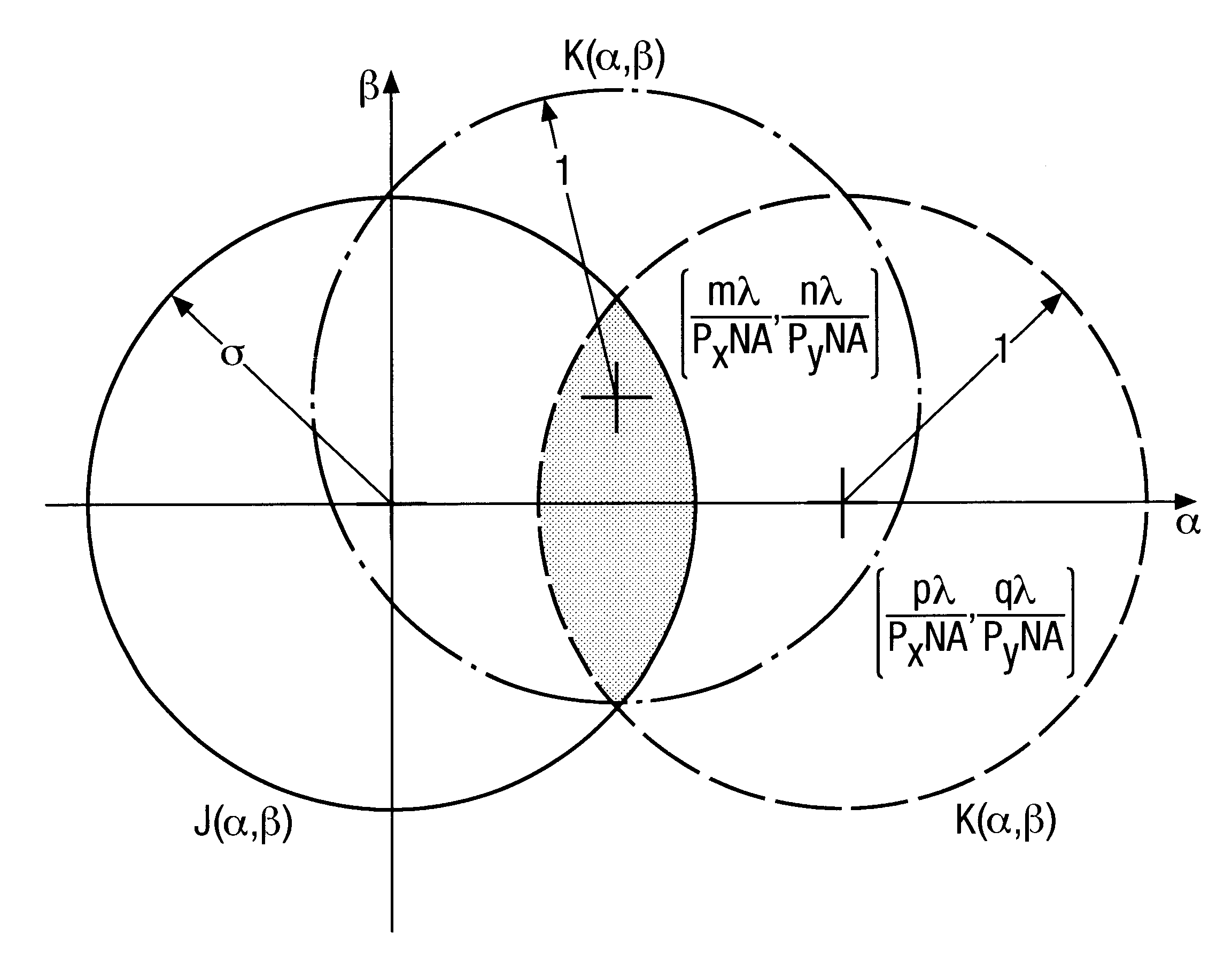
Illumination optimization for specific mask patterns
a mask pattern and optimization technology, applied in the field of microlithographic imaging, can solve the problems of poor contrast and end-of-line errors, and the cost of trial and error optimization of illumination configuration becomes very large, and achieve the effect of reducing a number of pitches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
