Patents
Literature
1303 results about "Heterodyne" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
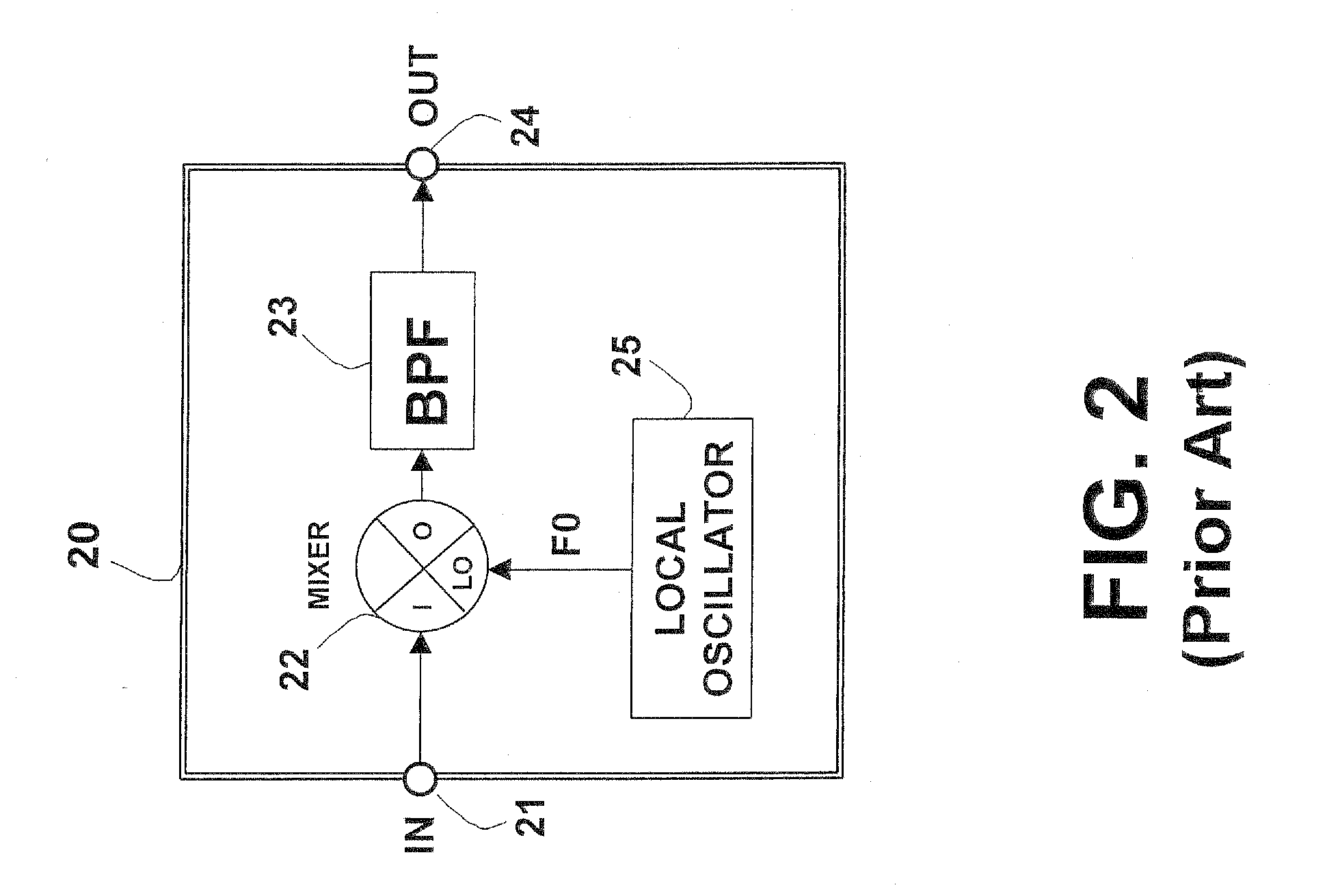
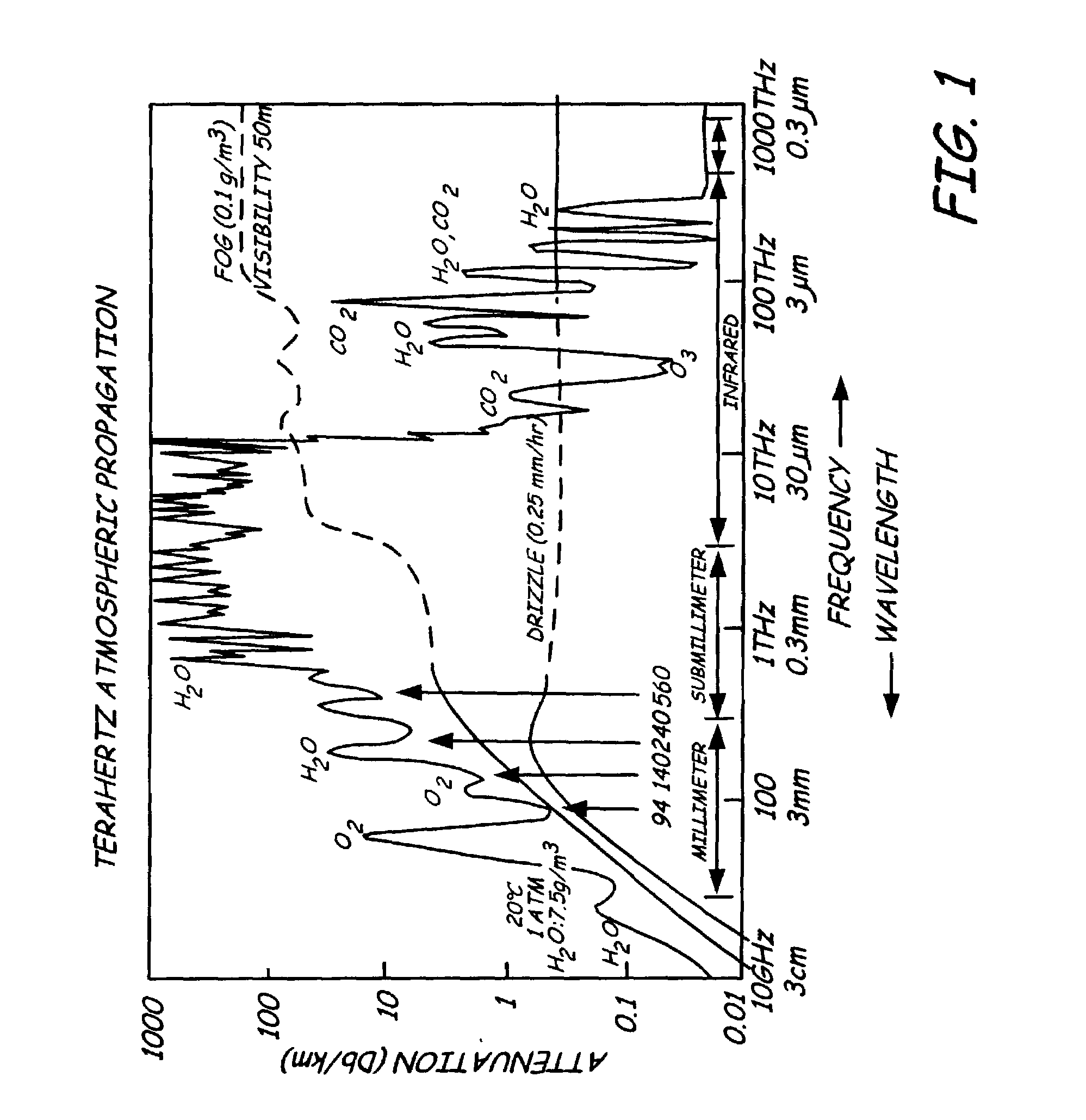
Heterodyning is a signal processing technique invented by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden that creates new frequencies by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f₁ and f₂ are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f₁ + f₂ of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f₁ − f₂. These frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodyne frequencies are related to the phenomenon of "beats" in acoustics.
Frequency encoding of resonant mass sensors
InactiveUS20050016276A1Sufficient ring timeImprove stabilityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayFrequency spectrum
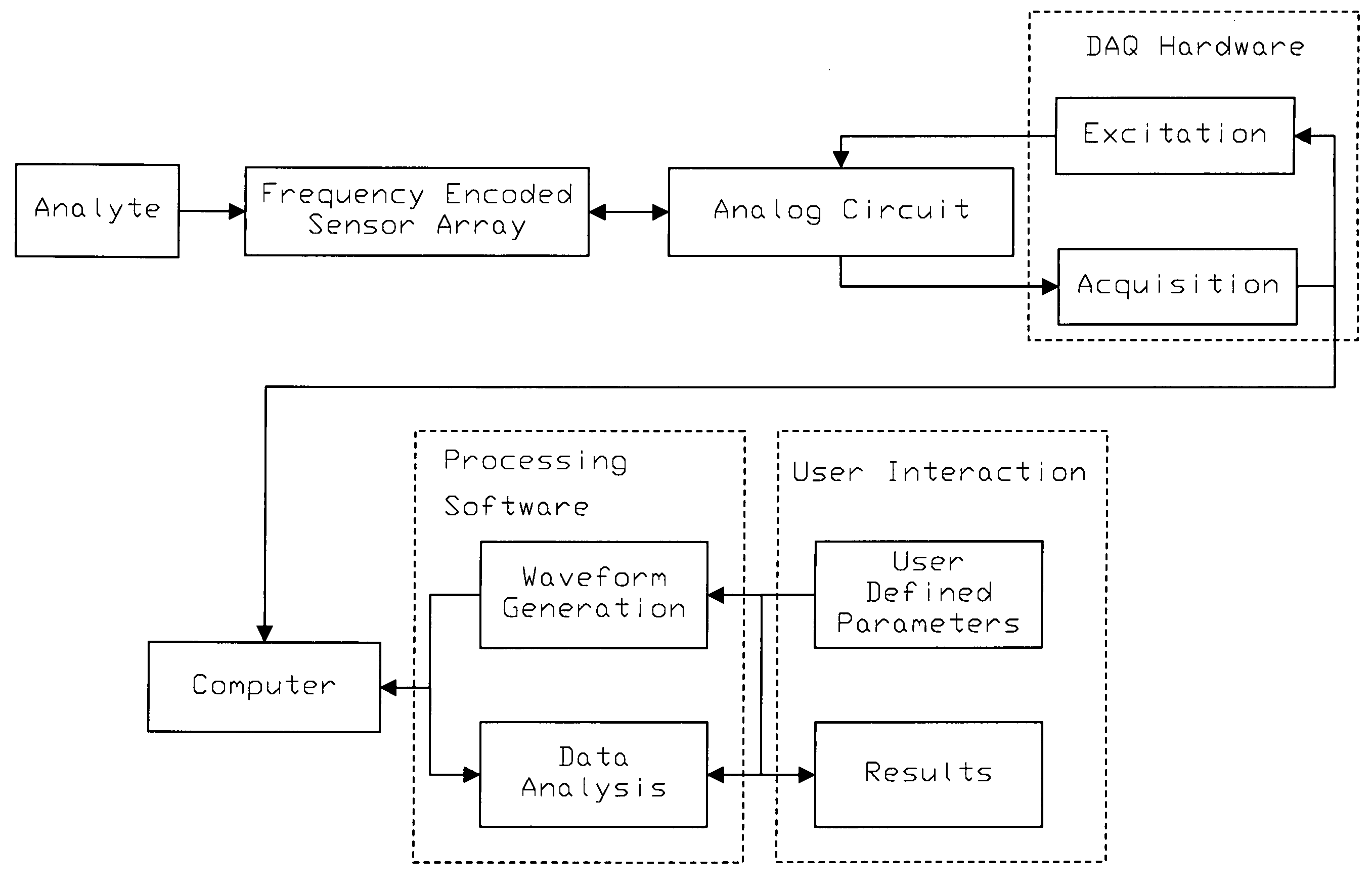
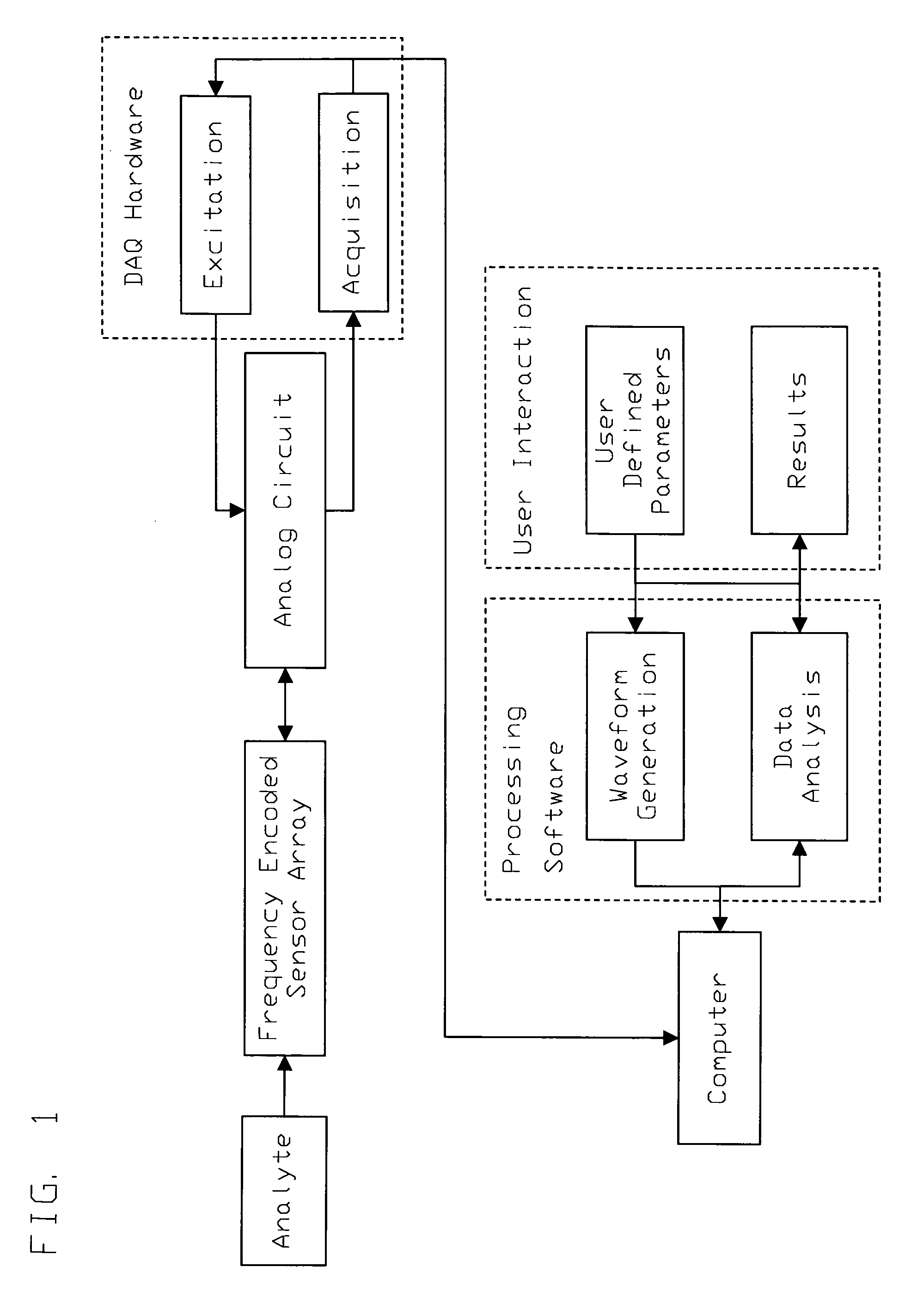
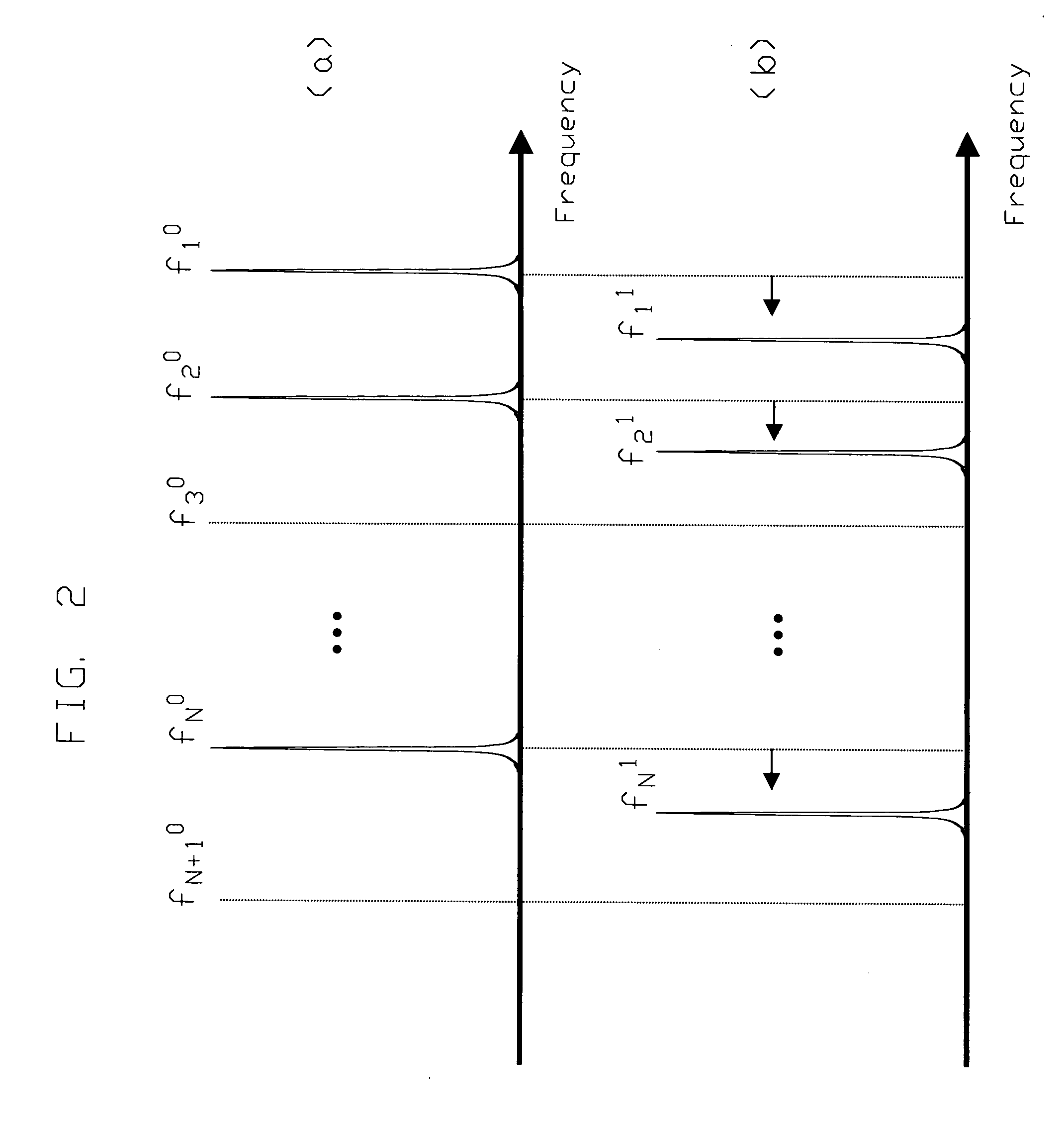
A method for the detection of analytes using resonant mass sensors or sensor arrays comprises frequency encoding each sensor element, acquiring a time-domain resonance signal from the sensor or sensor array as it is exposed to analyte, detecting change in the frequency or resonant properties of each sensor element using a Fourier transform or other spectral analysis method, and classifying, identifying, and / or quantifying analyte using an appropriate data analysis procedure. Frequency encoded sensors or sensor arrays comprise sensor elements with frequency domain resonance signals that can be uniquely identified under a defined range of operating conditions. Frequency encoding can be realized either by fabricating individual sensor elements with unique resonant frequencies or by tuning or modifying identical resonant devices to unique frequencies by adding or removing mass from individual sensor elements. The array of sensor elements comprises multiple resonant structures that may have identical or unique sensing layers. The sensing layers influence the sensor elements' response to analyte. Time-domain signal is acquired, typically in a single data acquisition channel, and typically using either (1) a pulsed excitation followed by acquisition of the free oscillatory decay of the entire array or (2) a rapid scan acquisition of signal from the entire array in a direct or heterodyne configuration. Spectrum analysis of the time domain data is typically accomplished with Fourier transform analysis. The methods and sensor arrays of the invention enable rapid and sensitive analyte detection, classification and / or identification of complex mixtures and unknown compounds, and quantification of known analytes, using sensor element design and signal detection hardware that are robust, simple and low cost.
Owner:PALO ALTO SENSOR TECH INNOVATION
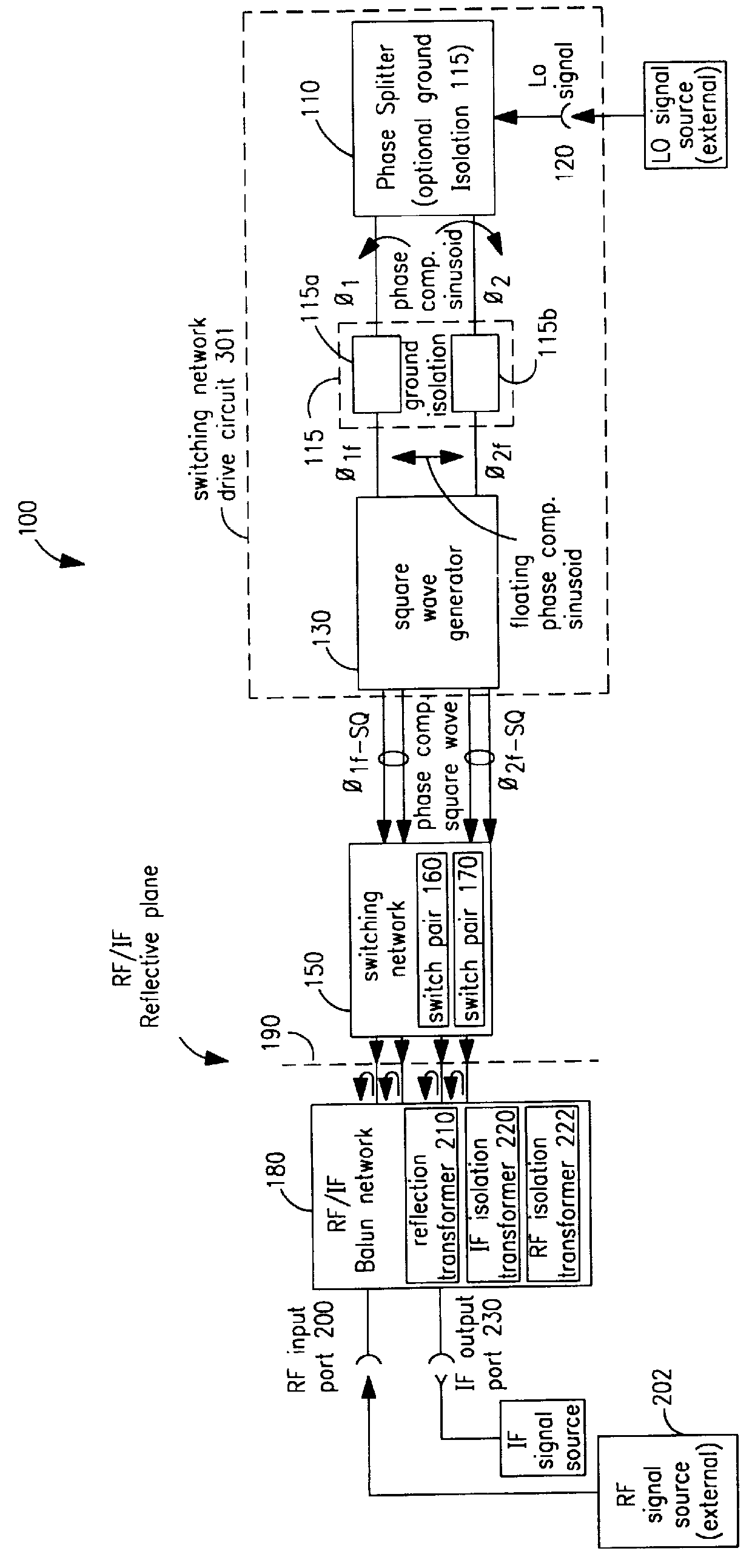
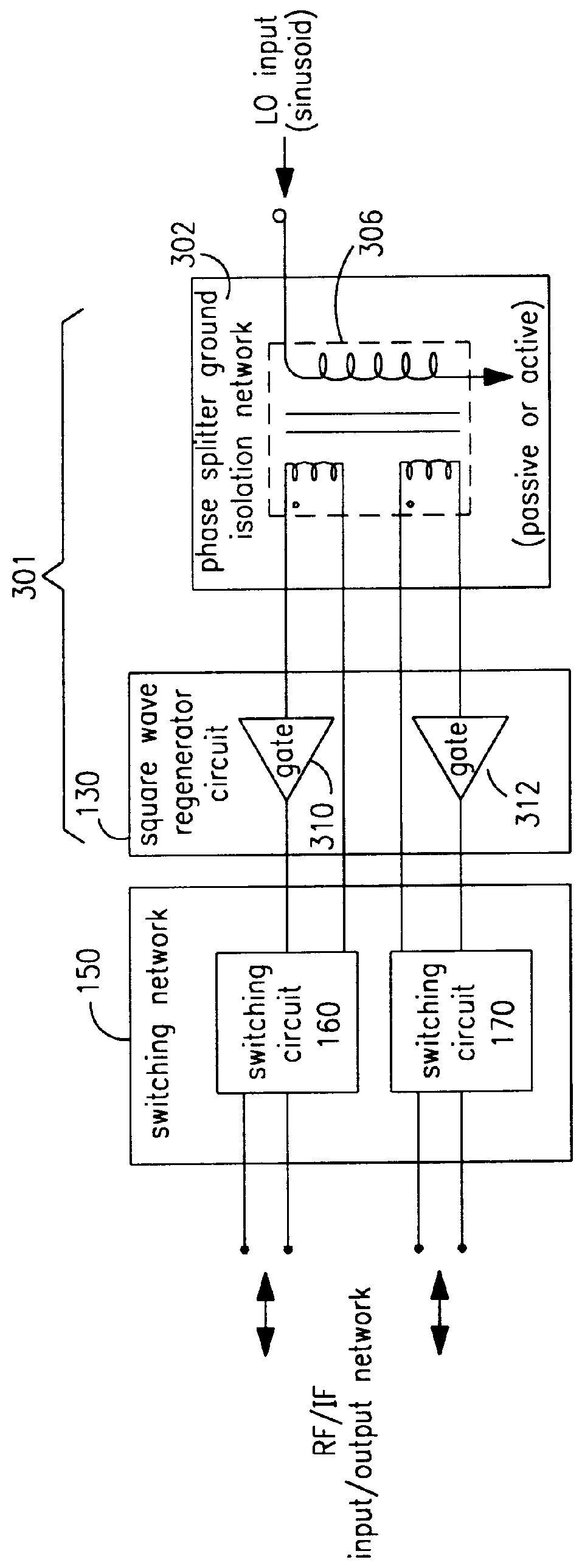
Structure and method for super FET mixer having logic-gate generated FET square-wave switching signal
InactiveUS6144236AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio receiverTransformer
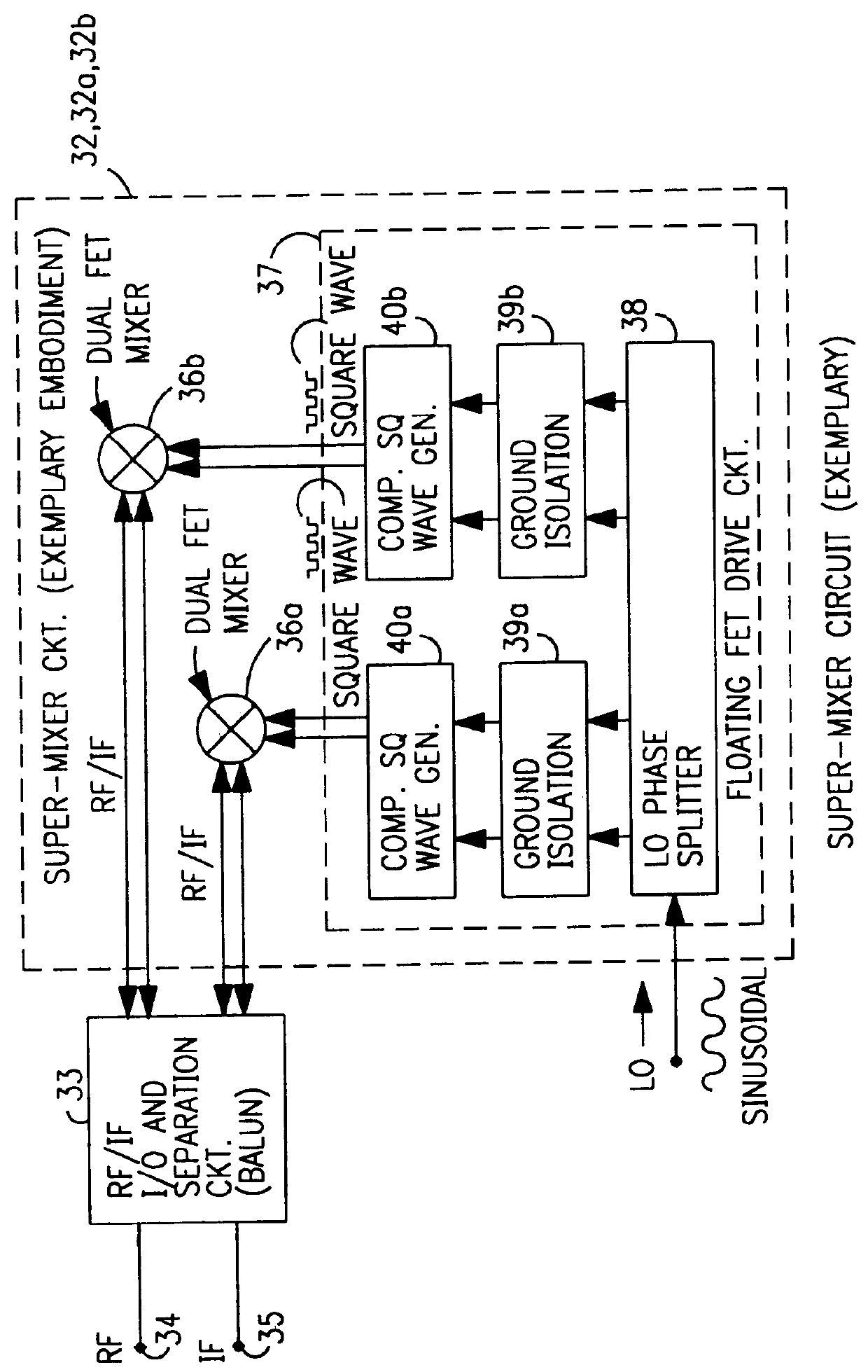
A mixing method and mixer structure provide a circuit topology suitable for use in radio receivers, transmitters, tuners, instrumentation systems, telemetry systems, and other systems and devices performing frequency conversion in either homodyne or heterodyne implementations. The inventive mixer may be used for wireless communication devices including radios, cellular telephones, and telemetry systems whether land, sea, airborne, or space based, and whether fixed or mobile. The mixer provides superior intermodulation and harmonic distortion suppression and features excellent conversion loss, noise figure, port match, and port isolation as a result of its circuit topology. The mixer device circuit combines the advantages of series mixing FETs, a triple balanced design using a balanced passive reflection transformer, a precise local oscillator phase splitter, and square wave gate drive having high slew rate signal characteristics to achieve high levels of performance. It is power conservative and offers the advantage of long battery life in portable devices such as portable radios and cellular telephones as it requires only a modest amount of DC and local oscillator drive power, and is useful for operation over at least a multi-decade bandwidth.
