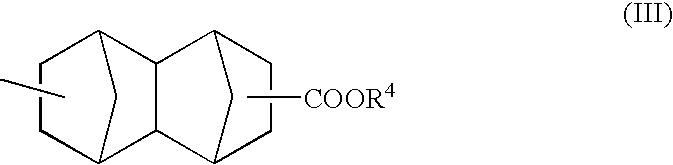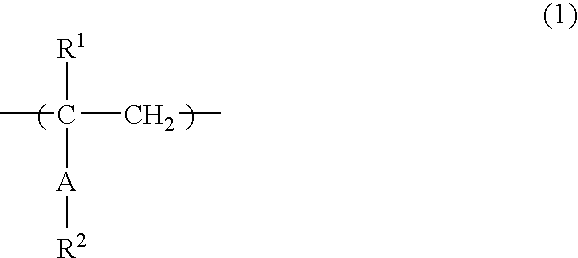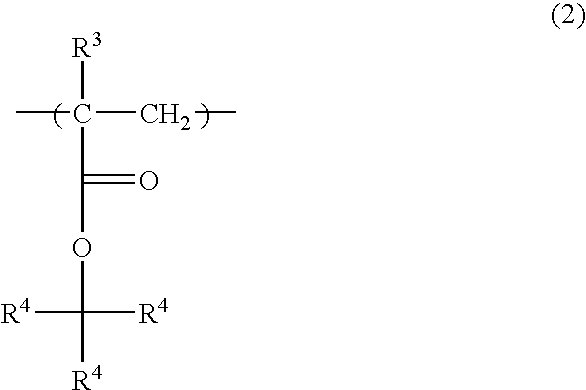Patents
Literature
514 results about "Depth of focus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
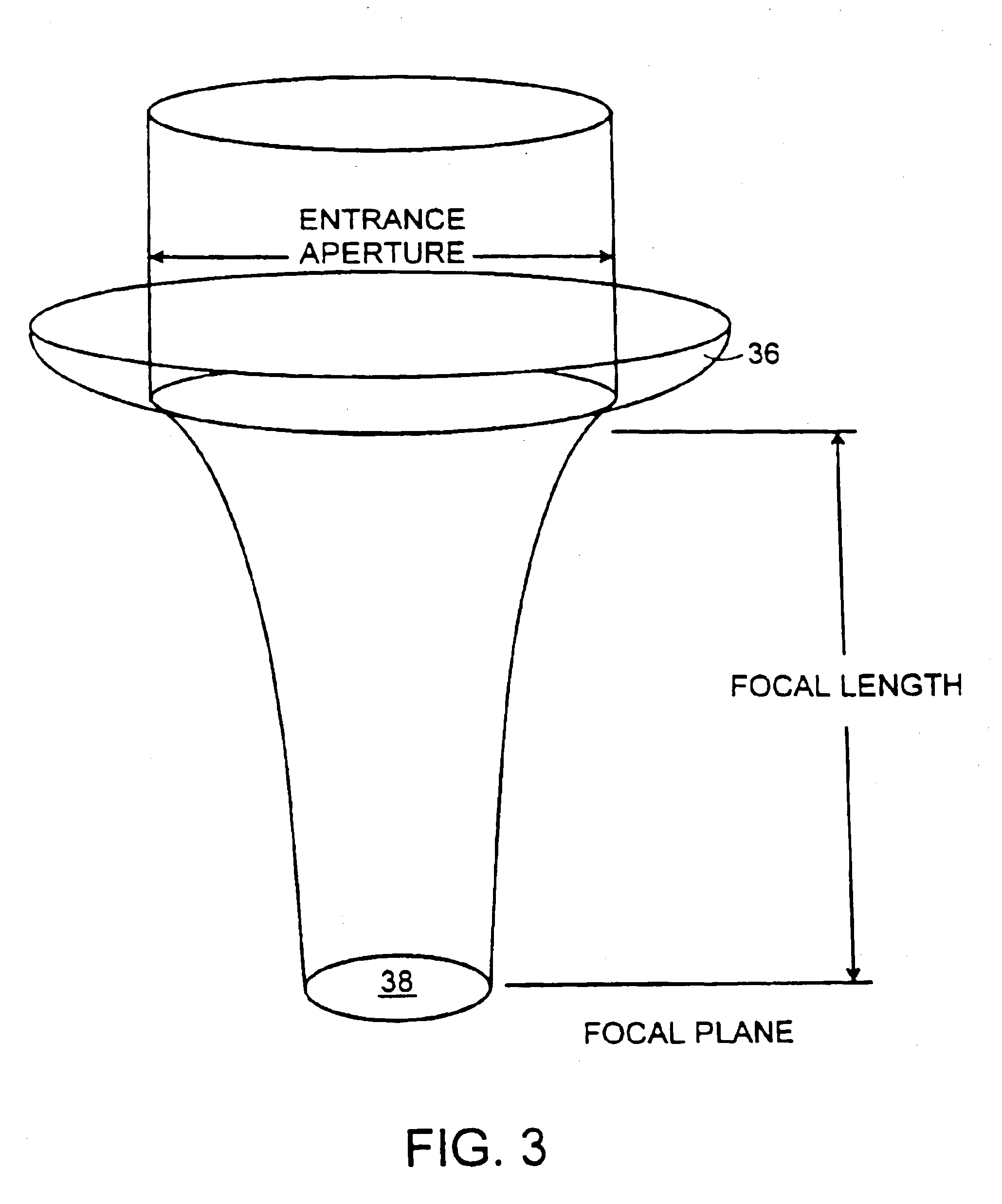
Depth of focus is a lens optics concept that measures the tolerance of placement of the image plane (the film plane in a camera) in relation to the lens. In a camera, depth of focus indicates the tolerance of the film's displacement within the camera and is therefore sometimes referred to as "lens-to-film tolerance".
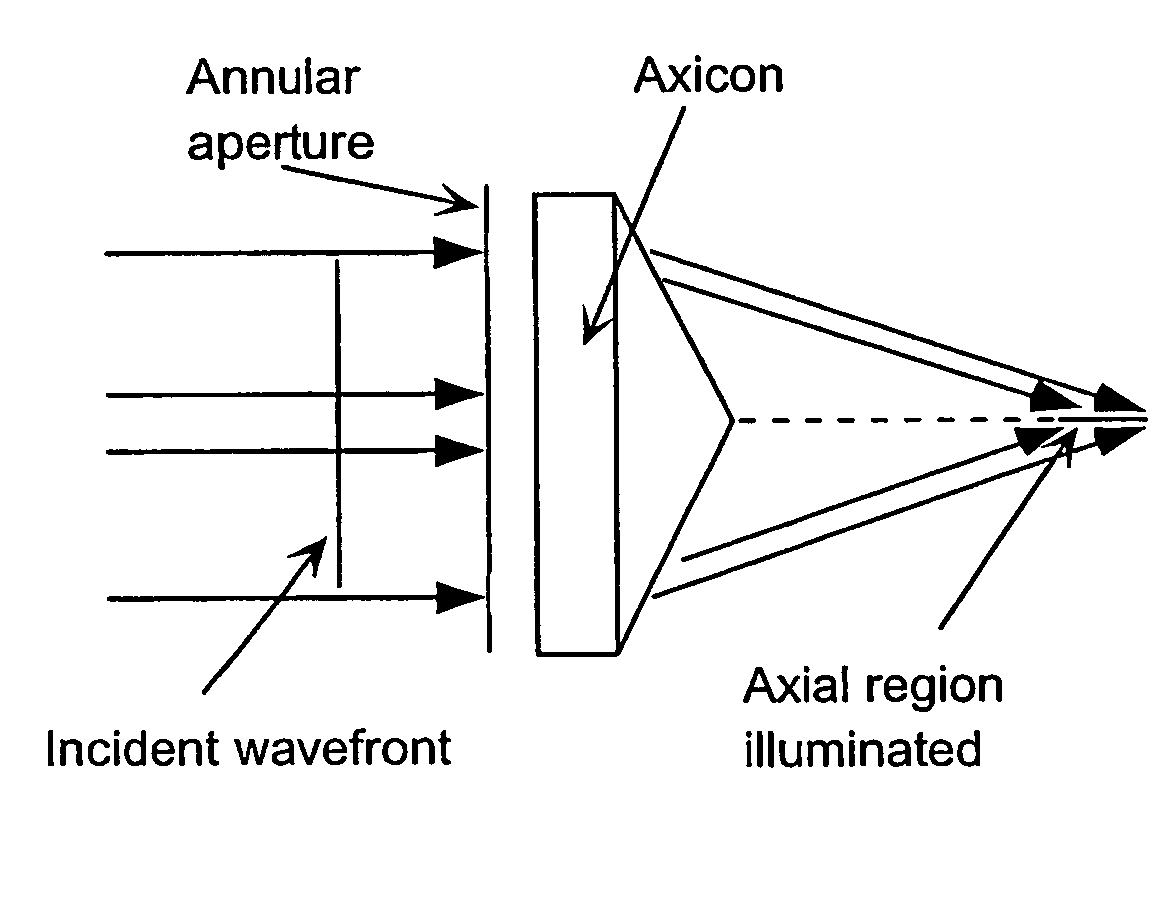
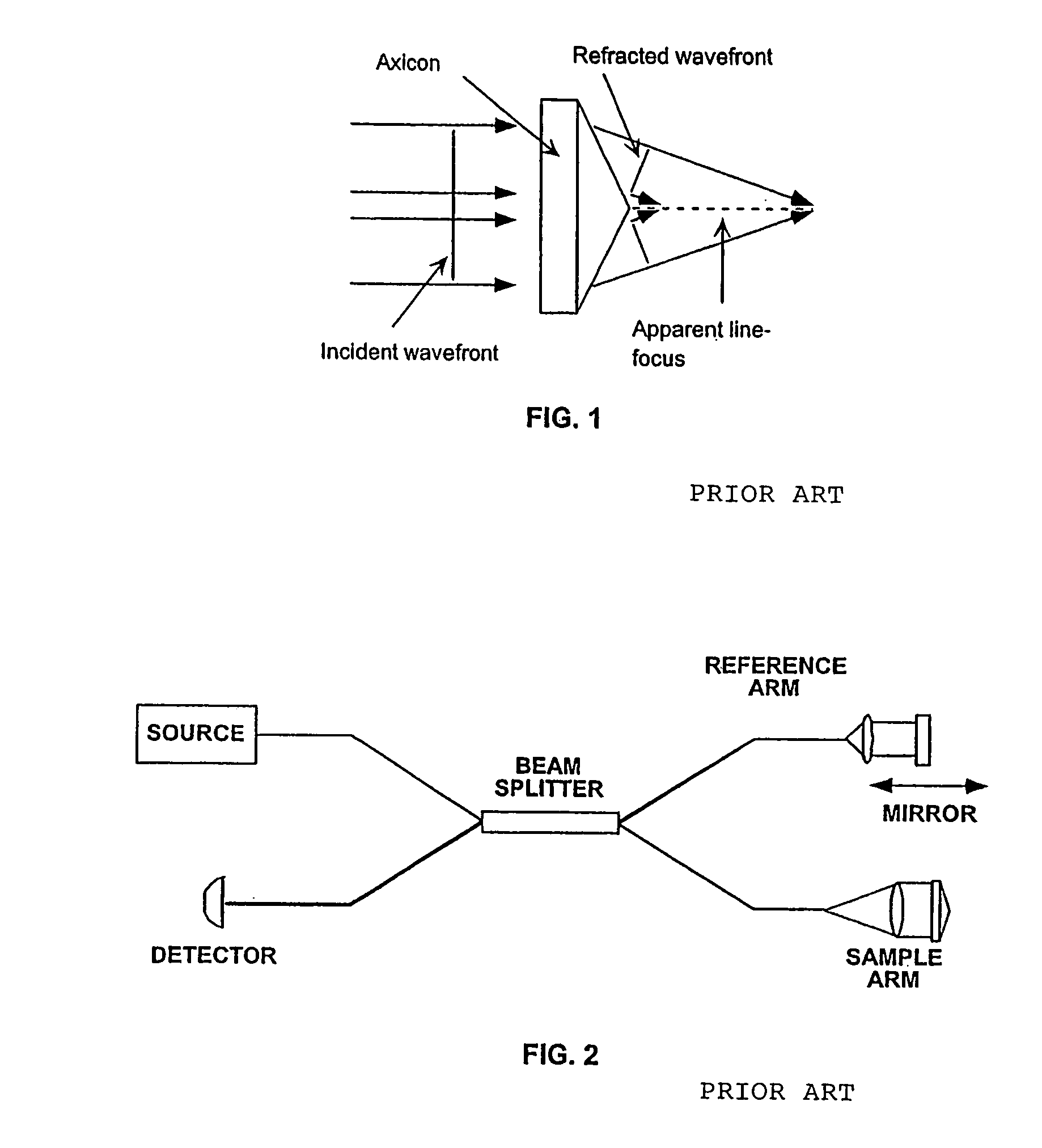
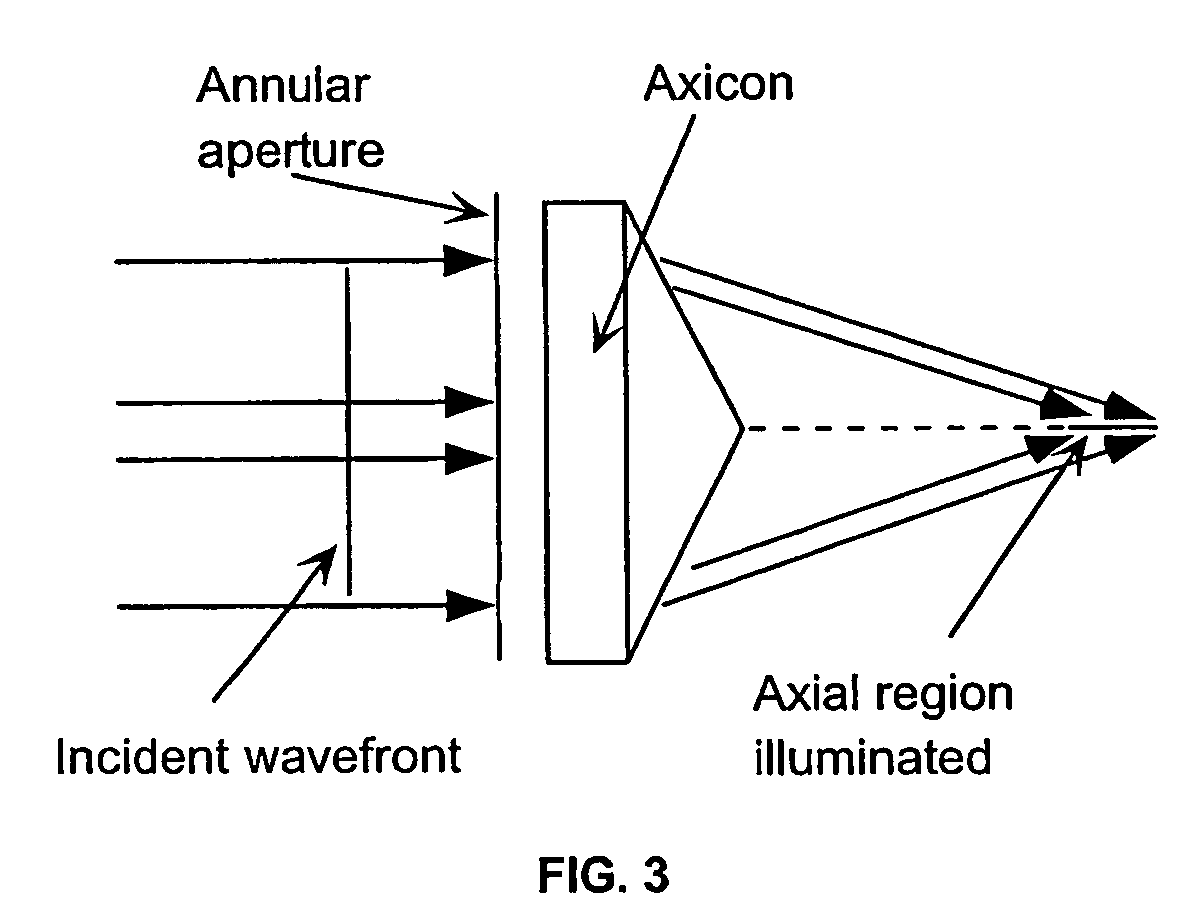
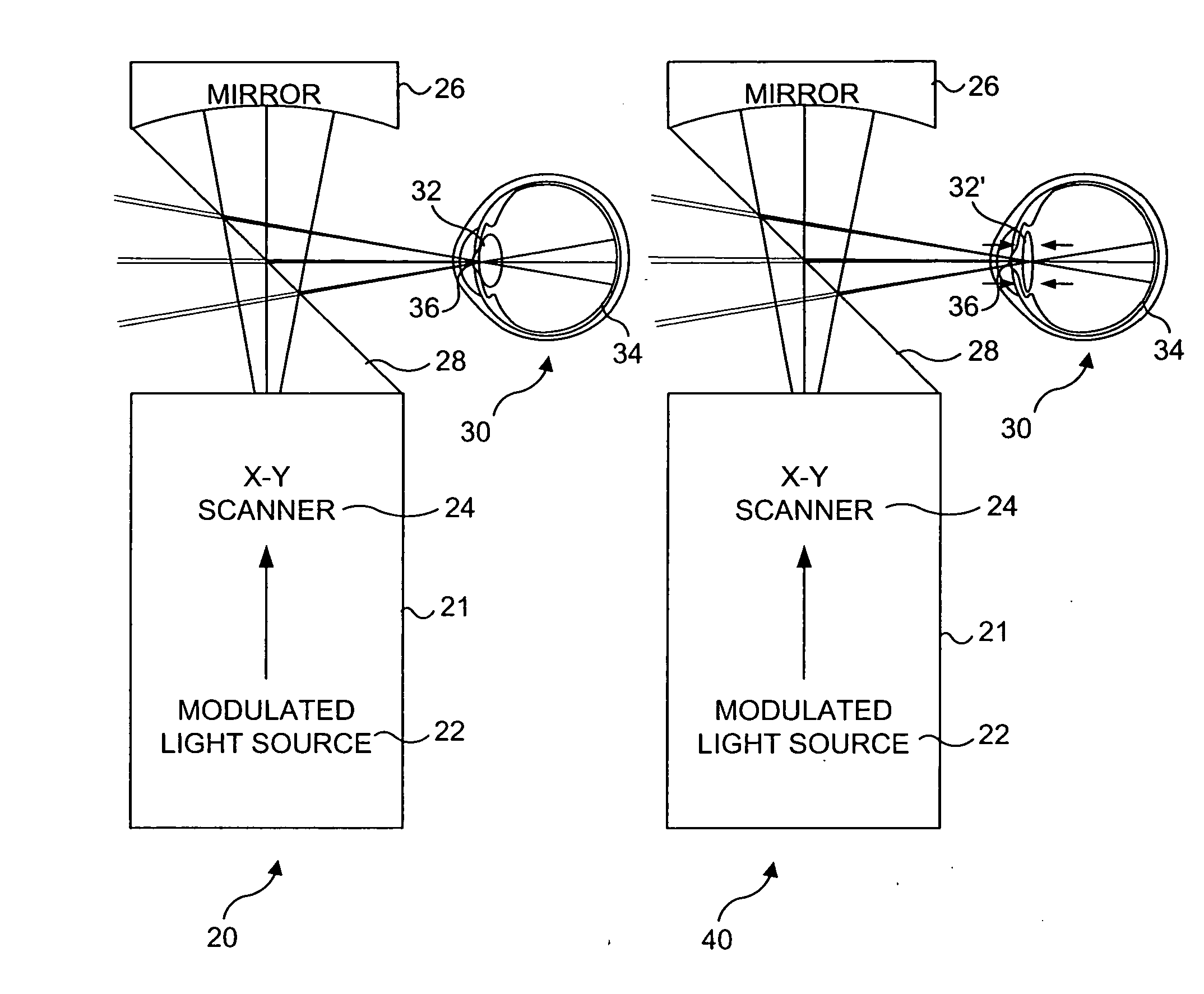
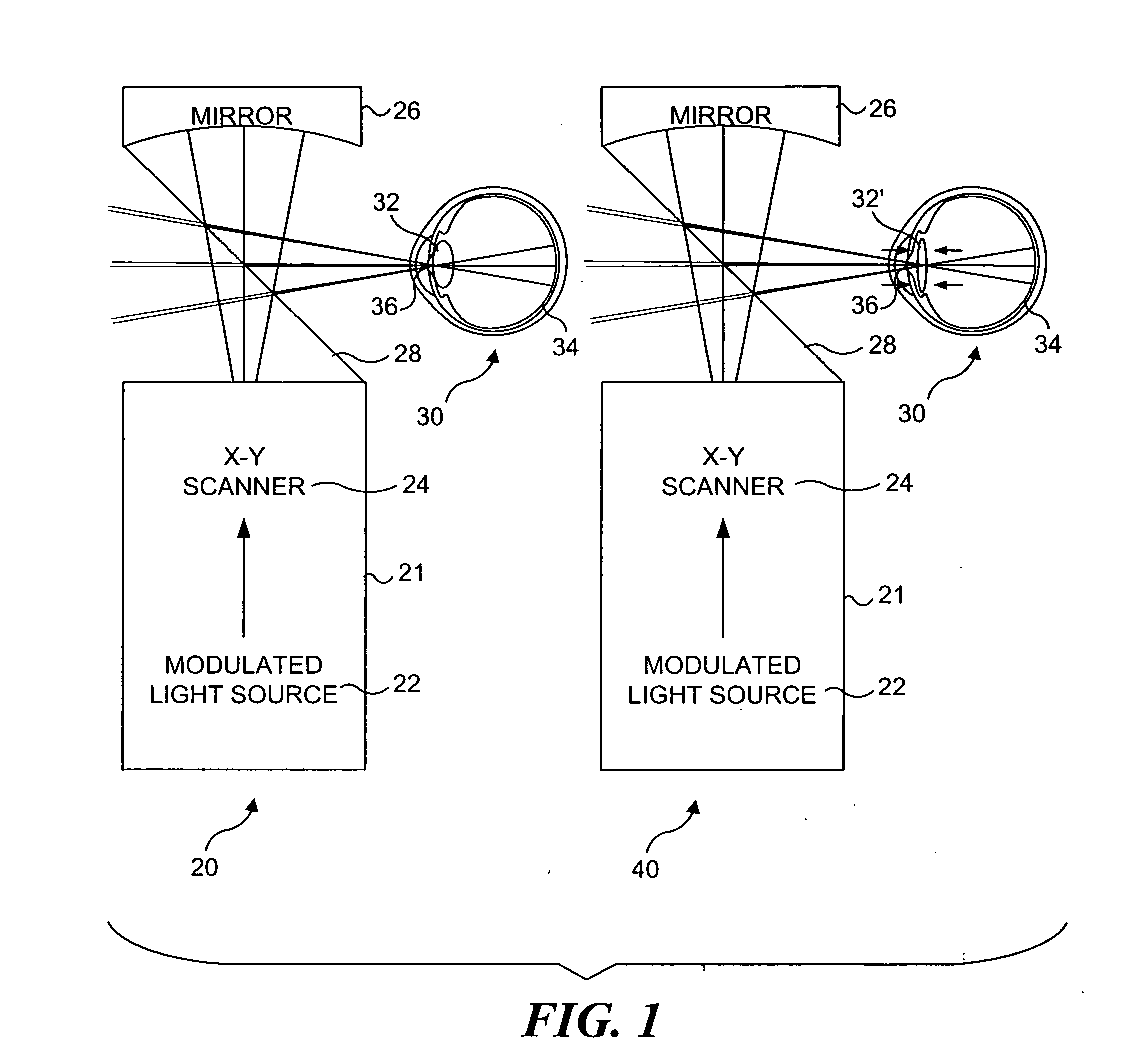
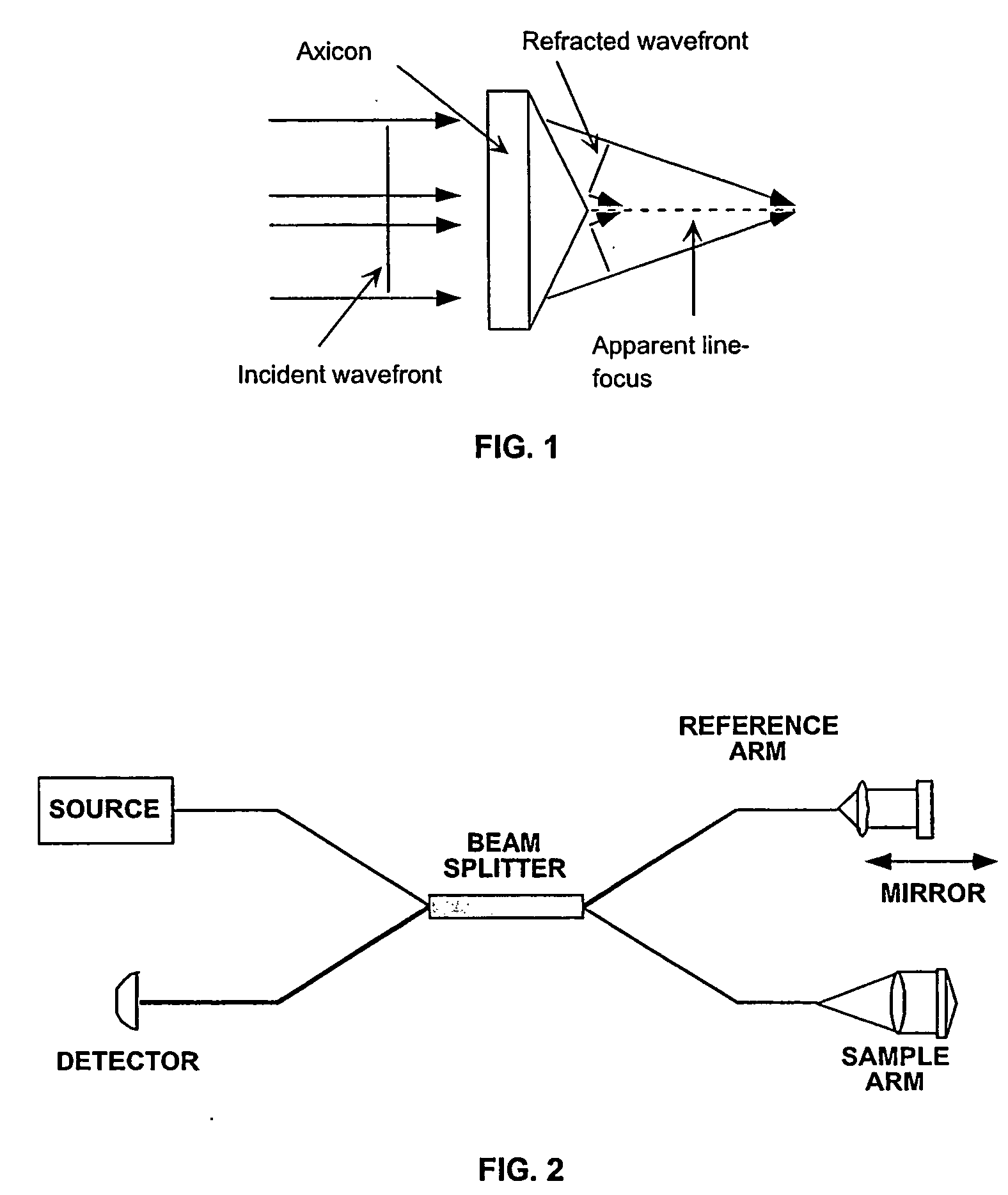
Apparatus and method for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS7310150B2Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
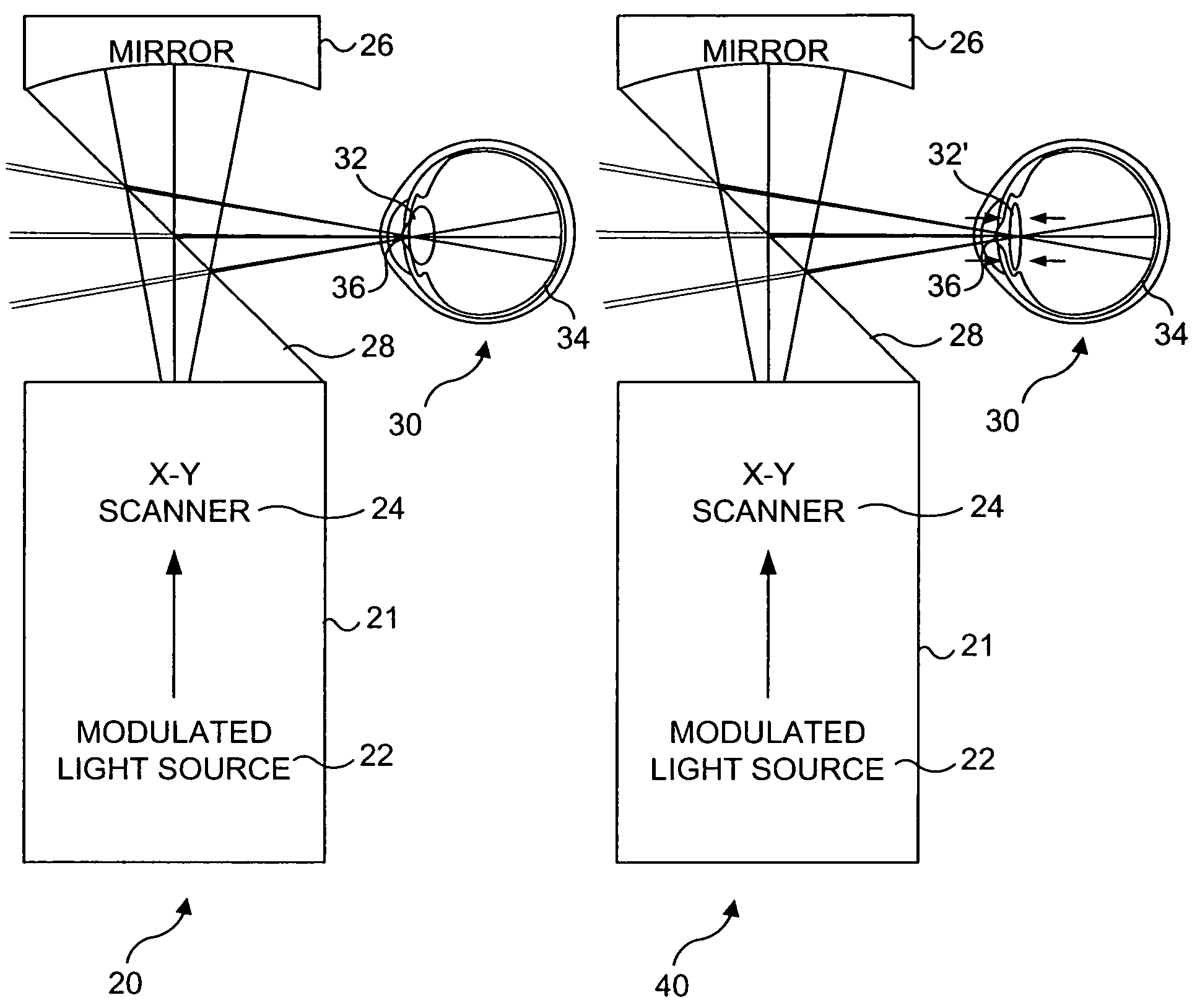
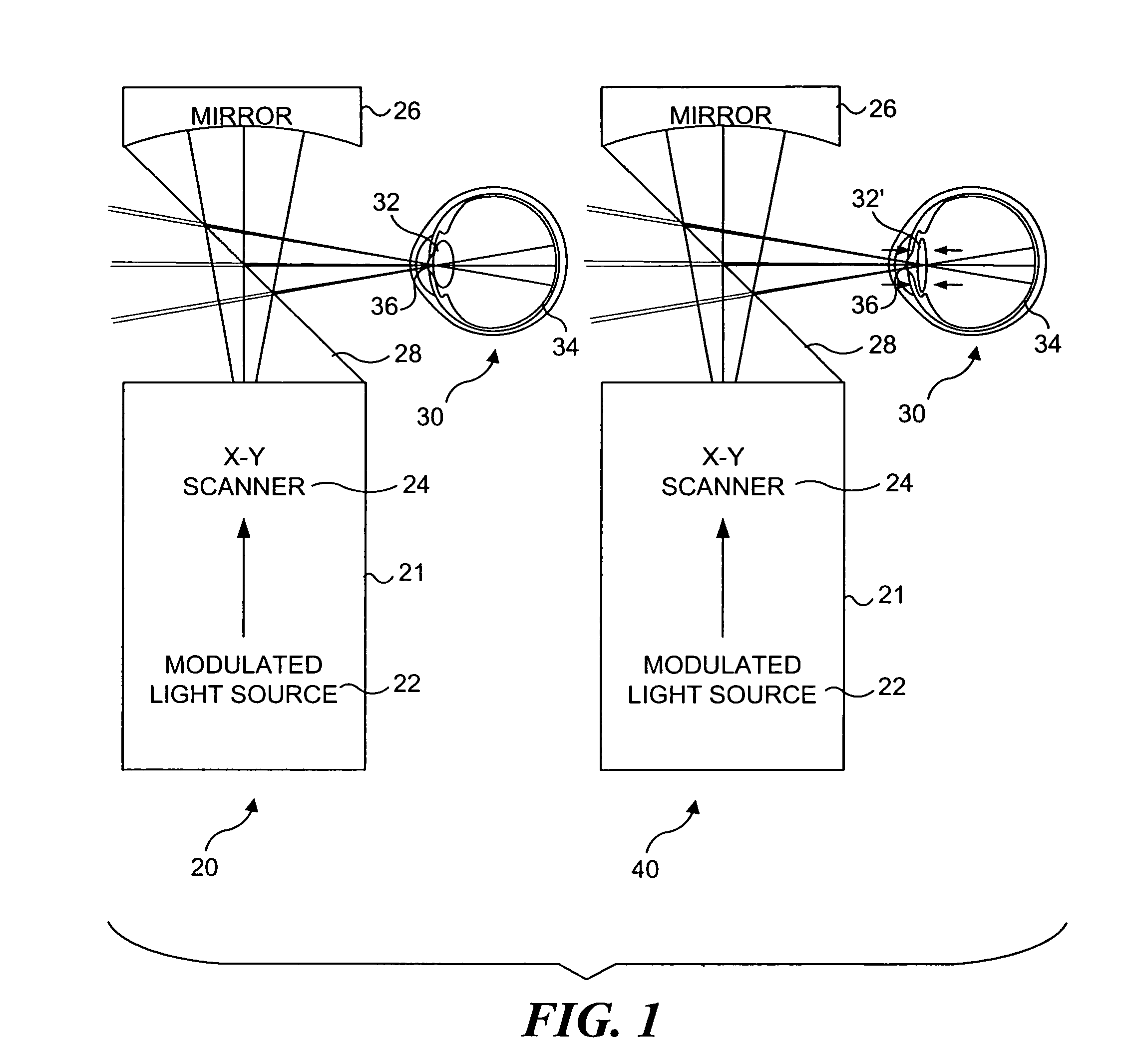
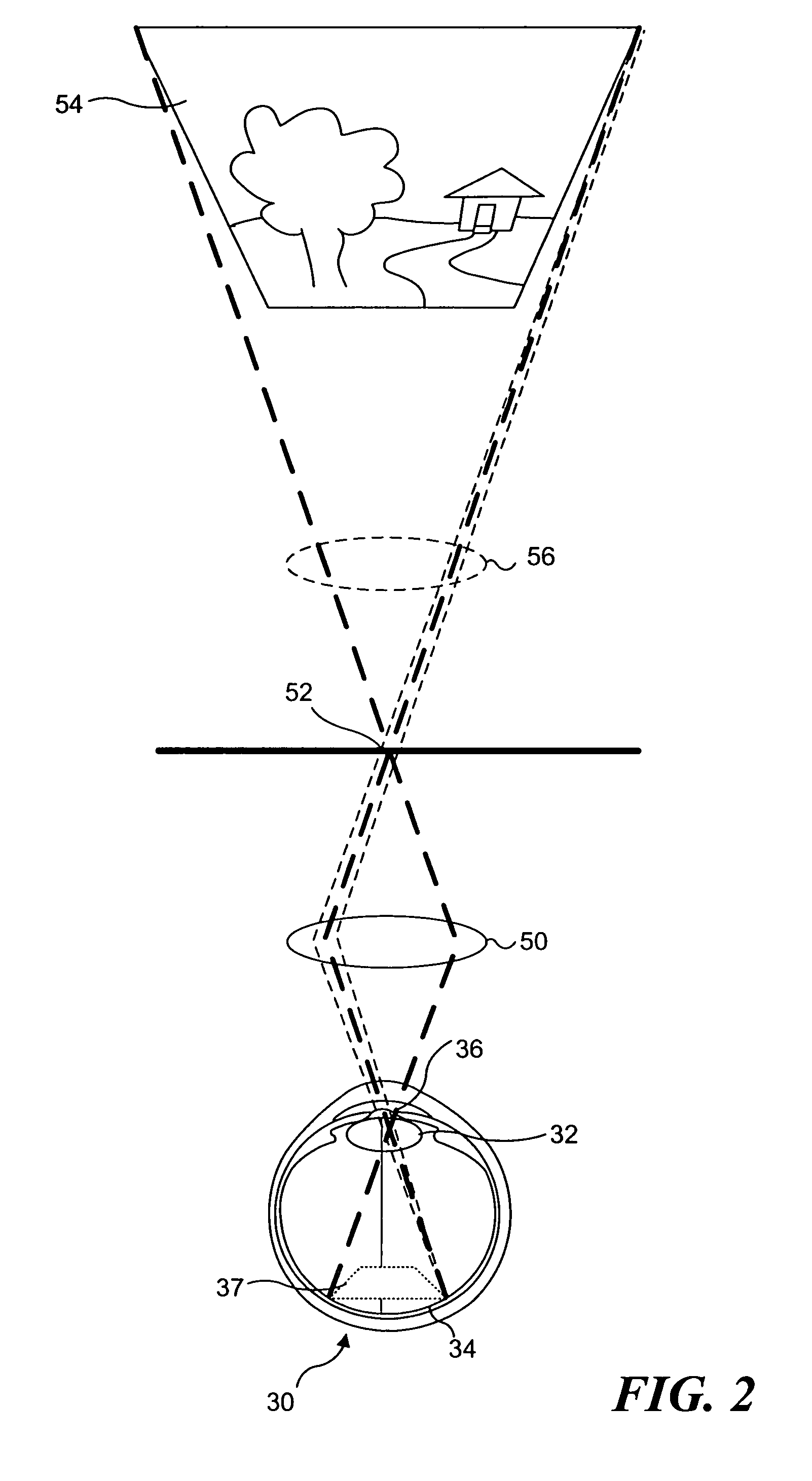
A system, apparatus and method for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus can be provided. For example, an optical ranging system including a light source can be used. Certain exemplary arrangement can be provided, e.g., a first arrangement for directing light from the light source to the sample, a second arrangement for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, and a third arrangement for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image can be utilized. Further, for example, an optical element can be provided which can have a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about μ5 m, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method utilizing compensation features in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS7202148B2Increased process windowReduce depthRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFlare
A photolithography and etch process sequence includes a photomask having a pattern with compensation features that alleviate patterning variations due to the proximity effect and depth of focus concerns during photolithography. The compensation features may be disposed near isolated or outermost lines of a device pattern. A photoresist pattern is formed to include the compensation features and the pattern etched to form a corresponding etched pattern including the compensation features. After etching, a protection material is formed over the layer and a trim mask is used to form a further photoresist pattern over the protection material. A subsequent etching pattern etches the protection material and removes the compensation features and results in the device lines being formed unaffected by proximity effects. Flare dummies may additionally be added to the mask pattern to increase pattern density and assist in endpoint detection. Flare dummies, like the compensation features, are subsequently removed by a photolithography and etching process sequence.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Exposure apparatus including micro mirror array and exposure method using the same
InactiveUS7061582B2High resolutionShort amount of timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistImage resolution
An exposure method and apparatus for use in exposing a photoresist on a semiconductor wafer do not employ an aperture for shaping the exposure light. The exposure apparatus includes a light source unit, a reflecting mirror unit having a micro mirror array (MMA) and a control unit that controls the MMA, and a pattern transfer unit that transfers the pattern of a photomask onto the photoresist. The angles of inclination of the respective mirrors of the MMA are adjusted to reflect incident light in a manner that shapes the incident light. Accordingly, it is possible to form a pattern having the highest degree of resolution and optimum depth of focus (DOF) in the shortest amount of processing time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and Apparatus for Rendering Focused Plenoptic Camera Data using Super-Resolved Demosaicing
