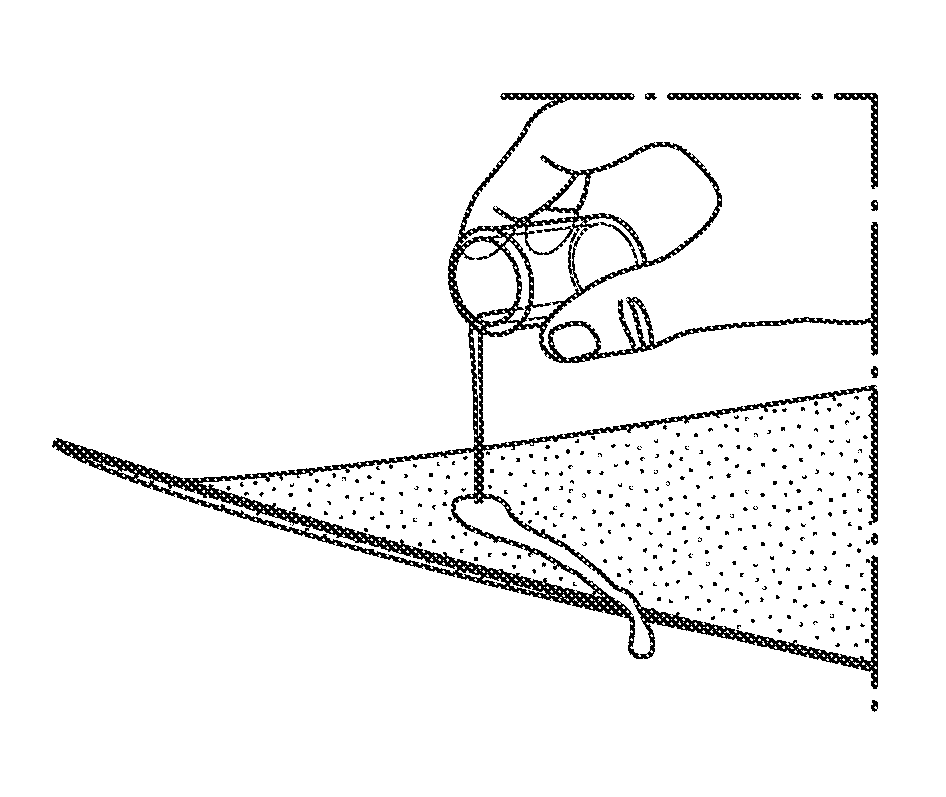
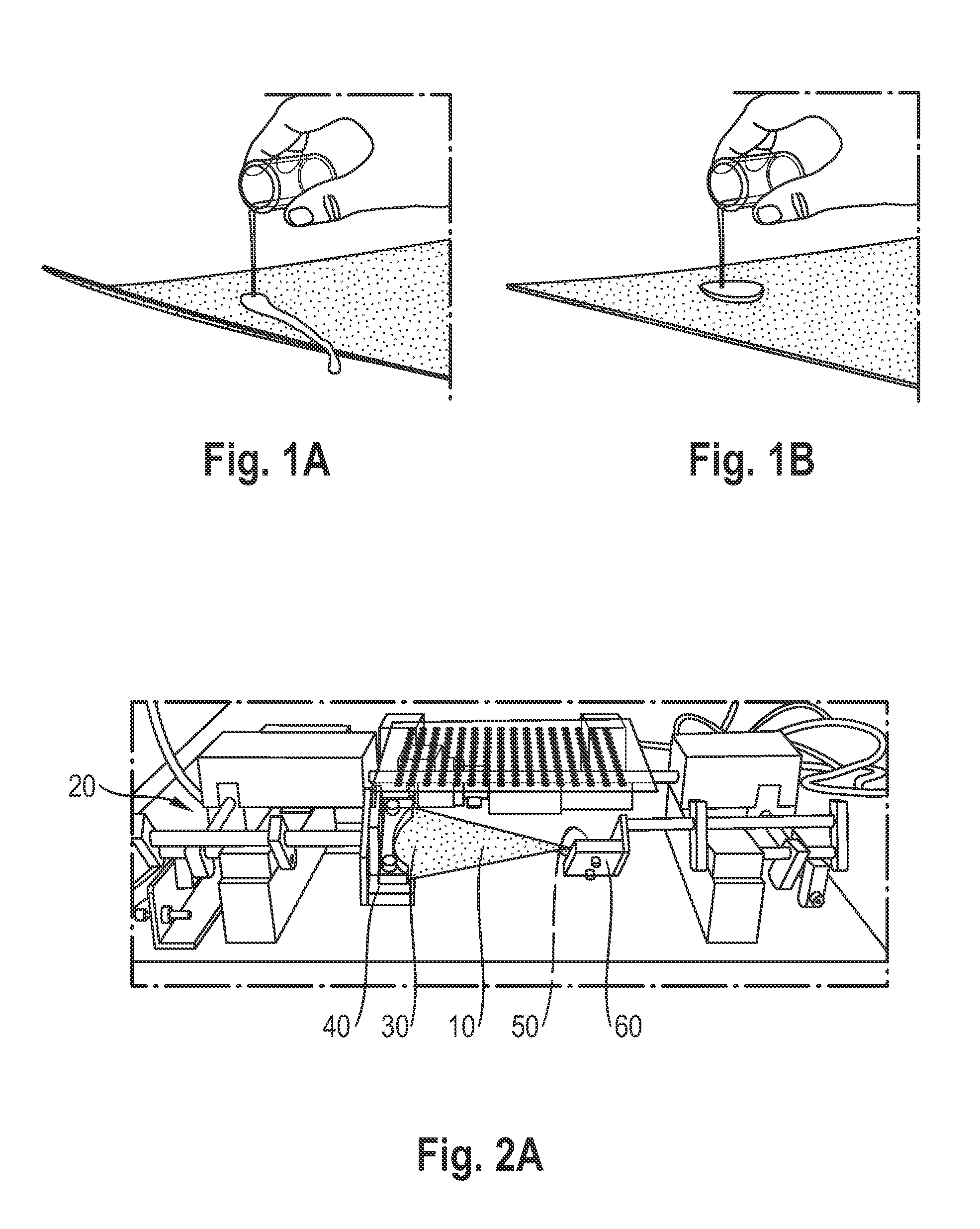
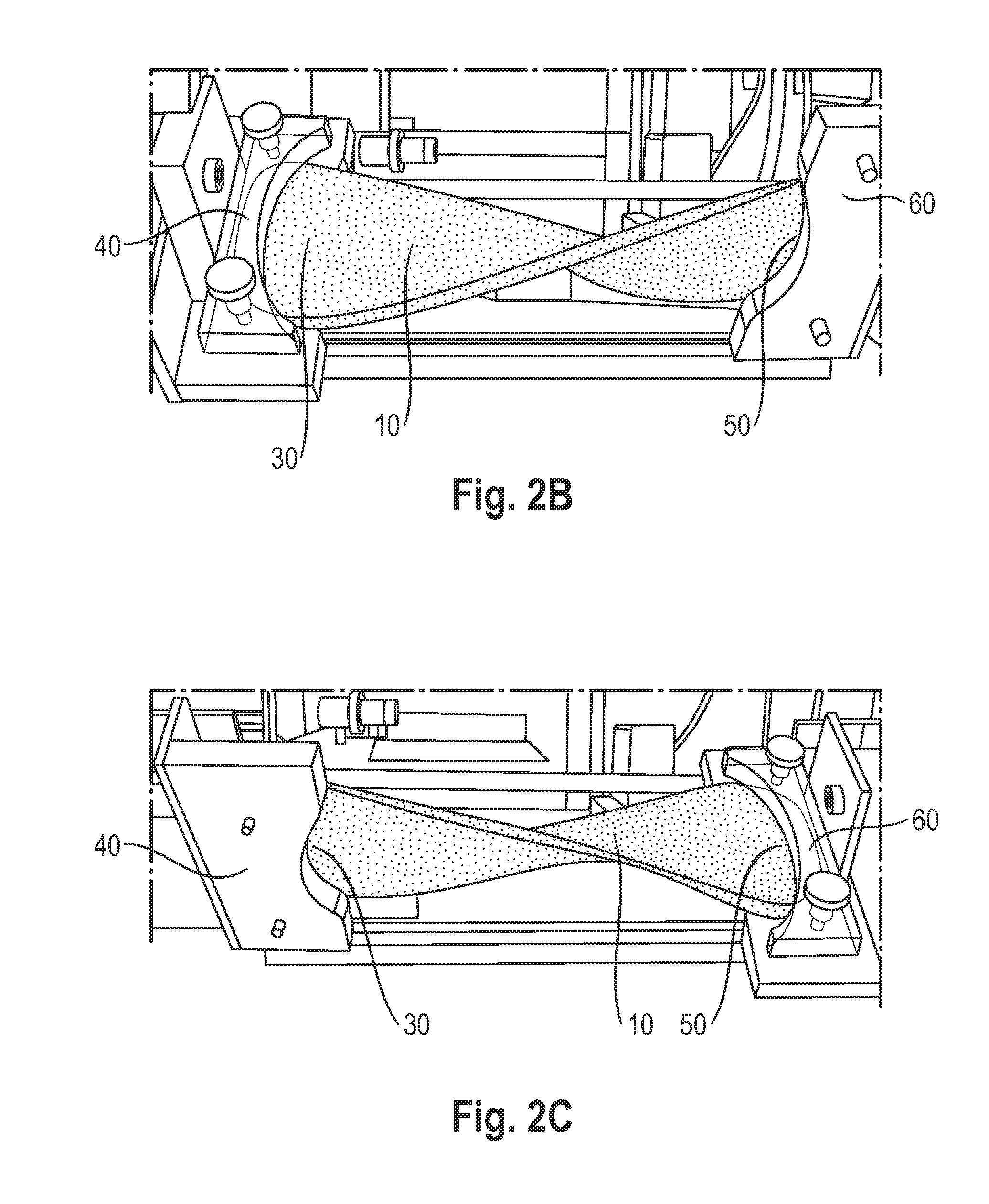
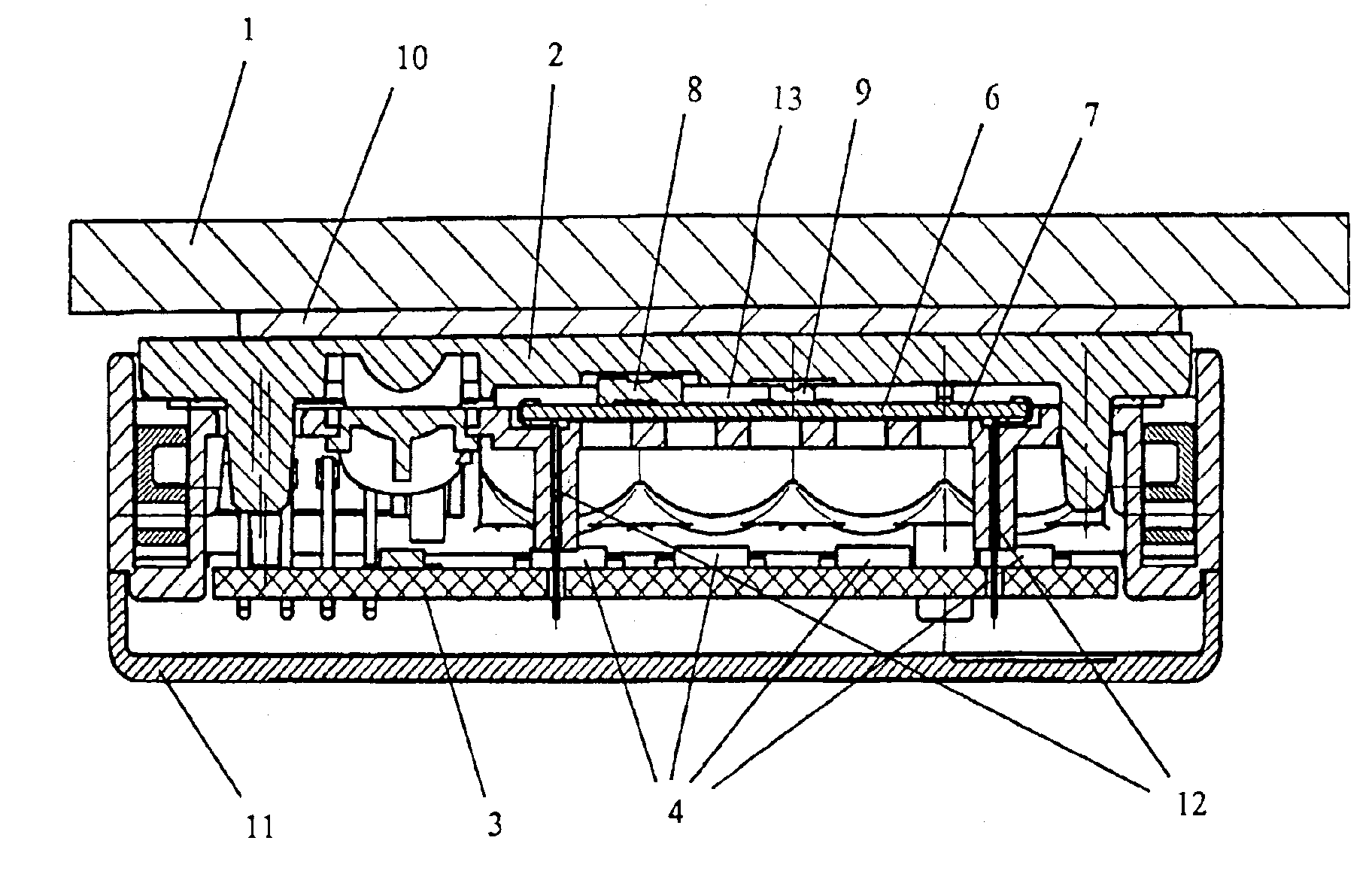
Patents
Literature
2248results about "Weighing by absorbing component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
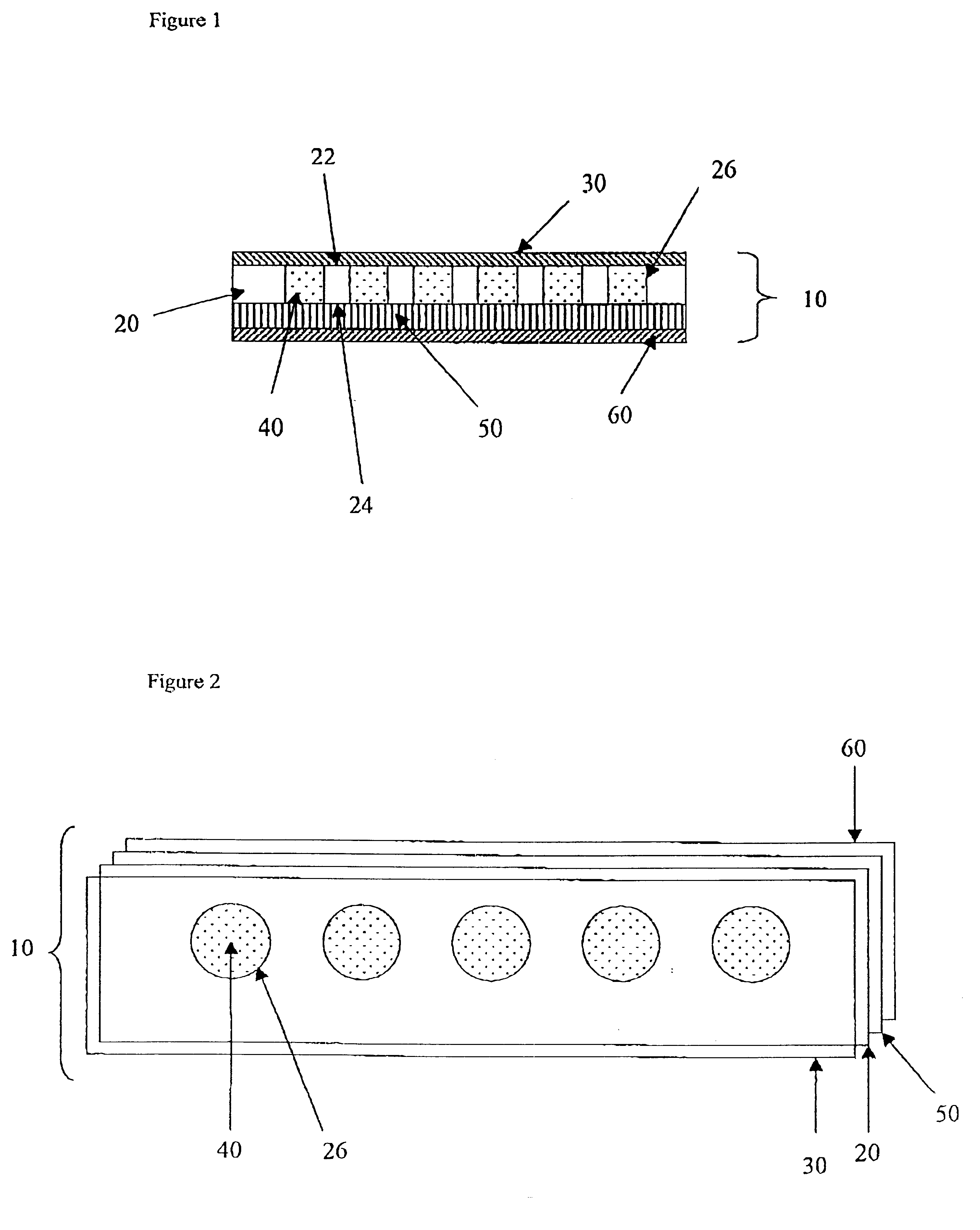
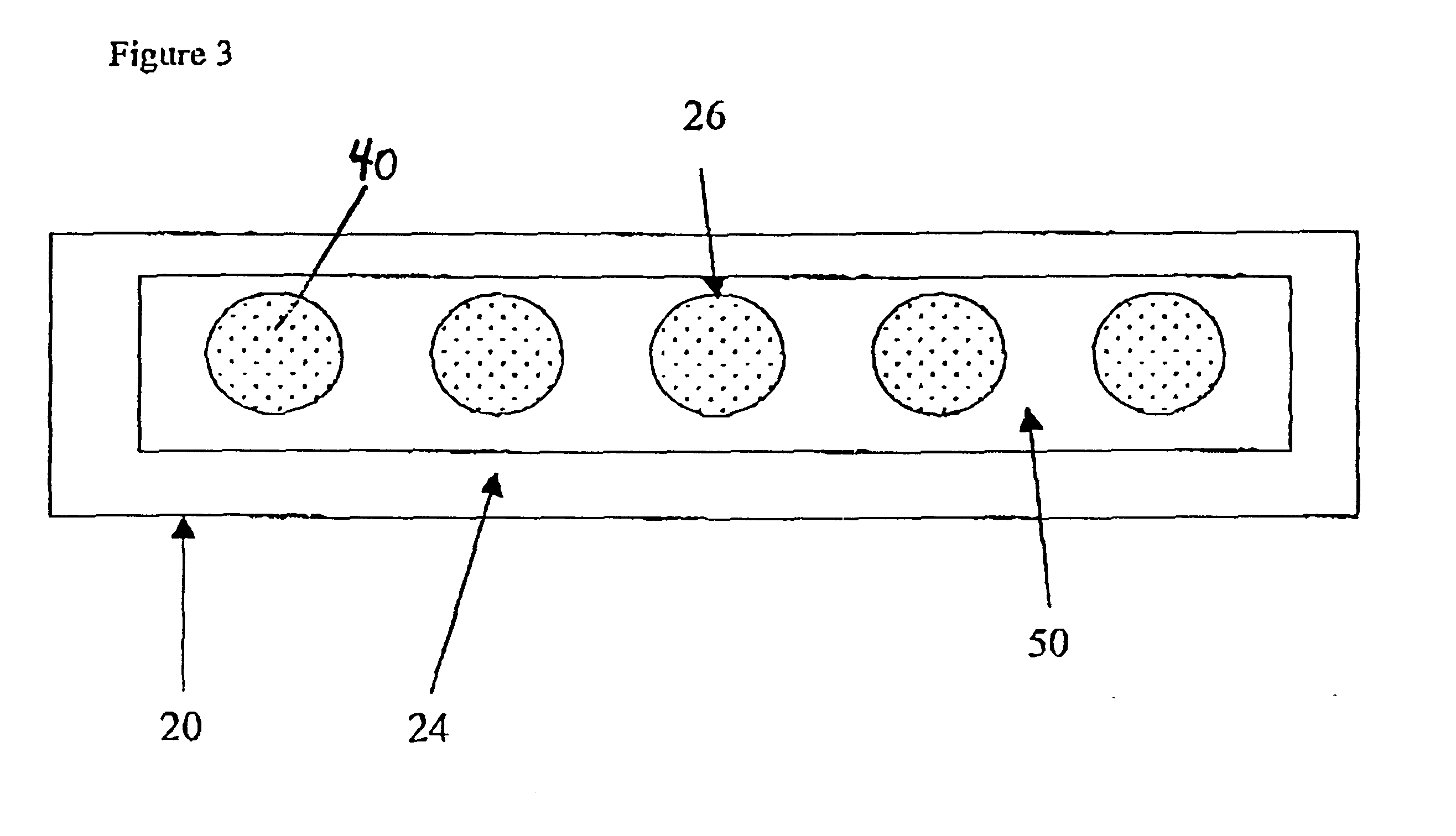
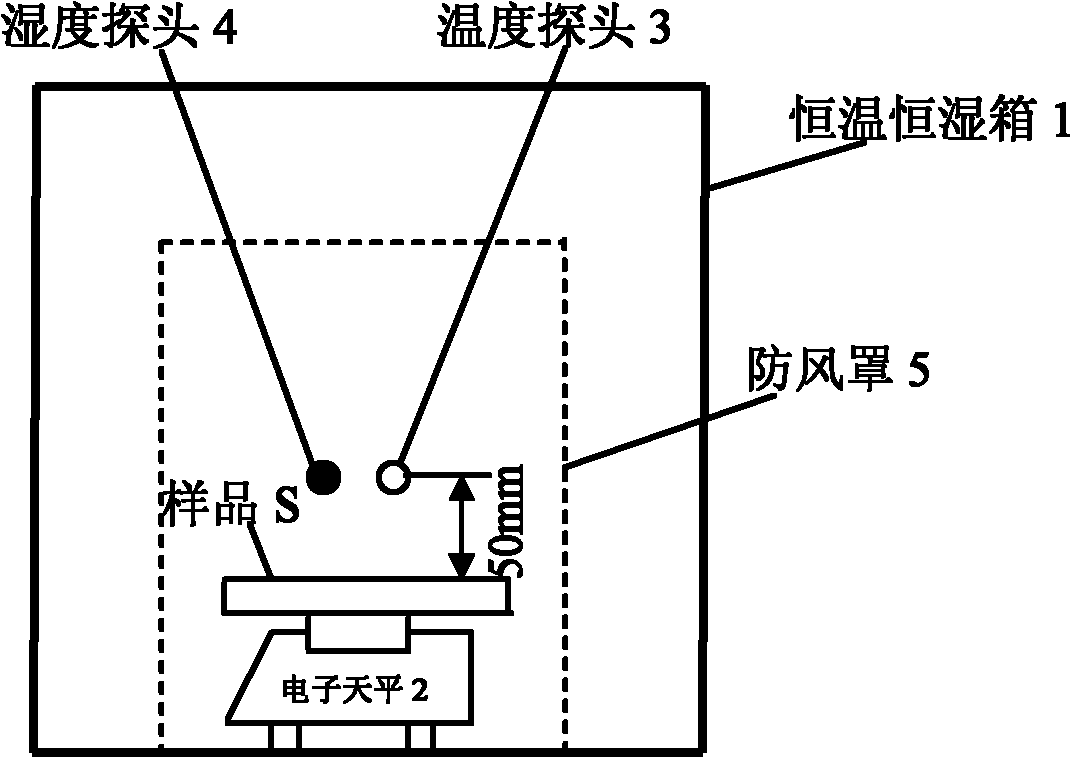
Absorbent structure having enhanced intake performance characteristics and method for evaluating such characteristics
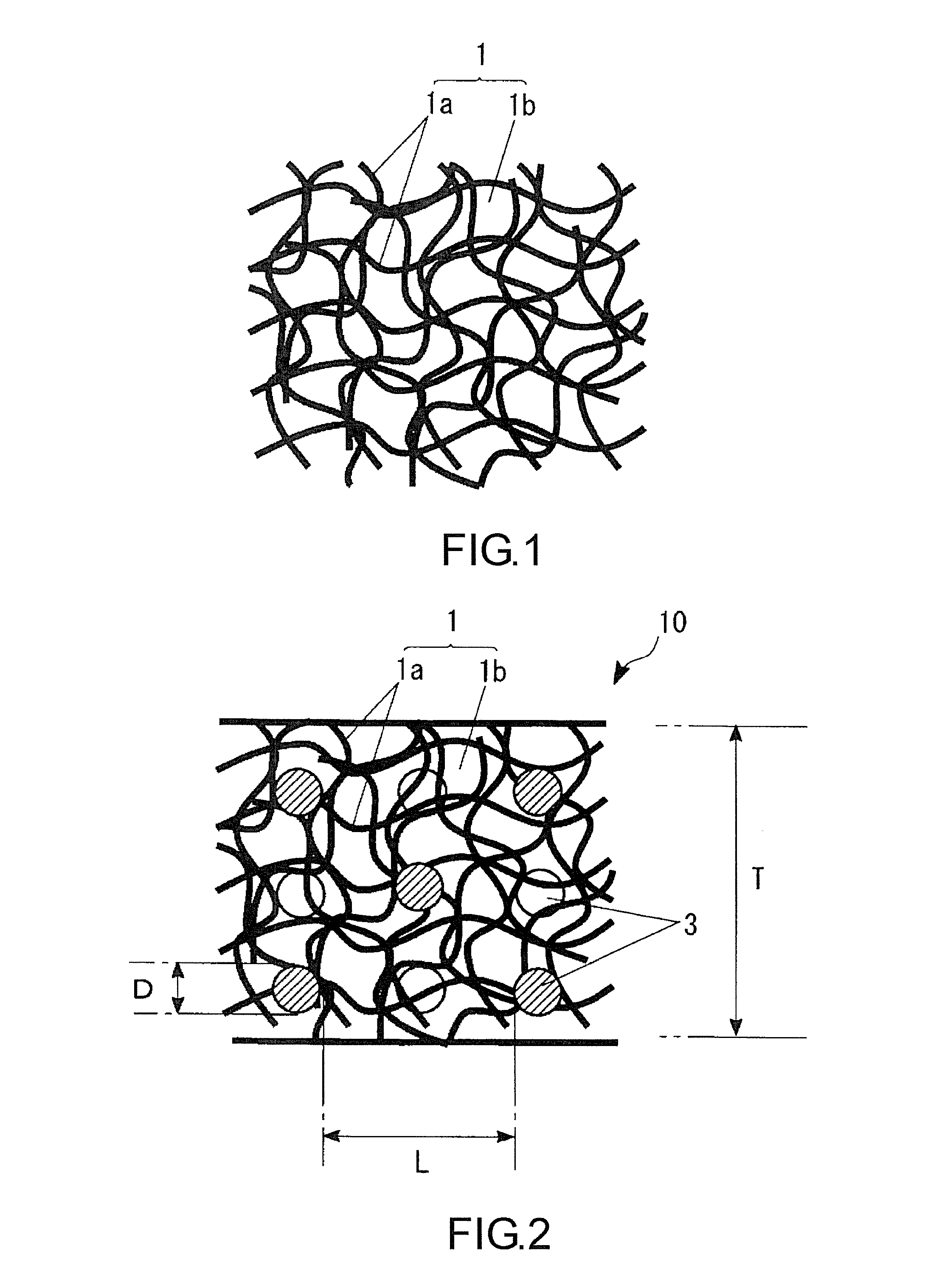
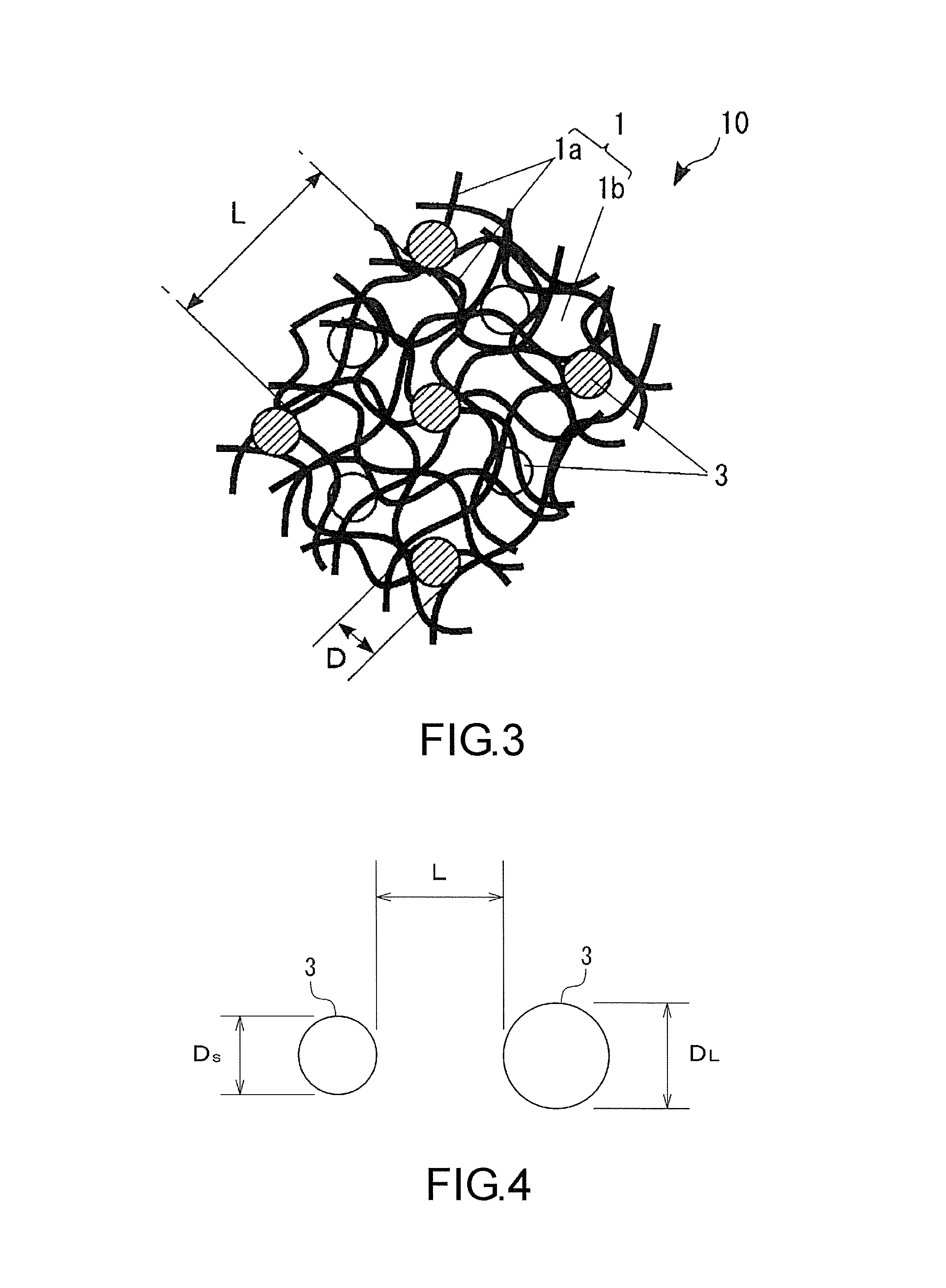
An absorbent structure is constructed of hydrophilic fibers and superabsorbent material and has a permeability as determined by an Absorbent Structure Permeability Test and a normalized retention capacity as determined by a Retention Capacity Test. The absorbent structure has an intake factor of at least about 3 wherein the intake factor is defined as the absorbent structure permeability divided by the normalized retention capacity. In another embodiment, the absorbent structure is constructed at least in part of a superabsorbent material and has an intake factor of at least about 3 and less than about 50.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Moisture sensor for skin
ActiveUS20060248946A1Broaden applicationReduce decreaseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial moisture contentEngineeringLotion
A moisture sensor for skin is disclosed. With the moisture sensor, a user can determine that her skin is too dry, and can conveniently apply a skin-care product. In addition, in one embodiment, the sensor can assist in identifying different types of skin-care products to apply. As one example, a skin-care product is a type of lotion. As another example, a skin-care product is a type of shampoo.