Owner:DRS SIGNAL SOLUTIONS
Multi-color hetereodyne interferometric apparatus and method for sizing nanoparticles
A nanoparticle sensor is capable of detecting and recognizing single nanoparticles in an aqueous environment. Such sensor may find applications in broad areas of science and technology, from the analysis of diesel engine emissions to the detection of biological warfare agents. Particle detection is based on interferometric detection of multi-color light, scattered by the particle. On the fundamental level, the detected signal has a weaker dependence on particle size (ÿ R3), compared to standard detection methods (ÿ R6). This leads to a significantly larger signal-to-noise ratio for smaller particles. By using a multi-color or white excitation light, particle dielectric properties are probed at different frequencies. This scheme samples the frequency dependence of the particle's polarizability thereby making it possible to predict the composition of the particle material. The detection scheme also employs a heterodyne or pseudoheterodyne detection configuration, which allows it to reduce or eliminate noise contribution from phase variations, which appear in any interferometric measurements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
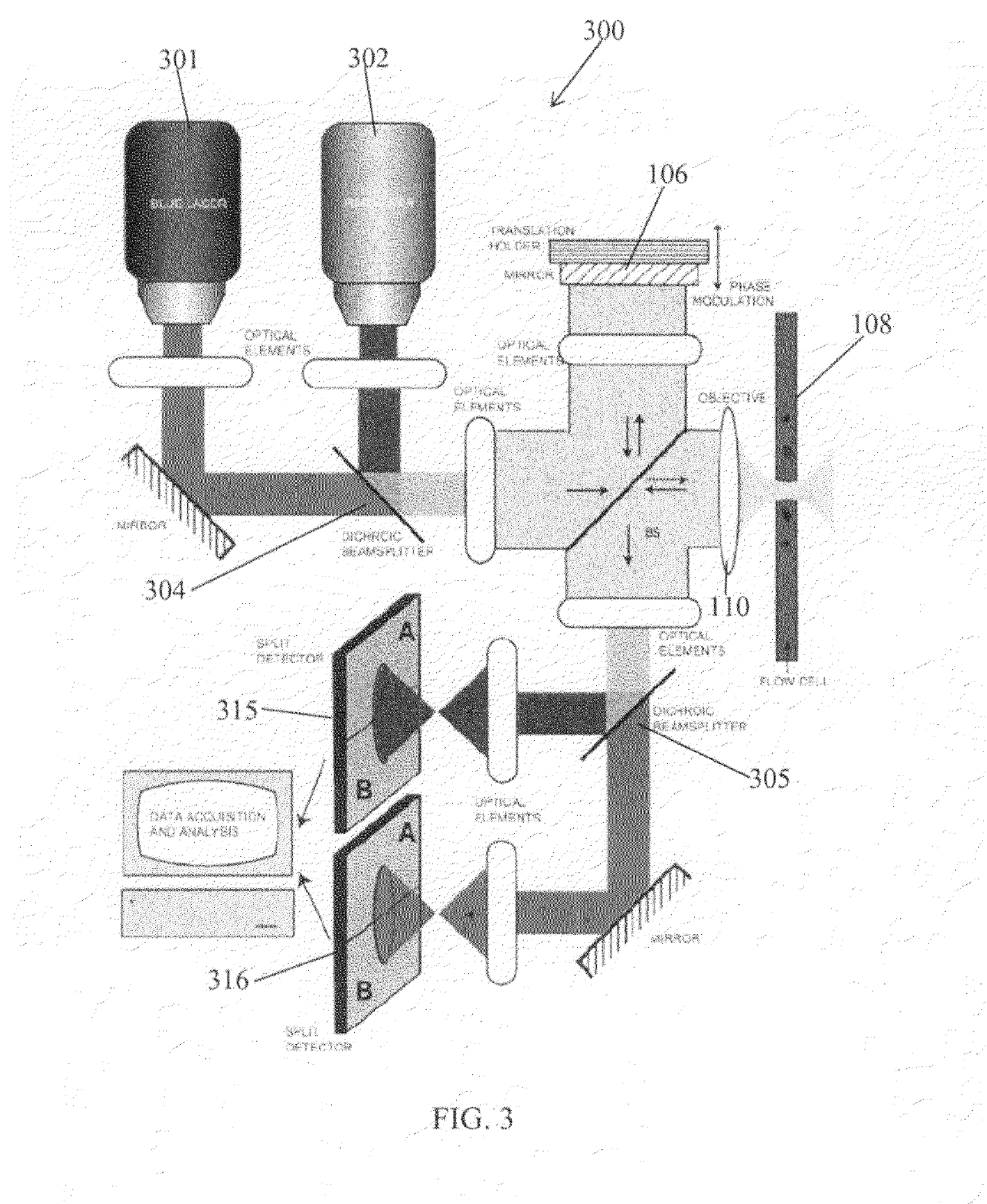
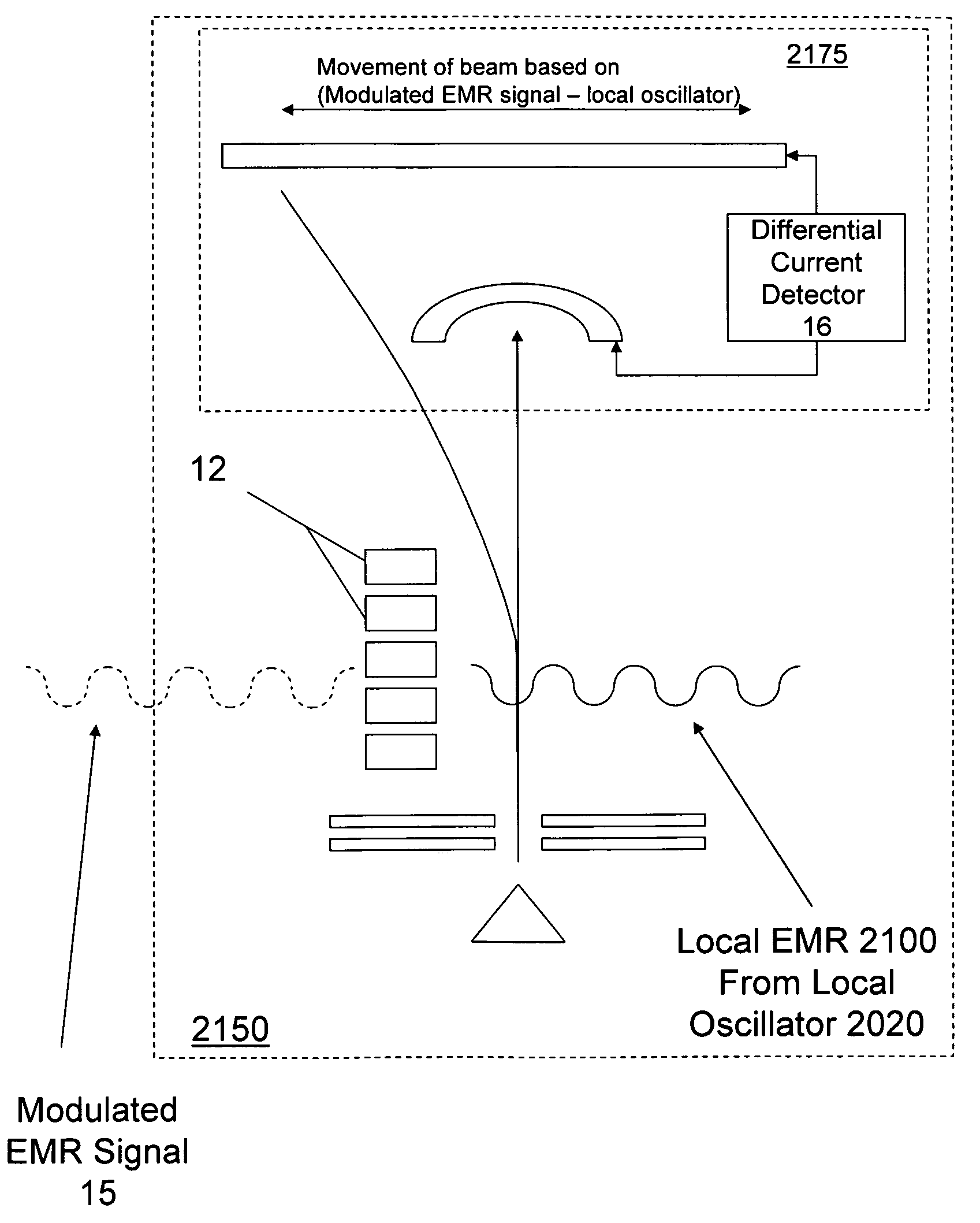
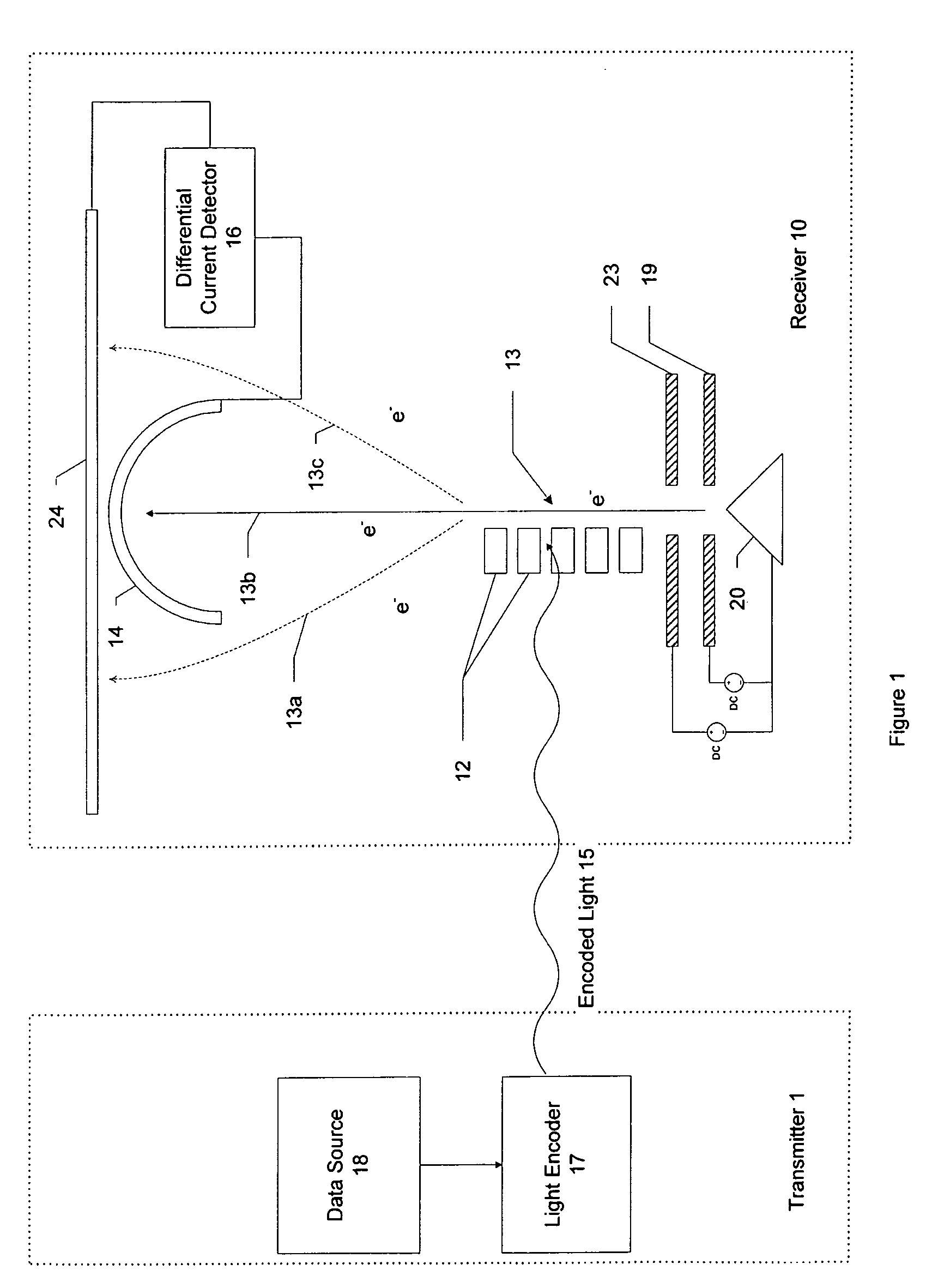
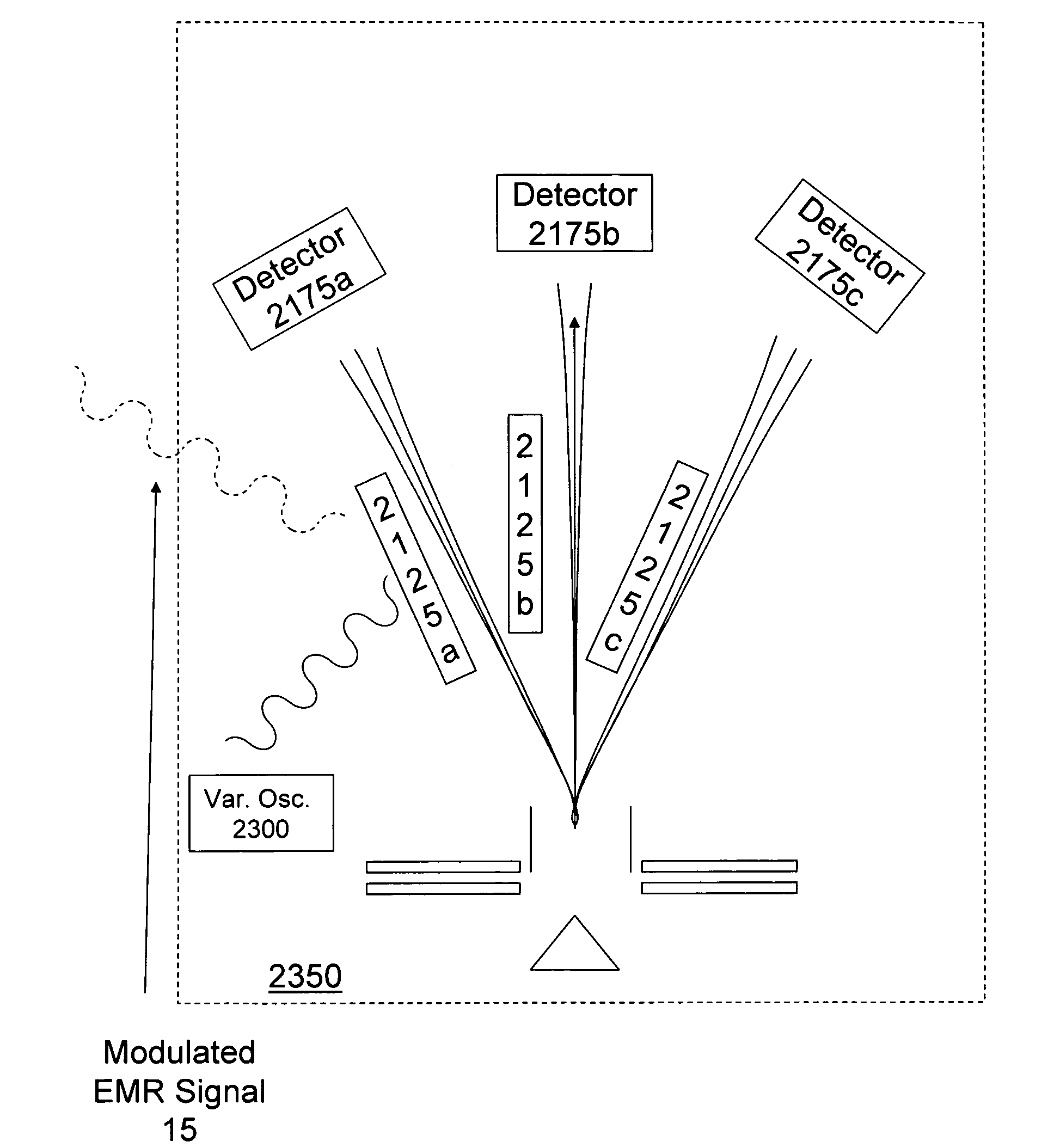
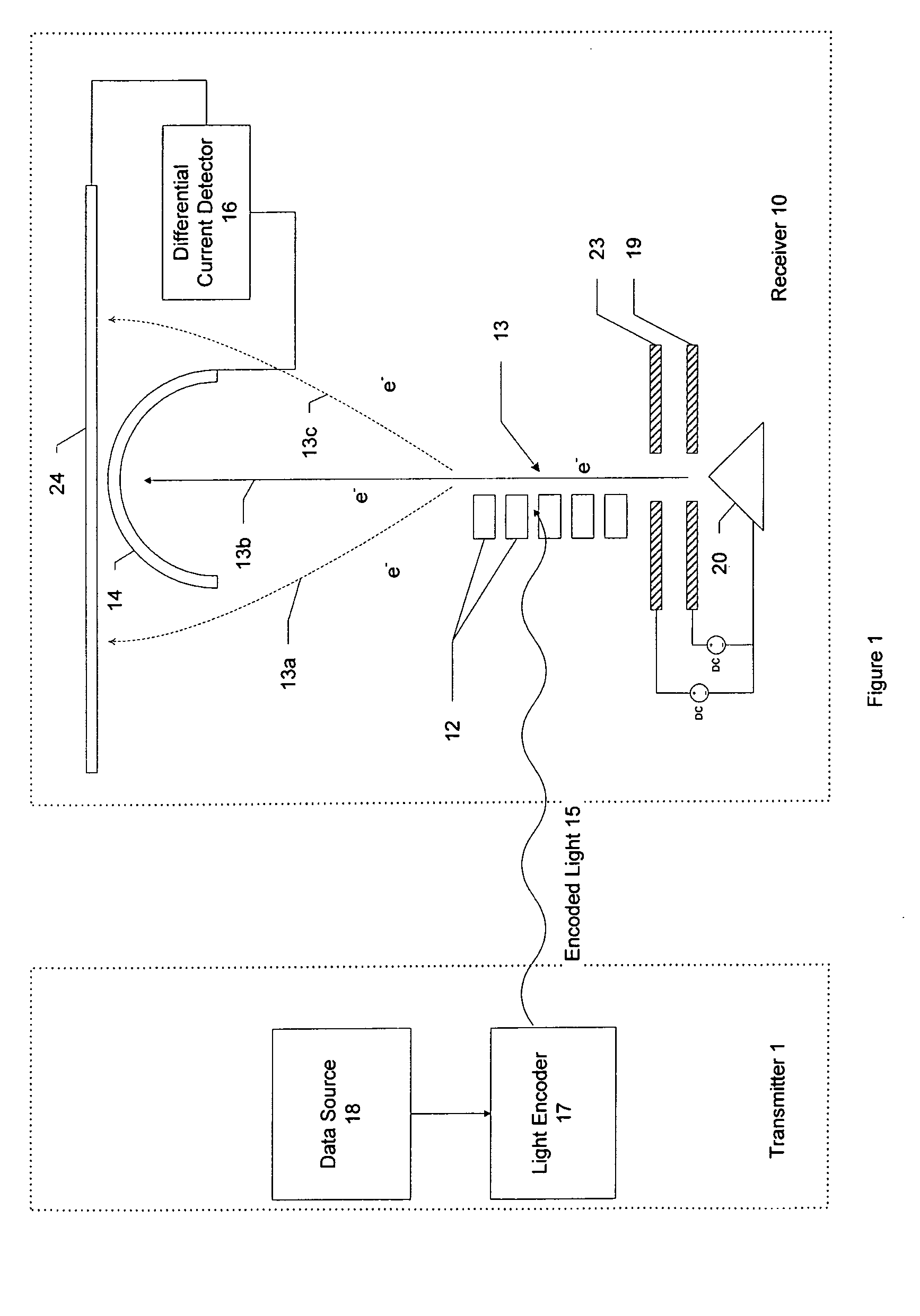
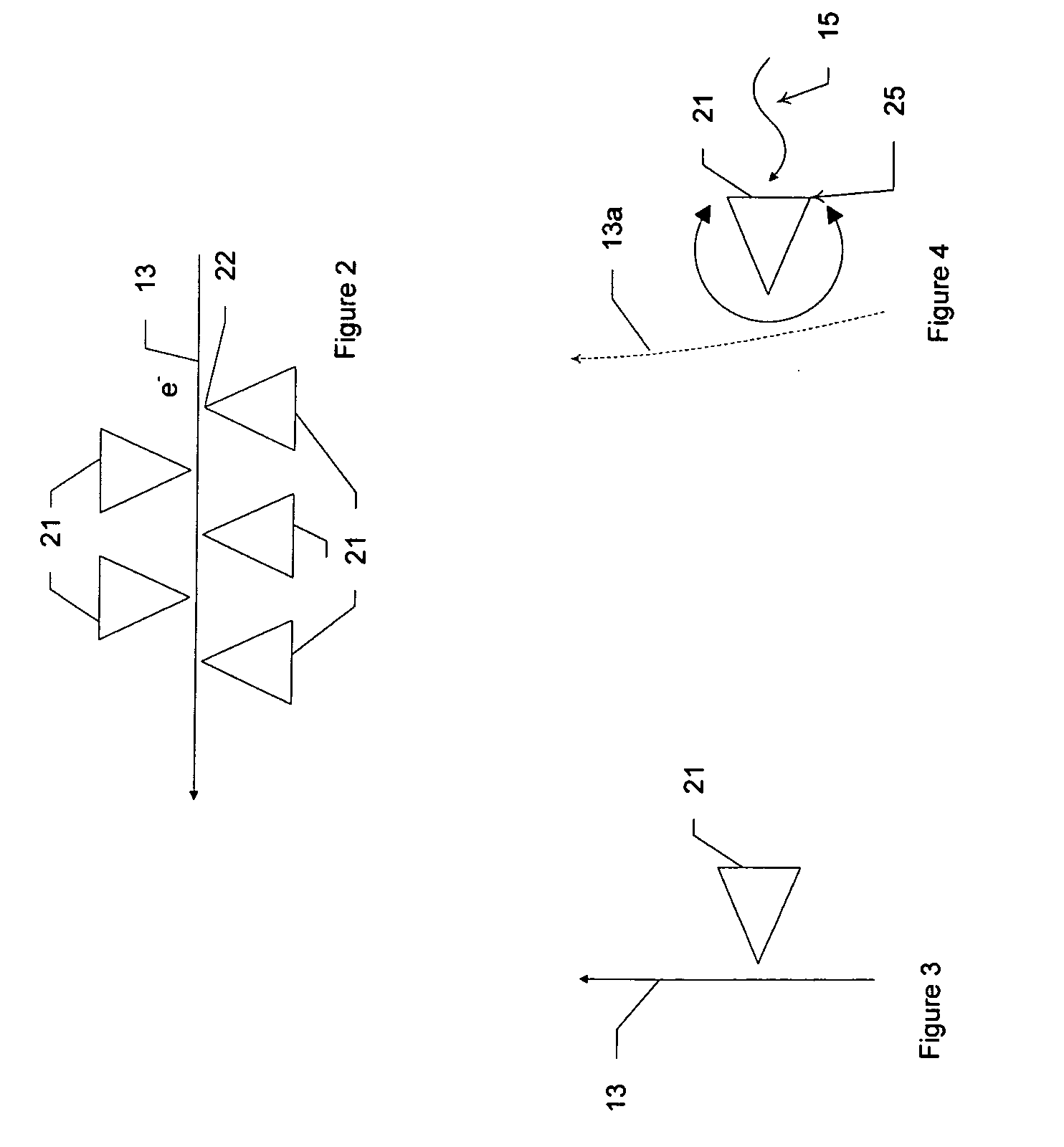
Heterodyne receiver array using resonant structures
An electronic receiver array for decoding data encoded into electromagnetic radiation (e.g., light) is described. The light is received at an ultra-small resonant structure. The resonant structure generates an electric field in response to the incident light and light received from a local oscillator. An electron beam passing near the resonant structure is altered on at least one characteristic as a result of the electric field. Data is encoded into the light by a characteristic that is seen in the electric field during resonance and therefore in the electron beam as it passes the electric field. Alterations in the electron beam are thus correlated to data values encoded into the light.
Owner:ADVANCED PLASMONICS
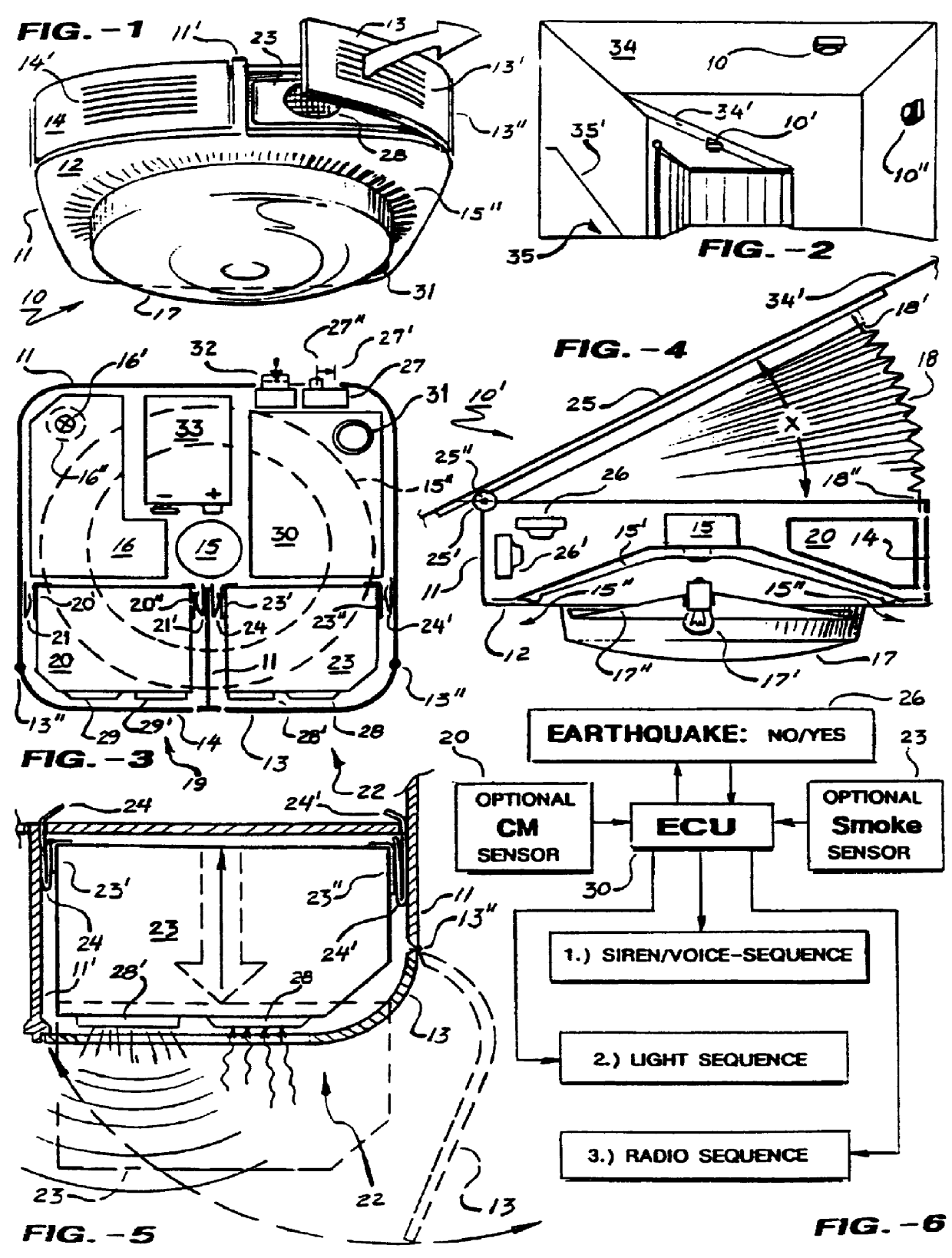
Quake-alerter w/radio-advisory and modular options
An improved safety related compact hand-portable apparatus for home or office use, EQ-Alert TM is ceiling or shelf mountable, activating upon sensing a minimum-threshold earthquake preferably of about 3.25 / Rictor-scale intensity, instantly emitting a series of approximate 110-decibel level siren-alarms; preferably along with activation of a safety-lamp to illuminate an immediate floor-area in event of community power-outage. A preferably dry-cell powered dc / electronic IC-chip timer-circuit, limits duration of the audible-alarm, triggered by sufficient movement of an internal omni-directional mercury n.o. / jiggle-switch. Upon completion of the timed audible-alarm and optional voice-chip announcement, the timer-circuit sequences a conventional integral superheterodyne-AM / radio user has preset to a local Conelrad / news-station, for ongoing notification of any earthquake rescue procedures. Optional provision for plug-in circuit-modules, facilitates adding of allied safety-units, such as substantially conventional smoke-alarm, and carbonmonoxide-alarm detectors, sharing the audio-transducer and IC-microprocessor; to issue forth separate short programed voice-announcements as to the detected hazards.
Owner:YOUSIF MARVIN J
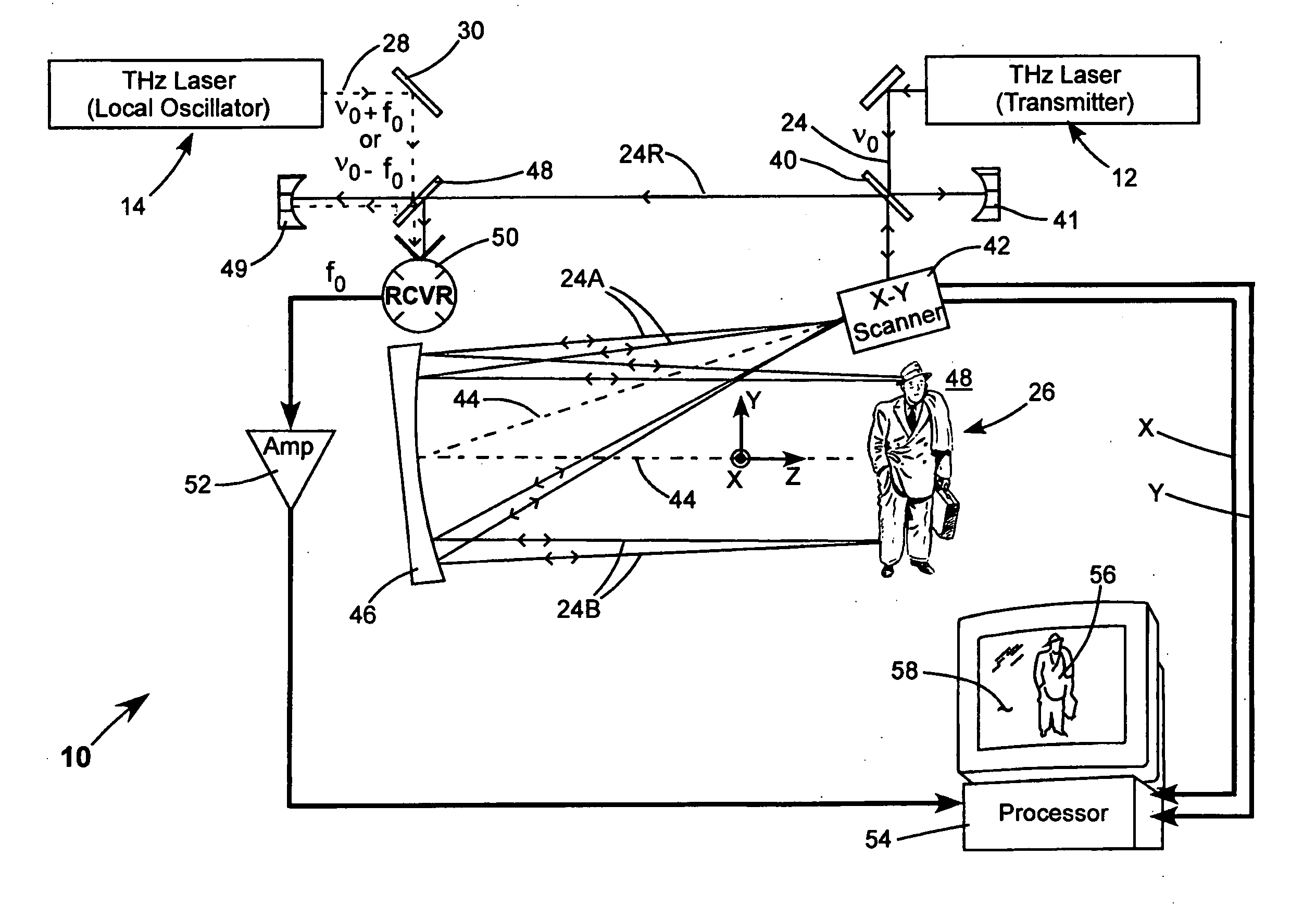
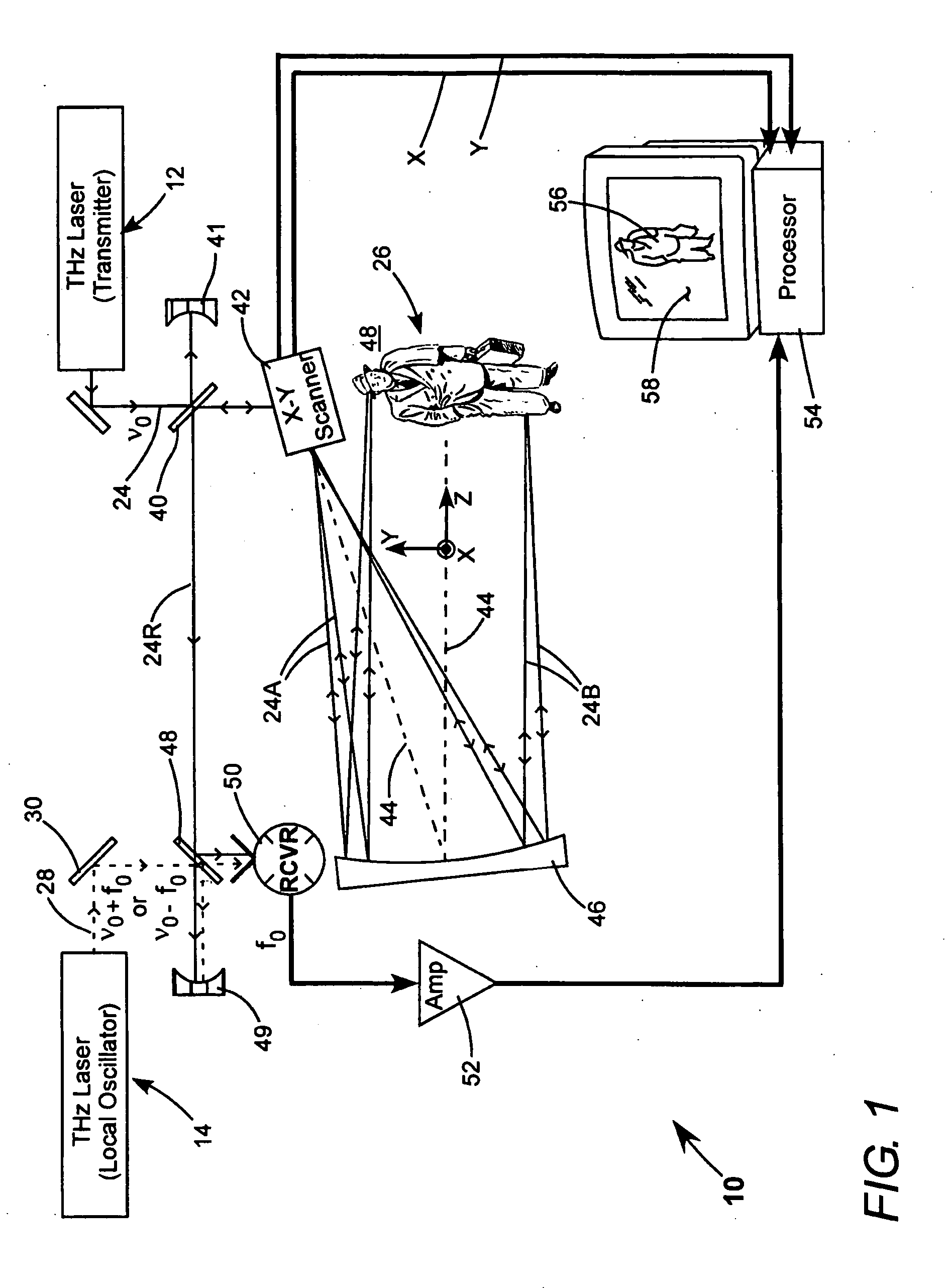
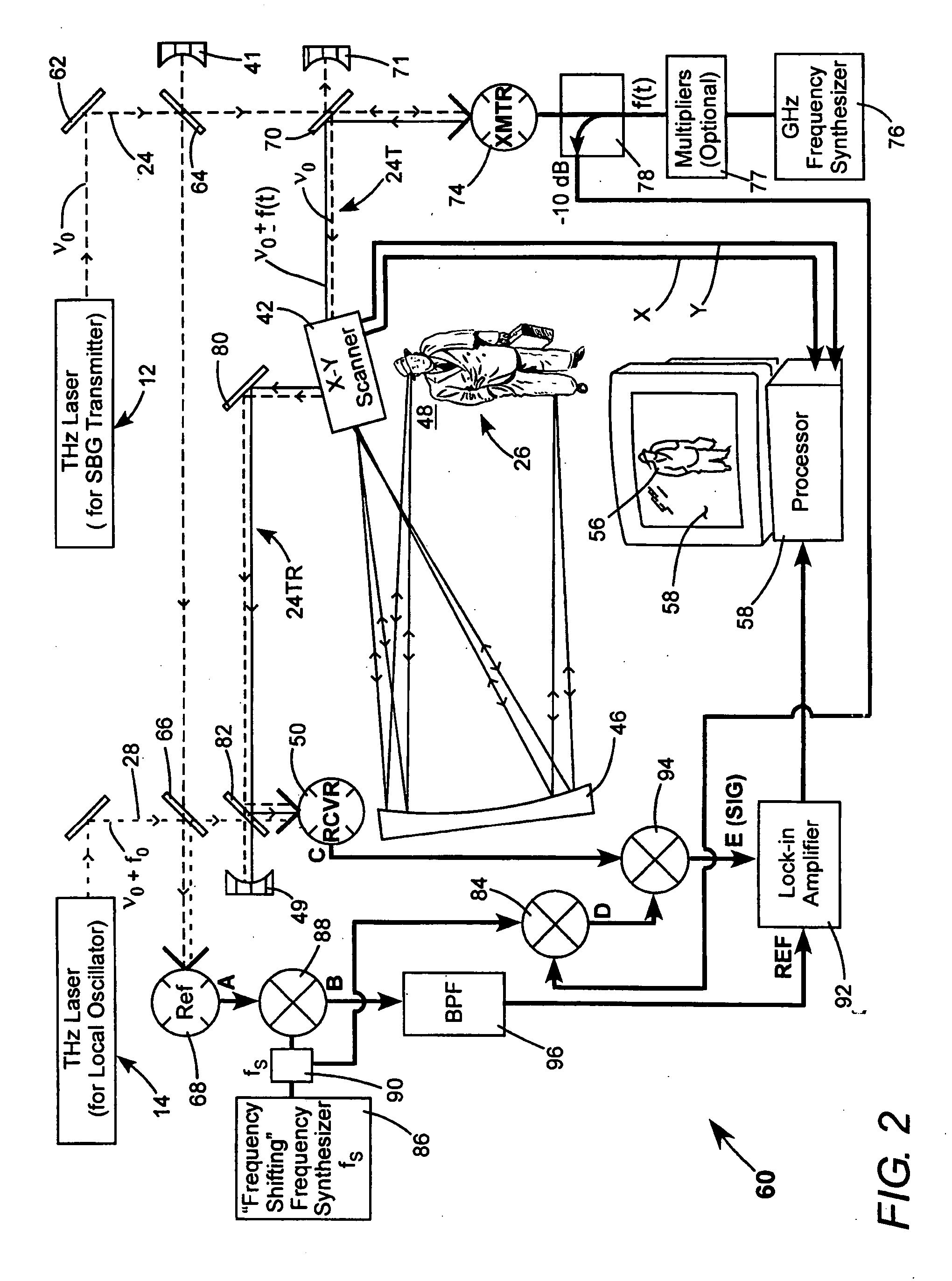
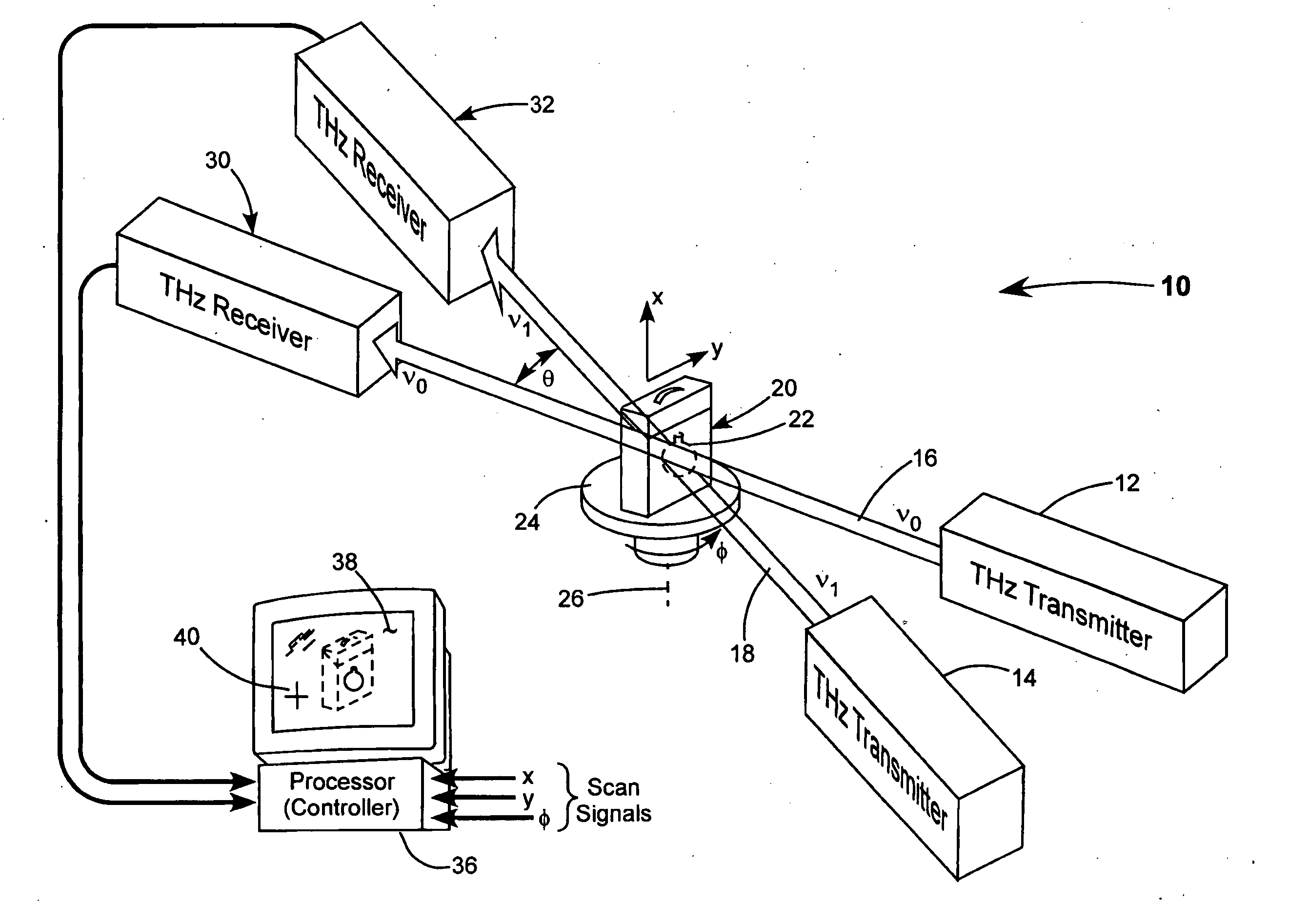
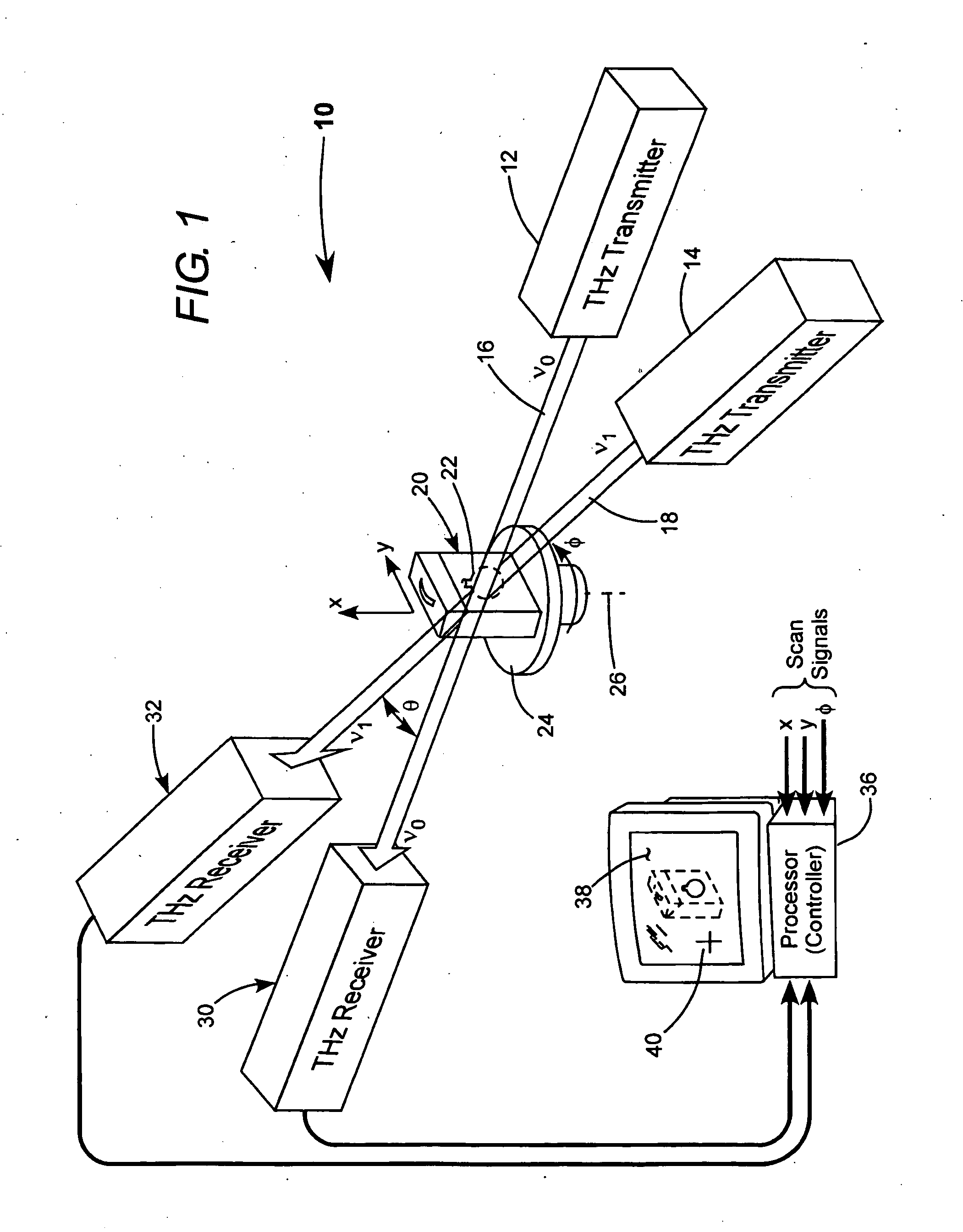
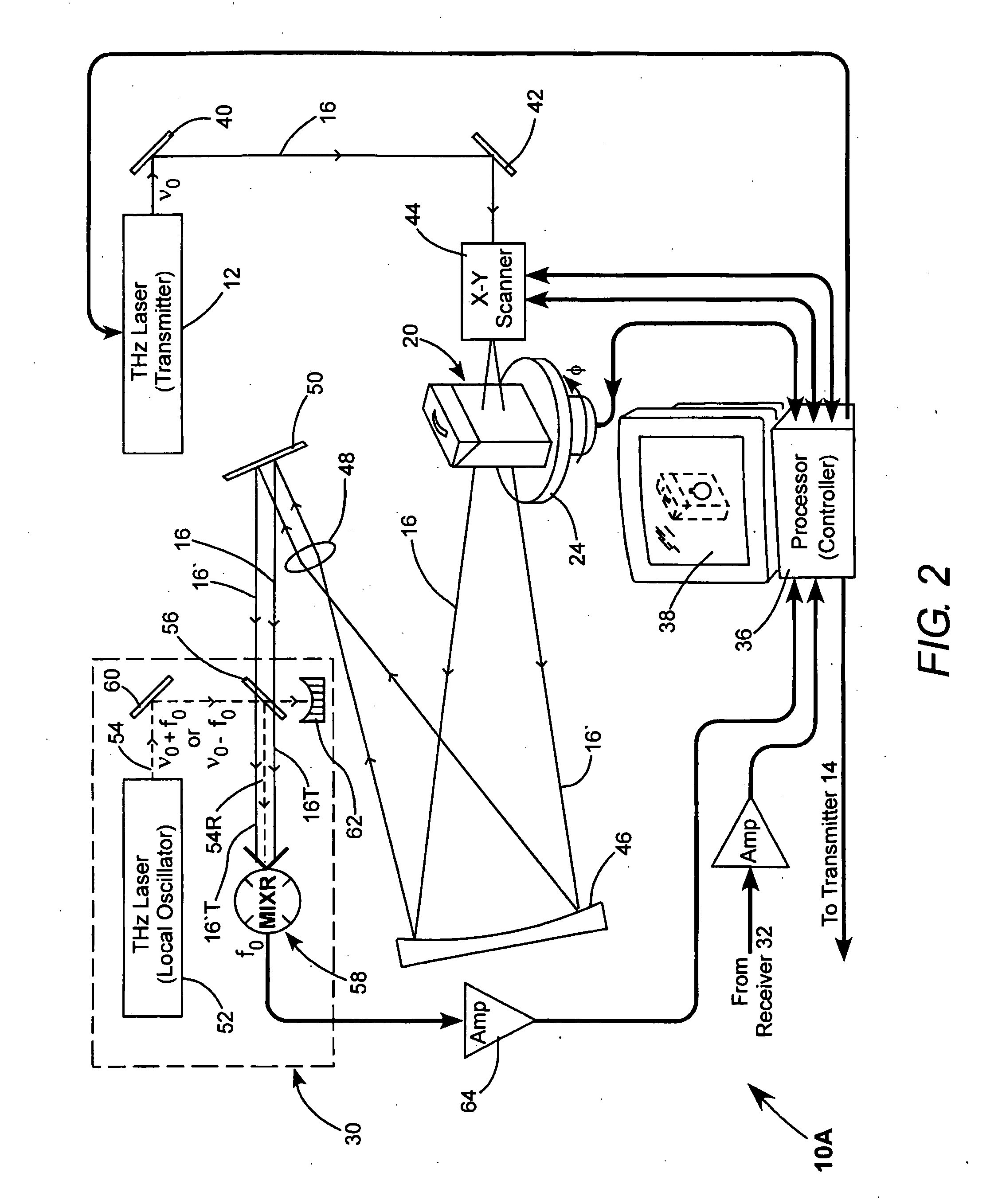
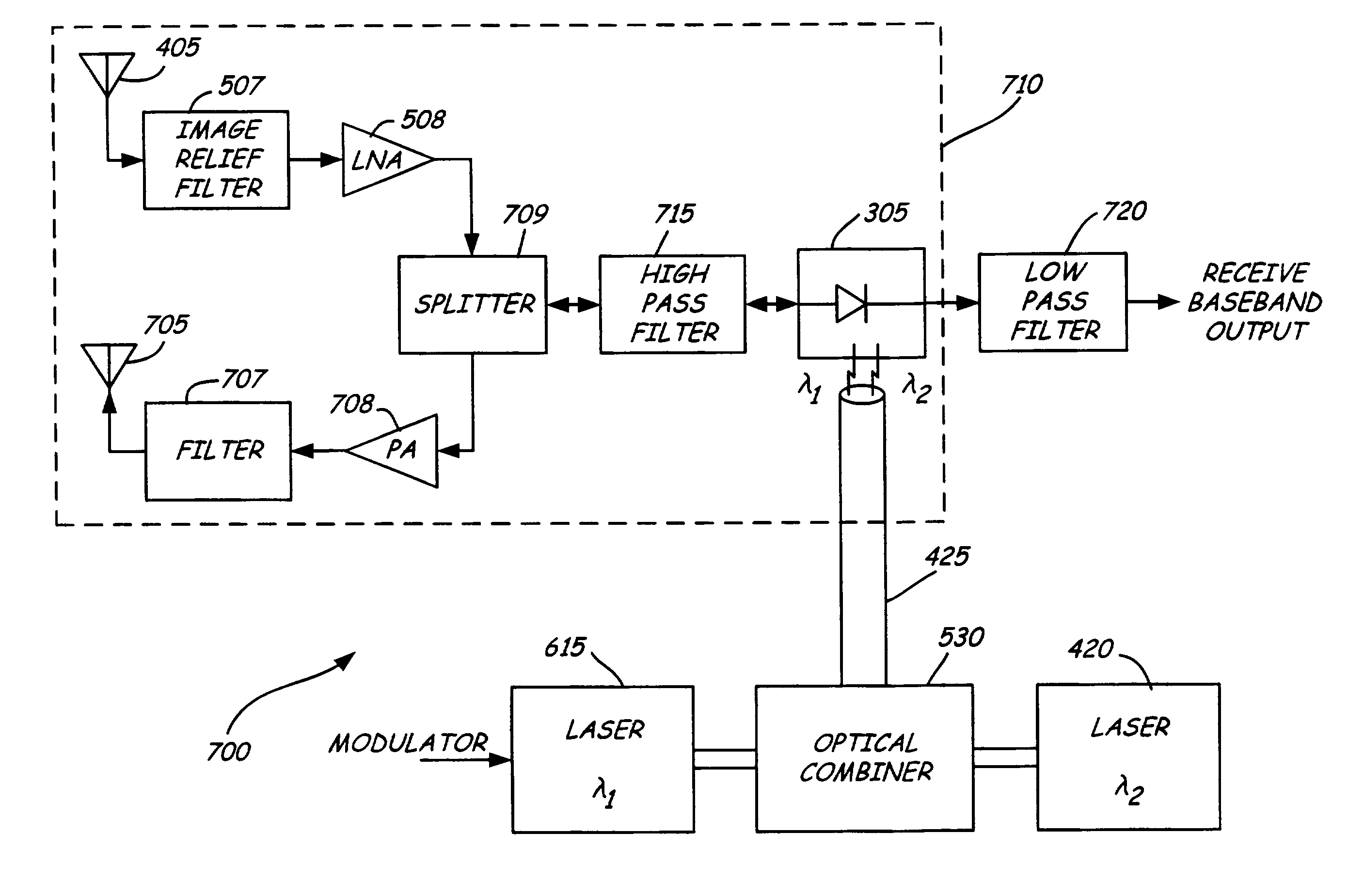
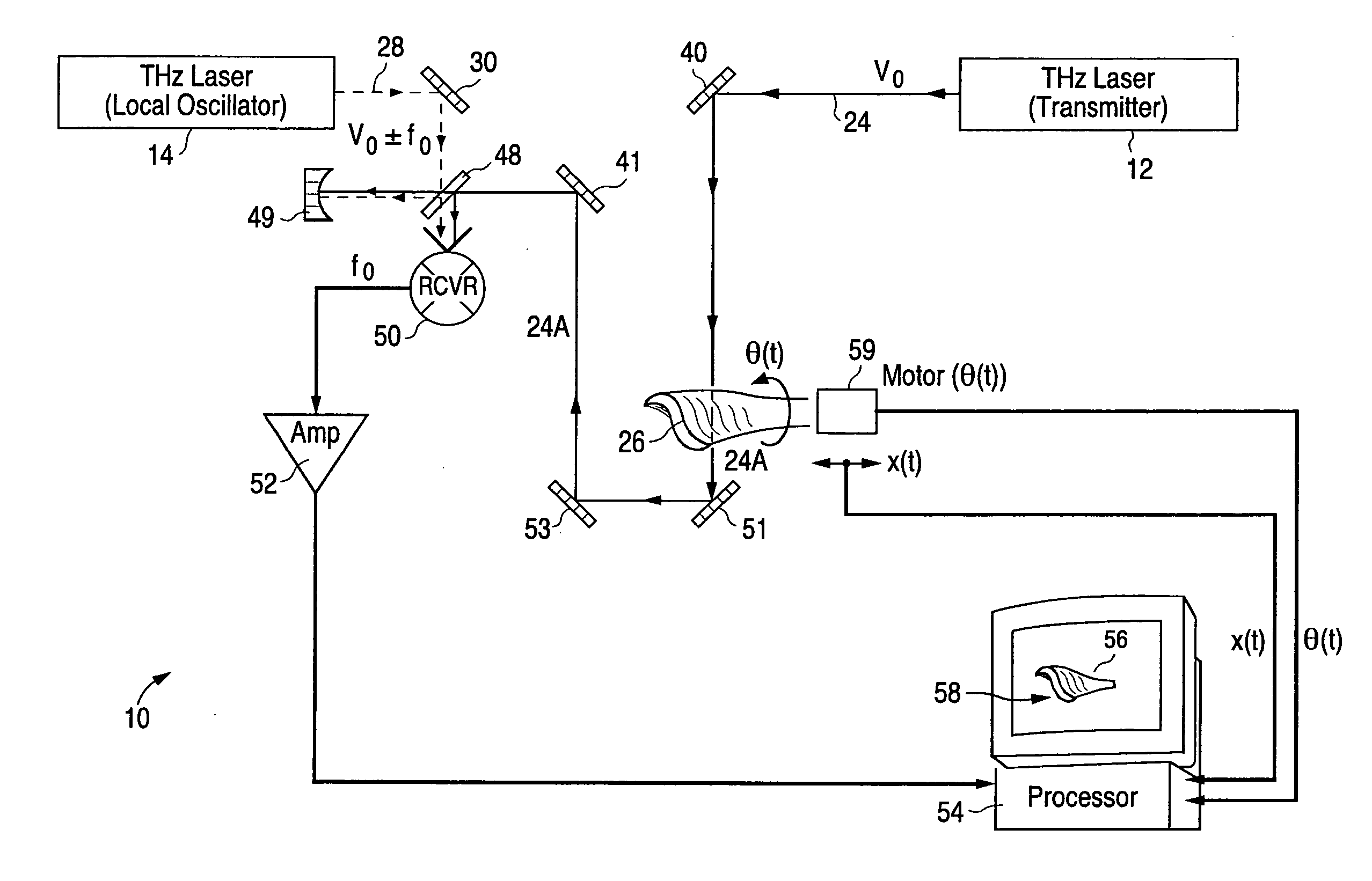
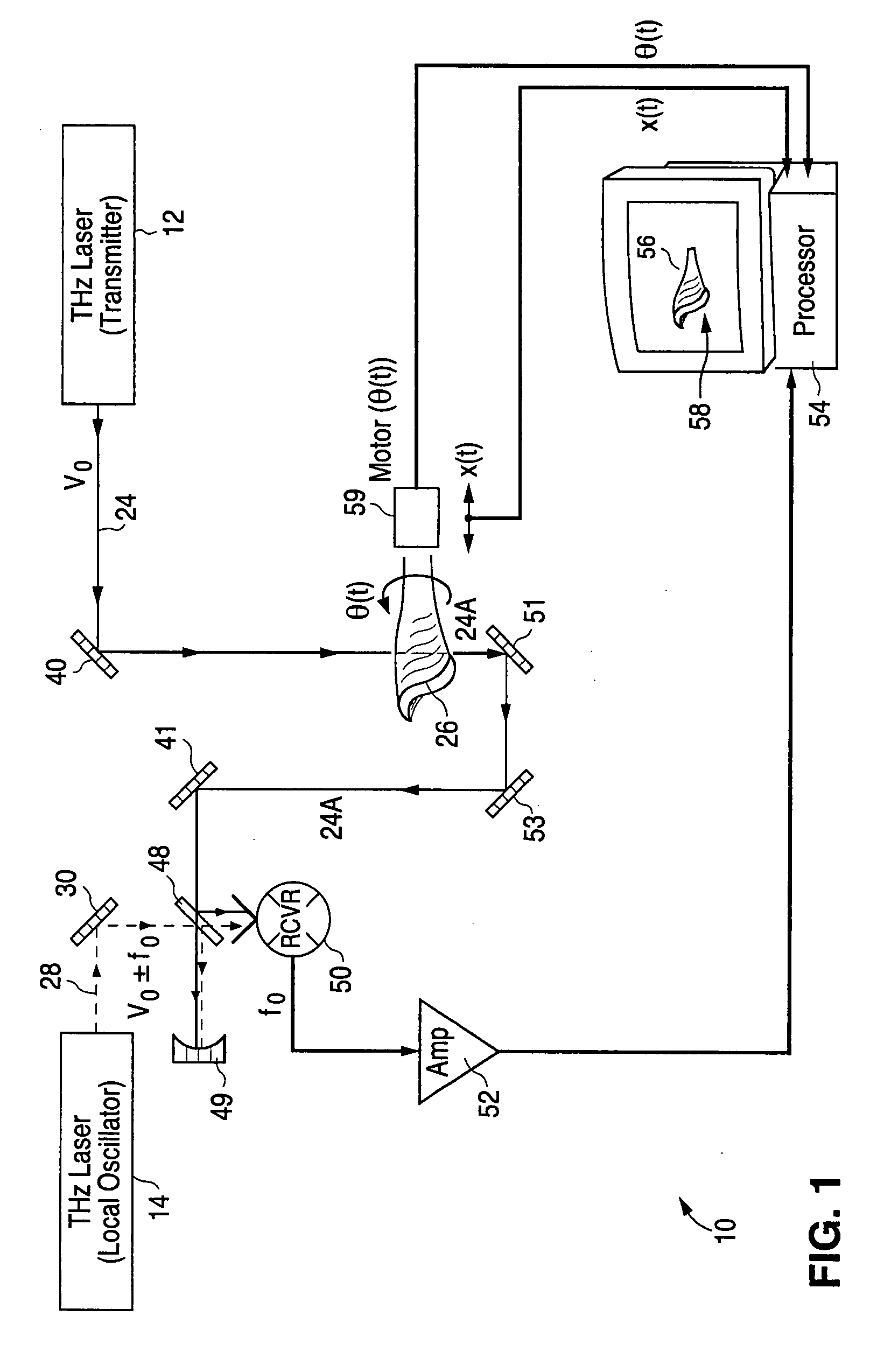
Detection of hidden objects by terahertz heterodyne laser imaging
A THz-frequency heterodyne imaging method is used to remotely detect objects concealed in or under a person's clothing. One THz-frequency beam is scanned over a person being examined. A portion of the beam penetrates the persons clothing and is reflected by an object concealed under the person's clothing. The reflected portion the beam is mixed with another beam of THz-frequency radiation having a different frequency to provide a signal having an intermediate frequency (IF) including image data representative of the concealed object.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Apparatus and method for frequency shifting of a wireless signal and systems using frequency shifting
ActiveUS20080146146A1Expand coverageIncreased reach and distanceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsMultiple carrier systemsResidenceOperating energy
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
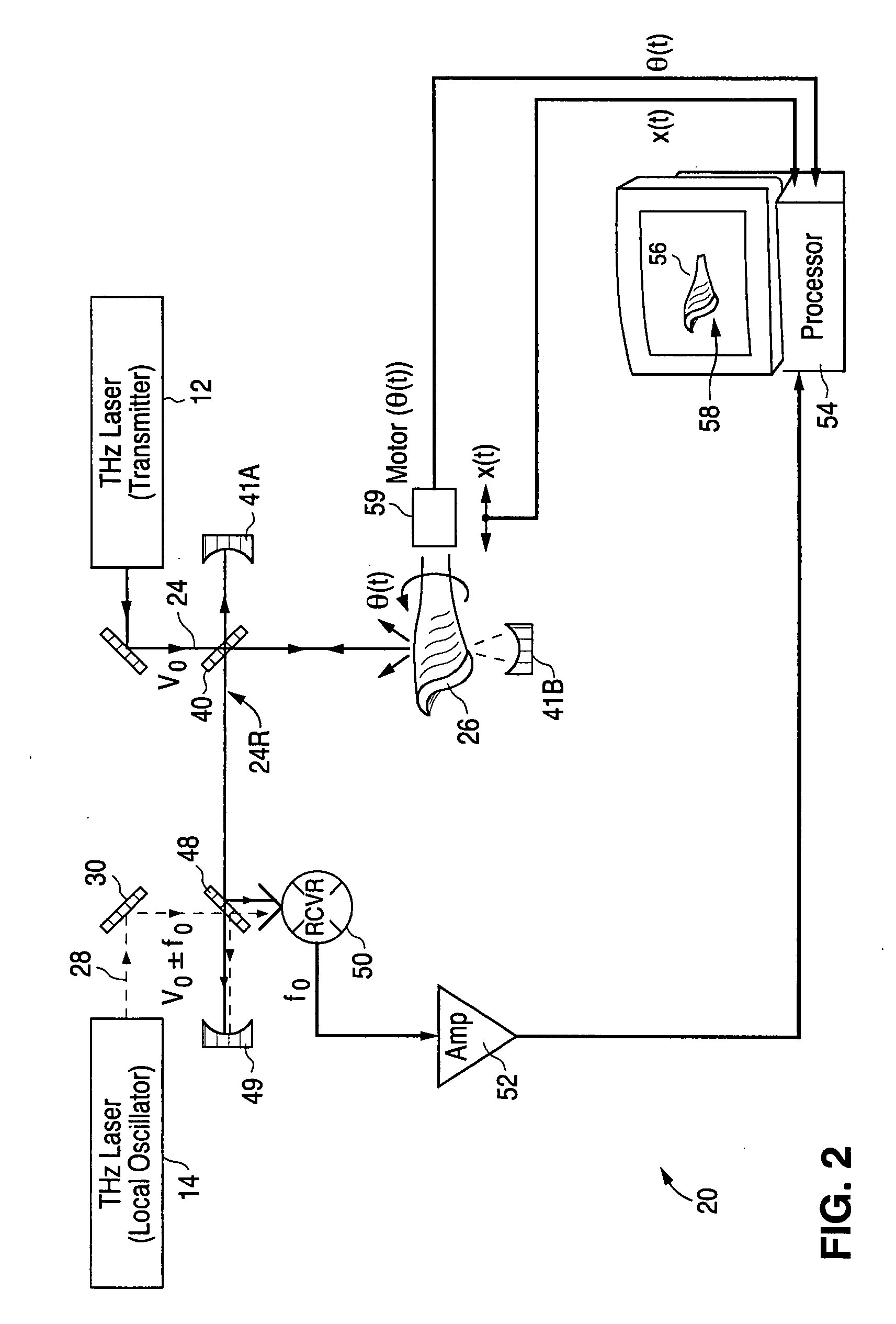
Identification of hidden objects by terahertz heterodyne laser imaging
A method for inspecting a package to identify an object concealed in the package includes passing two beams of THz-radiation through the package. The frequency of THz radiation in one beam is different from that in the other, and the beams are at an angle to each other. Each of the transmitted beams is used to form an image of the package and the object. The absorption coefficient of the object is determined from the two images. The material of the object is determined from the absorption coefficients at the two frequencies. The method is useful for detecting explosive material concealed in baggage.
