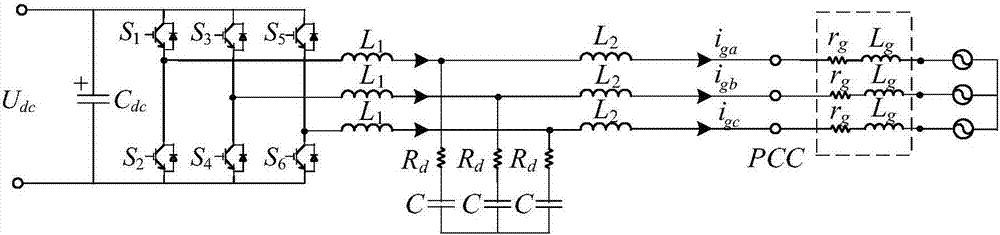
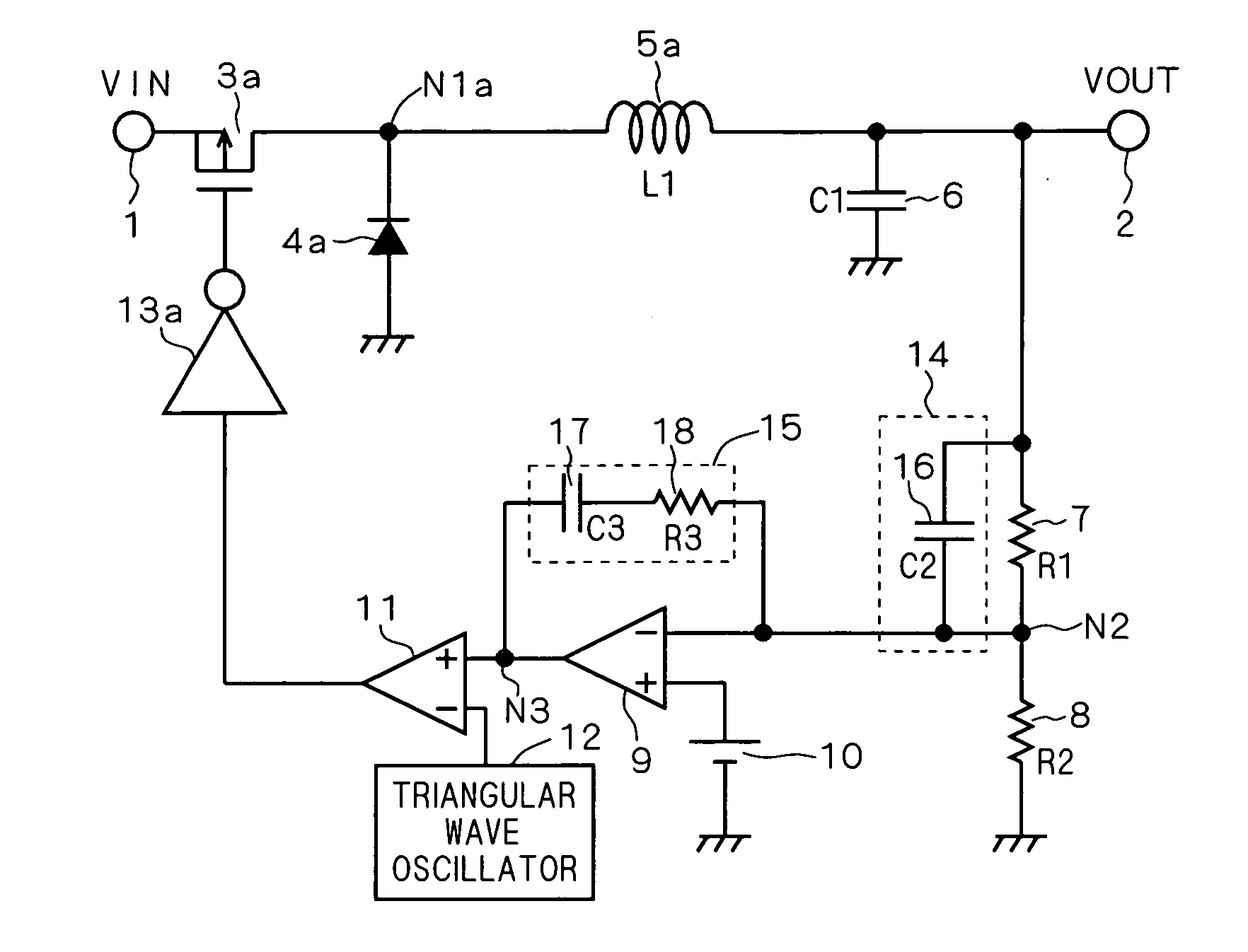
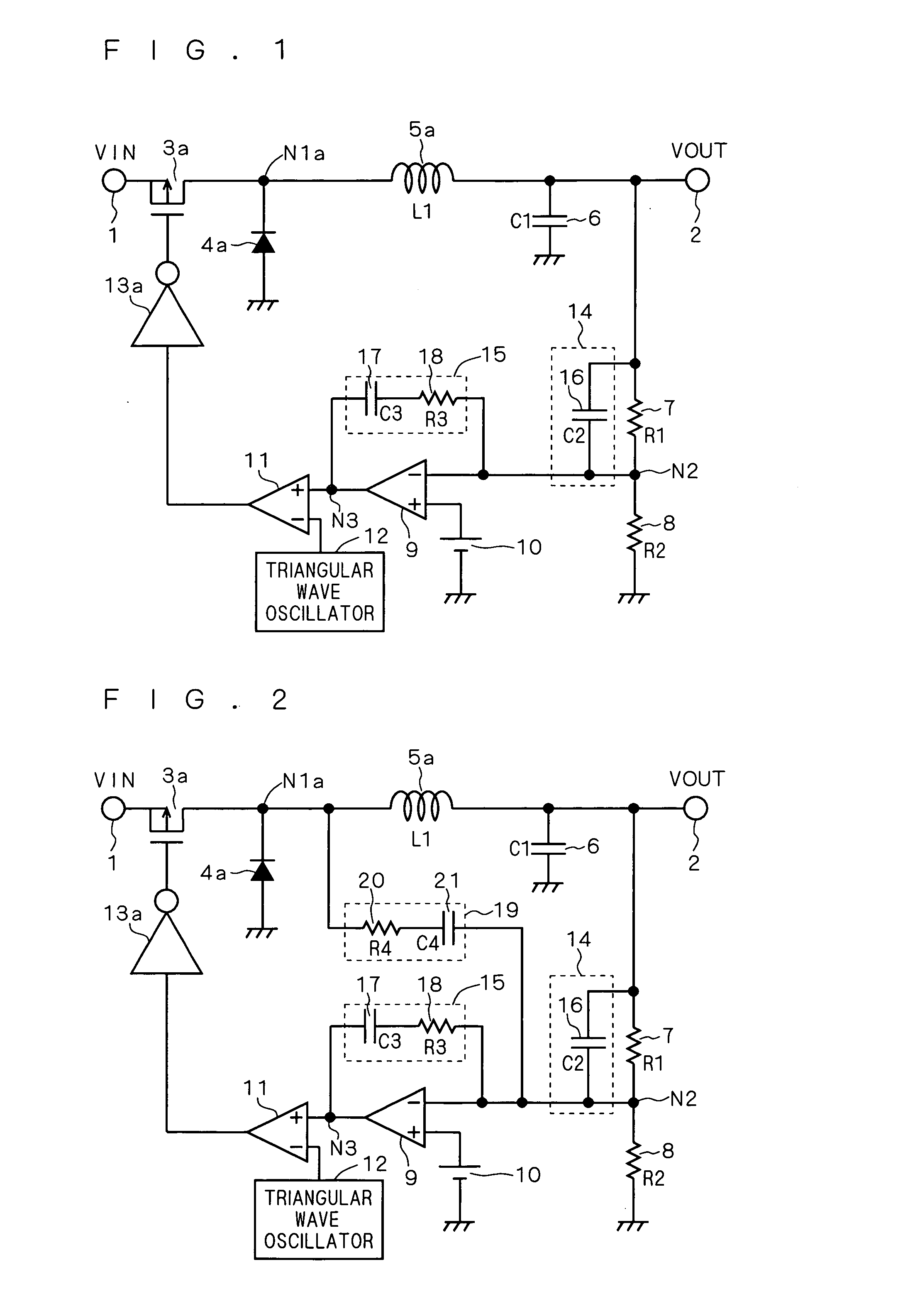
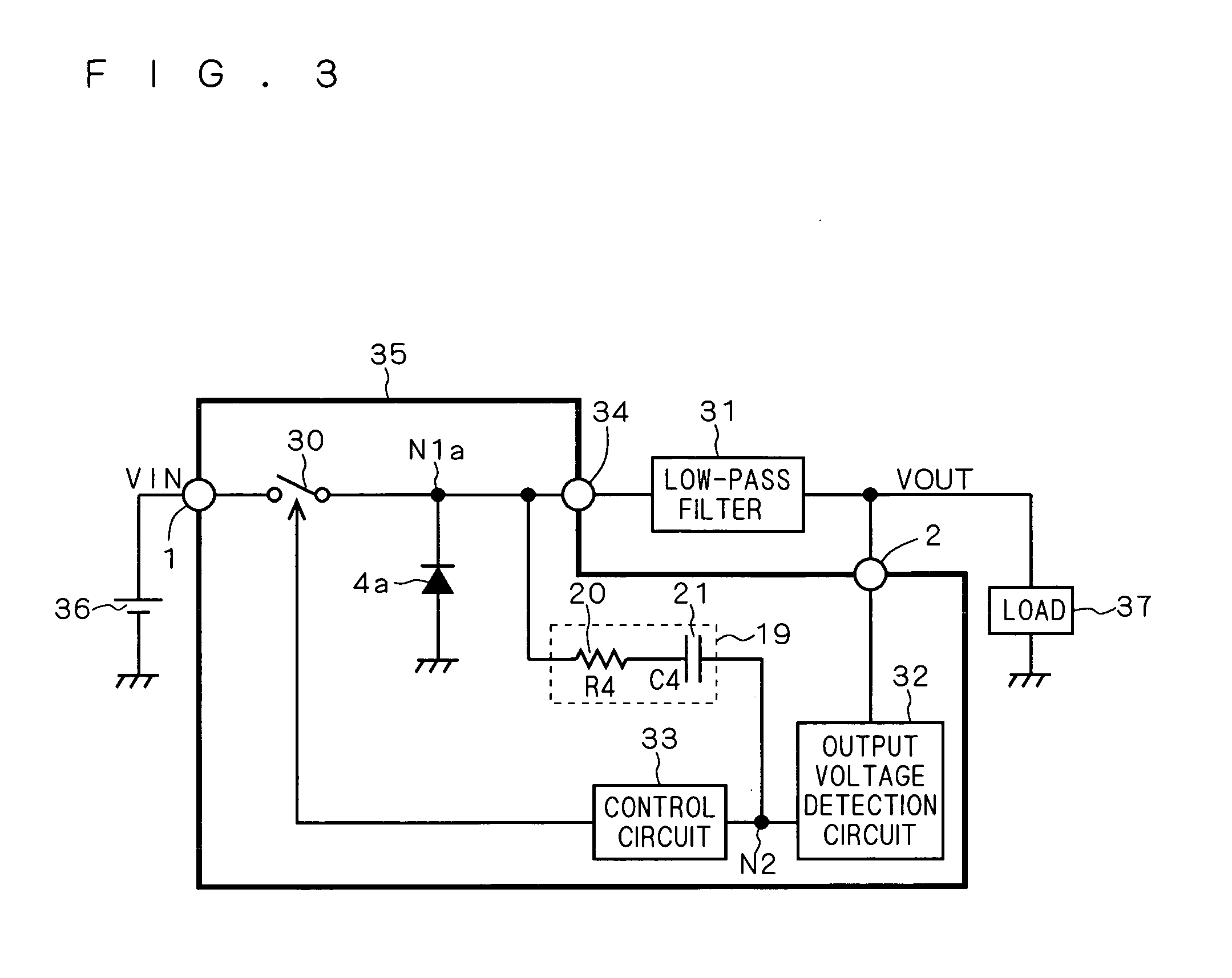
Patents
Literature
372 results about "Phase margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
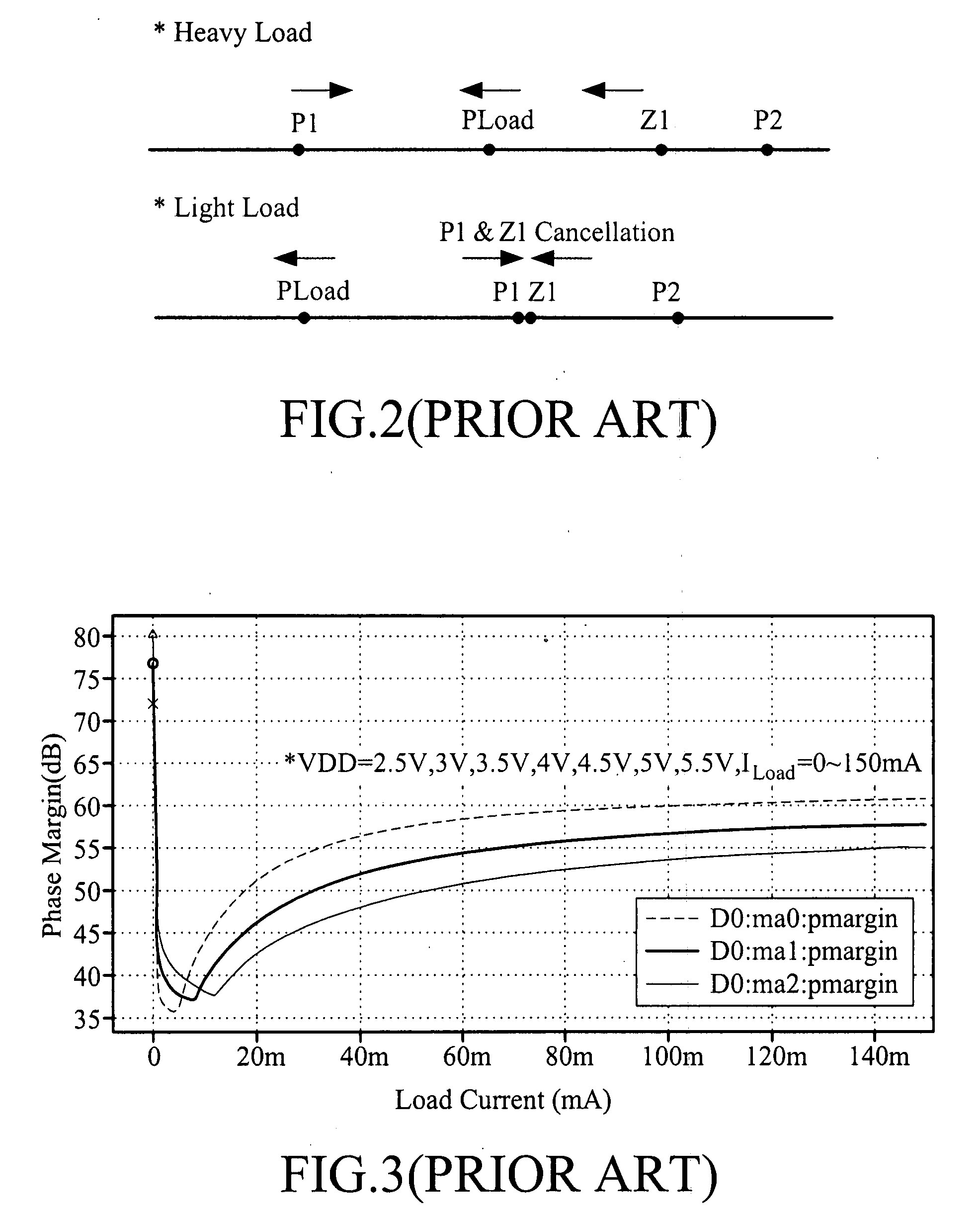
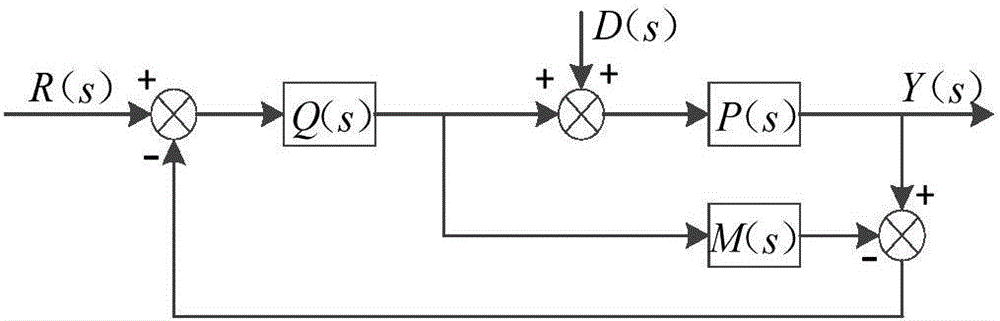
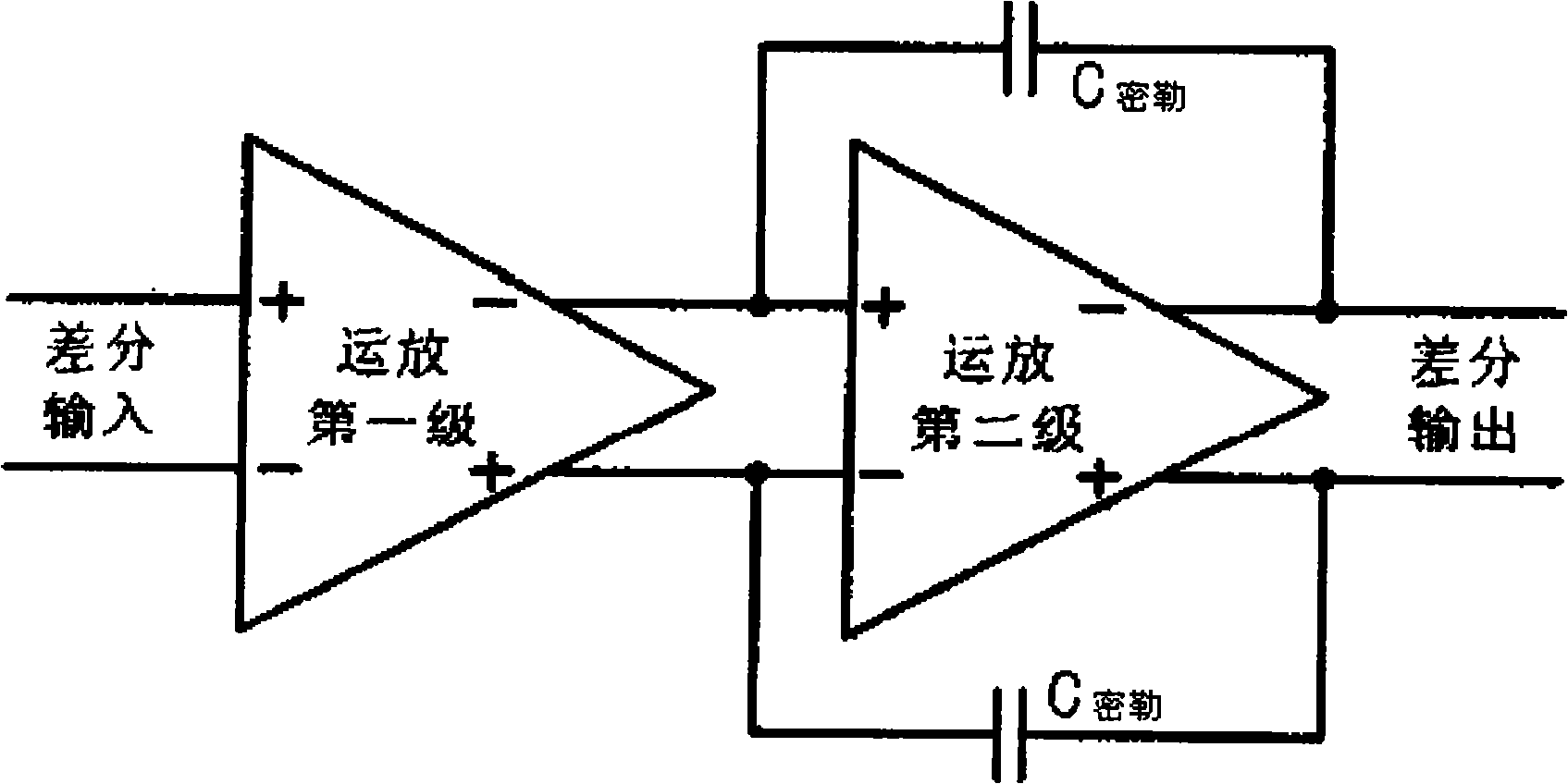
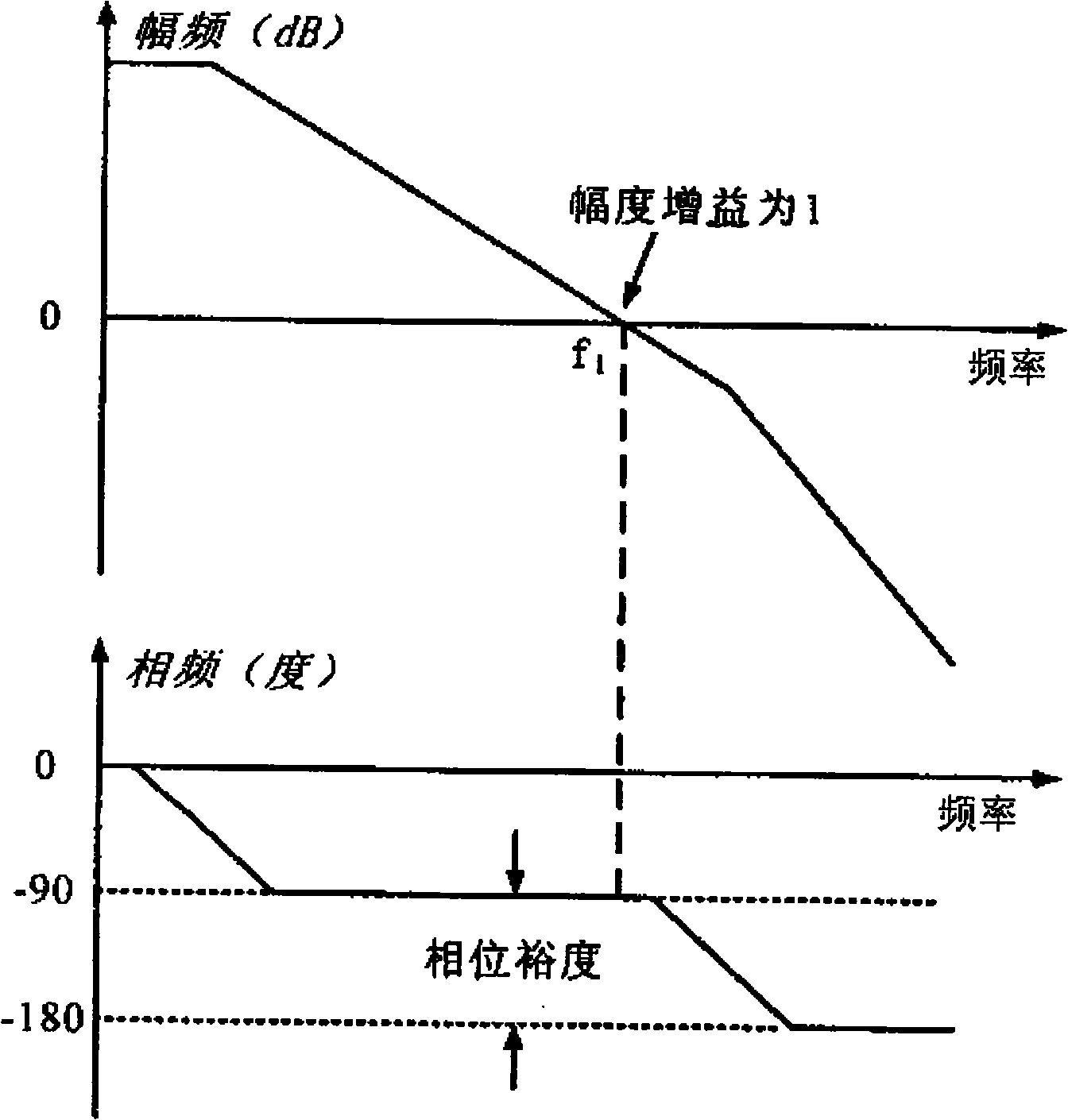
In electronic amplifiers, the phase margin (PM) is the difference between the phase and 180°, for an amplifier's output signal (relative to its input) at zero dB gain or output is same as of input. PM=180∘+|Δϕ|.
