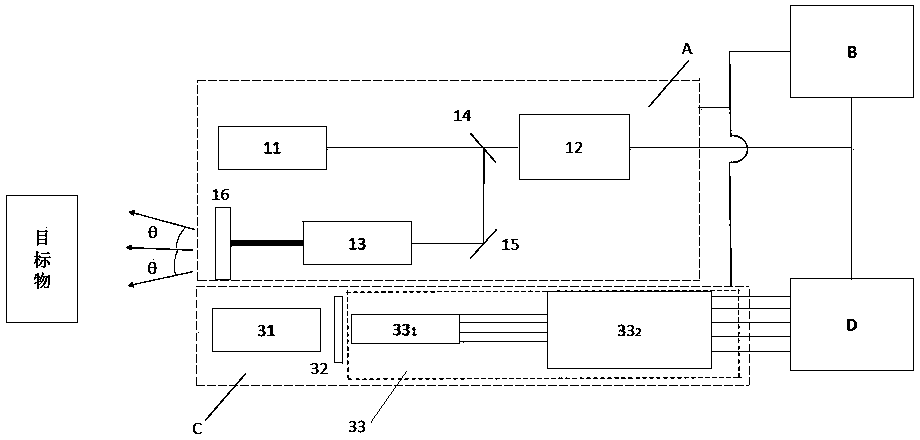
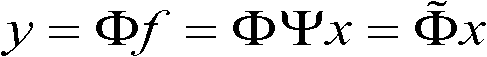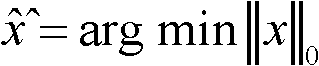Patents
Literature
752 results about "Laser imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
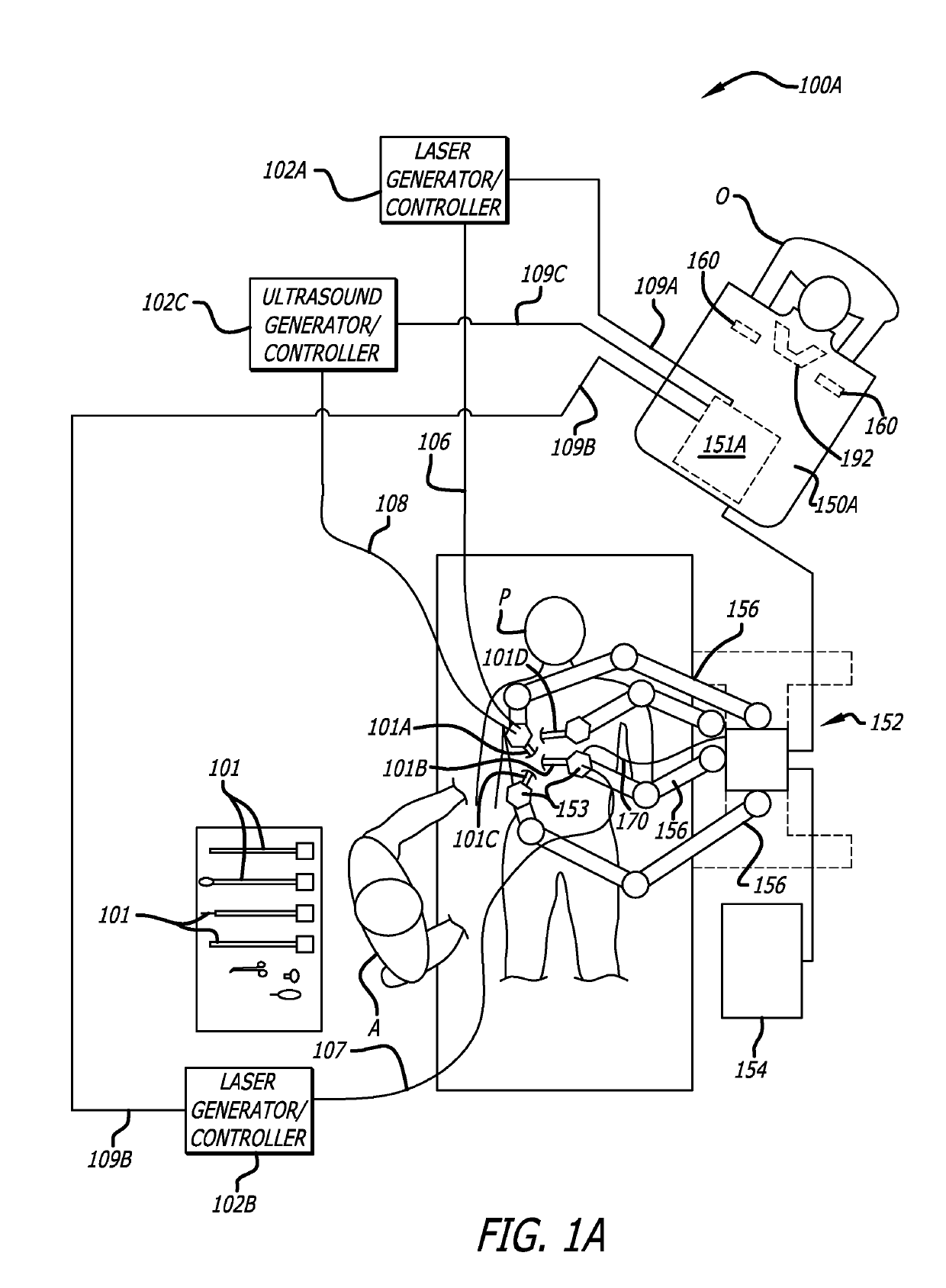
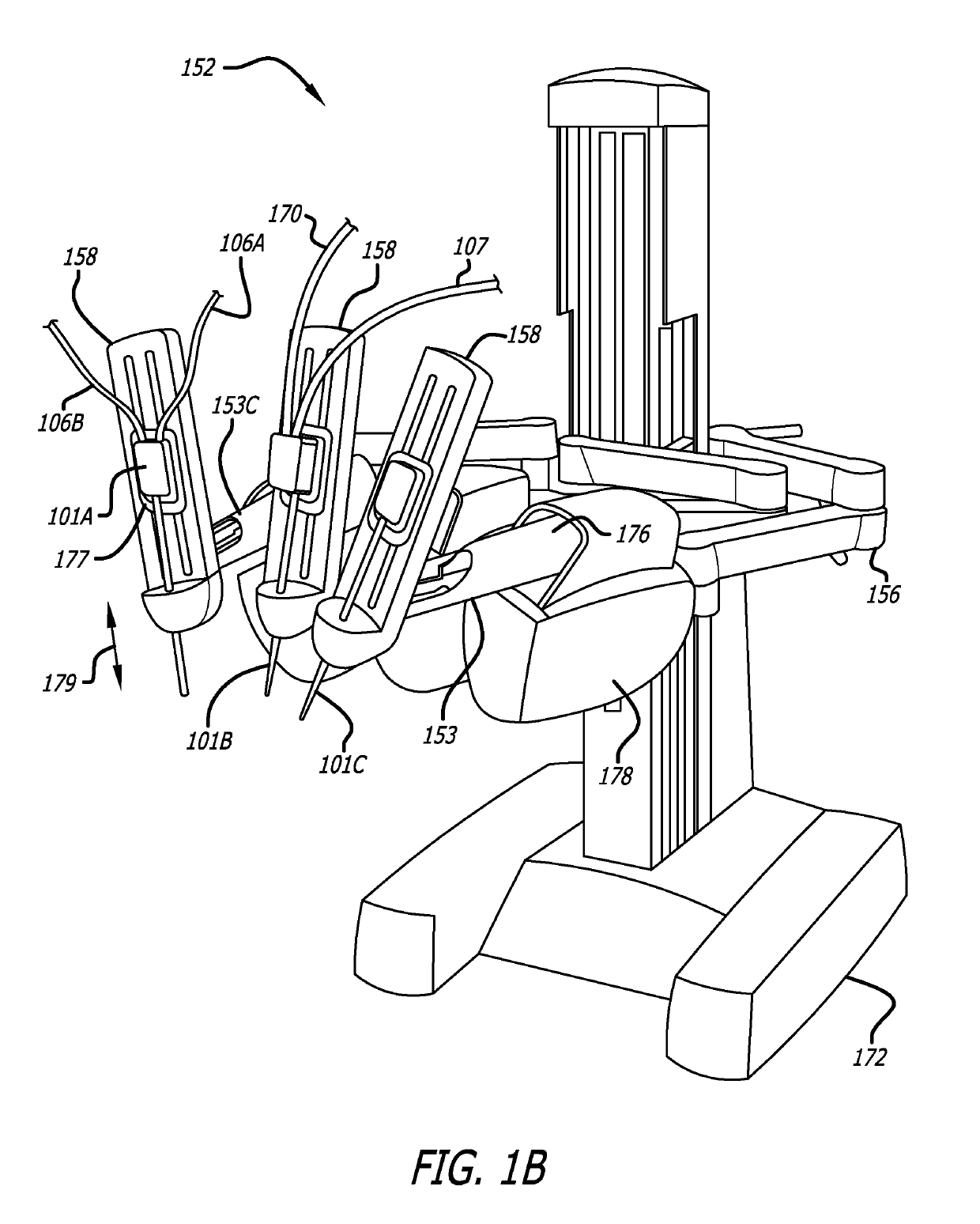
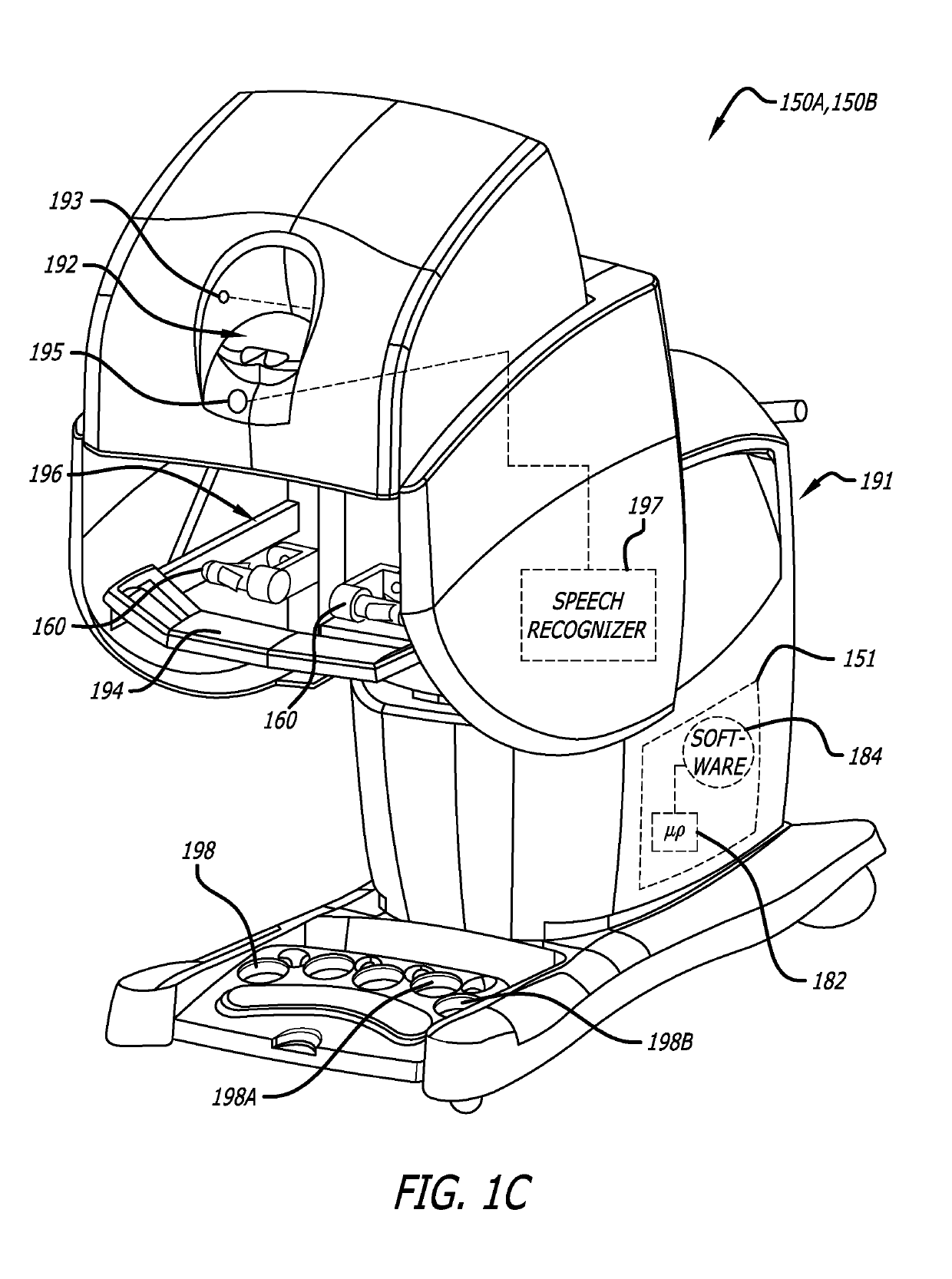
Surgical tools for laser marking and laser cutting
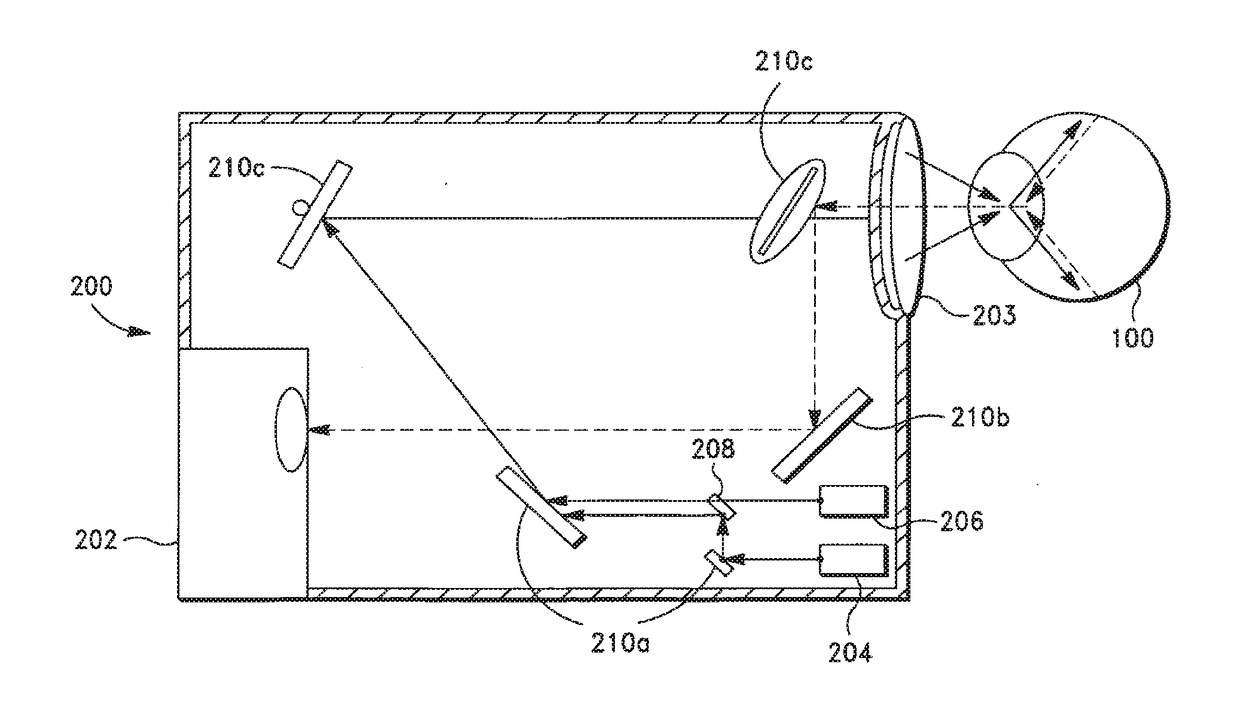
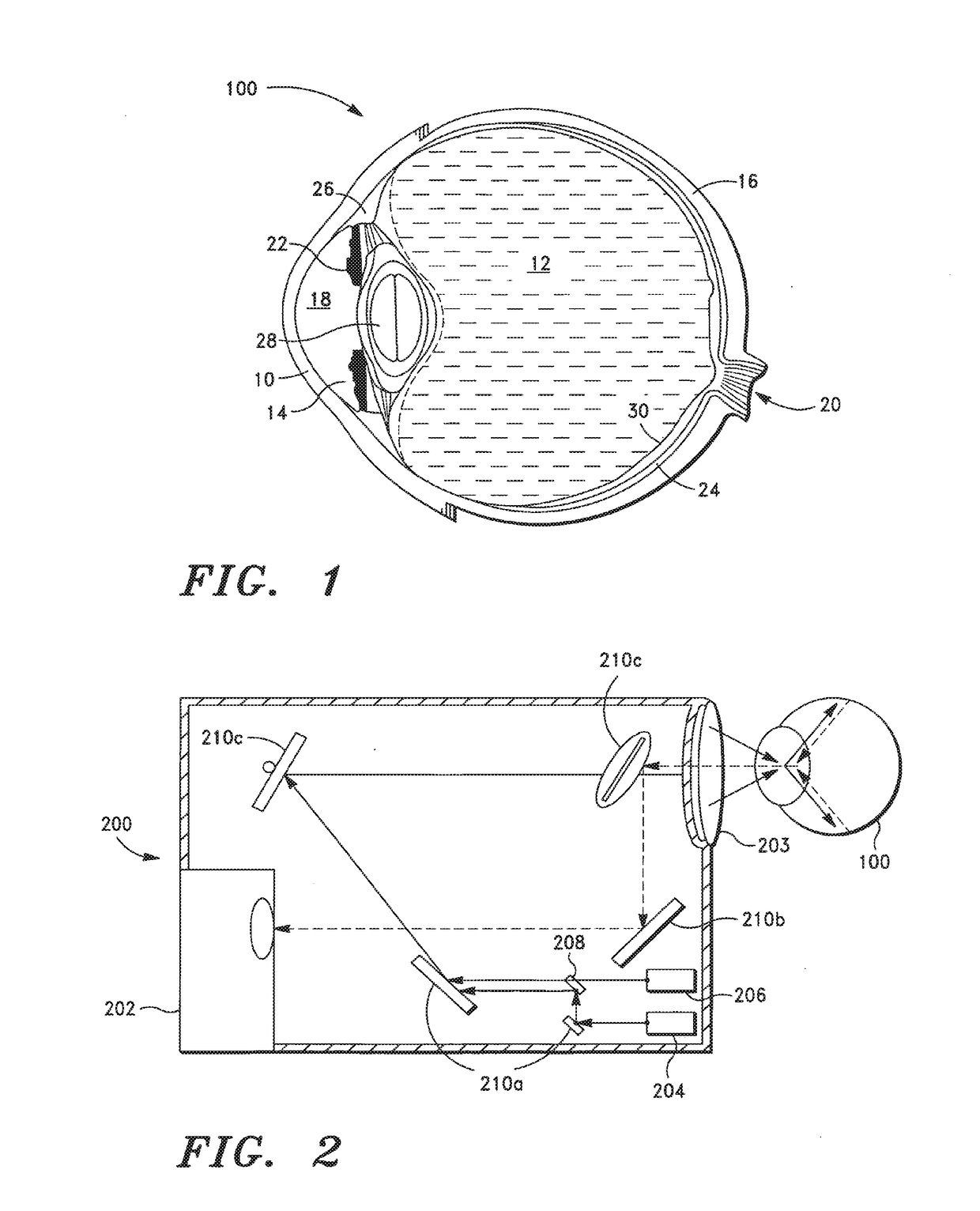
ActiveUS10368838B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsRobotic armDisplay device
In one embodiment of the invention, a robotic surgical system includes a combined laser imaging robotic surgical tool, a control console, and a laser generator / controller. The tool is mounted to a first robotic arm of a patient side cart. The tool has a wristed joint and an end effector coupled together. The end effector has a laser-emitting device to direct a laser beam onto tissue in a surgical site and an image-capturing device to capture images of the tissue in the surgical site. The control console, in communication with the tool, receives the captured images of tissue in the surgical site and displays the captured images on a display device to a user. The laser generator / controller is coupled to the tool and the control console to control the emission of the laser beam onto tissue of the surgical site.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
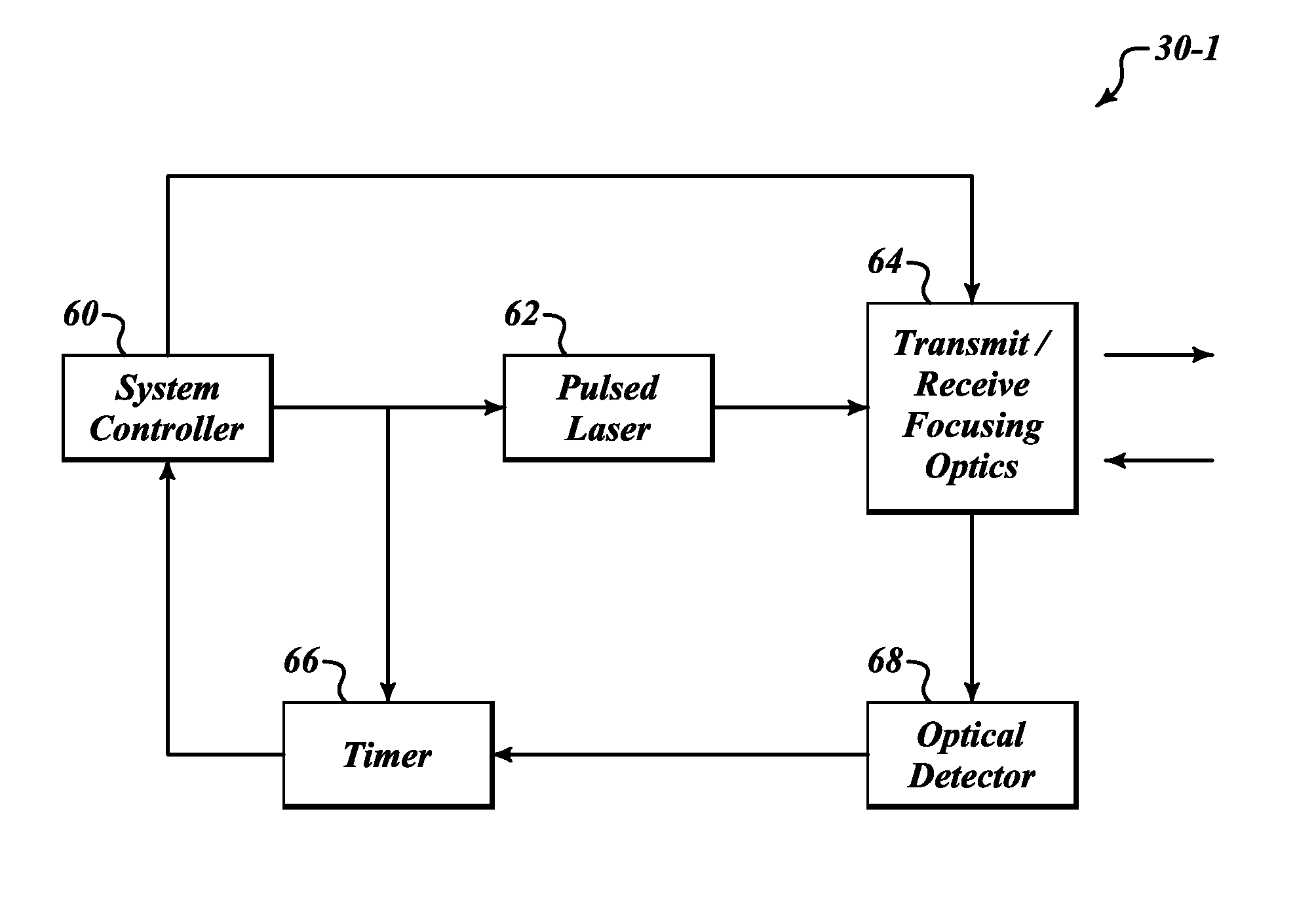
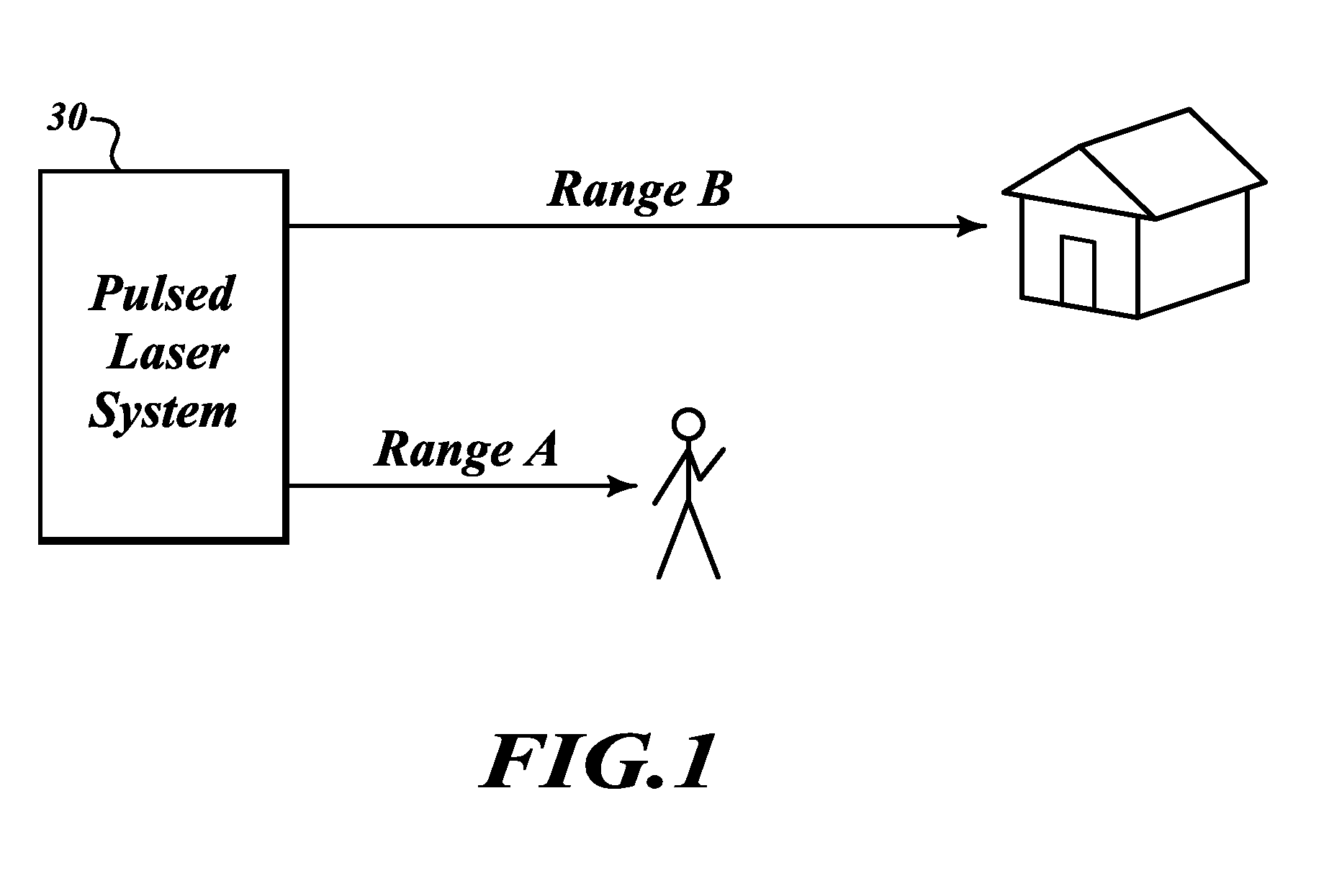
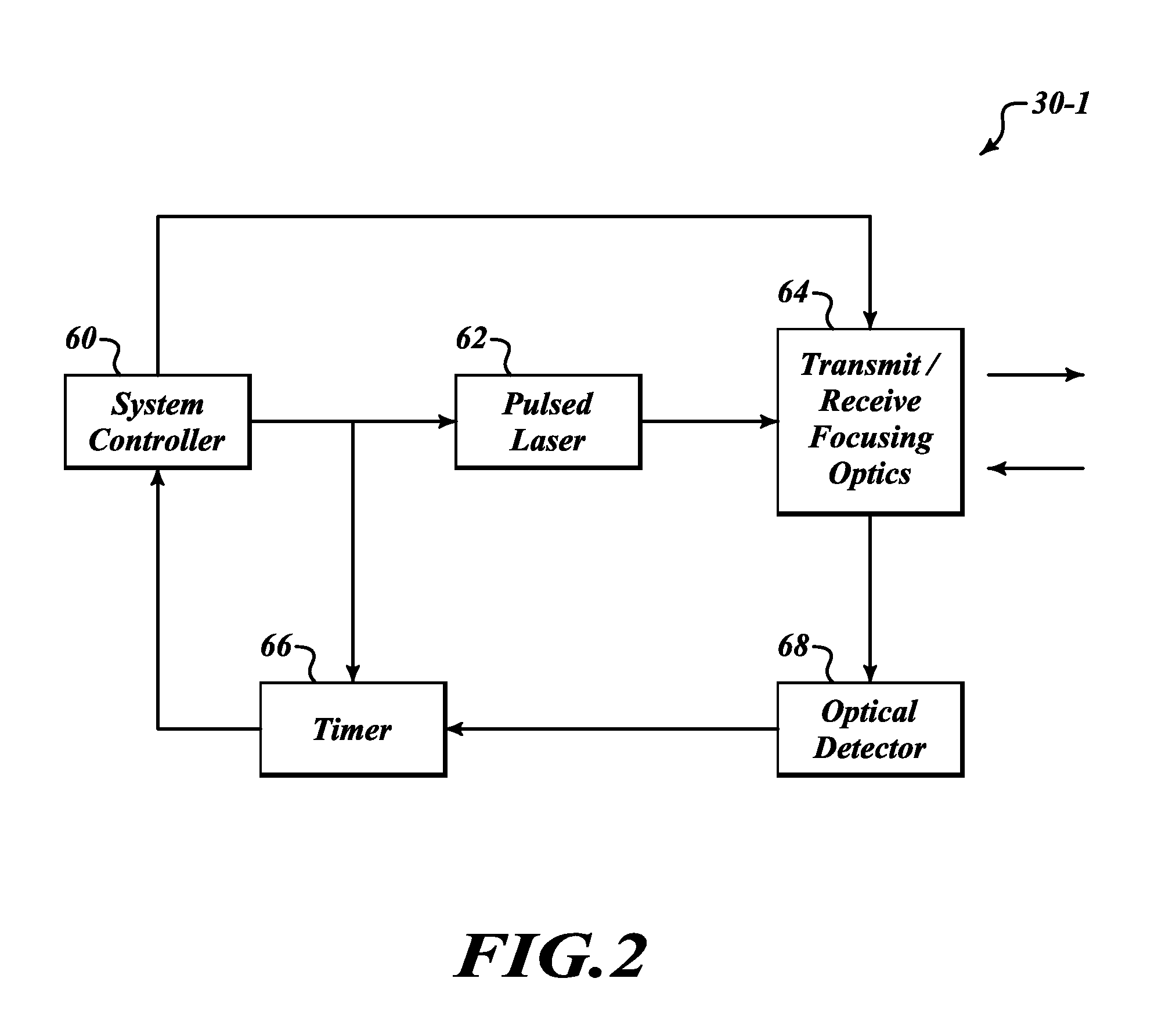
Systems and methods for safe laser imaging, detection and ranging (LIDAR) operation
InactiveUS20090273770A1Realize automatic adjustmentOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser imagingField of view
A Laser Imaging, Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) system that automatically adjusts laser output so that no eye damage occurs to human targets. In one example, a component automatically measures range to targets in a field of view and determines the closest targets based on the measured range. A laser device outputs a laser beam and a controller adjusts one of pulse repetition frequency, power, or pulse duration of the laser device based on the measured range of the closest target in order to comply with a predefined eye safety model.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Integrated laser imaging and spectral analysis system
A system for analyzing an object has two operating modes such as scanned imaging mode and stop scan spectral analysis mode. A beam scanner is optically connected to a laser to receive laser beams from the laser. Beam scanner also scans the beams if the system is in the scanned imaging mode. A lens (e.g., an objective lens) is optically coupled to the beam scanner to focus the beams received from the beam scanner. A sensor is optically coupled to the lens to receive the beams that reflect from the object. The sensor may detect characteristics of the beam such as color and intensity. A spectrometer is optically coupled to the objective lens. During stop scan spectral analysis mode, spectrometer generates wavelength spectrum data.