Owner:COHERENT INC
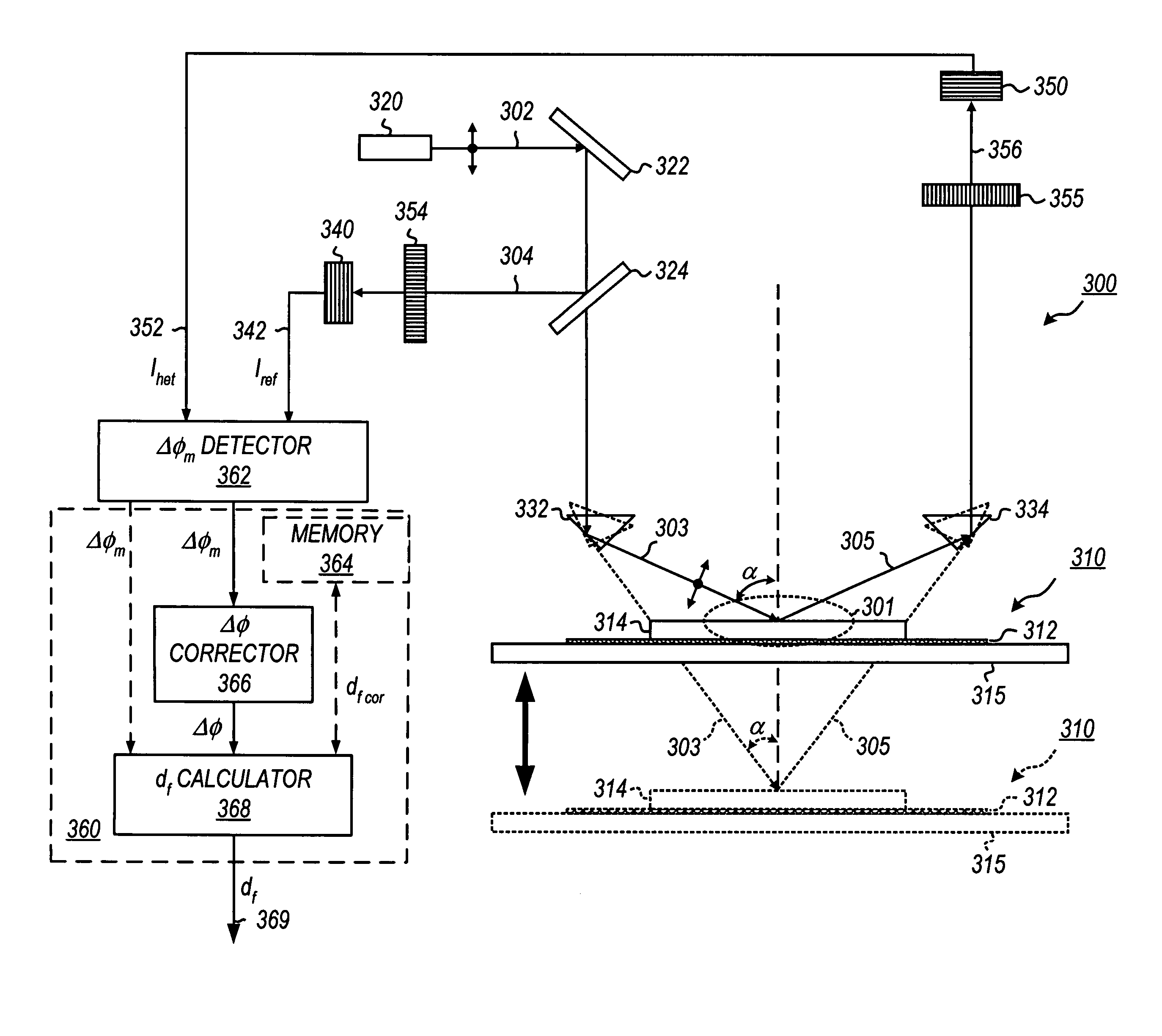
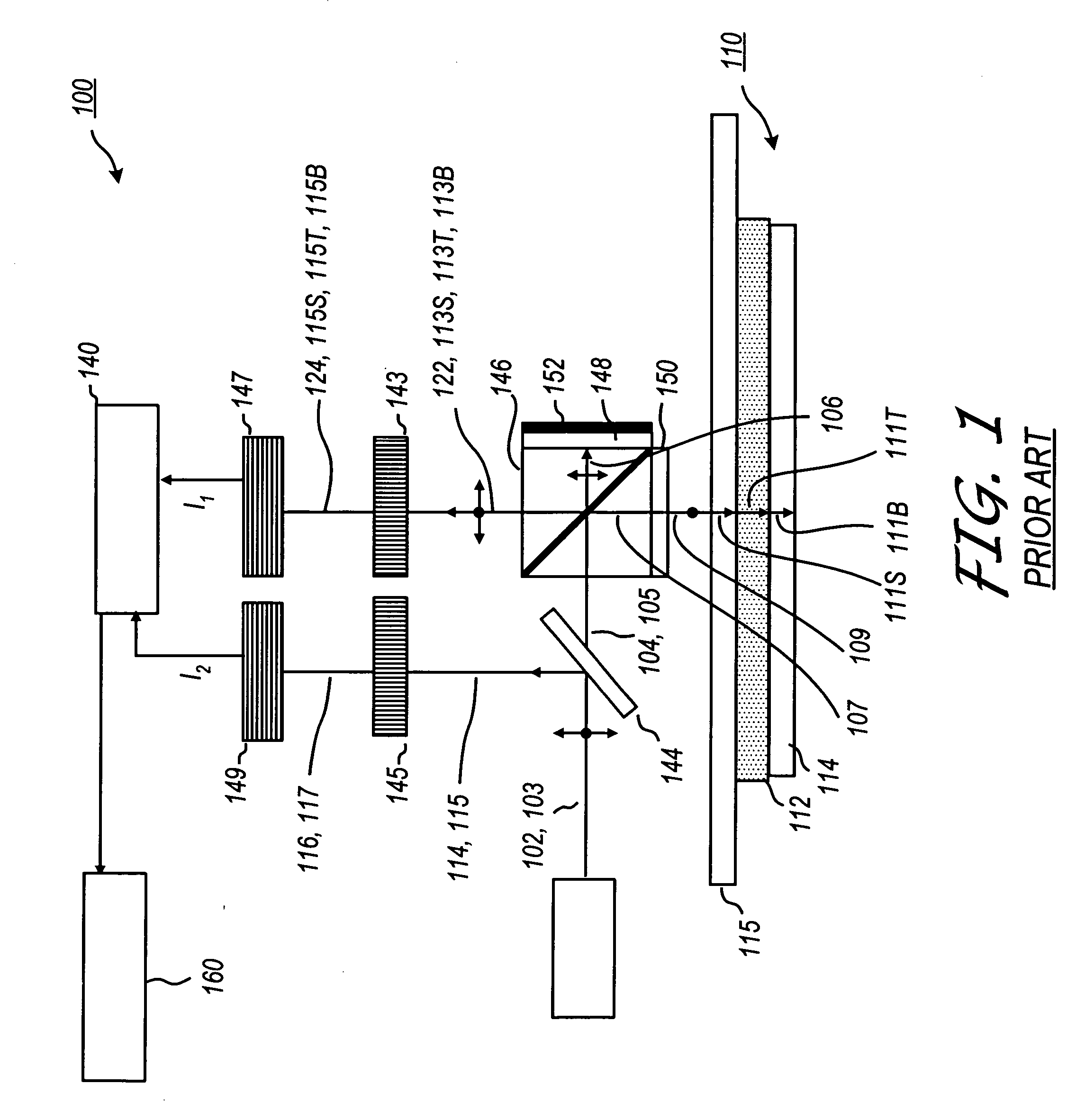
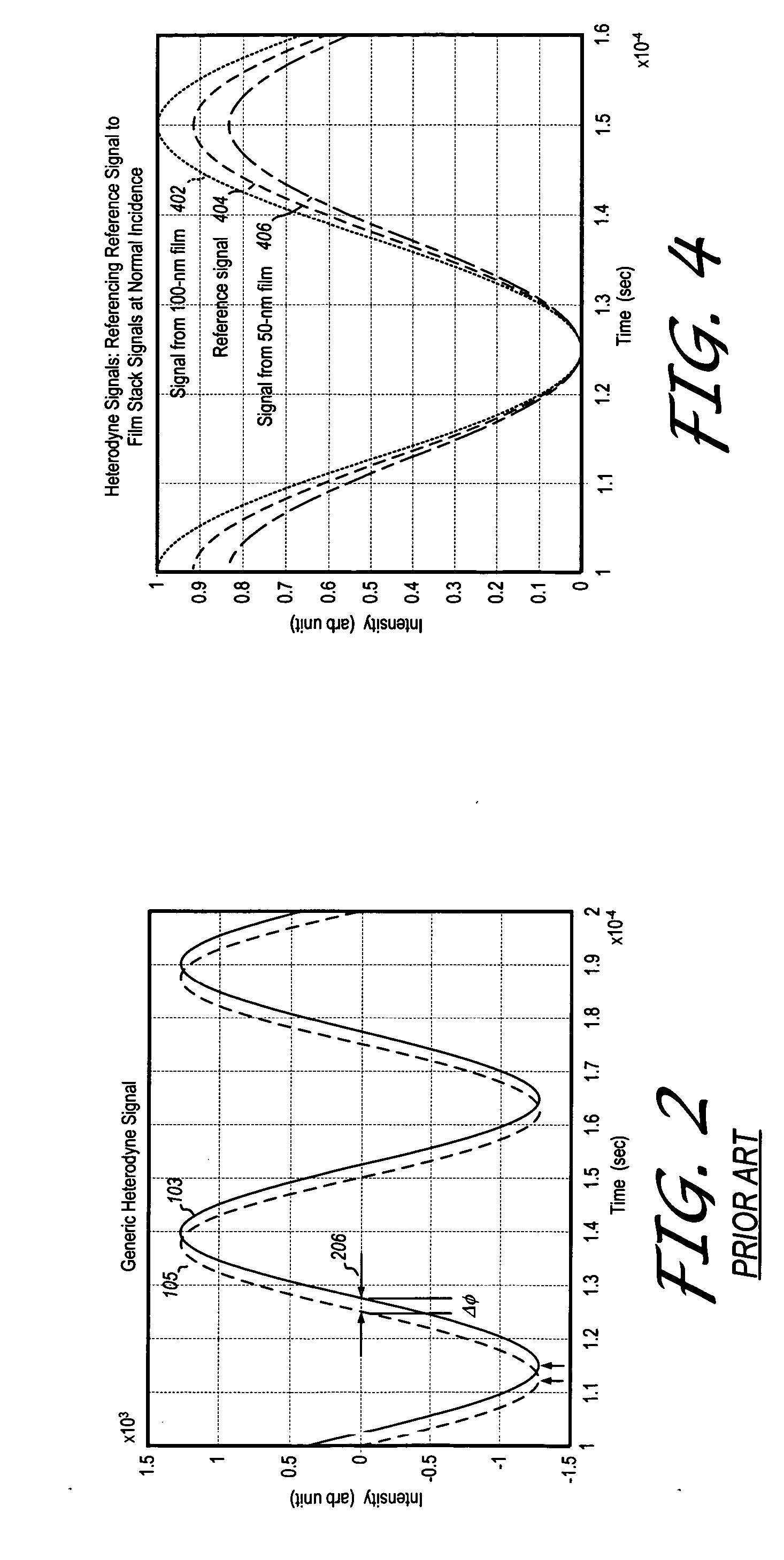
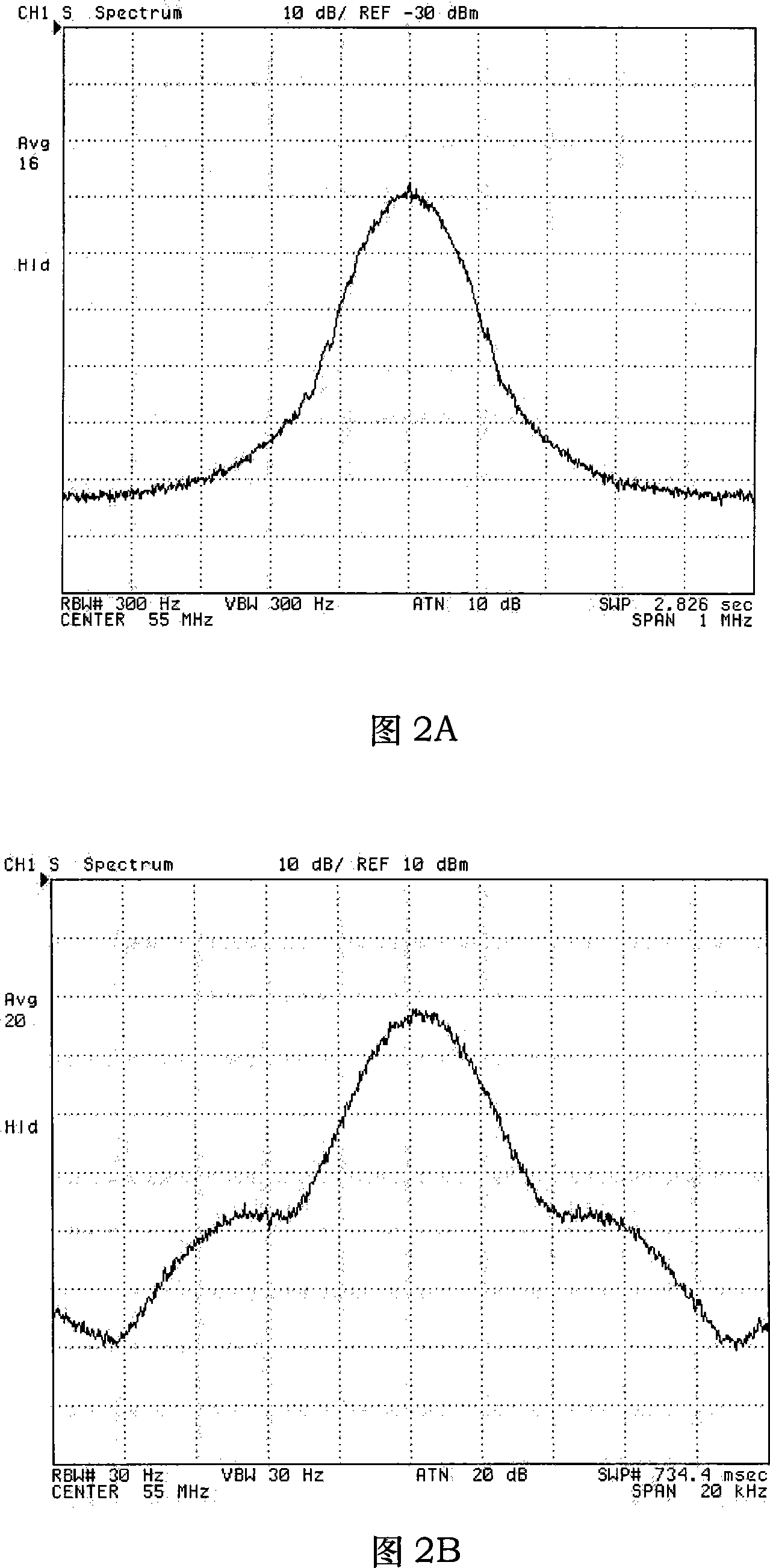
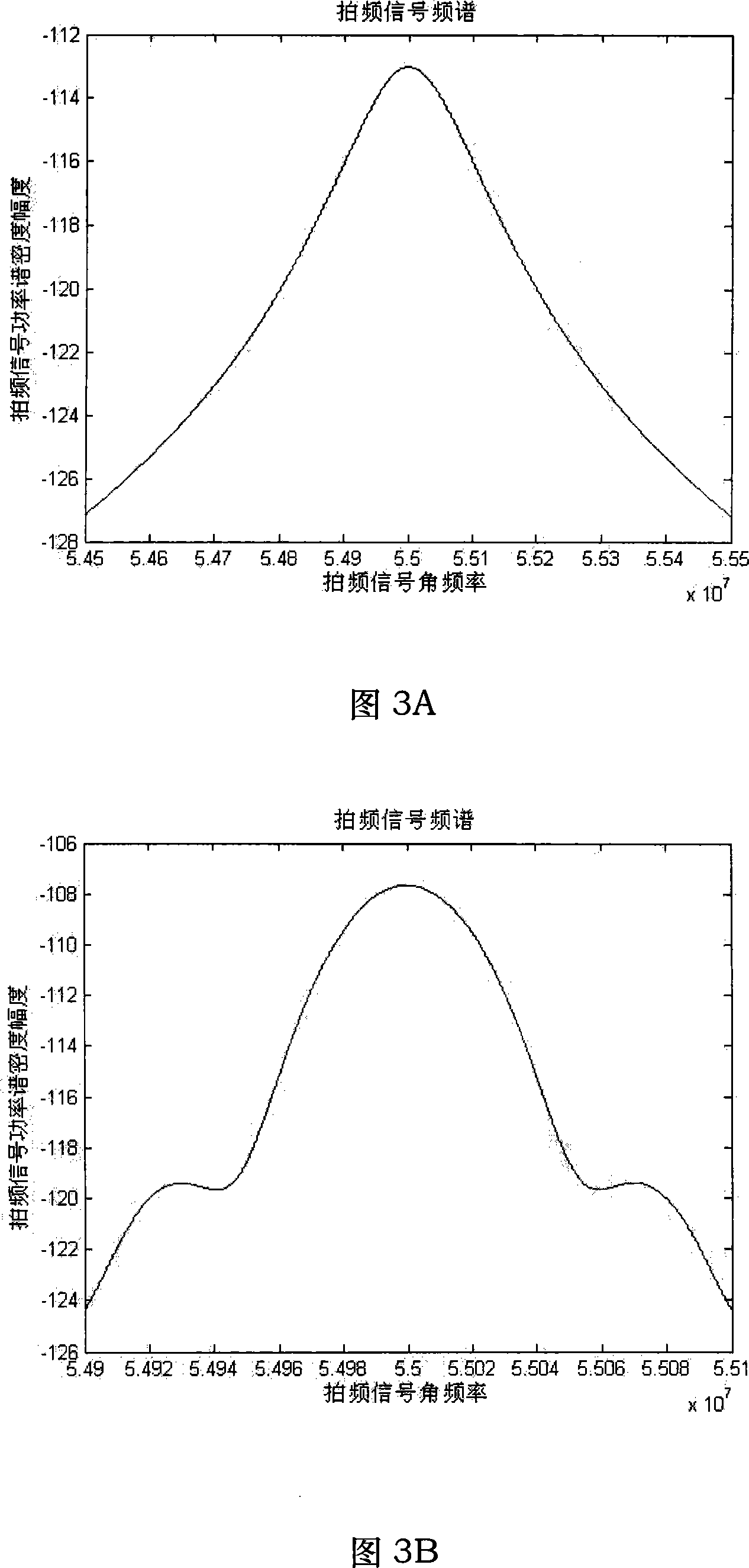
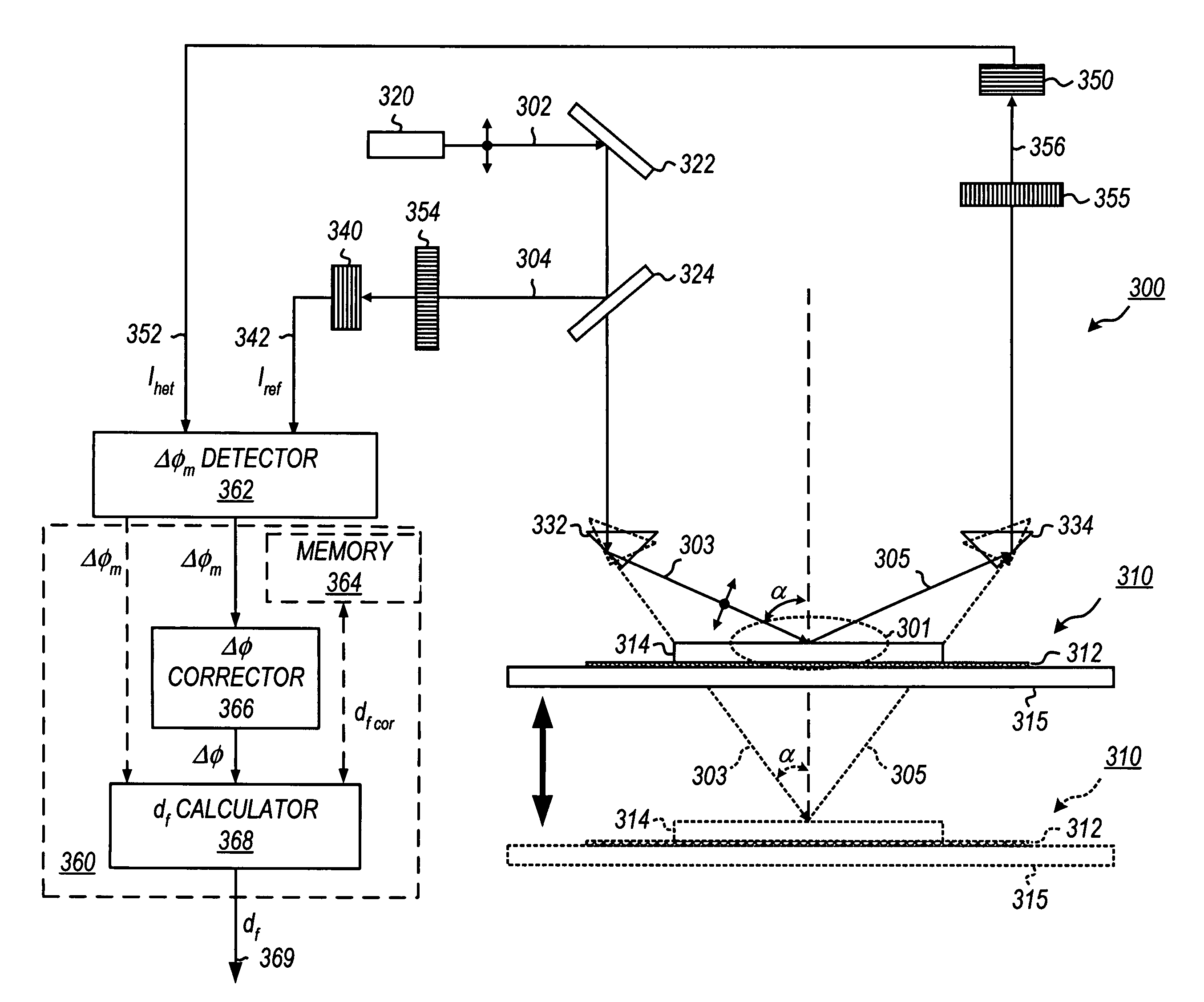
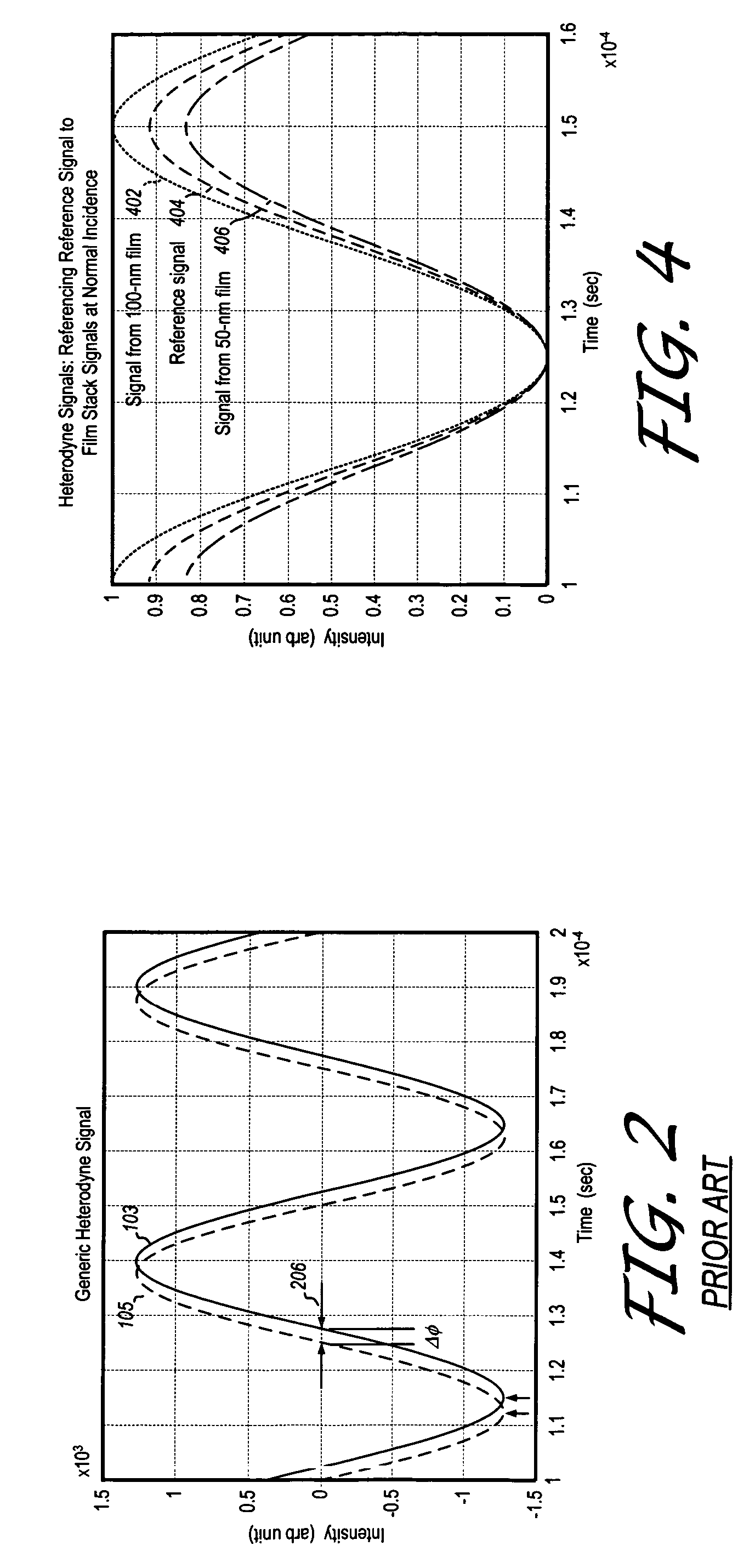
Heterodyne reflectomer for film thickness monitoring and method for implementing
The present invention is directed to a heterodyne reflectometer system and method for obtaining highly accurate phase shift information from heterodyned optical signals, from which extremely accurate film depths can be calculated. A linearly polarized light comprised of two linearly polarized components that are orthogonal to each other, with split optical frequencies, is directed toward a film causing one of the optical polarization components to lag behind the other due to an increase in the optical path in the film for that component. A pair of detectors receives the beam reflected from the film layer and produces a measurement signal, and the beam prior to incidence on the film layer and generates a reference signal, respectively. The measurement signal and reference signal are analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift. The detected phase shift is then fed into a thickness calculator for film thickness results. A grating interferometer may be included with the heterodyne reflectometer system with a grating, which diffracts the reflected beam into zeroth- and first-order bands, which are then detected by separate detectors. A detector receives the zeroth-order beam and generates another measurement signal. Another detector receives the first-order beam and generates a grating signal. The measurement signal from the grating and reference signal may be analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift, which is related to the thickness of the film. Conversely, either measurement signal may be analyzed with the grating signal by a phase detector for detecting a grating phase shift. The refractive index for the film may be calculated from grating phase shift and the heterodyne phase shift. The updated refractive index is then used for calculating thickness.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
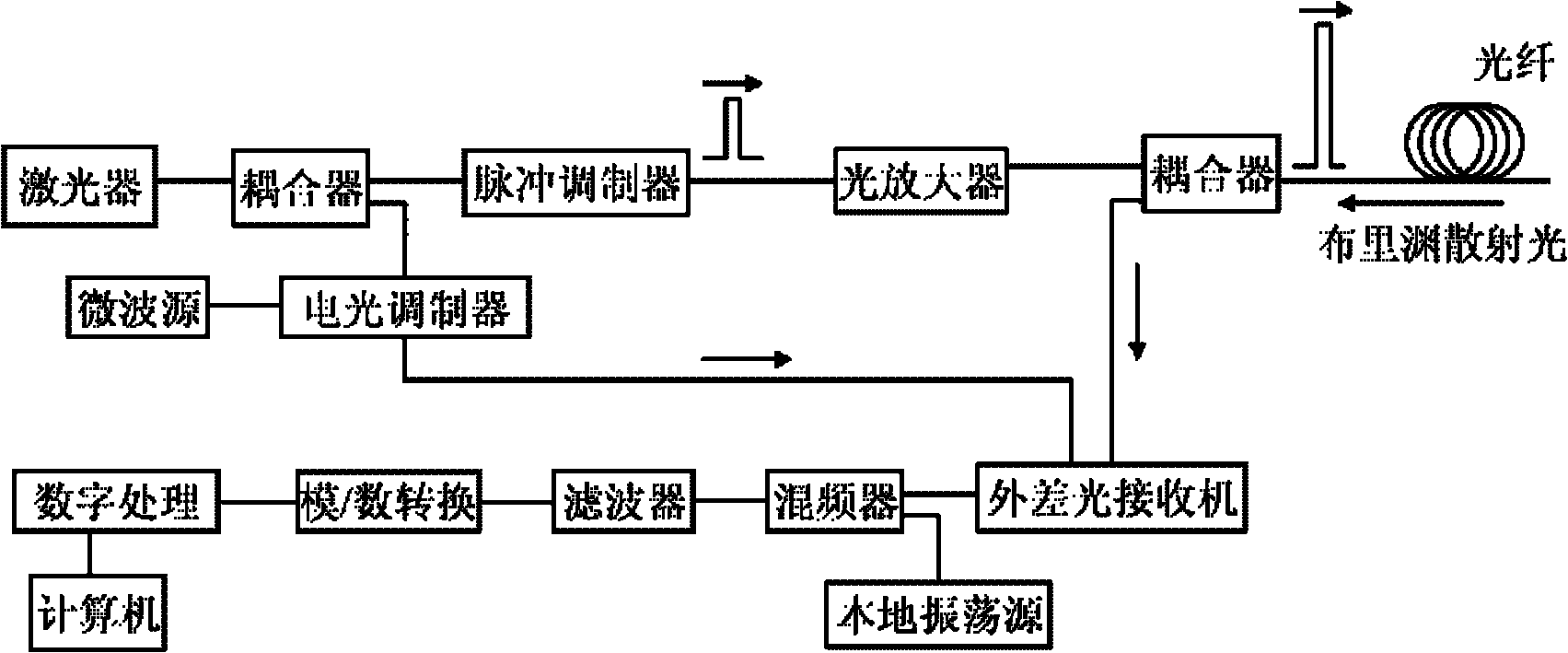
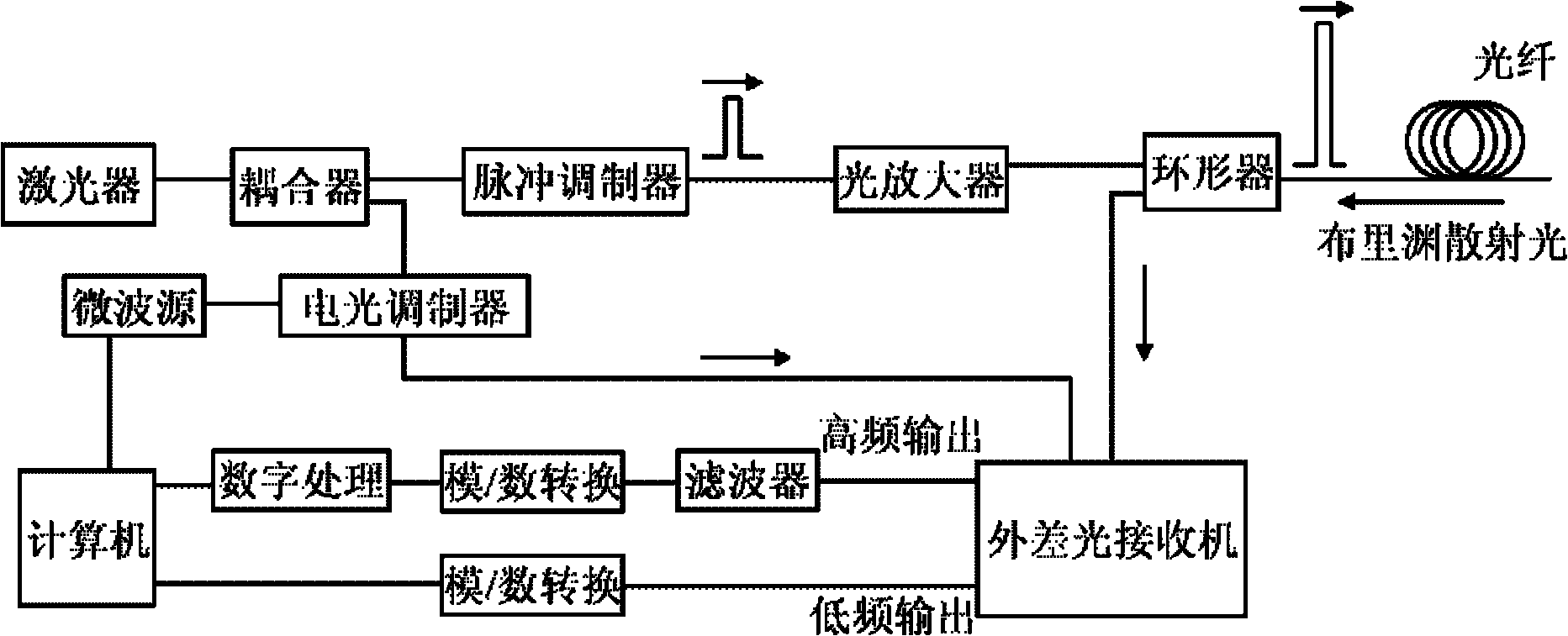
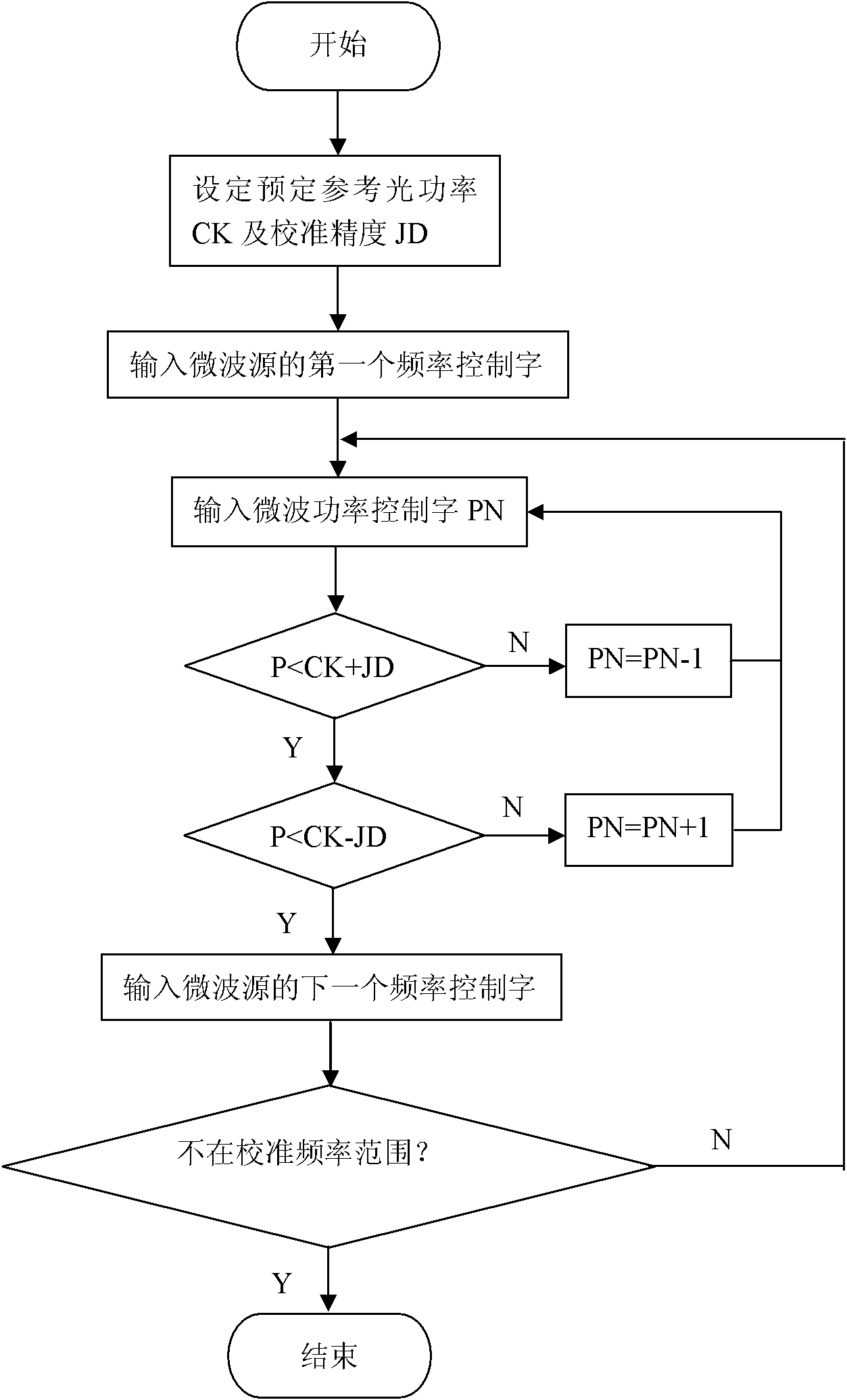
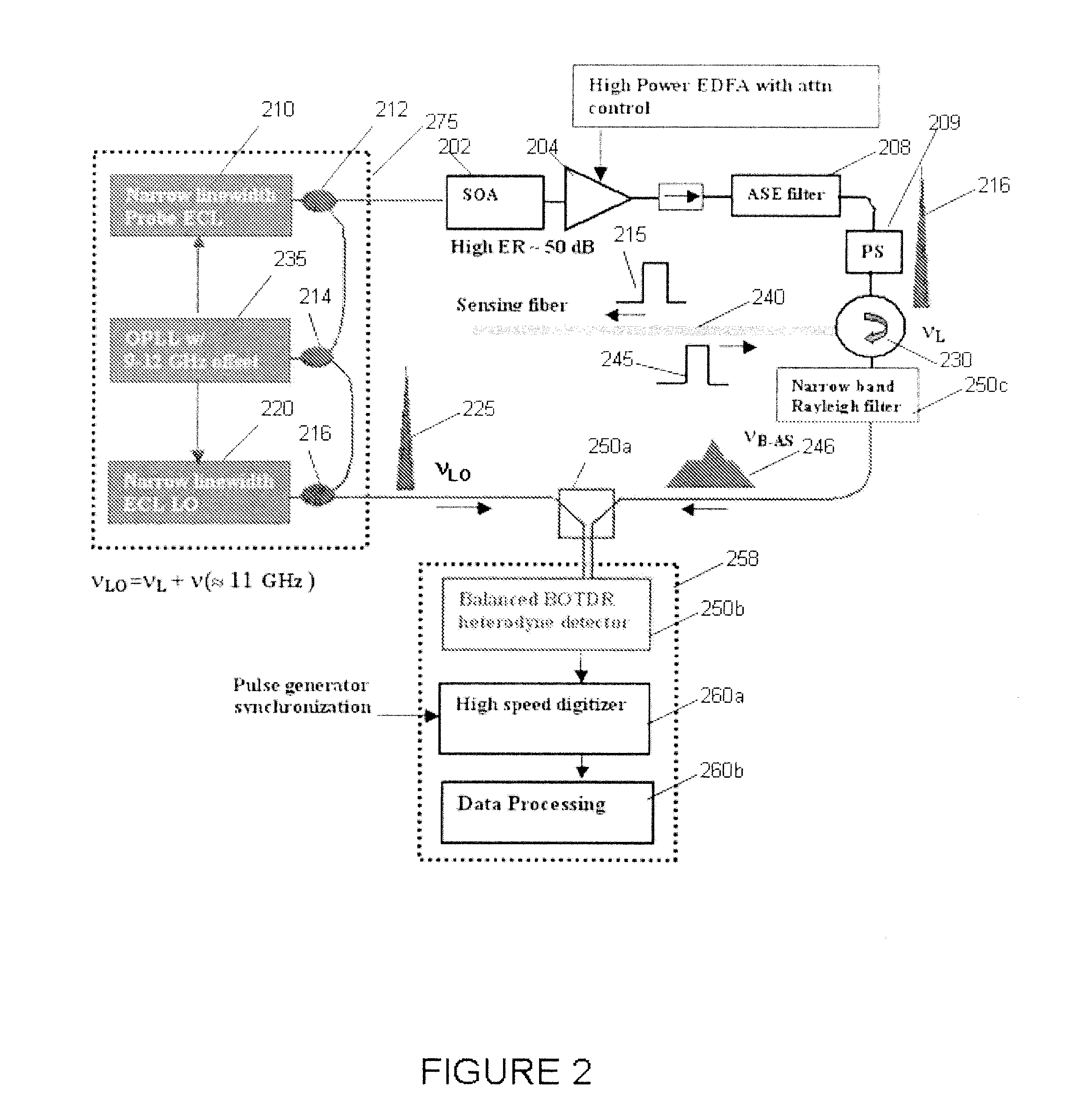
BOTDR (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) for calibrating optical power of reference light and calibrating method thereof
InactiveCN101839698AAccurate measurementHigh measurement accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationTime domainOptical power
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Electro optical microwave communications system
A wideband communications system uses a photomixer, a radio frequency (RF) mixer, and an antenna. The photomixer is comprised of high speed phototransistors that are illuminated by two laser beams. The laser beams are generated by two lasers, one tunable, and conveyed to the photomixer via fiber optic cables. The two beams are mixed by the photomixer to generate a radio heterodyne signal that is mixed with antenna signals to generate an intermediate frequency (IF) signal based on the differences of the generated heterodyne frequency and the antenna signals. Conventional fiber optic means may be used to convey the IF signals, along with the fiber optic cables to the photomixer, to and from a remote RF head located at some distance from the rest of the communications system to overcome losses in transmission lines.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
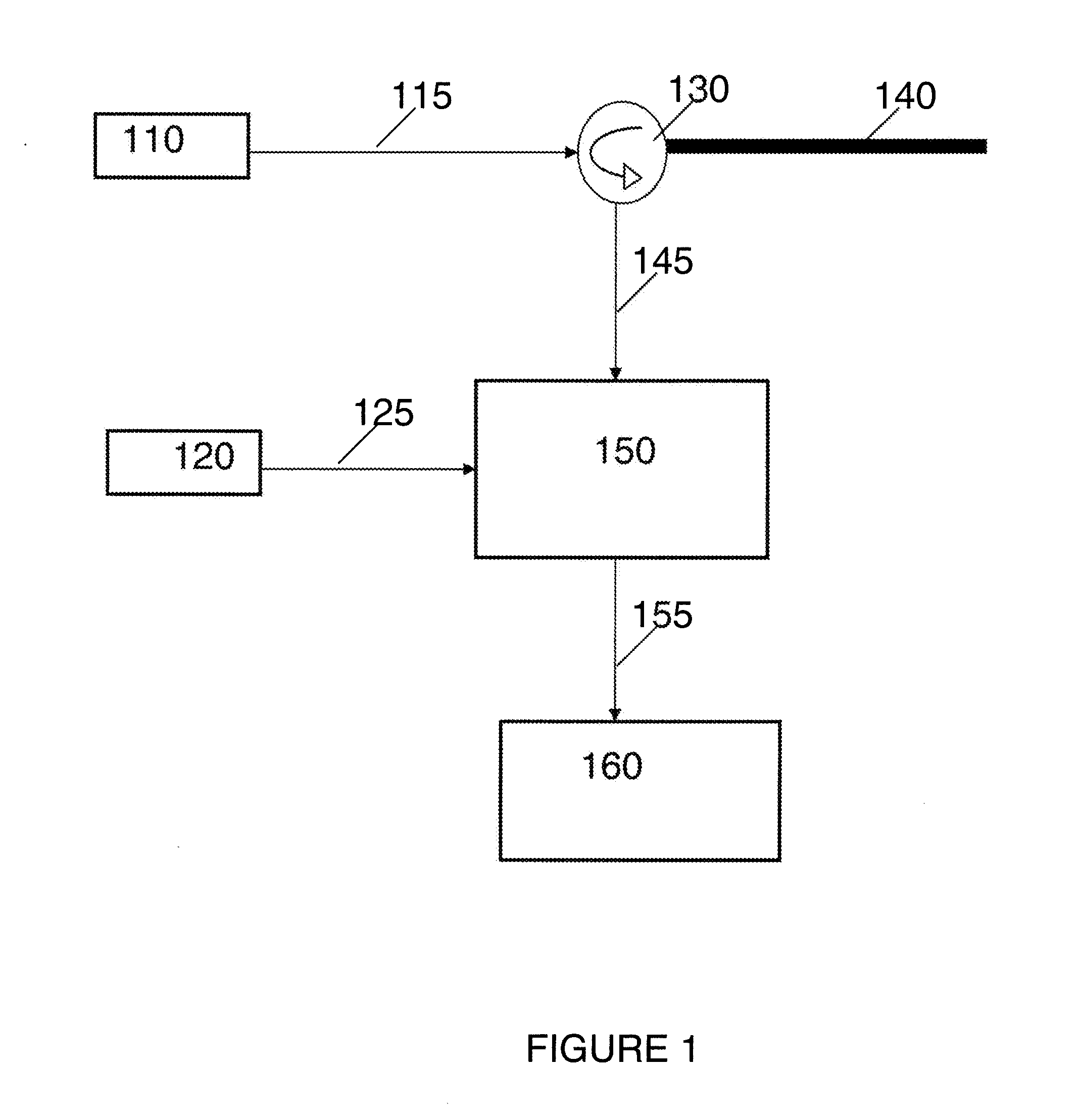
System and method for using coherently locked optical oscillator with brillouin frequency offset for fiber-optics-based distributed temperature and strain sensing applications
InactiveUS20110090936A1Efficient detectionReduce frequencyThermometer detailsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationExternal cavity laserLine width
Systems and methods are disclosed for distributed temperature and strain sensing along a length of an infrastructure. Two optical sources, such as, external cavity lasers with a narrow linewidth, are used for launching a probe signal into a sensing fiber coupled to the infrastructure, and for producing a local oscillation signal, respectively. The optical sources are coherently locked with a predefined frequency offset with respect to each other, the predefined frequency offset being in the order of the Brillouin frequency shift. The optical sources are included in an optical phase lock loop (OPLL) system. A balanced heterodyne receiver for narrow band detection at radio frequency (RF) bandwidth receives an optical signal generated by coherent mixing of a backscattered probe signal with the Brillouin frequency shift and the local oscillation signal, and produces an output indicative of one or both of a measured temperature and a measured strain.