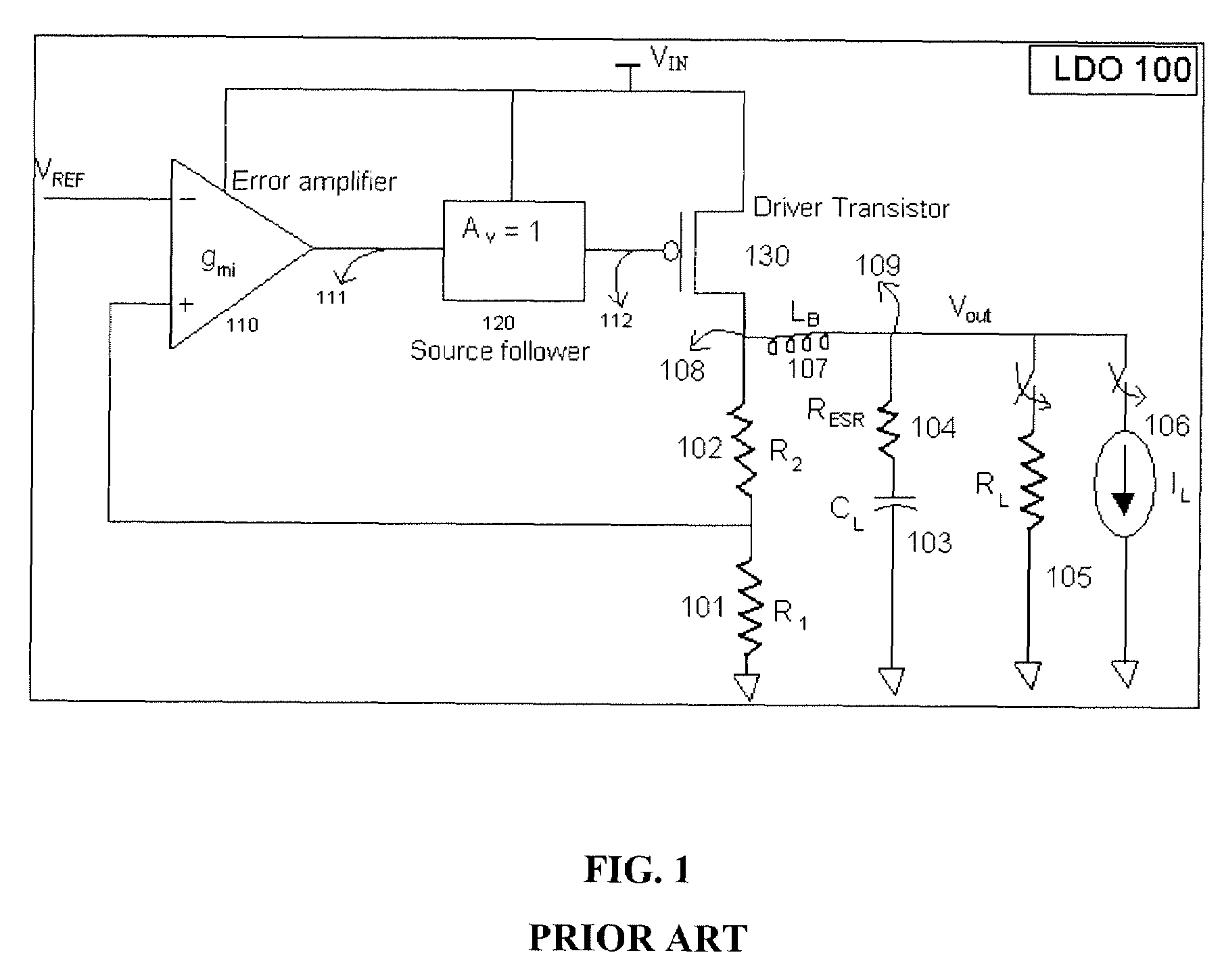
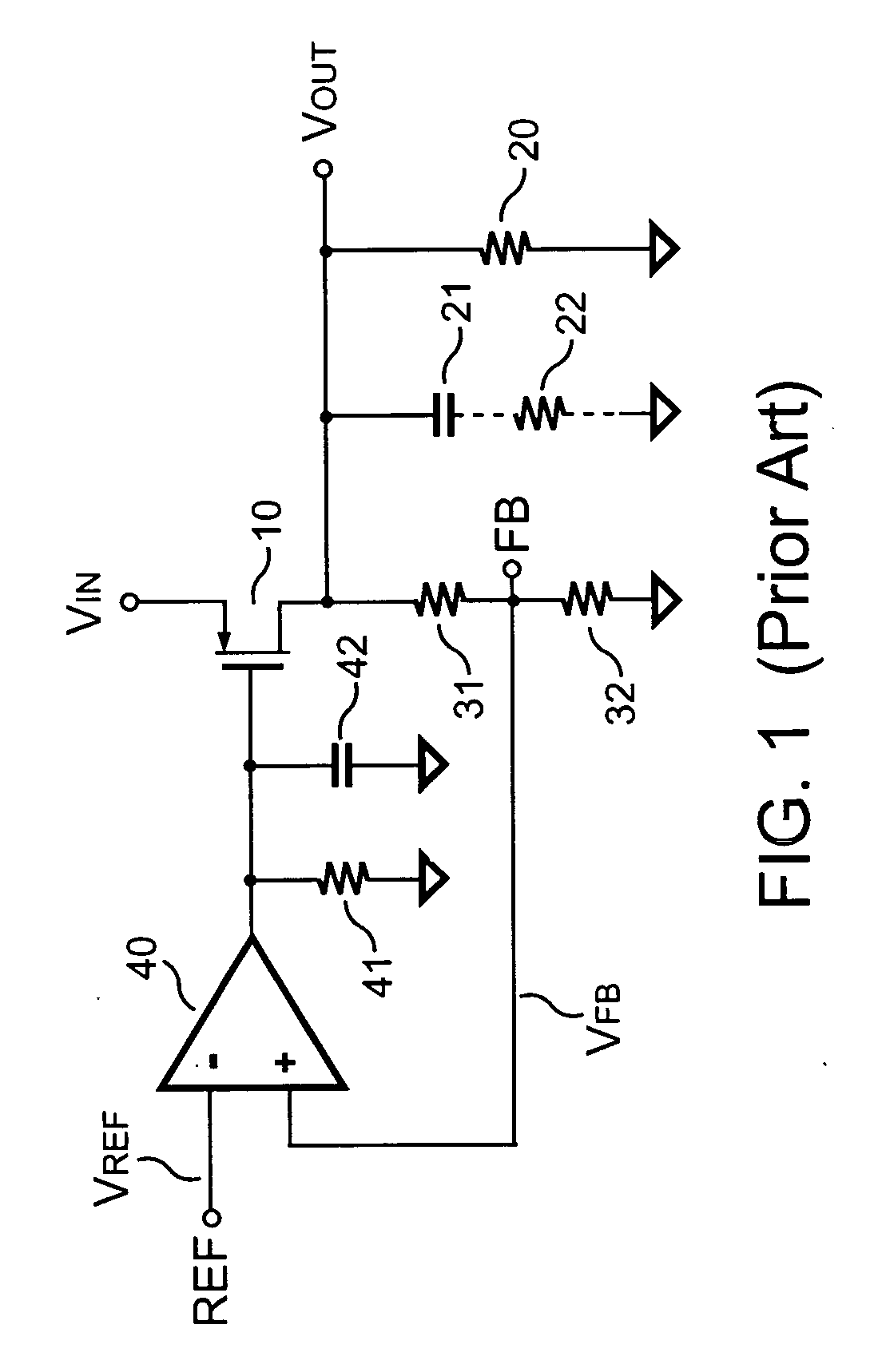
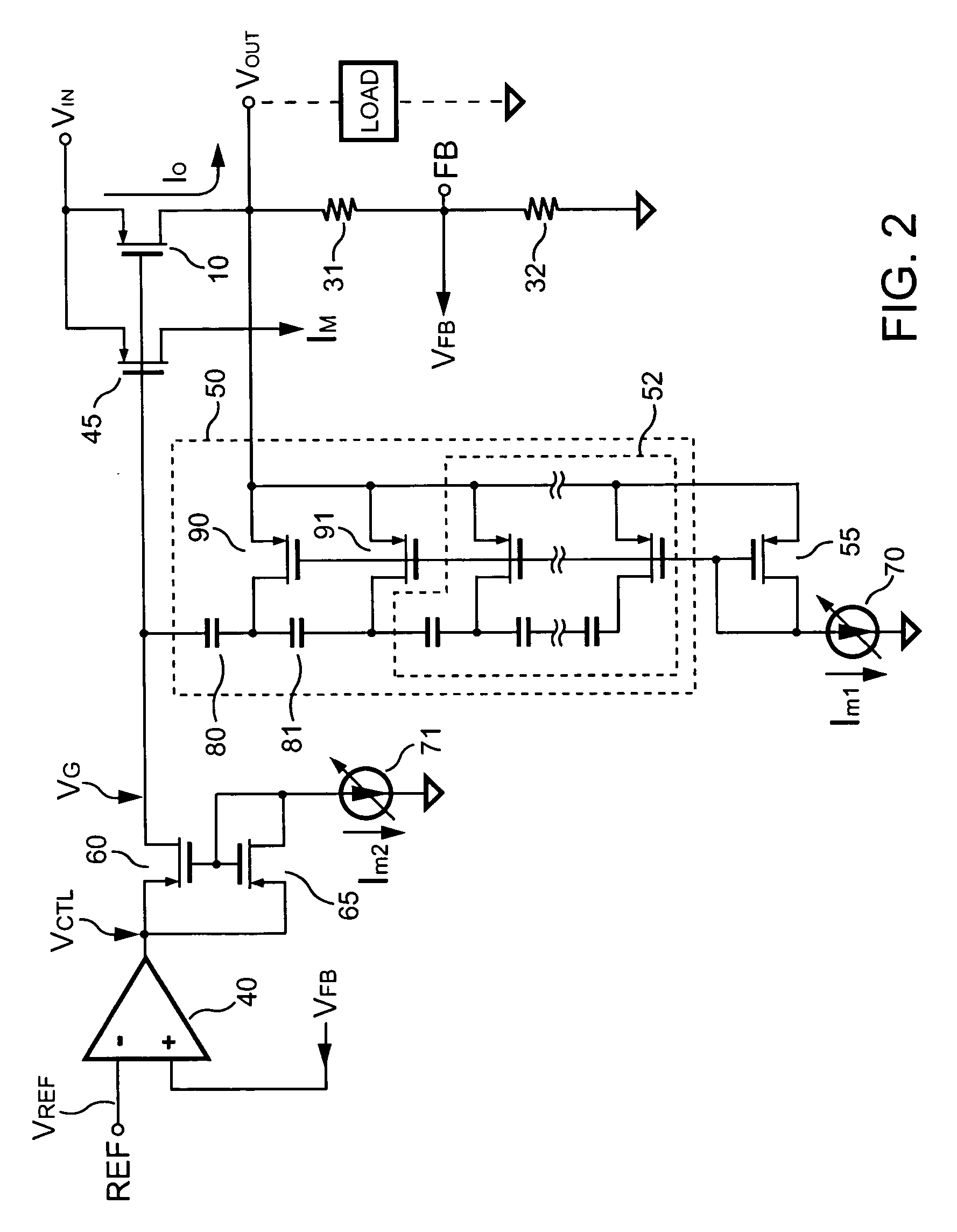
Low dropout regulator
InactiveUS20070159146A1Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
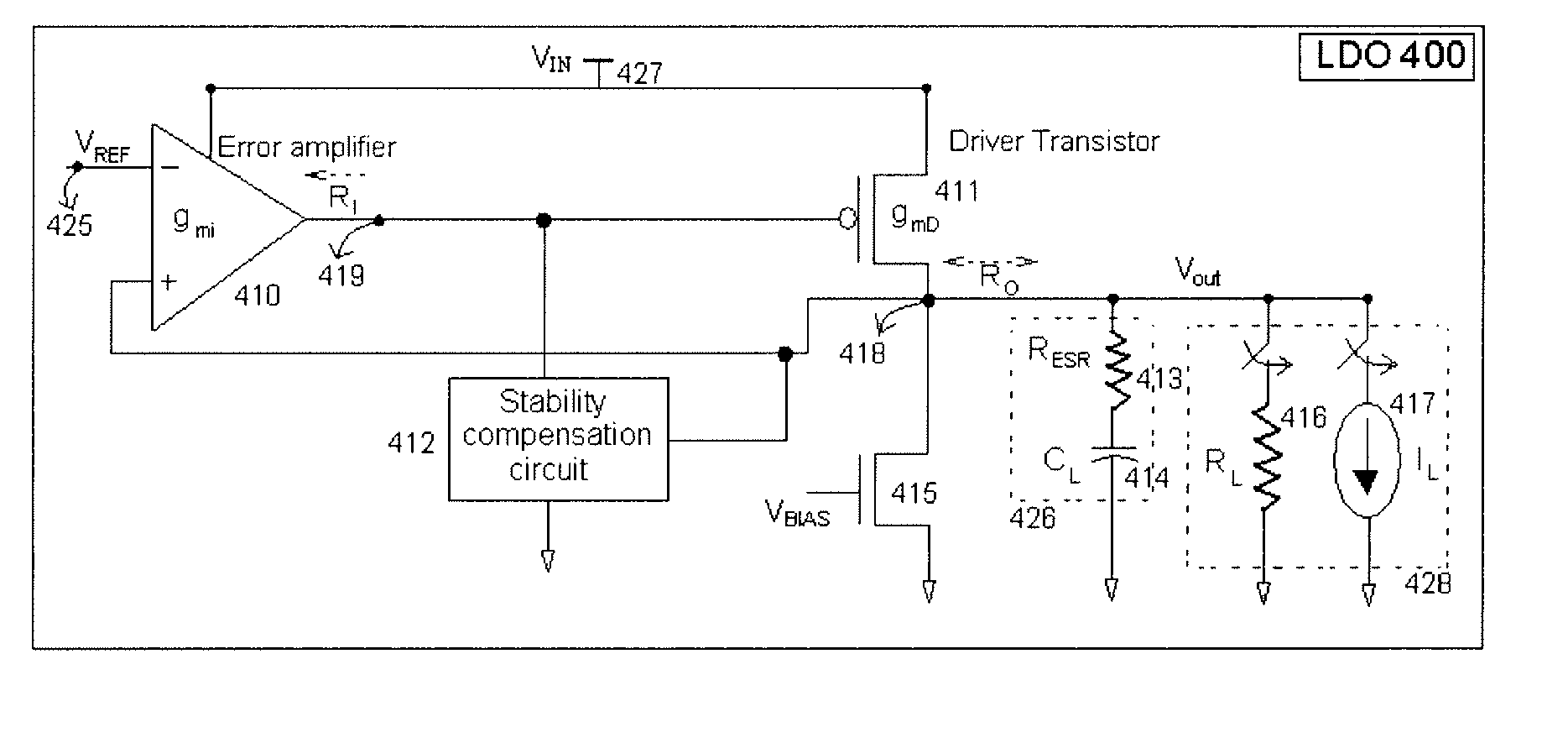
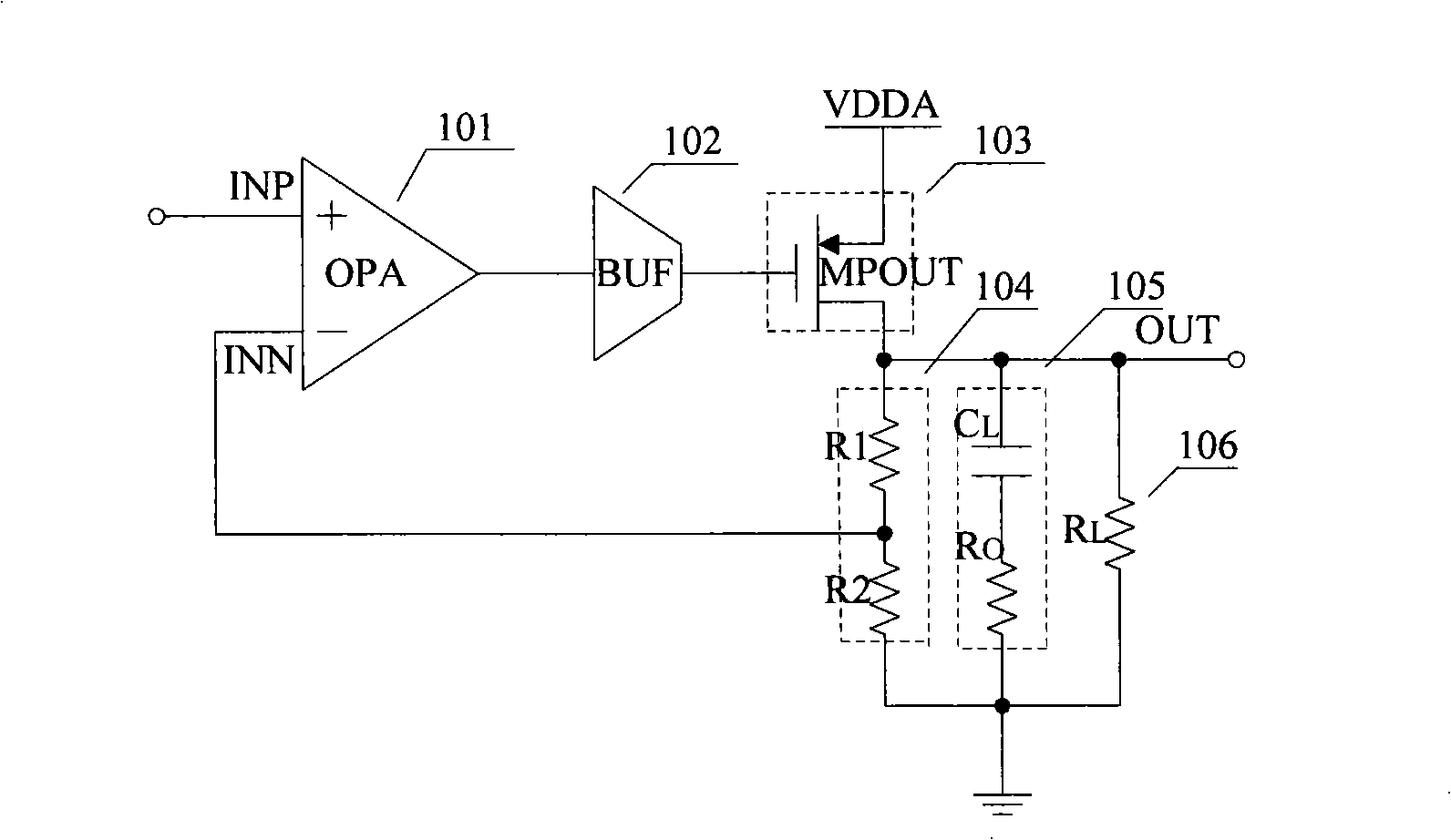
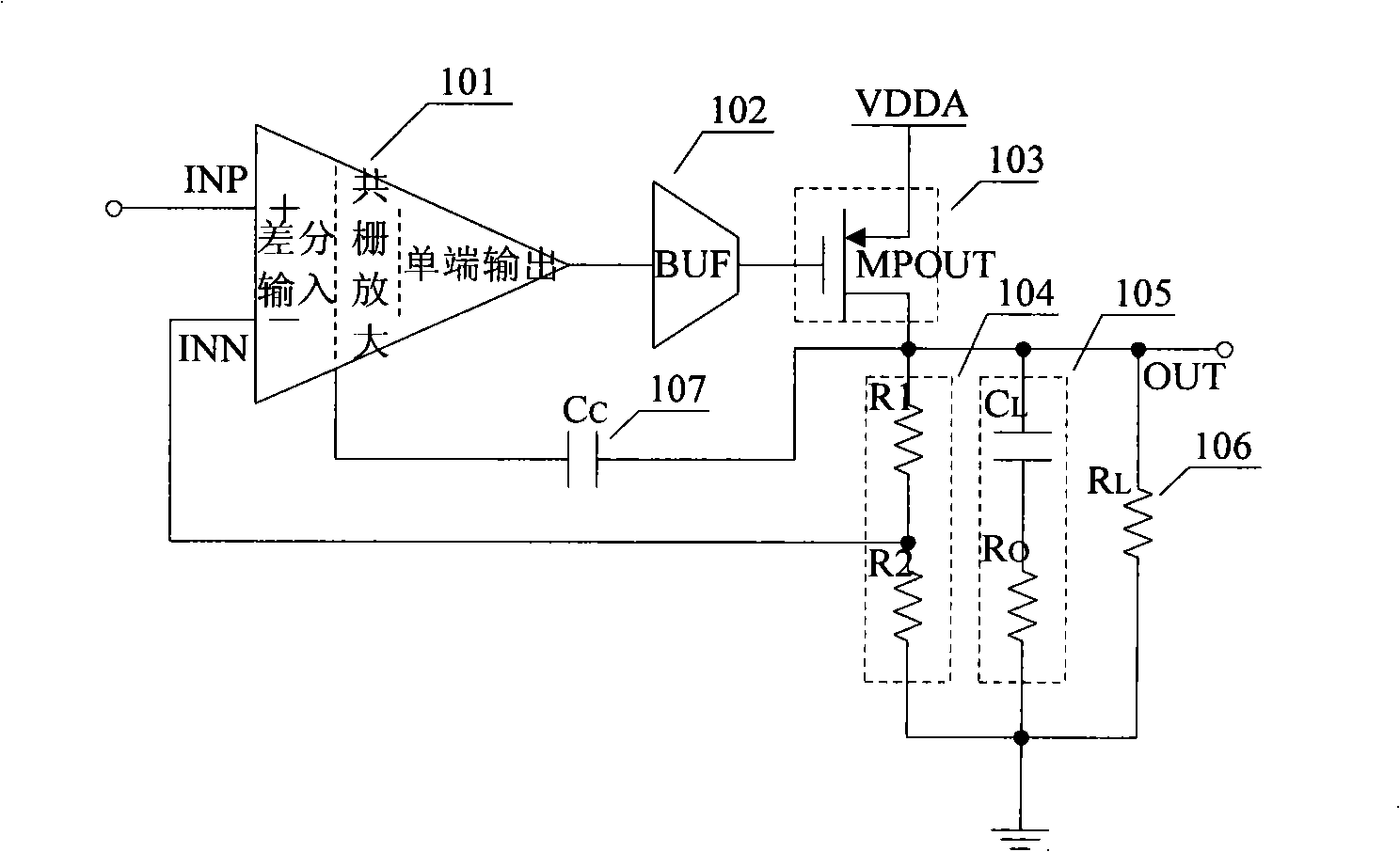
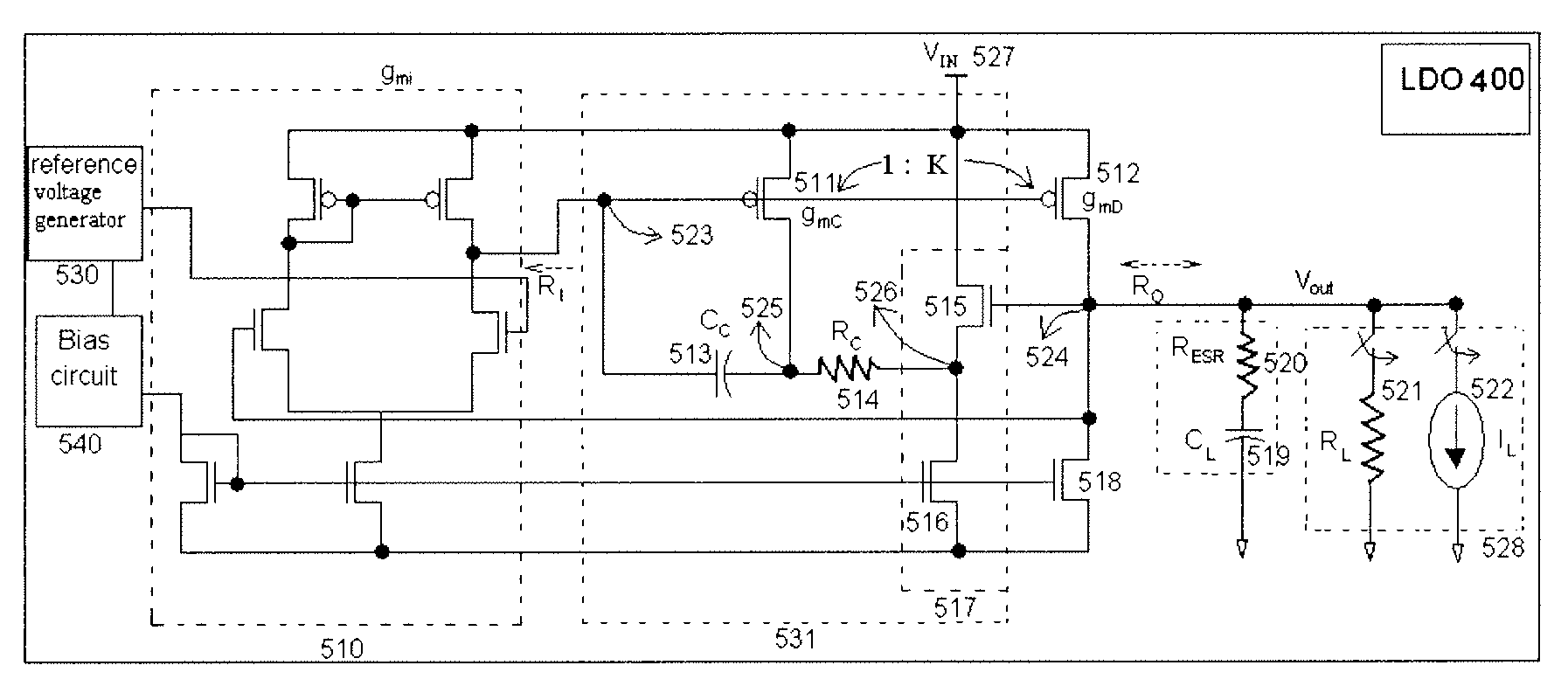
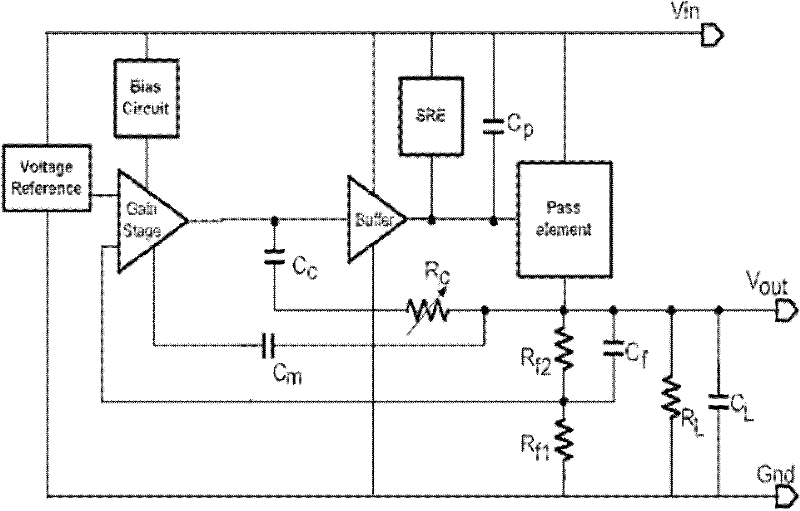
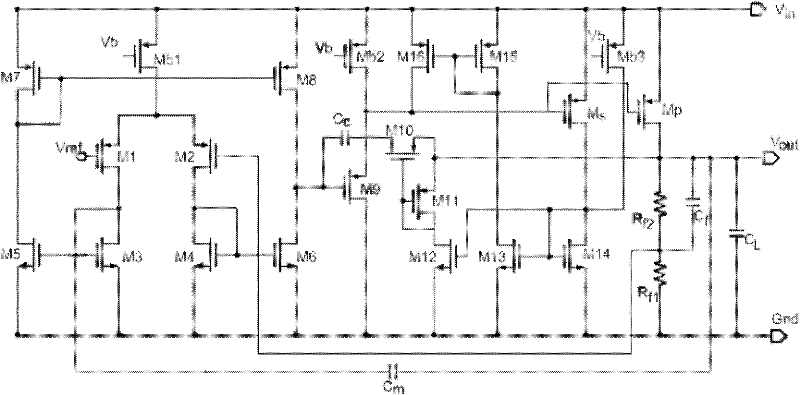
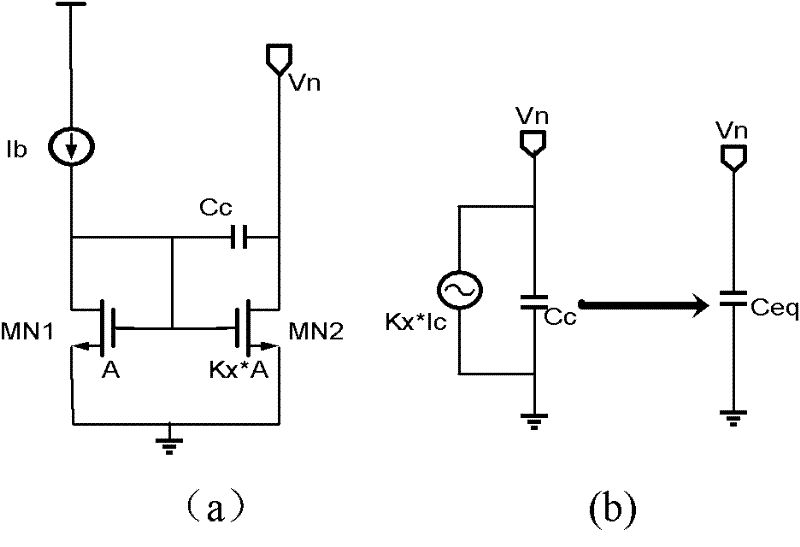
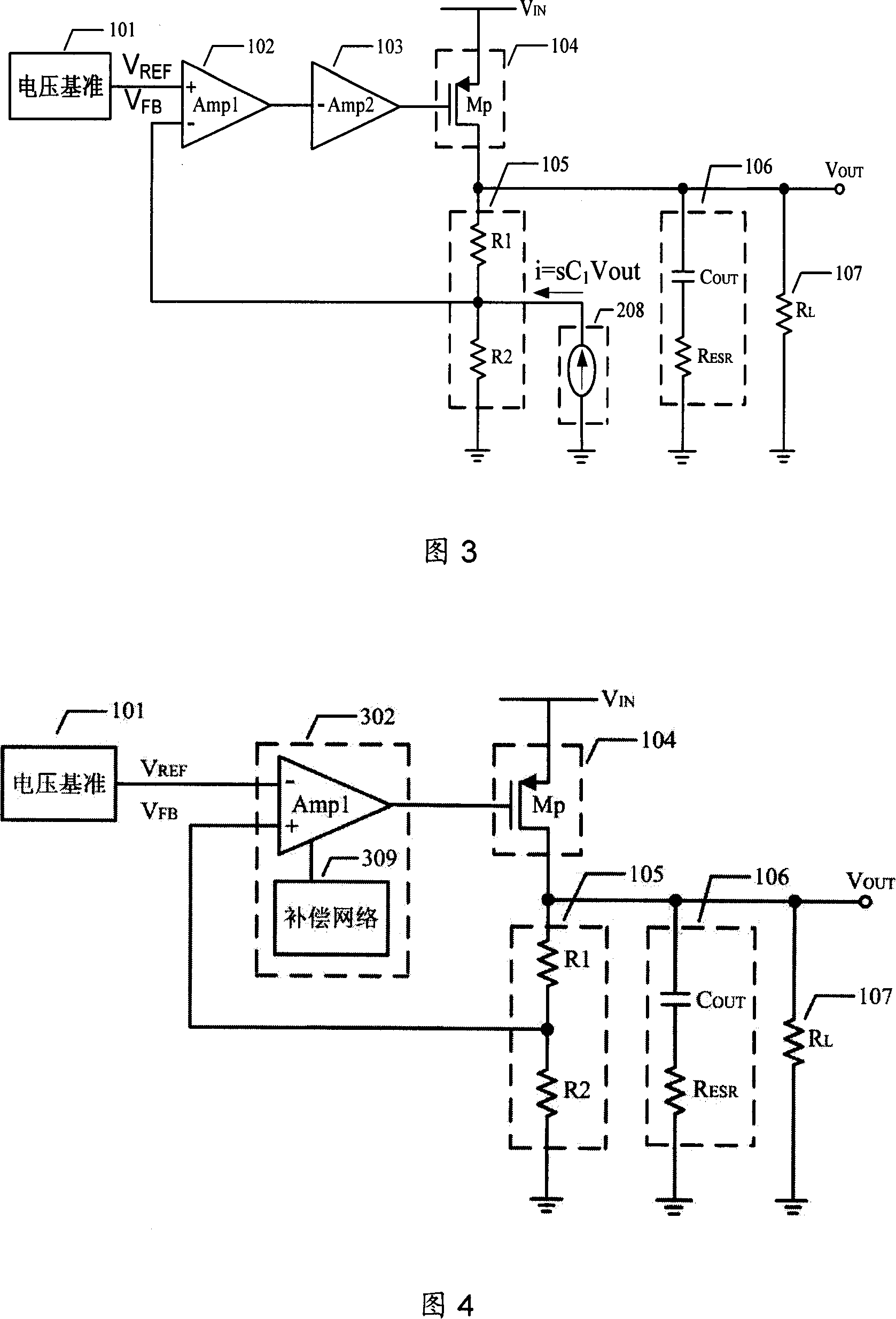
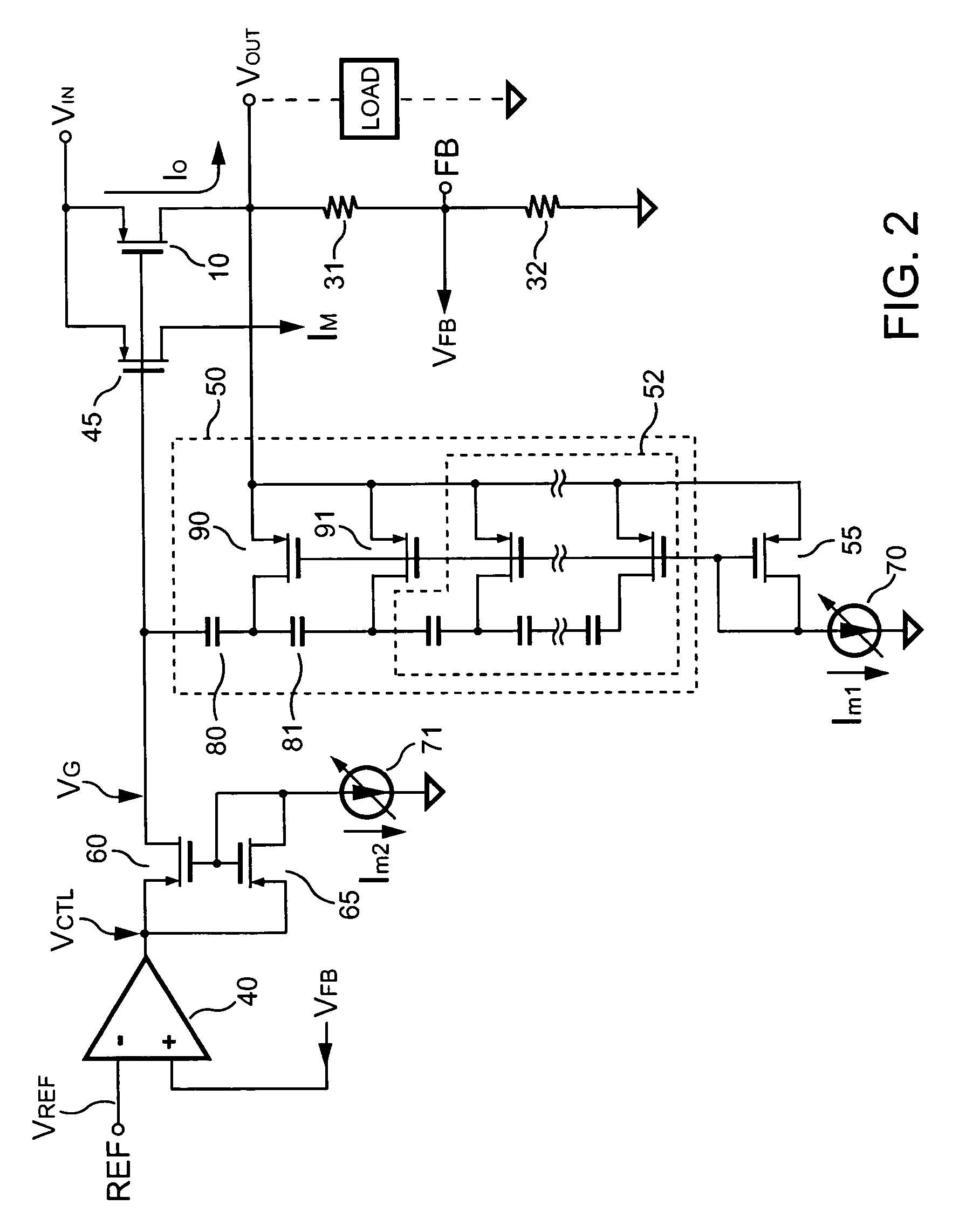
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
InactiveCN101339443AIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent range
A low dropout linear voltage regulator with wide output current range and low pressure difference, comprises an error amplifier in the folding common source and common gate structure, a buffer circuit, a driving element, a feedback circuit, a load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit and a multistage Miller compensation circuit, wherein the buffer circuit changes the low frequency pole into a medium frequency pole and a high frequency pole; the large load capacitance of the load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit pushes the main pole to the low frequency, causing the gain crossover point to push inwards, and generating a medium frequency zero point for counteracting the medium frequency pole connected serially with the equivalent series resistance; the stride multilevel Miller compensation circuit generates a medium high frequency pole and a medium high frequency zero point slightly smaller than the medium high frequency pole for advancing the phase margin, thereby not only adding the unity gain bandwidth, but also saving considerable chip area. When the output current has a large change range, the structure provided by the invention generates wider unity gain bandwidth, provides the phase margin of greater than 85 degrees, ensures the stability of the system and advances the low pressure difference linear voltage stabilization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Adaptive pole and zero and pole zero cancellation control low drop-out voltage regulator
InactiveUS20080157735A1Good phase marginBandwidth of loop will become largeElectric variable regulationEngineeringControl theory
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
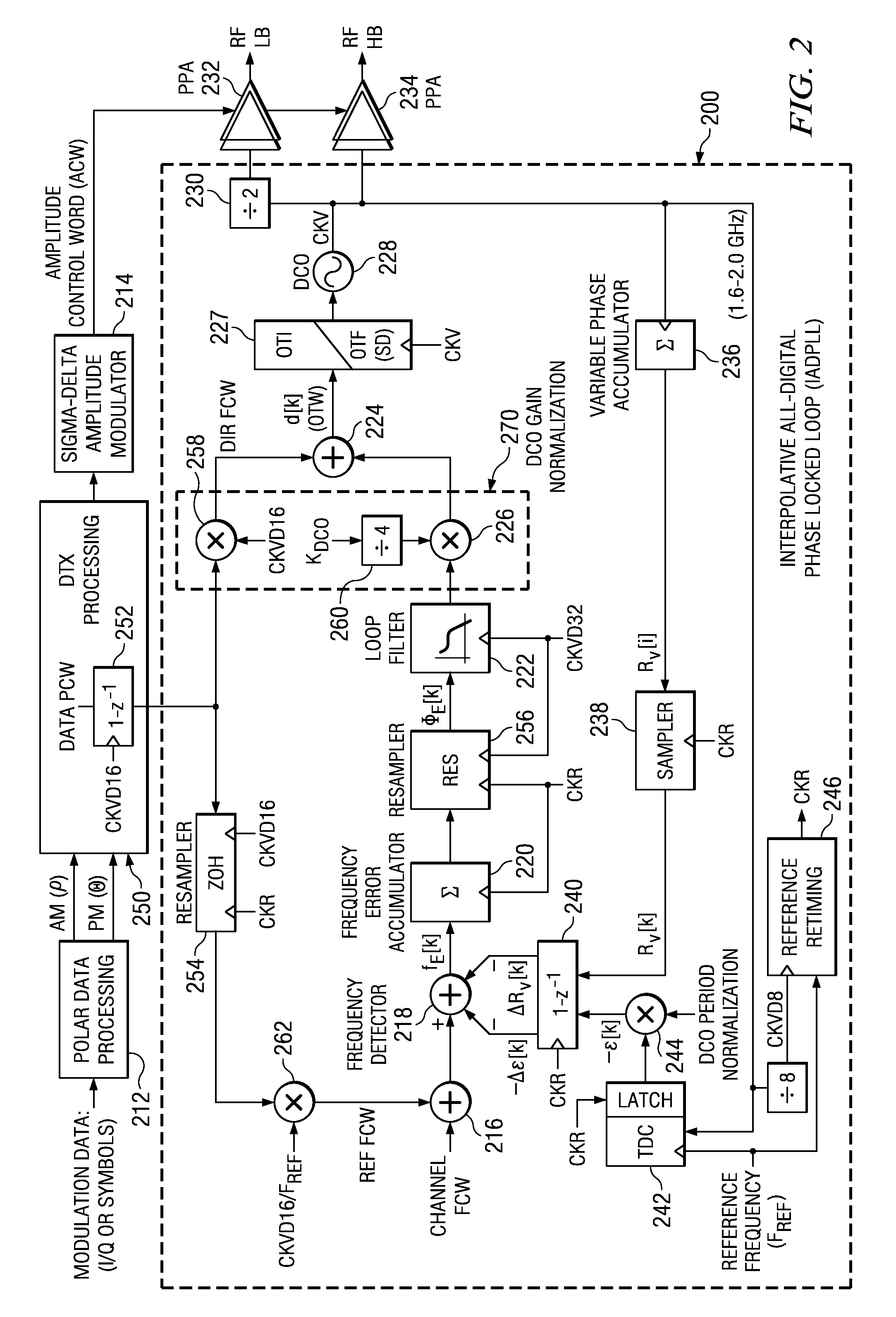
Digital Phase Locked Loop with Gear Shifting
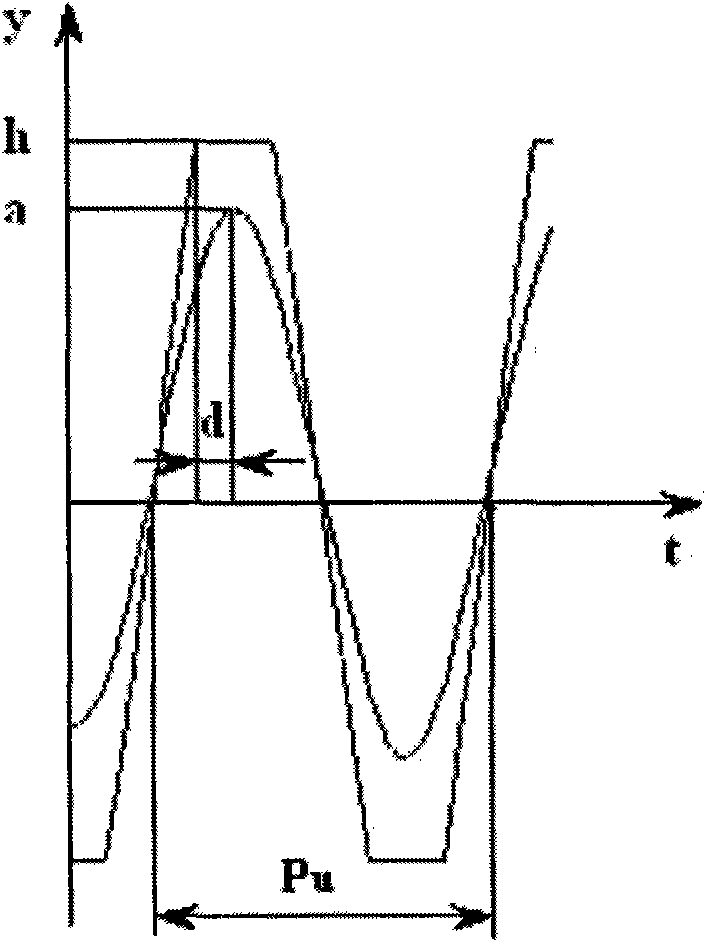
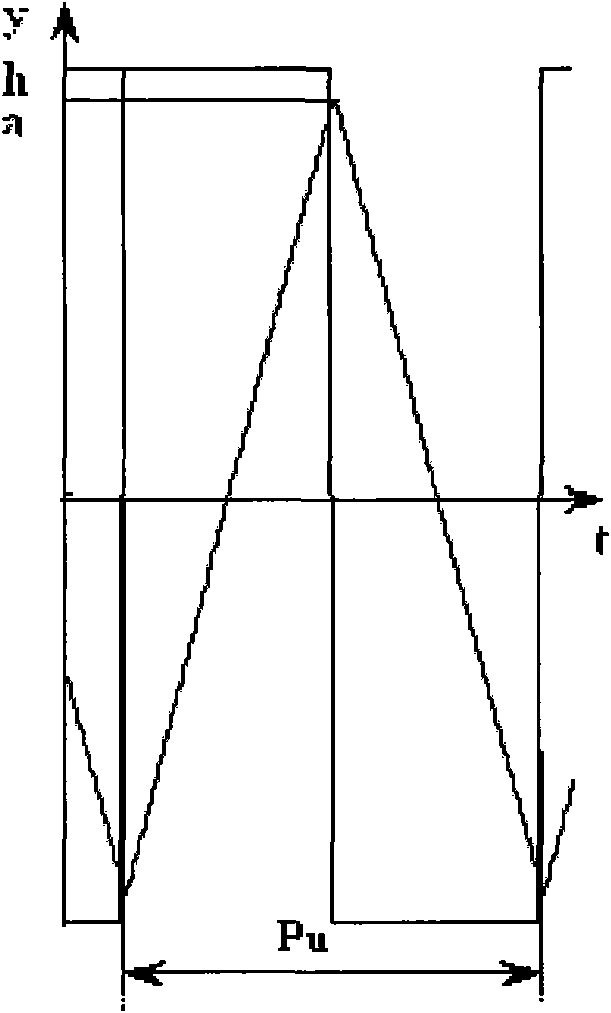
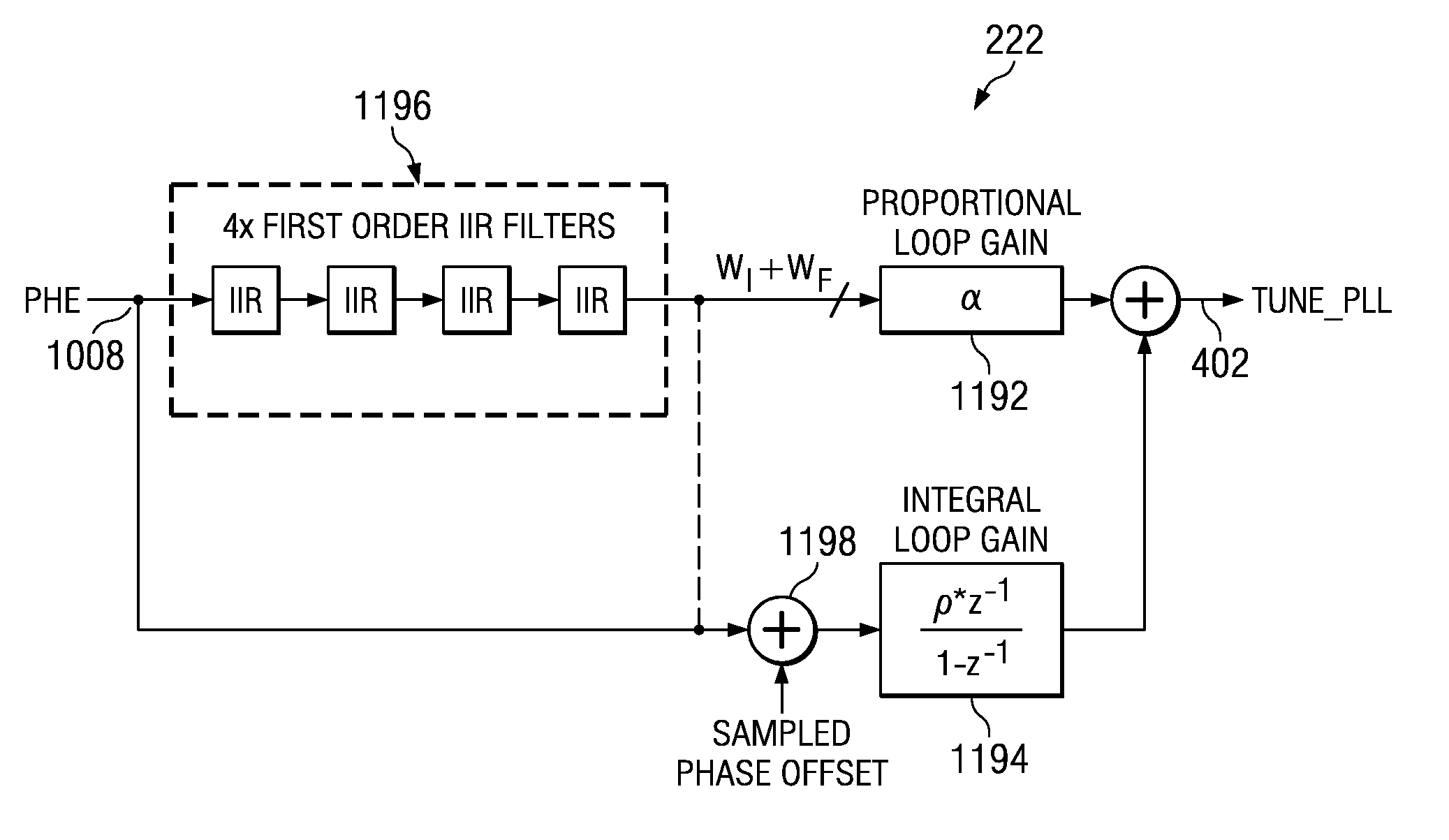
ActiveUS20080315960A1Pulse automatic controlTransmission path divisionProportional controlPhase difference
An embodiment of the present invention provides a phase locked loop that operates on clock signals derived from an RF clock signal generated by the phase locked loop. A frequency reference input provides a reference clock. A controllable oscillator generates the RF clock signal. A phase detection circuit operates on the reference clock to provide digital phase error samples indicative of a phase difference between the reference clock and the RF clock. A programmable filter is connected to receive the phase error samples and connected to provide a filtered output having a gain and a phase margin to the controllable oscillator. The programmable filter includes a proportional loop gain control having a programmable loop gain coefficient (alpha-α) and an integral loop gain control having a programmable loop gain coefficient (rho-ρ). Alpha and rho are configured to be programmatically changed simultaneously and are selected such that the gain is changed and the phase margin remains substantially unchanged
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Clock and data recovery circuit having wide phase margin
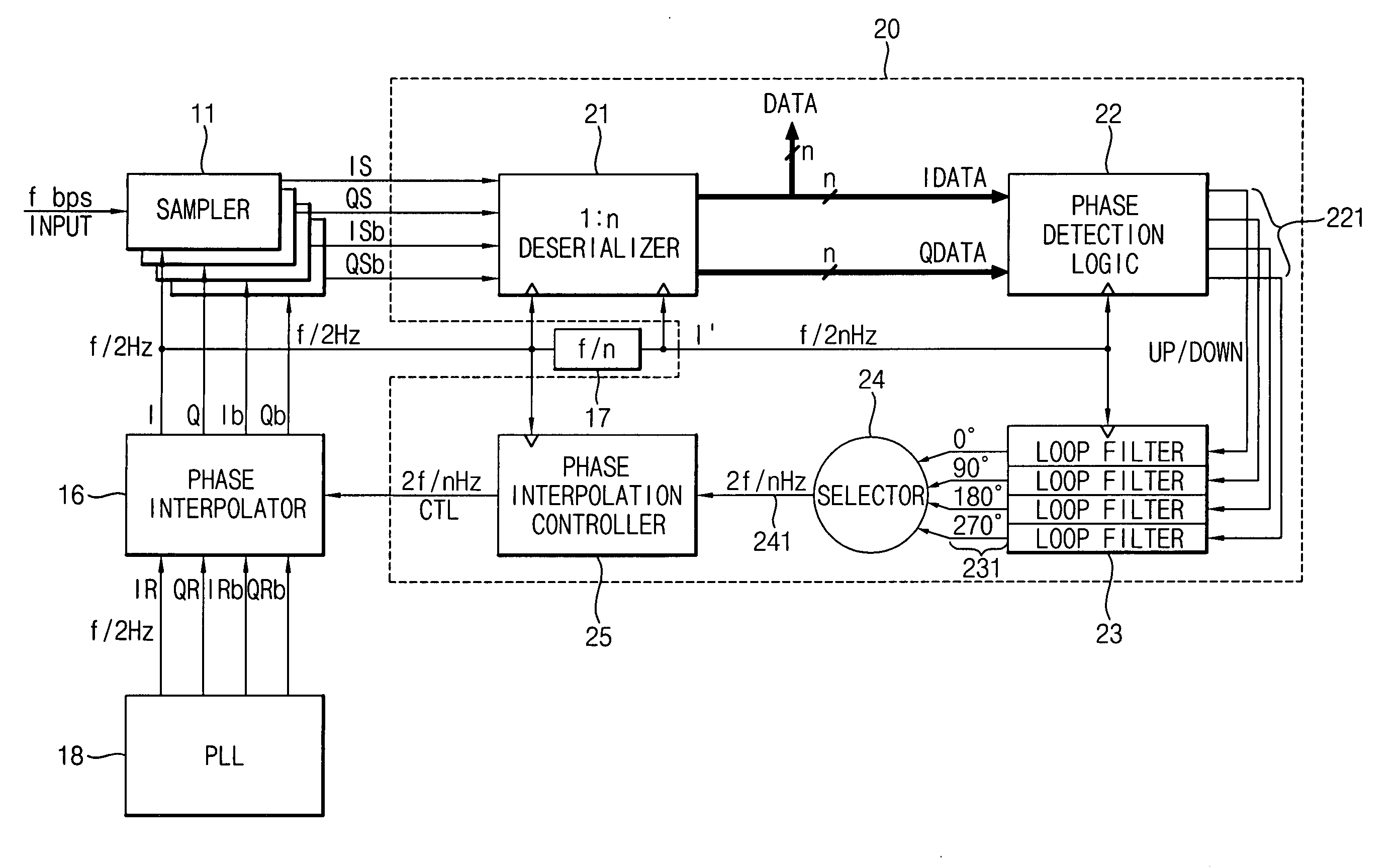
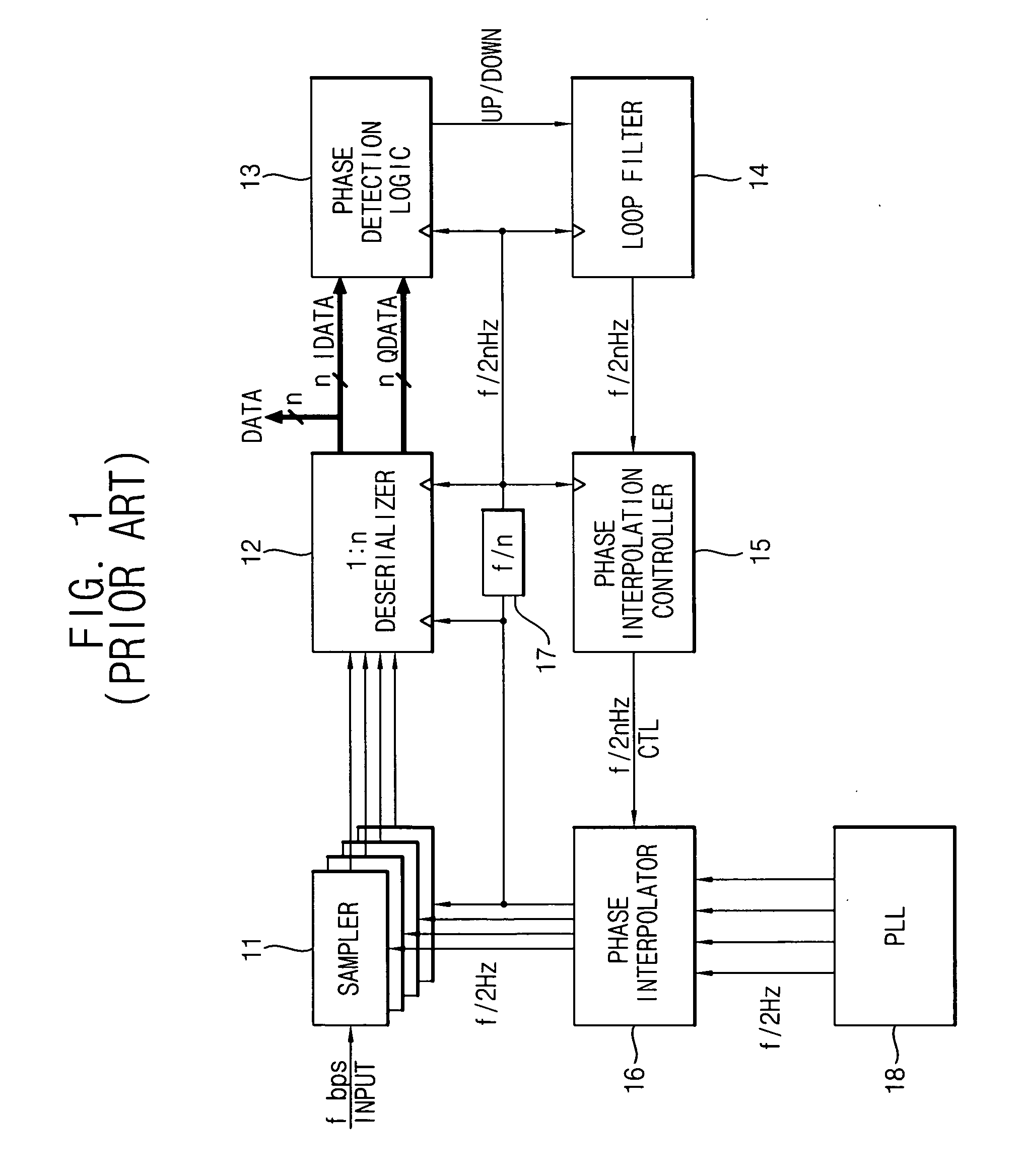
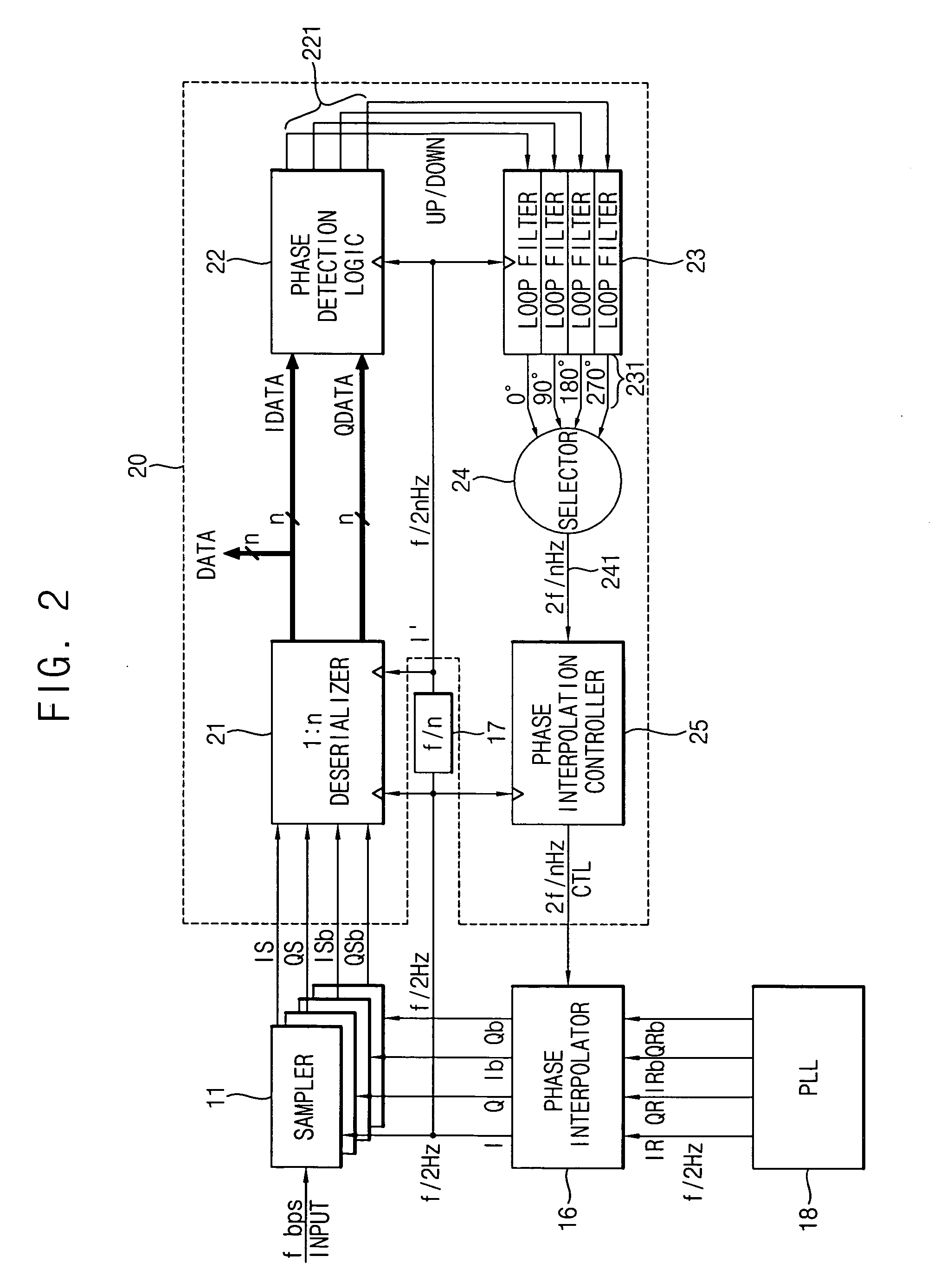
InactiveUS20070047683A1Wide phase marginIncrease speedPulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversSerial samplingPhase control
A clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit includes a sampler, a CDR loop and a phase interpolator. The sampler samples serial data in response to a recovery clock signal to generate a serial sampling pulse. The CDR loop transforms the serial sampling pulse into parallel data, generates a plurality of phase signals with a first speed based on the parallel data, and generates a phase control signal with a second speed higher than the first speed based on the plurality of phase signals. The phase interpolator generates the recovery clock signal by controlling a phase of a reference clock signal in response to the phase control signal. Therefore, the CDR circuit may recover data and a clock with a relatively high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
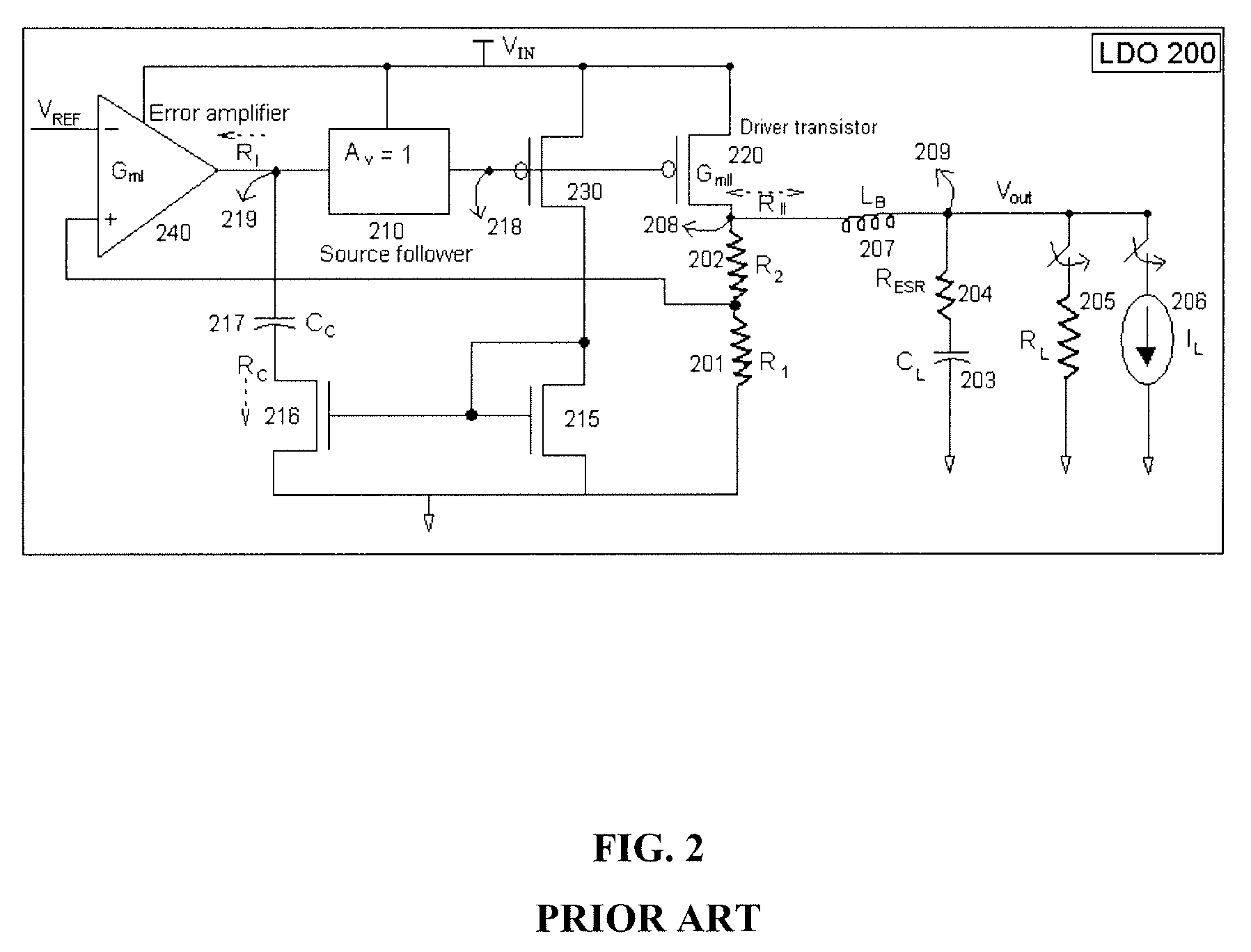
Low dropout regulator with stability compensation
InactiveUS7589507B2Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Double ring low differential voltage linear voltage stabilizer circuit
InactiveCN1949121AImproved Load Transient ResponseImprove dynamic performanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLoad circuit
