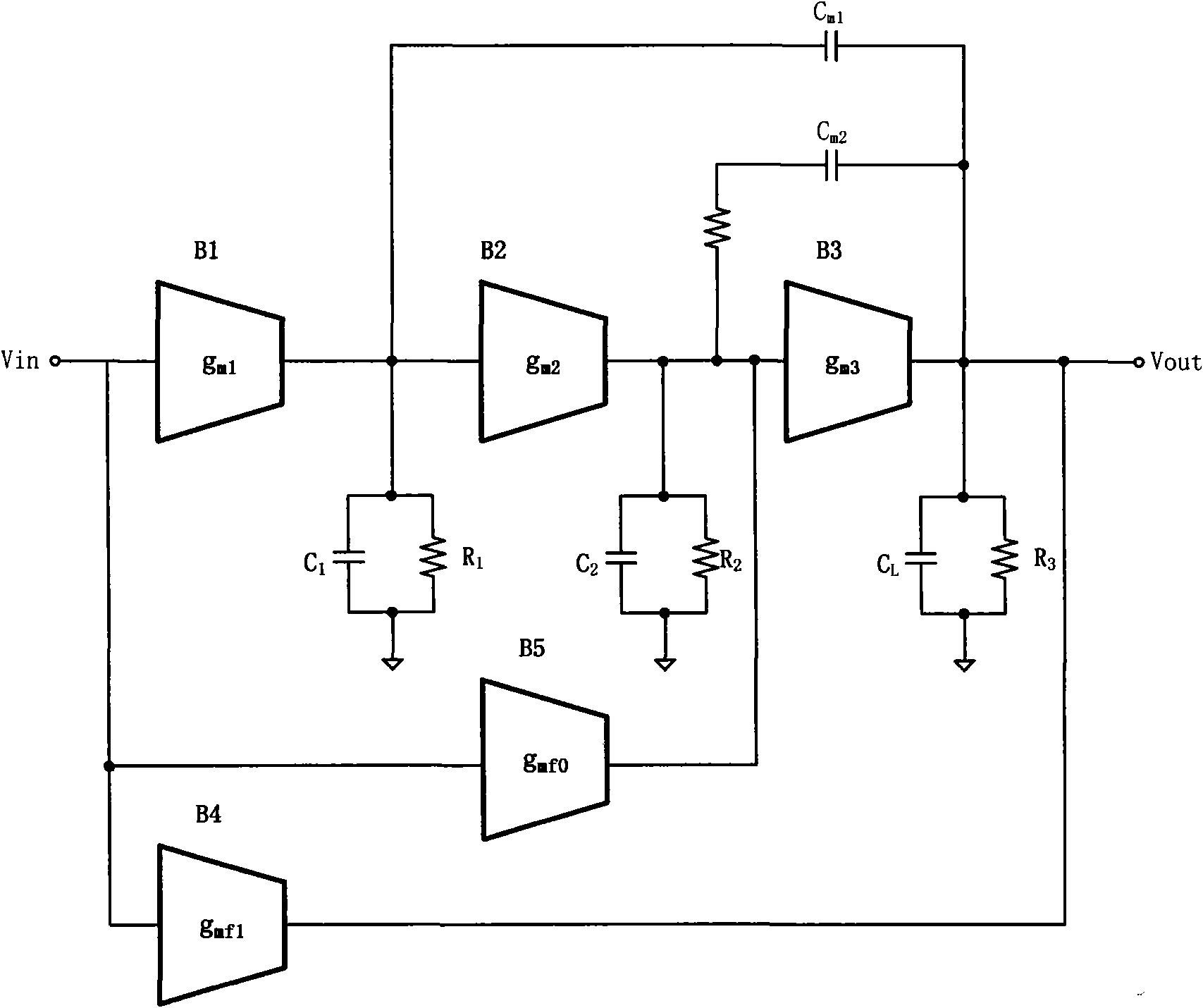
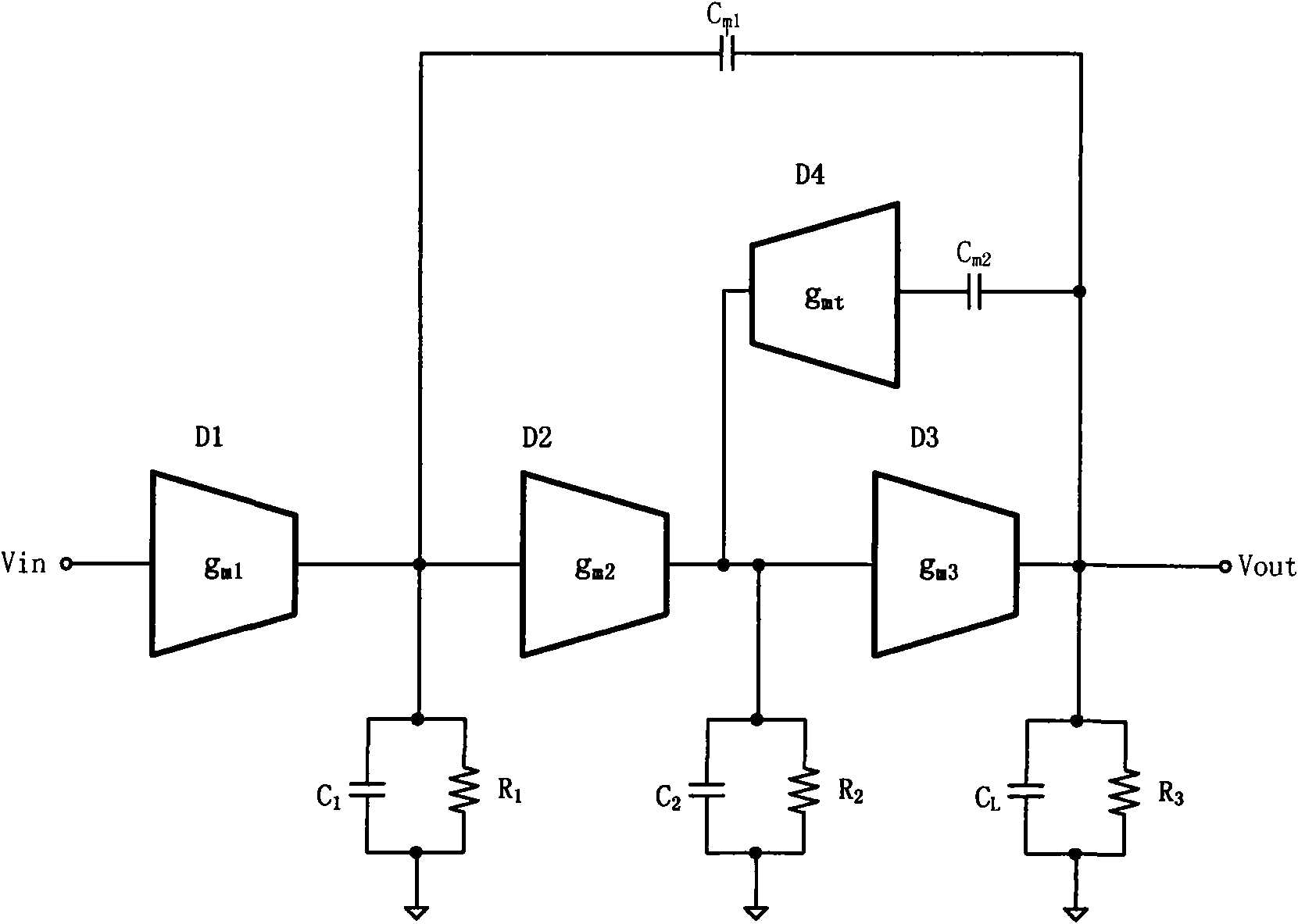
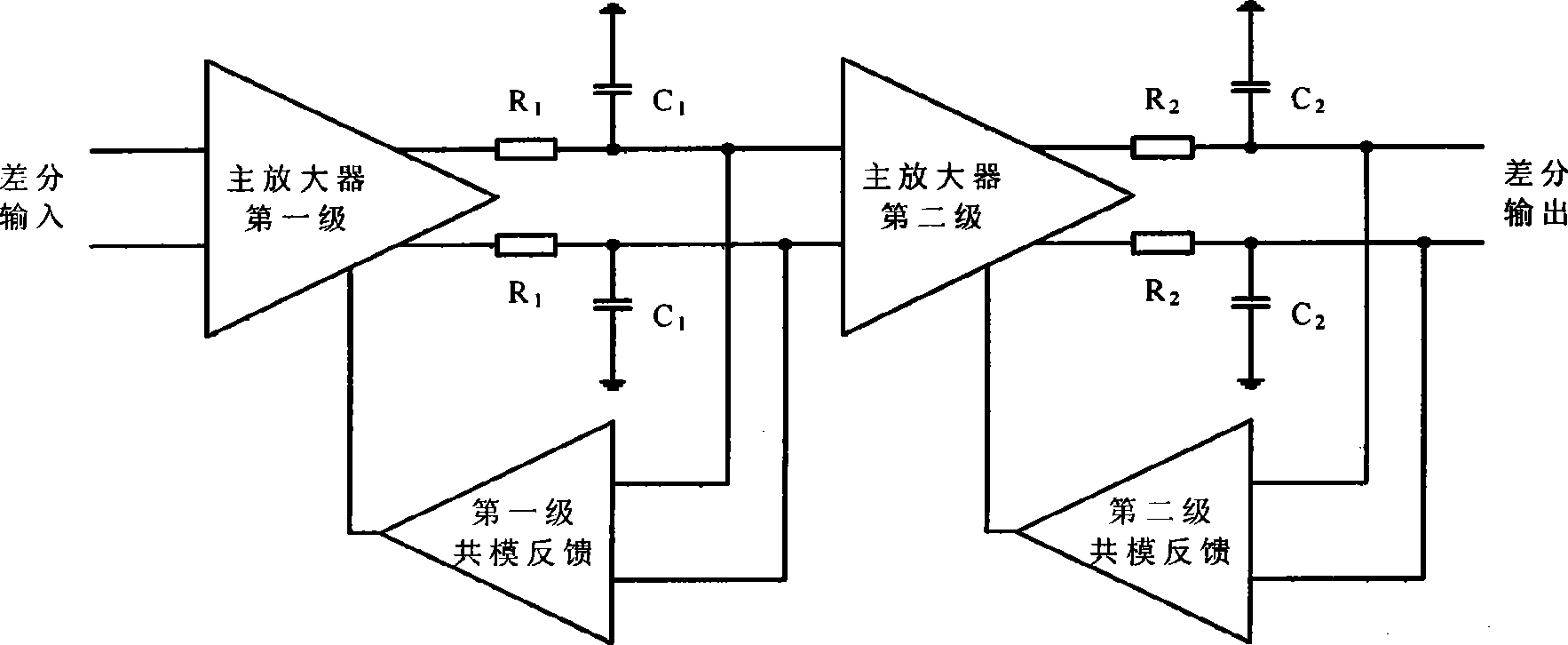
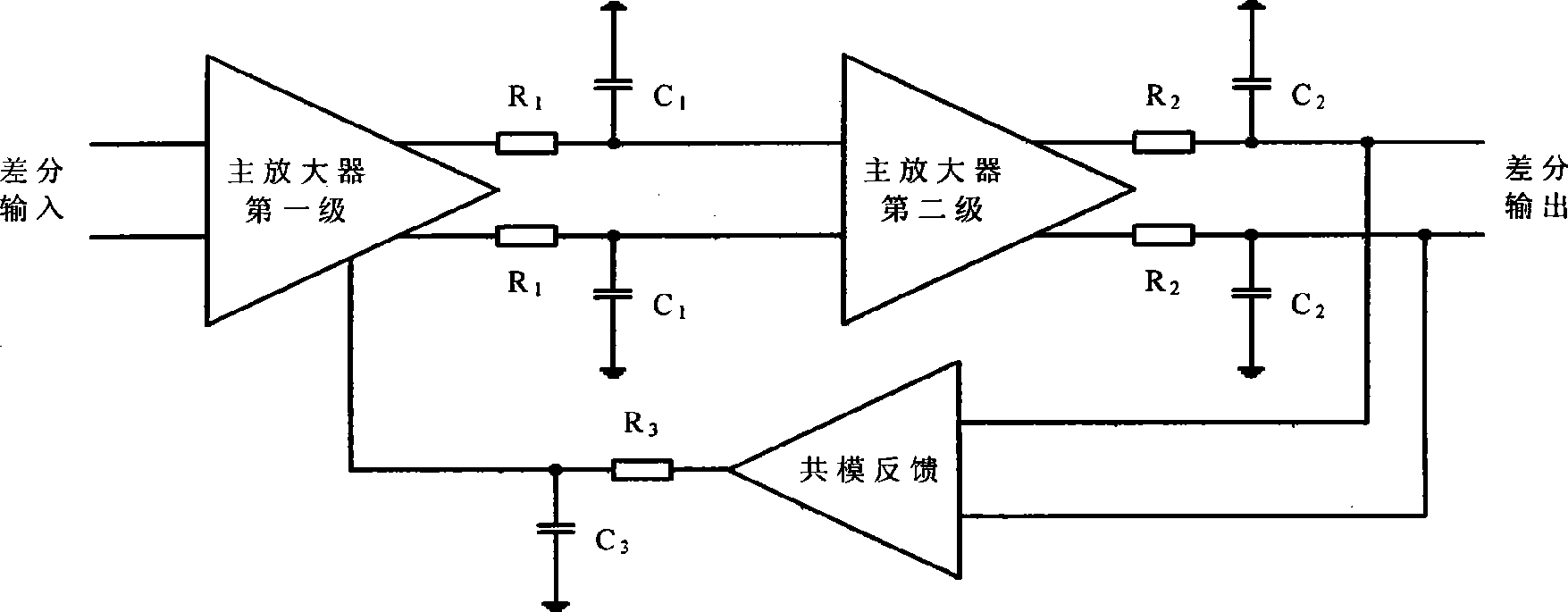
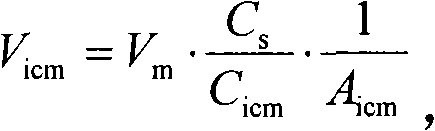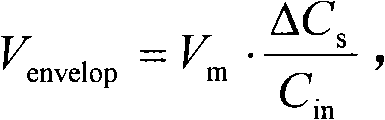Patents
Literature
450 results about "Common mode feedback" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for dynamic insertion loss control for 10/100/1000 mhz ethernet signaling
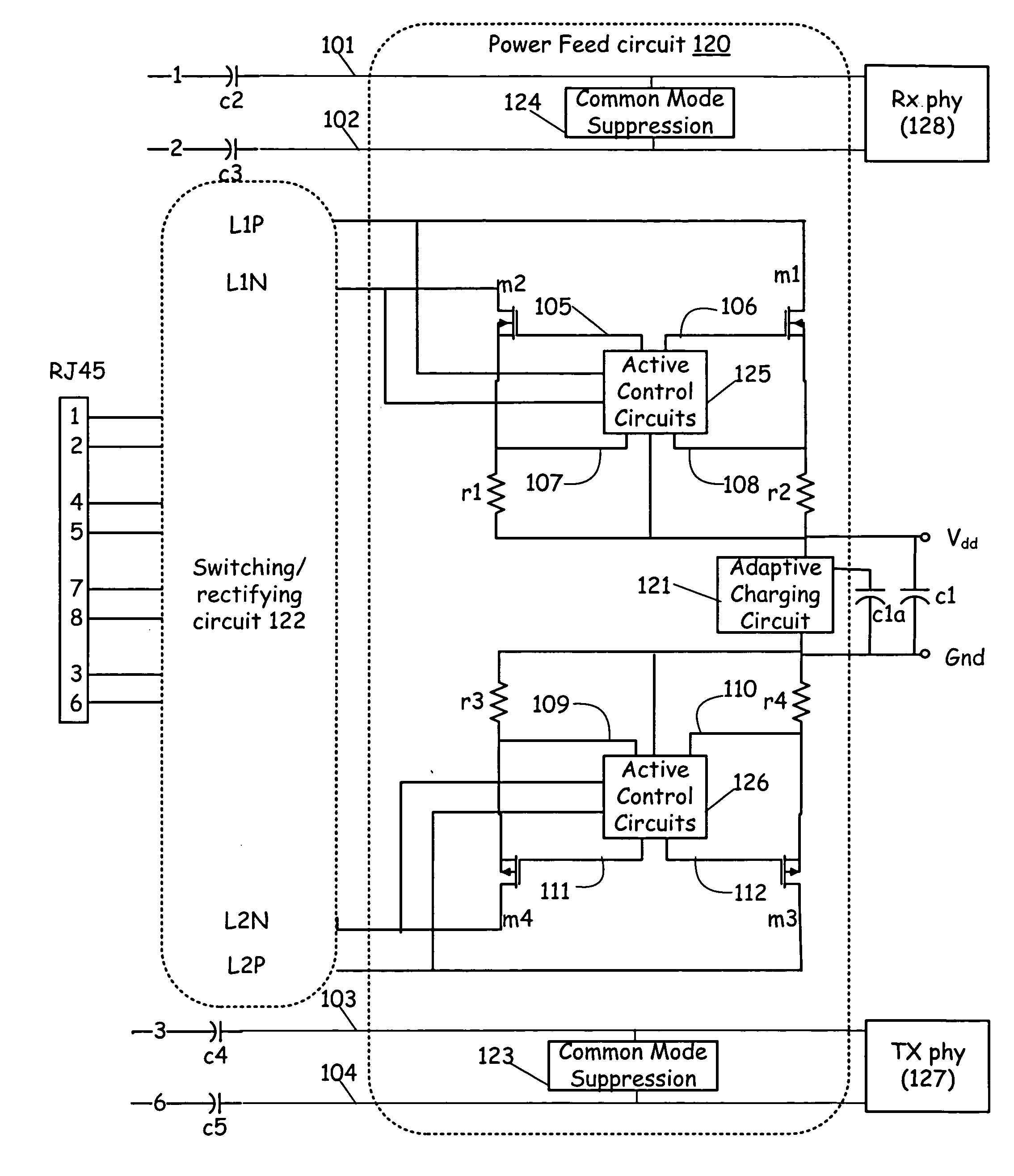
ActiveUS20060238250A1Suppression of insertion lossReduced insertion lossResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital data processing detailsNetworking protocolNetwork connection
The present invention provides for dynamic insertion loss control for a 10 / 100 / 1000 megahertz Ethernet power on differential cable pairs. A power feed circuit supplies power to a network attached device (PD). An insertion loss control circuit limits power loss in a coupled power feed circuit. The insertion loss control circuit determines an insertion loss limit and senses an average power of the power signals to produce a common mode feedback signal to the power feed circuit. The insertion loss limit is determined for the received signals based on a differential RMS of the received Ethernet power signals as seen by a differential transistor pair. Alternatively, the insertion loss limit may be determined logically by the higher layers of the network protocol based on the AC differential portion of the network power signal. When the insertion loss limit is determined based on the differential RMS, the insertion loss control circuit is operable to automatically reduce the insertion loss based upon transmission losses experienced over the network connection between the power sending equipment and network-attached device.
Owner:KINETIC TECH INT HLDG LP
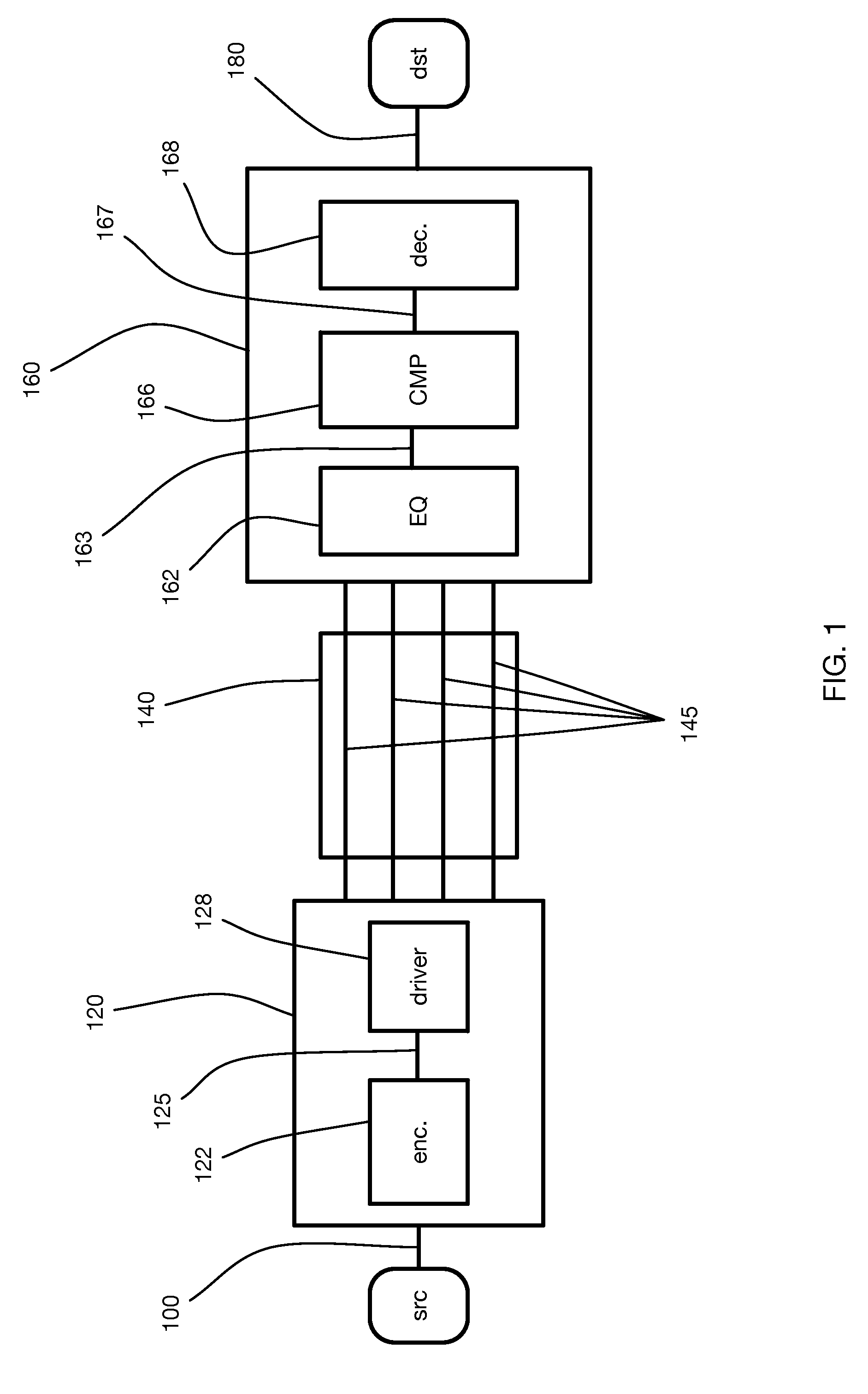
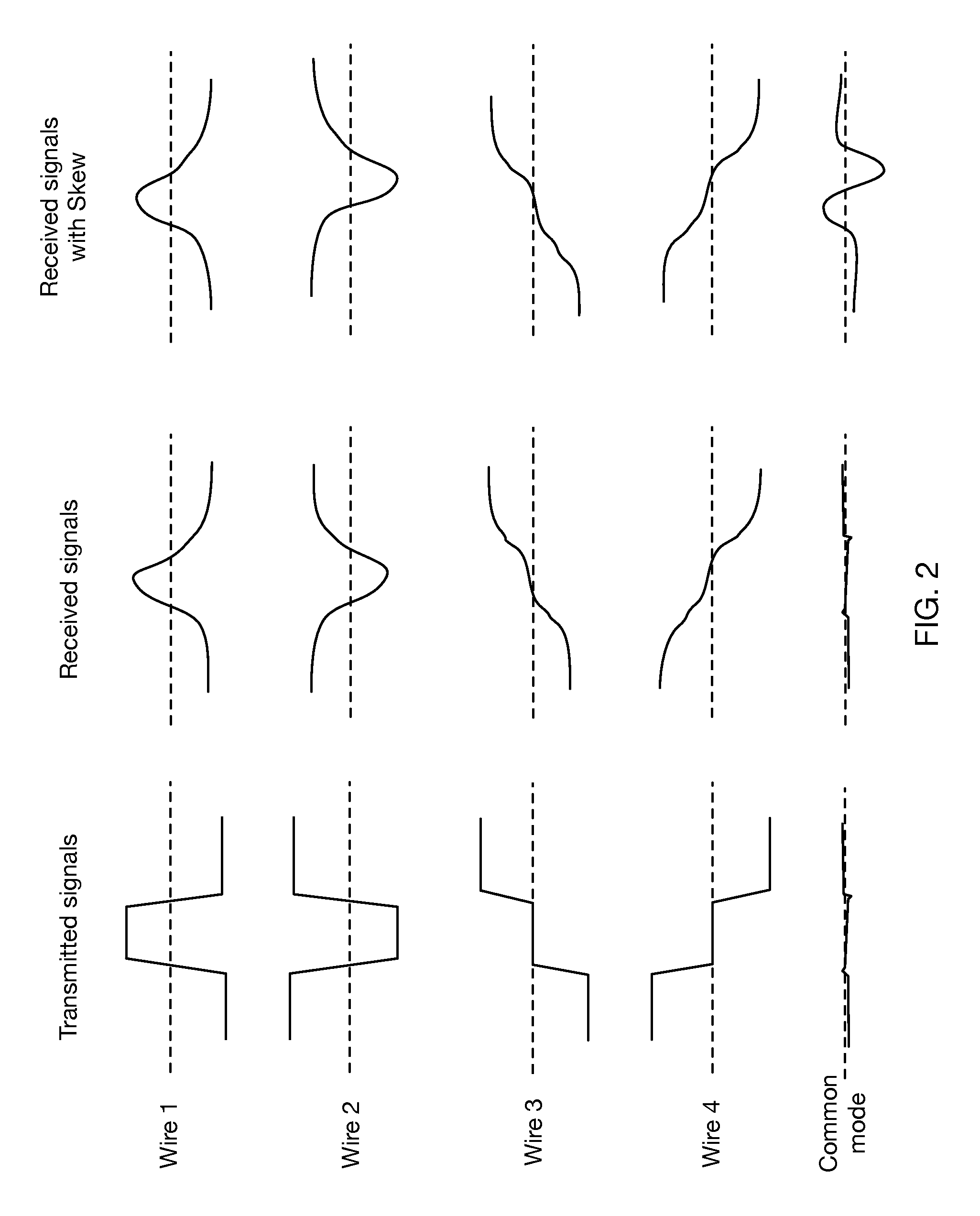
Multiwire linear equalizer for vector signaling code receiver
ActiveUS9106465B2Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersSignal onEqualization
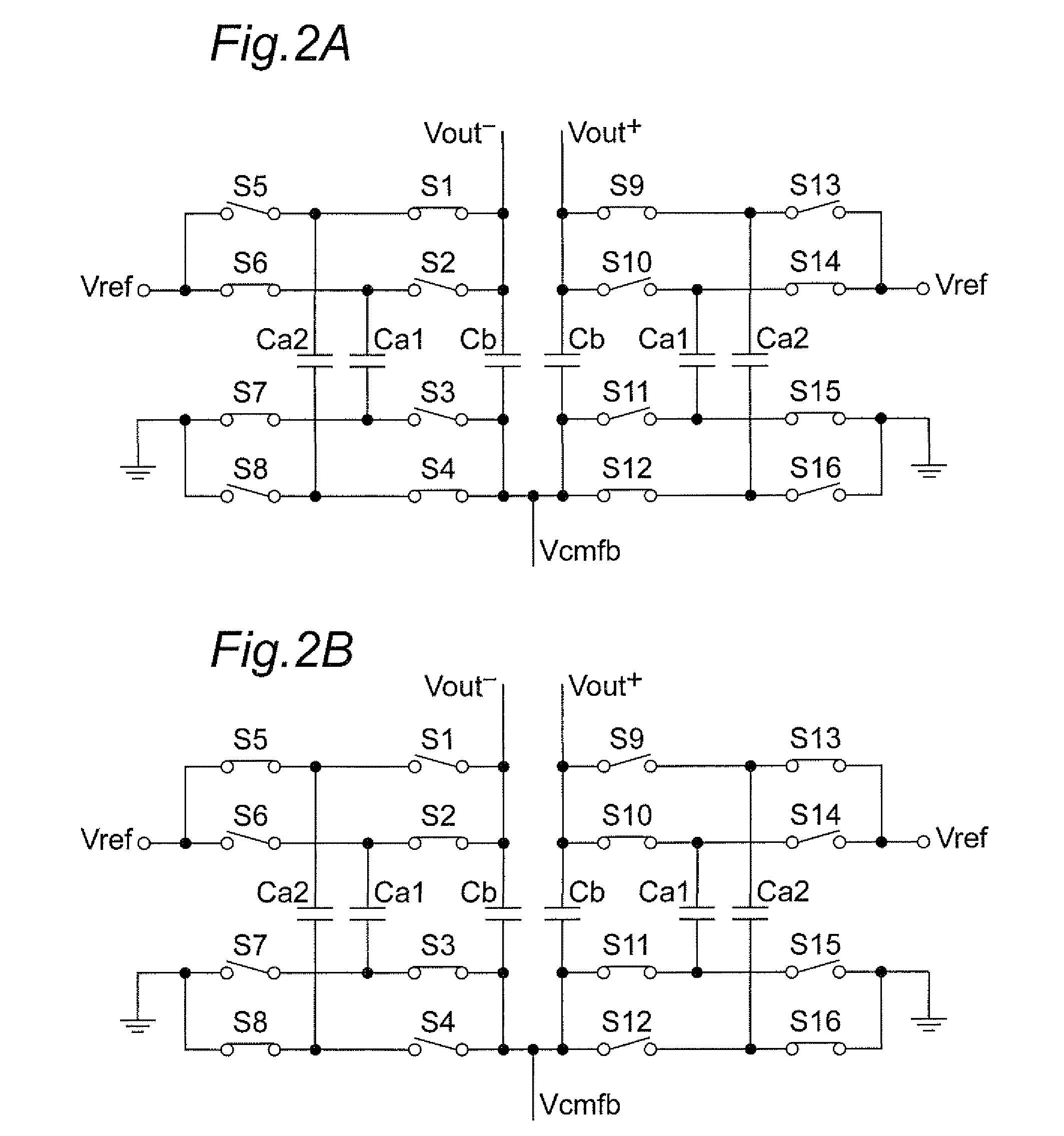
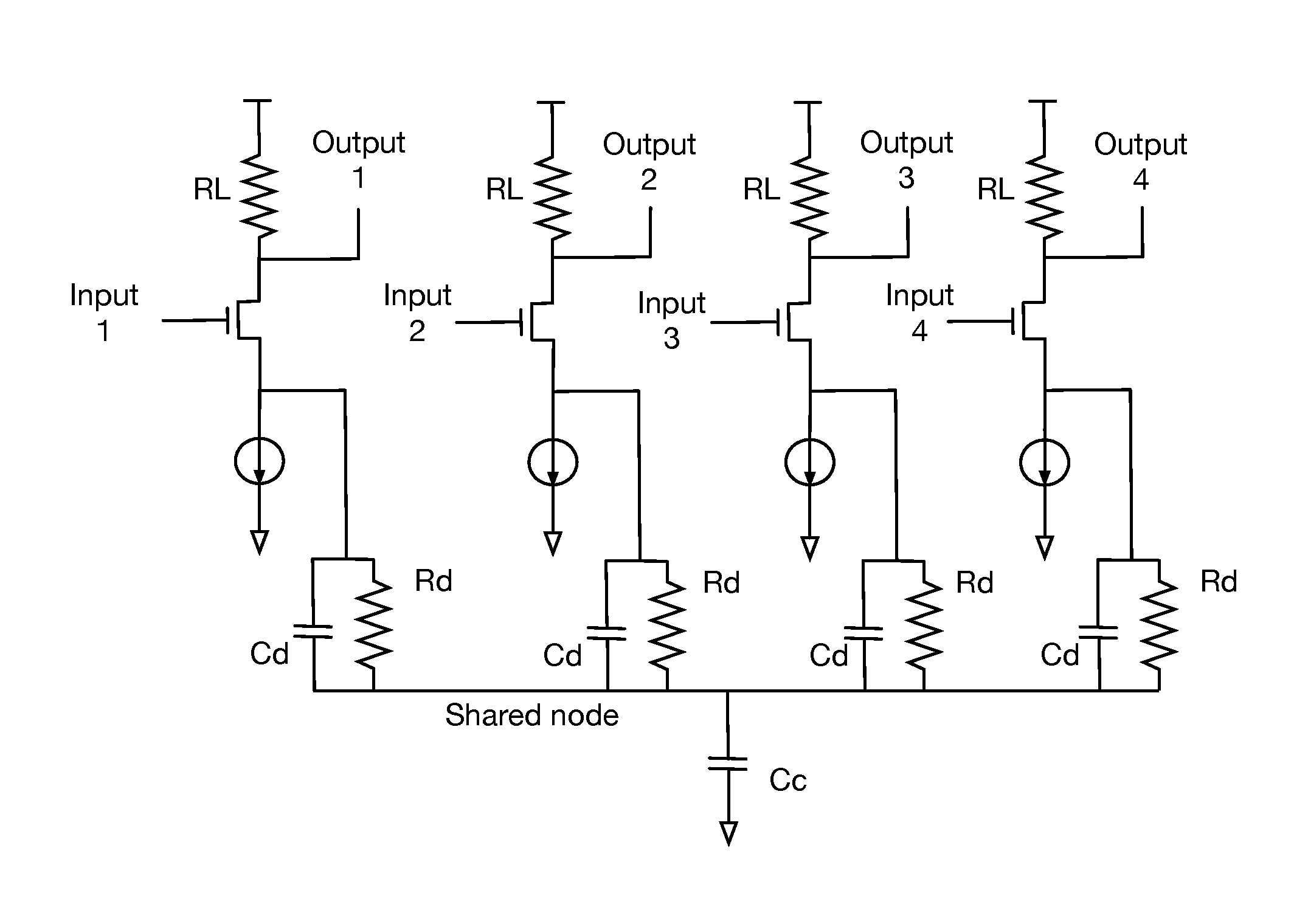
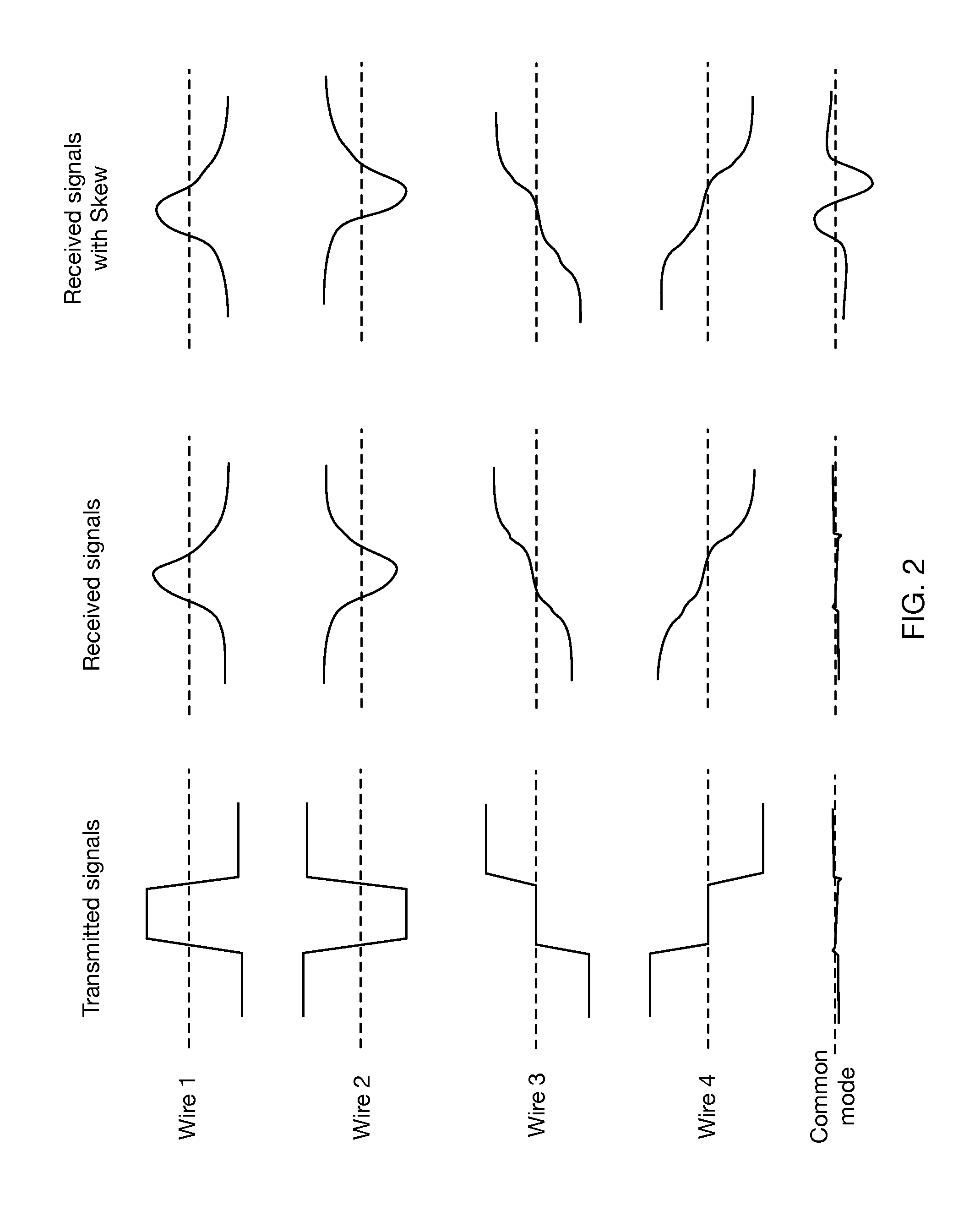
Continuous-time linear equalization of received signals on multiple wire channels while maintaining accurate common mode signal values. Multiwire group signaling using vector signaling codes simultaneously transmits encoded values on multiple wires, requiring multiple receive signals to be sampled simultaneously to retrieve the full transmitted code word. By misaligning transitions on multiple wires, skew introduces a transient common mode signal component that is preserved by using frequency-selective common mode feedback at the receiver to obtain accurate sampling results.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Discrete time amplifier circuit and analog-digital converter
ActiveUS20090115523A1Simple circuit configurationShorten convergence timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierA d converter
