Patents
Literature
1636 results about "Intermodulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
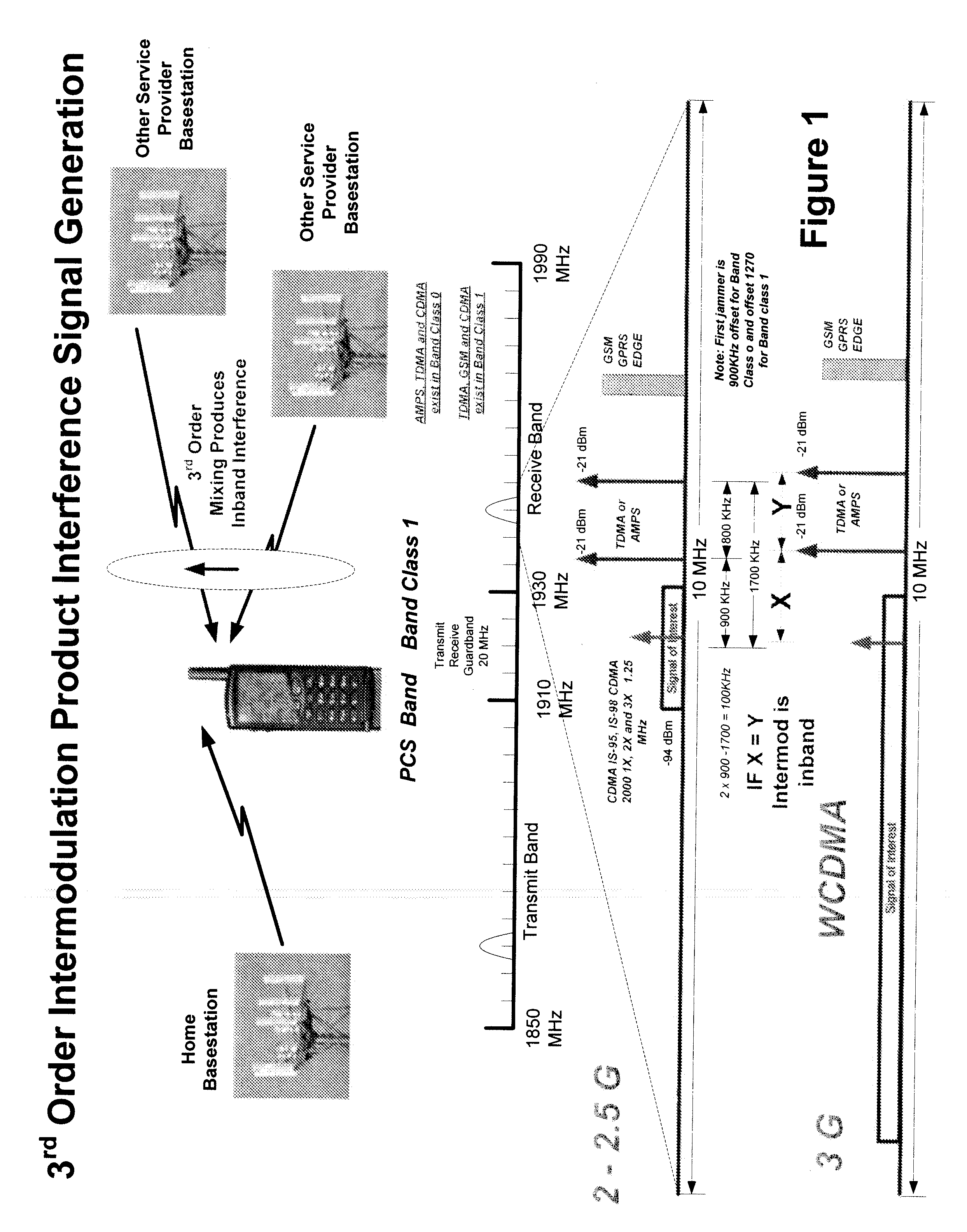
Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by nonlinearities or time variance in a system. The intermodulation between frequency components will form additional components at frequencies that are not just at harmonic frequencies (integer multiples) of either, like harmonic distortion, but also at the sum and difference frequencies of the original frequencies and at sums and differences of multiples of those frequencies.
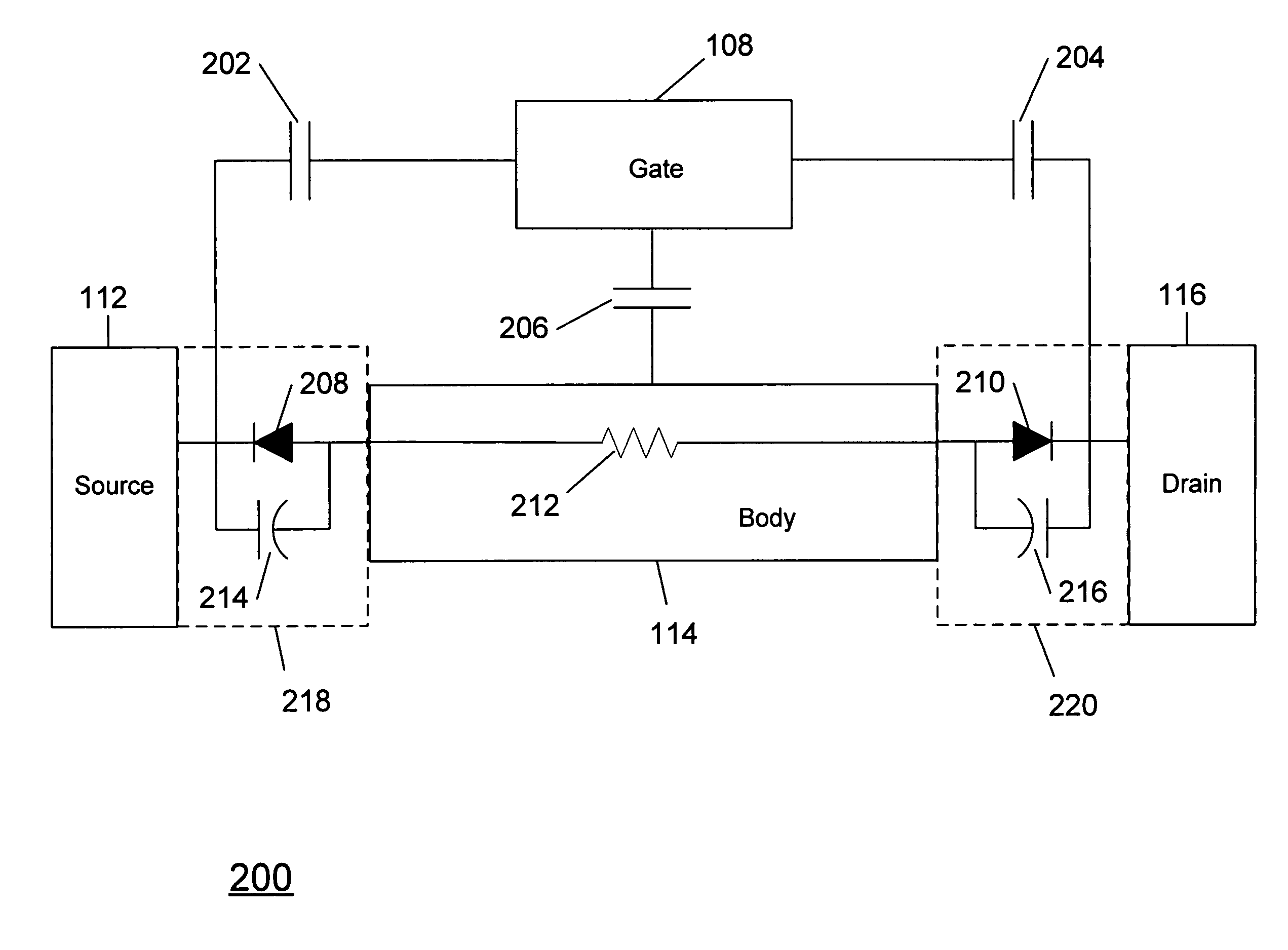
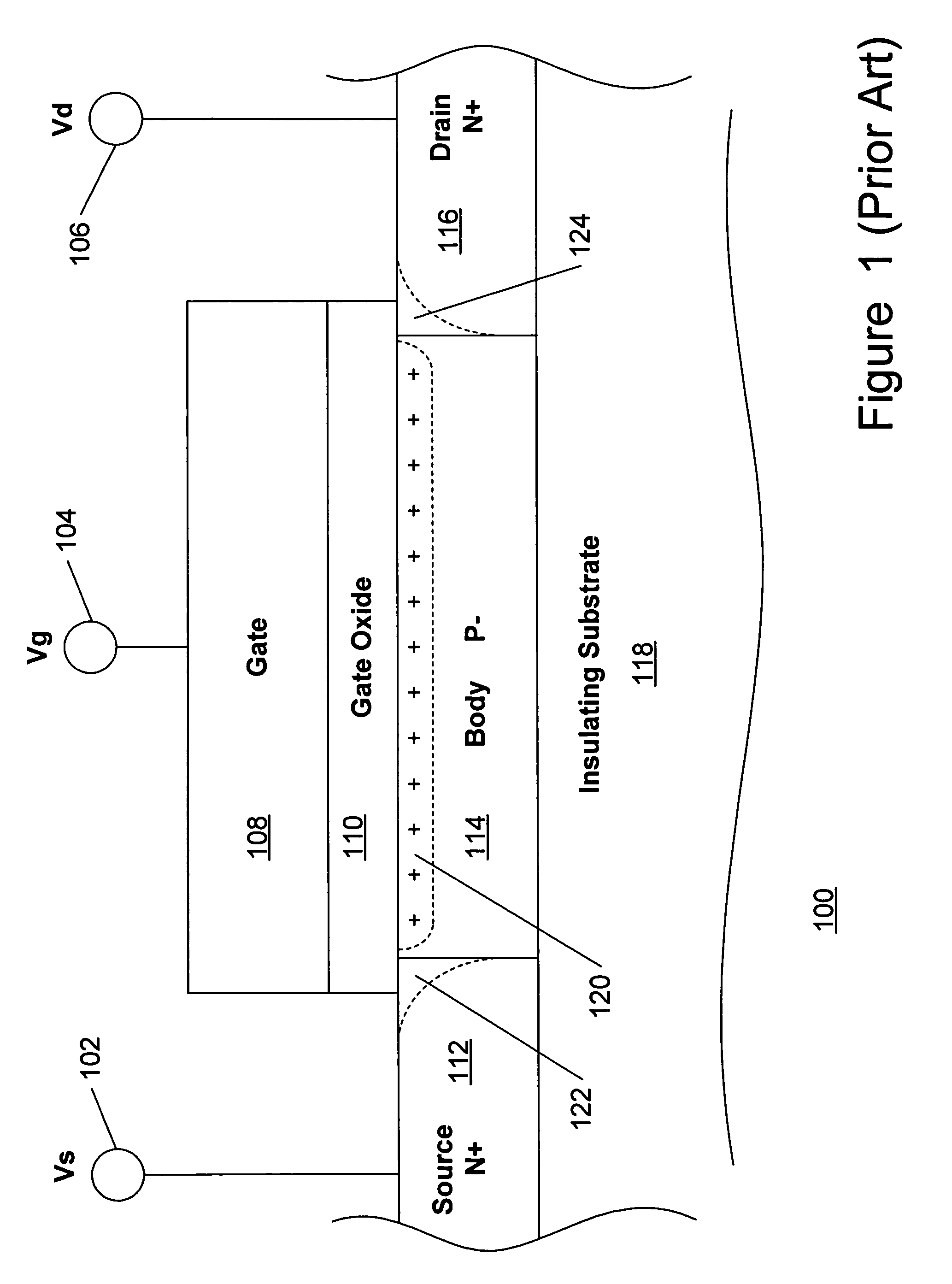
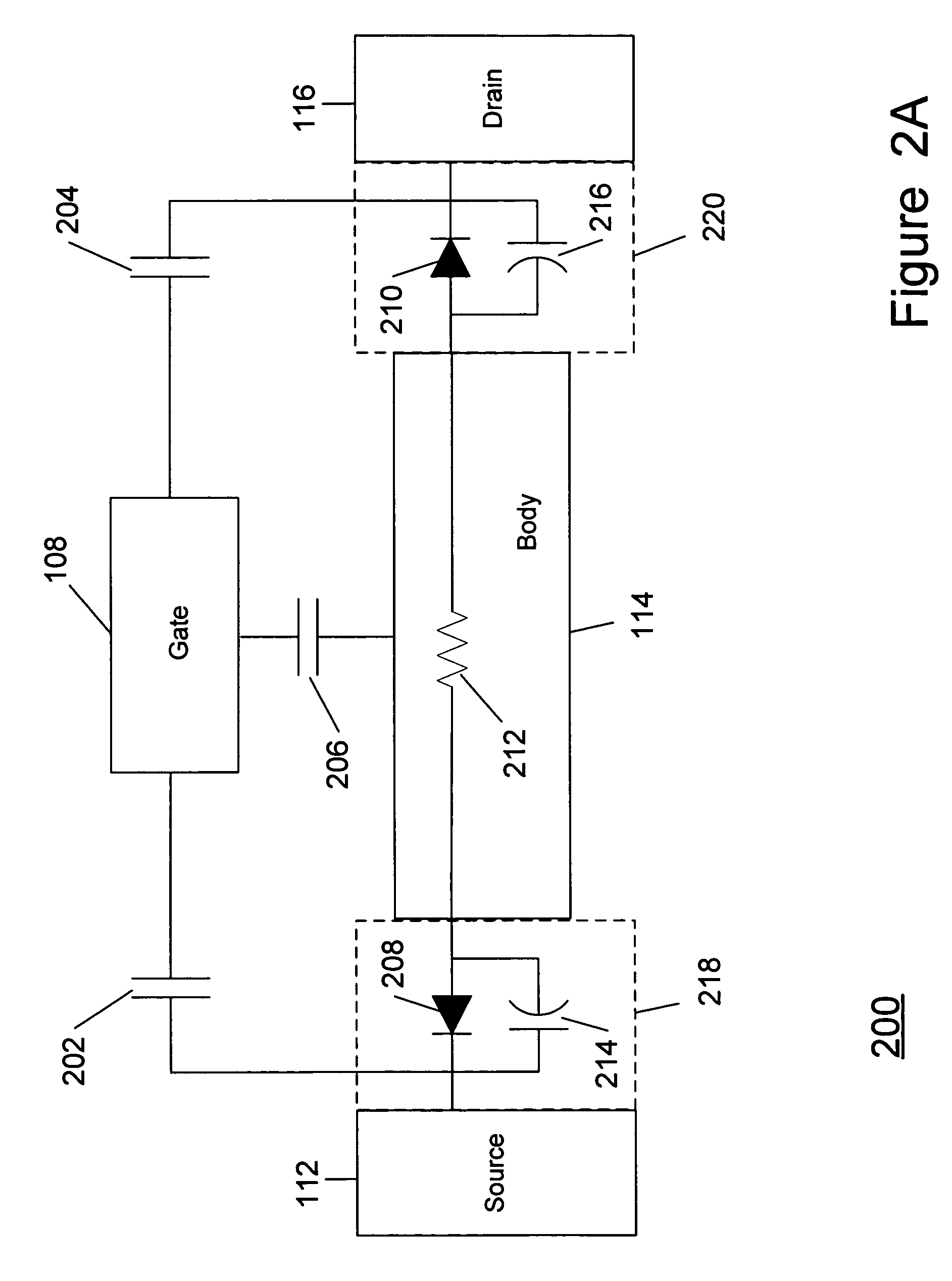
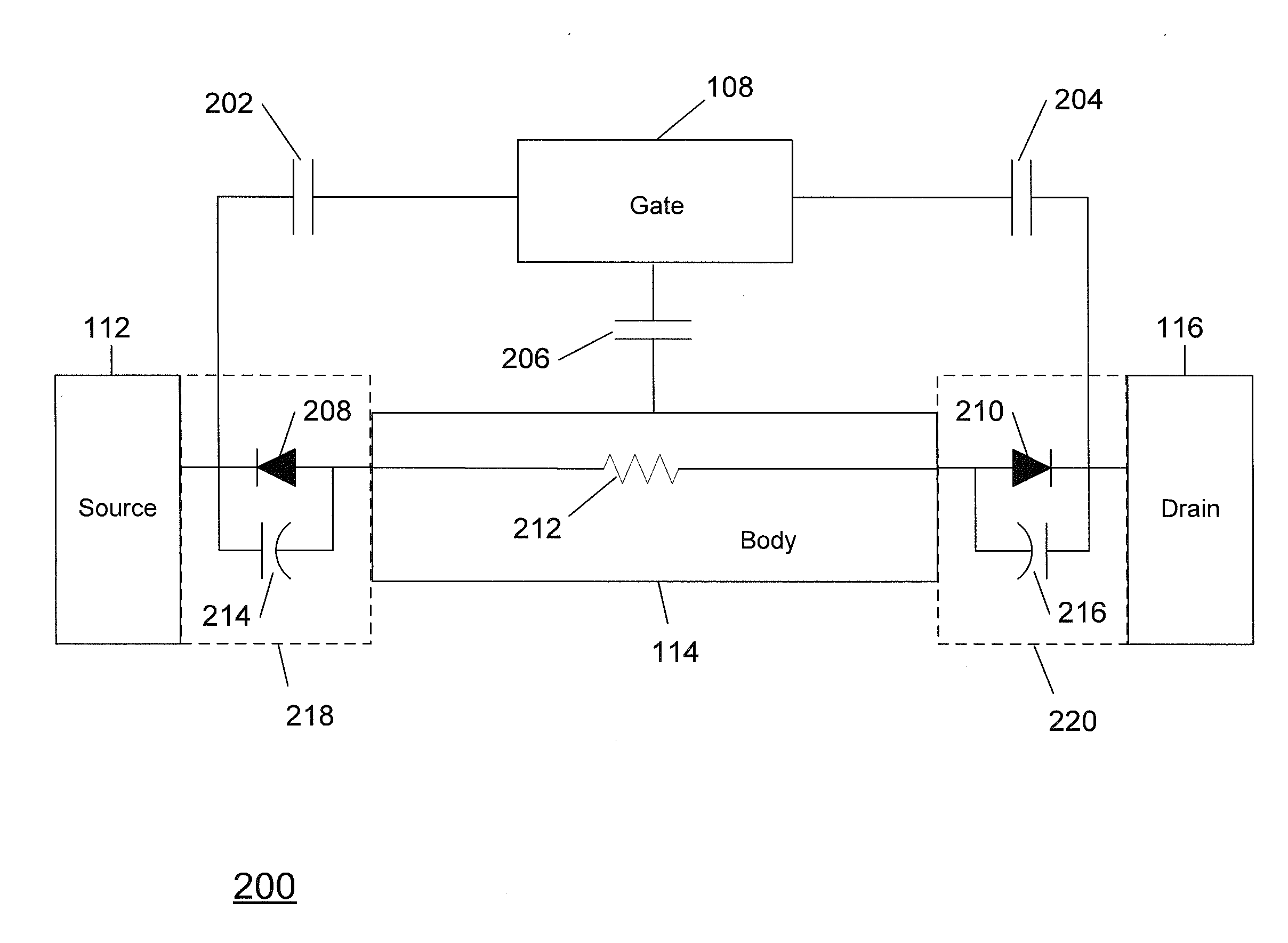
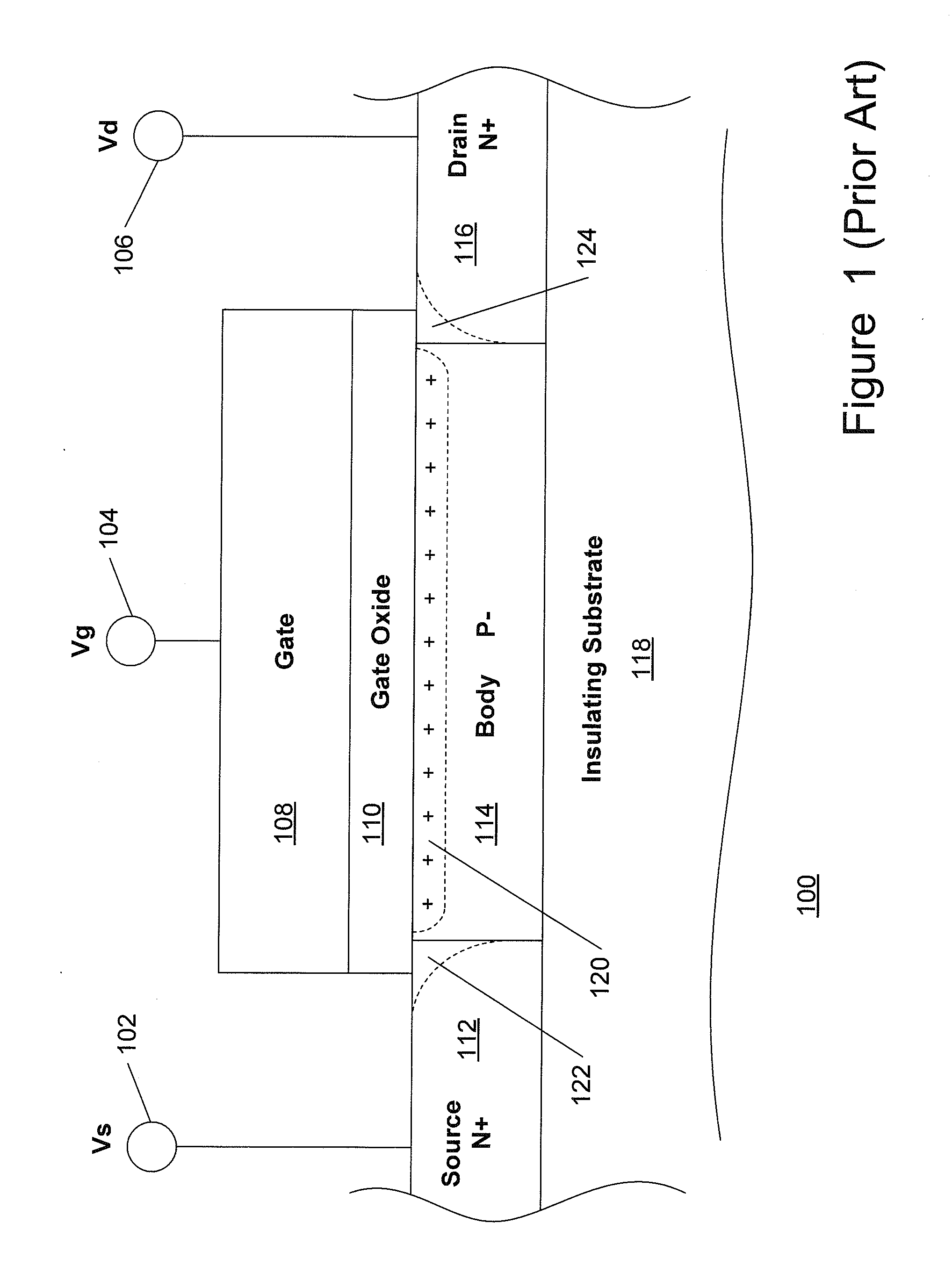
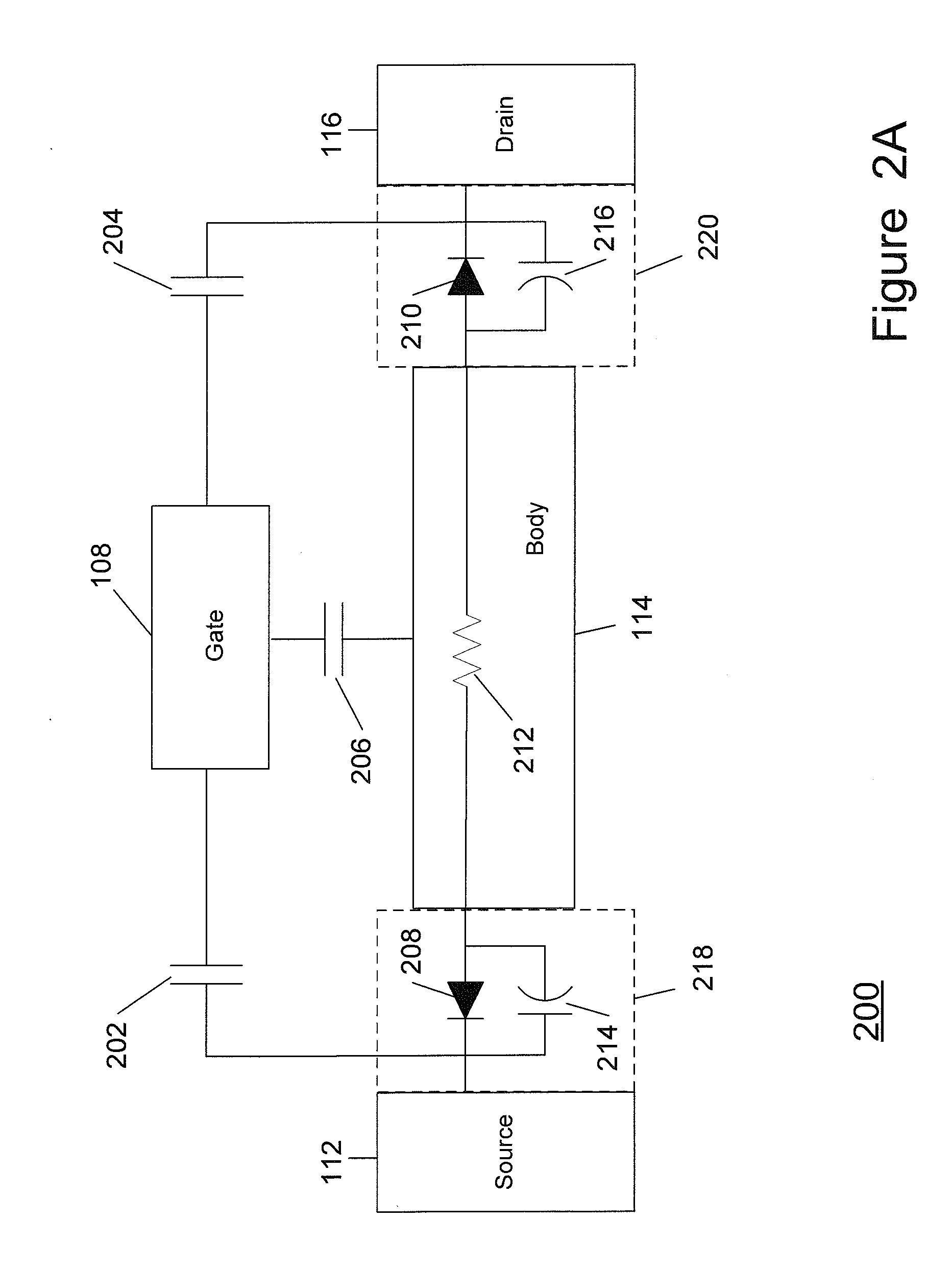
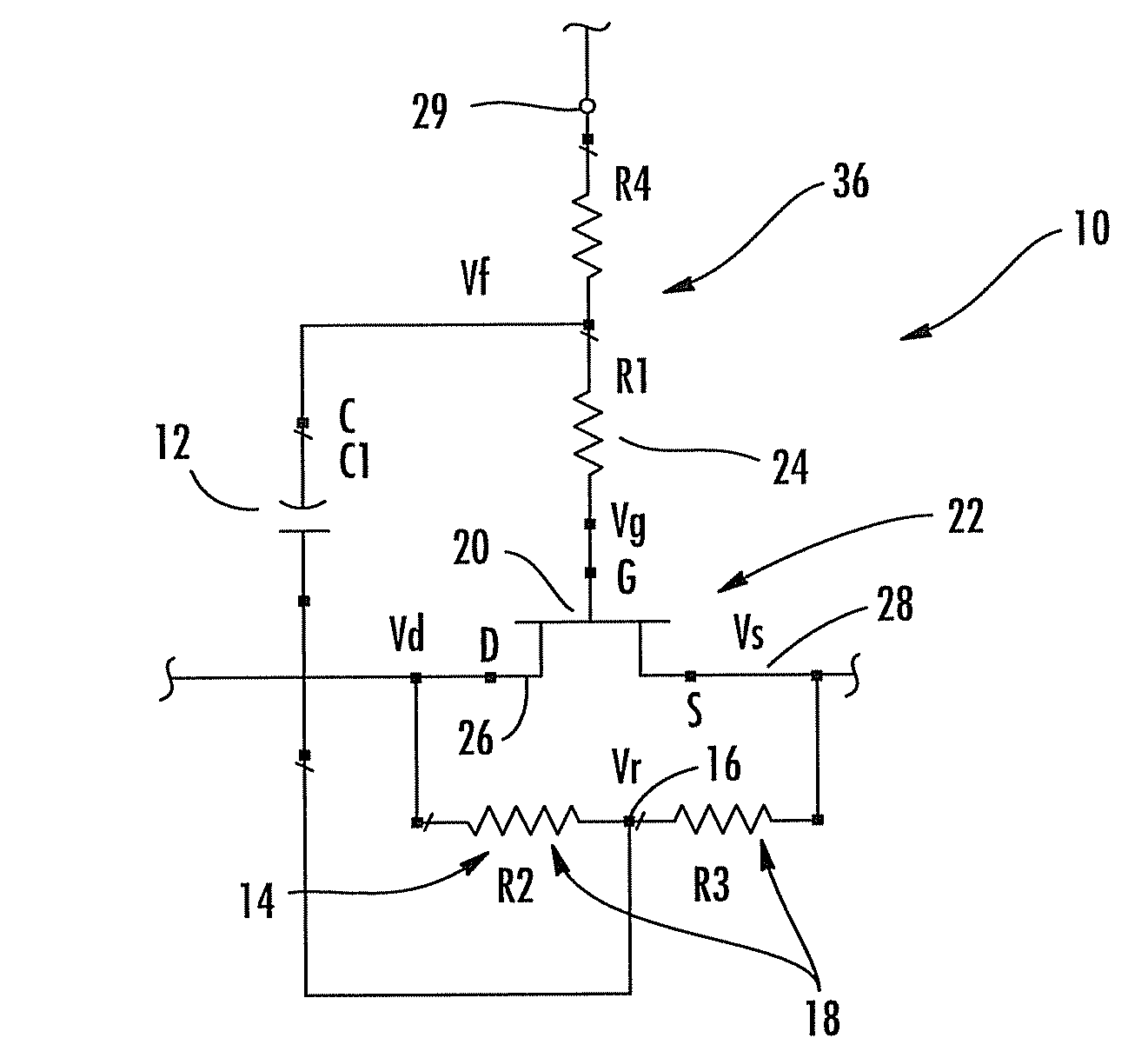
Method and apparatus for use in improving linearity of MOSFET's using an accumulated charge sink
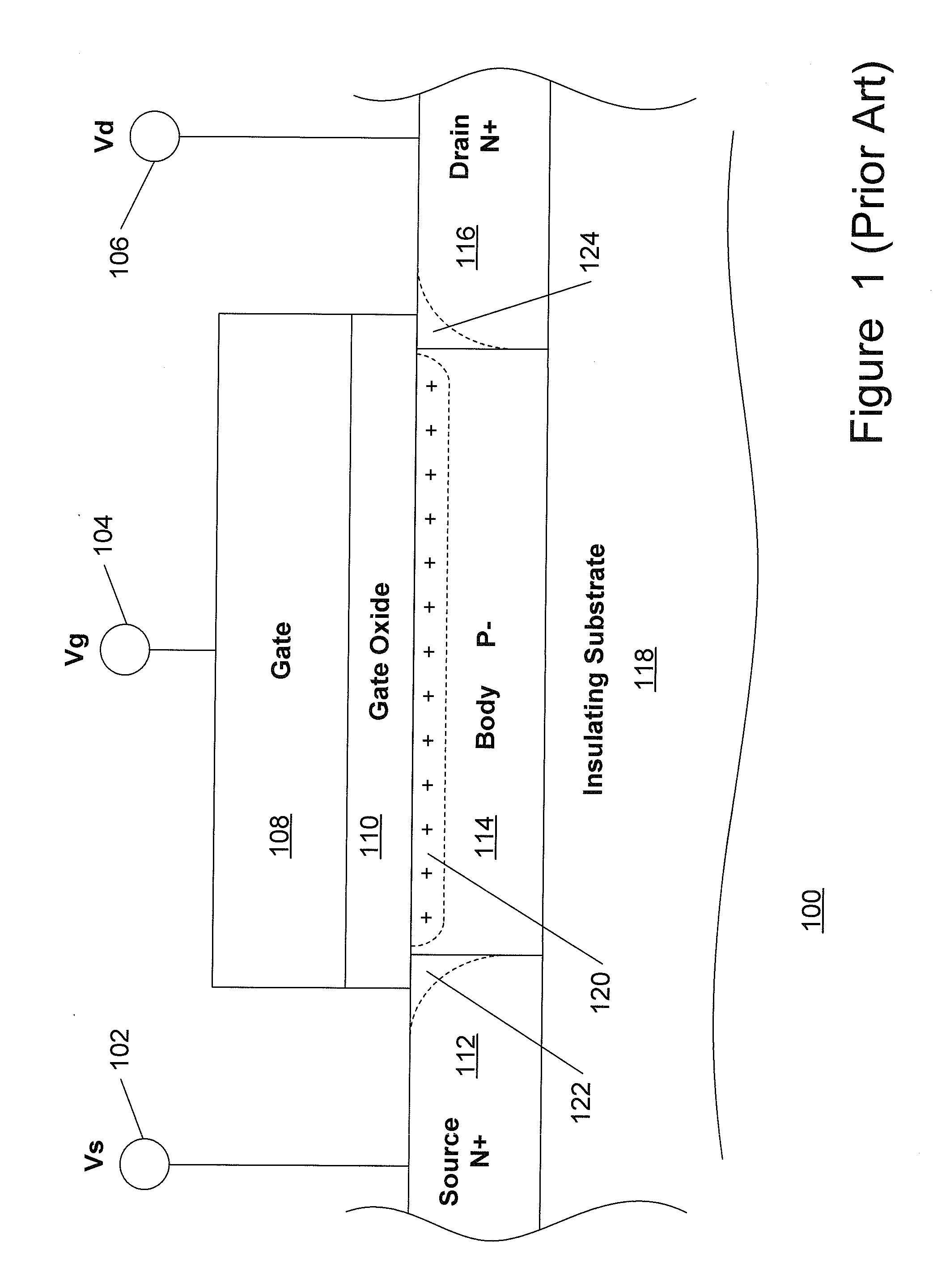
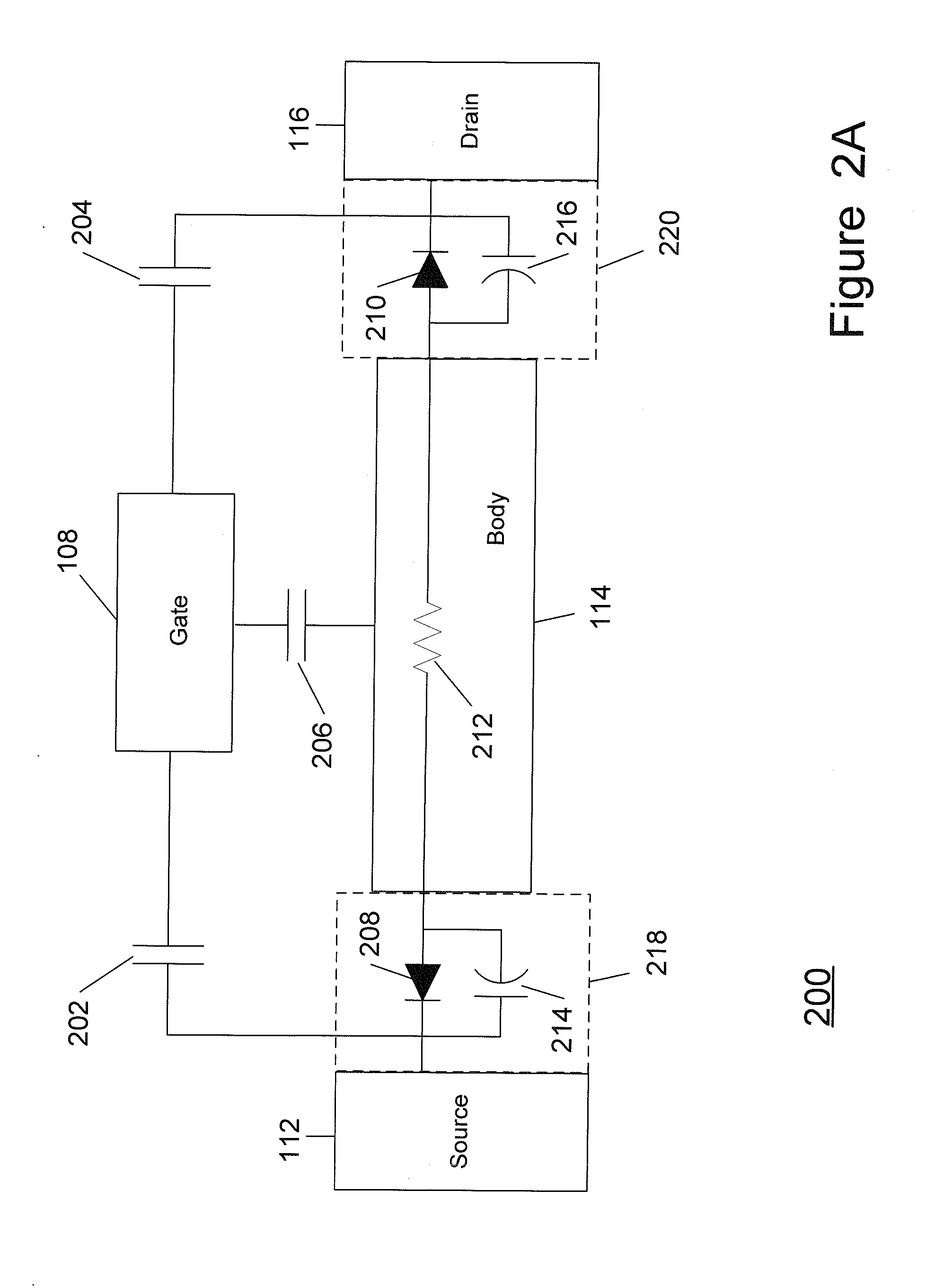
ActiveUS7910993B2Improving nonlinear responseImprove harmonicsSolid-state devicesElectronic switchingCapacitanceMOSFET
A method and apparatus for use in improving the linearity characteristics of MOSFET devices using an accumulated charge sink (ACS) are disclosed. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one exemplary embodiment, a circuit having at least one SOI MOSFET is configured to operate in an accumulated charge regime. An accumulated charge sink, operatively coupled to the body of the SOI MOSFET, eliminates, removes or otherwise controls accumulated charge when the FET is operated in the accumulated charge regime, thereby reducing the nonlinearity of the parasitic off-state source-to-drain capacitance of the SOI MOSFET. In RF switch circuits implemented with the improved SOI MOSFET devices, harmonic and intermodulation distortion is reduced by removing or otherwise controlling the accumulated charge when the SOI MOSFET operates in an accumulated charge regime.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
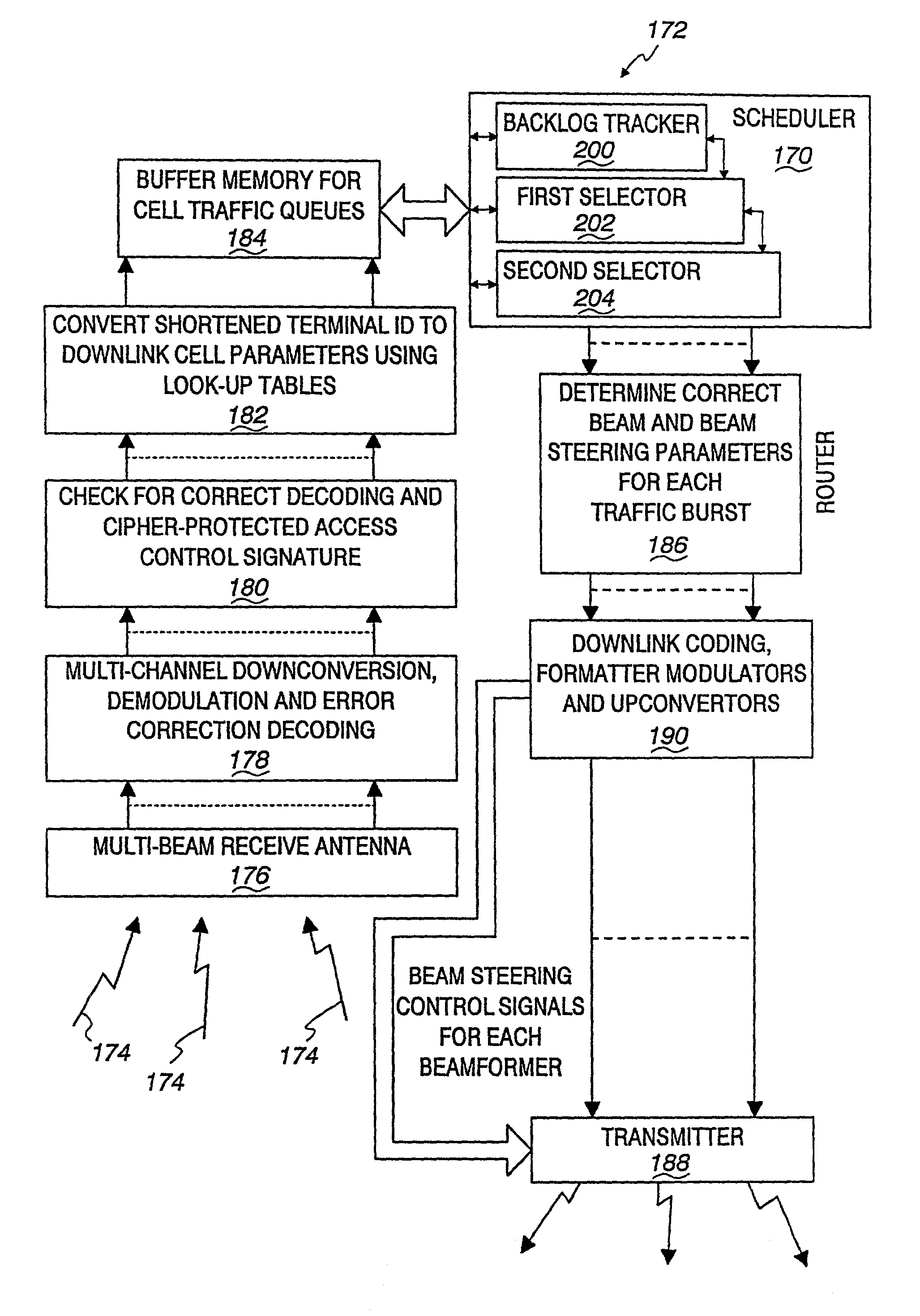
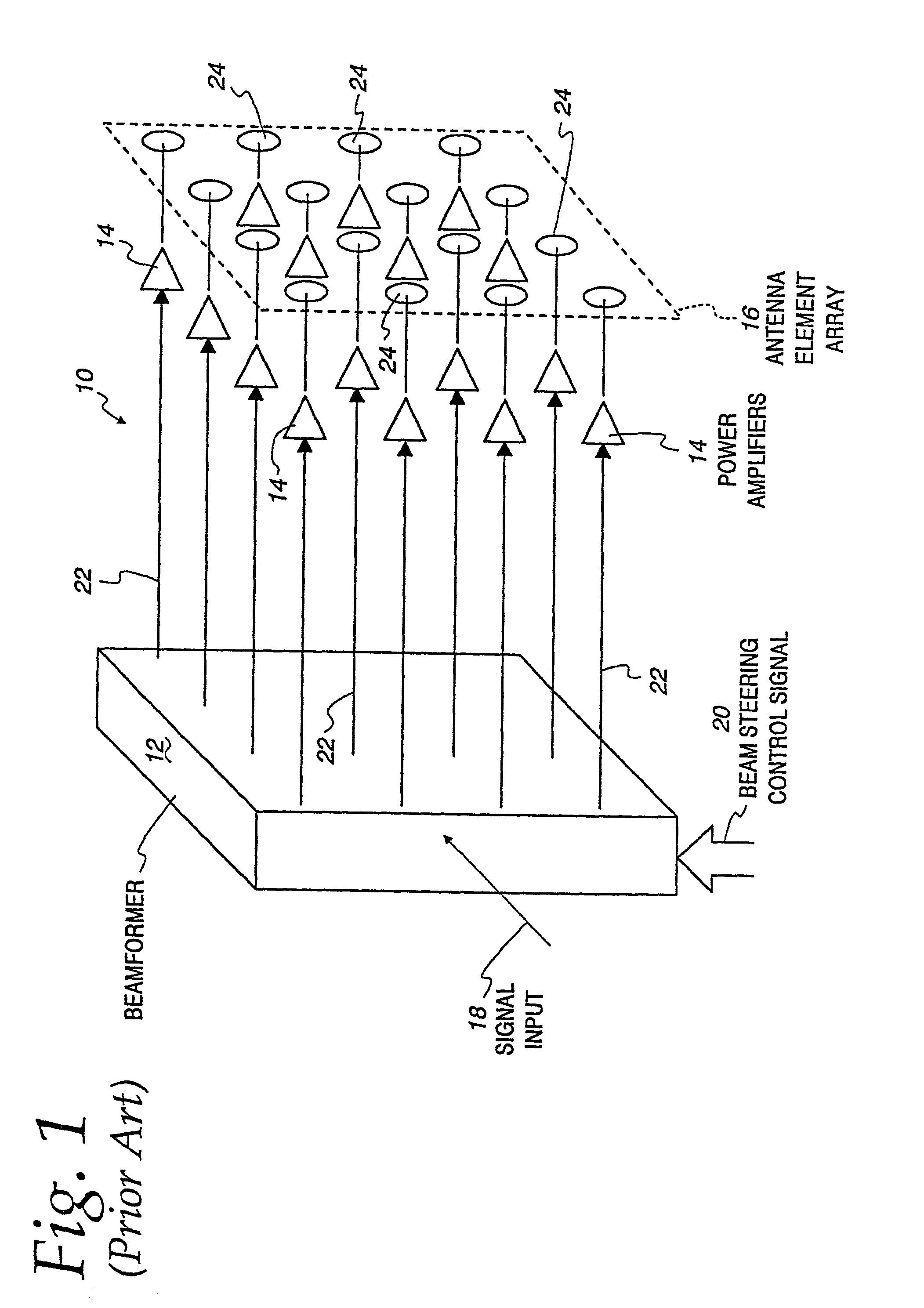
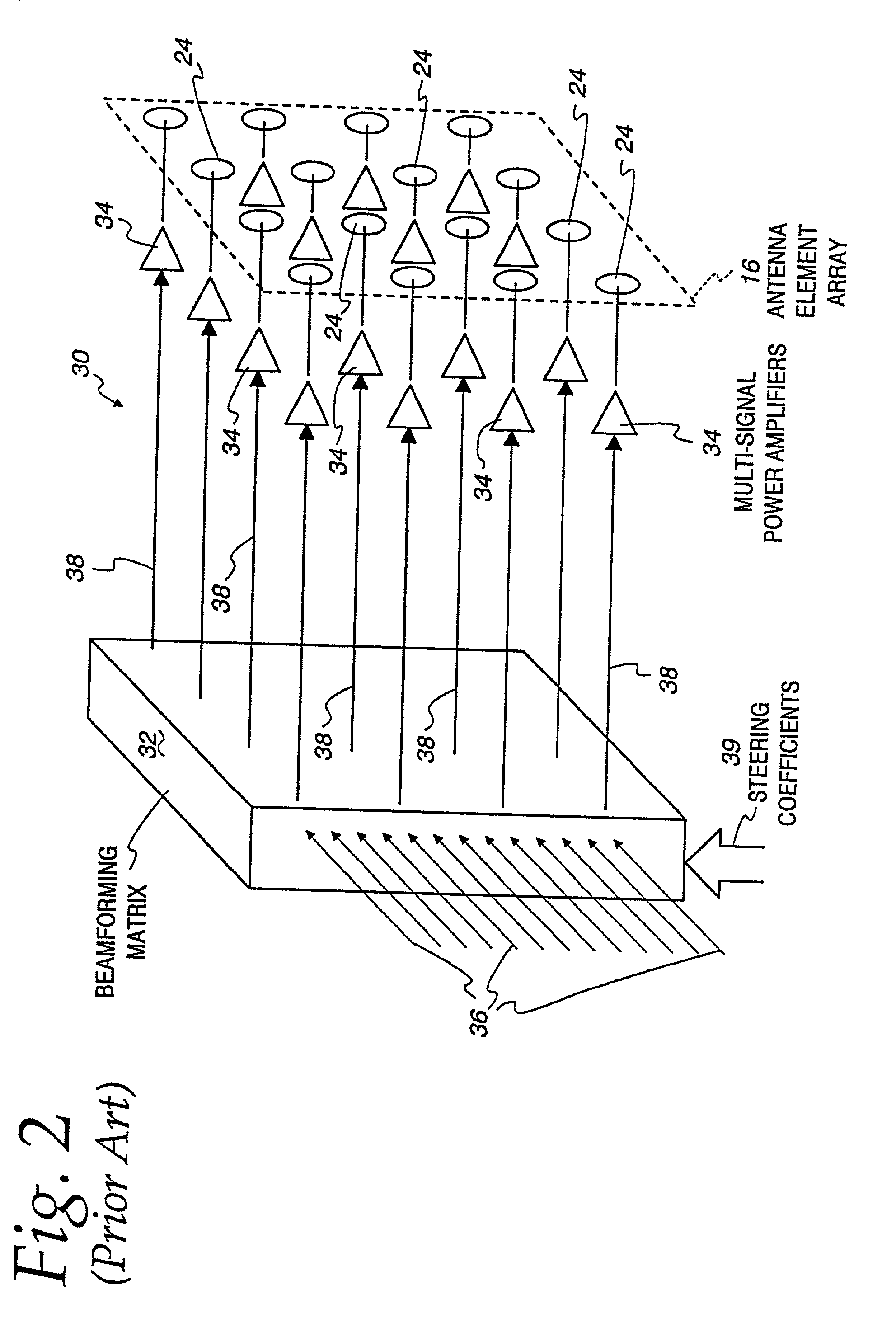
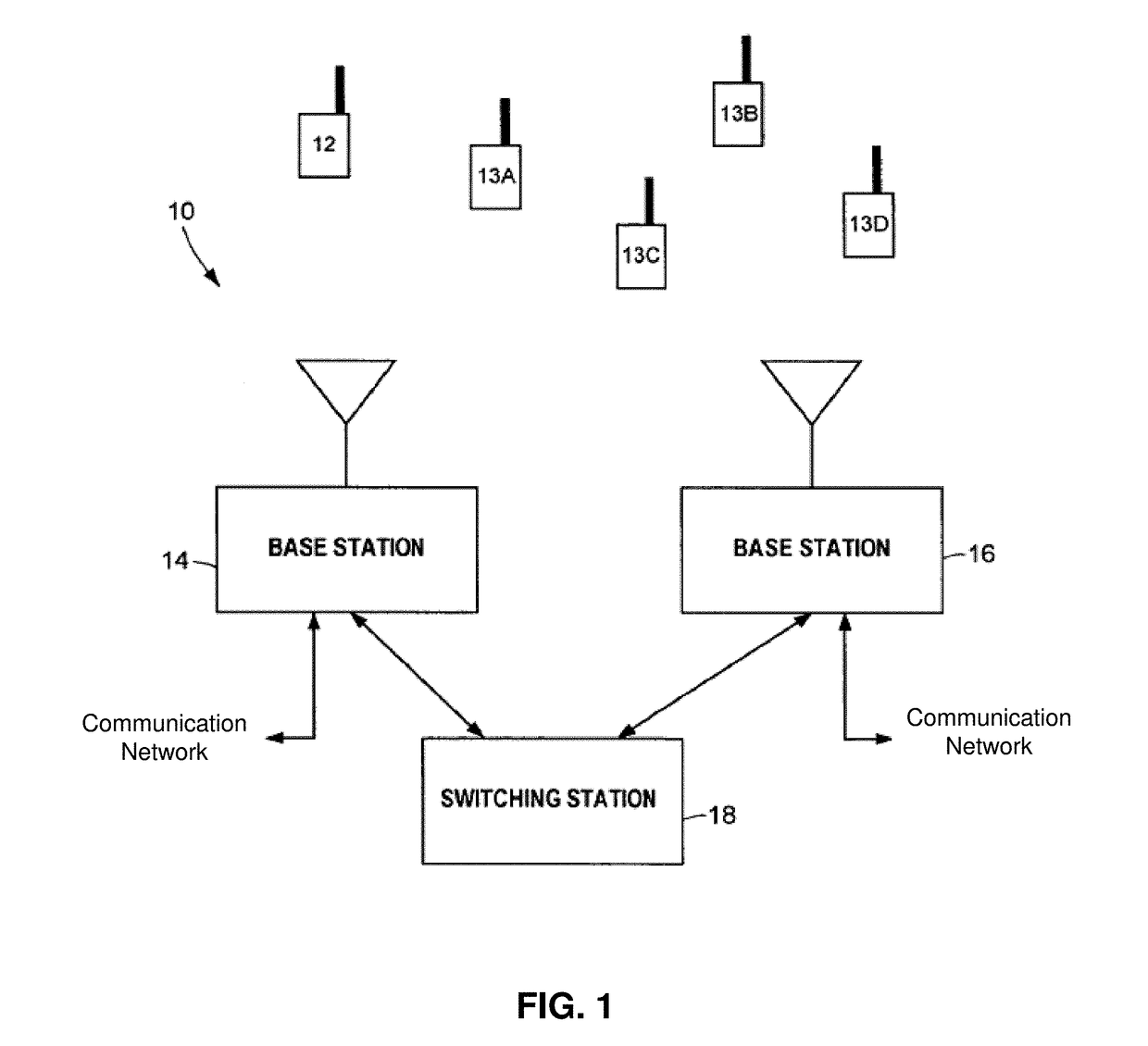
Multi-signal transmit array with low intermodulation
InactiveUS7027454B2Reduce unwanted out-of-band radiationImprove transmission efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsSteering controlAntenna element
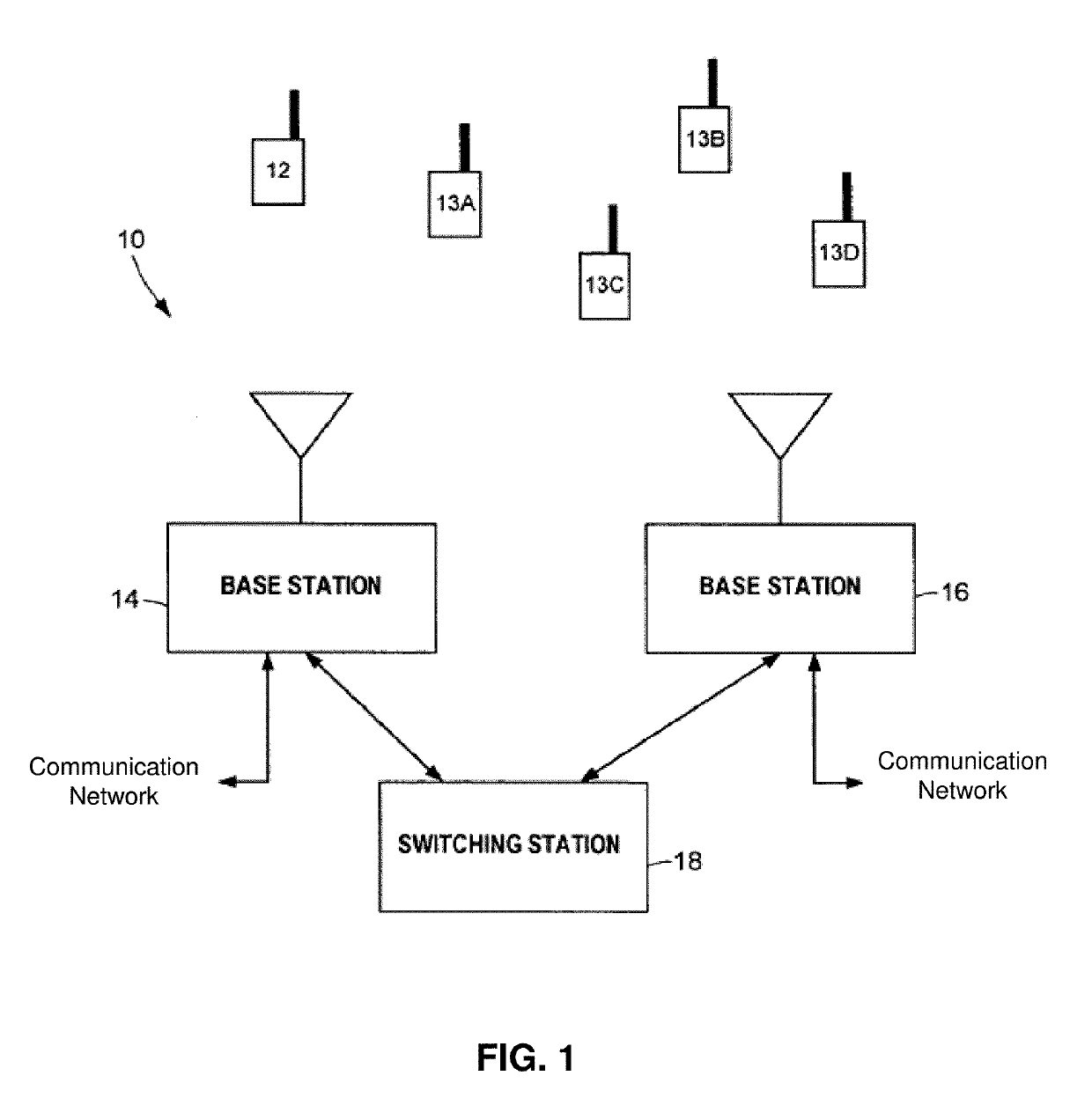
