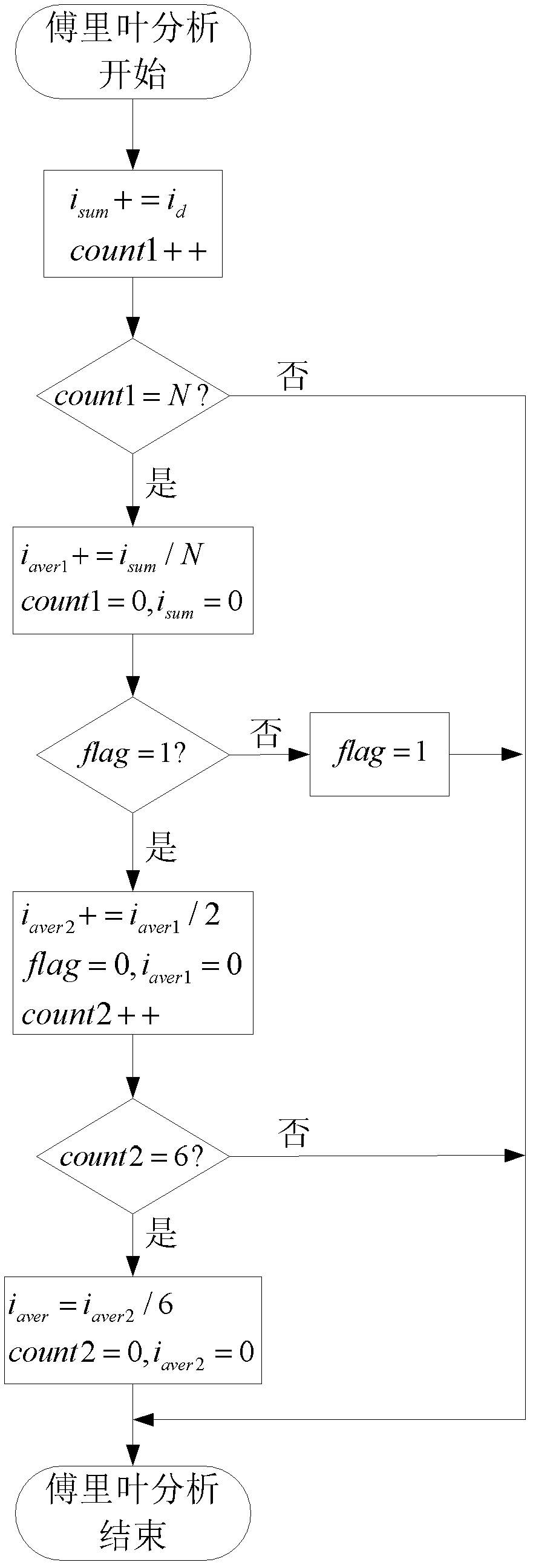Patents
Literature
412 results about "Fourier analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, Fourier analysis (/ˈfʊrieɪ, -iər/) is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fourier, who showed that representing a function as a sum of trigonometric functions greatly simplifies the study of heat transfer.
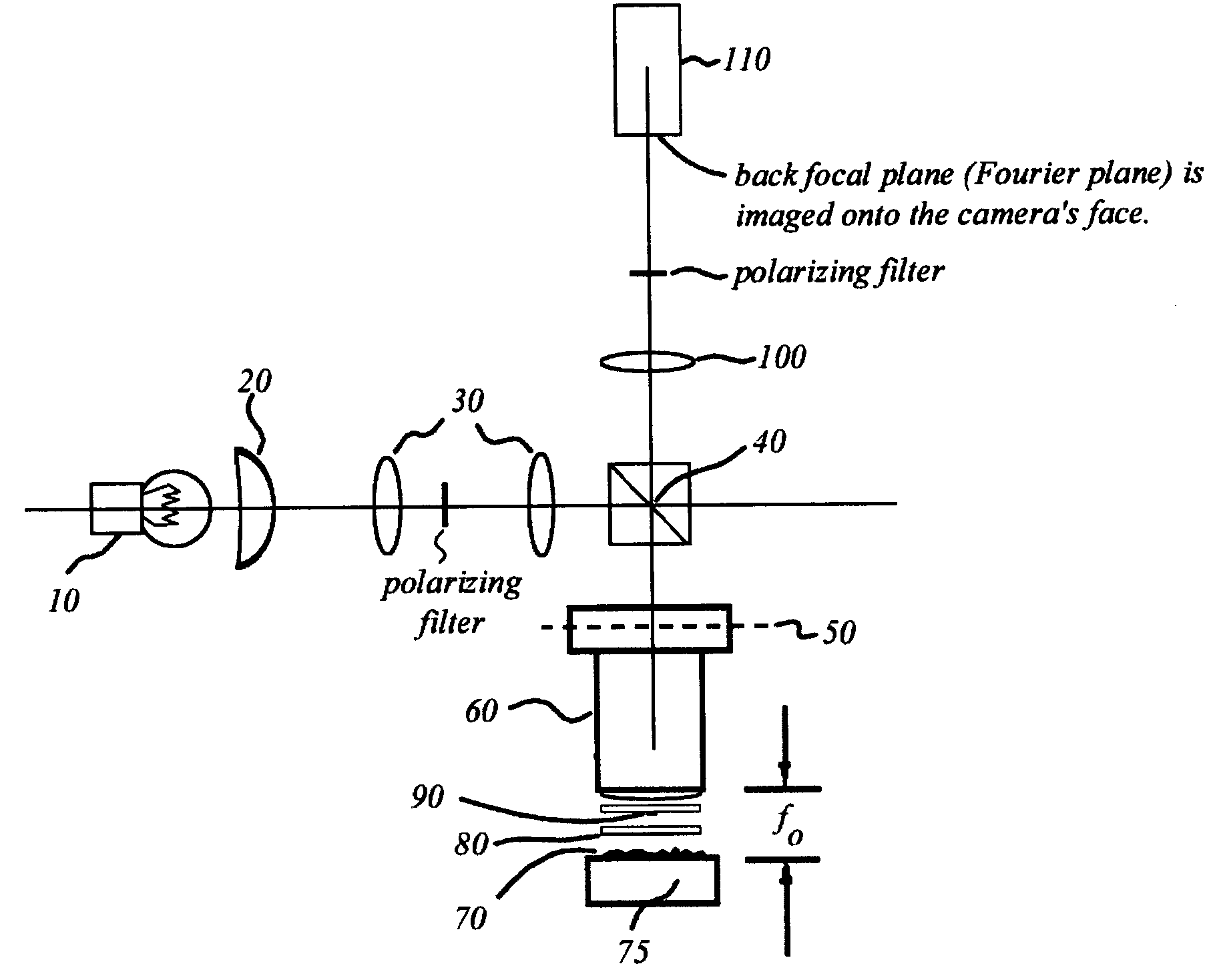
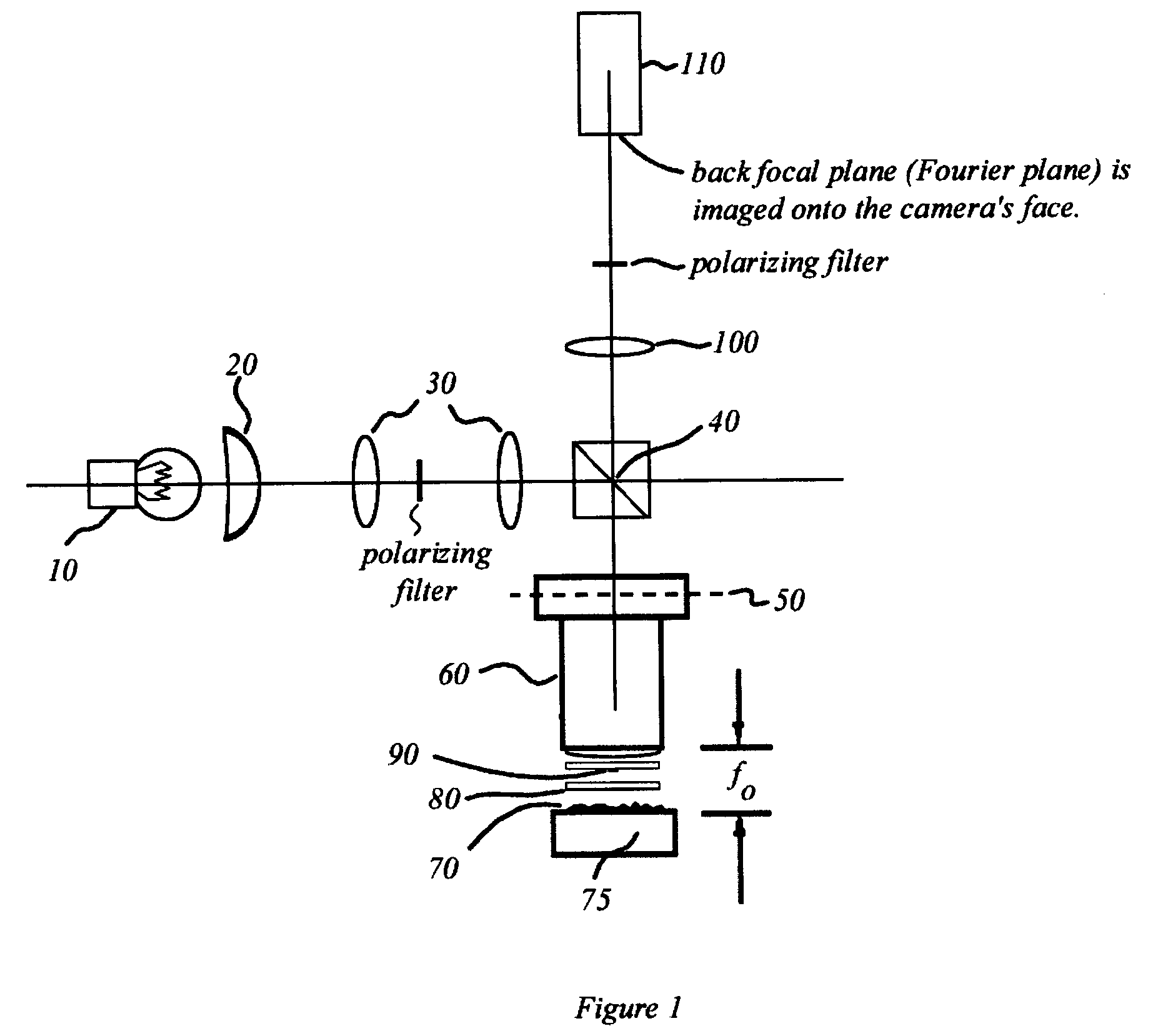
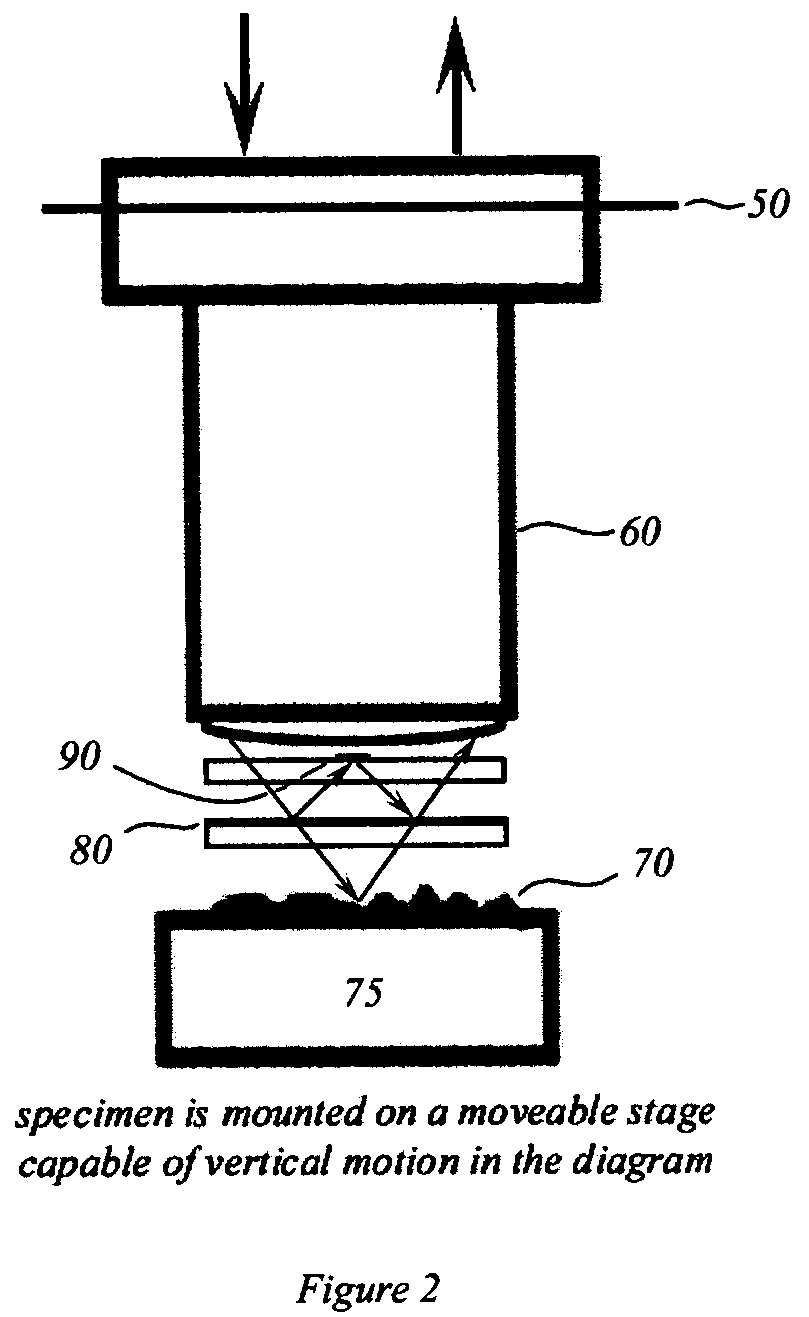
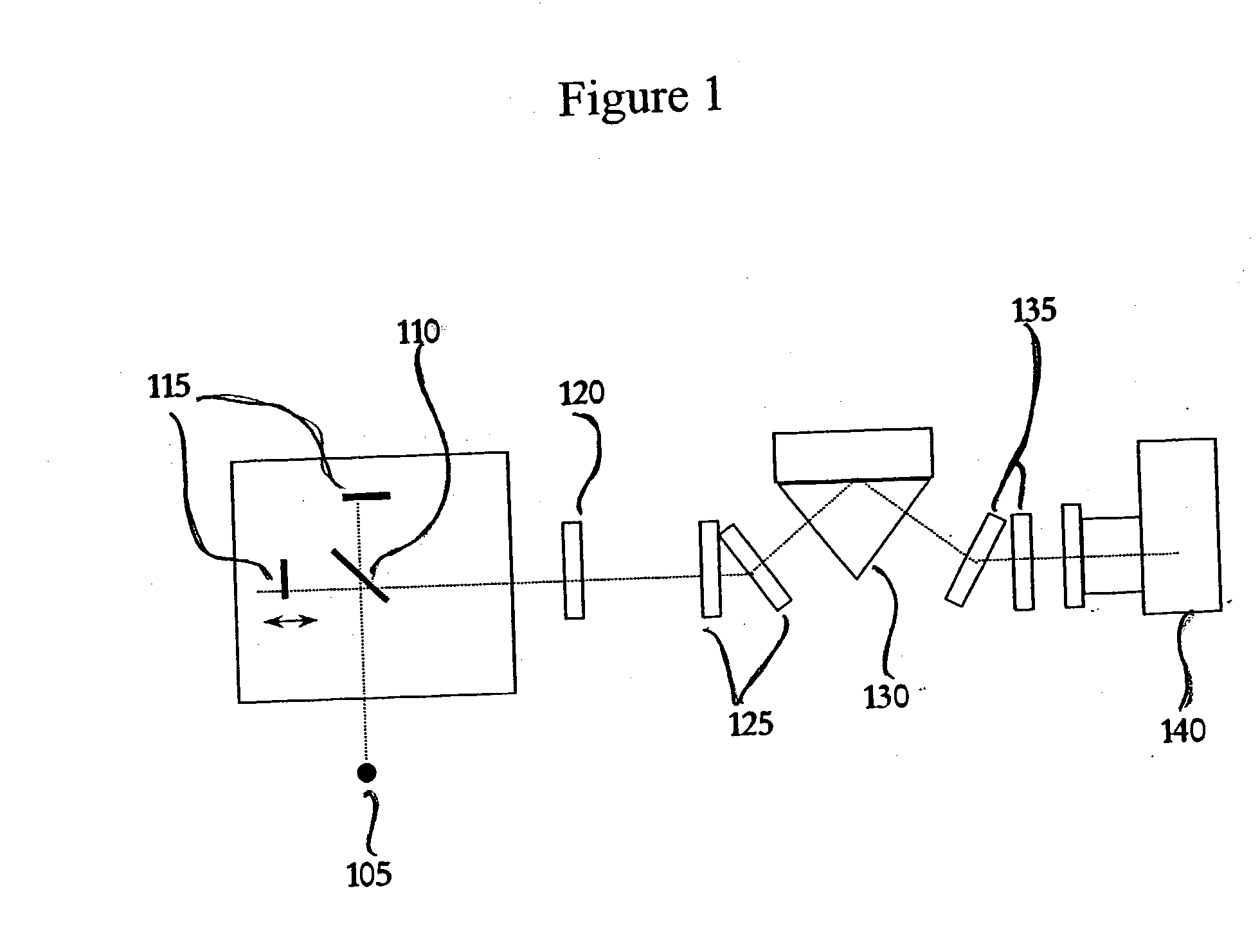
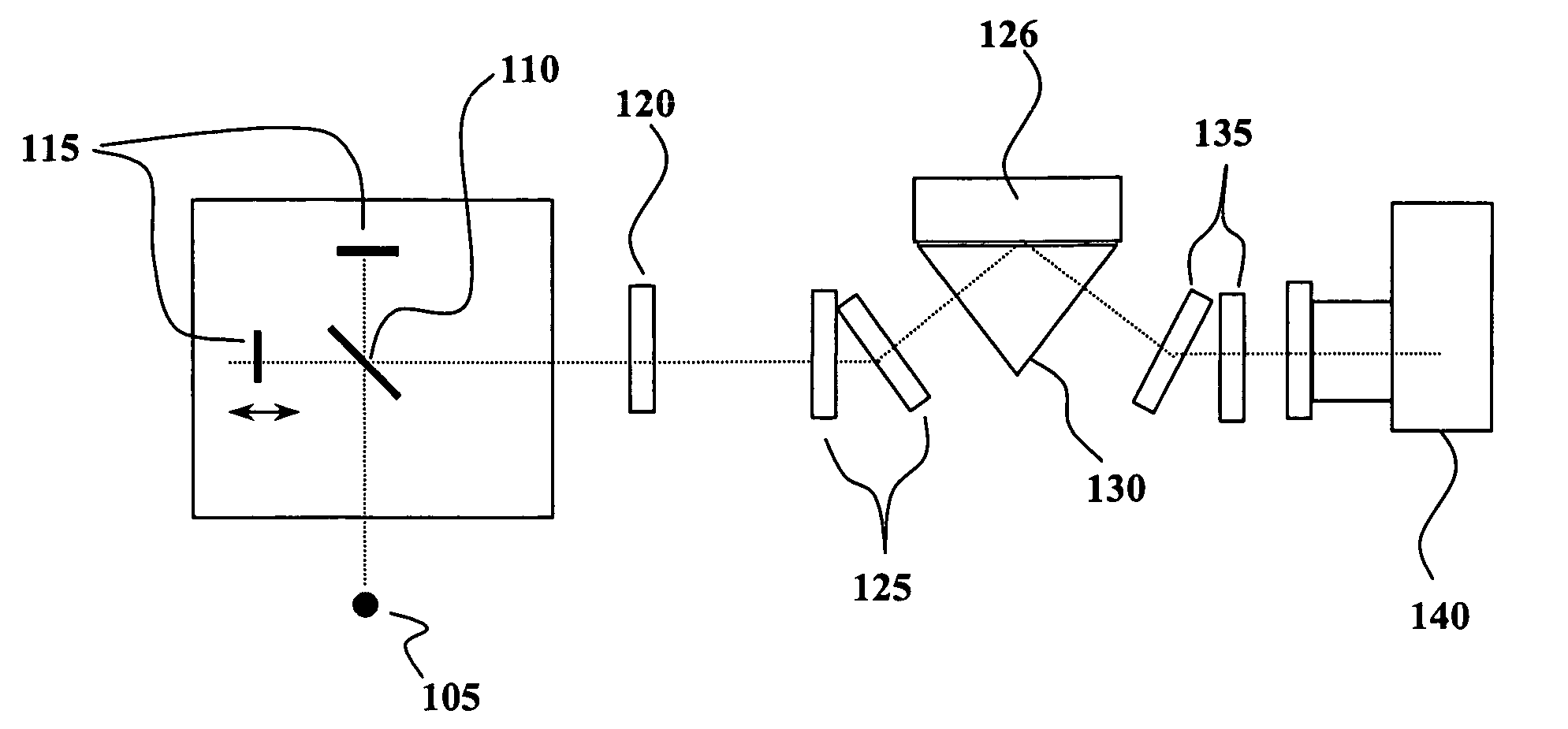
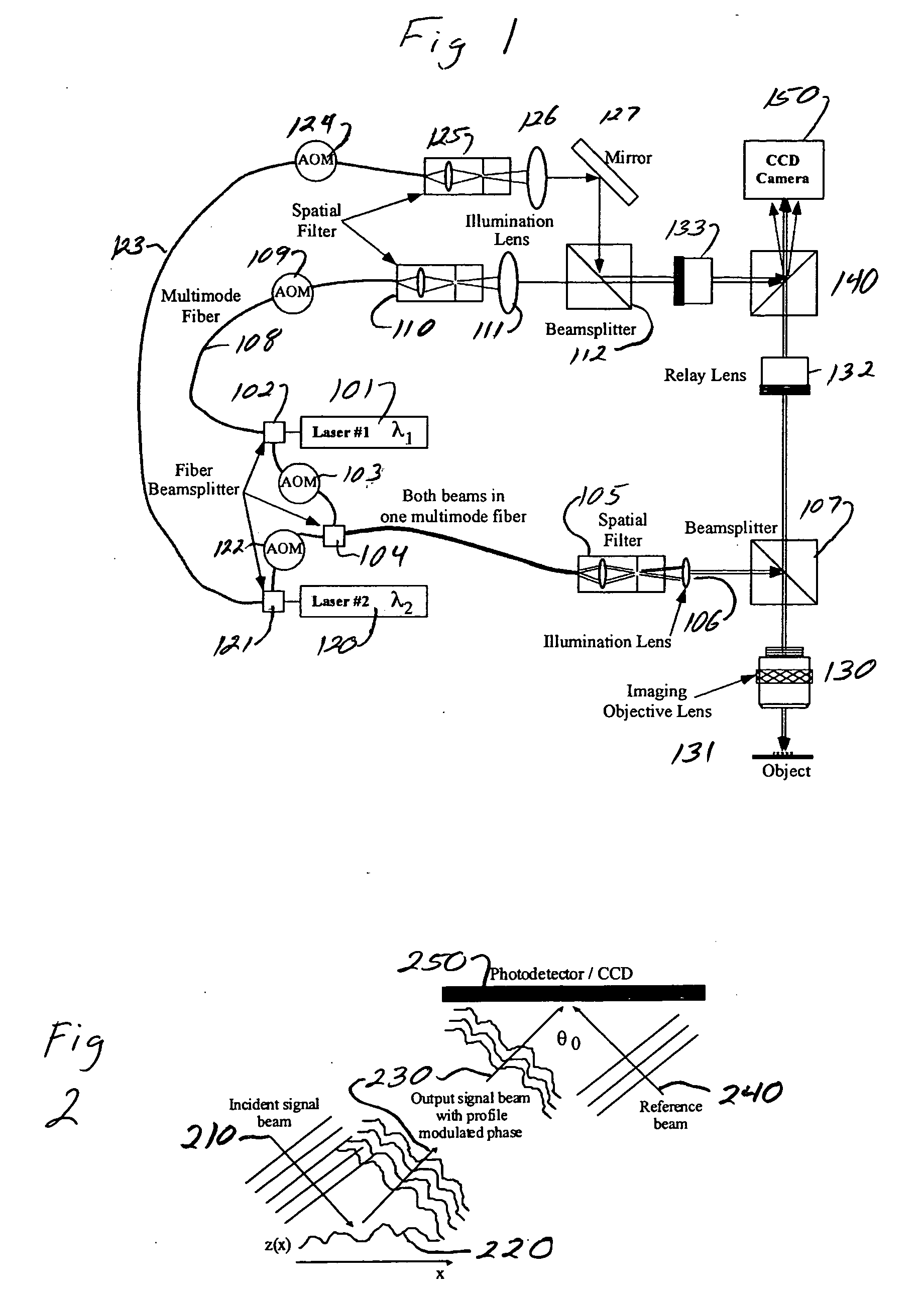
Interferometric back focal plane scatterometry with Koehler illumination
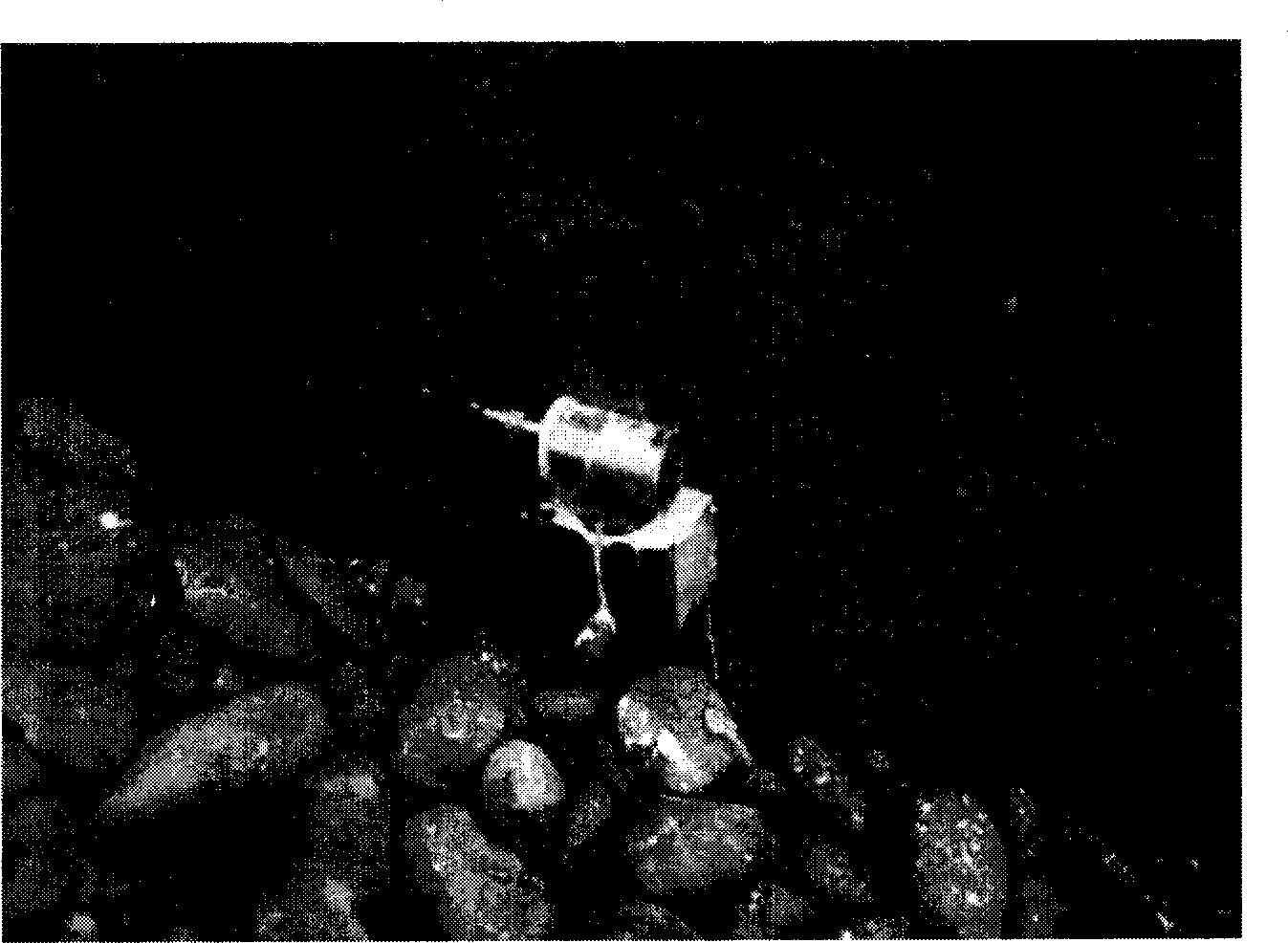
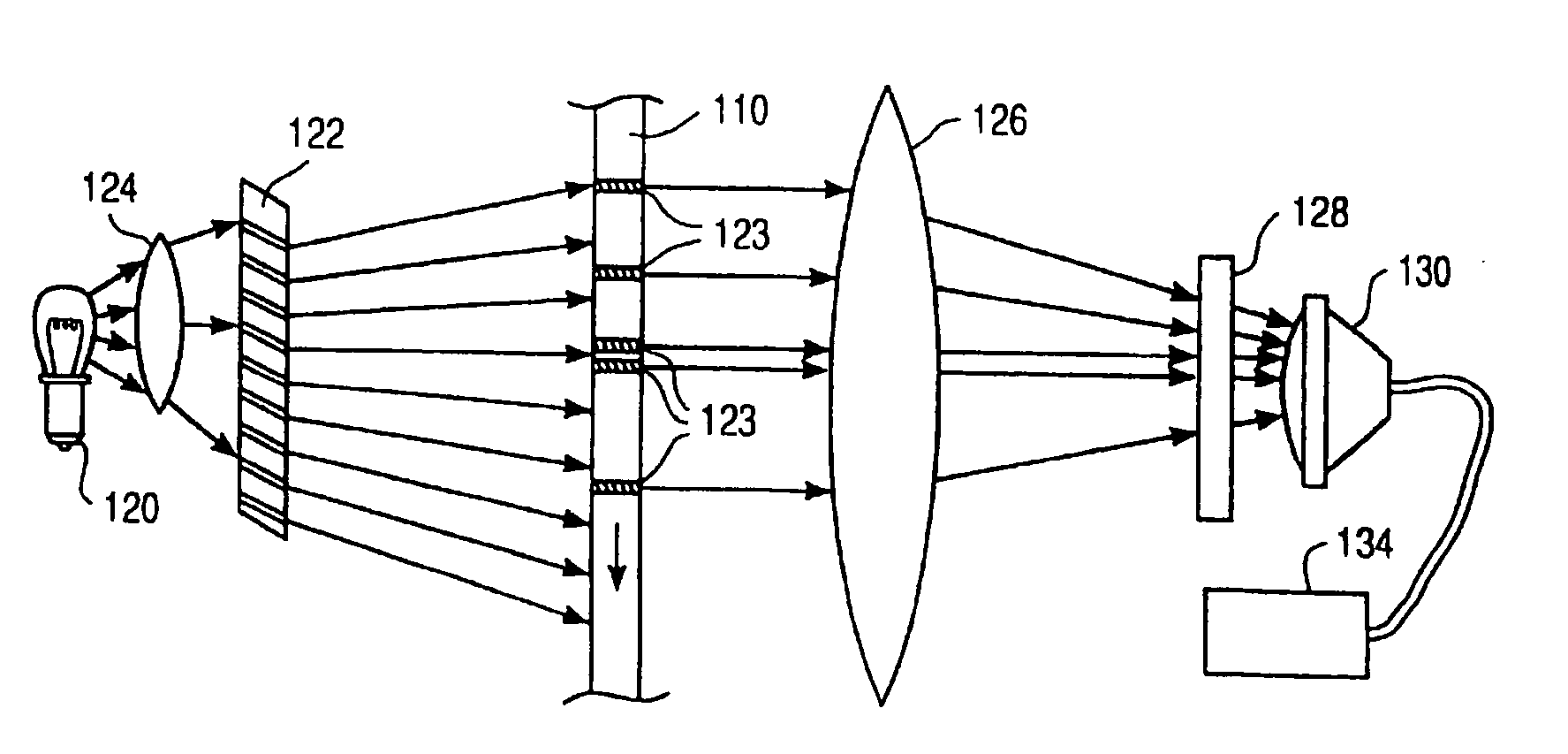
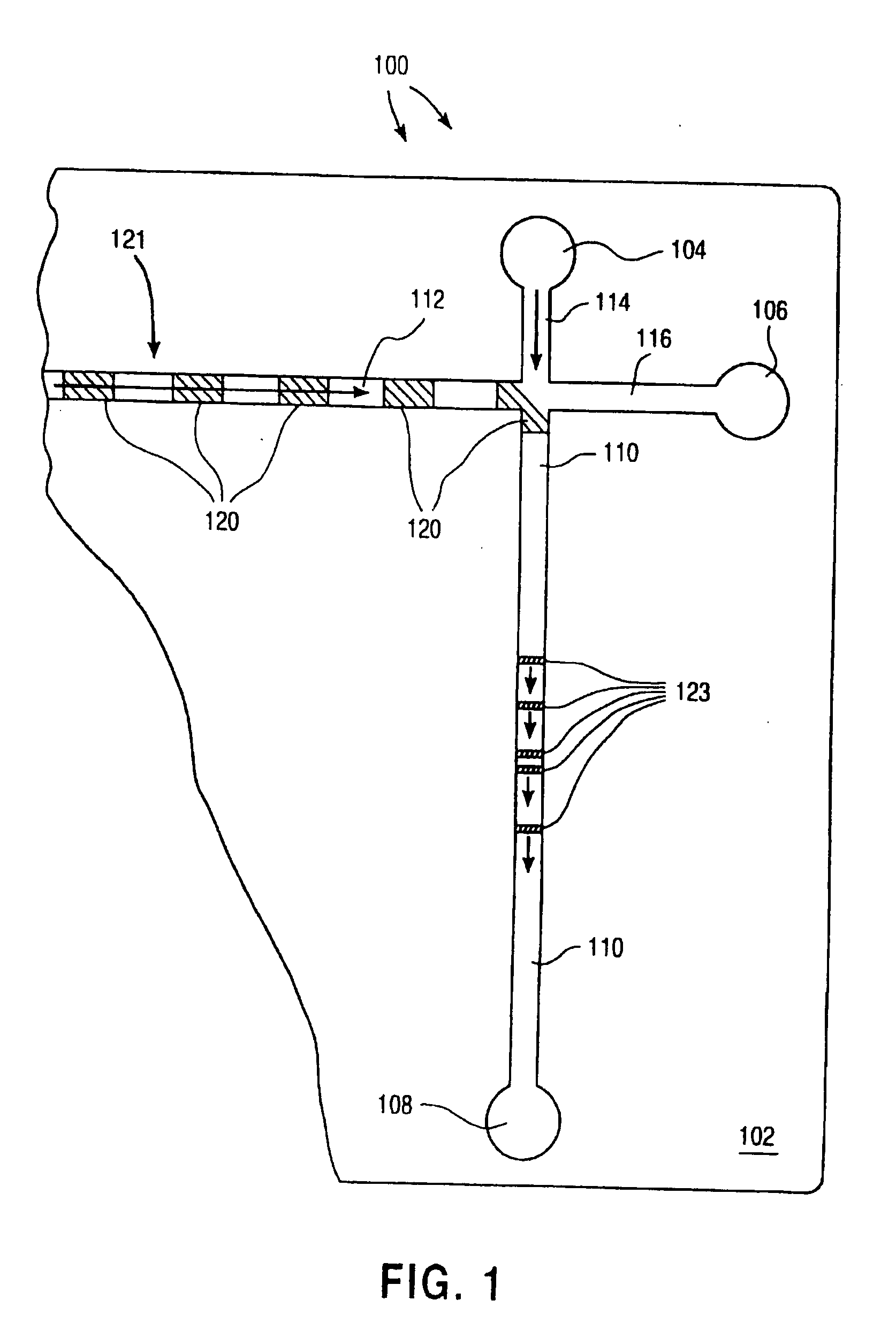
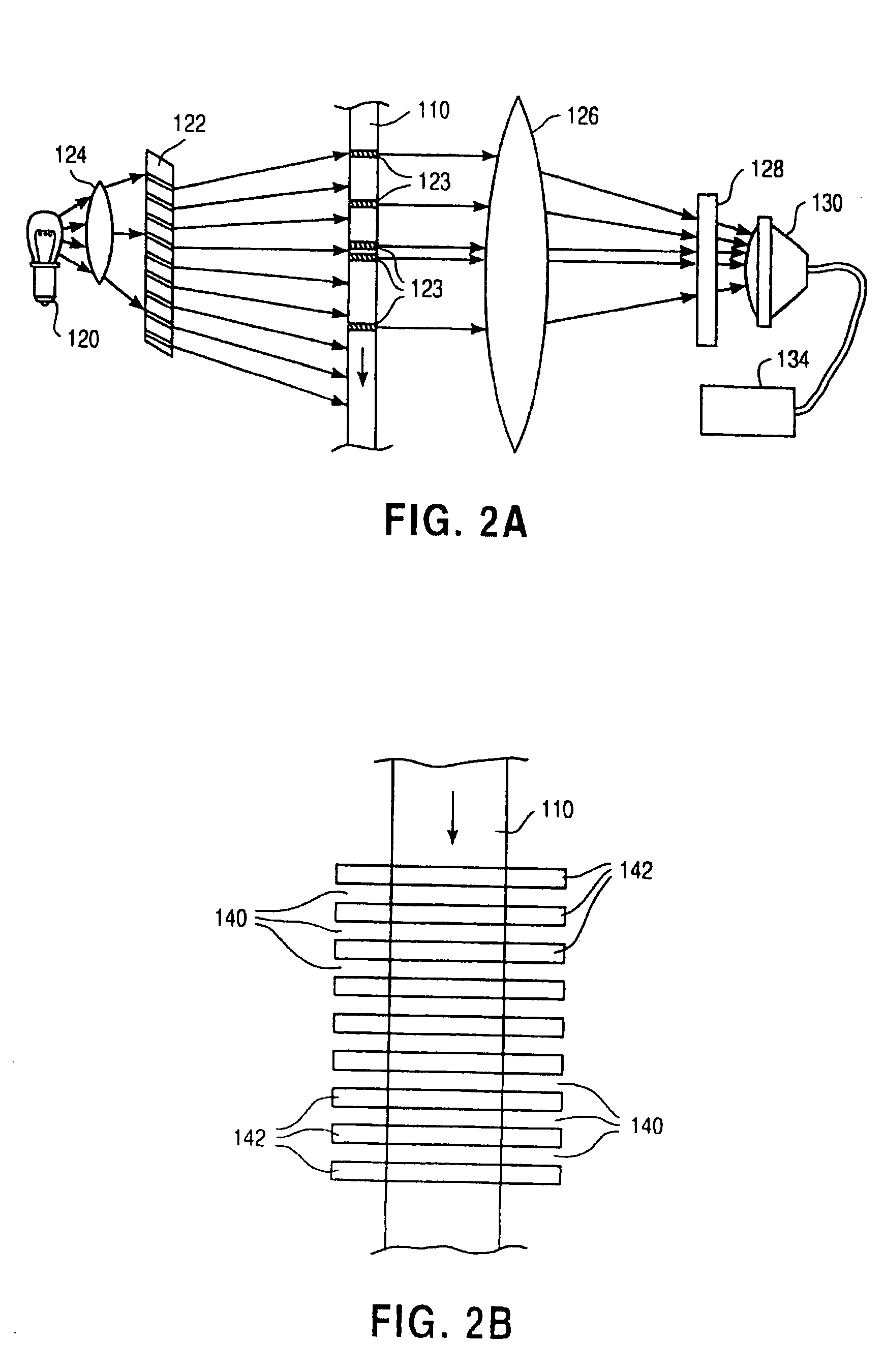
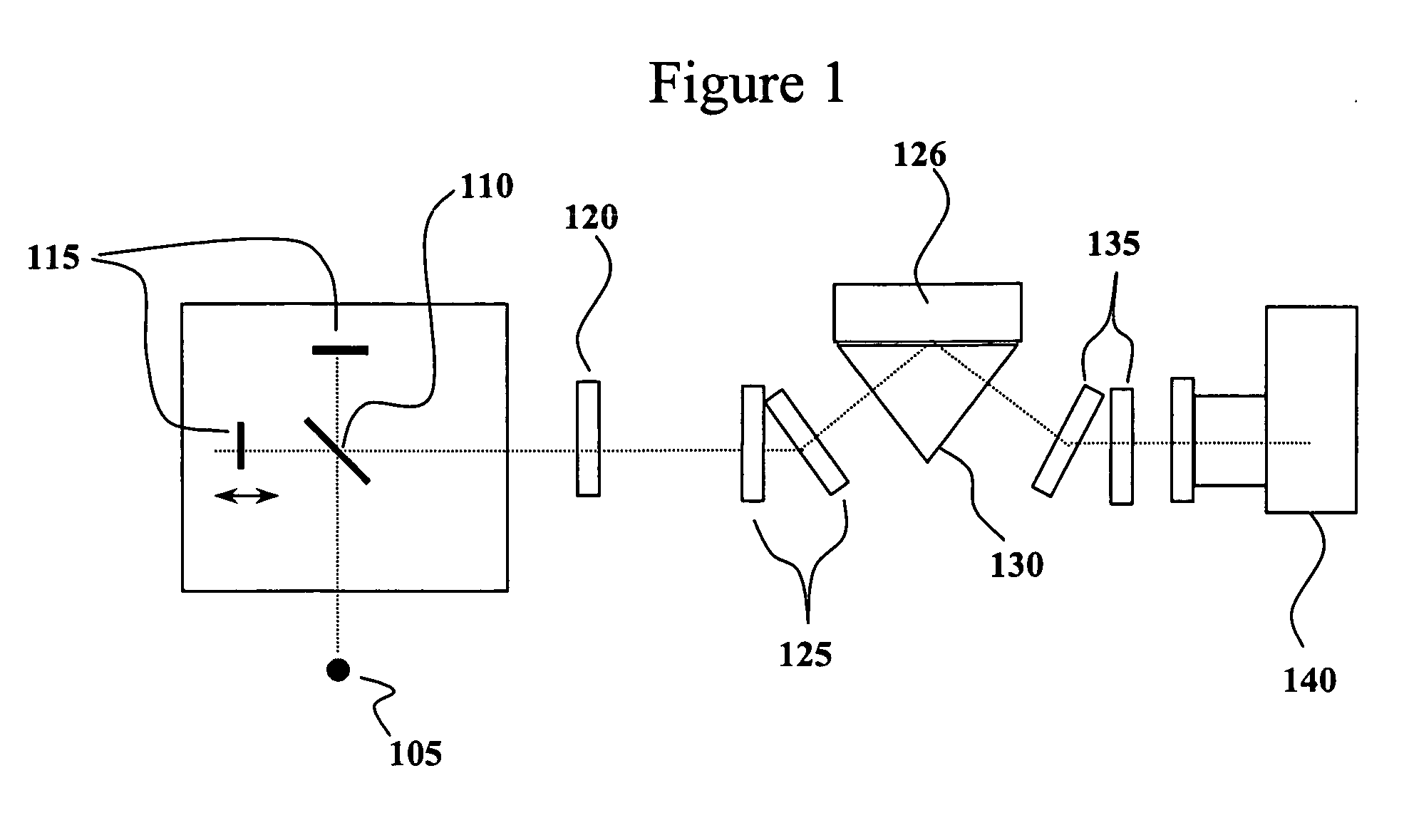
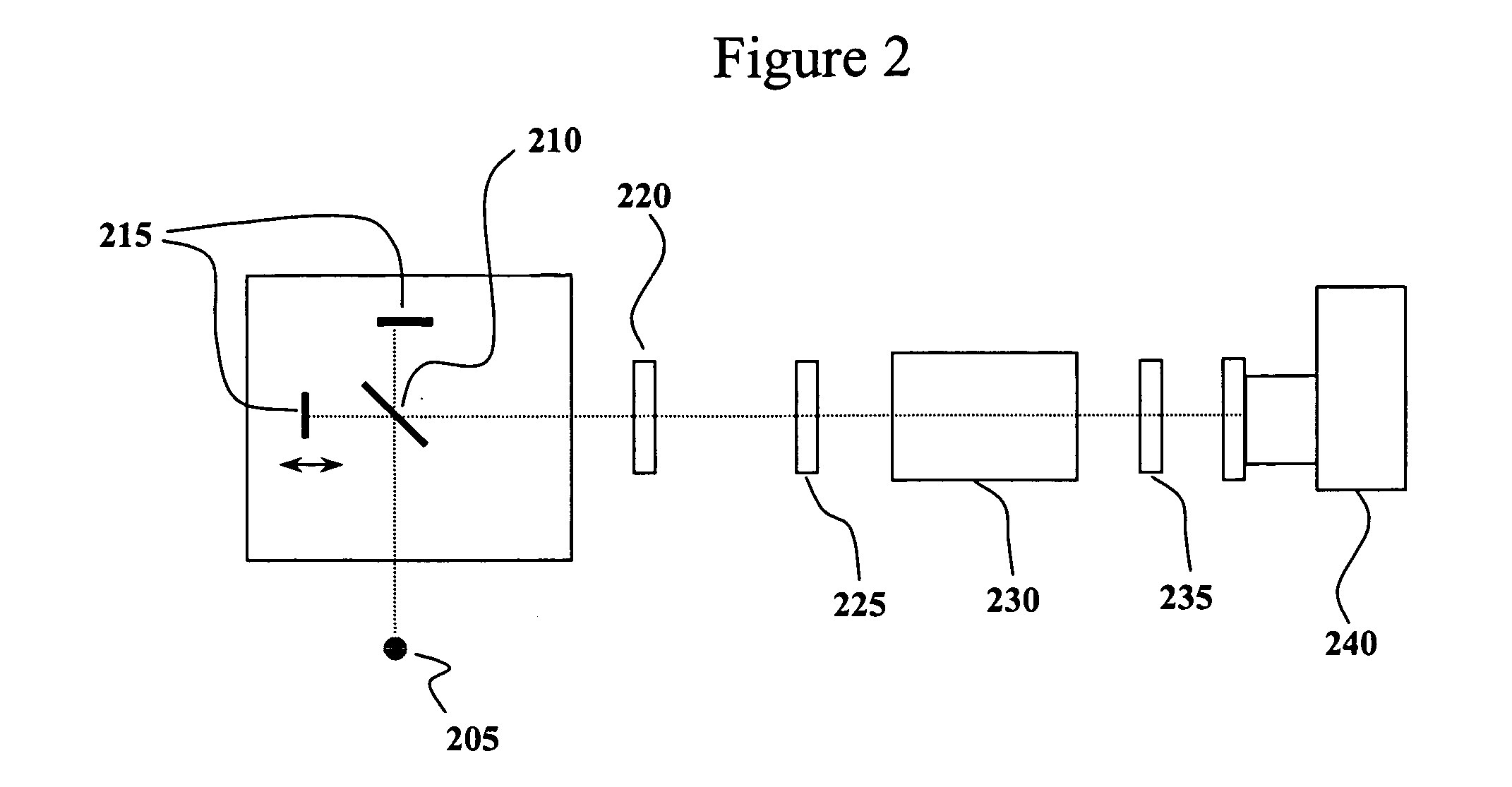
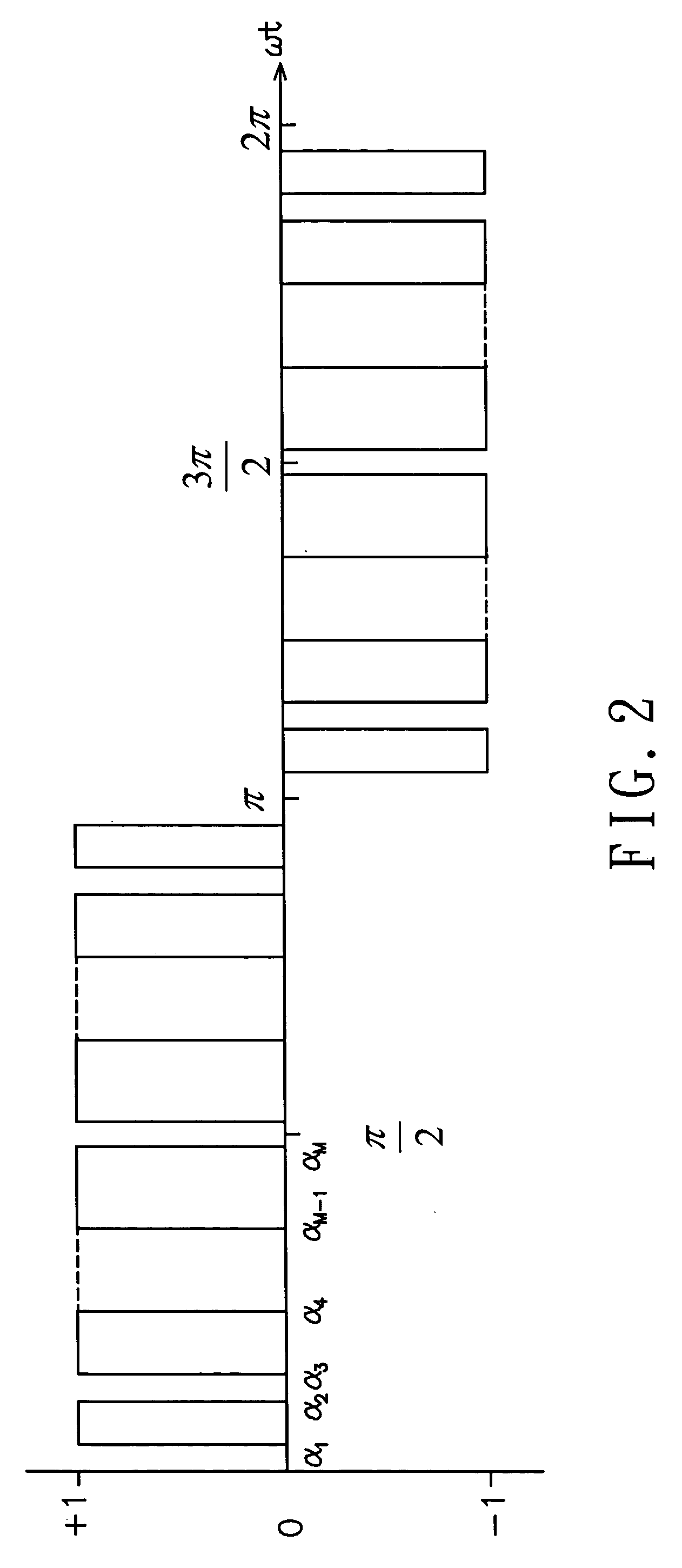