ActiveUS20130128068A1Television system detailsSolid-state device signal generatorsCurrent pointDemosaicing
A super-resolved demosaicing technique for rendering focused plenoptic camera data performs simultaneous super-resolution and demosaicing. The technique renders a high-resolution output image from a plurality of separate microimages in an input image at a specified depth of focus. For each point on an image plane of the output image, the technique determines a line of projection through the microimages in optical phase space according to the current point and angle of projection determined from the depth of focus. For each microimage, the technique applies a kernel centered at a position on the current microimage intersected by the line of projection to accumulate, from pixels at each microimage covered by the kernel at the respective position, values for each color channel weighted according to the kernel. A value for a pixel at the current point in the output image is computed from the accumulated values for the color channels.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
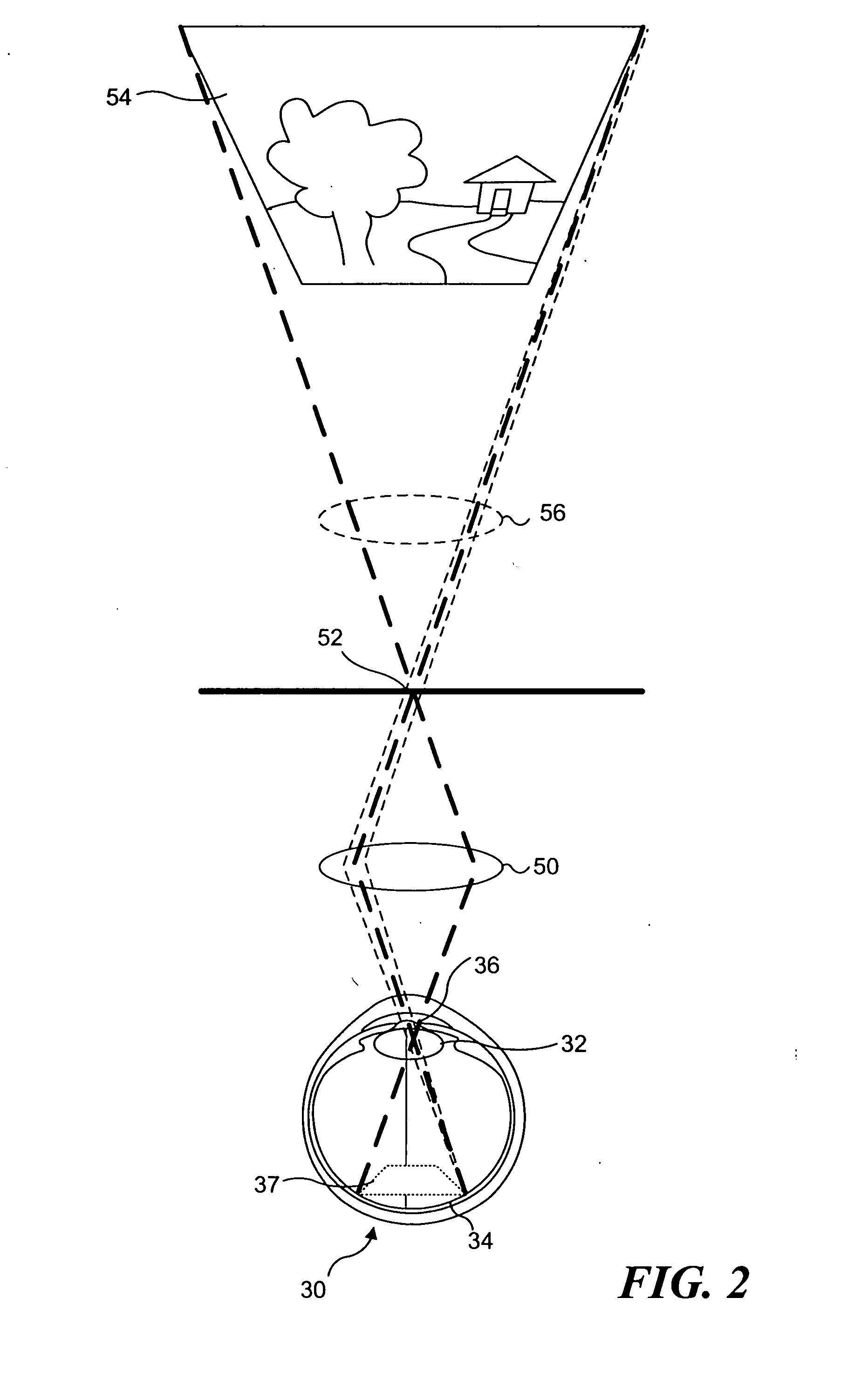
Materials and methods for simulating focal shifts in viewers using large depth of focus displays
ActiveUS20060232665A1Improve interactivityEnhances perceived realismTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceDepth of field
A large depth of focus (DOF) display provides an image in which the apparent focus plane is adjusted to track an accommodation (focus) of a viewer's eye(s) to more effectively convey depth in the image. A device is employed to repeatedly determine accommodation as a viewer's gaze within the image changes. In response, an image that includes an apparent focus plane corresponding to the level of accommodation of the viewer is provided on the large DOF display. Objects that are not at the apparent focus plane are made to appear blurred. The images can be rendered in real-time, or can be pre-rendered and stored in an array. The dimensions of the array can each correspond to a different variable. The images can alternatively be provided by a computer controlled, adjustable focus video camera in real-time.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
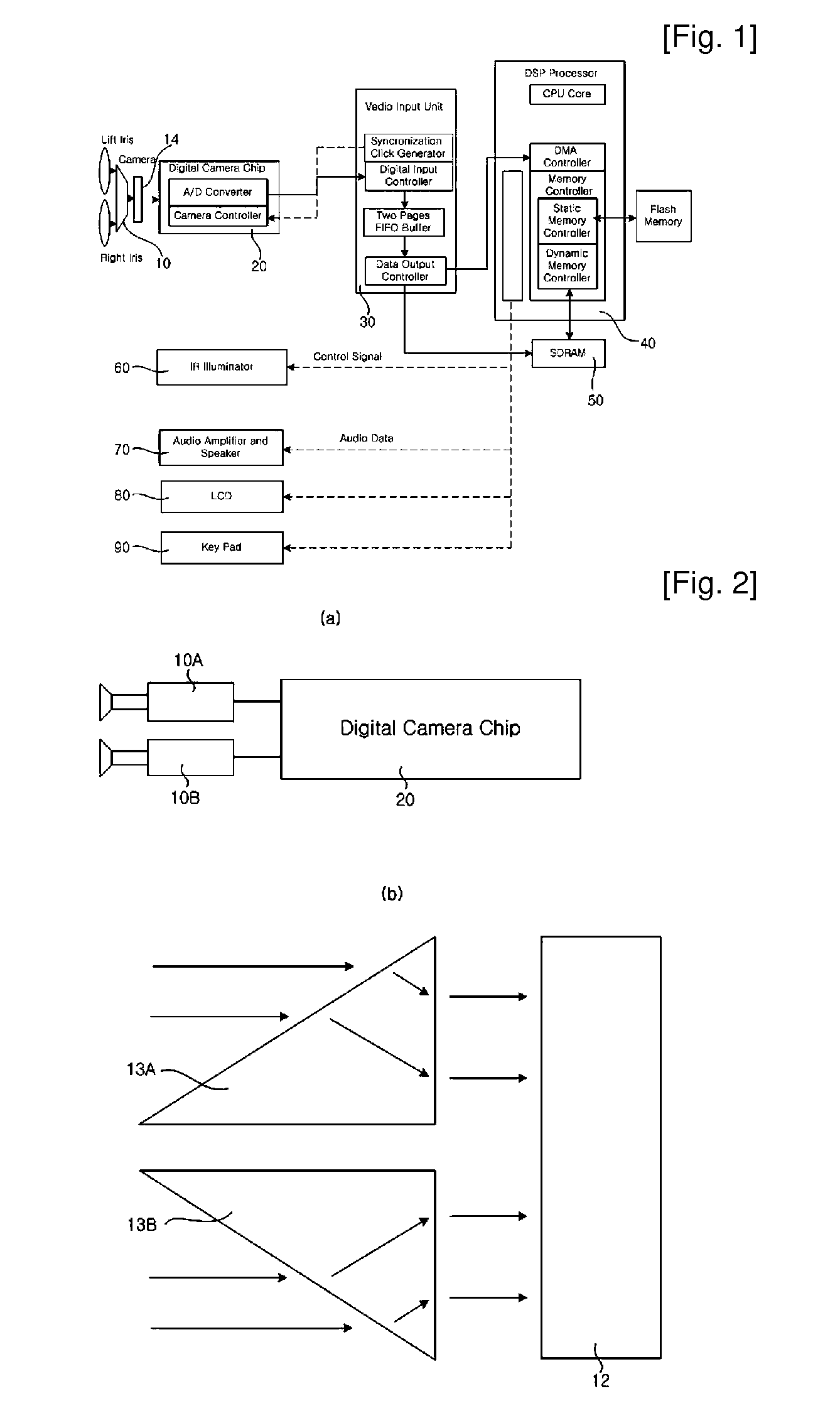
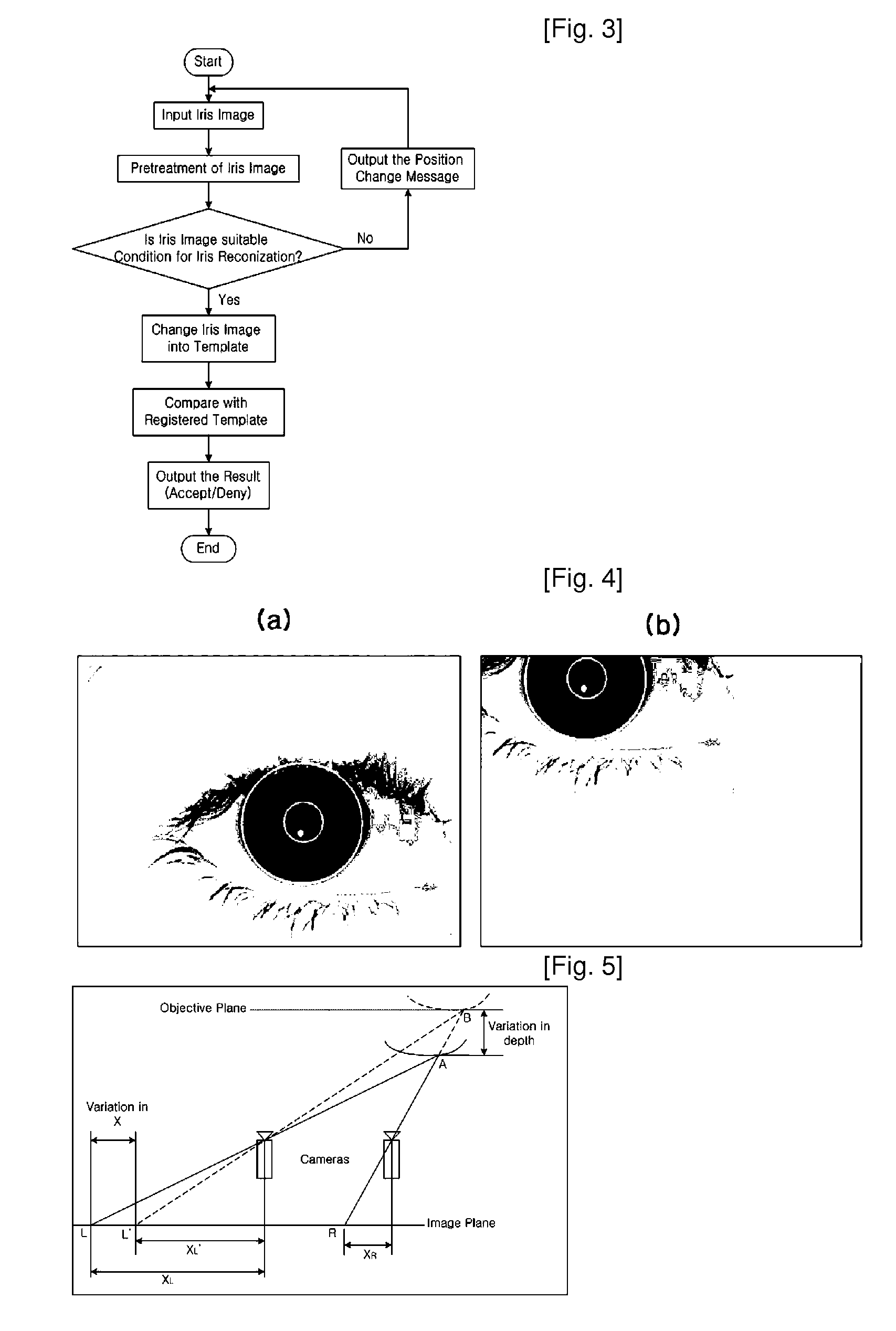
Iris Identification System and Method Using Mobile Device with Stereo Camera
InactiveUS20080292144A1Easy to getImprove recognition rateLighting and heating apparatusAcquiring/recognising eyesCamera lensStereo cameras
The present invention relates to a face recognition and / or iris recognition system and method using a mobile device equipped with a stereo camera, which acquire a stereo image of a user's face using at least two cameras or a method corresponding thereto and, even when the size of the stereo image is varied according to distance, correct the size of the stereo image. The stereo camera uses a single-focus lens with a long depth of focus to acquire a focused iris image over a wider range. When the user is not located at a position suitable for iris recognition, a message is sent to the user such that an iris image suitable for recognition is acquired. Furthermore, an iris image correction process according to distance is performed to prevent recognition rate from decreasing even when the size of the iris image is changed.