Owner:IPVENTURE
Mass sensor and mass sensing method
InactiveUS6457361B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mass sensor including: a connecting plate having one or more slit(s) and / or opening portion(s) formed therein and / or having a thin-walled portion and a thick-walled portion formed therein; a diaphragm joined with the connecting plate at respective side surfaces; a piezoelectric element; a sensing plate with the piezoelectric element being provided at least at one part on at least one surface of the sensing plate, which has its side surface joined with a side surface of the connecting plate in the direction perpendicular to the joining direction of the diaphragm and the connecting plate; and a sensor substrate with which at least a part of side surfaces of the connecting plate as well as the sensing plate are joined, and the diaphragm, the connecting plate, the sensing plate, and the piezoelectric element form a resonating portion. The mass sensor can conveniently be used for determining the mass of a substance to be sensed by measuring changes in resonant frequencies caused by changes in the mass of the diaphragm on which a catching substance for catching a substance to be sensed by reacting only with the object of sensing is applied.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Multilateration enhancements for noise and operations management
InactiveUS20060191326A1Data augmentationGood serviceDirection finders using radio wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementNoise monitoringMultilateration
Multilateration techniques are used to provide accurate aircraft tracking data for aircraft on the ground and in the vicinity of an airport. From this data, aircraft noise and operations management may be enhanced. Aircraft noise may be calculated virtually using track data in real-time and provided to a user to determine noise violations. Tracking data may be used to control noise monitoring stations to gate out ambient noise. Aircraft emissions, both on the ground and in the air may be determined using tracking data. This and other data may be displayed in real time or generated in reports, and / or may be displayed on a website for viewing by airport operators and / or members of the public. The system may be readily installed in a compact package using a plurality of receivers and sensor packages located at shared wireless communication towers near an airport, and a central processing station located in or near the airport.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Device and method for detecting a substance of a liquid
ActiveUS7468608B2Eliminates high-frequency lossEliminates interfering inductanceAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersResonancePiezo electric
A device for detecting at least one substance of a fluid includes at least one piezo-acoustic resonator with at least one piezo layer, an electrode arranged on the piezo-electric layer, at least one other electrode arranged on the piezo-electric layer and a surface section used for sorption of the substance of the fluid. The piezo-electric layer, the electrodes and the surface section are disposed in such a way that electric control of the electrodes leads to an oscillation of the resonator at a resonance frequency which depends upon the amount of the substance which is sorbed on the surface section. The thickness of the pioelectric layer is in the region of 0.5 to 20 μm and the resonance frequency of the oscillation ranges from 500 MHz to 2 GHz. The device is a mass sensor with a piezo-acoustic high-frequency thin film resonator.
Owner:BIOMENSIO LTD
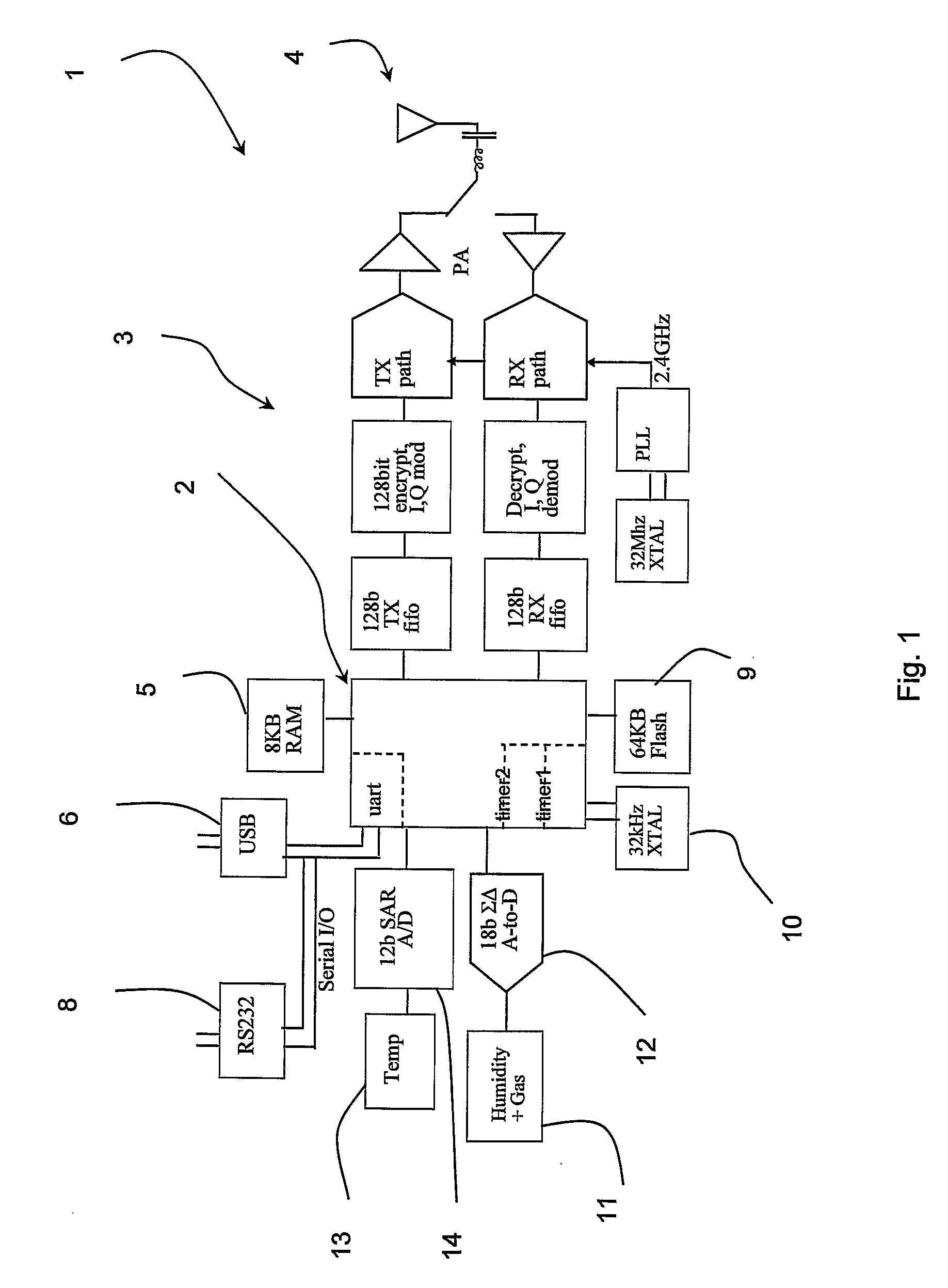
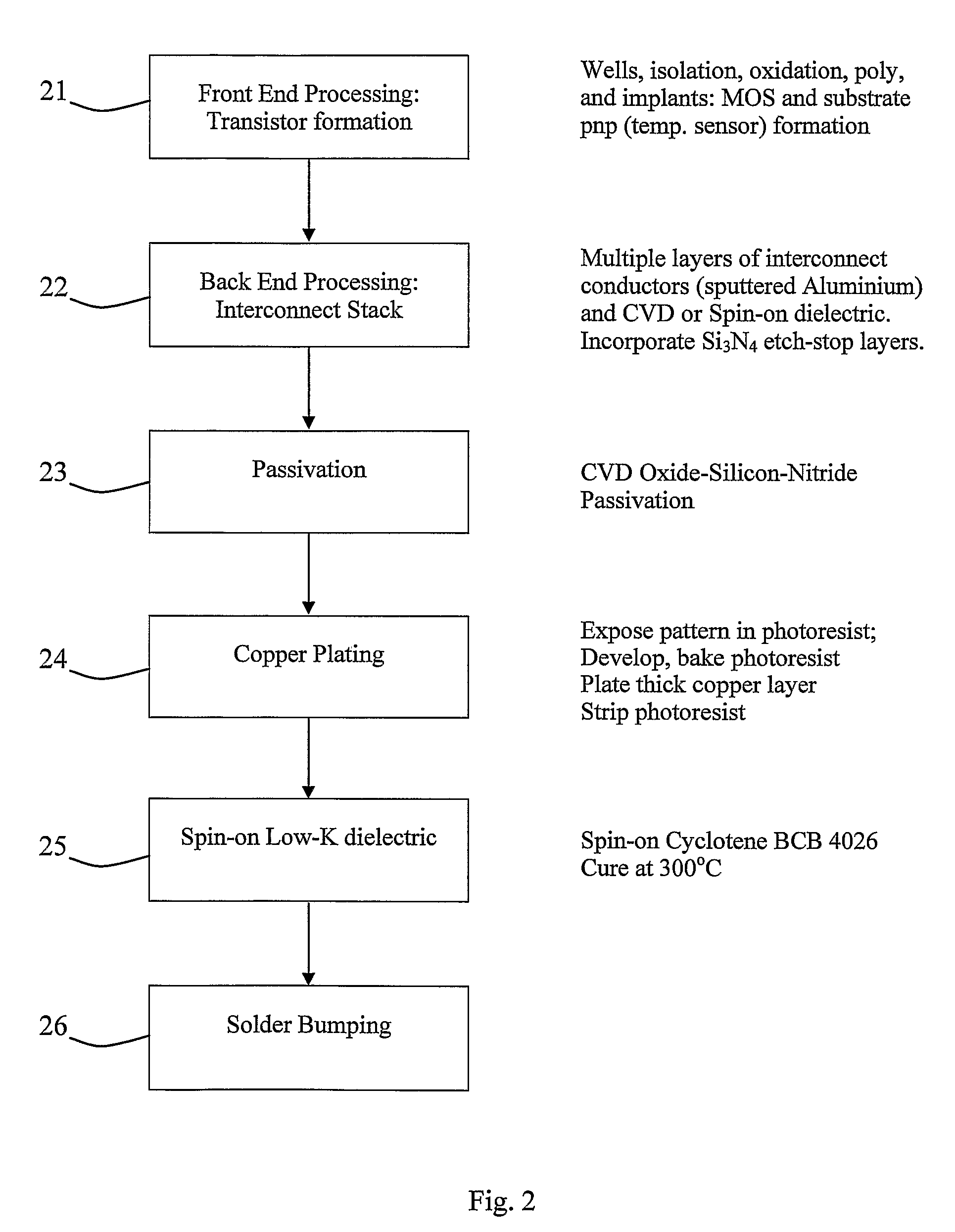
Integrated Electronic Sensor
ActiveUS20090141767A1Improve response characteristicsSufficient free space volumeThermometer detailsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrocontrollerLine sensor
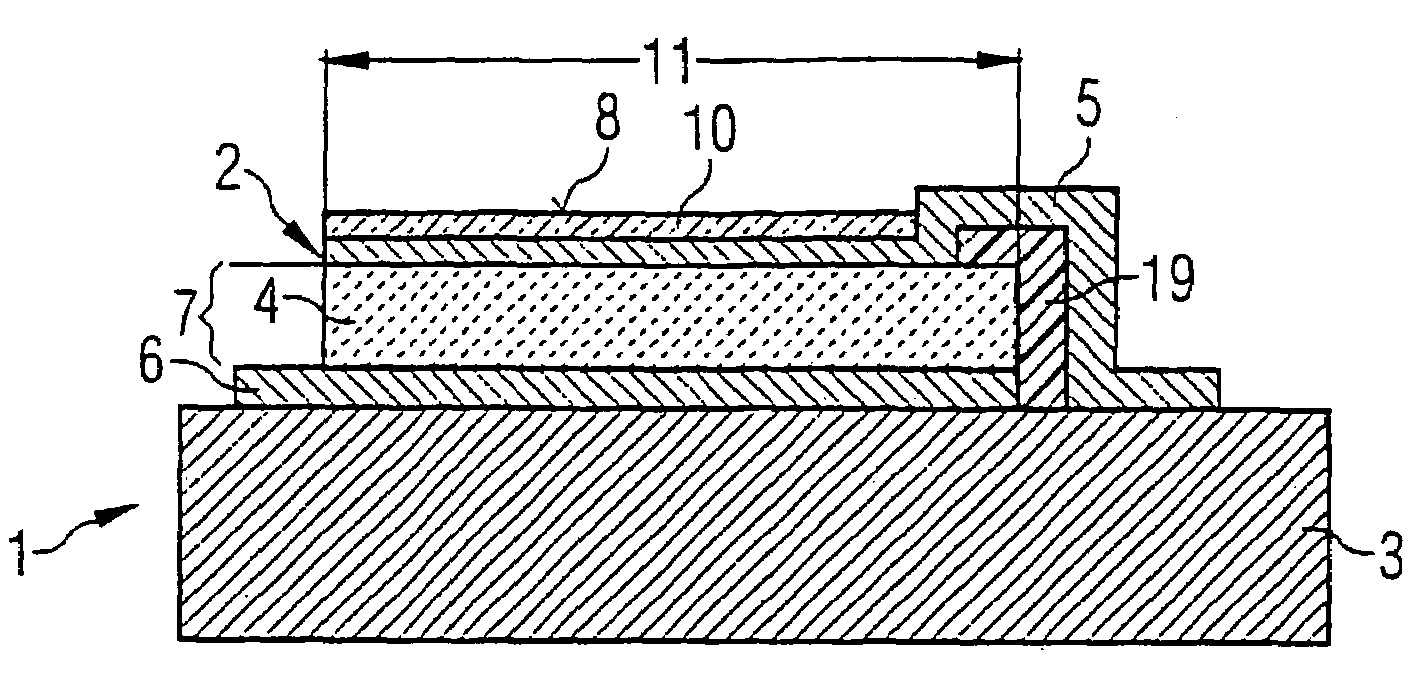
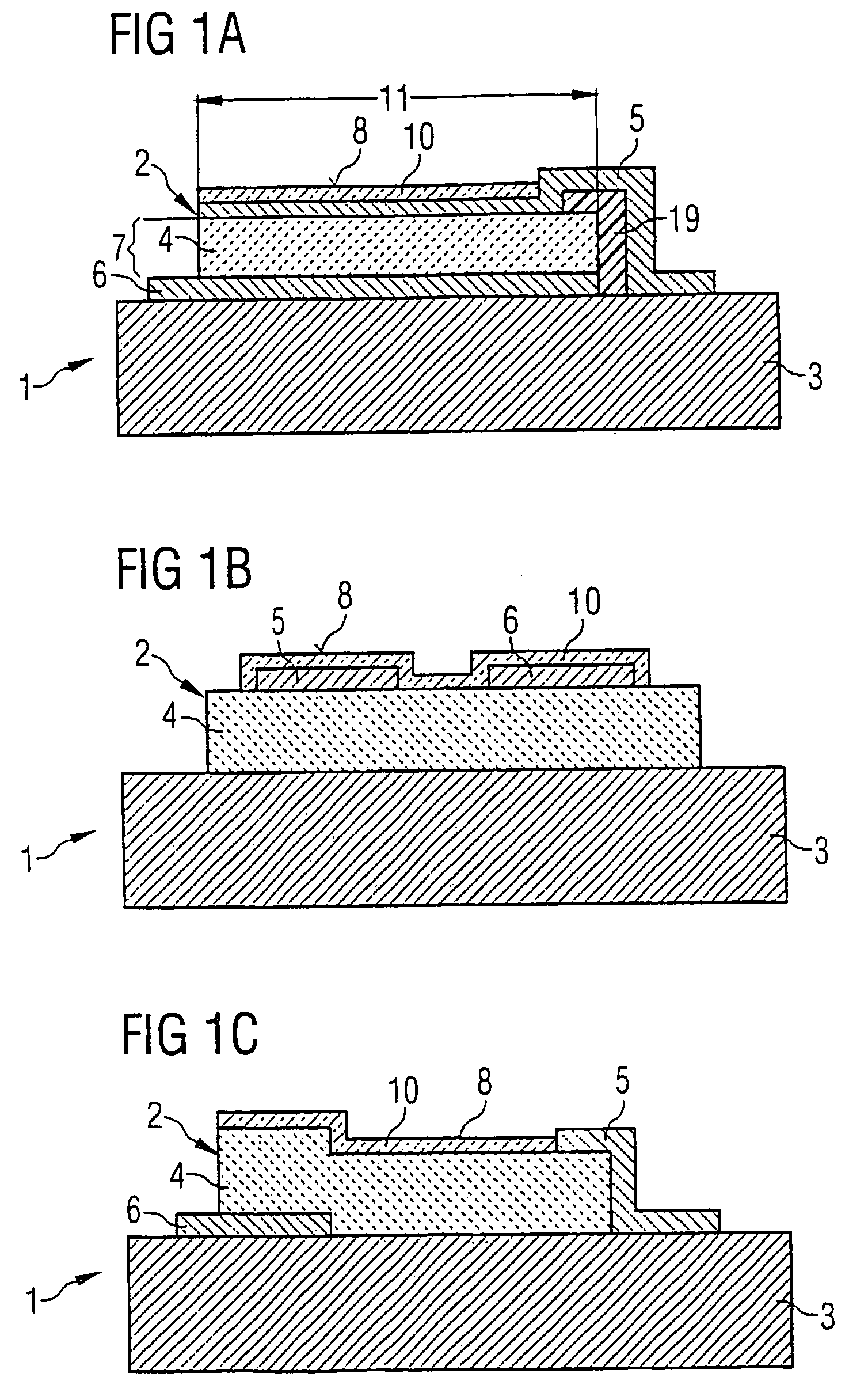
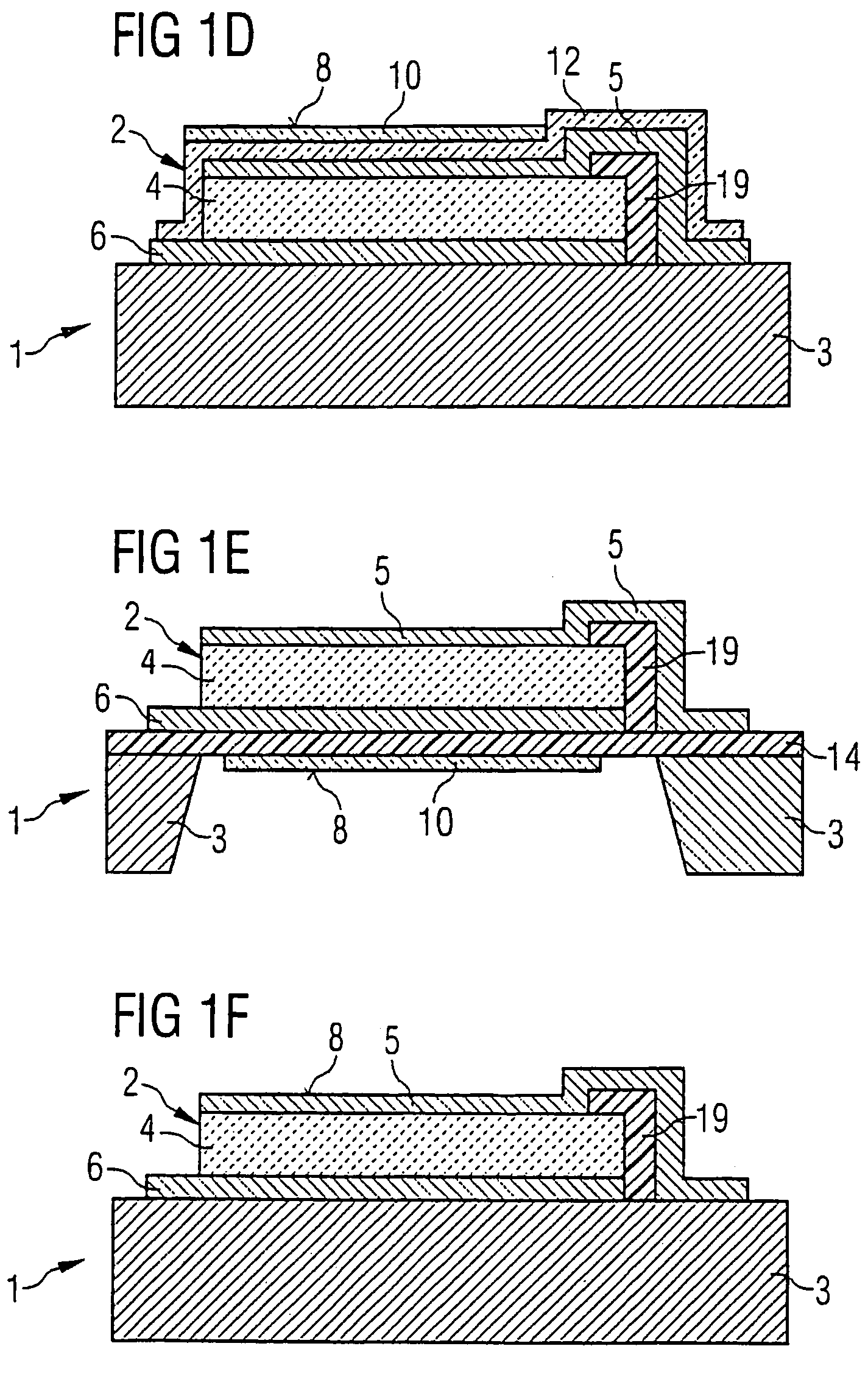
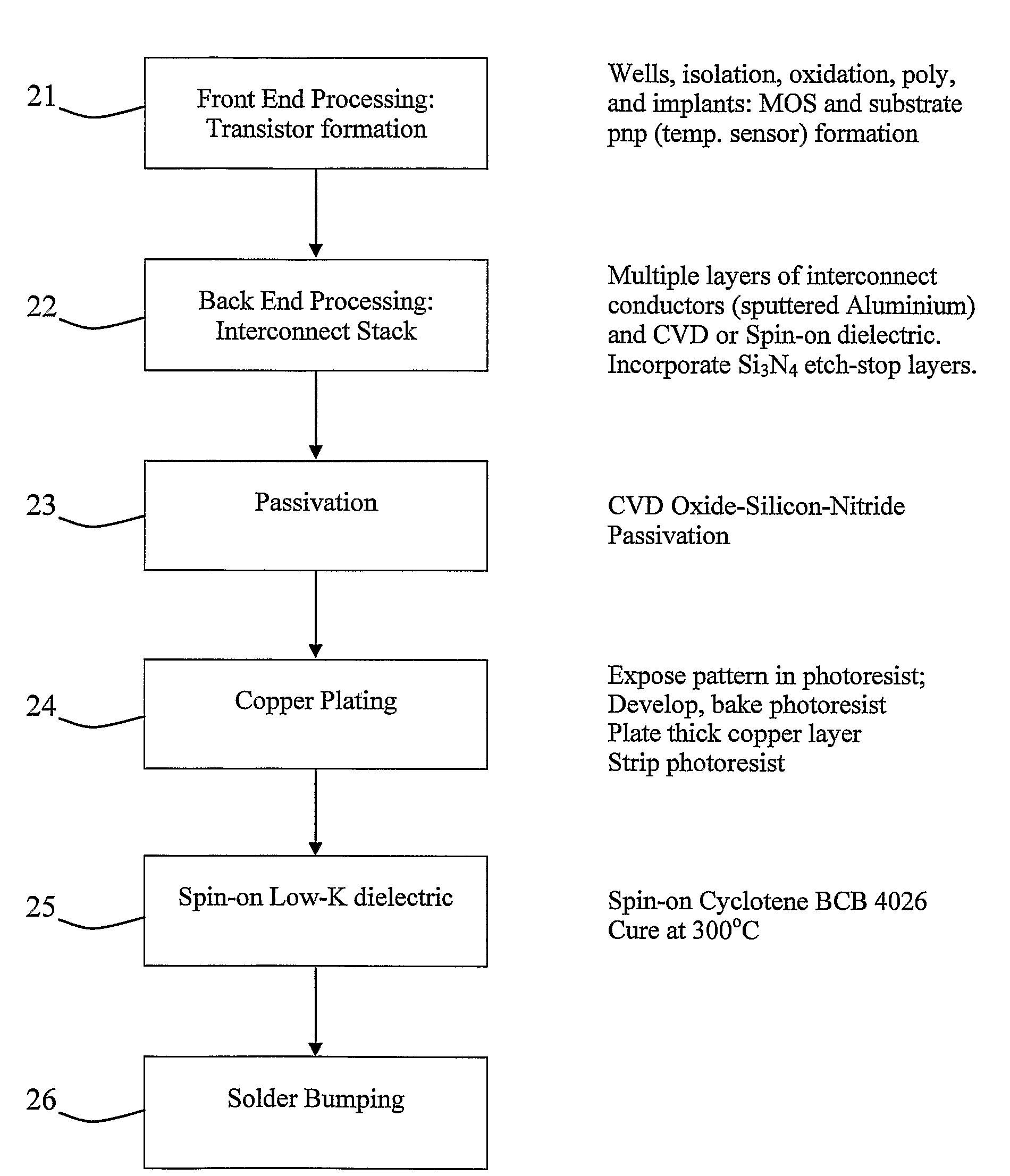
