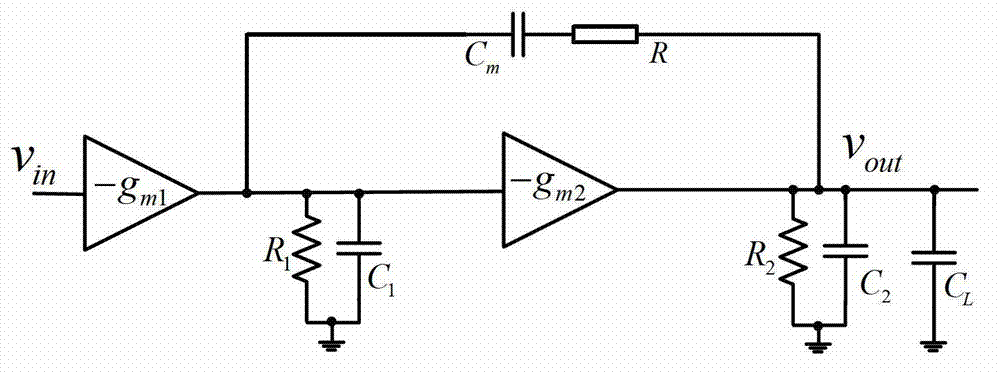
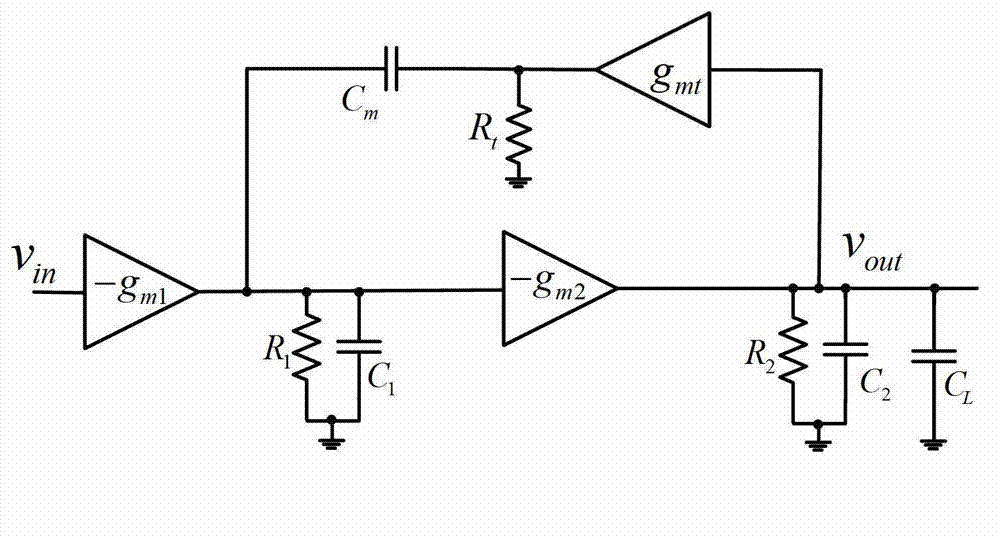
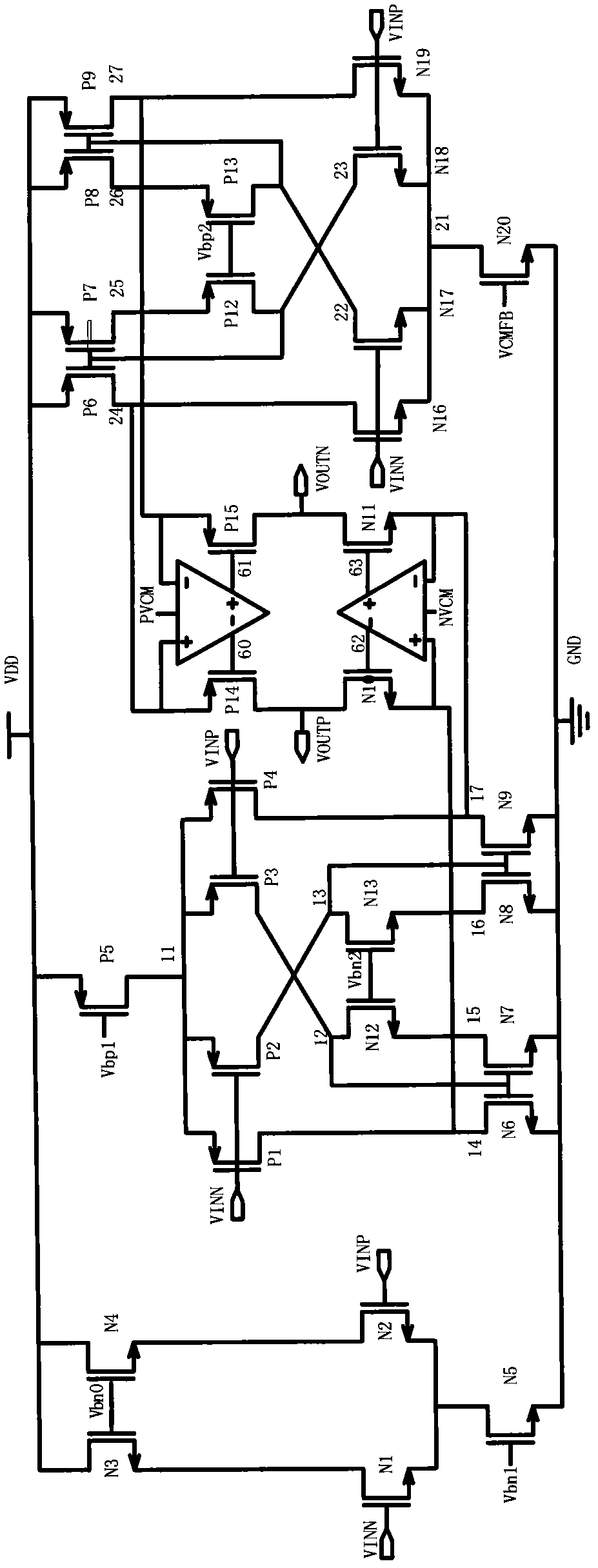
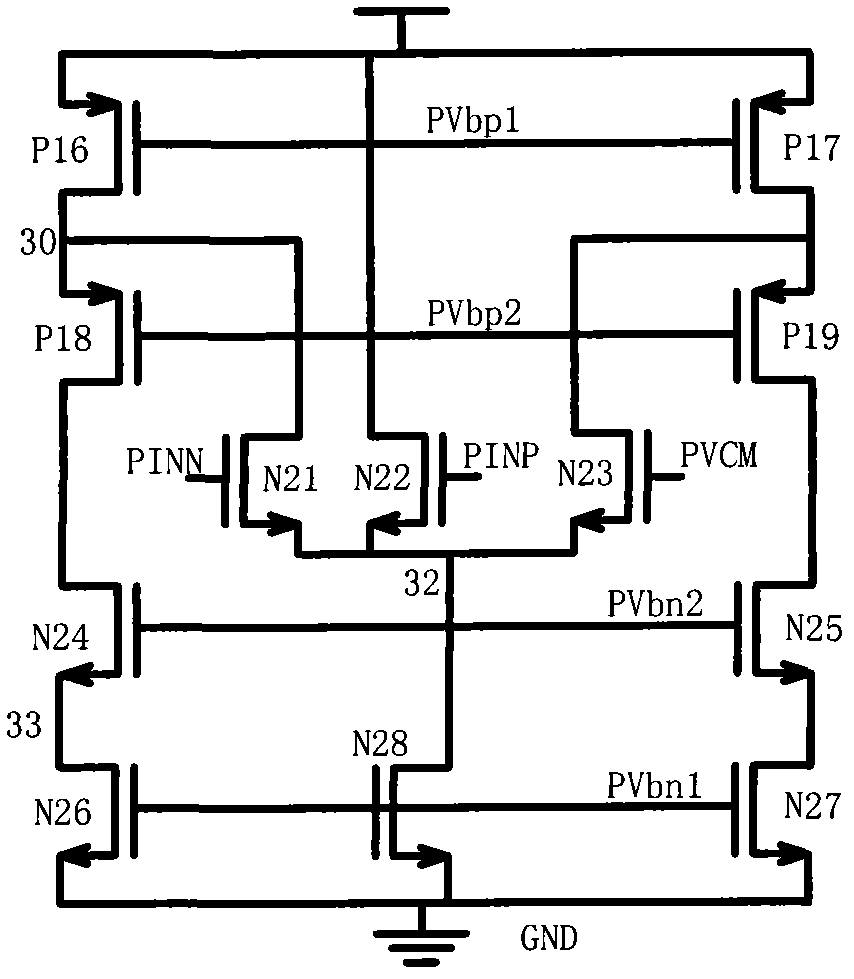
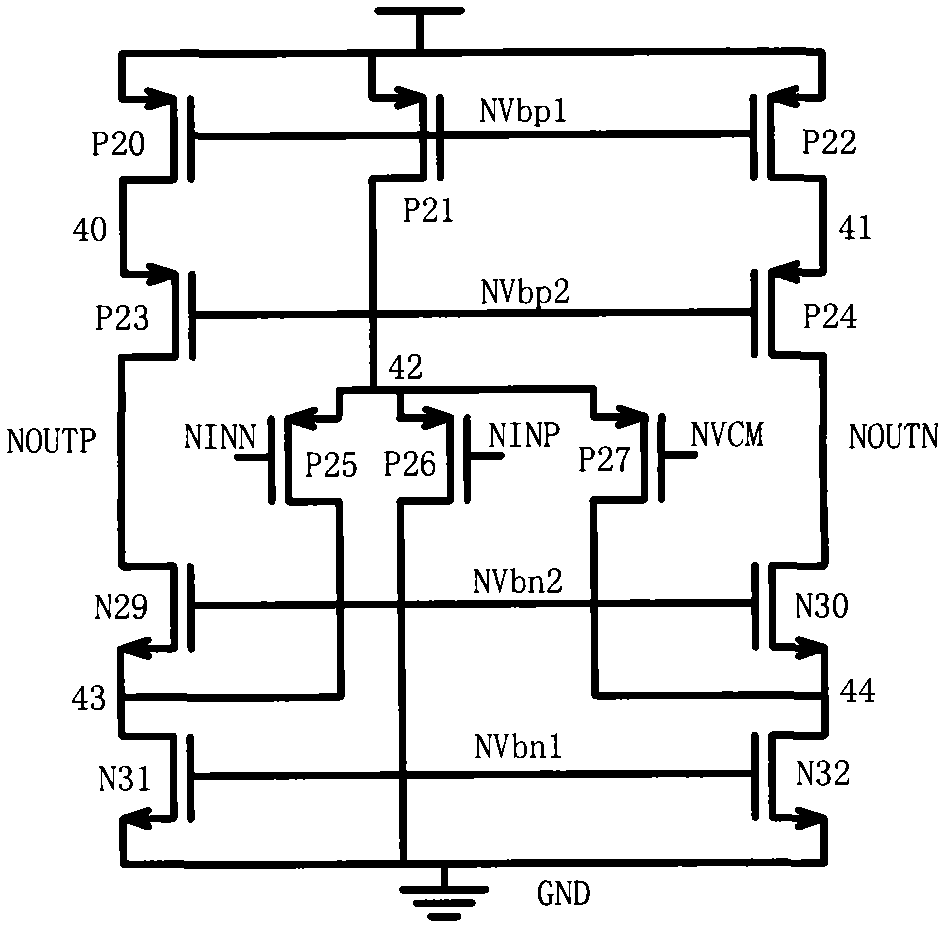
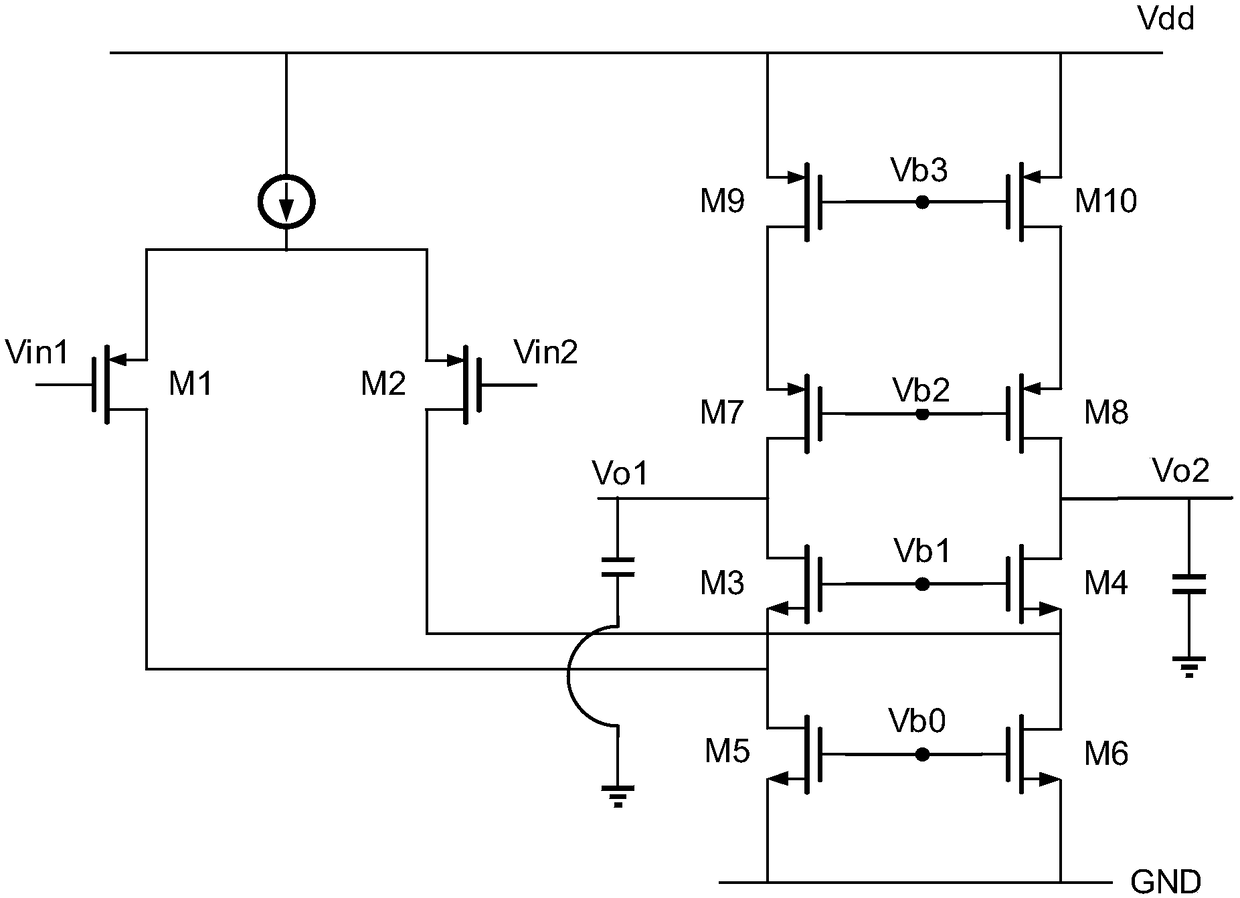
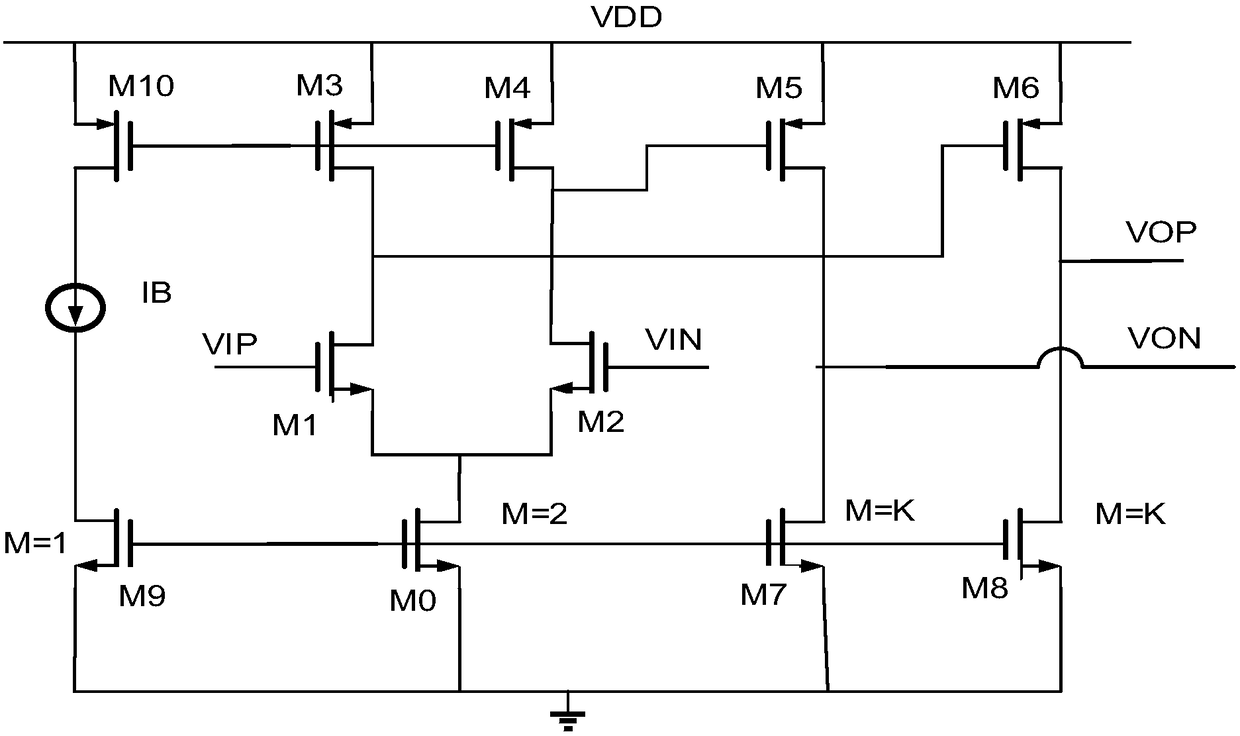
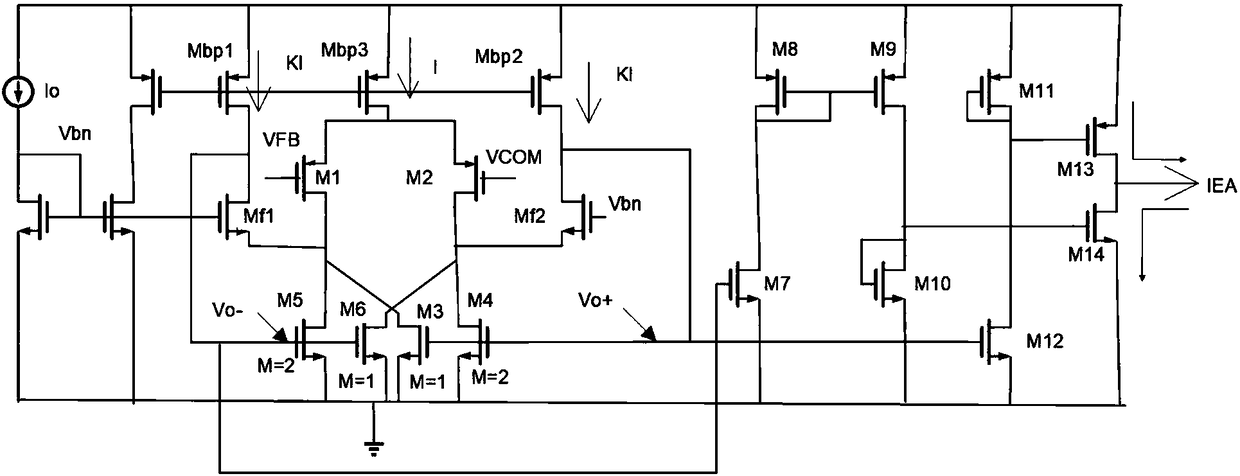
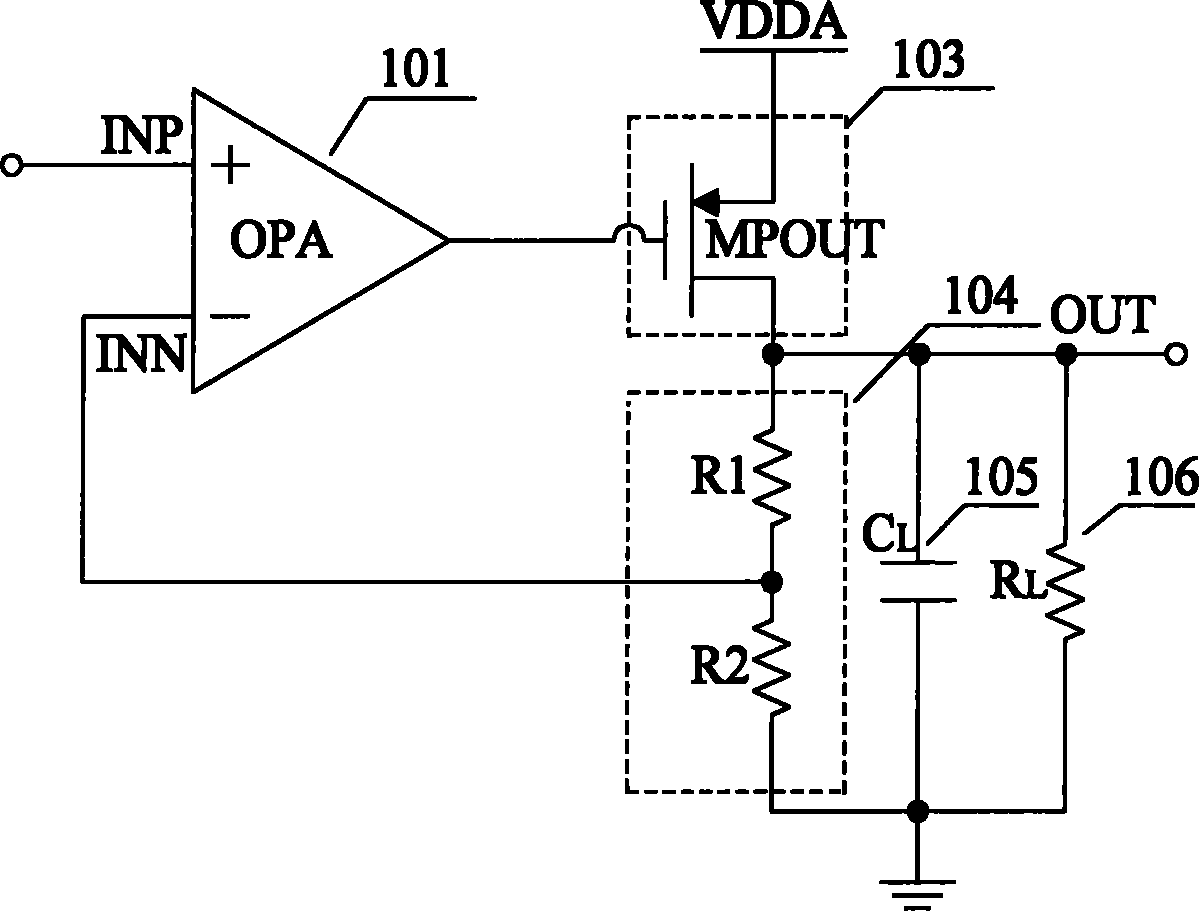
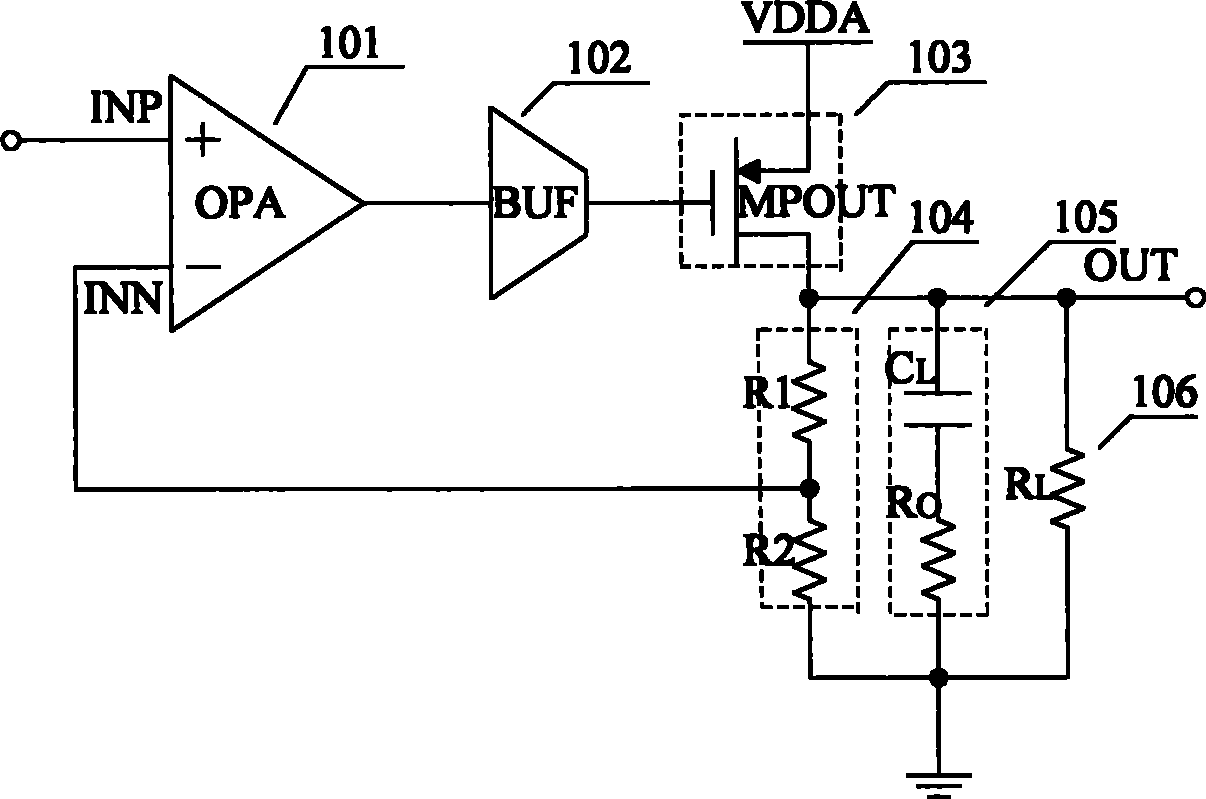
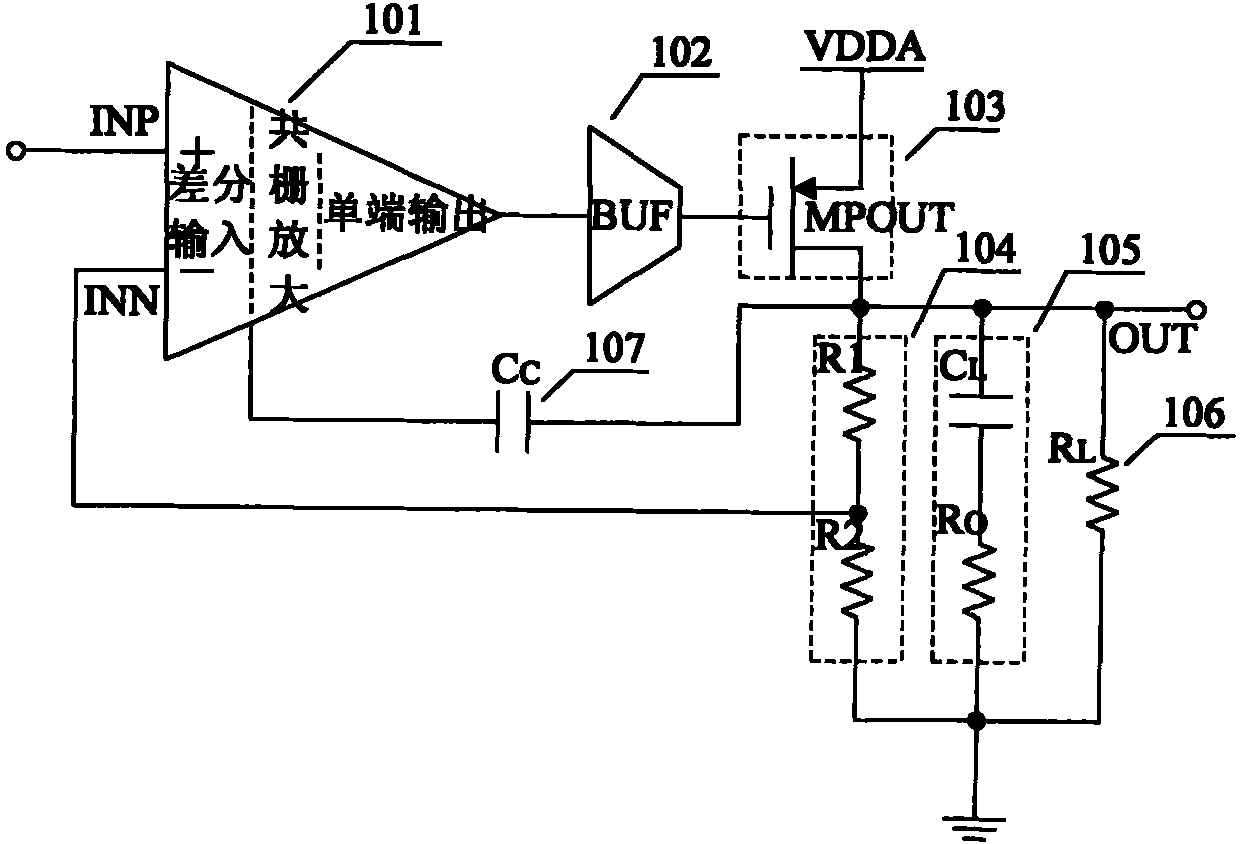
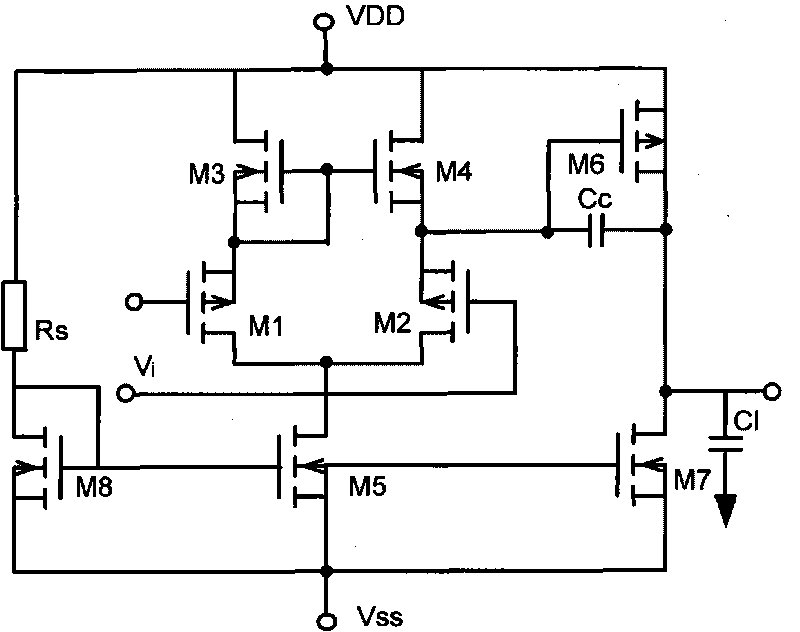
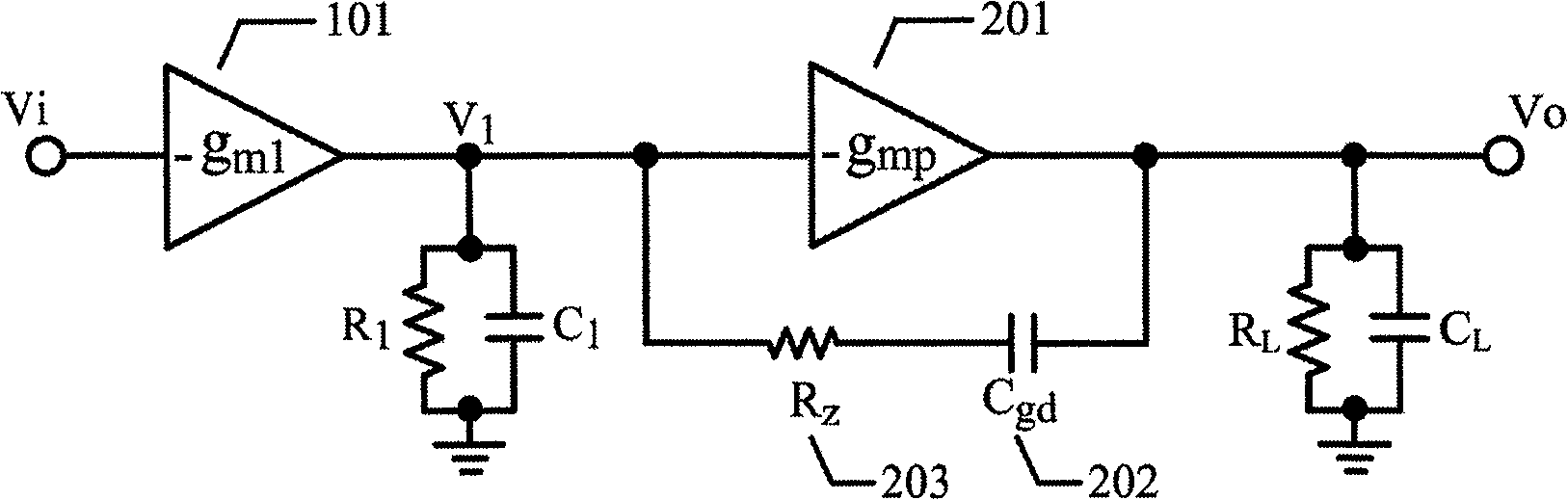
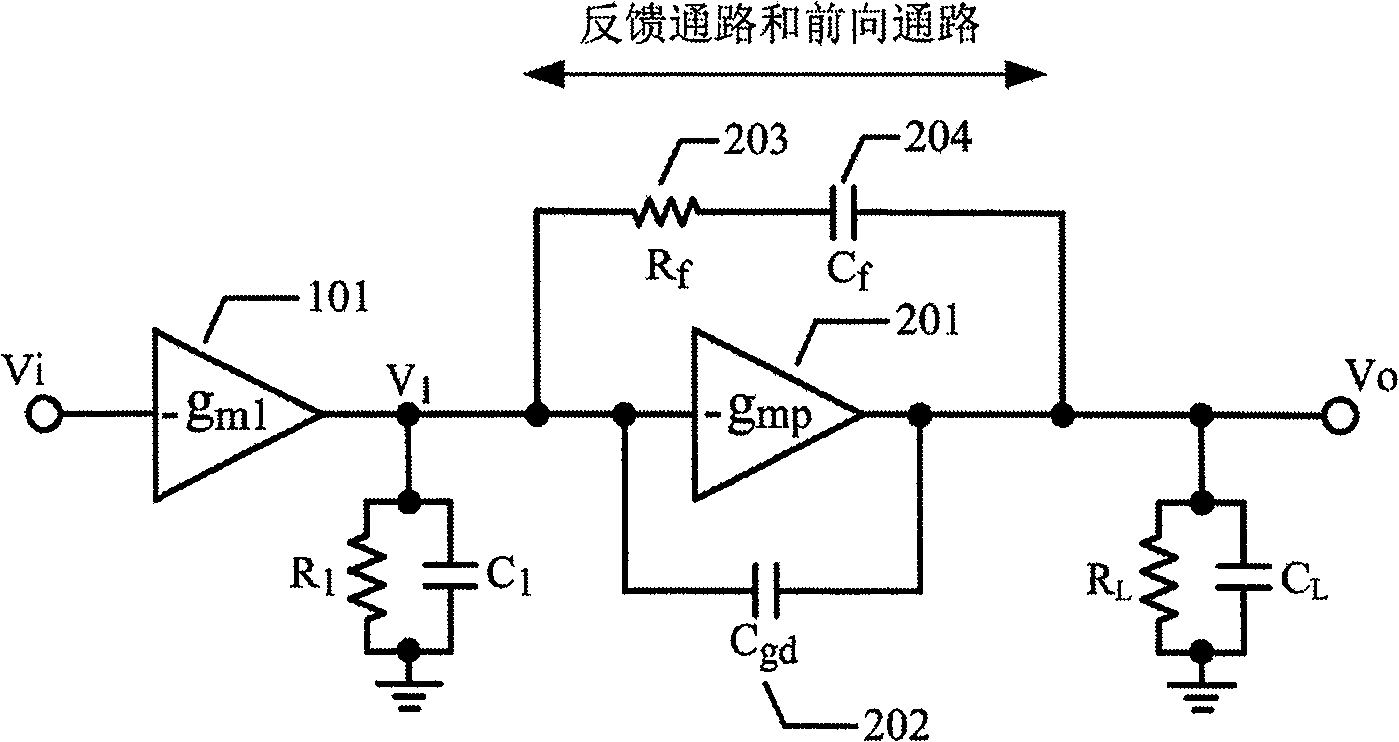
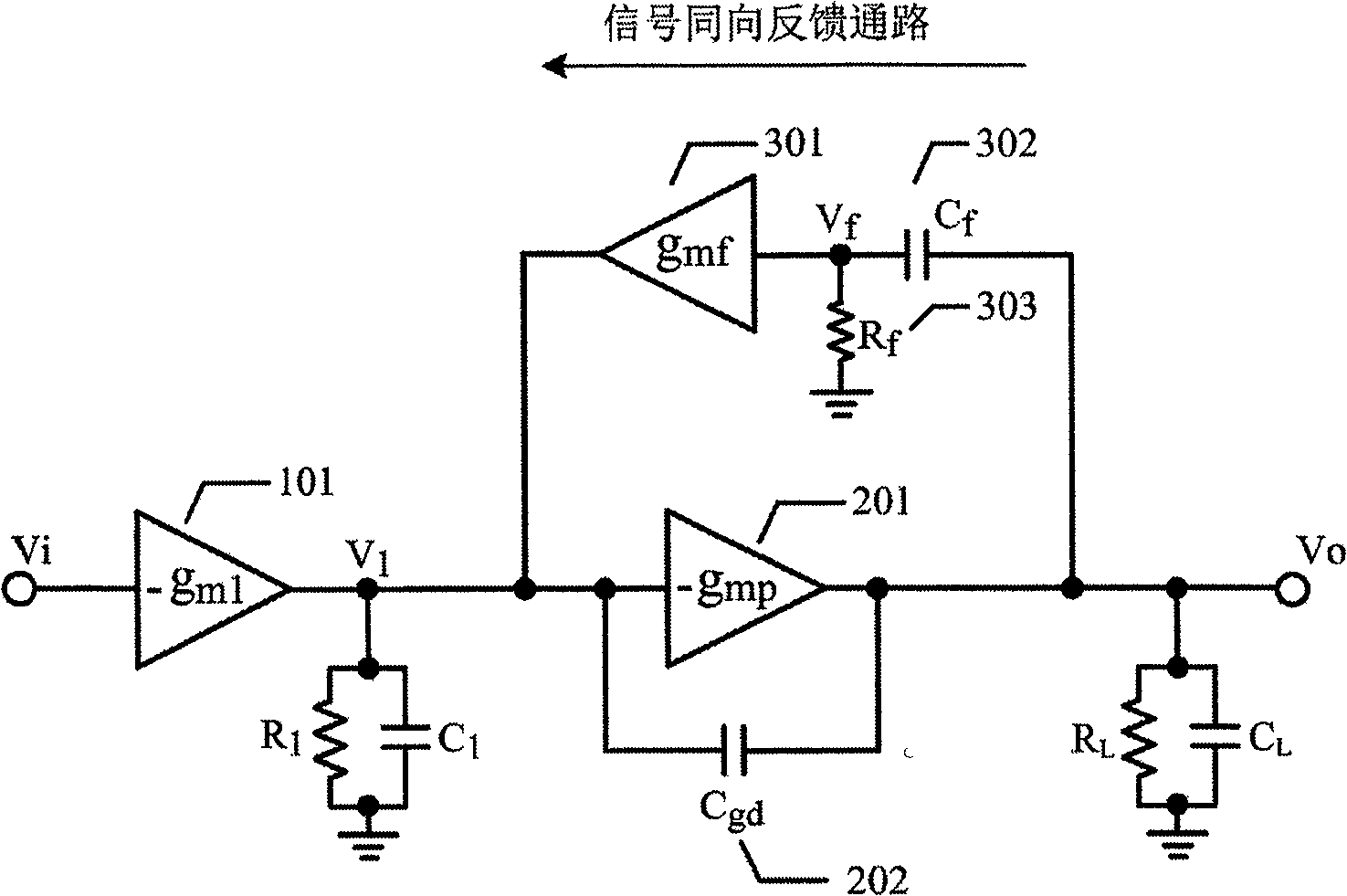
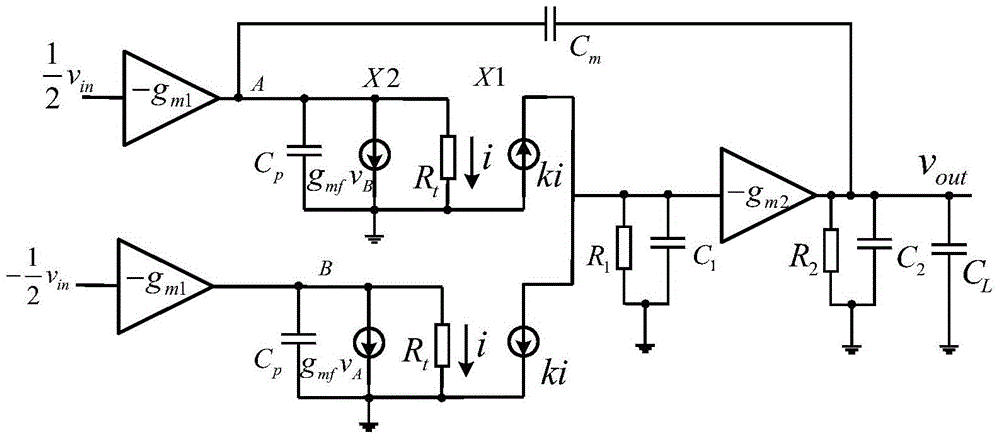
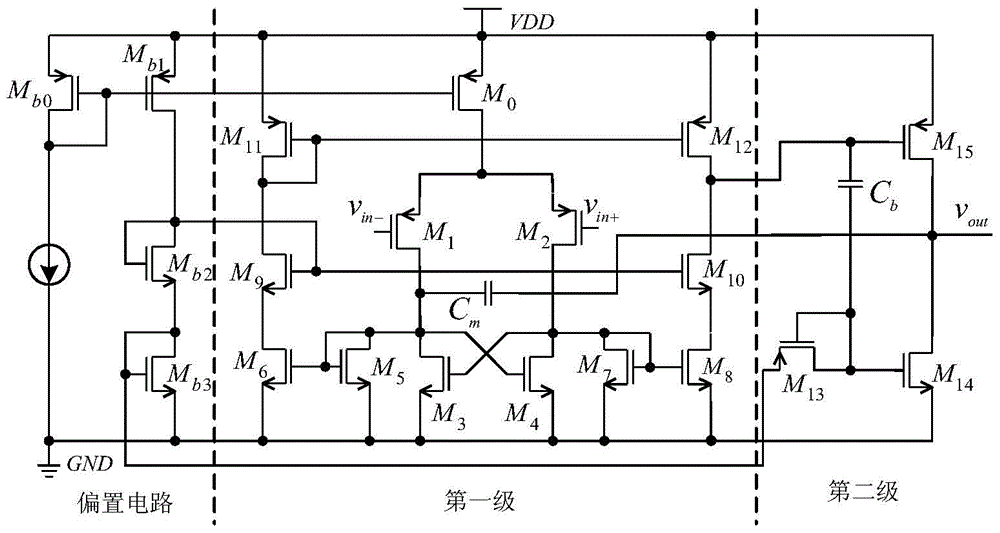
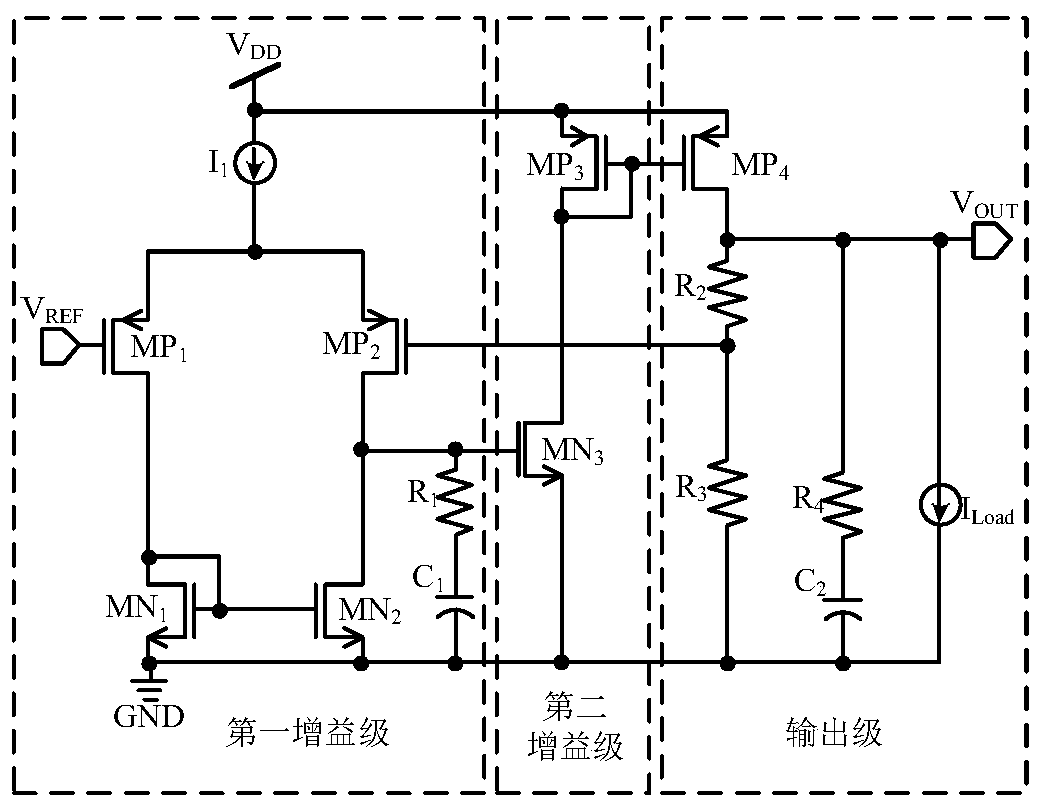
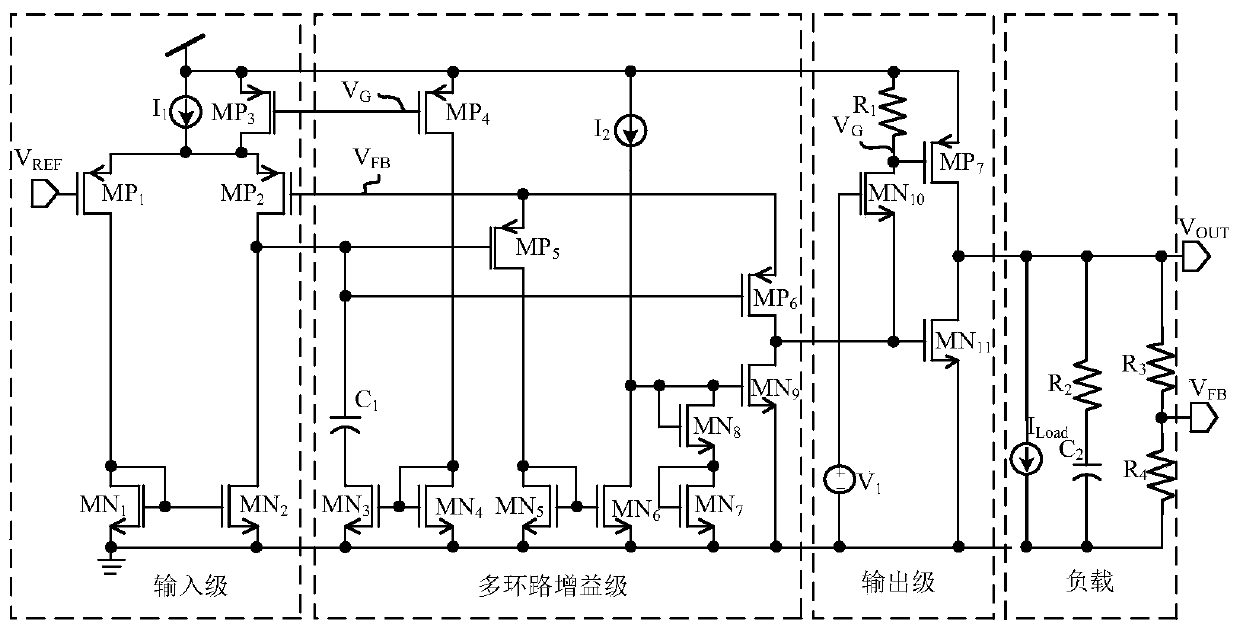
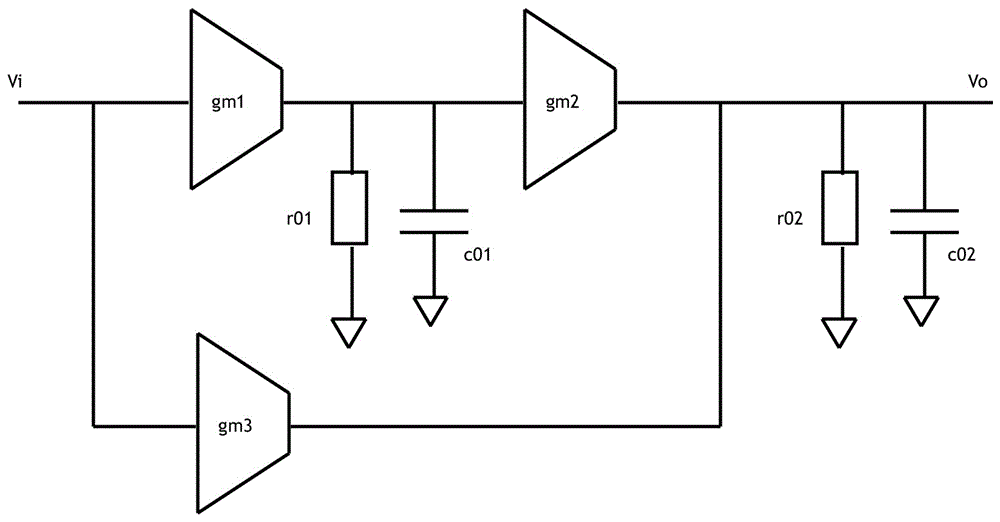
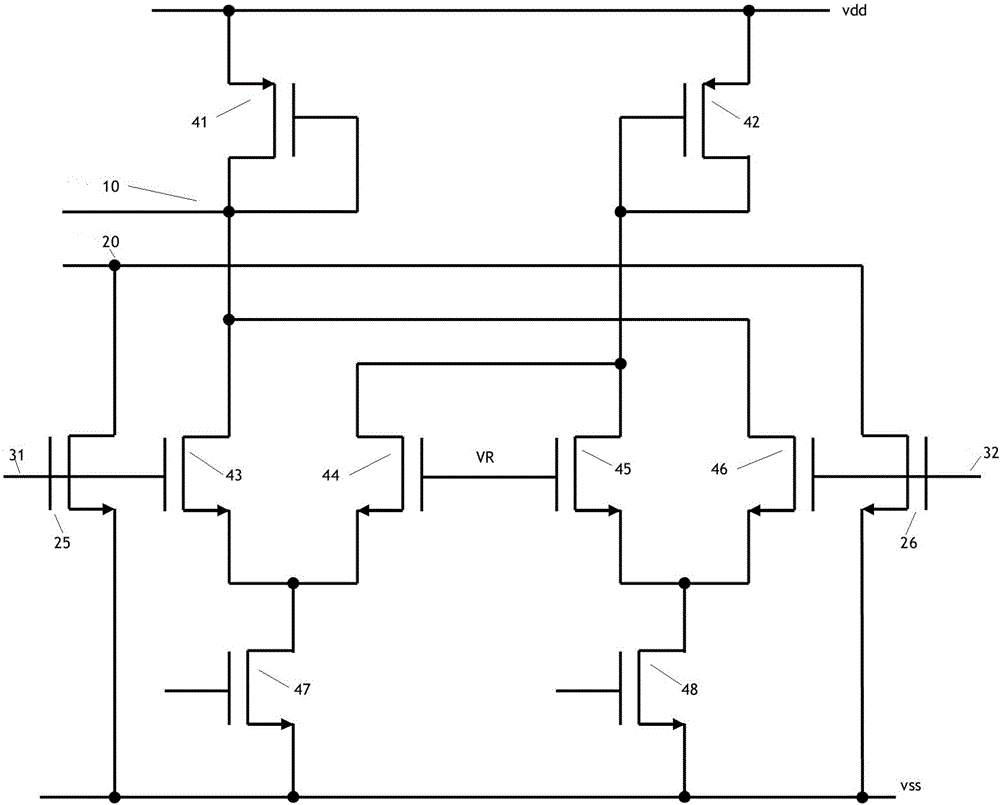
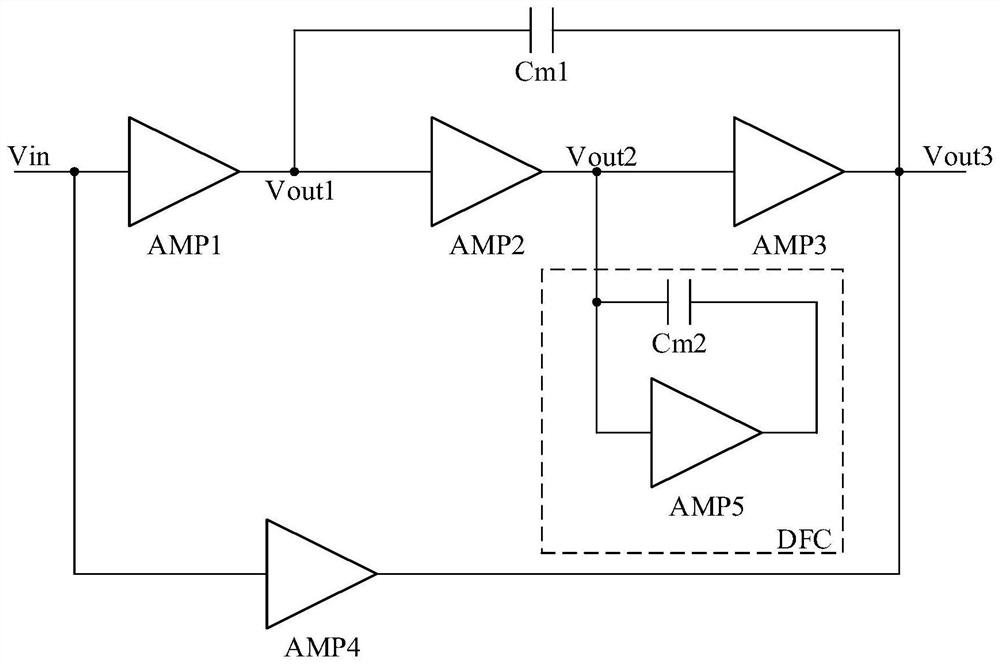
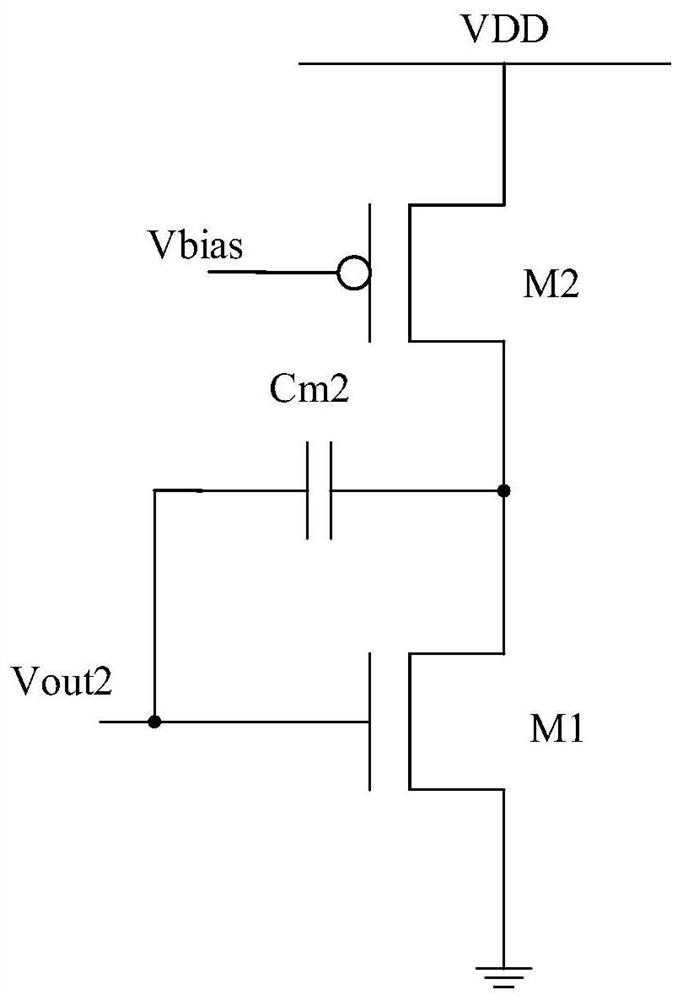
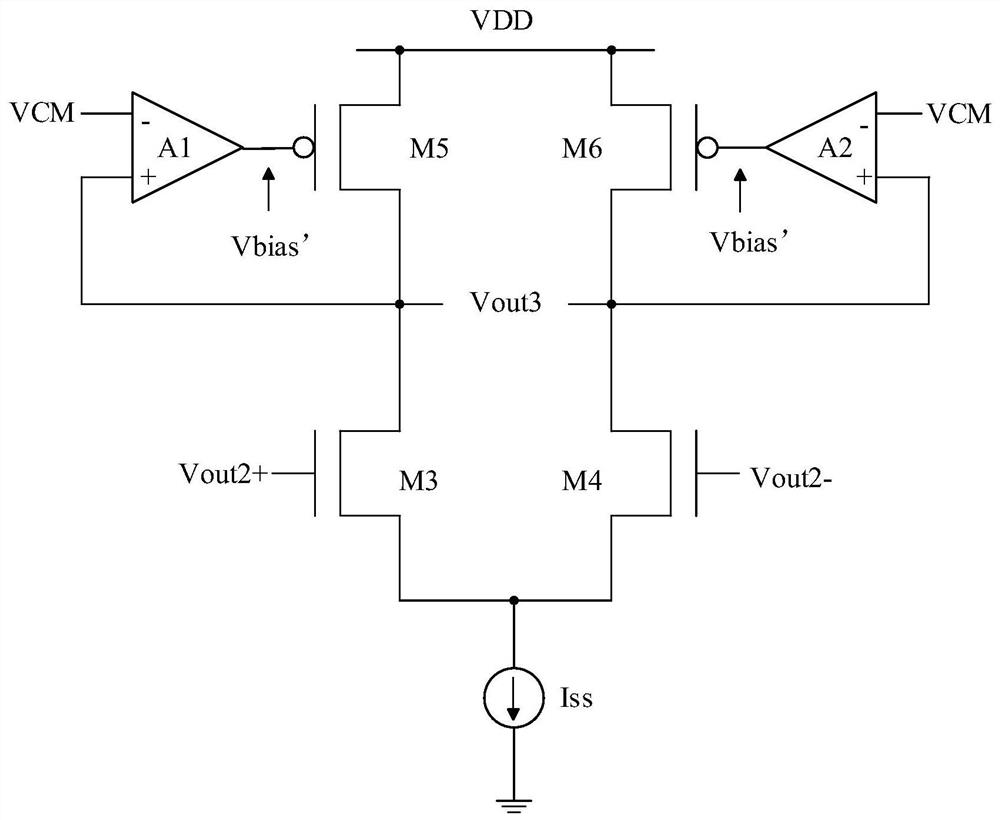
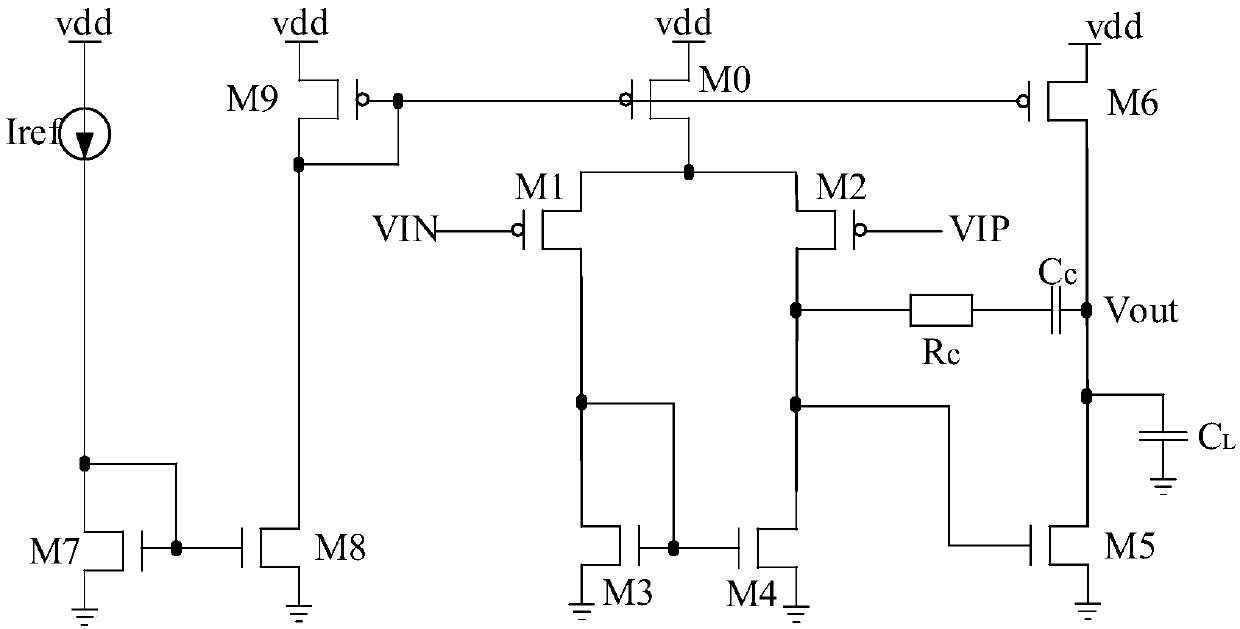
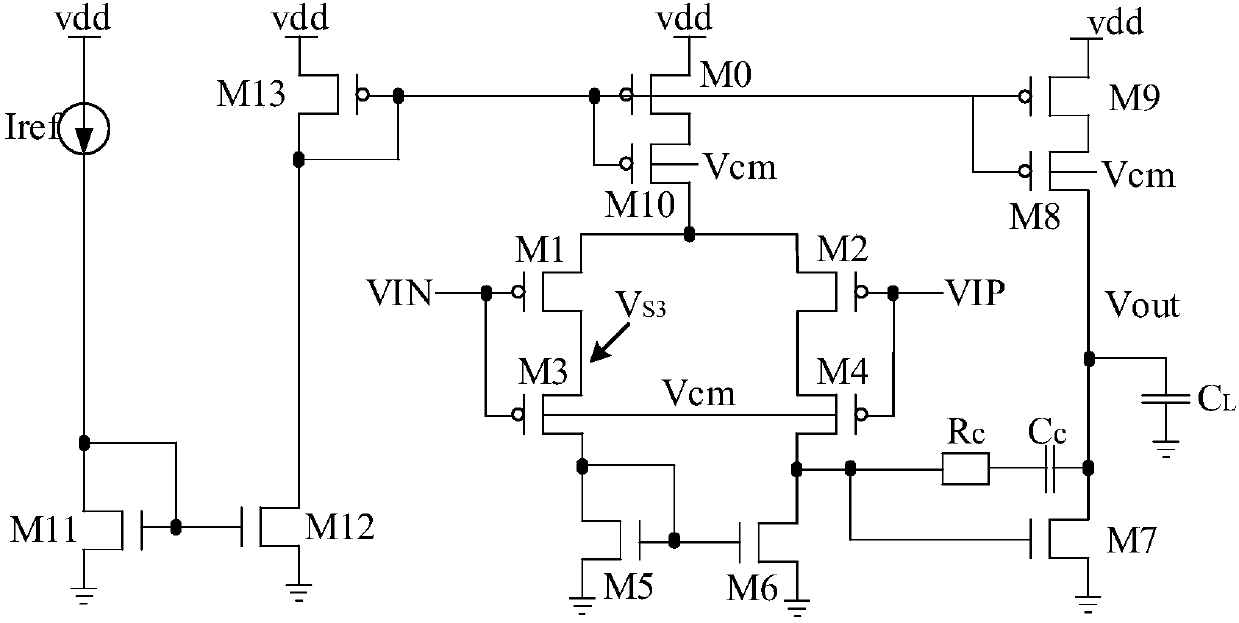
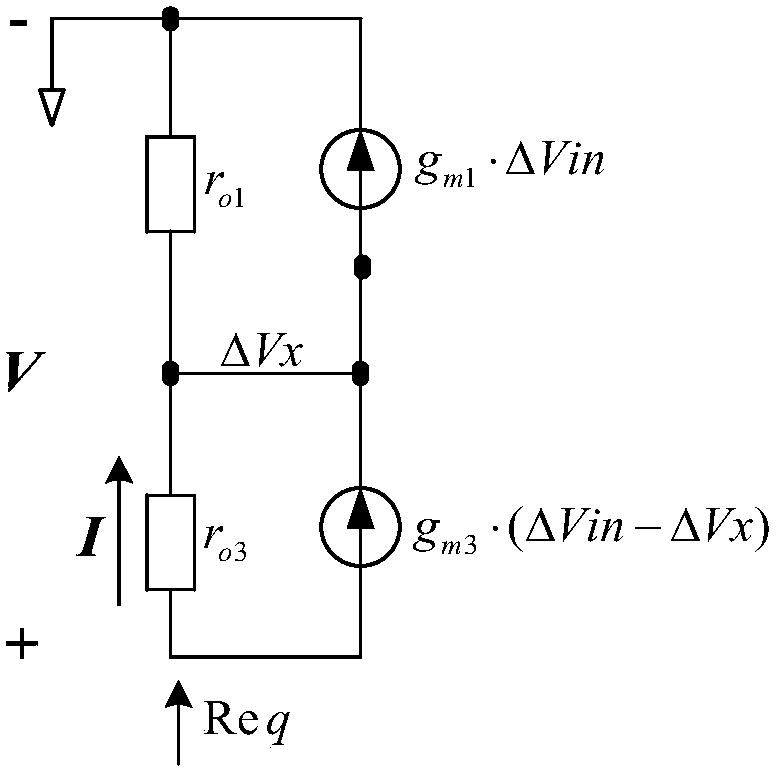
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Increased unity-gain bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
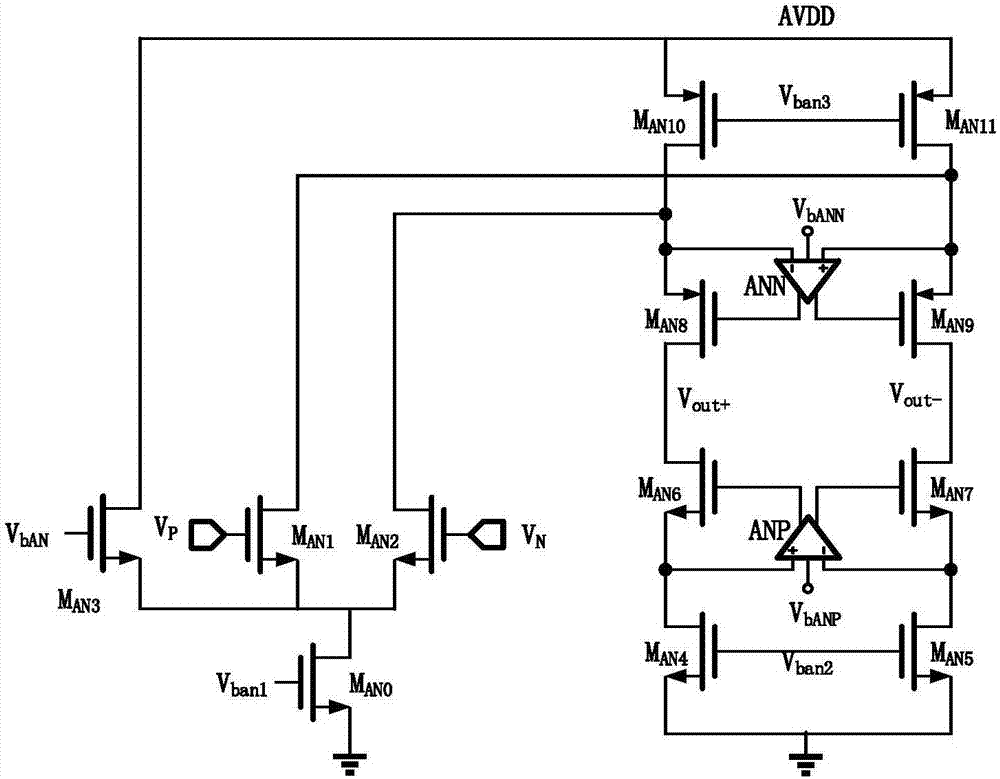
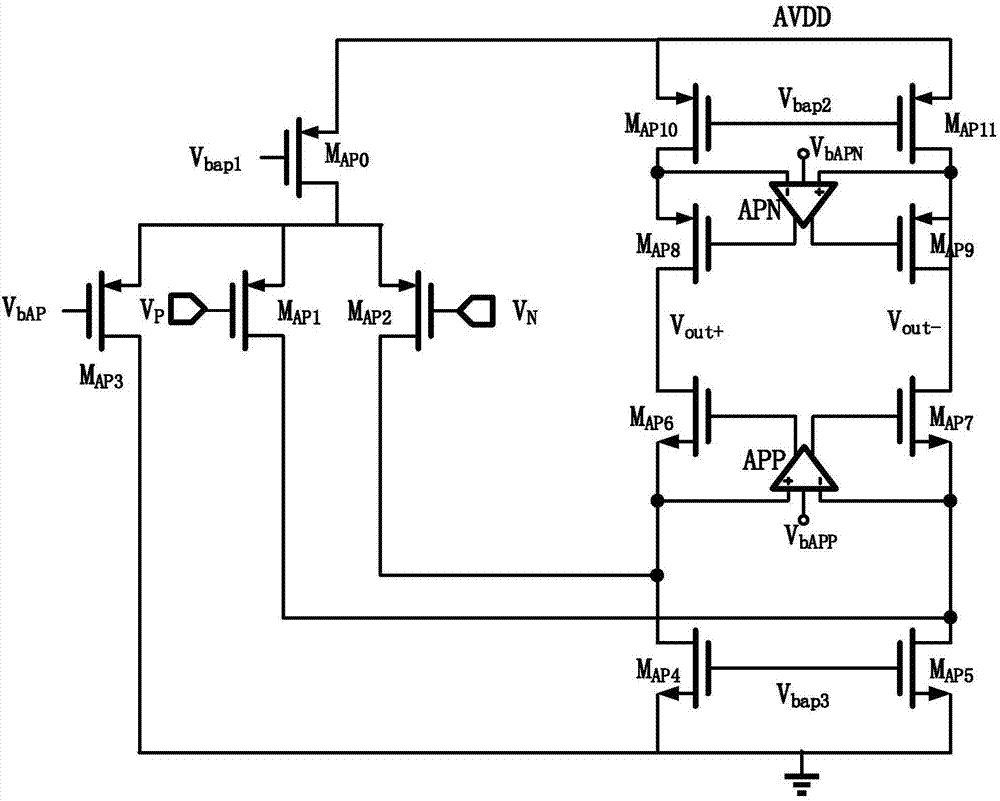
Method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier
InactiveUS6924701B1Increased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierCascode
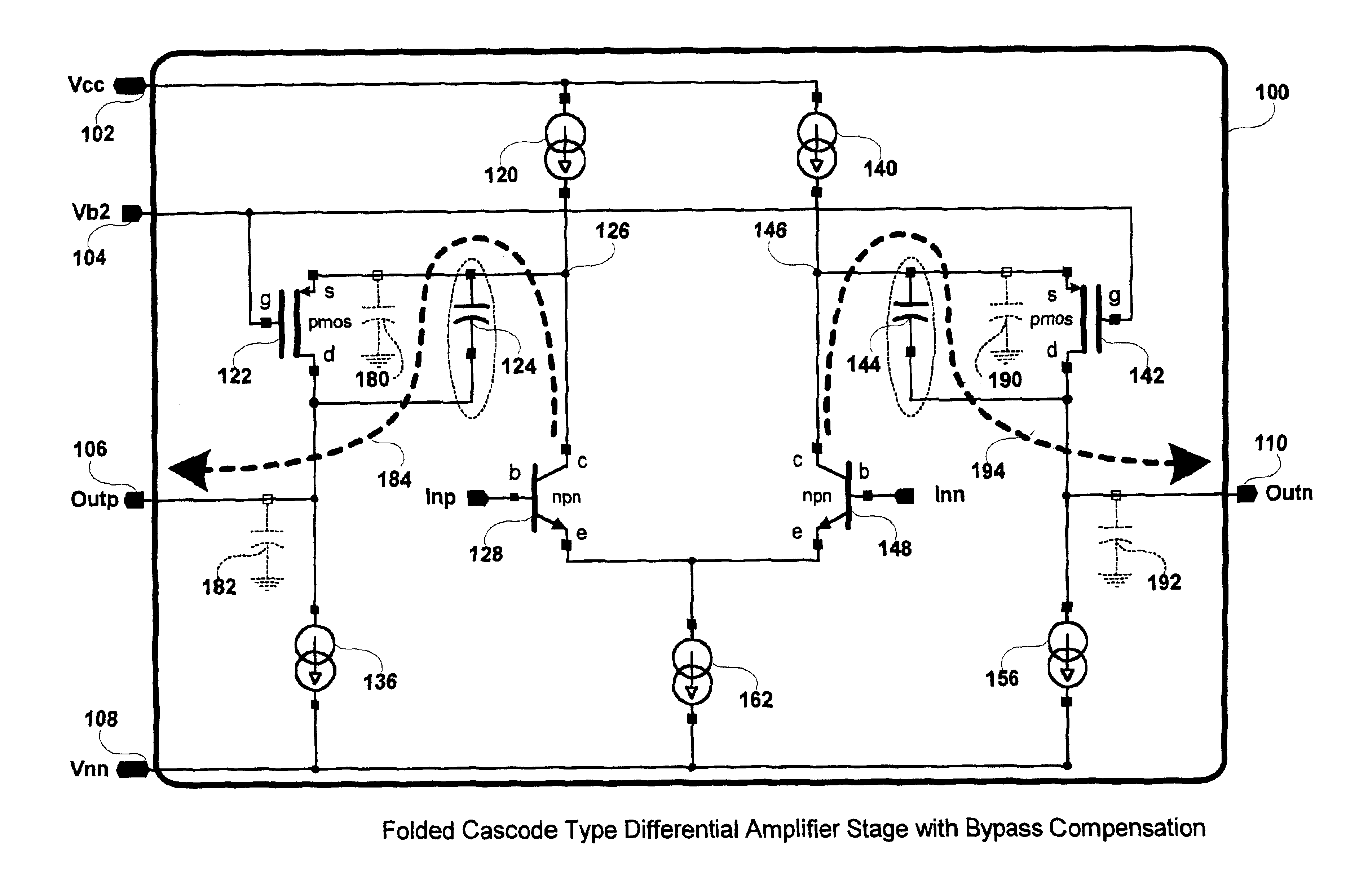
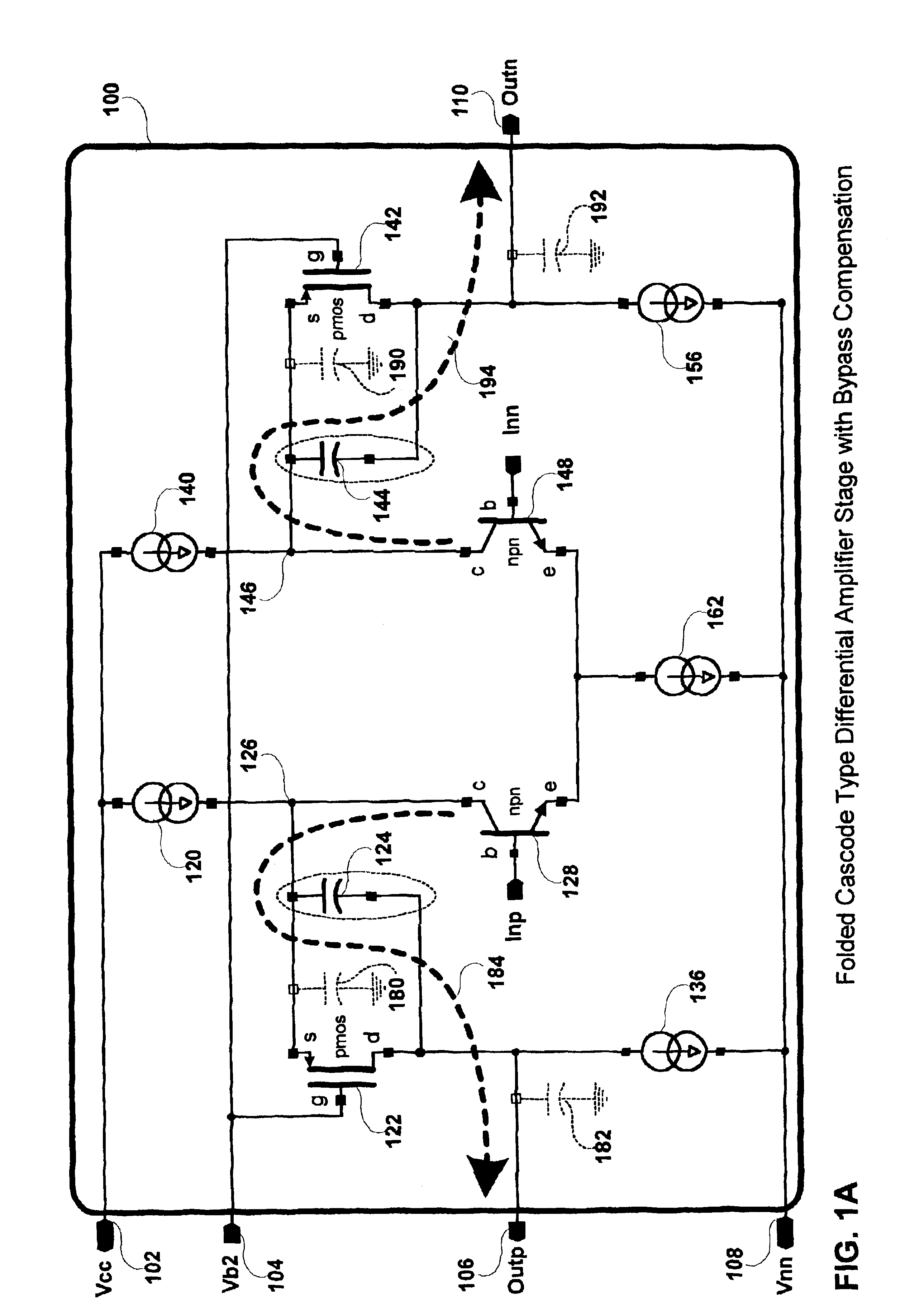
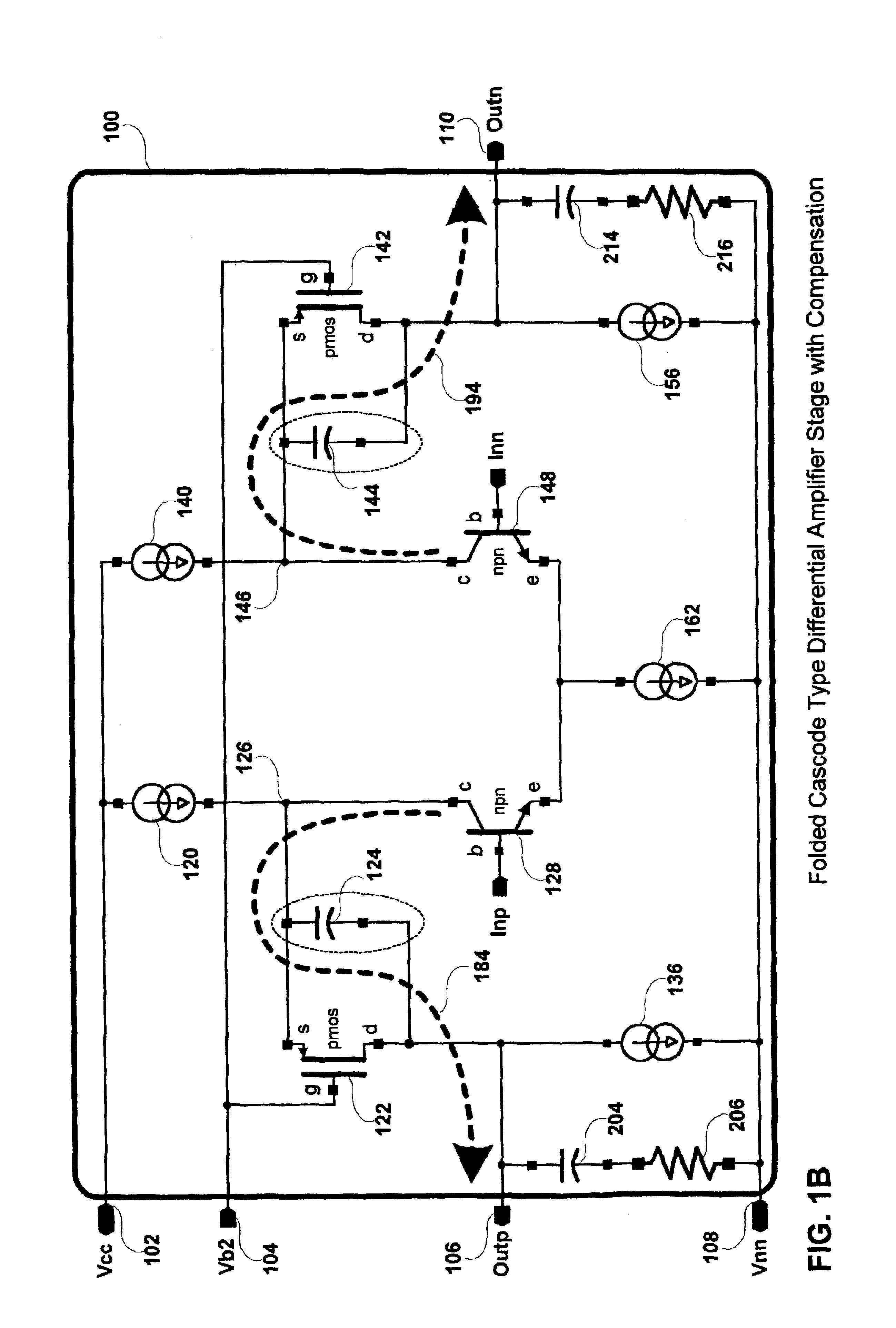
A method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier is disclosed which significantly improves the unity gain bandwidth of the amplifier. In an embodiment of the invention the amplifier includes at least one compensated pair of cascode coupled transistors including: an input transistor, a cascode transistor, and a bypass element. The input transistor exhibits a first transition frequency. The cascode transistor is cascode coupled to the input transistor. The cascode transistor exhibits a second transition frequency less than or equal to the first transition frequency of the input transistor. The bypass element couples across a corresponding current interface of the cascode transistor to substantially bypass the cascode transistor at a pole frequency thereof.