Owner:IRITECH
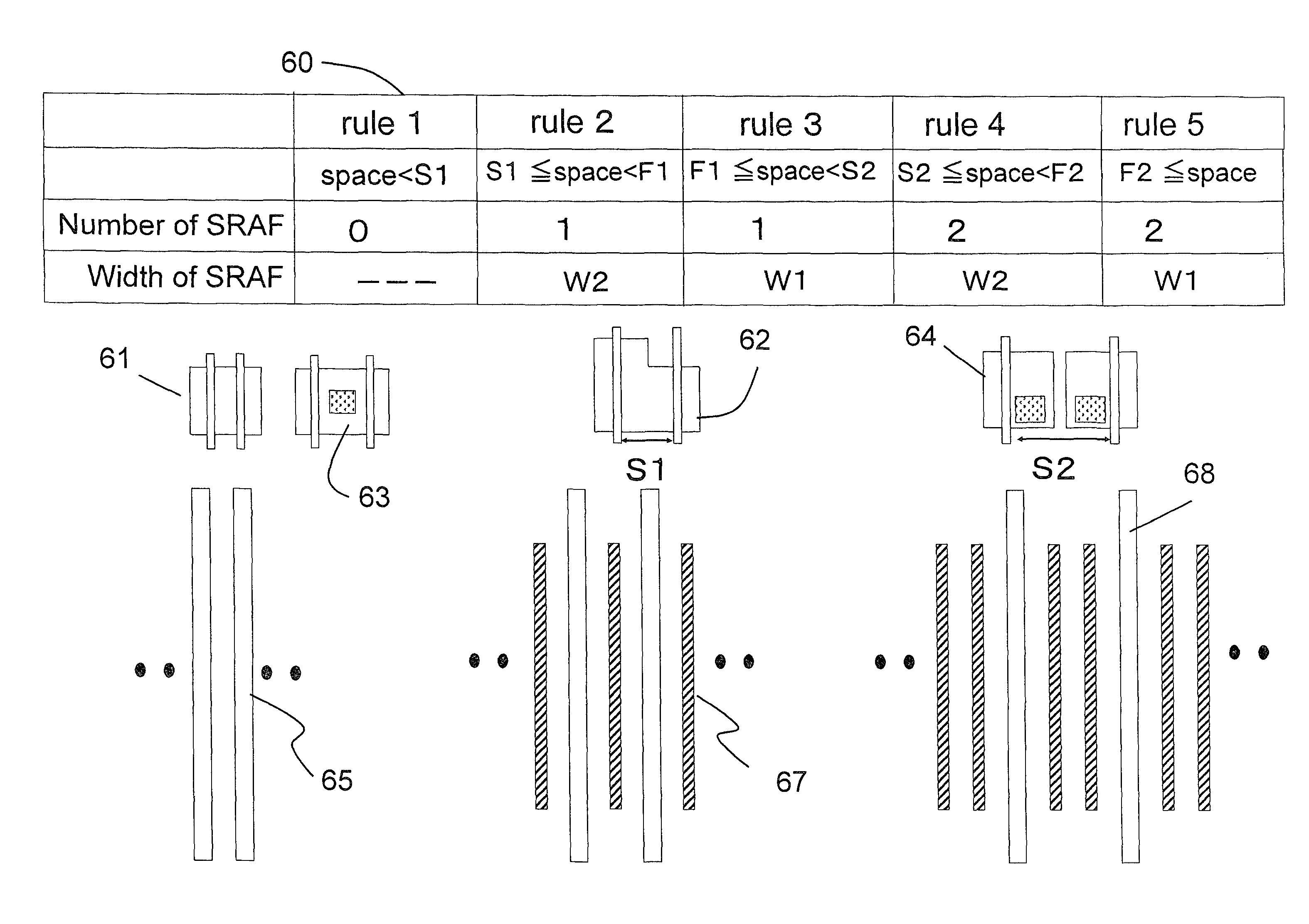
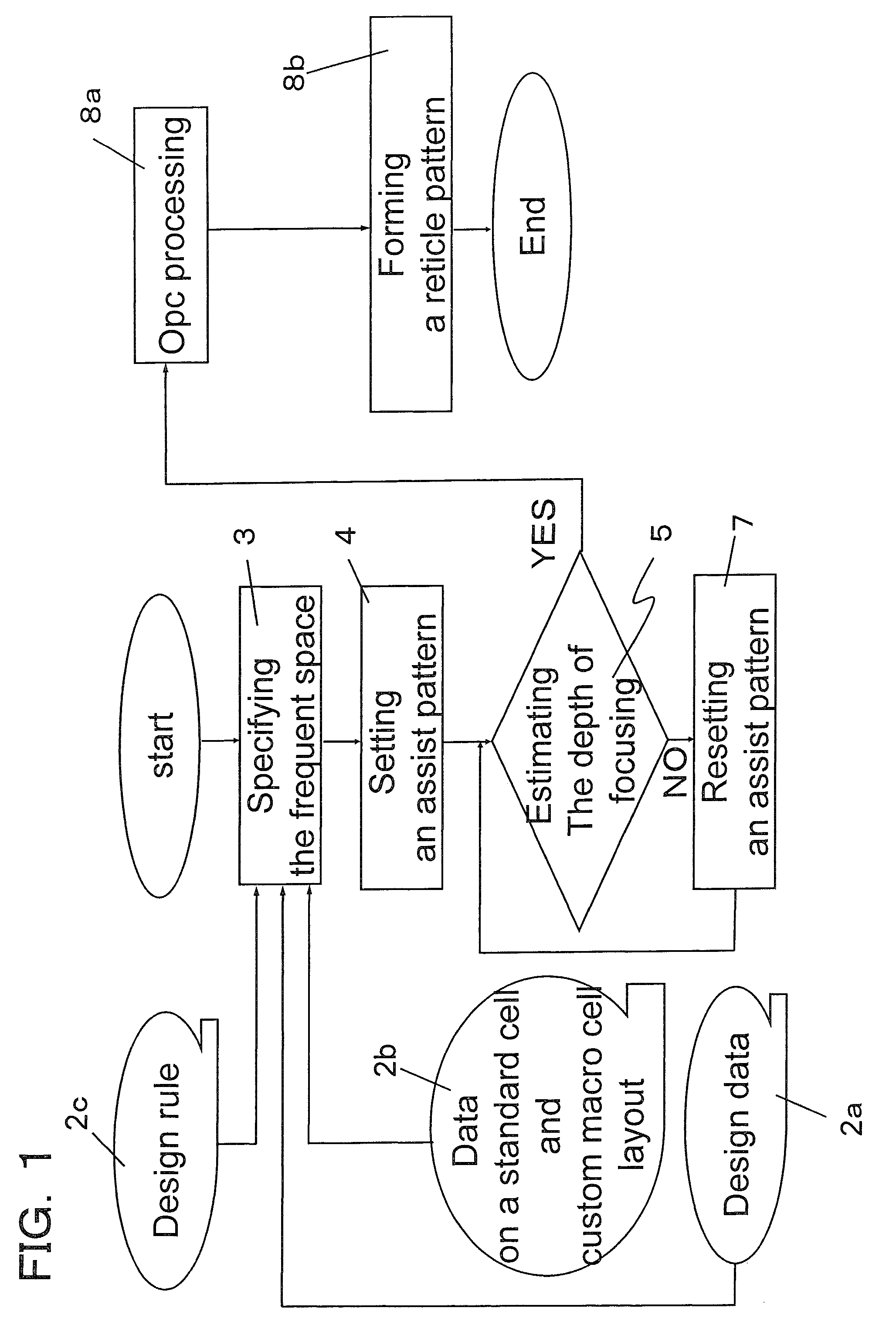
Creating method of photomask pattern data, photomask created by using the photomask pattern data, and manufacturing method of semiconductor apparatus using the photomask
A method for creating a pattern on a photomask includes steps of recognizing a space between main patterns by using pattern data which indicate the main patterns to be adjacently transferred onto a wafer, determining a 1st rule about arrangement of an assist pattern on the photomask, the assist pattern being adjacent to the main patterns and not being transferred onto the wafer, estimating a depth of focus in the presence of the assist pattern among the main patterns, determining a 2nd rule about arrangement of the assist pattern on the photomask to improve the depth of focus in the presence of the 1st assist pattern among the main patterns in a group having one or more number of appearance times of the space between main patterns, and correcting the assist pattern on the photomask using the assist pattern data on the basis of the 2nd rule.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
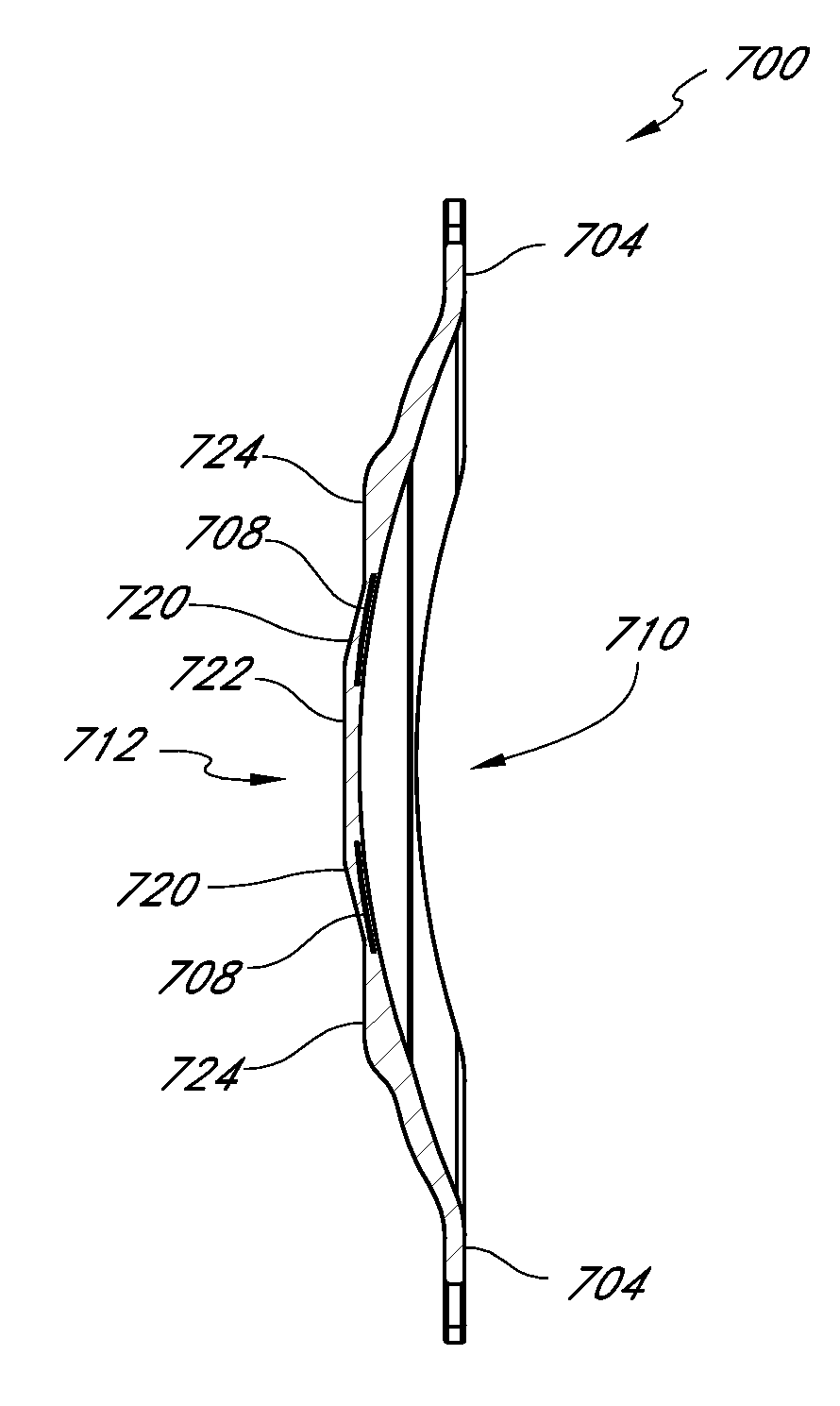
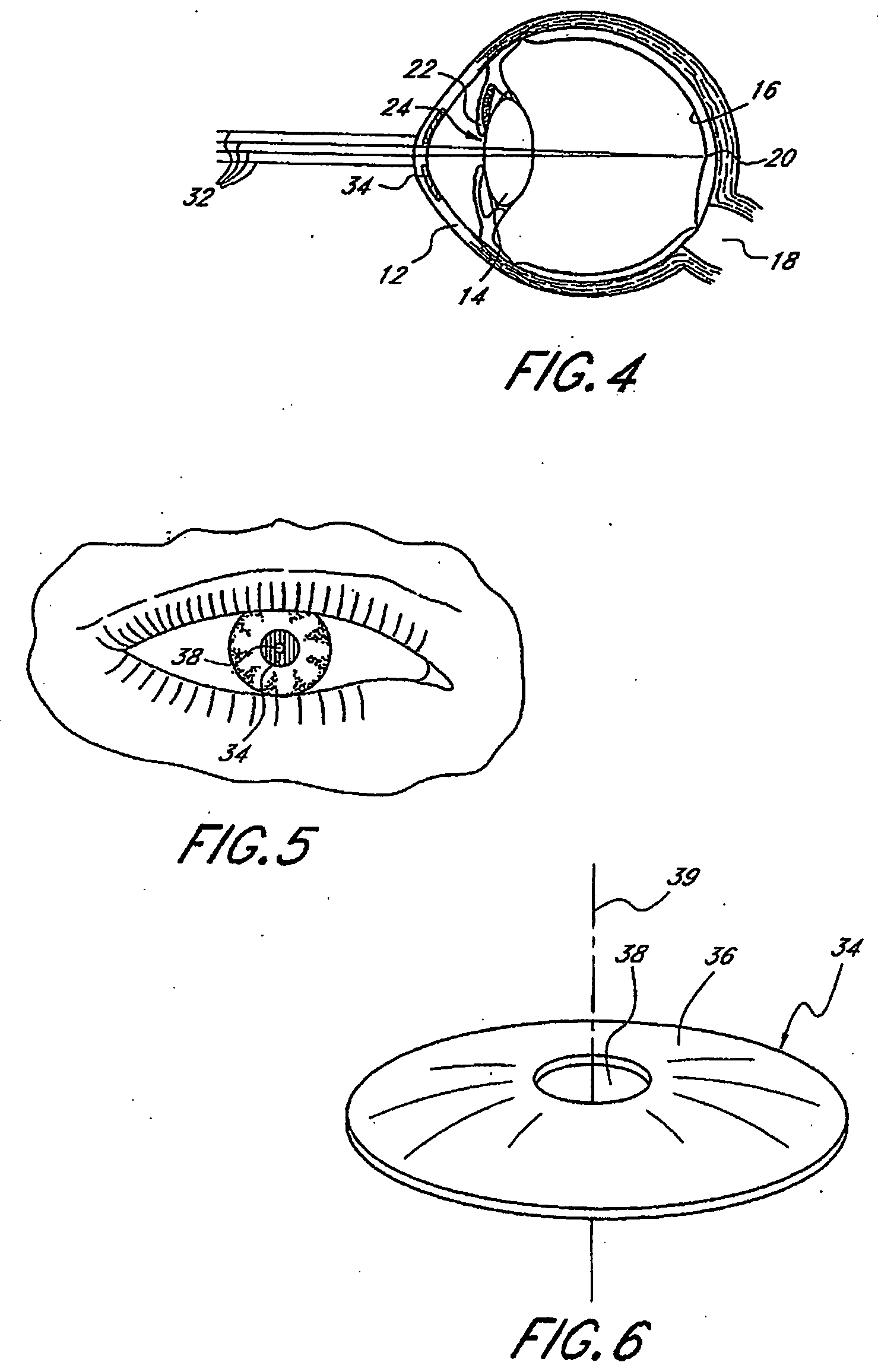
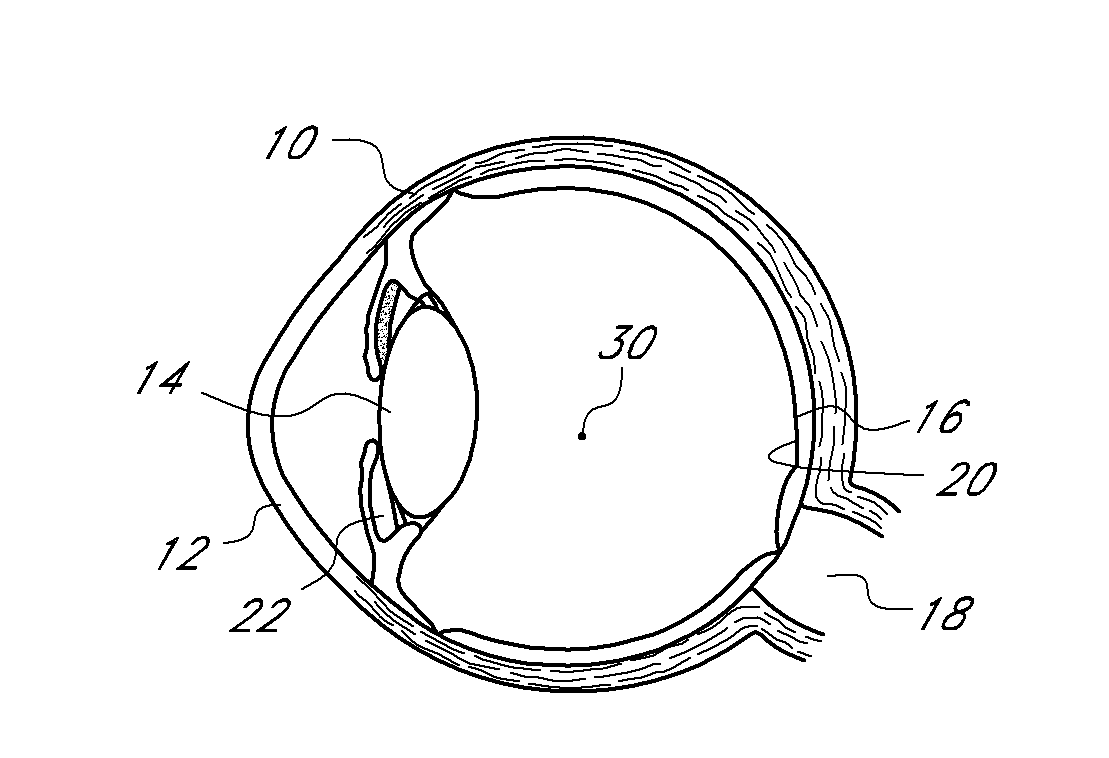
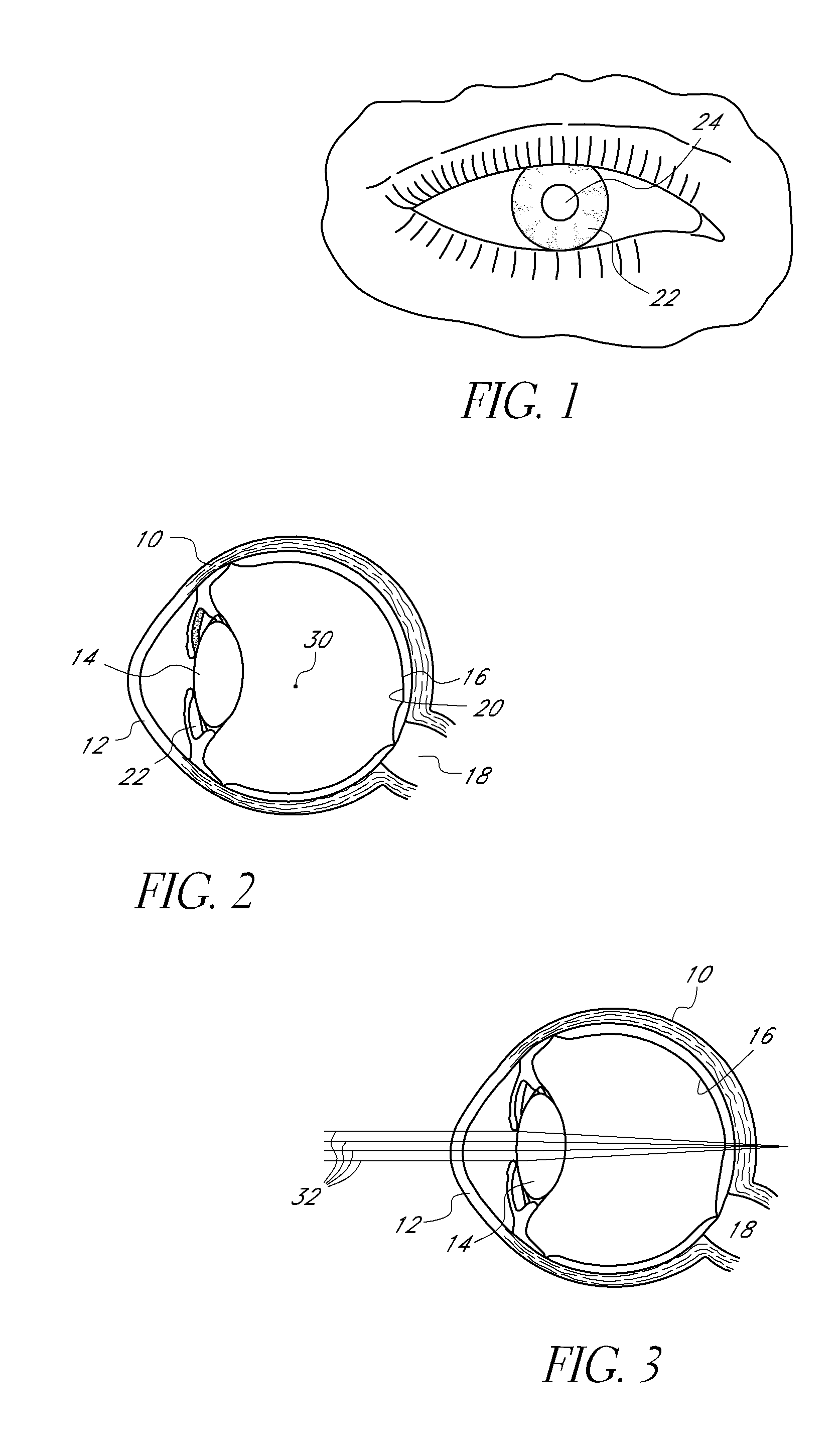
High performance corneal inlay
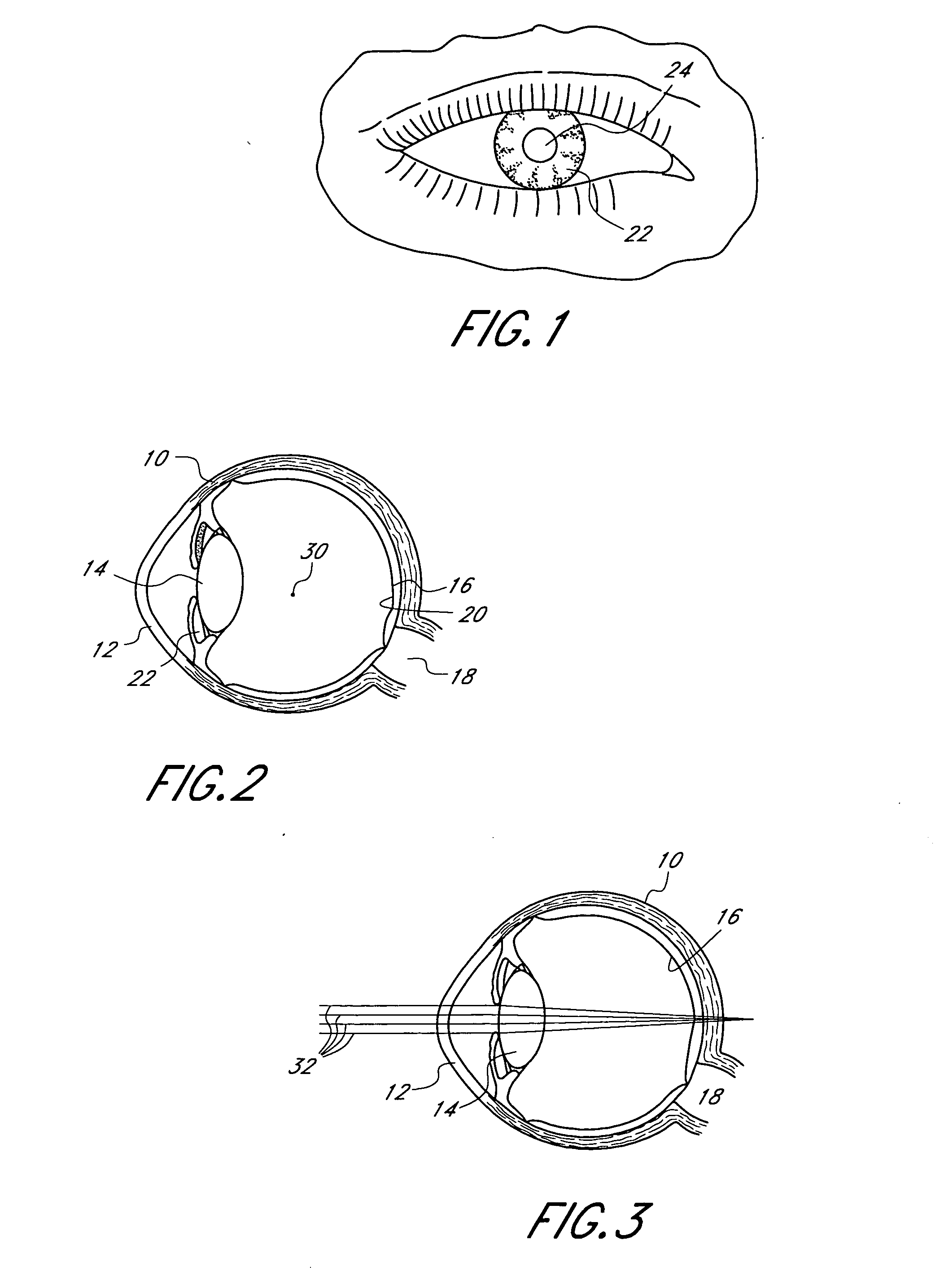
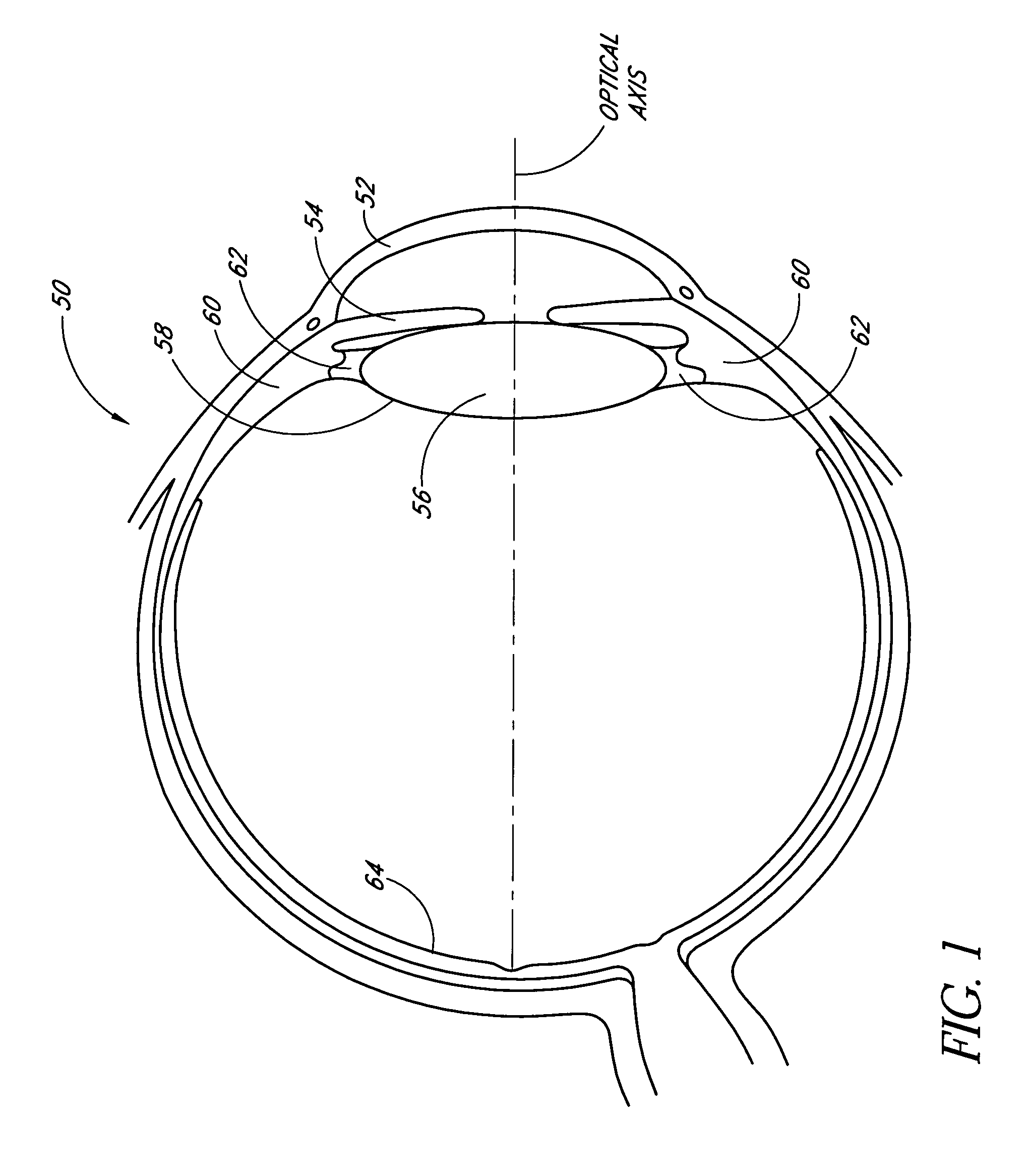
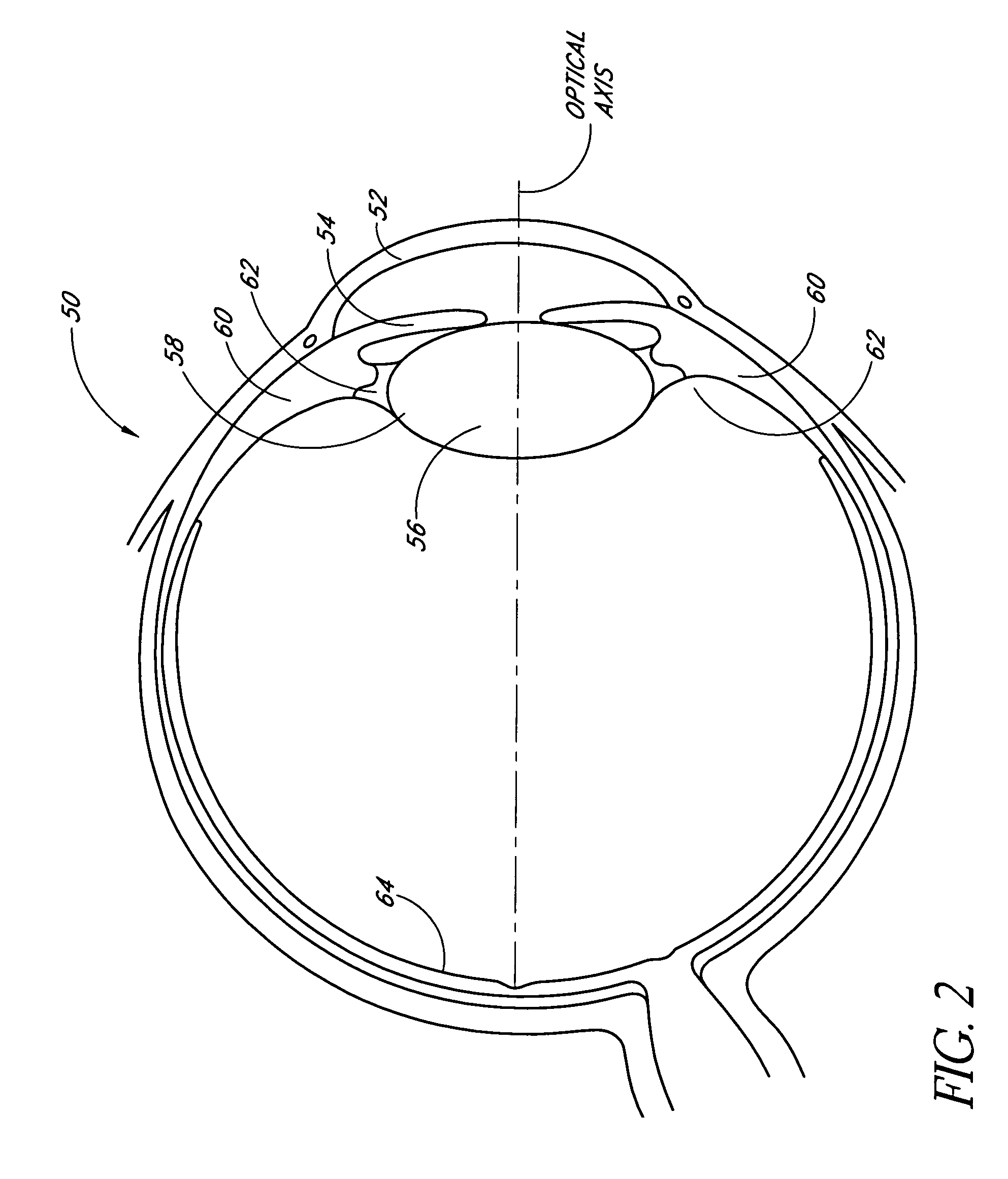
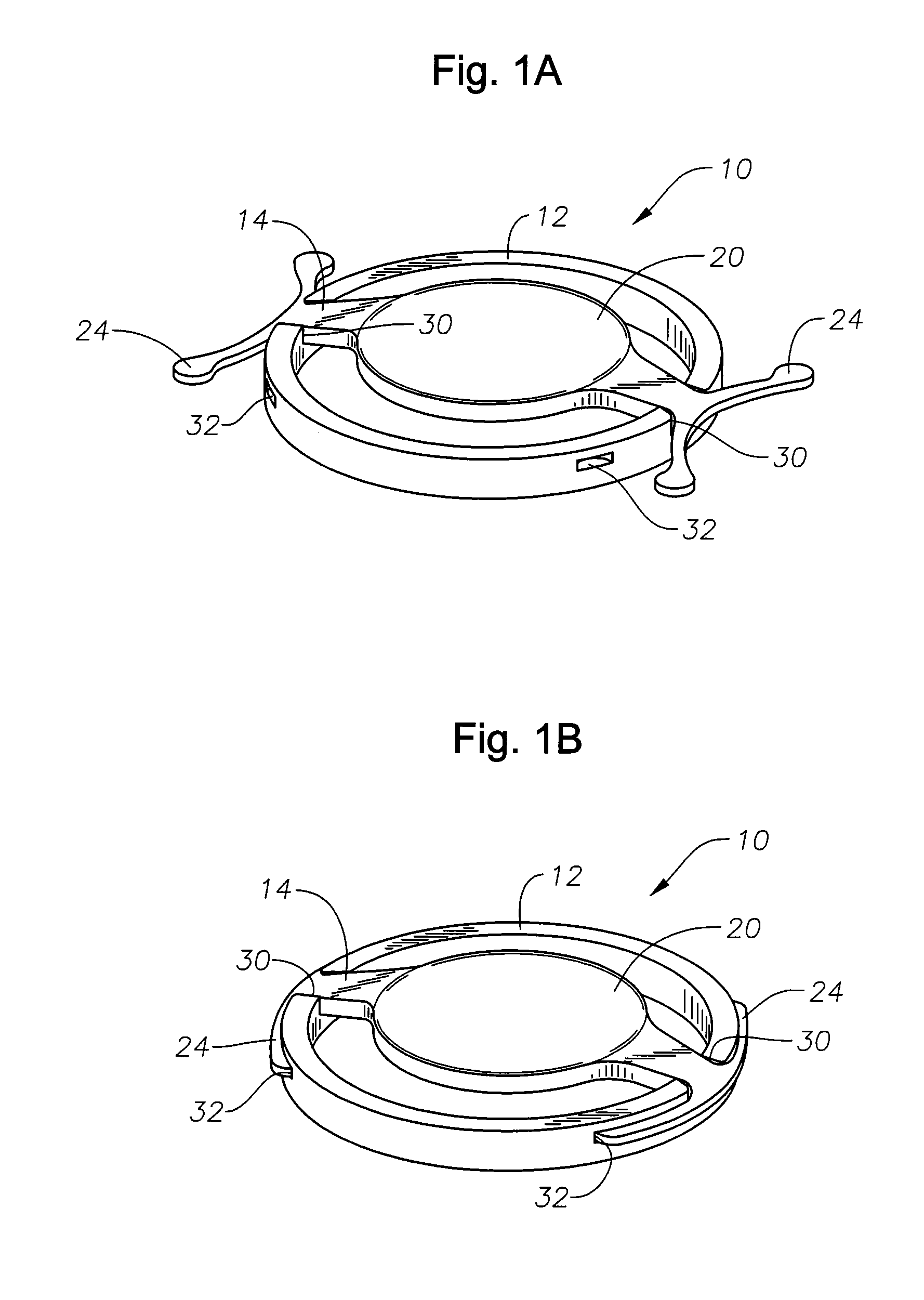
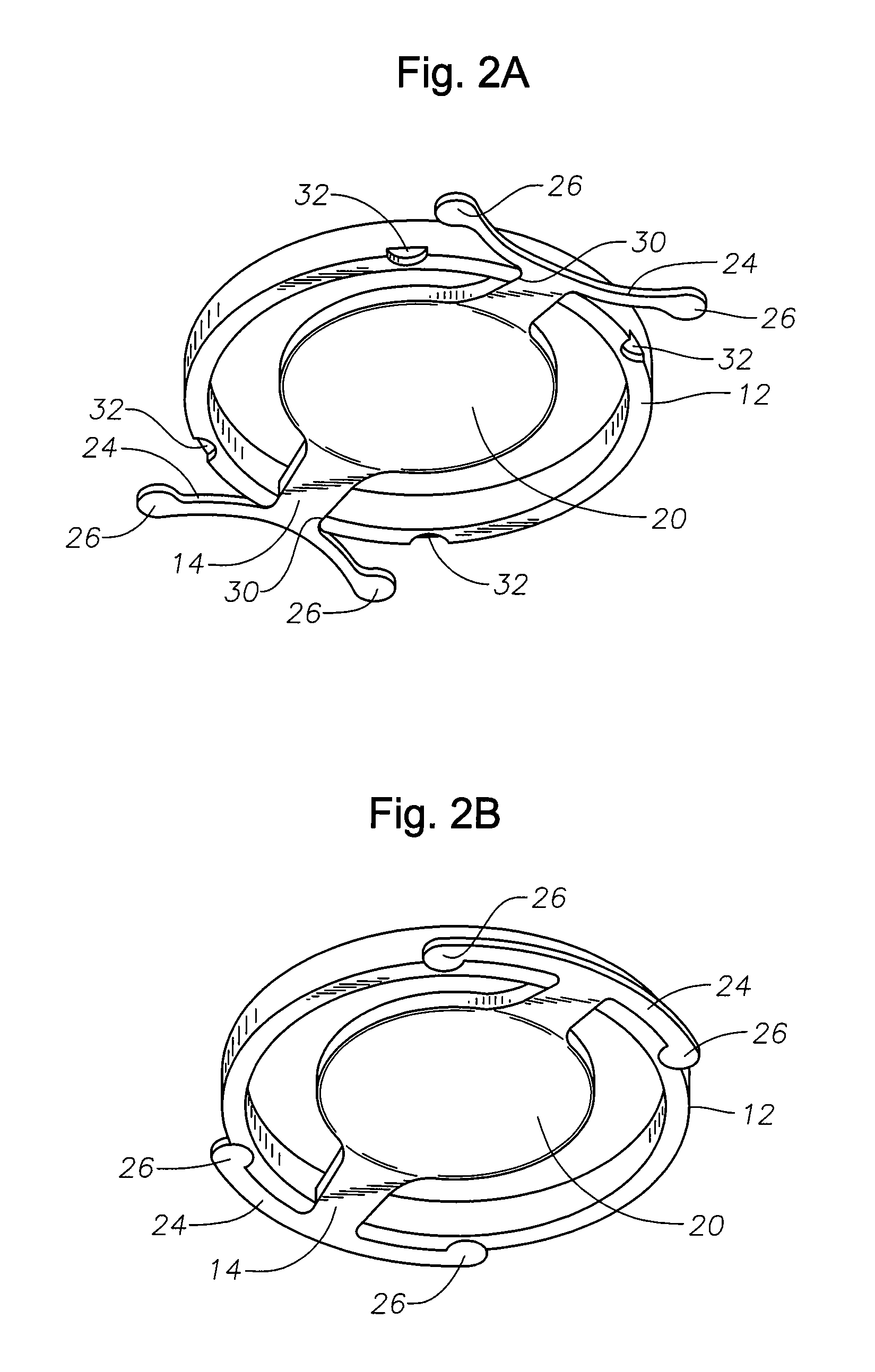
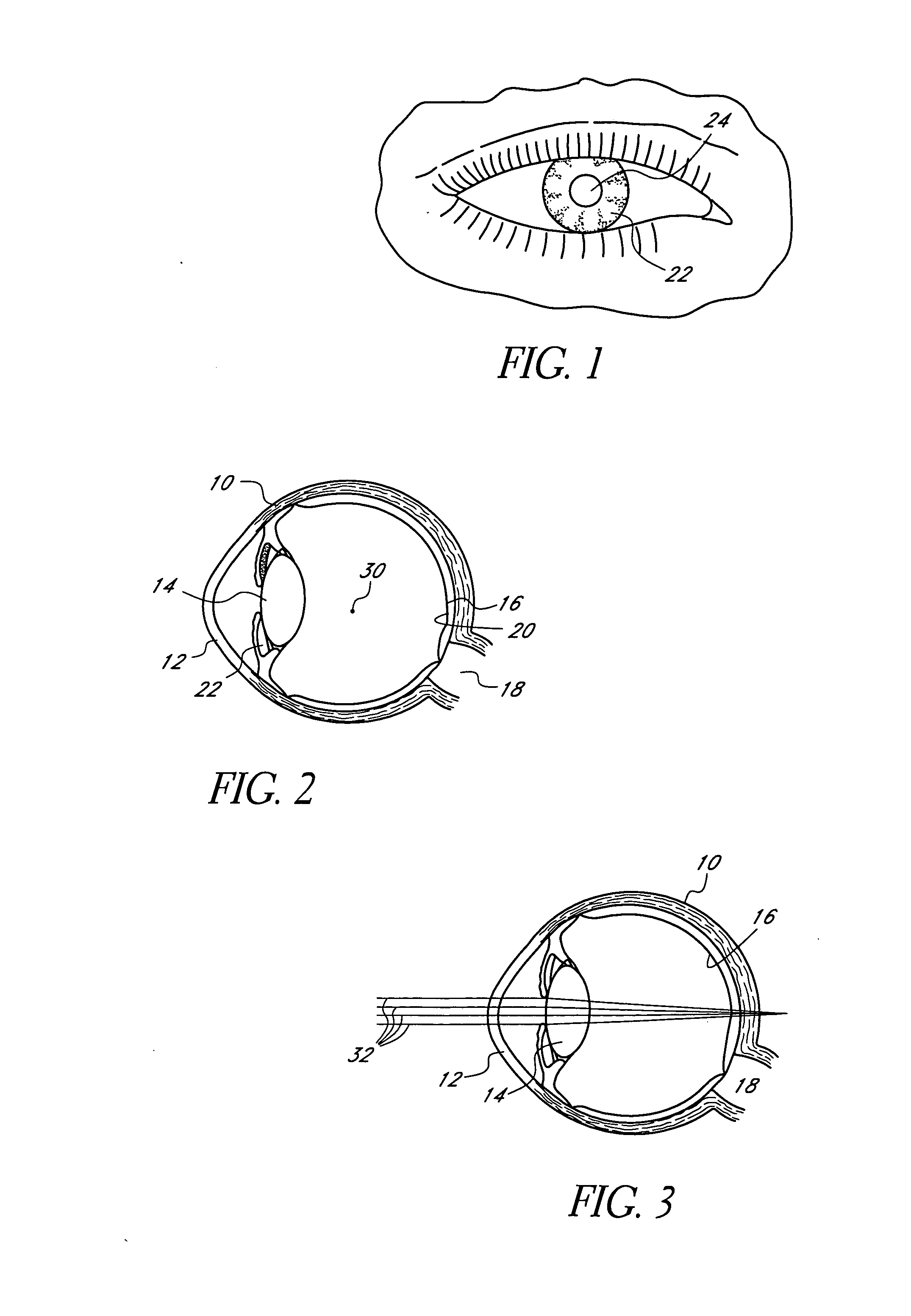
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
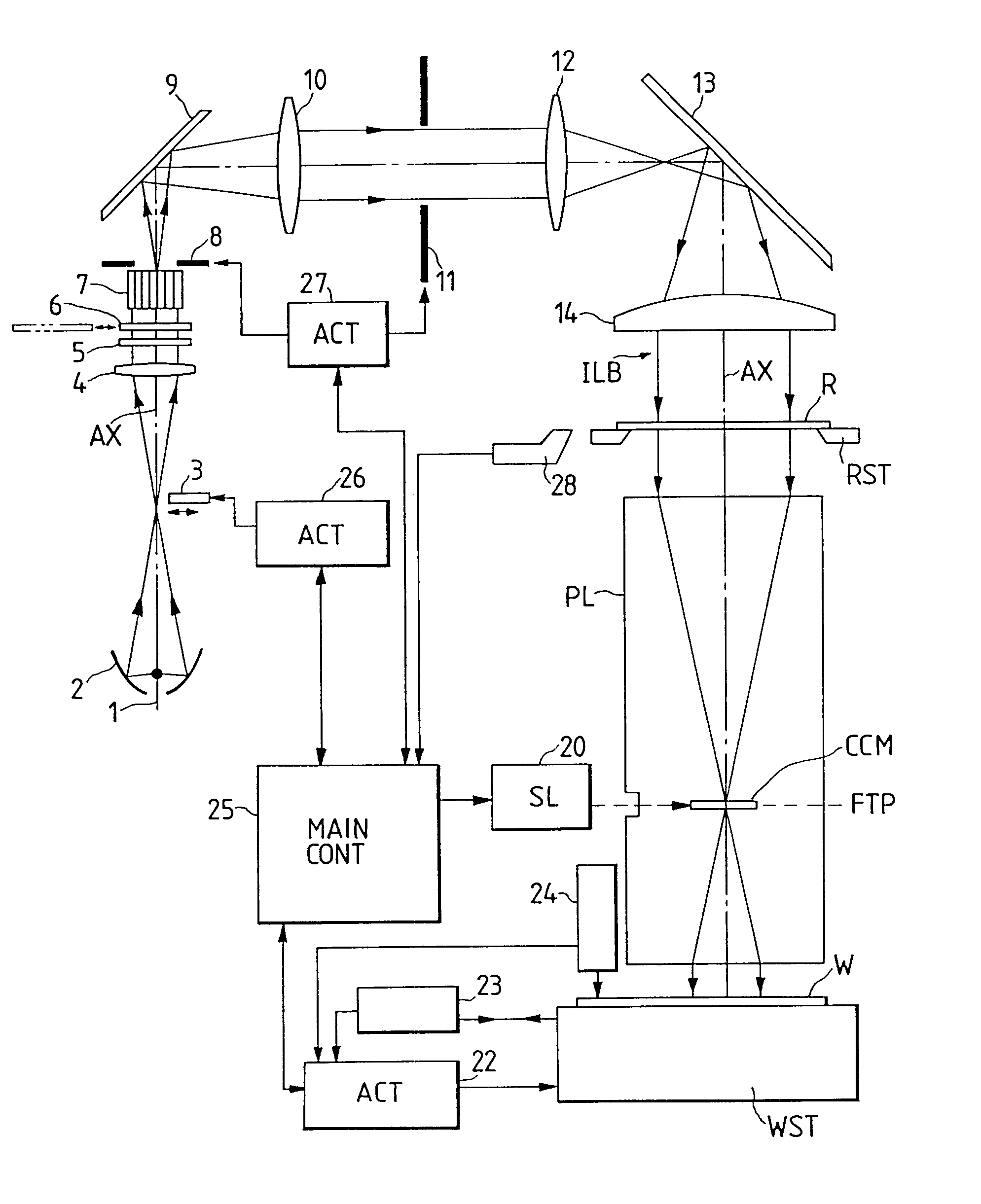
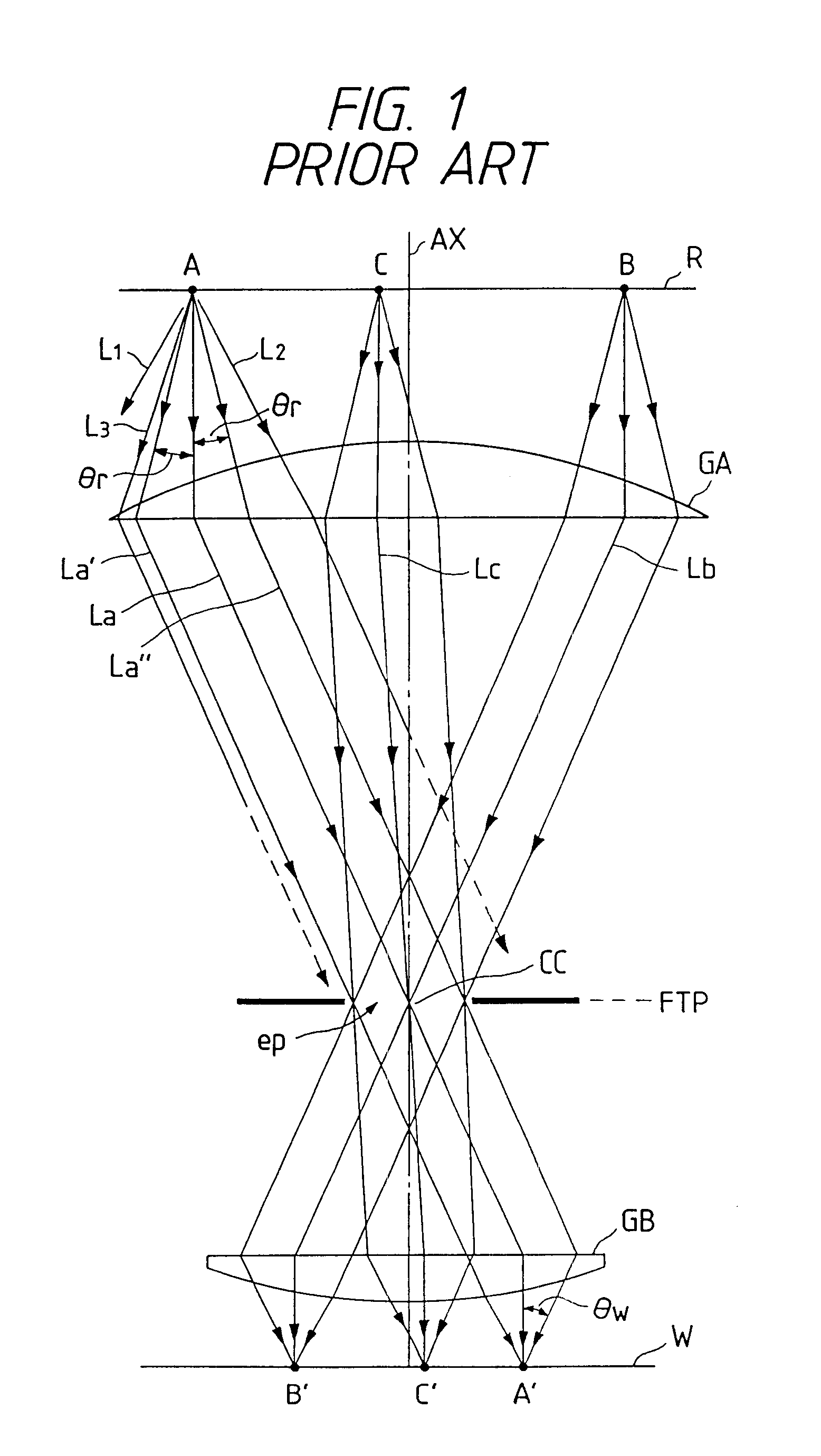
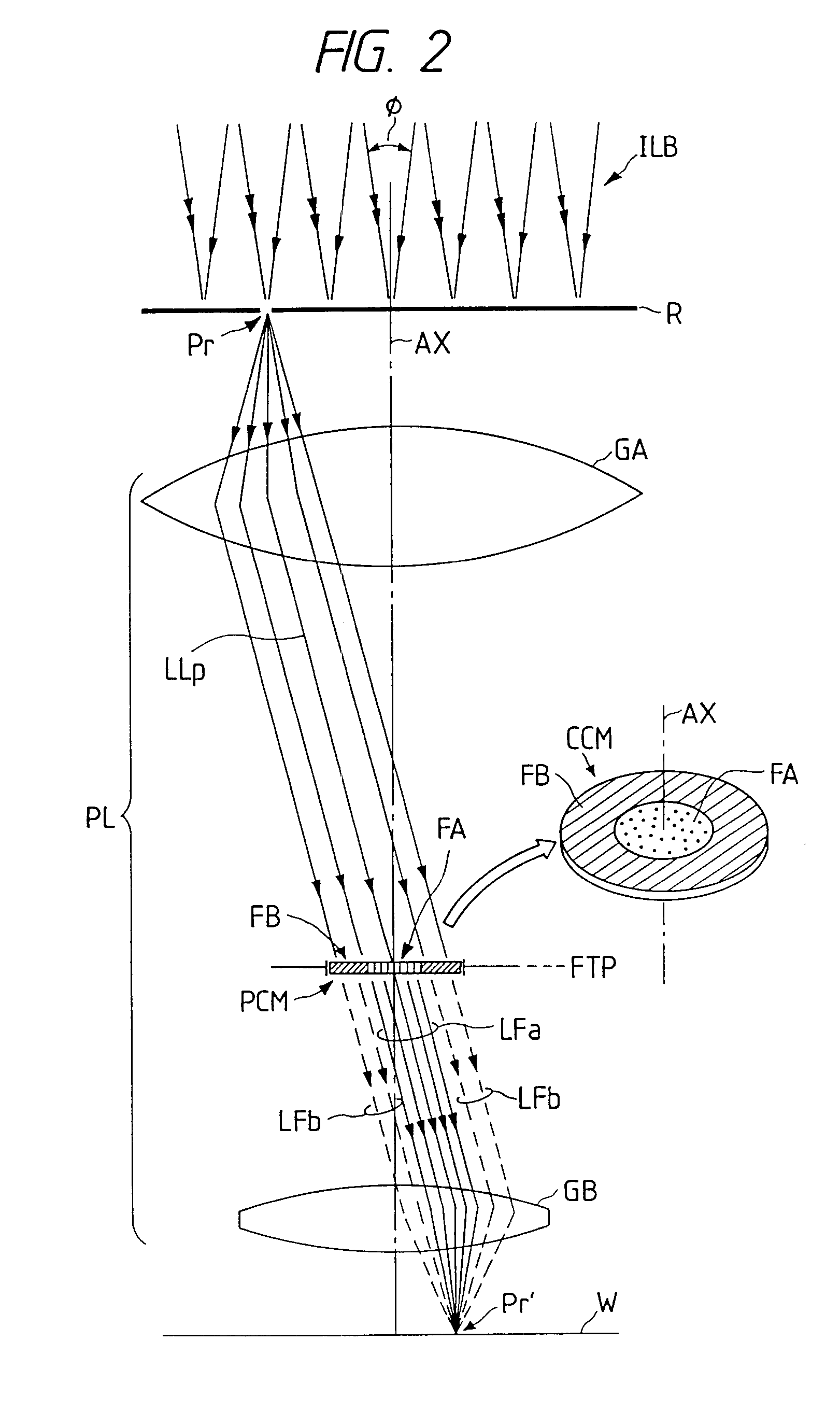
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6404482B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
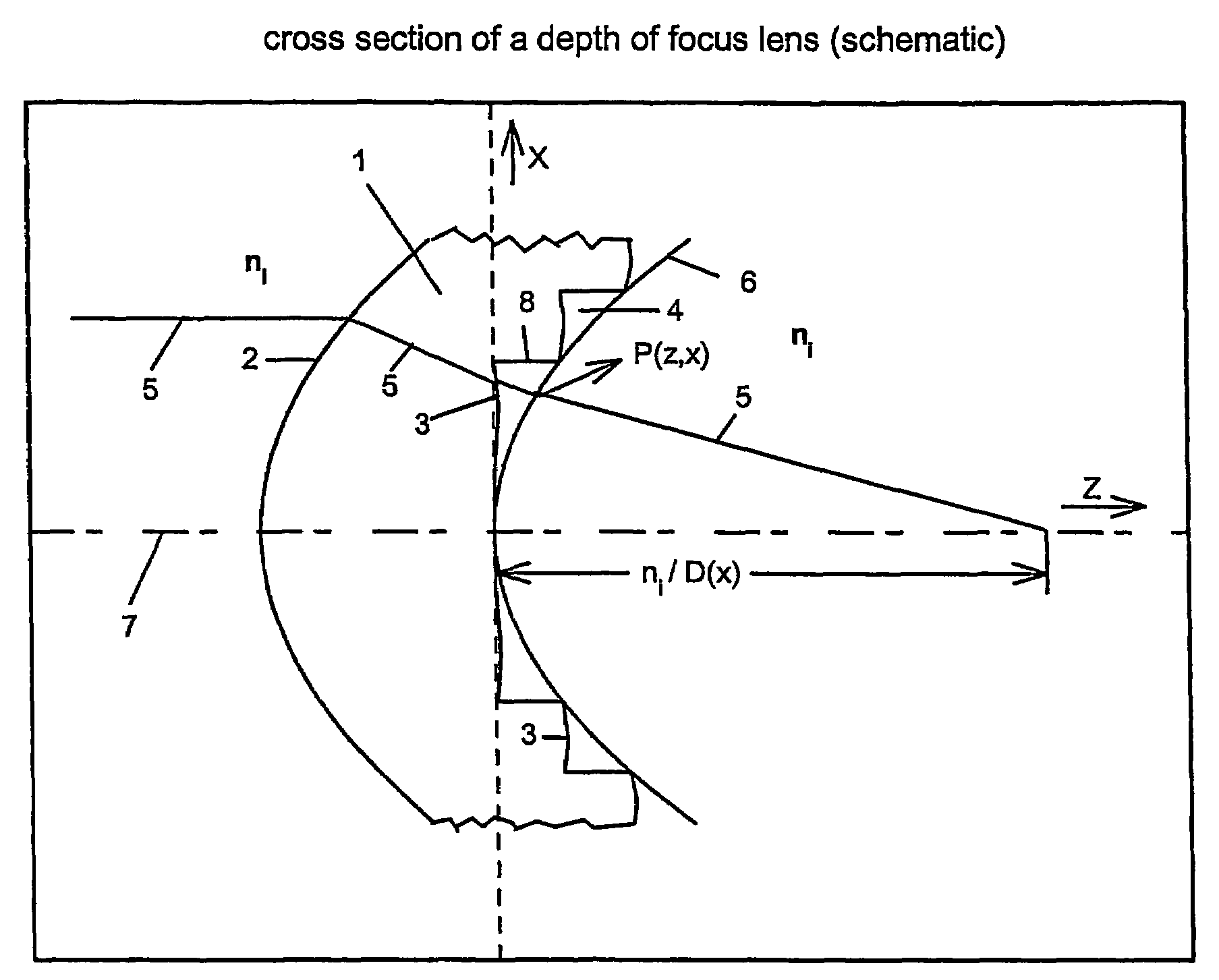