A transmitter is provided for simultaneously transmitting a plurality of signals in a plurality of directive beams to corresponding destination stations, each destination station located in a separate fan within a service area. The transmitter includes a plurality of beamformers, each beamformer receiving one of the signals to be transmitted to an associated fan, each of the beamformers having a plurality of outputs for each different signal to be transmitted. A plurality of Butler matrices each receive one of the plurality of outputs from the plurality of beamformers for each different signal to be transmitted, each Butler matrix having a plurality of outputs in phased relationship to one another, wherein each of the signals to be transmitted is simultaneously provided across the outputs of each Butler matrix in a phased relationship. An antenna is provided with an aperture within which a two-dimensional array of antenna elements are disposed, wherein equal fractions of adjacent antenna elements are connected to the outputs of each Butler matrix, and wherein each of the plurality of signals are simultaneously transmitted by the entire two-dimensional array of antenna elements. Each of the plurality of beamformers receives steering control signals for steering the direction of each beam within its respective fan.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
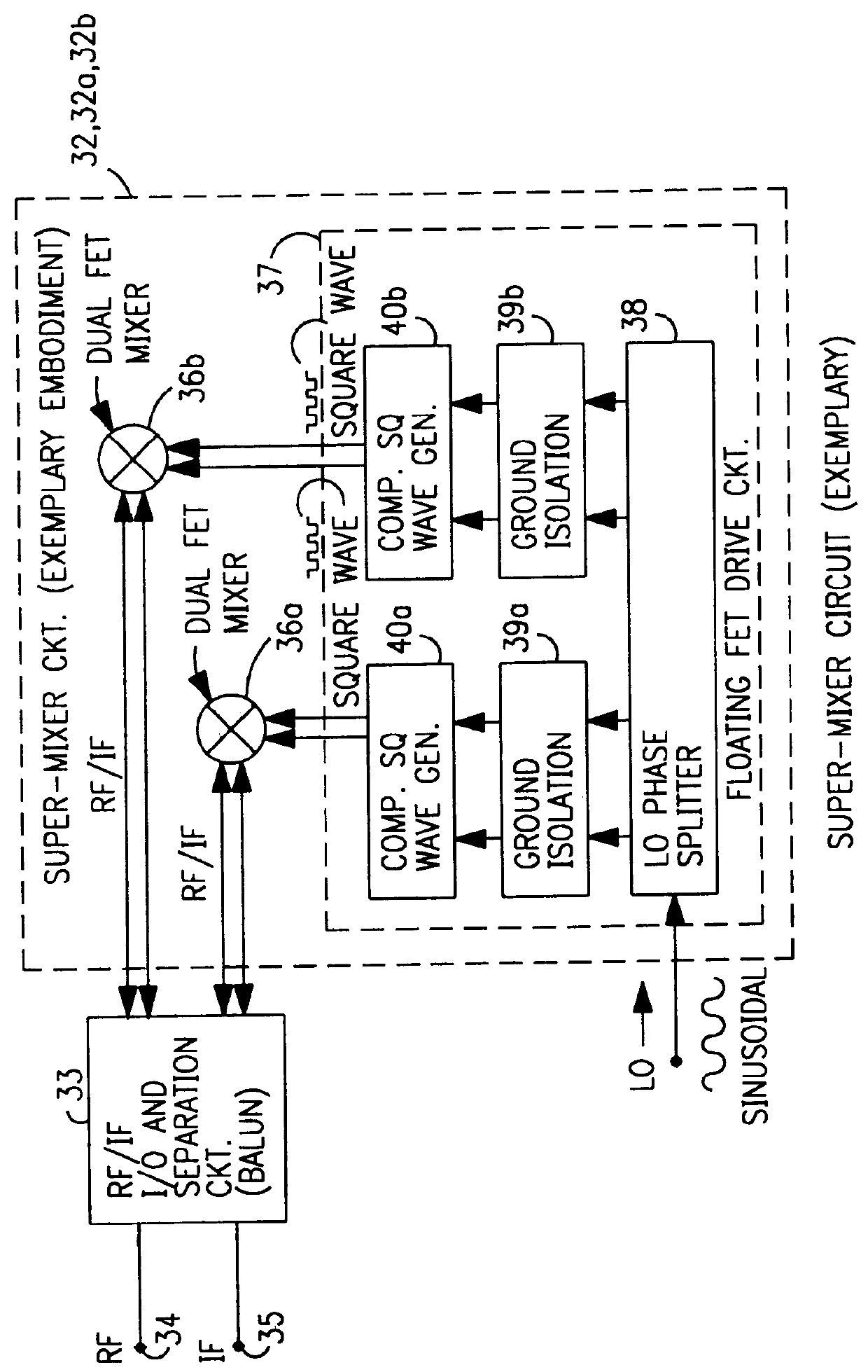
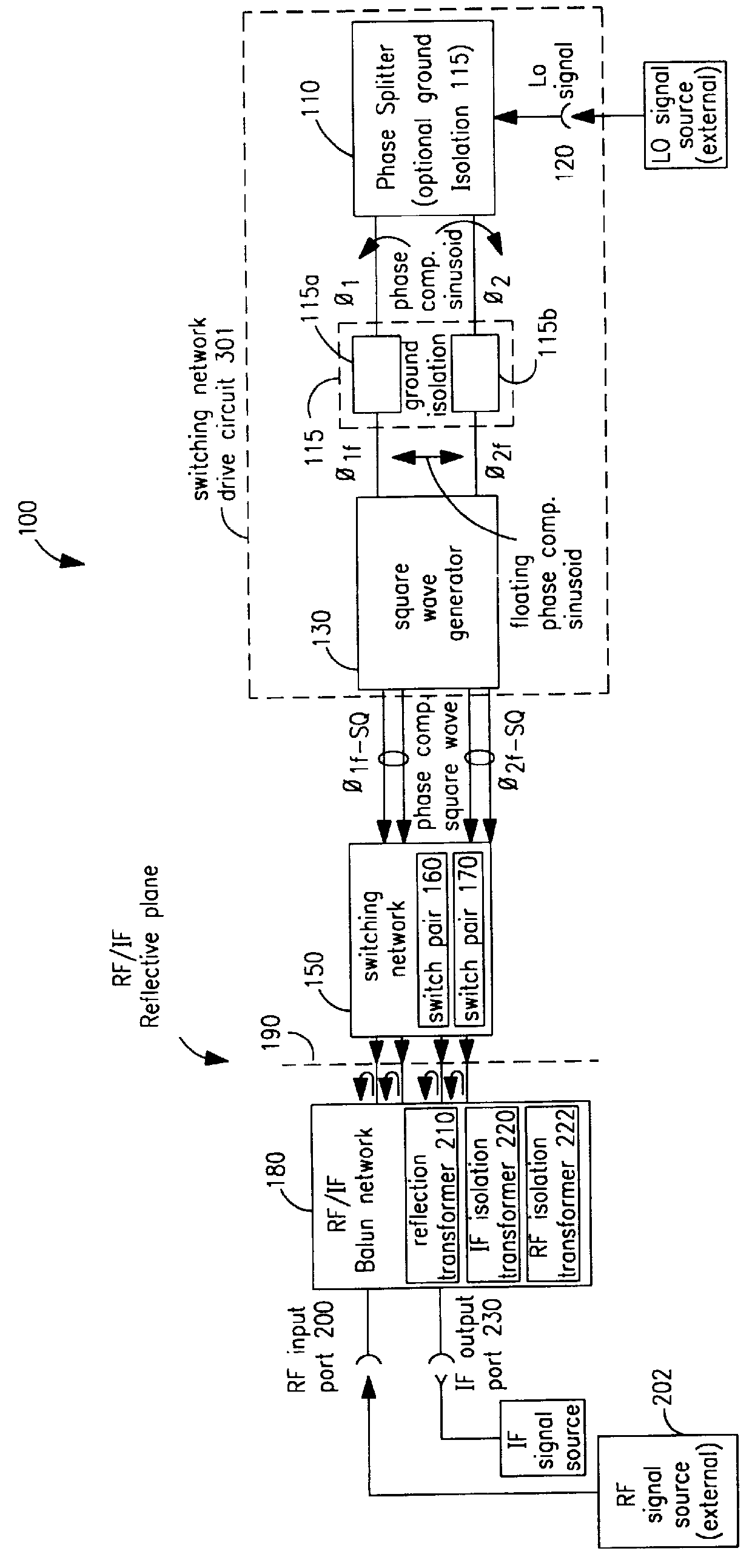
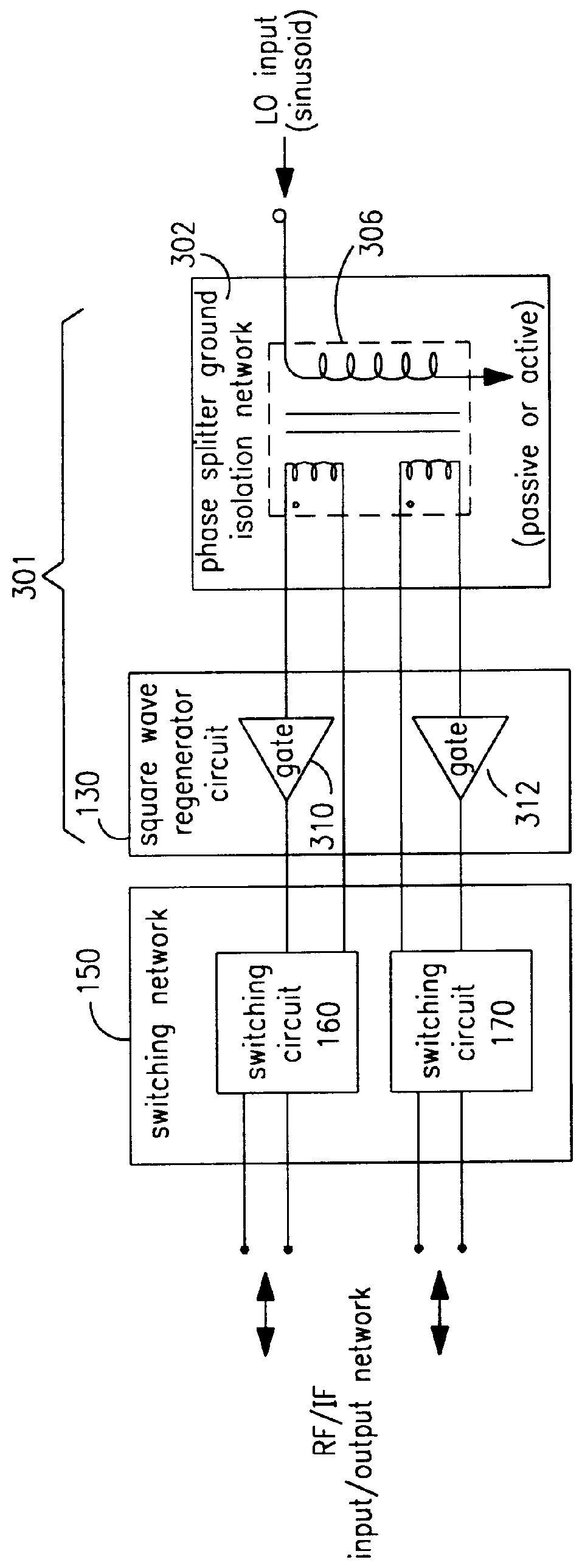
Structure and method for super FET mixer having logic-gate generated FET square-wave switching signal
InactiveUS6144236AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio receiverTransformer
A mixing method and mixer structure provide a circuit topology suitable for use in radio receivers, transmitters, tuners, instrumentation systems, telemetry systems, and other systems and devices performing frequency conversion in either homodyne or heterodyne implementations. The inventive mixer may be used for wireless communication devices including radios, cellular telephones, and telemetry systems whether land, sea, airborne, or space based, and whether fixed or mobile. The mixer provides superior intermodulation and harmonic distortion suppression and features excellent conversion loss, noise figure, port match, and port isolation as a result of its circuit topology. The mixer device circuit combines the advantages of series mixing FETs, a triple balanced design using a balanced passive reflection transformer, a precise local oscillator phase splitter, and square wave gate drive having high slew rate signal characteristics to achieve high levels of performance. It is power conservative and offers the advantage of long battery life in portable devices such as portable radios and cellular telephones as it requires only a modest amount of DC and local oscillator drive power, and is useful for operation over at least a multi-decade bandwidth.
