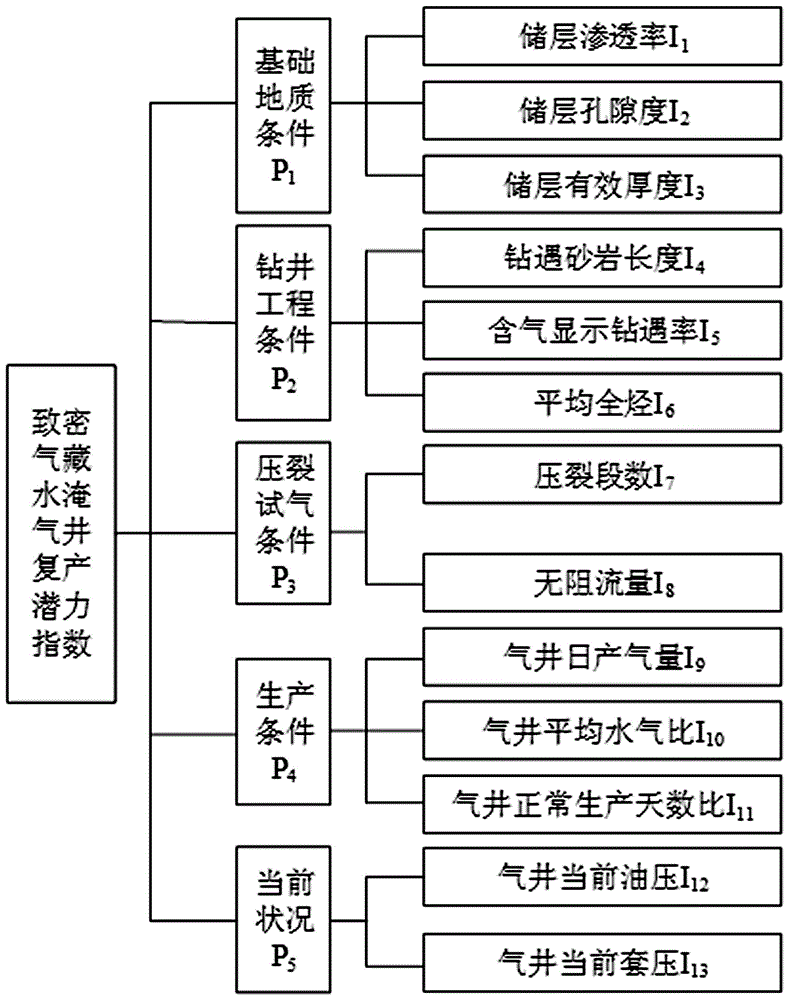
Method for evaluating reproduction potential of tight gas reservoir watered gas well
The invention belongs to the gas field exploitation research field, and especially relates to a method for evaluating reproduction potential of a tight gas reservoir watered gas well. The method includes the following steps: determining a reproduction goal of a tight gas reservoir watered gas well on the basis of the geological and exploitation features of the gas well; utilizing a hierarchy analysis method to establish a hierarchical structure model for different reproduction potential evaluations of the watered gas well; through the hierarchical structure model, constructing a judging matrix and determining weights of all evaluation factors; and utilizing a fuzzy mathematics comprehensive evaluation method to make remark and grading standards for all indexes, and establishing a target gas well comprehensive evaluation transformation matrix. A fuzzy mathematics comprehensive evaluation calculating model for a target gas well is determined on the basis of the weights of the indexes and the target gas well comprehensive evaluation transformation matrix, so that reproduction potential comprehensive evaluation values of the watered gas well are obtained and an optimal reproduction sequence of the gas well is determined. The method of the invention enables degrees of the advantages and disadvantages of the evaluation factors and comprehensive evaluation of reproduction potential of the watered gas well to be obtained, and is a scientific and effective method for reproduction of the tight gas reservoir watered gas well.
Owner:SINOPEC NORTH CHINA OIL & GAS CO
Apparatus and methods for culturing and/or transporting cellular structures
InactiveUS20100196871A1Easy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnimal reproductionDiffusionLiquid medium
An apparatus for culturing and / or transporting embryos, oocytes or other cellular structures, comprising a housing (12) having a gas space (28) and a media space (18) for a liquid medium separated from one another by a barrier (16) having one or more gas permeable regions to allow gas diffusion from the gas space to the media space, and an essentially gas-tight gas closure means (14) adapted to restrict the passage of gas into the container from the exterior environment, and liquid closure means (14, 16) adapted to engage with the housing to form a liquid-tight seal for retaining liquid in the media space. The barrier preferably comprises an at least partly gas-permeable insert (16) that when inserted into the housing forms together with the housing a gas space (28) and a liquid media space (18) in gas communication with one another via diffusion through the insert. The insert may be at least partly porous, the pores of the insert comprising at least part of the gas space.