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Split compensation two-stage operational amplifier based on inverter input structure
InactiveCN103199807AInhibition effectOffset the impactDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceFrequency compensation
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics and relates to the frequency compensation technology of operational amplifiers in analog integrated circuits. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier comprises a two-stage operational amplifier. A first-stage operational amplifier is composed of N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tubes (M1N, M2N, M3 and M4) and P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tubes (M1P, M2P and M0). A second-stage operational amplifier is composed of a PMOS tube M5P and an NMOS tube M5N. A traditional Miller capacitor is divided into a Cm1 portion and a Cm2 portion to finish frequency compensation of the operational amplifier. A first frequency compensation capacitor Cm1 is connected with the position between the output end of the first operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. A second frequency compensation capacitor Cm2 is connected with the position between a connection point of a source of the NMOS tube M2N and a drain of the NMOS tube M4 in the first-stage operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier has strong robustness and higher unit grain bandwidth and output slew rate due to the fact that non-dominant poles and stray parameter are not related.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Complementary circulation folding gain bootstrapping operational amplifier circuit with preamplifier
InactiveCN102075151AIncrease unity gainHigh gainAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierOperational transconductance amplifier
The invention discloses a complementary circulation folding grain bootstrapping operational amplifier circuit with preamplifier, belonging to the technical field of operational amplifier. The circuit comprises a preamplifier formed by N-typed transistors (N1, N2, N3, N4); the unit grained band width of the operational amplifier is improved by the complementary input of P-typed transistors (P, P2, P3, P4) and the N-typed transistors (N16, N17, N18, N19), and using the circulation folding gain bootstrapping operational transconductance amplifier structure. The circuit has the characteristics of high unit gain bandwidth and low power consumption, and confirms to the researching and developing directions of integrated circuits.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low power broadband transconductance error amplifier
PendingCN108599731AImprove driving abilityIncreased unity-gain bandwidthAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a low power broadband transconductance error amplifier. A differential amplifier with a common mode feedback loop is designed at a first stage, so a common mode rejection ratioof a circuit is improved, and an output common mode level is stabilized. According to the design, gain and swing of the first stage can be further improved. Moreover, a common source level and classAB output level amplifier is employed at a second stage, the transconductance and circuit drive capability of the transconductance error amplifier are improved, and further a unit gain bandwidth of the circuit is improved. The design of a common mode negative feedback circuit is simplified, moreover, the power consumption is reduced, the stability of the circuit is improved, and the technical problem that the power consumption of the amplifier is increased to a certain degree due to the fact that the design of the traditional common mode negative feedback circuit is relatively complex is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
InactiveCN101339443BIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceIntermediate frequency
