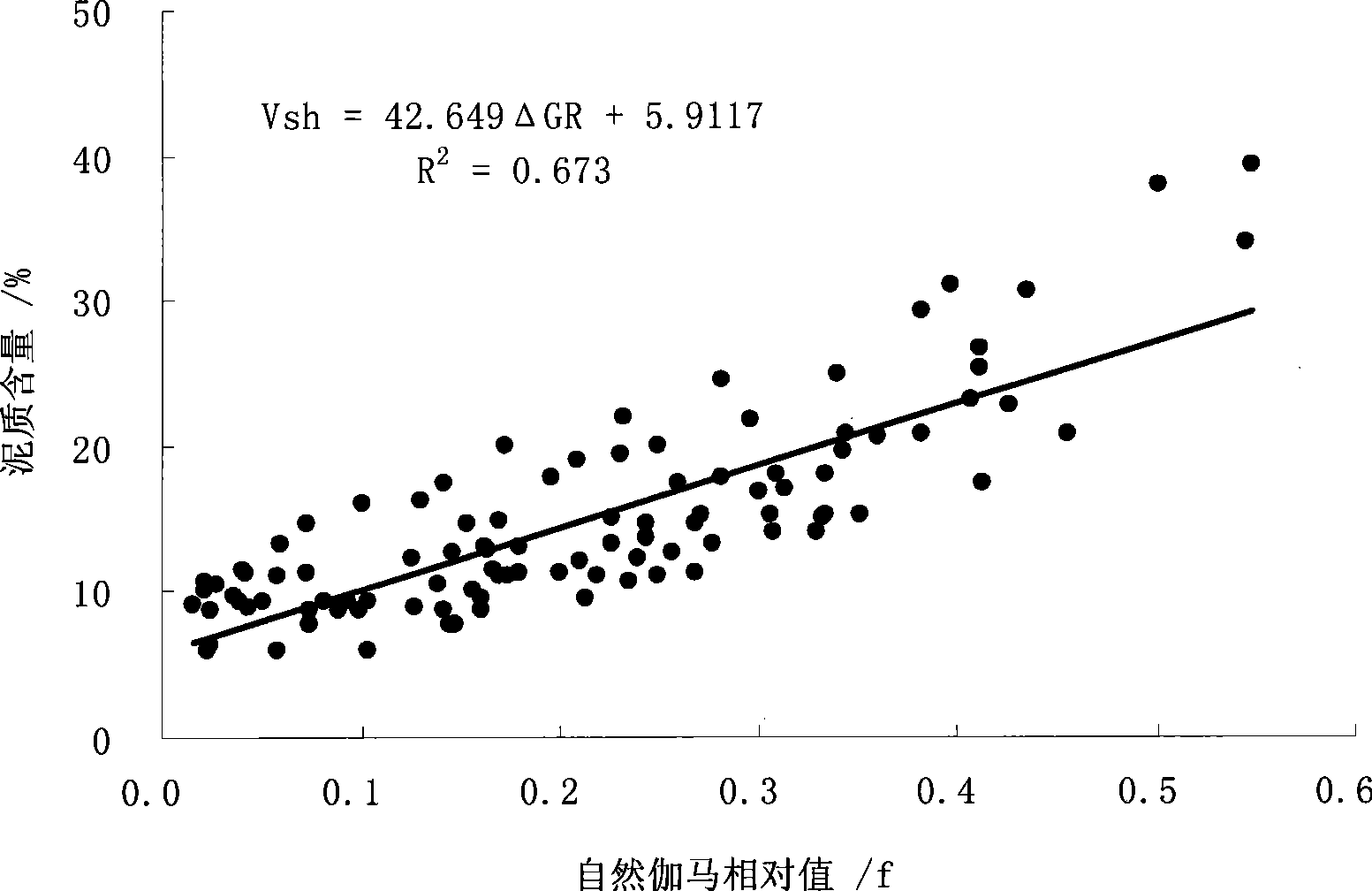
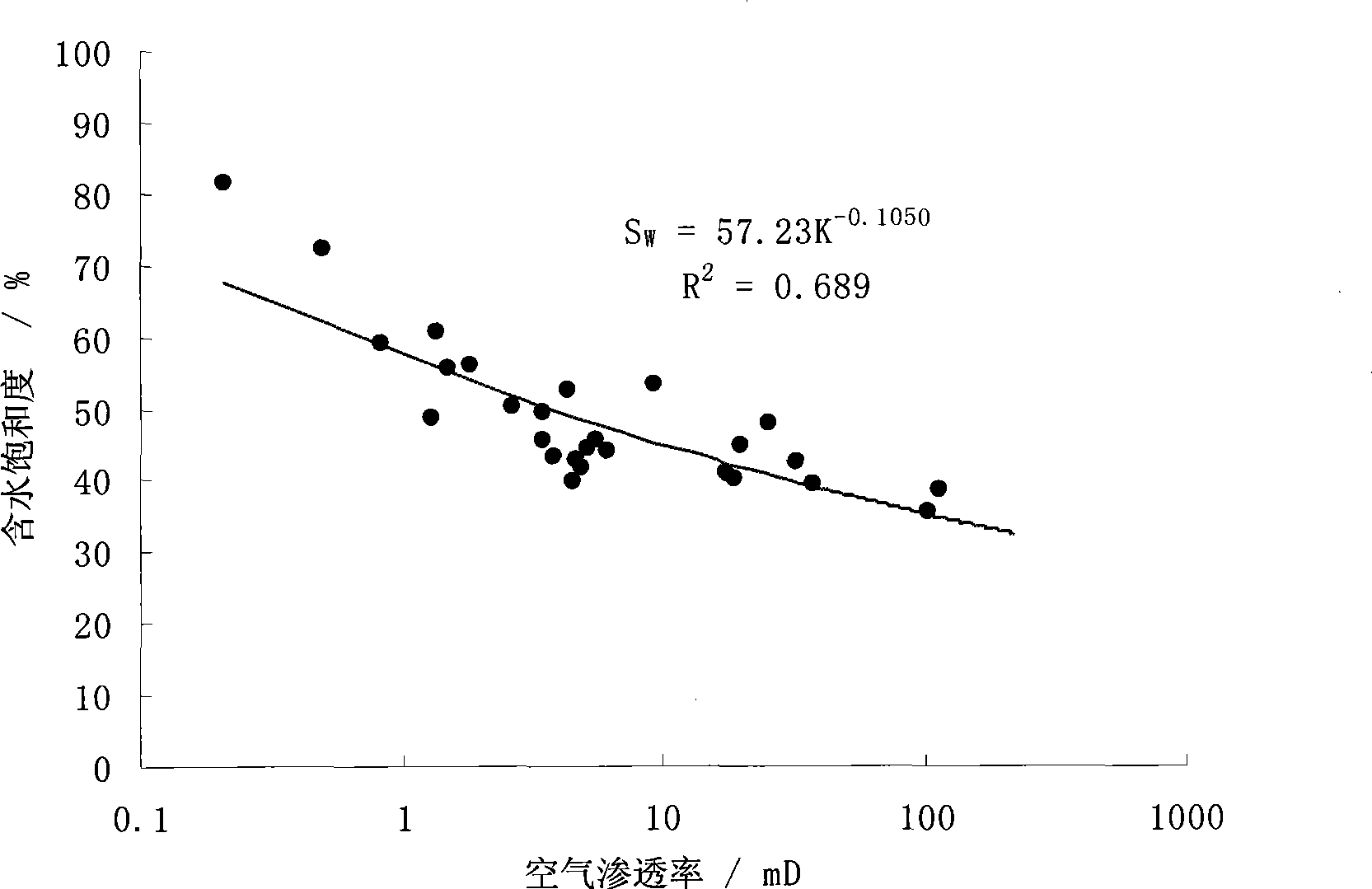
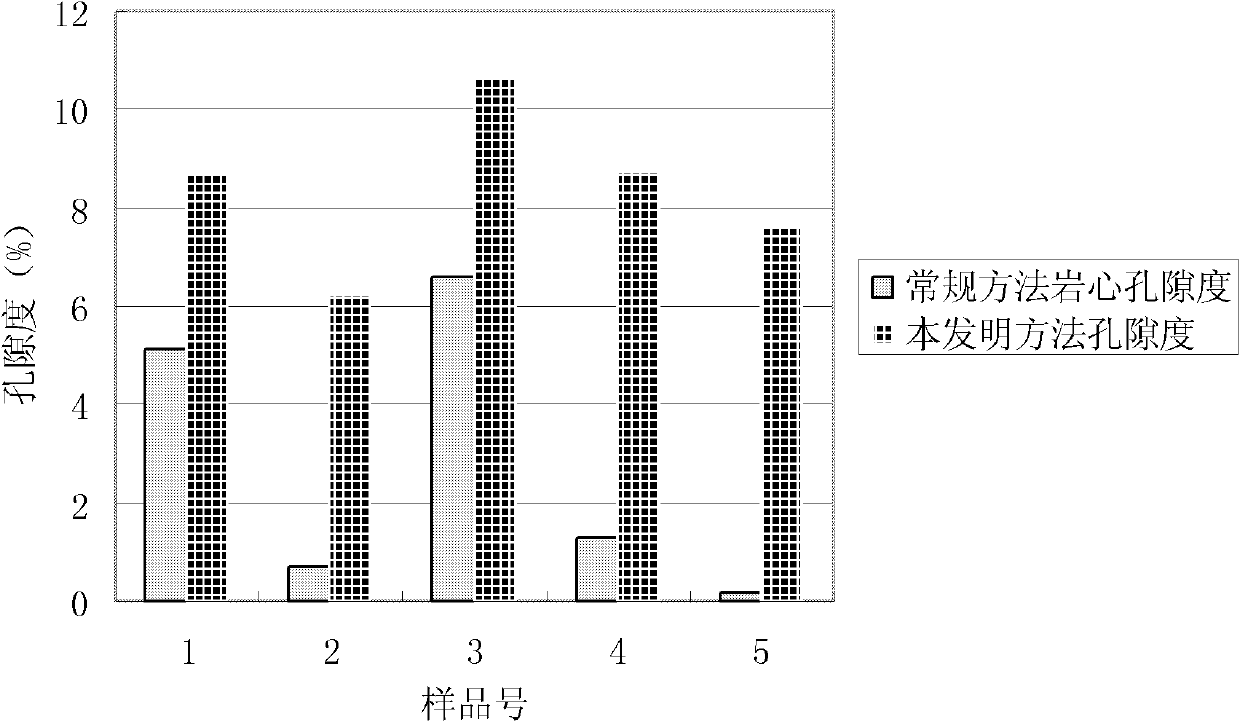
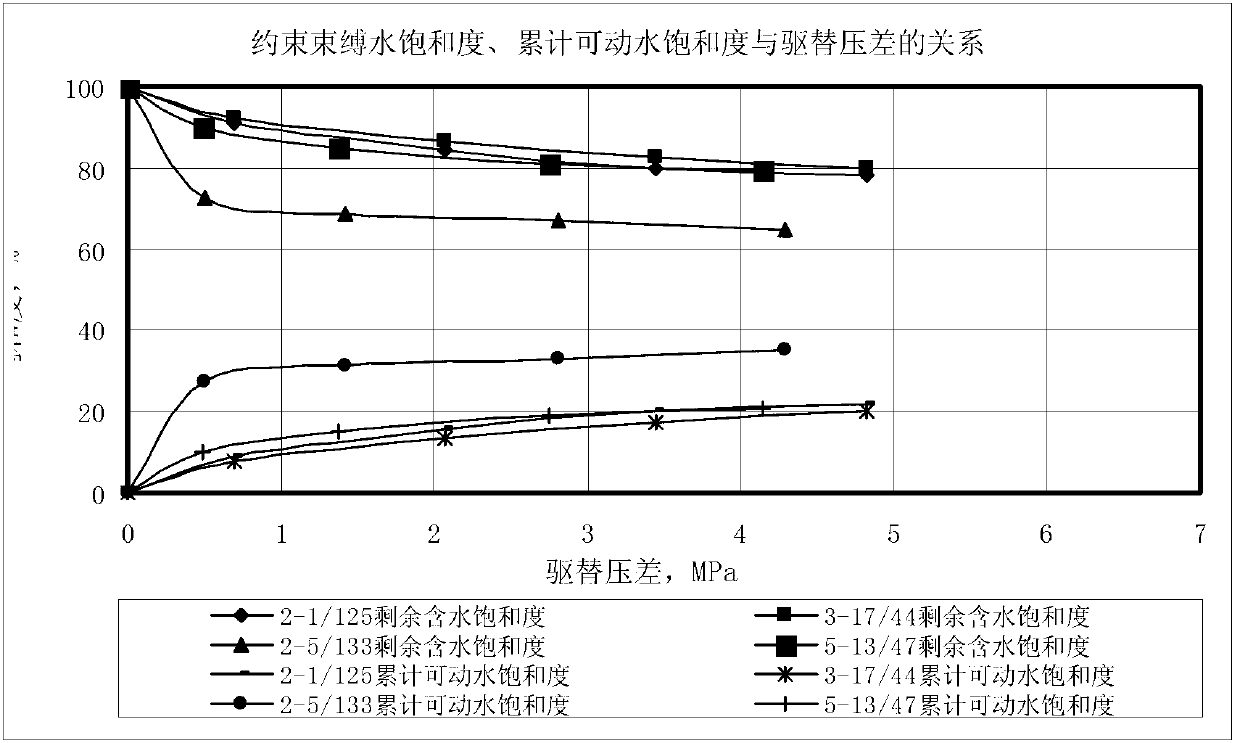
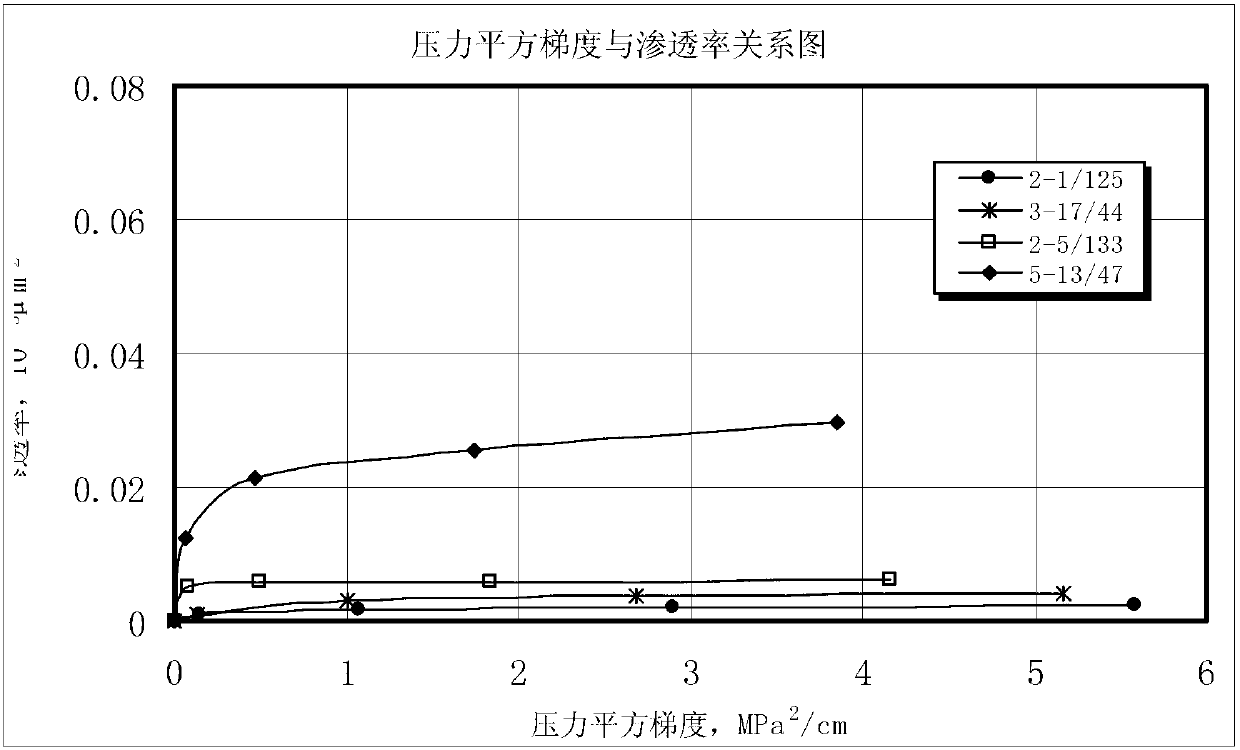
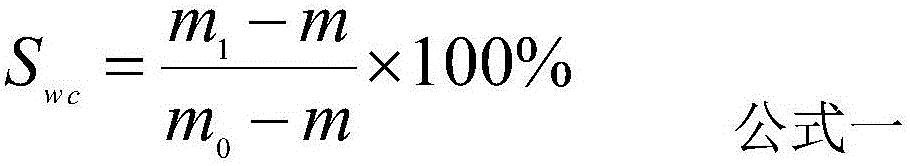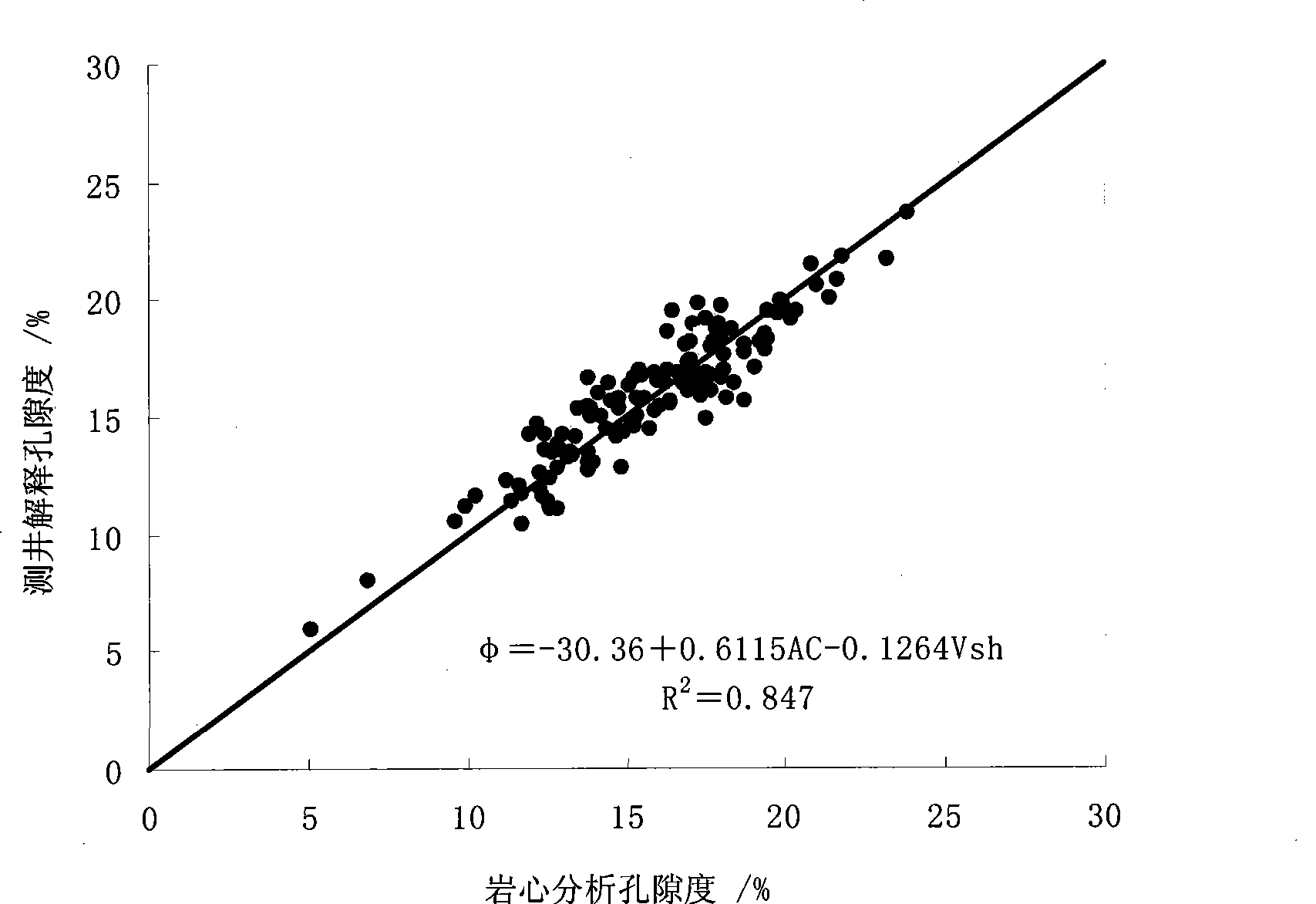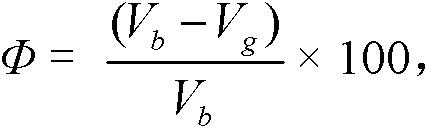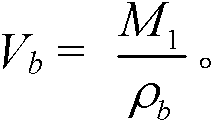Patents
Literature
1016 results about "Water saturation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Water saturation. 1. n. [Formation Evaluation] The fraction of water in a given pore space. It is expressed in volume/volume, percent or saturation units. Unless otherwise stated, water saturation is the fraction of formation water in the undisturbed zone.
