Patents
Literature
747results about "Modulation transference balanced arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS20050239430A1Enhanced inhibitory effectLess harmonic suppressionModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
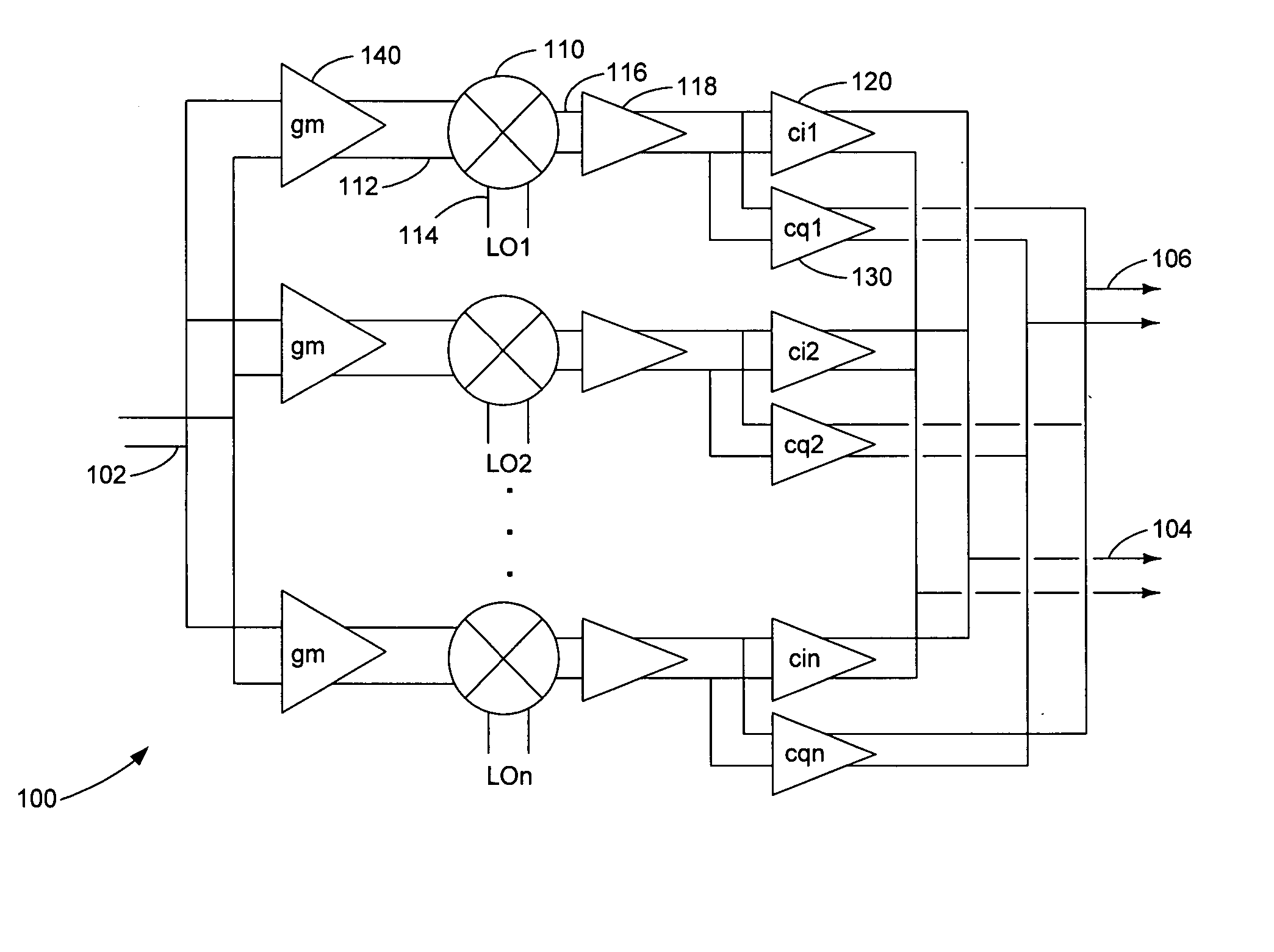
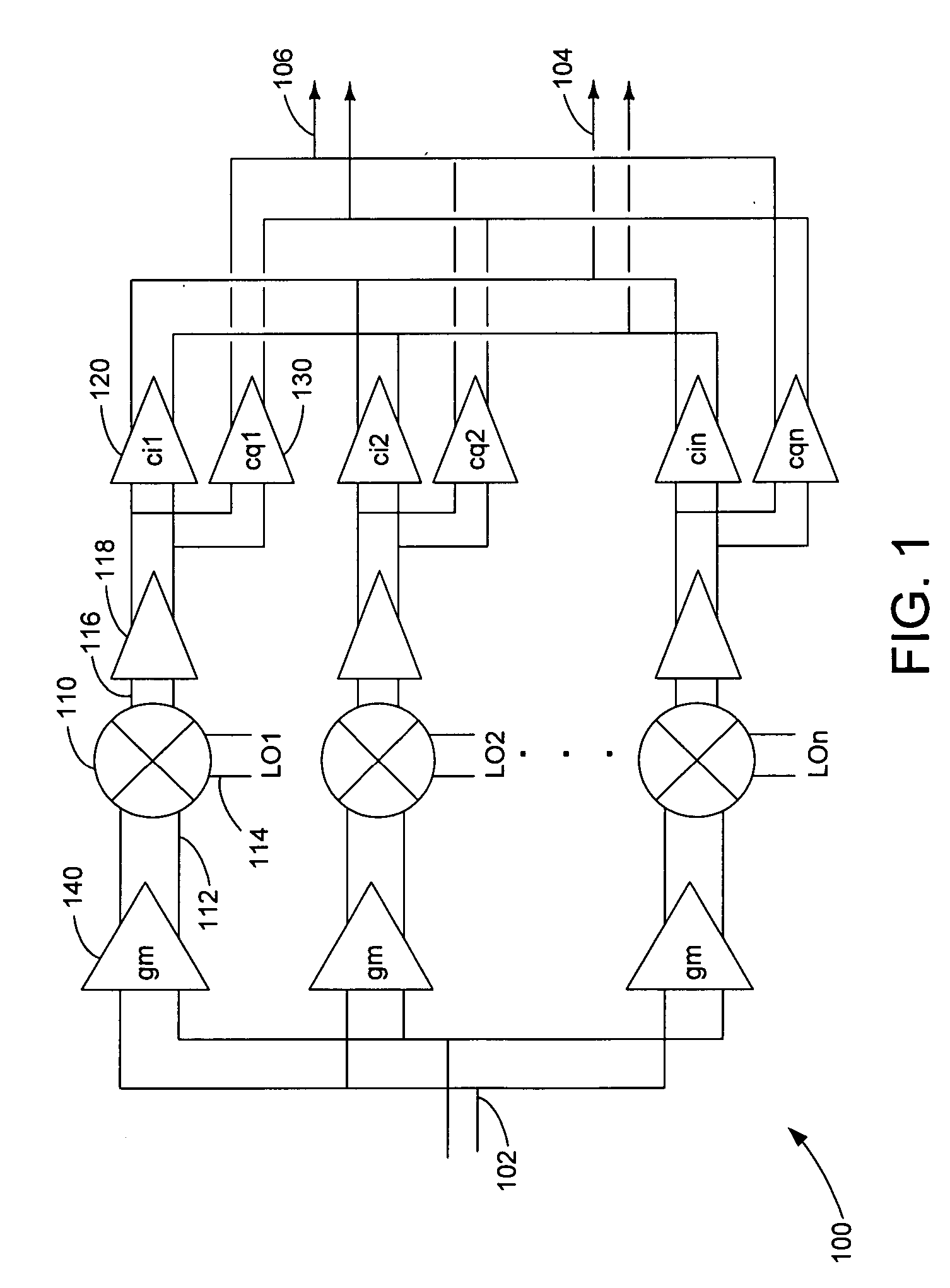
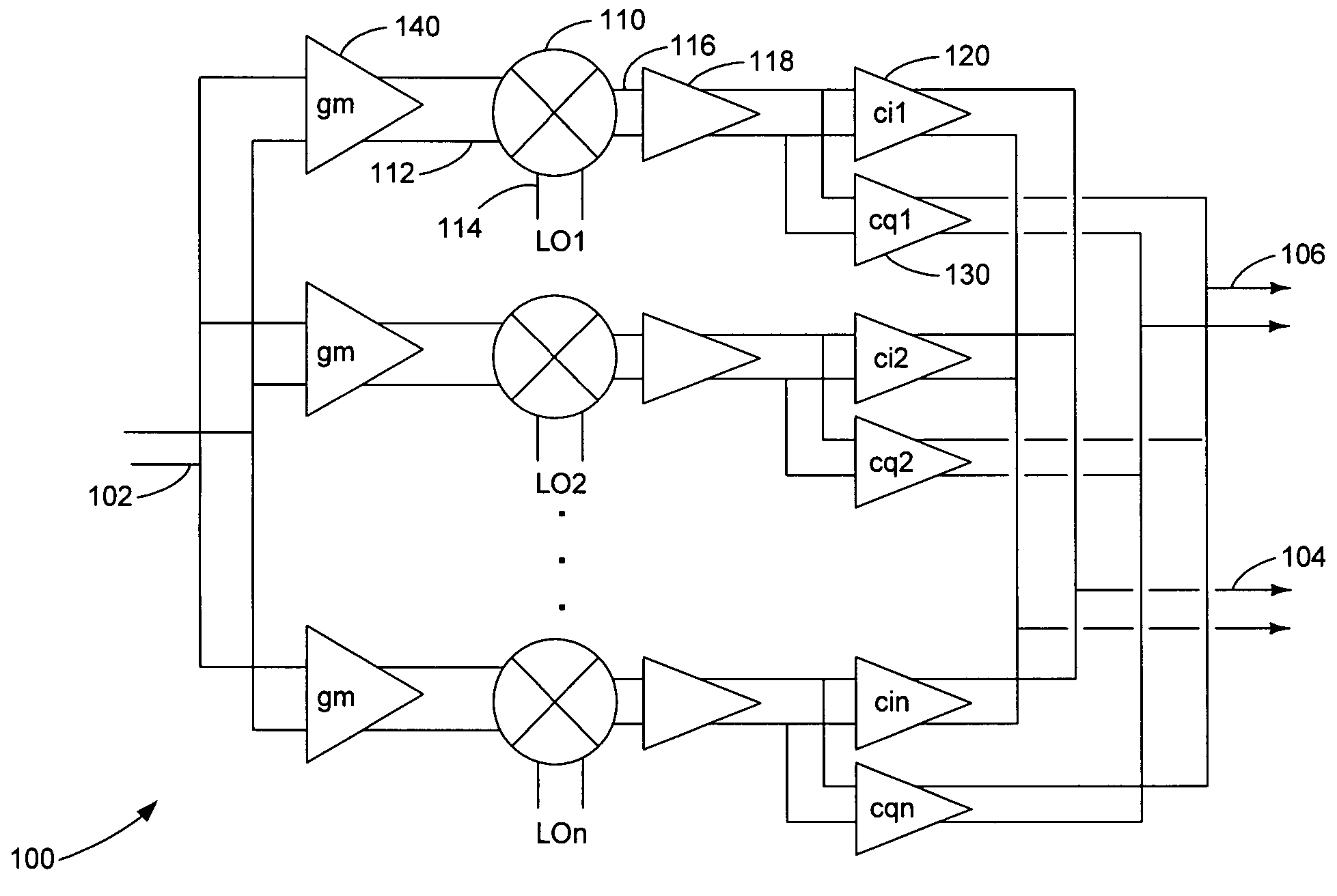
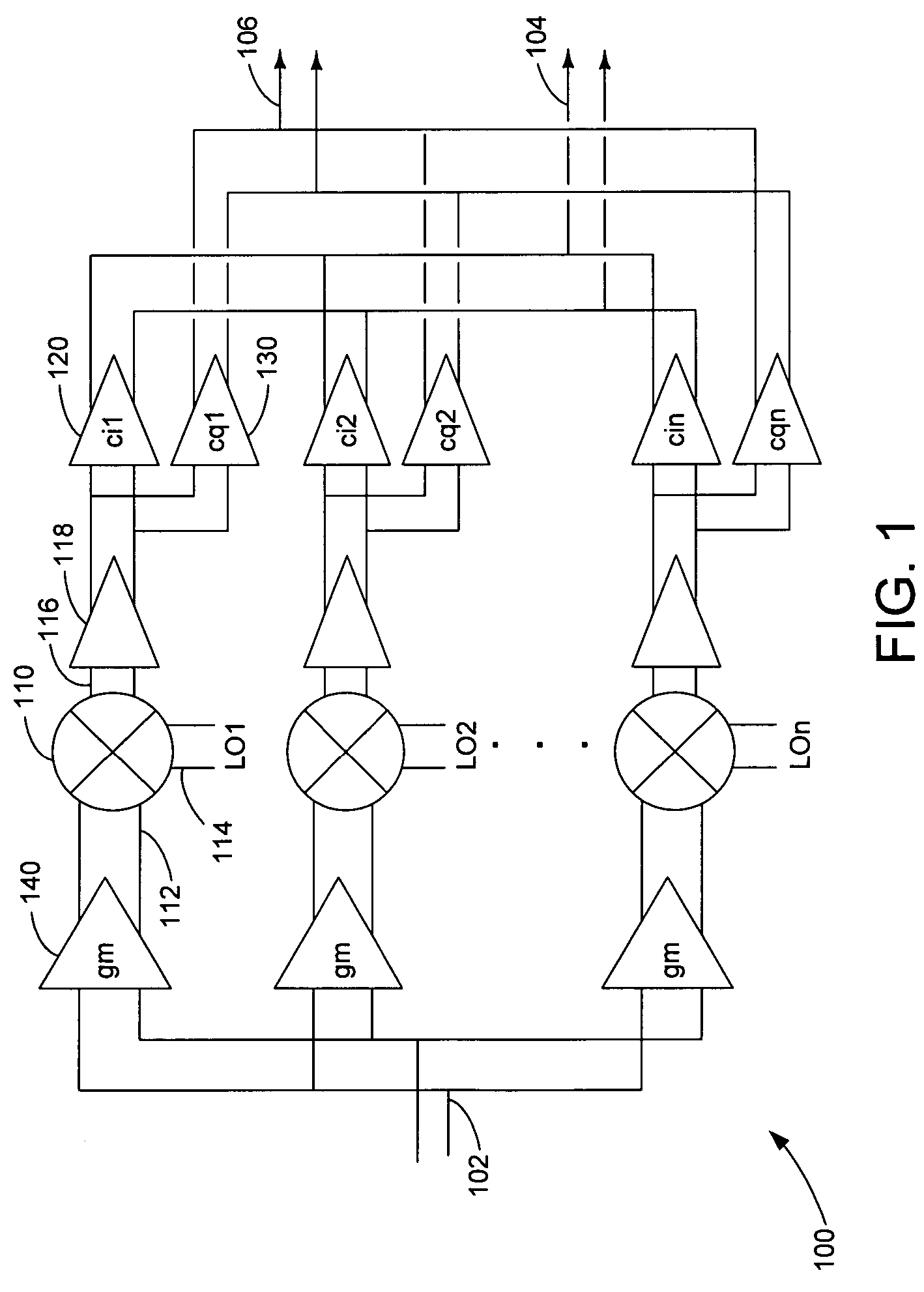
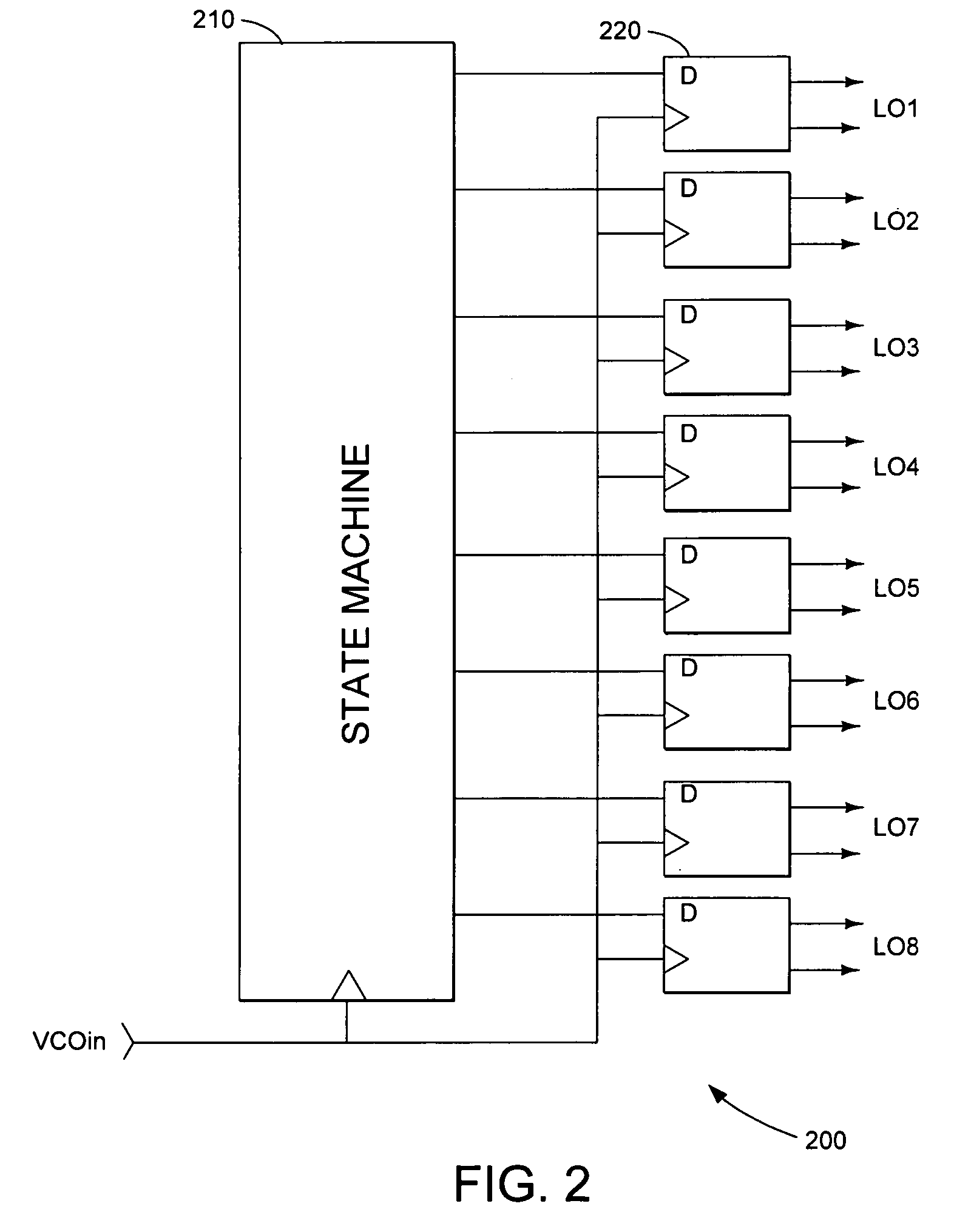
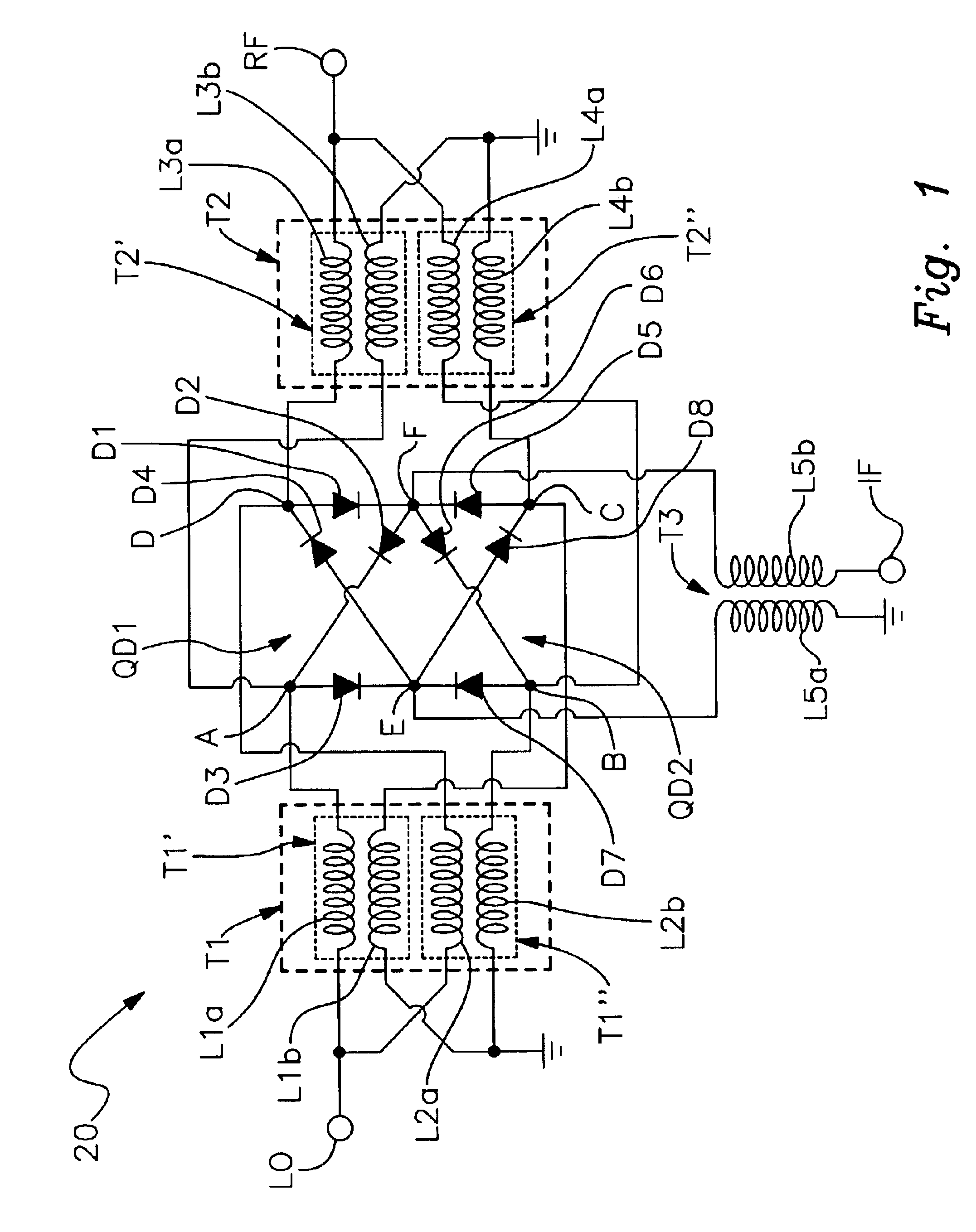
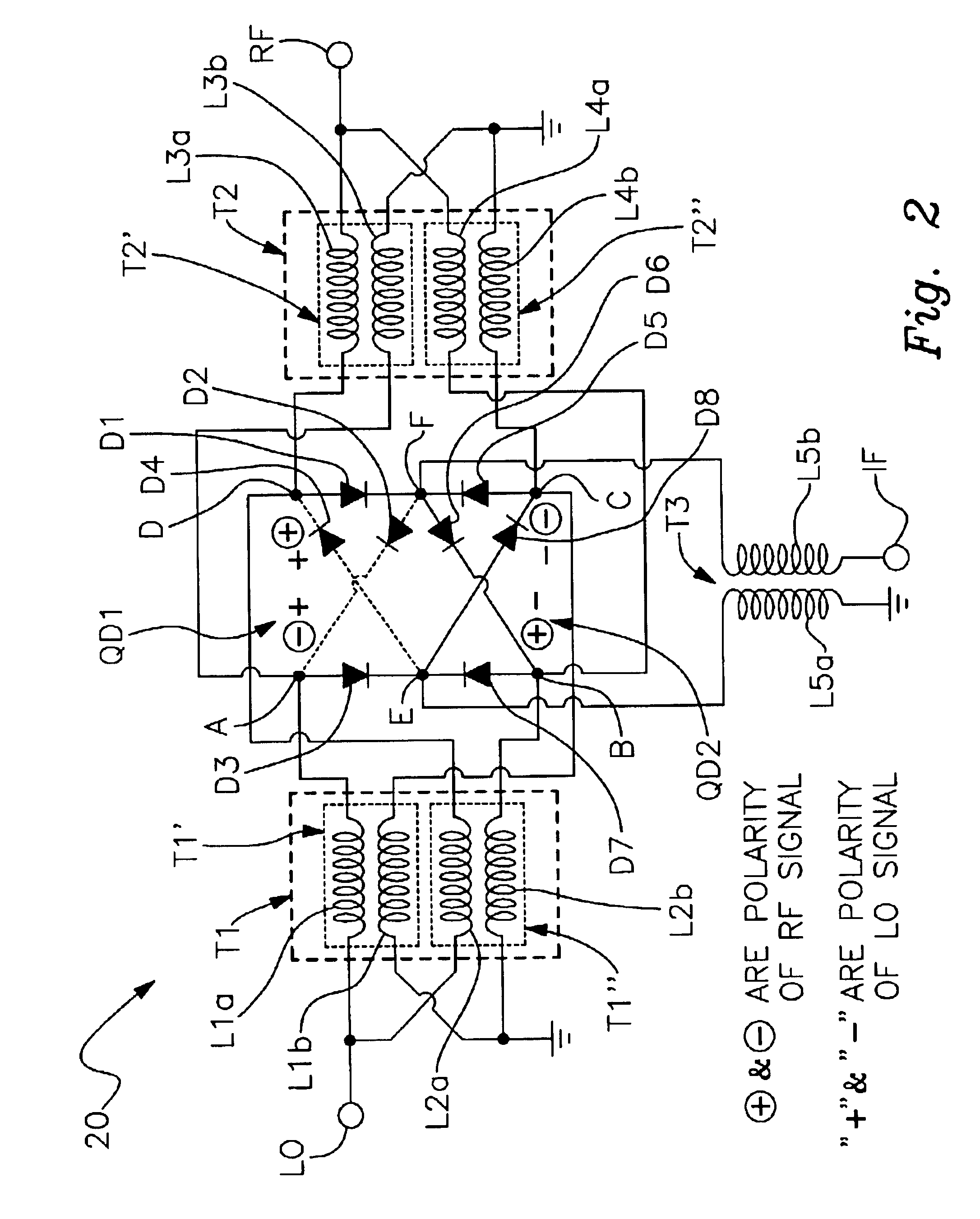
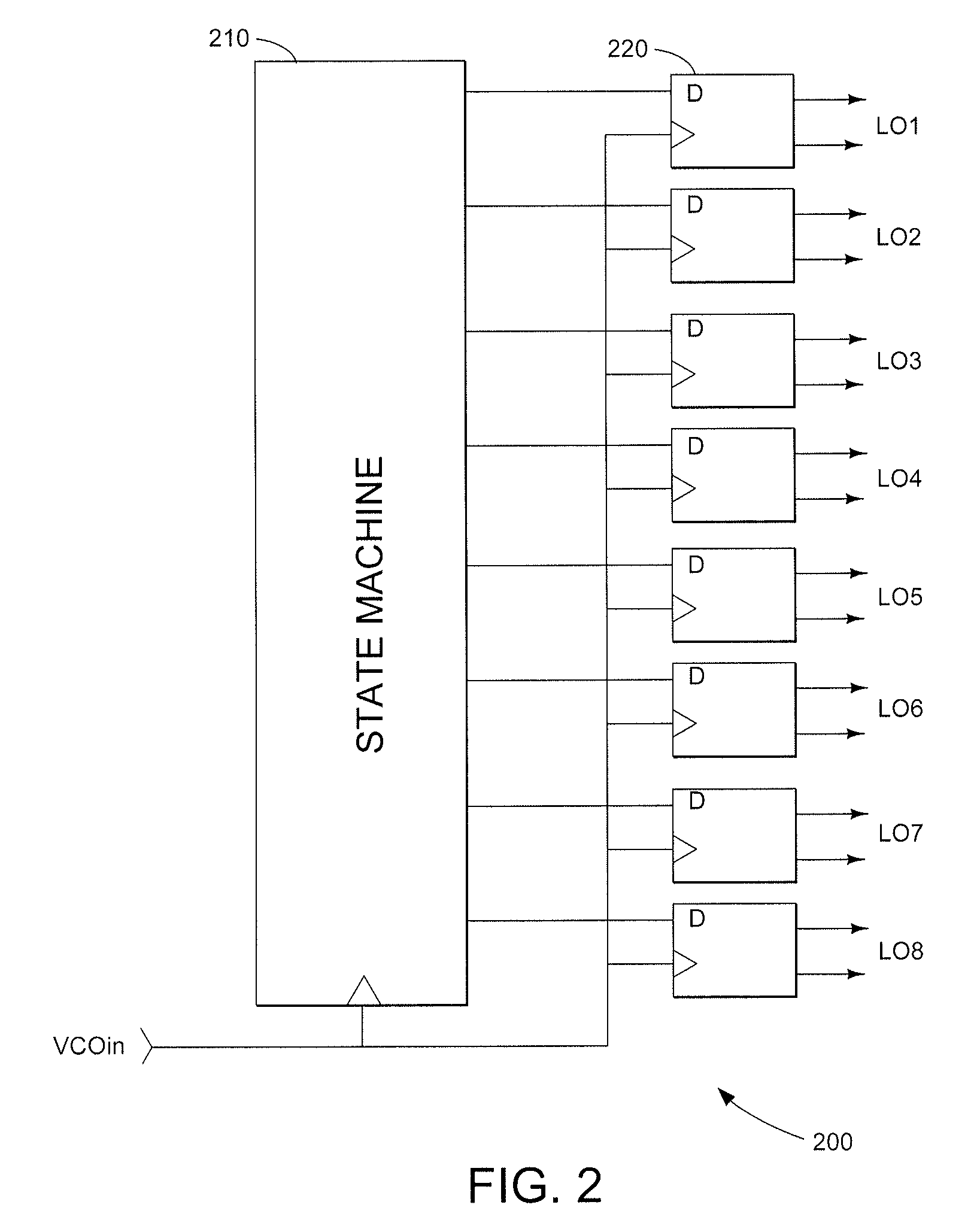
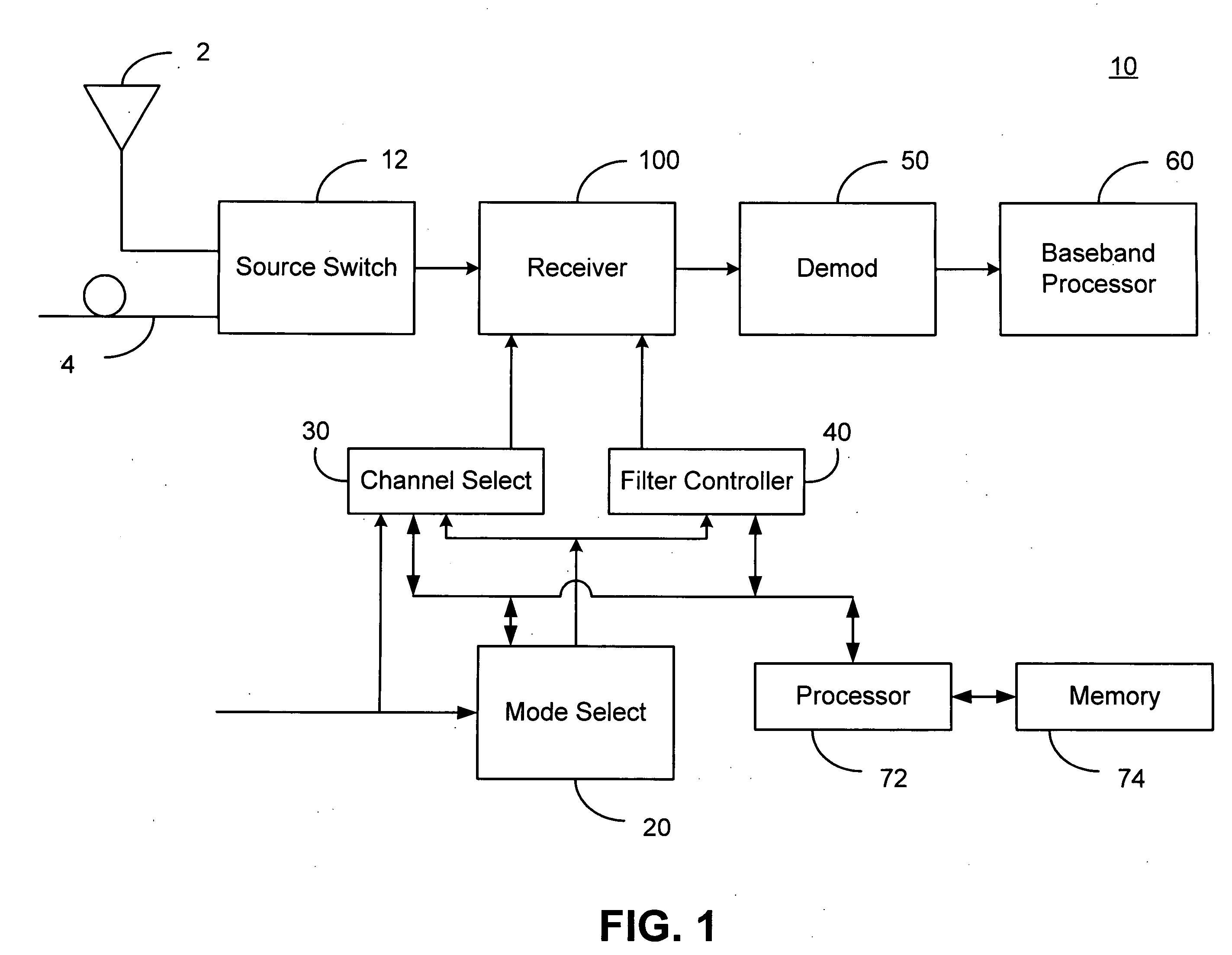
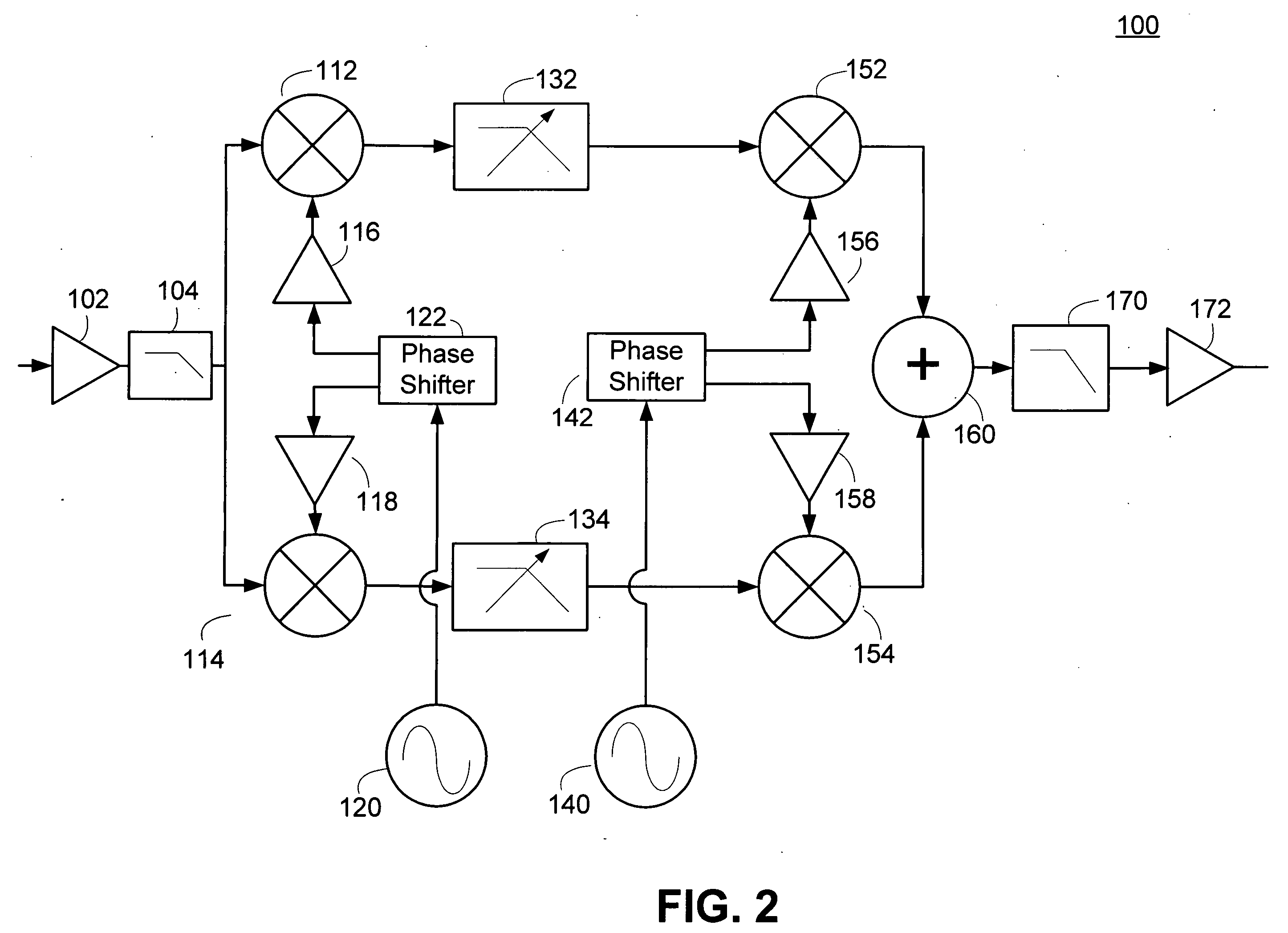
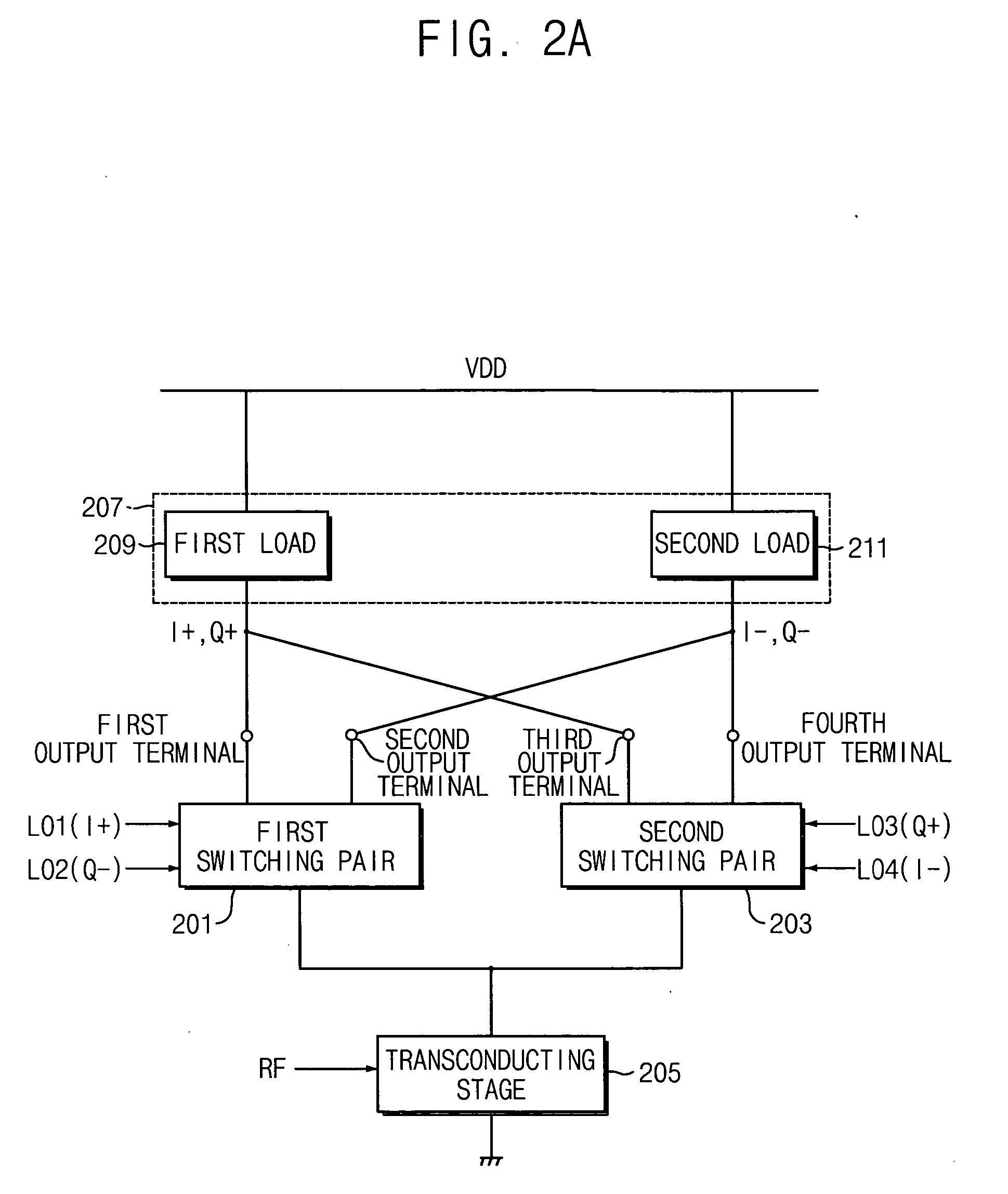
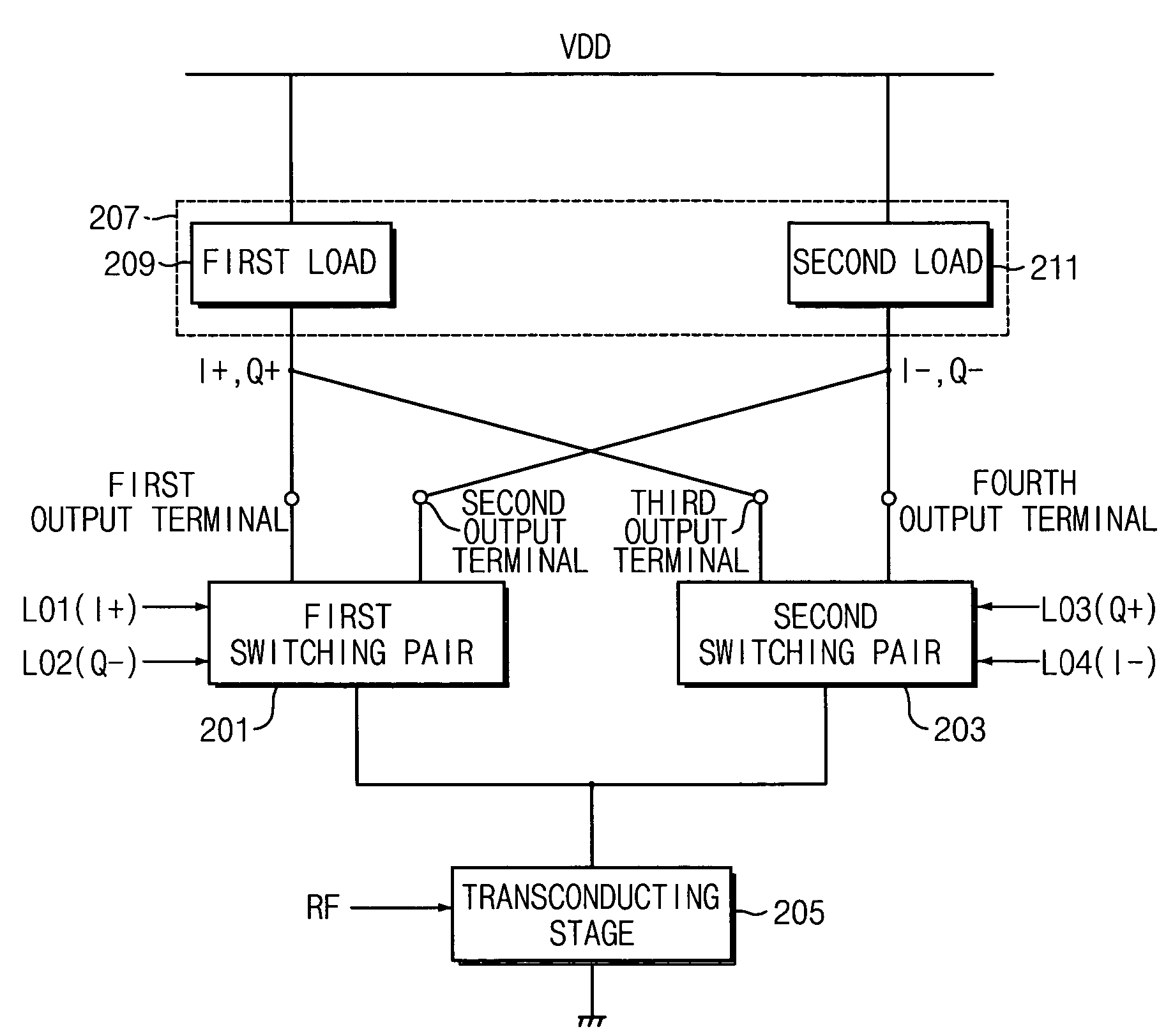
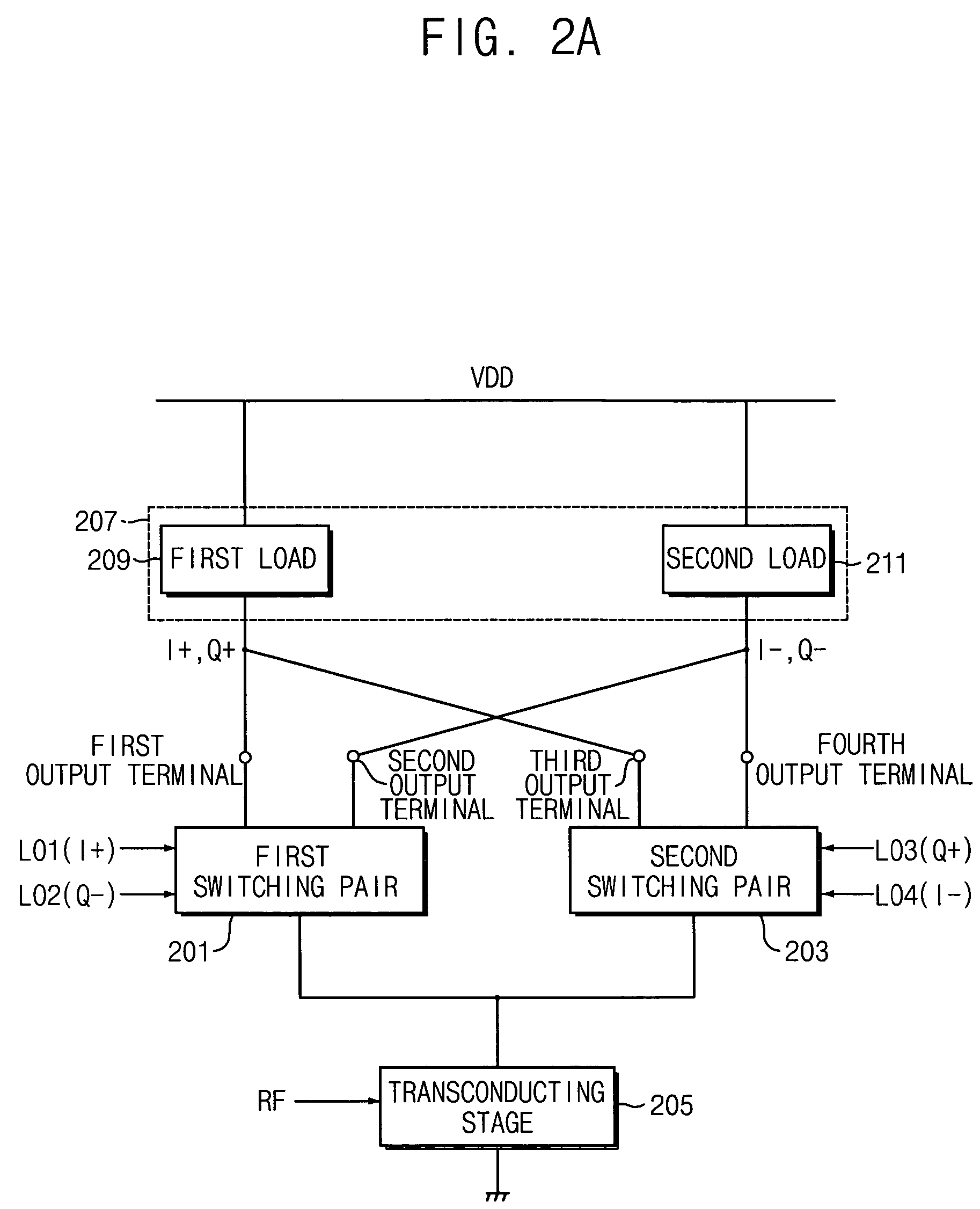