Owner:DRS SIGNAL SOLUTIONS
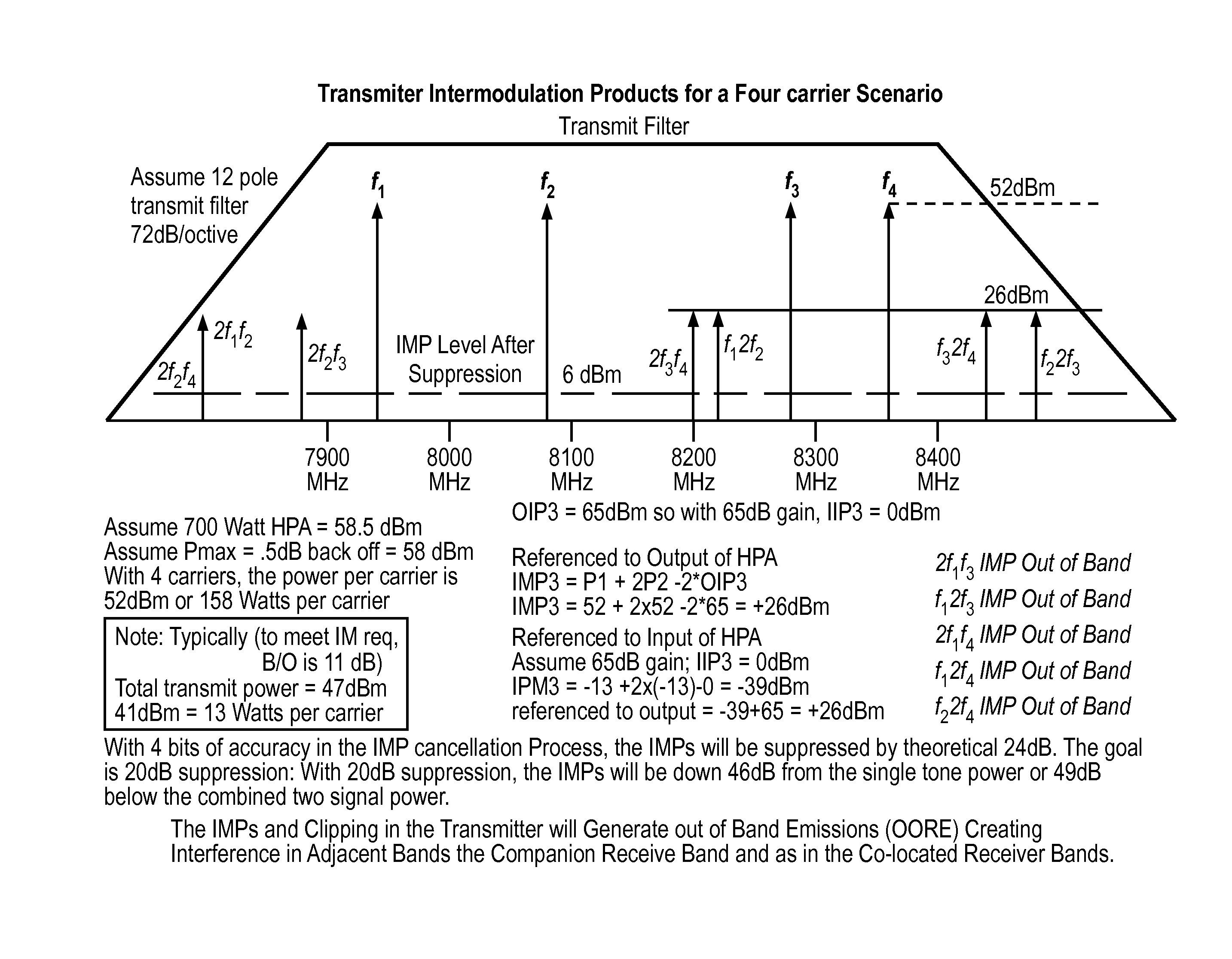
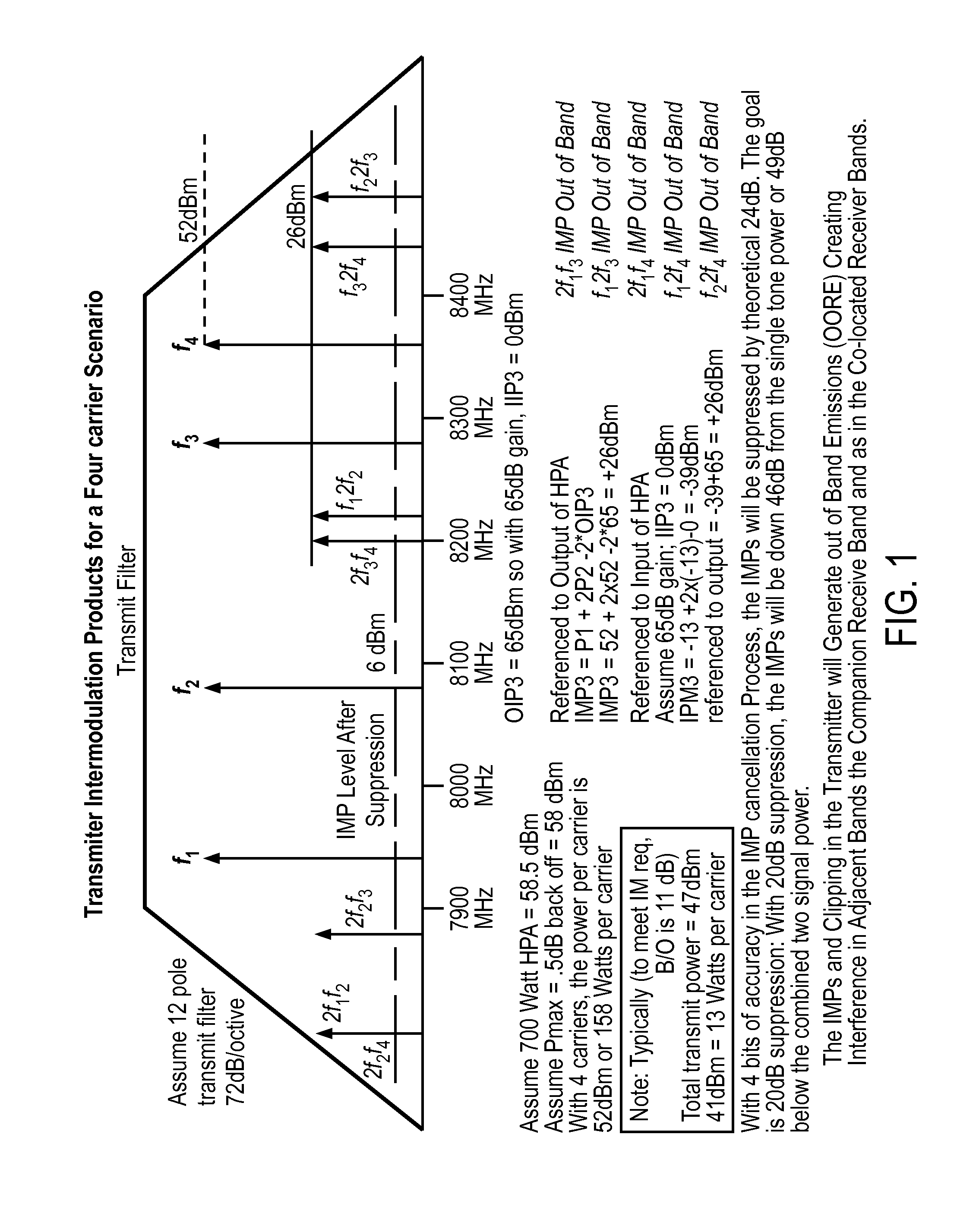
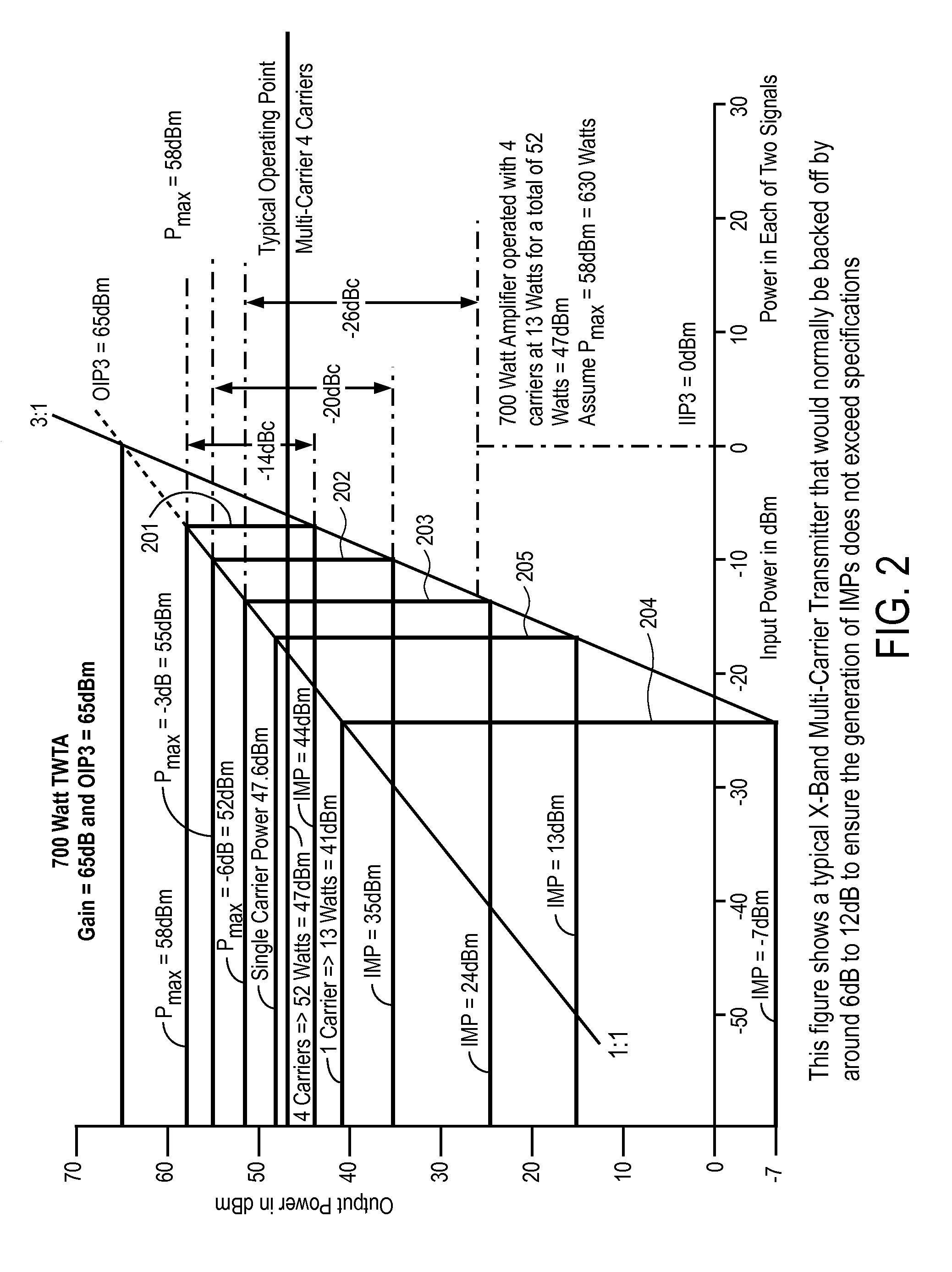
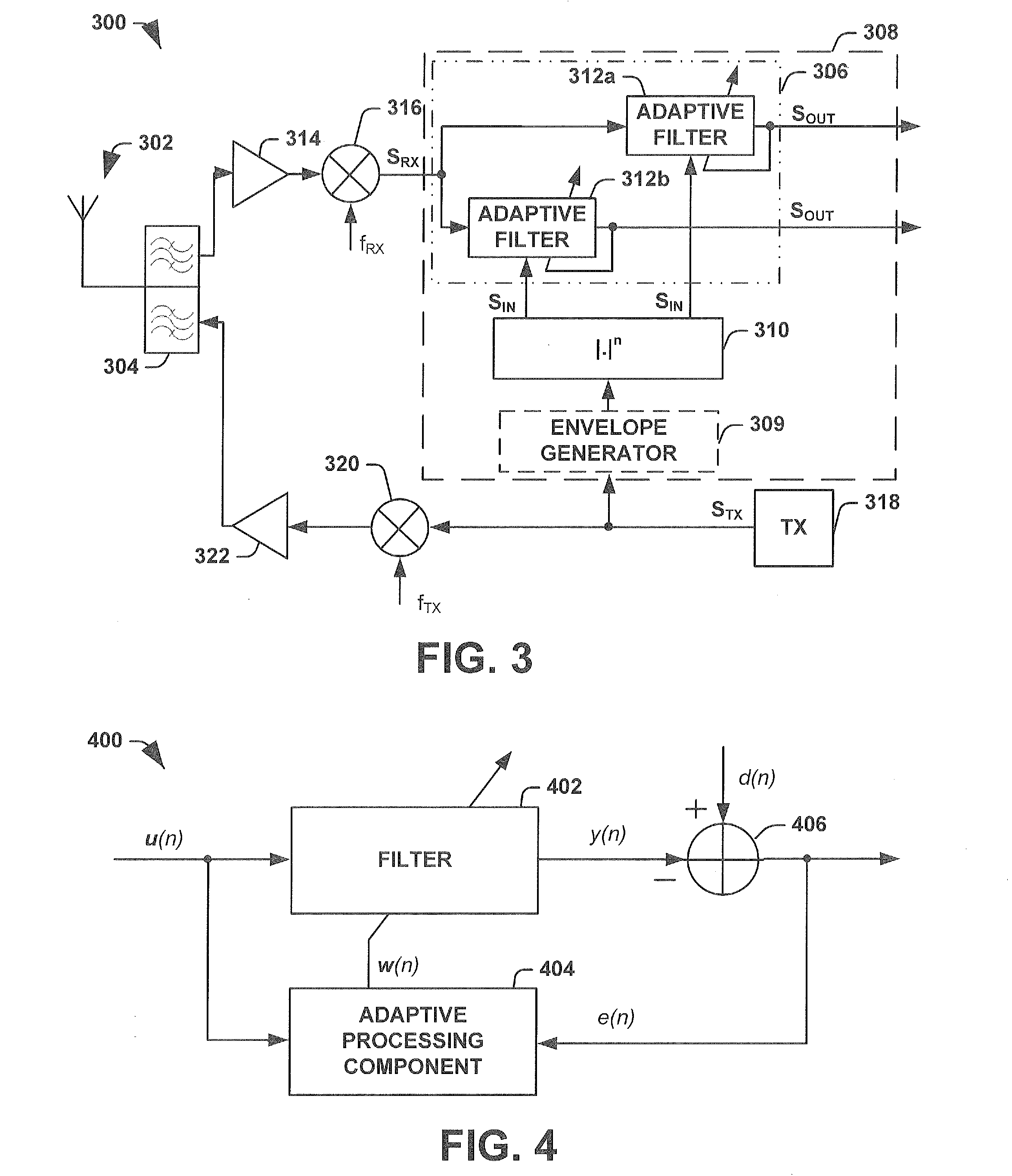
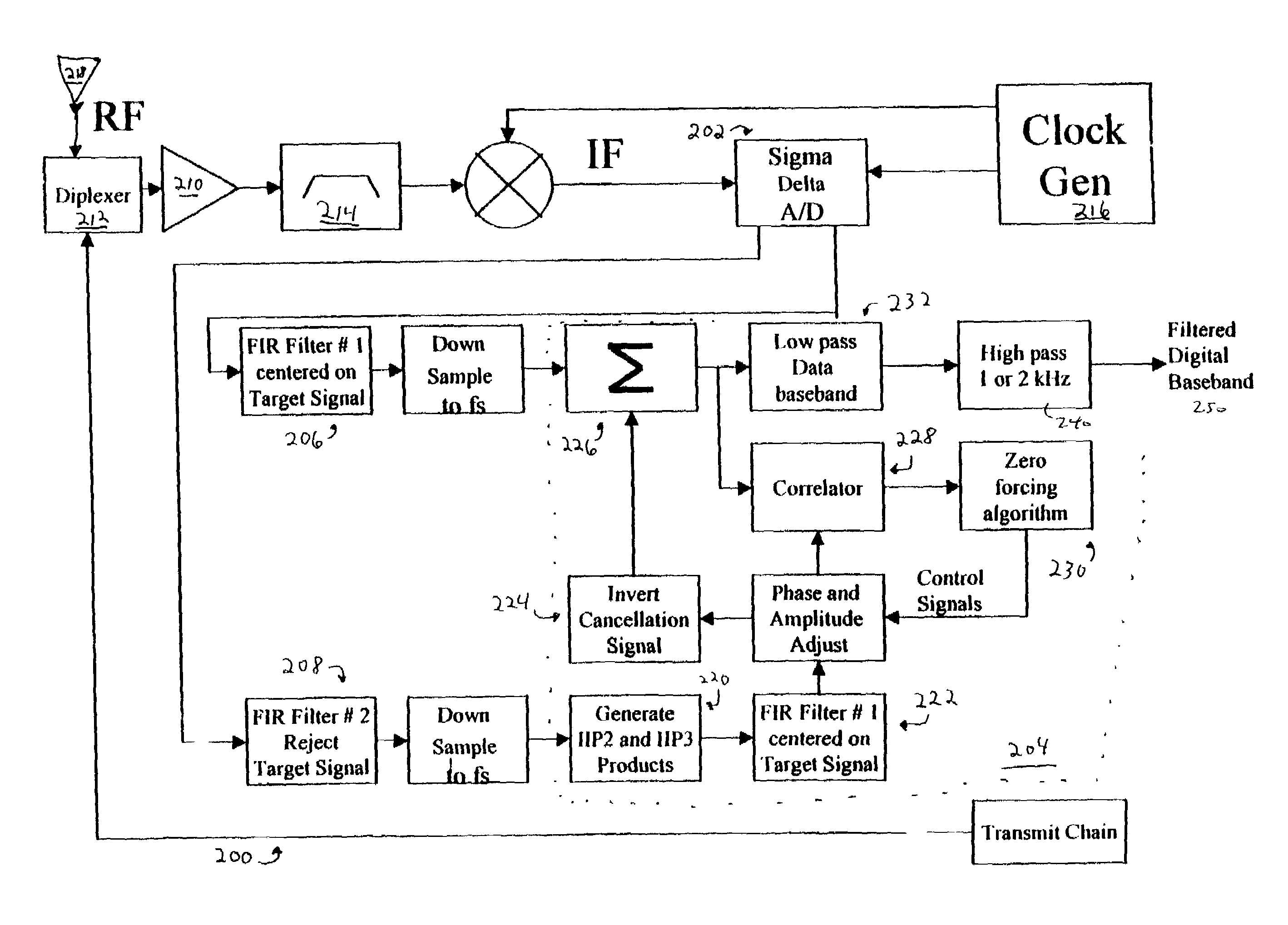
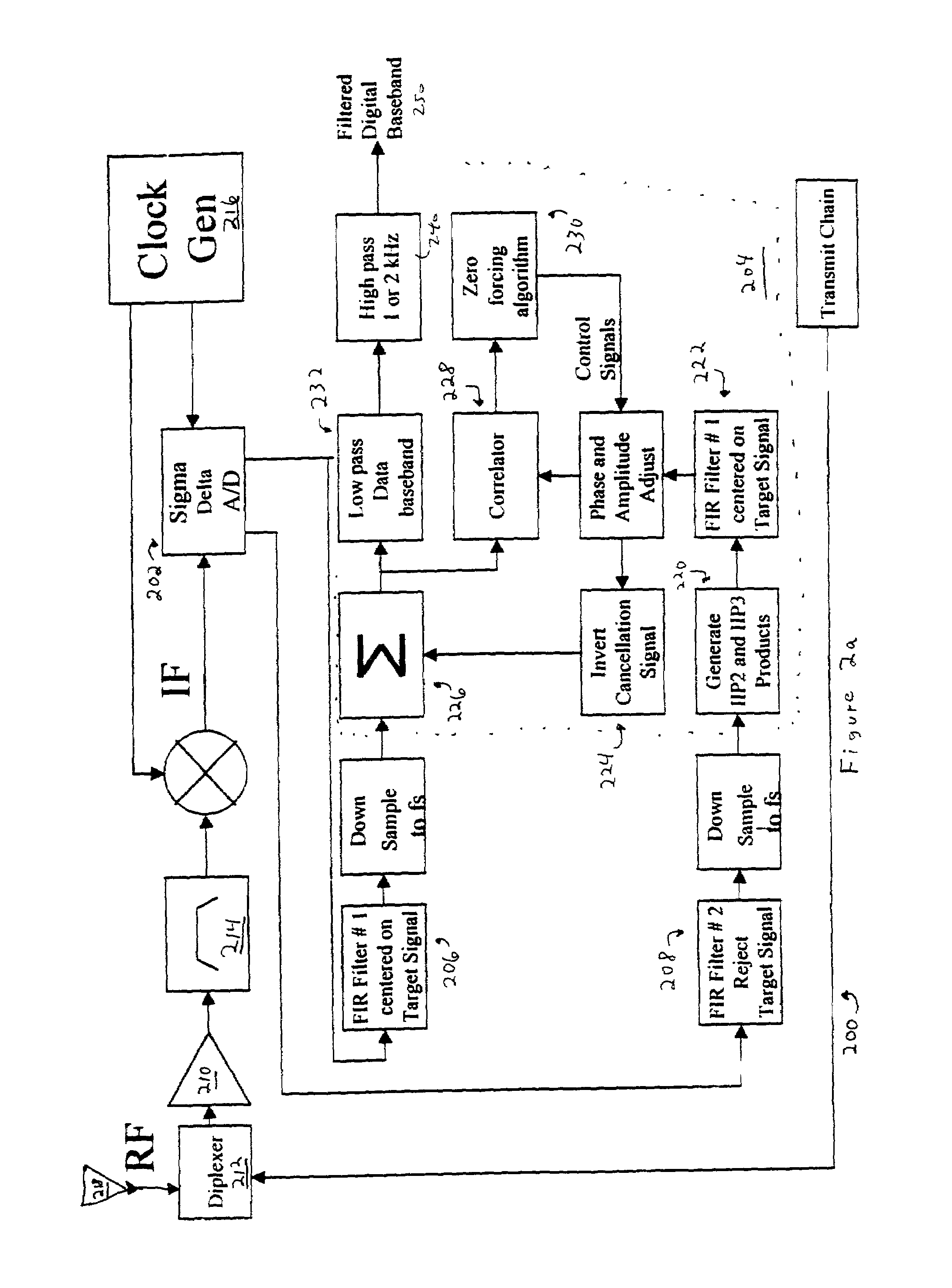
Mitigation of transmitter passive and active intermodulation products in real and continuous time in the transmitter and co-located receiver
ActiveUS20110075754A1Secret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLinear componentEngineering
A transmitter channel interference mitigation processing method for cancellation of intermodulation products are described. In one embodiment, a method comprising generating continuous and real time IMP cancellation signals (ICS) in the baseband digital signal set of the transmitter based on a transmitter signal set, combining digital IMP cancellation signals with a digital baseband transmitter signal set such that the digital cancellation signals, when converted to analog signals and transmitted as part of an analog transmitter signal set, are cancelled by and so cancel the IMPs generated by the non-linear components in the analog transmitter hardware, including digitally generating the IMP cancellation signals using a process based on a power series description of a non-linear process generating the IMPs, generating 3rd order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three signals of the transmitter signal set to create 3rd order IMP cancellation signals, generating 5th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five signals of the transmitter signal set to create 5th order IMP cancellation signals, generating 7th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five or seven signals of the transmitter signal set to create 7th order IMP cancellation signal, generating odd order IMP cancellation signals (ICS) by digitally multiplying an odd number of digital signals and combining multiplied digital signals with the transmitter baseband digital signals, creating IMP cancellation signals in the receiver, and cancelling one or both of active and passive IMPs generated in a transmitter path that fall within a receiver passband.
Owner:FINESSE WIRELESS LLC
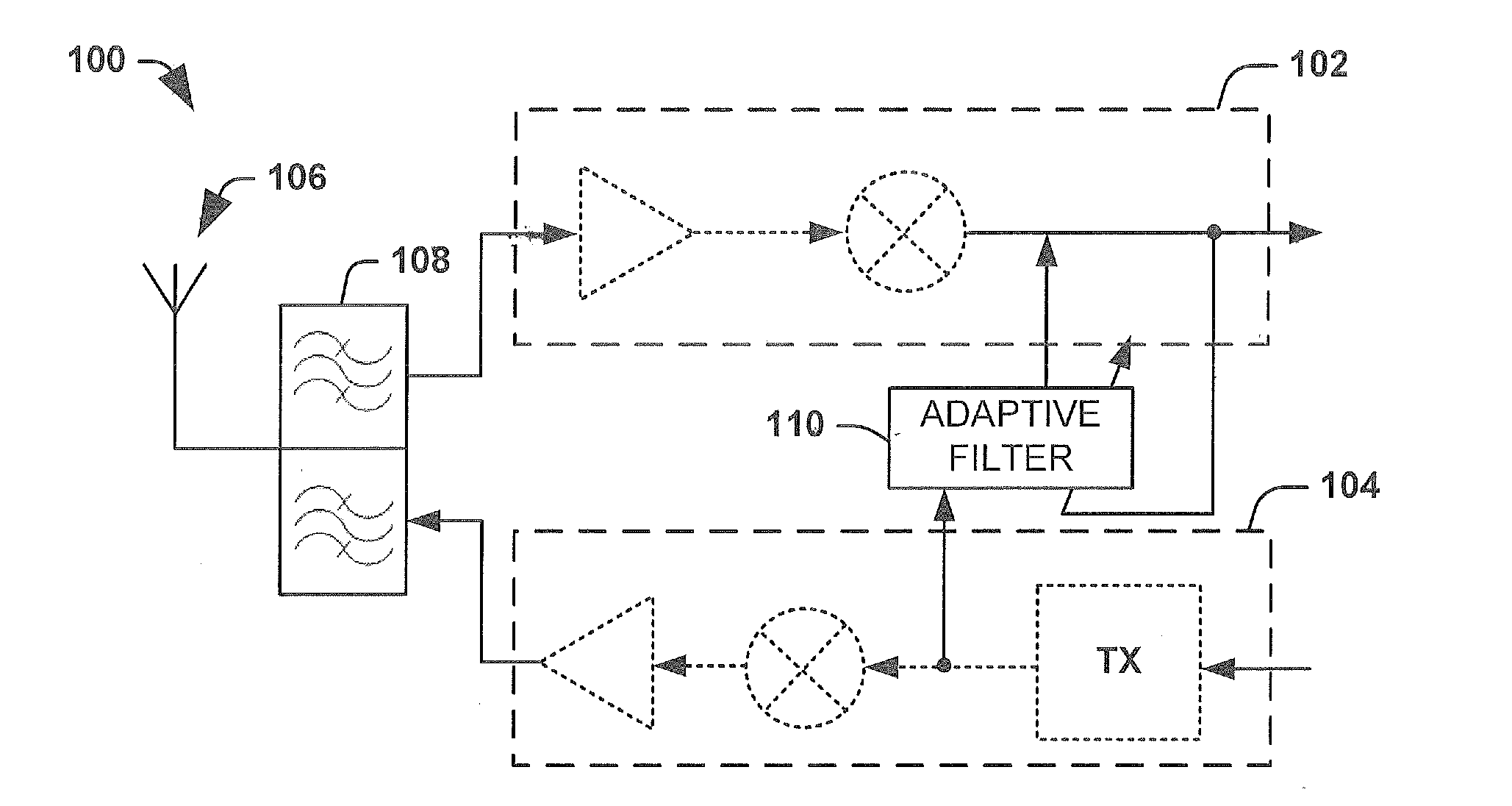
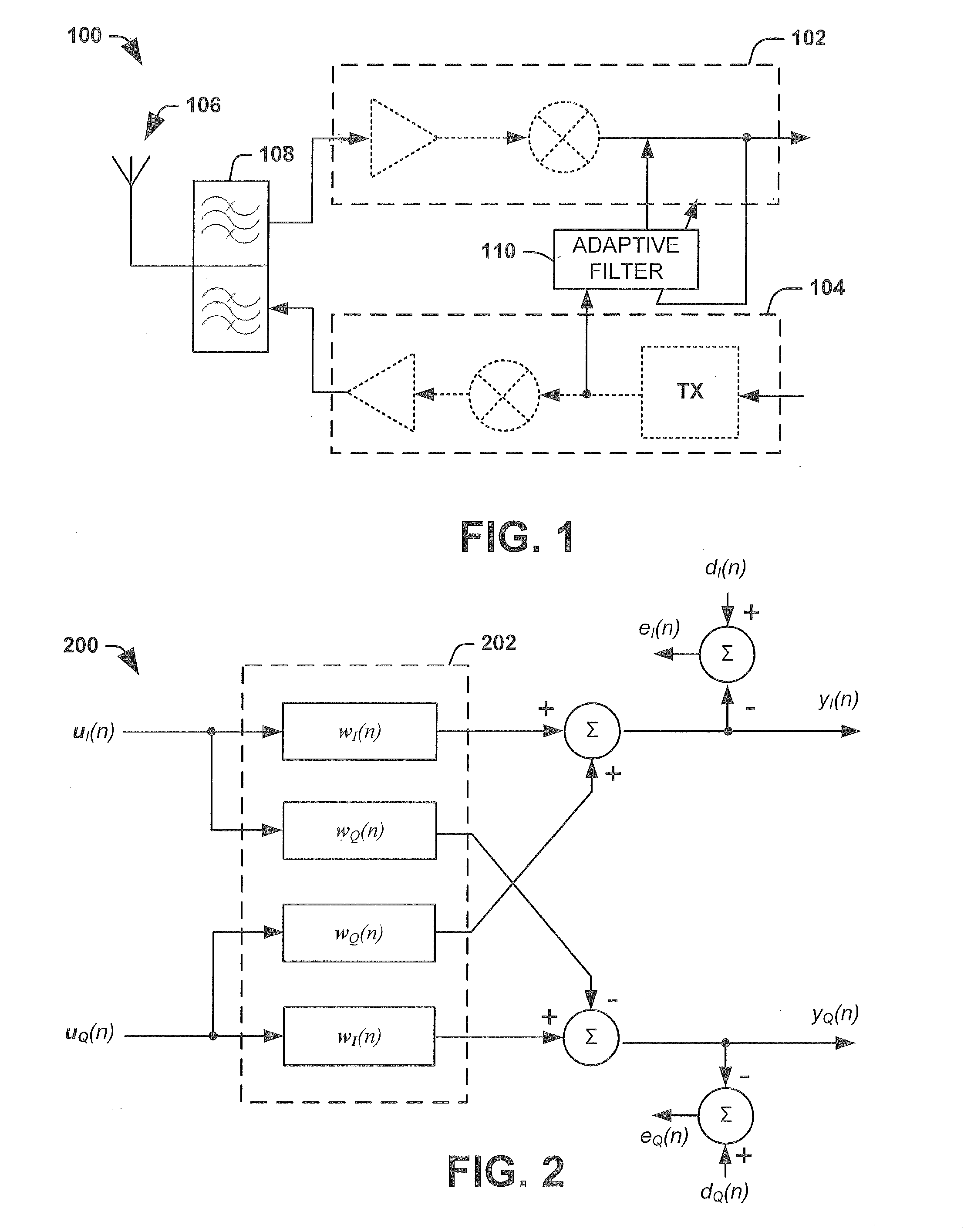
Simplified adaptive filter algorithm for the cancellation of tx-induced even order intermodulation products
InactiveUS20120140685A1Modulated-carrier systemsLine-transmissionAdaptive filtering algorithmAdaptive filter
One embodiment of the present invention relates to an adaptive filtering apparatus comprising first and second real valued adaptive filters, respectively configured to receive an adaptive filter input signal based upon a transmission signal in a transmission path. The first real valued adaptive filter is configured to operate a real valued adaptive filter algorithm on the input signal to estimate a first intermodulation noise component (e.g., an in-phase component) in a desired signal and to cancel the estimated noise. The second real valued adaptive filter is configured to operate a real valued adaptive filter algorithm on the input signal to estimate a second intermodulation noise component (e.g., a quadrature phase component) in the desired signal and to cancel the estimated noise. Accordingly, each filter operates a real valued adaptive algorithm to cancel a noise component, thereby removing complex cross terms between the components from the adaptive filtering process.
Owner:INTEL CORP
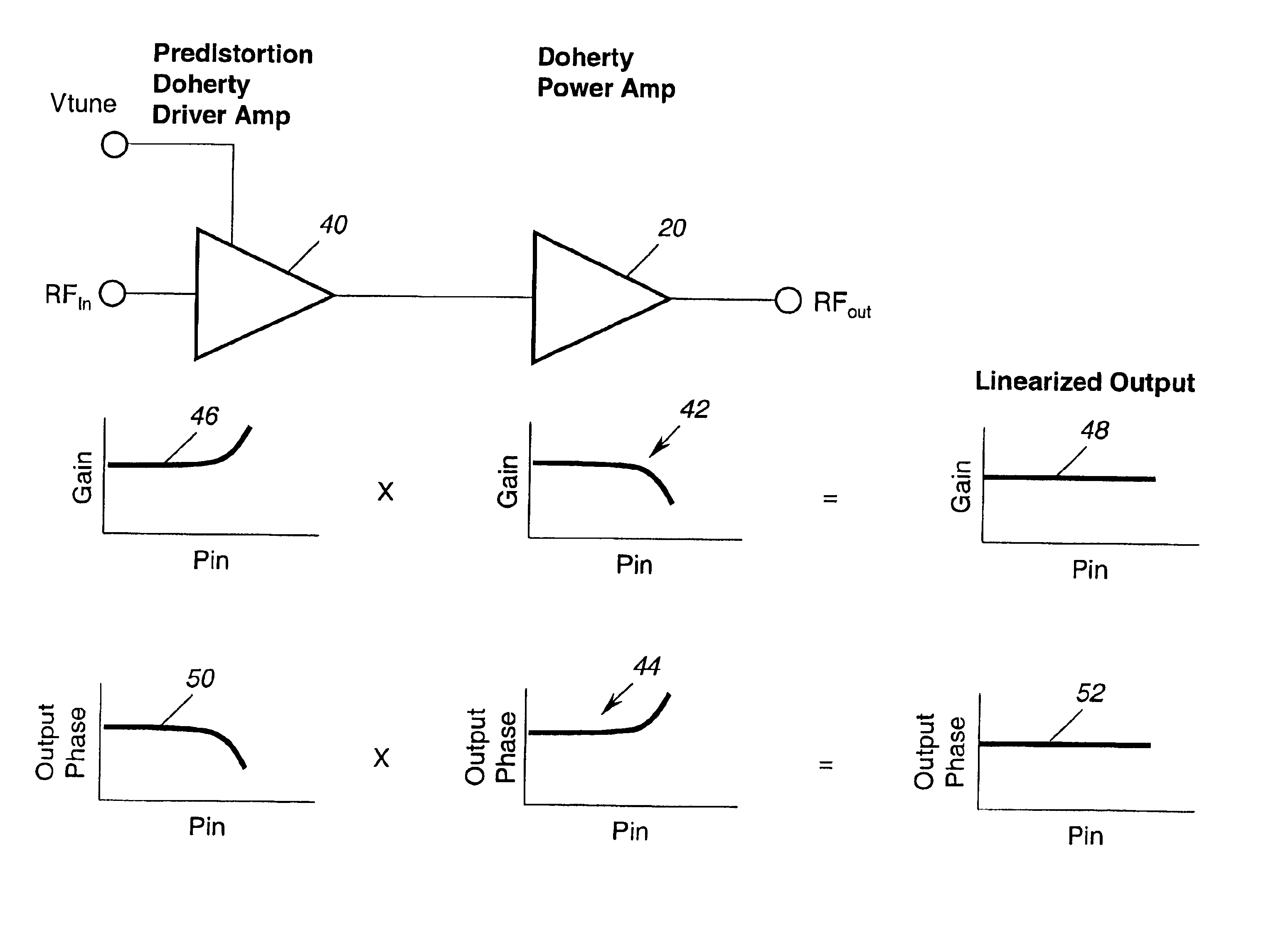
Application of the doherty amplifier as a predistortion circuit for linearizing microwave amplifiers
InactiveUS6864742B2Reducing intermodulation (IM) distortionImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A predistortion circuit for a microwave amplifier and more particularly to predistortion circuit configured as a Doherty amplifier. The predistortion circuit is adapted to be coupled to a downstream Doherty amplifier to precompensate for the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier as the input power level is increased while simultaneously reducing the intermodulation (IM) distortion. In order to provide precompensation, the precompensation circuit is operated at bias level to provide gain expansion and phase compression to cancel out the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier to provide a higher overall linear power added efficiency (PAE).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
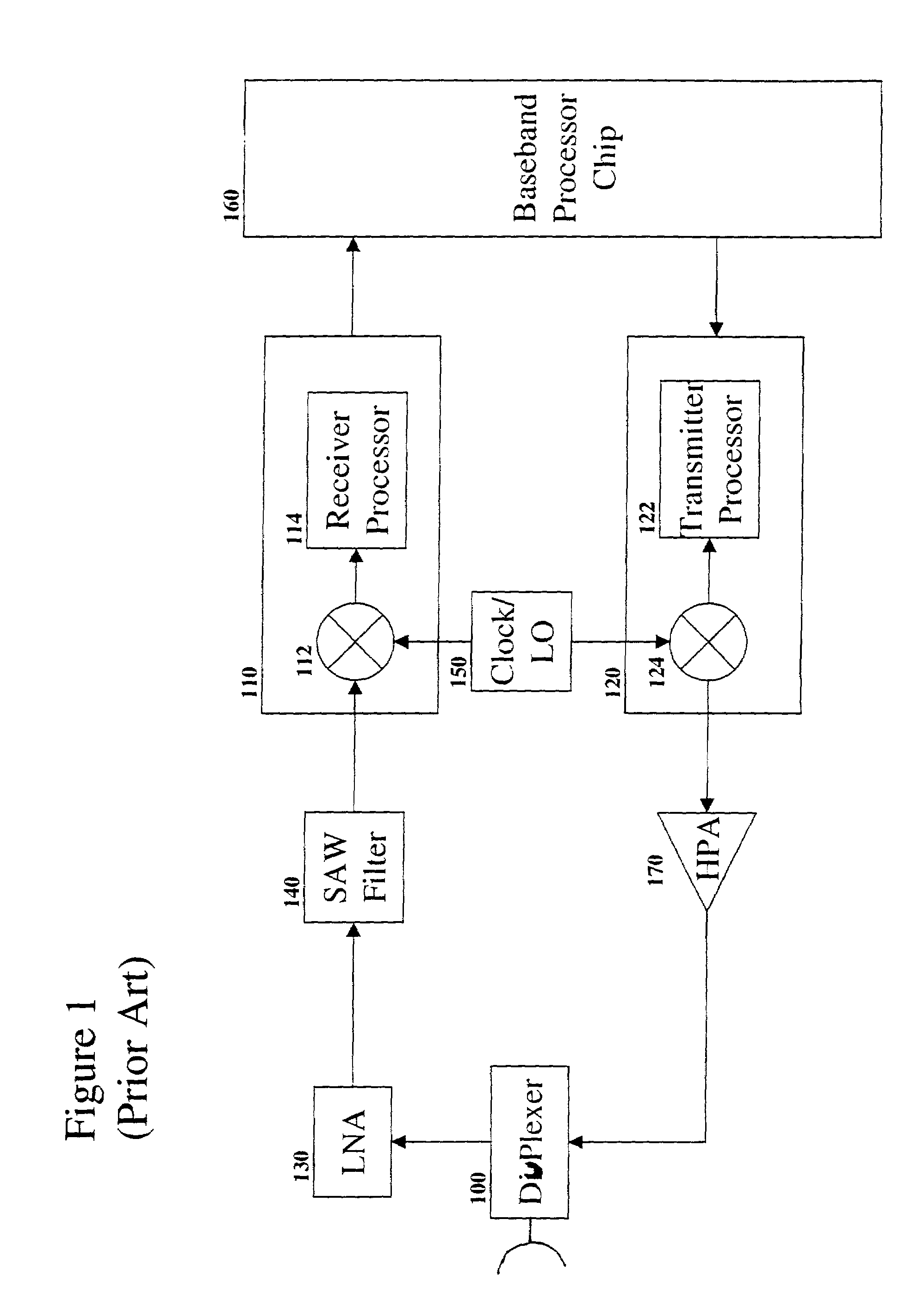
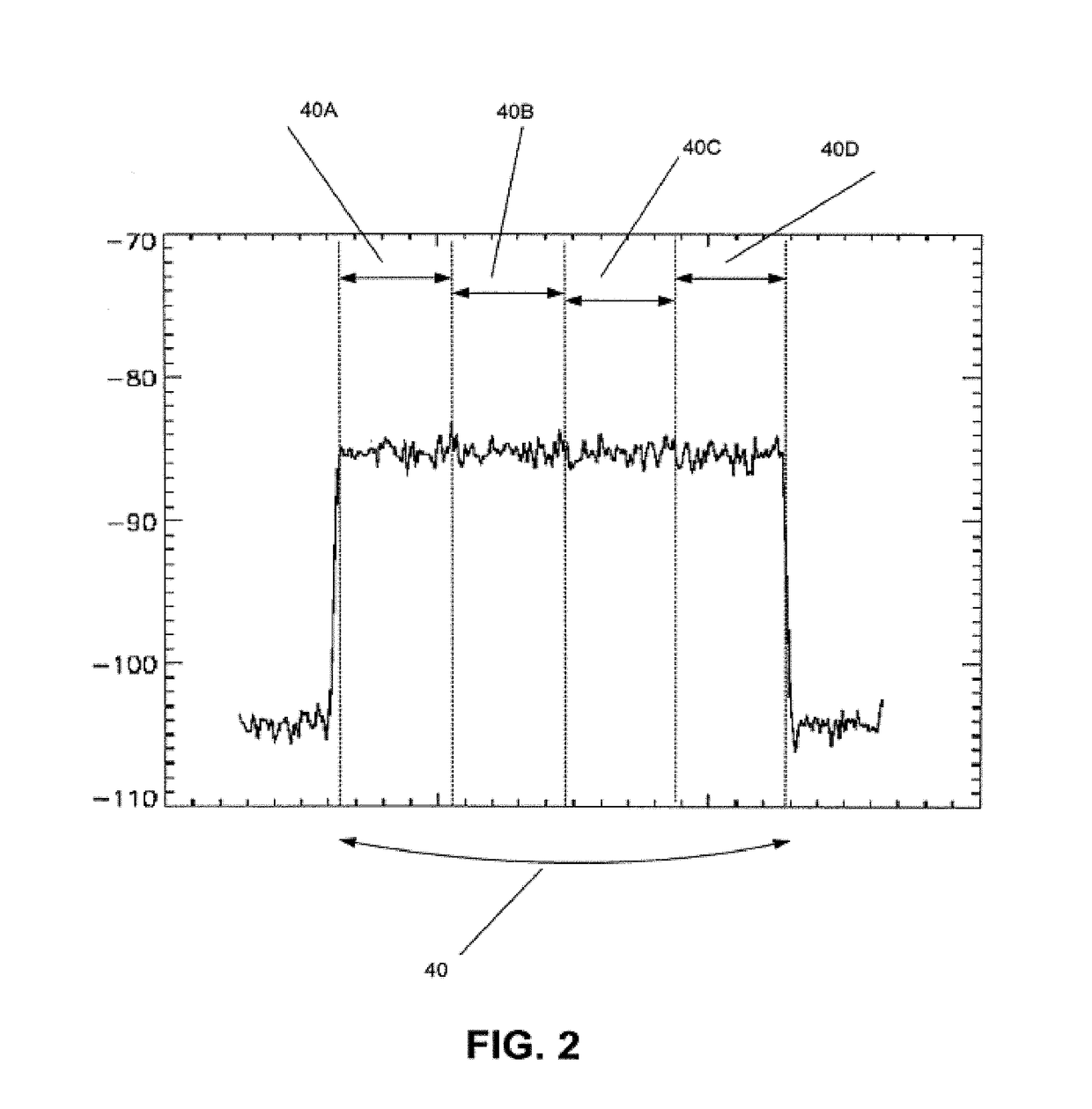
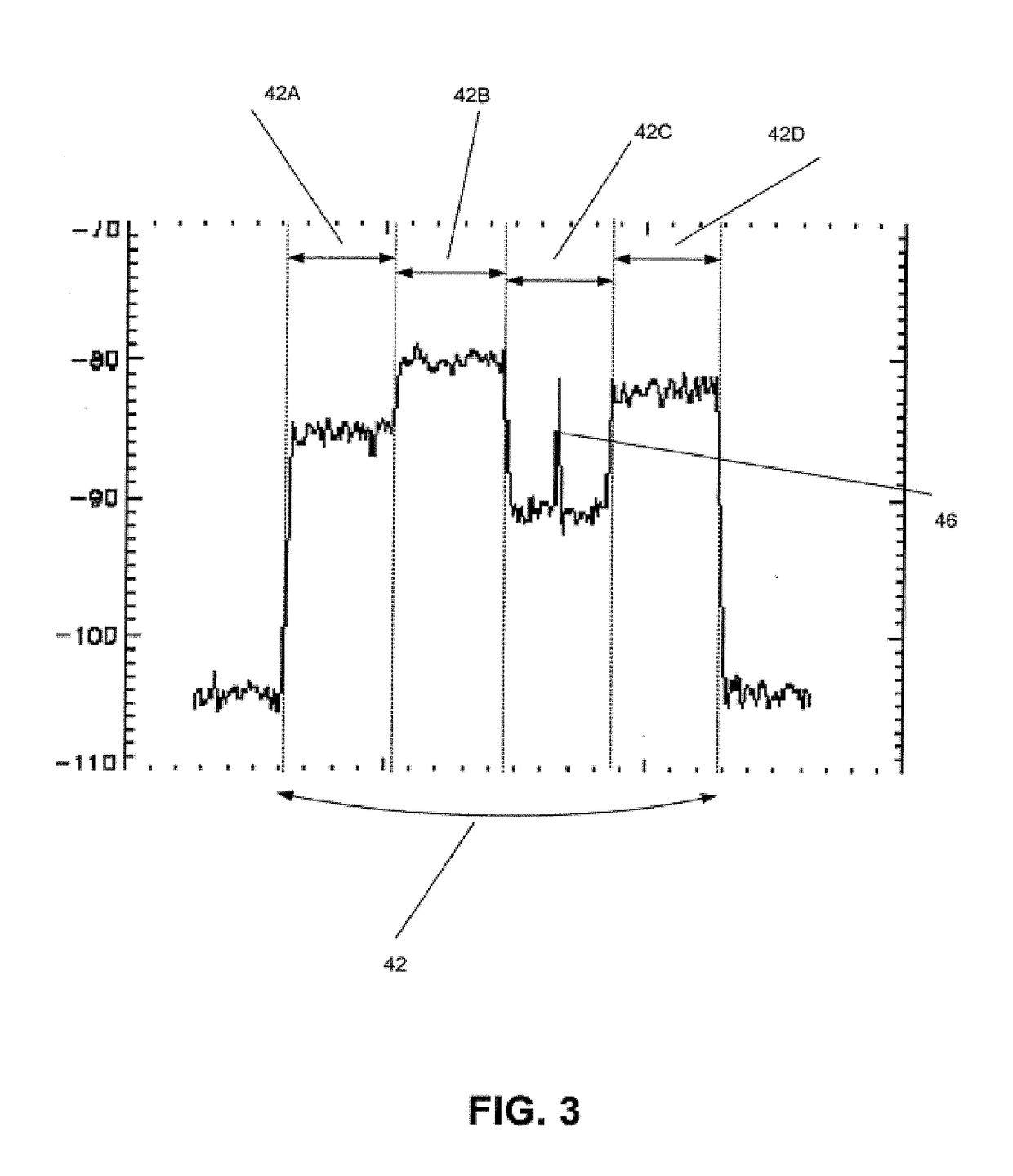
Digital baseband receiver in a multi-carrier power amplifier
InactiveUS20020127986A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionTransmissionBaseband receiverCarrier signal
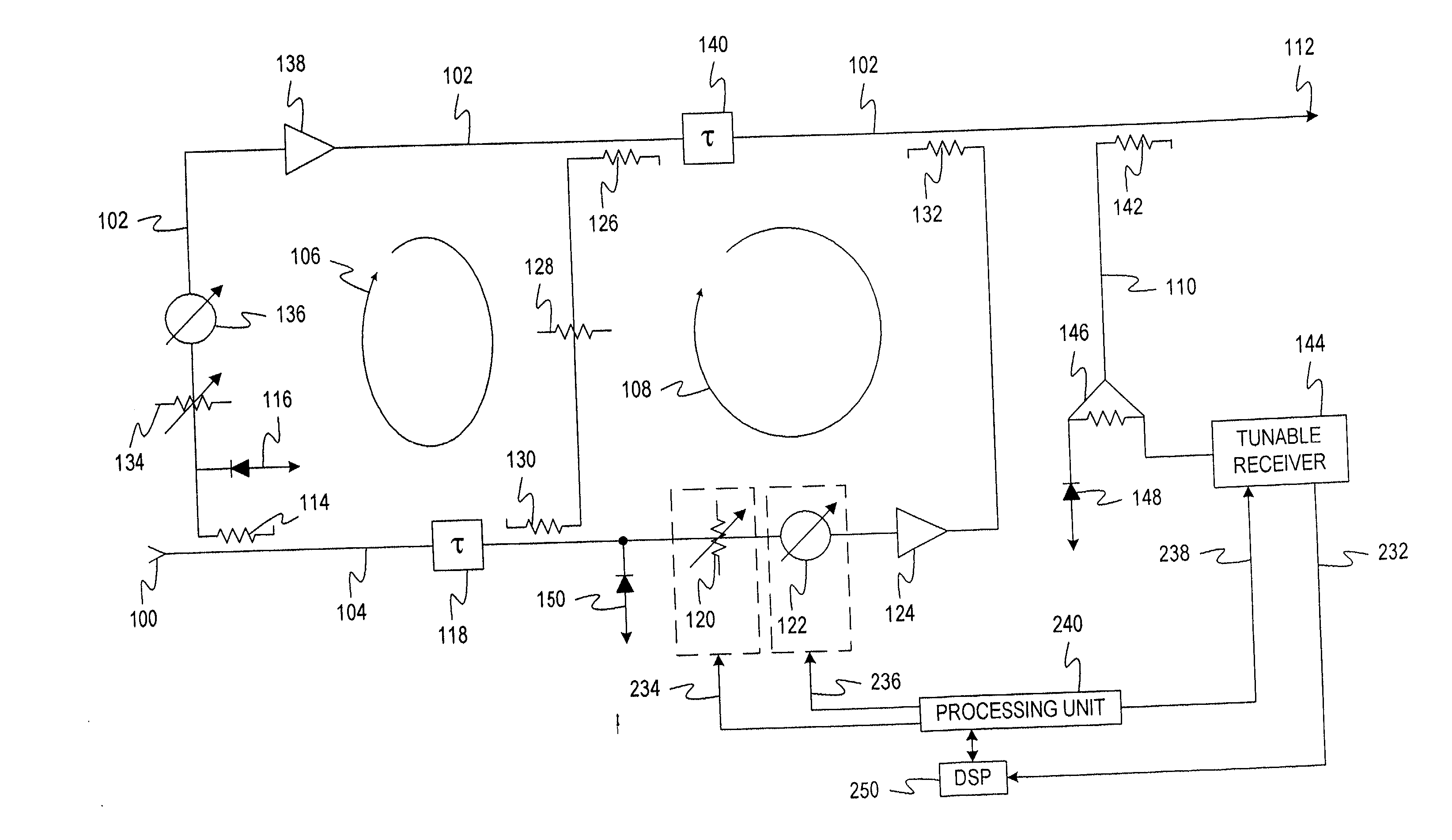
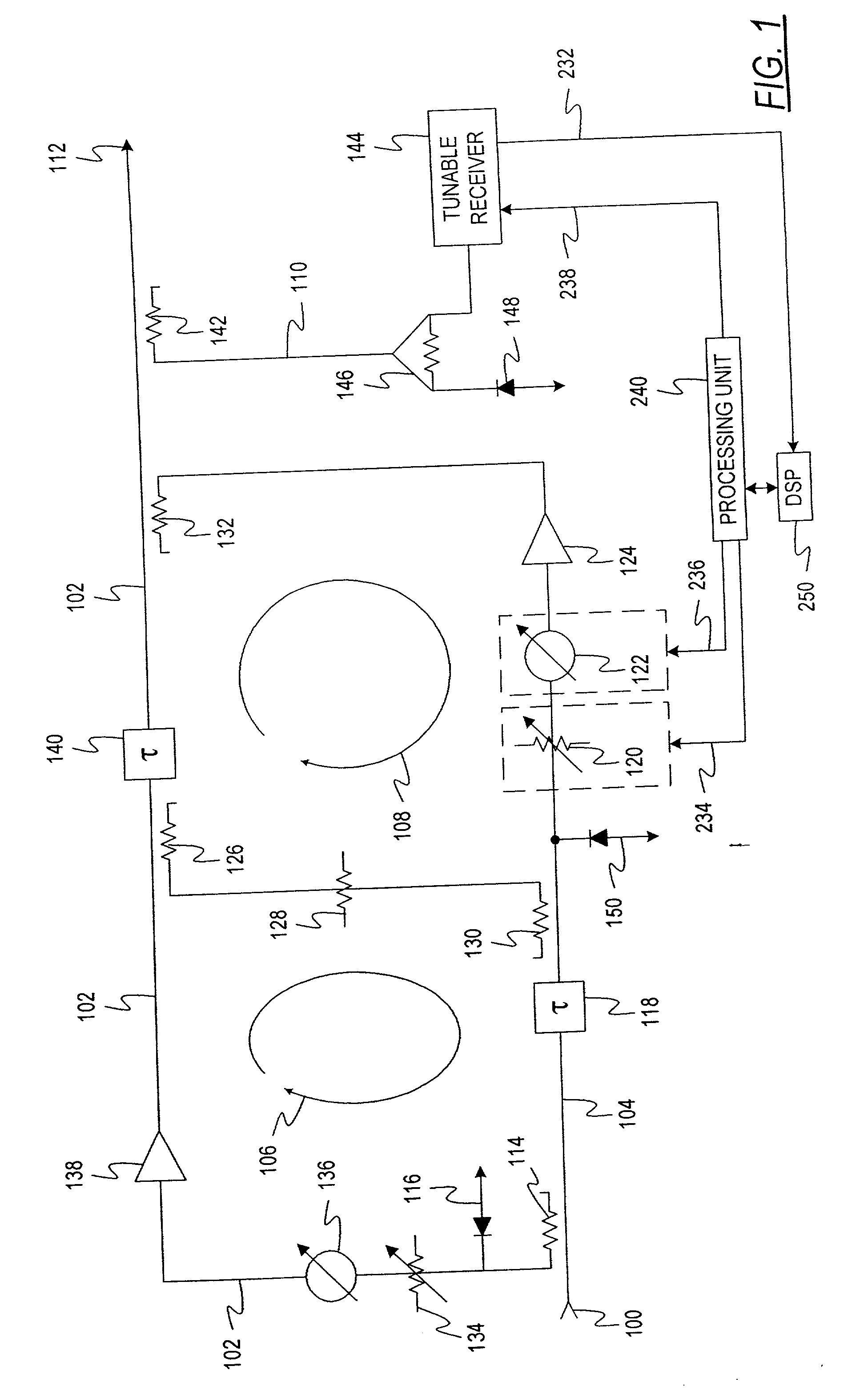
