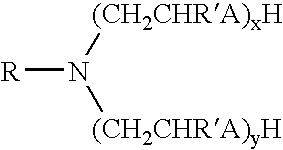
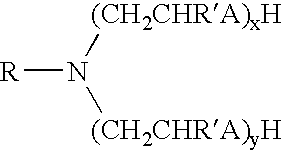
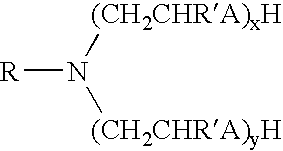
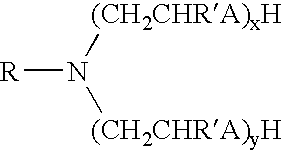
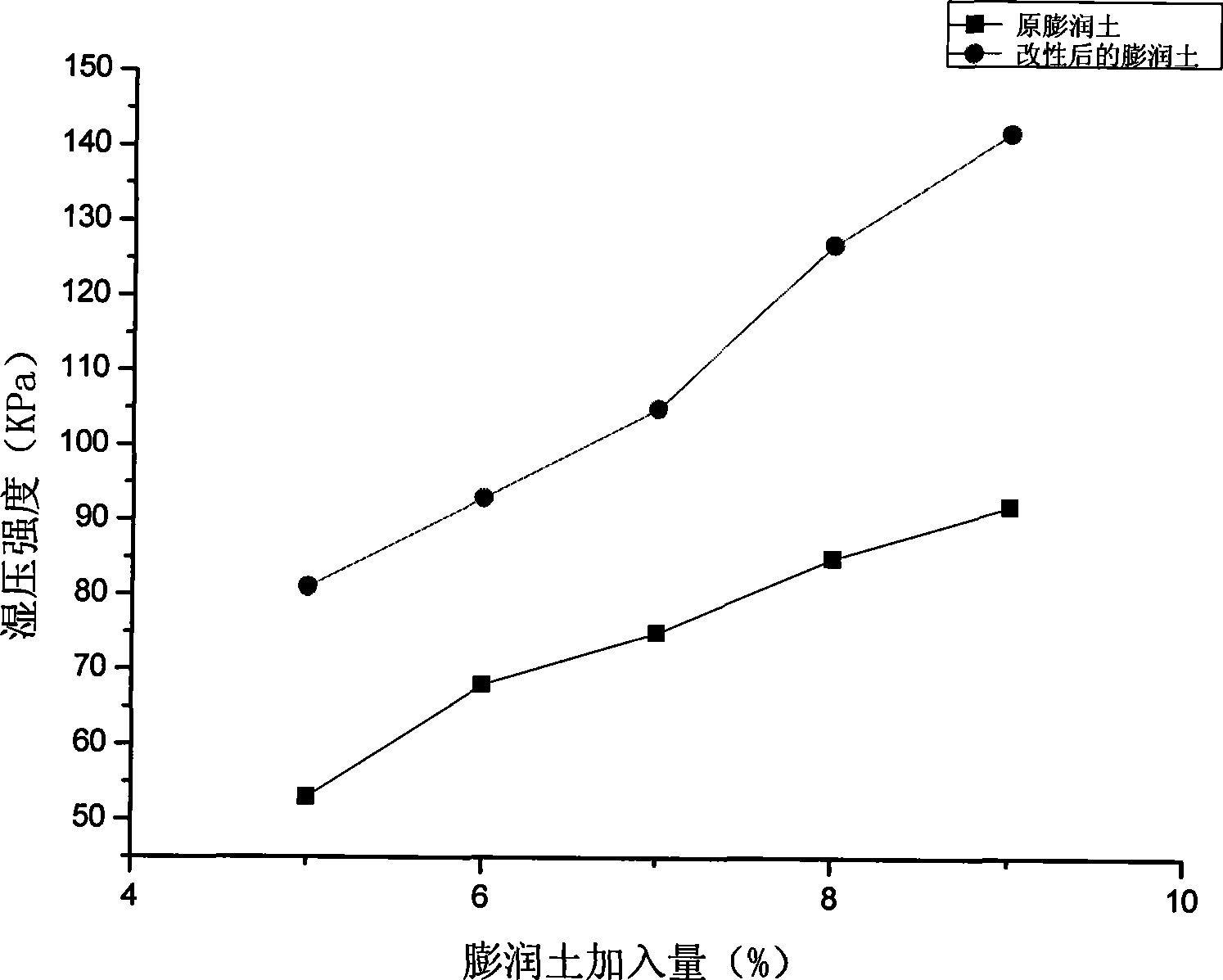
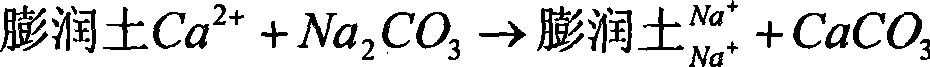Patents
Literature
94 results about "Water wet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Answer 1: Being a liquid, water is not itself wet, but can make other solid materials wet. Wetness is the ability of a liquid to adhere to the surface of a solid, so when we say that something is wet, we mean that the liquid is sticking to the surface of a material.
Compositions and methods for the removal of oil-based filtercakes
A method of servicing a wellbore comprising providing a composition comprising a mutual solvent precursor, an acid precursor, and an aqueous fluid, and contacting the