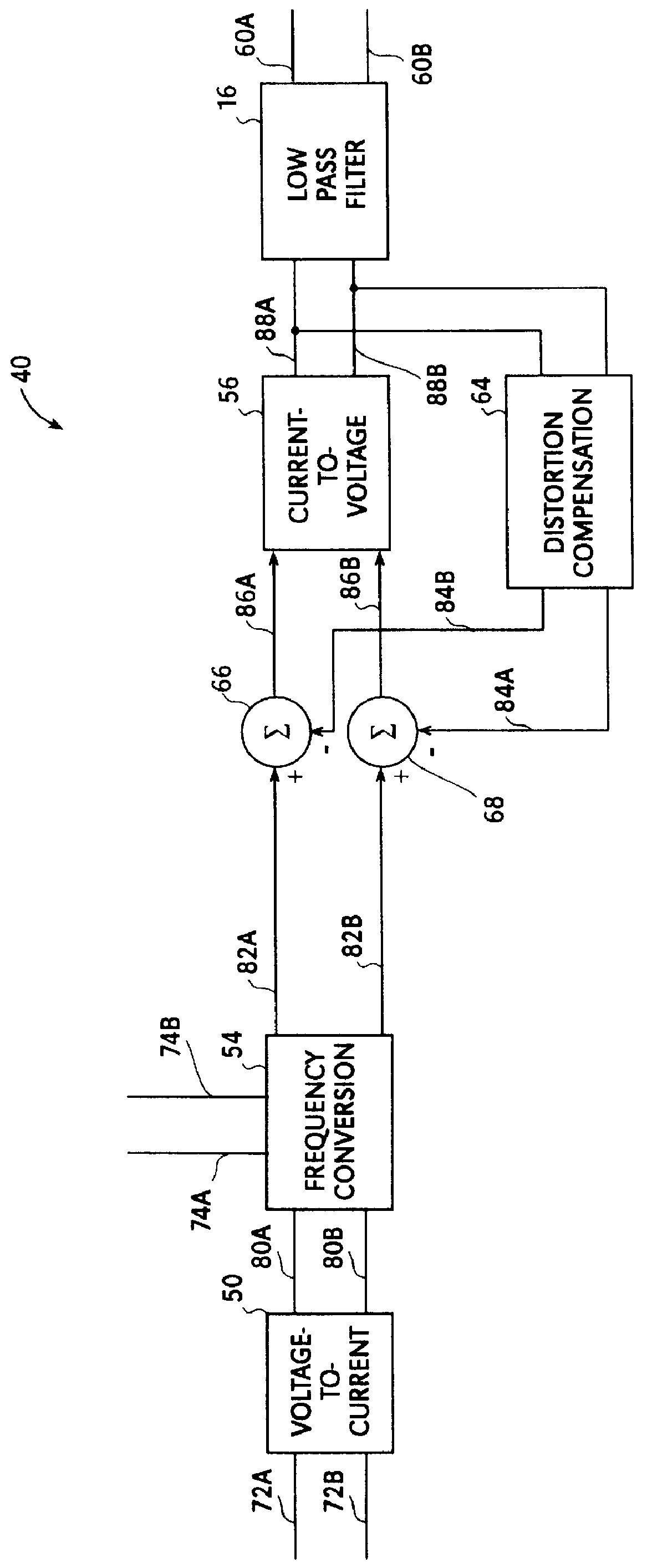
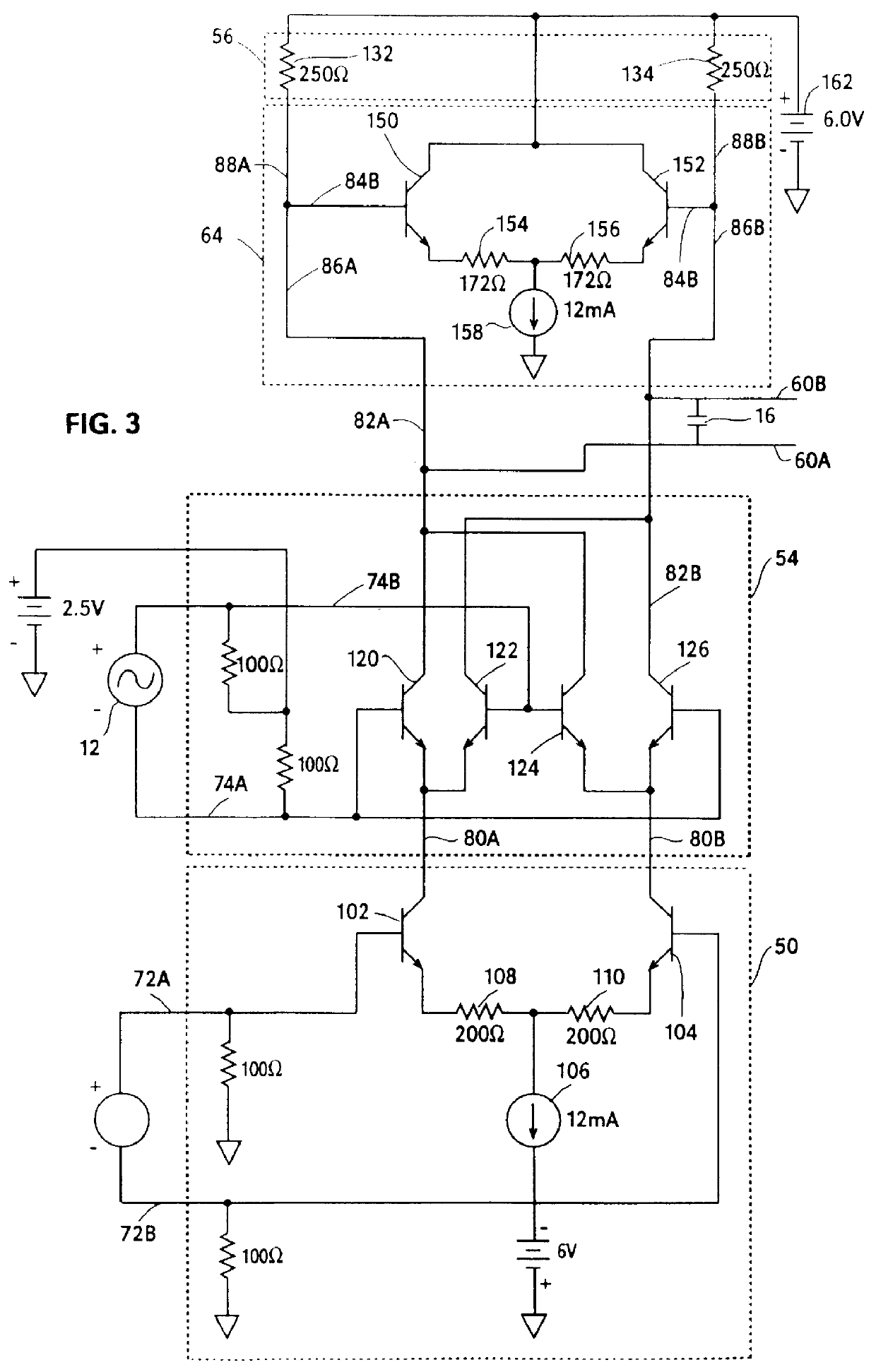
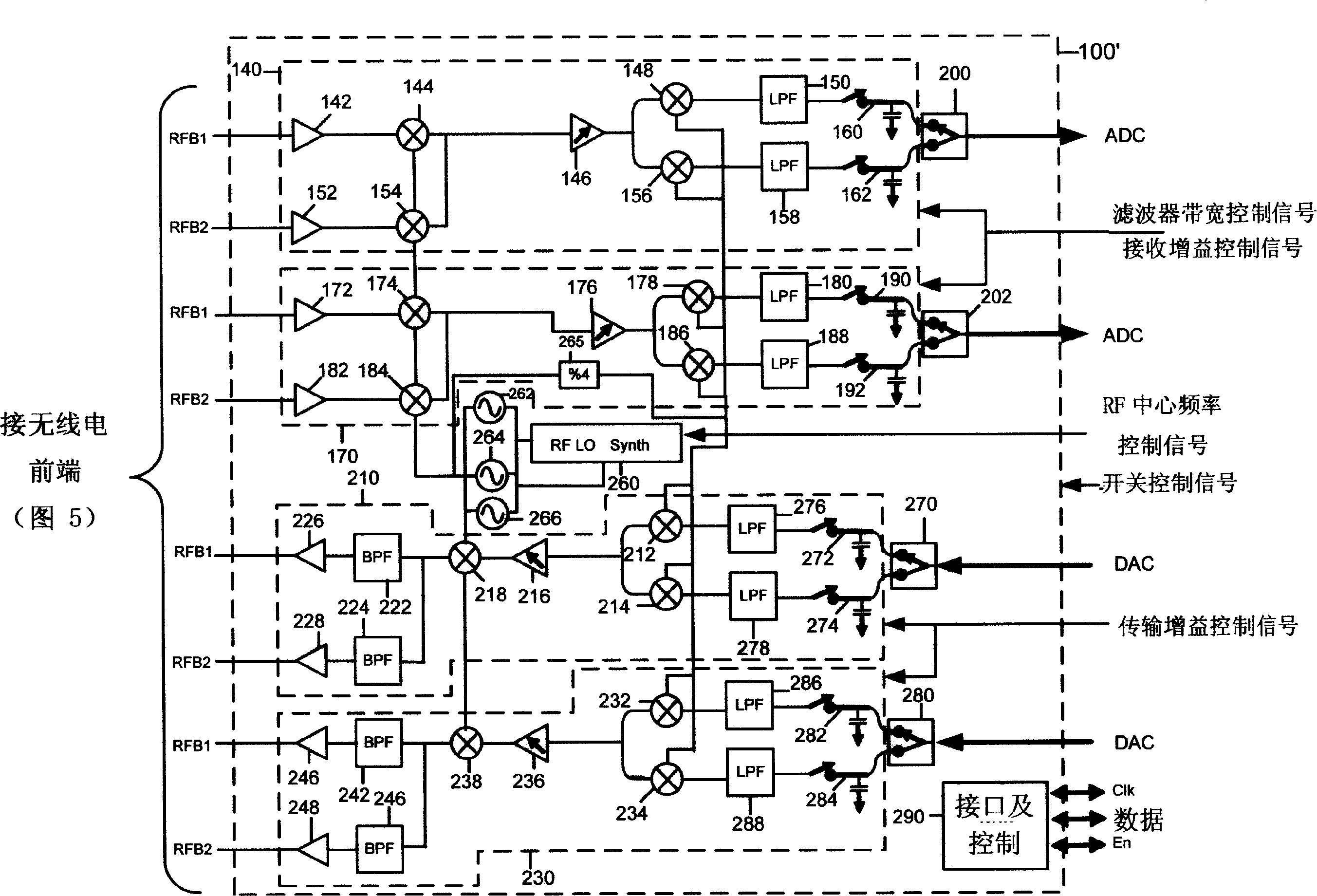
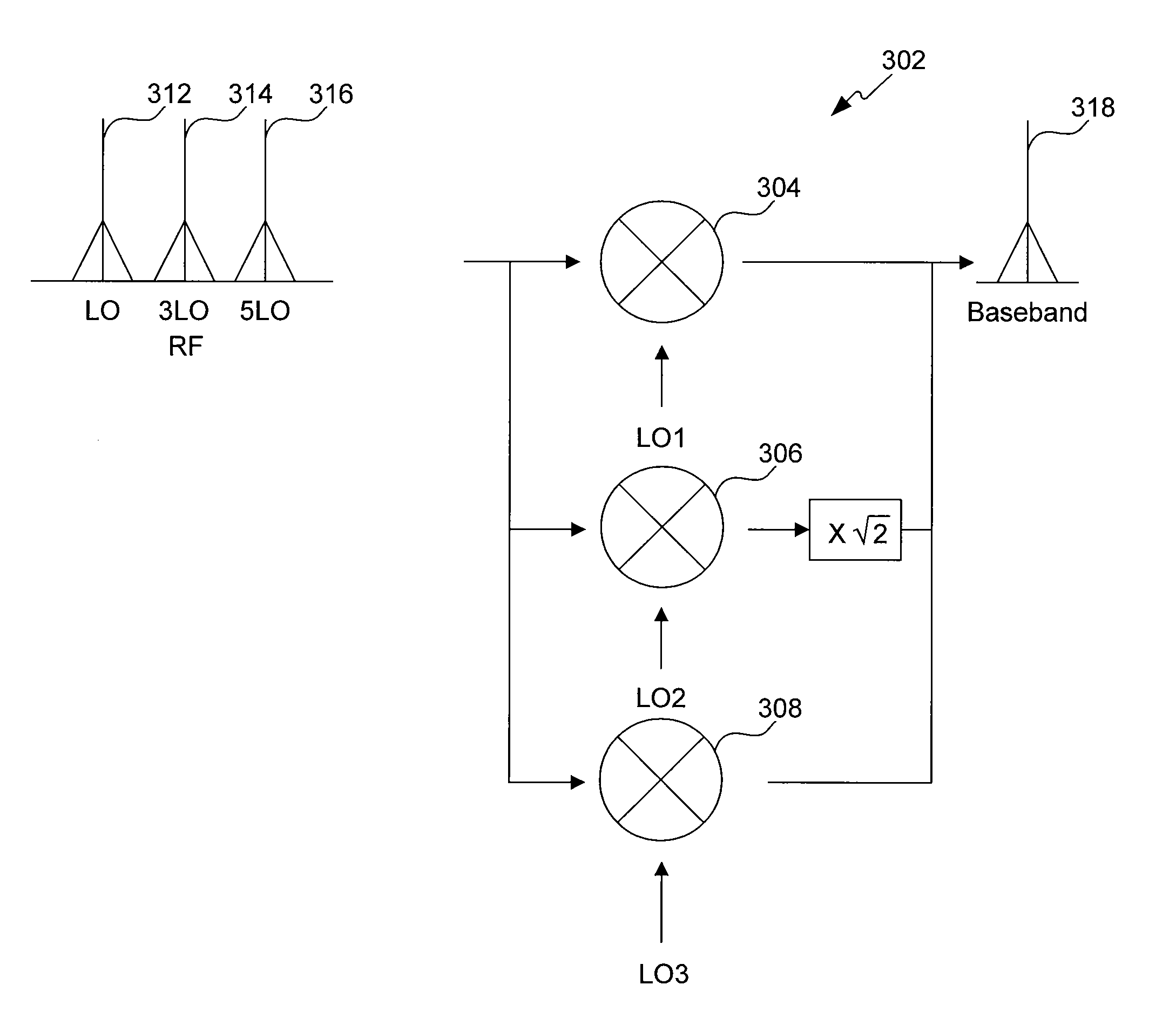
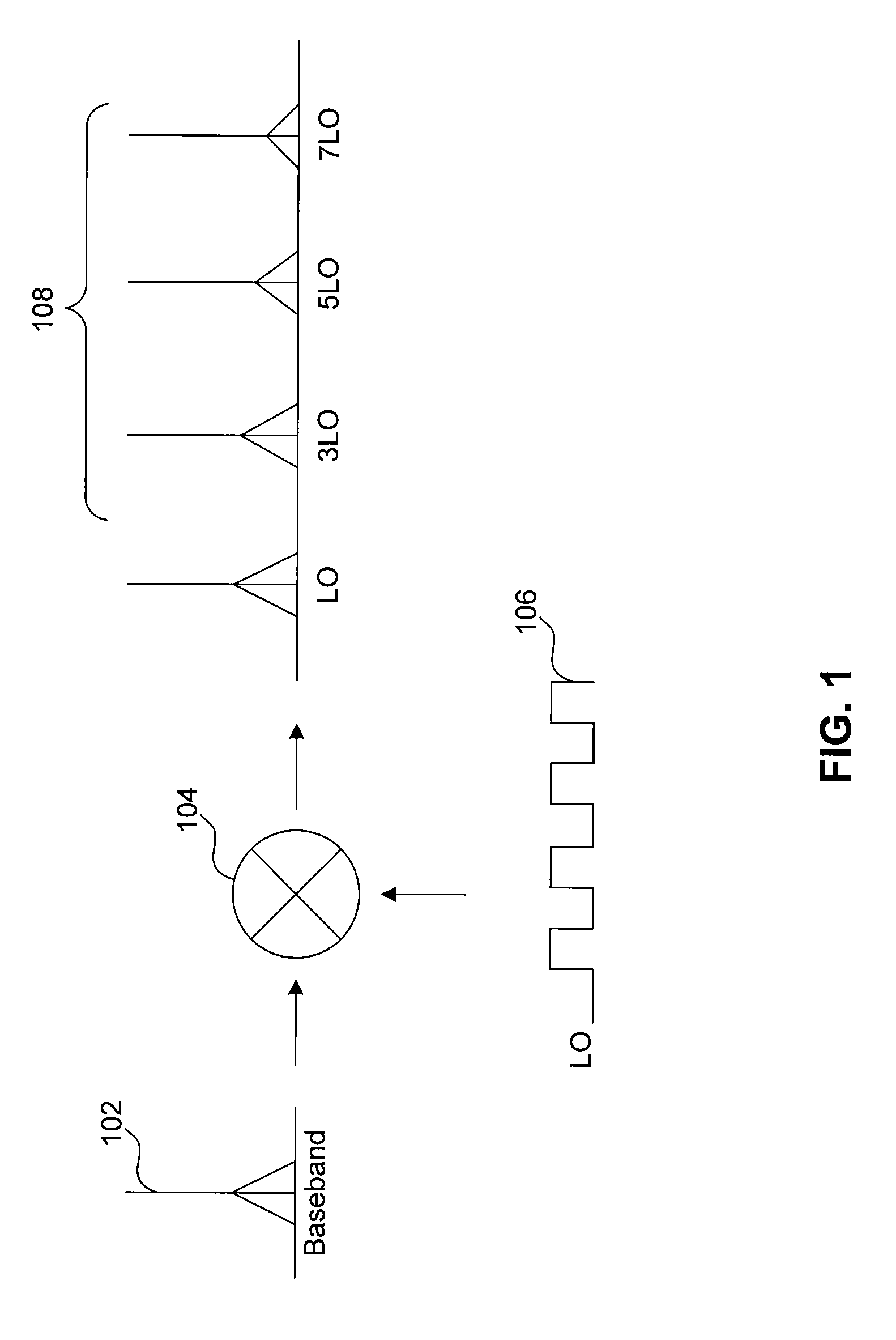
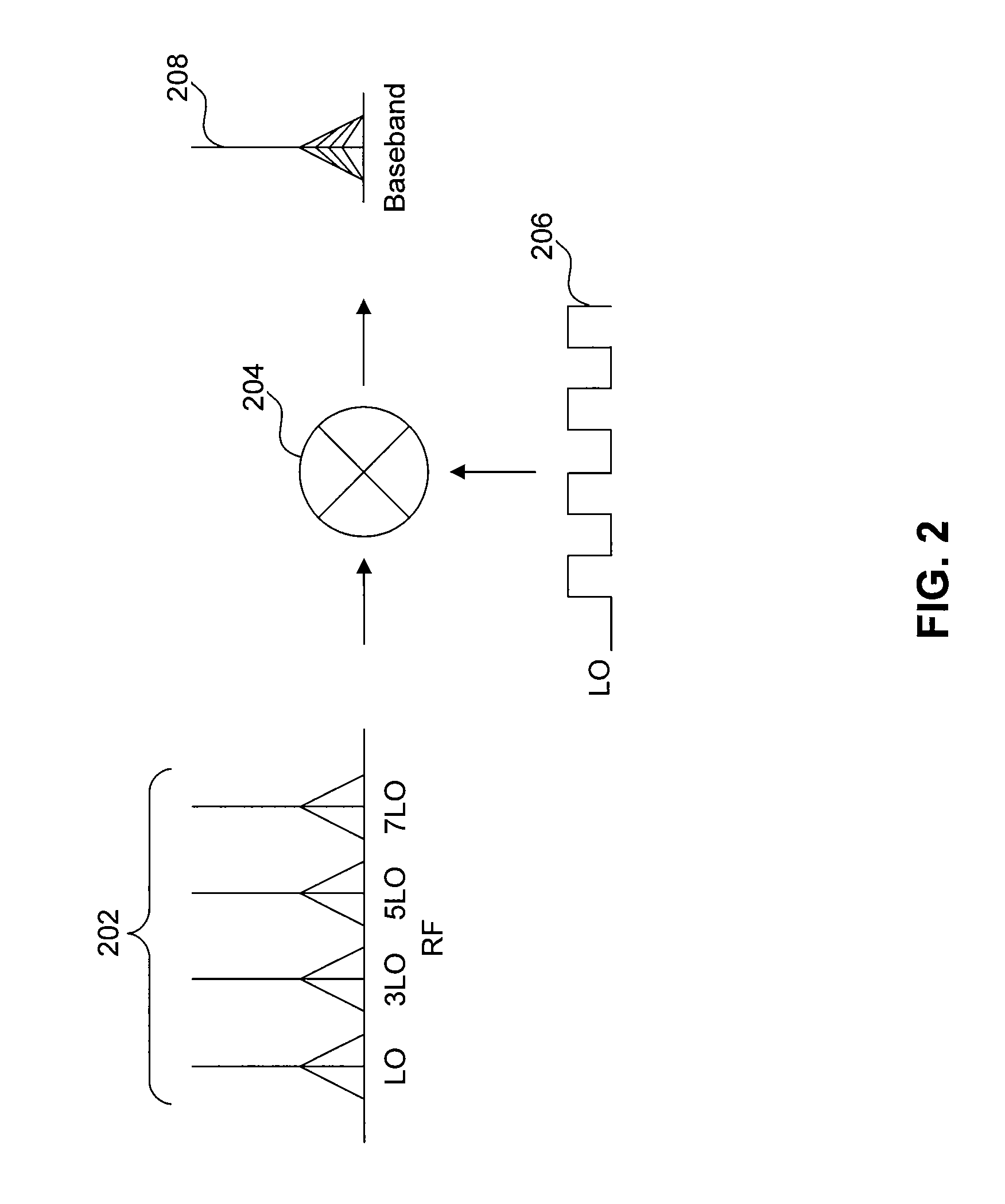
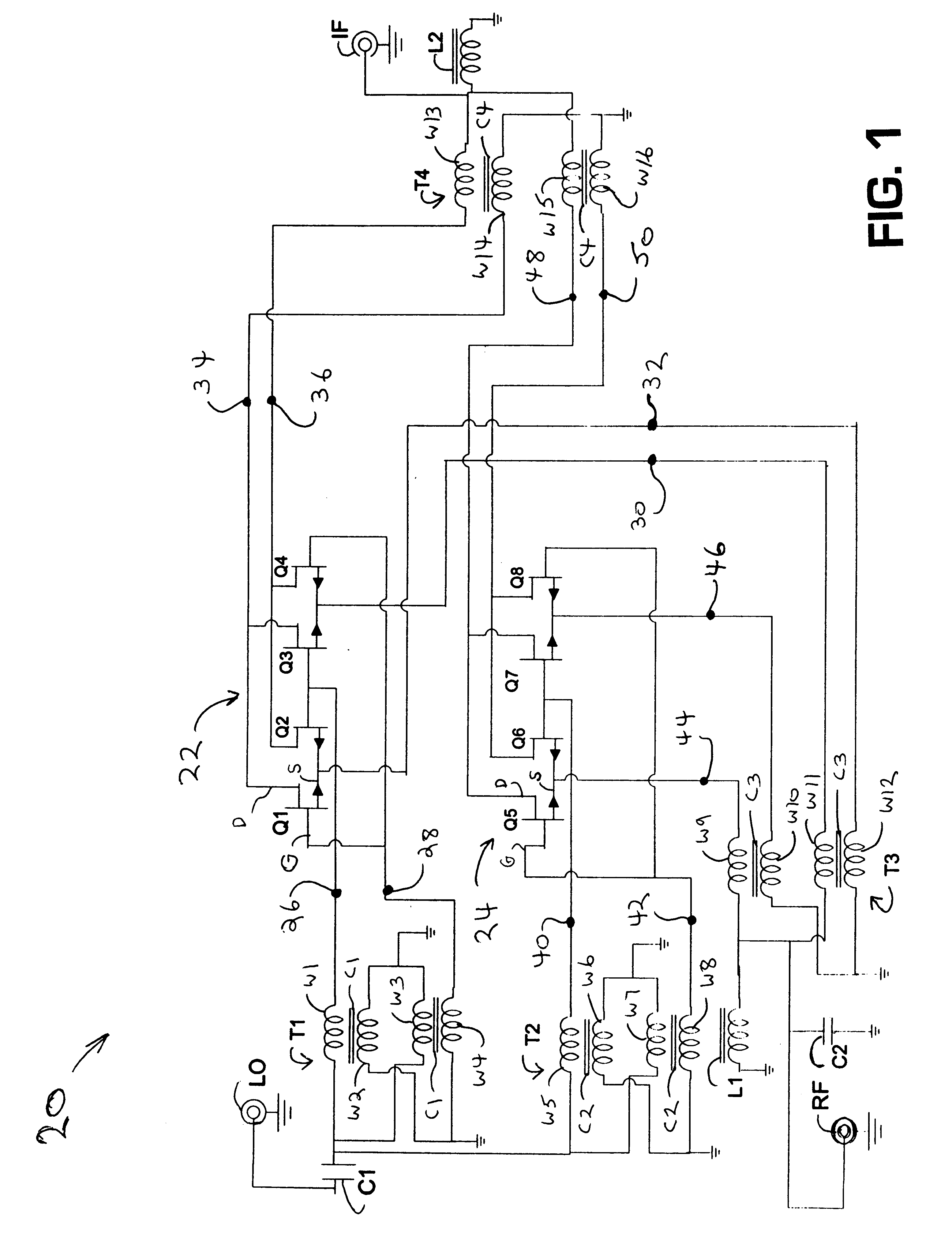
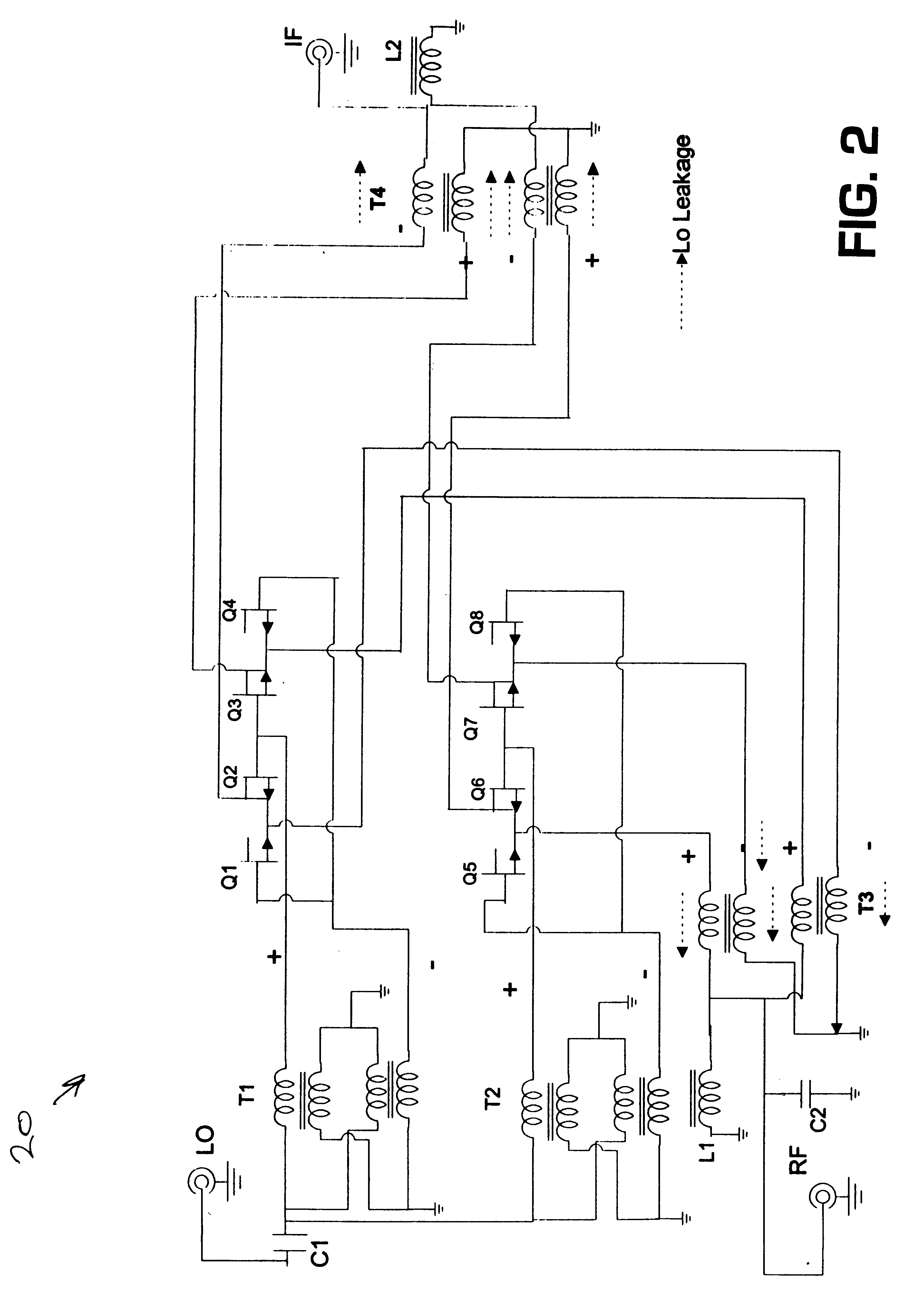
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Structure and method for super FET mixer having logic-gate generated FET square-wave switching signal
InactiveUS6144236AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio receiverTransformer
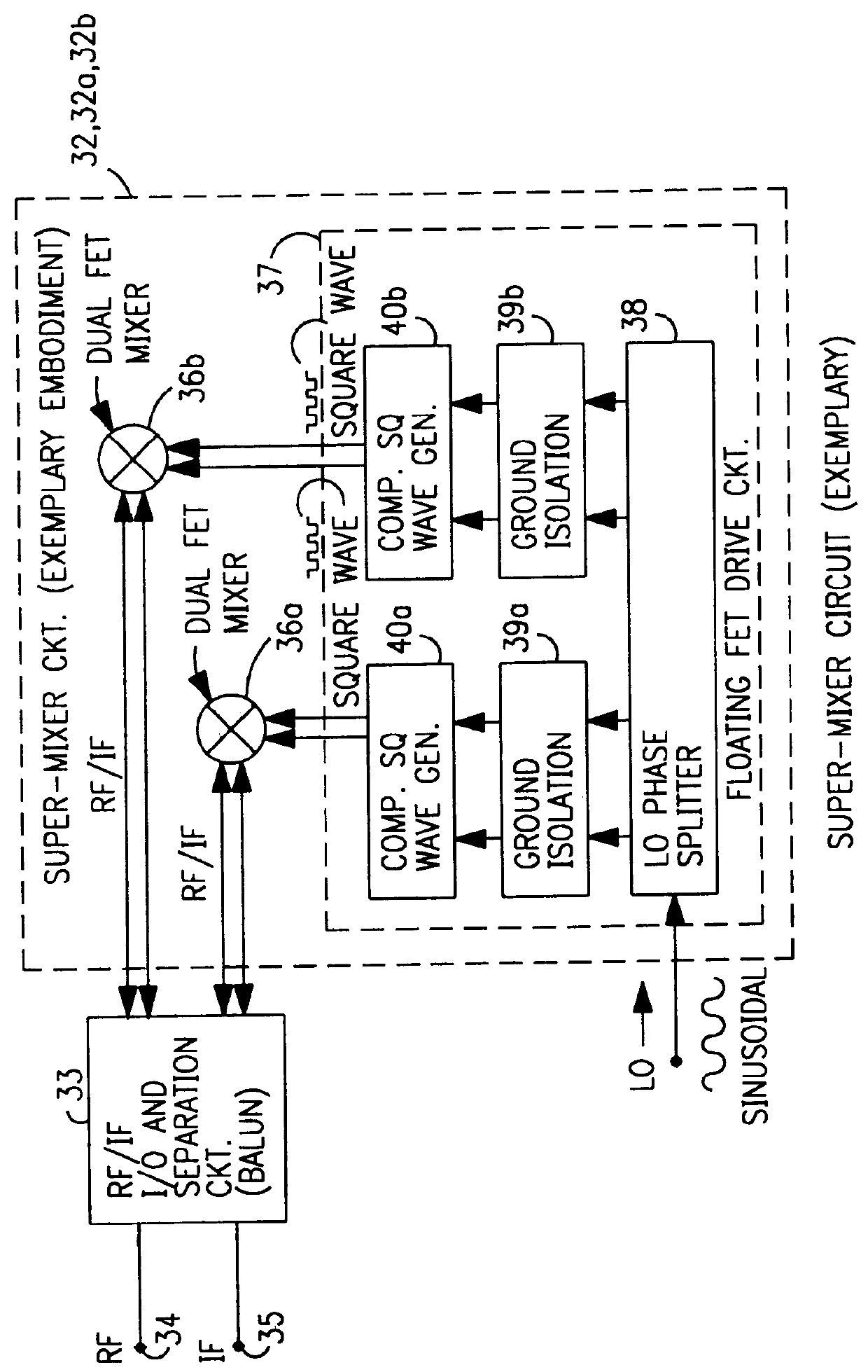
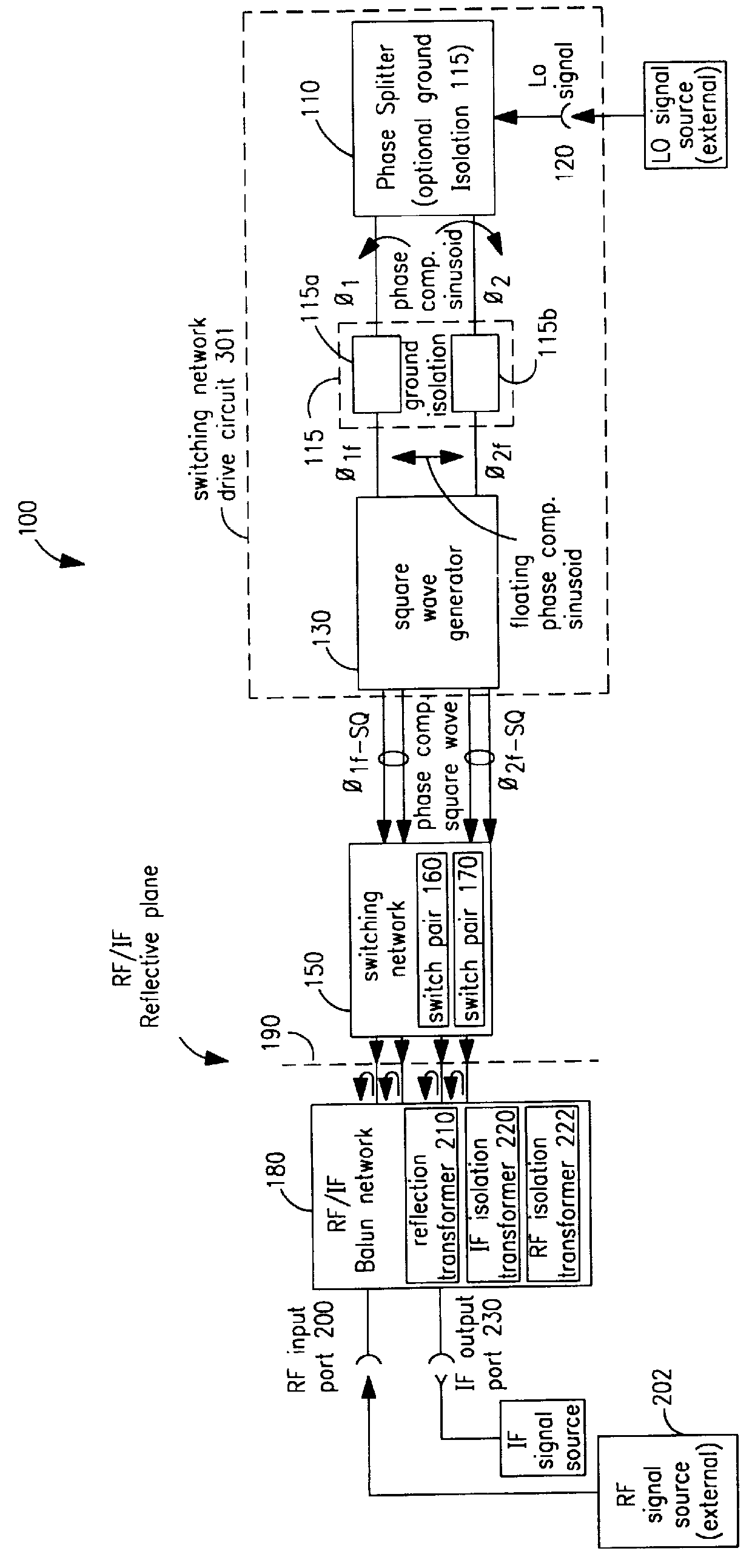
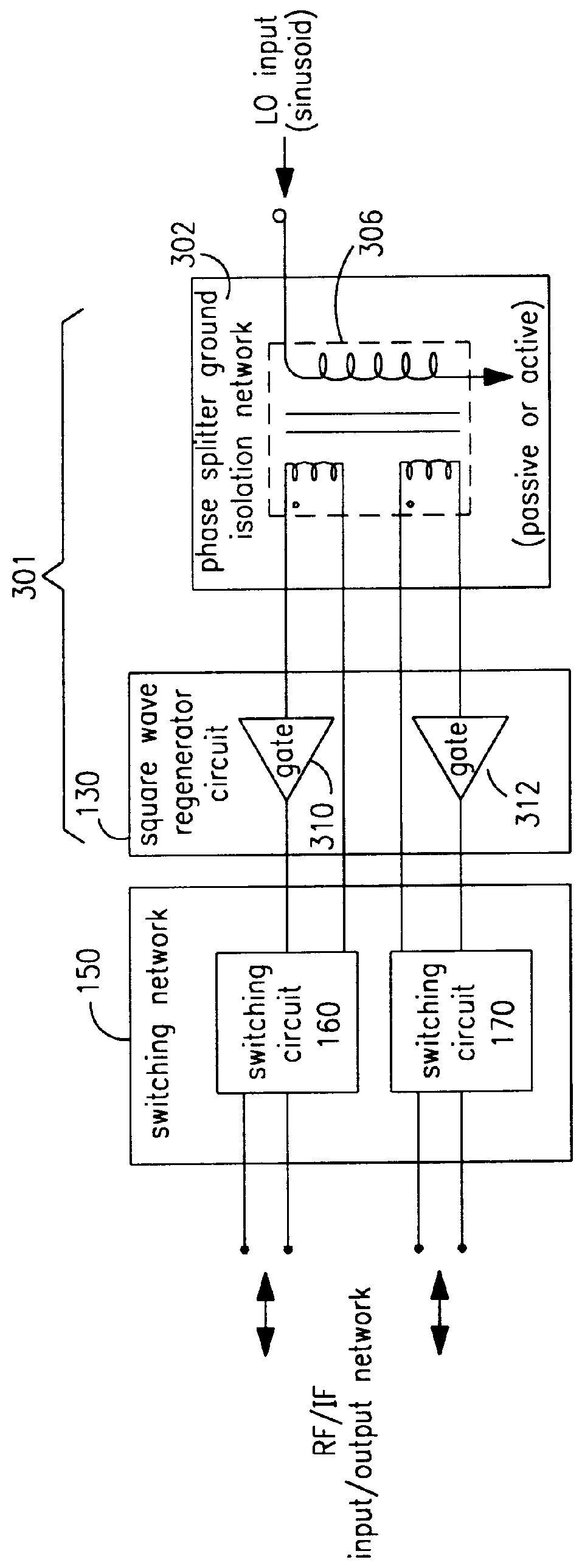
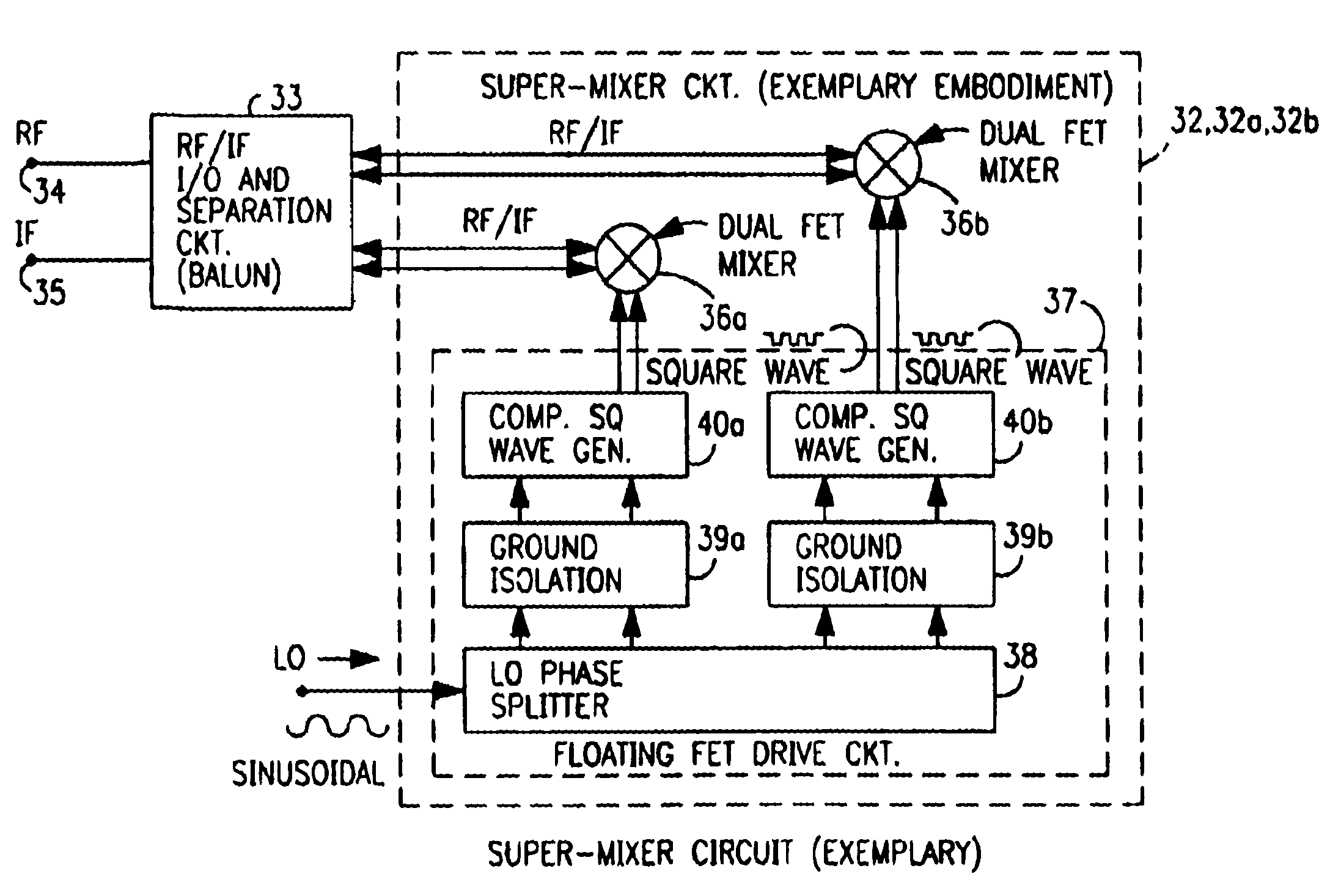
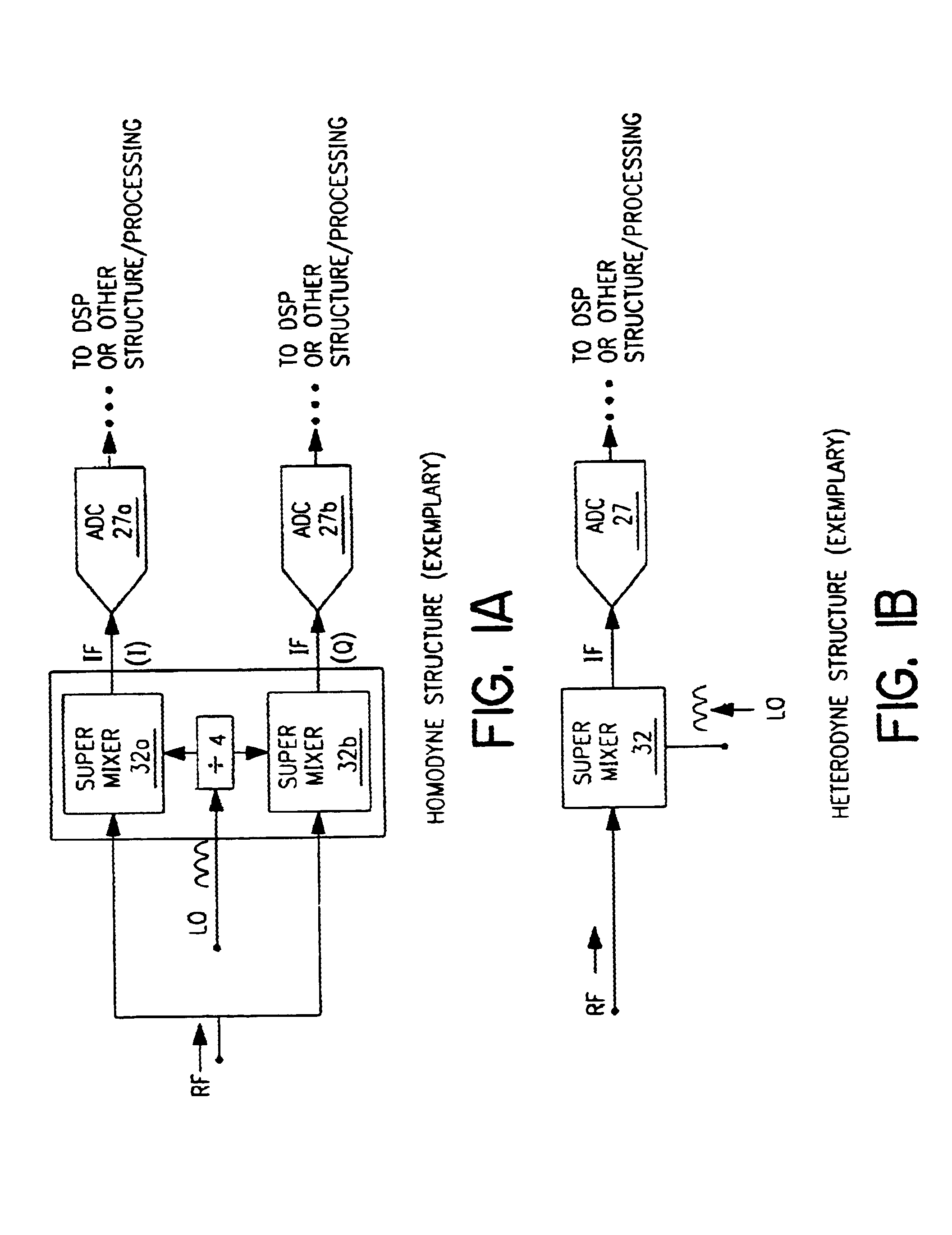
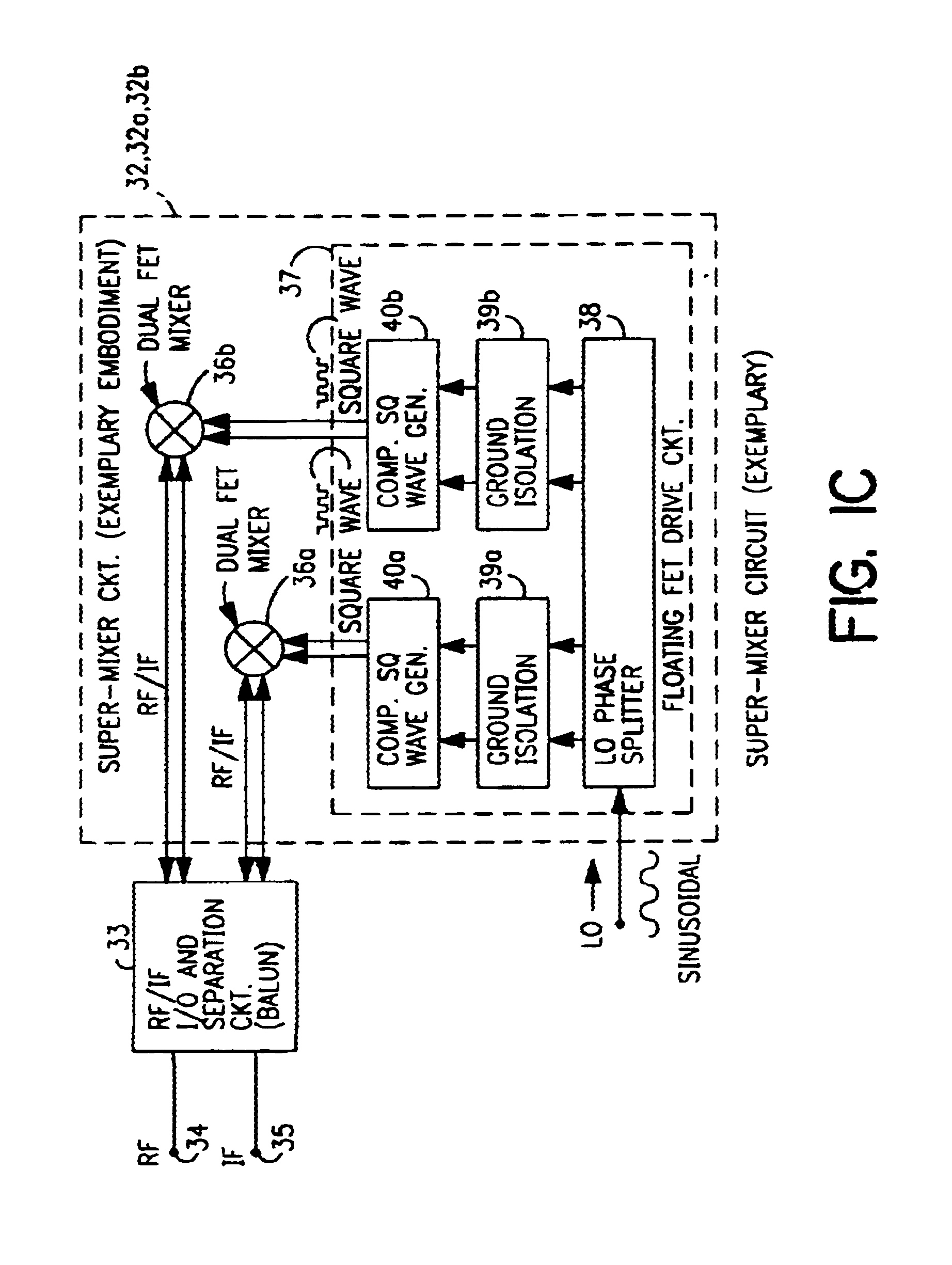