The present invention is intended to attain simplified circuit configuration and low current consumption in a discrete time amplifier circuit and an AD converter, to improve the convergence from the transient response state to the steady state of the amplifier circuit and to reduce noise and distortion owing to the variation in the output common-mode voltage. The discrete time amplifier circuit and the AD converter are provided with a switched-capacitor common-mode feedback (CMFB) circuit capable of detecting and feeding back the output common-mode voltage at every sampling timing in the case that the circuit operates at double sampling timing (every ½ cycle).
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Multiwire Linear Equalizer for Vector Signaling Code Receiver
ActiveUS20150146771A1Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsSignal onEqualization
Continuous-time linear equalization of received signals on multiple wire channels while maintaining accurate common mode signal values. Multiwire group signaling using vector signaling codes simultaneously transmits encoded values on multiple wires, requiring multiple receive signals to be sampled simultaneously to retrieve the full transmitted code word. By misaligning transitions on multiple wires, skew introduces a transient common mode signal component that is preserved by using frequency-selective common mode feedback at the receiver to obtain accurate sampling results.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Operational transconductance amplifier input driver for class D audio amplifiers
ActiveUS7068103B2Reduced turn-on “popping”Lower noise floor characteristicDifferential amplifiersDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorAudio power amplifierCoupling
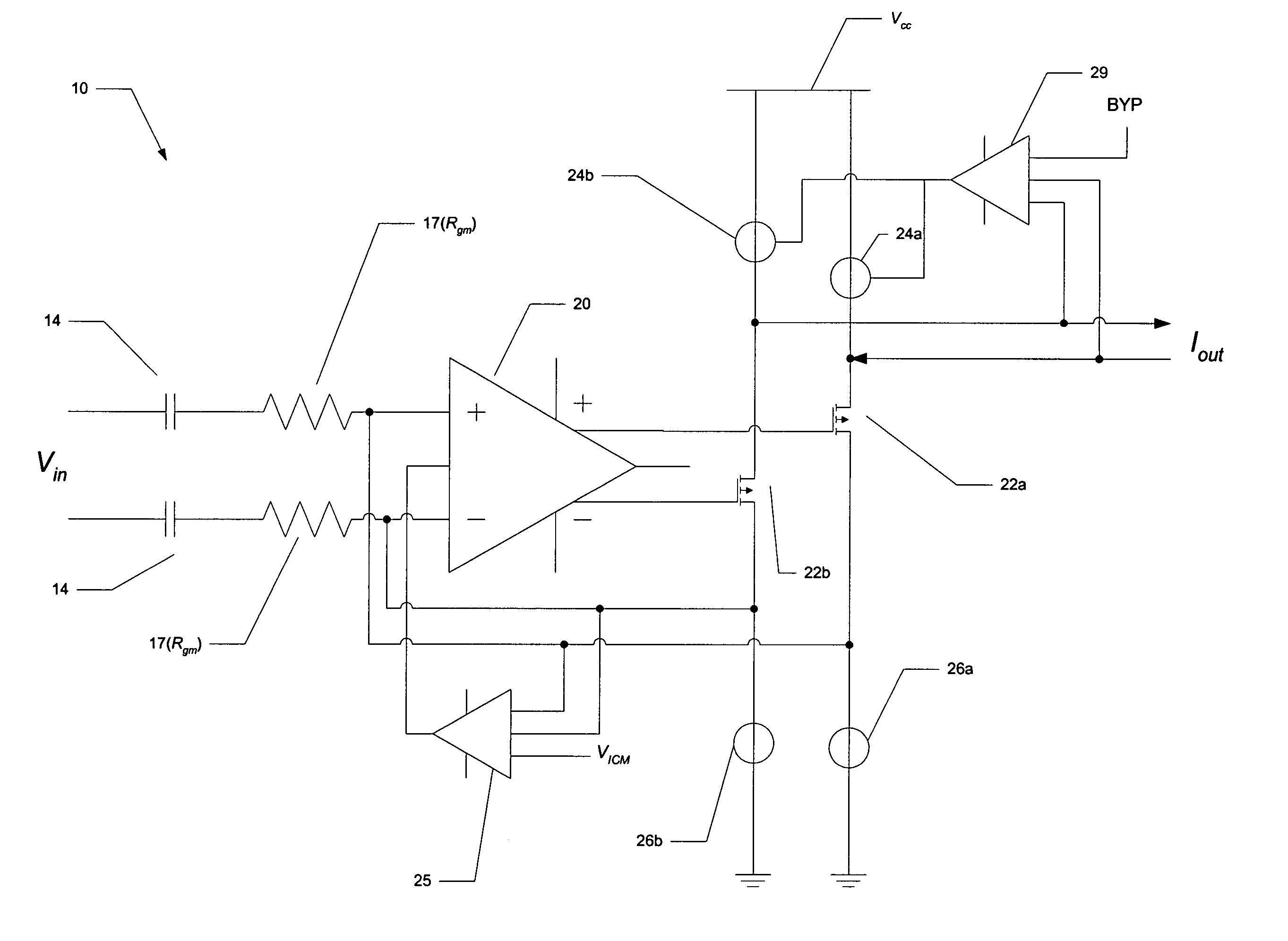
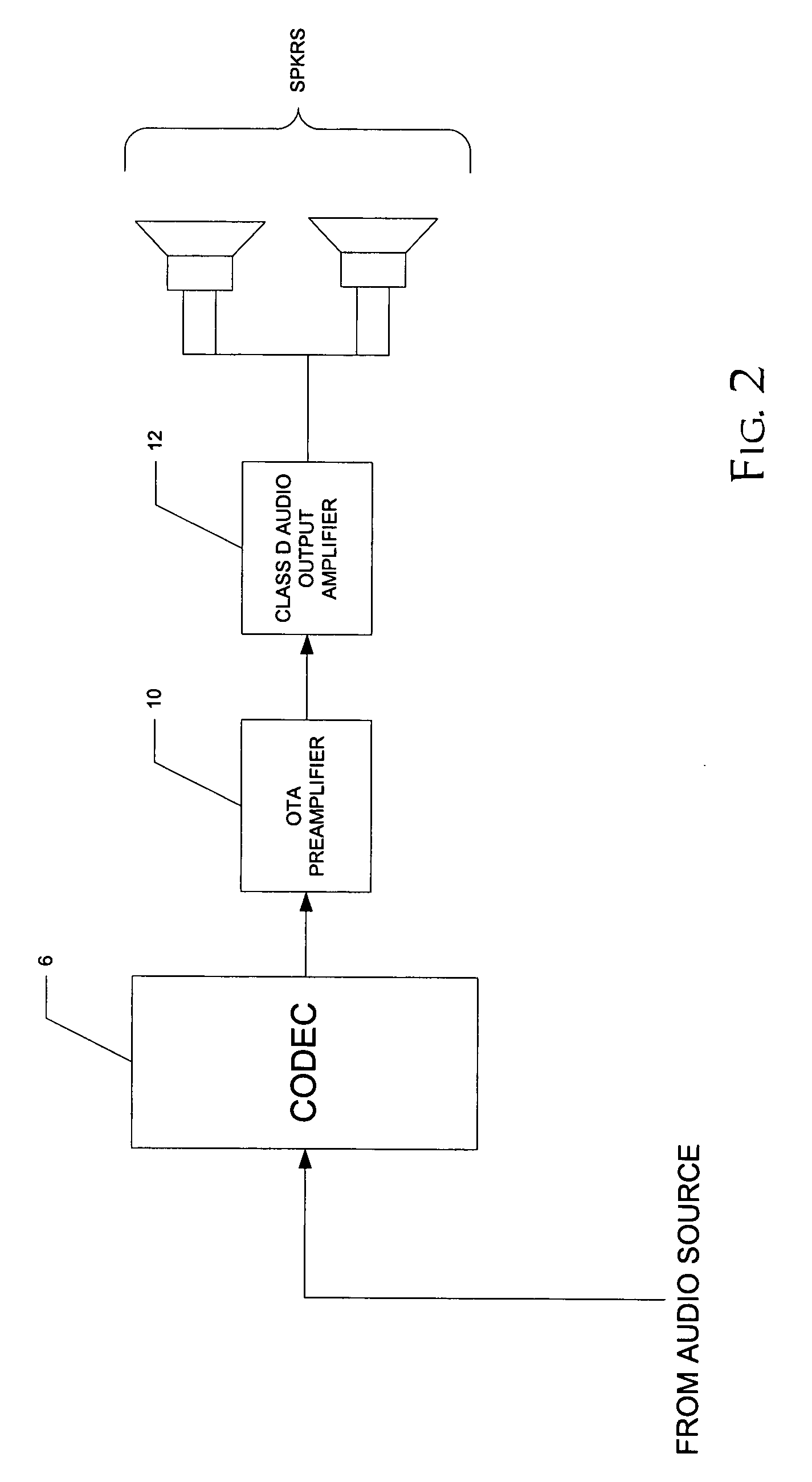
An audio preamplifier (10) based on an operational transconductance amplifier, in combination with a class D audio output amplifier (12) is disclosed. The input signal is coupled to the preamplifier (10) through a capacitor (14) in series with a resistor (17) that sets the transconductance of the preamplifier. The preamplifier (10) includes a differential operational amplifier (20) that drives output MOS transistors (22a, 22b), which are biased by current sources (24a, 26a; 24b, 26b). Feedback from the drain nodes of the output MOS transistors (22a, 22b) to the inputs of the differential operational amplifier (20), along with the series capacitor (14) and resistor (17) input coupling, ensures minimum offset voltage and current at the output of the preamplifier (10). Common mode feedback control amplifiers (25, 29) ensure proper bias of the components into the saturation region.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low drop-out voltage regulator with common-mode feedback
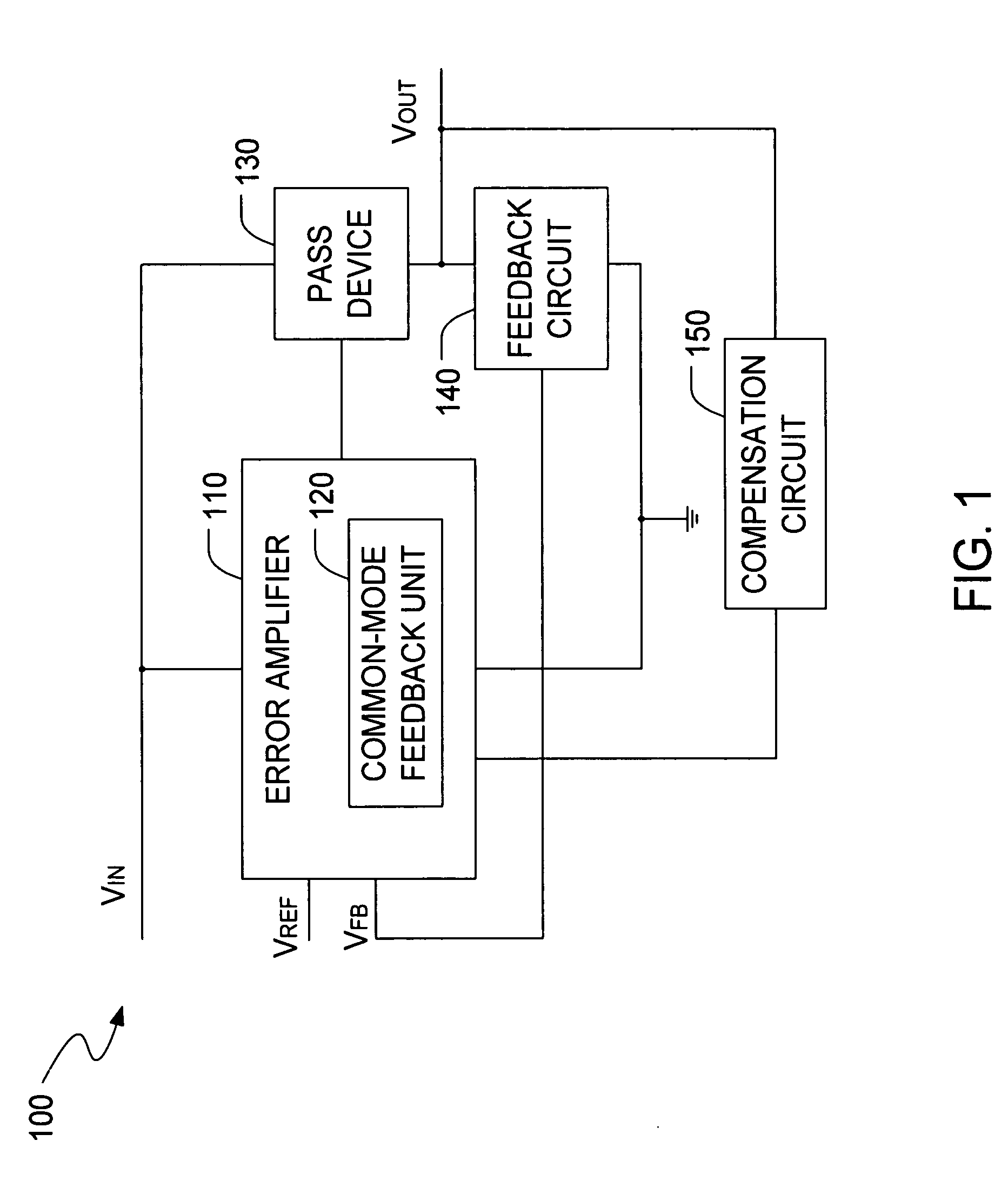
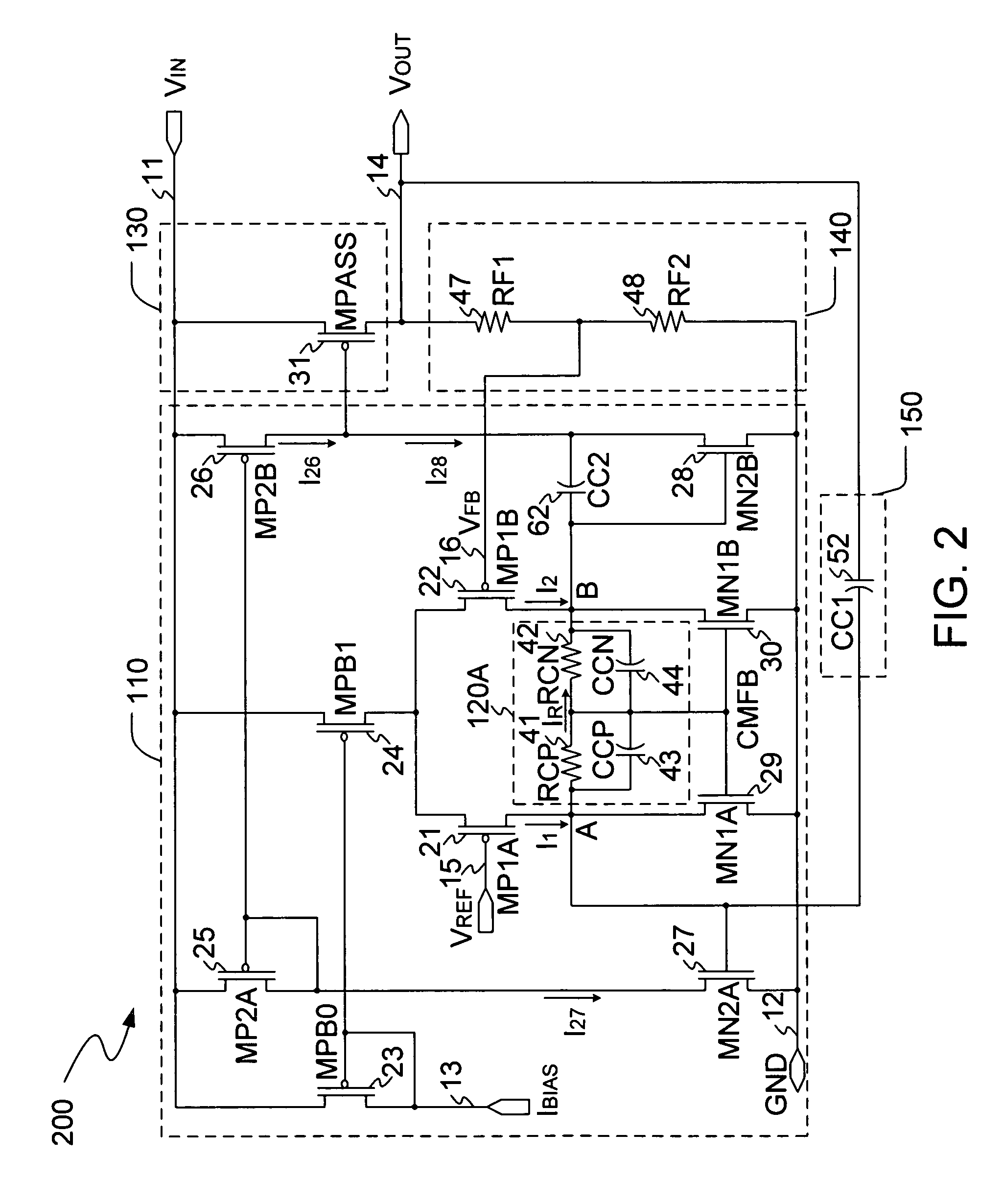
InactiveUS20060197513A1Increase conversion rateStable output voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
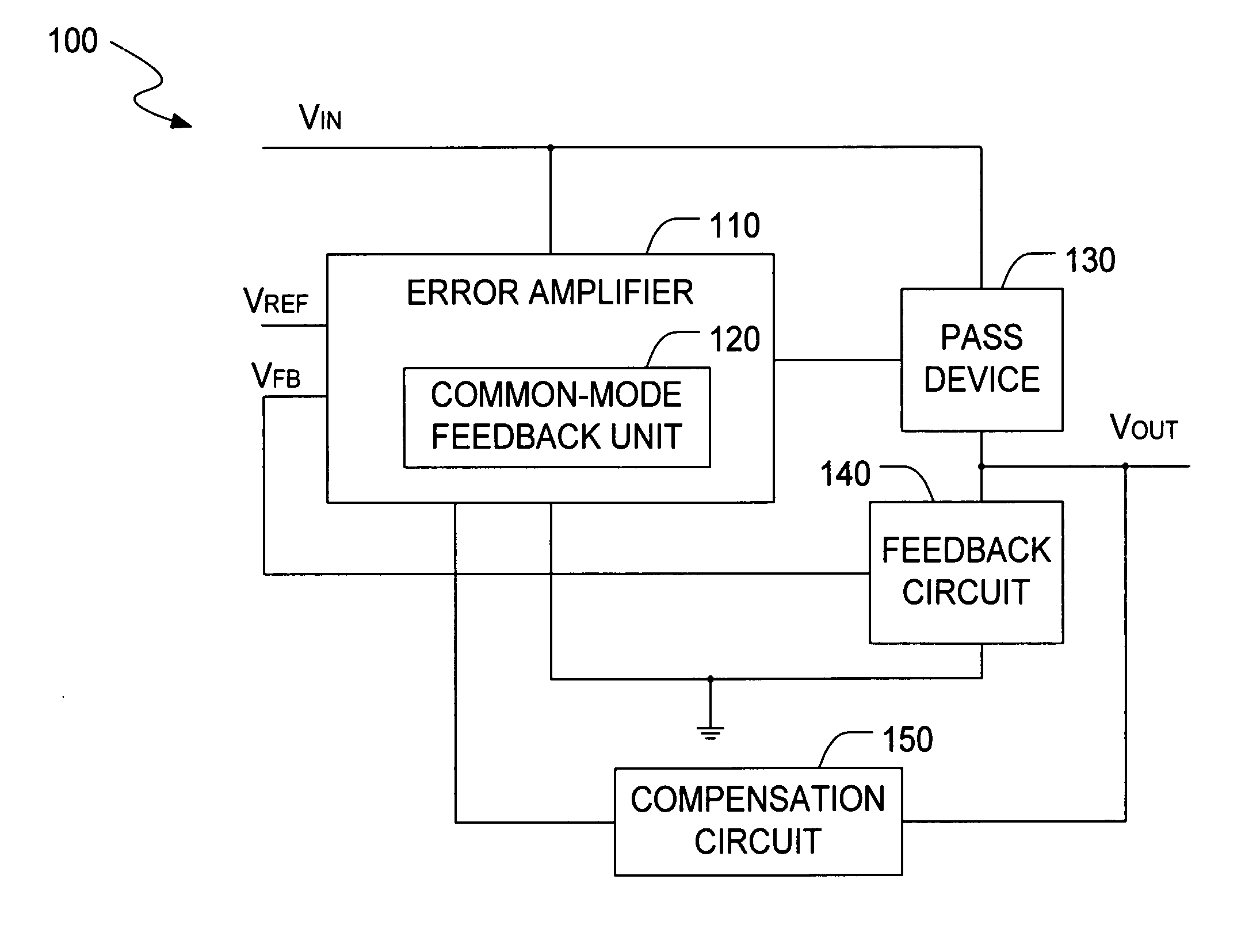