A power amplifier system and method for locating carrier frequencies across a frequency band, identifying the modulation format of each carrier, and locating and suppressing undesired intermodulation distortion (IMD) products generated by the power amplifier. The system includes an amplifier for amplifying RF carrier signals in a main signal path, a variable phase shifter and variable attenuator on a feed forward path, and a tunable receiver that digitizes a portion of the frequency band to baseband. The tunable receiver includes a tunable voltage controlled oscillator which provides an oscillating frequency to a mixer and is phase-locked to a highly stable reference oscillator. The mixer downconverts a desired RF based on the oscillating frequency to IF. A filter passes only a selected portion of the IF signals, and the filter has a passband sufficient to discern both narrowband and wideband carriers and their associated IMD products. Based on the locations of the carrier frequencies, a processing unit determines the IMD locations of the carrier frequencies, determines the IMD locations, and adjusts the variable phase shifter and variable attenuator on the feed forward path until the IMD products in the main signal path are suppressed below a desired threshold.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Simultaneous transmission of multiple signals through a common shared aperture
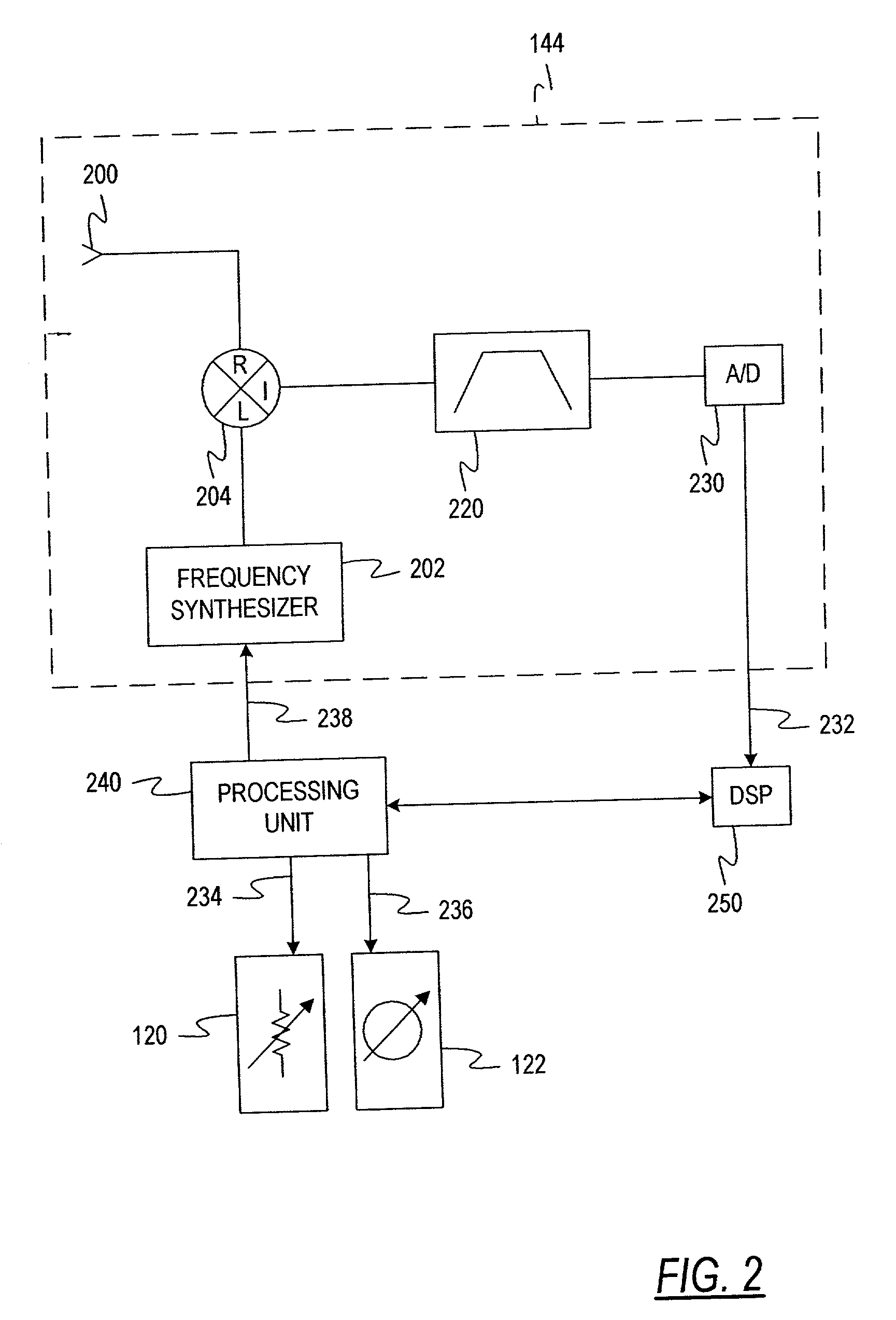
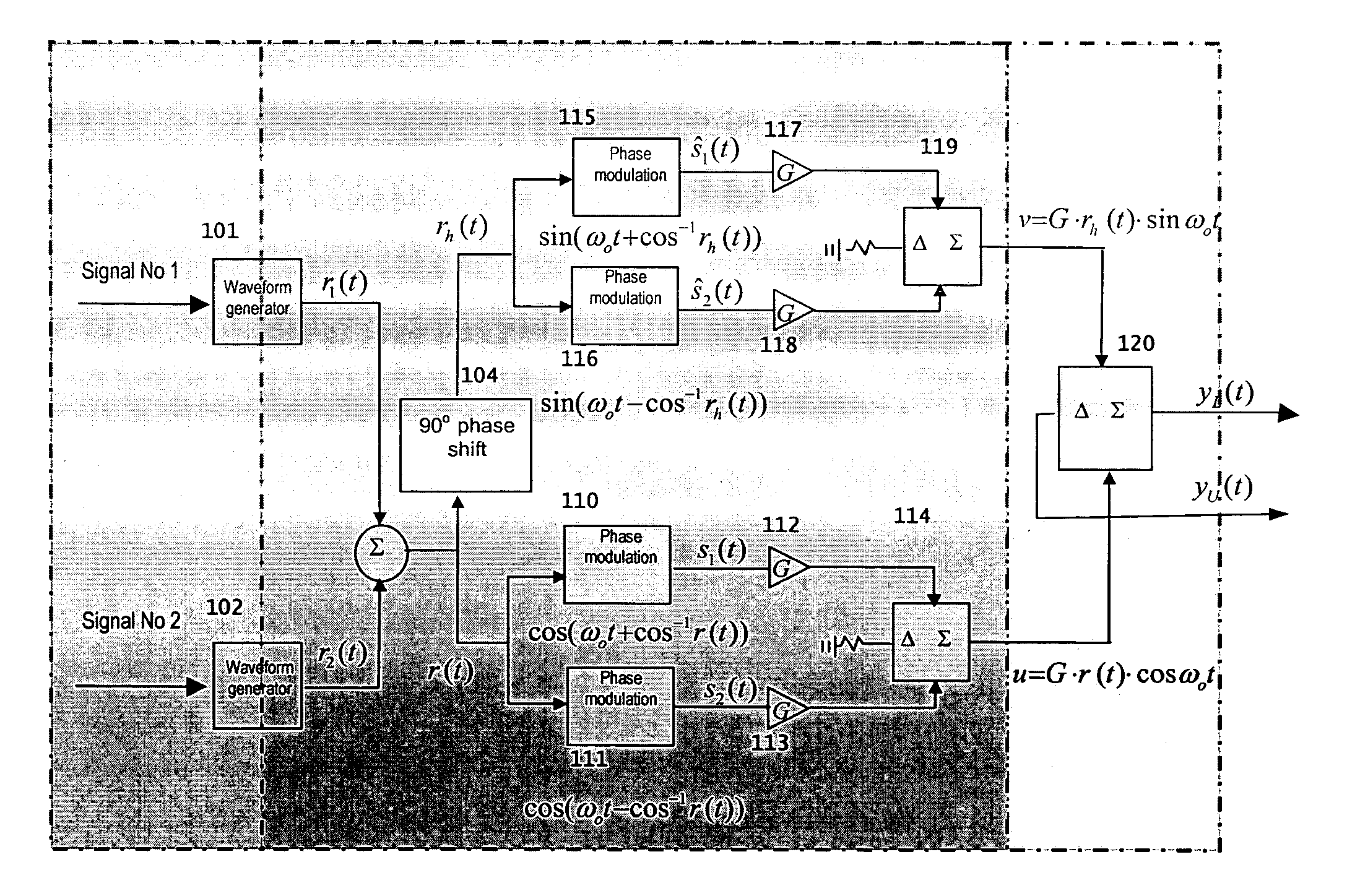
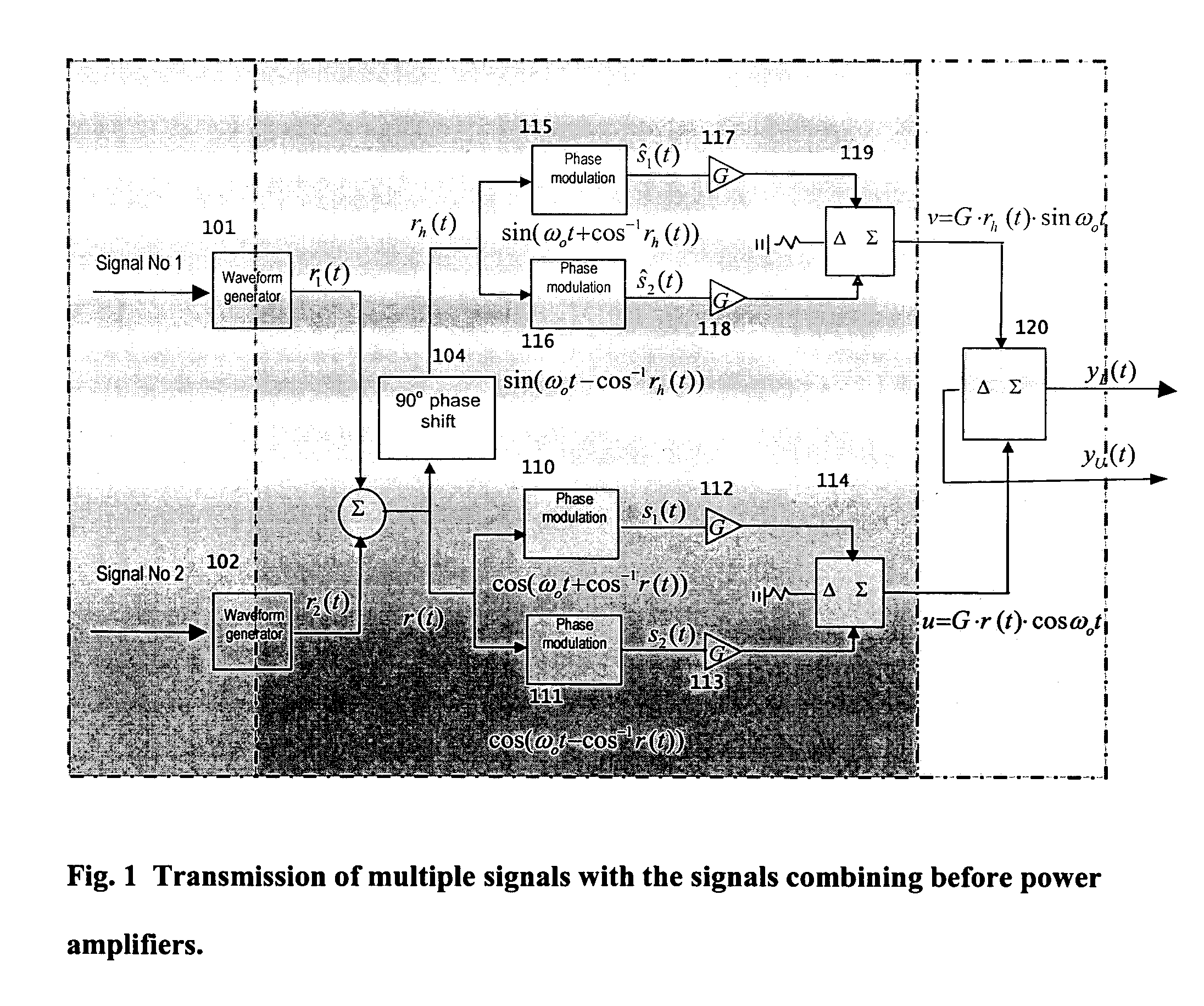
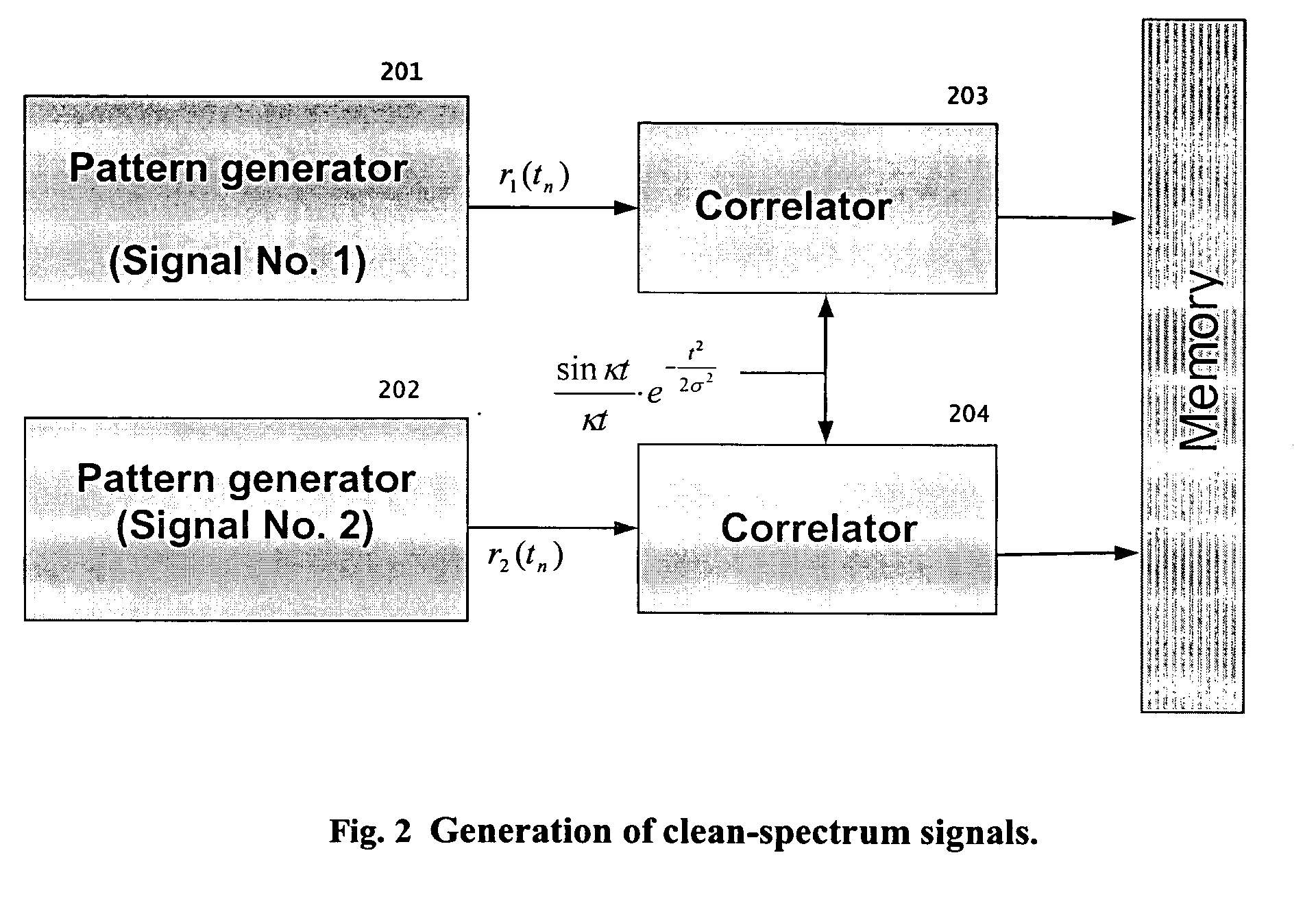
In phased array antennas, multiple signals that perform different functions, such as radar, electronic warfare (EW) and telecommunications, can each be simultaneously transmitted only through a different sub-aperture of the array. For maximum power and efficiency, the power amplifiers operate on one signal at a time. This patent provides the technique of forming a common waveform from multiple signals for transmission through a common aperture. To practically implement this technique in wideband operations, processes performing the required waveform-shaping and amplitude-to-phase-modulation are devised that can transmit the high-power diverse waveforms without serious intermodulations and spectral distortion through every element of the array.
Owner:NAVY THE U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECU OF THE
Radio receiver
Various apparatuses and methods are described to reduce interference in signals subject to intermodulation products and high power narrow band interfering signals on lower power wideband signals. Apparatuses and methods described herein also provide the capability for supporting multi-standards, multi-modes and multi-bands in wireless and wired applications with a single receiver or a receiver with minor variations. The receiver described herein samples the entire band in which there can be signals of interest or signals that can generate interference. All of these signals are sampled in one bit stream and the bit stream is processed to isolate signals of interest and interfering signals. The isolated interfering signals are then cancelled out of the signals of interest.
Owner:SMITH FRANCIS J
Method and Apparatus for use in Improving Linearity of MOSFETS using an Accumulated Charge Sink-Harmonic Wrinkle Reduction
ActiveUS20120267719A1Improving nonlinear responseImprove harmonicsSolid-state devicesPulse techniqueMOSFETHarmonic
A method and apparatus for use in improving linearity sensitivity of MOSFET devices having an accumulated charge sink (ACS) are disclosed. The method and apparatus are adapted to address degradation in second- and third-order intermodulation harmonic distortion at a desired range of operating voltage in devices employing an accumulated charge sink.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
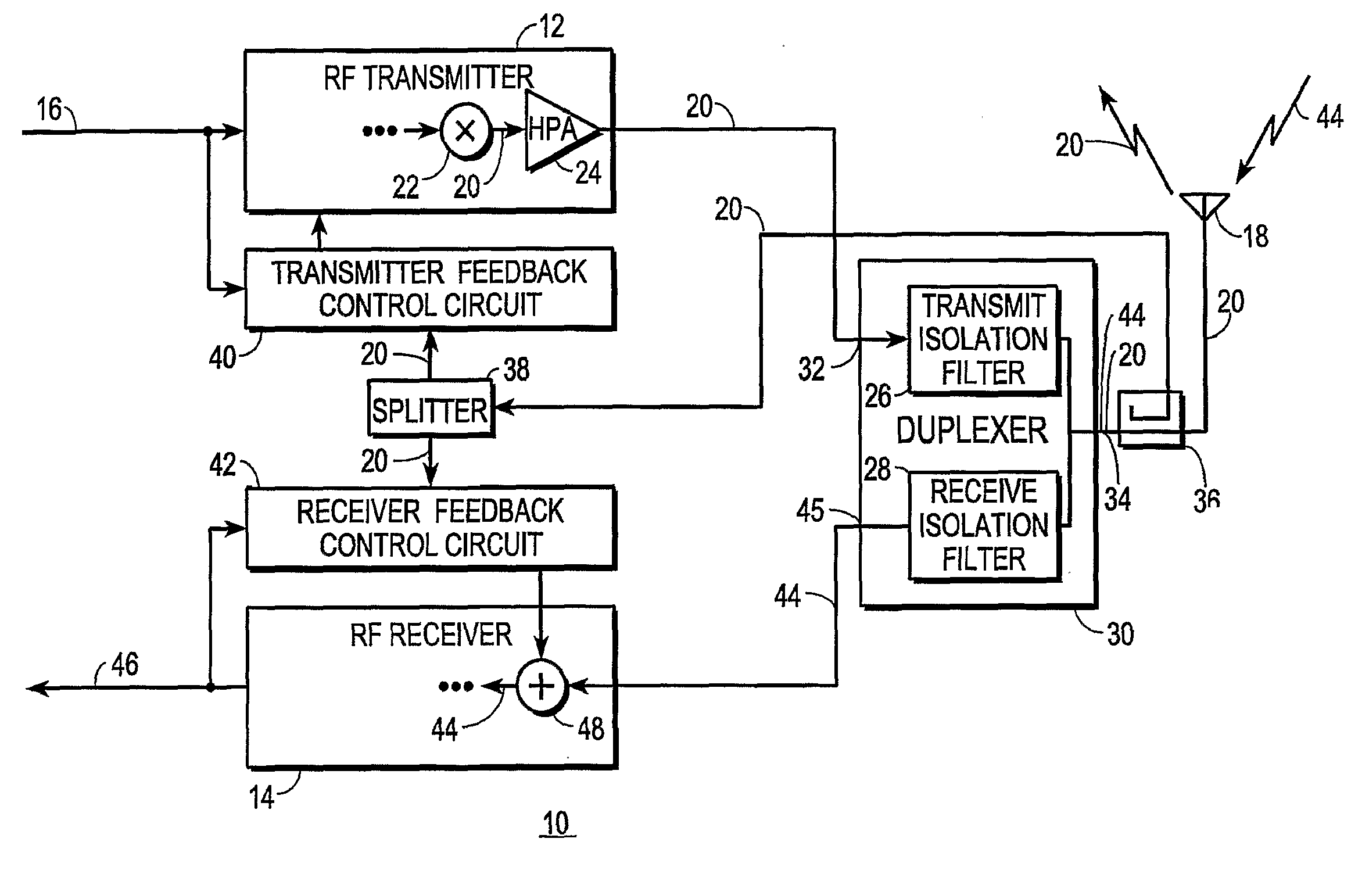
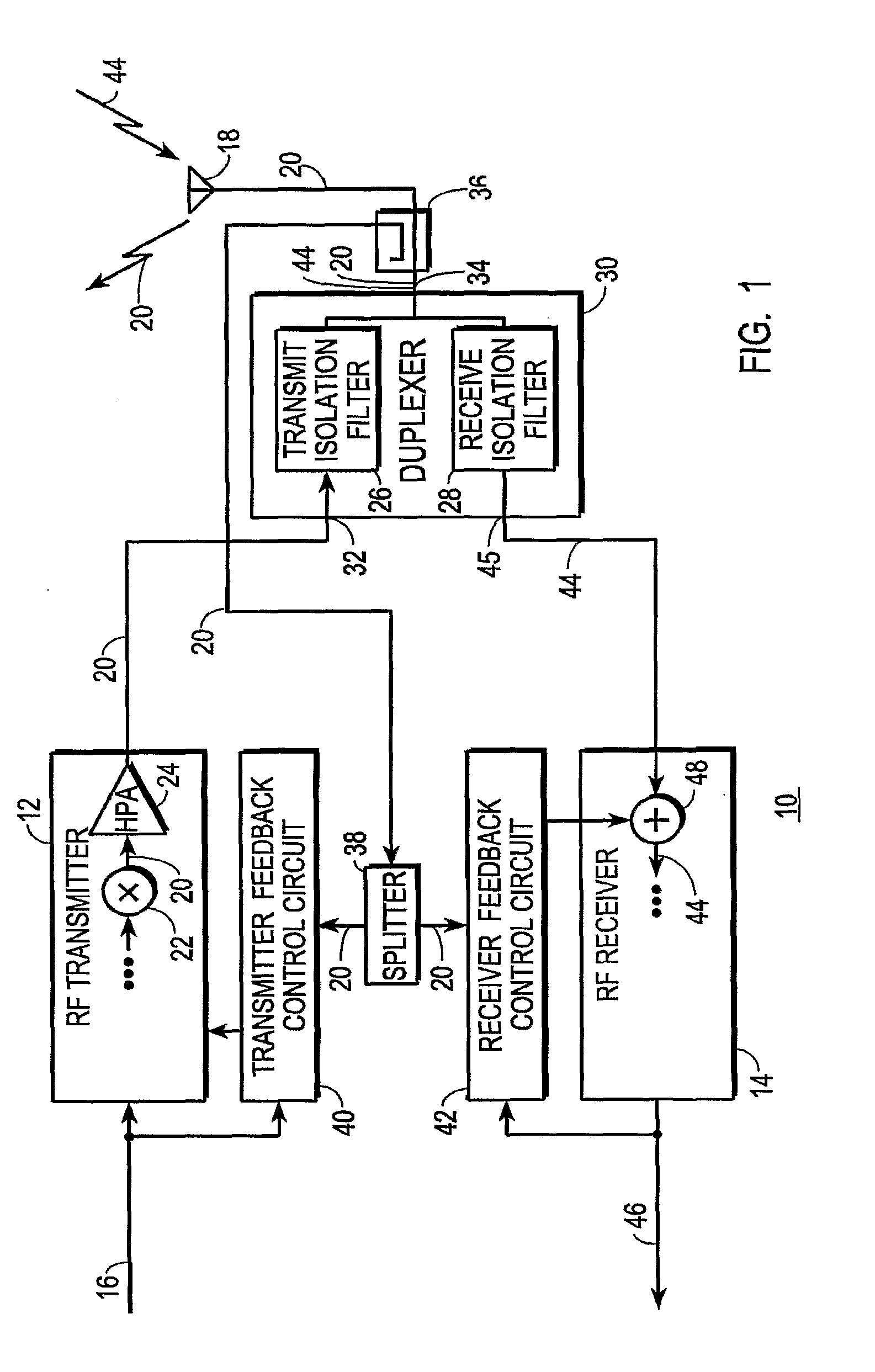
Transceiver with Compensation for Transmit Signal Leakage and Method Therefor
InactiveUS20100048146A1Simple and inexpensive duplexerAvoid inaccuraciesTransmissionTransceiverEngineering
A transceiver (10) includes an RF transmitter (12) and an RF receiver (14) coupled together through a duplexer (30) or non-filtering multiport device (30′). Either device may leak significant portions (56, 58) of the transmit signal (20) into the receive signal (44), and may significantly distort the transmit signal (20). Distortion is compensated in the transmitter (12) through the use of a linear predistorter (68) that is adjusted in response to an RF feedback signal obtained from the antenna-side of the device. Transmit signal leakage is compensated in the receiver (14) by producing an RF cancellation signal (106) that, when combined with the receive signal (44) at RF at least partially cancels the transmit signal portions (56, 58) leaked into the receive signal (44). Residual leakage signal and intermodulation products thereof may be cancelled digitally.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Method and Device for Preventing Interference at a Radio Receiver Device Caused by Several Radio Transmitter Devices