A single chip wireless sensor (1) comprises a microcontroller (2) connected to a transmit / receive interface (3), which is coupled to a wireless antenna (4) by an L-C matching circuit. The sensor (1) senses gas or humidity and temperature. The device (1) is an integrated chip manufactured in a single process in which both the electronics and sensor components are manufactured using standard CMOS processing techniques, applied to achieve both electronic and sensing components in an integrated process. A Low-K material (57) with an organic polymer component is spun onto the wafer to form a top layer incorporating also sensing electrodes (60). This material is cured at 300° C., which is much lower than CVD temperatures. The polyimide when cured becomes thermoset, and the lower mass-to-volume ratio resulting in K, its dielectric constant, reducing to 2.9. The thermoset dielectric, while not regarded as porous in the conventional sense, has sufficient free space volume to admit enough gas or humidity for sensing.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Wetness sensor using RF circuit with frangible link
InactiveUS8978452B2Material heat developmentMaterial moisture contentElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Capacitive humidity sensor
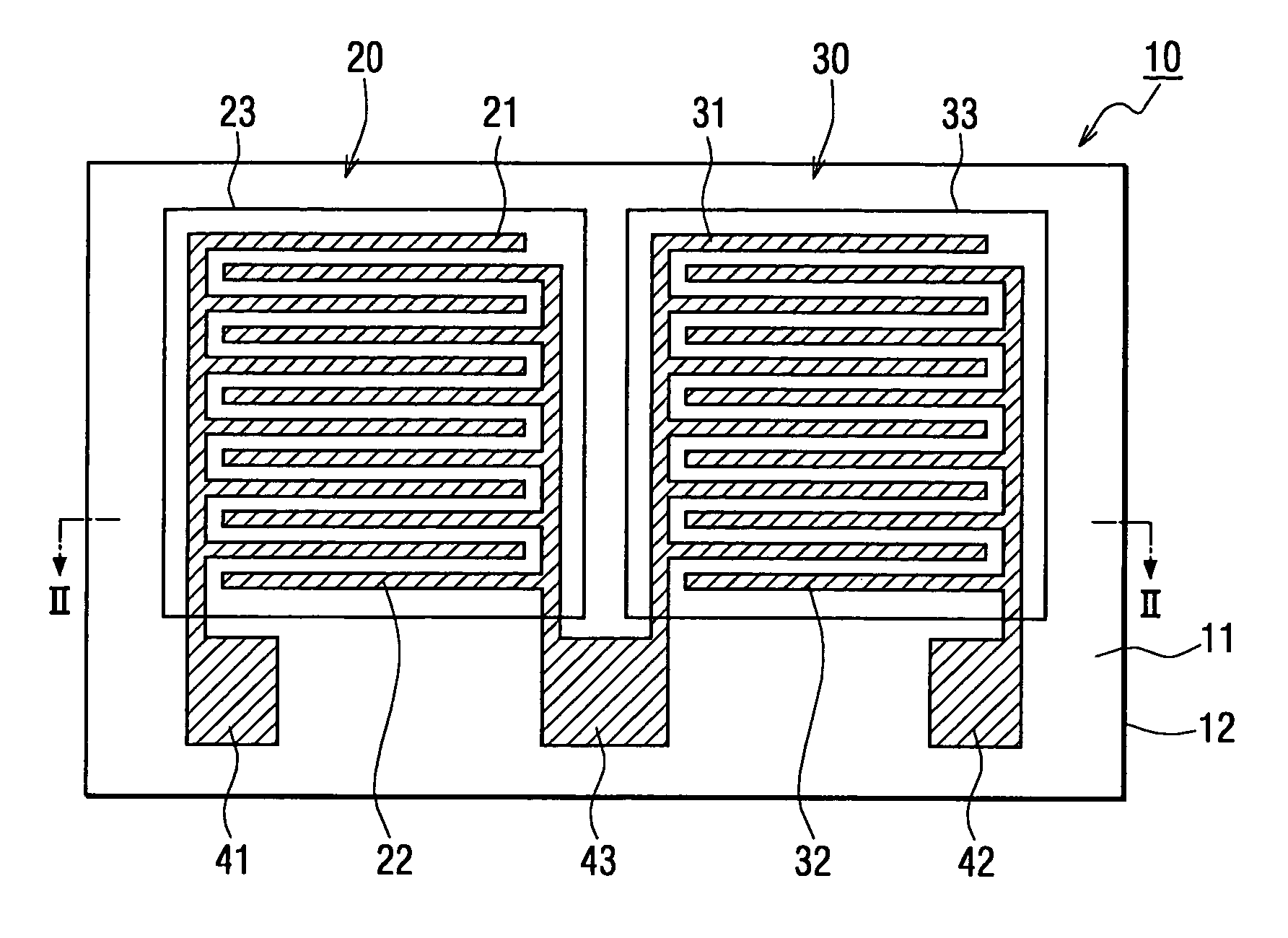
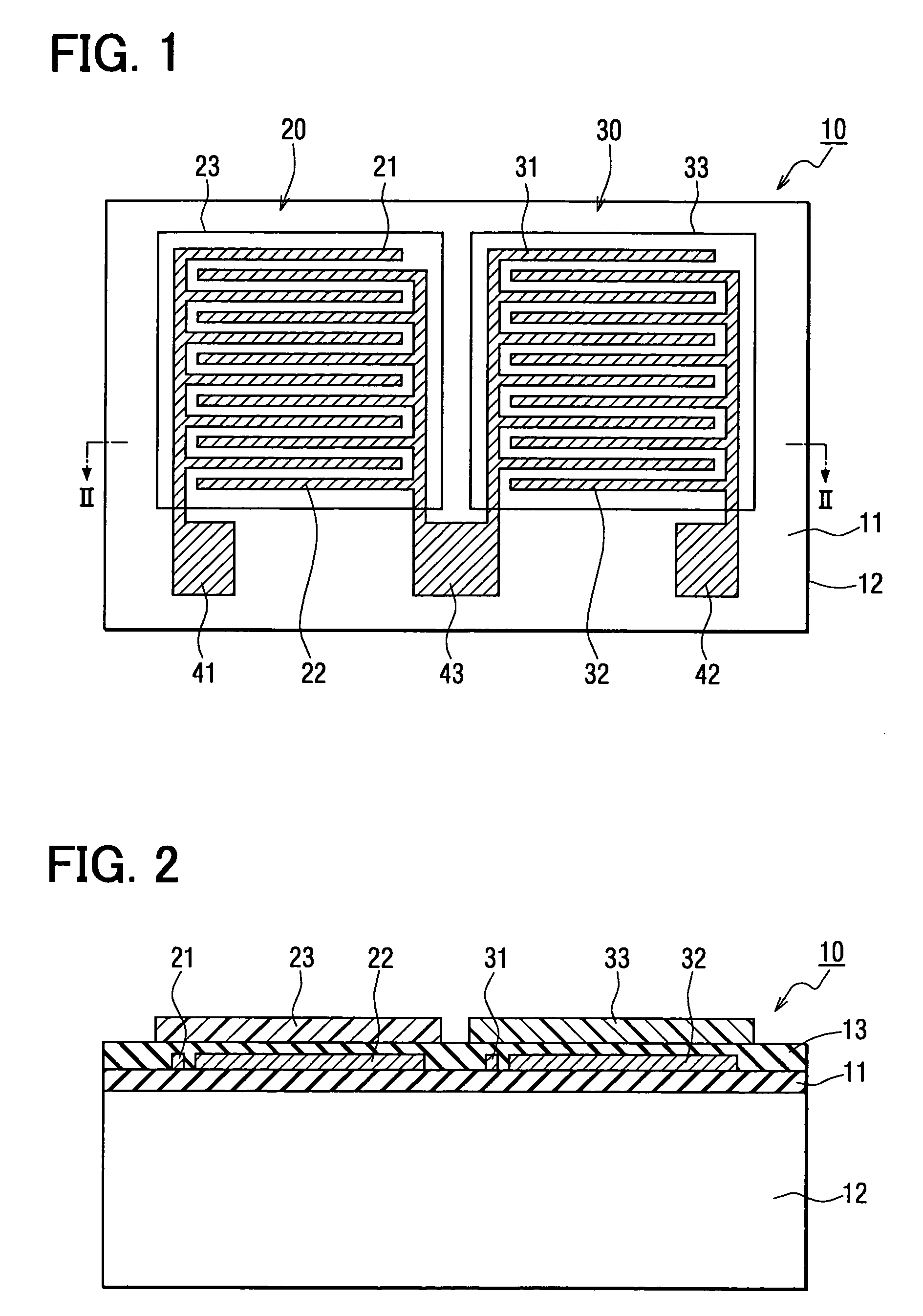
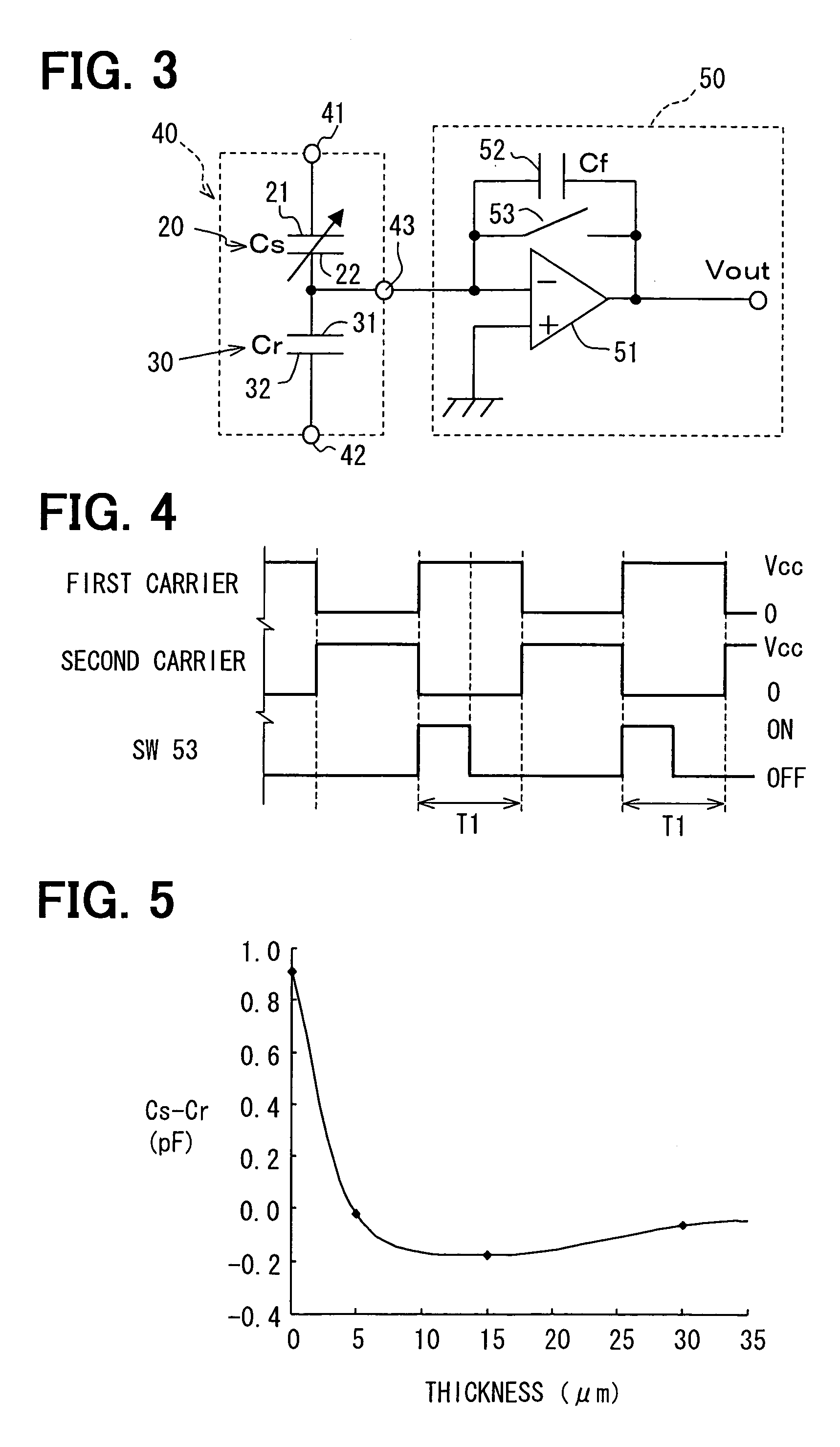
InactiveUS7032448B2Lower Offset VoltageSmall sizeResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing mechanical meansMoisture permeationMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes a detection portion and a reference portion. The detection portion includes detection electrodes and a moisture sensitive film. The reference portion includes reference electrodes and a moisture permeation film as a capacitance adjusting film. The capacitive humidity sensor detects humidity by converting a capacitance difference between a capacitance of the detection electrodes and a capacitance of the reference electrodes to an electric signal by using a capacitance-voltage conversion circuit. The moisture permeation film reduces offset voltage of the capacitive humidity sensor. Thus, an offset compensation circuit or the like is not required.
Owner:DENSO CORP
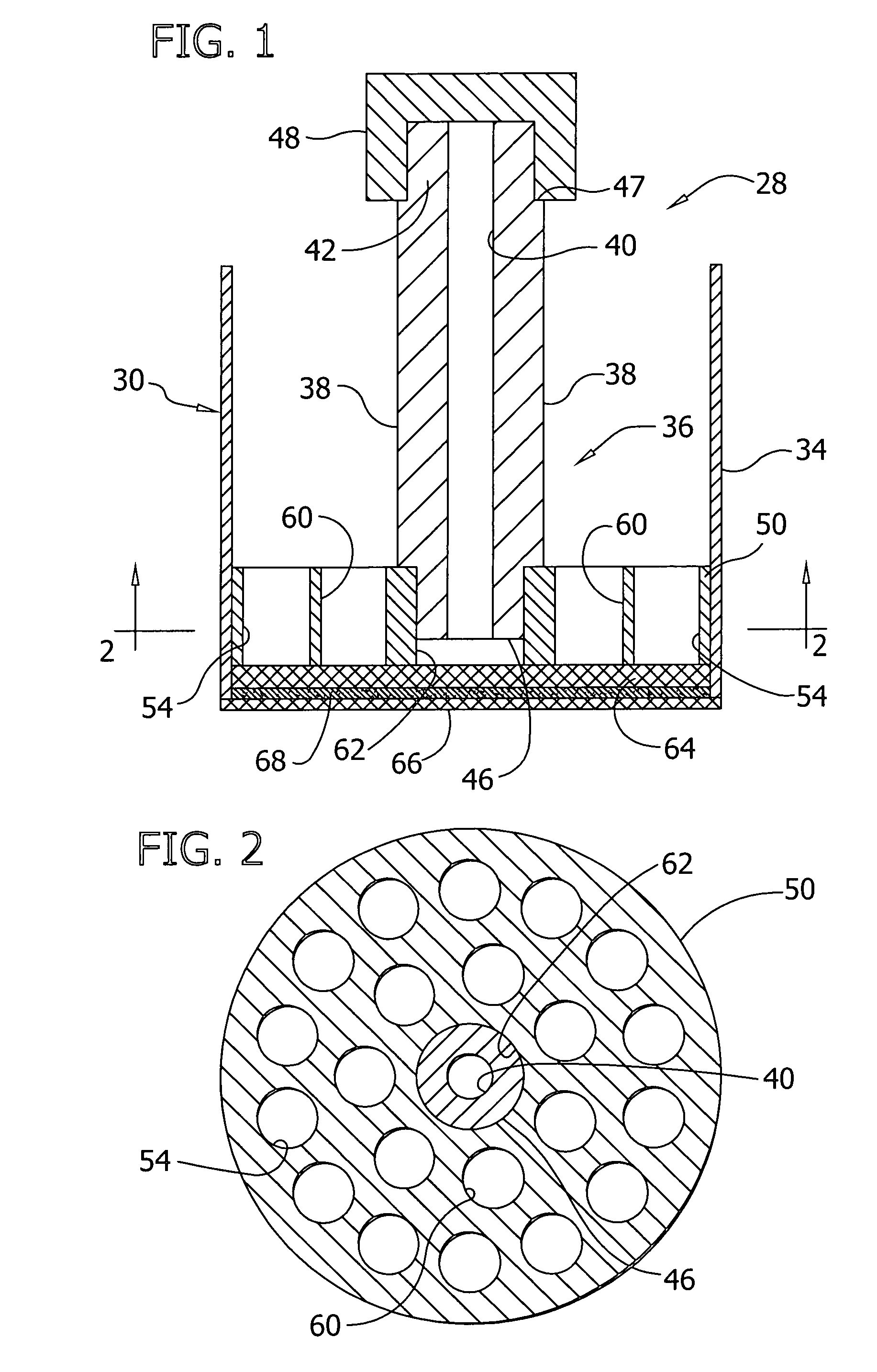
Composite material for a sensor for measuring shear forces
The present invention is related to a composite sheet material, a method of producing this material, and the application of this material as a sensor for monitoring and measuring shear forces (or lateral translation). In one embodiment, the present invention includes a composite sheet material having an upper and a lower surface comprising an elastomeric matrix, which is essentially non-conductive, and discrete electrically conductive elements within the matrix wherein the electrically conductive elements in a region of the composite sheet material are arranged into columns, and the orientation of these columns are in an essentially organized, non-random pattern with a majority of these columns oriented at angles less than about 90° and greater than about 15° to the lower surface of the composite sheet material. In another embodiment, the present invention provides for a method of forming the sensors.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECH
Piezoelectric cantilever sensors
ActiveUS7458265B2Less lengthVibration measurement in solidsWeighing by removing componentViscous liquidAnalyte
A piezoelectric cantilever with a non-piezoelectric, or piezoelectric tip useful as mass and viscosity sensors. The change in the cantilever mass can be accurately quantified by monitoring a resonance frequency shift of the cantilever. For bio-detection, antibodies or other specific receptors of target antigens may be immobilized on the cantilever surface, preferably on the non-piezoelectric tip. For chemical detection, high surface-area selective absorbent materials are coated on the cantilever tip. Binding of the target antigens or analytes to the cantilever surface increases the cantilever mass. Detection of target antigens or analytes is achieved by monitoring the cantilever's resonance frequency and determining the resonance frequency shift that is due to the mass of the adsorbed target antigens on the cantilever surface. The use of a piezoelectric unimorph cantilever allows both electrical actuation and electrical sensing. Incorporating a non-piezoelectric tip (14) enhances the sensitivity of the sensor. In addition, the piezoelectric cantilever can withstand damping in highly viscous liquids and can be used as a viscosity sensor in wide viscosity range.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