Owner:ROBIO SYST
On-site shale gas desorption analyzer
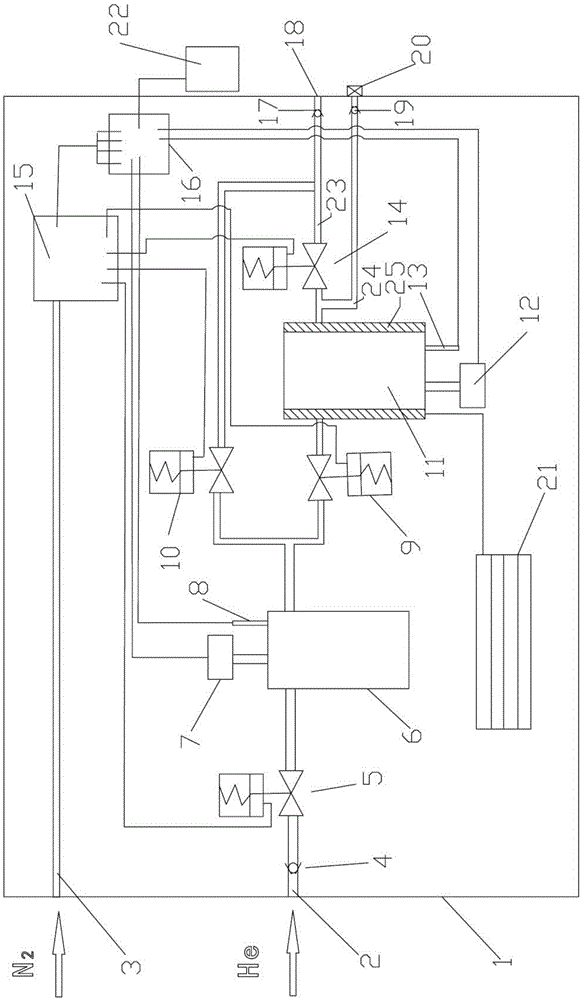
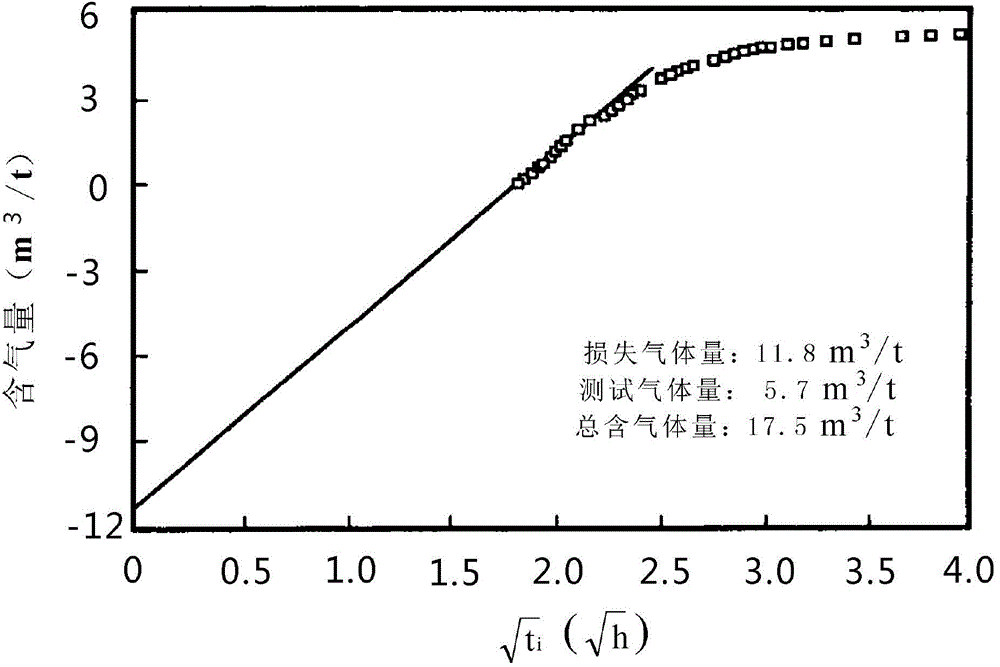
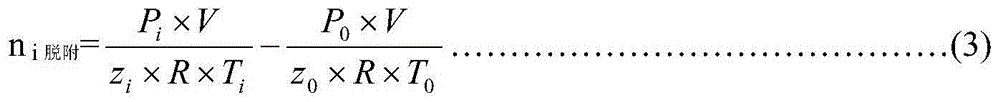
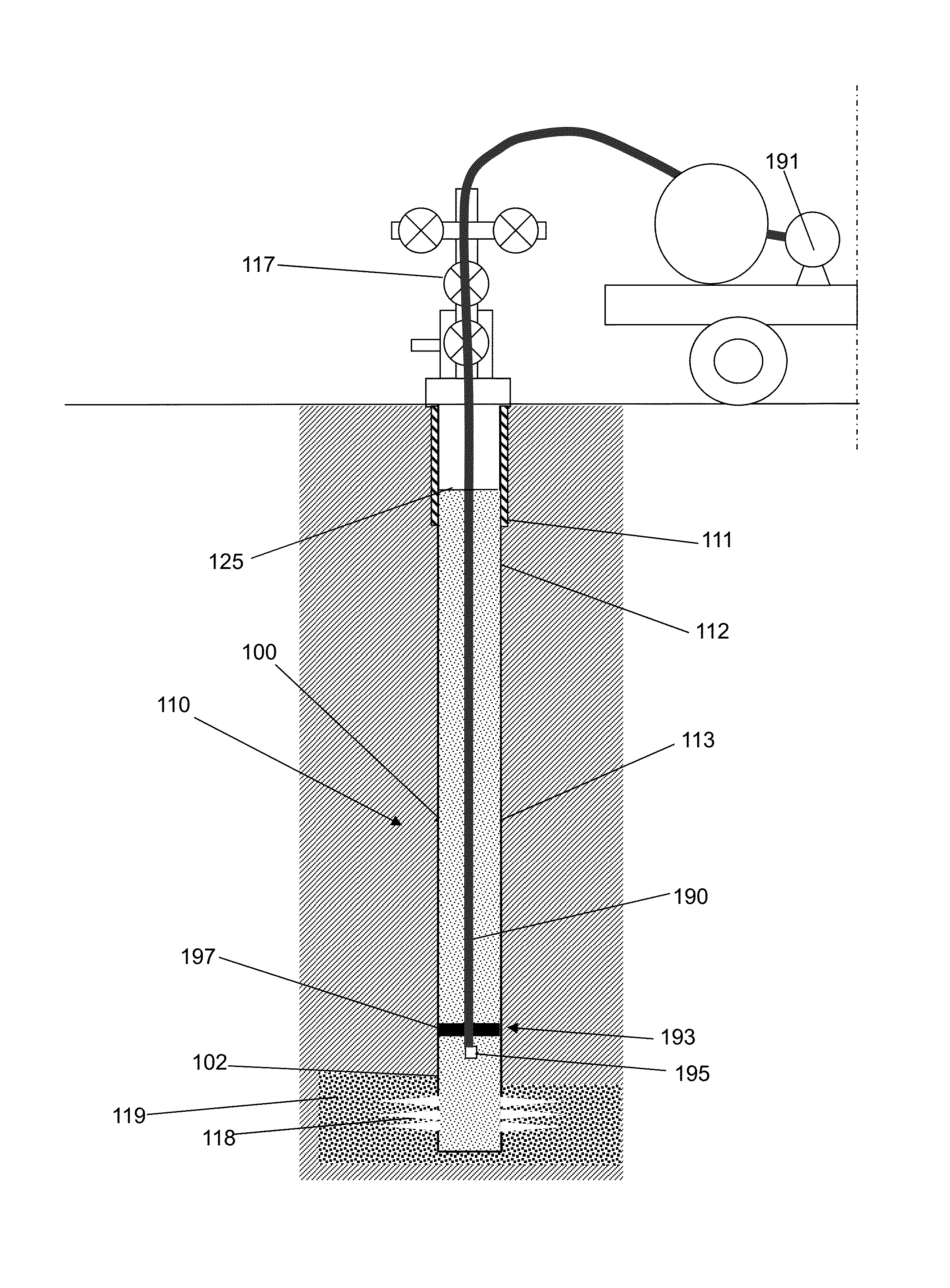
The invention discloses an on-site shale gas desorption analyzer. The on-site shale gas desorption analyzer disclosed by the invention is compact in overall structure and low in experimental environment requirements and is applied to convenient on-site testing of a vehicle-mounted room or simple room nearby a well site. The analyzer is low in power, and power of the analyzer can be supplied by a generator or supplied conventionally. According to the set of instrument, the content of gas of a shale gas site can be tested, the content of gas of tight gas reservoir, coal bed gas and other site rock cores also can be tested, and the accuracy is high. According to the well site customer test requirements, the rapid site shale gas desorption analyzer can be connected with an on-line gas analyzer, and gas components and change in the shale gas desorption process can be synchronously analyzed. The components of the shale gas can be rapidly determined, and the degassing rule can be researched. The on-site shale gas desorption analyzer is equipped with a rapid gas sample production joint, and the gas separated from rock core samples can be conveniently collected to be used for subsequent accurate testing and analysis in a lab, such as gas component analysis and gas isotope analysis in the lab.
