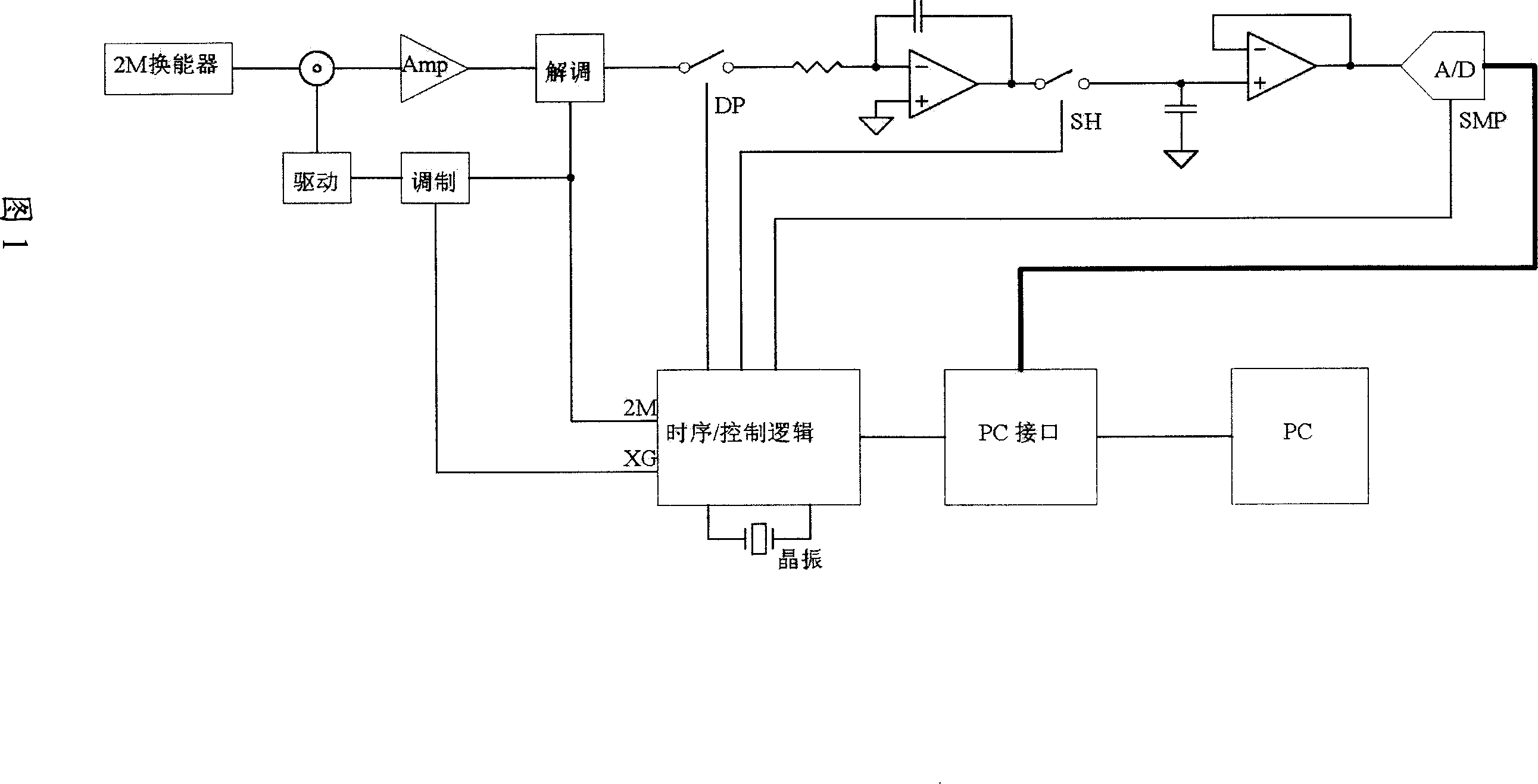
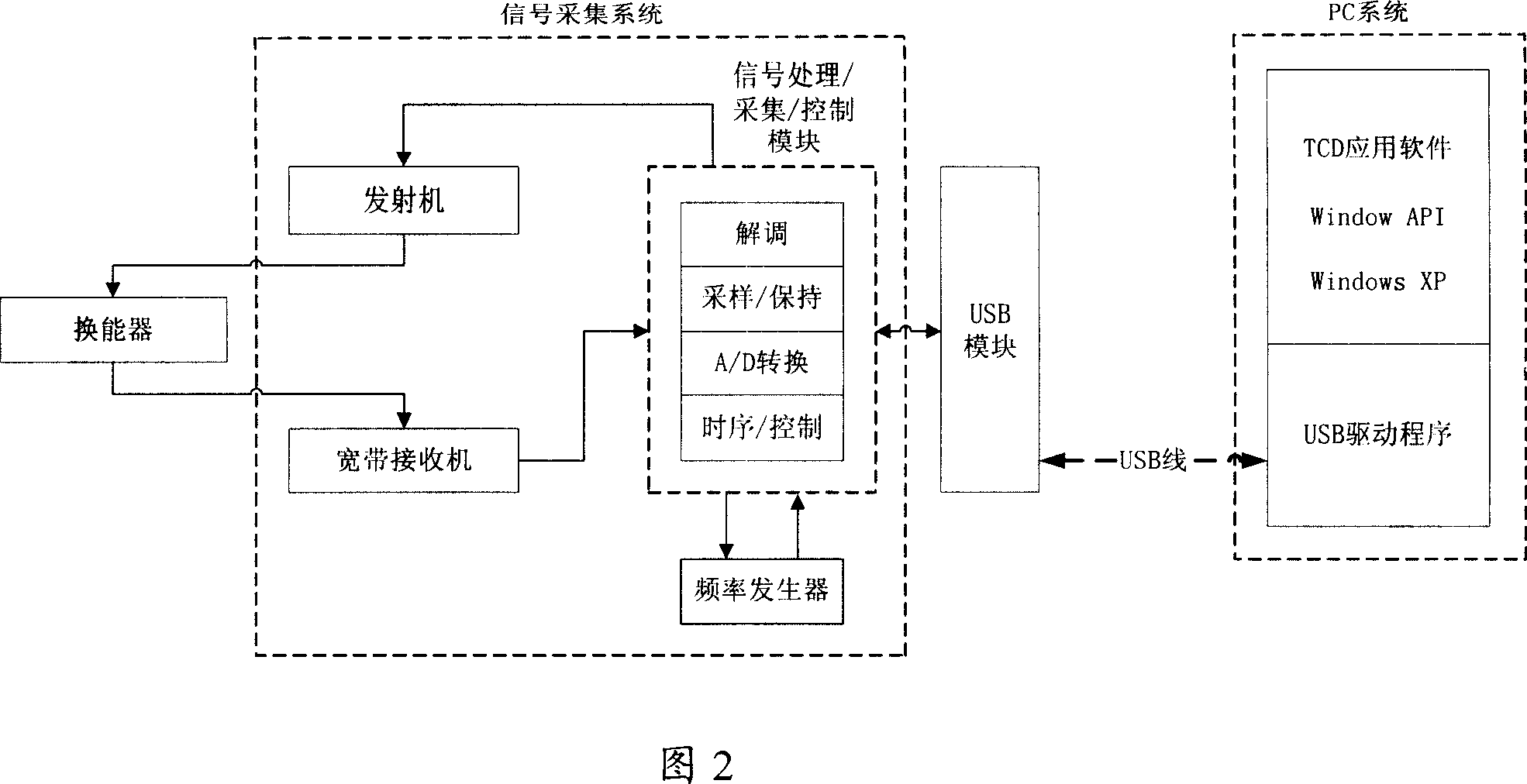
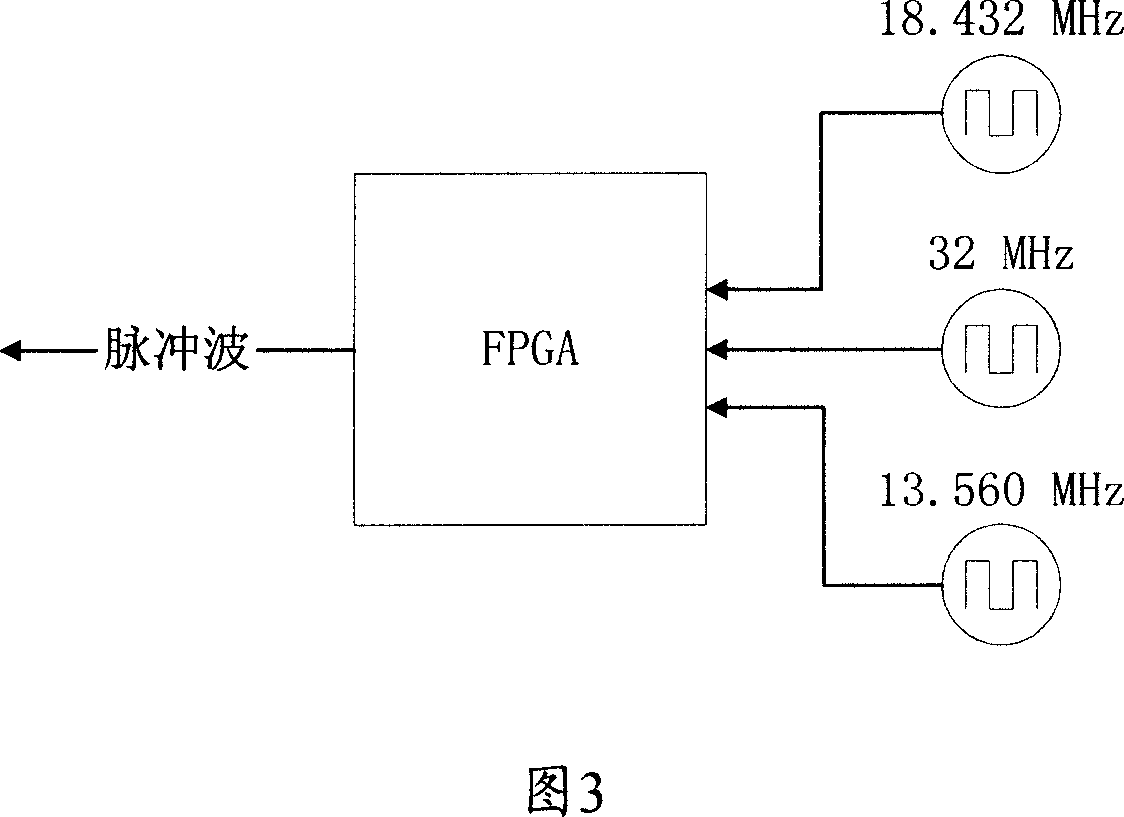
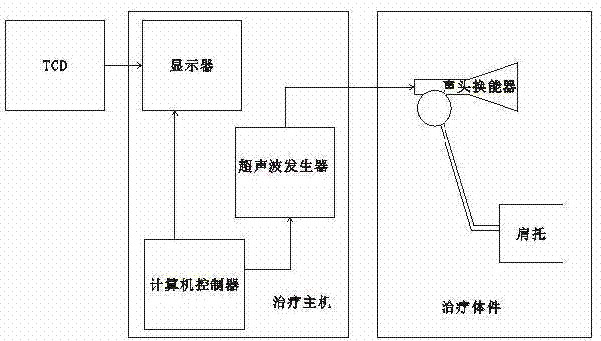
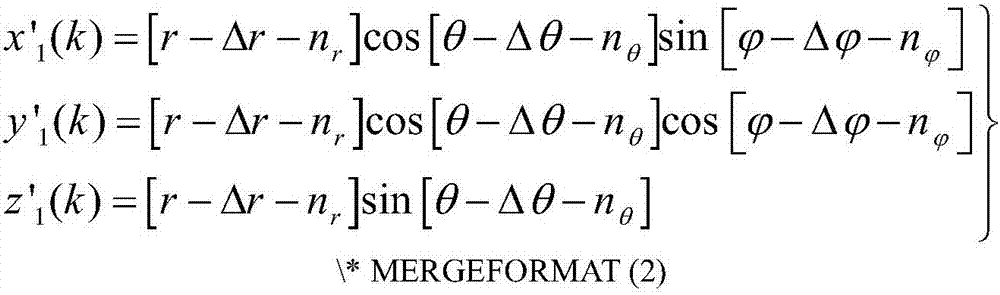Patents
Literature
69 results about "Transcranial Doppler" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
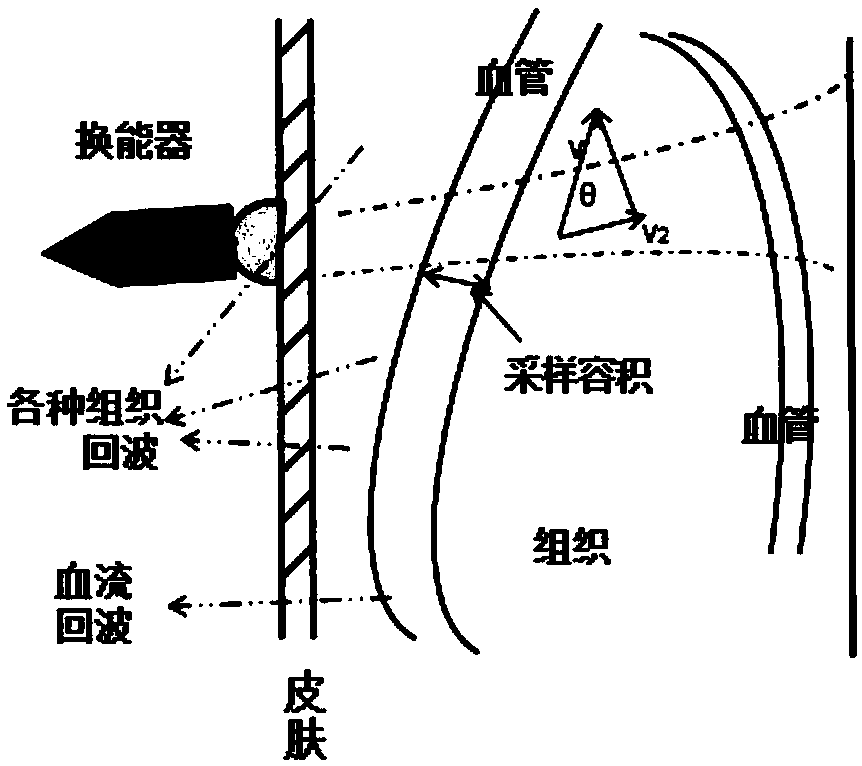
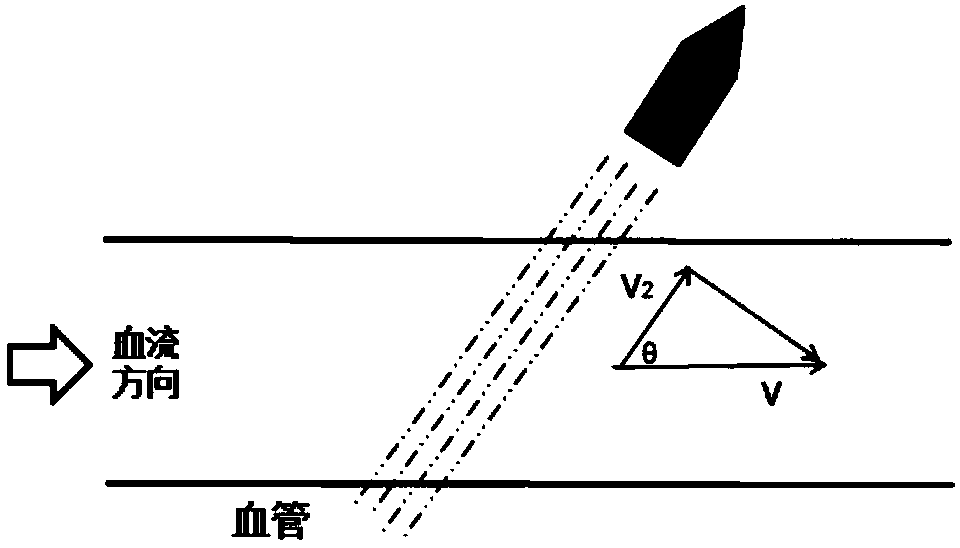
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) and transcranial color Doppler (TCCD) are types of Doppler ultrasonography that measure the velocity of blood flow through the brain's blood vessels by measuring the echoes of ultrasound waves moving transcranially (through the cranium). These modes of medical imaging conduct a spectral analysis of the acoustic signals they receive and can therefore be classified as methods of active acoustocerebrography. They are used as tests to help diagnose emboli, stenosis, vasospasm from a subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding from a ruptured aneurysm), and other problems. These relatively quick and inexpensive tests are growing in popularity. The tests are effective for detecting sickle cell disease, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, subarachnoid hemorrhage, arteriovenous malformations, and cerebral circulatory arrest. The tests are possibly useful for perioperative monitoring and meningeal infection. The equipment used for these tests is becoming increasingly portable, making it possible for a clinician to travel to a hospital, to a doctor's office, or to a nursing home for both inpatient and outpatient studies. The tests are often used in conjunction with other tests such as MRI, MRA, carotid duplex ultrasound and CT scans. The tests are also used for research in cognitive neuroscience (see Functional transcranial Doppler, below).