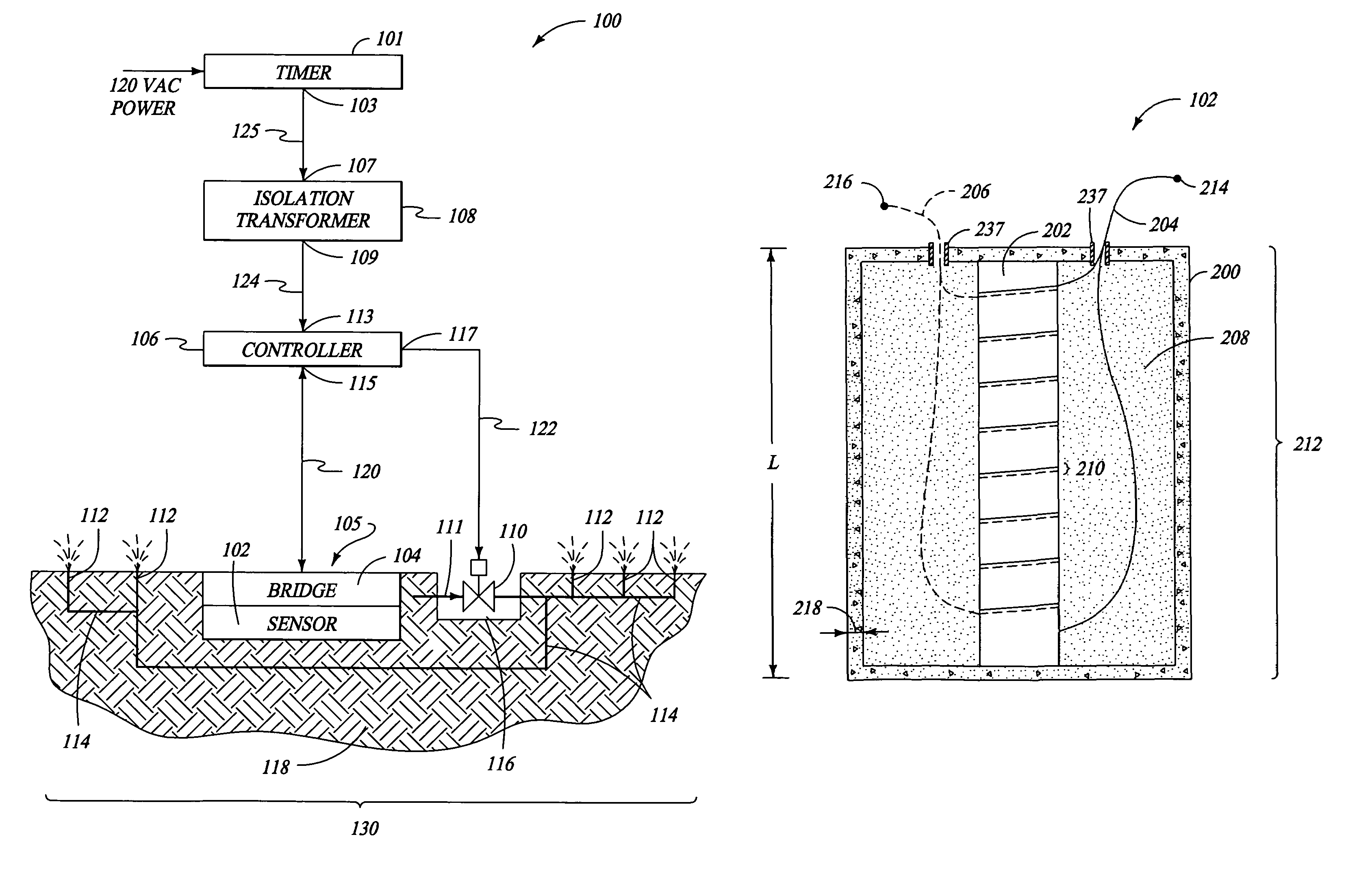
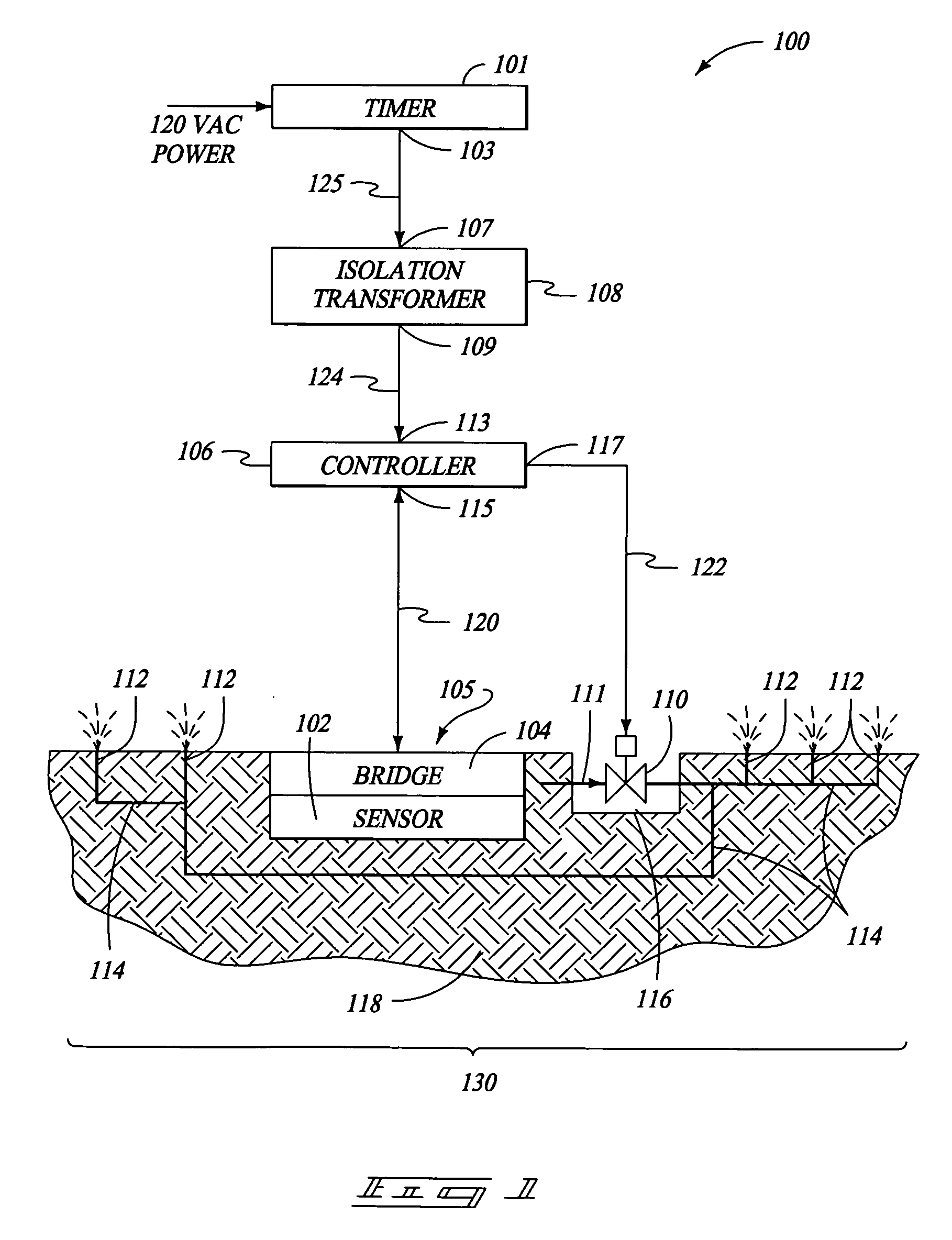
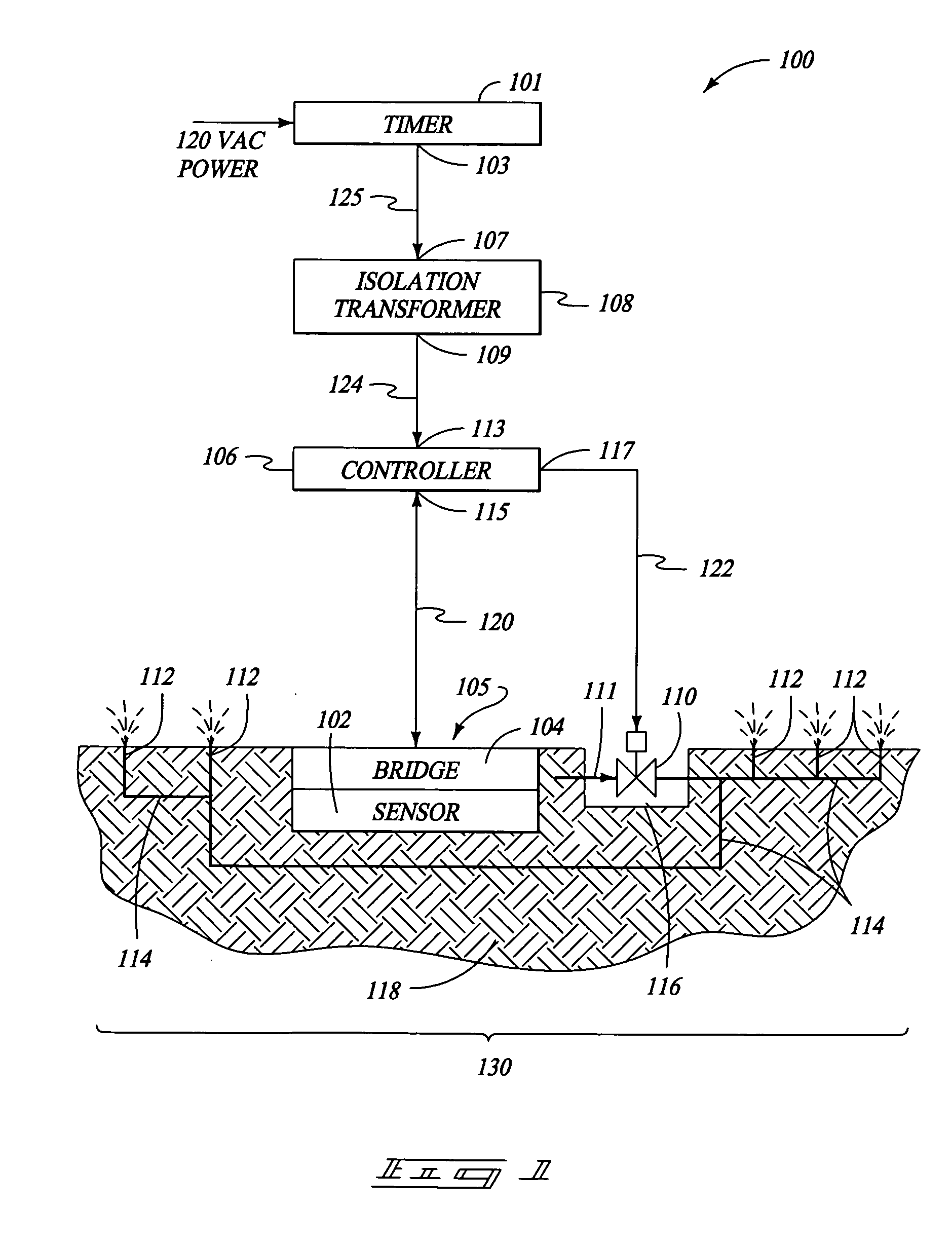
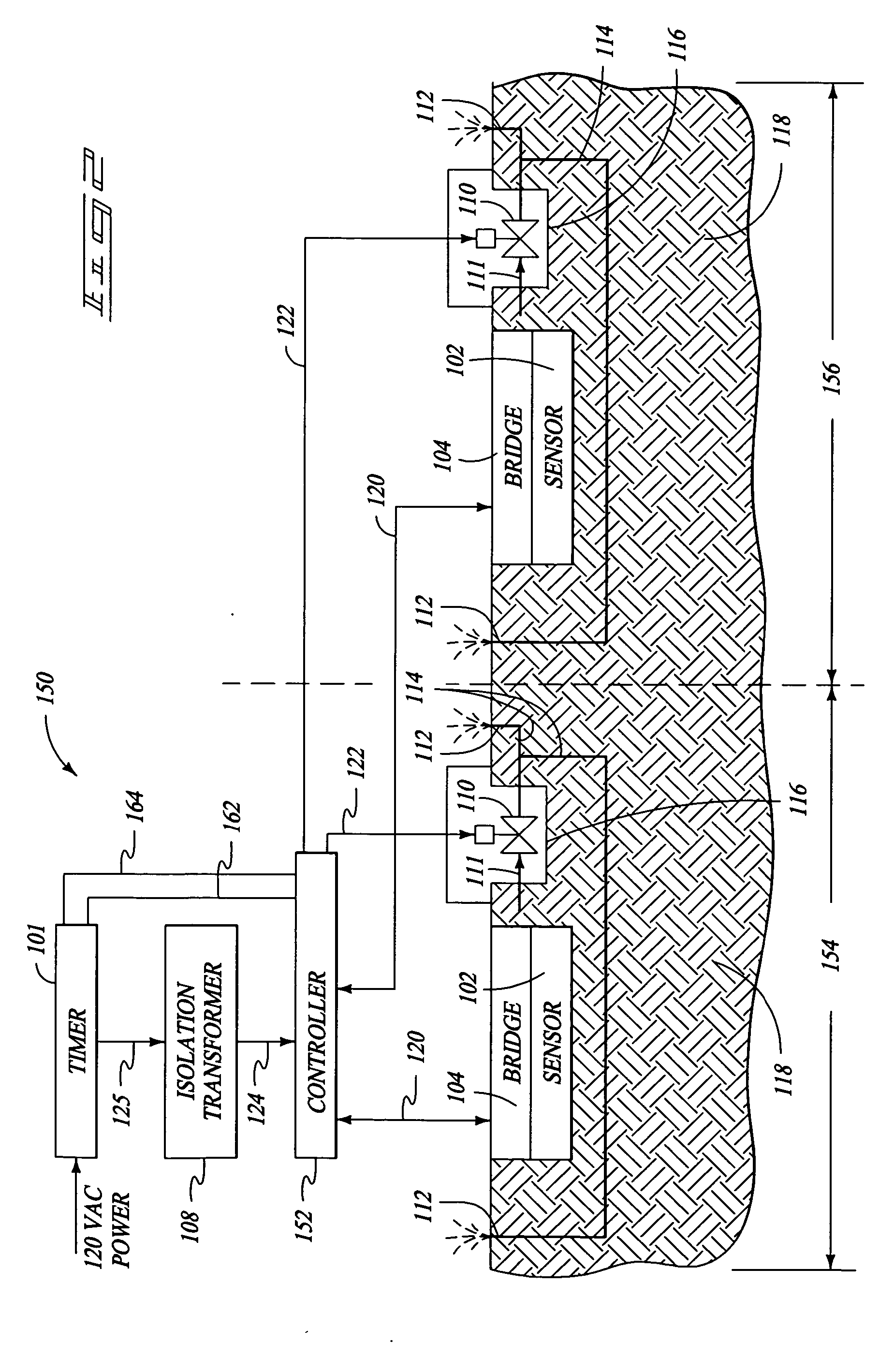
Moisture sensor sprinkler control systems
Irrigation systems, moisture sensors and related methods having a sensor embedded in the ground to sense moisture and help control watering. The sensor is responsive to capacitance changes from ground moisture variations. The sensor uses spaced insulated electrodes which are mounted within a granular filled chamber within a water-permeable shell. The sensor is mounted as part of a ground unit that also includes a high frequency driver that excites the sensor. The ground unit further has a detector circuit which produces a moisture indicating signal based on the capacitance which varies with ground moisture. Also disclosed are controllers that electrically isolate the ground units so that reliable moisture signals can be obtained and used to control irrigation. The controllers can be configured to provide multiple zone operation using a shared controller having shared or independent moisture adjusters.
Owner:BOWERS JOHN R +1
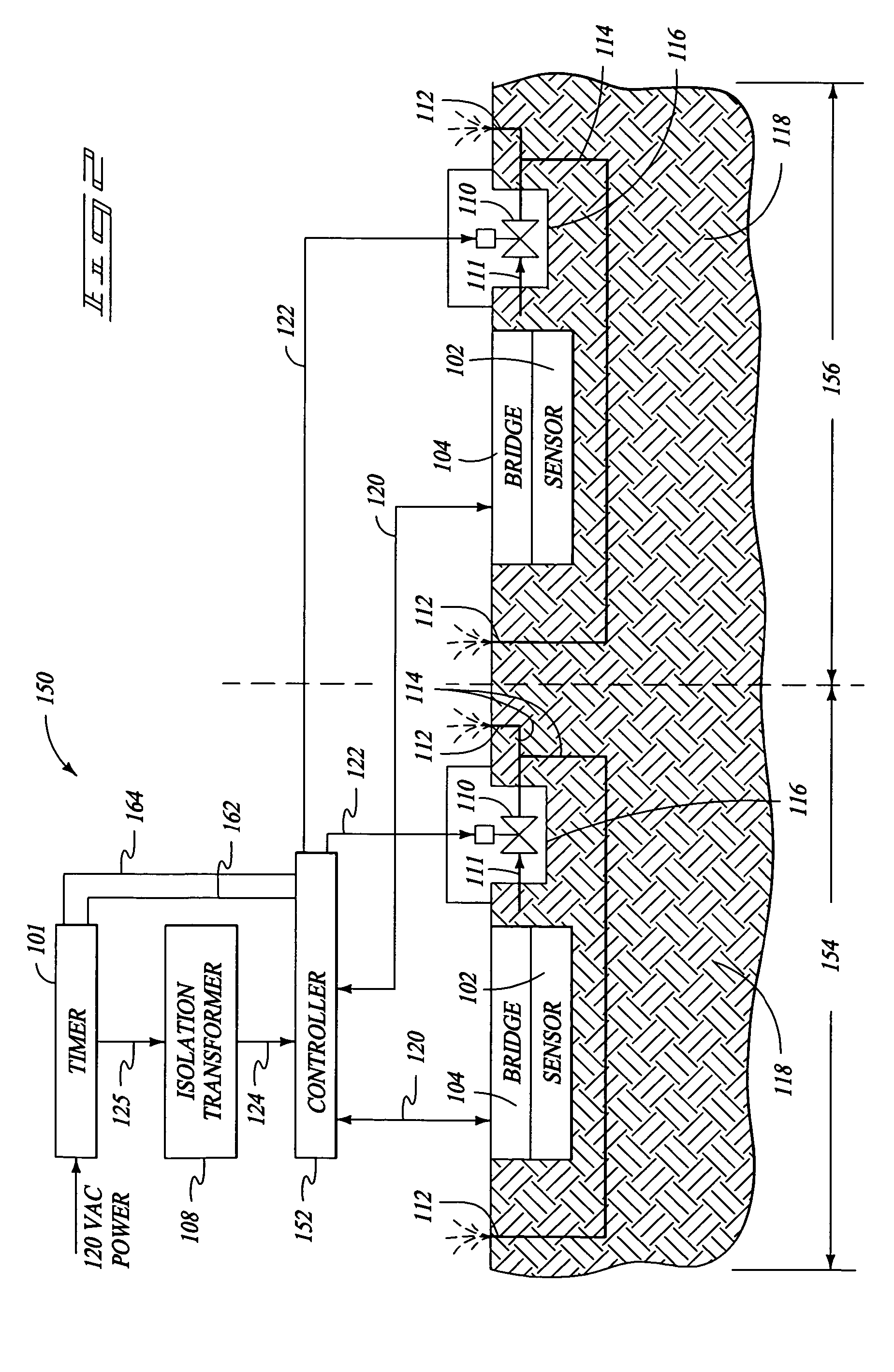
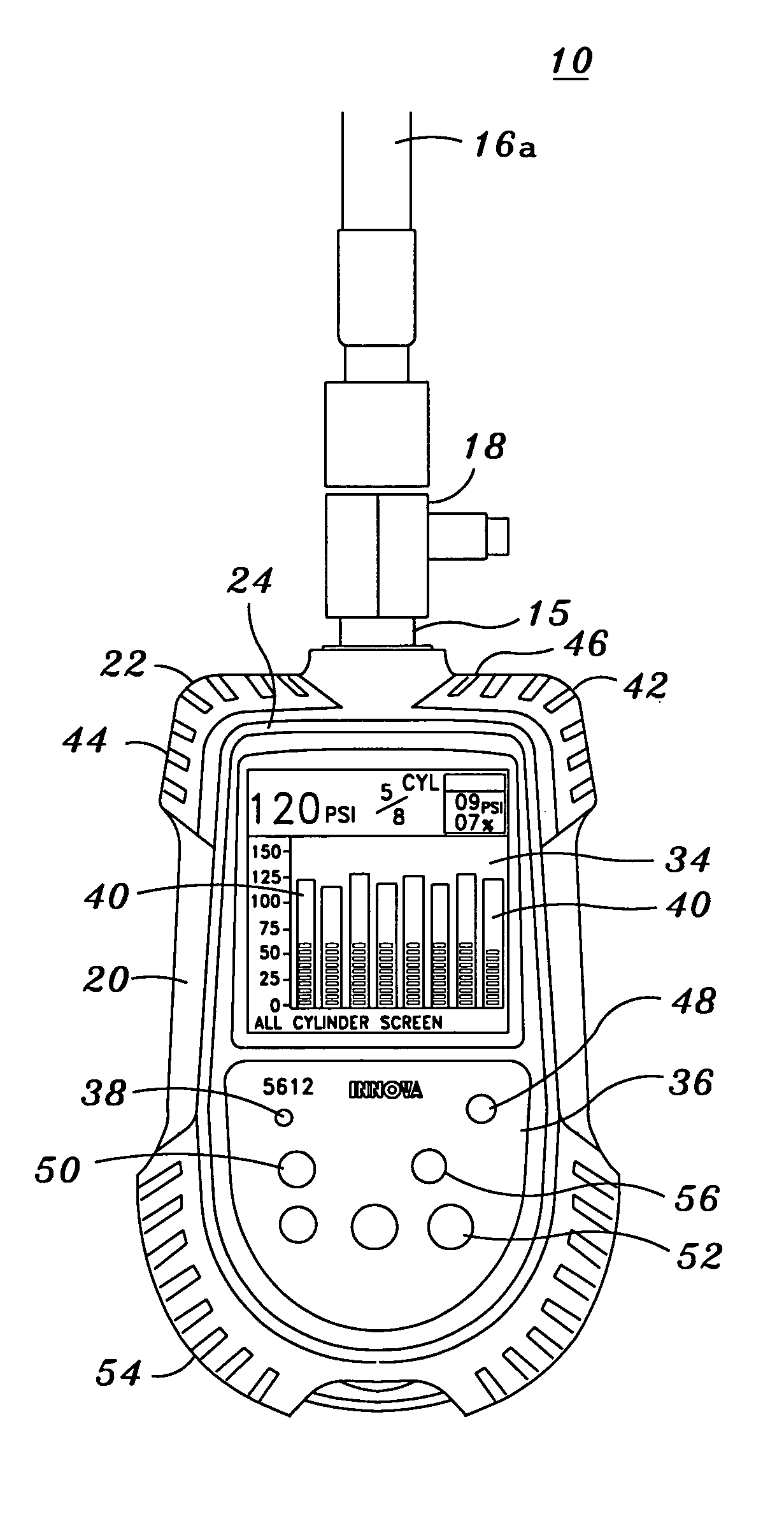
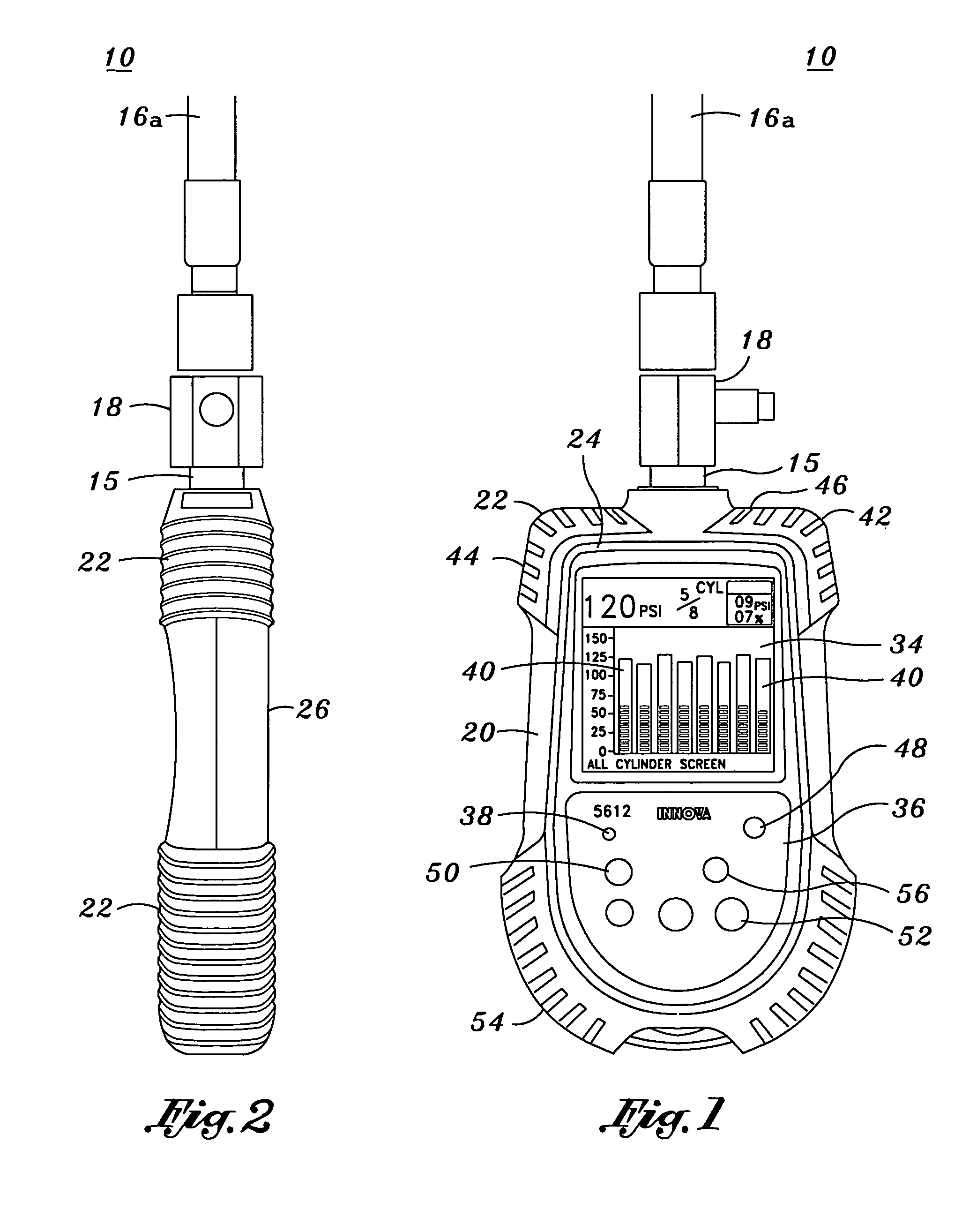
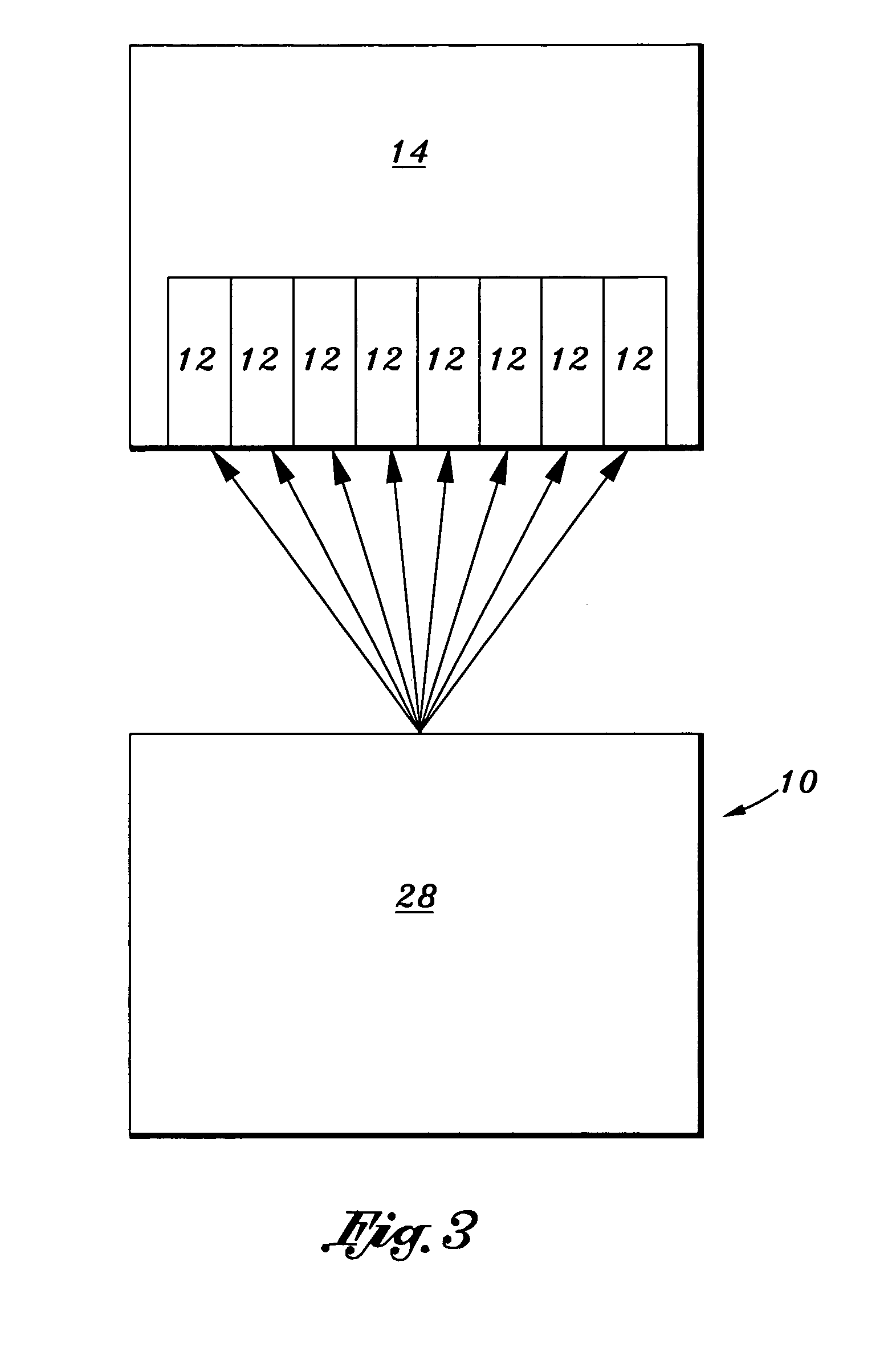
Digital compression gauge
InactiveUS6968733B2Internal-combustion engine testingFluid pressure measurementComparators circuitsDisplay device
There is provided a compression gauge assembly for diagnosing pressure variances of an engine cylinder(s). The gauge assembly comprises a gauge sensor in communication with the engine cylinder(s). The gauge sensor is operative to detect compression stroke pressures within the cylinder(s). A gauge controller is in communication with the gauge sensor. The gauge controller includes a comparator circuit operative to compare detected compression stroke pressures within the cylinder(s) and to derive the pressure variances therebetween. A gauge display is in communication with the gauge controller for displaying the derived pressure variances.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
Method for Evaluating Absorbency of an Absorbent Article
A method of evaluating the absorbency of an absorbent article comprises the steps of: (i) providing an absorbent article comprising a topsheet and having a longitudinal axis, a transverse axis, a first longitudinal end and a second longitudinal end; (ii) disposing the absorbent article in a flat configuration in a plane defined by the longitudinal axis and the transverse axis of the absorbent article; (iii) twisting the longitudinal ends in opposite directions in planes perpendicular to the longitudinal axis; (iv) twisting the longitudinal ends in directions opposite that of step (iii); (v) applying artificial bodily fluid to the topsheet of said absorbent article during steps (iii) and / or (iv); and (vi) repeating steps (iii) and (iv) after the artificial bodily fluid is applied to the topsheet.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Optoelectronic sensor device
InactiveUS6995354B2Produced cost-effectivelyFree spaceHeater elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamTransmitter
An optoelectronic sensor device for detecting precipitation on an outer surface of a transparent pane. The sensor device includes a beam guide attached to an inner surface of the pane and a circuit board offset from the inner pane surface. A beam transmitter is arranged on the circuit board to transmit, along a transmission beam path, a light beam toward the pane via the beam guide. A beam receiver is arranged on the circuit board to receive, along a reception beam path, a light beam reflected from the outer surface of the pane via the beam guide. A circuit substrate, electrically connected to the circuit board, is arranged parallel to the pane between the pane and the circuit board. An installation space separates the circuit substrate from the inner pane surface. A heating device is arranged on the circuit substrate in an area lying outside of the beam paths.