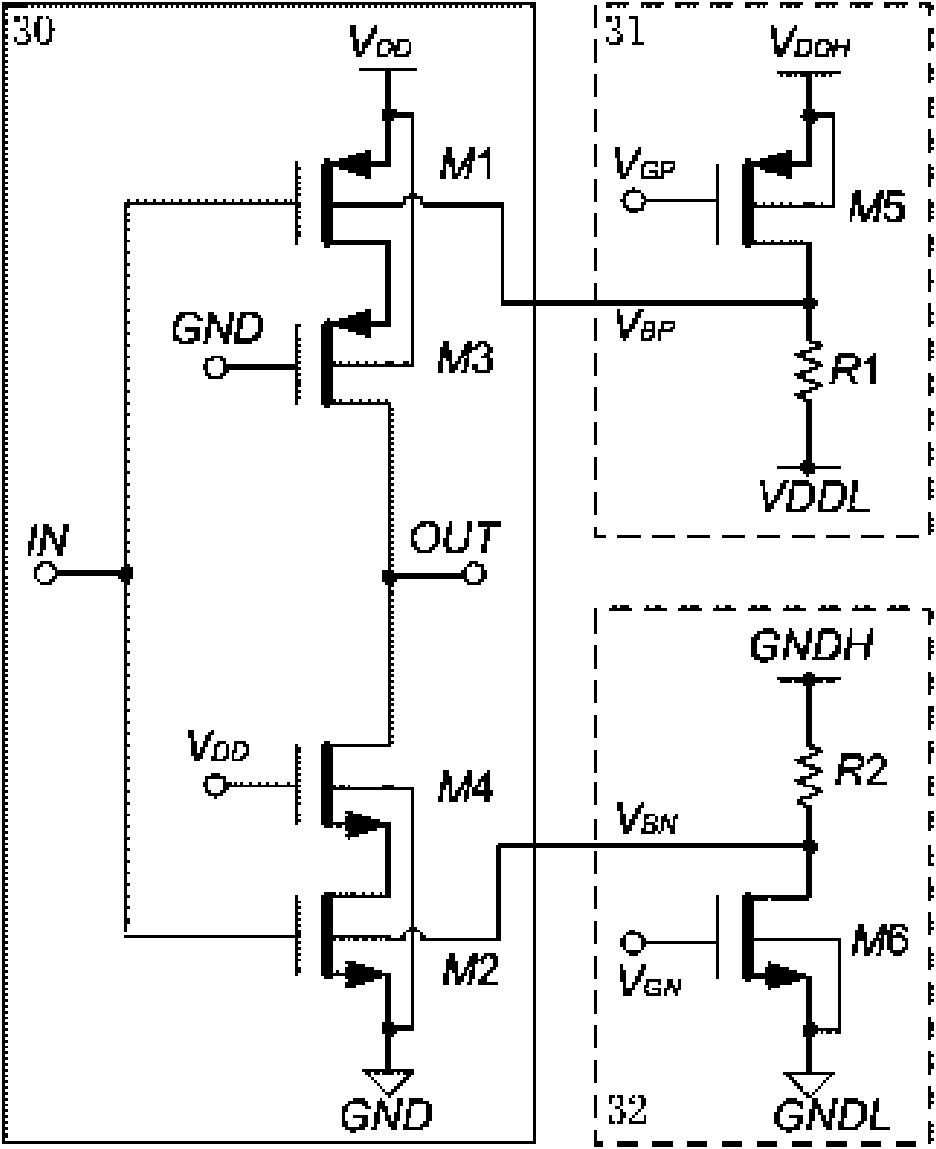
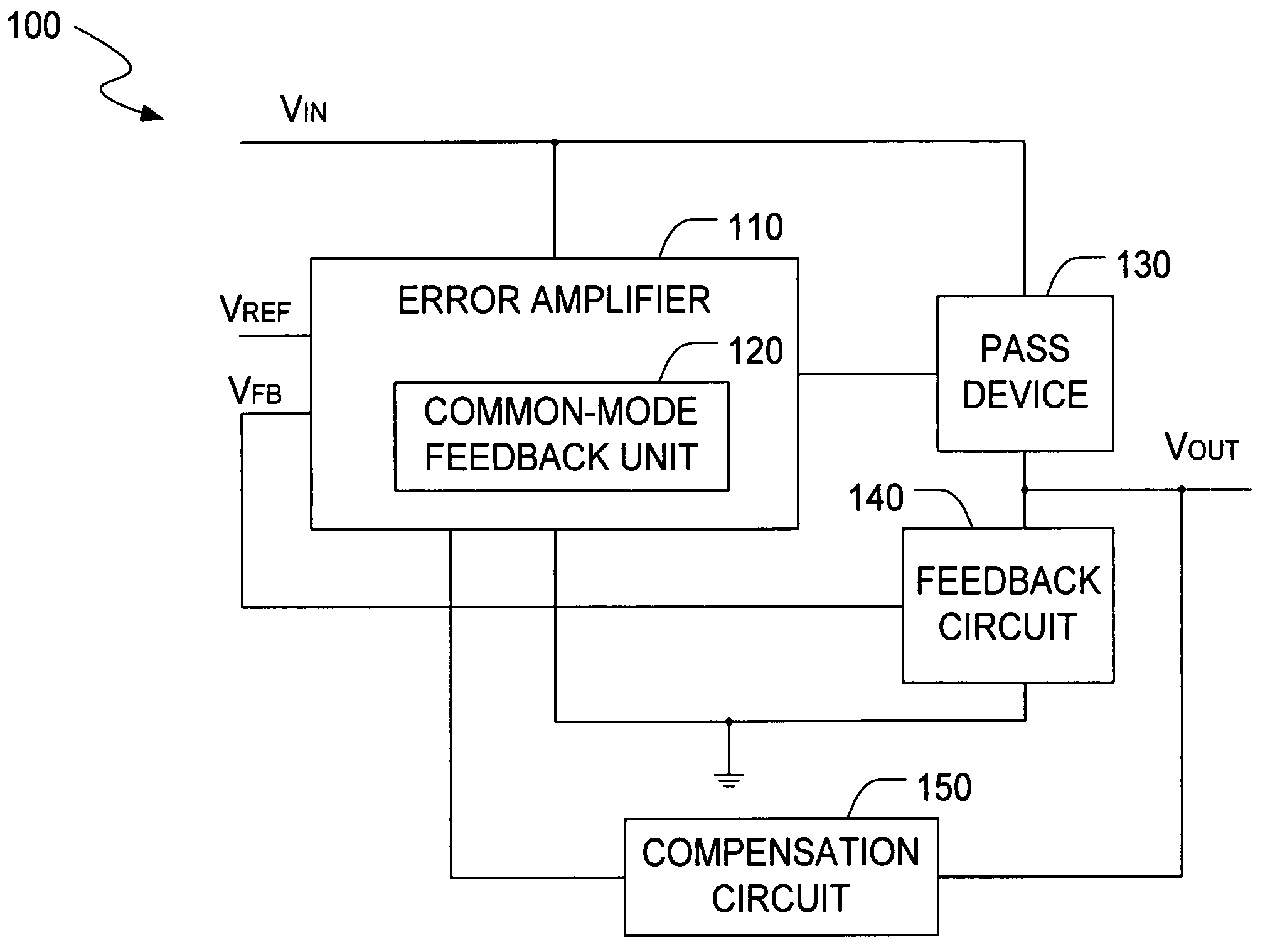
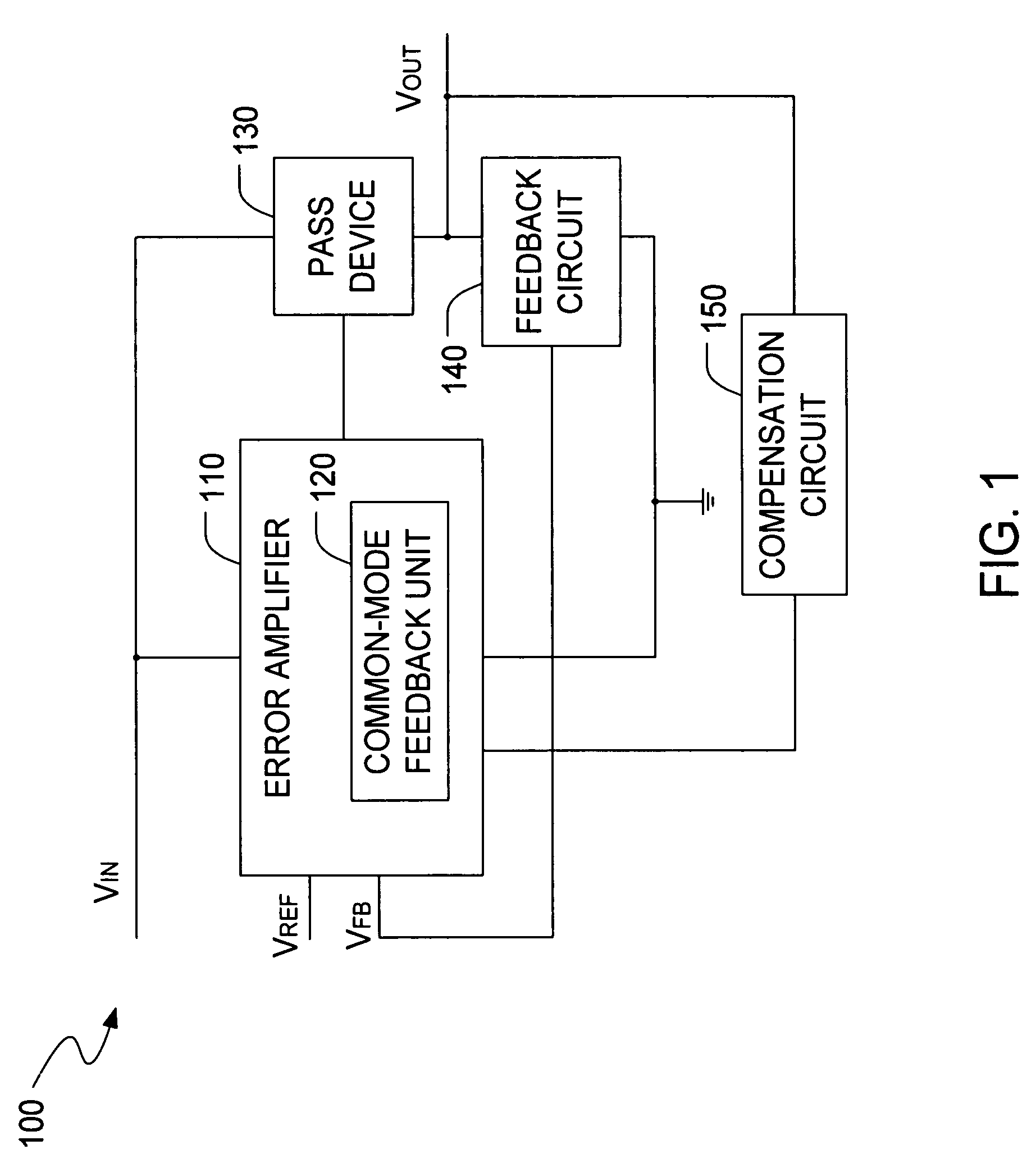
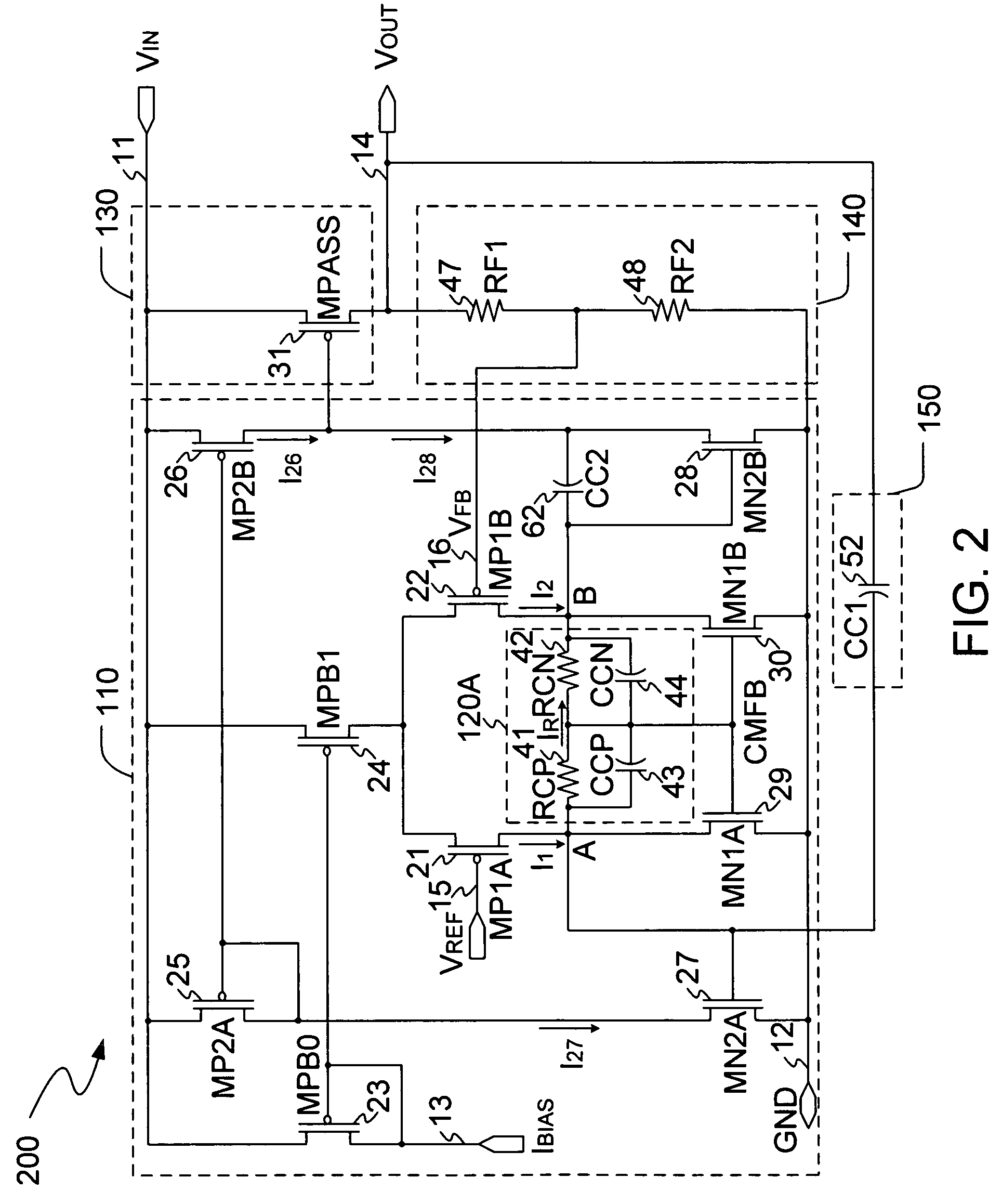
The present invention is a LDO voltage regulator circuit with common-mode feedback. The LDO voltage regulator includes an error amplifier with a common-mode feedback unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal to the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the pass device. A capacitor in the compensation unit provides frequency compensation to the LDO voltage regulator. The common-mode feedback unit incorporated into the error amplifier greatly improves a slew rate of a gate voltage of the pass device.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Multistage common mode feedback for improved linearity line drivers
ActiveUS7034611B2Reduce areaReduce total powerAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierHarmonic
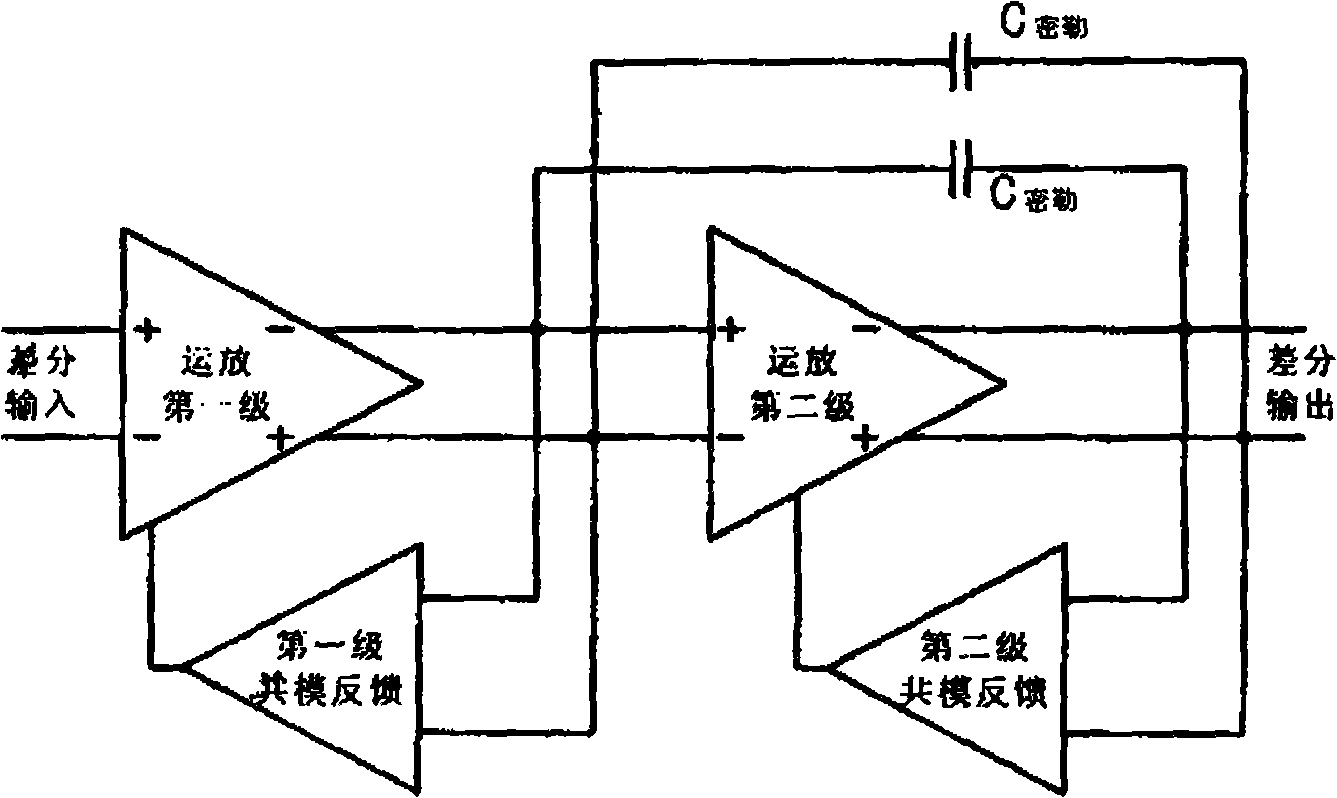
A technique to attenuate even-order harmonics of an output stage of a multistage nested Miller compensation circuit. In one example embodiment, this is accomplished by using a low-bandwidth low-swing amplifier in the common mode feedback loop to improve the even-order harmonic performance in the signal path. The technique uses a separate multistage loop for the common mode feedback loop to attenuate the even-order harmonics. The common mode feedback loop is the fourth stage and uses the third stage of the nested Miller compensation circuit. The fourth stage of the common mode feedback loop includes a single harmonic and uses a low voltage supply to achieve lower power consumption by the common mode feedback loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for phase-locked loop (PLL) for high-speed memory interface (HSMI)
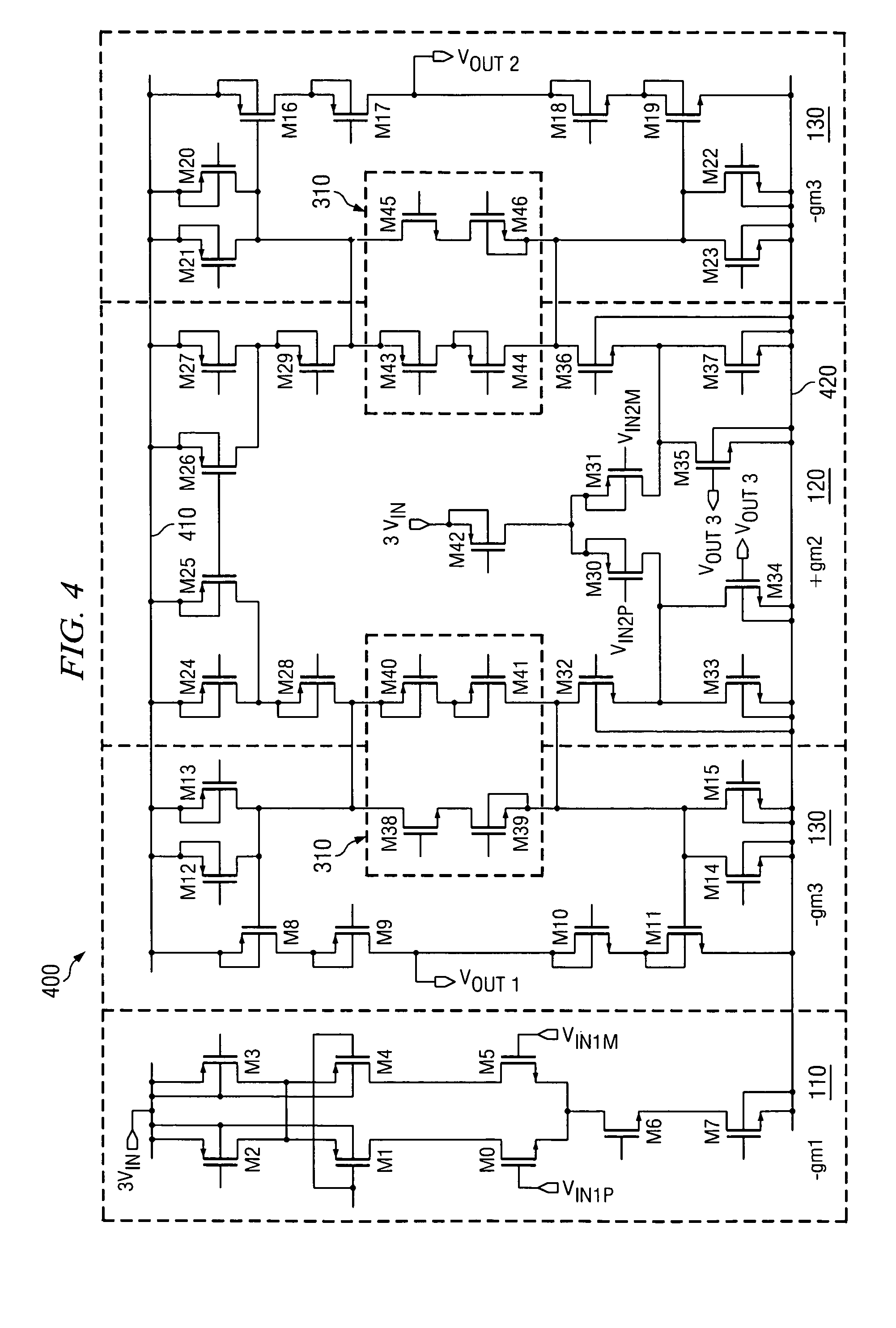
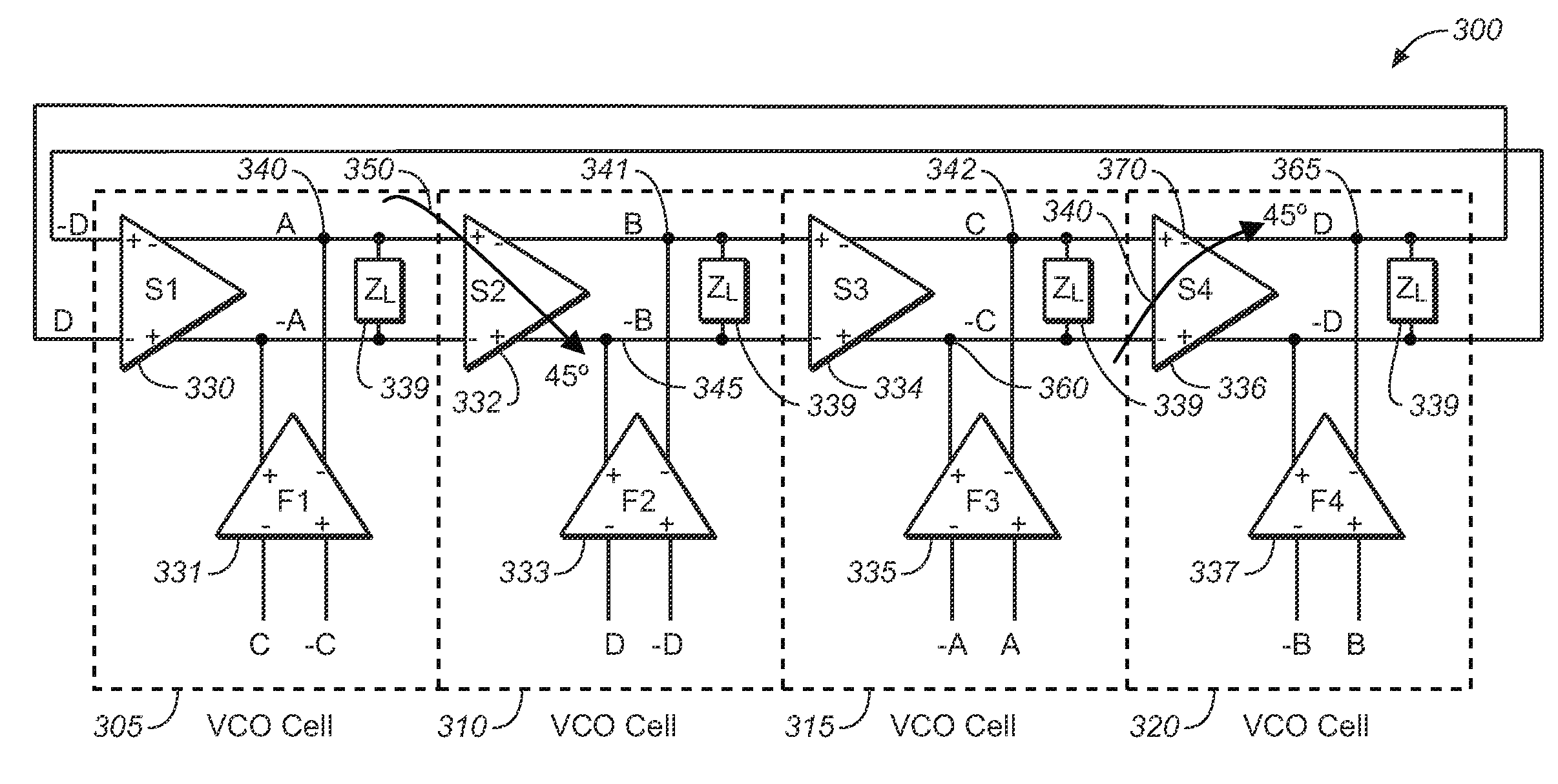
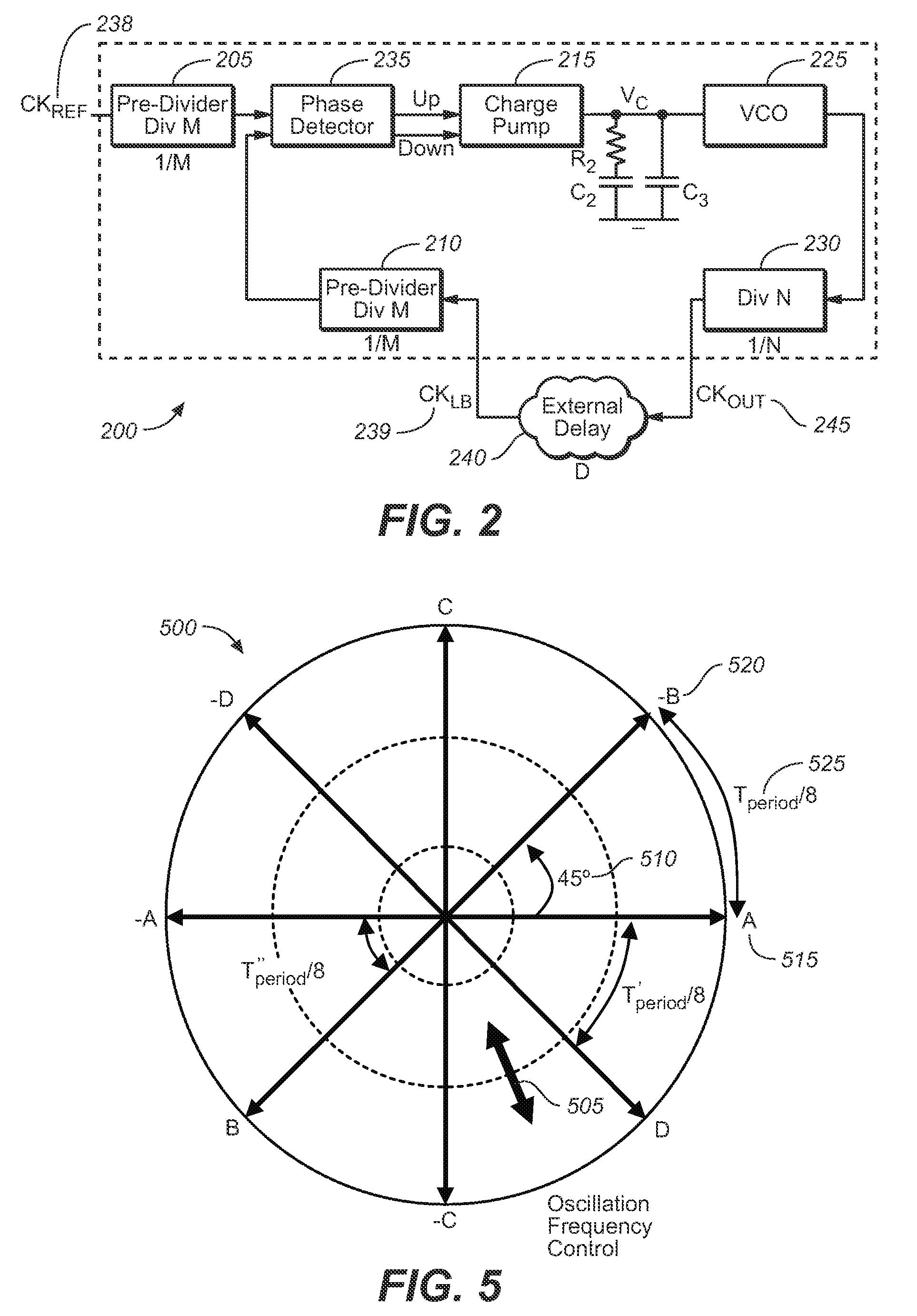
ActiveUS7659783B2Optimize allocationMeet the blocking requirementsPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationLoop filterDouble data rate
A phase-locked loop (PLL) to provide clock generation for high-speed memory interface is presented as the innovate PLL (IPLL). The IPLL architecture is able to tolerate external long loop delay without deteriorating jitter performance. The IPLL comprises in part a common mode feedback circuit with a current mode approach, so as to minimize the effects of mismatch in charge-pump circuit, for instance. The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) of the IPLL is designed using a mutually interpolating technique generating a 50% duty clock output, beneficial to high-speed double data rate applications. The IPLL further comprises loop filter voltages that are directly connected to each VCO cell of the IPLL. Conventional voltage-to-current (V-I) converter between loop filter and VCO is hence not required. A tight distribution of VCO gain curves is therefore obtained for the present invention across process corners and varied temperatures.