Owner:王思波
Method of determining reservoir pressure
A well test method for use in tight gas reservoirs prior to hydraulic fracture stimulation. The method can use injection of water using low-rate surface pumps into the reservoir below parting pressure. The measured rates and pressures are converted to sandface rate and pressure datasets for each stage. The technique can utilize either surface or bottom-hole pressure sensors. The resulting sandface datasets are analyzed using the baseline / calibration method or other analysis appropriate to stage data to determine reservoir flow properties. The small-volume, staged well test enables estimation of the flow properties of reservoir, including pressure and permeability, in hours rather than days.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
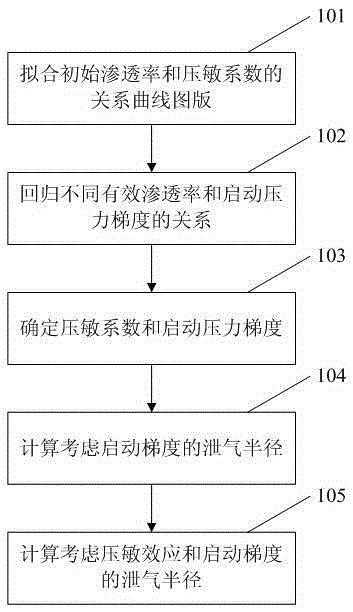
Method for calculating gas drainage radius by considering seepage mechanism of tight gas reservoir
InactiveCN106547930AReduce external dependencePlay a supporting roleFluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsInitial permeabilityCalculation methods
The invention provides a method for calculating a gas drainage radius by considering a seepage mechanism of a tight gas reservoir. The method for calculating the gas drainage radius by considering the seepage mechanism of the tight gas reservoir comprises the steps of 1, fitting a relation curve chart of initial permeability and a pressure-sensitive coefficient through a physical simulation experiment; 2, obtaining a relationship between effective permeability and a starting pressure gradient through the physical simulation experiment; 3, determining the pressure-sensitive coefficient and the starting pressure gradient through the chart; 4, calculating the gas drainage radius by considering