Owner:UNIPHASE A CA
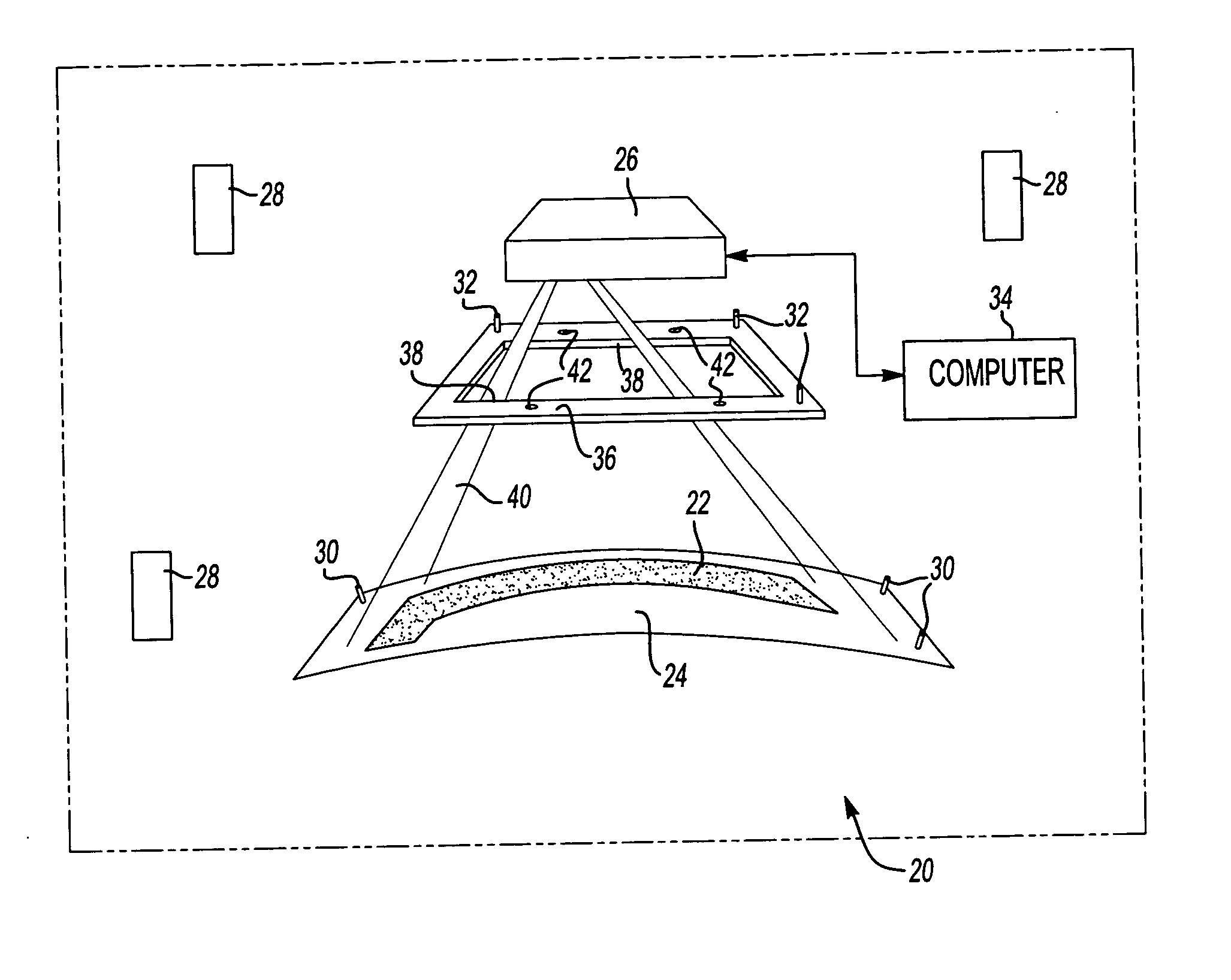
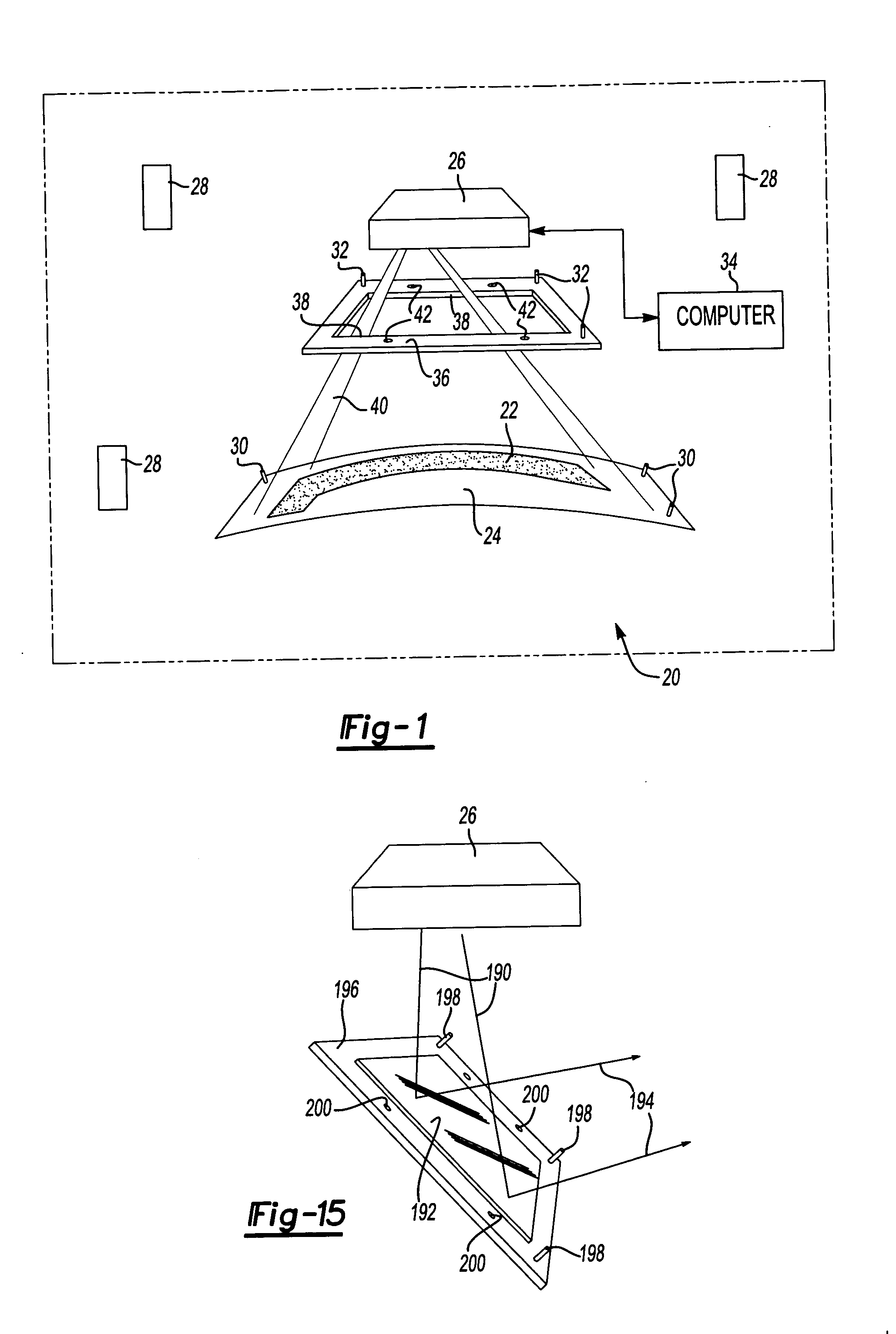
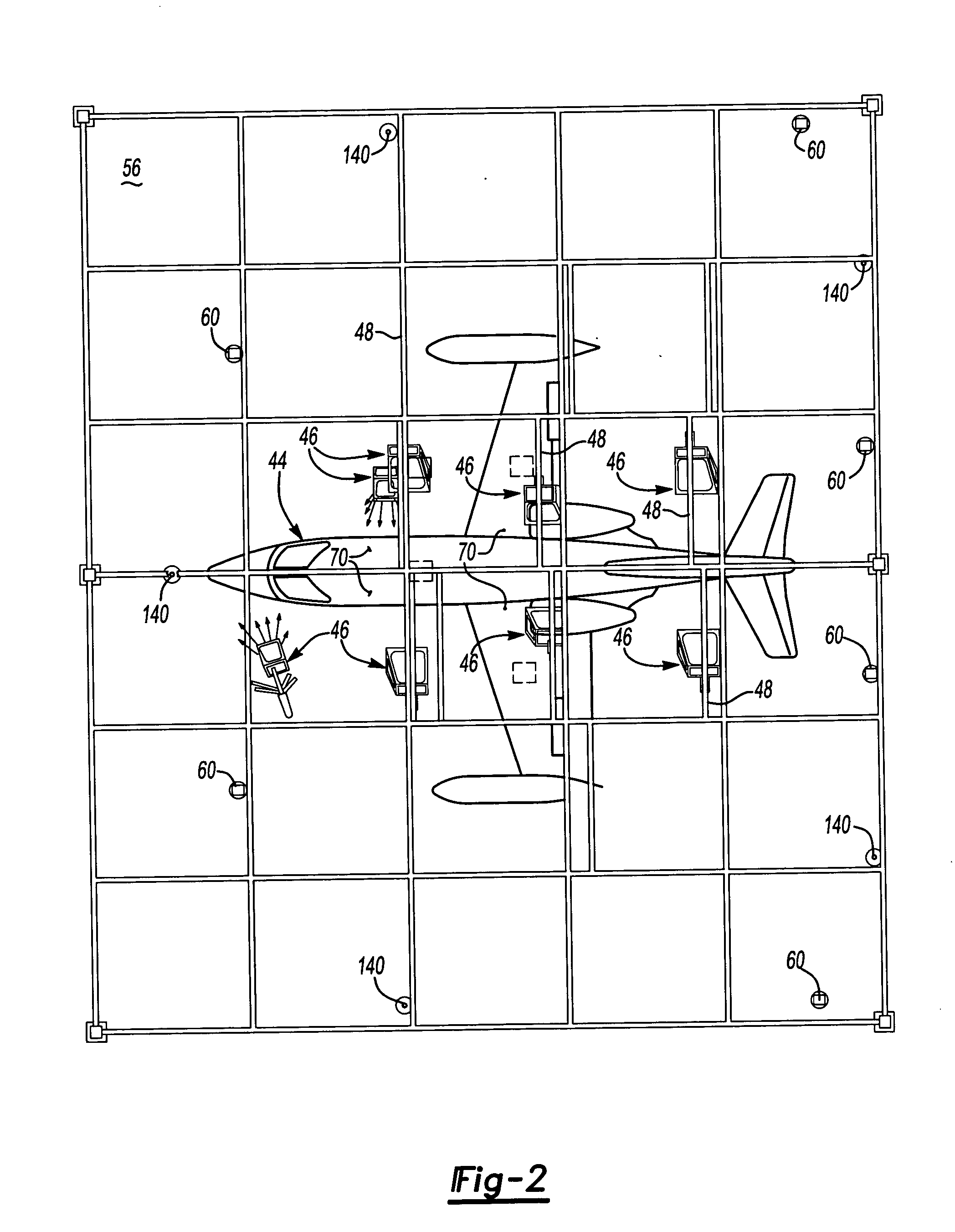
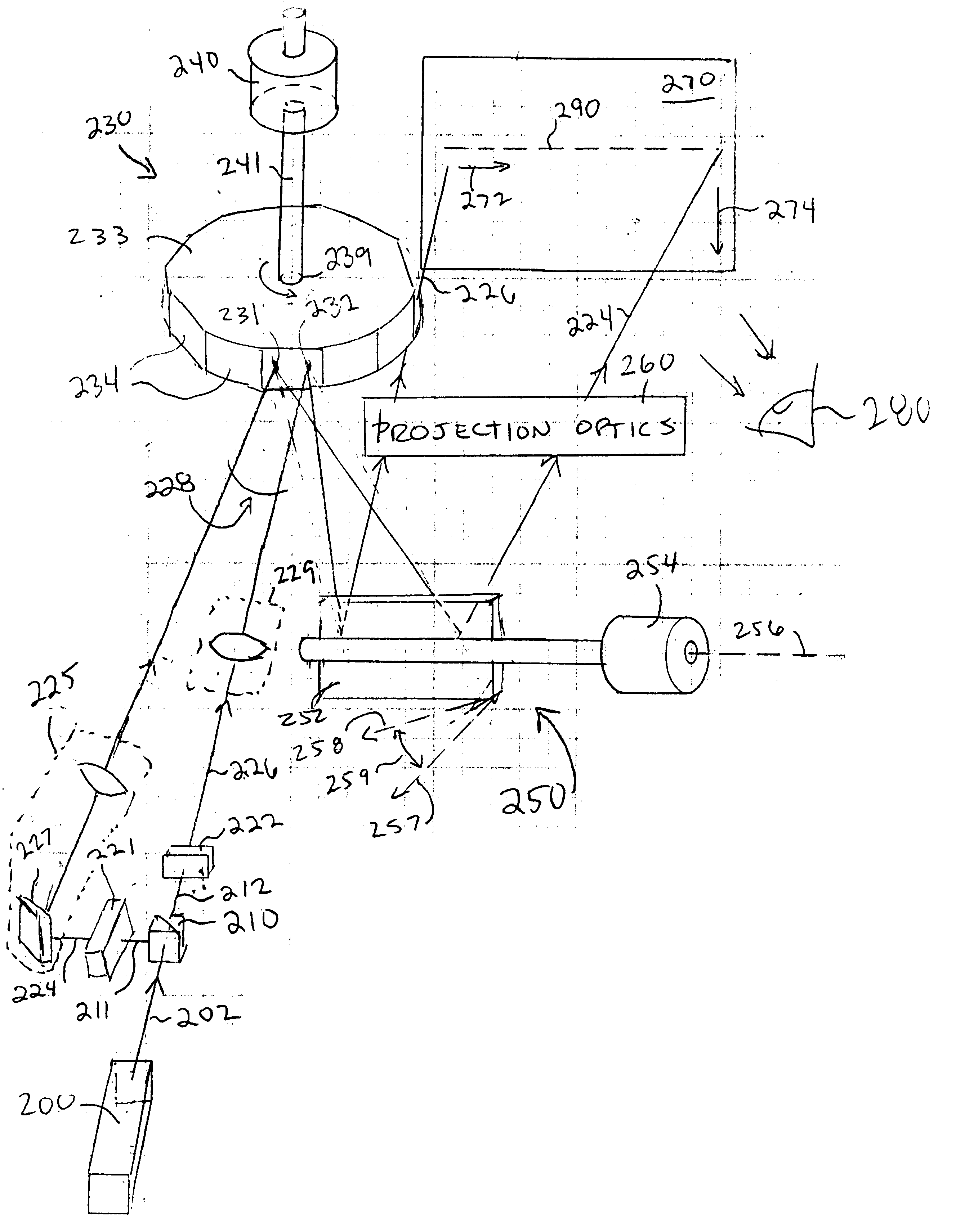
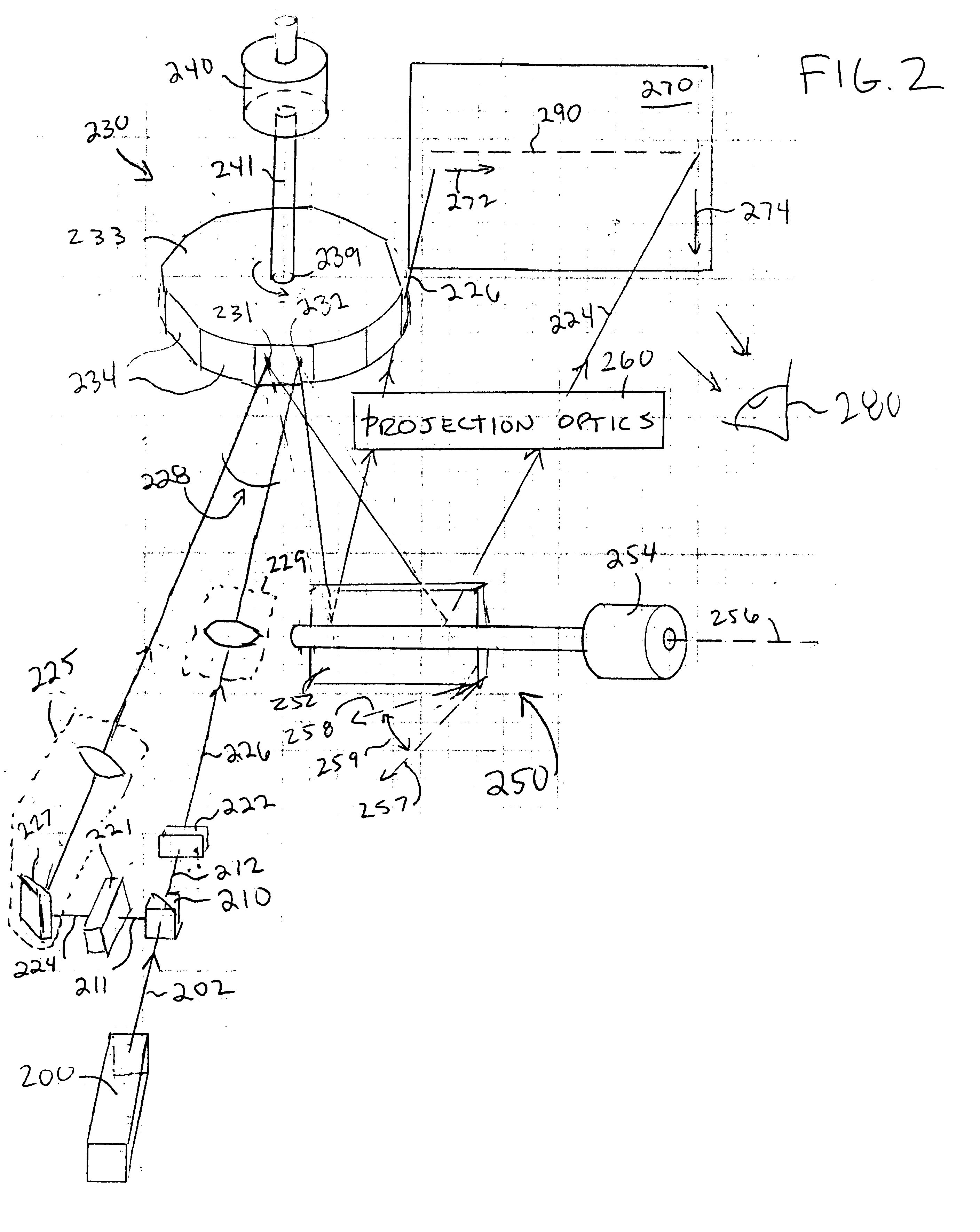
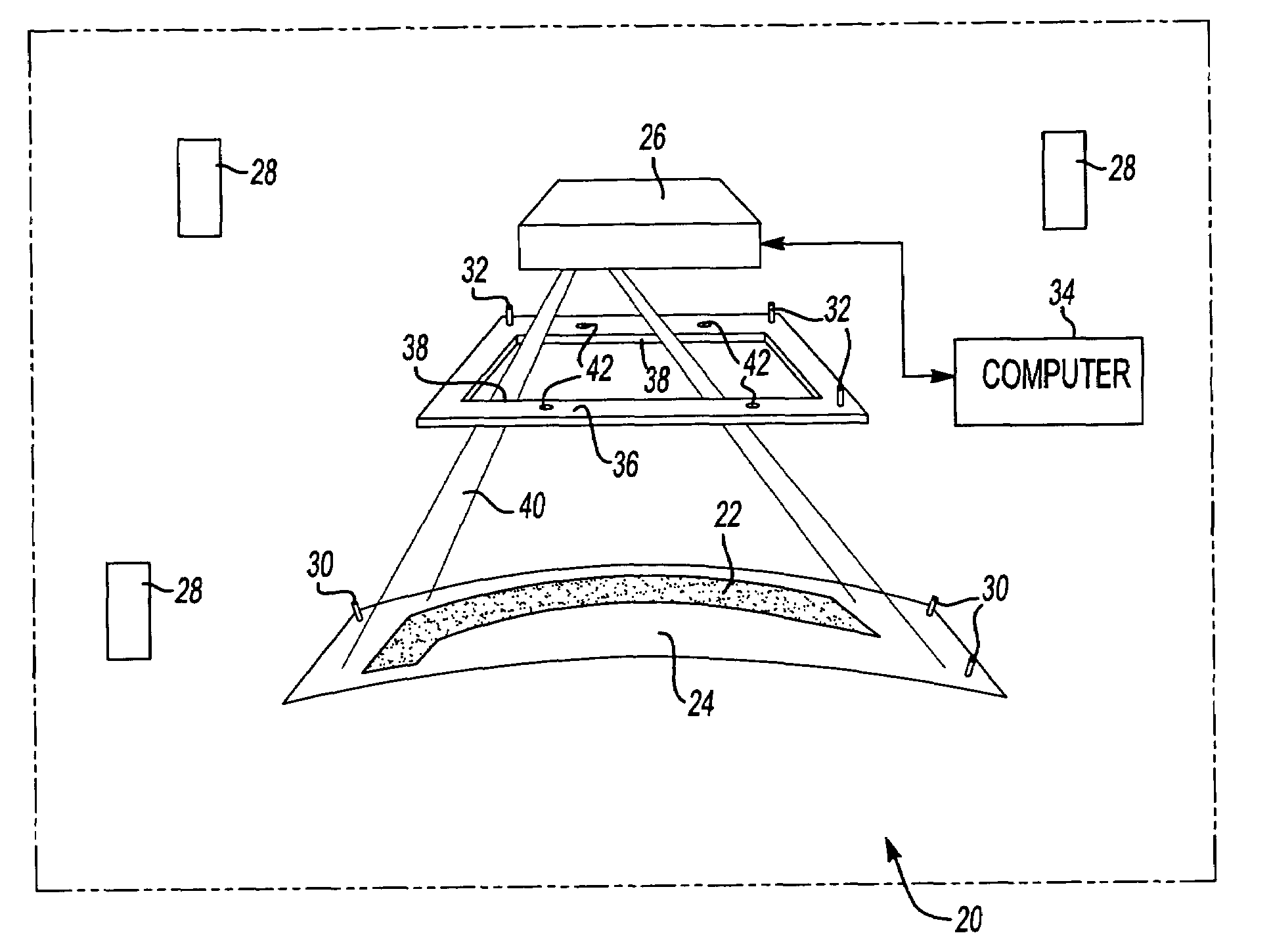
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS20050082262A1Easy to disassemblePrecise positioningProjectorsPosition fixationMetrologyKinematics
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
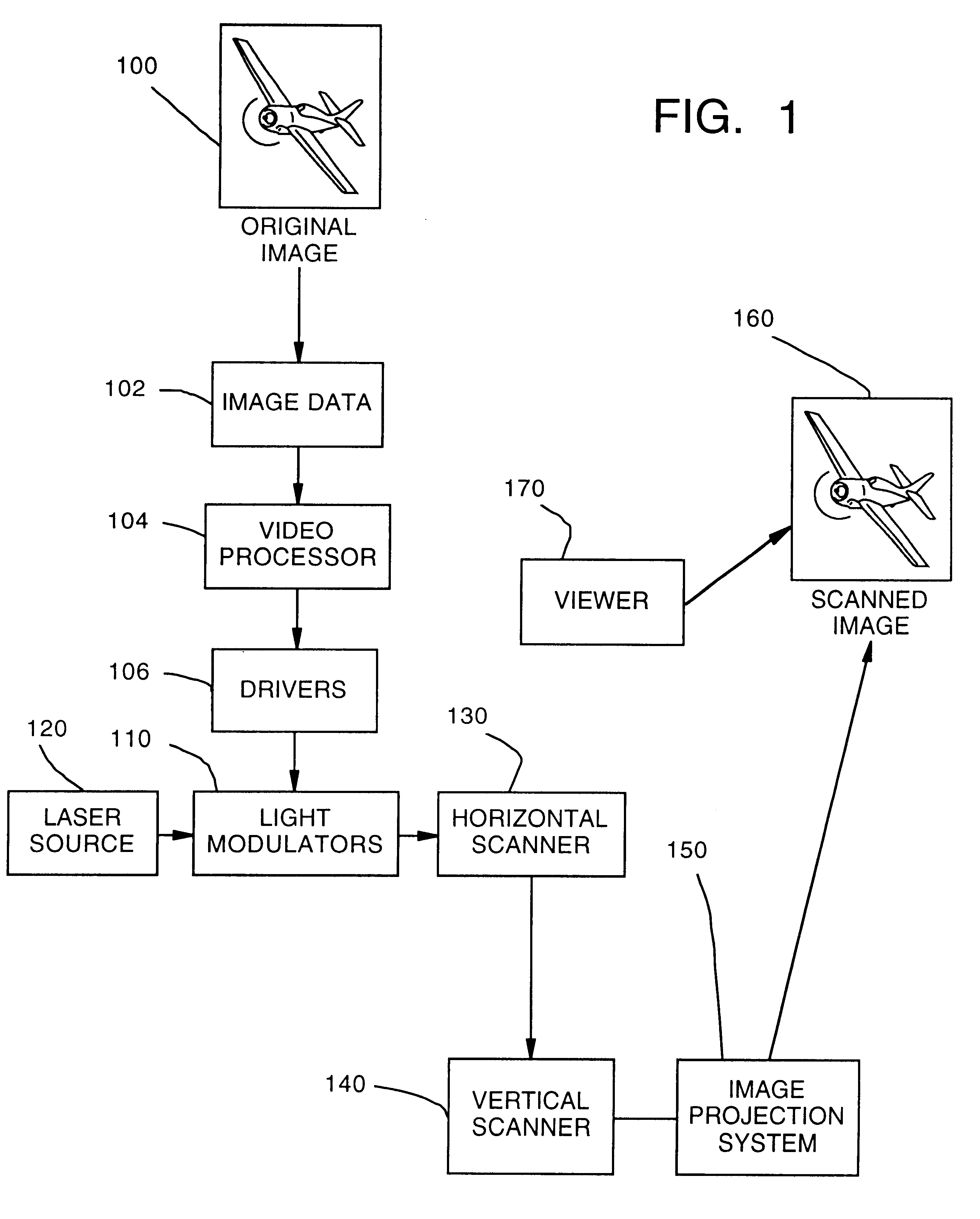
Laser imaging system with progressive multi-beam scan architecture
InactiveUS6351324B1Big cost advantageImprove system efficiencyPicture reproducers using projection devicesPicture signal generatorsColor imageBeam scanning
A progressive scan architecture for displaying a two-dimensional image by alternately scanning two or more laser beams, one after the other with a time delay between adjacent beams. The beams are arranged to become incident upon a polygon scanner in a row with an approximately uniform spatial separation and an approximately equal angle between adjacent beams. The polygon scanner scans horizontally and a galvanometer-driven mirror scans vertically. Adjacent lines are progressively scanned in sequence from top to bottom, which advantageously reduces or eliminates psycho-visual effects and is tolerant of non-linearities in the vertical scanner, allowing use of a low-cost galvo mirror. Typically, the beams in the row are arranged in pairs, and only one beam from each pair will be scanning at any one time. Embodiments are described in which the duty cycle is slightly less than 50% and the laser illumination is switched between two interleaved beam scans thereby allowing a single modulator to be used for both beams which provides significant cost advantages and improves system efficiency. For full-color images, each of the beams described can incorporate separate red, green and blue (RGB) components which are individually modulated by separate red, green, and blue modulators. The system can be scaled up with one or more additional pairs of beams to improve resolution and / or increase pixel count without requiring a high-speed polygon scanner or a highly-linear galvo scanner. Furthermore, the height of each facet in the polygon mirror need be only one beam diameter and its length need only be two beam diameters, which allows the system to approach the minimum pixel size attainable, which is useful to provide high efficiency and high brightness in the image.