Owner:REDFERN INTEGRATED OPTICS
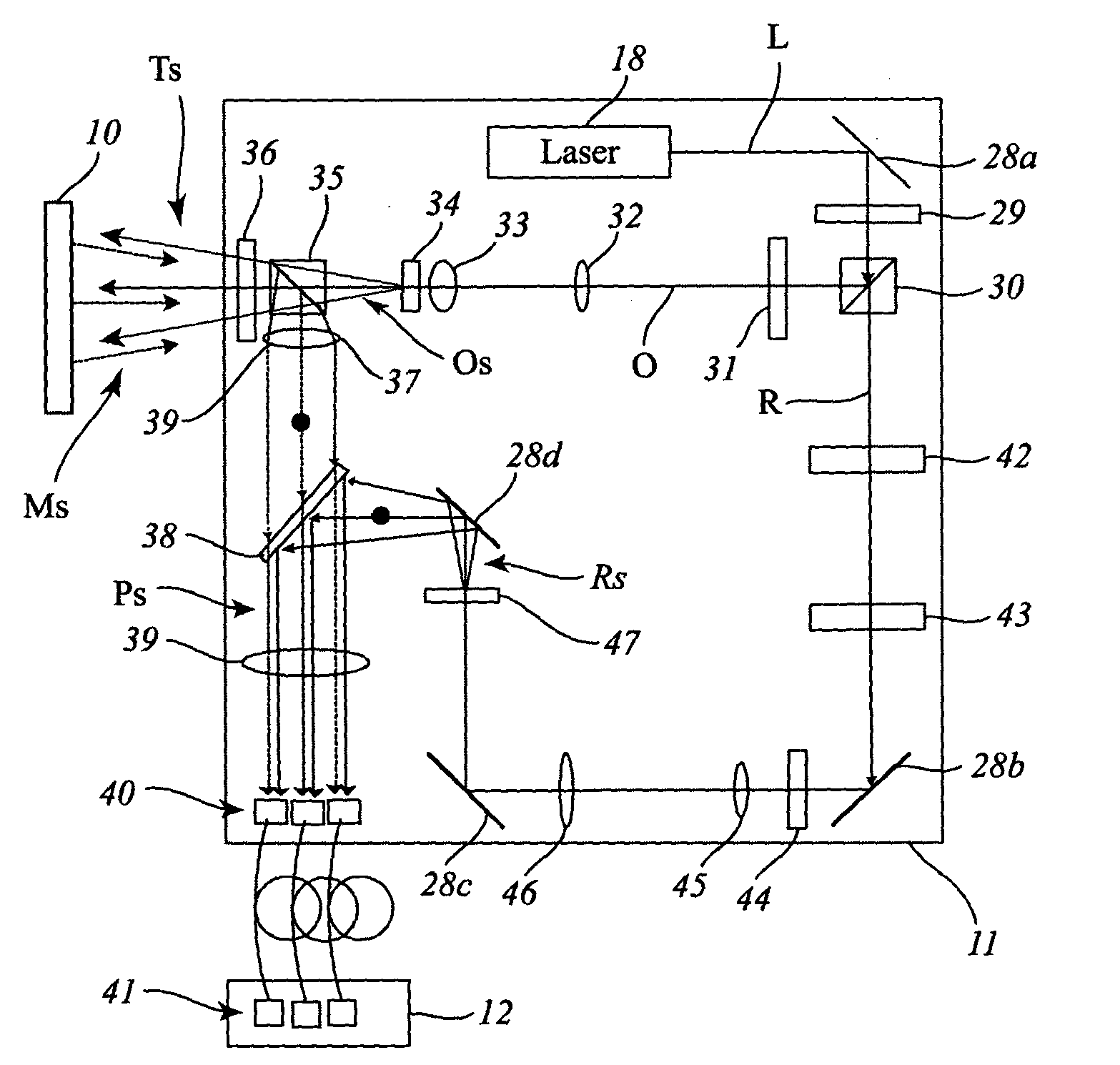
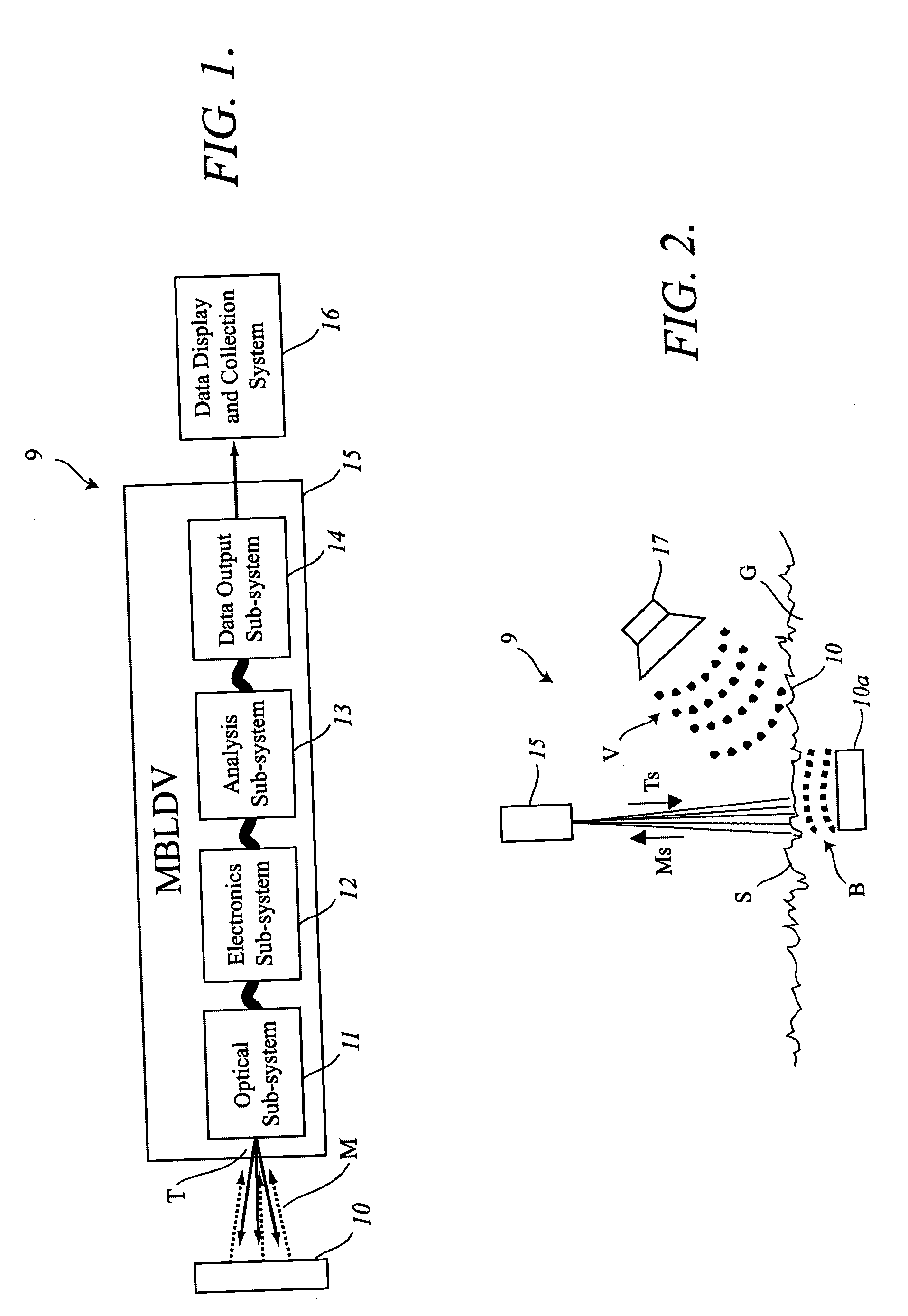
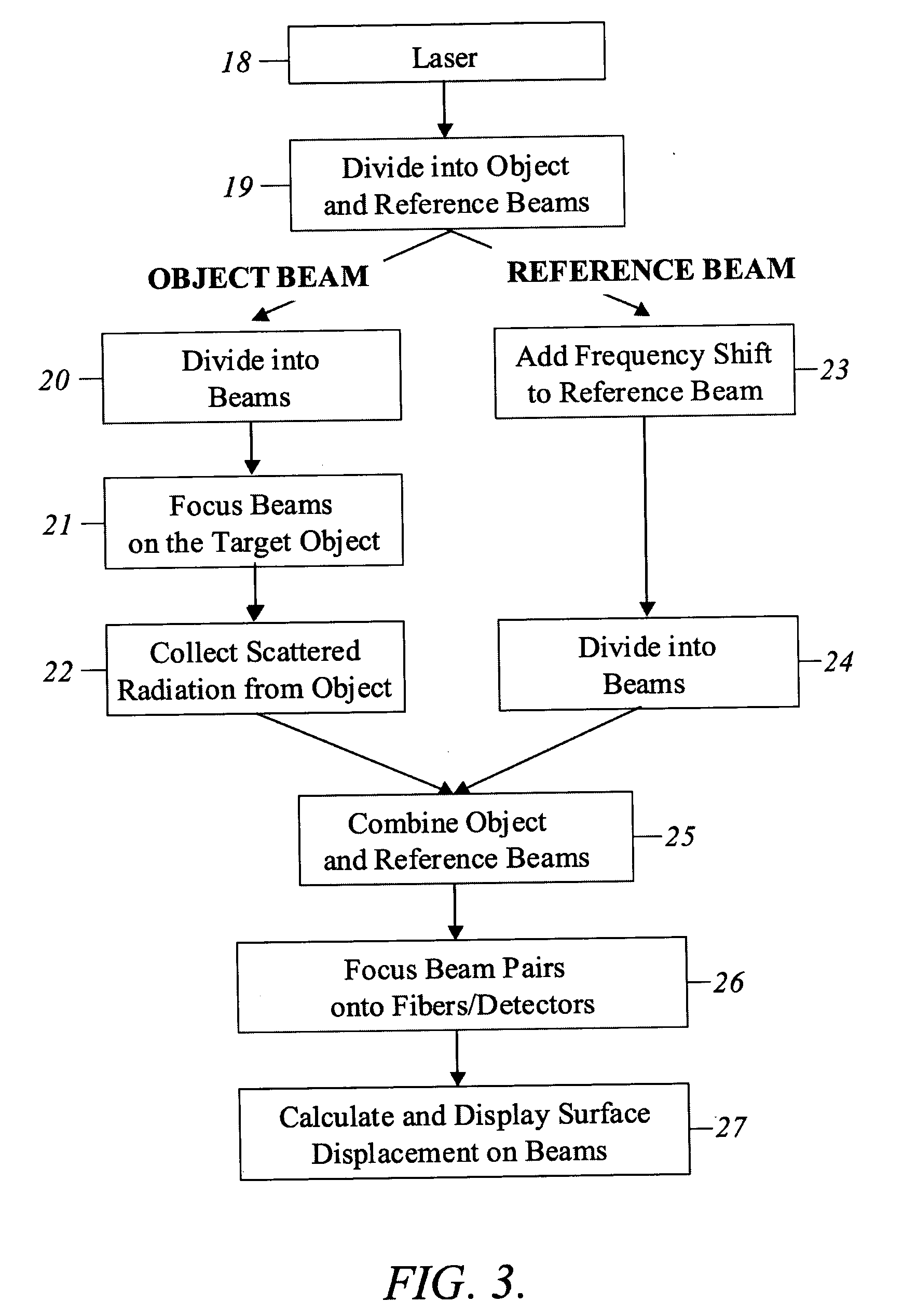
Multi-beam heterodyne laser doppler vibrometer
ActiveUS20050237533A1Accurate measurementImprove abilitiesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometer simultaneously measures velocity, displacement, and vibration history of multiple locations on an object. A beam of coherent light is split into an object beam and a reference beam. The object beam is divided into a plurality of object beams to simultaneously illuminate multiple locations on the object under inspection. The reference beam is frequency shifted and split into a corresponding plurality of frequency-shifted reference beams. A portion of each object beam is reflected by the object as a modulated object beam. The plurality of modulated object beams are collected and respectively mixed with the plurality of frequency-shifted reference beams to provide a plurality of beam pairs. Each beam pair may be focused onto a photodetector or an optical fiber connected to a photodetector.
Owner:METROLASER
Heterodyne receiver array using resonant structures
An electronic receiver array for decoding data encoded into electromagnetic radiation (e.g., light) is described. The light is received at an ultra-small resonant structure. The resonant structure generates an electric field in response to the incident light and light received from a local oscillator. An electron beam passing near the resonant structure is altered on at least one characteristic as a result of the electric field. Data is encoded into the light by a characteristic that is seen in the electric field during resonance and therefore in the electron beam as it passes the electric field. Alterations in the electron beam are thus correlated to data values encoded into the light.
Owner:ADVANCED PLASMONICS
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
ActiveUS20080304044A1Increase signal powerHigh frequencyOptical rangefindersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase noisePeak value
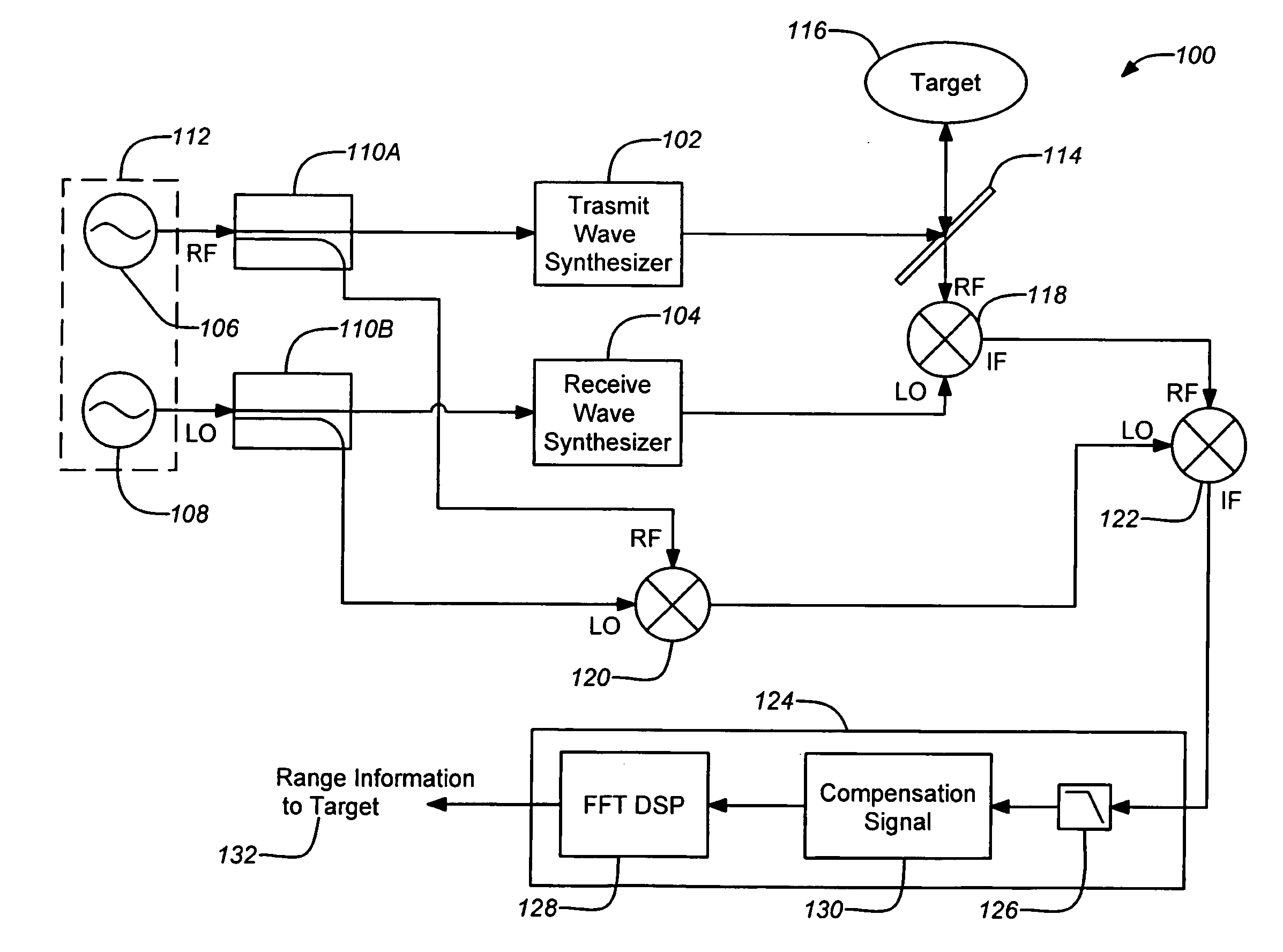
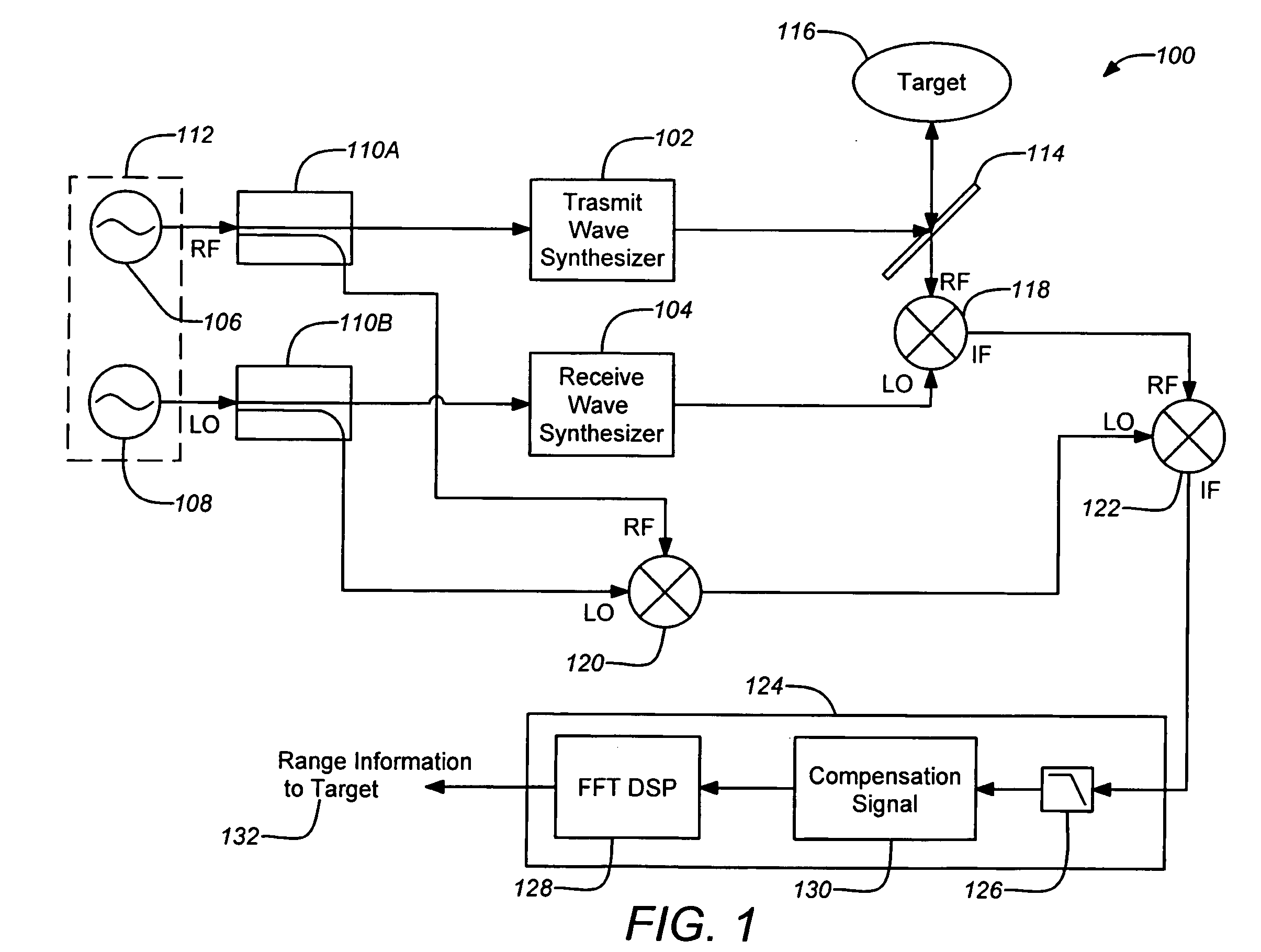
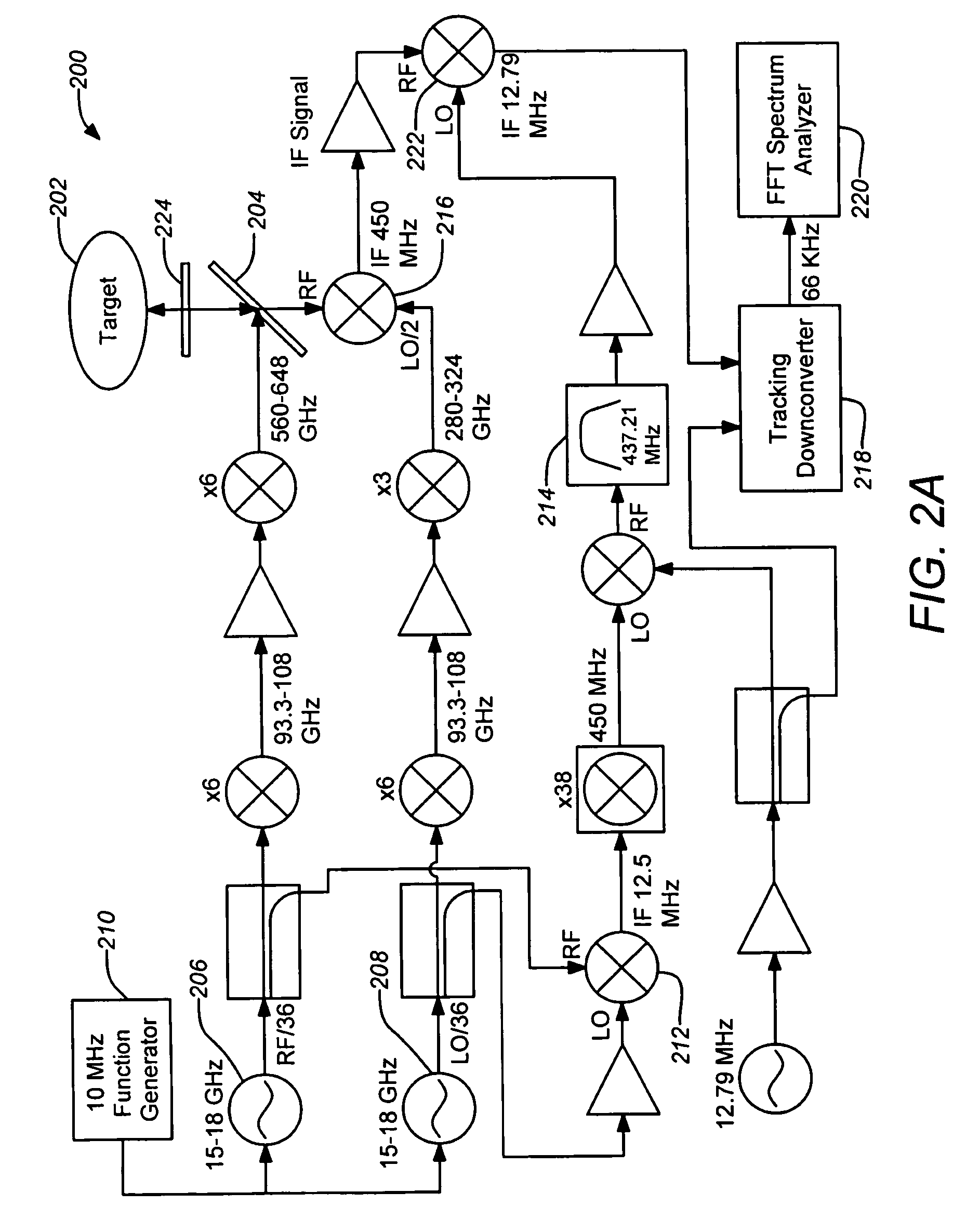
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz, is disclosed. The active target illumination inherent in radar solves the problem of low signal power and narrow-band detection by using submillimeter heterodyne mixer receivers. A submillimeter imaging radar may use low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform. Three-dimensional images are generated through range information derived for each pixel scanned over a target. A peak finding algorithm may be used in processing for each pixel to differentiate material layers of the target. Improved focusing is achieved through a compensation signal sampled from a point source calibration target and applied to received signals from active targets prior to FFT-based range compression to extract and display high-resolution target images. Such an imaging radar has particular application in detecting concealed weapons or contraband.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
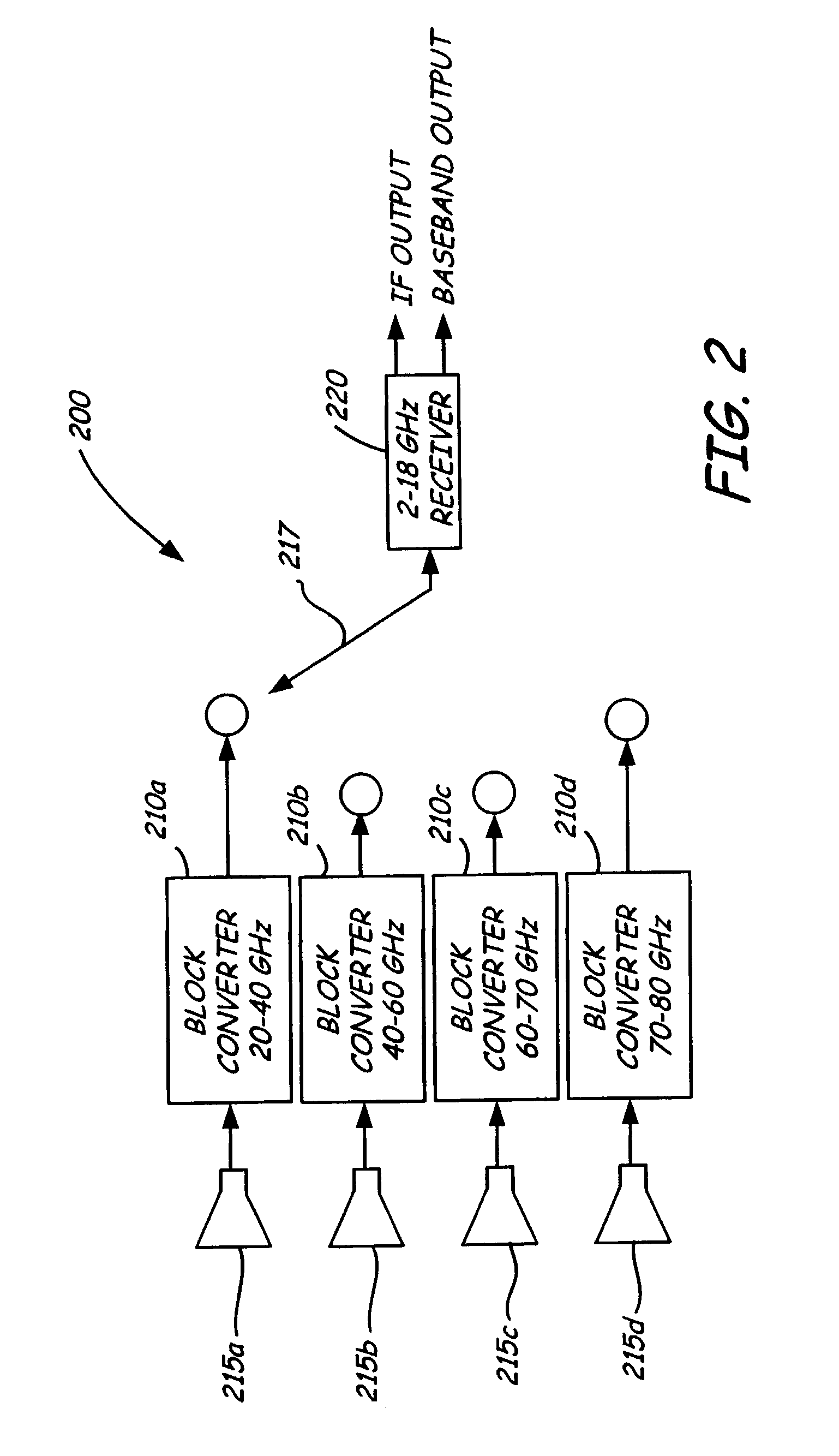
Radio communication equipment
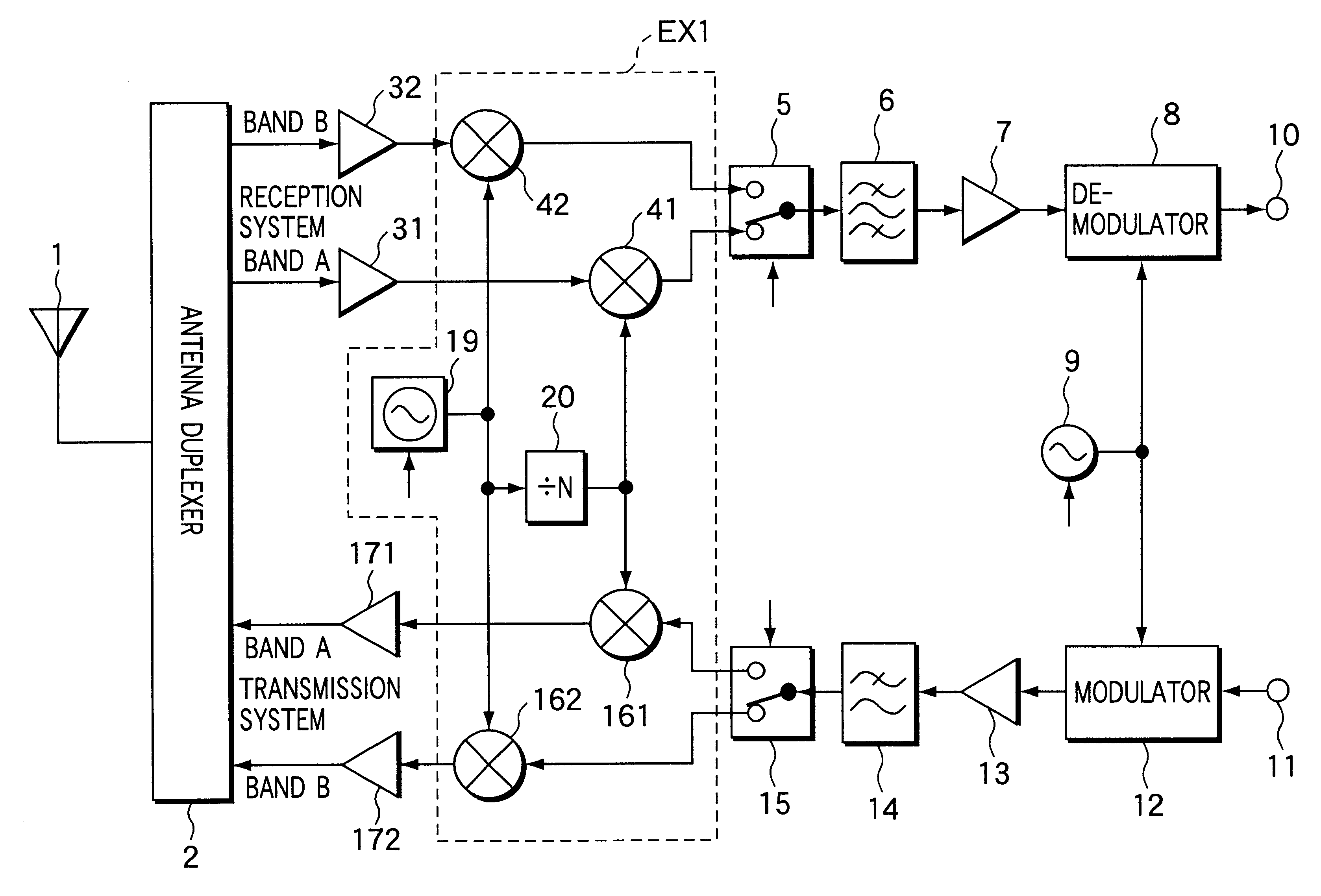