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
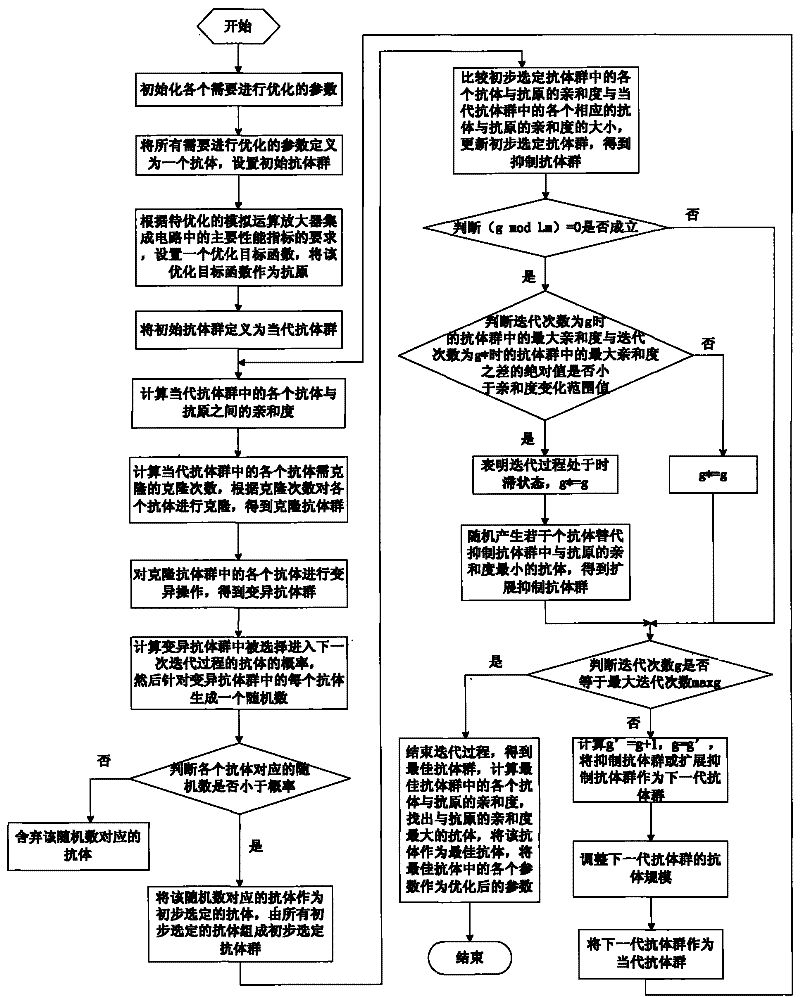
Method for optimizing integrated circuit of analog operational amplifier
InactiveCN101714176AReduced Power RequirementsHigh DC GainGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAnalog circuit designLow power dissipation
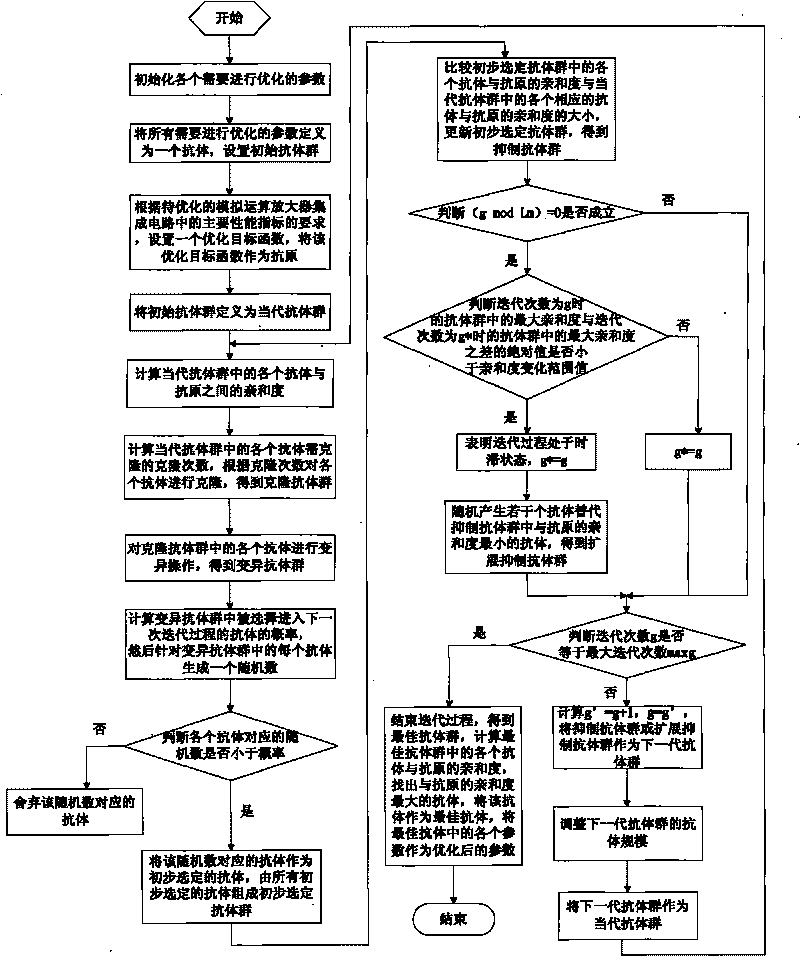
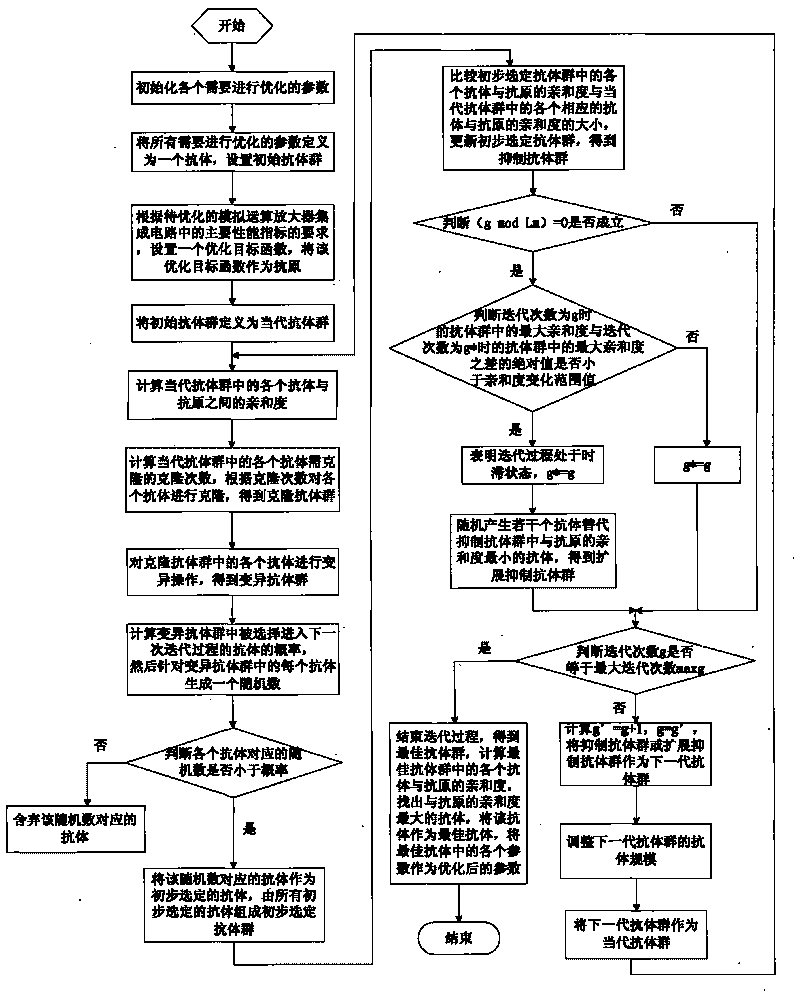
The invention discloses a method for optimizing an integrated circuit of an analog operational amplifier. The method has the advantages that according to the principle and requirement of an analog integrated circuit to be designed, the method can automatically design technical parameters and circuit parameters free from design parameters and the number of optimized targets by applying an intelligent optimized searching method of a Q-deviant immune network, can automatically search and find the optimal technical parameters and circuit parameters meeting the requirements of analog circuit performance indexes in a range of set values, namely meeting the requirements of high direct current gain, unit gain bandwidth, conversion velocity and low power consumption, and provides good foundation and accordance for high-performance analog integrated circuit technological design. Furthermore, the method is applicable to various analog circuit designs, is easy for transplanting, and has wide applicability and high universality.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
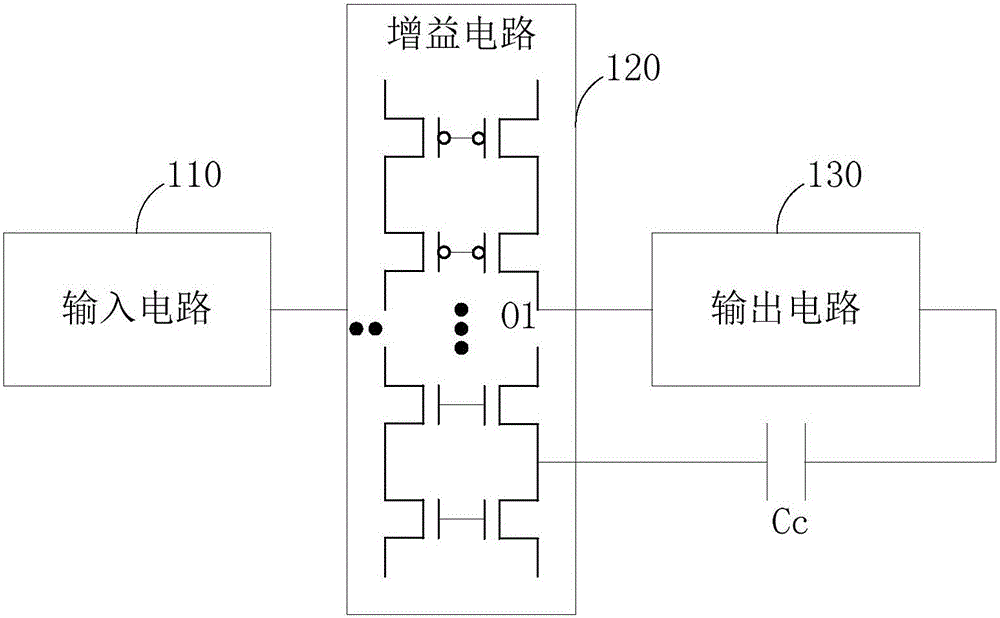
Frequency compensation circuit for operational amplifier
ActiveCN106026954AImplement frequency compensationImprove -3dB bandwidthDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
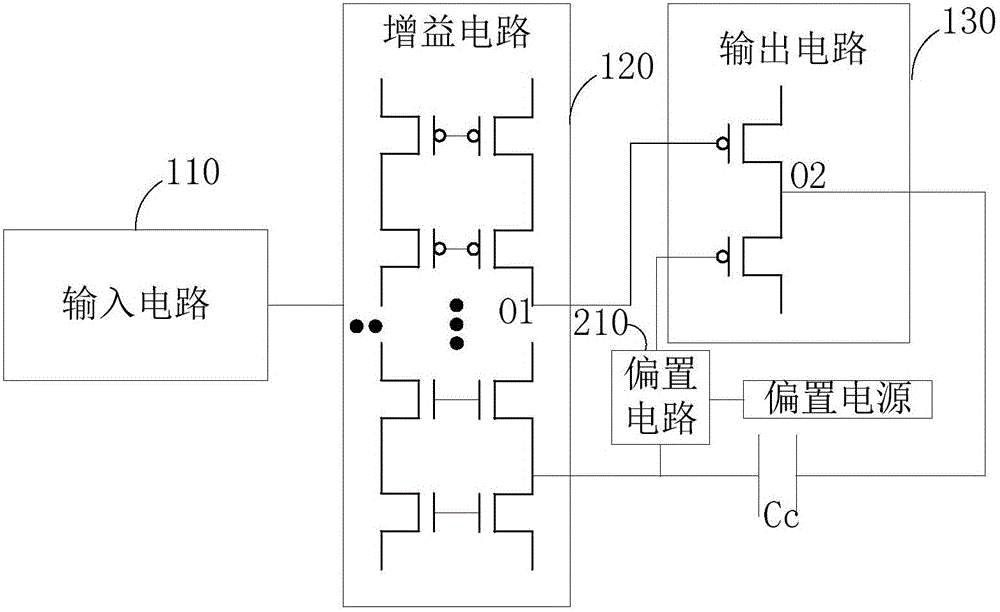
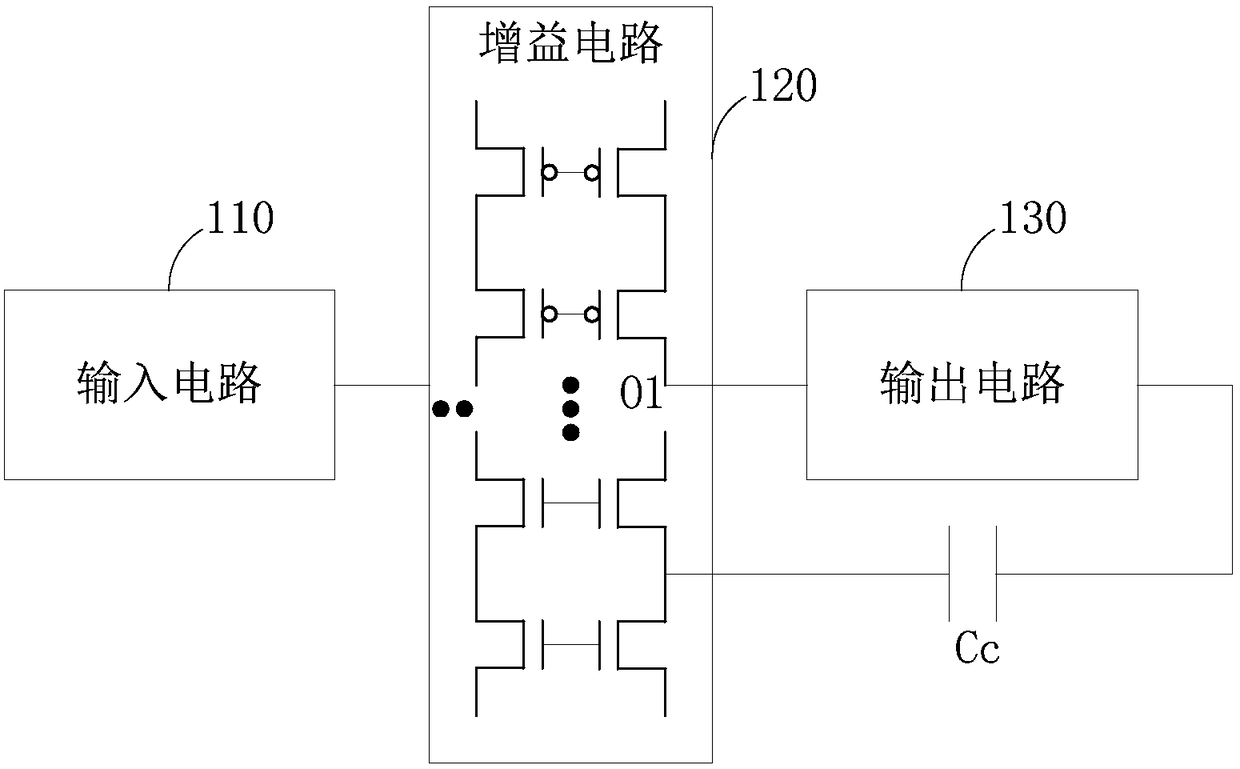
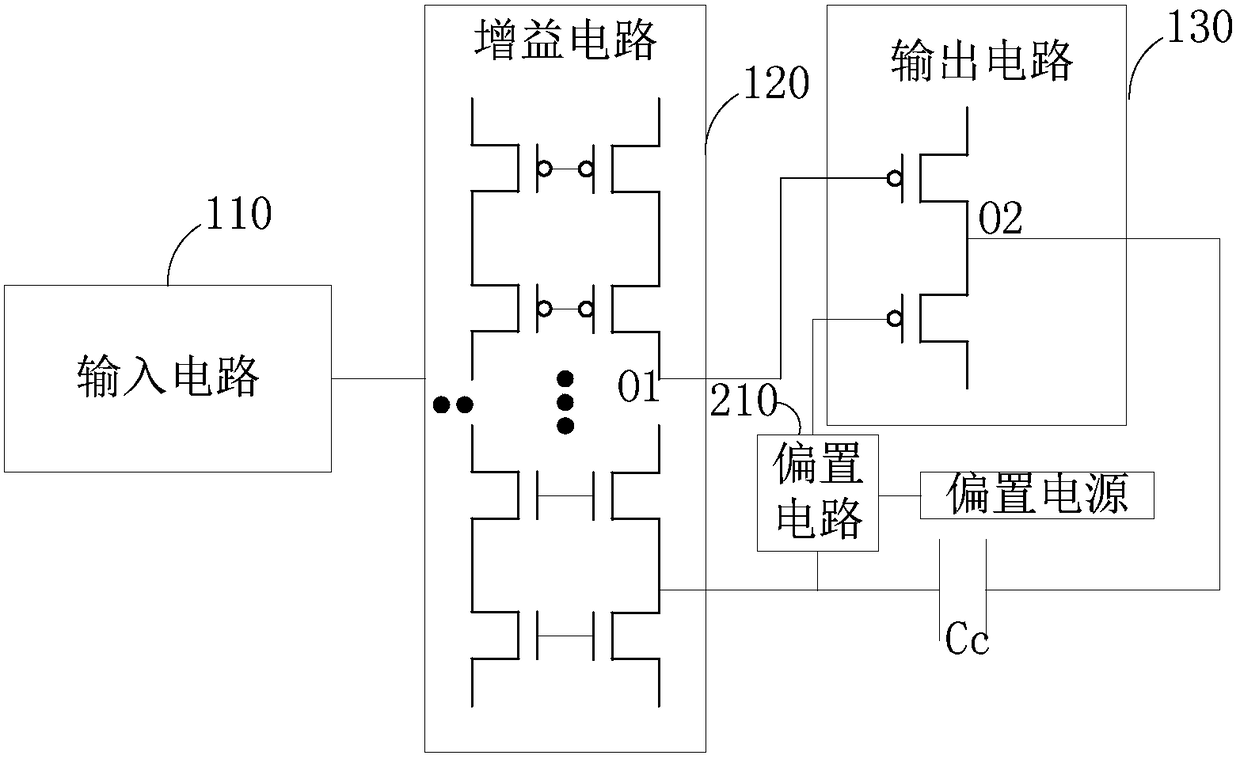
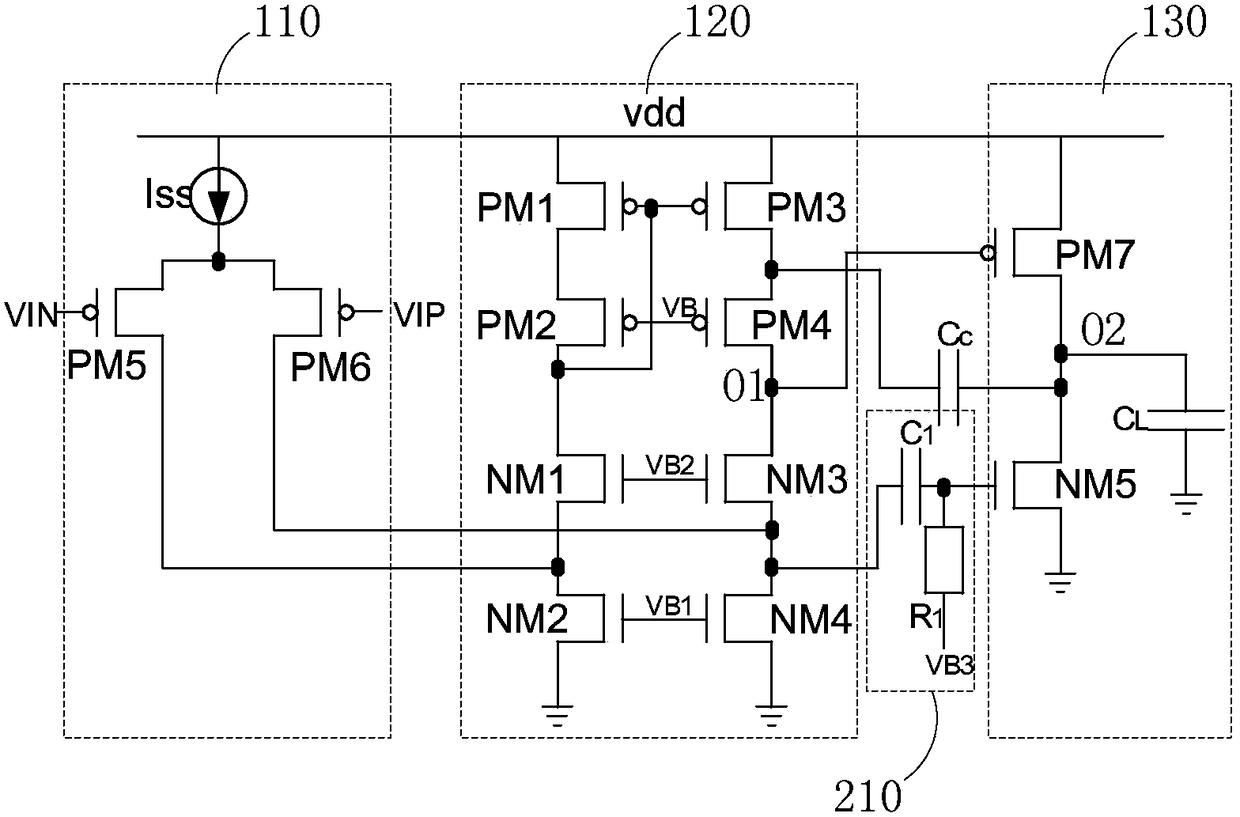