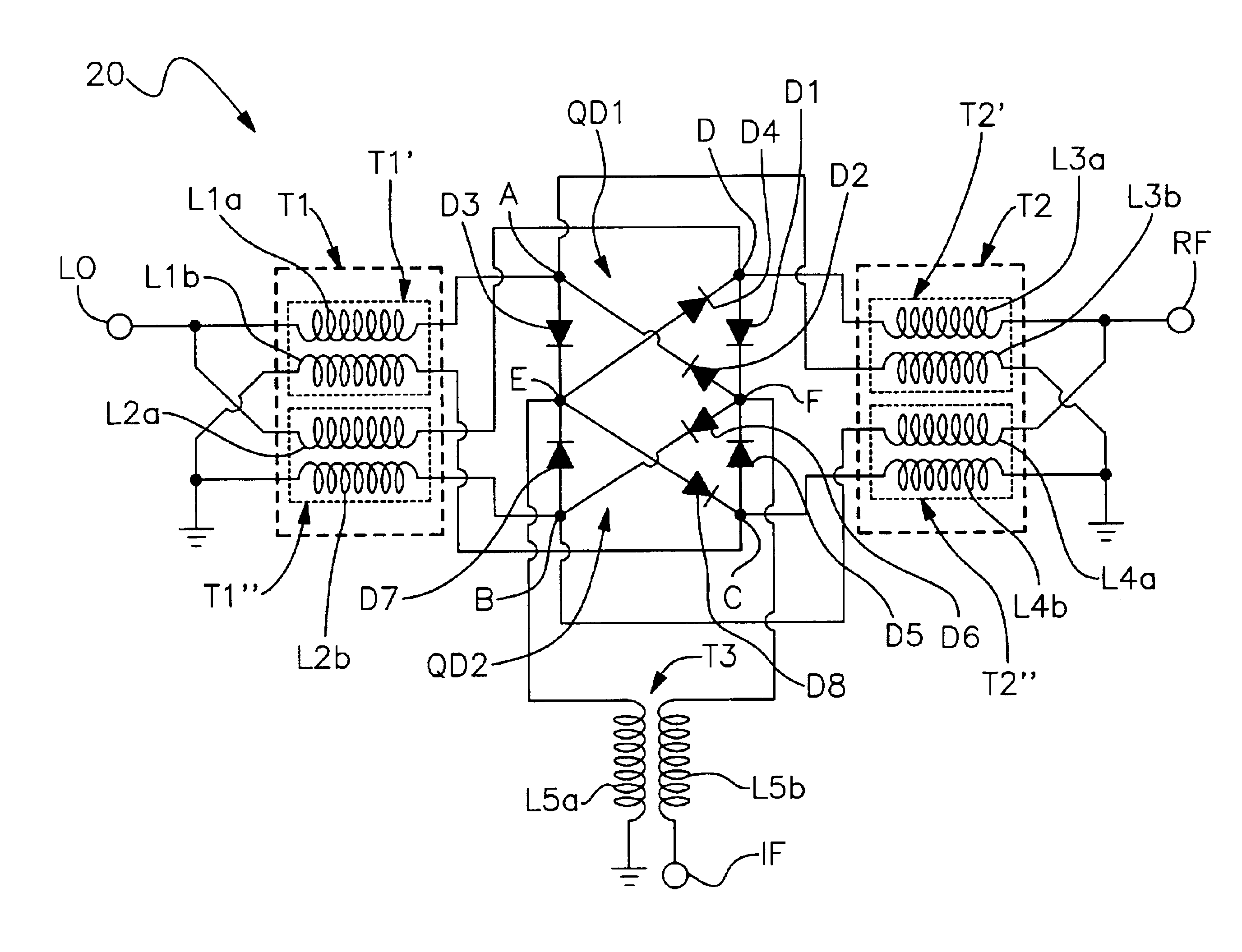
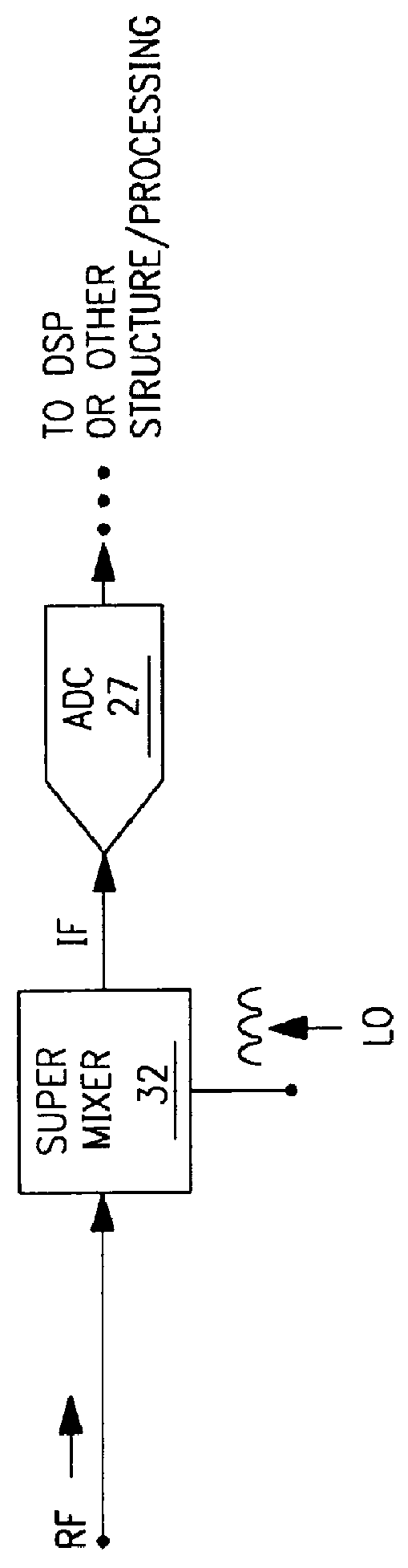
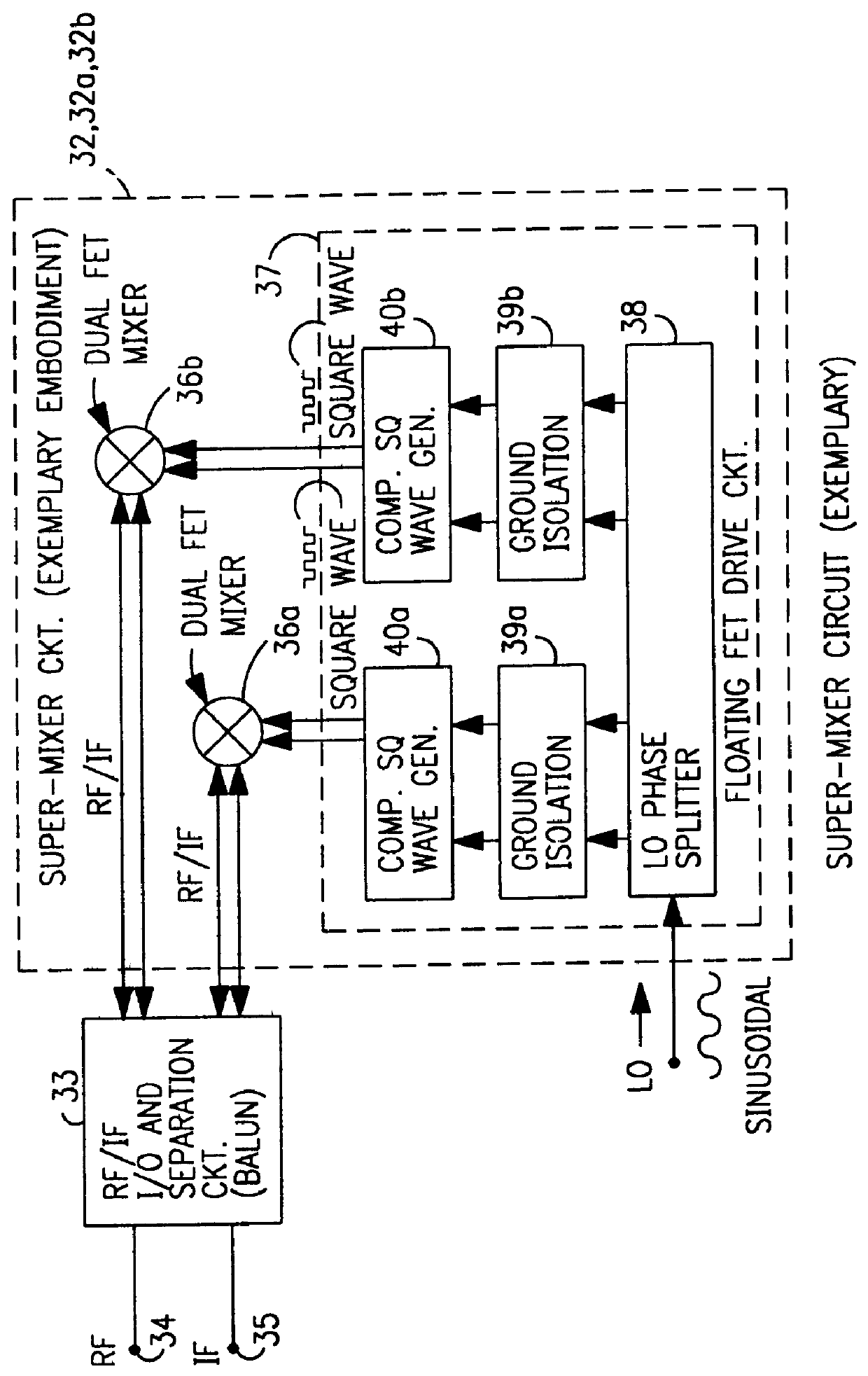
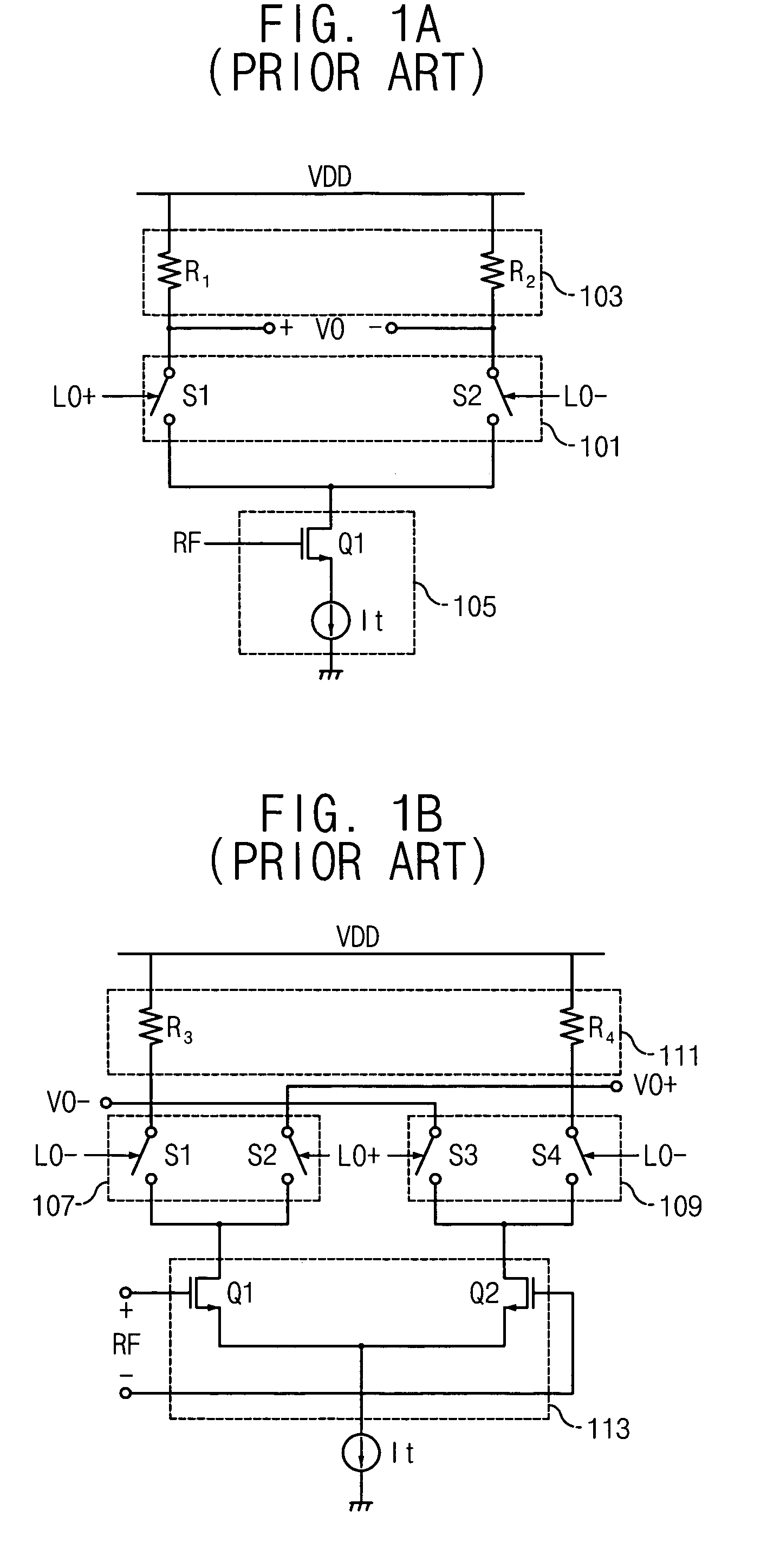
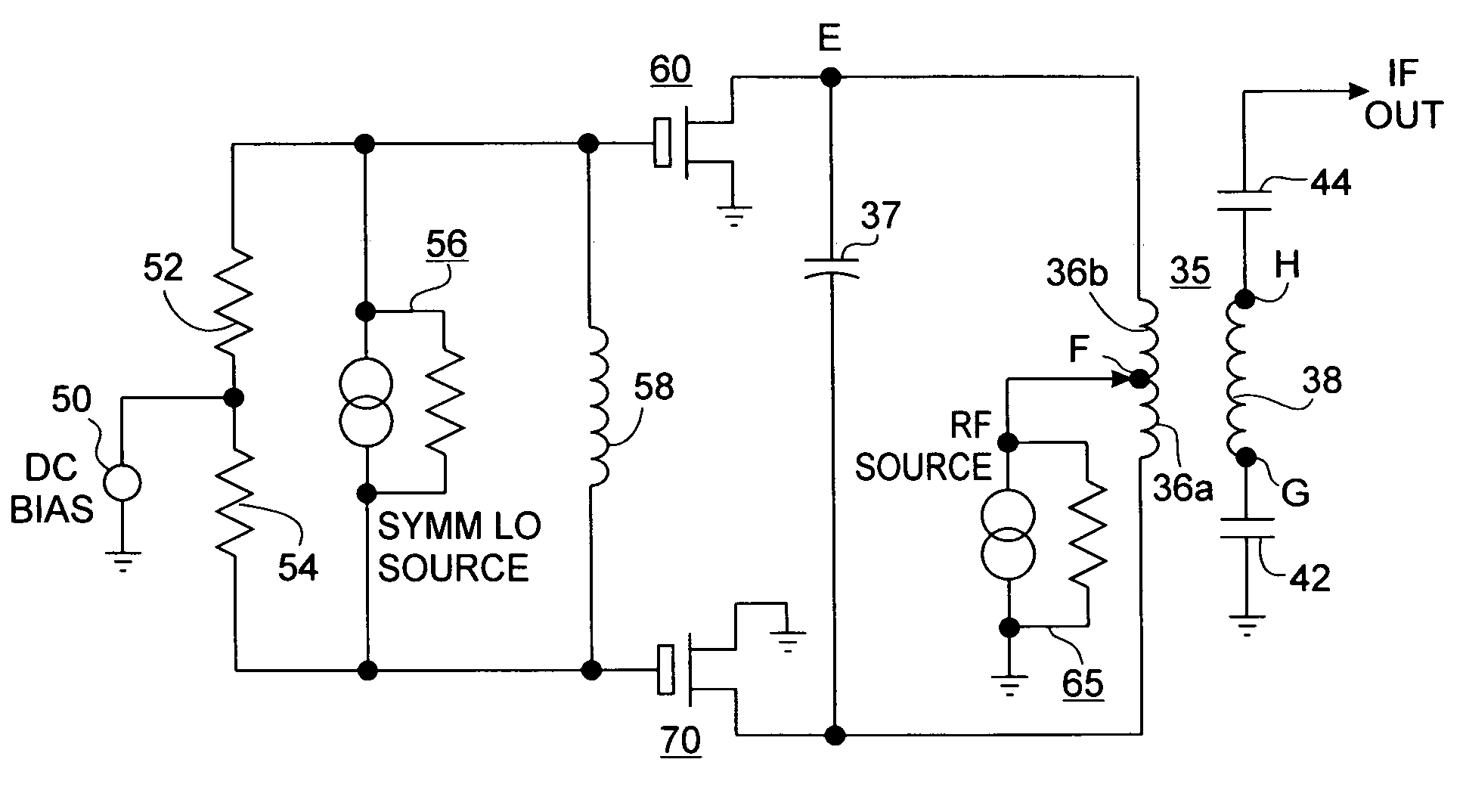
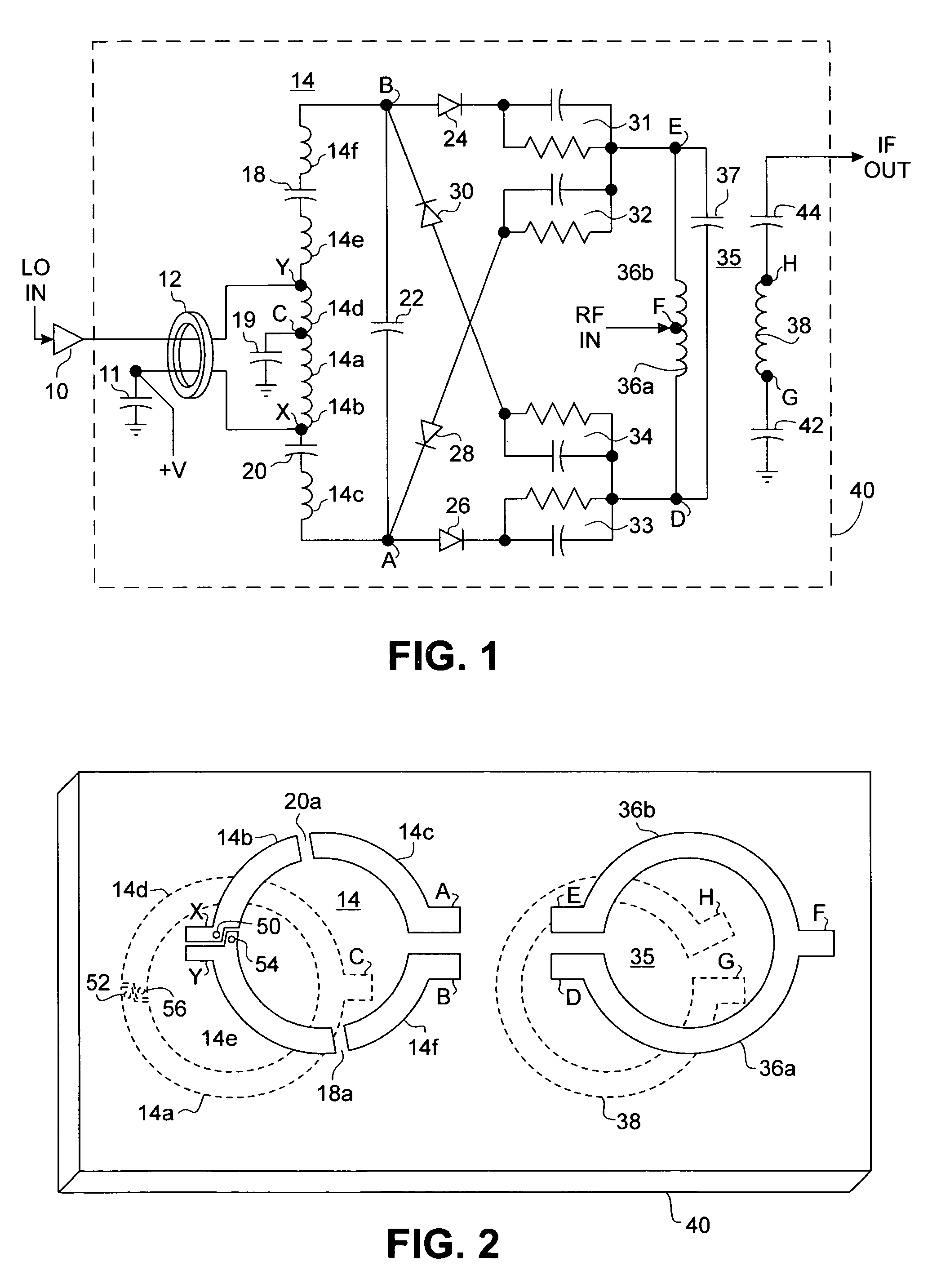
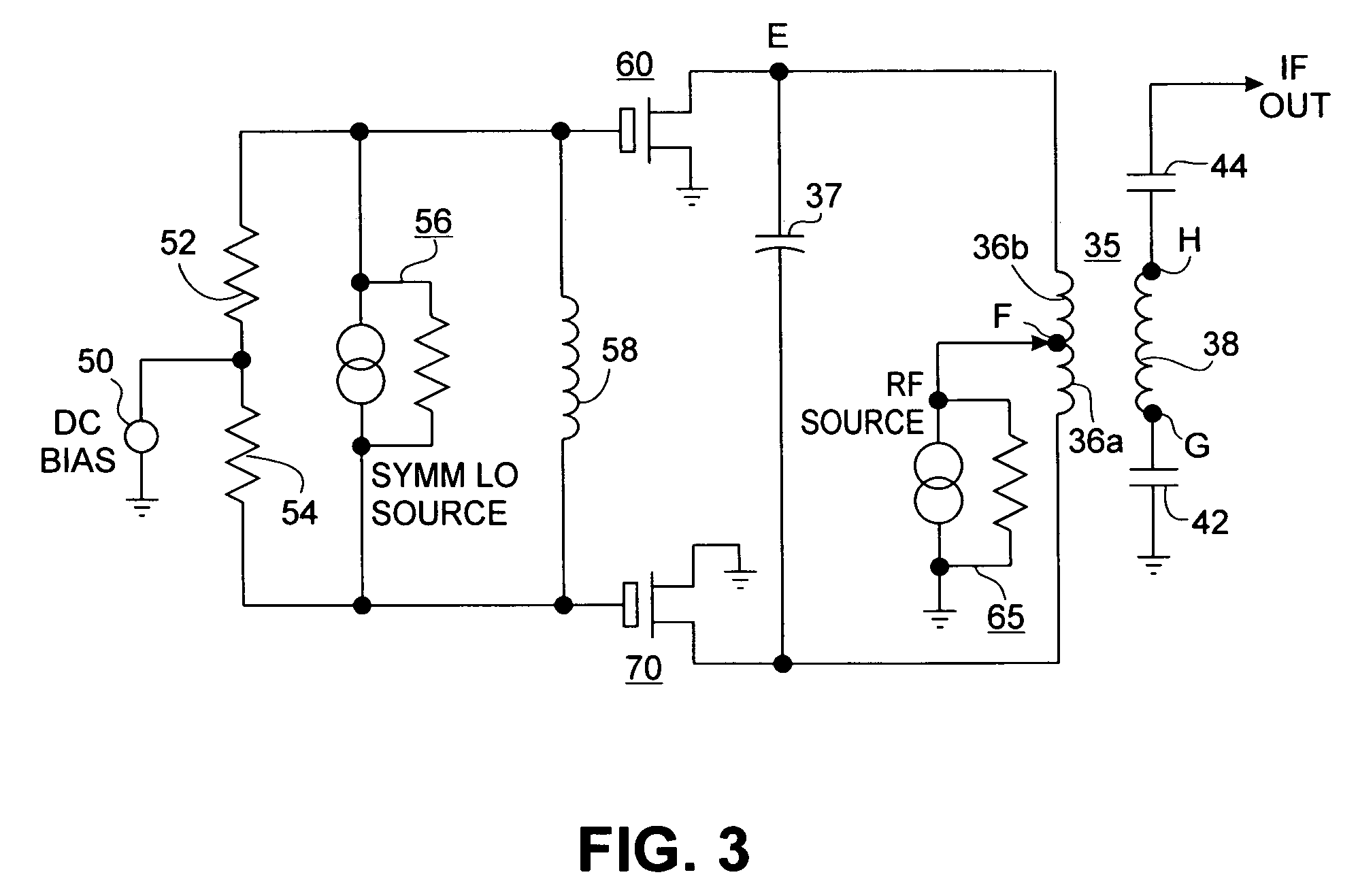
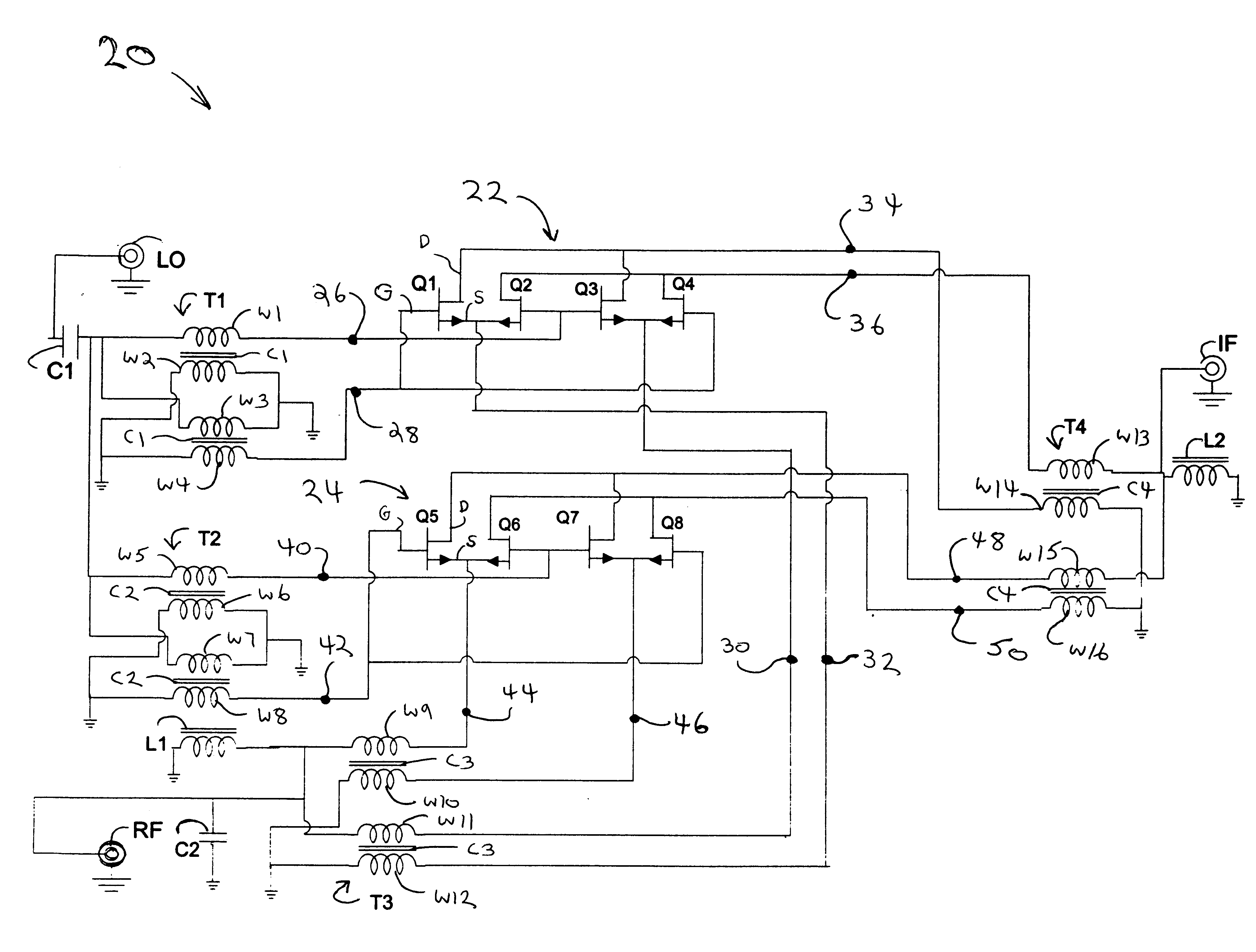
A mixing method and mixer structure provide a circuit topology suitable for use in radio receivers, transmitters, tuners, instrumentation systems, telemetry systems, and other systems and devices performing frequency conversion in either homodyne or heterodyne implementations. The inventive mixer may be used for wireless communication devices including radios, cellular telephones, and telemetry systems whether land, sea, airborne, or space based, and whether fixed or mobile. The mixer provides superior intermodulation and harmonic distortion suppression and features excellent conversion loss, noise figure, port match, and port isolation as a result of its circuit topology. The mixer device circuit combines the advantages of series mixing FETs, a triple balanced design using a balanced passive reflection transformer, a precise local oscillator phase splitter, and square wave gate drive having high slew rate signal characteristics to achieve high levels of performance. It is power conservative and offers the advantage of long battery life in portable devices such as portable radios and cellular telephones as it requires only a modest amount of DC and local oscillator drive power, and is useful for operation over at least a multi-decade bandwidth.