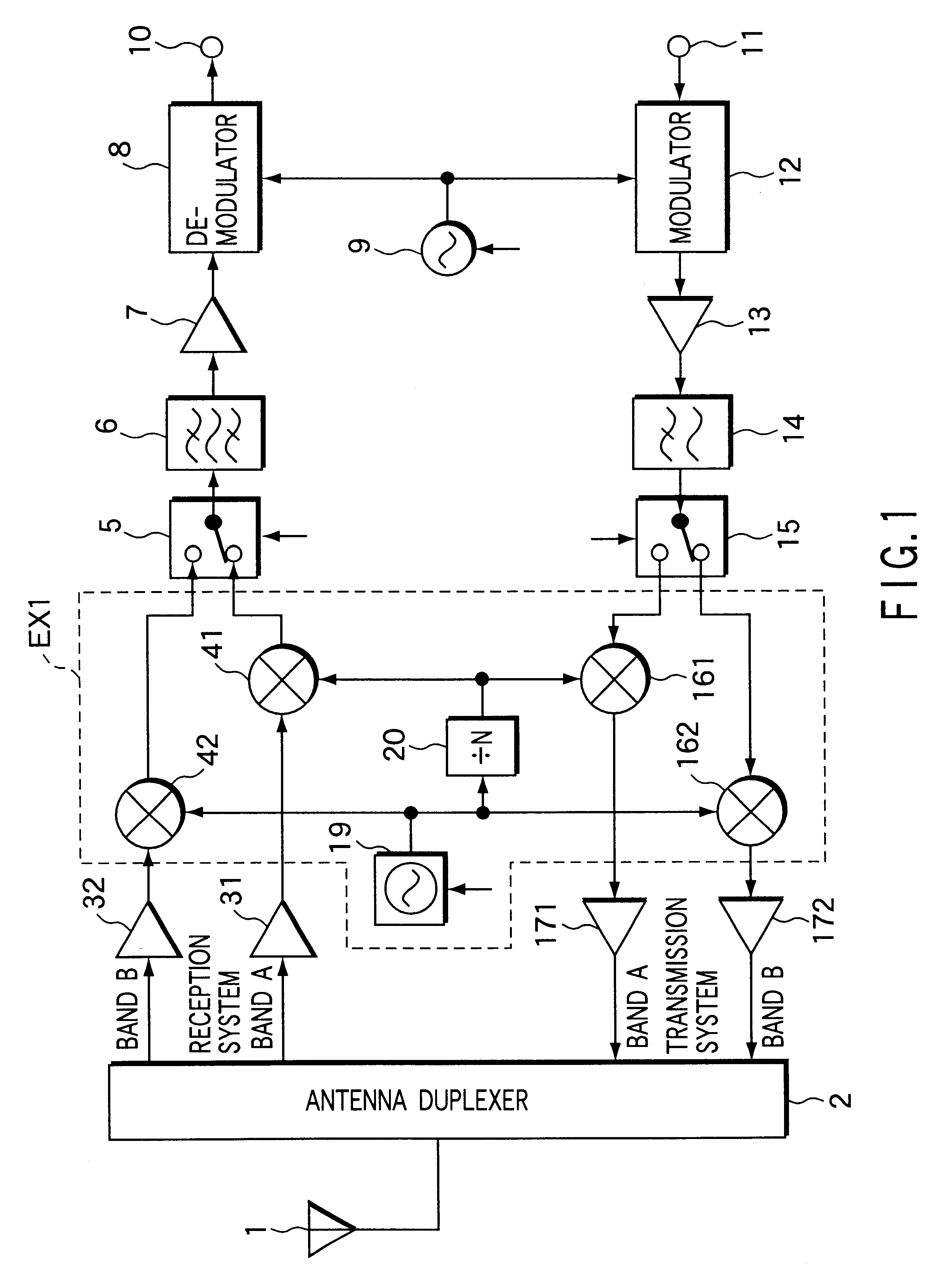
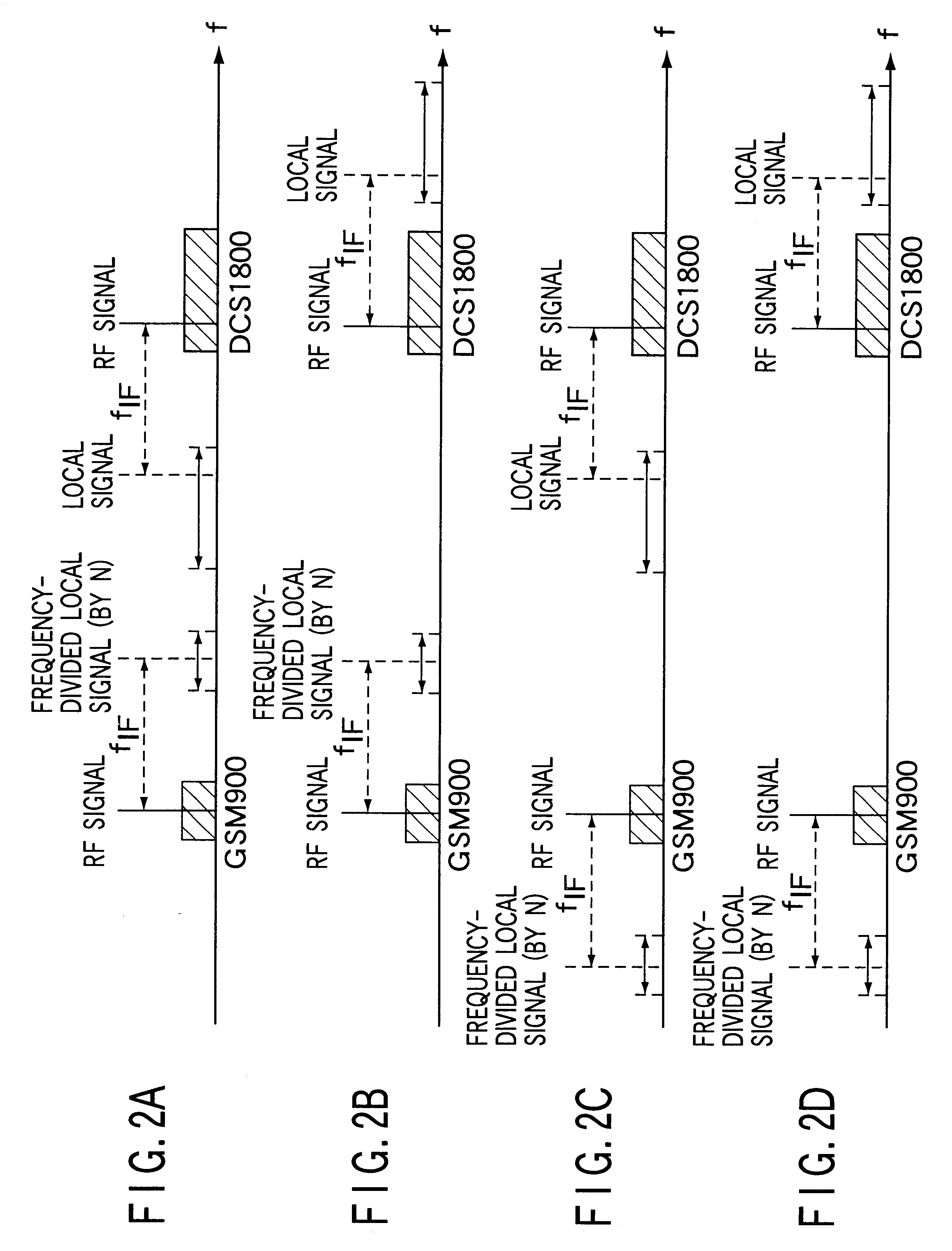
InactiveUS6393299B1Increase speedIncrease power consumptionSubstation equipmentTransmissionFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
In radiocommunication apparatus, two downconverters (41, 42) for use in reception system each heterodyne their respective received RF signal to an intermediate frequency. One of the downconverters employs a local signal generated by a synthesizer (19), and the other employs a signal obtained by dividing the frequency of the local signal by a factor of N. Two upconverters (161, 162) for use in transmission system each convert their respective input transmit signal to a transmit RF signal. One of the upconverters employs a local signal generated by the synthesizer (19) and the other employs a signal obtained by dividing the frequency of the local signal by a factor of N.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
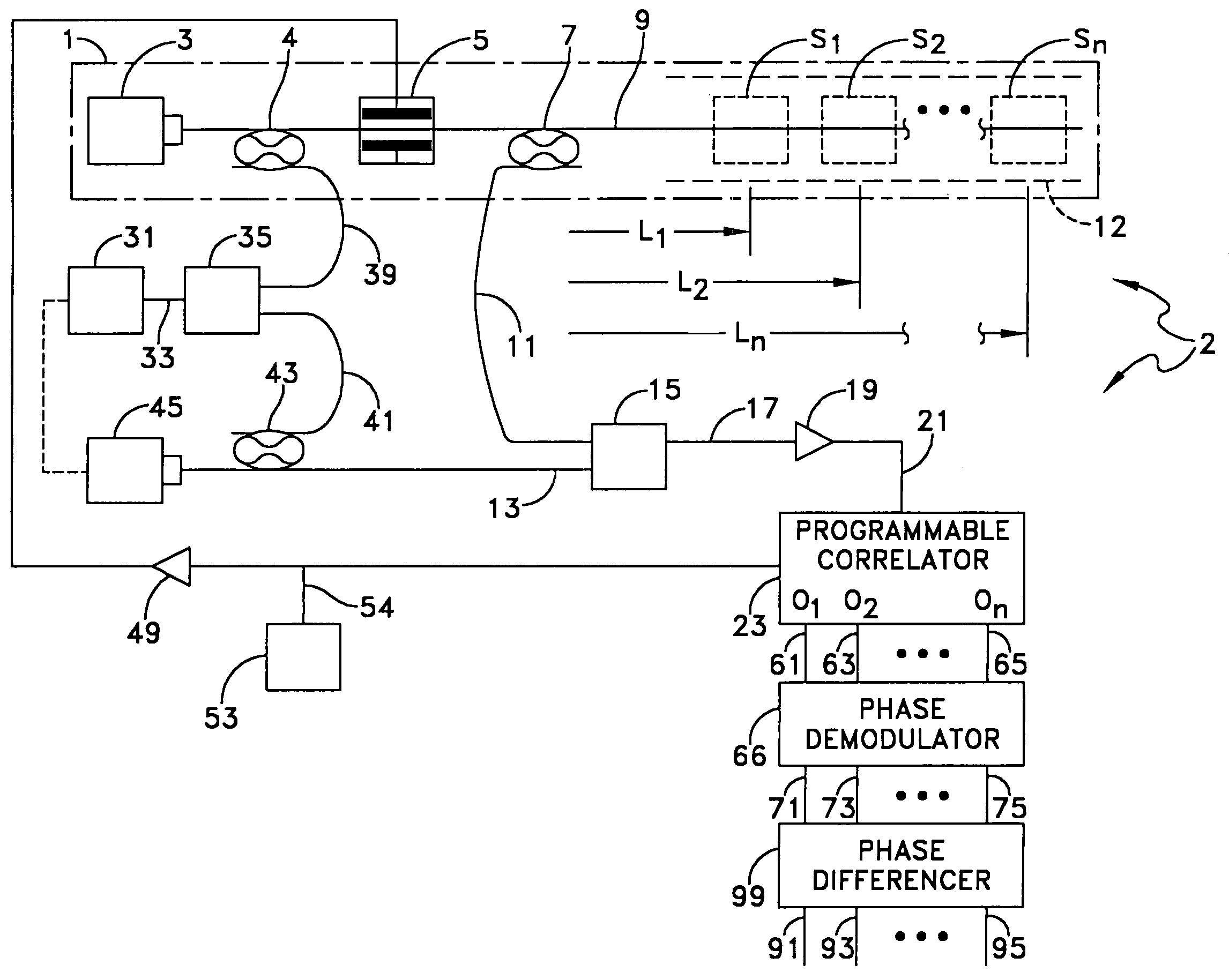
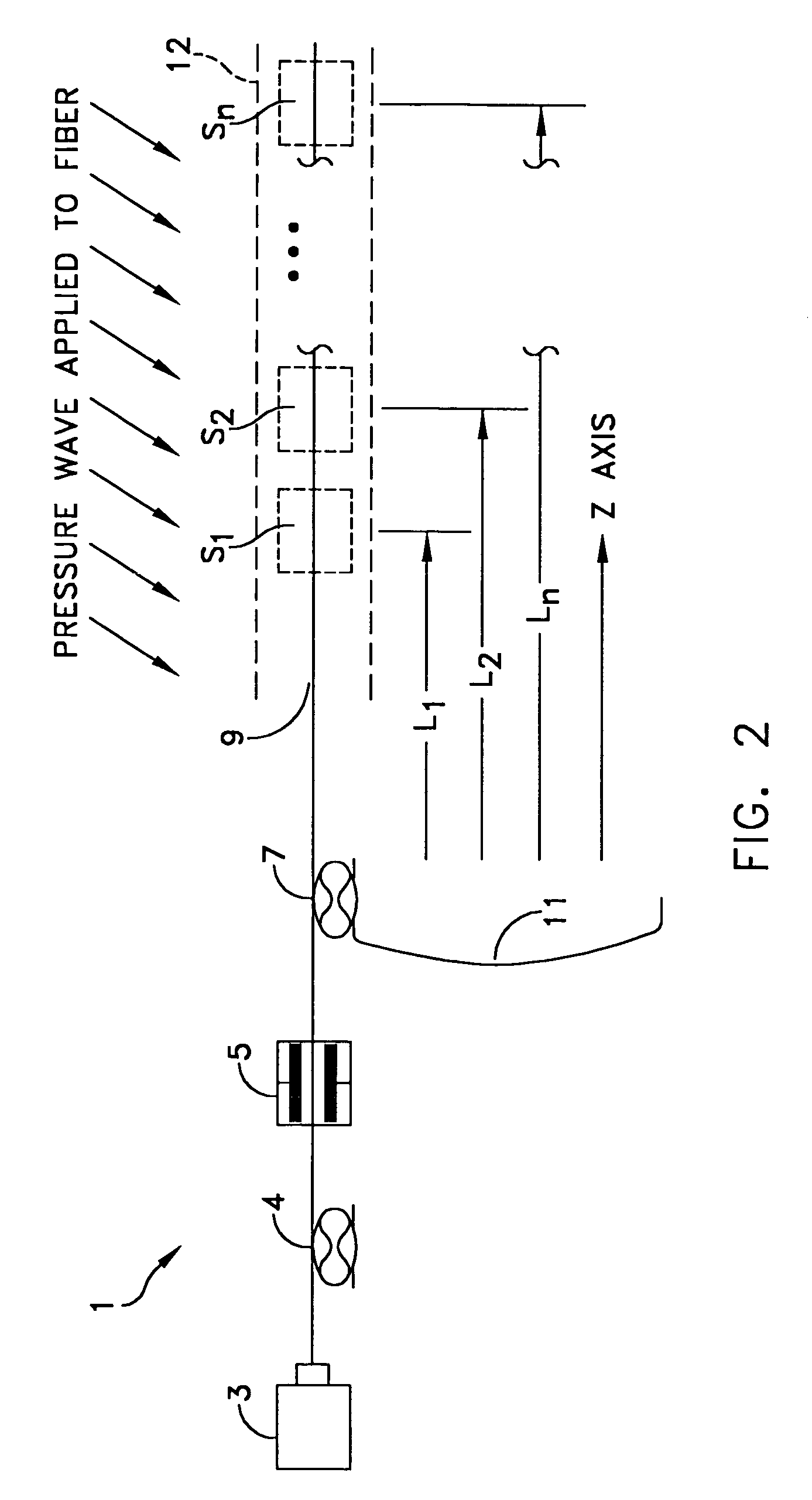
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS7030971B1To offer comfortLow costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringTime delays
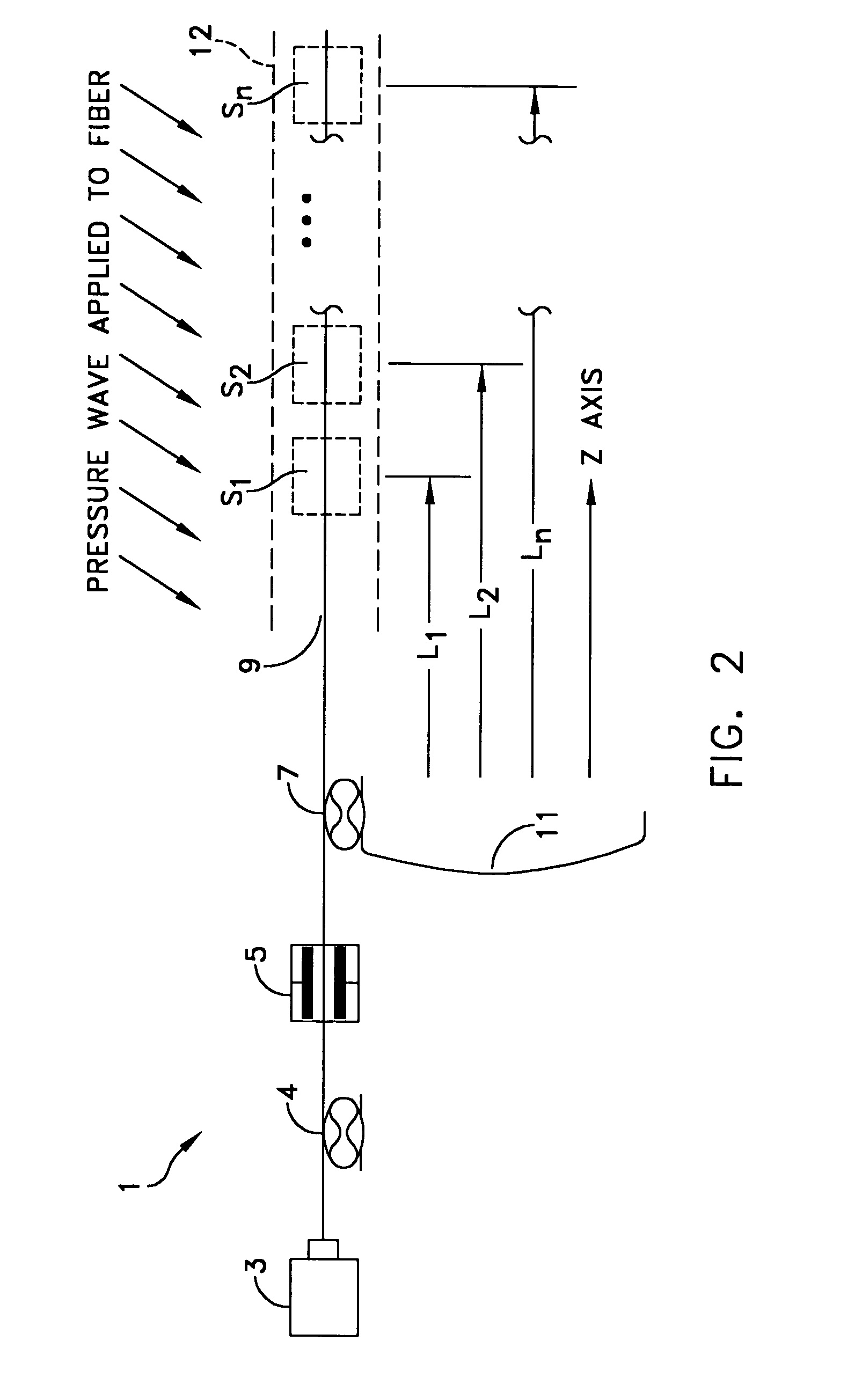
A CW lightwave modulated by a continuously reiterated binary pseudorandom code sequence is launched into an end of a span of ordinary optical fiber cable. Portions of the launched lightwave back propagate to the launch end from a continuum of locations along the span because of innate fiber properties including Rayleigh scattering. This is picked off the launch end and heterodyned to produce a r.f. beat signal. The r.f. beat signal is processed by a plurality (which can be thousands) of correlator type binary pseudonoise code sequence demodulators respectively operated in different delay time relationships to the timing base of the reiterated modulation sequences. The outputs of the demodulators provide r.f. time-domain reflectometry outputs representative of signals (e.g., acoustic pressure waves) incident to virtual sensors along the fiber at positions corresponding to the various time delay relationships.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE OFFICE OF NAVAL RES
Method and apparatus for waveform generation
InactiveUS7650080B2Less filteringWide bandwidthCode division multiplexOptical multiplexPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
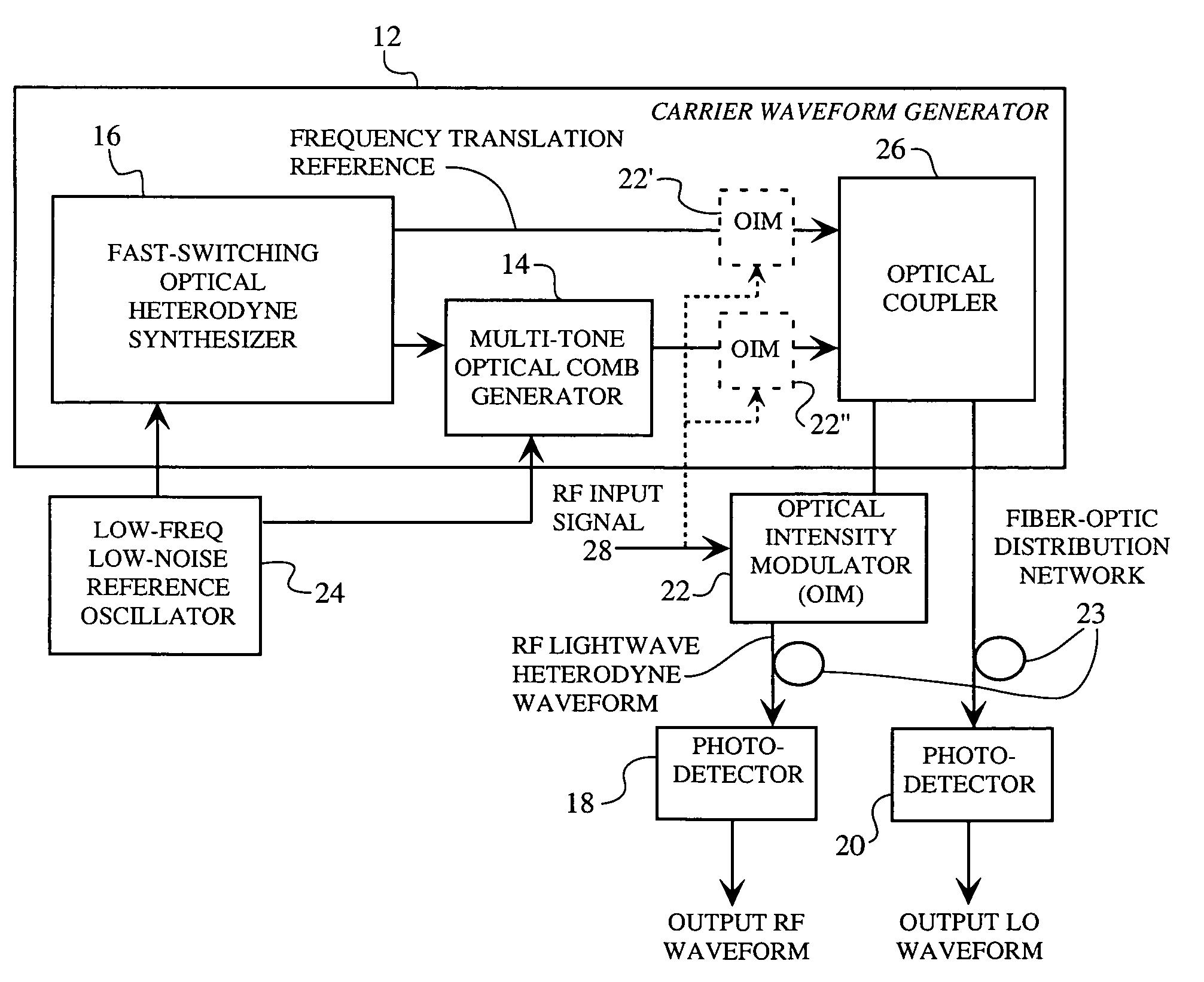
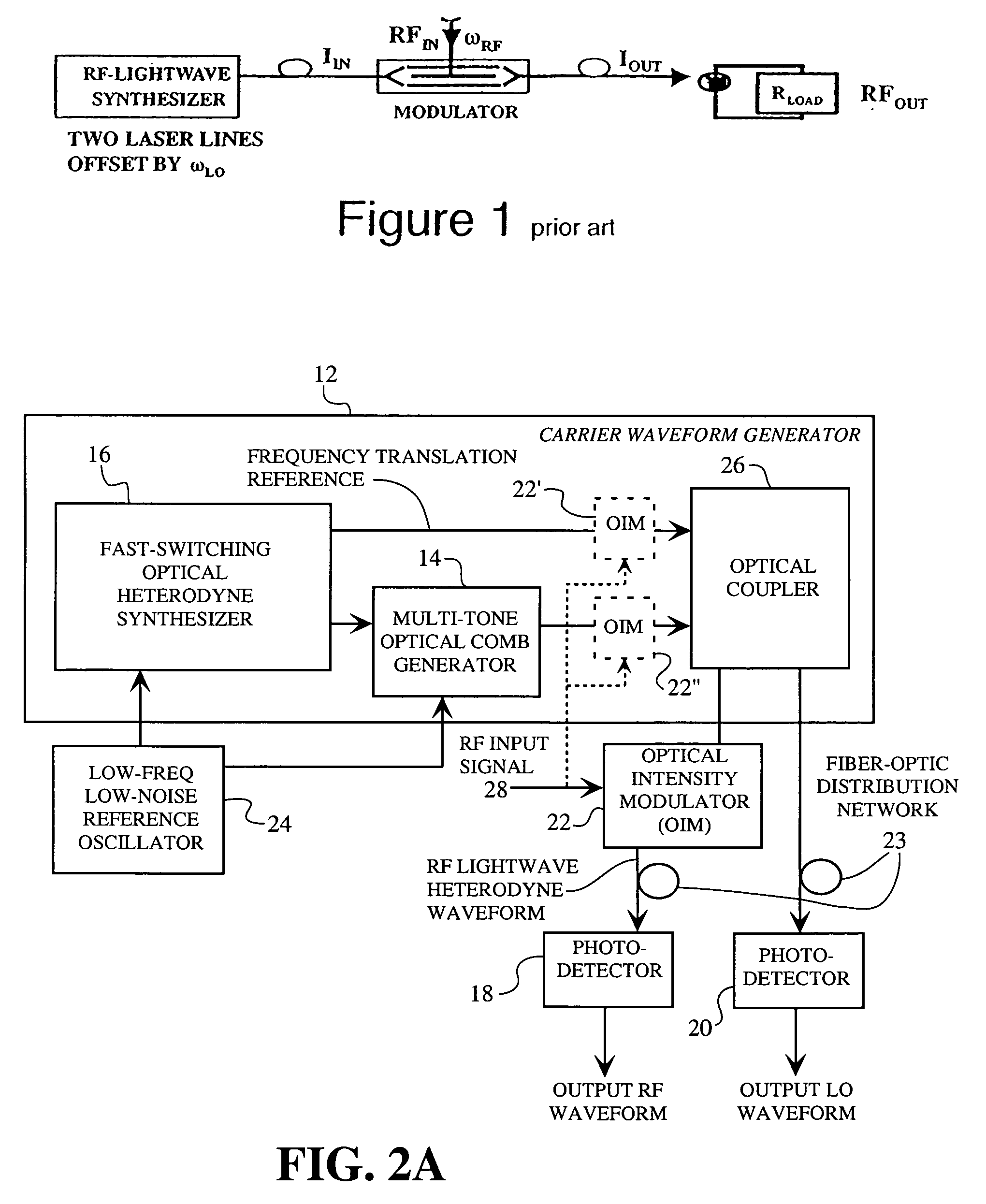
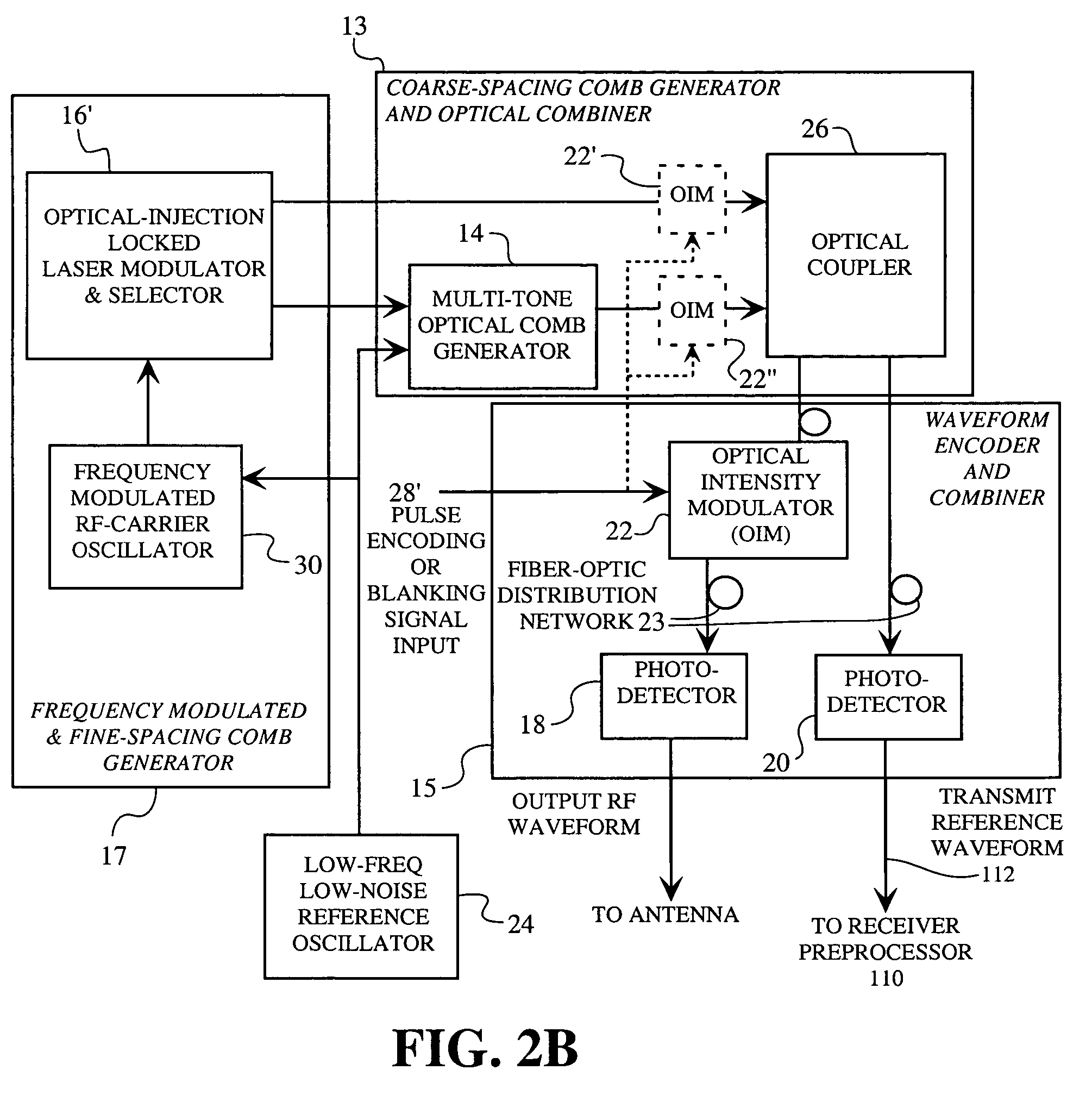
A spread spectrum waveform generator has a photonic oscillator and an optical heterodyne synthesizer. The photonic oscillator is a multi-tone optical comb generator for generating a series of RF comb lines on an optical carrier. The optical heterodyne synthesizer includes first and second phase-locked lasers, where the first laser feeds the multi-tone optical comb generator and the second laser is a single tone laser whose output light provides a frequency translation reference. At least one photodetector is provided for heterodyning the frequency translation reference with the optical output of the photonic oscillator to generate a spread spectrum waveform. A receiver pre-processor may be provided to operate on the spread spectrum waveform.