composition with oil wet solids in the wellbore. A method of servicing a wellbore comprising introducing an oil-based fluid into a wellbore, wherein the oil-based fluid forms oil wet solids in the wellbore, contacting the oil wet solids in the wellbore with a composition comprising a mutual solvent precursor; an acid precursor and an aqueous fluid, and allowing the oil wet solids to become water wet. A method of servicing a well bore comprising contacting a composition comprising a formate ester with oil wet solids in the well bore under conditions wherein the formate ester hydrolyzes to release formic acid, wherein the formic acid catalyzes the hydrolysis of additional formate ester, and wherein all or a portion of the formate ester converts at least a portion of the oil-wet solids to water-wet solids.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
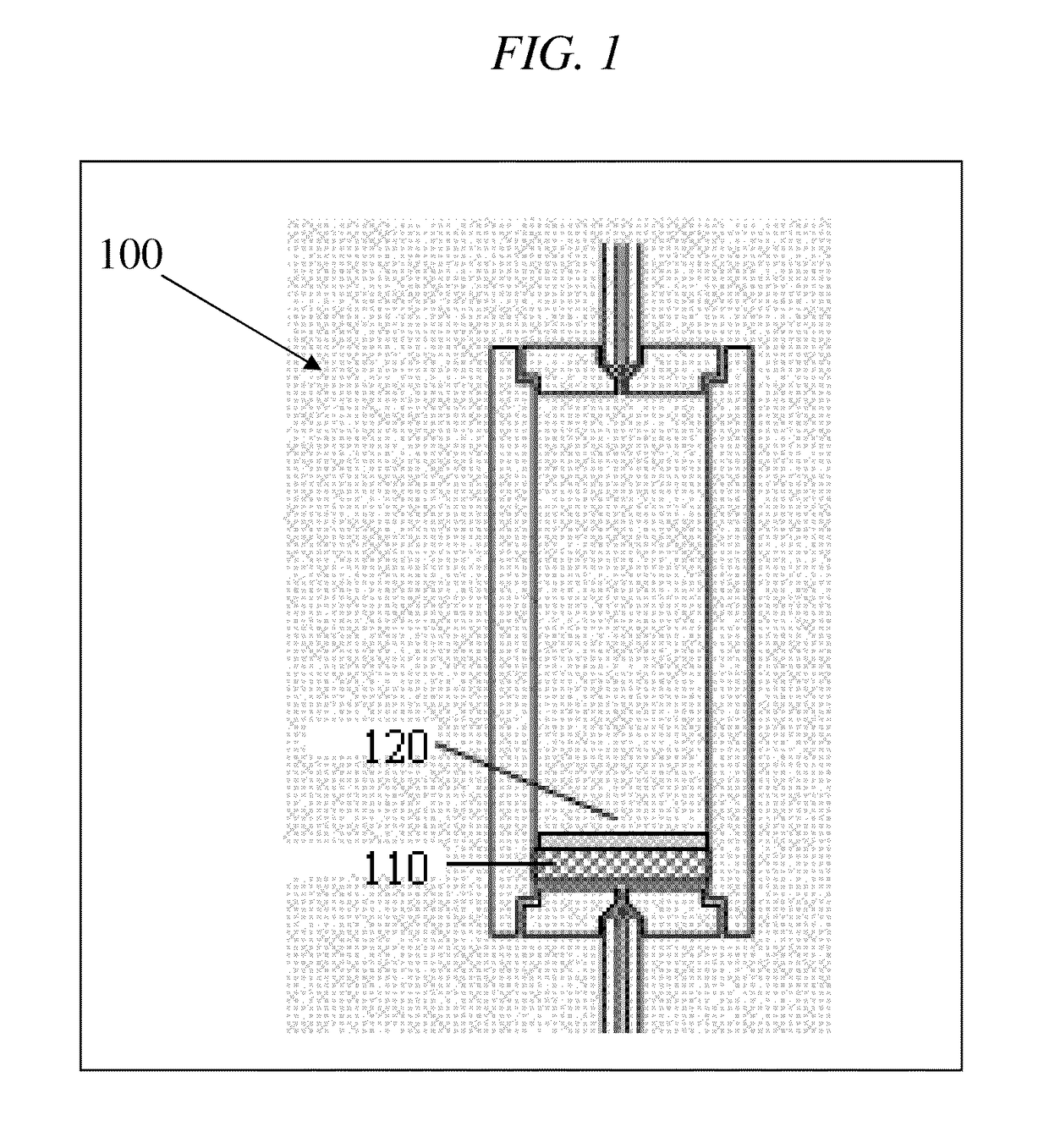
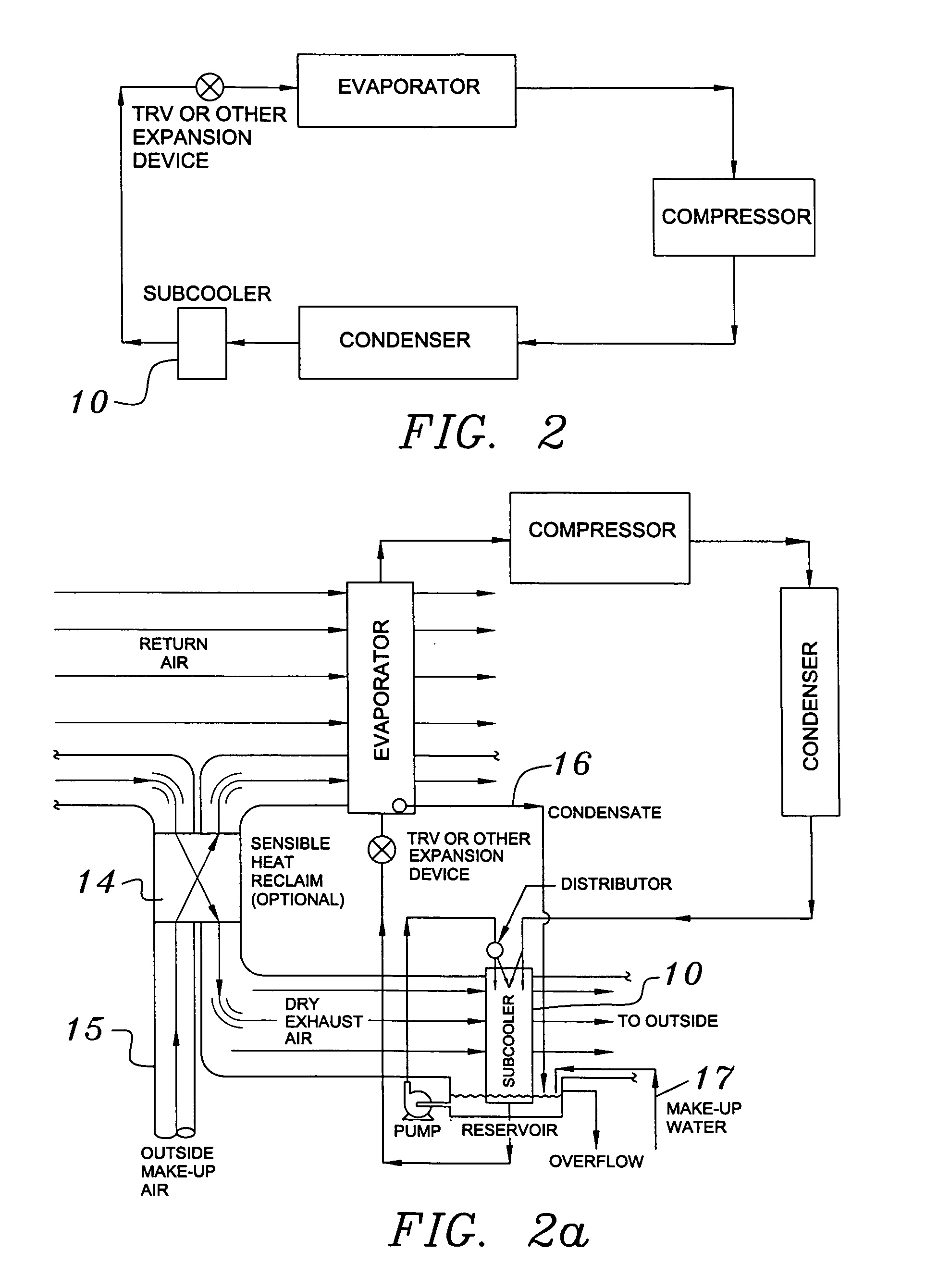
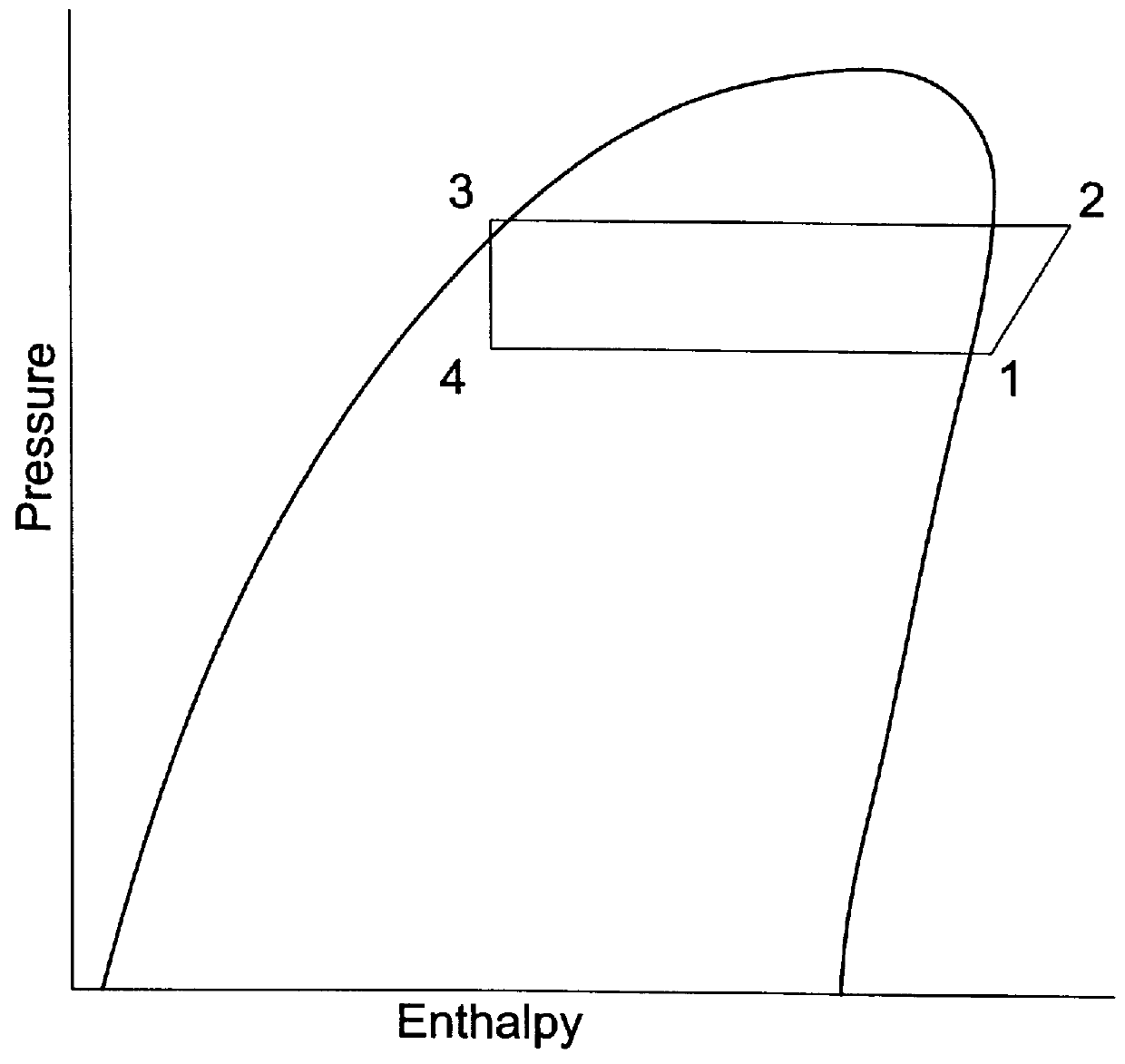
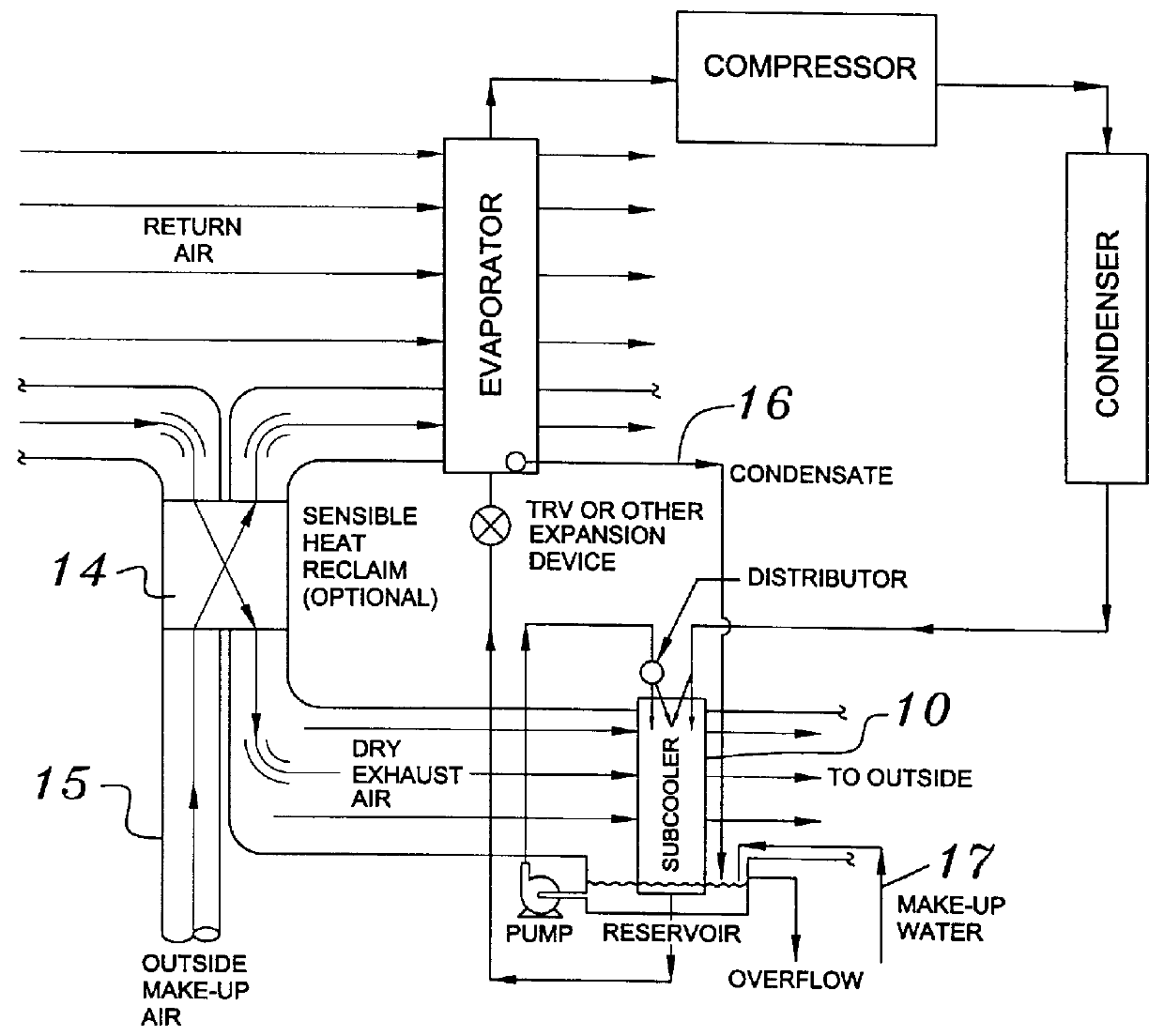
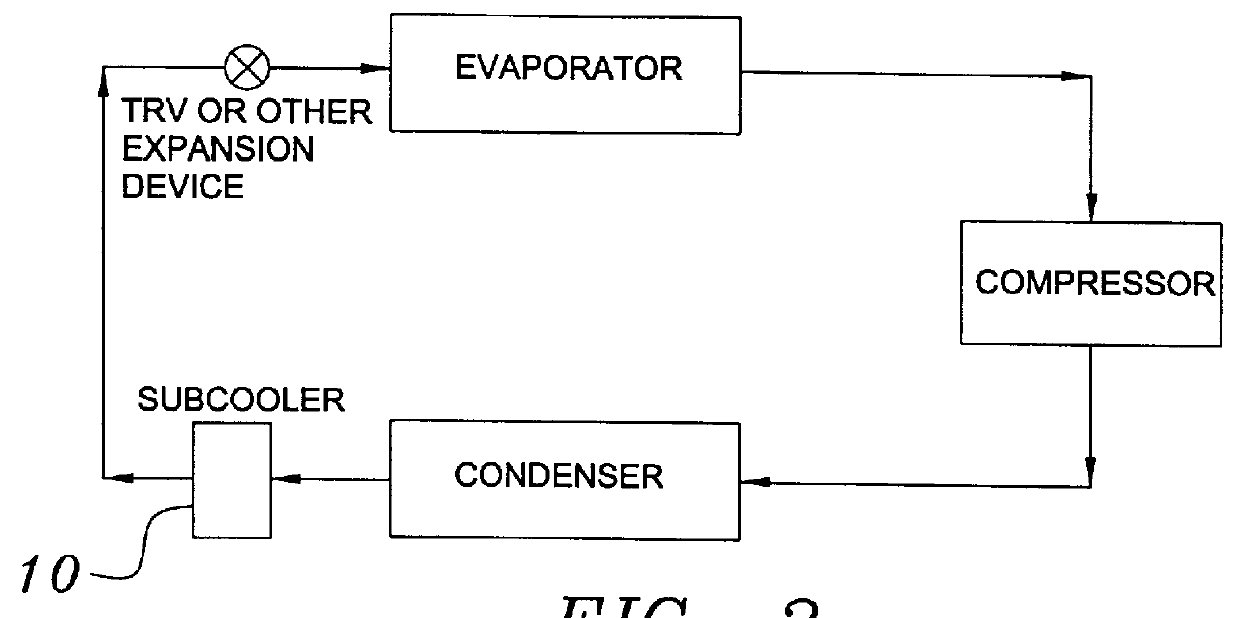
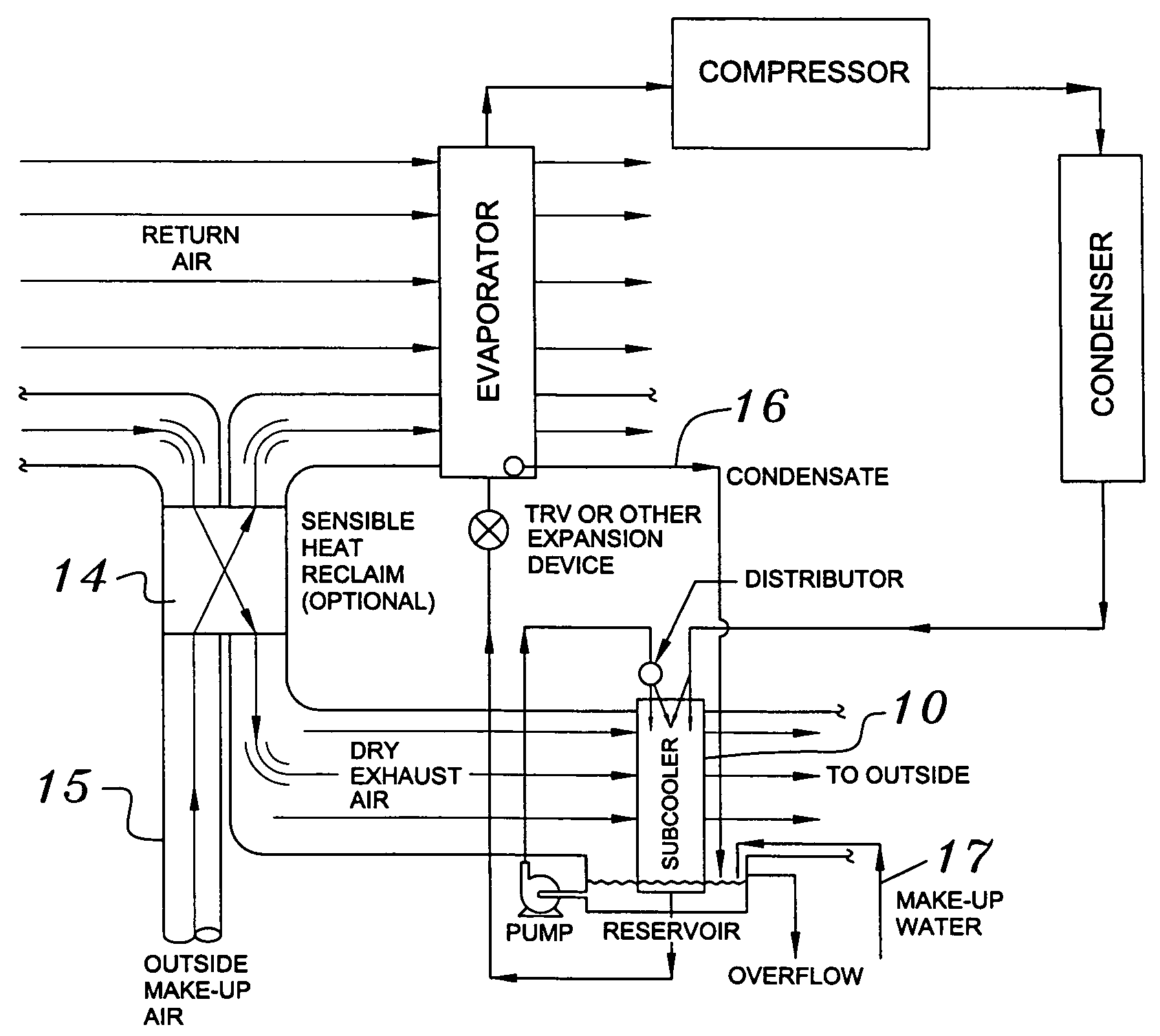
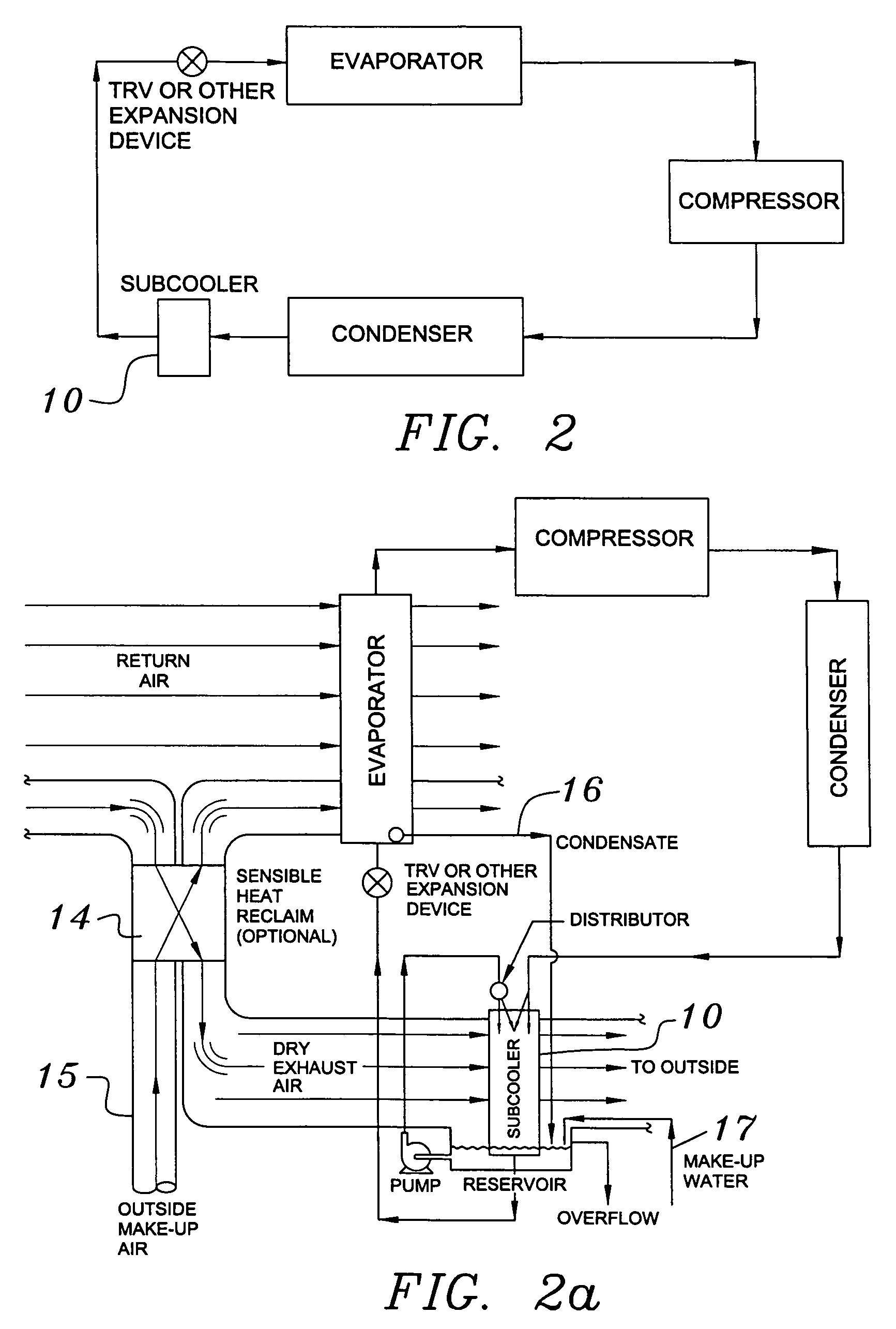
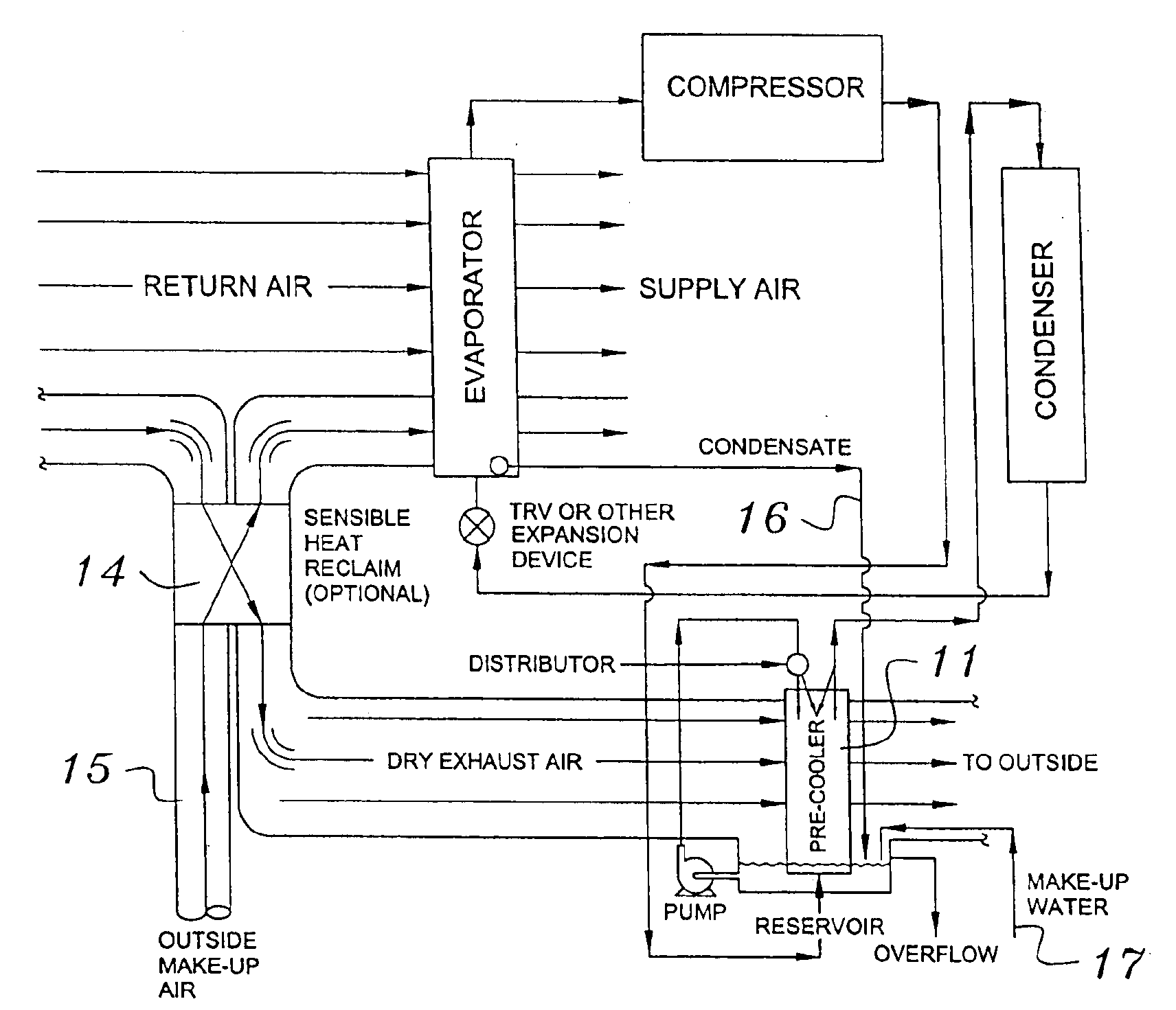
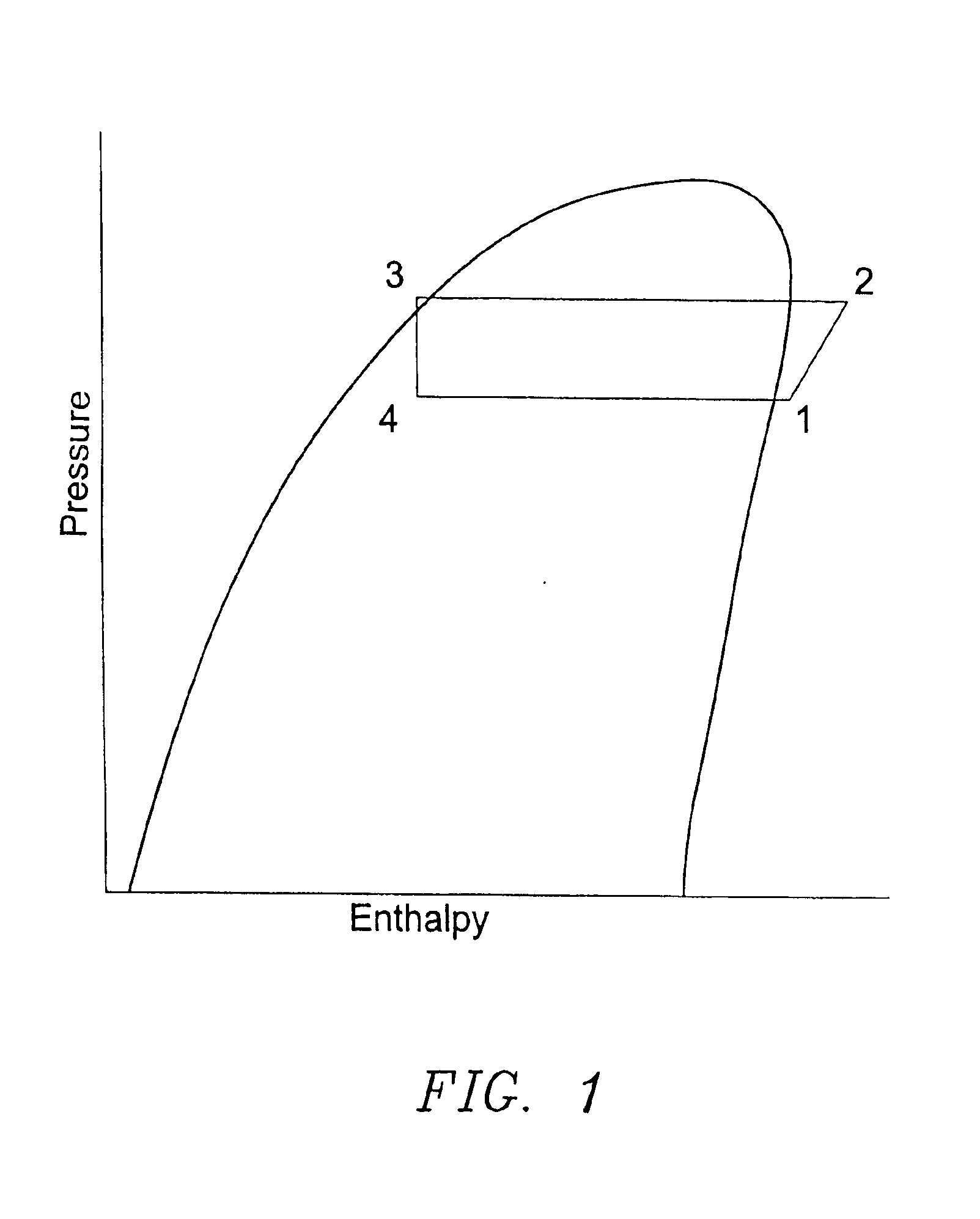
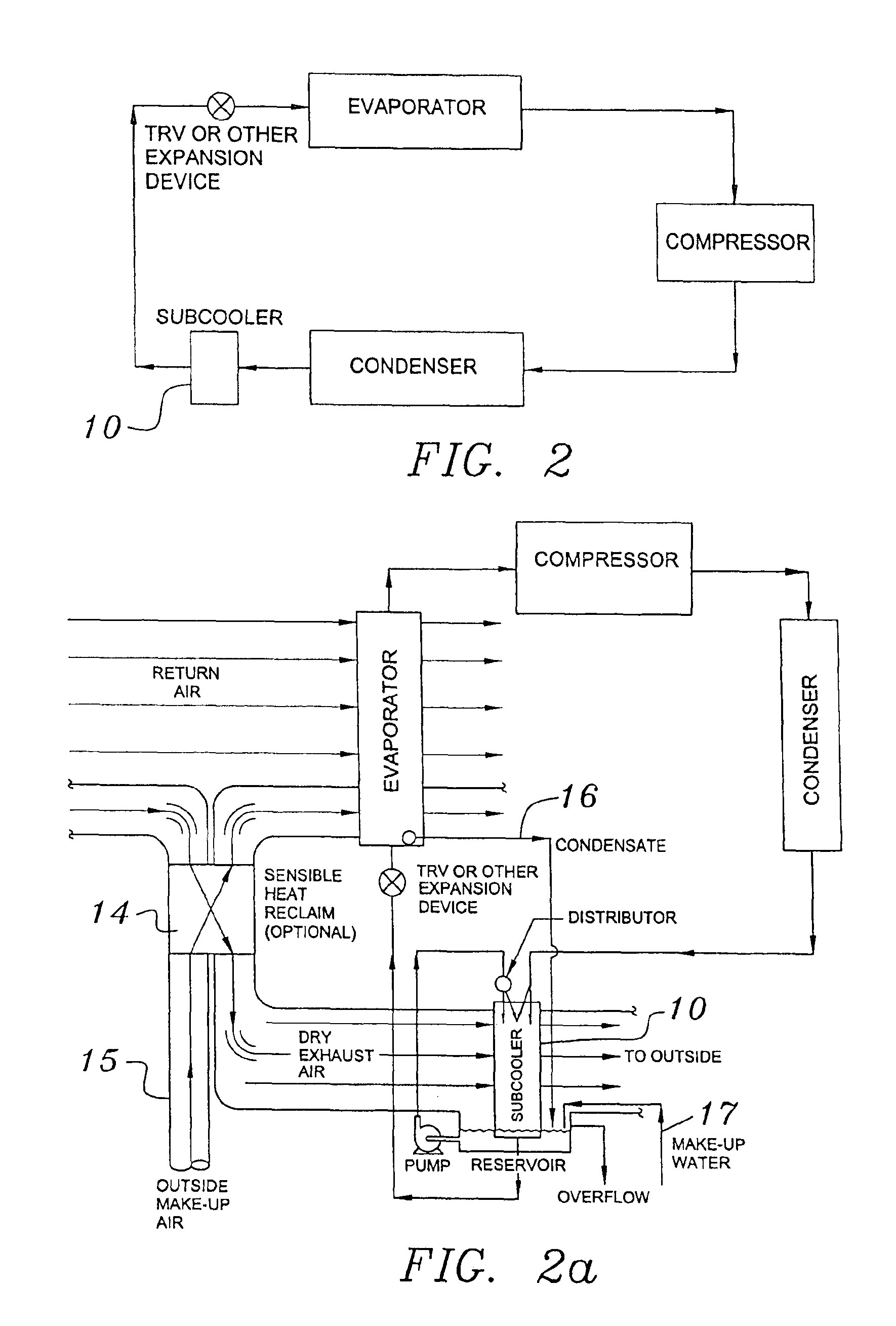
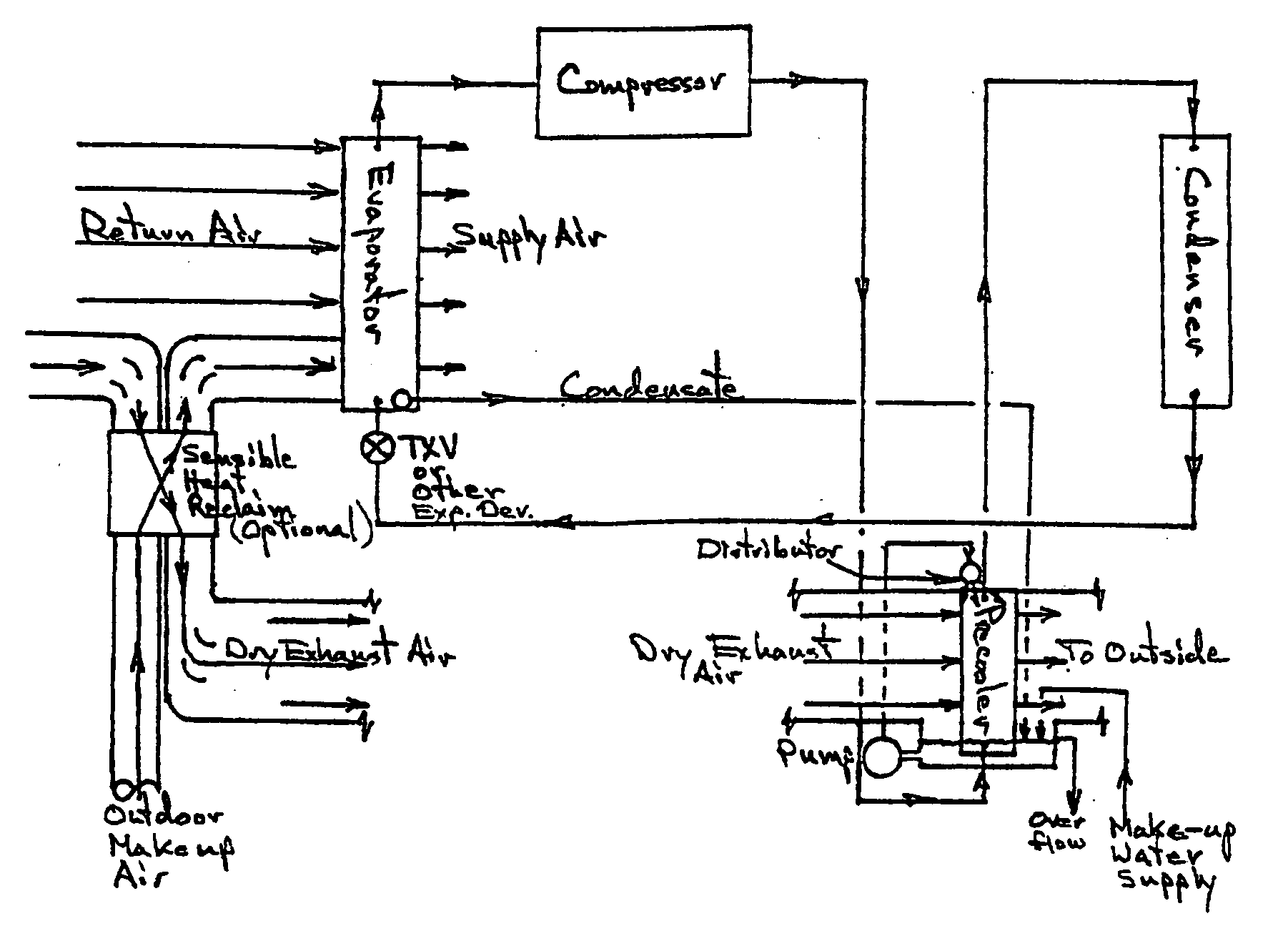
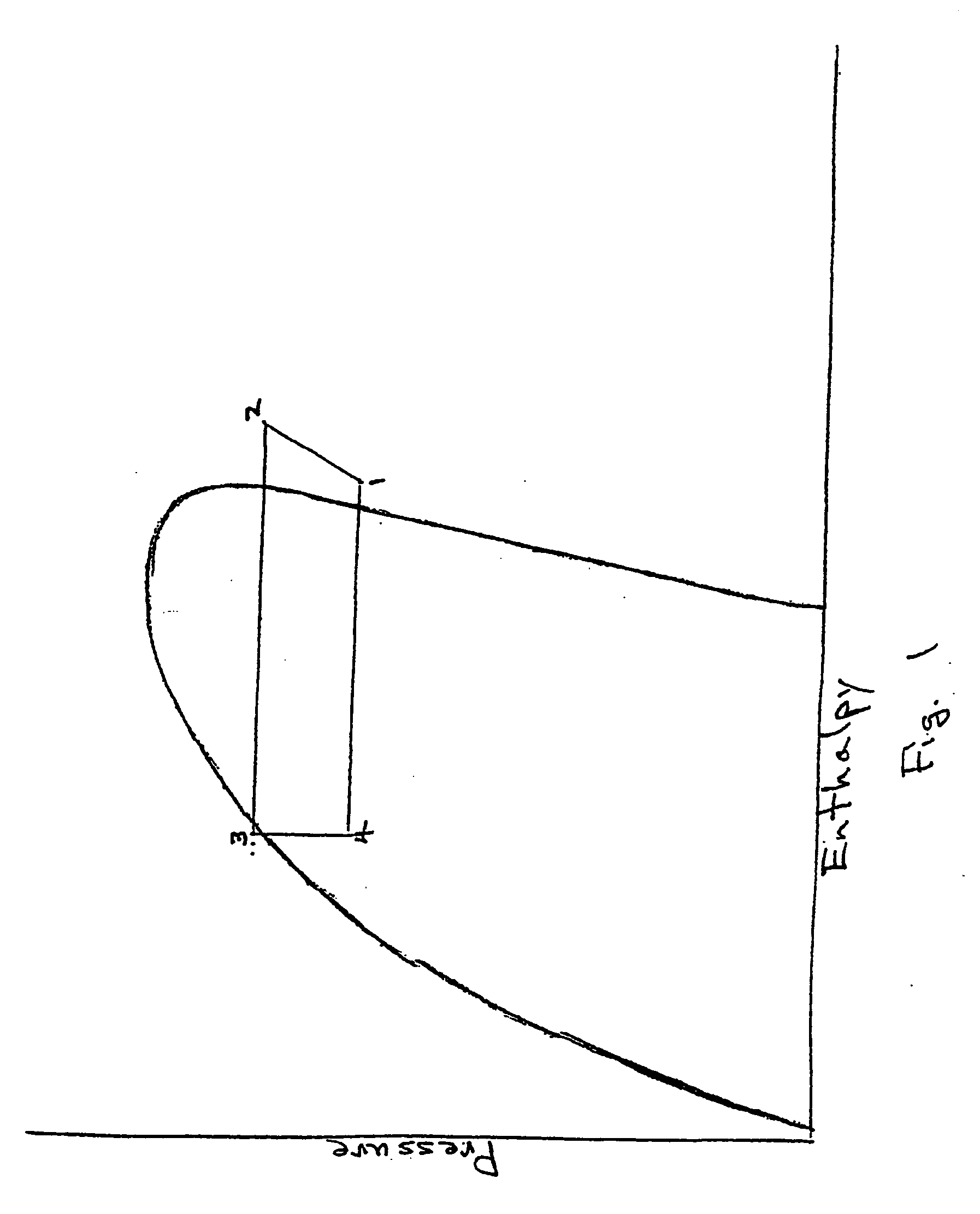
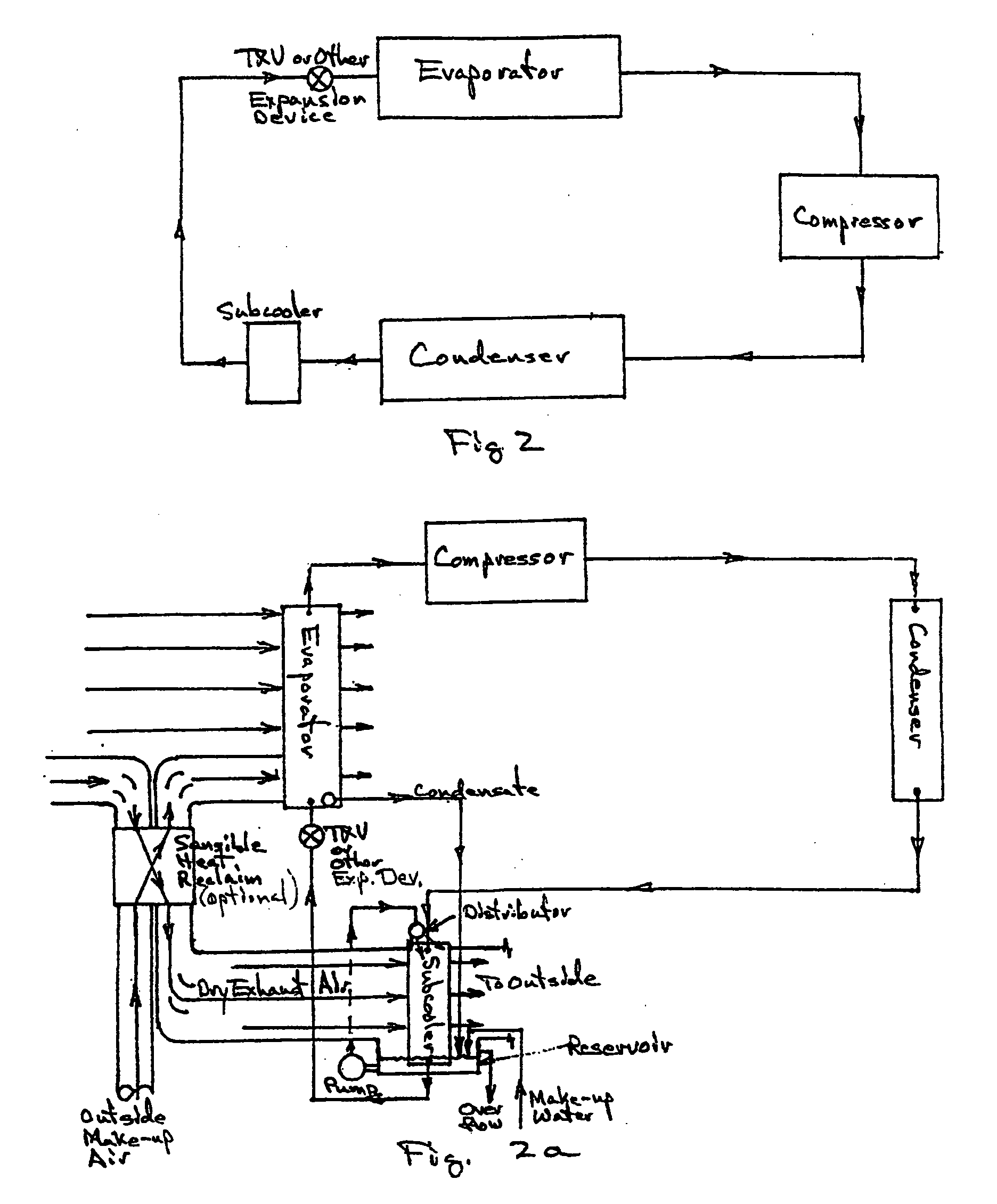
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS20050028545A1Improve cooling effectReduce power consumptionEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingDomestic cooling apparatusWater wetWater source
A system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration / heat pump system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and pass the dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. A system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling into the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system by evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. A combination subcooler / precooler system where the cold dry building exhaust air is used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted (or dry) subcooler and then used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
Composition of Wellbore Cleaning Agent
A cleaning agent, which comprises a mutual solvent, a carrier fluid, a nonionic surfactant and another nonionic surfactant as co-surfactant. The cleaning agent can be used, for example, to clean oil and water based drilling mud and water-wet the surface.