Owner:DRS SIGNAL SOLUTIONS
Radio system including mixer device and switching circuit and method having switching signal feedback control for enhanced dynamic range and performance
InactiveUS6654595B1Modulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsFrequency changerLocal oscillator signal
Radio system including mixer device and switching circuit and method having switching signal feedback control for enhanced dynamic range and performance. Radio apparatus including: local oscillator input port for receiving periodic sinusoidal local oscillator signal; drive circuit for generating a substantially square-wave two-voltage level switching signal including: phase splitter circuit, voltage potential isolation circuit, and square wave signal generation circuit; FET mixing device; input / output signal separation circuit; analog-to-digital converter; and feedback control circuit. Radio tuner apparatus including low-band signal processing circuit; high-band signal processing circuit including first mixer circuit operating as an up-frequency converter, amplifier circuit, second mixer circuit operating as a down-frequency converter, and feedback control circuit for adjusting a duty cycle of a mixer switching device; signal combining circuit and output processing circuit. Method for operating radio system, apparatus, and tuner. Method of operating switching circuit.
Owner:BAE SYST AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS
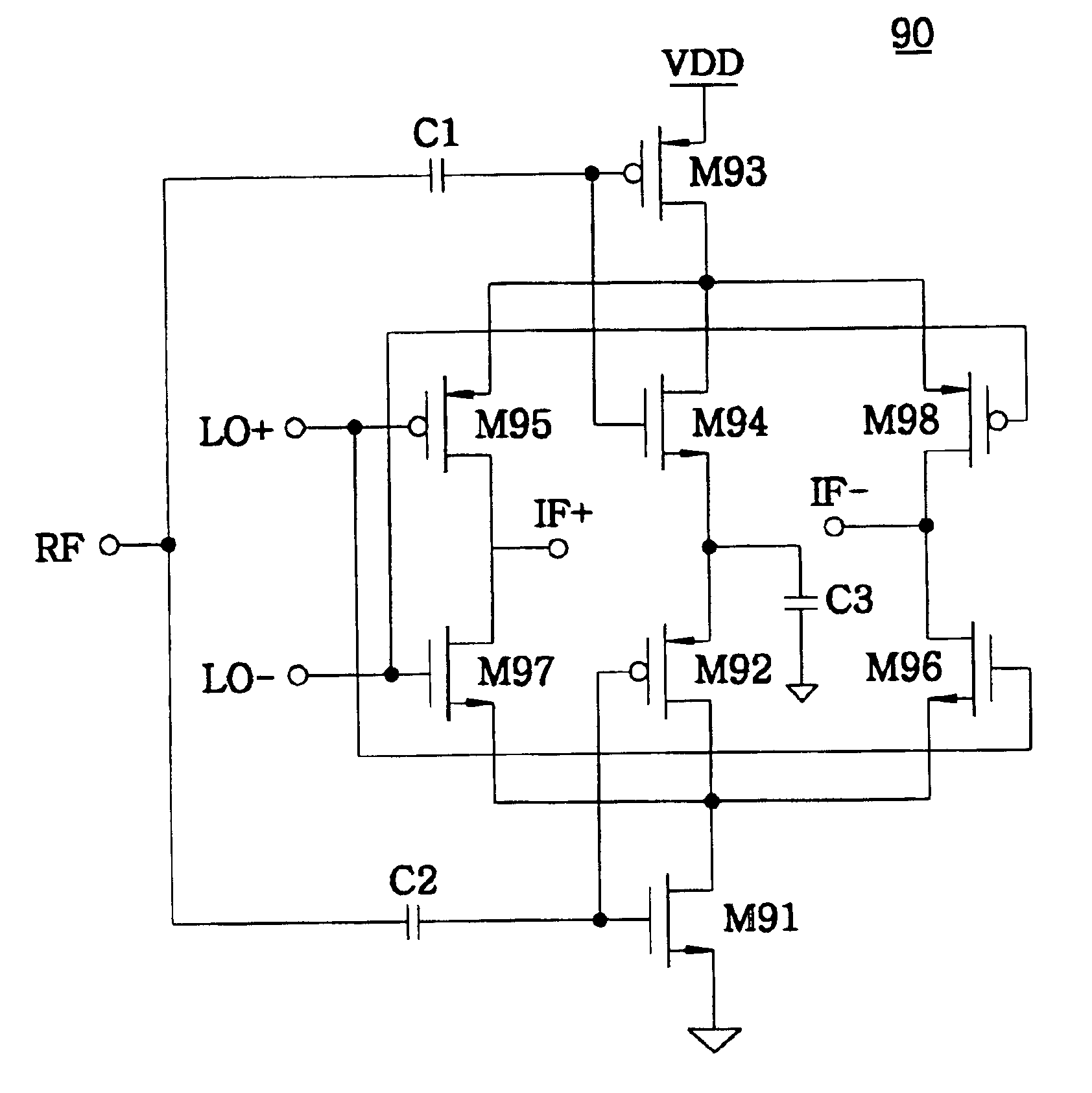
Current-reuse bleeding mixer
InactiveUS6892062B2Good performance in conversion gain and linearity and noise figureModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplitude demodulationLow noiseLocal oscillator
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS7519348B2Reduce leakageEnhanced inhibitory effectModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Triple balanced mixer
ActiveUS6917796B2Small sizeEasy to assembleModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionBalanced mixerPlanar substrate
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
Multiple-input multiple-output radio transceiver
InactiveUS7636554B2Easy to integrateLow cost manufacturingModulation transference balanced arrangementsSubstation equipmentTransceiverEngineering
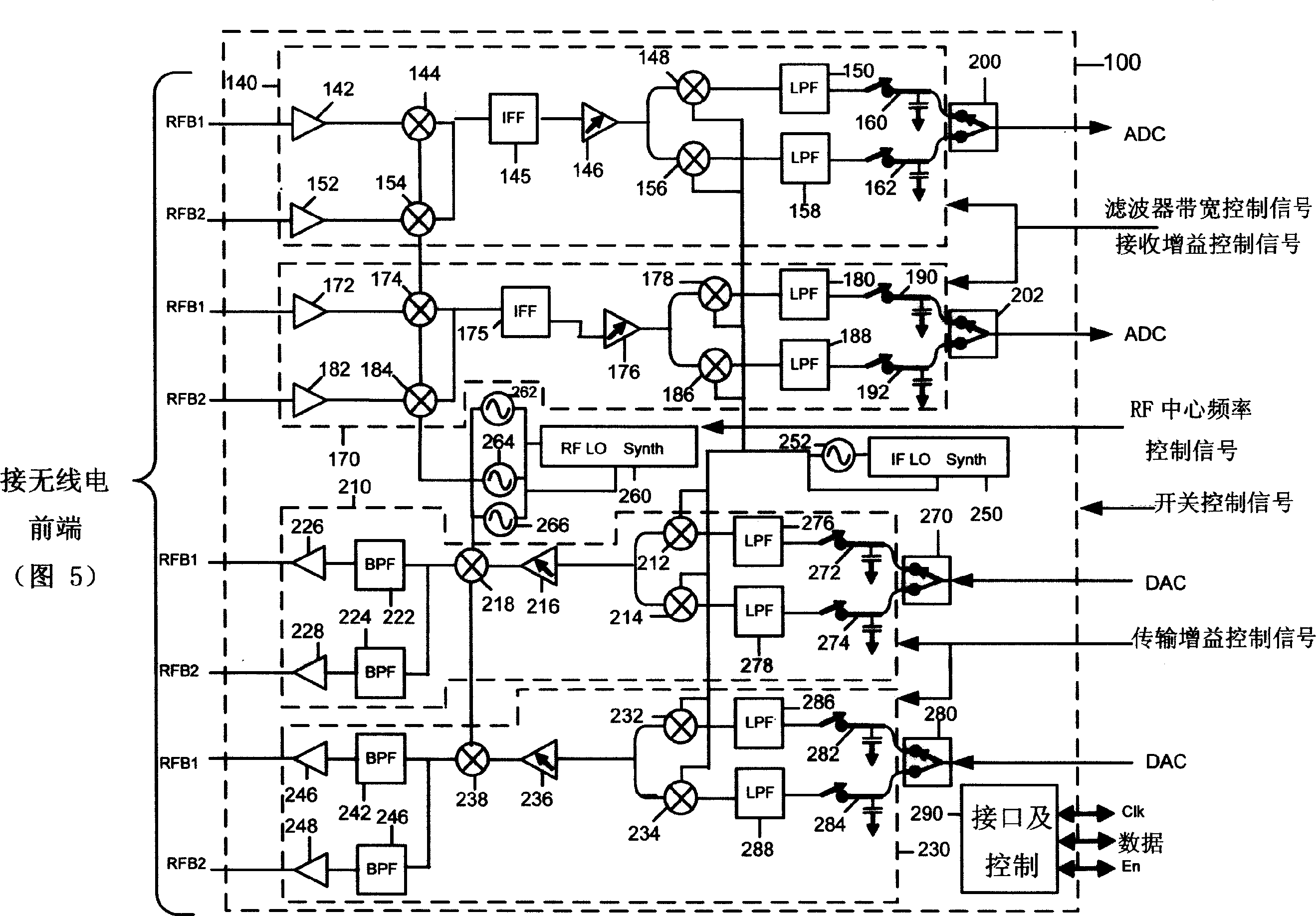
A MIMO radio transceiver to support processing of multiple signals for simultaneous transmission via corresponding ones of a plurality of antennas and to support receive processing of multiple signals detected by corresponding ones of the plurality of antennas. The radio transceiver provides, on a single semiconductor integrated circuit, a receiver circuit or path for each of a plurality of antennas and a transmit circuit or path for each of the plurality of antennas. Each receiver circuit downconverts the RF signal detected by its associated antenna to a baseband signal. Similarly, each transmit path upconverts a baseband signal to be transmitted by an assigned antenna.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
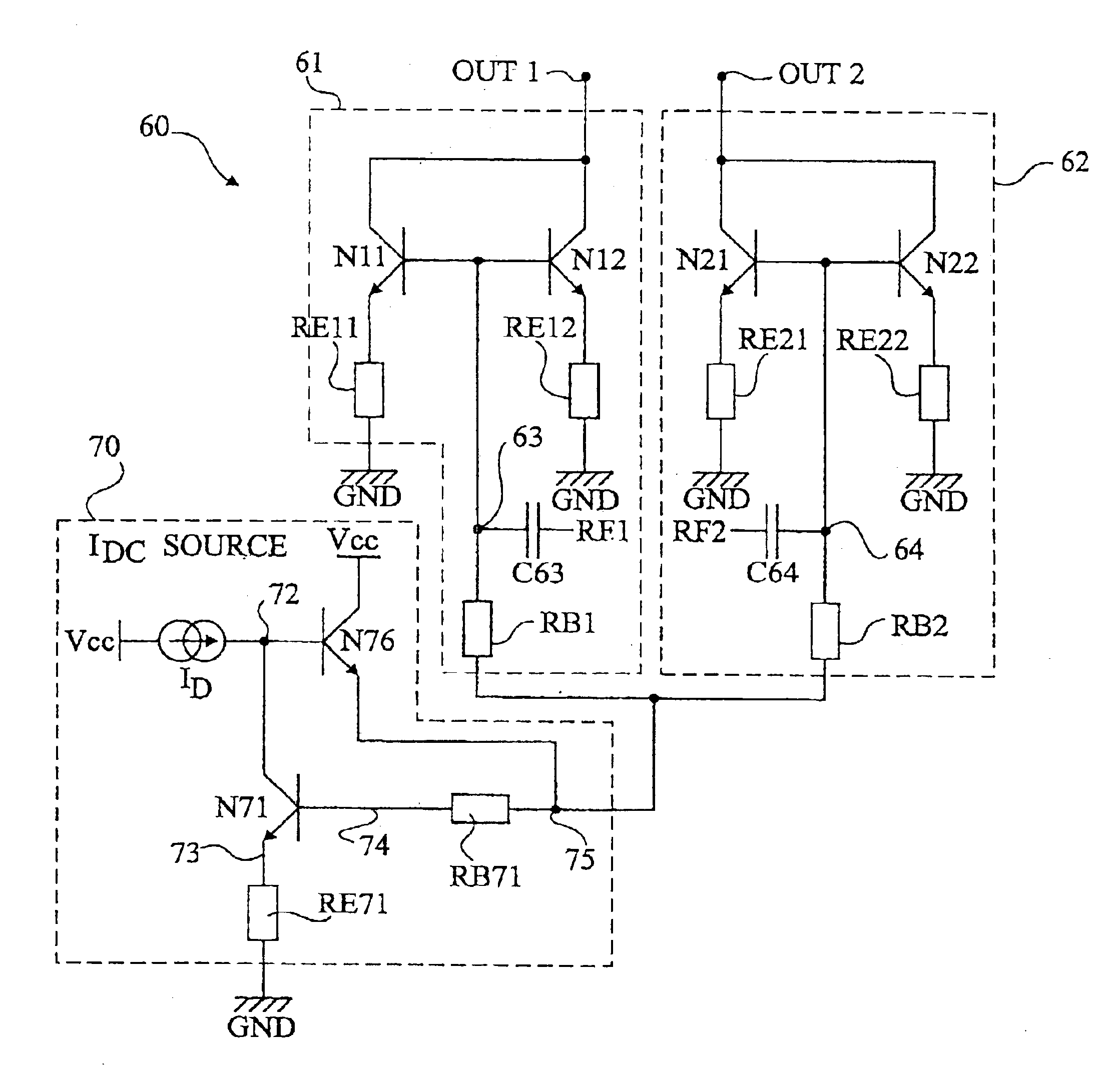
Class AB differential mixer
InactiveUS6882194B2Reduce power consumptionModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsLow voltageReference line
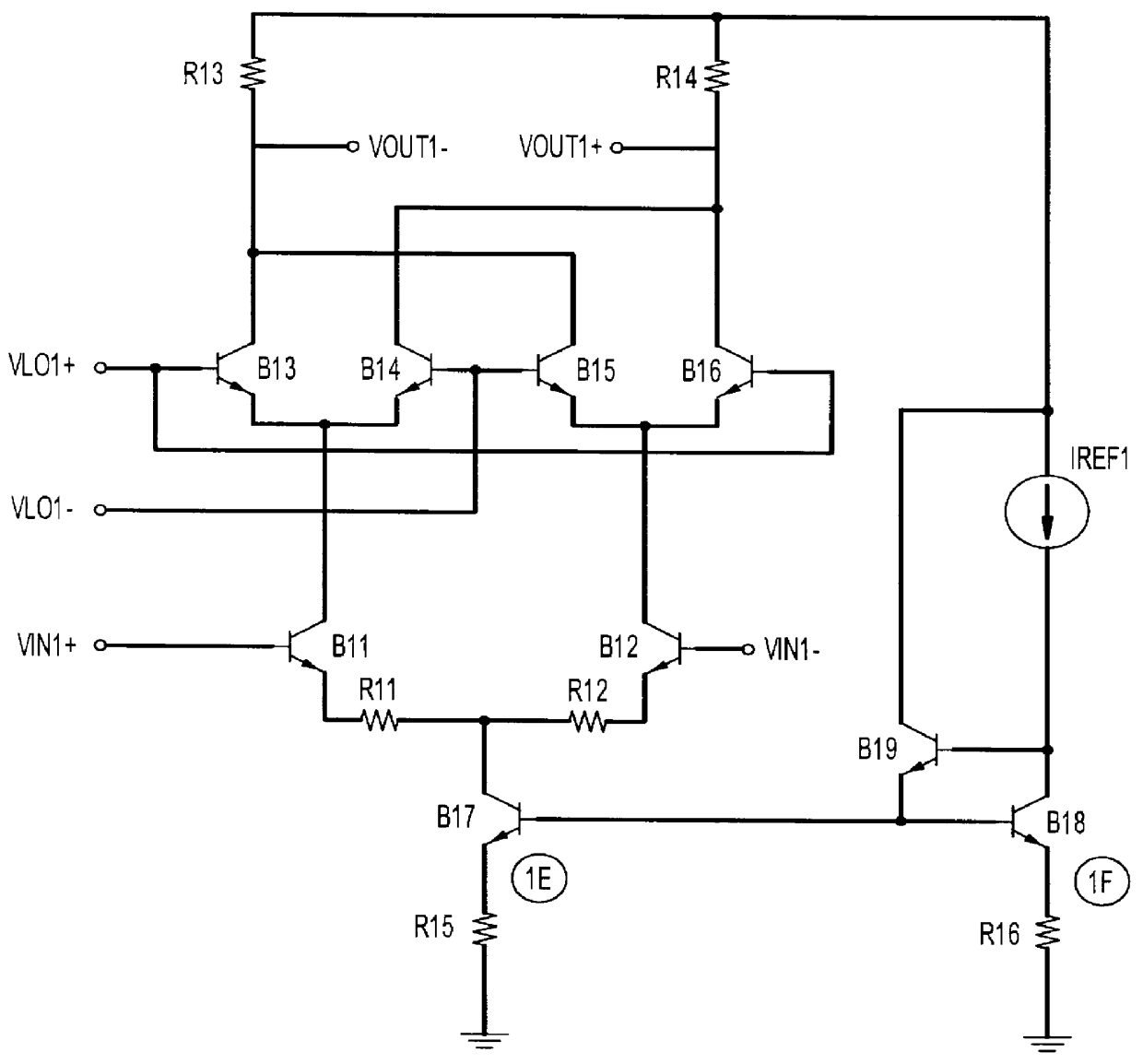
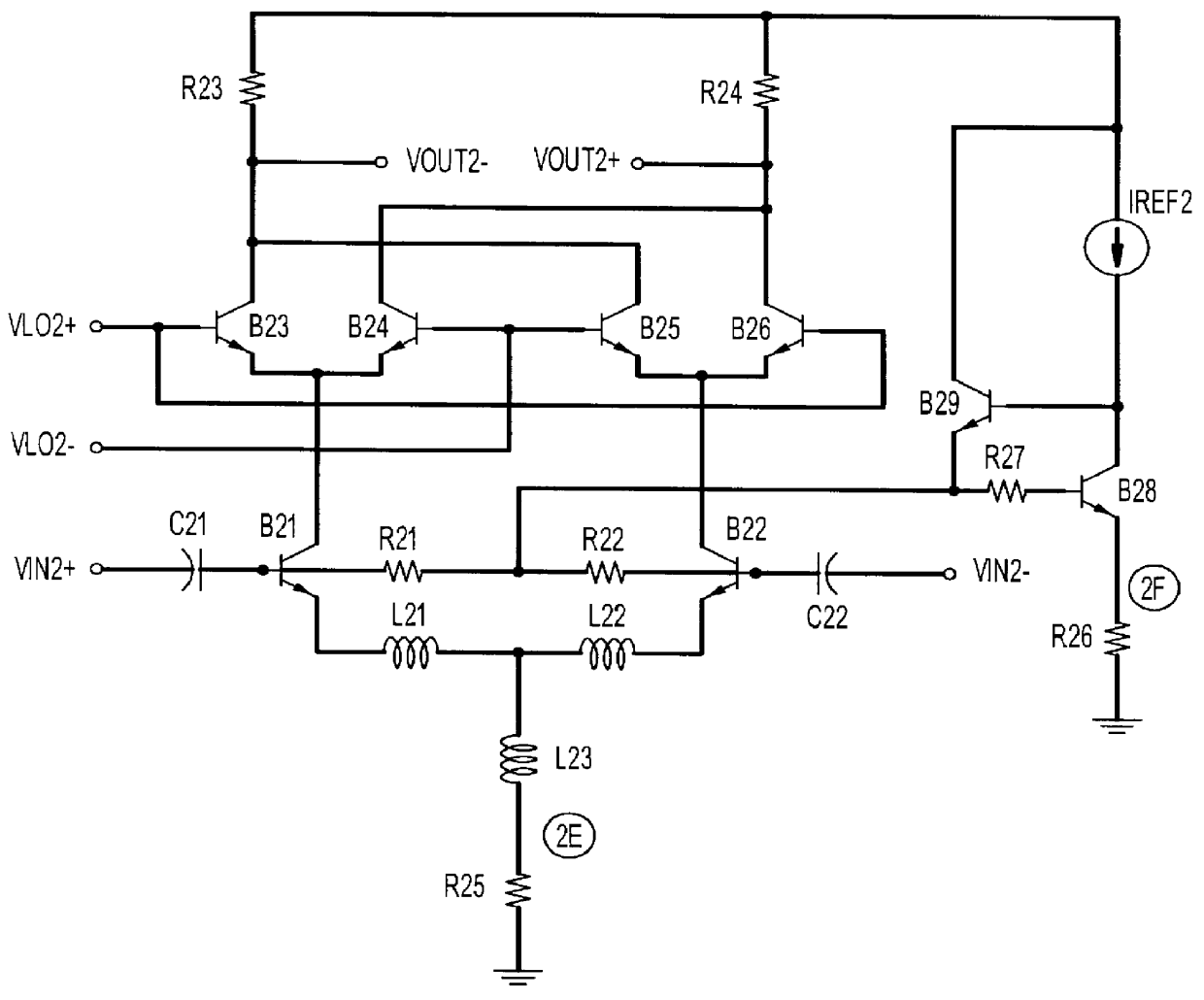
A differential mixer including at least two input / output stages, each stage including two identical branches, each branch of one of the two stages including at least two bipolar transistors the bases of which define a first pair of input / output terminals of the stage and are connected to a same D.C. current source individually by a respective isolating resistor; the collectors of which define a second pair of input / output terminals of the stage which forms a pair of input / output terminals of another stage of the mixer; and the emitters of which are individually connected to a low voltage reference line by a respective degenerative impedance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
High dynamic range time-varying integrated receiver for elimination of off-chip filters
ActiveUS20050164669A1Improve linearityLow costModulation transference balanced arrangementsSwitched capacitor networksQuadrature mixerOutput impedance
A quadrature mixer with an LO input is provided. The quadrature mixer receives a signal having a frequency FLO and a signal input having a frequency FSIG, and has an output that comprises an output impedance that is high at frequencies of |FLO−FSIG | and |FLO+FSIG| and low at other. A mixer coupled to the output impedance interacts with the output impedance such that an impedance presented at the signal input is high for signals at FSIG if FSIG is a predetermined signal frequency, and low at other frequencies.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Low noise mixer circuit with improved gain
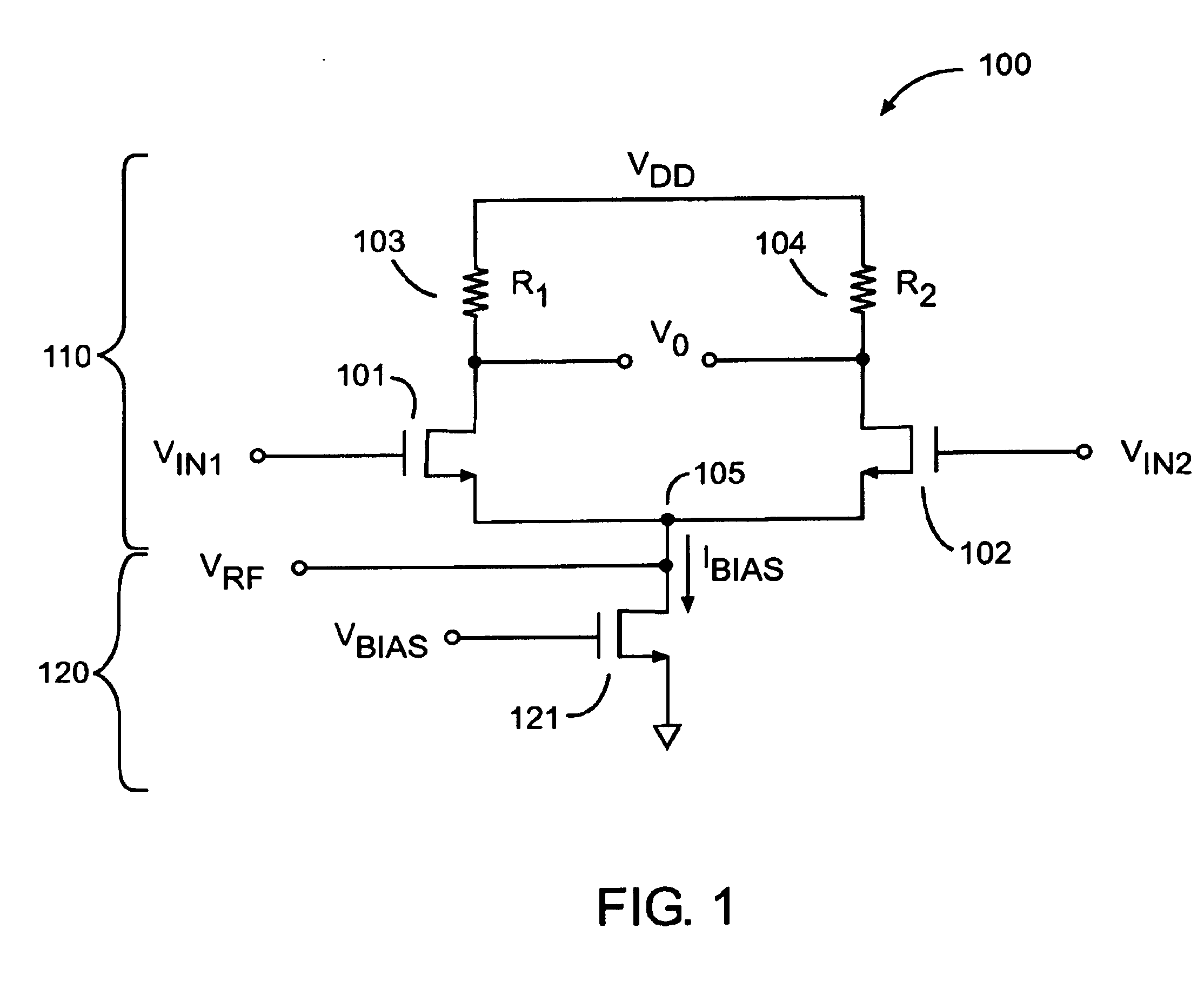
InactiveUS6947720B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio transmissionLow noiseGain stage
A mixer circuit of the present invention includes a gain stage configured to receive a first signal and a modulated bias current, and in accordance therewith, produce an output signal, the gain stage generating a first current and receiving the modulated bias current from a bias circuit on a common node. The bias circuit includes an input configured to receive a second signal, and in accordance therewith, generate the modulated bias current. The mixer circuit also includes a current shunt circuit for generating a second current. The first current, the second current, and the modulated bias current are coupled to the common node. In one embodiment, the first signal is approximately a square wave, and the frequency of the first signal is one-third the frequency of the second signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
InactiveUS20090143031A1Enhanced inhibitory effectAvoid interferenceModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:SHAH PETER
RF mixer with high local oscillator linearity using multiple local oscillator phases
InactiveUS20050233723A1Less sensitiveReduce noiseModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionSignal cancellationPhase difference
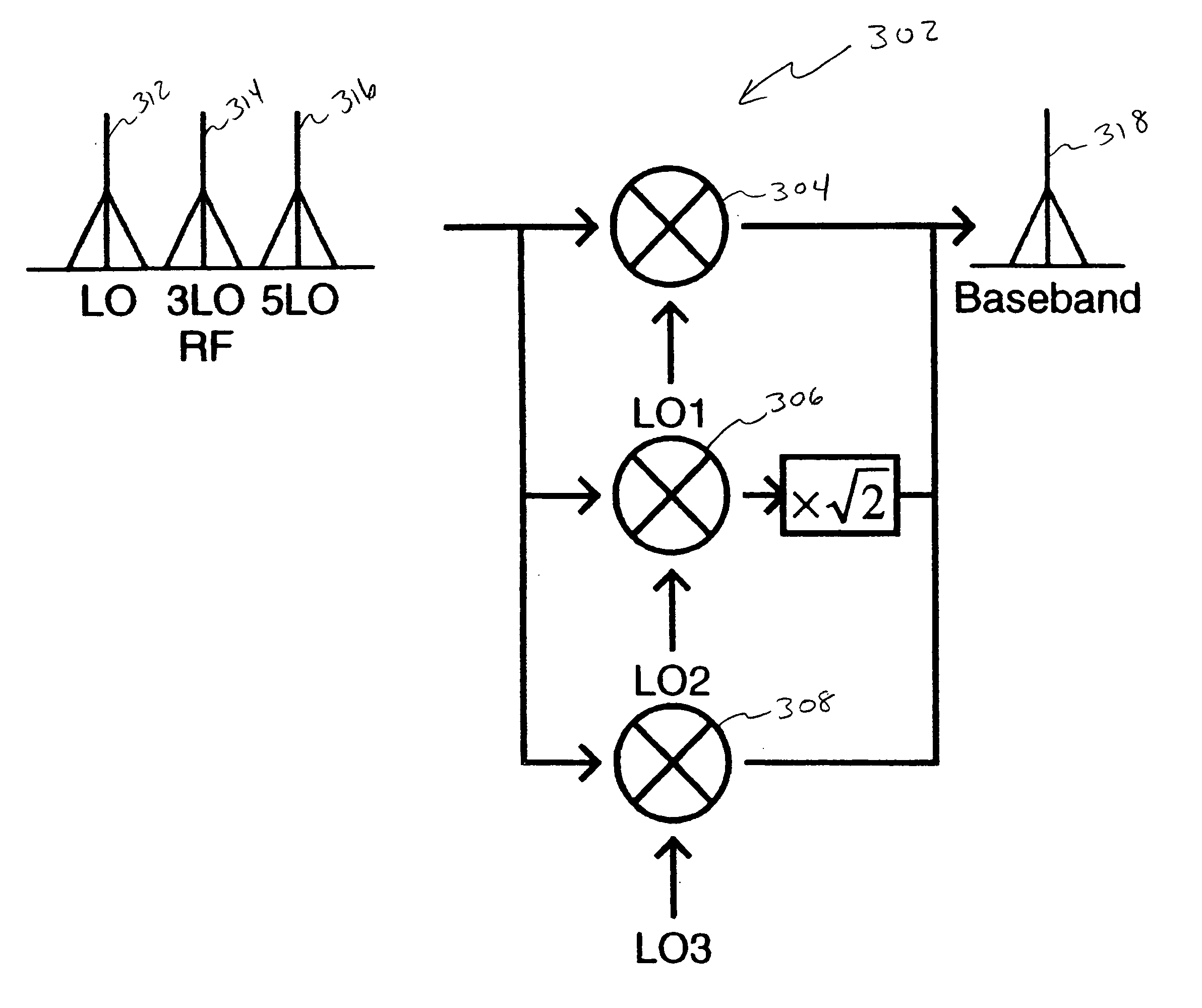