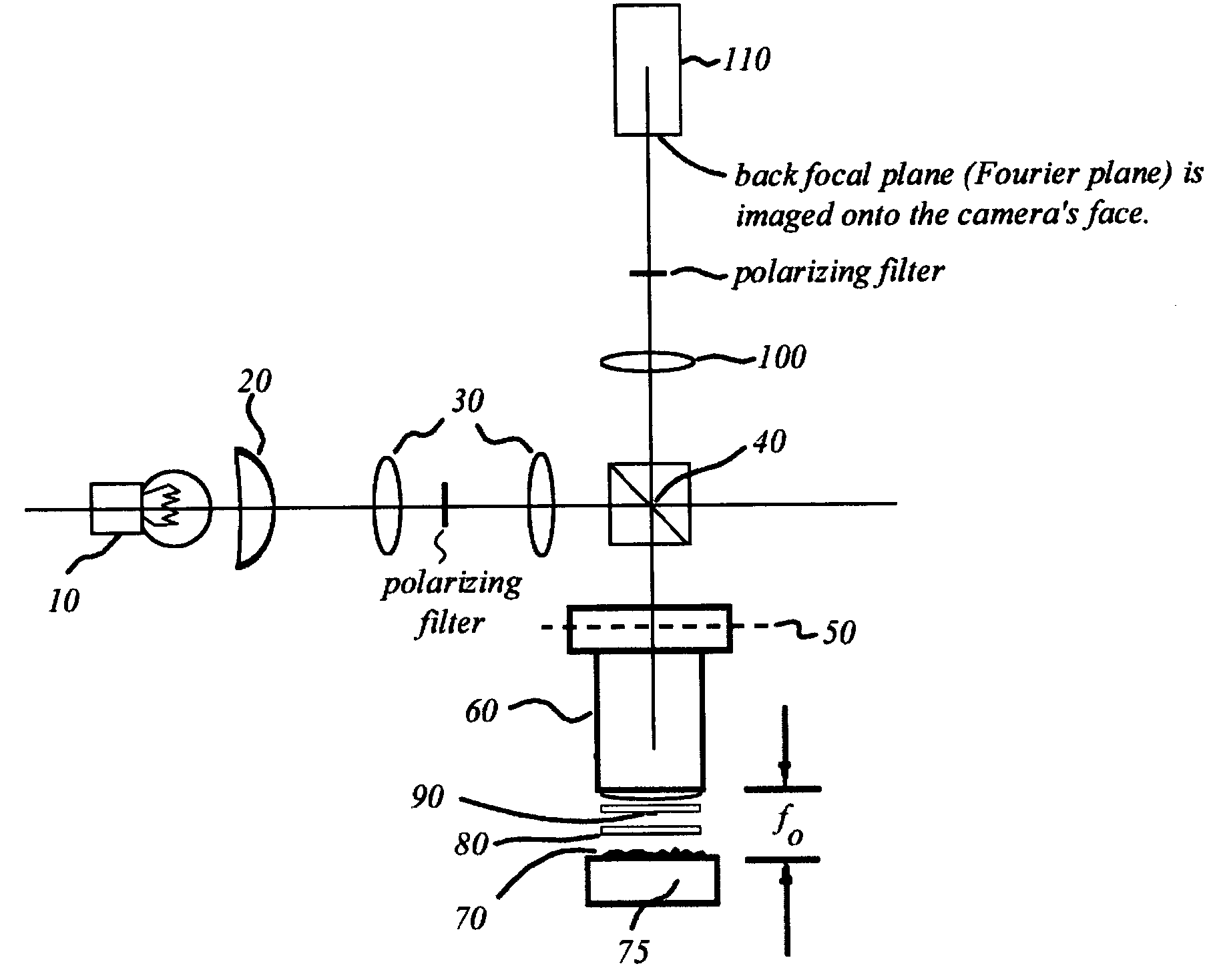
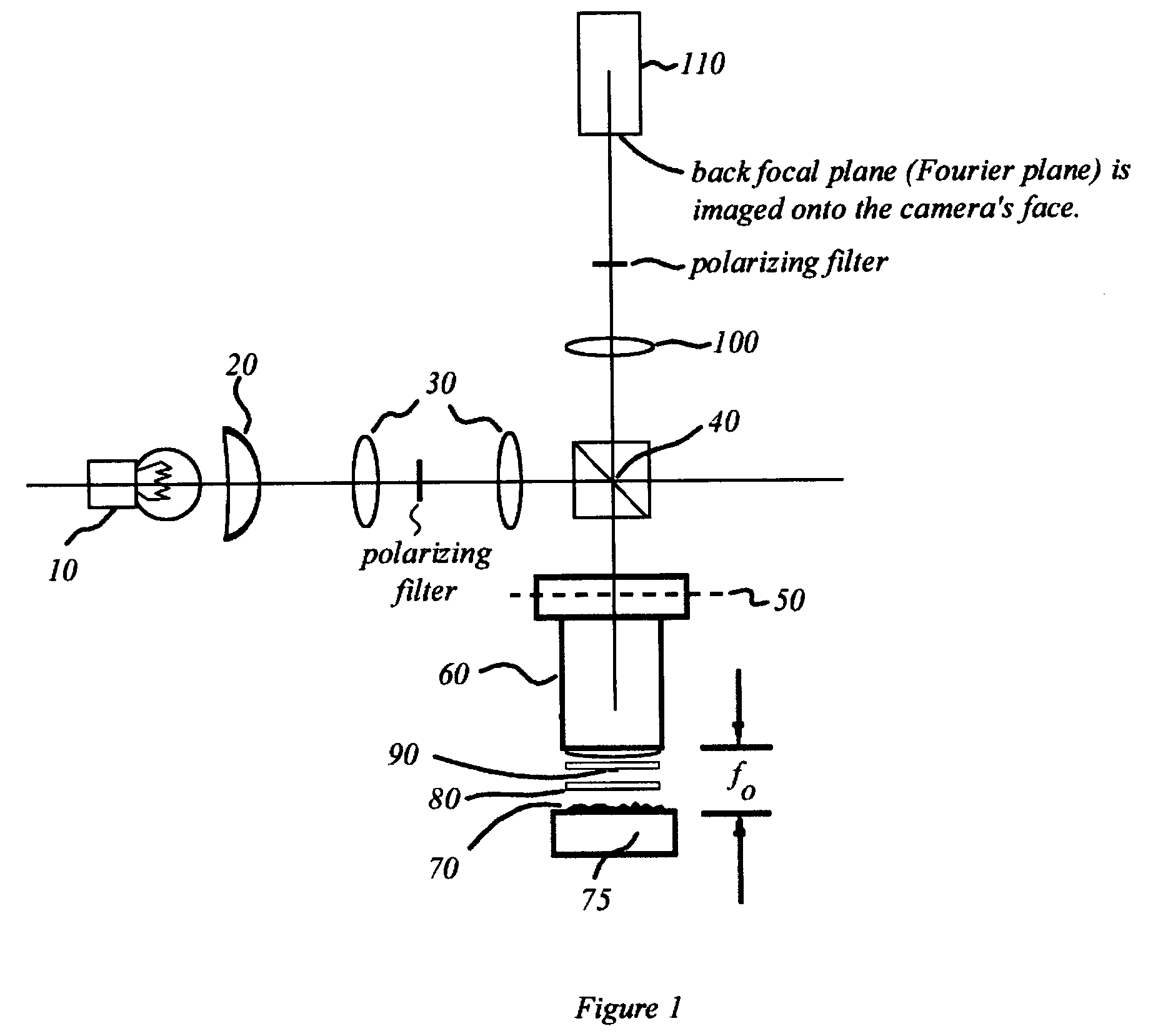
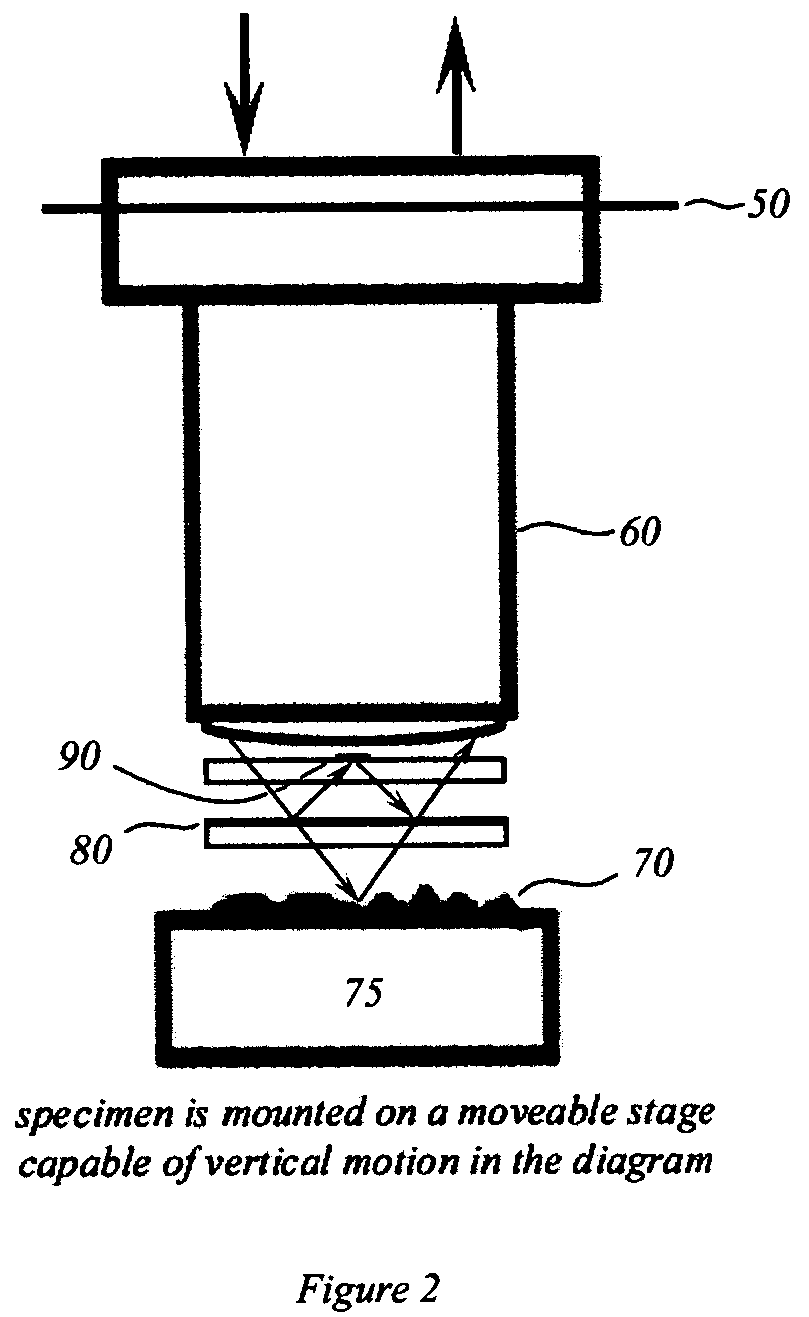
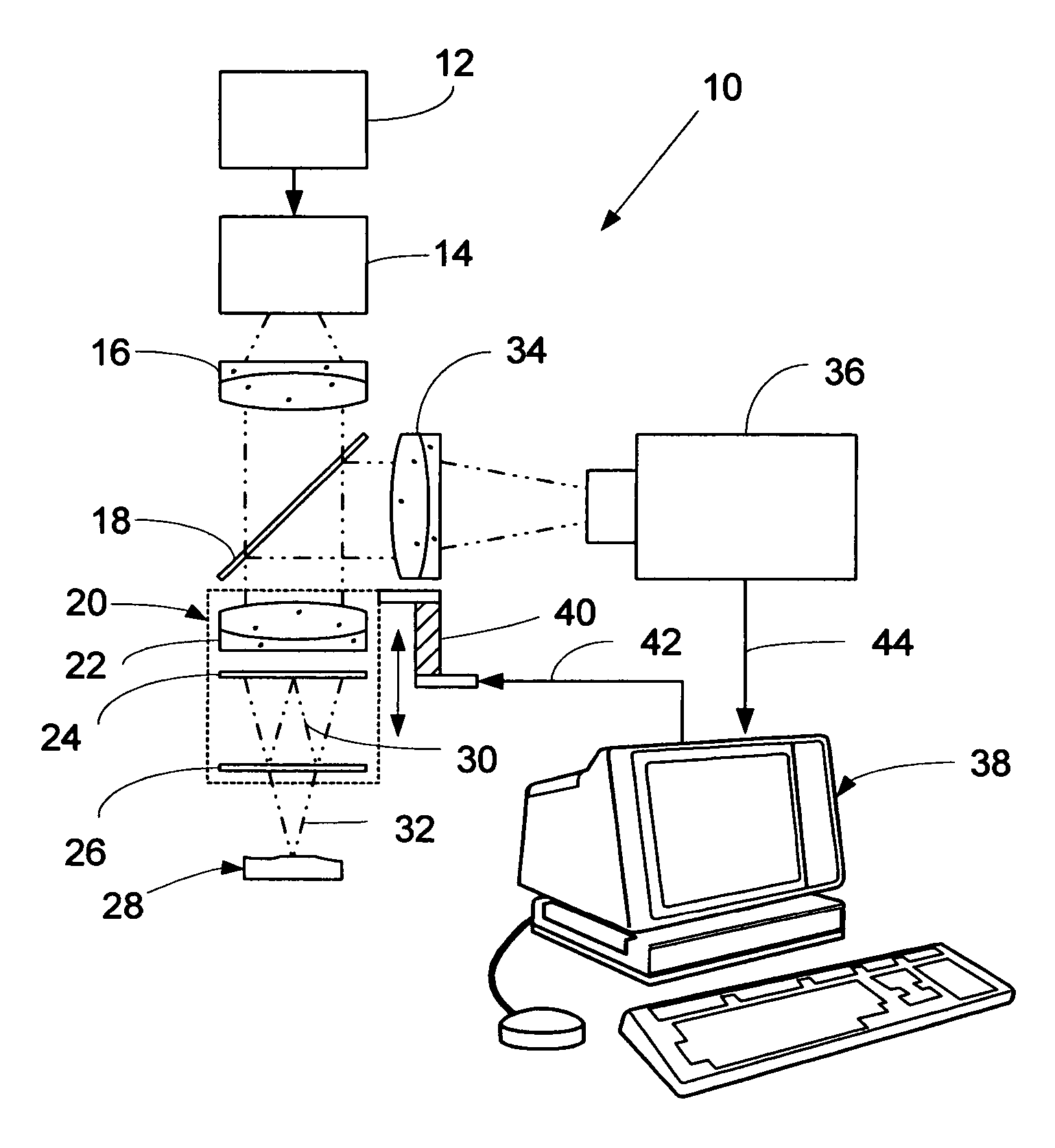
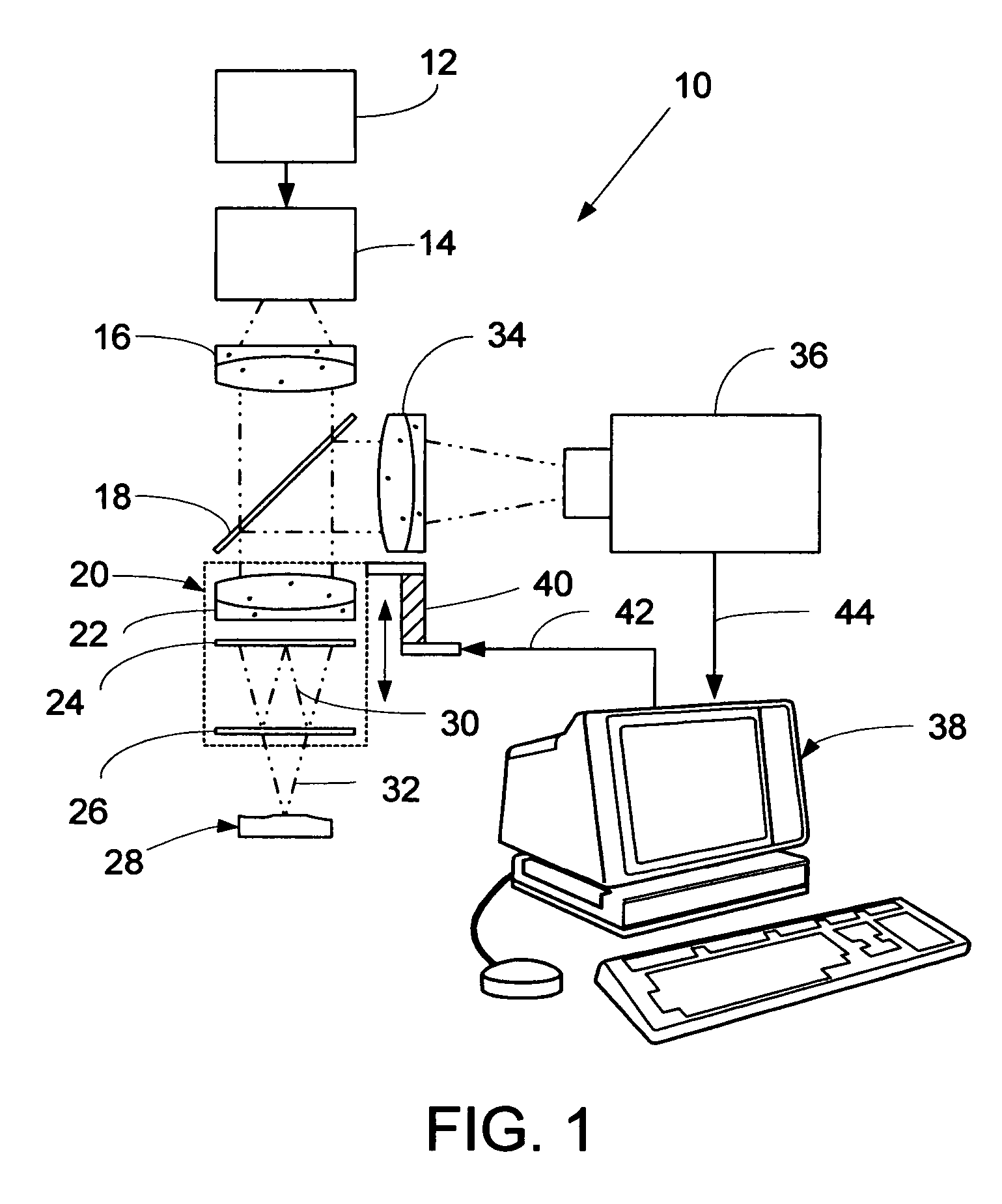
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
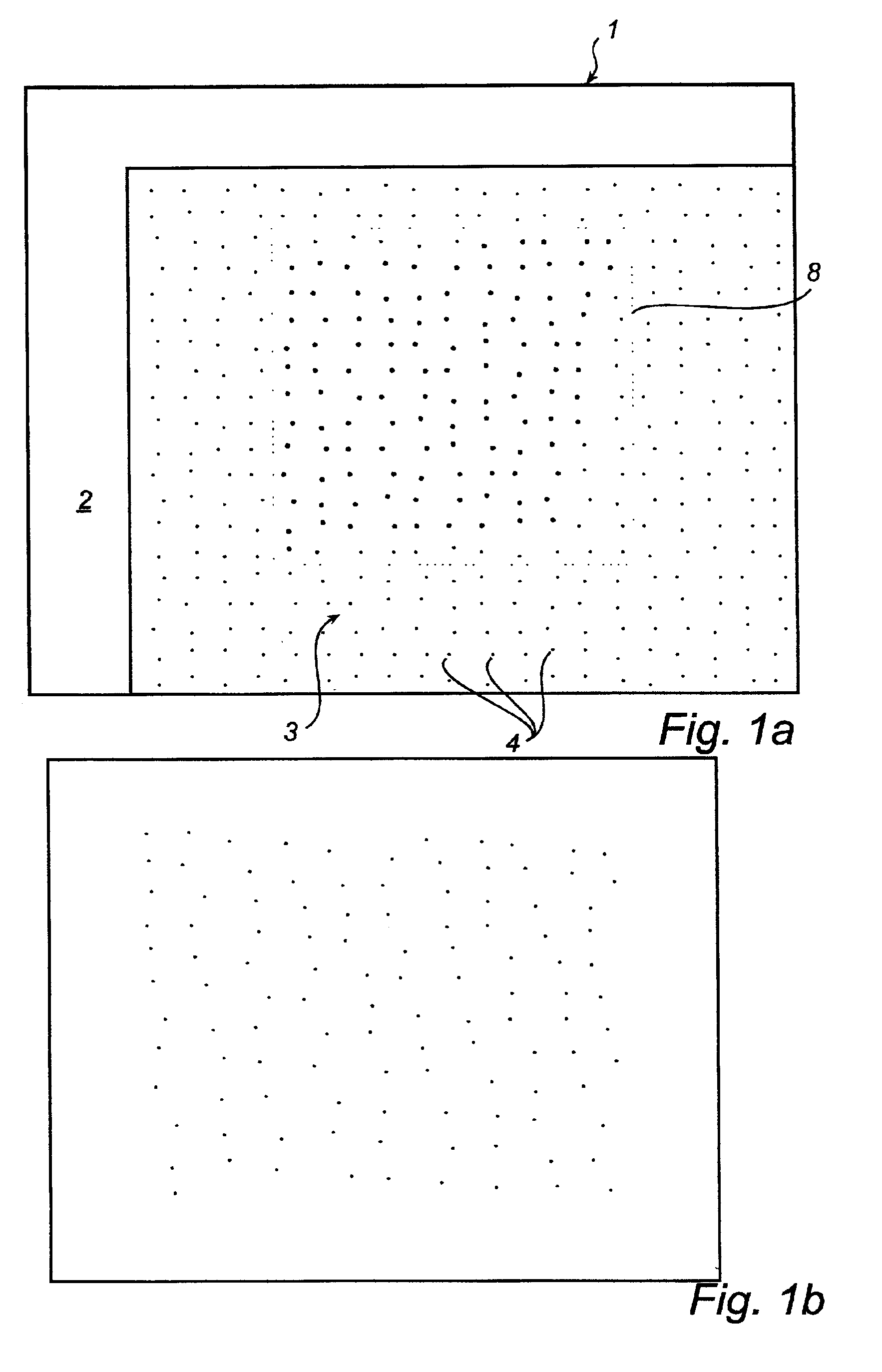
Identification of virtual raster pattern
InactiveUS7050653B2High precisionEffective calculationInput/output for user-computer interactionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGratingComputer graphics (images)
A method aims to identify a virtual raster pattern in an image of a surface that is provided with a plurality of position-coding marks. Each mark is associated with a respective intersection of raster lines belonging to the raster pattern. By means of the method, the virtual raster pattern is identified via Fourier analysis of the image. A computer program product and a device for position determination are also described.
