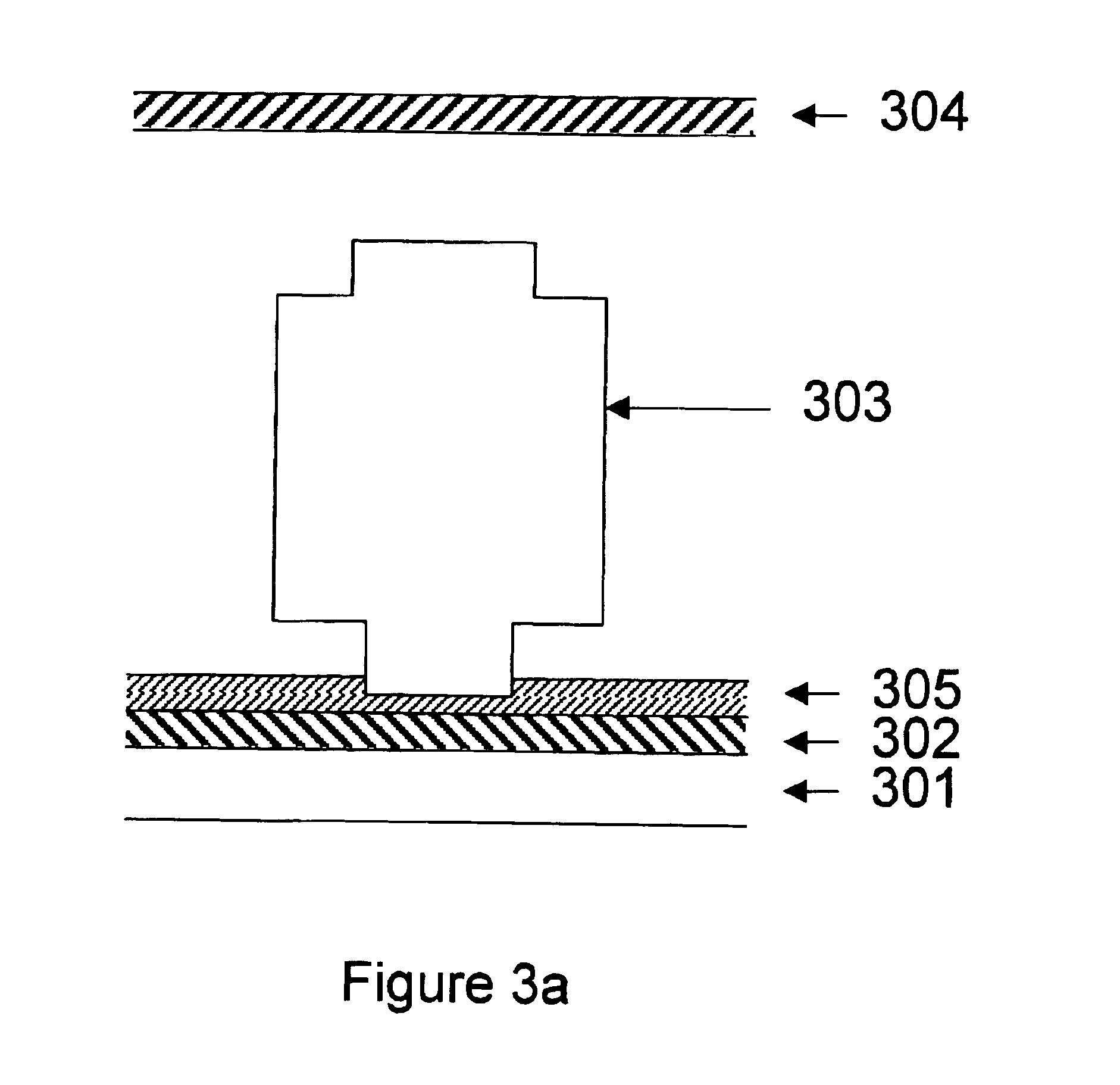
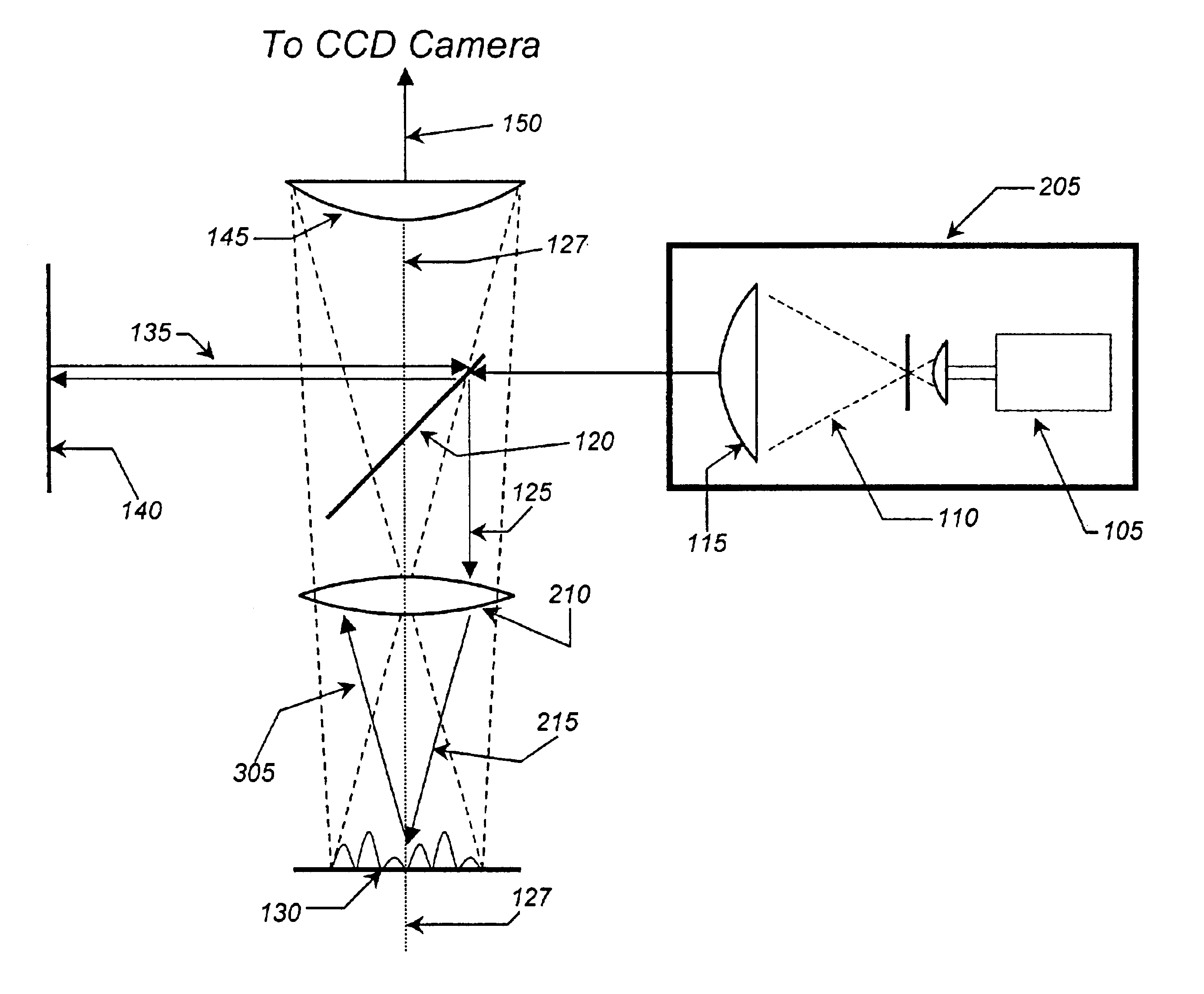
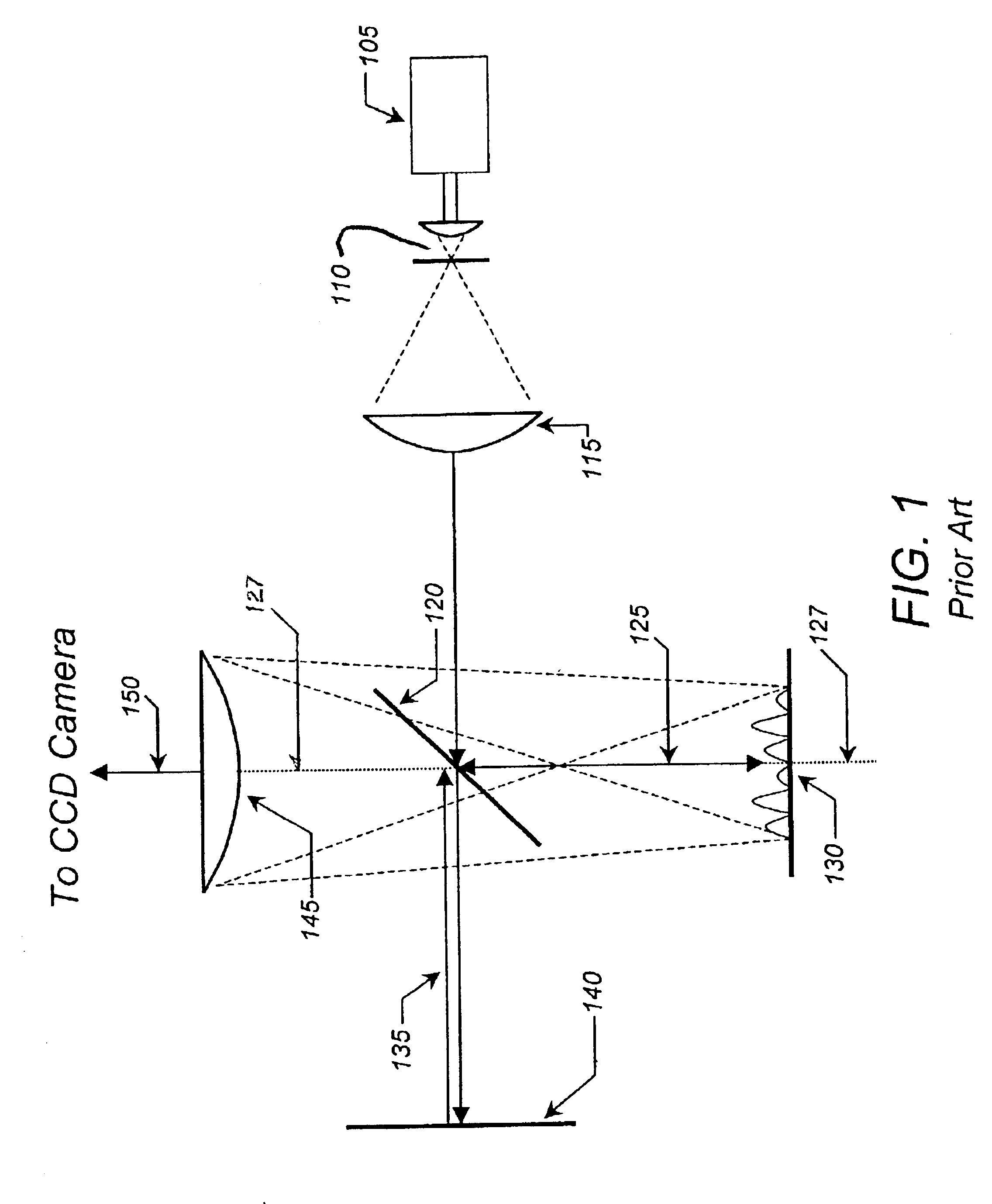
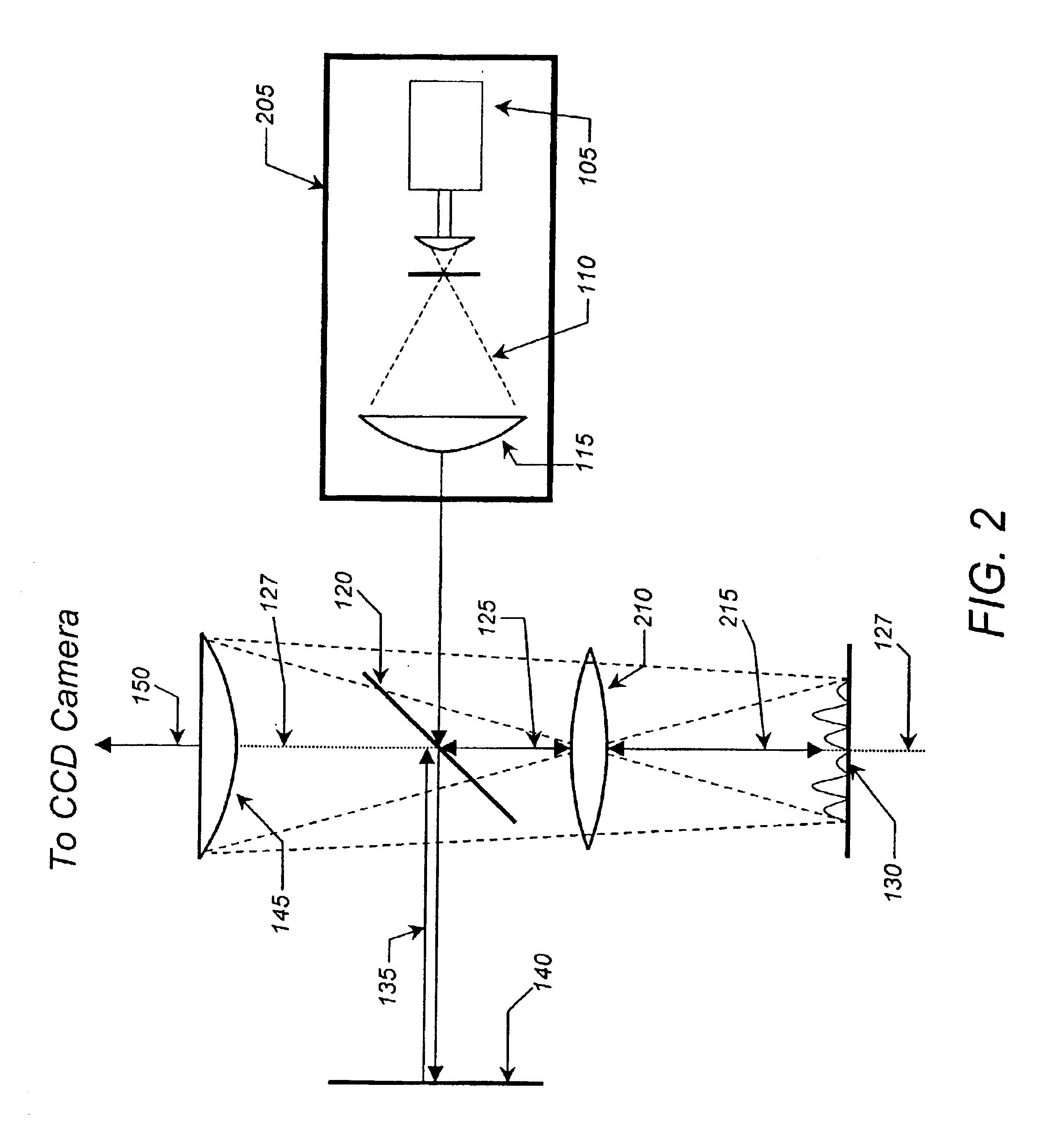
Patents
Literature
101 results about "Off-axis illumination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
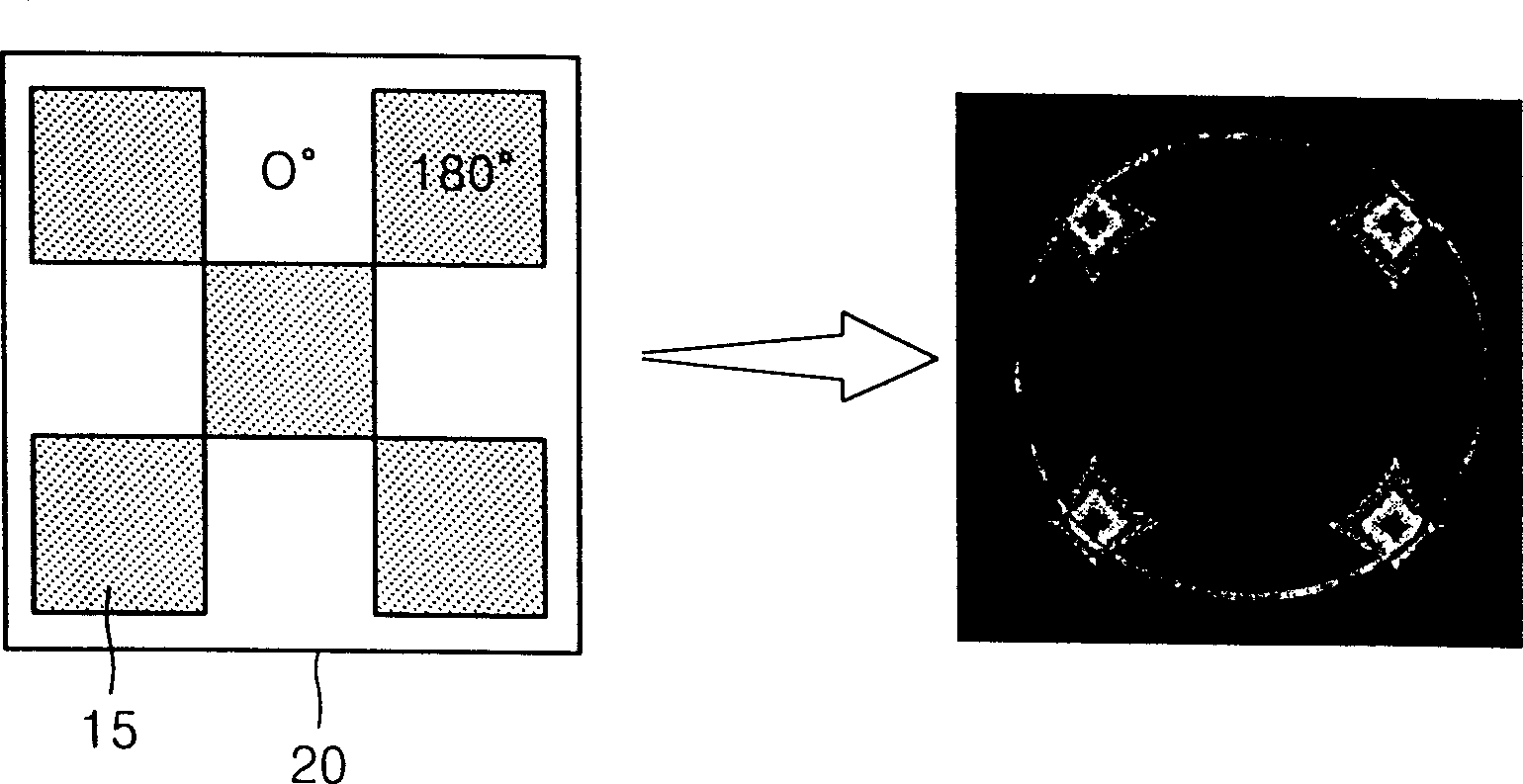
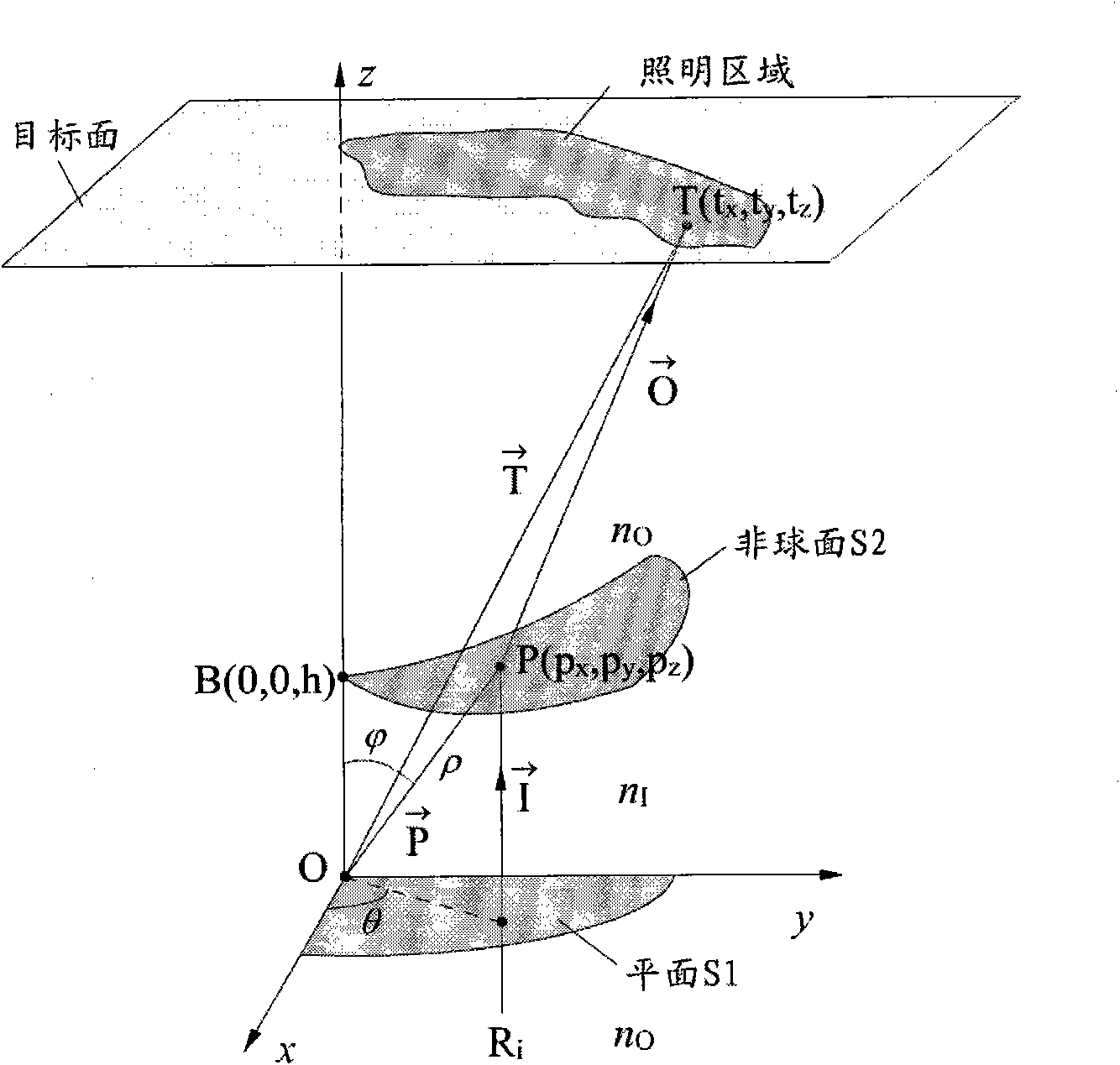
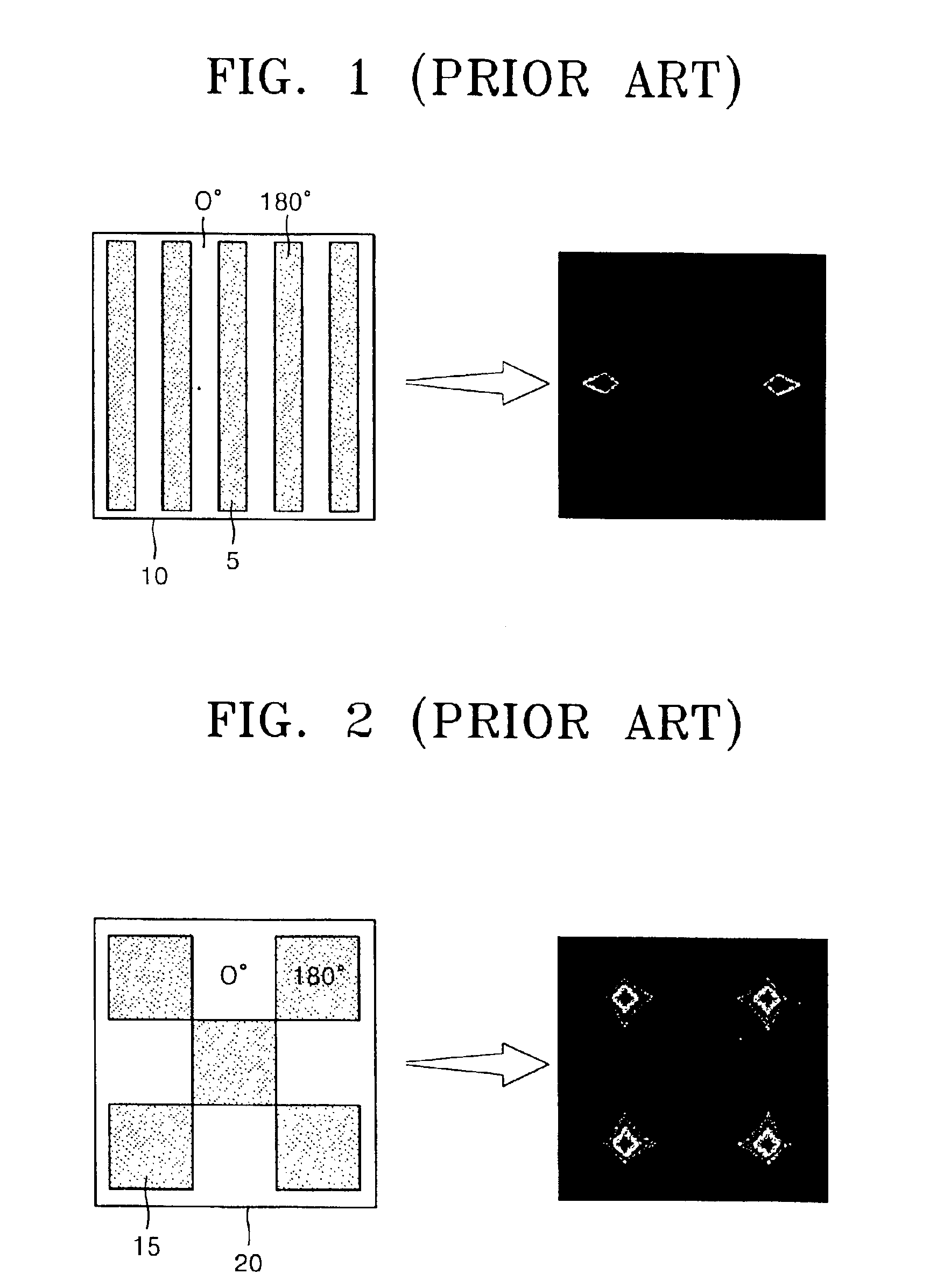
In photolithography, off-axis illumination is an optical system setup in which the incoming light strikes the photomask at an oblique angle rather than perpendicularly to it, that is to say, the incident light is not parallel to the axis of the optical system.
