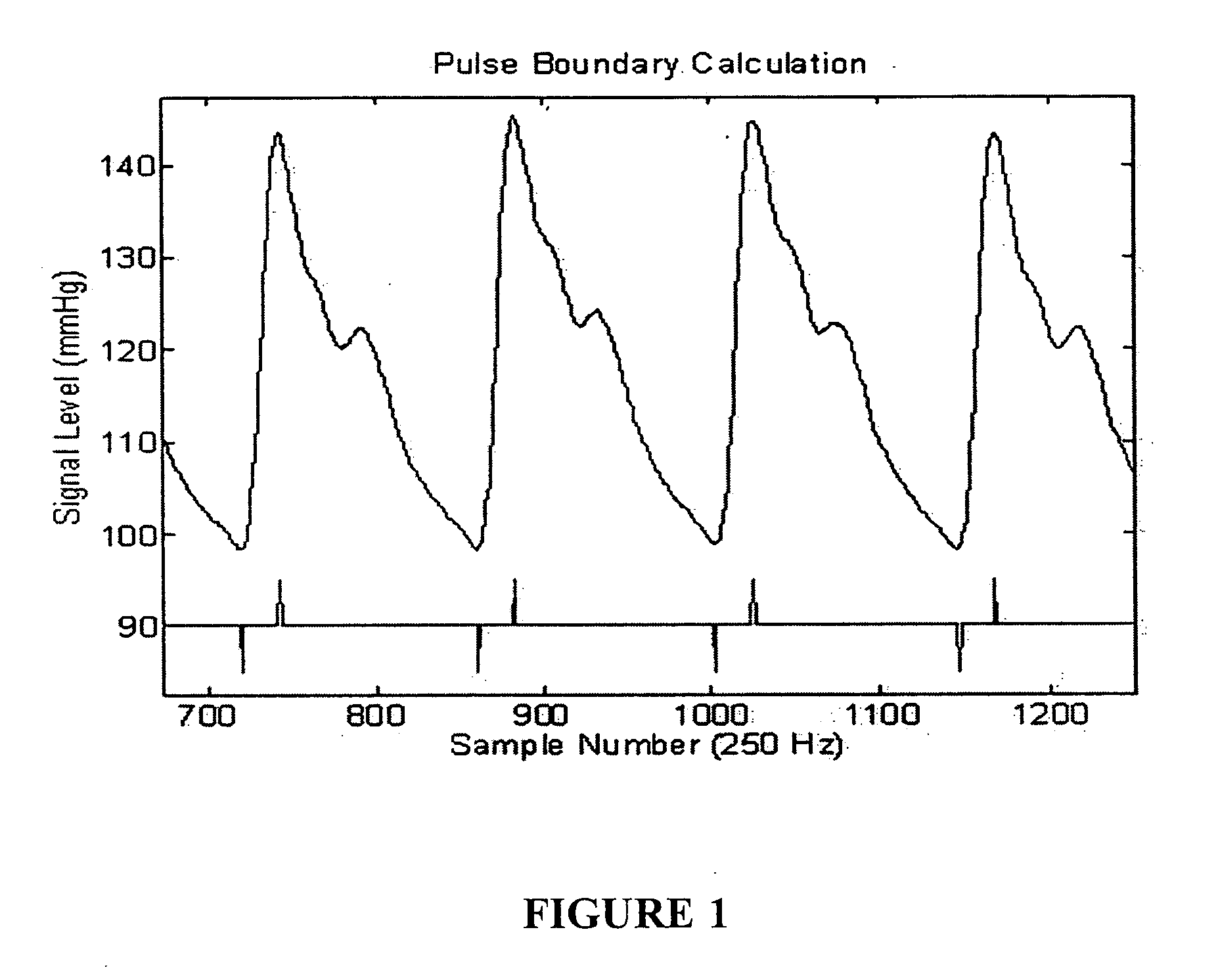
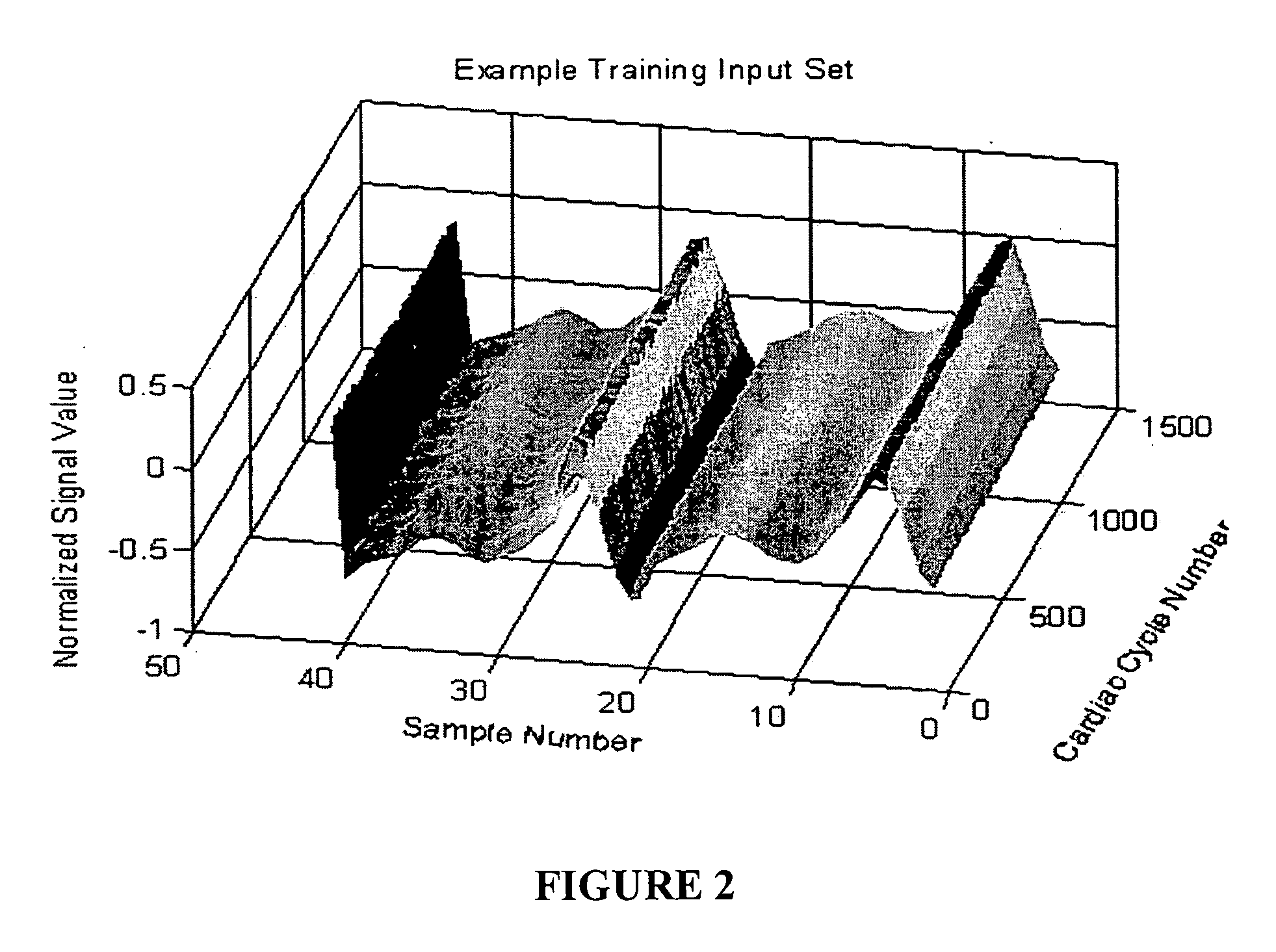
Patents
Literature
372results about "Diagnostics using vibrations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
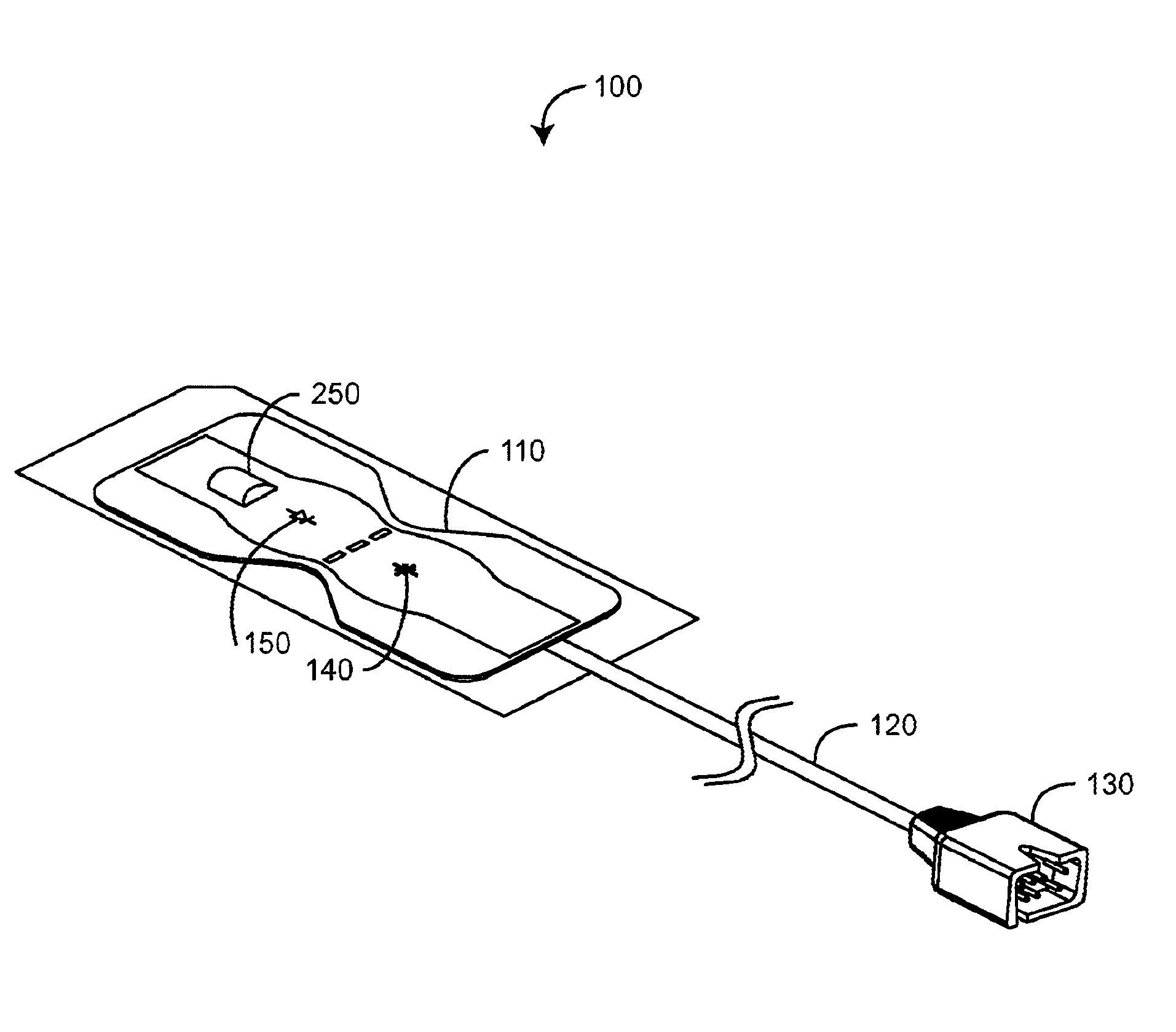
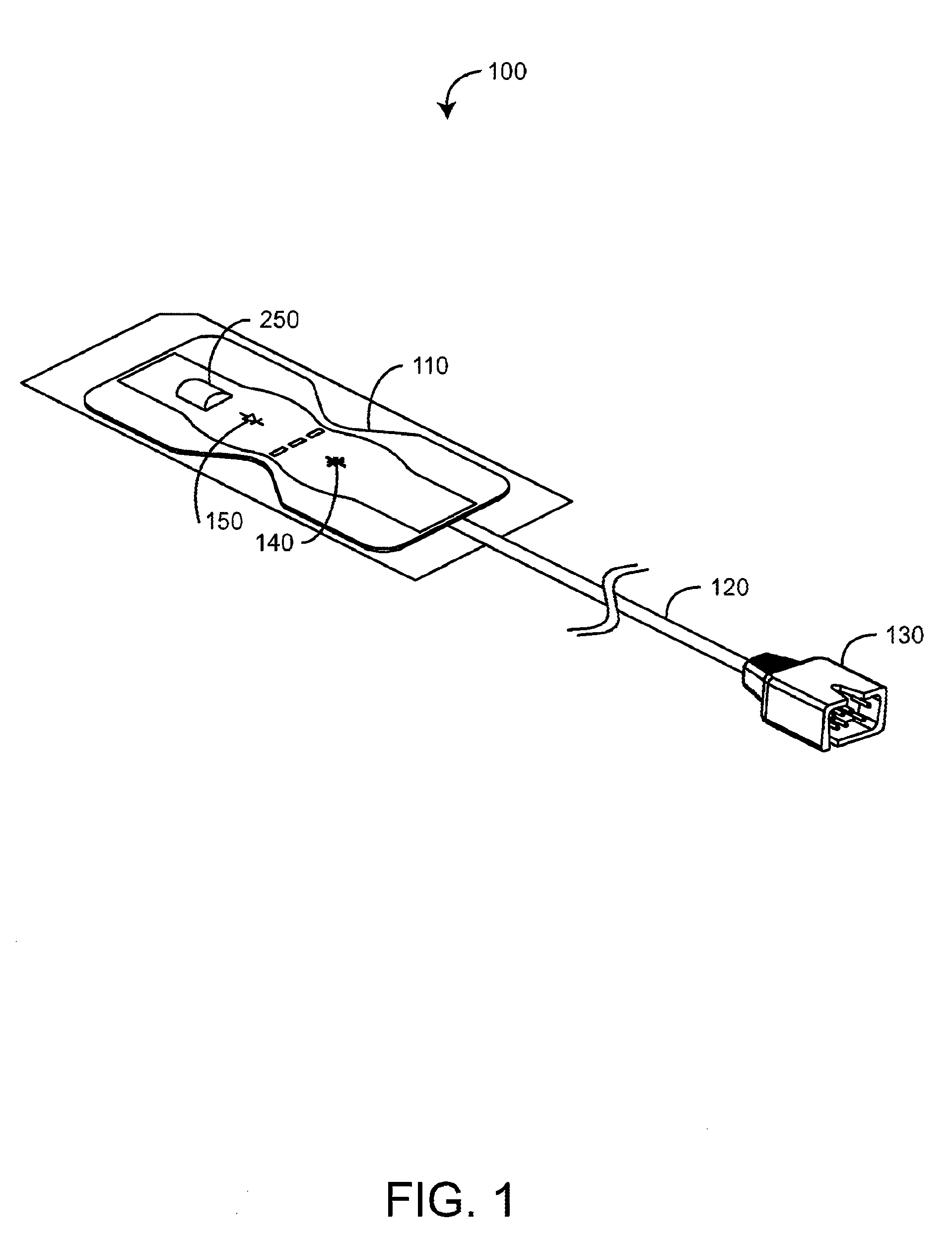
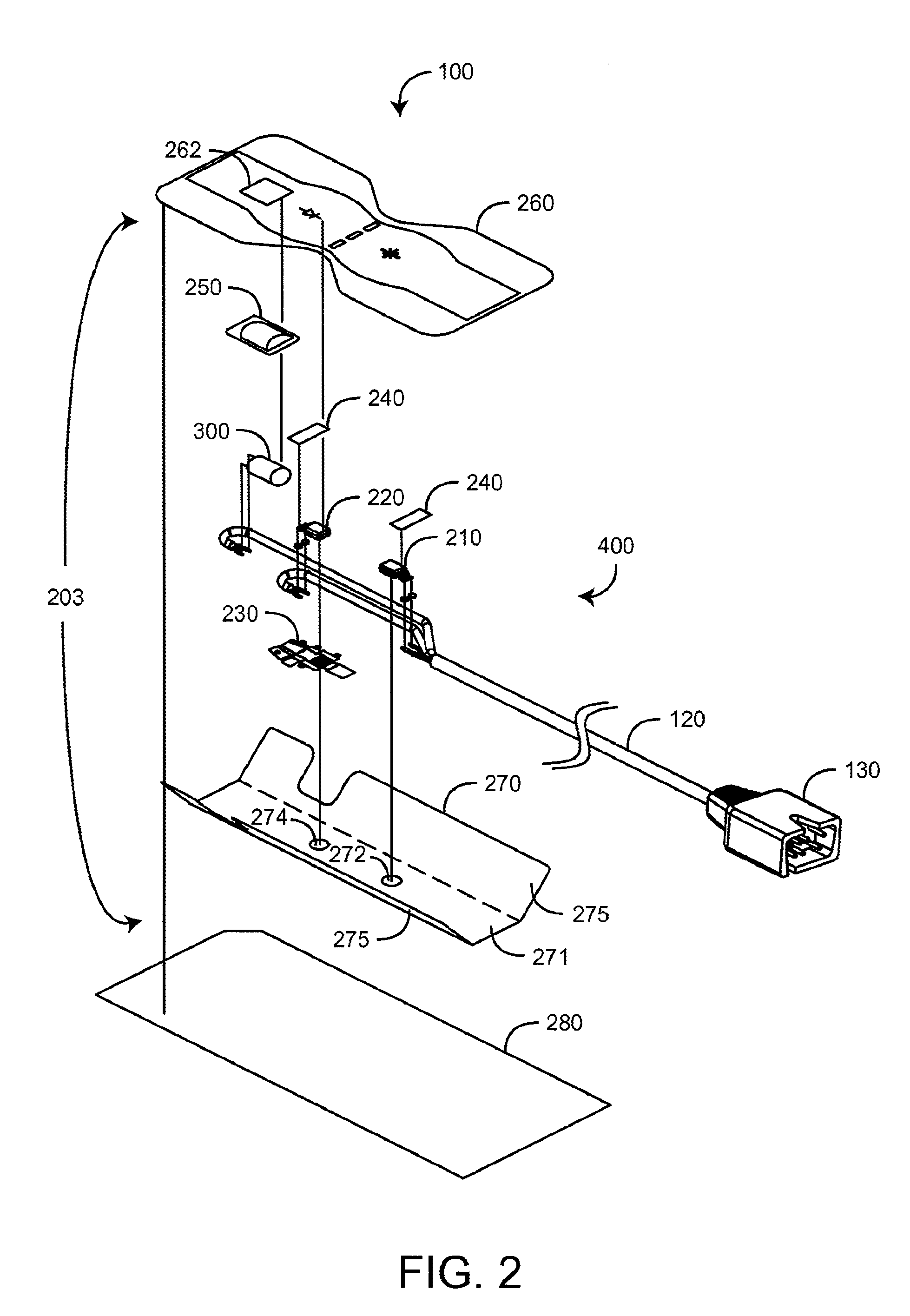