Owner:ANOTO AB
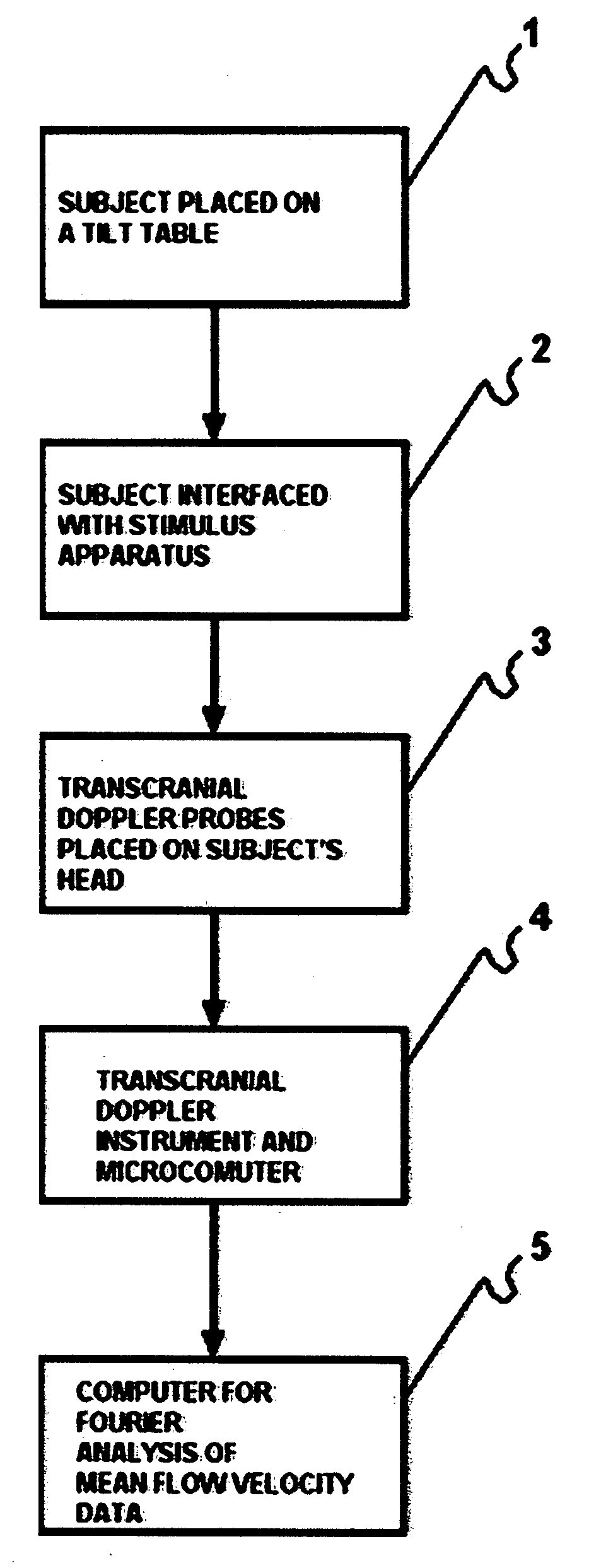
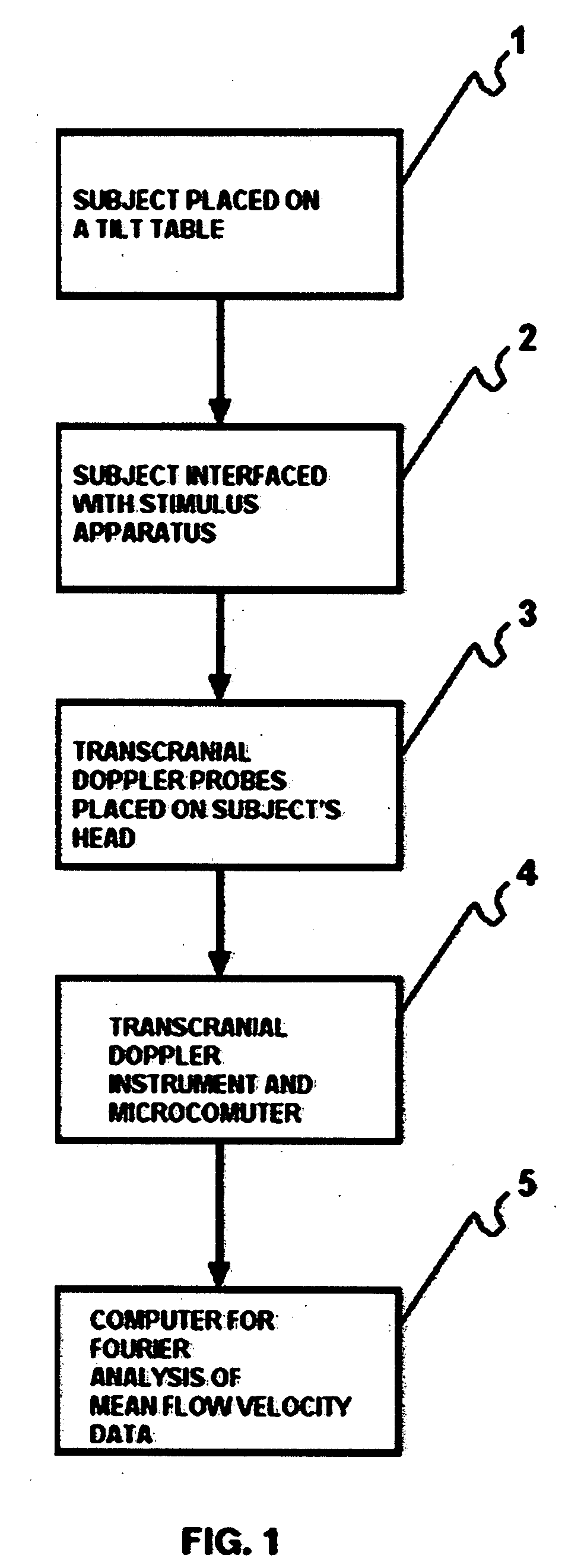
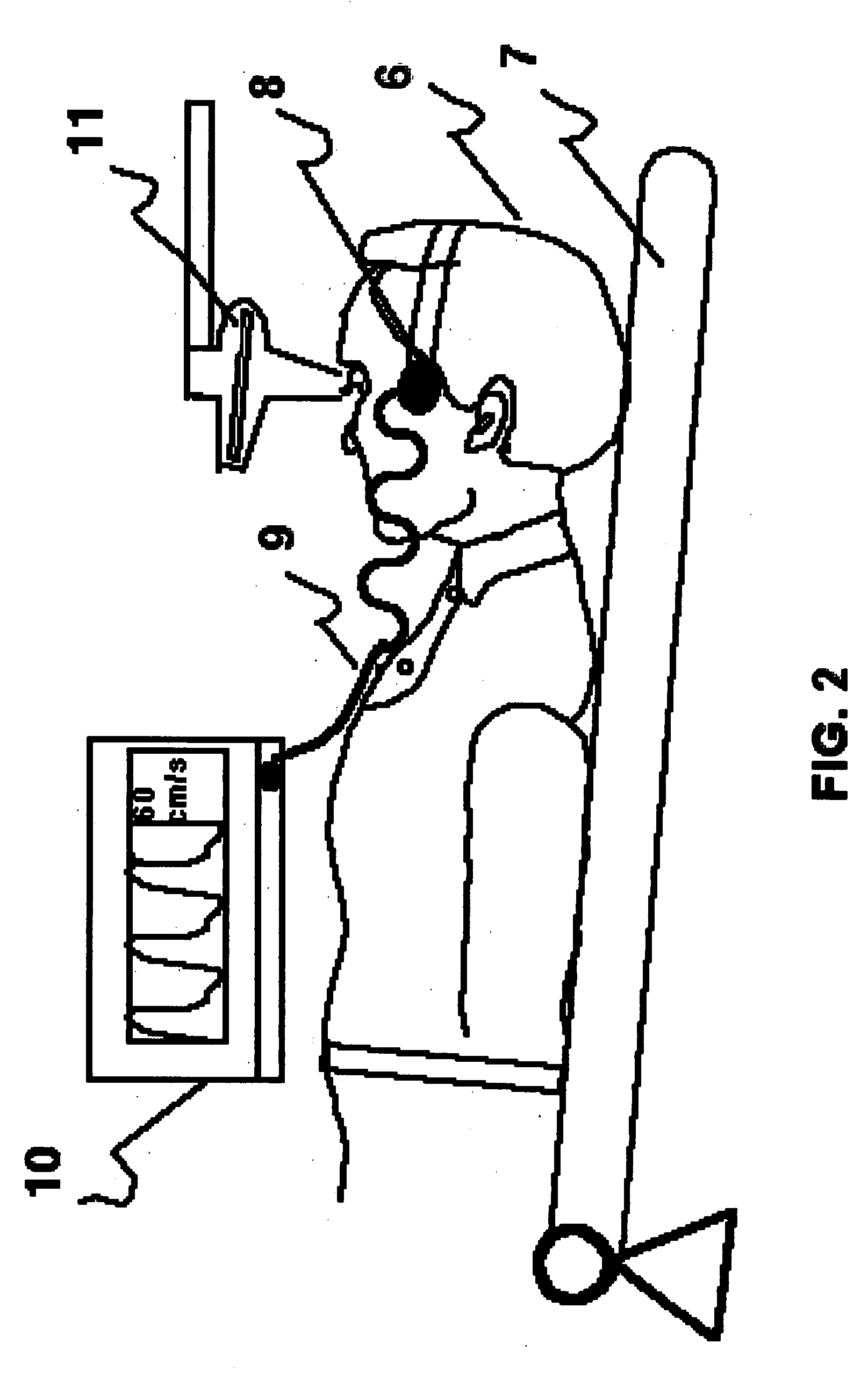
Method for inducing and monitoring long-term potentiation and long-term depression using transcranial doppler ultrasound device in head-down bed rest
InactiveUS20080221452A1Blood flow measurement devicesCatheterUltrasound deviceUltrasound attenuation
The present invention provides a method for monitoring long-term potentiation and long-term depression, comprising placing a subject in head down rest position and monitoring in real-time cerebral mean blood flow velocity using a transcranial Doppler device during psychophysiologic tasks. The method involves using Fourier analysis of mean blood flow velocity data to derive spectral density peaks of cortical and subcortical processes. The effect of head-down rest at different time intervals is seen as accentuation of the cortical peaks in long-term potentiation and attenuation of subcortical peaks in long-term depression. The effect of different interventions could be evaluated for research, diagnosis, rehabilitation and therapeutic use.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Microfluidic devices for electrophoretic analysis of materials
InactiveUS20070177147A1High-speed analysisOther chemical processesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The present invention provides a microfluidic system for electrophoretic analysis of materials in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry, biotechnology, molecular biology and numerous other fields. Light absorbance signals are received by a photodetector from periodically spaced regions along a channel in the microfluidic system. The signals received by the photodetector are modulated by the movement of species bands through the channel under electrophoretic forces. By Fourier analysis, the velocity of each species band is determined, and identification of the species is made based on its electrophoretic mobility in the channel.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Interference cancellation in an fmcw radar
ActiveUS20160124075A1Increase the number ofIncrease probabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterference cancelationRadar systems
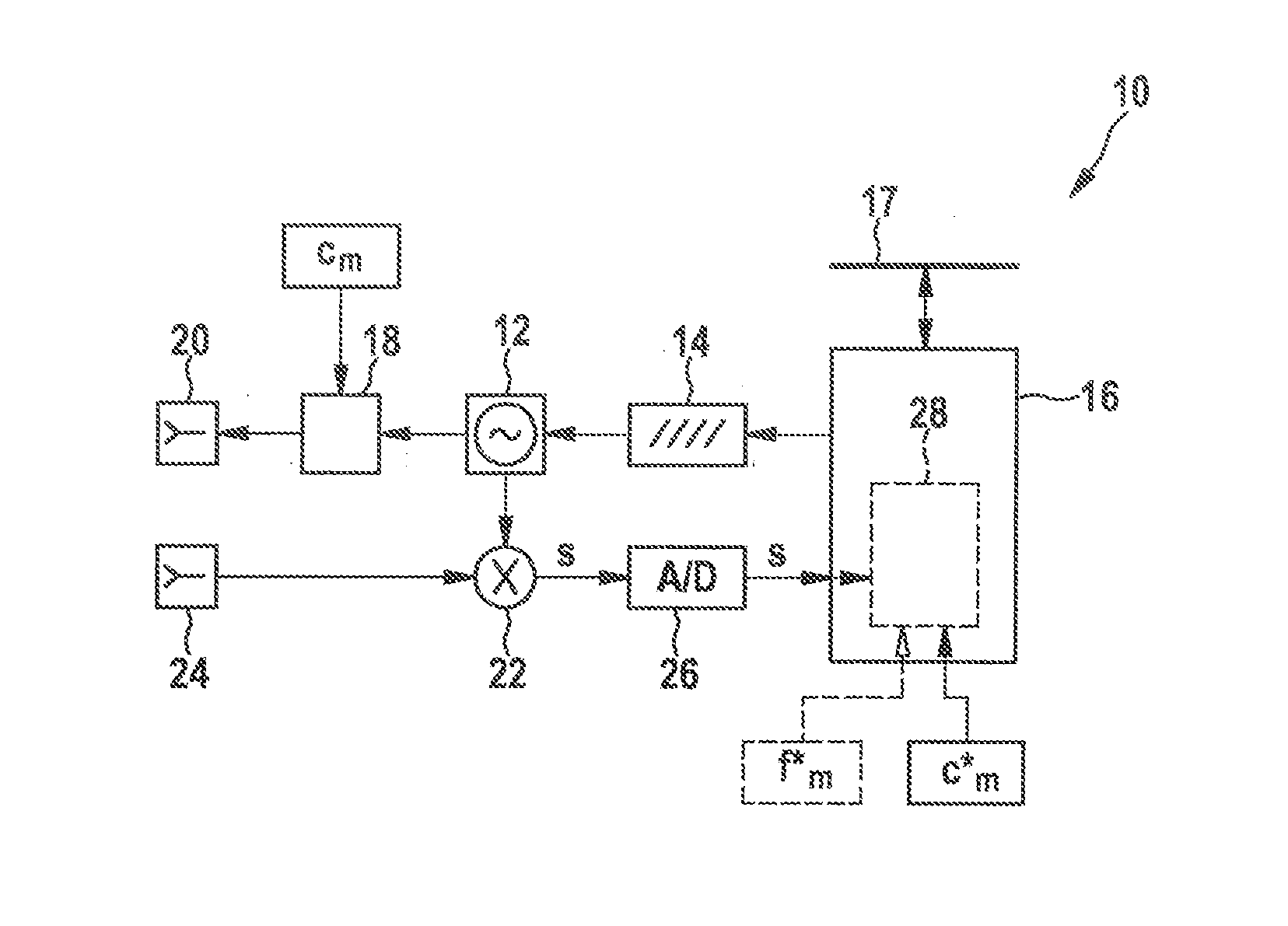
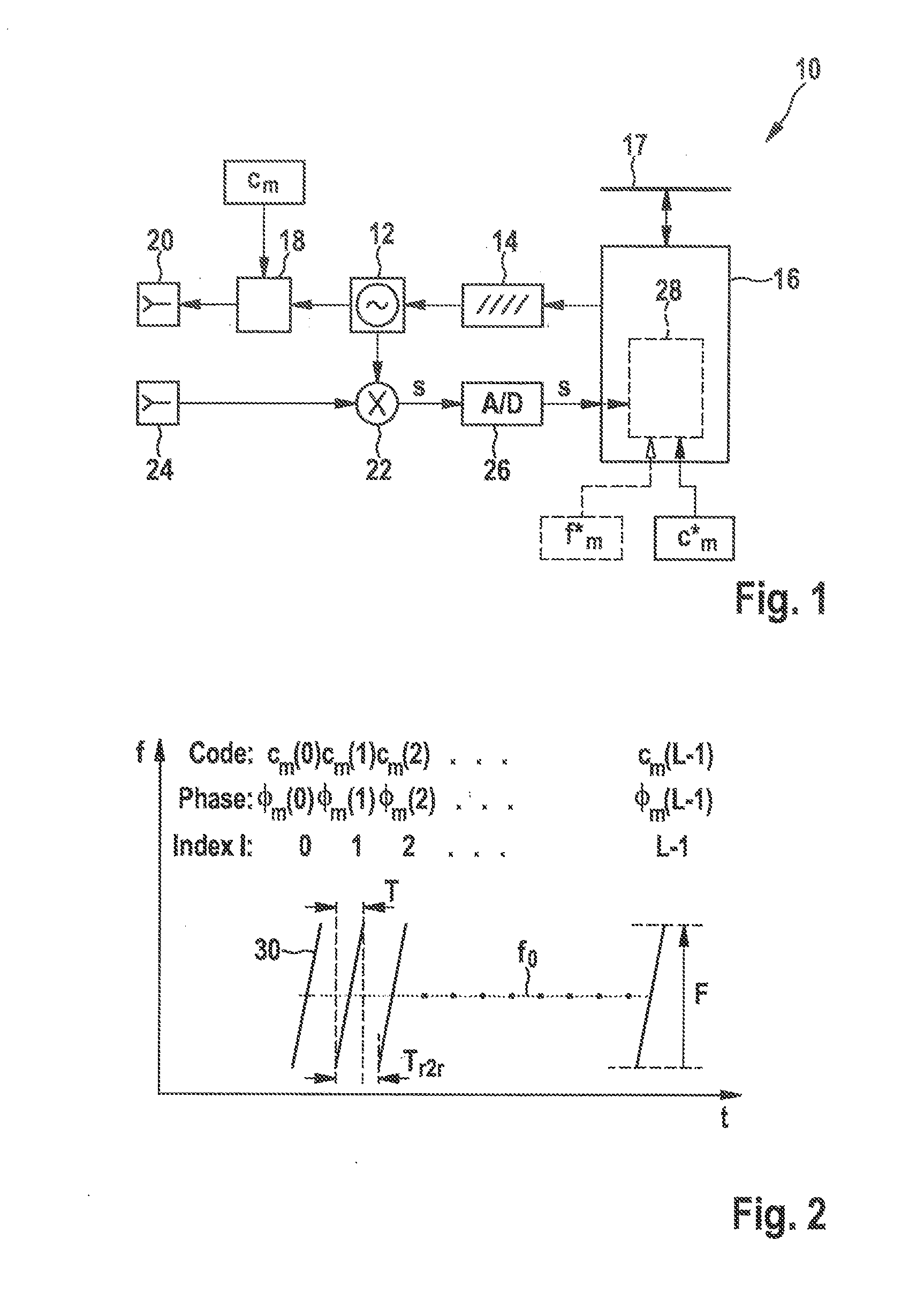
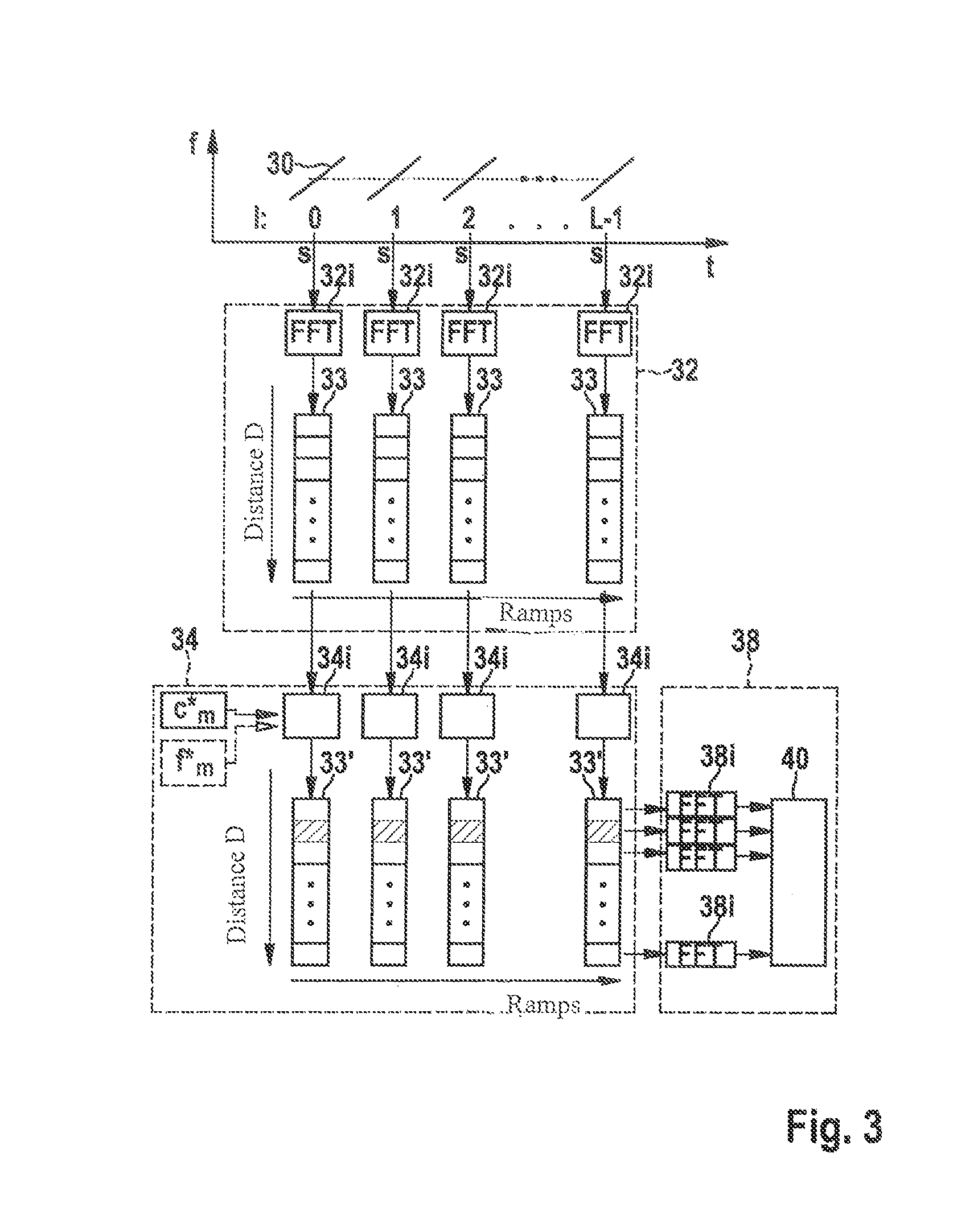
A radar system for transmitting a FMCW radar sensor signal encompassing a series of frequency modulation ramps and phase-modulated with a first code sequence orthogonal to a respective other code sequence with which a time-synchronized transmitted signal of another FMCW radar sensor is phase-modulated; the radar echoes are phase-demodulated with a code sequence correlating with the first code sequence; and a distance and / or a relative speed of a localized object is identified from a Fourier analysis frequency spectrum, in a first dimension over sampled radar echo values of a frequency modulation ramp, and in a second dimension over the phase-demodulated sequence of radar echoes of the ramps of the transmitted signal; and a vehicle fleet radar system having an FMCW radar sensor in which a code set satisfying a code set orthogonality condition with a code set of a radar sensor of another vehicle is used for phase modulation / demodulation.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
High throughput screening with parallel vibrational spectroscopy
InactiveUS20030175160A1Enhances signal developmentImprove performanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMeasurement device
Rapid spectrum assay of multiple samples with infrared light is made possible by devices and methods that increase total light throughput. Multiple wavelength scan with Fourier analysis is combined with large numbers of sample wells located within infrared light compatible solid materials. In particular, very large scale measurement devices and systems for their use are fabricated from lithography and other techniques used for semiconductor processing.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL HLDG
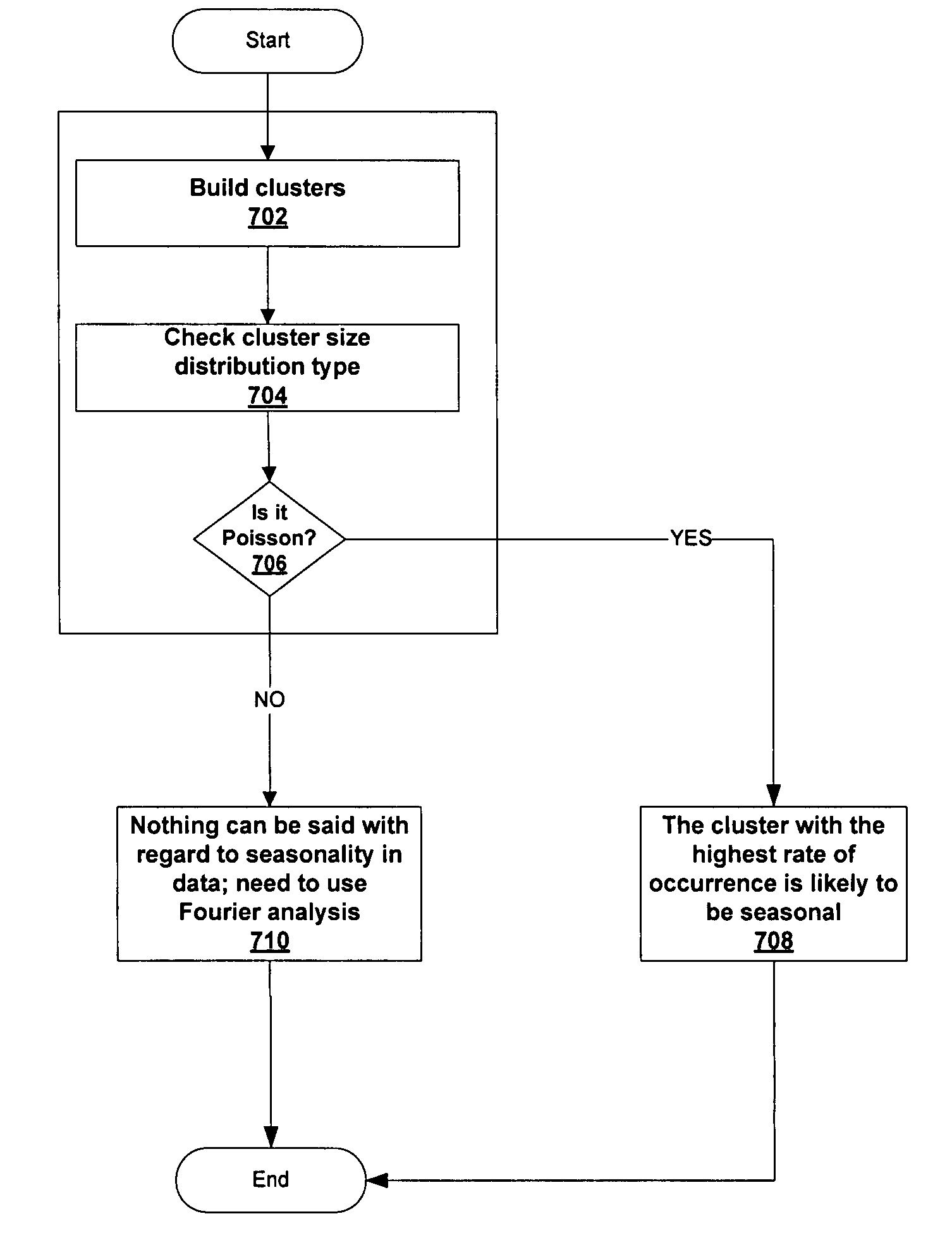
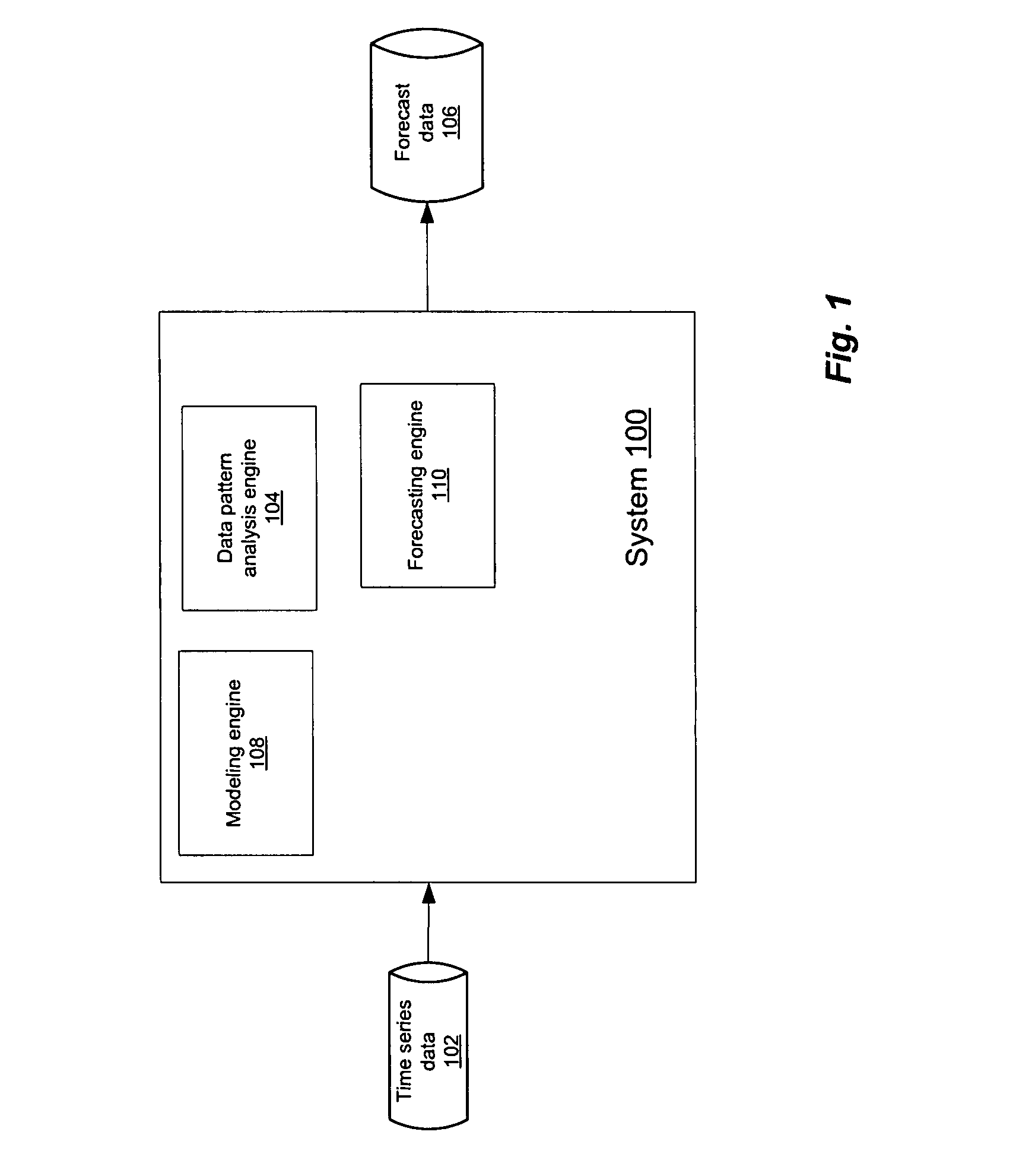
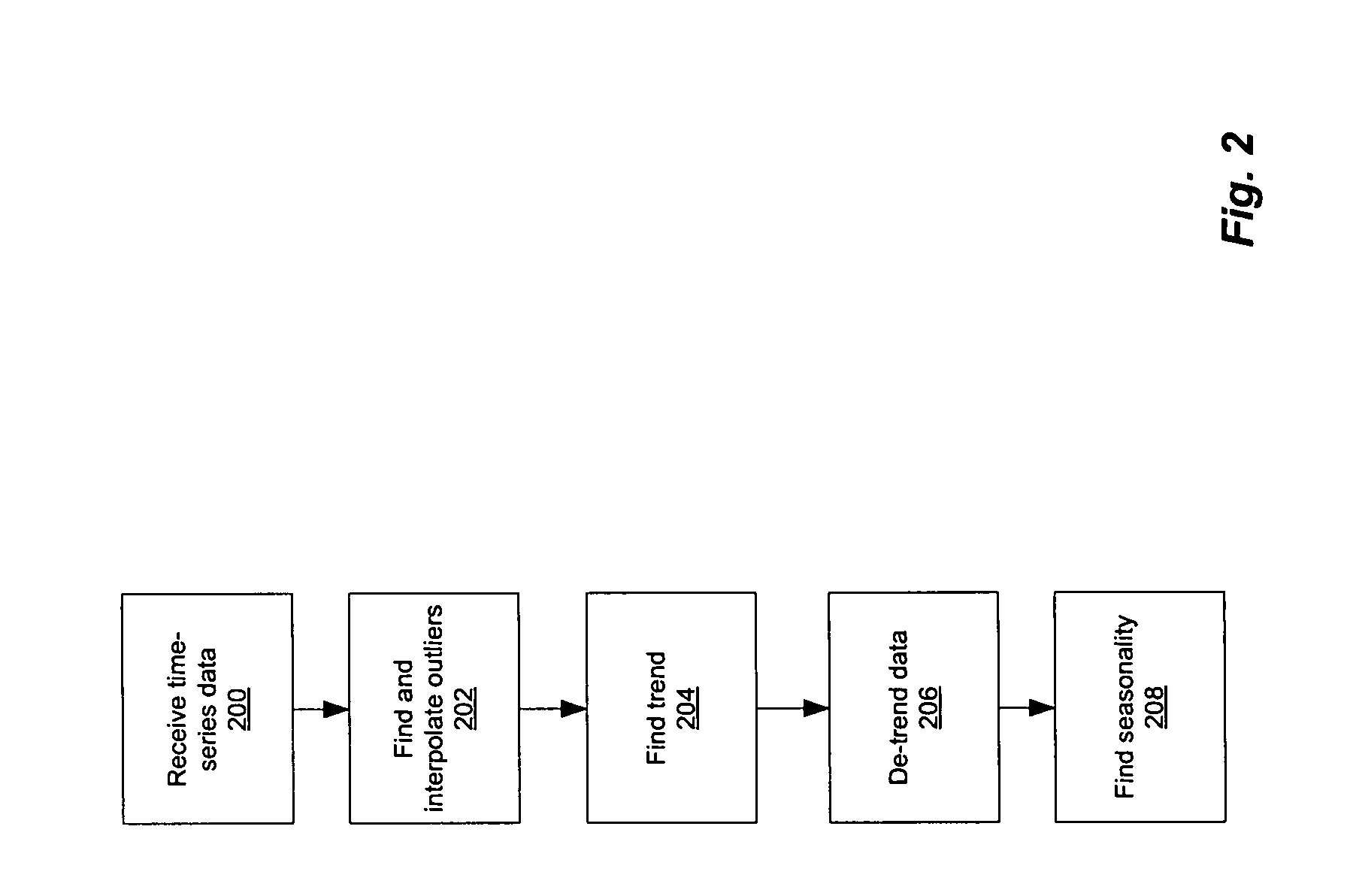
Computer storage capacity forecasting system using cluster-based seasonality analysis
ActiveUS7783510B1Easy to shapeAccurate predictionCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsData setDecomposition
A methodology for automatic a priori data pattern analysis is provided. Described methods allow consistent and objective determination of outliers; trend; seasonality; and level shifts; and the production of better models and more accurate forecasts. In addition, a two-step way to automatically determine seasonality and locate possible events in the data set is described. Decomposition of data into seasonal, trend and level components; detection of outliers and level-shift events in the time series based on statistical analysis of the time series; detection of seasonality based on statistical analysis of clusters of data, known as cluster-based seasonality analysis, or CBSA; evaluation of the goodness of fit of a model to data, using the existing goodness of fit indicator, R2; and seasonality analysis, using a sequence of cluster-based seasonality analysis (CBSA) and Fourier analysis are described.