Owner:WELLBORE CHEM LLC
Preparation method of cellulose nano-fiber/polylactic acid composite membrane
InactiveCN103387688AUniform diameter distributionReduce hydrogen bondingPaper material treatmentFiberChemical treatment
The invention provides a preparation method of a cellulose nano-fiber / polylactic acid composite membrane. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) treating raw materials; (2) performing chemical treatment; (3) performing mechanical treatment; (4) preparing a nano cellulose membrane; (5) preparing a nano cellulose / polylactic acid composite membrane material by using a mixing and dissolving method or an immersion method. The preparation method has the advantages that lignin and most of hemicellulose are removed by using a chemical method, and under a water wet swelling condition, water fills the positions in which most of the hemicellulose and the lignin are removed, so that the hydrogen bond acting force among fibrillae is reduced; then lignocellulose nano fibrillae with uniform morphological sizes and mesh gangles are prepared by adopting mechanical treatment. The nano celluloses prepared by grinding for 30 minutes and homogenizing are small in diameter size and are uniformly distributed, the diameters of the nano fibrillae is 15-50nm, and the length-diameter ratio is high and reaches 1200. The cellulose nano-fiber / polylactic acid composite membrane can be used as a substitute and the like for a flexible display, electronic paper, a solar battery, a flexible circuit and a glass substrate.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Compositions and Methods for the Removal of Oil-Based Filtercakes
A method of servicing a wellbore comprising providing a composition comprising a mutual solvent precursor, an acid precursor, and an aqueous fluid, and contacting the composition with oil wet solids in the wellbore. A method of servicing a wellbore comprising introducing an oil-based fluid into a wellbore, wherein the oil-based fluid forms oil wet solids in the wellbore, contacting the oil wet solids in the wellbore with a composition comprising a mutual solvent precursor; an acid precursor and an aqueous fluid, and allowing the oil wet solids to become water wet. A method of servicing a well bore comprising contacting a composition comprising a formate ester with oil wet solids in the well bore under conditions wherein the formate ester hydrolyzes to release formic acid, wherein the formic acid catalyzes the hydrolysis of additional formate ester, and wherein all or a portion of the formate ester converts at least a portion of the oil-wet solids to water-wet solids.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
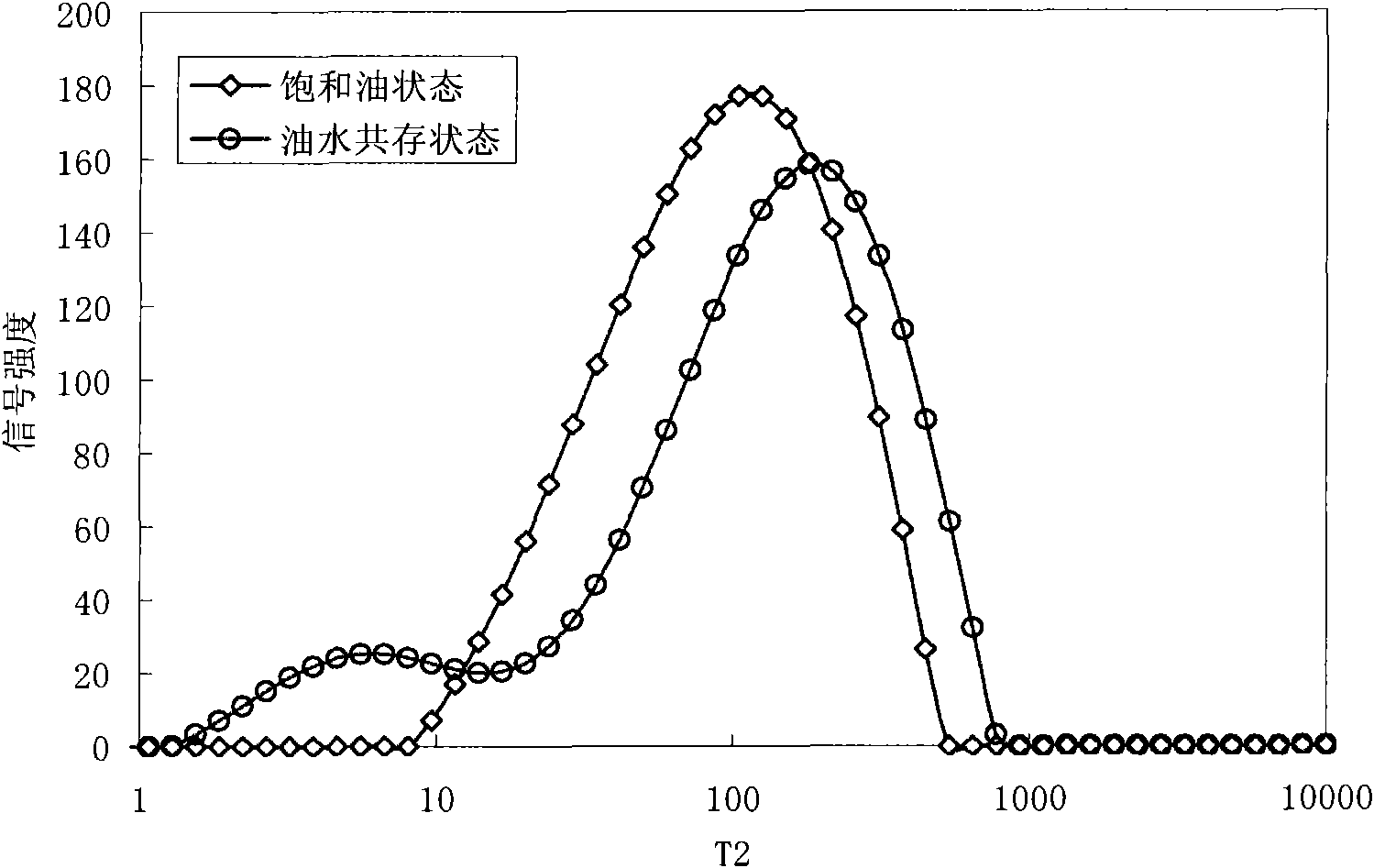
Method for judging wettability of reservoir rock
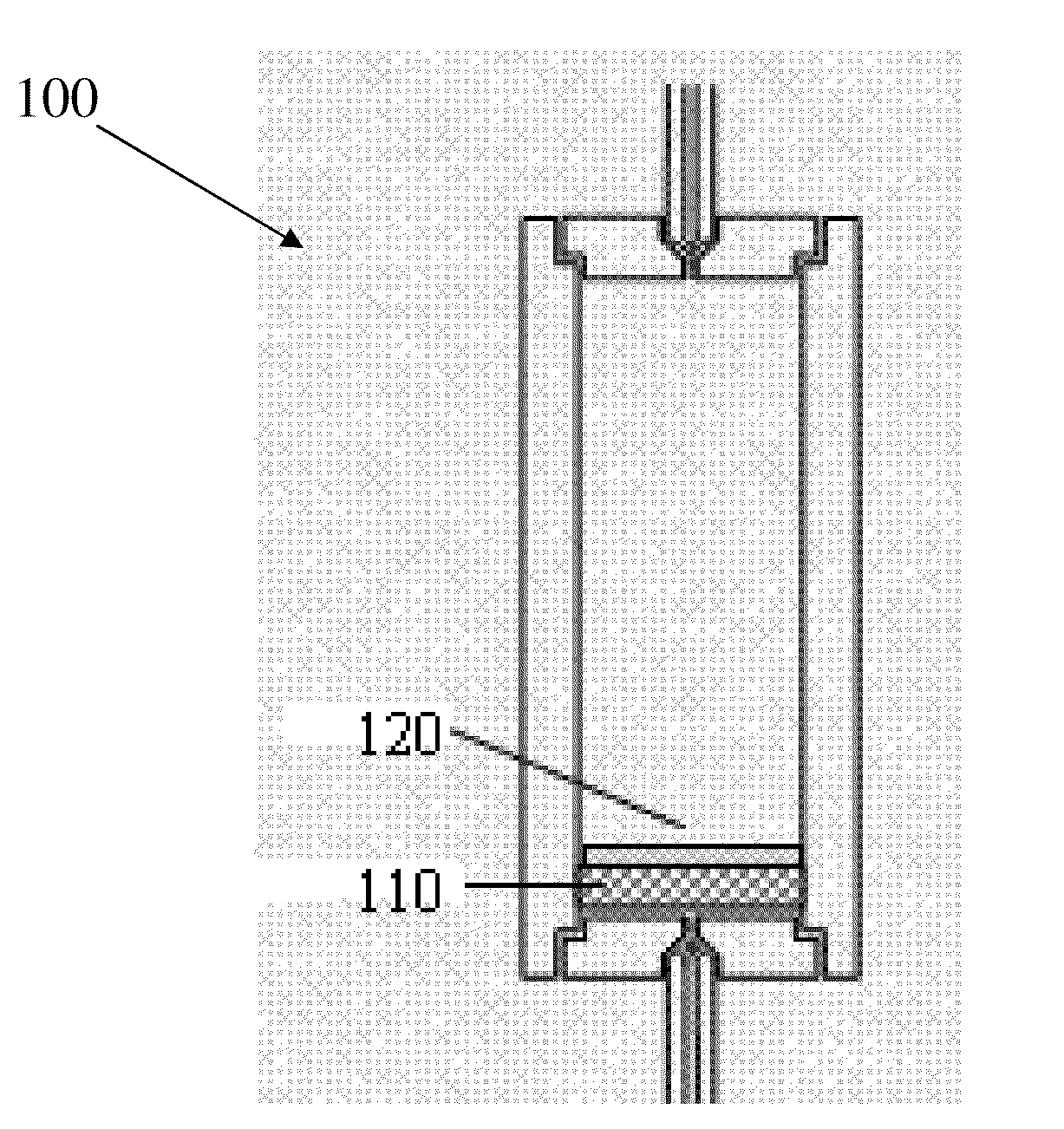
ActiveCN101915716AEasy to judge wettabilityWettability judgmentSurface/boundary effectAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
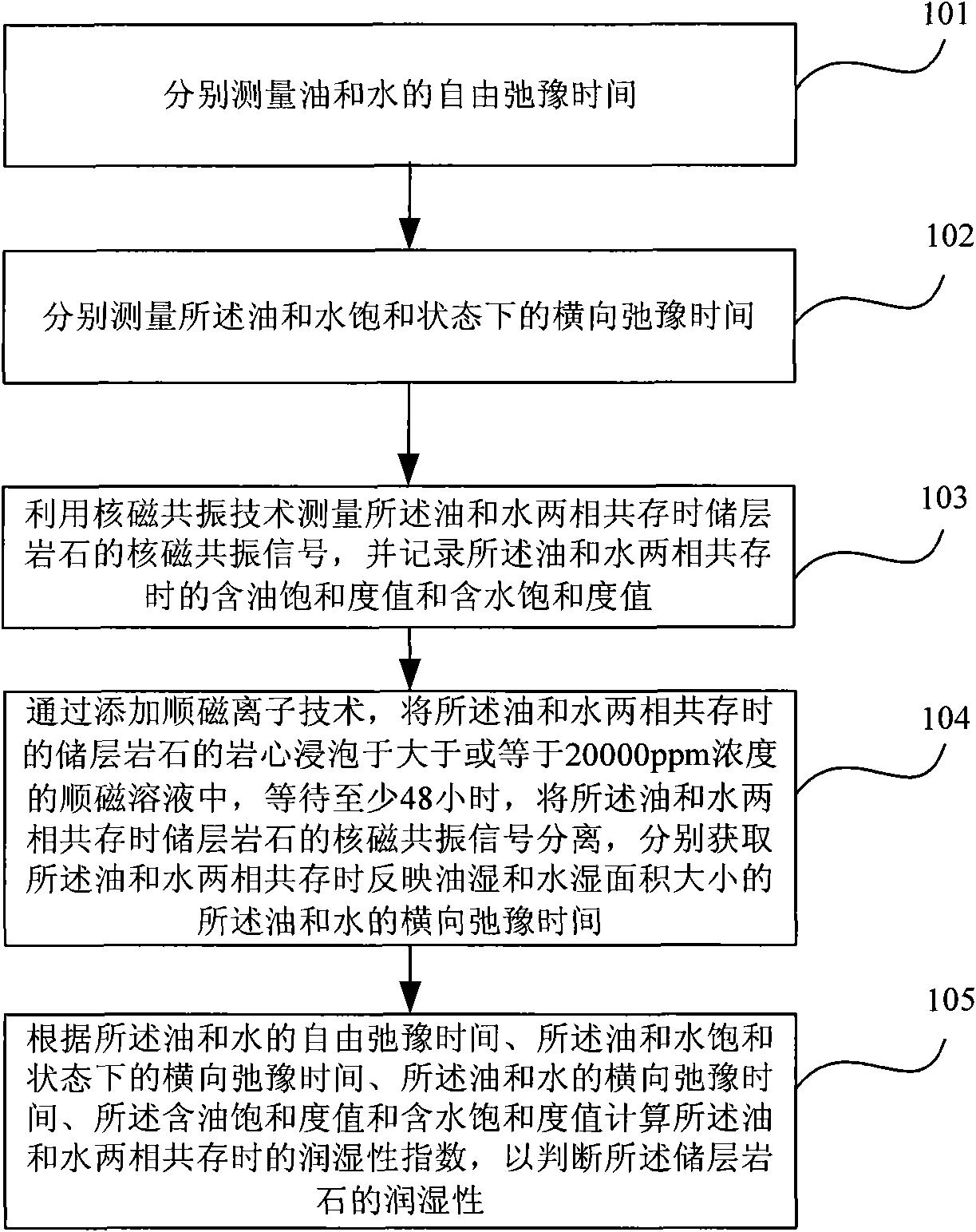
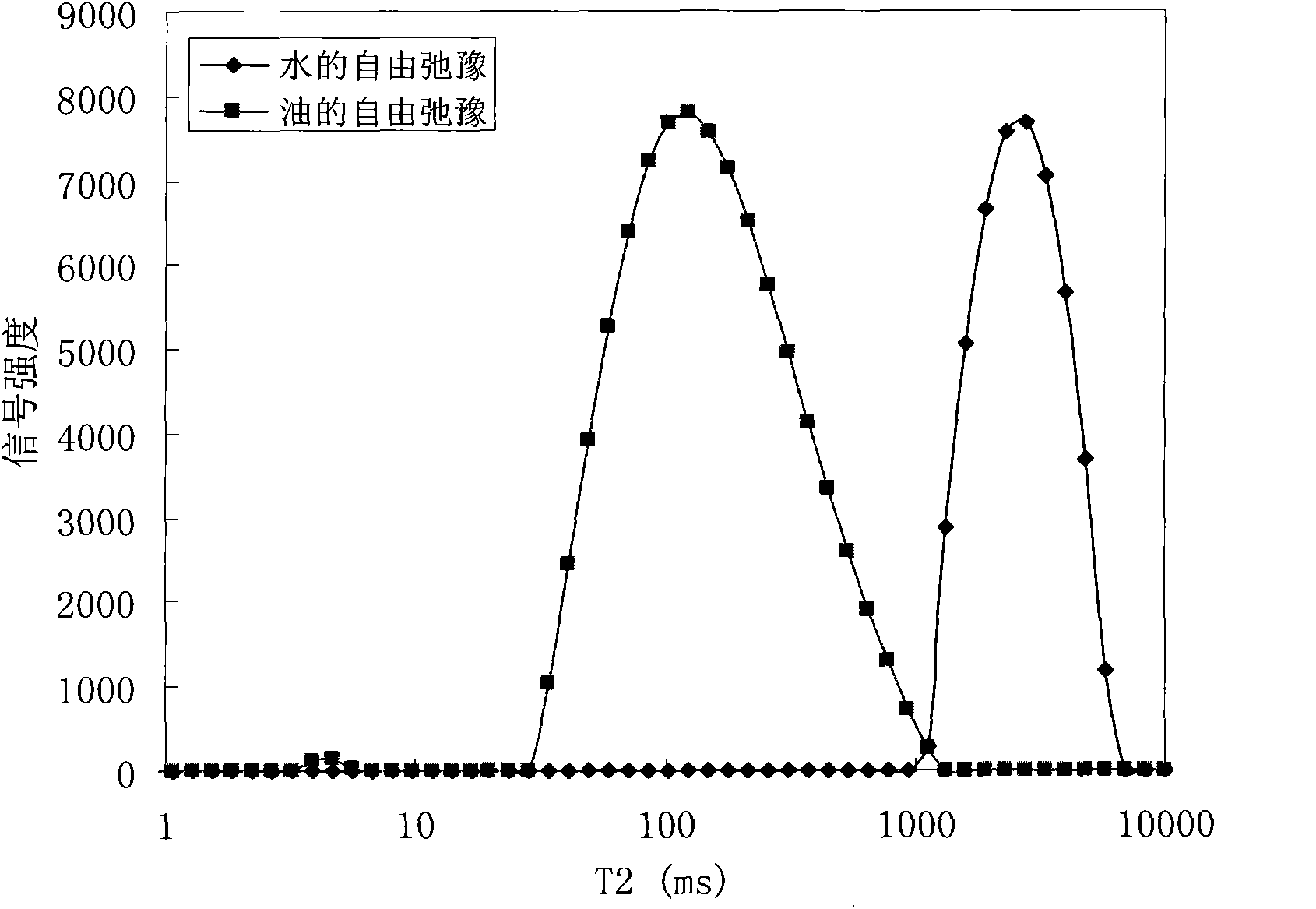
The invention provides a method for judging the wettability of a reservoir rock. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring free relaxation time of oil and water respectively; measuring transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in saturated states respectively; measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of an oil phase and a water phase by using nuclear magnetic resonance technology and recording an oil saturation value and a water saturation value in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase; dipping the rock core of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase in more than or equal to 20,000 ppm paramagnetic solution, waiting for at least 48 hours and separating the nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase to obtain the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water reflecting the size of an oil wet area and a water wet area; and calculating a wettability index in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase according to the free relaxation time of the oil and the water, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in the saturated states, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water, the oil saturation value and the water saturation value so as to judge the wettability of the reservoir rock.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Building exhaust and air conditioner condenstate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
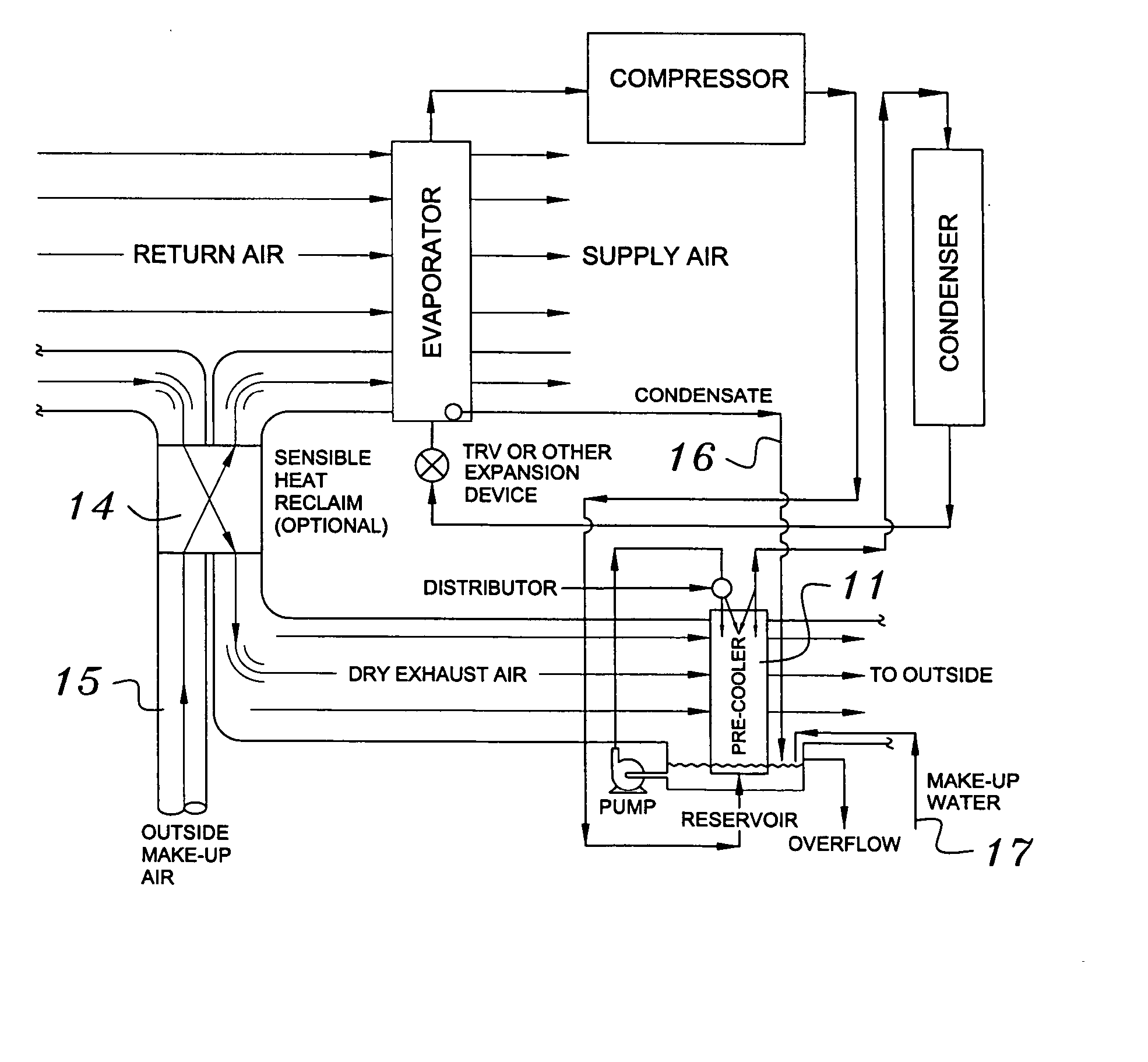
InactiveUS6070423AComprehensive understandingReduce the temperatureEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetIndoor air quality
First, a system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, subsequent to that subcooling accomplished by the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air. Said subcooling providing for an increased refrigeration capacity, and efficiency of the system. Secondly, a system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling before said hot gas passes into the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. Said precooler providing lower power consumption of the compressor, lower head pressure, increased mass flow of the refrigerant and improved efficiency of the primary condenser of the air conditioning or heat pump system. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air on either the subcooler or precooler. Finally, a combination subcooler and precooler system where the cold dry exhaust air is first used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted subcooler and then subsequently used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant passing through a dry surface precooler or alternately used to evaporatively cool the wetted surface of the precooler thereby evaporatively precooling the hot gas refrigerant passing through the precooler.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT RES INC +1
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS7150160B2Improve pumping efficiencyReduce power consumptionCondensate preventionDomestic cooling apparatusWater wetWater source
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
Preparation of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material for lithium ion power cell
InactiveCN101339995ANo danger of flammabilityImprove securityElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphorus compoundsWater wetPhosphate
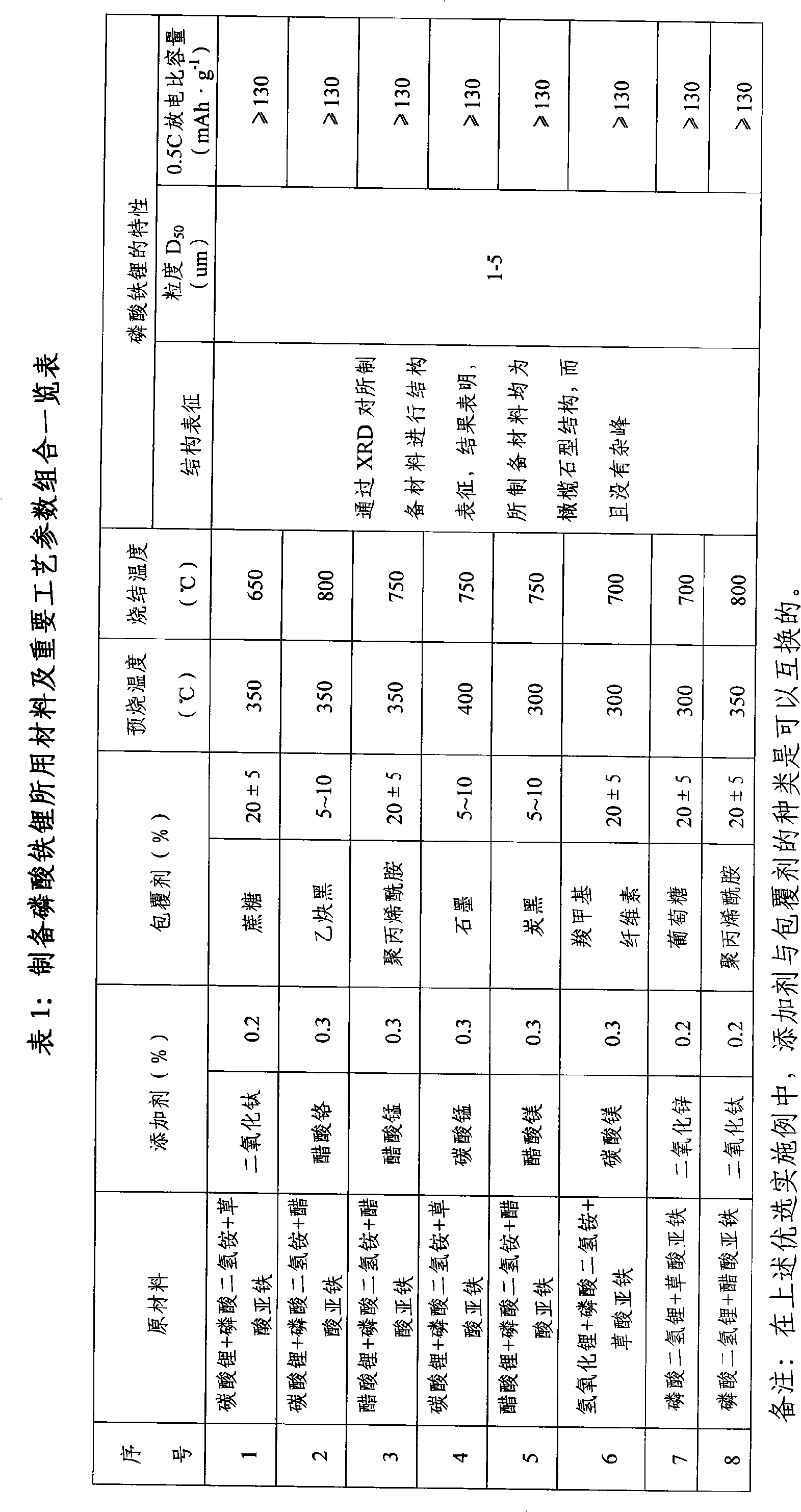
The invention discloses a preparation method of a lithium iron phosphate anode material used in a lithium-ion power battery. The preparation method takes ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide or lithium acetate and ferrous oxalate or ferrous acetate or takes the lithium dihydrogen phosphate and the ferrous oxalate or ferrous acetate as raw materials, the raw materials are prepared according to the ratio of Li, P and Fe of 1:1:1 or the ratio of LiH2PO4 to Fe of 1:1, and is added with micro amount of nano-metallic oxide or metal salt. After the process of mixing by a water wet method, spraying, drying, rolling and prilling, the mixture is pre-sintered for 10 minus or plus 2 hours at the constant temperature of 300-400 DEG C and is clad with carbon for prilling after being cooled; and then after the process of mixing by the water wet method, spraying, drying, rolling and prilling, the mixture is sintered for 10 minus or plus 2 hours at the temperature of 650-800 DEG C and then is cooled to obtain the lithium iron phosphate which is made after being crashed by gas stream and being compacted. The preparation method has the prominent advantages of safe preparation process, simple operation procedure, easy realization of industrialization and stable material performance of the product.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二一三研究所
Methods for using reversible phase oil-based drilling fluid
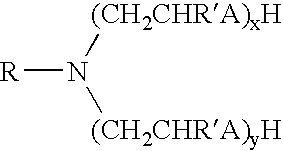
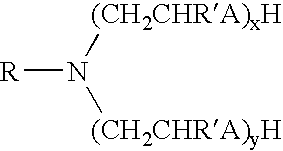
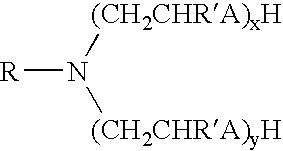