Owner:PHOTERA TECH
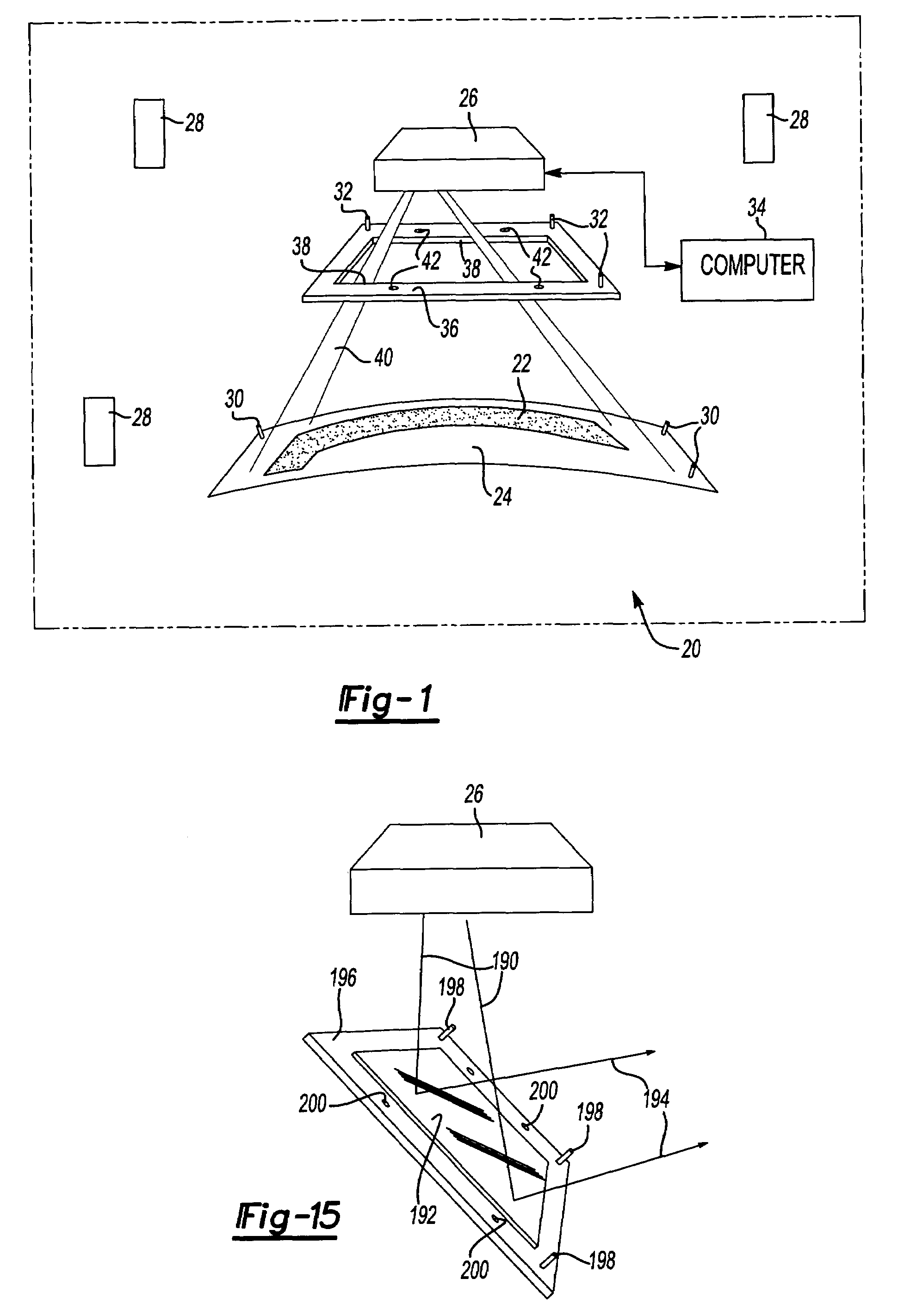
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS7545517B2Precise positioningEasy to disassembleProjectorsPosition fixationKinematicsLaser target
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
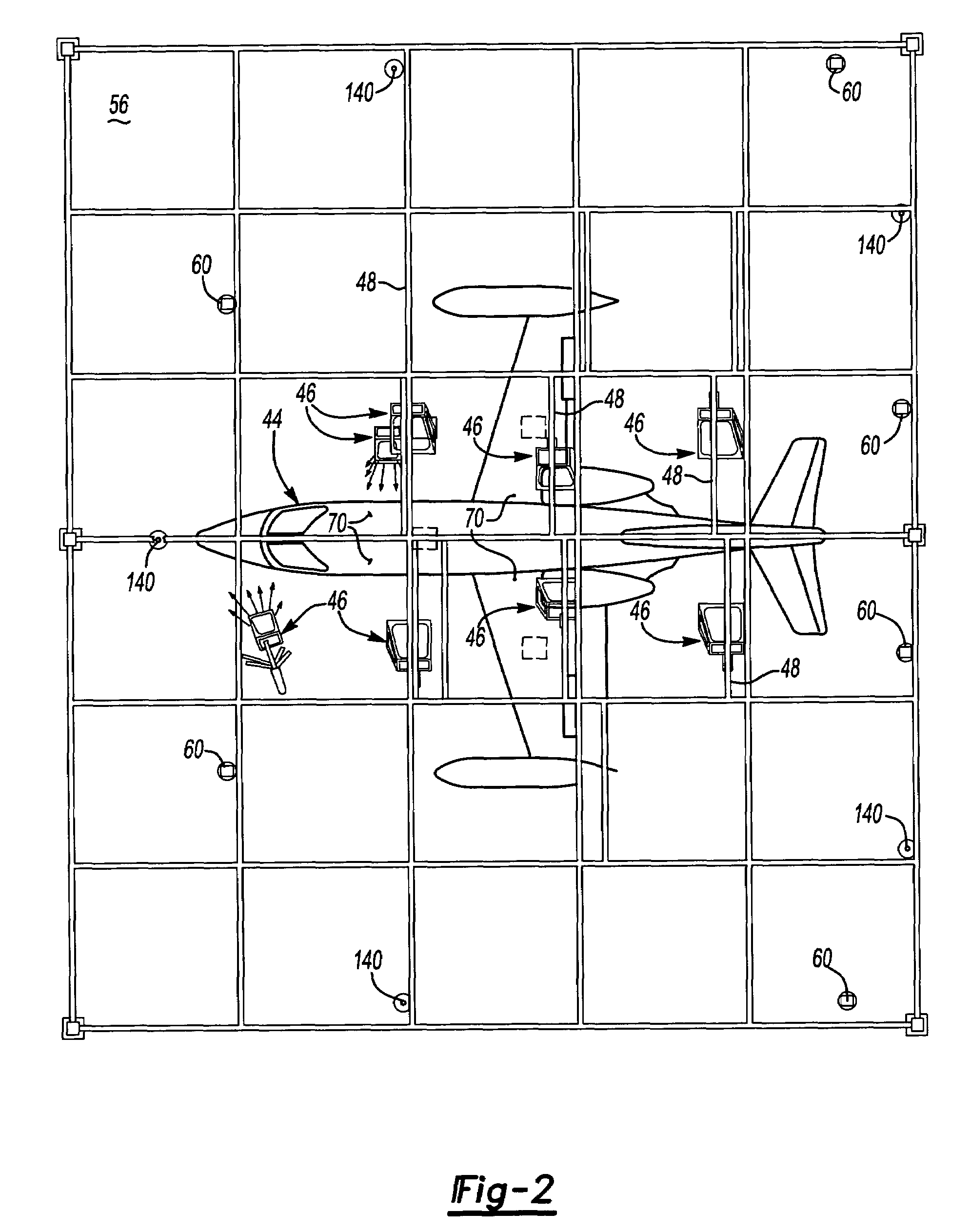
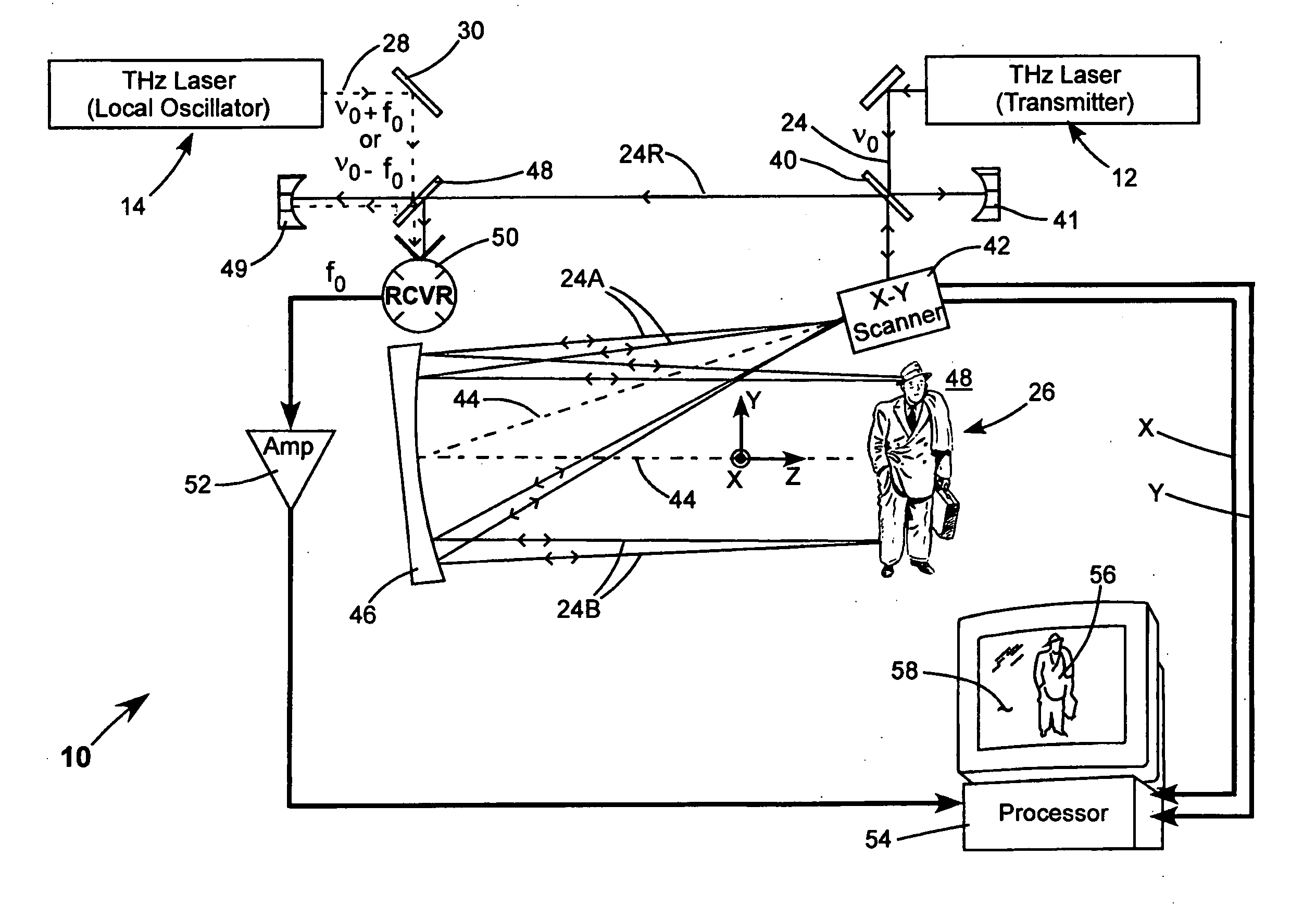
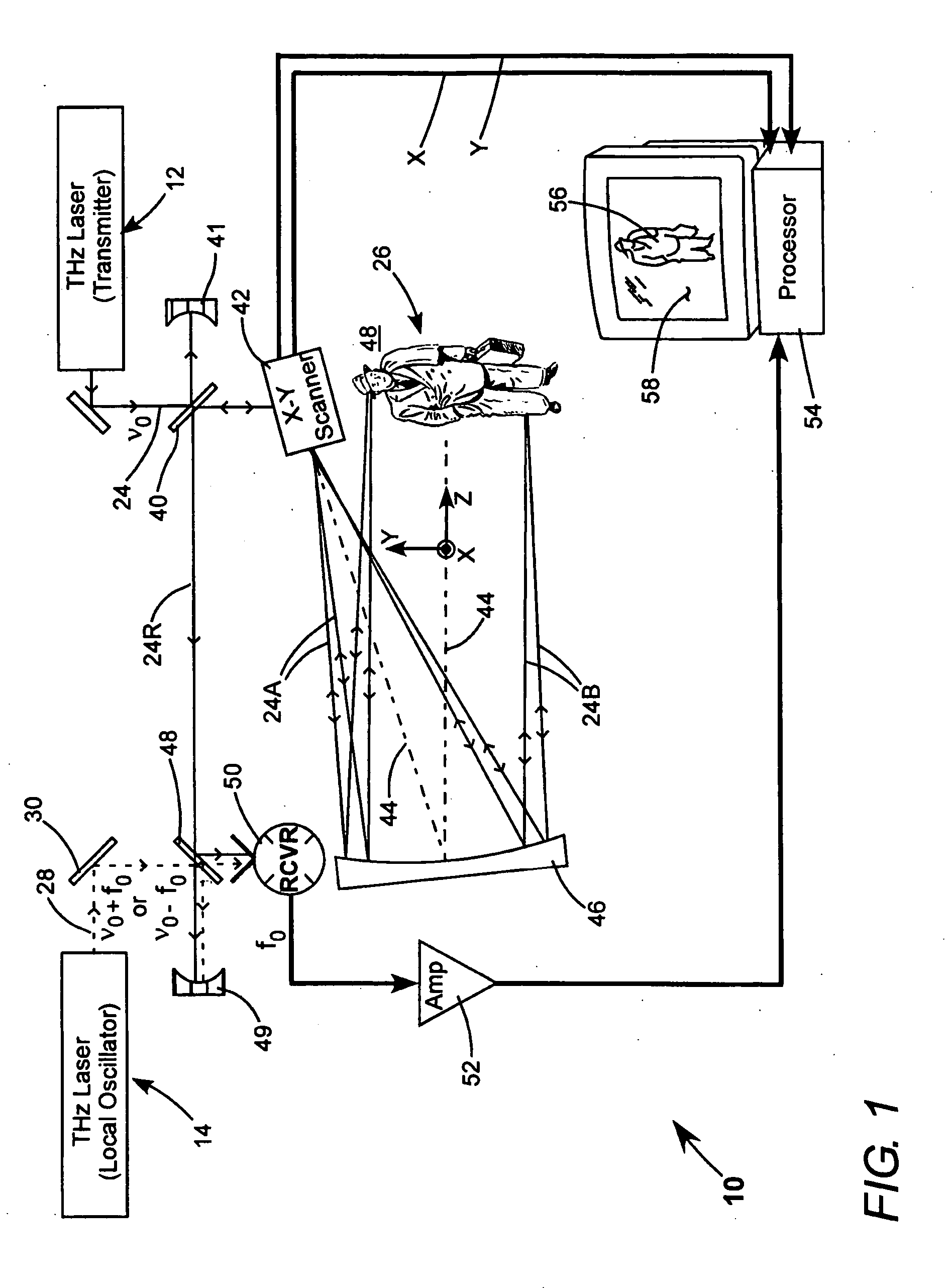
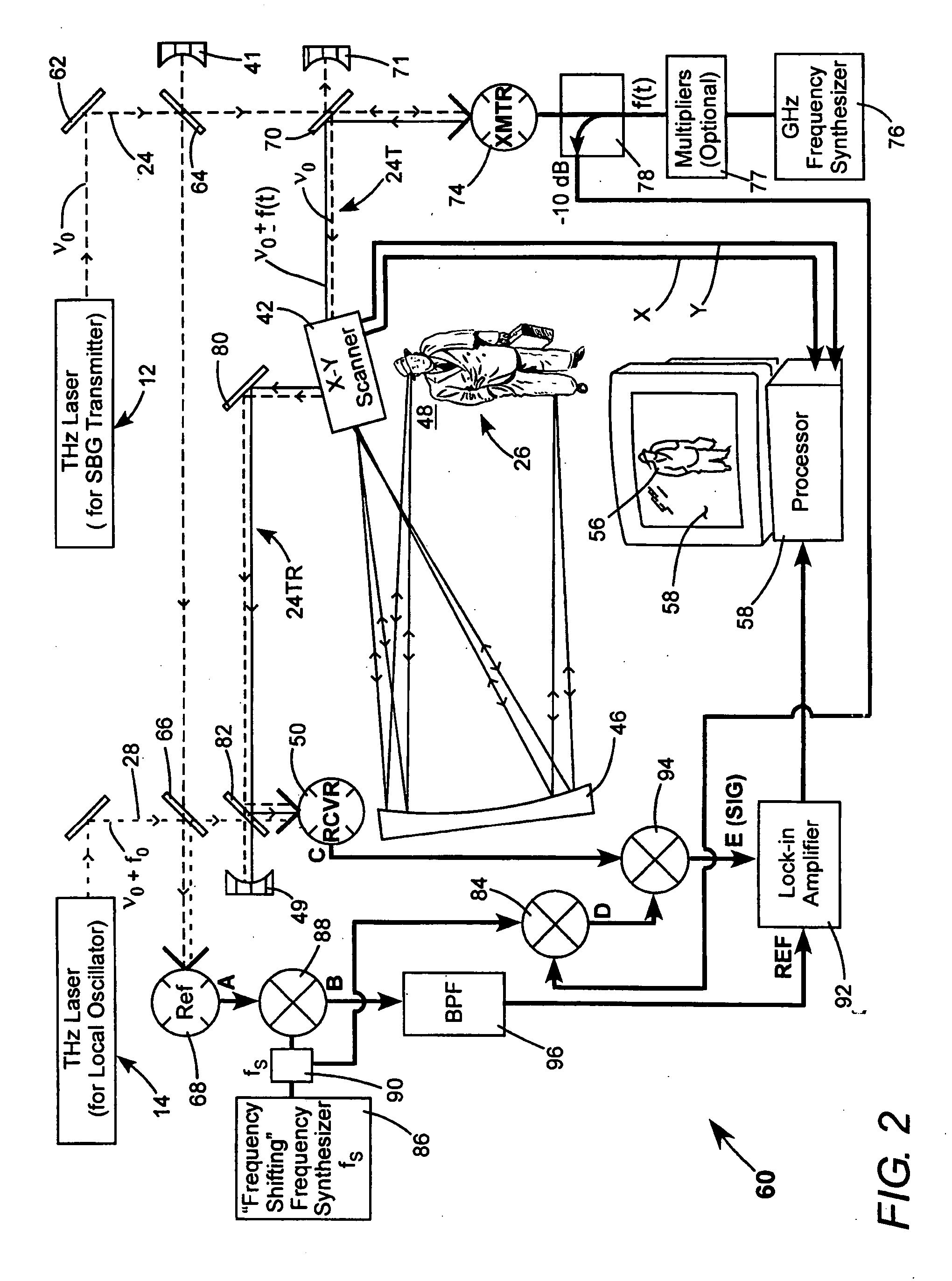
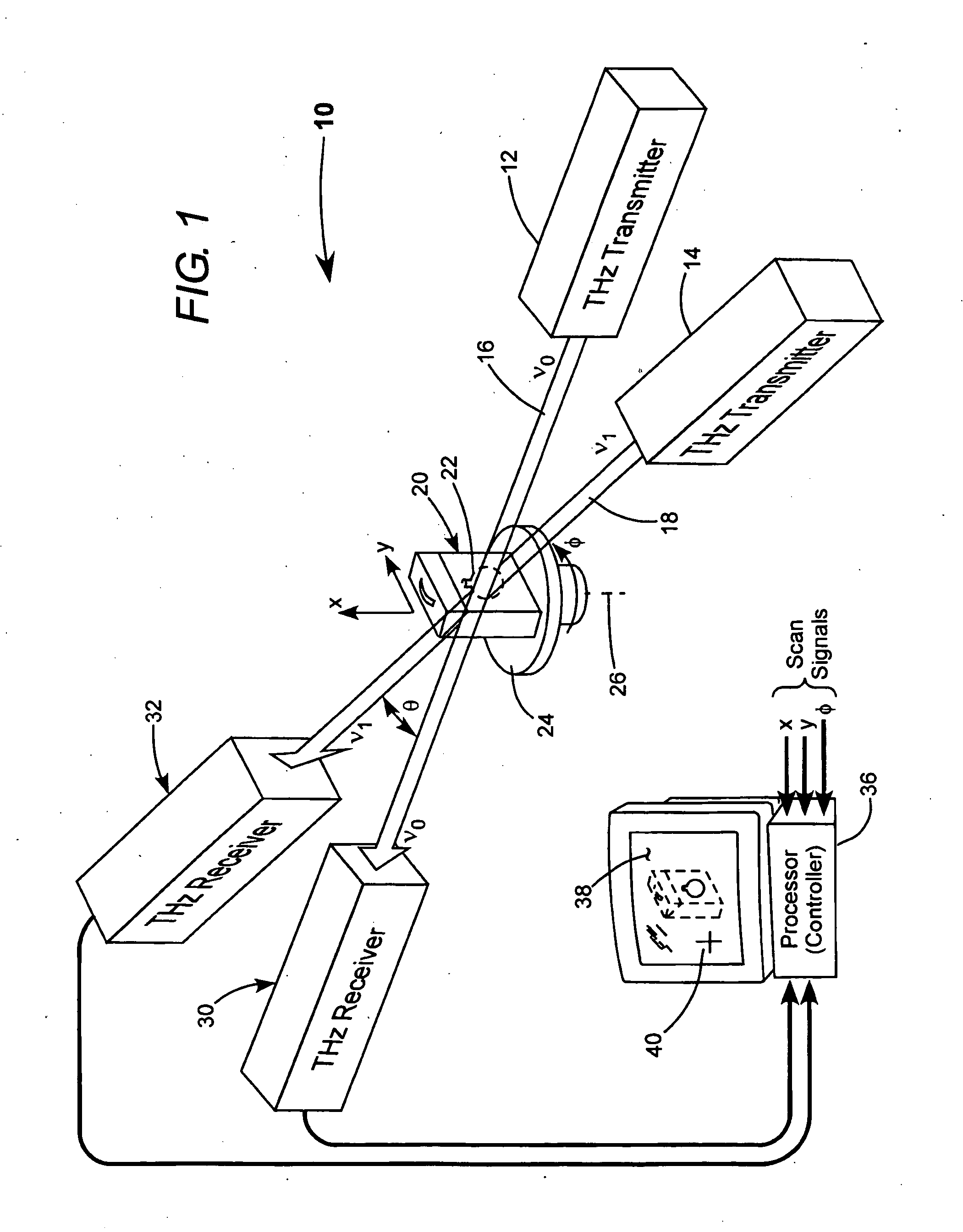
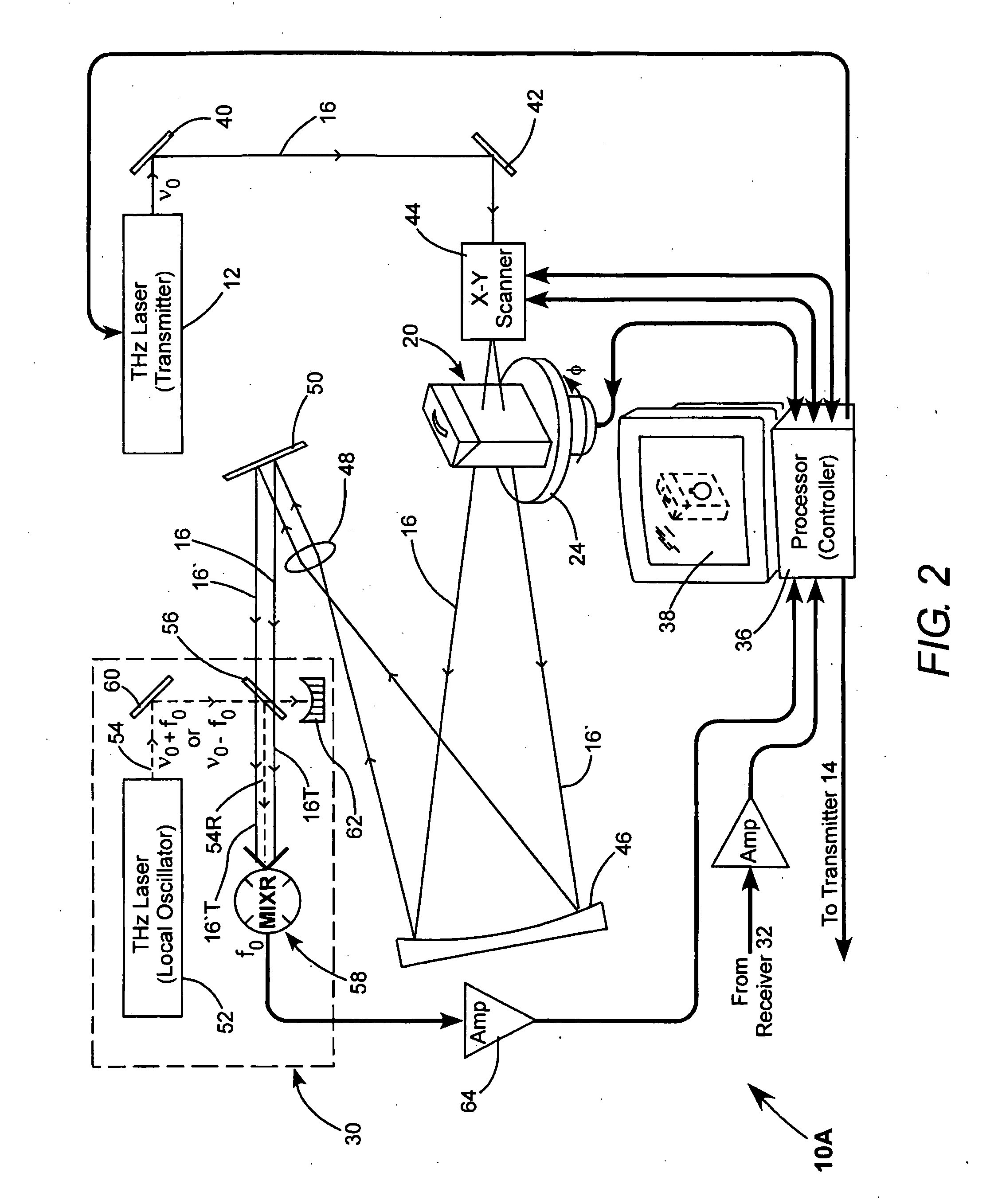
Detection of hidden objects by terahertz heterodyne laser imaging
A THz-frequency heterodyne imaging method is used to remotely detect objects concealed in or under a person's clothing. One THz-frequency beam is scanned over a person being examined. A portion of the beam penetrates the persons clothing and is reflected by an object concealed under the person's clothing. The reflected portion the beam is mixed with another beam of THz-frequency radiation having a different frequency to provide a signal having an intermediate frequency (IF) including image data representative of the concealed object.