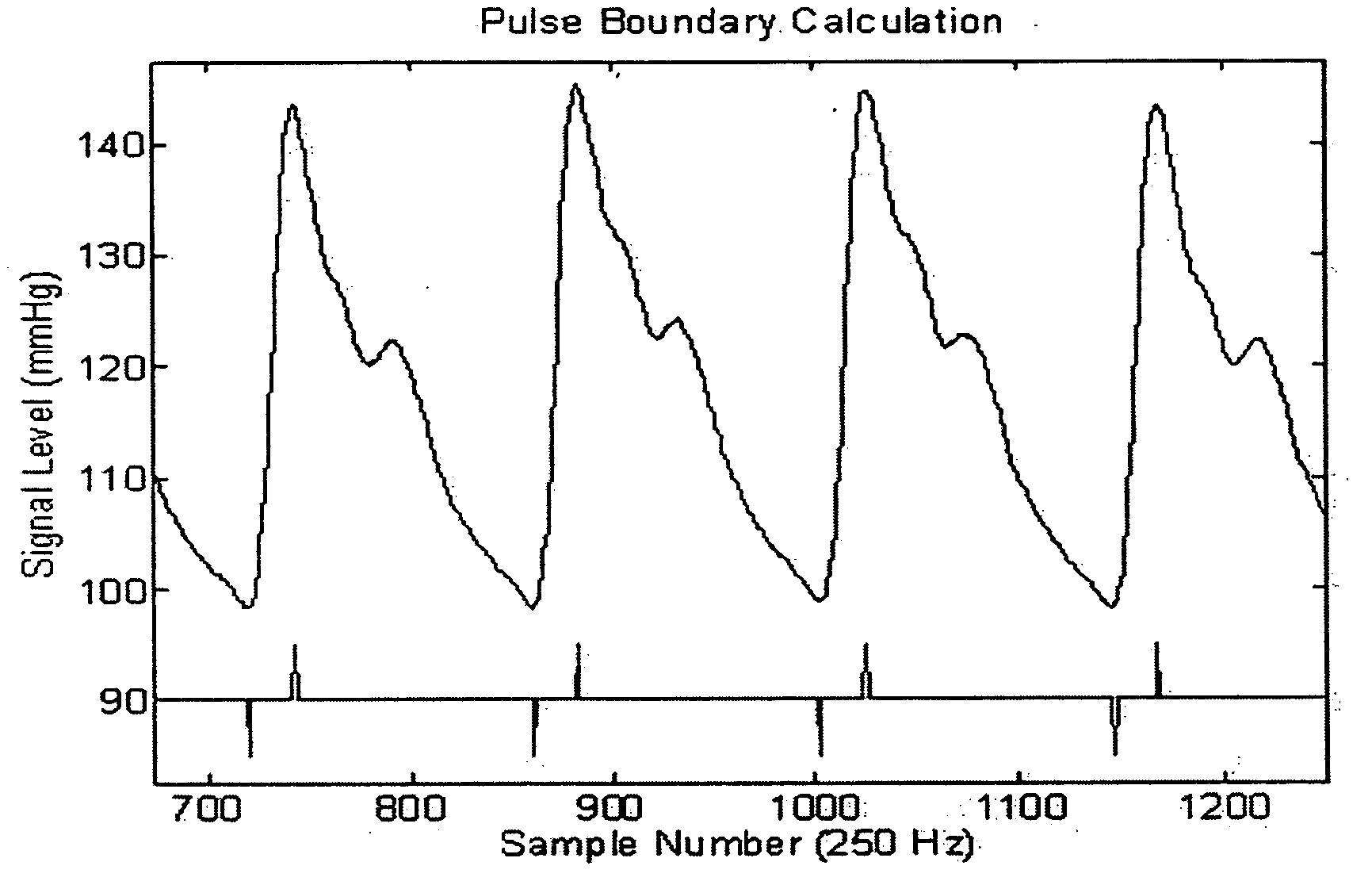
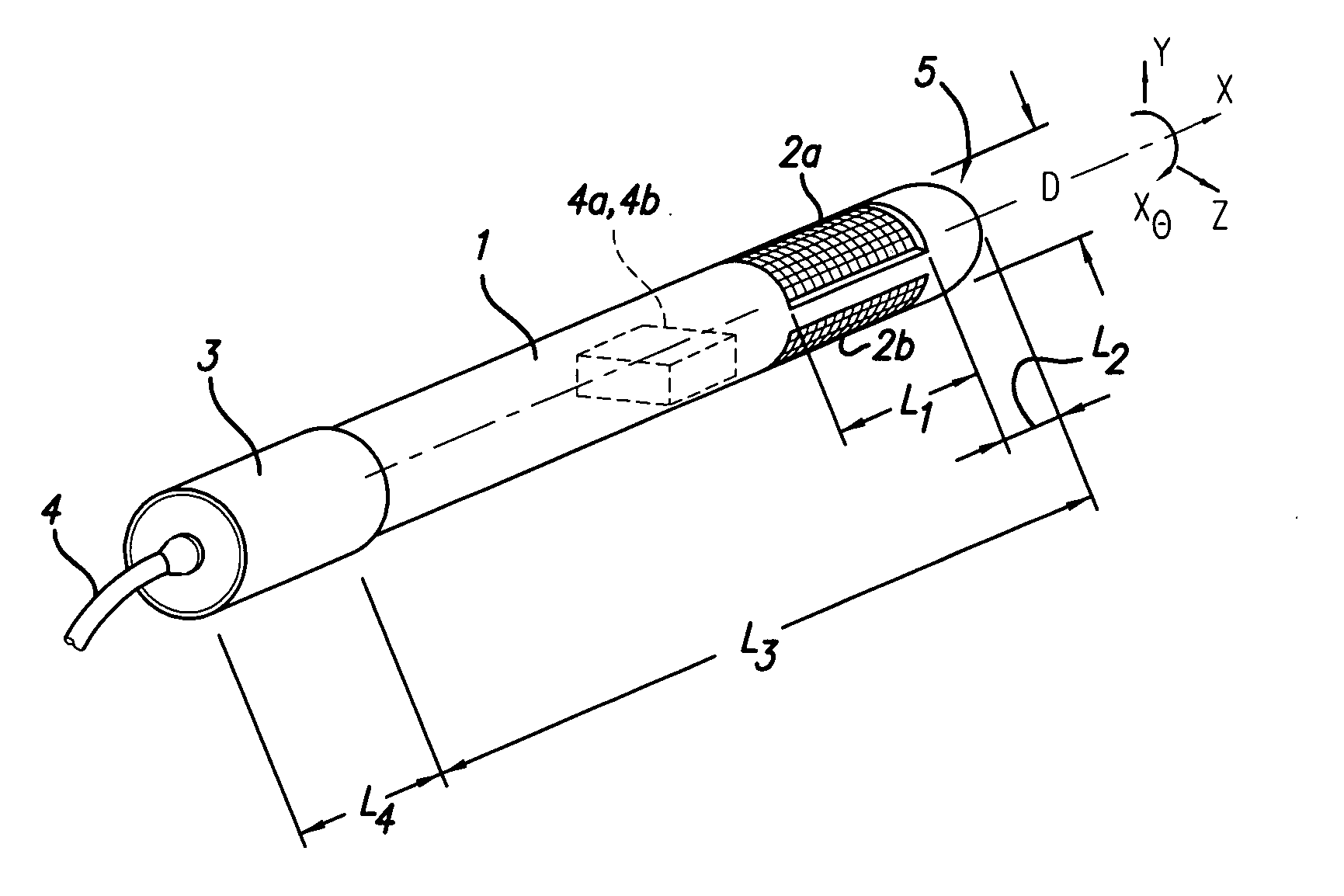
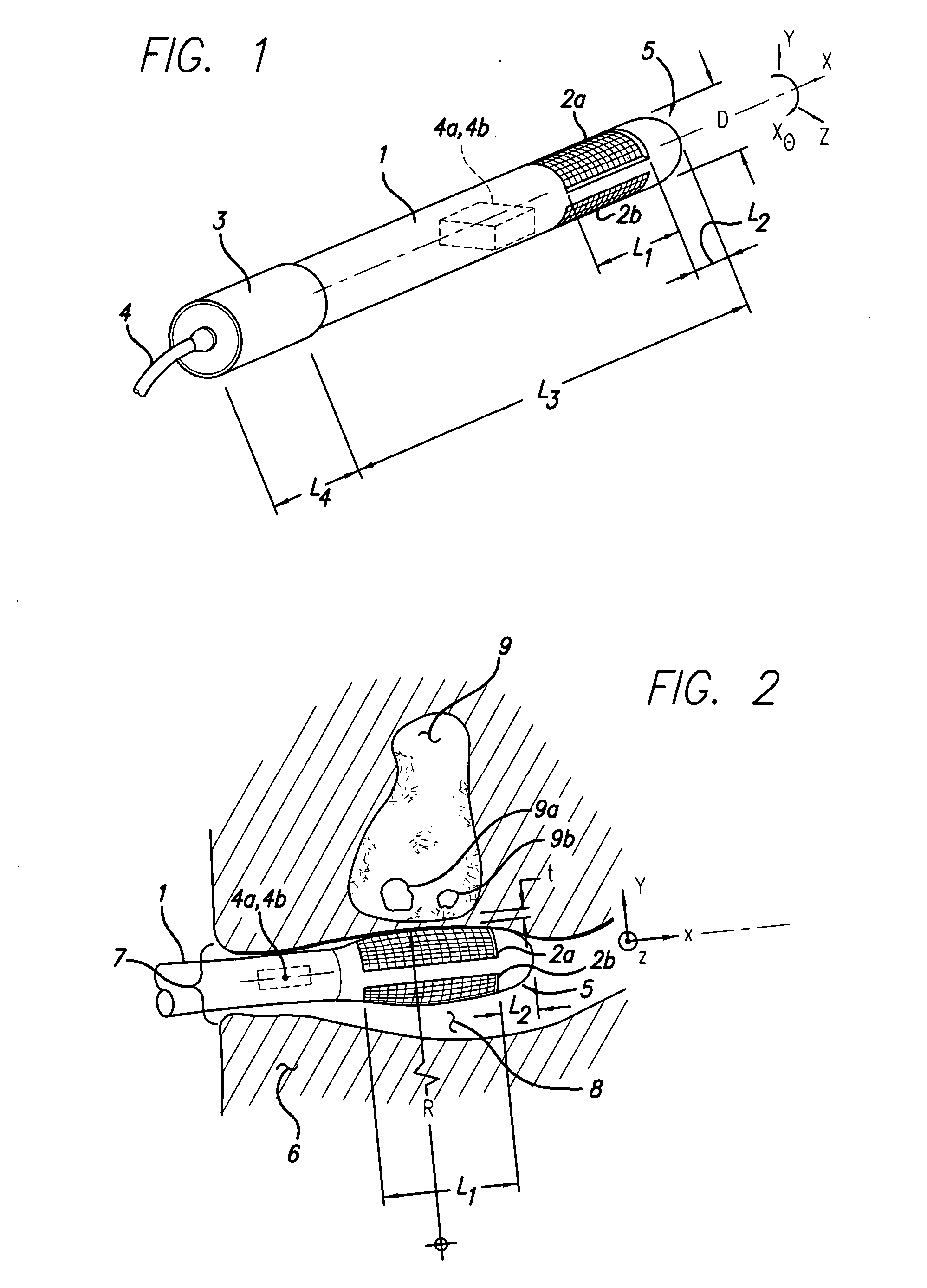
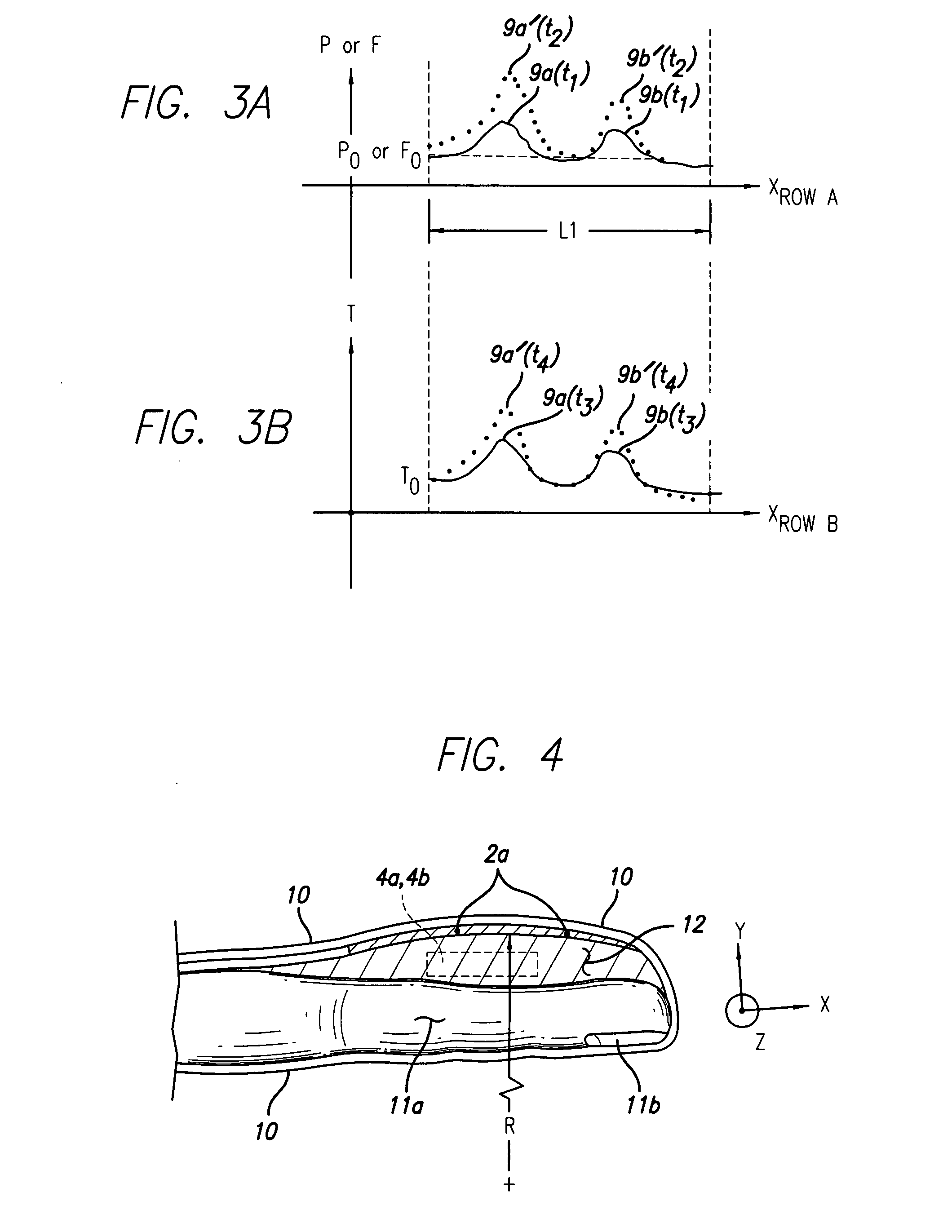
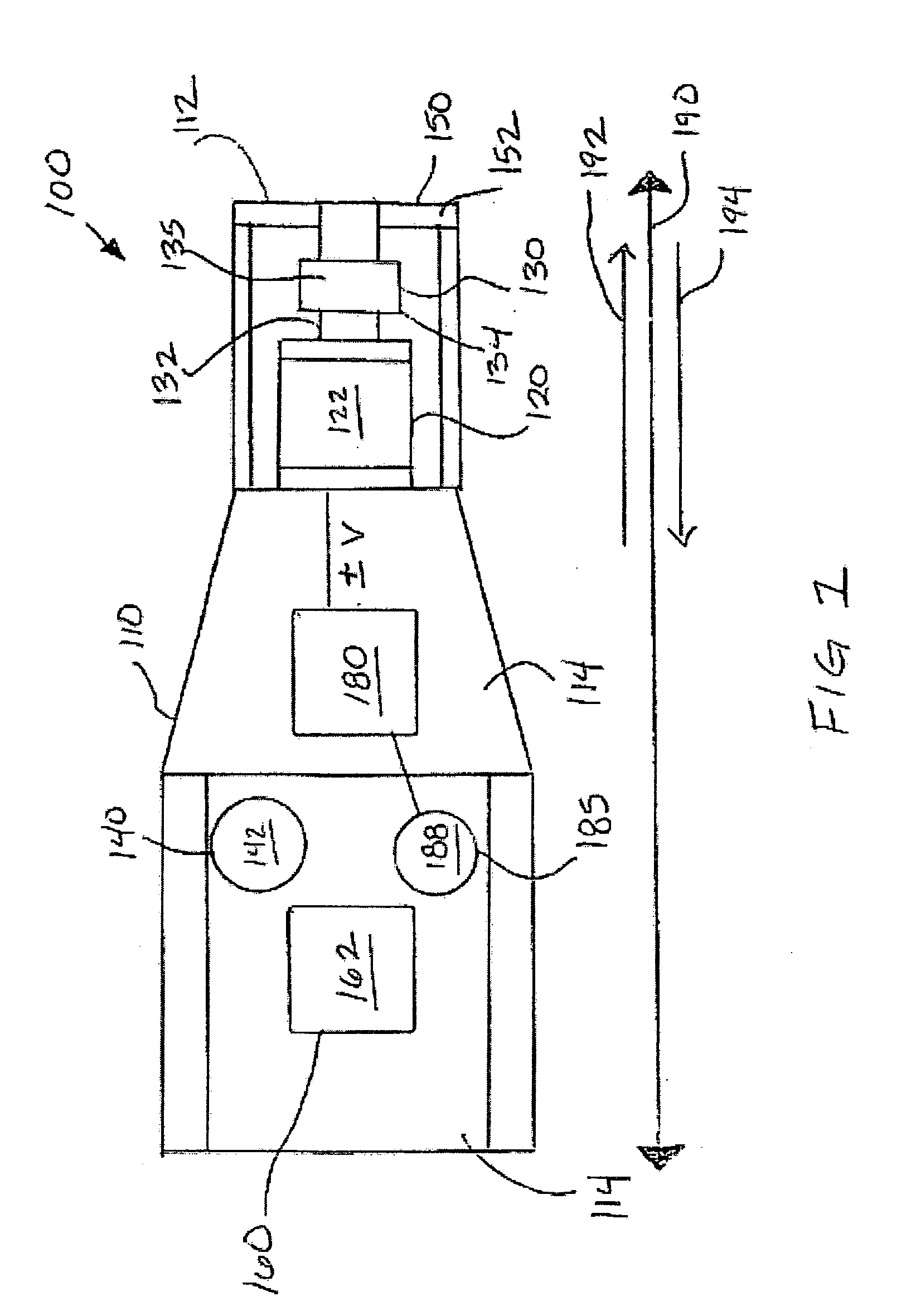
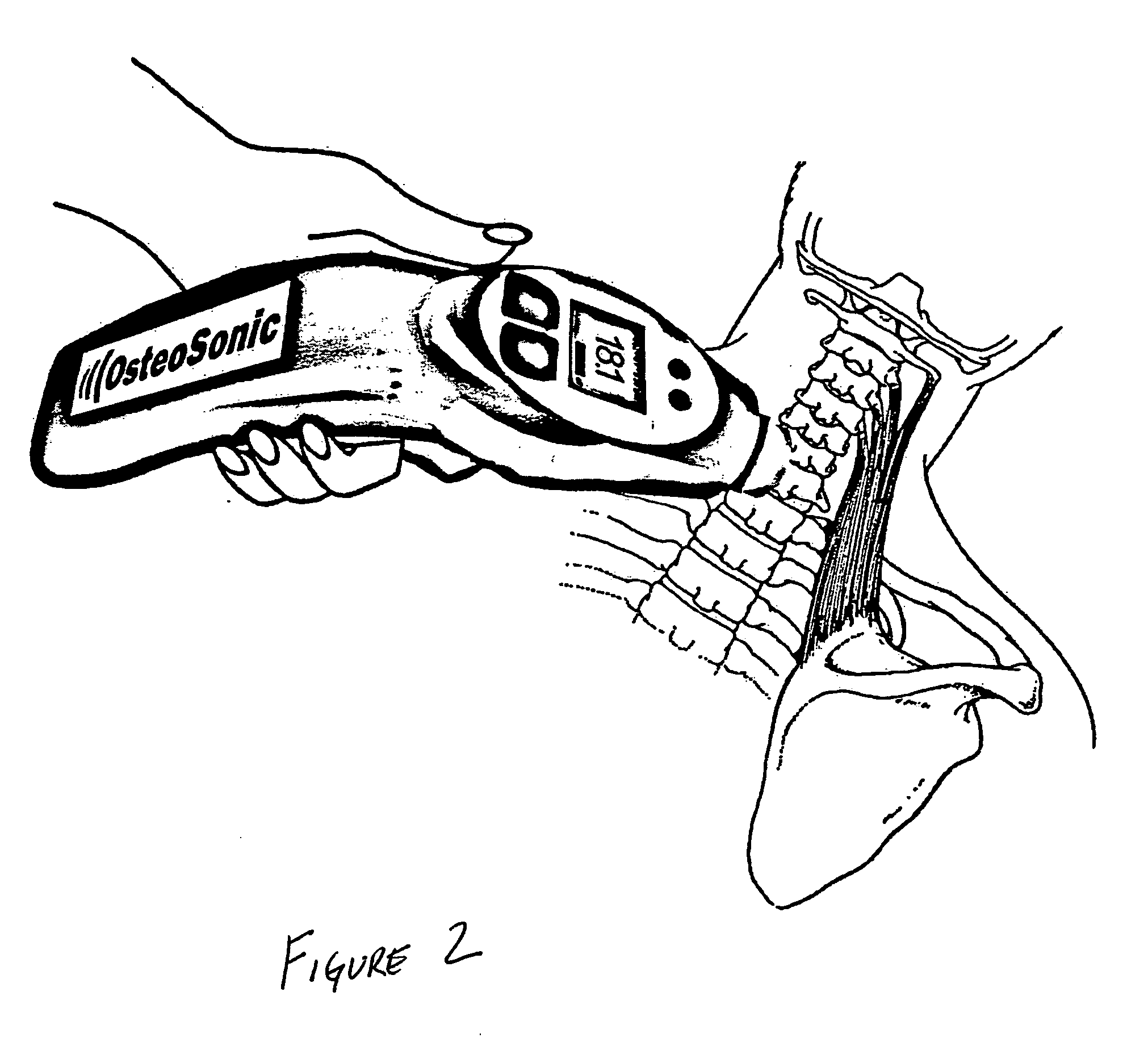
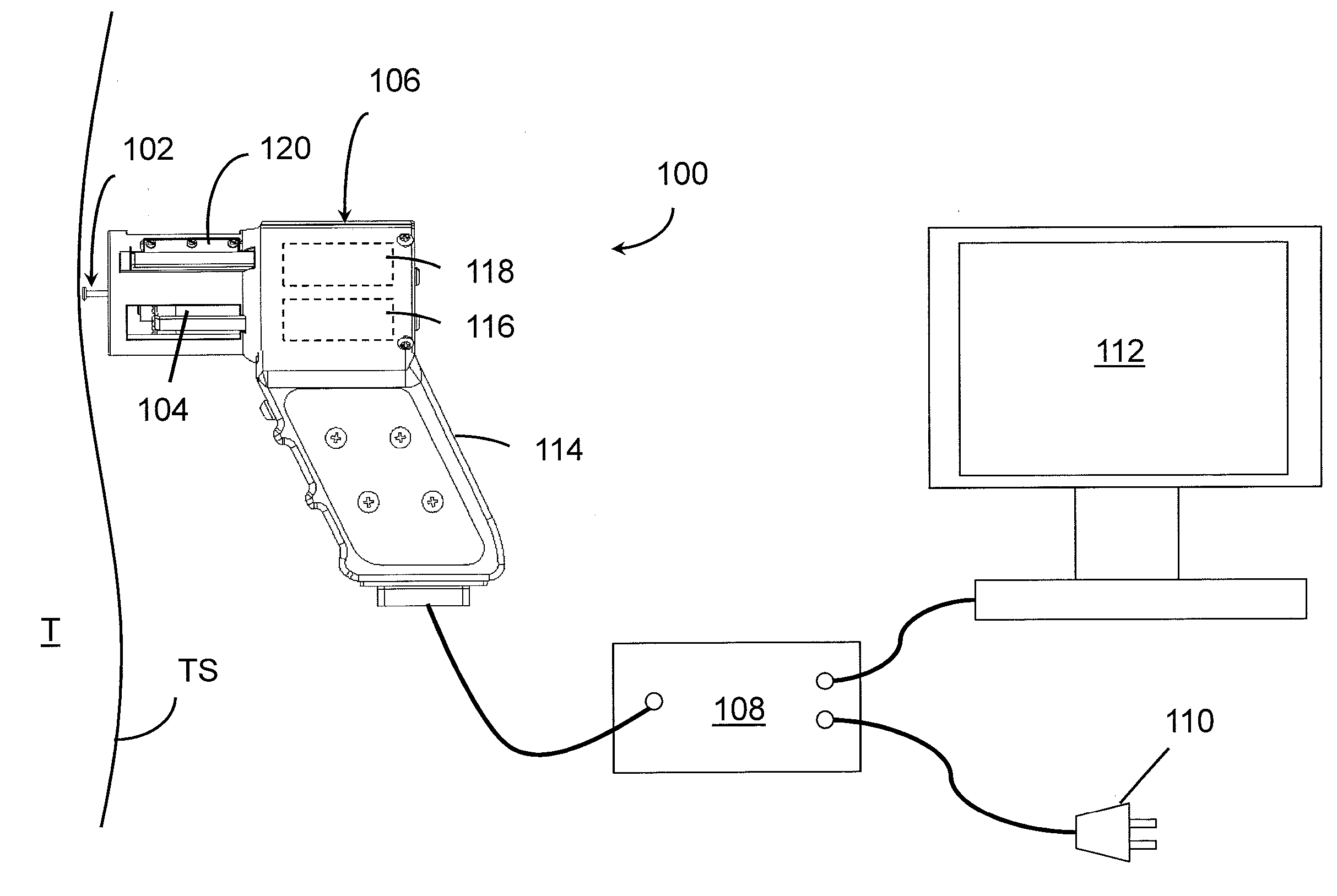
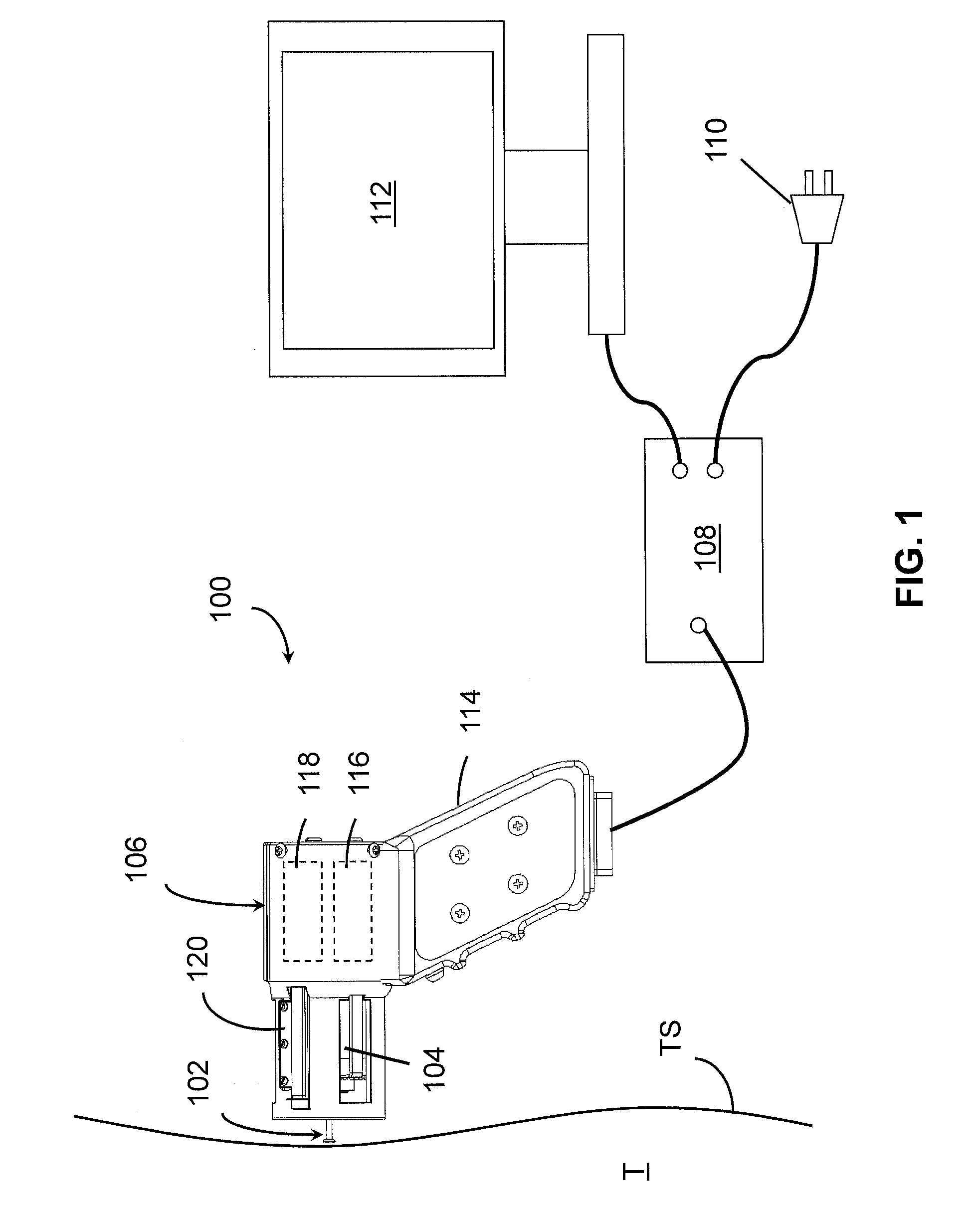