InactiveUS20090318087A1Minimizing noise/interferenceElectrical apparatus interference reductionWireless communicationRadio receptionRadio receiver
The present invention provides a method for reducing interference at a radio receiver device caused by several radio transmitter devices, comprising the steps of detecting simultaneous operation of at least two radio transmitter devices and a radio receiver device, determining that said simultaneous operation of said transmitter devices causes interference through frequency intermodulation effects at said radio receiver device, and controlling at least one of said radio transmitter devices and / or said radio receiver device, in order to reduce said interference.The invention furthermore provides a device for reducing interference between a radio receiver device and several radio transmitter devices, comprising a detection component, adapted for detecting simultaneous operation of at least two radio transmitter devices and a radio receiver device, and for determining that said simultaneous operation of said transmitter devices causes interference through frequency intermodulation effects at said radio receiver device, and a controller responsive to said detection component, adapted for controlling at least one of said radio transmitter devices and / or said radio receiver device for reducing said interference.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method for the terrestrially transmitting digital signals
InactiveUS6366309B1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsFrequency spectrumDigital radio
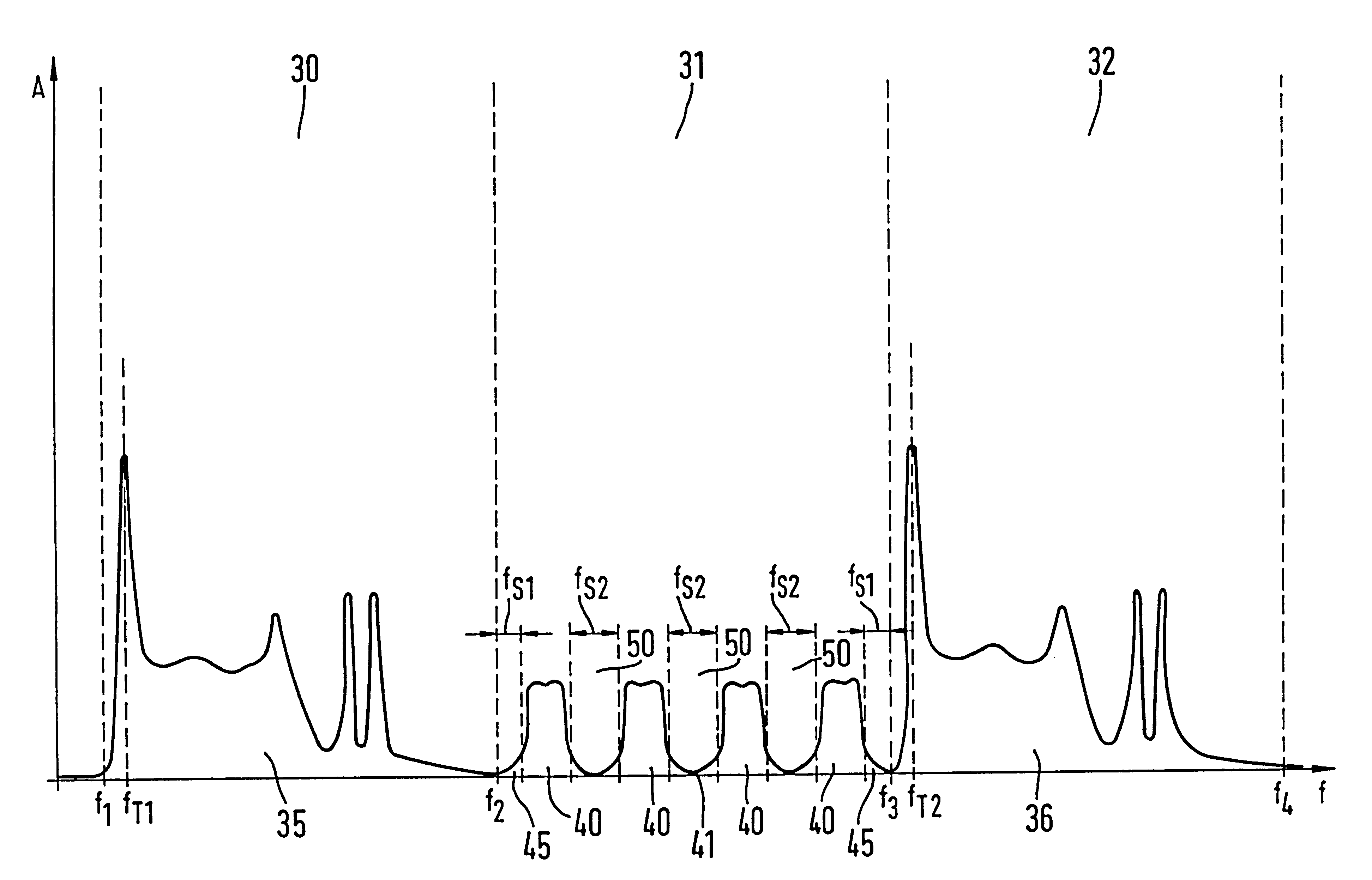
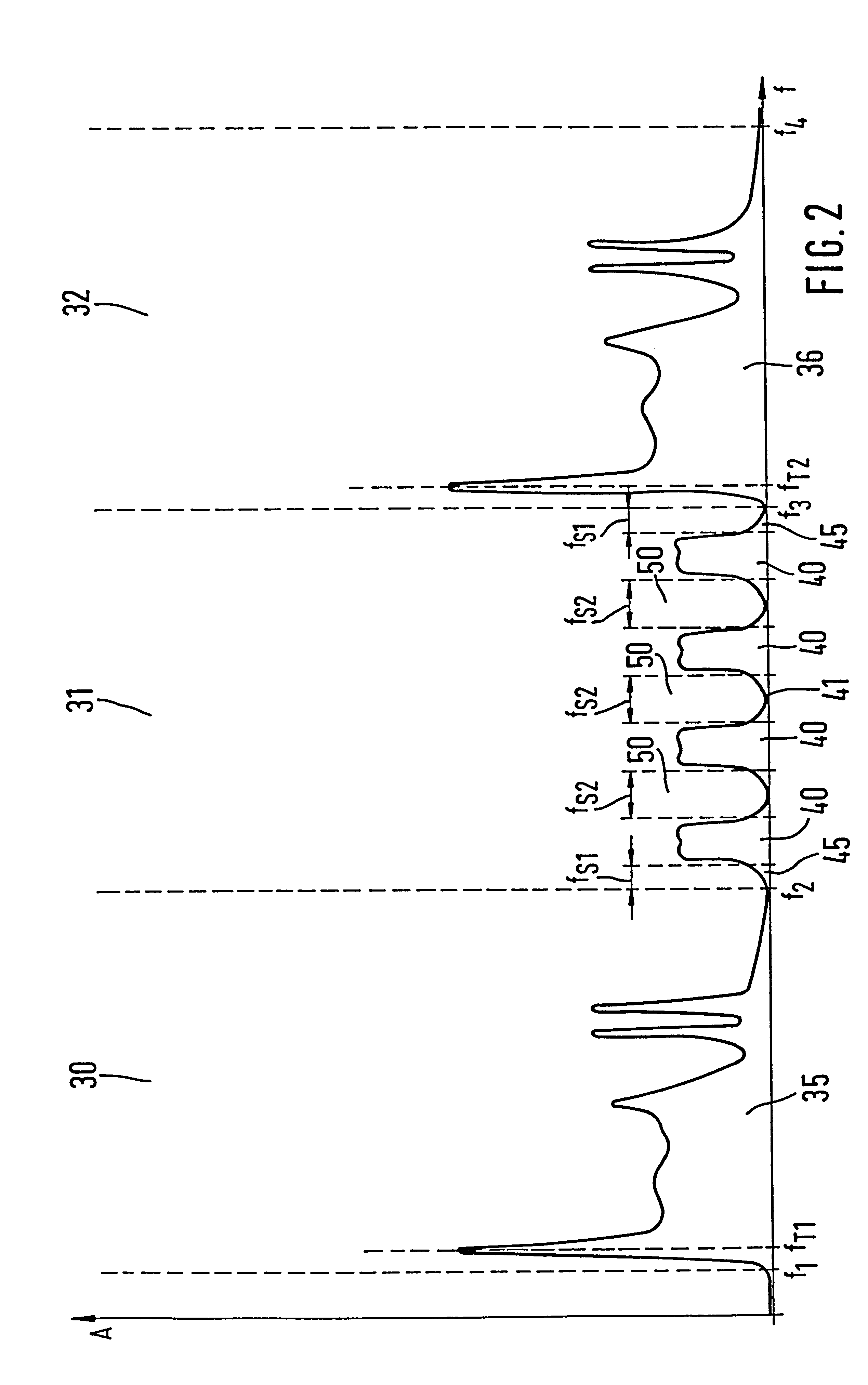
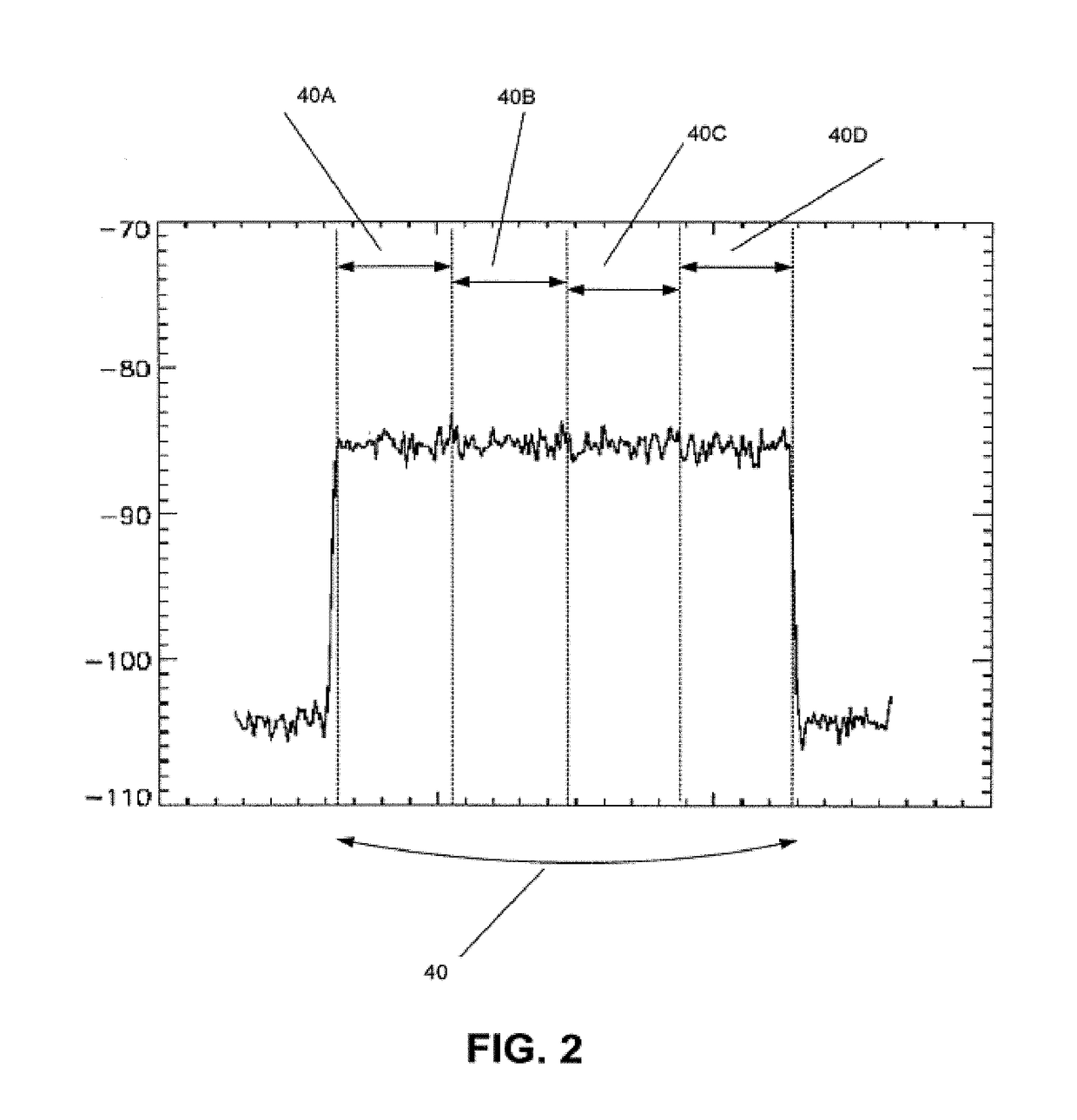
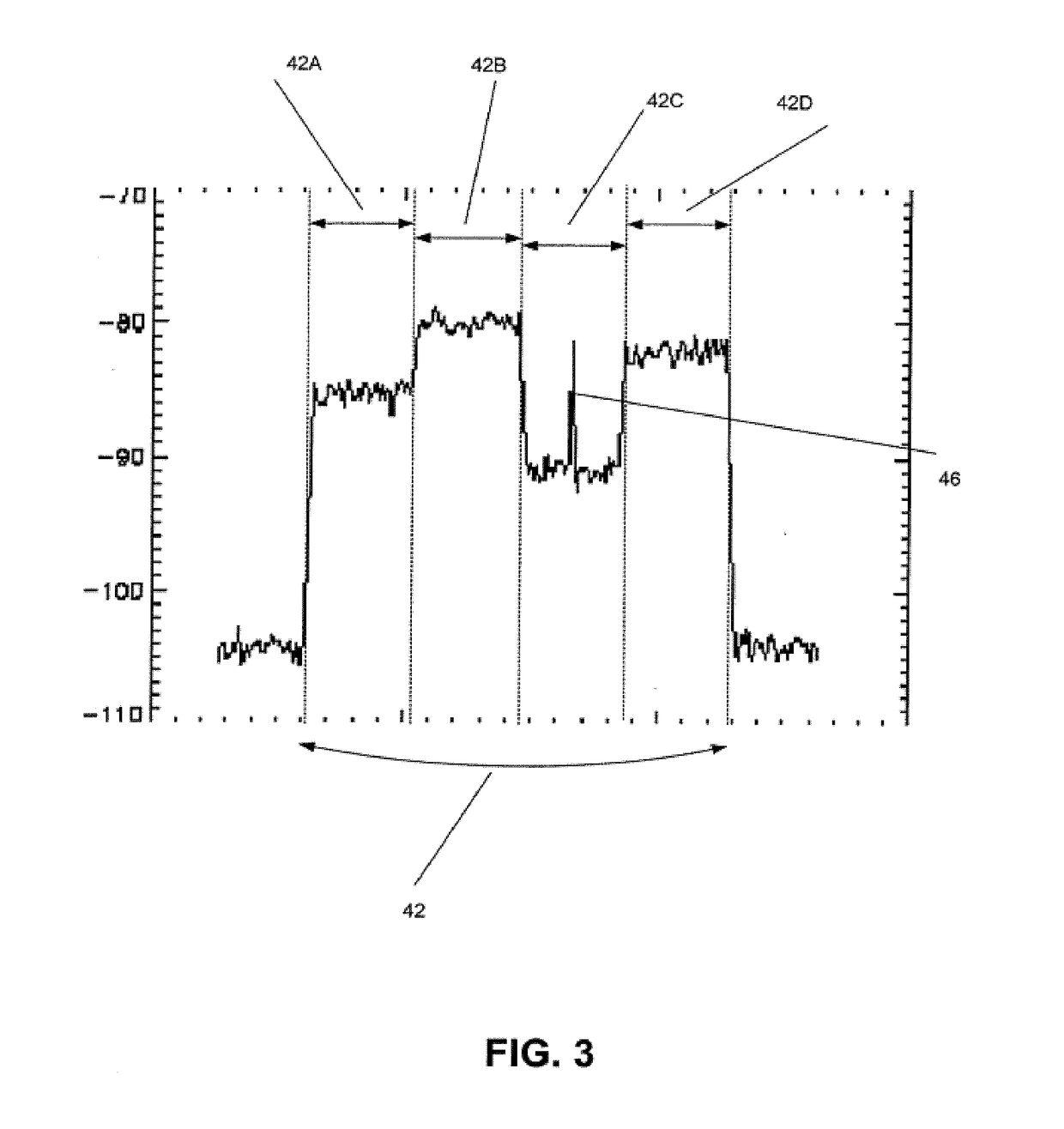
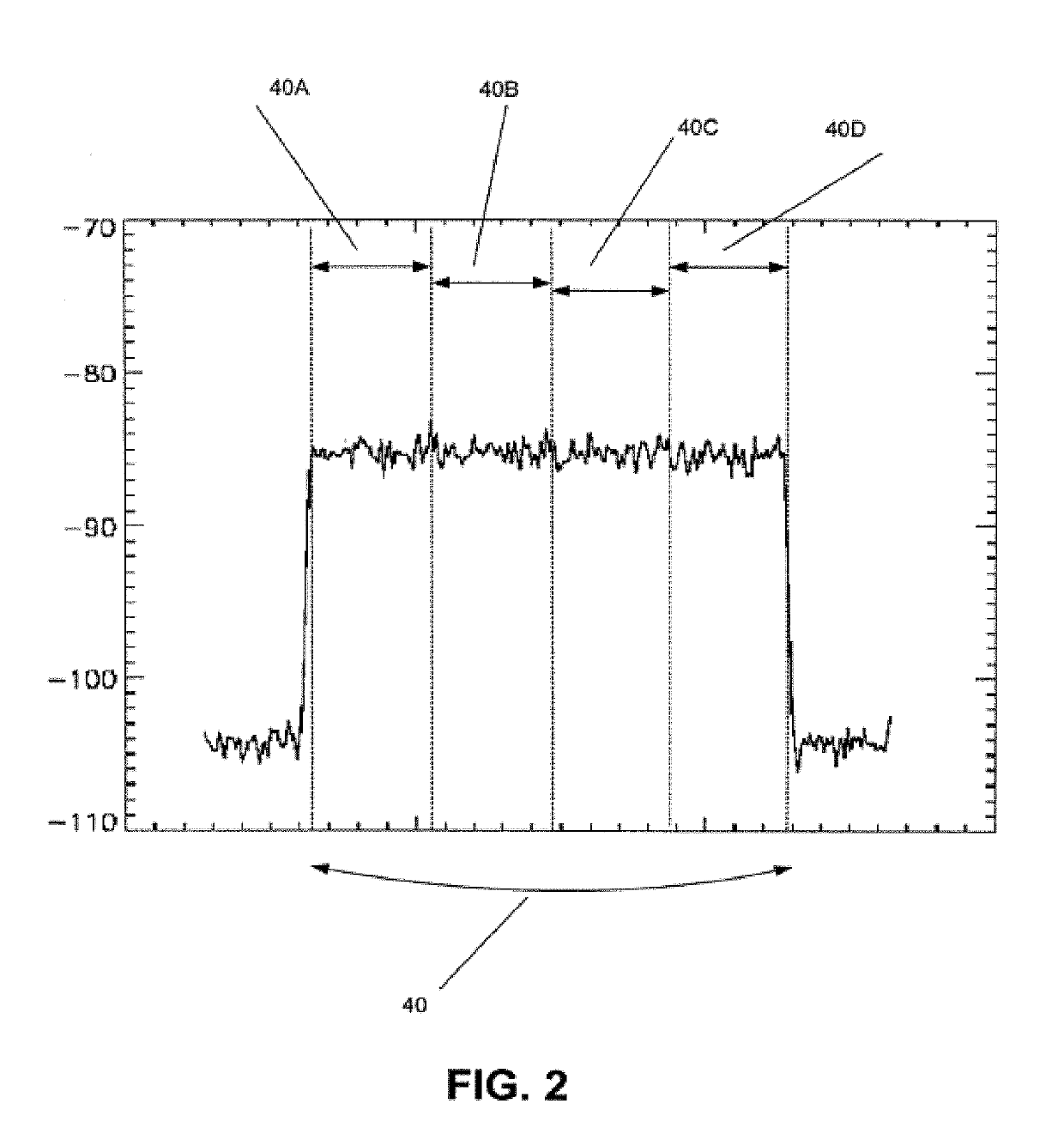
A method is proposed that is used for terrestrial transmission of at least one digital signal, in particular a digital radio and / or TV broadcasting signal. In this method, the at least one digital signal, reduced in its data quantity by coding, is modulated, preferably by the OFDM method, and converted into the frequency position of at least one channel, adjacent to at least one occupied or unoccupied channel (30, 32) for transmitting an analog TV broadcasting signal, and is broadcast in this frequency position. The dynamic scope and the amplitude of the spectrum (41) of the at least one digital signal must undershoot a respectively predetermined value that is markedly less than the dynamic scope or amplitude of the video carrier of the spectrum (35, 36) of the analog TV broadcasting signal, so that there will be only slight intermodulation and cross modulation with other digital signals or with analog signals of other channels. The spectrum (41) of the at least one digital signal is transmitted, separated from at least one adjacent channel (30, 31) by a protective frequency margin (45). When a plurality of digital signals are transmitted in the at least one channel (31), the frequency ranges of at least two digital signals are transmitted, separated from one another by a protective frequency margin (50).
Owner:NOLA SEMICON
Method and apparatus for locating faults in communications networks
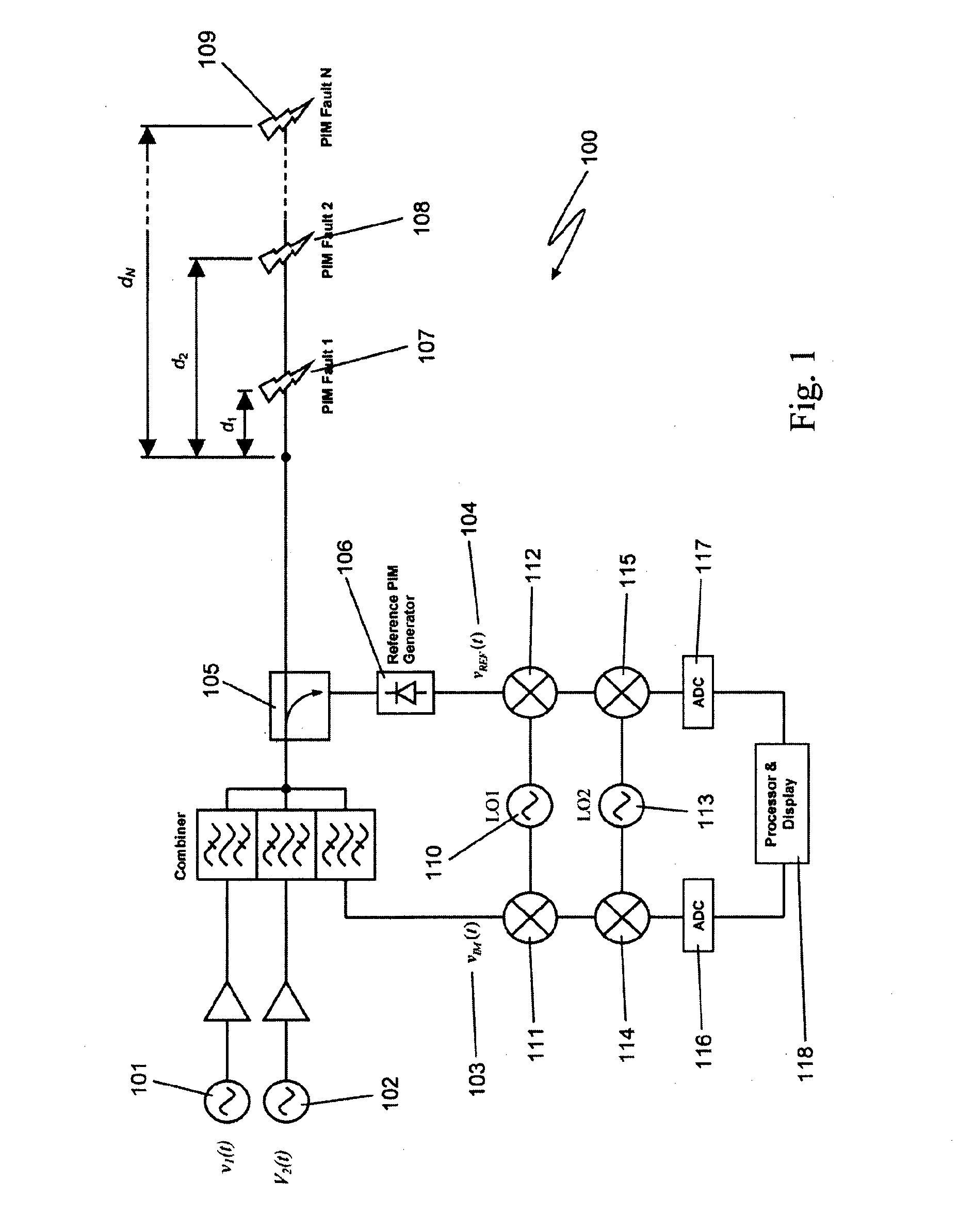
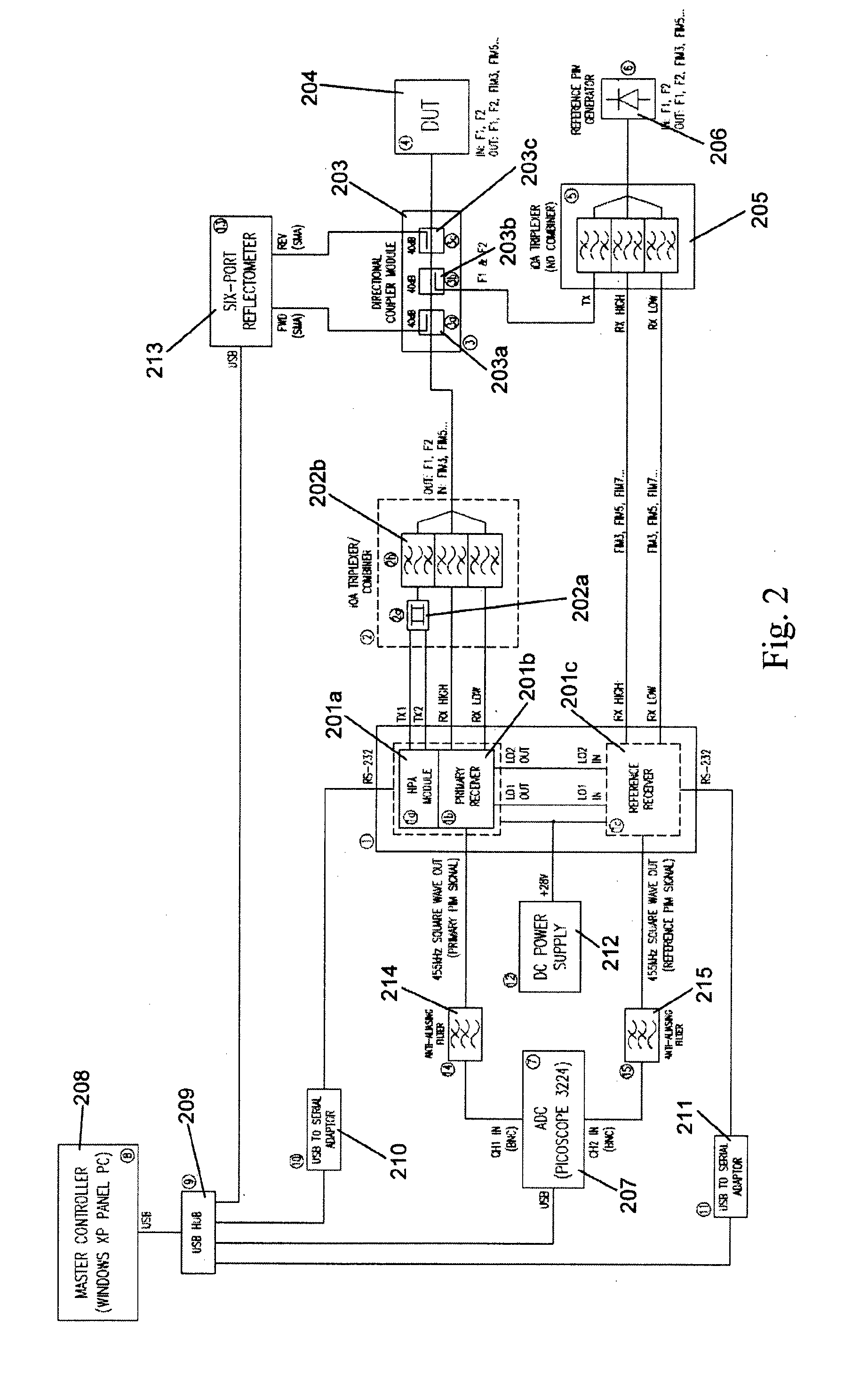
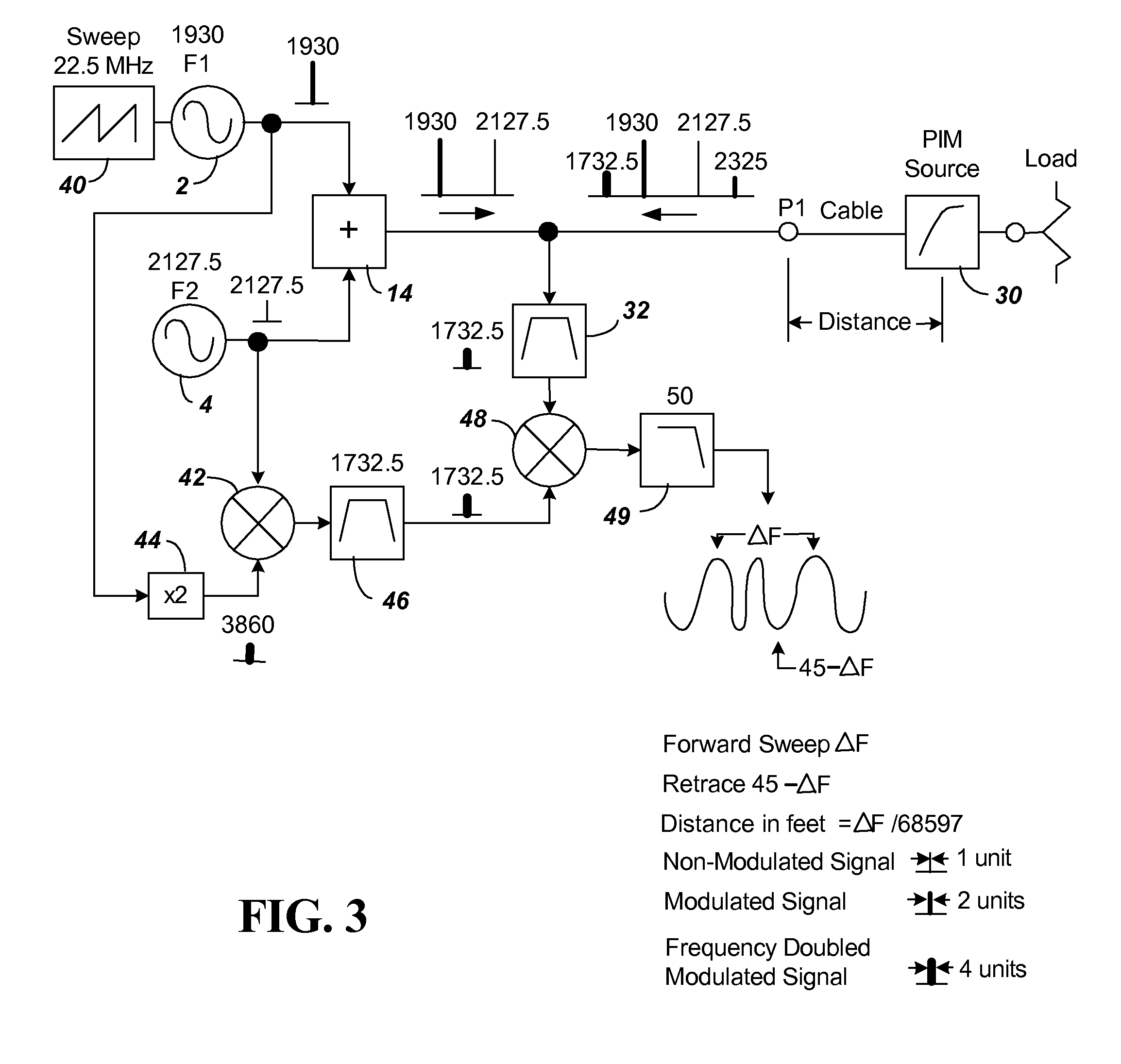
ActiveUS20130182753A1Smoother range profileEasy to identifySpectral/fourier analysisTransmitters monitoringCoaxial cableEngineering
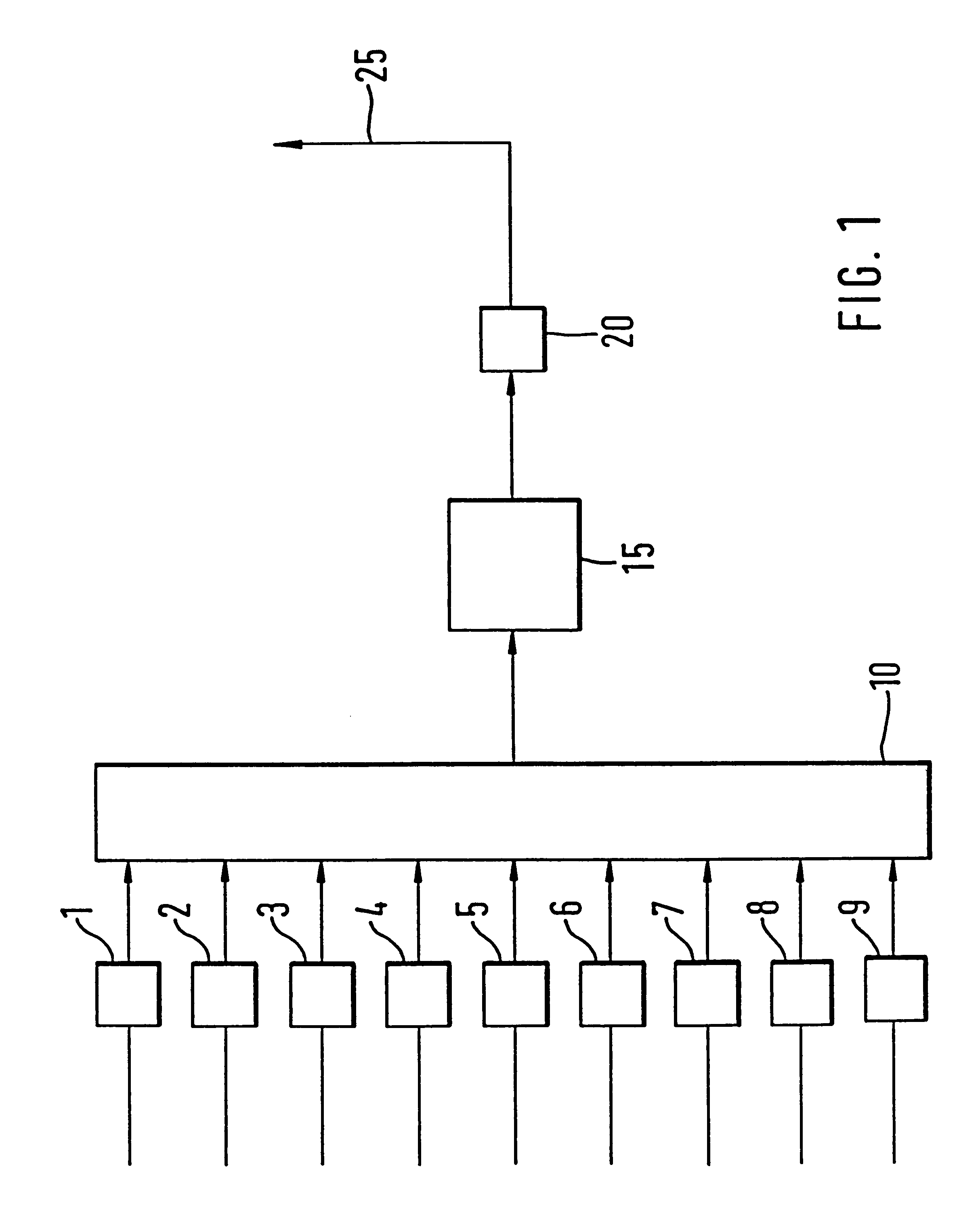
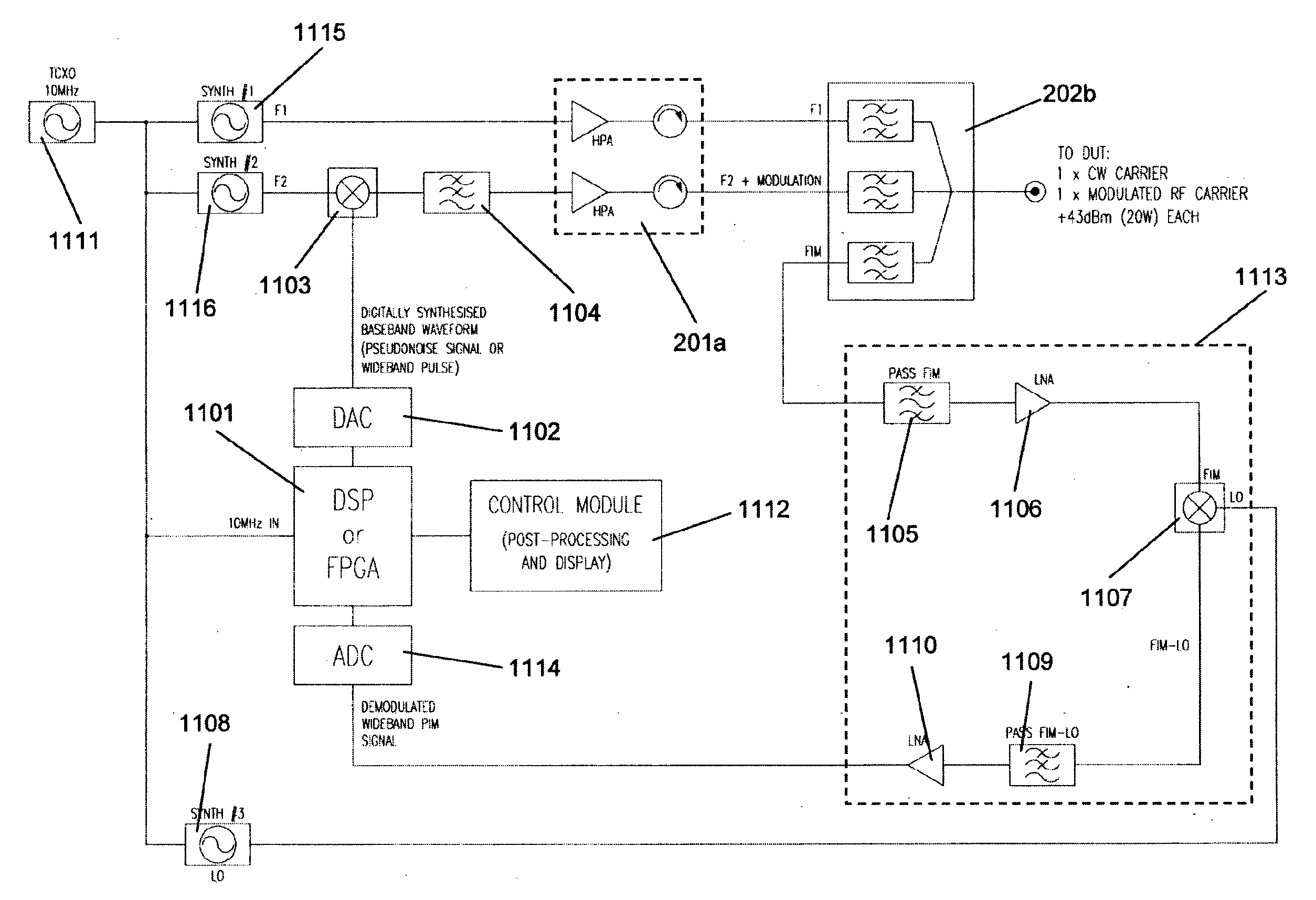
The present invention relates to a device for the location of passive intermodulation faults in a coaxial cable network. The test apparatus (100) according to one embodiment of the present invention utilises a pair of high-power, frequency-synthesised, unmodulated RF carriers v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) are generated inside the HPA module of the apparatus. The power and frequency of v1(t) (101) and v2(t) (102) can be independently set to a range of values, v1(t), v2(t) are combined inside the instrument and then applied to the input of the device under test (DUT). The PIM signals (107,108,109) generated in the DUT are combined to produce the primary PIM signal vIM(t) (103). The apparatus also includes two receivers (110,111,112,113,114,115) for the detection of vIM(t) 103 and vREF(t) (104). These signals are downconverted to 455 kHz. The two 455 kHz waveforms are digitised with a dual- channel A / D converter (116,117) and the amplitude ratio and phase offset between the digitised waveforms are calculated and stored.