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS6857285B2Improve pumping efficiencyReduce power consumptionEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetWater source
A system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration / heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and pass the dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. A system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling into the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigation or heat pump system by evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. A combination subcooler / precooler system where the cold dry building exhaust air is used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted (or dry) subcooler and then used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
Method for using reversible phase oil-based drilling fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS20040144118A1Improve pumping efficiencyReduce power consumptionEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetIndoor air quality
First, a system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, subsequent to that subcooling accomplished by the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality (or outside air) across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger or by using building exhaust air only to conductively subcool. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air. Said subcooling providing for an increased refrigeration capacity and efficiency of the system. Secondly, a system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling before said hot gas passes into the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality(or outdoor air) across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. Said precooler providing lower power consumption of the compressor, lower head pressure, increased mass flow of the refrigerant and improved efficiency of the primary condenser of the air conditioning, refrigeration or heat pump system. A combination subcooler and precooler system where the cold dry building exhaust air (or outdoor air) is first used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted (or dry) subcooler and then subsequently used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant passing through a dry surface precooler or alternately used to evaporatively cool the wetted surface of the precooler thereby evaporatively precooling the hot gas refrigerant passing through the precooler. Also, a system for providing suction gas postheating after the primary evaporator but before the refrigerant is drawn back into the compressor of a heat pump operating in the heating mode, by passing relatively warm building exhaust air through a postheat heat exchanger thereby adding normally wasted heat back into the heat pump system. Finally, a combination subcooler and postheater system whereby building exhaust air(or outdoor air) is first used to conductively subcool the liquid refrigerant and then the subcooler warmed building exhaust air (or outdoor air) is subsequently used to conductively warm the refrigerant passing through the postheater thereby adding normally wasted heat back into a heat pump system operating in the heating mode.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
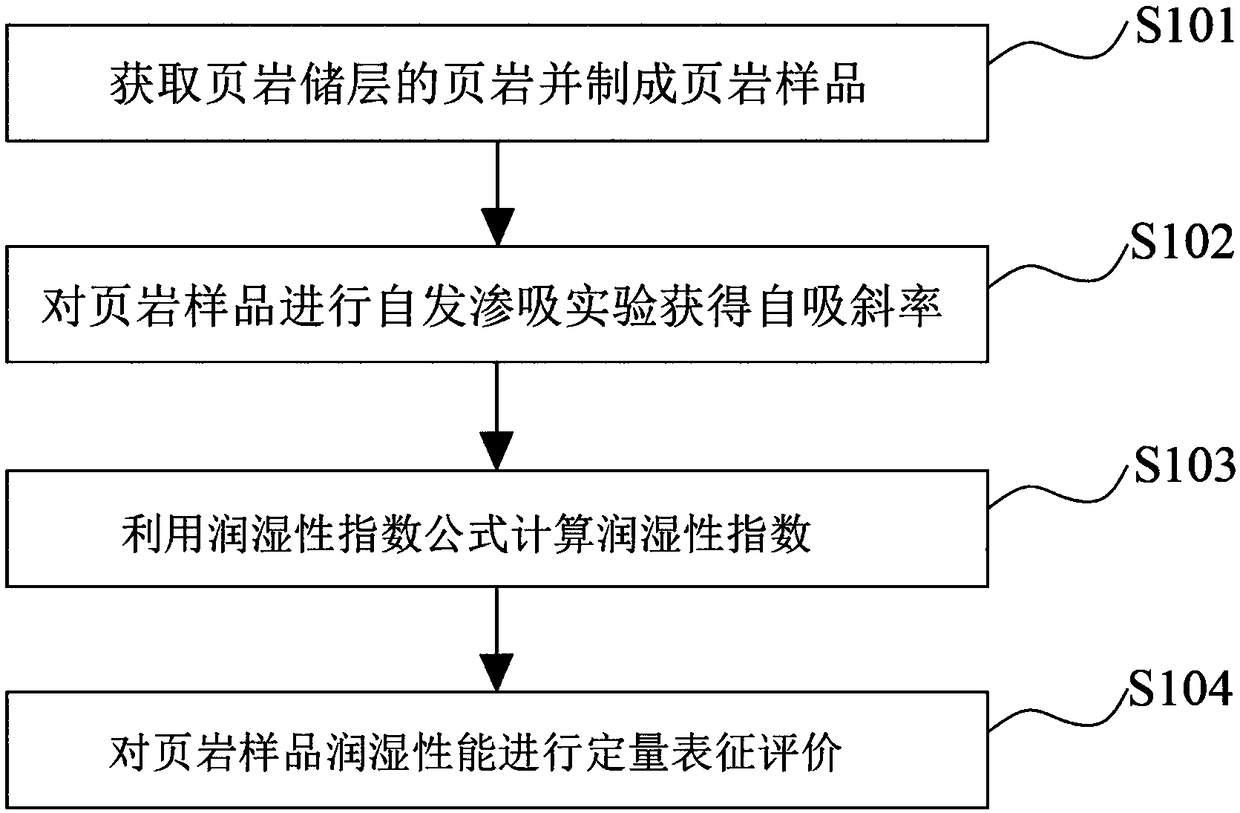
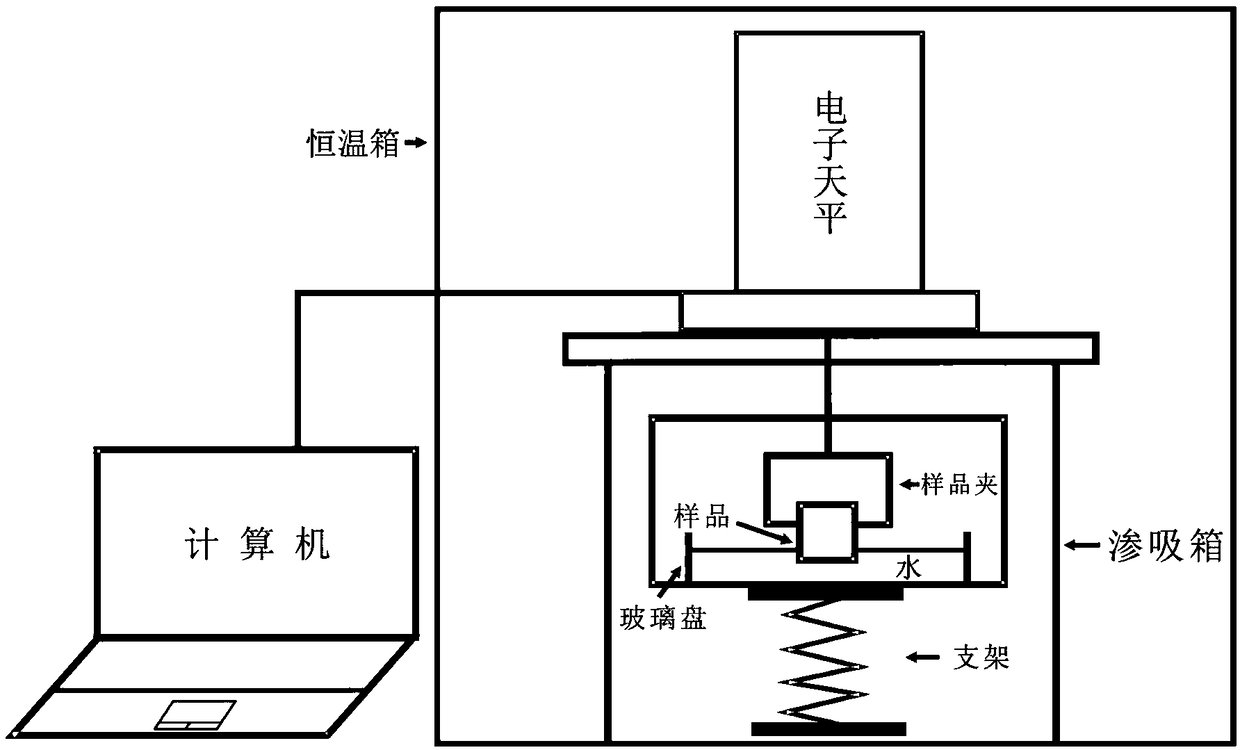
Method and device for quantitatively characterizing wettability of rocks in shale reservoir
ActiveCN108717031ASimple requirementsReduce penetrationWeighing by absorbing componentRecovery factorsSelf priming
The invention provides a method and device for quantitatively characterizing wettability of rocks in a shale reservoir. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining shale in the shale reservoir, and preparing a shale sample; performing a spontaneous infiltration experiment on the shale sample to obtain a self-priming slope; calculating a wettability index WI by using WI=(P1-T1)-(P2-T2); performing quantitative characterization evaluation on the wettability performance of the shale sample: the wettability index is within the range of -0.5 to 0; if the wettablity index is closer to -0.5,the water dampness behavior is stronger, otherwise, the shale sample is closer to blended water dampness; when the wettability index is 0, the shale reservoir is in blended dampness; the wettability index is within the range of 0 to 0.5; if the wettability index is closer to 0.5, the oil dampness behavior is stronger, otherwise, the shale sample is closer to blended oil dampness. According to themethod, by introduction of a new wettability index, the wettability of the shale reservoir can be accurately and quantitatively characterized; the method has important significance for designing an effective yield increase technology and estimating the ultimate recovery factor.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Composite titanium dioxide photocatalyst sol coating material component and coating method thereof
InactiveCN102653639AImprove hydrophilic propertiesImprove hydrophilicityPretreated surfacesCoatingsWater wetRoom temperature
The invention discloses a composite titanium dioxide photocatalyst sol coating material component which is good in water-wet behavior in case of no light lay irritation or insufficient light lay irritation and a coating method of the composite titanium dioxide photocatalyst sol coating material component, aiming at improving the water-wet behavior of the titanium dioxide photocatalyst in case of no light lay irritation or insufficient light lay irritation, wherein the coating material which is formed by proportioning titanium dioxide photocatalyst sol and hydroxyl-containing porous metal oxide sol in proper proportion is coated on the surface of a base material, and a layer of functional coating layer is formed on the surface of the base material after the coating layer is dried at normal temperature and solidified in a heating way. Under the condition of sufficient light lay irritation, the coating layer has the chemical decomposition or degradation characteristic of the titanium dioxide photocatalyst, can decompose or degrade the organic pollutant adhered to the surface face of the base material, and further has the physical hydrophilic soil release. The coating layer is good in the water-wet behavior in case of no light lay irritation or insufficient light lay irritation, so that the dirt on the surface can be easily washed to be removed by the means that the base material is washed by water, therefore, the cleanness of the base material can be kept.
Owner:GREENCOAT TECH
Methods for Using Reversible Phase Oil-Based Drilling Fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Use method of modified bentonite by lithiation in casting wet type clay sand
The invention discloses an application method of lithiation modified bentonite in casting green sand, which comprises the following steps: forming raw sand from 50 wt% to 90 wt% of old sand with the particle size being 15 Q(H) (circle minus square) and 50 wt% to 10 wt% of new sand with the particle size being 15 Q(H) (circle minus square); adding 2% to 10% of lithiation bentonite, 0% to 8% of calcium bentonite and 2% to 4% of casting coal powder by the weight of the raw sand every 100 weight parts of the raw sand, and mixing; adding 5% to 6% of water when wet-mixing casting sand, and mixing by a common sand roller mill; and dry-mixing the new sand, the old sand, the coal powder and the lithiation bentonite for 2 minutes, then, adding water and wet-mixing for 10 minutes, and finally obtaining the casting sand with the green compression strength being 130 to 140 KPa and the air permeability being 100 to 150.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Engineering formation wettability characteristics
ActiveUS20160272873A1Enhanced recovery of hydrocarbonPromote recoveryFluid removalDrilling compositionSaline waterWater wet