Owner:LEOPOLD KOSTAL GMBH & CO KG
Device for metering a urea soulution
InactiveUS20050011183A1High sensitivityIncrease surface areaInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusNitrogen oxidesState variable
A device for metering urea solutions permitting a reliable reduction of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas of an internal combustion engine is provided. This is achieved by the fact that the device for metering the urea solution includes a sensor unit for monitoring one or more physical state variables of an enzyme-free Urea solution.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
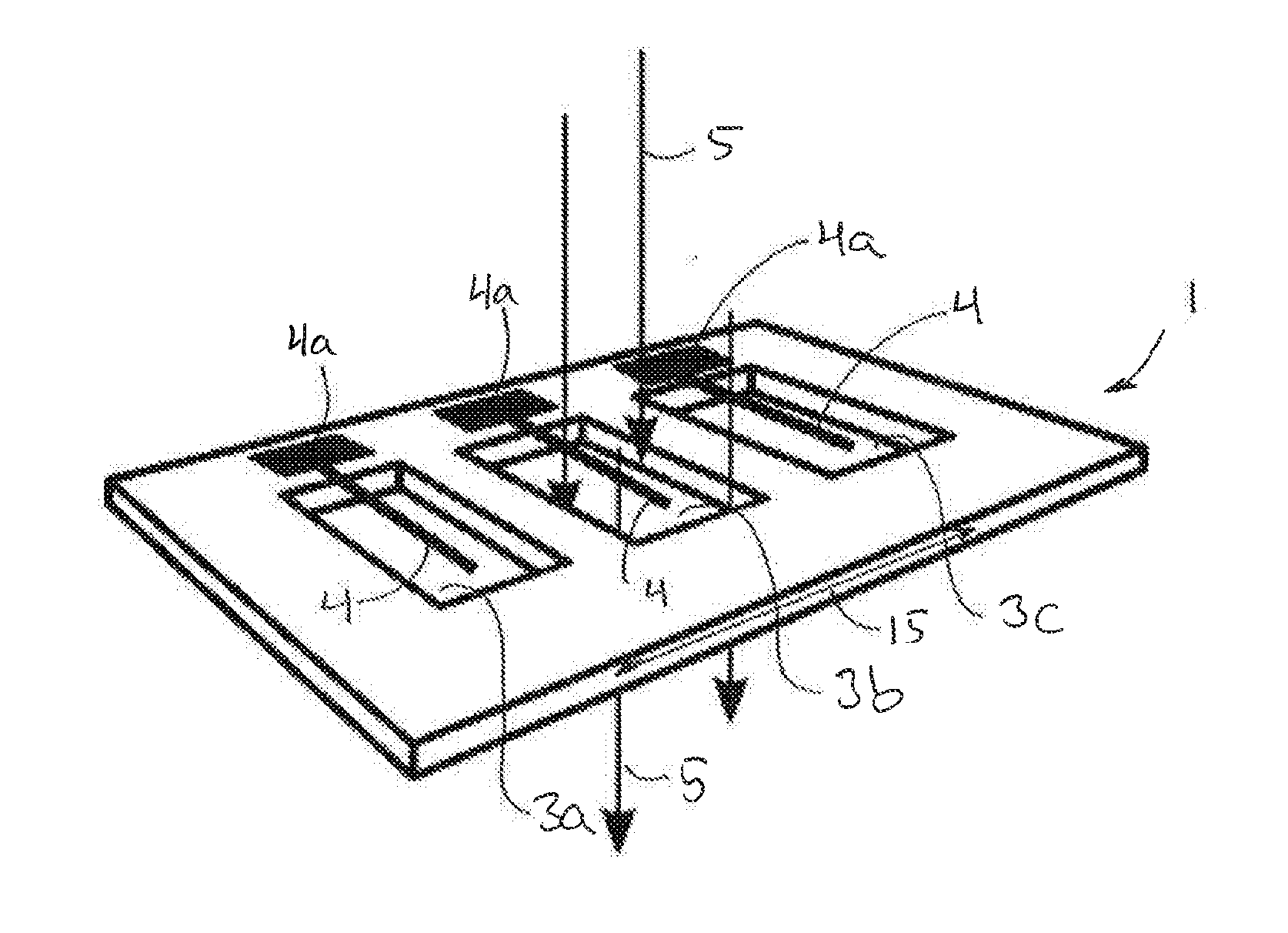
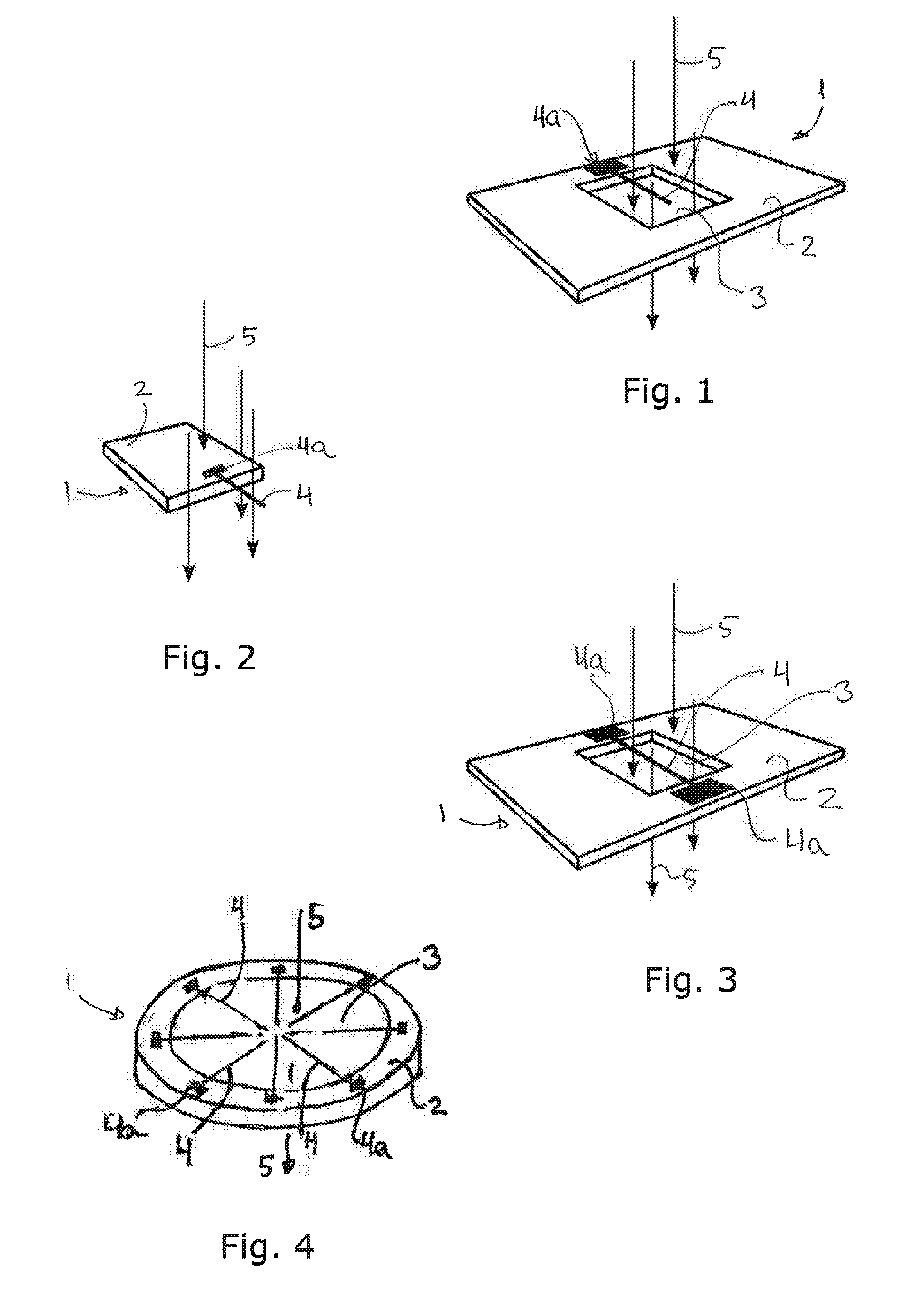
Resonant fiber based aerosol particle sensor and method
InactiveUS20140305191A1Increase speedMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle flowFiber
The present invention relates to methods and devices for determining the weight of small particles, typically being nano-sized particles by use of resonating fibers in the form of elongate members being driven into resonance by an actuator or e.g. thermal noise / fluctuation. The frequency shift in resonance frequency due to depositing of nano-sized particles is correlated with the mass deposited on the elongate member and the vibration frequency of the elongate member is determined by a detector. The read-out from the detector is transformed into a mass deposited on the elongate member. Particles are deposited by letting a fluid with the particles flow past the elongate member.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
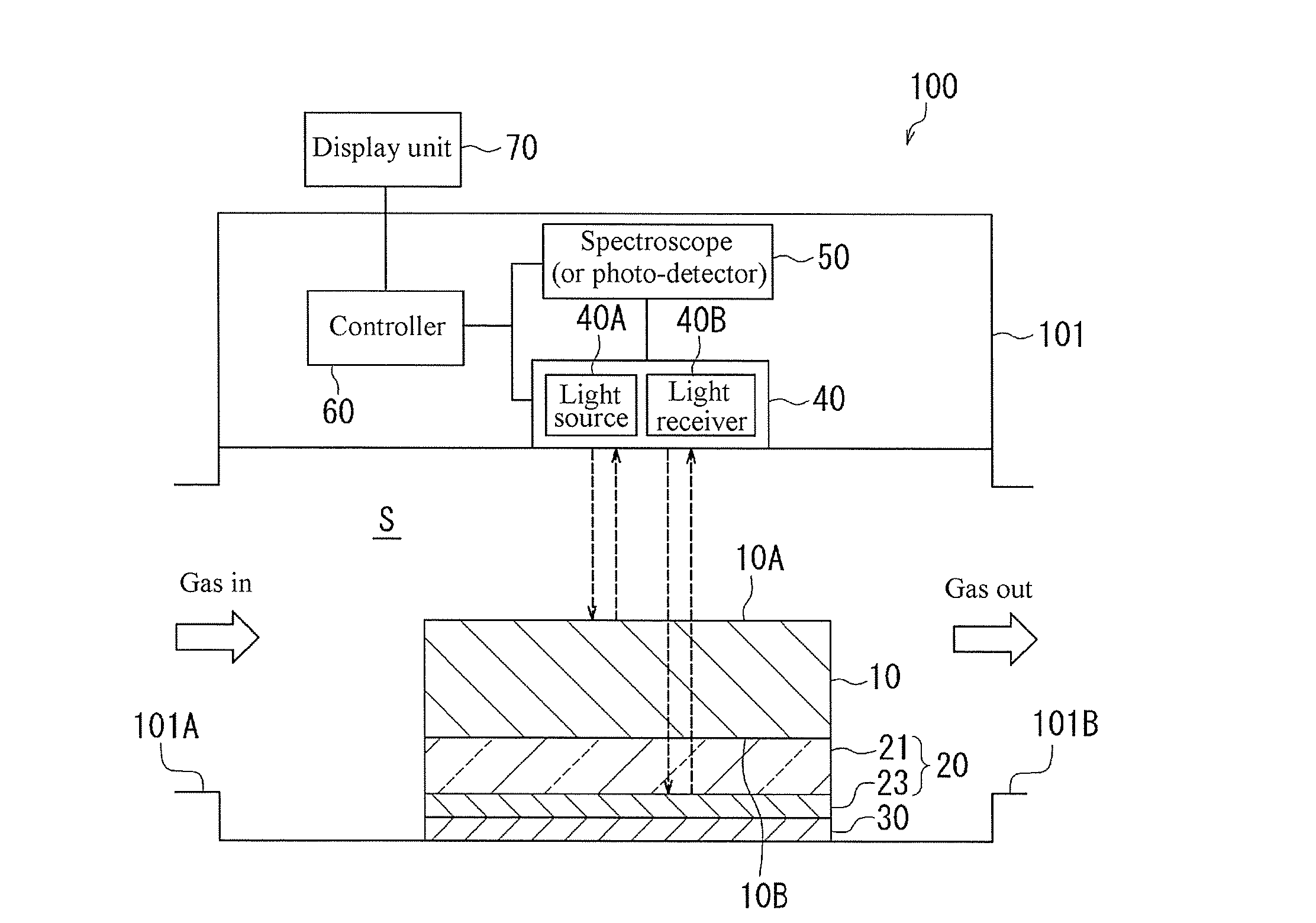
Sensor element, dew condensation sensor, humidity sensor, method for detecting dew condensation, and dew-point measurement device
InactiveUS20140186215A1Good precisionSimply performedComponent separationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsMeasurement deviceDew
A dew condensation sensor is described, including a nano-composite for generating local surface plasmon resonance, a light reflecting member disposed on one side of the nano-composite, a protection layer laminated on the light reflecting member, a light source / light receiver disposed facing the nano-composite, a spectroscope (or photo-detector) for detecting the light reflected by the light source / light receiver, a controller connected to the light source / light receiver and the spectroscope (or photo-detector) and used for overall control thereof, and a display unit connected to the controller. The dew condensation sensor detects occurrence of dew condensation based on the variation in the absorption spectrum, the absorption intensity or the reflected-light intensity of the local surface plasmon resonance of the nano-composite.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
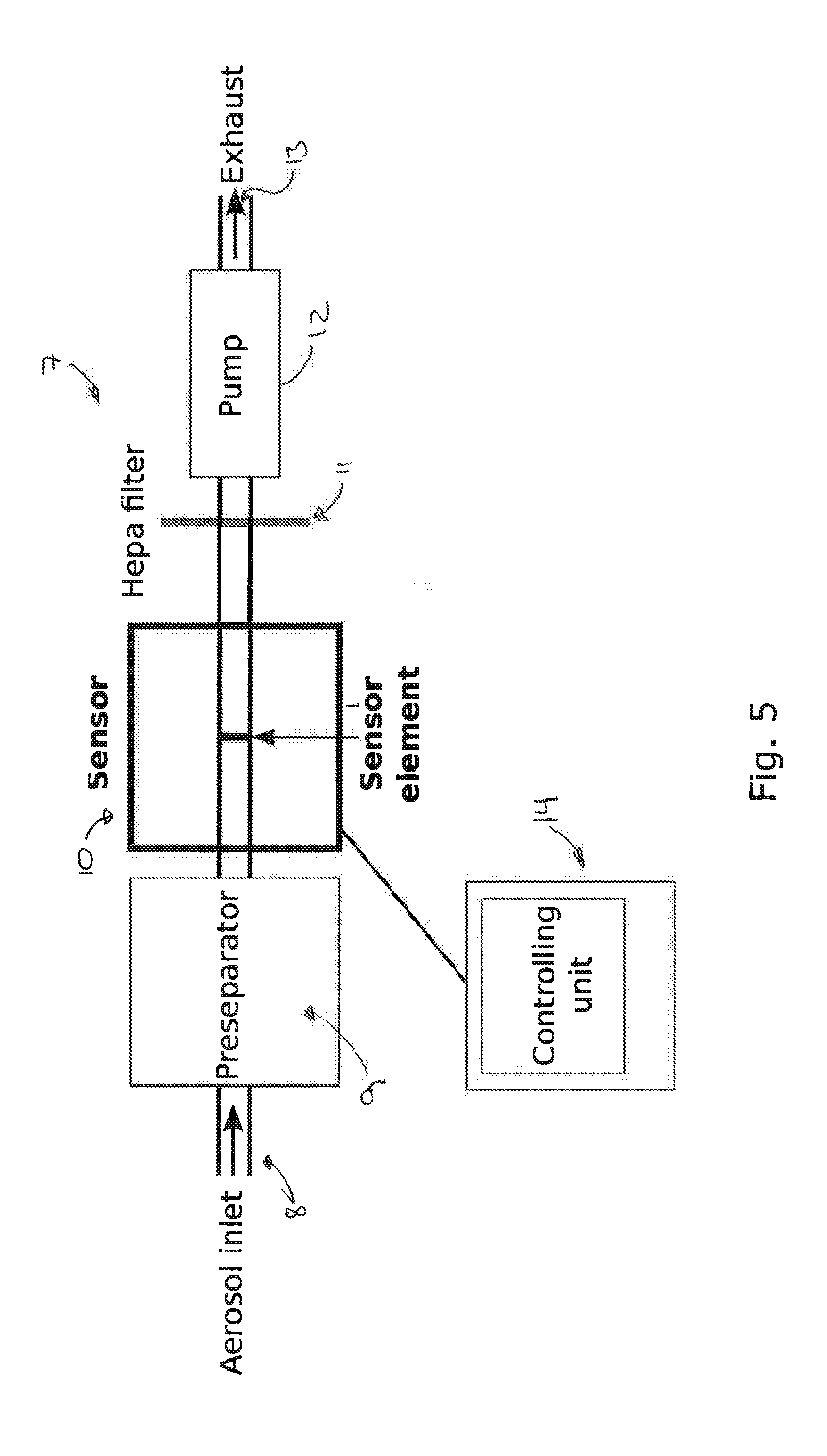
Hand-held trace vapor/particle sampling system
A sampling system that contains filter components for collecting and concentrating vapor and particles in high-volume flows. The sample is then vaporized and delivered to a detector at a low-volume flow. The invention also has a sampling probe that contains an air-jet to help dislodge particles from surfaces and a heating lamp to help vaporize compounds on surfaces or objects. The sampling system is especially useful for screening for explosives and other illicit chemicals and toxins on people, baggage, cargo, and other objects.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Mass sensor and mass sensing method
InactiveUS6326563B1Force measurement by measuring frquency variationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas phaseCompound (substance)