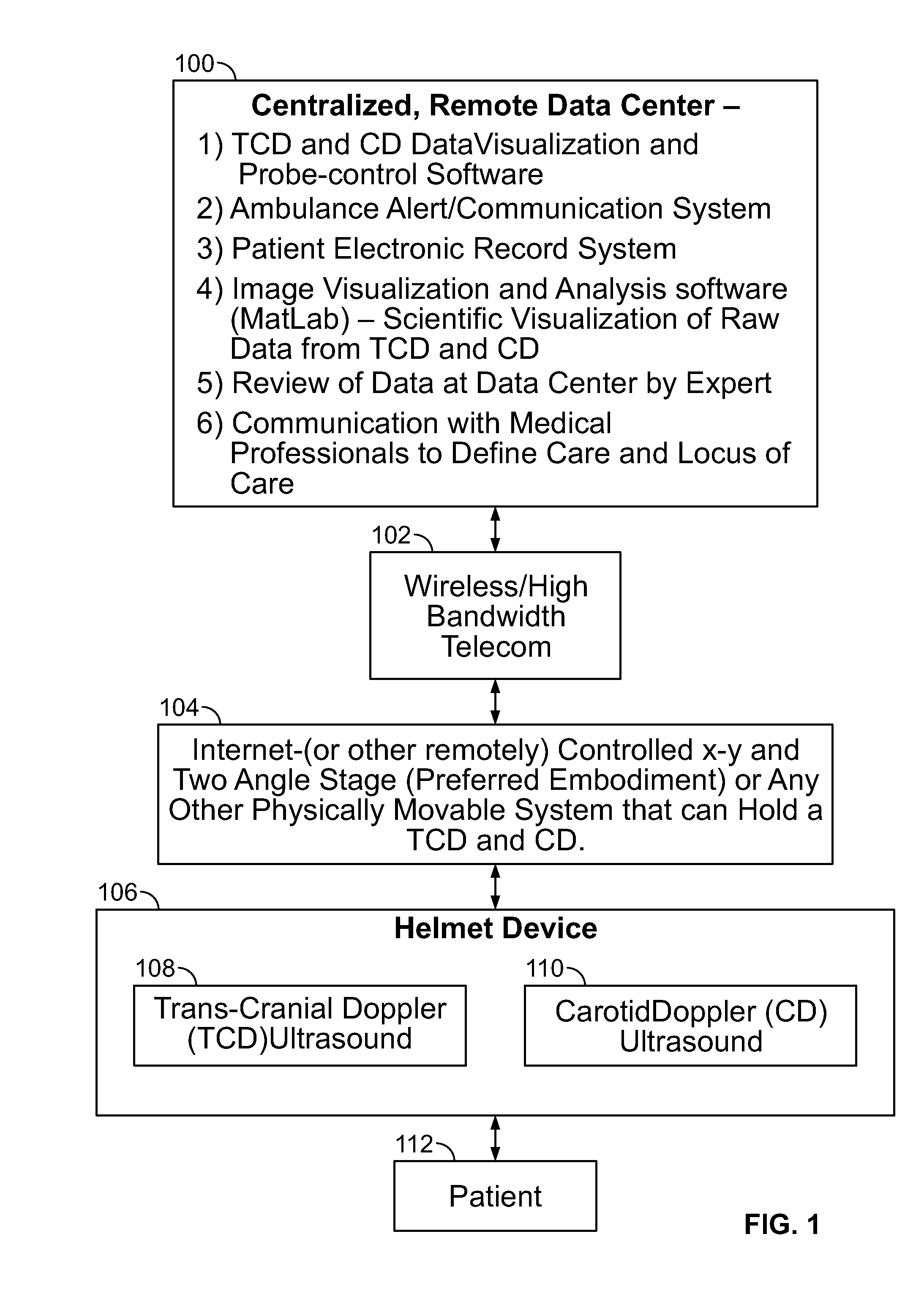
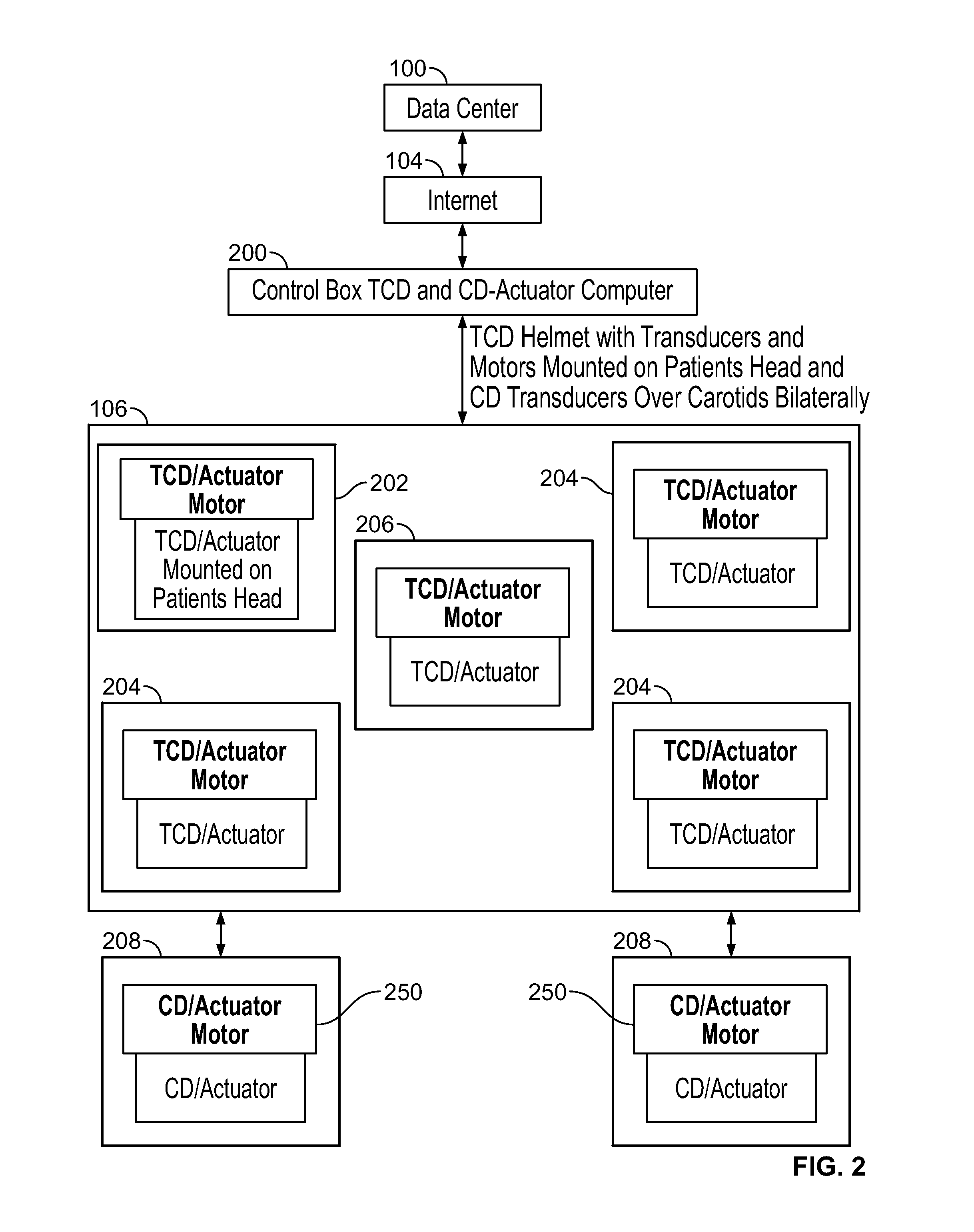
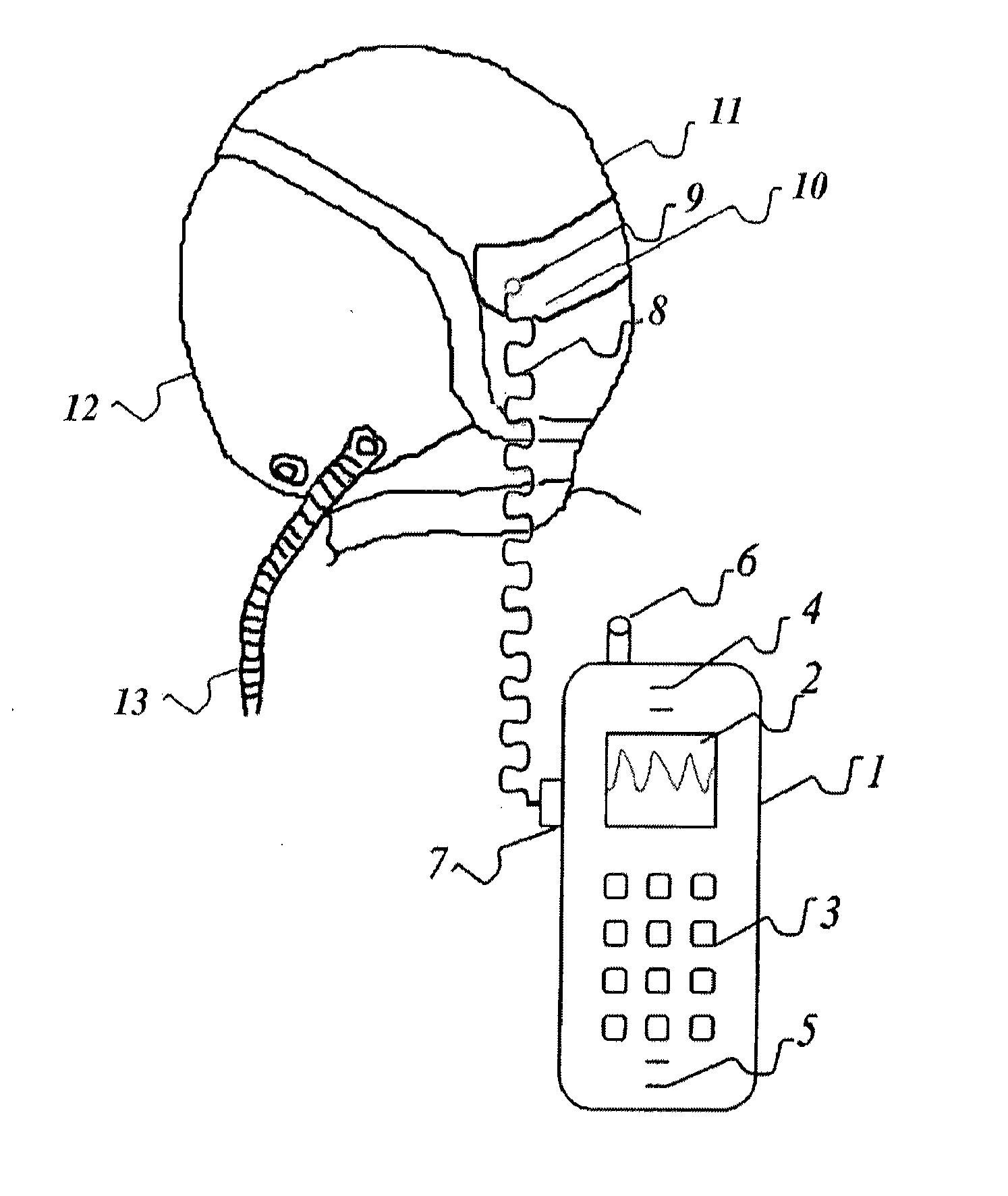
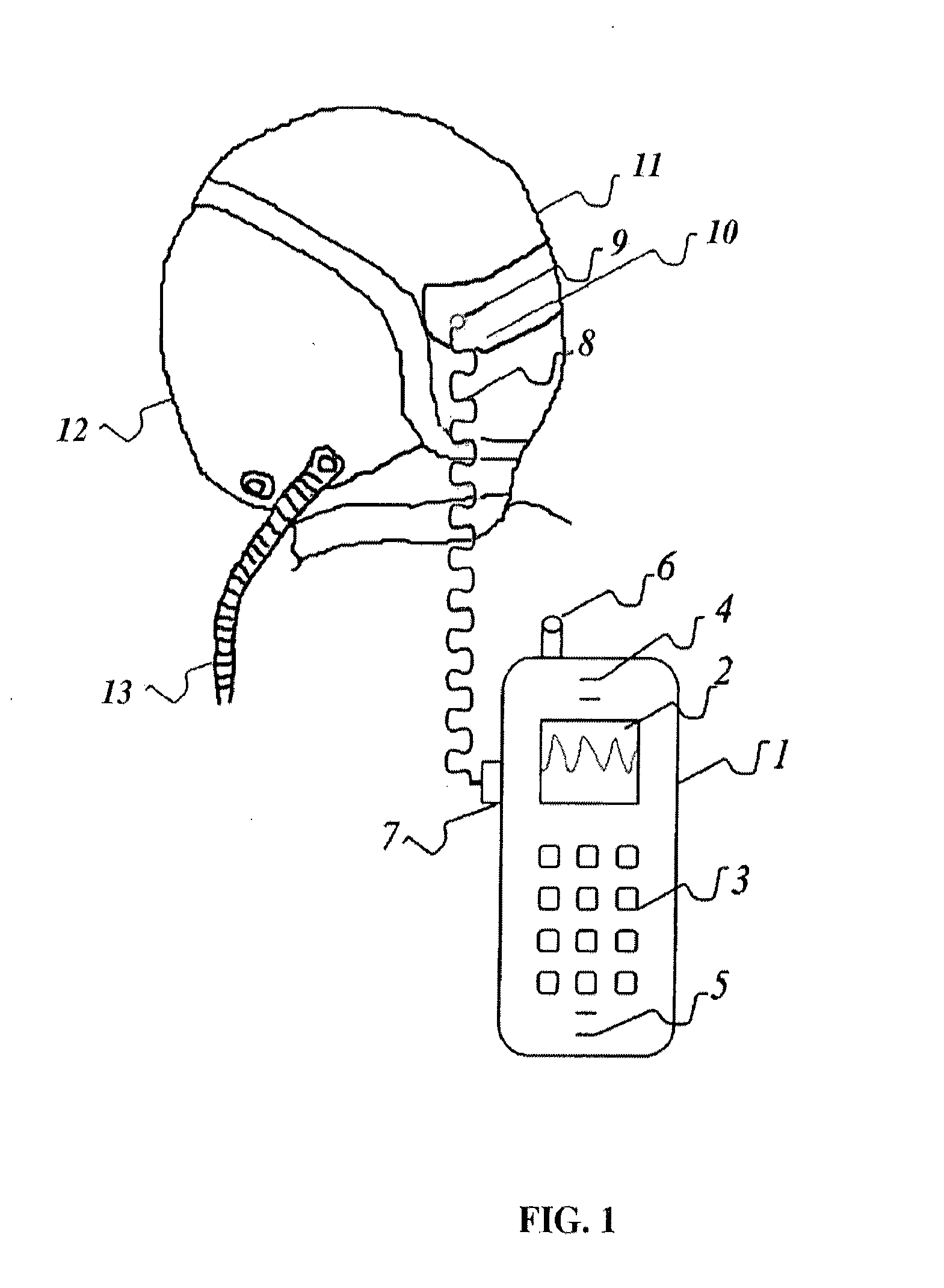
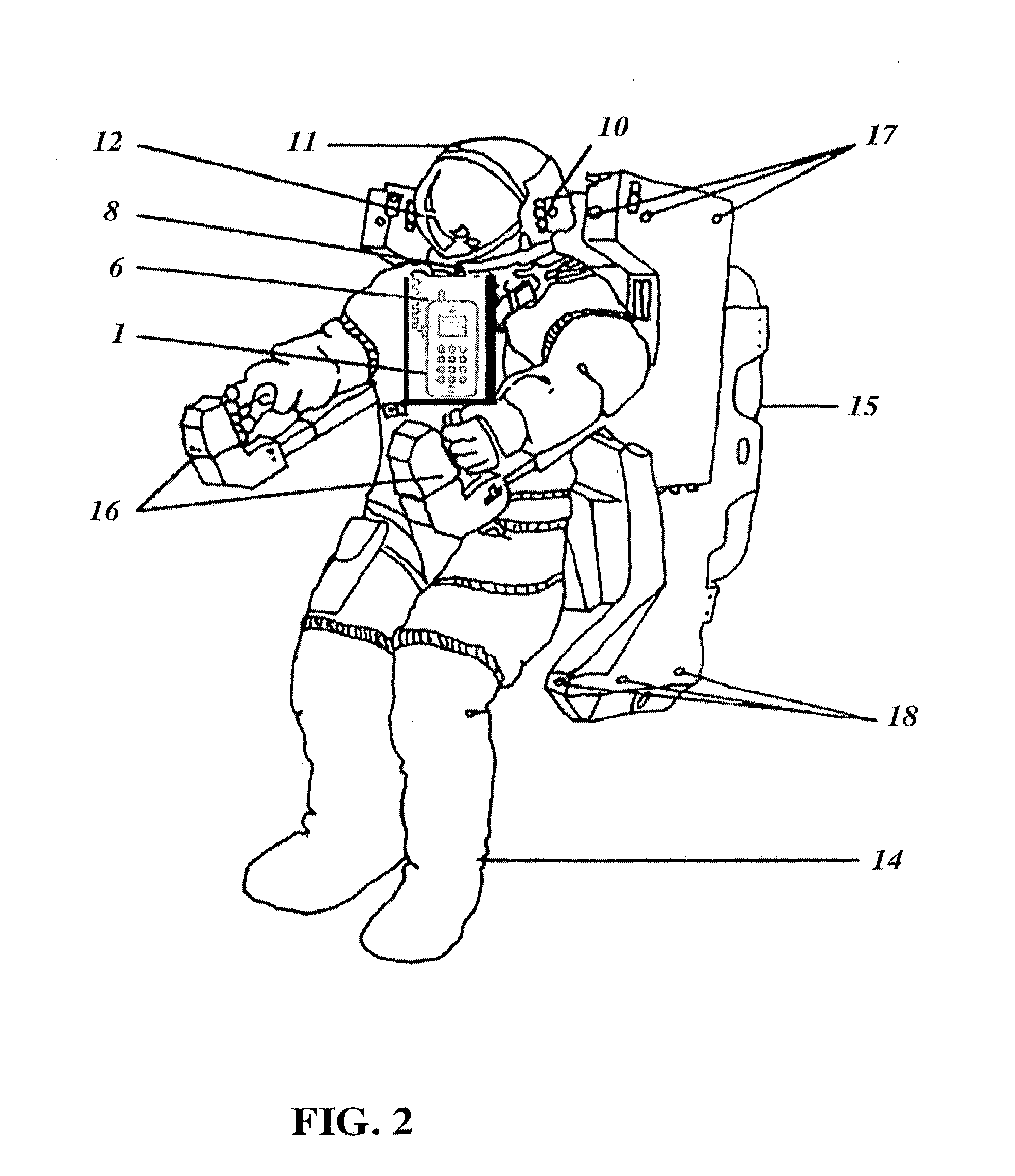
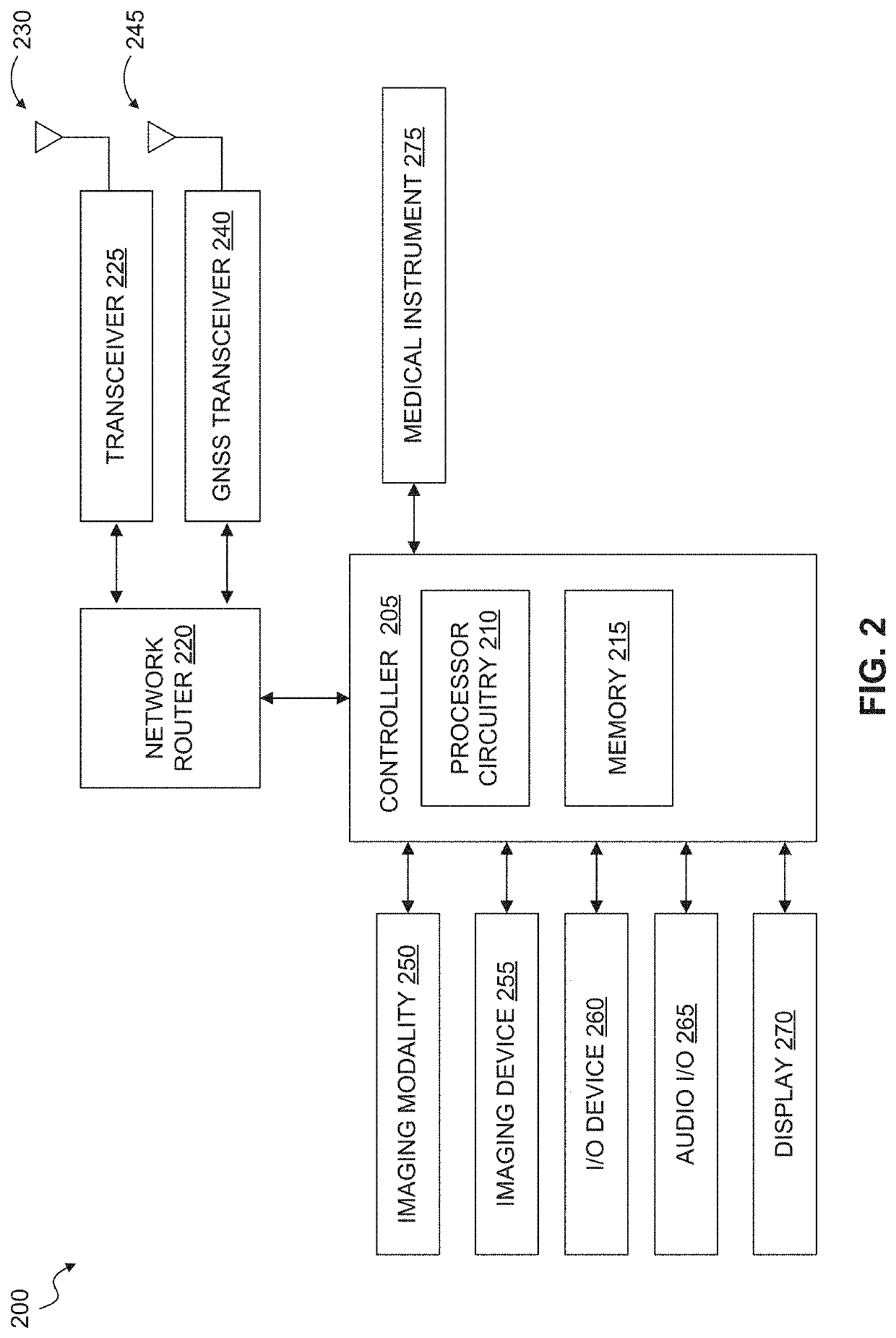
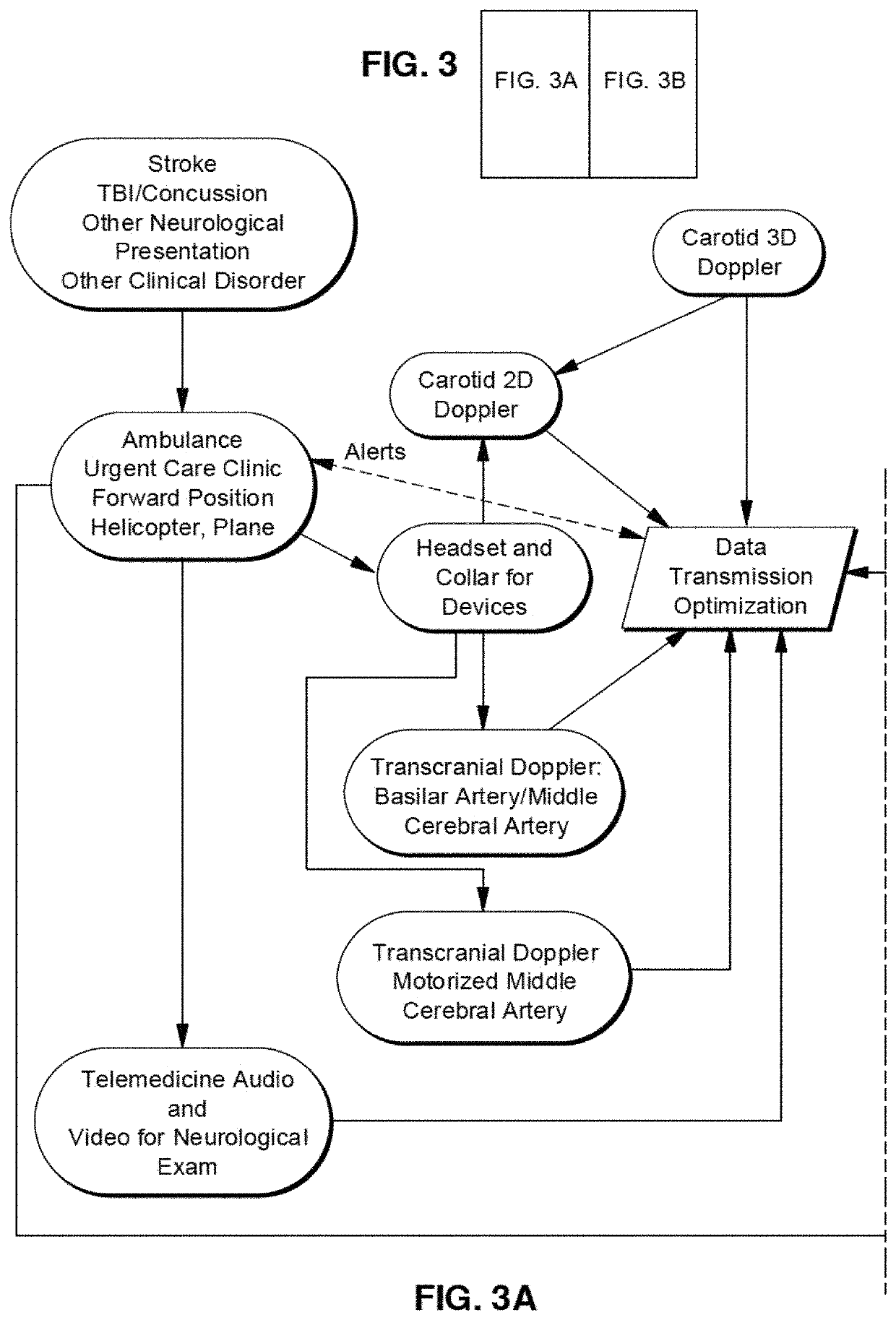
Mobile medicine communication platform and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170300654A1Increase elasticityReduce packet lossError preventionSimultaneous aerial operationsComputer networkTransceiver
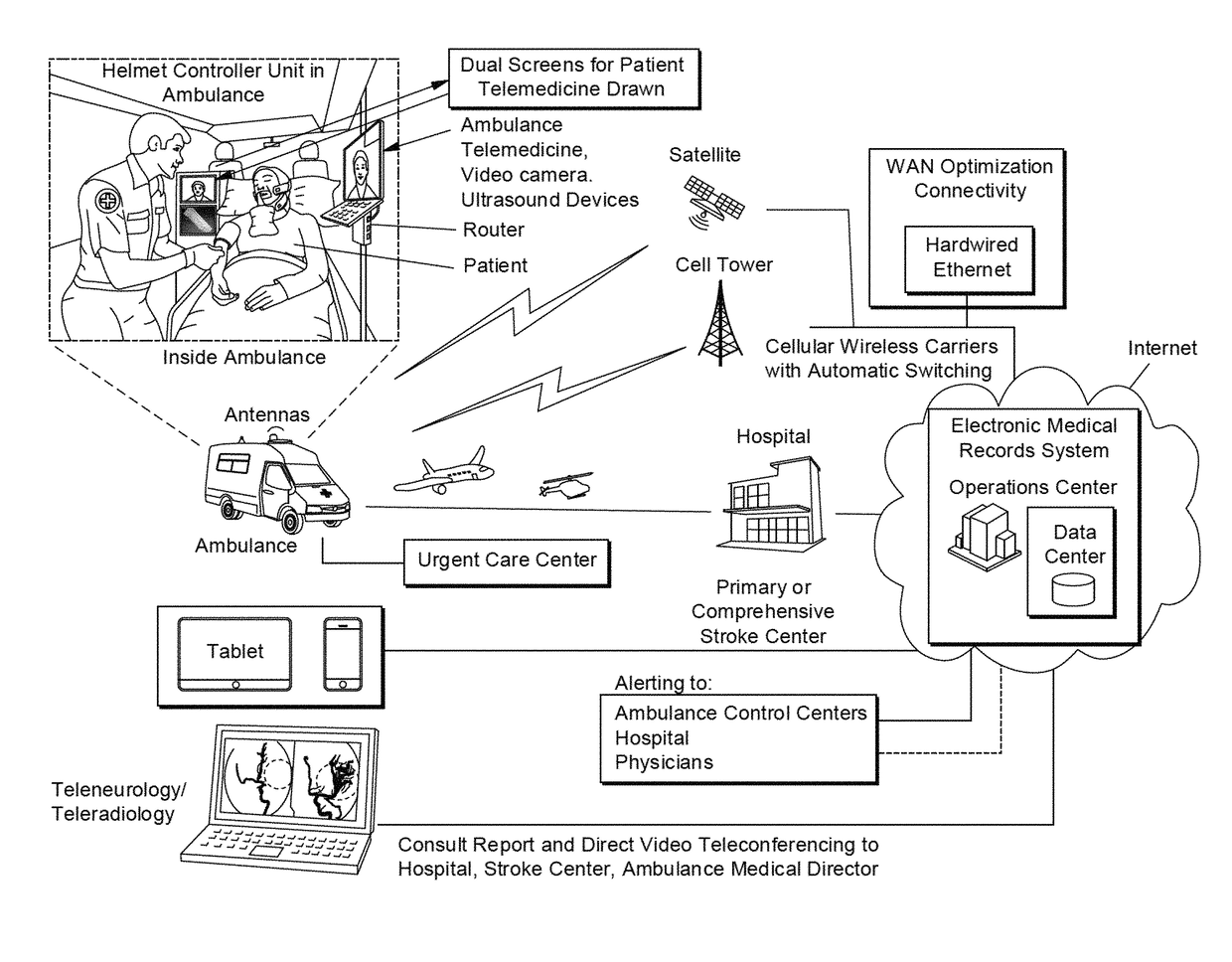
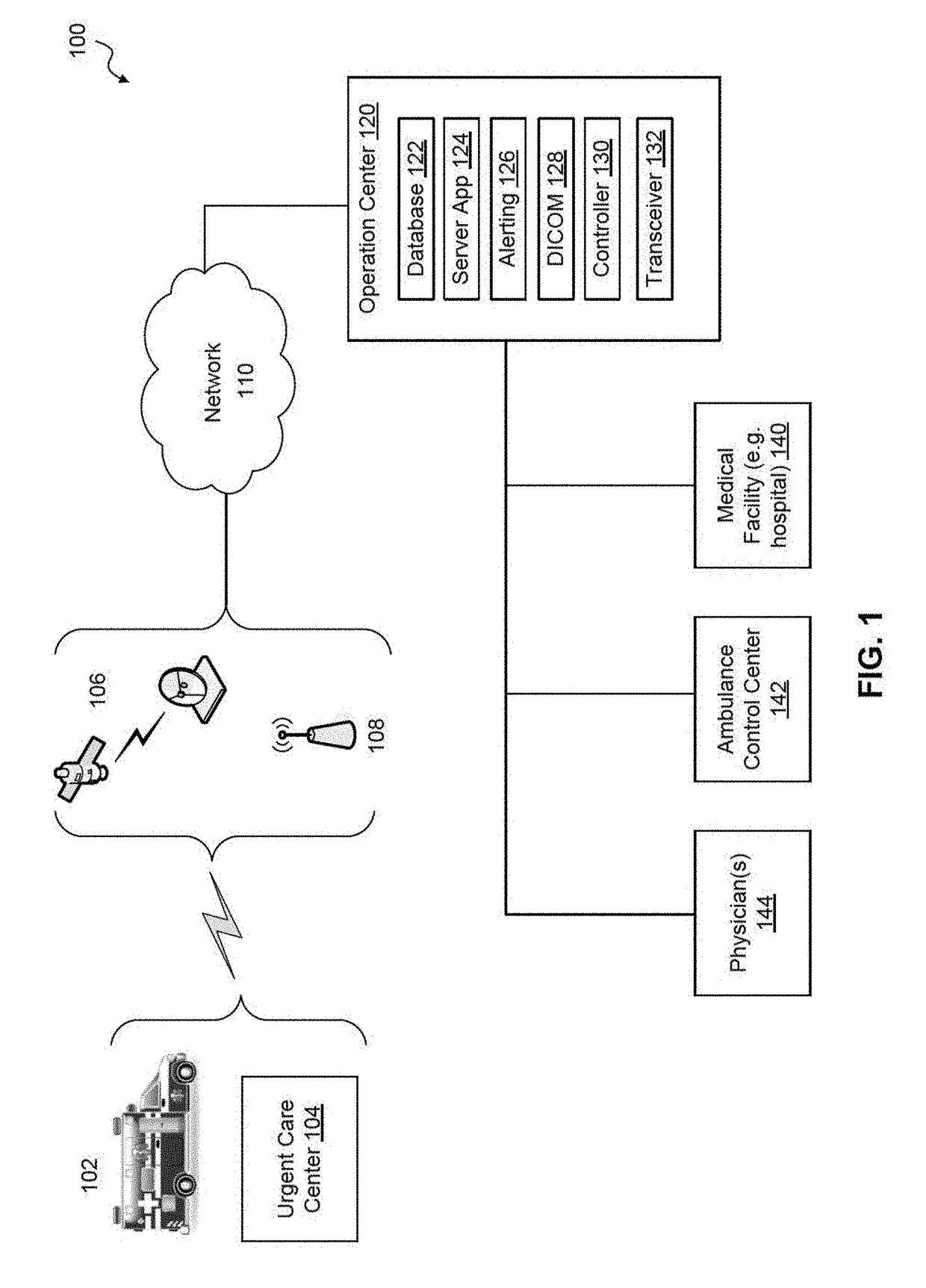
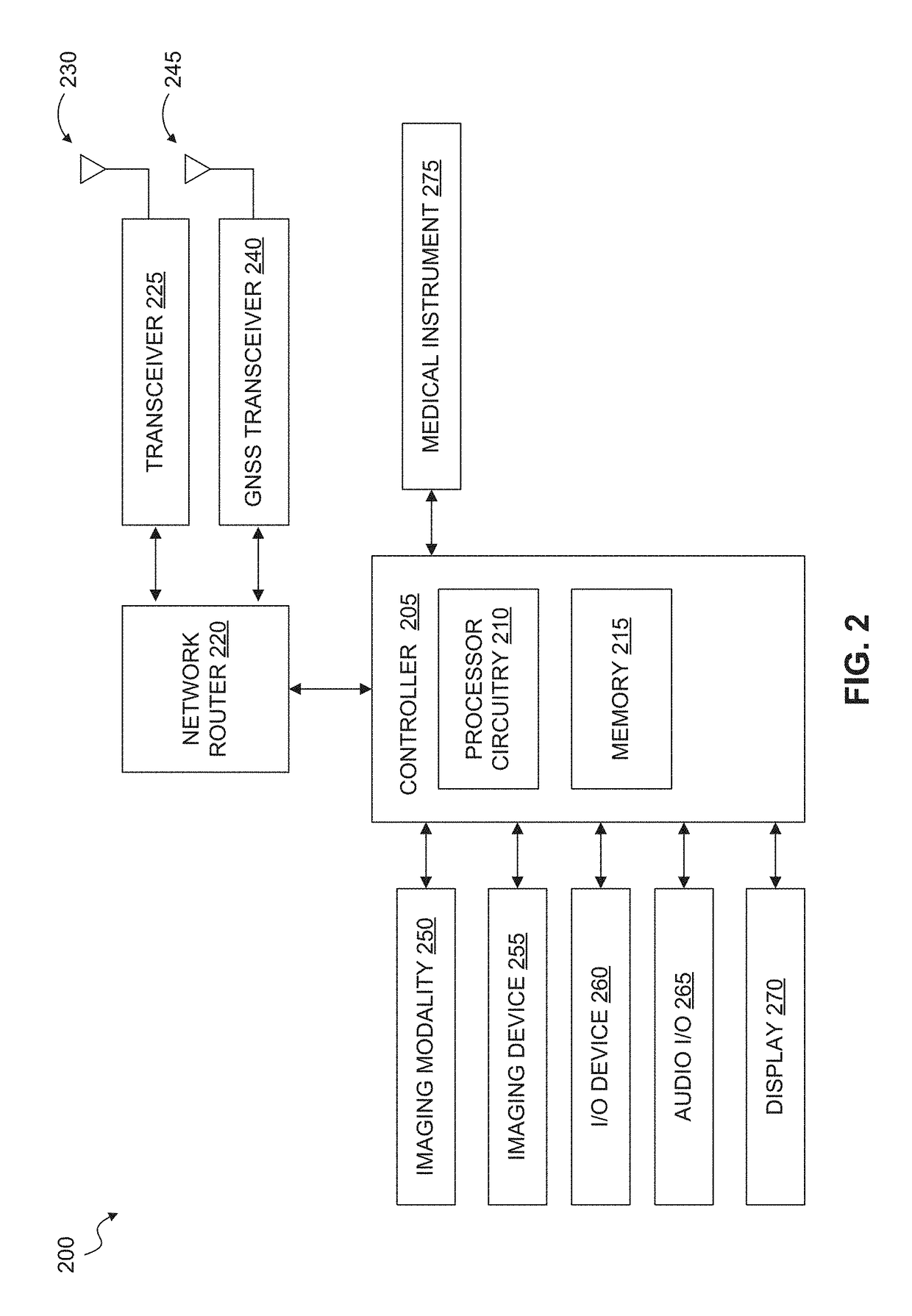
Telemedicine systems and methods are described. In a telemedicine system operable to communicate with a remote operations center, communications can be transmitted / received using a transceiver having an antenna. The antenna can include first and second di-pole antenna elements, the first di-pole antenna element being vertically polarized and the second di-pole antenna element being horizontally polarized. A controller of the system can establish, using the transceiver, a telemedicine session with the operations center using a Transport Morphing Protocol (TMP), the TMP being an acknowledgement-based user datagram protocol. The controller can also mask one or more transient network degradations to increase resiliency of the telemedicine session. The telemedicine system can include a 2D and 3D carotid Doppler and transcranial Doppler and / or other diagnostic devices, and provides for real-time connectivity and communication between medical personnel in an emergency vehicle and a receiving hospital for immediate diagnosis and treatment to a patient in need.
