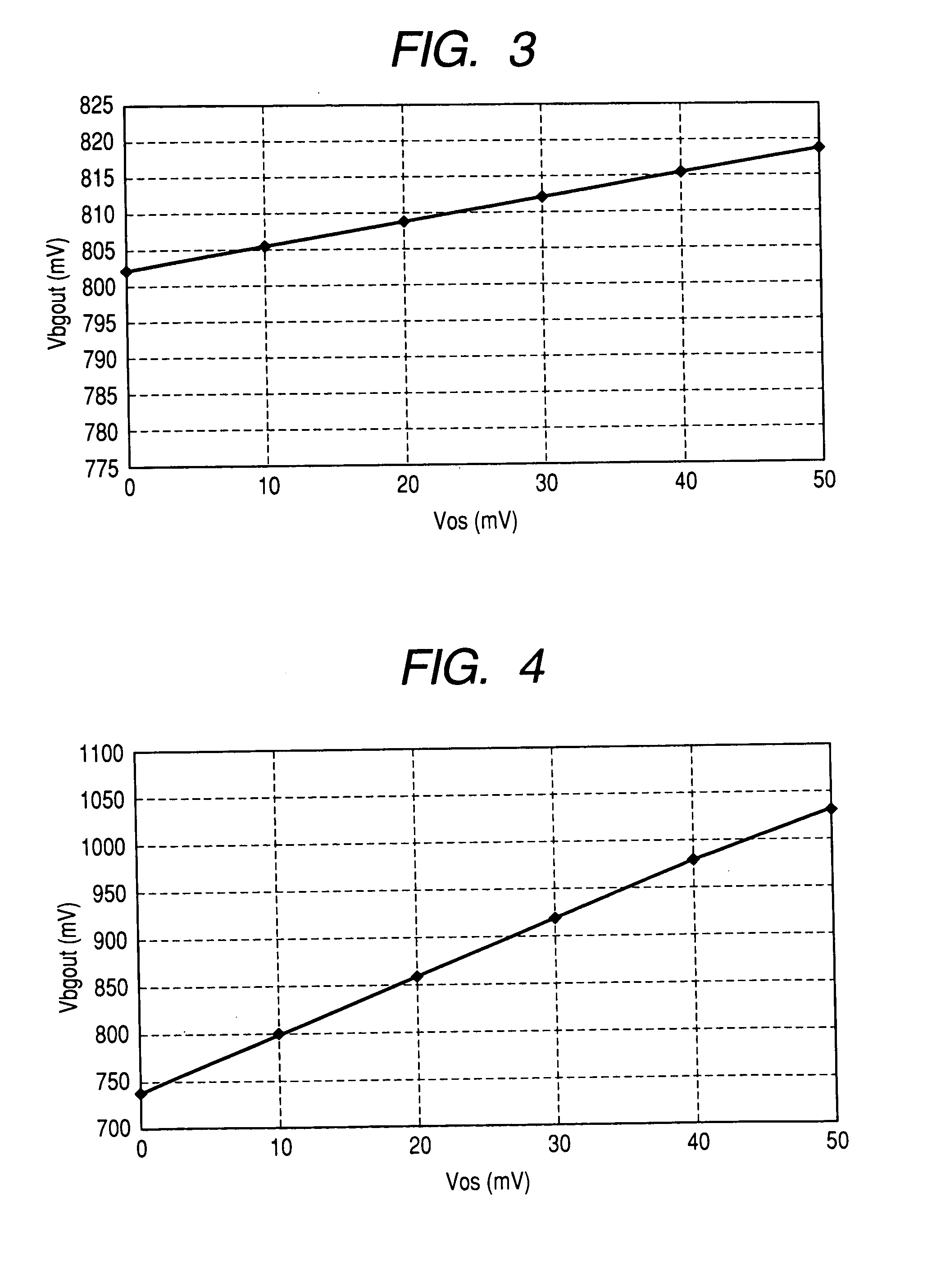
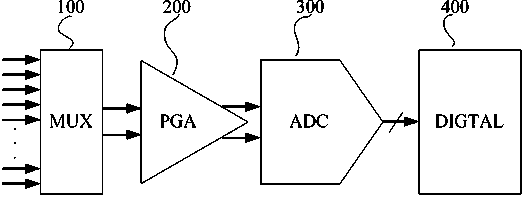
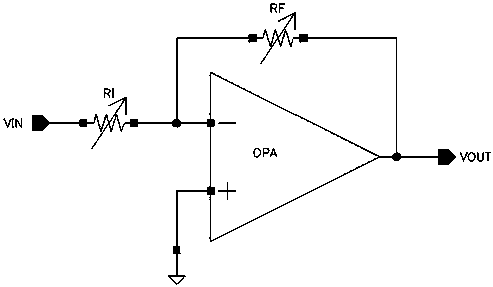
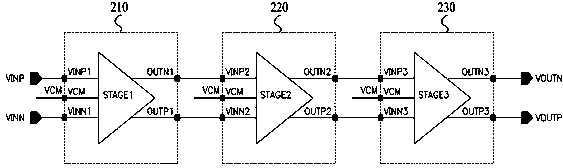
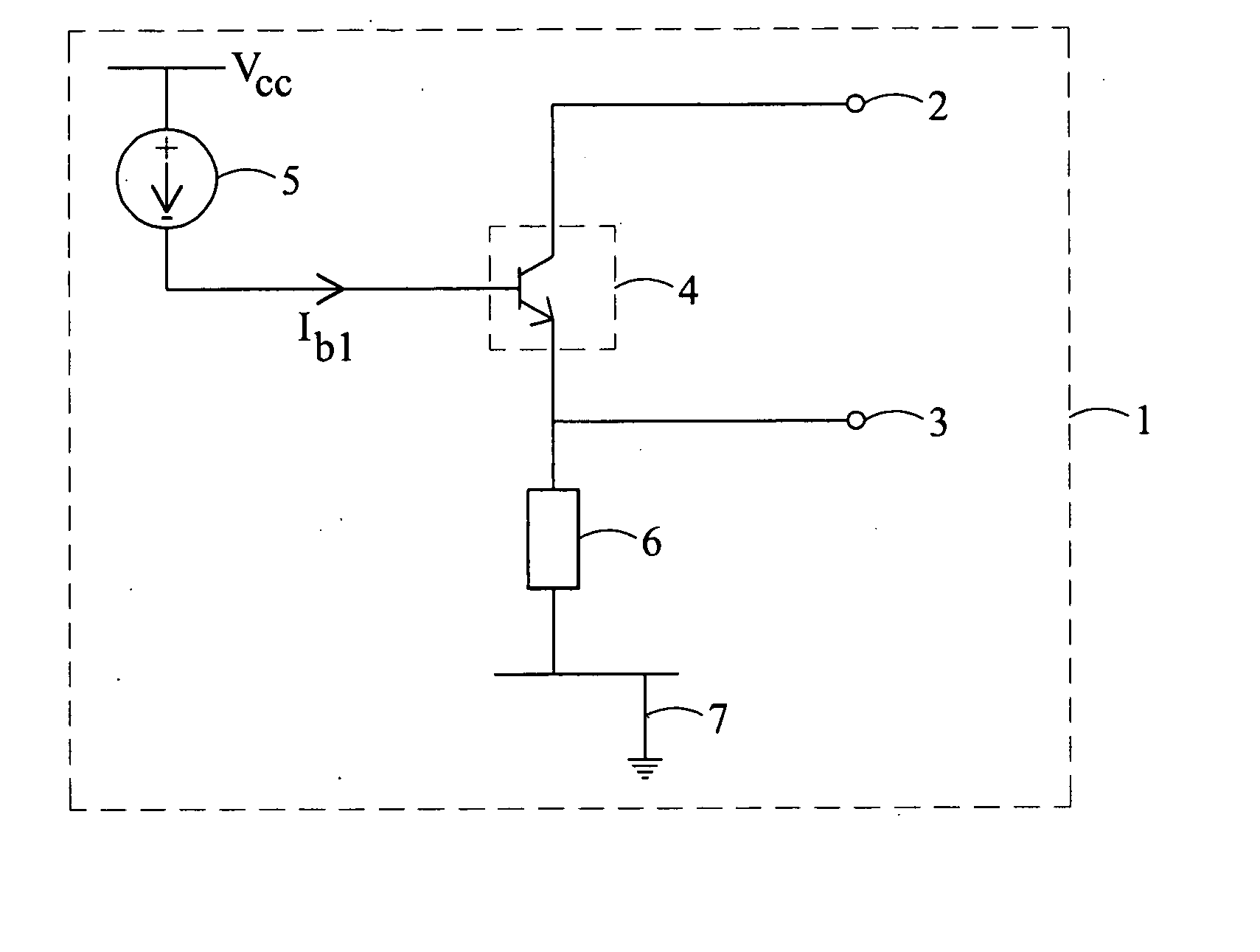Patents
Literature
164results about How to "Lower Offset Voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
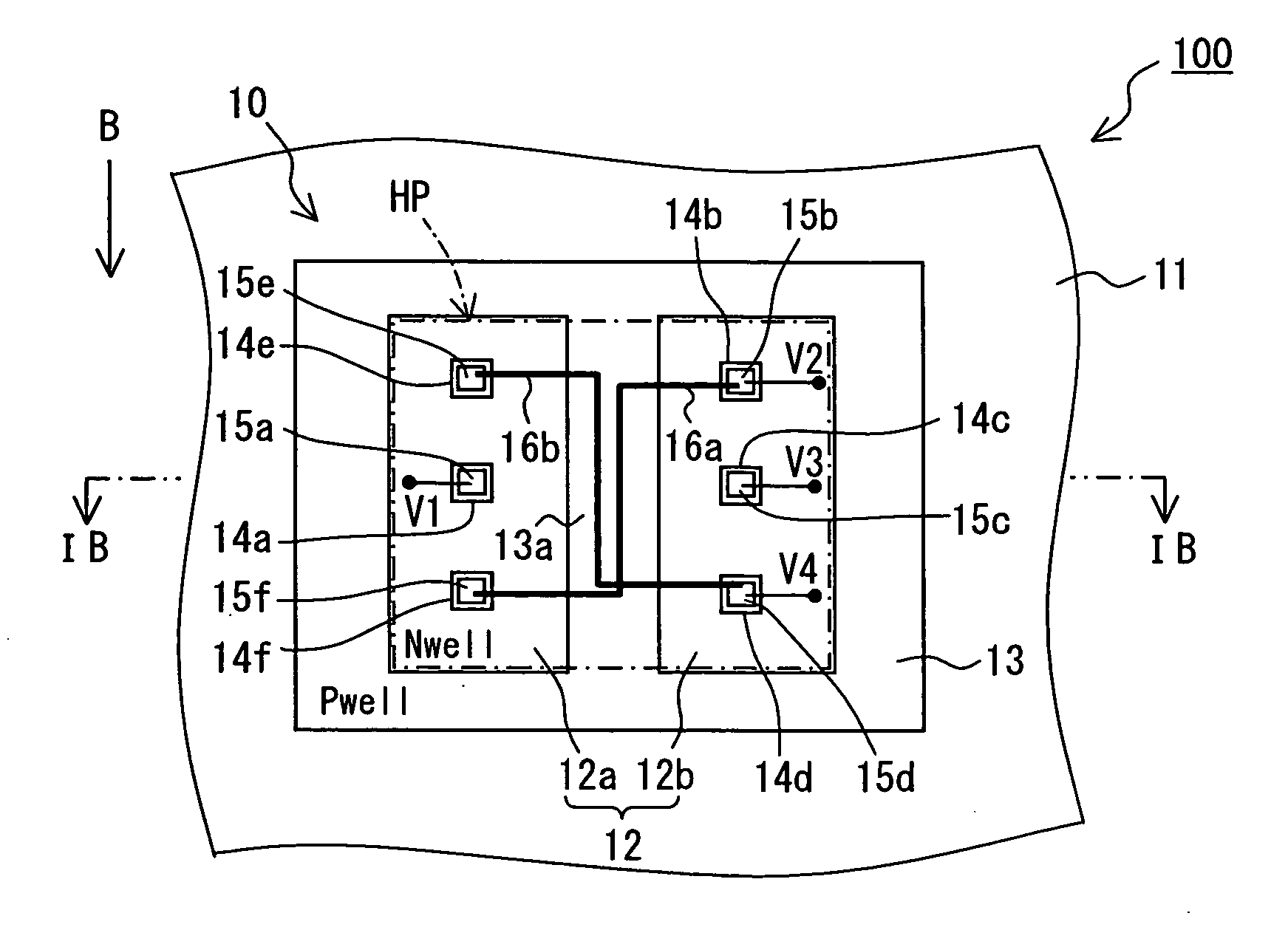
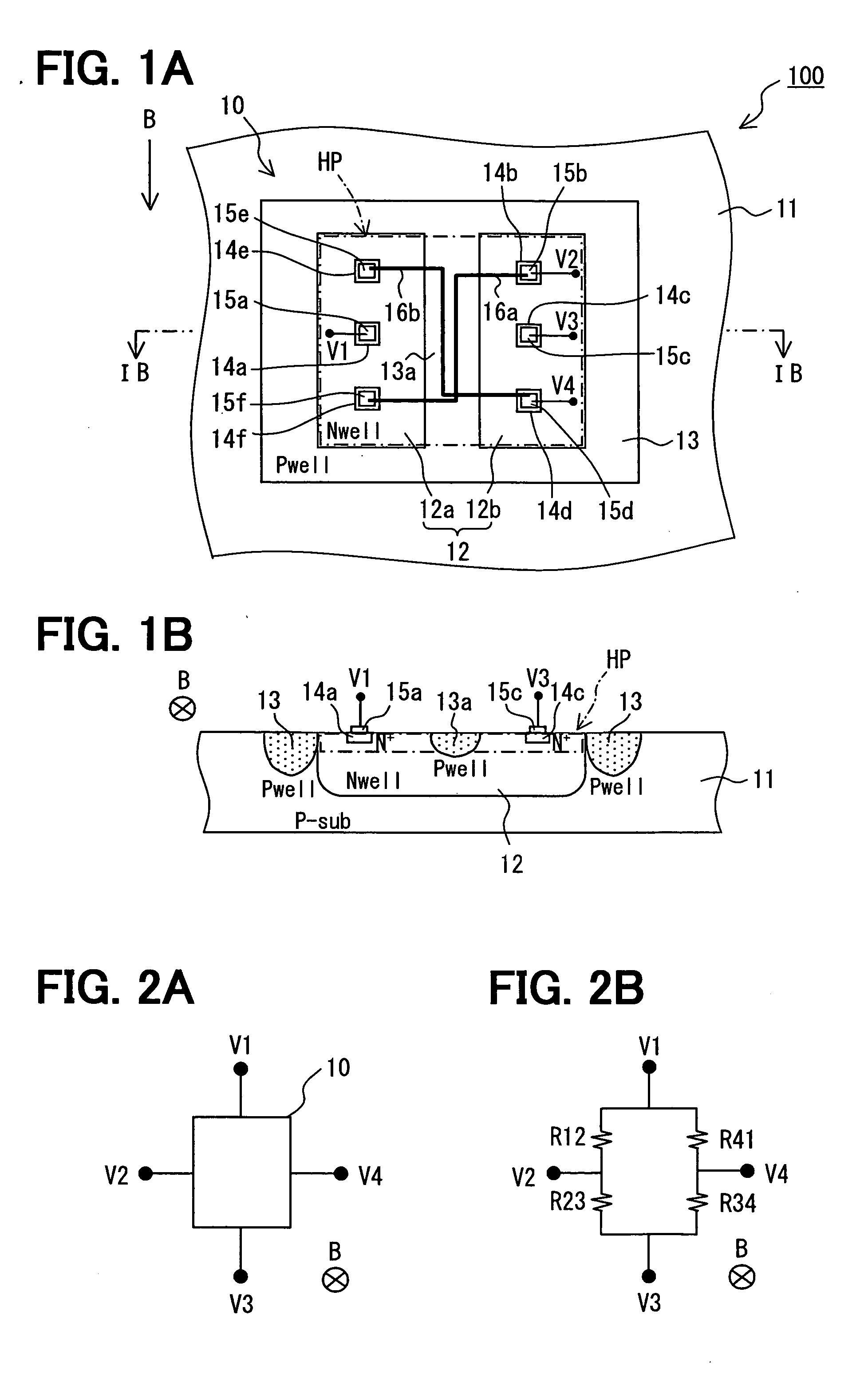
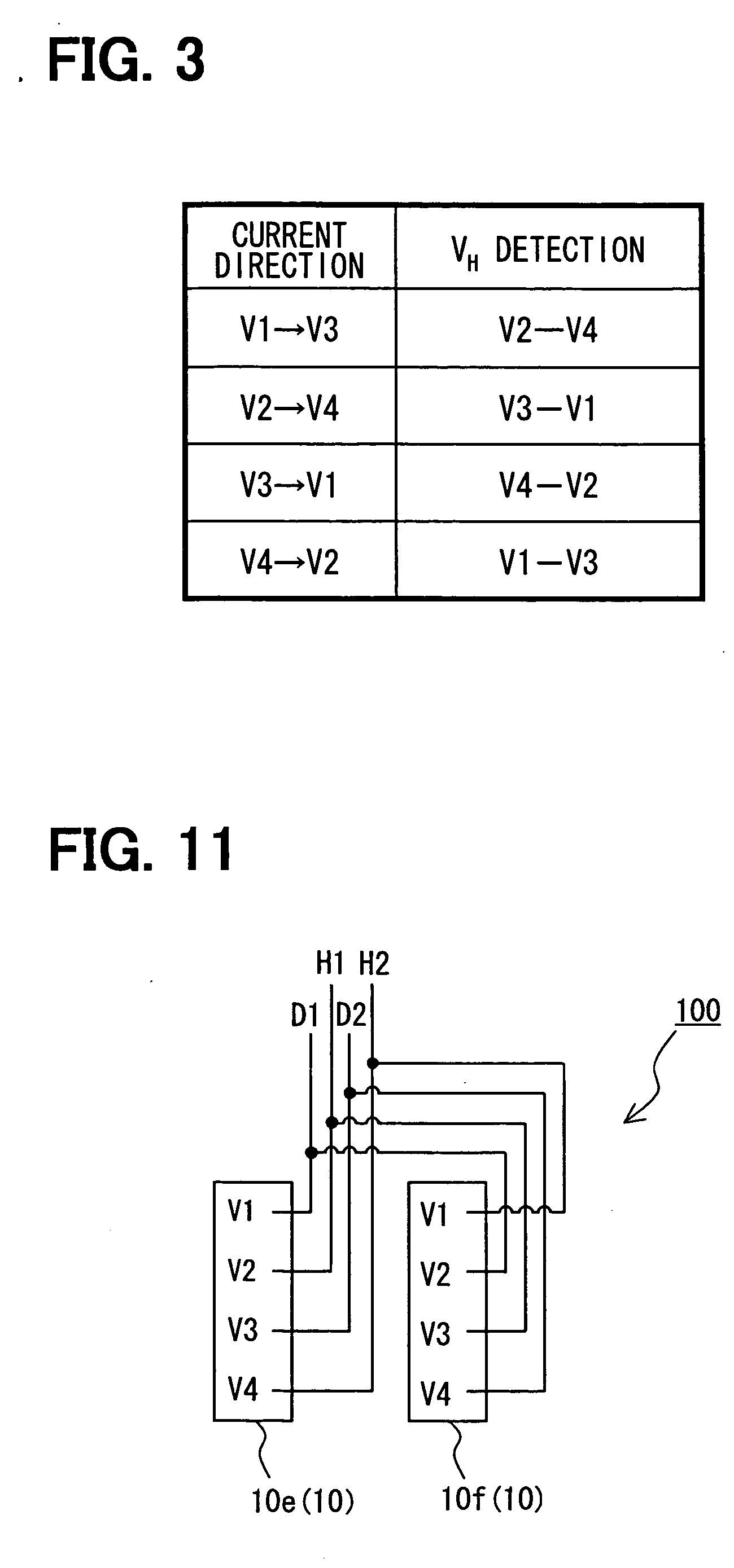
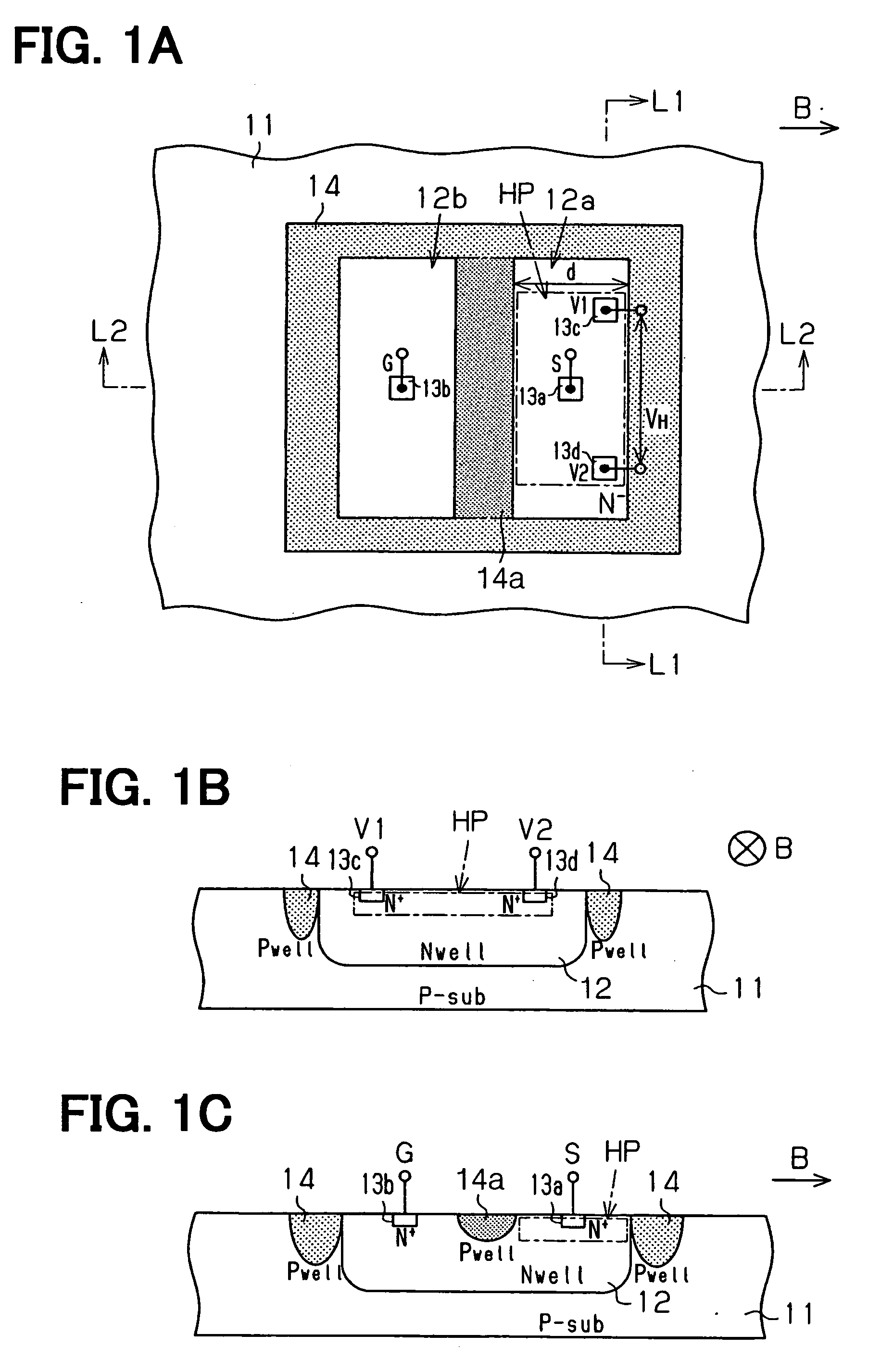
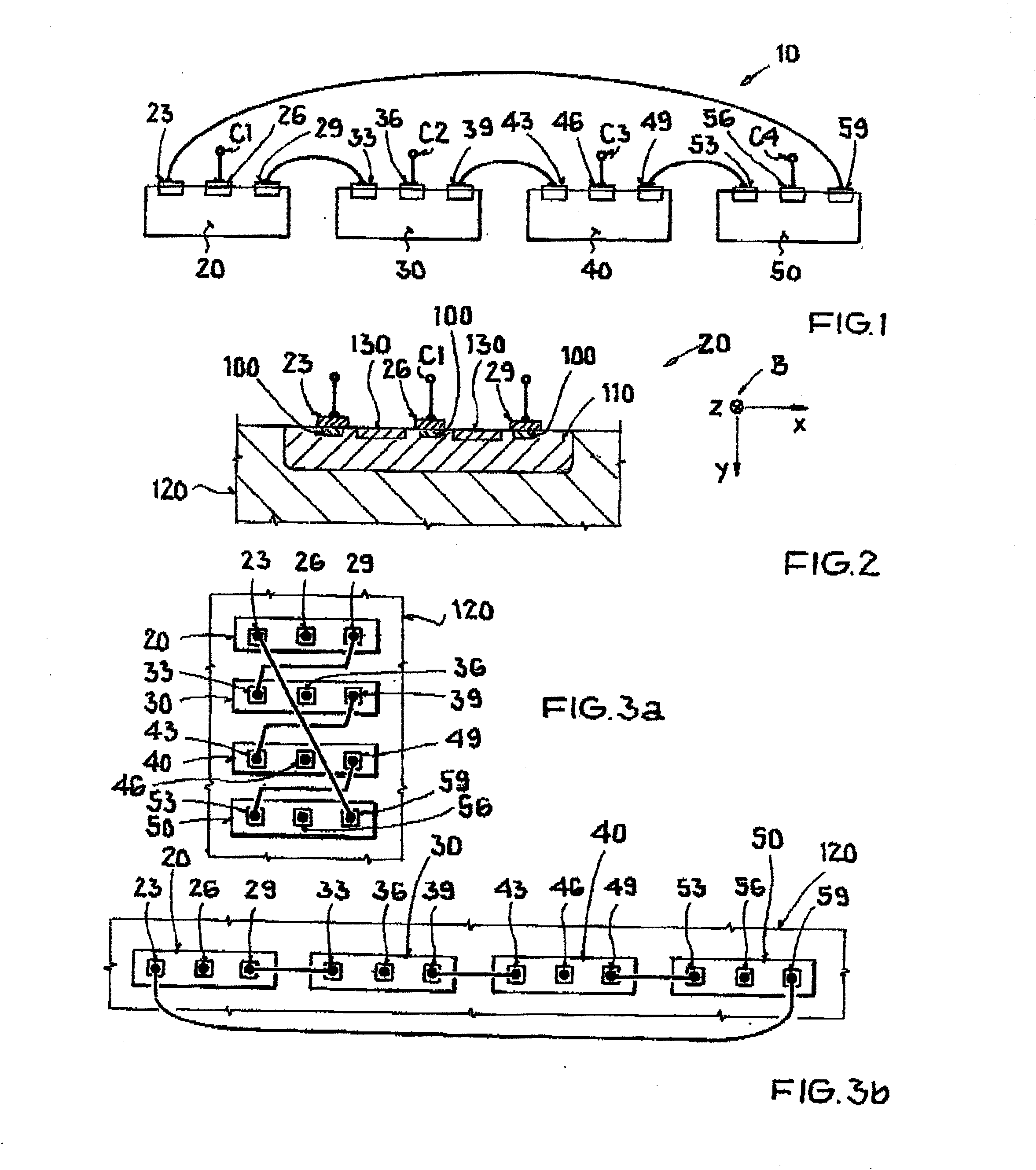
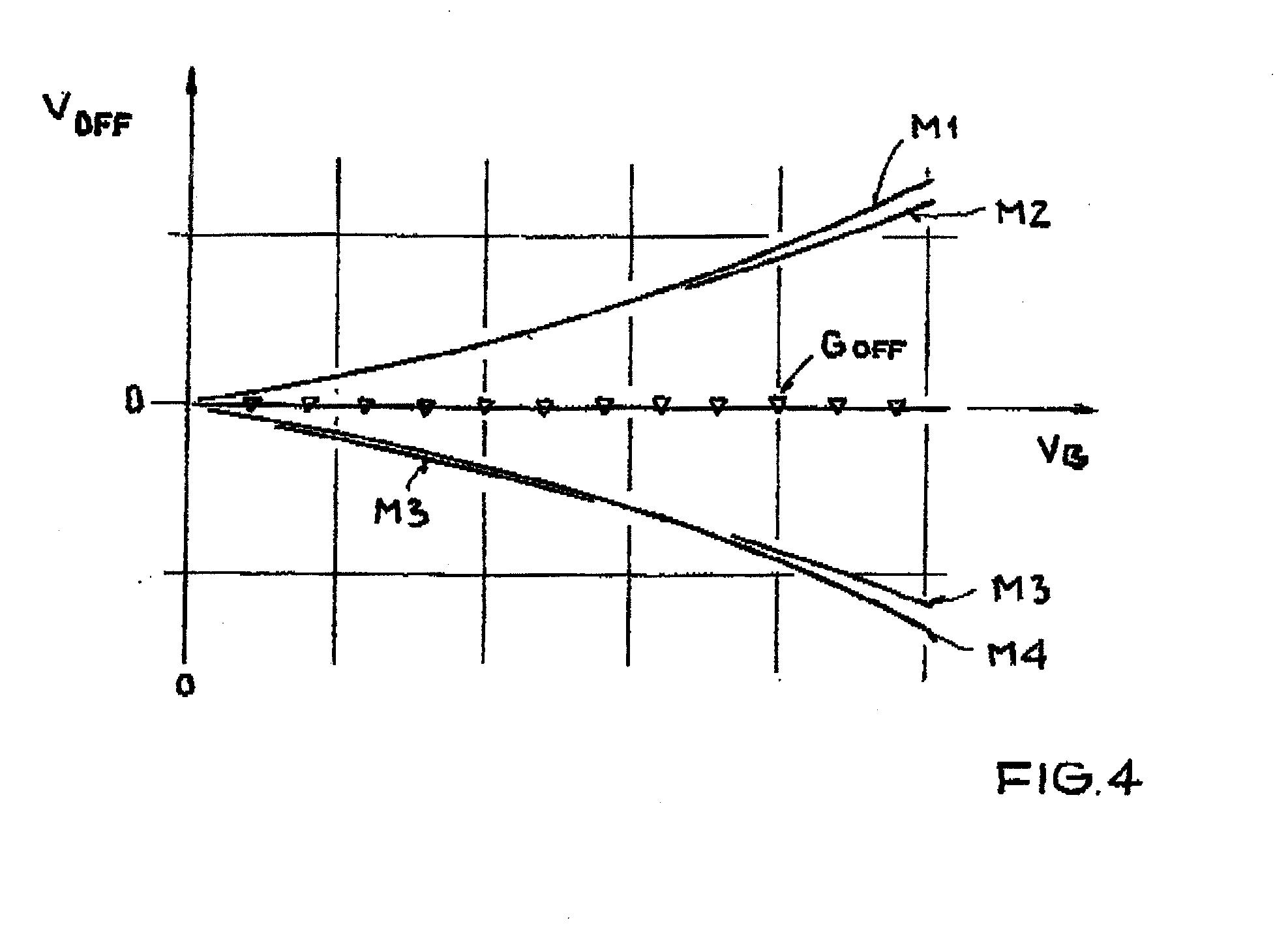
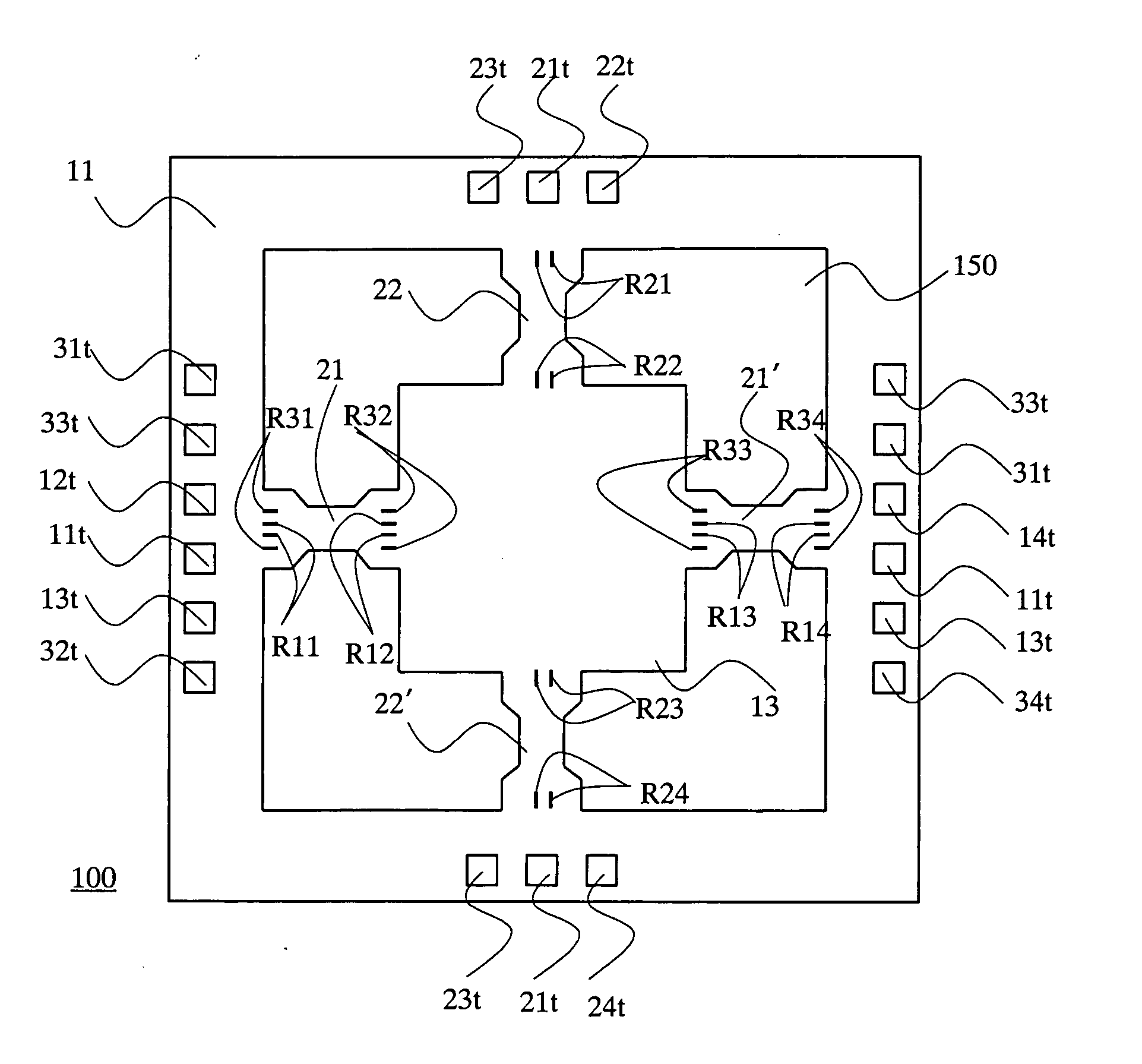
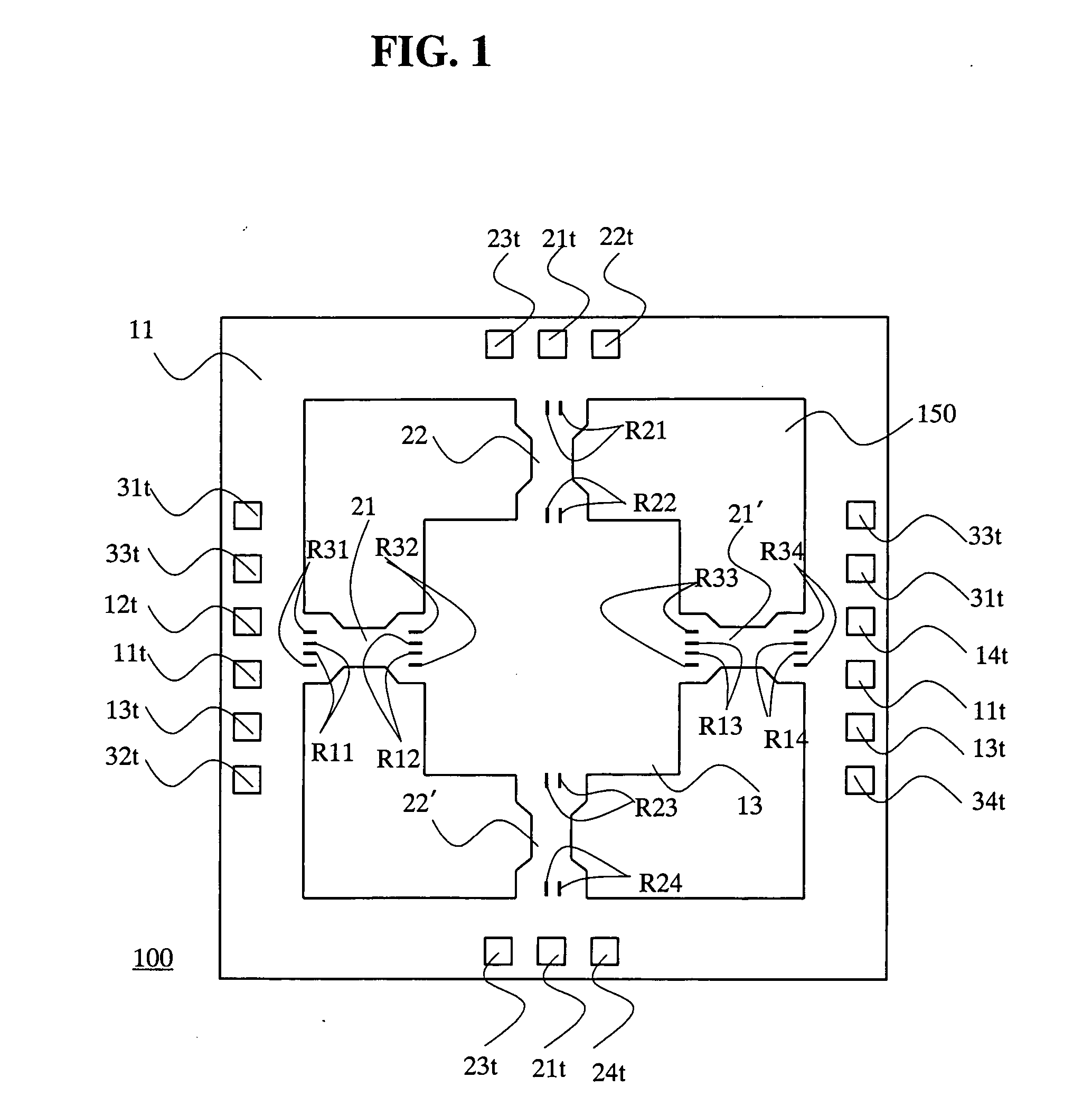
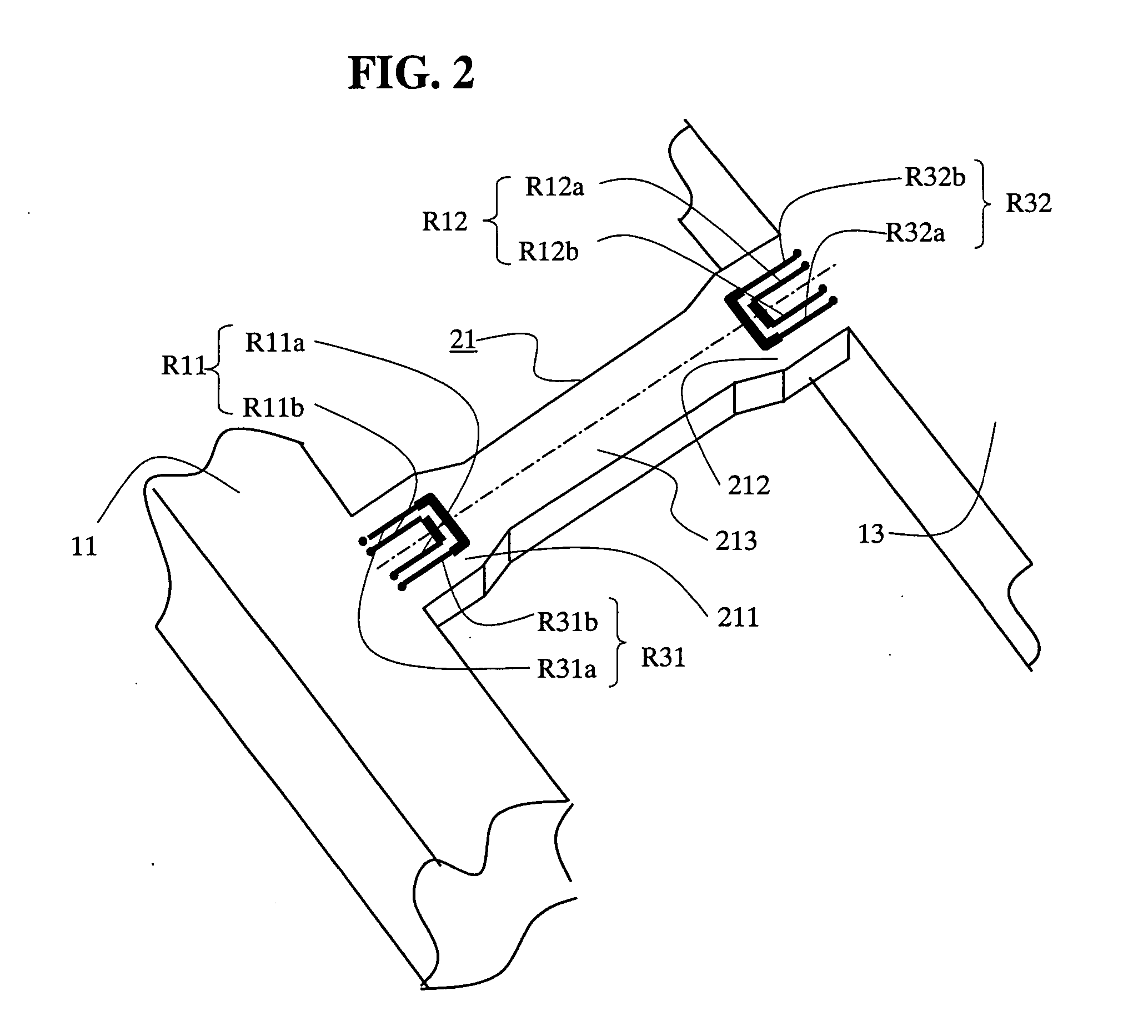
Magnetic sensor and method for detecting magnetic field
InactiveUS20070290682A1Lower Offset VoltageGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesDriving currentElectricity
A magnetic sensor includes: a substrate; a semiconductor region; a magnetic field detection portion; a pair of first electrodes; and two pairs of second electrodes. One pair of second electrodes includes first and second terminals, and the other pair includes third and fourth terminals. The first and third terminals are disposed on one side, and the second and fourth terminals are disposed on