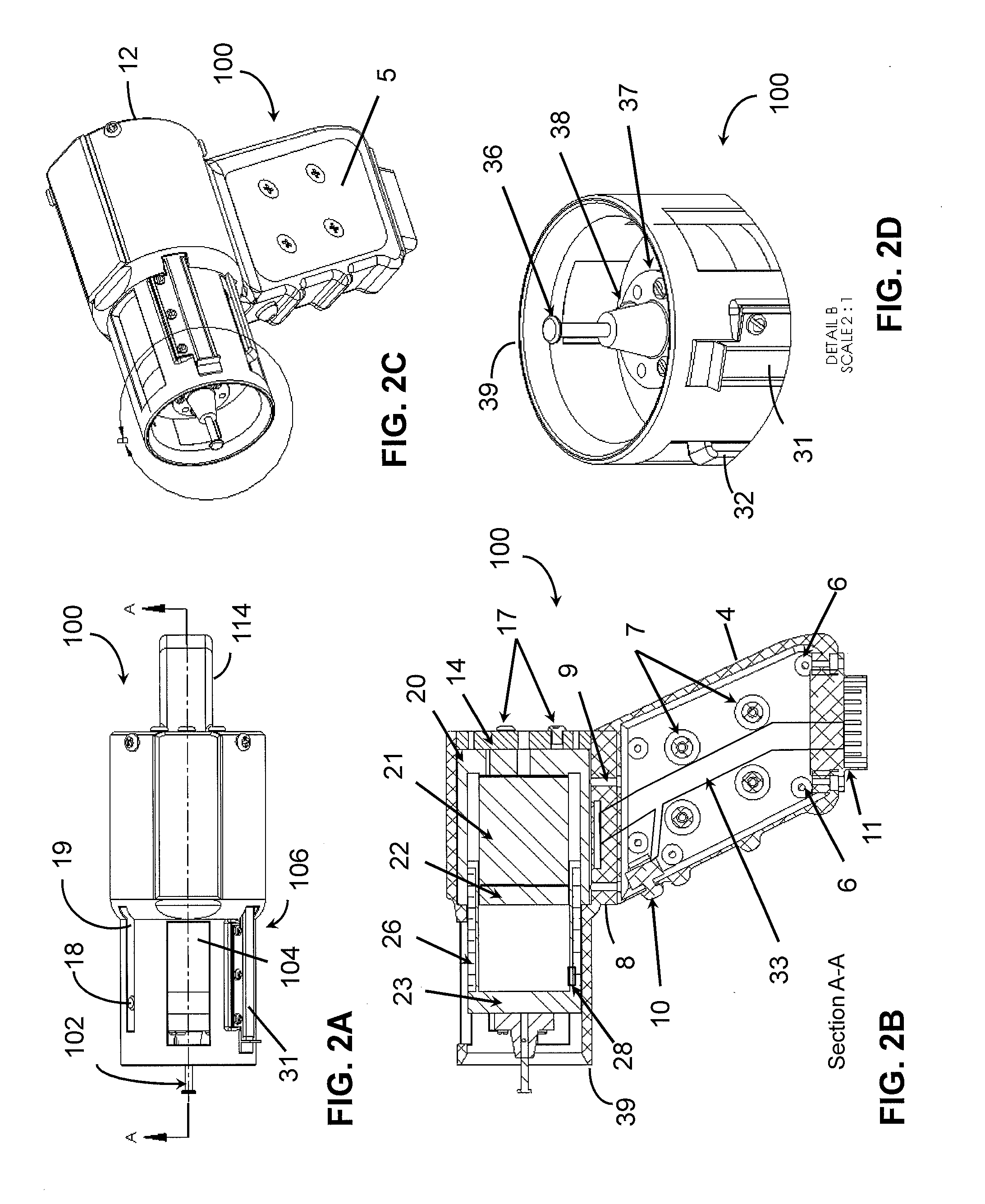
Disposable active pulse sensor
ActiveUS8764671B2Sufficient volumeDiagnostics using vibrationsCatheterOptical radiationUltrasound attenuation
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
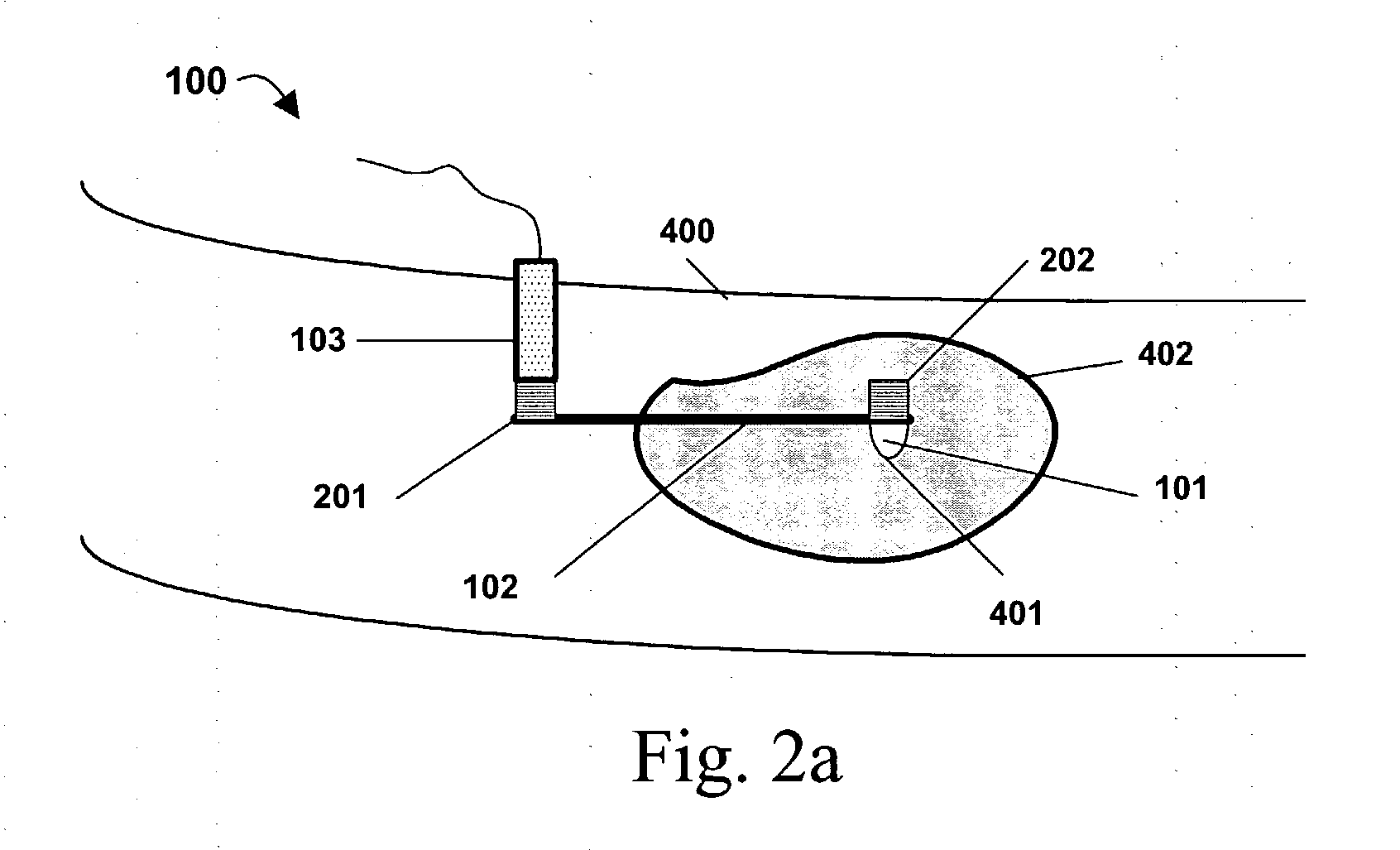
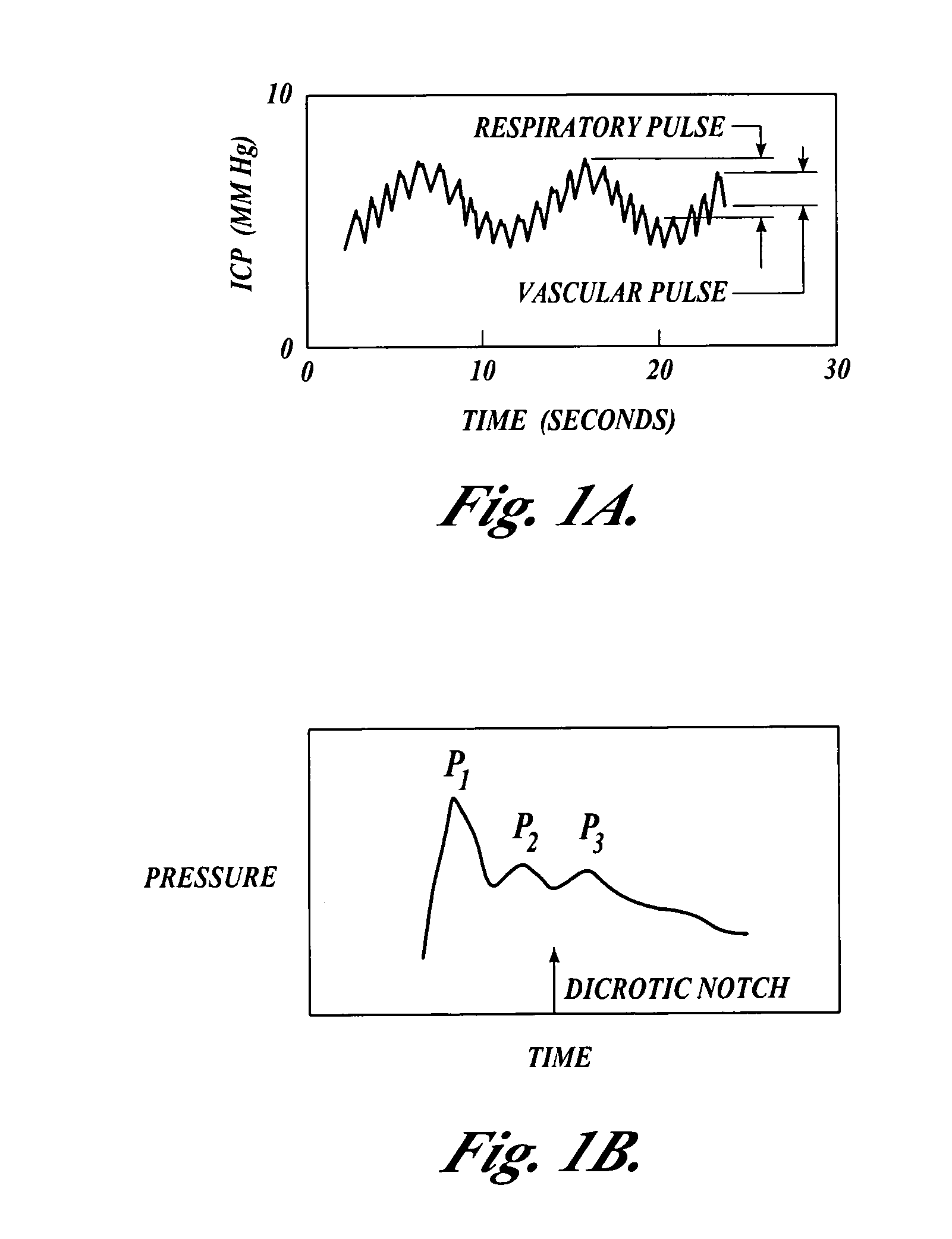