Owner:COHERENT INC
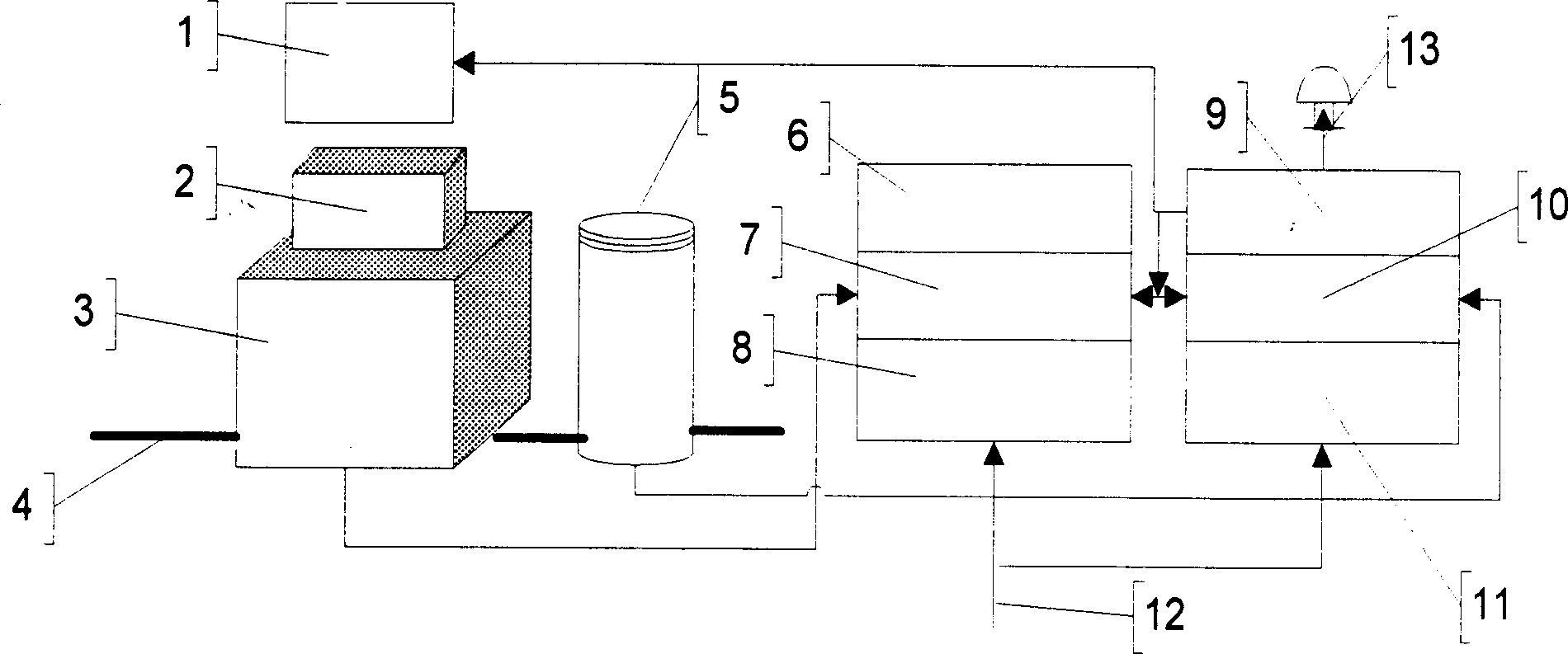
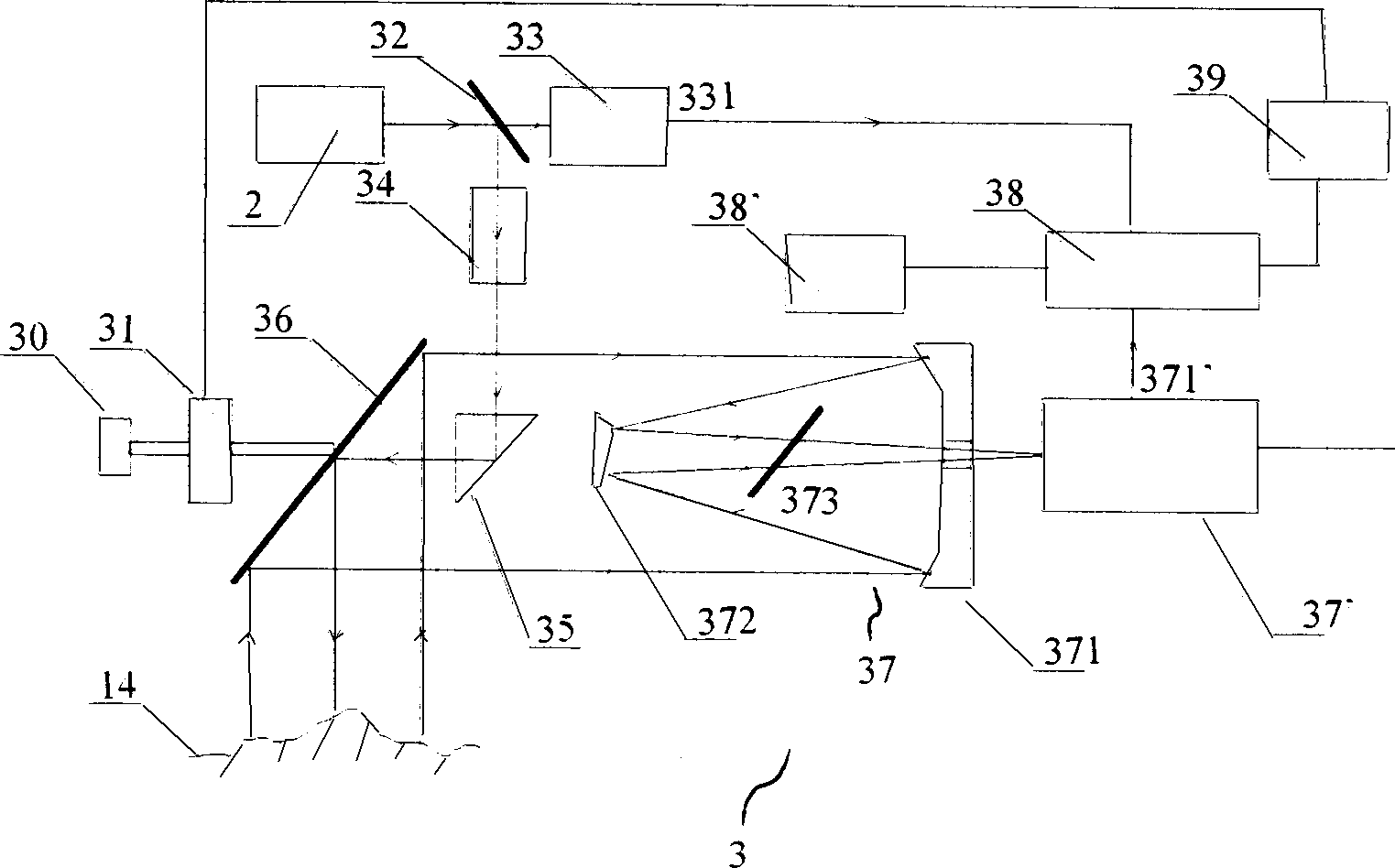
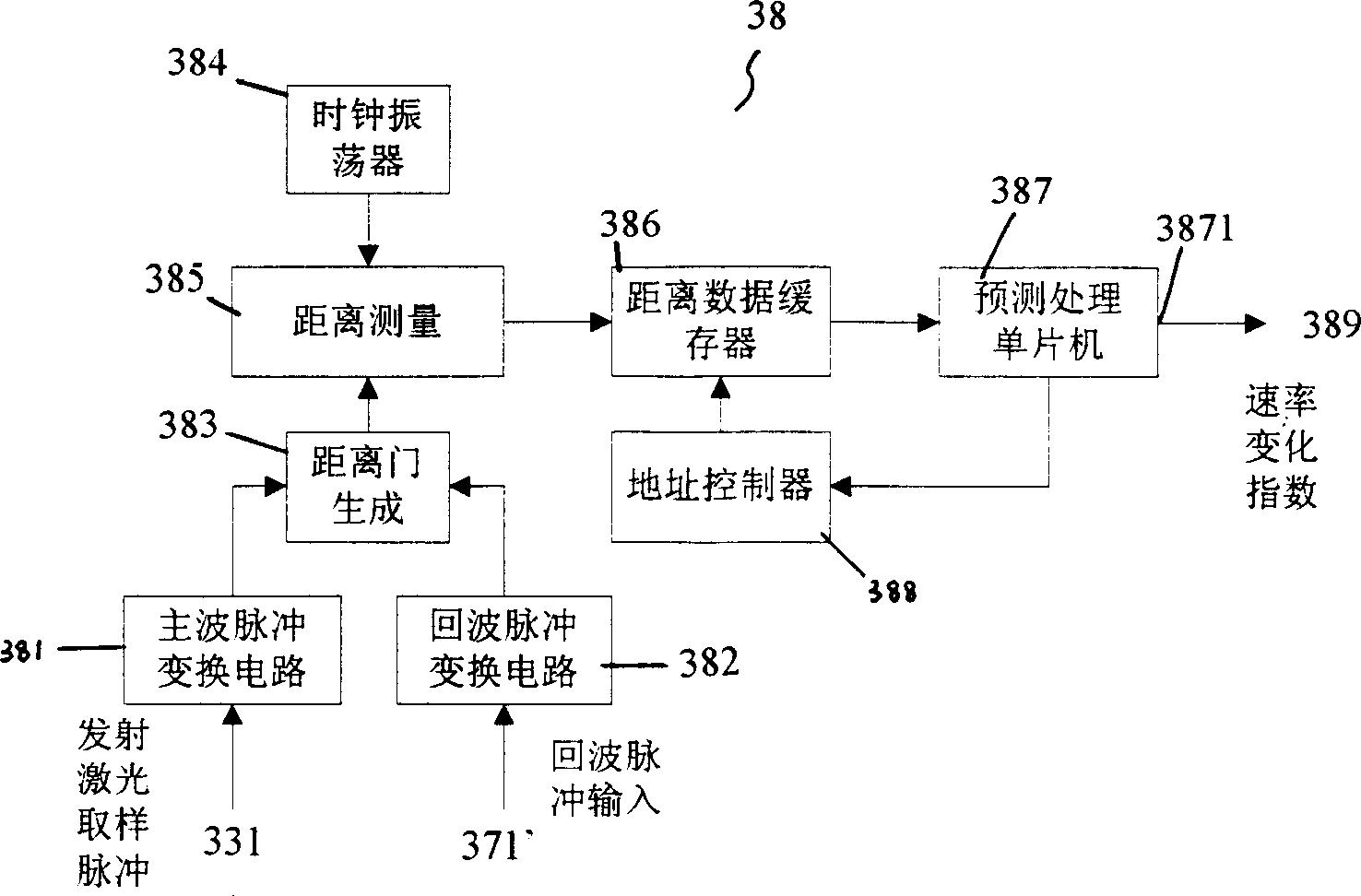
Laser imaging radar device and distance measurement method thereof
ActiveCN103616696AFast ranging speedProbe cycle shortenedElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringRange gate
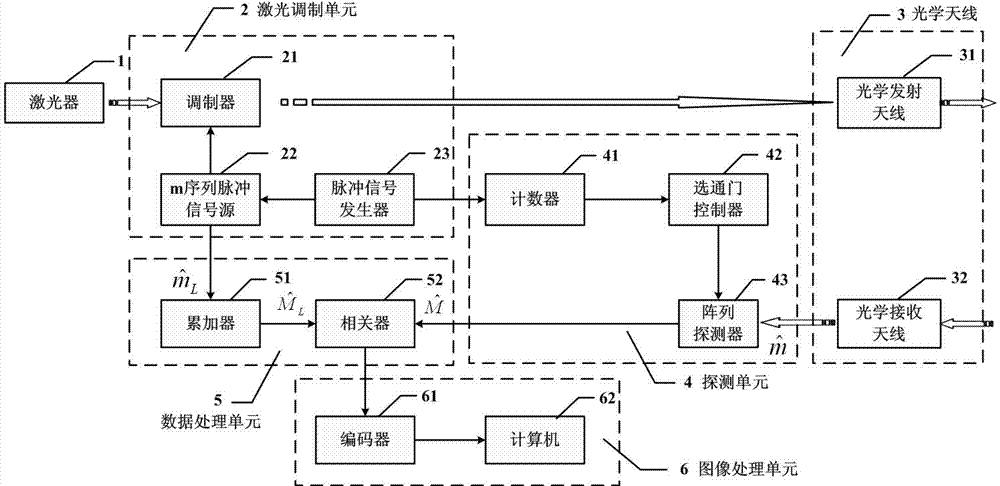
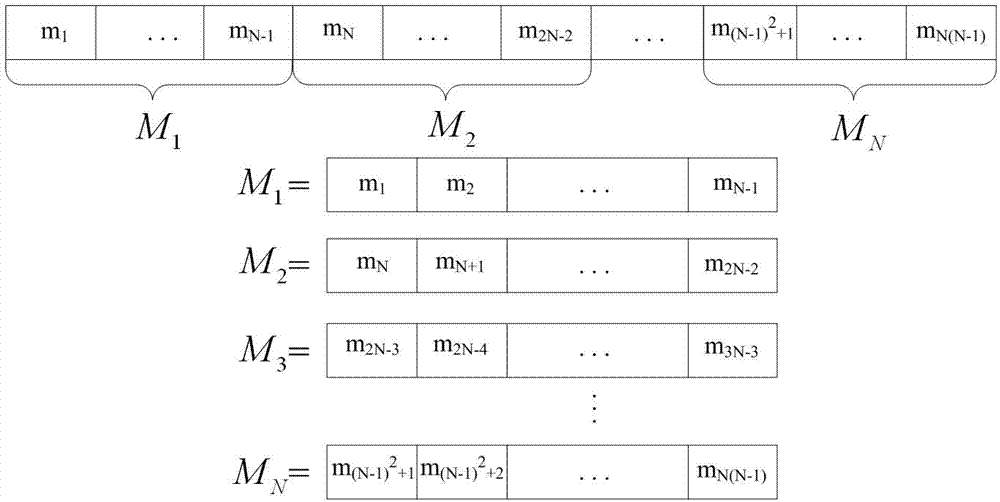
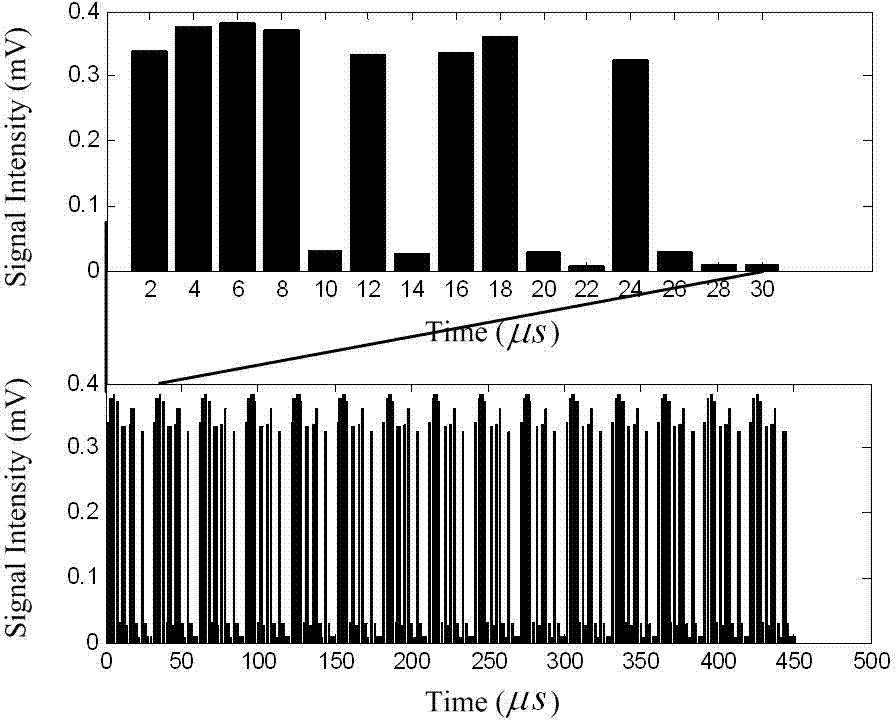
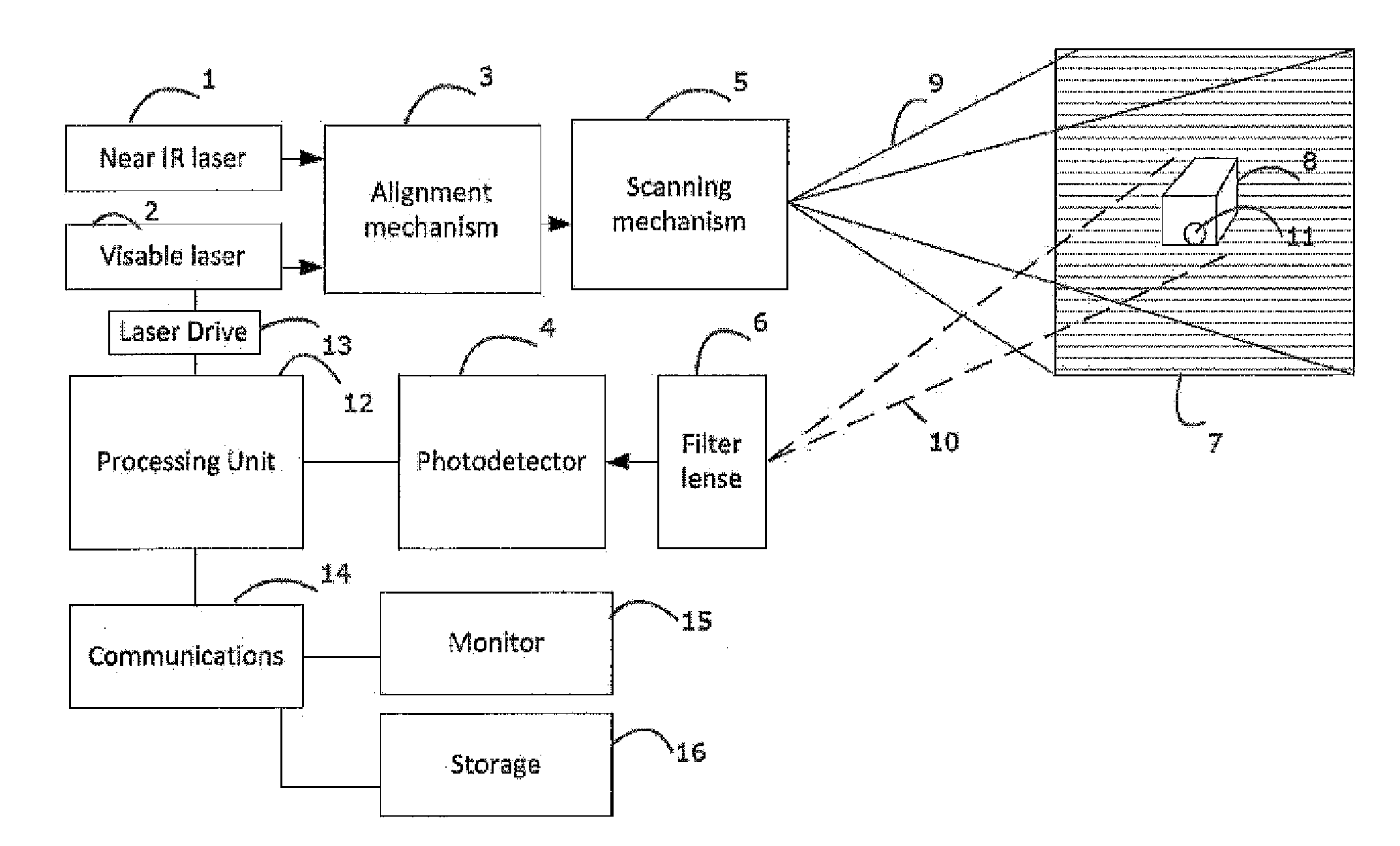
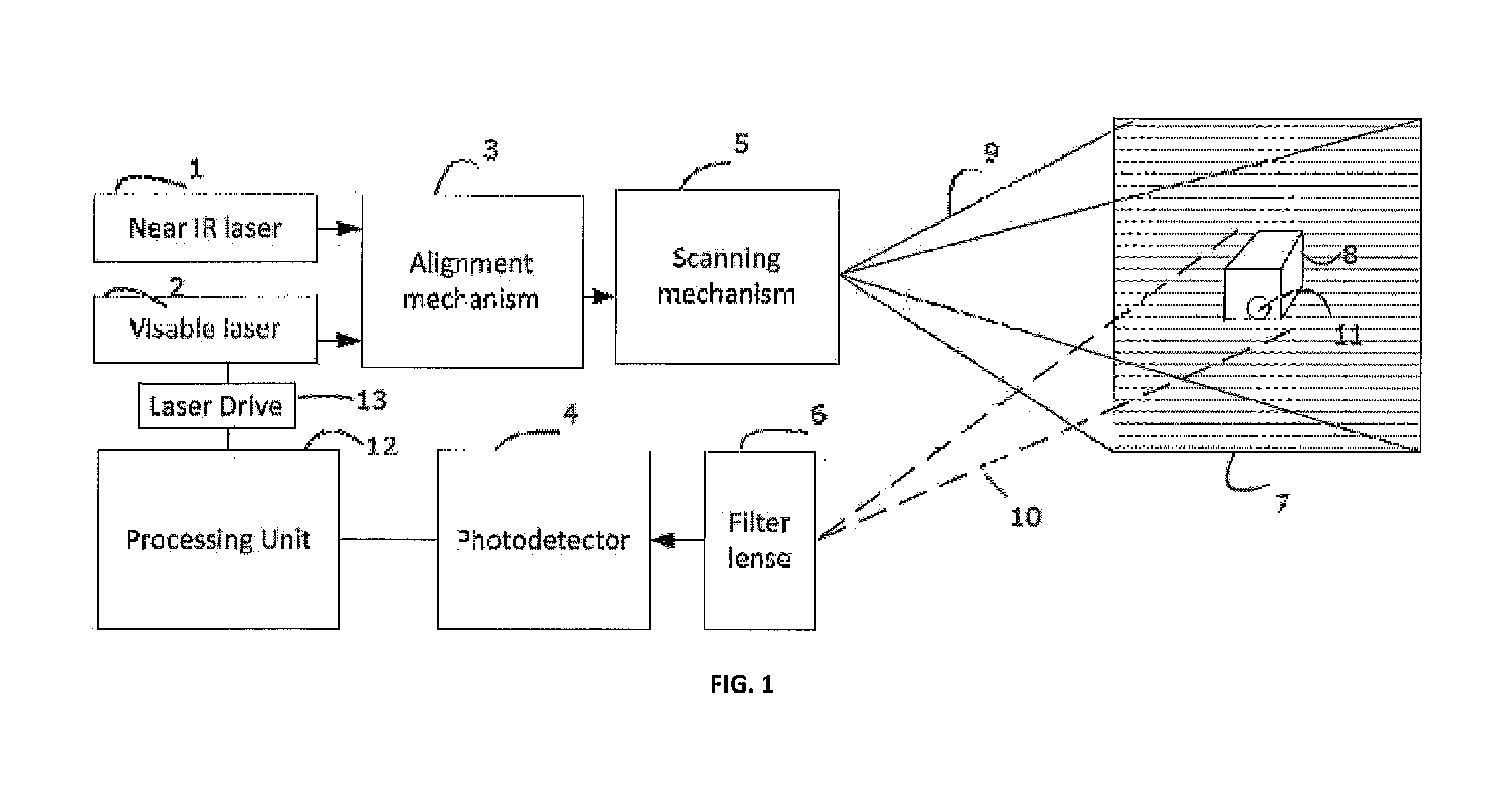
The invention provides a laser imaging radar device and a distance measurement method thereof. The laser imaging radar device and the distance measurement method thereof aims at the problem that an existing distance range gate laser imaging radar is low in distance resolution. The laser imaging radar device comprises a laser device, a laser modulation unit, an optical antenna unit, a detecting unit, a data processing unit and an image processing unit, wherein the detecting unit is composed of a counter, a gate controller and an array detector, and the data processing unit is composed of an accumulator and a correlator. According to the distance measurement method, an information loading process is carried out on laser signals with constant amplitude by using a phase code pulse amplitude modulation mode. The laser imaging radar device and the distance measurement method thereof have the advantages that the equipment and the method combine the advantages of long detecting distances of the distance ranging gate layer imaging radar and the advantage of high distance measurement resolution of the pulse phase coding mode, and meanwhile the detect of low distance measurement resolution of the distance ranging gate layer imaging radar and the detect of low imaging speed of the pulse phase coding mode are avoided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Identification of hidden objects by terahertz heterodyne laser imaging
A method for inspecting a package to identify an object concealed in the package includes passing two beams of THz-radiation through the package. The frequency of THz radiation in one beam is different from that in the other, and the beams are at an angle to each other. Each of the transmitted beams is used to form an image of the package and the object. The absorption coefficient of the object is determined from the two images. The material of the object is determined from the absorption coefficients at the two frequencies. The method is useful for detecting explosive material concealed in baggage.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Feedback mechanism for smart nozzles and nebulizers
ActiveUS20070299561A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove performanceSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesFluorescenceLaser light
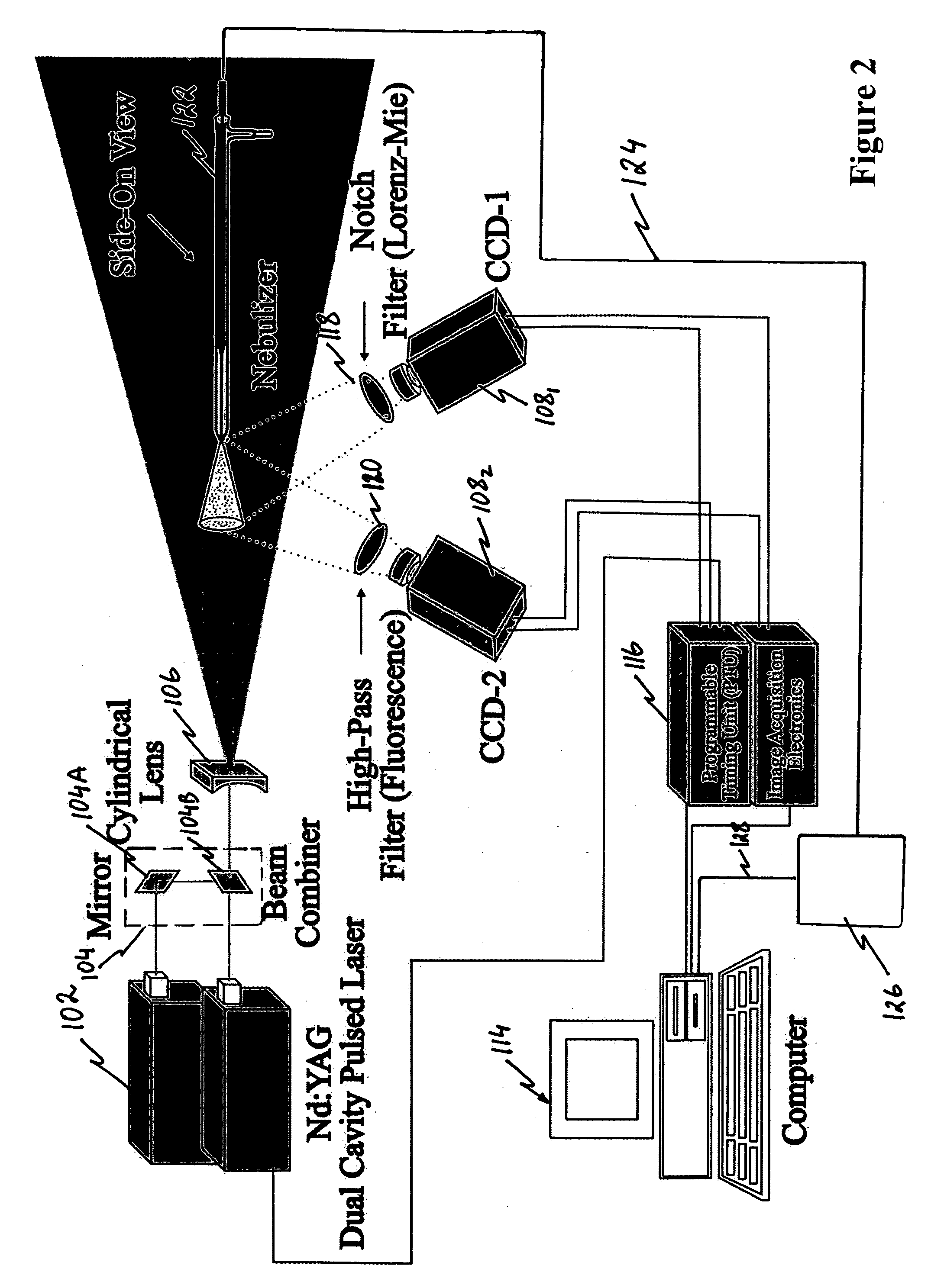
Nozzles and nebulizers that can be adjusted to produce an aerosol with optimum and reproducible quality based on the feedback information obtained using laser imaging techniques are provides. Two laser-based imaging techniques based on particle image velocimetry (PIV) and optical patternation are provided to map and contrast the size and velocity distributions for indirect and direct pneumatic nebulizations in plasma spectrometry. The flow field of droplets is illuminated by two pulses from a thin laser sheet with a known time difference. The scattering of the laser light from droplets is captured by a charge coupled device (CCD), providing two instantaneous images of the particles. Pointwise cross-correlation of the corresponding images yields a two-dimensional (2-D) velocity map of the aerosol velocity field. For droplet size distribution studies, the solution is doped with a fluorescent dye and both laser induced florescence (LIF) and Mie scattering images are captured simultaneously by two CCDs with the same field of view. The ratio of the LIF / Mie images provides relative droplet size information, which is then scaled by a point calibration method via a phase Doppler particle analyzer (PDPA). Two major outcomes are realized for three nebulization systems: 1) a direct injection high efficiency nebulizer (DIHEN); 2) a large-bore DIHEN (LB-DIHEN); and 3) a PFA microflow nebulizer with a PFA Scott-type spray chamber. First, the central region of the aerosol cone from the direct injection nebulizers and the nebulizer-spray chamber arrangement comprise fast (>13 m / s and >8 m / s, respectively) and fine (<10 μm and <5 μm, respectively) droplets as compared to slow (<4 m / s) and large (>25 μm) droplets in the fringes. Second, the spray chamber acts as a momentum separator, rather than a droplet size selector, as it removes droplets having larger sizes or velocities. Smart-tunable nebulizers may utilize the measured momentum as a feedback control for adjusting certain operation properties of the nebulizer, such as operating conditions and / or critical dimensions.