Methods and systems are provided to enhance recovery of hydrocarbons from a formation by altering wettability at a surface of the formation towards more water-wet. One method includes: providing a formation; providing an aqueous stream for injecting into the formation; adding a reducing agent to the aqueous stream; and injecting the aqueous stream with the reducing agent into the formation to alter a surface charge of the surface of the formation to become more water-wet to enhance recovery of hydrocarbons from the formation. The reducing agent is responsive to characteristics of the formation, characteristics of brine of the formation, and characteristics of hydrocarbons of the formation. Also provided is a method to select a brine composition to be injected into a formation to alter wettability at a surface of the formation towards more water-wet to enhance recovery of hydrocarbons from the formation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Shale reservoir microscopic wettability determination method and device
The invention provides a shale reservoir microscopic wettability determination method and a device. The method comprises the following steps of smashing a shale core to acquire a core sample with the particle diameter being less than 30mu m; adding 10mg of core sample into a glass tube, adding 10ml of saline solution for mixing, and aging for 48h; after finishing aging, separating the saline solution from the glass tube, and keeping saline and a wet sample; adding 10ml of in-place oil into the glass tube containing the wet sample, and aging for 48h; adding the kept saline into the glass tube with oil and rock powder, stirring and mixing, and settling for 24h; extracting an upper layer of crude oil and oil wettability substances in the settled glass tube, utilizing an organic solvent to clean and dry, and acquiring an oil wetting substance; drying a water wettability rock kept in the glass tube, and acquiring a water-wet mineral; utilizing a scanning electron microscope and an XRD (X-Ray Diffraction) analytical test to confirm the components of the oil wetting substance and the water-wet mineral, and generating a determination result. The invention provides the shale reservoir microscopic wettability determination method with open type conditions, simplicity and practicability.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and water chutes for adjusting water-wet distribution of water-storage type evaporative cooling wall
The invention discloses a method for adjusting the water-wet distribution of a water-storage type evaporative cooling wall, which comprises the following steps that: 1) preparing a plurality of water chutes, wherein the water chute has a wide opening and a narrow bottom, and a plurality of water outlets are formed at the bottom of the water chute in a way of intercepting a water flow form top down or guiding a water flow from top down according to the requirements; 2) clamping the water chutes (with openings upwards) in transverse seams of a decorative brick layer of a water-storage type evaporative cooling wall of which the water-wet distribution is required to be adjusted; 3) when the water flow runs from top down, because one edge of each water chute is arranged against the evaporativecooling wall, the water flow is collected to the water chute; 4) because the bottom of the water chute is provided with the water outlets according to the requirement for intercepting or guiding the water flow, draining the water flow out from the water outlets to adjust the water-wet distribution of the water-storage type evaporative cooling wall. The method and the water chutes of the inventionare simple in structure and clever in design, and can make porous water-storage bodies arranged below windows of the water-storage type evaporative cooling wall or on some concave-convex structures of the water-storage type evaporative cooling wall absorb moisture sufficiently, and are of benefit to energy conservation and environmental protection.
Owner:何玉成
Organic matter/mineral complex and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101445250AImprove performanceEasy to useContaminated soil reclamationSilicon compoundsWater wetSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to the technical field of remediation of heavy metal polluted soil by in situ passivation, particularly to an organic matter / mineral complex and a preparation method thereof. In the complex, the mineral is sodium bentonite, and the organic matter is pig manure and degradation liquid thereof; the solvent includes hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, copper sulfate and silver nitrate; and the weight ratio of the organic matter and the mineral is 1:(1-6). The preparation method comprises the steps of adding water-wetted dry pig manure into effective microorganism (EM) liquid, culturing at 25DEG C for 30 days, centrifuging, collecting supernatant, filtering to obtain degradation liquid, adding buffered degradation liquid into slurry form sodium bentonite, preparing into 10% suspension, adjusting pH value to 3-11, allowing reaction under controlled temperature for 0.5-3 h, cooling, centrifuging, collecting sediment, and air-drying. The complex has the advantages of simple principle, safe and feasible preparation method, stable product properties, and good usability; and can be widely used for remediation of various kinds of soil by passivation.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Rotation burning type burning device
The provides a rotatablely burning type incinerator for incinerating the wastes, characterized in that: a circulating water wet wall type gas cooling room including an exhaust gas energency drain, air vent, shade and aeration tank is mounted on the most top of a double layer rotary flow layer type incinerator of JP 2985058 and the circulating water wet wall type gas cooling room is integrated with the double layer rotary flow layer type incinerator.
Owner:五味吉男 +1
Cleaning fracturing outlet liquid recovery oil displacement and plugging relief technology
PendingCN101608543AEnhanced overall recoveryImprove wettabilityFluid removalMultistage water/sewage treatmentRock coreWater wet
The invention relates to a cleaning fracturing outlet liquid recovery oil displacement and plugging relief technology, comprising the following steps: cracking glue; adding a flocculating agent, an adhesive mud removing agent or a bactericide to accumulate suspended matters and sterilize; filtering and recovering the suspended matters; finely filtering the suspended matters again through a precise filter; and adding a biological enzyme preparation, and the like into the filter liquor. The invention thoroughly solves the problem of the environment pollution of fracturing outlet liquid, can effectively displace the remaining oil of an oil layer, thereby enhancing the recovery ratio of crude oil; and in addition, the invention has environmental-friendly characteristics, can obviously improve the property of rock cores, recovers the percolation rate of a stratum, enhances the water-wet effect and the expand preventing and sand firming effect, prevents incrustations being accumulated again, reduces the oil-water interfacial tension and enhances the recovery ratio of the crude oil.
Owner:SUNCOO PETROLEUM TECH
Fracturing process in oil and water well by means of biological enzyme preparation
InactiveCN1766283AImprove work efficiencyDoesn't take into account the reverse dischargeFluid removalWater wetFracturing fluid
The invention discloses an oil field oil-water well fracturing craft method of biological enzyme agent, which is characterized by the following: building the mixed biological enzyme agent and water or biological acid or antisludging agent or liquid nitrogen as fracturing fluid; forcing the fracturing fluid into the oil well or water well through the fracturing vehicle; pressing the fracturing fluid into the crack; opening the well after 72 hours. The biological enzyme agent penetrates the hole throat then enters into the microscopic hole gap, which attaches the rock surface and denudes the raw oil to improve the earth penetration factor. The method improves the water wet effect and washes the spalling oil film, which improves the recovery factor of raw oil.