Owner:MICREL
Transconductance/C complex band-pass filter
ActiveUS7002403B2Guaranteed smooth progressPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A complex filter such as the channel select filter in a radio transceiver is implemented using a transconductance / C topology to benefit from the ability to tune such filters and thereby stabilize the output transfer function of the filter over variations in temperature, power supply voltage and process. The topology is based on an active R / C biquadratic topology to achieve the additional benefit of independently controlled stages. The problem created by the R in the output impedance is can be overcome by separately tuning the R value along with the transconductance / C ratio, by implementing the R as a transconductance amplifier having common mode feedback, or by implementing the transconductance amplifiers of the topology using Nauta transconductors, and unbalancing the common mode circuit of the Nauta transconductor to achieve a differential resistance that can be used to implement the R in the output impedance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
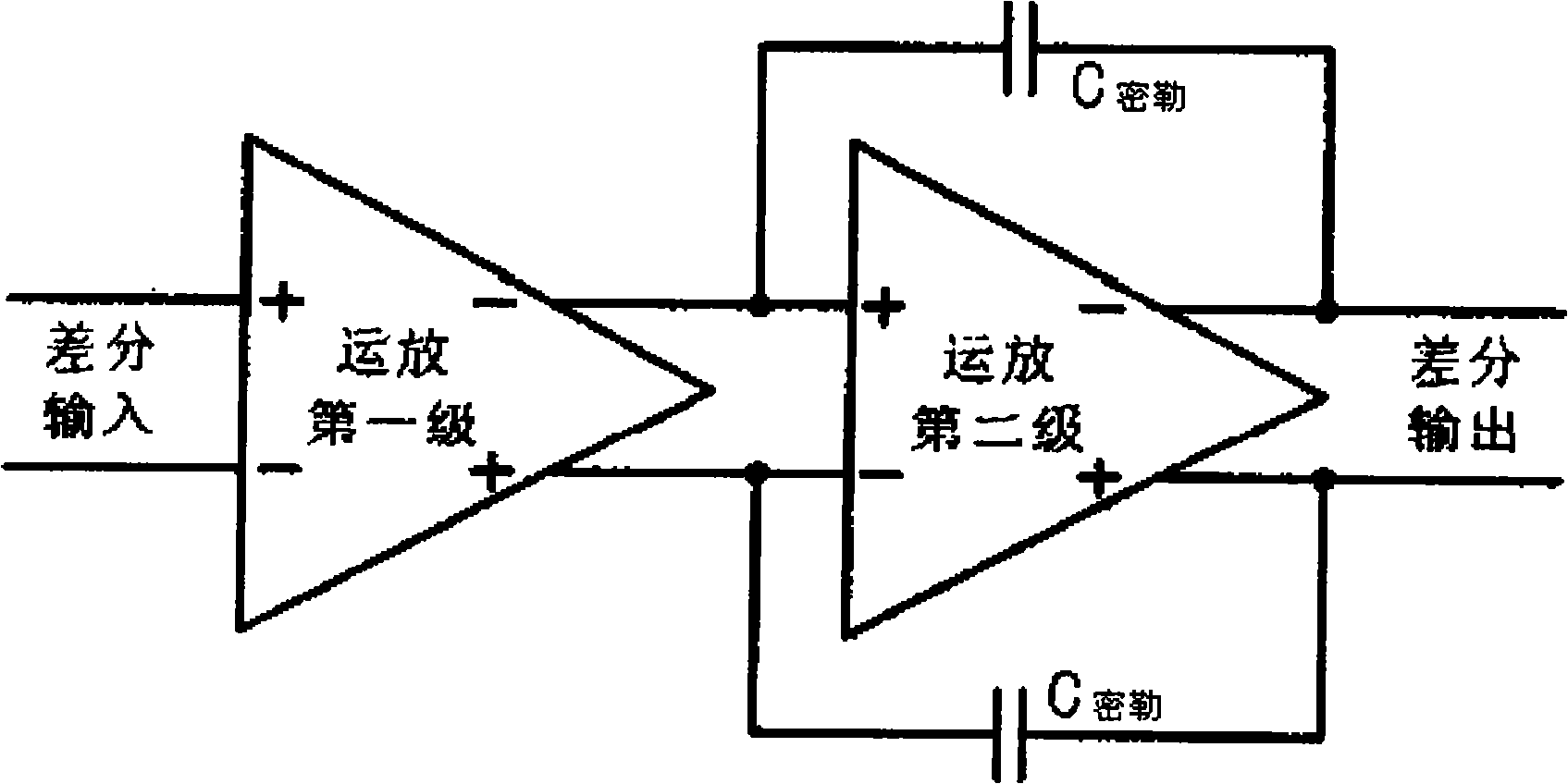
High-bandwidth low-power consumption frequency-compensation three-stage operational amplifier
InactiveCN101917169AGood compensationIncrease separation resistanceEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLoad circuitWireless communication protocol
The invention belongs to the technical field of analog IC (Integrated Circuit) design, in particular to a high-bandwidth low-power consumption frequency-compensation three-stage operational amplifier. The amplifier comprises an input stage, a second stage, an output stage, a common mode feedback stage, a comprehension circuit, an internal feedforward circuit, wherein the second stage is connectedwith the input stage, the output stage is connected with the second stage and used for amplifying a signal output by the second stage and driving an external load circuit, the common mode feedback stage extracts the common mode level of the differential output stage and stabilizes the common mode level, the comprehension circuit comprises a traditional trsanscondutance comprehension circuit, a miller comprehension circuit and a resistor for separating a high-frequency zero pole, and the internal feedforward circuit is used for comprehending an internal additional pole and forming a push-pull circuit together with the output stage to reduce static power consumption. The three-stage operational amplifier realizes high gain, high bandwidth and high stability under the condition of little DC power consumption and can be used in a high-speed analog-digital conversion circuit, such as a sigma-delta modulator suitable for the bandwidth of an LTE (Line Terminator Equipment) wireless communication protocol.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
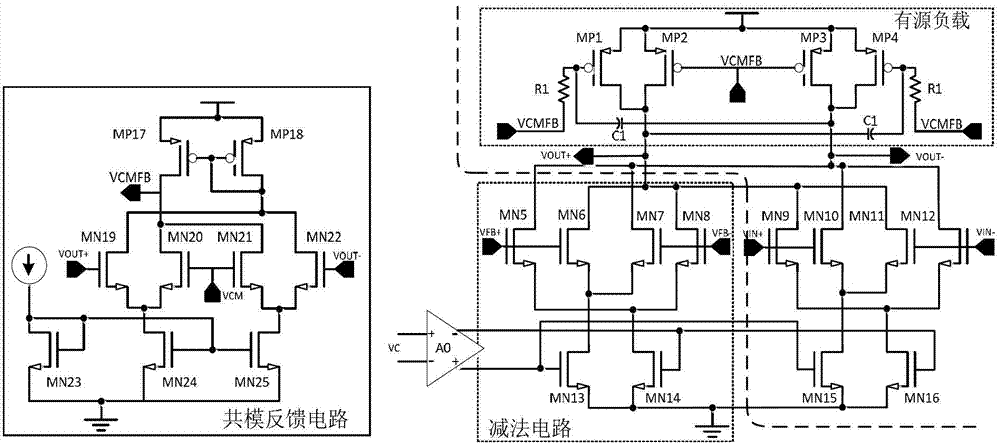
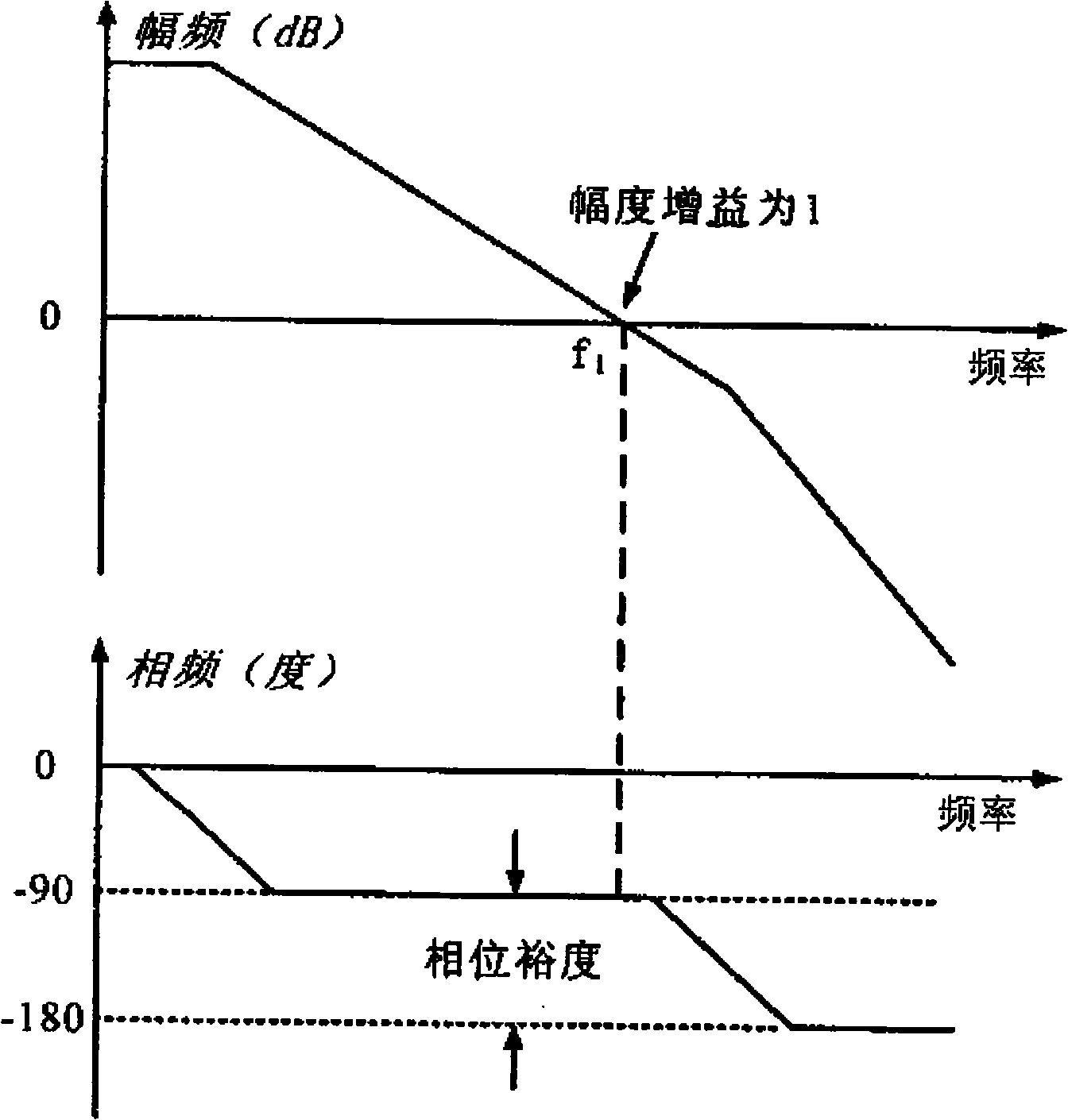
Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
InactiveCN101373956AImprove phase marginImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesDual stageControl signal
The invention discloses a common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method of a dual-stage amplifier, which belongs to the analog integrated circuit design field. One common-mode feedback circuit is adopted in the dual-stage amplifier to reduce the area and the power consumption of the feedback circuit; the dual-stage amplifier adopts a fully-differential input / output structure; a differential output terminal is used for sampling the common-mode output level; a first-stage amplifying circuit thereof comprises a controllable biasing circuit; a common-mode feedback control signal controls the first-stage common-mode output level and the second-stage common-mode output level of the amplifier at the same time through the controllable biasing circuit; a feedback amplifier is realized by adopting a dual-stage operational amplifier with miller compensation. The left half plane zero point generated by the feedback amplifier in a loop circuit counteracts a certain left half plane pole in a prime amplifier, thereby forming a stable compensation loop circuit. The common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method has the advantages of less feedback circuit elements, lower feedback circuit power consumption, high low-frequency loop gain and better compensation phase margin.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Method and apparatus for stabilizing RF power amplifiers