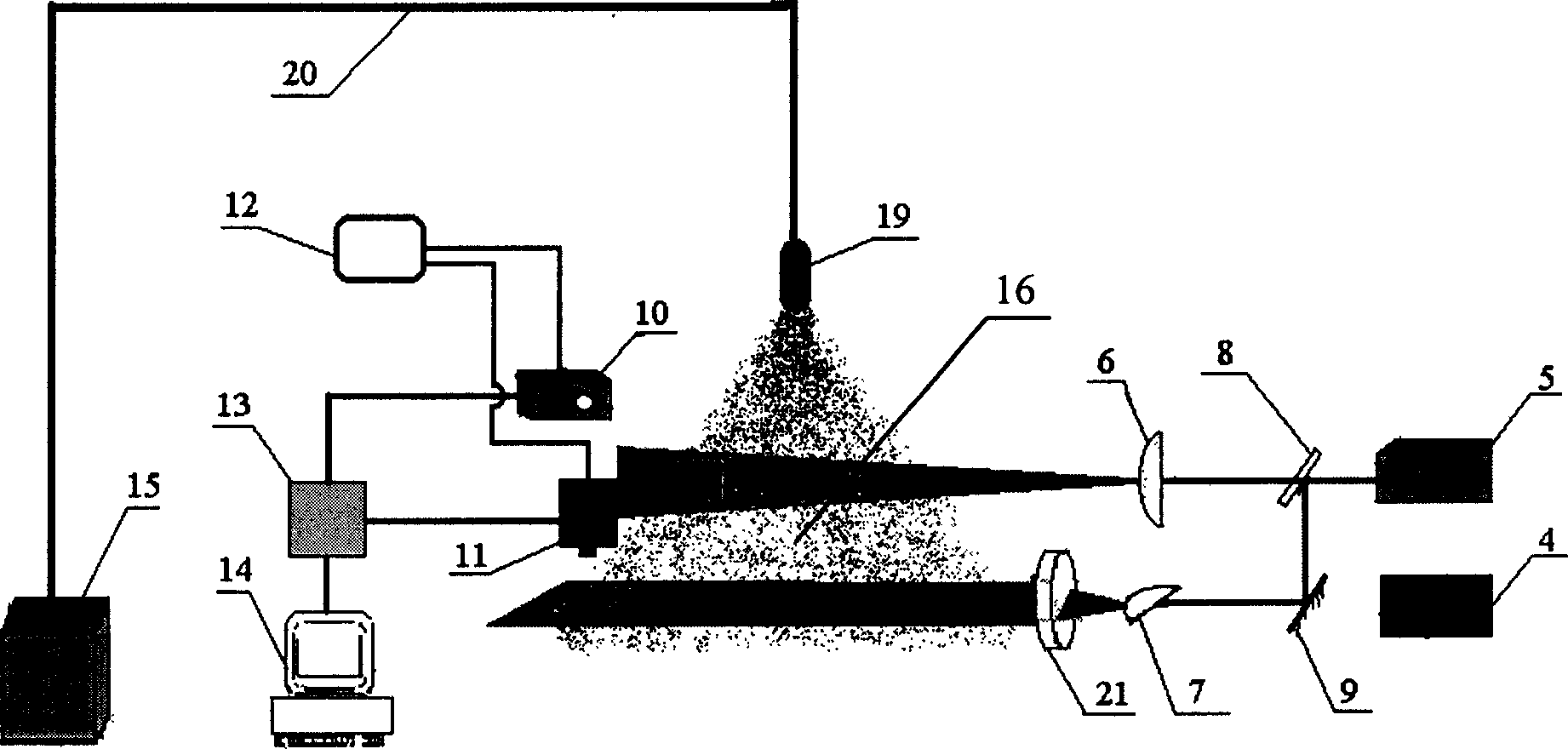
Particle field total-field measurement process and apparatus based on laser sheet optical image-forming
InactiveCN1464288ASolve the limitation that only the flow field velocity can be measuredSolve the shortcomings of single-point measurement methodsMeasurement devicesMeasurement deviceFull field
The present invention is whole particle field measuring method and equipment based on laminar laser imaging and features that particles in test flow field are illuminated with orthogonal laminar laser beams and two CCD cameras are used to take the particle motion locus images both in the direction perpendicular to the flow field and in the direction parallel to the flow field separately. The equivalent diameters of particles are determined via particle image distinction and statistical analysis of covered pixels, and the particle motion speeds, including magnitudes and directions, are determined via the distinction and analysis of particle motion locus image, so as to obtain the size spectrum and speed field distribution of particles in the imaging plane. The present invention needs no addition of tracing particle, and may be used widely in the two-phase and multi-phase flow field measurement in various fields.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Adaptive variable-speed scanning laser imager
InactiveCN1424591AImprove imaging effectElectromagnetic wave reradiationMobile laser scanningLaser imaging
A laser imaging apparatus with self-adaptable speed change scanning is used to obtain 3-D image of a target and belongs to the technical field of observation and imaging to ground. The apparatus is mainly used in 3-D imaging of the ground target on the basis of the observation to ground with laser scanning, and also used in 3-D laser imaging of close target and tomographic scan. A close loop mainly achieves the speed change scanning of a scanning lens driven by a scanning motor, and the basis for the scanning is the condition of fluctuation of the ground target. Electrical signal, mechanical rotation, laser detection and the like links to achieve the close loop. The close loop consists of four components, they are the components of optical members and of laser detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for laser material manipulation
InactiveUS20060119743A1Television system detailsColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayLaser imaging
A laser material manipulation system is provided for material manipulations such as laser ablation, laser deposition and laser machining. The system includes a laser for emitting laser pulses and a laser imaging device having an array of controllable imaging elements. The laser imaging device receives the laser pulses emitted from the laser, forms a laser image through the controllable imaging elements, and projects the laser image onto a target material which needs to be manipulated. The projected laser image manipulates the material according to a desired manipulation pattern. The laser can be a femtosecond laser. The laser imaging device can be a liquid crystal display (LCD) or a digital micromirror device (DMD). An SEM can be used for monitoring the material distribution and dynamically adjust the laser image according to the monitor result.
Owner:CHOSEN TECH
System and Method for Multi-Color Laser Imaging and Ablation of Cancer Cells Using Fluorescence
ActiveUS20140187967A1Reduce deficiencyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSurgical instrument detailsCancer cellWound care
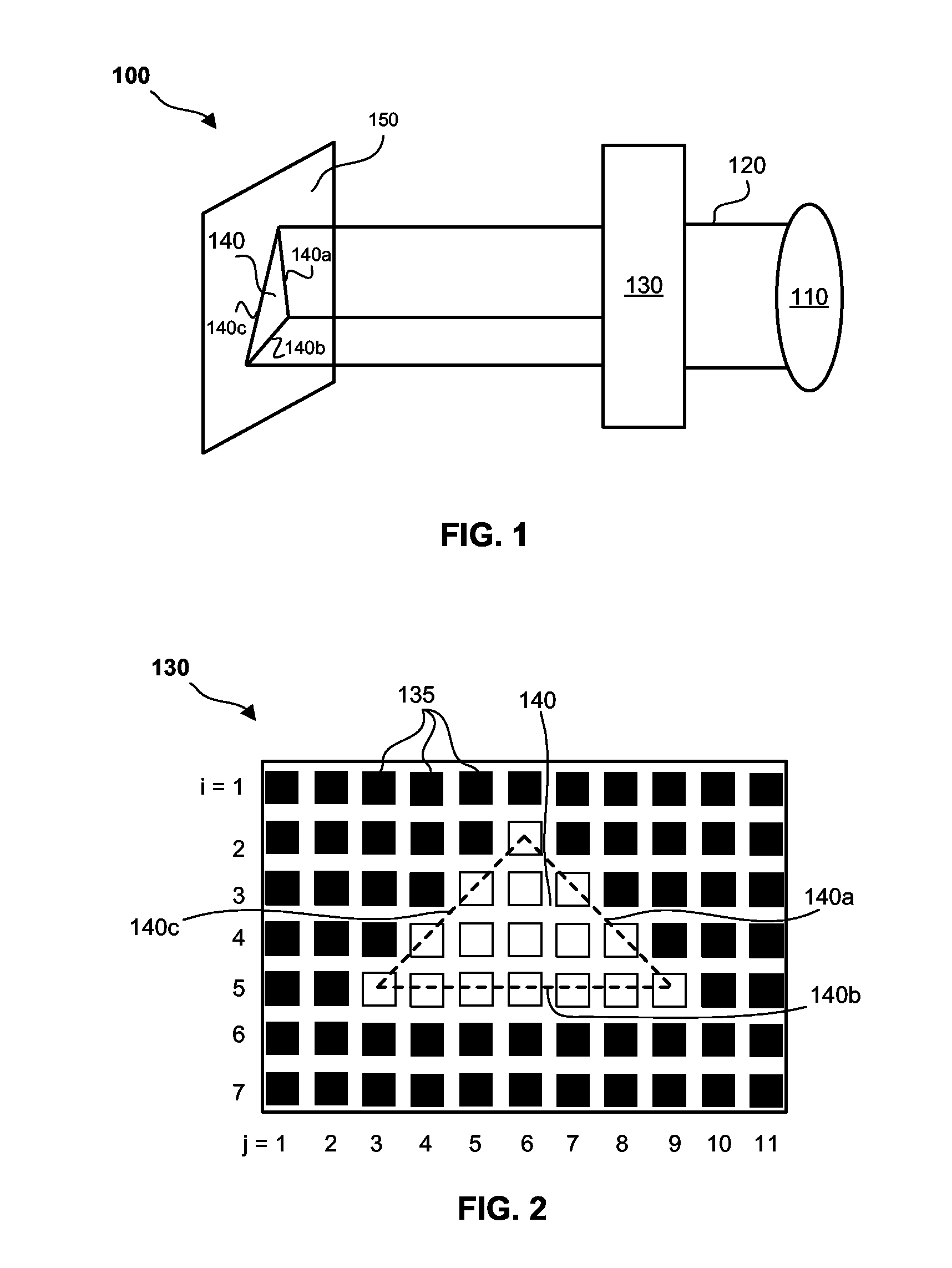
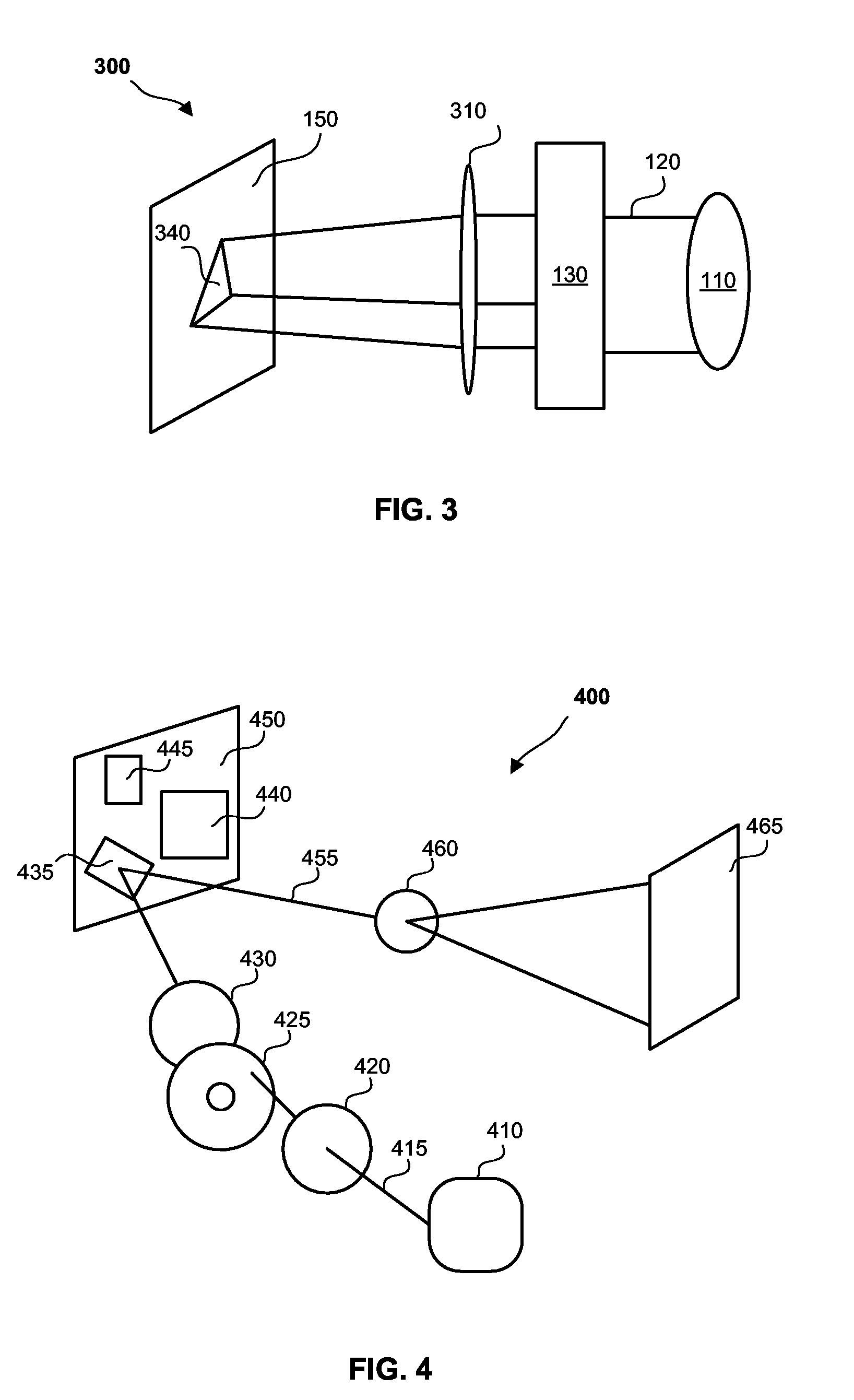
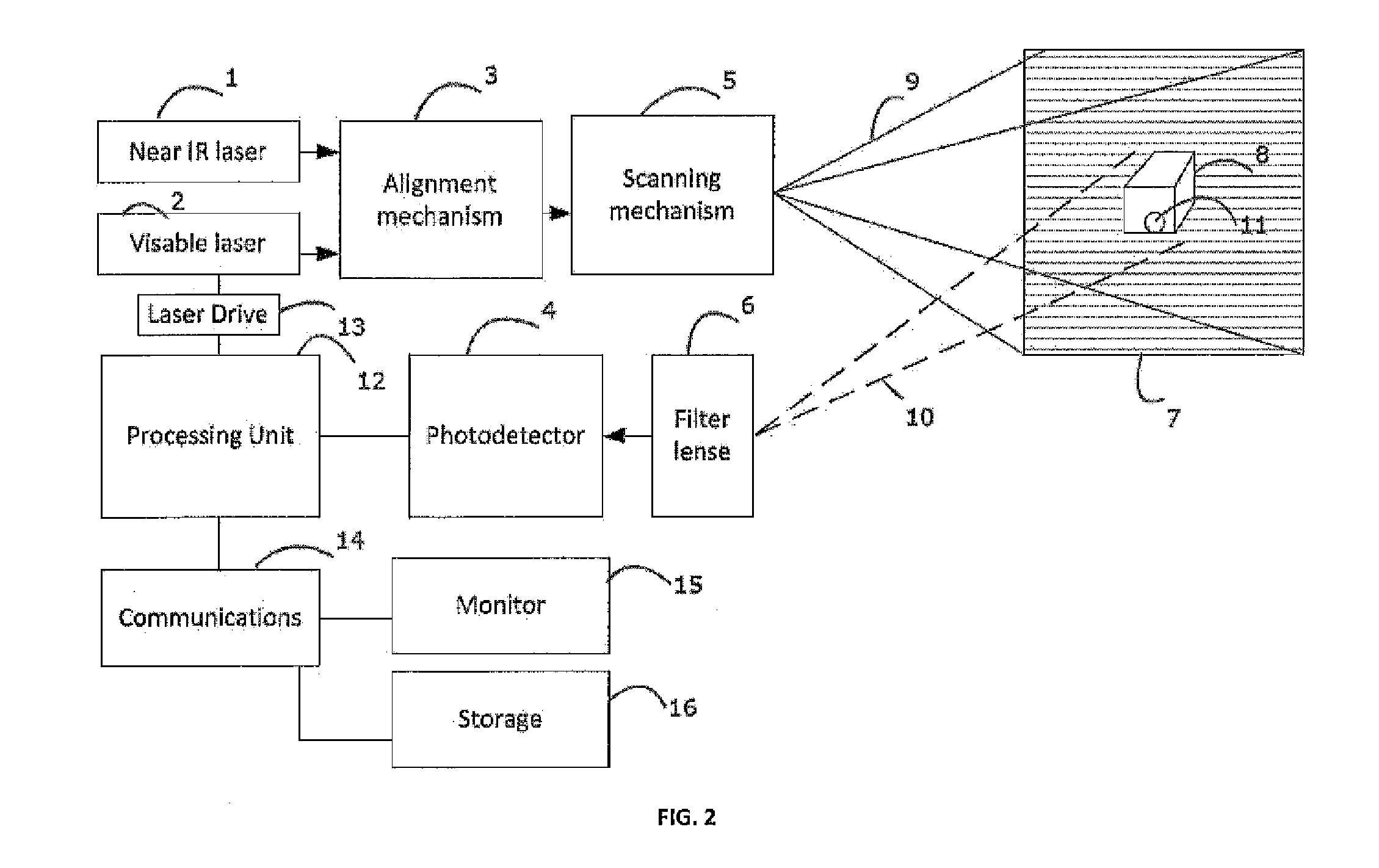
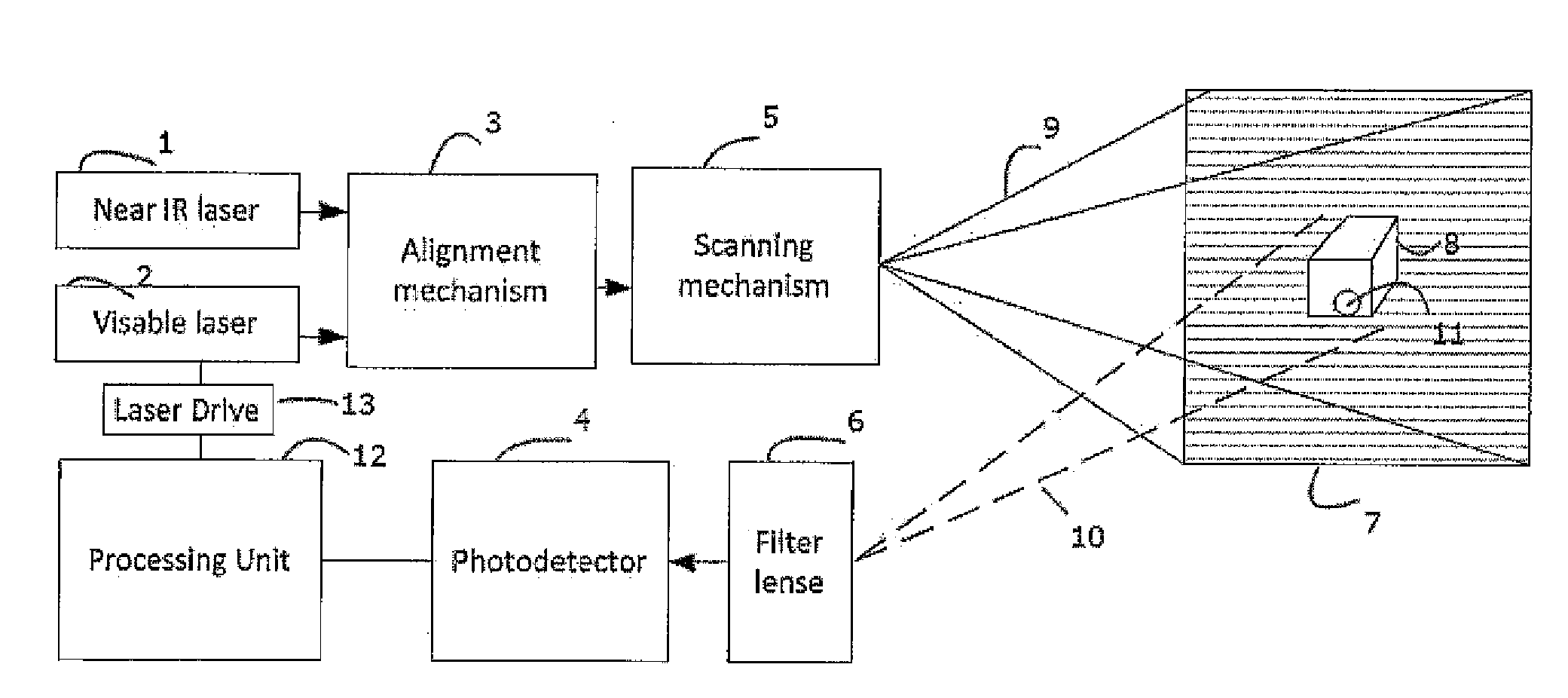
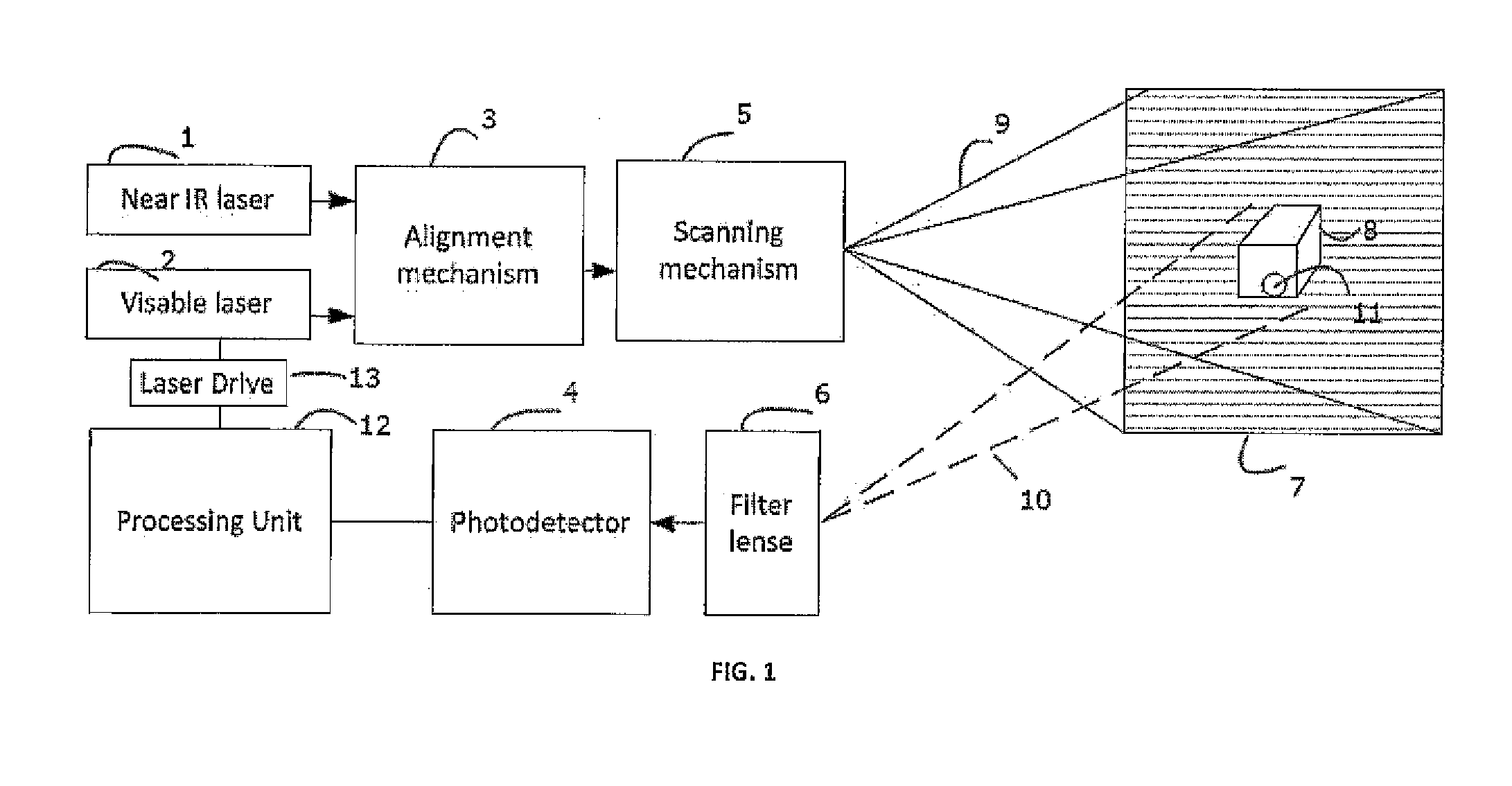
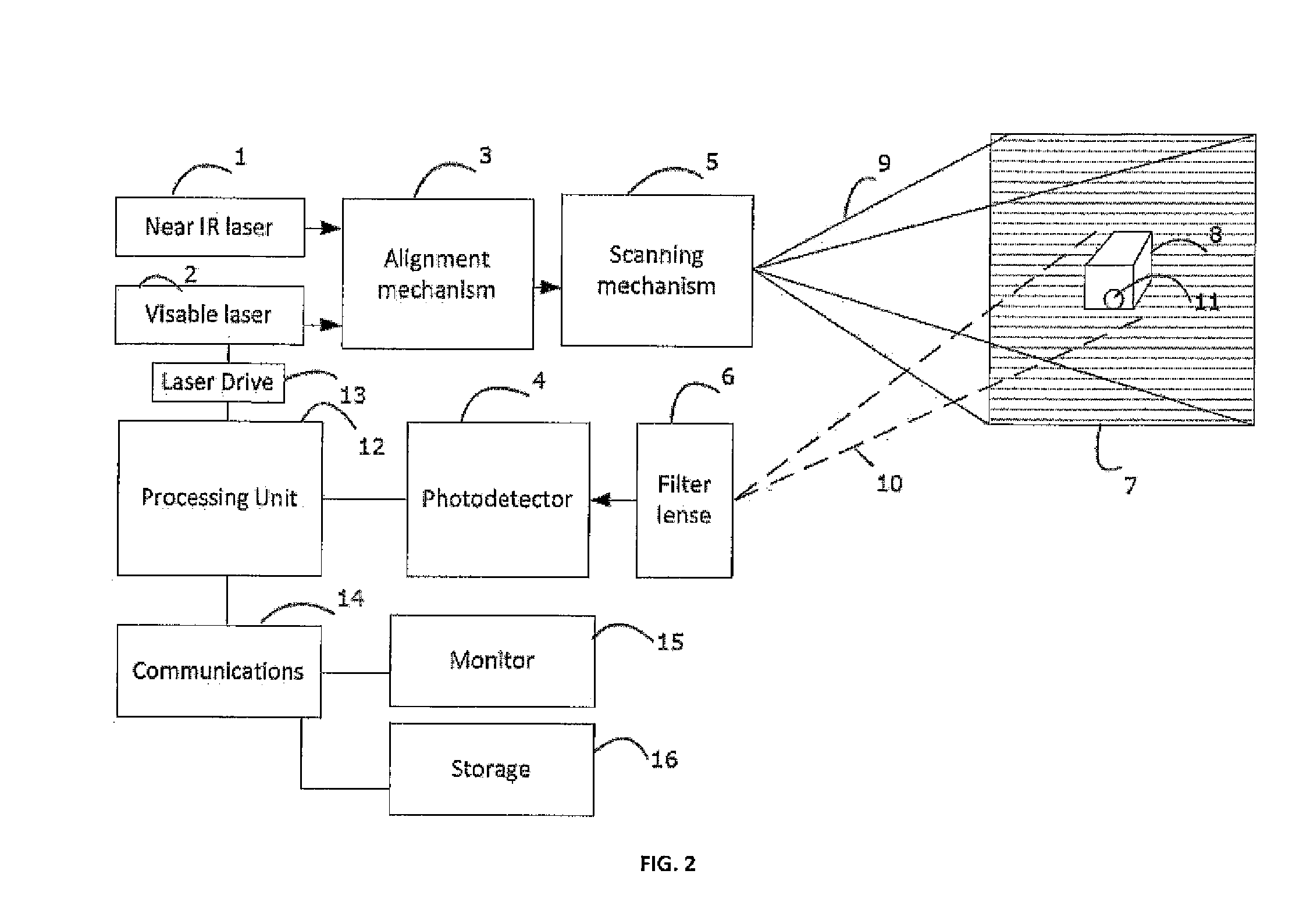
A fluorescence imaging device detects fluorescence in parts of the visible and invisible spectrum, and projects the fluorescence image directly on the human body, as well as on a monitor, with improved sensitivity, video frame rate and depth of focus, and enhanced capabilities of detecting distribution and properties of multiple fluorophores. Direct projection of three-dimensional visible representations of florescence on three-dimensional body areas advantageously permits view of it during surgical procedures, including during cancer removal, reconstructive surgery and wound care, etc. A NIR laser and a human visible laser (HVL) are aligned coaxially and scanned over the operating field of view. When the NIR laser passes over the area where the florescent dye is present, it energizes the dye which emits at a shifted NIR frequency detected by a photo diode. The HVL is turned on when emission is detected, providing visual indication of those positions.