The invention discloses double ring low voltage difference linear voltage regulator circuit. It includes error amplifier, secondary amplifier, power tube, compensating unit, output sampling network, load capacitance and load circuit, feed-forward amplifier, pull-up driving tube, pull-down driving tube, and sampling tube. It includes two loop circuits that the main one includes the error amplifier, secondary amplifier, pull-up driving tube, power tube, and output sampling network which form negative feedback loop to stably output voltage VOUT; the additional one includes feed-forward amplifier, sampling tube, pull-down driving tube, and power tube which refer to output voltage, form feed back loop to dynamically compensate circuit and further stably output voltage VOUT, and refer to load current, form positive feedback loop to increase load step change for the response circuit. The invention can supply better transient response, periphery circuit selecting, and phase margin for the circuit.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
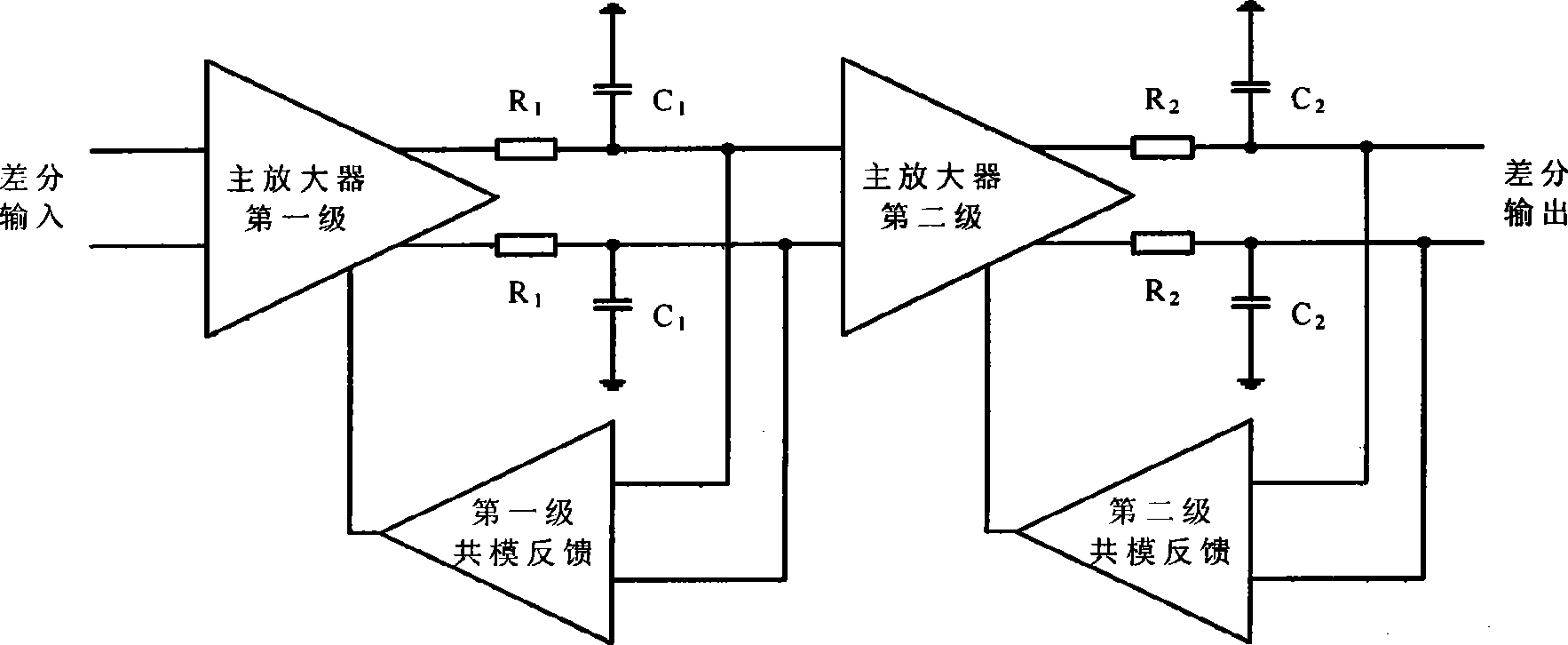
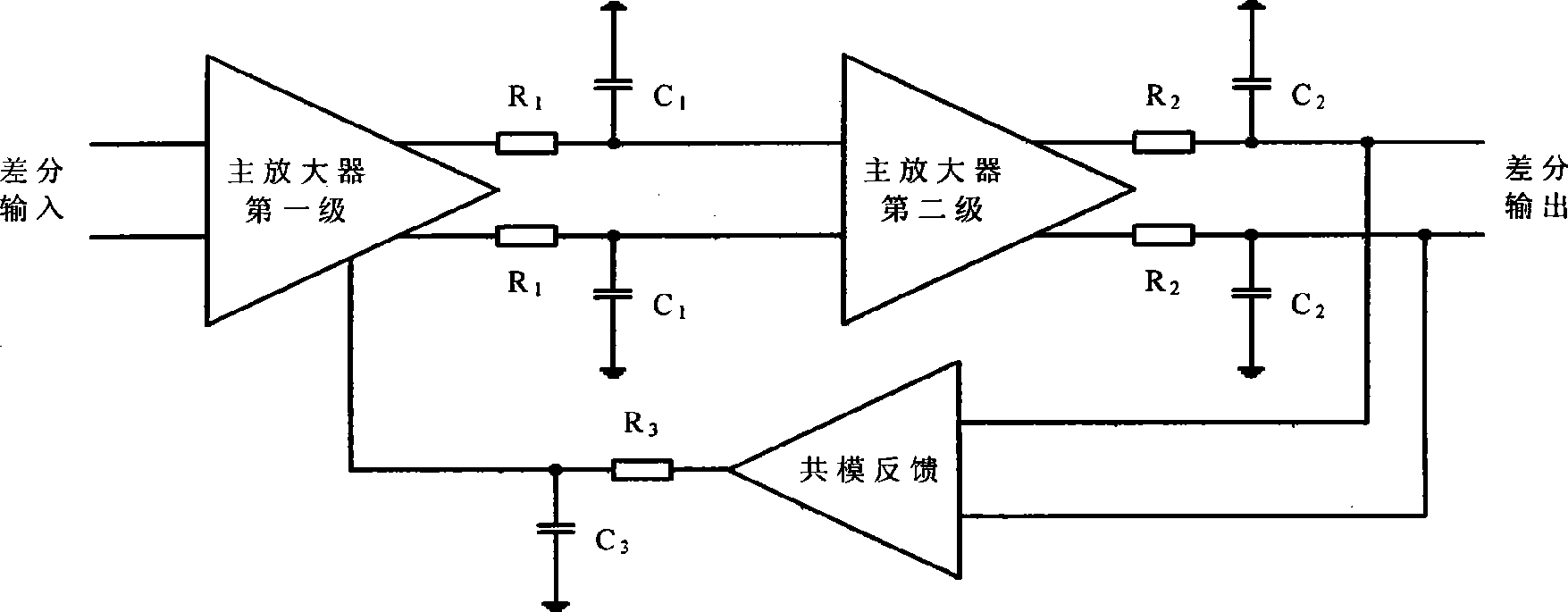
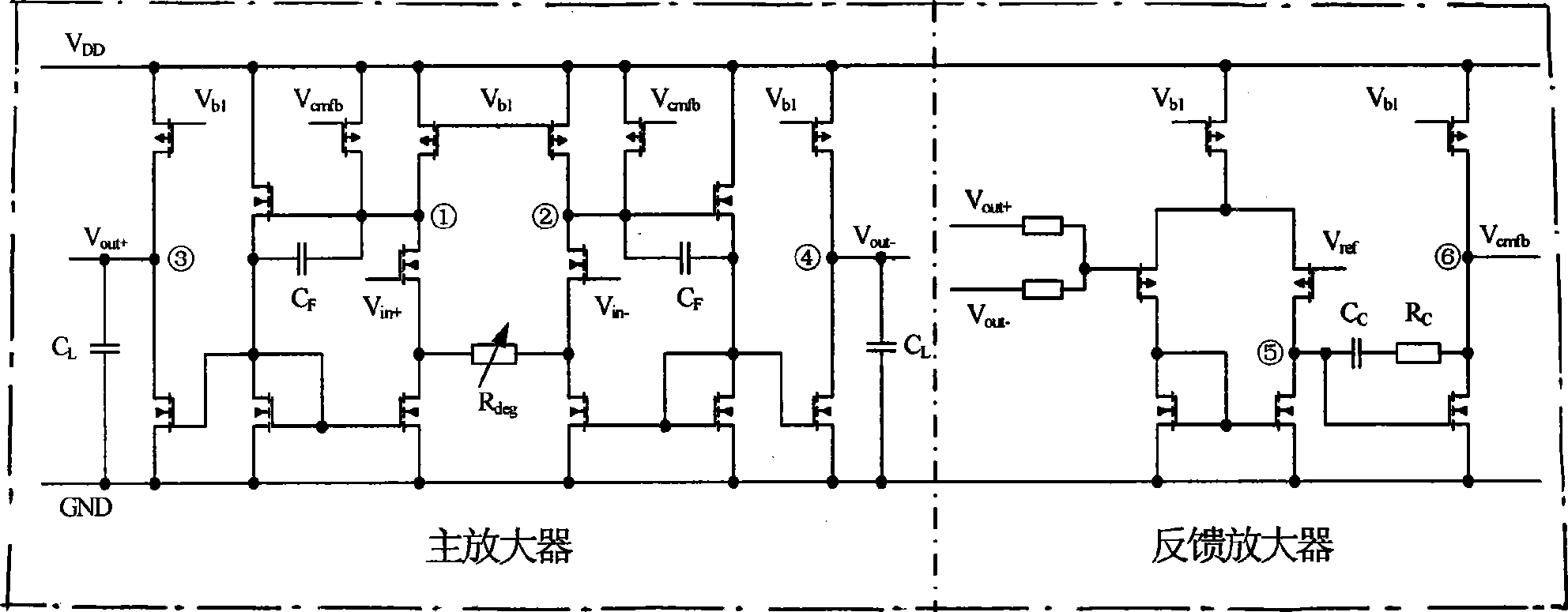
Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
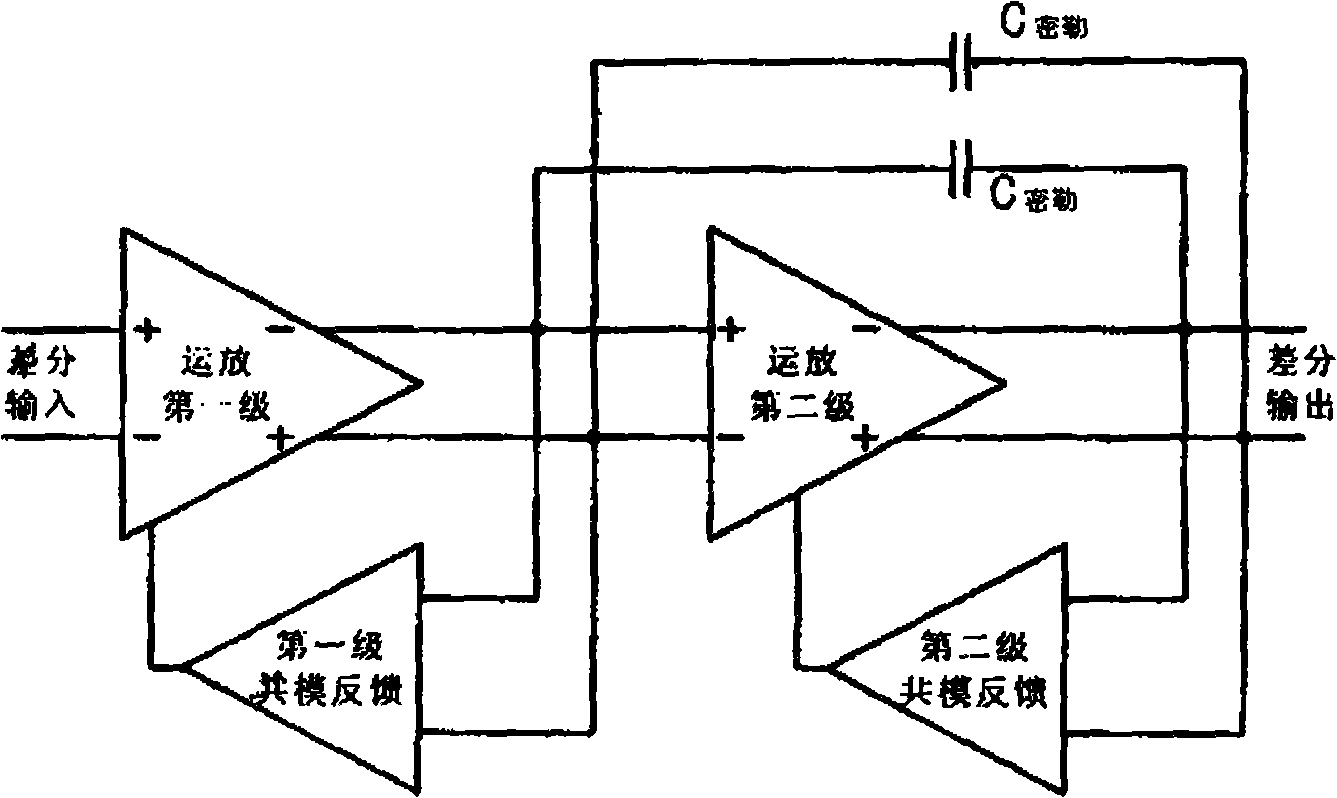
InactiveCN101373956AImprove phase marginImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesDual stageControl signal
The invention discloses a common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method of a dual-stage amplifier, which belongs to the analog integrated circuit design field. One common-mode feedback circuit is adopted in the dual-stage amplifier to reduce the area and the power consumption of the feedback circuit; the dual-stage amplifier adopts a fully-differential input / output structure; a differential output terminal is used for sampling the common-mode output level; a first-stage amplifying circuit thereof comprises a controllable biasing circuit; a common-mode feedback control signal controls the first-stage common-mode output level and the second-stage common-mode output level of the amplifier at the same time through the controllable biasing circuit; a feedback amplifier is realized by adopting a dual-stage operational amplifier with miller compensation. The left half plane zero point generated by the feedback amplifier in a loop circuit counteracts a certain left half plane pole in a prime amplifier, thereby forming a stable compensation loop circuit. The common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method has the advantages of less feedback circuit elements, lower feedback circuit power consumption, high low-frequency loop gain and better compensation phase margin.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
LDO (Low DropOut Regulator) based on dynamic zero pole tracking technology
InactiveCN102541134AImprove stabilityElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
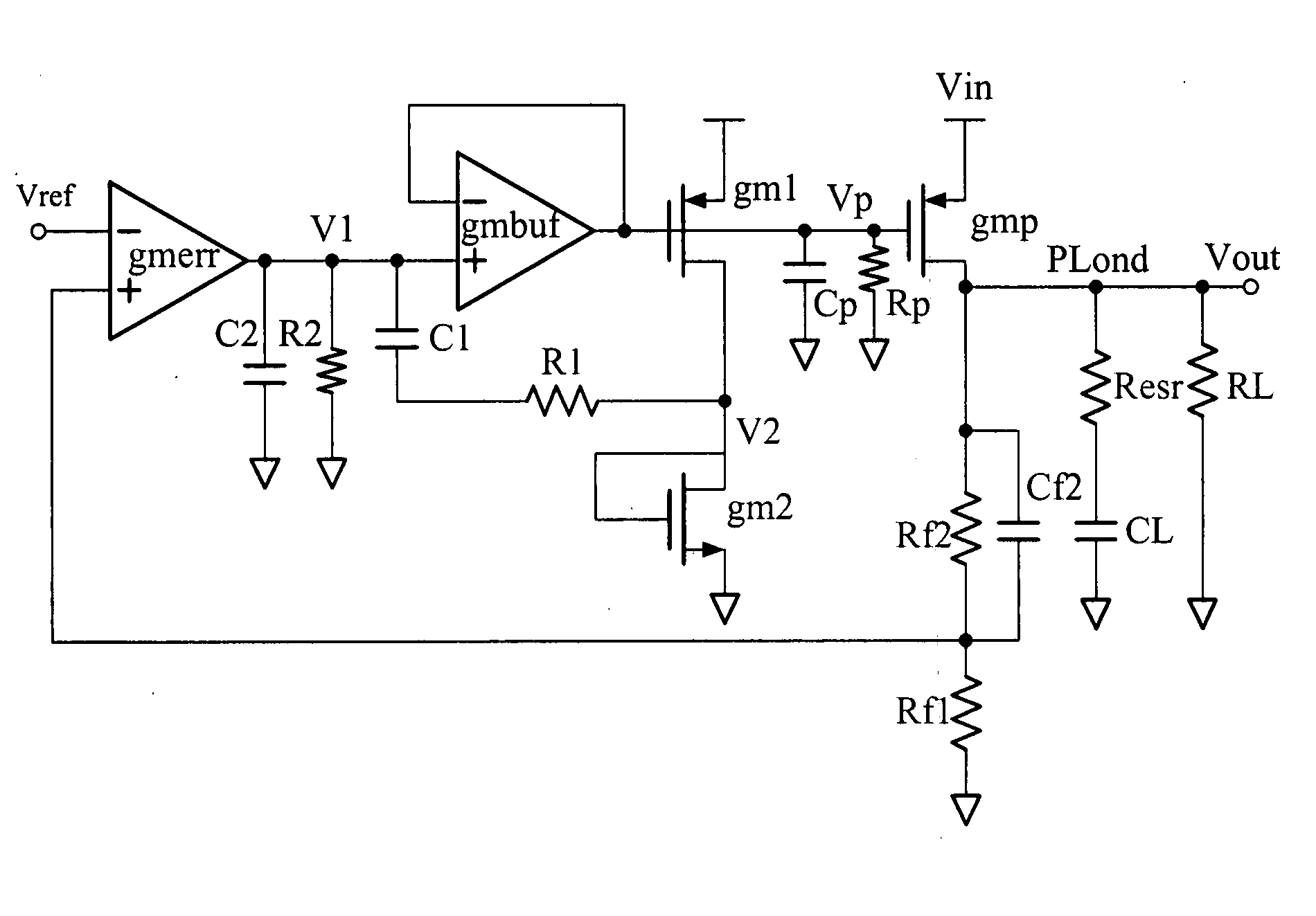
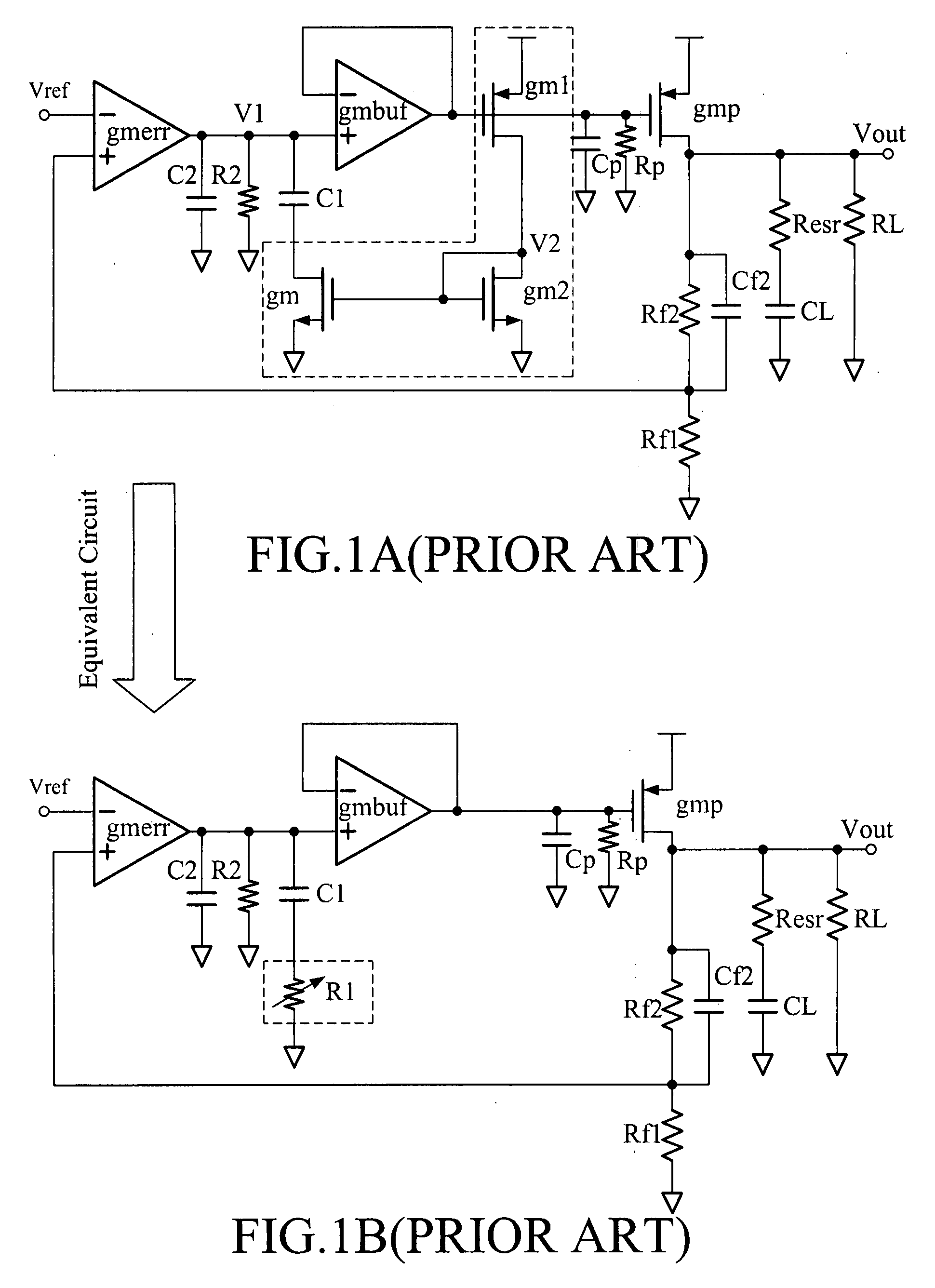
The invention discloses an LDO (Low DropOut Regulator) based on a dynamic zero pole tracking technology, belonging to the field of power supply management. The LDO is provided to solve the problem of the stability of a traditional LDO loop, and specifically comprises an error amplifier, a buffer and a slew-rate enhancement circuit. The LDO is characterized by further comprising a first capacitor, a second capacitor and a variable resistor, wherein one end of the first capacitor is connected with the output end of the error amplifier, the other end of the first capacitor is connected with one end of the variable resistor, one end of the second capacitor is connected with the error amplifier, and the other end of the second capacitor is connected with the other end of the variable resistor and is taken as the output end of the LDO. According to the LDO based on the dynamic zero pole tracking technology, disclosed by the invention, the first capacitor and the variable resistor form a compensative network as a dynamic zero pole of a system; and in addition, a phase margin of the LDO loop is compensated by utilizing the second capacitor in a current multiplication mode so that the stability of the LDO loop is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
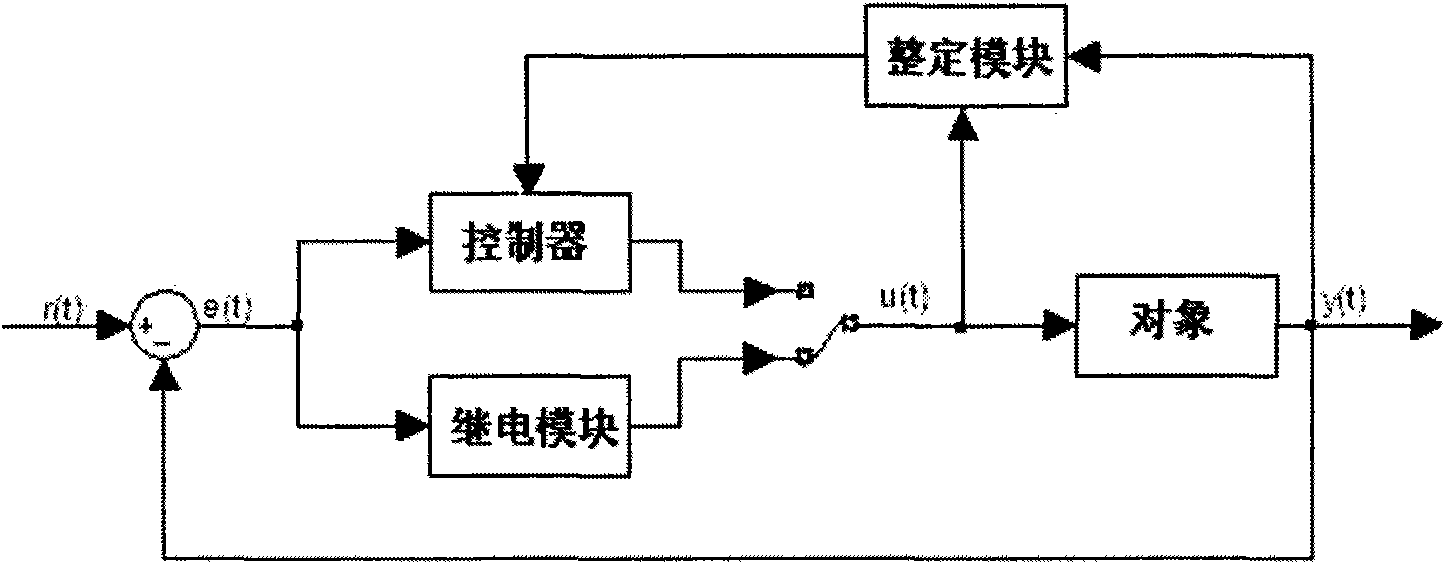
Relay feedback based AC servo system automatic setting method
InactiveCN101552589ARealize automatic tuningMotor parameters estimation/adaptationMovement controlMotion control
A relay feedback based AC servo system automatic setting method belonging to the motion control technology field comprises a speed ring setting process and a position ring setting process. The method comprises the following steps: setting the parameters of saturated relay with delay; bringing the relay identification link into the closed speed ring (or position ring) to cause the system to establish a limit ring quickly; evaluating the system delay and the limit oscillation period parameter; identifying the AC servo system model; and setting the PID control parameter automatically by the PID parameter setting principle such as pole assignment method and amplitude phase margin method according to the identified model parameters; By combining the saturated relay feedback and he PID parameter setting principle such as ITAE method and amplitude phase margin method, the invention can accomplish the parameter automatic setting to the controller of AC servo motor.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Digital phase locked loop with gear shifting
An embodiment of the present invention provides a phase locked loop that operates on clock signals derived from an RF clock signal generated by the phase locked loop. A frequency reference input provides a reference clock. A controllable oscillator generates the RF clock signal. A phase detection circuit operates on the reference clock to provide digital phase error samples indicative of a phase difference between the reference clock and the RF clock. A programmable filter is connected to receive the phase error samples and connected to provide a filtered output having a gain and a phase margin to the controllable oscillator. The programmable filter includes a proportional loop gain control having a programmable loop gain coefficient (alpha—α) and an integral loop gain control having a programmable loop gain coefficient (rho—ρ). Alpha and rho are configured to be programmatically changed simultaneously and are selected such that the gain is changed and the phase margin remains substantially unchanged.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