Owner:HRL LAB
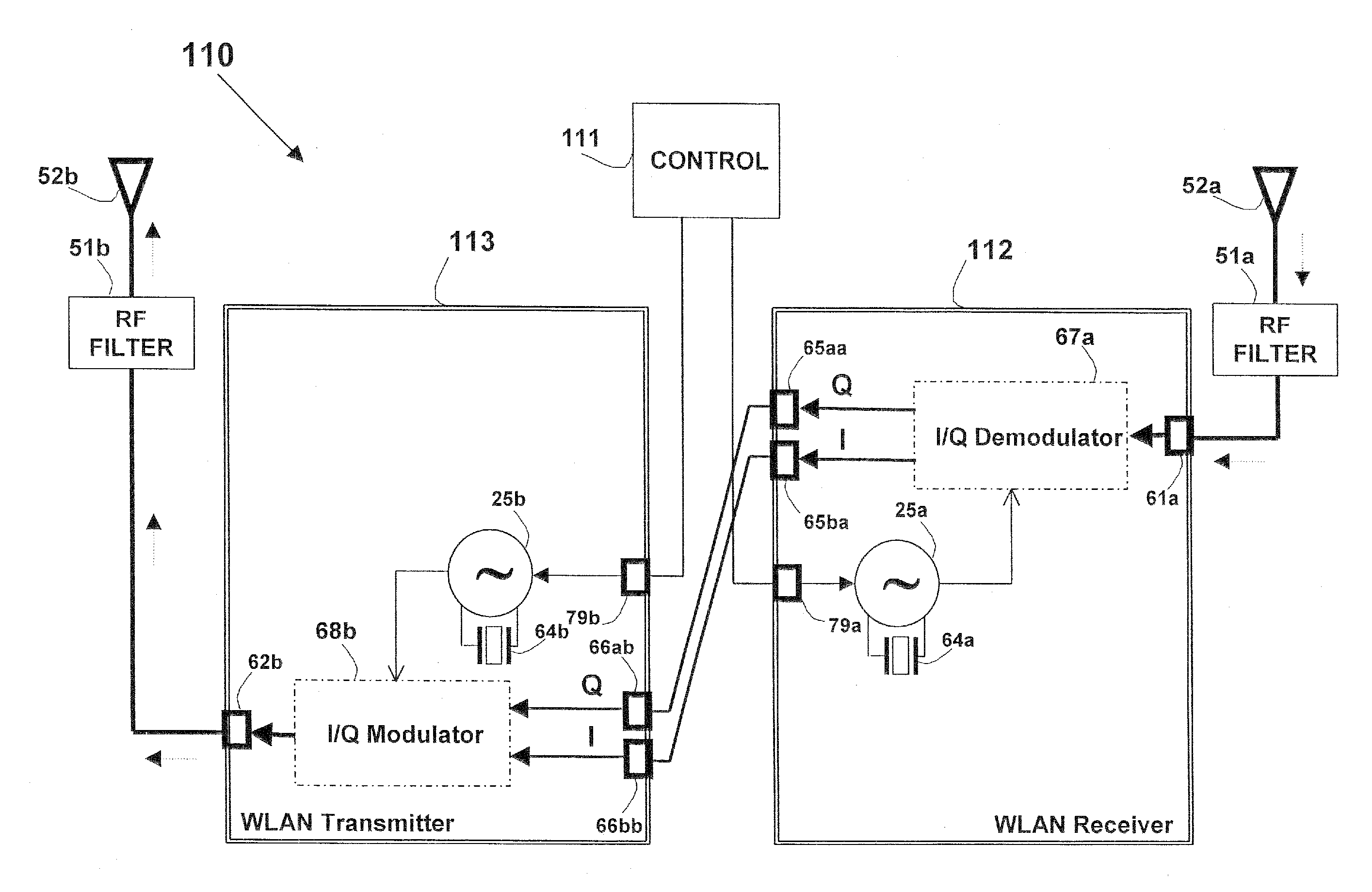
Hybrid heterodyne transmitters and receivers
ActiveUS20060111074A1Improves system manufacturabilityImprove performanceError preventionAnalogue conversionDigital signal processingData stream
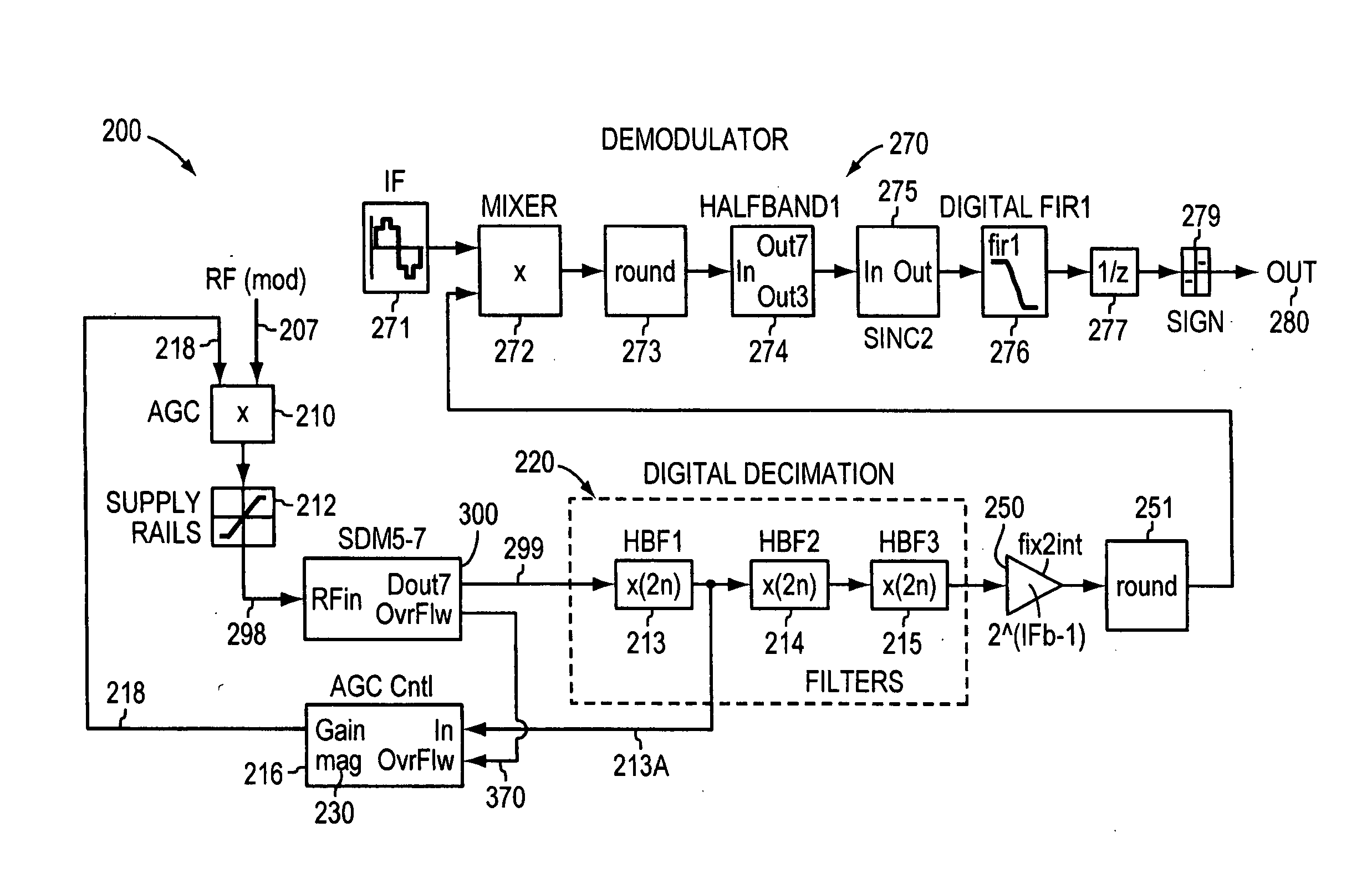
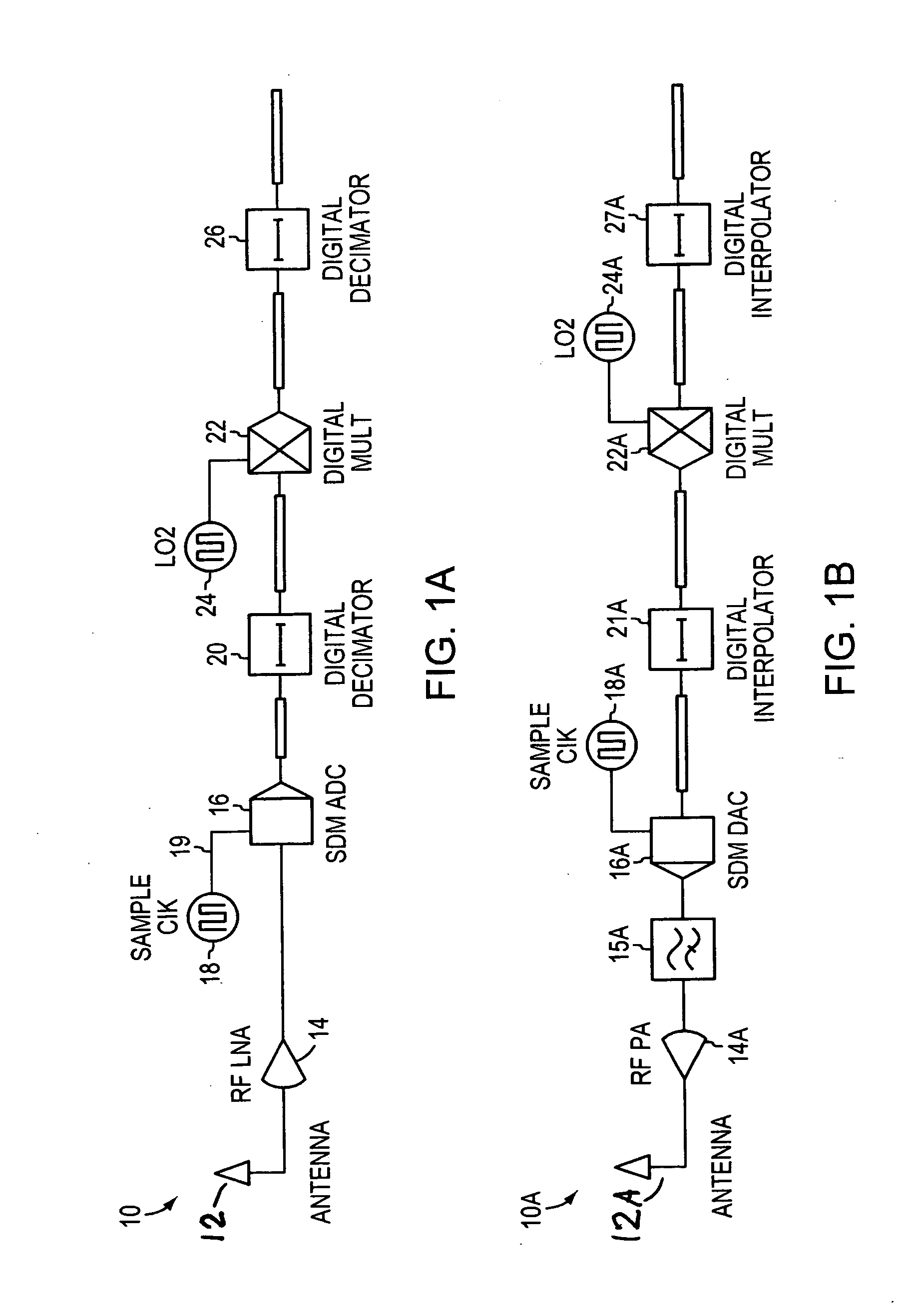
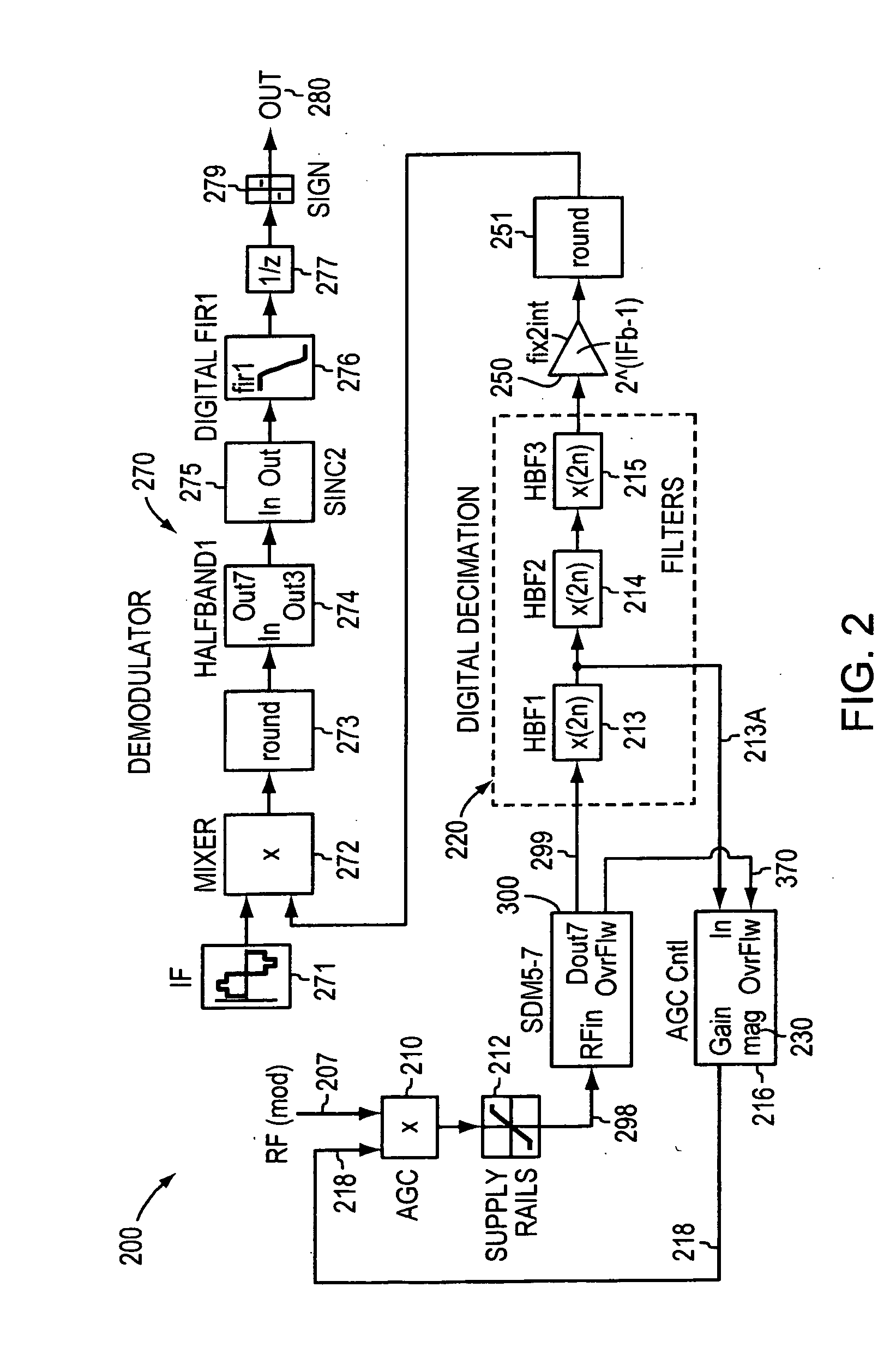
Disclosed are hybrid heterodyne transmitters and receivers for use in communications systems, or other systems, and the corresponding methods for hybrid heterodyne transmitting and receiving. A heterodyne receiver for converting a continuous time modulated signal to a discrete time digital baseband signal includes a sigma-delta modulator. The sigma-delta modulator is a sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter constructed and arranged to receive a modulated signal at an RF carrier frequency and provide a quantized output at a first intermediate frequency. The heterodyne receiver may also include a digital mixer constructed and arranged to receive a data stream quantized by the sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter and receive a signal at a second mixing frequency. The digital mixer then provides digital signals representative of a baseband signal suitable for digital signal processing.
Owner:INTRINSIX
Terahertz heterodyne tomographic imaging system
A method of forming a three-dimensional internal image of an object includes illuminating the object with terahertz (THz) radiation and detecting THz radiation that is either transmitted through, reflected from or backscattered from the object. The detected radiation is used to form a series of two-dimensional images of the object at different angles or positions. The recorded two-dimensional images are electronically processed using computer aided tomography (CAT) algorithms to form the three-dimensional image of the object.
Owner:COHERENT INC
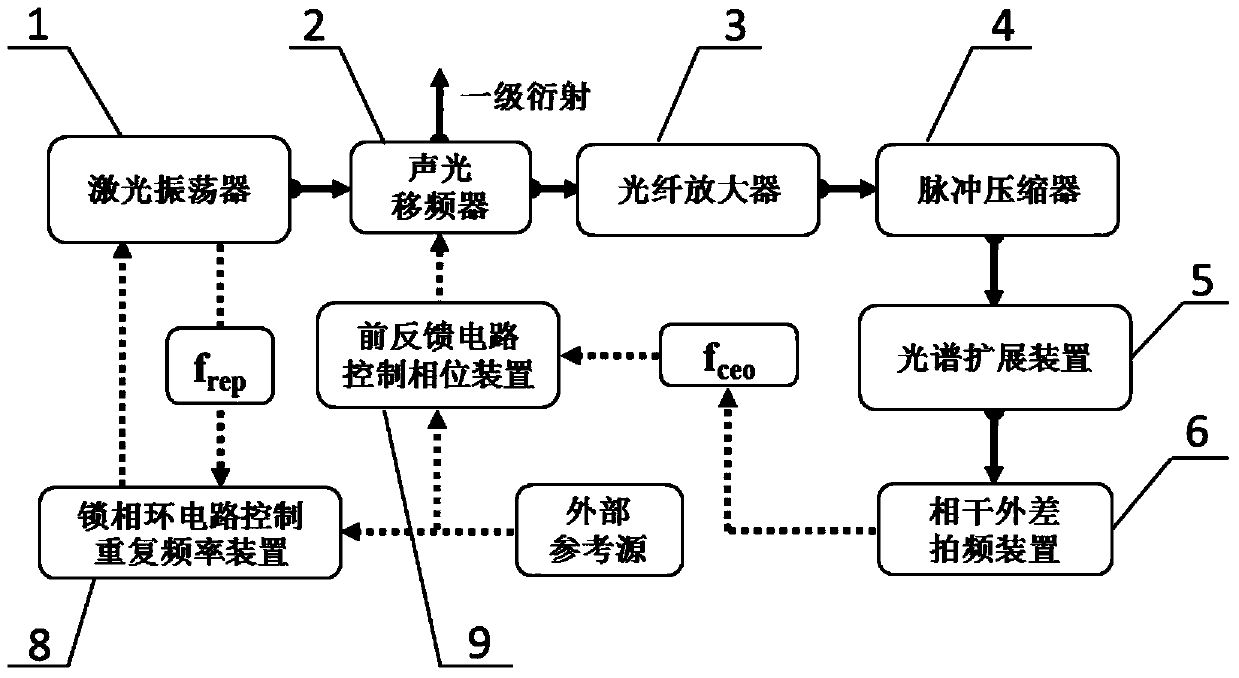
Low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency
ActiveCN103633537AImprove stabilityCarrier envelope phase shift frequency precise controlOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLow noisePhase locked loop circuit
The application provides a low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency. The low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency comprises an optical path structure and a circuit structure, wherein the optical path structure comprises an oscillator, an acousto-optic frequency shifter, an optical fiber amplifier, a pulse compressor, an optical fiber spread spectrum device and a coherent heterodyne beat device; and the circuit structure comprises a feed-forward circuit control phase device and a phase-locked loop circuit control repetition frequency device. The fiber laser oscillator can ensure long-time operation of a system, so that the stability of the system is superior to that of a system adopting a solid laser oscillator; through the technologies of optimizing intracavity net dispersion of the fiber oscillator, introducing an inner cavity modulator in the oscillator, adopting the feed-forward acousto-optic frequency shifter, and the like, the low noise fiber laser frequency combs device can be realized; and meanwhile, due to the application of the acousto-optic frequency shifter, the carrier envelope phase shift frequency of the optical frequency combs can be accurately regulated, so that the optical frequency combs device with precise phase position regulation and secular stability is provided for realizing applications such as optical frequency standard, attosecond science and non-linear optics.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for reducing heterodyne interference nonlinear error first harmonic component
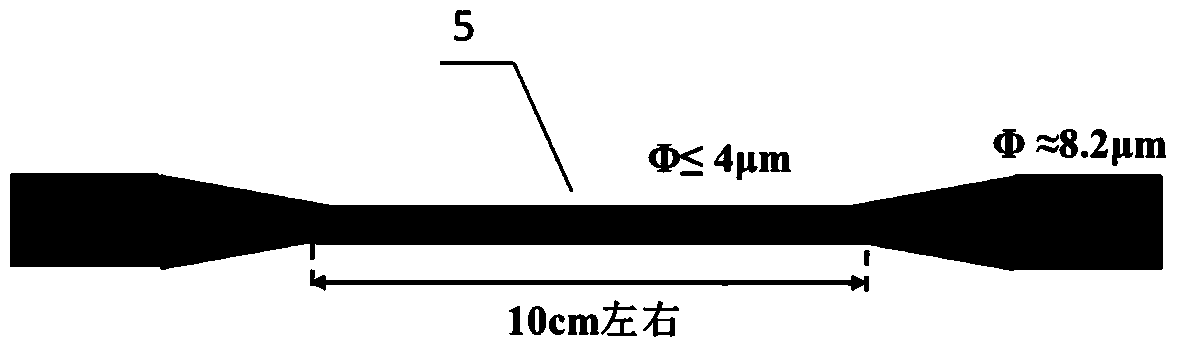
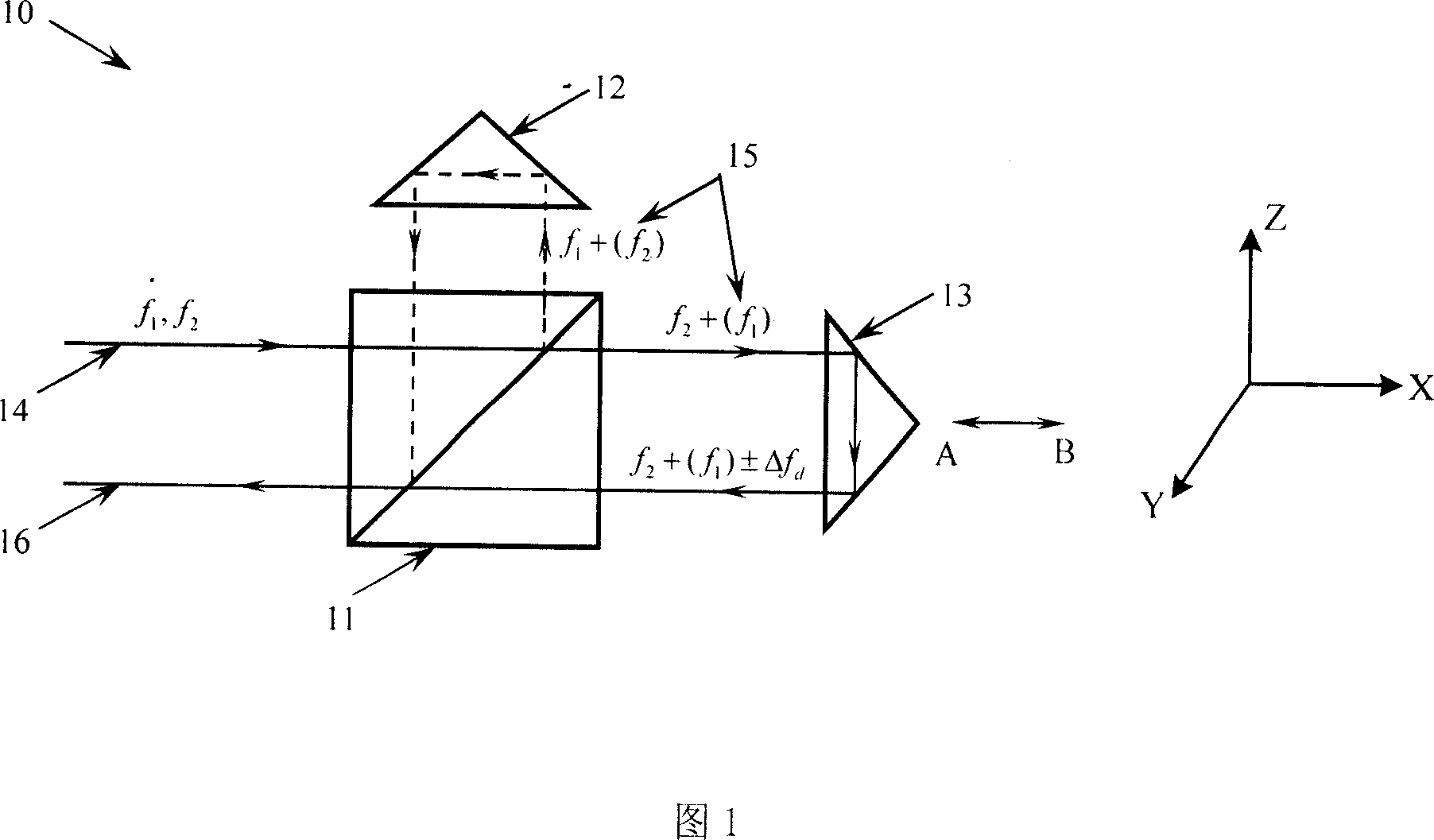
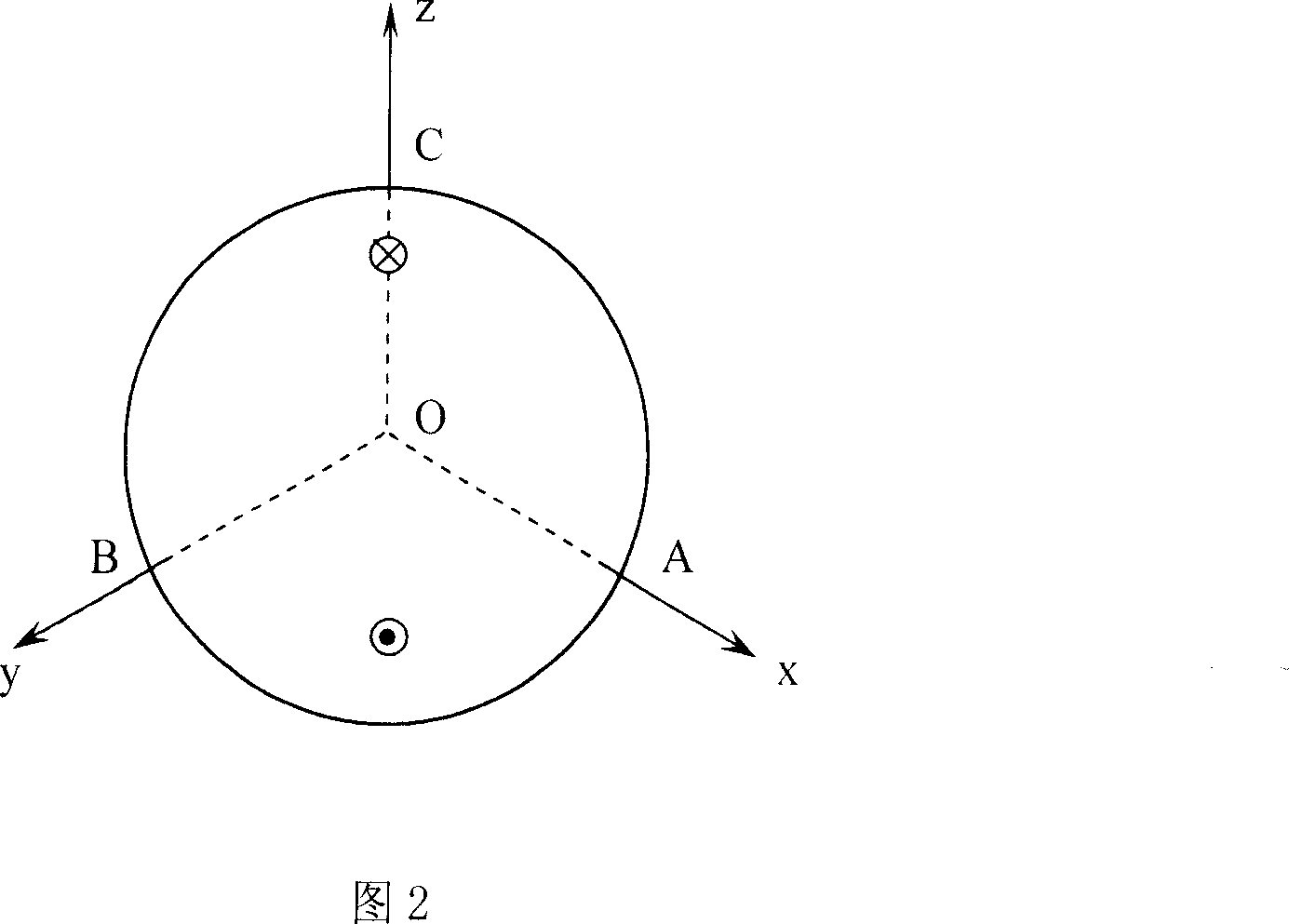
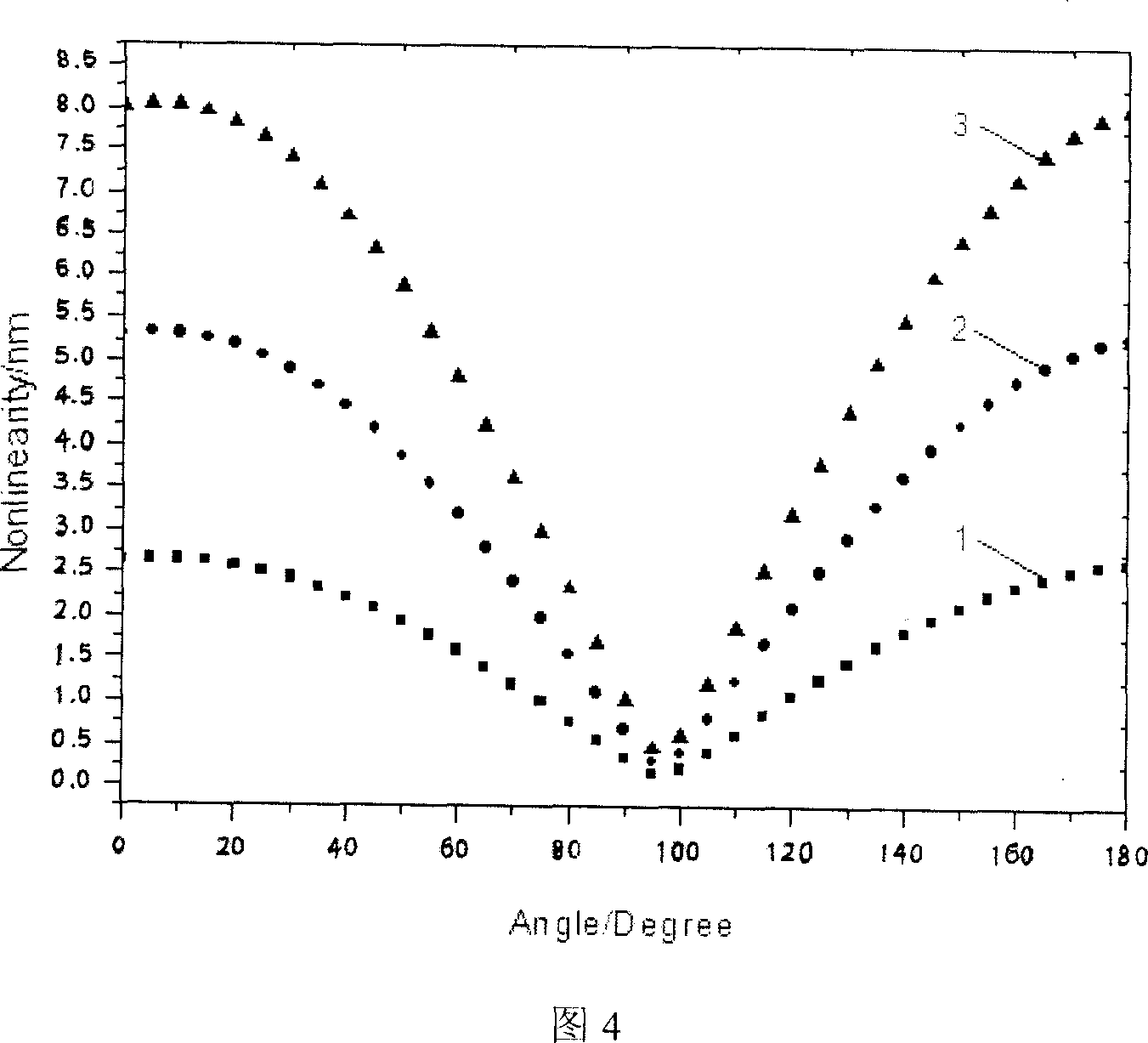
InactiveCN101067546AReducing Nonlinear Errors of Laser Heterodyne InterferometrySimple methodUsing optical meansRotary stagePrism
The invention relates to a method of reducing the heterodyne interference non-linear error first harmonic component and its equipment, the existing kinds of system and the method are all very complex. The invention includes: the light beams which contains two frequencies, two polarization directions and sends out by the double frequency laser; this light beam divides into two bunches of light after the spectroscope, the reflected light forms the reference signal after the analyzer by the photo detector receive; the transmitted light enters the polarization spectroscope to divide into two bunches of light which includes the reflected light of polarization direction vertical paper surface and parallel paper surface transmitted light, the reflected light reflects to the polarization spectroscope after the reference pyramid prism, the transmitted light after survey pyramid prism installed on the swivel table also reflects the polarization spectroscope; above two bunches of light converge in the polarization spectroscope place, and formed the survey signal by the reflector reflection after the analyzer by the photo detector; swivel table axial revolves the survey pyramid prism along the survey pyramid prism heading, swivel table anti-clockwise or clockwise axial revolves 97 degree. The invention uses to increase the heterodyne interference measuring accuracy.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and device for frequency translation in powerline communications
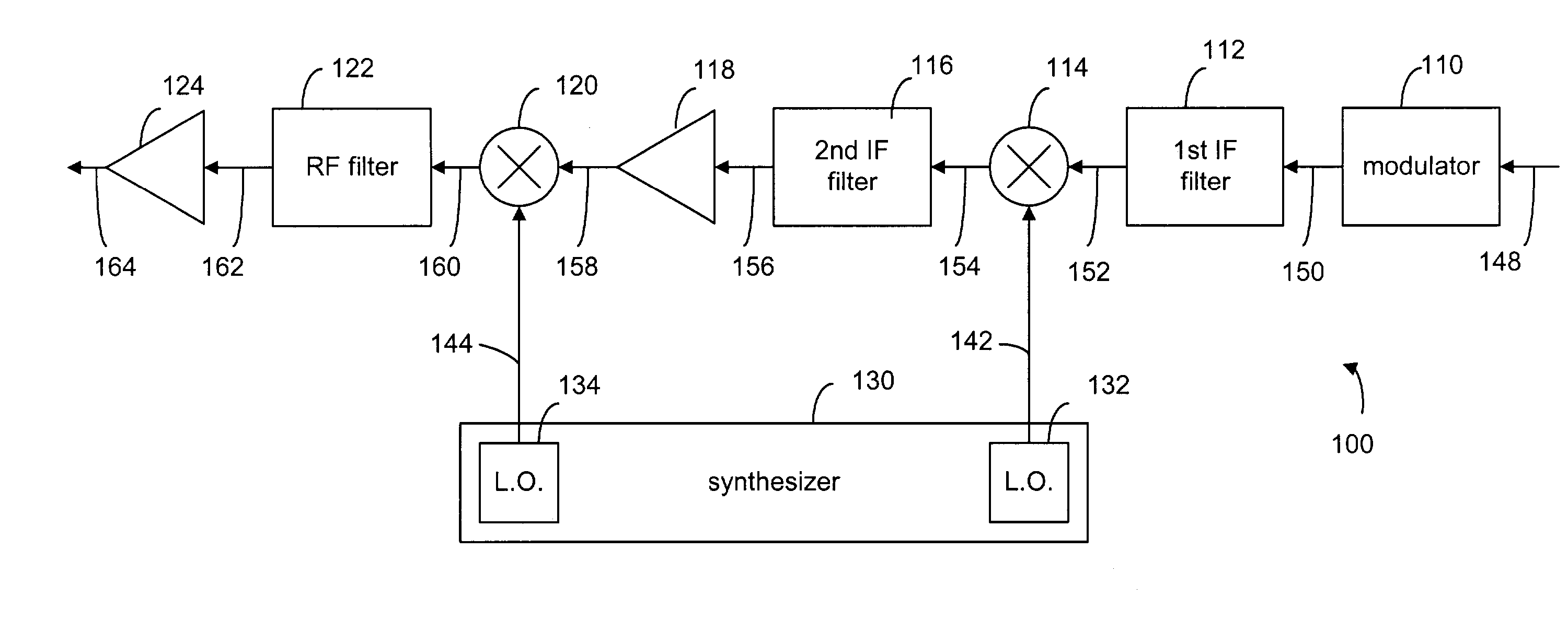
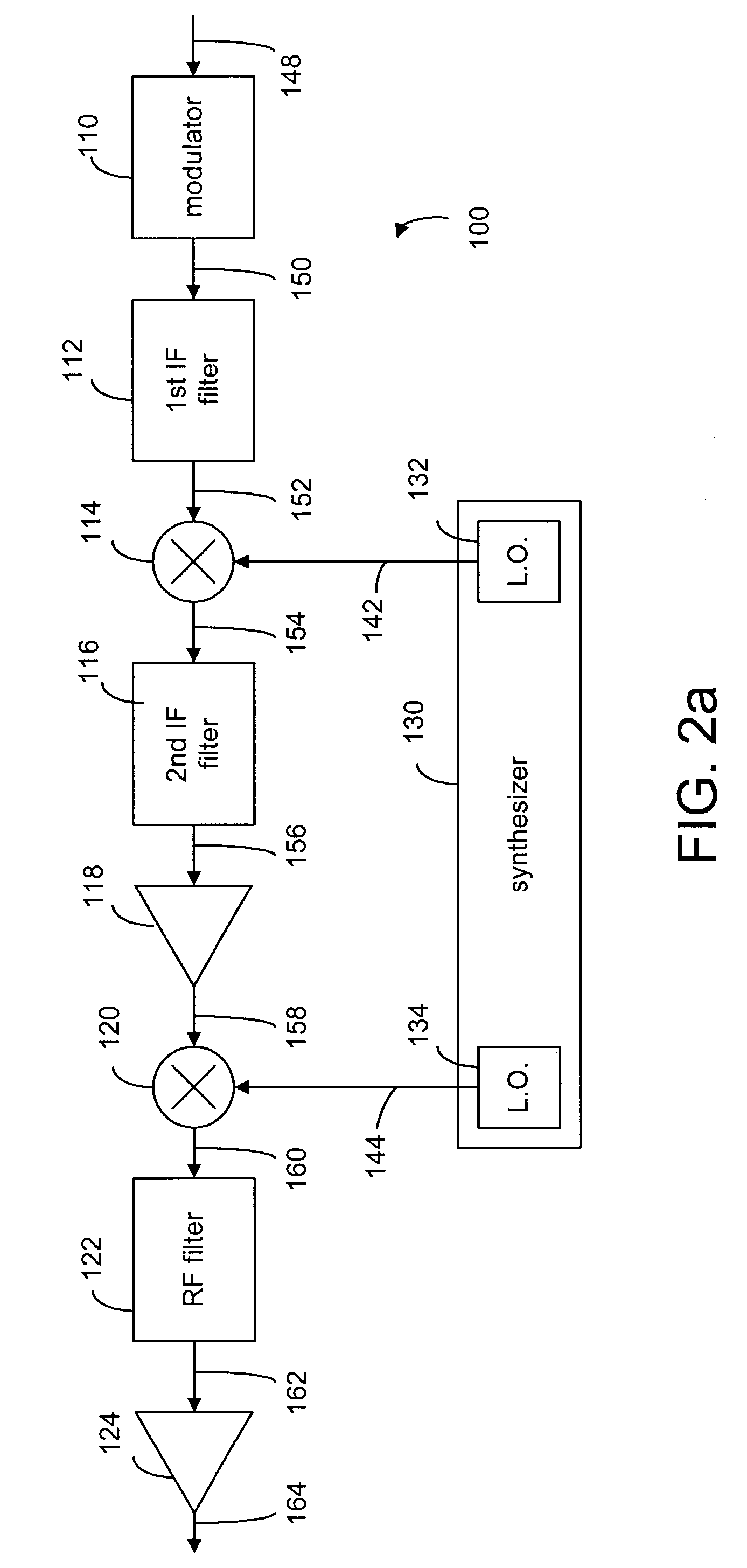
InactiveUS6985715B2Enhance communication signalHigh selectivitySystems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsLocal oscillator signalModem device
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving RF signals for broadband communications using power lines as communication medium. A super-heterodyne structure is used to translate the signals from one frequency to another so as to avoid interference sources, which may corrupt the communication signals. In the heterodyne structure, a plurality of local oscillators are used to mix the local oscillator signals with the communication signals for frequency translation. A plurality of frequency filters are used to filtered out unwanted signals. The communication signals are imparted onto or received from the power lines via couplers operatively connected to modems.