Owner:ACCUVEIN
On-board colorful three-dimensional scanning laser radar
ActiveCN103954971AEnhanced color resolutionImprove stabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringLaser source
An on-board colorful three-dimensional scanning laser radar comprises a laser emission unit, a scanning unit, a signal detection signal, a time sequence control circuit and a computer data processing unit, wherein the scanning unit comprises a motor driver, a motor, a polyhedral scanning rotating mirror and an angle encoder, and the motor driver, the motor and the polyhedral scanning rotating mirror are sequentially connected, the angle encoder is connected with the motor, and the laser emission unit comprises a laser driver, a colorful laser source, an optical emission system and a PIN detector which are sequentially connected. The signal detection signal comprises a receiving optical system, a colorful laser signal detector and a multi-channel data acquisition unit which are sequentially connected. The time sequence control circuit is respectively connected with the laser driver, the PIN detector and the multi-channel data acquisition unit. The on-board colorful three-dimensional scanning laser radar can simultaneously obtain colorful laser spectral information and laser point cloud information of a target ground feature, accordingly obtains a colorful laser imaging of a target through three-dimensional reconstruction and strengthens the colorful resolution capability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Remote Laser Treatment System With Dynamic Imaging
ActiveUS20180303667A1Eliminate needTrack displacementLaser surgeryAnti-theft devicesTherapeutic DevicesThe Internet
An integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus, and associated systems and methods that allow a physician (e.g., a surgeon) to perform laser surgical procedures on an eye structure or a body surface with an integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus disposed at a first (i.e. local) location from a control system disposed at a second (i.e. remote) location, e.g., a physician's office. In some embodiments, communication between the integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus and control system is achieved via the Internet®. Also, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus includes a dynamic imaging system that verifies the identity of a patient, and is capable of being used for other important applications, such as tracking and analyzing trends in a disease process. Further, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus determines the geographical location of the local laser generation unit of the system using GPS.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Uptically variable security devices
InactiveCN1423598AGood anti-counterfeiting measuresOther printing matterSynthetic resin layered productsHot stampingEngineering
A security article (10) includes a light transmissive substrate (12) having a first surface and an opposing second surface, with the first surface having an optical interference pattern (14) such as a holographic image pattern or an optical diffraction pattern thereon. A color shifting optical coating (16) is formed on the substrate such as on the interference pattern or on the opposing second surface of the substrate, with the optical coating providing an observable color shift as the angle of incident light or viewing angle changes. Various processes can be utilized to form the security article (10), such as vacuum coating processes, lamination, laser scribing, and laser imaging. The security article (10) can be affixed to a variety of objects through various attachment mechanisms, such as pressure sensitive adhesives or hot stamping processes, to provide for enhanced security measures such as anticounterfeiting.
Owner:光学涂层实验公司
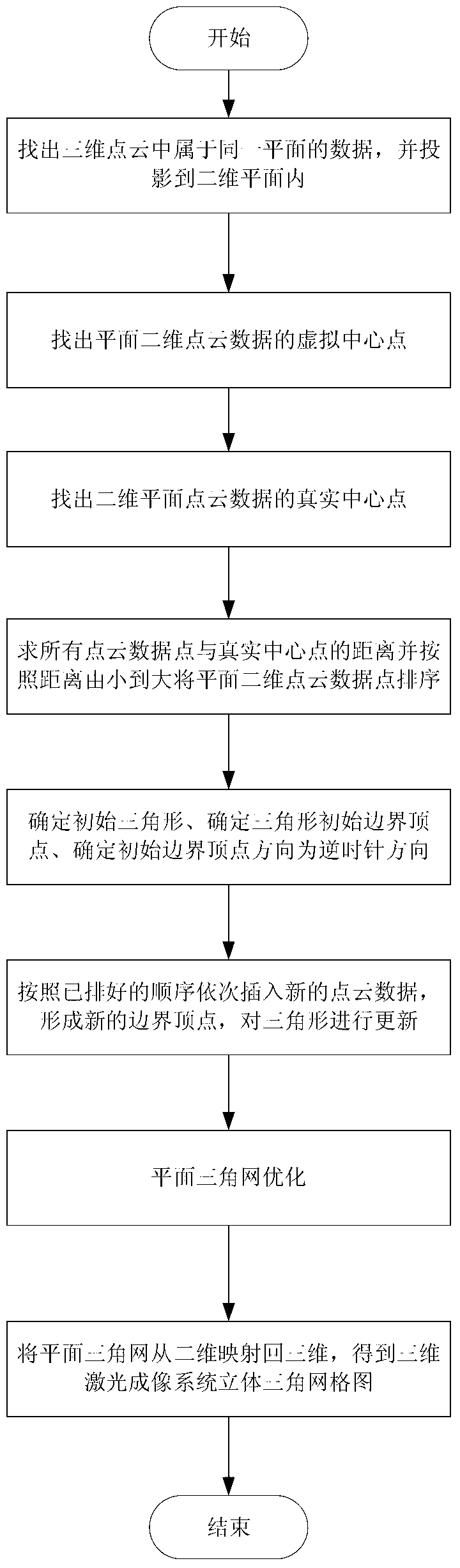
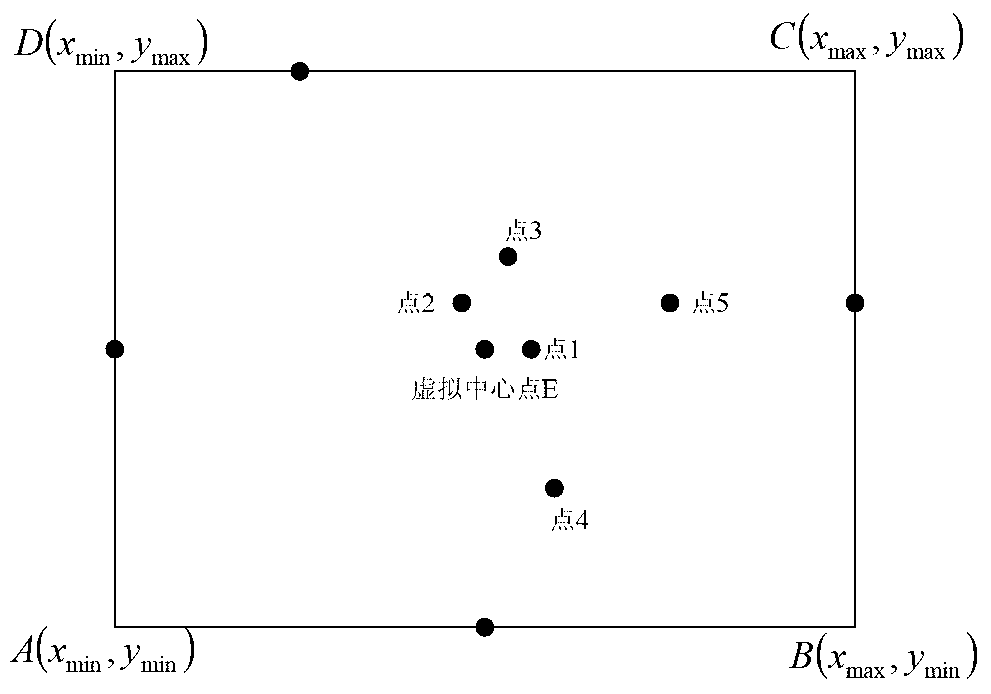
Three-dimensional laser imaging system planar point cloud data triangularization processing method
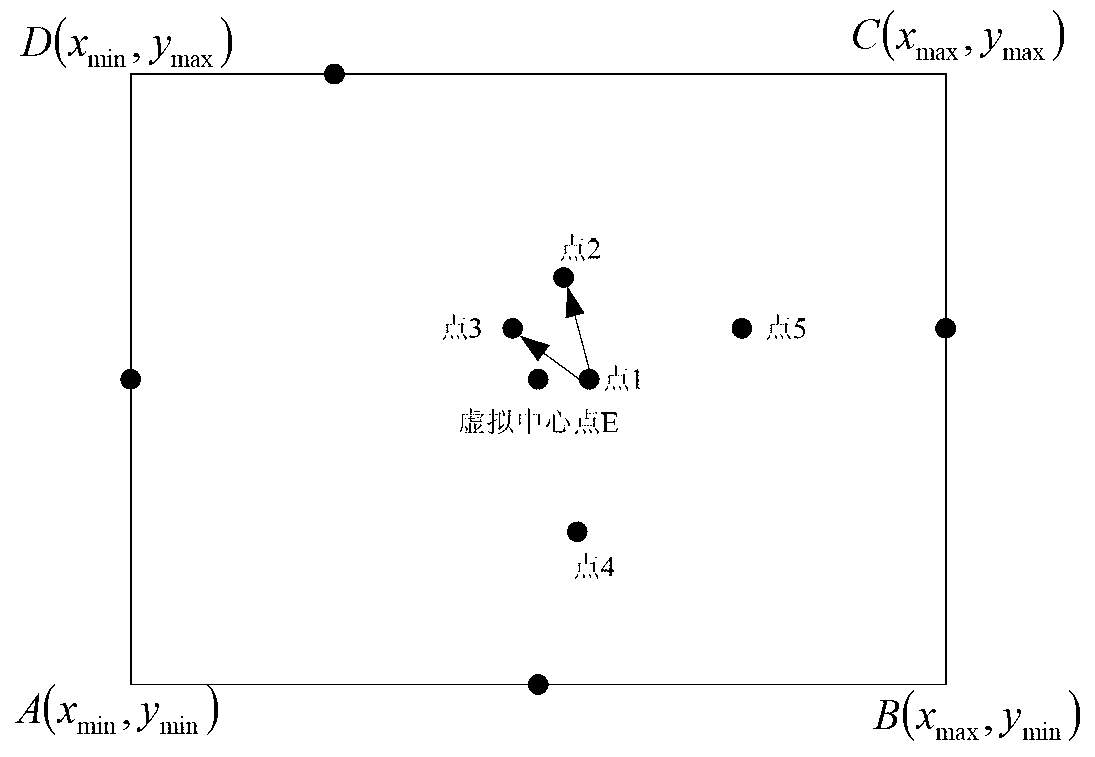
The invention discloses a three-dimensional laser imaging system planar point cloud data triangularization processing method. According to the three-dimensional laser imaging system planar point cloud data triangularization processing method, firstly, three-dimensional point cloud data which are on the same plane are obtained from three-dimensional point cloud data, the three-dimensional point cloud data which are on the same plane are projected to a two-dimensional plane to form plane two-dimensional point cloud data, a virtual central point of the two-dimensional point cloud data is calculated, a point which is closest to the virtual central point is used as an actual central point of scattered data, distances between discrete points and the actual central point are compared, the two-dimensional point cloud data are presorted to find an initial triangle and initial boundary vertexes, the initial boundary vertexes are sorted anticlockwise, all the two-dimensional point cloud data are inserted into according to the arrayed sequence, boundary vertex update and triangle update are conducted, and planar point cloud data of a plane triangulation network are mapped back to a three-dimensional coordinate to generate three-dimensional triangular network model of an article to be scanned. Compared with the prior method, the three-dimensional laser imaging system planar point cloud data triangularization processing method has the advantages that the train of thought is simple and clear, programming is easy to achieve, and planes with holes or concave surfaces or other complex surface conditions can be processed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
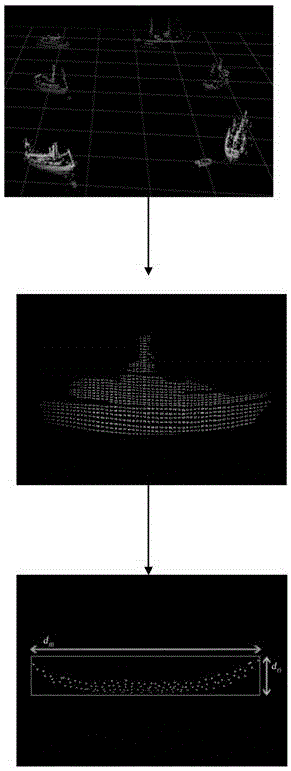
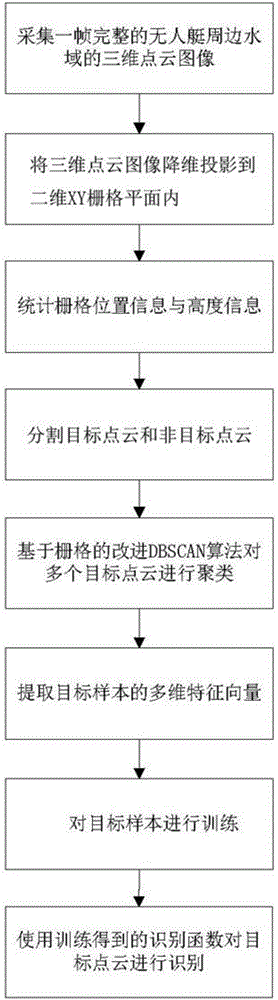
Treatment method for surface target of unmanned ship based on laser imaging radar
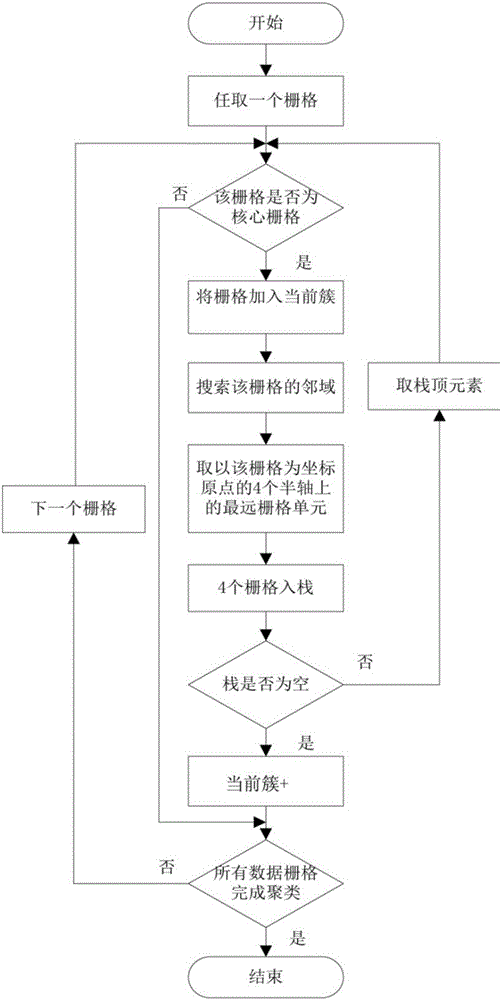
InactiveCN106355194AReduce the impactReduce extraction timeCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudReduction treatment
The invention provides a treatment method for a surface target of an unmanned ship based on a laser imaging radar.The method based on the unmanned ship of the laser image radar comprises the following steps: S1, generating a three-dimensional cloud point image on the water surface around the unmanned ship by the laser imaging radar, the three-dimensional cloud point image comprises a target cloud point and a non-target cloud point;conducting dimension reduction treatment to the three-dimensional cloud point image, projecting the three-dimensional cloud point image to a two-dimensional XY-grid plane, counting the position information and height information of each grid, S2, cutting the target cloud point and non-target point cloud, S3,clustering the target point cloud obtained after being cut, extracting the position information of each target, forming the target sample set, extracting multi-dimensional eigenvector collected by the target sample; S4, training the target sample set,obtaining the obtained identifying function, and identifying the target point cloud by the identifying function. The treatment method provided in the invention can detect and identify the target of the water surface around the unmanned ship accurately.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUST IND TECH RES INST +2