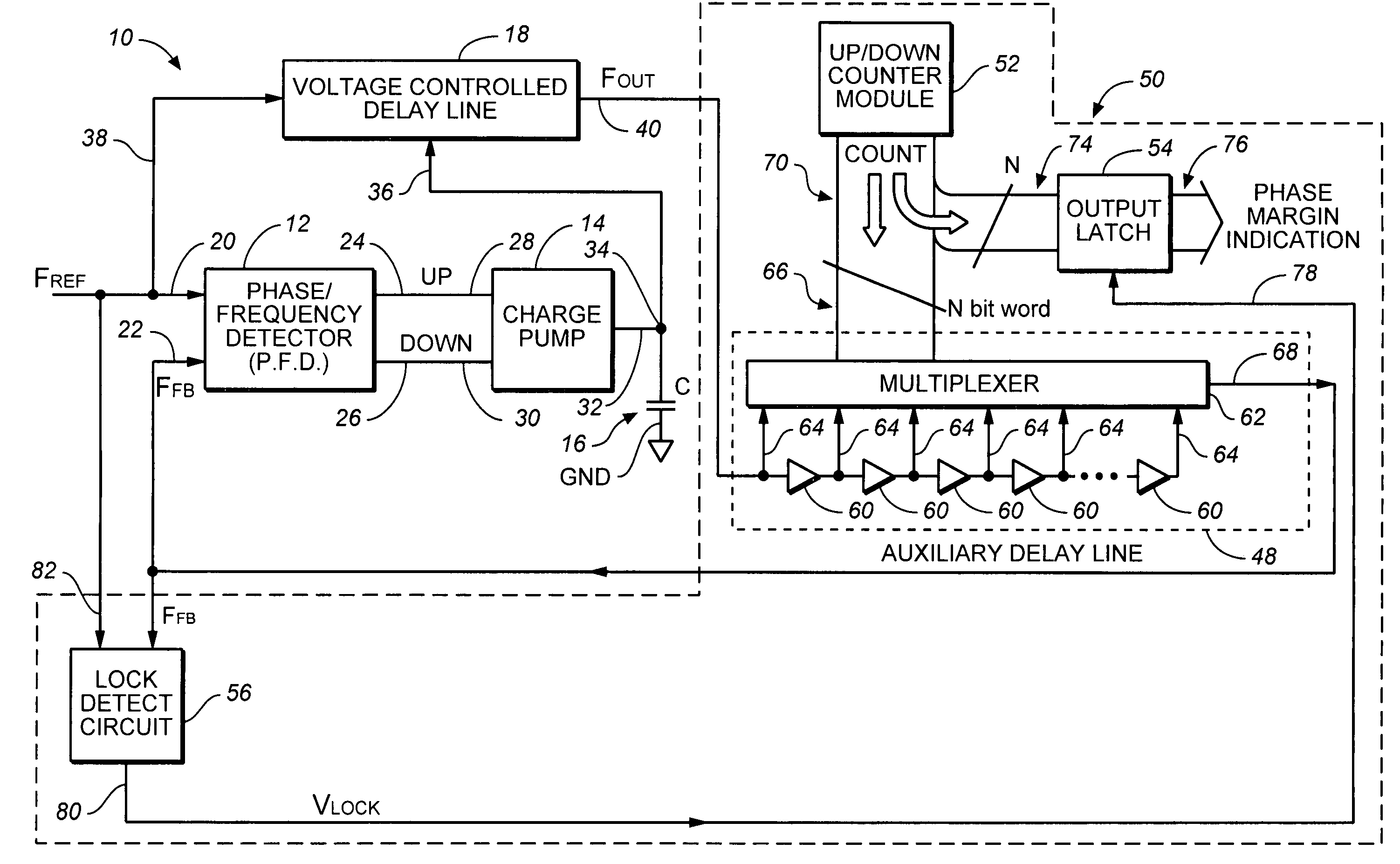
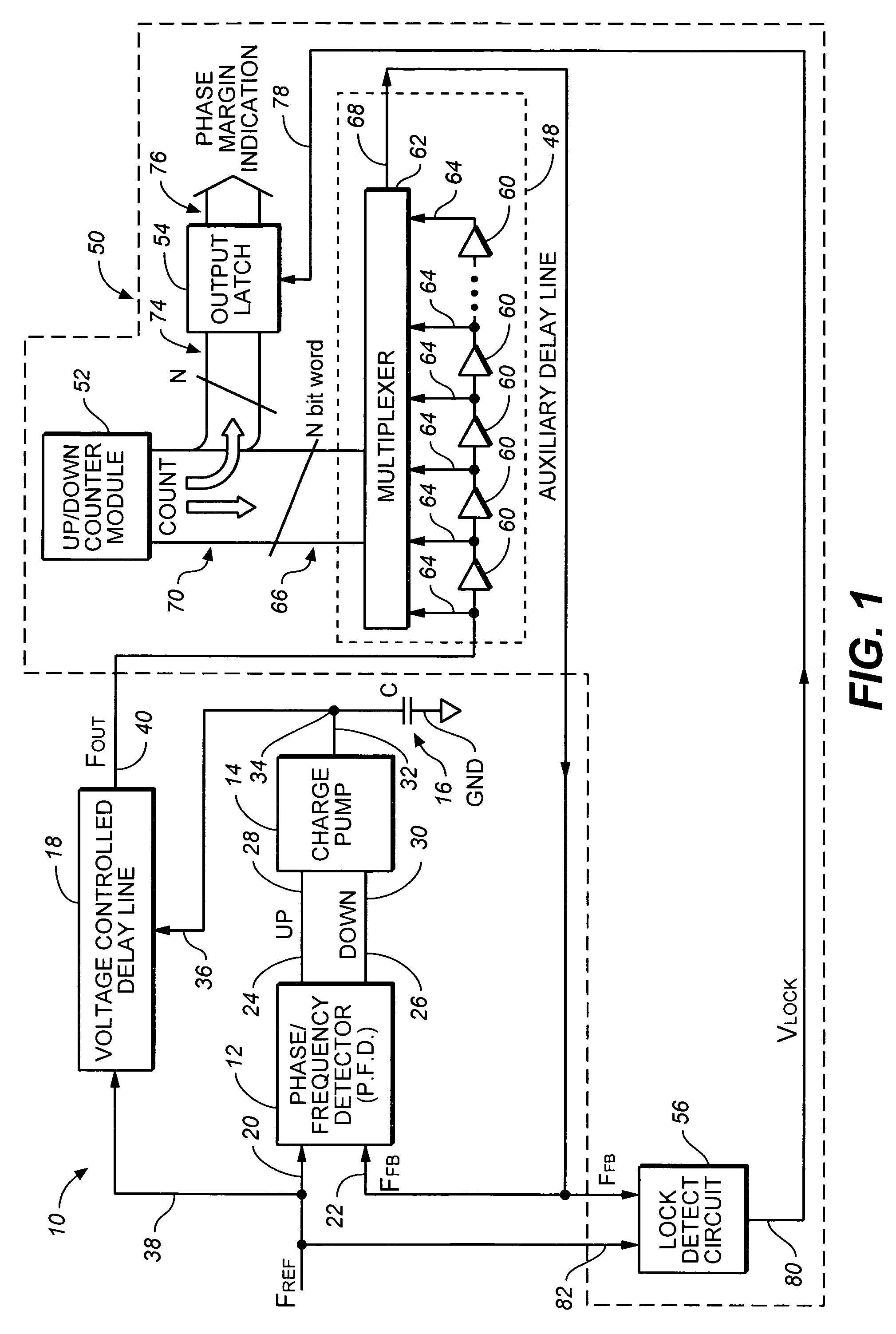
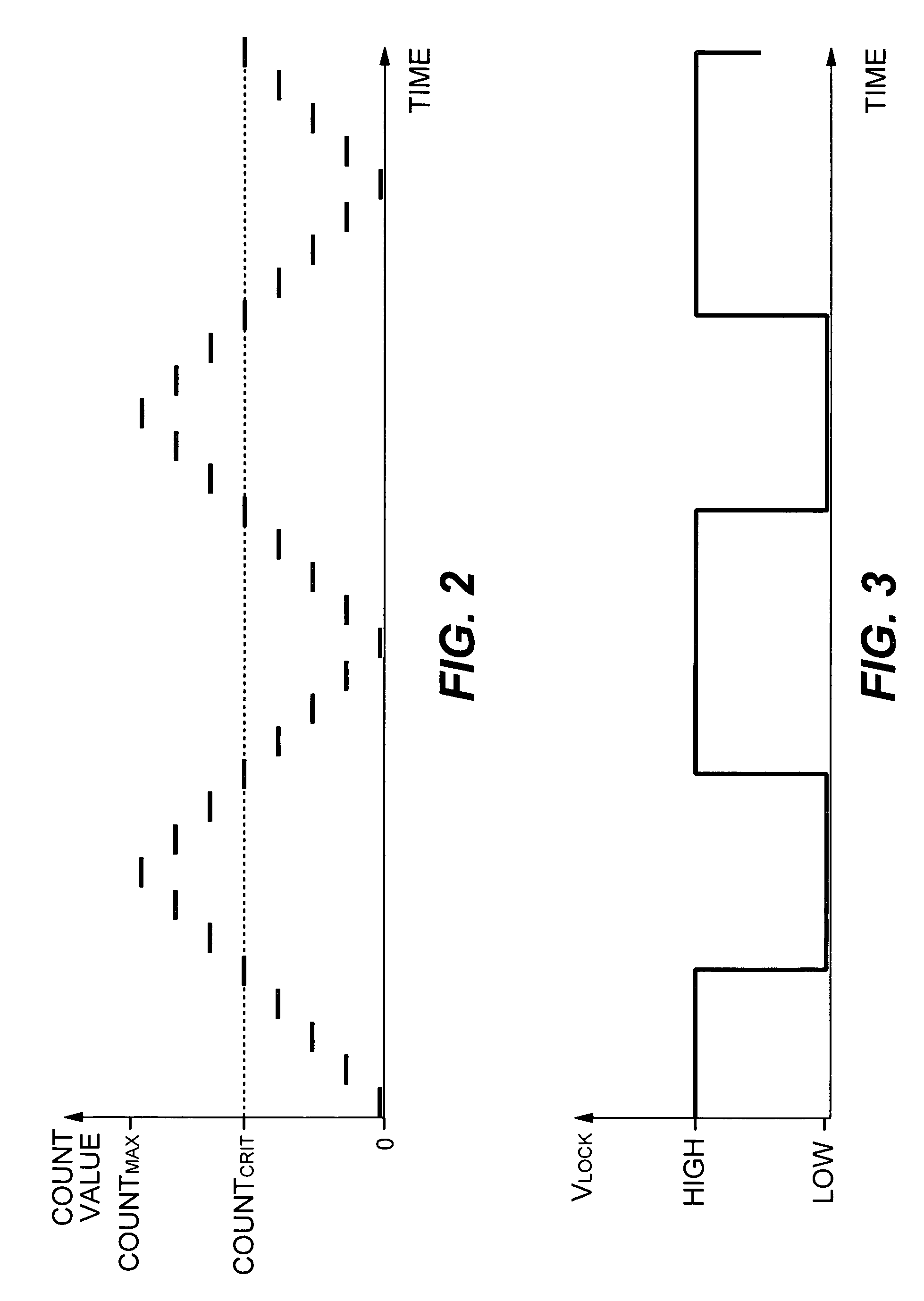
Delay-locked loop with built-in self-test of phase margin
ActiveUS7042971B1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopEngineering
A method and apparatus for measuring phase margin of a delay-locked loop (DLL) is provided in which a reference clock is applied to a reference input of the DLL. An auxiliary variable delay is coupled within the DLL and is varied until the DLL becomes unstable. A phase margin output is generated as a function of a value of the variable delay at which the DLL becomes unstable.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Hybrid Interleaving Structure with Adaptive Phase Locked Loop for Variable Frequency Controlled Switching Converter
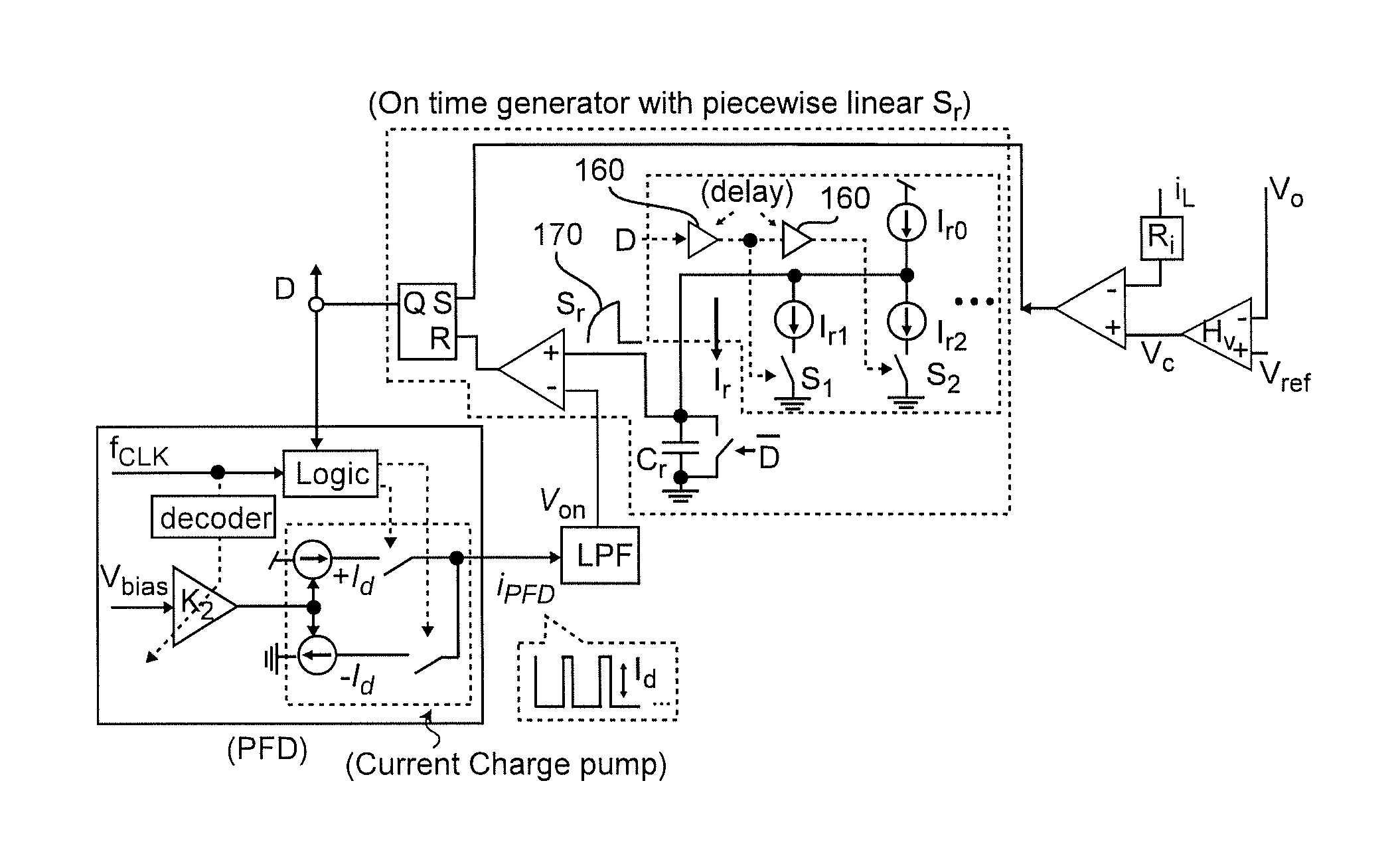
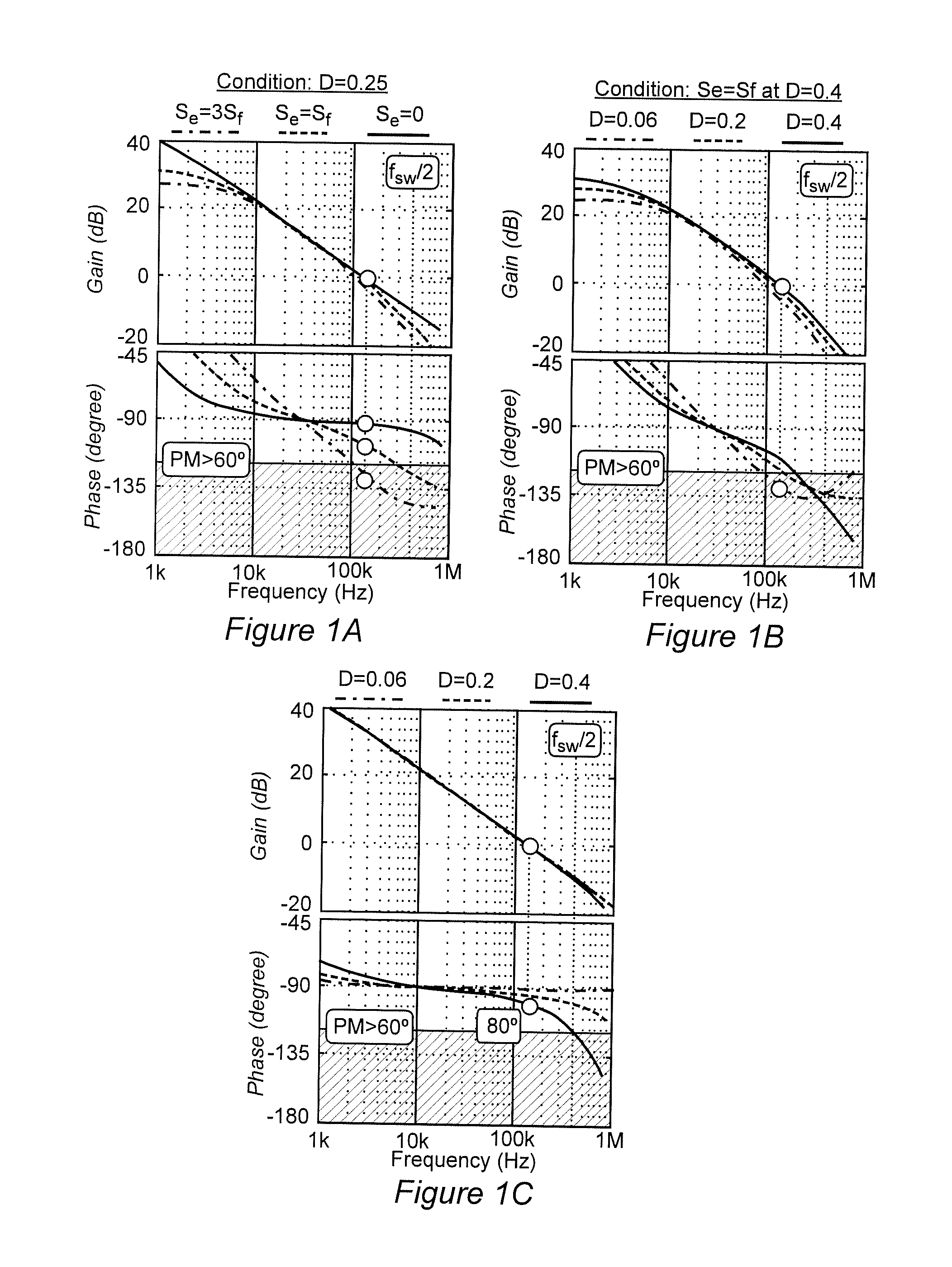
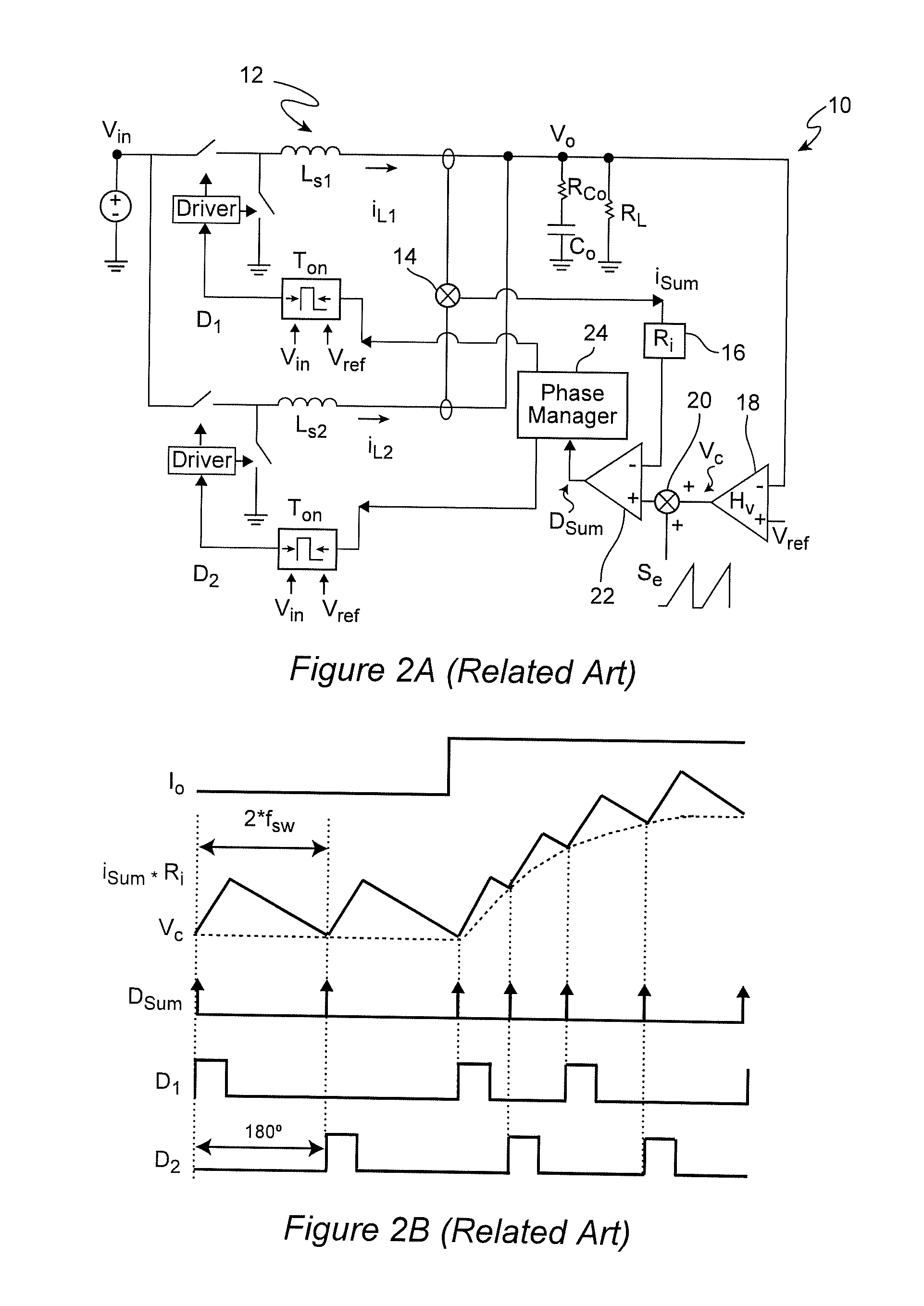
ActiveUS20150277460A1Reduce noiseSufficient phase marginPulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionPhase cancellationBand width
In a multi-phase power converter using a phase-locked loop (PLL) arrangement for interleaving of pulse frequency modulated (PFM) pulses of the respective phases, improved transient response, improved stability of high bandwidth output voltage feedback loop, guaranteed stability of the PLL loop and avoidance of jittering and phase cancellation issues are achieved by anchoring the bandwidth at the frequency of peak phase margin. This methodology is applicable to multi-phase power conveners of any number of phases and any known or foreseeable topology for individual phases and is not only applicable to power converters operating under constant on-time control, but is extendable to ramp pulse modulation (RPM) control and hysteresis control. Interleaving of pulses from all phases is simplified through use of phase managers with a reduced number of PLLS using hybrid interleaving arrangements that do not exhibit jittering even when ripple is completely canceled.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Low dropout voltage regulator providing adaptive compensation
InactiveUS20050242796A1Improve transient responseHigh bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedEngineering
A method and apparatus to dynamically modify internal compensation of a low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator is provided. The LDO voltage regulator includes an output pass transistor, an error amplifier, a bias transistor and a compensation network. The compensation network is connected between a gate and a drain of the output pass transistor to compensate for the feedback loop. The compensation network and the bias transistor generate pole-zero pairs to perform a maximum 45 degrees phase shift before reaching the crossover frequency in the LDO voltage regulator. Therefore a minimum 45 degrees phase margin is provided for the feedback loop in various load conditions. Furthermore, the pole-zero pairs produced in the LDO voltage regulator are adaptively adjusted according to load conditions, so that the bandwidth is optimized and faster transient response is achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
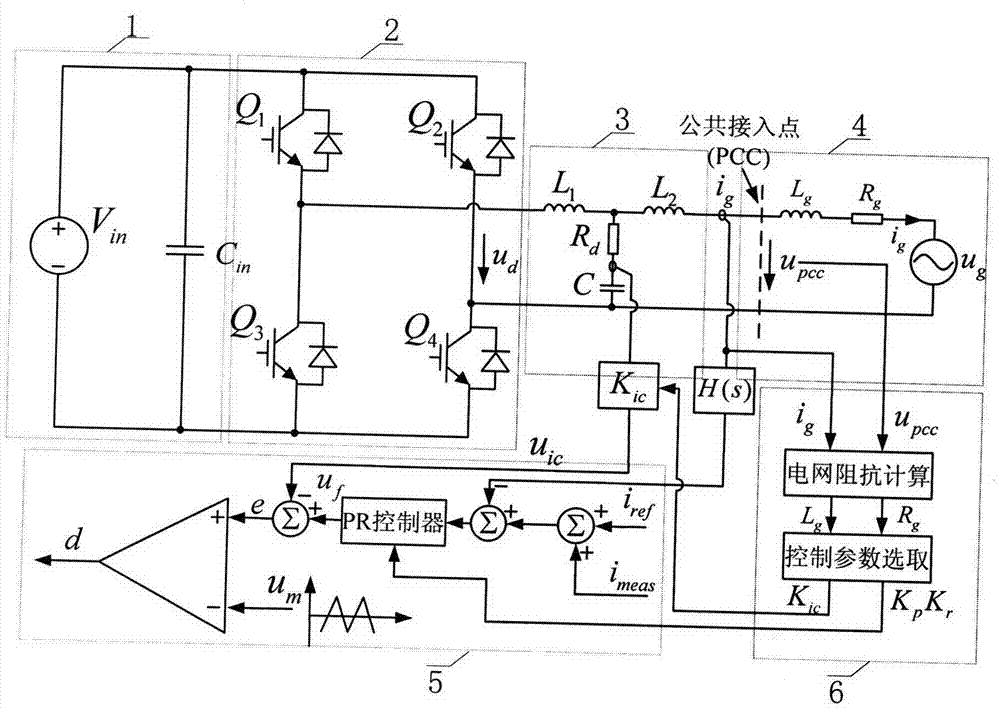
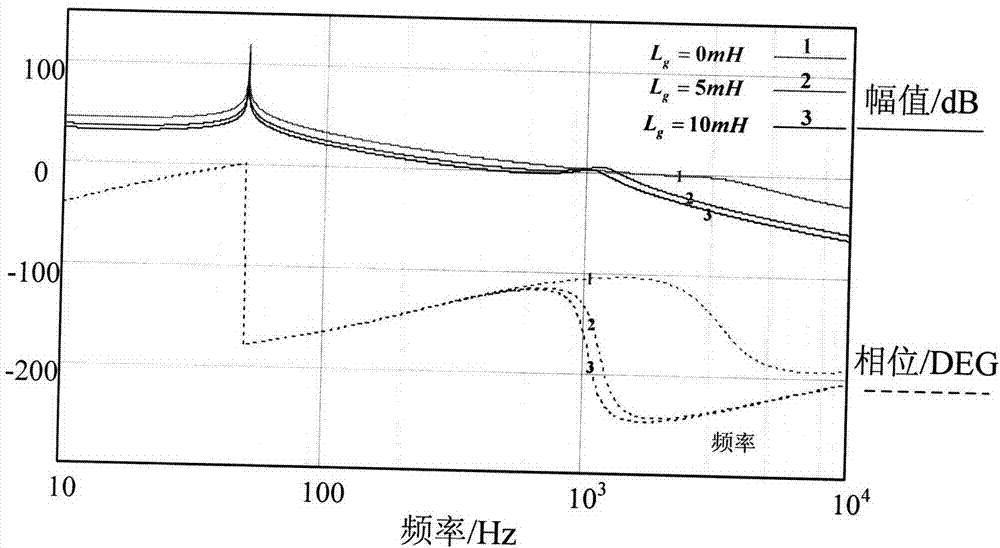
Method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of grid-connection inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions
ActiveCN103545838AReasonable frequency characteristicsPR parameter increaseAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDamping factorGrid impedance
The invention relates to a method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of a grid-connected inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions. Most existing methods are used for optimally controlling fixed impedance of grids at present, but grid access conditions of grid-connected inverters are dynamic and varied, so that adaptive control under different grid impedance conditions has high application value. The method includes measuring impedance information of a weak grid by a harmonic injection process; enabling a controller to adaptively modify loop parameters and active damping coefficients; ensuring a wide stability margin and a proper control bandwidth of a control system. The method has the advantages that the novel method for adaptively controlling the hybrid damping is based on real-time measurement on impedance of the grid, and optimal control parameters in a DSP (digital signal processor) are automatically selected, so that the control bandwidth and a phase margin of the inverter under different grid impedance access conditions can be guaranteed, and the grid-connected inverter can safely and reliably run under the various grid impedance conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
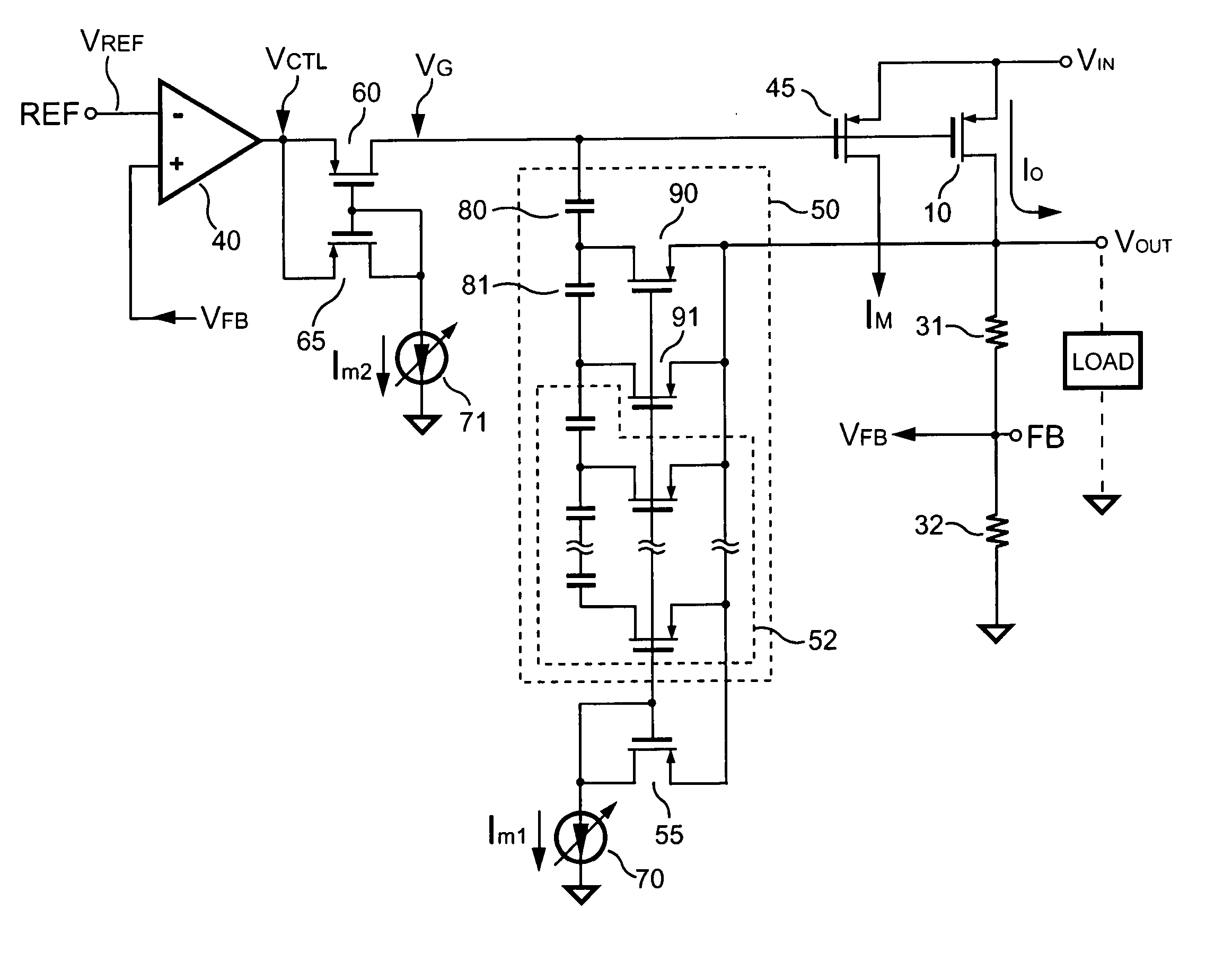
Efficient frequency compensation for linear voltage regulators
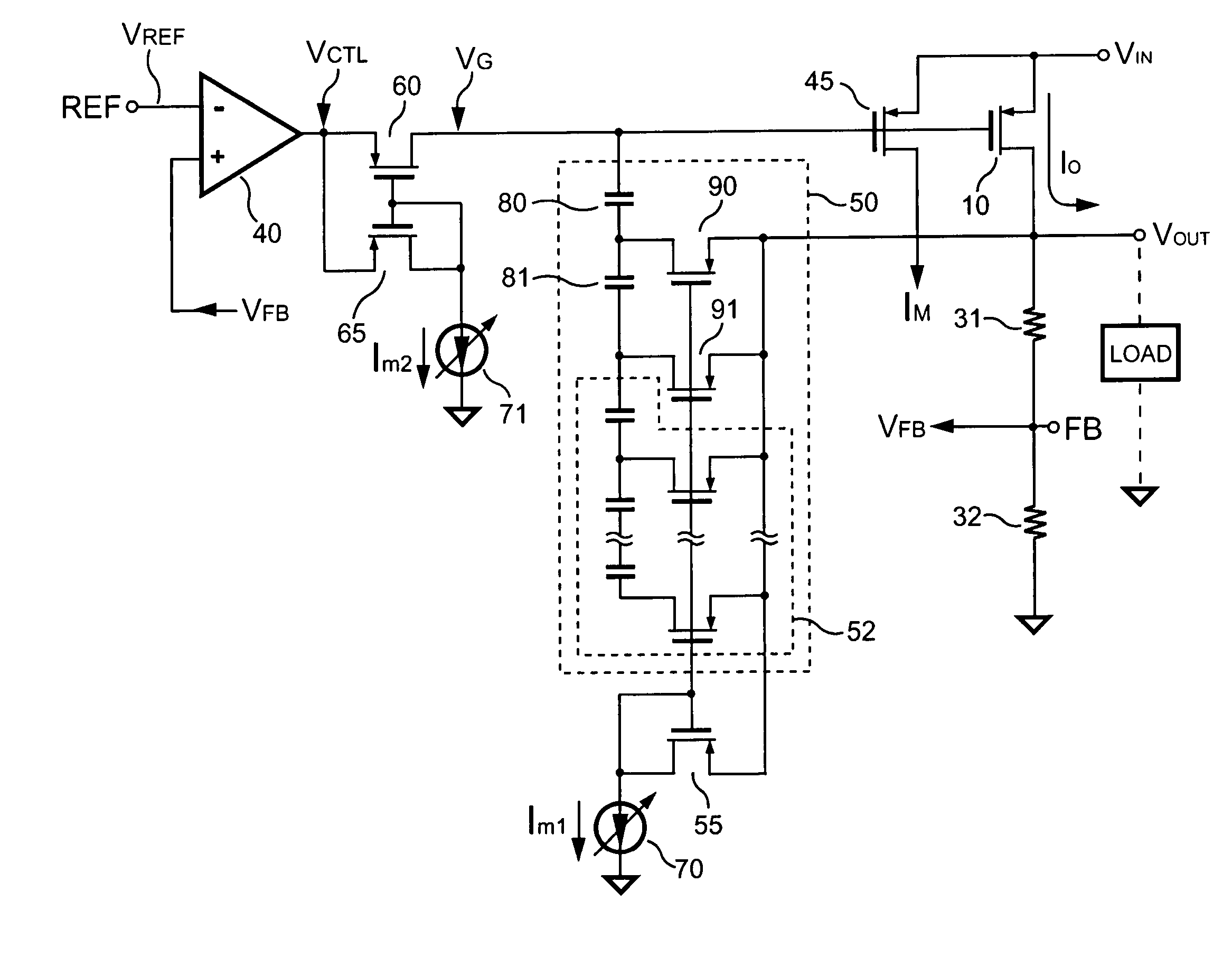
ActiveUS6975099B2Small overall compensation elementEqual and improved phase marginElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorFrequency compensation
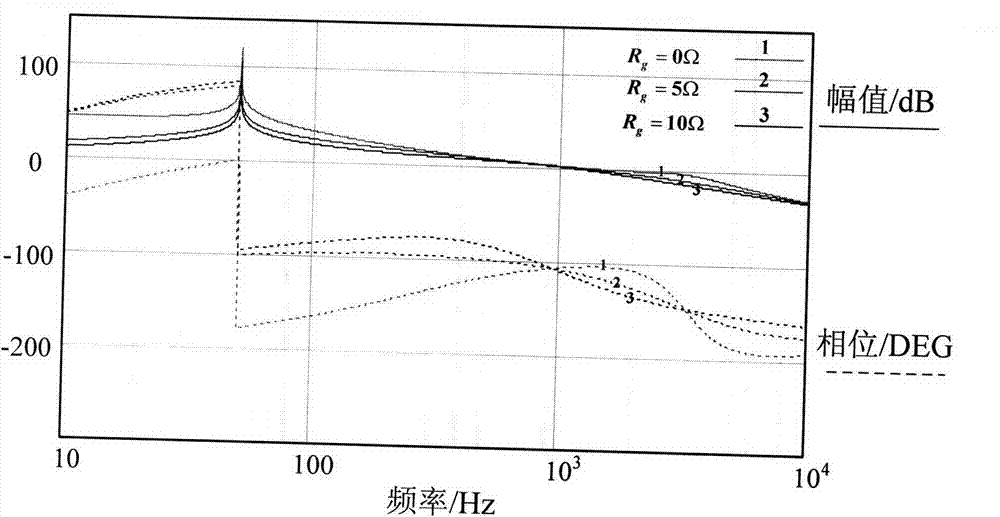