The invention provides a frequency compensation circuit for an operational amplifier. The frequency compensation circuit comprises a gain circuit, an output circuit and a tail current source bootstrap circuit of the gain circuit, wherein a grounding end of the gain circuit is connected with a first end and a second end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit; an output end of the gain circuit is connected with a first input end of the output circuit and an input end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit respectively; an output end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit is connected a bias voltage, and connected with a second input end of the output circuit through a first resistor; and the second input end of the output circuit is connected with the output end of the gain circuit through a first capacitor. Based on an RC network consisting of the first resistor and the first capacitor, the operational amplifier generates a left-half plane null point z, and the left-half plane null point z and a first non-main pole of the operational amplifier can be counteracted by adjustment of the magnitude of the RC, so that frequency compensation of the operational amplifier is realized. Meanwhile, the unit gain bandwidth of the operational amplifier can be increased remarkably.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Band gap reference voltage source and electronic equipment
PendingCN109388171AReduce generationHigh bandwidthElectric variable regulationCapacitanceComputer module
The invention discloses a band gap reference voltage source and electronic equipment. The band gap reference voltage source consists of a starting module and a band gap core module; when the band gapreference voltage source compensates for a loop, if a secondary pole of the band gap reference voltage source is equal to a zero point, the second capacitance value required for achieving a stable condition is far smaller than compensation capacitance required by a band gap reference voltage source in the prior art, and obviously, a main pole of the provided band gap reference voltage source is far greater than that of the band gap reference voltage source in the prior art. Therefore, the provided band gap reference voltage source can effectively increase loop bandwidth and achieve the purposes of reducing the loop compensation difficulty of the band gap reference voltage source, increasing unit gain bandwidth and reducing the required compensation capacitance.