A mass sensor includes a diaphragm, a sensing plate having a piezoelectric element arranged on at least a part of at least one surface joining respective sides, a connecting plate sandwiched by the diaphragm and the sensing plate, wherein the diaphragm, the sensing plate, the piezoelectric element, and the connecting plate form a resonating portion. The connecting plate is bridged across the side surfaces of a concave portion formed in a sensor substrate, and the sensing plate is joined to at least the bottom portion of the concave portion. Change in the mass of the diaphragm is measured by measuring change in the resonant frequencies of the resonating portion accompanying the change in the mass of the diaphragm. The mass sensor enables the easy and accurate measurement of a minute mass of a nanogram order including microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses, or chemical substances, or the thickness of vapor-deposited films.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
QCM sensor and QCM sensor device
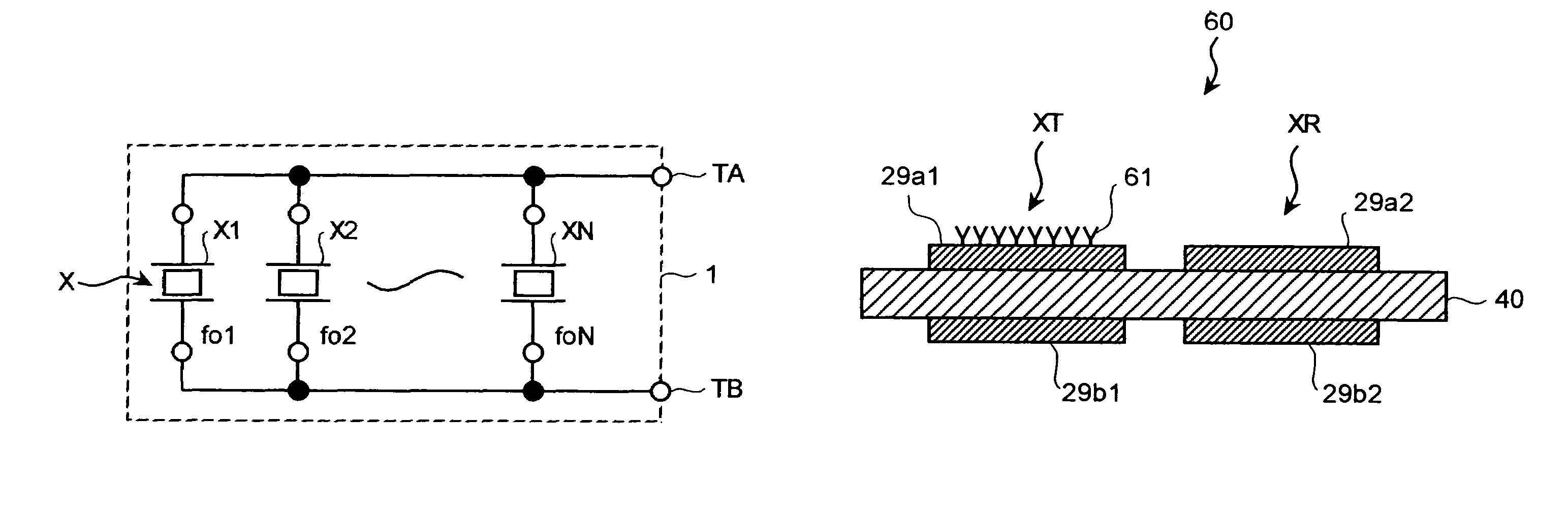
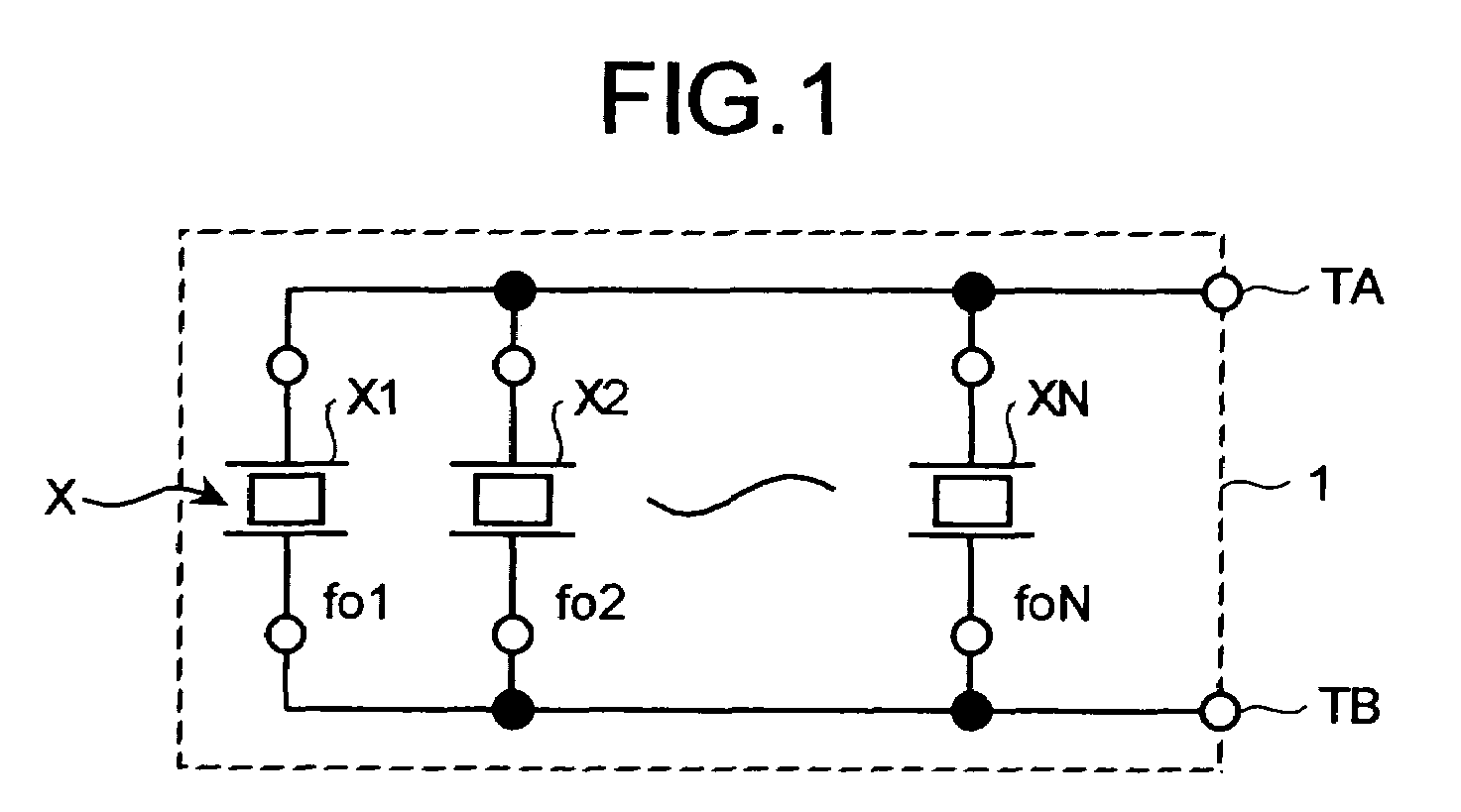
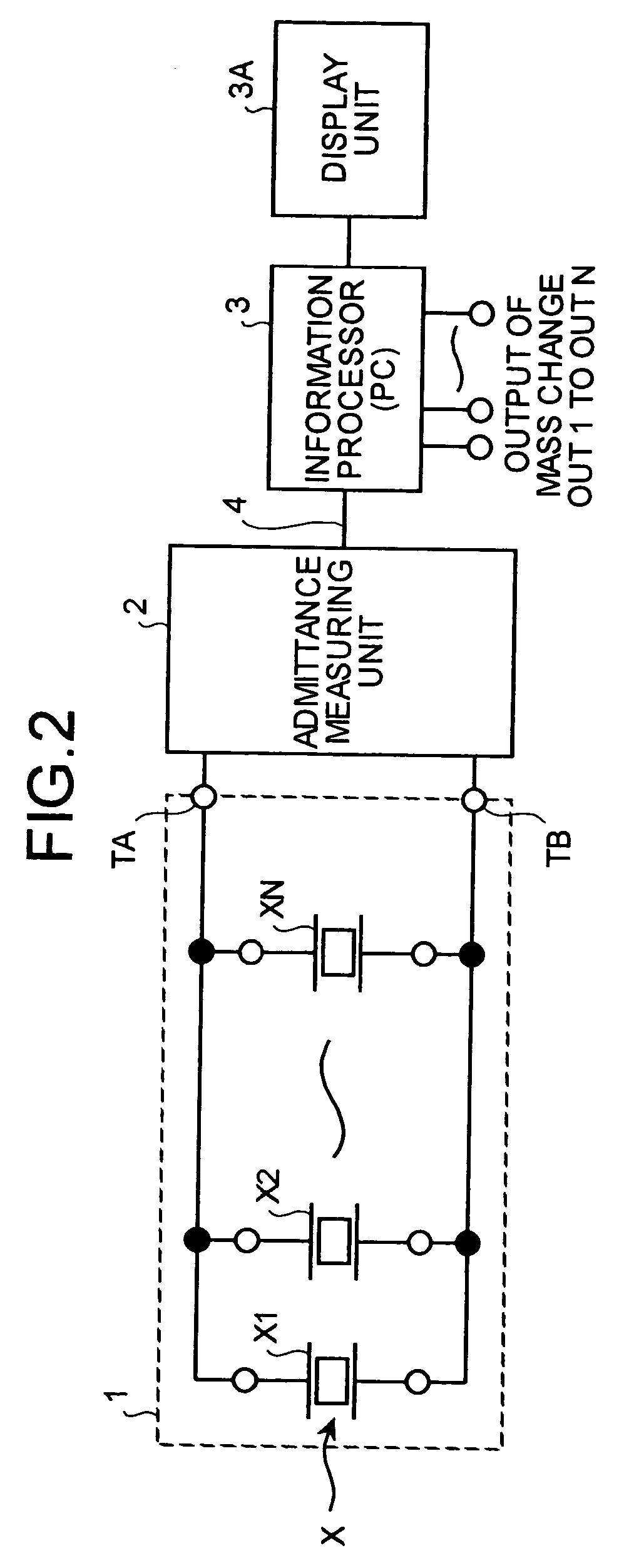
ActiveUS7036375B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesQuartz crystal resonatorResonance
A plurality of quartz crystal resonators having different resonance frequencies are connected in parallel. A combined admittance of the resonators is measured. Equivalent circuit constants of all the resonators are obtained by a method of least squares from admittance characteristics. A change in the resonance frequency is measured and mass of a substance adsorbed to a piezoelectric transducer is calculated.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Method for correcting weight measurement errors during microwave heating
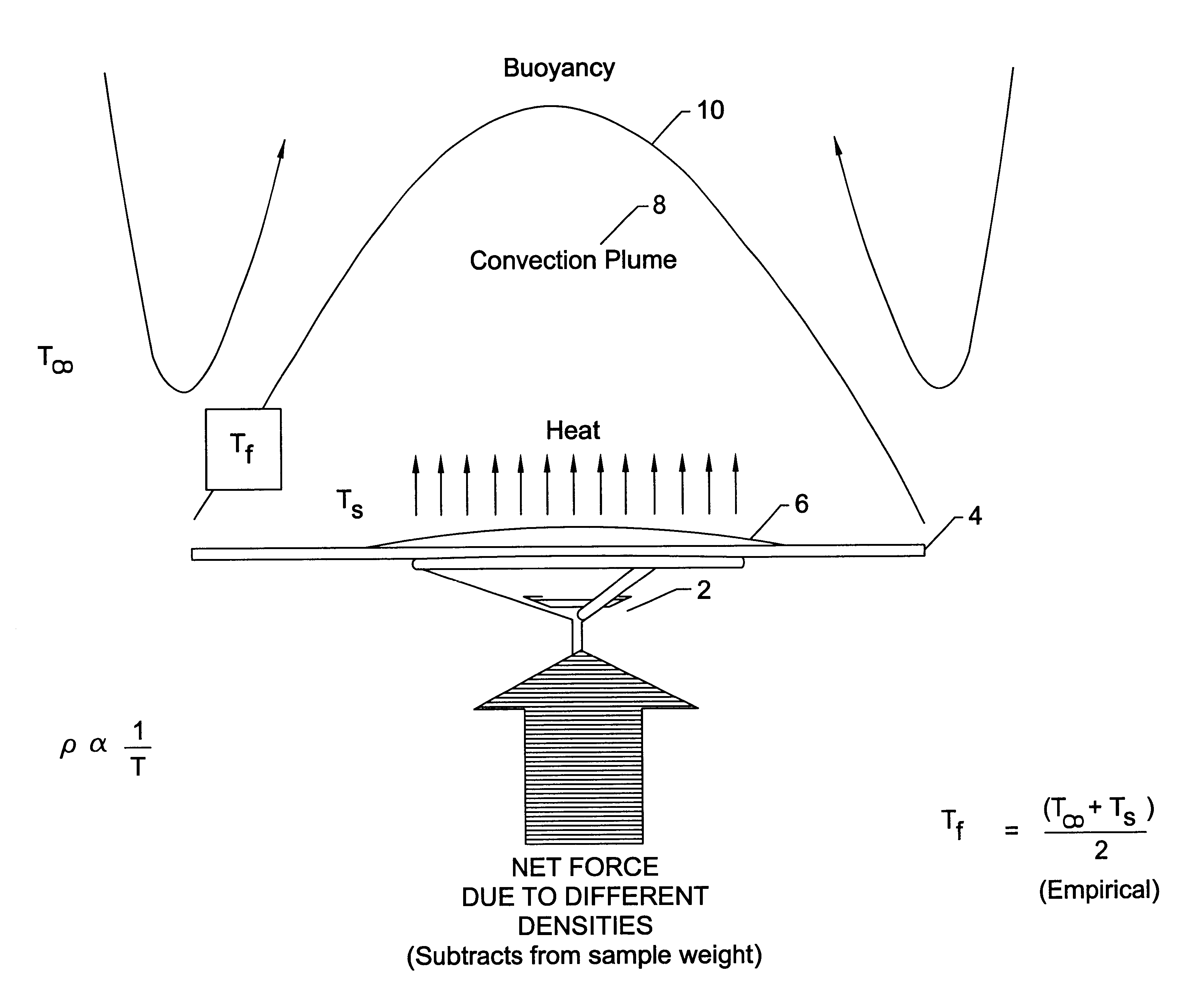
InactiveUS6268570B1Accurate sample weight measurementAccurate weighingWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationMaterial moisture contentObservational errorMicrowave
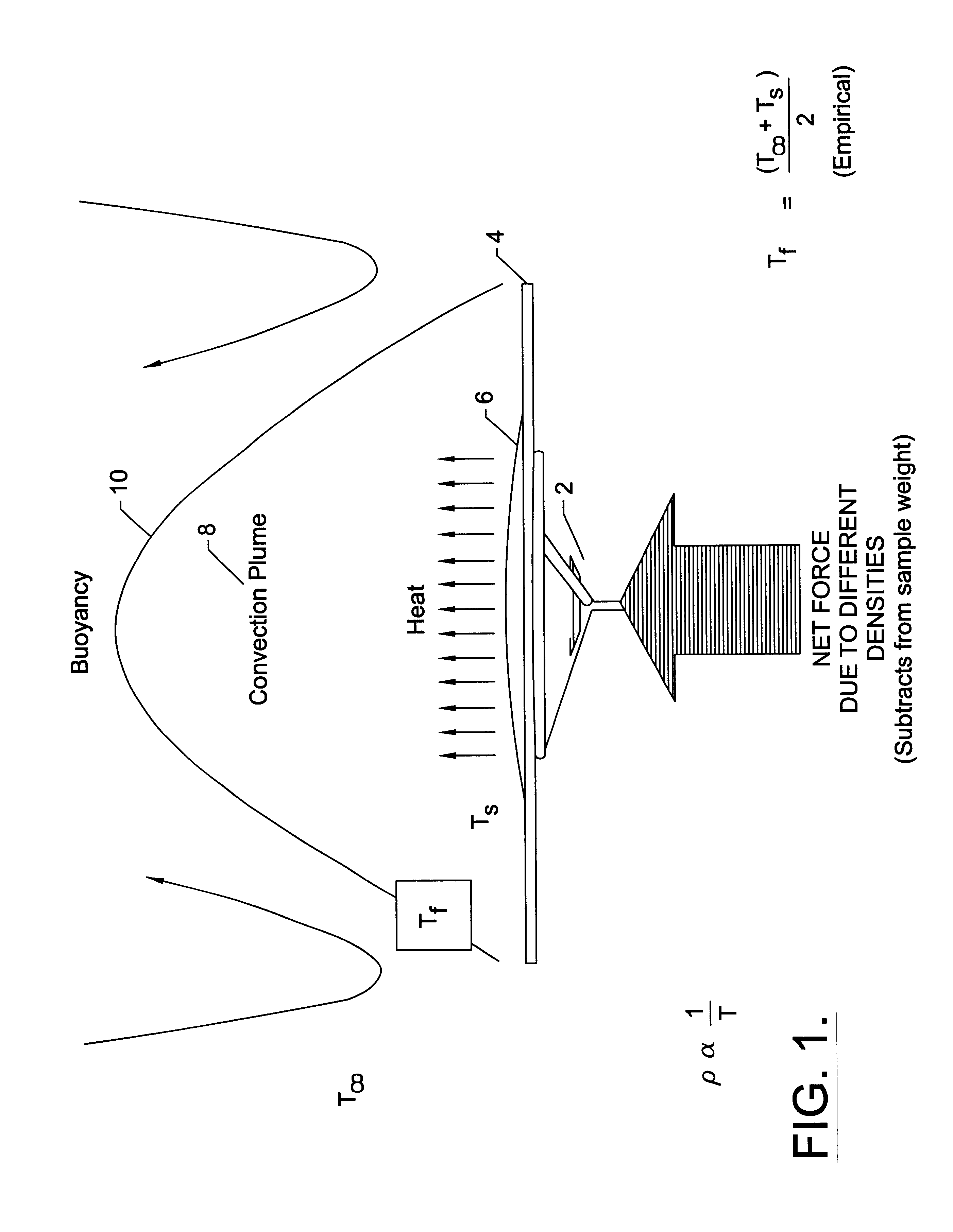
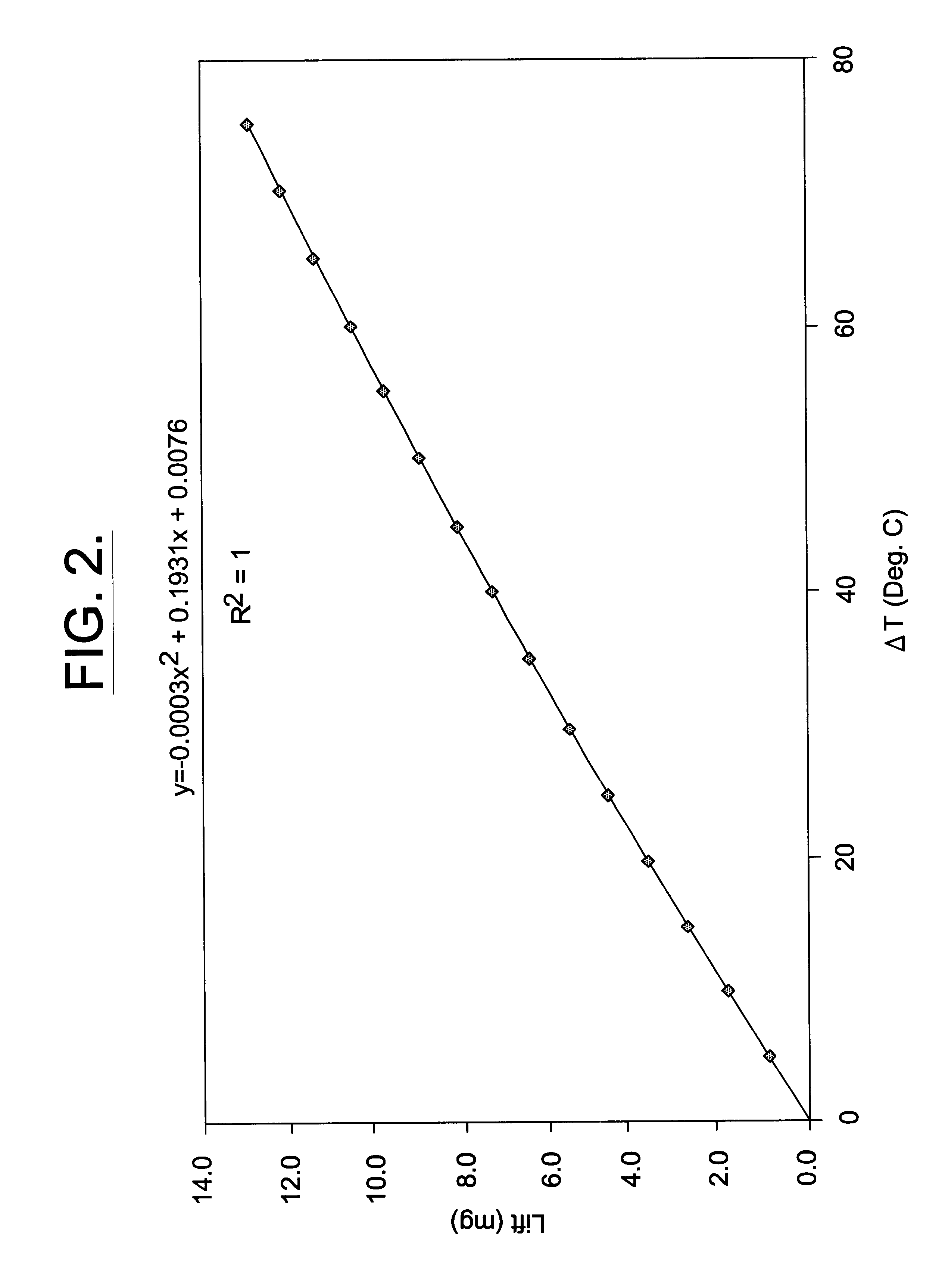
The invention is a method of measuring an apparent weight of a substance, while concurrently measuring a surface temperature of the substance and an ambient air temperature surrounding the substance, then predicting buoyancy forces acting upon the substance based on these temperature measurements. Thereafter, the true weight of the substance can be determined by correcting the apparent weight by the predicted buoyancy forces acting upon the substance.
Owner:CEM CORP
Solar Powered Umbrella Table
A solar umbrella and table apparatus with attached chairs features stand-alone AC power, generated from solar energy. The apparatus features an umbrella having solar collection devices and a table with attached seating chairs. The electrical system of the apparatus converts collected solar energy to an electrical voltage. Batteries store the energy provided by the solar panels. Inverters convert the DC voltage output from the storage batteries to 120 volts AC. Power outlet terminals are located on the umbrella and table apparatus allow 120 volts AC powered devices to access the output of the sine wave power inverters.
Owner:PORTIS JR MATTHEW N +1
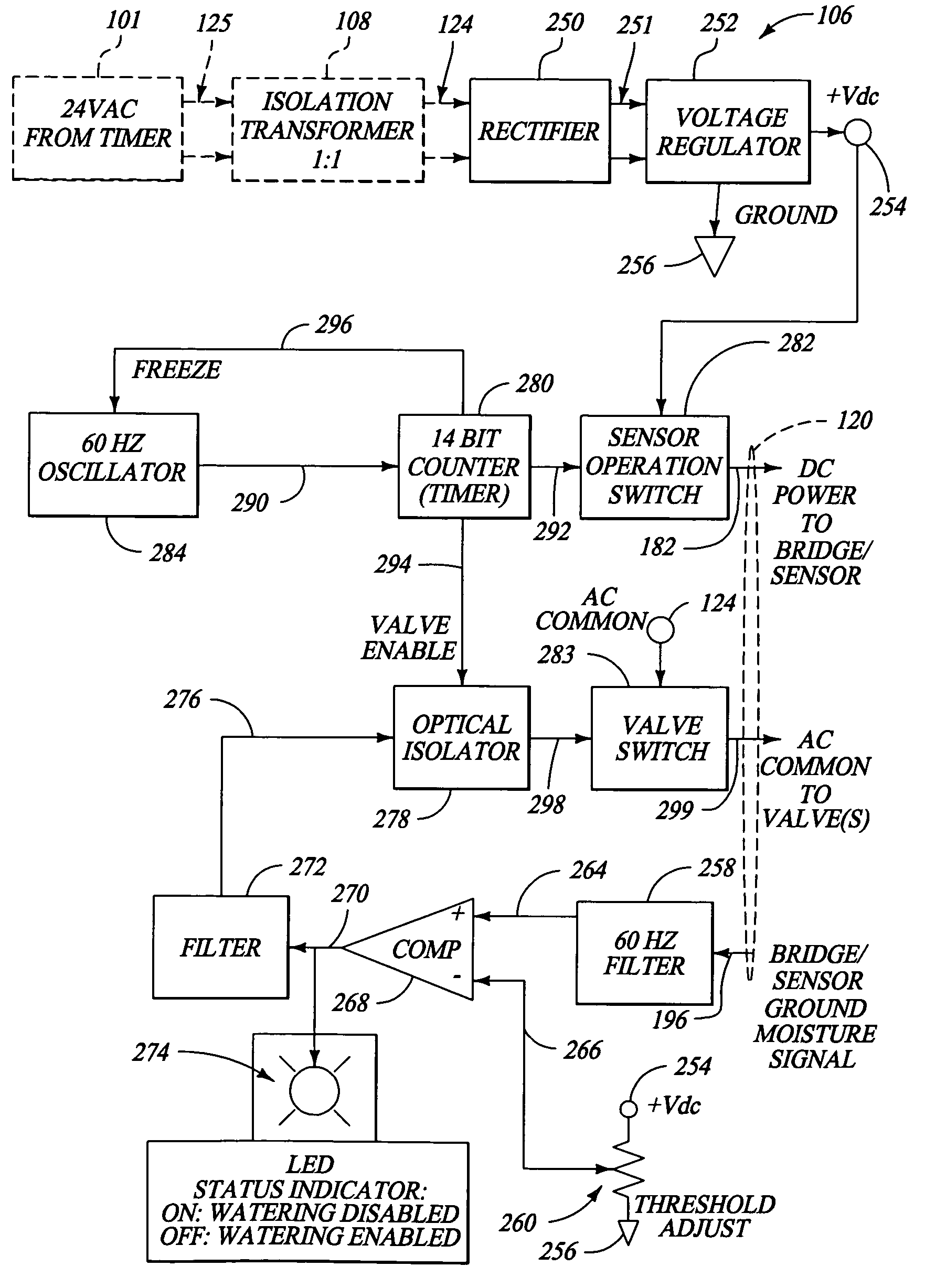
Apparatus and method to detect moisture
ActiveUS6906530B2Accurate and practicalResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingEngineeringElectric conductance
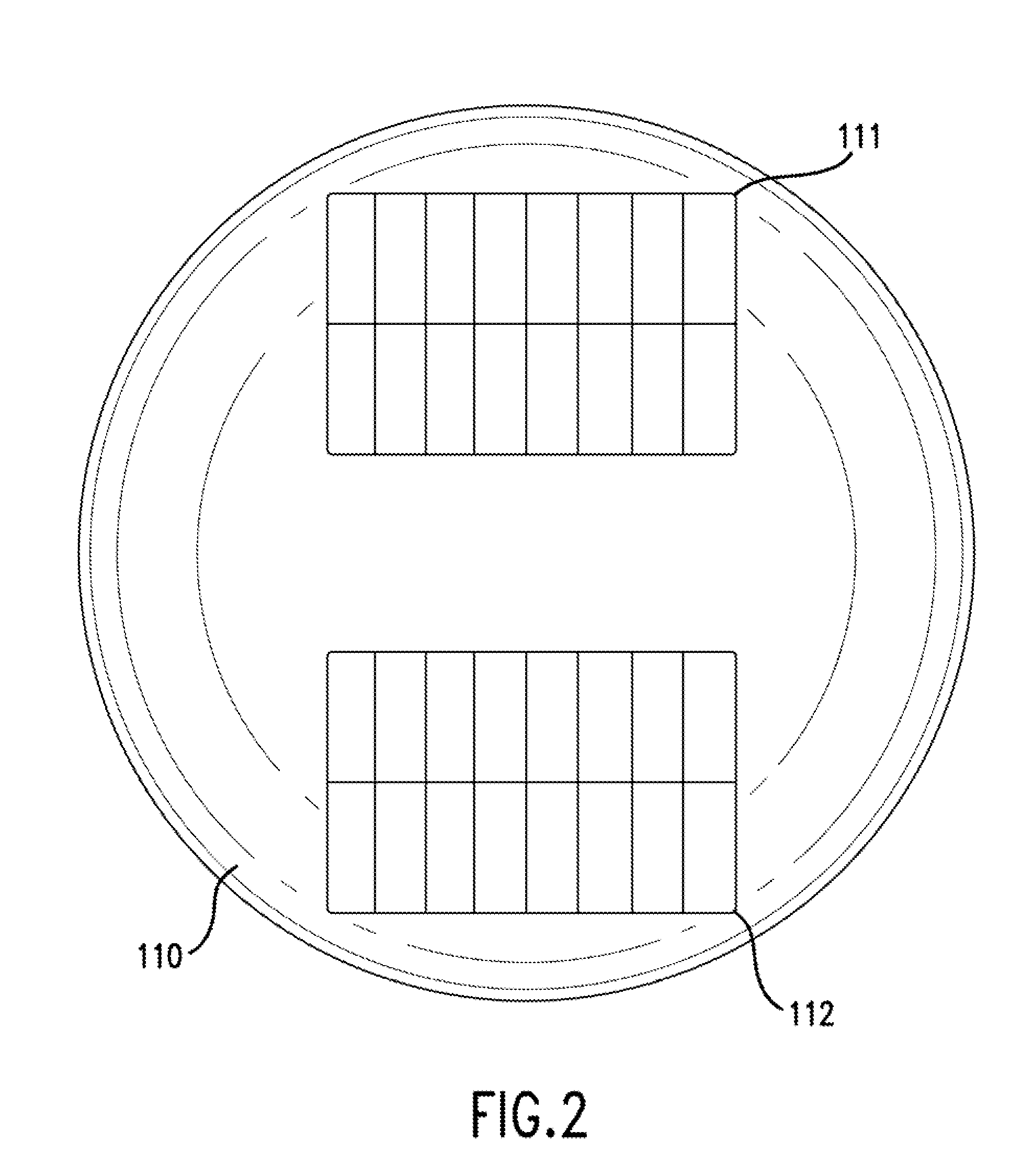
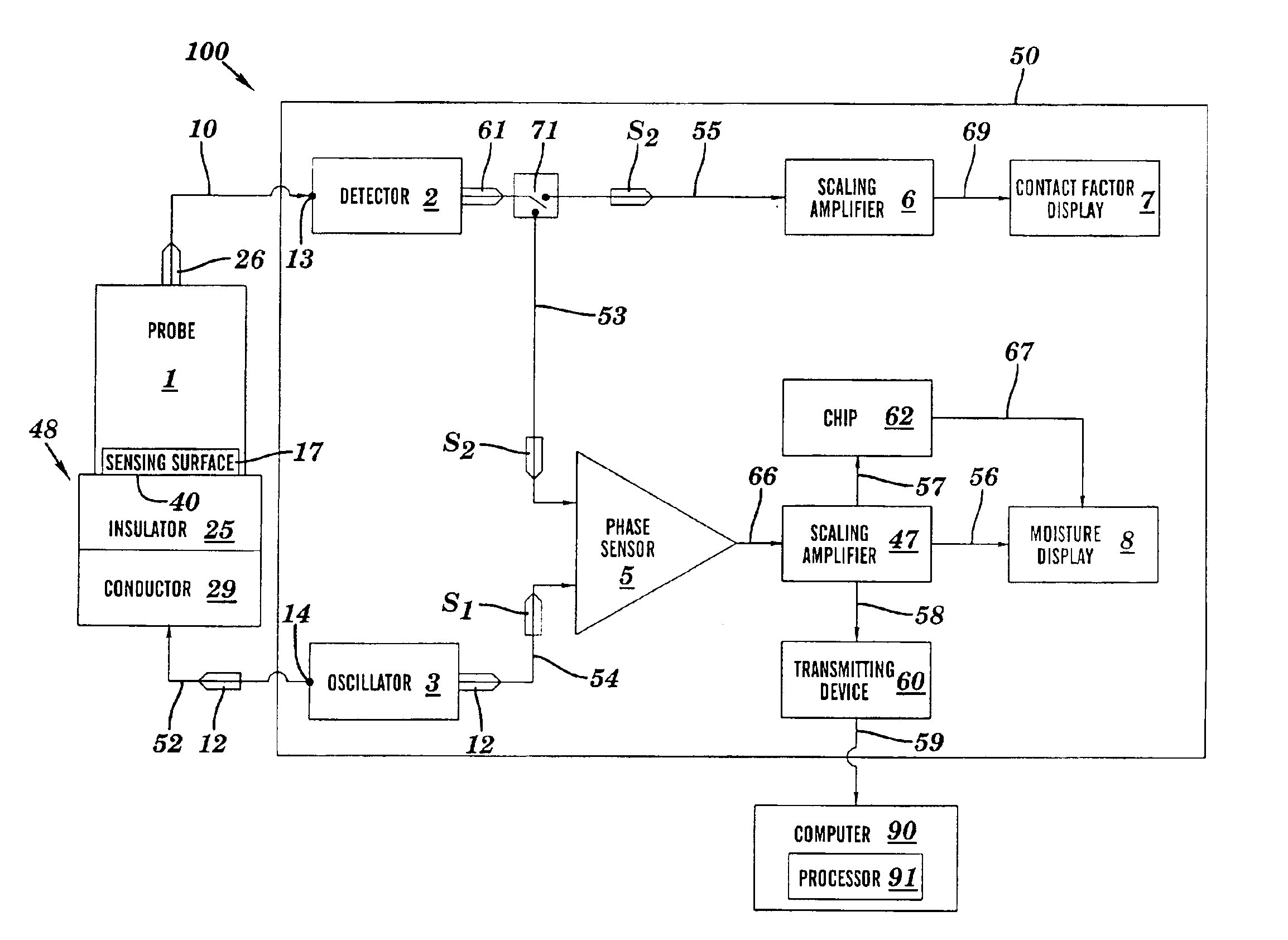
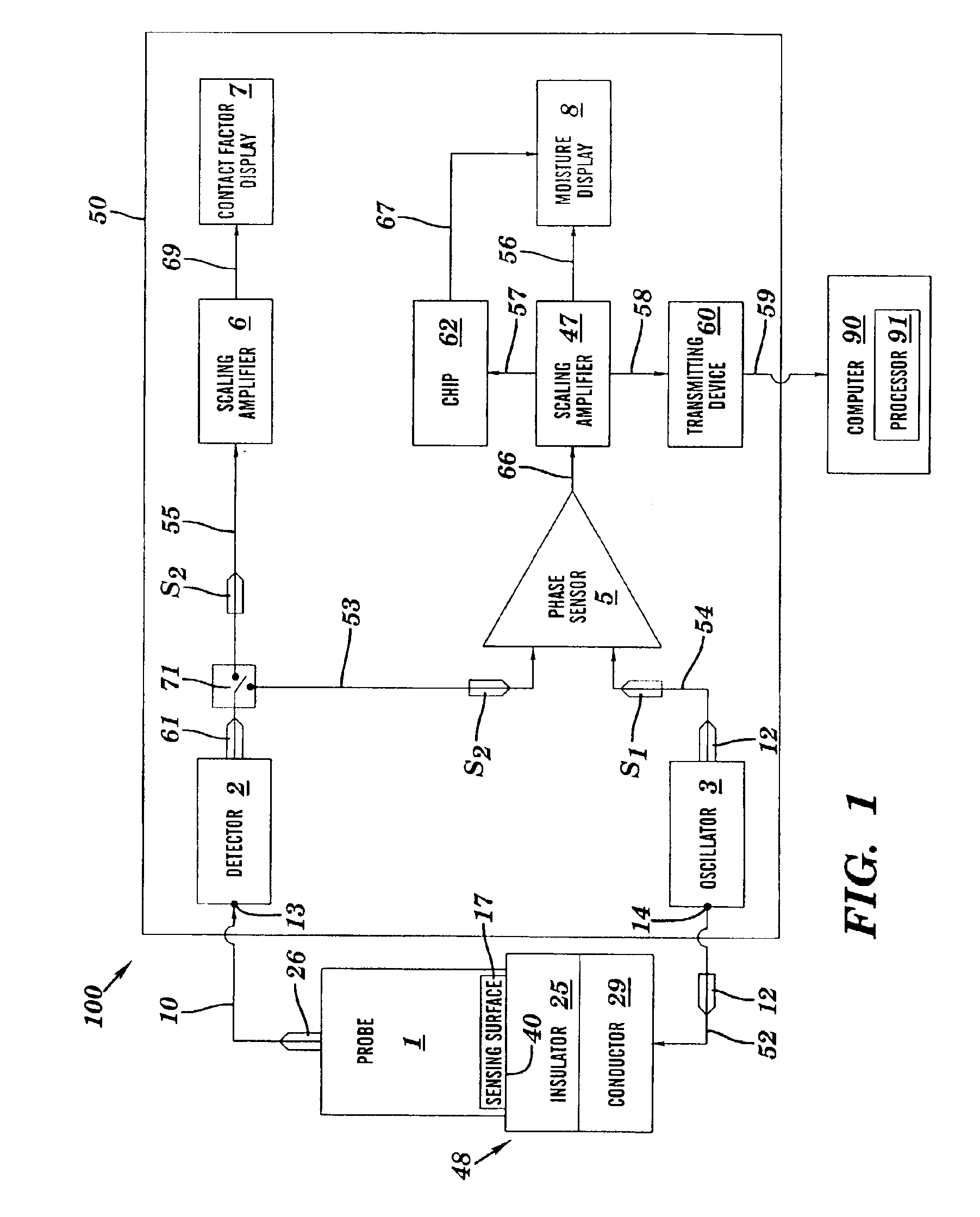
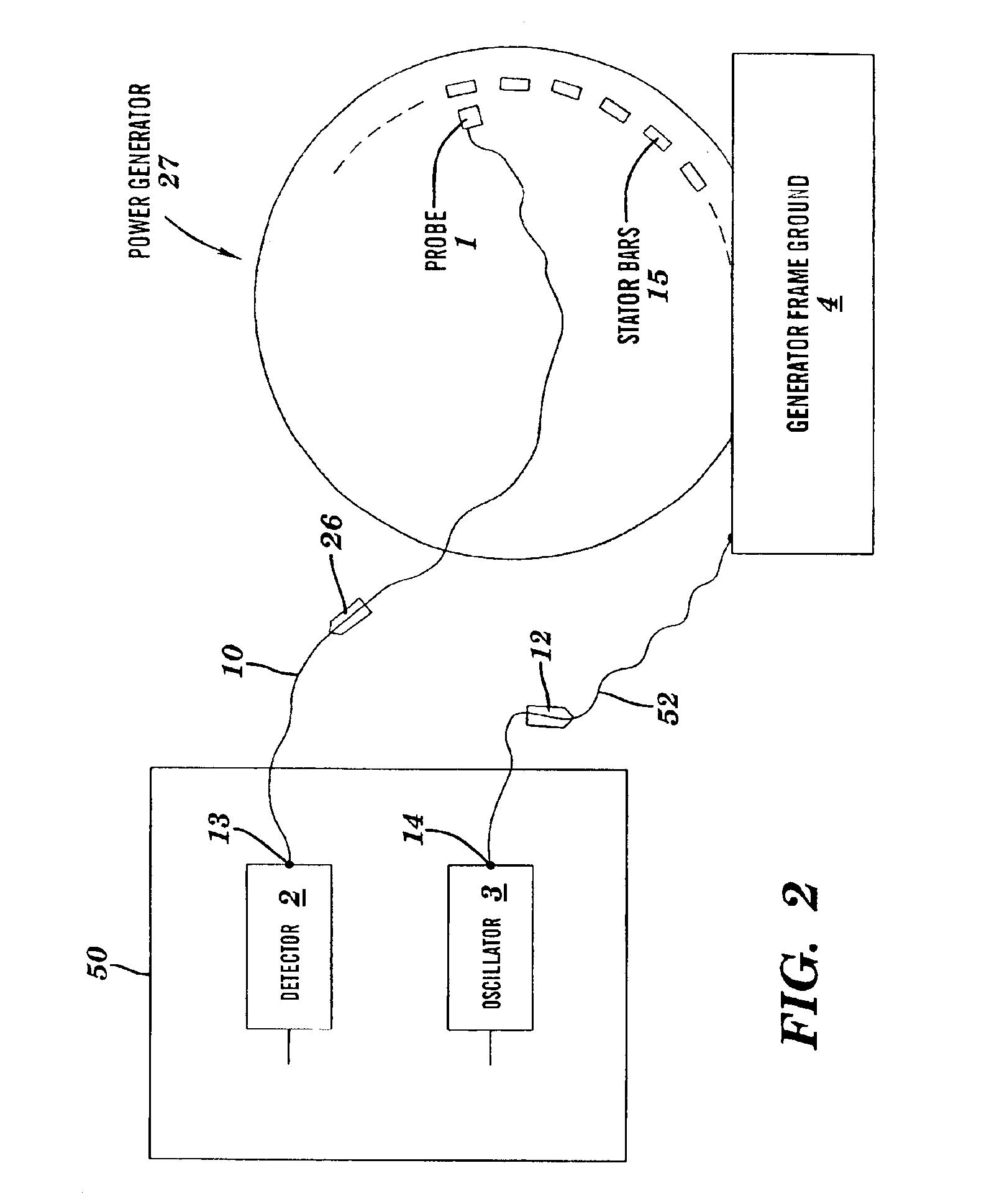
A method and apparatus for detecting moisture. An oscillatory electrical signal S1 generated by an oscillator is propagated into a body that includes an electrically insulative material. A signal due to S1 emerges from the body as an oscillatory electrical signal S2. The signals S1 and S2 differ in phase by Δφ, wherein Δφ is indicative of moisture along a path traversed by S1 within the insulative material, and wherein the conductance σ of the insulative material is also indicative of the moisture along the path traversed by S1 within the insulative material. S2 is received at a sensing surface of a sensing part (e.g., probe, sensing antenna, etc.) and then transmitted to a moisture detecting device. The moisture detecting device determines from S1 and S2 a measure M of the moisture as a function of Δφ or as a function of σ.