An RF mixer includes a plurality of submixers coupled to a single input transistor pair and a single tail current source. An input LO signal is divided into multiple individual waveforms, each having a different phase. The phase differences are even in that the phase difference between any two time-adjacent individual waveforms is approximately equal to the phase difference between any other two time-adjacent individual waveforms. The submixers are appropriately scaled so that the individual waveforms, when summed, create a piecewise linear LO signal. The submixers also combine the individual waveforms with an input baseband signal to produce an output signal or to produce a baseband signal from an input mixed signal. In order to reduce noise in the system, only one submixer is active at any time. Further, polarities of some individual waveforms are reversed so that to avoid signal cancellation when by combining waveforms of opposite polarities.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
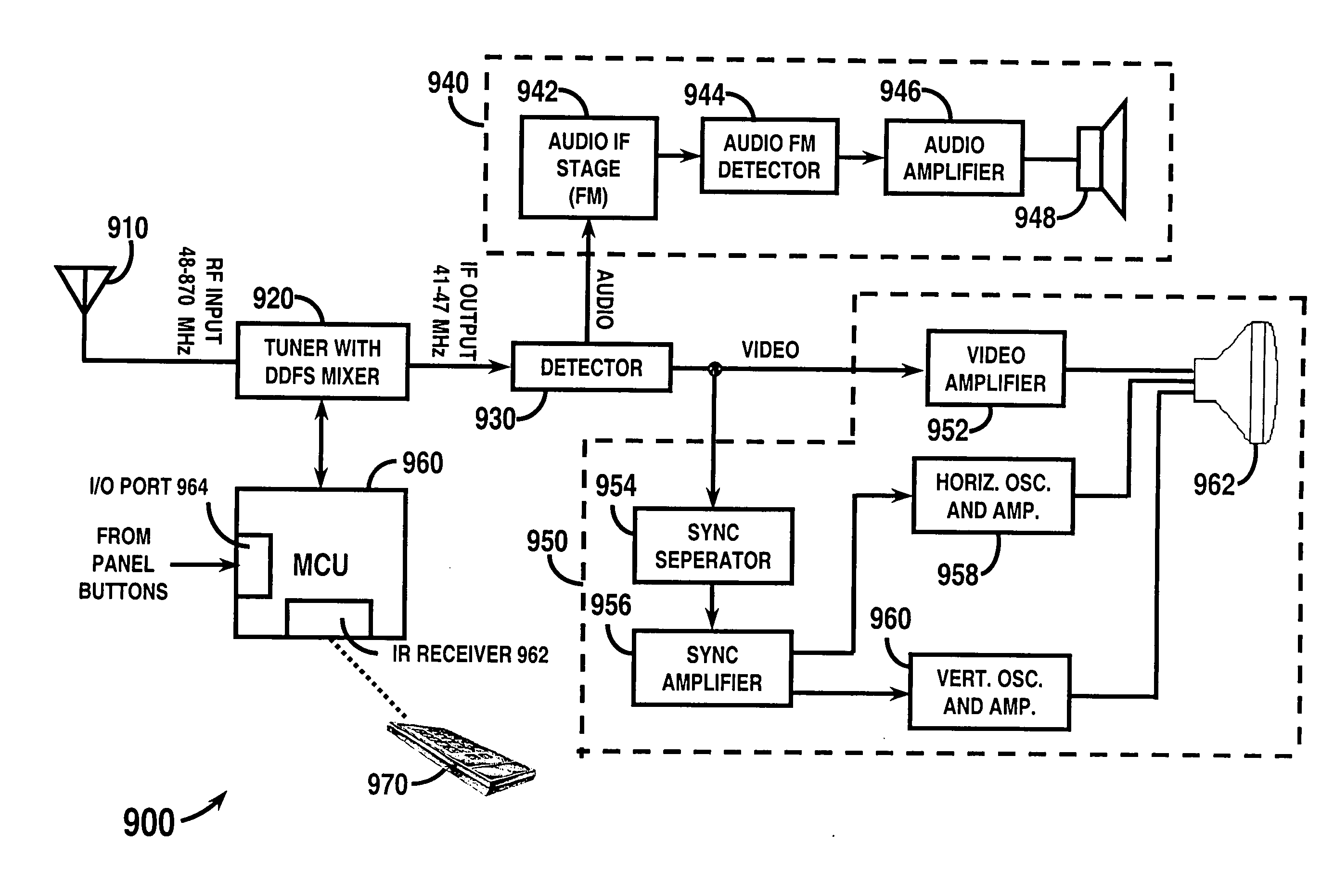
Tuner using a direct digital frequency synthesizer, television receiver using such a tuner, and method therefor
InactiveUS20050117071A1Television system detailsModulation transference balanced arrangementsTelevision receiversIntermediate frequency
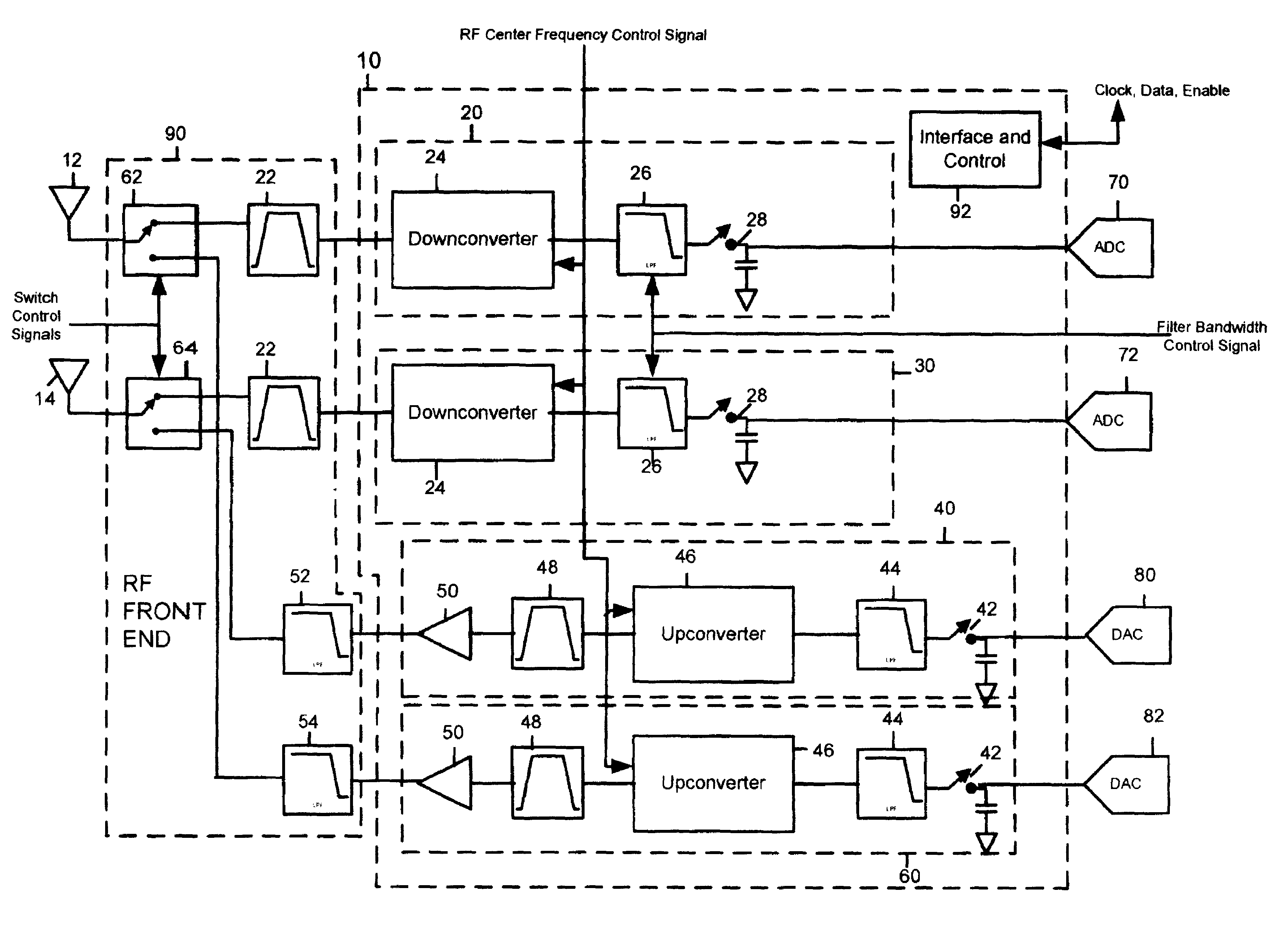
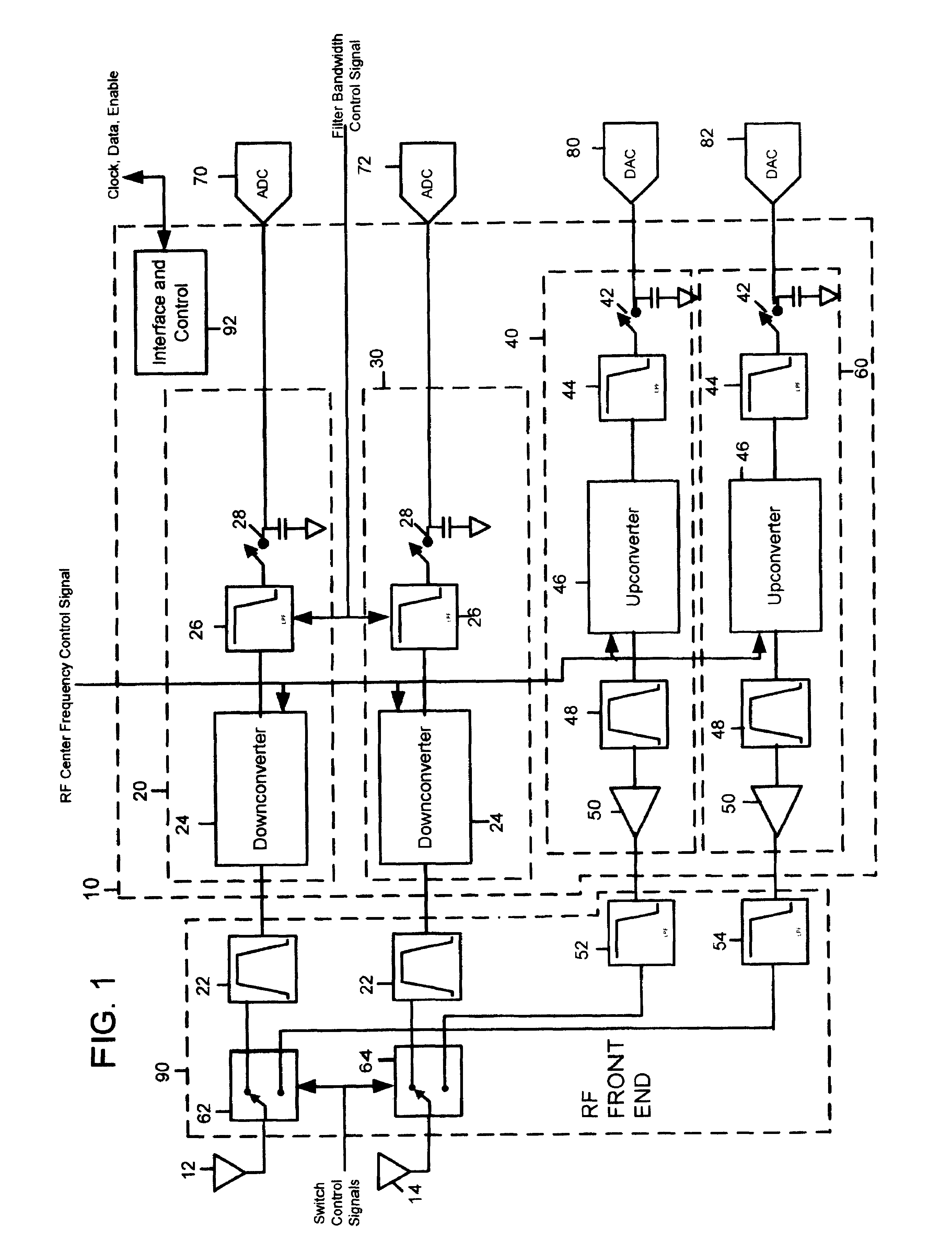
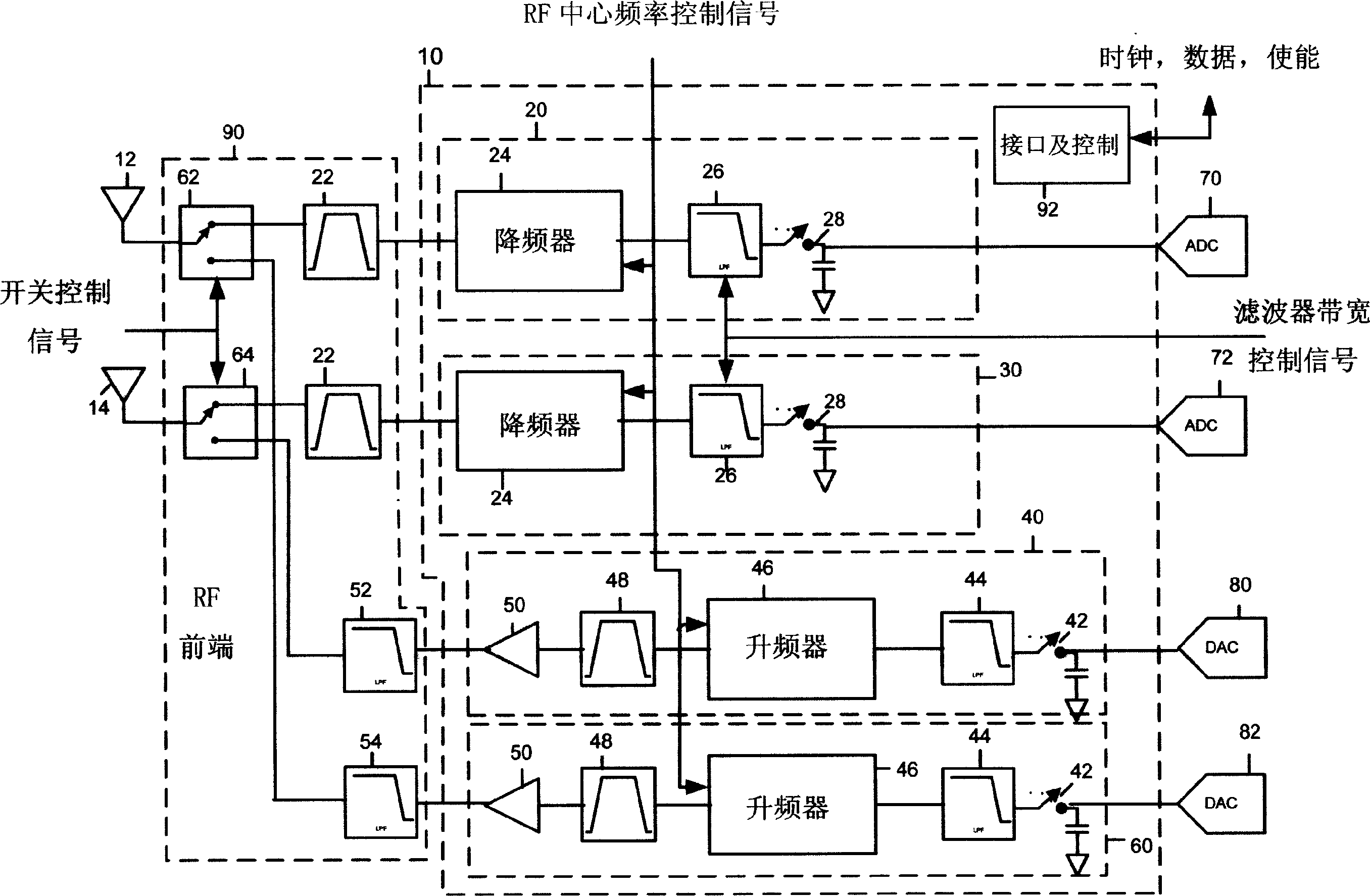
A television tuner (920) is adapted for use in a television receiver (900) that receives a radio frequency (RF) signal from an input device (910) and outputs audio and video information from a selected channel in response thereto. The television tuner (920) includes a direct digital frequency synthesizer (206) and a mixer (220). The direct digital frequency synthesizer (206) has an output for providing a digital representation of a mixing signal. The mixer (220) has a signal input for receiving a television signal, a mixing input coupled to the output of said direct digital frequency synthesizer (206), and an output for providing an intermediate frequency (IF) television signal.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
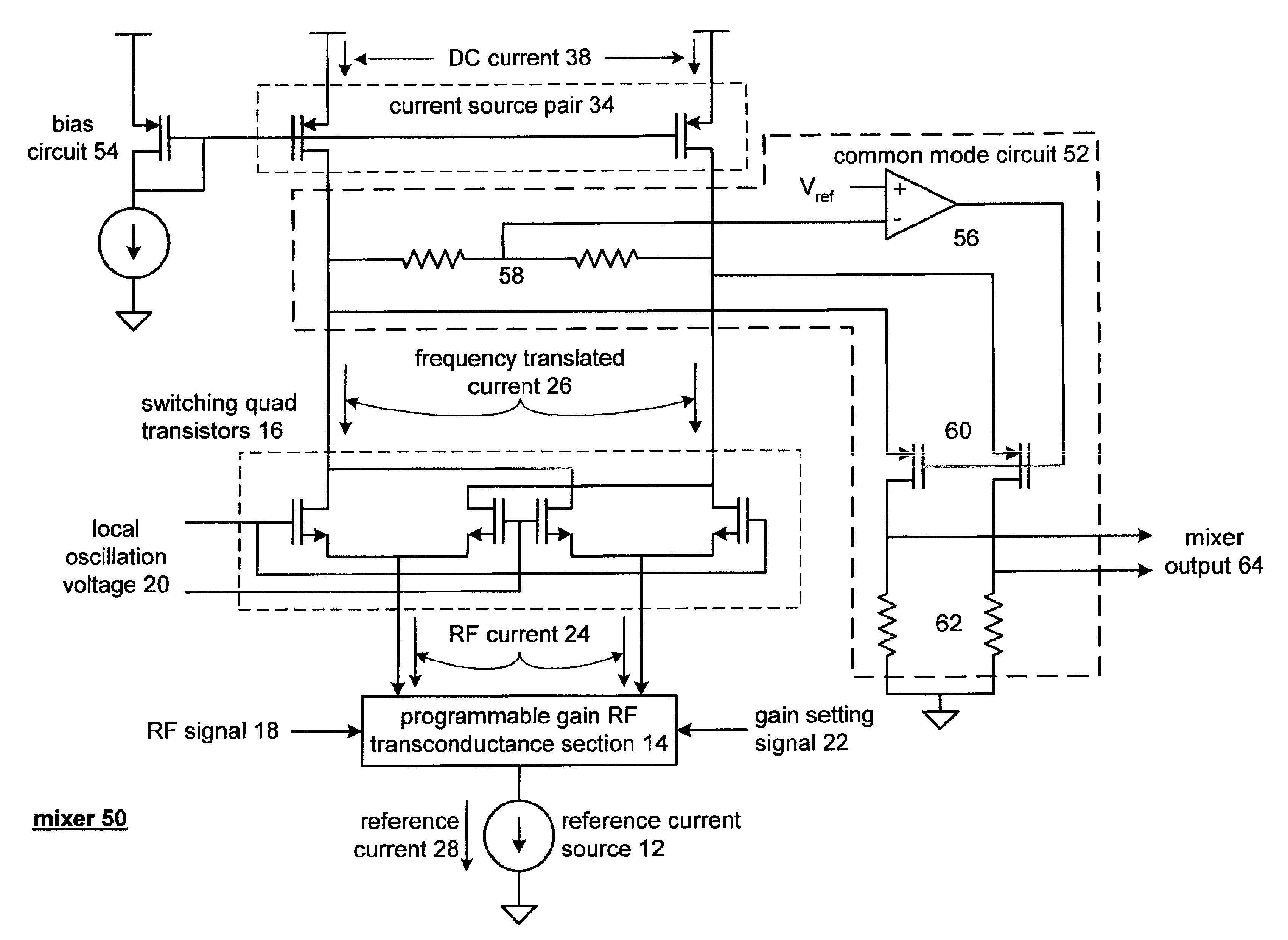
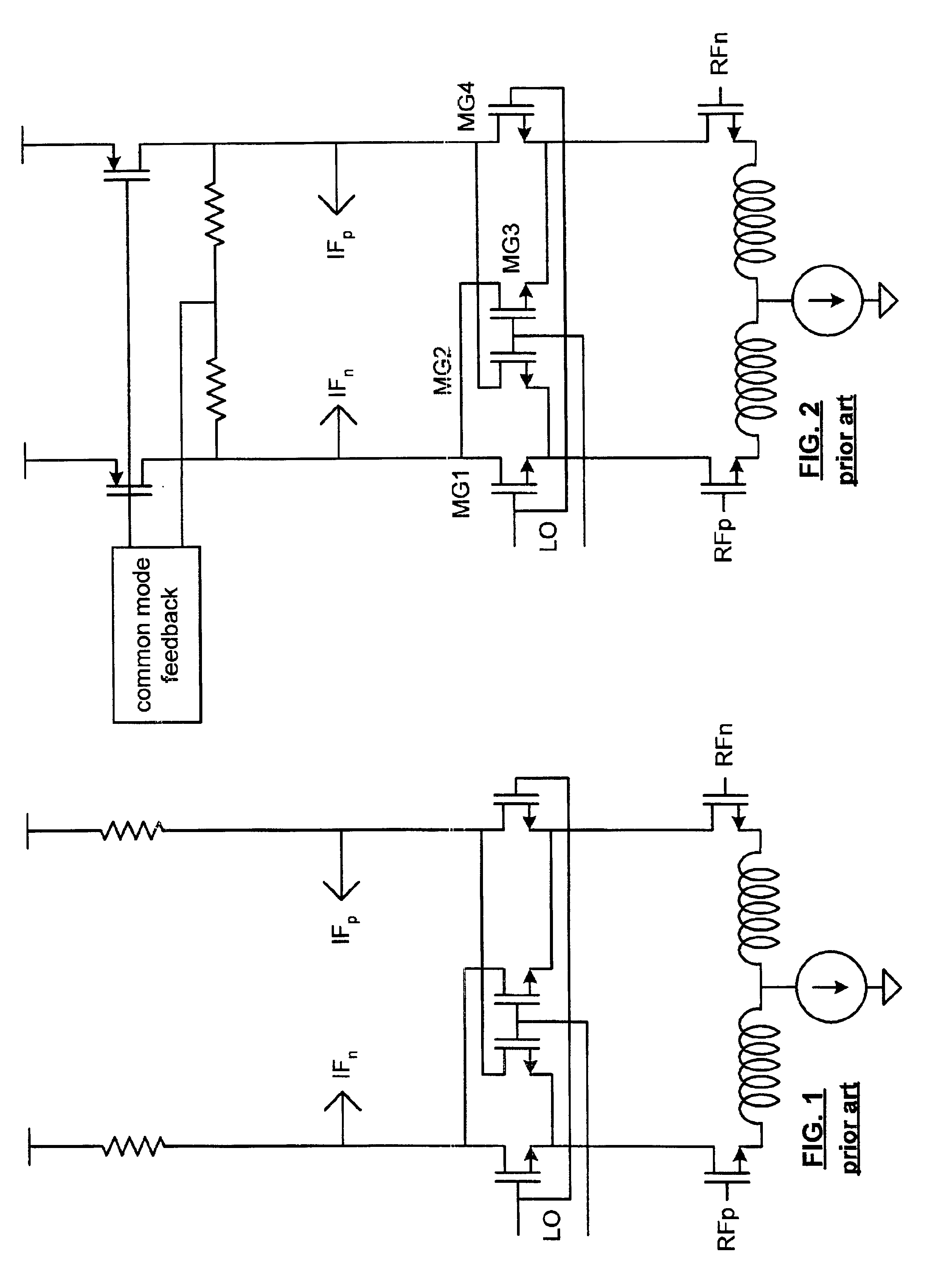
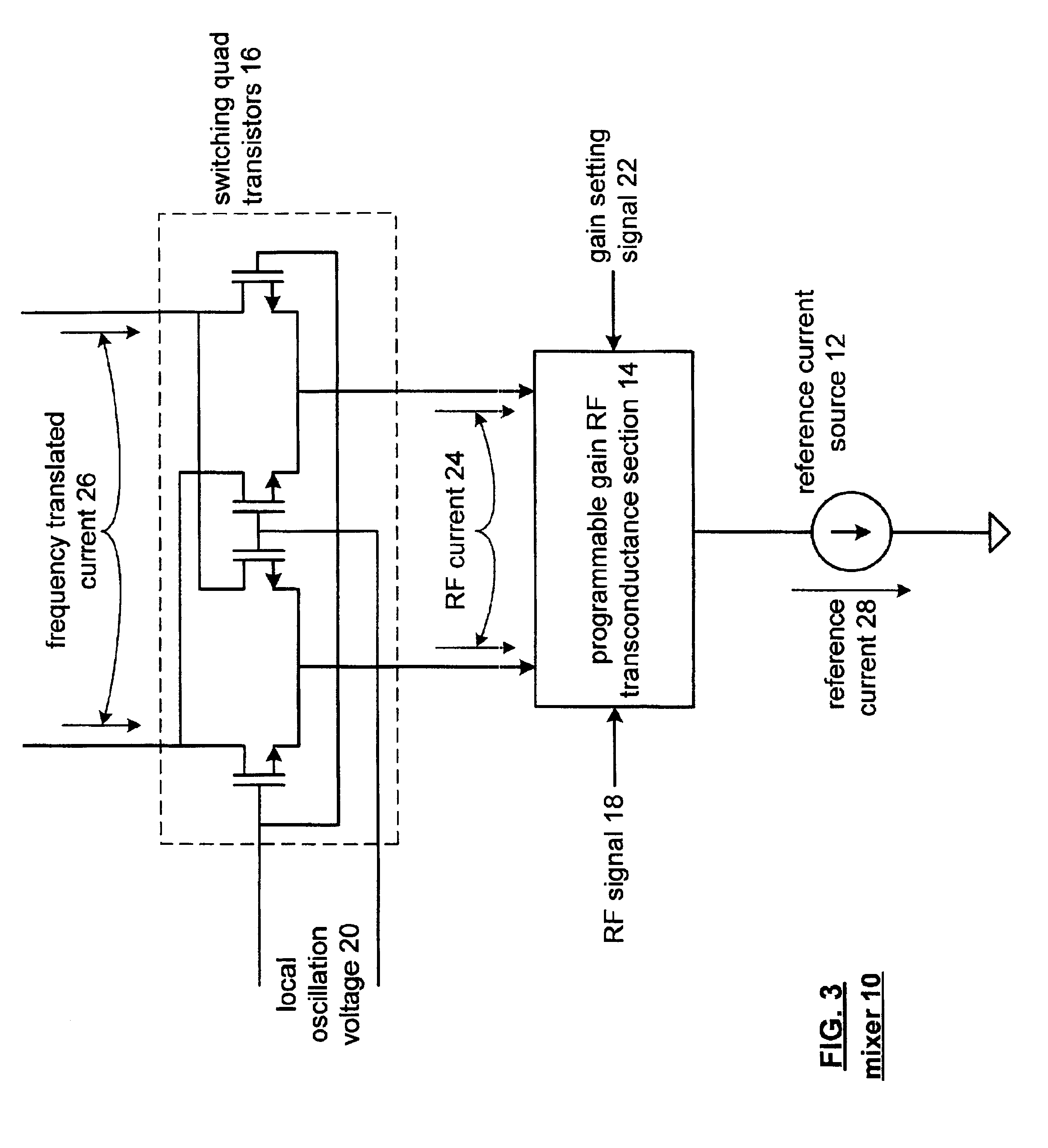
Mixer having low noise, controllable gain, and/or low supply voltage operation
InactiveUS6865382B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsLow noiseReference current
A mixer includes a reference current source, a programmable gain RF transconductance section or an RF transconductance section, switching quad native transistors or switching quad transistors, and a folded-cascoded common mode output section or an output section. When the mixer included the programmable gain RF transconductance section, the gain of the mixer is adjustable. When the mixer includes the switching quad native transistors, flicker noise of the mixer is reduced. When the mixer includes the folded-cascoded common mode output section, the mixer operates reliably from low supply voltages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High dynamic range time-varying integrated receiver for elimination of off-chip filters
ActiveUS7460844B2Improve linearityLow costModulation transference balanced arrangementsSwitched capacitor networksQuadrature mixerOutput impedance
A quadrature mixer with an LO input is provided. The quadrature mixer receives a signal having a frequency FLO and a signal input having a frequency FSIG, and has an output that comprises an output impedance that is high at frequencies of |FLO−FSIG | and |FLO+FSIG| and low at other. A mixer coupled to the output impedance interacts with the output impedance such that an impedance presented at the signal input is high for signals at FSIG if FSIG is a predetermined signal frequency, and low at other frequencies.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Wideband distributed mixers
ActiveUS20050064840A1Modulation transference balanced arrangementsModulation transference by distributed inductance and capacitanceIntermediate frequencyFrequency mixer
A wideband distributed mixer capable of operation over a wide range of frequencies is provided. The mixer can include a plurality of N mixer stages and monolithic transmission lines integrated together on a common semiconductor substrate. The length of each transmission line between adjacent stages can be predetermined such that an IF signal output from each stage is in-phase with the IF signal output from any preceding stage, allowing the mixer to output a mixed IF signal that is a constructive sum of the IF output signals from each constituent stage. The number of mixer stages as well as the design architectures and topologies for each stage can be varied according to the needs of the application.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
InactiveUS6909882B2Stabilized reception characteristicImprove receiver sensitivityResonant long antennasModulation transference balanced arrangementsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
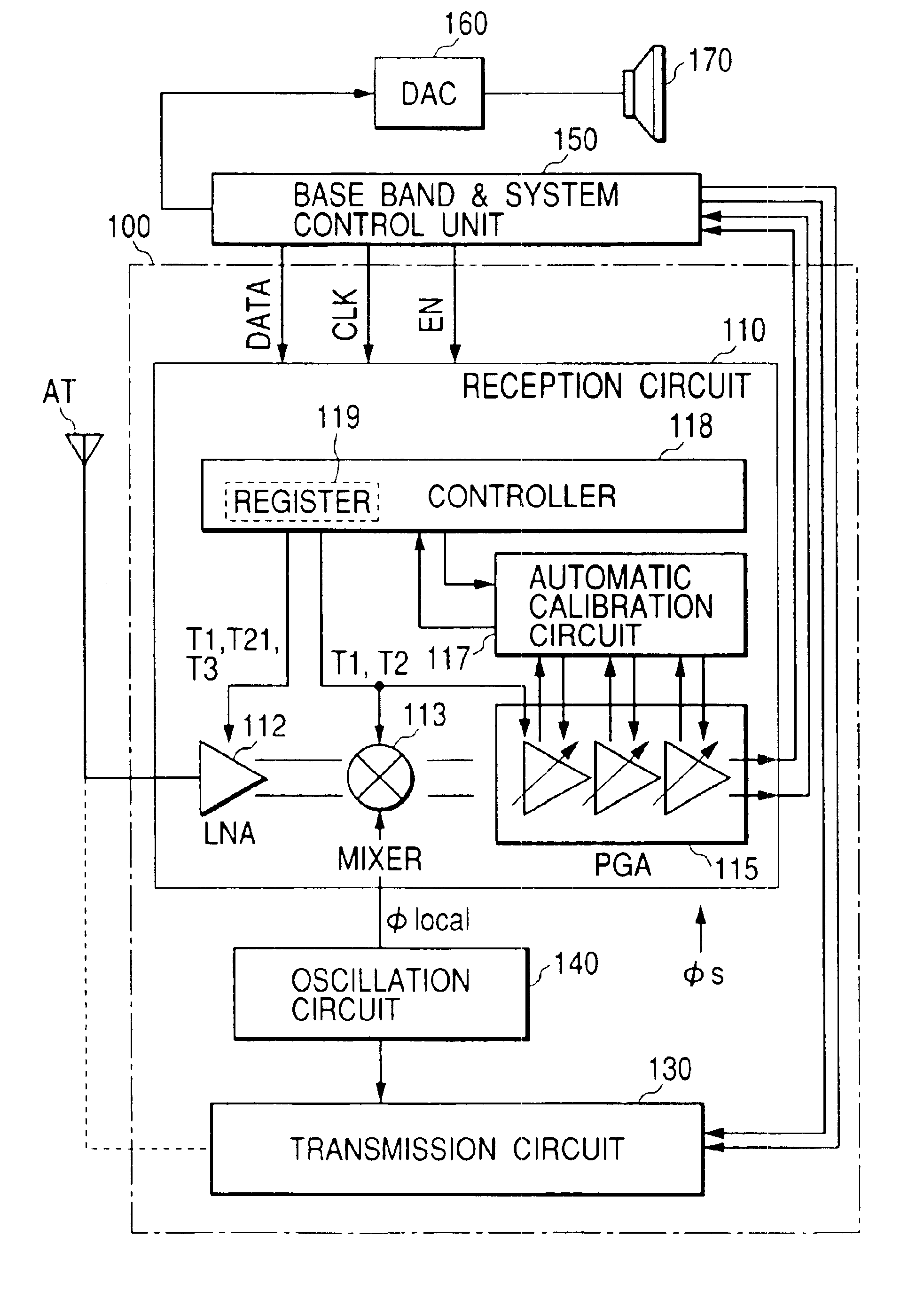
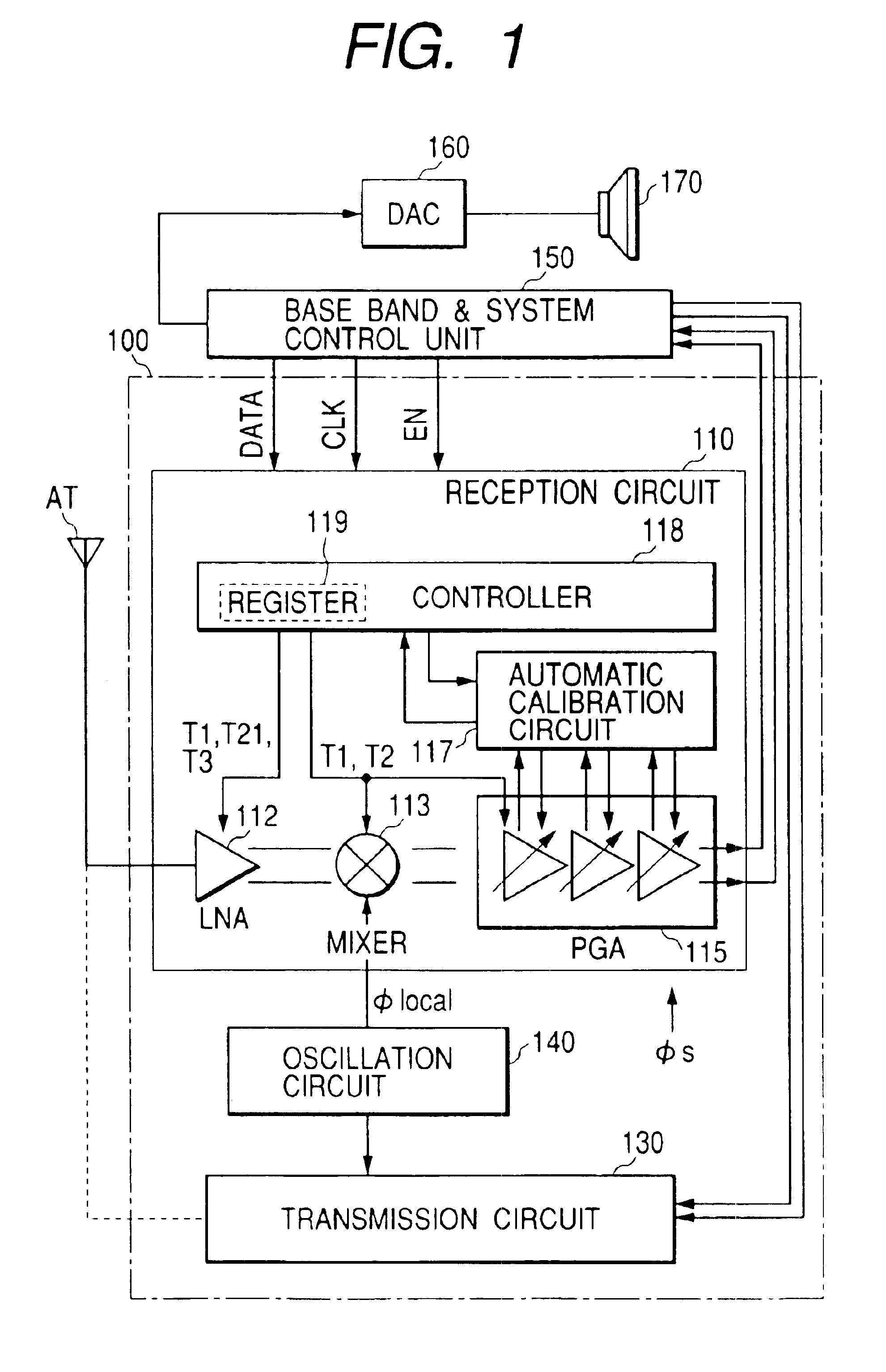
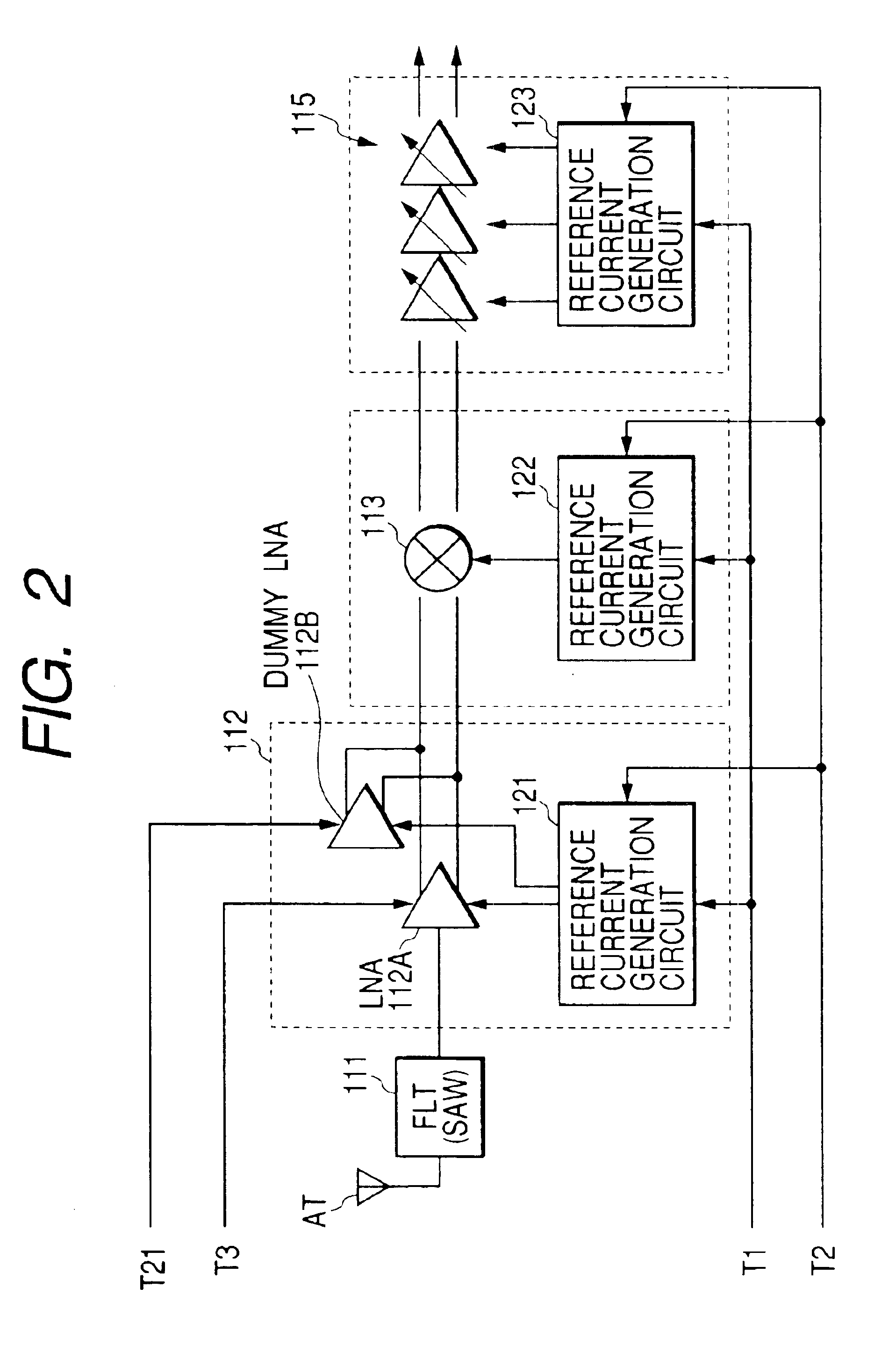
The invention provides a signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit of the direct conversion system, which includes a dummy amplifier having the same circuit configuration as a low noise amplifier being the first stage amplifier, in which the DC offset calibrations on the subsequent stage amplifiers are carried out during shifting into the reception mode in a state that the low noise amplifier is deactivated and the dummy amplifier is activated. Thereby, the invention achieves to suppress generation of the DC offsets resulting from the leakage noises of the local oscillator during shifting into the reception mode, and to enhance the reception sensitivity.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Harmonic reject receiver architecture and mixer
InactiveUS20060160518A1Reducing mixer responseReduced responseModulation transference balanced arrangementsMultiplex with amplitude-modulated carrierLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
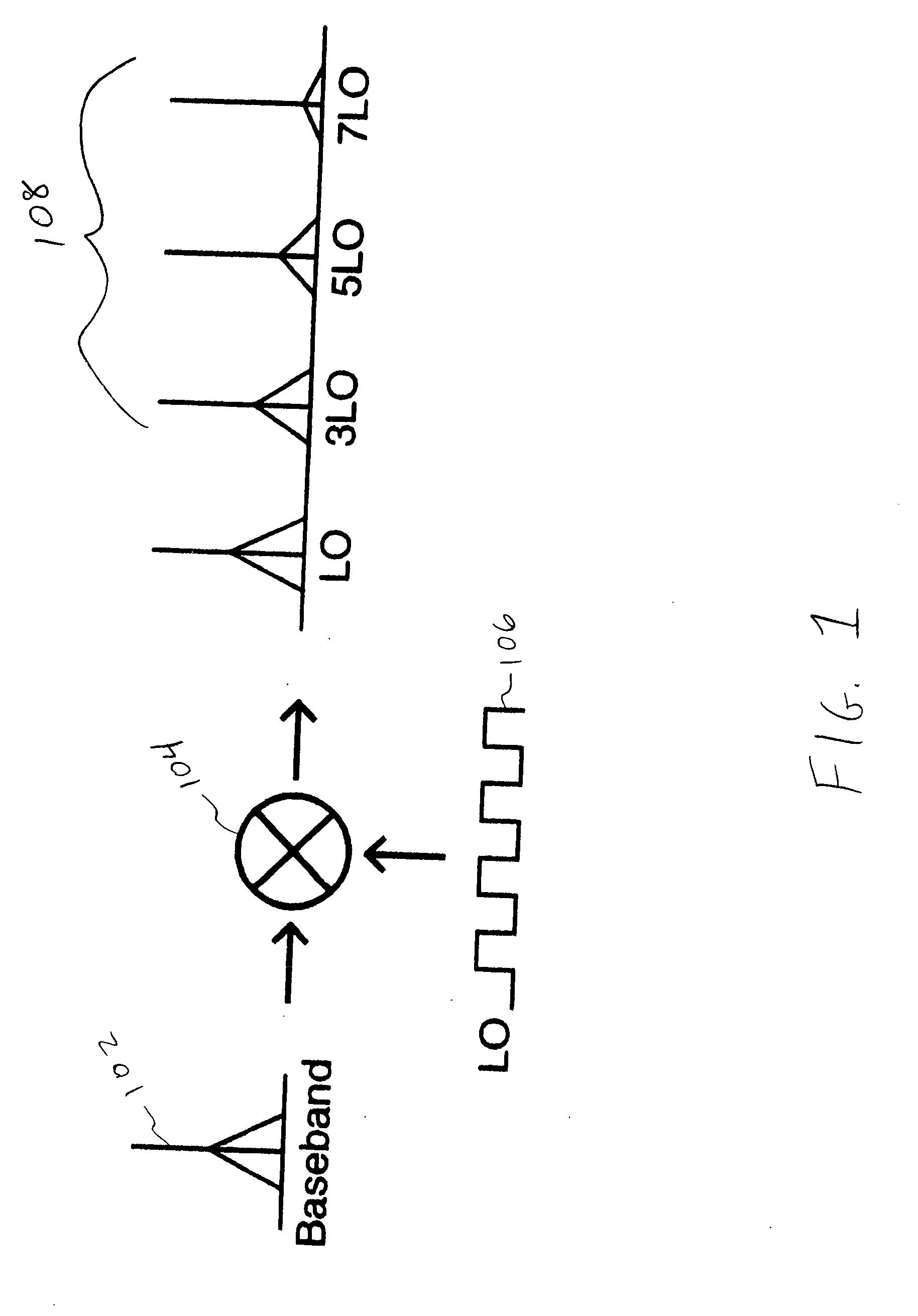
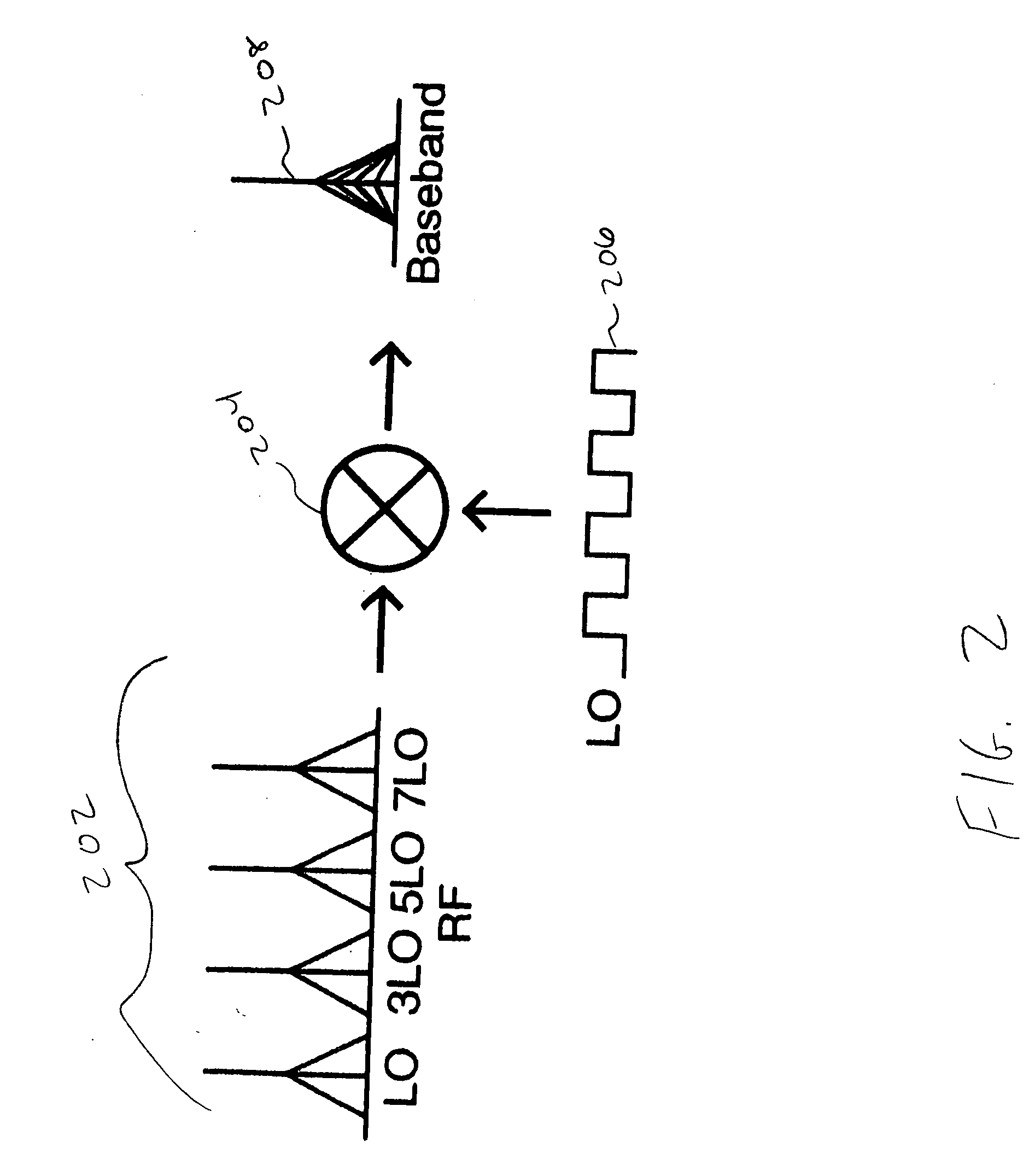