the starting gradient; and 5, calculating the gas drainage radius by considering a pressure-sensitive effect and the starting gradient. According to the method for calculating the gas drainage radius by considering the seepage mechanism of the tight gas reservoir, external dependency of Chinese energy is greatly reduced; Chinese energy structure adjustment is promoted; and the method has an important support effect for stable production of natural gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of fracturing subterranean formations with crosslinked fluid
ActiveUS9194223B2Particular applicabilityHigh viscosityFluid removalDrilling compositionApparent viscosityFracturing fluid
Subterranean formations, such as tight gas formations, may be subjected to hydraulic fracturing by introducing into the formation a fracturing fluid of an aqueous fluid, a hydratable polymer, a crosslinking agent and proppant. The fluid enters the reservoir through an entrance site. The apparent viscosity of the fluid decreases distally from the entrance site such that at in situ conditions:(a) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid 100 feet from the entrance site is less than 10 percent of the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid at the entrance site;(b) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid 15 minutes after introduction into the entrance site is less than 15% of the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid at the entrance site; and / or(c) the apparent viscosity of the fracturing fluid is less than 10 cP within 15 minutes after being introduced through the entrance site.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Identification method for unconventional superpressured tight gas effective reservoir
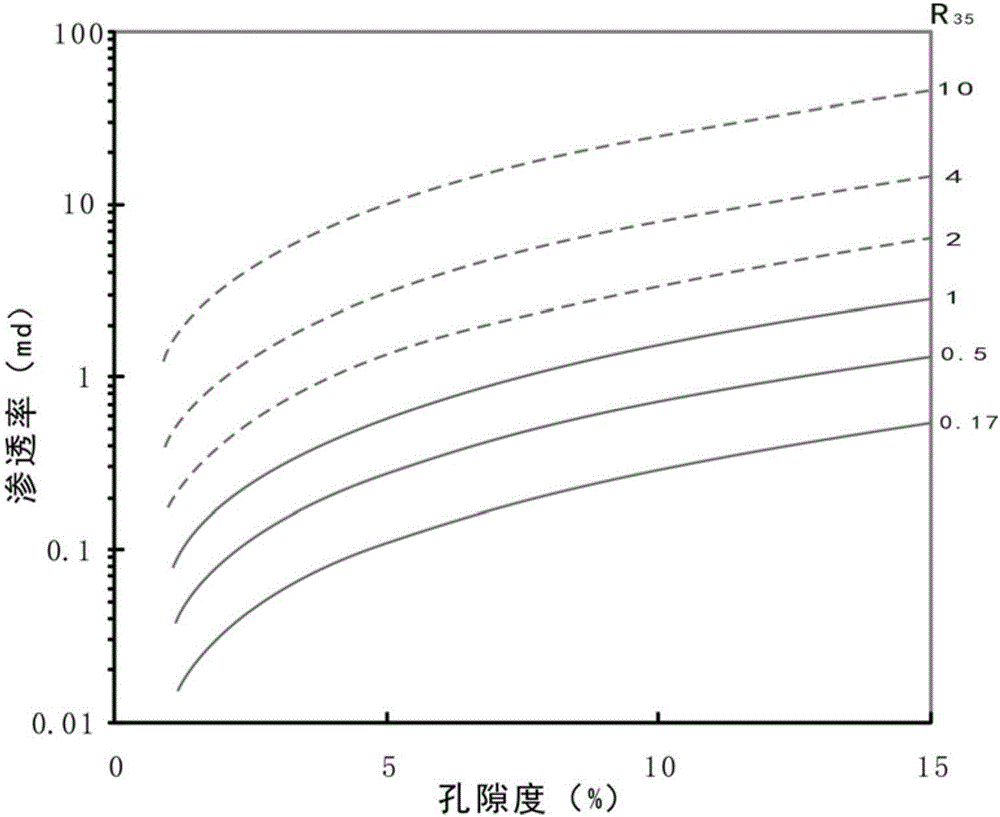