Intra-ocular lens or contact lens exhibiting large depth of focus
ActiveUS7287852B2Increase depth of focusLarge depth of fieldIntraocular lensOptical partsIntra ocular lensContact lens
Owner:FIALA WERNER J
Materials and methods for simulating focal shifts in viewers using large depth of focus displays
InactiveUS7428001B2Improve interactivityEnhances perceived realismTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceDepth of focus
A large depth of focus (DOF) display provides an image in which the apparent focus plane is adjusted to track an accommodation (focus) of a viewer's eye(s) to more effectively convey depth in the image. A device is employed to repeatedly determine accommodation as a viewer's gaze within the image changes. In response, an image that includes an apparent focus plane corresponding to the level of accommodation of the viewer is provided on the large DOF display. Objects that are not at the apparent focus plane are made to appear blurred. The images can be rendered in real-time, or can be pre-rendered and stored in an array. The dimensions of the array can each correspond to a different variable. The images can alternatively be provided by a computer controlled, adjustable focus video camera in real-time.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Accommodating intraocular lens system with aberration-enhanced performance
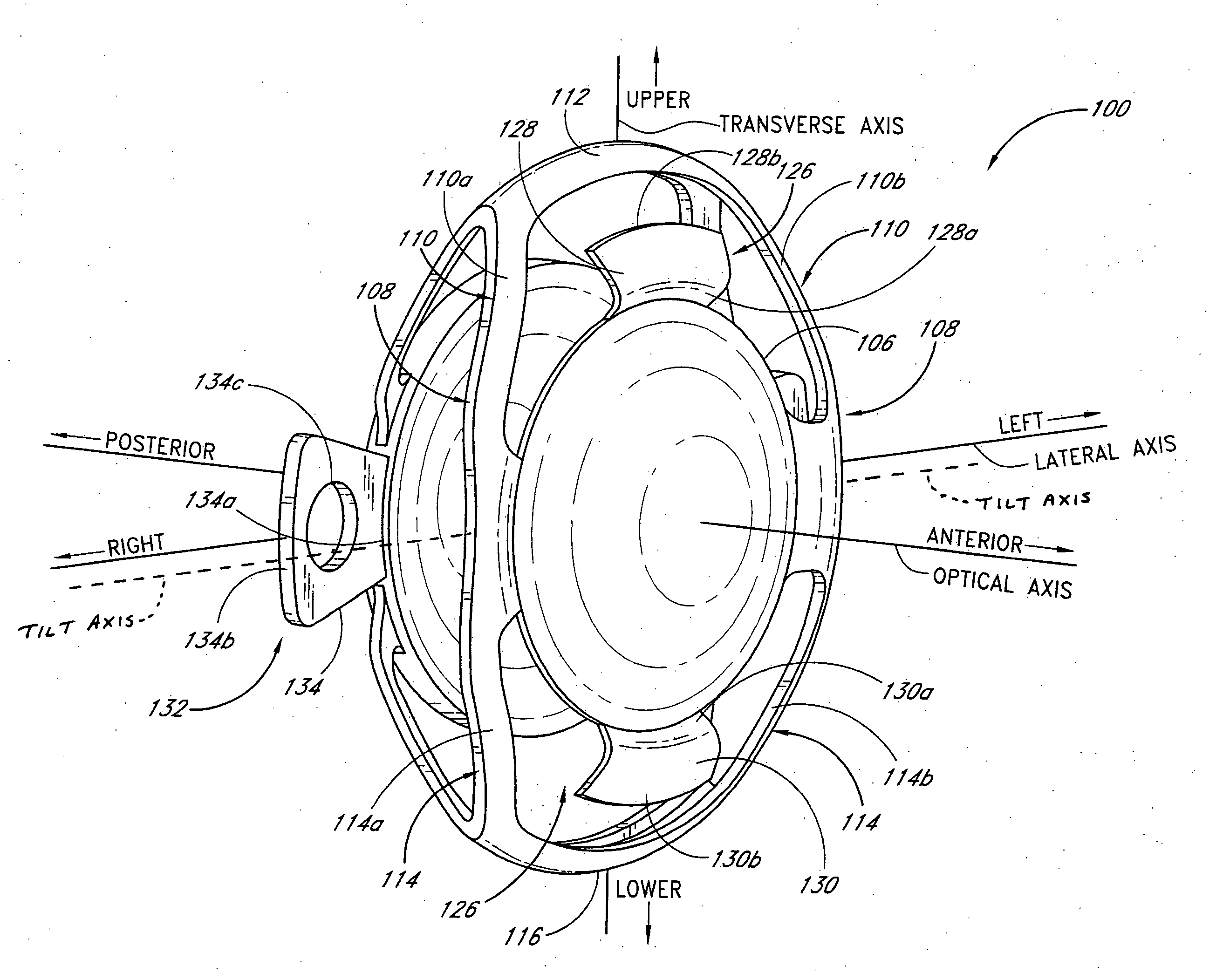
An accommodating intraocular lens implantable in an eye. The lens comprises an anterior portion having an anterior biasing element and an anterior optic having refractive power. The lens further comprises a posterior portion having a posterior biasing element and a posterior optic having refractive power. The anterior optic and the posterior optic are relatively moveable in response to action of the ciliary muscle to change the separation between the optics and the refractive power of the lens. The lens has an aberration-inducing force characteristic of about 