Single-photon-counting compression-sampling laser three-dimensional imaging method
InactiveCN102375144AReduce collectionSave storage spaceElectromagnetic wave reradiationInformation processingLaser imaging
The invention provides a single-photon-counting compression-sampling laser three-dimensional imaging method which is applicable to the fields of topographic mapping, information processing, digital image processing, high-precision topographic reconnaissance and the like. The method is a non-scanning laser three-dimensional imaging method on the basis of single-photon unit-detector compression sampling, a range-gated imaging method is introduced to correct a time-measuring vector obtained on the basis of single-photon-counting compression sampling, and a high-precision three-dimensional image is obtained through reconstruction by adopting a compression perceiving and restoring algorithm. The method has a better practical value and broad application prospects in the technical fields of laser imaging and digital image processing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
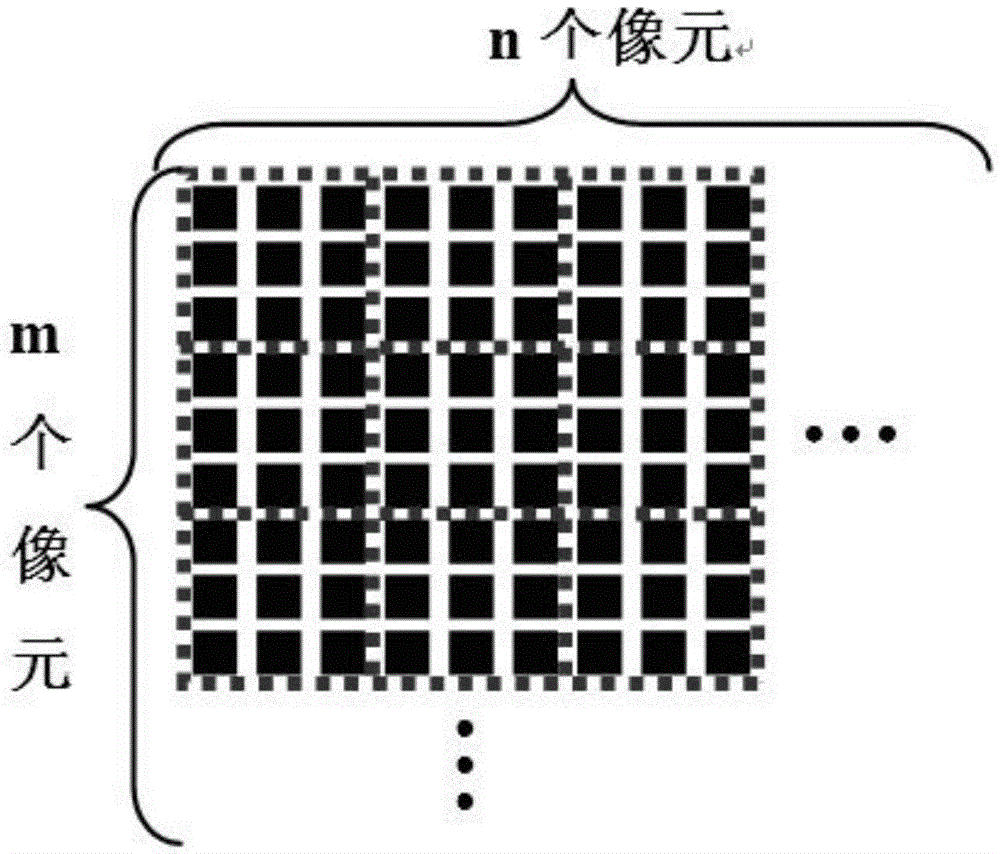
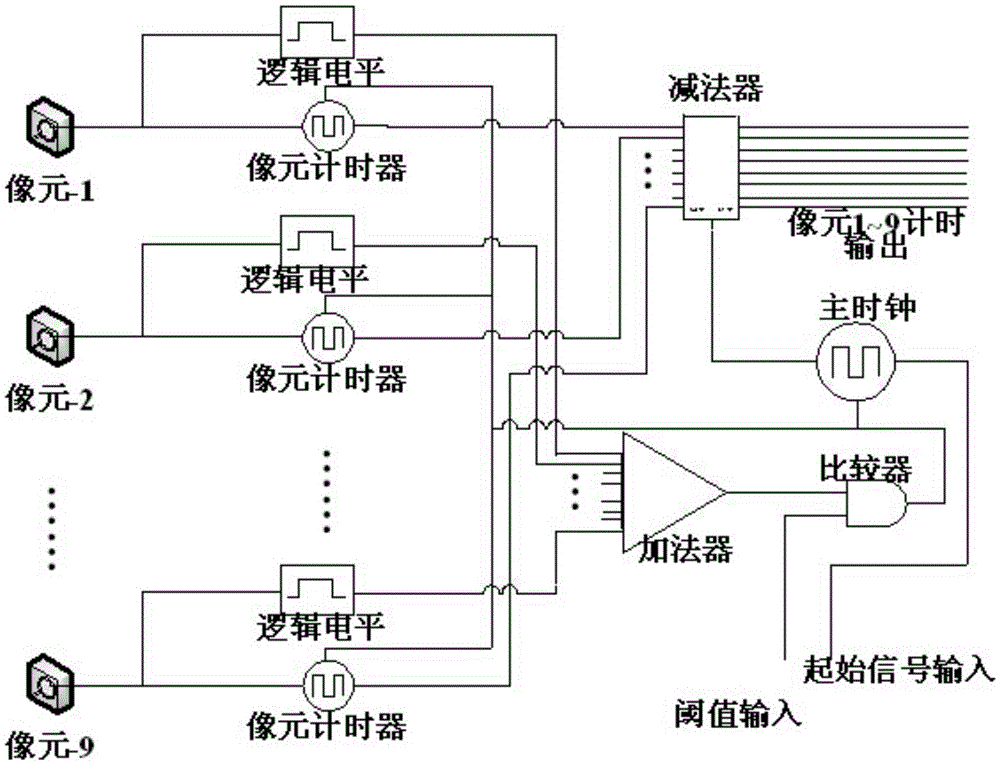
Photon-counting imaging laser radar for filtering noise in real time by adopting adjacent pixel element threshold value method
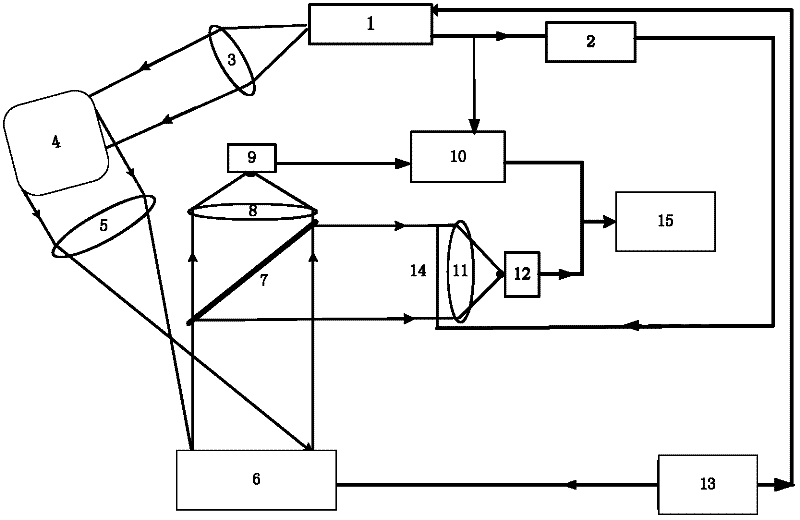
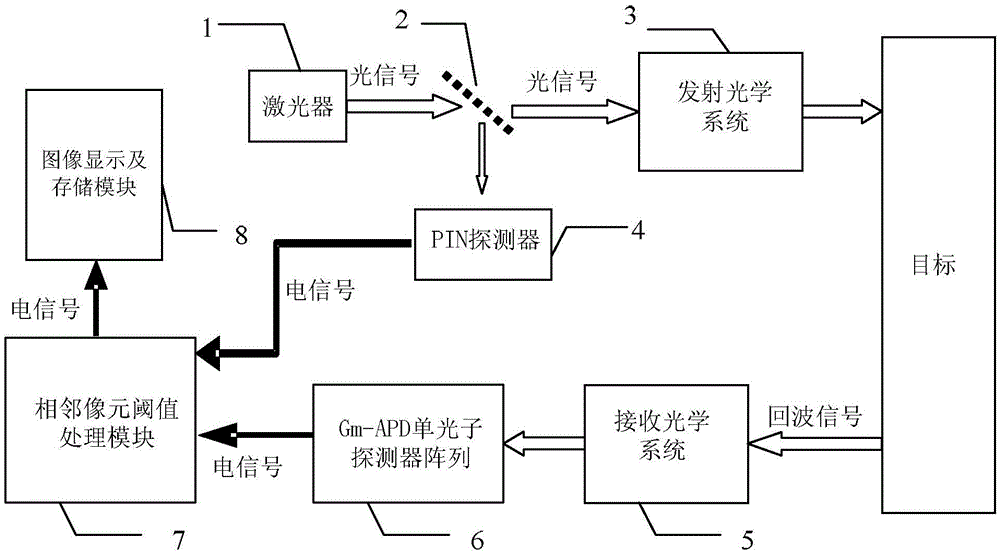
InactiveCN105607073AImprove performanceReduce volumePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterTime correlation
The invention relates to a photon-counting imaging laser radar for filtering noise in real time by adopting an adjacent pixel element threshold value method, and the radar relates to the technical field of laser radar. The problem that the photon-counting imaging laser radar noise filtering technology can not meet the real-time application requirement is solved. A pulse laser signal enters a beam splitter to form two signals; one signal is processed through a PIN detector and is outputted to an adjacent pixel element threshold value processing module; the other signal is collimated through a optical transmitting system to radiate a target; the other signal is spread by the target and outputted an echo signal, the echo signal passes through a receiving optical system and a Gm-APD single-photon detector array, the adjacent pixel element threshold value processing module records the echo signal comprising time correlation and compares the signal with an initial signal, so as to obtain the round-trip time difference of the pixel corresponding to the Gm-APD single-photon detector array, the round-trip time difference is calculated to obtain a distance value of the corresponding pixel target, and a target 3D distance image is obtained finally. The radar is suitable for filtering the noise in laser imaging.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
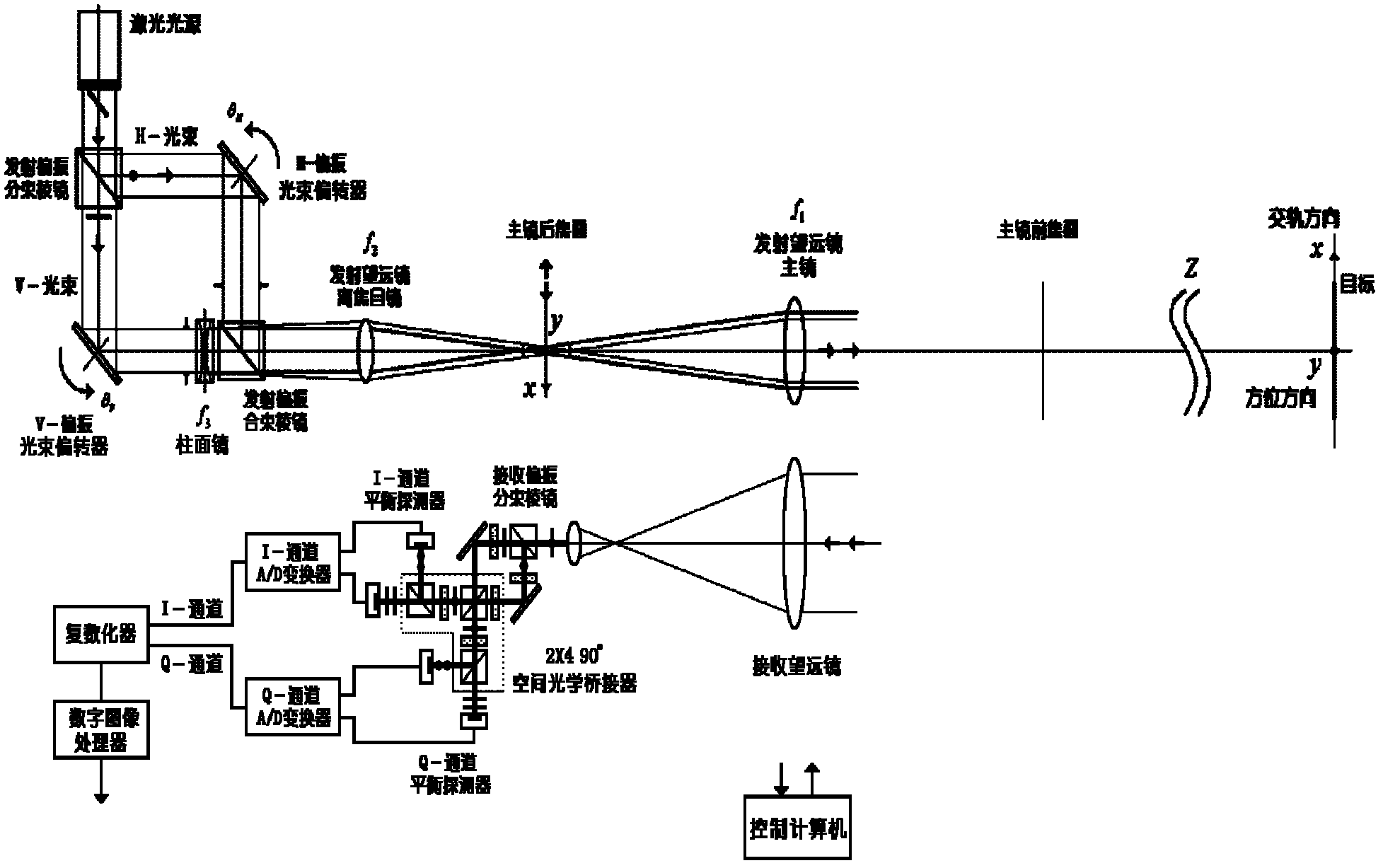
Orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
ActiveCN102435996AReduce the effects of phase interferenceBig optic toesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingRadar systems
The invention relates to an orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar comprises a laser light source, a transmission polarization beam splitter, a horizontal polarization optical path beam deflector, a horizontal polarization optical path transform lens, a vertical polarization optical path beam deflector, a vertical polarization optical path transform lens, a transmission polarization beam combiner, a transmitter telescope ocular, a transmitter telescope primary lens, a receiver telescope, a receiving polarization beam splitter, a 2 * 490 DEG optical bridge, an inphase channel balanced detector, an inphase channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel balanced detector, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a pluralizing processor, a digital image processor and a control computer. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar automatically eliminates phase changes and interference of atmosphere, motion platforms, optical radar systems and speckles, has high resolution imaging in larger optical footprint and larger receiving aperture, does not need optical delay lines, does not need real-time beat frequency signal phase synchronization, does not have shadows during imaging, and can be used for various lasers with single-module and single-frequency properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
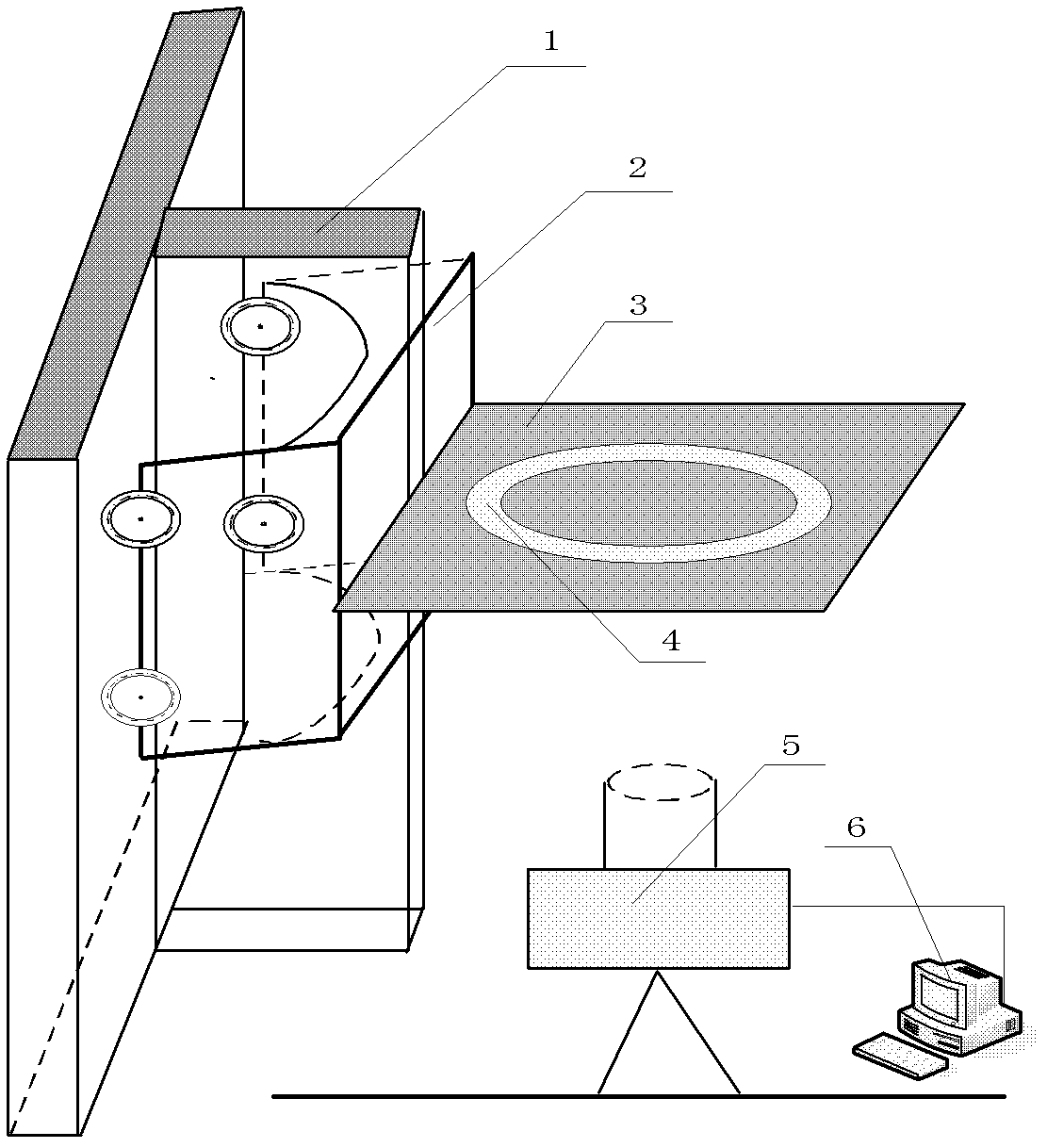
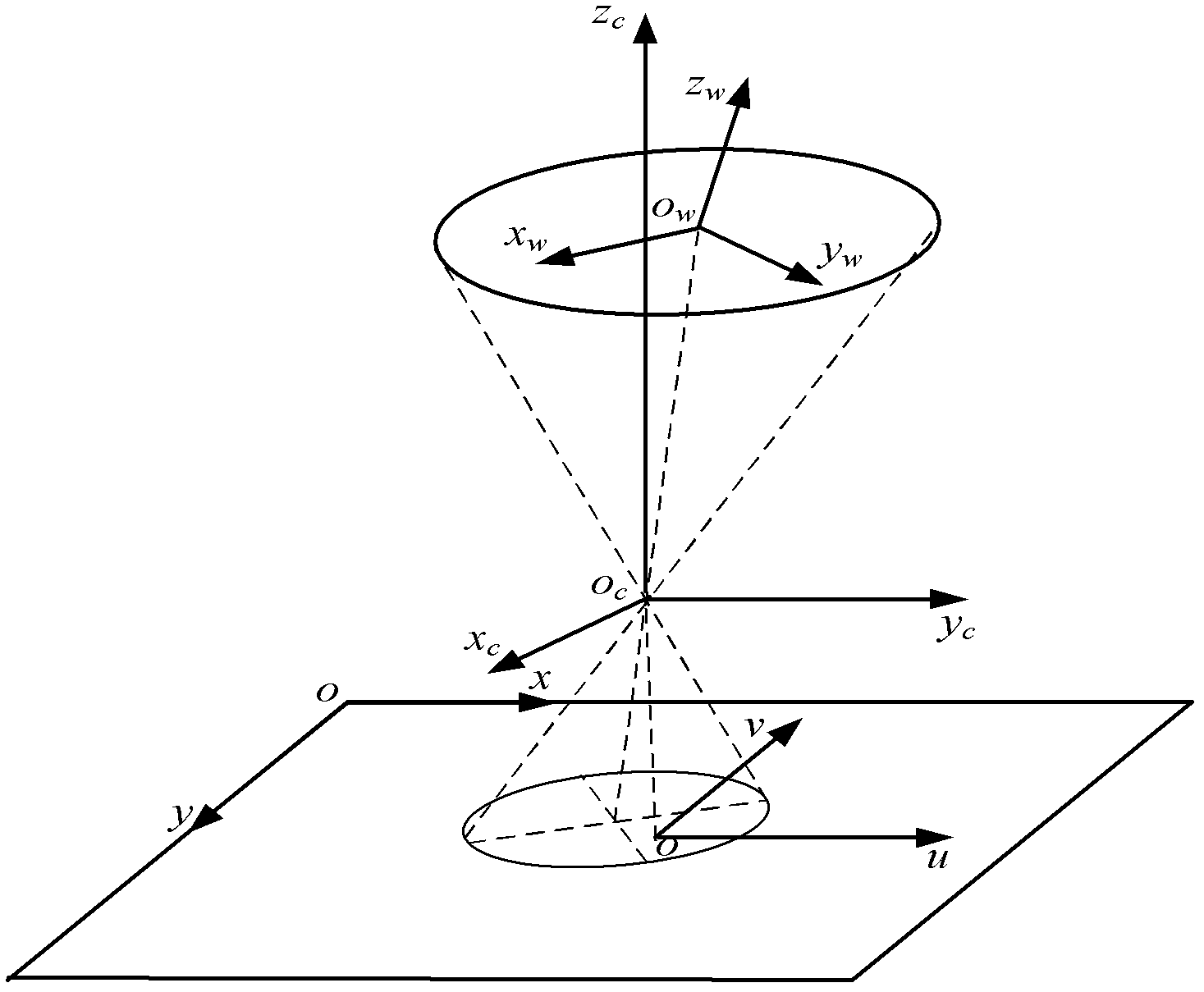
Device and method for detecting elevator guide rail perpendicularity based on visual measurement
Disclosed are a device and a method for detecting elevator guide rail perpendicularity based on visual measurement. An elevator guide rail perpendicularity detecting robot is used for carrying a luminous ring perpendicularly mounted on the robot to travel on a guide rail, and a camera alignment ring is mounted at the bottom end of the guide rail to input camera images into a computer. Circle center coordinates of the luminous ring and the height of a corresponding luminous ring are precisely calculated, and then a change curve of the perpendicularity of an elevator to be measured is drawn and is displayed on a display screen of the computer in real time. By the aid of full-automatic intelligent detection, errors caused by laser imaging are avoided, and errors caused by manual intervention are decreased. Operation is convenient, detecting precision is high, and calculating speed is fast. The device and the method are applicable to various places, and can be applied to not only detecting the perpendicularity of the elevator at installation and maintenance stages, but also detecting torsion of the guide rail and detecting rails, circular parts and the like in other industries.
Owner:SHANGHAI RO INTELLIGENT SYST
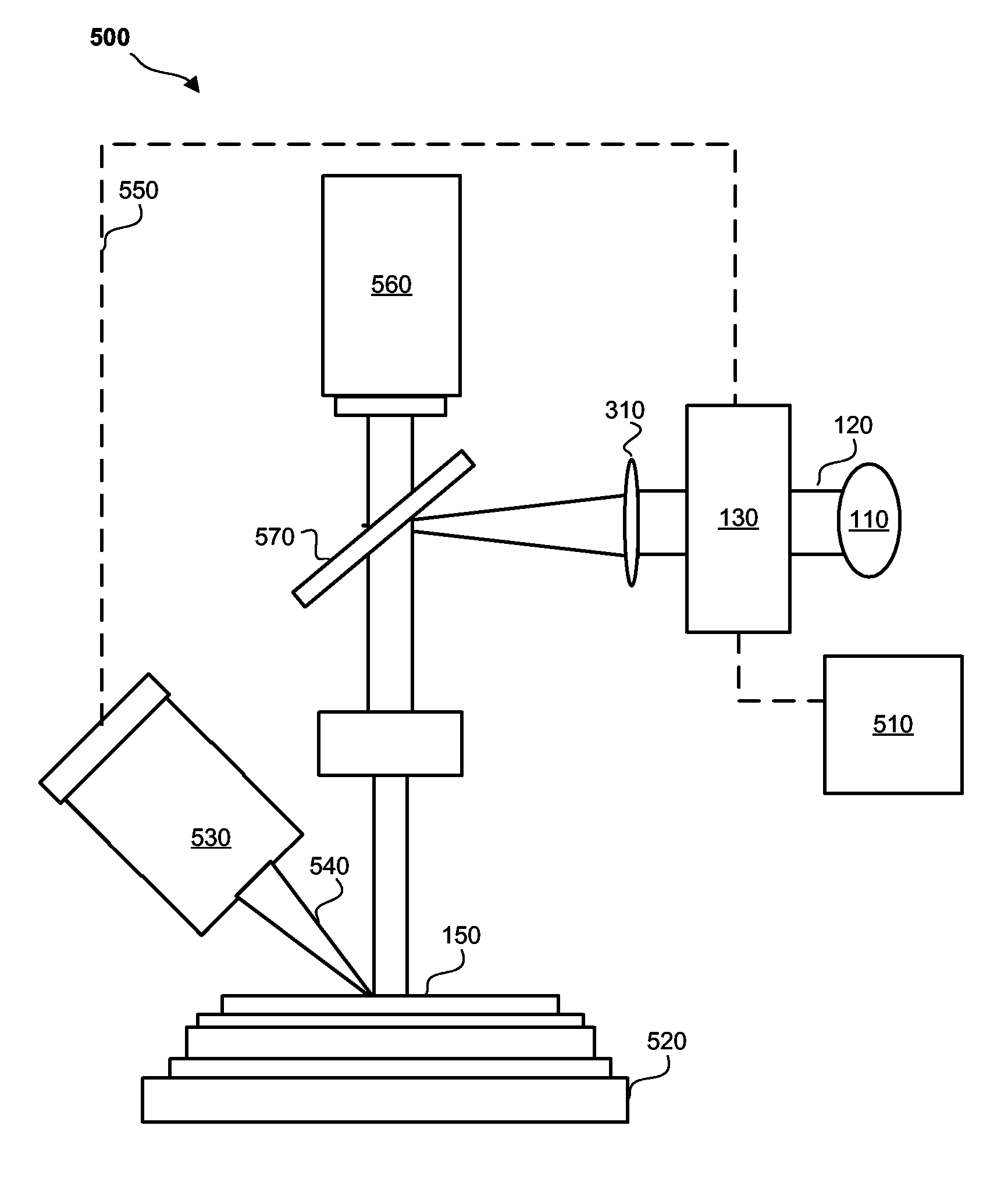
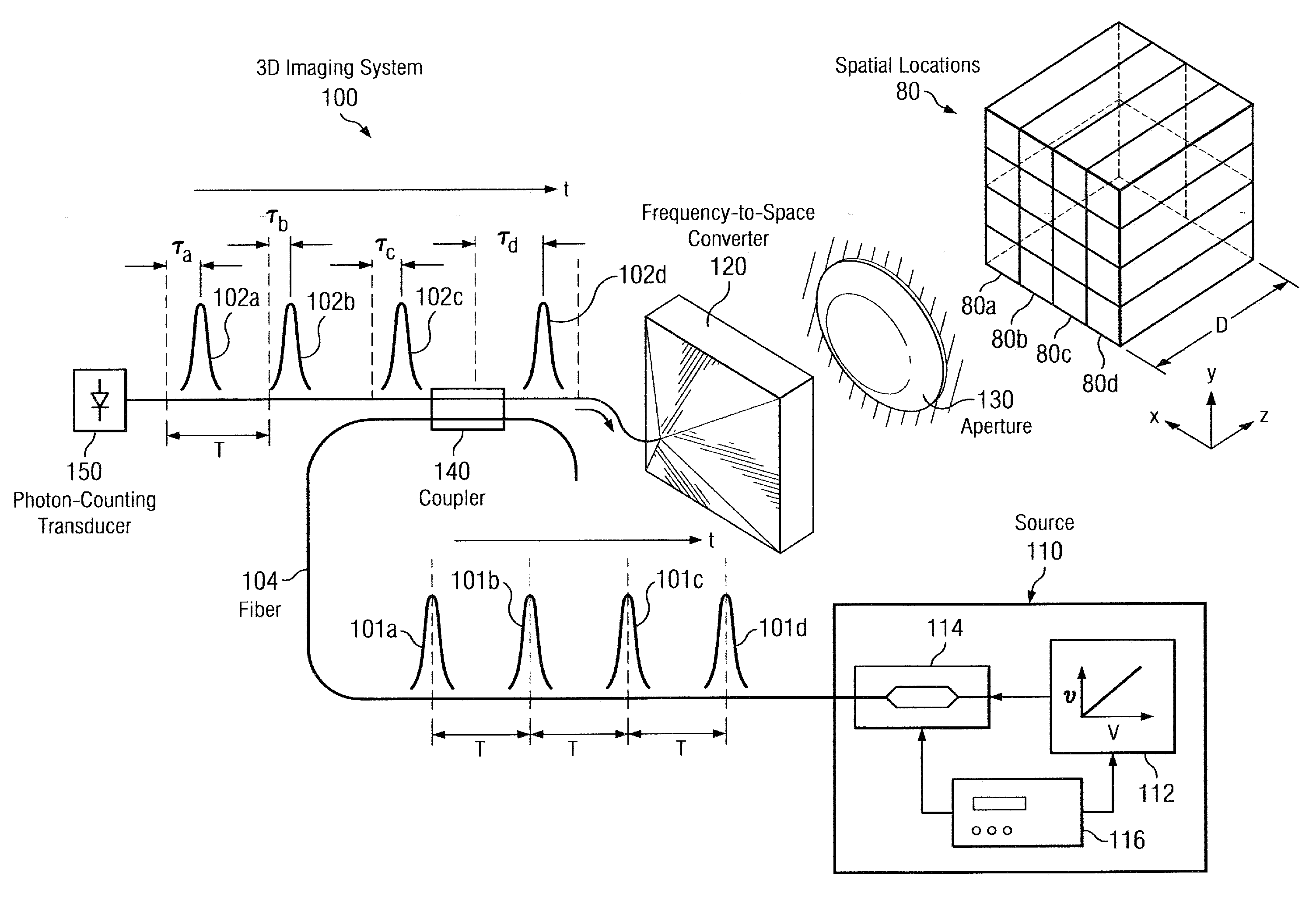
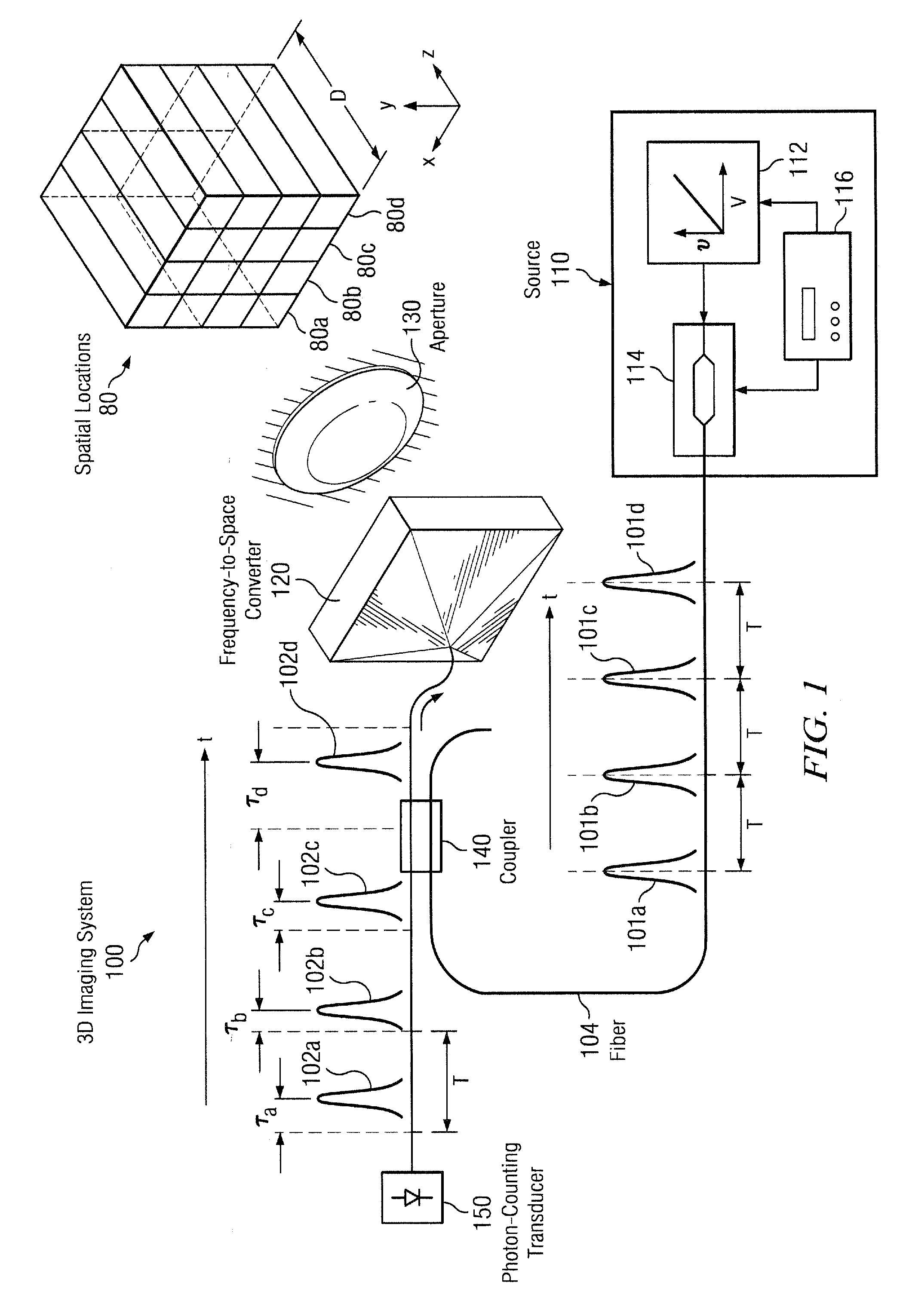
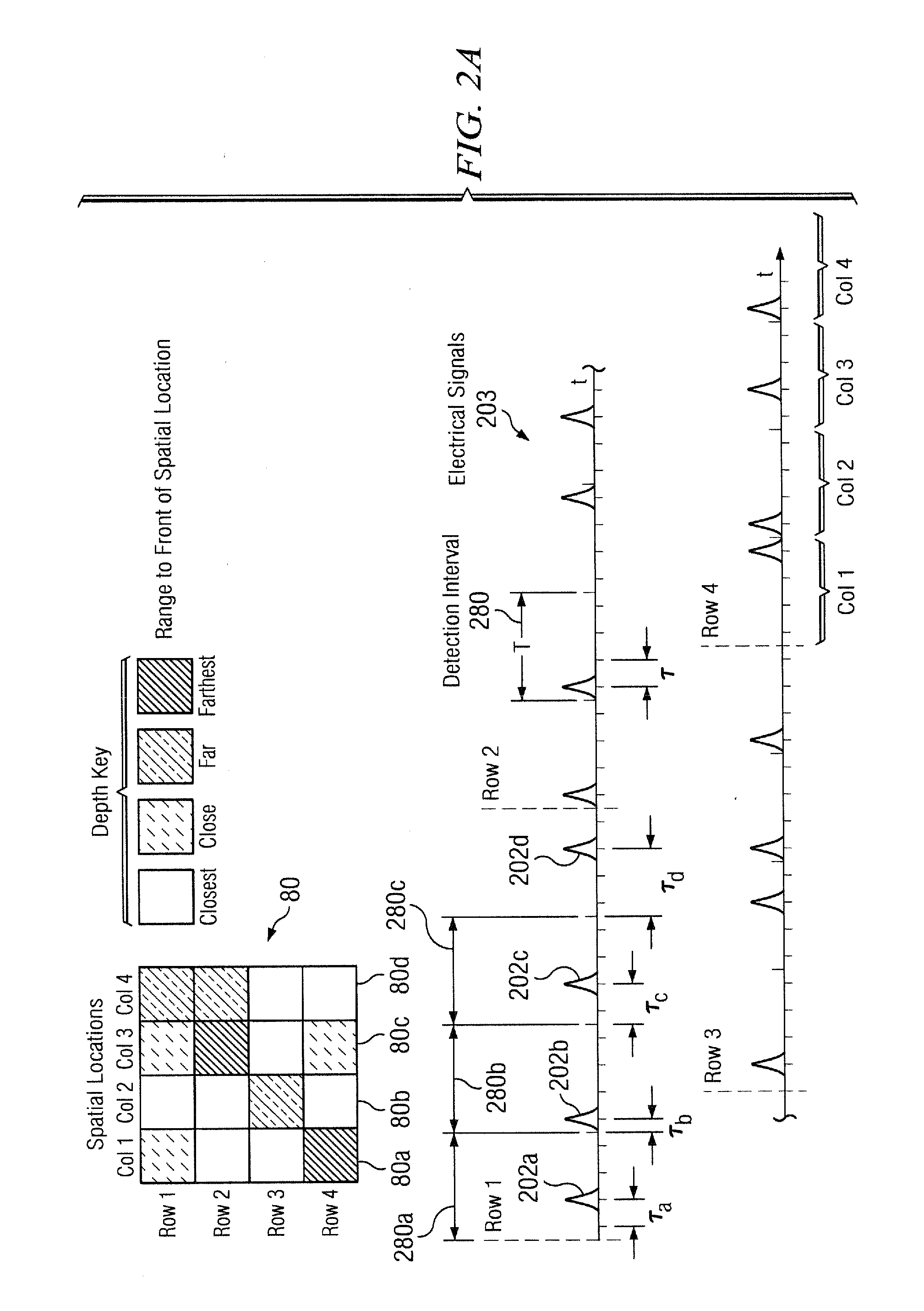
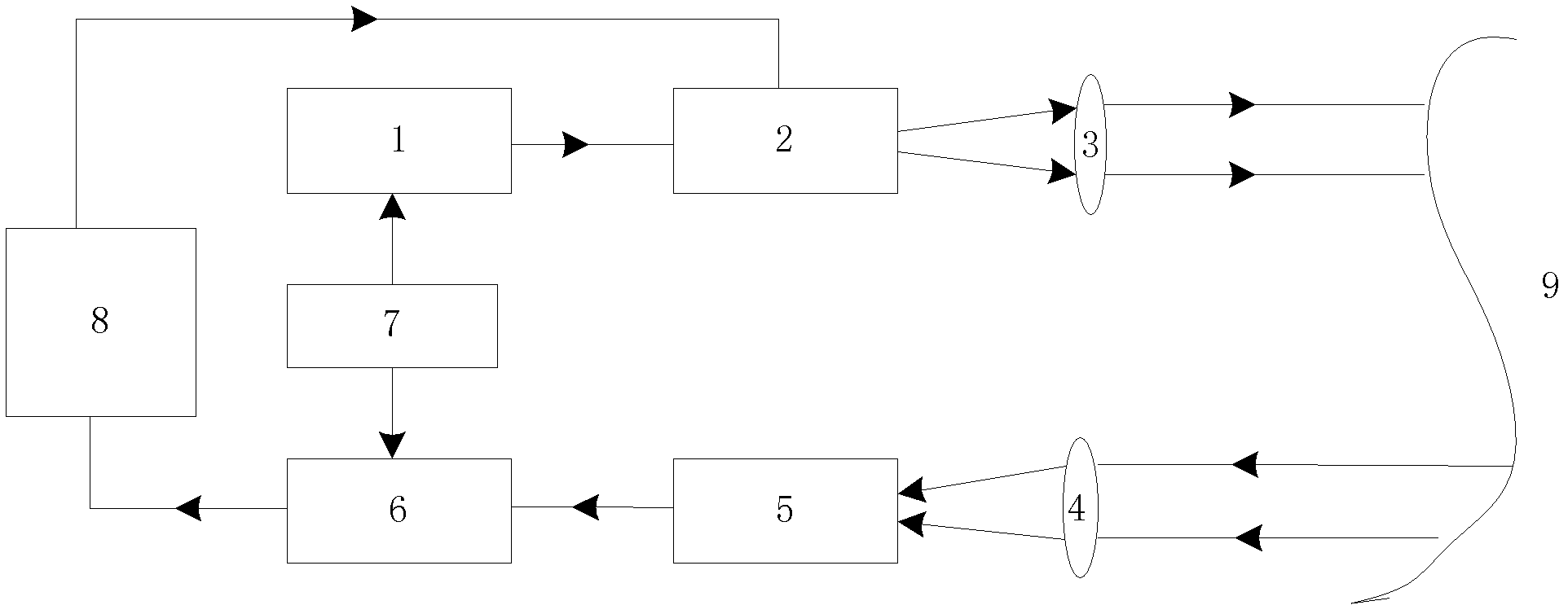
Single-transducer, three-dimensional laser imaging system and method
ActiveUS20110199621A1Little timing jitterBetter range resolutionUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser imagingTransducer