the other side. The first and fourth terminals are electrically coupled, and the second and third terminals are electrically coupled. The magnetic field detection portion and the first and second electrodes provide a vertical Hall element. One of the first and second electrodes supplies a driving current, and the other one detects the Hall voltage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
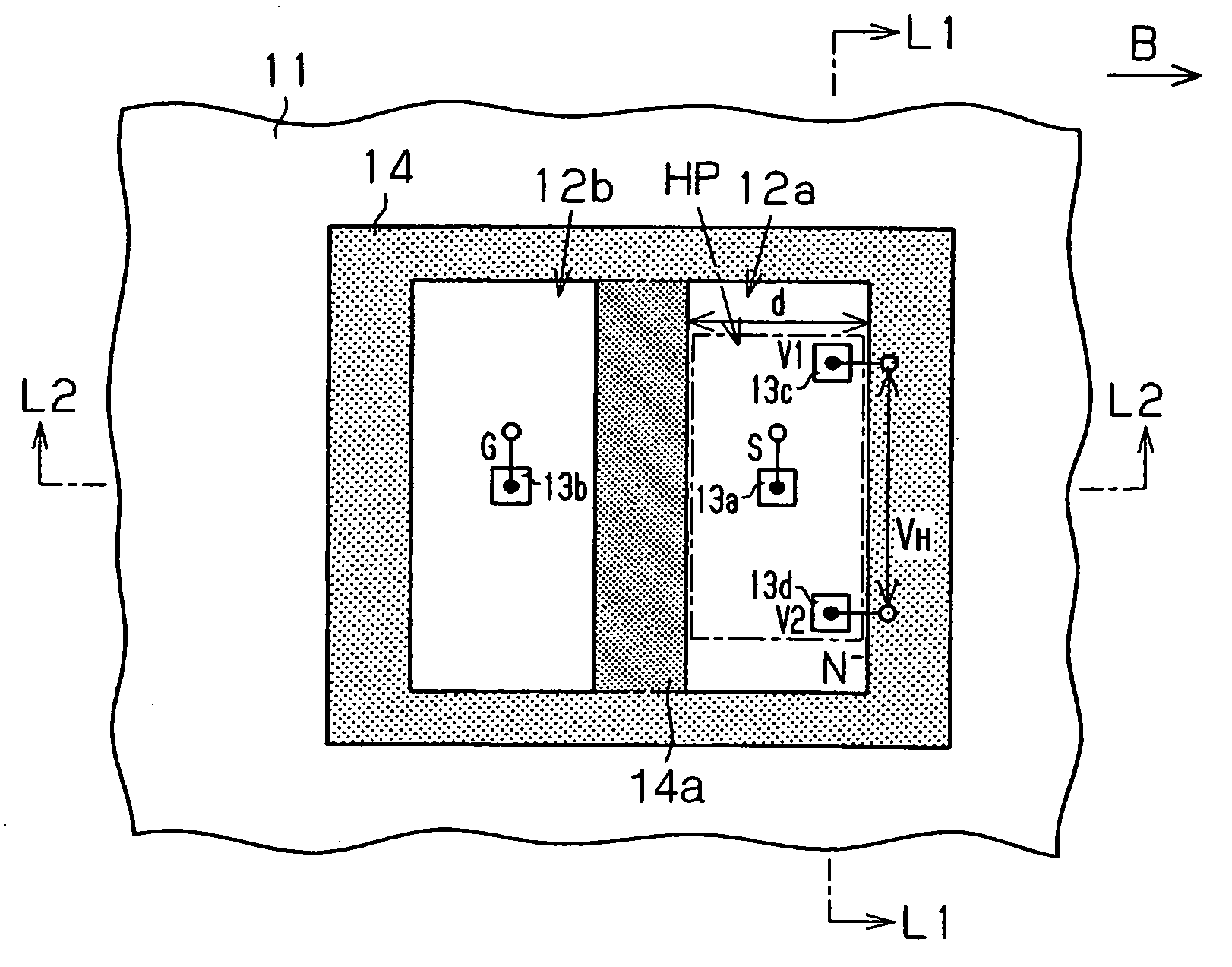
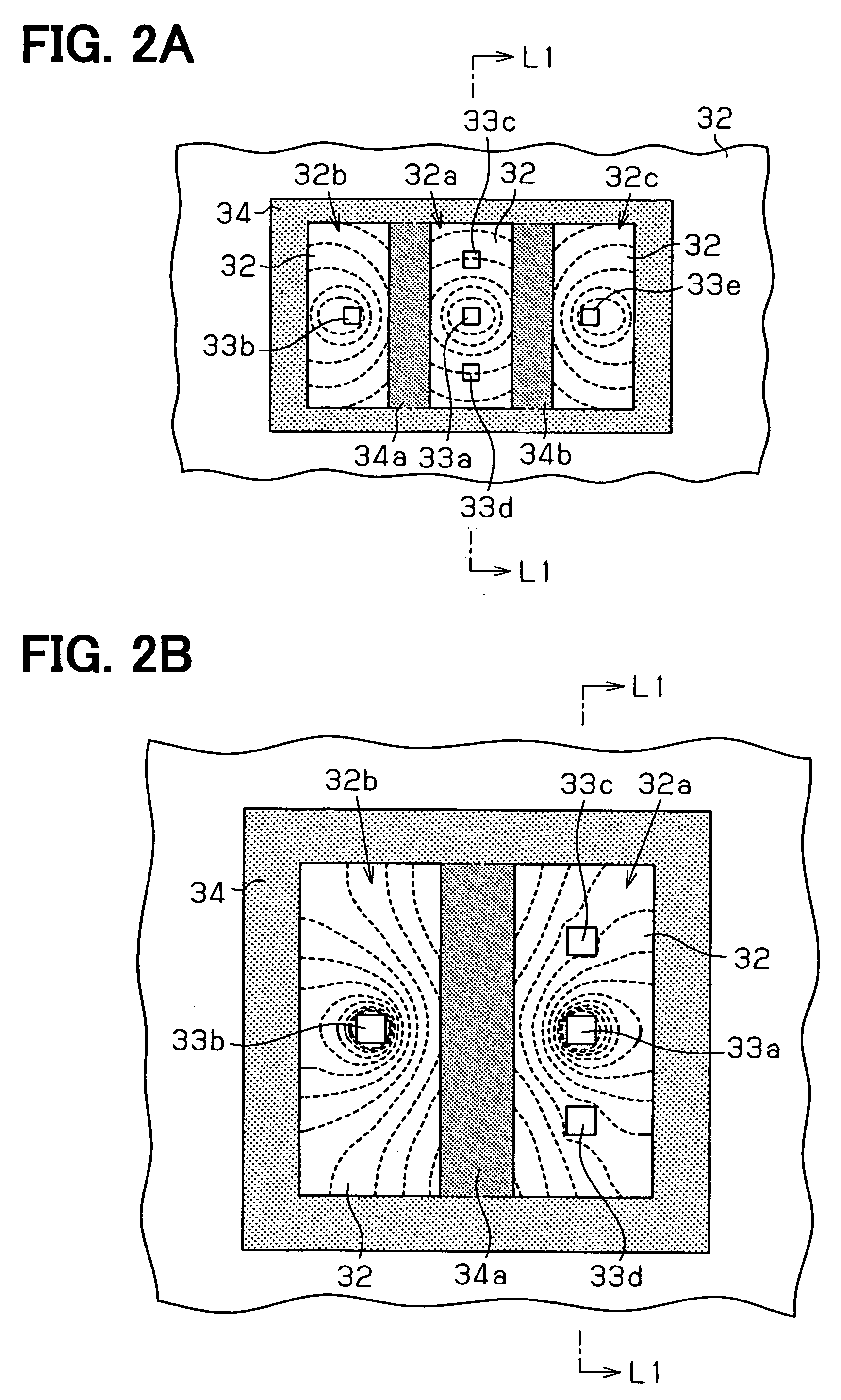
Vertical Hall device and method for adjusting offset voltage of vertical Hall device
InactiveUS20060097715A1Easily and accurately determinedReduce device voltageSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A vertical Hall device includes: a semiconductor substrate including a magnetic field detection portion, a current portion and an output portion. The output portion includes a pair of output terminals. The current portion is capable of supplying the current to the magnetic field detection portion and retrieving the current from the magnetic field detection portion. The current portion is sandwiched between a pair of the output terminals in such a manner that the current portion is disposed apart from a line connecting between a pair of the output terminals.