70 mg to about 115 mg to allow aberration-inducing relative movement of the optics when the lens is in the eye, thereby adding optical aberration to the lens which increases depth of focus of the lens. In one variation, the lens has an aberration-inducing force characteristic of 70 mg to 115 mg. Related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VISIOGEN
Masked intraocular implants and lenses
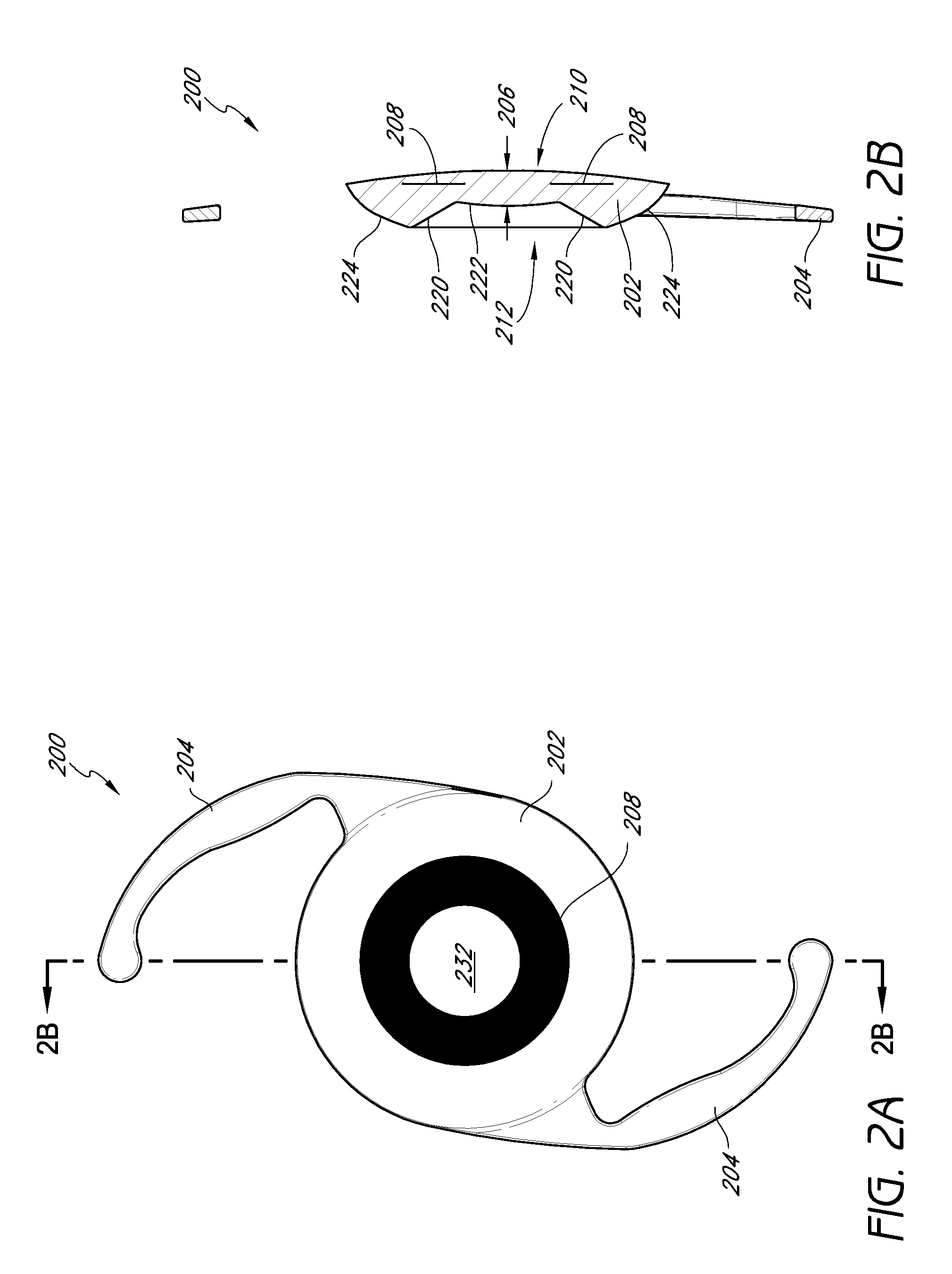
ActiveUS20110040376A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusOptical articlesIntraocular lensMedicineOptical power
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implants can improve the vision of a patient, such as by increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. In particular, the intraocular implants can include a mask having an annular portion with a relatively low visible light transmission surrounding a relatively high transmission central portion such as a clear lens or aperture. This construct is adapted to provide an annular mask with a small aperture for light to pass through to the retina to increase depth of focus. The intraocular implant may have an optical power for refractive correction. The intraocular implant may be implanted in any location along the optical pathway in the eye, e.g., as an implant in the anterior or posterior chamber.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
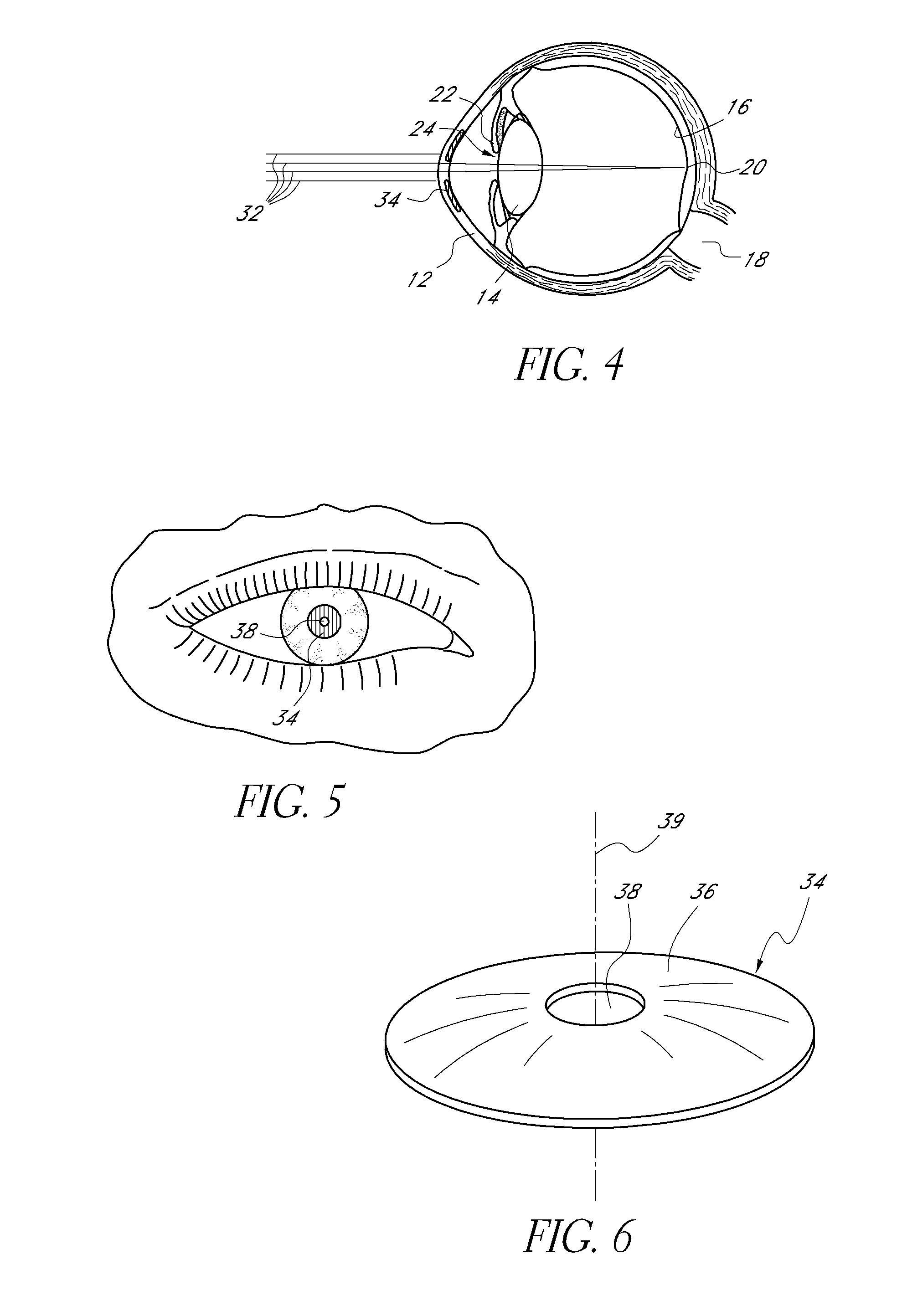
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
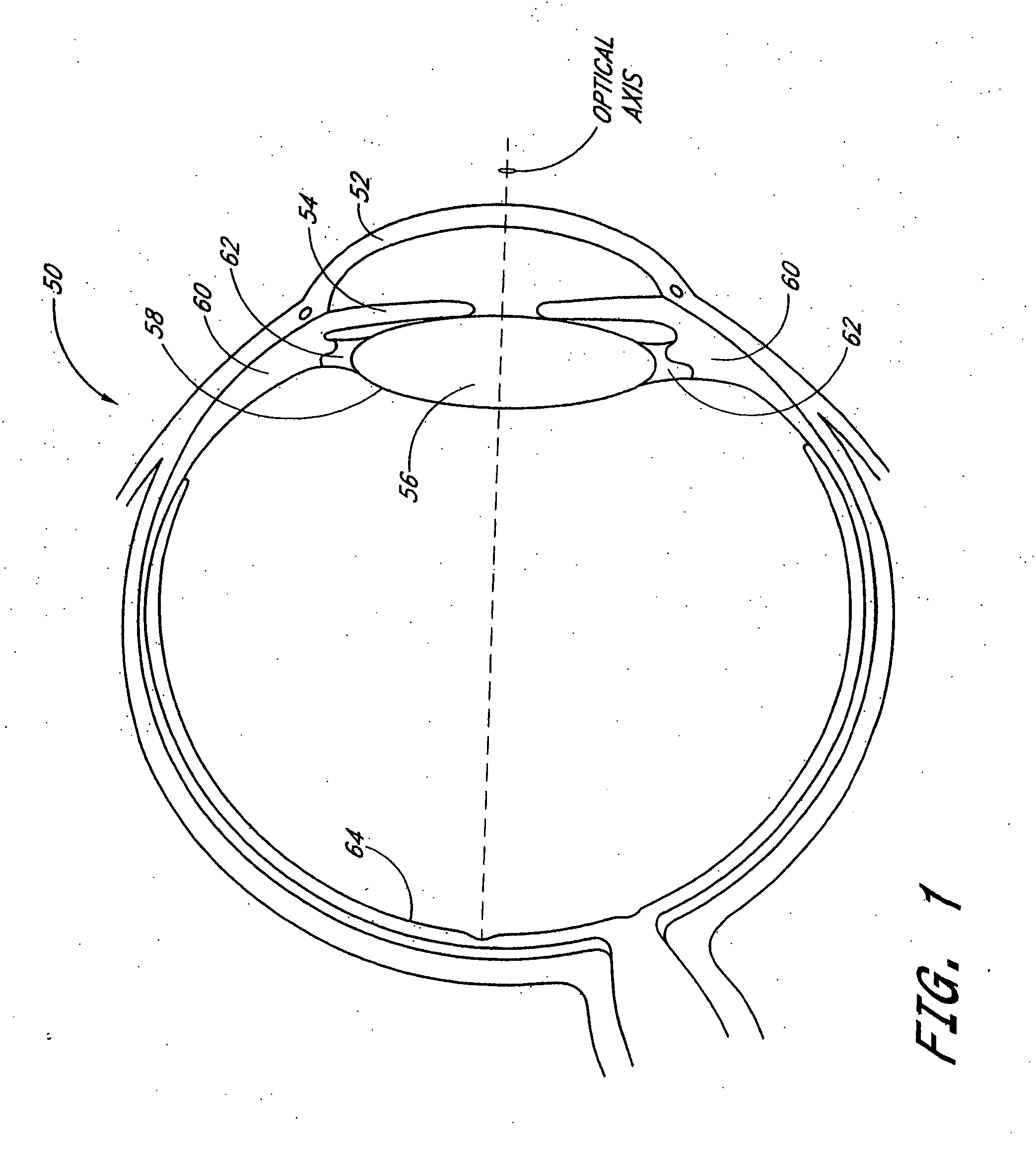
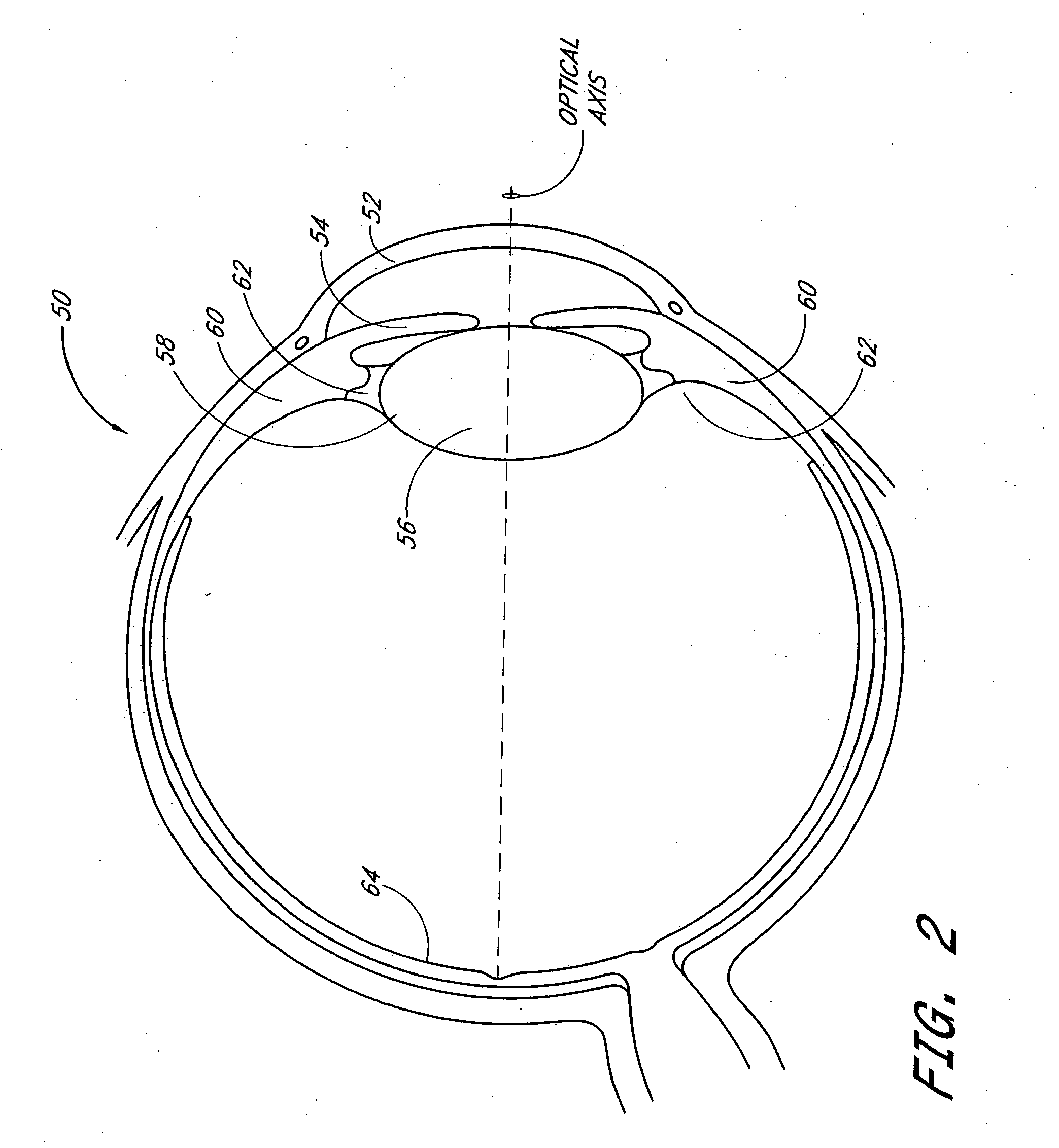
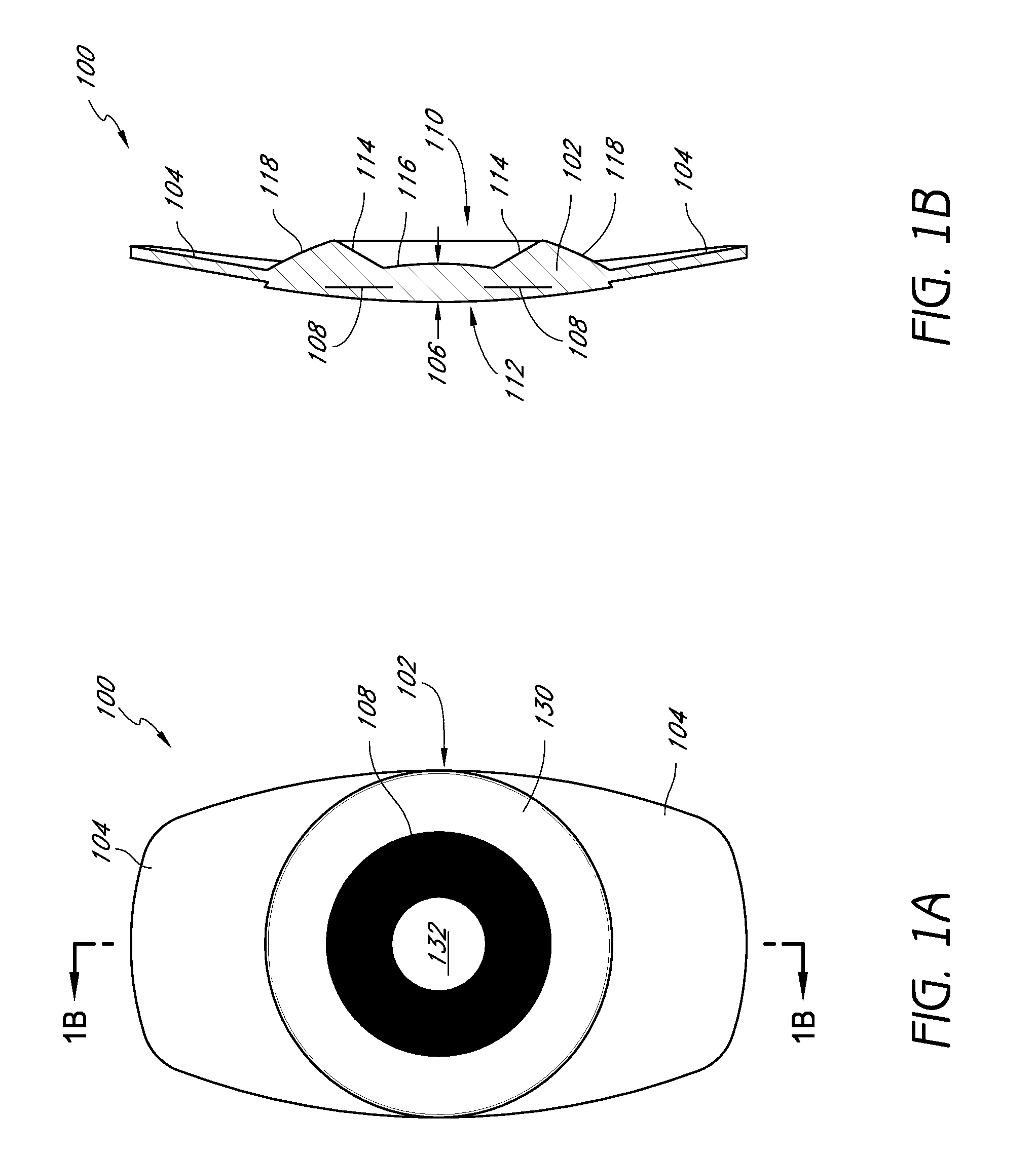
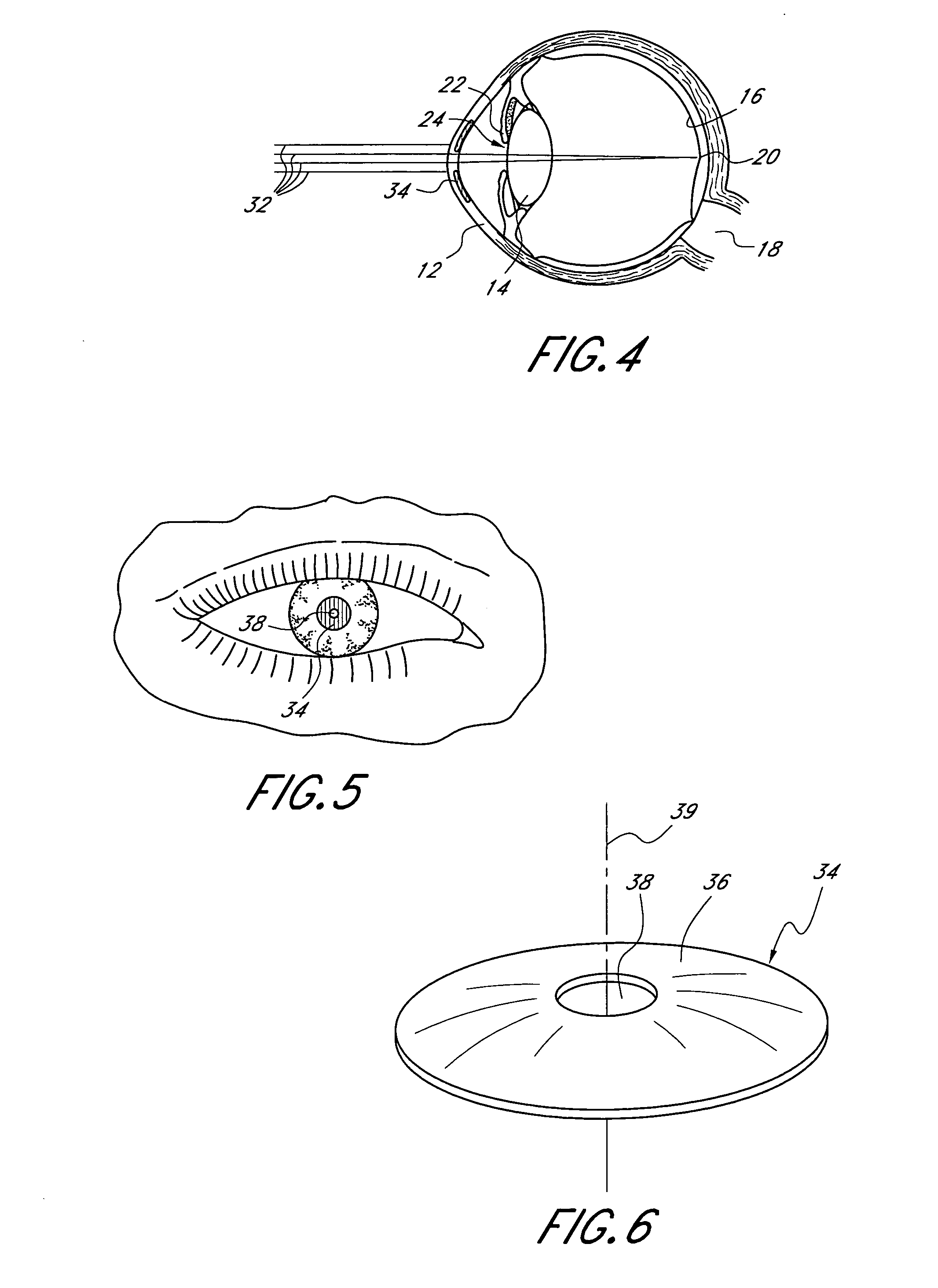
InactiveUS20050033420A1Increase depth of focusEliminate visible diffraction patternSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern from the same
InactiveUS20040110085A1Small line edge roughnessHigh resolutionRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityMethacrylate