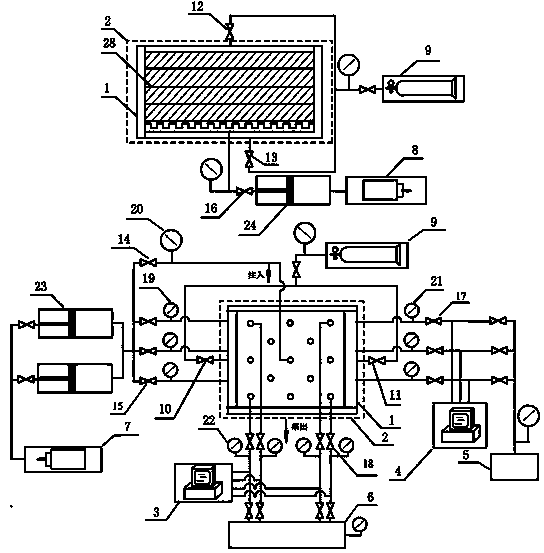
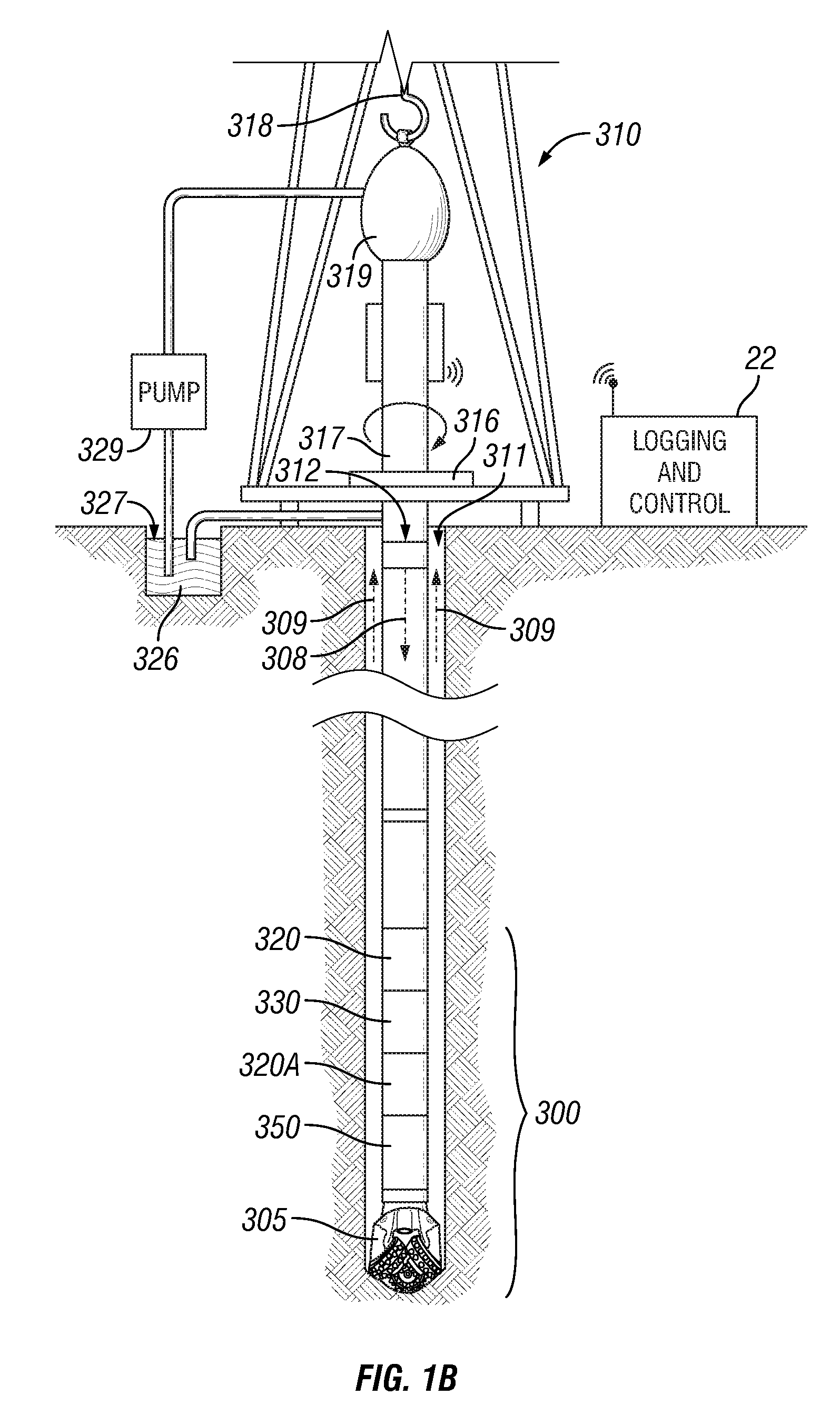
Oil-gas well hydraulically-created-fracture expansion visualization experiment method and oil-gas well hydraulically-created-fracture expansion visualization experiment device
ActiveCN103485759AFor the purpose of visualizationSurveyEarth material testingEpoxyHigh pressure water
The invention relates to an oil-gas well hydraulically-created-fracture expansion visualization experiment method and an oil-gas well hydraulically-created-fracture expansion visualization experiment device. The device is composed of a rock sample chamber, a crustal loading unit, a simulation fracturing string, a high-speed camera, a high-pressure pumping unit, a data measuring and collecting unit and the like, and four transparent observation ports are formed on a top cover of the rock sample chamber. The method includes firstly, preparing a flat-plate-type rock sample, performing high-pressure-water cutting to preform a natural fracture, and filling the natural fracture with epoxy resin to form a filled-type fracture; secondly, performing water saturation on the rock sample for 3-5 days, and using epoxy resin to wrap the rock sample after water saturation; thirdly, loading three-axis stress on the rock sample, drilling a borehole under the condition that the three-axis stress is applied on the rock sample, and mounting the simulation fracturing string; finally, connecting a high-pressure pipeline with a constant-flux pump, pumping fracturing liquid, recording a fracture expansion path by the high-speed camera, and measuring pumping pressure changes by a pressure transmitter. By the method and the device, the hydraulically-created-fracture expansion path can be visualized on a plane, and a novel experiment method is provided for studying on a hydraulically-created-fracture expansion mechanism.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method for calculating oil saturation of reservoir
ActiveCN102434152ASolve the difficulty of low accuracy in quantitative evaluation of saturationIn line with the actual lawBorehole/well accessoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
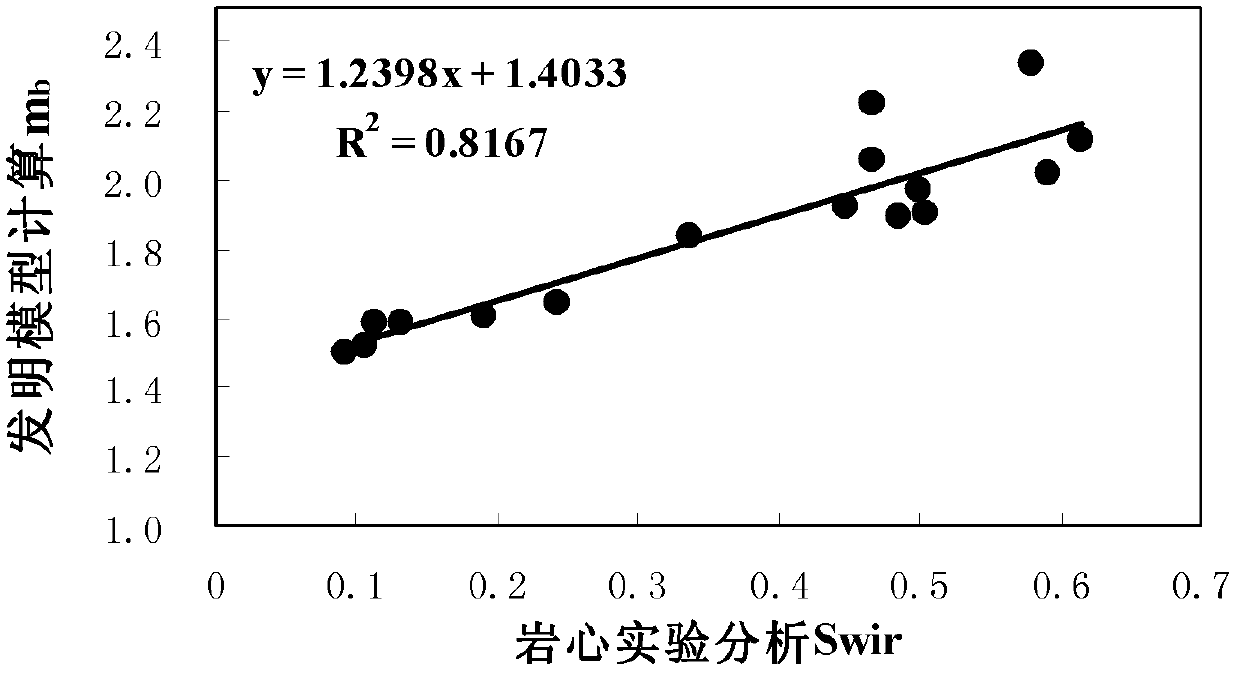
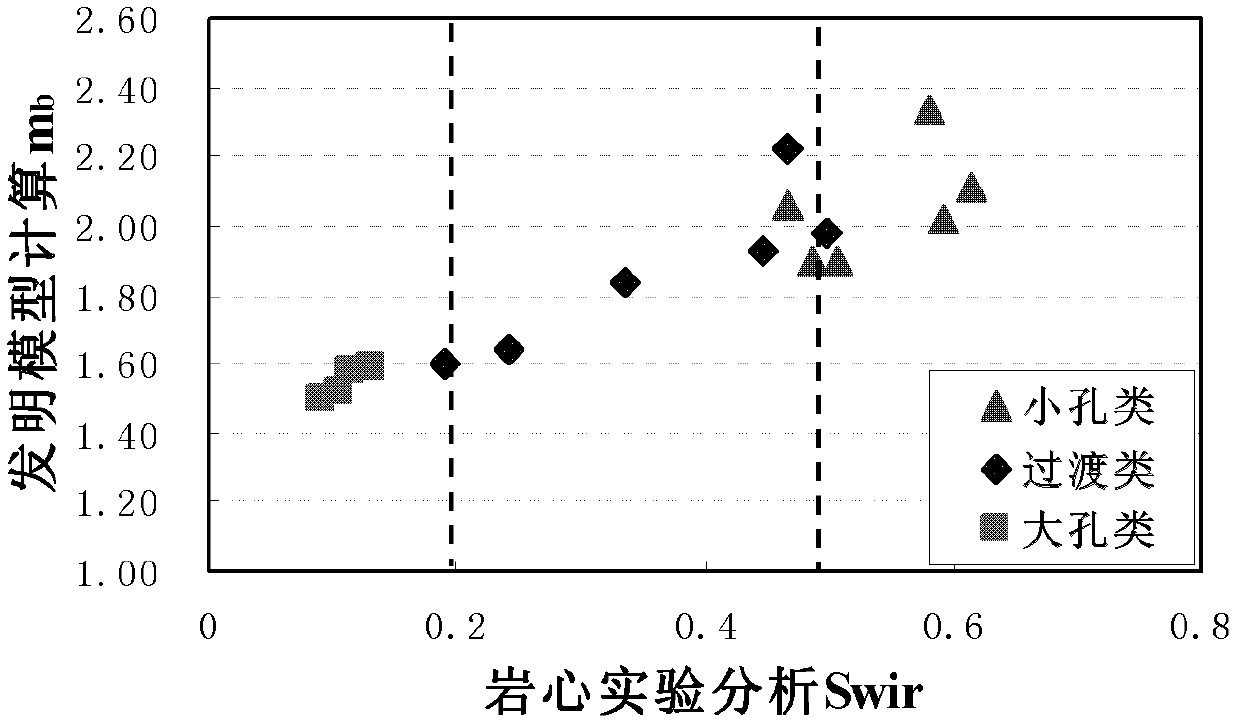
The invention discloses a method for calculating oil saturation of a reservoir. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a reservoir oil saturation model including a free fluid porosity phi f, a bound fluid porosity phi b, as well as corresponding macropore bond index mf, micropore bond index mb and micropore bond index characteristic value parameters; measuring a core porosity phi of a selected core sample; carrying out a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum experiment and an electric petrophysical experiment on the selected core sample to determine the core porosity phi and bound water saturation Swir of the selected core sample, the free fluid porosity phi f and bound fluid porosity phi b, stratum water resistivity Rw of a saturated rock sample, saturated water rock resistivity Ro of each rock sample, and resistivity Rt of each rock under different conditions of water saturation Sw; determining parameters of a reservoir oil saturation model by adopting an optimization data fitting method; establishing a relationship between the core micropore bond index mb and the bound water saturation Swir; classifying reservoir cores according to the bound water saturation; and determining a saturation index n of each type of cores by using the optimization fitting algorithm.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
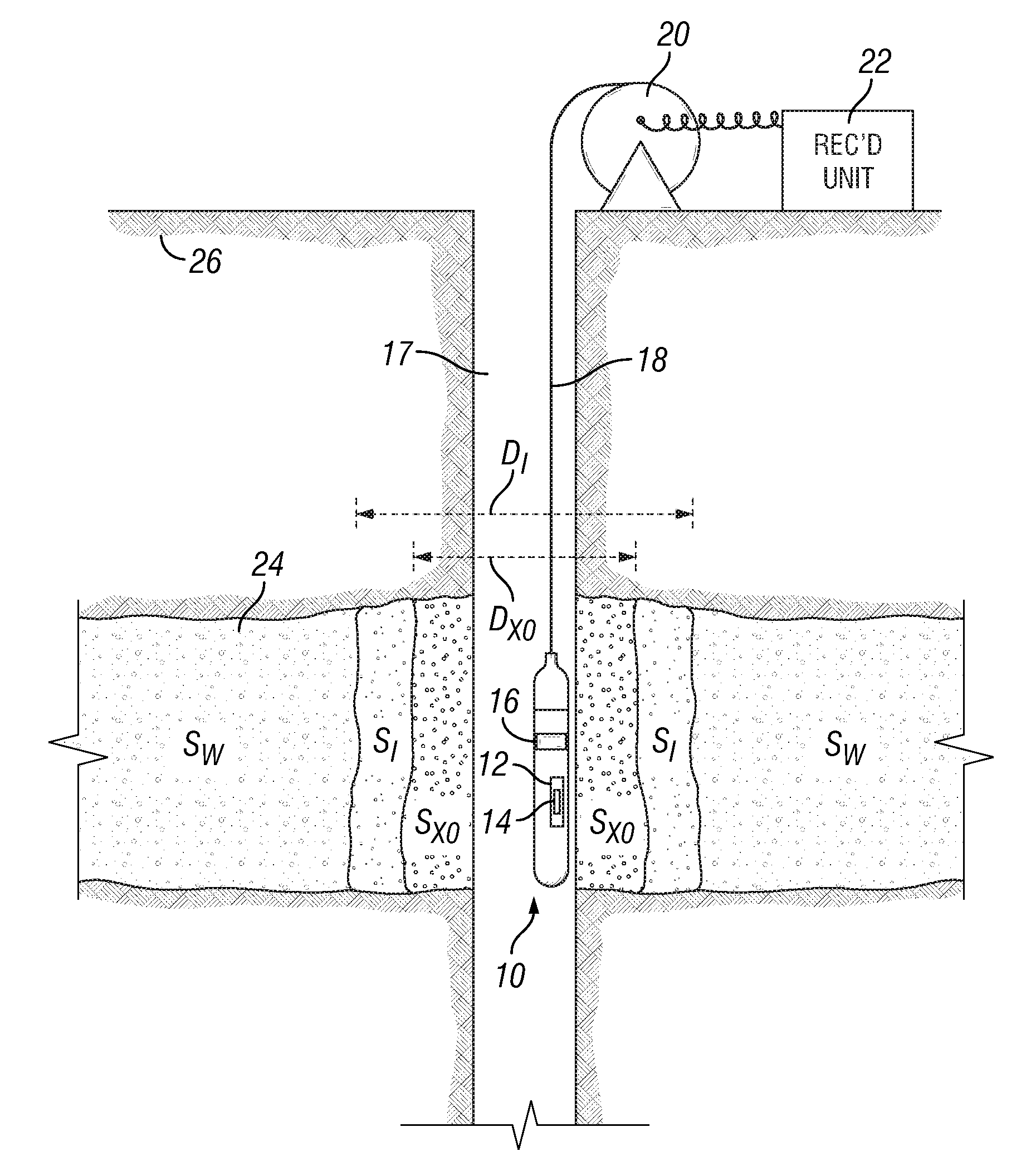
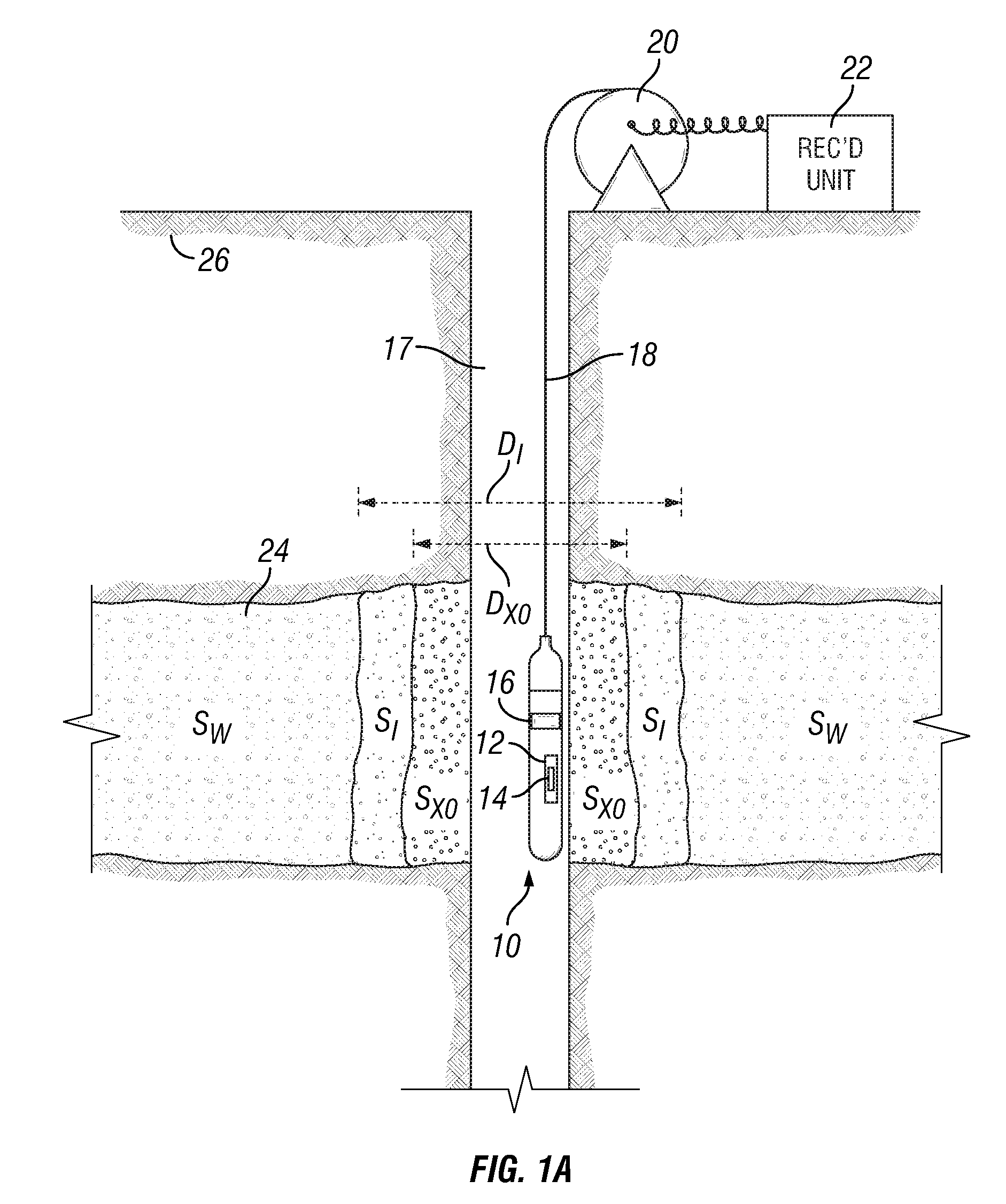
Estimating petrophysical parameters and invasion profile using joint induction and pressure data inversion approach
ActiveUS20100185393A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyRate of penetrationSegregation effect
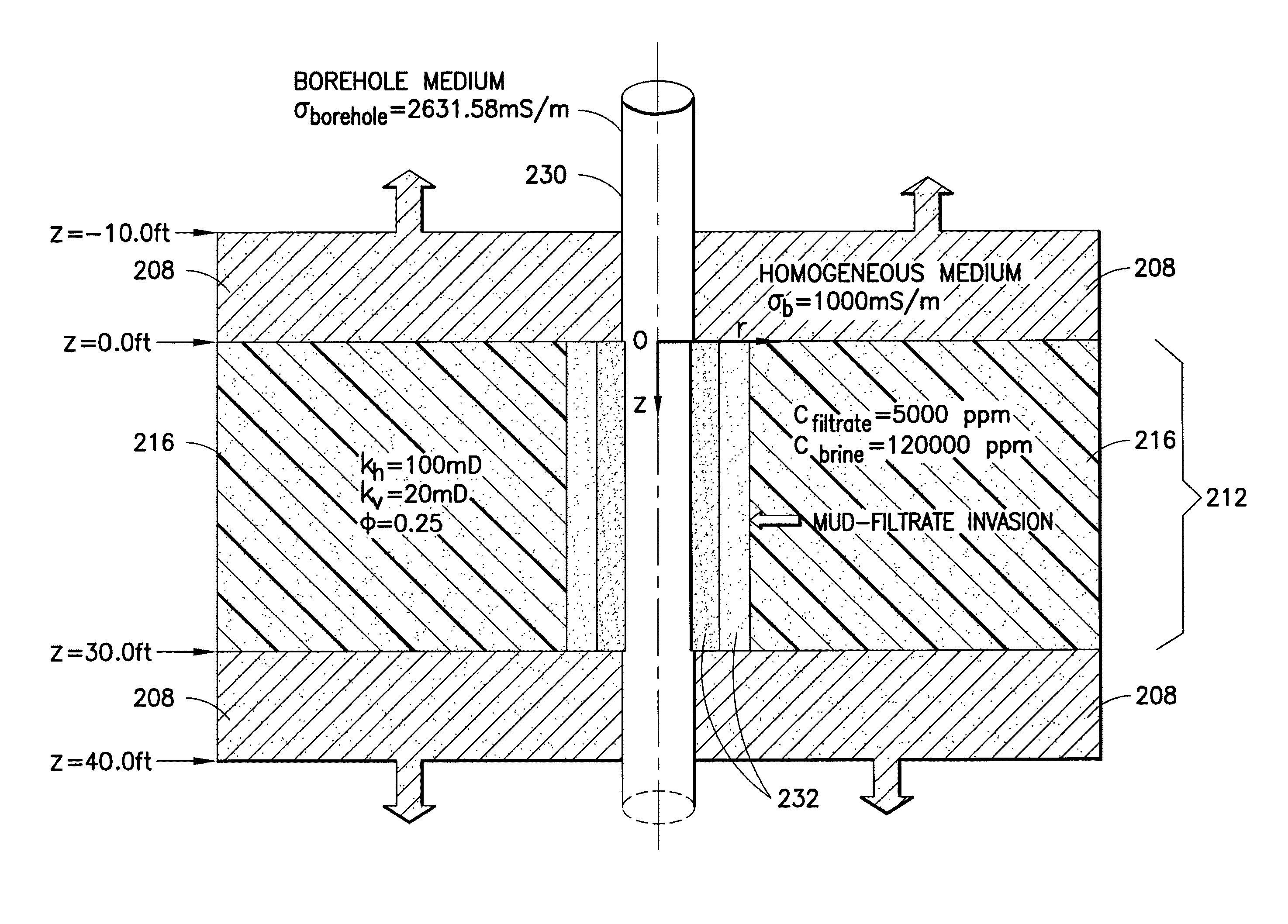
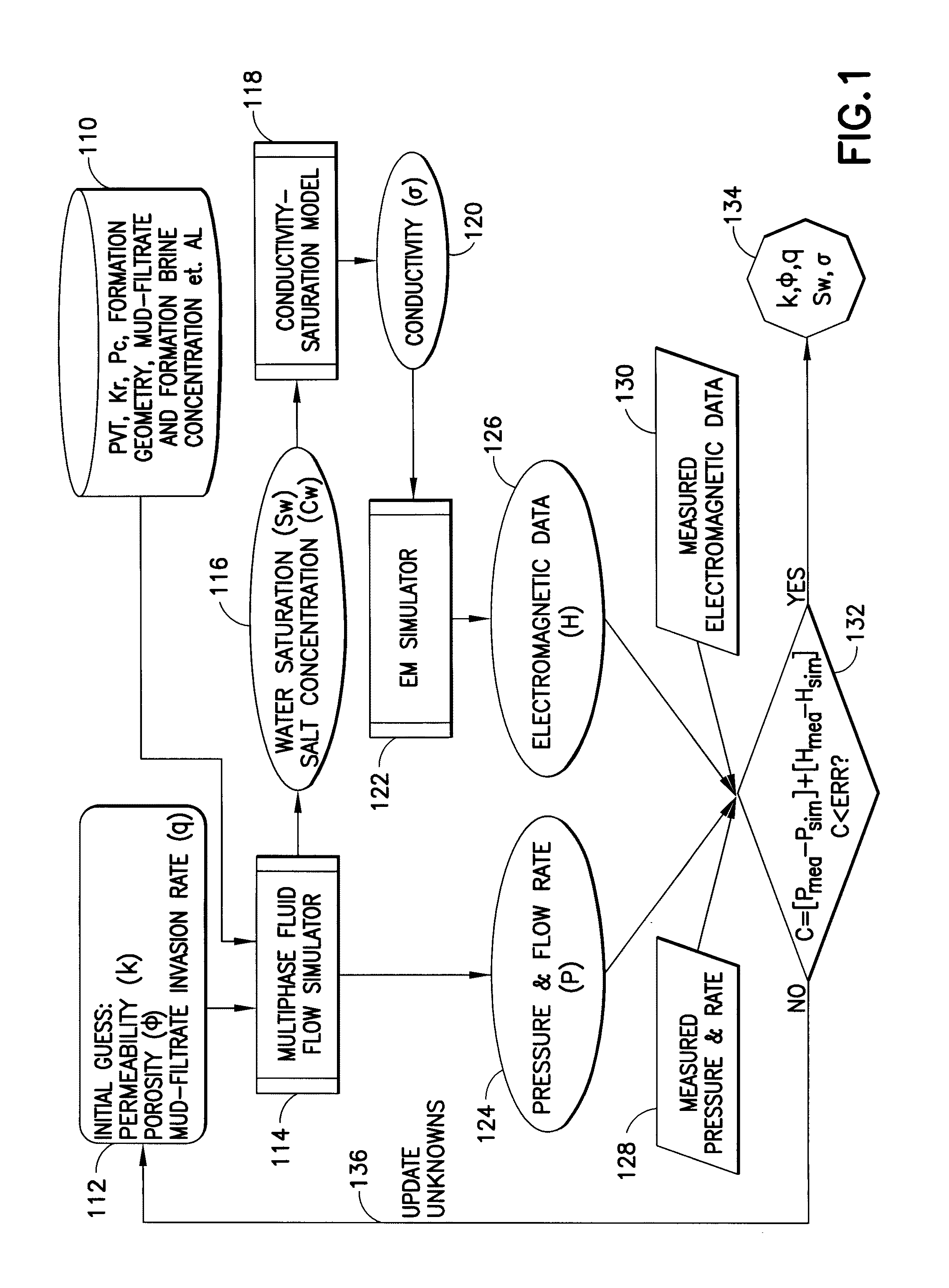
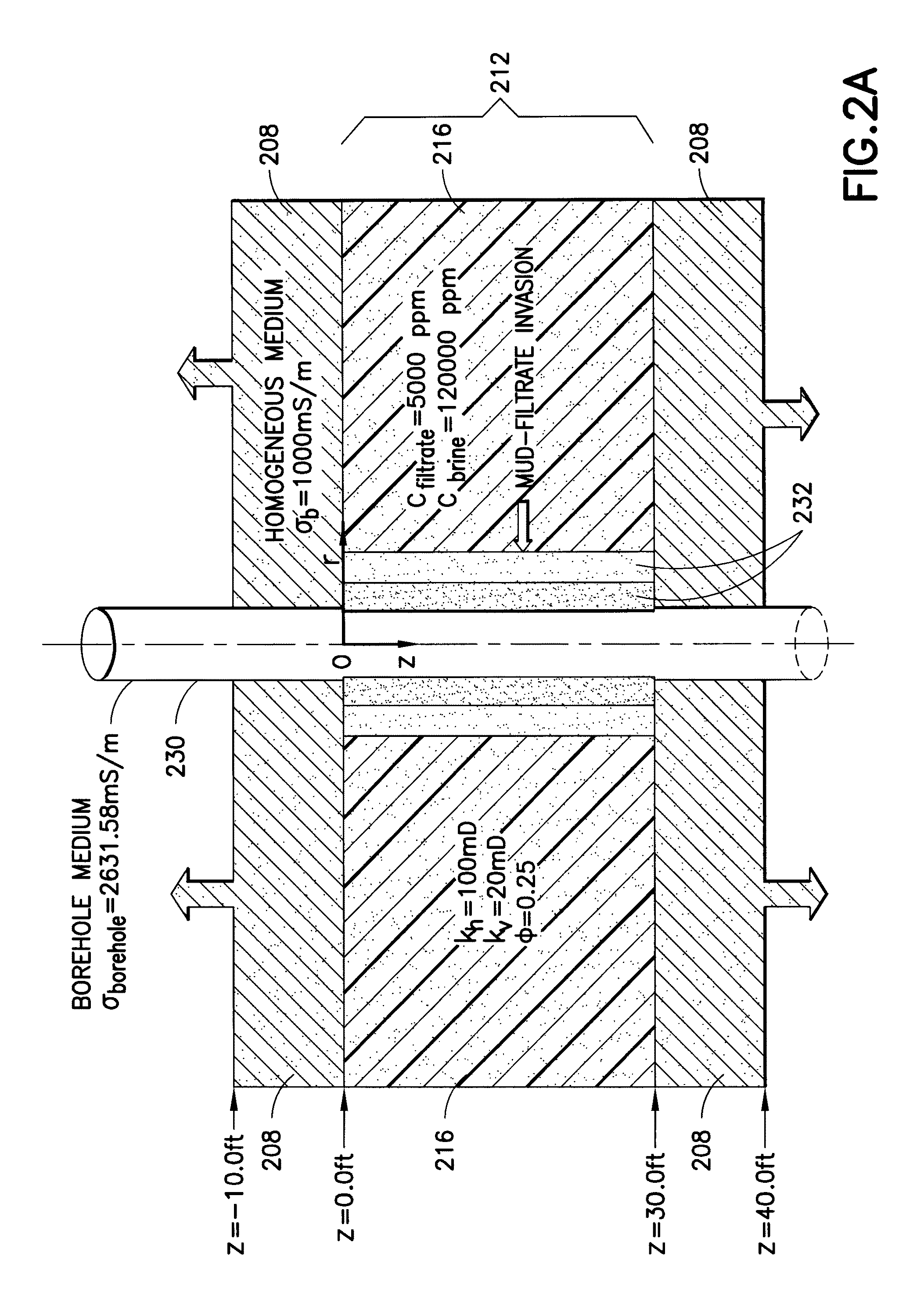
Methods and related systems are described relating to an inversion approach for interpreting the geophysical electromagnetic data. The inversion can be constrained by using a multiphase fluid flow simulator (incorporating pressure data if available) which simulates the fluid flow process and calculates the spatial distribution of the water saturation and the salt concentration, which are in turn transformed into the formation conductivity using a resistivity-saturation formula. In this way, the inverted invasion profile is consistent with the fluid flow physics and moreover accounts for gravity segregation effects. Jointly with the pressure data, the inversion estimates a parametric one-dimensional distribution of permeability and porosity. The fluid flow volume is directly inverted from the fluid-flow-constrained inversion of the electromagnetic data. The approach is not limited by the traditional interpretation of the formation test, which is based on a single-phase model without taking into account invasion or assuming that the fluid, for example mud-filtrate, has been cleaned up from the formation testing zone. The joint inversion of the electromagnetic and pressure data provides for a more reliable interpretation of formation permeability. One advantage of the approaches described herein, is its possible generalization to three-dimensional geometries, for example dipping beds and highly deviated wells.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Archie mode method for confirming initial oil saturation of oil layer