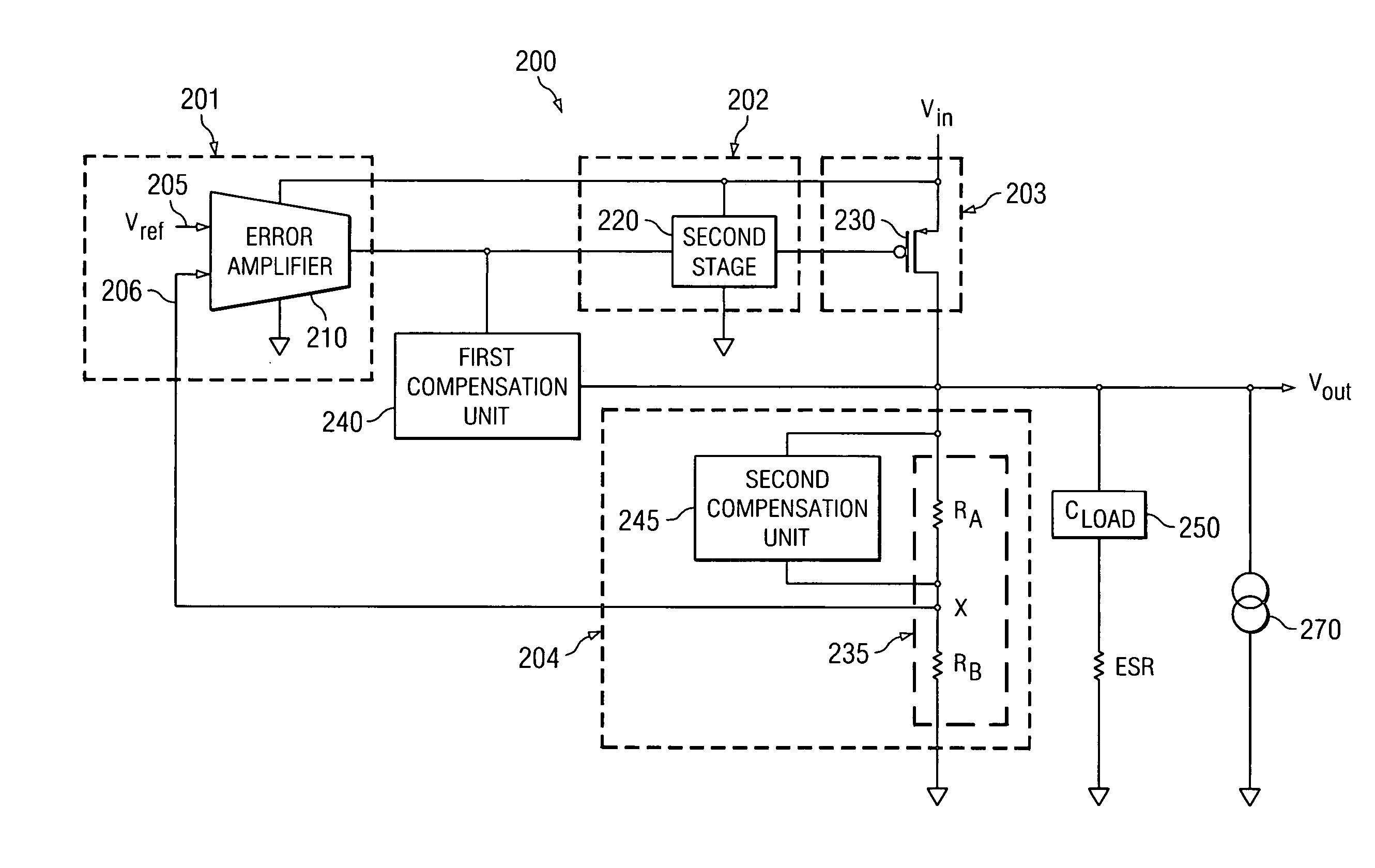
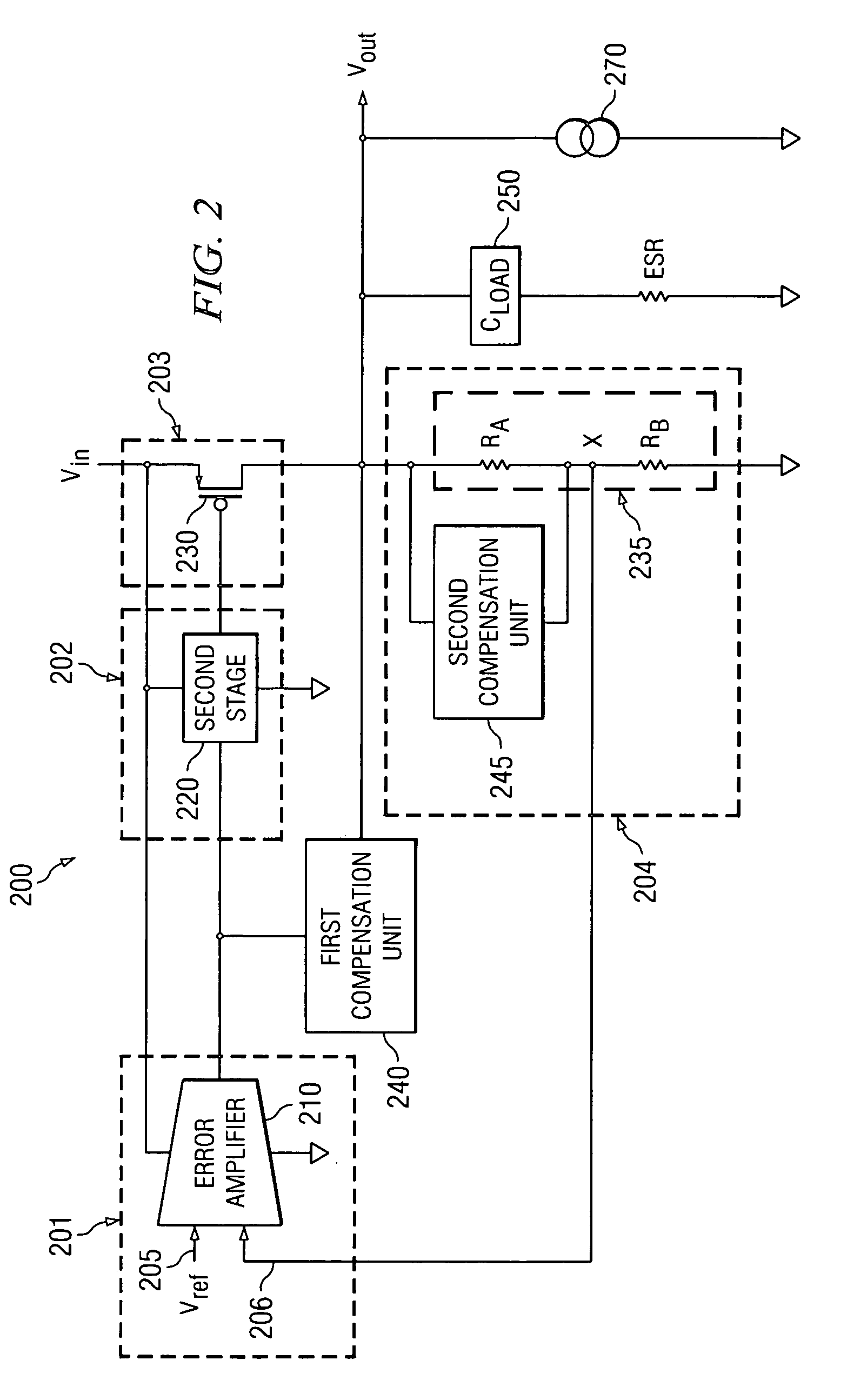
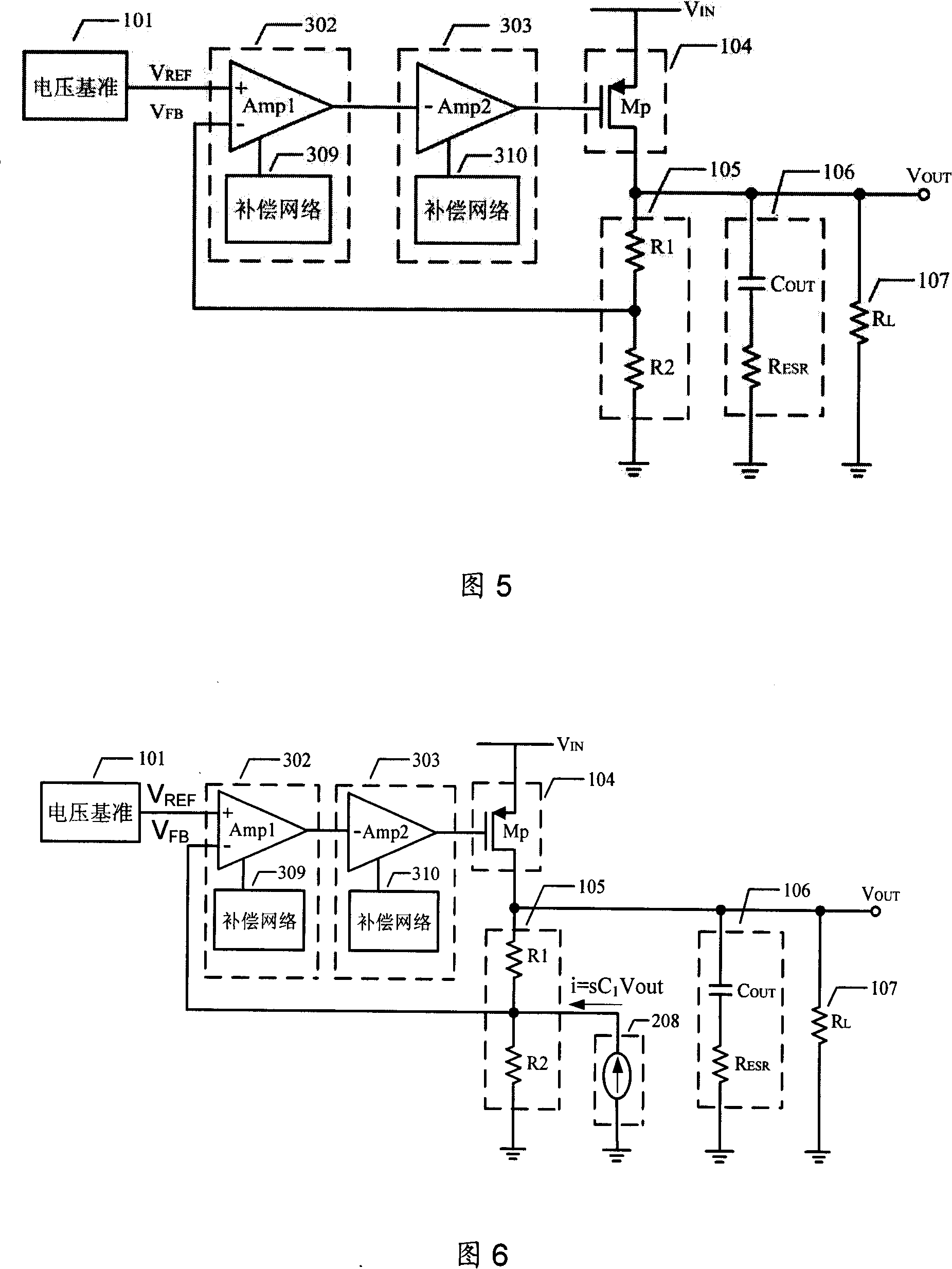
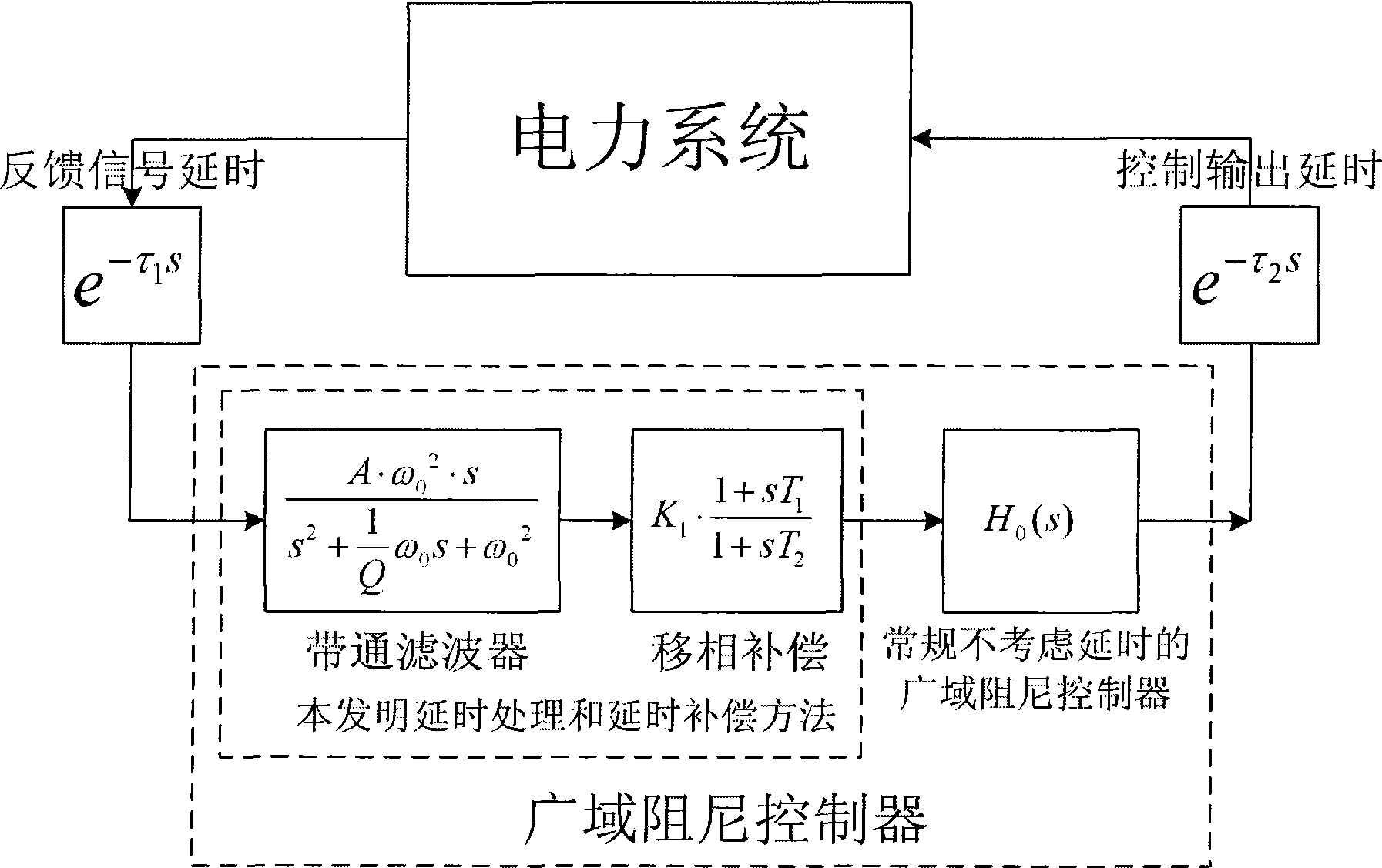
The present application describes a frequency compensation scheme for a linear voltage regulator circuit, or its special case, a low-drop out voltage regulator (LDO). According to one embodiment, the frequency compensation scheme includes two circuits, an inner loop compensation circuit (240), and a circuit (245) at the output in parallel with one of the resistors of the output voltage divider (235). These two compensation elements (240, 245) are not interdependent and may be adjusted separately to provide more optimal frequency compensation. Advantages include smaller compensation circuit elements, die or board area savings, better phase margin over process technology variations and operating conditions, and ease of design adjustment.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
PIlambdaDmu controller parameter setting method based on parameter stability domain
InactiveCN103092069AEasy to controlImprove dynamic characteristicsControllers with particular characteristicsGenetic algorithmControl theory
The invention discloses a PIlambdaDmu controller parameter setting method based on a parameter stability domain. The method includes the following steps: judging if the input and the output of a controller system are stable, then determining parameter stability domain boundary curves at phase margin upper limit and at the position of phase margin appearing, determining a value range of two boundary curve frequency on the condition of ensuring parameters with practical significance, confirming the range of parameter Ki and Kp in the stability domain on the boundary curve, inserting a plurality of points on two boundary curves, determining a plurality of groups of points which are equal in Kp value respectively on the two boundary curves, obtaining a value range of Ki corresponding to the plurality of groups of points, determining an optimum value of Ki corresponding to each group of points by adopting a genetic algorithm, and finally determining an optimal solution through integral time absolute error (ITAE). According to the PIlambdaDmu controller parameter setting method based on the parameter stability domain, stable phase margin of a system and dynamic characteristics are both considered, and controller parameters are set by means of the genetic algorithm. A controller which is set by using the method can well control a system on the condition of meeting given stable phase margin, and therefore the fact that a system has better dynamic characteristics is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
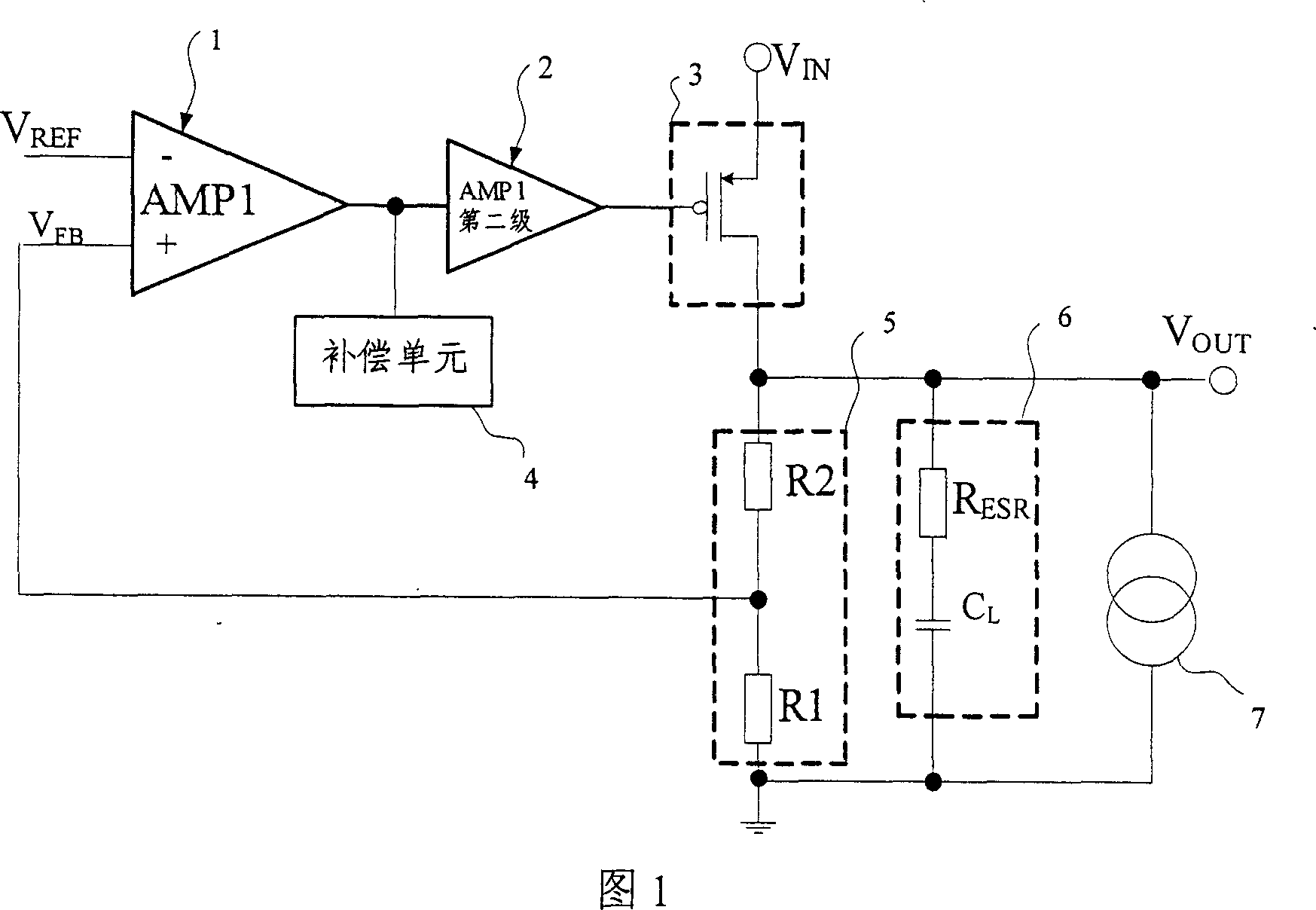
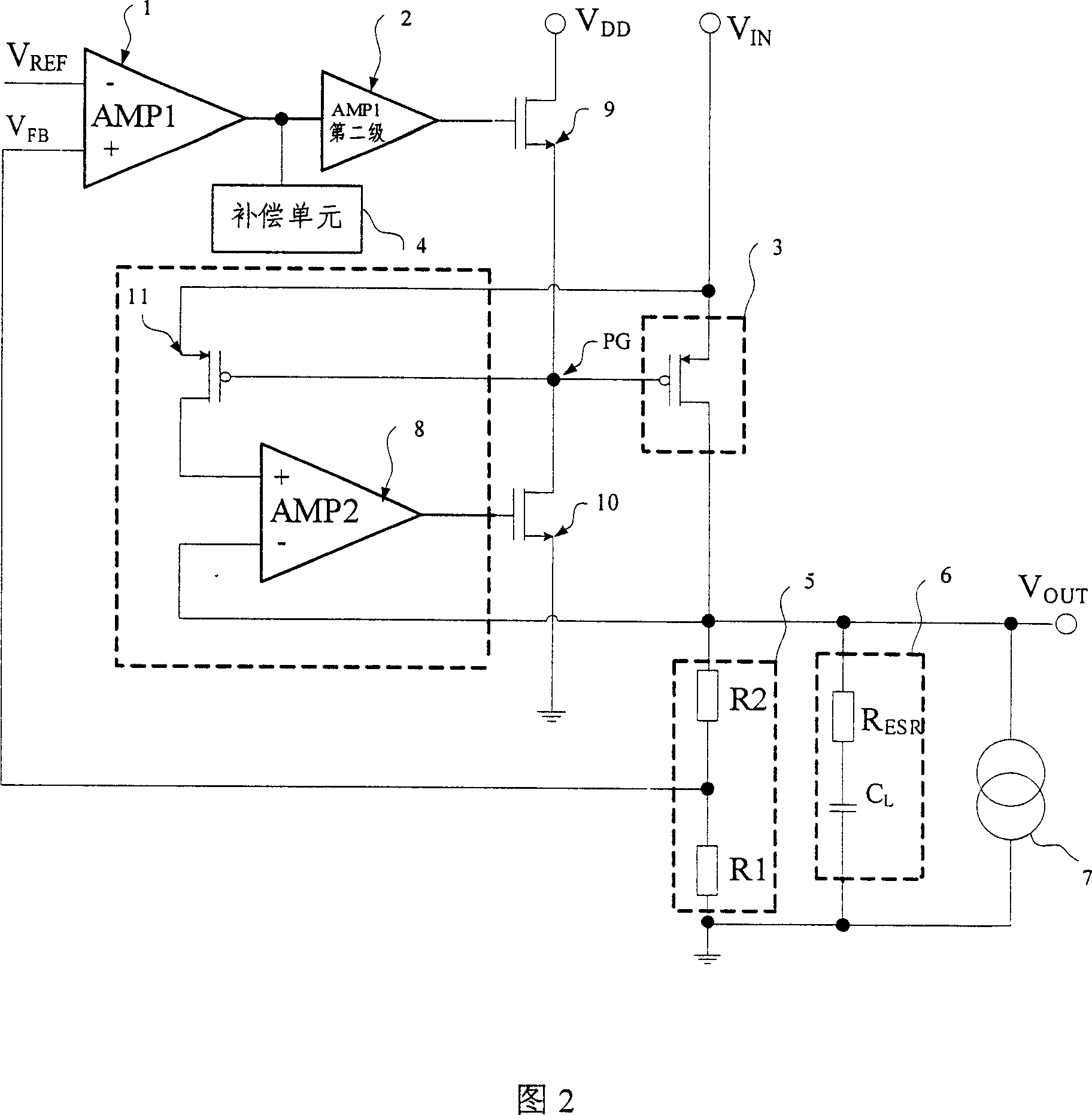
Low dropout linear regulator with quick transient response and high stability
InactiveCN103838286AGuaranteed stabilityChange does not happenElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCapacitance
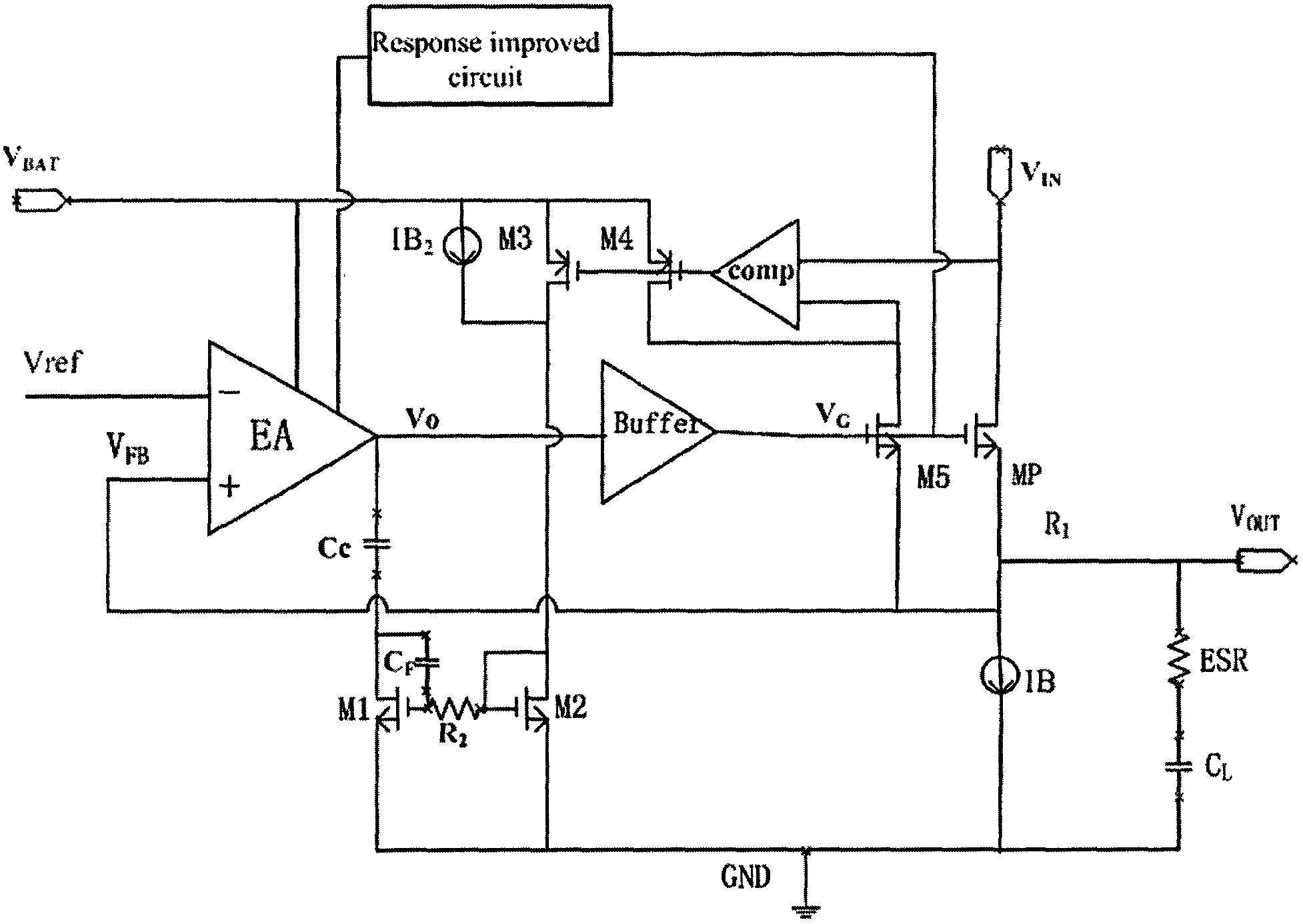
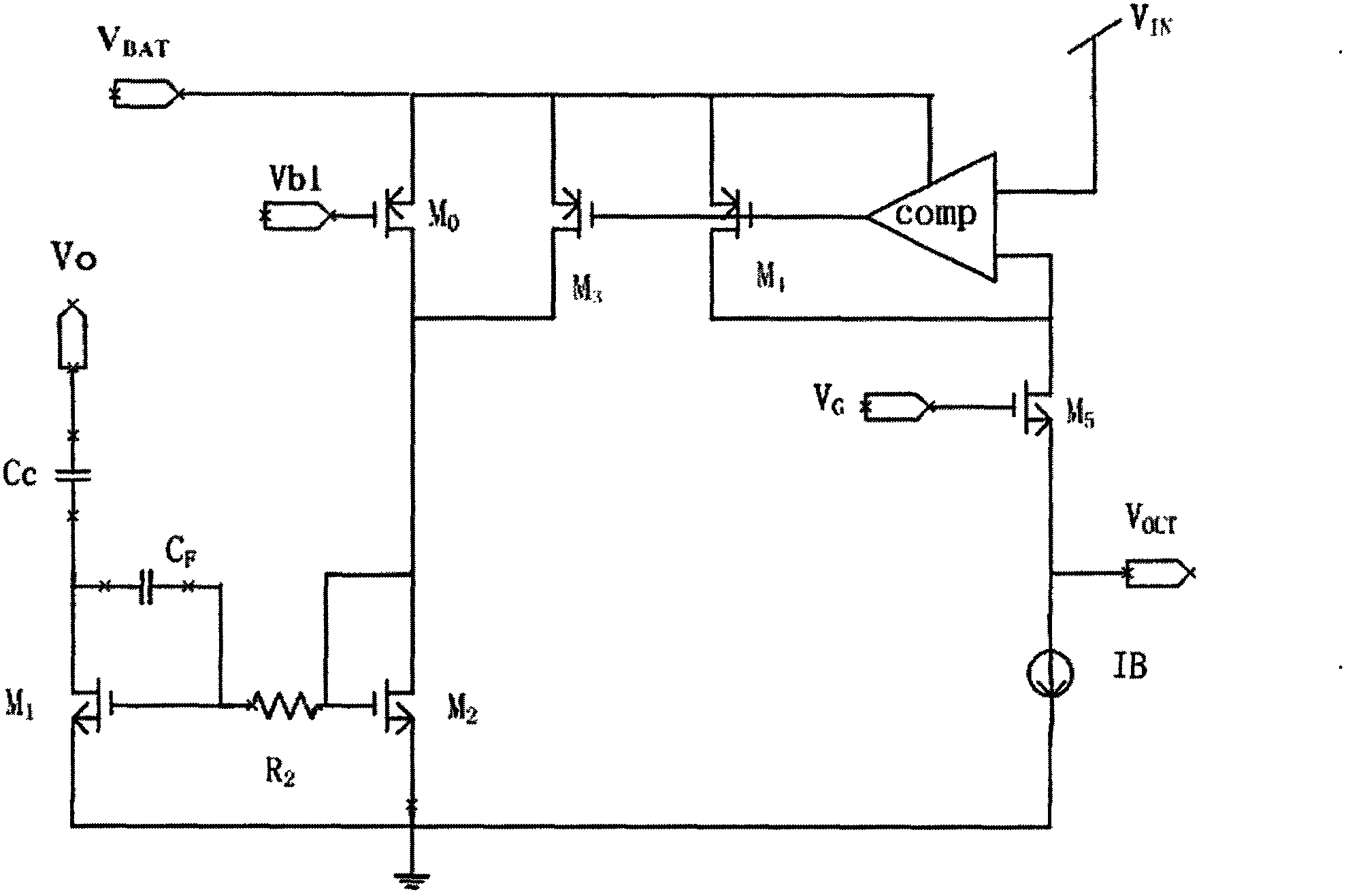
The invention discloses a low dropout linear regulator with quick transient response and high stability. The low dropout linear regulator comprises a power adjusting pipe, an error amplifier circuit and an ESR resistor. The error amplifier circuit comprises a main operational amplifier circuit and a buffering drive circuit. The low dropout linear regulator further comprises a transient response improving circuit and a compensation network circuit. The low dropout linear regulator has the advantages that a compensation network is provided to guarantee that when load currents change, phase margin doe not change, and stability of the low dropout linear regulator is guaranteed; an induction capacitor is additionally arranged on the compensation network, so that change of poles can be quickly tracked, moment stability can be maintained when load current jump occurs, and oscillation of output voltages is prevented; a transient response improving circuit structure is designed to improve load transient response, it is guaranteed that output of the transient response improving circuit has quick transient response capacity when the load currents of the output end jump, and grain and the phase margin can not change greatly.
Owner:ZUNYI NORMAL COLLEGE
Grid connected inverter control method with network voltage feedforward lag compensation under weak power grid
InactiveCN107026477ASuppression of background harmonicsImprove phase marginSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid connected inverterHarmonic
The present invention discloses a grid connected inverter control method with the network voltage feedforward lag compensation under a weak power grid. Aiming at a grid connected inverter stability problem caused by the network voltage direct feedforward on the weak power grid condition, the present invention provides the control method of the network voltage feedforward lag compensation. The method guarantees the situation that the fundamental wave gains of a grid connected inverter and the network voltage direct feedforward control are same in a manner of adding a low-pass filtering link in a network voltage feedforward channel, realizes the astable error tracking of a fundamental wave, not only can inhibit a power grid background harmonic wave, but also enables the phase margin of the grid connected inverter to be increased greatly on the weak power grid, and enables the power grid adaptability of the grid connected inverter to be improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device provided with feedback circuit including resistive element and capacitive element
