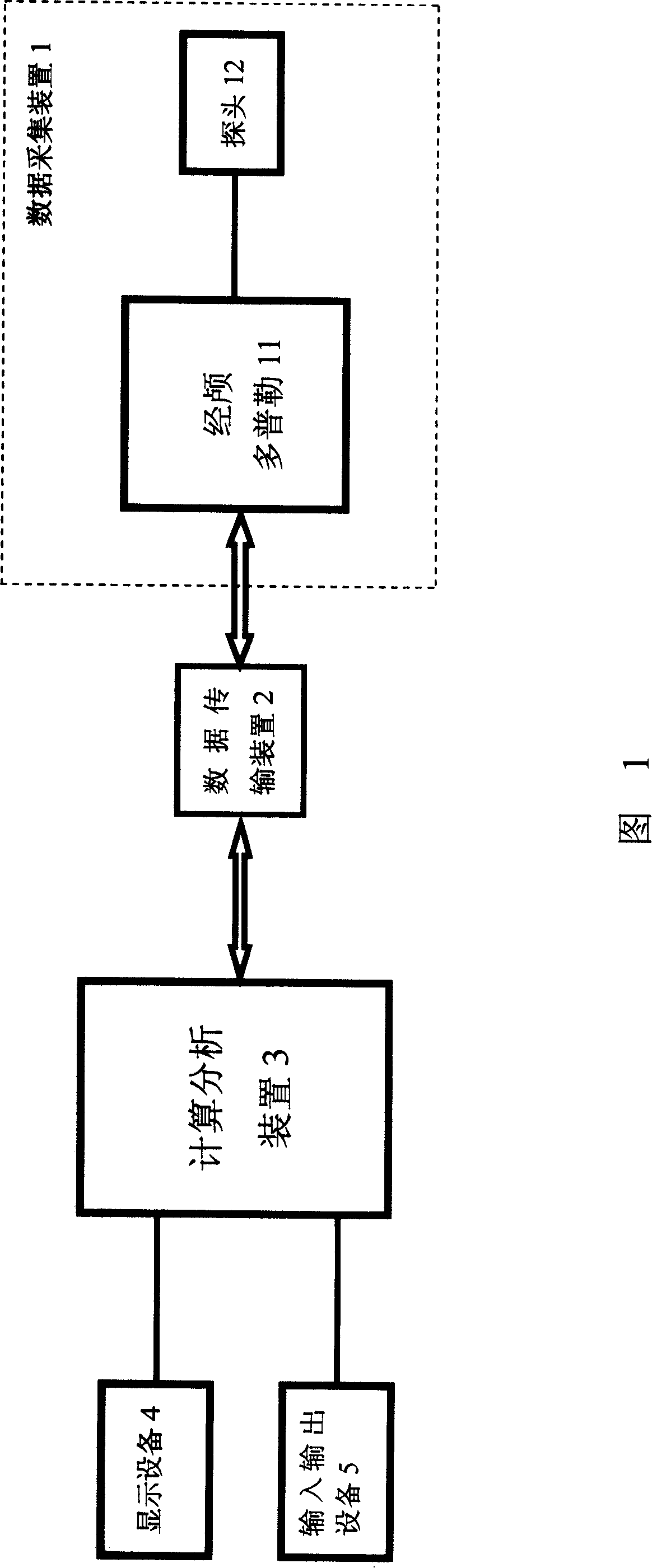
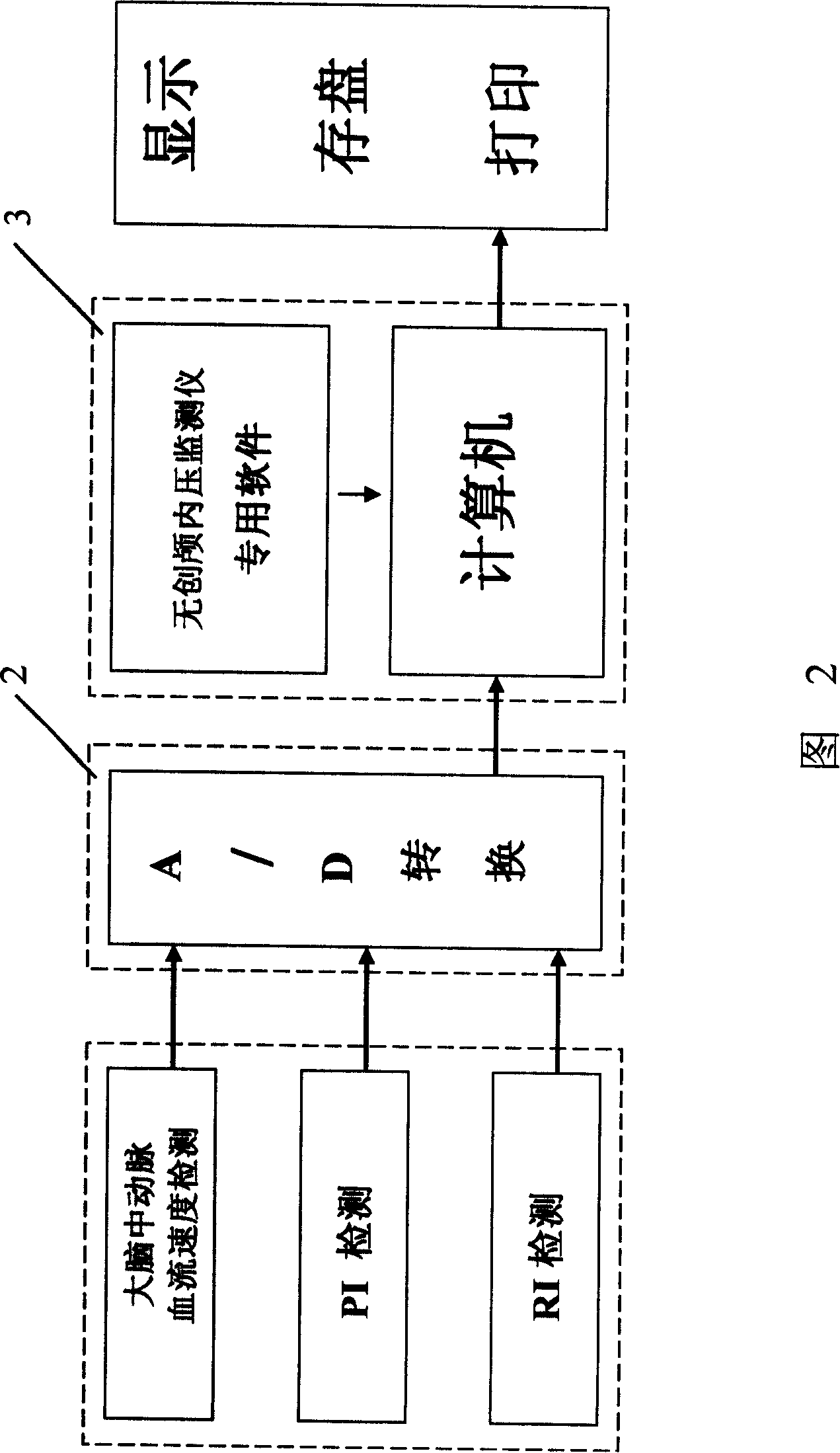
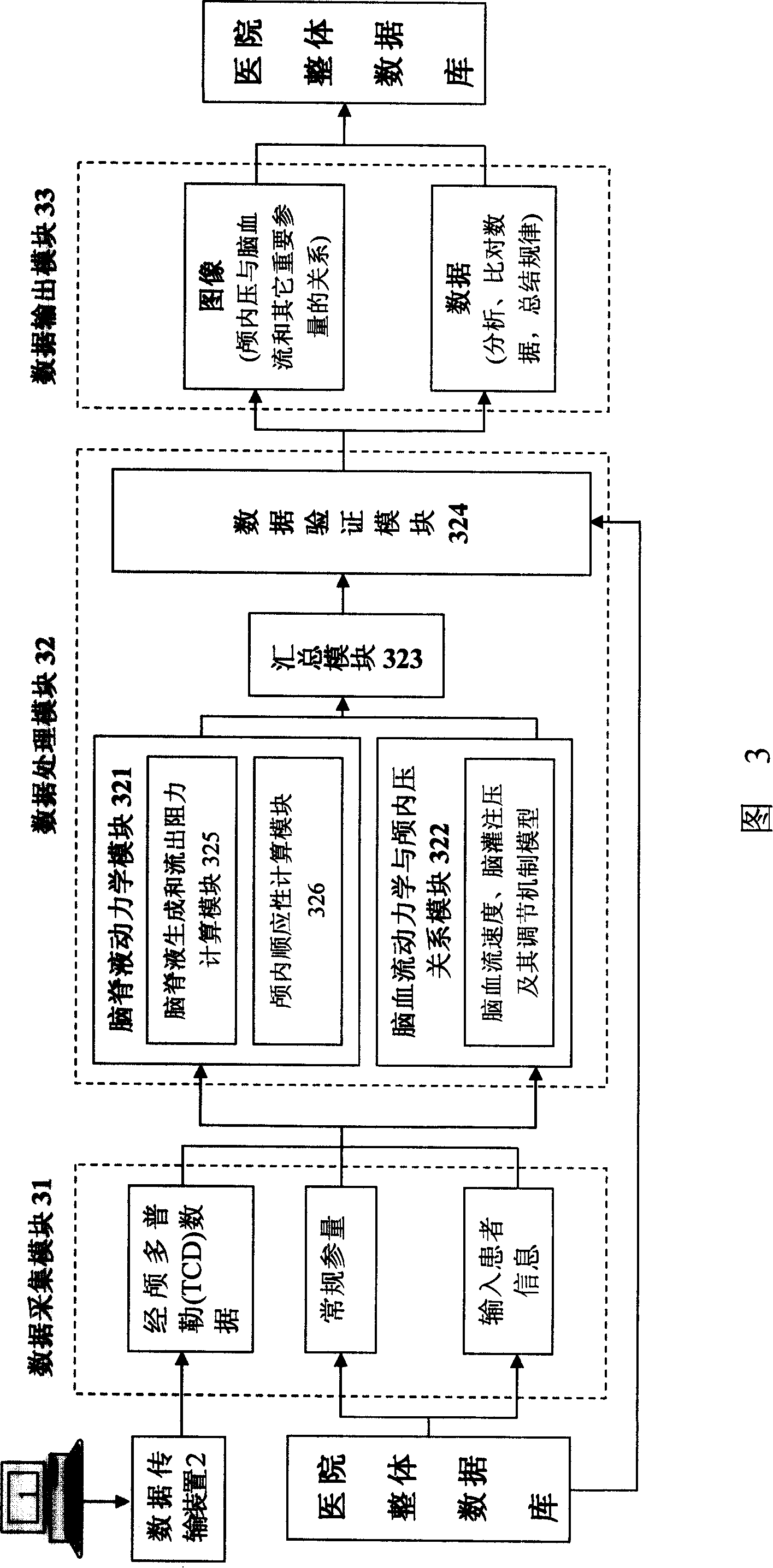
Noninvasive intracranial pressure monitoring equipment
A technology for monitoring equipment and intracranial pressure, applied in diagnostic recording/measurement, sensors, diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate measurement of ICP value, complex reasons for impedance changes, differences in impedance measurement, etc., to achieve convenient detection methods and benefit Rehabilitation, timely effect of treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] The mathematical model for determining CSF production and outflow resistance is:
[0088] R=P 0 t / PVI log[P (t) / P p ×(P p -P 0 ) / (P (t) -P 0 )]
[0089] The graph measured in this embodiment is as Figure 6 As shown, the abscissa in the graph is time, and the ordinate is intracranial pressure. The star-shaped curve in the figure represents the ICP data curve measured by the invasive monitor, and the solid line curve represents the mathematical model estimation based on the generation and outflow resistance of cerebrospinal fluid in the present invention. out the ICP