Owner:AMPERION
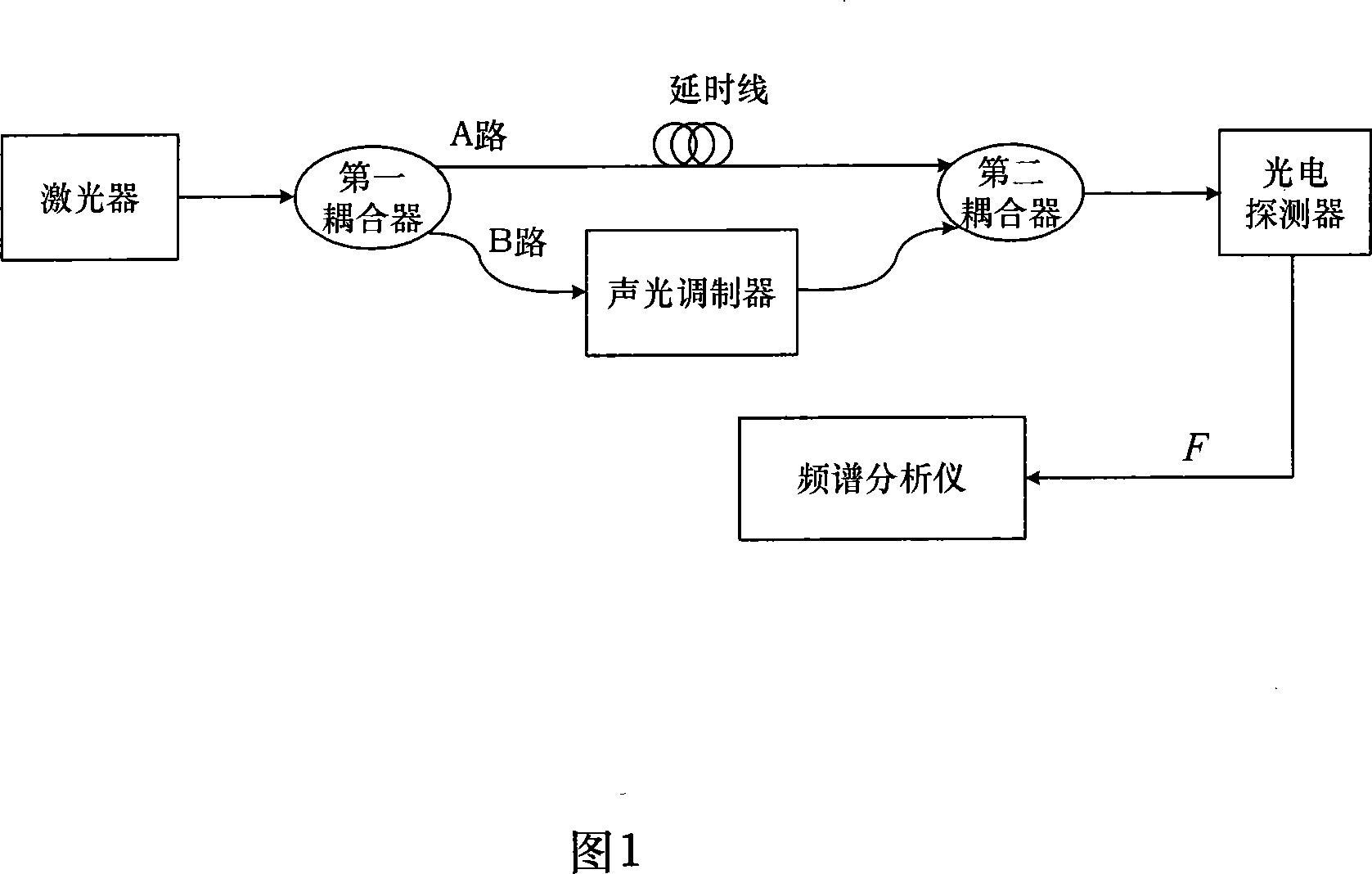
Device for measuring linewidth of narrow linewidth laser based on optical fiber time-delay self heterodyne method as well as method for measuring thereof
InactiveCN101201243ARealize high-precision testingReduce volumeUsing optical meansThree levelSpectrum analyzer
The invention discloses a device of measuring the line-width of a laser with narrow line-width and a method of measuring the line-width based on a optical fiber delay self-heterodyne method; in the hardware device, an optical fiber delay line is connected between a first and a second couplers; an acousto-optic modulator is connected between the first and the second couplers; the measured laser is connected to the input of the first coupler, and a photoelectric detector is connected to the output of the second coupler; the photoelectric detector is connected with a spectrum analyzer. In the line-width measurement, simulation models of the line-width triangle v of the laser and the spectrum-width triangle f of the photoelectric current heterodyne signal are built in the frequency shift delay self-heterodyne methodology, and the function relation between the line-width triangle v of the laser and the spectrum-width triangle f of the photoelectric current heterodyne signal is obtained fitting of the three-level proportion function model. The invention presents that with the short optical fiber delay self-heterodyne method, the device can eliminate the deficiency of greatly reduced measuring precision because of not enough delayed time in the delay self-heterodyne method when the length of the delay optical fiber is less than 6 times coherence length of the laser, so as to provide an effective method of precisely measuring the line-width of the laser with narrow line-width in projects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Heterodyne reflectometer for film thickness monitoring and method for implementing
Owner:VERITY INSTR
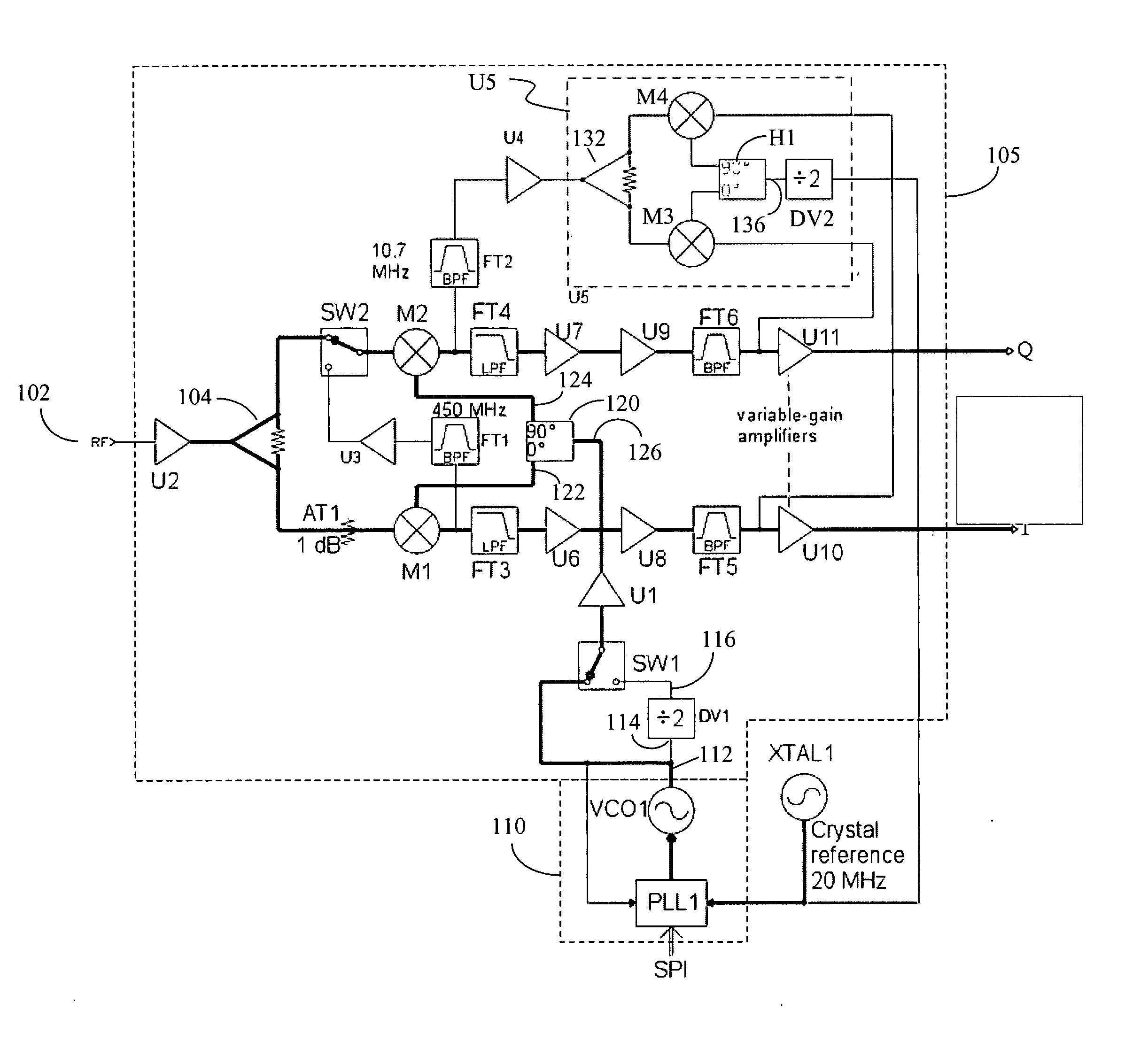
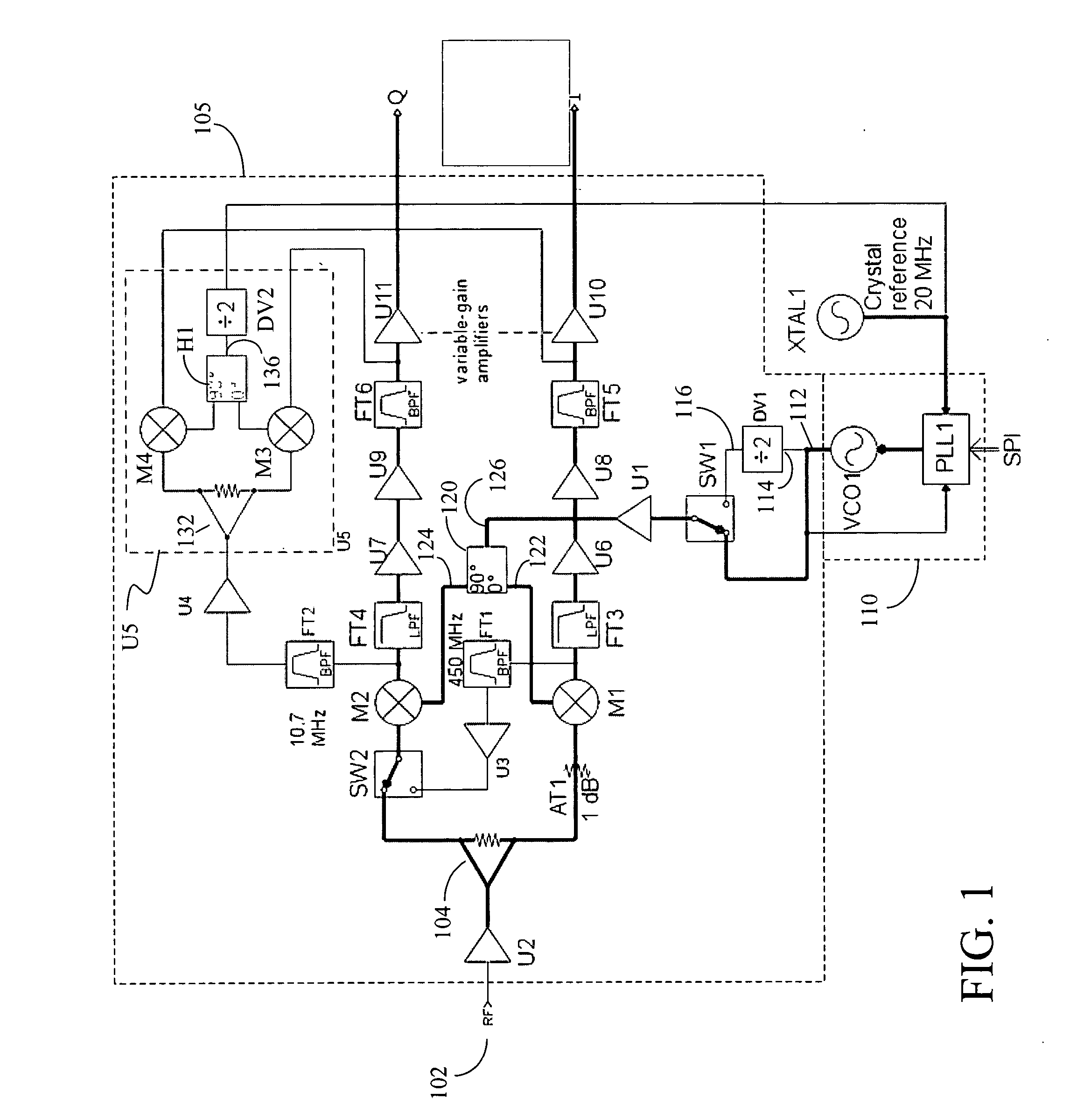
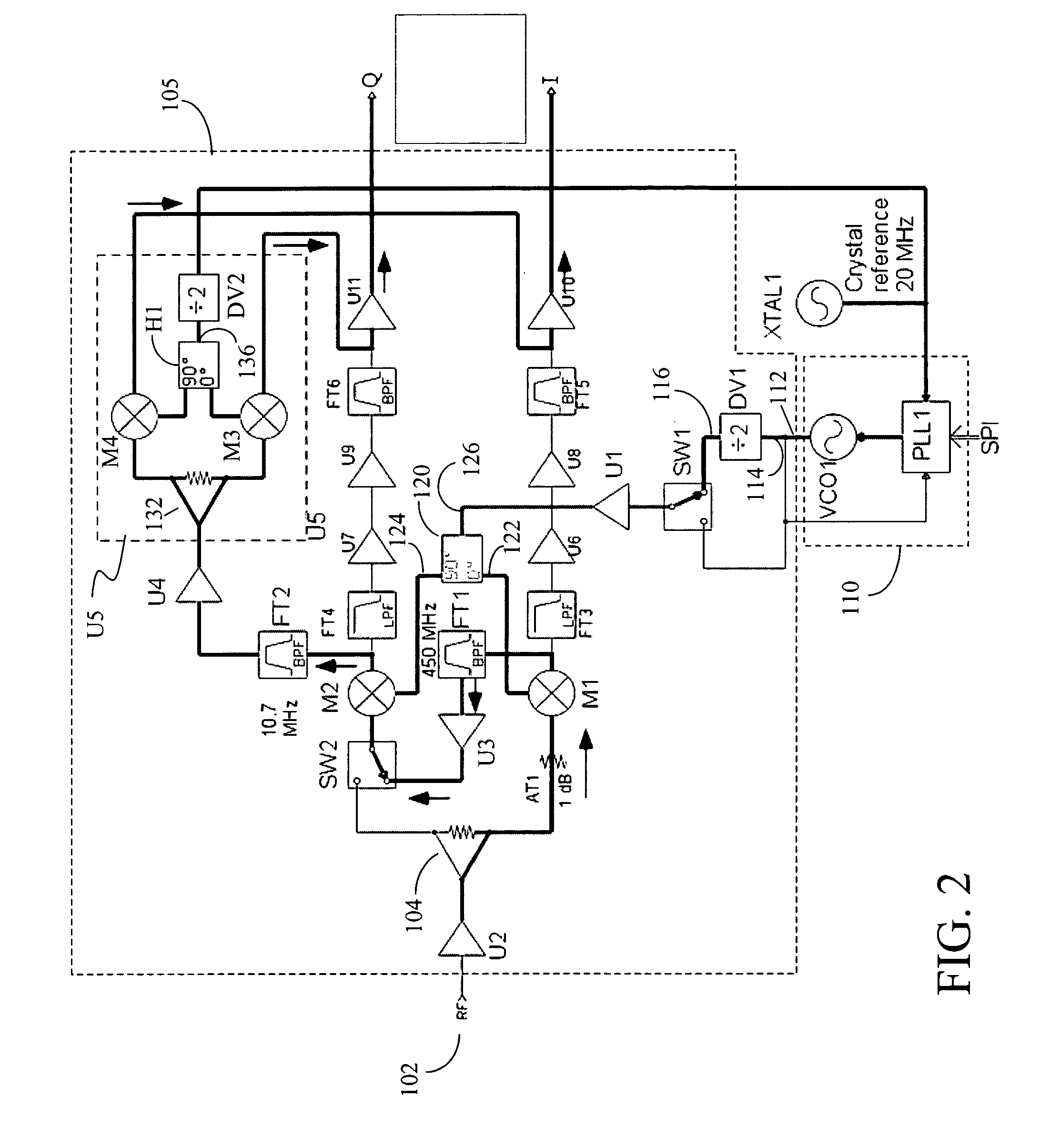
Configurable homodyne/heterodyne radio receiver and RFID reader employing same
InactiveUS20070111697A1Facilitate listen-before-talk functionHigh sensitivityNear-field transmissionAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayRadio receiverReceiver function
The embodiments of the present invention provide a configurable homodyne / heterodyne RF receiver including first and second mixers. The configurable homodyne / heterodyne RF receiver functions as a homodyne receiver when the first and second mixers are configured to operate in parallel, and as a heterodyne receiver when the first and second mixers are configured to operate in series. The embodiments of the present invention further provides an RFID reader employing the configurable homodyne / heterodyne RF receiver to facilitate a listen-before-talk function.
Owner:TRIQUINT SEMICONDUCTOR
Method and device for calibrating phase modulation of spatial light modulators by utilizing heterodyne interference
InactiveCN102109414ALight wave intensity is highLarge degree of phase modulationOptical measurementsTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorPhase difference
The invention discloses a method for calibrating phase modulation degree of spatial light modulators, and the method is used for detecting the phase modulation information by utilizing a heterodyne interference technology. In the method, two beams of coherent optical waves are led to generate a frequency difference by an acousto-optic frequency phase shifter, and the two beams of coherent optical waves are respectively used as a measuring beam and a reference beam; then the effective display area of the spatial light modulator is divided into two parts, a gray value written into one part is 0, and the part is taken as a reference area; the change range of the gray value of the other part is 0-255, and the other part is taken as a test area; the measuring beam is modulated by the spatial light modulators of the reference area and the test area and then interfered with the reference beam; then two photoelectric detectors at an interference field are utilized to respectively detect a reference signal and a measured signal; and the phase difference between the two photoelectric detectors is the phase modulation degree to be measured, therefore, the corresponding relation between the gray value and the phase modulation degree can be established, so that the phase modulation degree of the spatial light modulators can be calibrated.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
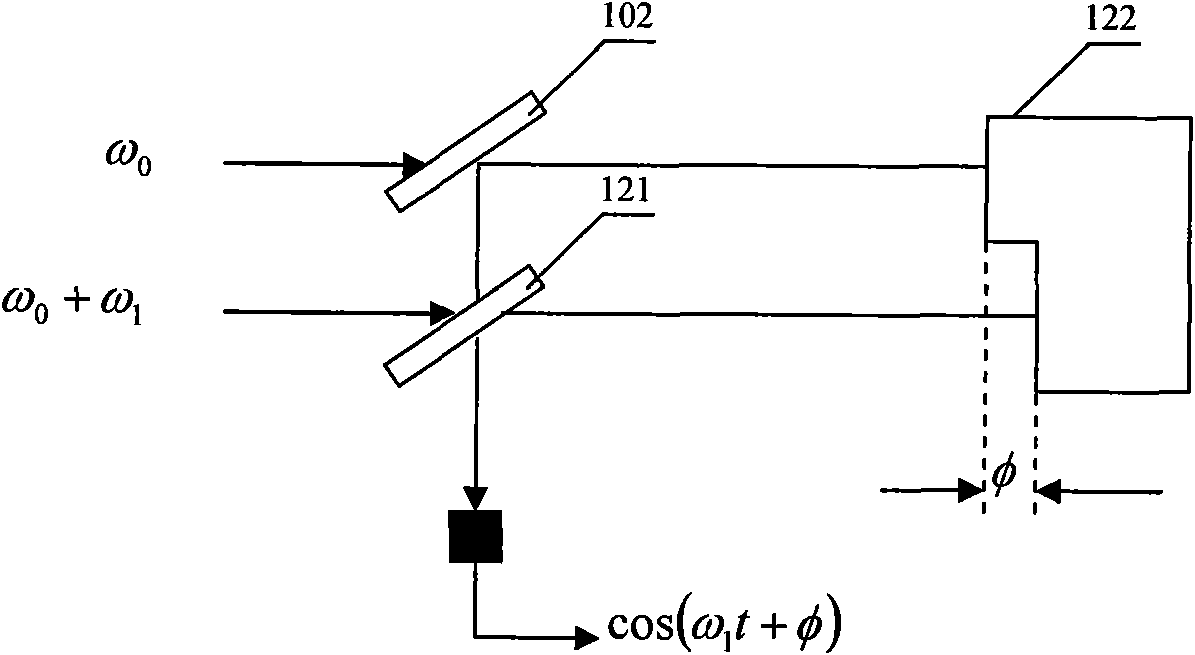
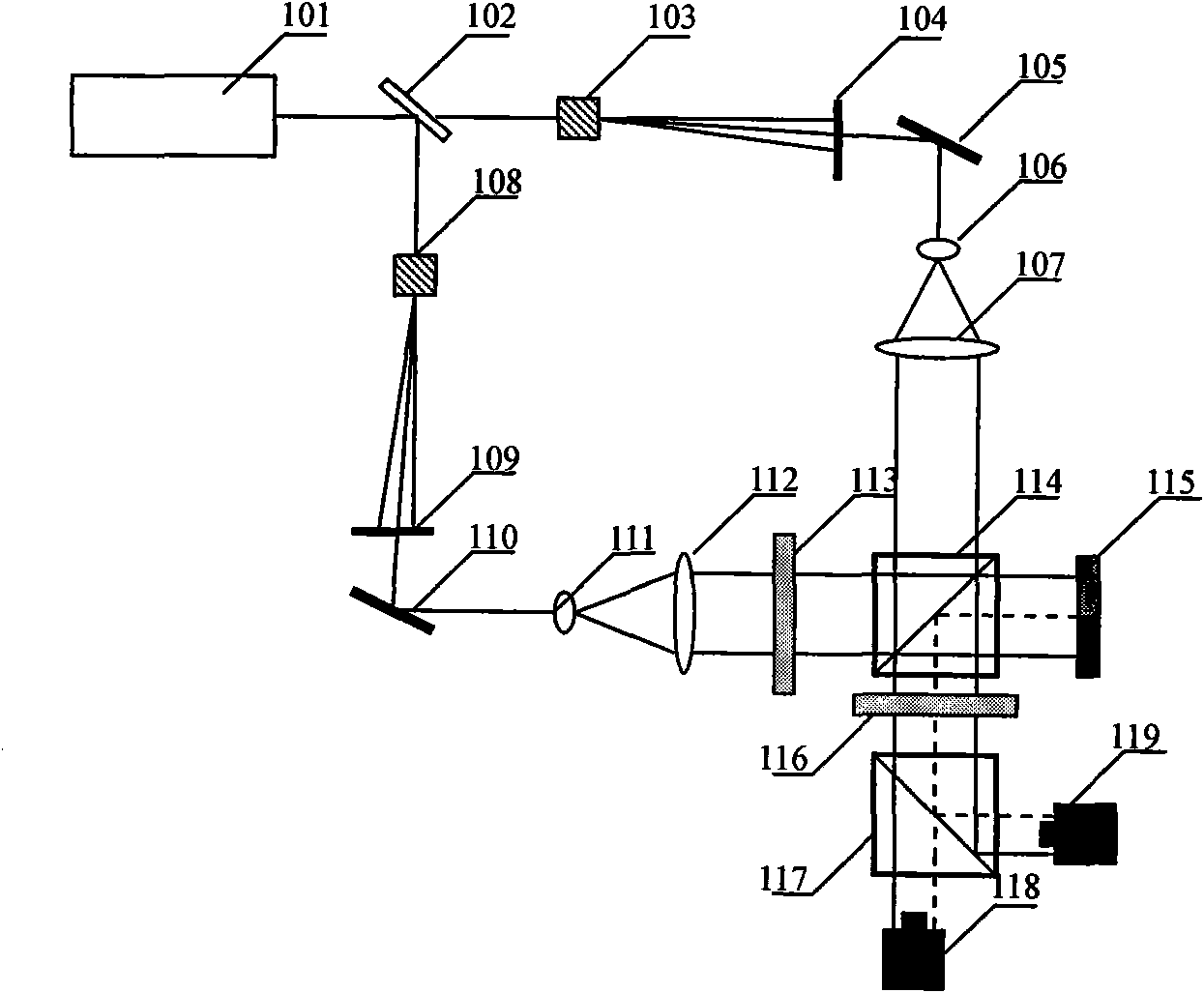
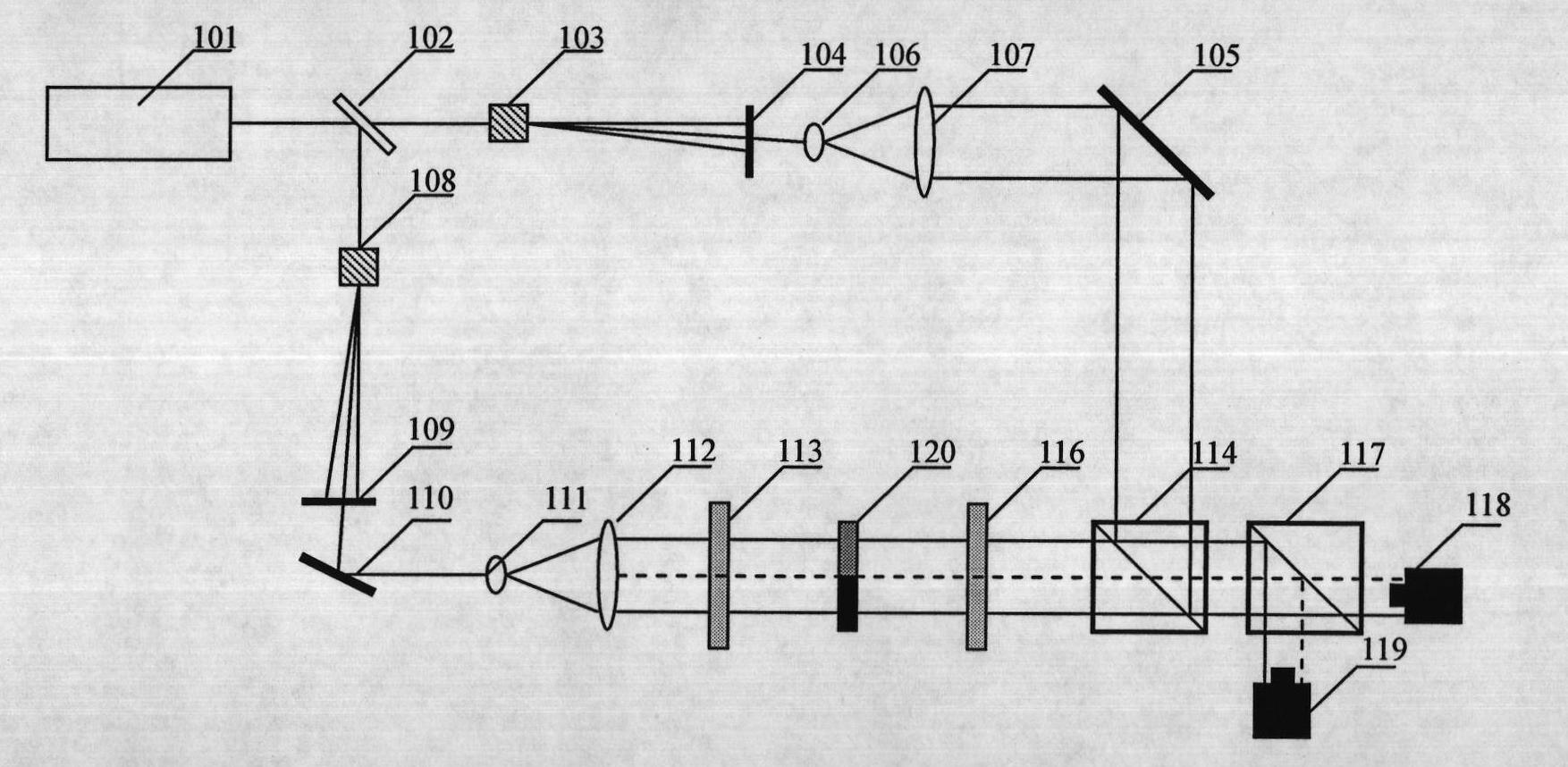
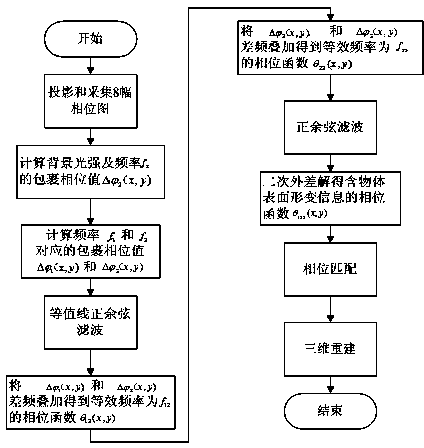
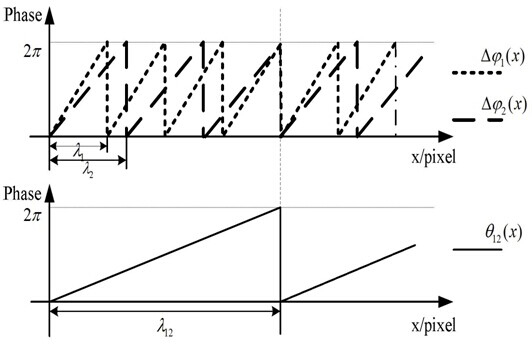
Heterodyne three-frequency unequal range phase displacement solution phase method
ActiveCN104330052AQuality improvementAccurate measurementImage analysisUsing optical meansGratingMiddle frequency
The invention relates to a heterodyne three-frequency unequal range phase displacement solution phase method, and the method is as follows: selecting three frequencies, firstly adopting four-step phase shift method to obtain the package phase and average light intensity of the middle frequency, adopting two-step phase shift method to obtain the package phase corresponding to the two frequencies under the condition with known light intensity, obtaining the true phase according to the heterodyne method, adopting the contour line sine and cosine filtering method in the optical grating projection three-dimensional measurement, using stripe direction information for filtering the package phase on isophasal line, the method uses less projection picture for exactly measuring and uses the stripe direction information for filtering the package phase picture for effectively removing the inconsistent points in the package phase picture, the heterodyne three-frequency unequal range phase displacement solution phase method is used in the phase method three-dimensional shape measurement for effectively raising the measuring efficiency and measuring accuracy.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
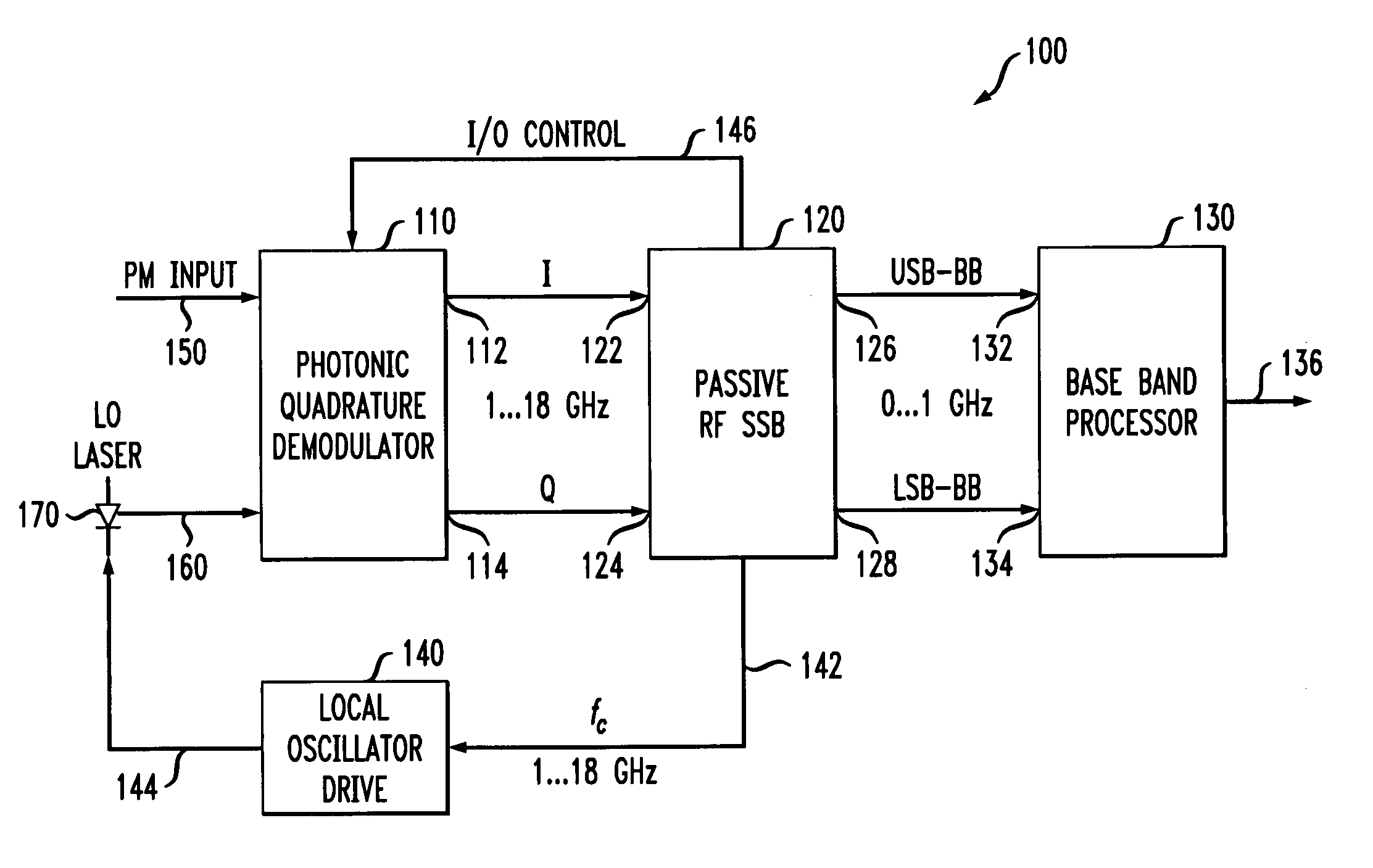
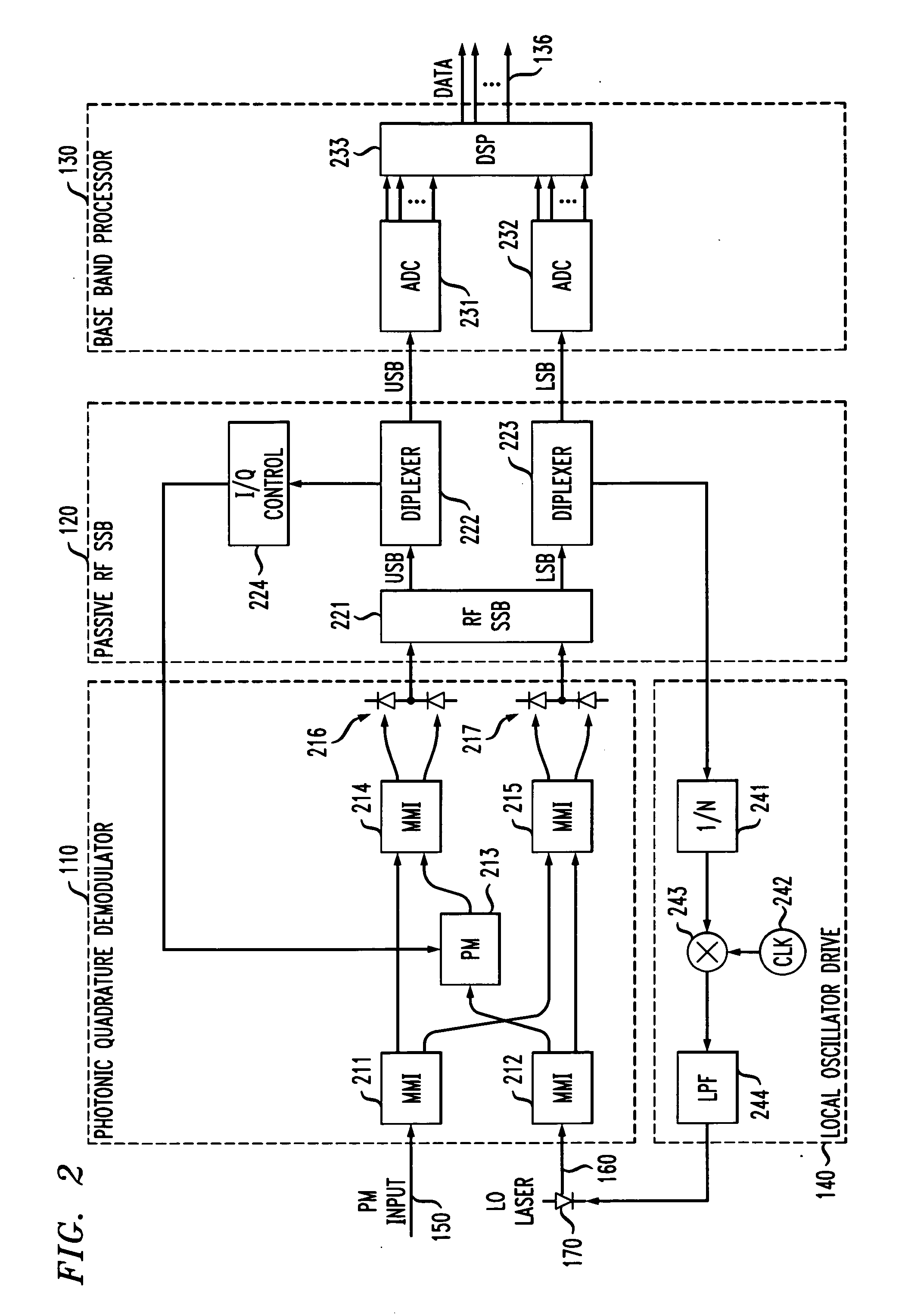
Optical heterodyne receiver and method of extracting data from a phase-modulated input optical signal
An optical heterodyne receiver and a method of extracting data from a phase-modulated input optical signal. In one embodiment, the optical heterodyne receiver includes: (1) a photonic quadrature demodulator having first and second optical inputs and first and second electrical outputs and configured to generate at the first and second electrical outputs an in-phase signal and a quadrature-phase signal, respectively, in response to receiving a modulated optical signal at the first optical input and a reference optical oscillator signal at the second optical input, (2) a passive radio frequency single sideband demodulator coupled to the photonic quadrature demodulator and configured to extract at least one sideband of the in-phase signal or the quadrature-phase signal and (3) at least one analog-to-digital converter coupled to the passive radio frequency single sideband demodulator and configured to receive and sample the at least one sideband.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual differential signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS7274441B2To offer comfortReduce noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com