There is provided a positive type resin composition comprising (A) a resin component comprising within the principal chain a structural unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester and incorporating an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group on an ester side chain section, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, and (C) an organic solvent, wherein the component (A) comprises both a structural unit derived from a methacrylate ester and a structural unit derived from an acrylate ester. According to such a resist composition, a resist pattern can be formed which displays little surface roughness and line edge roughness on etching, and also offers excellent resolution and a wide depth of focus range.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
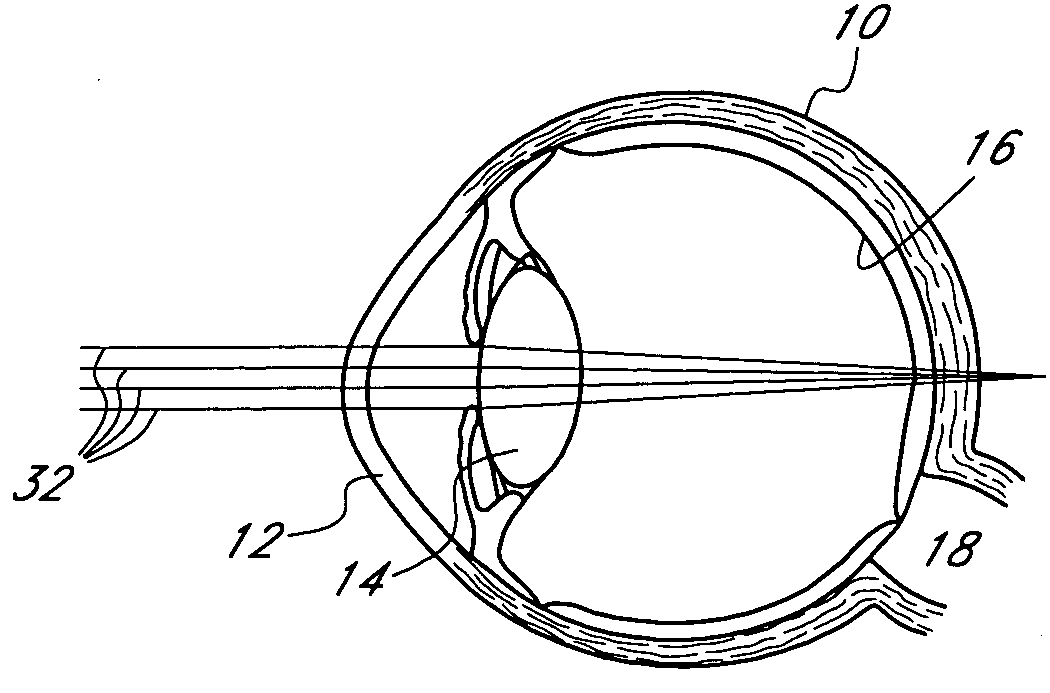
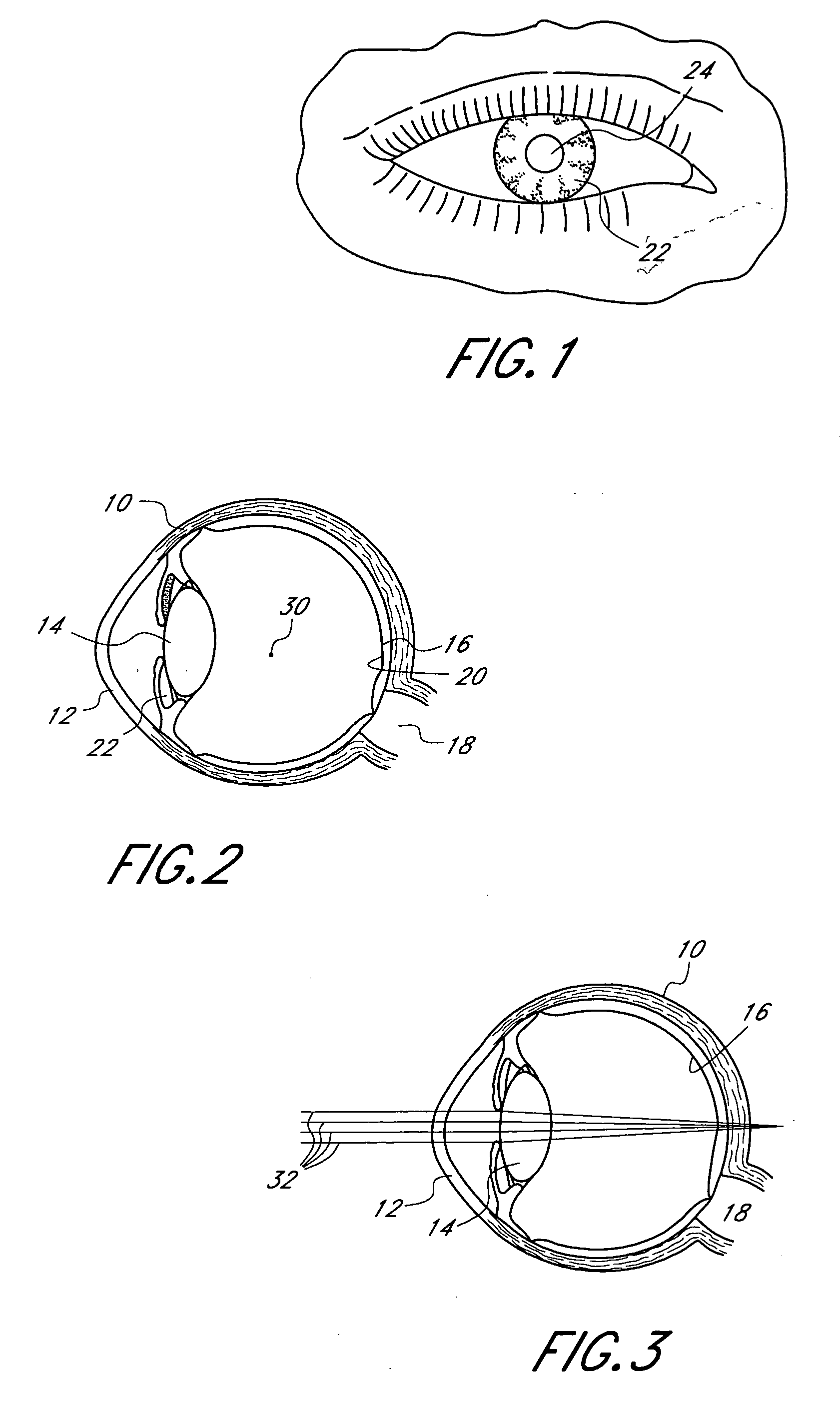
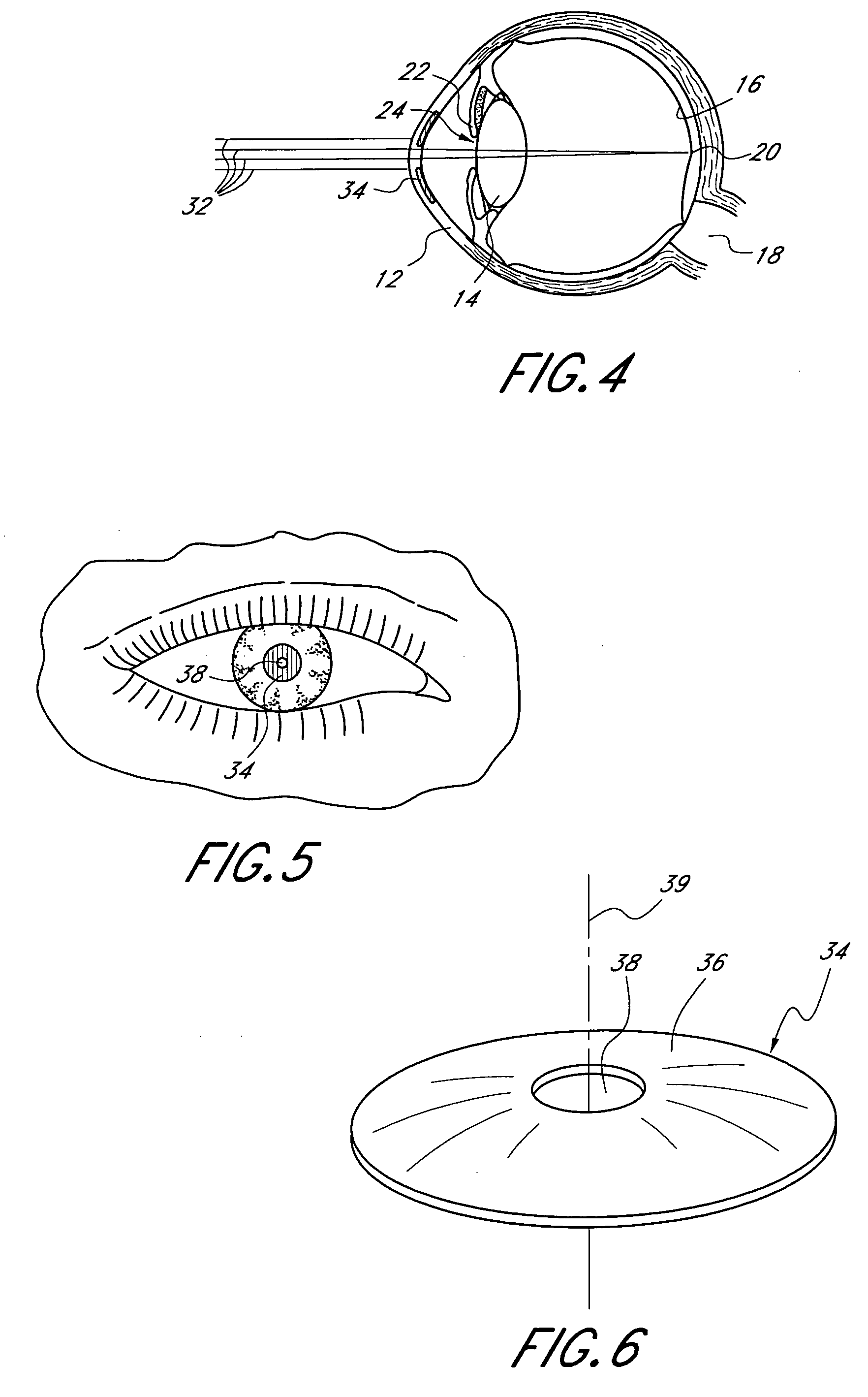
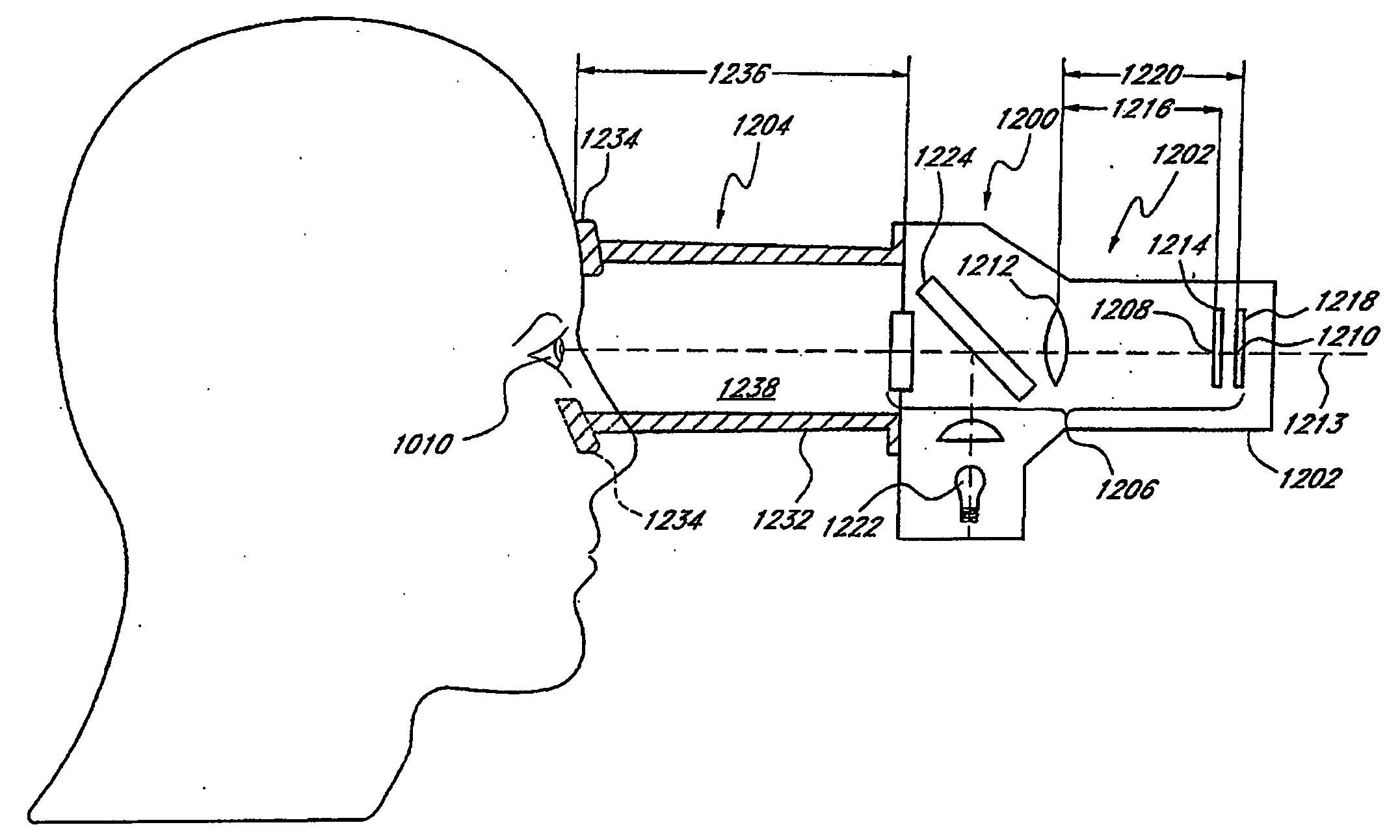
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
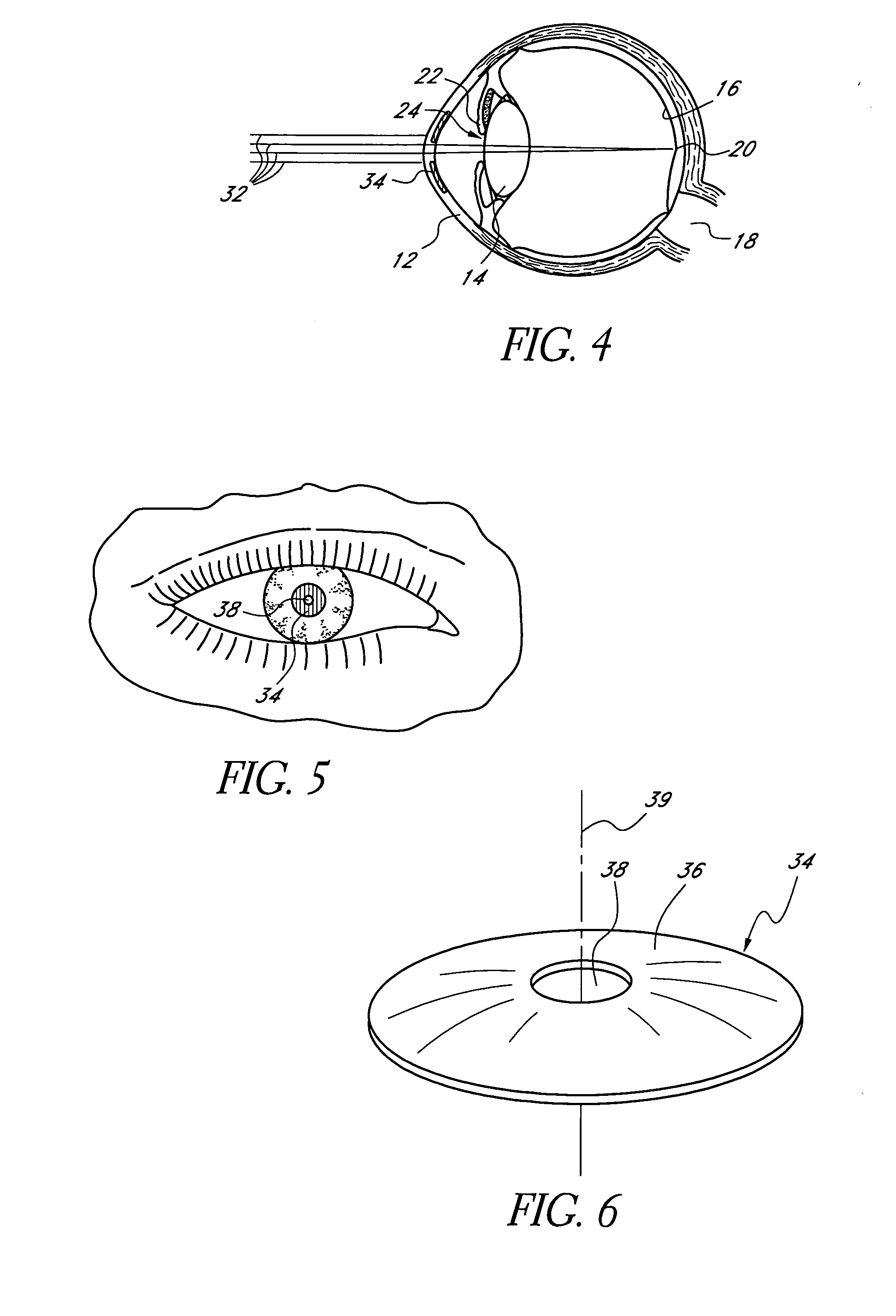
InactiveUS20050046794A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentEye diagnosticsOptometryDepth of focus
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Intra-ocular lens or contact lens exhibiting lardge depth of focus
ActiveUS20060176572A1Easy to manufactureIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensOptical partsIntra ocular lensDepth of focus
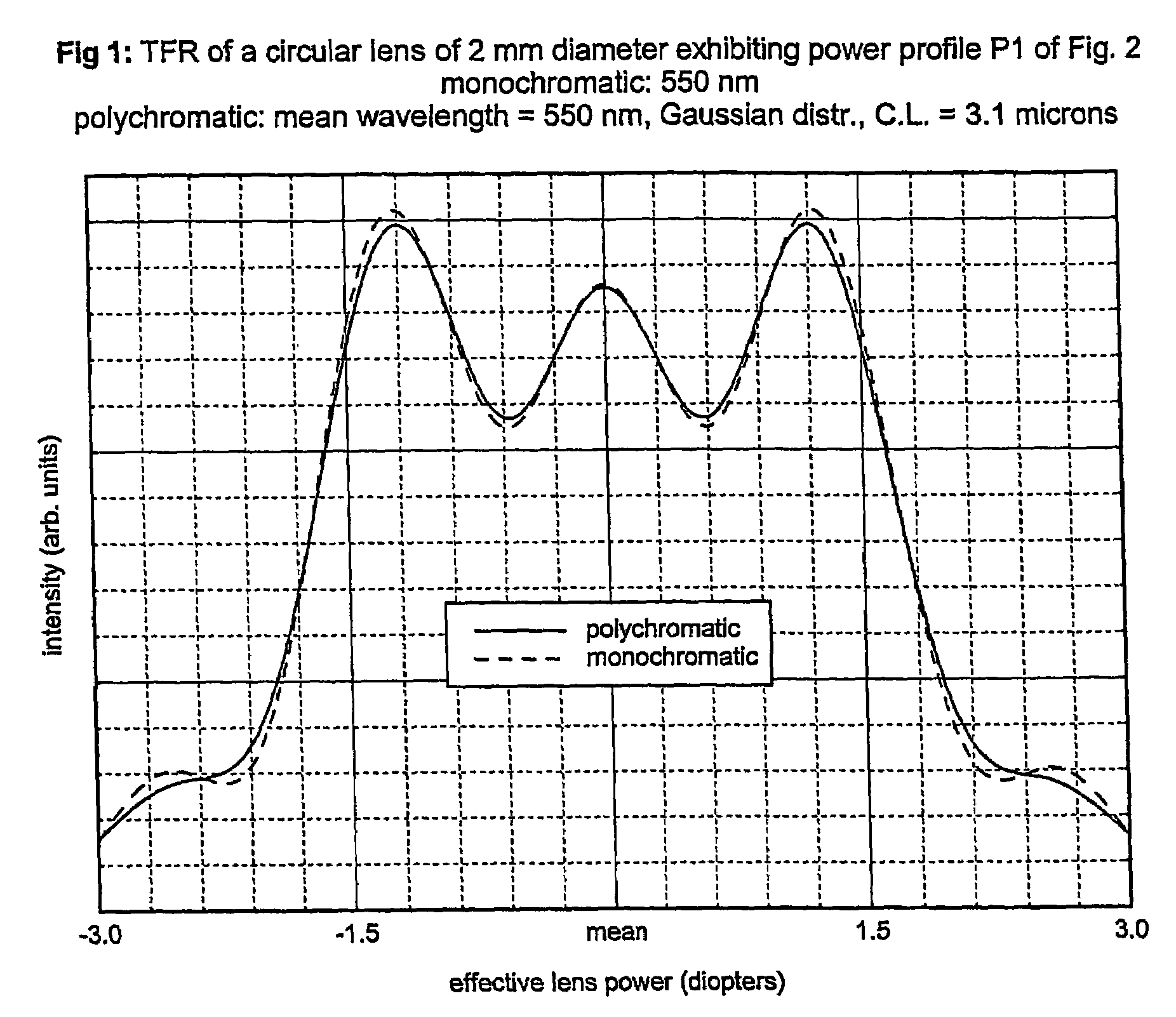
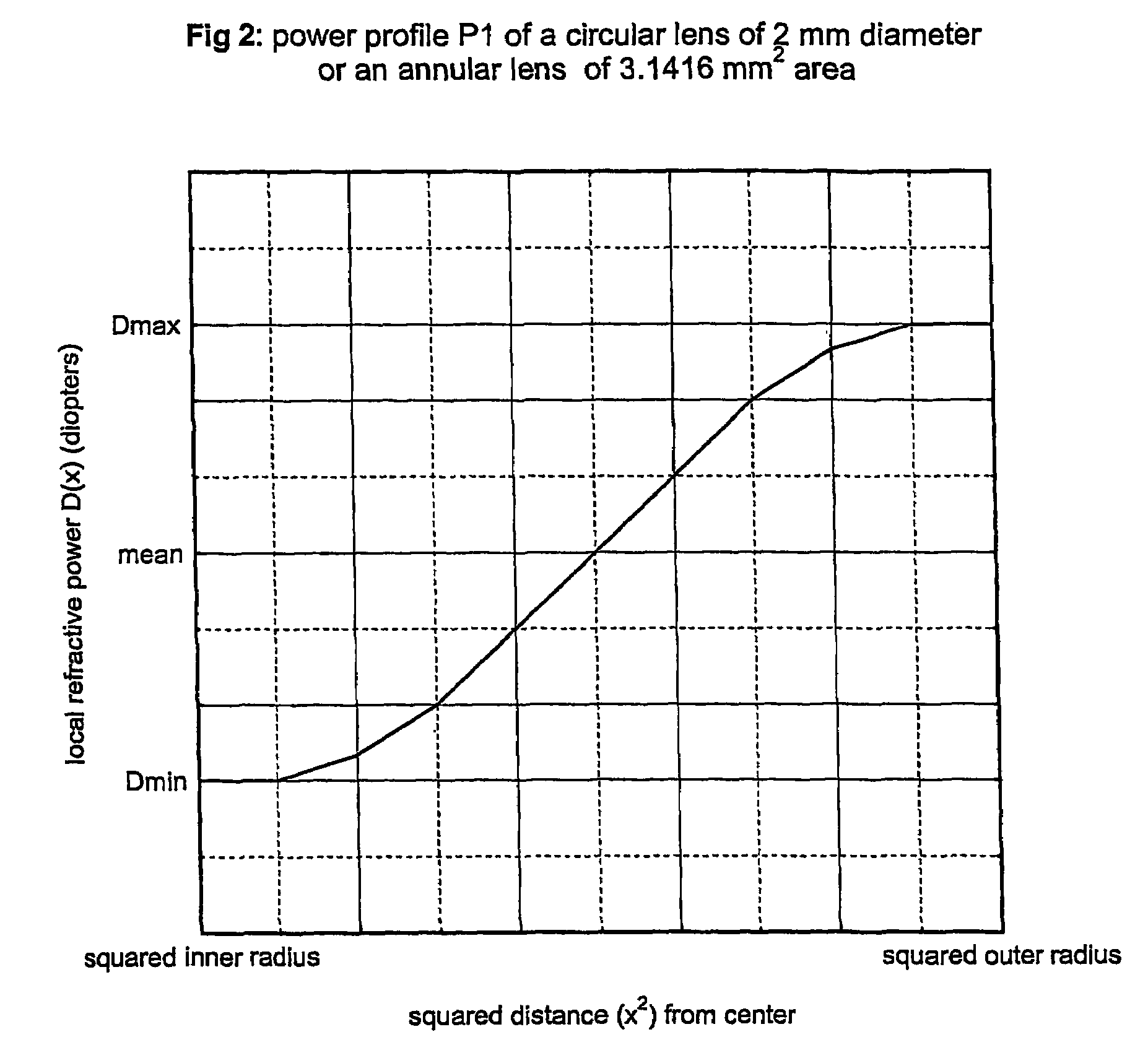
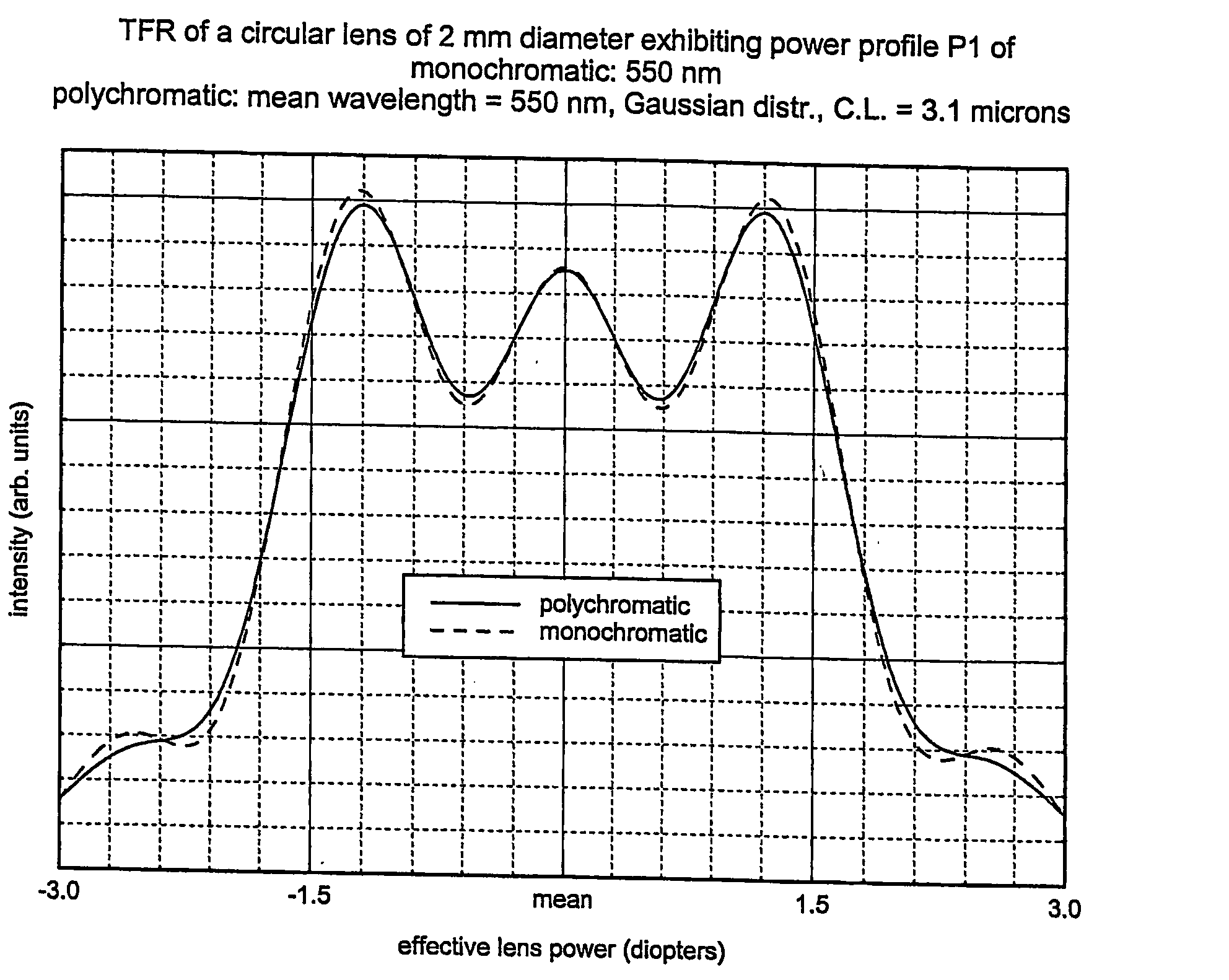
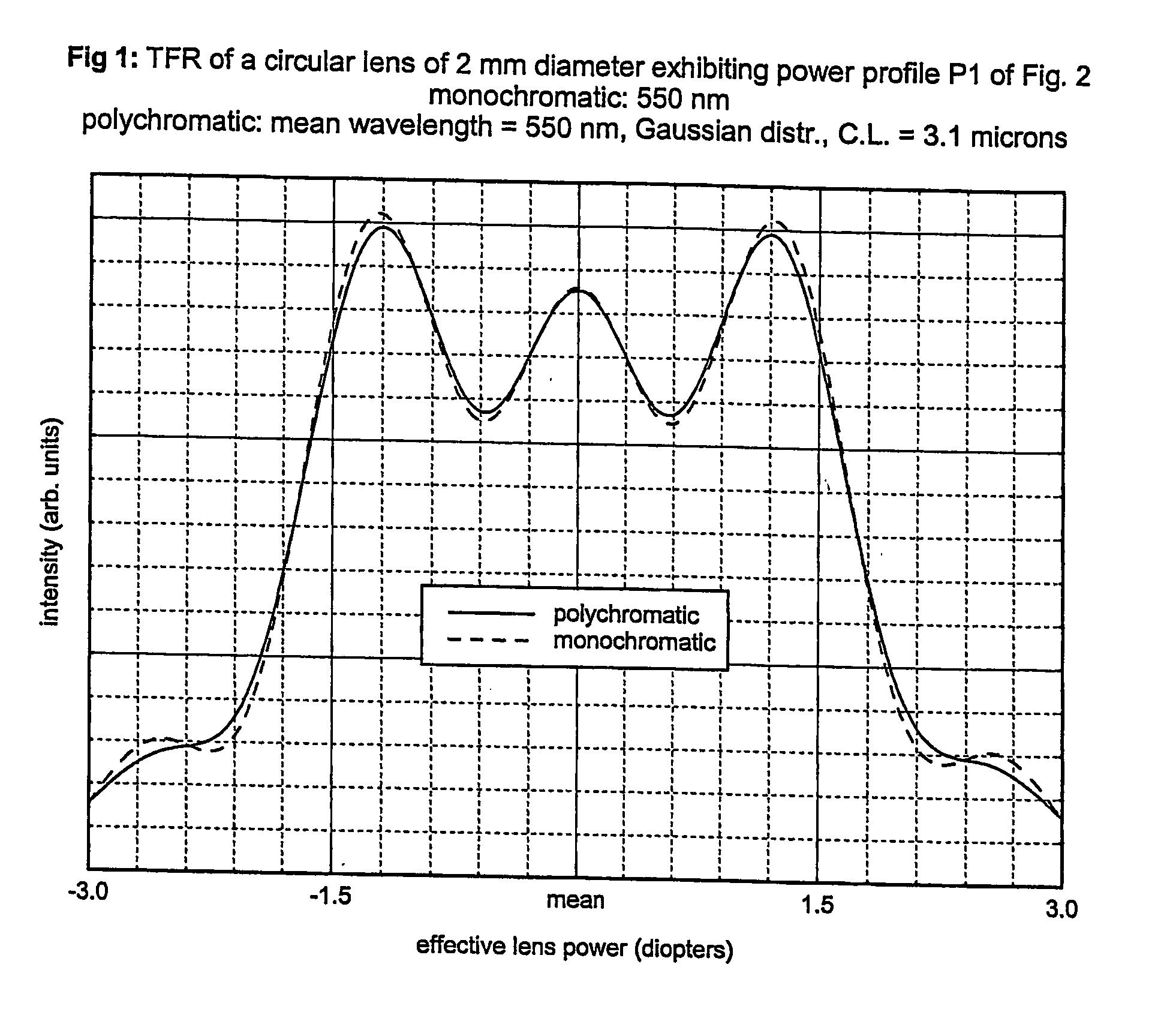
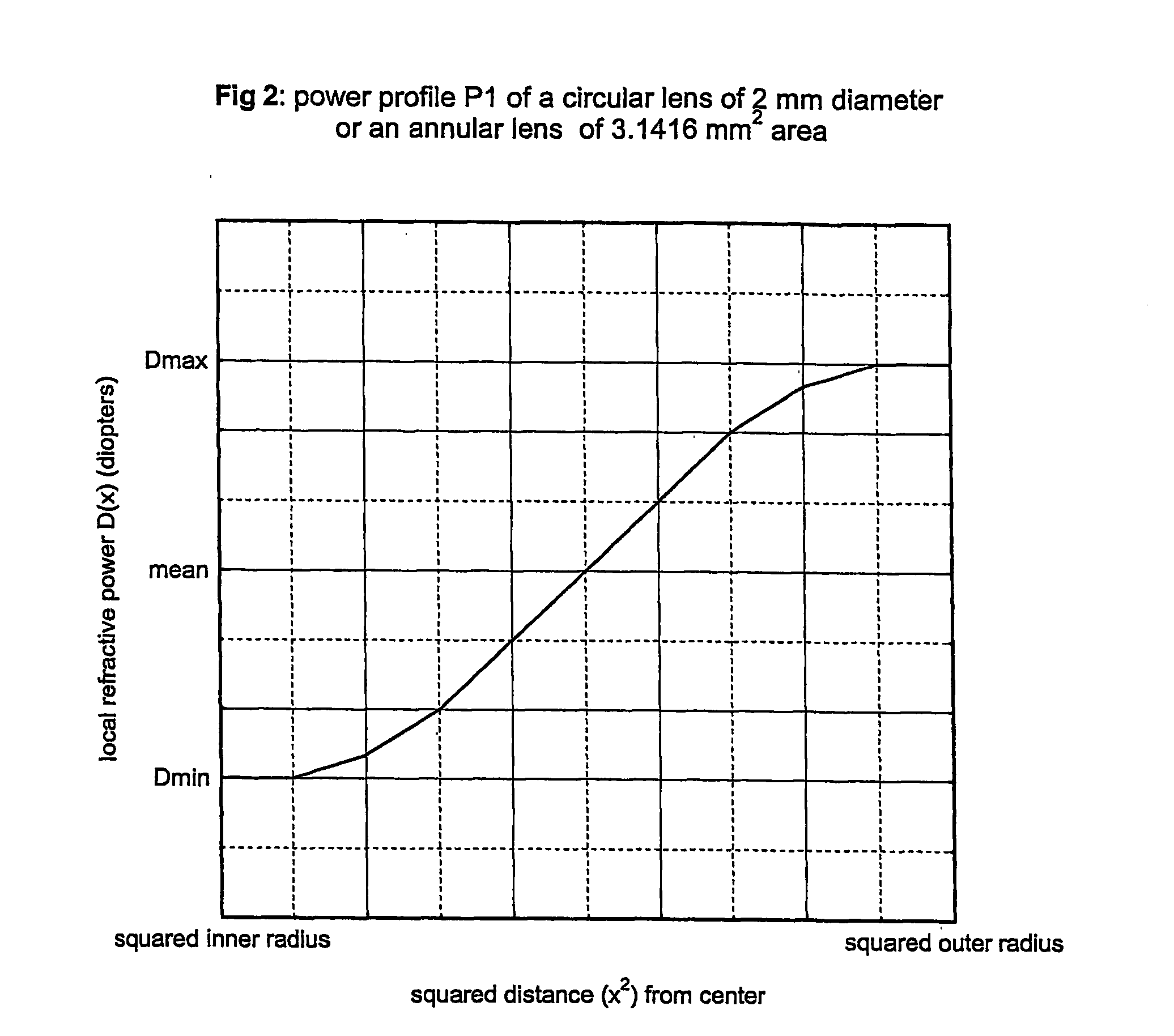
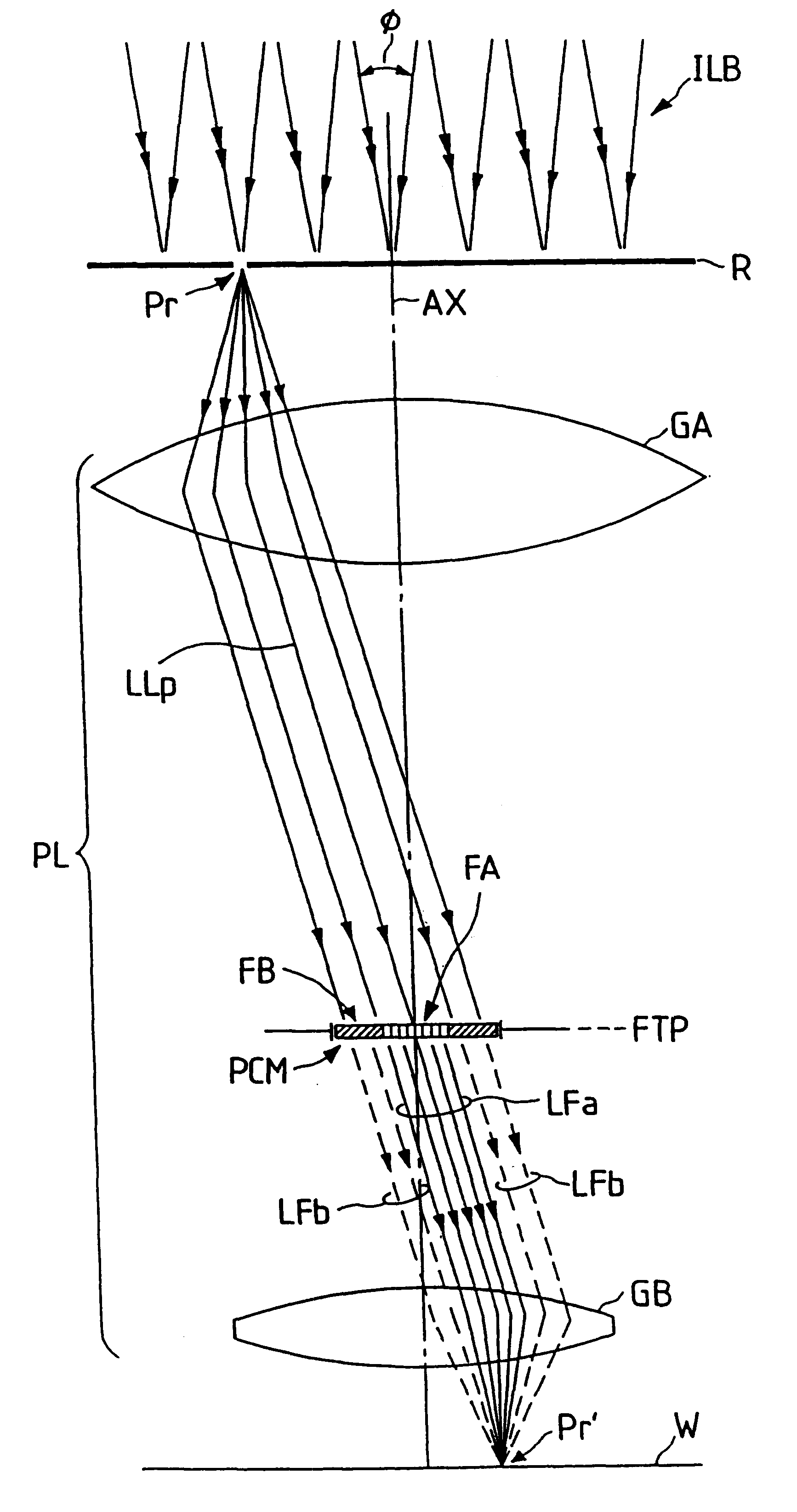
Circular and annular lens zones are disclosed which, at a given lens area, exhibit a depth of focus of a lens of considerably smaller area. The large depth of focus is achieved by imparting the lens zones a refractive power profile. An assembly of such large depth of focus lens zones represents a lens of large diameter which lens, in polychromatic light, exhibits essentially the same depth of focus as the lens zones from which it is composed.