InactiveUS20070139112A1Process stabilityReduce decreasePush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for use in power amplifiers for reducing the peak voltage that transistors are subjected to. A power amplifier is provided with first and second switching devices and an inductor connected between the switching devices. The switching devices are driven such that the switching devices are turned on and off during the same time intervals. Differential RF power amplifiers are also provided with inductive networks coupled at various nodes of the power amplifiers. In some examples, techniques are used to stabilize differential power amplifiers by stabilizing common-mode feedback loops.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
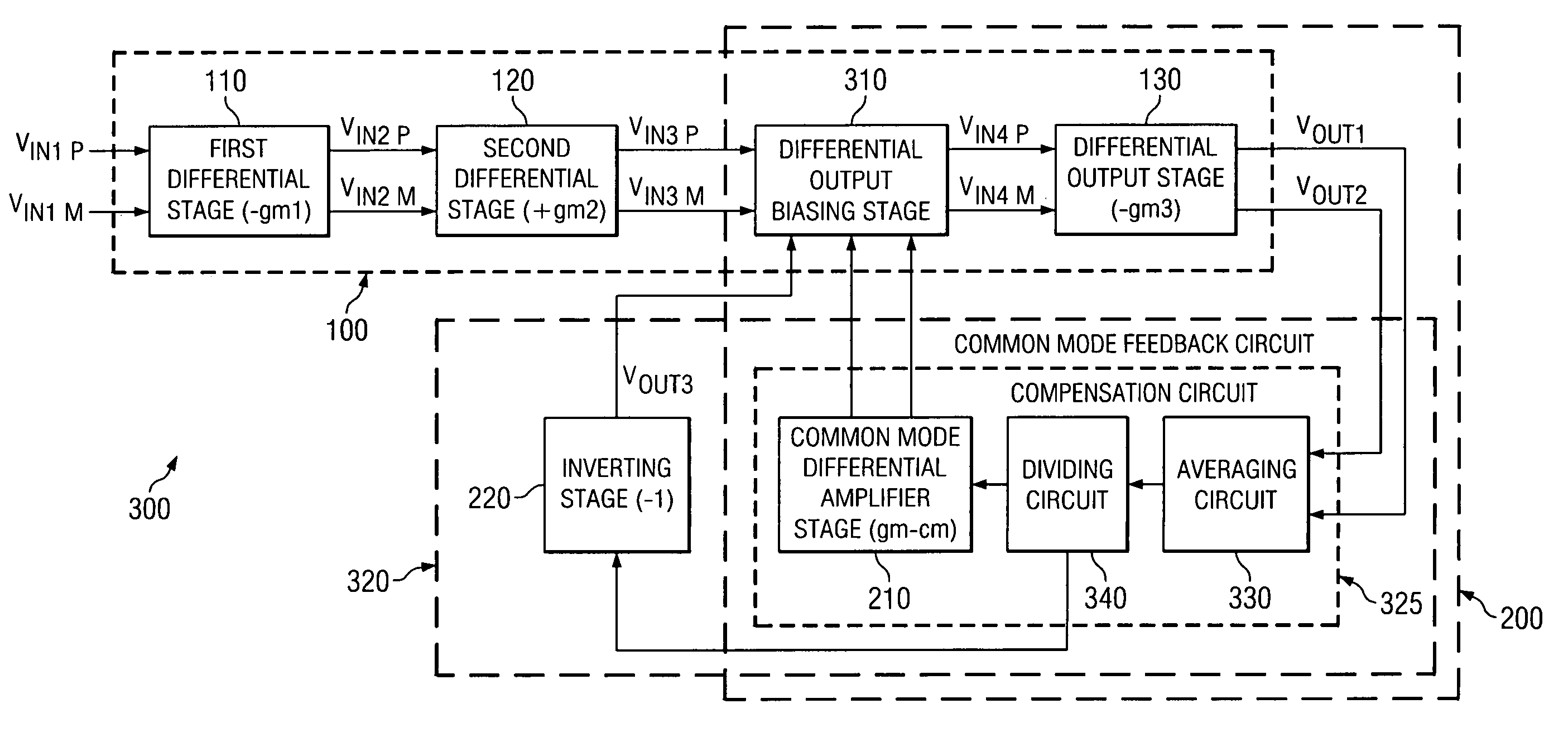
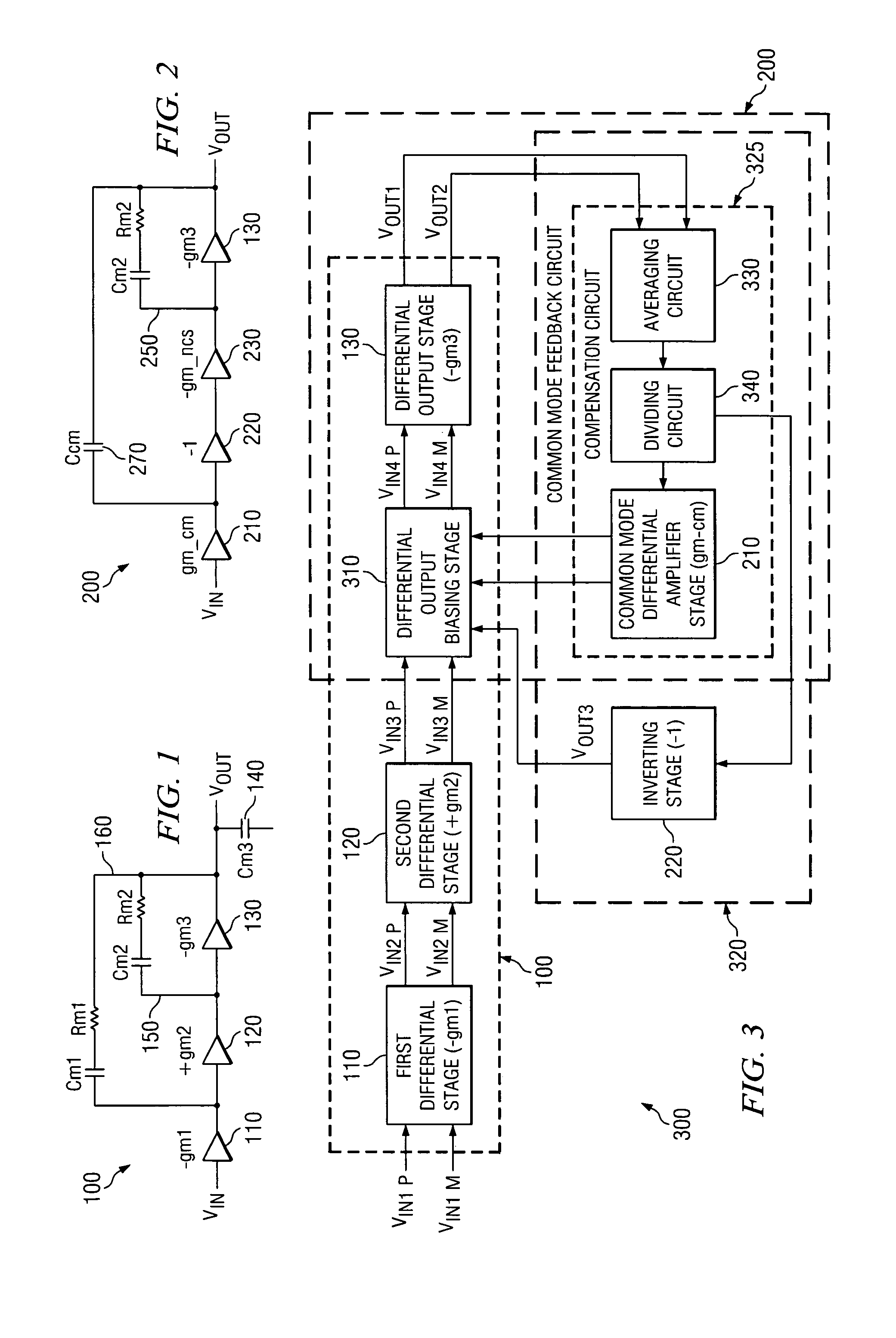
Differential amplifiers with enhanced gain and dynamic range
ActiveUS7253686B2Differential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Differential amplifier embodiments are provided for amplifying input signals with enhanced gain and dynamic range. They include first and second amplifier stages and at least one common-mode feedback circuit that is arranged to mirror and adjust a tail current to control the common-mode level of a respective one of the stages. The stages are configured with cascode elements to obtain high impedances that enhance their signal gain and the common-mode feedback circuit is configured to controllably lower the output voltage of a current source that provides the tail current to thereby enhance the amplifier's dynamic range. The amplifier embodiments are particularly suited for use in applications where they must operate with reduced supply voltages and operate in alternating operational modes.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Low power comsumption, low noise and high power gain distributed amplifiers for communication systems
ActiveUS7579913B1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power gainAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers wit coupling networksLow noiseDistributed amplifier
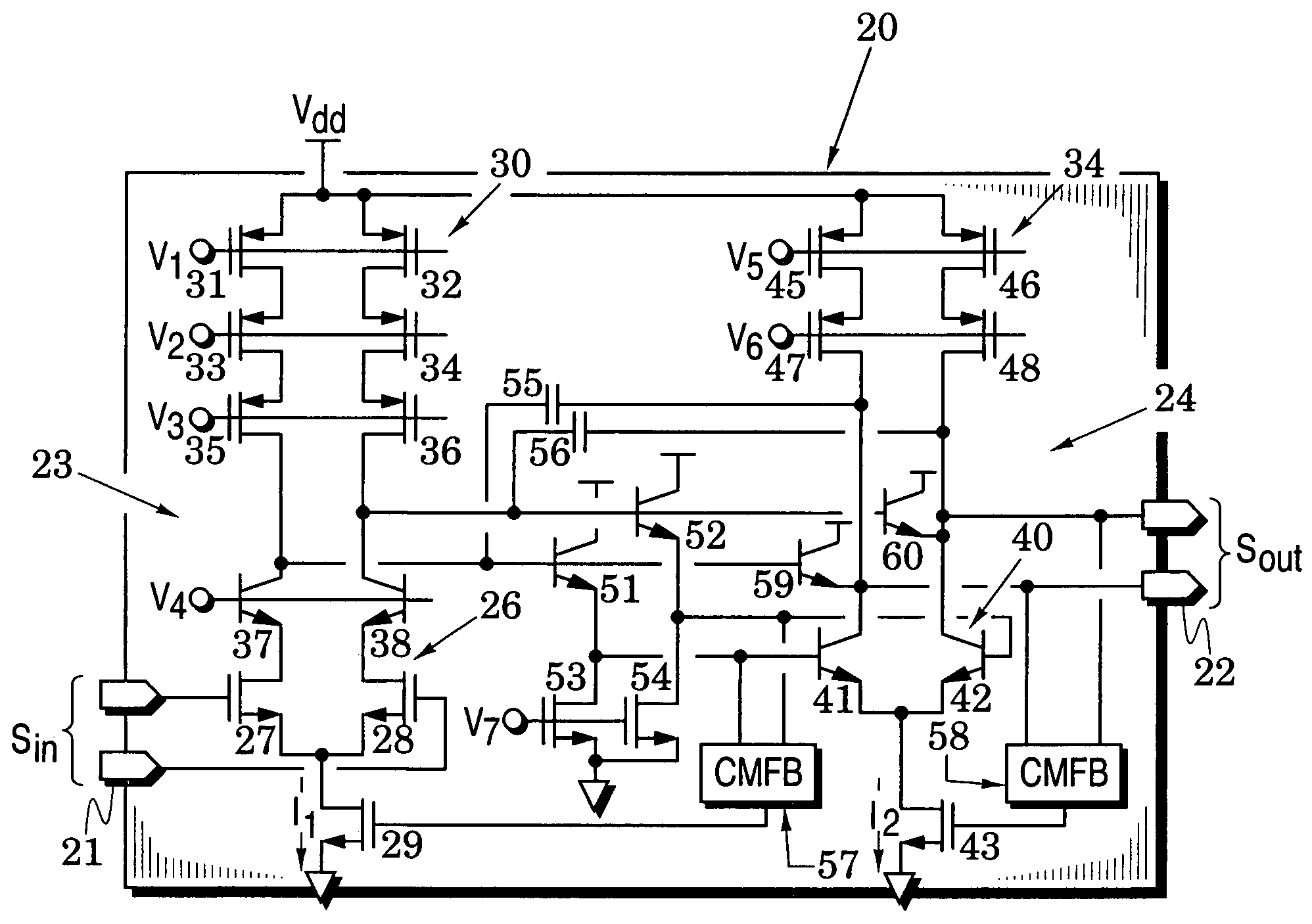
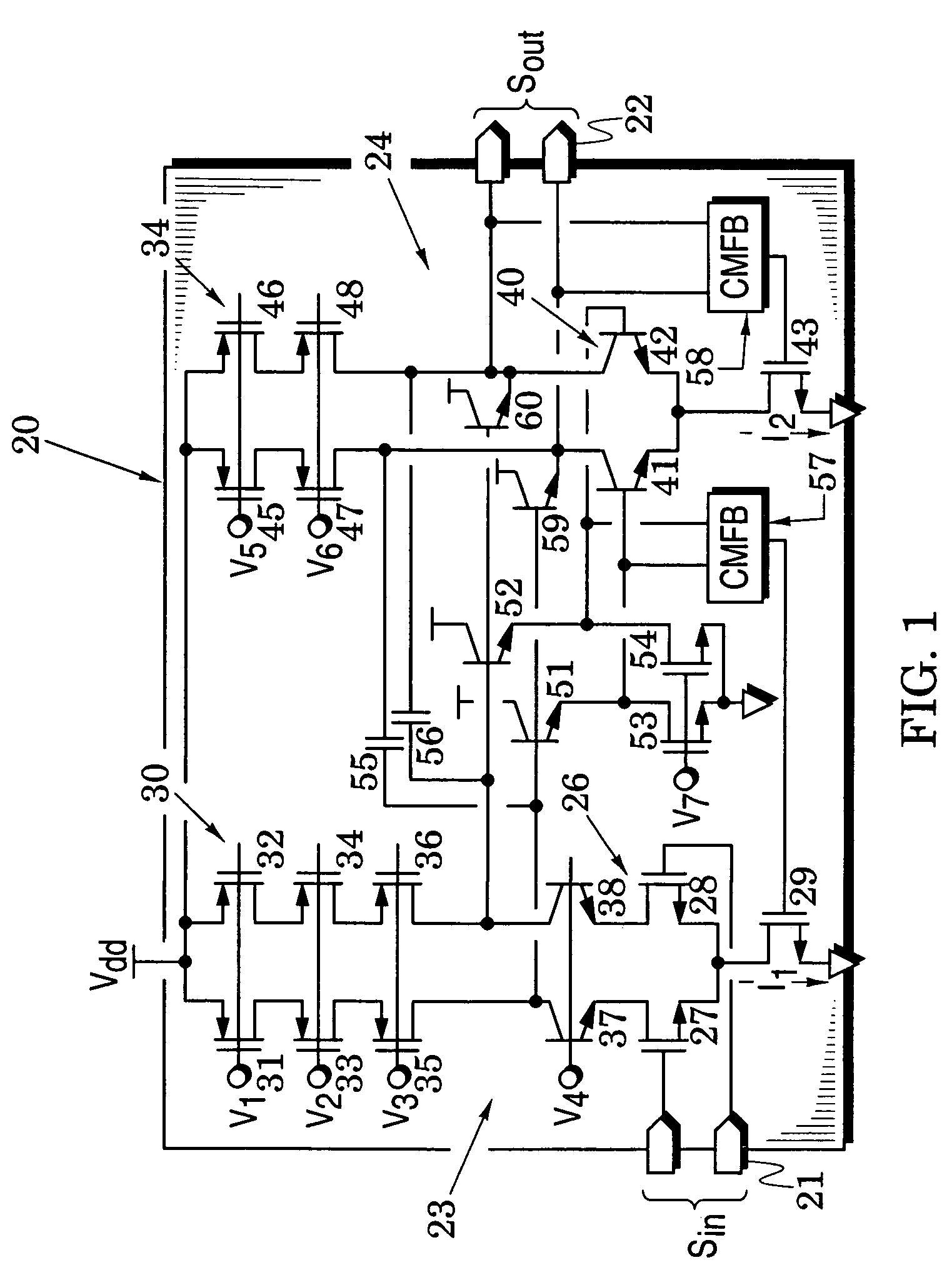
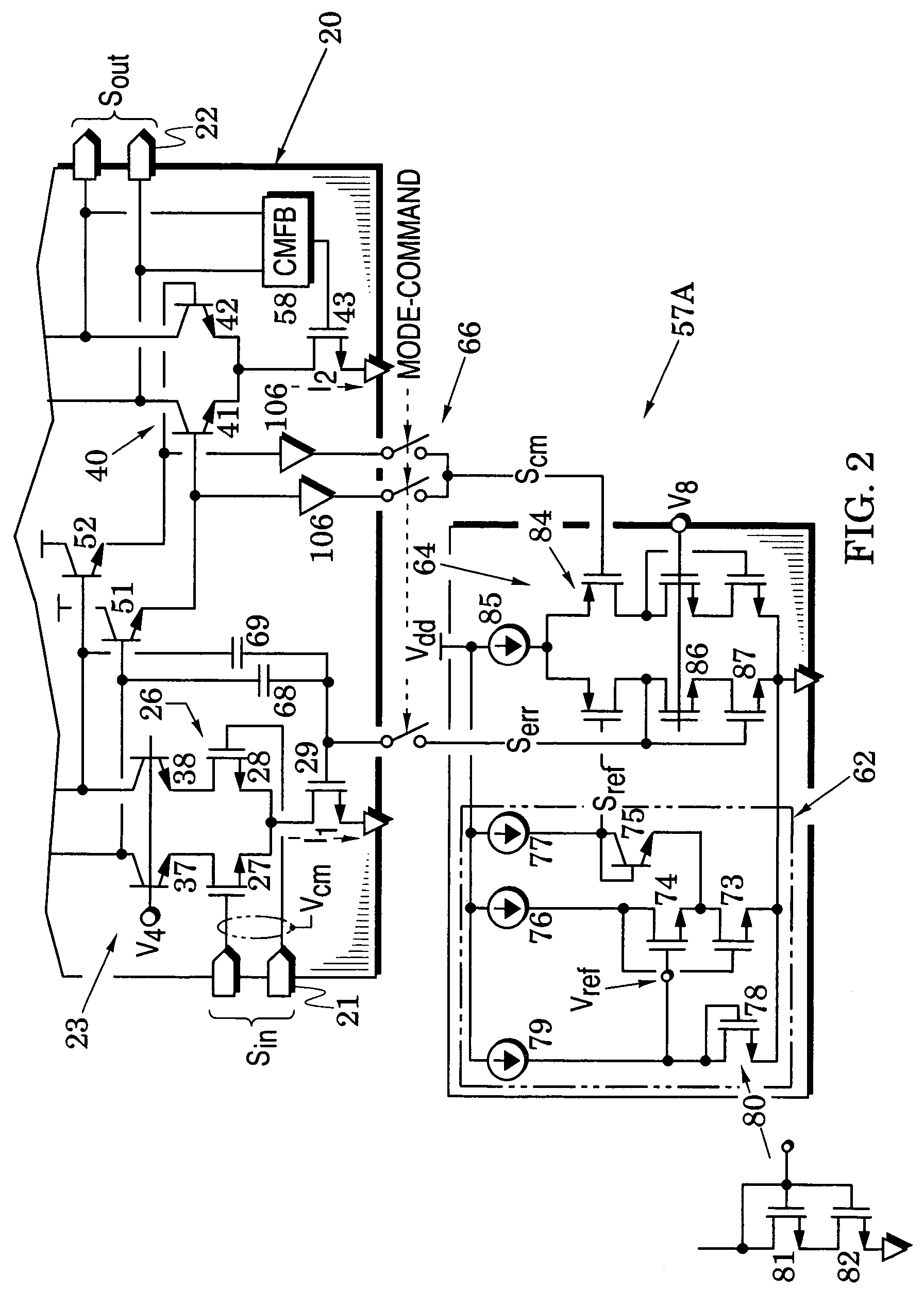
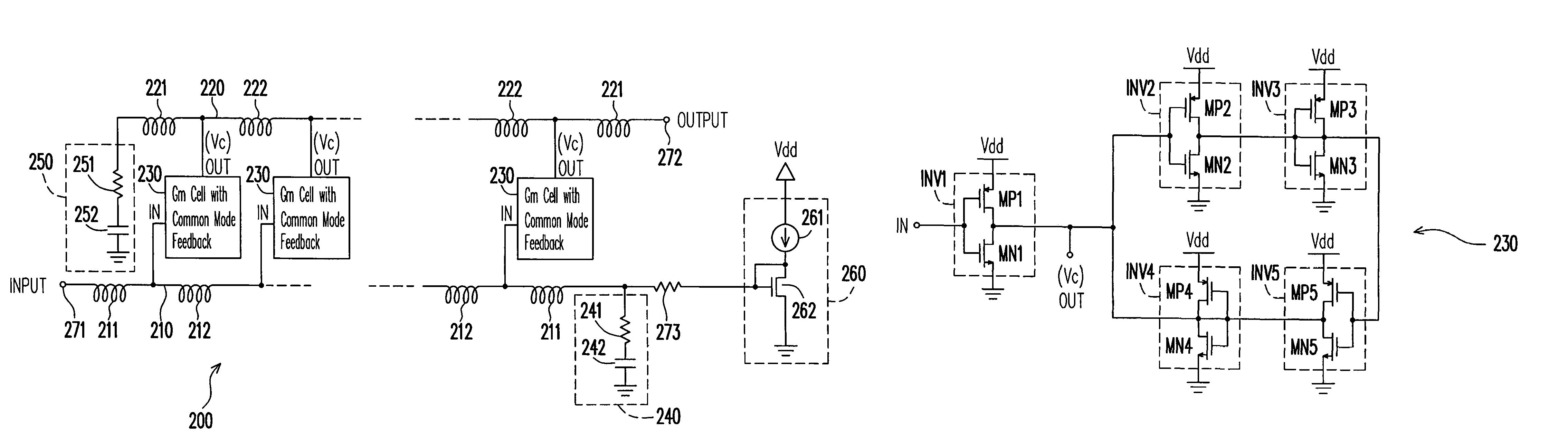
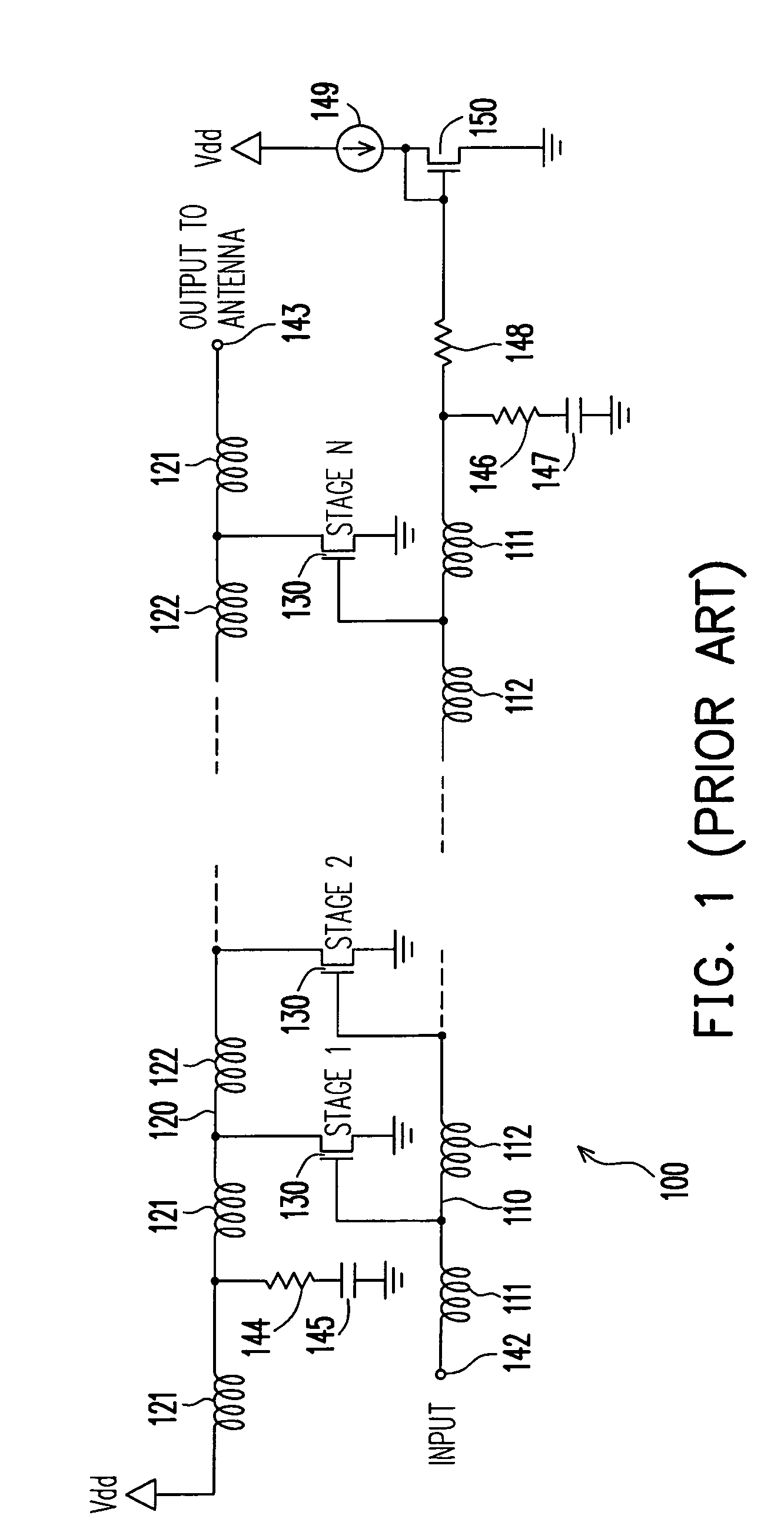
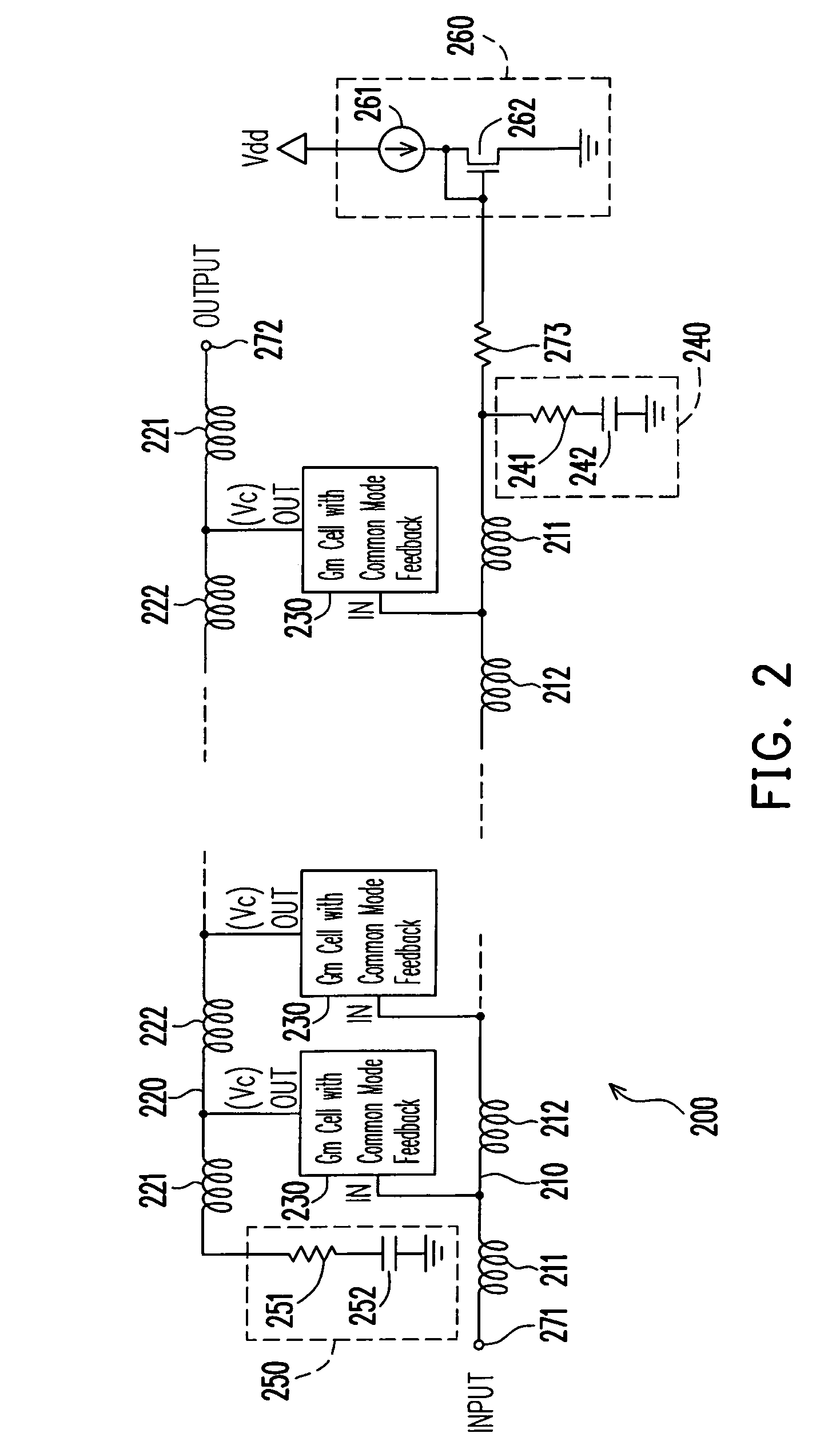
Provided is a distributed amplifier in communication systems, including: an input transmission line; an output transmission line; an input impedance match and an output impedance match, for providing termination of the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively and for preventing signal reflection in the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively; multi-stage Gm cells with common mode feedback, the input transmission line being coupled to the output transmission line by the transconductance of the Gm cells; and an input gate bias circuit, for providing bias for the multi-stage Gm cells. In at least one of the Gm cells, one inverter performs V / I conversion while other inverters provide negative resistance to control common mode of output voltage and to enhance DC gain of the Gm cell. Due to common mode feedback, no output gate bias is needed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Calibration circuit and method thereof
ActiveUS7259569B2Spectral/fourier analysisModulation transference balanced arrangementsControl signalFrequency mixer
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ultra linear high frequency transconductor structure
InactiveUS6346856B1Differential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A transconductor block including a Czarnul tuning network, transconductance resistors, an input voltage follower amplifier, a common mode circuit, PMOS transistors coupled in cascode configuration, an input current source, and high gain amplifiers that drive NMOS transistors at the output. The input voltage follower amplifier receives a differential input signal including a common mode voltage and applies the differential input signal to the Czarnul tuning network. The Czarnul tuning network includes series resistors and is coupled in parallel with the transconductance resistors. The common mode circuit receives the differential input signal and a reference common mode voltage and provides a bias voltage and a common mode feedback voltage. The common mode circuit asserts the common mode feedback voltage to the output PMOS transistors to establish a DC output current and to minimize drift of the common mode voltage of the transconductance block. Also, the bias voltage is level shifted from the common mode signal. The high gain amplifiers maintain the output of the Czarnul tuning network and transconductance resistors at the bias voltage. The high gain amplifiers are coupled to the input current sources and to the NMOS transistors in a negative feedback configuration. The high gain amplifiers drive the NMOS transistors to reflect an output current that corresponds to the input voltage signal.