The invention relates to an Archie mode method for determining oil layer initial oil saturation, comprising the following steps: (1) inspecting the structure of oil pool and the geological condition of a reservoir bed, and collecting relevant sampling data; (2) correcting initial oil saturation and initial water saturation data; (3) calculating the average value of the initial oil saturation or the initial water saturation according to a downhole single sand layer, namely, a substratum; (4) calculating the average value of average degree of porosity according to the single sand layer, namely, the substratum, and reading the corresponding stratum deep direction-finding resistivity data by well logging curve; (5) collecting the data and drawing; (6) establishing the Archie mode of different reservoir bed types for a single layer with approximate reservoir bed deposition and oil pool and reservoir formation characteristics; and (7) calculating the initial oil saturation for the unsampled oil layer requiring the calculation of the initial oil saturation by using the Archie saturation formula. The initial oil saturation calculated by applying the method has high precision.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD +1
Method for determining stratum water saturation
InactiveCN101649738AThe calculation result is accurateCalculations are reliableBorehole/well accessoriesRock coreWell logging
The invention relates to petroleum well-logging technology, in particular to a method for determining stratum water saturation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a serial core of geologic feature; obtaining porosity Phi of the core and saturated core stratum water specific resistance Rw; and solving and substituting cementation index m(Rw, Phi) and saturation index n(Rw, Phi) ina common Archie water saturation computation model to calculate accurate stratum water saturation Sw. The method realizes corresponding change along with different physical properties of reservoir stratums and changes in stratum water specific resistance to ensure more accurate and reliable results, thereby having better application effect.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Quantitative calculation method for oil (GAS) saturation of fractured reservoir
ActiveUS20120109603A1Improve accuracySurveyComputation using non-denominational number representationRock coreWell logging
A quantitative calculation method for oil (gas) saturation of fractured reservoir during petroleum exploitation is provided. The method comprises: obtaining the fracture porosity and calculating resistivity index at different depth of fractured reservoir with known full diameter core data and imaging logging data; establishing the percolation network model of matrix and fracture combination with known pore structure feature; calibrating the numerical simulation results obtained from percolation network model based on the data of core experiment and sealed coring analysis results, then obtaining the relationship between the resistivity index (I) and water saturation (Sw) at different fracture porosity; calculating the oil (gas) saturation of fractured reservoir through selecting an interpolation function. The oil (gas) saturation calculated with said method is 0.67, however 0.49 with common method in some fractured reservoir. The accuracy is improved by more than 0.18 in the studied fractured reservoir.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
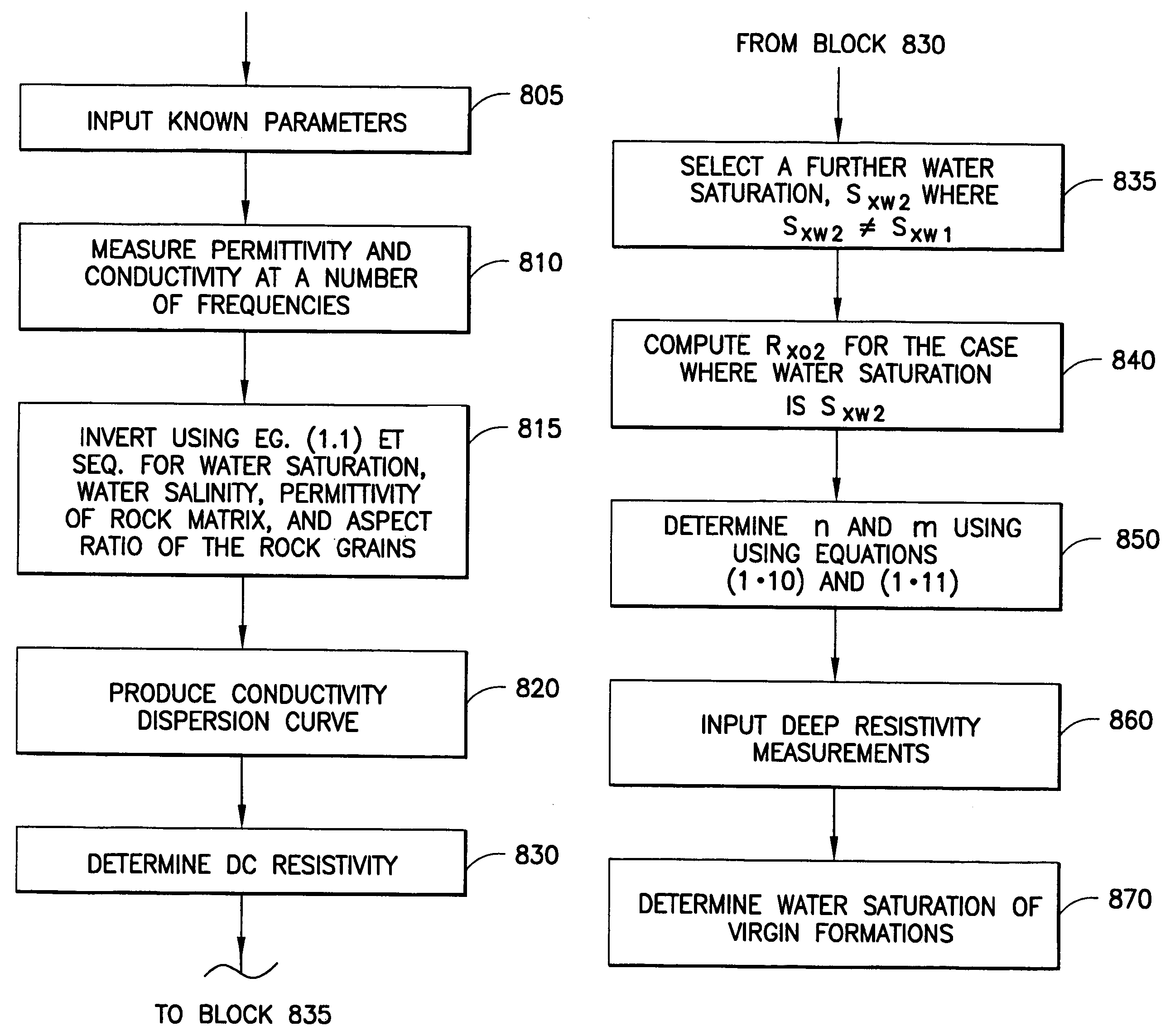
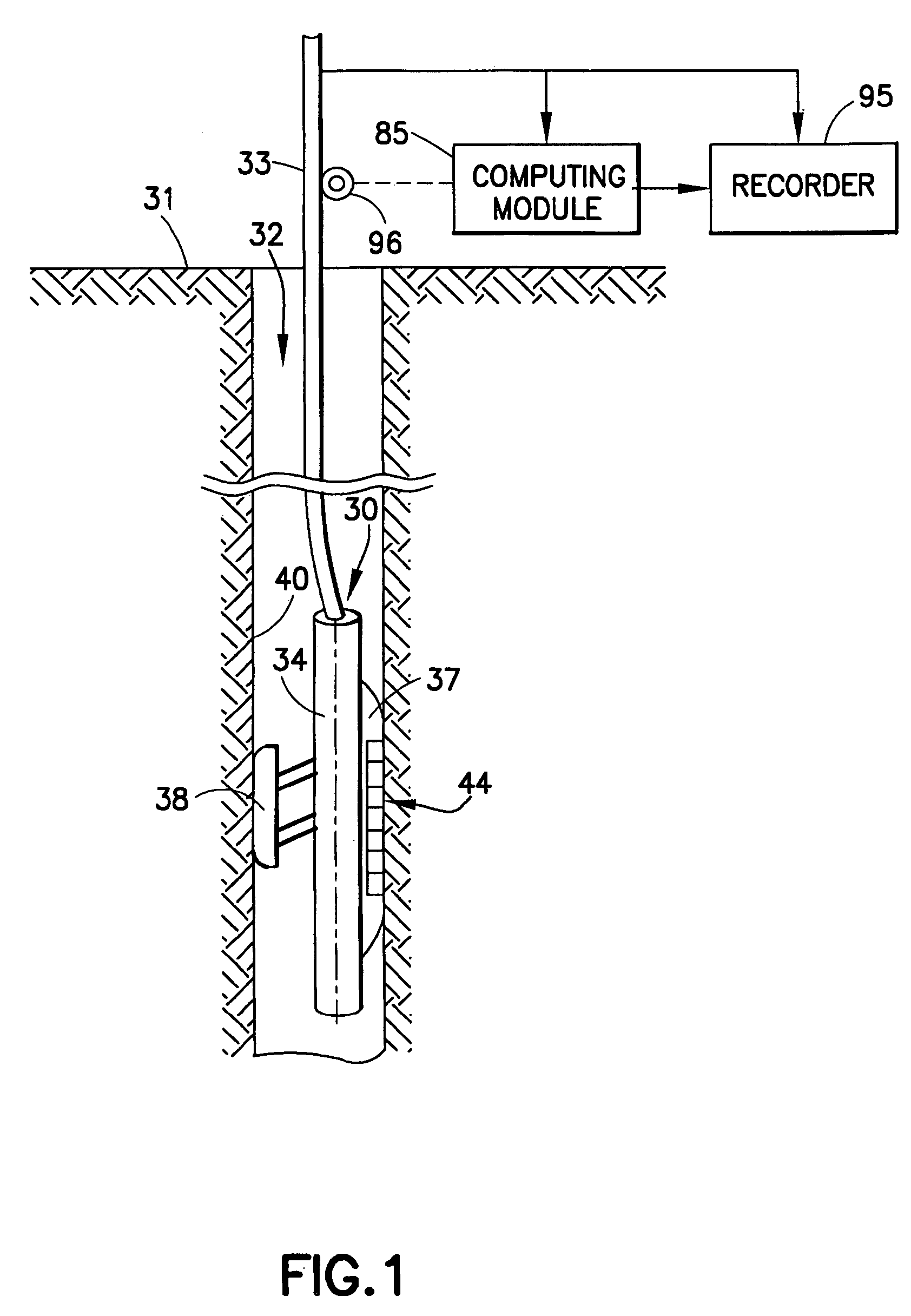
Technique for determining properties of earth formations using dielectric permittivity measurements
ActiveUS20070061082A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentDielectricDielectric permittivity
Techniques for determining formation characteristics use measurements of dielectric permittivity at a number of frequencies. Determined characteristics include the vertical and horizontal formation dielectric constant and conductivity, the formation water conductivity, the water saturation, the cementation and the saturation exponents. In laminated formations these profiles can be determined for each lamina. Also, formation dielectric properties are used in determination of the rock type.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for reducing permeability restriction near wellbore
InactiveUS6945327B2Improve breathabilityEfficient removalSurveyFluid removalRetrograde condensationHydraulic fracturing
Method is provided for increasing the productivity of gas wells producing from reservoirs where retrograde condensation occurs around the wells. An oil-wetting surfactant is injected in a solvent to oil wet the formation for a selected distance around a well or a hydraulic fracture intersecting the well. A pre-flush liquid, such as carbon dioxide, alcohol or similar products and mixtures thereof, may be used to reduce water saturation before injection of the surfactant. The method may also be applied to increase the productivity of oil wells producing from reservoirs where breakout of solution gas occurs near the well.