ActiveUS20060164055A1Stable output voltageImprove response speedDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceDevice material
The present invention provides a switching power supply circuit capable of stabilizing an output voltage as well as increasing a response speed of the output voltage by improving a phase margin of an open loop as a whole of the switching power supply circuit. The switching power supply circuit according to the present invention includes a resistor and a capacitor in addition to a configuration of a conventional switching power supply circuit. The resistor is connected between a node and the capacitor. The capacitor is connected between the resistor and another node. The resistor and the capacitor configure a phase compensation circuit. The phase compensation circuit has a cut-off frequency in accordance with a resonance frequency of an inductor and a capacitor by adjusting a resistance value of the resistor and a capacitance of the capacitor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Fractional-order PID control design method based on phase margin and cutoff frequency
InactiveCN106338913AImprove featuresEasy to tuneControllers with particular characteristicsFurnace temperatureTemperature control
The invention discloses a fractional-order PID control design method based on the phase margin and cutoff frequency, and relates to the technical field of process control application. Aimed at characteristics of large inertia, nonlinearity and model uncertainty in furnace temperature control of an intermediate-frequency induction electric furnace, the method is provided. A controller is derived from internal model control (IMC) and a fractional-order filter, only two adjustable parameters are included, convenience is provided for setting of controller parameters, and parameter setting of the fractional-order (PID) gamma controller is realized based on the phase margin and cutoff frequency of a control system. The method enables that a temperature control system has high set value tracking and interference inhibiting features, and enables higher robustness during parameter perturbation of the system.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS HEBEI ACADEMY OF SCI
Low pressure difference linearity voltage stabilizer for enhancing performance by amplifier embedded compensation network
InactiveCN101140478AImprove performanceIncrease phase marginElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLinear regulator
A low voltage differential linear regulator utilizes an embedded compensation network in an amplifier to improve performance, which embeds a compensation network composed of resistances and capacitances into an amplifier to increase one or a plurality of pole-zero pairs with their pole-zero frequency lower than pole frequency in a transfer function of a feedback loop without changing static operating point of the amplifier and increasing static current. Frequency of the pole-zero pairs can be accurately confirmed to enhance stability of the feedback loop of the low voltage differential linear regulator, expand loop unit gain bandwidth and increase phase margin and DC and low-frequency gain of the loop, thus enhancing performance of the low voltage differential linear regulator.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
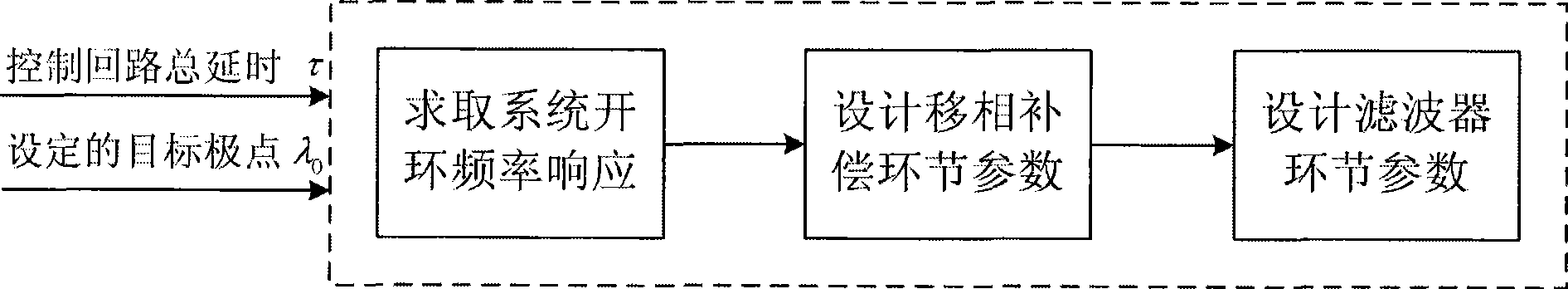
Sdelayed time processing and compensating system for wide domain damped control of electric power system
ActiveCN101465550AImprove phase marginIncrease the control linkPower oscillations reduction/preventionWide areaTime delays
The invention relates to a delayed time processing and compensating system for wide-area damper control of an electric power system and belongs to the stability and control technical field of the electric power system; the delayed time processing and compensating system is characterized in that: the system is composed of a controlled electric power system, a feedback signal time delay circuit of the electric power system, a band-pass filter, a dephasing compensator, a time delay free wide-area damping controller and a control output signal time delay circuit which are sequentially connected in series in a closed loop way; wherein, the setting wide-area damper controlling target is that a pole point which is corresponding to the low damping low-frequency oscillation mode on a complex plane is shifted left to the condition that lambda0 is equal to sigma0 + jomega0, and then according to actually measured frequency response of the electric power system, a phaseshift link circuit is used for counteracting retarding phase produced at the low-frequency oscillation point owning to time delay of a control circuit, and the phase margin of the system is improved by the band-pass filter for making up the lost phase margin caused by phaseshift owning to time delay, thus preventing the system from losing stability. The system leads the wide-area damping controller to still keep the system stability when the size of the total time delay of the control circuit is 0ms-600ms, and the damping effect is the same as the effect without time delay.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
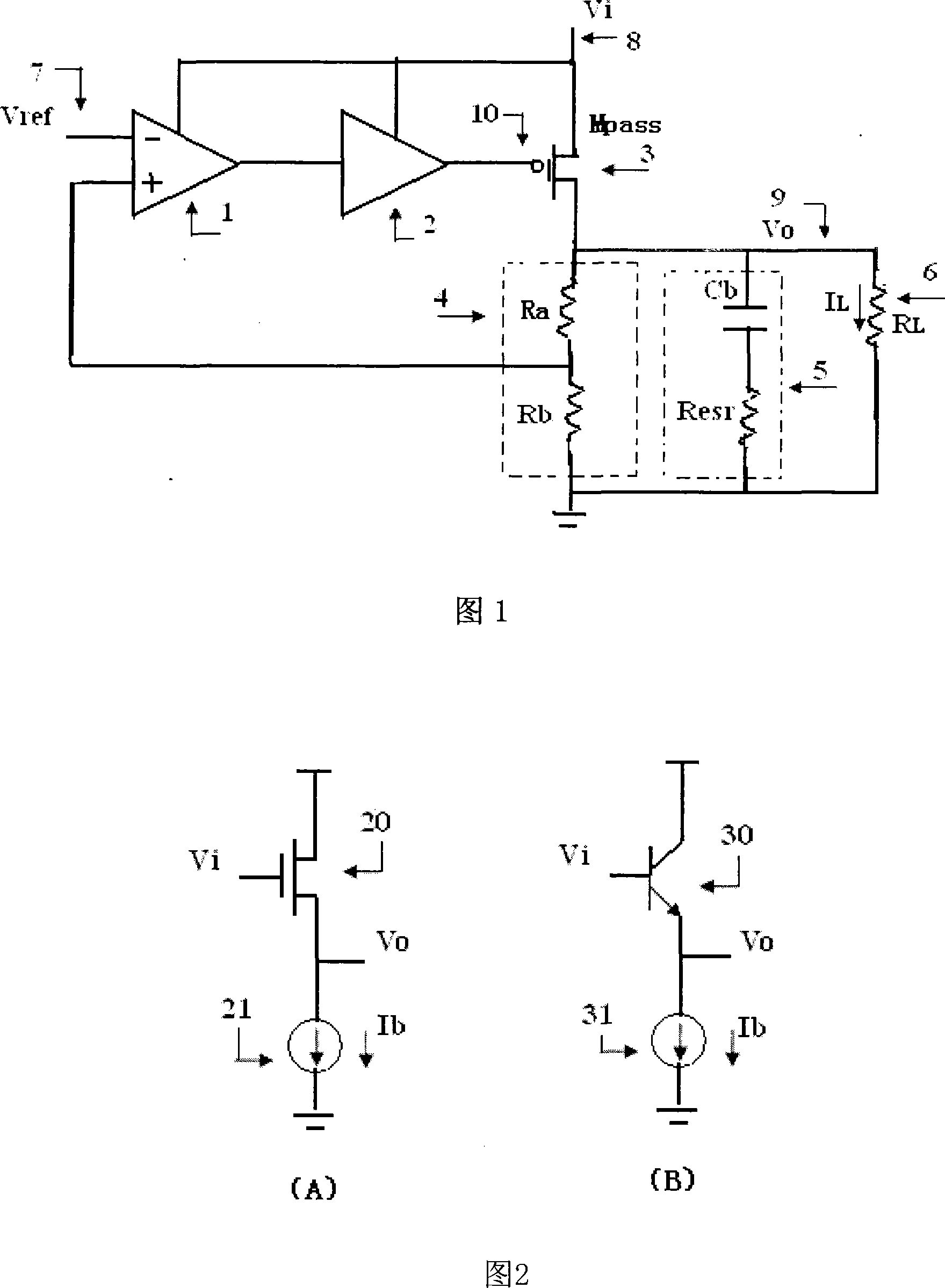
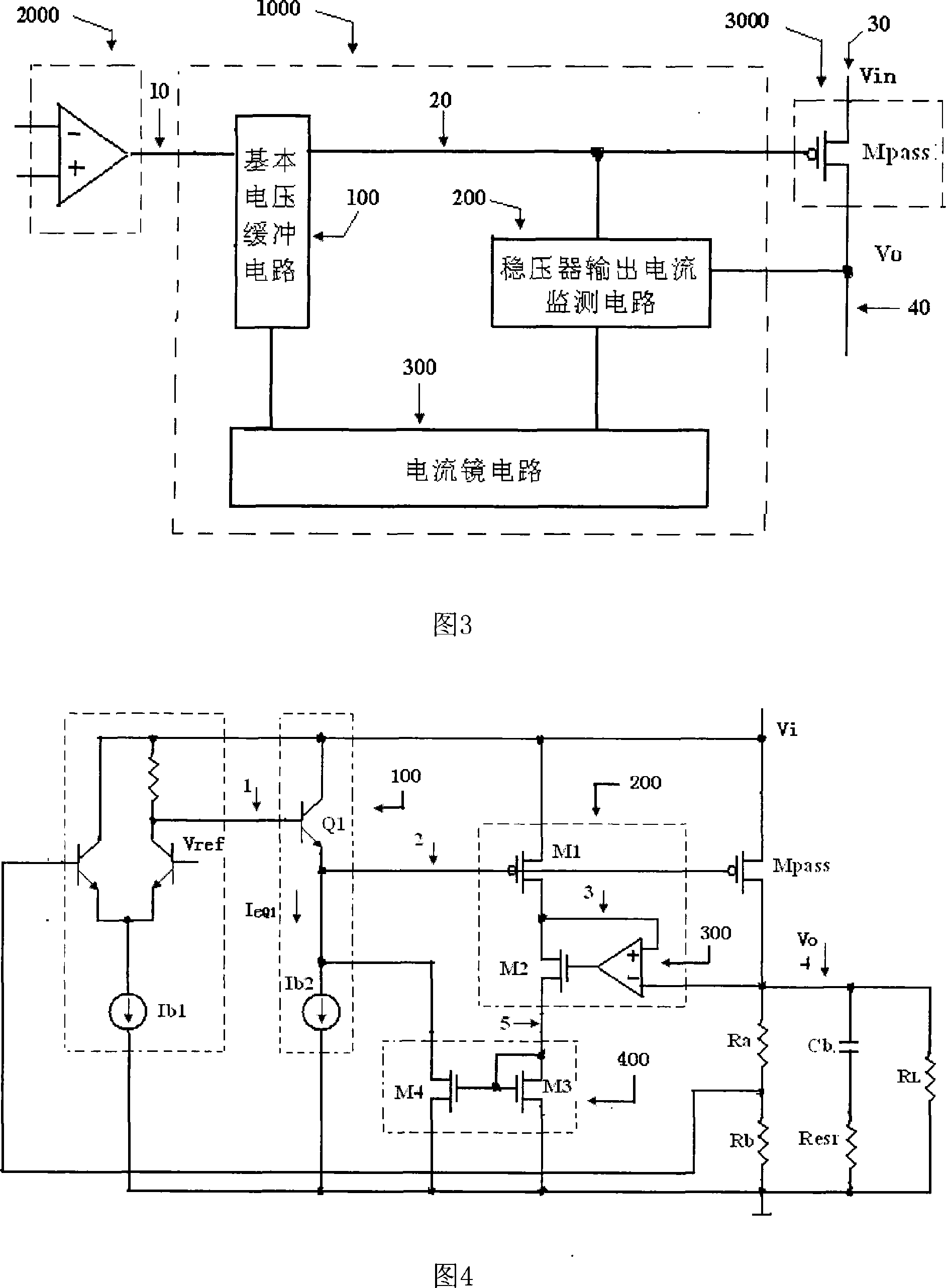
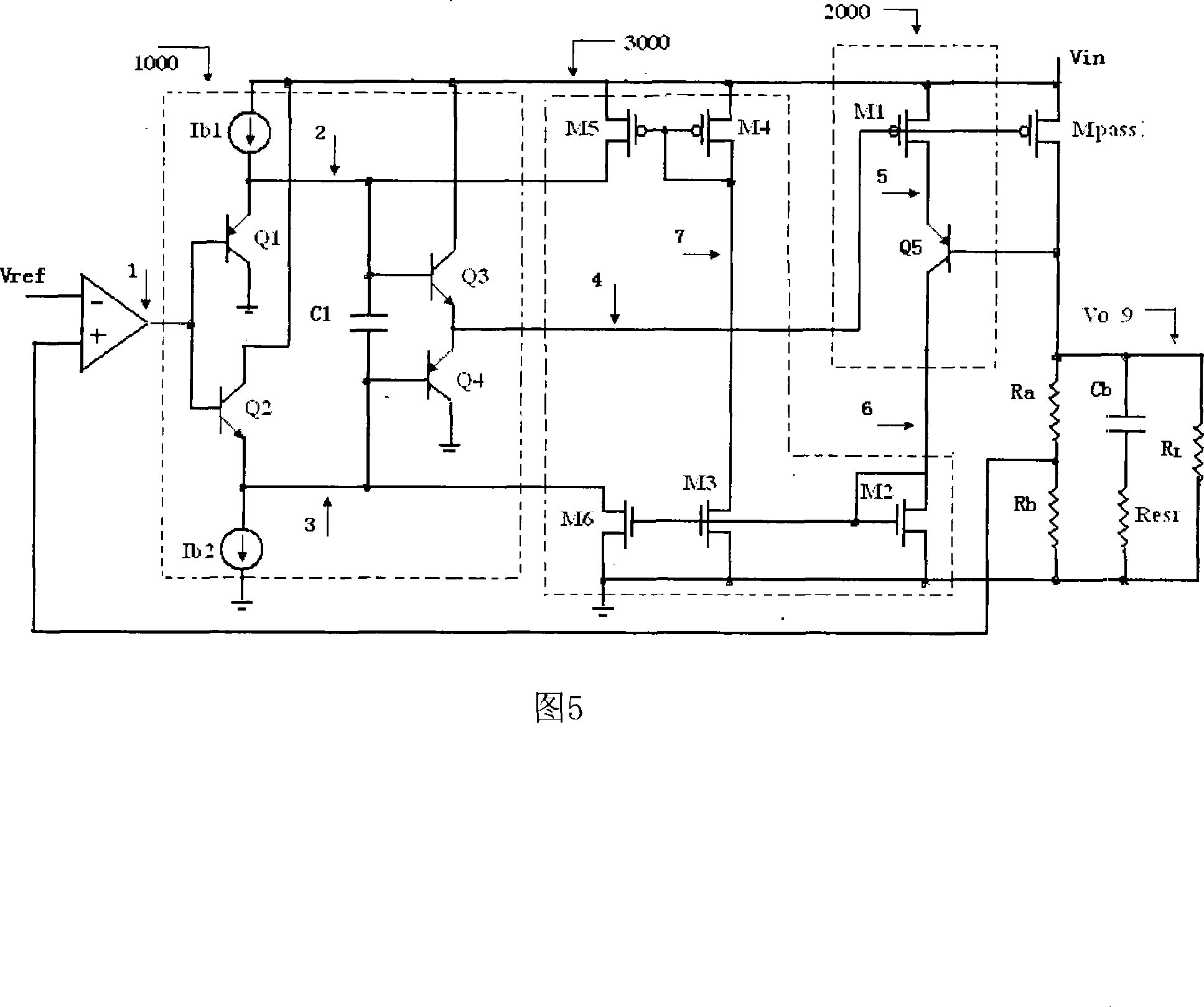
Voltage buffer circuit for linear potentiostat
InactiveCN101105696AReduce transient responseReduce inhibitionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