Owner:DENSO CORP
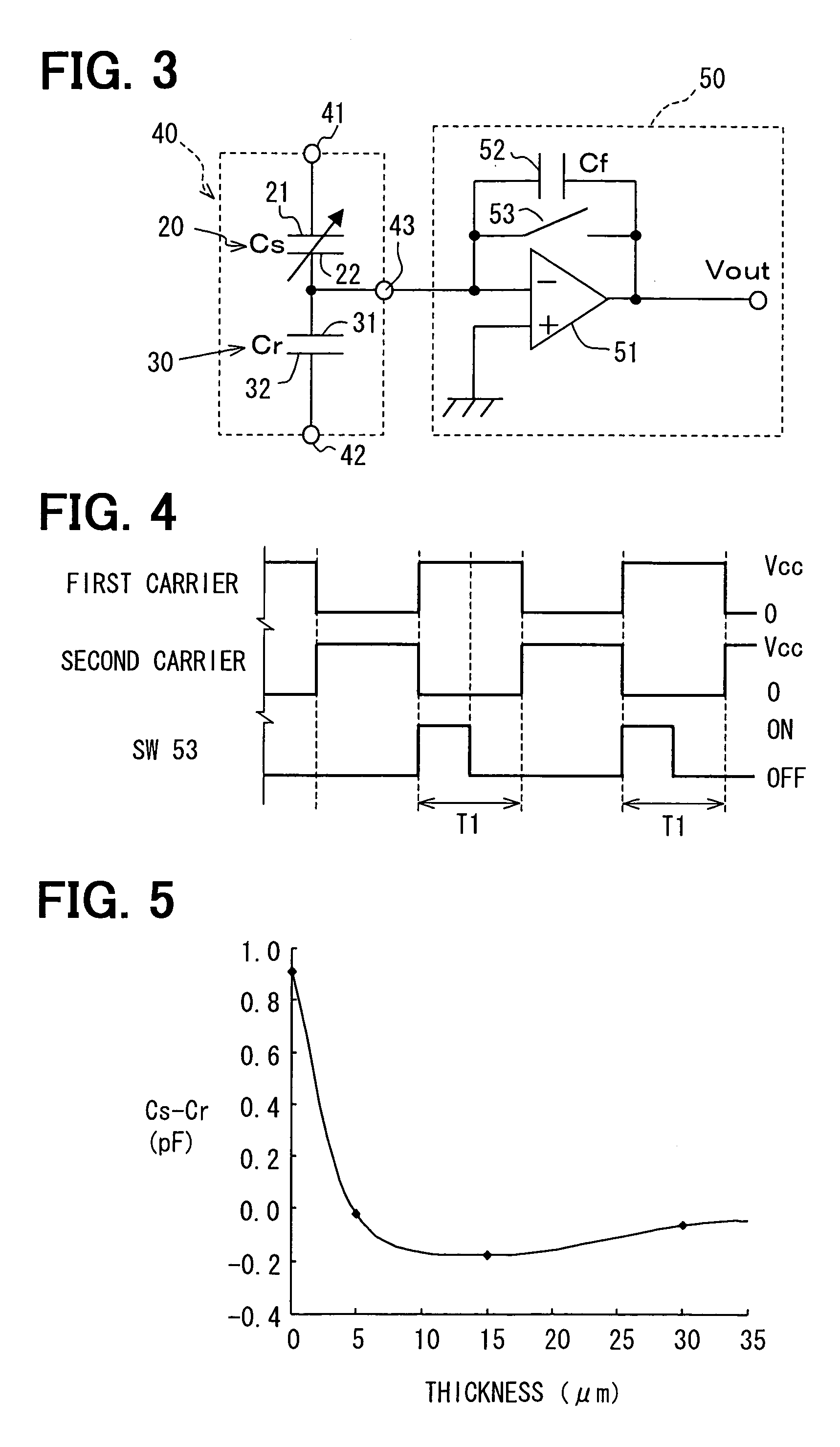
Capacitive humidity sensor
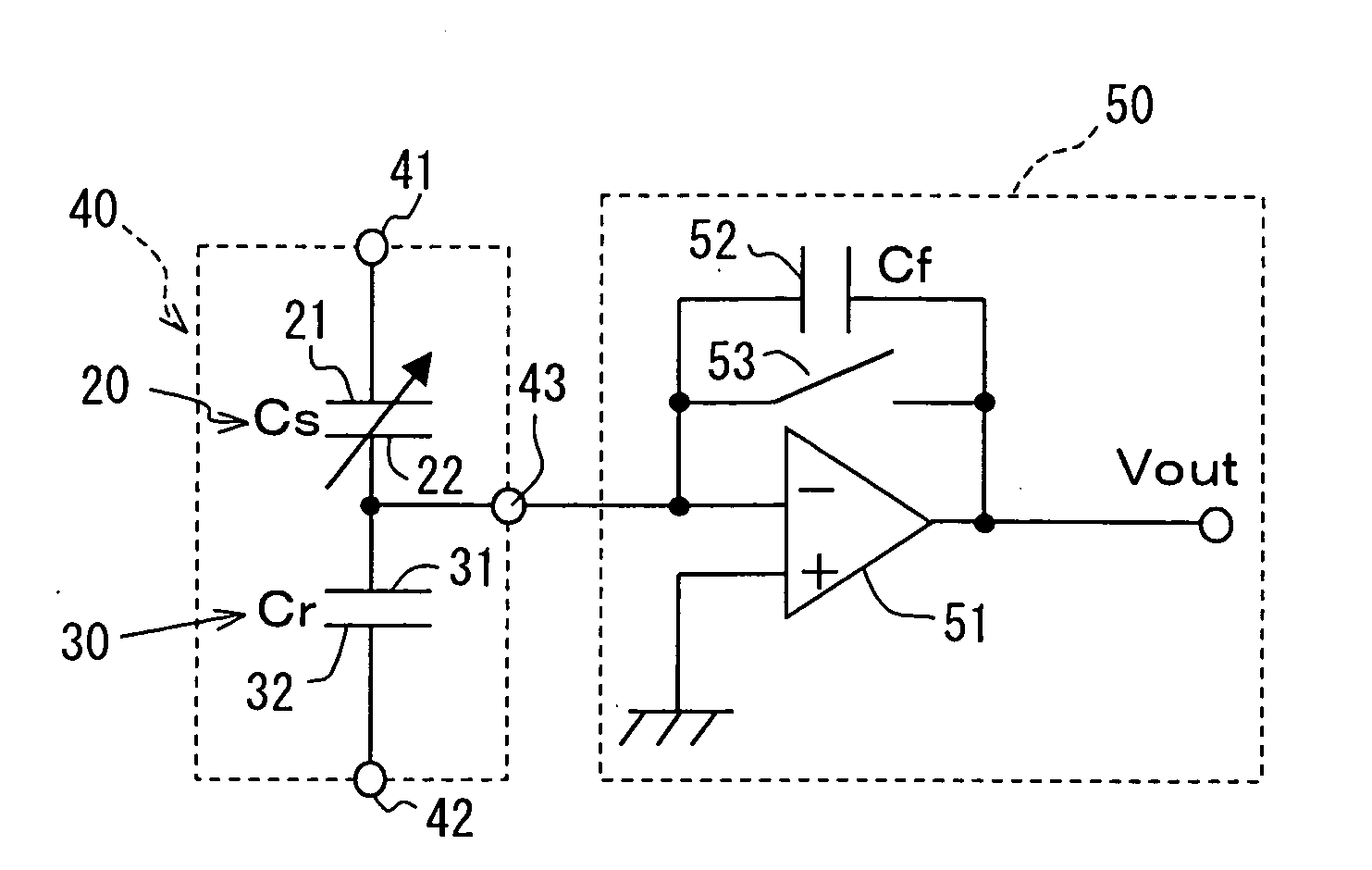
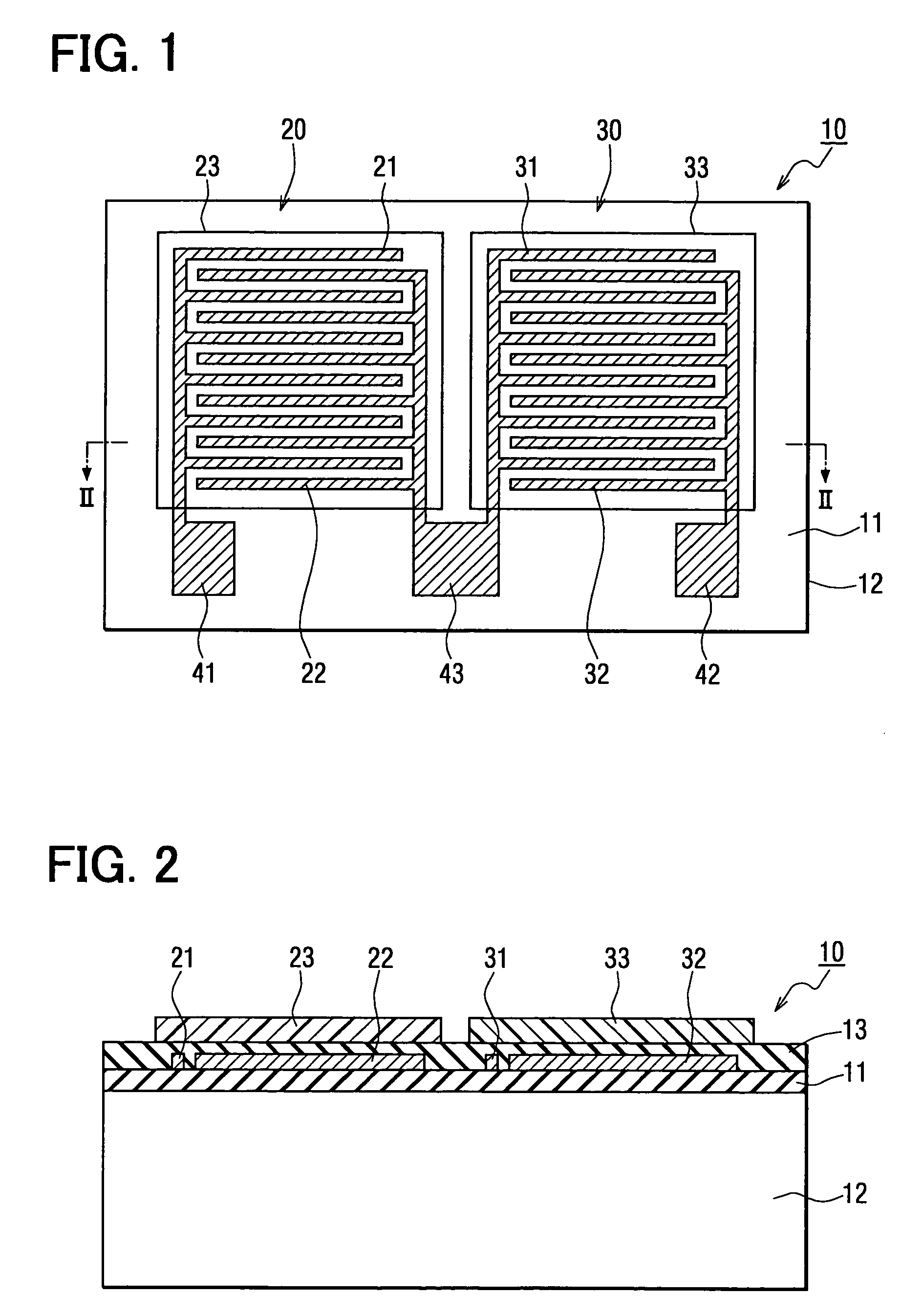
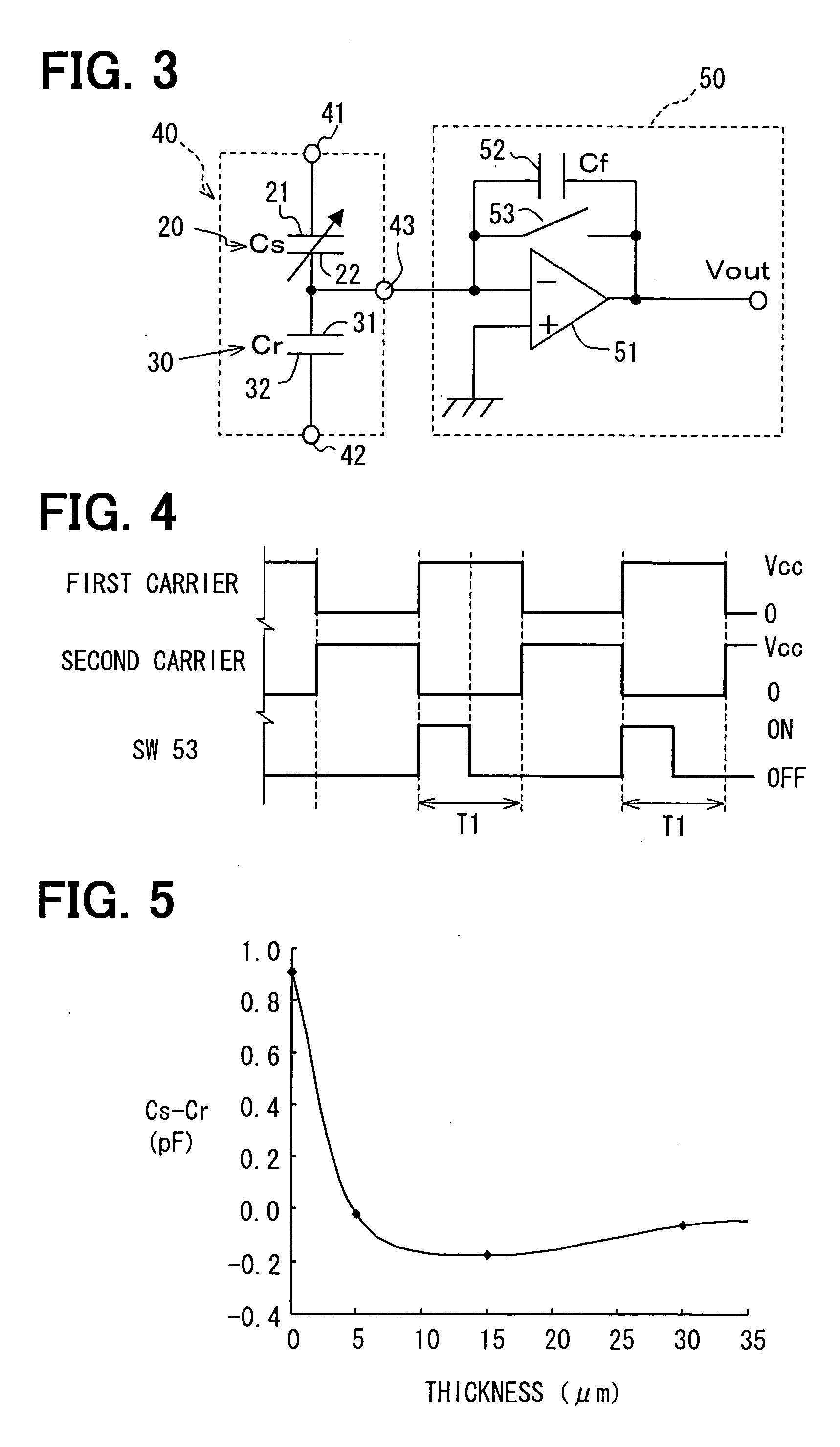
InactiveUS7032448B2Lower Offset VoltageSmall sizeResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing mechanical meansMoisture permeationMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes a detection portion and a reference portion. The detection portion includes detection electrodes and a moisture sensitive film. The reference portion includes reference electrodes and a moisture permeation film as a capacitance adjusting film. The capacitive humidity sensor detects humidity by converting a capacitance difference between a capacitance of the detection electrodes and a capacitance of the reference electrodes to an electric signal by using a capacitance-voltage conversion circuit. The moisture permeation film reduces offset voltage of the capacitive humidity sensor. Thus, an offset compensation circuit or the like is not required.
Owner:DENSO CORP
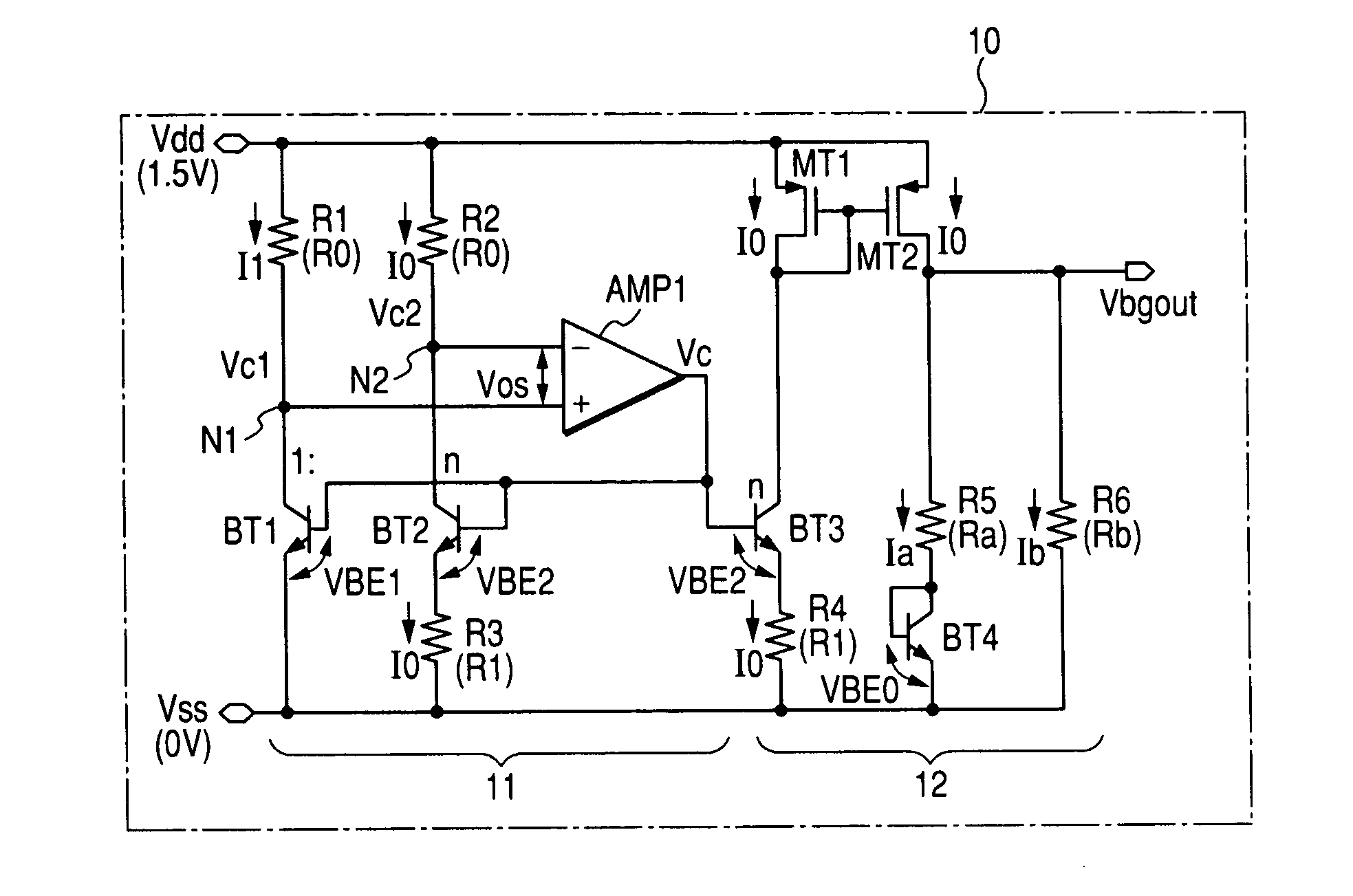
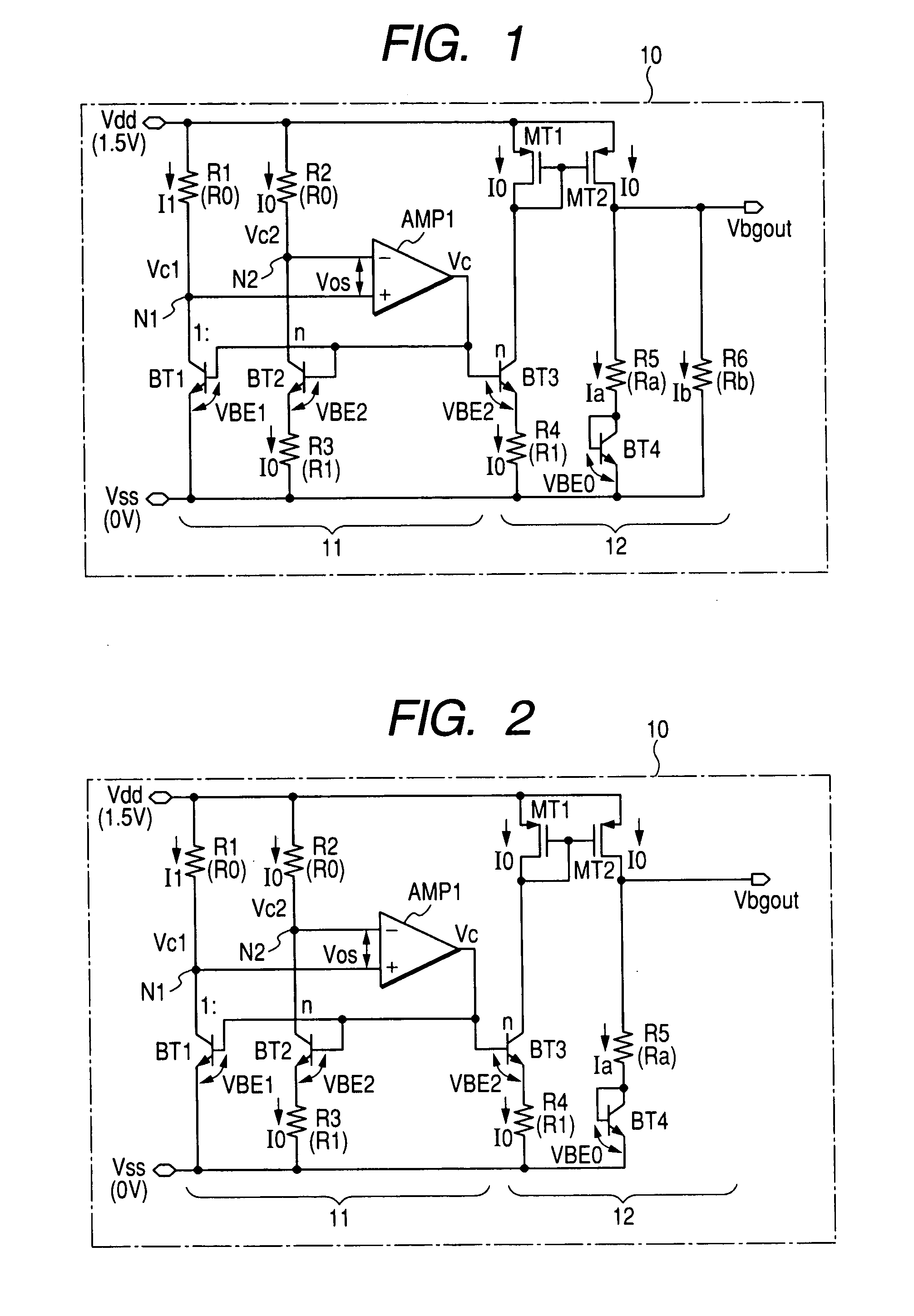
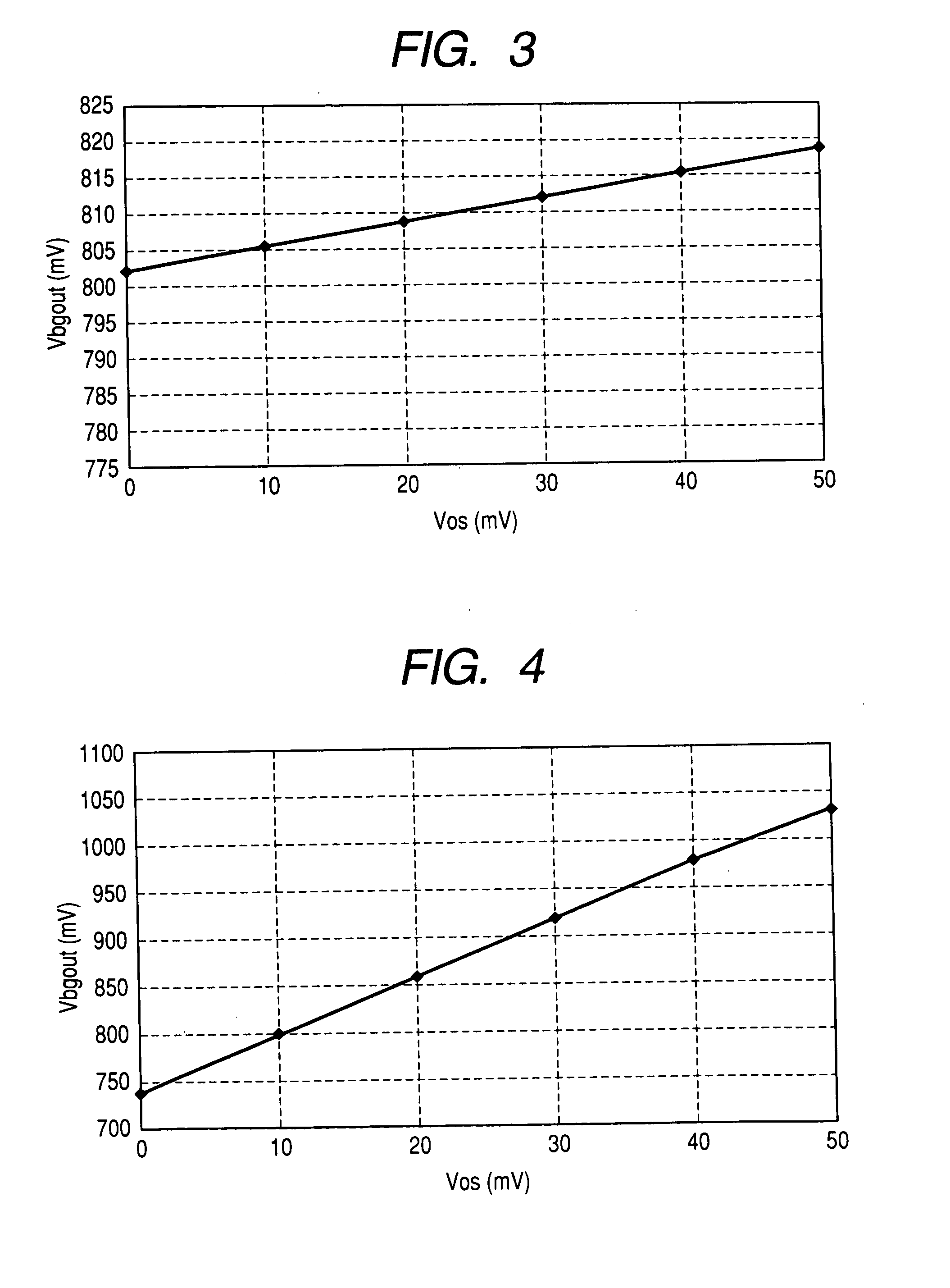
Reference voltage generating circuit, a semiconductor integrated circuit and a semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus
InactiveUS20070052405A1The output voltage is accurateAvoid output voltageStatic storageElectric variable regulationVoltage referenceEngineering
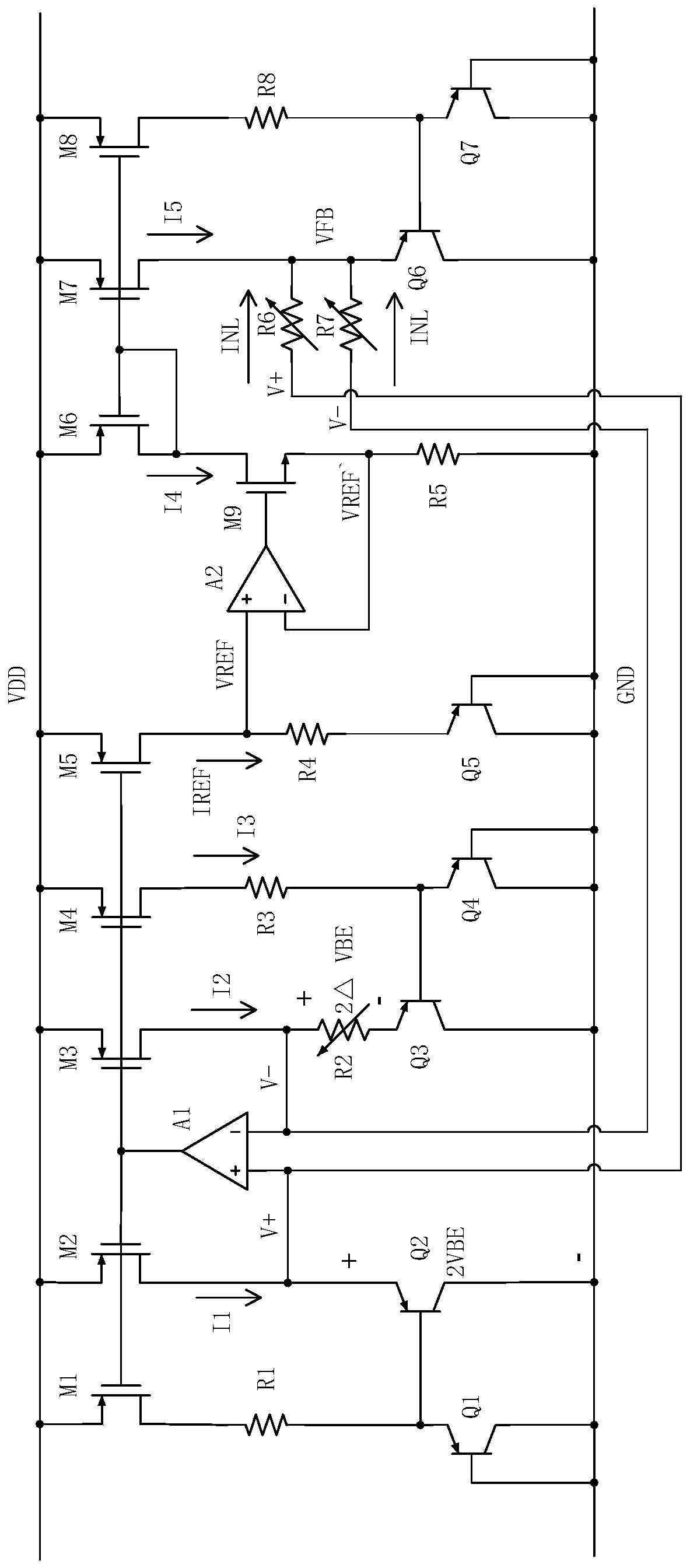
The present invention provides a band gap type reference voltage generating circuit and a semiconductor integrated circuit having the same, capable of generating a reference voltage of about 1.2V or less whose temperature dependency is low, and realizing reduced offset voltage dependency of a differential amplifier. A band gap part has: a first resistor and a first bipolar transistor connected in series between power supply voltage terminals; a second resistor, a second bipolar transistor, and a third resistor connected in series between the power supply voltage terminals; and a differential amplifier that receives voltages generated by the first and second resistors, and an output of the differential amplifier is applied to the bases of the two transistors. The output part has a third bipolar transistor having a base to which the output of the differential amplifier is applied, a fourth resistor connected in series with the third bipolar transistor, a current mirror circuit for transferring current flowing in the third bipolar transistor, and a fifth resistor and a diode for converting the transferred current to voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Capacitive humidity sensor
InactiveUS20040182153A1Reduce the differenceReduce capacitance differenceUsing mechanical meansCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricMoisture permeationMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes a detection portion and a reference portion. The detection portion includes detection electrodes and a moisture sensitive film. The reference portion includes reference electrodes and a moisture permeation film as a capacitance adjusting film. The capacitive humidity sensor detects humidity by converting a capacitance difference between a capacitance of the detection electrodes and a capacitance of the reference electrodes to an electric signal by using a capacitance-voltage conversion circuit. The moisture permeation film reduces offset voltage of the capacitive humidity sensor. Thus, an offset compensation circuit or the like is not required.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Hall sensor
ActiveUS20130015853A1Lower Offset VoltageMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesHall elementEngineering
A Hall sensor is provided having a first Hall element with a first terminal contact and with a second terminal contact and with a third terminal contact, a second Hall element with a fourth terminal contact and with a fifth terminal contact and with a sixth terminal contact, a third Hall element with a seventh terminal contact and with an eighth terminal contact and with a ninth terminal contact, and a fourth Hall element with a tenth terminal contact and with an eleventh terminal contact and with a twelfth terminal contact. The first Hall element and the second Hall element and the third Hall element and the fourth Hall element are connectable in series.