Owner:MONOSPHERE
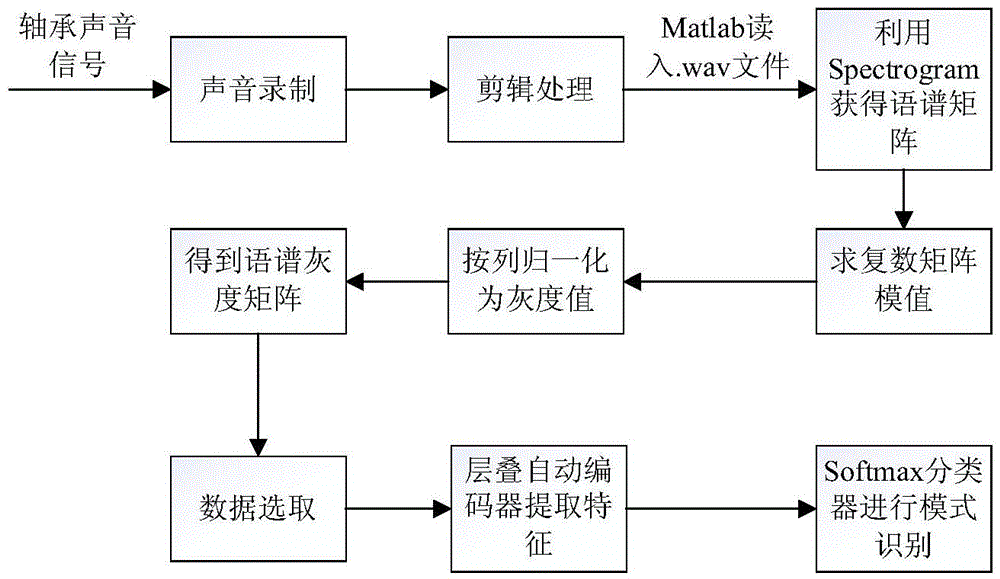
Rolling bearing sound signal fault diagnosis method based on short-time Fourier transform and sparse laminated automatic encoder
InactiveCN104819846AEasy to digFeature Effectively ImplementedMachine bearings testingFast Fourier transformFourier analysis
The invention discloses a rolling bearing sound signal fault diagnosis method based on short-time Fourier transform and a sparse laminated automatic encoder. According to the method of the invention, firstly a smart mobile phone is used for acquiring a sound signal of the rolling bearing fault; then short-time Fourier analysis is performed on the sound signal for obtaining a spectrogram matrix; then the modulus value of the matrix is acquired and gray scale normalization processing is performed; then the normalized data are selected and input into a deep studying network for automatically extracting characteristics; and finally the characteristic which is extracted by a neural net is input into a Softmax classifier for identifying the fault mode. The invention provides the rolling bearing sound signal fault diagnosis method based on smart mobile phone sound signal short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and the sparse laminated automatic encoder (SAE). Through testing result analysis, the rolling bearing sound signal fault diagnosis method can accurately determine the fault mode of the rolling bearing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
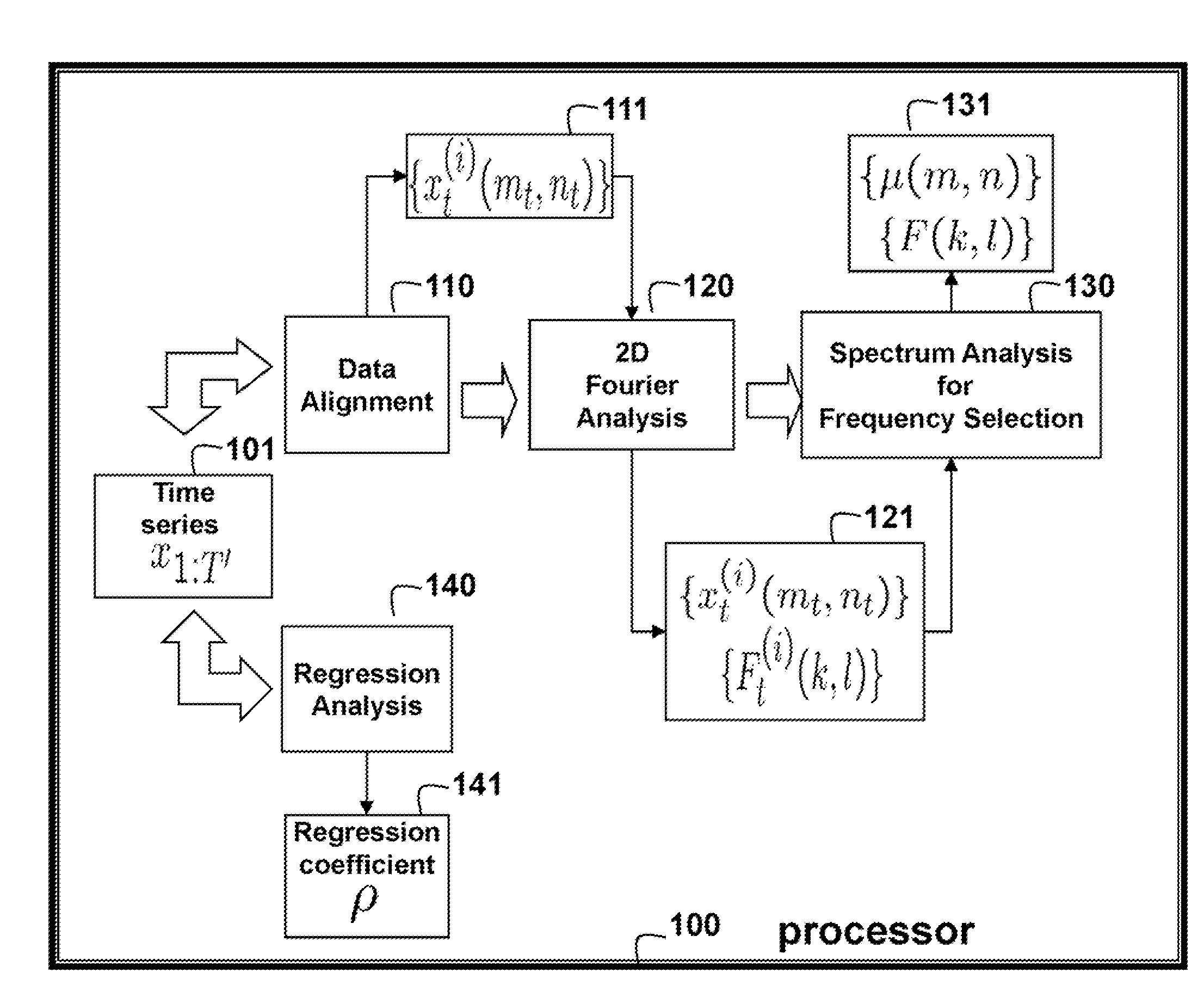
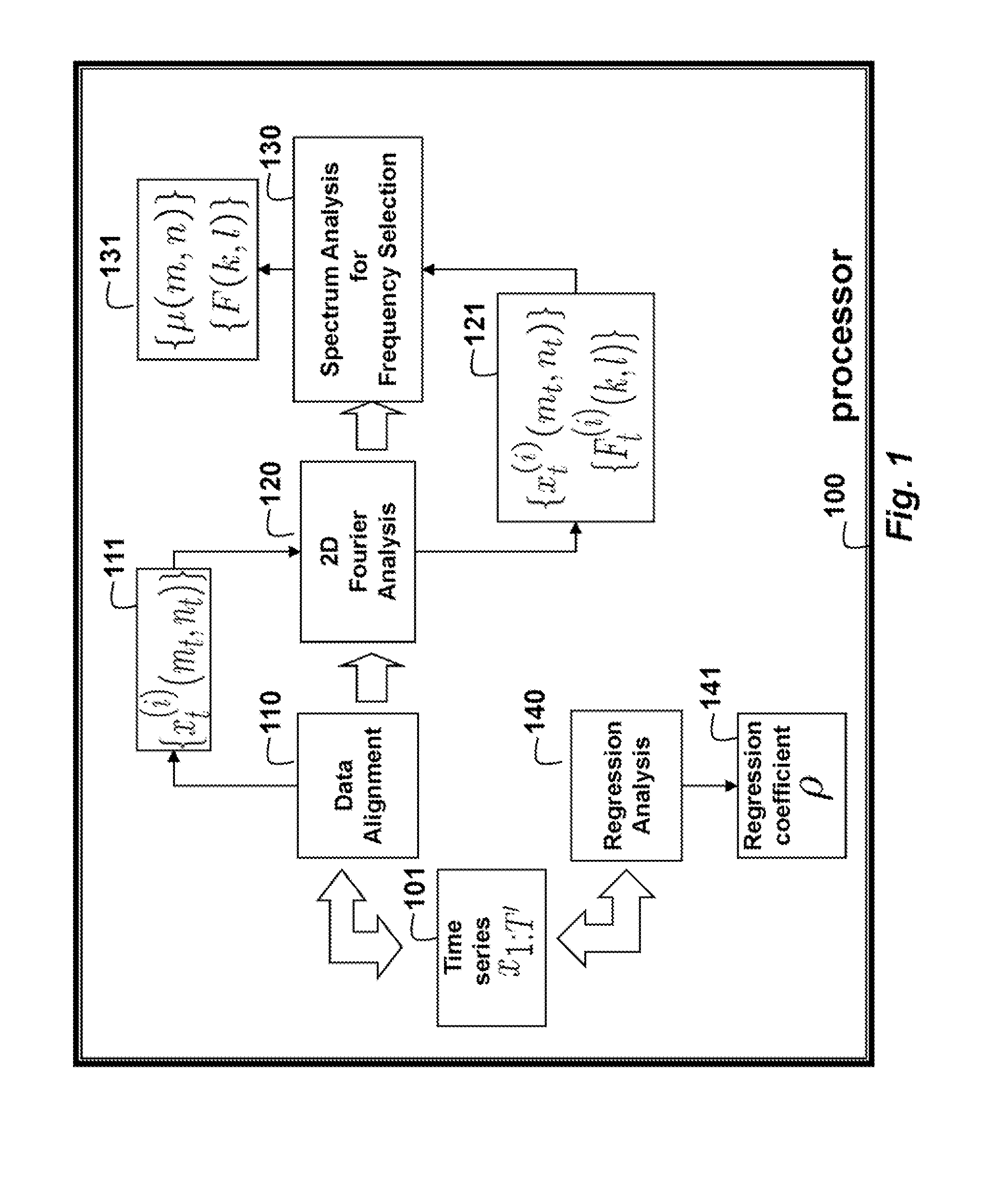
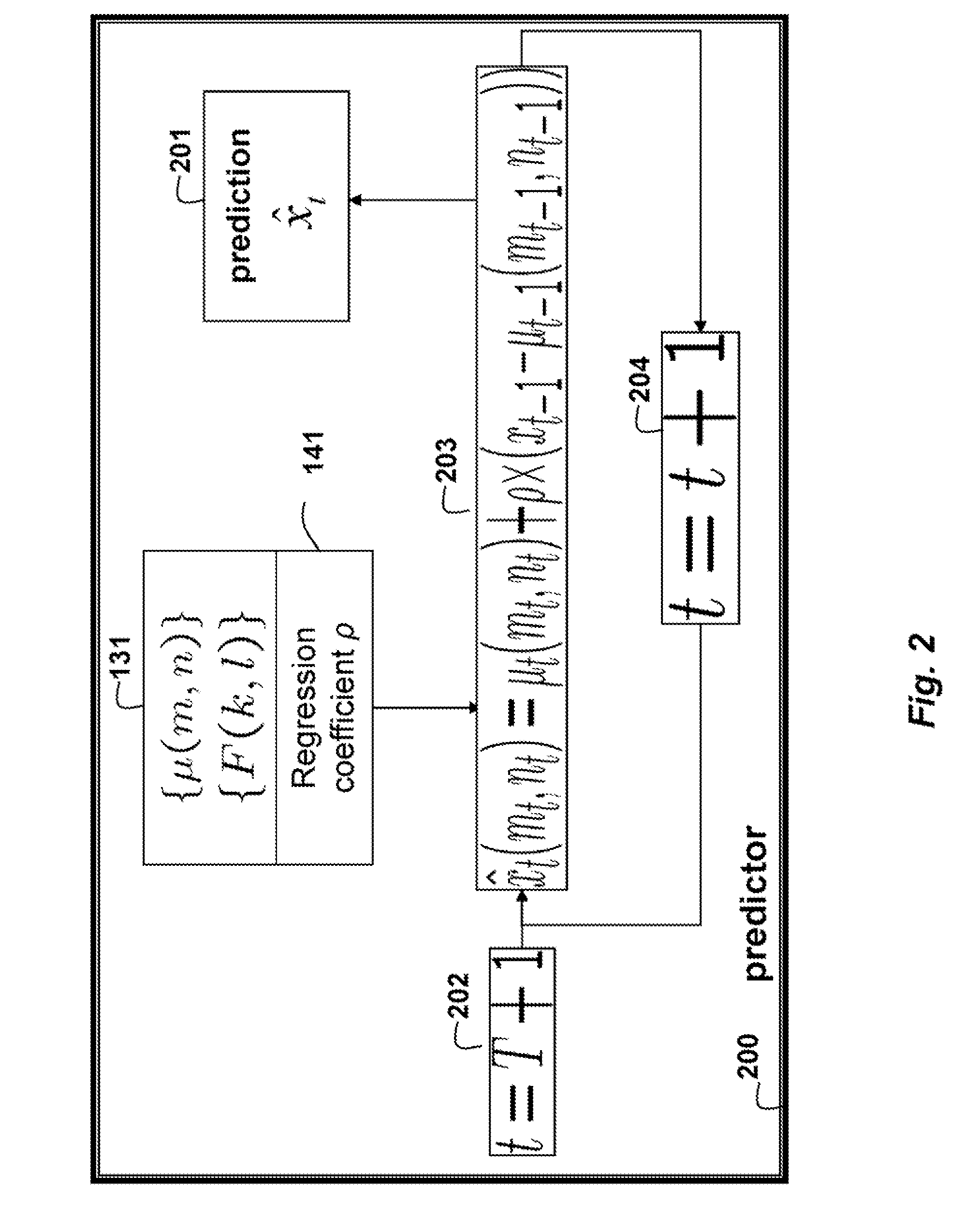
Method for Predicting Outputs of Photovoltaic Devices Based on Two-Dimensional Fourier Analysis and Seasonal Auto-Regression
InactiveUS20130262049A1Generation forecast in ac networkData processing applicationsRegression analysisPredictive methods
An output of a photovoltaic (PV) device is predicted by applying Fourier analysis to historical data to obtain frequencies and a mean of the frequencies in the data. Regression analysis is applied to the data to obtain a regression coefficient. Then, the prediction is a sum of the mean at the time step and a deviation from the mean at a previous time step, wherein the means are represented and approximated by selected frequencies, and the deviation for the previous time step is weighted by the regression coefficient.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs
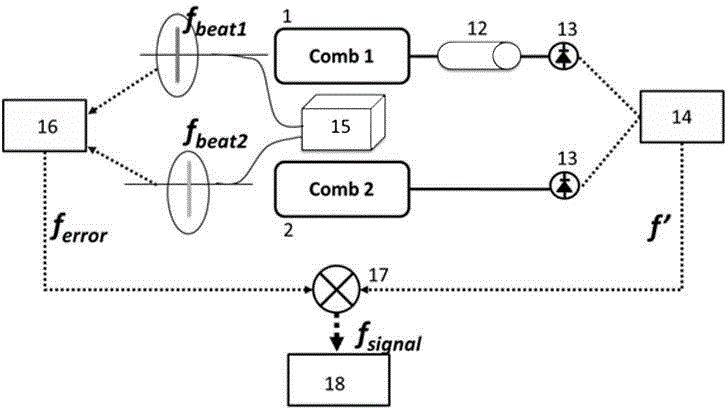
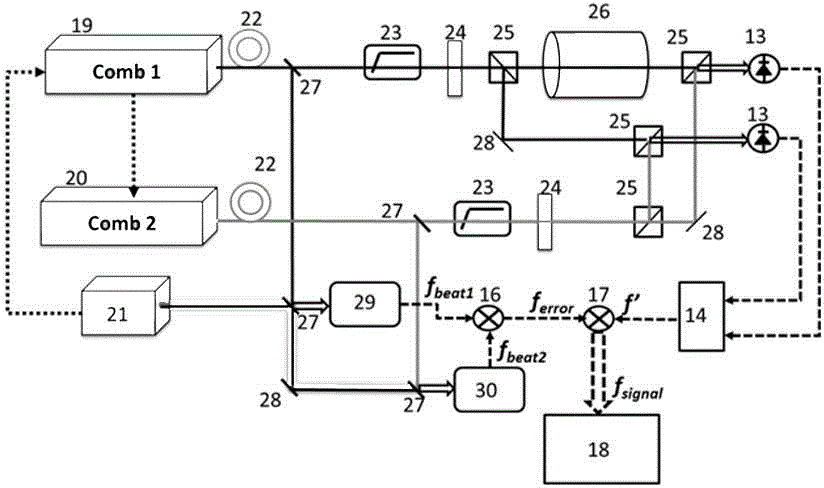
ActiveCN104316186AReduce volumeReduce maintenance difficultyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsFourier analysisVIT signals
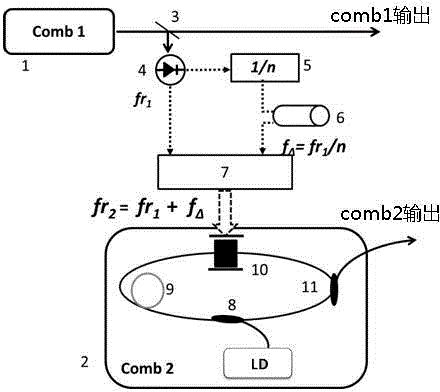
The invention discloses a spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs. The measurement method is characterized in that firstly, an annular laser resonant cavity based on a phase modulator is actively modulated by use of a first optical frequency comb controllable in time domain and frequency domain so that the annular laser resonant cavity is converted into a second optical frequency comb having tiny difference in repetition frequency with the first optical frequency comb, and spectrum detection is performed on the two optical frequency combs to obtain an interference signal carrying the information of a sample to be tested, and meanwhile, frequency beating is performed on the two optical frequency combs and continuous frequency stabilized laser, respectively, the difference frequency signal of two obtained beat frequency signals is mixed with the interference signal, and a signal obtained by virtue of detection mixing is taken as a spectral signal for Fourier analysis so as to reduce the optical information of the sample to be tested. The spectral measurement method has the advantages that the error of the spectral detection due to own phase drift of a dual-optical comb system can be eliminated, and therefore, the resolution and the detection accuracy of the spectral measurement can be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
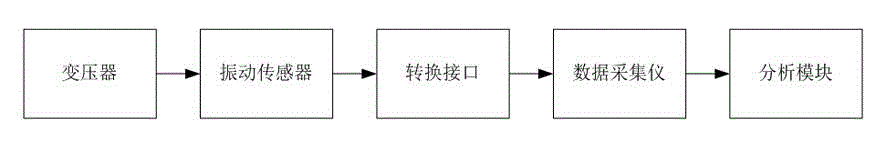
System and method for diagnosing and preliminarily positioning loosening faults of iron core of power transformer
ActiveCN102721465AAccurately reflect loose fault characteristicsDetect loose faultsSpectral/fourier analysisVibration measurement in solidsTransformerComputerized system
The invention discloses a system and a method for diagnosing and preliminarily positioning loosening faults of an iron core of a power transformer, and belongs to the technical field of intelligent diagnosis of faults of power transformers. The system for diagnosing and preliminarily positioning faults comprises vibration sensors, a signal acquisition instrument and a computer system. The method for diagnosing and preliminarily positioning faults includes that vibration signals are measured by the three vibration sensors mounted on the top of the transformer, Fourier analysis is carried out for the signals to obtain characteristic quantities, which include a 50Hz component, a 150Hz component and a 300Hz component, of the loosening faults of the iron core, the 300Hz component is used as a main characteristic quantity, a certain position of the iron core is determined to be loosened when amplitudes of the components of the certain position are increased to certain values, and the faults can be positioned by means of comparing the differences of the three characteristic quantities of signals of each position. By the aid of the system and the method, characteristics of the loosening faults of the iron core can be accurately reflected, and the loosening faults of the iron core of the power transformer can be effectively detected.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
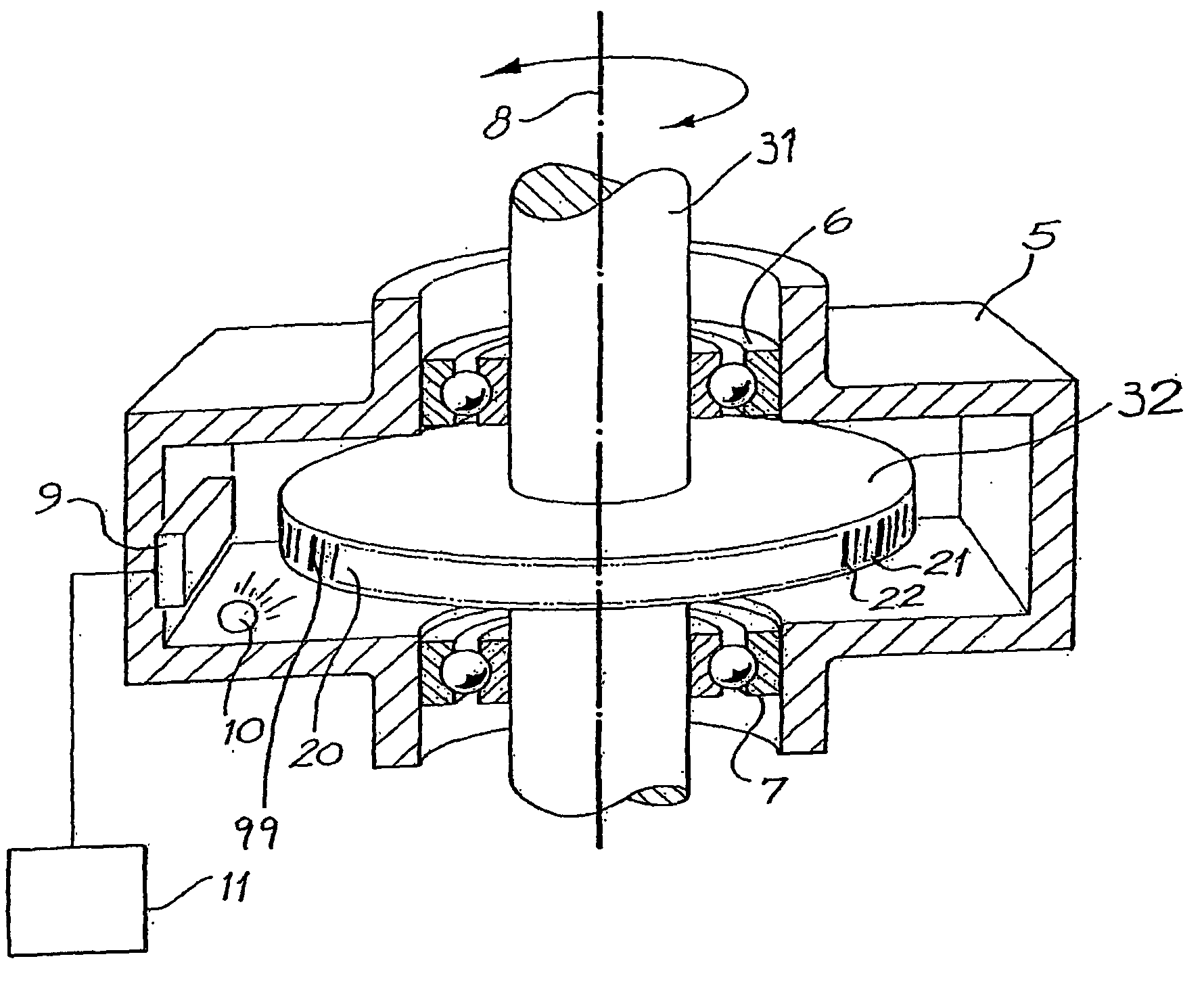
Position encoder using statistically biased pseudorandom sequence
InactiveUS20040015323A1Improve accuracyDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsManchester codeTransmittance
A position sensor encodes absolute position via n consecutive members of a pseudorandom sequence of bits, where each bit (30a-30k) comprises a region of high transmission or reflectivity adjacent to a region of low transmission or reflectivity. The pseudorandom sequence is chosen such that every series of n consecutive bits (30a-30k) in the sequence is predominantly formed from a predetermined bit value (1 or 0). The light transmitted or reflected from the series is therefore detected as a substantially periodic intensity pattern (42), which can be processed via Fourier analysis to yield an accurate interpolation of relative position. An example is given of a pseudorandom sequence, which can be represented as a cyclic Manchester code, in which at least 8 members of every series of 11 consecutive bits has a bit value of 1.