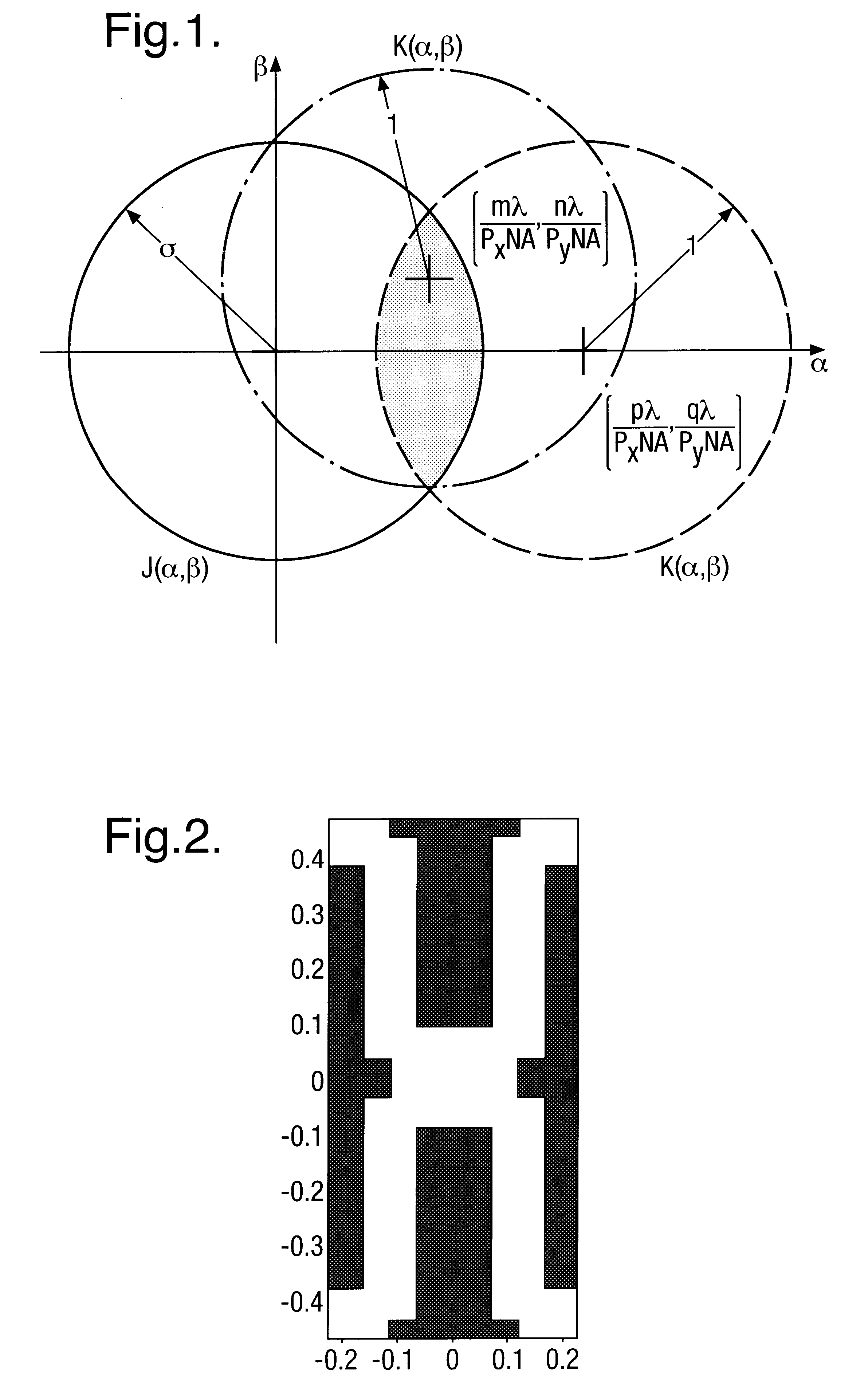
The technique for calculating Jtot outlined above was applied to a brick wall isolation pattern. A 150 nm pattern was shrunk to 130 nm and 110 nm design rules and imaged with a step and scan lithography system having a numerical aperture (NA) of 0.8. The isolation pattern for the 130 nm design rule is shown in FIG. 2.