Owner:SHANGHAI AWINIC TECH CO LTD
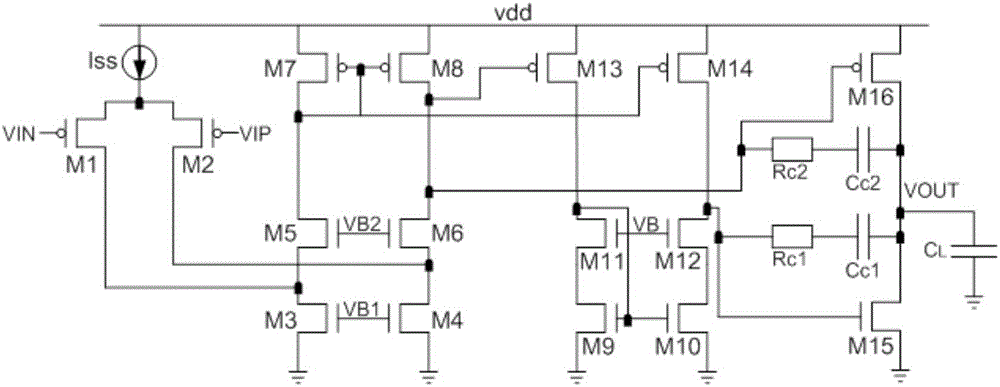
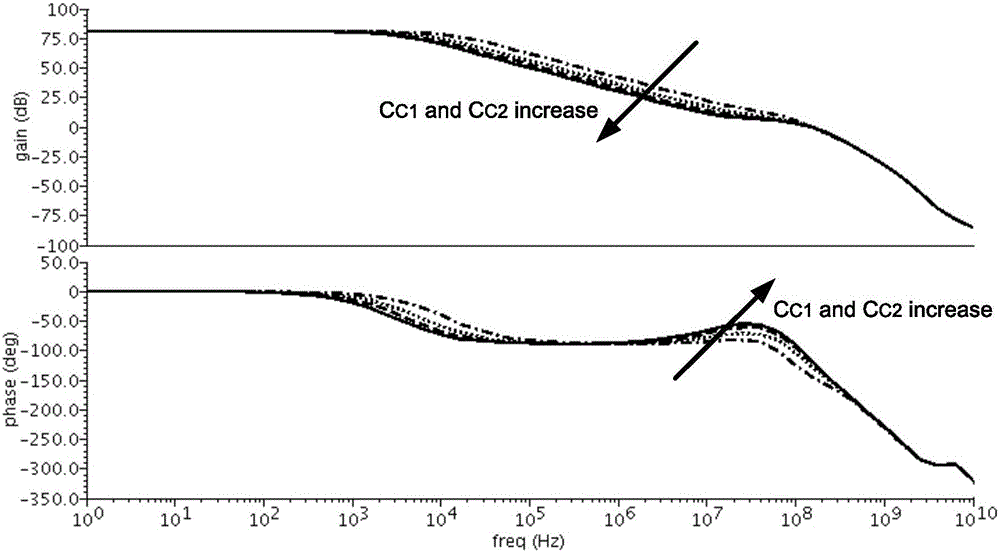
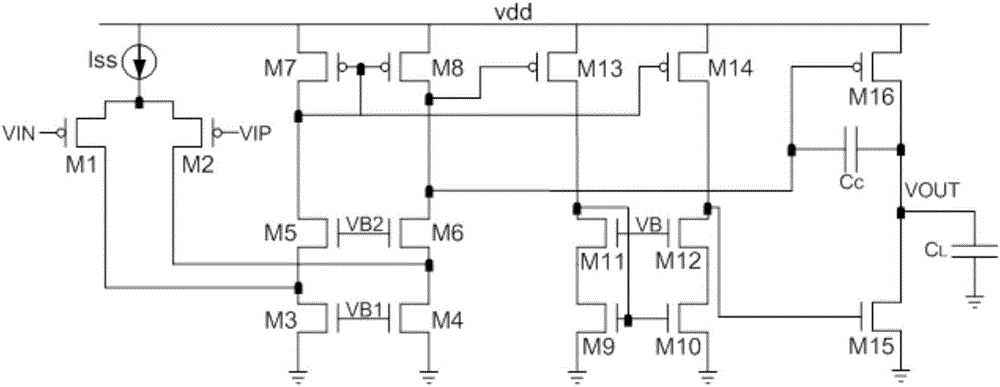
Frequency-compensated transconductance amplifier
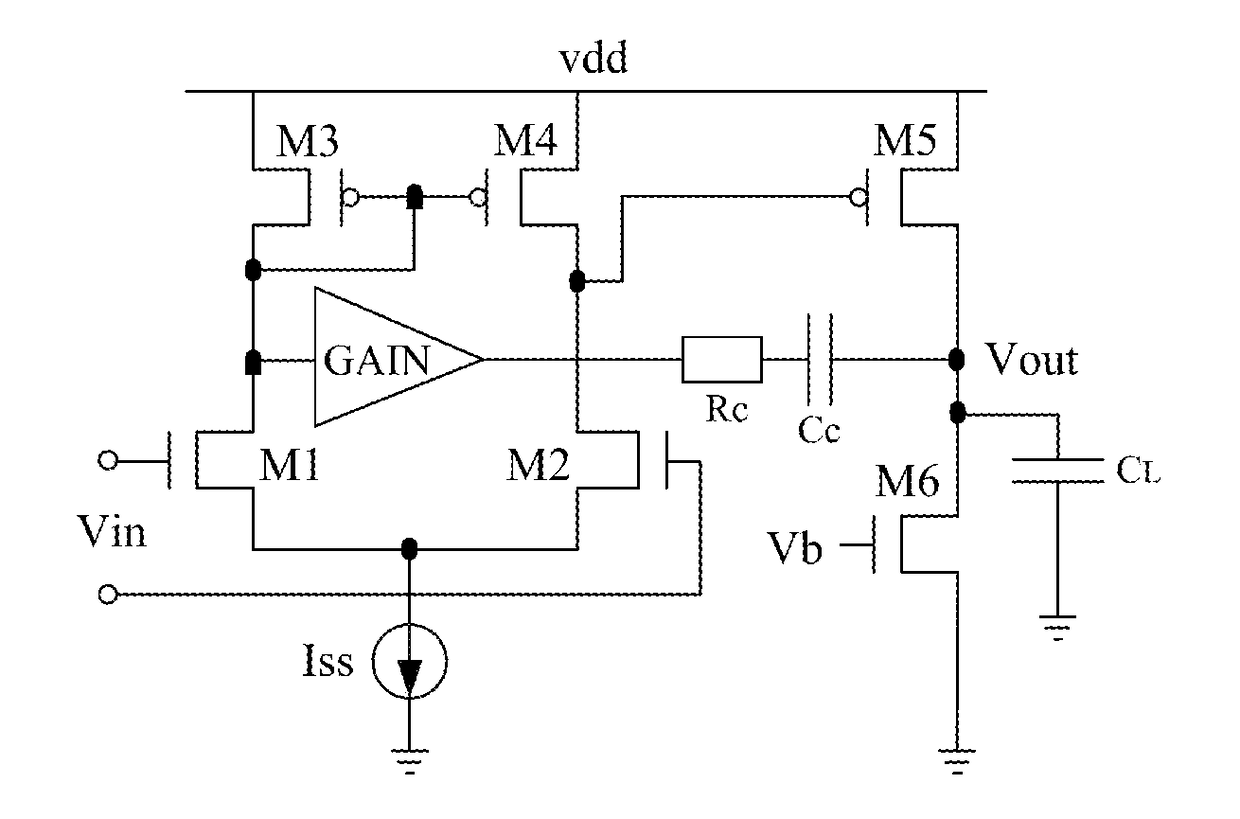
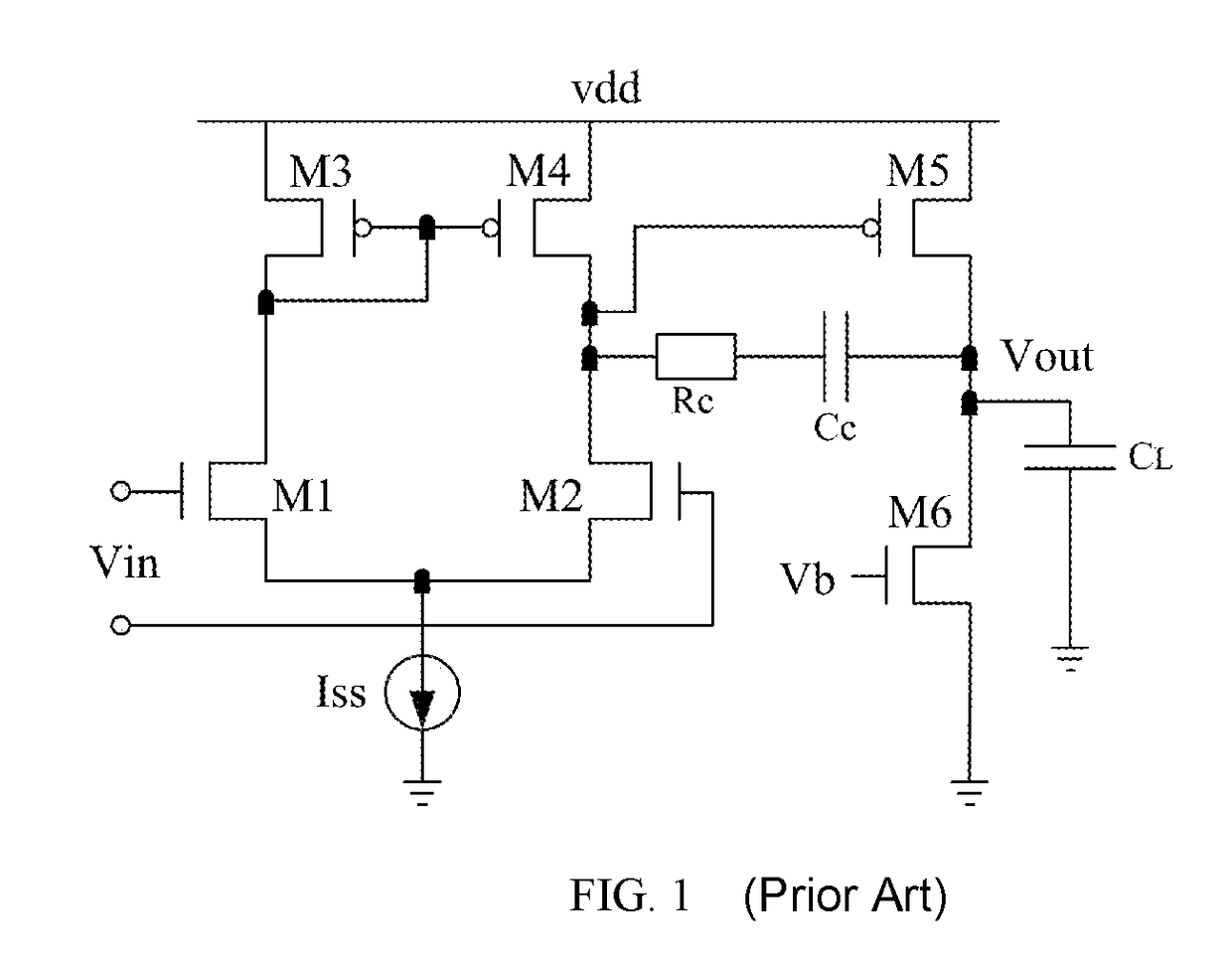
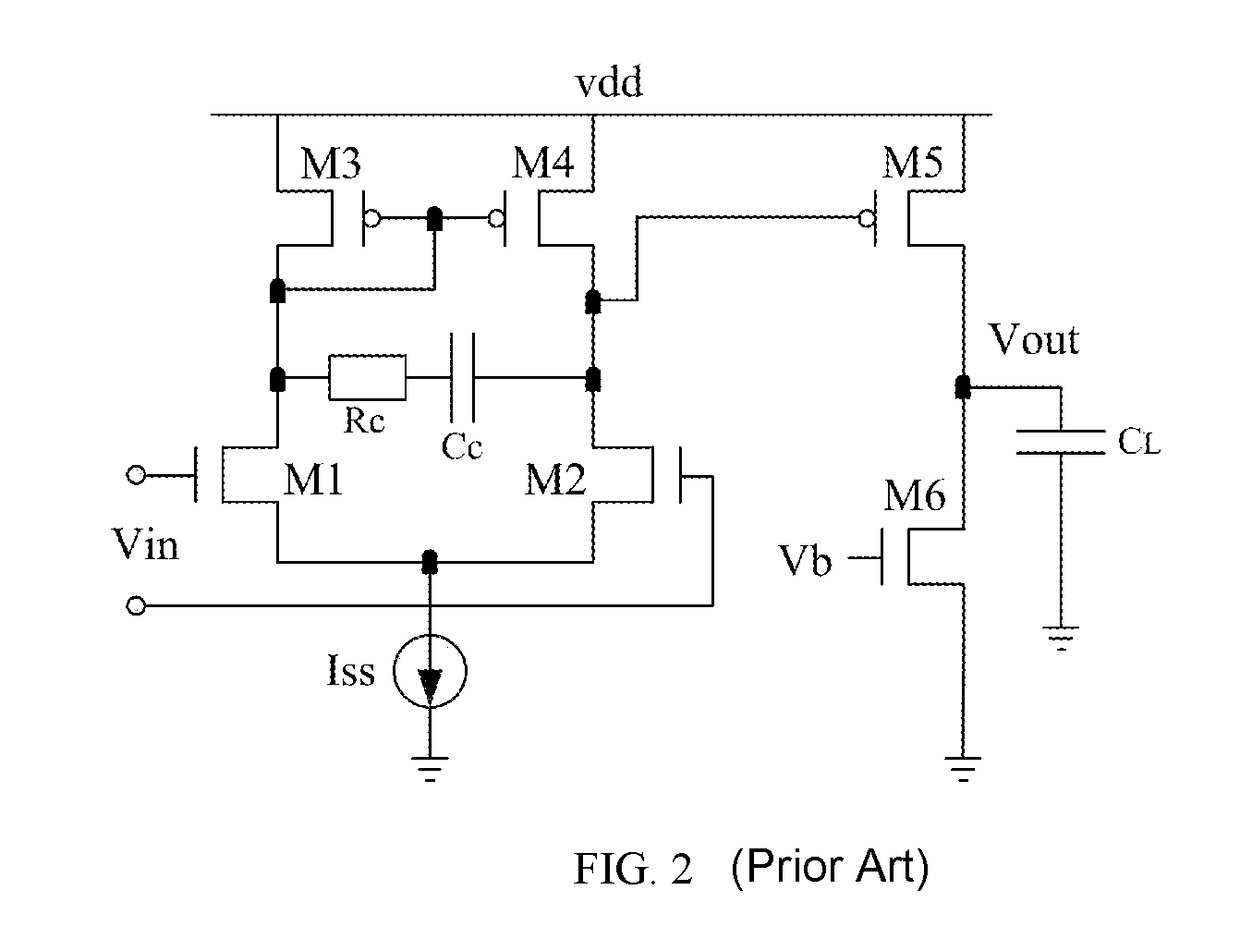
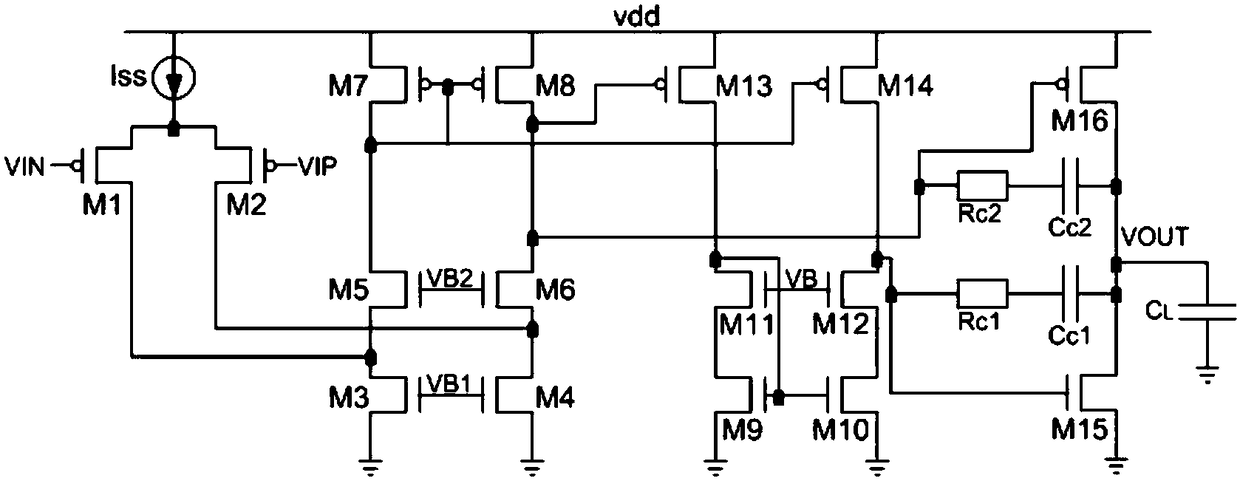
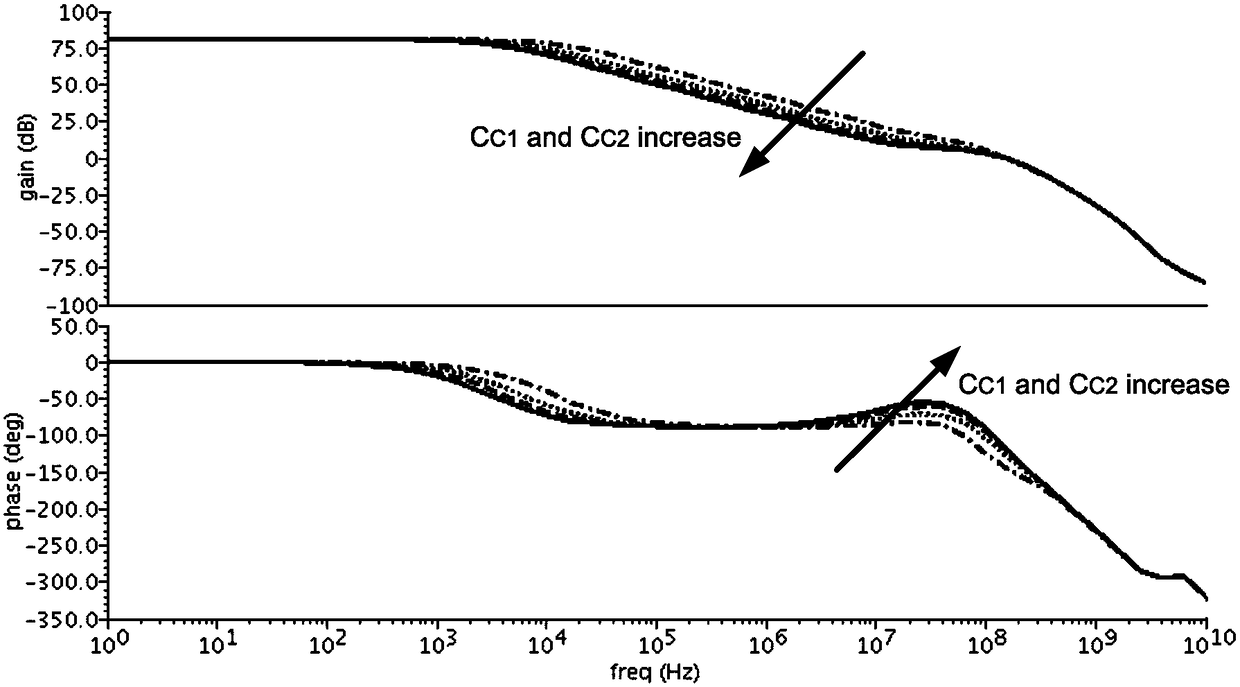
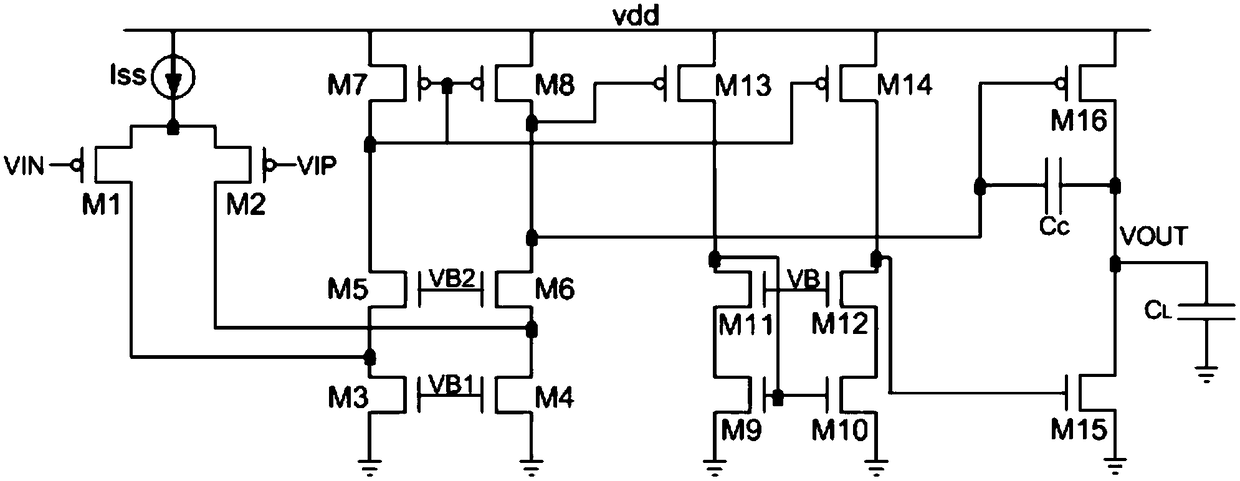
ActiveUS20180054168A1Improve amplitude-frequency characteristic curveIncreased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
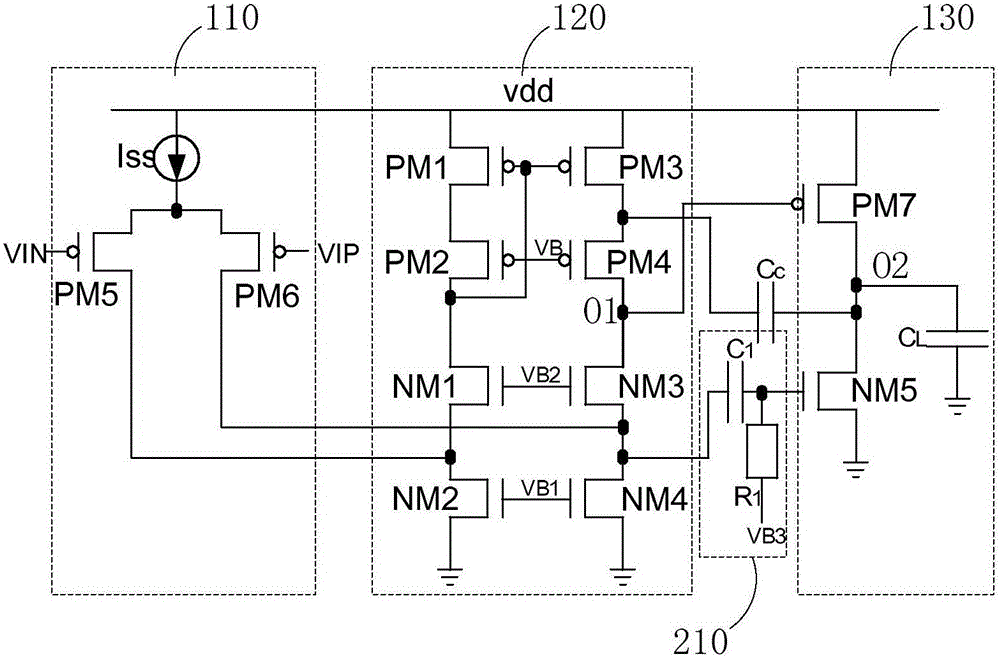
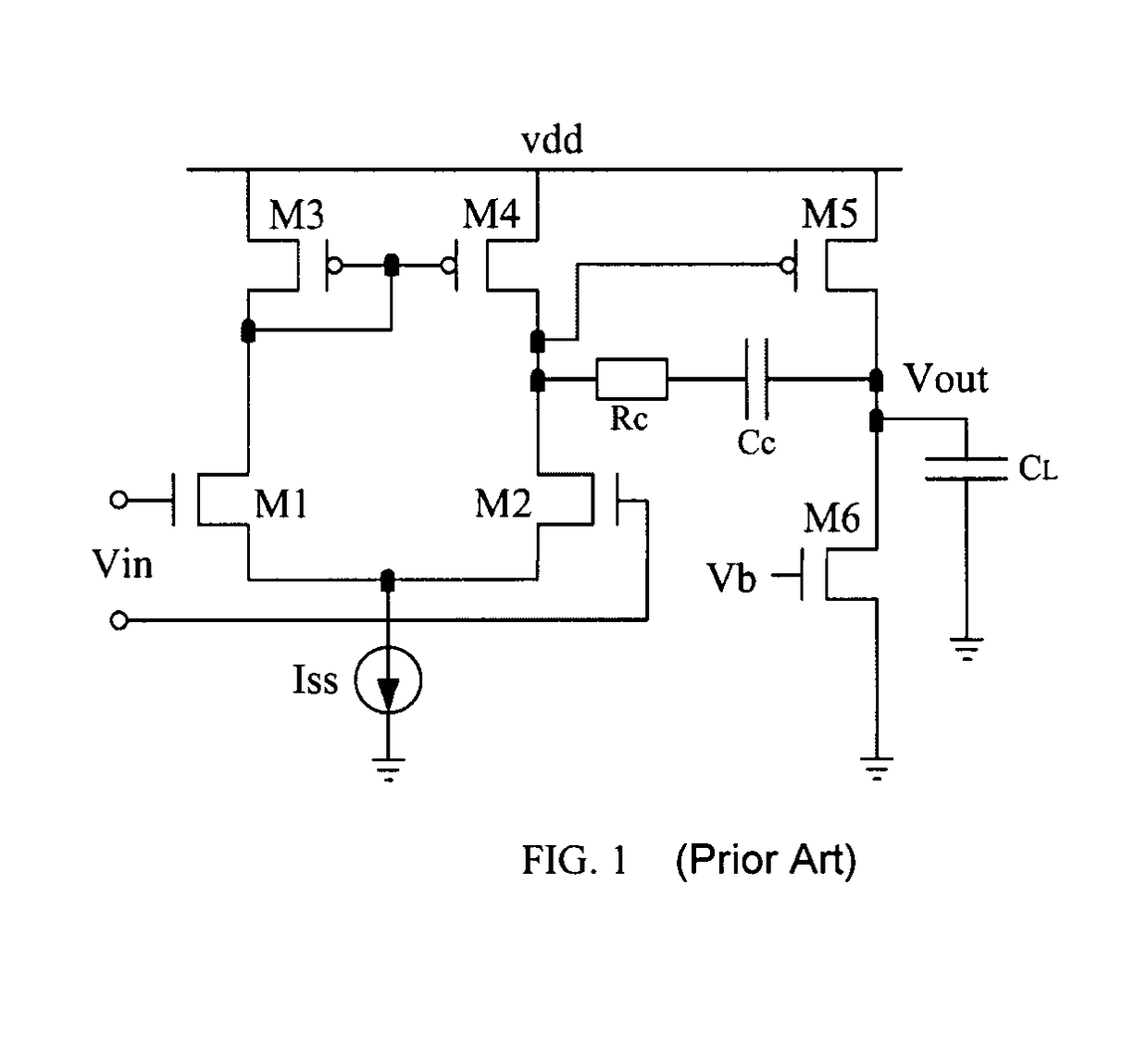
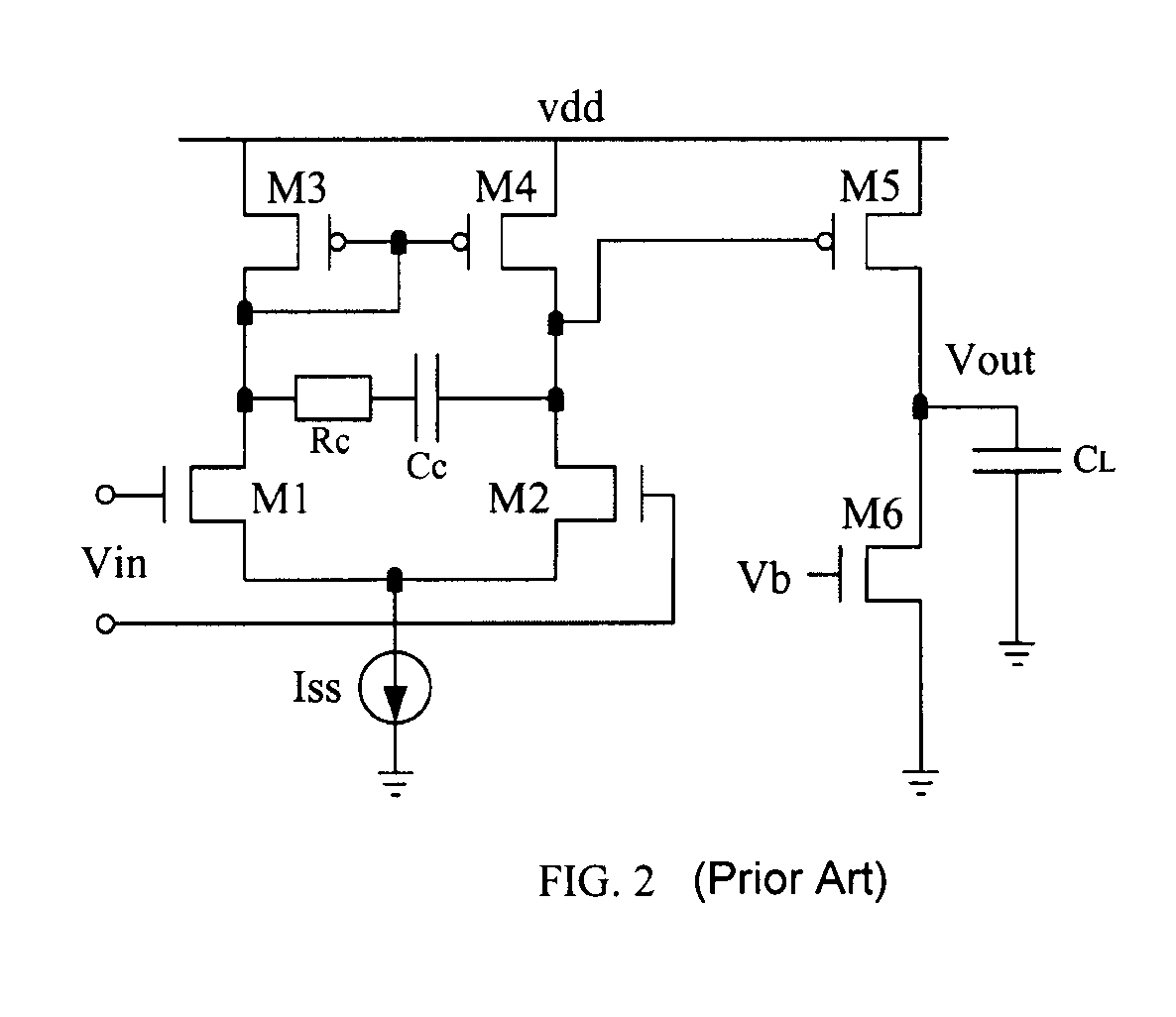
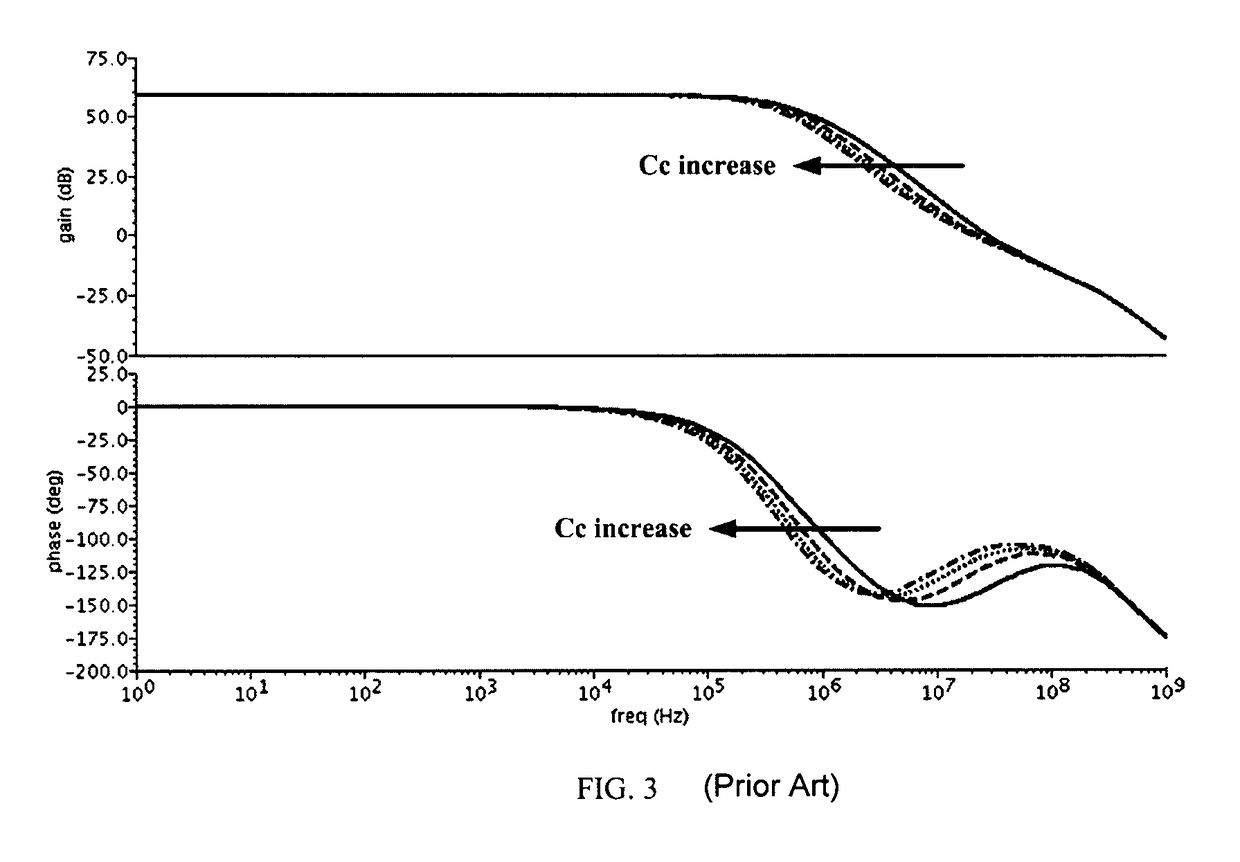
The present invention provides a frequency-compensated transconductance amplifier, includes an input stage consisting of NMOS transistors M1 and M2, a first-stage active load consisting of PMOS transistors M3 and M4, a first-stage tail current source consisting of a constant current source Iss, a second-stage input transistor consisting of a PMOS transistor M5, a second-stage constant current source consisting of an NMOS transistor M6, a load capacitor consisting of a capacitor CL, and a frequency compensation network formed by sequentially connecting a gain stage GAIN, a compensating resistor Rc and a compensating capacitor Cc in series.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Operational amplifier for pipeline analog to digital converter
ActiveCN107888194AImprove output swingHigh bandwidthAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceDigital down converter