Disclosed herein are a system and method for three-dimensional imaging using a single transducer. A laser in a transmitter emits a sequence of short pulses, each of which is at a different center wavelength (frequency). A dispersive element in the transmitter spatially separates the pulses according to wavelength, with different pulses mapped to different spatial locations in a target volume via a lens. The pulses travel to the target, which scatters or back-reflects the pulses towards the dispersive element via the lens. The lens collects the returned pulses and transmits them to a single transducer via the dispersive element. The transducer measures the time of arrival for each returned pulse. Because the arrival time depends on the range to the object in the portion of the target illuminated by the corresponding emitted pulse, the measured arrival time can be used to reconstruct a 3D (angle-angle-range) image of the object.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Seam tracking method based on template matching
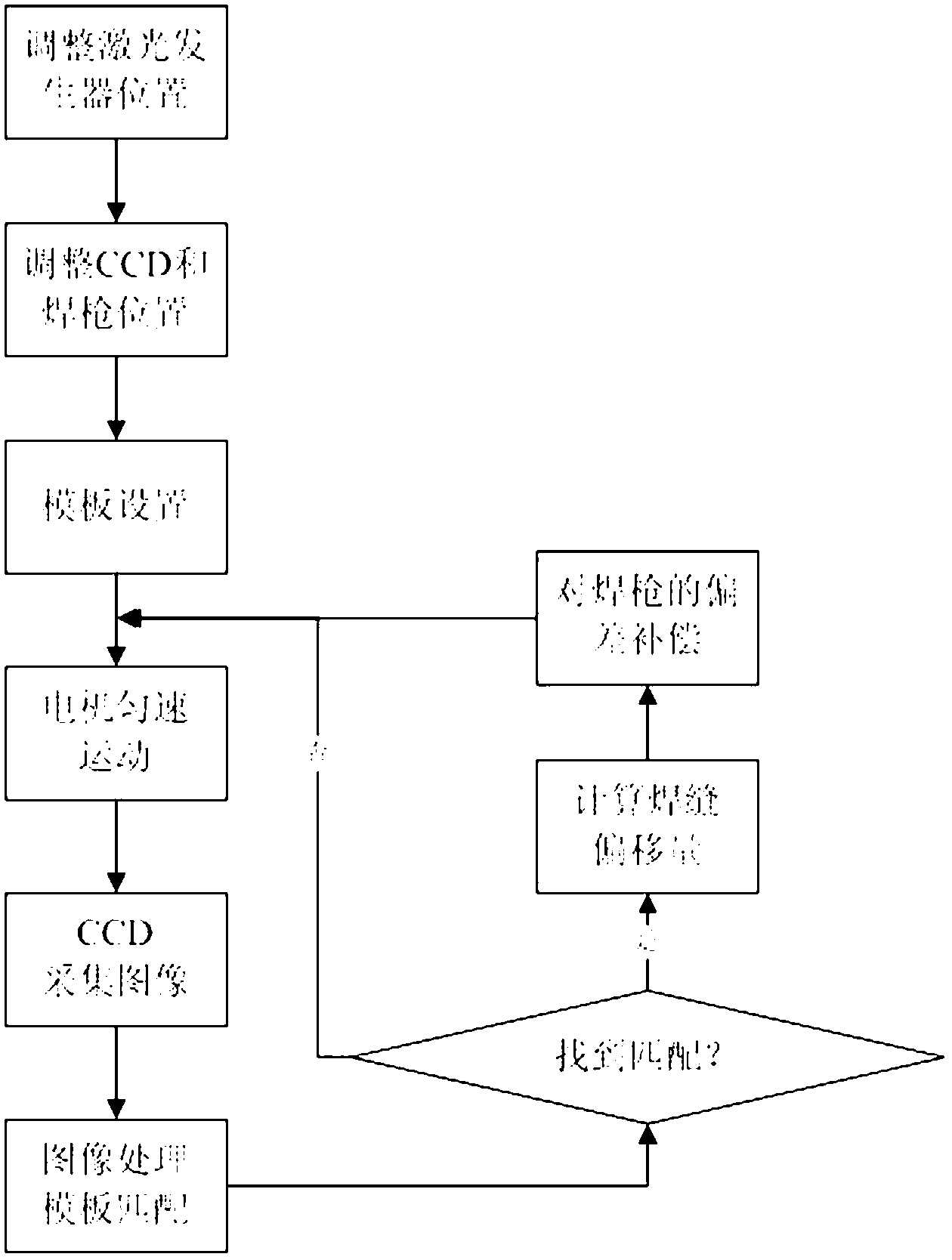
InactiveCN103008881AQuality assuranceEasy to operateLaser beam welding apparatusTemplate matchingLaser imaging
The invention discloses a seam tracking method based on liner laser imaging, and the seam tracking method comprises the following steps of step1, equipment calibration: adjusting a linear laser source generator, adjusting the position of a welding gun, fixing a charge coupled device (CCD) camera right in front of the welding gun, collecting an image and transmitting the collected image to a computer; step 2, setting a template; step 3, setting an interesting area; step 4, carrying out the template matching and acquiring a position deviation of the center of a weld seam; step 5, if an image which is matched with the template is found, compensating the deviation of the position of the welding gun; step 6, returning to the step 3 if no image which is matched with the template is found; and step 7, stopping a motor if the finding times of the image which is matched with the template is greater than a set threshold value. Due to the adoption of the seam tracking method, the position of a seam can be precisely positioned in the welding position, the seam tracking accuracy and reliability can be improved, the method is applicable to the tracking of the seams in different shapes, and a purpose for automatically tracking the seam in the welding process can be realized.
Owner:THE 45TH RES INST OF CETC
Multielement photon counting laser ranging three-dimensional imaging system
ActiveCN104166142APlay ultra-high sensitivityRealize 3D Laser ImagingElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingLaser imaging
The invention discloses a multielement photon counting laser ranging three-dimensional imaging system. The system comprises a laser emitting unit used for emitting beam arrays, a control unit for controlling the beam arrays to be emitted and scanned, a receiving and detecting unit which receives echo optical signals through an optical lens and detects focal plane optical signals through a single-photon detector array formed by coupling optical fiber arrays, and a time measurement unit used for recording and analyzing multi-channel photon flying time. According to multielement photon counting three-dimensional imaging system, the single-photon detector array formed by coupling optical fiber arrays is used, multielement photon counting laser ranging of one-dimensional laser beam arrays is achieved, one-dimensional scanning is performed on the beam arrays in the vertical direction of arrangement of the beam arrays, and photon counting three-dimensional laser imaging is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
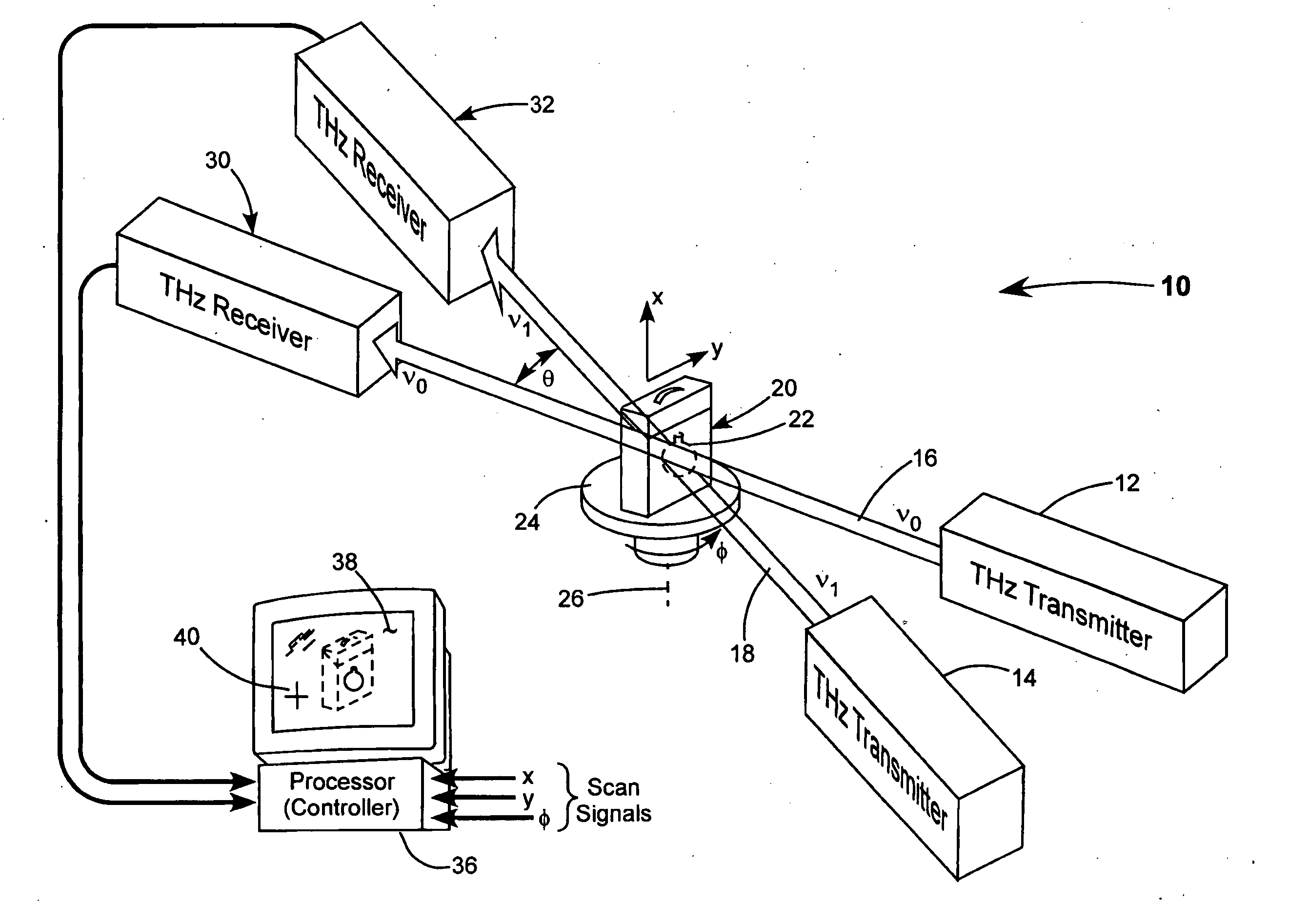
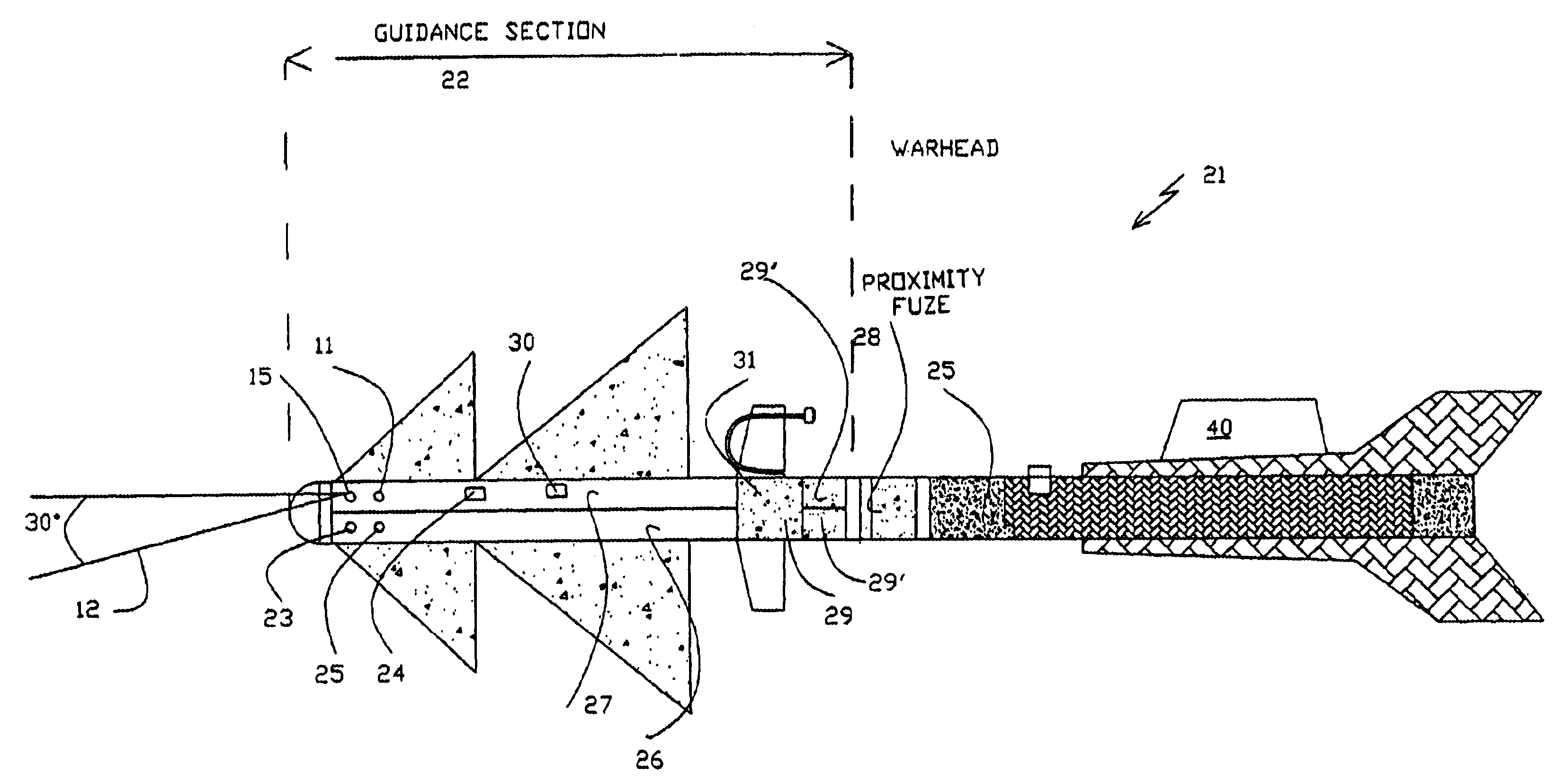
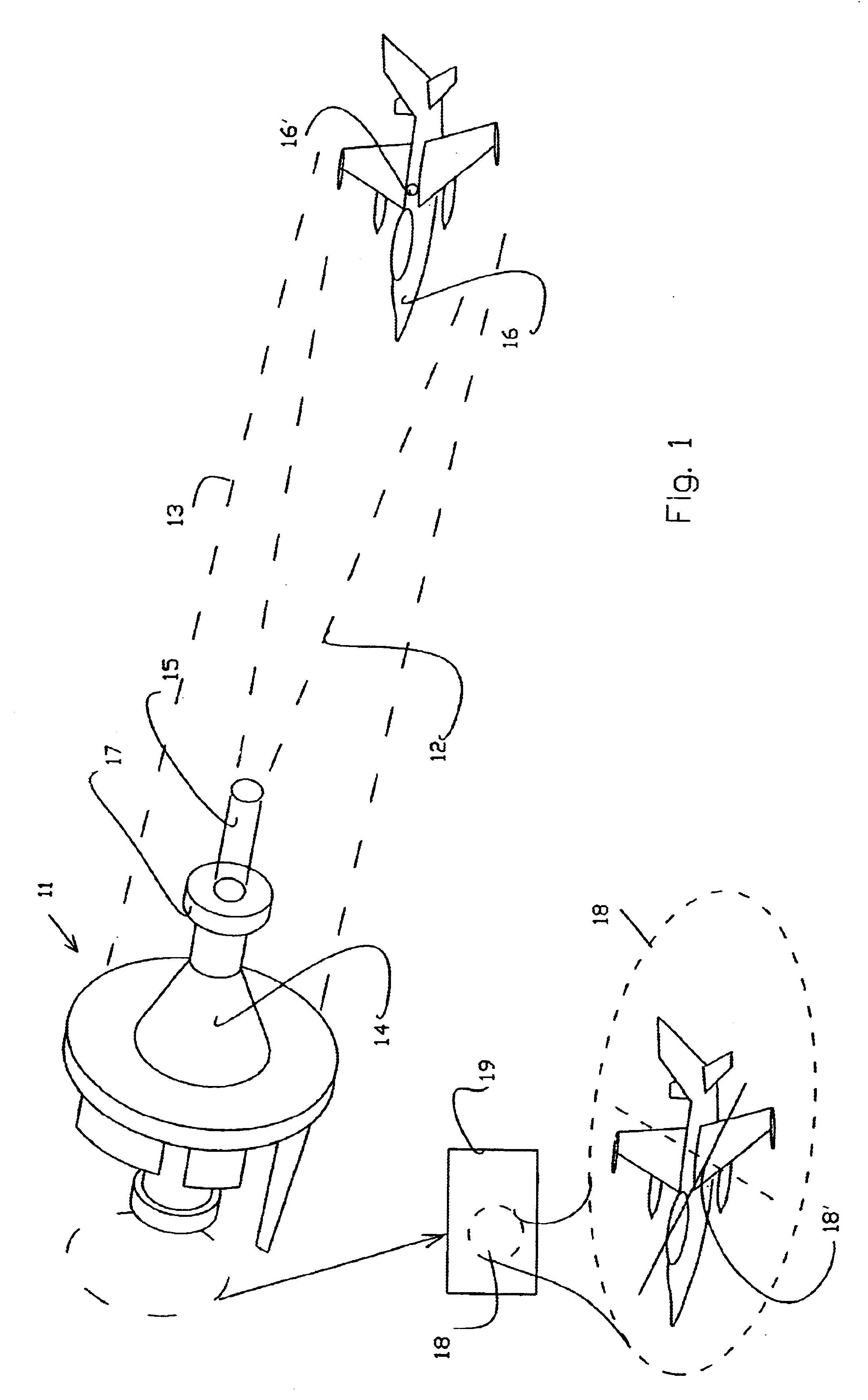
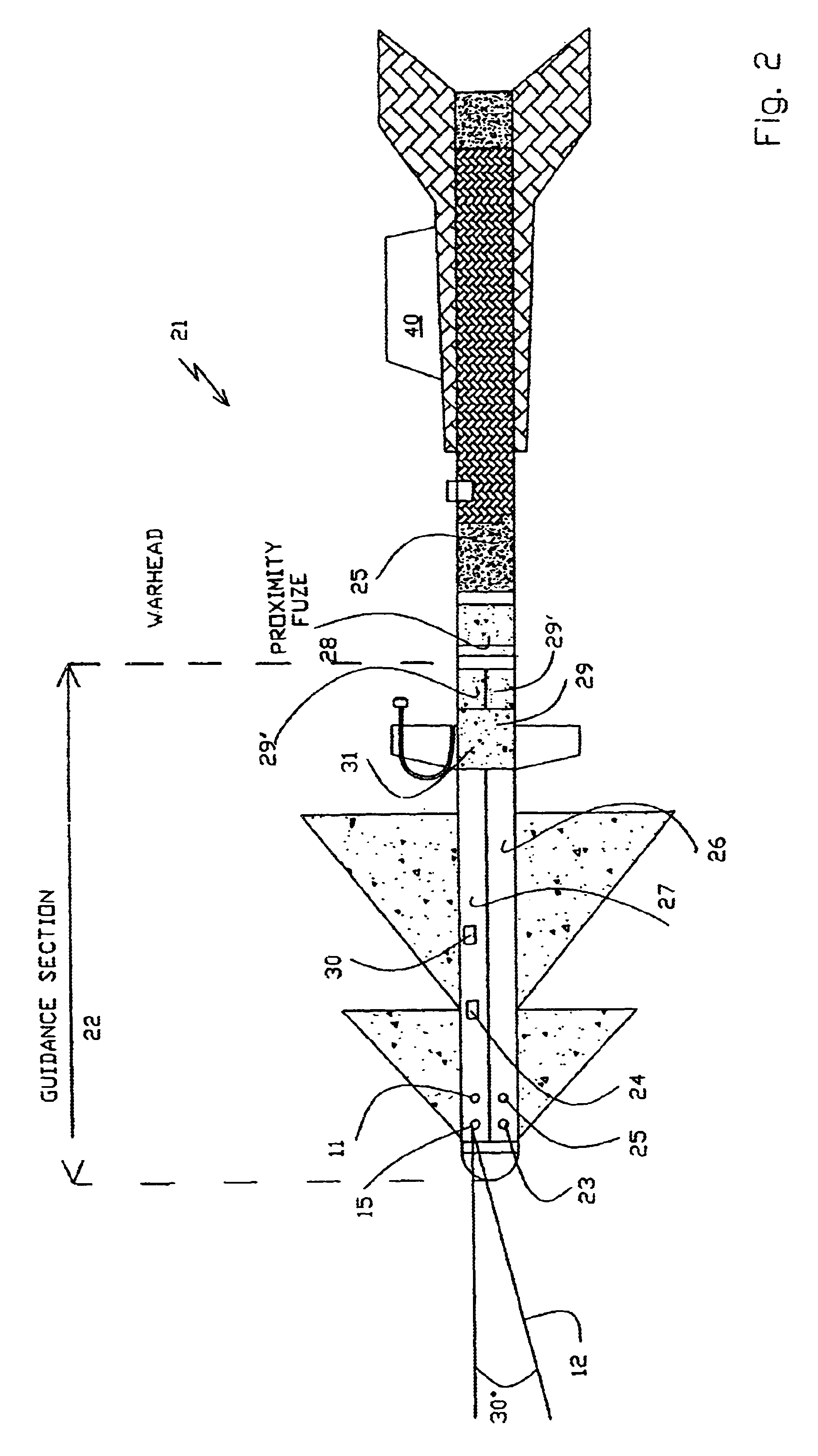
Method and system for active laser imagery guidance of intercepting missiles
A method for guiding an intercepting missile to a body-to-body contact with an airborne target in the atmosphere. The method includes the steps of guiding the intercepting missile to within an appropriate distance from the airborne target, illuminating the airborne target, using an illuminator carried by the intercepting missile, acquiring an image of the illuminated airborne target and, steering the missile in accordance with an aimpoint on the image.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Three-dimensional laser imaging method based on photon counting compressive sampling phased array
InactiveCN102608619AImprove signal-to-noise ratioGood drift resistanceElectromagnetic wave reradiationTerrainImaging processing
The invention provides a three-dimensional laser imaging method based on a photon counting compressive sampling phased array, which is applicable to the fields of all-weather target identification, high-precision terrain survey, precise nondestructive examination and the like, and belongs to the technical field of laser imaging and image processing. The three-dimensional laser imaging method includes steps that at first, a pulse signal generator generates pulse signals and drives a laser device to transmit laser pulse, and a liquid crystal optical phased array is adopted to modulate illuminating laser via a certain measurement matrix so as to illuminate for a target; optical pulse reflected by the target is received by a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode, a time-correlated single photon counter is used for recording the numbers of photons returned at different time intervals, and the numbers of the photons returned at different time intervals are integrated so as to obtain a measured vector quantity; and the measured matrix and the measured vector quantity are brought into a compressive sampling recovery algorithm, so that a three-dimensional image of the target is reconstructed. The three-dimensional laser imaging method has a good practical value and a wide application prospect in the technical field of laser imaging and digital image processing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and Method for Laser Imaging and Ablation of Cancer Cells Using Fluorescence
ActiveUS20140187879A1Reduce deficiencySurgical instrument detailsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCancer cellWound care
A fluorescence imaging device detects fluorescence in parts of the visible and invisible spectrum, and projects the fluorescence image directly on the human body, as well as on a monitor, with improved sensitivity, video frame rate and depth of focus, and enhanced capabilities of detecting distribution and properties of multiple fluorophores. Direct projection of three-dimensional visible representations of florescence on three-dimensional body areas advantageously permits view of it during surgical procedures, including during cancer removal, reconstructive surgery and wound care, etc. A NIR laser and a human visible laser (HVL) are aligned coaxially and scanned over the operating field of view. When the NIR laser passes over the area where the florescent dye is present, it energizes the dye which emits at a shifted NIR frequency detected by a photo diode. The HVL is turned on when emission is detected, providing visual indication of those positions.
Owner:ACCUVEIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com