Owner:TDK MICRONAS GMBH +1
Vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system
InactiveCN104485993AImplement instant voice communication technologySave spaceClose-range type systemsFrequency spectrumVoice communication
The invention discloses a vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system. The vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system comprises a sending module and a receiving module. The sending module comprises a digital audio acquisition unit, an RS coding unit, a PWM (pulse width modulation) unit, an LED (light emitting diode) drive unit and an LED transmitting unit, which are connected successively in circuit; the receiving module comprises a PIN photoelectric detection unit, a signal extraction unit, a PWM modulation unit, an RS decoding unit and a digital audio output unit, which are connected successively in circuit. The wireless digital voice communication system realizes instant voice communication between strange vehicles; an LED-based lamp is integrated with automobile lighting and communication without the need of an additional signal emission source installation space and occupation of scarce frequency spectrum resource. The voice signal transmission is high-speed and reliable, high in integration level, strong in anti-interference ability and low in cost, and bigger communication distance and more reliable communication are realized; moreover, a detector has high accuracy, high responsivity, low dark current, higher communication rate, stronger anti-interference ability and high reliability of a transmission channel.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Reading circuit used for sensor
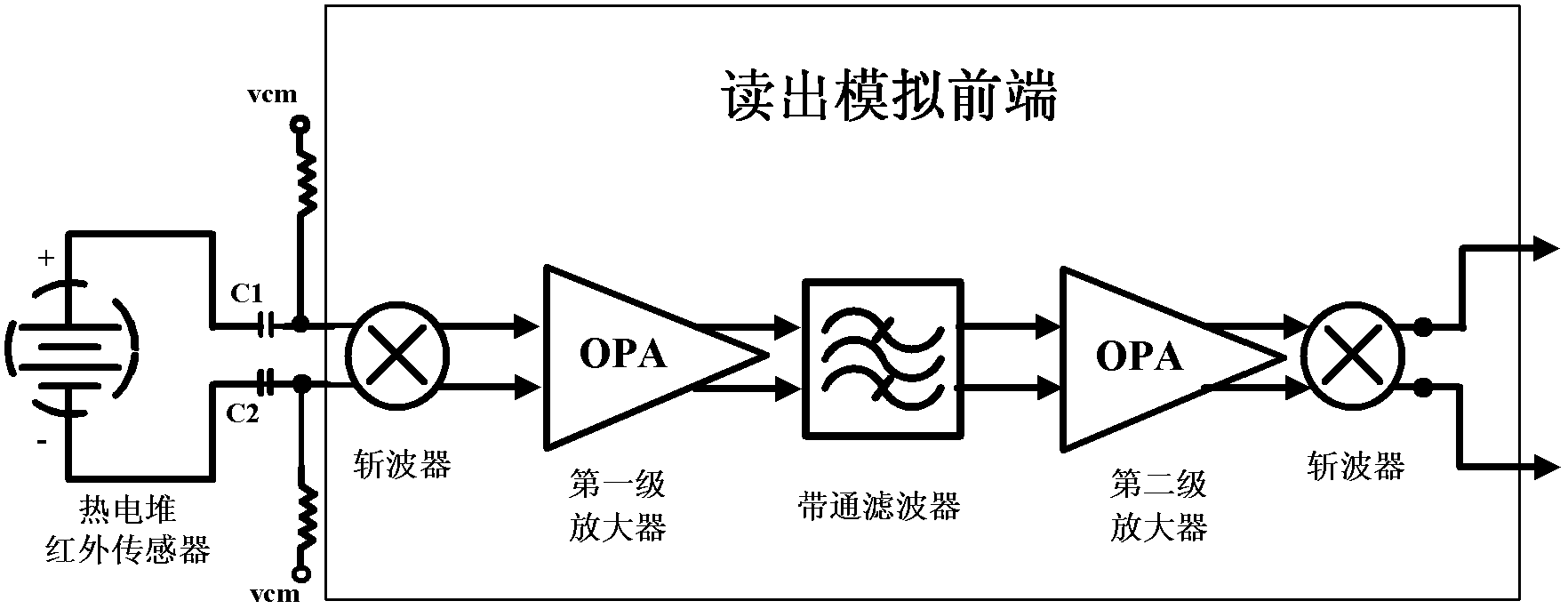
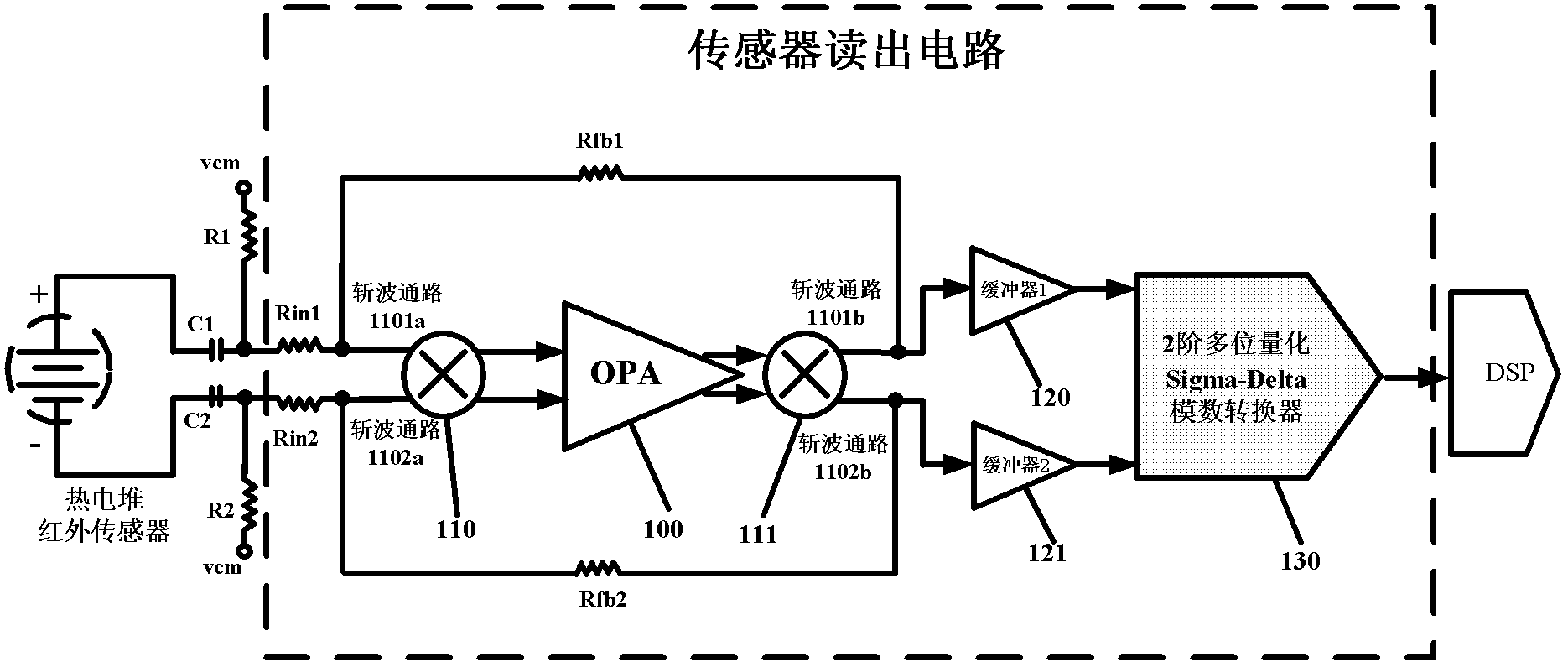
ActiveCN103308183AImprove detection accuracyHighly integratedPyrometry using electric radation detectorsEngineeringDigital converter
The invention relates to a reading circuit used for a sensor. The reading circuit comprises two levels of operational amplifiers, a chopper, a buffer and a 2-order 3-bit quantized Sigma-Delta analog / digital converter; the two levels of operational amplifiers amplify a weak voltage signal outputted from the sensor by a resistance ratio under a closed loop work state; the input / output chopper is used for reducing the direct current detuning voltage and low-frequency 1 / f noise of the operational amplifiers; the buffer performs isolation protection on the output signal of the operational amplifiers and provides a certain voltage driving capacity at the same time; and the 2-order 3-bit quantized Sigma-Delta analog / digital converter converts the amplified sensor voltage signal into a digital code and outputs to a DSP (digital signal processor) for processing.
Owner:中科芯未来微电子科技成都有限公司
High-speed low-kickback-noise dynamic comparer and circuit
InactiveCN107888171AReduce reset timeShorten the working cycleMultiple input and output pulse circuitsUltrasound attenuationDynamic noise
The invention discloses a dynamic comparator with high speed and low kick noise, which belongs to the field of analog integrated circuits. Its structure includes: pre-amplification stage, current compensation branch for suppressing kickback noise, positive feedback regeneration stage composed of N-channel transistor and P-channel transistor cross-coupling unit, current between pre-amplification stage and positive feedback regeneration stage A control unit, a reset control unit, an offset calibration unit, and an inverter output driver stage. The two current compensation branches that suppress the kickback noise compensate the current attenuation of the main channel to ensure a constant working current of the input pair tube, thereby suppressing the influence of the kickback noise on the input signal, thereby increasing the size of the input pair tube and reducing offset voltage, increasing the response speed. Compared with the traditional comparator, the invention satisfies the requirement of high speed and low power consumption, and exhibits excellent kickback noise suppression ability.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
Semiconductor device
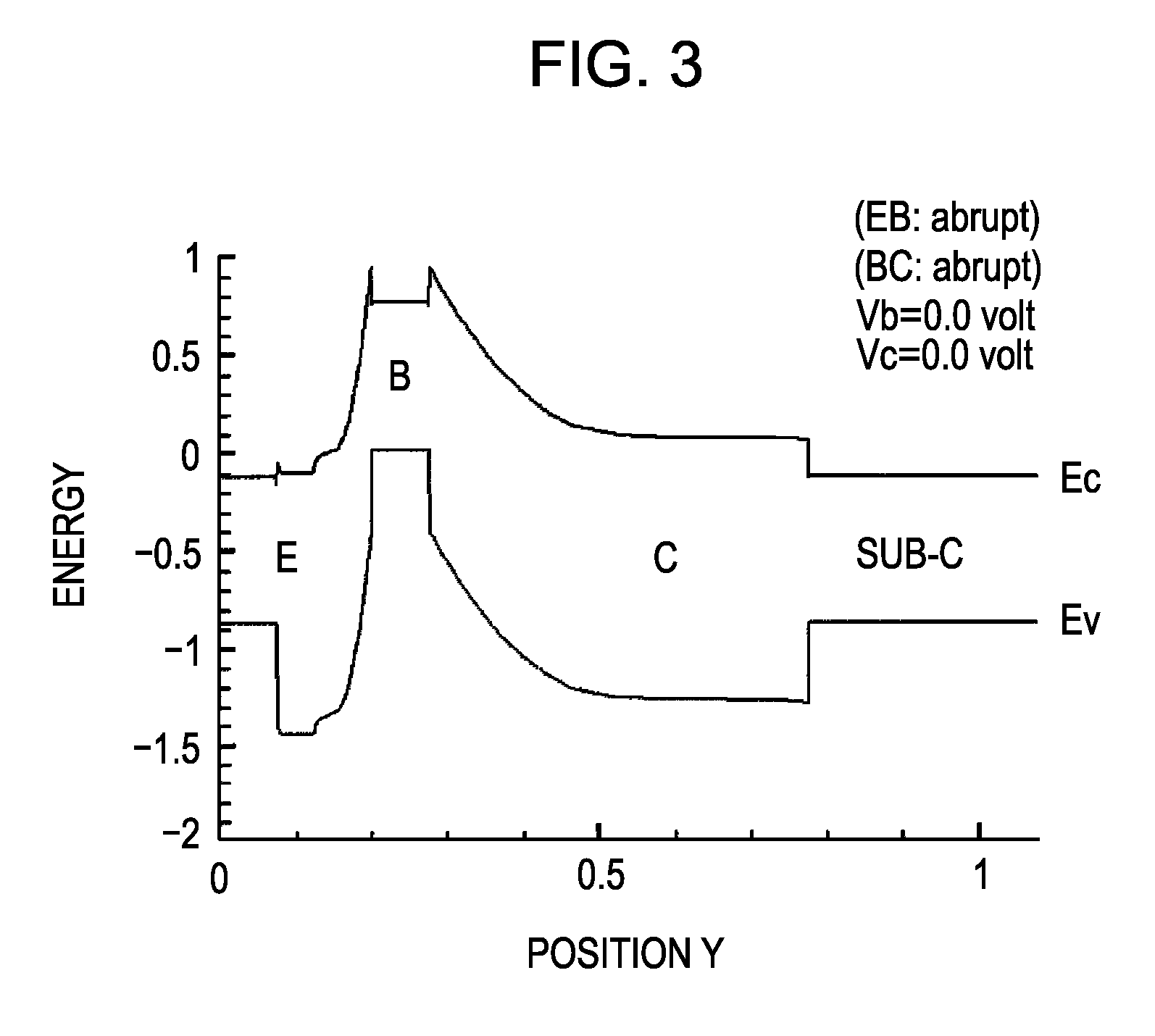
ActiveUS20070023783A1Decrease thicknessEasy to produceSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorDevice material
A semiconductor device includes an emitter layer: a base layer; and a collector layer, wherein the collector layer and the emitter layer each include a heavily doped thin sublayer having a high impurity concentration, and each of the heavily doped thin sublayers has an impurity concentration higher than those of semiconductor layers adjacent to each heavily doped thin sublayer.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Semiconductor acceleration sensor using doped semiconductor layer as wiring
InactiveUS20040016981A1Reduce impactMinimize fluctuationAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesElectricityStress induced
A semiconductor acceleration sensor is provided, which has the capability of preventing a situation that detection accuracy of acceleration deteriorates due to undesirable thermal stress induced when a metal layer wiring is used in the acceleration sensor. This sensor comprises a frame, a weight, at least one pair of beams made of a semiconductor material, via which said weight is supported in the frame, and at least one resistor element formed on each of the beams to thereby detect acceleration according to piezoelectric effect of the resistor element. The sensor also includes a doped semiconductor layer formed in a top surface of each of the beams as a wiring for electrically connecting with the resistor element.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
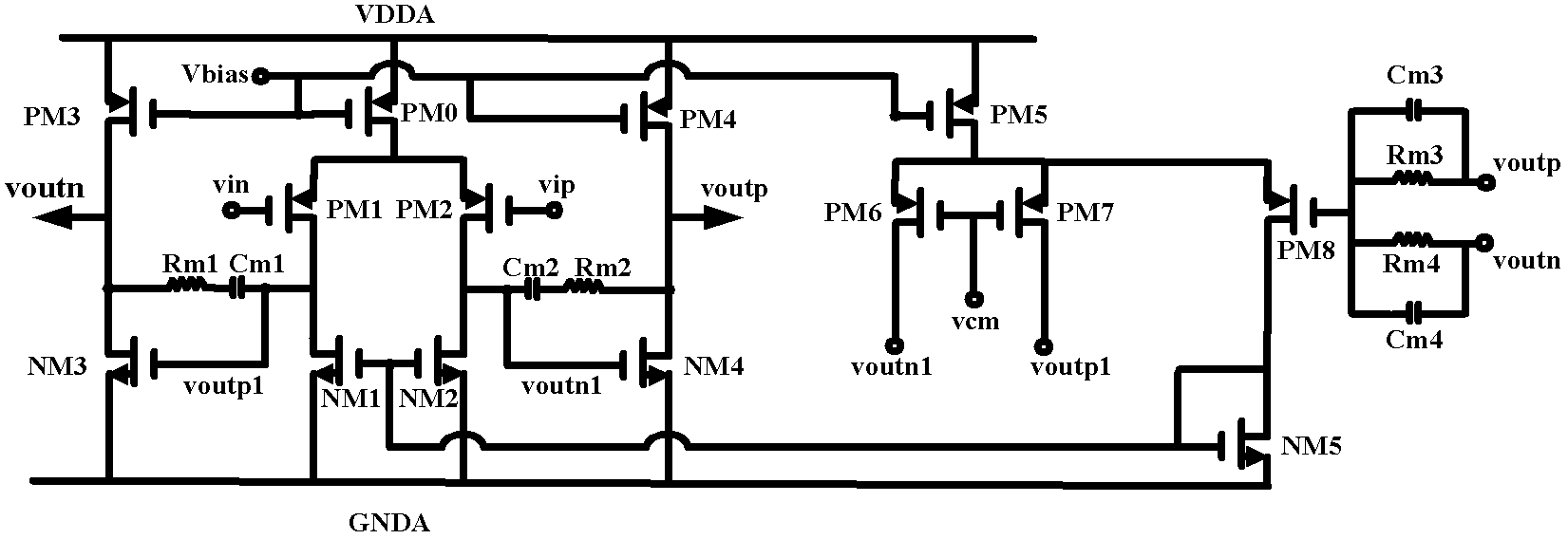
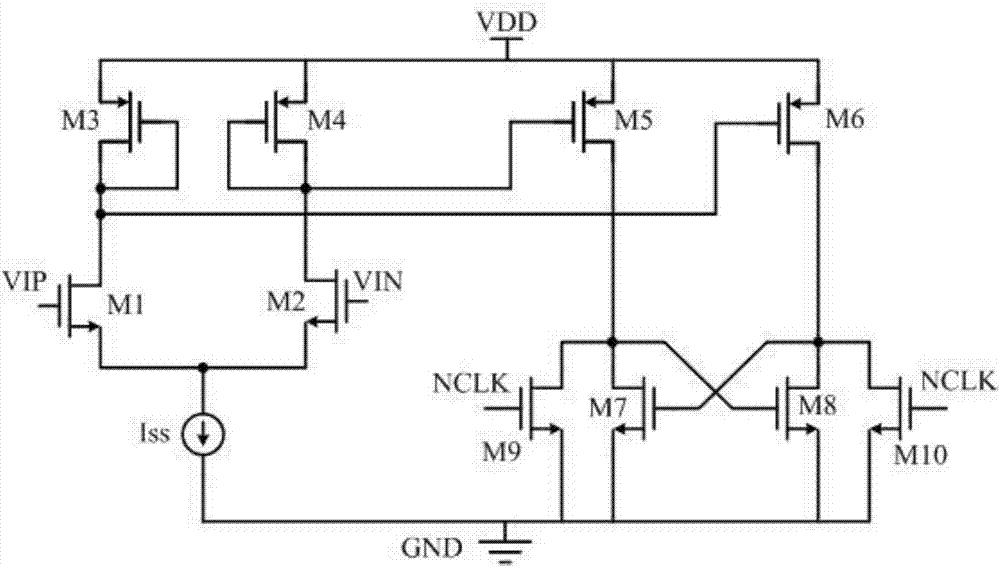
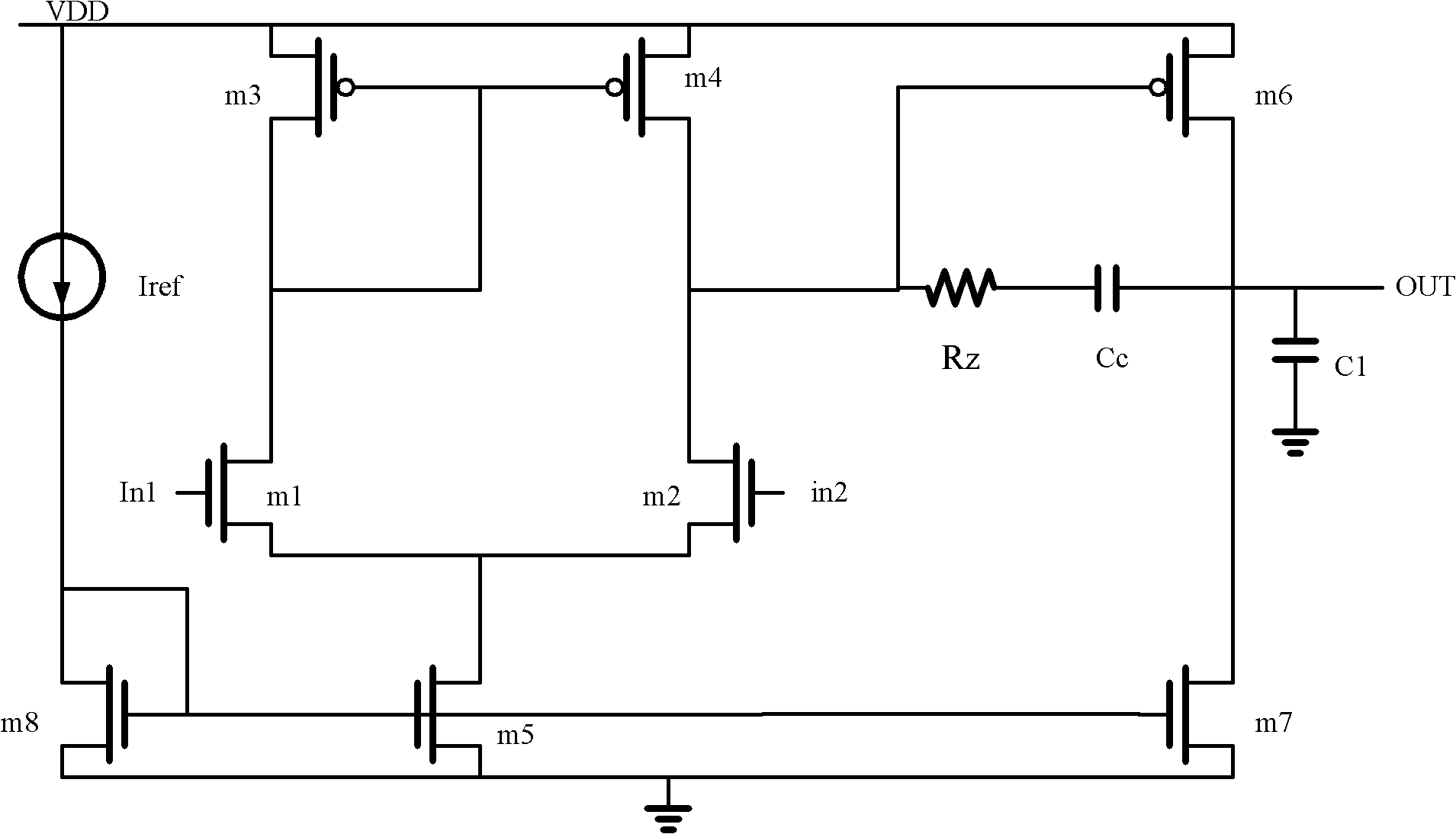
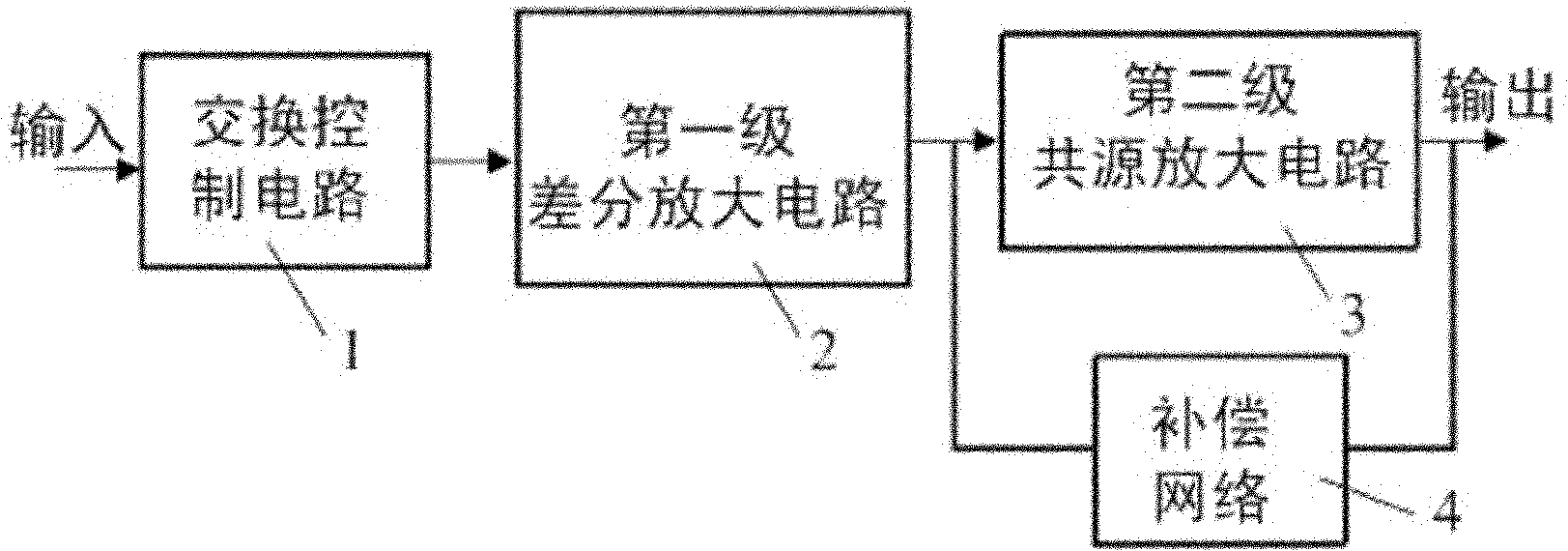
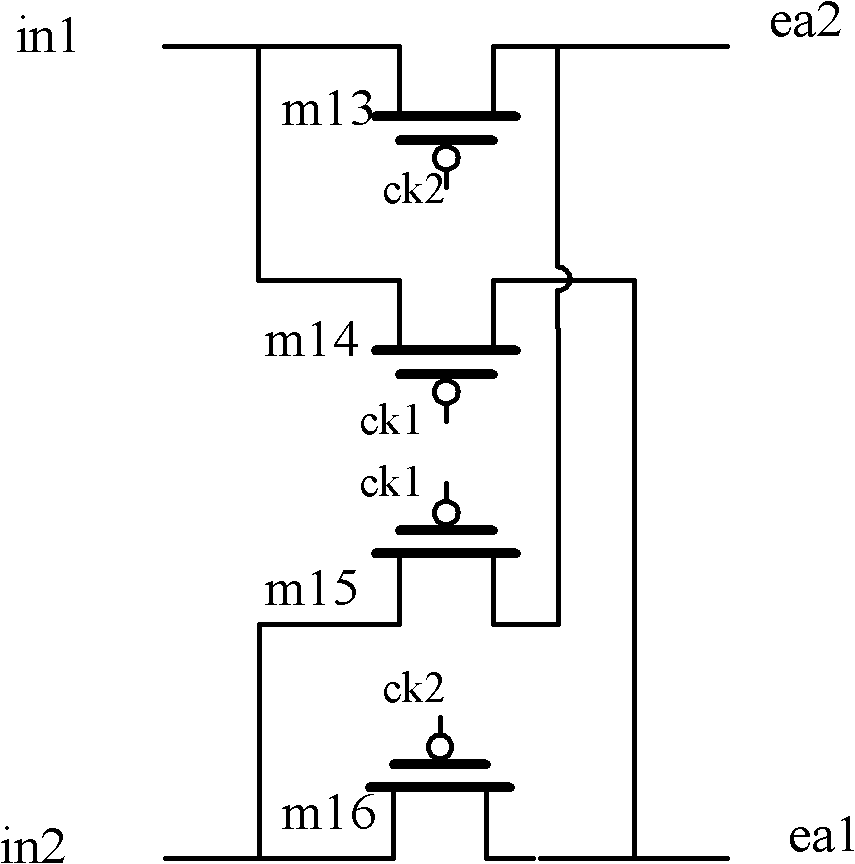
Circuit structure for reducing input offset voltage of two-stage operational amplifier
ActiveCN102130659ALower Input Offset VoltageLower Offset VoltageDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCMOSAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a circuit structure for reducing input offset voltage of a two-stage operational amplifier, which comprises a switching control circuit, a first-stage differential amplification circuit, a second-stage common-source amplification circuit and a compensation network, wherein the output end of the switching control circuit is connected with the input end of the first-stage differential amplification circuit, the output end of the first-stage differential amplification circuit is connected with the input end of the second-stage common-source amplification circuit, and the compensation network is further connected between the input end and the output end of the second-stage common-source amplification circuit. The circuit structure has the benefits that the offset of theoperational amplifier is reduced by adopting an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) switching tube to control and exchange signals at the positive and the negative input ends and the signals at the output end of the operational amplifier; as only the MOS switching tube is increased in the circuit, the circuit structure only needs very small area and very low power consumption; and the circuit does not affect the gain of the operational amplifier, the phase margin, the power supply voltage rejection ratio, the common-mode input range and other performance indexes while reducing the input offset voltage of the operational amplifier, and can be applied in mainstream CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) circuit systems.