Owner:BISHOP INNOVATION PTY LTD
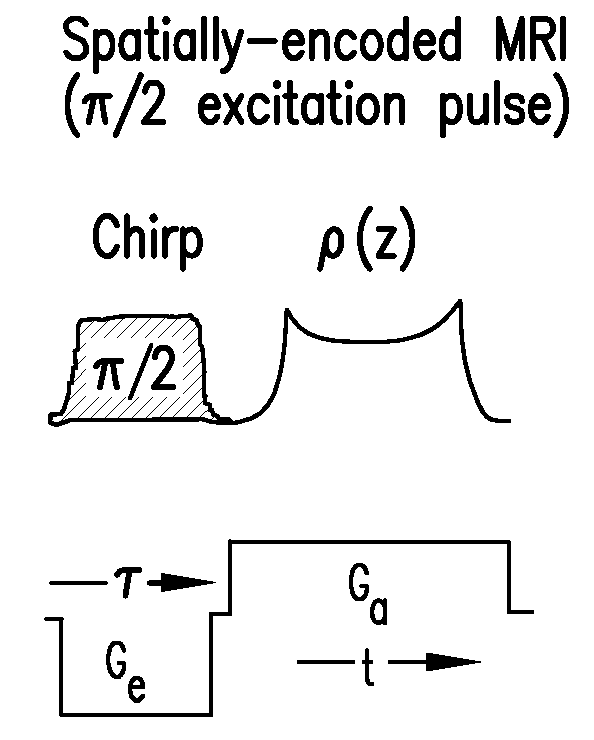
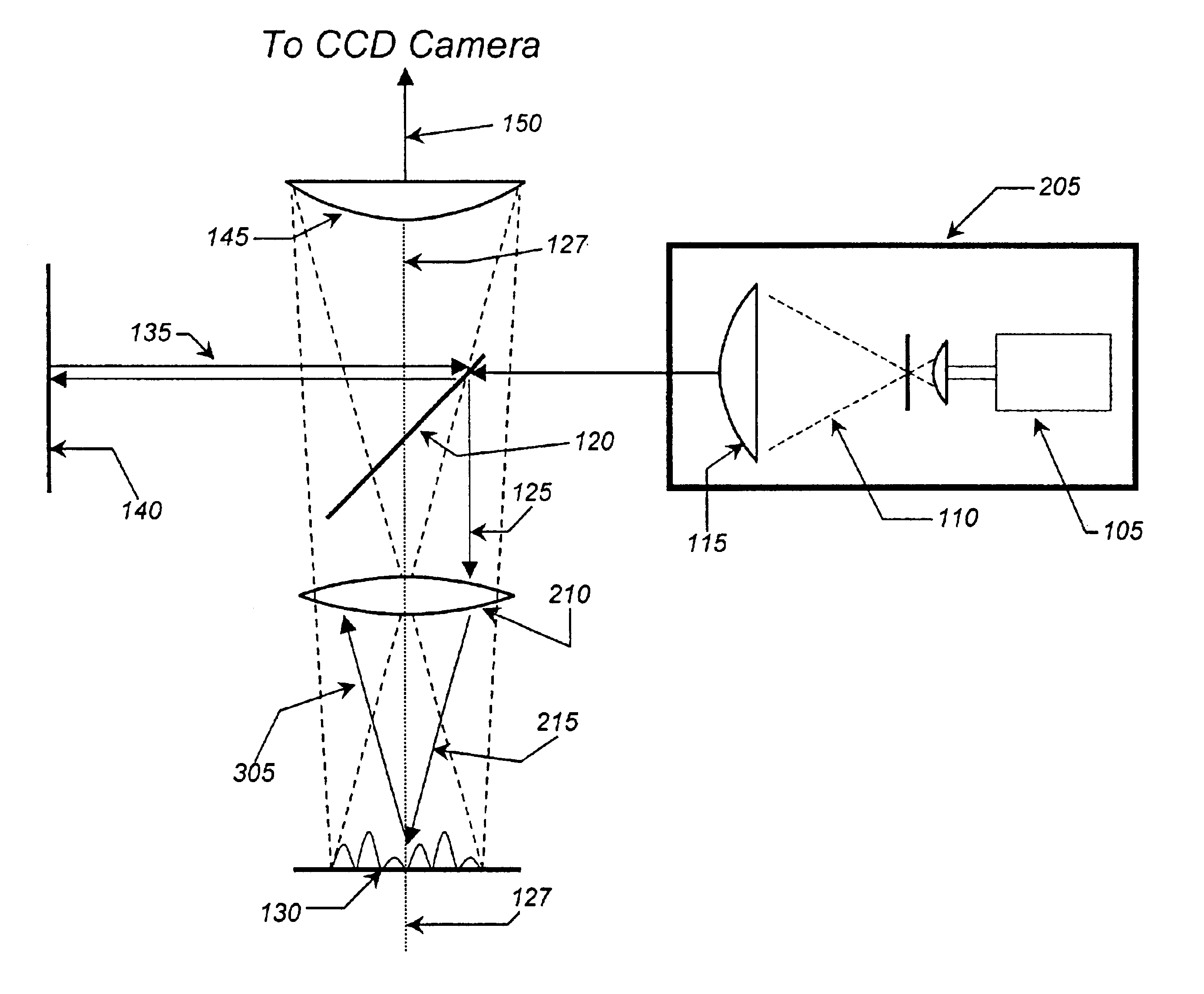
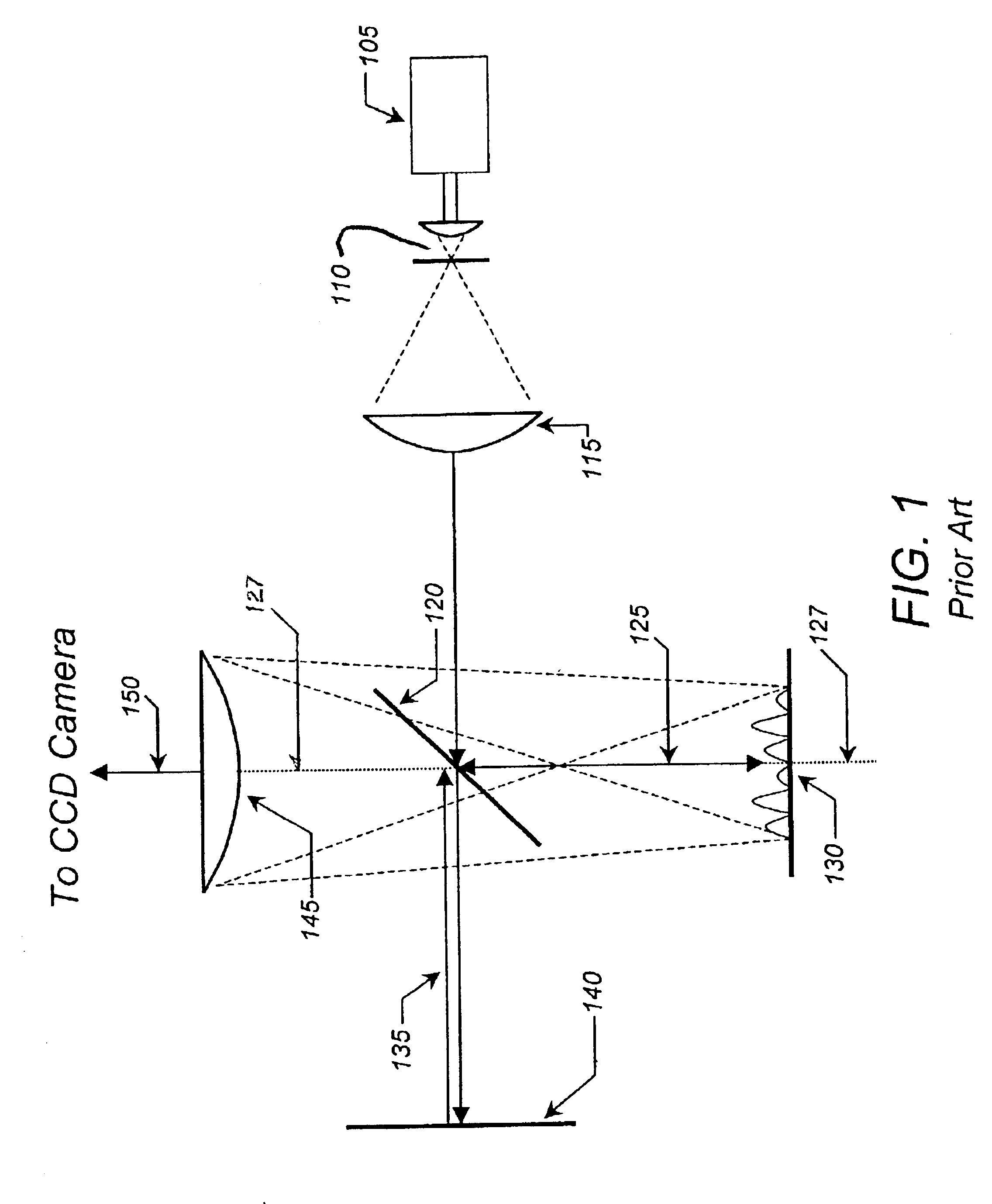
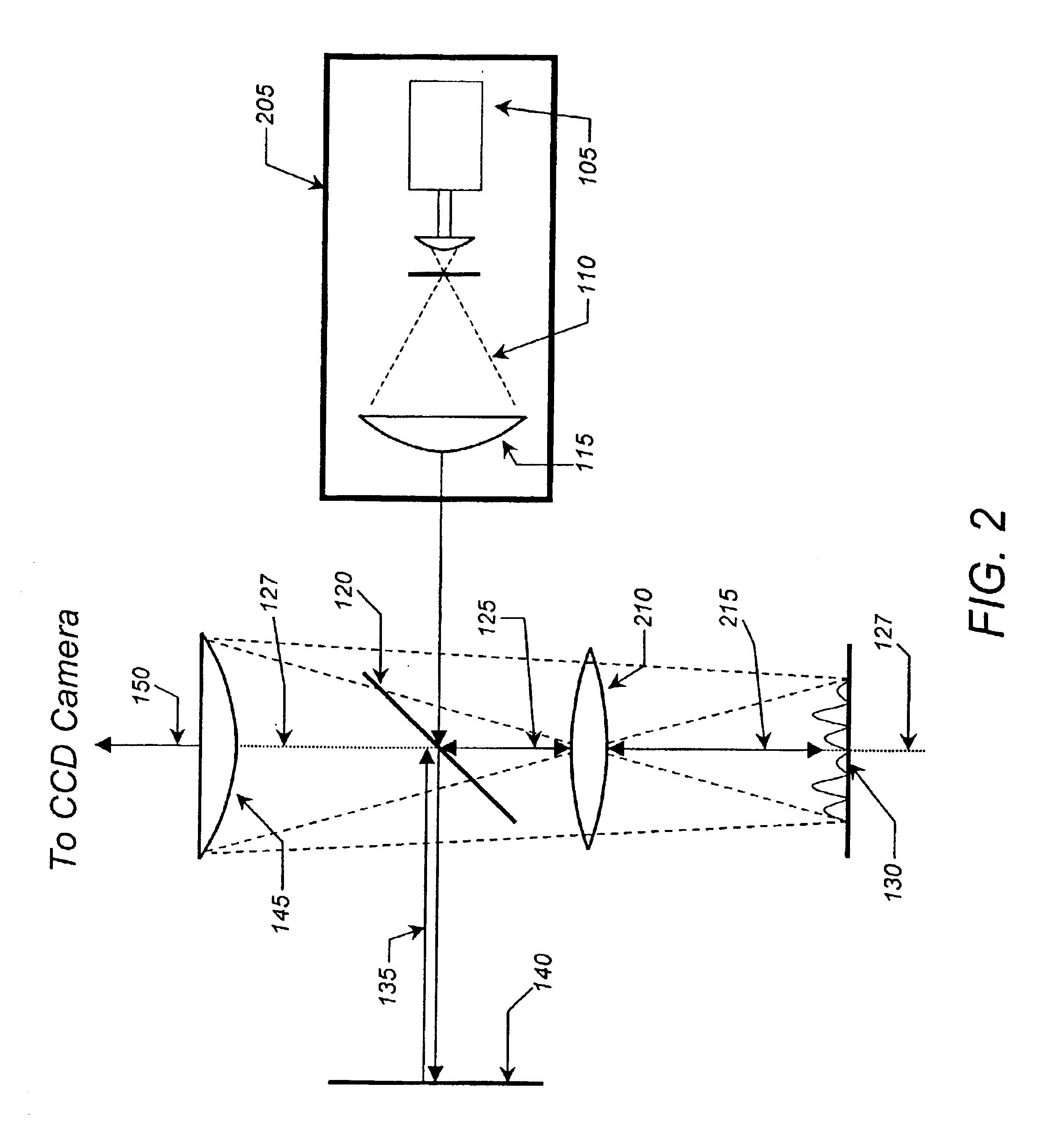
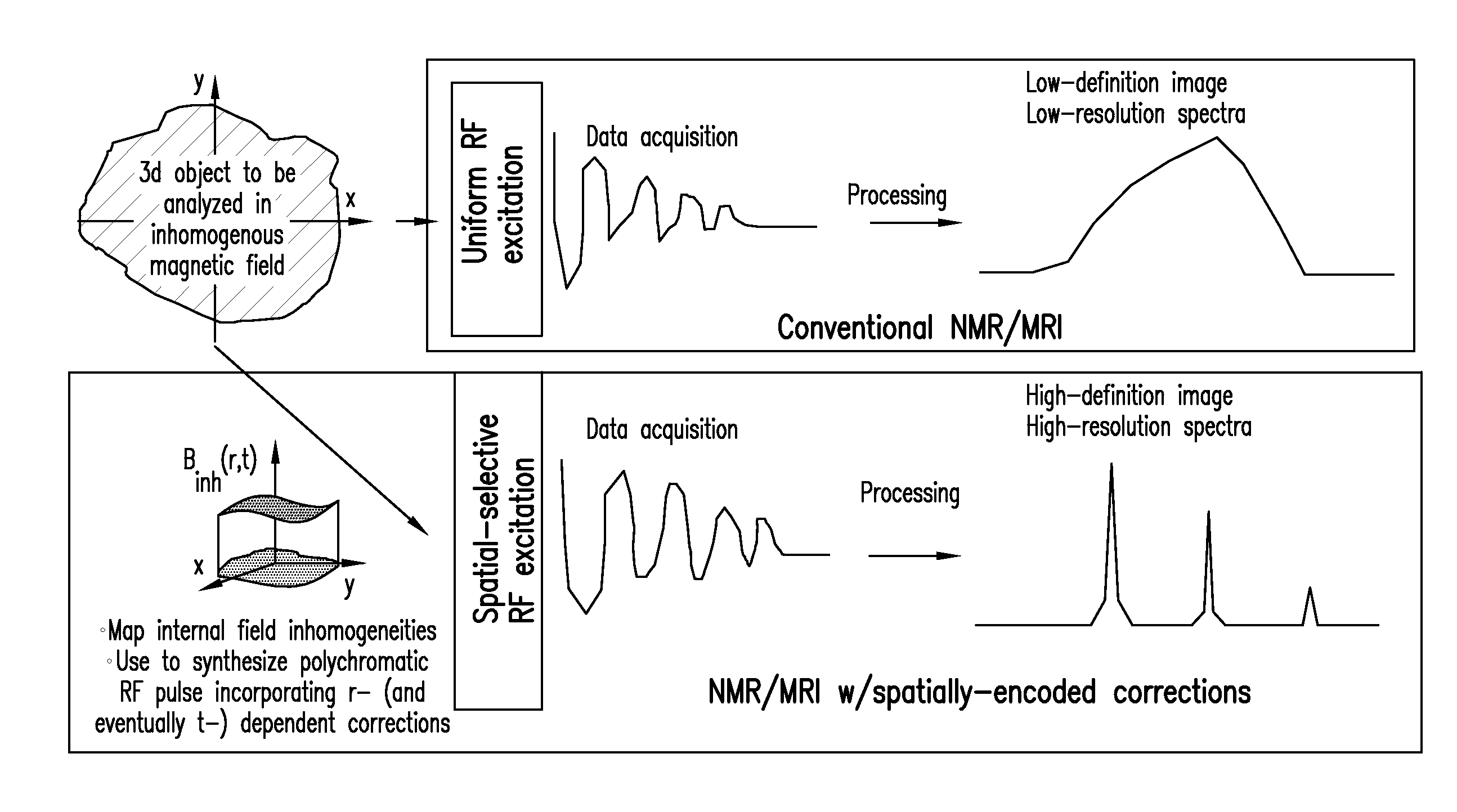
Method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution spectral data or high definition images in inhomogeneous environments
InactiveUS20100001727A1High definitionReduce complicationsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData treatment
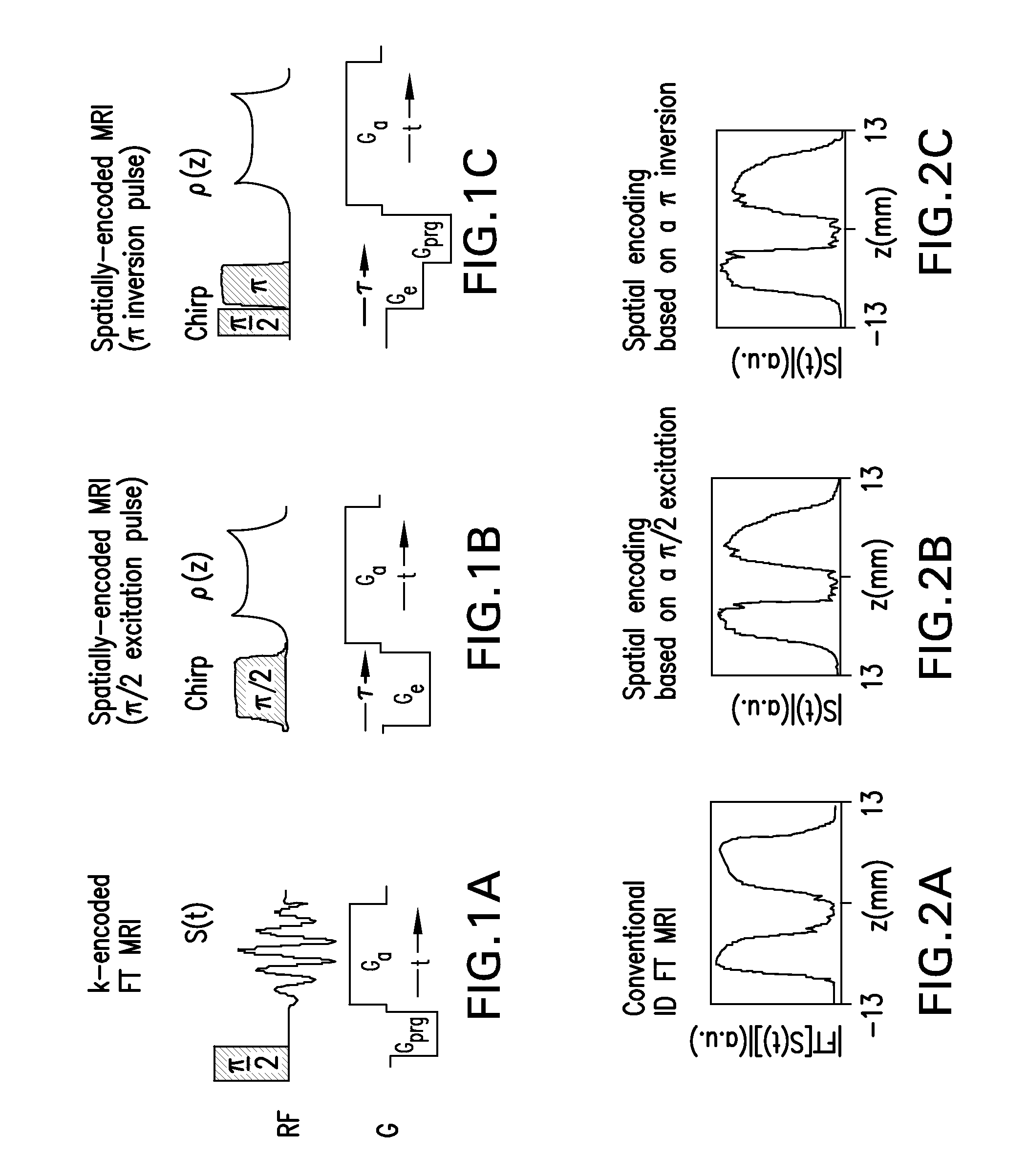
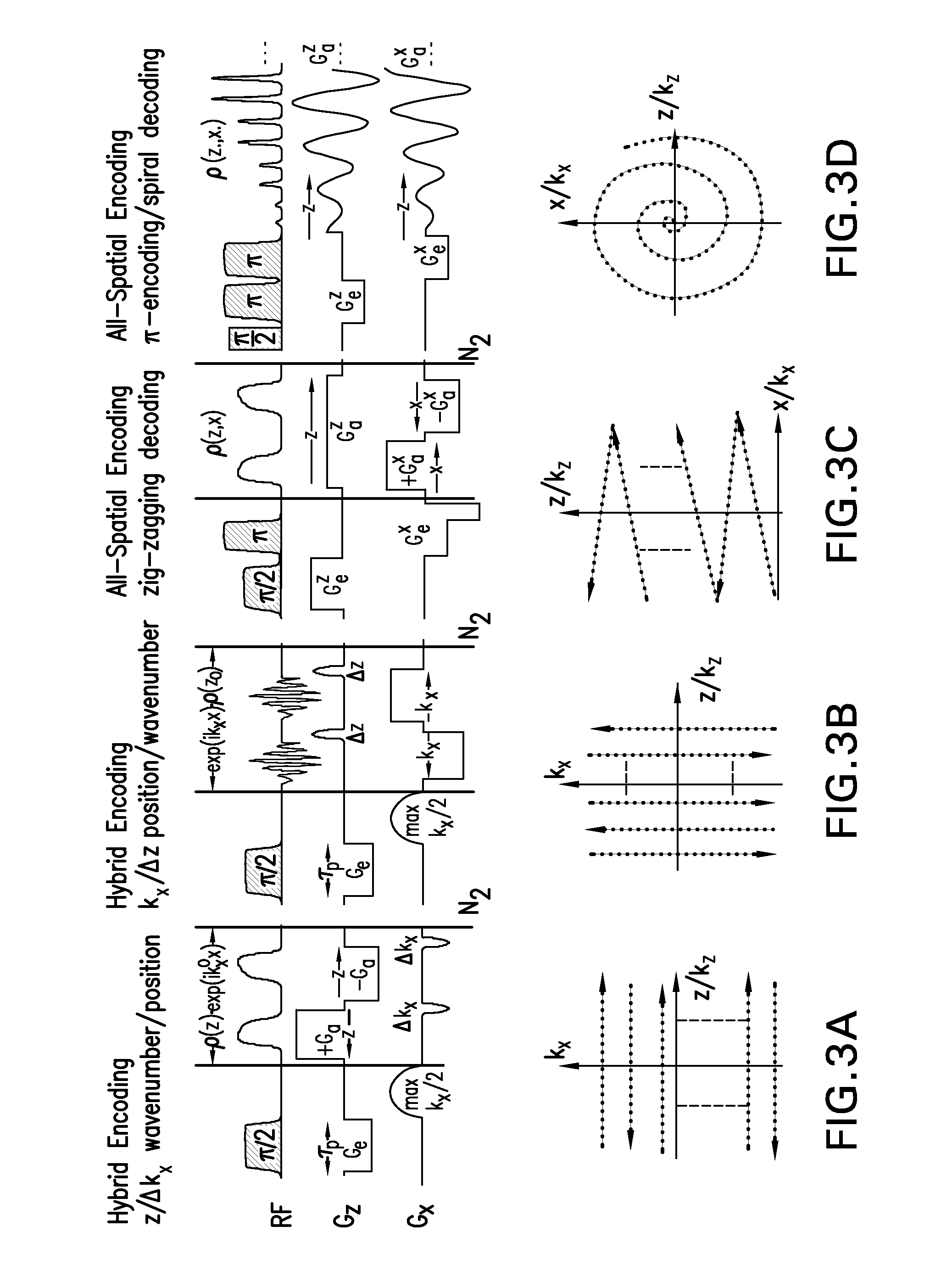
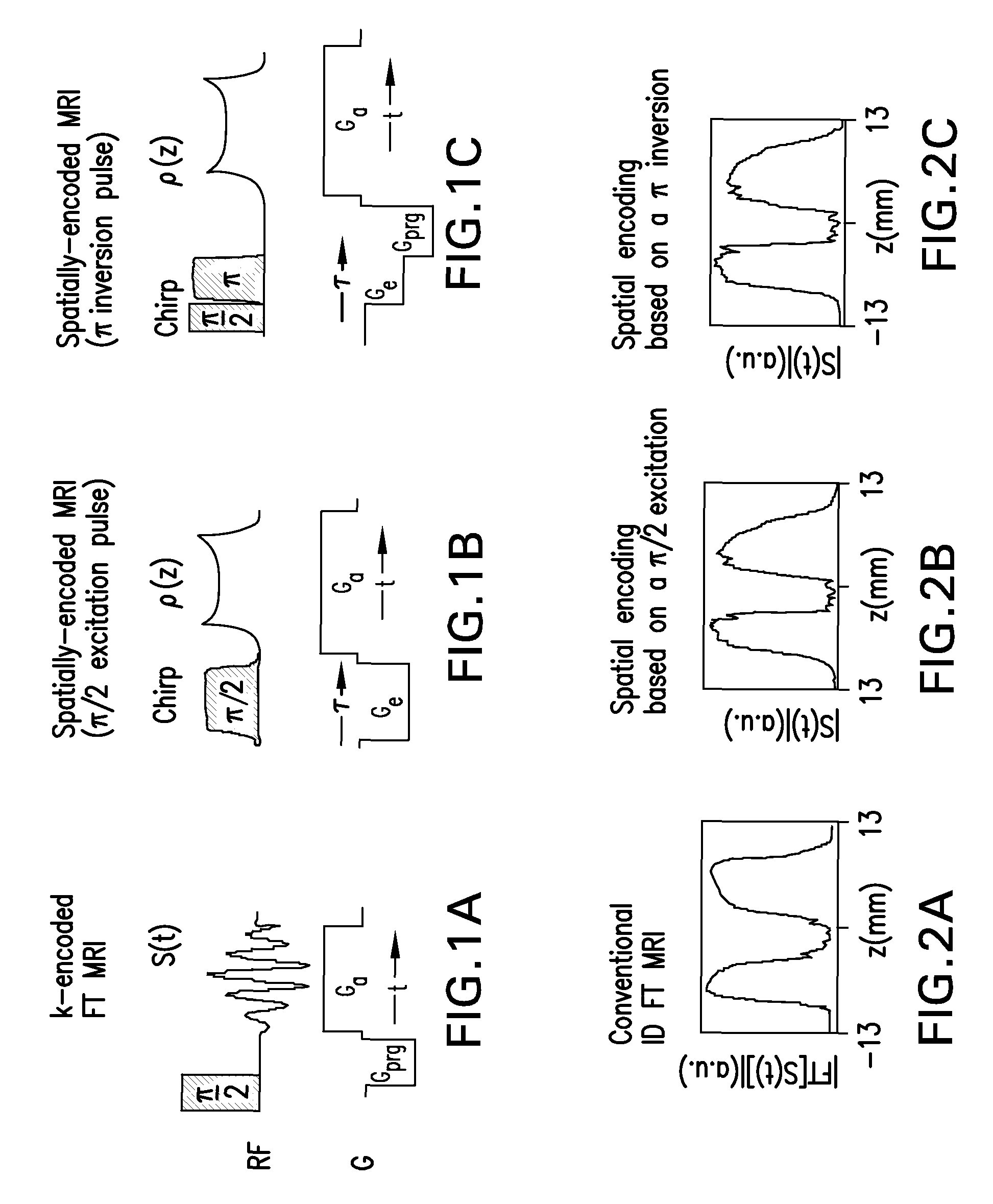
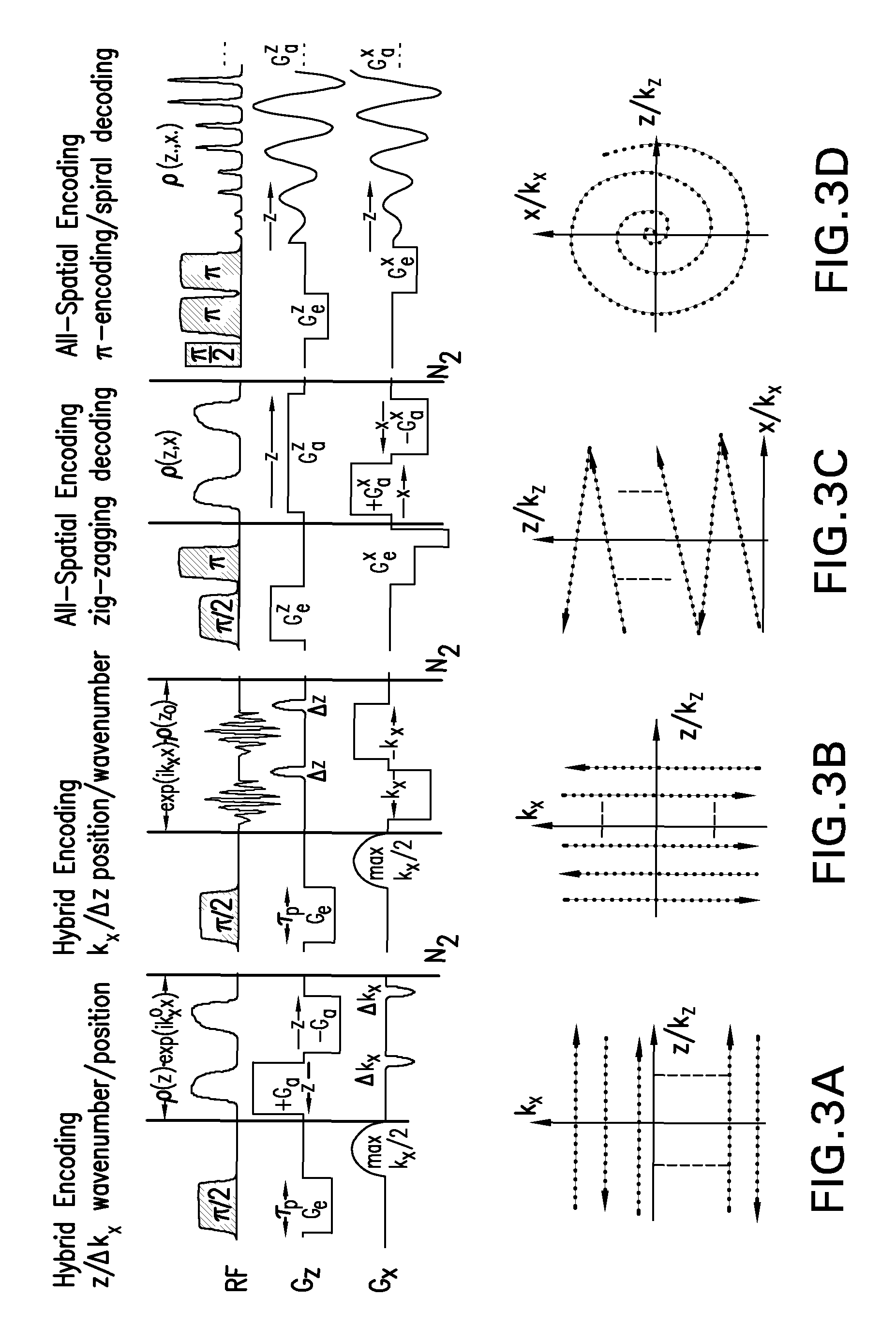
A method and apparatus for treating a sample for acquiring high-definition magnetic resonance images (MRI images) or high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra even in the presence of magnetic field distortions within one or multiple scans. The spatial nature and temporal dependence of the field inhomogeneities are determined a priori using any of several literature procedures. A static or oscillating magnetic field gradient is applied on the sample so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with different resonance frequencies. A phase- and amplitude-modulated radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied in unison with the magnetic field gradient so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with a homogeneous excitation / inversion profile. The nature of the spatially-selective RF irradiation is tailored in such a way that, when added on top of the effects of the inhomogeneities, the spins' evolution phases and their signal amplitudes at the time of the acquisition become independent of the inhomogeneities. The spin signals thus created are captured and decoded, so as to obtain the spins' response as if the inhomogeneity was not present. The collected data is processed to a suitable rearrangement and Fourier analysis procedure to retrieve a final undistorted image or spectrum. The magnetic field gradient can be oscillated to impose this kind of inhomogeneity corrections on multiple spatial dimensions sequentially, or simultaneously.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
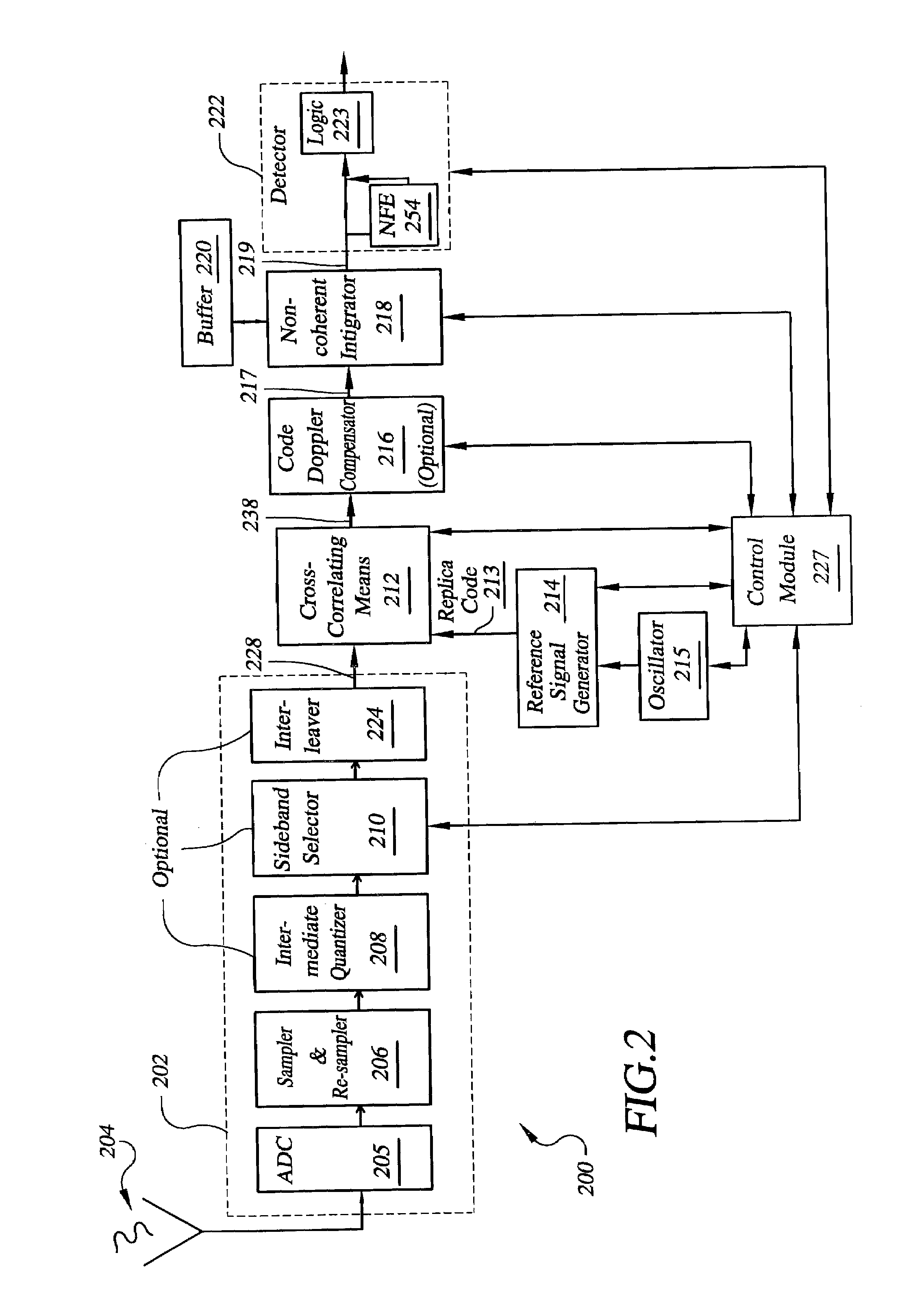
System for direct acquisition of received signals
ActiveUS7224721B2High degree of parallelismQuick alignmentAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingTime correlationData acquisition
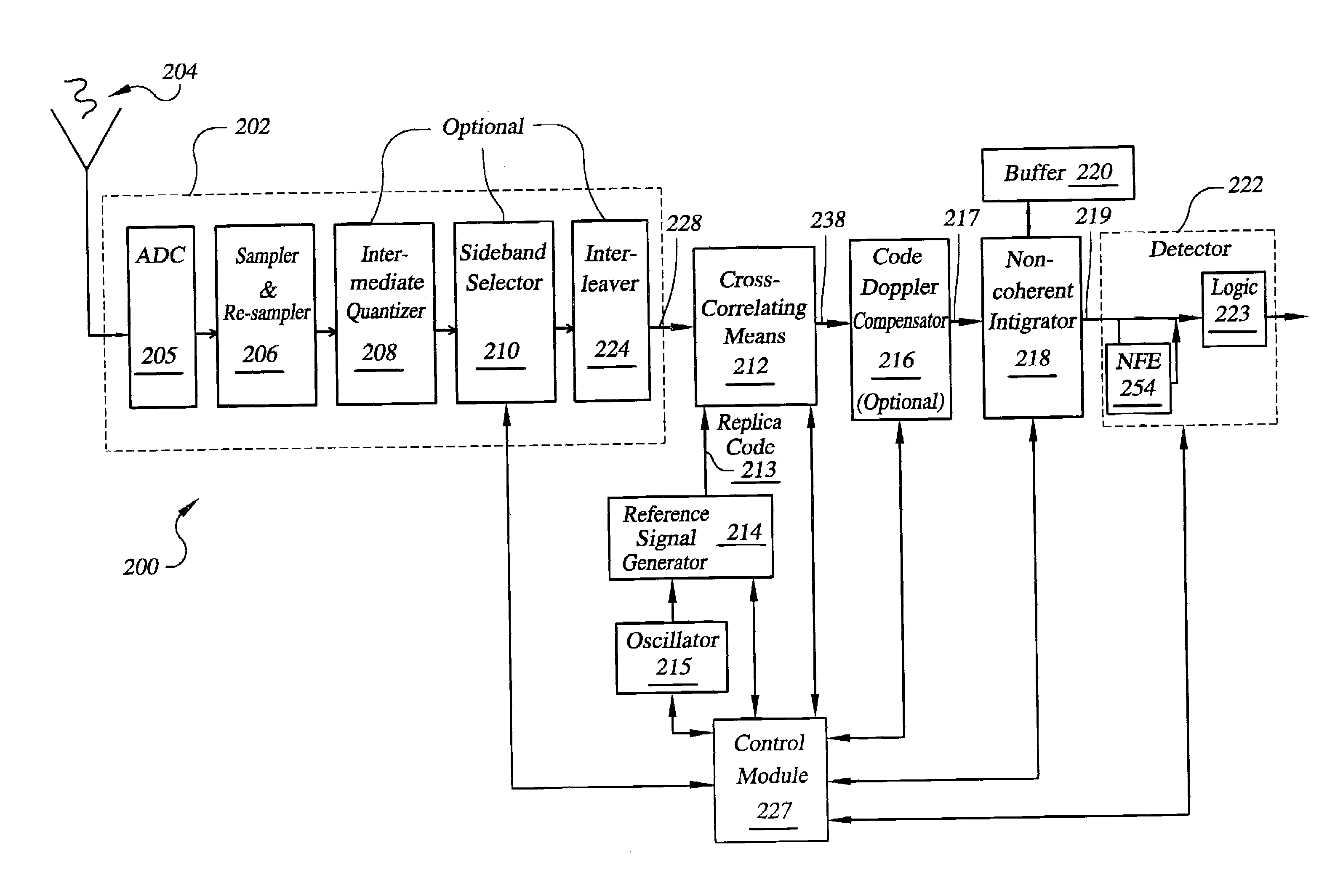
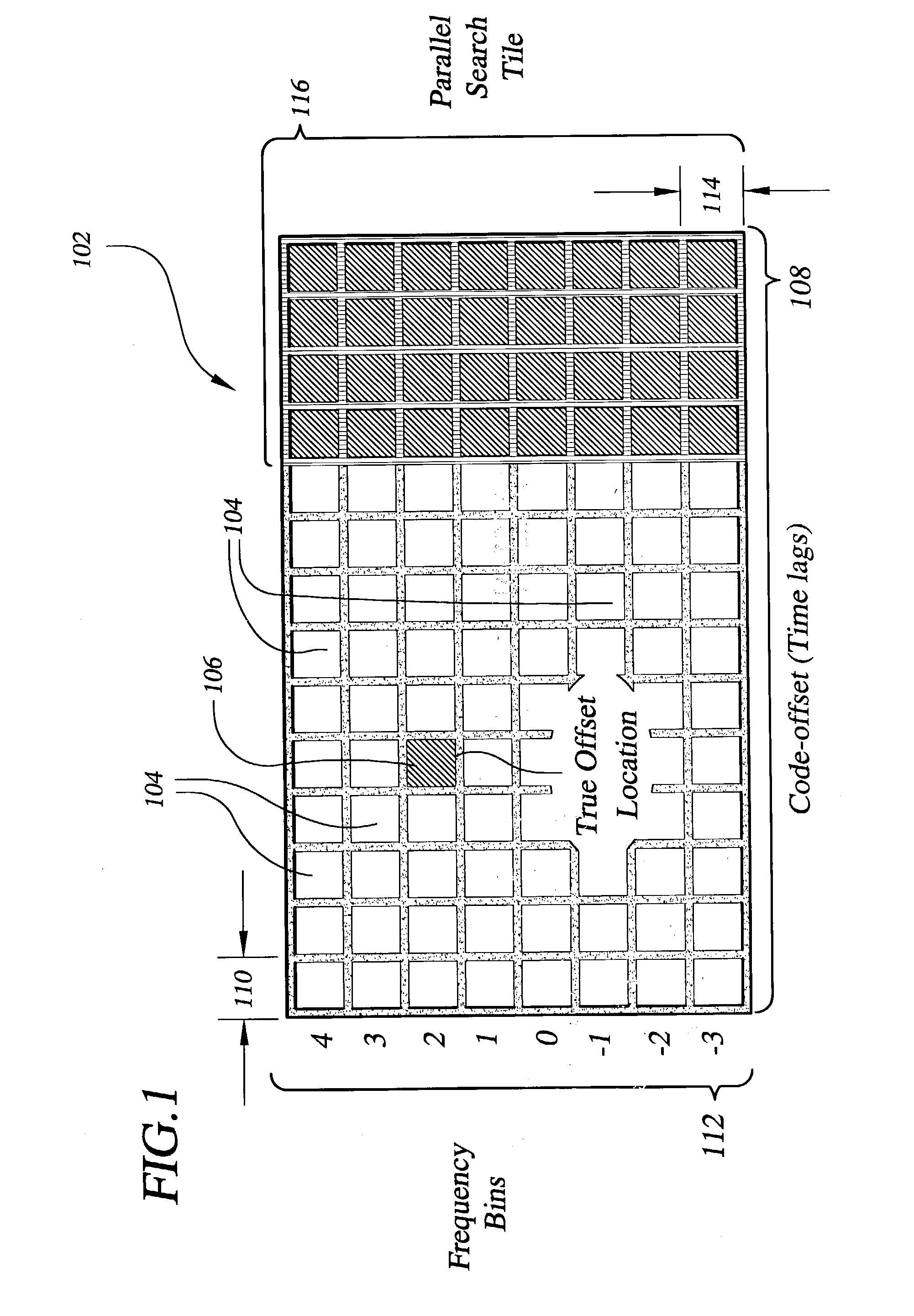
Signal processing architectures for direct acquisition of spread spectrum signals using long codes. Techniques are described for achieving a high of parallelism, employing code matched filter banks and other hardware sharing. In one embodiment, upper and lower sidebands are treated as two independent signals with identical spreading codes. Cross-correlators, in preferred embodiments, are comprised of a one or more banks of CMFs for computing parallel short-time correlations (STCs) of received signal samples and replica code sequence samples, and a means for calculating the cross-correlation values utilizing discrete-time Fourier analysis of the computed STCs. One or more intermediate quantizers may optionally be disposed between the bank of code matched filters and the cross-correlation calculation means for reducing word-sizes of the STCs prior to Fourier analysis. The techniques described may be used with BOC modulated signals or with any signal having at least two distinct sidebands.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
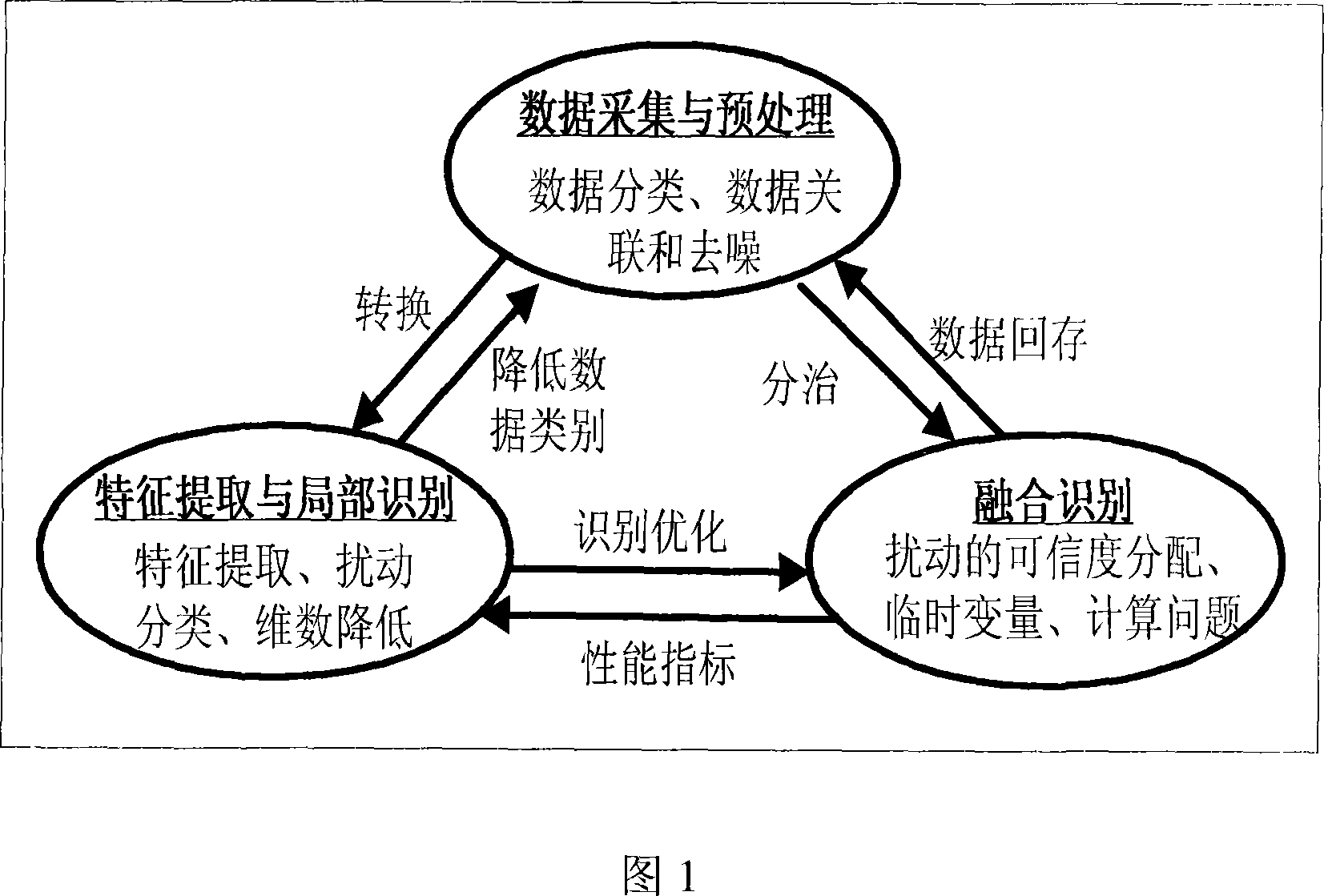
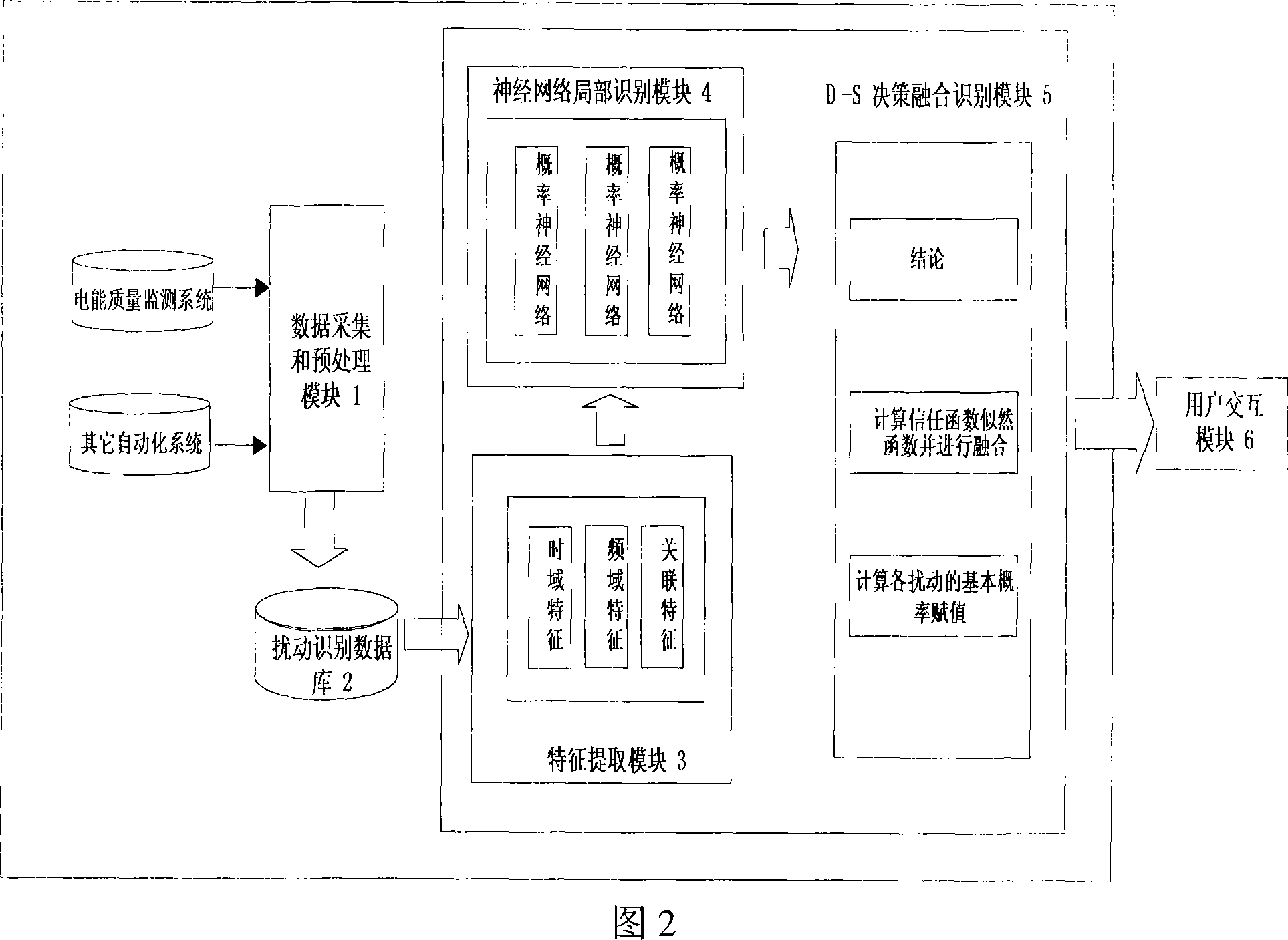
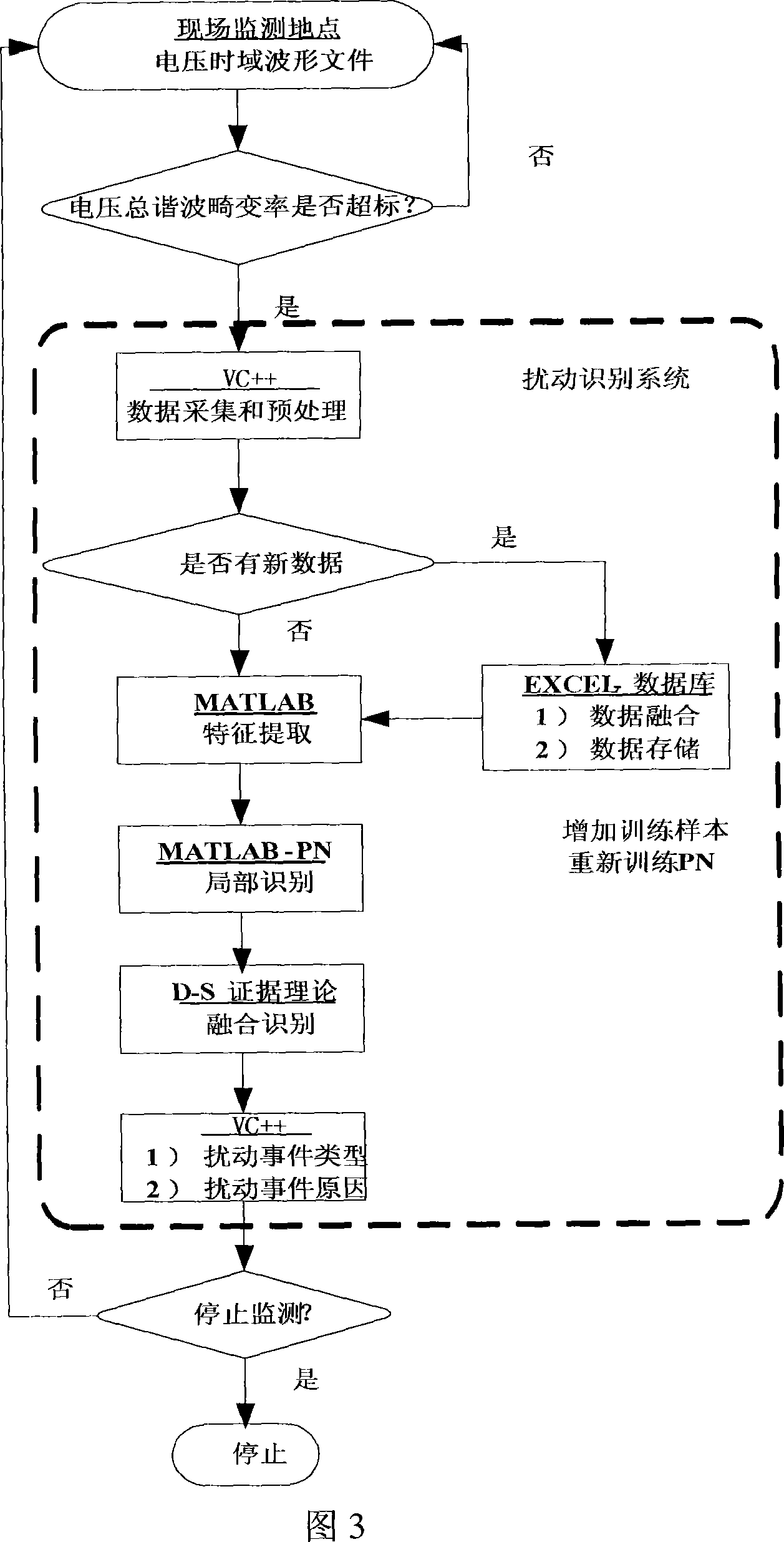
Electrical energy power quality disturbance automatic identification method and system based on information fusion
InactiveCN101034389ARealize intelligent identificationOvercome the disadvantage of strong subjectivityData processing applicationsData acquisition and loggingPower qualityNerve network
The invention is a automatic identification method and system based on the power quality disturbances of the information fusion, characterized by: collecting the transient and steady-state measurement datum associated with the power quality disturbances from the Power Quality Monitoring System and other automation systems, disposing of noise such as pretreatments; Using the method combining Fourier analysis, small wave multi-resolution decomposition and analysis of the correlation functions, distilling the from the disturbance datum, establishing the disturbance eigenvector, and as a the input characteristic vector of three probabilistic neural networks, realizing the mapping from a feature space to the disturbance space; the output of three probabilistic neural networks regarded as the evidence body of independent of each other, realizing Information Fusion by the use of D-S evidence theory, obtaining recognition results. This invention through the correct selection and extraction of disturbance eigenvectors, can input neural network parallel in classification and reflect the disturbance situation from the various aspects, thus effectively enhancing the correct identification rate of disturbance, a first step in Intelligent Recognition of the power quality disturbances.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO
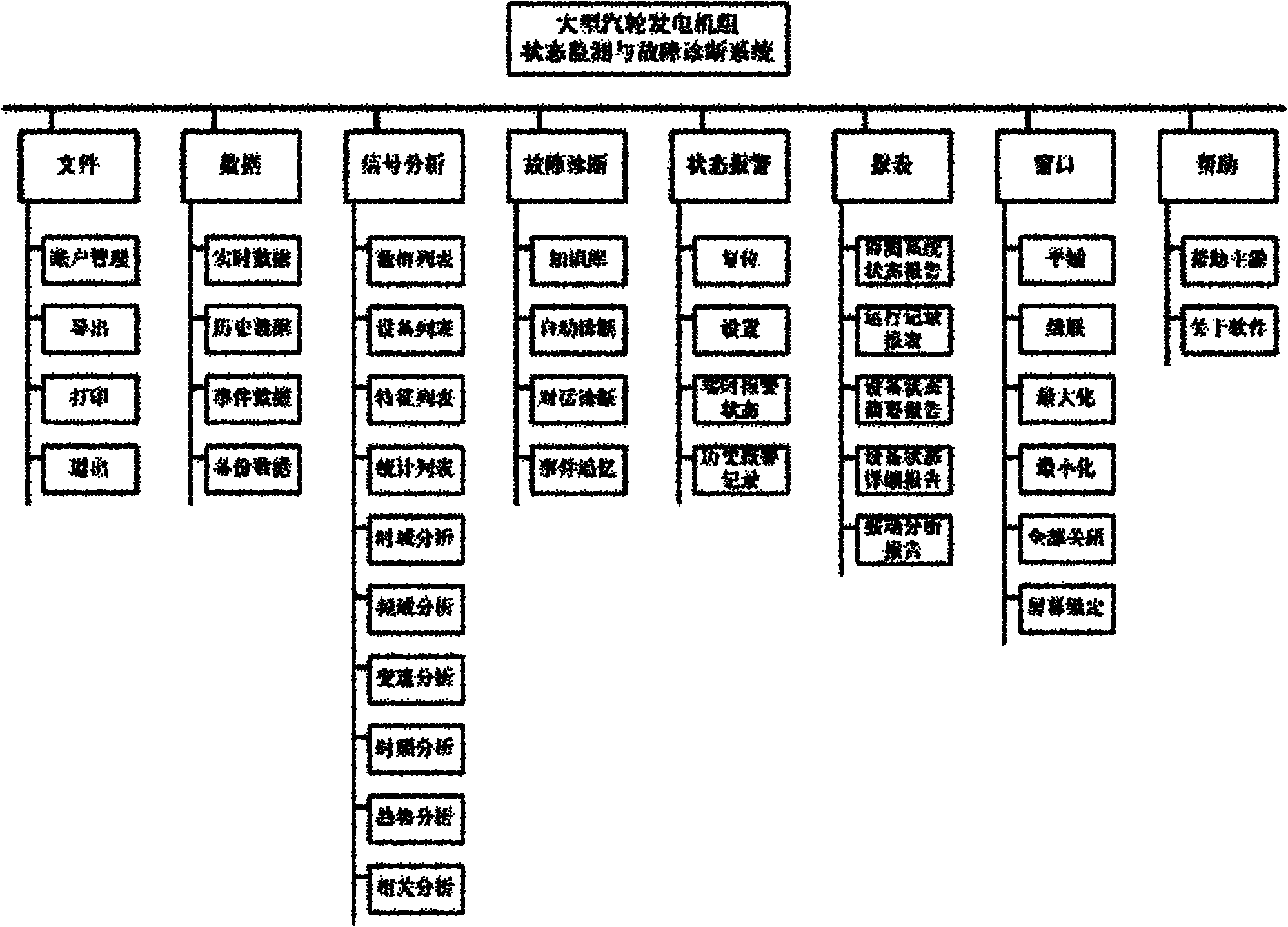
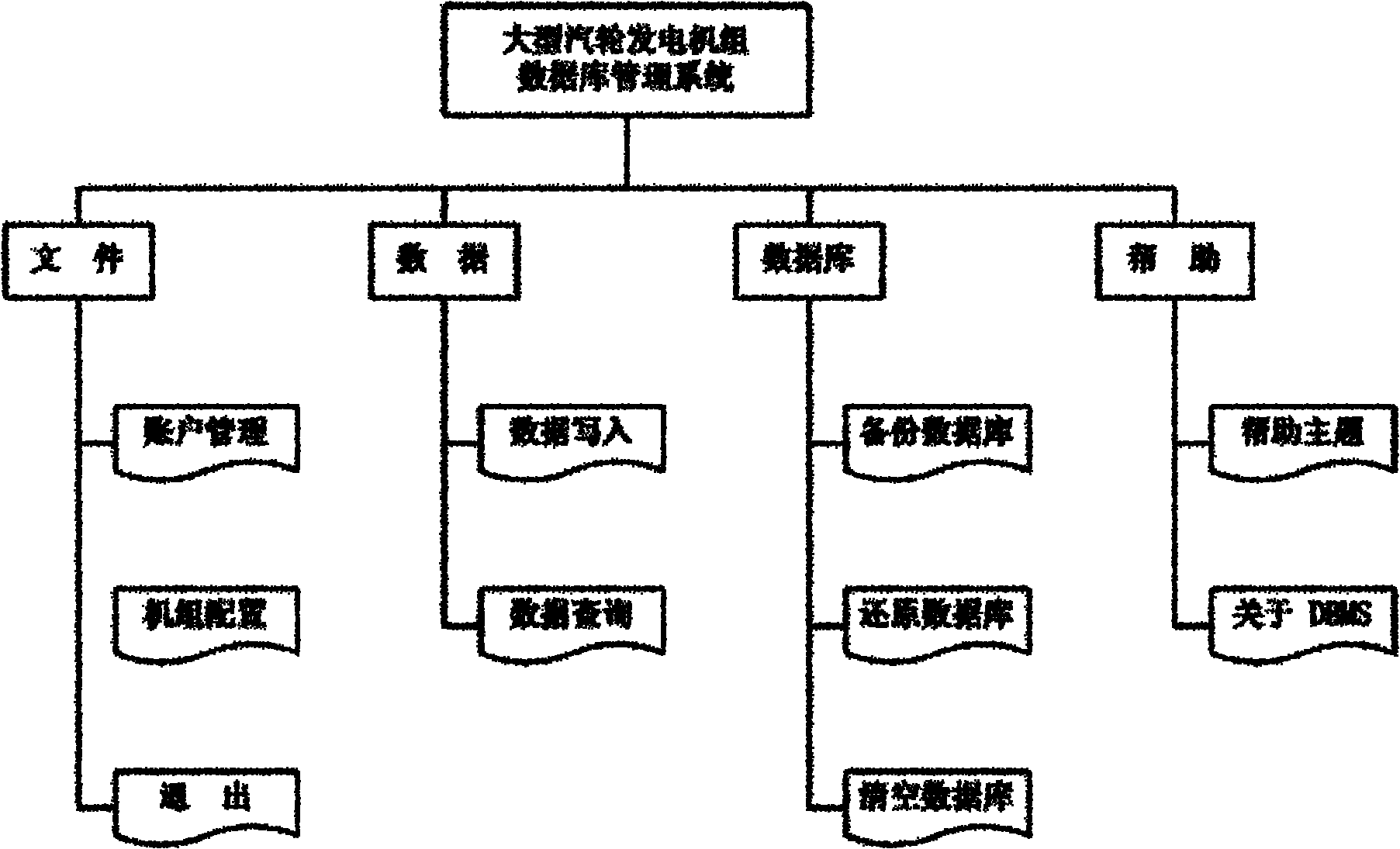
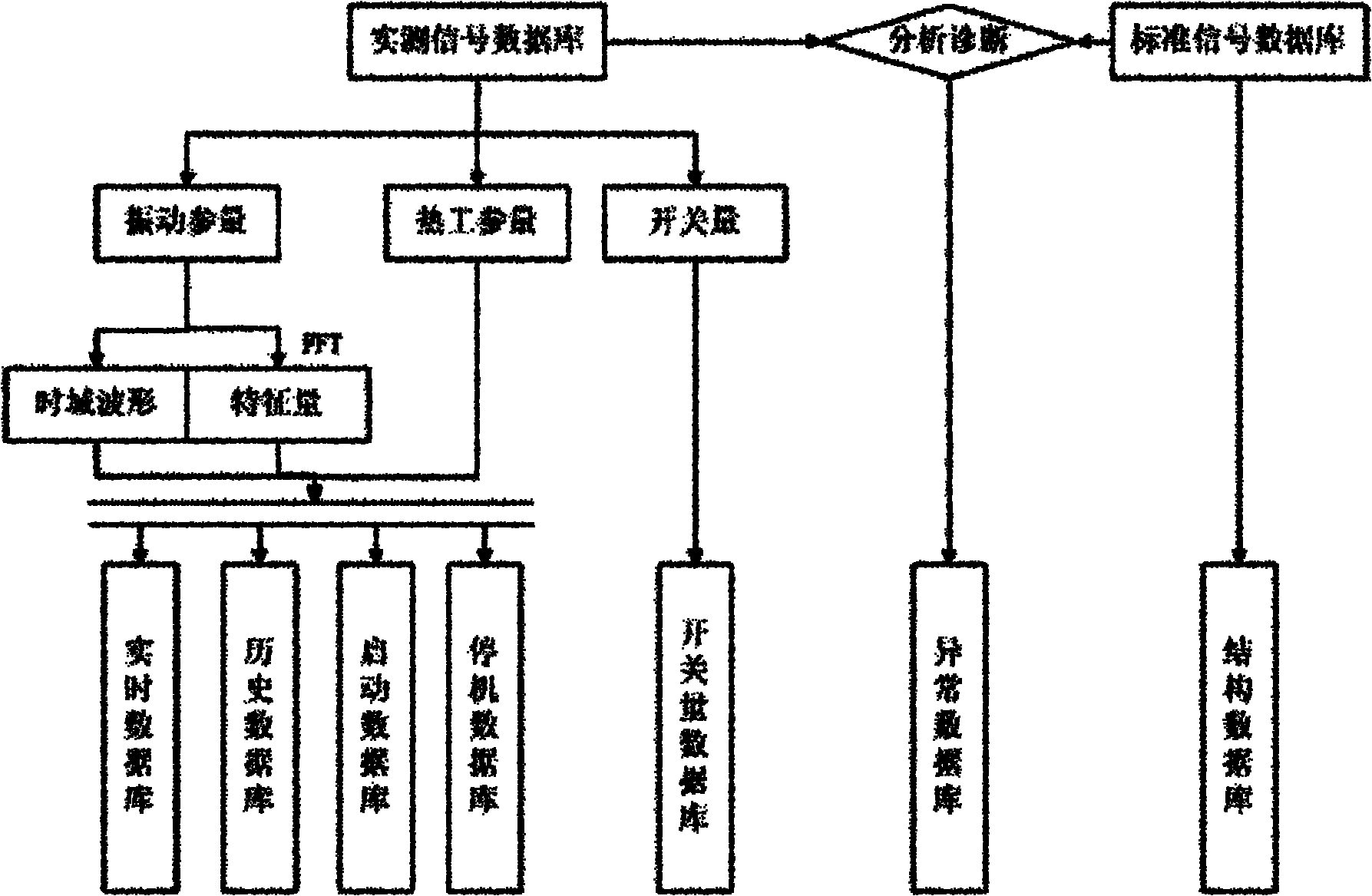
Distributed remote vibration monitoring and fault diagnosis system of large steam turbine-generator
InactiveCN102086784AQuick installation and layoutImprove accuracyMachines/enginesSafety/regulatory devicesSelf organizing map neural networkWeb service