Receiver architectures and methods of processing harmonic rich input signals employing harmonic suppression mixers are disclosed herein. The disclosed receivers, mixers, and methods enable a receiver to achieve the advantages of switching mixers while greatly reducing the mixer response to the undesired harmonics. A harmonic mixer can include a plurality of mixers coupled to an input signal. A plurality of phases of a local oscillator signal can be generated from a single local oscillator output. Each of the phases can be used to drive an input of one of the mixers. The mixer outputs can be combined to generate a frequency converted output that has harmonic rejection.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Bias circuit for transconductance amplifier
InactiveUS6023196AModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSignificant errorVoltage reference
In low-voltage circuits, there is often insufficient voltage to use a current source to bias a transconductance amplifier stage. This is particularly true in mixers where a switching circuit must be stacked on top of the transconductance input stage. One way around this problem is to get "double-duty" out of the input differential pair, using it both for gain stage and for DC bias. This is done by AC coupling in a high-frequency input signal, while using a low-frequency, DC-coupled circuit to establish the proper bias level. One common technique is to use a simple current mirror scheme to establish the DC level. Proper biasing using this technique requires good matching of resistance. In some implementations of transconductance amplifiers, particularly those that use inductors as degeneration elements, series resistance of the inductor and interconnect resistance can cause significant errors in the bias current. This invention addresses that problem by using an operational amplifier with a current-sensing resistor and a low-frequency feedback loop to compensate automatically for any resistance errors. The operational amplifier drives the feedback voltage (generated in accordance with the sensed voltage at the current-sensing resistor and applied to one input of the operational amplifier) towards a reference voltage that is applied to the other input of the operational amplifier to bias the transistor(s) in the transconductance amplifier for desired operating conditions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Frequency conversion circuit, radio frequency wave receiver, and radio frequency transceiver
InactiveUS20050117664A1Reduce power consumptionModulation transference balanced arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsTuned radio frequency receiverFrequency conversion
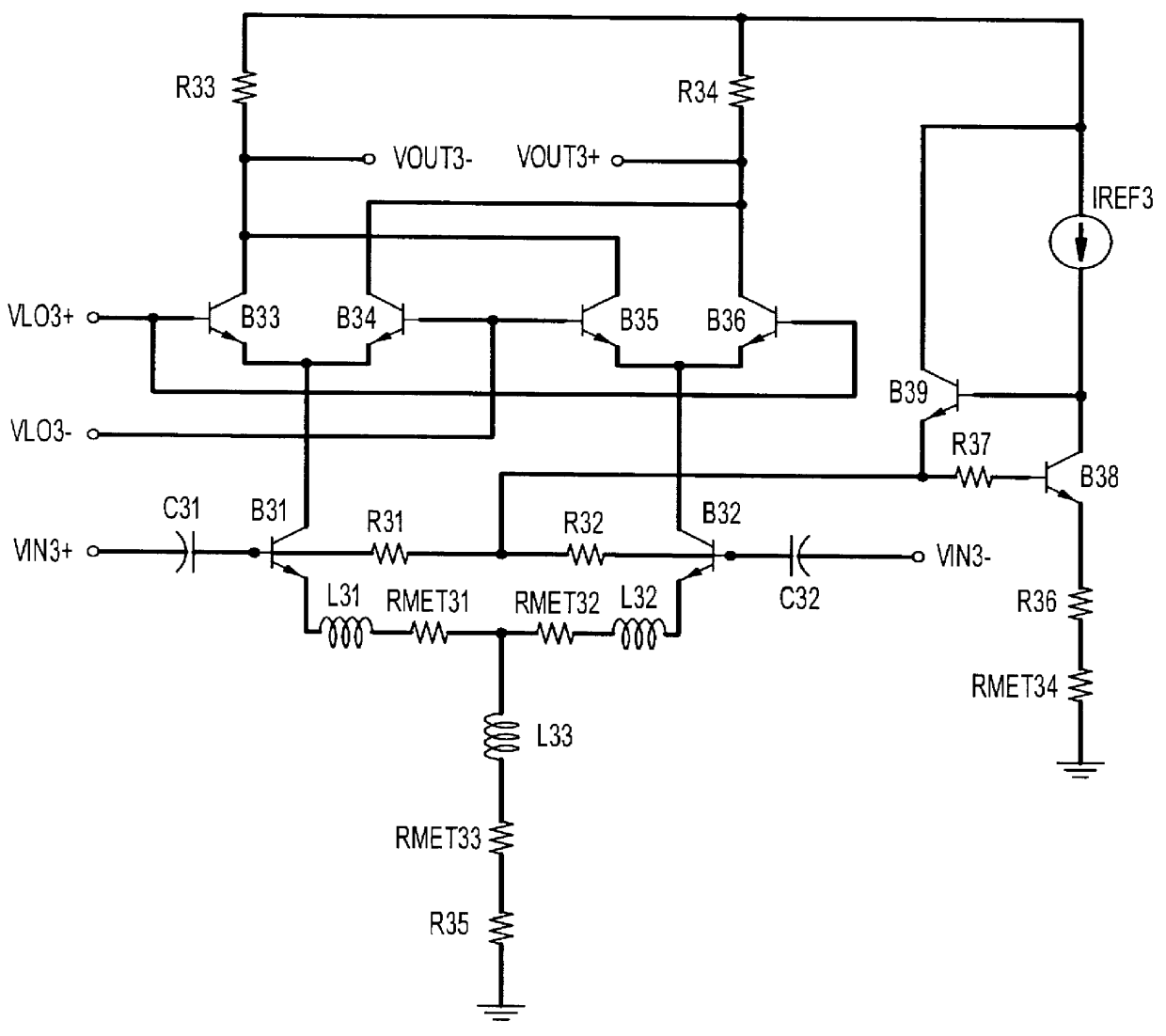
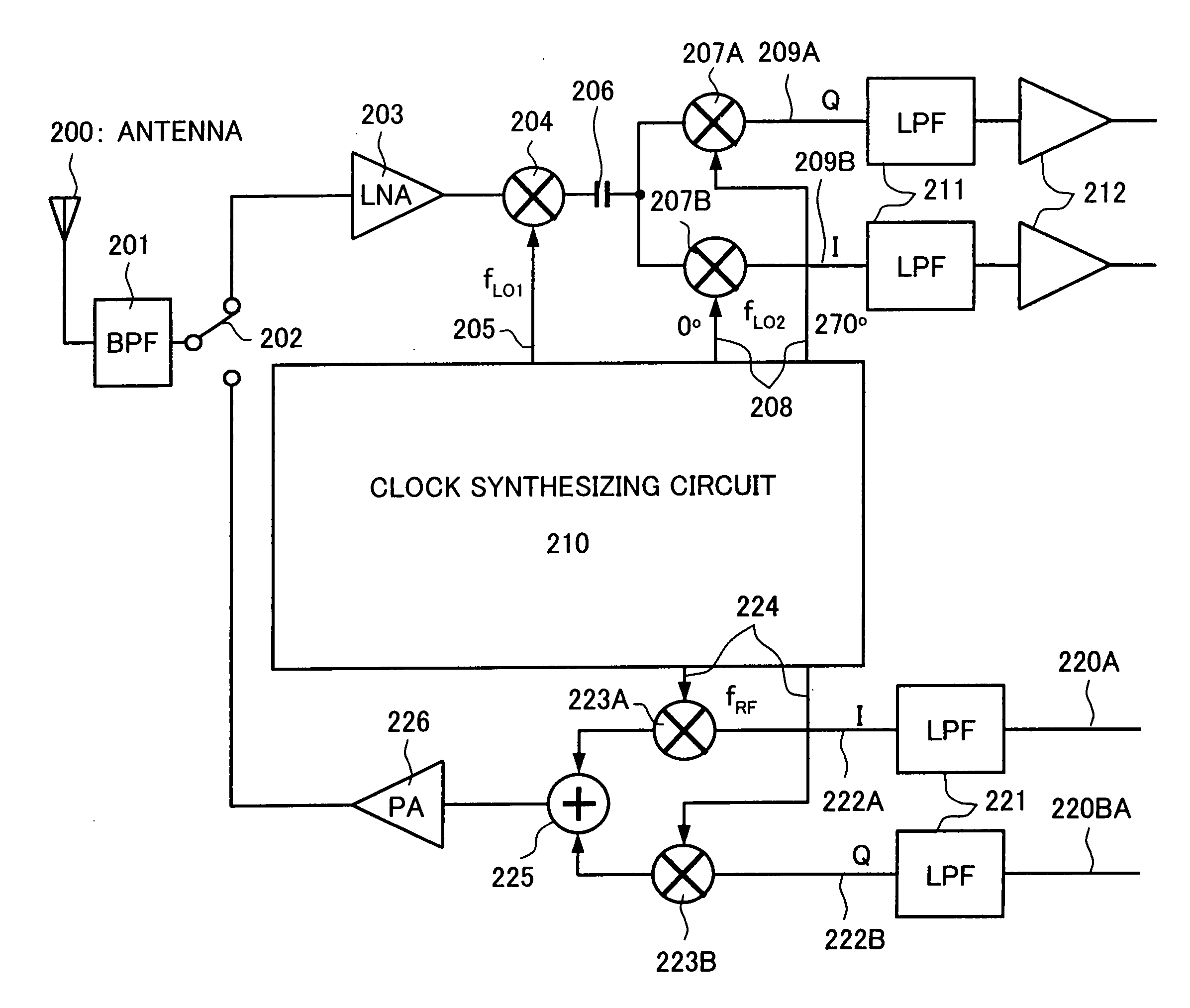
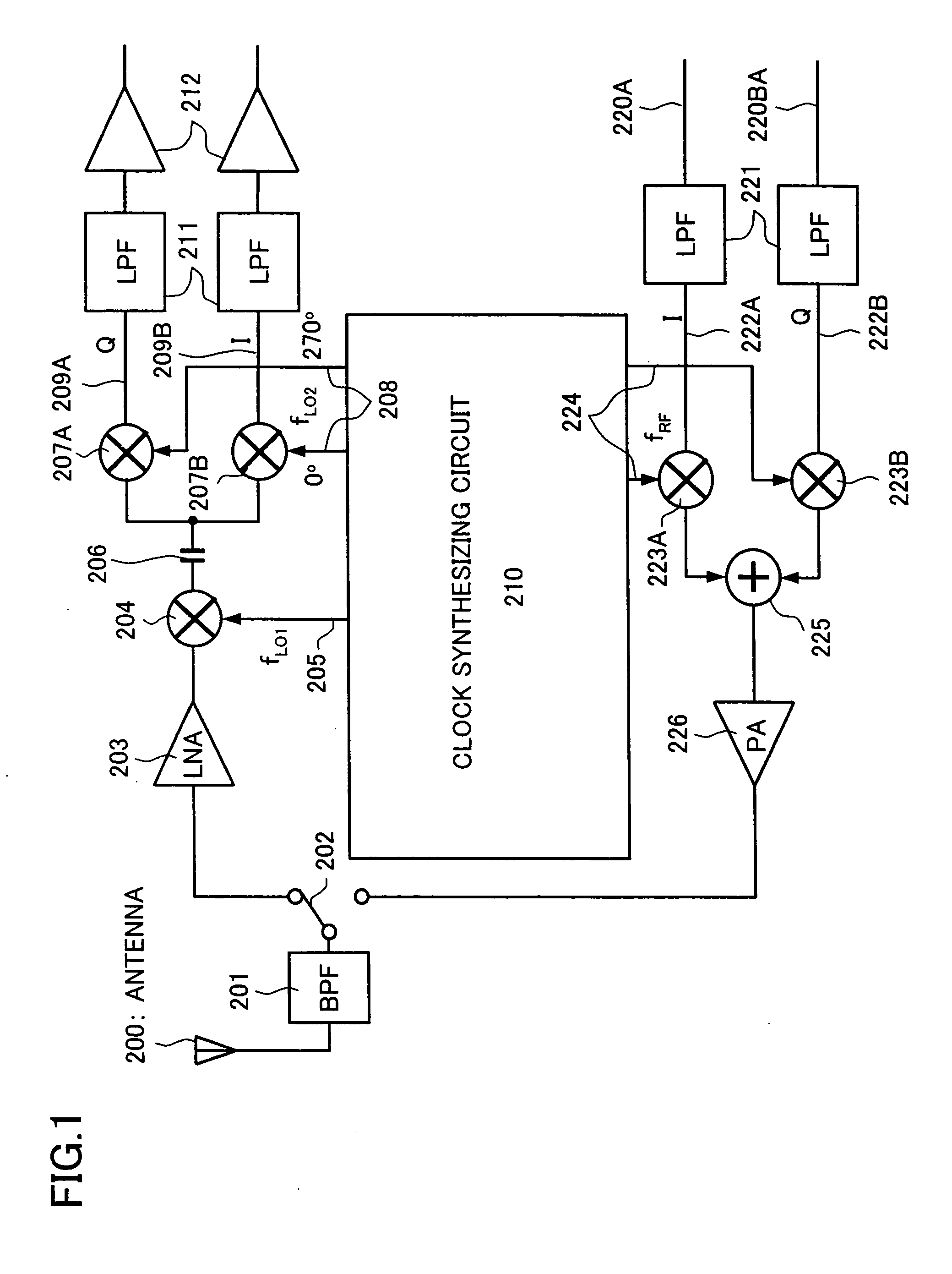
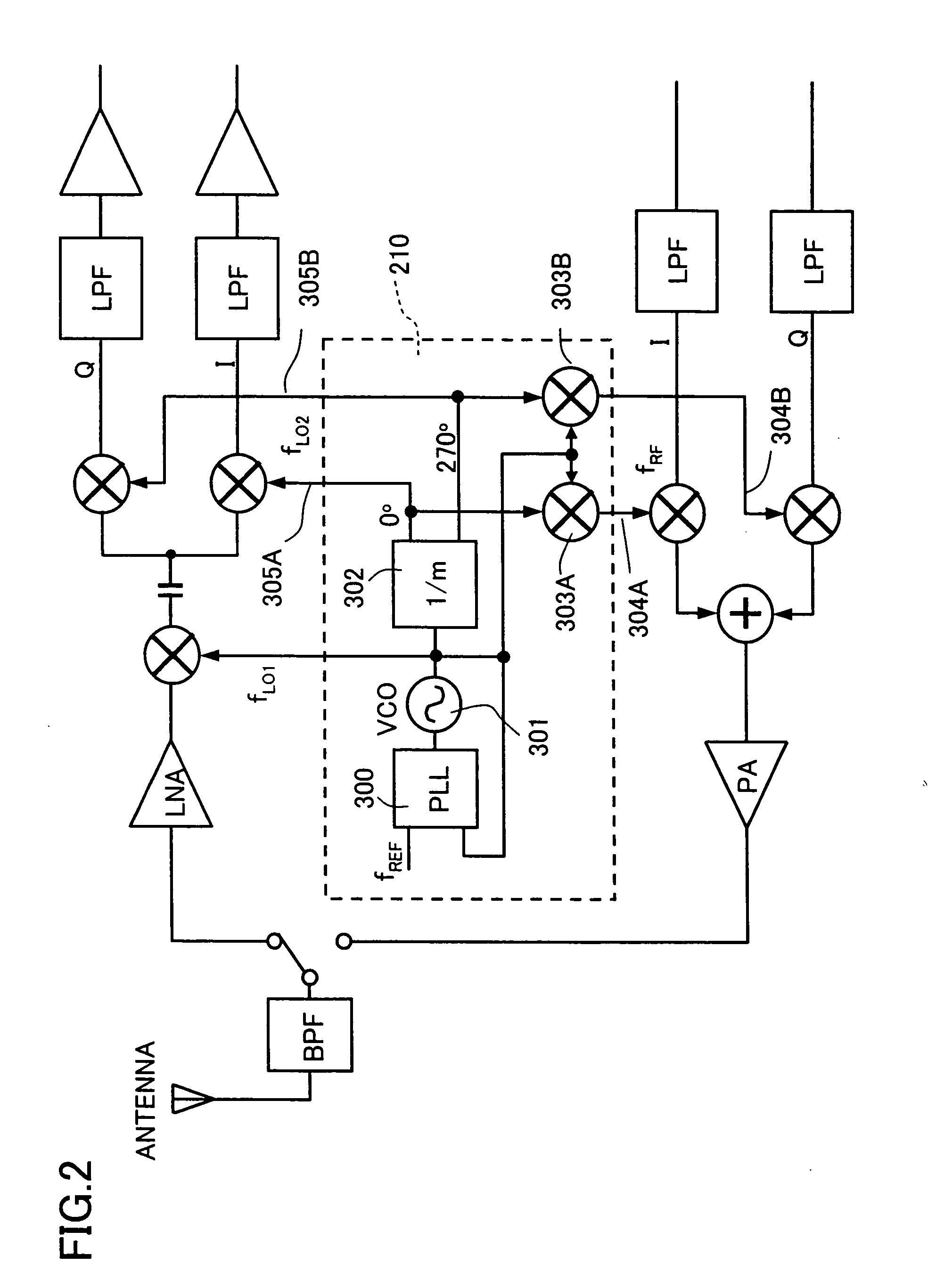
A frequency conversion circuit of the present invention includes: (i) a first mixer for mixing the radio frequency signal having a frequency fRF with a first oscillation signal having a frequency fLO1 so that the radio frequency signal is downconverted into an intermediate frequency signal; and (ii) a second mixer for mixing the intermediate frequency signal sent from the first mixer with two local oscillation signals so that the intermediate frequency signal is downconverted into two base-band signals having different phases. The second local oscillation signals have phases of 0° and 270°, respectively. These frequencies satisfies: fLO1=k×fRF(k>1) fLO2=fLO1 / m, (m>1) k=m / (m−1). This arrangement ensures (i) a small frequency conversion circuit that can be mounted on an integrated circuit, (ii) a radio frequency receiver including the frequency conversion circuit, and (iii) a radio frequency transceiver including the radio frequency receiver.
Owner:SHARP KK
Mixer circuit
InactiveUS6871057B2Increase working frequencyMinimum errorModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
A mixer circuit used in a radio receiver for mixing two frequencies and providing an intermediate frequency which is the difference of the two frequencies. Excellent image rejection is provided by decreasing an amplitude error and a phase error of an output IF signal in differential form.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Radio system including FET mixer device and square-wave drive switching circuit and method therefor
InactiveUS6108529AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio equipmentLocal oscillator signal
A radio comprising an FET mixing device for multiplying a first-frequency signal with a second frequency signal to generate a third frequency analog mixer output signal. A local oscillator input port receives a periodic sinusoidal local oscillator signal at a local oscillator frequency from an external local oscillator source. A drive circuit generates a substantially square-wave two-voltage level switching signal for driving said mixing device. An analog-to-digital converter generates a digital representation of said third frequency analog mixer output signal.
Owner:DRS SIGNAL SOLUTIONS
Mixer circuit for direct conversion transceiver with improved IP2
InactiveUS20050170806A1Improved IP characteristicImprove featuresModulation transference balanced arrangementsVibration massagePhase shiftedFrequency mixer
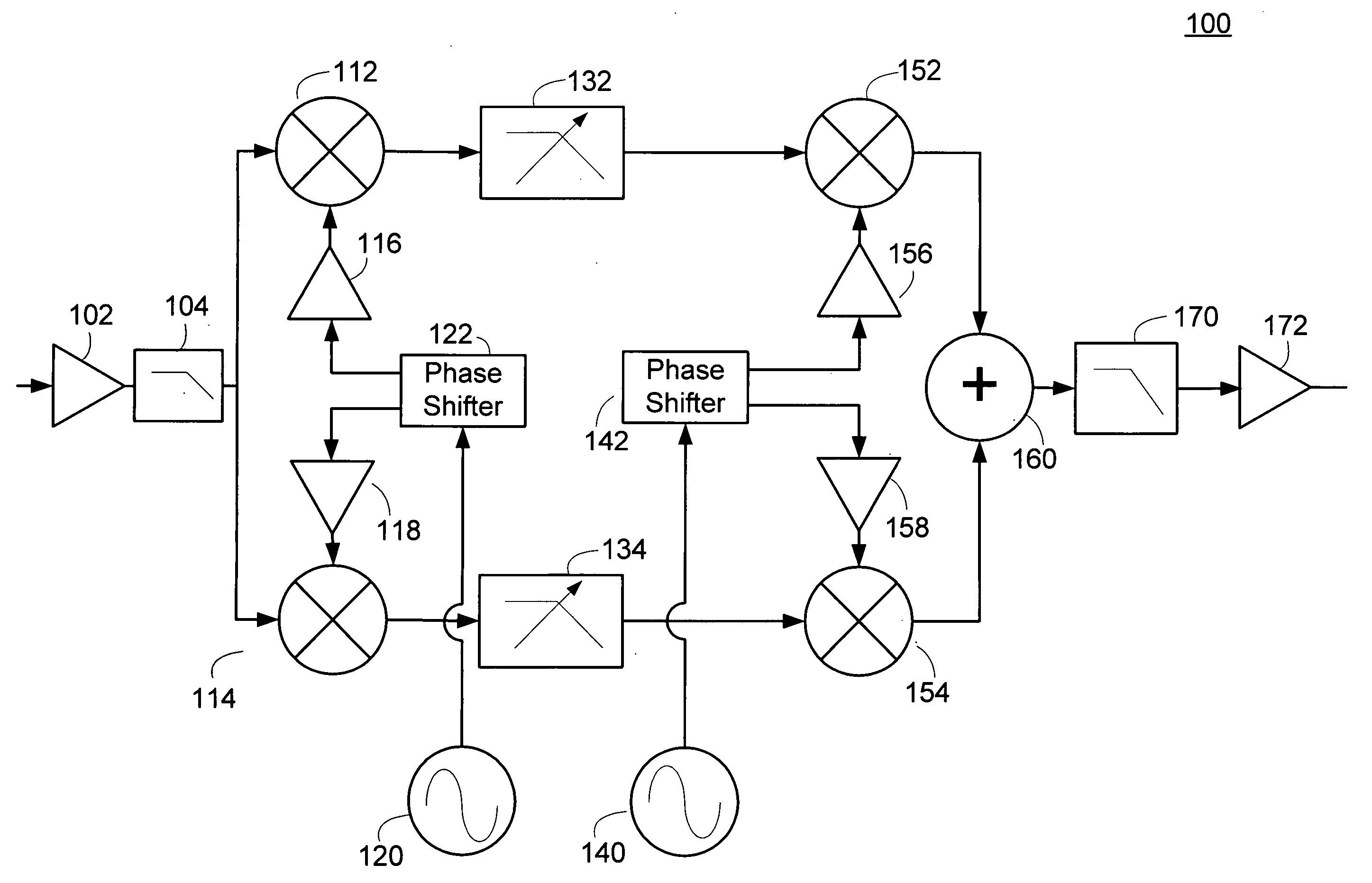
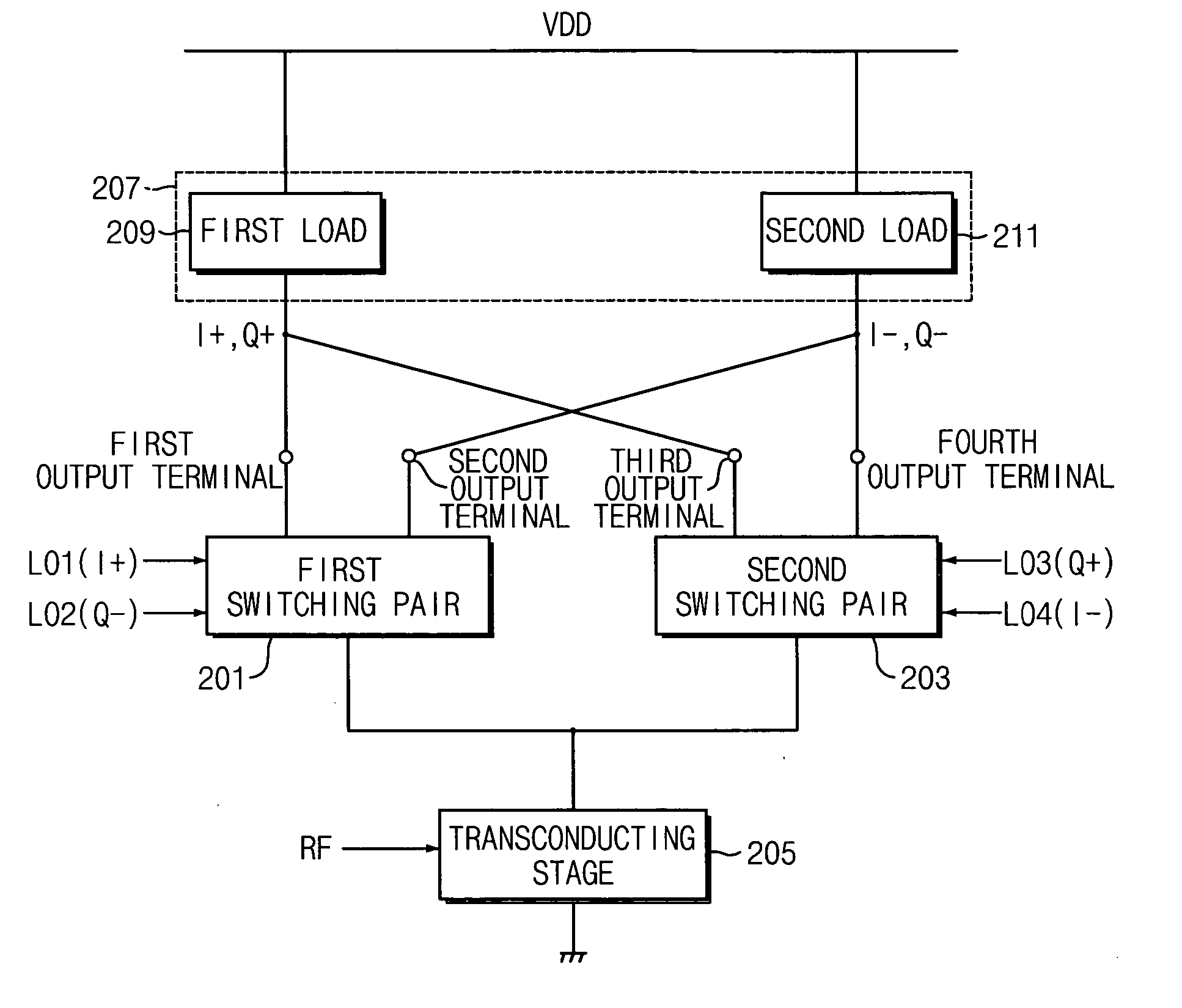
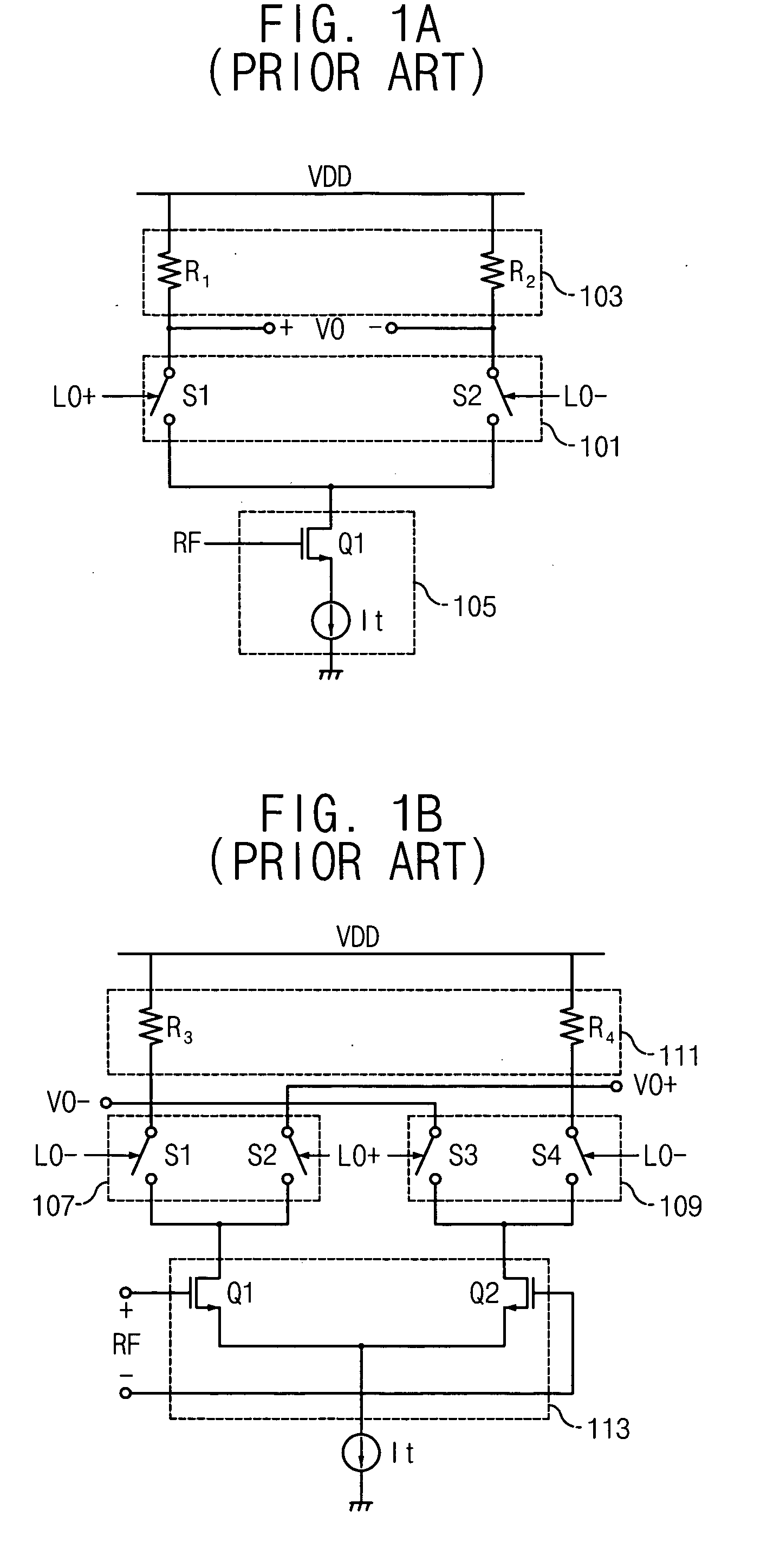
A mixer for direct conversion transmitters and receivers using four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other to control a plurality of switches for outputting signals that are orthogonal each other. Two output signals that are orthogonal to each other do not mutually interfere and have a predetermined small signal gain. Further, a mixer may include four or eight switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other for outputting signals that are orthogonal to each other on an I-Q plot. The signals outputted from the switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals remove I-Q mismatch and a DC component, and improve IP2 characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mixer circuit for direct conversion transceiver with improved IP2
InactiveUS7457606B2Enhanced IPImprove featuresModulation transference balanced arrangementsVibration massageTransceiverPhase shifted