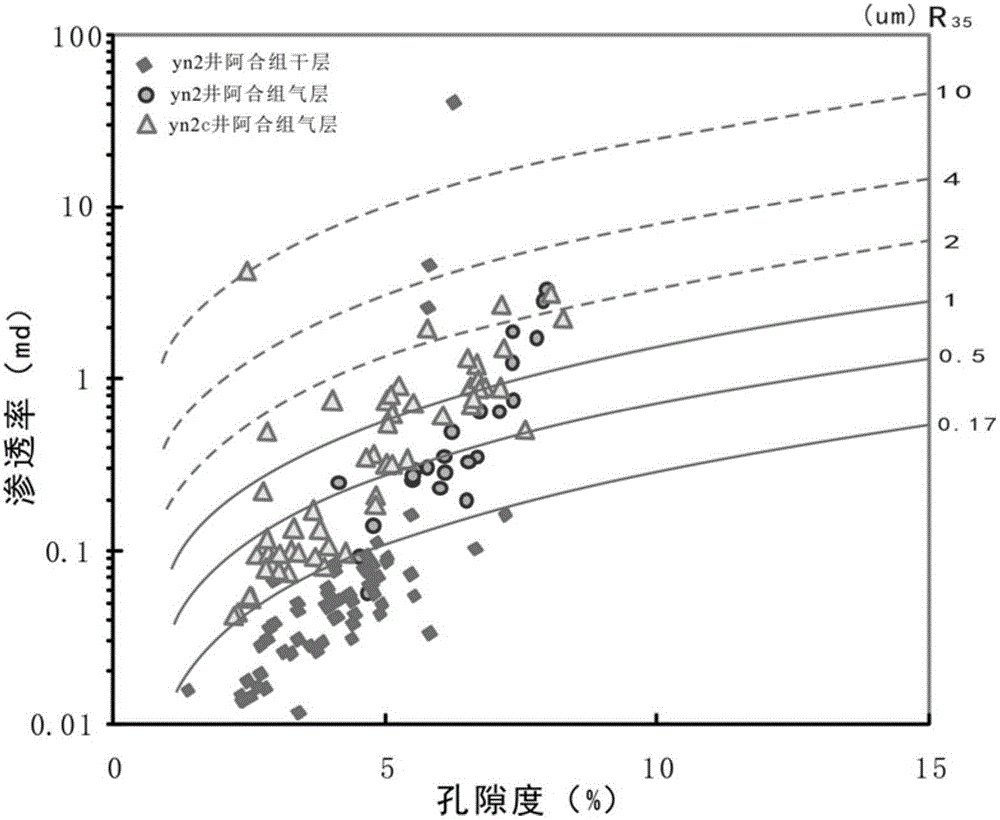
ActiveCN106599482AEfficient identificationQuick identificationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPorosityThroat
The invention provides an identification method for an unconventional superpressured tight gas effective reservoir. The identification method comprises the steps of acquiring the porosity, permeability, pore throat radius distribution characteristics and high-pressure mercury injection data of a rock core of a gas-producing layer section of a production well of a superpressured tight gas reservoir; by utilizing a linear regression equation, establishing relational expressions between a throat radius representation value and the porosity and between the throat radius representation value and the permeability, and establishing a projection chart of the porosity, the permeability and the throat radius representation value; by utilizing data of the production well, projecting porosity values and permeability values of the gas layer and a dry layer to the projection chart; selecting the throat radius representation value, which optimally separates the dry layer from the gas layer, as a throat threshold value for identifying the unconventional superpressured tight gas effective reservoir; and projecting to-be-identified reservoir porosity and permeability data to the projection chart, and judging reservoir effectiveness according to the positions of a projection point and a curve of the throat radius representation value. The method is simple, quick, convenient and accurate.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
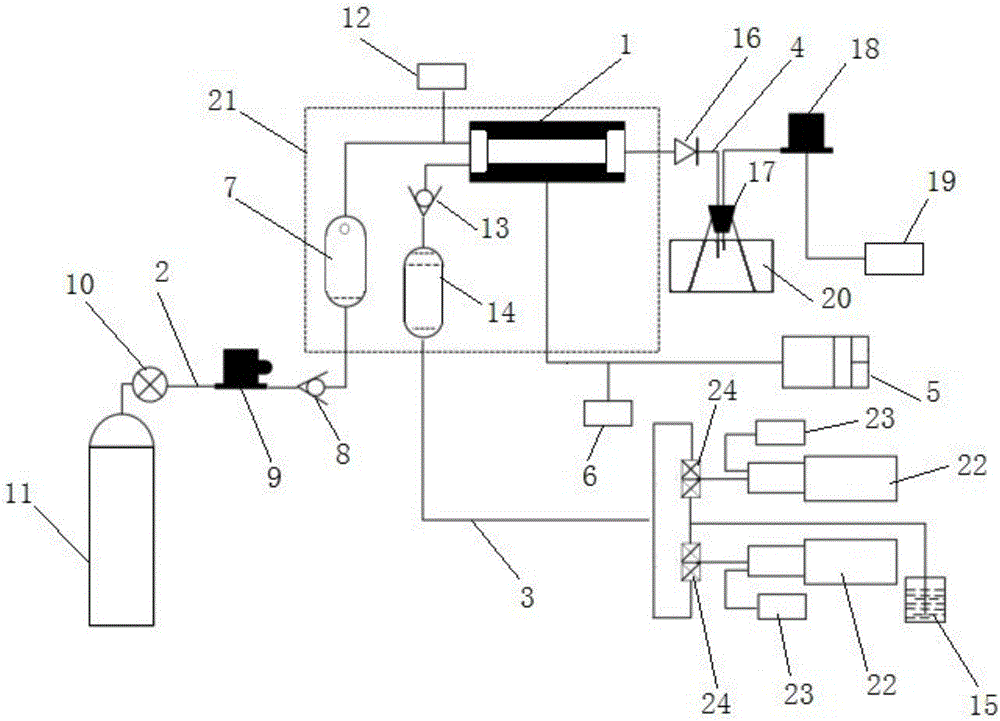
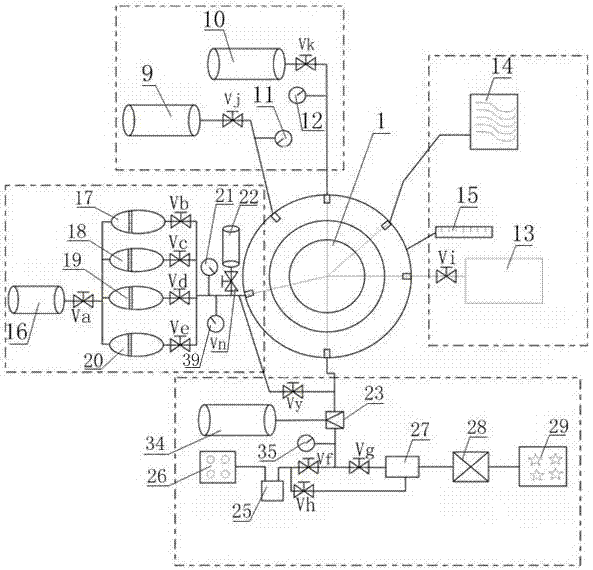
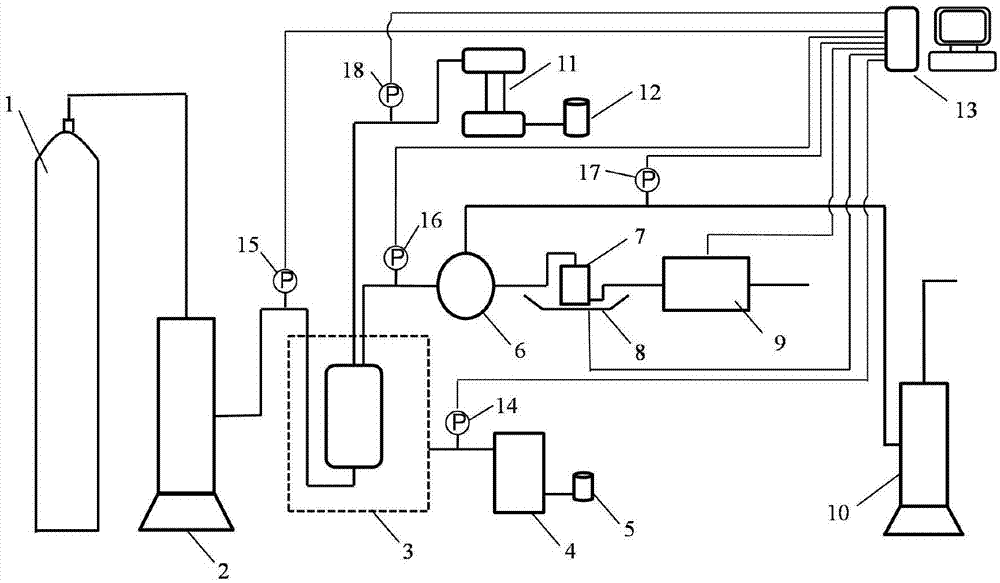
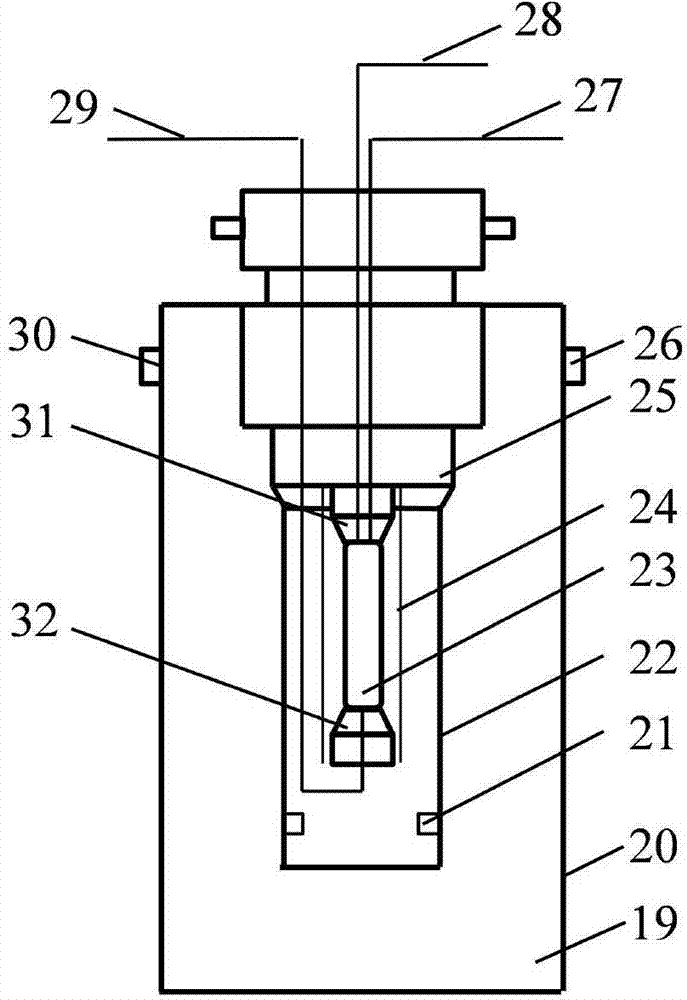