Owner:XIAN JIEHANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
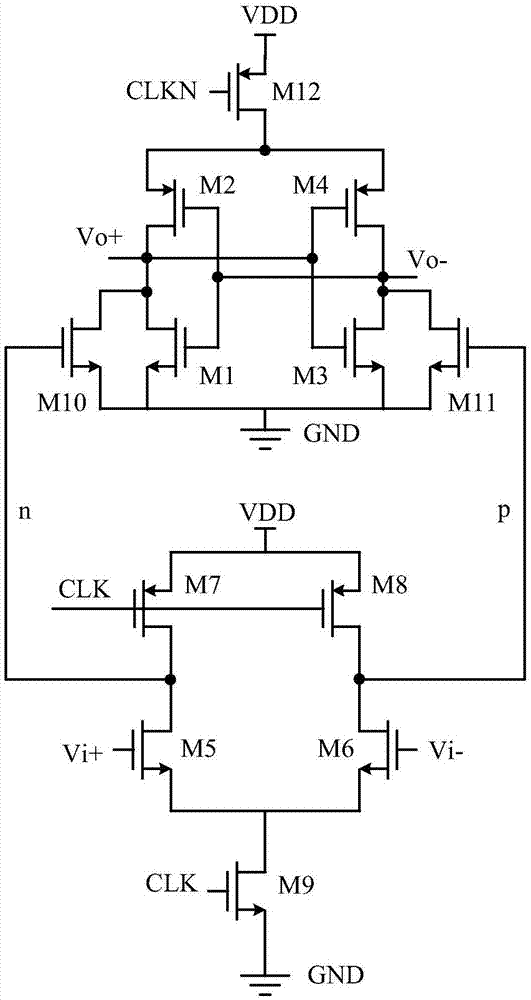
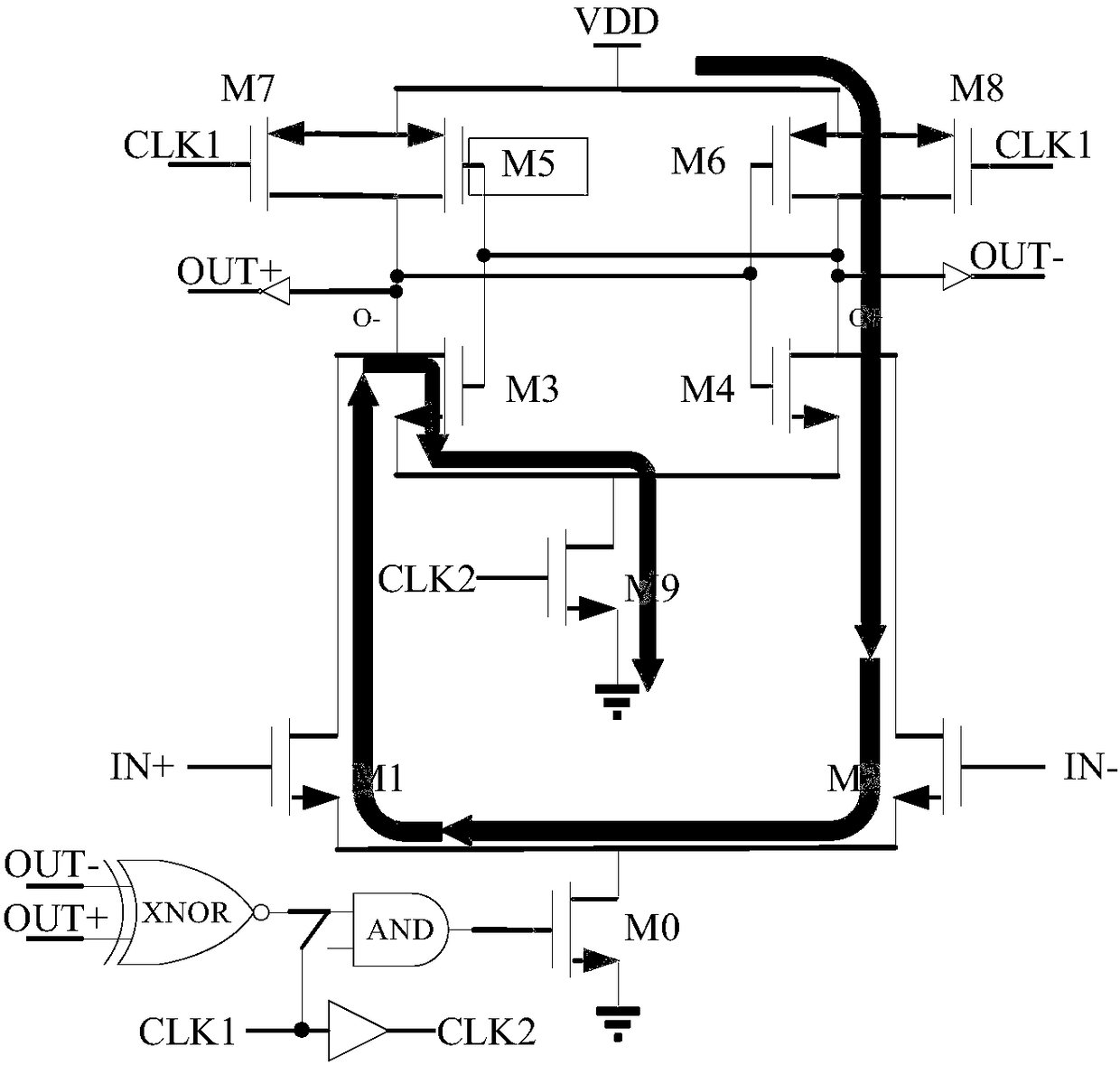
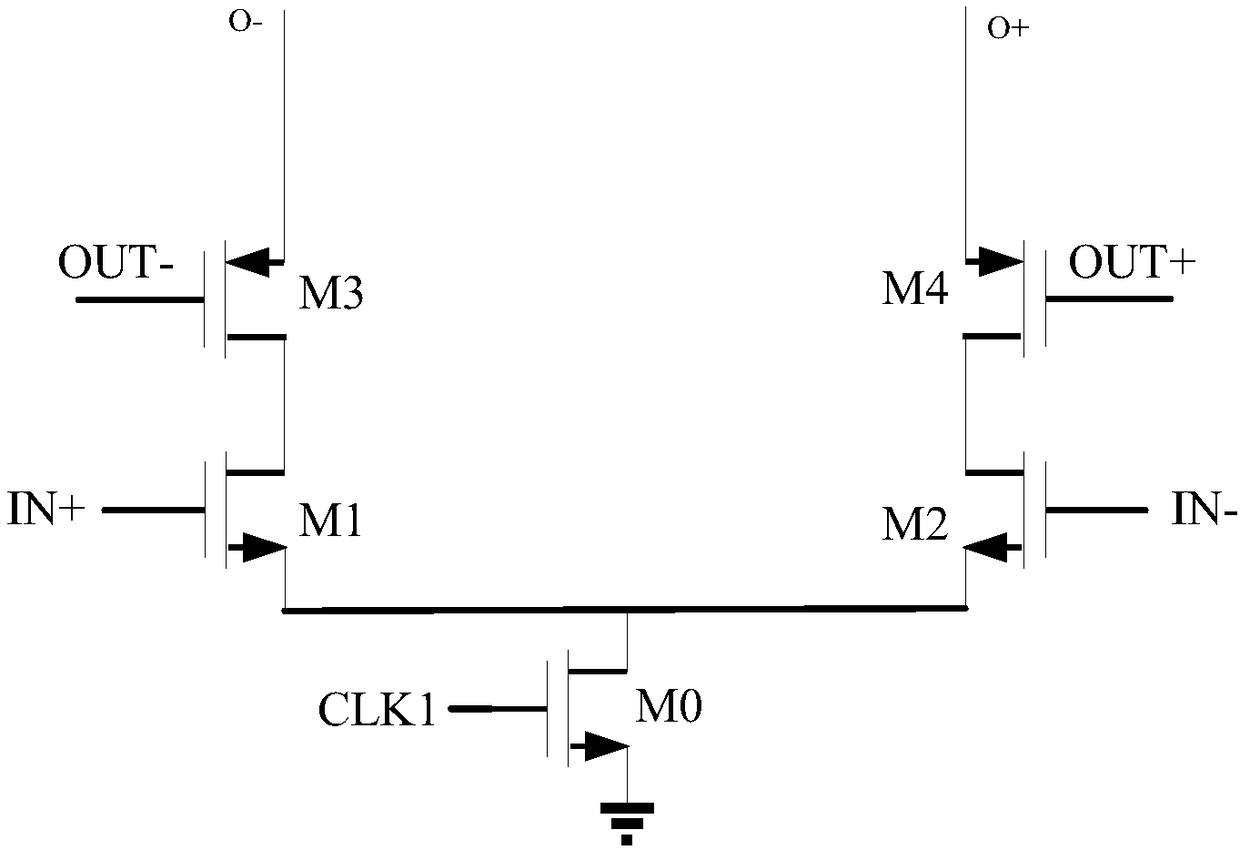
Dynamic comparator
InactiveCN108540130ALower Offset VoltageReduce power consumptionPower saving provisionsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectricityAmplifier
The invention discloses a dynamic comparator. The dynamic comparator comprises a pre-amplifier and a positive feedback latch, wherein the pre-amplifier is controlled by a clock signal CLK1 and outputsignals OUT+ and OUT- of a comparator; the positive feedback latch is controlled by a clock signal CLK2; when the CLK1 and the CLK2 are at a low level, a tail current tube of the pre-amplifier and a tail current tube of the positive feedback latch are both in a cut-off state, two switch tubes of the positive feedback latch enter a conductive state, two outputs of the latch reach a power voltage, the latch enters a reset stage, and two switch tubes of the pre-amplifier are controlled by the OUT+ and the OUT- to enter a conductive state; and when the signal CLK1 and the signal CLK2 sequentiallyreach a high level, the tail current tube of the pre-amplifier and the tail current tube of the positive feedback latch both enter a conductive state, the pre-amplifier works in an amplification state, amplifies an input signal and sends the amplified input signal to a latch node of the latch, the positive feedback latch works and outputs a comparison result, and after the two output signals OUT+and OUT- of the comparator pass through inverters, either of the two output signals increases and controls the corresponding switch tube (M3 or M4) of the pre-amplifier to enter a cut-off state, so that a path is cut off.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
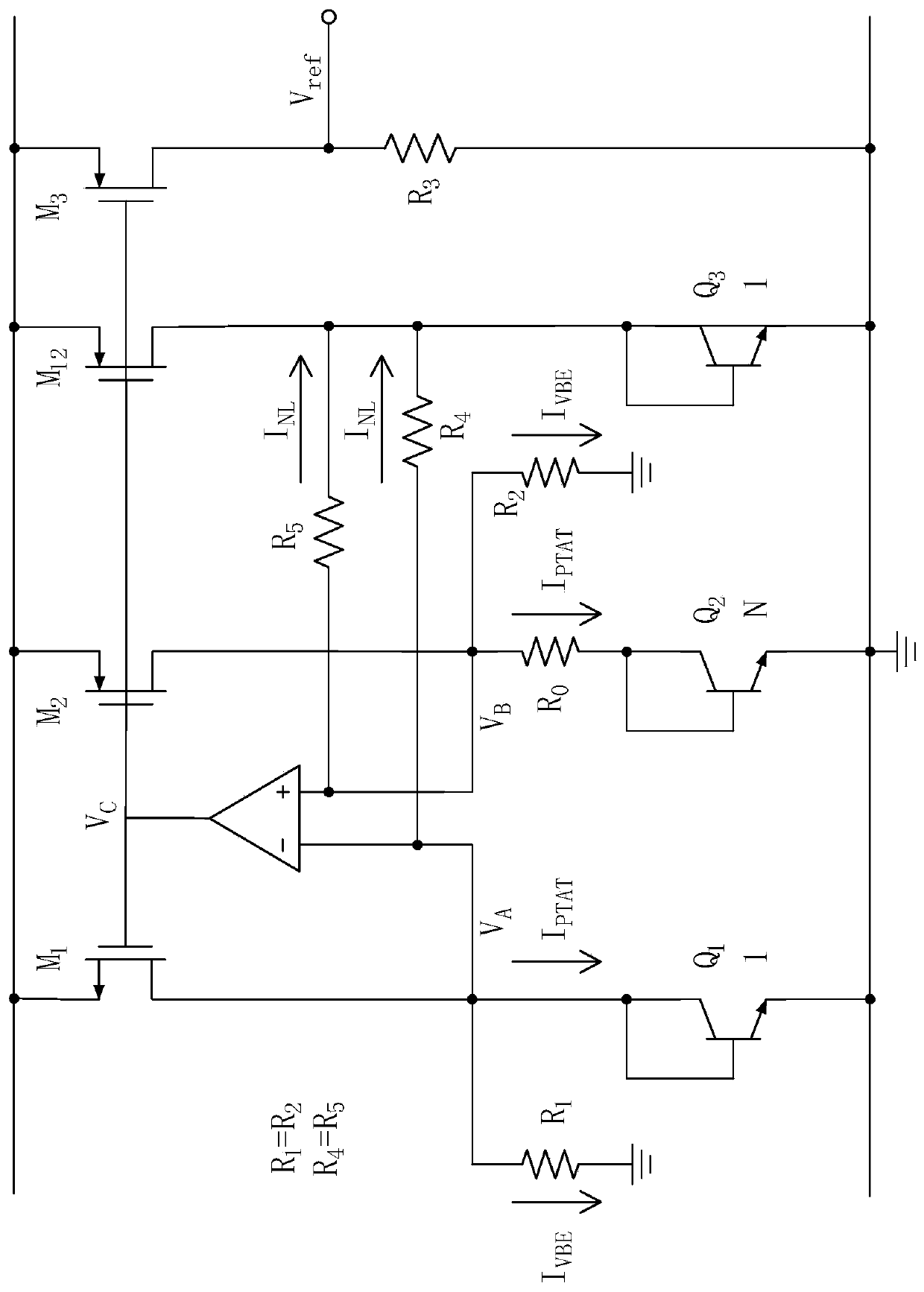
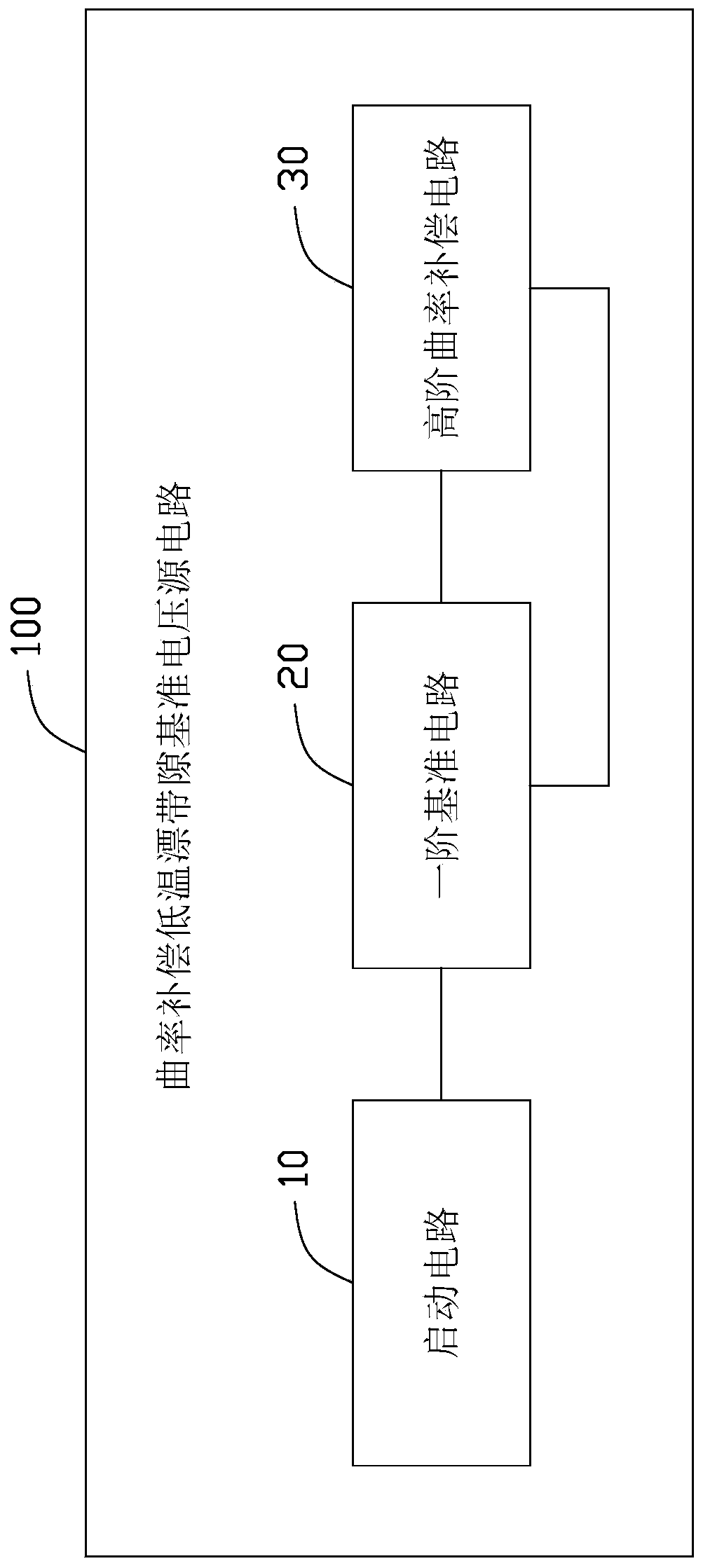
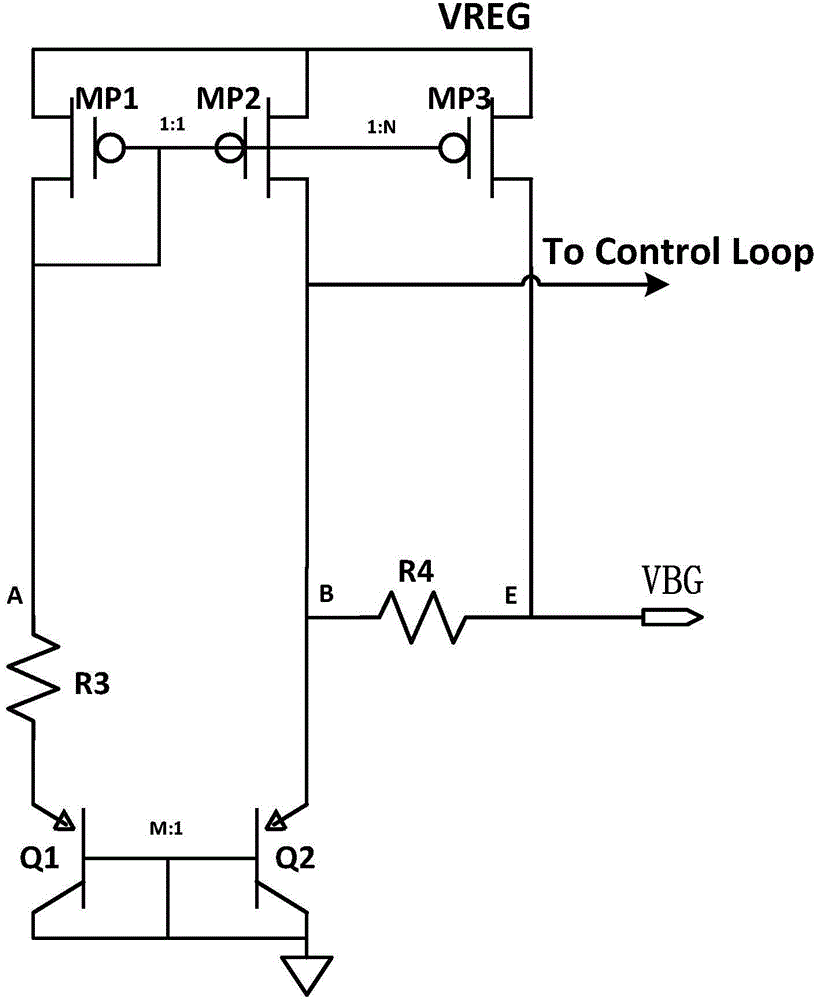
Curvature compensation low-temperature drift band-gap reference voltage source circuit
The embodiment of the invention provides a curvature compensation low-temperature drift band-gap reference voltage source circuit. The curvature compensation low-temperature drift band-gap reference voltage source circuit is used for generating a reference voltage, and comprises a starting circuit, a first-order reference circuit and a high-order curvature compensation circuit; the starting circuit is used for providing starting voltage for a voltage reference source circuit so as to prevent the voltage reference source circuit from working in a zero state region, the first-order reference circuit is used for generating low-temperature coefficient reference voltage, and the high-order curvature compensation circuit is used for performing high-order temperature curvature compensation on thefirst-order reference circuit. According to the technical scheme, influence of input offset voltage and noise of an operational amplifier is effectively reduced in a multi-stage PNP superposition mode, and meanwhile, a high-order curvature compensation method is provided for the multi-stage PNP superposition band-gap reference source circuit, so that the temperature drift coefficient of the band-gap reference source is effectively reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Current feedback operational amplifier circuit
ActiveCN102368680ALower Offset VoltageOvercome the disadvantage of large static errorNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDifferential amplifiersCommon emitterCommon base
The invention discloses a current feedback operational amplifier circuit comprising a power supply, a bias current supply unit, a first common base-common emitter current mirror, a second common base-common emitter current mirror, a static bias circuit, an input buffer stage, a voltage conversion stage and a drive output unit, wherein the drive output unit comprises a bias voltage circuit and an output buffer stage; the bias current supply unit is respectively connected with the input buffer stage through the first common base-common emitter current mirror and the second common base-common emitter current mirror and used for supplying bias current; and the static bias circuit is respectively connected with the inverted input end of the input buffer stage and the voltage conversion stage and used for stabilizing a static working point of the inverted input end. The current feedback operational amplifier circuit has the advantages of lower offset voltage, stronger on-load capacity and higher conversion rate and is beneficial to improvement of the precision and the linearity of the entire operational amplifier.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Band-gap reference source with low offset voltage and high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio)
ActiveCN105320205AReduces the impact of channel length modulation effectsLower Offset VoltageElectric variable regulationChannel length modulationEngineering
The invention discloses a band-gap reference source with low offset voltage and a high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio). The band-gap reference source comprises a first P-channel field-effect transistor, a second P-channel field-effect transistor, a third P-channel field-effect transistor, a fourth P-channel field-effect transistor, a first resistor, a second resistor, a third resistor, a first bipolar transistor, a second bipolar transistor and a voltage feedback circuit. According to the band-gap reference source with the low offset voltage and the high PSRR, with the adoption of a double-layer current mirror structure and addition of biasing resistors, influence of channel length modulation effects of current mirrors is reduced, the accuracy of current multiplication coefficients is guaranteed, and maladjustment of output voltage is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Reference voltage generating circuit, a semiconductor integrated circuit and a semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus
InactiveUS7268529B2Reducing offset voltage dependencyThe output voltage is accurateStatic storageElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage reference
The present invention provides a band gap type reference voltage generating circuit and a semiconductor integrated circuit having the same, capable of generating a reference voltage of about 1.2V or less whose temperature dependency is low, and realizing reduced offset voltage dependency of a differential amplifier. A band gap part has: a first resistor and a first bipolar transistor connected in series between power supply voltage terminals; a second resistor, a second bipolar transistor, and a third resistor connected in series between the power supply voltage terminals; and a differential amplifier that receives voltages generated by the first and second resistors, and an output of the differential amplifier is applied to the bases of the two transistors. The output part has a third bipolar transistor having a base to which the output of the differential amplifier is applied, a fourth resistor connected in series with the third bipolar transistor, a current mirror circuit for transferring current flowing in the third bipolar transistor, and a fifth resistor and a diode for converting the transferred current to voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Programmable gain amplifier
InactiveCN103944523ASolve output saturationHigh Common Mode Rejection RatioGain controlDifferential amplifiersProgrammable-gain amplifierThree level
The invention discloses a programmable gain amplifier which comprises three levels of amplifying circuits. The same-phase input end and the opposite-phase input end of the first-level amplifying circuit serve as the same-phase input end and the opposite-phase input end of the programmable gain amplifier respectively and form a pair of differential input ends of the programmable gain amplifier; the same-phase input end of the second-level amplifying circuit is connected with the opposite-phase output end of the first-level amplifying circuit, and the opposite-phase input end of the second-level amplifying circuit is connected with the same-phase output end of the first-level amplifying circuit; the same-phase input end of the third-level amplifying circuit is connected with the opposite-phase output end of the second-level amplifying circuit, and the opposite-phase input end of the third-level amplifying circuit is connected with the same-phase output end of the second-level amplifying circuit; the same-phase output end and the opposite-phase output end of the third-level amplifying circuit form a pair of differential output ends. The programmable gain amplifier can be used for amplifying micro physiological signals in the field of medical electronics so that high-precision gain can be achieved; meanwhile, adjustment can be achieved within a certain gain dynamic range, and the requirement for different amplitudes of input signals is met.