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Device Manufacturing Method and Substrate
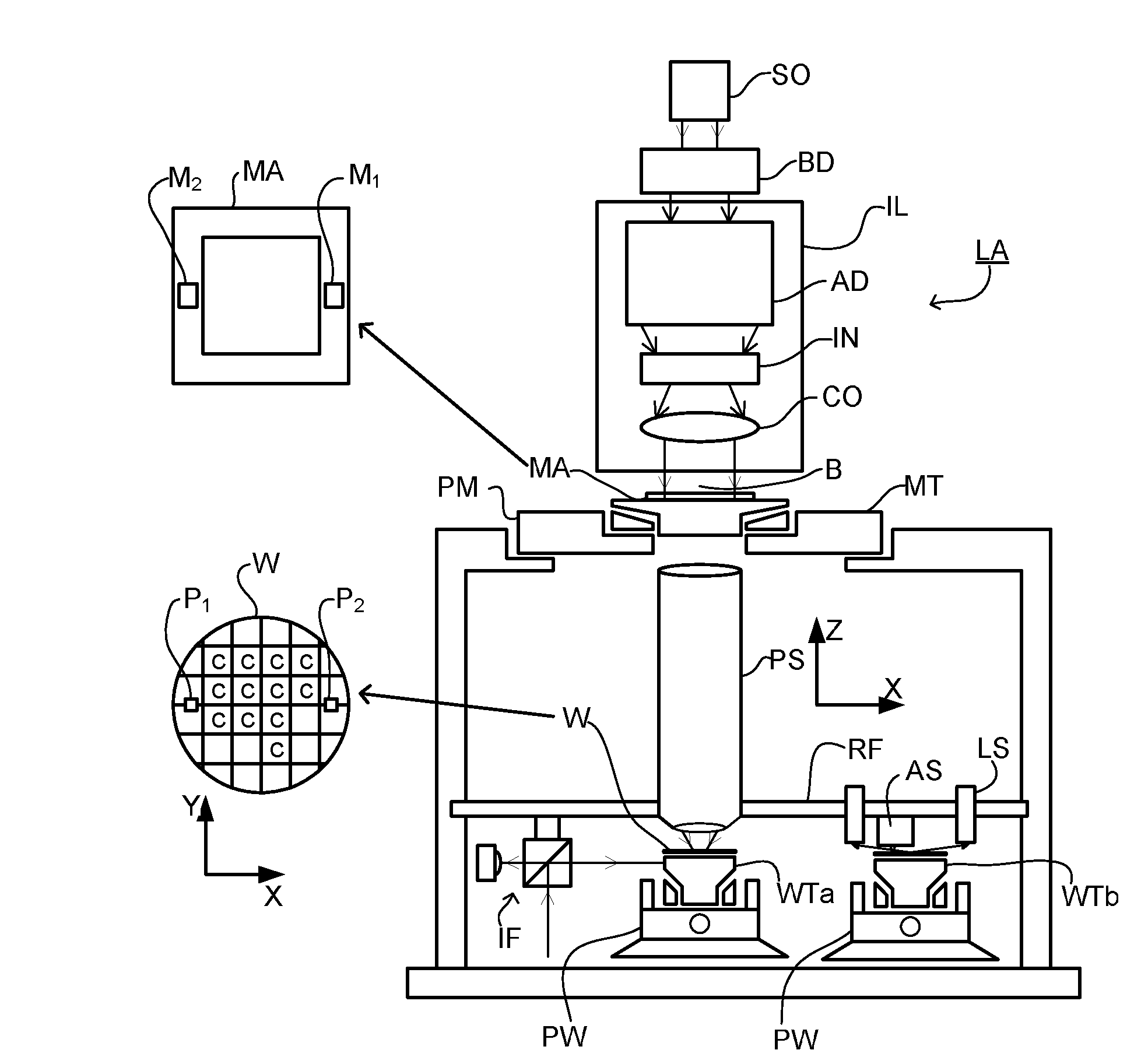
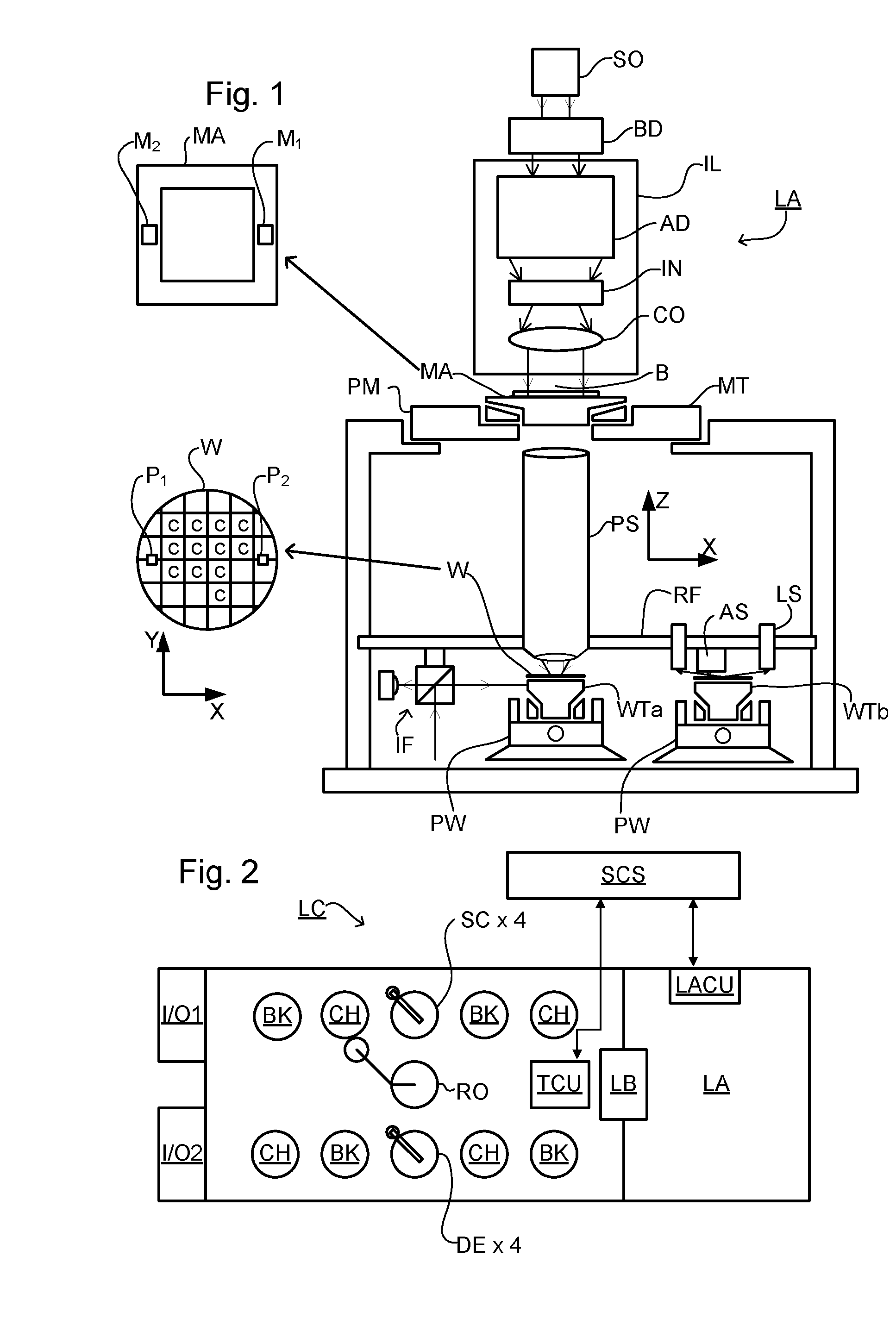
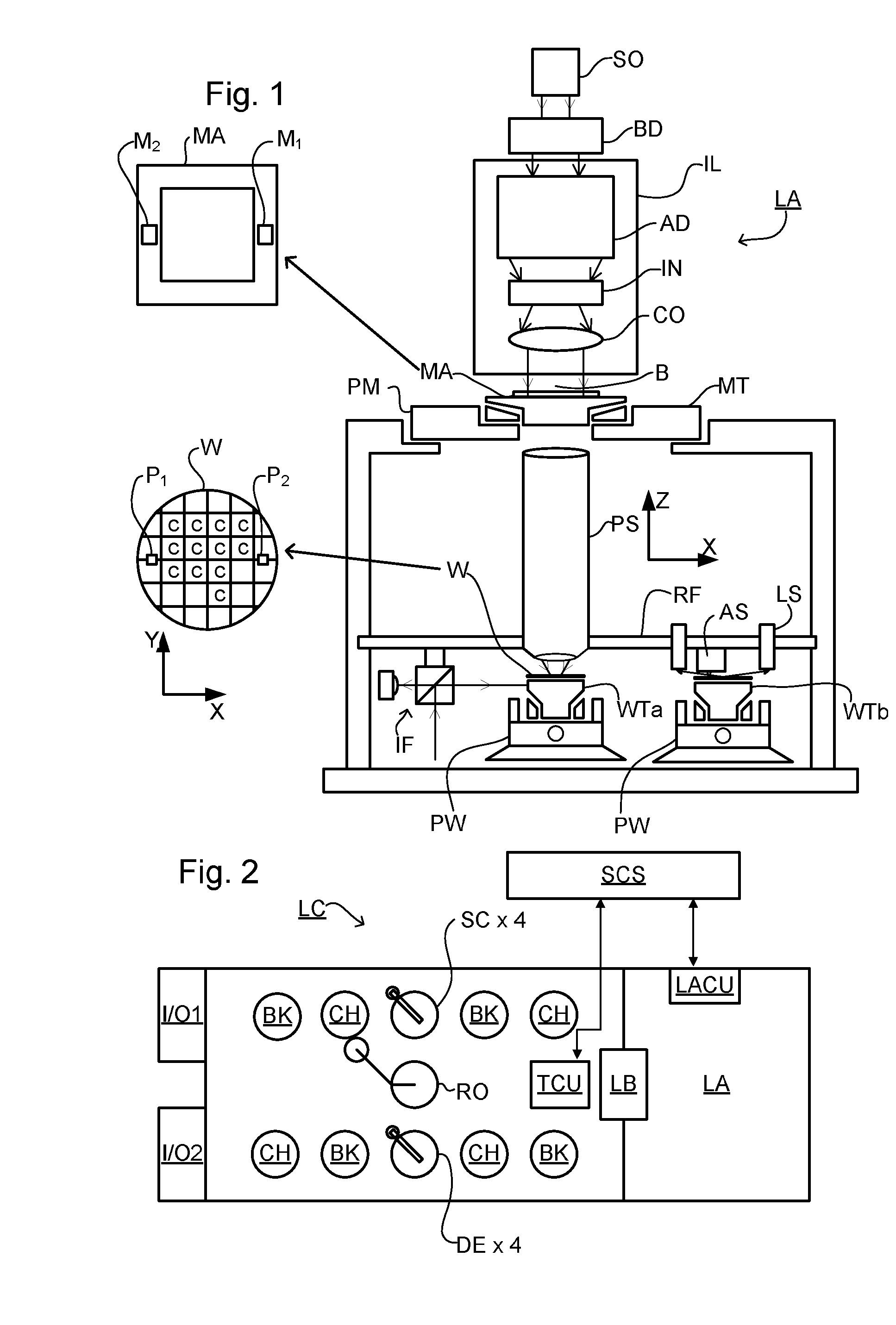
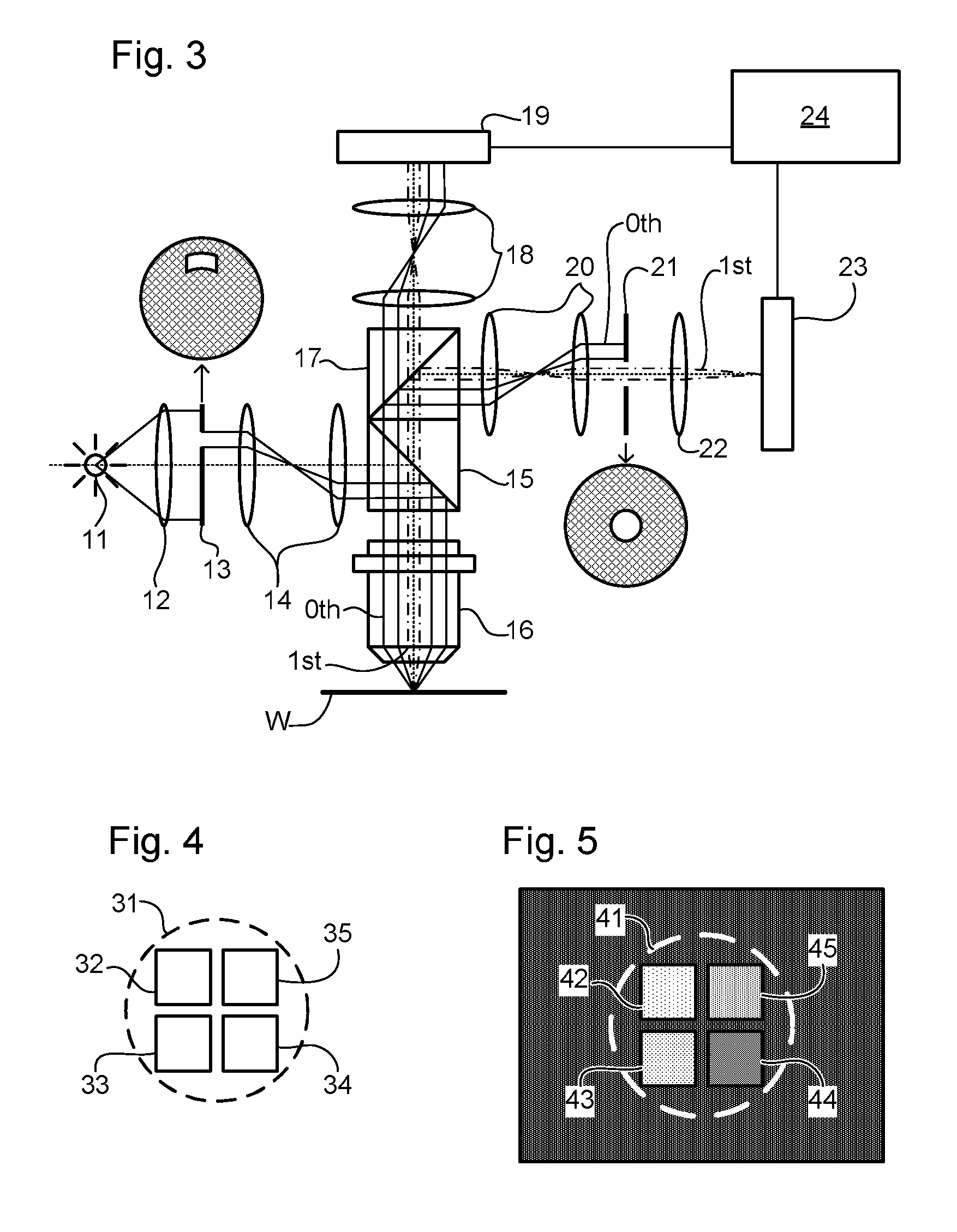
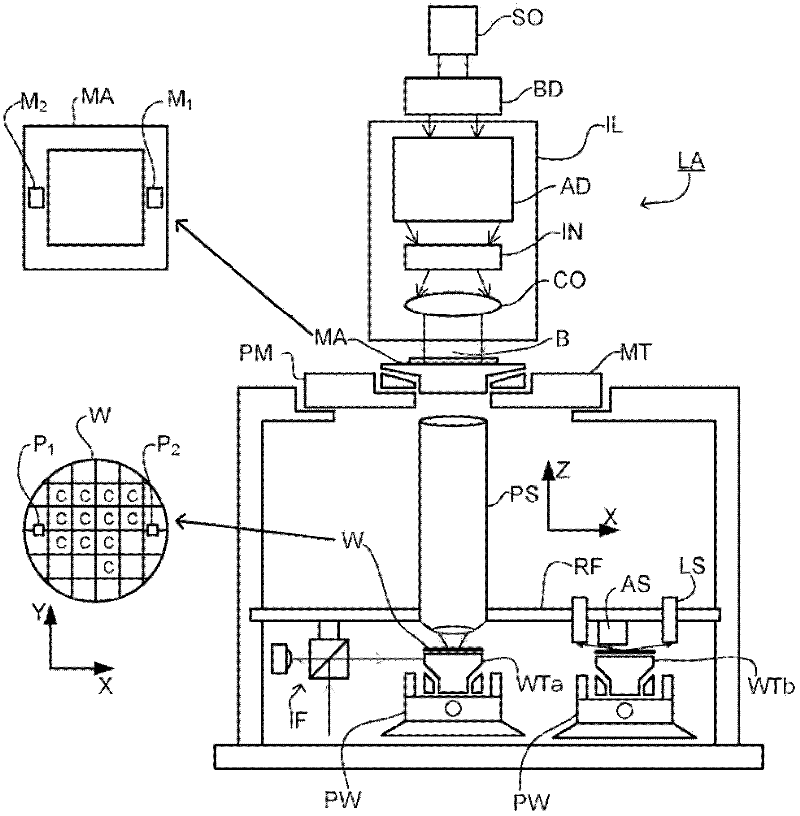
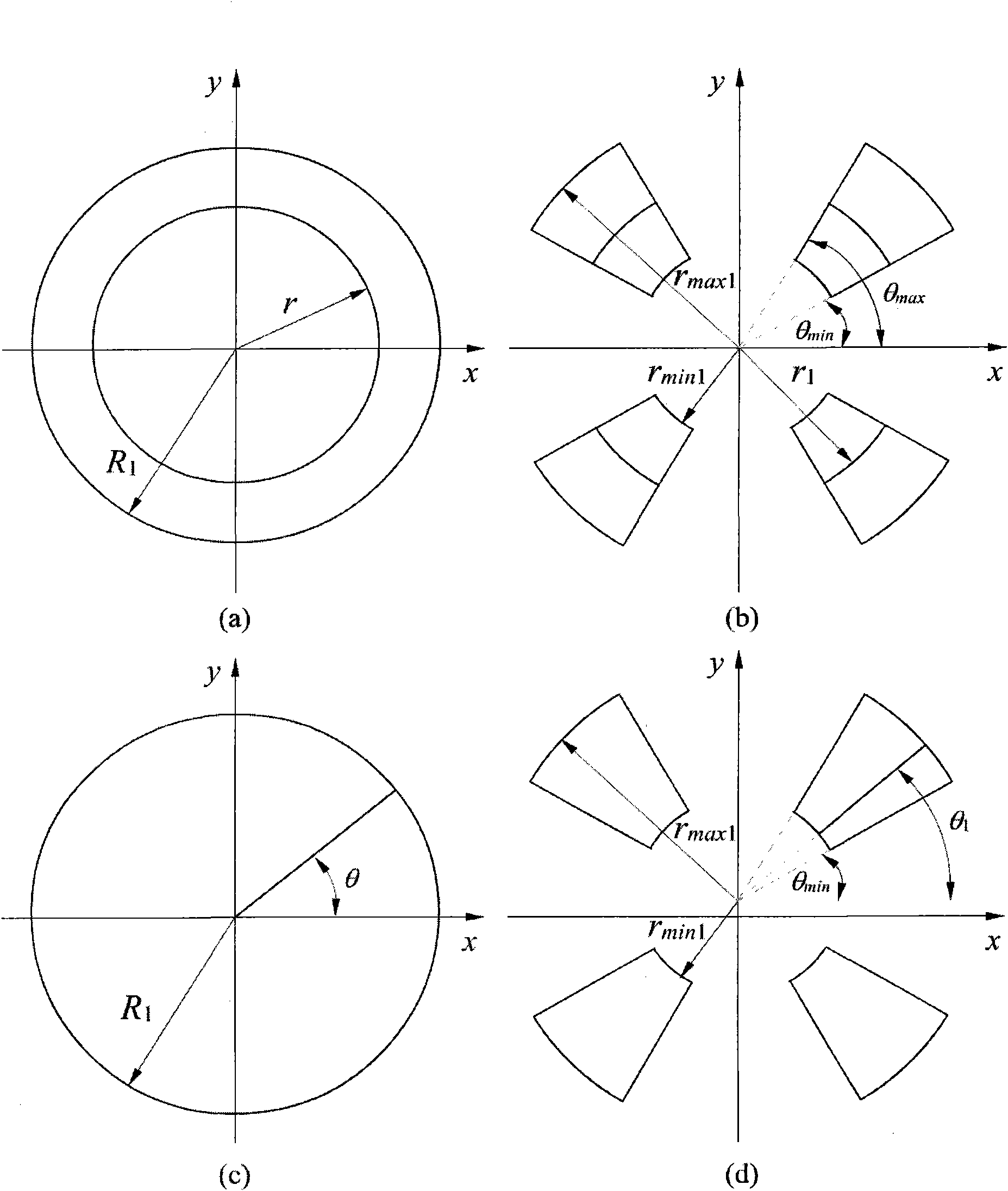
ActiveUS20110043791A1Made preciselySmall targetPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansMetrologyGrating
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Contact printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050068639A1Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusRefractive indexOff-axis illumination
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for calibration-free eye tracking
ActiveUS20060110008A1Extended durationImage enhancementImage analysisCorneal surfaceAngular distance
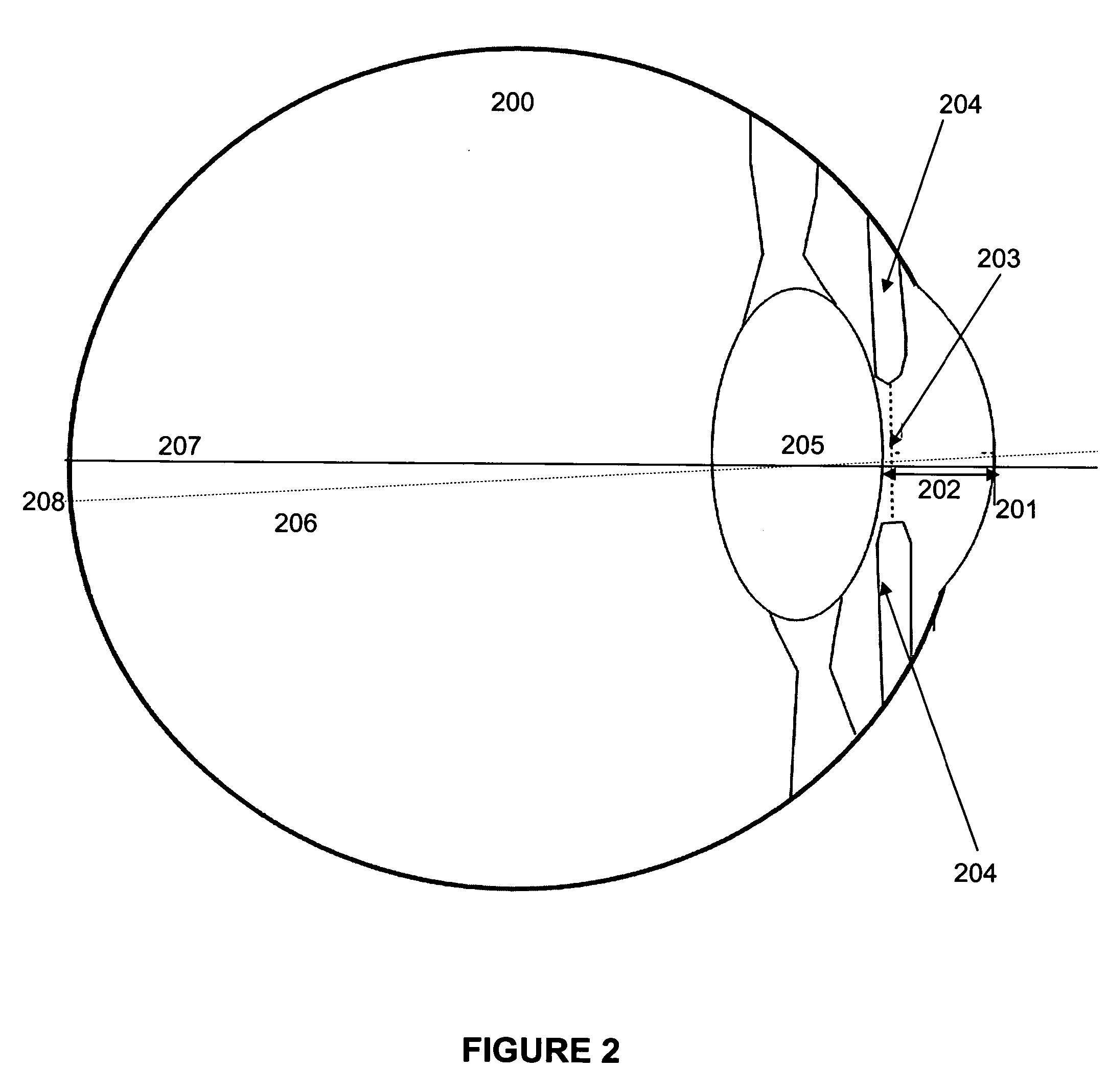
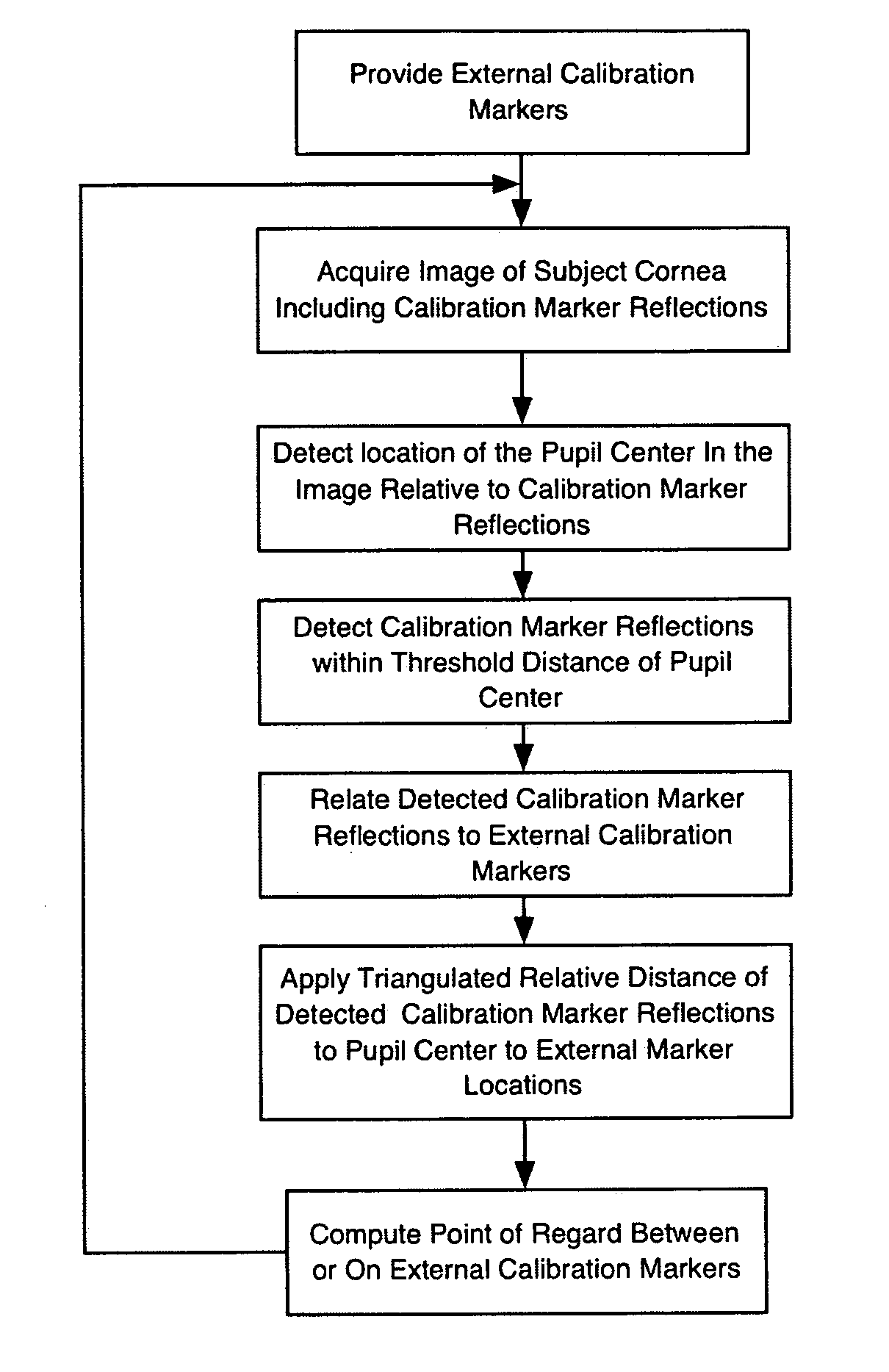
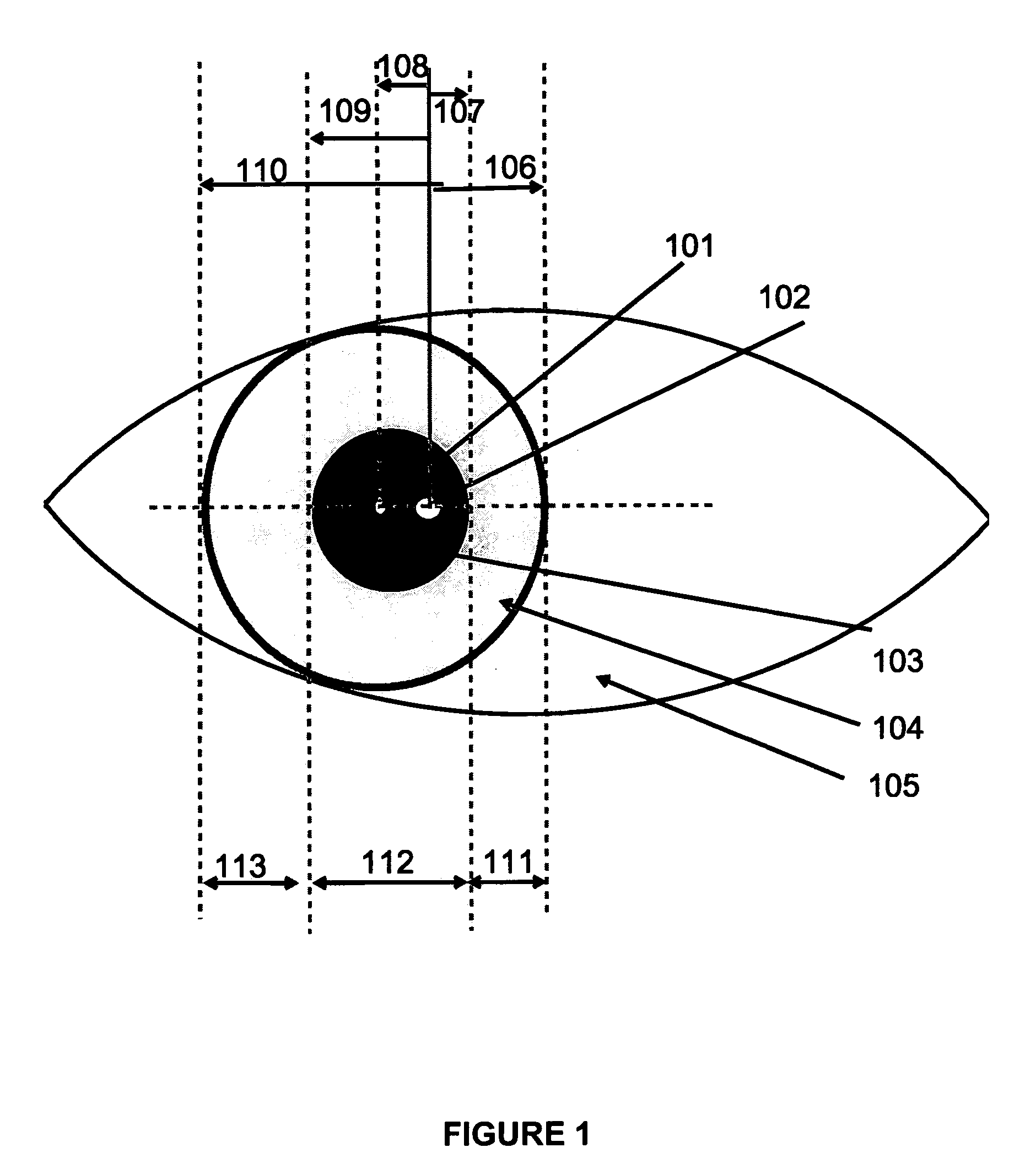
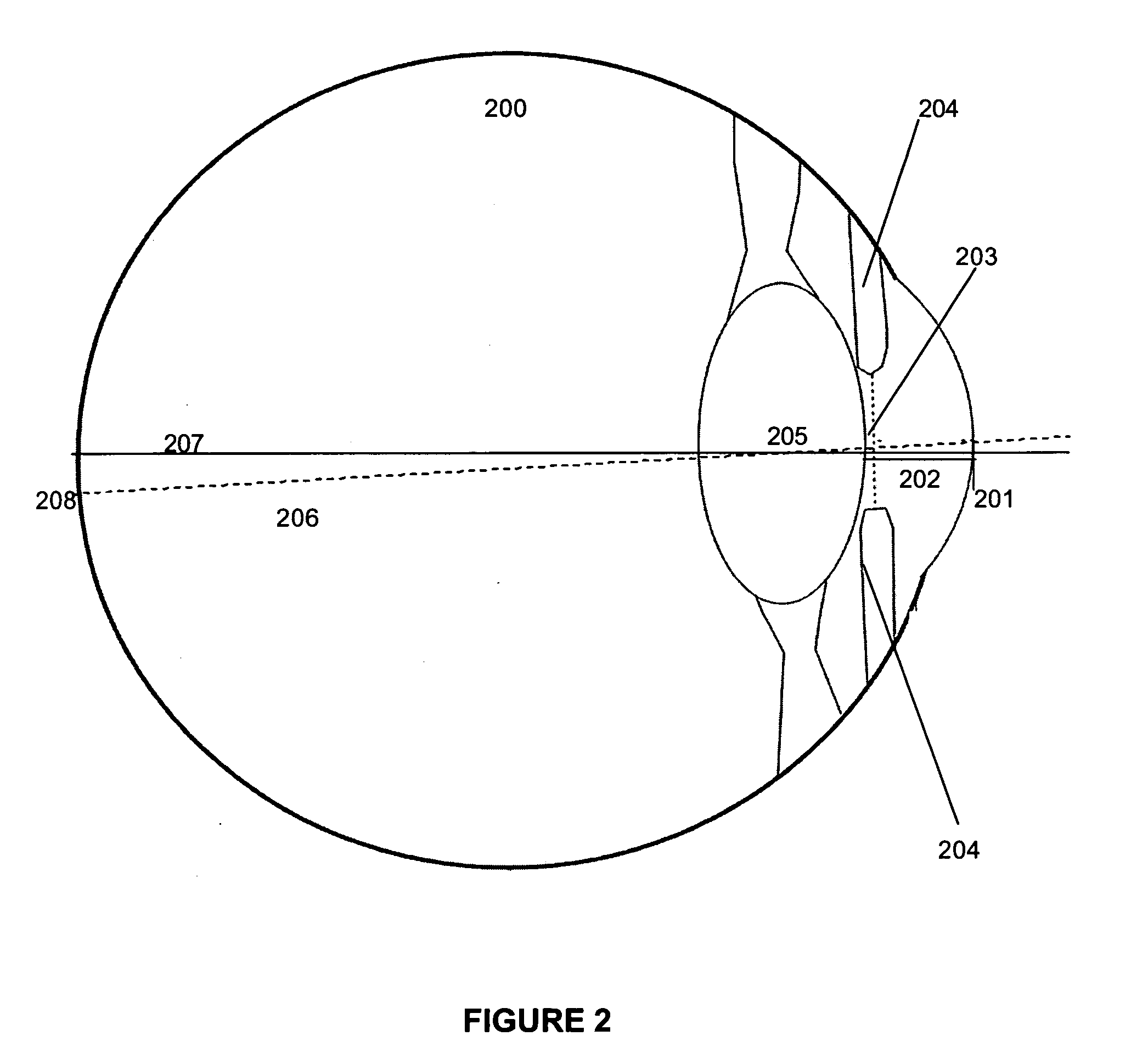
A system and method for eye gaze tracking in human or animal subjects without calibration of cameras, specific measurements of eye geometries or the tracking of a cursor image on a screen by the subject through a known trajectory. The preferred embodiment includes one uncalibrated camera for acquiring video images of the subject's eye(s) and optionally having an on-axis illuminator, and a surface, object, or visual scene with embedded off-axis illuminator markers. The off-axis markers are reflected on the corneal surface of the subject's eyes as glints. The glints indicate the distance between the point of gaze in the surface, object, or visual scene and the corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene. The marker that causes a glint to appear in the center of the subject's pupil is determined to be located on the line of regard of the subject's eye, and to intersect with the point of gaze. Point of gaze on the surface, object, or visual scene is calculated as follows. First, by determining which marker glints, as provided by the corneal reflections of the markers, are closest to the center of the pupil in either or both of the subject's eyes. This subset of glints forms a region of interest (ROI). Second, by determining the gaze vector (relative angular or Cartesian distance to the pupil center) for each of the glints in the ROI. Third, by relating each glint in the ROI to the location or identification (ID) of a corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene observed by the eyes. Fourth, by interpolating the known locations of each these markers on the surface, object, or visual scene, according to the relative angular distance of their corresponding glints to the pupil center.
Owner:CHENG DANIEL +3
Method and apparatus for calibration-free eye tracking using multiple glints or surface reflections
InactiveUS20050175218A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementCorneal surfaceAngular distance
A system and method for eye gaze tracking in human or animal subjects without calibration of cameras, specific measurements of eye geometries or the tracking of a cursor image on a screen by the subject through a known trajectory. The preferred embodiment includes one uncalibrated camera for acquiring video images of the subject's eye(s) and optionally having an on-axis illuminator, and a surface, object, or visual scene with embedded off-axis illuminator markers. The off-axis markers are reflected on the corneal surface of the subject's eyes as glints. The glints indicate the distance between the point of gaze in the surface, object, or visual scene and the corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene. The marker that causes a glint to appear in the center of the subject's pupil is determined to be located on the line of regard of the