Owner:FIALA WERNER J
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6310679B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Apparatus for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS20050018200A1Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
An apparatus for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus, comprising an optical ranging system comprising a light source, a means for directing light from the light source to the sample, a means for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, a means for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image; and an optical element having a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about 5 μm, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cursor control device
InactiveUS20060028442A1Improve dynamic rangeLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSelf adaptiveComputer science
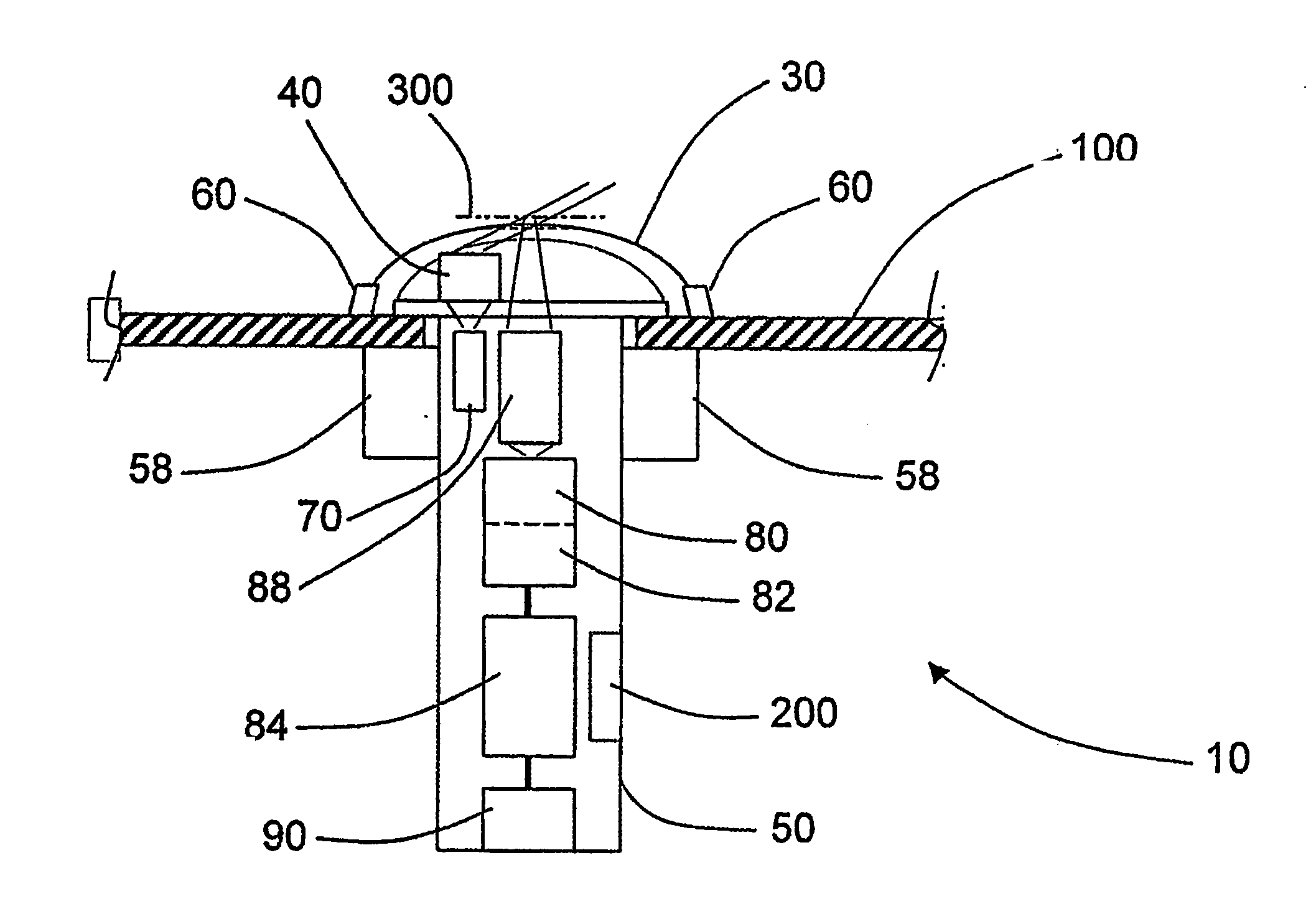
A cursor control device (700) having a light source (70) and an image sensor (80) for optically tracking motion. The device (700) includes an upwardly facing dome (710) or window (32) that provides a visual and tactile interface for user interaction. The user's hand or finger, bare or gloved, or other object controlled by the user, can be moved in close proximity or touching the dome (710), and means are provided to discriminate against the motion of objects that are not close to the dome in order to prevent unwanted cursor motion. Said means can include optics (40) having a limited depth of focus, adaptive illumination processing for controlling the intensity of light emitted from the light source (70) to optimize sensor operation, and / or processing for projecting cursor motion in accordance with a detected level of confidence in the sensor data.