Owner:D J GEISEL TECH INC 50 +1
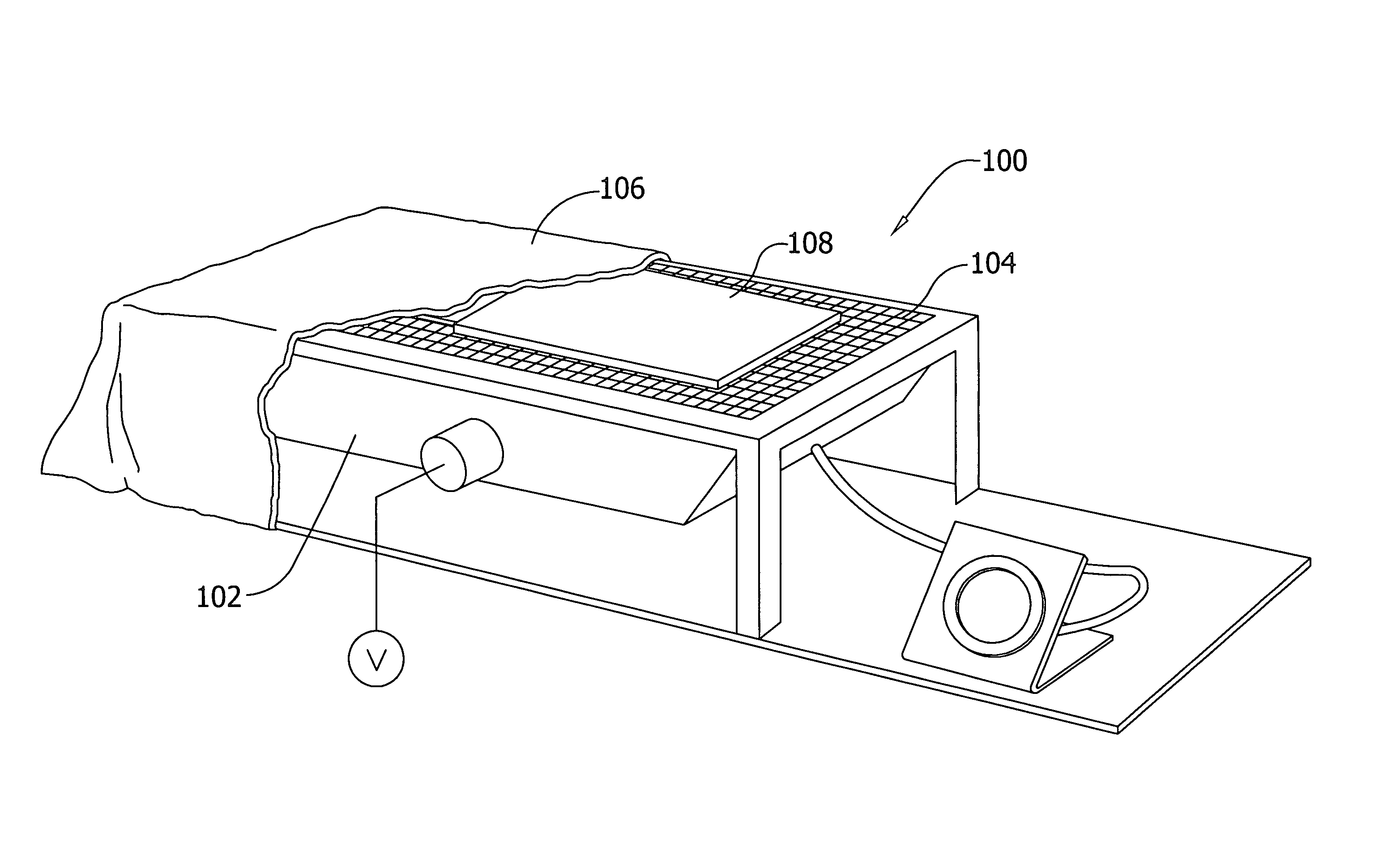
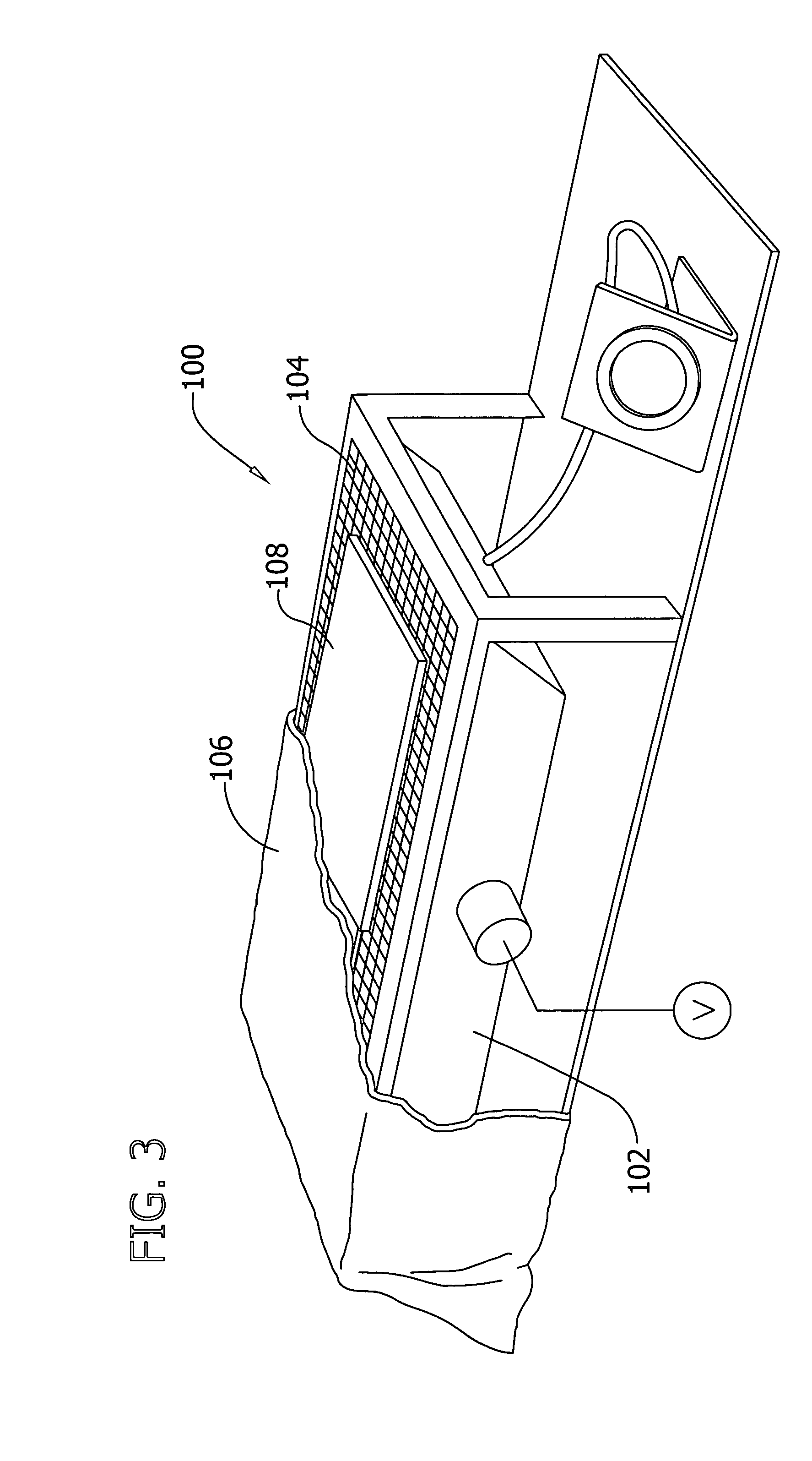
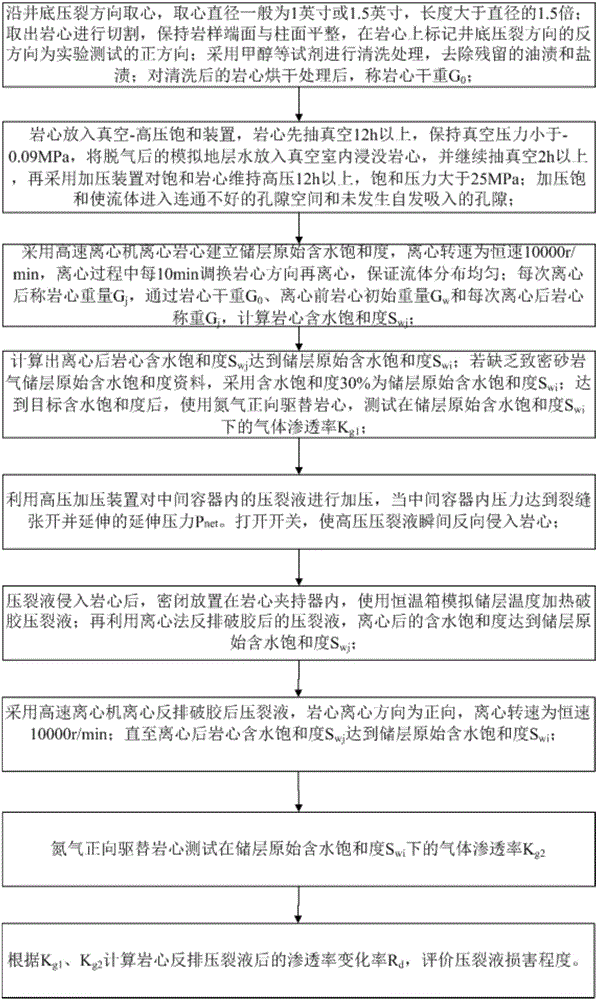
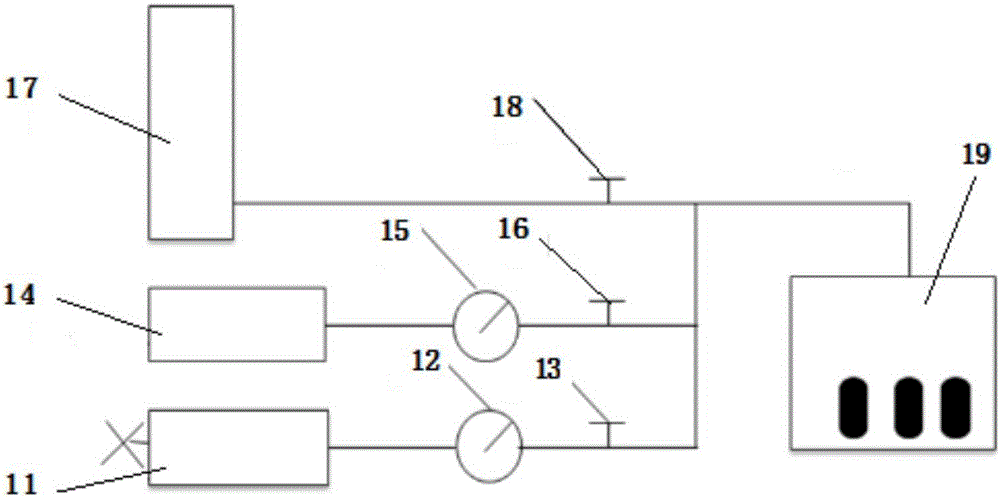
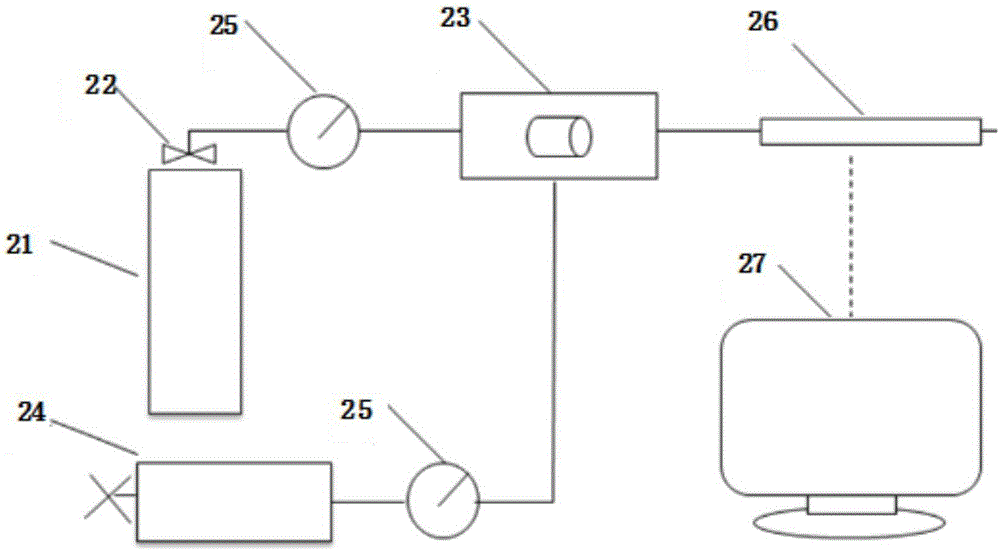
Tight sandstone gas reservoir fracturing fluid damage experimental evaluation method
InactiveCN106153518AConforms to seepage characteristicsExperimental test pressure is smallPermeability/surface area analysisWeighing by absorbing componentRock coreFracturing fluid
The invention belongs to the field of oil-gas field development and relates to an experimental evaluation method for fracturing fluid damage in an unconventional tight sandstone oil-gas exploration and development process. The method includes: subjecting fracturing fluid to high-pressure instant reverse injection into a rock core, and simulating flow invasion damages of fracturing fluid in cracks in a continuous extension process after a stratum is fractured by the fracturing fluid; adopting a high-speed centrifuge to set up original water saturation of a reservoir; under the condition of the original water saturation of the reservoir, adopting nitrogen for testing permeability before and after injection of the fracturing fluid into the rock core, and judging fracturing fluid damage degrees according to gas log permeability change rate. By complete simulation of a fracturing fluid injection mode in a fracturing process, adoption of nitrogen for testing permeability accords with seepage characteristics of the tight sandstone gas reservoir, and defects of high experimental displacement pressure, long displacement time, large experimental data errors and the like are avoided.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
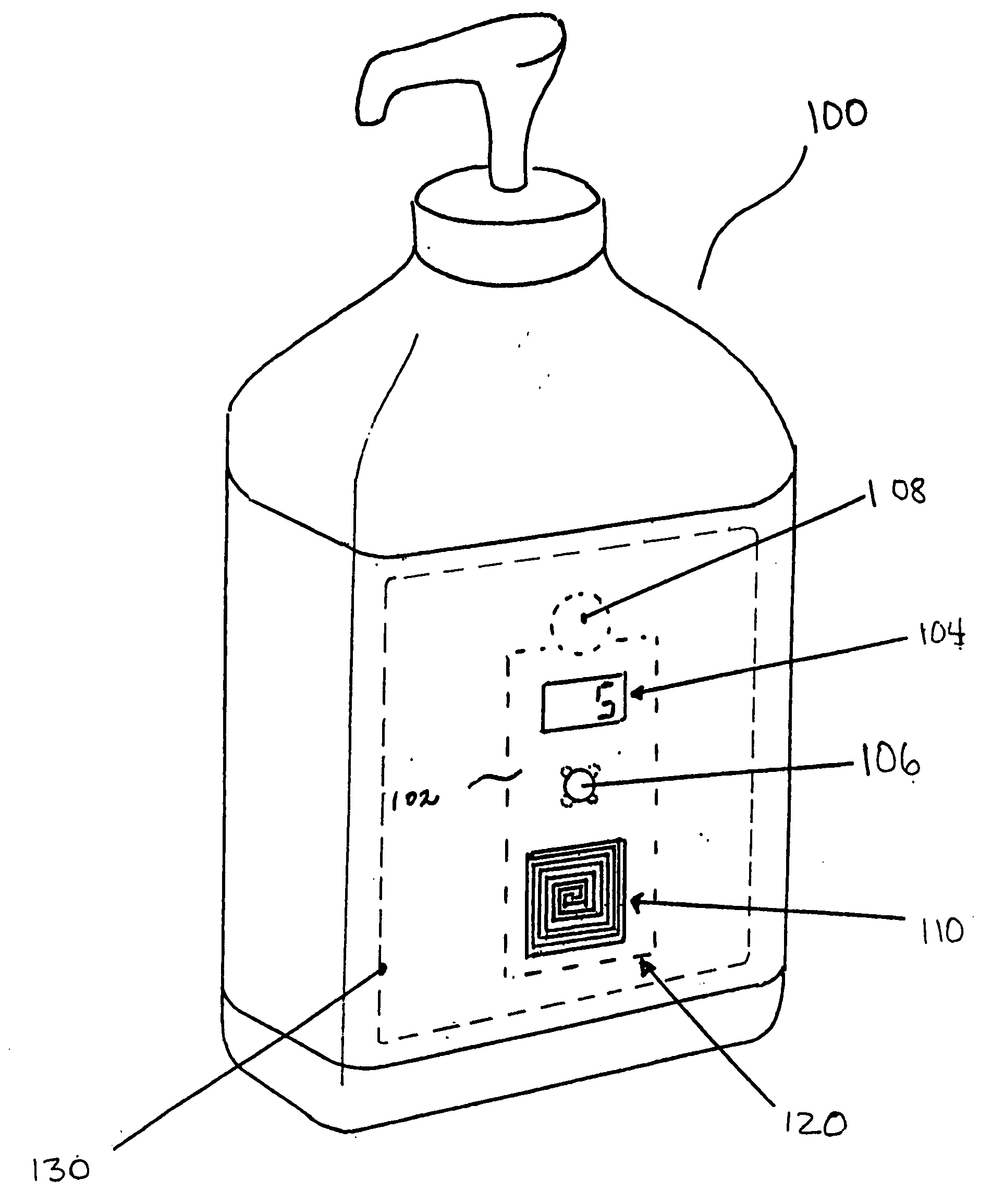
Irreversible humidity indicator cards
An irreversible humidity indicator card comprising an intermediate carrier member containing one or more holes, a clear, water vapor permeable first outer layer secured to the first side of the carrier member, a deliquescent material contained within the holes in the carrier member, a dark colored, absorbent sheet material secured to the back side of the carrier member to cover the holes in the carrier member and a second outer layer which covers the colored absorbent sheet material and a portion or all of the back side of the intermediate carrier member.