The invention relates to a voltage buffer circuit used in a linear voltage regulator. The circuit consists of a basic voltage buffer circuit, an output current monitoring circuit and a current mirror circuit; wherein the input end of the basic voltage buffer circuit is connected with the output end of a voltage difference amplifier of the linear voltage regulator which is also the output of a dynamic bias power source buffer circuit; the output end of the output current monitoring circuit is connected with the input end of the current mirror circuit; the output end of the current mirror circuit is in parallel connection with a static bias current source. Under the condition that the static power loss of voltage regulator circuit is not increased, the impact of a pole of the output end of the voltage buffer circuit to system phase margin and stability is reduced; the invention doesn't need the traditional linear voltage regulator and utilizes an outer wave filtering capacitance equivalent series resistance to generate zero point, which lowers the system cost, reduces use difficulty and reduces the impact of the equivalent series resistance to the transient state response and noise restraint capacity of the voltage regulator circuit; a chip upper frequency compensation capacitance is not needed, which saves chip area.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP NO 771 RES INST
Method for compensating frequency of wideband common mode feedback loop of two-stage operational amplifier
InactiveCN101355346ASimple designReduce power consumptionDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesRing circuitControl signal
The invention discloses a method for compensating the frequency of a broadband common mode feedback ring circuit for a two-stage operational amplifier, belonging to the field of analog integrated circuit design. A broadband feedback amplifier in the two-stage operational amplifier with the Miller compensation is used as the common mode feedback ring circuit so as to reduce the area and the power consumption of the common mode feedback circuit; the two-stage operational amplifier has only one main pole in the range of the unit gain bandwidth, a fully differential input and output structure is adopted, the sampling of the common mode output level is performed by the differential output end; and a control signal fed back by the common mode simultaneously controls the output level of a first-stage common mode and the output level of a second-stage common mode of the operational amplifier through a controllable bias circuit. The frequency of the main pole of the broadband feedback amplifier is far higher than the unit gain bandwidth of the operational amplifier, therefore the margin of phase position of the common mode ring circuit is basically equal to that of the operational amplifier, thereby forming the stable feedback ring circuit. The method has the advantages of few elements for a common mode feedback circuit, lower power consumption of the common mode feedback circuit and simpler and more convenient circuit design.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
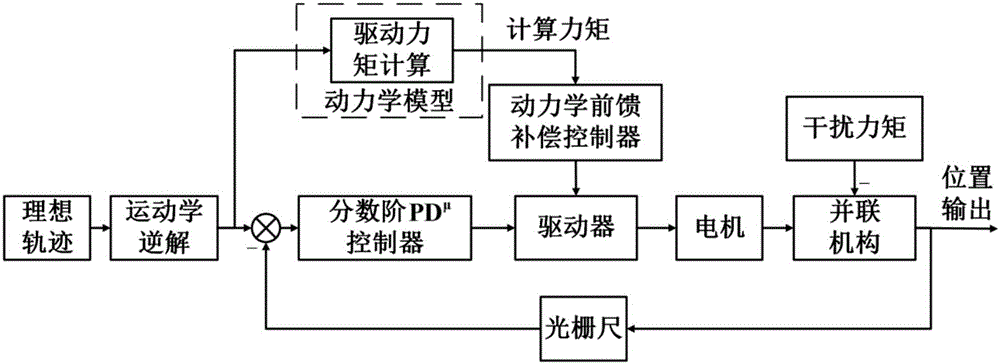
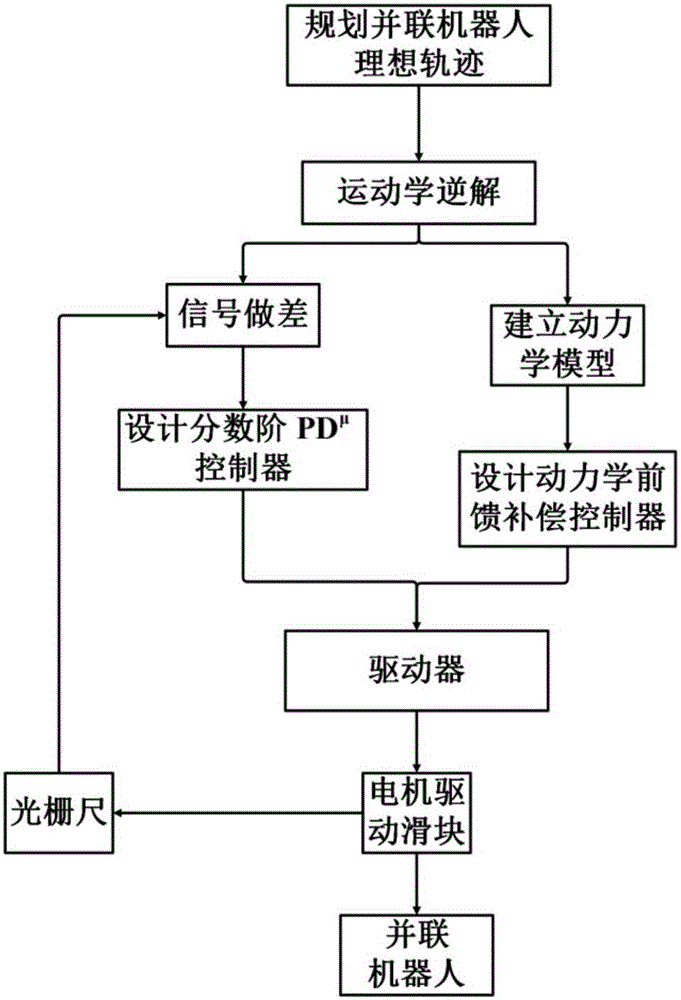
Parallel robot motion control method with fast response and robust performance
The invention discloses a parallel robot motion control method with fast response and robust performance, which belongs to the field of electromechanical control. The method comprises steps: an ideal displacement instruction for each driving shaft is obtained through inverse solution according to a parallel robot expected trajectory; and a fractional order PDmu controller is used to ensure a control system to be stable and have a quick response ability through selecting an ideal cutoff frequency, a phase margin and a robust design criterion. During the motion process, a grating ruler is used for feeding back the actual motion state of each driving shaft, the PDmu controller gives the motion control amount according to the ideal displacement instruction and the feedback state, and the motion control amount is sent to a motor driver to drive the motor to rotate. In addition, a dynamic model for the parallel robot is built, a driving torque command is obtained according to the model, the driving torque command sends a compensation signal to a driver through a dynamic feedforward compensation controller, disturbance torque of the parallel robot during a linkage process is compensated, system robustness is enhanced, and the parallel robot can be ensured to complete planning motion.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low dropout voltage regulator providing adaptive compensation
InactiveUS7091710B2Improve transient responseHigh bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedCrossover frequency
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Voltage regulator
ActiveCN1987710AReduce your own power consumptionWide range of workElectric variable regulationAutomatic controlEngineering
The voltage adjuster includes band-gap reference voltage source, voltage detection and feed back unit, auto bias circuit, frequency compensation circuit, and driver output circuit. The reference voltage source generates reference voltage and bias current. The voltage detection and feed back unit detects voltage output from the voltage adjuster, and feeds back the output voltage to the auto bias circuit and the control circuit of the drive tube or controlling bias circuit and driving capability automatically. The frequency compensation circuit guarantees tolerance of phase in whole loop and speed of transient response of voltage adjuster to make steady operation, and quick transient response of adjuster close loop. Features are: very low own power consumption, wide operating range, realized by standard CMOS technique, simplified design of voltage adjuster effectively, and raised performance of adjuster.