The invention discloses an operational amplifier for a pipeline analog to digital converter. The operational amplifier comprises a first main operational amplifier and a second main operational amplifier; the first main operational amplifier comprises a first common source common gate P type transistor pair, a second common source common gate P type transistor pair, a first common source common gate N type transistor pair and a first common source N type transistor pair, which are connected in sequence, and the source electrode of the first common source N type transistor pair is connected with a first tail current N type transistor; the second main operational amplifier comprises a third common source common gate P type transistor pair and a second common source N type transistor pair, which are connected in sequence, and the source electrode of the second common source N type transistor pair is connected with a second tail current N type transistor, wherein the drain electrode of thefirst common source common gate P type transistor pair is connected with the drain electrode of the third common source common gate P type transistor pair through a compensation capacitor. Compared with the prior art, the operational amplifier can greatly improve the gain and the precision of the operational amplifier in the case of low voltage.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
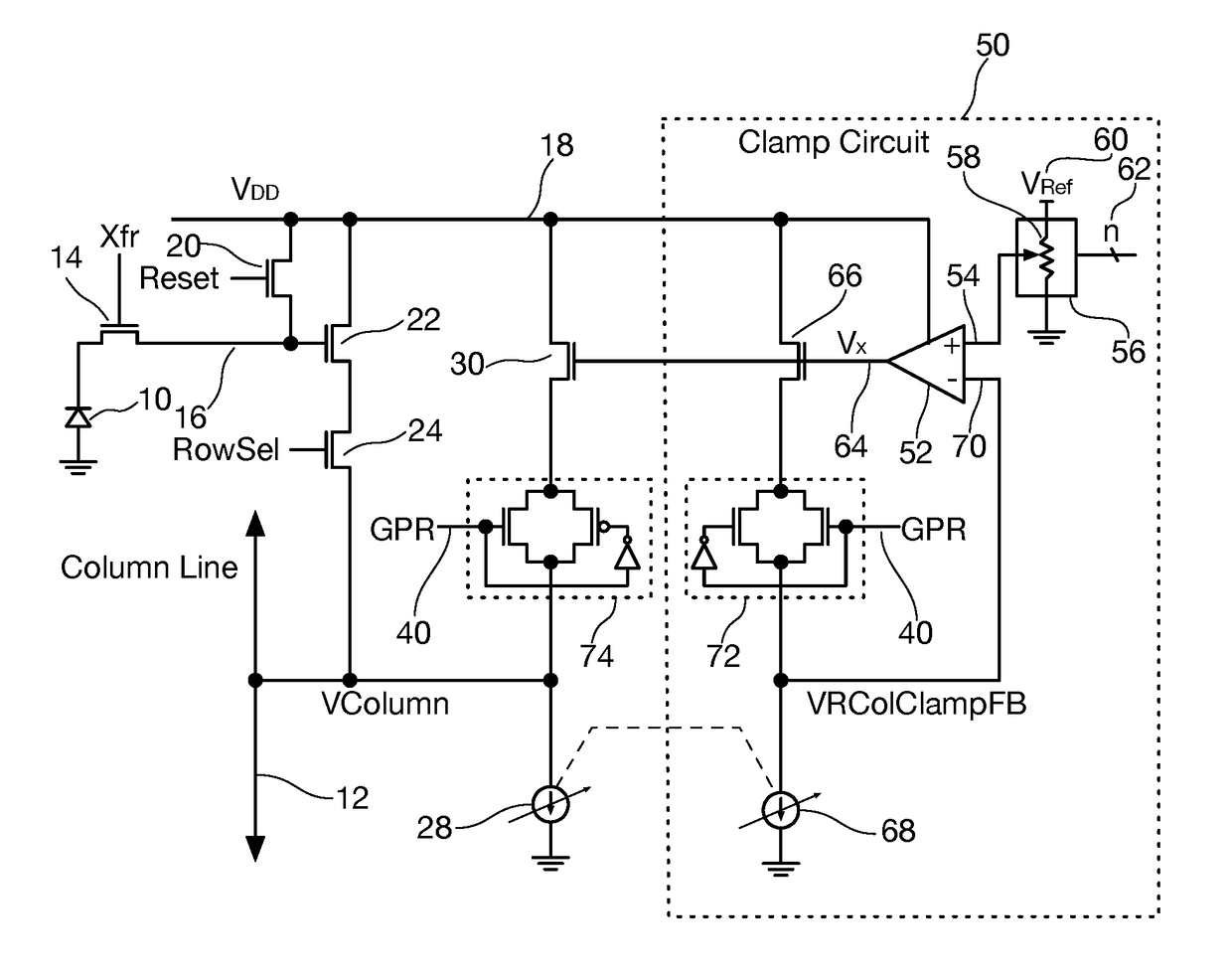
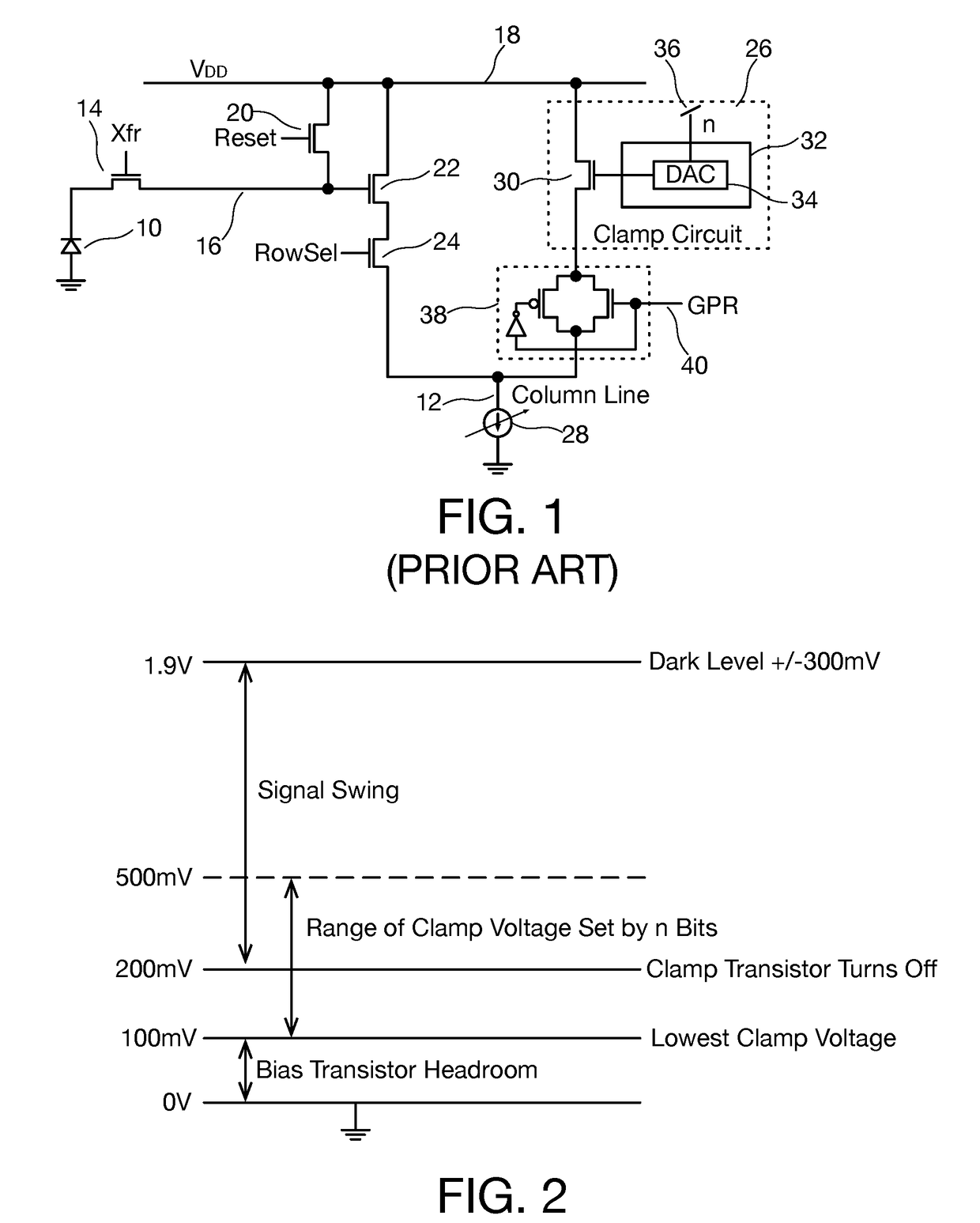
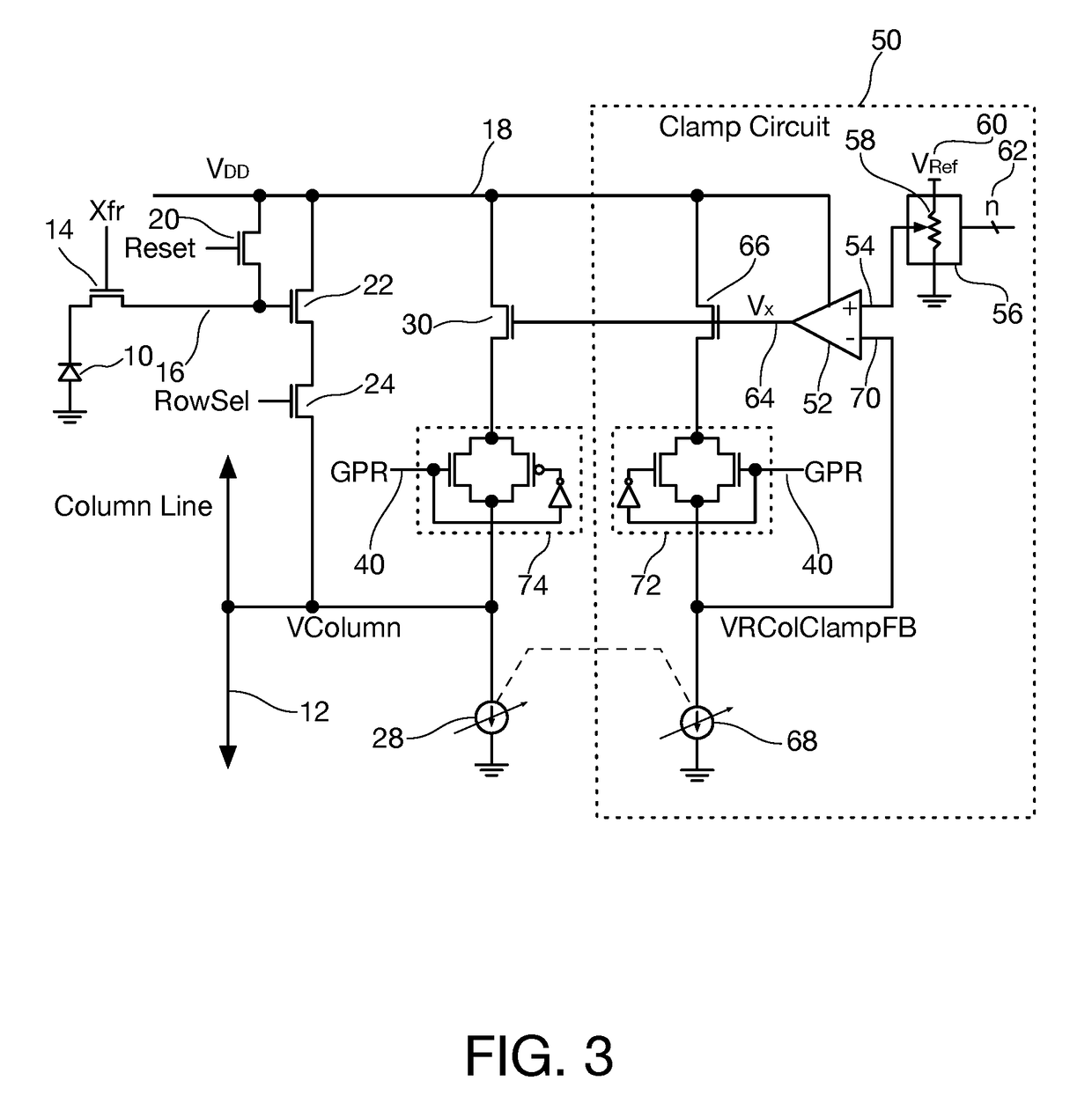
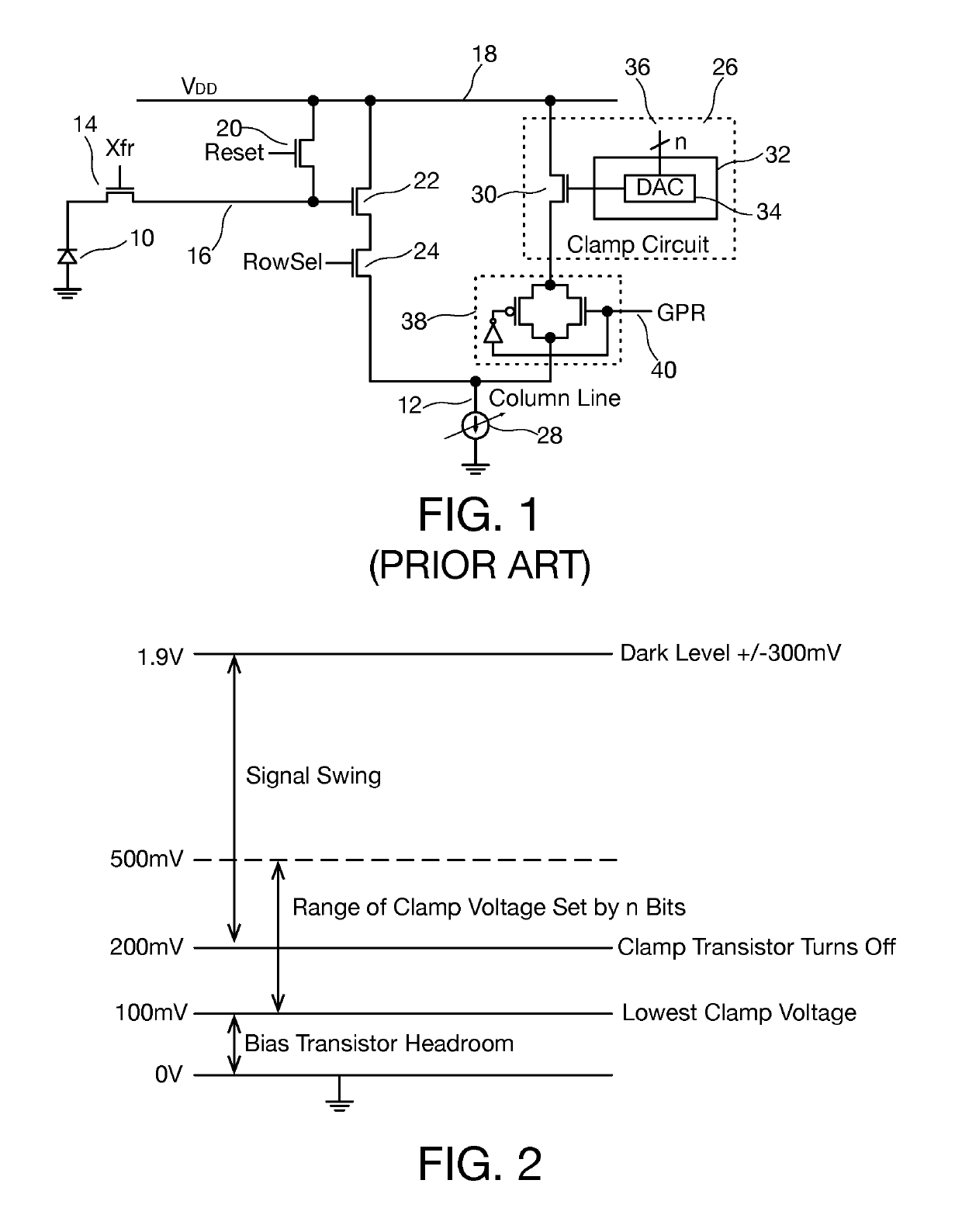
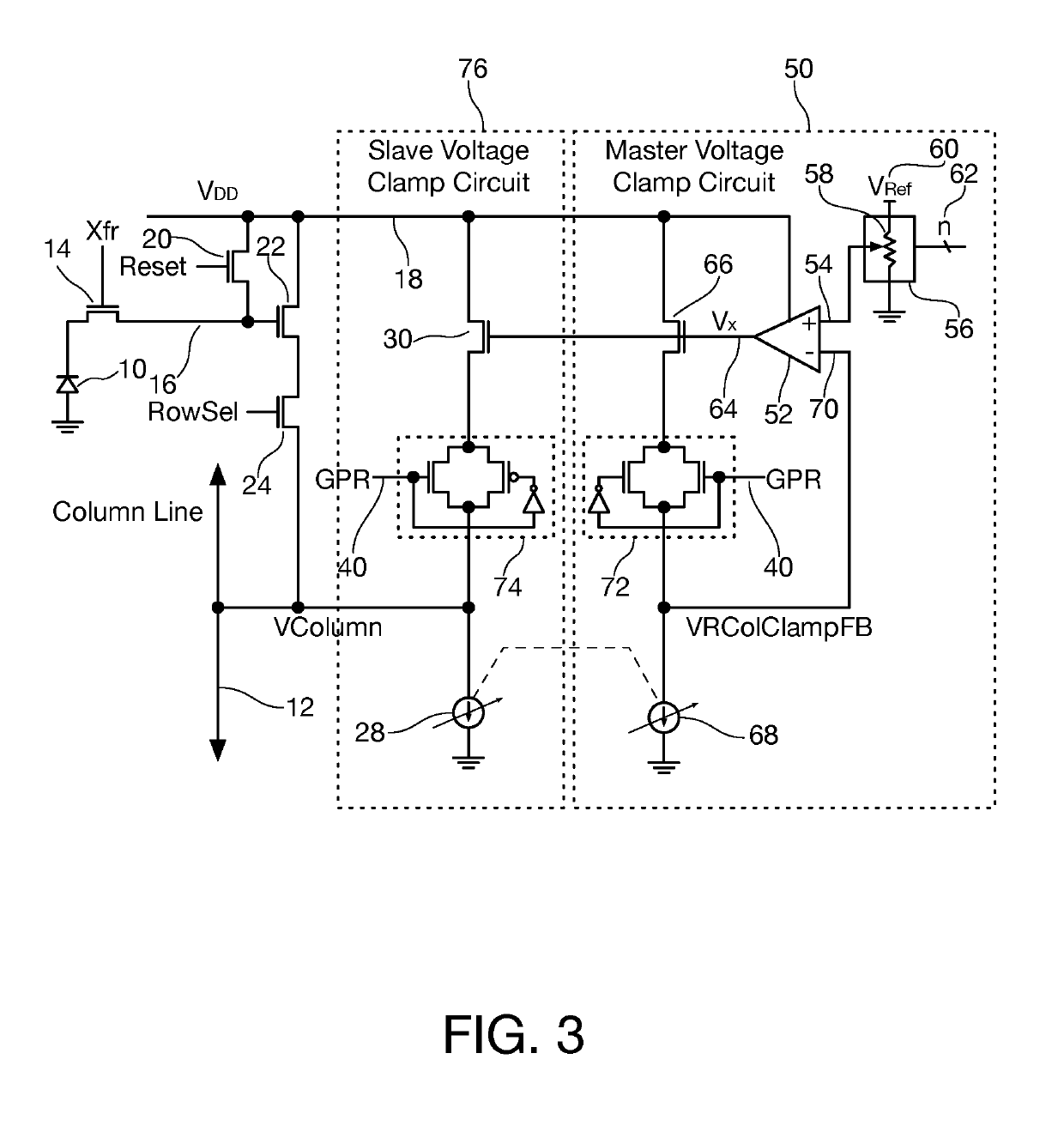
Column line clamp circuit
ActiveUS20180176497A1Closer matchIncrease exposure and brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVoltage referenceEngineering
In an imaging array having a plurality of pixel sensors arranged in a plurality of rows and columns, pixel data being read out on column lines of the array, a column line voltage clamp circuit for column lines of the array includes a master voltage clamp circuit coupled to provide a reference voltage clamp level on a reference node, and a slave voltage clamp circuit coupled to each column line in the imaging array, each slave voltage clamp circuit configured to clamp voltage on the column line to a column voltage clamp level derived from the reference voltage level.