Owner:BR INVENTION HLDG LLC
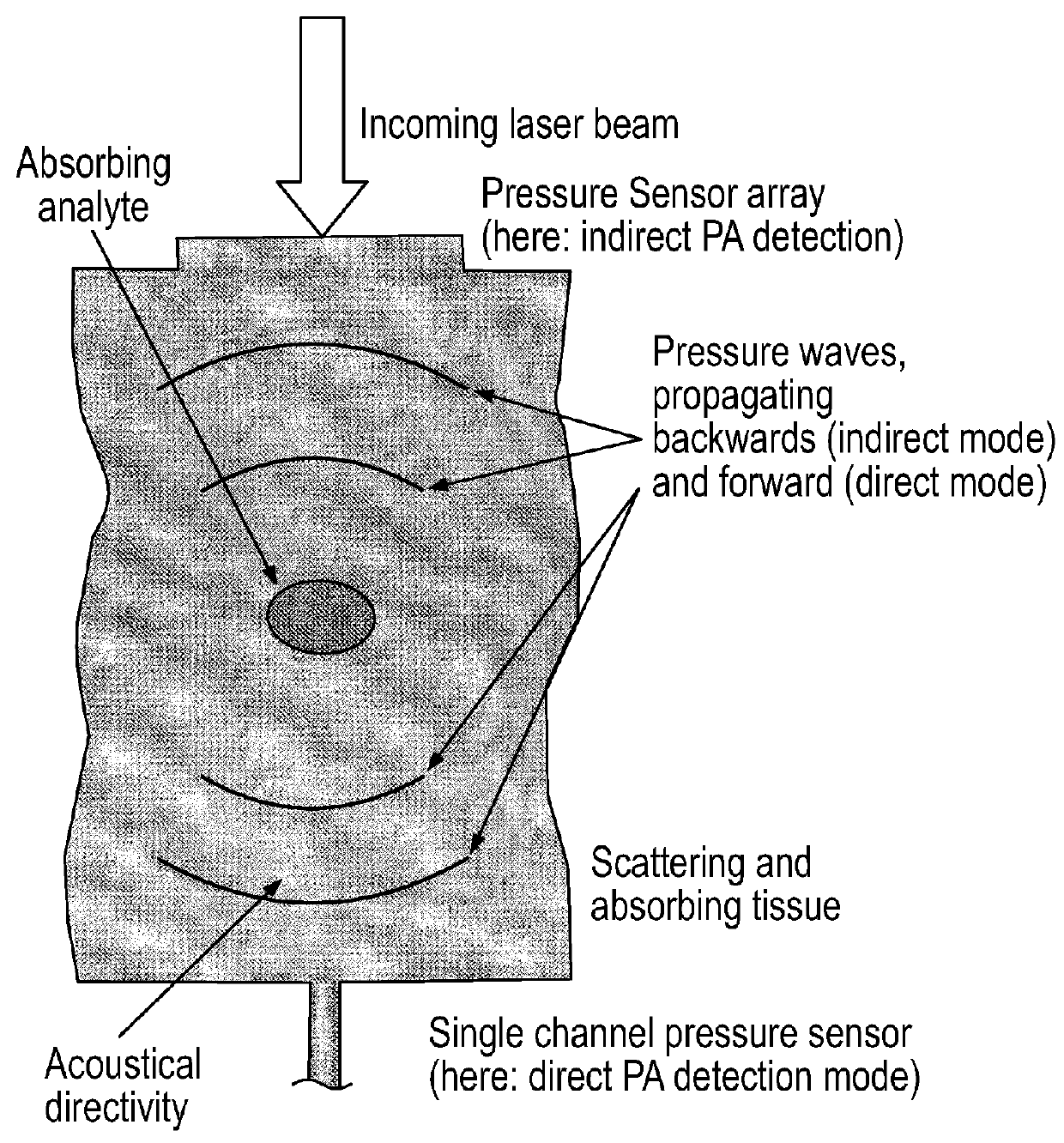
Emboli detection in the brain using a transcranial doppler photoacoustic device capable of vasculature and perfusion measurement
InactiveUS20140194740A1Rapid determinationQuick classificationBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionBrain vasculatureTriage
A device, method, and system for detecting emboli in the brain is disclosed. A transcranial Doppler photoacoustic device transmits a first energy to a region of interest at an internal site of a subject to produce an image and blood flow velocities of a region of interest by outputting an optical excitation energy to said region of interest and heating said region, causing a transient thermoelastic expansion and produce a wideband ultrasonic emission. Detectors receive the wideband ultrasonic emission and then generate an image of said region of interest from said wideband ultrasonic emission. A Doppler ultrasound signal will also be deployed to image the region of interest. Doppler presents changes in velocity to map blood flow. Additionally, a dye can be given to visualize the brain vasculature and a perfusion measurement can be made in various regions of the brain along with the transcranial Doppler and the photoacoustic screening. Systems are taught using resultory medical data for better triage within an enhanced stroke ecosystem.
Owner:CEREBROSONICS L L C
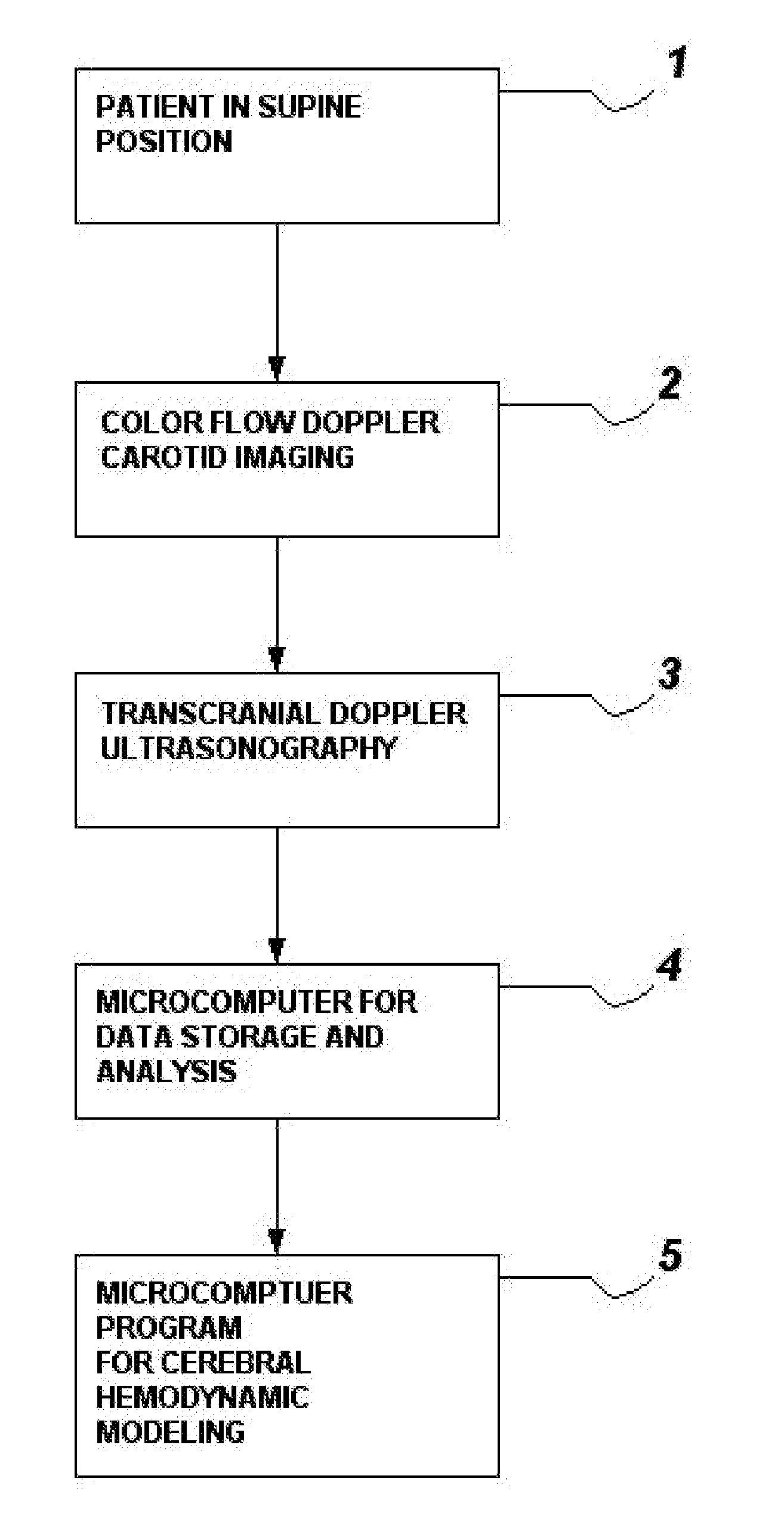
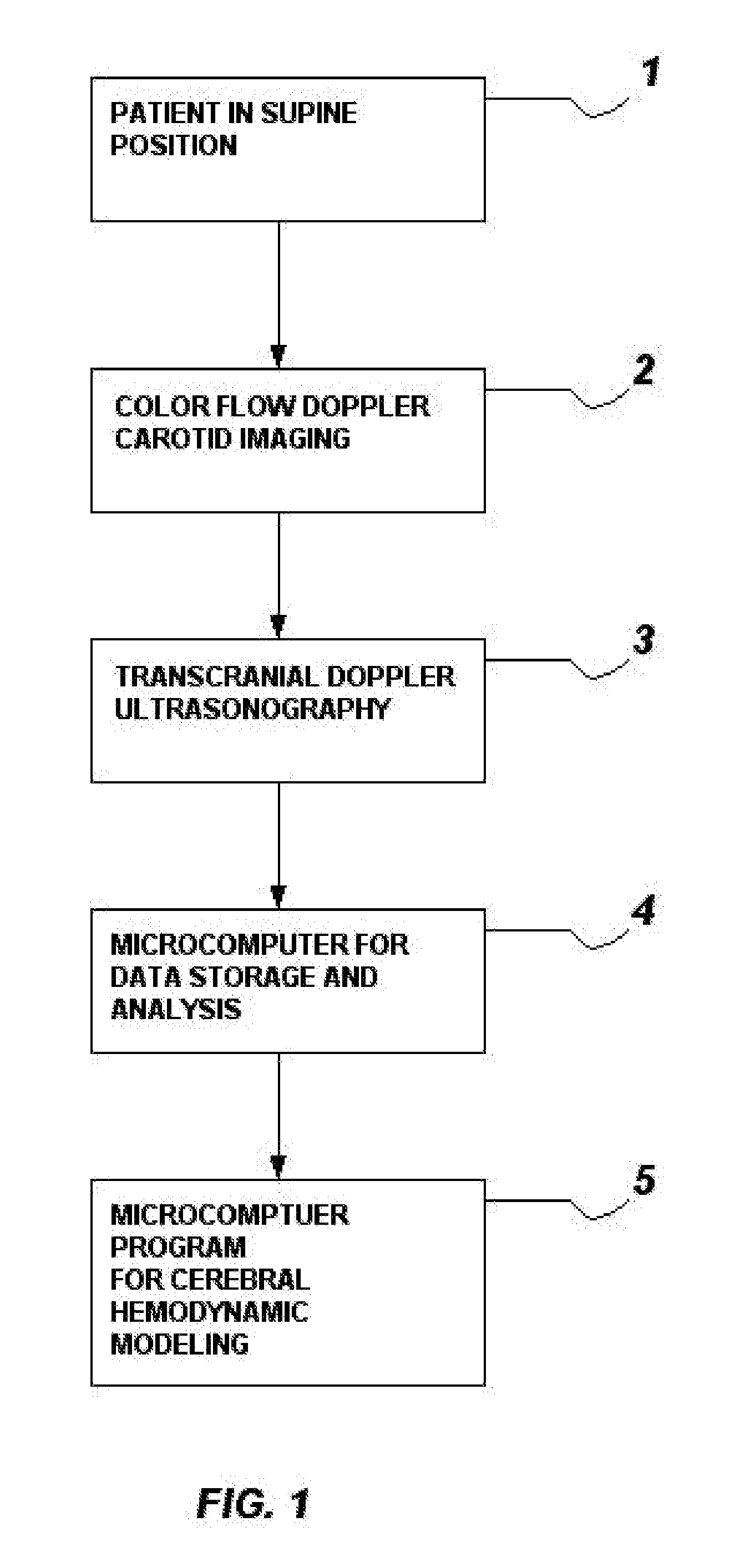
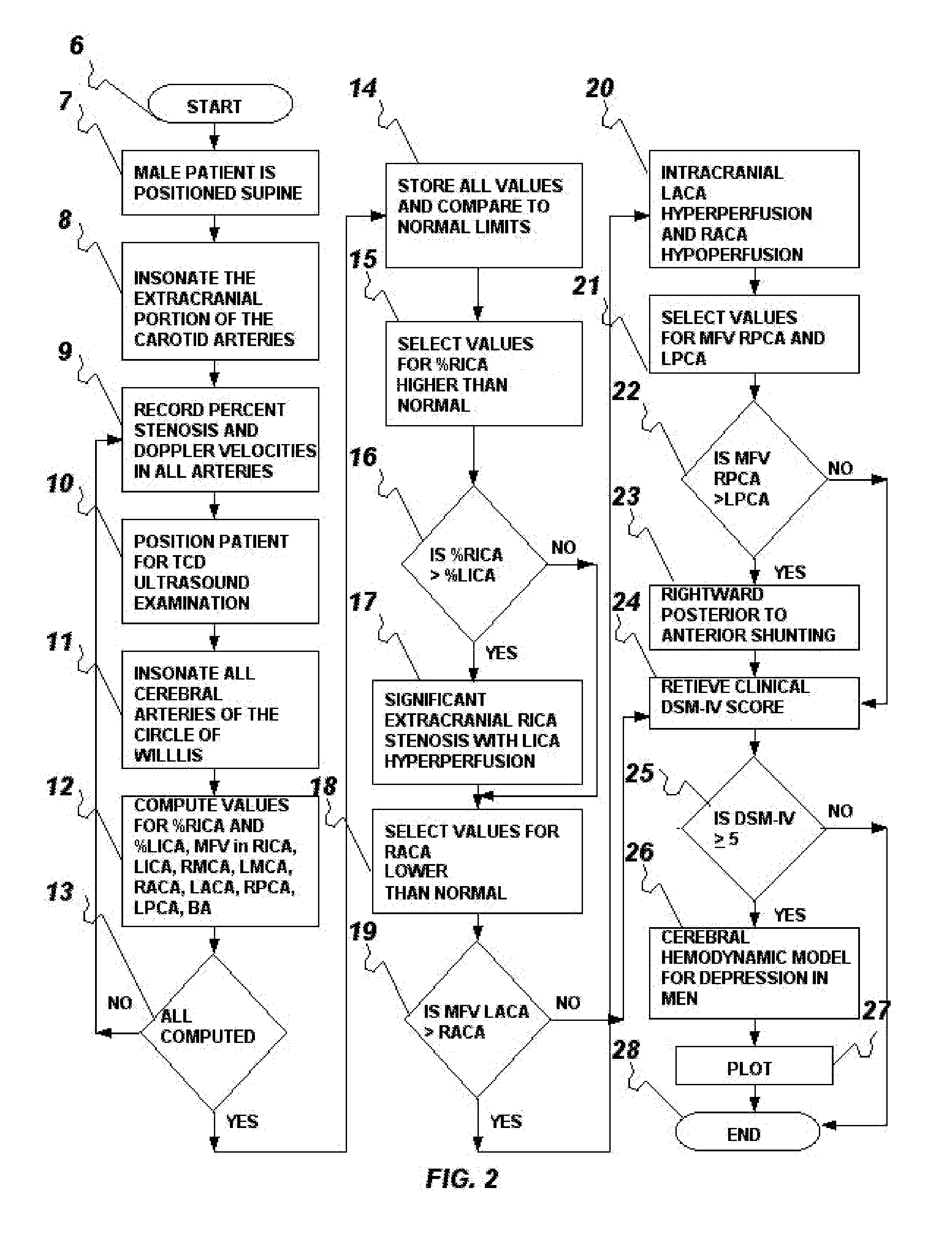
Method and system for evaluation of the hemodynamic model in depression for diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS20090054774A1Less computation timeLow costBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsLeft posterior cerebral arteryLeft posterior
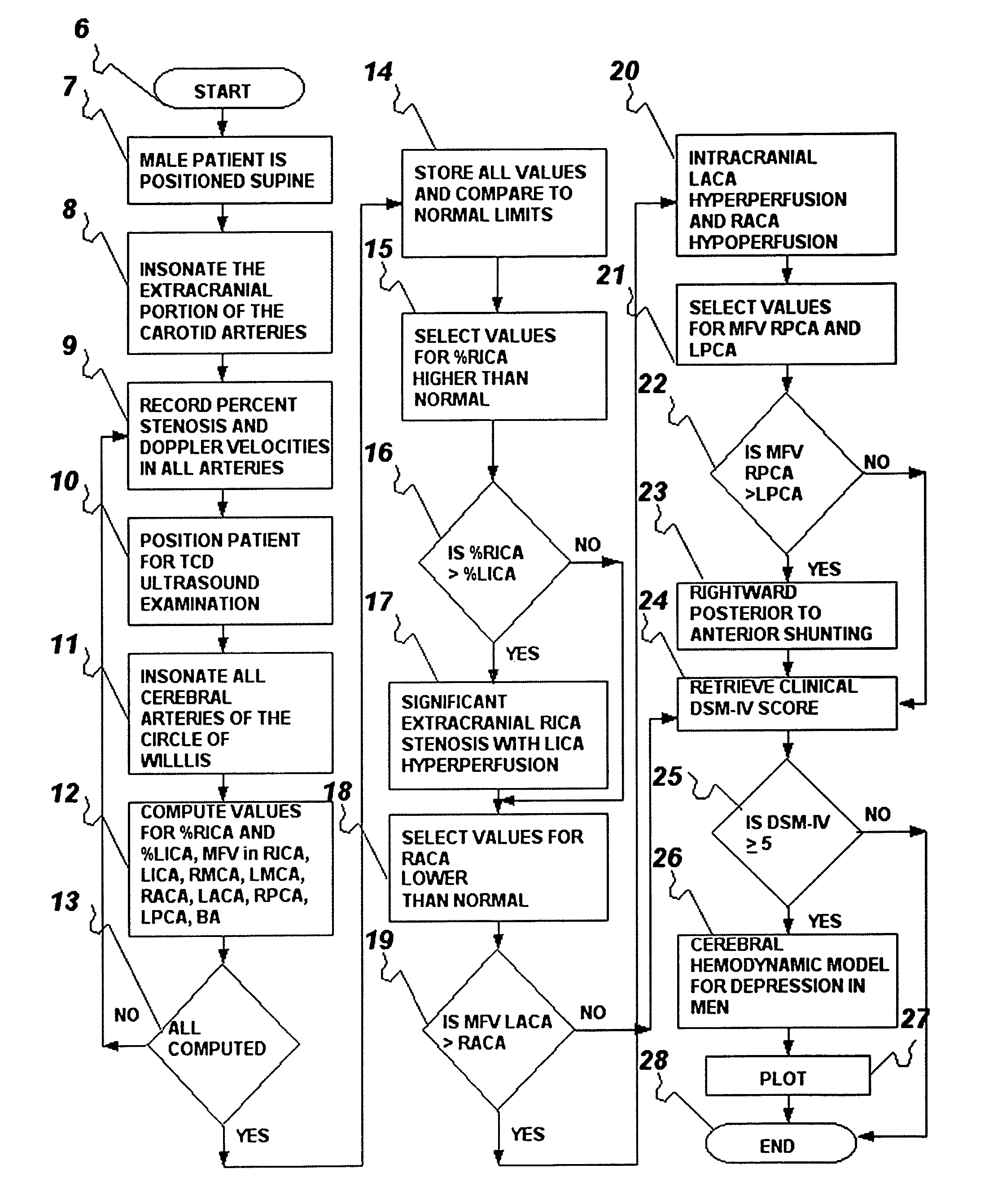
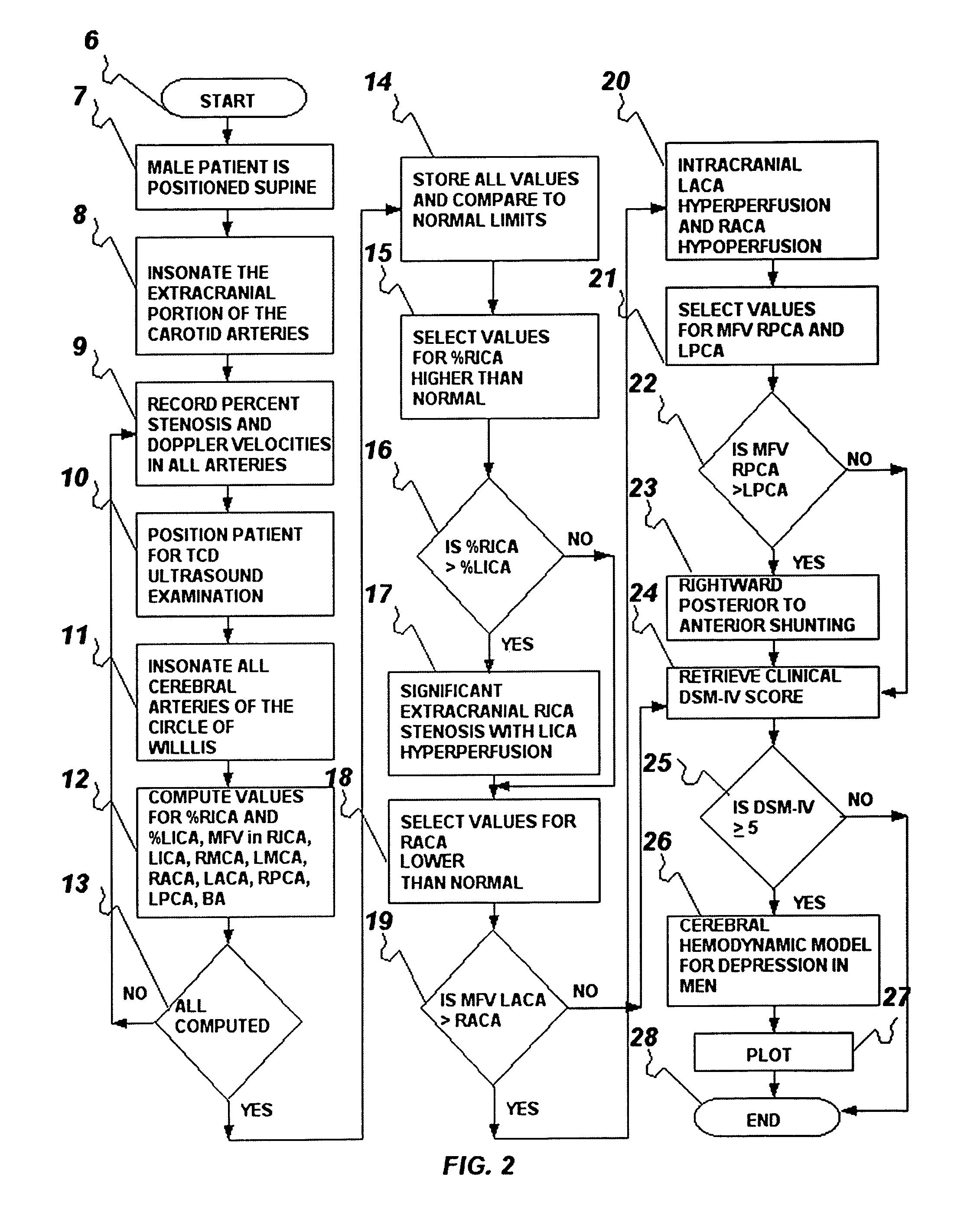
The present invention provides a method and system for determining the cerebral hemodynamic model for depression, using carotid duplex ultrasound to establish percent stenosis of the extracranial right and left internal carotid arteries and transcranial Doppler ultrasound instrument to measure mean flow velocity within the cerebral including the right and left internal carotid arteries, right and left middle cerebral arteries, right and left anterior cerebral arteries, right and left posterior cerebral arteries, and basilar artery. The percent carotid stenosis and the mean flow velocity values in cerebral arteries are used to determine the cerebral hemodynamic model associated with depression in men and women, respectively.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Ultrasound monitoring systems, methods and components
InactiveUS20110251489A1Convenient and stable positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsMonitoring systemEngineering
Ultrasound monitoring systems and components used in ultrasound monitoring systems, such as Transcranial Dopper (TCD) systems, are disclosed. Components include framework systems for mounting, locating and maintaining one or more ultrasound probes in contact with an anatomical surface, adjustable probe mounting systems, and probe interface components providing an acoustically transmissive interface between a probe mounting system and the emissive face of the ultrasound probe.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
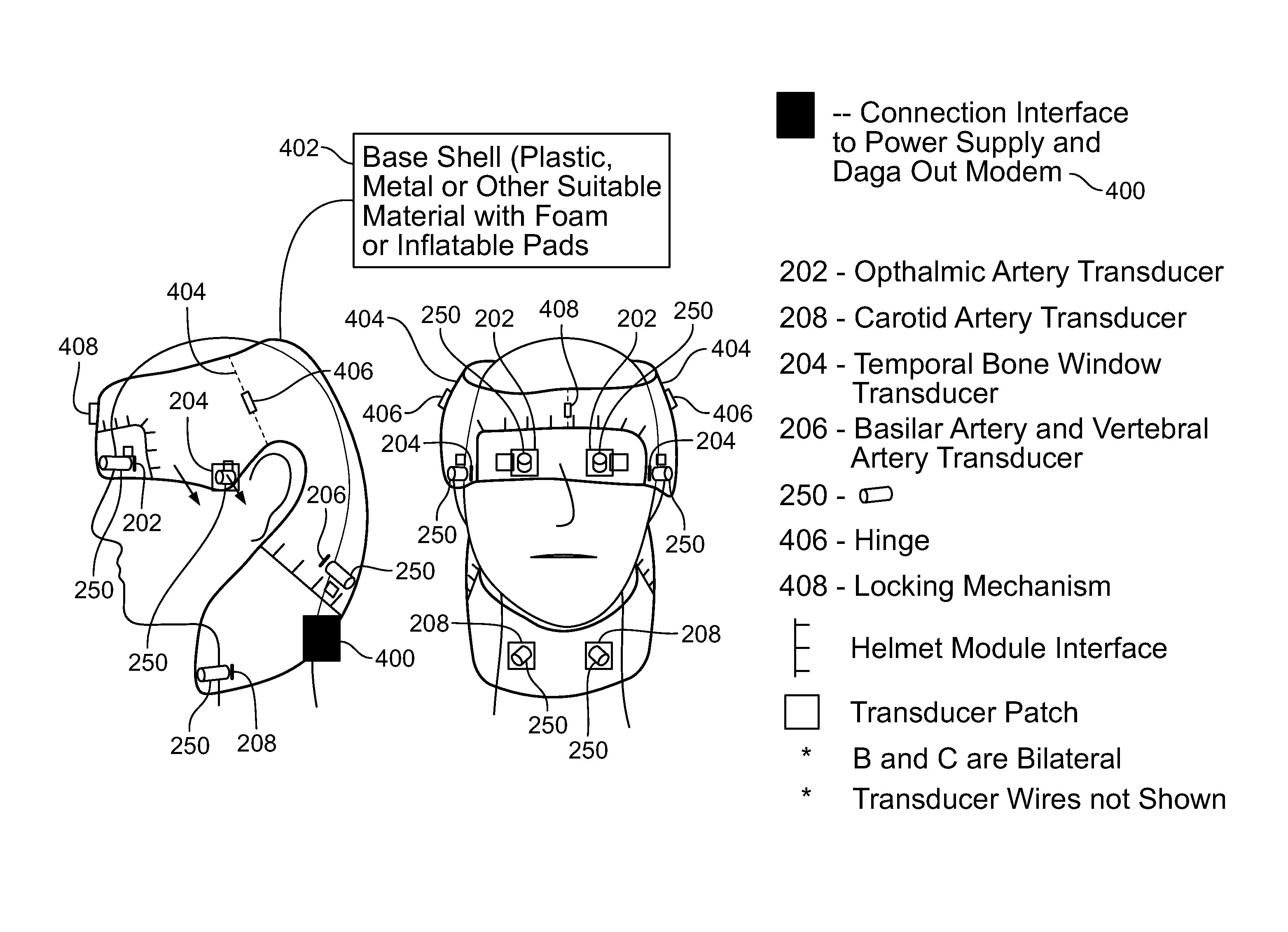
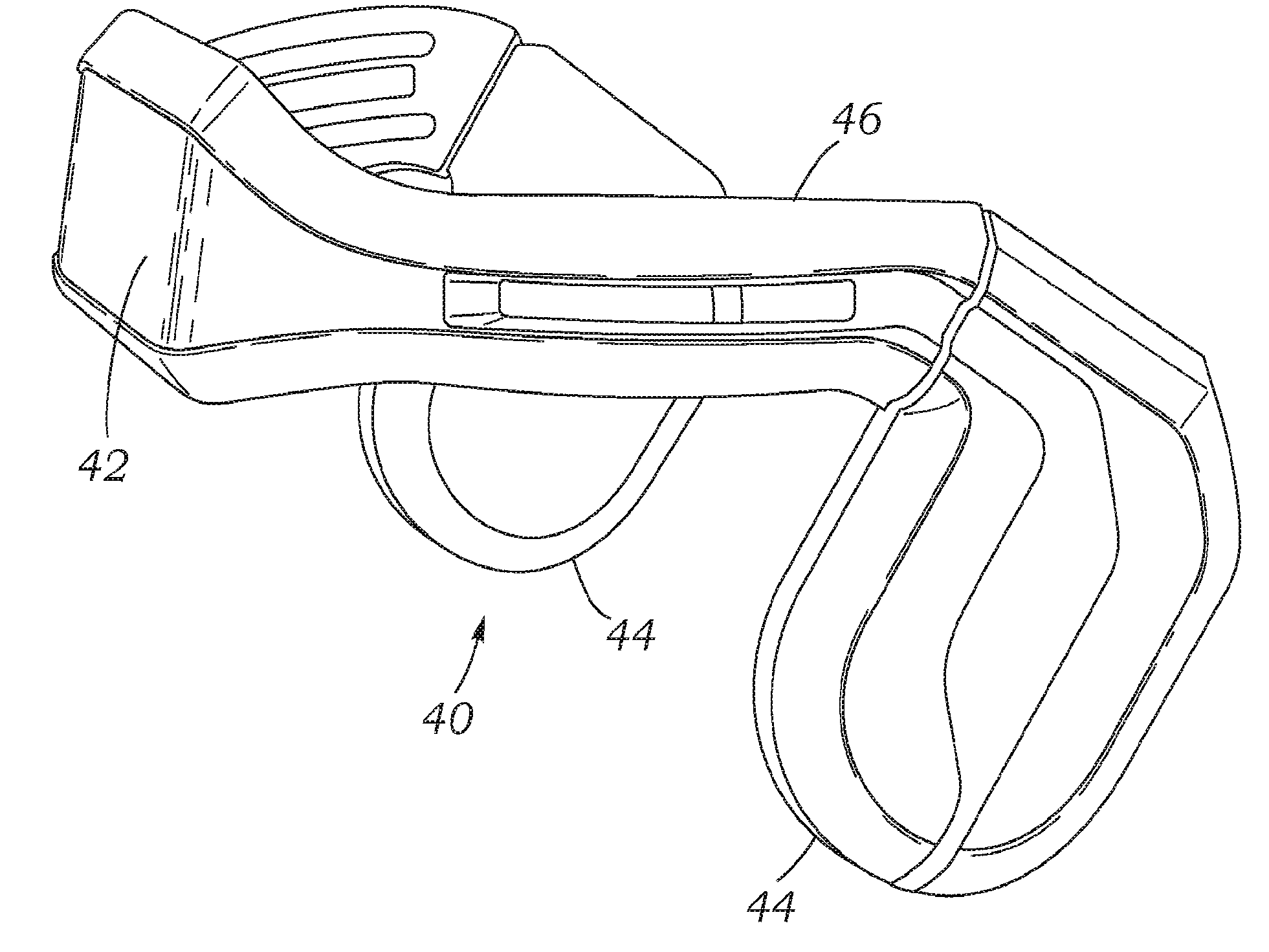
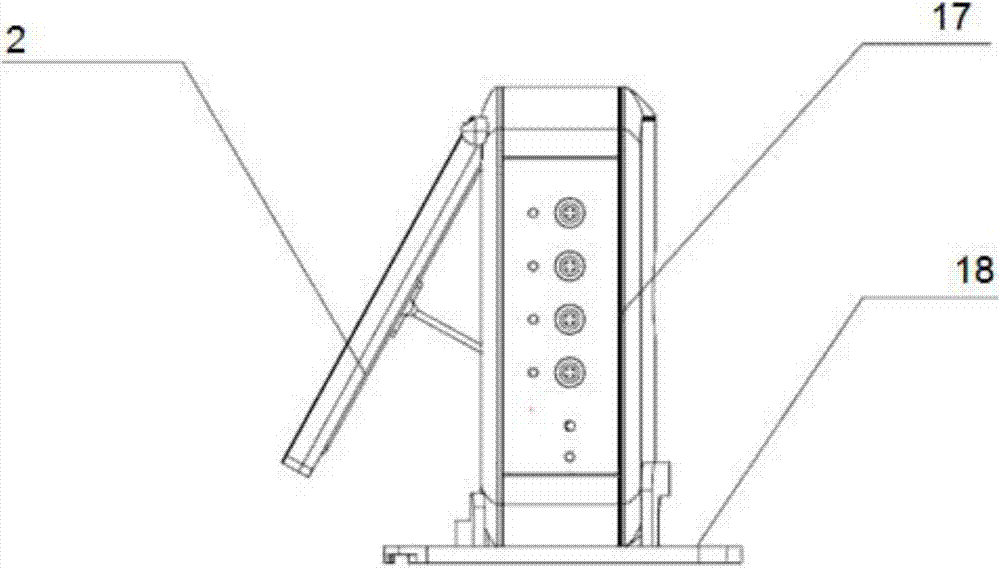
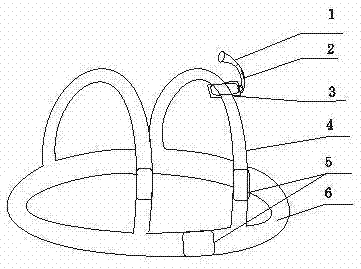
Helmet Apparatus and System with Carotid Collar Means On-Boarded
InactiveUS20160030001A1Quick cureSave brain cellMedical imagingHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSonificationEngineering
Apparatus for helmeting with carotid collars works in conjunction with a transcranial Doppler, phased array photoacoustic device to transmit a first energy to a region of interest at an internal site of a subject to produce an image and blood flow velocities of a region of interest by outputting an optical excitation energy to said region of interest and heating said region, causing a transient thermoelastic expansion and produce a wideband ultrasonic emission. Systems integrate and register the signals for use in, for example, acute stroke care.