Owner:CONEXANT
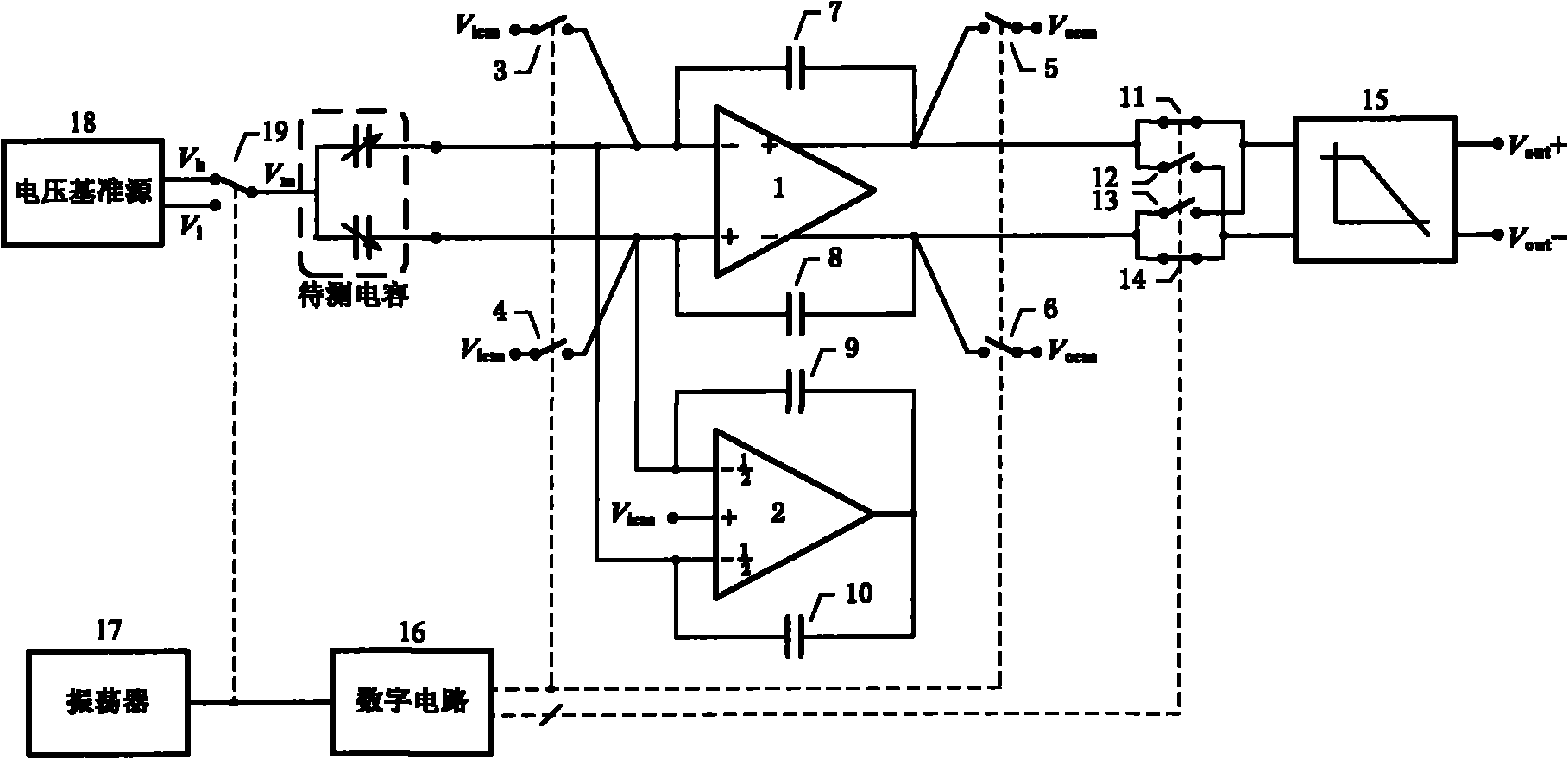
High accuracy capacitive readout circuit with temperature compensation
ActiveCN102072737ASolving high impedance node biasing issuesHigh precisionMitigation of undesired influencesIntegratorSwitching cycle
The invention discloses a high accuracy capacitive readout circuit with temperature compensation, belonging to the design field of integrated circuits. The circuit realizes high accuracy capacitive readout owing to the adoption of a chopping modulation technology, and can simultaneously realize temperature compensation by adjusting temperature characteristics of internal voltage reference. The circuit comprises an oscillator, a voltage reference source, a full-differential operational amplification unit, a common-mode operational amplification unit, a low pass filter, a switch device and a digital circuit. The voltage reference source generates a square wave in cooperation with a single-pole double throw switch, and the square wave is applied to an intermediate polar plate of a differential capacitance to be detected in order to implement modulation. The full-differential operational amplification unit and a feedback capacitance constitute a charge integrator to detect a transfer charge formed by the variation of the capacitance to be detected. Demodulation is realized by the switch device and the low pass filter. Both an input end and an output end of the full-differential operational amplification unit are set through a switch cycle. The common-mode operational amplification unit and the feedback capacitance constitute a common-mode feedback loop which is connected with the input end of the full-differential operational amplification unit to play the role of inputting common-mode voltage stably.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Circuit for reducing second order intermodulation
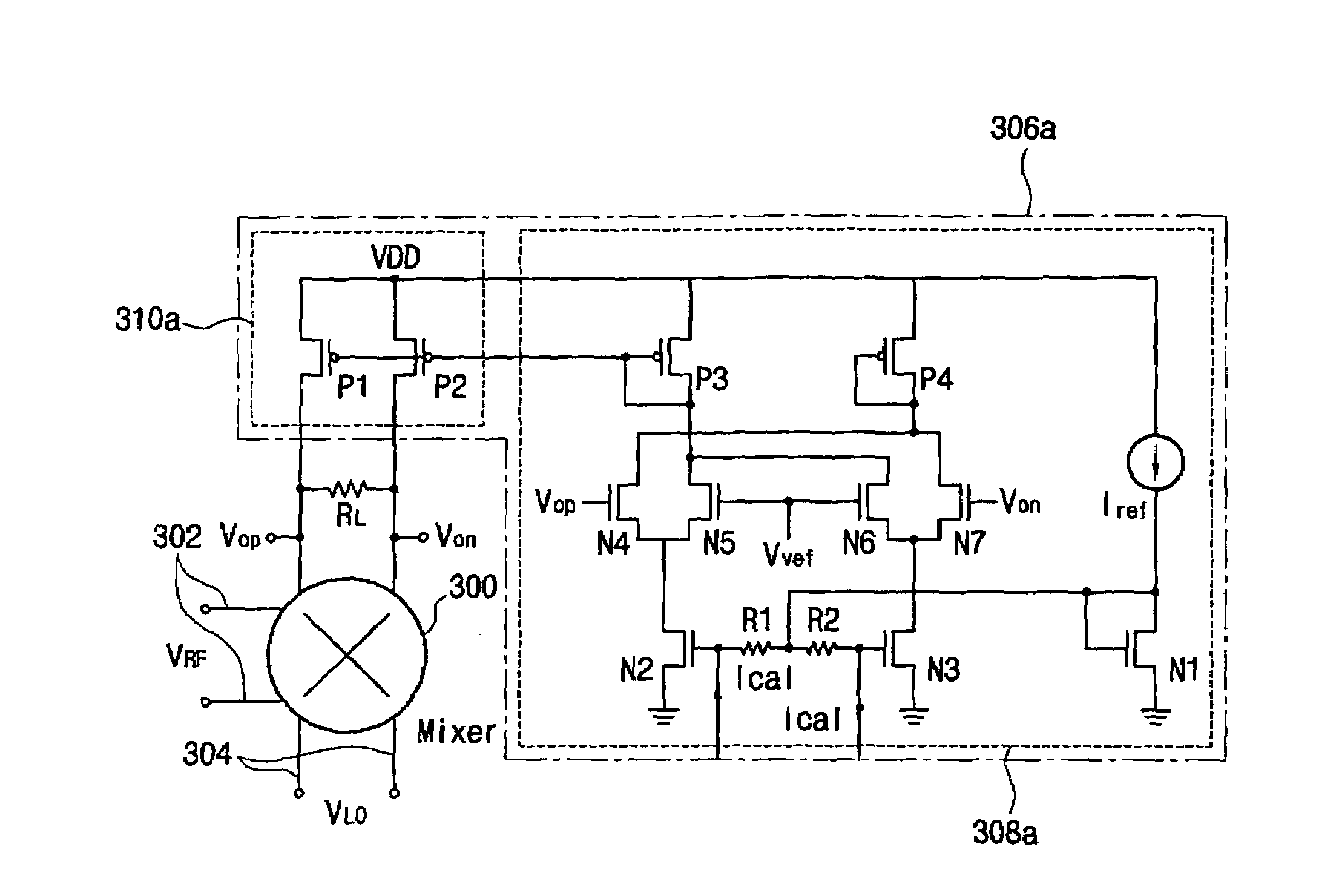
InactiveUS7421263B2Improve linearityReduce areaRadio transmissionFrequency mixerDirect-conversion receiver
A circuit for calibrating a second order intercept point (IP2) and for reducing second order intermodulation (IM2) includes a common mode feedback circuit and a load impedance operatively connected between first and second output terminals of a mixer in a direct conversion receiver. The common mode feedback circuit reduces second order intermodulation of the mixer by detecting an output voltage of the mixer and adjusting a gain of the mixer. The IP2 is controlled by controlling the gain of the common mode feedback circuit. The second order intermodulation (IM2) may be reduced and the linearity of a device may be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
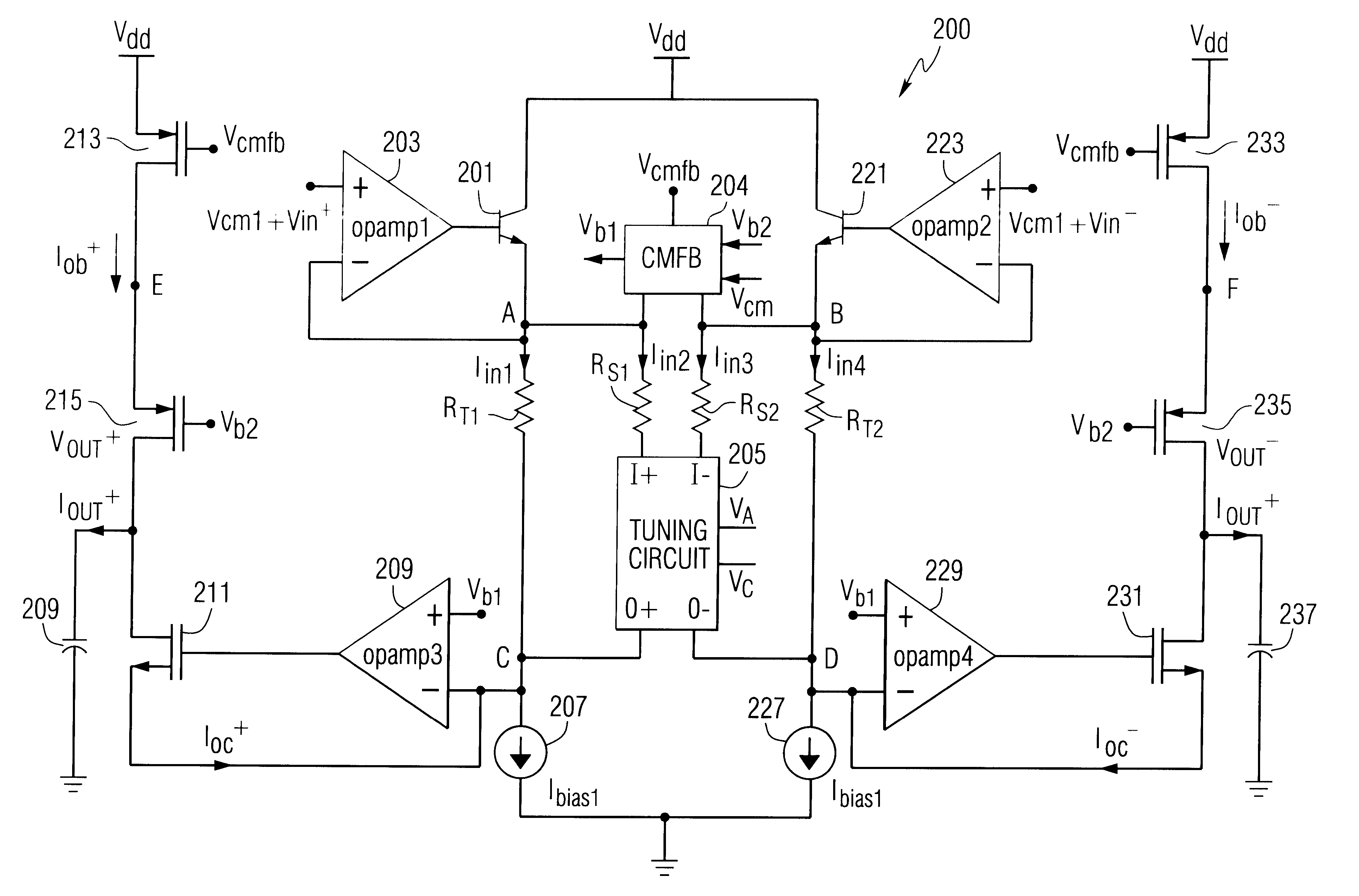
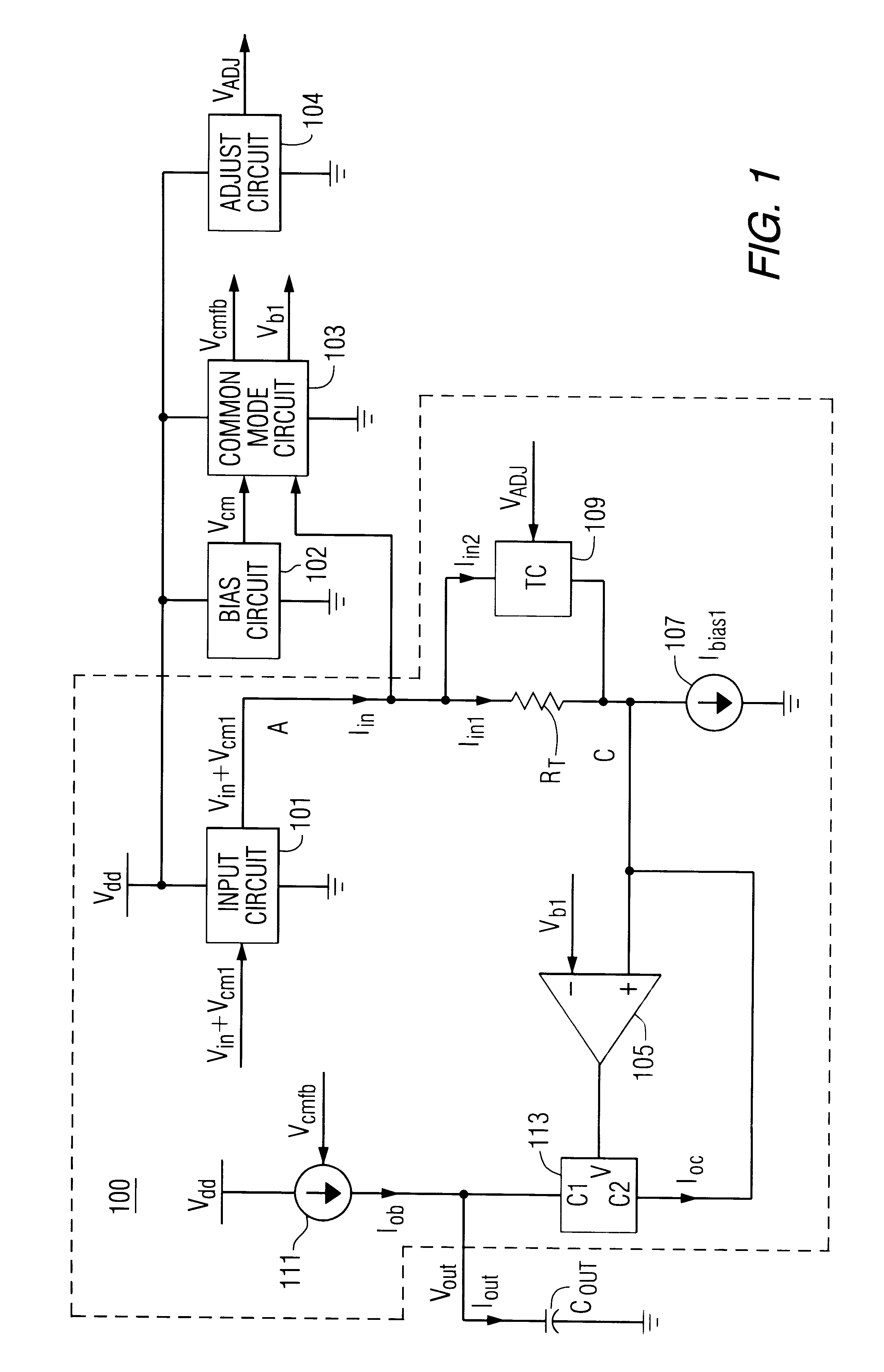
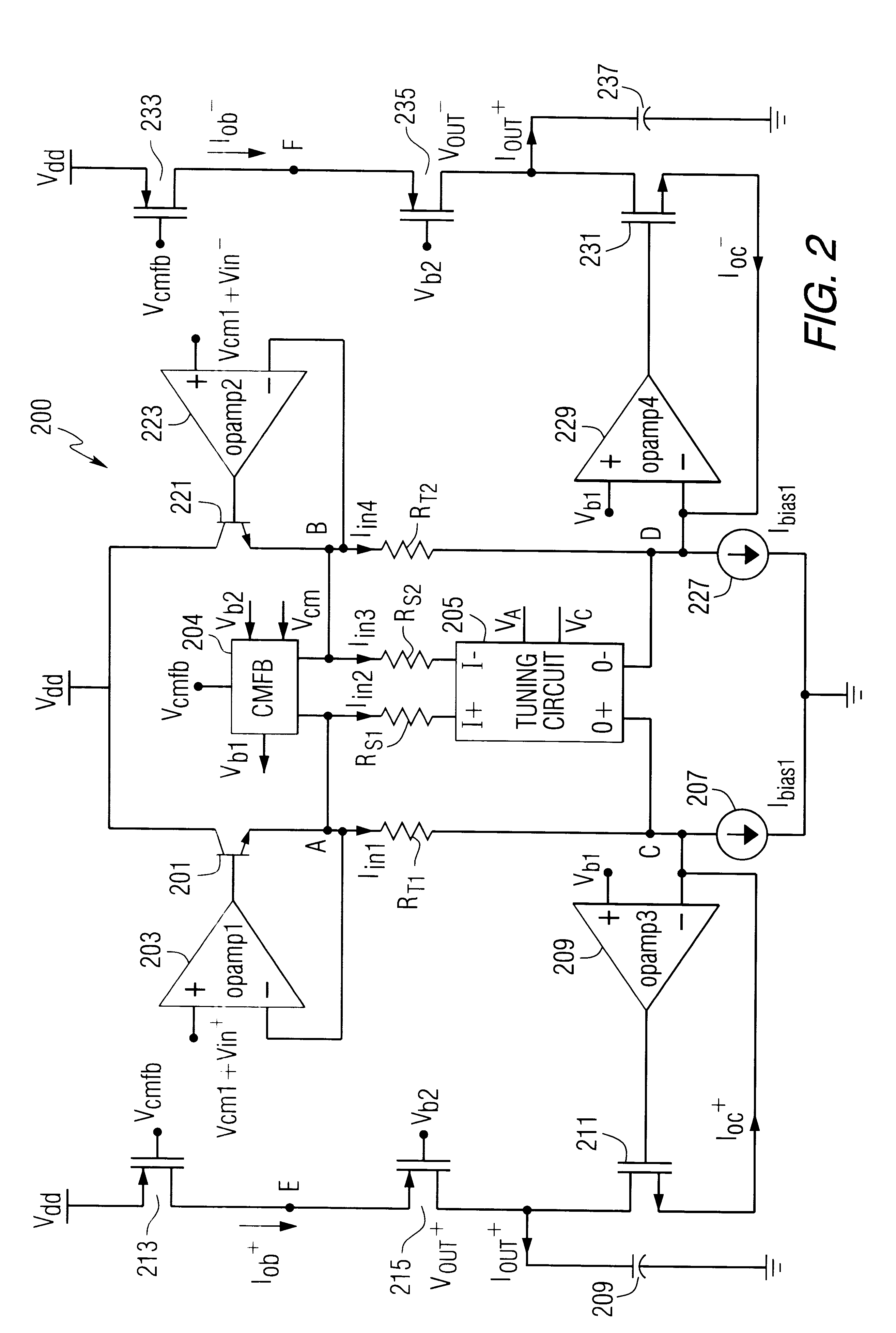
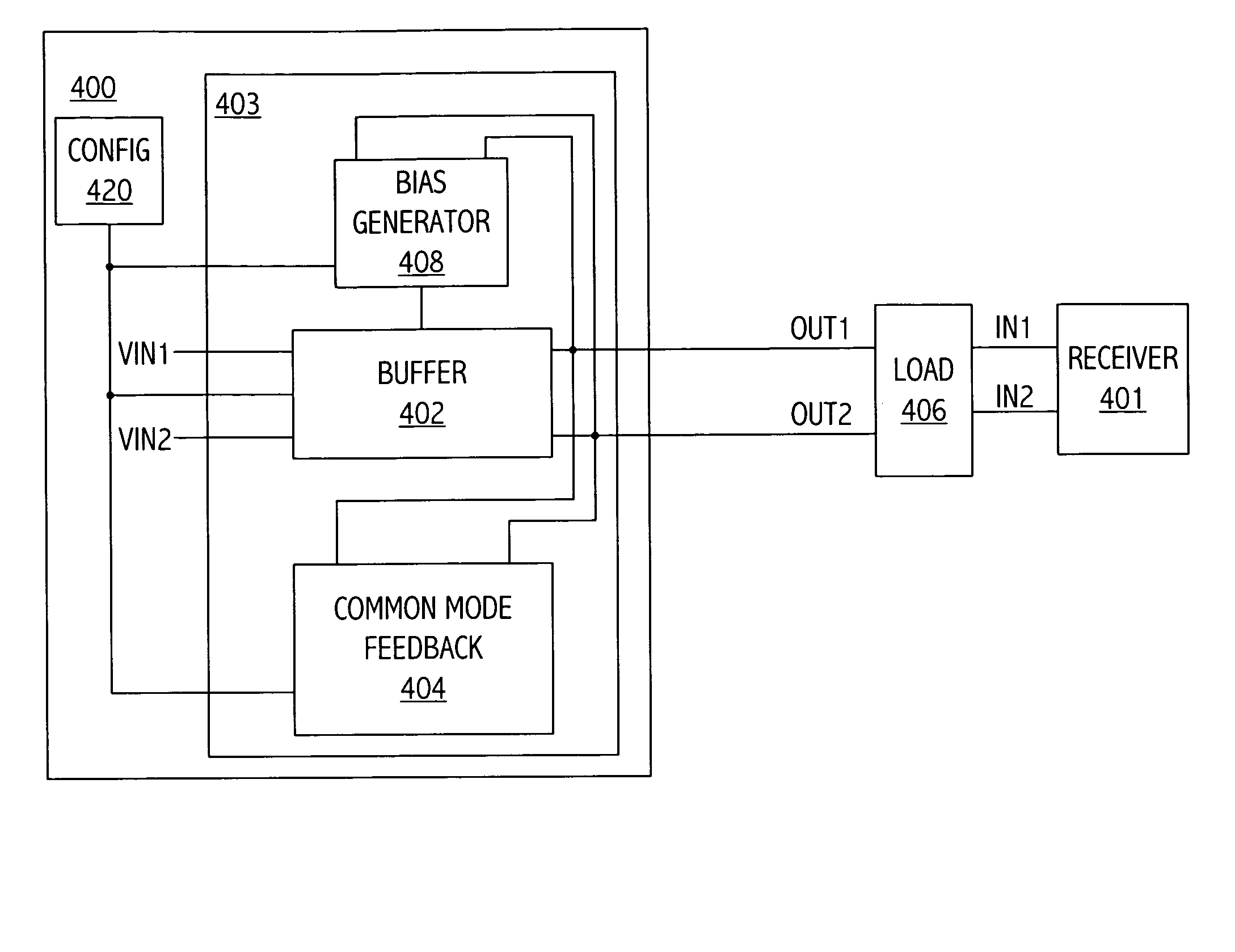
Multi-Stage Fully Differential Amplifier with Controlled Common Mode Voltage
ActiveUS20130169361A1Cancel noiseNoise minimizationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Disclosed are systems and methods to achieve a low noise, fully differential amplifier with controlled common mode voltages at each stage output but without the requirement of a common mode feedback loop. Common mode voltages are adjusted by adjusting the currents flowing through the load impedances (bias currents) wherein the currents are derived from one or more voltage-to-current converters based on an impedance that matches to the load impedances of the stages of the amplifier. The amplifier invented is primarily used for amplification of low frequency signals. The amplifier has one or more gain stages applying only one conduction type of transistors of an IC technology that has the lowest transition frequency between 1 / f noise and white noise to achieve a low chopping or autozeroing frequency.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
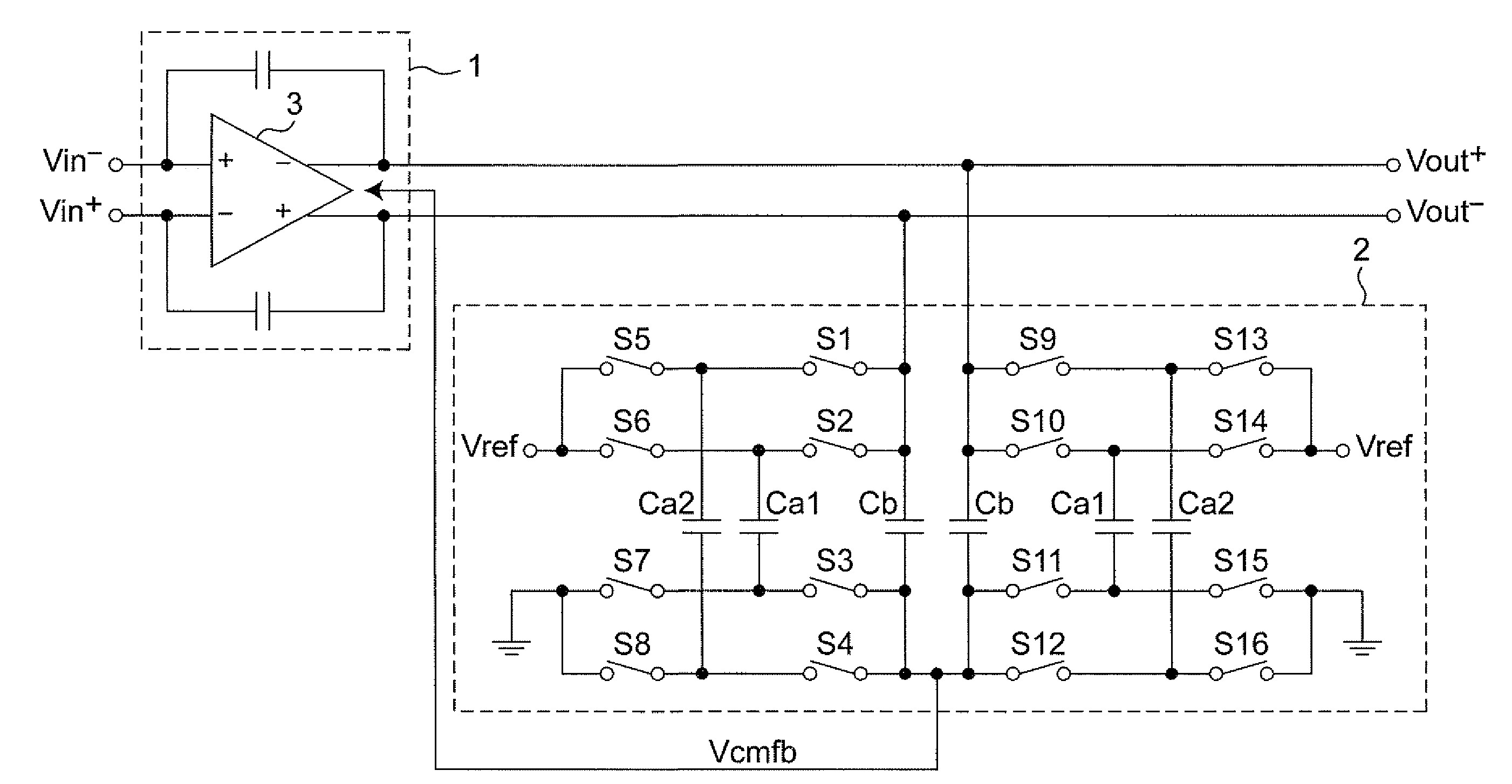
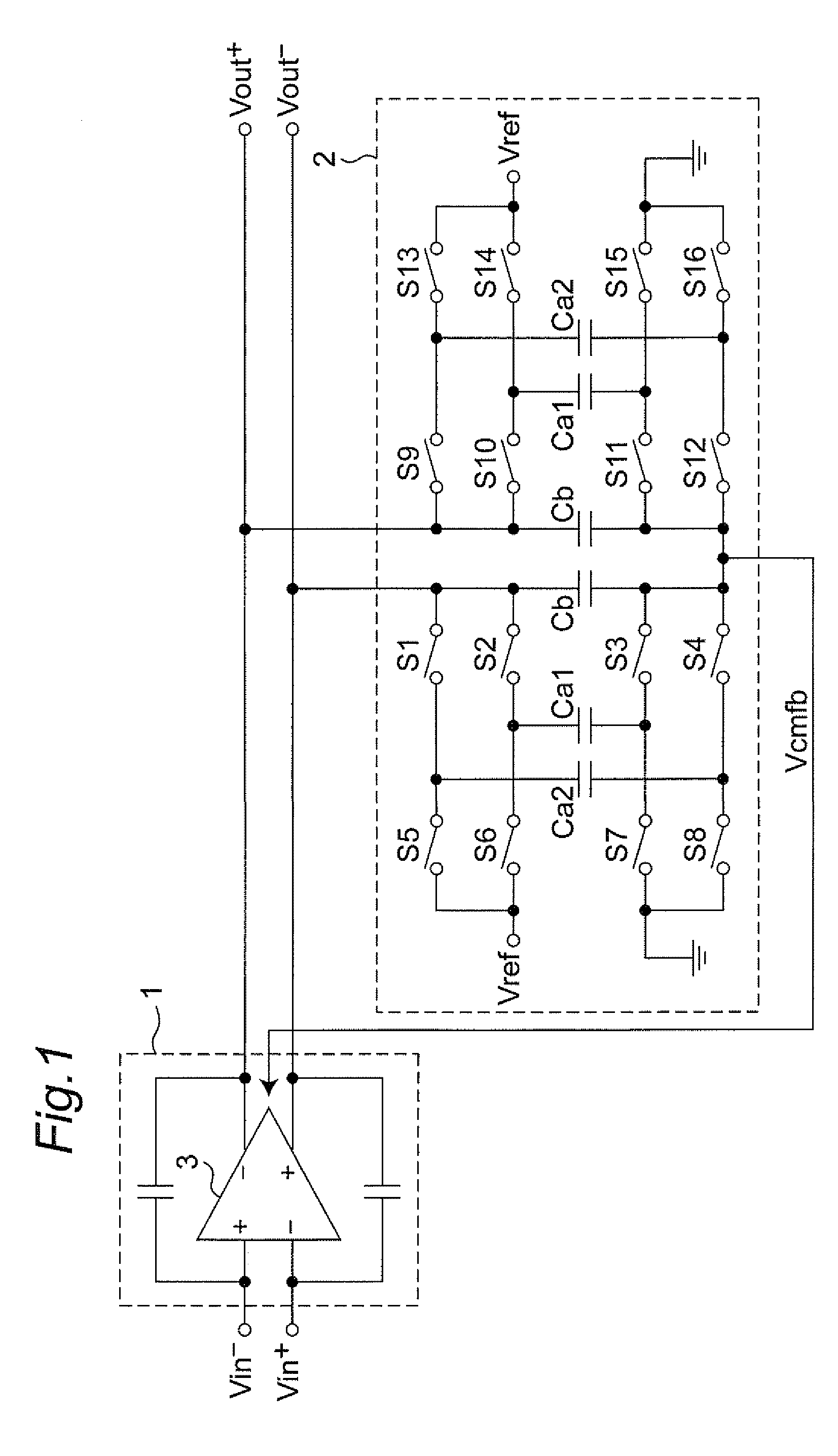
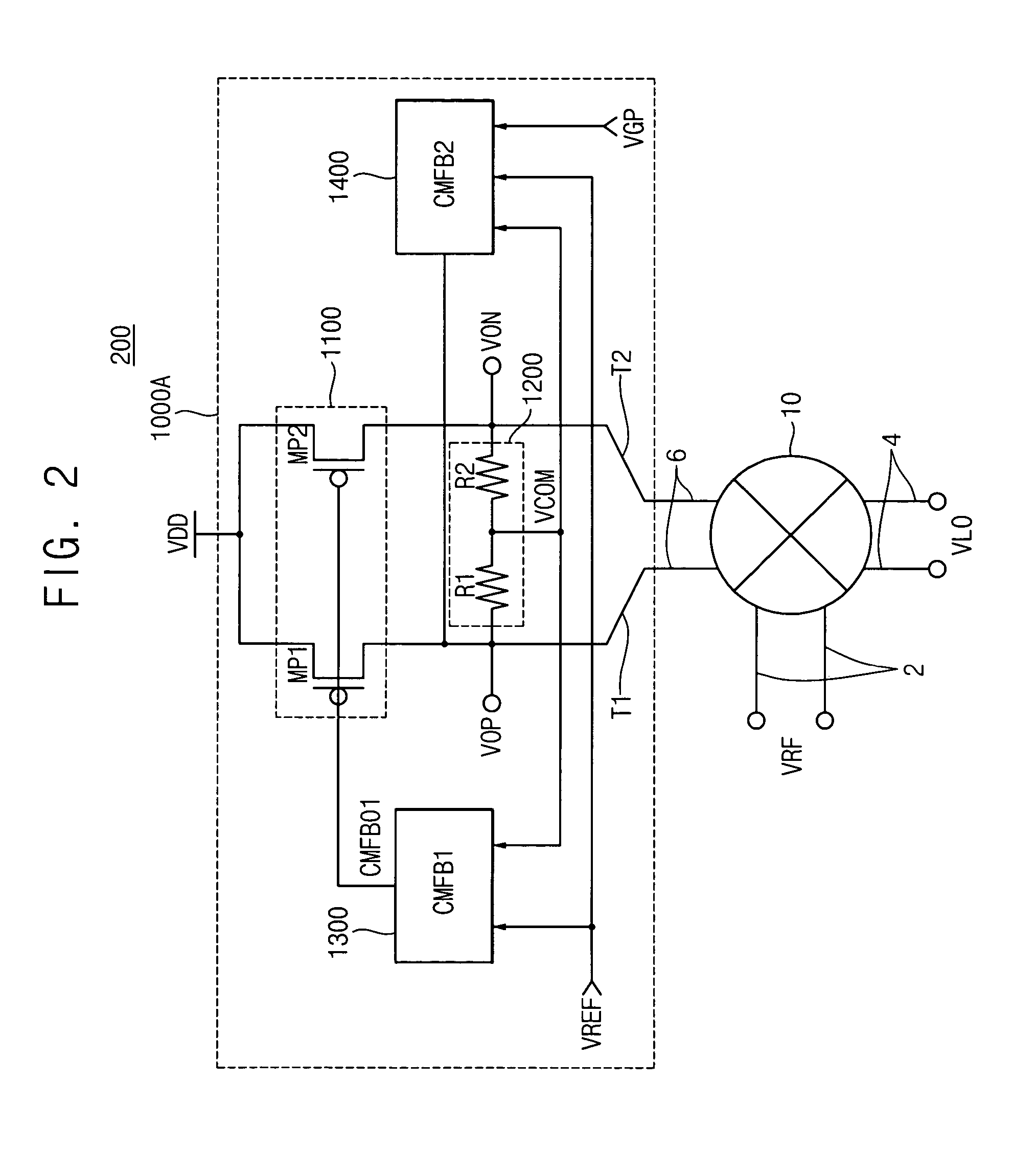
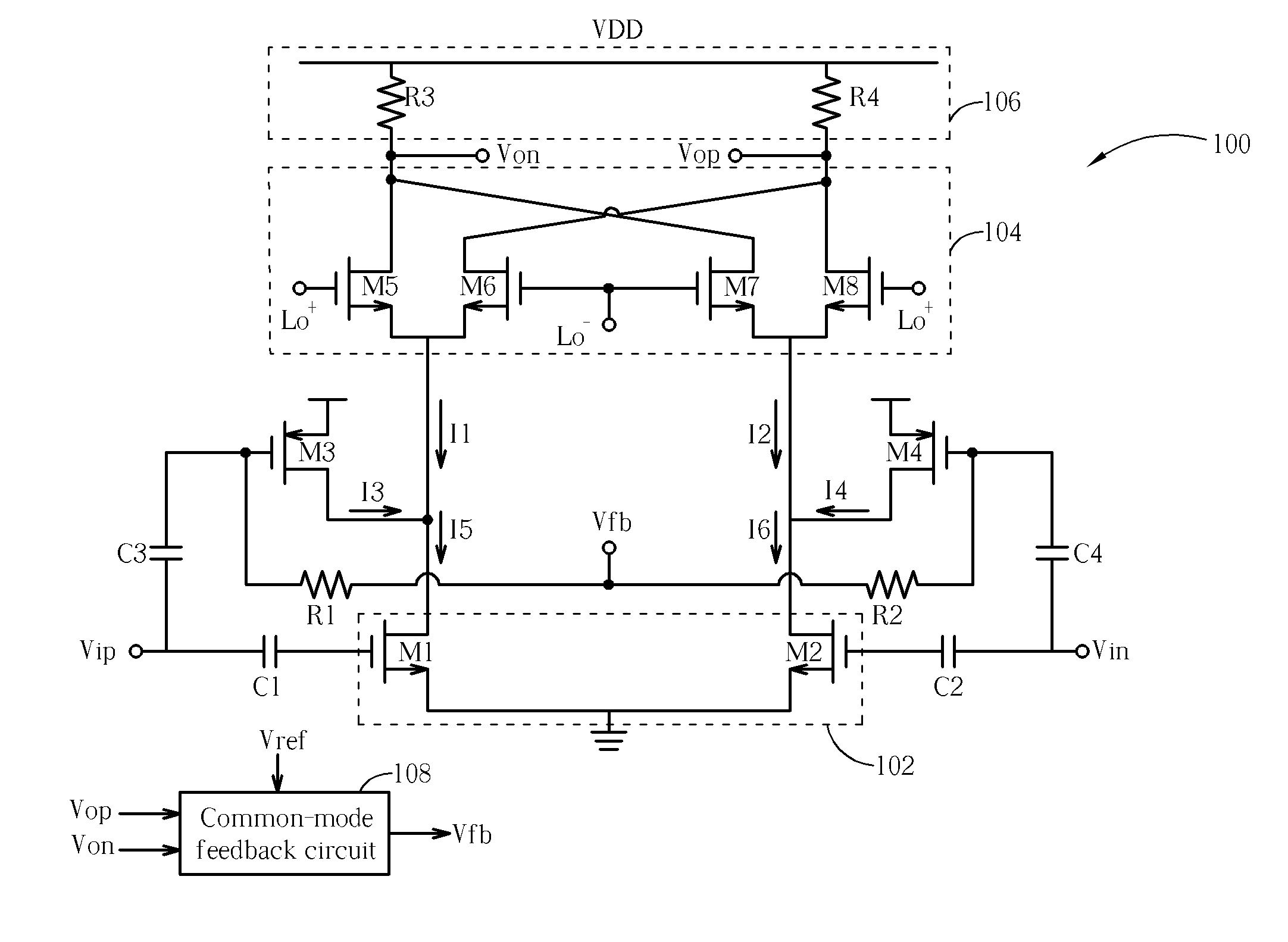
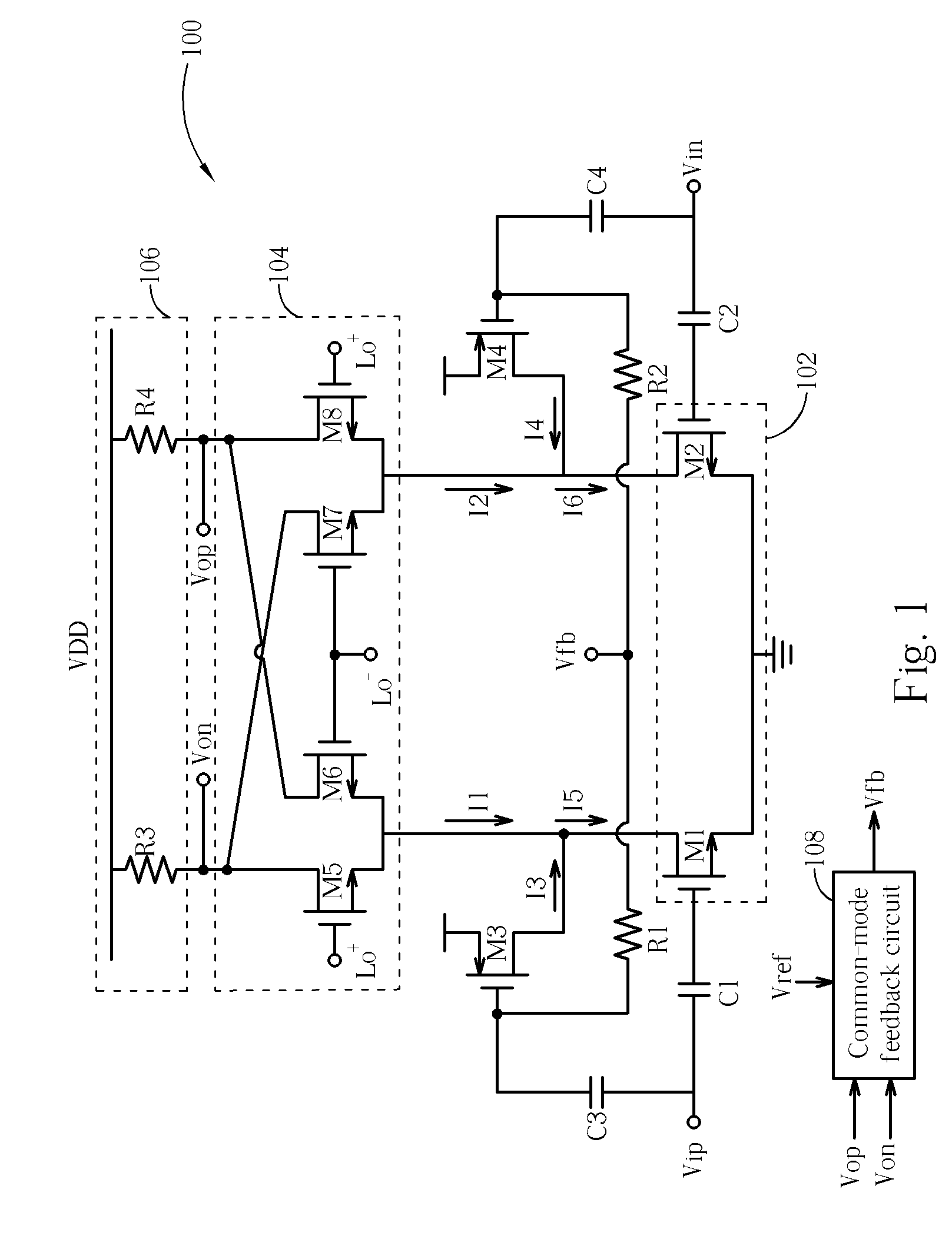
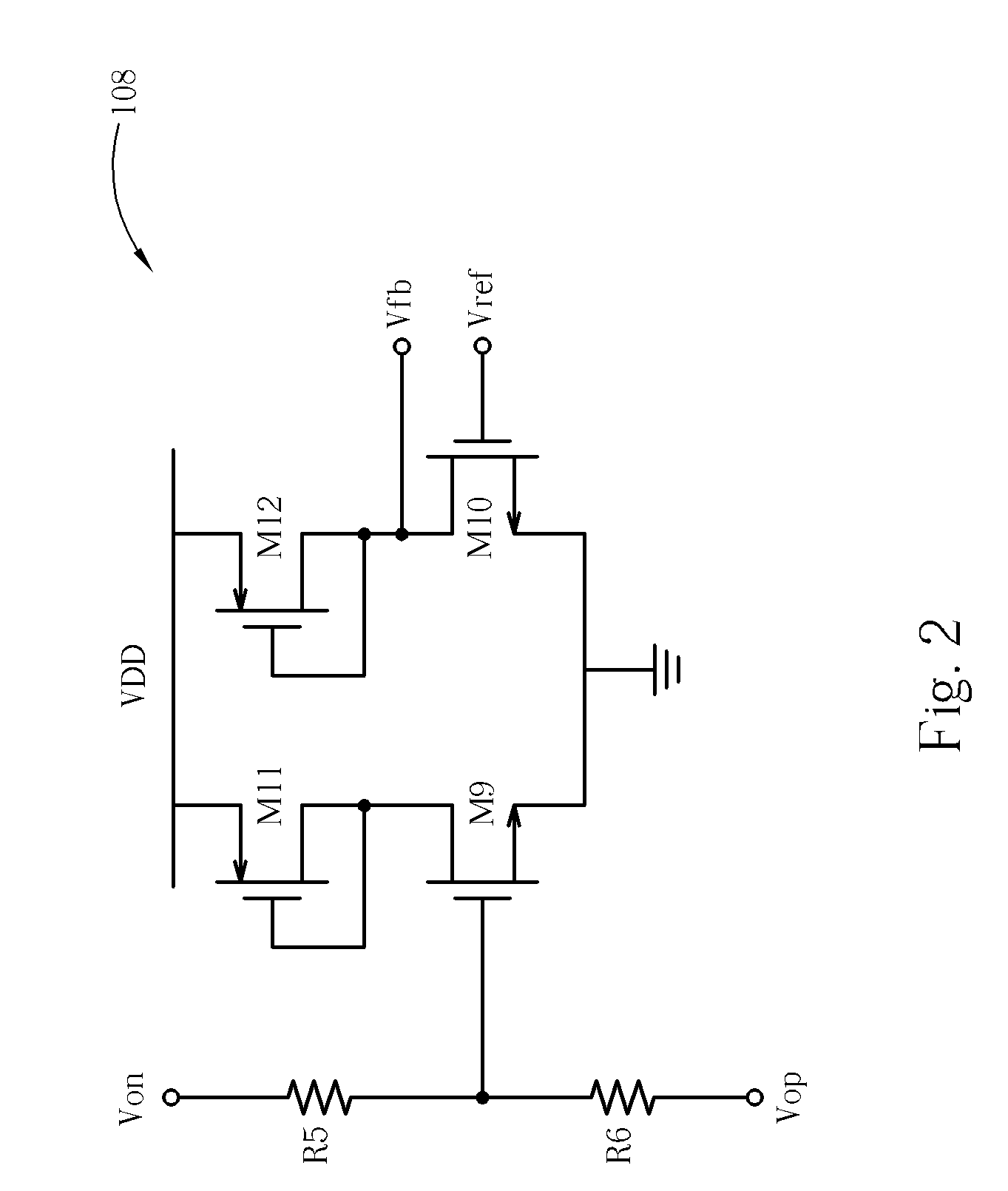
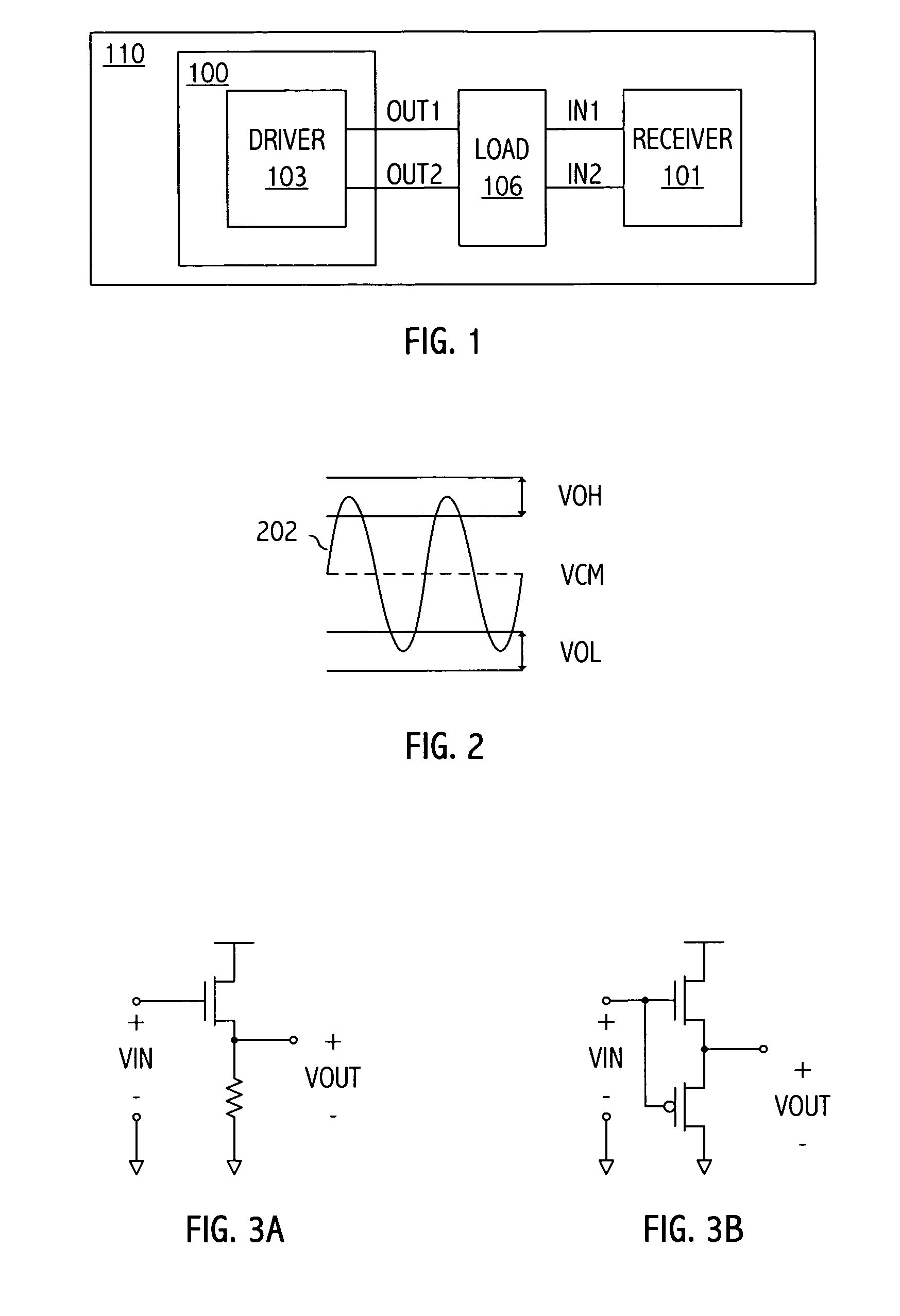
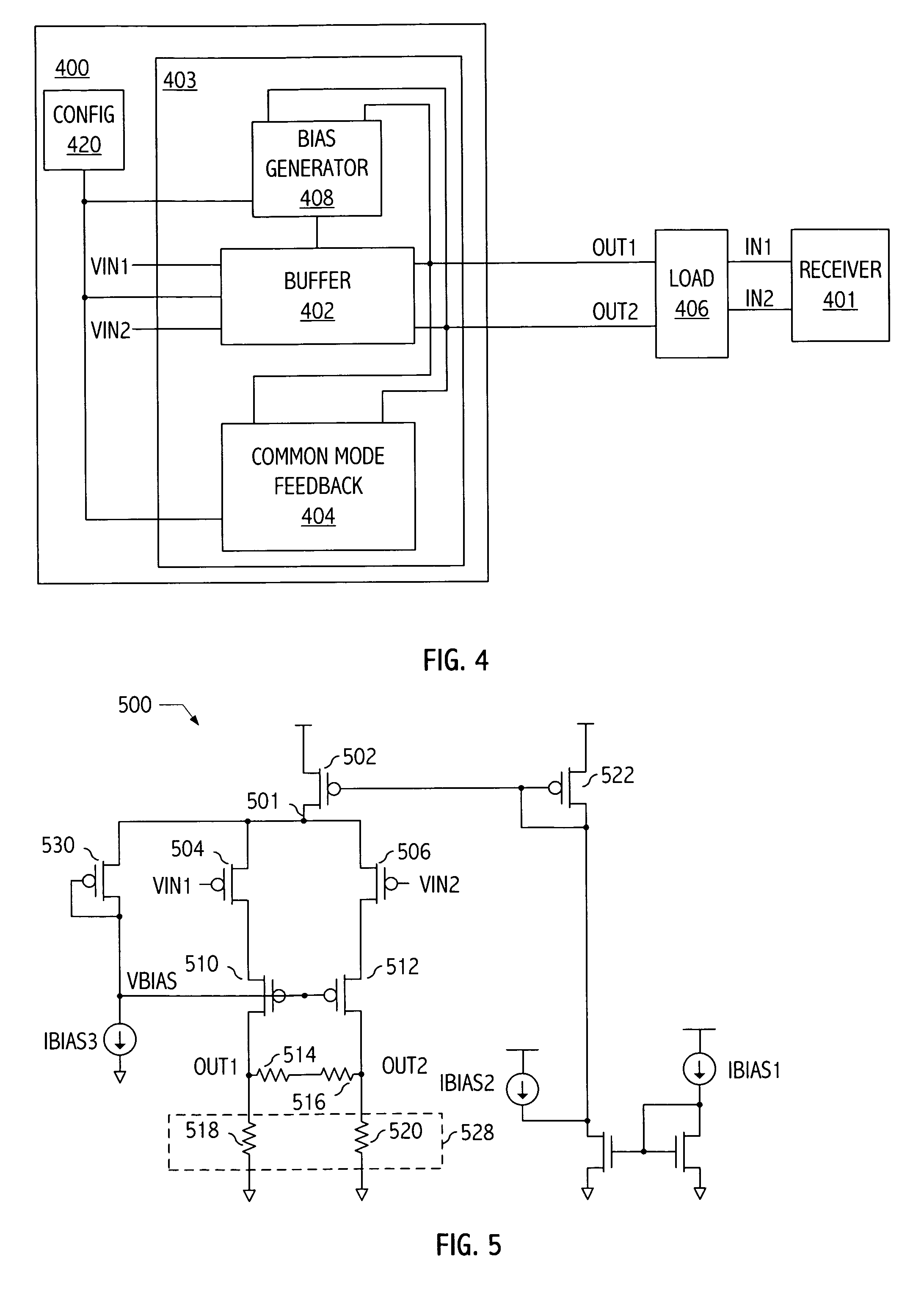
Output driver with common mode feedback
A complementary metal-oxide semiconductor output driver provides a differential output signal having a particular differential voltage swing and a particular common mode voltage to a differential output node for various types of load circuits coupled to the differential output node. The load circuit may have any impedance within a particular impedance range. A current source provides a current with a variable current component that adjusts the differential voltage swing of the differential output signal. A common mode feedback circuit adjusts the common mode voltage of the differential output signal by sourcing current to the differential output node or sinking current from the differential output node. At least a portion of a current flowing into a load circuit coupled to the differential node is provided by the current source, thereby reusing current from the current source.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
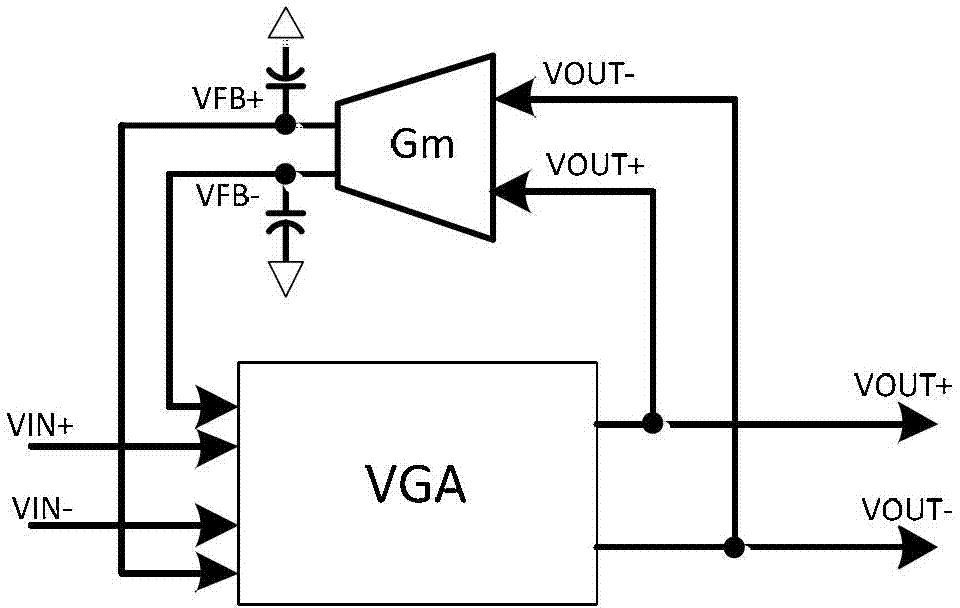
Variable gain amplifier for linearity optimization at low gain
InactiveCN101826843AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDifferential amplifiersEngineeringLinearity