subject's eye, and to intersect with the point of gaze. Point of gaze on the surface, object, or visual scene is calculated as follows. First, by determining which marker glints, as provided by the corneal reflections of the markers, are closest to the center of the pupil in either or both of the subject's eyes. This subset of glints forms a region of interest (ROI). Second, by determining the gaze vector (relative angular or cartesian distance to the pupil center) for each of the glints in the ROI. Third, by relating each glint in the ROI to the location or identification (ID) of a corresponding marker on the surface, object, or visual scene observed by the eyes. Fourth, by interpolating the known locations of each these markers on the surface, object, or visual scene, according to the relative angular distance of their corresponding glints to the pupil center.
Owner:CHENG DANIEL +3
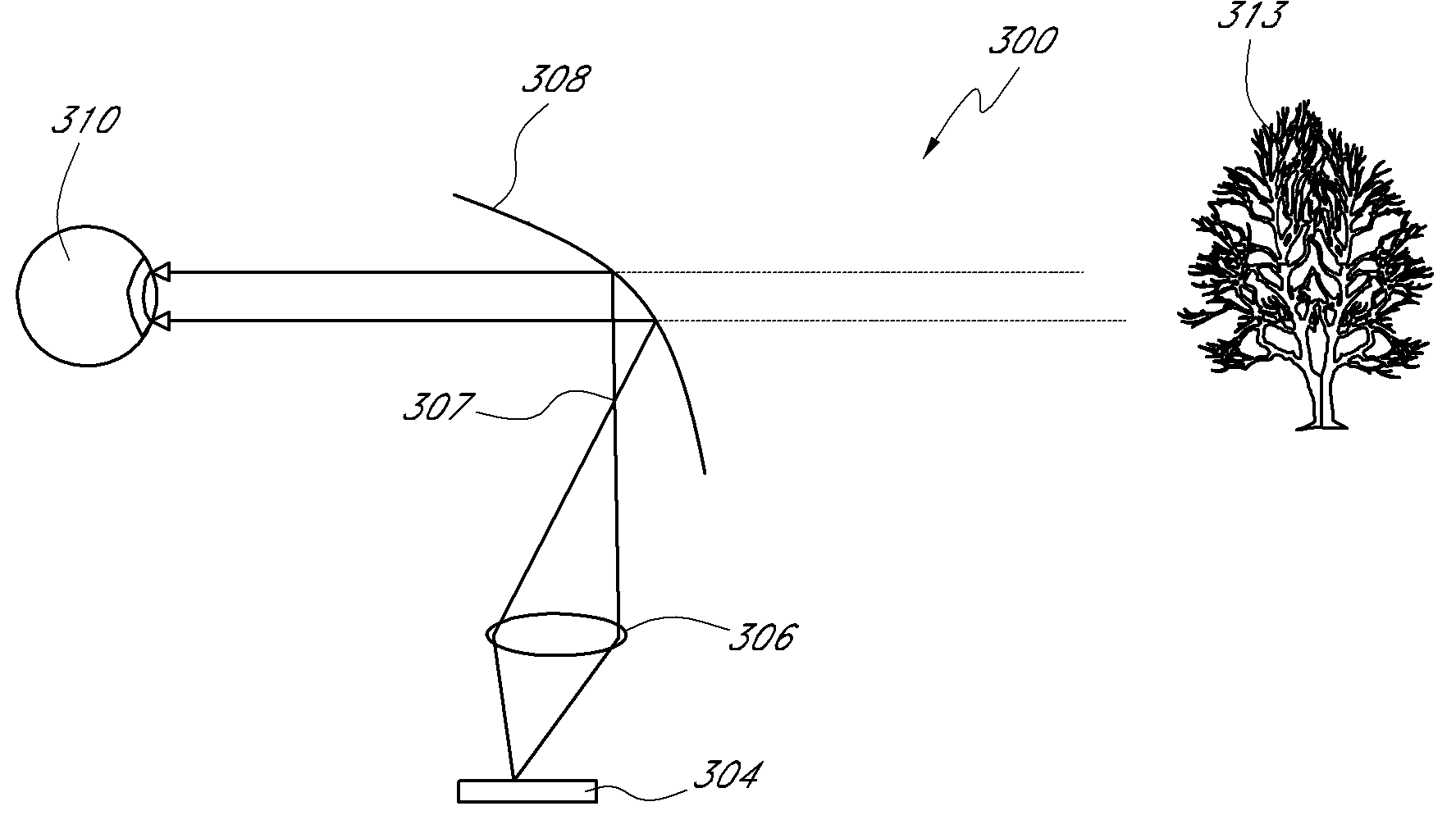
Personal Display Using an Off-Axis Illuminator
Certain embodiments include a head mounted display for displaying images that can be viewed by a wearer when the display is worn on the wearer's head. The display can include a spatial light modulator having an array of pixels selectively adjustable for producing spatial patterns. The array of pixels can define a substantially planar reflective surface on the spatial light modulator. The display can further include a light source. The display can also include illumination optics disposed to receive light from the light source and direct light onto the planar reflective surface of the spatial light modulator at an angle with respect to the surface normal of the planar reflective surface. The display can include imaging optics disposed with respect to the spatial light modulator to receive light from the spatial light modulator. The display can further include a curved reflector disposed to reflect light from the imaging optics so as to form a virtual image such that the image may be viewed by an eye of the wearer. The display can also include headgear for supporting the spatial light modulator, imaging optics, and reflector. In certain embodiments, only rays of light incident on the planar reflective surface of the spatial light modulator at an angle with respect to the surface normal of the planar reflective surface contribute to the virtual image viewable by the eye.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Metrology method and apparatus, lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method and substrate
ActiveUS8411287B2Made preciselyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansGratingMetrology
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
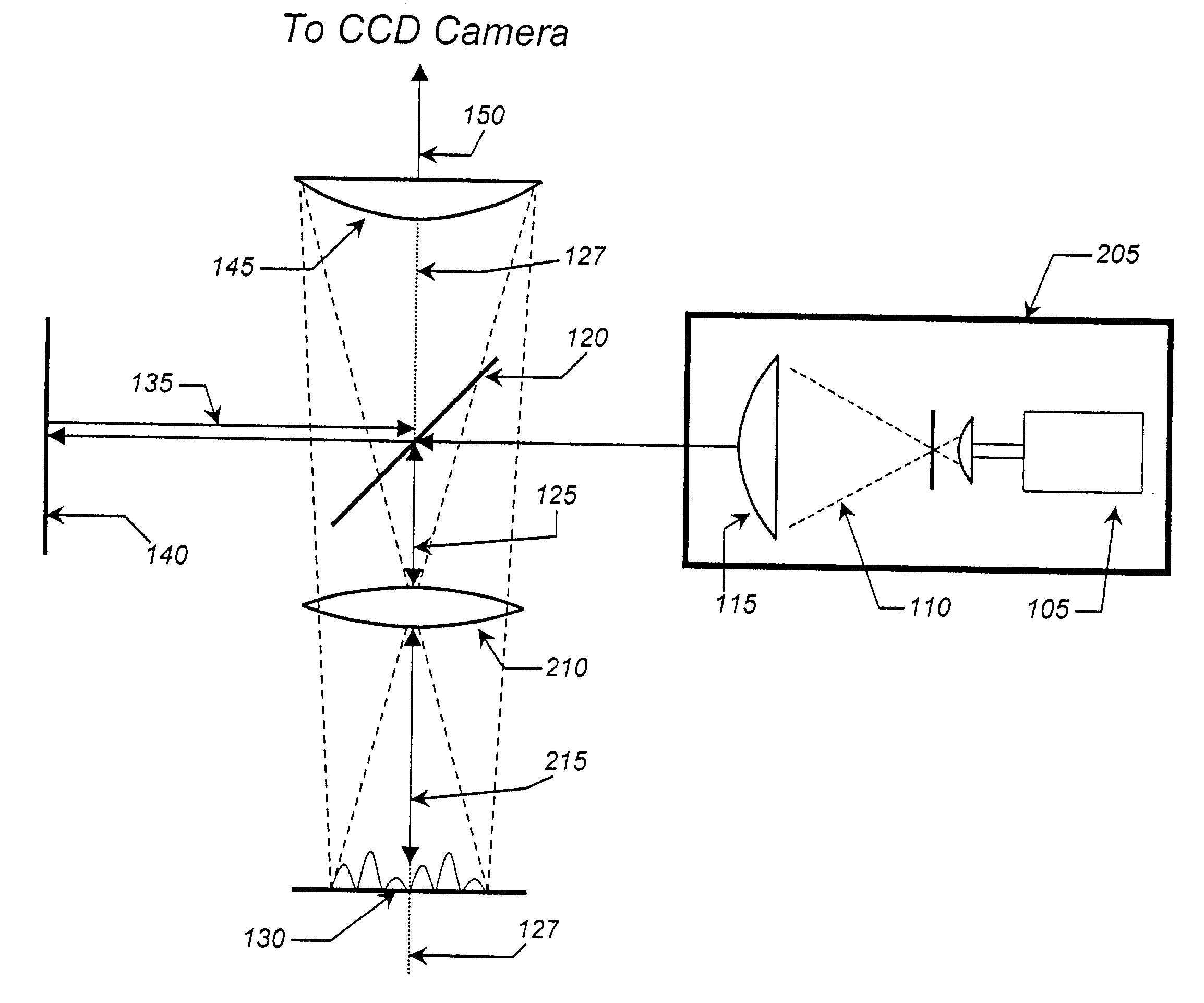
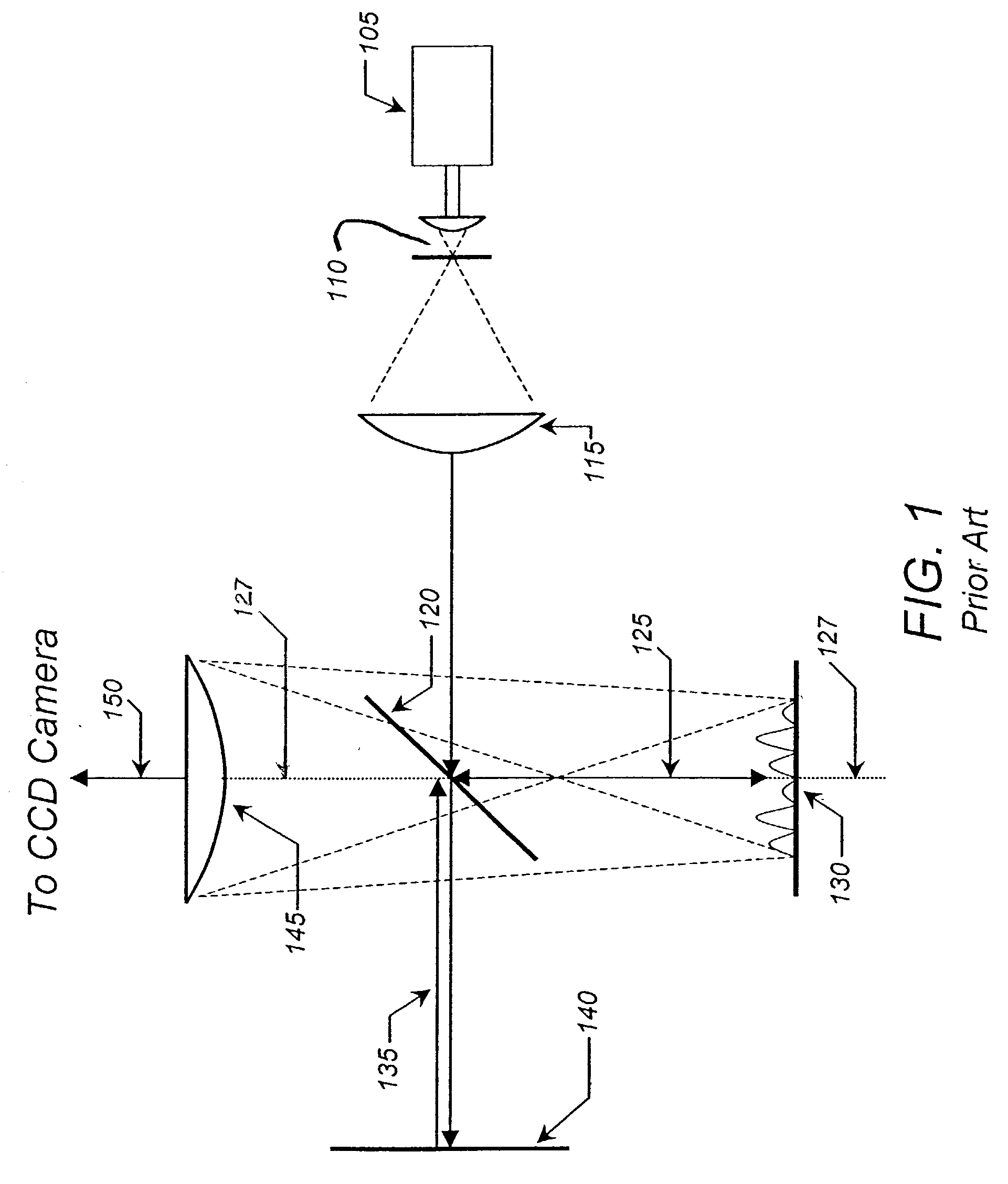
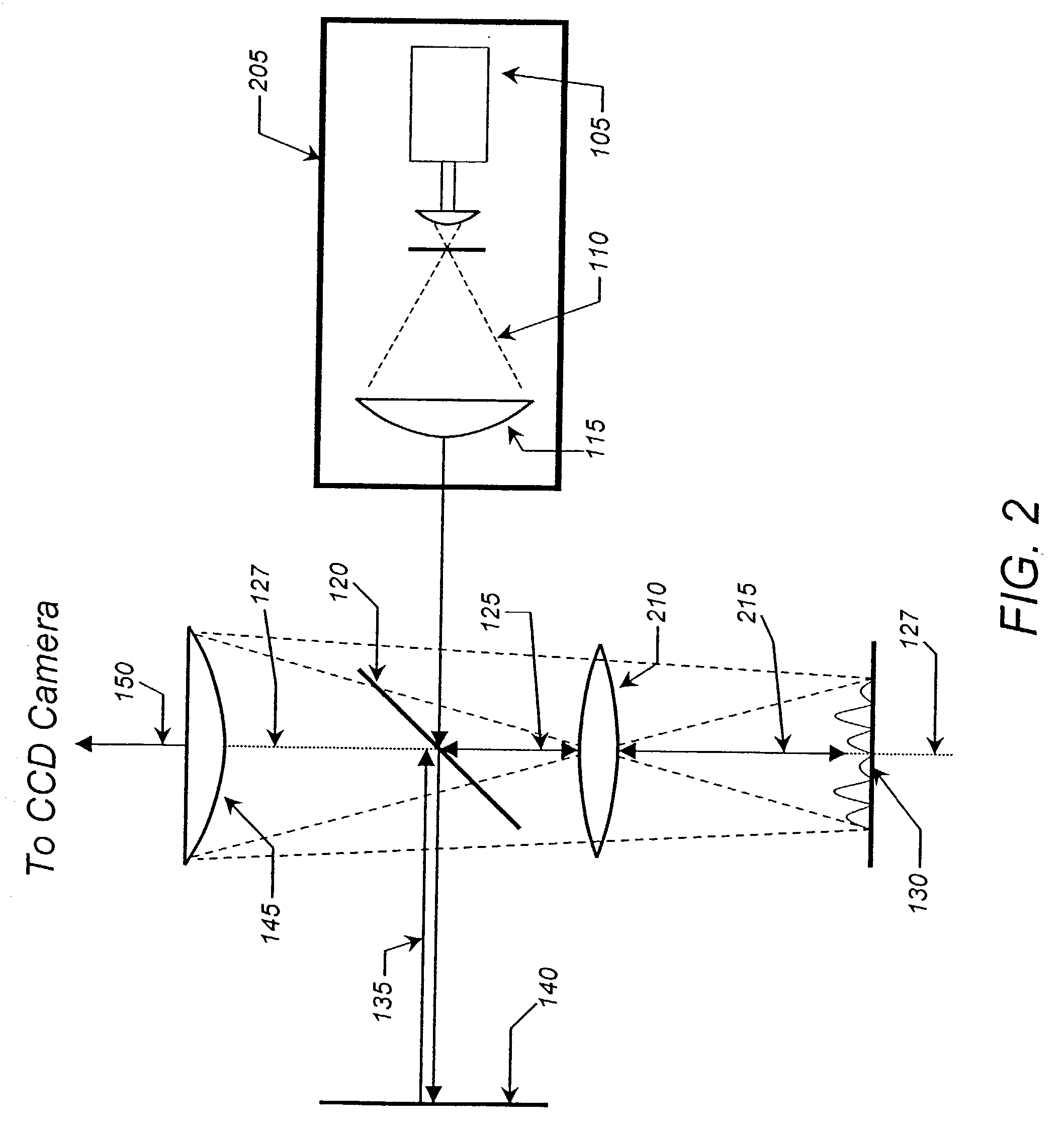
Handheld portable fundus imaging system and method
InactiveUS20130057828A1Reduce restrictionsLow costOthalmoscopesPhotographyCamera lensOff-axis illumination
A system and method for fundus imaging wherein selective illumination of a sector of the field of view of the fundus, using off-axis illumination, provides images of acceptable clarity, resolution, and size, with significantly reduced reflections, in a compact system. By rotating illumination around the optical axis, sectors of the fundus may be selectively and sequentially illuminated. An image of the entire field of view of the fundus is obtained by combining images, e.g. two or more half images, obtained within a single shutter exposure or capture period. An illumination system using LED light sources and a rotatable occluder provides for a lightweight, handheld and portable fundus imaging system. It may take the form of a fundus camera, a fundus imaging lens module for regular camera, or an adapter which couples to the standard lens of a camera to create a low cost fundus camera.