The invention discloses a distributed remote vibration monitoring and fault diagnosis system of a large steam turbine-generator, comprising a database subsystem in which steam turbine-generator vibration data is stored, a workstation subsystem capable of providing real-time status monitoring, historical data analysis and fault symptom analysis, and a Web server subsystem provided with remote monitoring and fault diagnosing software, wherein, the subsystems are connected with one another by the Ethernet, and are integrated by a Web services technique. A method combining a traditional fault diagnosing technique based on Fourier analysis, a novel independent component analysis feature extraction technique, a Hilbert-yellow time frequency analysis technique, an empirical decomposition algorithm trend analysis technique and a self-organizing map neural network is adopted for monitoring and diagnosing in the system, thus improving the monitoring real time and the accuracy of diagnosis. The system has strong universality and reliability; and the system configuration can be adjusted, thus conveniently realizing distributed remote monitoring and diagnosis based on the internet as a medium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High throughput screening with parallel vibrational spectroscopy
InactiveUS7033542B2Improve performanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSpectroscopy
Rapid spectrum assay of multiple samples with infrared light is made possible by devices and methods that increase total light throughput. Multiple wavelength scan with Fourier analysis is combined with large numbers of sample wells located within infrared light compatible solid materials. In particular, very large scale measurement devices and systems for their use are fabricated from lithography and other techniques used for semiconductor processing.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL HLDG
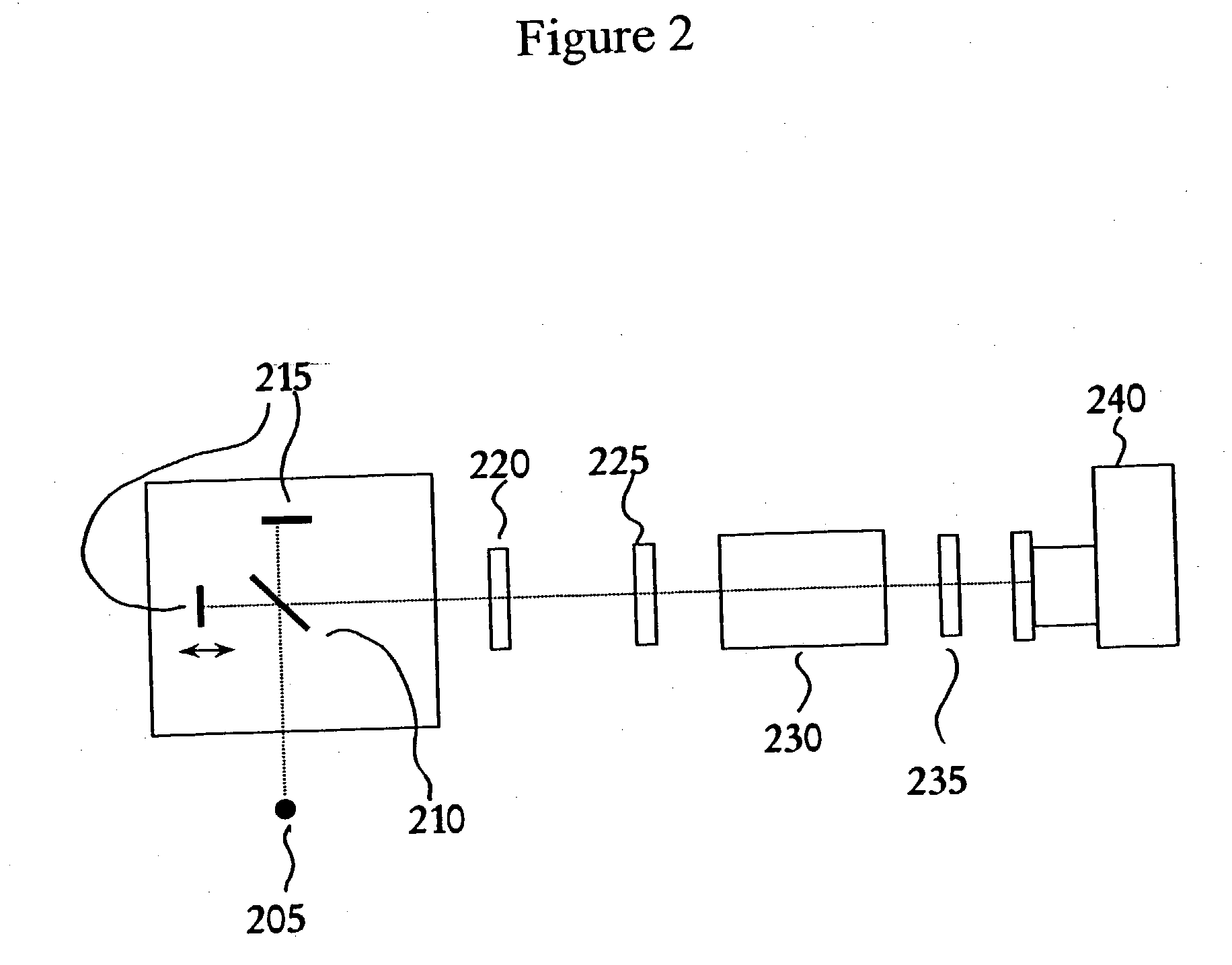
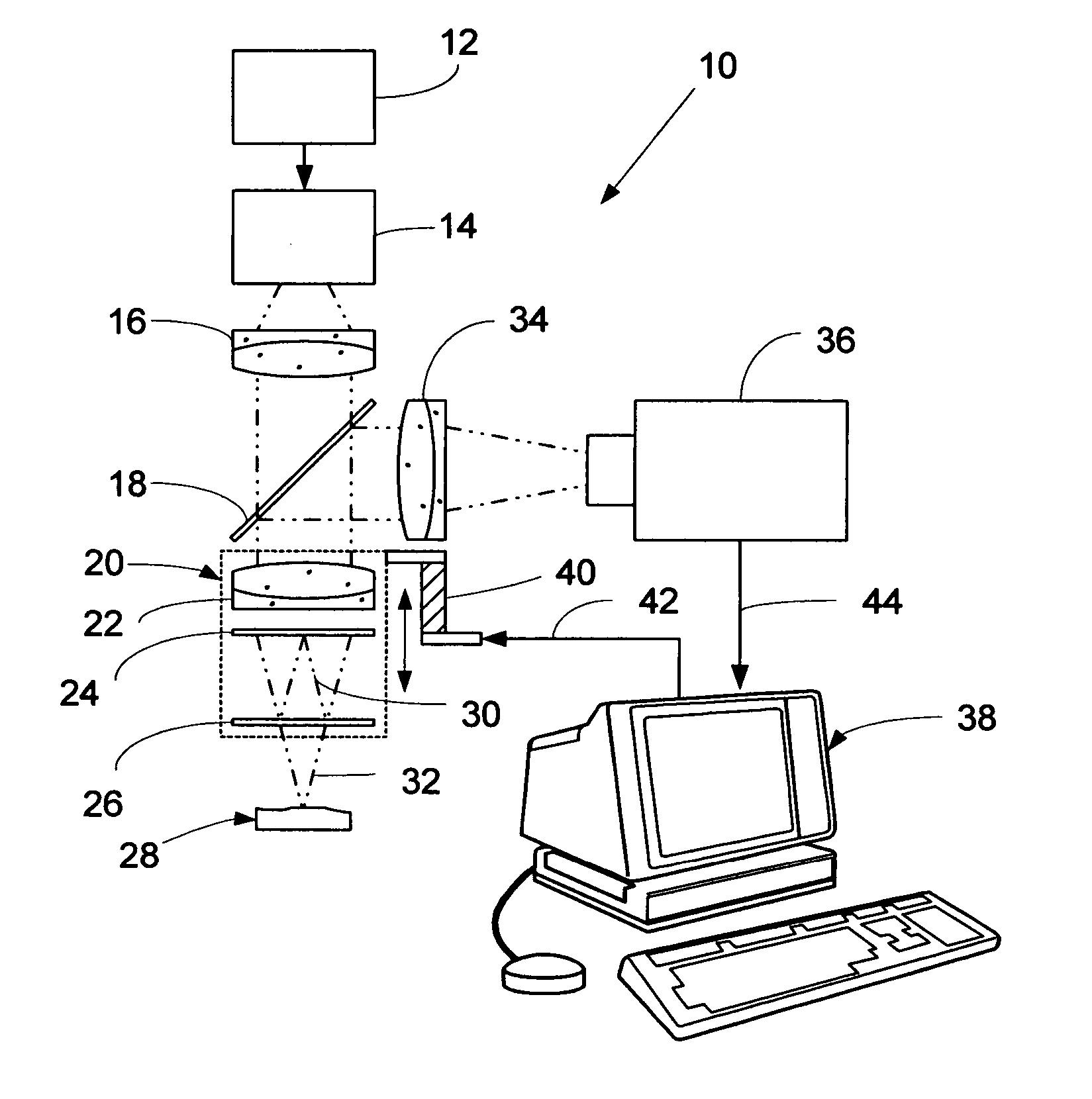
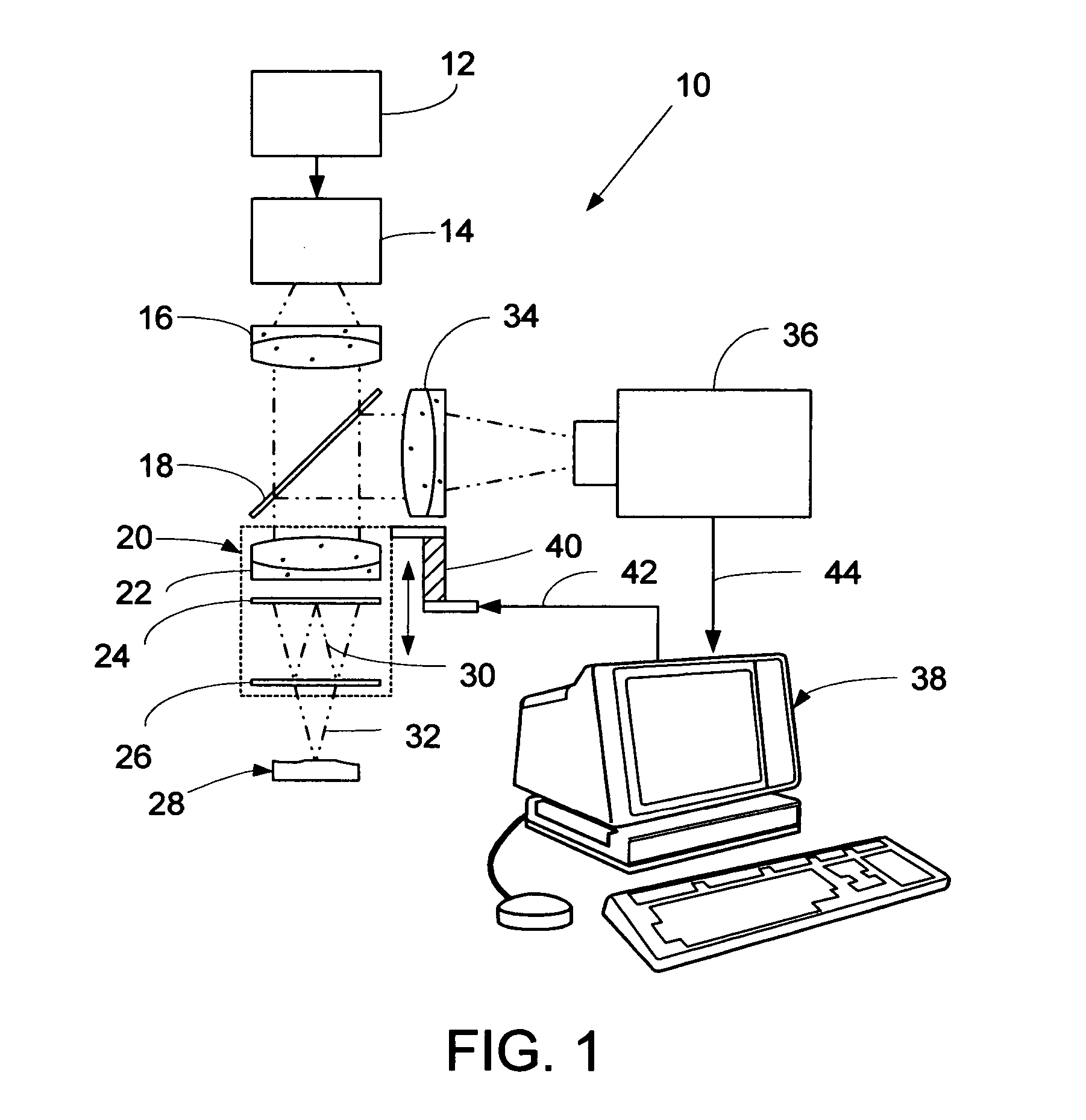
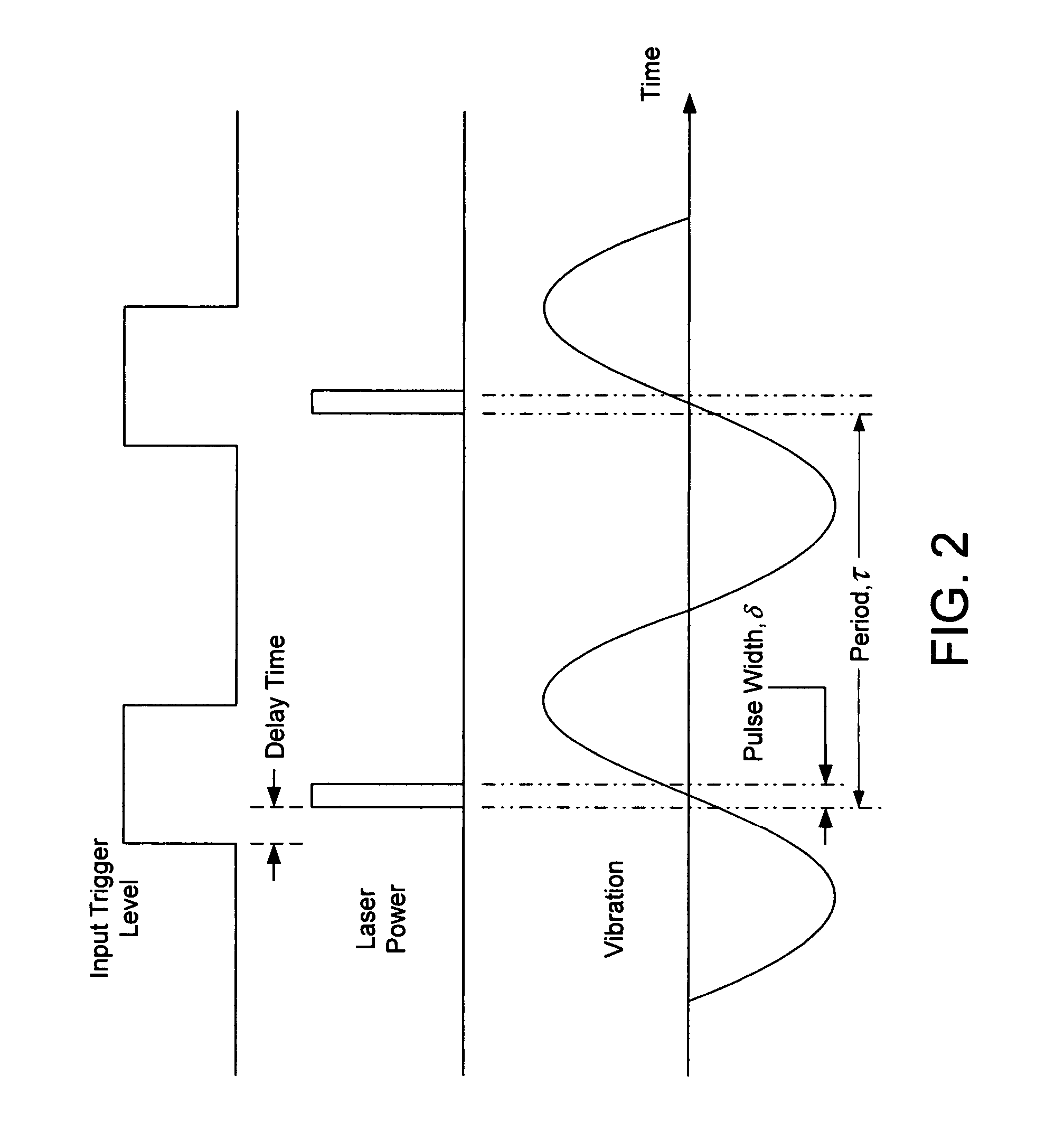
Stroboscopic interferometry with frequency domain analysis
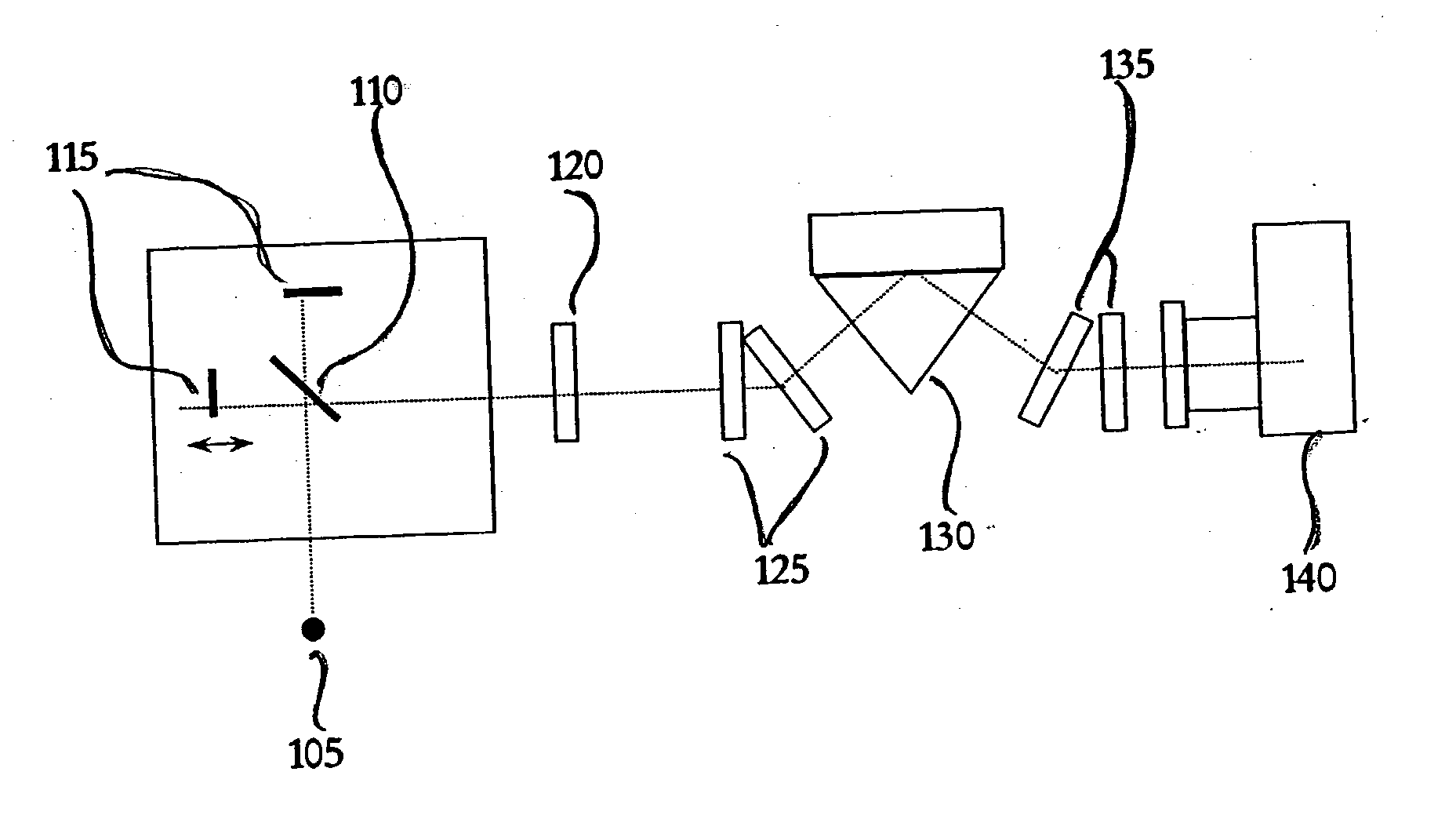
ActiveUS20050007599A1Issue to overcomeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansDigital signal processingTwo dimensional detector
A computer-based stroboscopic interferometric microscope system for measuring the topography of a microscopic vibratory object includes an interferometric microscope equipped with a multiple-color (e.g., LED) or white-light source, a mechanical scanning apparatus for varying the optical path difference between the vibratory object and a reference surface, a camera having a two-dimensional detector array, and digital signal processing apparatus for determining surface height from interference data. Interferograms for each of the detector image points in the field of view are generated simultaneously by scanning the object in a direction approximately perpendicular to the object surface illuminated stroboscopically while recording detector data in digital memory. Recorded interferograms for each image point are then transformed into the spatial frequency domain by Fourier analysis, and the surface height for each corresponding object surface point is obtained by examination of the complex phase as a function of spatial frequency. A complete three-dimensional image of the object surface is then constructed from the height data and corresponding image plane coordinates. The three-dimensional image may be presented on a display or hard copy or written to a storage medium.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
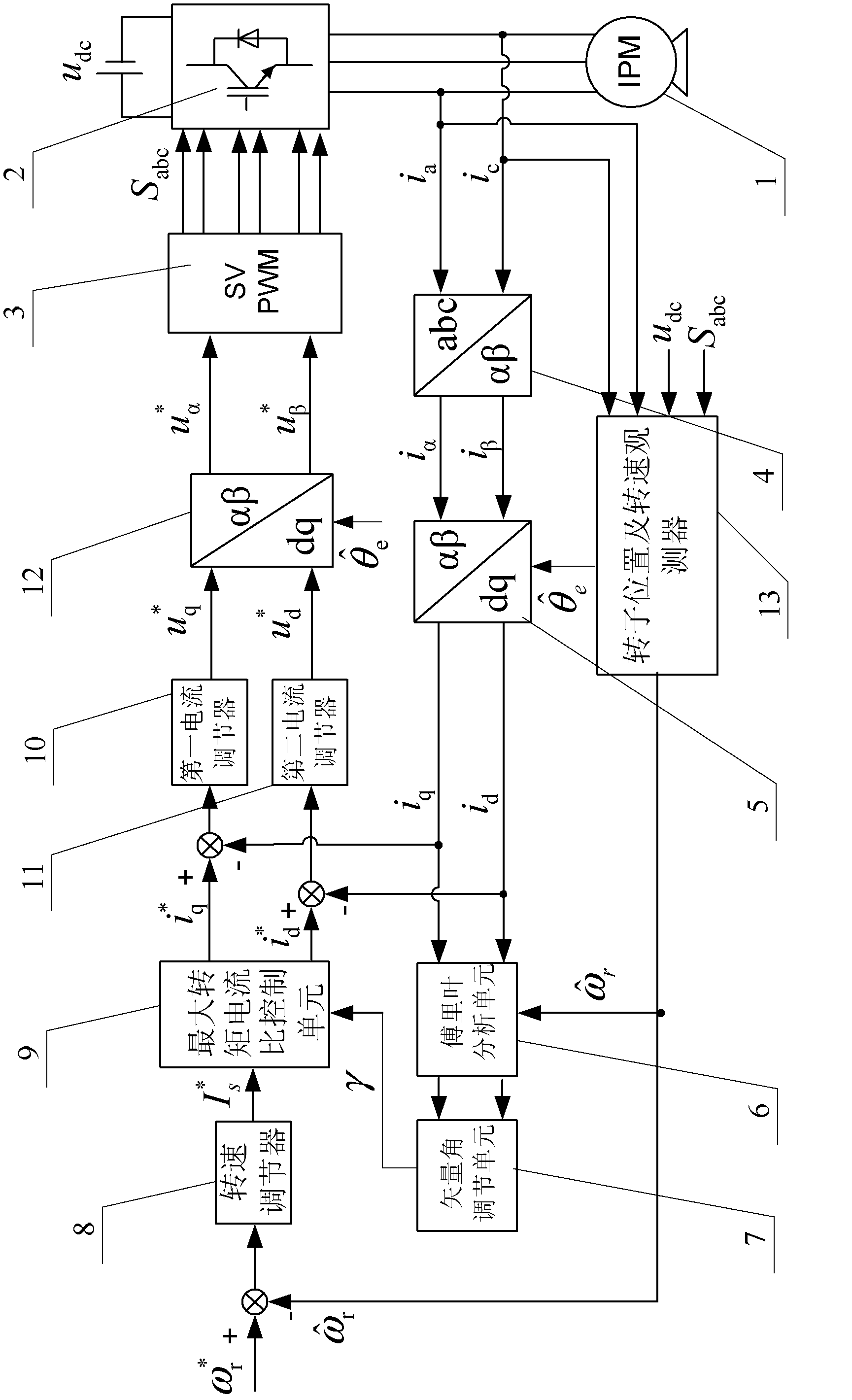
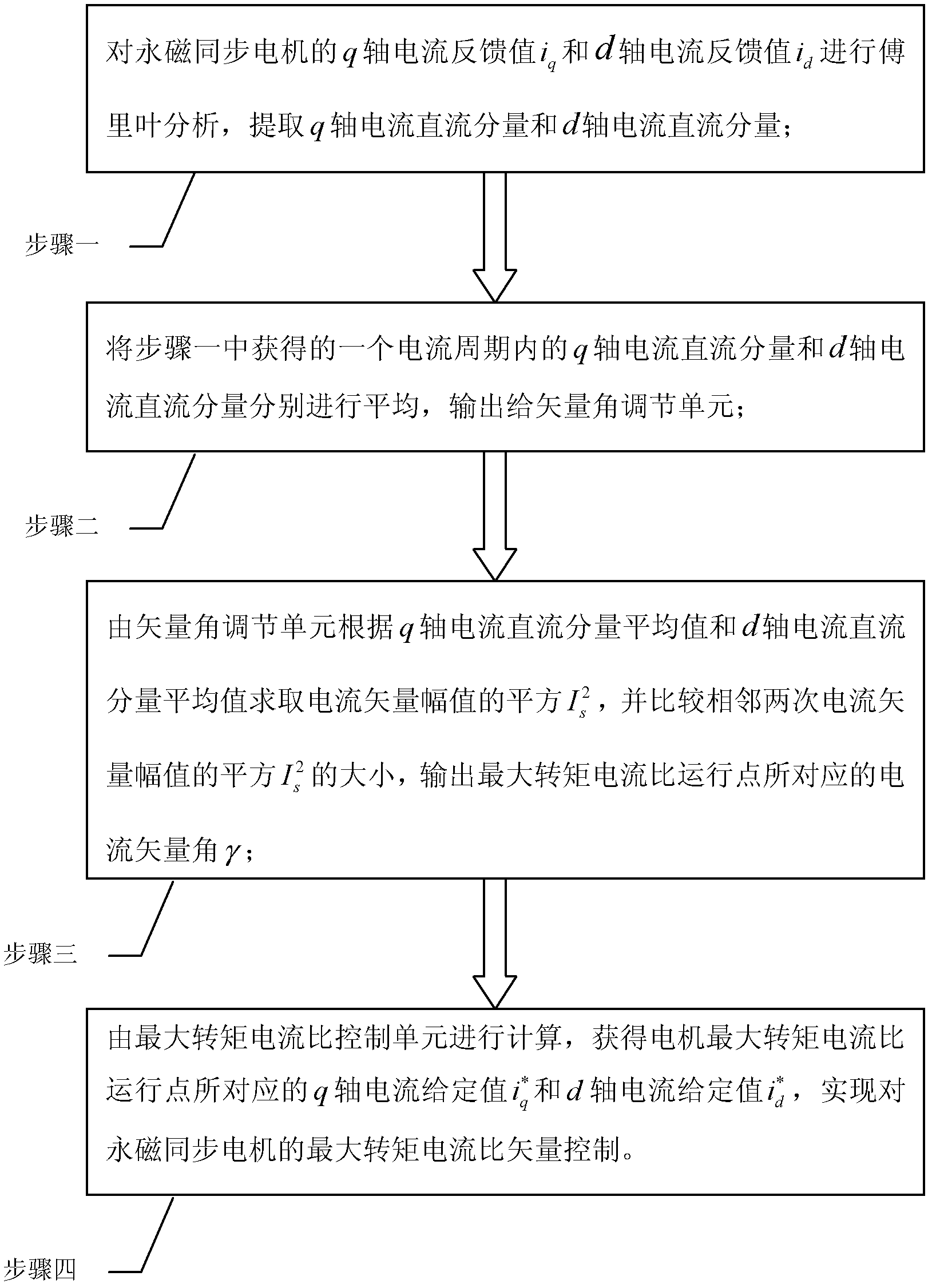
Maximum torque per ampere vector control system and control method for position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102594250AImprove overload capacityImprove power densityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsOperating pointAmpere
The invention discloses a control method of a maximum torque per ampere vector control system for a position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the field of motor control. The problems of complexity of a computing method and low accuracy of an obtained current set value in the conventional maximum torque per ampere control strategy are solved. The control system comprises a permanent magnet synchronous motor, an inverter, a space vector pulse width modulation unit, a three-phase-two-phase coordinate conversion unit, a static-rotational coordinate conversion unit, a Fourier analysis unit, a vector angle regulation unit, a rotating speed regulator, a maximum torque per ampere control unit, a first current regulator, a second current regulator, a rotational-static coordinate conversion unit and a rotor position and rotating speed observer. According to the control method, the magnitude of current amplitude is automatically regulated and compared on the basis of a current vector angle gamma, and an operating point with maximum torque per ampere is automatically searched. The system and the method are applied to maximum torque per ampere vector control over the motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
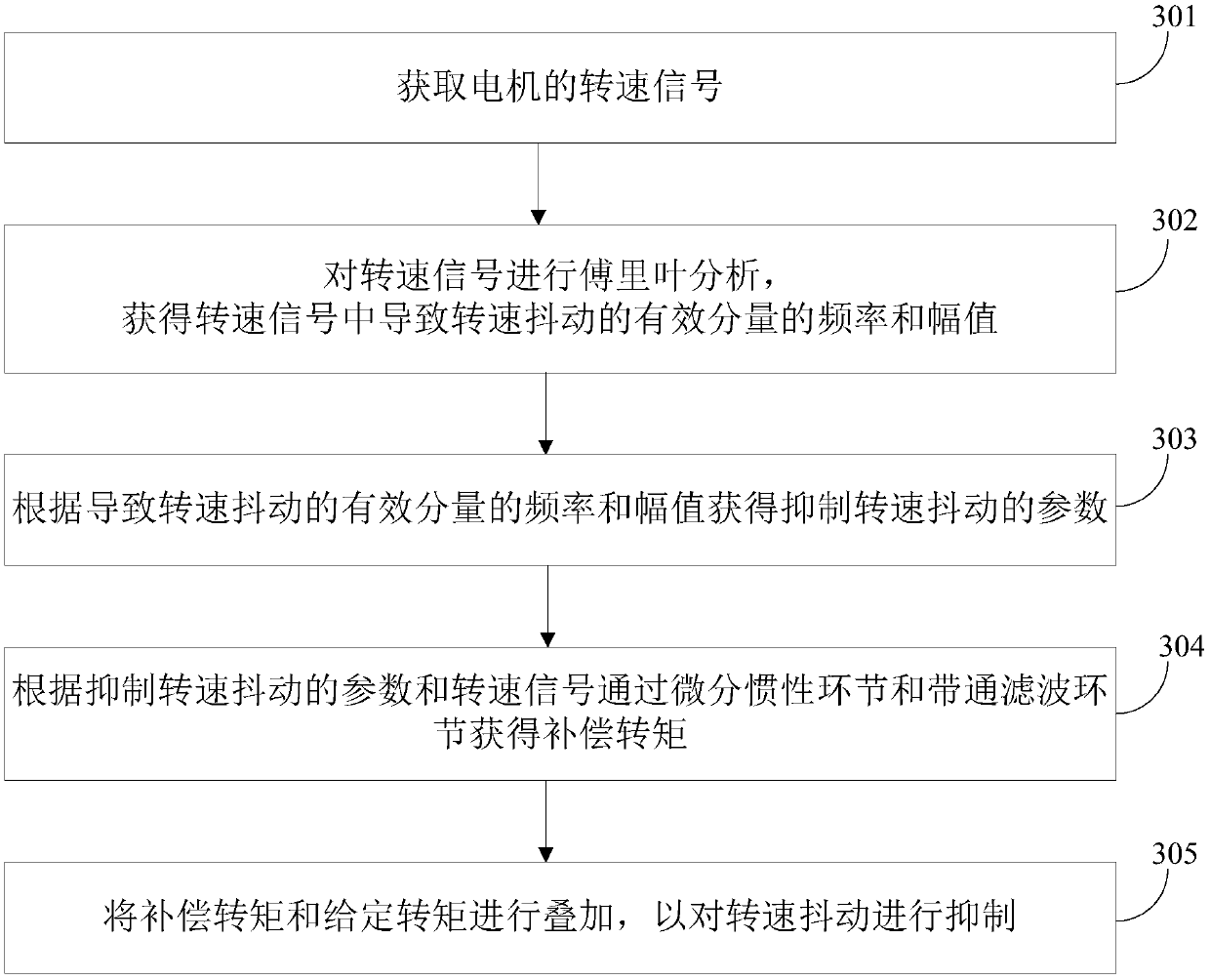
Method, device and system for suppressing shaking of electric automobile
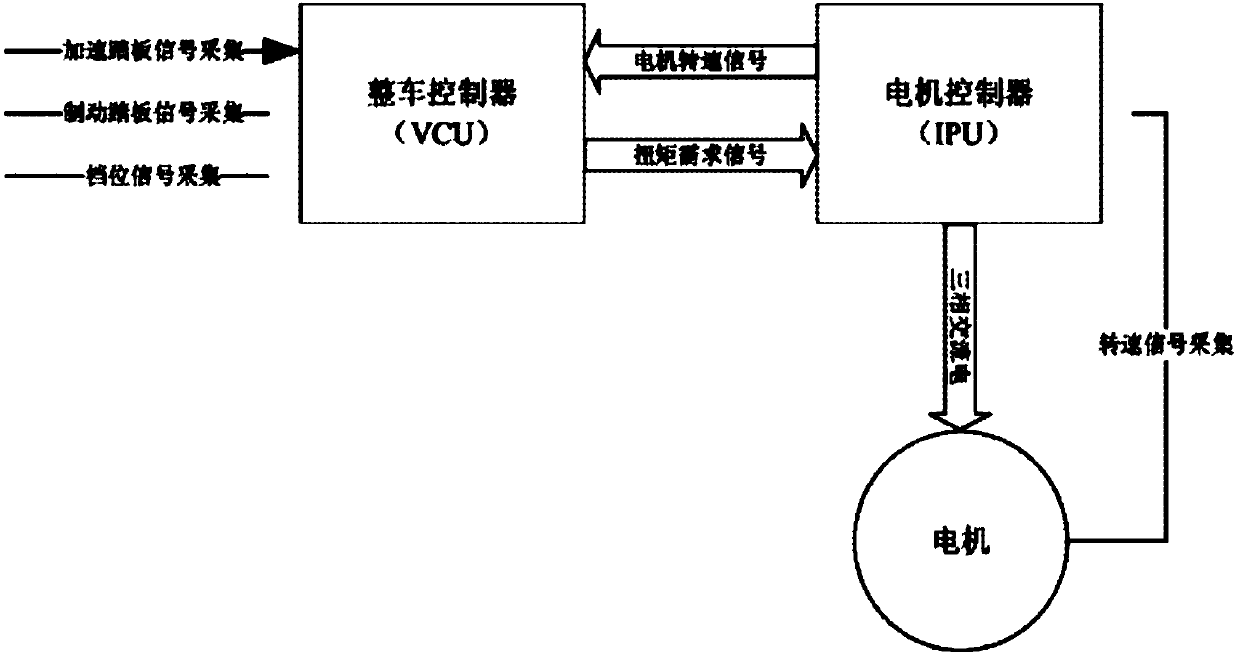
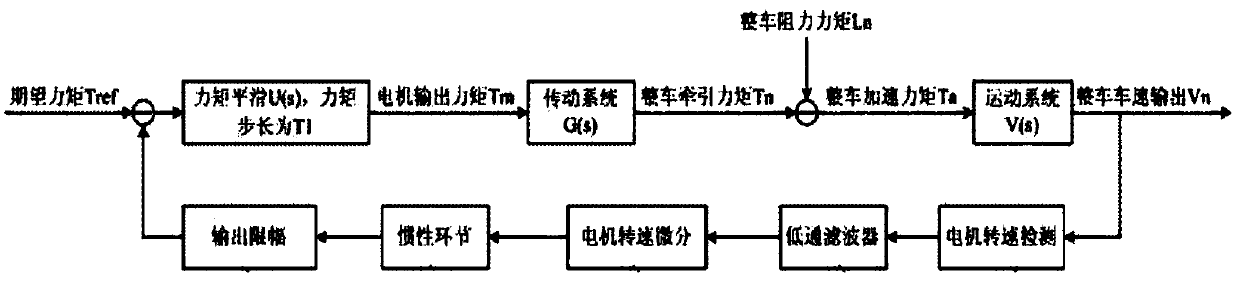
ActiveCN108068659ASuppress jitterSolve the problem of direct deviation in the extraction of rotational speed fluctuationsSpeed controllerElectric machinesBand-pass filterLinear relationship