Owner:ELY & ASSOCS
Shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method
ActiveCN104697915AAvoid damageGood reproducibilityWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBound waterHydrogen
The invention discloses a shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method. The shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method comprises the following steps that shale gas reservoir rock is collected, and a natural core is manufactured; the relaxation characteristic of hydrogen-contained fluid in core pores is measured through a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of clay water is obtained; the core is processed to obtain a saturated core, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of saturated fluid and a summation curve are obtained; a T2 distribution map of effective fluid is obtained; a T2 distribution map of irreducible fluid and saturability Swi of bound water are obtained; a T2 distribution map of surplus water and water saturation Sw are obtained; the T2 distribution maps of the fluids are converted into a pore size distribution map, the shale clay deadline and the irreducible fluid deadline are obtained, and then the shale micropore size and fluid distribution are obtained. The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is adopted, the pore size and distribution of the shale and size and distribution positions of water drops in the pores are analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively, and the result is reliable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for determining reserve volume of nonhomogeneous sandstone reservoir
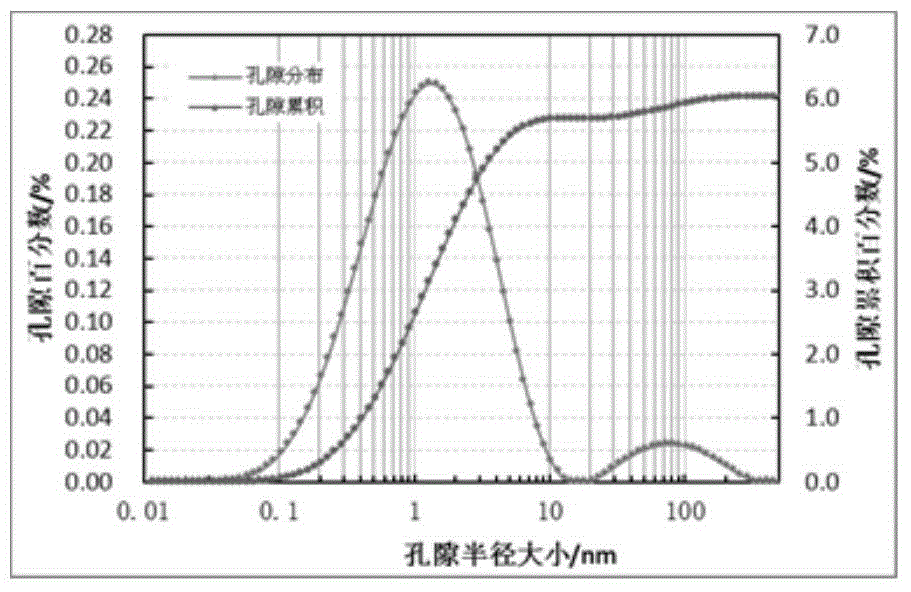
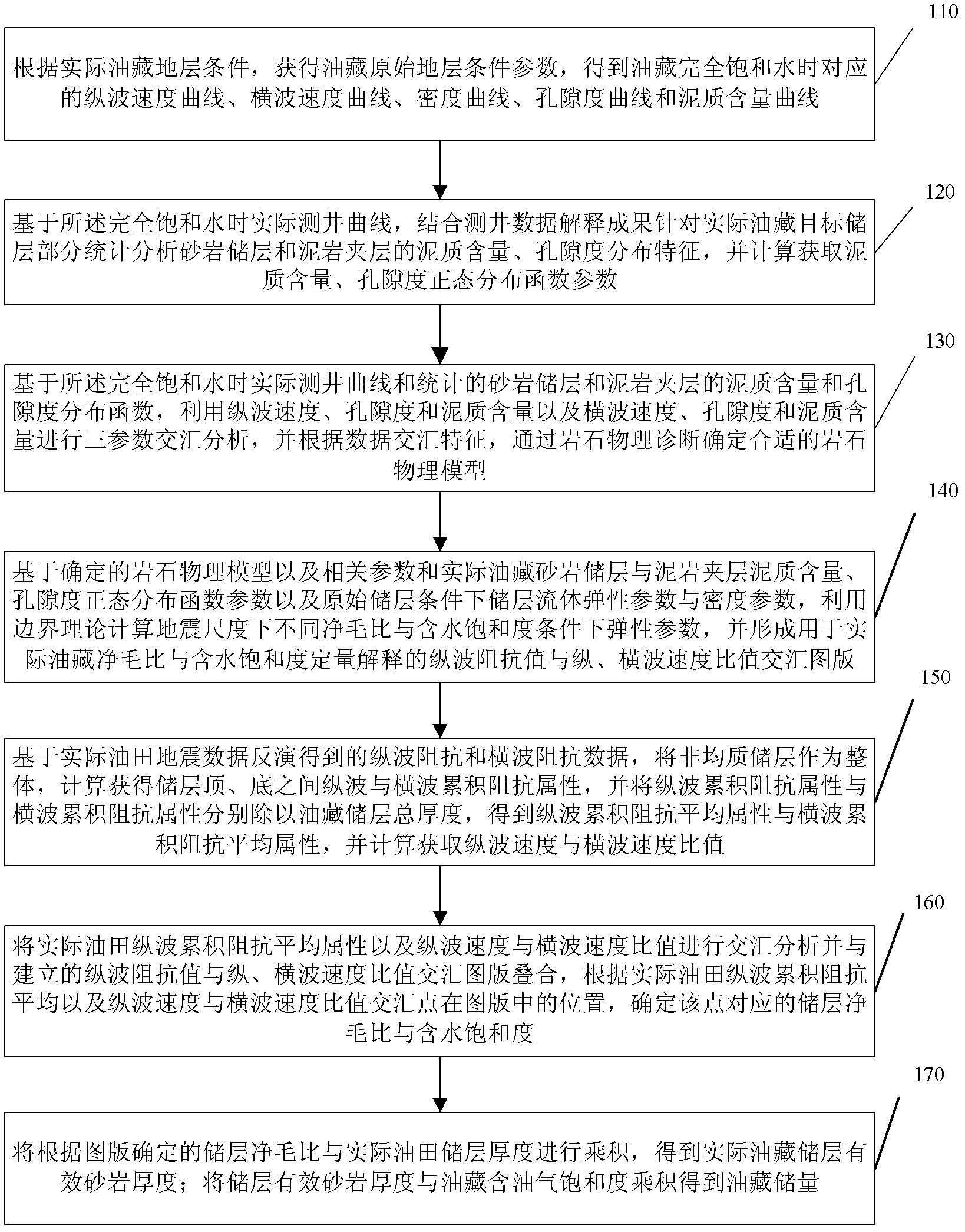
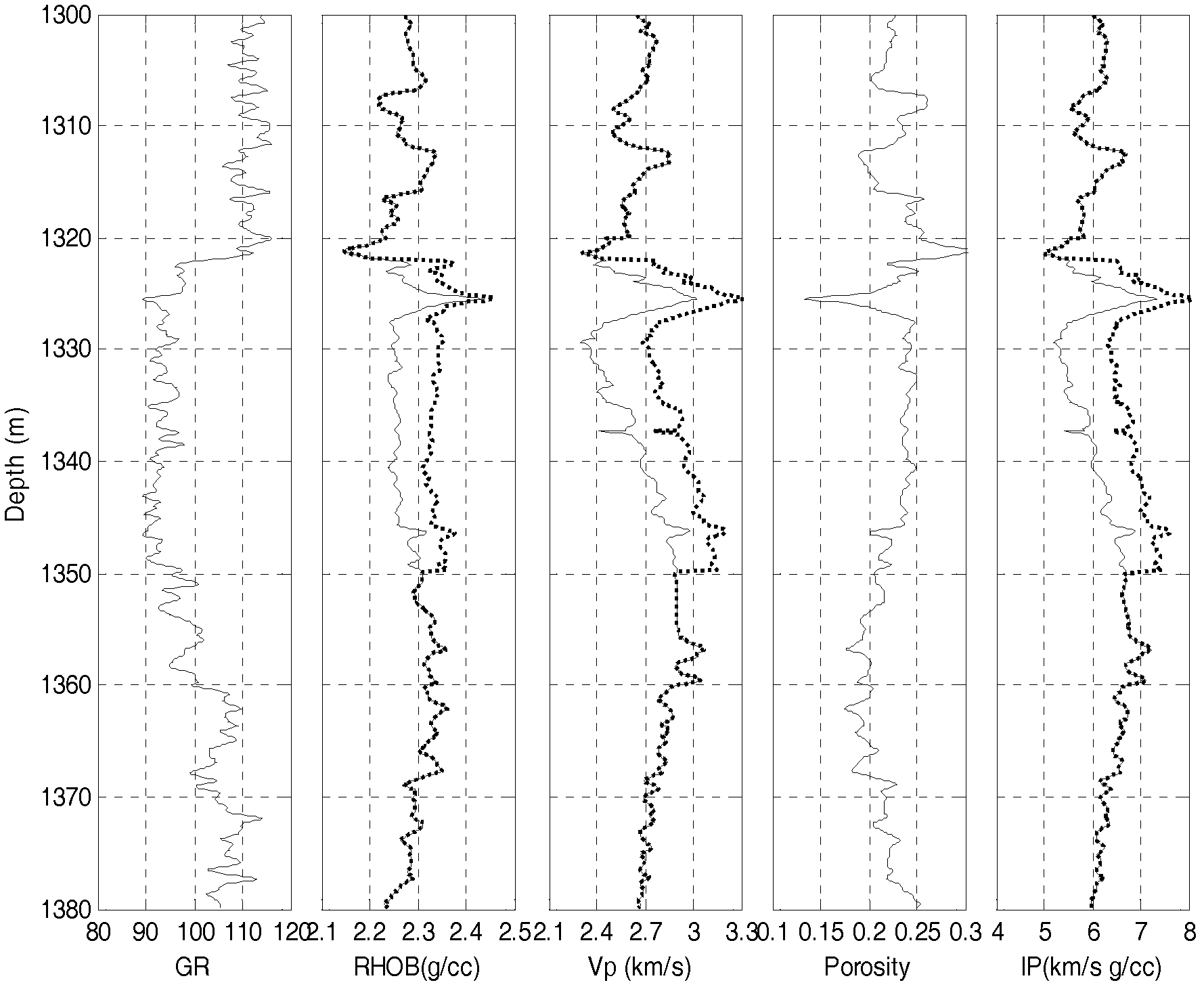
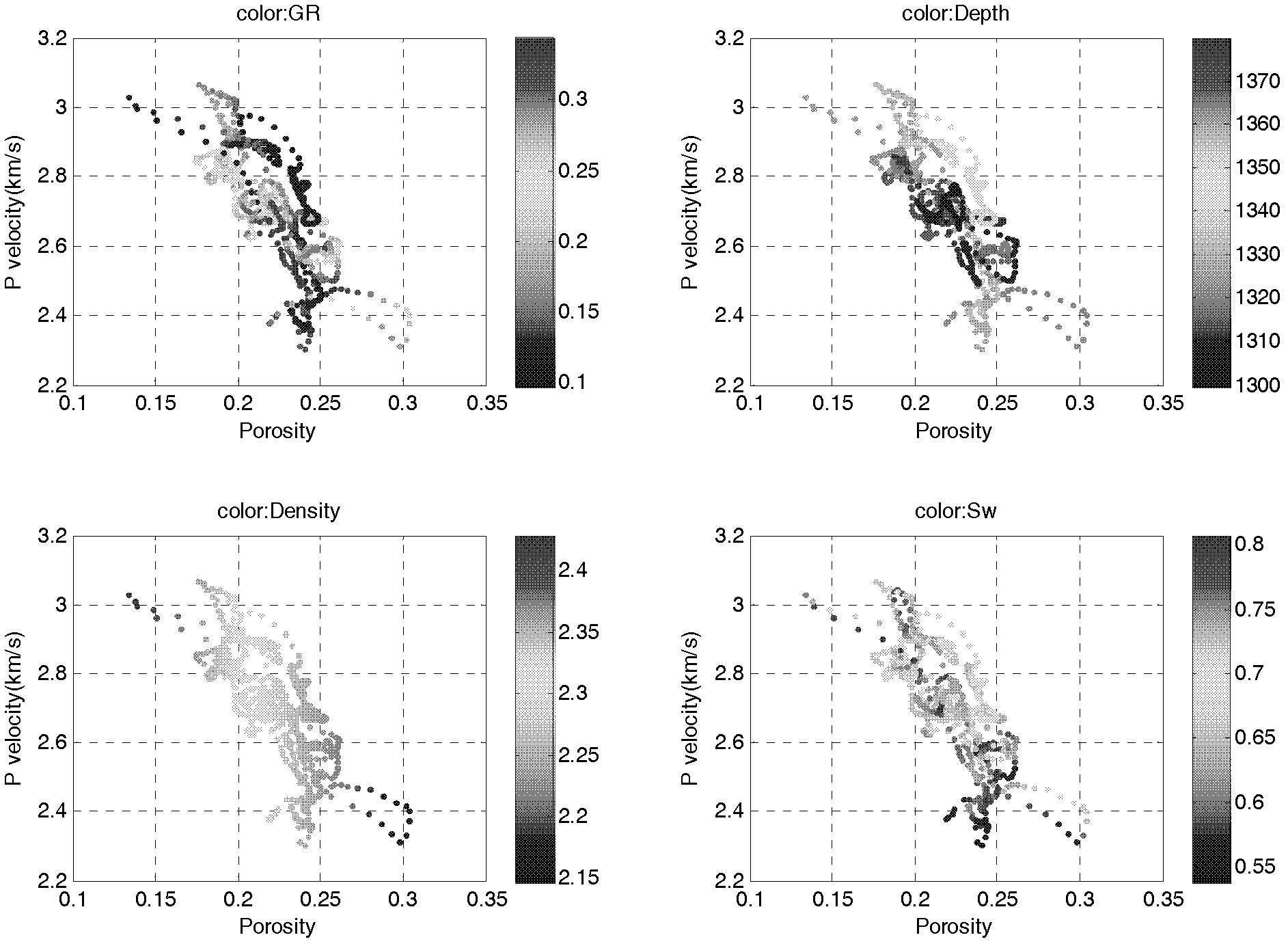
InactiveCN102426390AHigh precisionReduce drilling riskSeismology for water-loggingGeomorphologyBoundary theory
The invention relates to a method for determining reserve volume of a nonhomogeneous sandstone reservoir. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining original stratum conditional parameters of an oil reservoir, carrying out logging data liquid displacement to obtain a corresponding elastic parameter curve corresponding to saturated water of a reservoir; based on saturated water loggingcurve as well as shale content and porosity distribution function of the sandstone reservoir and a mudstone interlayer which are obtained by statistics, determining a rock physical model by utilizingrock physical diagnosis, and calculating relation between elastic parameter variation of the nonhomogeneous sandstone reservoir and water saturation and net gross ratio of the reservoir; calculating accumulated impedance attribute by utilizing earthquake impedance data, quantitatively interpretating effective sandstone thickness and oil-gas-bearing saturation of the reservoir by virtue of the built template, and producting to obtain the reserve volume of the oil reservoir. In the method provided by the invention, elastic parameter calculation in earthquake scale and plate establishment are carried out, and earthquake accumulated impedance attribute is utilized, thus quantitative evaluation on the net gross ratio and the saturation of the nonhomogeneous sandstone reservoir is realized, andthe aim of determining the reserve volume is achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
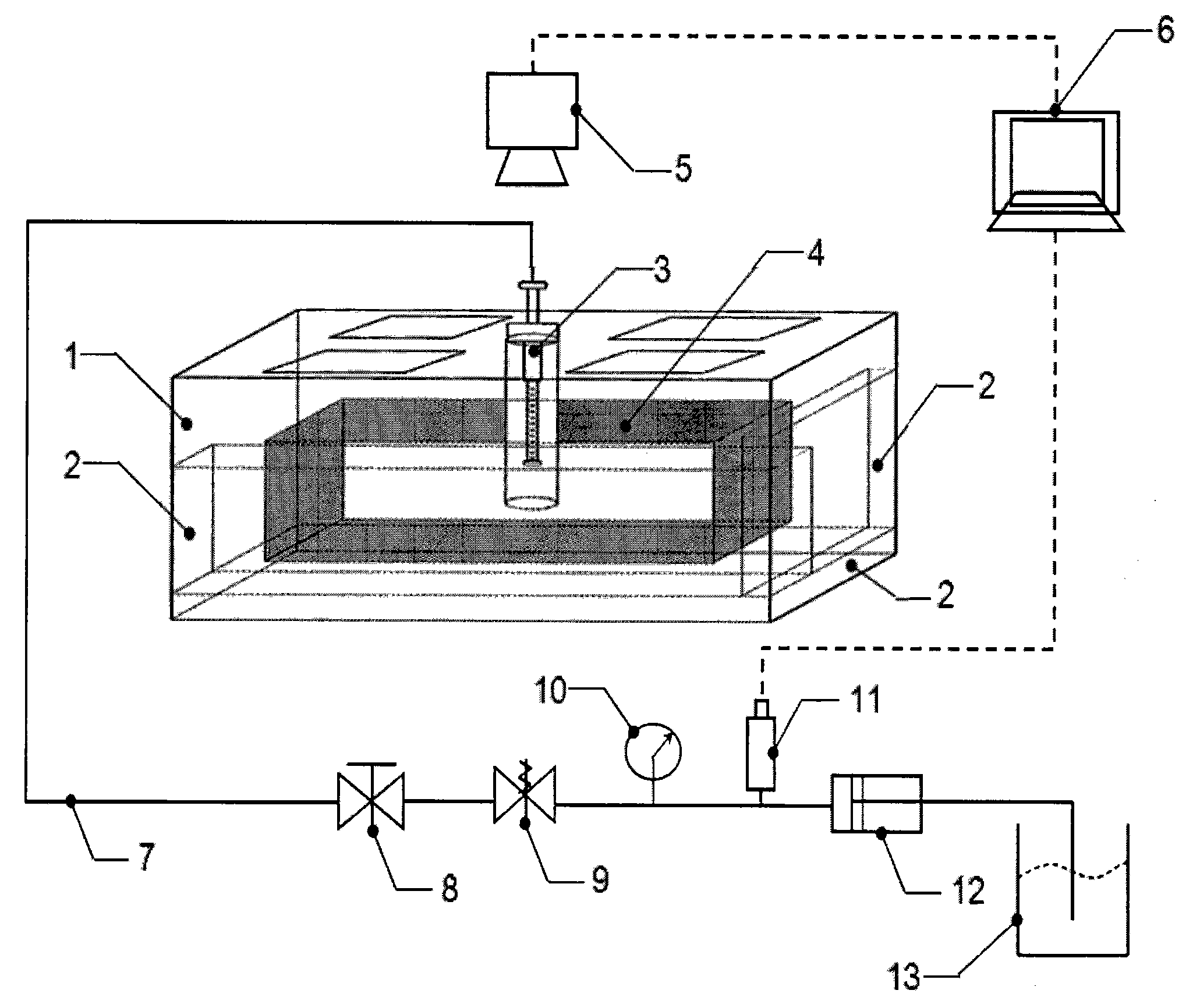
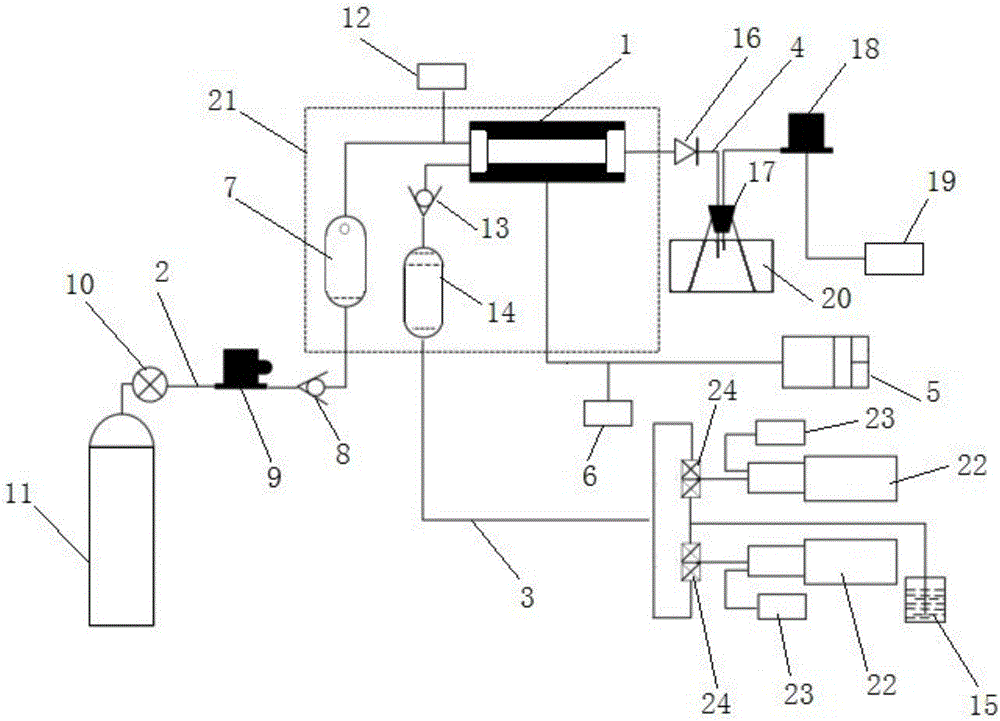
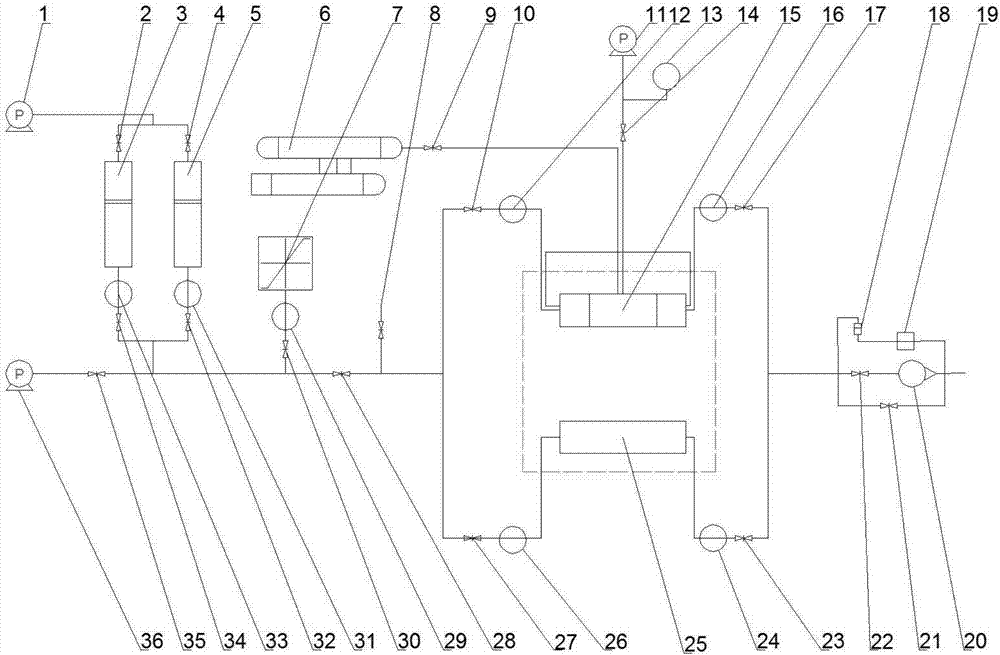
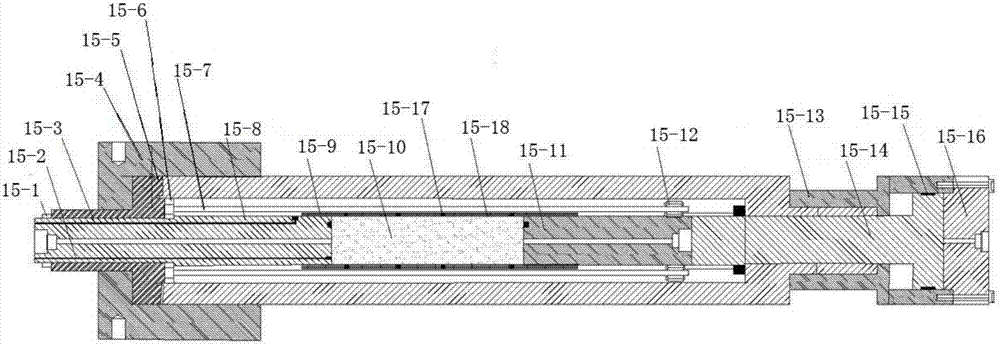
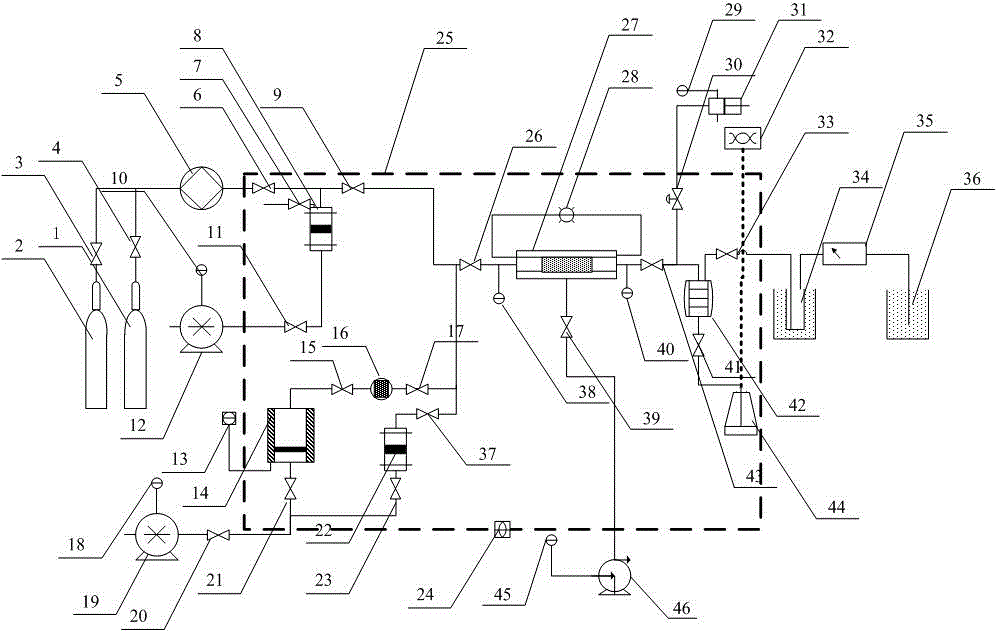
Three-dimensional physical simulation experimental apparatus of heterogeneous bottom-water reservoir and saturation determining method thereof
The invention discloses a three-dimensional physical simulation experimental apparatus of a heterogeneous bottom-water reservoir and a saturation determining method thereof. The apparatus comprises a core holder (1), a confining pressure pump (9), a constant-pressure constant-speed displacement valve A (7), a piston container A (23), an oil-gas-water meter B (4), a back pressure device A (5), an oil-gas-water meter A (3), a back pressure device B (6), a constant-temperature tank (2), a constant-pressure constant-speed displacement valve B (8), a piston container B (24), a pressure meter A (19), a pressure meter B (21), a pressure meter C (20) and a pressure meter D (22). The apparatus is suitable for planar and vertical heterogeneous displacement experimental researches, research on influence of edge-bottom water upon displacement, and real-time analysis on oil (gas) and water saturation distribution.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
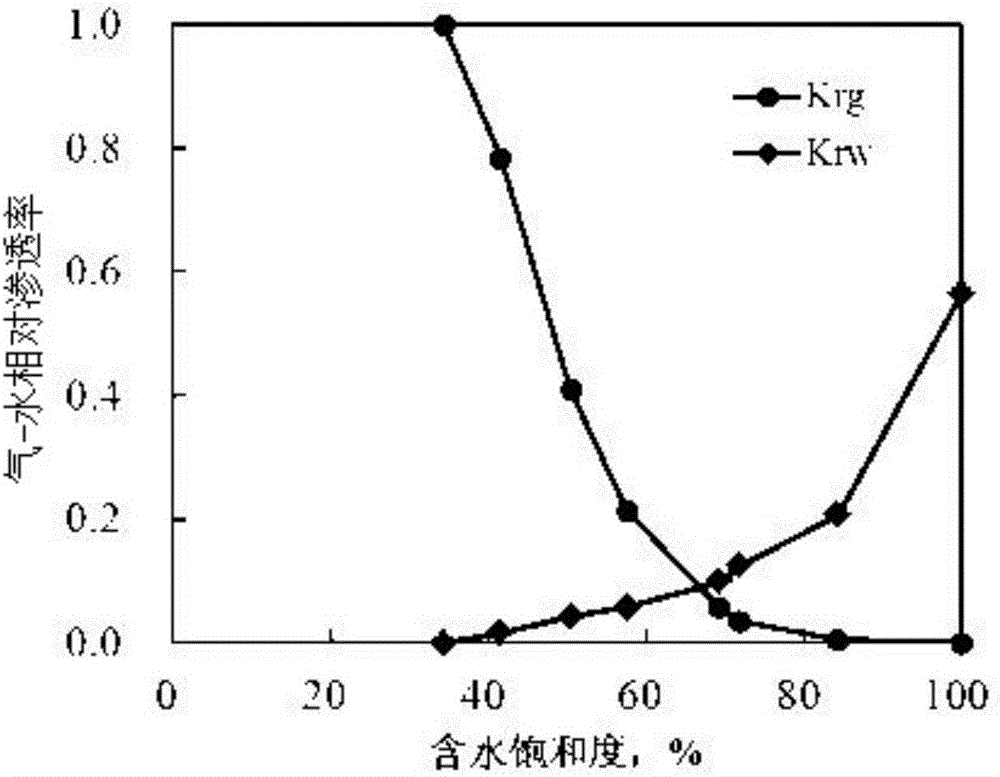
Method for testing gas-water relative permeability curve by using tight sandstone steady state method
ActiveCN106525690AIn line with the actual situationHigh reference valuePreparing sample for investigationPermeability/surface area analysisMeasurement pointDisplacement pressure
The invention provides a method for testing a gas-water relative permeability curve by using a tight sandstone steady state method. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a stone core; preparing simulation stratum water; vacuuming till the simulation stratum water is saturated; connecting an experiment device and heating to experiment temperature; putting the stone core into the experiment device, pressurizing, releasing the pressure, testing the mass and the liquid phase permeability of the stone core; establishing irreducible water saturation; controlling the flowing speed of gas, and injecting the simulation stratum water at a relatively slow flowing speed, after the gas flow at an outlet is stable, increasing the flowing speed of liquid, and measuring a next point till displacement pressure meets the maximum set value and the flowing speed of the gas at the outlet is reduced to 0.1mL / minute, and terminating the experiment; according to improved phase permeability equations, calculating water saturation and relative permeability of different points. By adopting the method, two-phase permeation characteristics in the tight gas reservoir production process under stratum conditions can be simulated, the influence of the temperature on gas-water viscosity is taken into account, the influence of pressurization on the water content of the stone core is also taken into account, the irreducible water saturation and the relative permeability curve can be relatively accurate and reliable, and high-value data can be provided for gas reservoir production evaluation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for estimating formation hydrocarbon saturation using nuclear magnetic resonance measurements