Owner:STEIN STUART +1
Device and Methods for Targeting of Transcranial Ultrasound Neuromodulation by Automated Transcranial Doppler Imaging
InactiveUS20150151142A1Overcome deficienciesReduce amountSurgeryChiropractic devicesSonificationBlood vessel
Methods and systems for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation as well as targeting such neuromodulation in the brain are disclosed. Automated transcranial Doppler imaging (aTCD) of blood flow in the brain is performed and one or more 3-dimensional maps of the neurovasculature are generated. Ultrasound energy is delivered transcranially in conjunction to induce neuromodulation. One or more brain regions for neuromodulation are targeted by using brain blood vessel landmarks identified by aTCD components. The landmarks are used for initial targeting of the neuromodulation to one or more brain regions of interest and / or for maintaining neuromodulation targeting despite user or device movements. Acoustic contrast agents may be employed to generate broadband ultrasound waves locally at the site of target cells. Transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation may be achieved by having confocal ultrasound waves differing in acoustic frequency by a frequency effective for neuromodulation interfere to generate vibrational forces in the brain that induce neuromodulation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
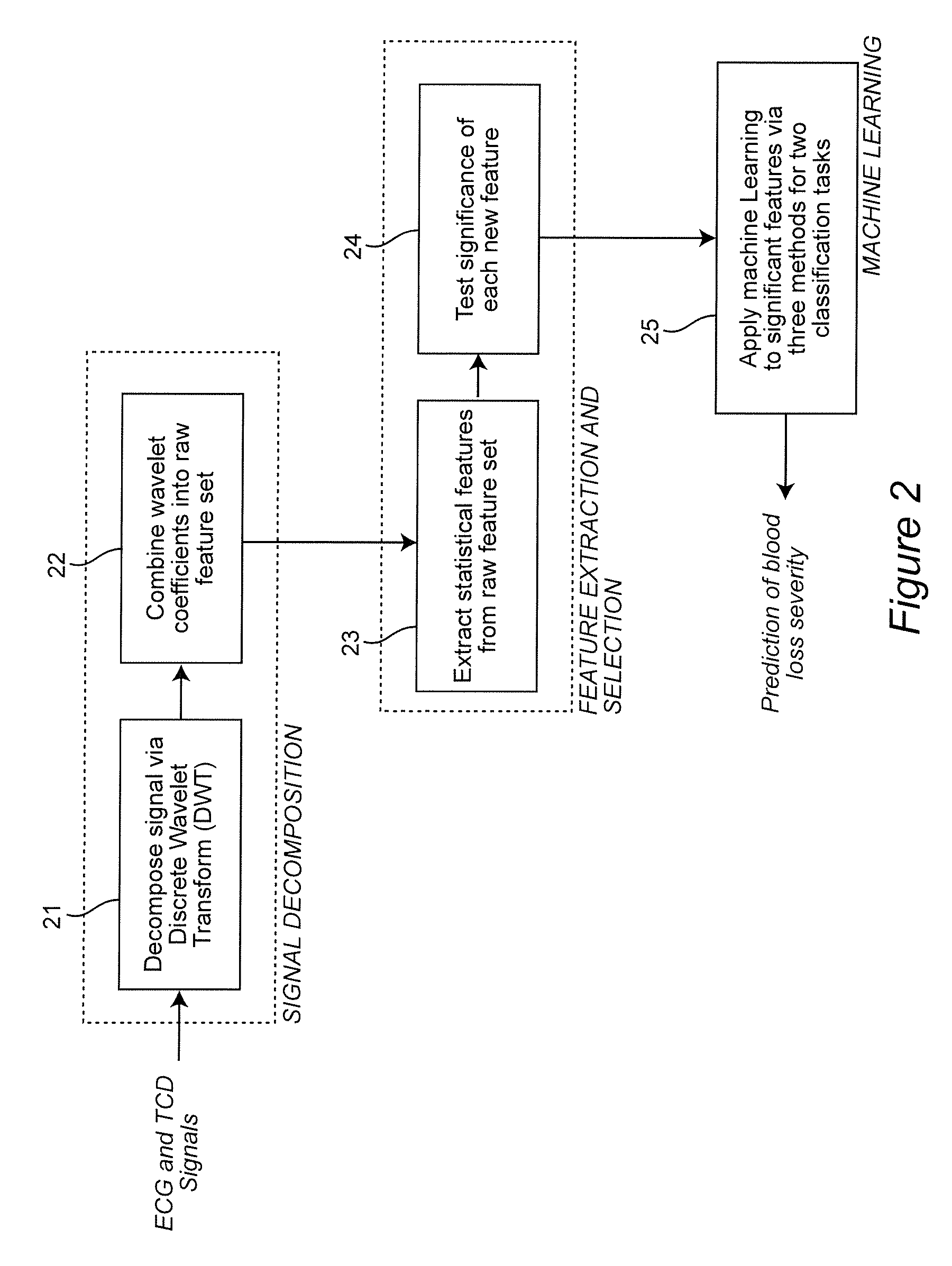
Combining predictive capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to predict hemorrhagic shock
InactiveUS8762308B2Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
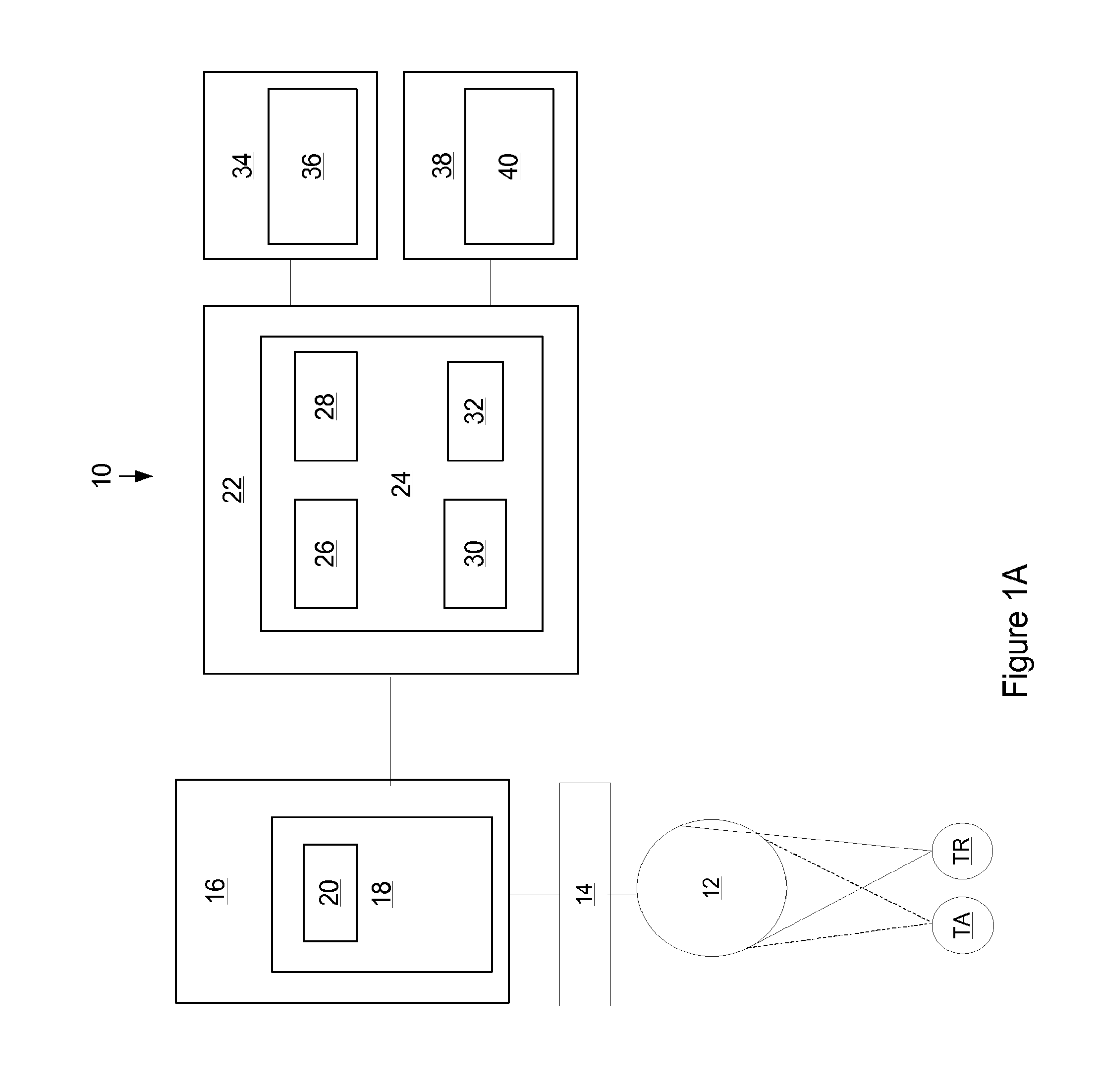
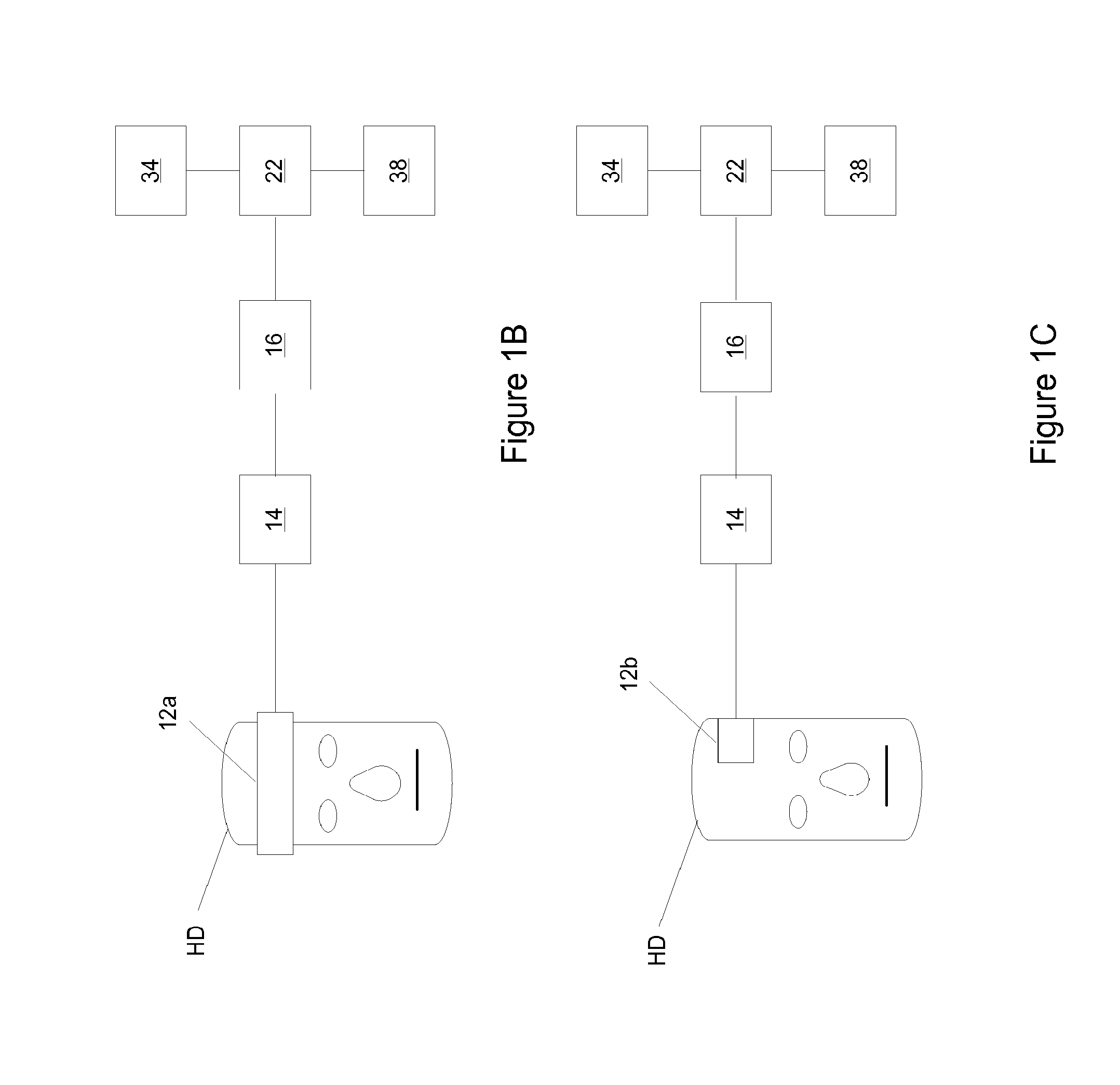
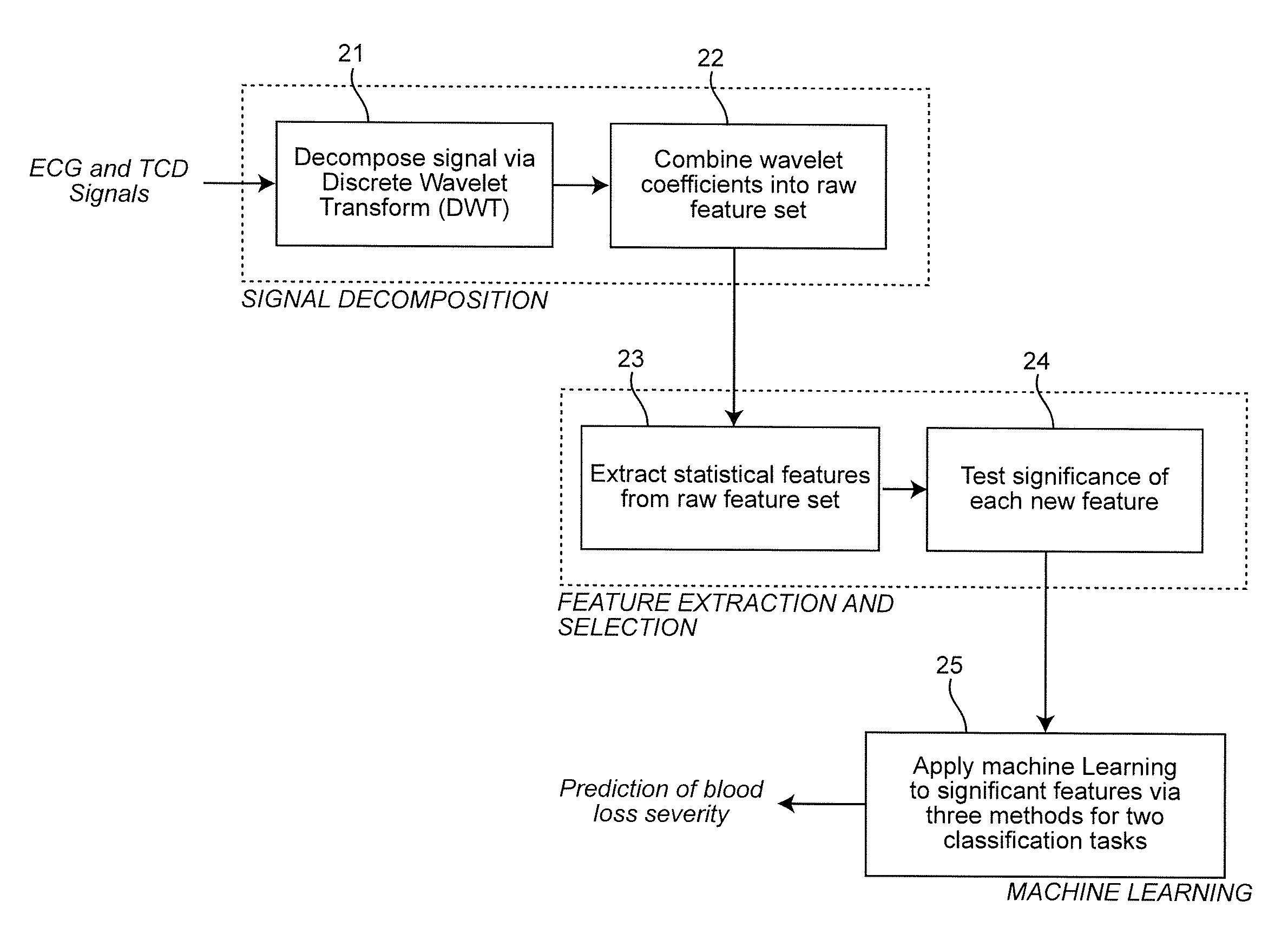
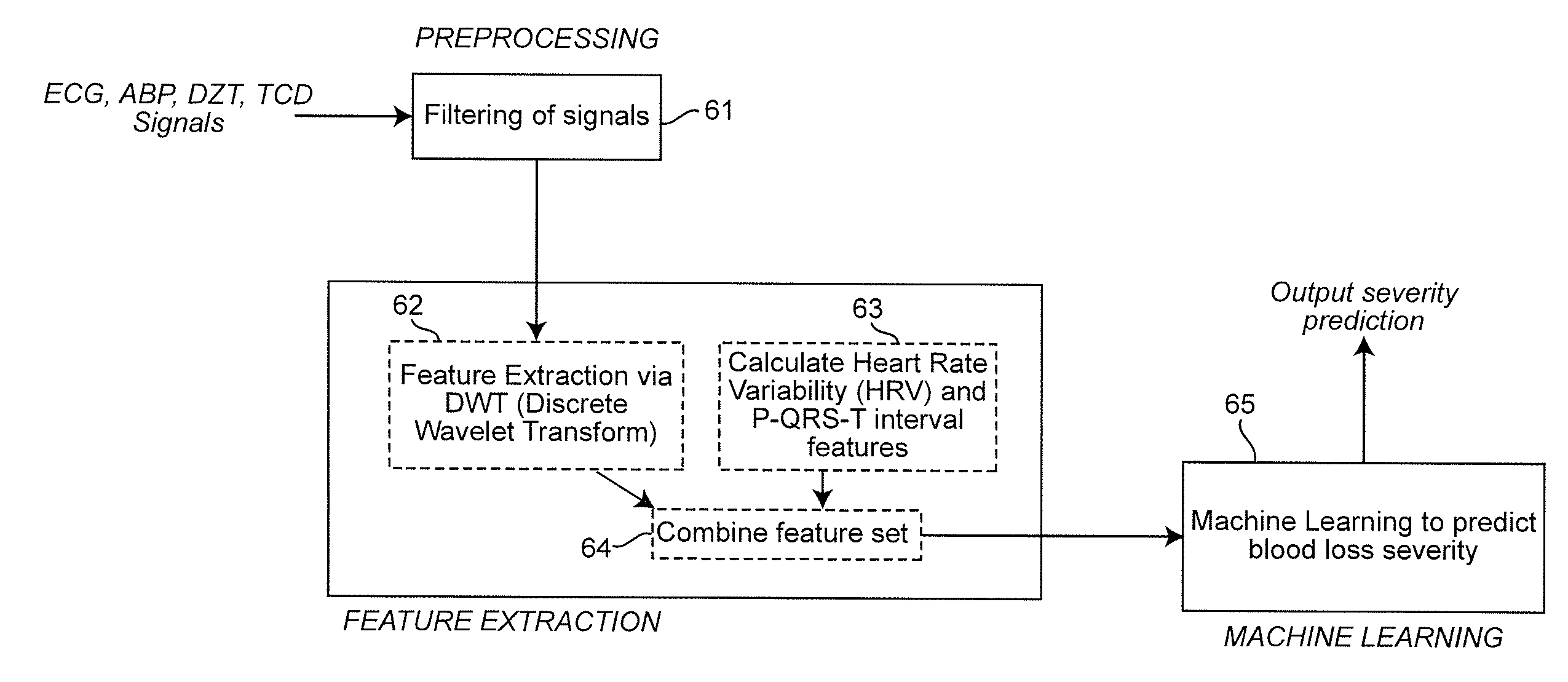
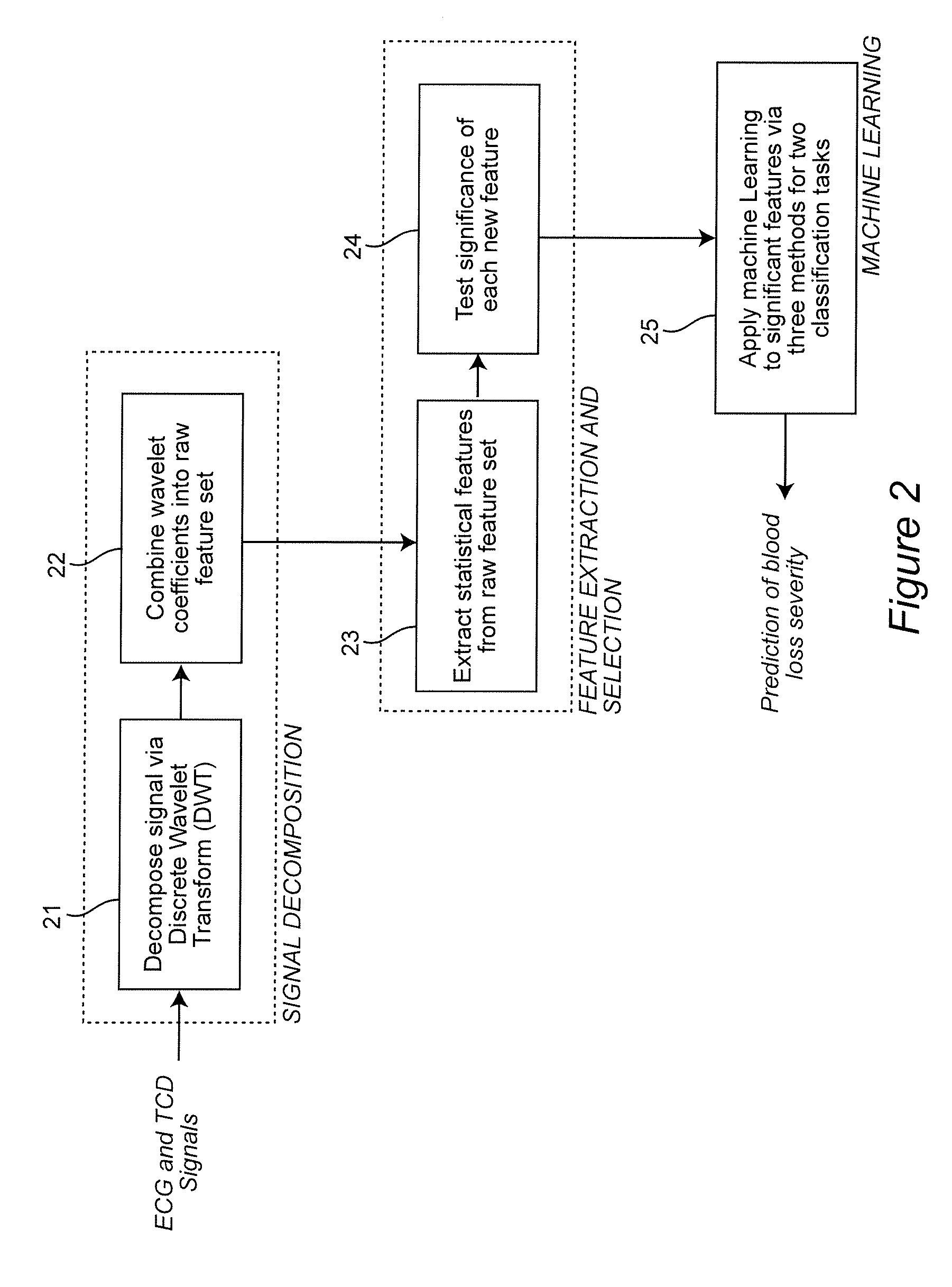
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
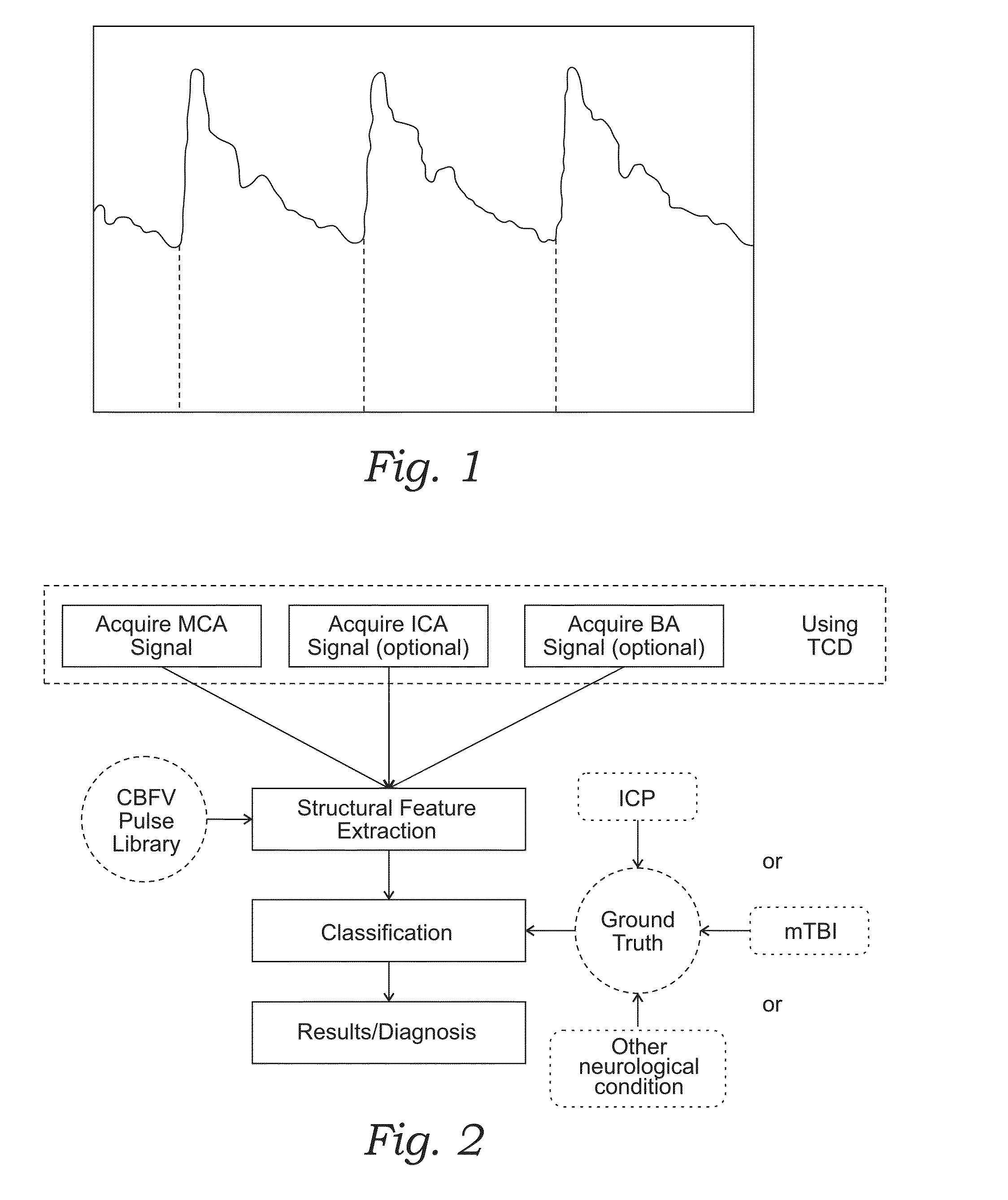
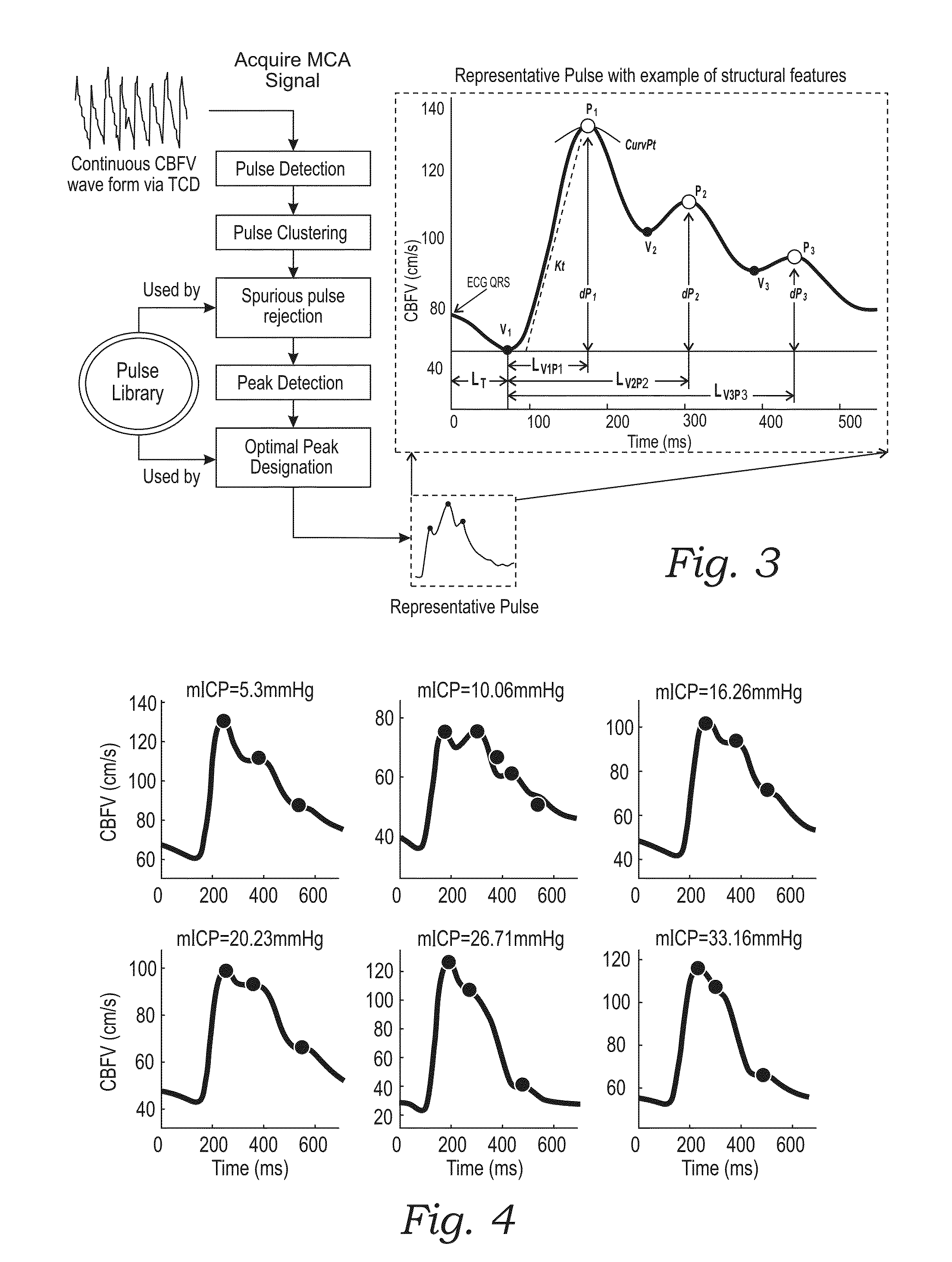
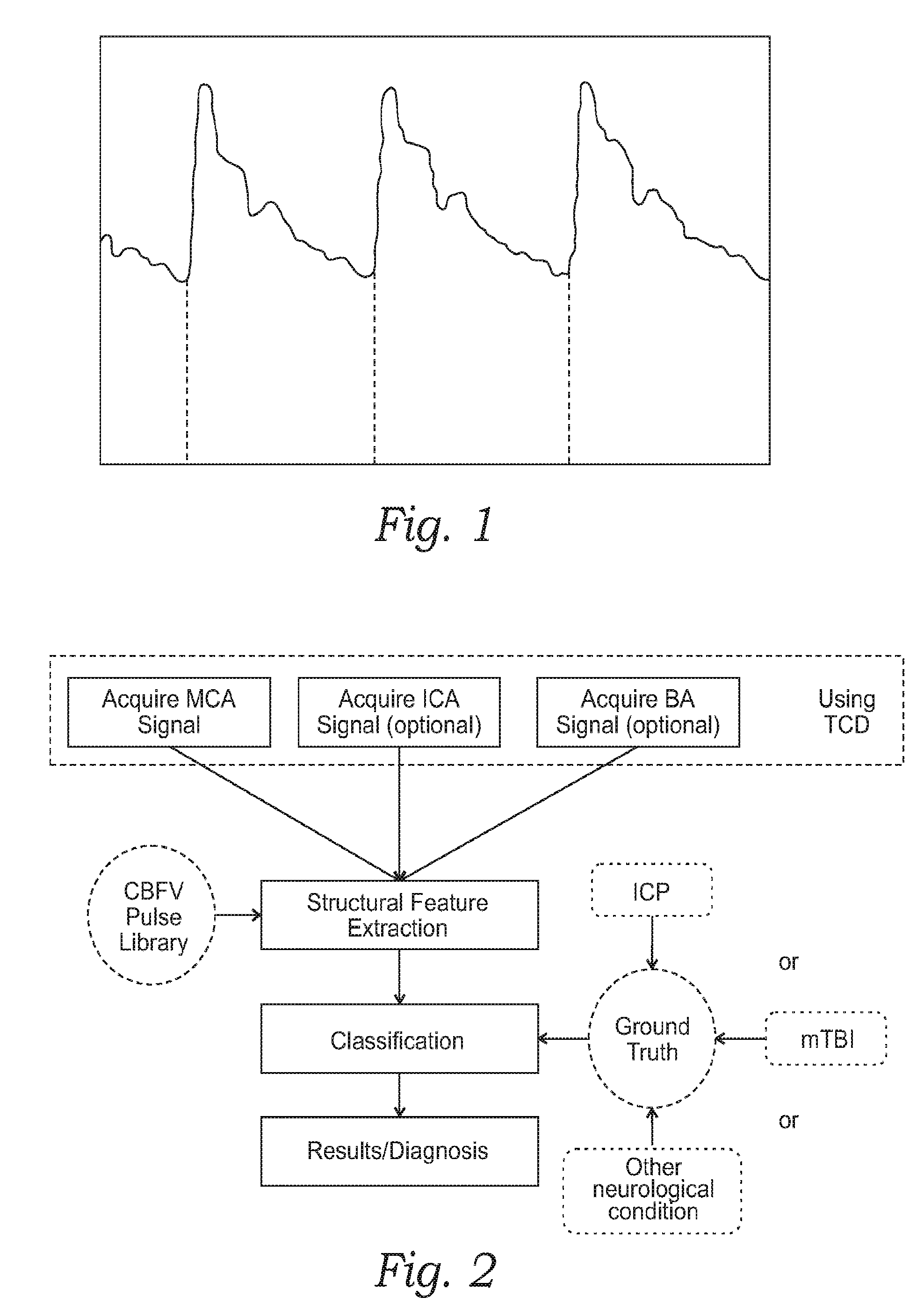
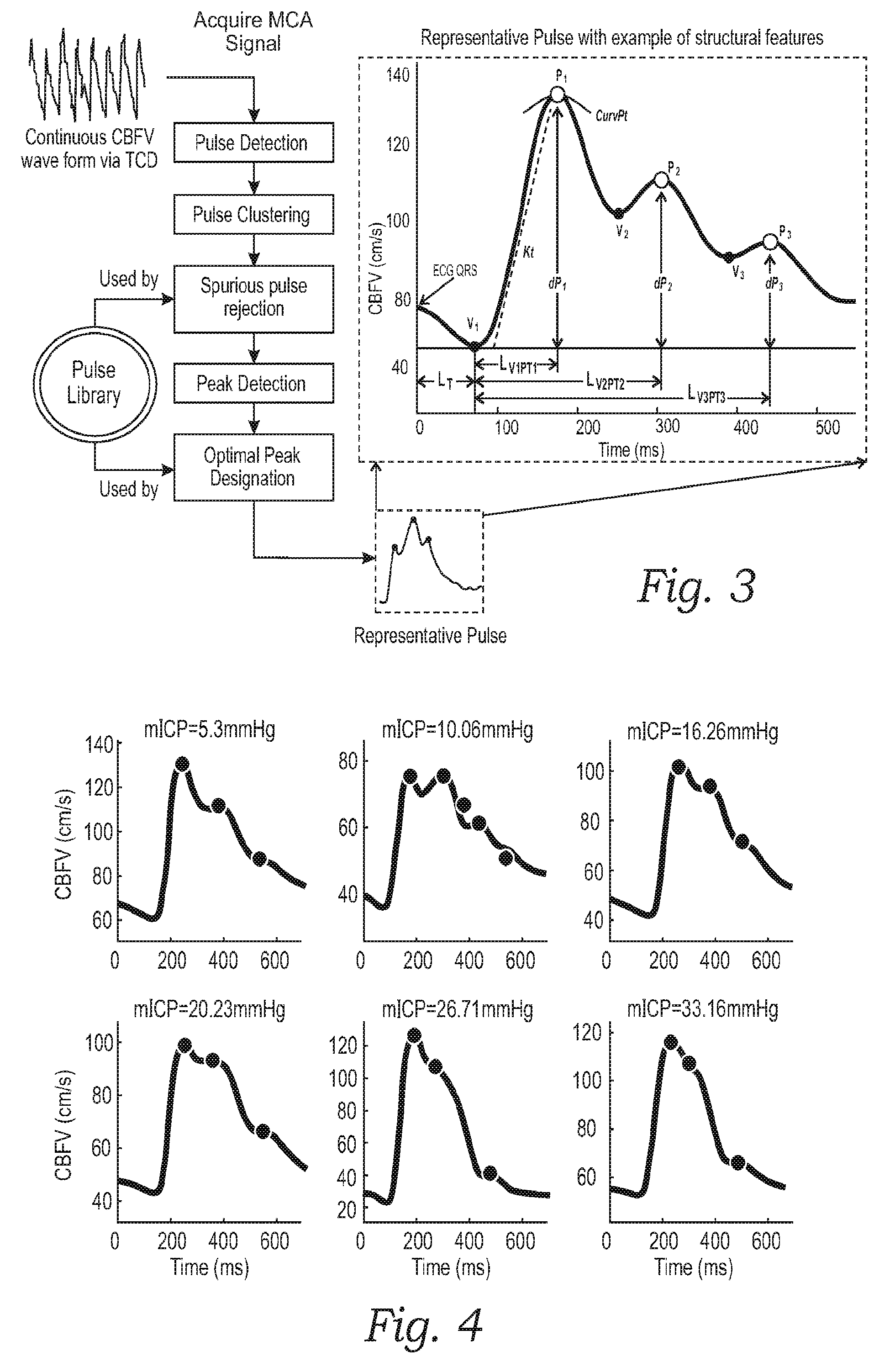
Monitoring structural features of cerebral blood flow velocity for diagnosis of neurological conditions
InactiveUS20160256130A1Improve reliabilityLow accuracyIntracranial pressure measurementTomographyDiseaseNervous system
The systems and methods described herein include a non-invasive diagnostic tool for intracranial hypertension (IH) detection and other neurological conditions like mild and moderate TBI that utilizes the transcranial Doppler (TCD) measurement of cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) in one or more cerebral vessels. A headset includes a TCD scanner which automatically locates various cerebral arteries and exerts an appropriate pressure on the head to acquire good CBFV signals.
Owner:NEURAL ANALYTICS INC
Monitoring structural features of cerebral blood flow velocity for diagnosis of neurological conditions
InactiveUS20160278736A1Quantitative precisionImprove accuracyMedical imagingSurgical instrument detailsDiseaseNervous system