Owner:MASIDAH CORP
Hyperspectral microscope for in vivo imaging of microstructures and cells in tissues
InactiveUS20070160279A1Improve image contrastImprove visibilityDiagnostics using spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansOff-axis illuminationIn vivo
An optical hyperspectral / multimodal imaging method and apparatus is utilized to provide high signal sensitivity for implementation of various optical imaging approaches. Such a system utilizes long working distance microscope objectives so as to enable off-axis illumination of predetermined tissue thereby allowing for excitation at any optical wavelength, simplifies design, reduces required optical elements , significantly reduces spectral noise from the optical elements and allows for fast image acquisition enabling high quality imaging in-vivo. Such a technology provides a means of detecting disease at the single cell level such as cancer, precancer, ischemic, traumatic or other type of injury, infection, or other diseases or conditions causing alterations in cells and tissue micro structures.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Contact or proximity printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050007567A1Avoid stickingElectric discharge tubesPhoto-taking processesLithographic artistImage resolution
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact or proximity printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:TAKUMI TECH
Hyperspectral microscope for in vivo imaging of microstructures and cells in tissues
InactiveUS7945077B2Increase contrastImprove visibilityDiagnostics using spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseOff-axis illumination
An optical hyperspectral / multimodal imaging method and apparatus is utilized to provide high signal sensitivity for implementation of various optical imaging approaches. Such a system utilizes long working distance microscope objectives so as to enable off-axis illumination of predetermined tissue thereby allowing for excitation at any optical wavelength, simplifies design, reduces required optical elements, significantly reduces spectral noise from the optical elements and allows for fast image acquisition enabling high quality imaging in-vivo. Such a technology provides a means of detecting disease at the single cell level such as cancer, precancer, ischemic, traumatic or other type of injury, infection, or other diseases or conditions causing alterations in cells and tissue micro structures.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Contact printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS6961186B2Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistSolid mass
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
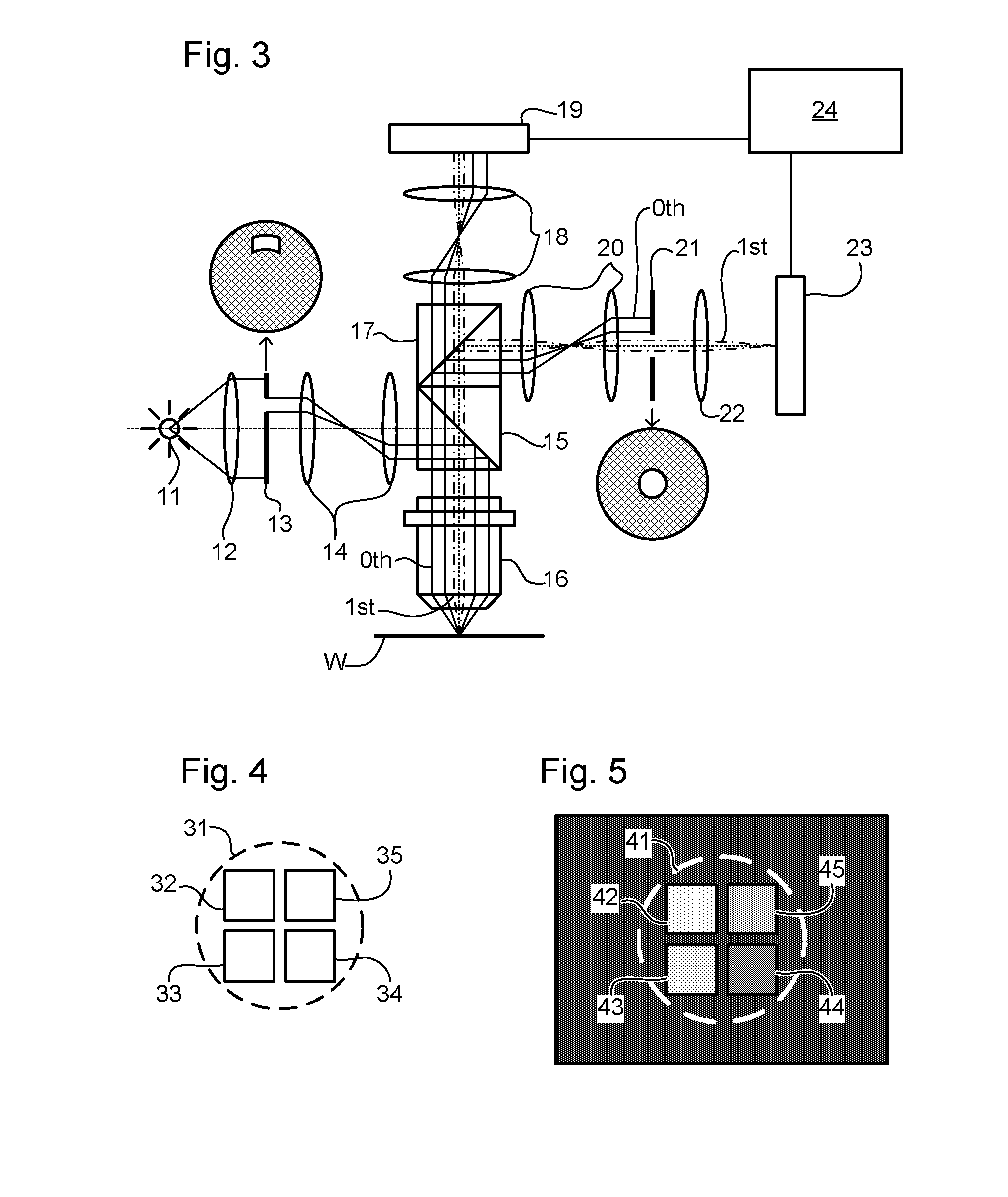
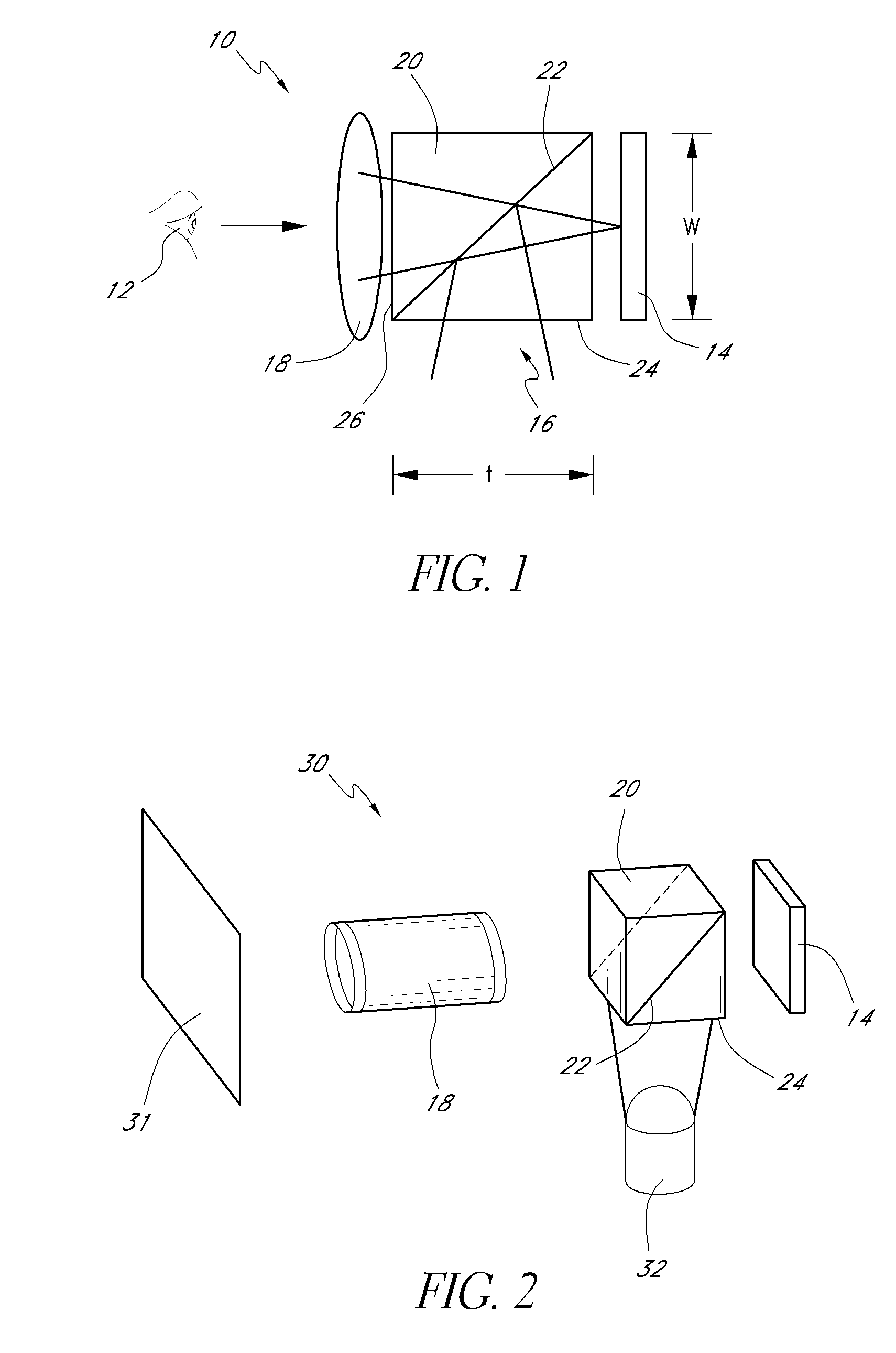
Off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS6747771B2Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording an off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes: reflecting a reference beam from a reference mirror at a non-normal angle; reflecting an object beam from an object at an angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; digitally recording the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
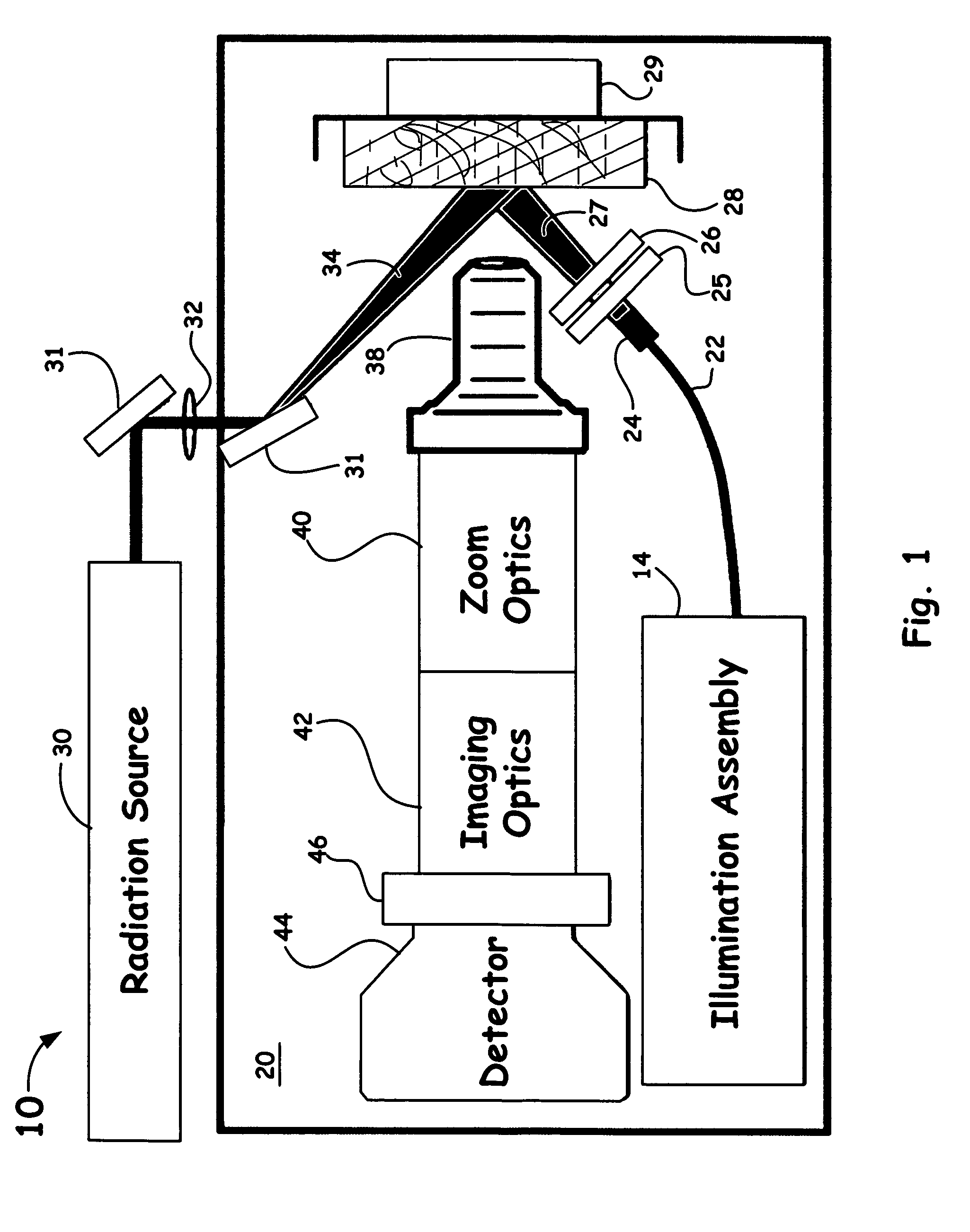
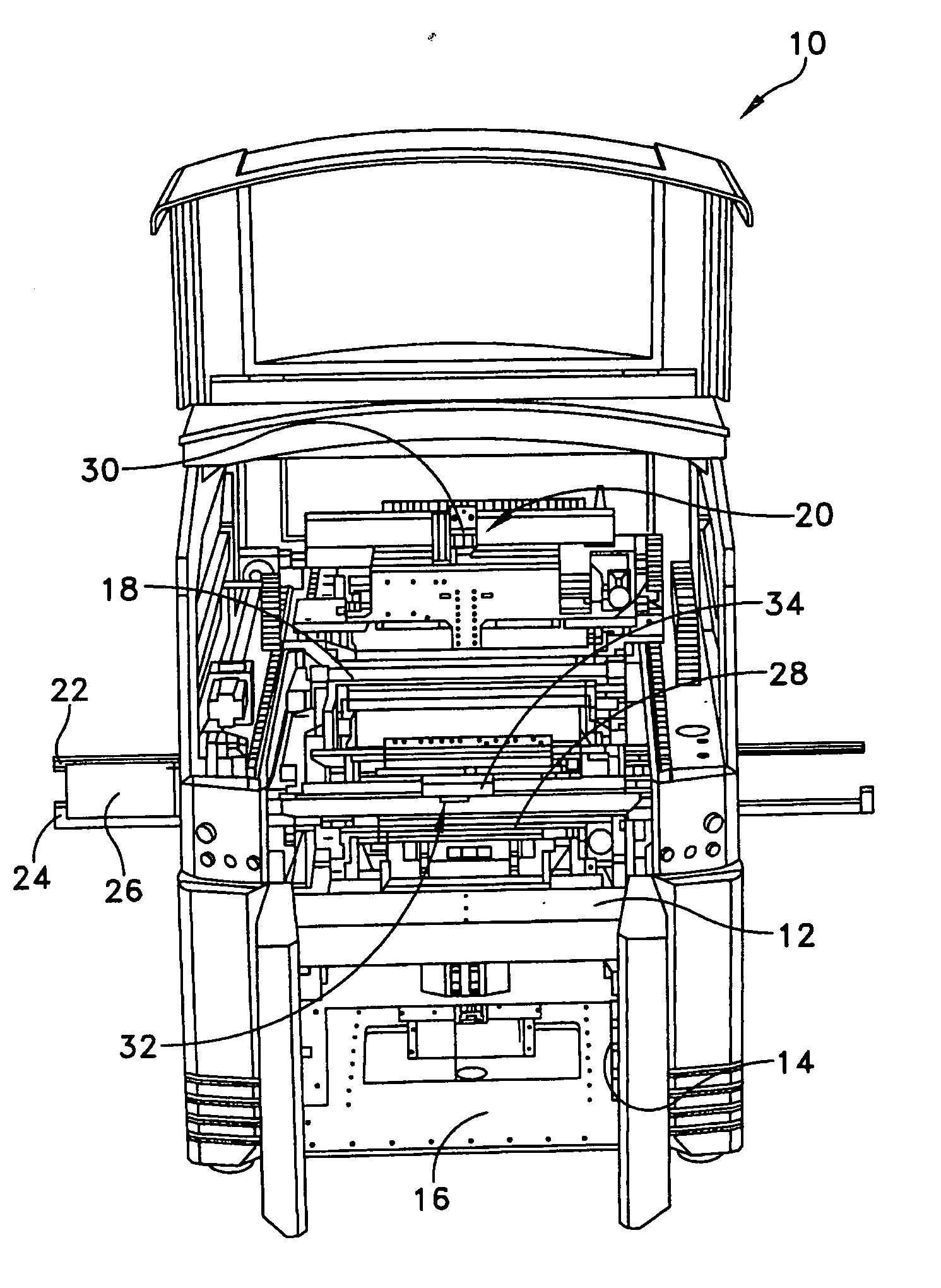
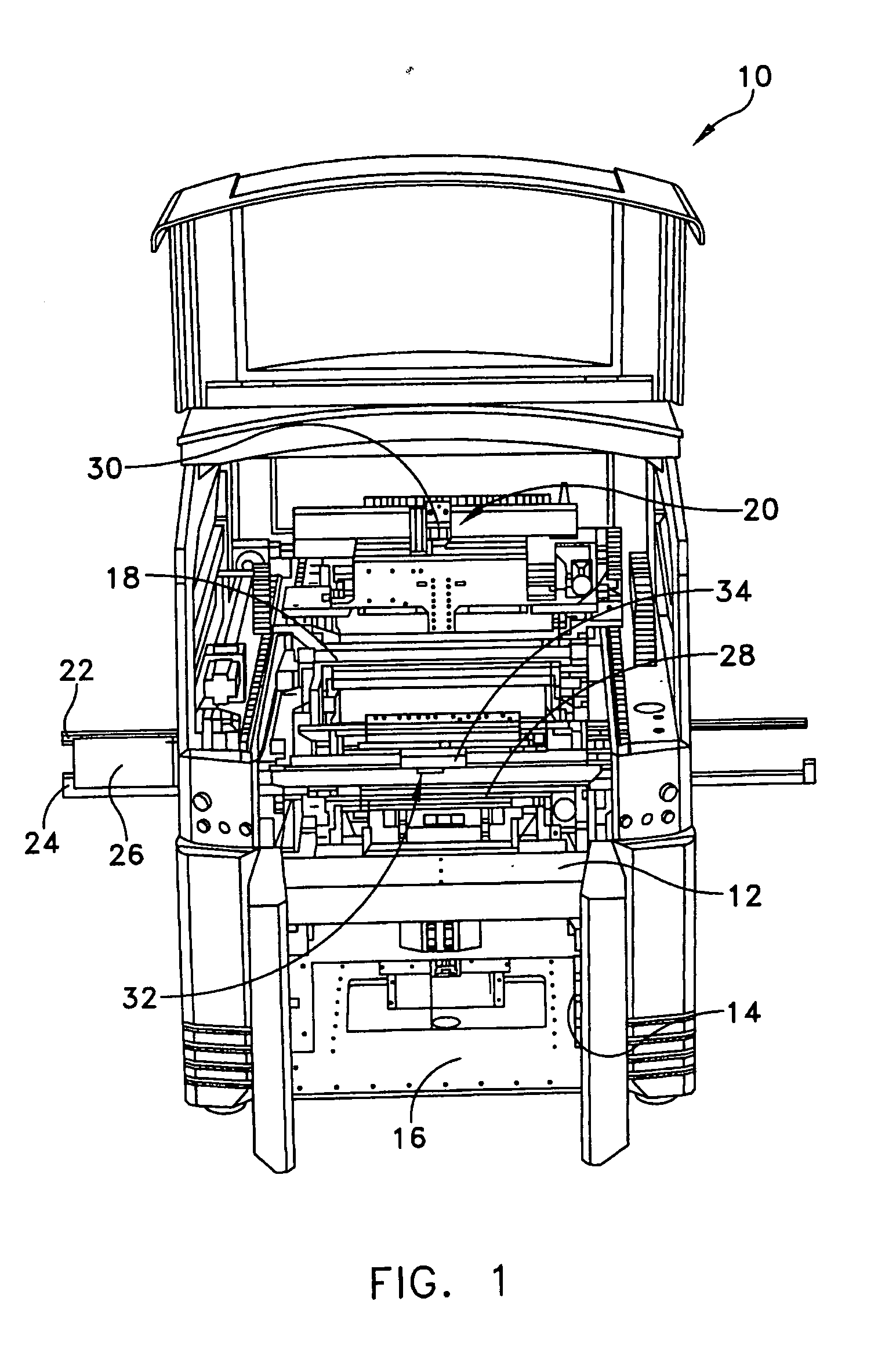
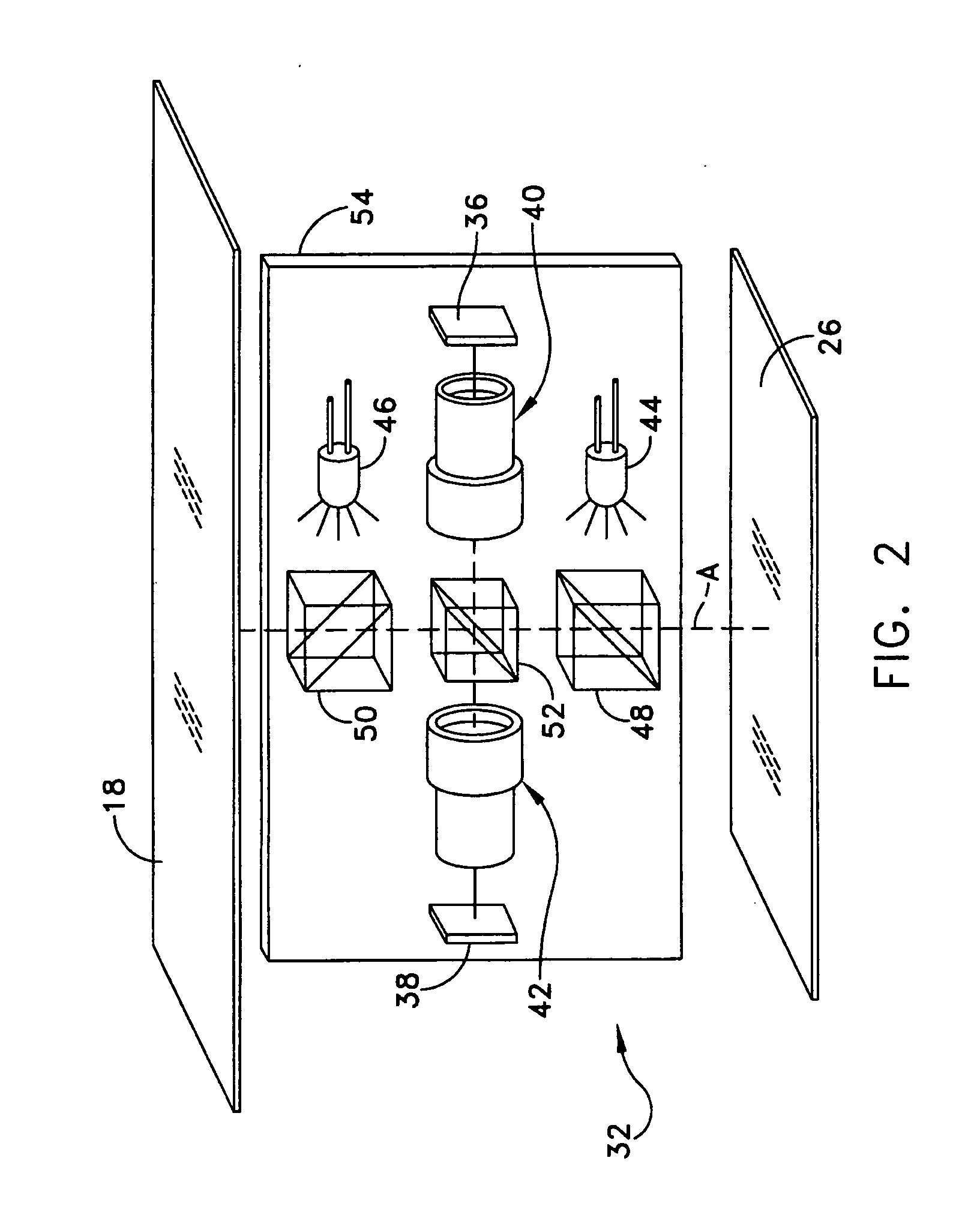
Off-axis illumination assembly and method
ActiveUS20070175343A1Accuracy in determineInking apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsOff-axis illuminationEngineering
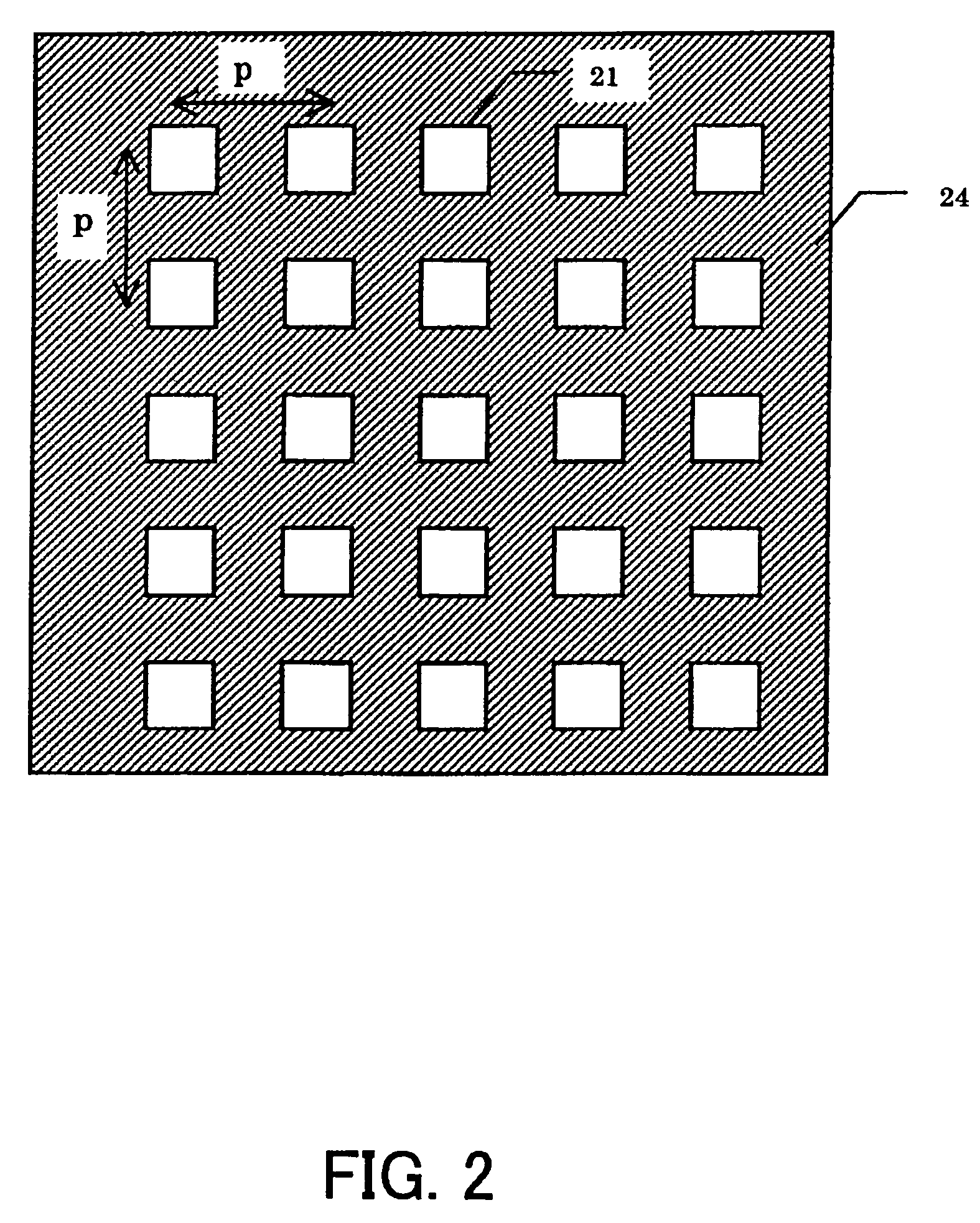
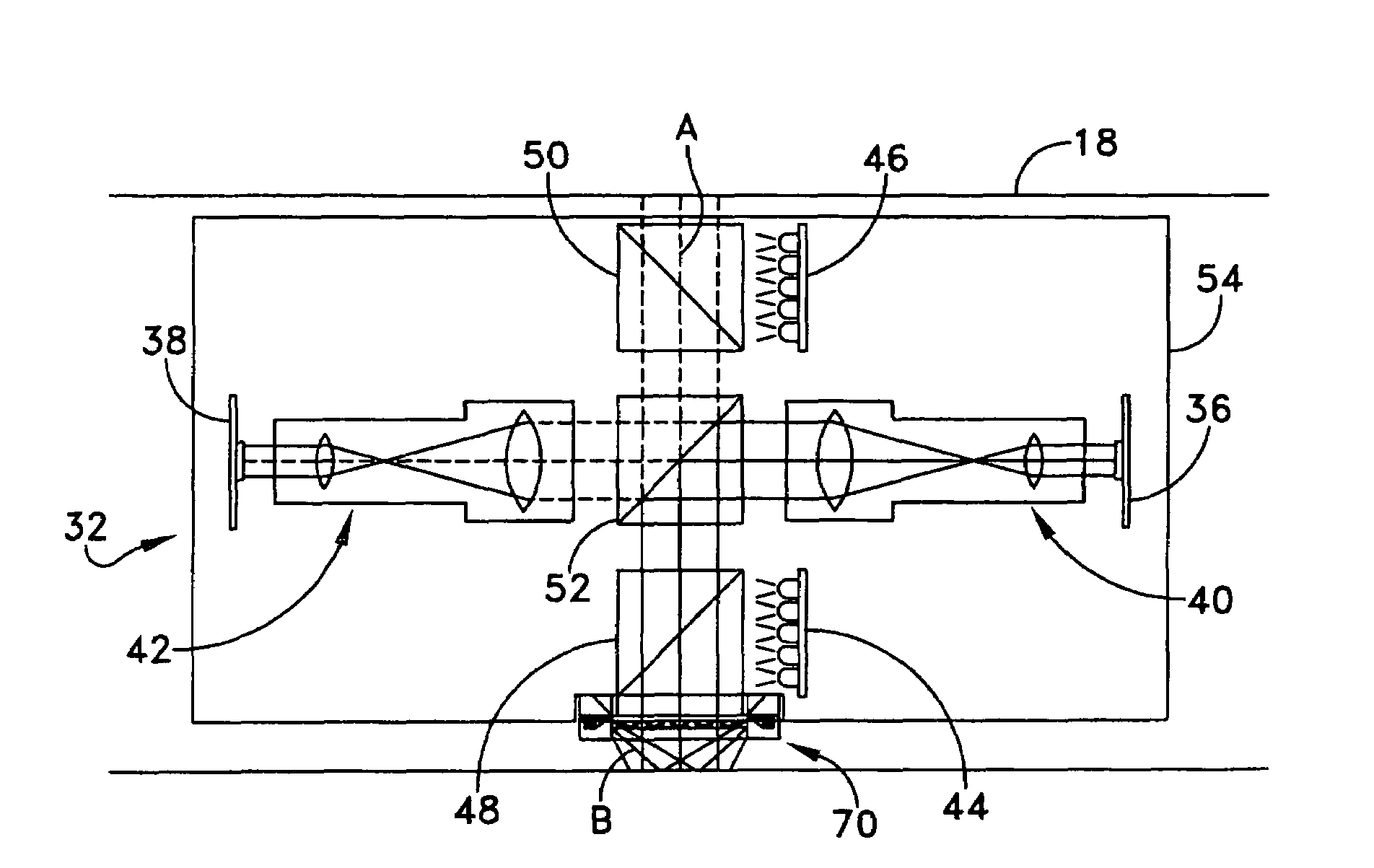
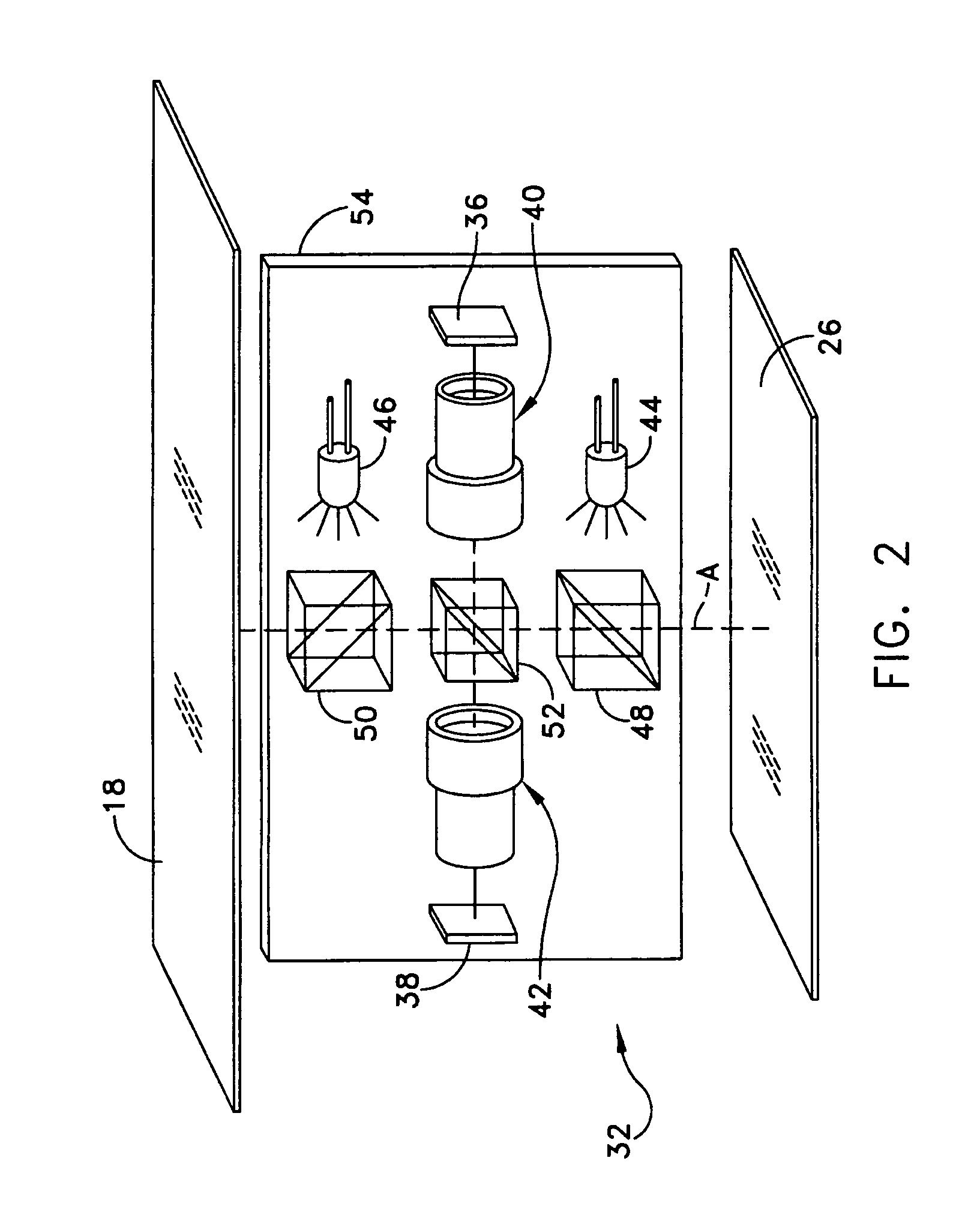
A stencil printer is provided for depositing solder paste onto a surface of an electronic substrate. The stencil printer includes a frame and a stencil coupled to the frame. The stencil has a plurality of apertures formed therein. The stencil printer further includes a dispenser coupled to the frame. The stencil and the dispenser are adapted to deposit solder paste onto the electronic substrate. The stencil printer further includes an imaging system constructed and arranged to capture an image of the electronic substrate. The imaging system includes a camera assembly, an on-axis illumination assembly adapted to generate light substantially along a first axis generally perpendicular to the surface of the electronic substrate, and an off-axis illumination assembly adapted to generate rays of light substantially along a second axis extending at an angle with respect to the first axis. A controller is coupled to the imaging system to control movement of the imaging system to capture an image.
Owner:SPEEDLINE TECH
Metrology method and apparatus, lithographic apparatus, lithographic processing cell and substrate comprising metrology targets
ActiveCN102483582APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMetrologyGrating
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Methods for enhancing photolithography patterning
ActiveUS20090214984A1Increased process windowSecond pitchSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOff-axis illuminationProcess window
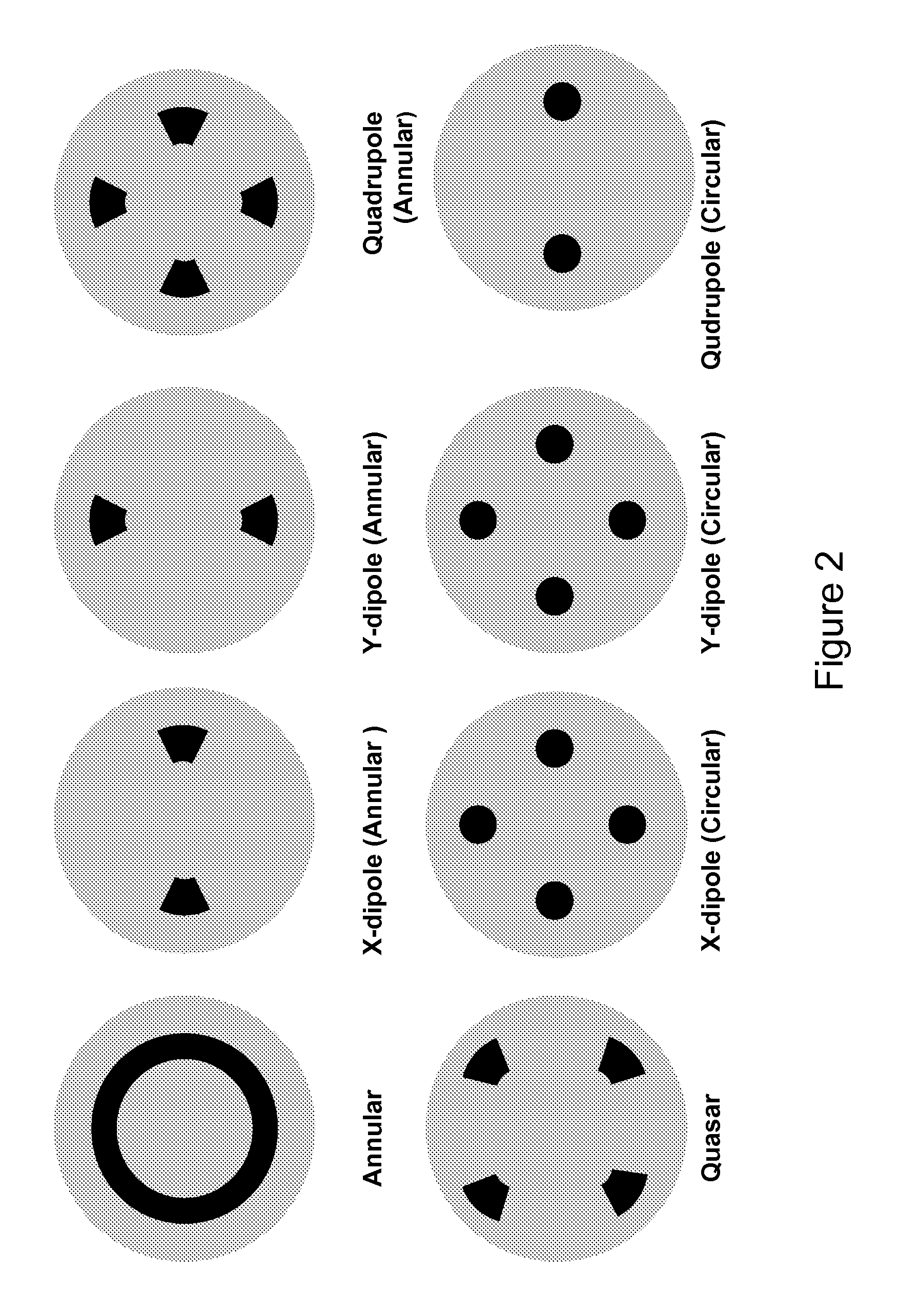