The invention discloses a method, device and system for suppressing shaking of an electric automobile. The method, device and system are used for suppressing the shaking of the electric automobile andimproving the driving comfort level. The method includes the steps that a rotation speed signal of a motor is obtained; Fourier analysis is conducted on the rotation speed signal, and the frequency and the amplitude of an effective component, causing rotation speed shaking, in the rotation speed signal are obtained, wherein rotation speed shaking is shaking caused by the non-linear relationship between traction torque and the resistance moment of the electric automobile; according to the frequency and the amplitude of the effective component causing rotation speed shaking, a parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking is obtained; according to the parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking and the rotation speed signal, compensation torque is obtained through a differential inertial element and a band-pass filtering element; and the compensation torque and given torque are superposed so as to suppress the rotation speed shaking. Due to the fact that the shaking of the electric automobile is suppressed, mechanical resonance generated in the shaking process is reduced, and therefore hardware wear of the electric automobile is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Recording multiple spatially-heterodyned direct to digital holograms in one digital image
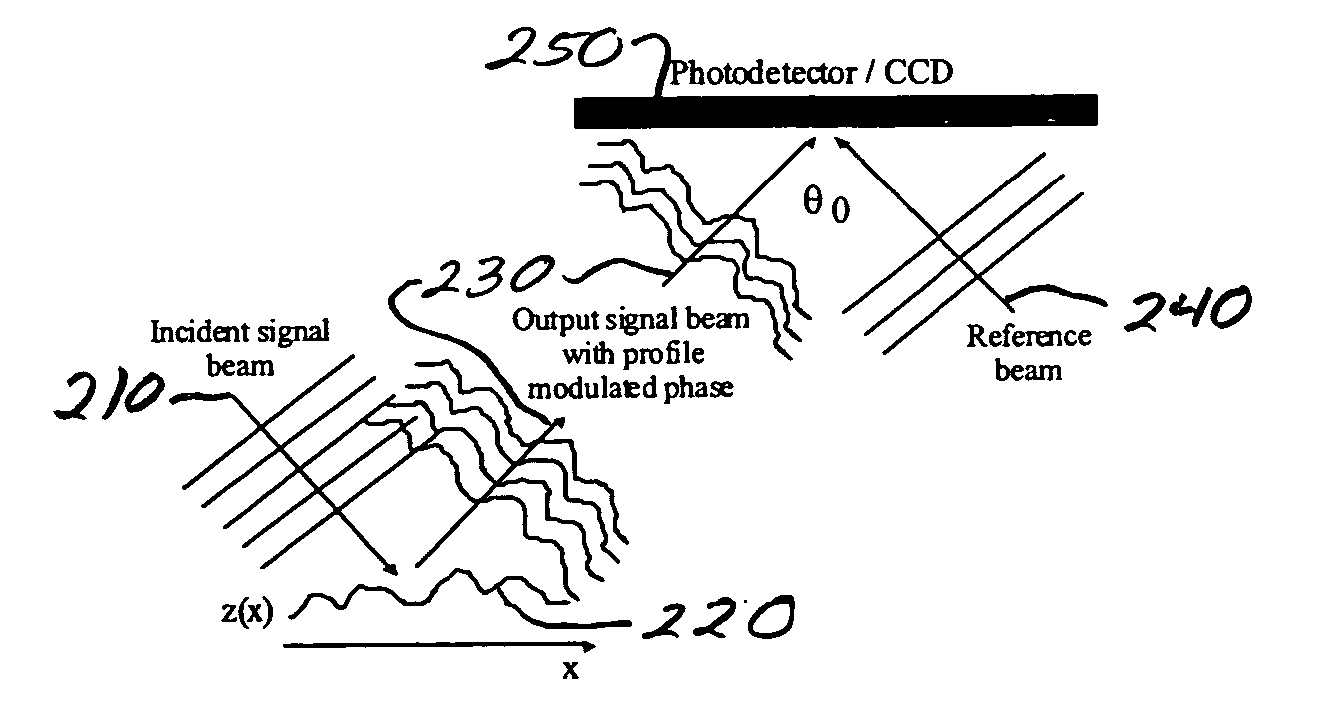
ActiveUS20040213464A1Reduction of common-modeReduction of correlated noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansBeam angleLight beam
Systems and methods are described for recording multiple spatially-heterodyned direct to digital holograms in one digital image. A method includes digitally recording, at a first reference beam-object beam angle, a first spatially-heterodyned hologram including spatial heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded first spatially-heterodyned hologram by shifting a first original origin of the recorded first spatially-heterodyned hologram to sit on top of a first spatial-heterodyne carrier frequency defined by the first reference beam-object beam angle; digitally recording, at a second reference beam-object beam angle, a second spatially-heterodyned hologram including spatial heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded second spatially-heterodyned hologram by shifting a second original origin of the recorded second spatially-heterodyned hologram to sit on top of a second spatial-heterodyne carrier frequency defined by the second reference beam-object beam angle; applying a first digital filter to cut off signals around the first original origin and define a first result; performing a first inverse Fourier transform on the first result; applying a second digital filter to cut off signals around the second original origin and define a second result; and performing a second inverse Fourier transform on the second result, wherein the first reference beam-object beam angle is not equal to the second reference beam-object beam angle and a single digital image includes both the first spatially-heterodyned hologram and the second spatially-heterodyned hologram.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
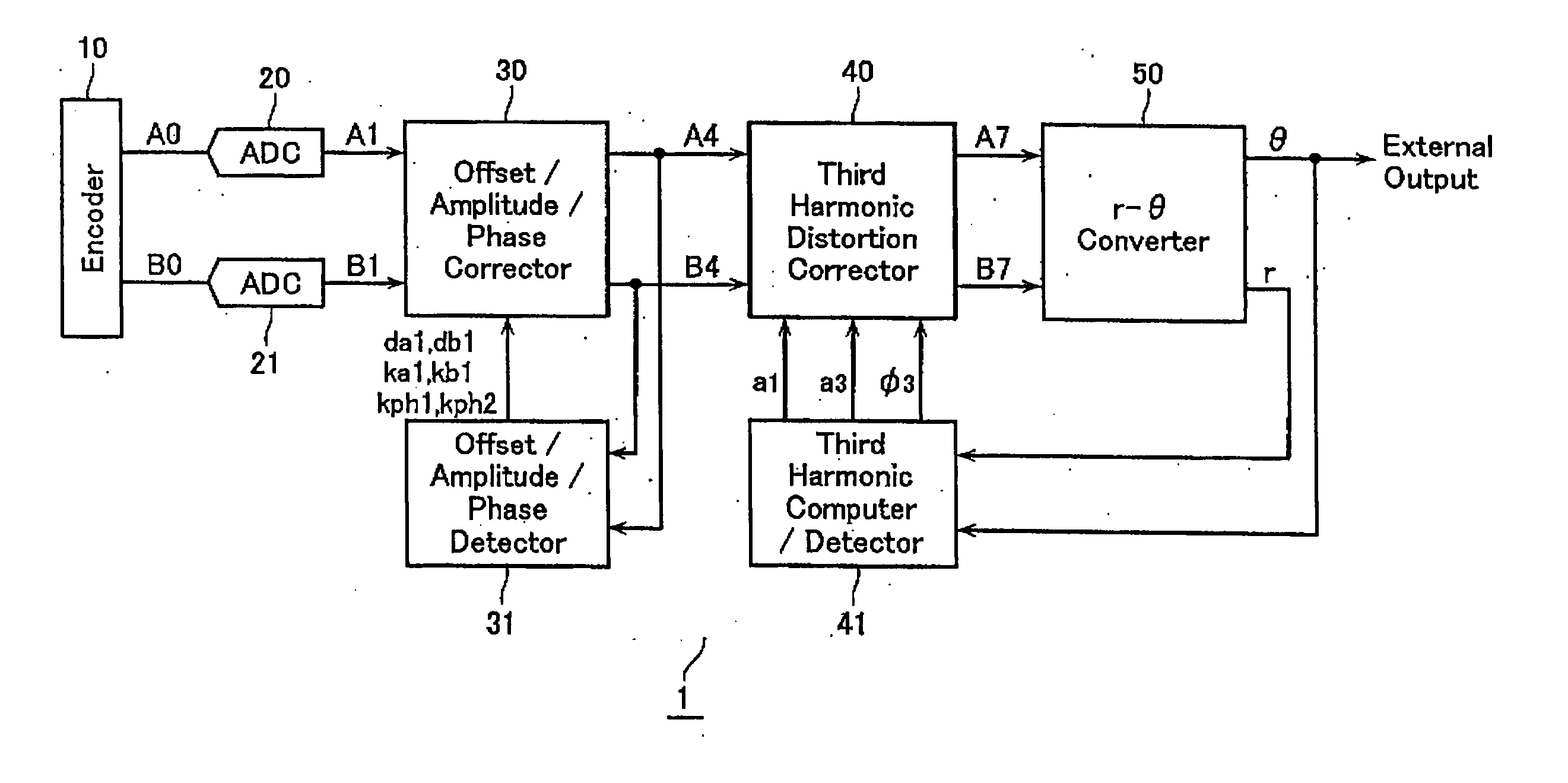
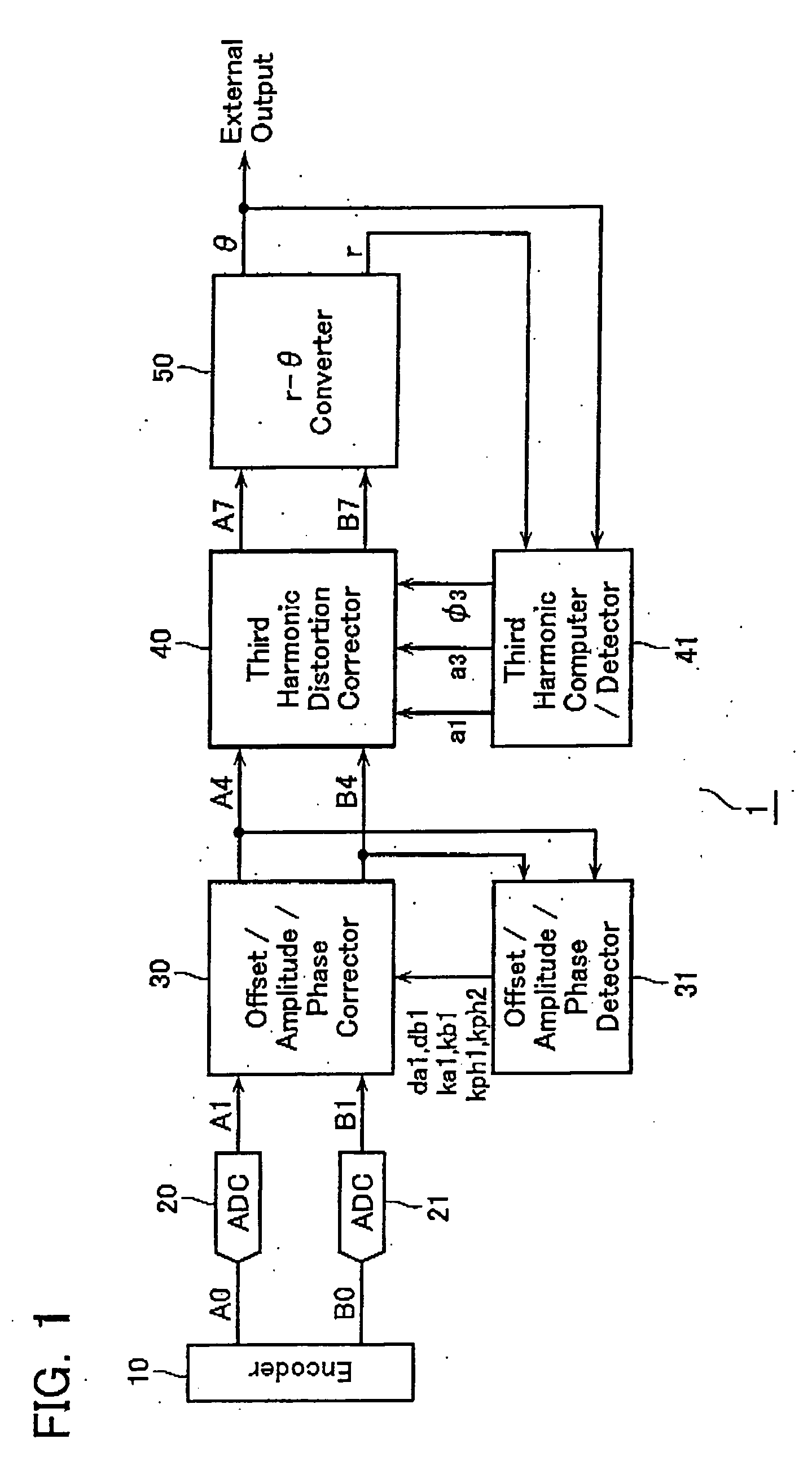
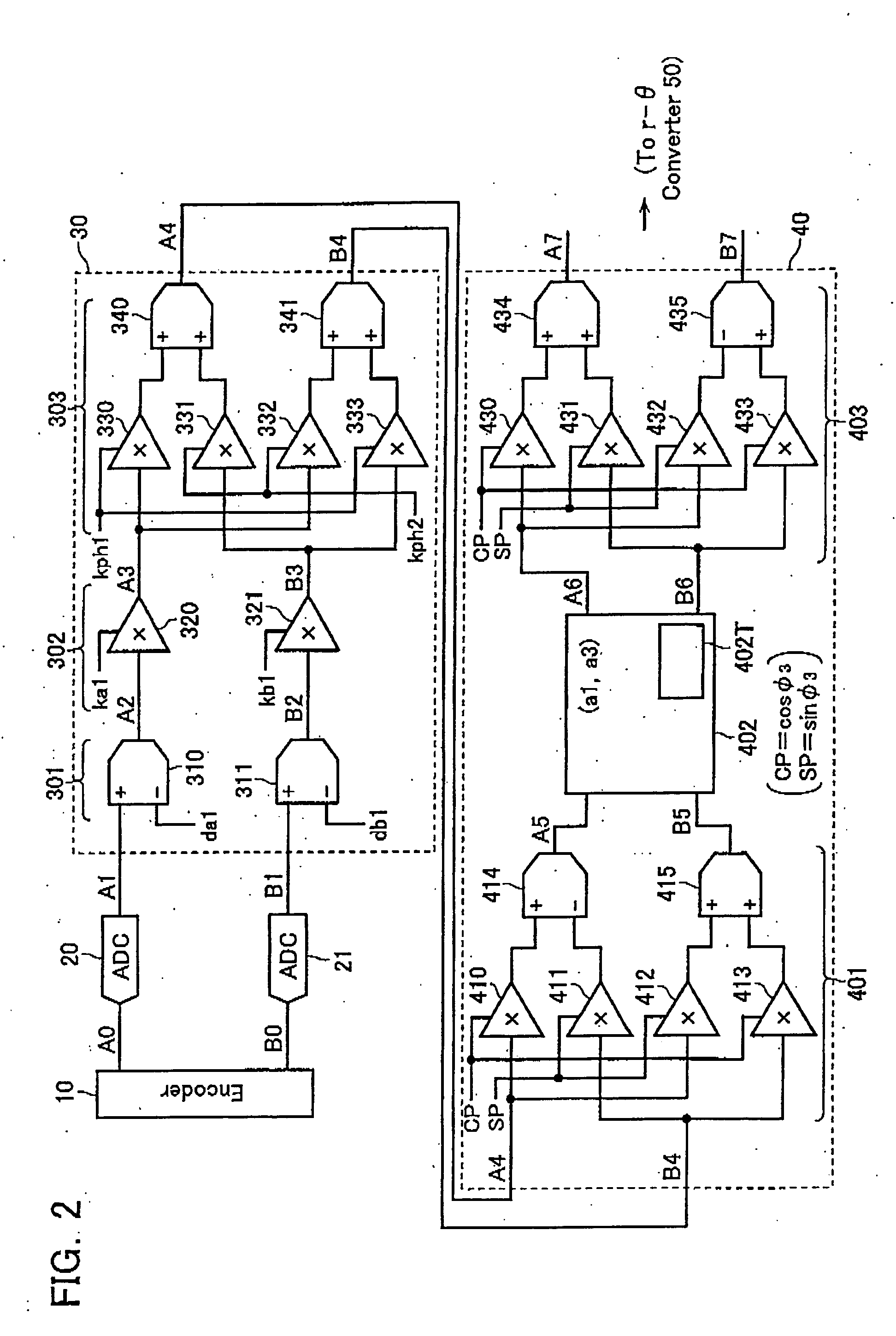
Encoder output signal correction apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060077083A1Improve interpolation accuracyComponent with highElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersSignal correctionThird harmonic
A third harmonic distortion corrector is equipped for correcting a third harmonic distortion contained in a two-phase sinusoidal signals with different phases output from an encoder. A third harmonic calculator / detector calculates the amplitude a3 and the phase φ3 of the third harmonic using Fourier analysis, based on change in radius r of the Lissajous waveform output from a r-θ converter. The third harmonic distortion corrector corrects the third harmonic distortion of the two-phase sinusoidal signal A4, B4 based on the amplitude a3 and the phase φ3 of the third harmonic calculated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Noise suppression based on bark band wiener filtering and modified doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS7492889B2Slow constantEliminate artifactsInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisNoise estimationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
In a noise suppresser, an input signal is converted to frequency domain by discrete Fourier analysis and divided into Bark bands. Noise is estimated for each band. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. The noise suppresser further includes a circuit to adjust a noise suppression factor inversely proportional to the signal to noise ratio of each frame of the input signal. A noise estimate is subtracted from the signal in each band. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the signals back to the time domain and overlapping and combined windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS6747771B2Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording an off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes: reflecting a reference beam from a reference mirror at a non-normal angle; reflecting an object beam from an object at an angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; digitally recording the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution spectral data or high definition images in inhomogeneous environments
InactiveUS7944206B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData treatment