The systems and methods described herein include a non-invasive diagnostic tool for intracranial hypertension (IH) detection and other neurological conditions like mild and moderate TBI that utilizes the transcranial Doppler (TCD) measurement of cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) in one or more cerebral vessels. A headset includes a TCD scanner which automatically locates various cerebral arteries and exerts an appropriate pressure on the head to acquire good CBFV signals.
Owner:NEURAL ANALYTICS
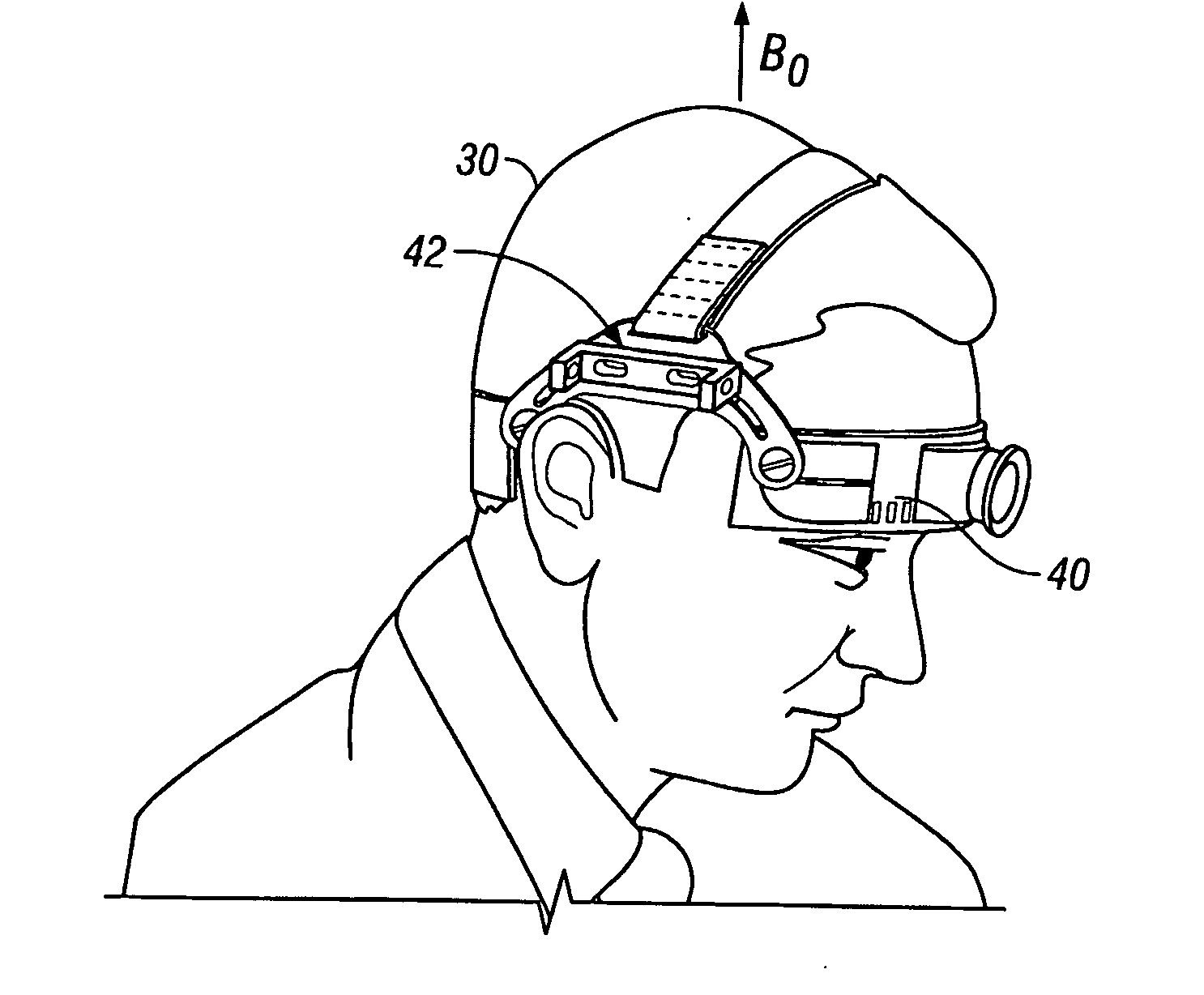
In vivo brain elasticity measurement by magnetic resonance elastography with vibrator coil
InactiveUS20070161891A1Altered mechanical propertyReduced patient functional outcomeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsMagnetic field gradientVoxel
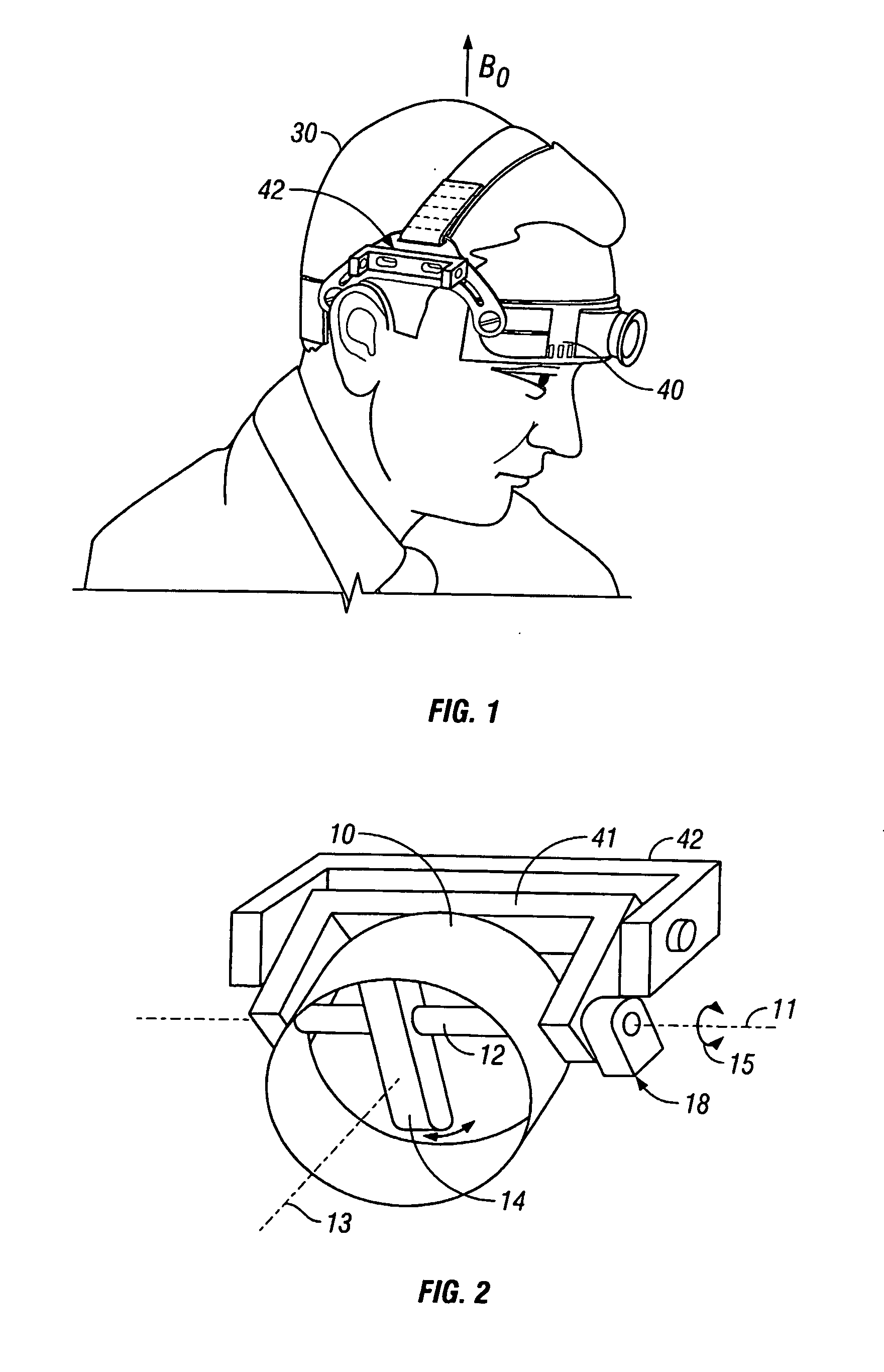
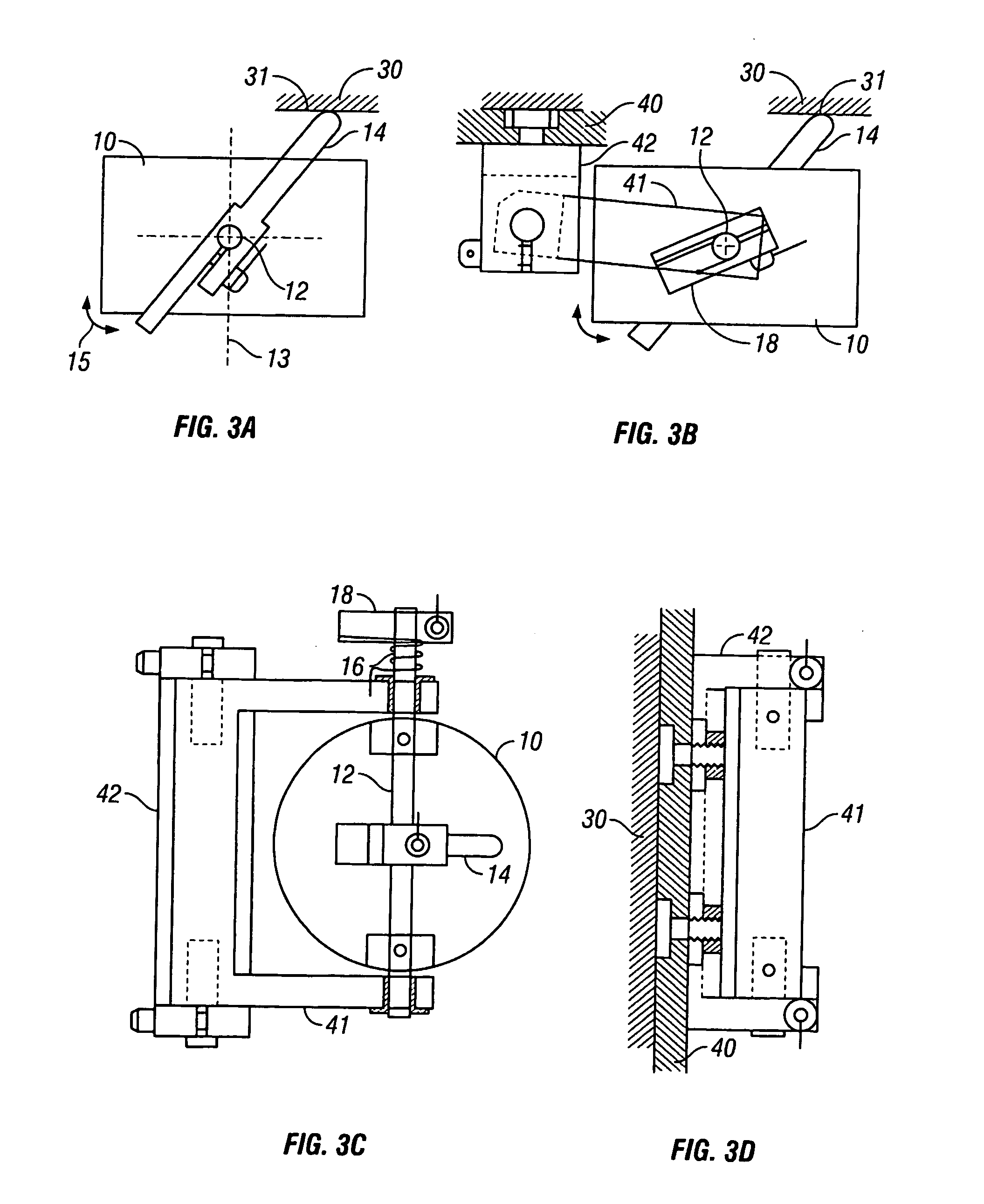
A vibrator coil (10) is applied to the skull (30) by adaptation of a commercially available transcranial Doppler monitoring harness (40) during MR applies mechanical waves in the acoustic waves through the skull to the brain. Utilizing magnetic resonance elastography (MRE), non-invasive estimation of tissue elastic properties in three dimensions occurs. The propagation of the acoustic waves through brain tissue, coupled to phase alteration of voxel isochromats in the presence of applies motion encoding magnetic field gradients allows measurements of brain elasticity.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF HEALTH & HUMAN
Transcranial Doppler plane annular phased array probe
InactiveCN103549977AReduce large differencesVariable apertureBlood flow measurement devicesTime delaysArray element
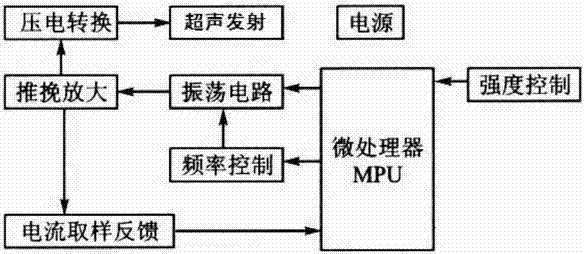
The invention provides a transcranial Doppler plane annular phased array probe, which comprises a piezoelectric vibrator, a metal shielding casing, an electronic tuning circuit, a coaxial cable, a case, a back lining, a matching layer and an acoustic lens, wherein the piezoelectric vibrator comprises more than one array element ring in annular distribution to form concentric circles, each array element ring adopts independent lead wire control, the areas of all array elements are identical, in addition, the path differences of all array elements are identical, each independent array element is excited by adopting specific time delay, and the dynamic focusing in the spreading direction of ultrasonic beams can be achieved. The plane annular phased array is utilized, each array element is respectively subjected to time delay during the emitting or receiving, and the emitting focusing or the receiving focusing is realized, so focal points can be continuously adjusted, the ultrasonic beams can be effectively and controllably narrowed, the depth of field is long, the transcranial Doppler plane annular phased array probe has the advantages of variable aperture, variable focal point, variable trace and the like, the lateral resolution ratio of a system can be comprehensively improved, and the signal to noise ratio is effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