The invention discloses a variable gain amplifier (VGA) for linearity optimization at low gain, belonging to the technical field of analogue integrated circuits. The variable gain amplifier adopts pseudo-indexes to approximately realize linear variation by decibel. The variable gain amplifier is formed by a variable transconductance array, a bias current array, a digital control circuit, a transistor variable load connected with a diode, and a common-mode feedback circuit. The VGA realizes the variable gain of the VGA through changing the bias current of the variable transconductance and the variable load and realizes the linearity optimization when the gain of the VGA is low. Since the bias current of the variable transconductance array is very small at low gain, the variation of the width-to-length ratio effective value of the variable transconductance array does not have great impacts on the overall power consumption of the VGA. A circuit structure can be realized by using a CMOS technology.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Data bit (dB) linear variable gain amplifier
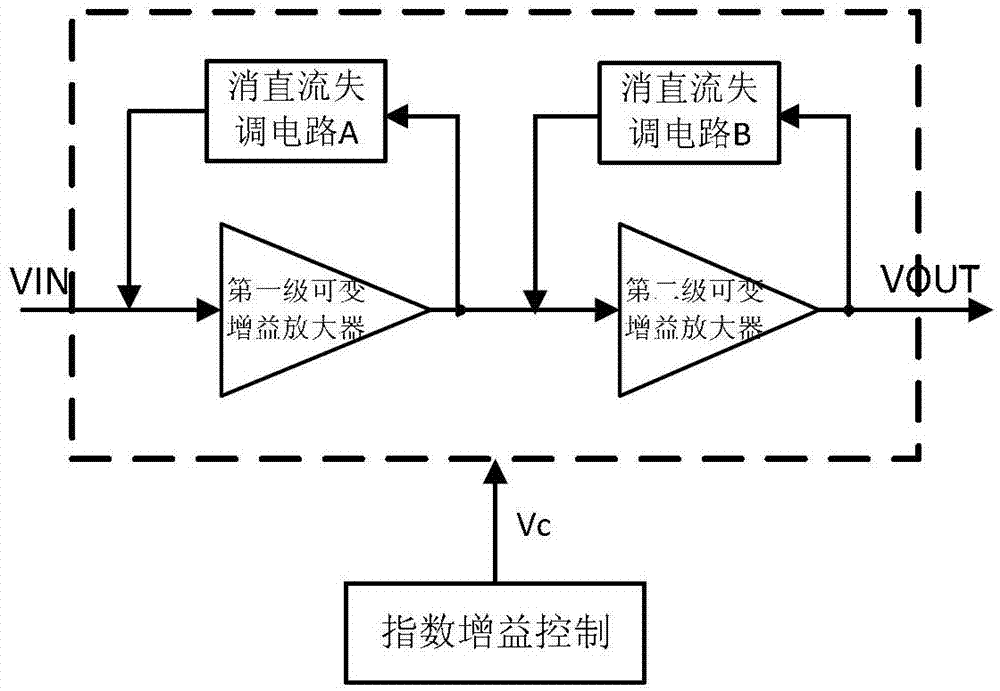
InactiveCN103036517AReduce gainEliminate the effect of DC offsetGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
The invention discloses a data bit (dB) linear variable gain amplifier. The dB linear variable gain amplifier is formed by a premier variable gain amplifier, a removing direct current offset circuit A, a secondary variable gain amplifier, and a removing direct current offset circuit B which are used for amplifying signals or weakening and removing direct current offset. Control voltage and gain of the amplifiers are enabled to be in an exponential relationship by an index gain control circuit. Each removing direct current offset circuit is formed by a GM-C tan-conductance filter and a common-mode feedback circuit. Input of the premier variable gain amplifier is used as input of the whole circuit. Output of the premier variable gain amplifier is connected with input of the secondary variable gain amplifier. Output of the secondary variable gain amplifier is used as output of the whole circuit. The dB linear variable gain amplifier is improved based on a Gilbert unit, is used in an automatic gain control circuit, and enables the amplifier to have larger broadband and better linear degree.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for compensating frequency of wideband common mode feedback loop of two-stage operational amplifier
InactiveCN101355346ASimple designReduce power consumptionDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesRing circuitControl signal
The invention discloses a method for compensating the frequency of a broadband common mode feedback ring circuit for a two-stage operational amplifier, belonging to the field of analog integrated circuit design. A broadband feedback amplifier in the two-stage operational amplifier with the Miller compensation is used as the common mode feedback ring circuit so as to reduce the area and the power consumption of the common mode feedback circuit; the two-stage operational amplifier has only one main pole in the range of the unit gain bandwidth, a fully differential input and output structure is adopted, the sampling of the common mode output level is performed by the differential output end; and a control signal fed back by the common mode simultaneously controls the output level of a first-stage common mode and the output level of a second-stage common mode of the operational amplifier through a controllable bias circuit. The frequency of the main pole of the broadband feedback amplifier is far higher than the unit gain bandwidth of the operational amplifier, therefore the margin of phase position of the common mode ring circuit is basically equal to that of the operational amplifier, thereby forming the stable feedback ring circuit. The method has the advantages of few elements for a common mode feedback circuit, lower power consumption of the common mode feedback circuit and simpler and more convenient circuit design.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
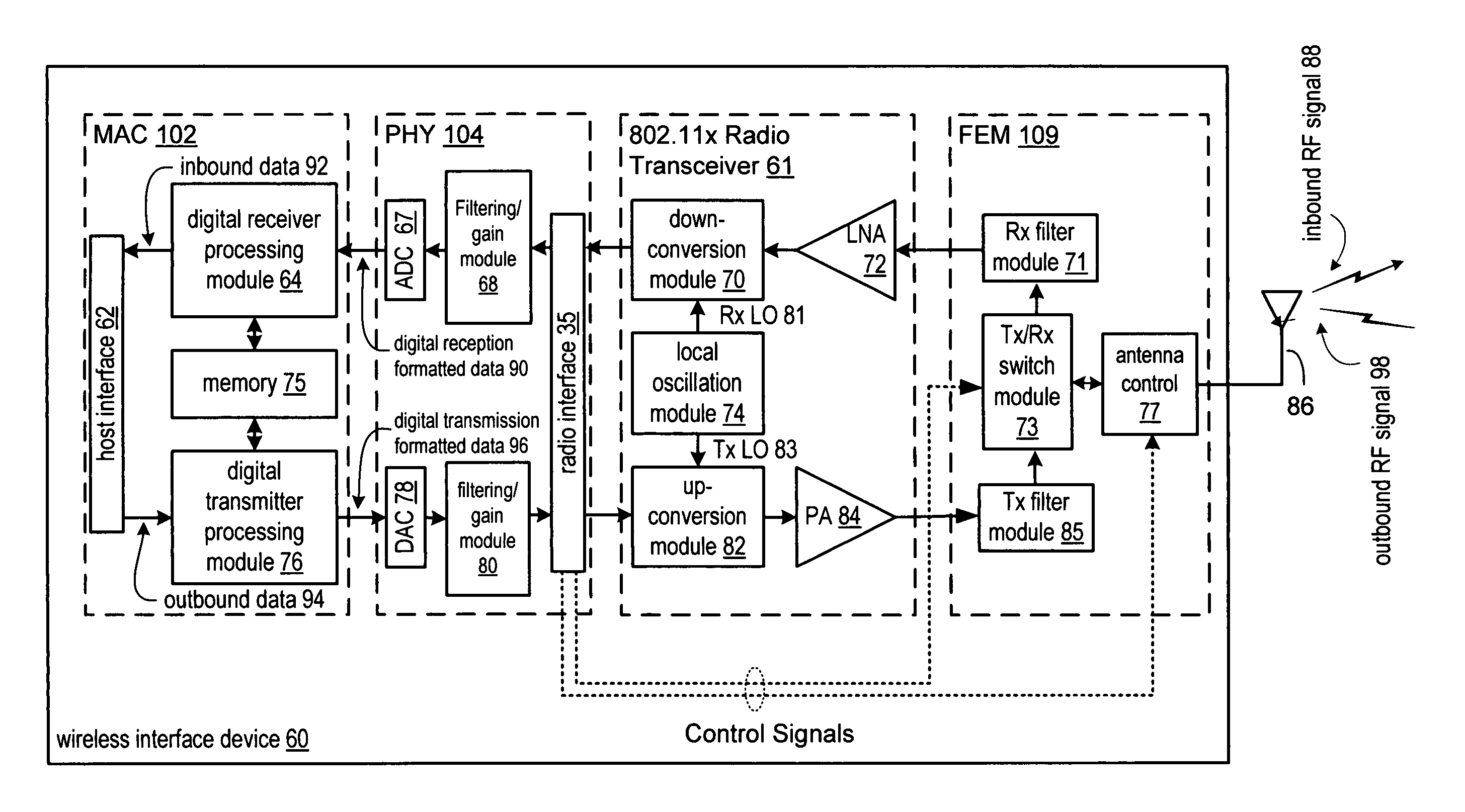
RX dual-band mixer
A dual-band input transceiver block is formed to operably receive one of a 2.4 GHz radio frequency signal or a 5.0 GHz radio frequency transceiver signal in a manner that minimizes duplication of circuitry and creates a combined circuit path for RF front end input stages for much of the input stage. More specifically, the embodiments of the present invention include separate amplification and mixing stages whose outputs are combined by a stabilized load with circuitry for removing a common mode feedback signal. As such, downstream components, such as amplifiers, filters, analog-to-digital converters, and other input path circuit elements, are not duplicated and may be used regardless of whether the dual-band transceiver is operating in a first or second frequency band. Operation is, in the described embodiment, only one frequency input at a time though the invention is not limited to such operation. More specifically, a first input section is operably coupled to receive a first local oscillation input and a first frequency band signal input. A second input section is coupled to receive a second local oscillation input and a second frequency band signal input. Outputs of the first and second input sections are produced to a stabilized load with a common mode feedback block for removing a common mode feedback signal. As such, an output signal is produced having a regulated DC level and having any common mode feedback signal eliminated there from.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low noise mixer
ActiveUS20070142018A1Decreasing flicker noise phenomenonModulation transferenceTransmissionLow noiseLoad circuit