A method and apparatus for treating a sample for acquiring high-definition magnetic resonance images (MRI images) or high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra even in the presence of magnetic field distortions within one or multiple scans. The spatial nature and temporal dependence of the field inhomogeneities are determined a priori using any of several literature procedures. A static or oscillating magnetic field gradient is applied on the sample so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with different resonance frequencies. A phase- and amplitude-modulated radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied in unison with the magnetic field gradient so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with a homogeneous excitation / inversion profile. The nature of the spatially-selective RF irradiation is tailored in such a way that, when added on top of the effects of the inhomogeneities, the spins' evolution phases and their signal amplitudes at the time of the acquisition become independent of the inhomogeneities. The spin signals thus created are captured and decoded, so as to obtain the spins' response as if the inhomogeneity was not present. The collected data is processed to a suitable rearrangement and Fourier analysis procedure to retrieve a final undistorted image or spectrum. The magnetic field gradient can be oscillated to impose this kind of inhomogeneity corrections on multiple spatial dimensions sequentially, or simultaneously.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Impact and vibration method for measuring natural frequency of bridge lower structure
InactiveCN1804563AEasy to operateEasy to testVibration measurement in solidsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention relates to an impulse vibrating method for testing the bridge substructure natural frequency of vibration which uses avoirdupois weight to stroke the pier and tests the vibrating response of the pier to analyze and compute the natural frequency of vibration. It uses avoirdupois weight to stroke the pier top part and tests the speed and hastens response of the bridge. It usually dose multi-stroke and uses the recording wave mode superposition to dispel the noise to obtain the accurate response wave mode. It reads the response wave mode to do Fourier analysis to ascertain Fourier frequency spectrum and combines with the peak spectrum to ascertain the natural frequency of vibration of bridge.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of designing an RPWM inverter with unwanted harmonic elimination
InactiveUS20070242489A1Increase frequencyCompletely suppress the low-order harmonic componentsDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationHarmonicSideband
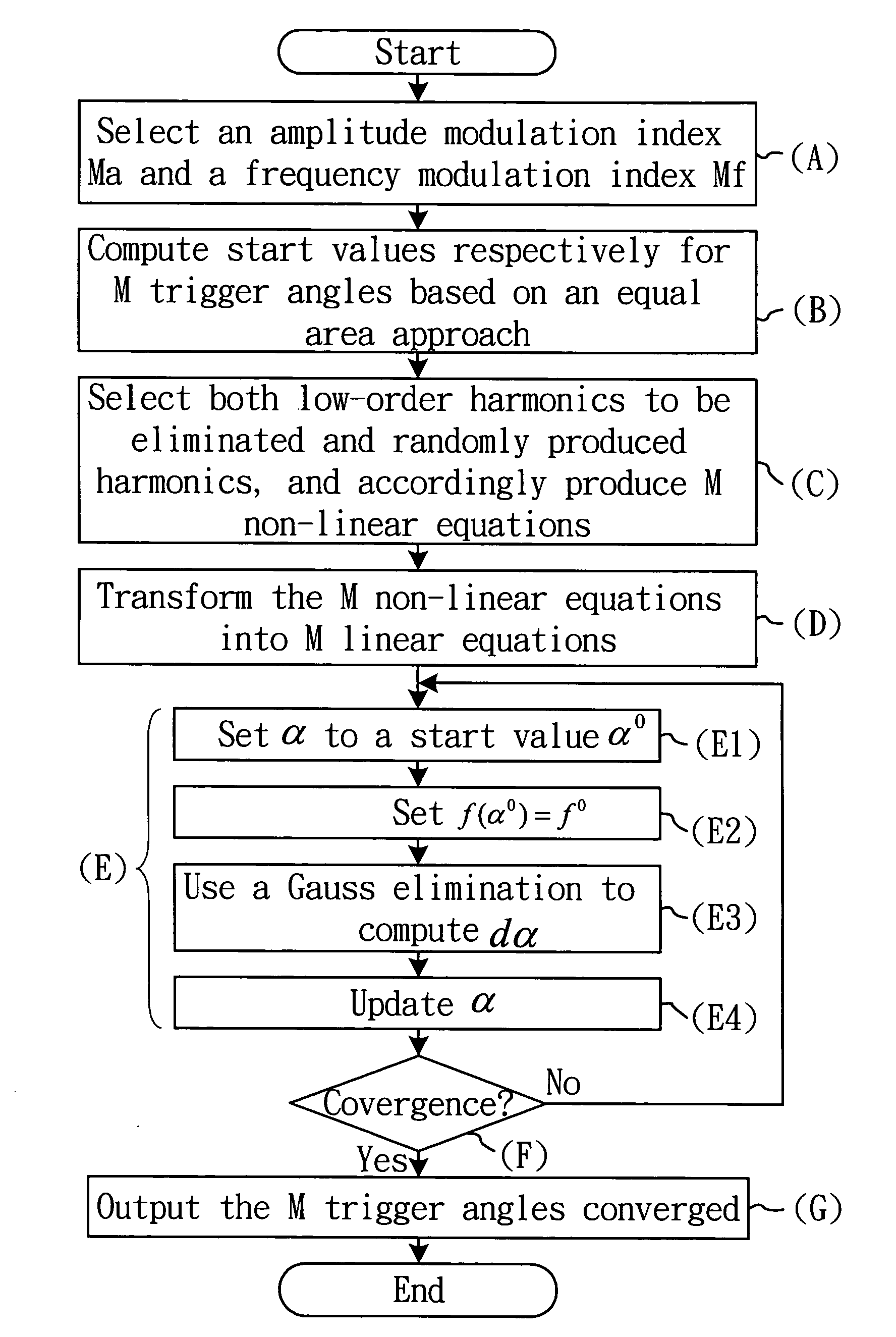
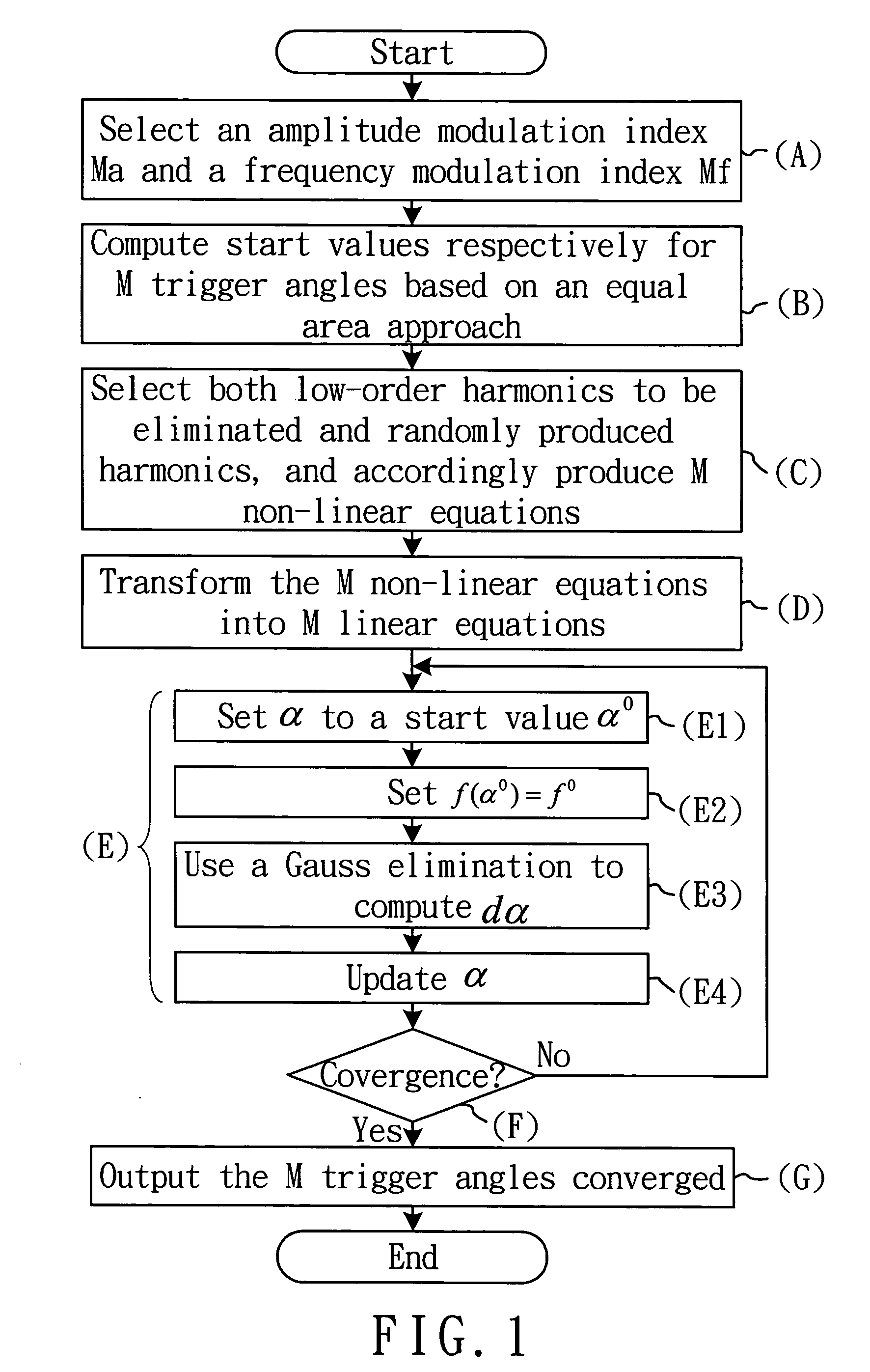
A method of designing a random pulse width modulation (RPWM) inverter with unwanted harmonic elimination, which first uses a Fourier analysis and a numerical analysis to eliminate the unwanted harmonic components, next uses the equal area approach to produce switching angles to be used as start values for solving non-linear equations, next selects low-order harmonics to be eliminated and randomly sampled harmonics to solve the equations and obtain pluralities of switching angles for eliminating different harmonics, next applies pluralities of harmonics to a random probability function to thereby obtain a harmonic distribution, and finally uses a random sampling to evenly disperse the higher side-band harmonic components and effectively suppress the low-order harmonic components.
Owner:TATUNG UNIVERSITY +1
Interference scatterometer
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Stroboscopic interferometry with frequency domain analysis
ActiveUS7177029B2Issue to overcomeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansDigital signal processingTwo dimensional detector
A computer-based stroboscopic interferometric microscope system for measuring the topography of a microscopic vibratory object includes an interferometric microscope equipped with a multiple-color (e.g., LED) or white-light source, a mechanical scanning apparatus for varying the optical path difference between the vibratory object and a reference surface, a camera having a two-dimensional detector array, and digital signal processing apparatus for determining surface height from interference data. Interferograms for each of the detector image points in the field of view are generated simultaneously by scanning the object in a direction approximately perpendicular to the object surface illuminated stroboscopically while recording detector data in digital memory. Recorded interferograms for each image point are then transformed into the spatial frequency domain by Fourier analysis, and the surface height for each corresponding object surface point is obtained by examination of the complex phase as a function of spatial frequency. A complete three-dimensional image of the object surface is then constructed from the height data and corresponding image plane coordinates. The three-dimensional image may be presented on a display or hard copy or written to a storage medium.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
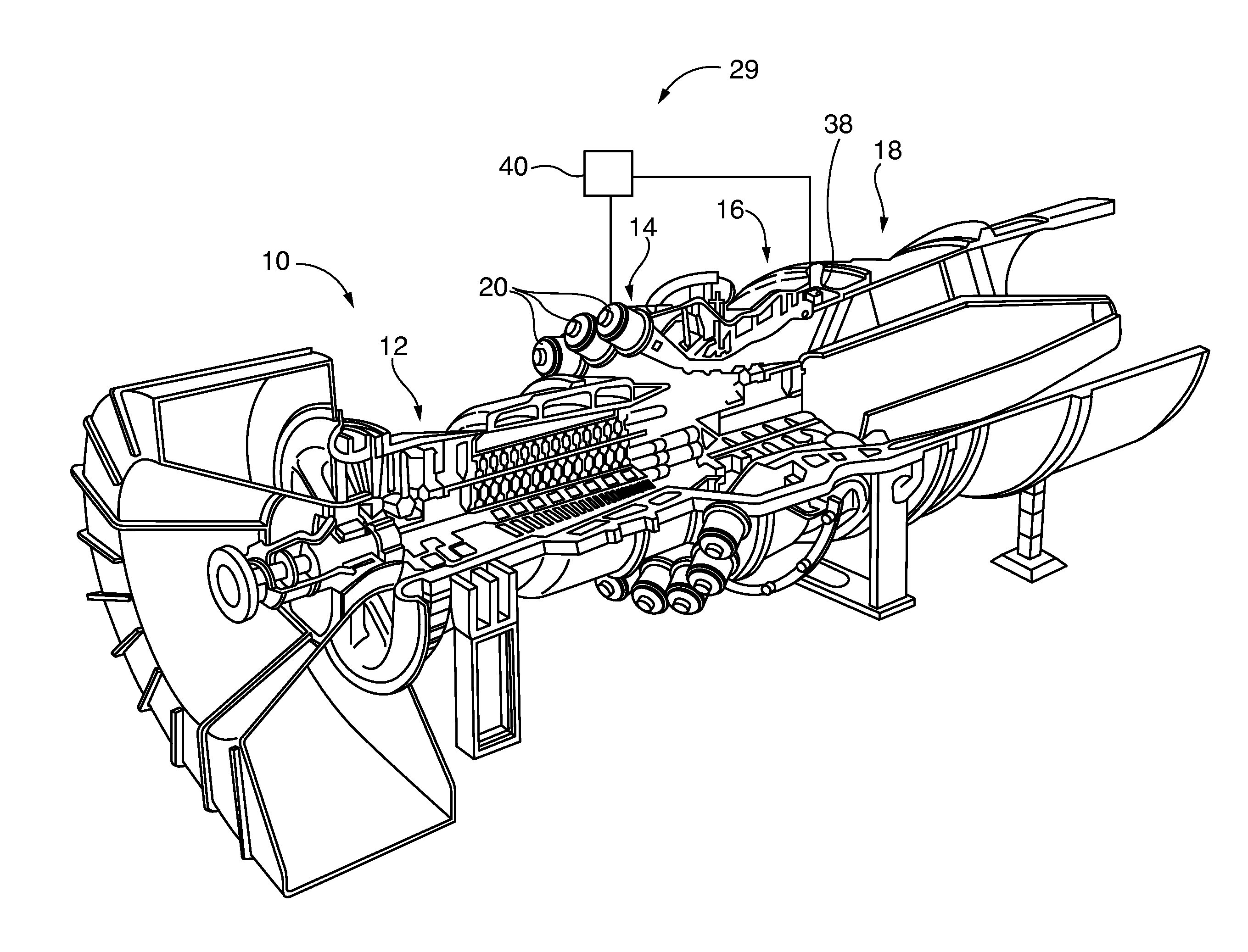
Multi functional sensor system for gas turbine combustion monitoring and control
ActiveUS20150168228A1Optimizing engine controlImprove performanceContinuous combustion chamberGas-turbine engine testingCombustion chamberEngineering
Thermoacoustic sensors, such as dynamic pressure sensors, in the combustor measure vibratory responses of the combustor. An integrated monitoring and control system controller correlates sensor readings with combustion thermoacoustic properties in order to identify combustion anomalies by wavelet or Fourier analysis techniques; determine bulk temperature characteristics within the combustor with dominant mode frequency analysis techniques; and optionally determines absolute active path temperatures within the combustor with acoustic pyrometry transmission and time-of-flight analysis techniques. In some embodiments all of the monitoring functions are performed with a commonly shared array of thermoacoustic sensors that function as both combustion dynamics thermoacoustic vibration / wave receivers and acoustic transmitters. The monitored combustion properties are used for controlling gas turbine combustion.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com