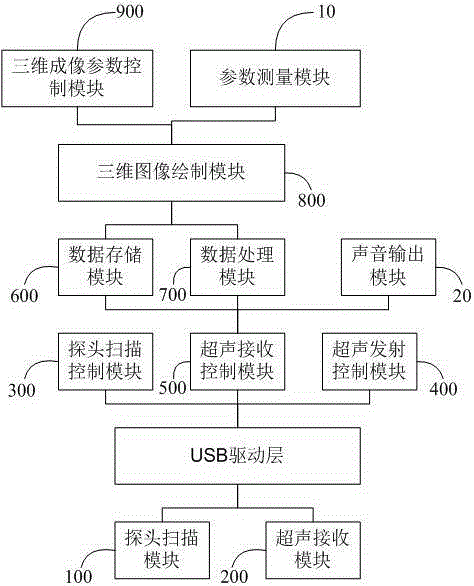
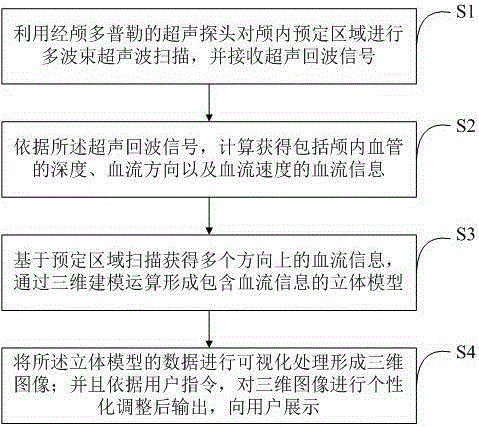
Transcranial Doppler intracranial blood flow three dimensional information display method and system
InactiveCN105232086AEasy diagnosisReduce dependencyBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsPersonalizationSonification
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Cerebral blood flow regulation function monitor system and method for detecting cerebral circulation critical closing pressure
ActiveCN1883383ARealize automatic adjustment functionEliminate the pitfalls of artificial gradingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCollection systemEngineering
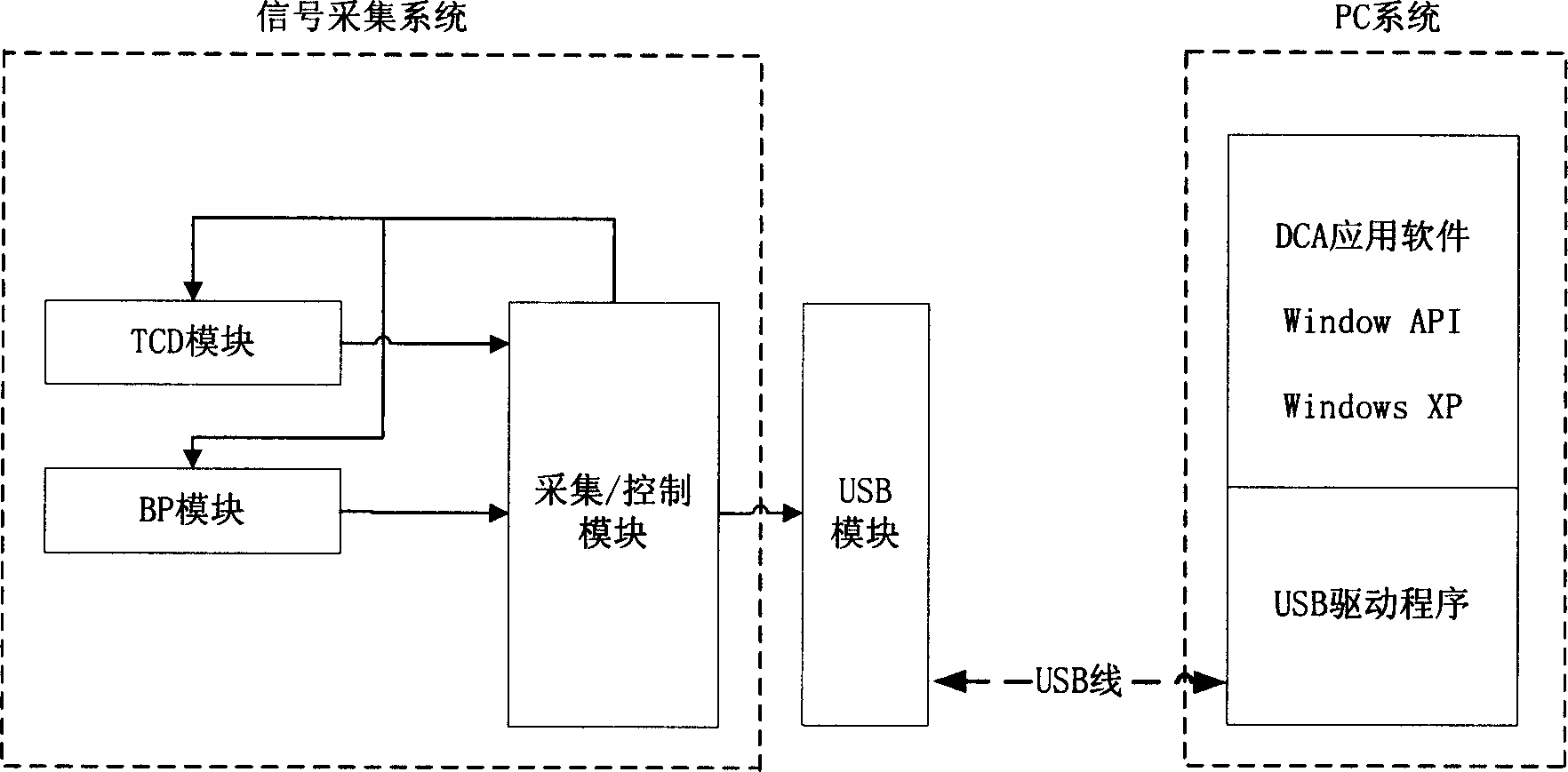
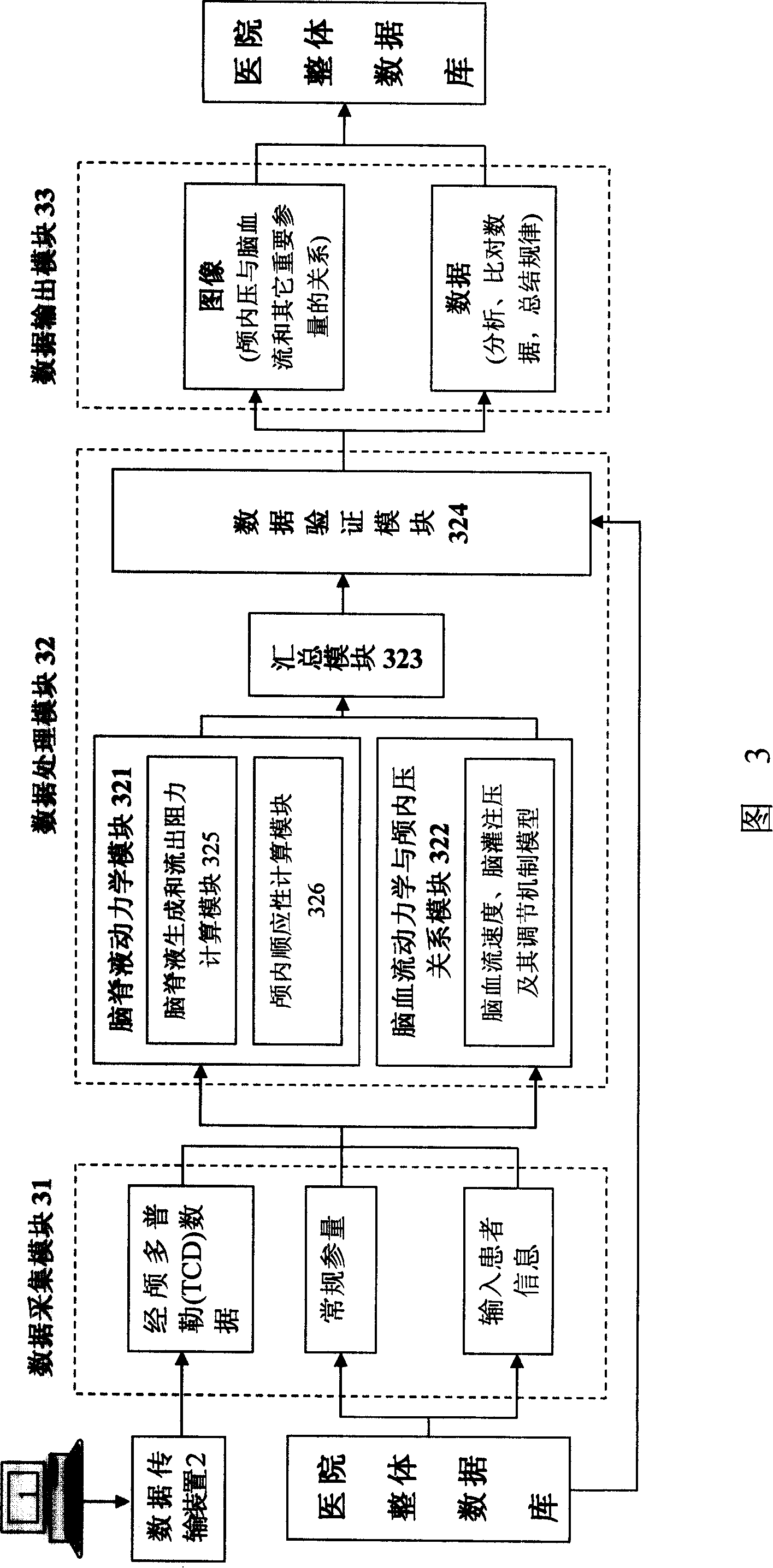
A cerebrovascular regulation function monitor system and a method for detection of cerebrovascular circulation critical closing pressure, wherein the cerebrovascular regulation function monitor system includes a signal collection system for in-phase sampling analog signal of transcranial doppler (TCD) signal and continuous artery pressure signal and further converting the analog signals into correspondent digital signals and a signal processing / displaying system connected with the signal collection system via interfaces for processing the digital signals to obtain the cerebrovascular critical closing signal and displaying them. The method and system realize a non-invasion detection and monitor of cerebrovascular autoregulation function in clinical practice.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD +1
Noninvasive intracranial pressure monitoring equipment
ActiveCN101224108AAccurately judge the prognosisAccurate diagnosis of brain deathUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringData acquisitionNon invasive
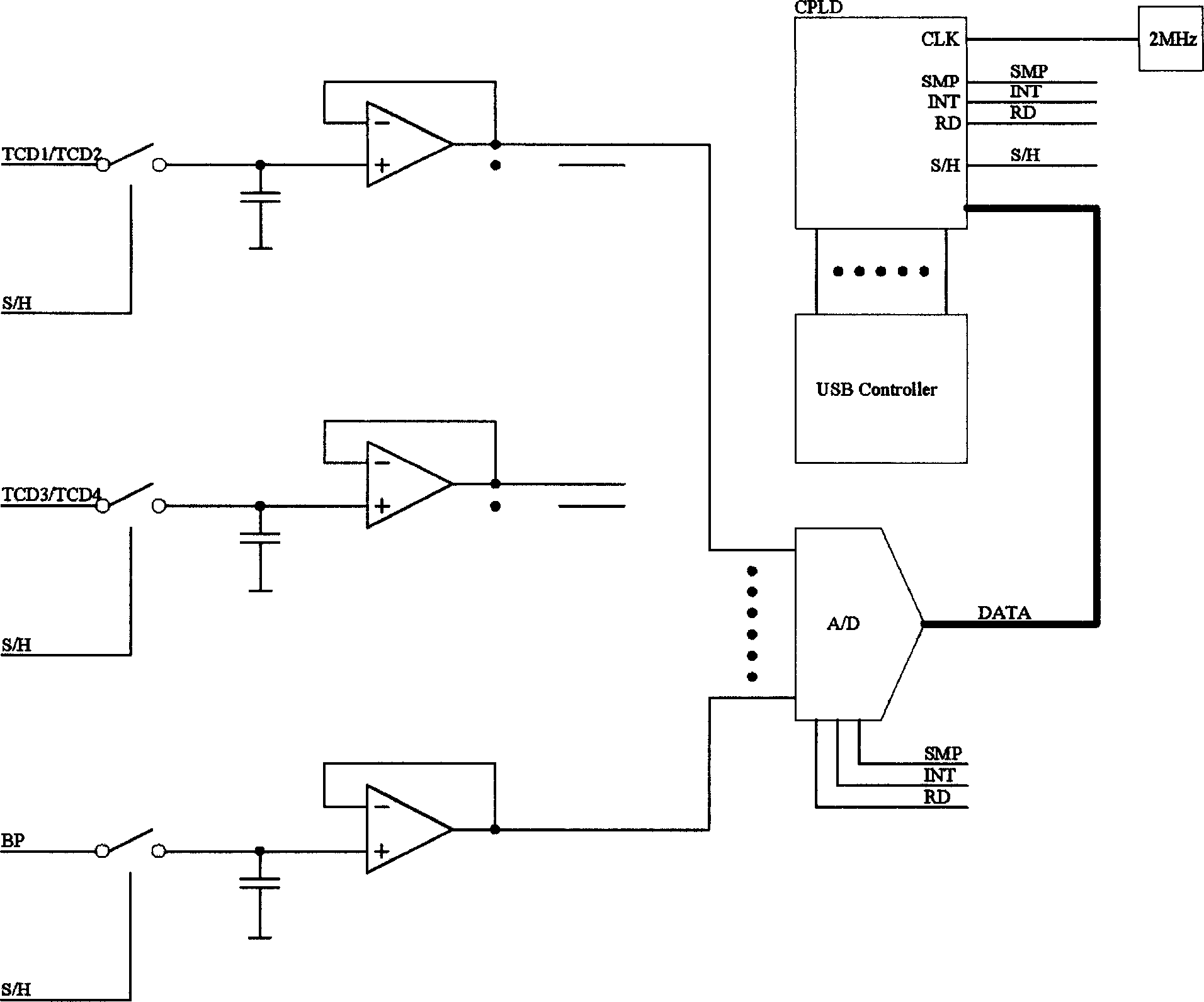
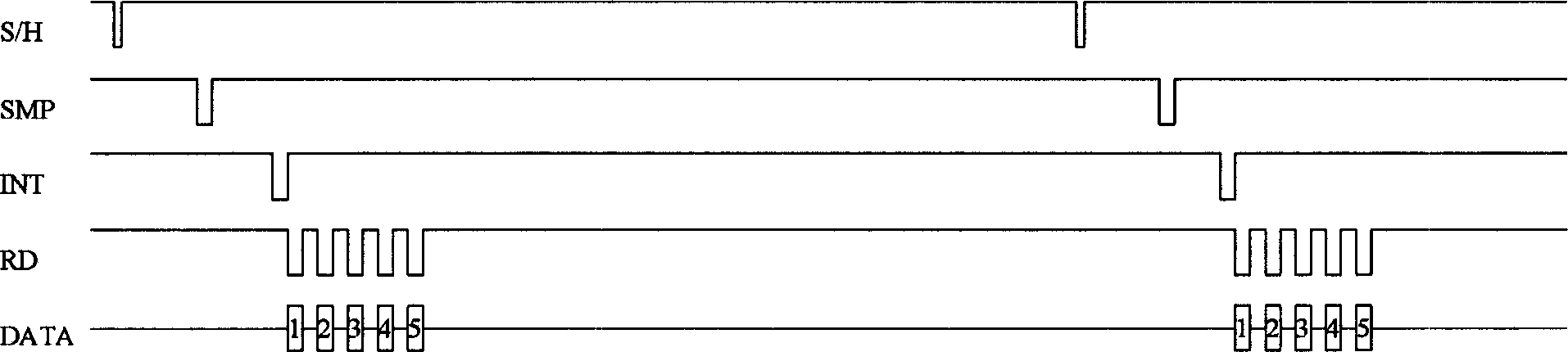
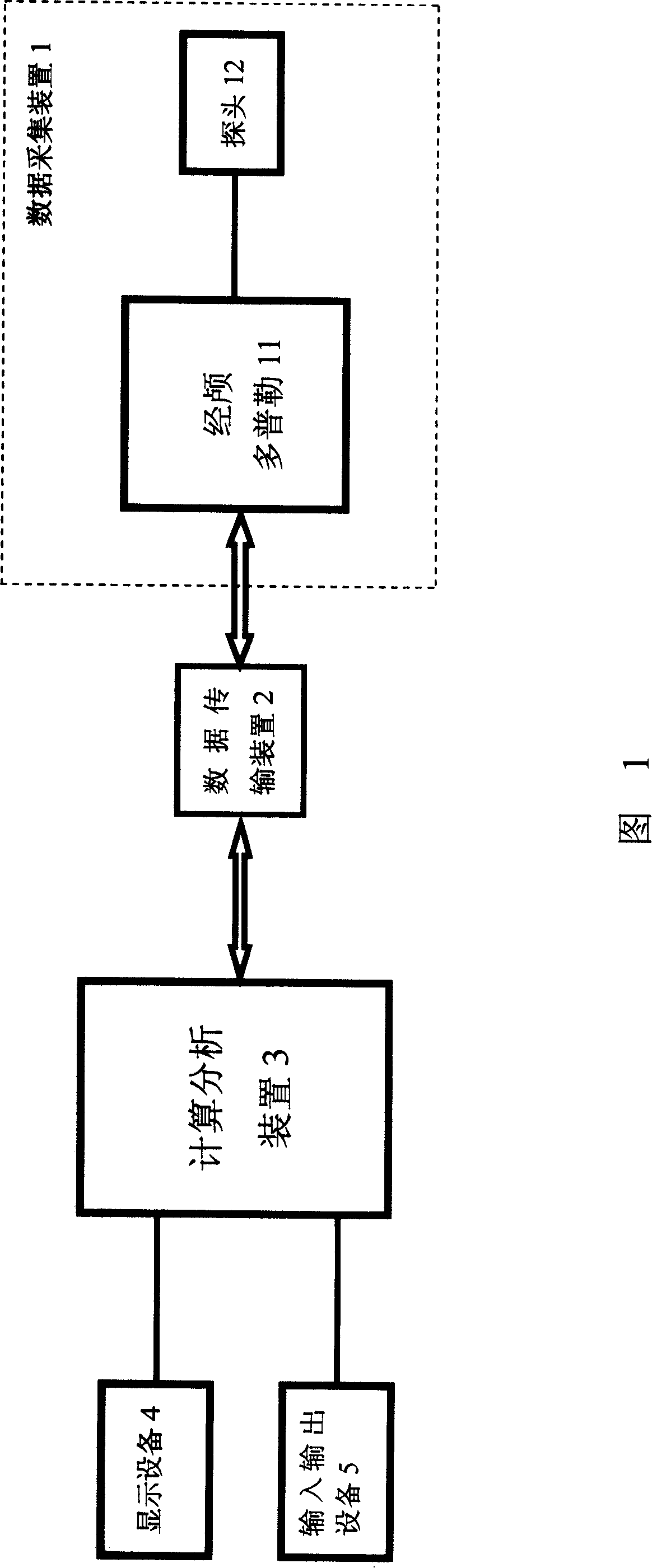
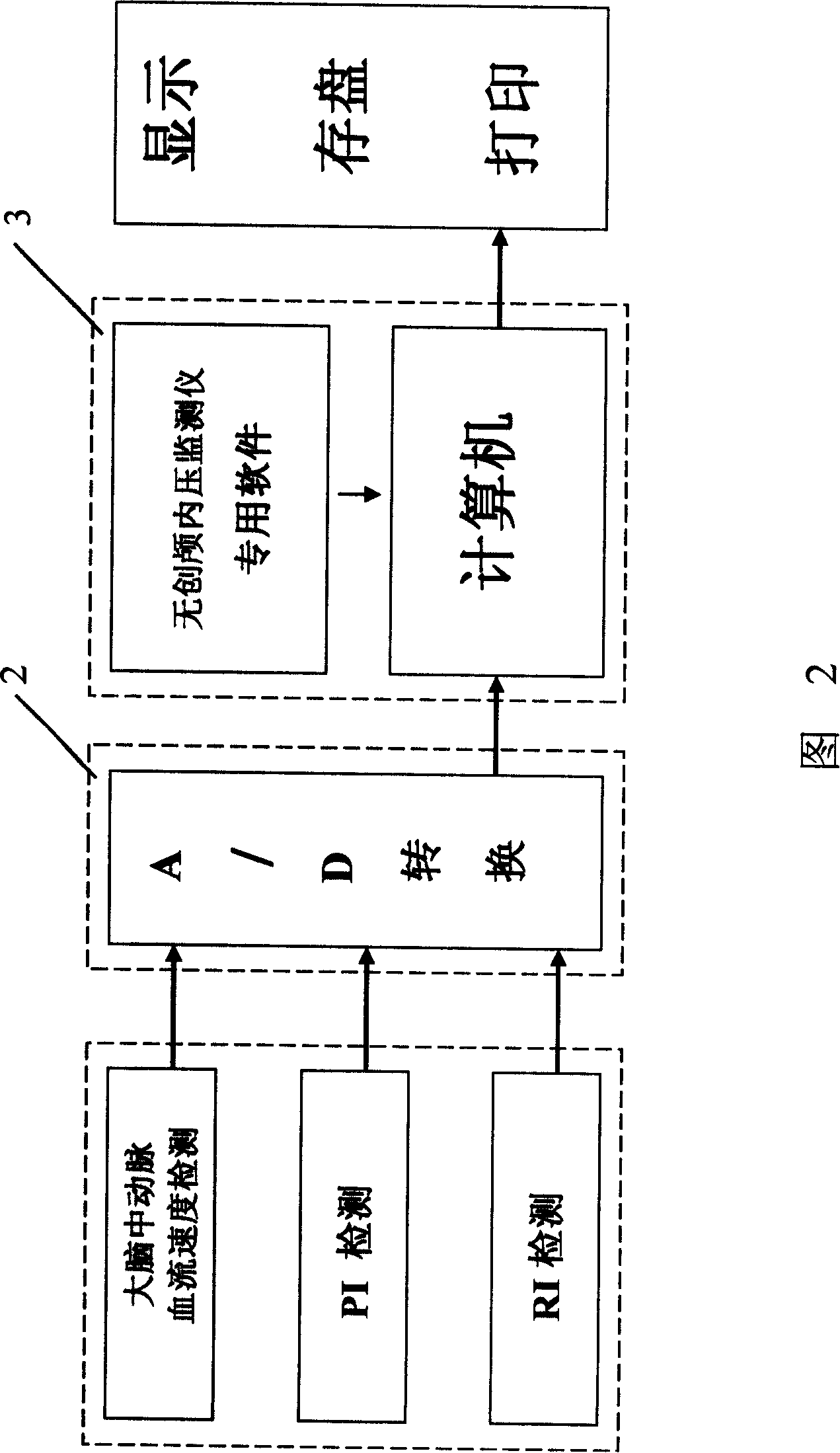
The invention relates to a non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring equipment, which comprises: a data collection device, which is a transcranial Doppler instrument; a data transmission device, which is used for converting the analog signal of the data collection device to the digital signal; a calculation and analysis device, which is a computer with a data analysis software, the calculation and analysis device receives the output signal of the data transmission device and can call the data in a database by a network; a display equipment, which is used for displaying the analysis results of the calculation and analysis device; an input-output equipment, which is used for the input of the operation command and the output of the analysis results of the calculation and analysis device. The invention can realize the long-term continuous detection, which not only has a convenient detection way, but also has reliable conclusions and high measurement accuracy.