ActiveUS20090206834A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFluid saturation
A method for estimating fluid saturation in a formation penetrated by a wellbore from nuclear magnetic resonance measurements made at a plurality of lateral depths into the formation from the wellbore includes estimating a bound water volume, a total porosity and a free water volume at each of the lateral depths from the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements. A minimum water saturation is estimated at each lateral depth from the total porosity, the free water volume and the bound water volume at each lateral depth. A value of water saturation is estimated at each lateral depth from the minimum water saturation at each lateral depth. A relationship between lateral depth and water saturation is determined. Water saturation is estimated at a selected lateral depth greater than the greatest lateral depth of the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
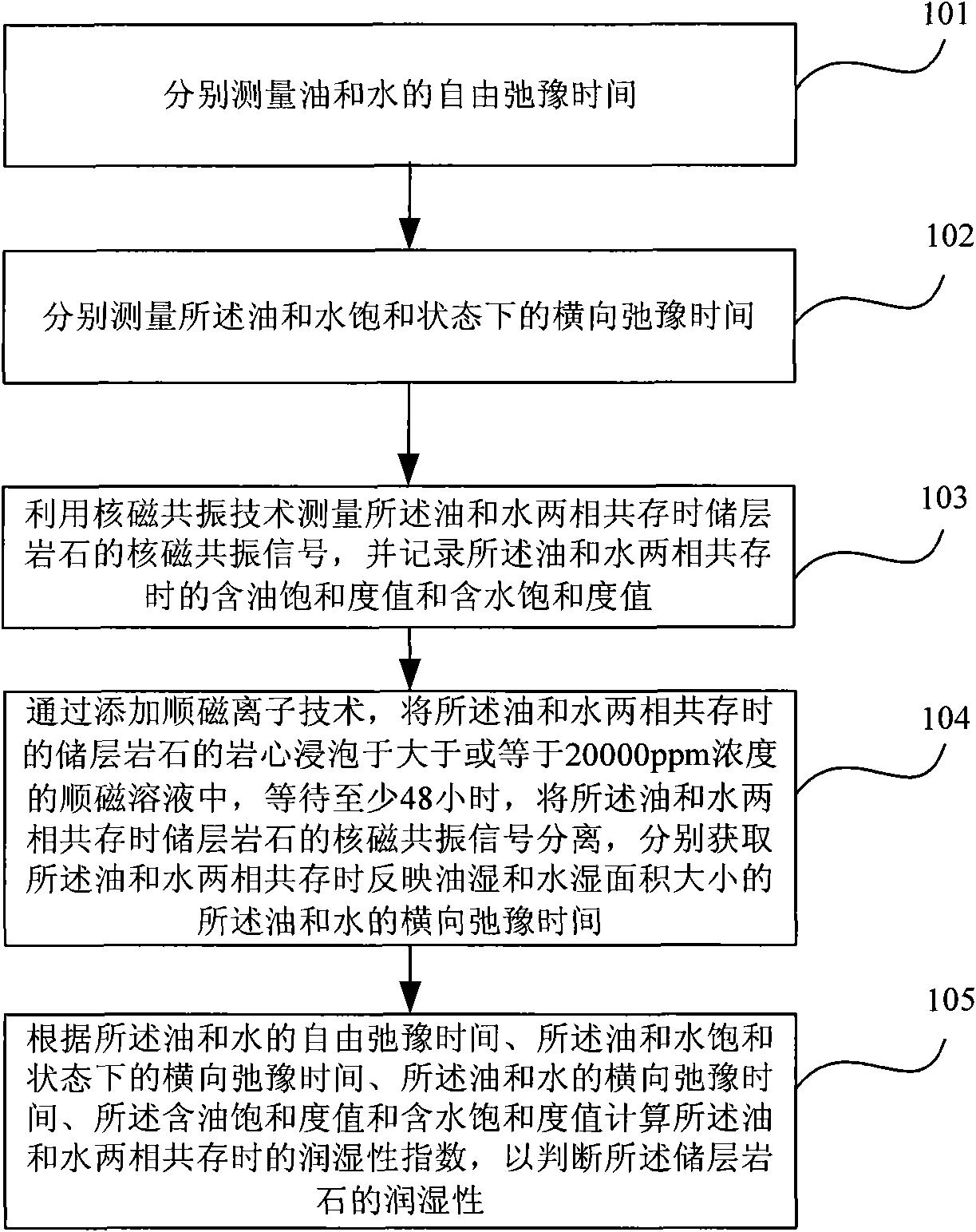
Method for judging wettability of reservoir rock
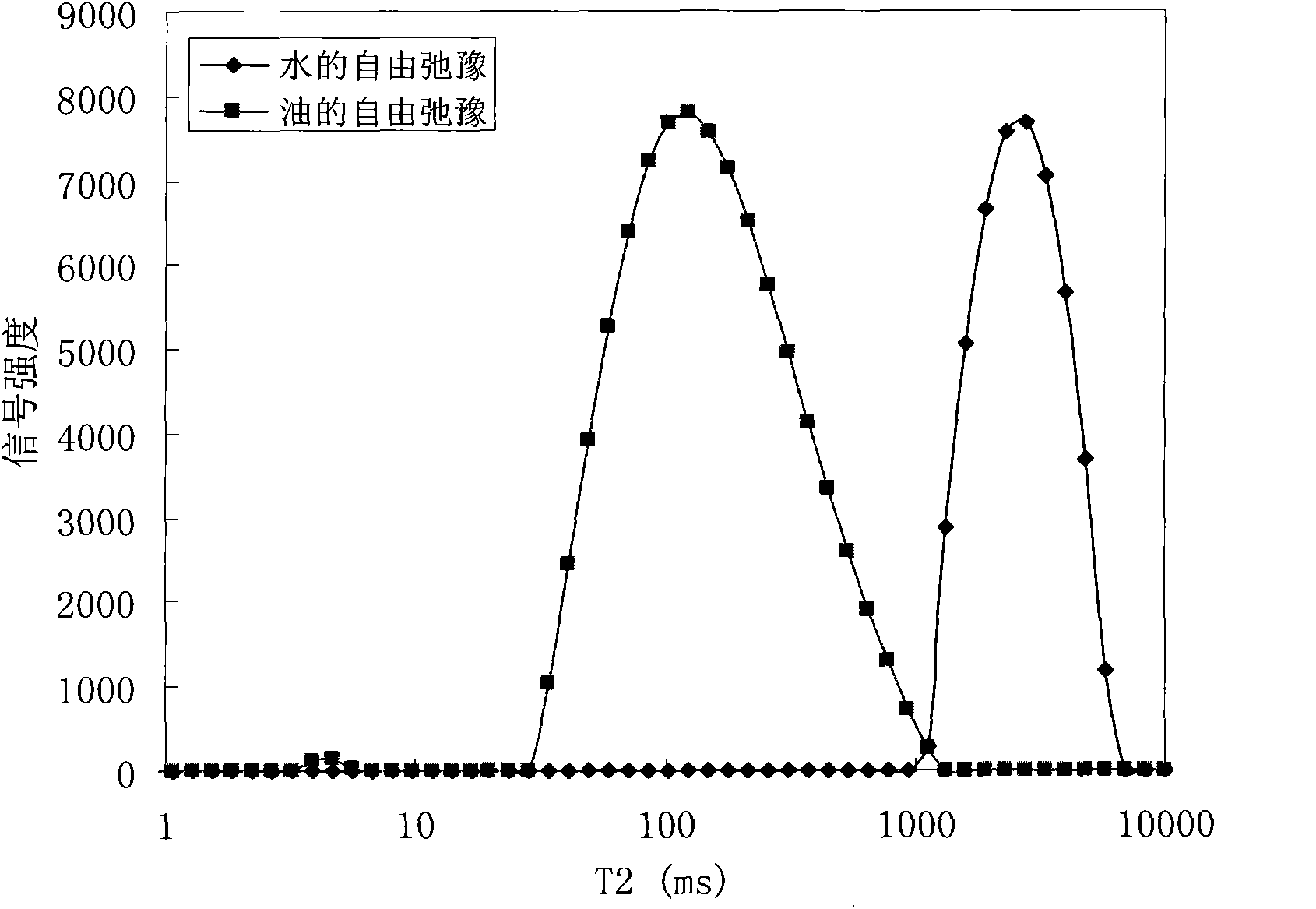
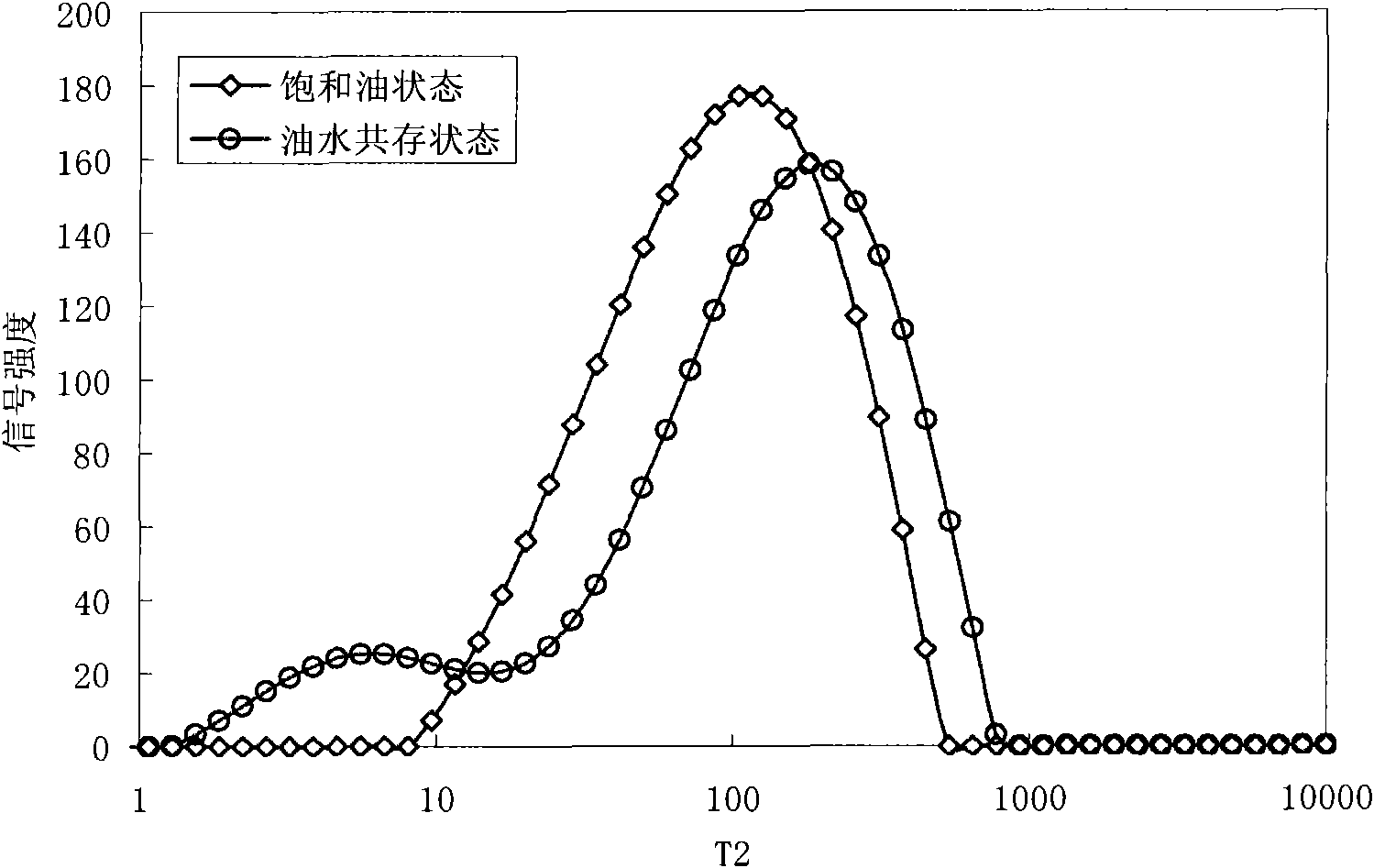
ActiveCN101915716AEasy to judge wettabilityWettability judgmentSurface/boundary effectAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention provides a method for judging the wettability of a reservoir rock. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring free relaxation time of oil and water respectively; measuring transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in saturated states respectively; measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of an oil phase and a water phase by using nuclear magnetic resonance technology and recording an oil saturation value and a water saturation value in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase; dipping the rock core of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase in more than or equal to 20,000 ppm paramagnetic solution, waiting for at least 48 hours and separating the nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase to obtain the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water reflecting the size of an oil wet area and a water wet area; and calculating a wettability index in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase according to the free relaxation time of the oil and the water, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in the saturated states, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water, the oil saturation value and the water saturation value so as to judge the wettability of the reservoir rock.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Technique for determining properties of earth formations using dielectric permittivity measurements
ActiveUS7363160B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentDielectricFormation water
Techniques for determining formation characteristics use measurements of dielectric permittivity at a number of frequencies. Determined characteristics include the vertical and horizontal formation dielectric constant and conductivity, the formation water conductivity, the water saturation, the cementation and the saturation exponents. In laminated formations these profiles can be determined for each lamina. Also, formation dielectric properties are used in determination of the rock type.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
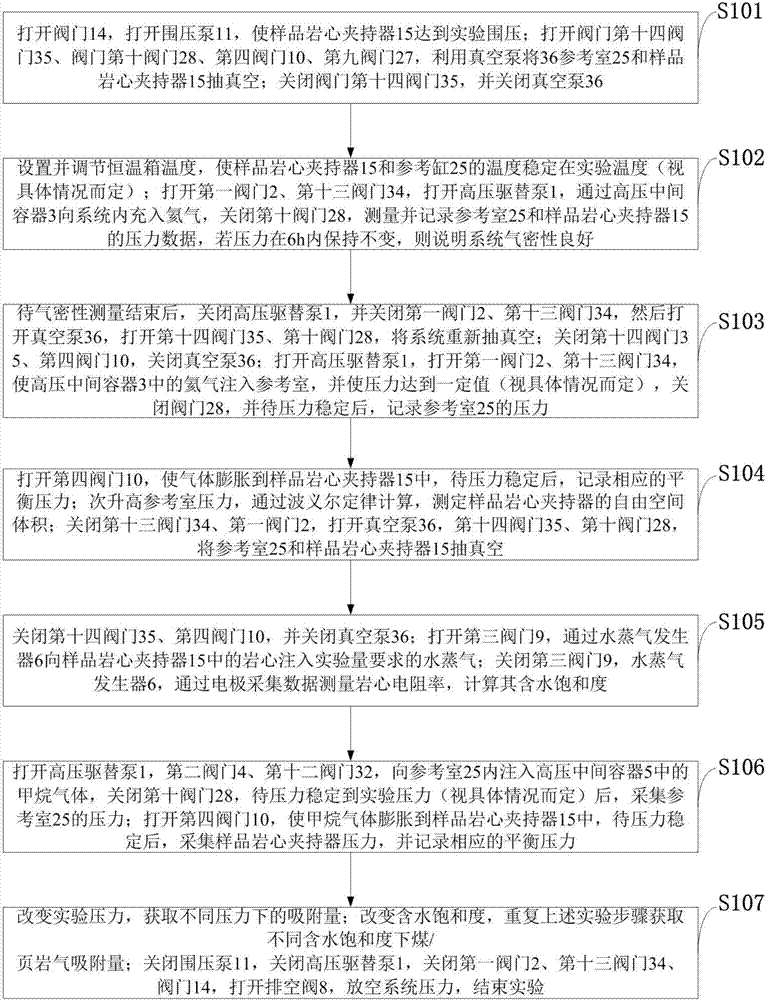
Method for evaluating shale gas adsorption through coal/shale ultrahigh pressure gas absorption and seepage experiment
The invention discloses a method for evaluating shale gas adsorption through a coal / shale ultrahigh pressure gas absorption and seepage experiment. The method comprises the steps that a core is selected and put in a sample cylinder, a confining pressure pump is started to make the sample cylinder reach an experimental confining pressure, and vacuumizing is performed; the temperatures of the sample cylinder and a reference cylinder are stabilized at experimental temperature; helium gas is injected into the reference cylinder, and the pressure of the reference cylinder is measured; after the reference cylinder and the sample cylinder are balanced in pressure, the pressure of the sample cylinder is measured; the pressure of the reference cylinder is increased sequentially, and free space volume measurement of the sample cylinder is completed; systematic vacuumizing is performed; water steam is injected into the sample cylinder; methane having set pressure is injected into the reference cylinder, and the pressure of the reference cylinder is acquired; a balancing valve is turned on, and the pressure of the sample cylinder is acquired; the pressure of the reference cylinder is increased sequentially, and the shale gas adsorption experiment is completed under certain water saturation. By adopting the method, the porosity, the permeability, the adsorbing capacity and gas-water seepage of the experimental core, electrical resistivity change of the core in the experimental process and the influence of different water saturations on absorption and desorption amounts can be respectively measured.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
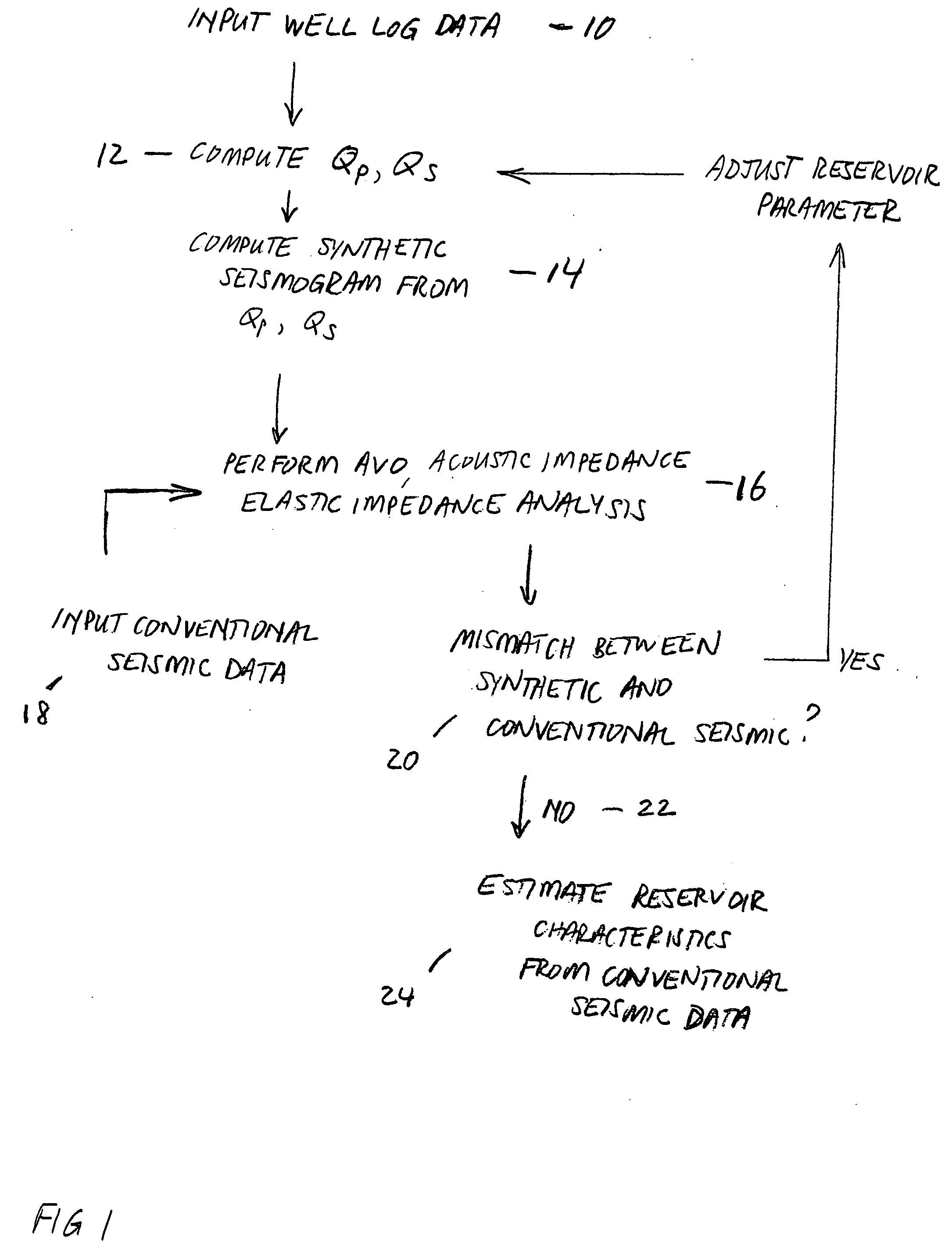
Method for determining formation quality factor from well log data and its application to seismic reservoir characterization
ActiveUS7088639B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic surveyWell logging
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Device and method for testing gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation curve of high-temperature high-pressure high-sulfur-content gas reservoir
ActiveCN104568678ARapid determinationAccurate measurementSurface/boundary effectPermeability/surface area analysisGas phaseData acquisition