A method for fabricating a a semiconductor device that includes: providing a substrate prepared with a photoresist layer; providing a photomask comprising a first and a second pattern having a respective first and second pitch range; providing a composite aperture comprising a first and a second off-axis illumination aperture pattern, the first off-axis aperture pattern having a configuration that improves the process window of the first pitch range and the second off-axis aperture pattern having a configuration that improves the process window for a second pitch range; exposing the photoresist layer on the substrate with radiation from an exposure source through the composite aperture and the photomask; and developing the photoresist layer to pattern the photoresist layer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +2
High-magnification three-dimensional imaging microscope based on double-light source off-axis illumination and imaging method
InactiveCN101900875AEasy to findSynchronous adjustment caliberMicroscopesIlluminanceOff-axis illumination
The invention discloses a high-magnification three-dimensional imaging microscope based on double-light source off-axis illumination and an imaging method and relates to a device for acquiring a left path of image and a right path of image by a CCD (Charge Coupled Device), a method for changing focus depth, a method for acquiring and separating two paths of images, a system calibrating method and a three-dimensional coordinate calculating method of a target. The three-dimensional imaging microscope mainly comprises a left off-axis light source, a right off-axis light source, a concentrated projecting assembly, a microobjective and a CCD, wherein the left off-axis light source and the right off-axis light source are symmetrical. The imaging method comprises the following steps of: calibrating the relation of microscope defocusing amount and double-image distance; acquiring an image; processing the image; recognizing a target; calculating a two-dimensional coordinate; and converting the two-dimensional coordinate into a three-dimensional coordinate. A left and right image synchronous acquiring method comprises a two-color method and a polarization method, and an asynchronous acquiring method comprises an LED switching illumination method. The three-dimensional coordinate of an object can be rapidly calculated. An illuminating light beam is converged on entrance pupils of the microobjective, the diameter of the light beam is limited by a variable diaphragm, and the focus depth is changed, thereby maintaining the illumination of the image surface to be basic invariant.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
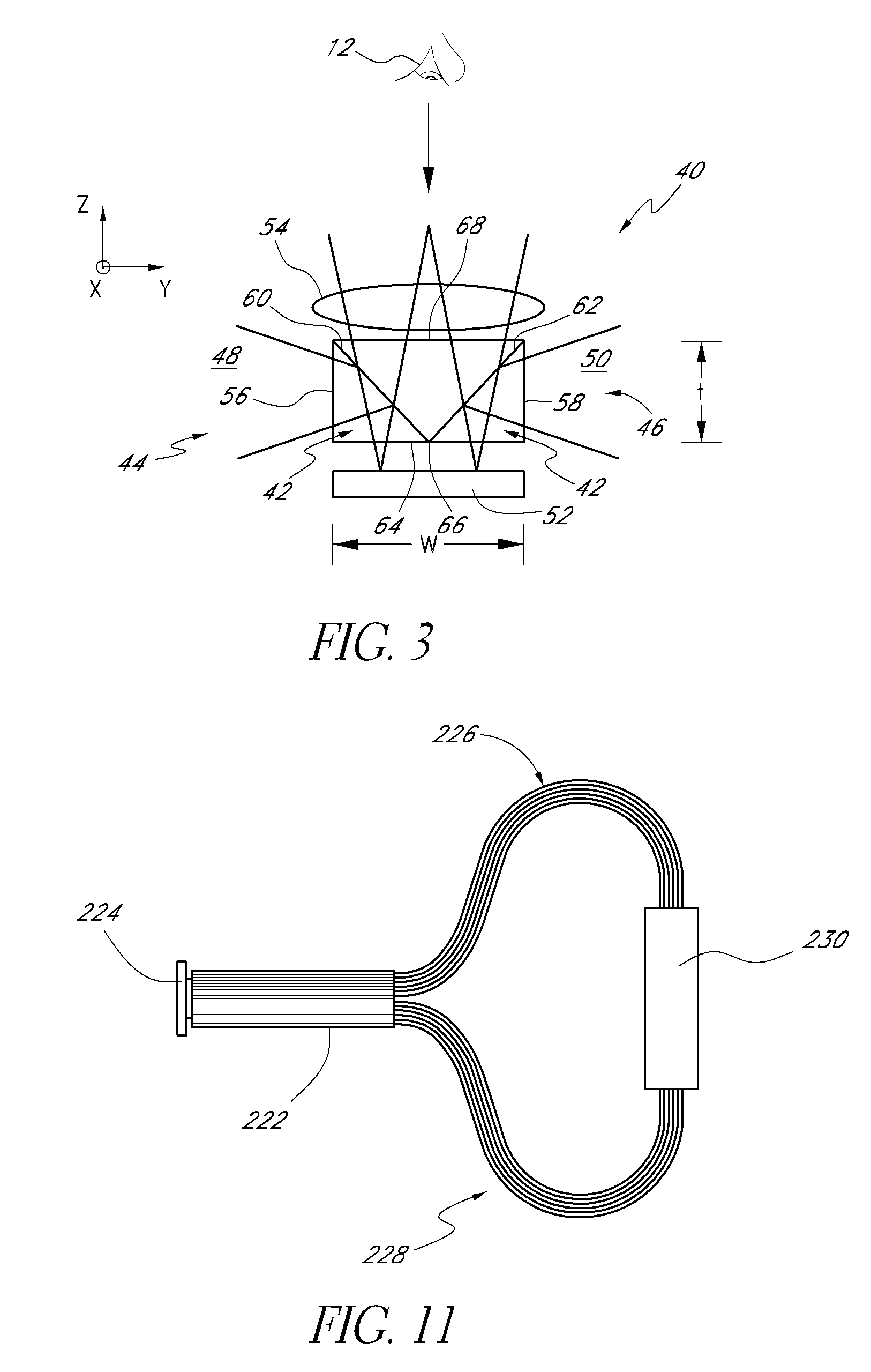
Content-based fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS20040042015A1Cost effectiveHigh resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for content-based fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method includes calculating an illumination angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens as a function of data representing a Fourier analyzed spatially heterodyne hologram; recording a content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
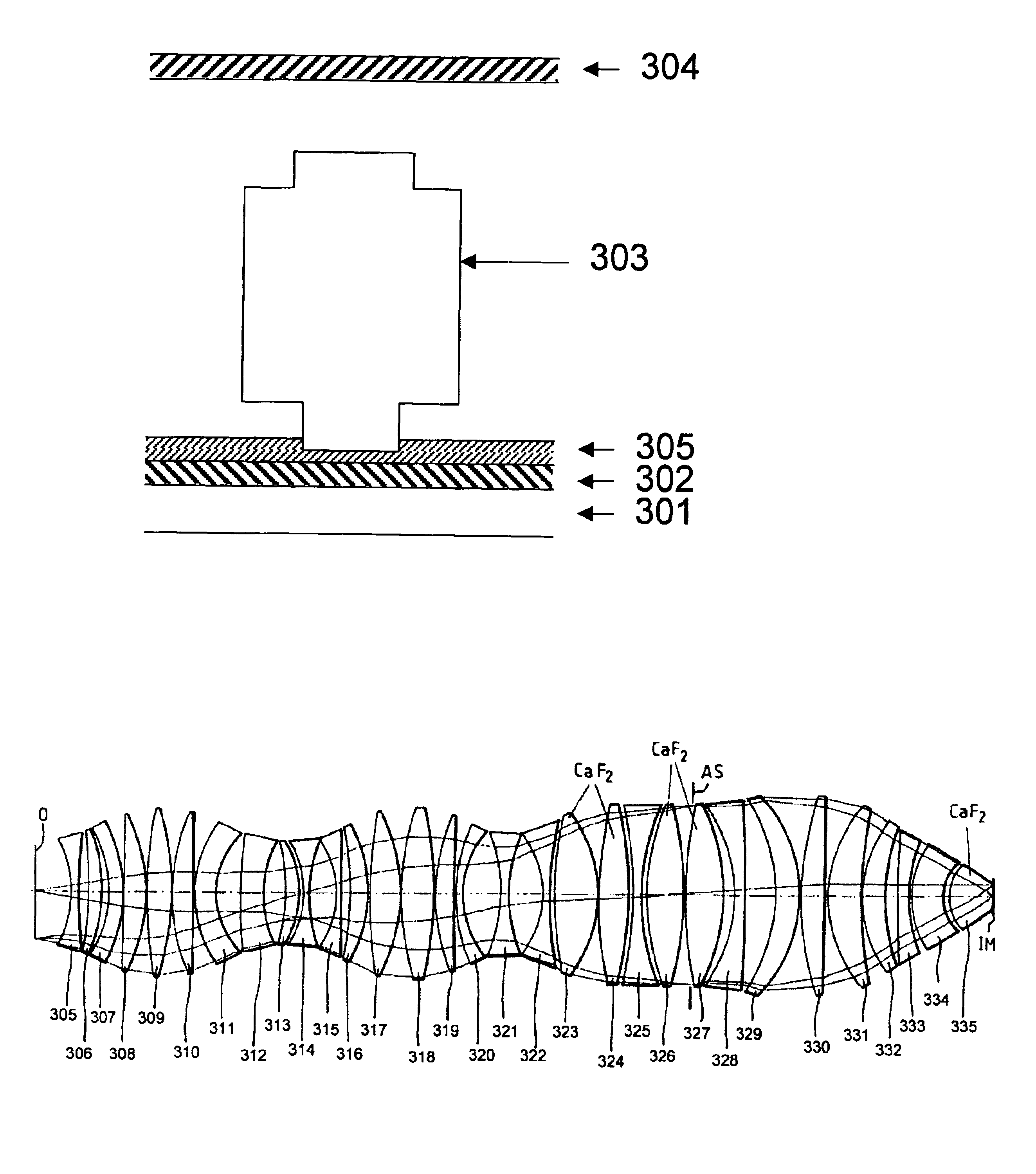
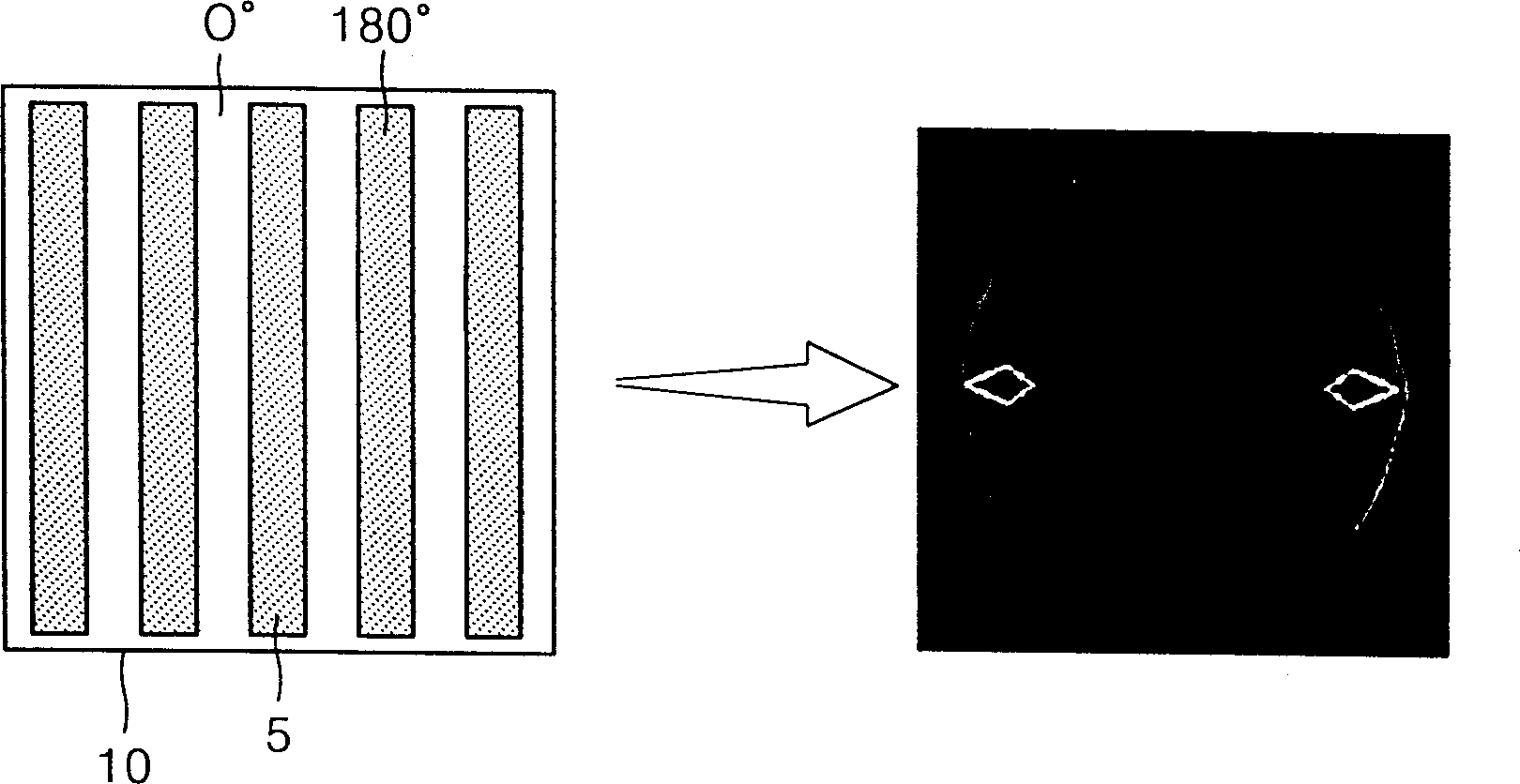
Photomask for off-axis illumination and its producing method
InactiveCN1437069AEasy to handleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhase gratingOff-axis illumination
A photomask (50) comprises a transparent substrate; opaque patterns formed on a front surface of the substrate; and phase gratings (150) formed on a back surface of the substrate, allowing off-axis illumination (OAI) of an incident light source beyond an OAI limit of an exposure equipment. A photomask comprises a transparent substrate; opaque patterns formed on a front surface of the substrate, for defining a floodlighting portion for forming patterns; and phase gratings formed on a back surface of the substrate, allowing OAI of an incident light source beyond an OAI limit of exposure equipment, allowing use in an outmost region of an aperture and allowing modified illumination having a shape suitable for a layout of the opaque patterns. An independent claim is also included for a method of fabricating a photomask comprising forming opaque patterns for defining a floodlighting portion for forming patterns, on a front surface of a substrate; and forming phase gratings on a back surface of the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photolithography exposure device for implementing off-axis illumination by using free-form surface lens
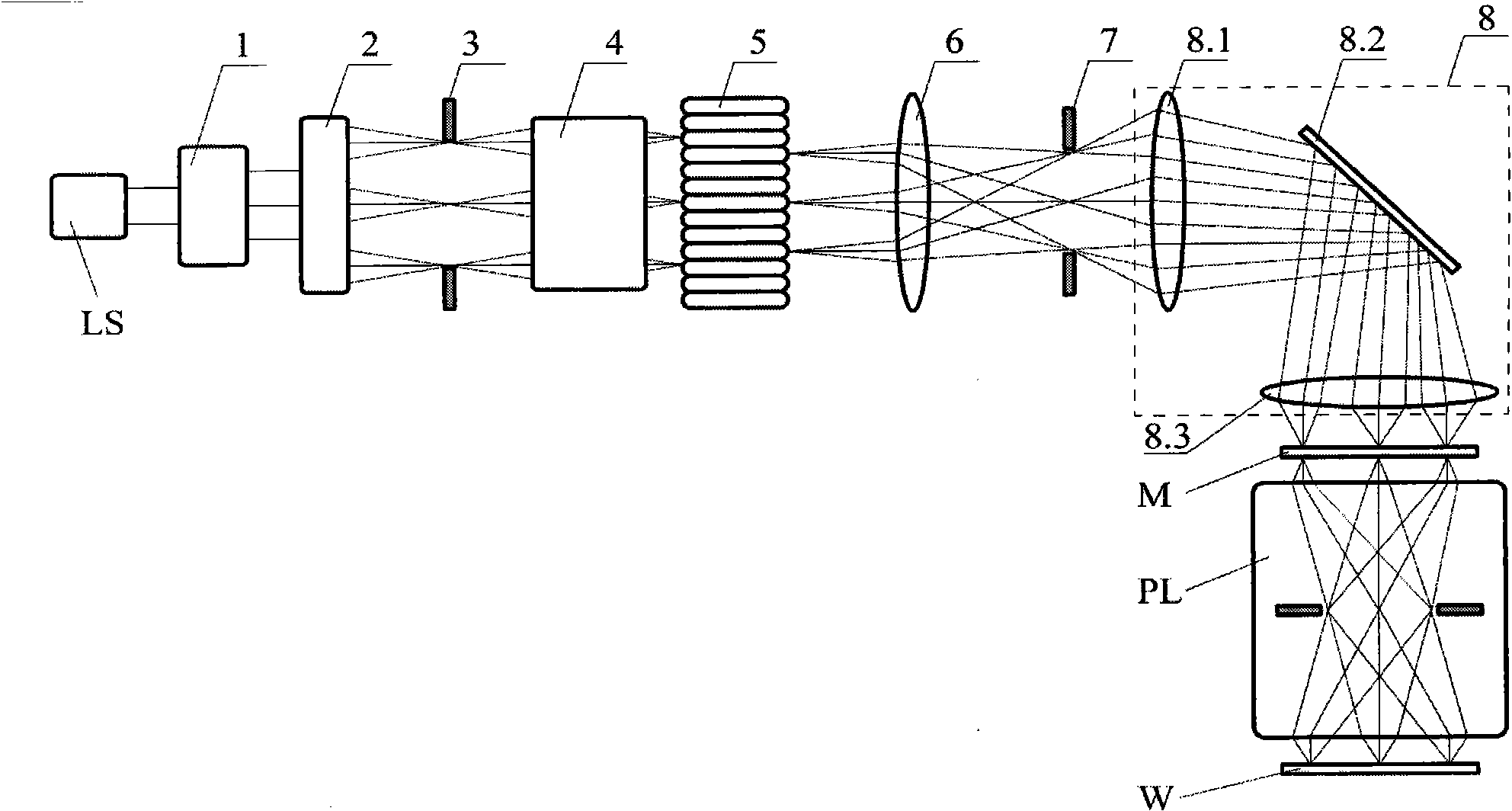
InactiveCN101916047AGood beam shaping effectImprove energy utilizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam expanderIntegrator