Owner:百睦好科技(北京)有限公司
Combining Predictive Capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to Predict Hemorrhagic Shock
InactiveUS20120136224A1Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device
InactiveCN102429651AHigh precisionGood clinical applicabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSonification
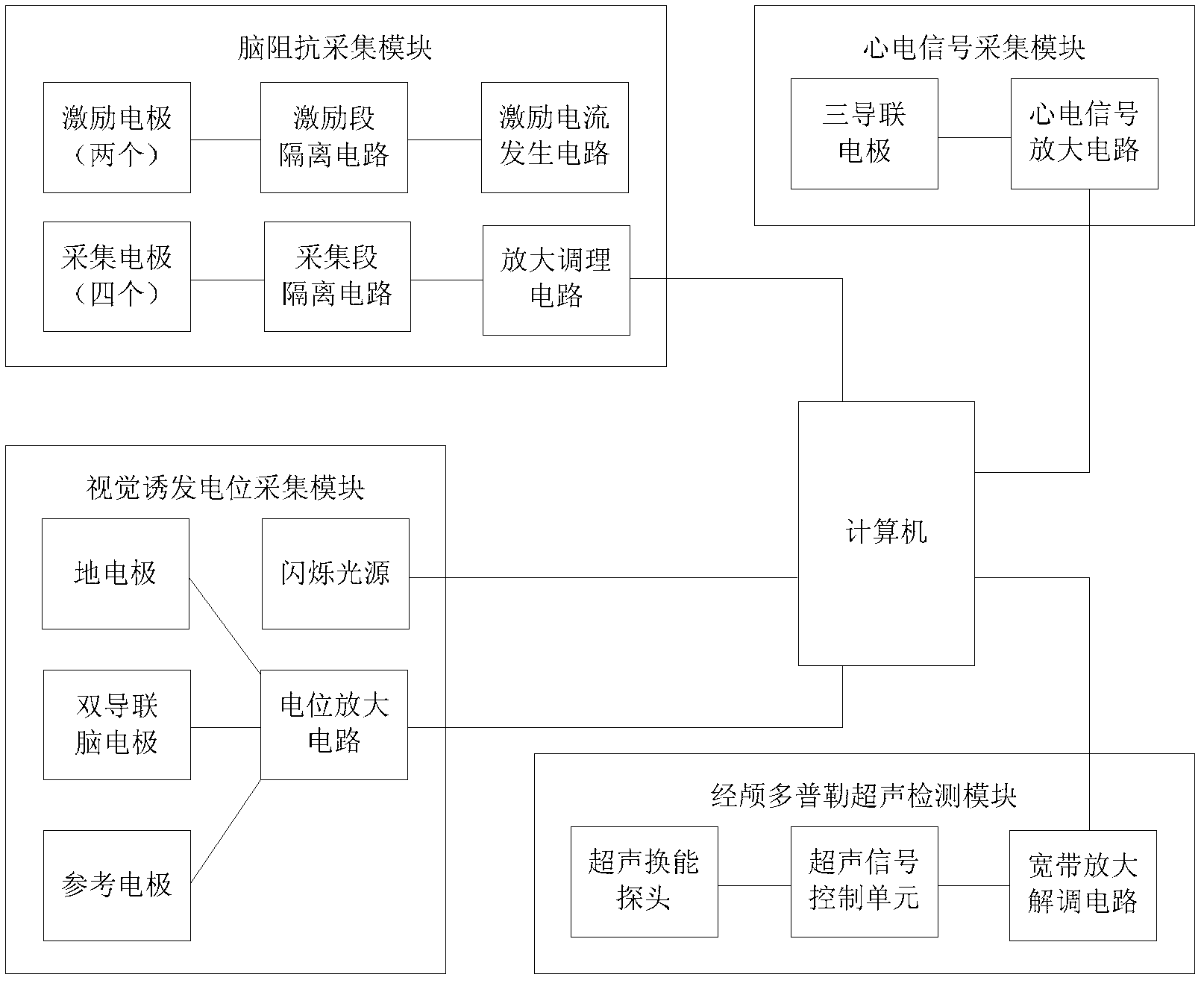
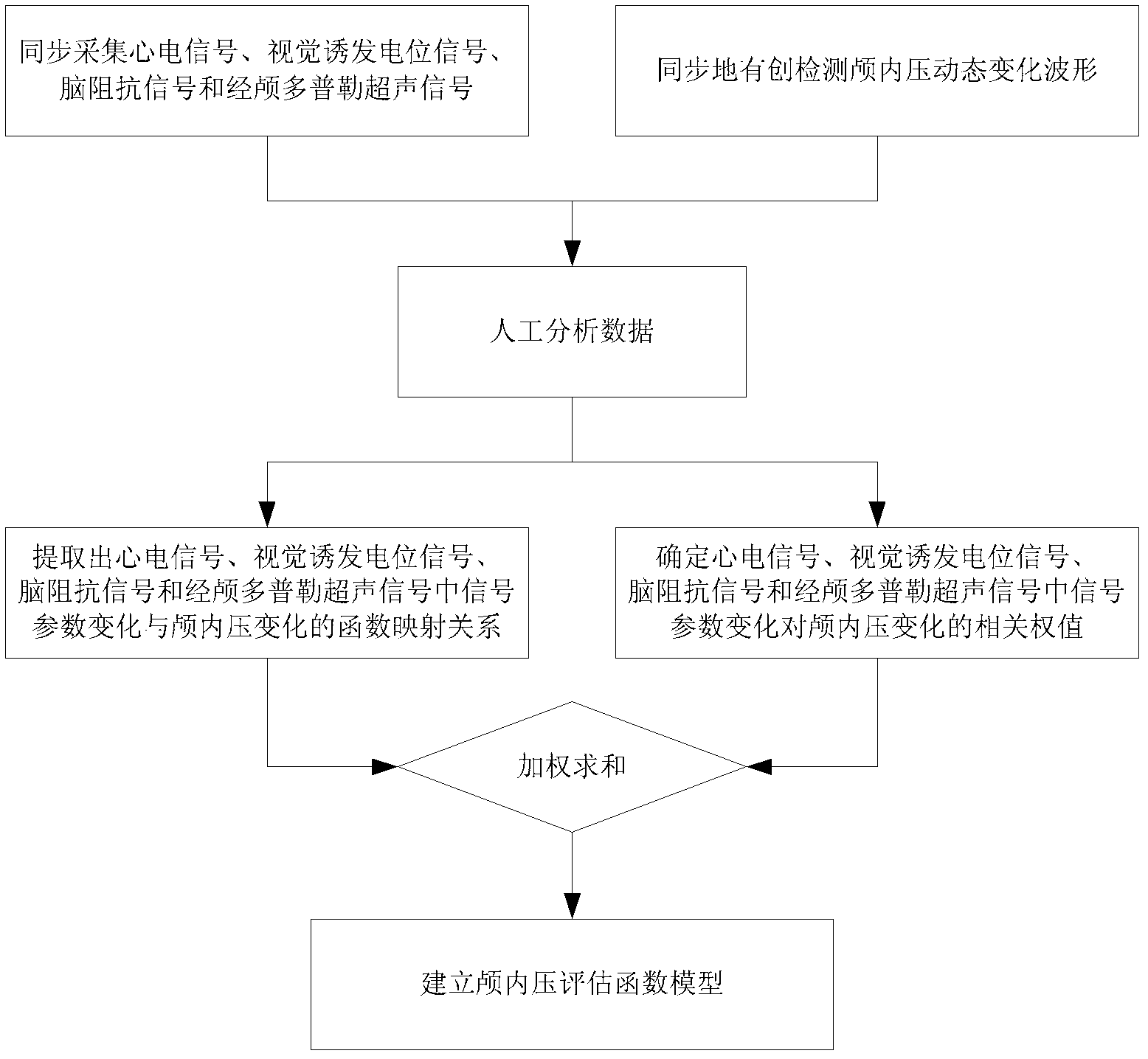
The invention provides a multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-establishing an intracranial pressure evaluation function model for recording a function mapping relation between the change of the intracranial pressure and the changes of an electrocardiosignal, a visual evoked potential signal, a brain impedance signal and a transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal and setting in a computer; and synchronously acquiring the electrocardiosignal, the visual evoked potential signal, the brain impedance signal and the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal into a computer and inputting the signals serving as the intracranial pressure evaluation function model to obtain the dynamic change process waveform of the intracranial pressure of an inspected object by performing multi-parameter and multi-direction operation. Due to the adoption of the method, invasive intracranial pressure detection is avoided; the device for implementing the method is easy to obtain; and meanwhile, various physiological and pathological signal parameters causing the change of the intracranial pressure are considered comprehensively in the intracranial pressure evaluation function model, so that the intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method has higher clinical detection accuracy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Cerebral blood flow regulation function monitor system
ActiveCN100399990CRealize automatic adjustment functionEliminate the pitfalls of artificial gradingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCollection systemEngineering
A cerebrovascular regulation function monitor system and a method for detection of cerebrovascular circulation critical closing pressure, wherein the cerebrovascular regulation function monitor system includes a signal collection system for in-phase sampling analog signal of transcranial doppler (TCD) signal and continuous artery pressure signal and further converting the analog signals into correspondent digital signals and a signal processing / displaying system connected with the signal collection system via interfaces for processing the digital signals to obtain the cerebrovascular critical closing signal and displaying them. The method and system realize a non-invasion detection and monitor of cerebrovascular autoregulation function in clinical practice.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD +1
Digital ultrasonic transcranial Doppler digital demodulation signal processing method and device
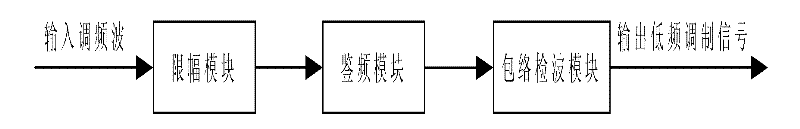
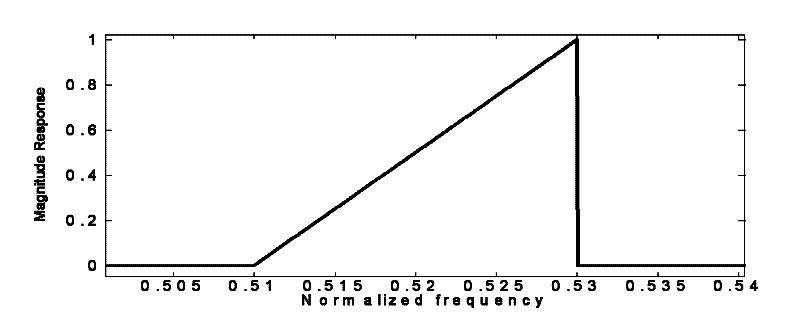
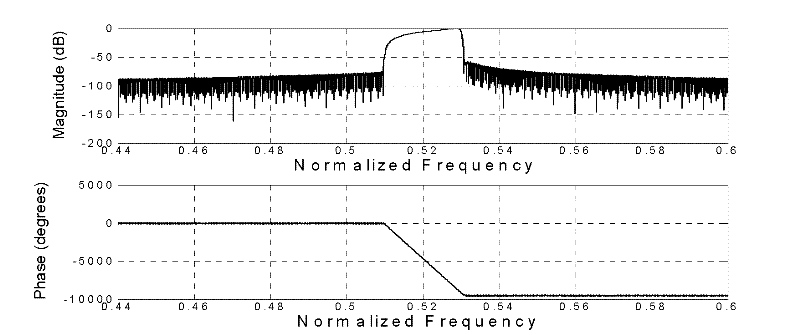
InactiveCN102176121ASolve the shortcomings of single frequency scanning distance, low precision, etc.Achieve full depth scanBlood flow measurement devicesSimulator controlFrequency spectrumSonification
The invention discloses a digital ultrasonic transcranial Doppler digital demodulation signal processing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: performing the A / D (analog / digital) sampling on an input frequency-modulated wave which is a non-demodulated ultrasonic echo signal, and then performing the amplitude limiting through a digital comparator; detecting a modulation signal reflected on the frequency conversion in a frequency-modulated save subjected to the amplitude limiting; and taking the absolute value of the modulation signal, responding the changes of the amplitude of the modulation signal to an envelope line, and acquiring a low-frequency modulation signal through a down-sampling low-pass filter. The device comprises an AD converter, at least two large-capacity high-speed caches FIFO (first in first out), a DSP digital signal processor), and an FPGA (field programmable gate array). According to the invention, the wide frequency band scanning and the full-depth scanning can be realized, the timeliness and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the system are improved, a blood flow dynamic parameter is accurately extracted, the SNR of a detecting signal is improved, and the quality of a frequency spectrum image is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
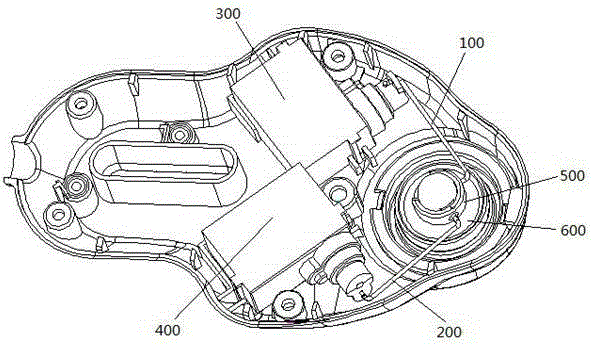
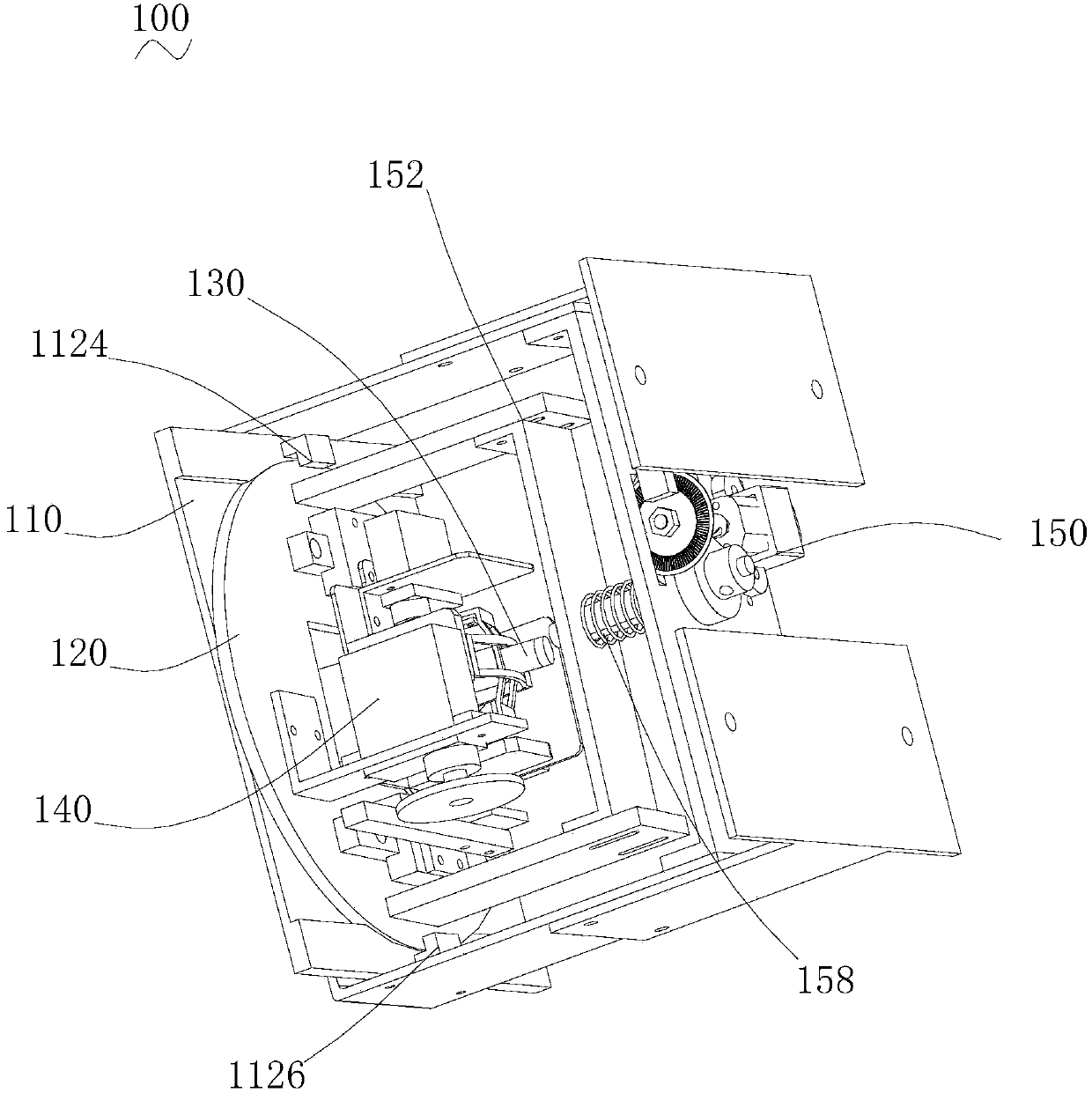
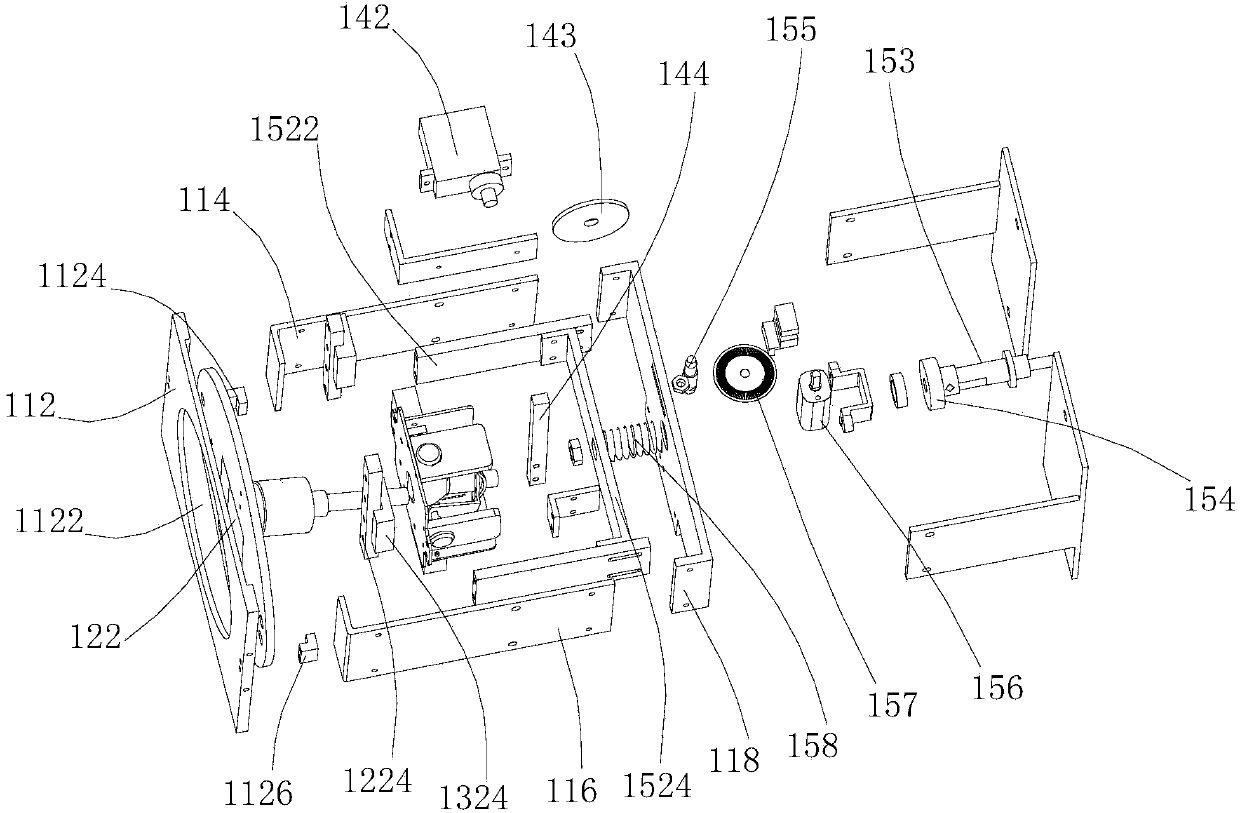
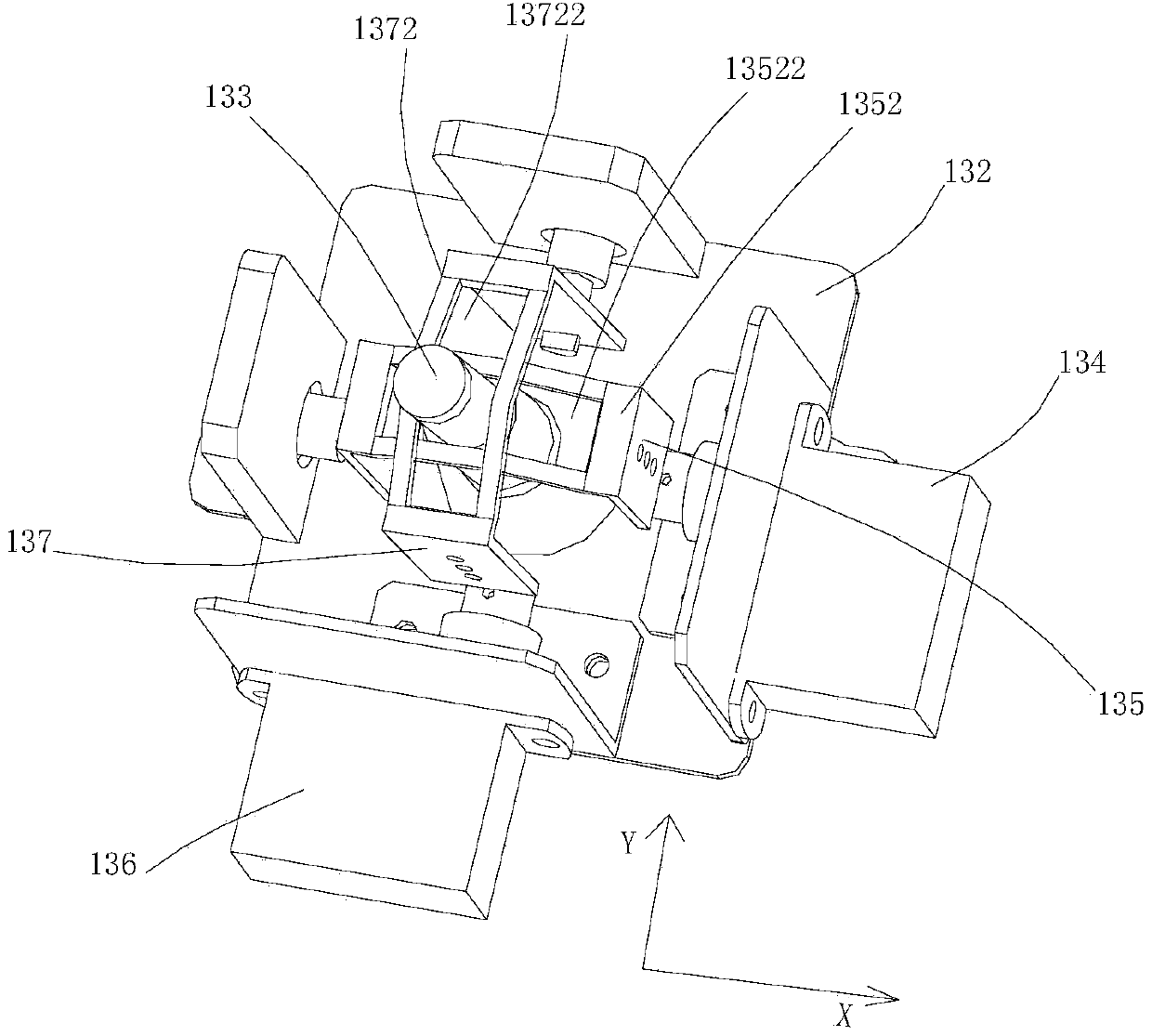
Cerebral blood flow detection probe bracket
The invention relates to a cerebral blood flow detection probe bracket which comprises a frame, a rotary disc rotatably installed on the frame, a space adjusting mechanism which is fixedly connected with the rotary disc and is provided with a sleeve rod capable of rotating around two direction axes, a translational driving mechanism for driving the space adjusting mechanism to translate, and a rotation driving mechanism for driving the rotary disc to rotate. According to the cerebral blood flow detection probe bracket, the space adjusting mechanism can drive a transcranial Doppler ultrasonic probe to rotate around two direction axes through the sleeve rod. The rotating rotary disc can drive the space adjusting mechanism to rotate so as to drive the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic probe to rotate. The translational driving mechanism can drive the space adjusting mechanism to drive the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic probe to translate relative to the rotary disc. Therefore, the cerebral blood flow detection probe bracket can drive the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic probe to carry out multiple movements during manual search and can finish automatic search.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
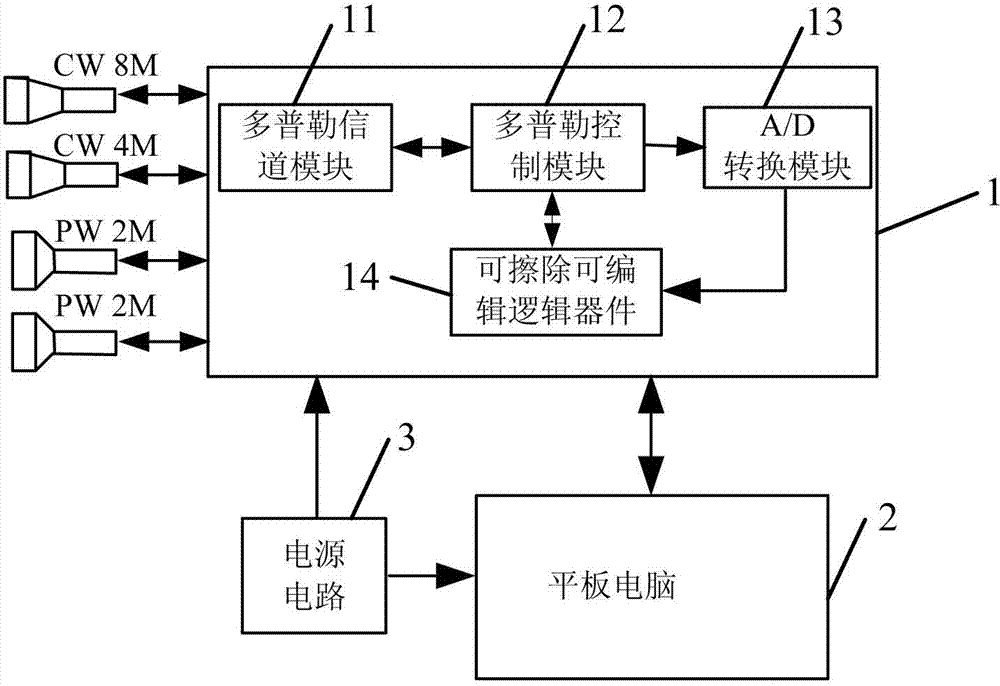
Ultrasound transcranial Doppler blood flow detector and control method thereof
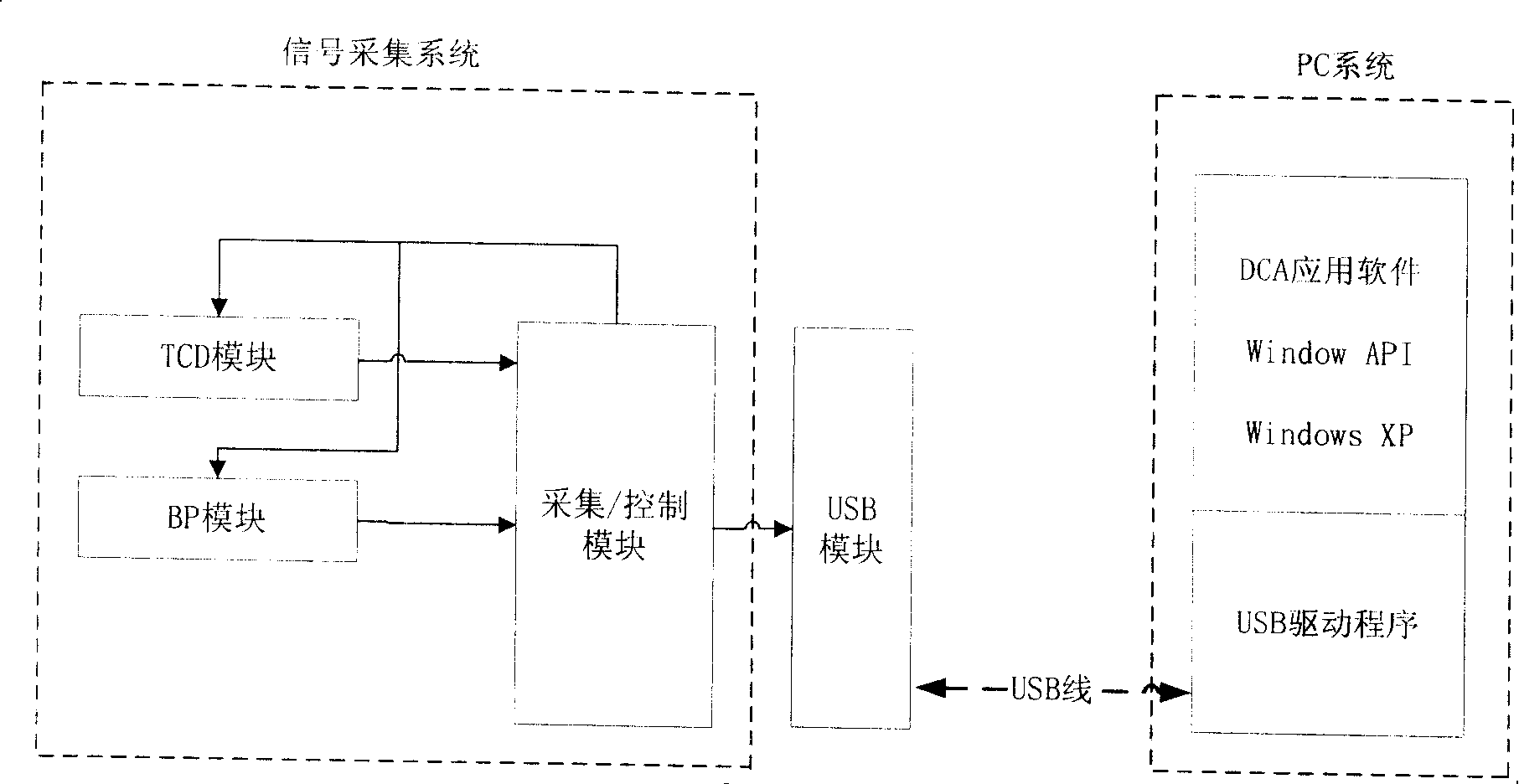
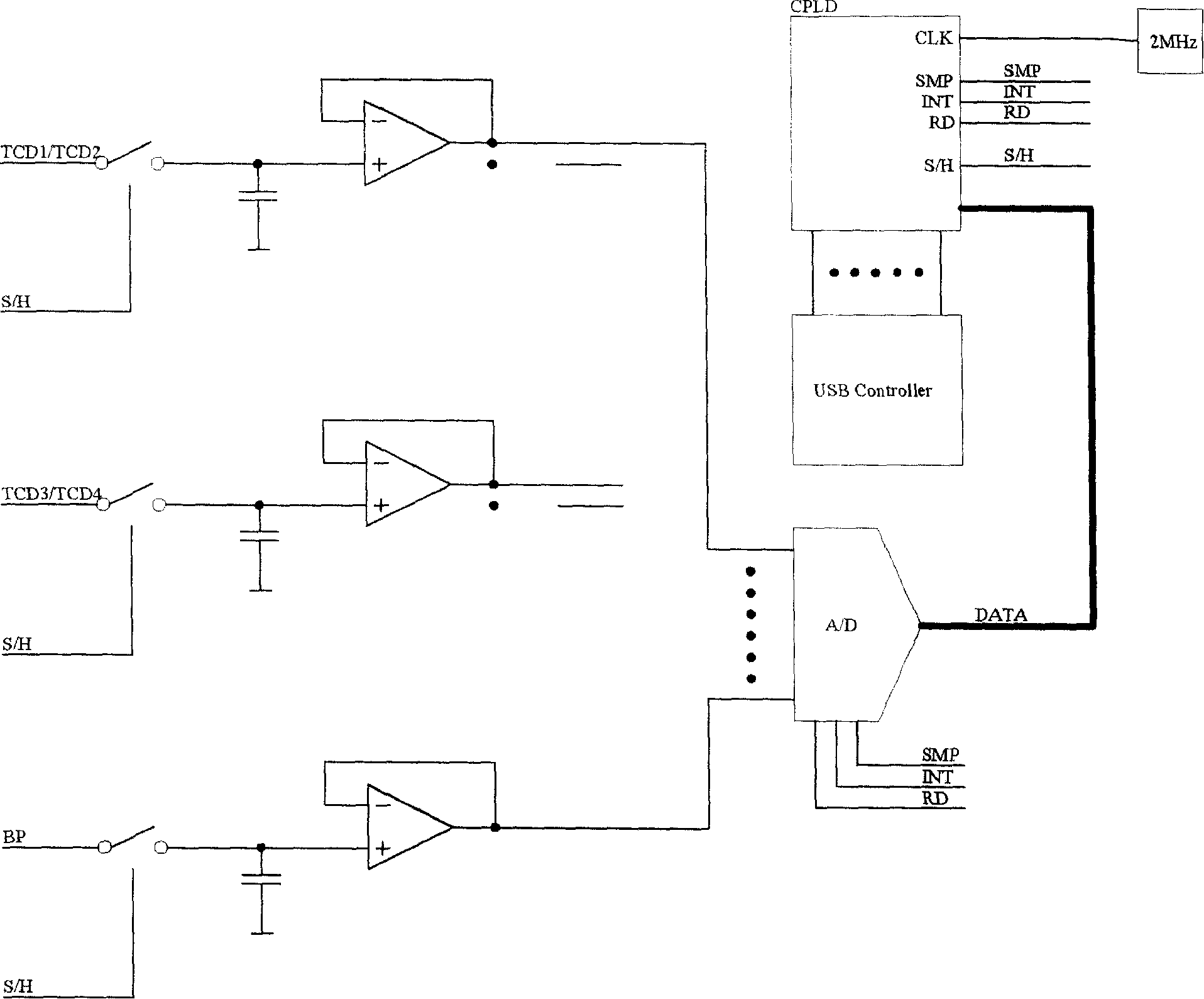
InactiveCN103876781AExtended working hoursCompact structureBlood flow measurement devicesTranscranial DopplerPower circuits
The invention discloses an ultrasound transcranial Doppler blood flow detector and a control method thereof. The ultrasound transcranial Doppler blood flow detector comprises a case, a power source circuit and a plurality of ultrasonic probes. The detector comprises a tablet personal computer used for inputting information and displaying the detection information, and a detection circuit board, wherein the detection circuit board comprises a Doppler channel module, a Doppler control module, an A / D conversion module and an erasable and editable logic device, the output end of the Doppler channel module is connected with the input end of the Doppler control module, the output end of the Doppler control module is connected with the input end of the A / D conversion module, the output end of the A / D conversion module is connected with the input end of the erasable and editable logic device, and the output end of the erasable and editable logic device is connected with the input end of the Doppler control module. The detection circuit board is used for receiving Doppler signals and outputting the detection information to the tablet personal computer. The tablet personal computer and the detection circuit board are connected through a connector. The detector is easy to produce, low in open source cost of an operation system, small in size and convenient to move and carry.