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing a gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation curve of a high-temperature high-pressure high-sulfur-content gas reservoir. The testing device comprises a displacement system, a stratum condition simulation system, a back-pressure system, a data testing system and a data acquisition system. The testing method comprises the following steps: selecting and treating a rock core; preparing rock core saturated stratum water and liquid sulfur; simulating a high-temperature and high-pressure environment of the stratum; determining the condition of liquid sulfur phase permeability under irreducible water saturation; performing a phase permeation test on filling of gas-liquid sulfur according to a set ratio; recording the amount VSi of liquid sulfur and the gas amount Vgi generated totally; correcting the stratum condition; calculating the relative permeability Krs of the liquid sulfur phase, the relative permeability Krg of the gas phase and the gas saturation Sg of a rock sample at each moment and the like. The device and the method disclosed by the invention can be used for safely, conveniently, rapidly, accurately and efficiently measuring the high-temperature high-pressure gas-liquid sulfur phase permeation data and providing scientific data support for making a reasonable development scheme for the high-sulfur-content gas reservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for obtaining oil-water common-layer original oil-containing saturation degree and method for estimating non-test oil-water common-layer original oil-containing saturation degree
InactiveCN101413388ABorehole/well accessoriesNuclear radiation detectionCalculation errorPoor correlation
The invention relates to a method for acquiring the initial oil saturation of an oil-water layer and a method for estimating the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer of untested oil, which relate to a method for calculating the initial oil saturation in a reserve parameter log interpretation. The method solves the problem of large calculation error in the prior method for acquiring the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer. In the method for acquiring the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer, the initial oil saturation of a tested oil layer of the oil-water layer is calculated by application of an initial oil saturation model of the oil layer first, and corrected according to interpenetration data and oil testing data to obtain the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer of tested oil. The method is suitable for the oil-water layer with poor correlation between the initial oil saturation and the resistivity and can be used for calculating the petroleum reserve by the volumetric method. The method for estimating the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer of the untested oil according to the interpenetration data and the oil testing data is to estimate the initial oil saturation of the oil-water layer of the untested oil by applying and researching the average moisture content of the oil-water layer of a working area.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD
Method for measuring porosity of mud shale
ActiveCN102252948AAvoid the inconvenience of drilling coreEliminate the effects ofPermeability/surface area analysisRHOBOrganic matter
The invention provides a method for measuring the porosity of mud shale. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: selecting a whole mud shale sample block to be detected; measuring the mass M0; measuring the total volume V0 of the block; computing the block density rhob of the mud shale; rhob=M0 / V0, grinding the sample; weighing a certain quantity M1 of the ground sample, wherein the M1 is less than or equal to the M0; distilling and extracting the weighed sample until the water yield is maintained to be stable; recording the volume Vw of the extracted water; taking out the distilled and extracted sample; drying until the mass is stable; recording the mass M2 of the sample; taking out the dried sample; measuring the volume Vg of particles; and computing the porosity phi of the sample, phi=(Vb-Vg) / Vg *100%, wherein Vb=M1 / rhob, the method provided by the invention can avoid inconvenience in drilling out the core of mud shale, eliminate the absorption of organic matters on measurement gases, avoid organic matters from blocking a pore throat, can measure non-communication pores before the mud shale is ground and can simultaneously determine the water saturation, oil saturation and gas saturation of the mud shale.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Tight sandstone gas reservoir fracturing fluid damage experimental evaluation method
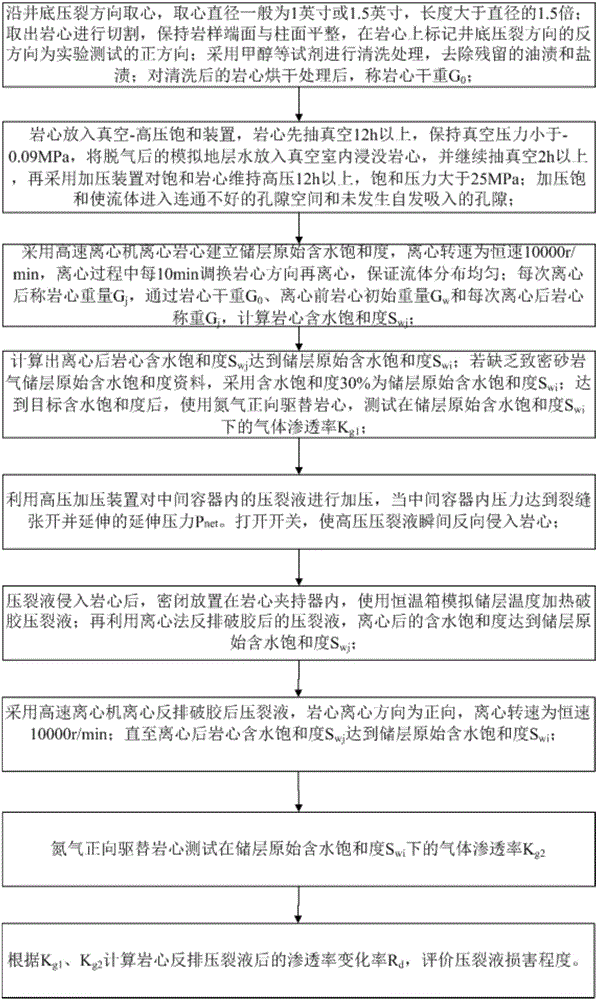
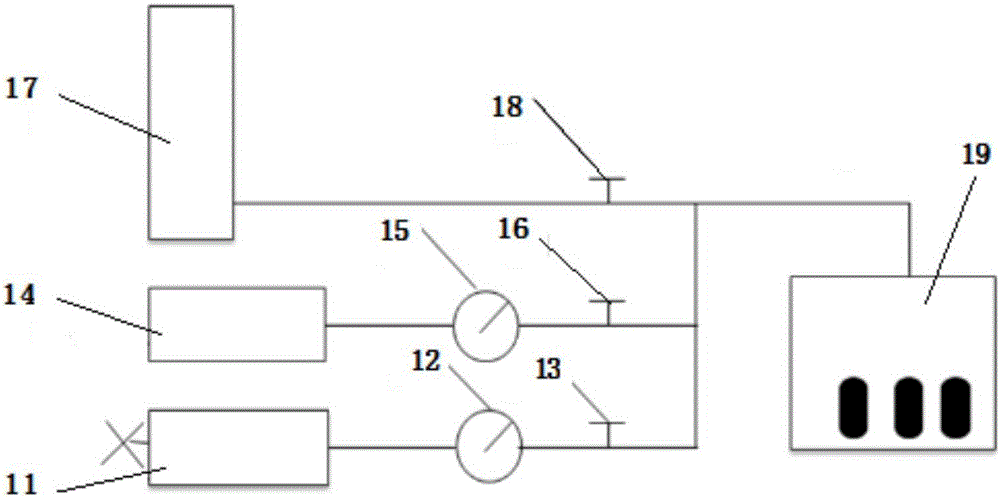
InactiveCN106153518AConforms to seepage characteristicsExperimental test pressure is smallPermeability/surface area analysisWeighing by absorbing componentRock coreFracturing fluid
The invention belongs to the field of oil-gas field development and relates to an experimental evaluation method for fracturing fluid damage in an unconventional tight sandstone oil-gas exploration and development process. The method includes: subjecting fracturing fluid to high-pressure instant reverse injection into a rock core, and simulating flow invasion damages of fracturing fluid in cracks in a continuous extension process after a stratum is fractured by the fracturing fluid; adopting a high-speed centrifuge to set up original water saturation of a reservoir; under the condition of the original water saturation of the reservoir, adopting nitrogen for testing permeability before and after injection of the fracturing fluid into the rock core, and judging fracturing fluid damage degrees according to gas log permeability change rate. By complete simulation of a fracturing fluid injection mode in a fracturing process, adoption of nitrogen for testing permeability accords with seepage characteristics of the tight sandstone gas reservoir, and defects of high experimental displacement pressure, long displacement time, large experimental data errors and the like are avoided.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Source rock volumetric analysis