The invention discloses a photolithography exposure device for implementing off-axis illumination by using a free-form surface lens. The photolithography exposure device comprises a laser source, a beam expander, a free-form surface lens beam shaper, a filtering diaphragm, a varifocal optical system, an optical integrator, a collimation optical system, a field diaphragm, a relay optical system, a mask, a photolithography projection objective and photoresist, wherein the relay optical system comprises a front lens group, a middle reflection lens and a rear lens group; the position of the filtering diaphragm and the position of the front surface of the optical integrator form a pair of conjugate positions of the varifocal optical system; the position of the rear surface of the optical integrator and the position of the field diaphragm form a pair of conjugate positions of the collimation optical system; the position of the field diaphragm and the position of the mask form a pair of conjugate positions of the relay optical system; and the position of the mask and the position of the photoresist form a pair of conjugate positions of the photolithography projection objective. The photolithography exposure device has the advantages of good shaping effect and high energy utilization rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rapid acquisition fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS20040042056A1Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOff-axis illuminationDigital recording
Systems and methods are described for rapid acquisition of fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording a plurality of off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne holograms, each of the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne holograms including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes digitally recording, with a first illumination source of an interferometer, a first off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; and digitally recording, with a second illumination source of the interferometer, a second off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS20040042057A1Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording an off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes: reflecting a reference beam from a reference mirror at a non-normal angle; reflecting an object beam from an object at an angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; digitally recording the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Photomask and methods for manufacturing and correcting photomask
ActiveUS20110294045A1Increase contrastReduce mask costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentTarget surfaceOff-axis illumination
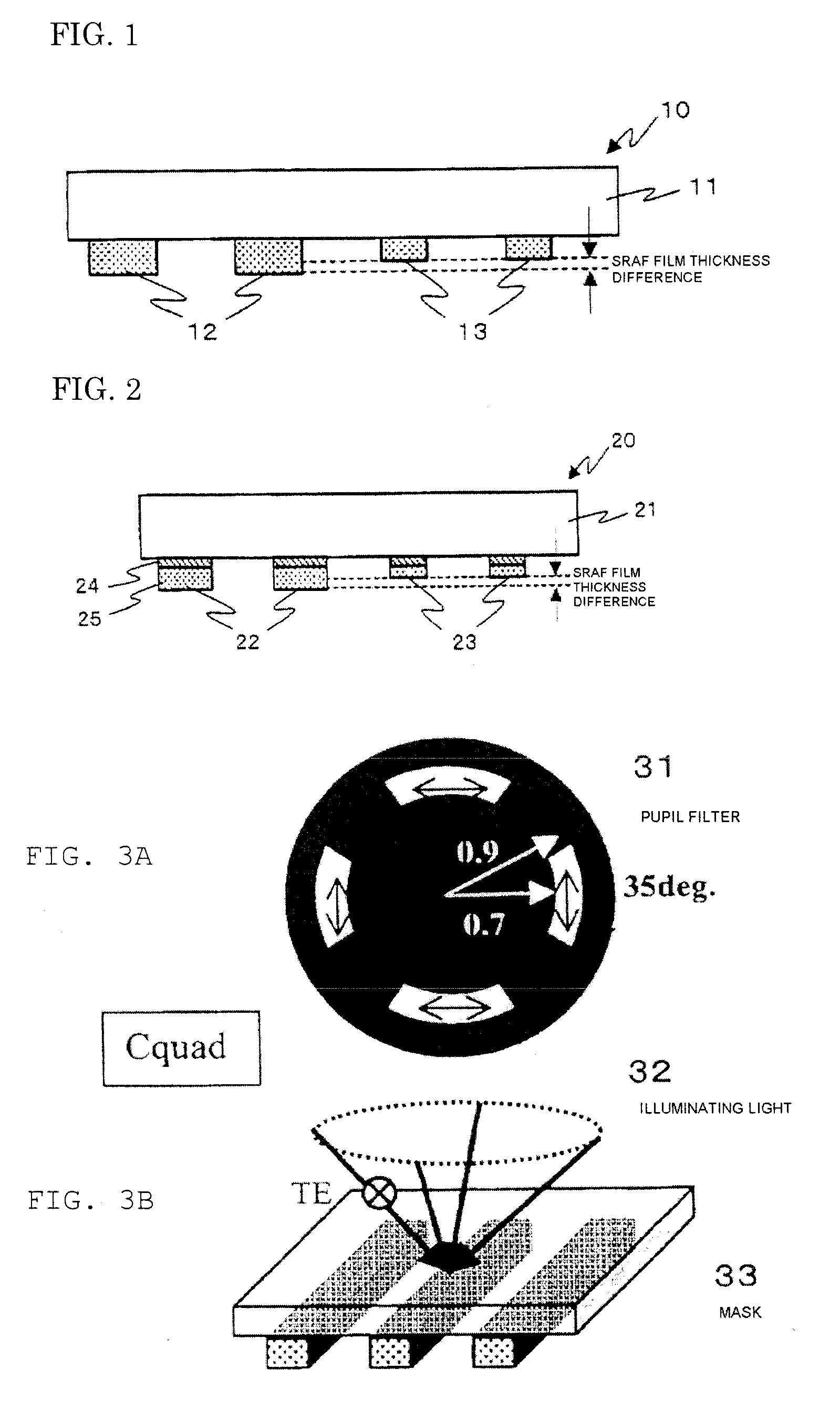
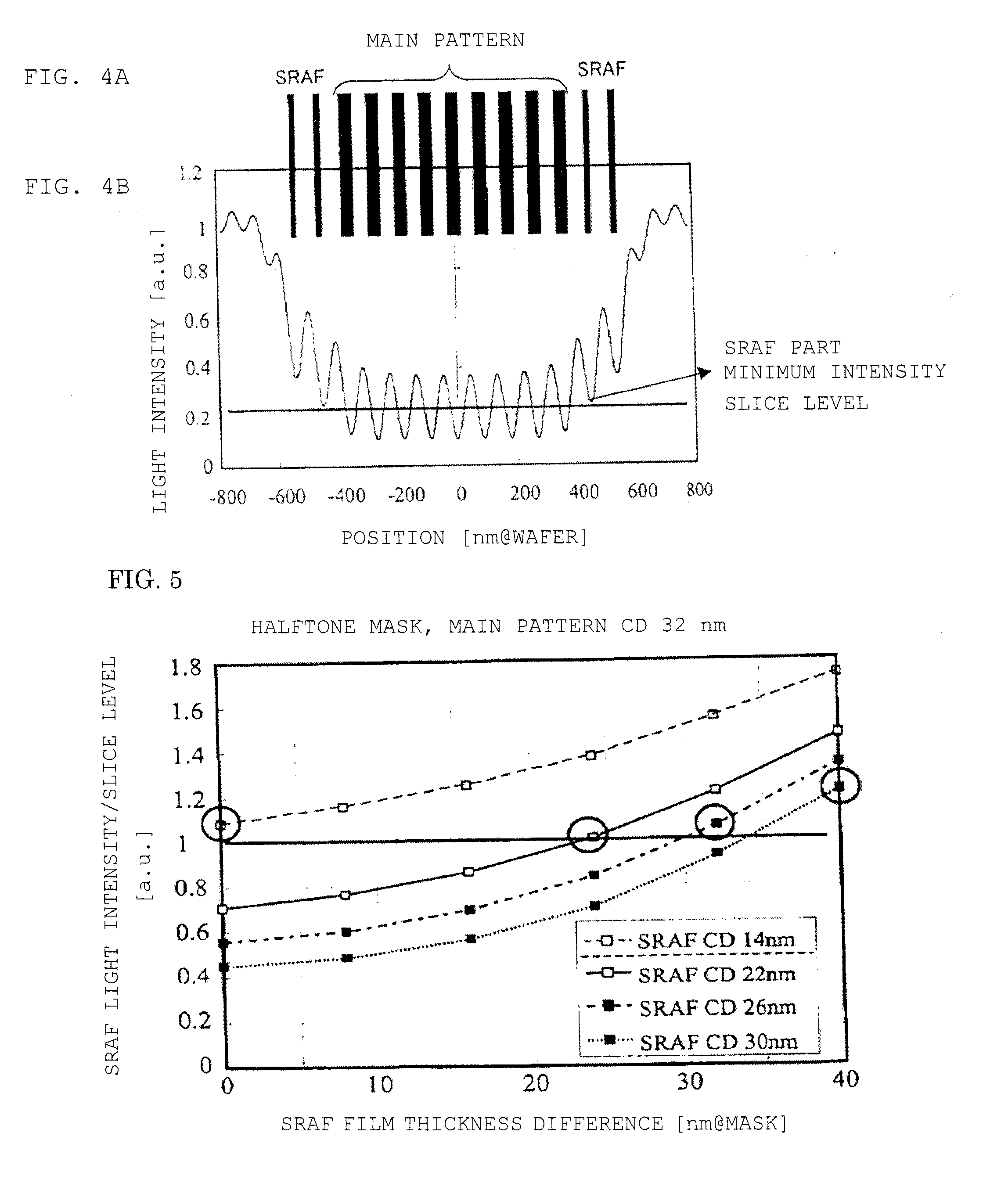
The present invention provides a halftone mask comprising an assist pattern and a manufacturing method of the halftone mask, which uses an ArF excimer laser as an exposing source, is used for a projection exposure by an off axis illumination, does not resolve the assist pattern while keeping the focal depth magnification effect as the assist pattern, and may form a transferred image having high contrast of a main pattern. A photomask is a photomask comprising the main pattern which is transferred to a transfer-target surface by the projection exposure and the assist pattern which is formed nearby the main pattern and not transferred, characterized in that the main pattern and the assist pattern are each constituted from a semi-transparent film made of the same material, a retardation of 180° is generated between the light transmitting through the main pattern and the light transmitting through a transparent region of a transparent substrate, and a predetermined retardation within the scope of 70° to 115° is generated between the light transmitting through the assist pattern and the light transmitting through the transparent region of the transparent substrate.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060197934A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOff-axis illuminationLength wave
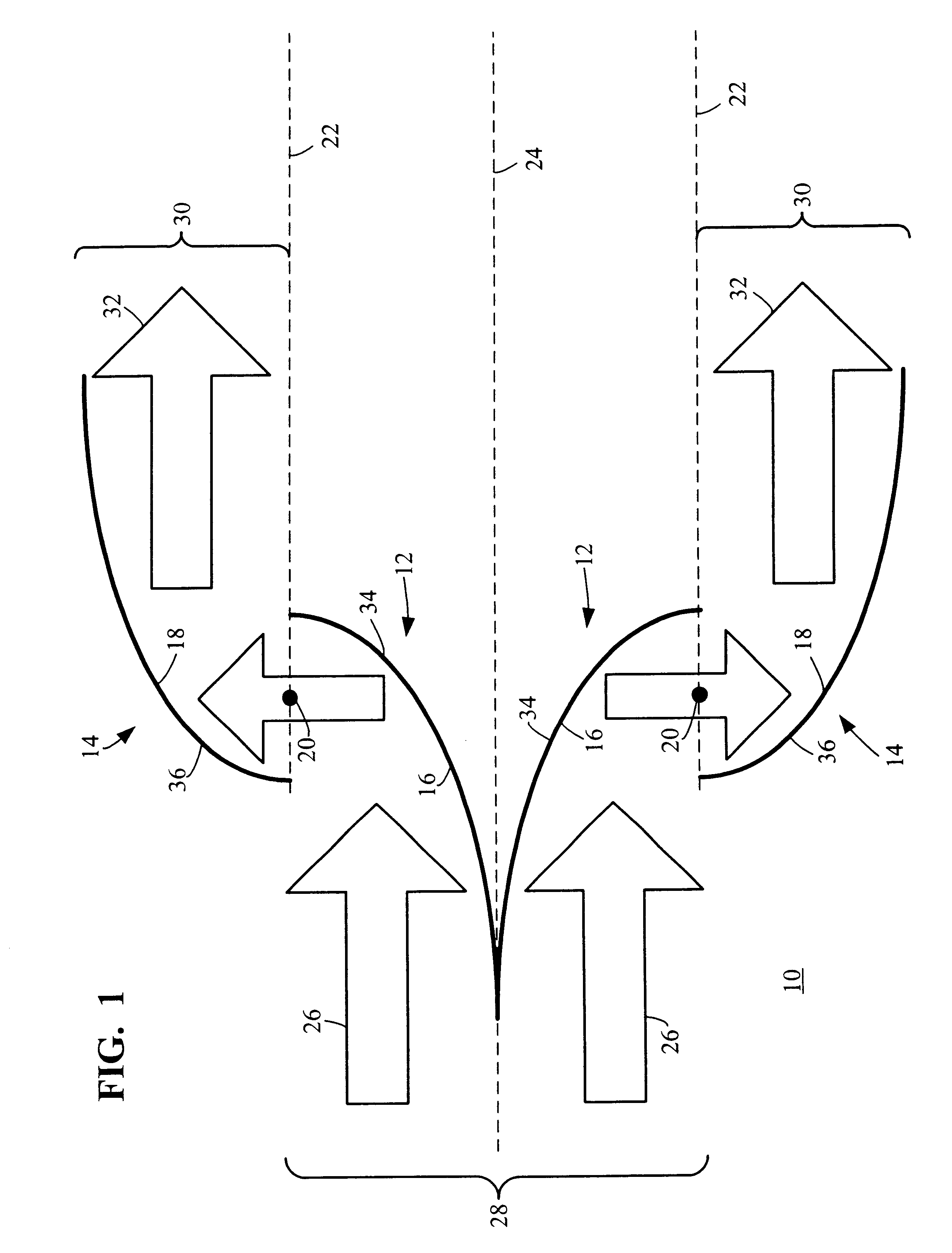
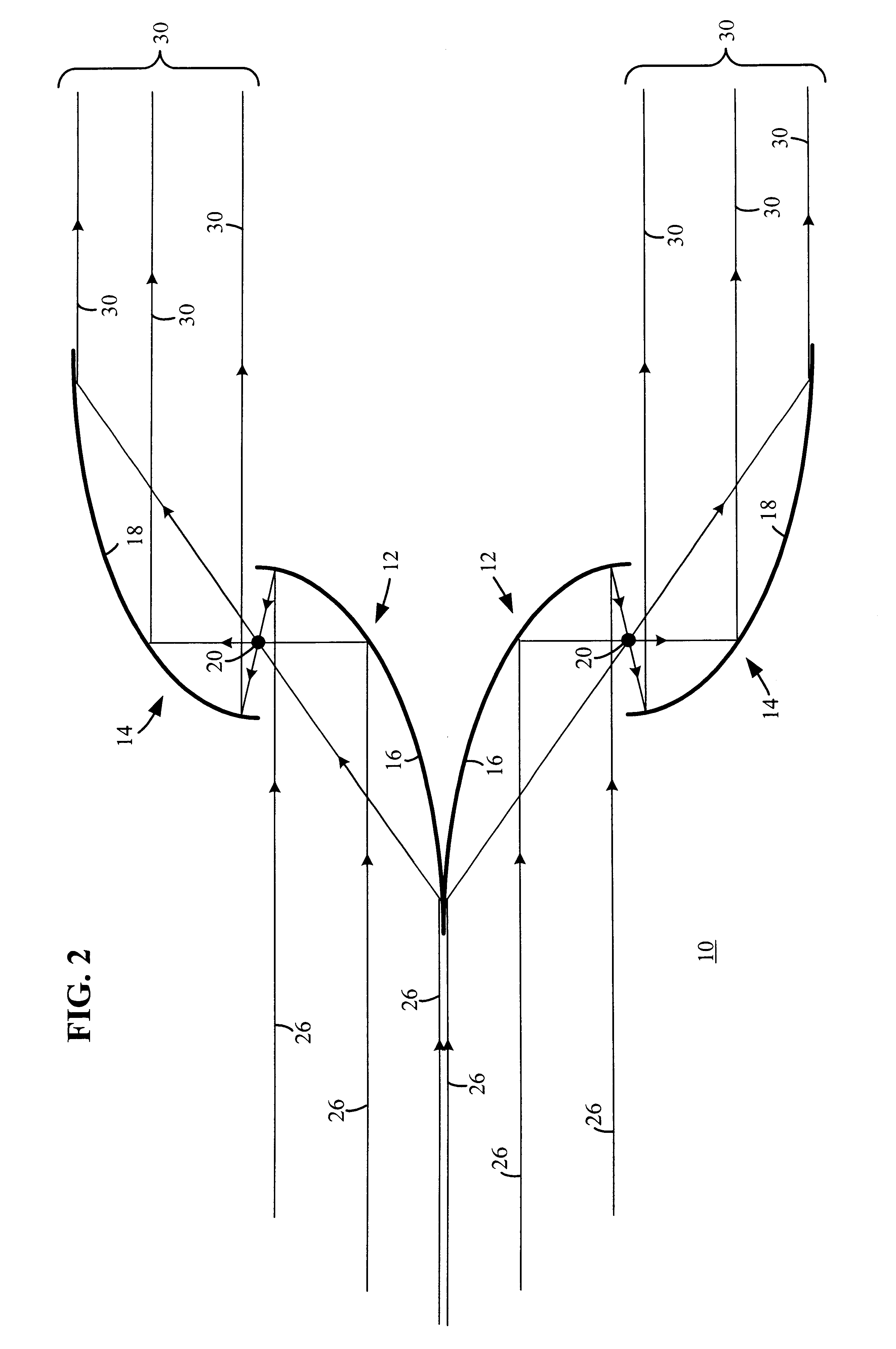
An exposure method for exposing a dense contact hole pattern onto a plate via a projection optical system includes the step of illuminating one of a binary mask and an attenuated phase shifting mask which one has the dense contact hole pattern by utilizing light from a light source and an illumination optical system, wherein the illuminating step uses an off-axis illumination that is polarized in a tangential direction when a value that is directed to half of a interval between centers of two adjacent contact holes in the dense contact hole pattern and is normalized by λ / NA is 0.25×√2 or smaller, where λ is a wavelength of the light, and NA is a numerical aperture of the projection optical system at an image side.
Owner:CANON KK
Off-axis illumination assembly and method
A stencil printer is provided for depositing solder paste onto a surface of an electronic substrate. The stencil printer includes a frame and a stencil coupled to the frame. The stencil has a plurality of apertures formed therein. The stencil printer further includes a dispenser coupled to the frame. The stencil and the dispenser are adapted to deposit solder paste onto the electronic substrate. The stencil printer further includes an imaging system constructed and arranged to capture an image of the electronic substrate. The imaging system includes a camera assembly, an on-axis illumination assembly adapted to generate light substantially along a first axis generally perpendicular to the surface of the electronic substrate, and an off-axis illumination assembly adapted to generate rays of light substantially along a second axis extending at an angle with respect to the first axis. A controller is coupled to the imaging system to control movement of the imaging system to capture an image.