Owner:KAELUS
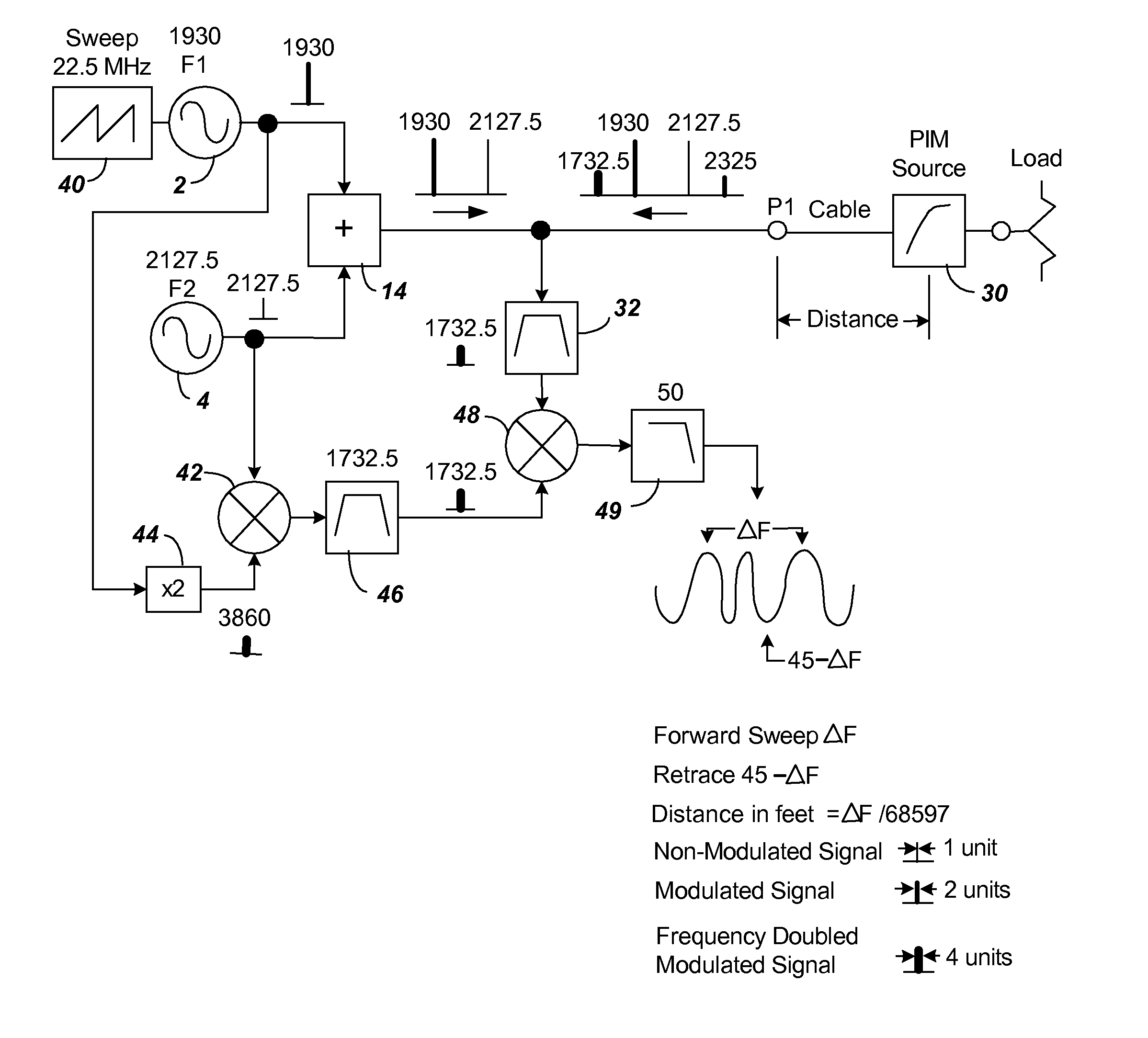
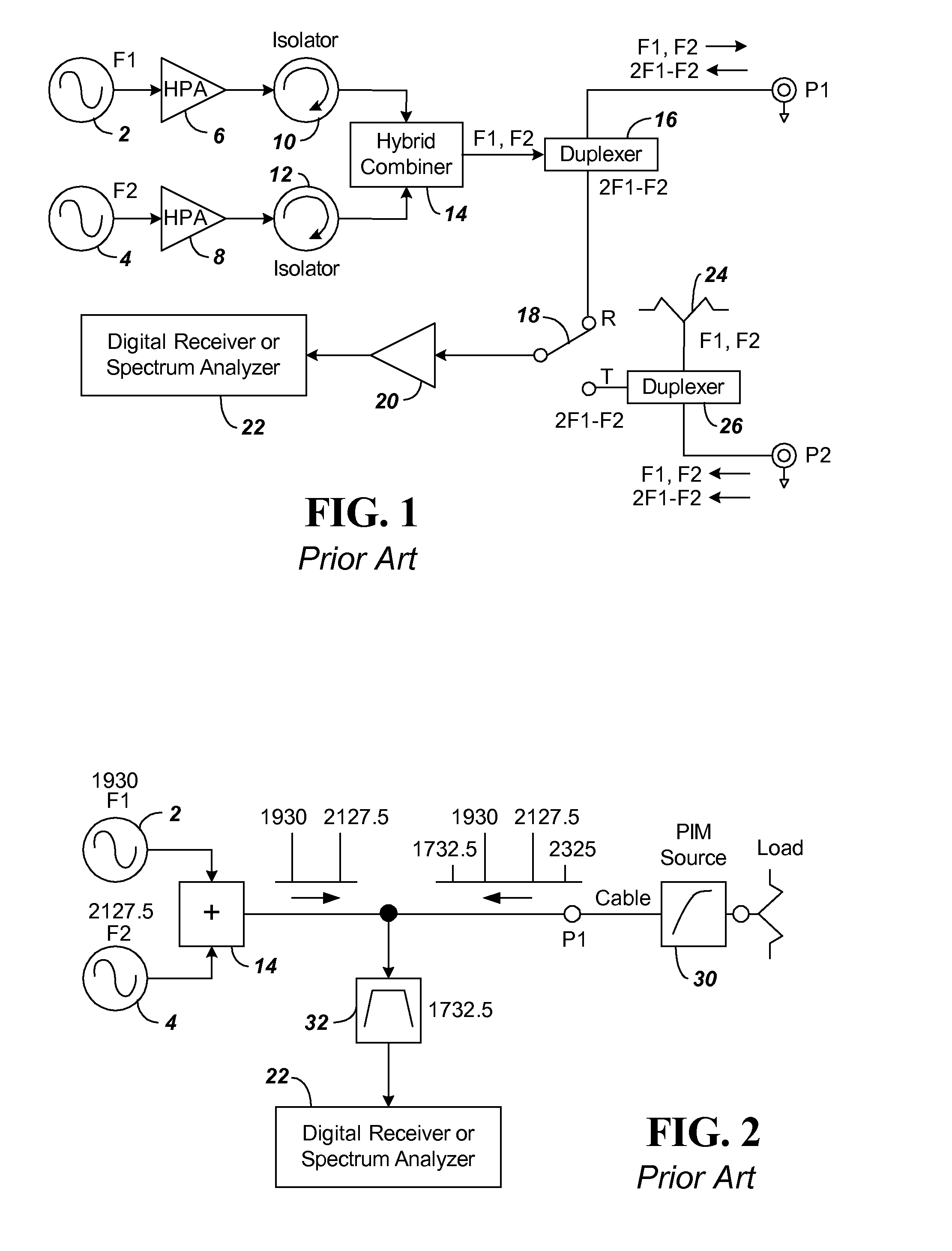
Passive intermodulation (PIM) distance to fault analyzer with selectable harmonic level
ActiveUS20100164504A1Eliminate distractionsSpectral/fourier analysisTransmitters monitoringAudio power amplifierTransceiver
A distance to PIM measurement circuit is made using a device such as an AWS transceiver that has separate transmit and receive bands. With a typical AWS transceiver placed in close proximity to a PCS transceiver, the AWS device will include a band reject filter to eliminate interference from the PCS signals. The PIM measurement circuit includes two frequency sources F1 and F2 that are provided through a combiner for characterization of the PIM circuit. To enable distance determination, an FM measurement is created by using a offset sweep generator attached to one of the two frequency sources. To avoid frequencies blocked by the band reject filter, a desired harmonic of a test PIM harmonic signal is selected outside the band of the band reject filter. In one embodiment, a reference signal is provided by mixing a signal from an ×M multiplier connected to the F1 source with an ×N multiplier signal connected to the F2 source, the mixed output being filtered to select the desired harmonic reference signal to avoid the band reject filter. In another embodiment, a reference signal is created by generating all harmonics of the combined F1 and F2 signal using a series connected amplifier and clipping diodes with a filter again used to select the desired harmonic reference signal to avoid the band reject filter.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
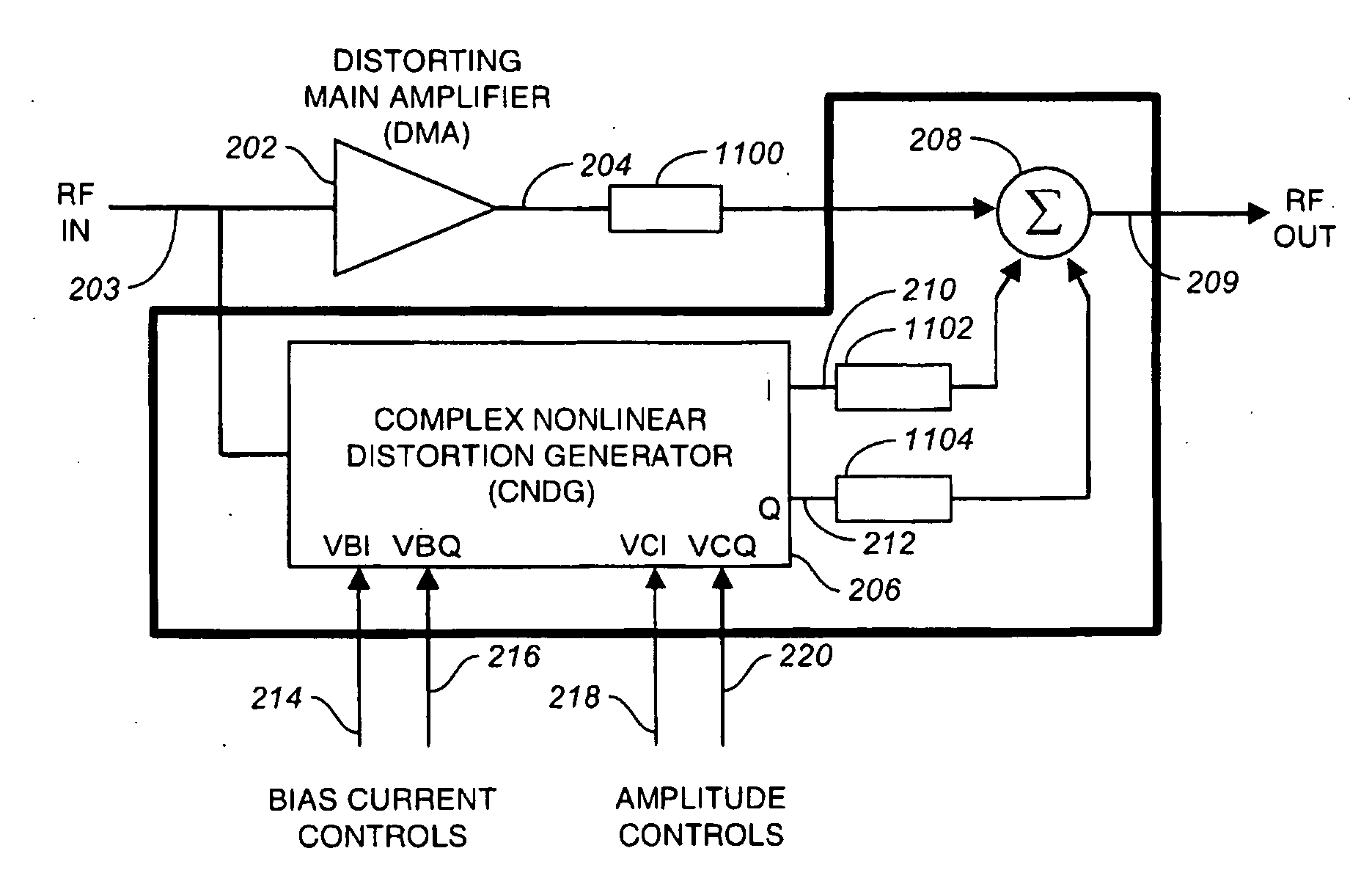
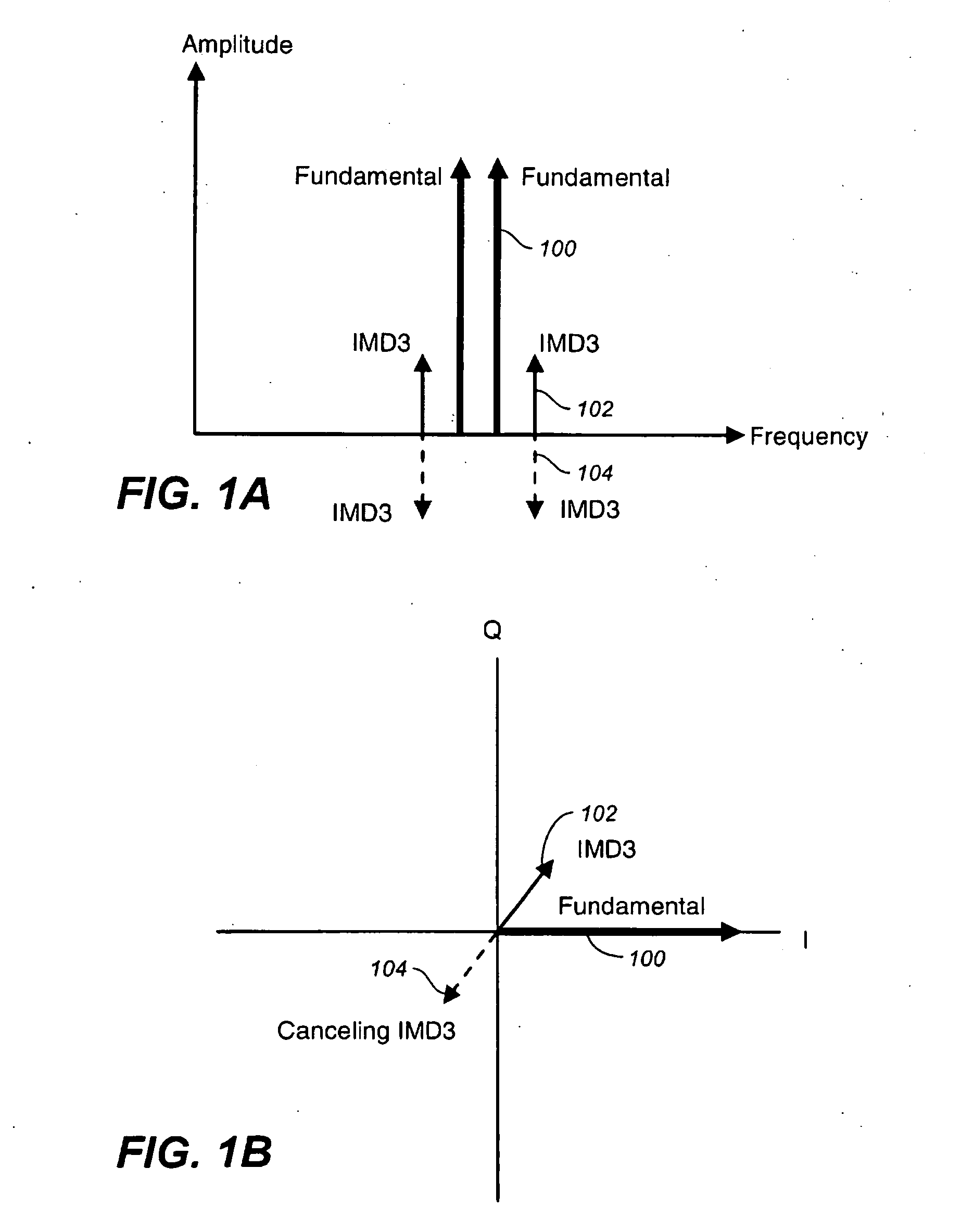
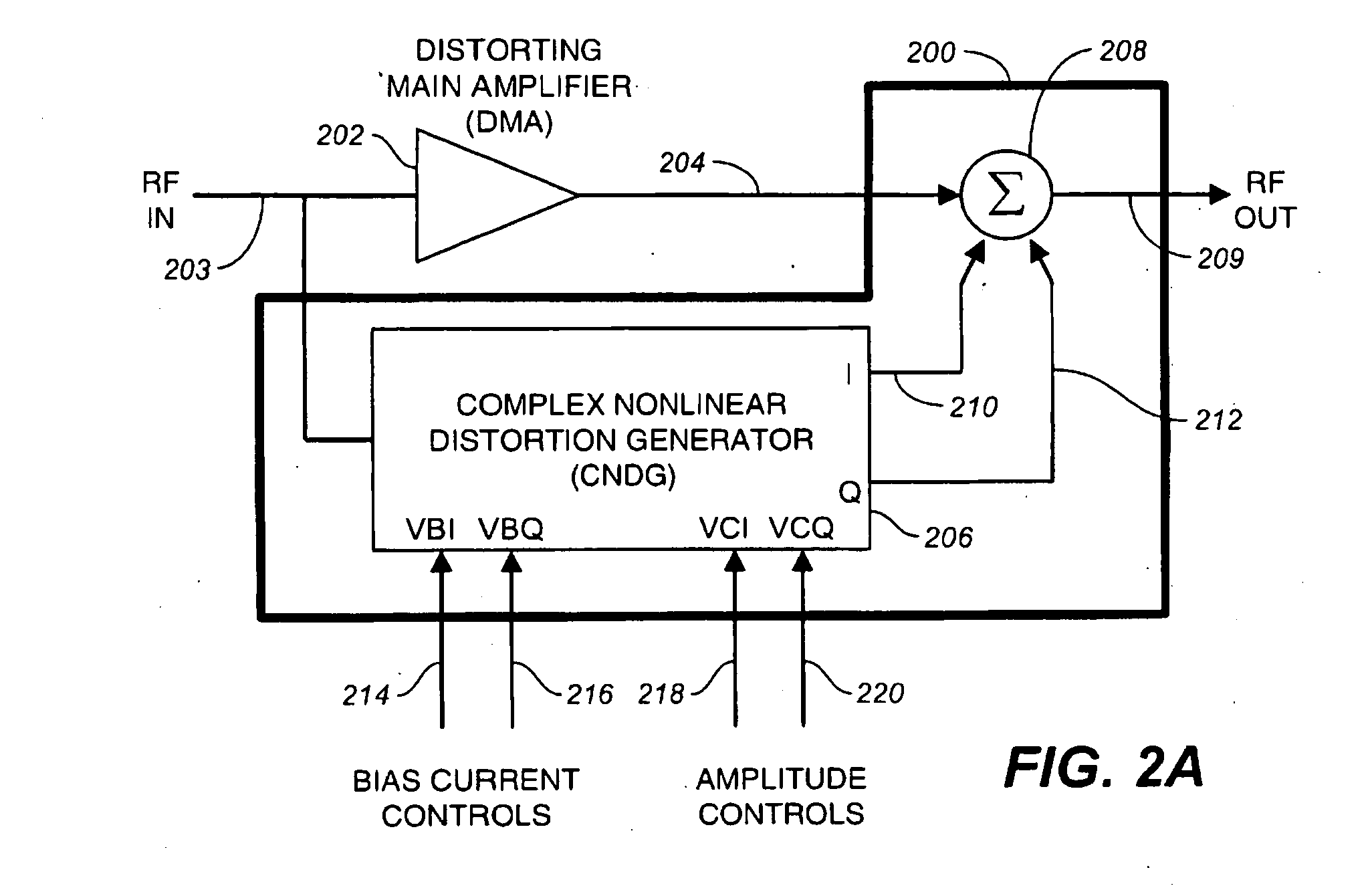
High efficiency RF system linearizer using controlled complex nonlinear distortion generators
InactiveUS20100225389A1Reduces nonlinear intermodulation distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationNonlinear distortionFour quadrants
A linearizer reduces nonlinear intermodulation distortion in radio frequency and microwave systems by first directly generating in-phase and quadrature nonlinear intermodulation products of the system input. Controllable amounts of each phase are then added back into the system such that the vector sum of nonlinear intermodulation products at the output is reduced or eliminated by destructive interference, while the fundamentals are substantially unaffected. The quadrature distorted signals are generated with two lightly-biased and thus overdriven differential pairs having gain-determining degeneration impedances that are in quadrature with each other. The amount of each quadrature phase summed to the output is controlled with electronically tunable four-quadrant variable attenuators. The quadrature phasing enables rapidly convergent tuning to minimize distortion using conventional scalar spectral analysis. The advantages of a linearizer using rectangular vector coordinate system are significant.
Owner:TEETZEL ANDREW M
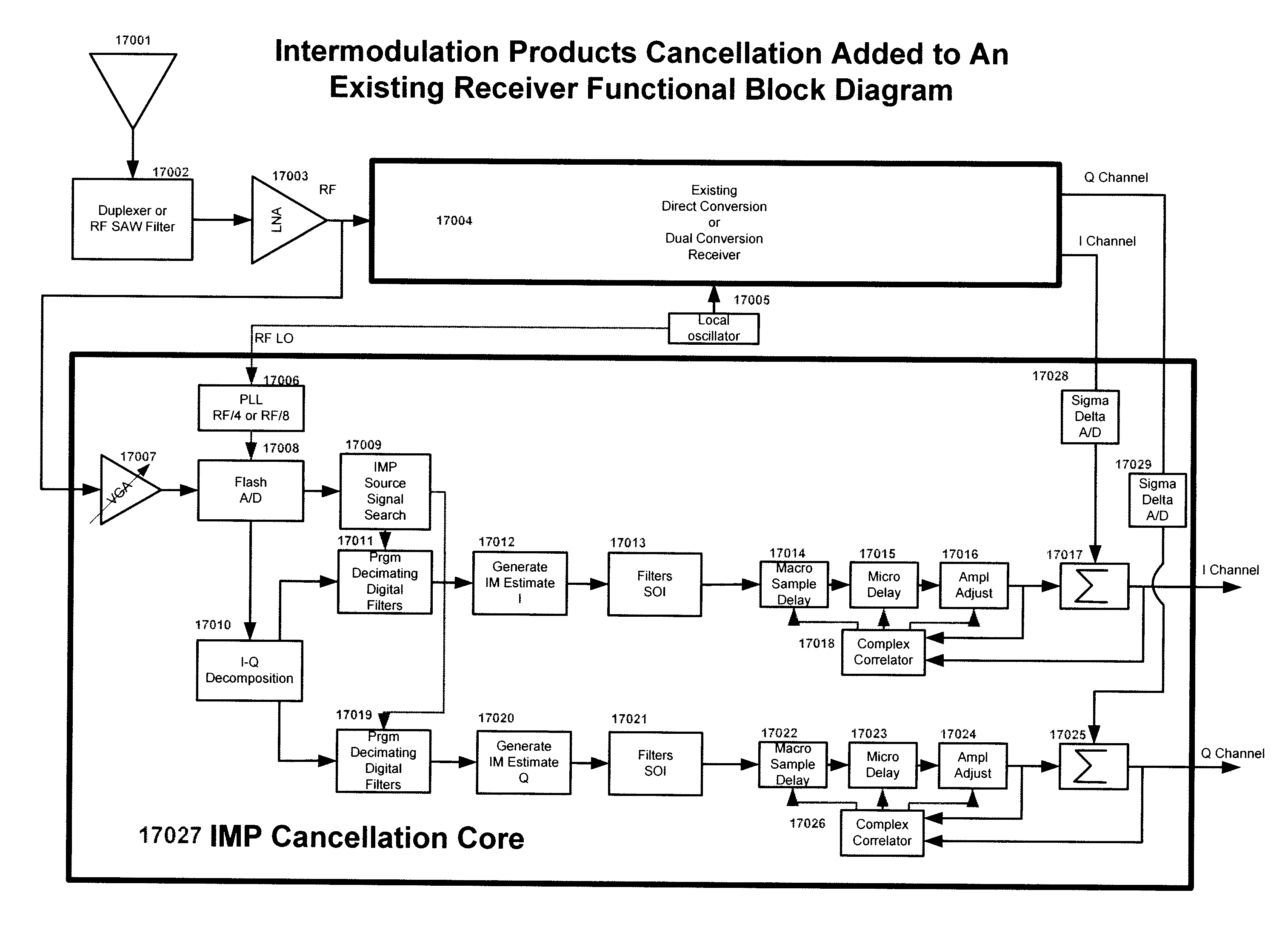
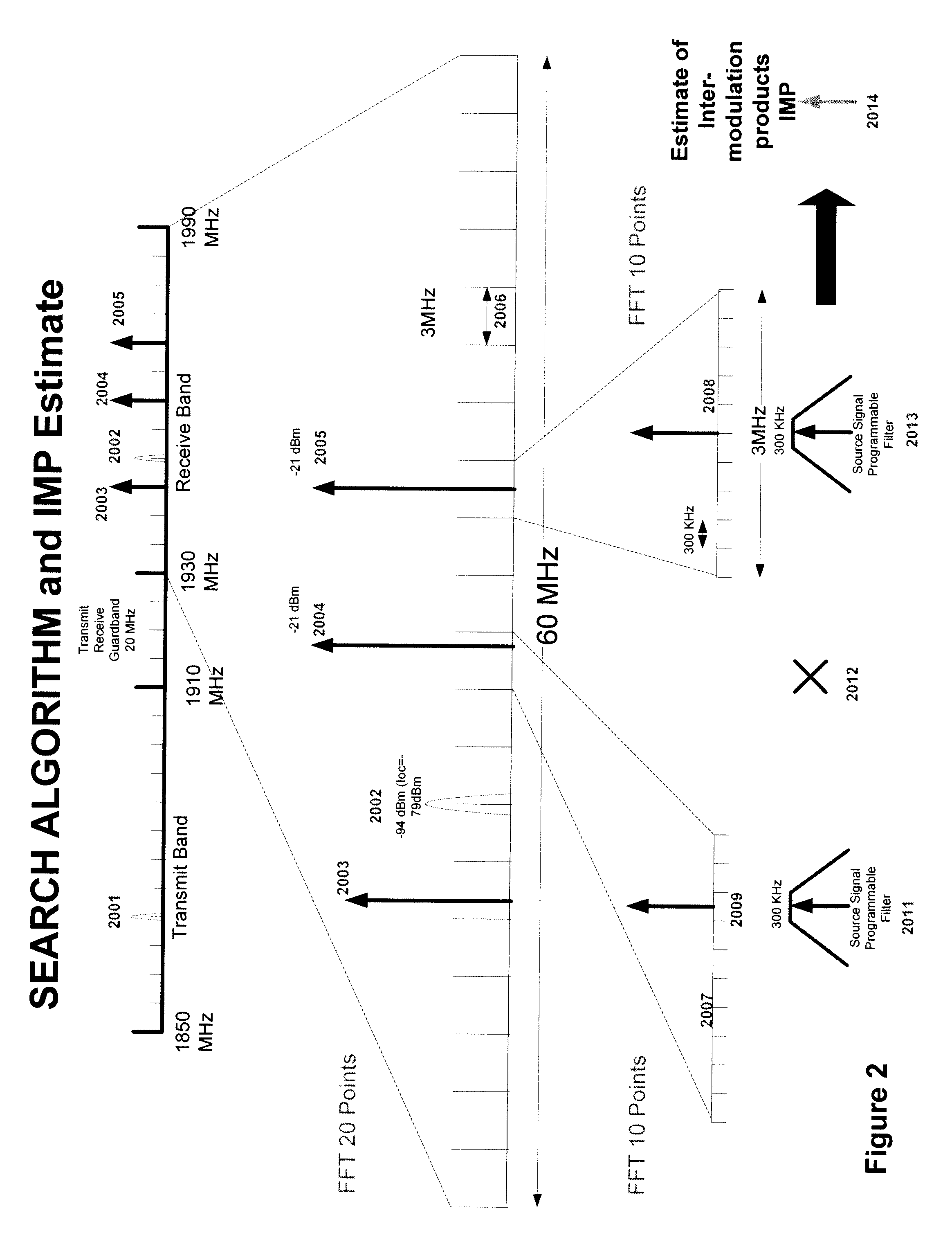
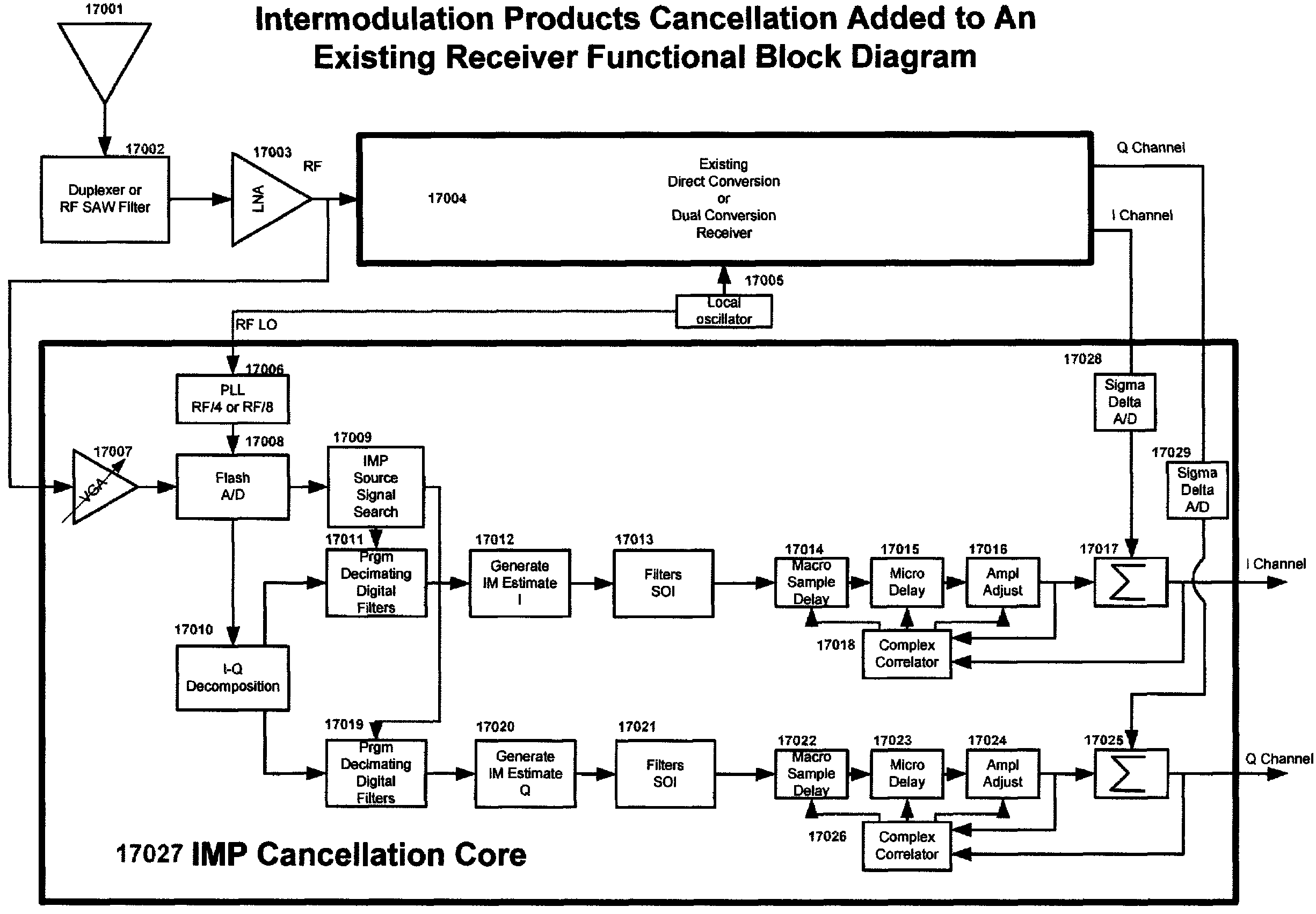
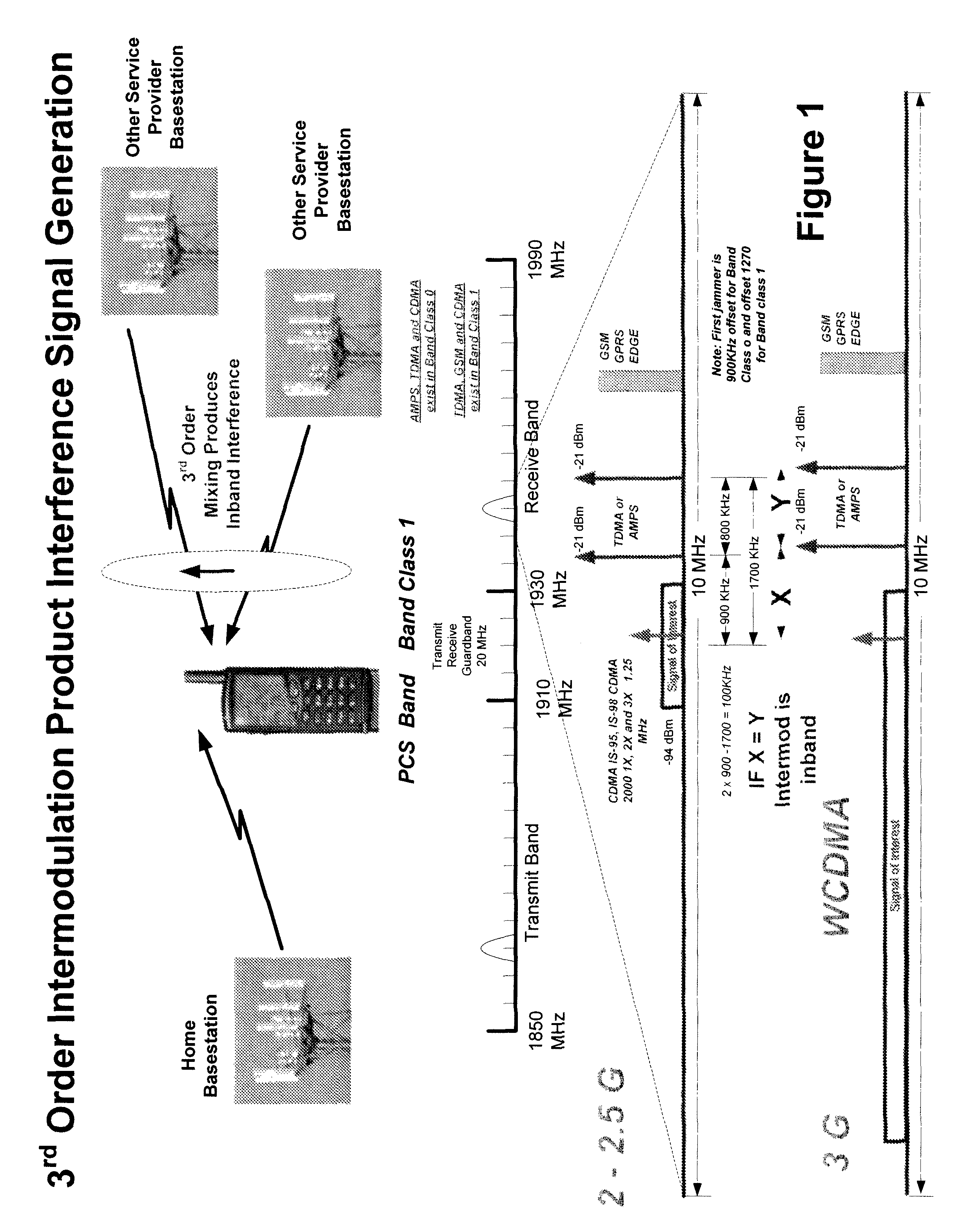
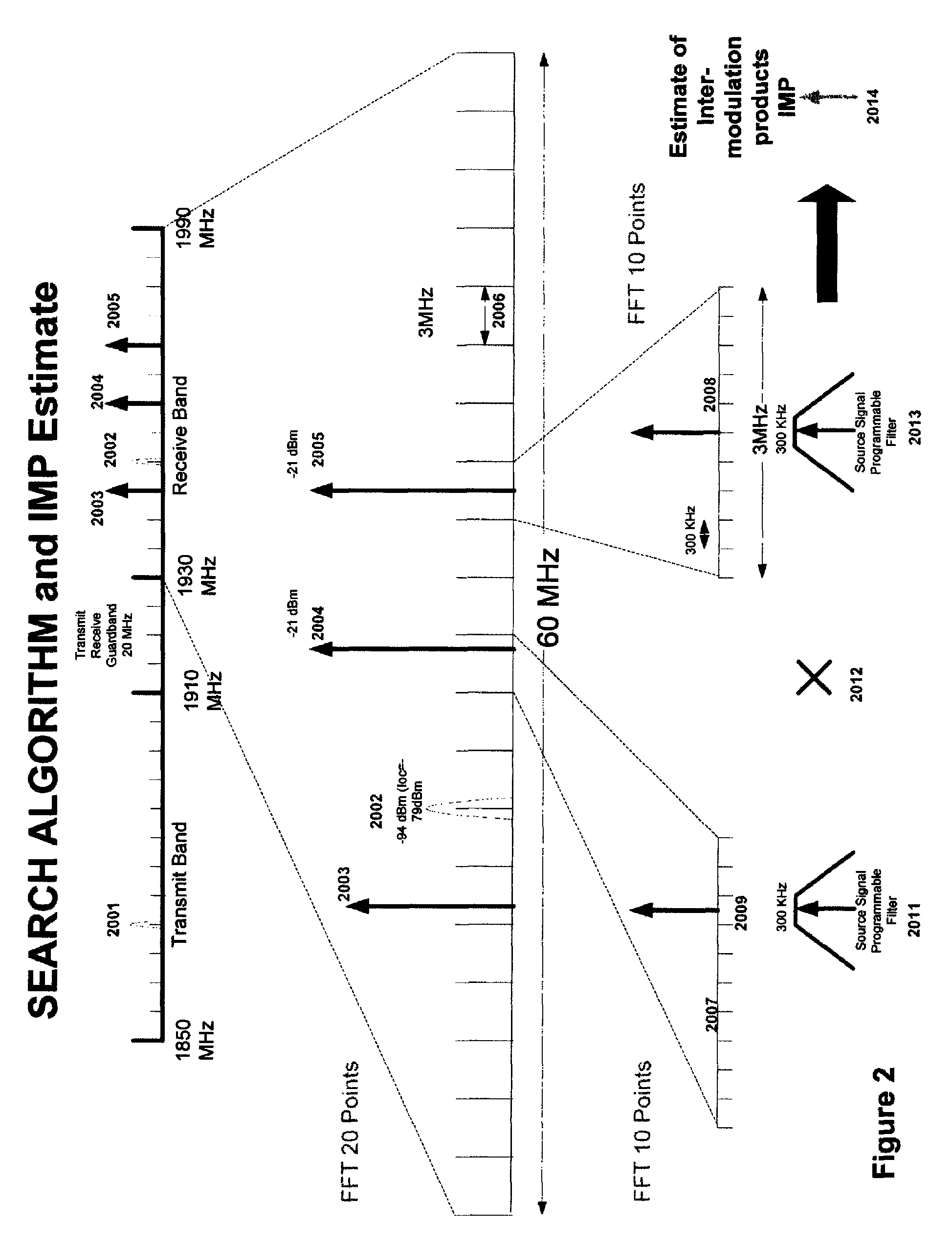
Multi-mode - multi-band direct conversion receiver with complex i and q channel interference mitigation processing for cancellation of intermodulation products
Multi-mode-multi-band direct conversion receiver with complex I and Q channel interference mitigation processing for cancellation of intermodulation products are described. In one embodiment, a method comprising over sampling of the entire receiver passband to acquire the IMP source signals that can generate IMPs within the SOI, using these signals to generate a coherent complex I-Q channel estimates of the interference and (after phase and amplitude adjustment) using these estimates to cancel the SOI inband IMPs in the I and Q channels independently and simultaneously in near real time, generating estimates of 2nd and 3rd order IMP products, adjusting the phase and amplitude of the estimates and using the estimates to cancel the SOI inband IMPs on the I ad Q channels independently and simultaneously in real time or very near real time, sampling of the transmitter feed thru signal and blocking signals and computing the cross modulation products estimate and adjusting the phase and amplitude and using the estimate to cancel the SOI inband cross modulation products energy in real time or near real time in the I and Q channels of the receiver, using the cross modulation cancellation to cancel of the effects of the on chip transmitter feed thru to support building a single transceiver chip with full duplex operation with cancellation being done independently and simultaneously on the I and Q channels of the receiver, and creation of an estimate of the DC offset in the receiver and adjusting the amplitude of the DC offset in a near real time closed loop fashion to cancel the DC offset in the I and Q channels independently and simultaneously and adjusting the rate of update to match system parameters.