InactiveUS20110144913A1Reduces and eliminates erroneous TOC valueIncrease compressional slownessElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisTotal organic carbonSource rock
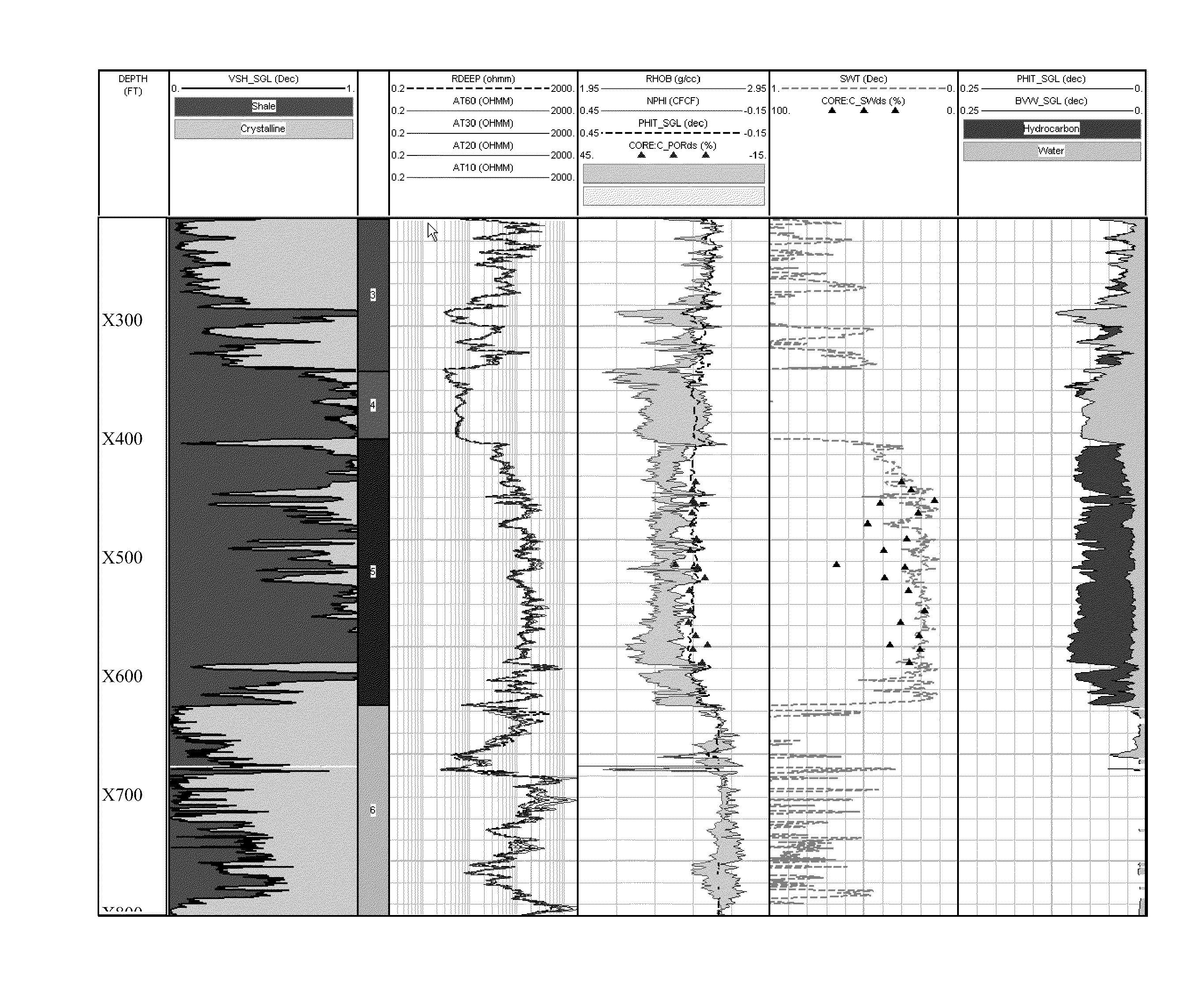
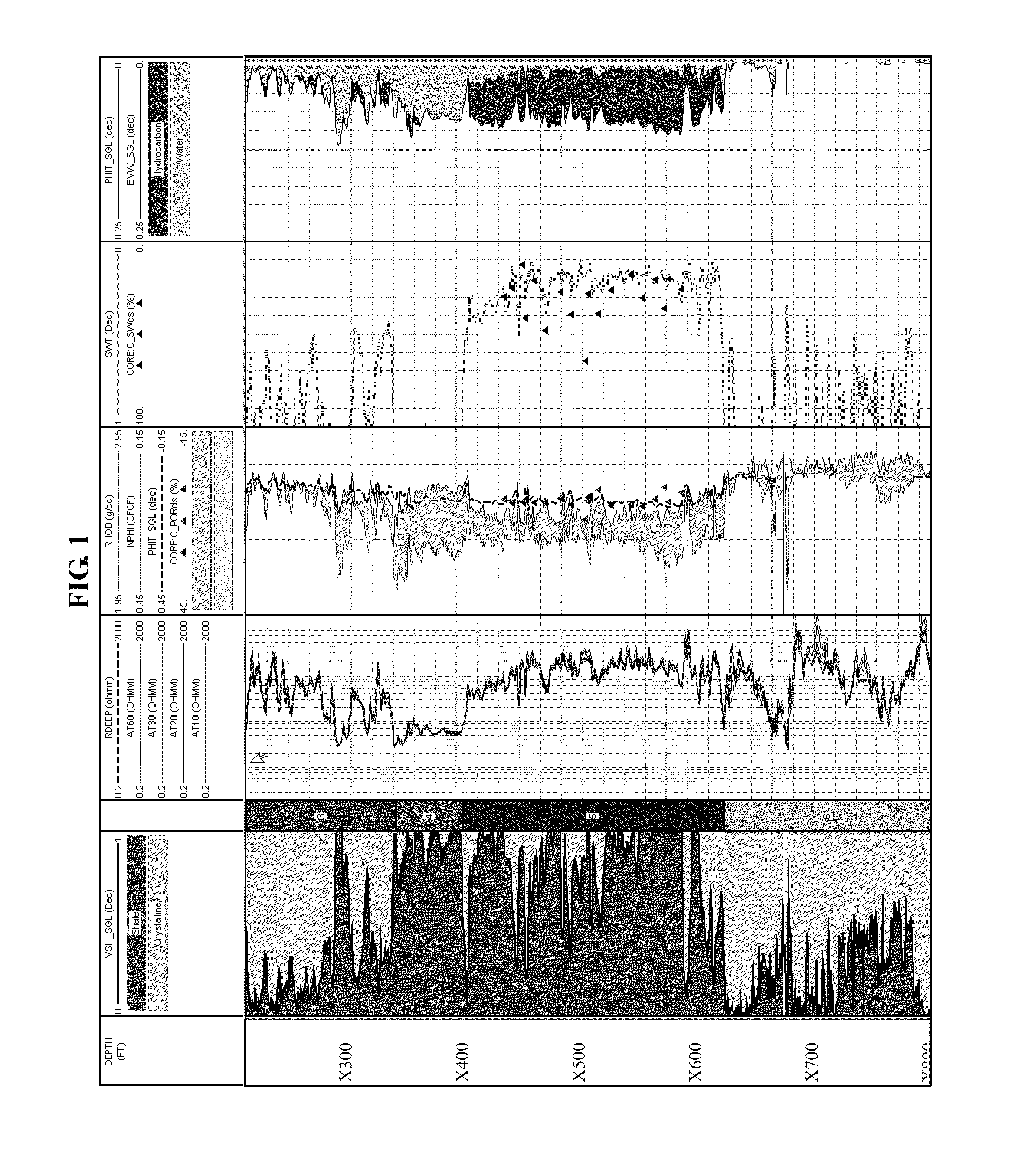
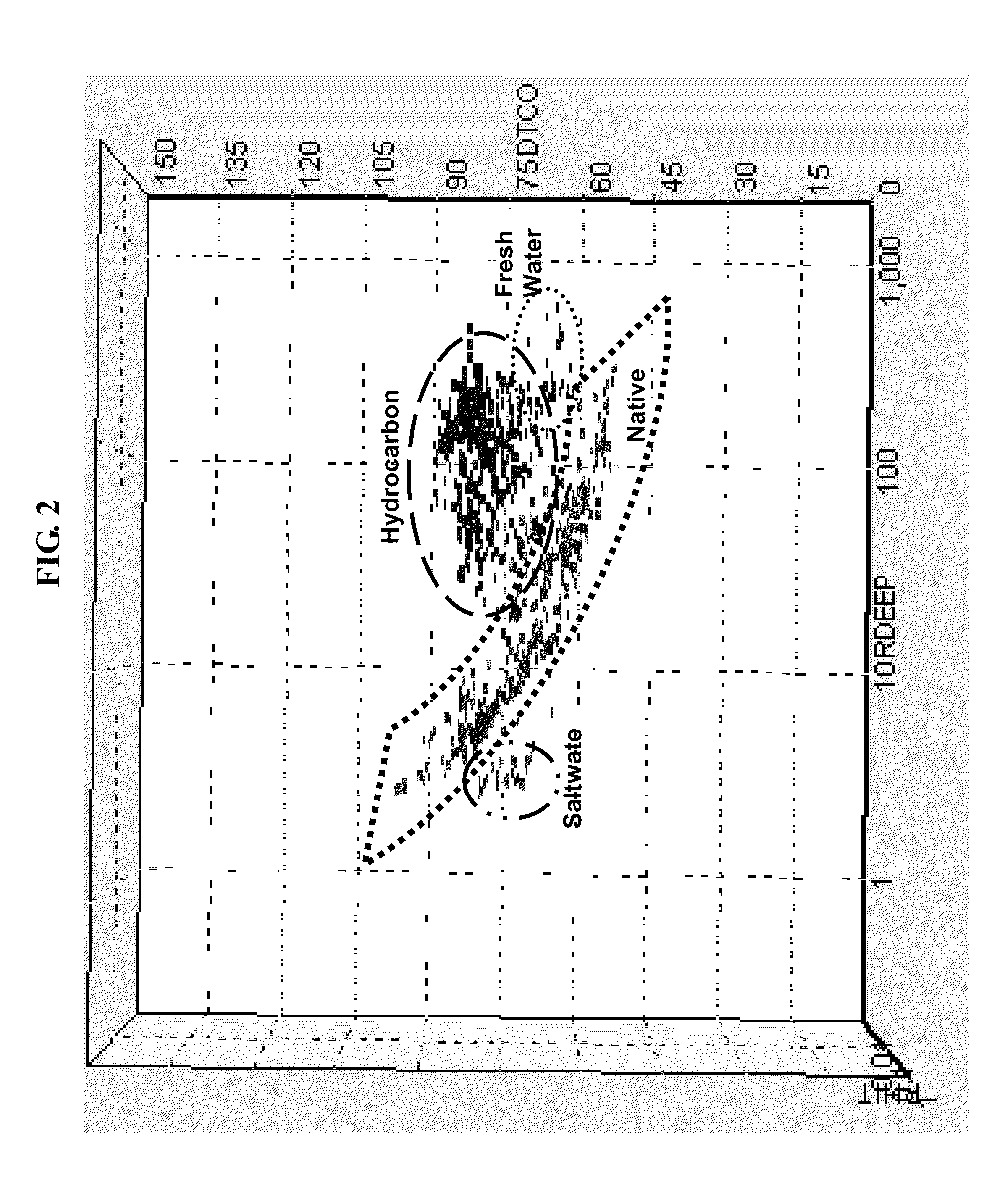
An empirical method of measuring water saturation in hydrocarbon bearing formations is described. The system described herein accurately calculates water saturation, formation volume, total organic carbon, and other formation parameters under a variety of formation conditions.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
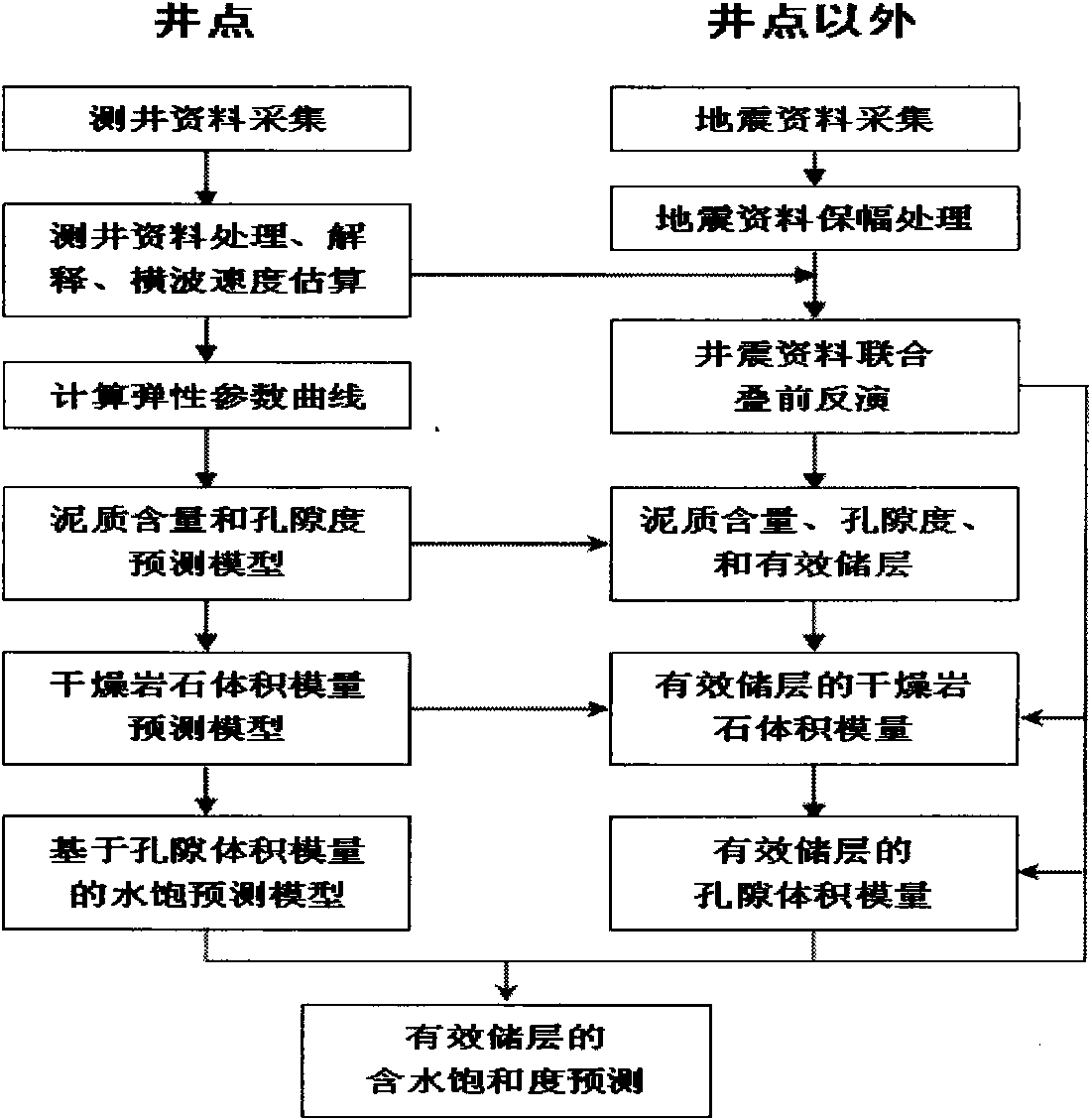
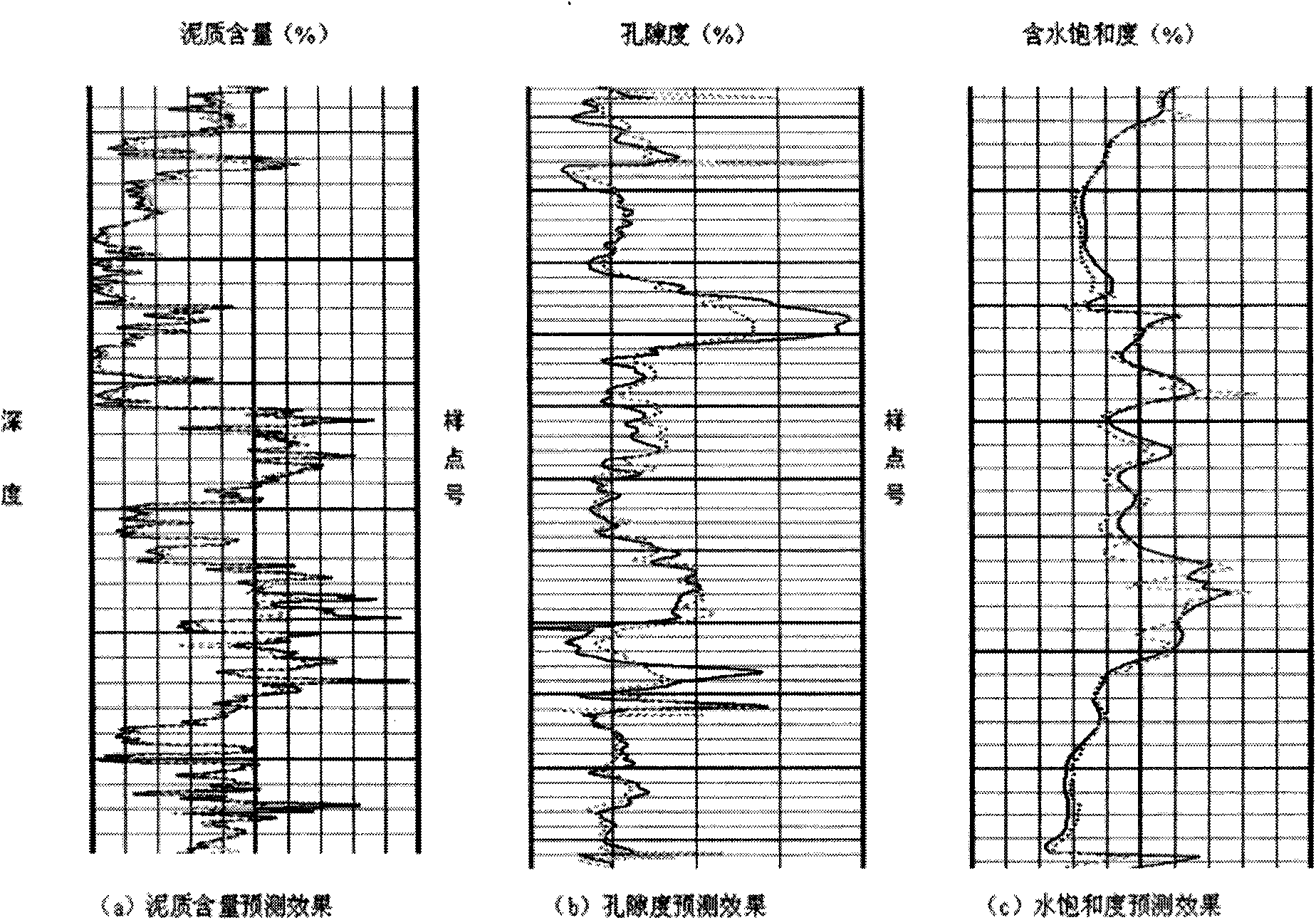
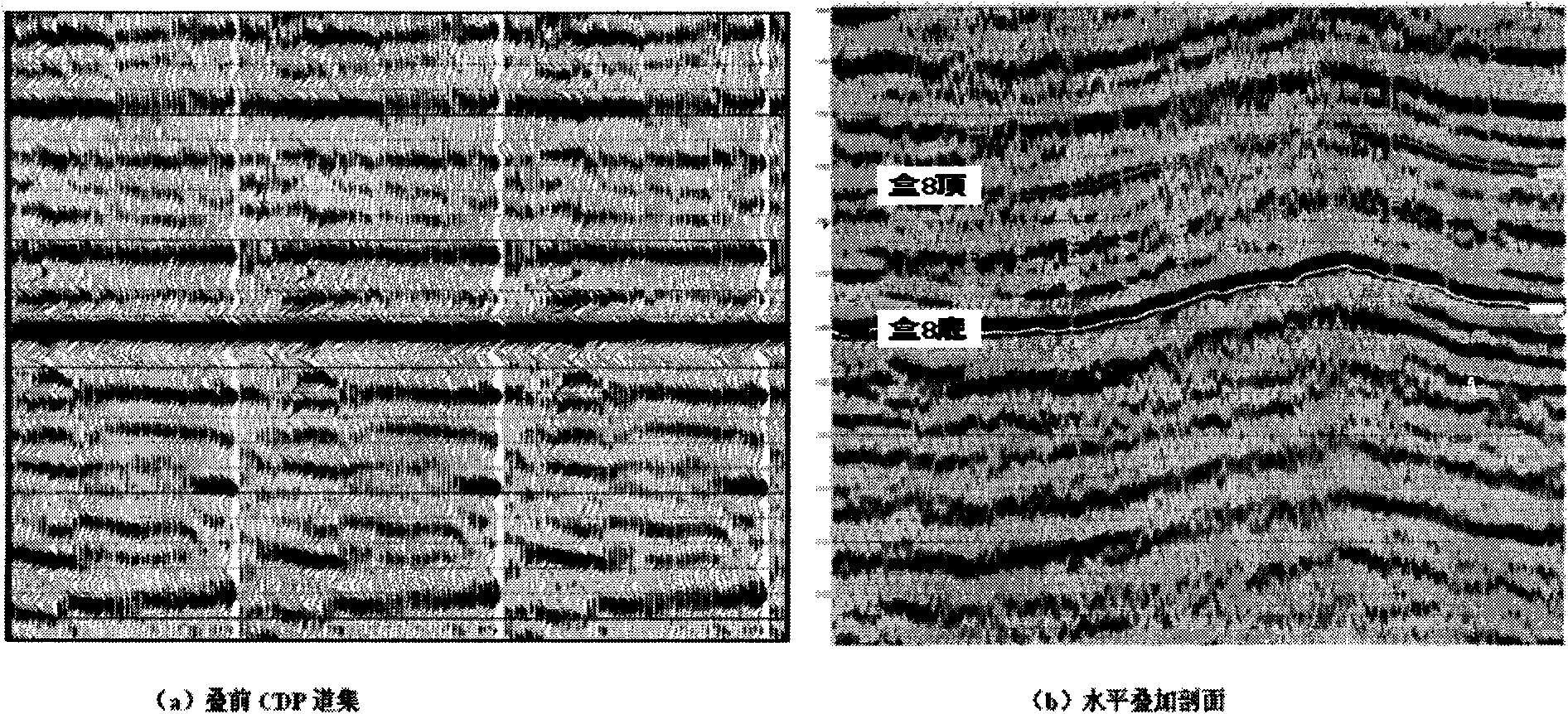
Method for quantificationally predicting sandstone reservoir fluid saturation by combining well and seism
InactiveCN101887132ARealize Quantitative PredictionGood geological effectSeismology for water-loggingReservoir fluidSeismic trace
The invention discloses a method for quantificationally predicting sandstone reservoir fluid saturation by combining a well and seism in geophysical prospecting for petroleum. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring and processing seismic data and log data to obtain each parameter curve; respectively determining the relationships among the shale content, the porosity and an elastic parameter of the well; establishing prediction models of the shale content and the porosity; calculating a pore volume modulus and a dry rock volume modulus to establish a modulus prediction model; establishing an effective reservoir water saturation prediction model; performing prestack seismic inversion by utilizing prestack seismic trace gathers and the log data to obtain an inversion data volume of each elastic parameter; calculating the dry rock volume modulus to solve the pore volume modulus by the obtained elastic inversion volume; and solving the water saturation by using the pore volume modulus. In the method, prestack seismic data and the log data are fully utilized for quantificationally predicting reservoir saturation; and good geological effects on predicting oil and gas saturation are achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
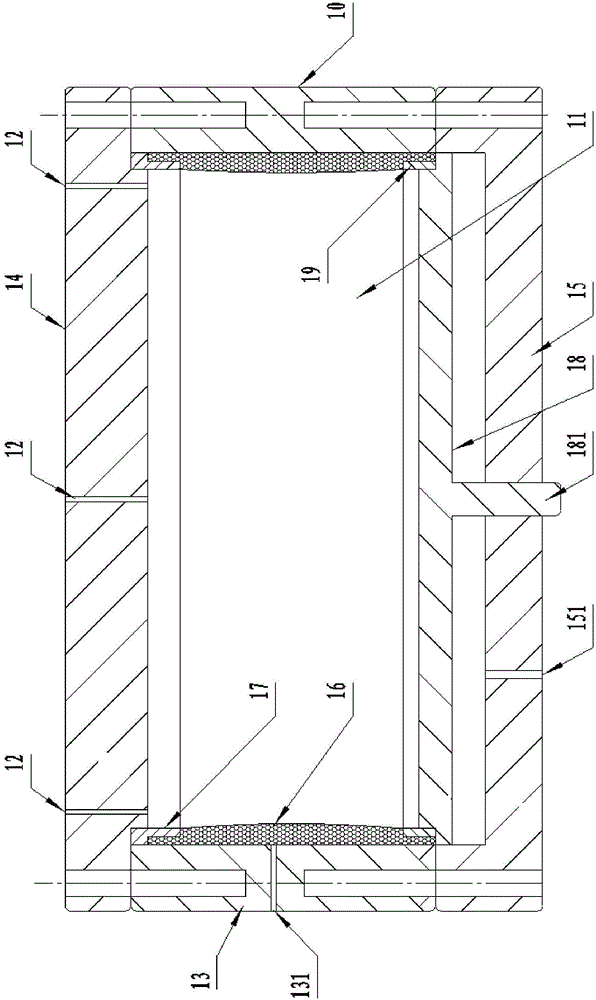
Simulation experimental analog method for low permeability oilfield planar five-spot well pattern carbon dioxide flooding
The invention provides a simulation experimental analog method for low permeability oilfield planar five-spot well pattern carbon dioxide flooding, which comprises the following steps: I. choosing a core and drilling five blind holes corresponding to five through holes (12) in a planar five-spot well pattern simulation holder (10) in the surface of the core; II. placing the core into the planar five-spot well pattern simulation holder (10); III. injecting water and raw oil into the planar five-spot well pattern simulation holder (10) in sequence, and establishing the irreducible water saturation; IV. injecting carbon dioxide into the planar five-spot well pattern simulation holder (10) by using a gas injecting device (31), and collecting and measuring experimental parameters through produced fluid collection and calibration equipment (21). The method can be used for simulating the displacement performance of a one-injection and four-production five-spot well pattern, and simulating the interwell fluid channeling with cracks so as to avoid the phenomenon of the overlarge starting pressure gradient of one-way flow, so that simulation is more proximate to a real situation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Tool and method for determining formation parameter
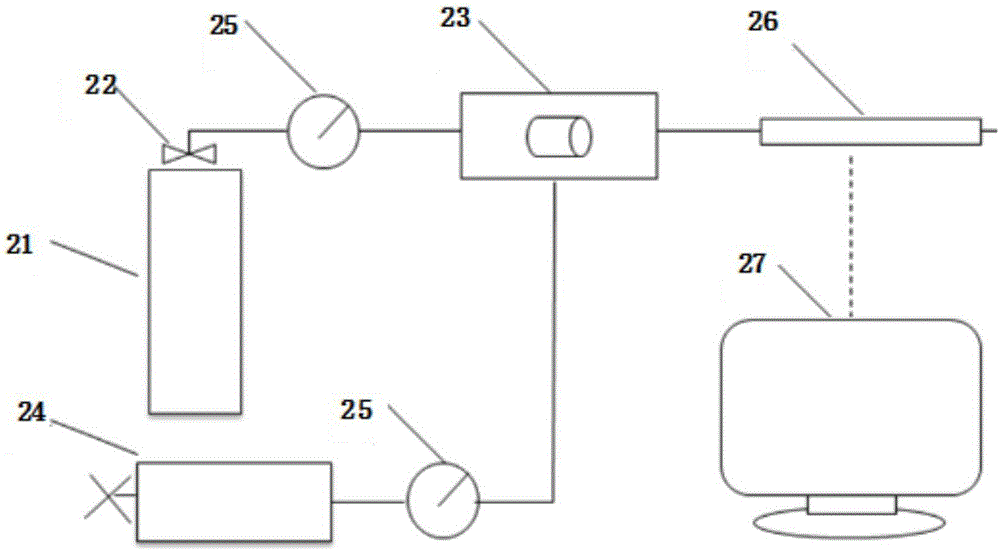
ActiveUS20090255669A1Good estimateReduces some of the uncertaintiesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyStreamflowOil well
An apparatus and method of measuring a parameter characteristic of a rock formation in an oil well is provided with a device for generating a sensing field within a volume of the rock formation and a device for causing a flow through the volume in the presence of the sensing field, further including sensors responsive to changes in the volume, wherein a sensor response is indicative of the amounts of fluid, particularly hydrocarbon and water saturations and irreducible hydrocarbon and water saturations. Measurements can be made before the flow affects the measuring volume and after onset of the flow through the measuring volume.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Determination device and method of constraint irreducible water saturation in reservoir rock core
InactiveCN103278418AReliable principleReasonable structureWeighing by removing componentRock coreDisplacement control
The invention discloses a determination device and method of constraint irreducible water saturation in a reservoir rock core. The device mainly comprises a high-pressure nitrogen source, a humidifier, a rock core holding device, an oil-water displacement pump, a loop pressure pump, a return pressure control pump, a gas metering instrument and a liquid metering instrument, wherein the rock core clamping device is arranged in a constant-temperature box; the high-pressure nitrogen source is connected with the inlet end of the rock core clamping device through the humidifier; the oil-water displacement pump is also connected with the inlet end of the rock core clamping device through an oil-water displacement control valve; the loop pressure pump is connectd with the rock core clamping device through a loop pressure control valve, and applies confining pressure to the rock core; and the outlet end of the rock core clamping device is connected with the return pressure control pump, and is also connected with the gas metering instrument and the liquid metering instrument respectively. The device is reliable in principle, is reasonable in structure, and is simple and convenient to operate, is utilized for determining the constraint irreducible water saturation in the reservoir rock core, can achieve the highest pressure of 70Mpa and the highest temperature of 150 DEG C, and remedies the defects of an existing gas reservoir log analysis and gas well production dynamic analysis method as well as the technique application.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