Evaluation instrument for damage of aqueous phase trapping of high-temperature high-pressure tight gas reservoir
ActiveCN104764859ASolve the problem that is not easy to take outMaterial analysisTrappingGas cylinder
The invention discloses an evaluation instrument for the damage of aqueous phase trapping of a high-temperature high-pressure tight gas reservoir. The evaluation instrument comprises a rock-core holder system, a liquid displacement system, a gas displacement system, a gas-liquid metering system and a data acquisition system, wherein the rock-core holder system comprises a rock-core holder 3, a confining pressure pump 4, a confining pressure sensor 14 and a temperature-rising / temperature-controlling device 21; the liquid displacement system comprises a liquid storage tank 12, a liquid metering pump 11 and a liquid displacement pressure sensor 18; the gas displacement system comprises a gas cylinder 1, an inlet pressure stabilizing tank 2, a pressure returning device 6 and a pressure returning stabilizing tank 10; the gas-liquid metering system comprises a gas-liquid separator 7, an electronic scale 8 and a gas flow meter 9; and the temperature-rising / temperature-controlling device 21 and the confining pressure sensor 14 and the like are connected with a computer 13 to form the data acquisition system. The evaluation instrument disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the automation degree is high, the function is complete, the damage process of the aqueous phase trapping of the tight gas reservoir under the operation links such as drilling, completion, workover and yield increase can be simulated, and the damage degree of the aqueous phase trapping can be evaluated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
Large-area tight gas reservoir exploitation method