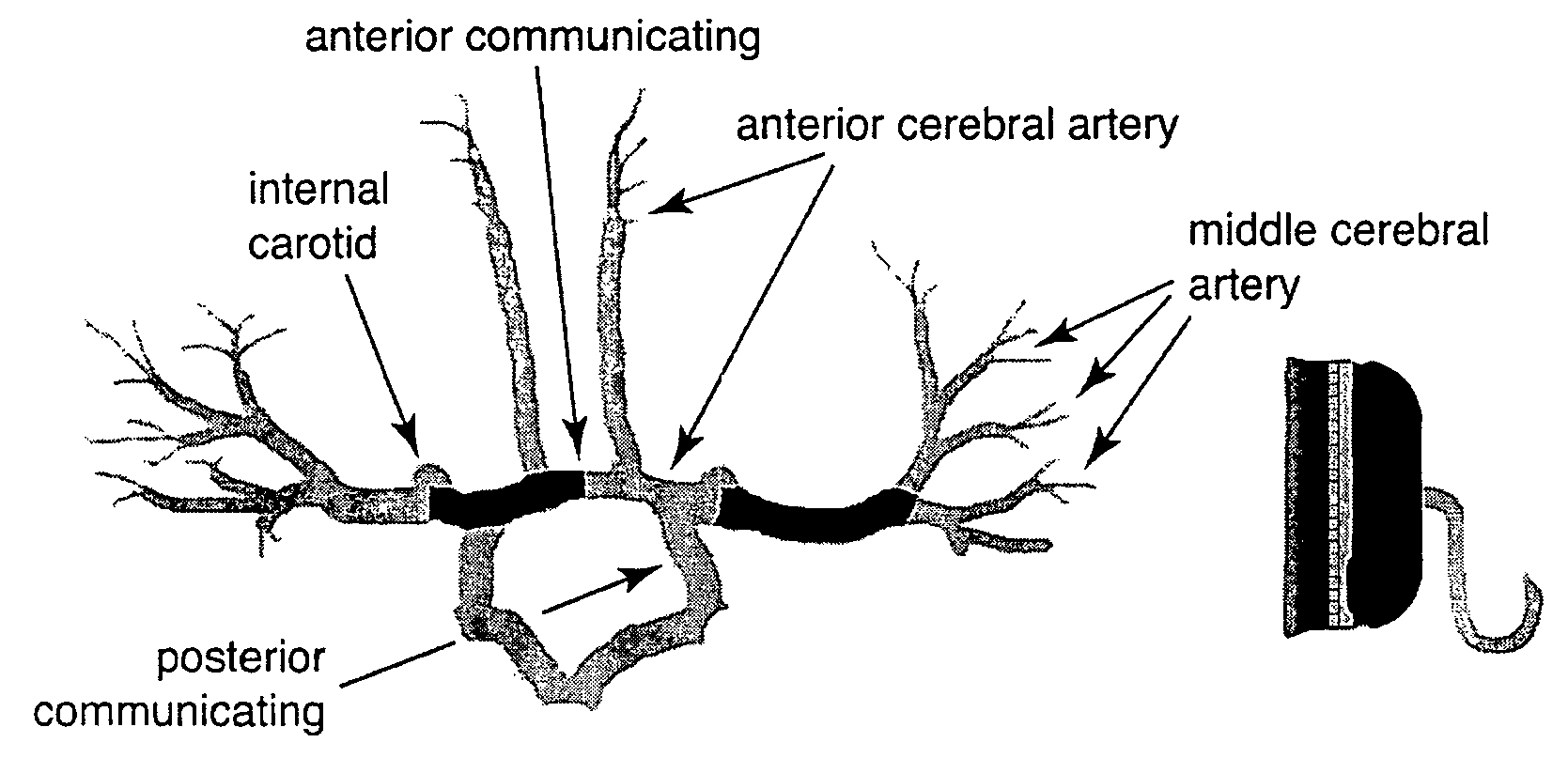
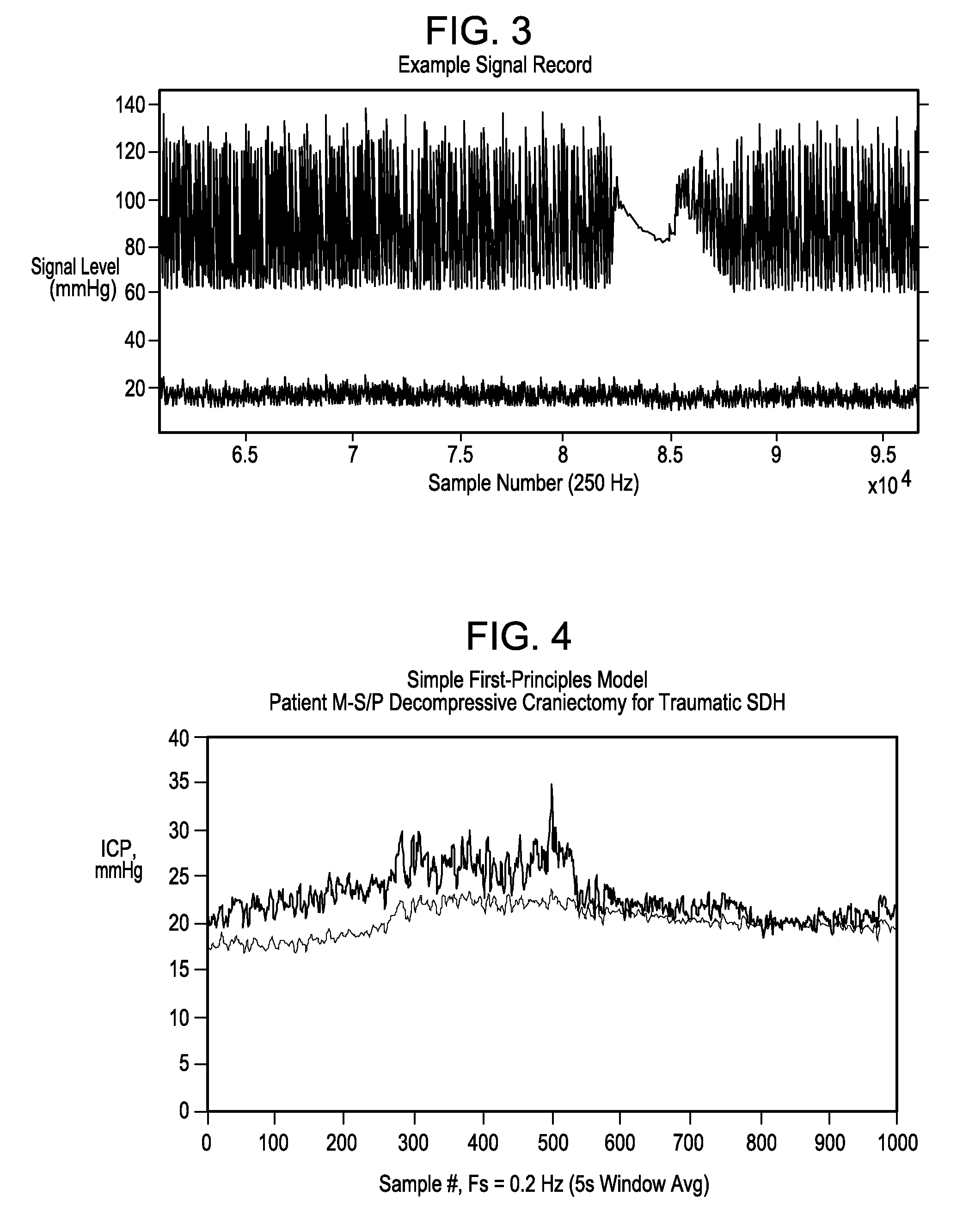
InactiveUS20050015009A1Accurate assessmentAccurate monitoringMedical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method, system and device for tissue characterization