Owner:CHANGSHA YUNTENG MICROELECTRONICS
Semiconductor acceleration sensor
InactiveUS20060065054A1Reduce outputCheap and highly sensitiveAcceleration measurement using interia forcesForce measurementElectricityClassical mechanics
A semiconductor acceleration sensor is disclosed which has a small difference in acceleration detection sensitivity among X, Y, and Z axes and a high detection sensitivity. The acceleration sensor has a mass portion in its center, a support frame surrounding the mass portion, and a plurality of flexible arms connecting the mass portion and the support frame. The flexible arm has wider portions on both ends and a narrower portion between the wider portions. Piezo resistors are restrictedly provided within a top surface region of the wider portion of the flexible arm, and through holes connecting metal wires and the piezo resistors are disposed on the mass portion / support frame. The plurality of flexible arms are symmetric with respect to the center of the mass portion, and each of the flexible arms is symmetric with respect to the center line of the flexible arm.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
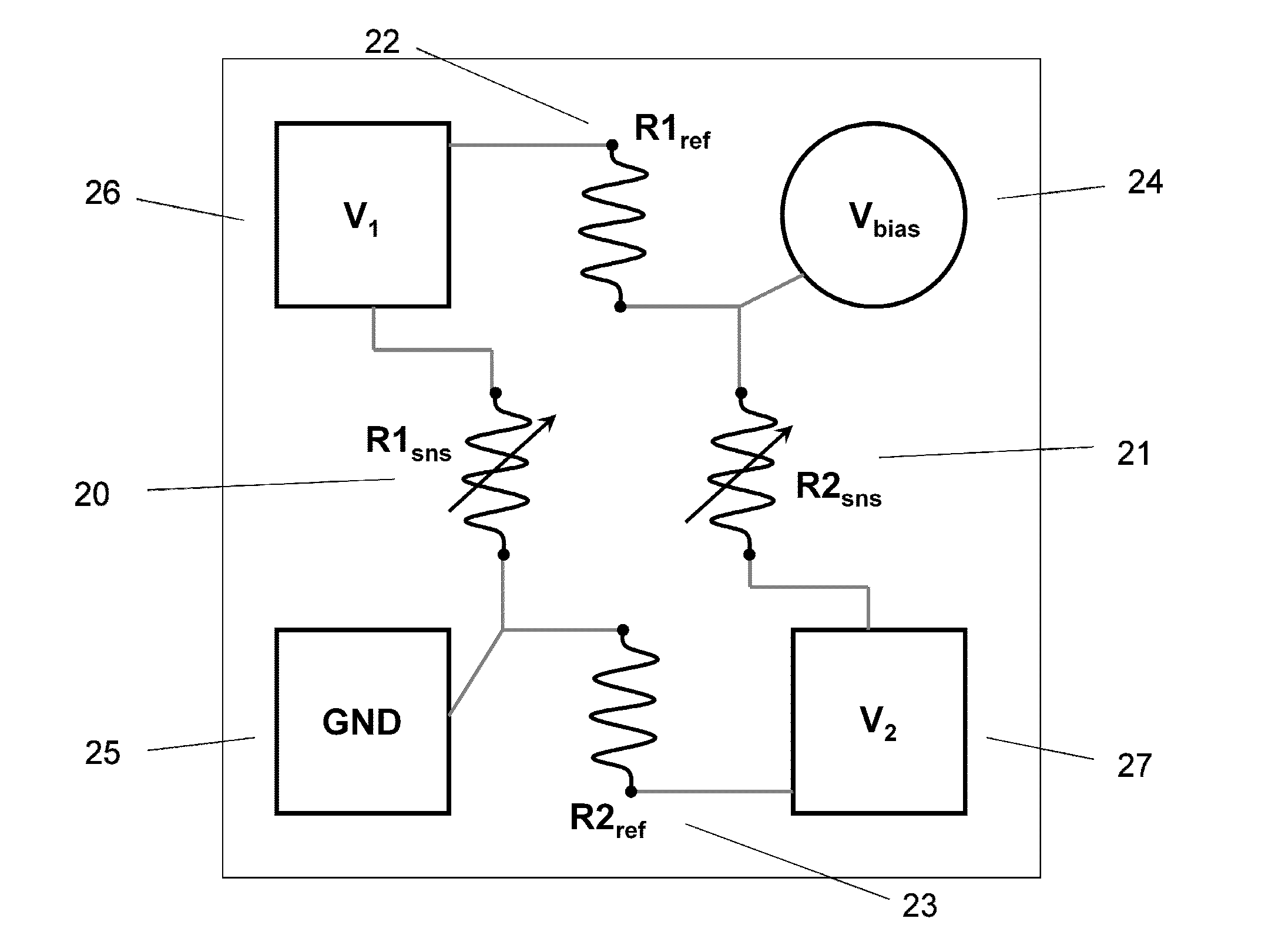
Single-chip referenced full-bridge magnetic field sensor
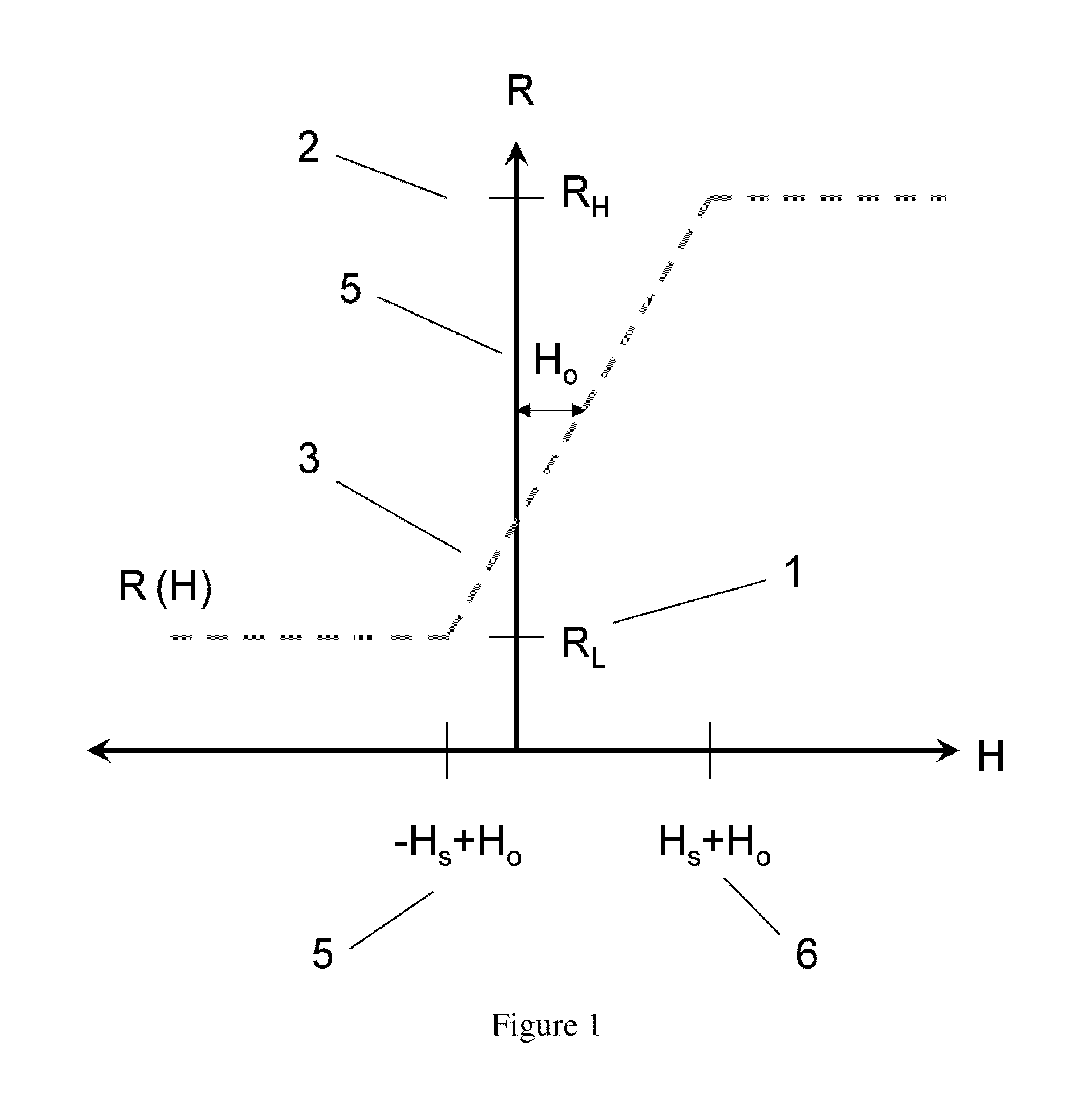
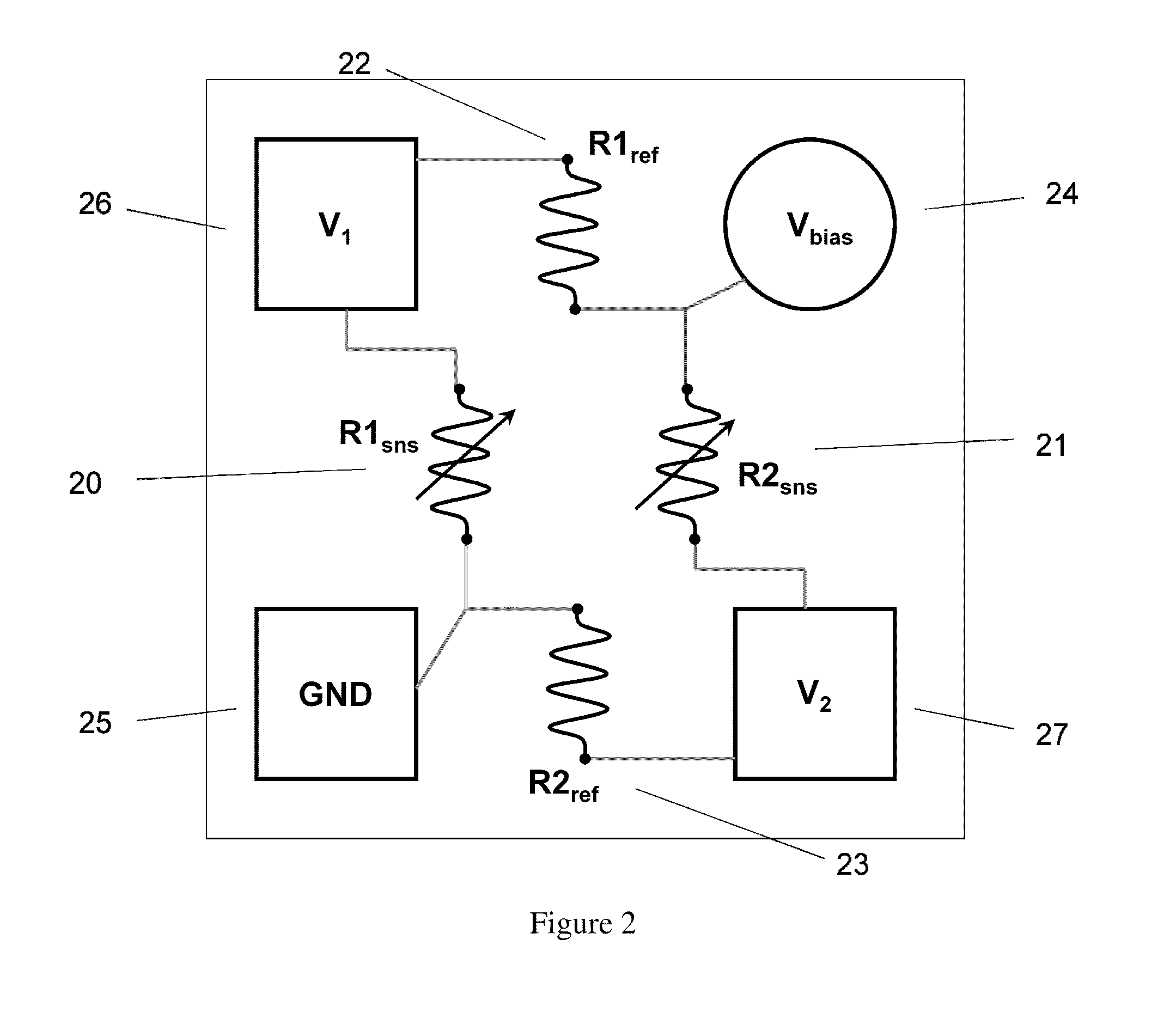
ActiveUS20140054733A1Improve temperature stabilityLower Offset VoltageMagnetic measurementsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceFull bridge
The present invention discloses a single-chip referenced full-bridge magnetoresistive magnetic-field sensor. The single-chip sensor is a Wheatstone bridge arrangement of magnetoresistive sensing elements and reference elements. The sensing elements and reference elements are formed from either magnetic tunnel junctions or giant magnetoresistive materials. The sensitivity of the reference and sensor elements is controlled through one or a combination of magnetic bias, exchange bias, shielding, or shape anisotropy. Moreover, the bridge output is tuned by setting the ratio of the reference and sensor arm resistance values to a predetermined ratio that optimizes the bridge output for offset and symmetry. The single-chip referenced-bridge magnetic field sensor of the present invention exhibits excellent temperature stability, low offset voltage, and excellent voltage symmetry.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Acceleration sensor device having piezo-resistors measuring acceleration
InactiveUS7716984B2Reduce damping periodTransmission easilyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsAir cycleEngineering
An acceleration sensor device comprising: an acceleration sensor chip comprising a mass portion, a support frame and flexible arms having piezo-resistors on their top surfaces; and an upper regulation plate having an IC circuit, which is larger in area than the support frame, bonded to a top surface of the support frame; wherein the acceleration sensor chip and the upper regulation plate are placed in a protection case with a lid. The regulation plate protrudes from outside walls of the support frame to partition the space accommodating the chip in the protection case by the protrusion and to prevent air circulation above and below the regulation plate, so that a temperature rise due to the IC circuit among the piezo-resistors provided on the top surfaces of the flexible arms is kept uniform to reduce offset voltage.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Vertical hall sensors with reduced offset error
ActiveUS20160111631A1Improve conductivitySuitable for measuringSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor chipElectrically conductive
A semiconductor chip for measuring a magnetic field based on the Hall effect. The semiconductor chip comprises an electrically conductive well having a first conductivity type, in a substrate having a second conductivity type. The semiconductor chip comprises at least four well contacts arranged at the surface of the well, and having the first conductivity type. The semiconductor chip comprises a plurality of buffer regions interleaved with the well contacts and having the first conductivity type. The buffer regions are highly conductive and the buffer region dimensions are such that at least part of the current from a well contact transits through one of its neighboring buffer regions.
Owner:MELEXIS TECH NV +1
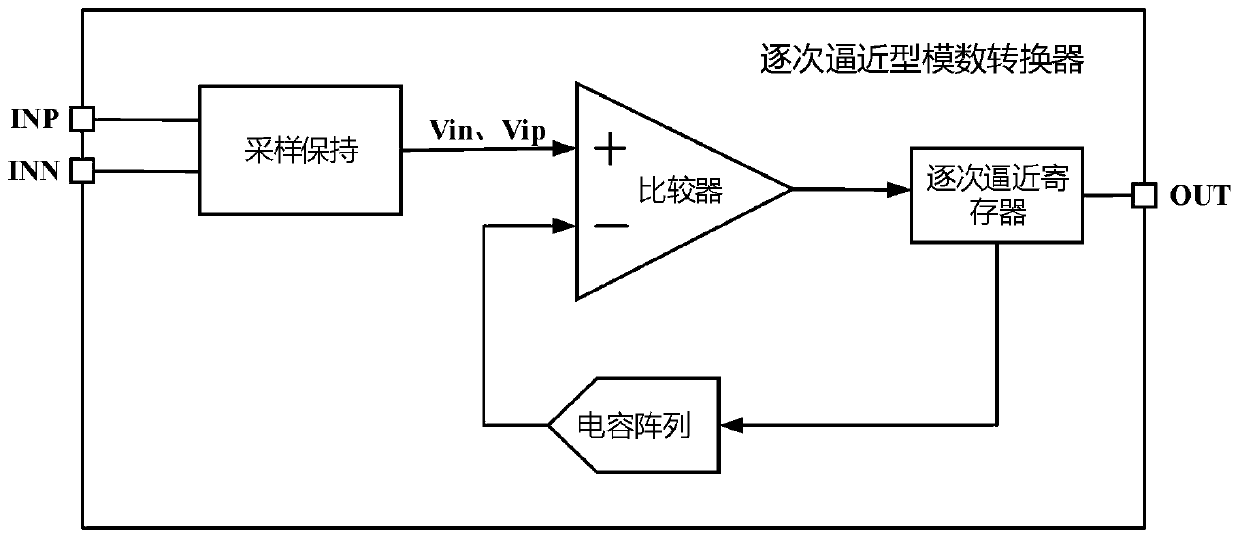
Ultra-low-power-consumption asynchronous successive approximation register type analog-to-digital converter
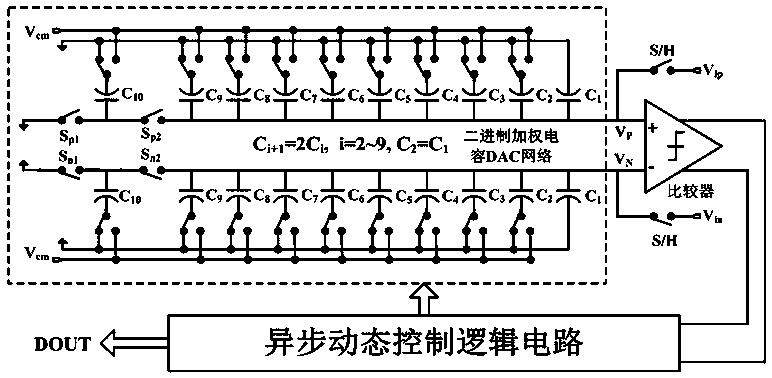
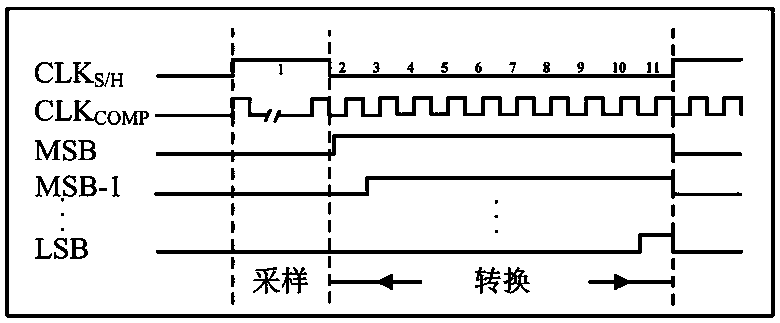
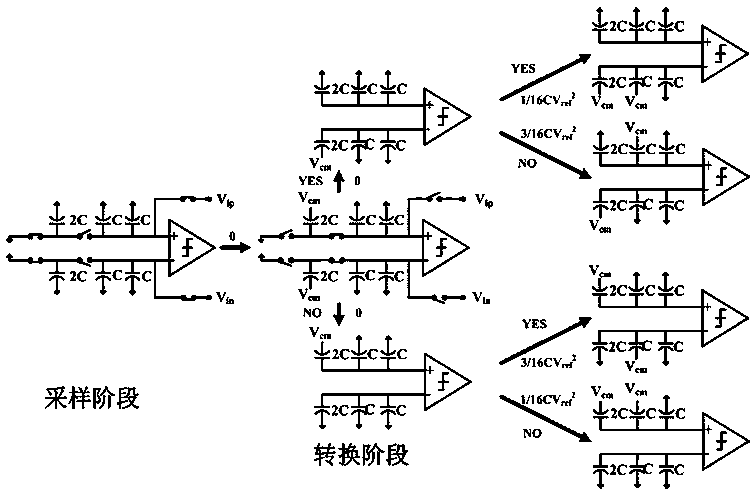
ActiveCN108449087AImprove linearityImprove conversion accuracyPower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsUltra low powerCapacitance
The invention belongs to the technical field of low-power-consumption integrated circuits, in particular to an ultra-low-power-consumption asynchronous successive approximation register type analog-to-digital converter. The analog-to-digital converter comprises two bootstrap sampling and holding switches S / H, four connection switches, two binary weighted capacitor DAC networks, a sub-threshold dynamic comparator and an asynchronous SAR control logic circuit, wherein the bootstrap sampling and holding switches S / H are used for sampling an analog differential input signal to upper pole plates ofthe two binary weighted capacitor DAC networks; and the four connection switches are controlled by the asynchronous SAR control logic circuit to determine a connection relationship between the upperpole plates of highest location capacitors of the binary weighted capacitor DAC networks, i.e. whether the upper pole plates of the highest location capacitors are connected with upper pole plates ofother non-highest location capacitors or connected with the ground.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
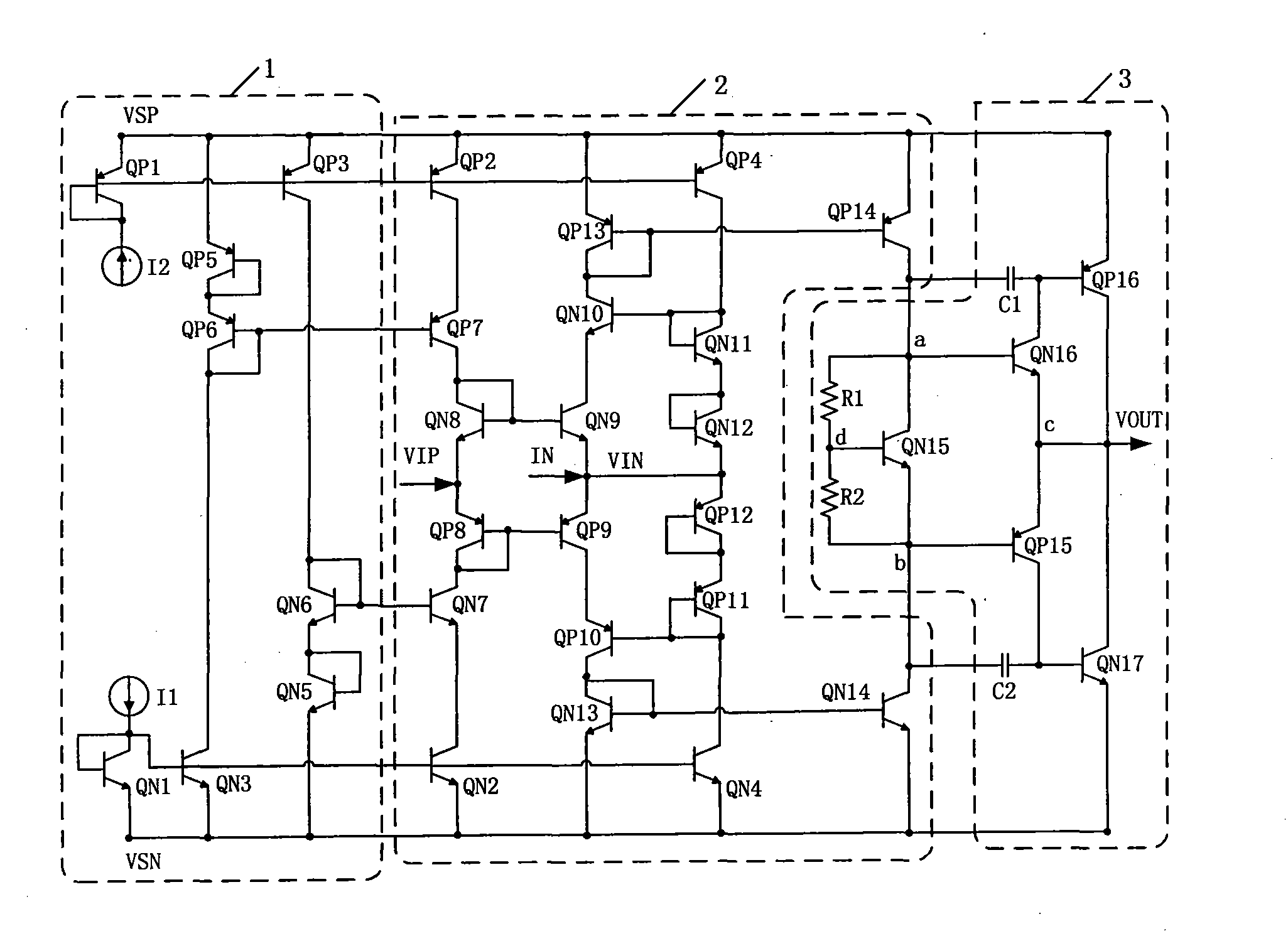
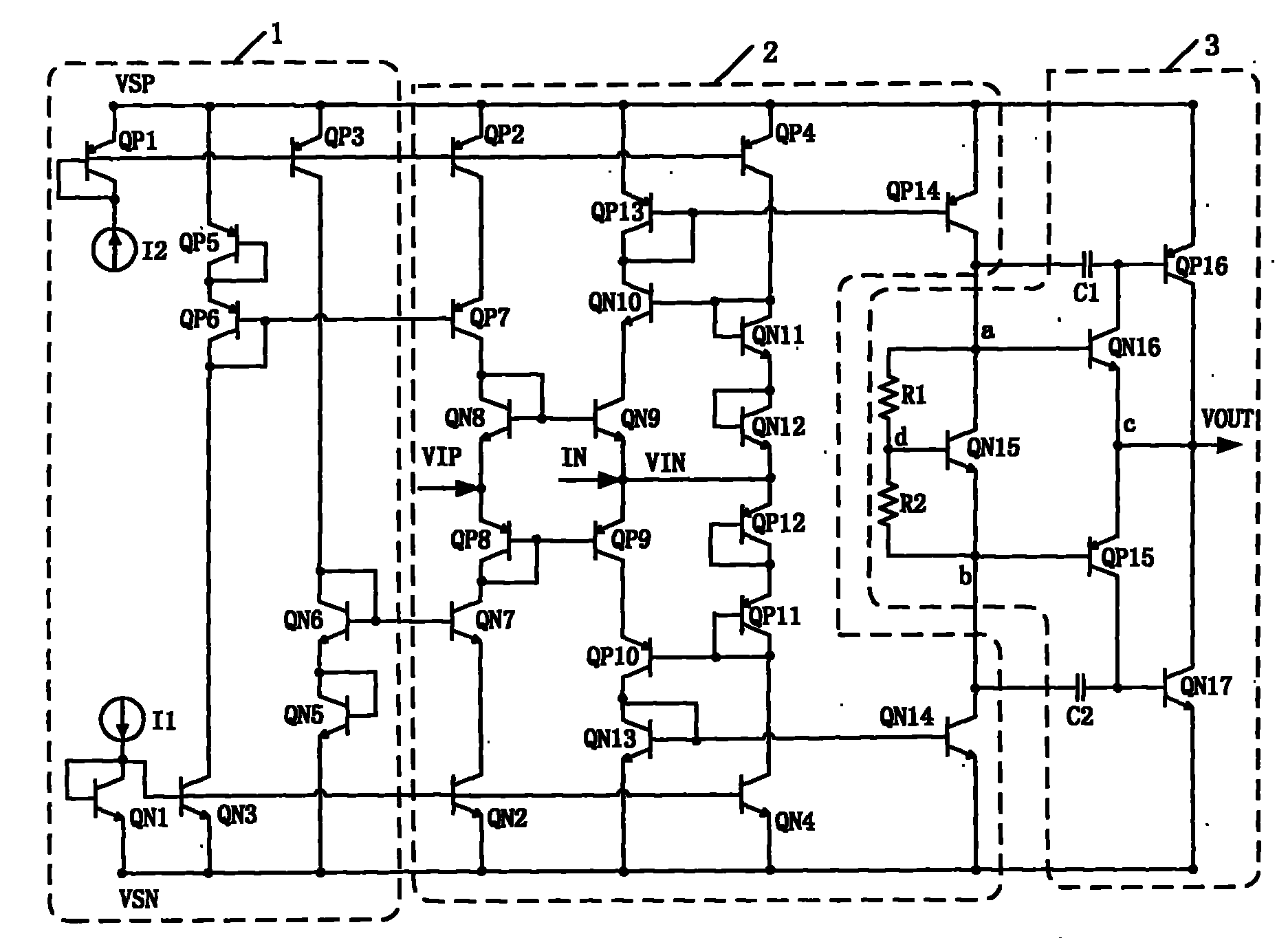
Fully differential amplifier with continuous-time offset reduction
ActiveUS20080204138A1Reducing voltage of firstLower Offset VoltageDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesSignal onEngineering
A fully differential amplifier circuit according to one embodiment includes a first section for generating first and second output signals on first and second outputs from first and second input signals; a first feedback loop coupled to the first section, the first feedback loop including a second section for adjusting the first output signal towards a common mode voltage level, and for reducing an offset voltage of the first output signal; a second feedback loop coupled to the first section, the second feedback loop including a third section for adjusting the second output signal towards the common mode voltage level, and for reducing an offset voltage of the second output signal; and a filter section positioned on the first and second feedback loops between outputs of the second and third sections and the first section.