Owner:NANJING KEJIN INDAL
Neuravionic System for Life Support in High Performance Avionics
InactiveUS20120165676A1Avoid lostAvoid makingBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsAviationNeuropsychological test
A system for life support in high performance avionics that utilizes cerebral blood flow velocity measurements and responses to real-time neuropsychological tests of brain function, to accomplish prevention of gravitational loss of consciousness, determination of cognitive state-of-being of the crewmember, regulation of autonomy-decision making level, while taking into account individualized +Gz-tolerance and cognitive abilities under +Gz-stress, comprising a transcranial Doppler device, attached to a microcomputer, operatively connected to the mainframe avionic computer.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Wide band via-skull Doppler system and method for frequency conversion cerebrovascular blood flow rate detection
ActiveCN1919146AMeet clinical needsLow costBlood flow measurement devicesFrequency waveFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a broad-frequency skull Doppler system and frequency conversion brain vessel blood speed detecting method, which comprises the following parts: frequency generator, time-sequence control mode, emitter, receiver, demodulation gathering conversing mode and PC system to communicate time-sequence control mode through PC interface, wherein the frequency generator can produce wave-carrying signal with multiple preset frequencies, which controls frequency generator to output different frequency wave-carrying signal.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD +1
Carotid Plaque Ultrasound Therapy Apparatus
ActiveCN102284141AAccurate timingClear positioningUltrasound therapyUltrasonic generatorTranscranial Doppler
Owner:LUOYANG KANGLI MEDICAL INSTR
Brain blood vessel analysis system
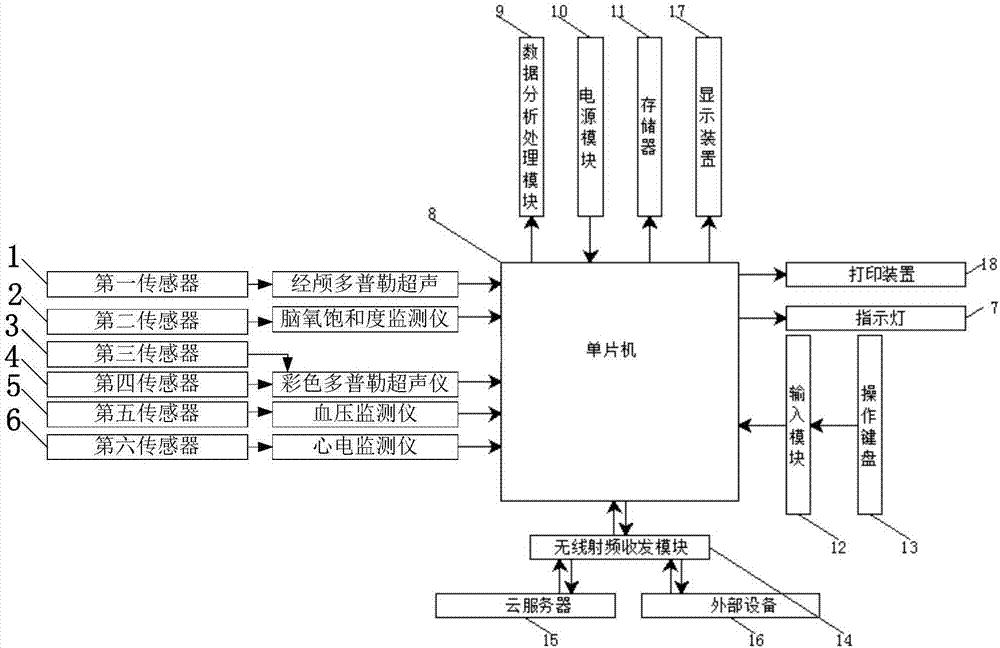
InactiveCN106890008AVarious detection methodsSafe storageBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionColour dopplerRadiology
The invention relates to a brain blood vessel analysis system. The system comprises a first sensor used for measuring the blood flow speed of the brain blood vessel and connected with a single-chip microcomputer by a transcranial Doppler ultrasonic instrument, a second sensor used for measuring the oxygen saturation of the brain and connected in a wired mode with the single-chip microcomputer by a brain oxygen saturation monitoring instrument, a third sensor used for measuring the carotid artery pressure and connected in a wired mode with the single-chip microcomputer by a colour Doppler ultrasonic instrument, a fourth sensor used for measuring the carotid artery diameter and connected in a wired mode with the single-chip microcomputer by the colour Doppler ultrasonic instrument, a fifth sensor used for measuring the blood pressure and connected in a wired mode with the single-chip microcomputer by a blood pressure monitor instrument, and a sixth sensor used for measuring the heart rate and connected in a wired mode with the single-chip microcomputer by an electro cardio monitoring device. The brain blood vessel analysis system is diverse in test method and safe in data storage, and remote examination can be conducted.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Method and system for evaluation of the hemodynamic model in depression for diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS7942820B2Less computation timeReduce complexityBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsLeft posterior cerebral arteryLeft posterior
The present invention provides a method for determining the cerebral hemodynamic model for depression, using carotid duplex ultrasound to establish percent stenosis of a right external carotid artery and a left external carotid artery, and transcranial Doppler ultrasound instrument to measure mean flow velocity within the cerebral arteries including the right and left internal carotid arteries, right and left middle cerebral arteries, right and left anterior cerebral arteries, right and left posterior cerebral arteries, and basilar artery. Percent carotid stenosis and mean flow velocity values in cerebral arteries are used to determine the cerebral hemodynamic model associated with depression in men and women, respectively.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
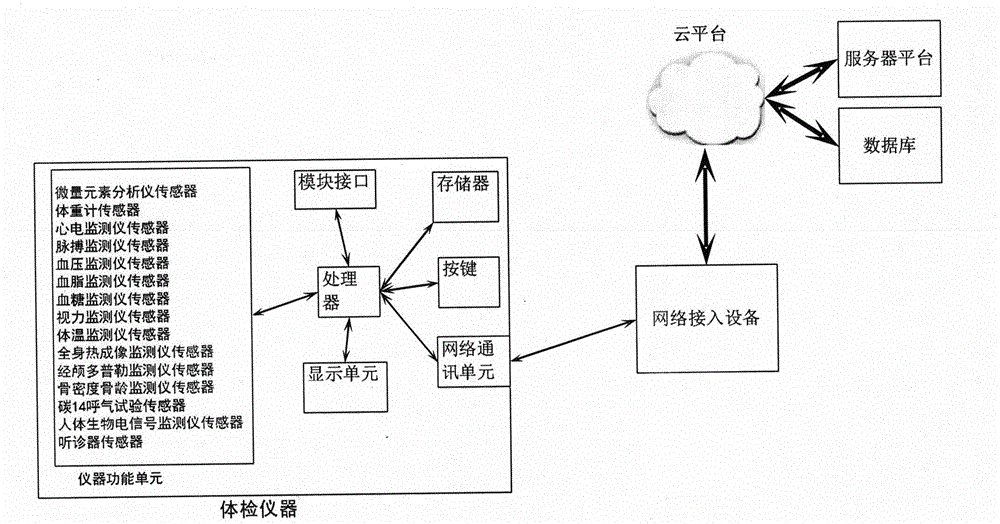
Physical examination system based on cloud computing
InactiveCN104970883AEasy to operateEasy to upgradeDiagnosticsSurgeryStomach cancerNetwork Access Device
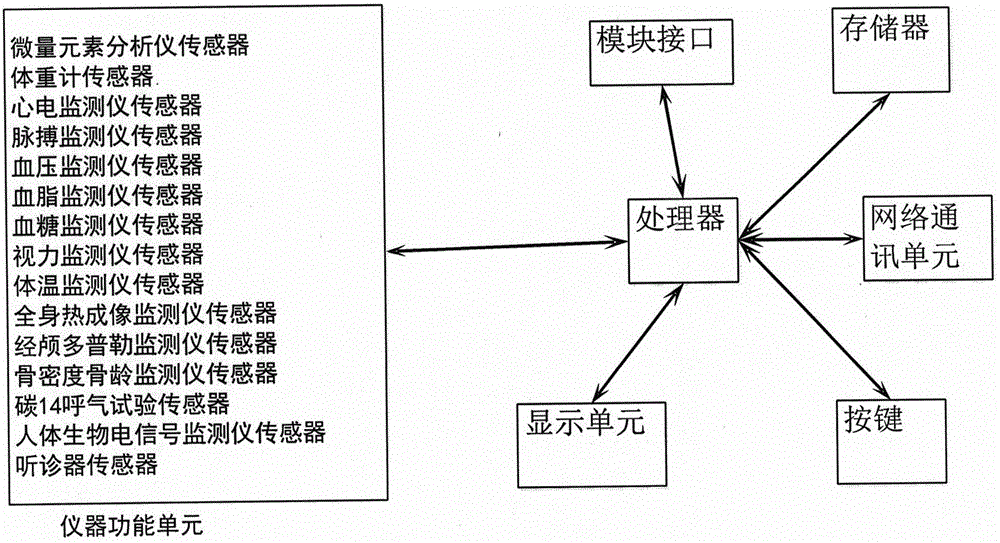
The invention discloses a physical examination system based on cloud computing. The physical examination system comprises a cloud microelement analyzer, a cloud weighing machine, a cloud electrocardioscanner, a cloud pulse monitor, a cloud blood pressure monitor, a cloud blood fat monitor, a cloud blood glucose monitor, a cloud vision monitor, a cloud body temperature monitor, a cloud whole-body thermal imaging monitor, a cloud transcranial Doppler monitor, a cloud bone mineral density and bone age monitor, a cloud carbon 14 breath test part, a cloud human body bio-electricity signal monitor and a cloud stethoscope. The physical examination system comprises a cloud platform, a server platform, a database, a network access device and physical examination instruments. The functions and the number of the physical examination instruments are not limited. The problems that physical examination is difficult and microelements for growth of teenagers are not balanced are solved. Serious diseases without subjective symptoms, for example, the stomach cancer, the colon cancer, the lung cancer, the breast cancer and the uterine cancer, can be found at the germination stage.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHIER TECH
Cerebral blood flow auto-regulation index output method, storage medium and ultrasonic equipment
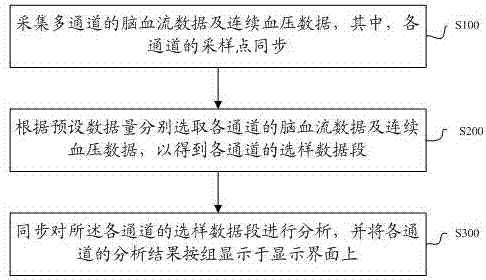
ActiveCN107296627AEasy to useBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsAuto regulationData segment
The invention discloses a cerebral blood flow auto-regulation index output method, a storage medium and ultrasonic equipment. The method includes: acquiring cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data of multiple channels, wherein sampling points of each channel are synchronous; selecting cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data of each channel according to preset data quantity to obtain a sample data segment of each channel; synchronously analyzing the sample data segment of each channel, and displaying analysis results of each channel on a display interface by groups. Since the cerebral blood flow data and continuous blood pressure data are acquired synchronously, the synchronously selected data segments are analyzed and the analysis results are displayed on the display interface by groups, real-time synchronous displaying of multiple groups of cerebral blood flow auto-regulation indexes in a transcranial Doppler system is realized, and convenience in use is brought to users.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Device for detecting cerebral blood flow regulation function
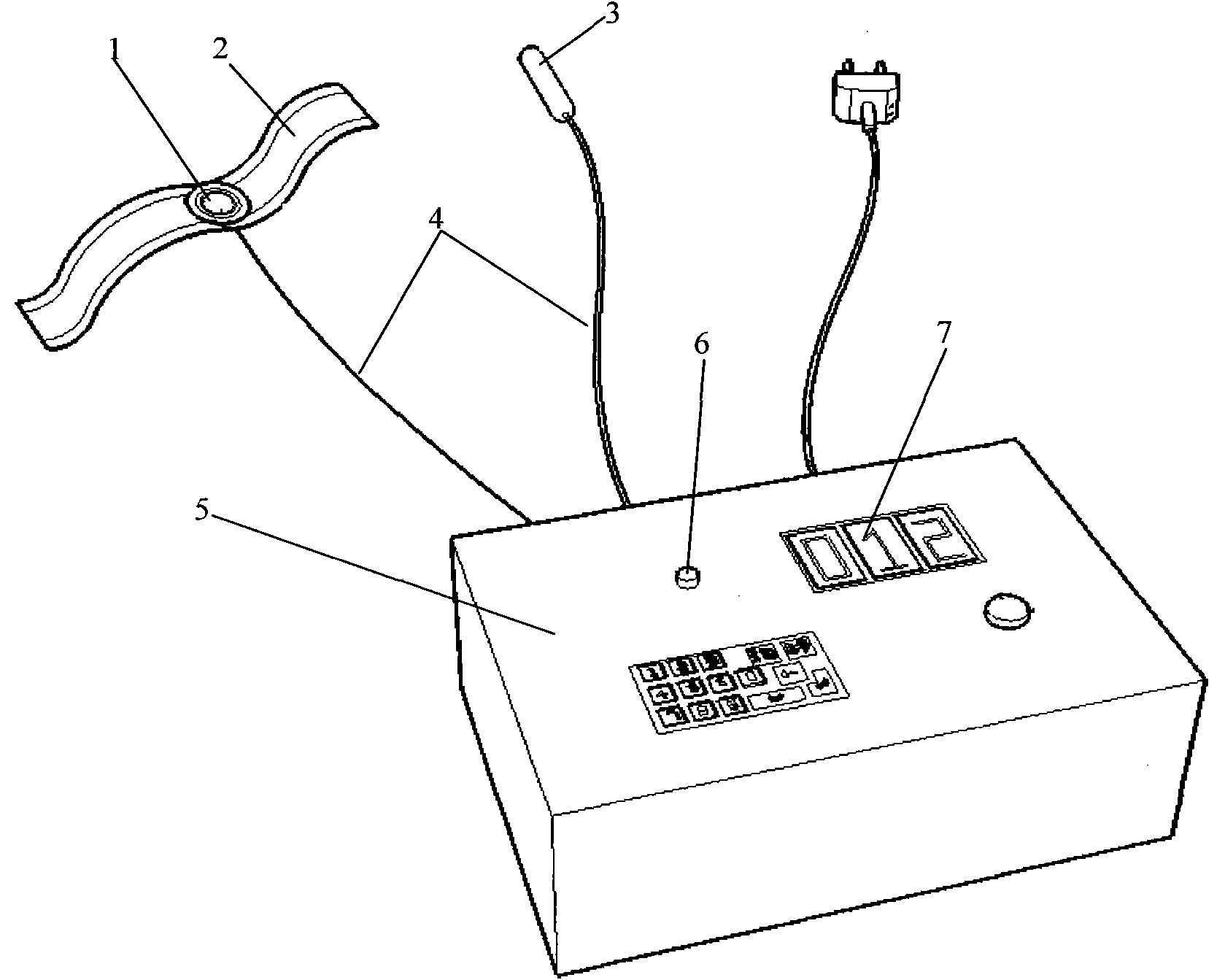
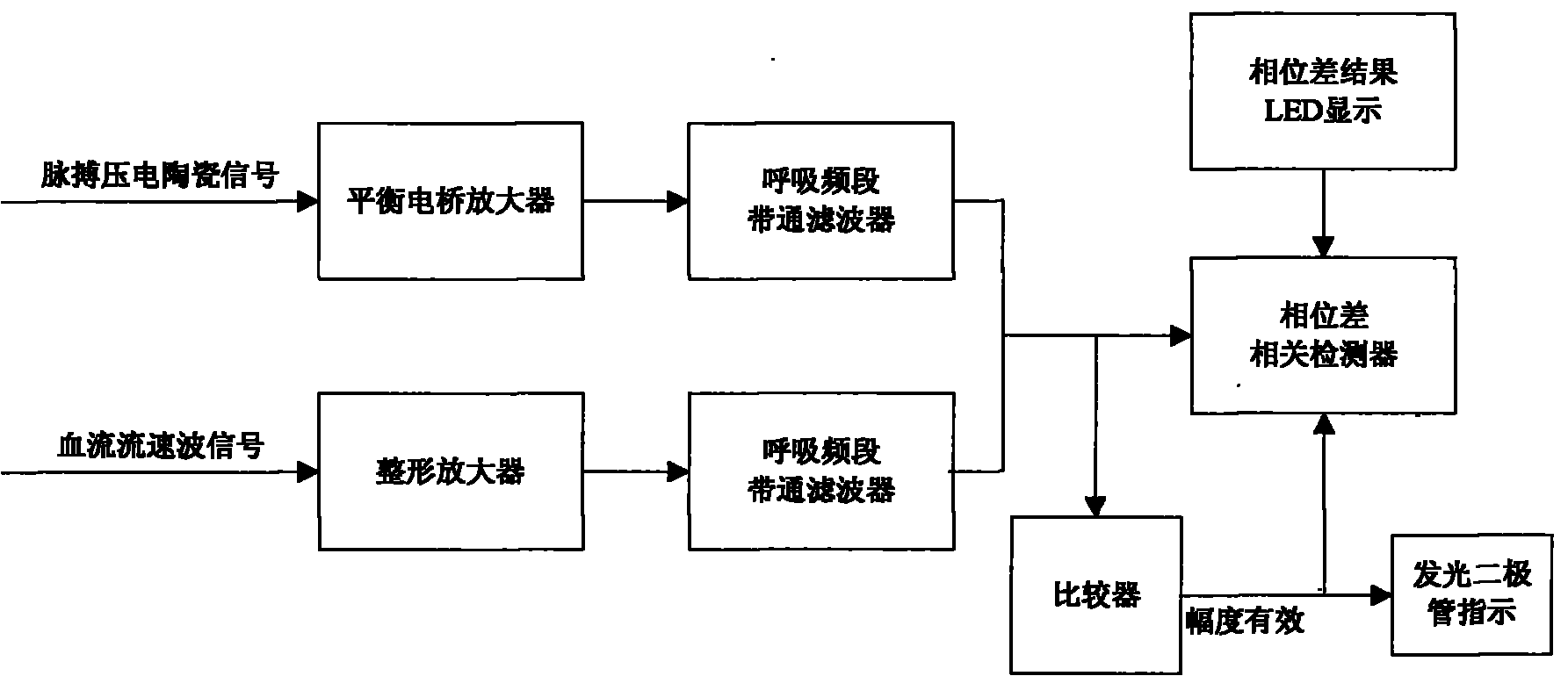
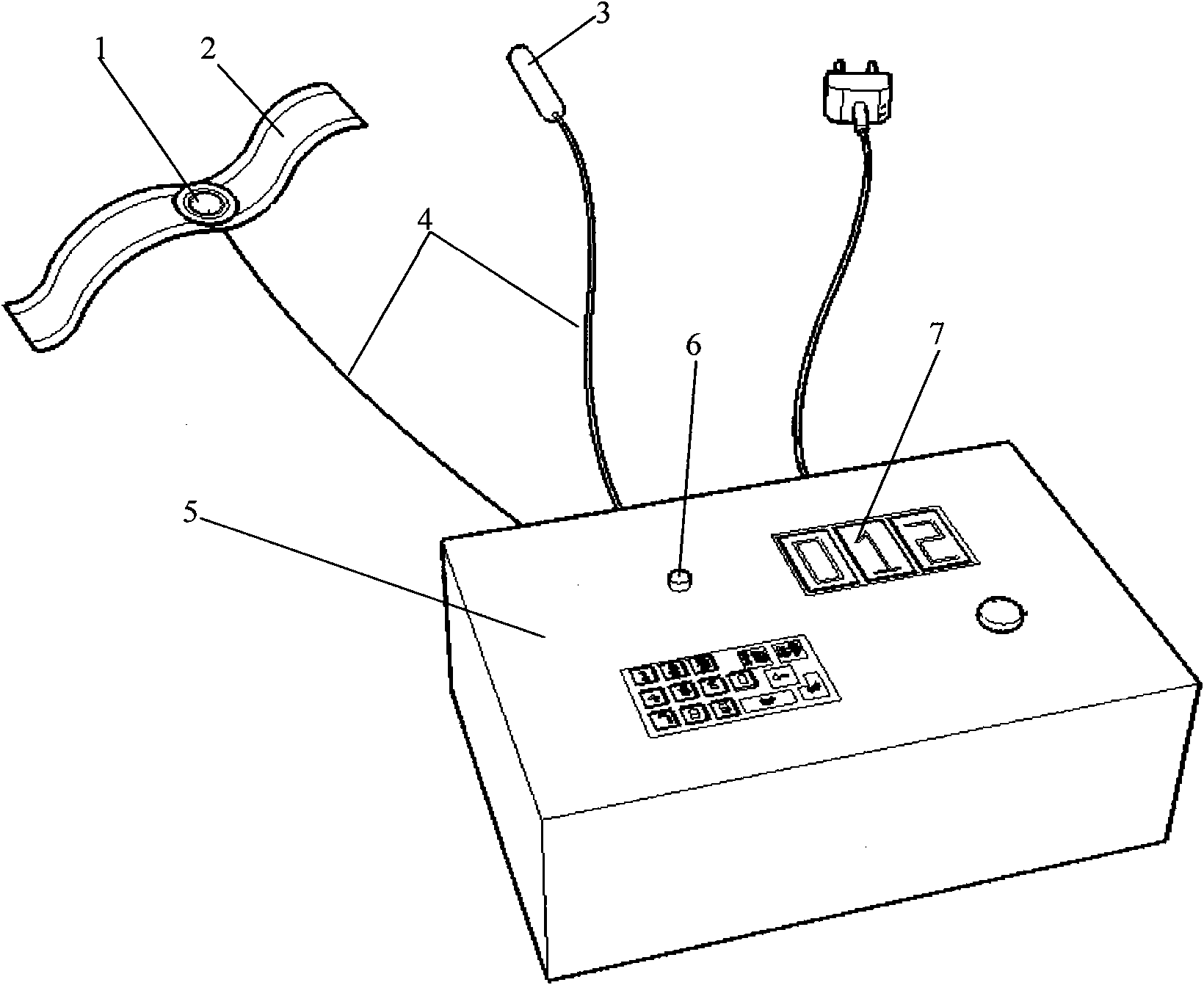
InactiveCN101889860AStrong self-regulation abilityImprove the safety of useBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase differencePrice ratio
The invention discloses a device for detection a cerebral blood flow regulation function, which belongs to the technical field of biomedical engineering. The device comprises a piezoelectric ceramic plate (1), a fixed elastic ribbon (2) of the piezoelectric ceramic plate (1), a trans-cranial Doppler probe module (3), a detection box (5), a light-emitting diode (6) and a phase difference result display LED (7), wherein the piezoelectric ceramic plate (1) is used for measuring pulse waves; the trans-cranial Doppler probe module (3) is used for measuring medium-sized artery blood flow velocity waves; the light-emitting diode (6) is arranged on the detection box (5) and is used for indicating effective characteristic waves; and the piezoelectric ceramic plate (1) and the trans-cranial Doppler probe module (3) synchronously measure signals and are connected with a respiratory frequency band characteristic wave extraction and phase difference detection circuit arranged in the detection box (5) through a connecting wire (4) respectively. The device needs no external artery blood pressure control, has high use safety, uses the piezoelectric ceramic plate to measure pulse pulsation signal waveforms from a wrist directly, and evaluates the cerebral blood flow regulation function according to phase changes of respiration characteristic waves of pulse and the cerebral blood flow, and has the advantages of use safety, simple and convenient operation, quick measuring and processing speed and high performance price ratio.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Mobile medicine communication platform and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS10534894B2Increase elasticityReduce packet lossError preventionAntenna supports/mountingsComputer networkTransceiver
Telemedicine systems and methods are described. In a telemedicine system operable to communicate with a remote operations center, communications can be transmitted / received using a transceiver having an antenna. The antenna can include first and second di-pole antenna elements, the first di-pole antenna element being vertically polarized and the second di-pole antenna element being horizontally polarized. A controller of the system can establish, using the transceiver, a telemedicine session with the operations center using a Transport Morphing Protocol (TMP), the TMP being an acknowledgement-based user datagram protocol. The controller can also mask one or more transient network degradations to increase resiliency of the telemedicine session. The telemedicine system can include a 2D and 3D carotid Doppler and transcranial Doppler and / or other diagnostic devices, and provides for real-time connectivity and communication between medical personnel in an emergency vehicle and a receiving hospital for immediate diagnosis and treatment to a patient in need.
Owner:BR INVENTION HLDG LLC
Portable module full-depth frequency-shift searching type transcranial doppler detection device and method
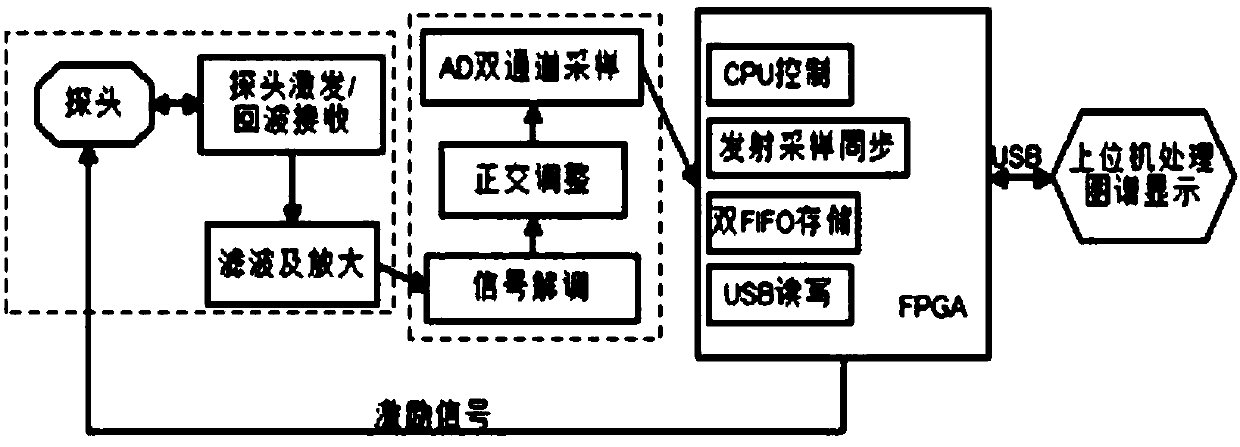
PendingCN108433742ASmall amount of calculationReduce positioningOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationDirection information
The invention discloses a portable module full-depth frequency-shift searching type transcranial doppler detection device and method. The device includes a probe, a probe excitation and echo receivingmodule, a wave filtering and amplifying module, a signal demodulation and orthogonal adjustment module, an AD dual-channel sampling module, a control module and an upper computer. The method includesthe steps that the probe emits a sound wave into the skull and receives a blood flow echo signal; wave filtering and amplification are carried out, actual blood flow frequency-shift signals are obtained after analog demodulation, and orthogonal adjustment is achieved; a data pack is formed, and control over transmission is achieved; preprocessing is conducted on received frequency-shift signals of actual flows, a full-depth frequency-shift searching method is utilized to obtain the blood flow distribution and direction information of the overall depth of an ultrasonic wave beam in the emitting direction, and after dispersed Fourier and pseudo-color conversion, blood flow forms a regional spectrogram according to selected demand depth. By means of the device and method, the blood flow distribution condition of the whole depth of the ultrasonic wave beam in the emitting direction can be displayed, the signal complexity is simplified, and therefore a system is much smaller and more portable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com