Owner:FOVEON
Three-stage transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105897206ADoes not lower the dominant pole-3dB wide bandwidthDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a three-stage transconductance amplifier design. The three-stage transconductance amplifier is characterized in that NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M3 / M4 / M5 / M6, PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M1 / M2 / M7 / M8 and a tail current source Iss form a folding input structure and a first stage; NMOS tubes M9 / M10 / M11 / M12 and PMOS tubes M13 / M14 form a second stage; an NMOS tube M15 and a PMOS tube M16 form a third stage; NMOS tubes M17 / M18, PMOS tubes M19 / M20 and a capacitor Cc form a compensation structure; the input end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the second stage of the transconductance amplifier; and the output end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the transconductance amplifier. A power supply of the transconductance amplifier is vdd1, a power supply of the compensation structure is vdd2 and a capacitor CL represents a load capacitor of the transconductance amplifier. According to the three-stage transconductance amplifier, a left half plane zero is introduced into a product of a gain A of a gain stage and the capacitor Cc, so that a dominant pole of a transmission function of the three-stage transconductance amplifier is not reduced, and the transconductance amplifier is guaranteed to have relatively large -3dB bandwidth and unity-gain bandwidth.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
LDO circuit using bidirectional asymmetry buffer structure to improve performance
InactiveCN100549898CImprove stabilityImprove transient response performanceElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationParasitic capacitance
An LDO circuit that uses a bidirectional asymmetric buffer structure to improve performance. A bidirectional asymmetric buffer structure is used to provide a feedback path with a signal reverse function and a forward path with a signal same direction function. The feedback path is used to realize the frequency of the LDO circuit. To compensate and improve the transient response performance, the forward path is used to offset the right half-plane zero point generated by the gate-drain parasitic capacitance of the LDO transmission element, thereby improving the stability of the system and expanding the unity gain bandwidth. The circuit has the advantages of simple structure, low power consumption, and can effectively eliminate the zero point of the right half plane.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
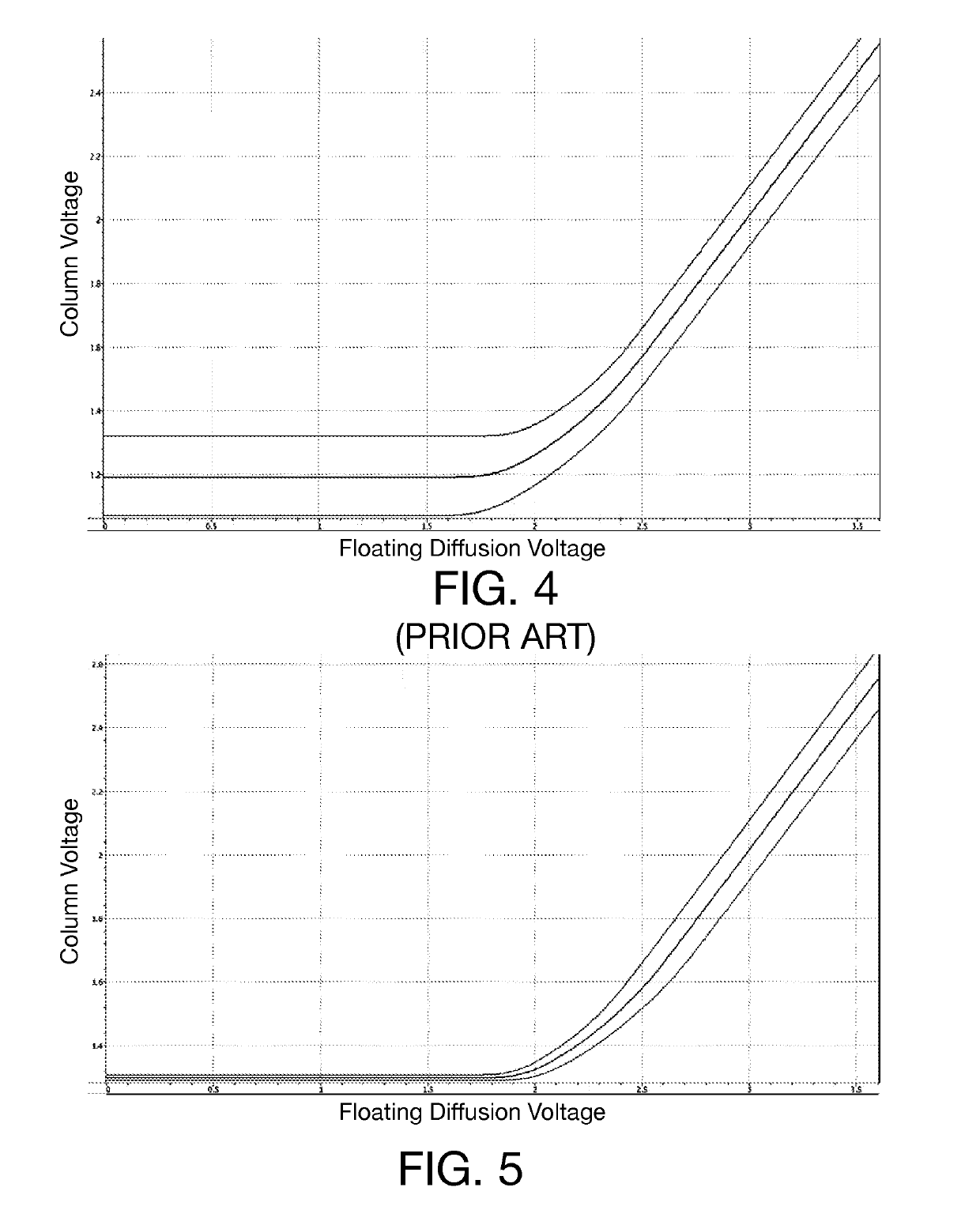
Column line clamp circuit for imaging array
ActiveUS10523885B2High precisionIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOn columnVoltage reference
Owner:FOVEON
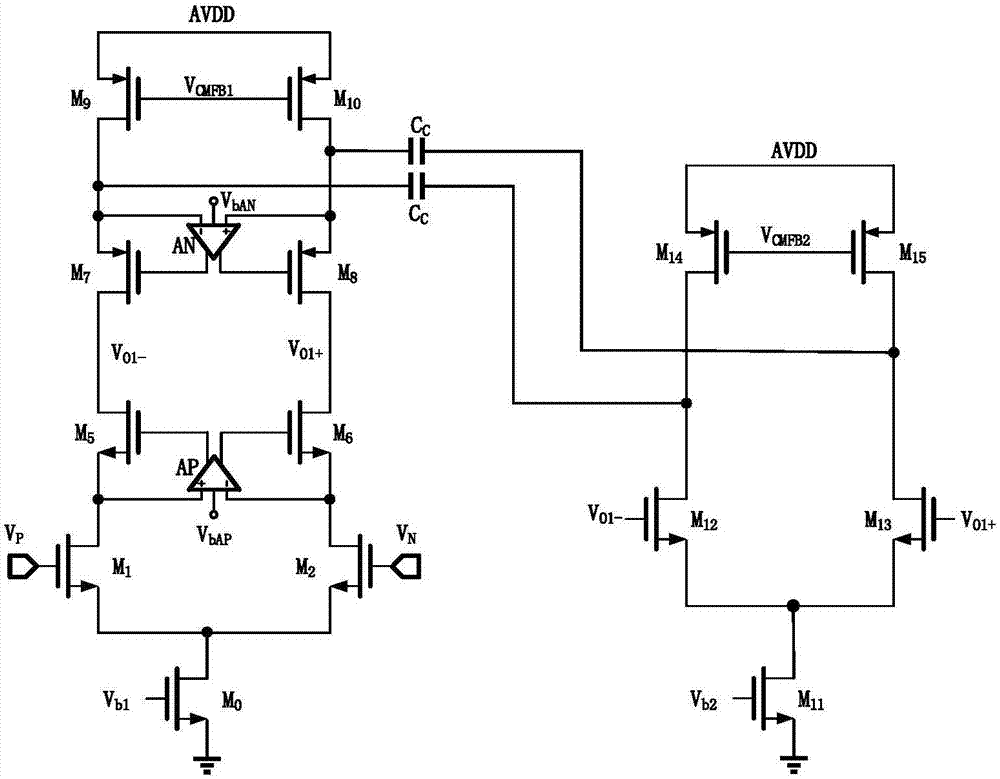
Continuous-time Common-Mode Feedback Circuit for High-Speed Fully Differential Operational Amplifiers
ActiveCN103354443BHigh gainIncreased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthControl circuitCommon mode feedback
The invention provides a CTCMFB circuit applied to a high-speed fully differential operational amplifier. The CTCMFB circuit comprises a common-mode voltage detection circuit, an error amplifier and a common-mode feedback control circuit, wherein the common-mode voltage detection circuit is used for detecting common-mode voltage output by the high-speed fully differential operational amplifier; the error amplifier is used for amplifying a comparison result of the common-mode voltage and expected common-mode voltage; the common-mode feedback control circuit is used for regulating the high-speed fully differential operational amplifier; the high-speed fully differential operational amplifier, the common-mode voltage detection circuit, the error amplifier and the common-mode feedback control circuit are mutually connected; and the error amplifier provides two channels of different output signals for the common-mode feedback control circuit so as to control the output common-mode voltage of the high-speed fully differential operational amplifier. The CTCMFB circuit applied to the high-speed fully differential operational amplifier has the advantages as follows: the structure is simple, the common-mode feedback loop gain is high, and the unity-gain bandwidth is large.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Preamplifier with an adjustable bandwidth
InactiveUS6175275B1Increased GSIncreased unity-gain bandwidthTelevision system detailsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierControl signal
A preamplifier includes an output stage having a bandwidth which is adjustable by a control signal. The output stage includes an amplifier with an adjustable bandwidth. The amplifier includes a main input for receiving an input current, a main output for providing an output voltage, a resistor connected between the main input and output. A current amplifier with an adjustable gain is connected for receiving the input current. A capacitor is connected between an output of the current amplifier and the main output. An inverting transconductance circuit is connected between the output of the current amplifier and the main output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Split Compensation Two-Stage Operational Amplifier Based on Inverter Input Structure
InactiveCN103199807BInhibition effectOffset the impactDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceFrequency compensation
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics and relates to the frequency compensation technology of operational amplifiers in analog integrated circuits. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier comprises a two-stage operational amplifier. A first-stage operational amplifier is composed of N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tubes (M1N, M2N, M3 and M4) and P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tubes (M1P, M2P and M0). A second-stage operational amplifier is composed of a PMOS tube M5P and an NMOS tube M5N. A traditional Miller capacitor is divided into a Cm1 portion and a Cm2 portion to finish frequency compensation of the operational amplifier. A first frequency compensation capacitor Cm1 is connected with the position between the output end of the first operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. A second frequency compensation capacitor Cm2 is connected with the position between a connection point of a source of the NMOS tube M2N and a drain of the NMOS tube M4 in the first-stage operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier has strong robustness and higher unit grain bandwidth and output slew rate due to the fact that non-dominant poles and stray parameter are not related.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A two-stage operational amplifier
InactiveCN103633954BIncrease the multiplication factorHigh gainDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
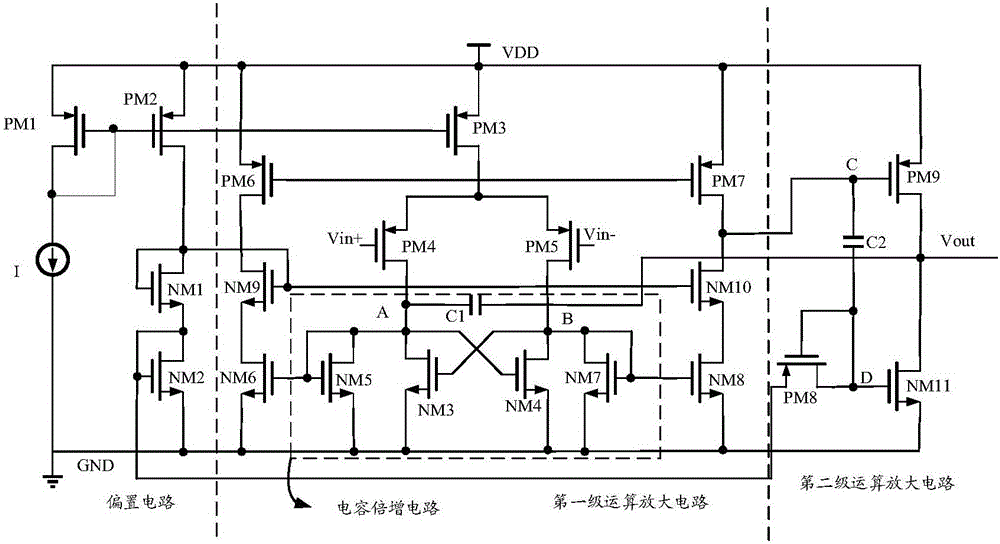
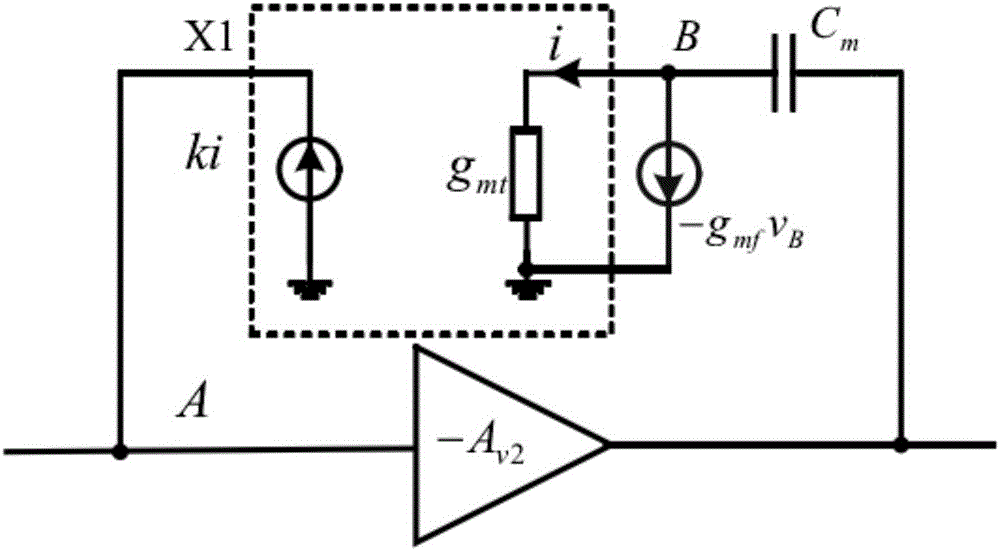
The invention relates to electronic circuit technology, in particular to the frequency compensation technology of operational amplifiers in analog integrated circuits. A two-stage operational amplifier according to the present invention includes a bias circuit, a first-stage amplifying circuit, and a second-stage amplifying circuit connected in sequence, and is characterized in that the first-stage amplifying circuit includes a capacitance multiplication module, and the The capacitance multiplying module is composed of a current-controlled current source and a voltage-controlled current source. The invention has the beneficial effects of increasing the capacitance multiplication factor, reducing the required compensation capacitance, saving chip area, not requiring an additional bias circuit, improving the gain and unity gain bandwidth of the operational amplifier, and simultaneously reducing systemic imbalance. The invention is particularly applicable to two-stage operational amplifiers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
ldo circuit with dynamic compensation and fast transient response
ActiveCN107797599BGuaranteed stabilityImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationLinear regionParasitic capacitance
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of analog integrated circuits, in particular to an LDO circuit with dynamic compensation and rapid transient response. The circuit comprises an input stage, a multi-loop gain stage, an output stage and a load stage. By introducing the dynamic bias mode, gain of the input stage, C1 in the multi-loop gain stage and a pole-zero doublet introduced by an MOS resistor RMN3 working in a deep linear region are related to load current ILoad, and the stability of loops within the whole load range is ensured. Meanwhile, due to the dynamic bias mode, the unity-gain bandwidth of the input stage becomes larger, and the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit is increased. In addition, MP6 and MN11 adopted in the multi-loop gain stage, sothat discharging of charges on an output cavity can be accelerated, and the circuit response speed during hopping from heavy load to light load is increased. Due to the MN9, discharging of charges ona power tube MP7 grid stray capacitor can be accelerated, and the response speed of the circuit during hopping from light load to heavy load is increased.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
An Operational Amplifier for Pipelined Analog-to-Digital Converters
ActiveCN107888194BImprove output swingHigh bandwidthAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceConverters
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A three-stage transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105897206BDoes not lower the dominant poleAchieve mutual cancellationDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a three-stage transconductance amplifier design. The three-stage transconductance amplifier is characterized in that NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M3 / M4 / M5 / M6, PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M1 / M2 / M7 / M8 and a tail current source Iss form a folding input structure and a first stage; NMOS tubes M9 / M10 / M11 / M12 and PMOS tubes M13 / M14 form a second stage; an NMOS tube M15 and a PMOS tube M16 form a third stage; NMOS tubes M17 / M18, PMOS tubes M19 / M20 and a capacitor Cc form a compensation structure; the input end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the second stage of the transconductance amplifier; and the output end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the transconductance amplifier. A power supply of the transconductance amplifier is vdd1, a power supply of the compensation structure is vdd2 and a capacitor CL represents a load capacitor of the transconductance amplifier. According to the three-stage transconductance amplifier, a left half plane zero is introduced into a product of a gain A of a gain stage and the capacitor Cc, so that a dominant pole of a transmission function of the three-stage transconductance amplifier is not reduced, and the transconductance amplifier is guaranteed to have relatively large -3dB bandwidth and unity-gain bandwidth.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105915188AIncrease the dominant pole frequencyIncrease the capacitance of the compensation capacitor to reduce the dominant pole frequencyDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthTransistor arrayCapacitance
The present invention provides a transconductance amplifier comprising an input circuit, a gain circuit and an output circuit which are successively connected. The gain circuit comprises a MOS transistor array composed of a plurality of MOS transistors, grids of the corresponding MOS transistors between every two adjacent columns of the MOS transistor array are connected, the MOS transistors in each column of the MOS transistors are successively connected, and compensation capacitors are arranged between asymmetrical connection points of the MOS transistors in the output column of the MOS transistor array and an output terminal of the output circuit. According to the transconductance amplifier, compared with a traditional frequency compensation technology, dominant pole frequency of the transconductance amplifier can be reduced through increasing capacitance values of the compensation capacitors, right half plane zero frequency of the transconductance amplifier can also be prevented from being reduced, so that a distance between the dominant pole frequency and the right half plane zero frequency of the transconductance amplifier can be increased, the influence of frequency compensation on frequency characteristics of the transconductance amplifier can be reduced, unity-gain bandwidth of the transconductance amplifier can be improved, and the problem that the transconductance amplifier is possibly unstable can be solved.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Signal amplification frequency compensation circuit applicable to RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader
InactiveCN106849883AIncrease slew rateIncreased unity-gain bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceFrequency compensation
The invention discloses a signal amplification frequency compensation circuit applicable to an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader. The signal amplification frequency compensation circuit comprises a bias circuit, a first stage operational amplifier circuit and a second stage operational amplifier circuit; the bias circuit is used for providing a temperature independent stable voltage for the first stage operational amplifier circuit and the second stage operational amplifier circuit to work; the first stage operational amplifier circuit is used for receiving a signal frequency to be amplified, performing first operation amplification processing on the signal frequency to be amplified, and acquiring a first amplified signal frequency; and the second stage operational amplifier circuit is used for performing second operation amplification processing on the first amplified signal frequency, acquiring an amplified signal frequency, and outputting the amplified signal frequency. In the embodiment of the invention, a capacitance multiplication technology with a voltage-controlled current source is designed, which improves the unity gain bandwidth and meanwhile reduces the offset voltage and obtains a greater slew rate, so as to make a loop more stable, reliable and accurate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SYSUR MICROELECTRONICS +1
transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105915188BIncrease the dominant pole frequencyIncrease the capacitance of the compensation capacitor to reduce the dominant pole frequencyDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthTransistor arrayCapacitance
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Frequency-compensated transconductance amplifier
ActiveUS10181821B2Improve amplitude-frequency characteristic curveIncreased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Method for optimizing integrated circuit of analog operational amplifier
InactiveCN101714176BReduced Power RequirementsHigh DC GainGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAnalog circuit designCircuit performance
The invention discloses a method for optimizing an integrated circuit of an analog operational amplifier. The method has the advantages that according to the principle and requirement of an analog integrated circuit to be designed, the method can automatically design technical parameters and circuit parameters free from design parameters and the number of optimized targets by applying an intelligent optimized searching method of a Q-deviant immune network, can automatically search and find the optimal technical parameters and circuit parameters meeting the requirements of analog circuit performance indexes in a range of set values, namely meeting the requirements of high direct current gain, unit gain bandwidth, conversion velocity and low power consumption, and provides good foundation and accordance for high-performance analog integrated circuit technological design. Furthermore, the method is applicable to various analog circuit designs, is easy for transplanting, and has wide applicability and high universality.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
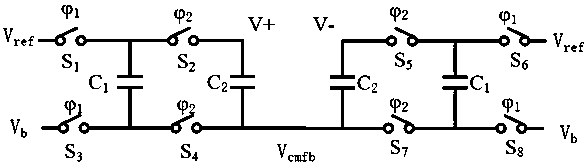
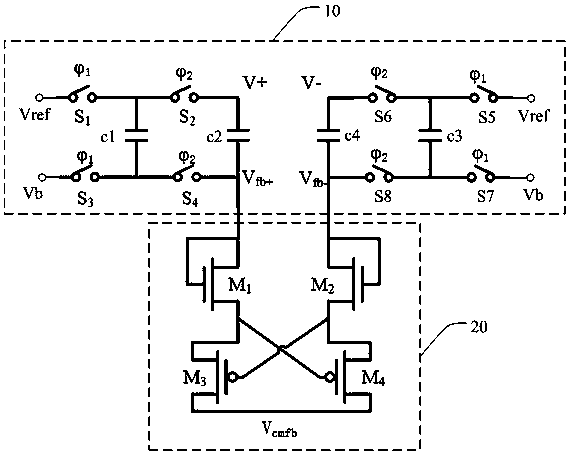
A Low Ripple Switched Capacitor Common Mode Feedback Circuit
ActiveCN105391409BSmall voltage rippleImprove output accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
An Active Feedforward Circuit Constitutes a Frequency Compensated Differential Operational Amplifier
ActiveCN104270107BLimiting Unity Gain Bandwidth IssuesIncreased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsCapacitanceNegative feedback
The invention relates to a differential operational amplifier by using active feed-forward circuit for frequency compensation, and mainly solves the technical problems that the zero pole separation of a multistage differential operational amplifier is caused as the current Miller frequency compensation method introduces Miller capacitance, and further unity-gain bandwidth of the differential operational amplifier is limited. According to the technical scheme, the differential operational amplifier comprises a first gain stage, a second gain stage and an active feed-forward amplification stage, wherein each of the first gain stage and the second gain stage comprises a first input node and a second input node; the active feed-forward amplification stage is composed of a circuit A (a control node is coupled to the first input nodes, and a control path is coupled to a second output node;) and a circuit B (a control node is coupled to the second input nodes, and a control path is coupled to a first output node;). The differential operational amplifier further comprises a common-mode negative feedback circuit, wherein the common-mode negative feedback circuit is composed of a high gain stage and an active feed-forward amplification stage. The unity-gain bandwidth performance of the fully differential operational amplifier can be effectively improved, and chip implementation area is reduced.
Owner:南京英锐创电子科技有限公司
Three-Stage Operational Amplifier Based on Damping Factor Frequency Compensation and DC Offset Cancellation
ActiveCN109309481BIncreased unity-gain bandwidthSuppress spike effectAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceDamping factor
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A Transconductance Amplifier Based on Self-biased Cascode Structure
ActiveCN105720936BIncrease DC GainIncreased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierReference current
The present invention provides a transconductance amplifier based on a self-biased cascode structure, which includes a self-biased cascode input stage structure composed of PMOS input transistors M1, M2, M3 and M4, and NMOS transistors M5, M6 and M7 The self-biased cascode first-stage load structure composed of M8, the second-stage common-source amplifier structure composed of NMOS transistor M9 and PMOS transistor M10, the bias circuit structure composed of NMOS transistors M11, M12 and PMOS transistor M13, The amplifier compensation capacitor CC, the amplifier load capacitor CL, the reference current source Iref and the PMOS transistor M0 that provides the constant current source function. The invention also provides a self-biased cascode transconductance amplifier using an NMOS transistor as an input transistor. Both the input tube and the load tube of the first-stage amplifier of the present invention adopt a self-biased cascode structure, which improves the output impedance of the first-stage amplifier and increases the DC gain of the first-stage amplifier; the MOS of the first-stage amplifier The substrate voltage of the tube is provided by the amplifier bias circuit; the connection mode of the compensation capacitor Cc realizes a higher quality factor.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com