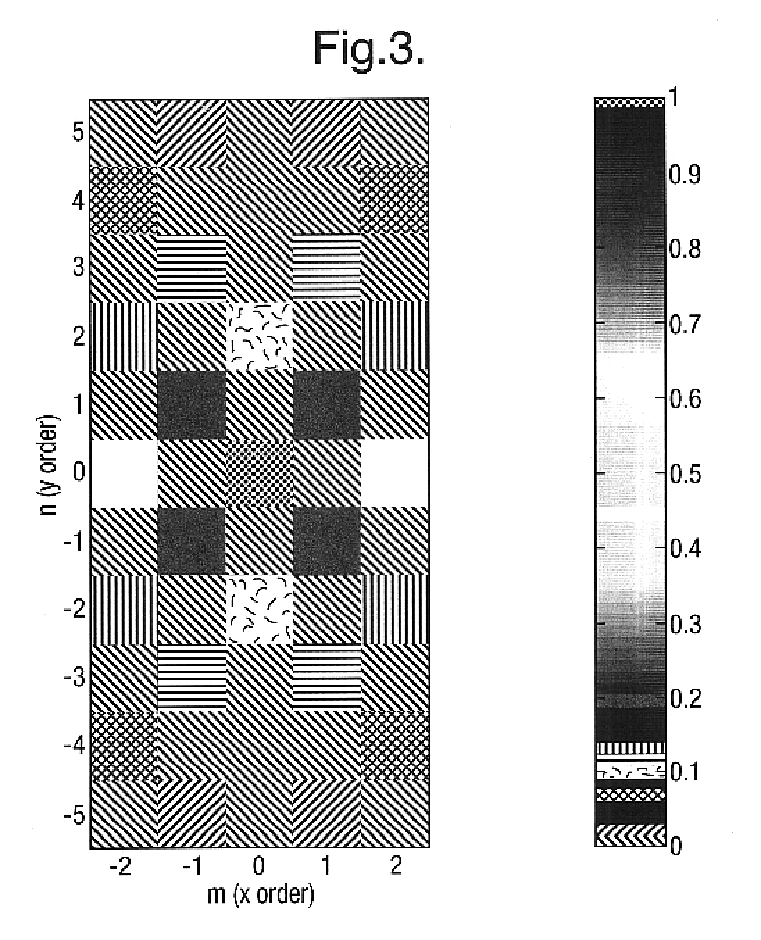
The magnitudes of the diffraction orders of this mask feature are plotted in FIG. 3. In FIG. 3, the largest order is the (0,0) order or the DC background light. The orders that contribute the most to imaging are the (±2,0) orders and represent the vertical bricks in the brick wall pattern. The other significant order is the (±1,±1) which represents the clear areas and defines the end of the isolation pattern. The higher orders also help to define two dimensional structures such as the end of each line. Since the diffraction orders are not constant, the orders change the weighting coefficients in the DOCC, which implies that the mask pattern influences the illumination s...
example 2
Using the gray scale to binary approach, a binary illumination configuration for the same brick wall isolation pattern was designed assuming a maximum outer σ of 0.88 and is shown in FIG. 6.
The performance of the optimized illumination configuration in FIG. 6 was then simulated for binary mask on a step and scan photolithography apparatus having NA=0.8 and λ=248 nm and compared to the simulated performance of annular illumination. In the simulation, the vector (thin-film) imaging resist model was used since the numerical aperture was above 0.7. In this model, the resist is 400 nm thickness of a type having a refractive index n=1.76−j0.0116), over 66 nm of another type having n=1.45−j0.3 on top of a polysilicon material having n=1.577−j3.588. The results with the annular illumination (σin=0.58 and of σout=0.88) and with the optimized illuminator (σout=0.88) are shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, respectively. In both FIGS. 7 and 8, cross section results in the middle of the isolation region and...
example 3
The results in FIGS. 7 and 8 for binary mask (BIM) were compared to simulation results for chromeless mask (CLM). A chromeless brick wall isolation pattern was designed from experimental results of software simulation in a manner known to those skilled in the art. The chromeless technology requires (0,0) order light so as to fully benefit from the DOF improvement produced by off axis illumination. Experimental results from the simulation confirm the need for (0,0) order light for which purpose the isolation layer should be dithered or half toned. The half tone pitch may be chosen such that the first order in the dithered direction does not fall into the projection pupil. In the example, the lines were dithered in the vertical direction with pitch less than λ / [NA(1+σout). The dithering duty cycle however should be tuned to optimize the amount of (0,0) order light for best DOF and pattern fidelity. In the simulation results for CLM the half tone pitch was 155 nm with 50% duty cycle (7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com