data. Quantitative relationship of CSF production and outflow resistance to intracranial pressure over time is shown. R in the equation is the generation and absorption resistance; PVI is the pressure-volume index, indicating the corresponding relationship between pressure and volume; P 0 is the initial intracranial pressure; P p is the peak intracranial pressure. Depend on Figure 6 It can be ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] The mathematical model for determining intracranial compliance is:
[0093] C = K * PVI P (C: Compliance, compliance)
[0094] C=1 / KP=0.4343(PVI) / P
[0095] In the formula: C is the intracranial compliance; k is the intracranial elastic coefficient
[0096] The brain is in a rigid cranial cavity, and the increase of a certain volume of the contents of the cranial cavity can keep the intracranial pressure constant, which is intracranial compliance. However, if the volume of the cranial cavity further increases, the compliance will decrease and the intracranial pressure will increase. Therefore, the relationship between the two is one of the factors that determine the intracranial pressure. The quantitative relationship between compliance and intracranial pressure can be expressed by this mathematical model. In the process of data processing, conventional paramet...
Embodiment 3
[0098] The model for determining the relationship between cerebral hemodynamics and intracranial pressure is:
[0099] ICP t =c(1)*ABP t +c(2)*PI t +c(3)*RI t+c(4)*CO2 t +c(5)*ABP t-1 +μ t
[0100] mu t =c(6)*μ t-1 +ε t
[0101] This calculation formula obtains the parameter c(1) of the basic parameter by establishing an autoregressive time series model on the data sequence, and then selects the first-period delay and first-order autoregression of the most important response quantity ABP as random disturbance items.
[0102] The simulation curve of the model is as Figure 8 shown.
[0103] The components in the rigid cranial cavity are brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood. An increase in any of these components can lead to an increase in intracranial pressure. Cerebral hemodynamics regulates the amount of intracranial blood volume, so it determines intracranial pressure. Key factor. This model contains the main factors affecting cerebral hemodynamics. Su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com