Owner:SMITH FRANCIS J
Method and apparatus for detecting and analyzing passive intermodulation interference in a communication system
A system that incorporates aspects of the subject disclosure may perform operations including, for example, receiving, via an antenna, a signal generated by a communication device, detecting passive intermodulation interference in the signal, the interference generated by one or more transmitters unassociated with the communication device, and the interference determined from signal characteristics associated with a signaling protocol used by the one or more transmitters. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for monitoring, detecting, testing, diagnosing and/or mitigating interference in a communication system
ActiveUS20190222329A1Transmitters monitoringLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignaling protocol
A system that incorporates aspects of the subject disclosure may perform operations including, for example, receiving, via an antenna, a signal generated by a communication device, detecting passive intermodulation interference in the signal, the interference generated by one or more transmitters unassociated with the communication device, and the interference determined from signal characteristics associated with a signaling protocol used by the one or more transmitters. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
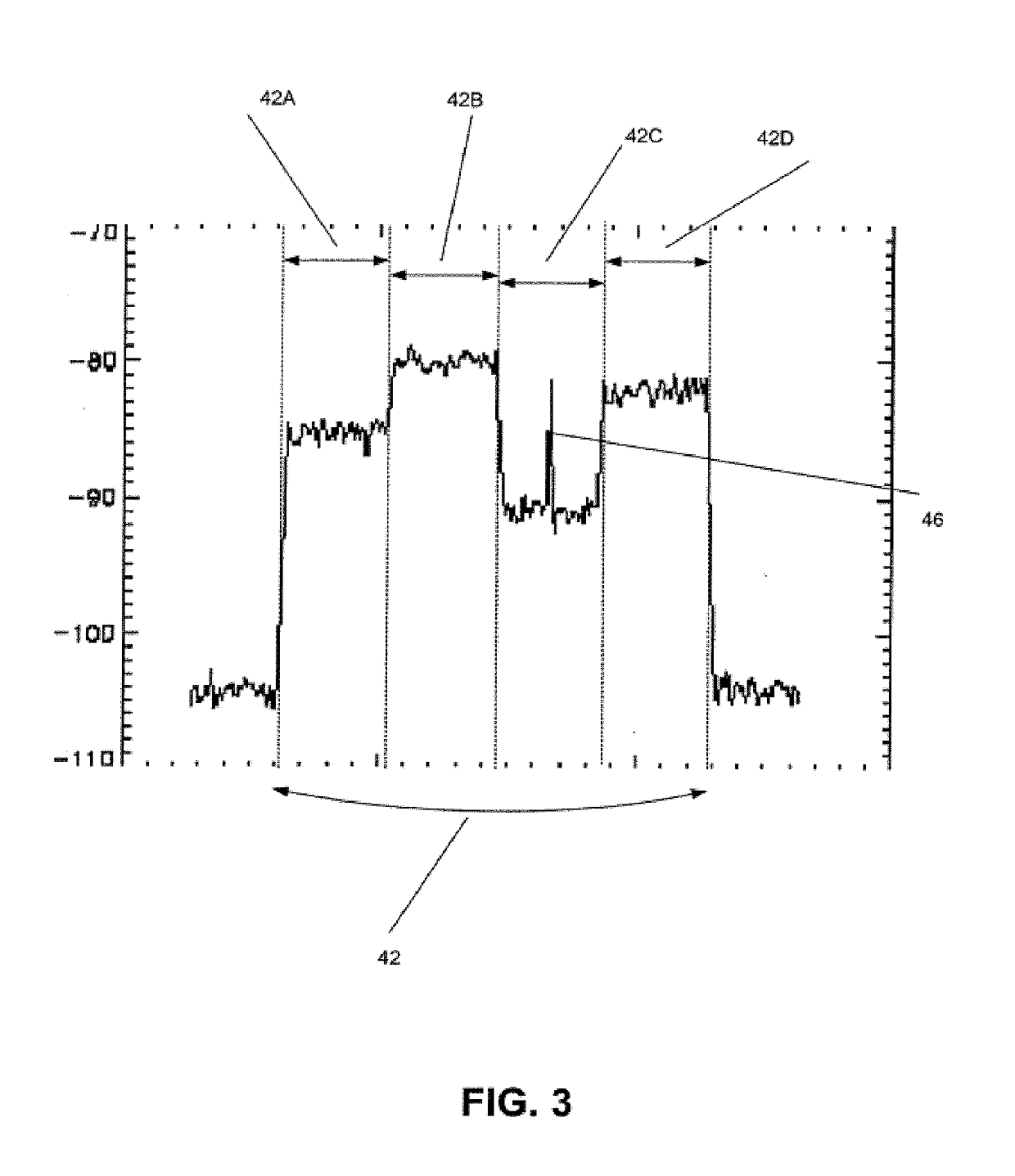
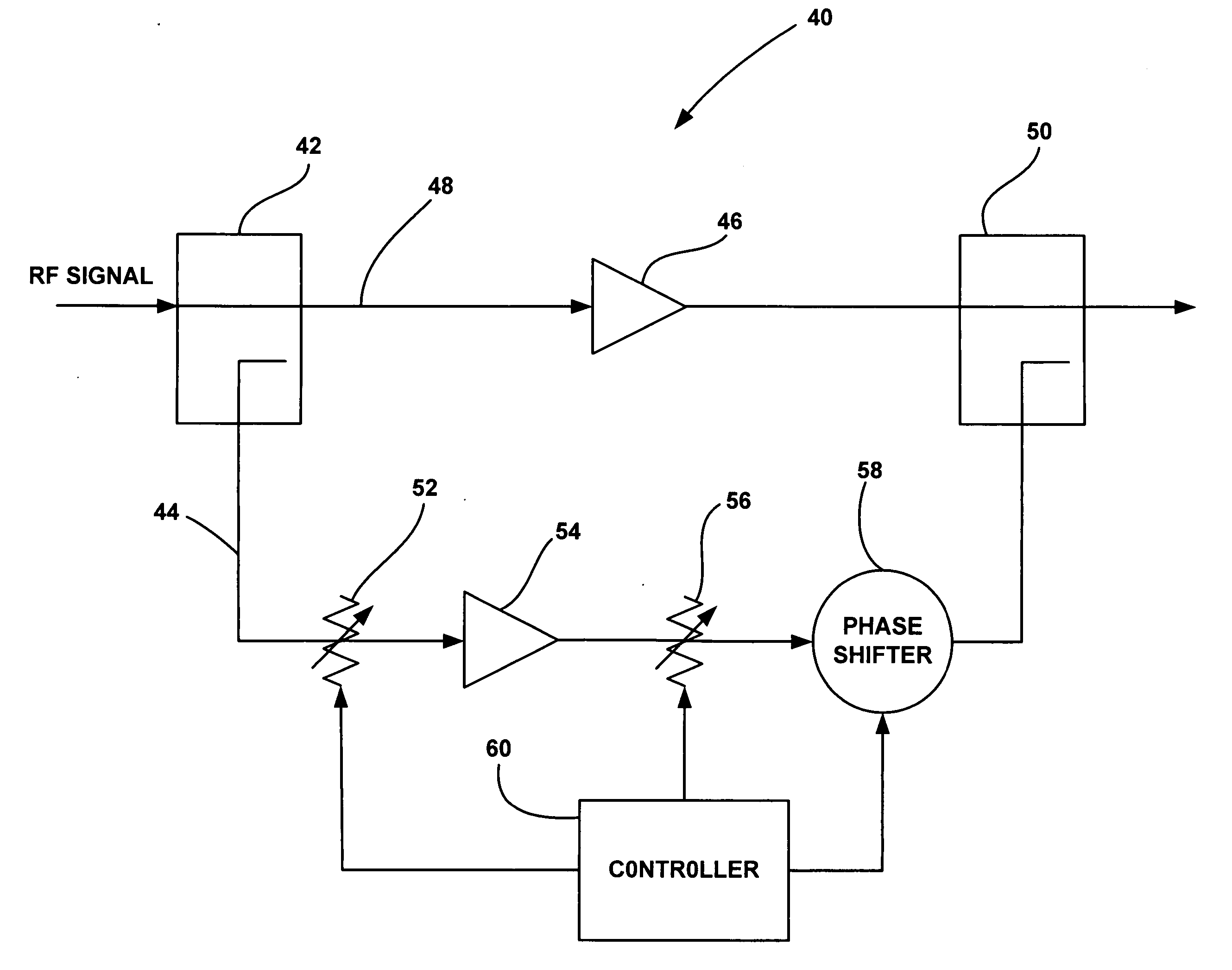
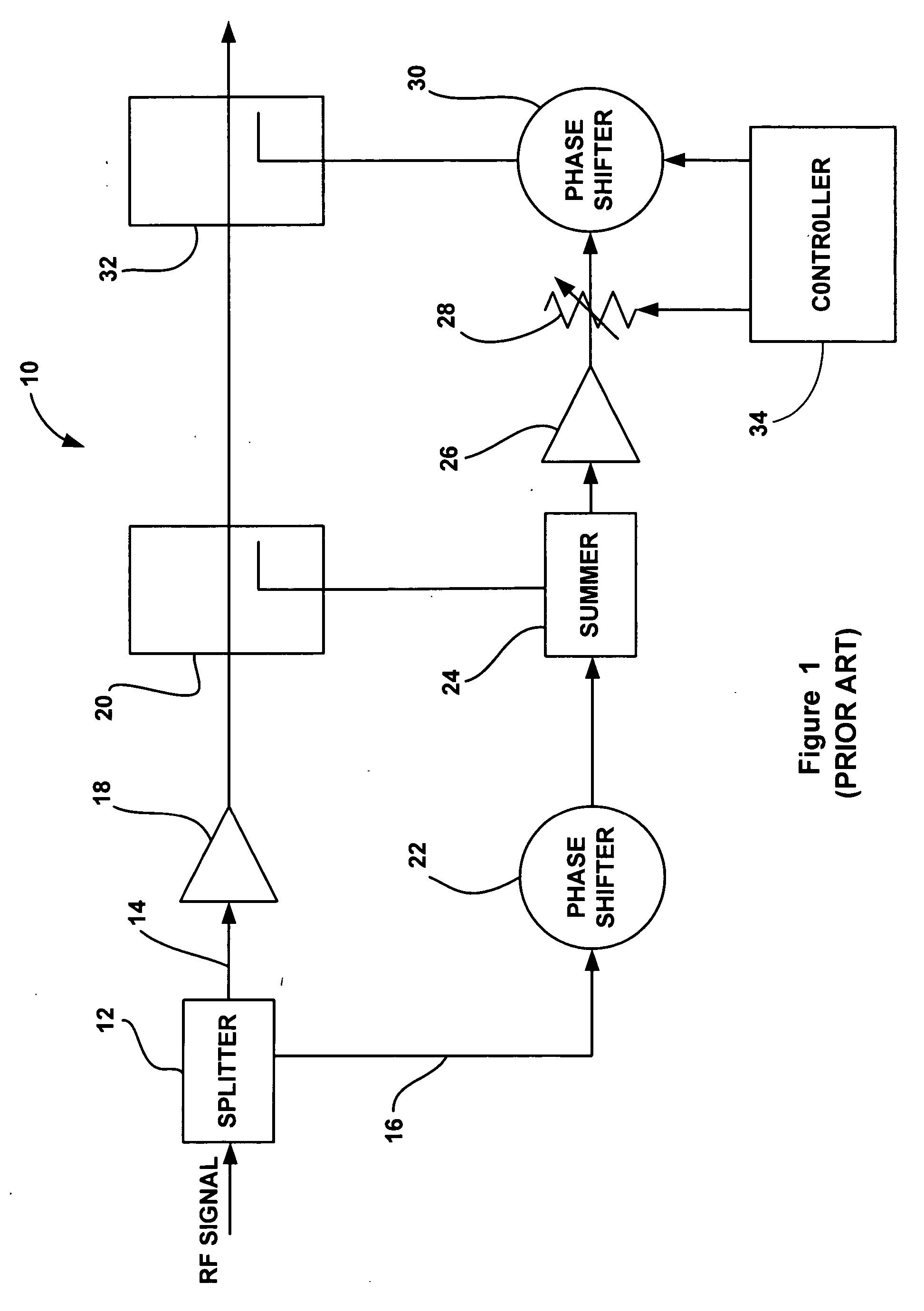
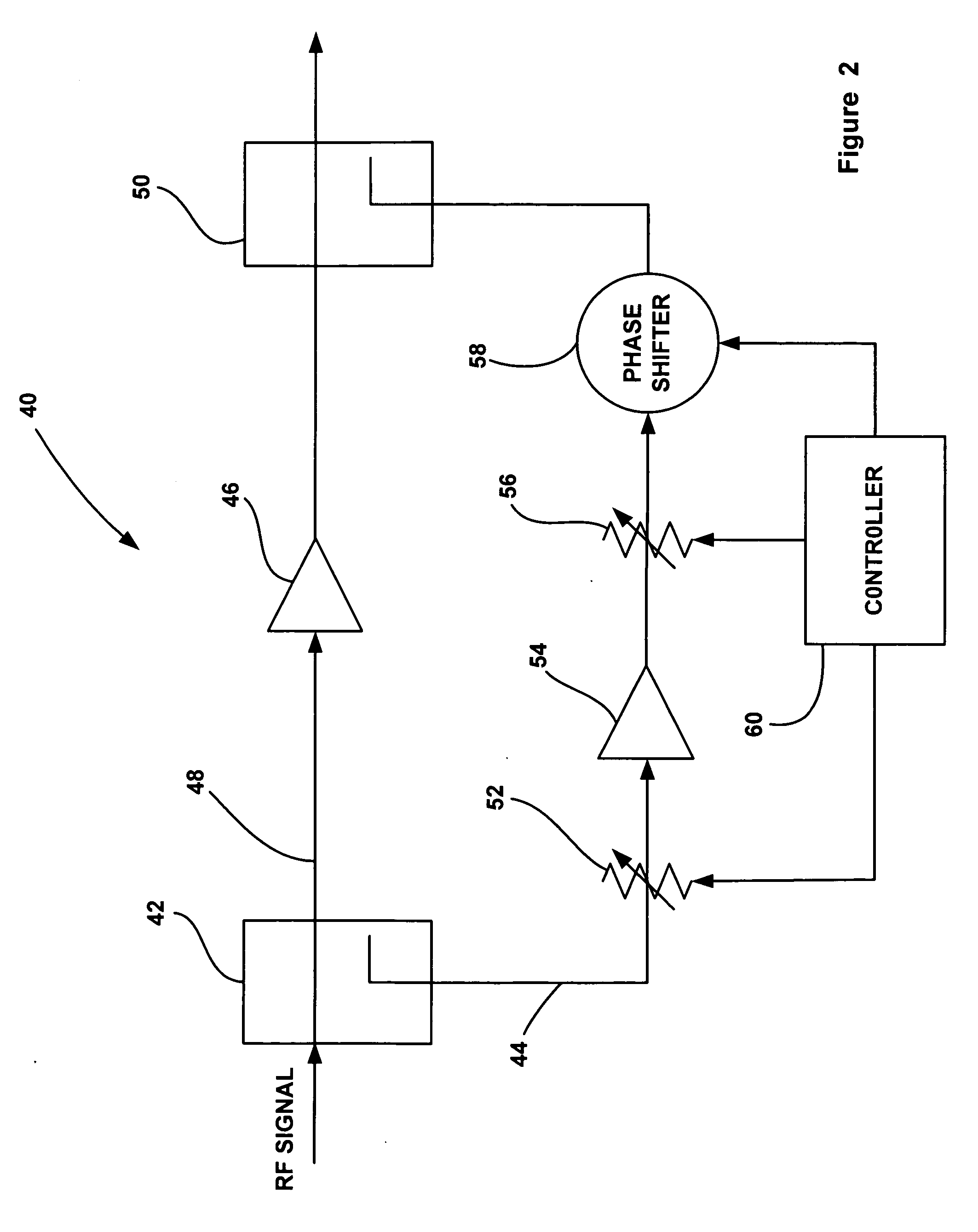
Feedforward spur cancellation approach using low IP amplifier
ActiveUS20060160502A1Resonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier circuit (40) that includes an error correction loop (44) having a lower IP3 error correction amplifier (54) than a main power amplifier (46) in a main signal path (48). A first attenuator (52) in the error loop (44) attenuates the RF signal, and provides more attenuation of intermodulation products in the RF signal and about the same attenuation for a main frequency of the RF signal for each dB of attenuation. The error amplifier (54) amplifies the attenuated RF signal from the first attenuator (52). A second attenuator (56) in the error loop (44) attenuates the RF signal from the error correction amplifier (54). A phase shifter (58) phase shifts the RF signal from the second attenuator (56). A coupler (50) couples the amplified RF signal and the phase shifted RF signal to cancel out intermodulation products in the amplified RF signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and Apparatus for Use in Improving Linearity of MOSFETs Using an Accumulated Charge Sink
ActiveUS20110169550A1Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceMOSFET
A method and apparatus for use in improving the linearity characteristics of MOSFET devices using an accumulated charge sink (ACS) are disclosed. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one exemplary embodiment, a circuit having at least one SOI MOSFET is configured to operate in an accumulated charge regime. An accumulated charge sink, operatively coupled to the body of the SOI MOSFET, eliminates, removes or otherwise controls accumulated charge when the FET is operated in the accumulated charge regime, thereby reducing the nonlinearity of the parasitic off-state source-to-drain capacitance of the SOI MOSFET. In RF switch circuits implemented with the improved SOI MOSFET devices, harmonic and intermodulation distortion is reduced by removing or otherwise controlling the accumulated charge when the SOI MOSFET operates in an accumulated charge regime.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
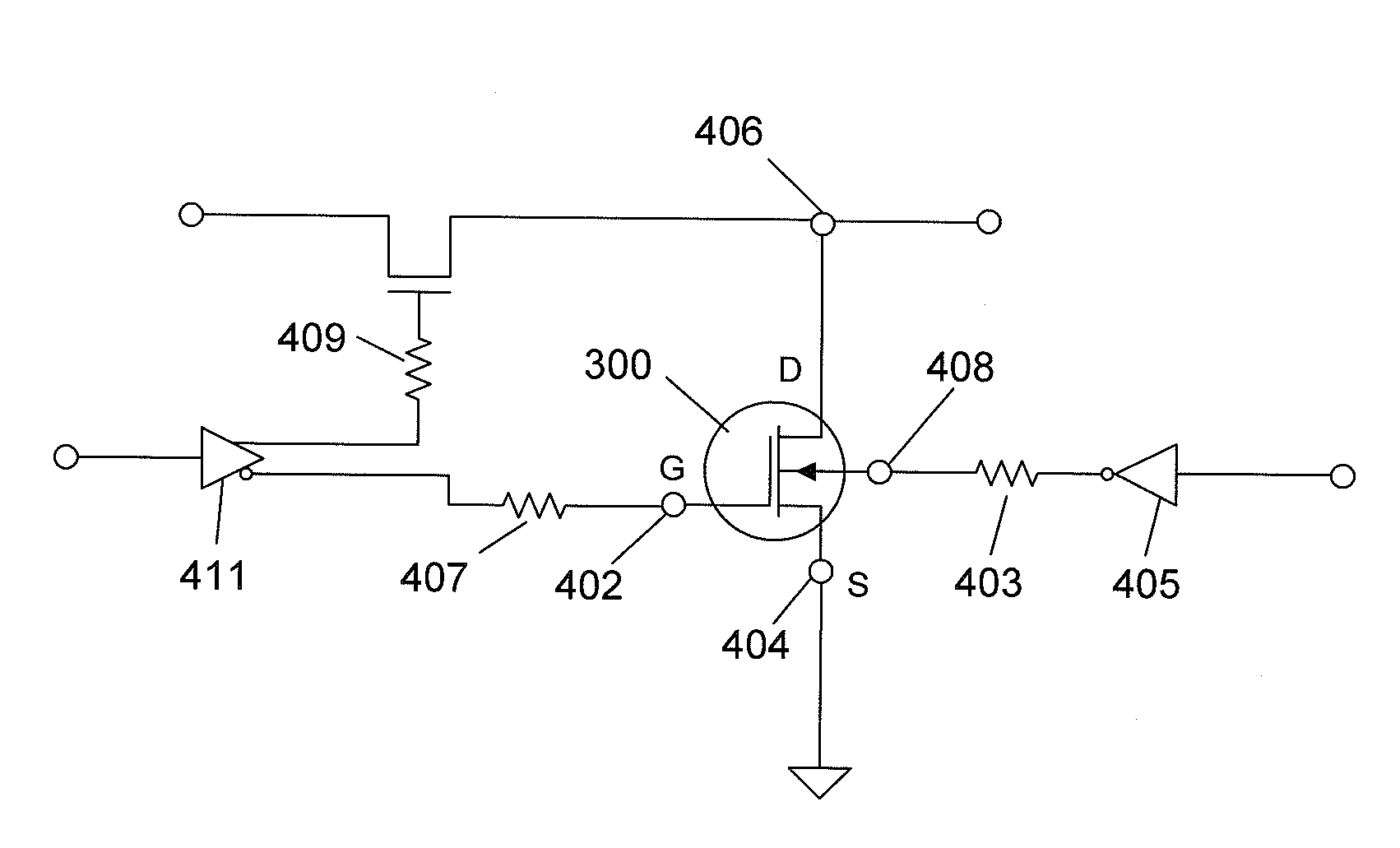
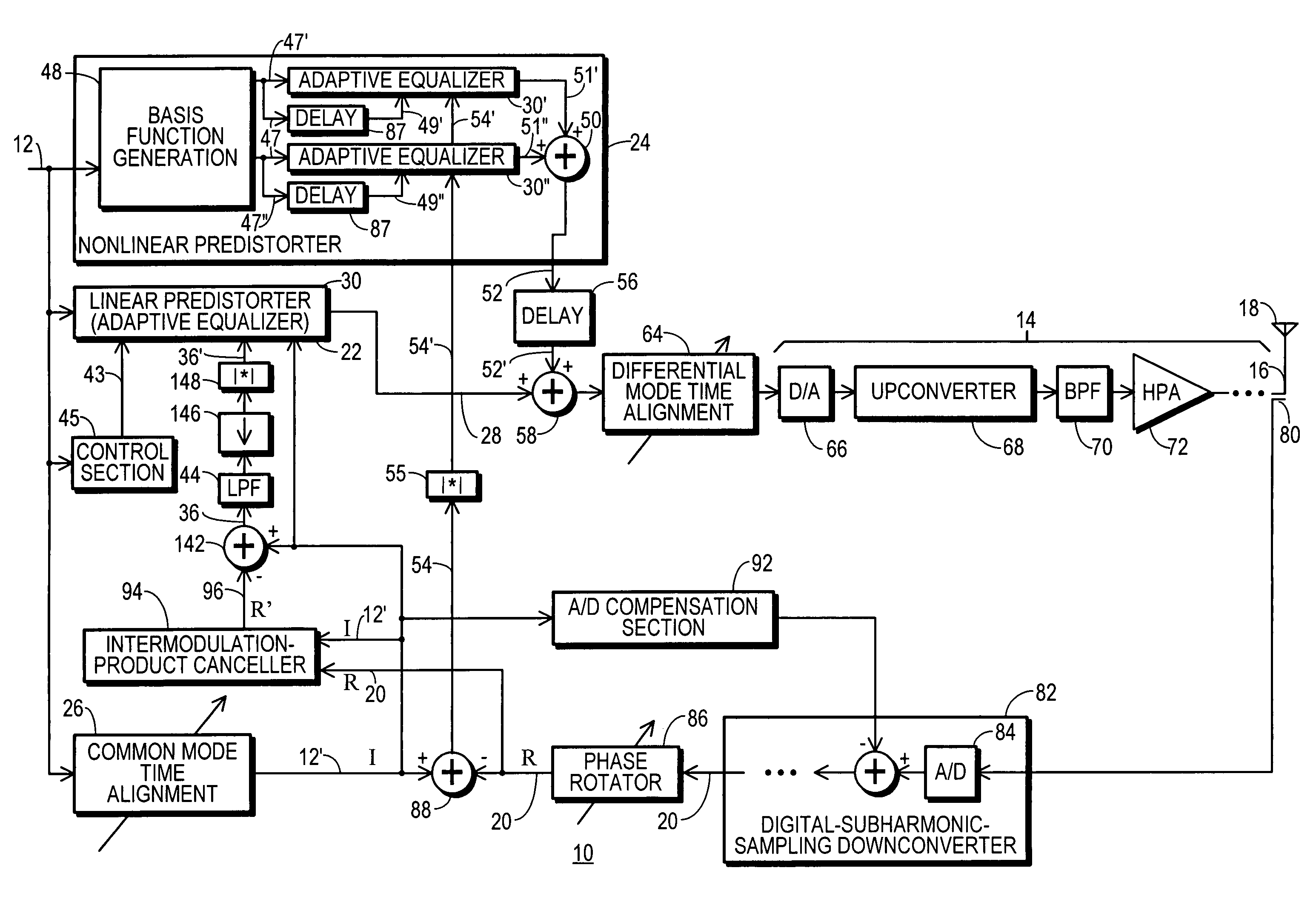
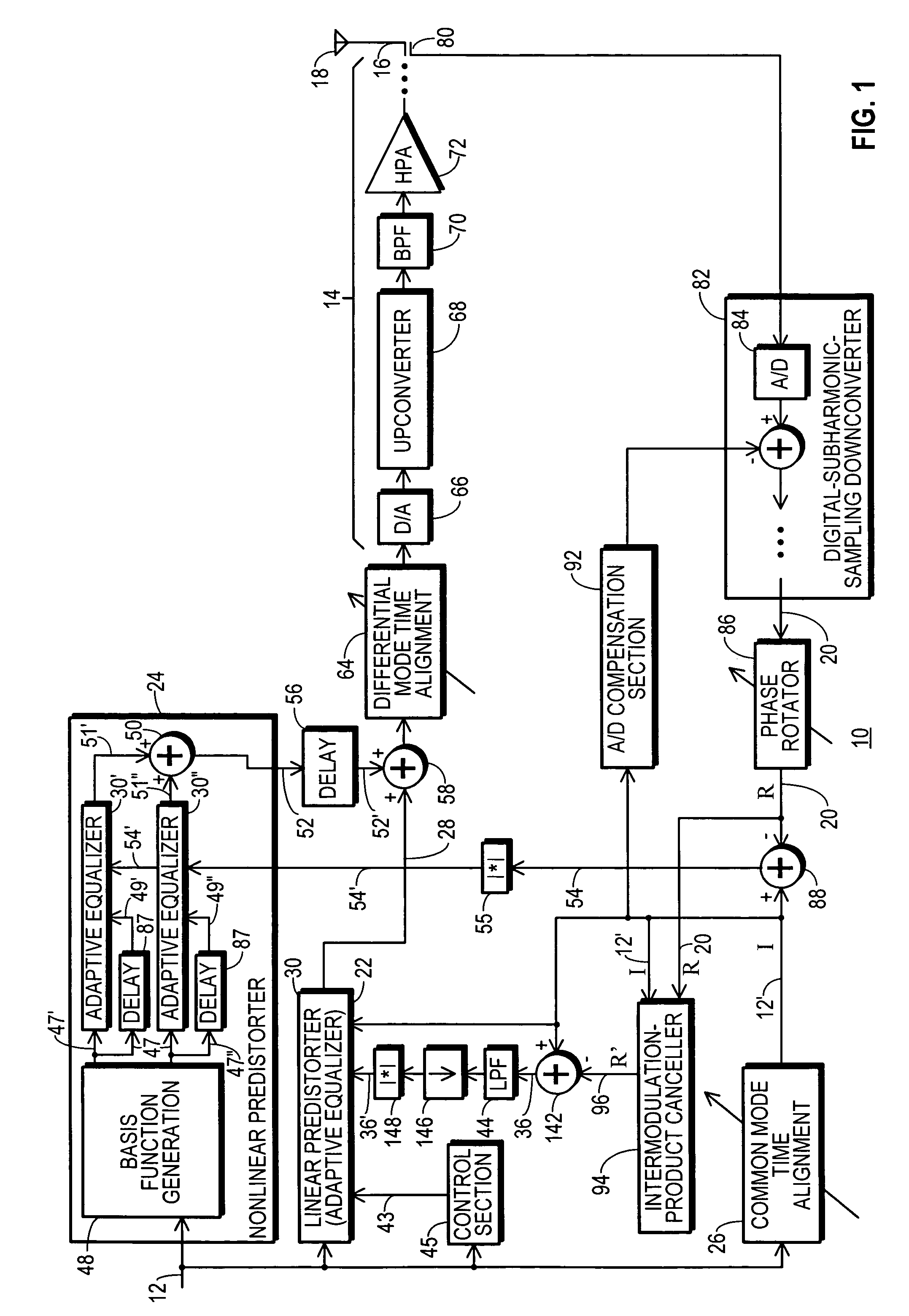
RF transmitter with predistortion and method therefor
InactiveUS20080144709A1Avoid feedbackMultiple-port networksAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSignal cancellationEngineering
An RF transmitter (10) includes a linear predistorter (22) and a nonlinear predistorter (24) which together drive analog transmitter components (14). The linear and nonlinear predistorters (22, 24) are implemented using a collection of adaptive equalizers (30). A feedback signal (20) is developed by downconverting an RF communication signal (16) obtained from the analog components (14). The feedback signal (20) are used in driving tap coefficients (34) for the adaptive equalizers (30′, 30″) in the nonlinear predistorter (24). An intermodulation-product canceller (94) uses signal cancellation to cancel intermodulation products from the feedback signal (20) and generate an intermodulation-neutralized feedback signal (96). The intermodulation-neutralized feedback signal (96) is used along with a modulated convergence factor (43) in driving tap coefficients (34) for the adaptive equalizer (30) in the linear predistorter (22).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Self forming in-the-ear hearing aid
InactiveUS20060098833A1Facilitate communicationEliminating any shearing actionEarplugsDeaf-aid setsEnvironmental soundsAssistive listening device
A soft-solid ear piece is formed to fit the typical human ear canal and will self form to fill the ear cavity by having an internal structure, endoskeleton, or bladder to expand to precisely fit the ear piece securely and comfortably in the ear canal. This self forming ear piece will enable ready-ware and custom molded hearing aids, hearing protectors, audio ear pieces, cell phone ear pieces and assistive listening devices to fit comfortably, securely, and free of acoustic feedback in the external ear canal. It creates an acoustic seal to optimally reduce peripheral leakage and intermodulation distortion delivering excellent acoustic performance while keeping environmental sounds blocked out.
Owner:JUNEAU ROGER P +4
Method and apparatus for monitoring, detecting, testing, diagnosing and/or mitigating interference in a communication system
ActiveUS20190052381A1Transmitters monitoringLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignaling protocol
A system that incorporates aspects of the subject disclosure may perform operations including, for example, receiving, via an antenna, a signal generated by a communication device, detecting passive intermodulation interference in the signal, the interference generated by one or more transmitters unassociated with the communication device, and the interference determined from signal characteristics associated with a signaling protocol used by the one or more transmitters. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
Multi-mode—multi-band direct conversion receiver with complex I and Q channel interference mitigation processing for cancellation of intermodulation products
Owner:SMITH FRANCIS J
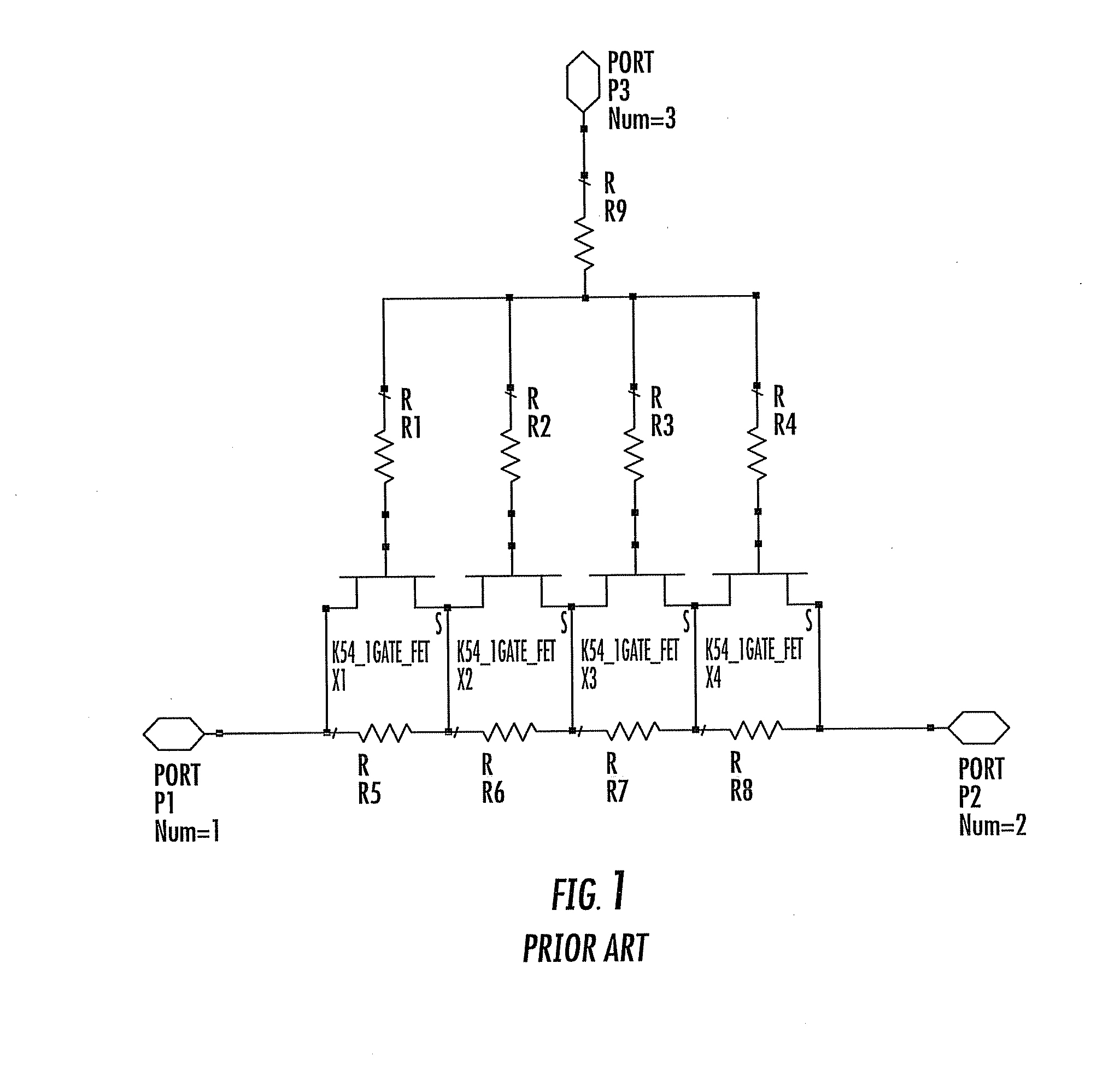
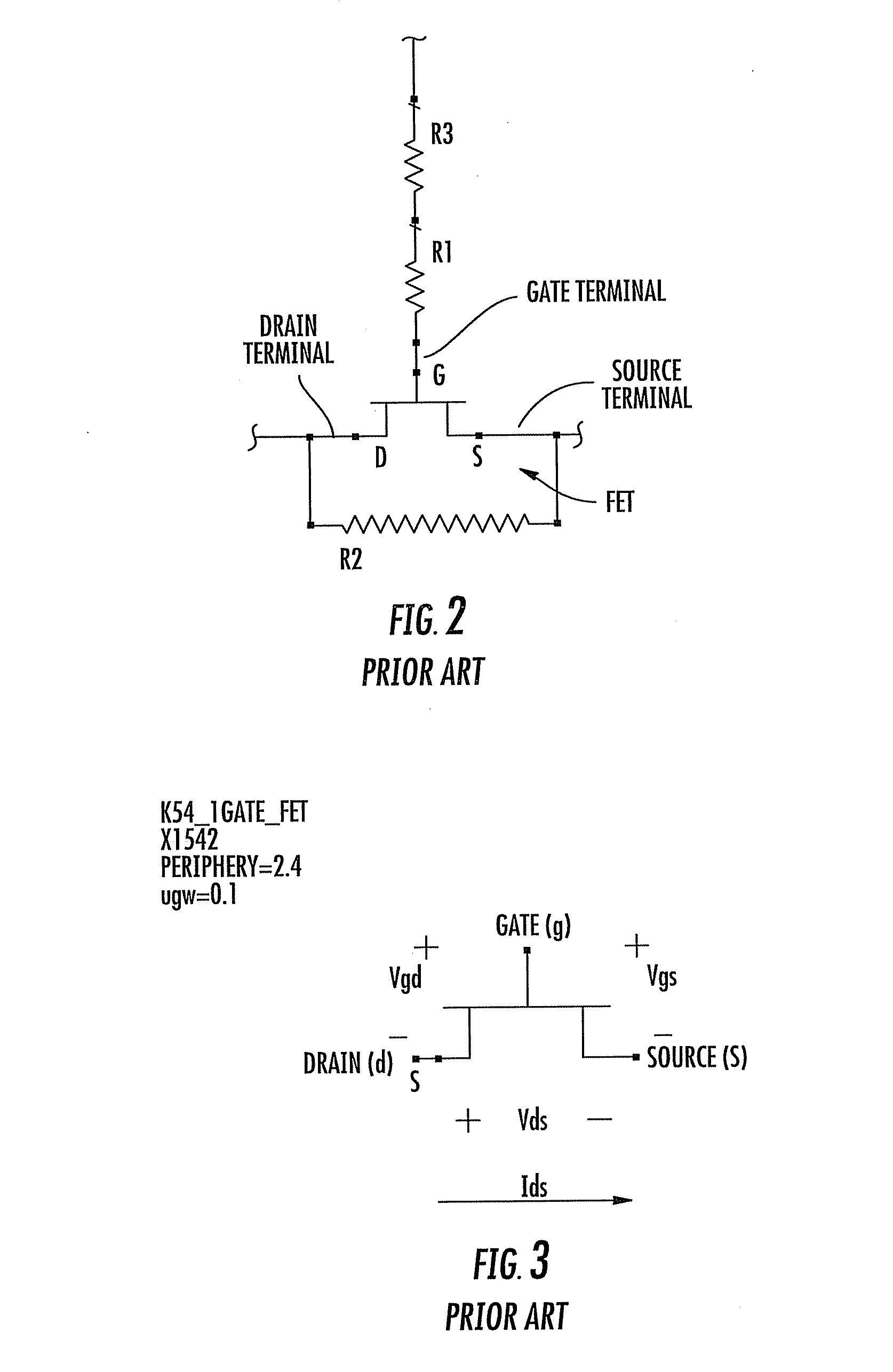
Radio frequency switch with improved intermodulation distortion through use of feed forward capacitor
A radio frequency (RF) switch using a field effect transistor has 2nd order intermodulation distortion improved through use of a feed forward capacitor electrically connected between the gate and a voltage coupler connected between the source and drain of the FET. With a control voltage provided at the gate through a gate feed resistor for operation of the FET, the feed forward capacitor feeds an RF voltage from the drain terminal and the source terminal to the gate terminal through the gate feed resistor.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Dual-frequency coaxial earphones with shared magnet
ActiveUS20100046783A1Minimized dimensionSolve the real problemTransducers for sound channels pluralityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsDual frequencyEngineering
A dual-frequency coaxial earphone has a shared magnet, which is interposed between a top board of a outer yoke and an outer disk of a inner yoke, wherein the outer yoke and the inner yoke each has a different polarity. A low-frequency voice coil of a low-frequency speaker part extends axially into and between an annular wall of the outer yoke and the outer disk of the inner yoke. An inner sleeve of the inner yoke extends into a first central opening of the outer yoke. Therefore, a high frequency of the high-frequency speaker part can pass through the inner sleeve so as to energize a central diaphragm of the low-frequency speaker part and to form a same phase as, and to output frequency synchronously with, the low-frequency speaker part. As such, the problem of intermodulation of distortion for the high and low acoustic frequencies can be solved, and that dimension of the earphone can be minimized.