Owner:SUNCOO PETROLEUM TECH
Surfactant for changing surface wettability of compact sandstone as well as preparation method and application of surfactant
InactiveCN107418546AReduce interfacial tensionReduce adhesionDrilling compositionWater wetRoom temperature
The invention relates to a surfactant for changing surface wettability of compact sandstone as well as a preparation method and an application of the surfactant. An oil phase solution is added to a water phase solution, and a dispersed and uniform phase is realized after 1-2 h under the action of an emulsifier. An initiator is added, the mixture is stirred and heated to 60-75 DEG C and reacts at the temperature for 12-18 h, and a colorless and clear liquid, namely, a high-molecular polymer, is prepared. A fluorocarbon surfactant and a biosurfactant are added at the room temperature, the mixture is stirred continuously for 4 h, and the surfactant for changing surface wettability of the compact sandstone is obtained. By the aid of the surfactant, the oil-water interface tension can be reduced, an oil wetted surface can be changed into a water wetted surface, the adhesion of oil drops on sandstone surfaces can be reduced, the flowability of crude oil in an original stratum can be improved, and the recovery percent of low-permeability oil reservoirs can be increased.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Glycols as an adjuvant in treating wastes using the Molten Salt Oxidation process
InactiveUS7288234B1Reducing/eliminating potentialReduce volatilityHydrogen sulfidesDispersed particle separationWater wetAdjuvant
An improved system and method for using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a processing fluid additive for safely and effectively treating water-wet hogout propellant as well as any other water-wet propellants, explosives and hazardous wastes (solids and liquids) to make them compatible with the MSO process. The method includes the step of applying liquid PEG to the hazardous waste to create a slurry or feedstock that when fed directly into the MSO reactor vessel prevents the occurrence of smelt-water explosions due to the accumulation of dangerous levels of sodium chloride, and / or sodium sulfide in the molten salt bath. The PEG possesses special qualities that make it ideal for this purpose. It is a low cost, low viscosity, commercially available, non-hazardous (per OSHA standards), water soluble, low toxicity chemical that burns cleanly leaving little or no residue.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Carbon-based nano wetting reversal agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111647392ALittle impact on rheologyStay hydrophilicCarbon compoundsDrilling compositionWater wetAlcohol
The invention discloses a carbon-based nano wetting reversal agent and application thereof. The carbon-based nano wetting reversal agent comprises modified nano graphene oxide, a surfactant and a solvent I, wherein the solvent I is selected from at least one of alcohol compounds. The novel carbon-based nano wetting reversal agent can be applied to drilling fluid, the surface of stratum rock can bekept in a hydrophilic state, the wettability of the surface of oil-wet rock is converted into water wettability, and the subsequent water injection of a water injection well or the improvement of therecovery ratio of an oil production well is facilitated.
Owner:NINGBO FENGCHENG ADVANCED ENERGY MATERIALS RES INST
Processing technology for drilled and cooled cylinder liner
The invention discloses a processing technology for a drilled and cooled cylinder liner, which comprises the following steps of: a, coating a coating, preparing a metal mold and a baffle plate, wetting a residual coating in an inner cavity of the metal mold by using water for removal, adding into a kiln, preheating, and preparing the coating from quartz powder of 150 to 200 meshes, bentonite, lead powder, platy lead powder, diatomite, water glass and water; b, smelting and pouring, namely adding new pig iron, a waste material, waste steel and an iron alloy material in turn, sampling for testing when the smelting temperature reaches 1,250 DEG C, adjusting the components of molten iron according to a test notice, cutting off electricity when the smelting temperature reaches 1,520+ / -5 DEG C (a thermocouple measures the temperature), standing for 2 to 3 minutes, and preparing for discharge; c, repairing a pouring system, quantizing a pouring ladle, and repairing according to the dimensional requirement of water gap flow; and d, demolding a casting, performing heat treatment on the casting, and delivering. The processing technology for the drilled and cooled cylinder liner is high in processing accuracy and strict in processes, and the processed product has high quality.
Owner:DALIAN BINCHENG PISTON MFG
Method for achieving water-passing oil-blocking type oil-water separation by using super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membrane
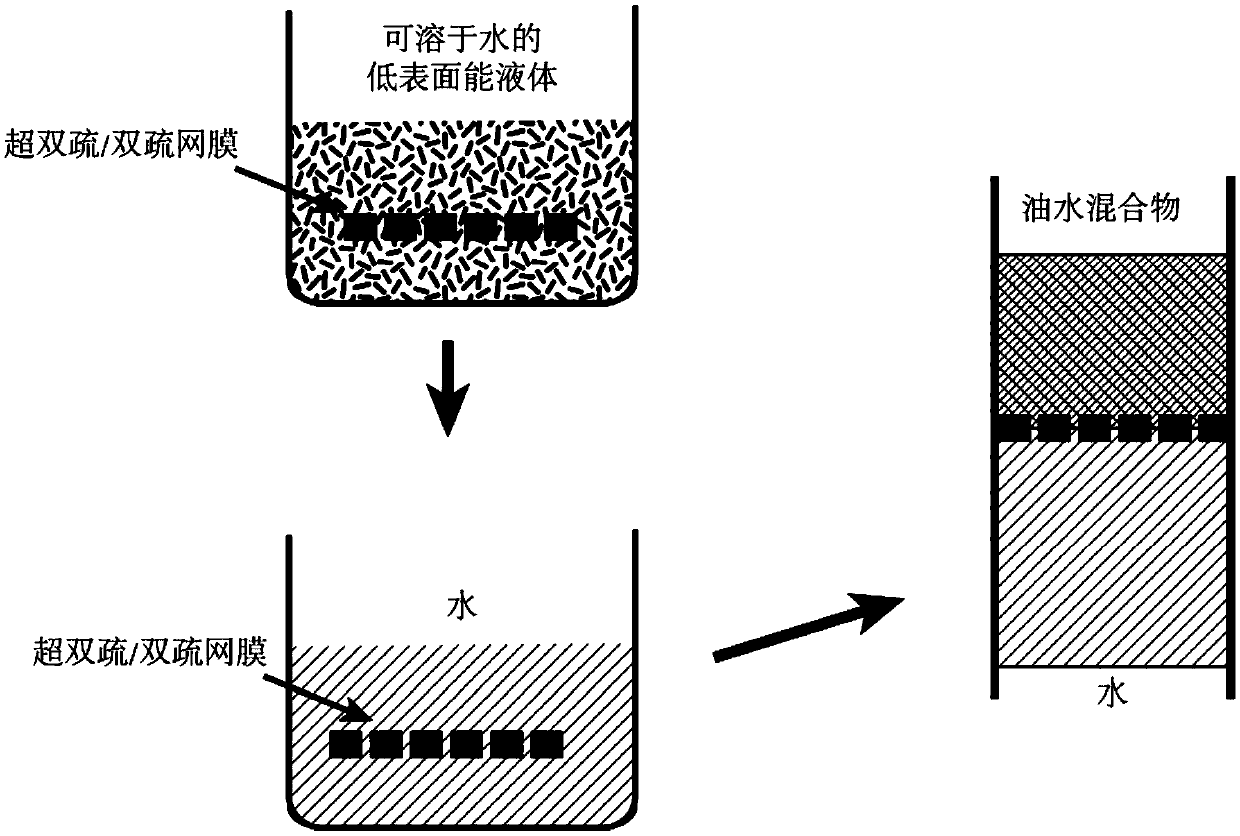
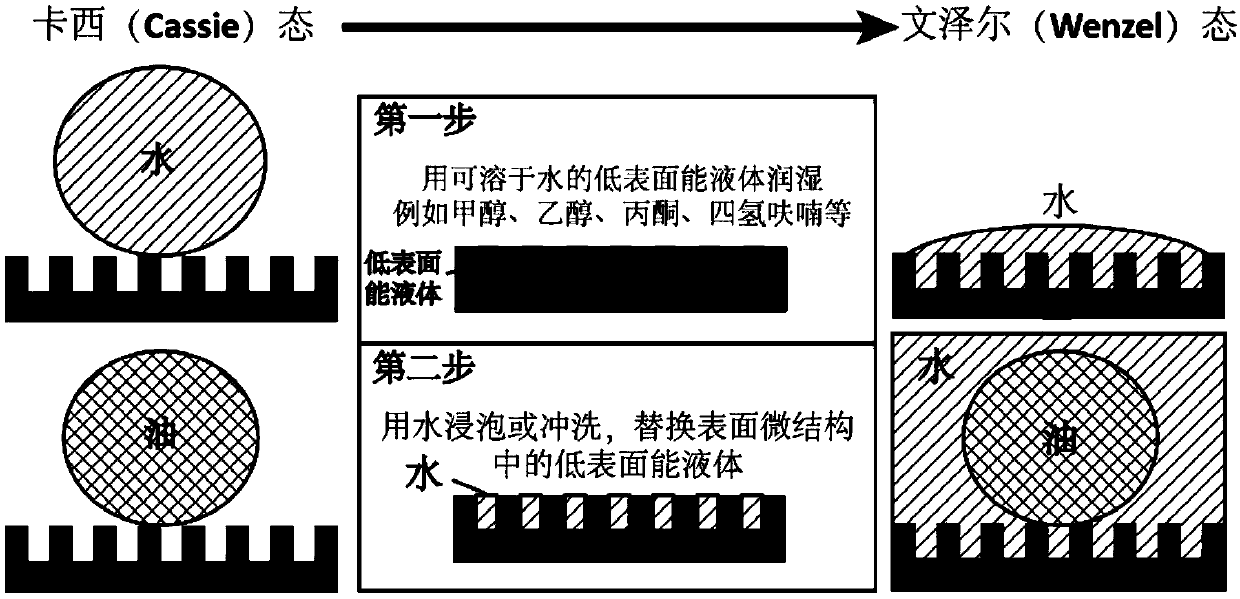
ActiveCN109647004ASeparate applicationNo limitWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisNon-miscible liquid separationWater wetFiltration
The invention relates to a method for achieving water-passing oil-blocking type oil-water separation by using a super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membrane, and relates to a water-passing oil-blocking type oil-water separation method. The purpose is to solve the problems that the existing filtration method is blocked easily by oil and the super-oleophobic super-hydrophilic or oleophobic hydrophilic material is prepared difficultly, so that the oil-blocking water-passing type oil-water separation is achieved difficultly. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a water-soluble liquid with low surface energy is enabled to wet a super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membrane by using a spraying or soaking mode; 2, the obtained super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membrane which is wetted by the water-soluble liquid with low surface energy is soaked in water, so that the super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membrane is wetted bywater; 3, when the oil-water mixture is driven by gravity or pressure to contact the two water-wetted net membranes, the water in the oil-water mixture freely passes through the super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net films, and the oil cannot pass through the super-double-hydrophobic or double-hydrophobic net membranes, so that the oil-blocking water-passing type oil-water separation is achieved. The method is used in the technical field of oil-water separation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for manufacturing sinter
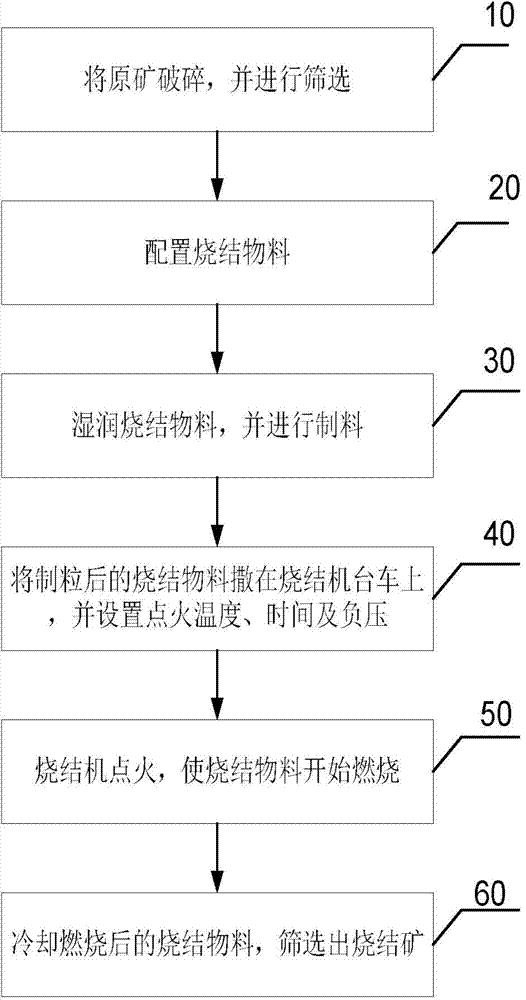
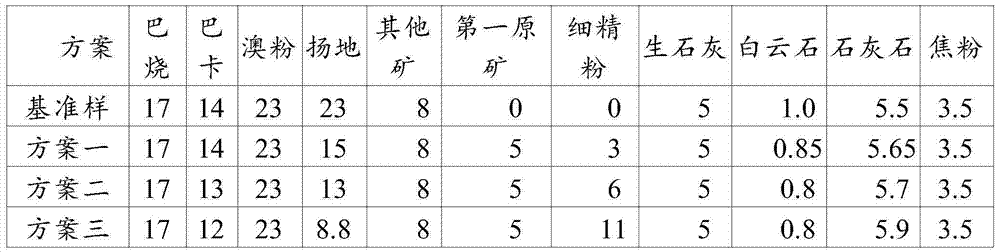
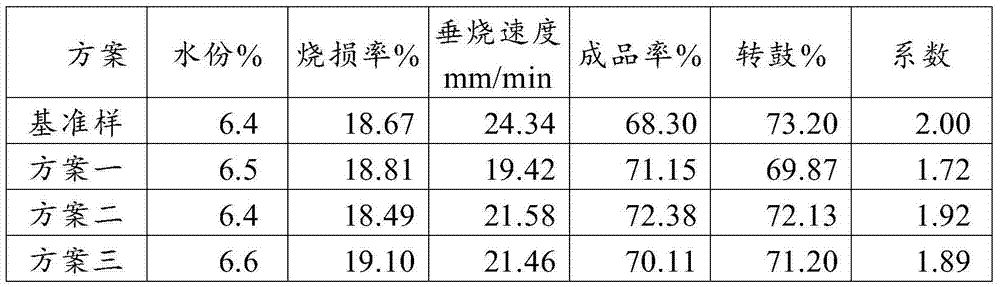
ActiveCN103924064AStable sintered compositionMineral blending cost reductionWater wetMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of mineral sintering, and in particular relates to a method for manufacturing sinter. The method comprises the following steps: crushing a raw ore, and screening by utilizing a first screen, wherein the screen underflow is a first raw ore, and the screen overflow is a second raw ore; preparing a sintering material; conveying the sintering material to a primary rotary drum mixer, and adding a water wetted sintering material; uniformly mixing the sintering material, conveying the mixture to a second rotary drum mixer, and granulating; uniformly spreading the granulated sintering material to a trolley of a sintering machine; igniting the sintering machine to burn the sintering material, and controlling the negative pressure of sintering to be 9,000-18,000Pa; and cooling the sintered sintering material, and screening the cooled sintering material by adopting a second screen, wherein the screen underflow is a sinter return ore, and the screen overflow is finished product sinter. According to the method for manufacturing the sinter, the raw ore can be appropriately applied, the sinter components are stable, and the ore preparation cost is reduced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com