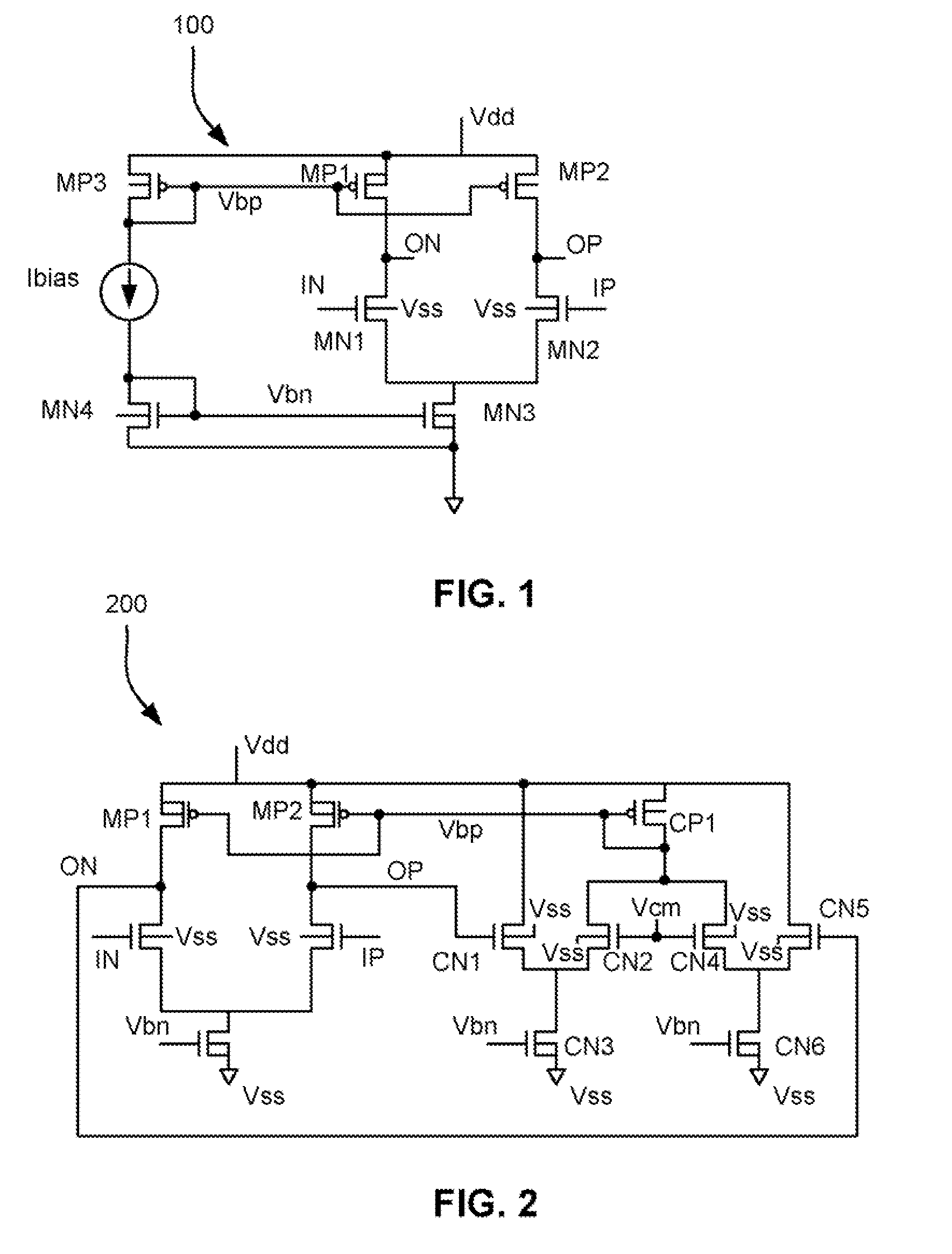
Owner:ZEST LABS INC
Apparatus for reducing offset voltage drifts in a charge amplifier circuit
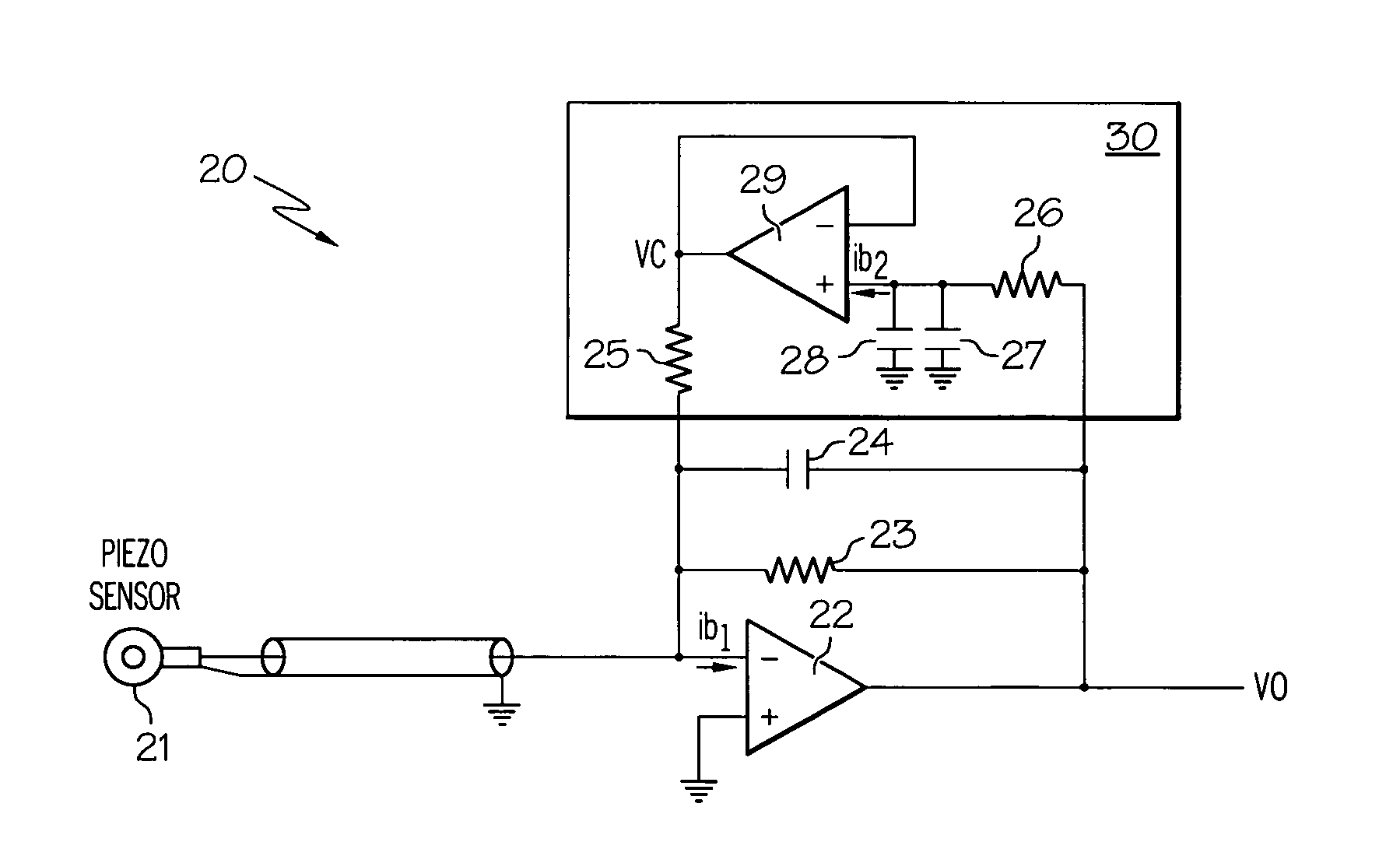
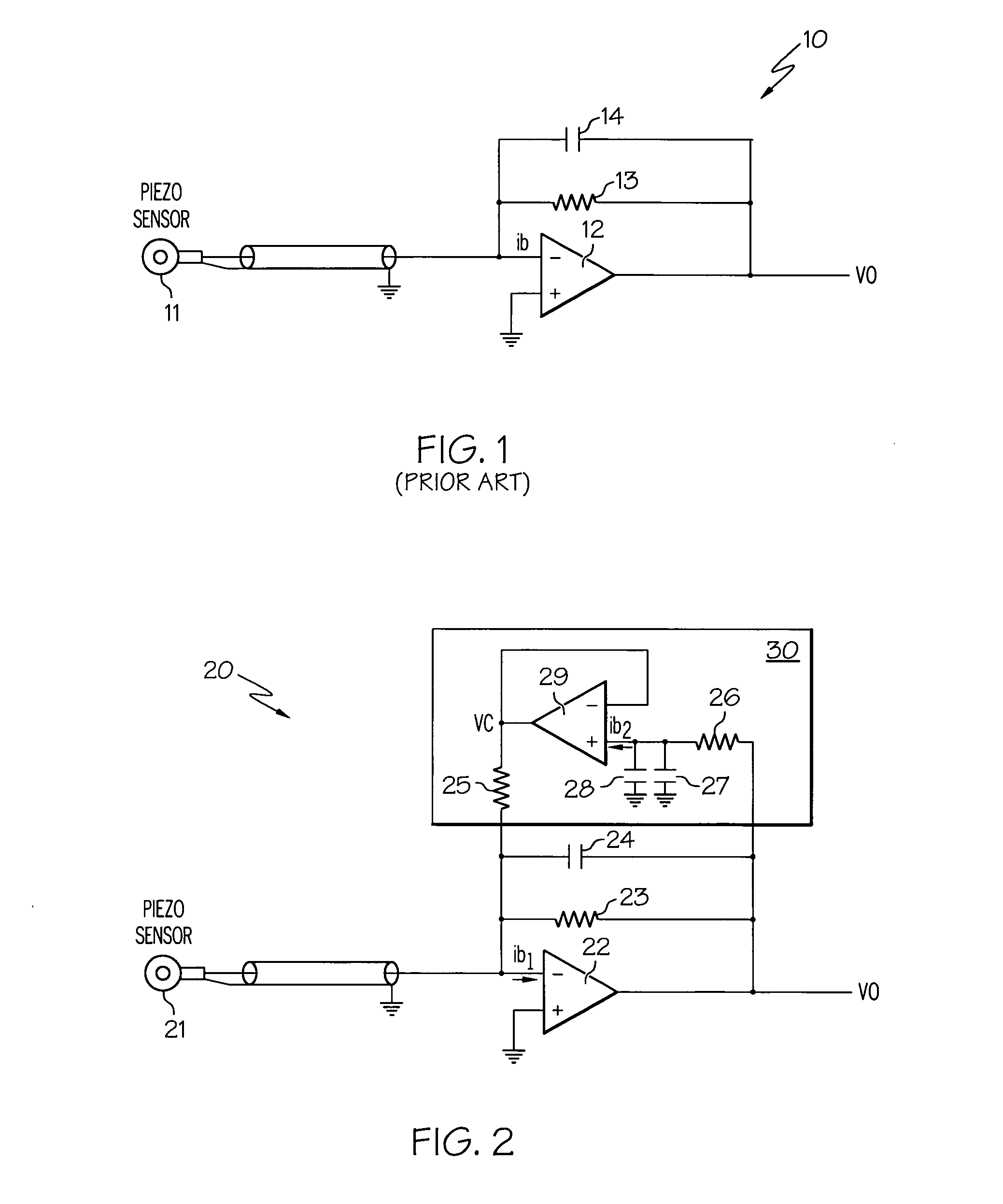
InactiveUS20070296496A1Reducing offset voltage driftLower Offset VoltageCharge amplifiersDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An apparatus for reducing offset voltage drifts in a charge amplifier circuit is disclosed. The apparatus includes a charge amplifier circuit and a bias current compensation circuit. The bias current compensation circuit supplies bias current to lower any offset voltage drift at the output of the charge amplifier.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Low offset input circuit and transmission system with the input circuit
InactiveUS20090304092A1High offset voltageSimple configurationPower amplifiersLine-transmissionLow offsetAdder–subtractor
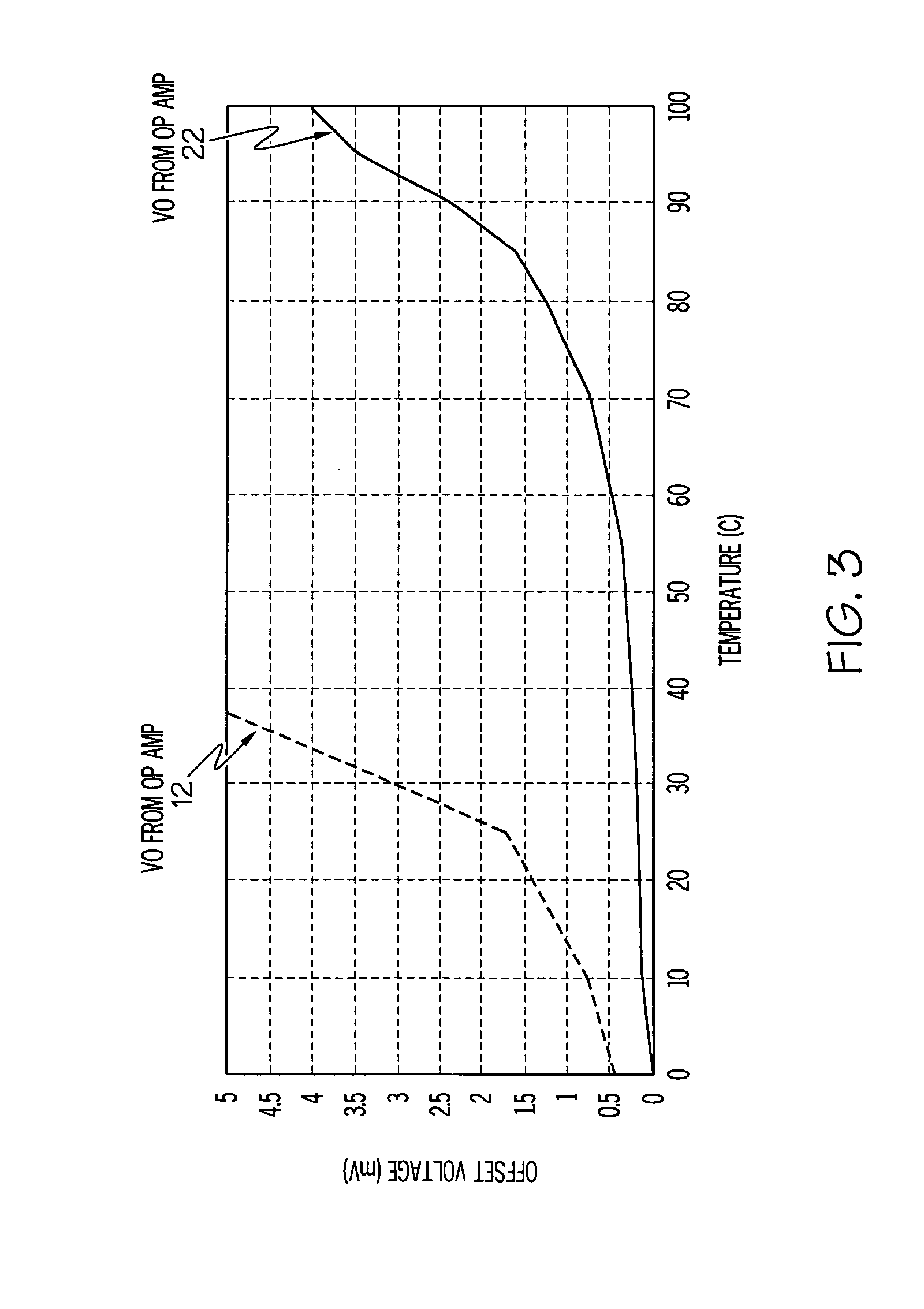
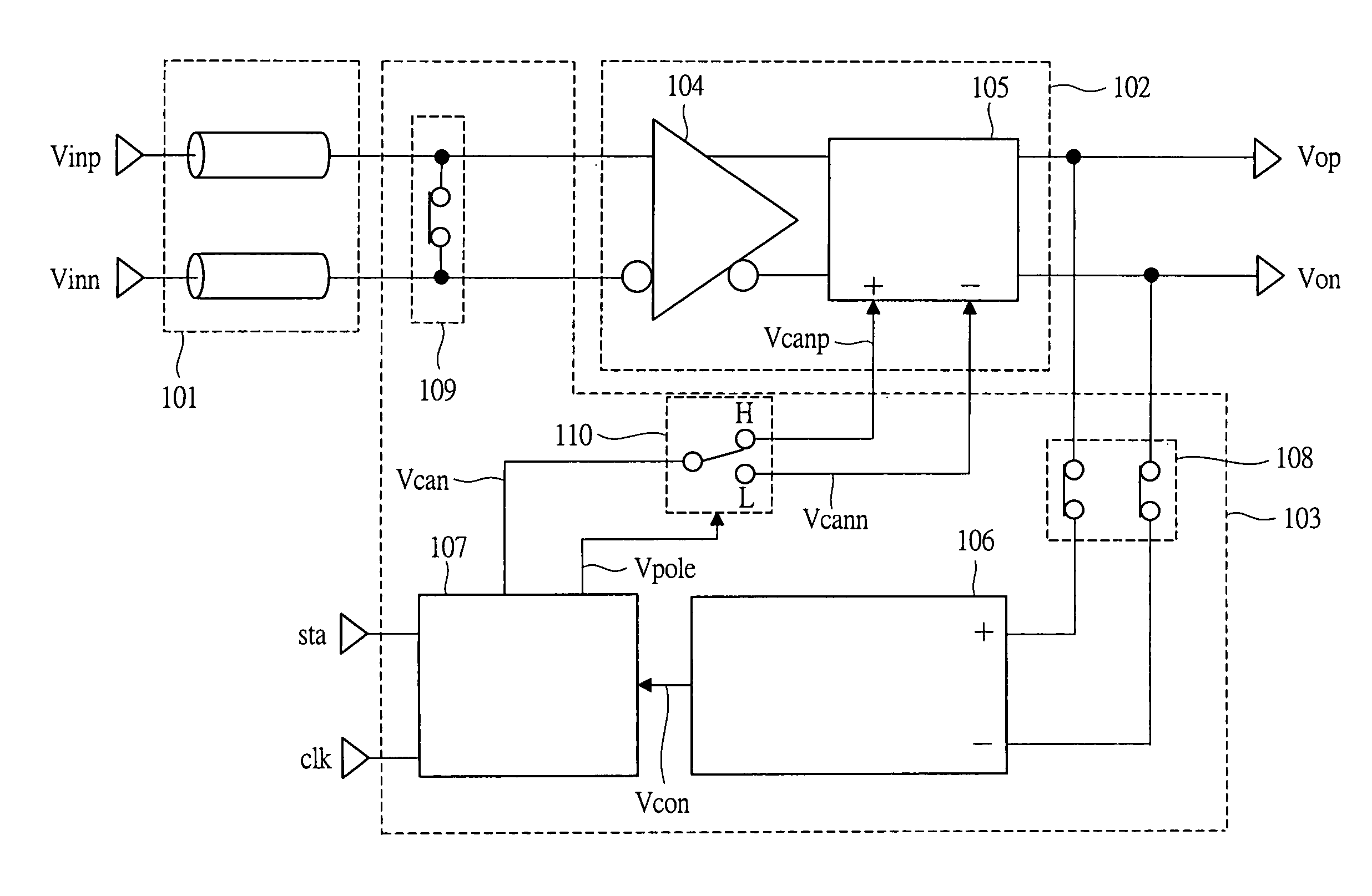
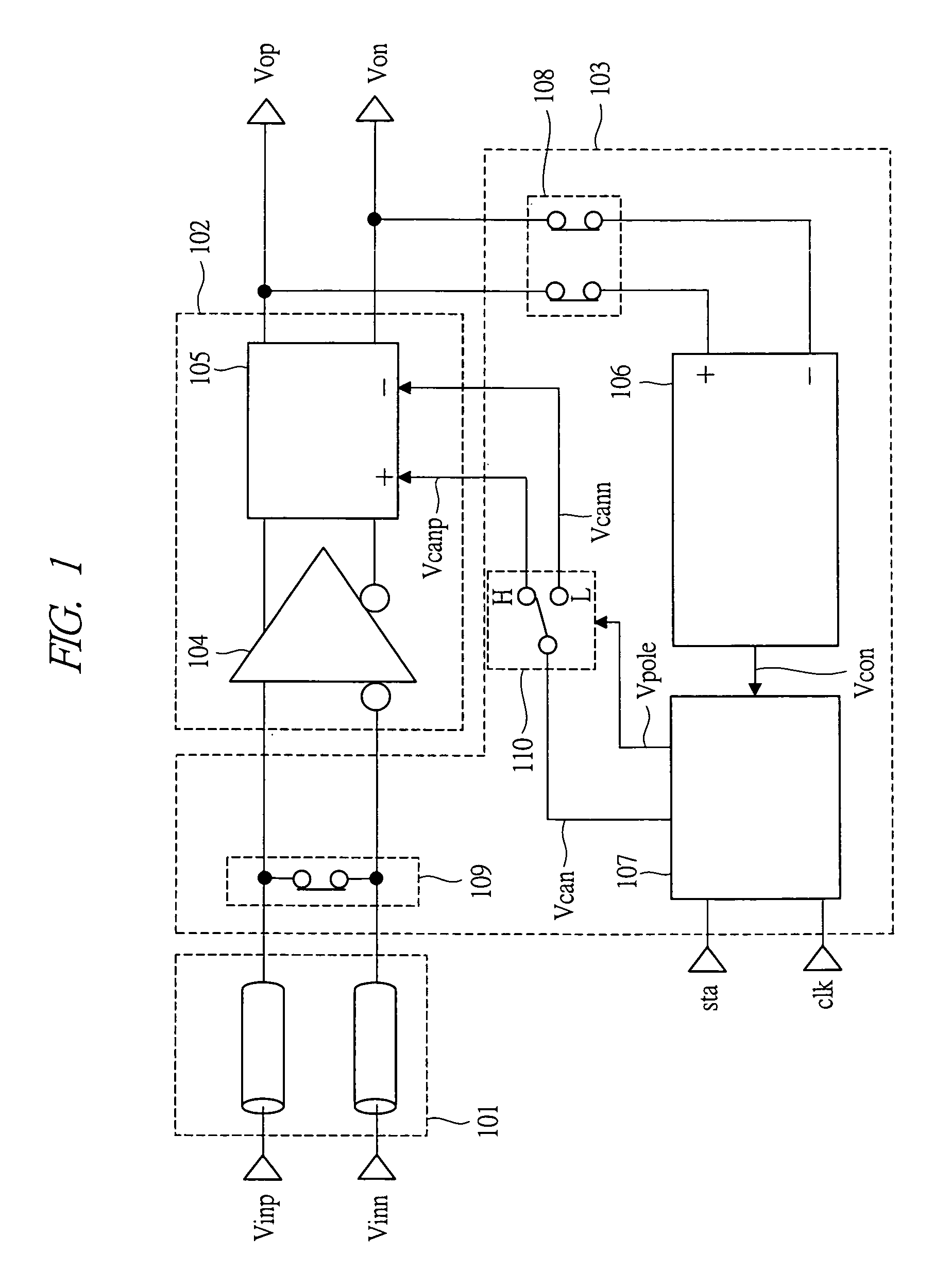
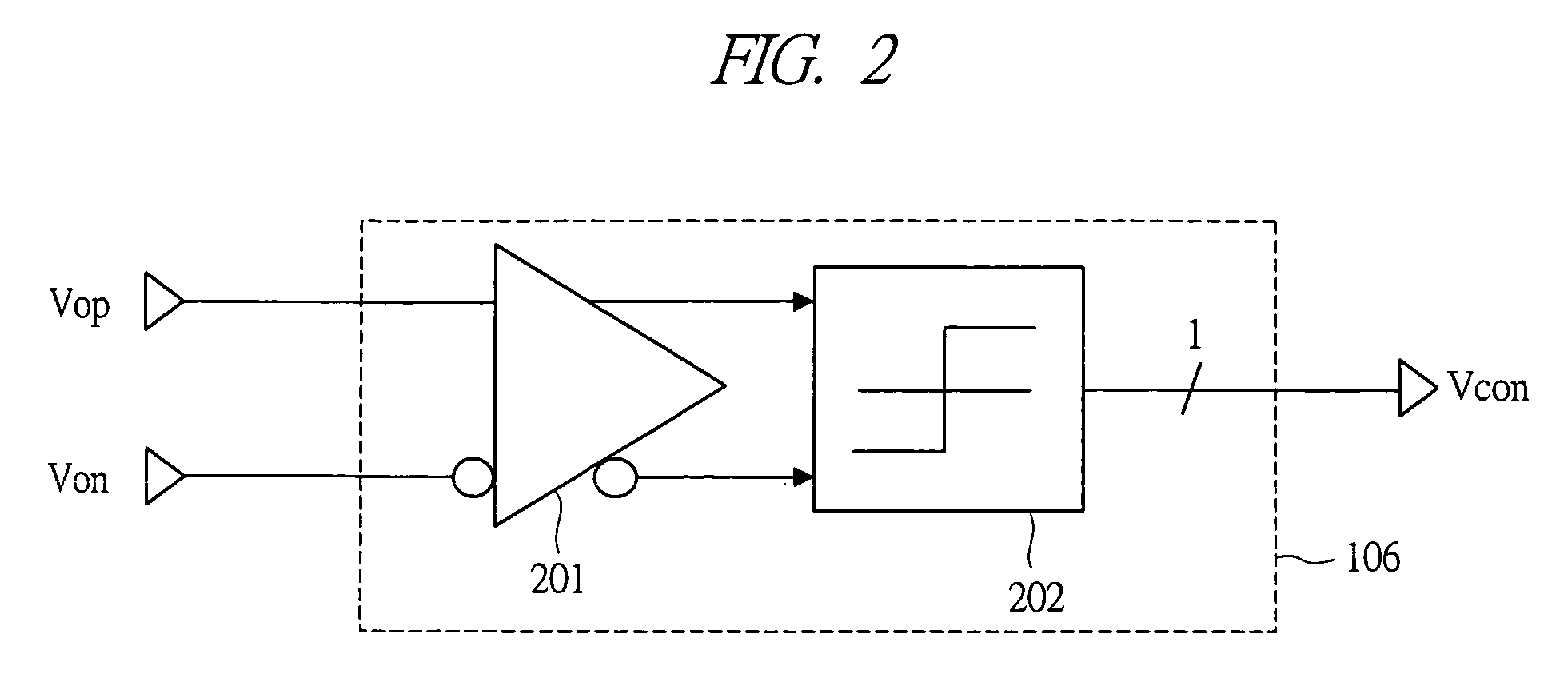
A low offset input circuit and a signal transmission system which can accommodate a high-speed interface and achieve reduction of an offset voltage are provided. An offset voltage compensating circuit block 103 having an input circuit block 108 including an input circuit 104 and an adder-subtractor circuit block 105, switches 108, 109, a detecting circuit block 106, and an adjusting and holding circuit block 107 is provided. To compensate for an offset voltage of the input circuit block 102, an offset voltage of the input circuit block 102 is detected at the detecting circuit block106 by turning on the switches 108, 109, and the detected offset voltage is held in the adjusting and holding circuit block 107, and negative feedback of the held offset voltage to the adder-subtractor circuit block 105 is performed. Thereby, signals Vop, Von having compensated offset voltages are outputted from the input circuit block 102.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Analogue switch
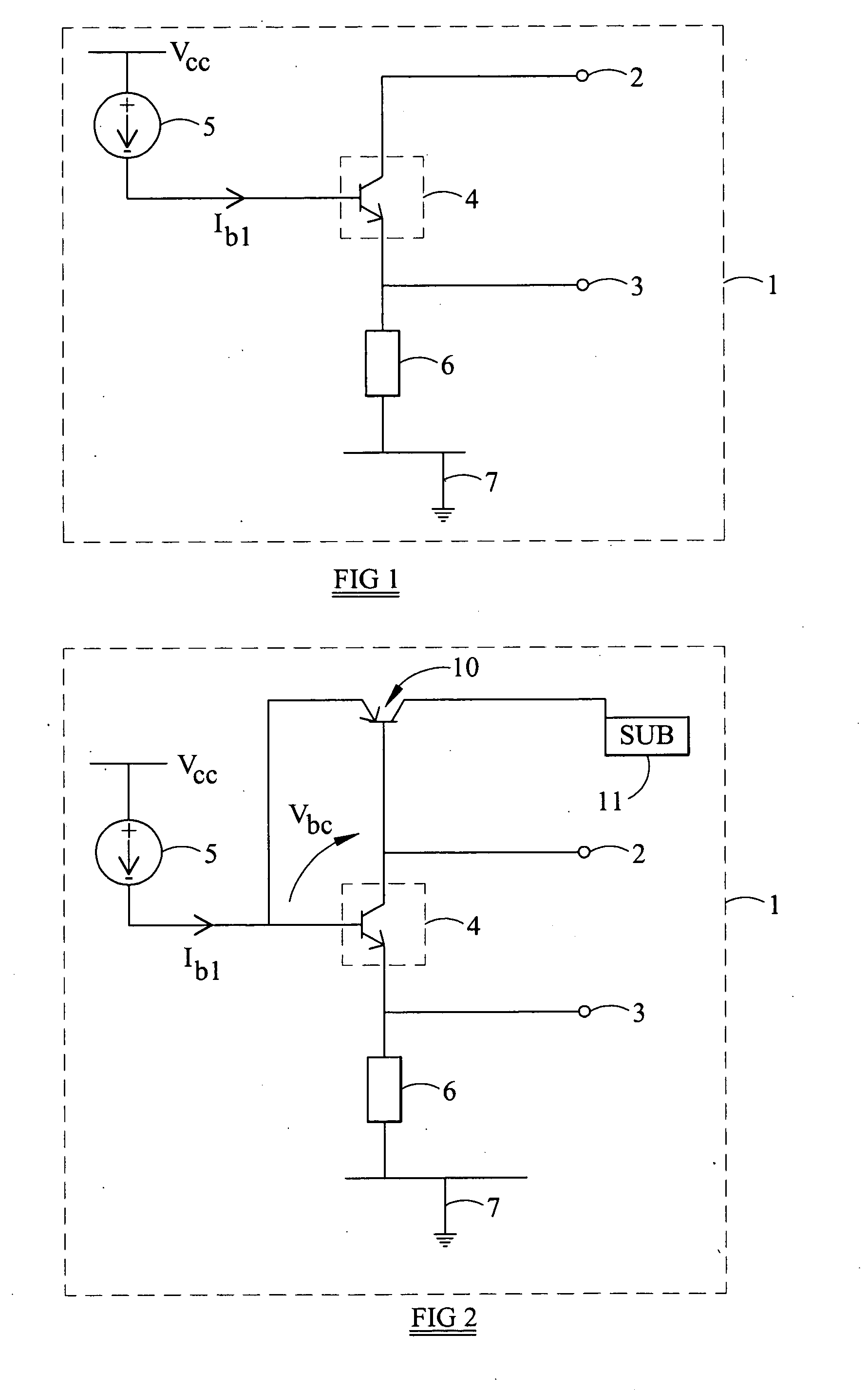
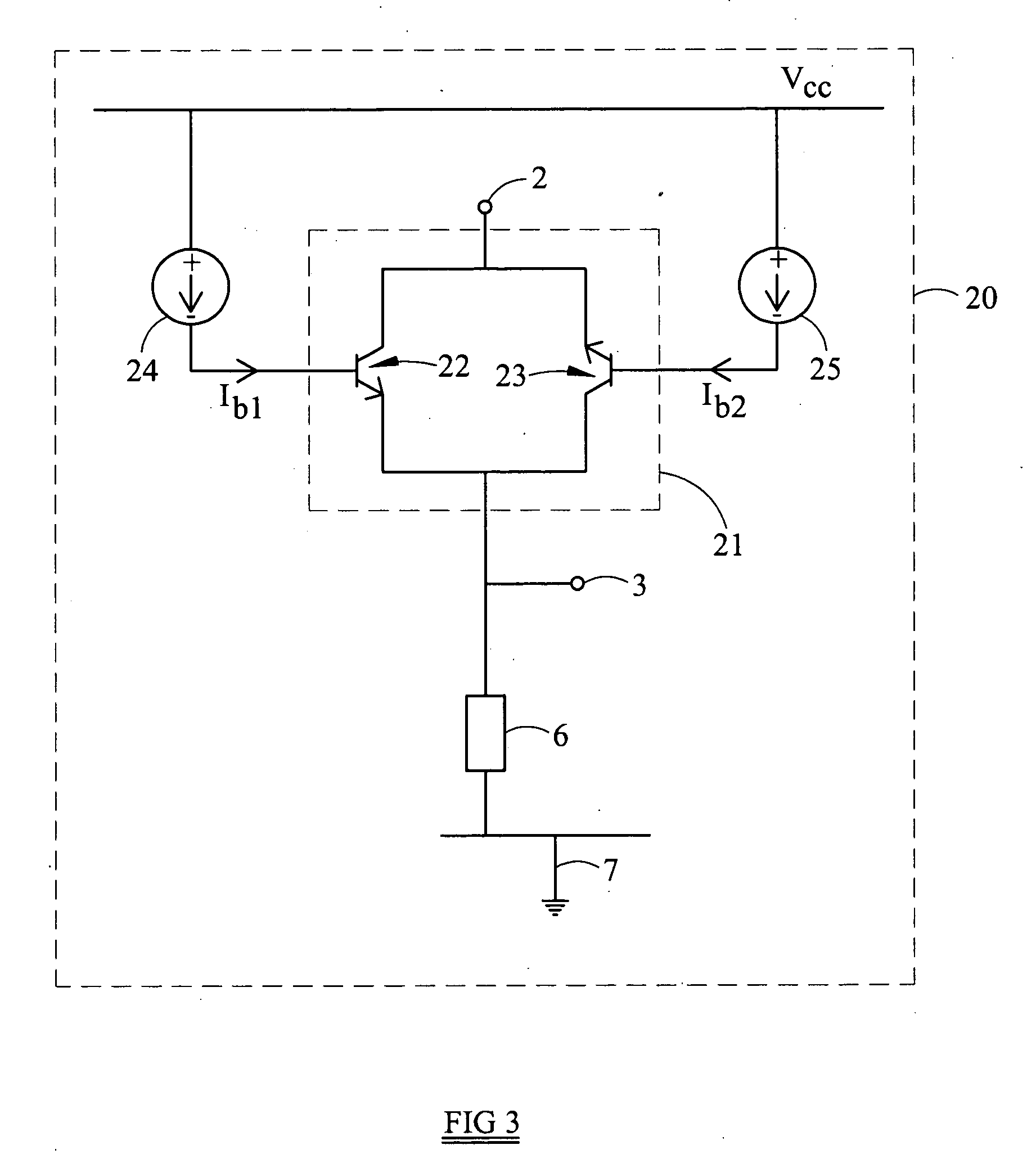
InactiveUS20060066385A1Easy to operateReduce switchingTransistorElectronic switchingTransistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A switching circuit (20) comprising first and second switch terminals (2,3) and a switch (21). The switch (21) comprises a first bipolar transistor (22), having a collector connected to the first switch terminal (2) and an emitter connected to the second switch terminal (3), and a second bipolar transistor (23), having an emitter connected to the first switch terminal (2) and a collector connected to the second switch terminal (3). The switch (21) can be turned on by supply of a control current to the base of either the first or the second bipolar transistor.