Owner:CHIPSEA TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
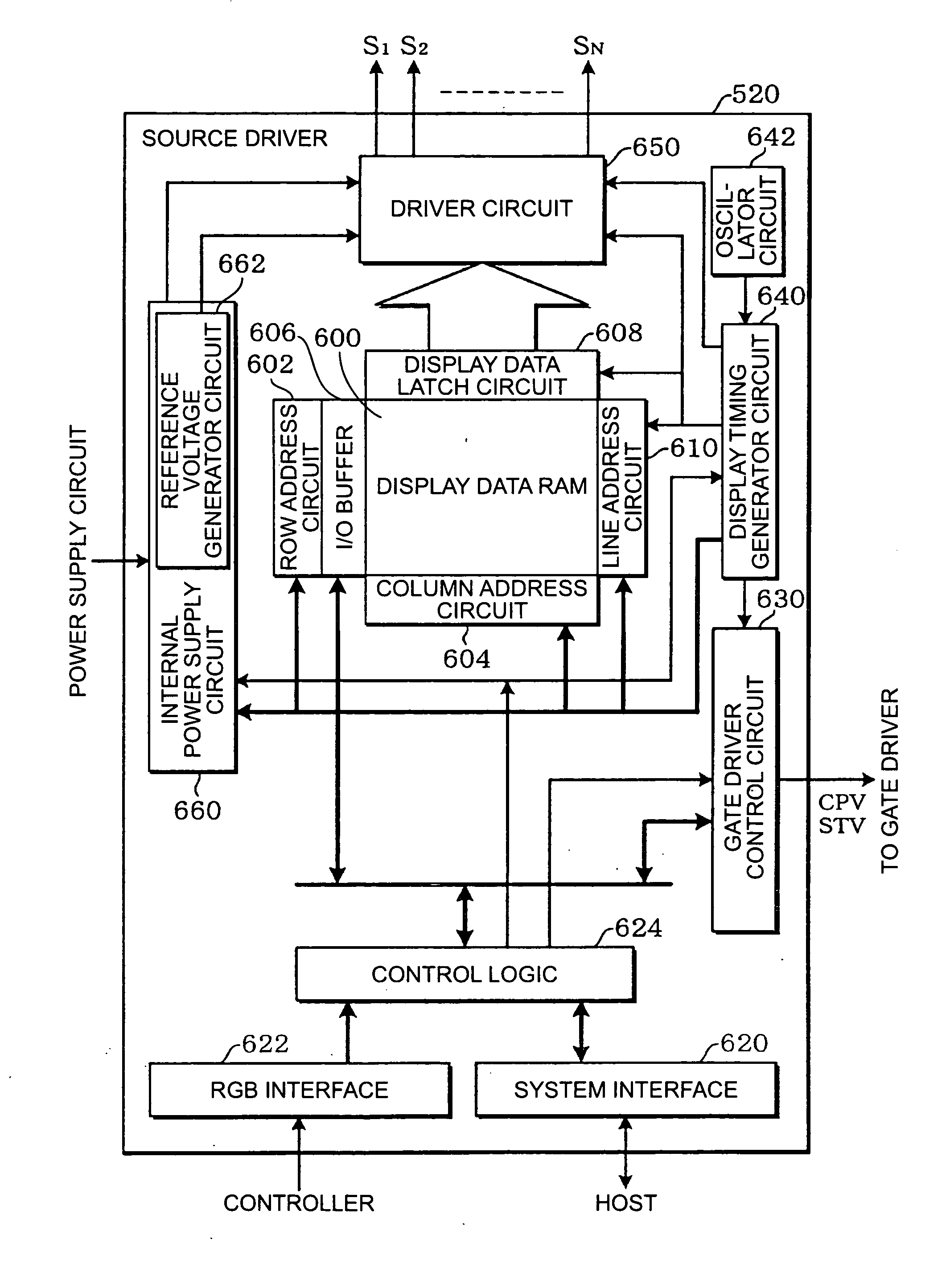
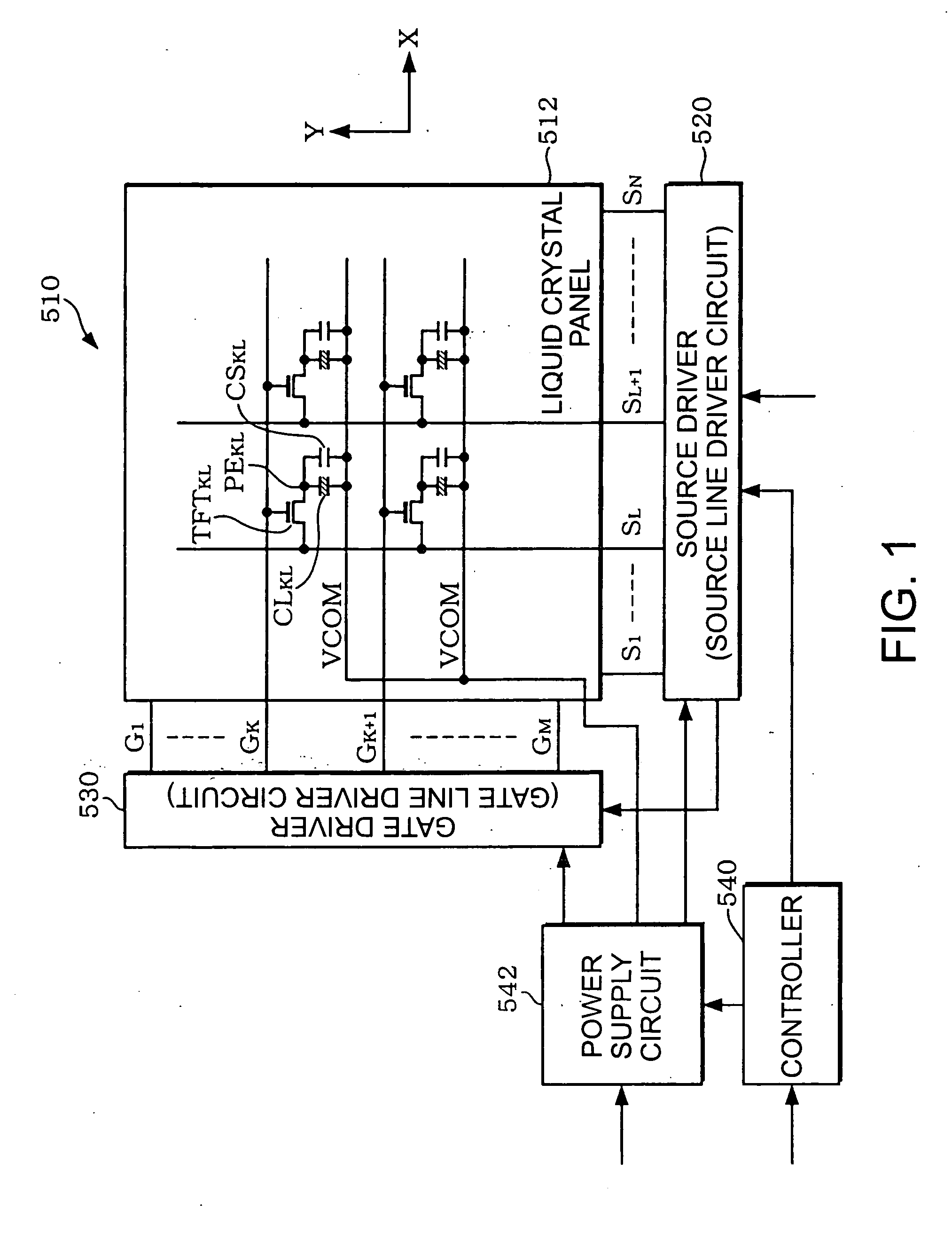
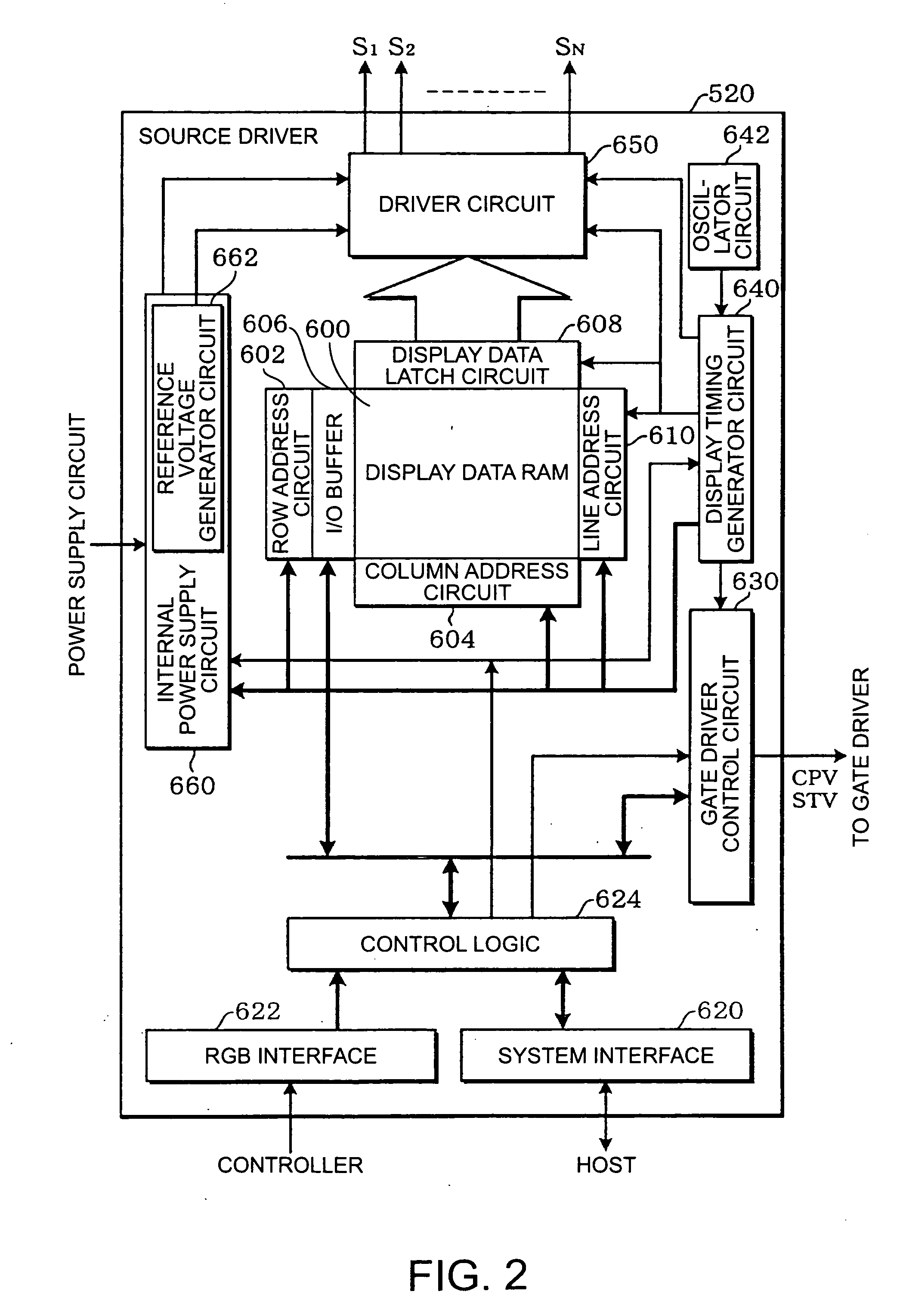
Source driver, electro-optic device, and driving method
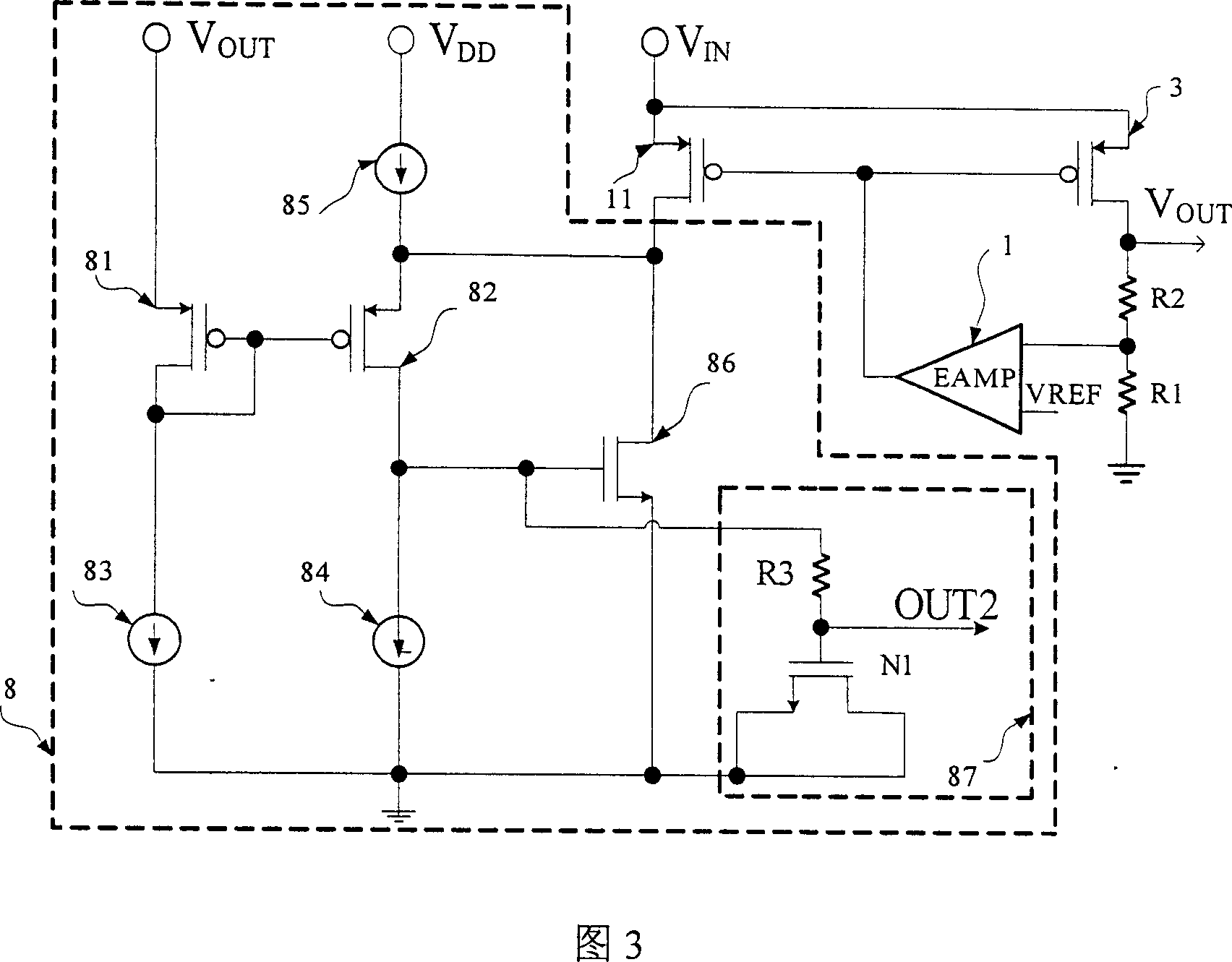
InactiveUS20060038764A1Low costReduction of examinationStatic indicating devicesEngineeringElectrical impedance
A source driver for driving a plurality of source lines of an electro-optic device, including a plurality of impedance conversion circuits each driving a respective one of the plurality of source lines in accordance with a grayscale voltage corresponding to display data; and a plurality of power save data storing circuits each storing power save data, wherein Each of the plurality of power save data storing circuits is provided for one of each of the plurality of impedance conversion circuits and a number of impedance conversion circuits, the number corresponding to the number of dots forming a pixel, each of the plurality of impedance conversion circuits includes a voltage follower circuit for driving one of the plurality of source lines and having a smaller phase margin without a load connected to an output thereof than with a load connected to the output thereof, and, an operating current of the voltage follower circuit included in the impedance conversion circuit is one of stopped and limited in accordance with the power save data stored in the power save data storing circuit corresponding to the impedance conversion circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
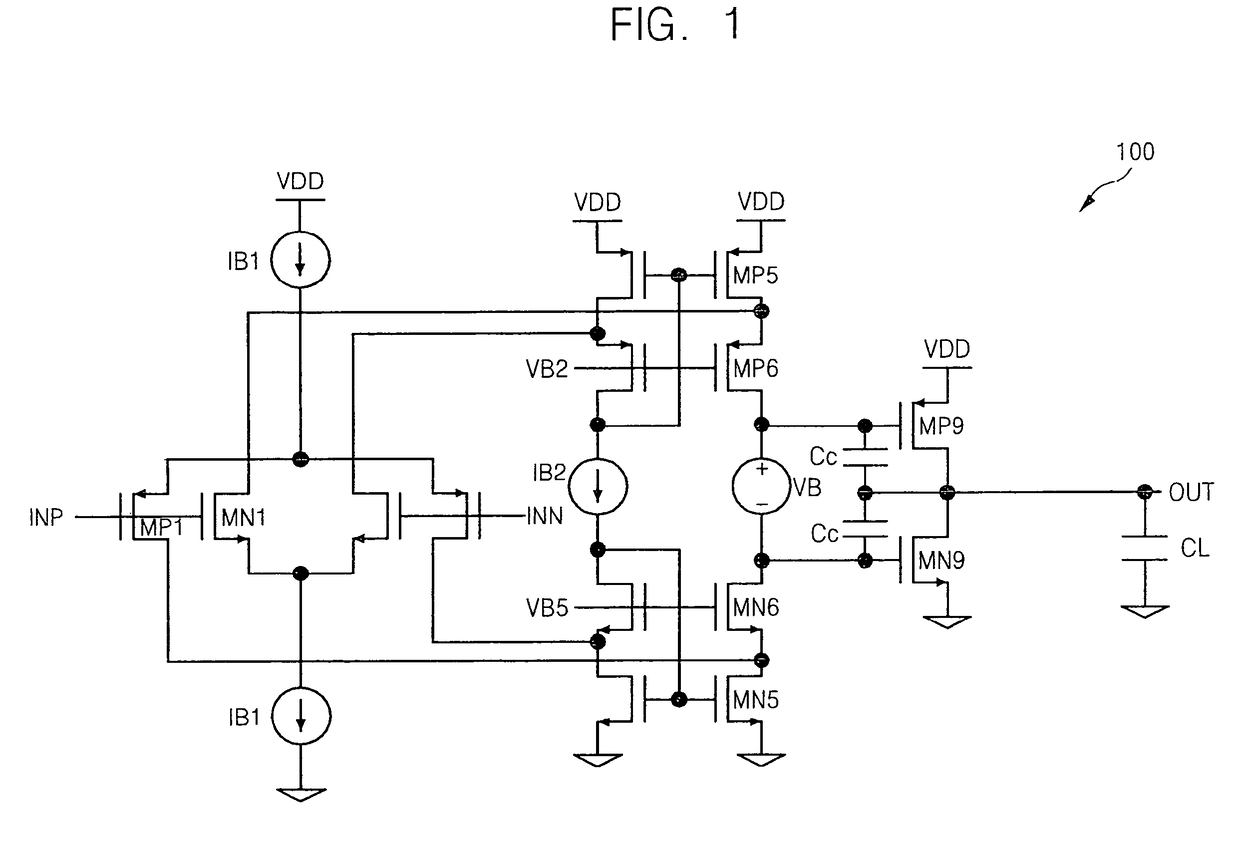
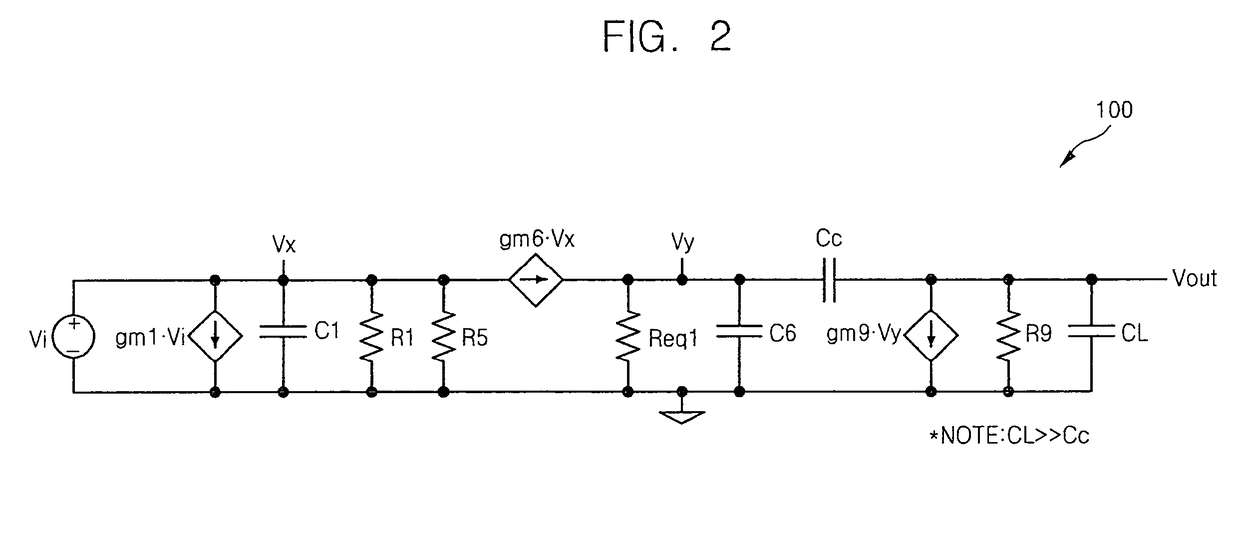
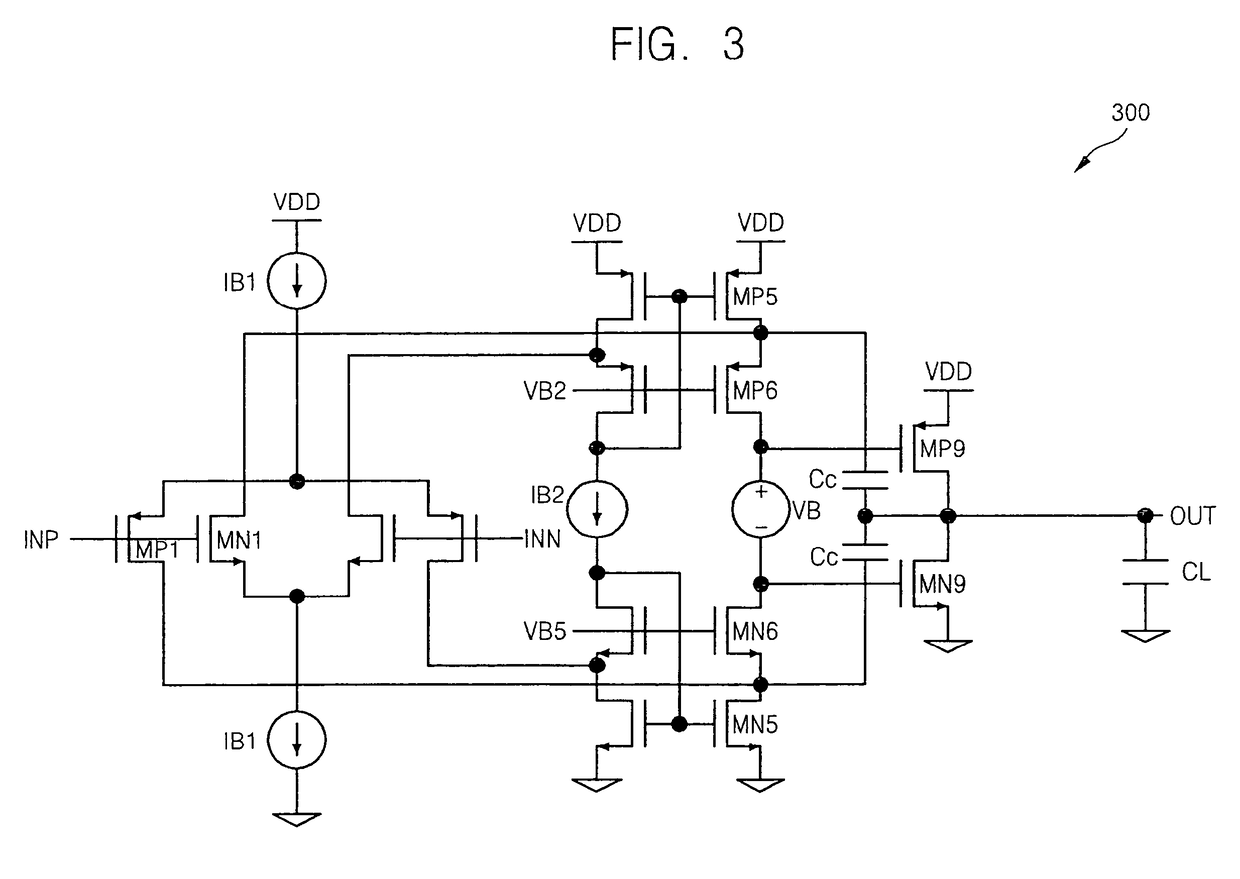
Folded cascode operational amplifier having improved phase margin
InactiveUS7907011B2Easy to operateAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceAudio amplifierFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com