Owner:ITAC SYST
System and method for aligning an optic with an axis of an eye
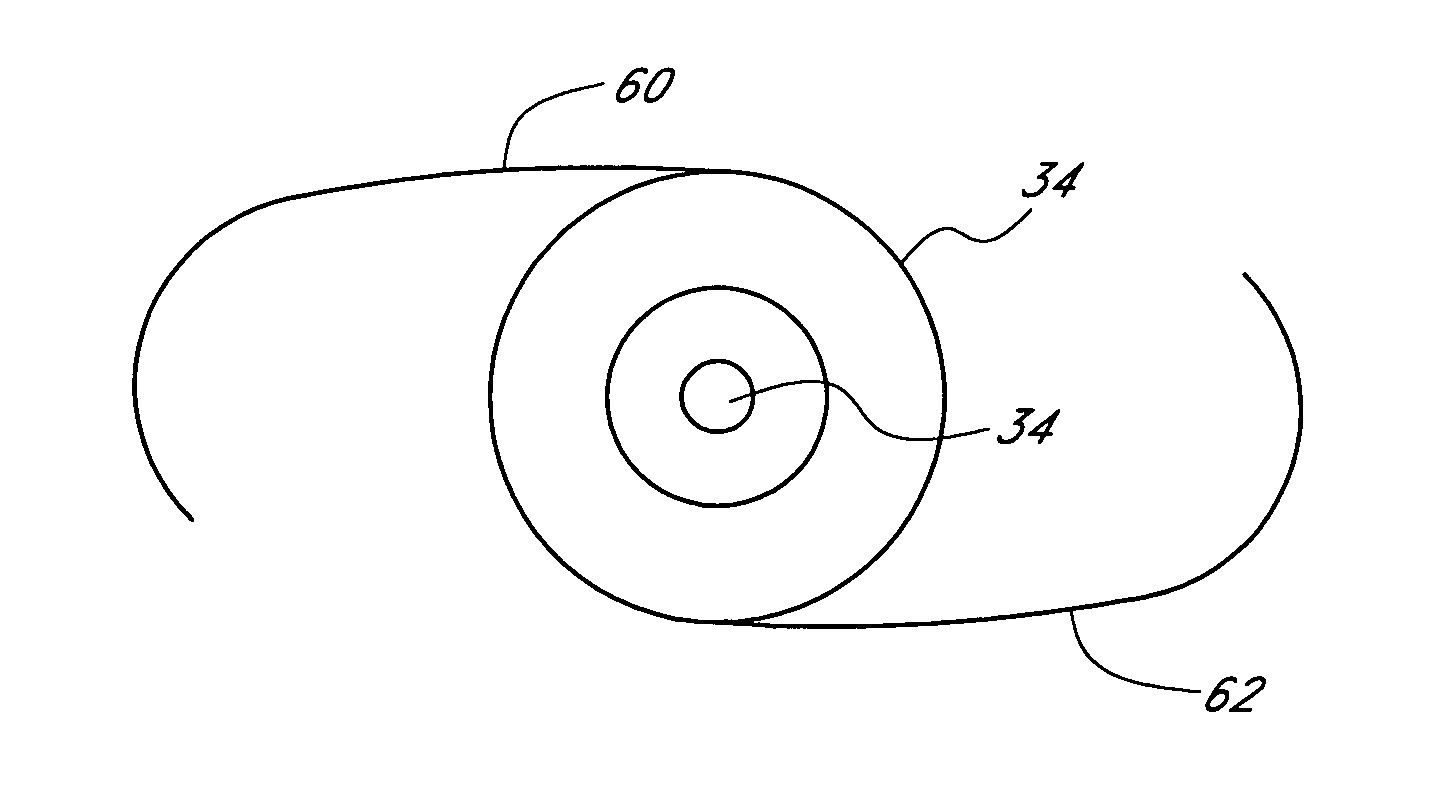
InactiveUS20060184243A1Increase depth of focusSmall sizeLaser surgeryEye implantsPupilComputer science
A method increases the depth of focus of an eye having a line of sight. A pharmacologic agent is applied to the eye to cause a reduction in the size of the pupil of the eye. The pupil is aligned with a visible feature of a mask comprising a pin-hole aperture. The pin-hole aperture is centered on a mask axis. The alignment causes the mask axis to be substantially aligned with the line of sight of the eye. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while maintaining the alignment of the visible feature of the mask and the pupil.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Illumination optimization for specific mask patterns
InactiveUS6871337B2Reduce in quantityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsDiffraction order
A method and apparatus for microlithography. The method and apparatus include optimizing illumination modes based on characteristics of a specific mask pattern. The illumination is optimized by determining an appropriate illumination mode based on diffraction orders of the reticle, and the autocorrelation of the projection optic. By elimination of parts of the illumination pattern which have no influence on modulation, excess DC light can be reduced, thereby improving depth of focus. Optimization of mask patterns includes addition of sub-resolution features to reduce pitches and discretize the probability density function of the space width.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Ocular mask having selective spectral transmission
ActiveUS20130268071A1Increase depth of focusEye-masksEye diagnosticsSpectral transmissionOptical axis
A mask is provided that is configured to increase the depth of focus of a patient. The mask can include an aperture configured to transmit along an optical axis substantially all visible incident light. The mask can further include a portion surrounding at least a portion of the aperture. The portion may be configured to be substantially opaque to visible electromagnetic radiation and be substantially transparent to electromagnetic radiation transmitted from an ocular examination device (e.g., substantially transparent to at least some non-visible electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between about 750 nm and about 1500 nm).
Owner:ACUFOCUS
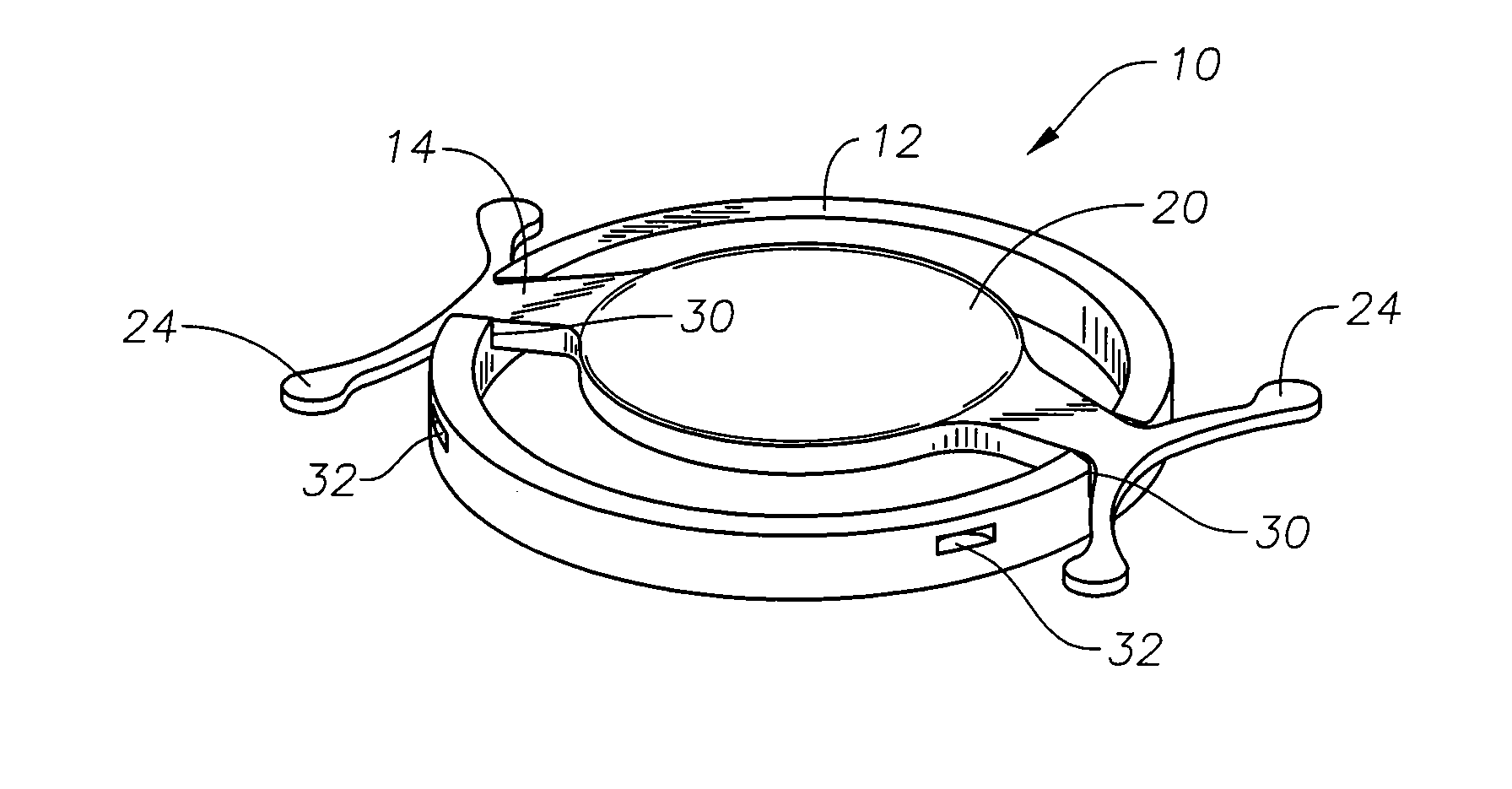
Single optic accommodative intraocular lens system
ActiveUS20100204788A1Add depthRestore accommodationGas turbine plantsIntraocular lensOphthalmologyCapsular ring
A single-optic accommodative lens system comprising two intraocular elements. The two intraocular elements are designed to be located within the capsular bag to extend depth of focus and / or restore accommodation following extraction of a natural lens. A first intraocular element comprises a circumferential capsular ring having interlock features to couple to and control the dynamic vault response of a second intraocular element. This second intraocular element comprises an intraocular lens (IOL) having an optic and a plurality of haptics and is designed to move axially in response to changes in the geometry of the eye capsule and thus provide a range of accommodative power. The IOL further comprises interlock features complementary to the interlock features of the first intraocular element for coupling the IOL to the capsular ring in a manner that provides for controlled movement of the IOL in response to capsular forces. Capsular force can be applied to the IOL from anterior, posterior and / or intermediate sections of the capsule equator, resulting in movement of the IOL and commensurate accommodation.
Owner:ALCON INC
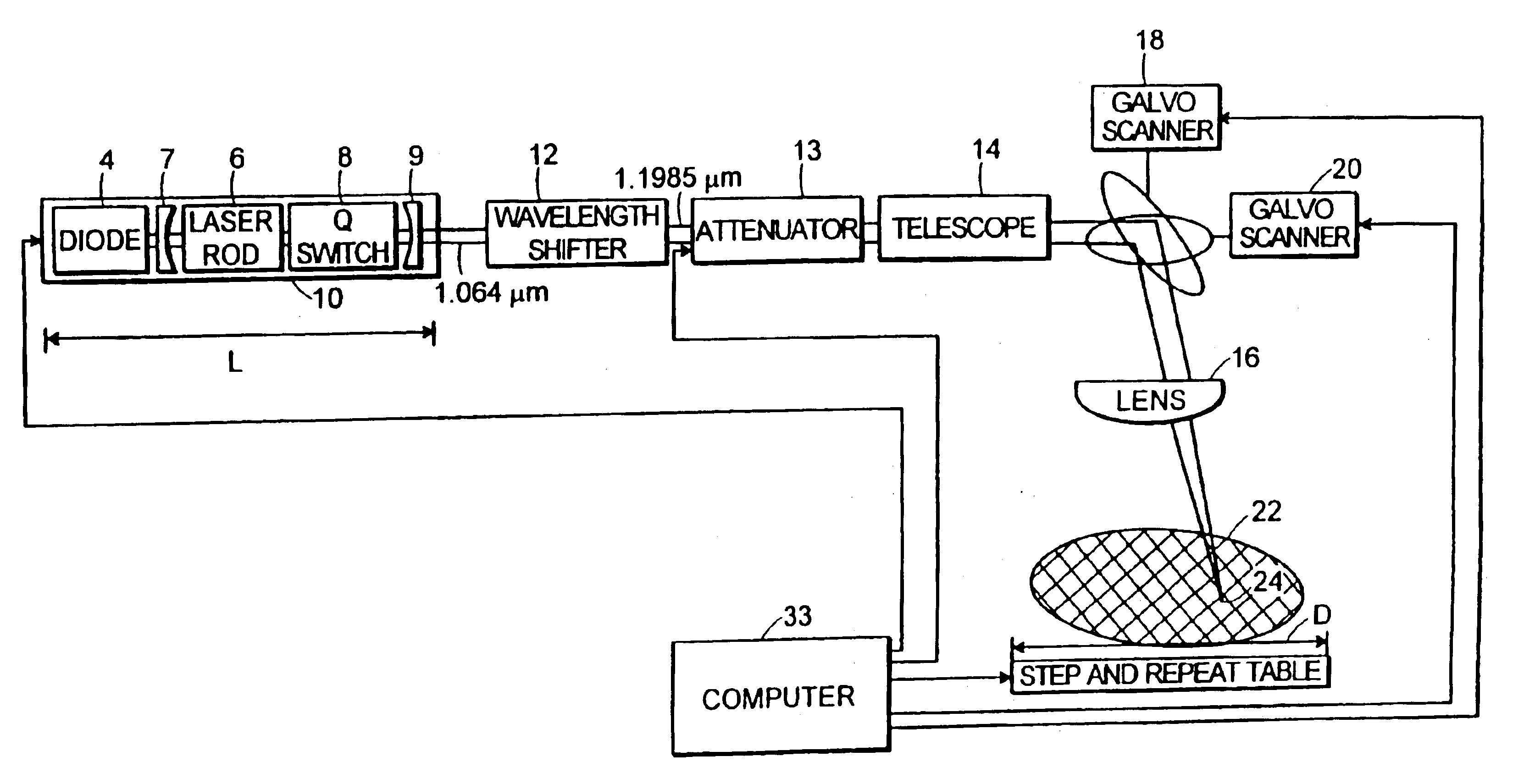
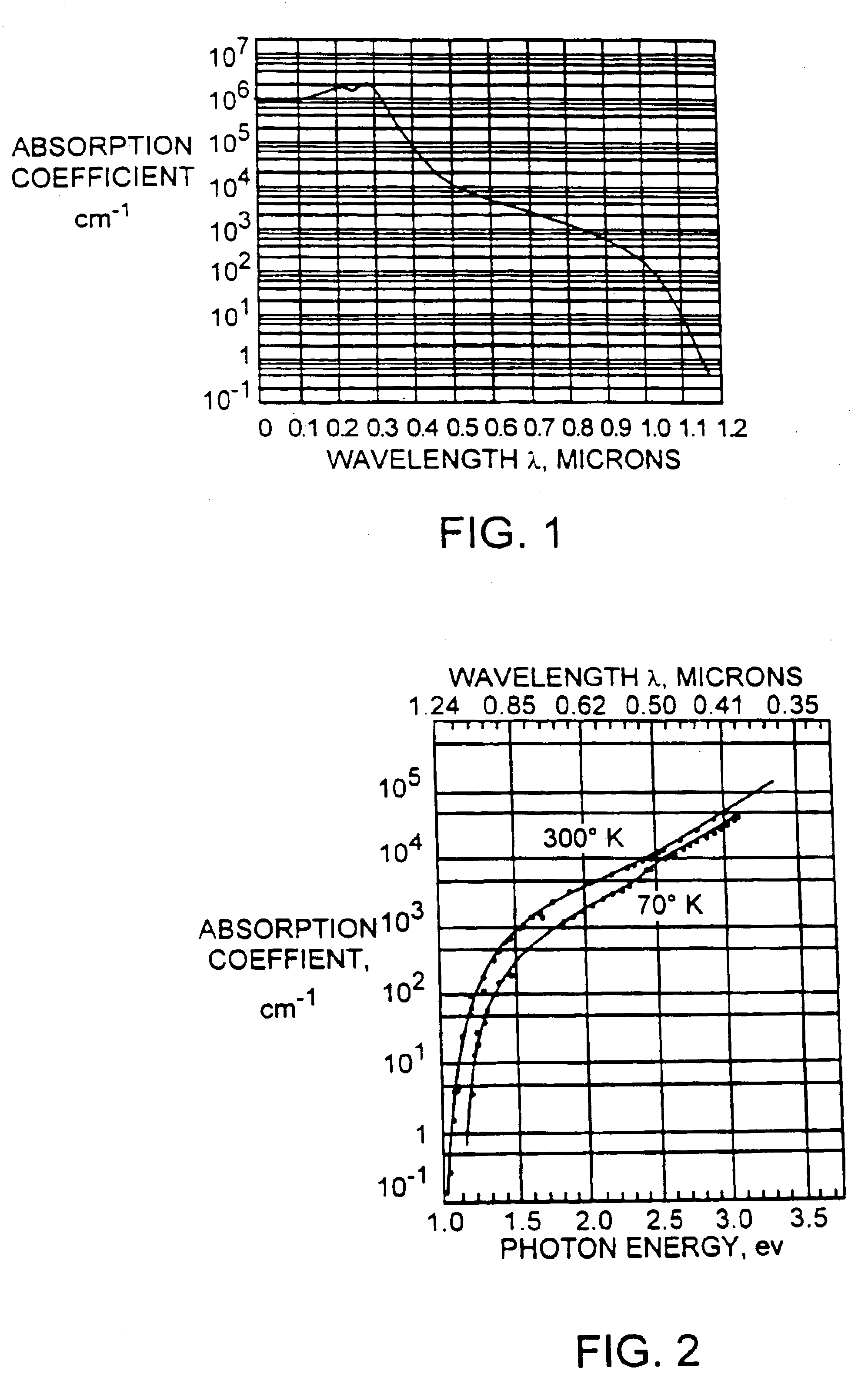
Laser processing
InactiveUS6878899B2Limit temperature riseAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingLength wave
A controlled, switched laser system for vaporizing a target structure on a substrate includes a diode-pumped, solid-state laser for producing a laser output, a controllable switch for controlling the on / off state and power level of the laser, and a wavelength shifter. The wavelength shifter shifts the wavelength of the laser output from a conventional wavelength to a wavelength beyond the absorption edge of the substrate but shorter than 1.2 μm in order to obtain a decrease in absorption of the laser output by the substrate due to the shift in the wavelength of the laser output. The wavelength shifter is removably insertable into the switched laser system so as to enable the switched laser system to operate at the conventional wavelength and at the wavelength beyond the absorption edge of the substrate. Heating of the substrate and hence damage to the substrate is limited due to the wavelength being beyond the absorption edge of the substrate. Good depth of focus of the laser beam output is maintained relative to spot size of the laser beam output due to the wavelength being less than about 1.2 μm.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
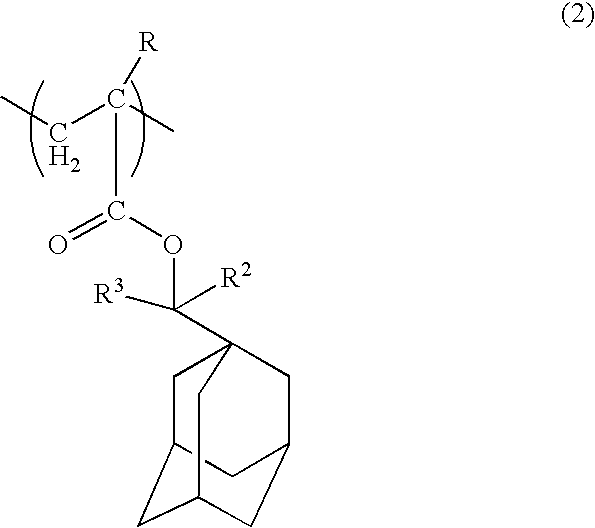
Fluorine-containing polymer, purification method, and radiation-sensitive resin composition
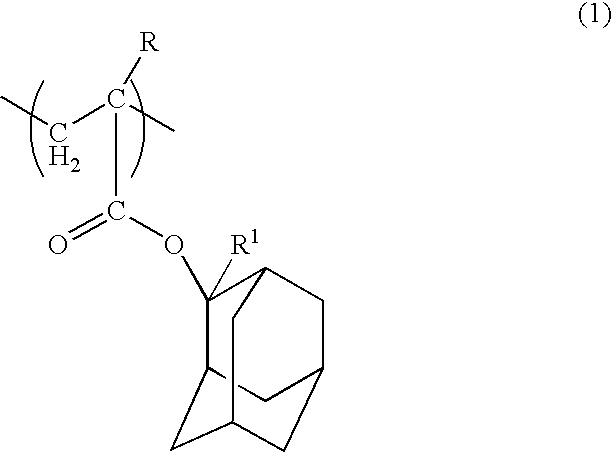
ActiveUS20090202945A1Great depth of focusQuantity minimizationPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPurification methodsNitrogen
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel fluorine-containing polymer, a radiation-sensitive resin composition for liquid immersion lithography which contains the fluorine-containing polymer, which leads to a pattern having an excellent shape and excellent depth of focus, wherein the amount of an eluted component in a liquid for liquid immersion lithography such as water that comes in contact with the resist during exposure in liquid immersion lithography is little, and which provides a larger receding contact angle between the resist film and the liquid for liquid immersion lithography such as water, and a method for purifying the fluorine-containing polymer. The present resin composition comprises a novel fluorine-containing polymer (A) containing repeating units represented by the general formulae (1) and (2) and having Mw of 1,000-50,000, a resin (B) having an acid-unstable group, a radiation-sensitive acid generator (C), a nitrogen-containing compound (D) and a solvent (E).
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
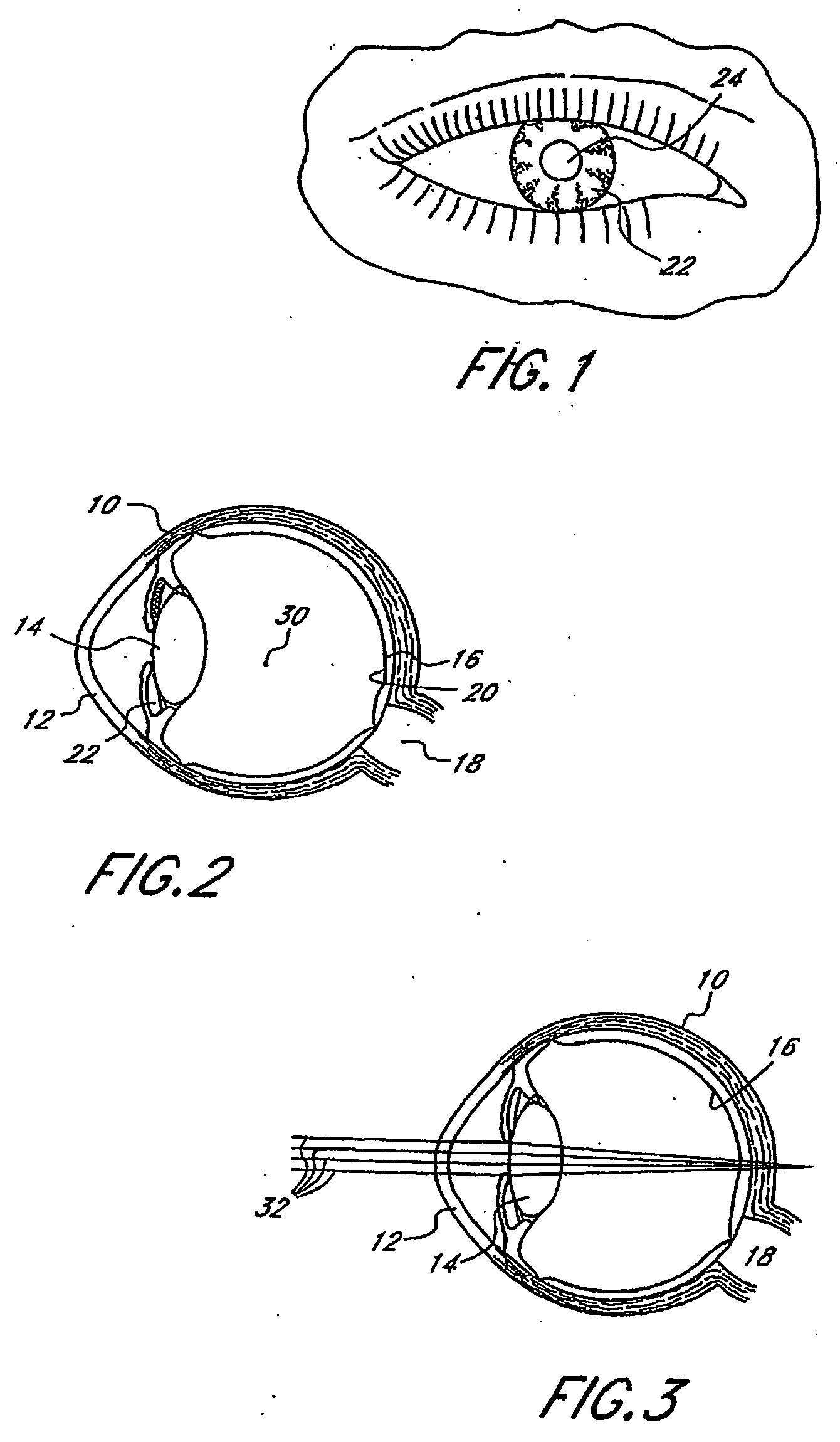
System and method for increasing the depth of focus of the human eye
InactiveUS6874886B2Increase depth of focusPrevent deviationSpectales/gogglesMembranesLight reflectionFace shield
A method and apparatus for increasing the depth of focus of the human eye is comprised of a lens body, an optic in the lens body configured to produce light interference, and a pinhole-like optical aperture substantially in the center of the optic. The optic may be configured to produce light scattering or composed of a light reflective material. Alternatively, the optic may increase the depth of focus via a combination of light interference, light scattering, light reflection and / or light absorption. The optic may also be configured as a series of concentric circles, a weave, a pattern of particles, or a pattern of curvatures. One method involves screening a patient for an ophthalmic lens using a pinhole screening device in the lens to increase the patient's depth of focus. Another method comprises surgically implanting a mask in the patient's eye to increase the depth of focus.
Owner:HEALTHCARE ROYALTY PARTNERS II
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
InactiveUS20040058269A1High resolutionIncreased focus rangePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsSolubilityResist
There is provided a positive type resist composition formed by dissolving (A) a resin component with a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester in the principal chain, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, and (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, in an organic solvent component (C), wherein the resin component (A) is a copolymer comprising (a1) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group, (a2) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a lactone containing monocyclic group or polycyclic group, (a3) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a hydroxyl group containing polycyclic group, and (a4) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a polycyclic group which is different from the unit (a1), the unit (a2) and the unit (a3). This composition provides a chemically amplified positive type resist composition which displays excellent resolution, enables the depth of focus range of an isolated resist pattern to be improved, and enables the proximity effect to be suppressed.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Method of making an ocular implant
InactiveUS20060271184A1Increase depth of focusEye implantsCosmetic implantsOcular implantBiomedical engineering
A method of making a mask configured to improve the depth of focus of an eye of a patient is provided. A substrate with a mask forming feature is provided. The mask forming feature comprises a forming surface that extends from an outer periphery. The forming surface is centered on a central axis of the mask forming feature. A release layer is formed on the forming surface. A mask layer is formed such that the release layer is between the mask layer and the substrate. The mask layer is formed of a biocompatible metal. A surface of the mask layer opposite the release layer is configured to not corrode. The mask layer is separated from the substrate.
Owner:HEALTHCARE ROYALTY PARTNERS II
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com