Computing model of mud shale oil gas saturability
ActiveCN104712329AAddressing Non-Archie PhenomenaImprove applicabilityInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelPhysical model
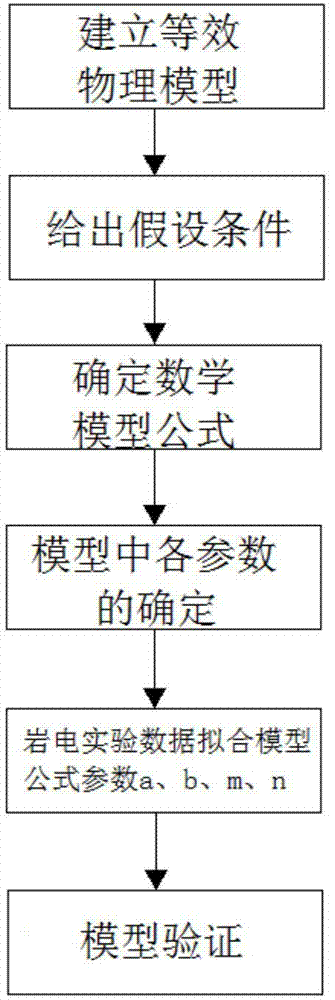
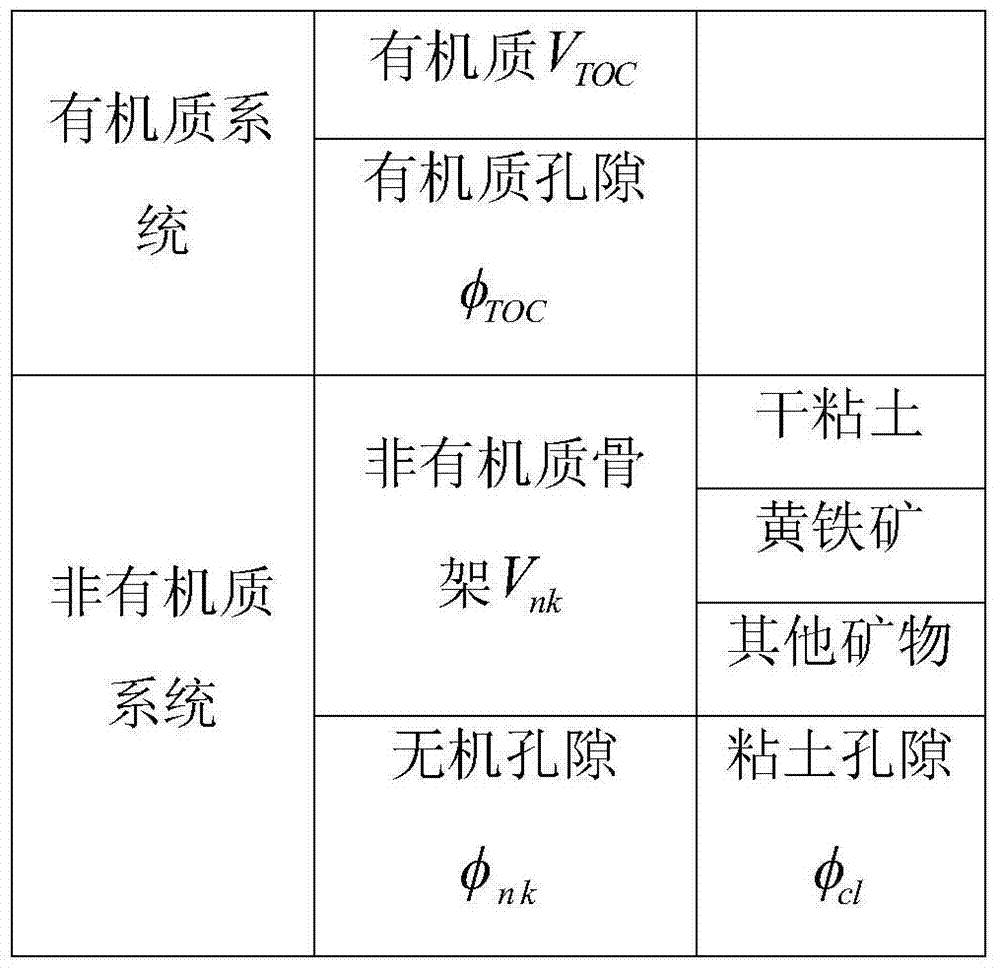
The invention discloses a computing model of mud shale oil gas saturability. The computing model comprises the steps that A. an equivalent physical model is established; B. an assumed condition is given out; C. a mathematical model formula is determined; D. various parameters in the model are determined; E. rock electric experimental data formula parameter a, b, m and n fitting is carried out; and F. model verification is carried out. The non-Archie phenomenon of a mud shale oil storage layer caused by the problems that framework minerals are complex, a pore structure is complex, and pore wettability is complex can be avoided, the oil gas saturability of the mud shale storage layer is accurately computed, help is provided for a logging evaluation storage layer and oil field development, the unparalleled advantages which other saturability models do not have are achieved on mud shale water saturability computing are achieved, practical application effect is obvious, and accordingly great promotion value is achieved. In current public-published literatures and commercial application software, similar method providing and application do not exist.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Test method for intrastratal nonhomogeneous model
The invention relates to a test method for an intrastratal nonhomogeneous model. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the porosity, the air permeability, the water phase permeability, the oil phase effective permeability and the bond water saturation of a plurality of natural reservoir cores serving as single-layer core models respectively; putting all the layers of cores with bond water into a nonhomogeneous multi-layer core holding device according to a reverse rhythm order, wherein the core holding device is provided with a plurality of liquid outlets, each liquid outlet is aligned with a layer of core respectively, a joint between two layers of correspondingly adjacent cores on the right tops of the cores is provided with a sealing gasket, and effluent liquid which passes through each layer of core flows out from the corresponding liquid outlet of each layer; adding 0 to 50MPa of ambient pressure; performing water displacement on the cores at a speed of between 0 and 10ml / min; recording the water breakthrough time, the accumulated oil yield during the water breakthrough time, the accumulated liquid yield, and displacement differential pressure at both ends of each layer of core; and finishing an experiment when the moisture content reaches 99.95 percent. By the test method, the variation rules of nonhomogeneous water displacing oil in each layer can be precisely reflected.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for macroscopically quantizing microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states
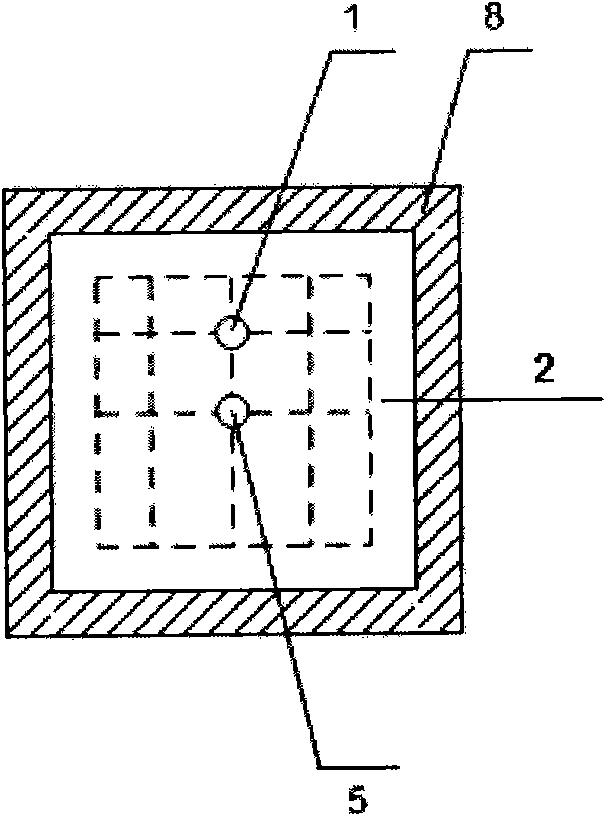
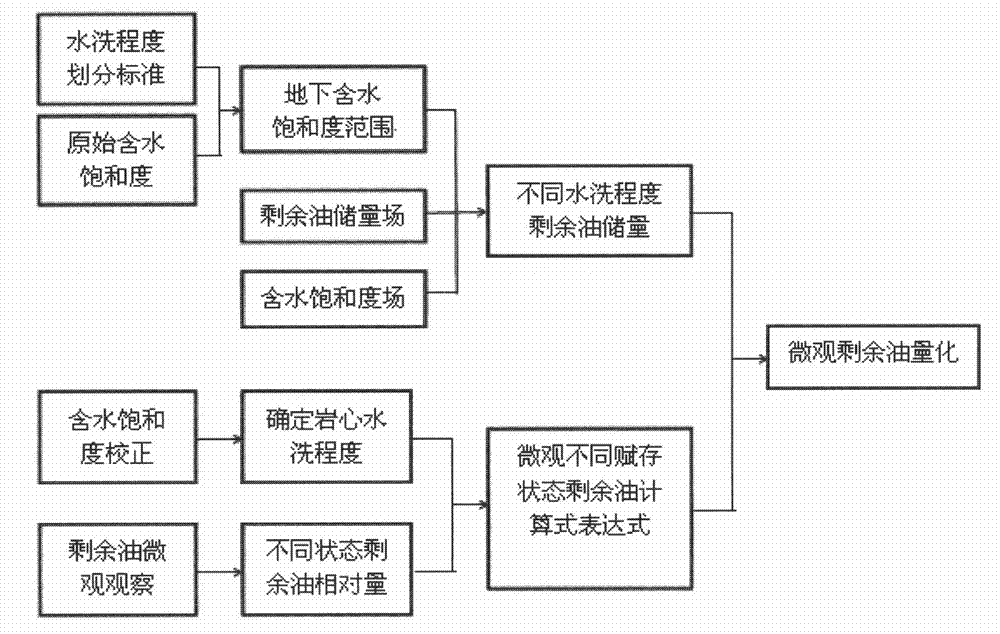
ActiveCN103206208ARaise the level of researchMeet the actual needs of developmentBorehole/well accessoriesRock coreMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a method for macroscopically quantizing microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states. The method includes the steps: acquiring a remaining oil reserve distribution field and a water saturation distribution field by macroscopic numerical simulation; determining the range of underground water saturation under the condition of different washing degrees according to washing degree differentiating standards and original water saturation, and obtaining macroscopic remaining oil reserve with different washing degrees according to the remaining oil reserve distribution field and the water saturation distribution field; determining the washing degree of a rock core in a current state by water saturation correction test for a coring well, determining the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states by microscopic observation test for oily slices of the coring well, and counting to obtain the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states under different washing degrees; and macroscopically quantizing the microscopic remaining oil by applying computation expression for microscopic remaining oil mass in different occurrence states according to the macroscopic remaining oil reserve with different washing degrees and the relative content of the microscopic remaining oil in different occurrence states under different washing degrees.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM EXPLORATION DEELOPMENT INST OF HENAN OILFIELD BRANCH SINOPEC
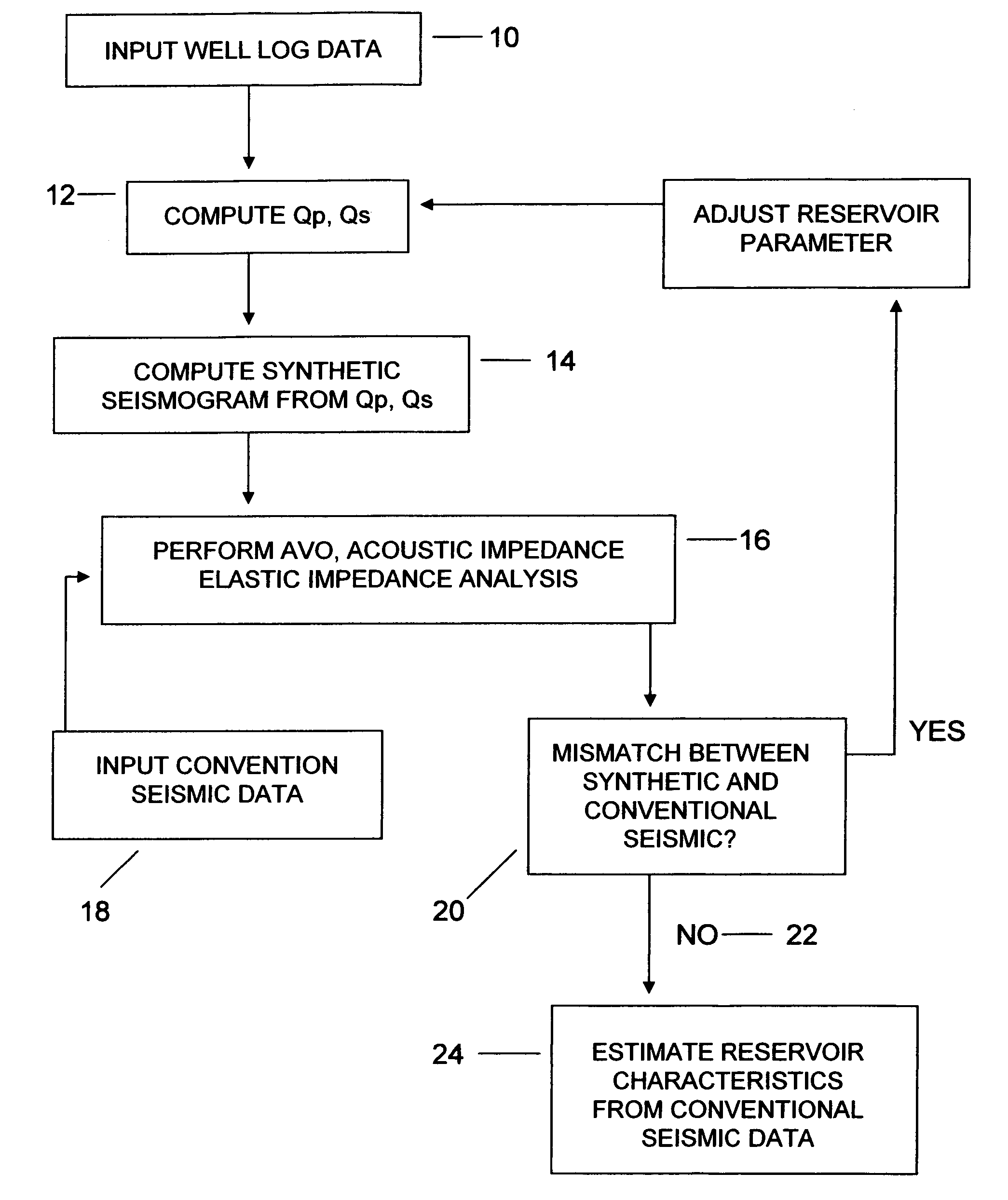
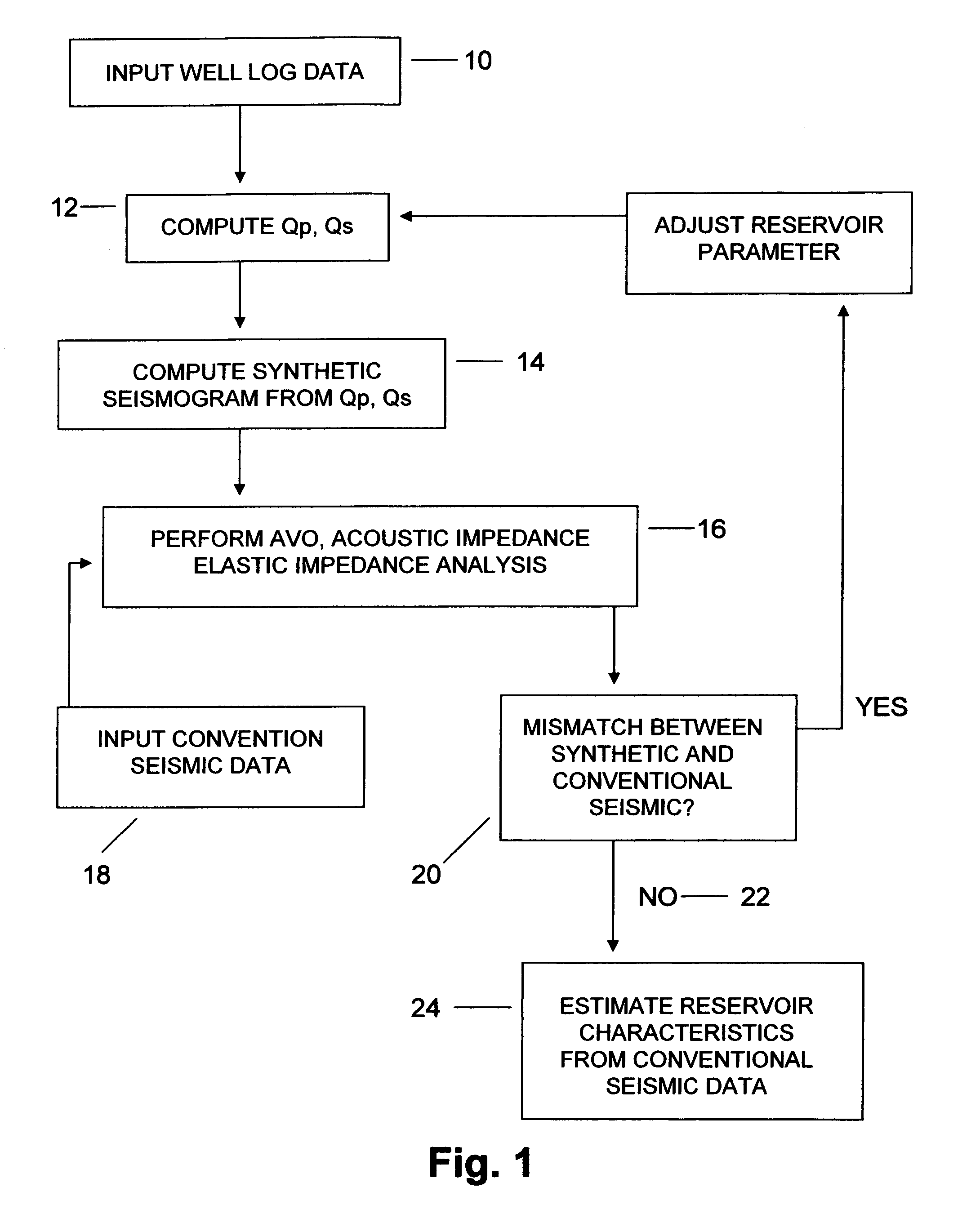
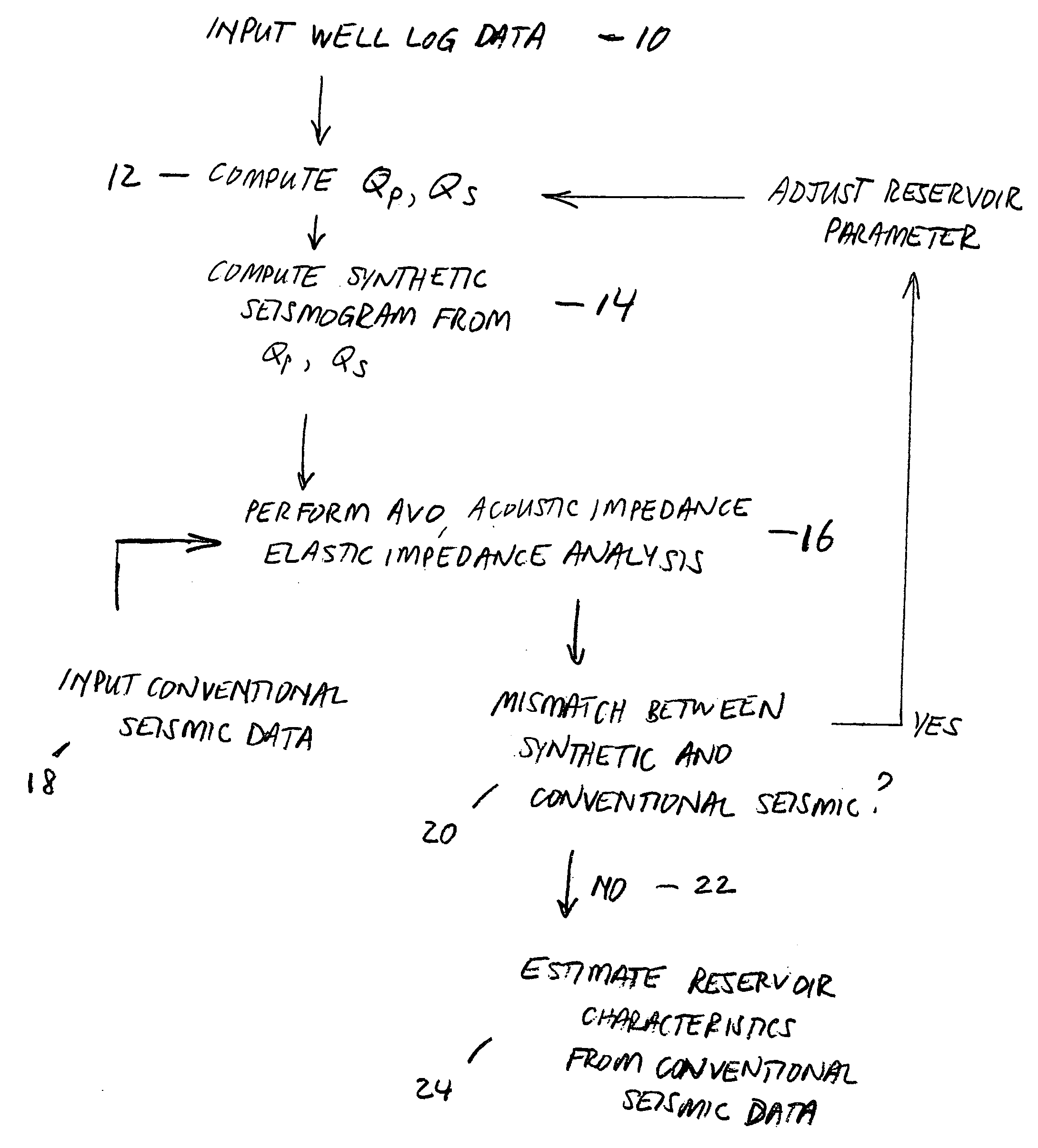
Method for determining formation quality factor from well log data and its application to seismic reservoir characterization
ActiveUS20060104158A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic surveyWell logging
A method for seismic characterization of subsurface Earth formations includes determining at least one of compressional velocity and shear velocity, and determining reservoir parameters of subsurface Earth formations, at least including density, from data obtained from a wellbore penetrating the formations. A quality factor for the subsurface formations is calculated from the velocity, the density and the water saturation. A synthetic seismogram is calculated from the calculated quality factor and from the velocity and density. The synthetic seismogram is compared to a seismic survey made in the vicinity of the wellbore. At least one parameter is adjusted. The synthetic seismogram is recalculated using the adjusted parameter, and the adjusting, recalculating and comparing are repeated until a difference between the synthetic seismogram and the seismic survey falls below a selected threshold.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com