A mixer for direct conversion transmitters and receivers using four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other to control a plurality of switches for outputting signals that are orthogonal each other. Two output signals that are orthogonal to each other do not mutually interfere and have a predetermined small signal gain. Further, a mixer may include four or eight switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals that are orthogonal each other for outputting signals that are orthogonal to each other on an I-Q plot. The signals outputted from the switches controlled by four phase-shifted local oscillation signals remove I-Q mismatch and a DC component, and improve IP2 characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mixer circuit arrangement and an image-reject mixer circuit arrangement
InactiveUS7016664B2Facilitate demodulationEasy to processModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier combinationsTransistor
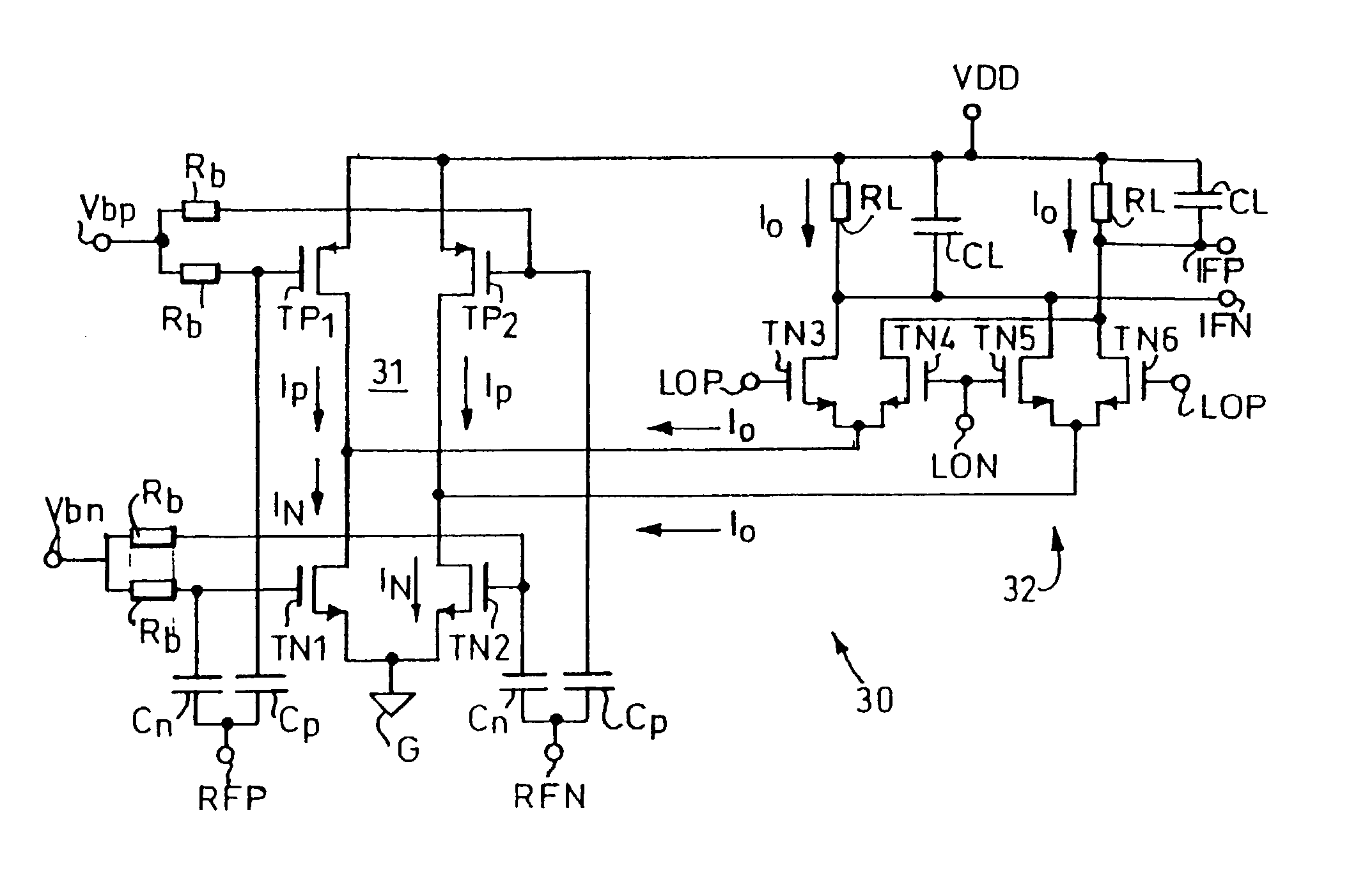
A mixer circuit arrangement 30 comprises a complementary transconductor circuit 31 and a mixer stage 32. The complementary transconductor circuit 31 includes two paths in parallel between a positive supply voltage VDD and ground G and is connected directly between the voltage supply terminals VDD and G. The first path includes a P-type MOS transistor TP1 and an N-type MOS transistor TN1 connected in series. Similarly, the second path includes a P-type MOS transistor TP2 and an N-type MOS transistor TN2 connected in series. The gate electrodes of the P-type transistors TP1 and TP2 are connected to a voltage bias Vbp via high value bias resistors Rb, and the gate electrodes of the N-type transistors TN1 and TN2 are connected to a second voltage bias Vbn via high value bias resistors Rb. The mixer stage 32 is connected between the output of the complementary transconductor circuit 31 and a load, the load also being connected to one of the supply terminals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Direct conversion receiver with reduced even order distortion
InactiveUS6021323AReduce distortion problemsReduces even order distortionModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPhase currentsLinear component
A mixer for use in a direct conversion receiver includes a compensating differential amplifier which injects equal amplitude opposite phase currents with respect to even order distortion currents. The compensating differential amplifier utilizes an ideal current source. The mixer is an active mixer which utilizes four switching transistors. The even order distortion is introduced by non-linear components which demonstrate strong off-channel signals.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Multiple-input multiple-output radio transceiver
InactiveCN1647404AModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio transmissionTransceiverMultiple input
A MIMO radio transceiver to support processing of multiple signals for simultaneous transmission via corresponding ones of a plurality of antennas and to support receive processing of multiple signals detected by corresponding ones of the plurality of antennas. The radio transceiver provides, on a single semiconductor integrated circuit, a receiver circuit or path for each of a plurality of antennas and a transmit circuit or path for each of the plurality of antennas. Each receiver circuit downconverts the RF signal detected by its associated antenna to a baseband signal. Similarly, each transmit path upconverts a baseband signal to be transmitted by an assigned antenna.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Printed circuit doubly balanced mixer for upconverter
InactiveUS7072636B2Minimization requirementsModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionBalanced mixerLocal oscillator signal
A doubly balanced upconverter mixer includes a local oscillator balun circuit comprising juxtaposed foil elements on opposite sides of an insulated substrate with electrical interconnections between the foil elements. An IF balun circuit also comprises series tuned and parallel tuned foil elements on opposite sides of the substrate in juxtaposition to each other. A diode switching network interconnects the baluns. A local oscillator signal is connected to the foil elements of the local oscillator balun circuit, an RF signal is coupled to one foil element of the IF balun circuit and an IF signal is taken from the other foil element of the IF balun circuit. Another embodiment incorporates MESFET type switches, the gates of which are supplied directly with a symmetrical local oscillator signal. This arrangement eliminates the need for the local oscillator balun.
Owner:ZENITH RADIO CORP
RF mixer with high local oscillator linearity using multiple local oscillator phases
InactiveUS7421259B2Less sensitiveReduce noiseModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionSignal cancellationPhase difference
An RF mixer includes a plurality of submixers coupled to a single input transistor pair and a single tail current source. An input LO signal is divided into multiple individual waveforms, each having a different phase. The phase differences are even in that the phase difference between any two time-adjacent individual waveforms is approximately equal to the phase difference between any other two time-adjacent individual waveforms. The submixers are appropriately scaled so that the individual waveforms, when summed, create a piecewise linear LO signal. The submixers also combine the individual waveforms with an input baseband signal to produce an output signal or to produce a baseband signal from an input mixed signal. In order to reduce noise in the system, only one submixer is active at any time. Further, polarities of some individual waveforms are reversed so that to avoid signal cancellation when by combining waveforms of opposite polarities.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dual double balanced mixer
InactiveUS6807407B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsOscillations generatorsLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
Popular searches
Pulse automatic control Computing operations for multiplication/division Input/output processes for data processing Differential amplifiers Amplifier details Dc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stages Antennas Television system scanning details Color television details Amplitude to angle modulation conversion
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com