Owner:JETVOX ACOUSTIC
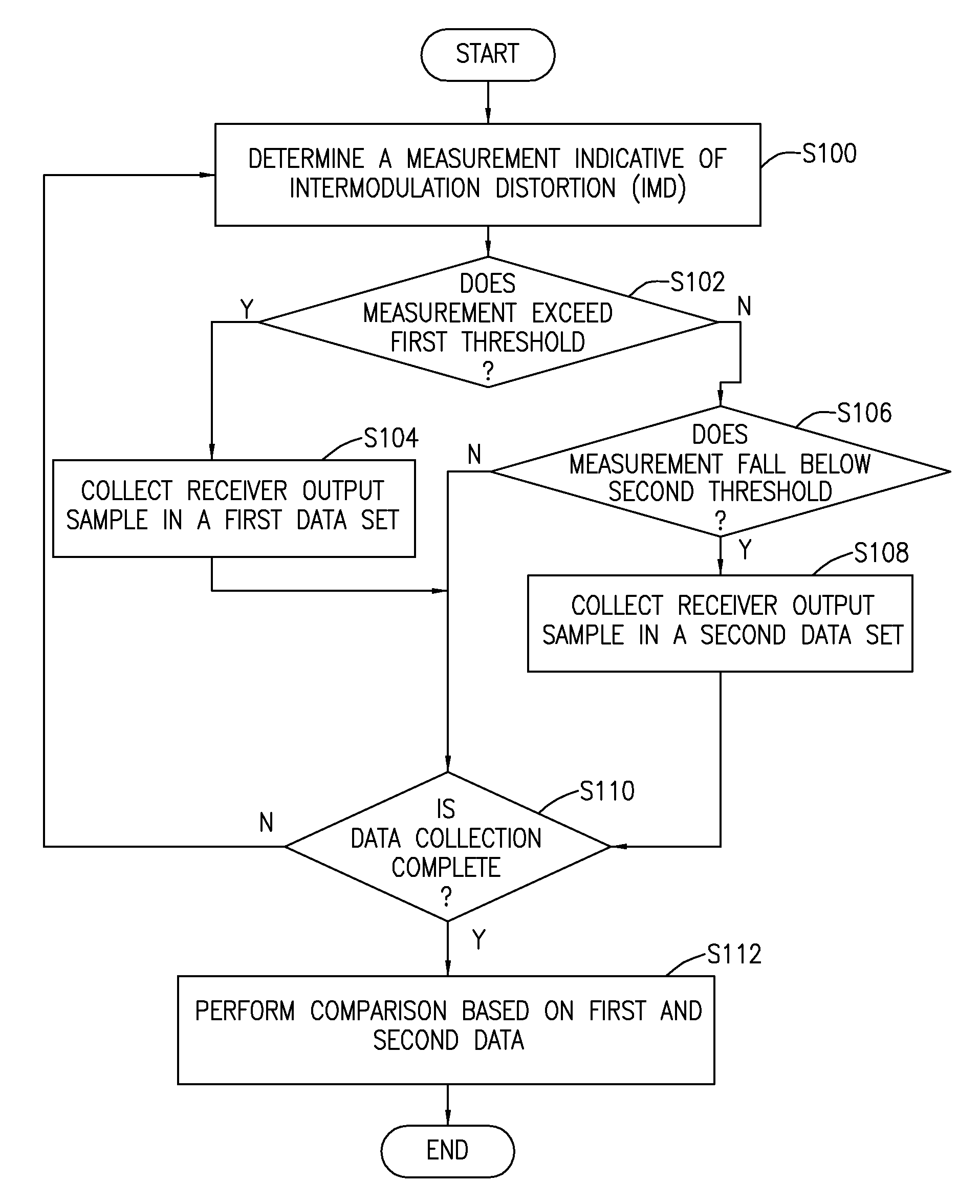
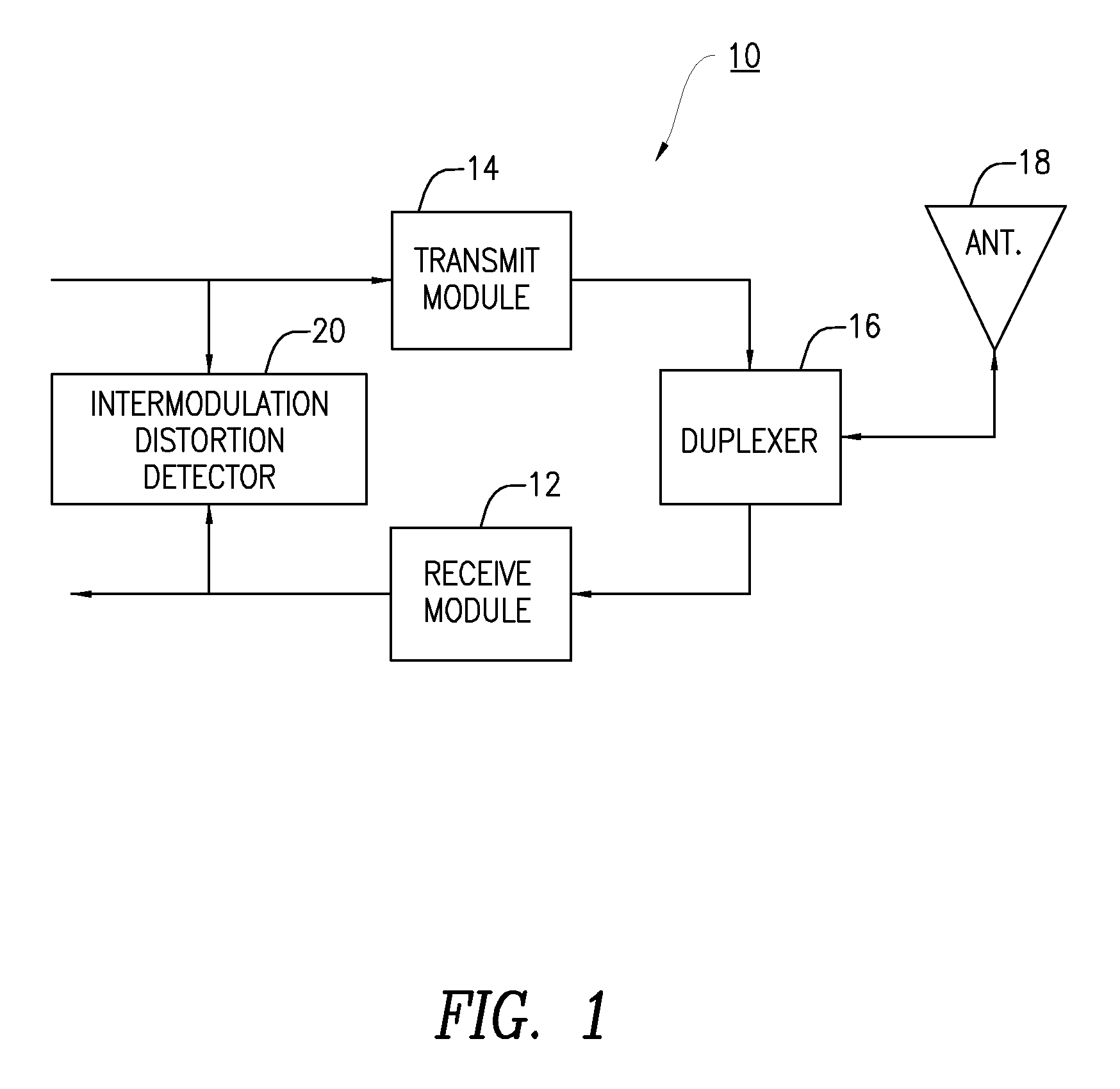
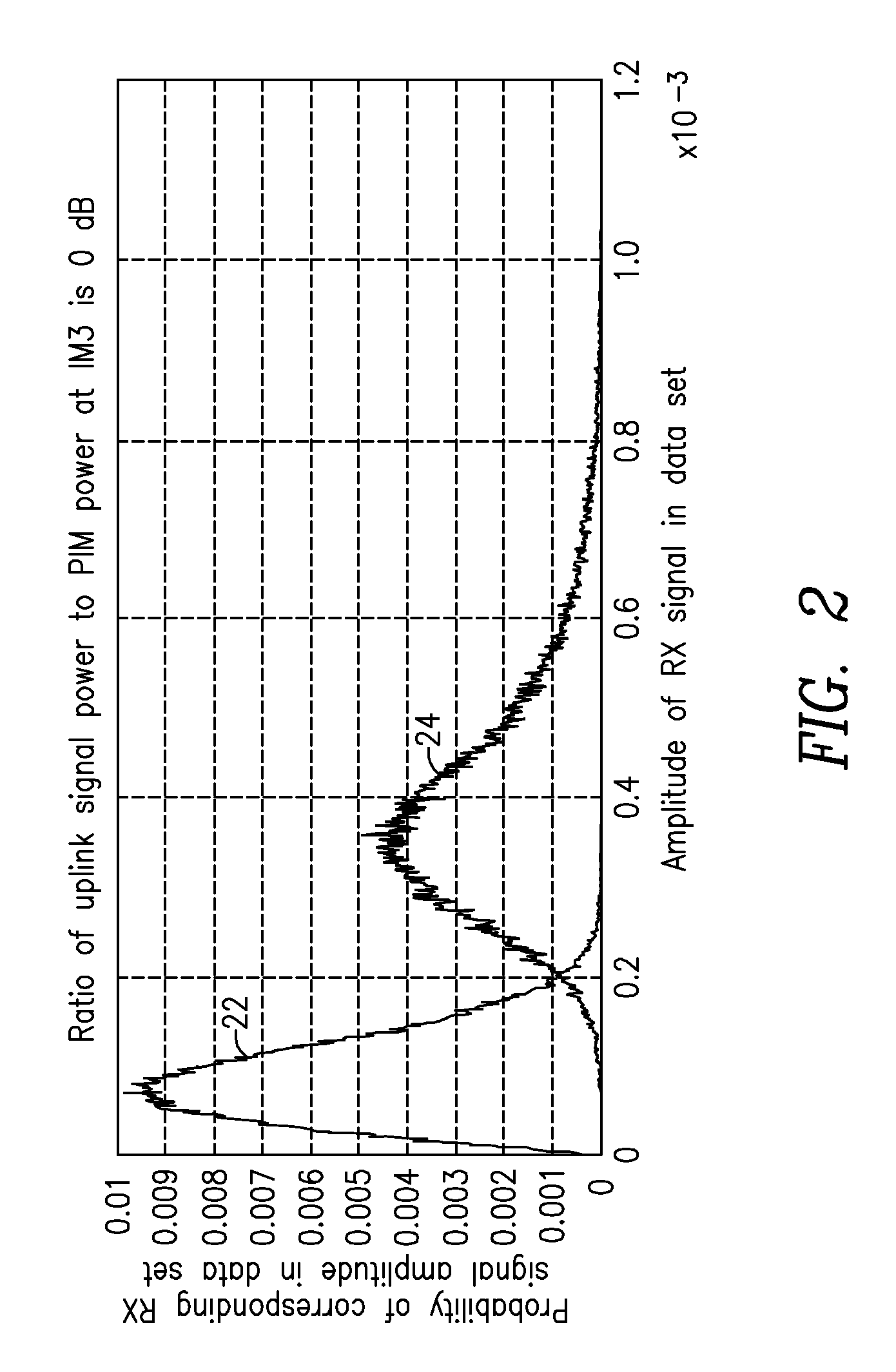
Passive intermodulation detection
A method, apparatus and receiver for detecting intermodulation distortion (IMD) affecting a received signal in a wireless receiver are provided. One method includes determining a measurement indicative of IMD based on at least one transmit signal. When the measurement indicative of IMD exceeds a first pre-determined level, at least one sample of an amplitude of a signal output by the wireless receiver is collected in a first data set. When the measurement indicative of intermodulation distortion does not exceed a second pre-determined level, the second predetermined level being less than the first predetermined level, at least one sample of an amplitude of the signal output by the wireless receiver is collected in a second data set. A comparison is performed based on data of the first data set and on data of the second data set to determine a measure of IMD.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
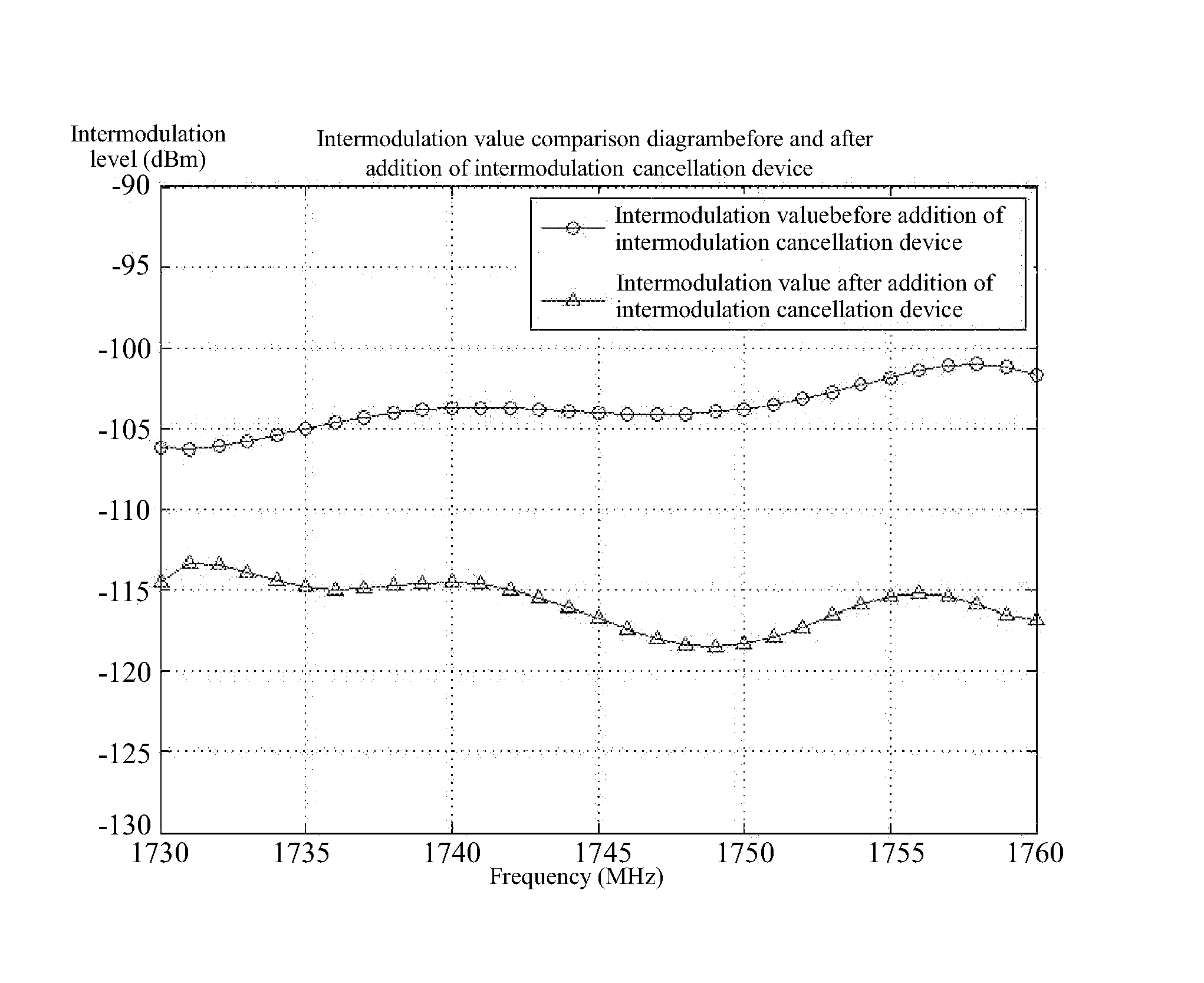
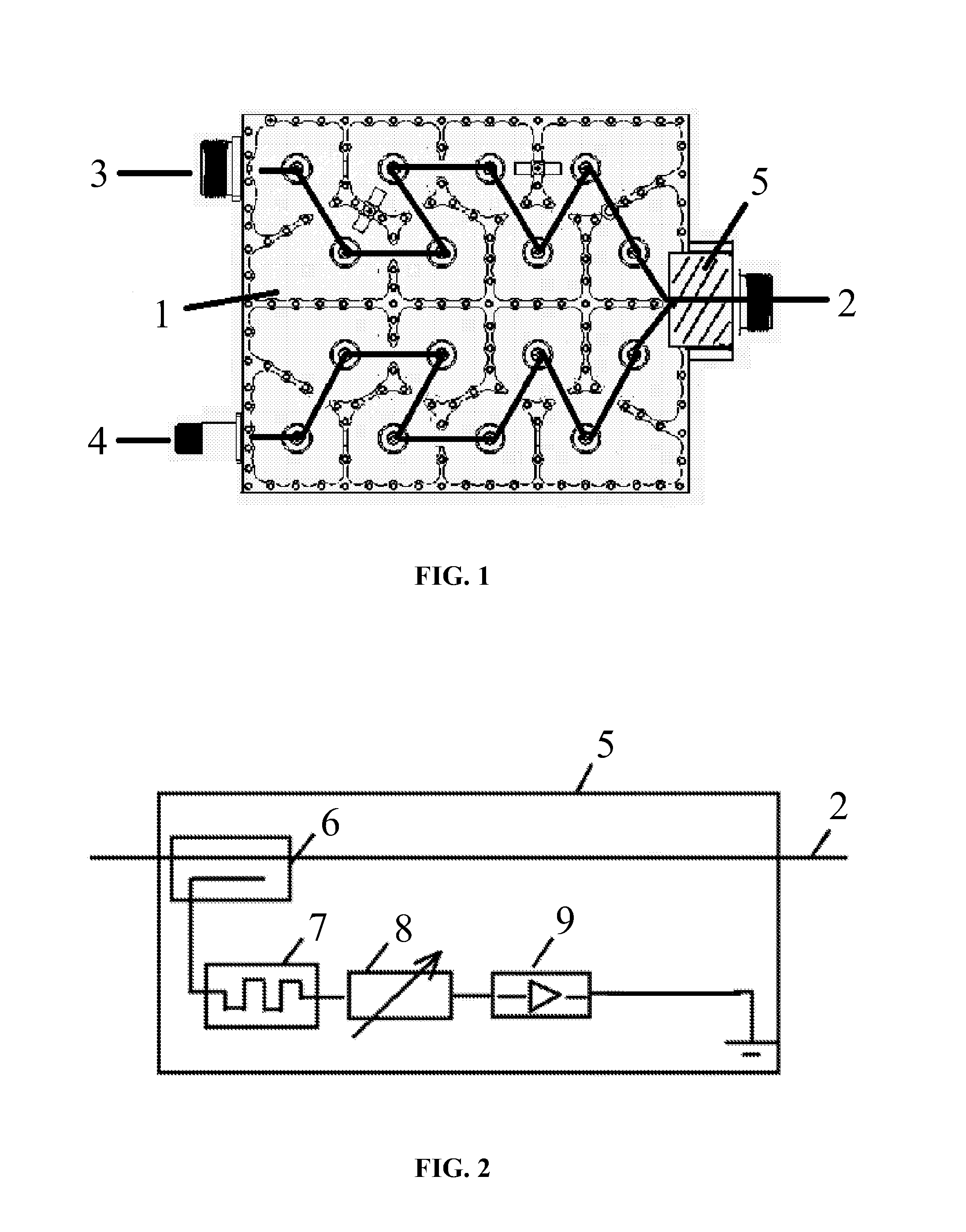
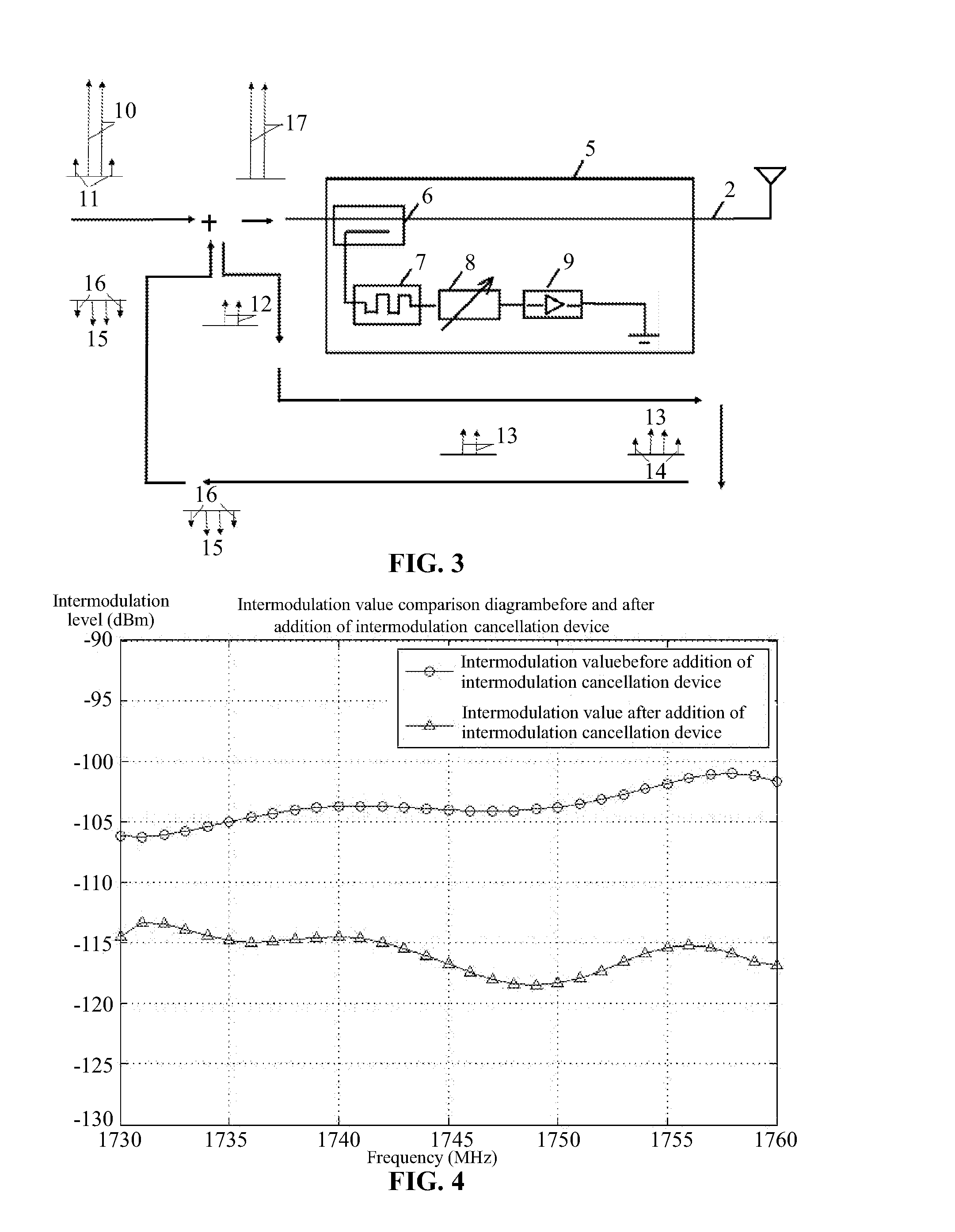
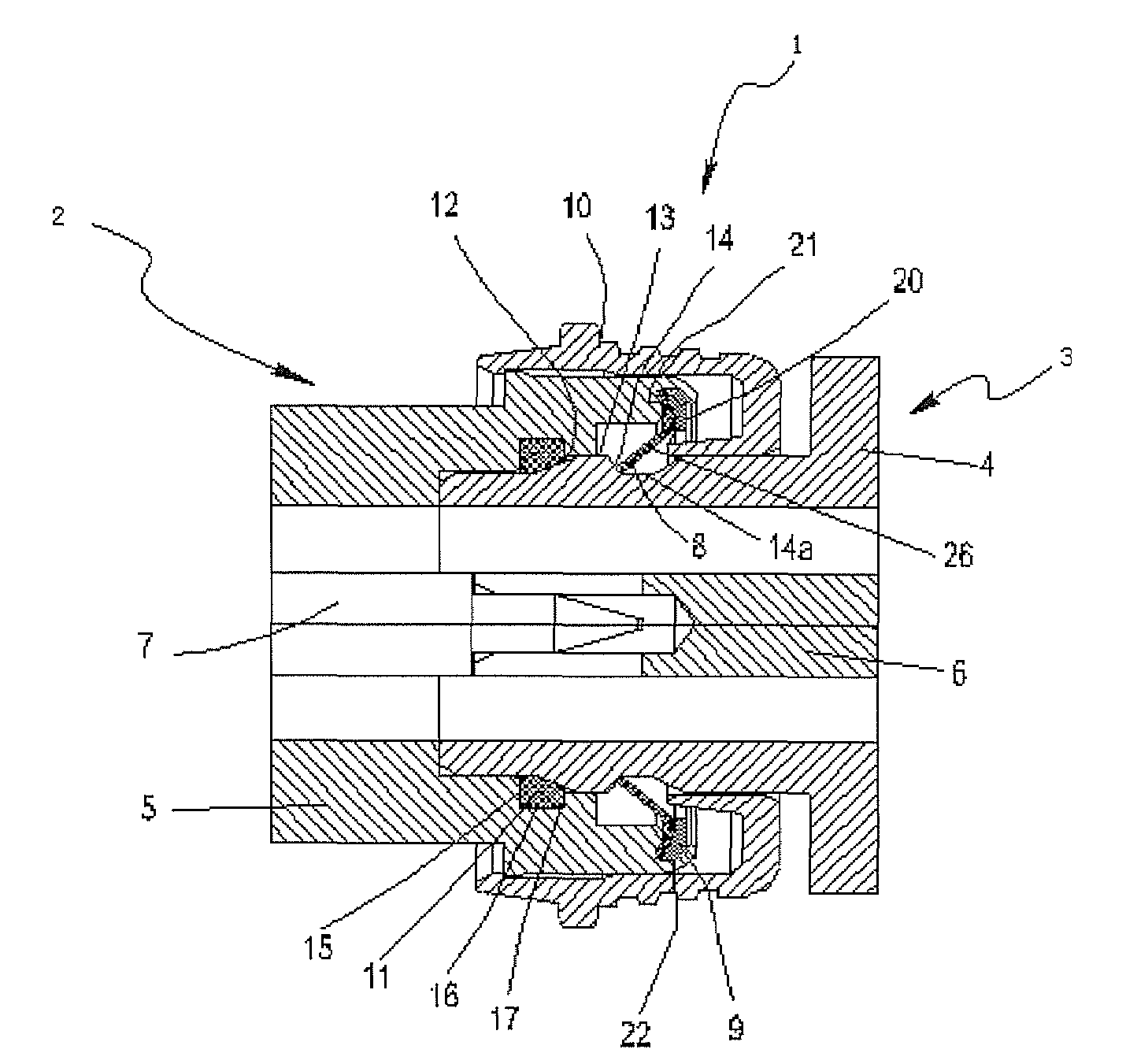
Intermodulation cancellation device
InactiveUS20150349819A1Simple structureEasy to operateAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersElectrical and Electronics engineeringInput/output
An intermodulation cancellation device, including: a power coupler, a regulating module, a nonlinear device, and an input / output port. When in use, a part of a transmitted signal including an intermodulation signal is coupled from a passive device by the power coupler via the input / output port. The coupled transmitted signal is processed for a first time by the regulating module and the nonlinear device, reflected at an end of the intermodulation cancellation device, and then processed for a second time to produce a power signal including a second intermodulation cancellation signal. The second intermodulation cancellation signal of the power signal and the intermodulation signal of the transmitted signal of the passive device have the same frequency and level and opposite phases. The power signal is superimposed on the transmitted signal of the passive device and a superimposed signal is output to the passive device via the input / output port.
Owner:WUHAN FINGU ELECTRONICS TECH
Electrical connector with self-locking by snap-fastening
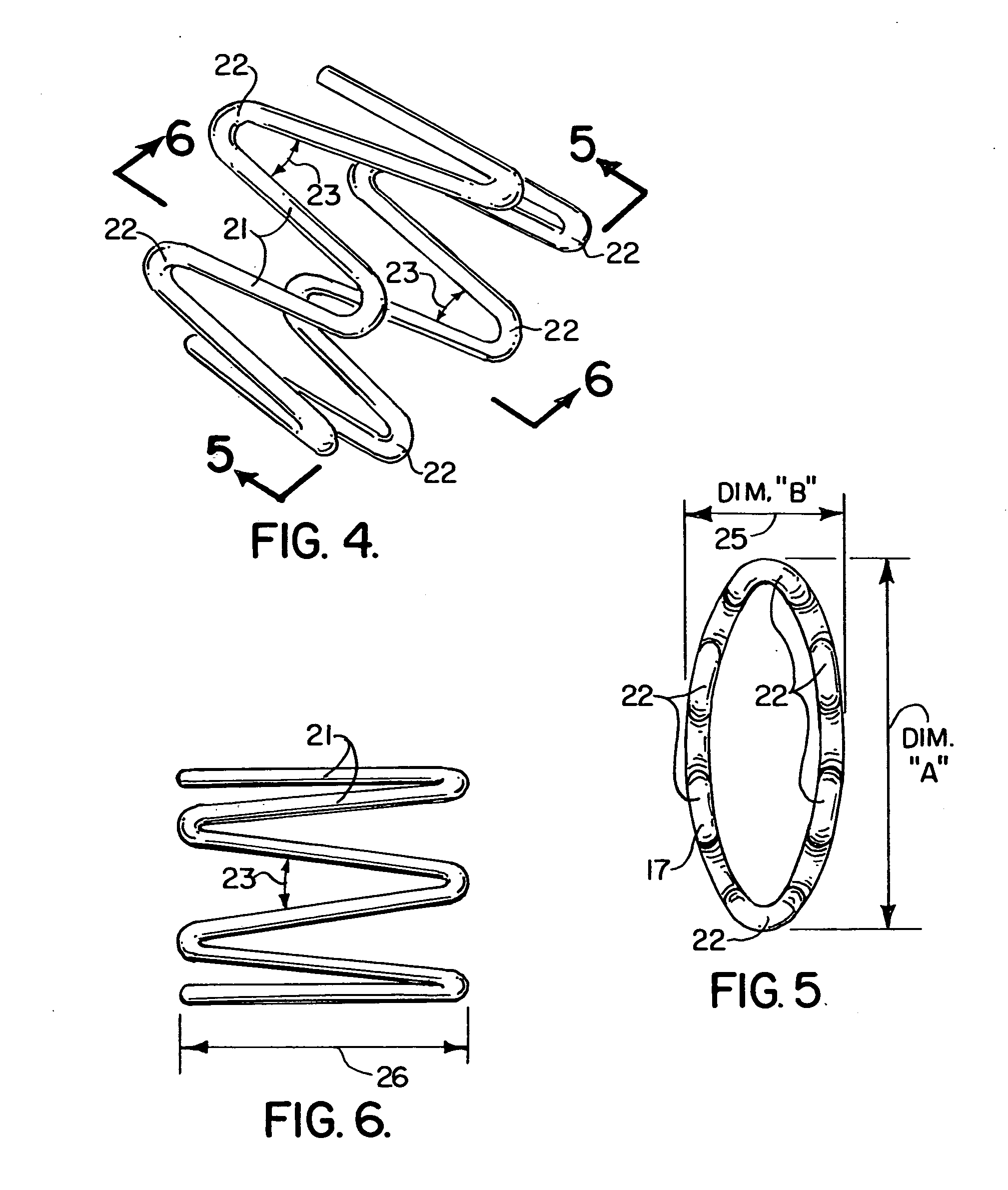
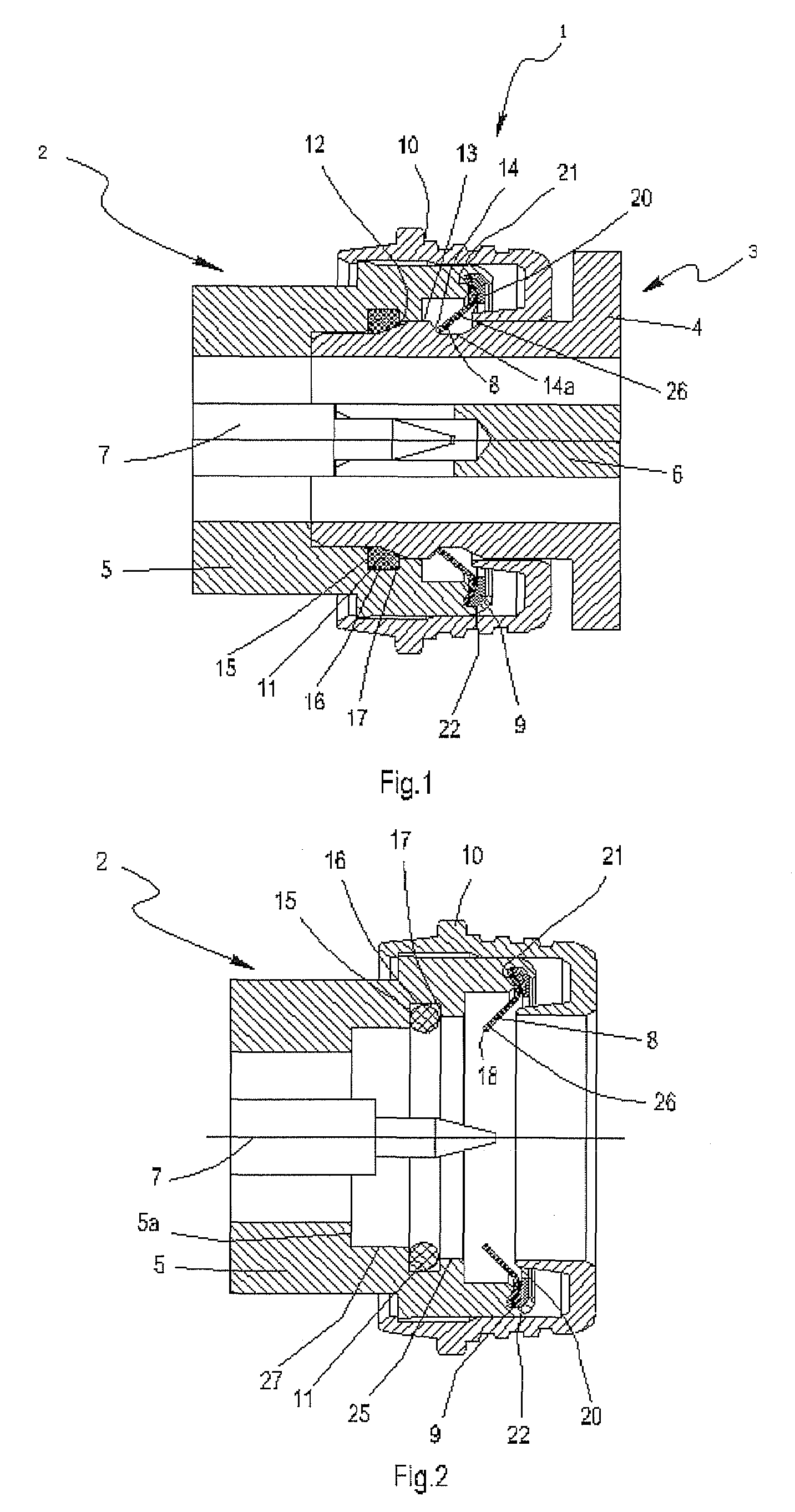
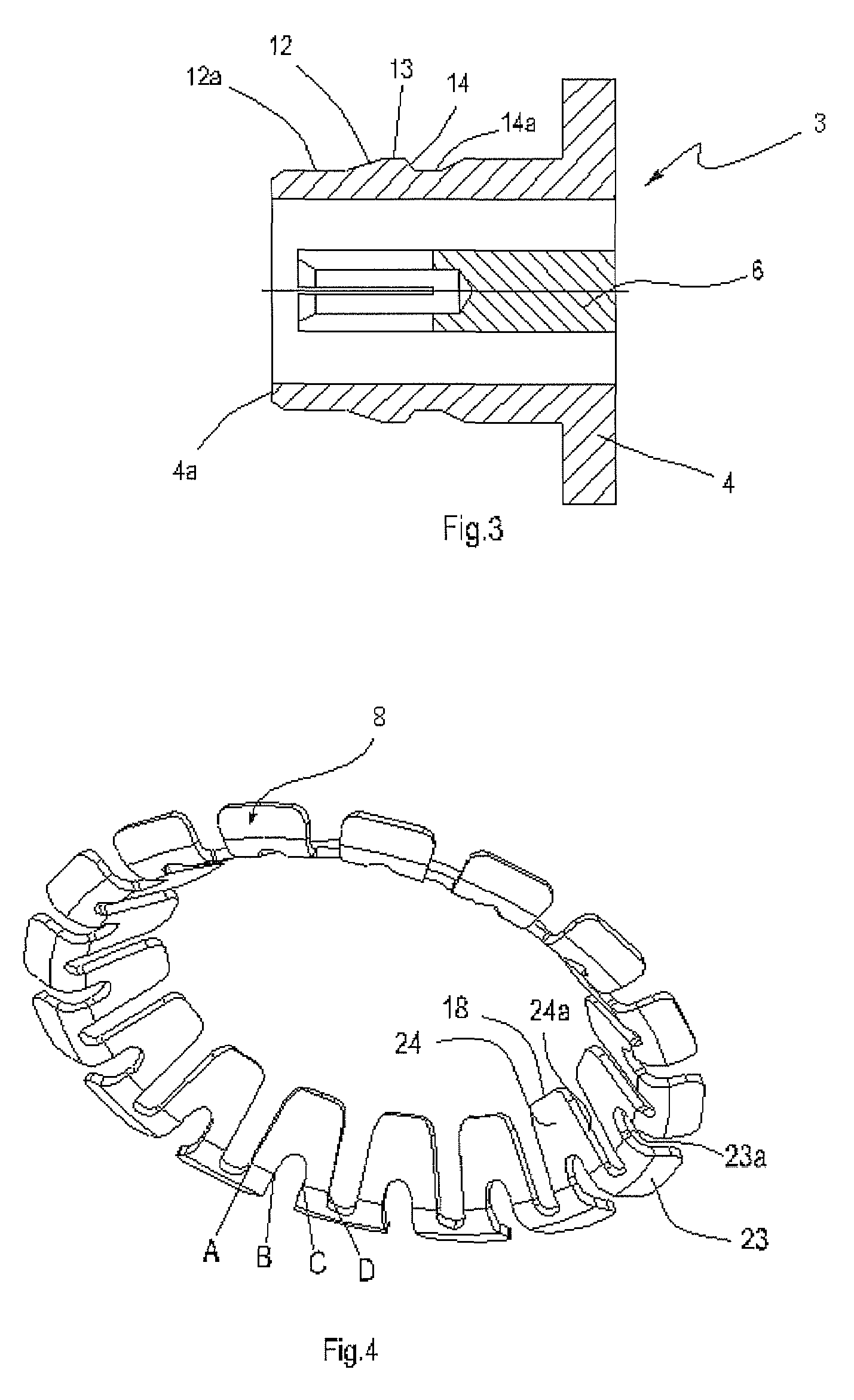
ActiveUS7351088B1Avoid reflectionsImprove intermodulationTwo pole connectionsCoupling device detailsElectrical conductorSelf locking
An electrical connector, a ring-like locking sheet with inner and outer teeth of which is fixed at the end of its plug connector; and a circumferential bulge, with trapezoid cross section which has an upslope, a flat top and a down-slope, is provided on the surface of the outer conductor of the socket connector. Therefore, in the process of connection, the inner teeth reach the max flexural deformation when go up along the slope to the flat top. When reach the down-slope, the deformed inner teeth gradually restore the original state in tangential direction of the down-slope, and finally stop at the down-slope or at the juncture of the down-slope and the flat top. The electrical connector according to the present invention can have a rigid zero clearance between the interfaces in connection, and at the same time can keep a very strong axial force. The RF coaxial connector according to the present invention has continuous impedance between the contact surfaces, reliable and stable contact, greatly reduced RF emission, as well as the same operating frequency, excellent RF performance and good passive intermodulation as those with threaded connection.
Owner:ANOISON ELECTRONICS JIANGSU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com