Owner:SPEEDLINE TECH
Fixing apparatus for ball lens
InactiveUS20150096608A1Reduce processing stepsEasy to operatePhotovoltaicsStands/trestlesDirect illuminationOff-axis illumination
The present invention relates to a fixing apparatus for ball lens used for facilitating installation of concentrator solar cell receiver module. The present invention can finish installing the fixing base for ball lens at a time and positioning the ball lens rapidly and accurately. It can also control the distance between the ball lens and the solar cell excellently. In addition, the present invention further has the function of sheltering the circuit of concentrator solar cell receiver module. When off-axis illumination of sunlight occurs, direct illumination of sunlight on, and consequently high-temperature burnout of, the circuit can be avoided. Thereby, the lifetime of the circuit can be extended effectively and the probability of failure can be reduced as well.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY COUNCIL INST O NUCLEAR ENERGY RES
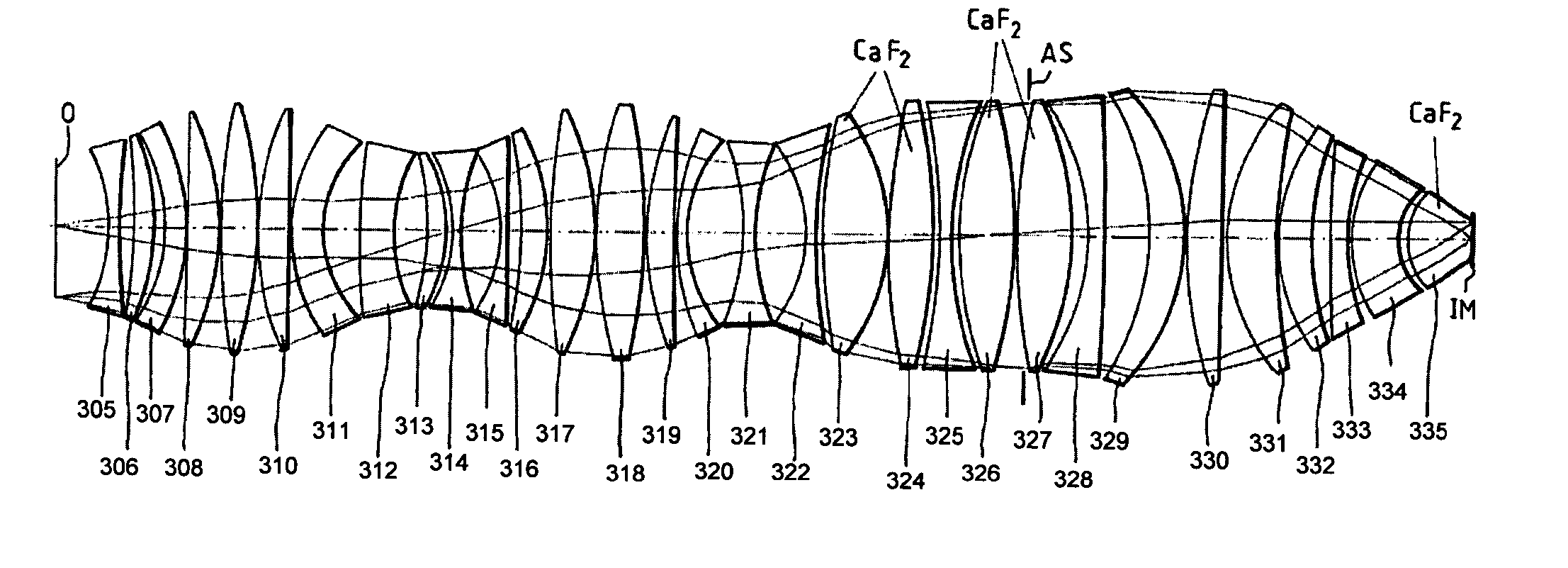
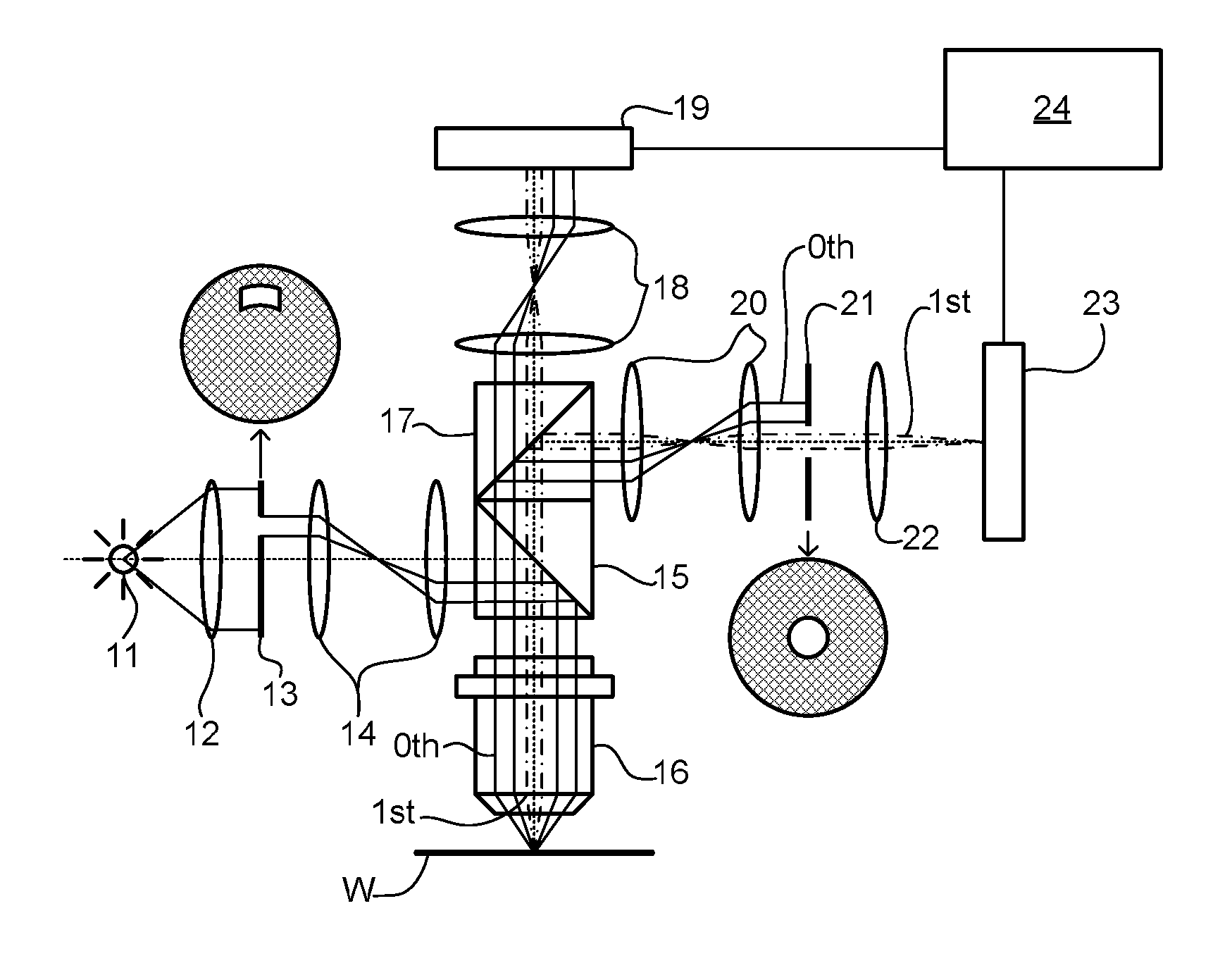
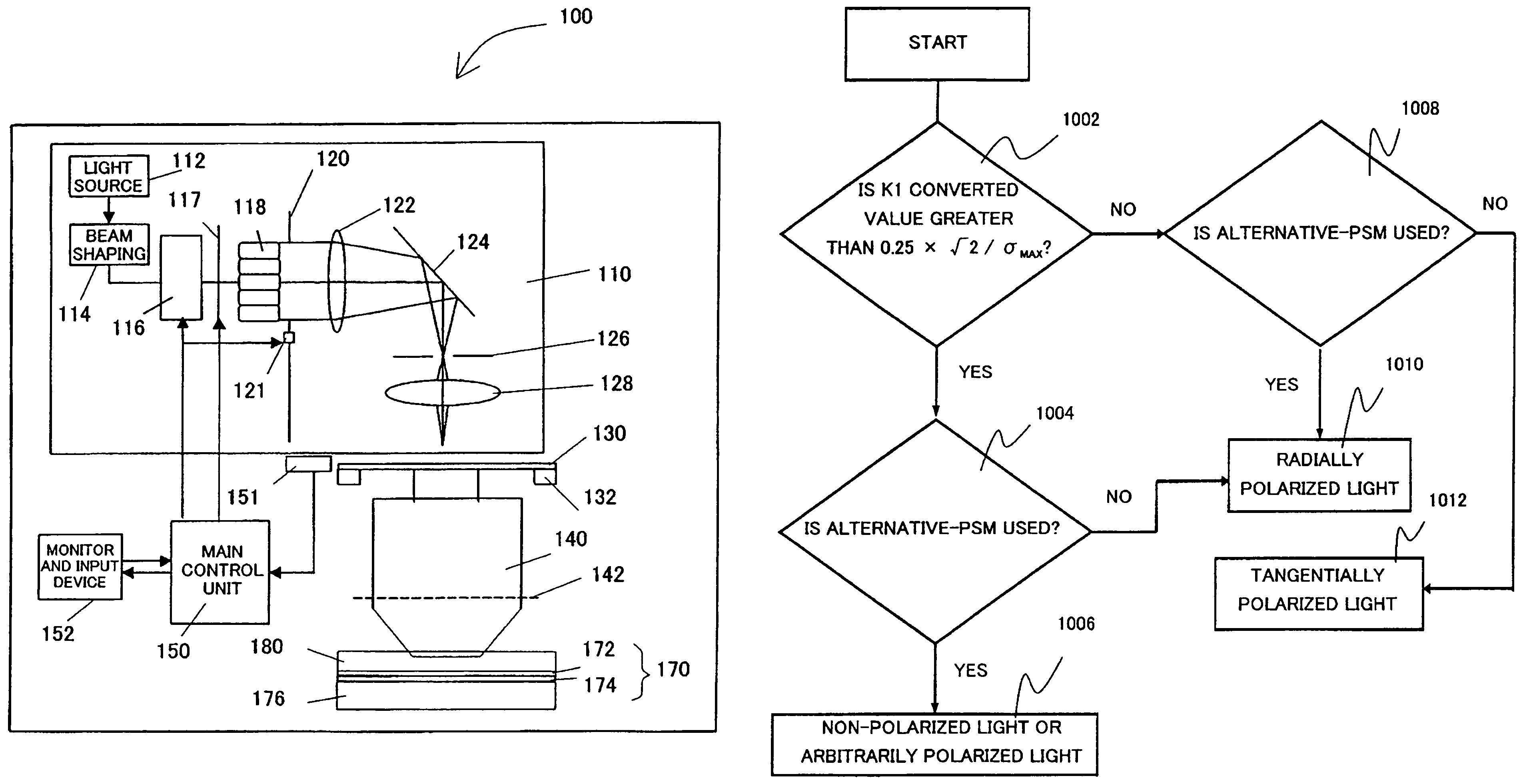
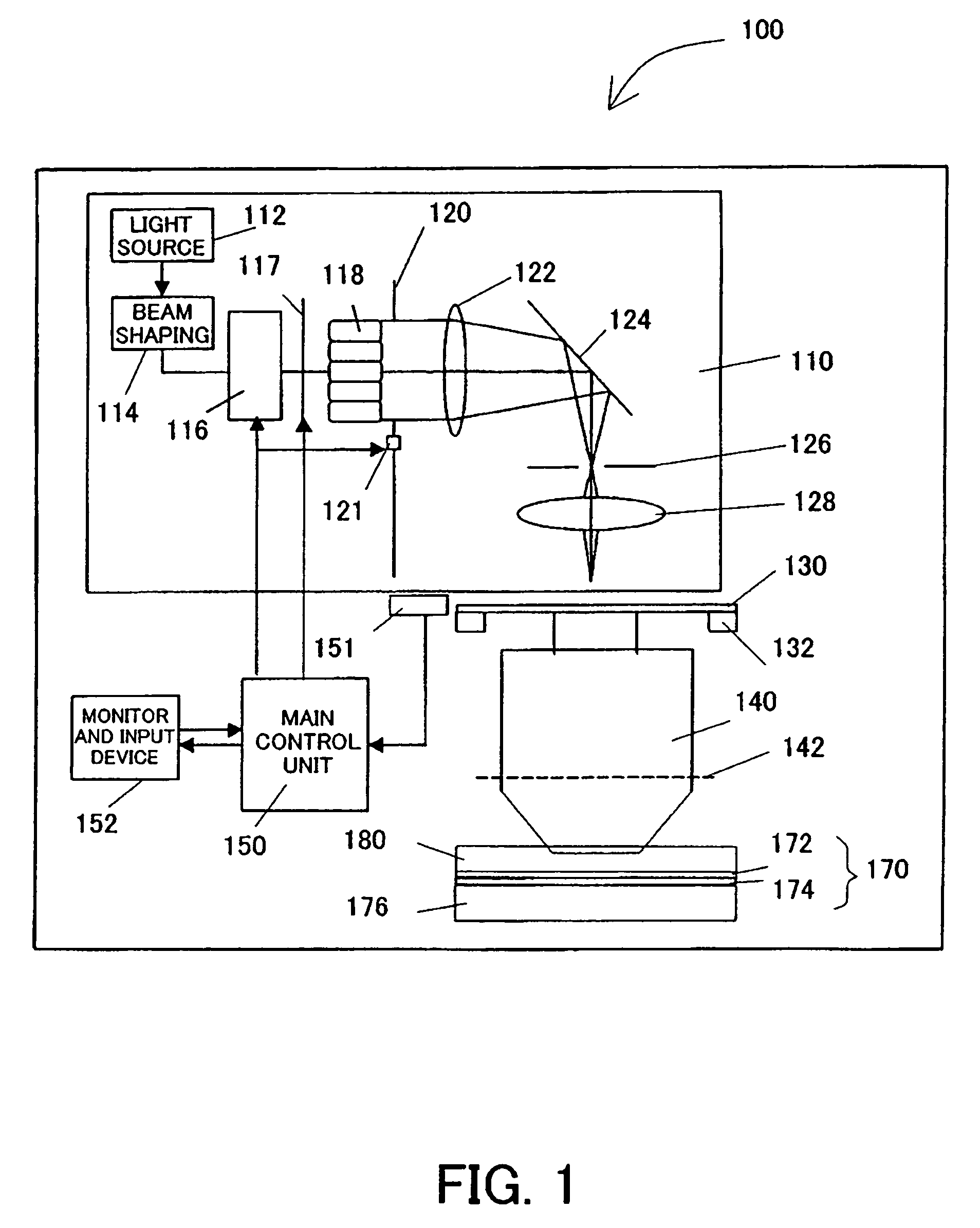
Methods and apparatus for off-axis lithographic illumination
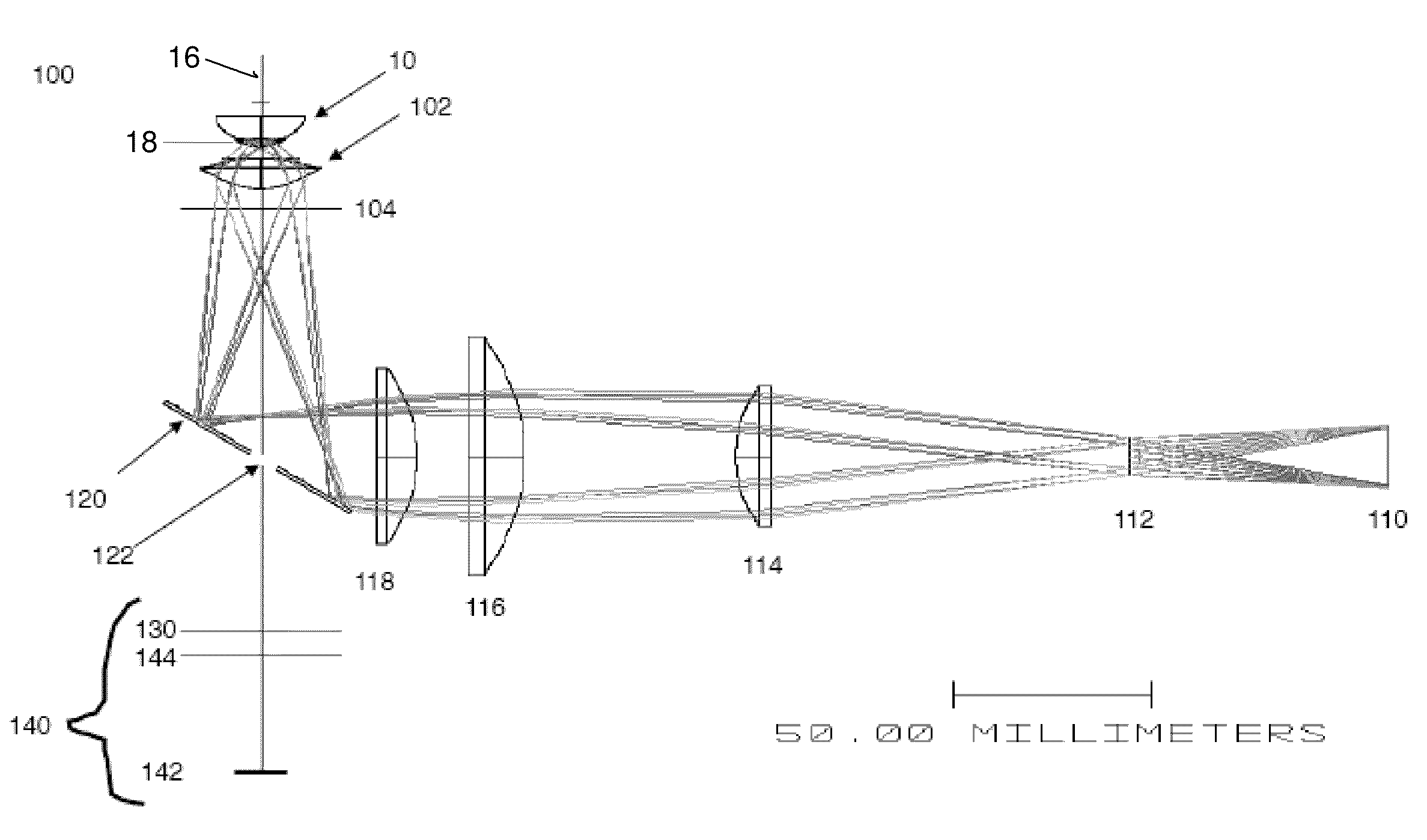
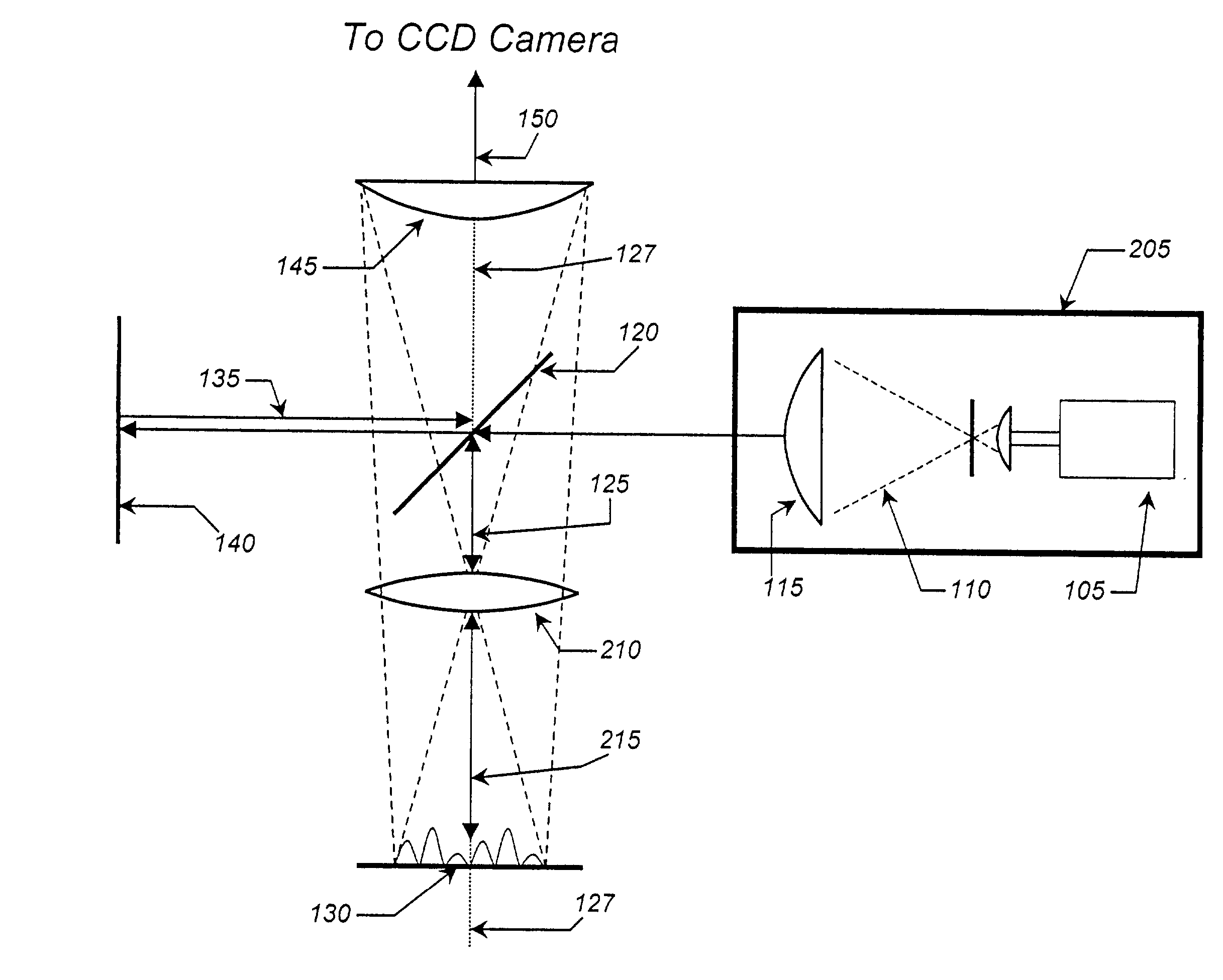
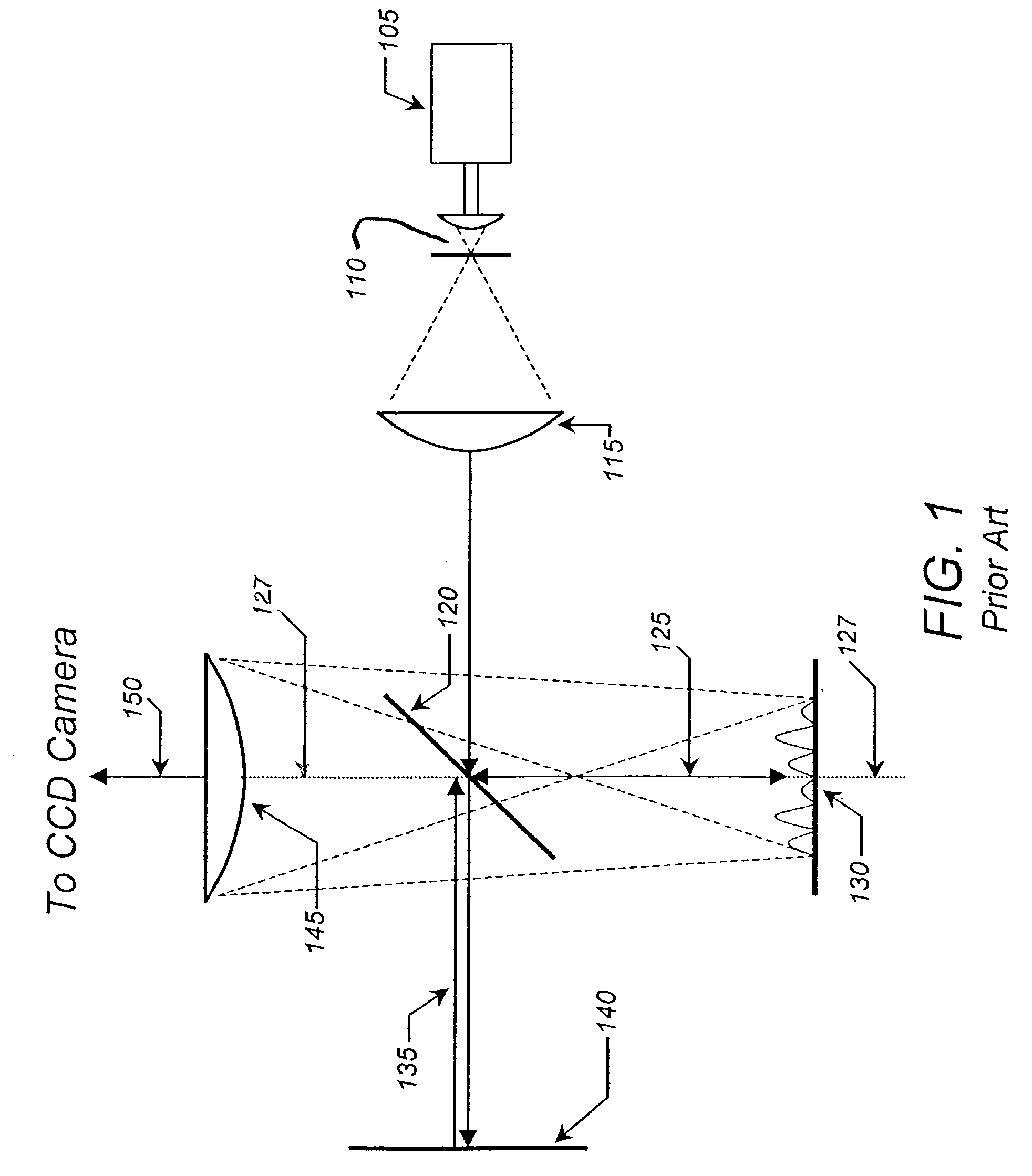
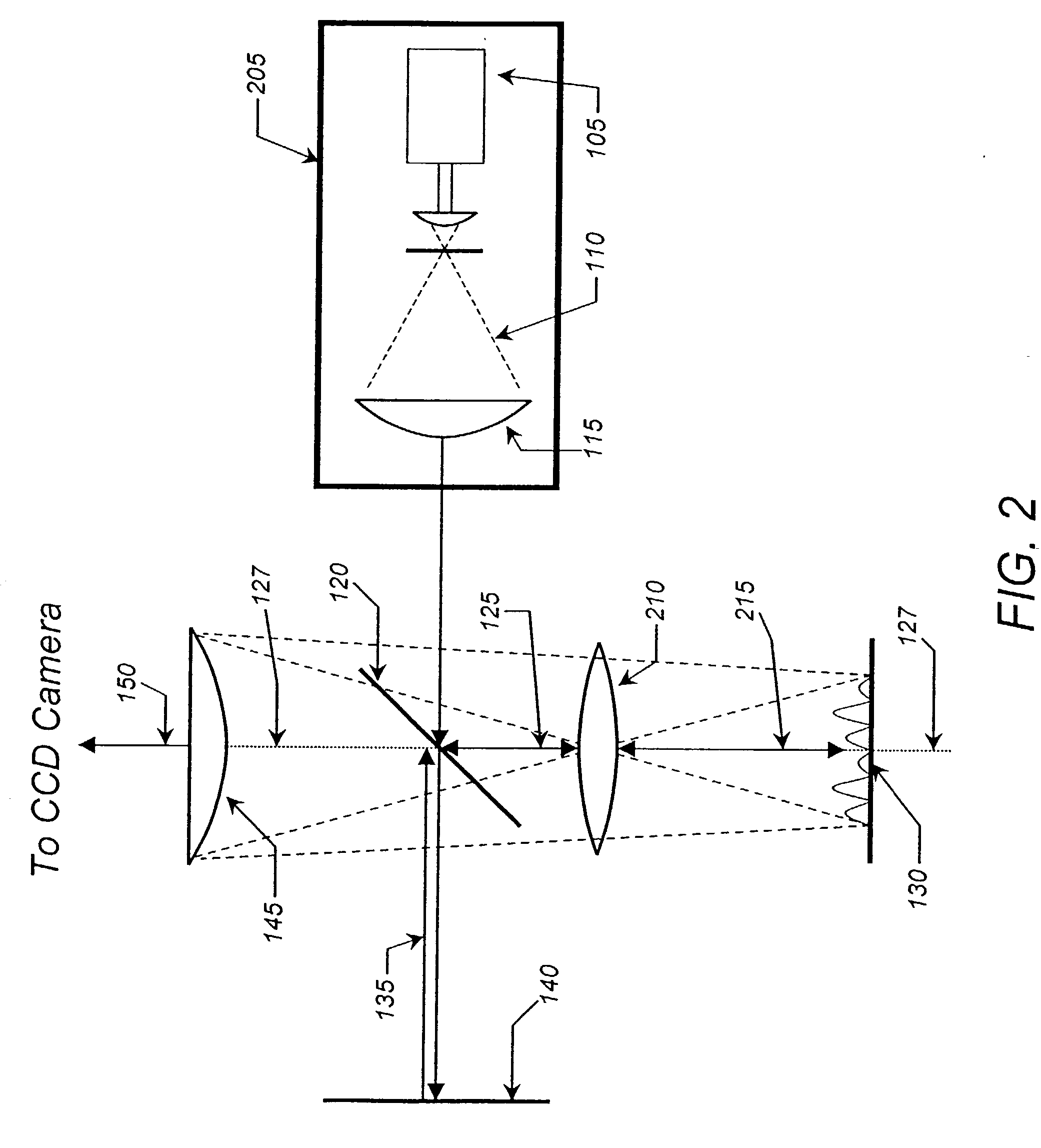
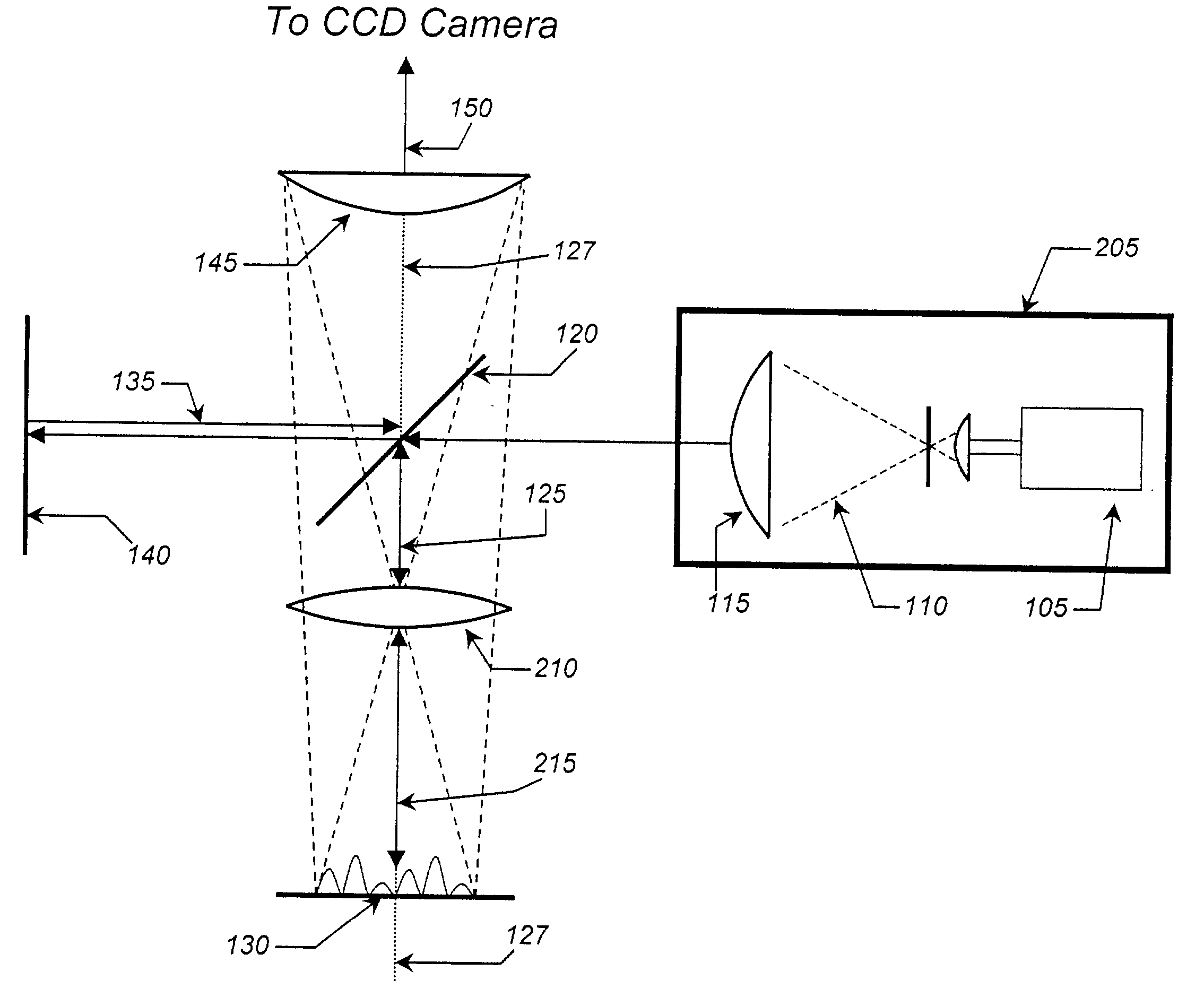
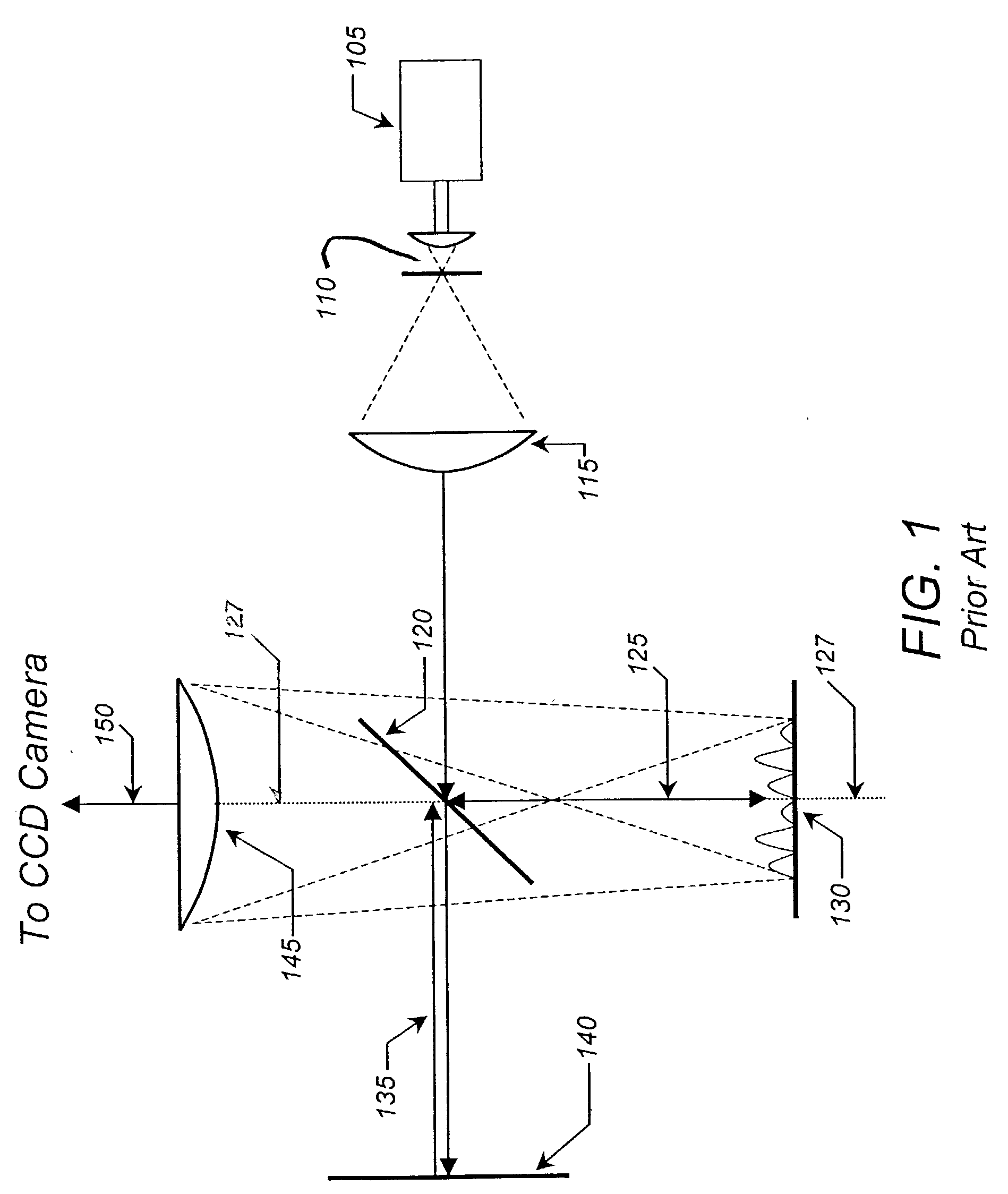
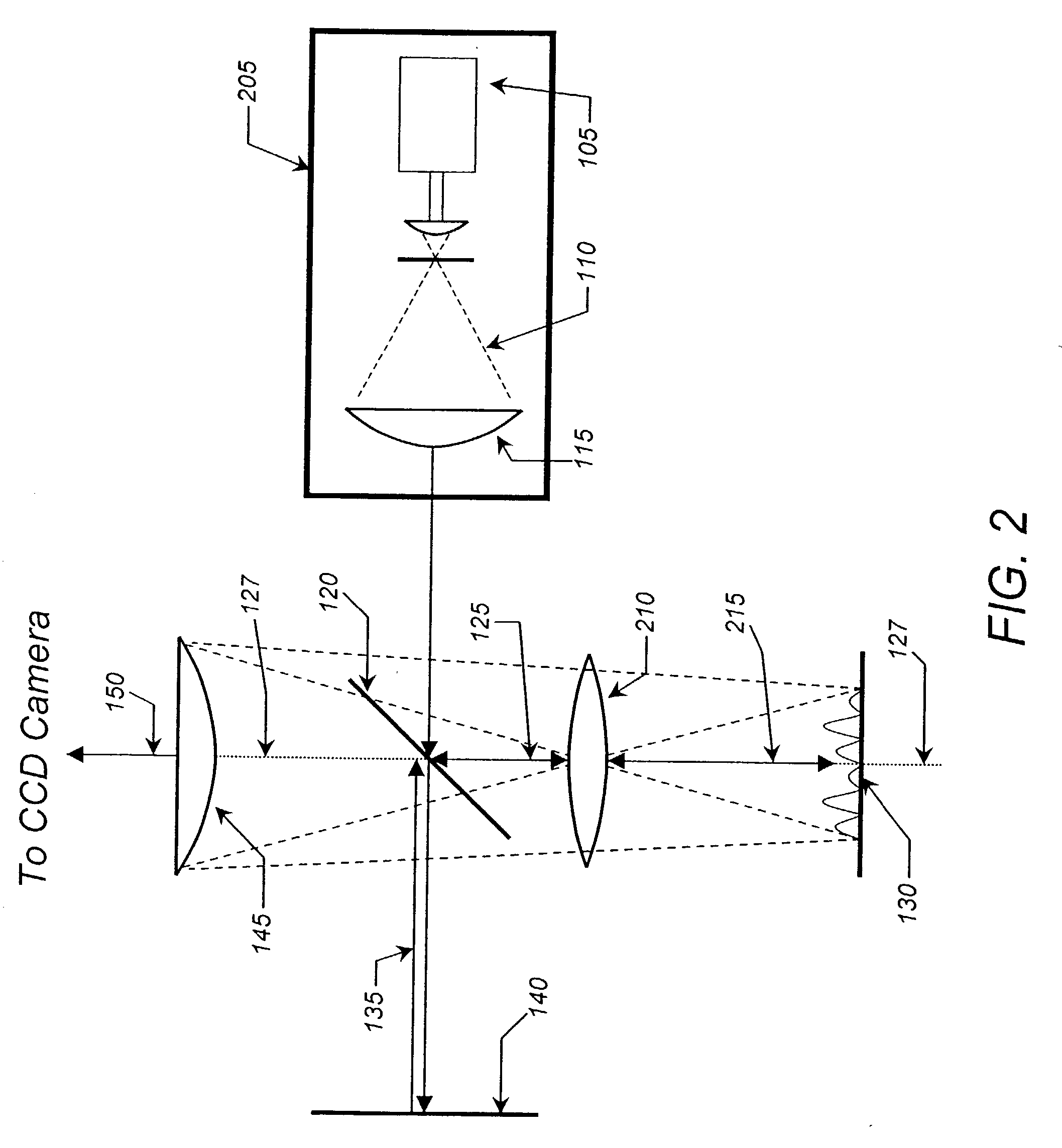
InactiveUS6703625B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistOptical axis
Methods and apparatuses for shaping an illumination pattern for off-axis lithography are disclosed. A disclosed apparatus includes a first and second reflecting objective. The first reflecting objective includes a first reflective surface that reflects input light having an on-axis illumination pattern through a first focal point. The second reflecting objective includes a second reflective surface that receives the reflected light through the first focal point and through a second focal point aligned with the first focal point, and reflects the reflected light through an output end as output light having an off-axis illumination pattern. A disclosed method includes receiving collimated light with a conventional illumination pattern centered on an optical axis, symmetrically reflecting the collimated light in multiple directions away from the optical axis and reflecting the reflected light to create output light having an off-axis illumination pattern symmetrical about the optical axis.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS7359033B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage resolutionOff-axis illumination