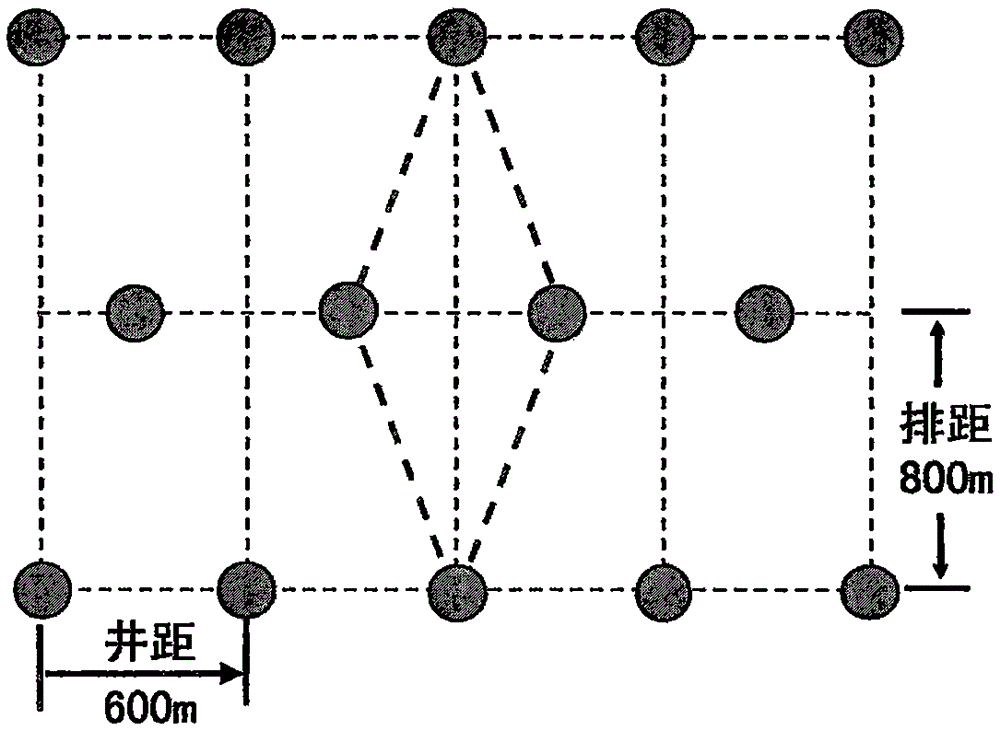
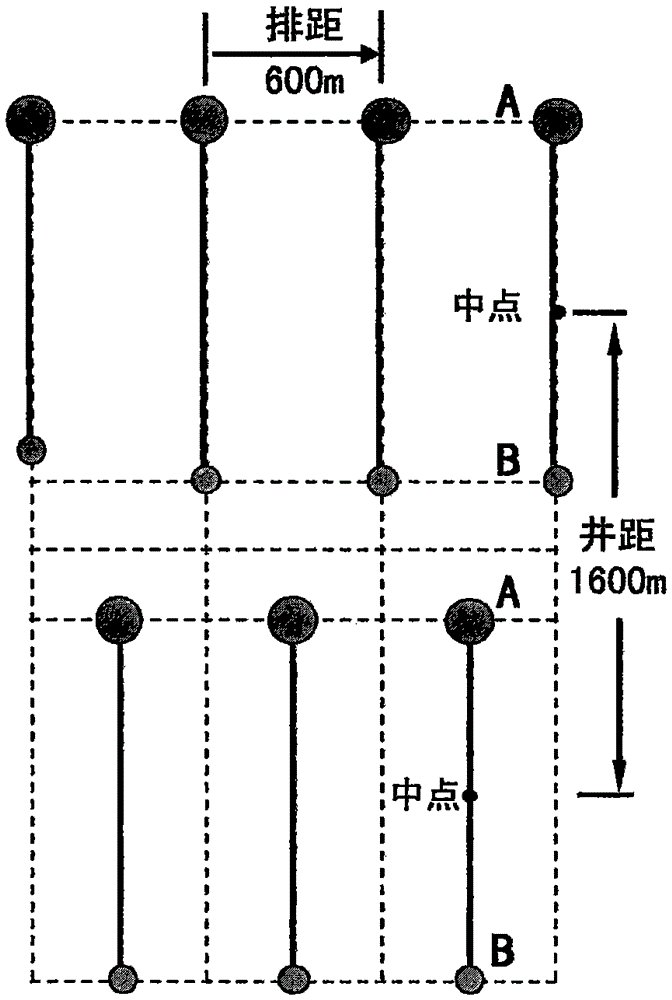
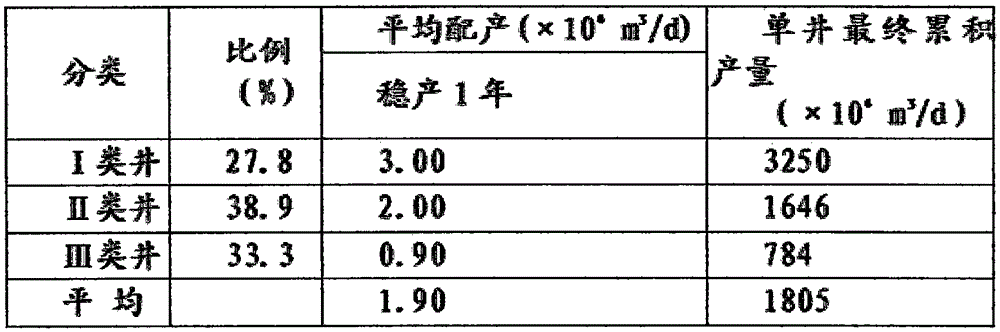
InactiveCN105545265AImprove the mining effectEnhanced overall recoveryFluid removalHorizontal wellsEnvironmental geology
The invention provides a large-area tight gas reservoir exploitation method. The large-area tight gas reservoir exploitation method comprises the following steps that a relative enrichment region is selected, the production building region gas bearing area and the proven geological reserve in the relative enrichment region are determined, the production building region gas bearing area is the area of a deployable well location, and then the production building region area of horizontal wells and the production building region area of vertical wells are determined according to geological and seismic data; the vertical well indexes and the horizontal well indexes are determined; the well pattern and well spacing of the vertical wells and the well pattern and well spacing of the horizontal wells are determined; the well number limit of the horizontal wells and the vertical wells is determined according to the well pattern and well spacing, the production building region area of the vertical wells and the production building region area of the horizontal wells; gas reservoir exploitation of the relative enrichment region comprises a gas reservoir production building period, a gas reservoir stable production period and a gas reservoir decline period, and the gas reservoir exploitation indexes are determined. The method is suitable for a large-area tight gas reservoir, the exploitation efficacy is improved, and the recovery rate is increased while the good exploitation benefit is achieved.
Owner:郭建林
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com