Disclosed is a mixer comprising: a switching circuit, having a first pair of differential signal nodes and a second pair of differential signal nodes, for switching according to a local oscillation signal; an amplifying stage circuit, for receiving an input signal and amplifying the input signal; a load circuit, for serving as the loading of the mixer and generating an output signal of the mixer; a common-mode feedback circuit, for receiving the output signal and generating a feedback signal according to the output signal; a first current source, for receiving the feedback signal and generating a first current according to the feedback signal; and a second current source, for receiving the feedback signal and generating a second current according to the feedback signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Output driver with common mode feedback
A complementary metal-oxide semiconductor output driver provides a differential output signal having a particular differential voltage swing and a particular common mode voltage to a differential output node for various types of load circuits coupled to the differential output node. The load circuit may have any impedance within a particular impedance range. A current source provides a current with a variable current component that adjusts the differential voltage swing of the differential output signal. A common mode feedback circuit adjusts the common mode voltage of the differential output signal by sourcing current to the differential output node or sinking current from the differential output node. At least a portion of a current flowing into a load circuit coupled to the differential node is provided by the current source, thereby reusing current from the current source.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Switch-capacitor integrator
InactiveCN101621292ARelax requirementsOptimize topologyElectric pulse generator detailsLogic circuitsCapacitanceIntegrator
The invention discloses a switch-capacitor integrator adopting novel C-class inverters and a switch-capacitor integrator realizing form of a pseudodifferential structure. The switch-capacitor integrator in a pseudodifferential structure comprises two novel C-class inverters (60) and capacitors such as a sampling capacitor CS, a compensation capacitor CC, an integrating capacitor CI, and the like, switches such as an NMOS switch S2, an NMOS switch S4, an NMOS switch S7, an NMOS switch S8, a CMOS switch S3, a CMOS switch S5, a bootstrap NMOS switch S1, a bootstrap NMOS switch S6, a bootstrap NMOS switch S9, and the like and a common mode feedback circuit (61) in the prior art, wherein the two novel C-class inverters (60) are respectively positioned in a positive branch and a negative branch of the integrator and differentially symmetrized to be in the pseudodifferential structure. The invention overcomes the effects of indexes of working efficiency, establishing time, integrating accuracy, power consumption, and the like on the switch-capacitor integrator by technical deviation through the bulk potential modulation effect of a bulk potential modulator in the novel C-class inverters and greatly improves the stability and the robustness of the integrator without obviously increasing the power consumption.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low drop-out voltage regulator with common-mode feedback
InactiveUS7323853B2Increase conversion rateStable output voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationDifferential signaling
The present invention is a LDO voltage regulator circuit with common-mode feedback. The LDO voltage regulator includes an error amplifier with a common-mode feedback unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal to the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the pass device. A capacitor in the compensation unit provides frequency compensation to the LDO voltage regulator. The common-mode feedback unit incorporated into the error amplifier greatly improves a slew rate of a gate voltage of the pass device.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
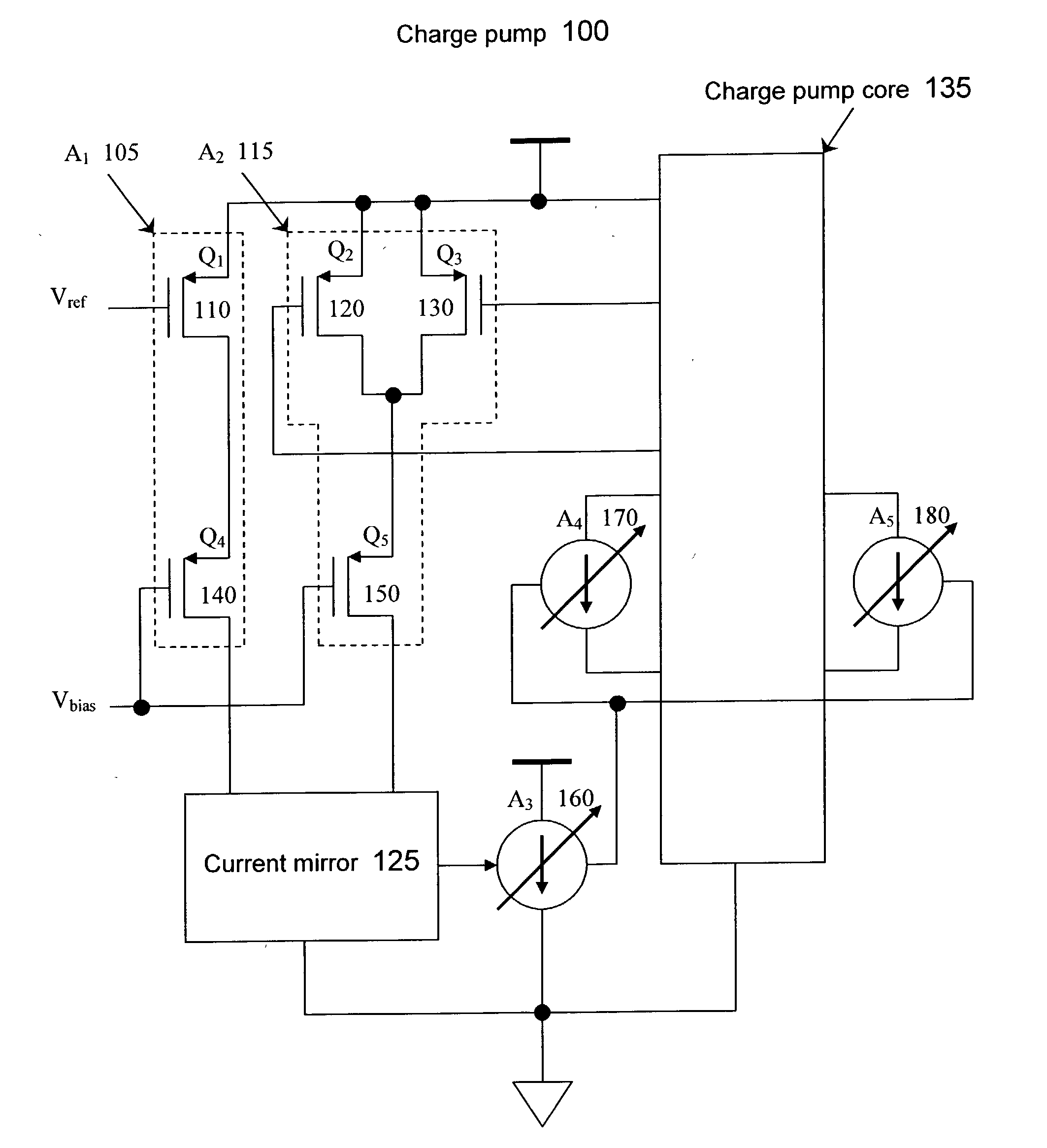
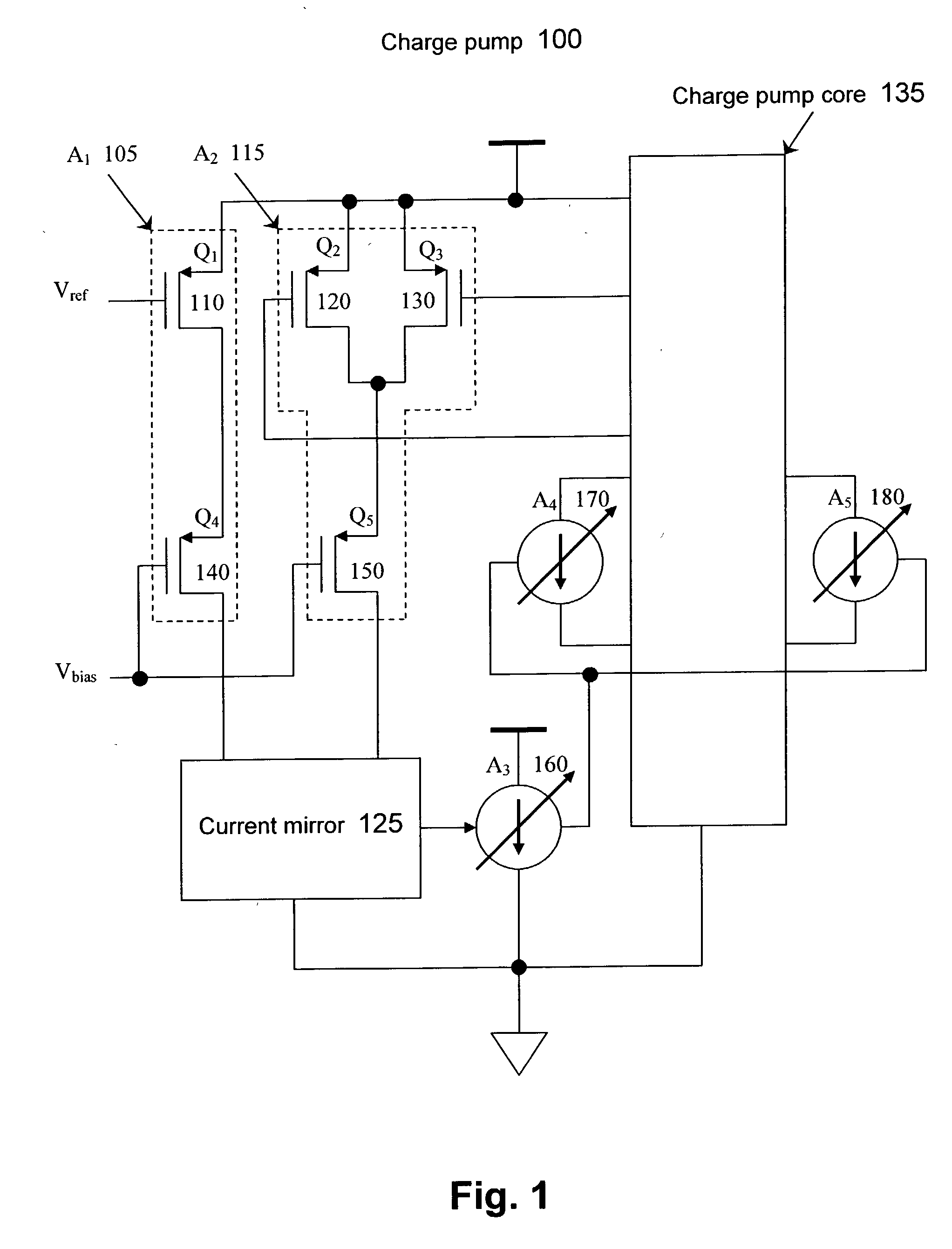
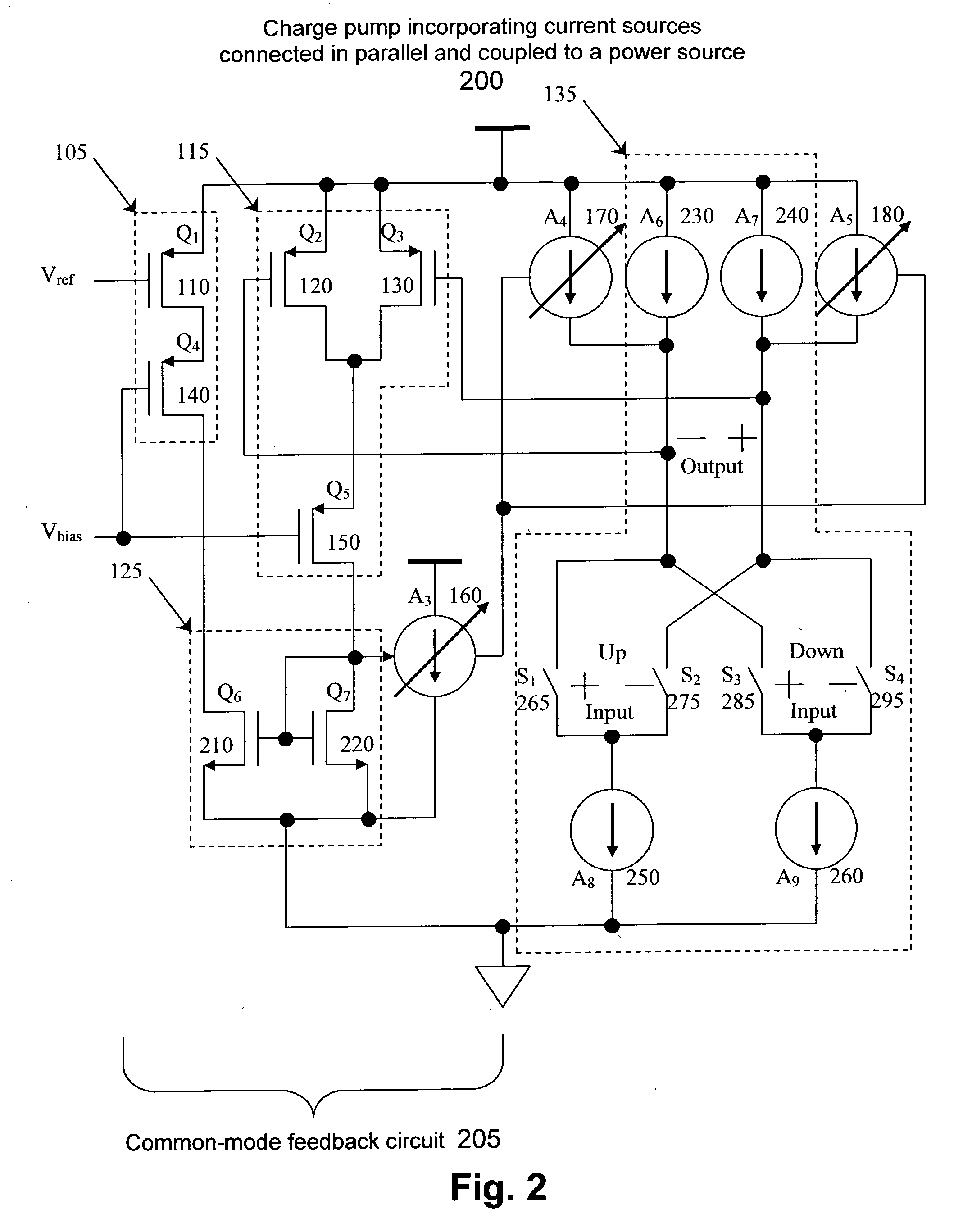
Common mode feedback technique for a low voltage charge pump
A charge pump includes a first current source, a second current source, and a current mirror. The first current source is included to set a common mode output voltage of a charge pump core based on a desired common mode input of the charge pump core. The second current source is included to receive the common mode output voltage from the charge pump core. A first input of the current mirror receives a signal from the first current source, and a second input of the current mirror receives a signal from the second current source.
Owner:INTEL CORP
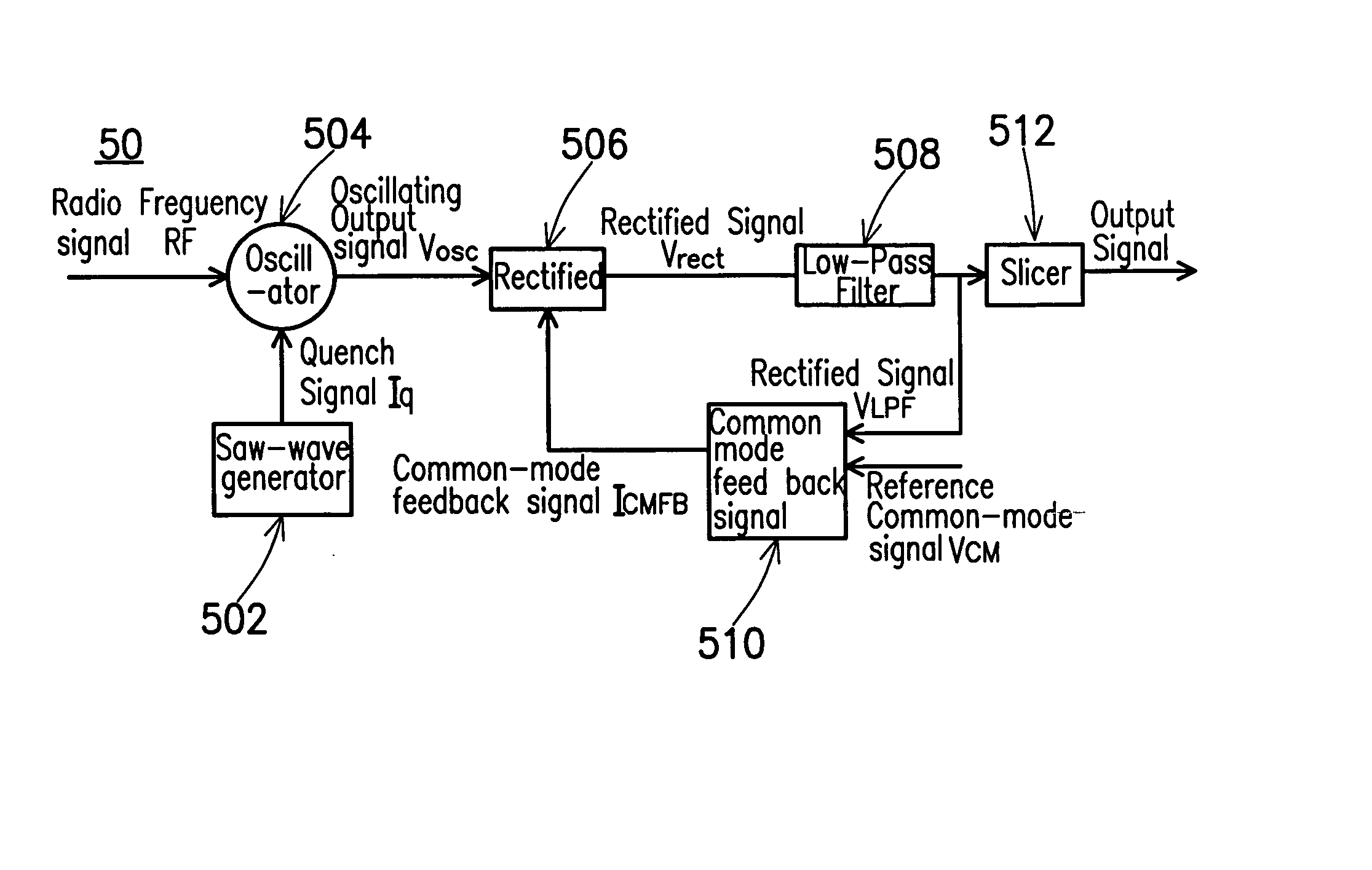
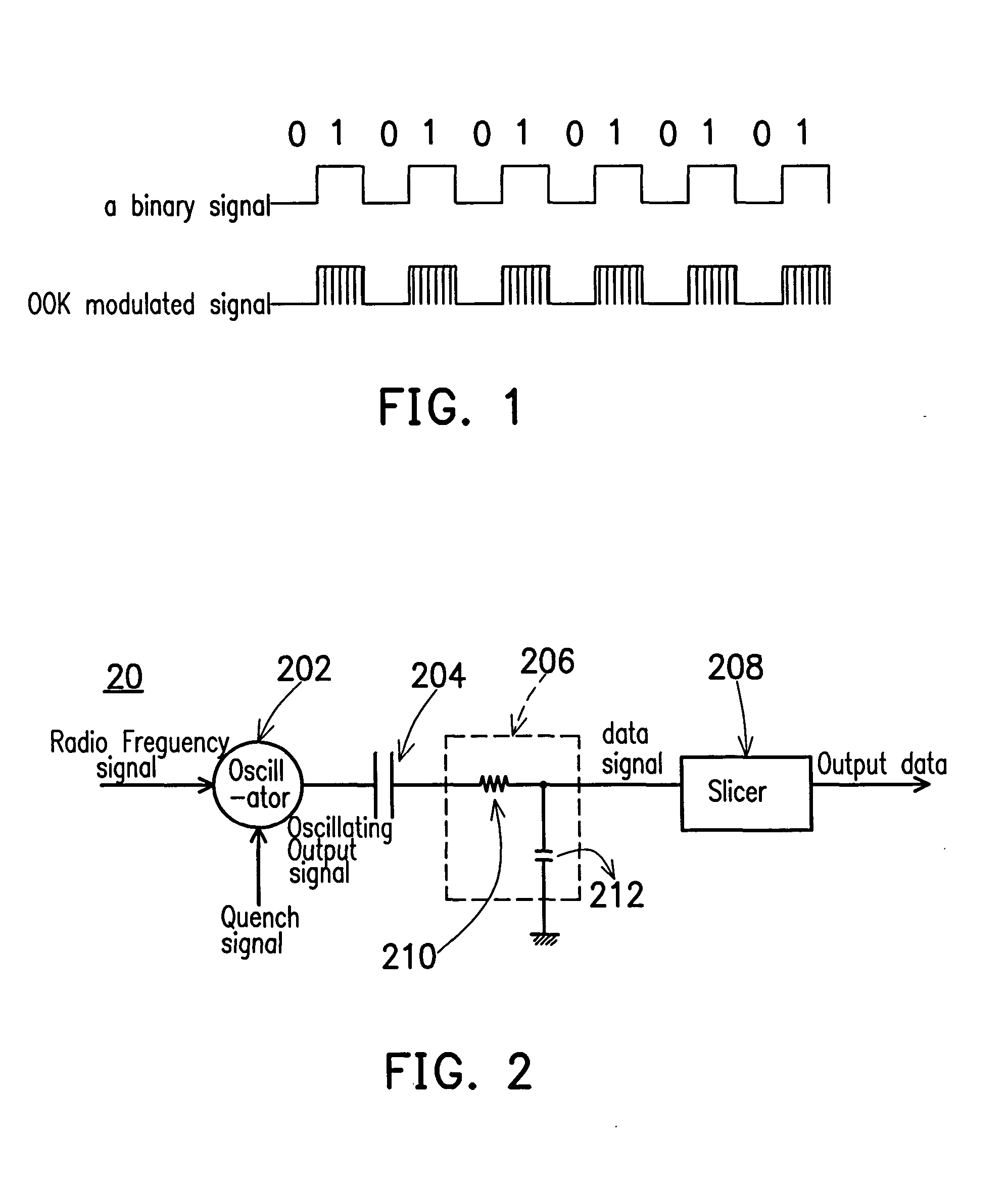
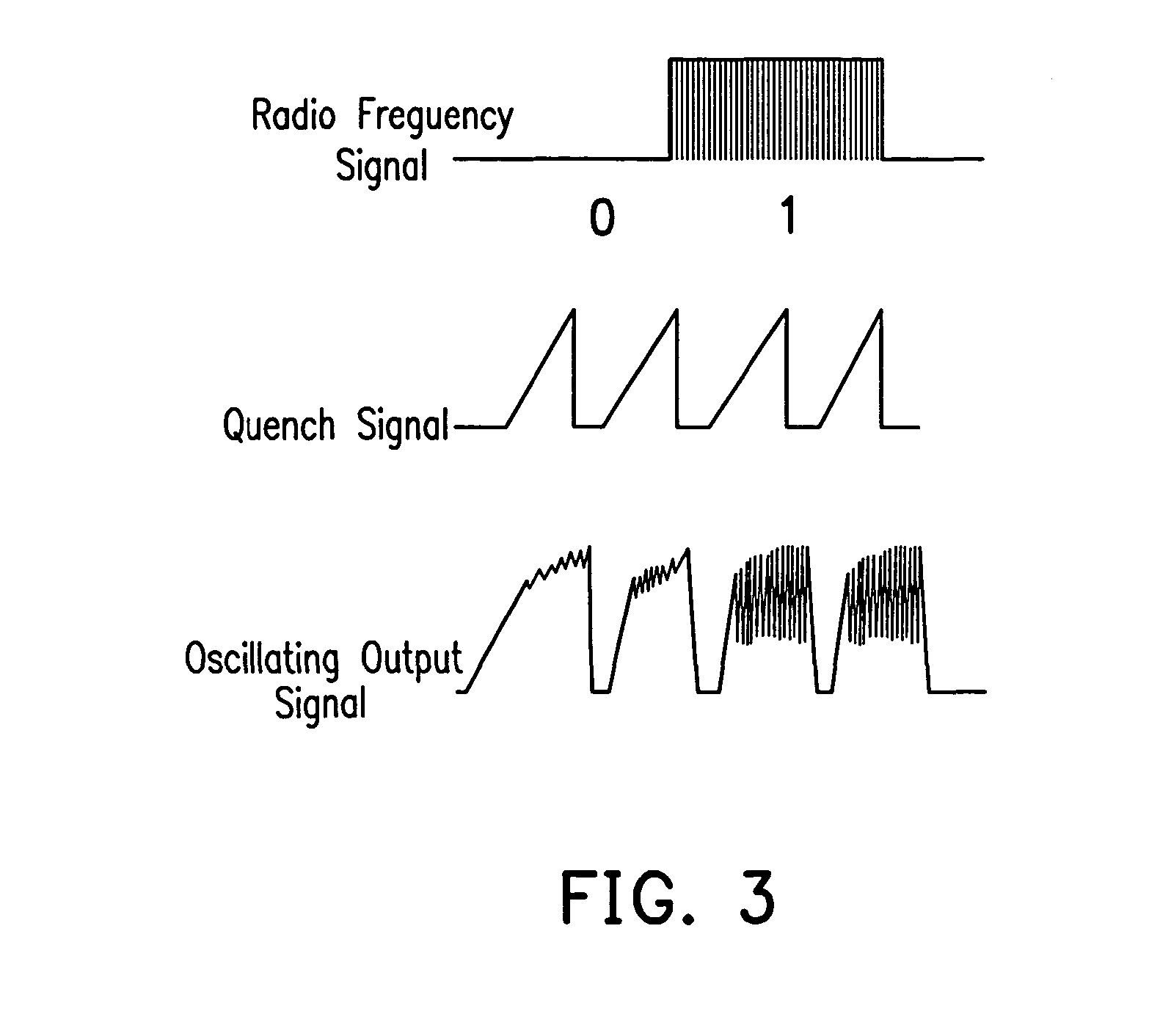
Super-regenerative radio frequency receiver and its data receiving method
InactiveUS20040229585A1Demodulator for amplitude-modulated oscillationsTransmissionTuned radio frequency receiverLow-pass filter
A high sensitivity of a Super-Regenerative Radio Frequency Receiver and its method is provided in the embodiment of the present invention. By using a common-mode feedback circuit and by replacing the rectifier with a feedback integral-rectifier, the rectifier, the low-pass filter, and the slicer will not be saturated during operation so that the output of the slicer is correctly generated, and the sensitivity of the Super-Regenerative Radio Frequency Receiver is greatly improved as a result.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com