Owner:SUD CHEM PERFORMANCE PACKAGING
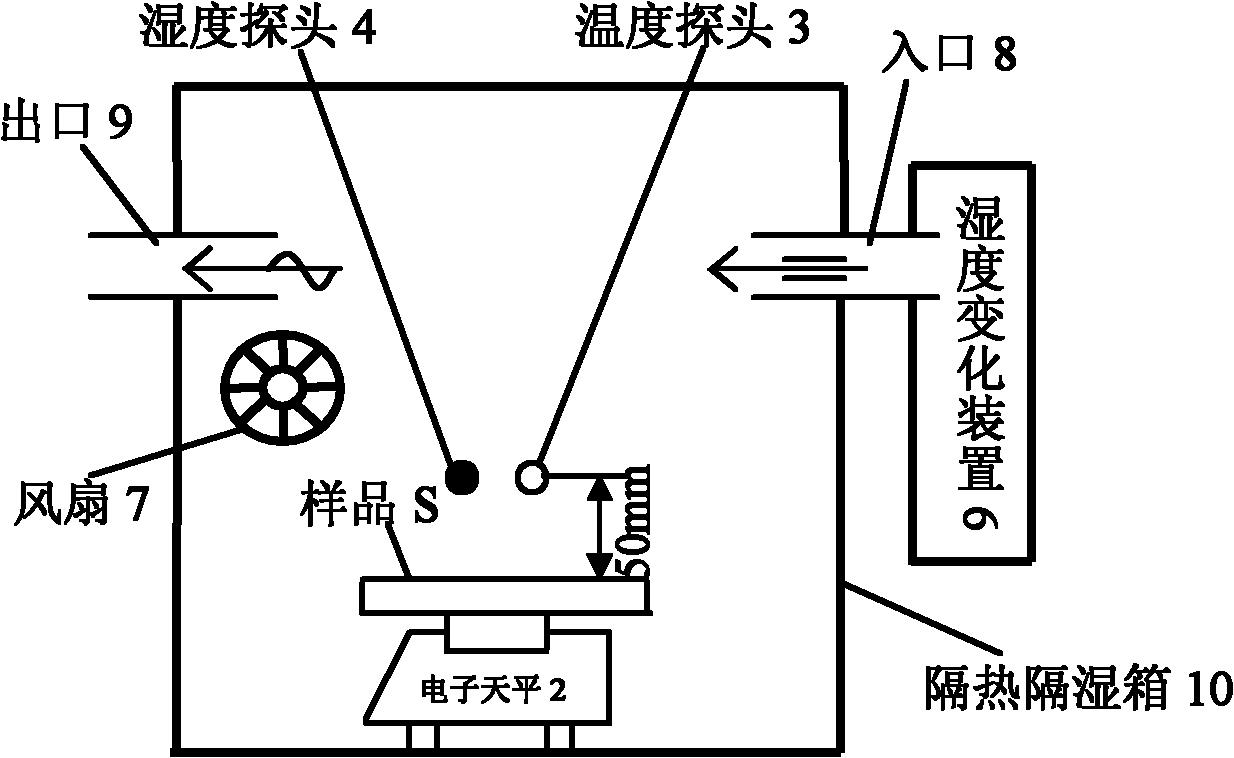
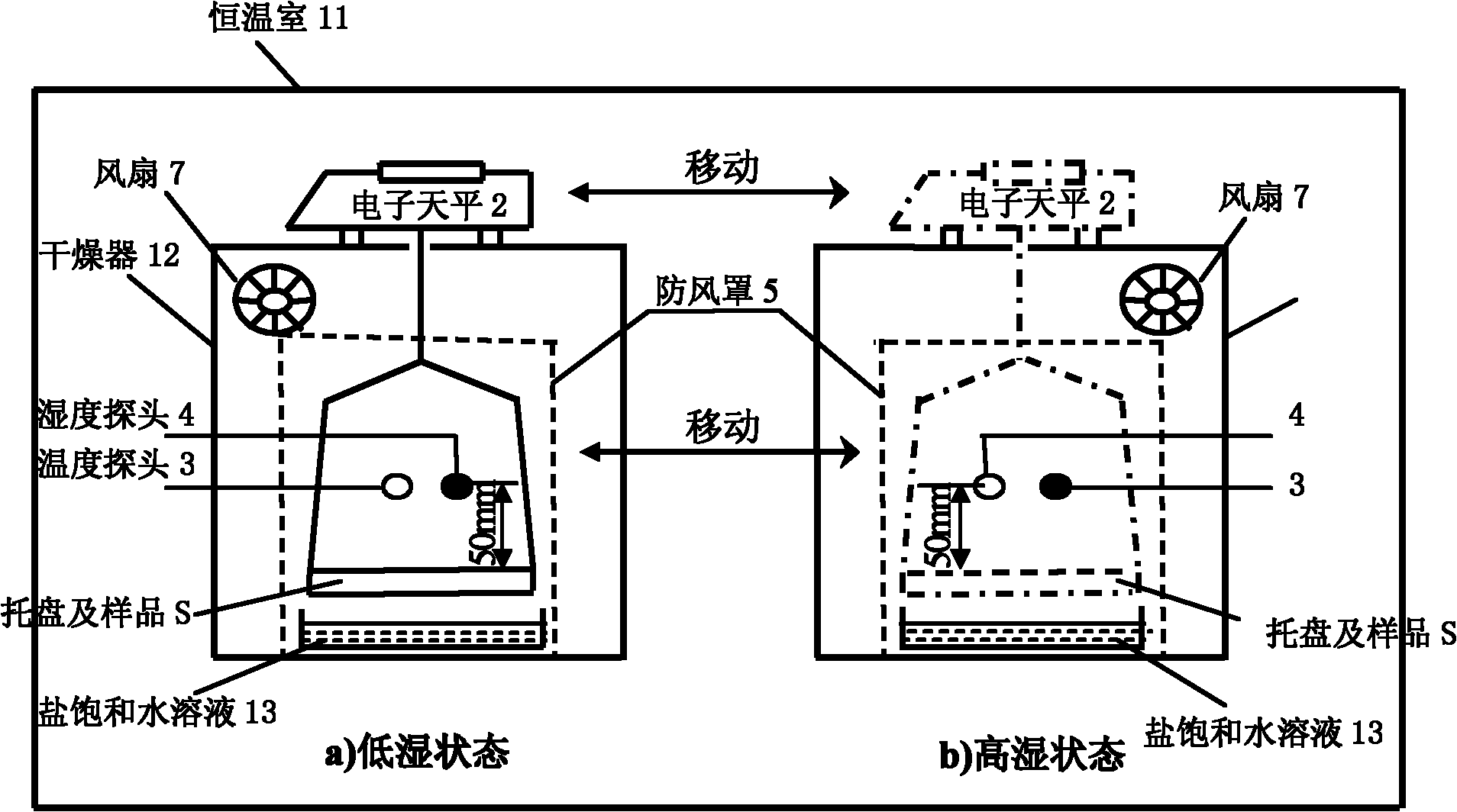
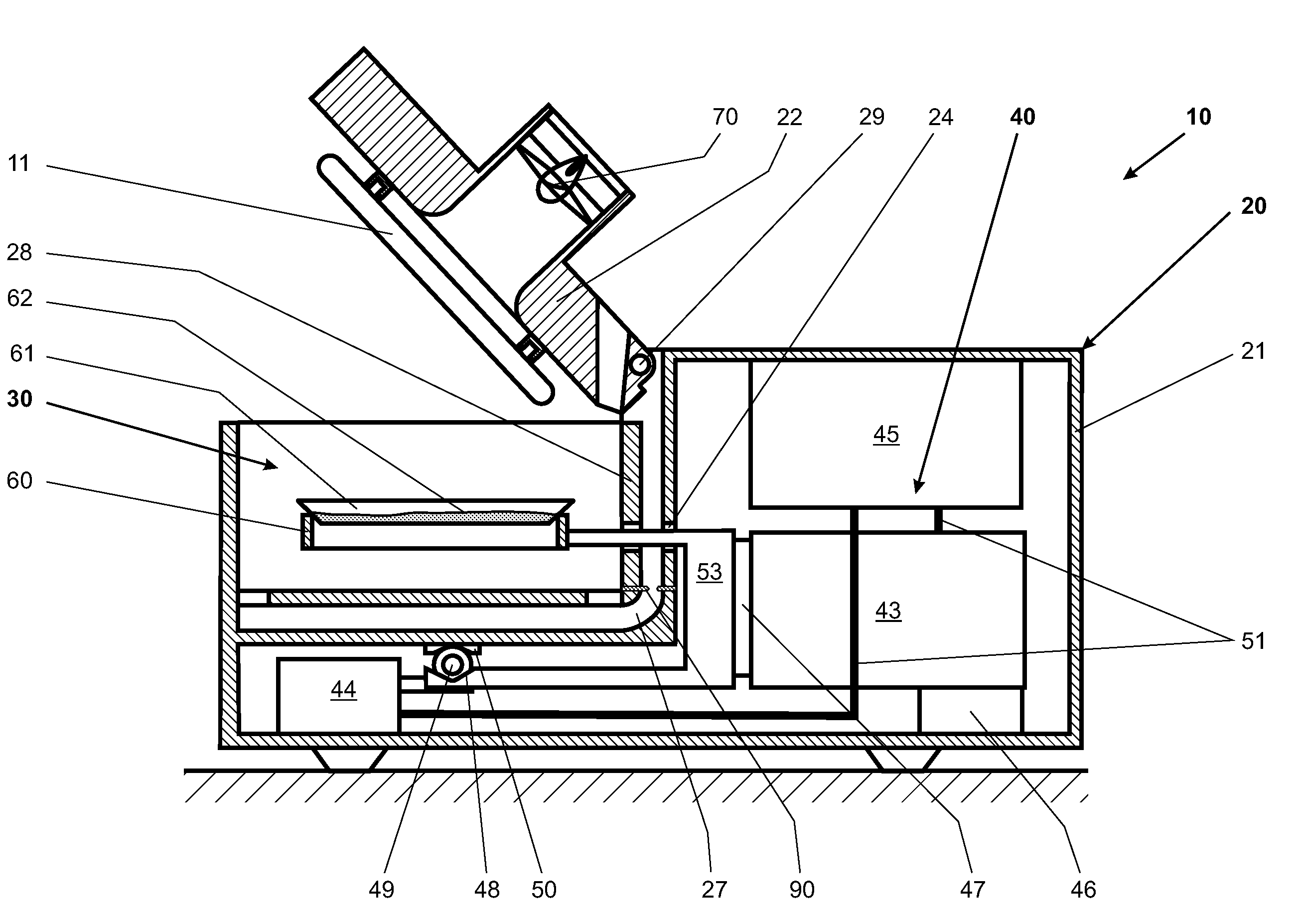
Performance testing equipment for humidifying function material and testing method
ActiveCN102252932AAccurate humidity controlImprove stabilityWeighing by removing componentWeighing by absorbing componentSaline waterEngineering
The invention discloses performance testing equipment for a humidifying function material and a testing method. The equipment disclosed by the invention comprises a relative humidity control part, a weighing part and a temperature and humidity monitoring part, wherein the relative humidity control part is a mechanical constant temperature cabinet system, a humidity change equipment system or a saturated saline water solution system and is provided with a closed space with adjustable temperature and humidity; a temperature probe and a humidity probe of the weighing part and the temperature andhumidity monitoring part are arranged in the closed space; the weighing part is an electronic balance; and the electronic balance, the temperature probe and the humidity probe are connected with a computer which is arranged outside the closed space. By means of different temperature and humidity control modes, the humidity absorption and release performances of the material are detected through ahumidity reaction method; the computer records the data of a detection sample which is weighed by the electronic balance in real time; and the humidity absorption and release capabilities of the sample are obtained by computing. The invention can accurately detect the humidifying performance of the material, and a testing result has good stability.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
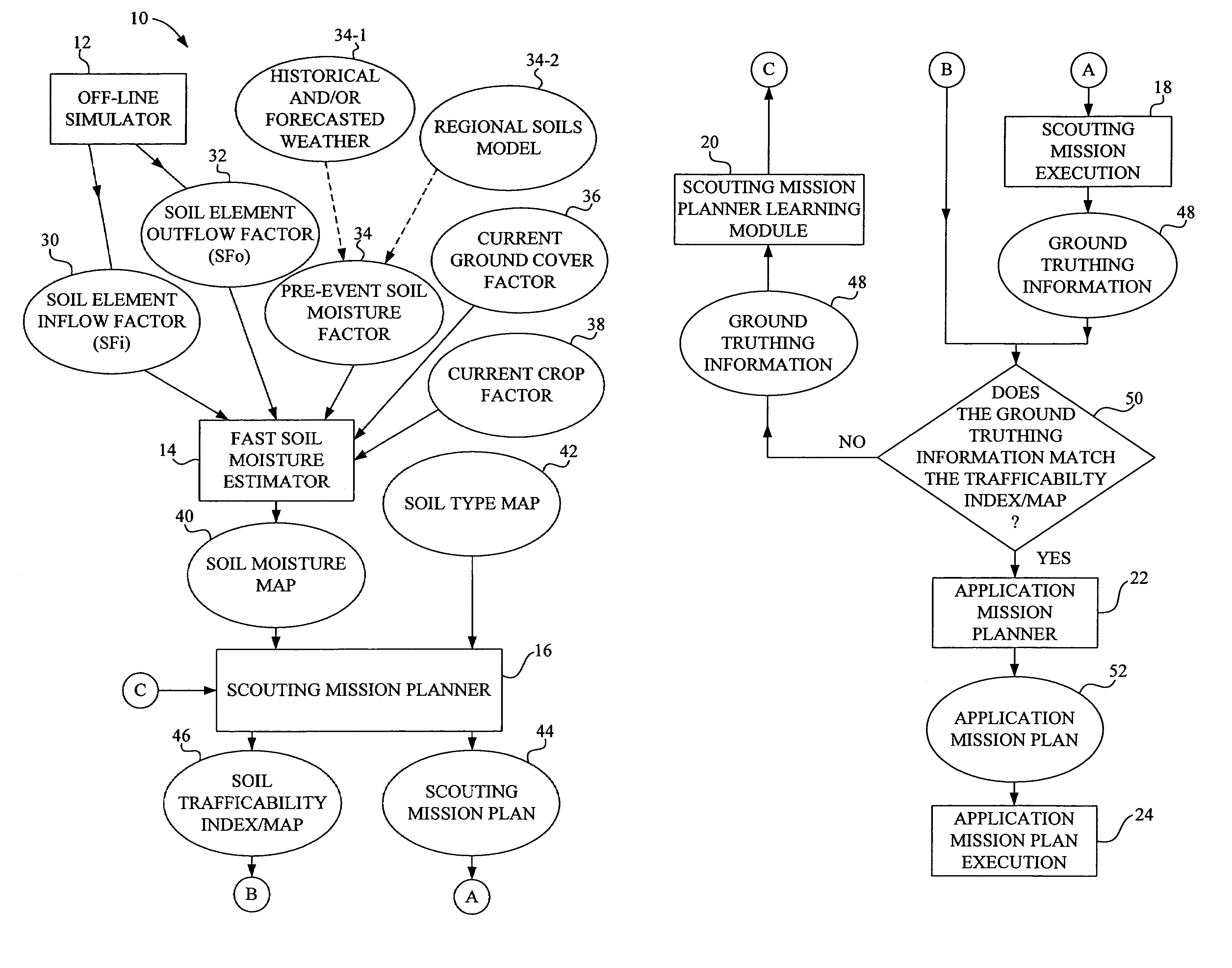
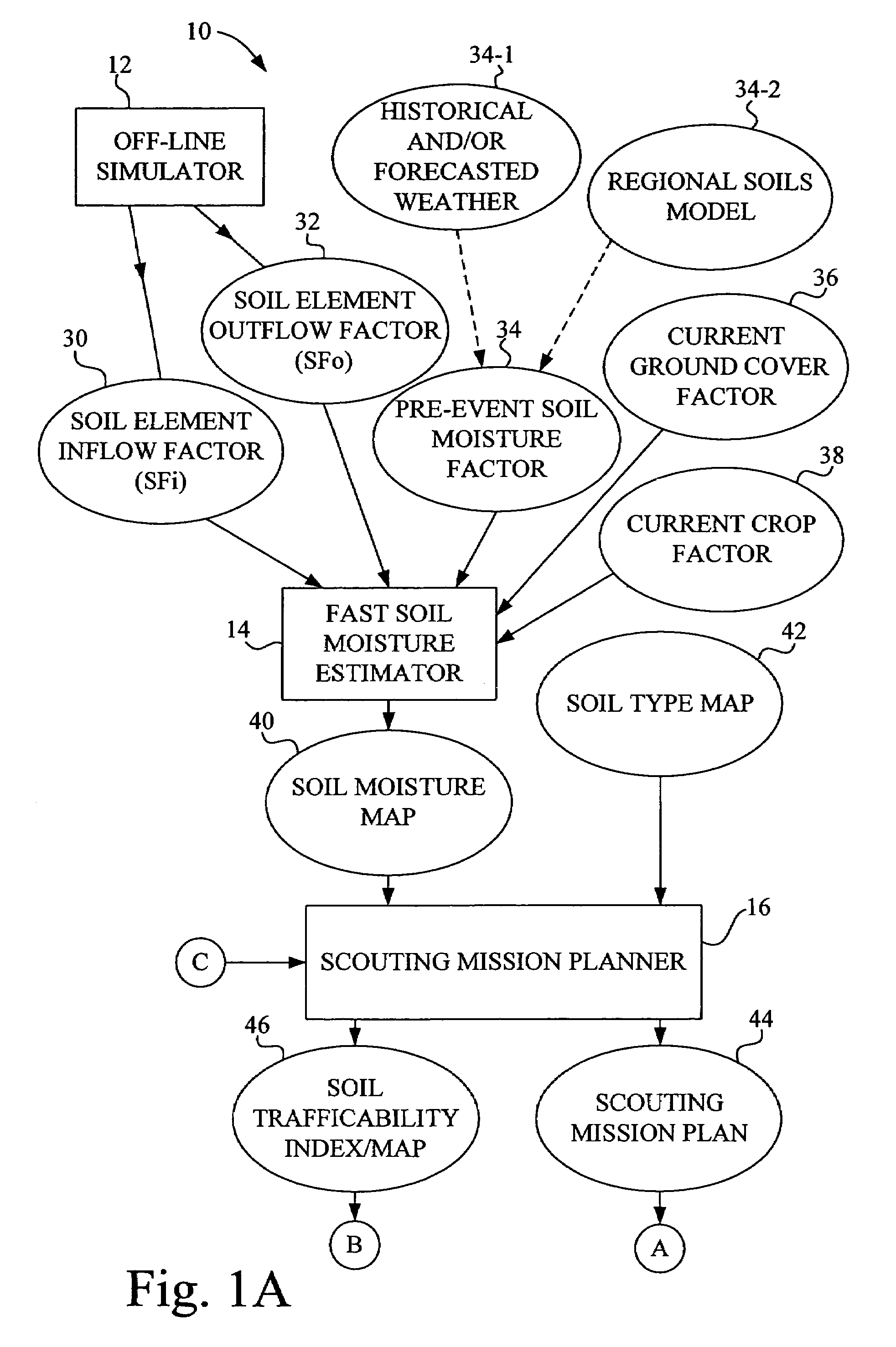
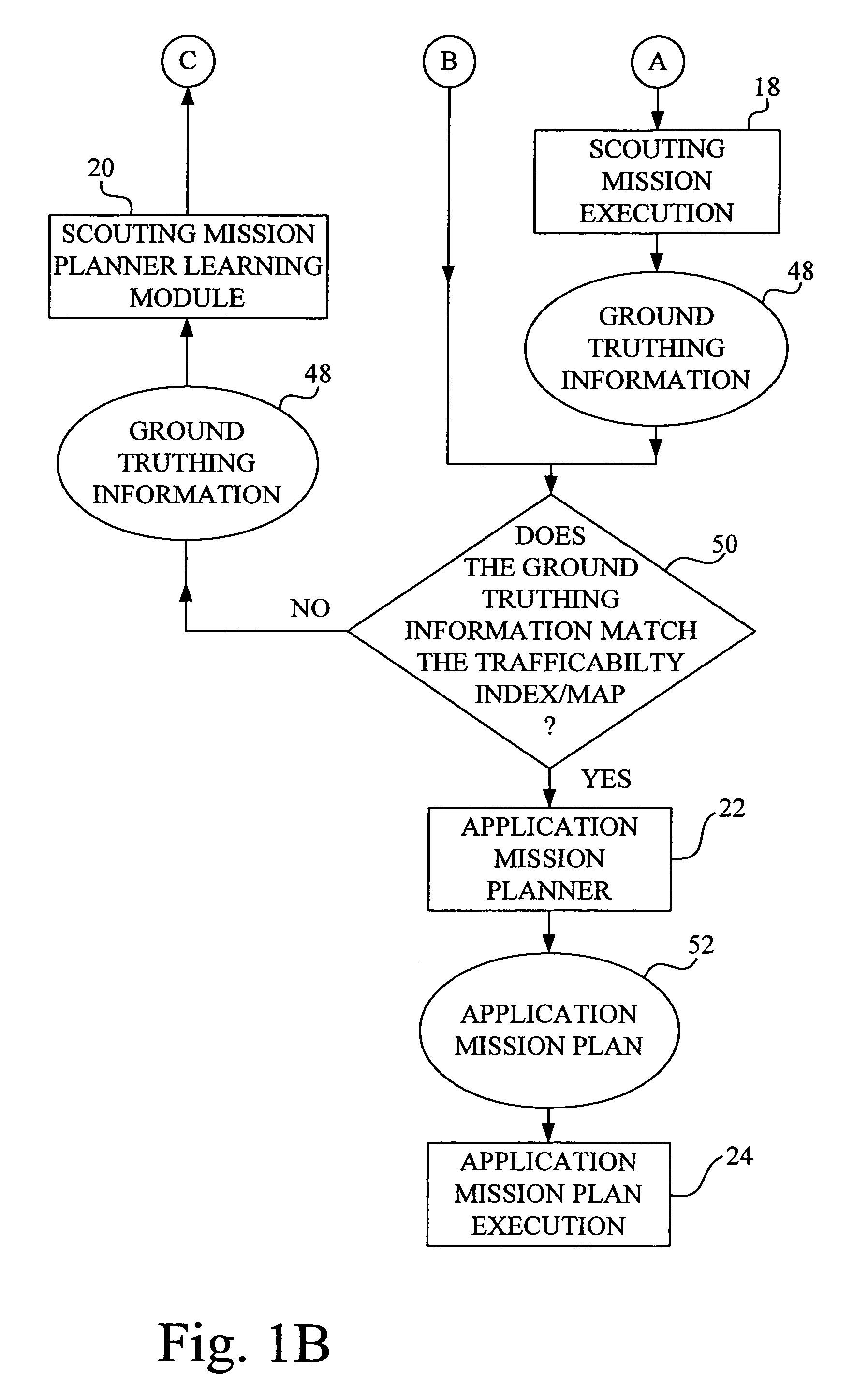
Method for determining field readiness using soil moisture modeling
ActiveUS7313478B1Data processing applicationsMeasurement arrangements for variableField elementSoil moisture content
A method for determining field readiness using moisture modeling of a plurality of fields in a region of interest includes (a) generating a detailed set of moisture factors covering a plurality of scenarios for each field element of the plurality of field elements for a particular field; (b) repeating act (a) for each field of the region of interest; (c) generating a general set of moisture factors for a particular field of the plurality of fields to be applied to each field element of the plurality of field elements in the particular field; (d) repeating act (c) for each field of the plurality of fields in the region of interest; and (e) estimating soil moisture for each field element in the region of interest based on the detailed set of moisture factors and the general set of moisture factors.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Functionalized particles for composite sensors
InactiveUS20050090015A1Low costEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSensor arrayDiffusion
A chemical sensor having a transducer element and a layer of composite material including a polymer matrix and a solid particulate filler disposed in the polymer matrix provides chemical sensors exhibiting improved properties. In particular, the device allows polymer matrix materials to be selected based primarily on diffusion properties, strength, stability and other physical characteristics substantially independent of limitations and compromises that arise when attempting to synthesize polymers having specific types of sensory groups chemically bound to the polymer. The invention also allows greater ability to modify sensor response characteristics by appropriate modification of the particulate filler, whereby a diverse sensor array may be fabricated more easily and at a lower cost.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOLECULAR INST
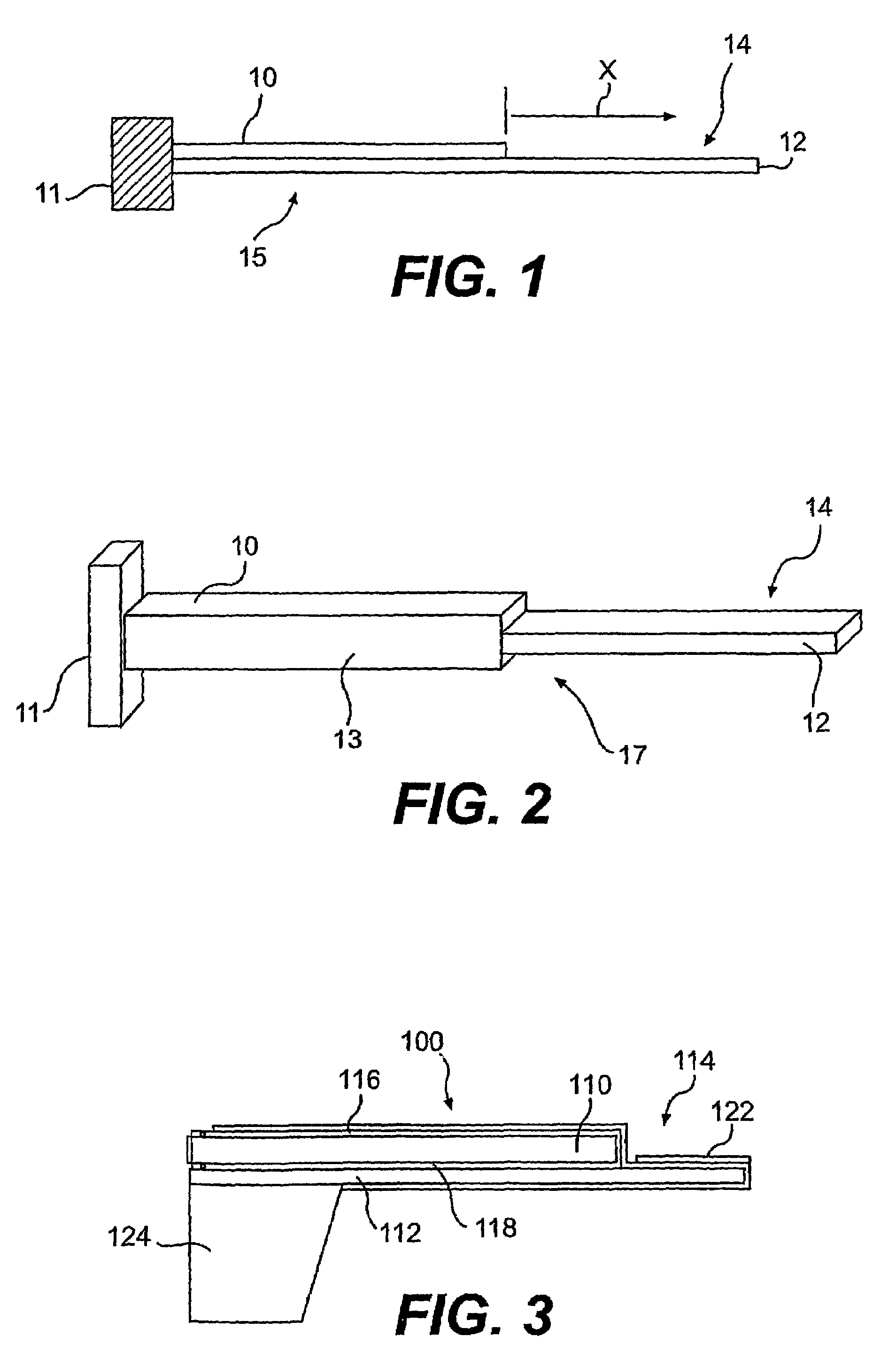
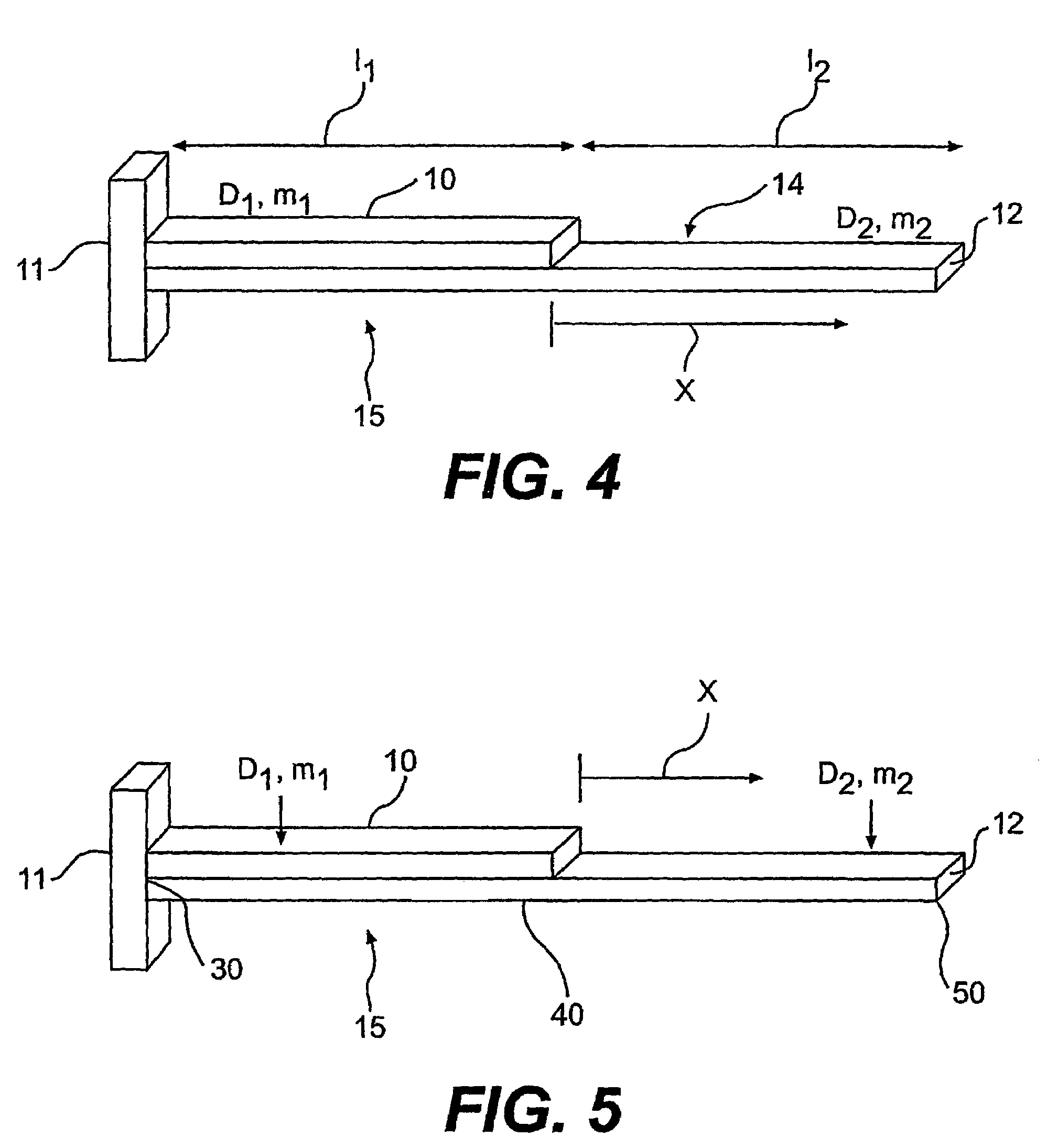
Moisture sensor sprinkler control systems
Irrigation systems, moisture sensors and related methods having a sensor imbedded in the ground to sense moisture and help control watering. The sensor is responsive to capacitance changes from ground moisture variations. The sensor uses spaced insulated electrodes which are mounted within a granular filled chamber within a water-permeable shell. The sensor is mounted as part of a ground unit that also includes a high frequency driver that excites the sensor. The ground unit further has a detector circuit which produces a moisture indicating signal based on the capacitance which varies with ground moisture. Also disclosed are controllers that electrically isolate the ground units so that reliable moisture signals can be obtained and used to control irrigation. The controllers can be configured to provide multiple zone operation using a shared controller having shared or independent moisture adjusters.
Owner:BOWERS JOHN R +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com