Owner:ZETEK
Error amplifier circuit
InactiveCN103414438ASmall rejection ratioHigh rejection ratioDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceEngineering
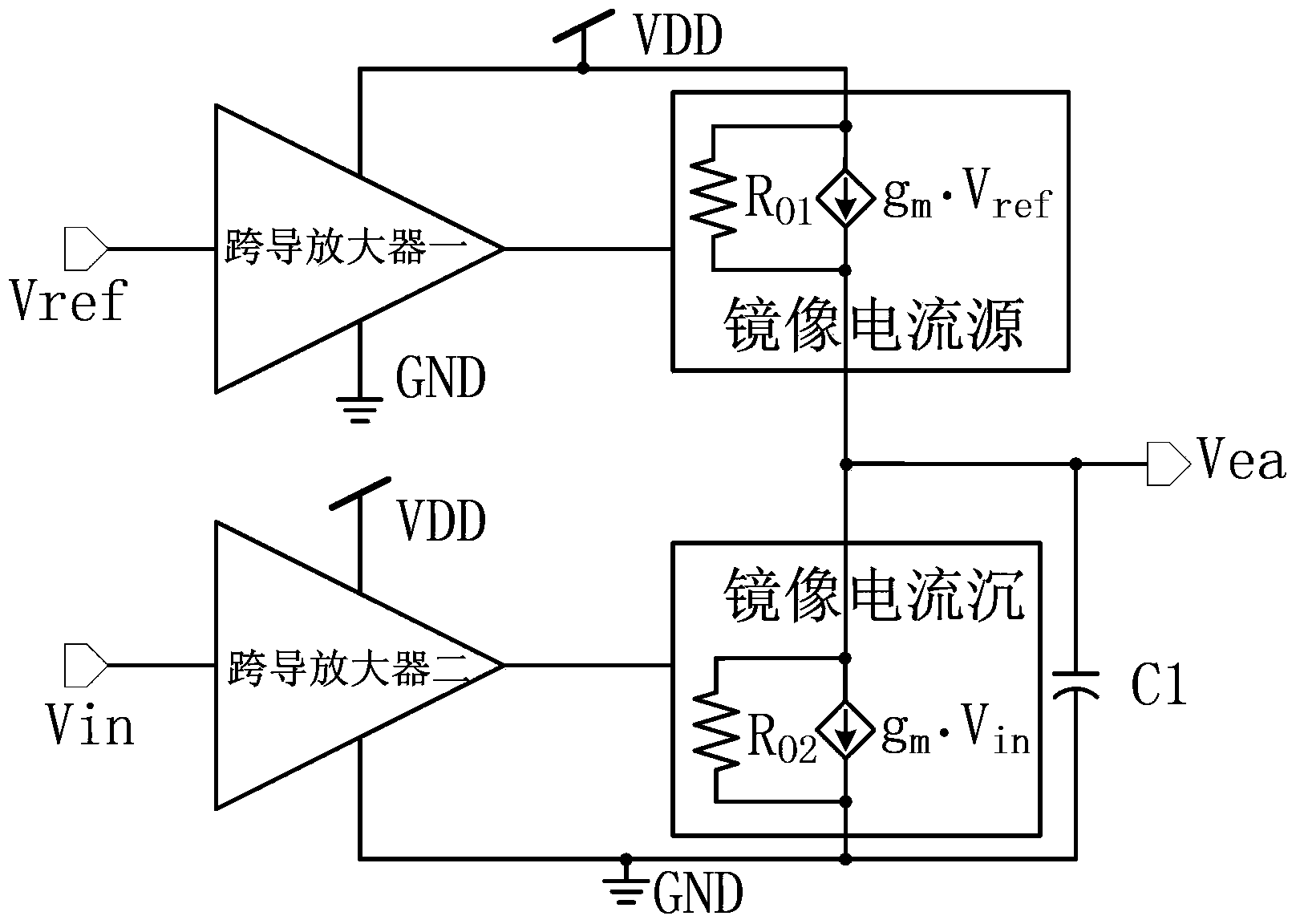
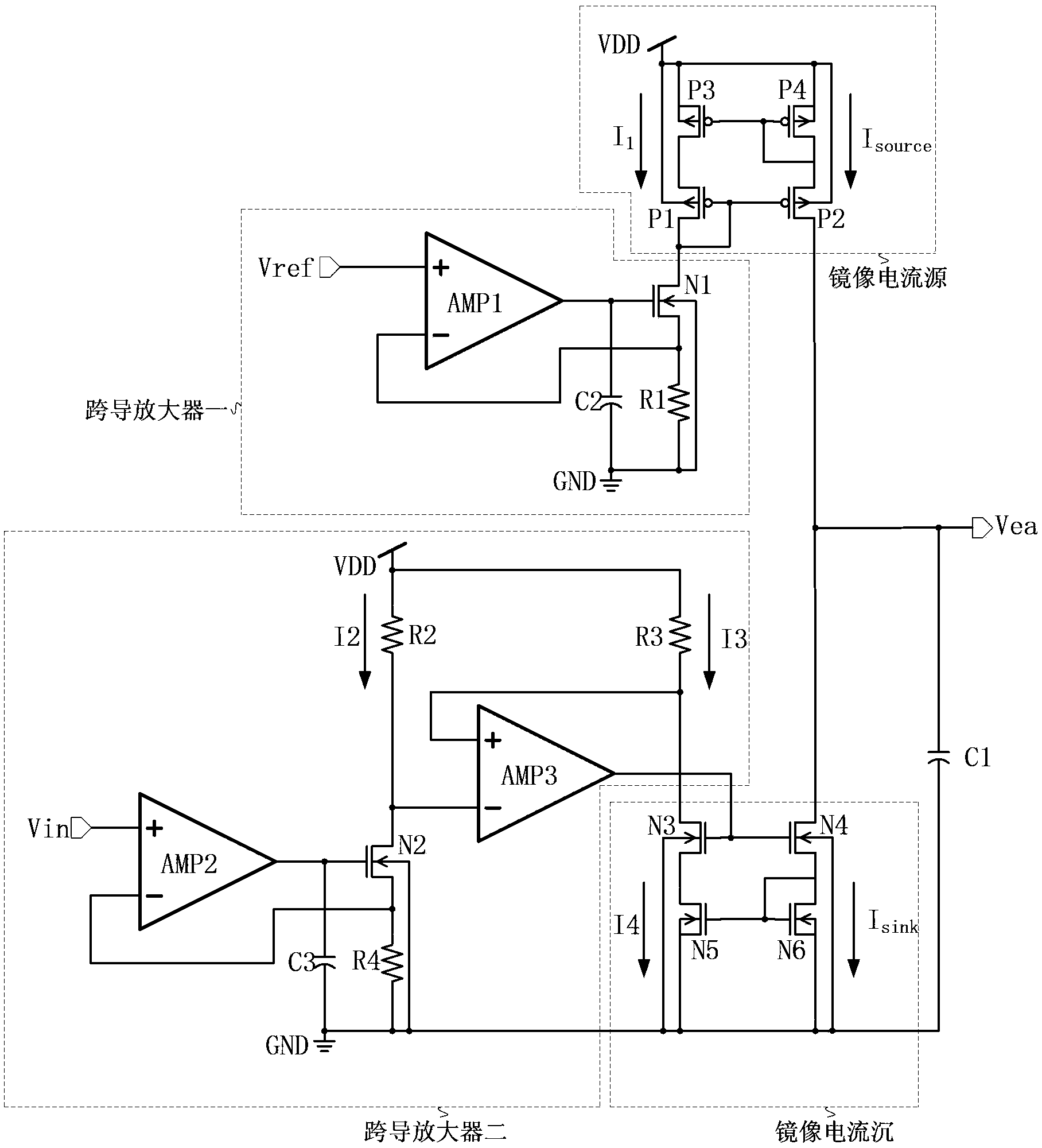
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics, and relates to an integrated circuit design technology, in particular to a novel current injection / pulling error amplifier circuit. The error amplifier circuit comprises a first transconductance amplifier, a second transconductance amplifier, a first image current source, a second image current source and a first capacitor C1, wherein the input end of the first transconductance amplifier is a first input end Vref of the error amplifier circuit, the output end of the first transconductance amplifier is connected with the first image current source, the input end of the second transconductance amplifier is a second input end Vin of the error amplifier circuit, the output end of the second transconductance amplifier is connected with the second image current source, and the output end of the first image current source and the output end of the second image current source are connected with one end of the first capacitor C1 to serve as an output end Vea of the error amplifier circuit. The error amplifier circuit has the advantages of being capable of adjusting the output voltage, improving the response speed and response accuracy of a system and improving the stability of the system, and is particularly suitable for an error amplifier.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Weak signal reading circuit
ActiveCN105897248AReduce the impact of readoutImprove signal-to-noise ratioLogic circuit interface arrangementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Audio power amplifier
The embodiment of the invention discloses a weak signal reading circuit comprising a chopper amplifying circuit. The chopper amplifying circuit comprises a first chopper, a second chopper, a third chopper, a fourth chopper, and a first operational amplifier. The input end of the first chopper is connected with a weak signal. The output end of the first chopper is connected with the input end of the first operational amplifier via the second chopper. The output end of the first operational amplifier is connected with the input end of the fourth chopper via the third chopper. The output end of the fourth chopper is connected with a first filter circuit. The first chopper and the fourth chopper are controlled by a first chopping signal. The second chopper and the third chopper are controlled by a second chopping signal. The frequency of the first chopping signal is lower than that of the second chopping signal. The weak signal reading circuit may decrease offset voltage due to chopping ripples, reduces influence of noise and the offset voltage on the reading of the weak signal, increases the signal-to-noise ratio of a signal and the precision of a signal processing system.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD
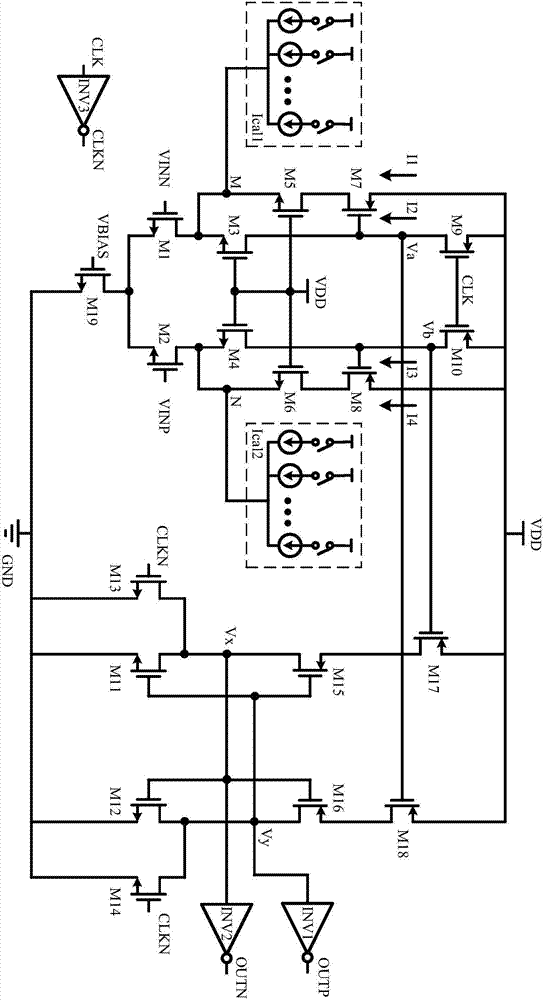
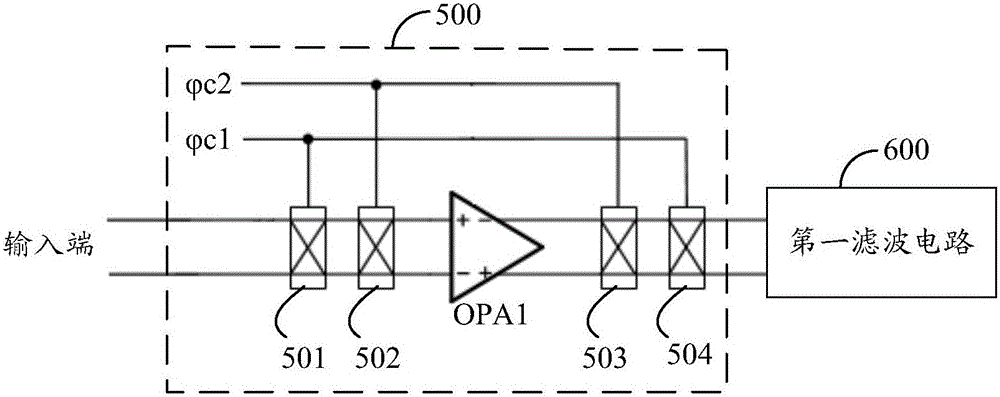
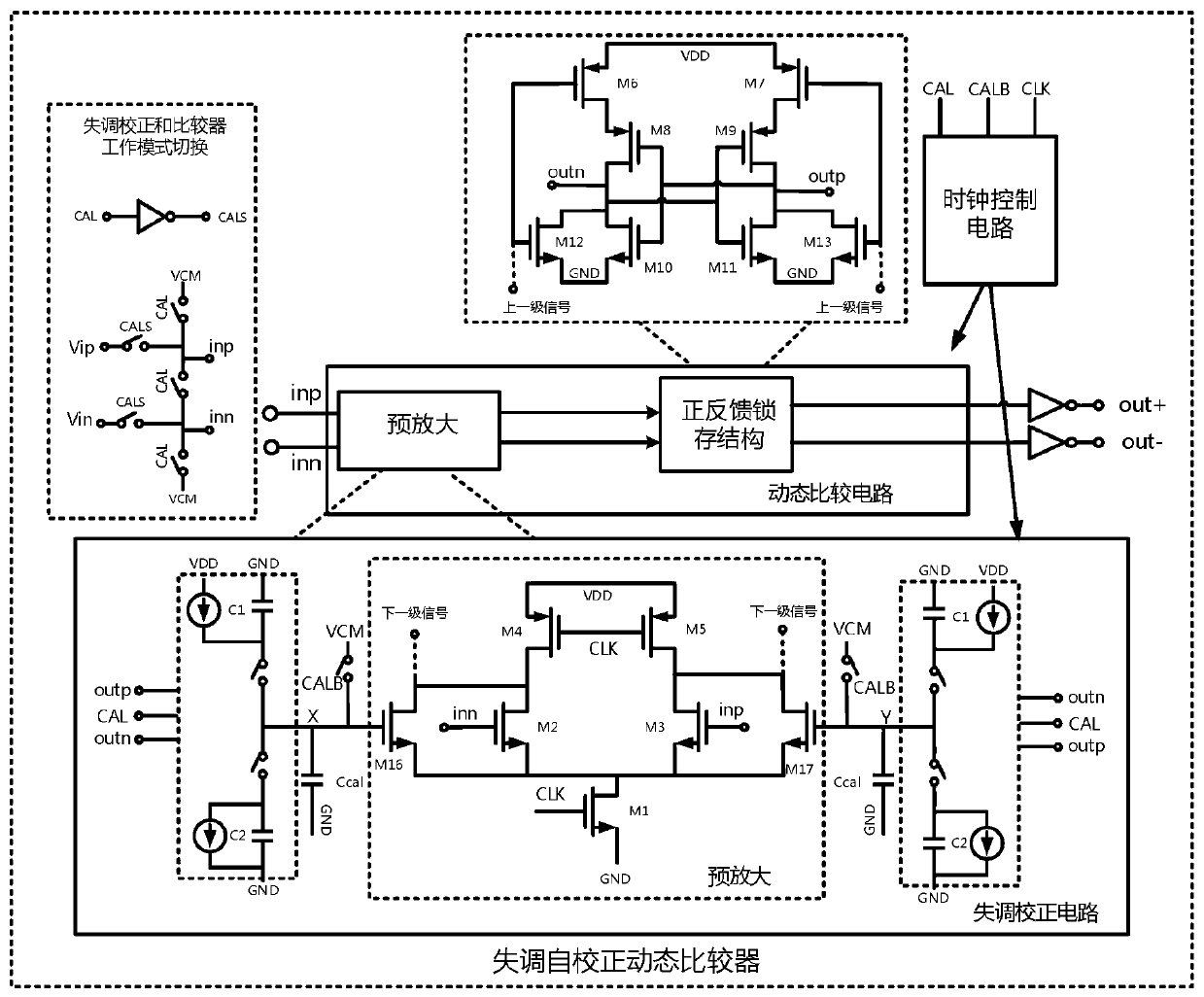
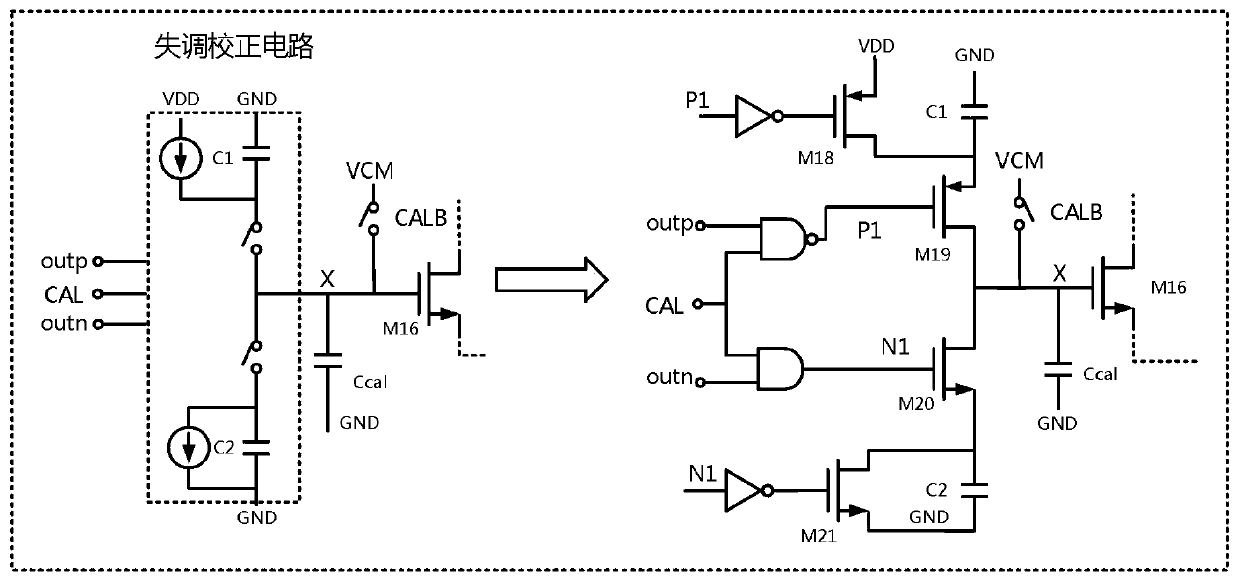
Offset self-correcting dynamic comparator for successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter
ActiveCN110474623AReduce power consumptionAvoid reducing static powerMultiple input and output pulse circuitsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceDigital down converter
The invention discloses an offset self-correcting dynamic comparator for a successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter. A dynamic comparator in a traditional successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter is improved; the dynamic comparator is enabled to perform offset correction, the on-off of NMOS and PMOS is controlled through clock signals generated by the output end of the comparator, and self-correction is performed according to the principle of charge redistribution so that introduction of an amplifier to reduce the static power consumption generated by offset can be avoided, and thus the power consumption of the comparator can be reduced. According to the dynamic comparator, the principle of charge redistribution is effectively utilized; the capacitance values of the correction capacitor and the charging and discharging capacitor can be adjusted to effectively improve the correction precision, and the correction process of the dynamic comparator is separated from the comparison process in the successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter system, so that the influence of the system on the offset correction process is avoided, the offset voltage of the dynamic comparator can be reduced, and the precision of the dynamic comparator is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com