Owner:CANON KK
Combined on-axis and off-axis illumination
InactiveUS20020141076A1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOff-axis illuminationPhysics
Owner:INTEL CORP
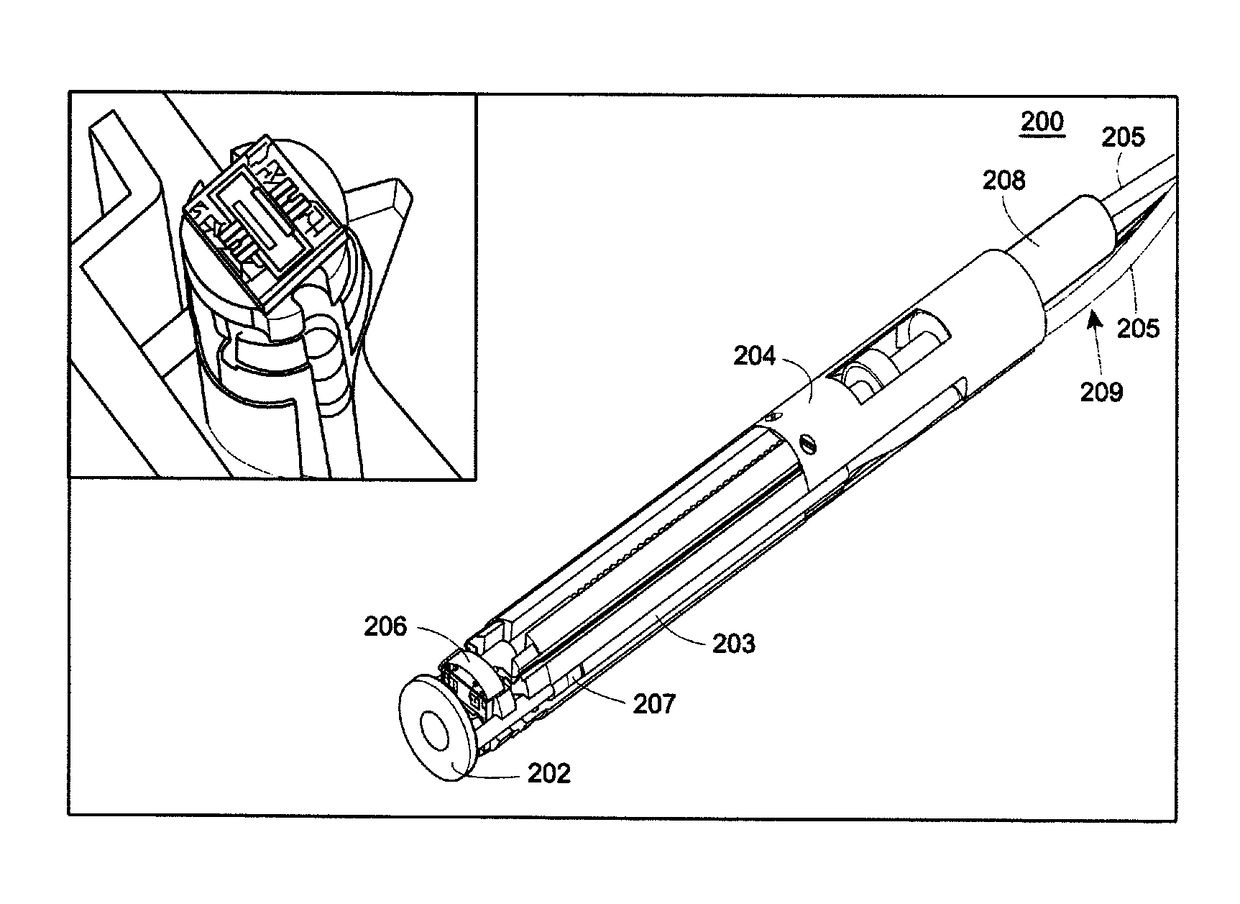
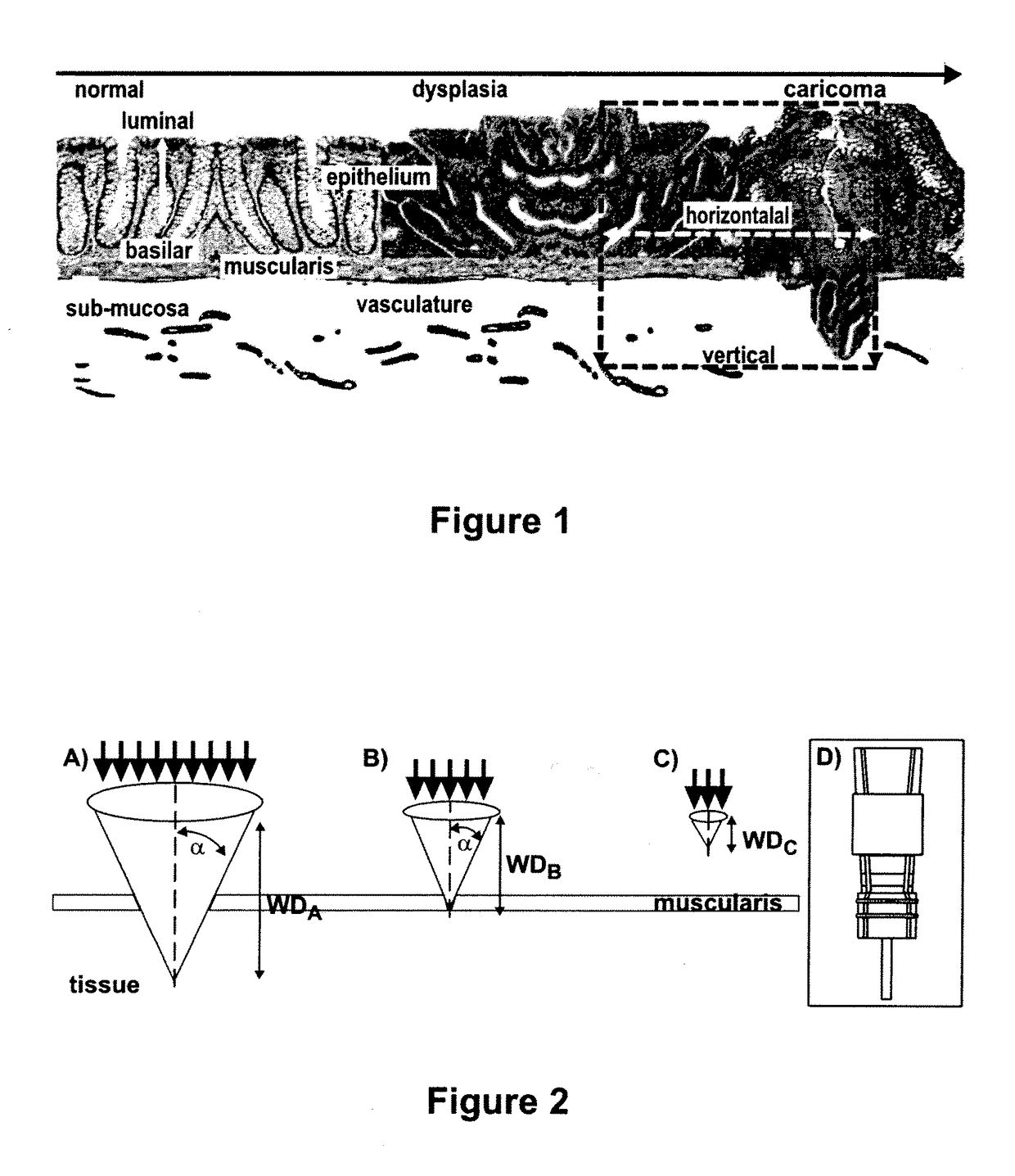
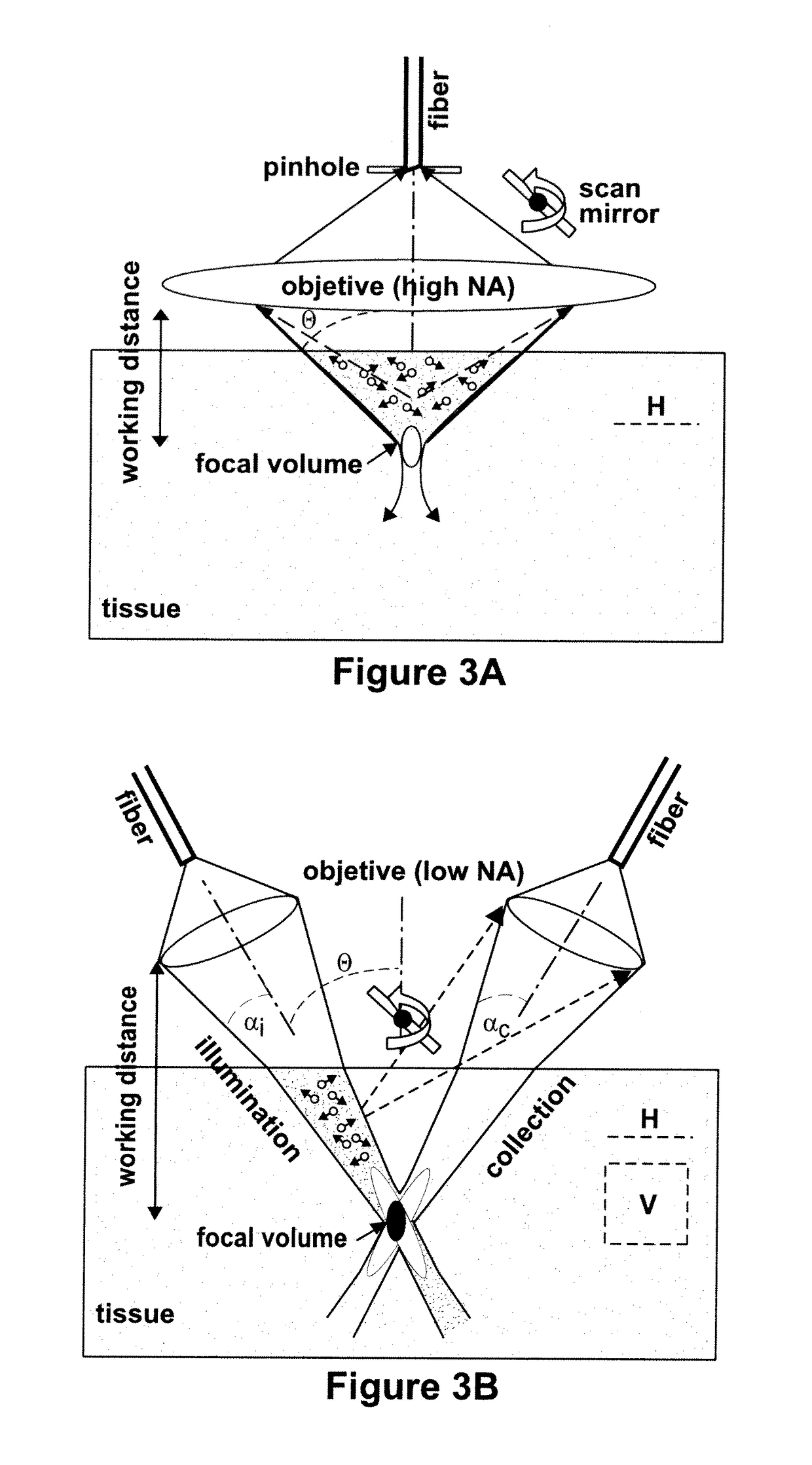
Targeted dual-axes confocal imaging apparatus with vertical scanning capabilities
ActiveUS9921406B2Overcome ambiguityLarge dynamic rangeDiagnostics using tomographySensorsEpitheliumFiber
An optical device is described that may be used as a microscope system for real-time, three-dimensional optical imaging. The device includes a miniature, fiber optic, intra-vital probe microscope that uses a dual-axes confocal architecture to allow for vertical scanning perpendicular to a surface of the sample (e.g., a tissue surface). The optical device can use off-axis illumination and collection of light to achieve sub-cellular resolution with deep tissue penetration. The optical device may be used as part of an integrated molecular imaging strategy using fluorescence-labeled peptides to detect cell surface targets that are up-regulated by the epithelium and / or endothelium of colon and breast tumors in small animal models of cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
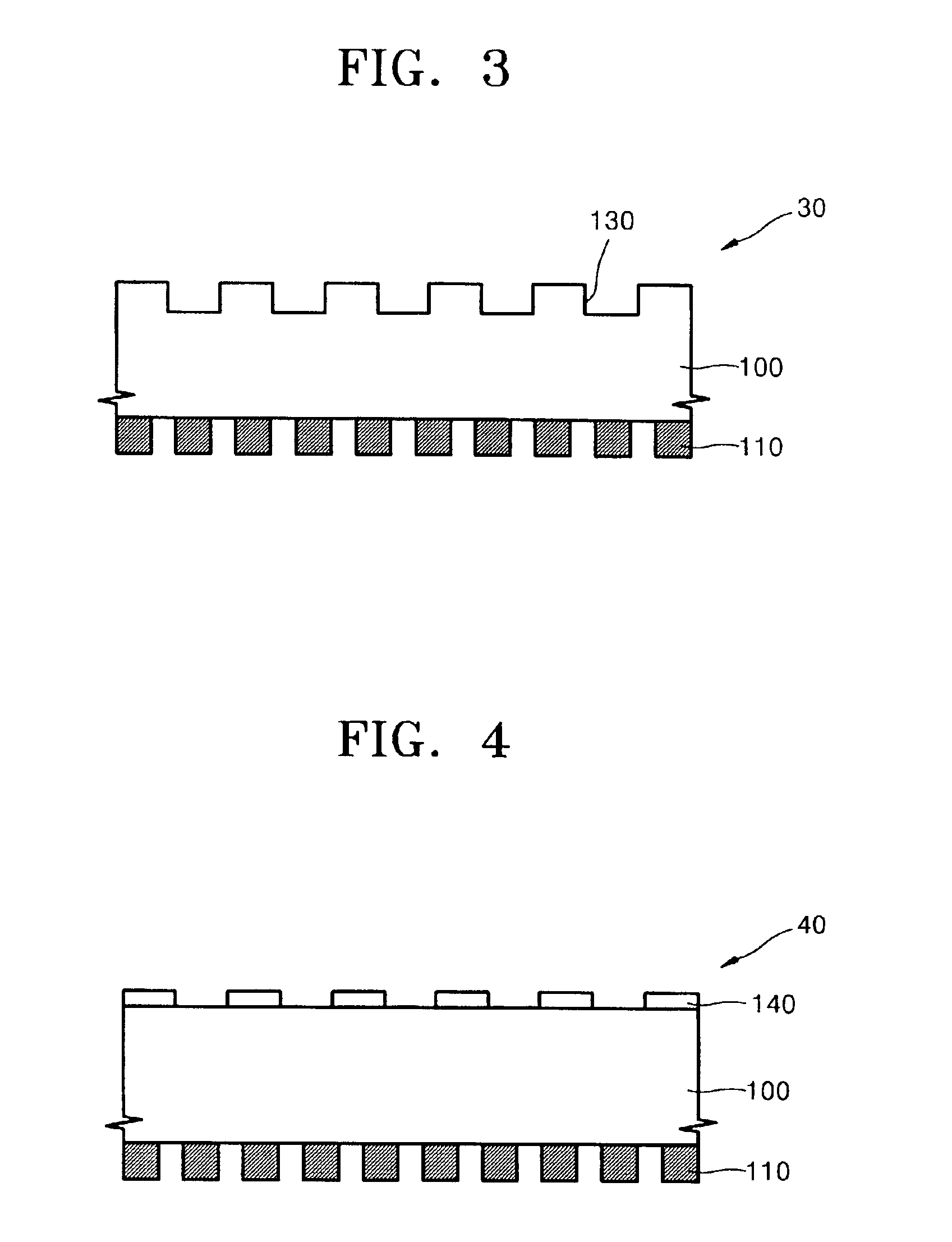
Photomask for off-axis illumination and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS6866968B2Suitable shapeImprove process capabilityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase gratingOff-axis illumination
A photomask that is capable of implementing off-axis illumination (OAI), and a method of fabricating the same, are provided. The photomask includes a transparent substrate, a plurality of opaque patterns formed on the front surface of the transparent substrate, for defining a floodlighting portion for forming patterns, and a plurality of phase gratings formed on the back surface of the transparent substrate, allowing off-axis illumination (OAI) of an incident light source beyond the OAI limit of exposure equipment, allowing use in the outmost region of an aperture, and allowing modified illumination having a shape suitable for the layout of the opaque patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com