InactiveUS20030220556A1Increase dynamical interactionEnhanced interactionDiagnostics using vibrationsSurgeryTissue characterizationEngineering
A method of characterizing a tissue present in a predetermined location of a body of a subject, the method comprising: generating mechanical vibrations at a position adjacent to the predetermined location, the mechanical vibrations are at a frequency ranging from 10 Hz to 10 kHz; scanning the frequency of the mechanical vibrations; and measuring a frequency response spectrum from the predetermined location, thereby characterizing the tissue.
Owner:VESPRO
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Prostate BPH and tumor detector also useable on other tissues
Prostate probe systems are disclosed for assessing one or both of BPH or prostate cancer. The prostate probe systems comprise either a force or pressure sensor mounted on or in a rectally insertable probe or a temperature sensor mounted on or in a rectally insertable probe, or both. Also disclosed are probe systems for evaluating a condition of a prostate gland. Finally, force or hardness mapping devices are disclosed for palpation-examination of patient anatomical tissues for abnormalities or assessing states of firmness.
Owner:SLIWA JOHN W +1
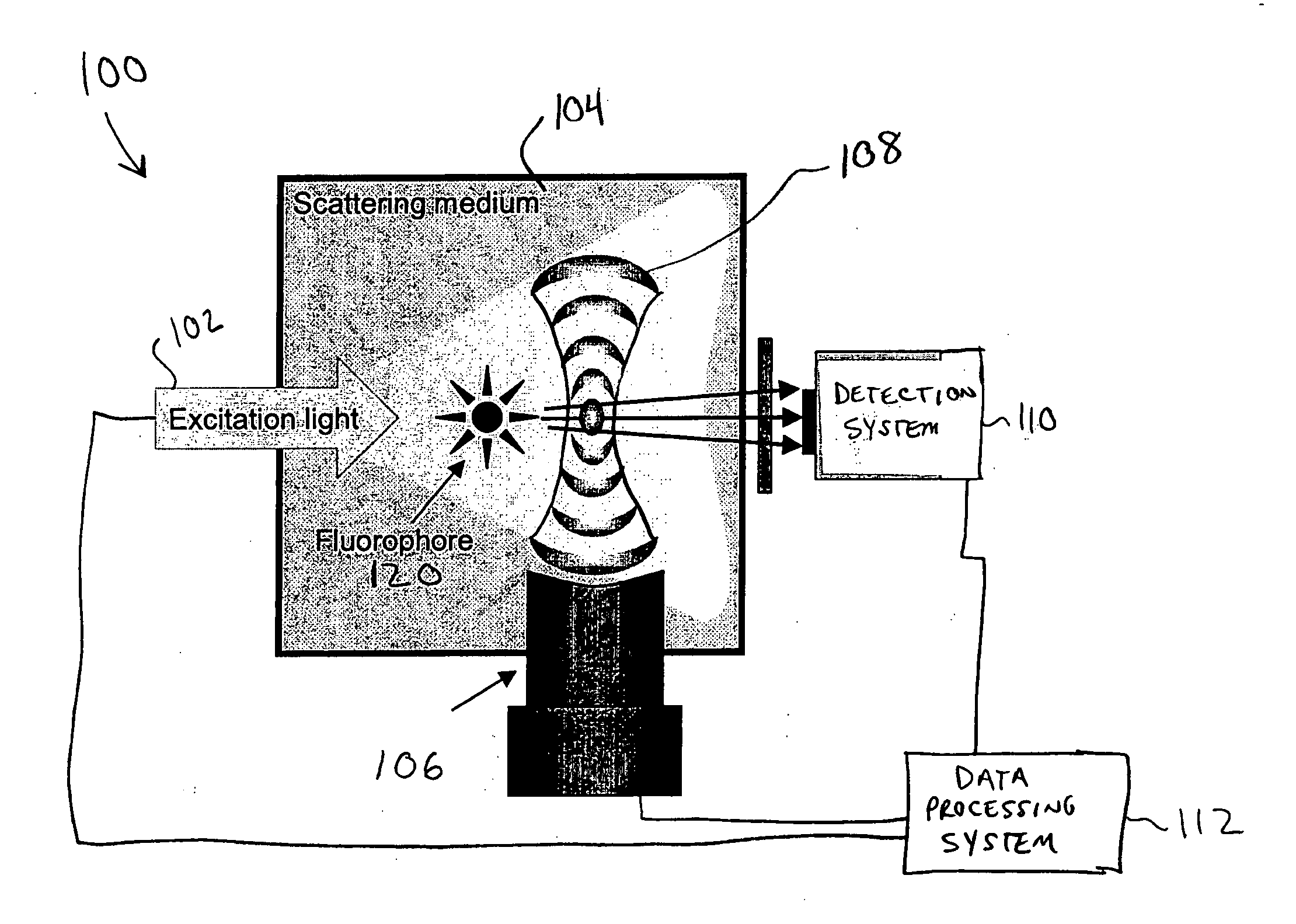
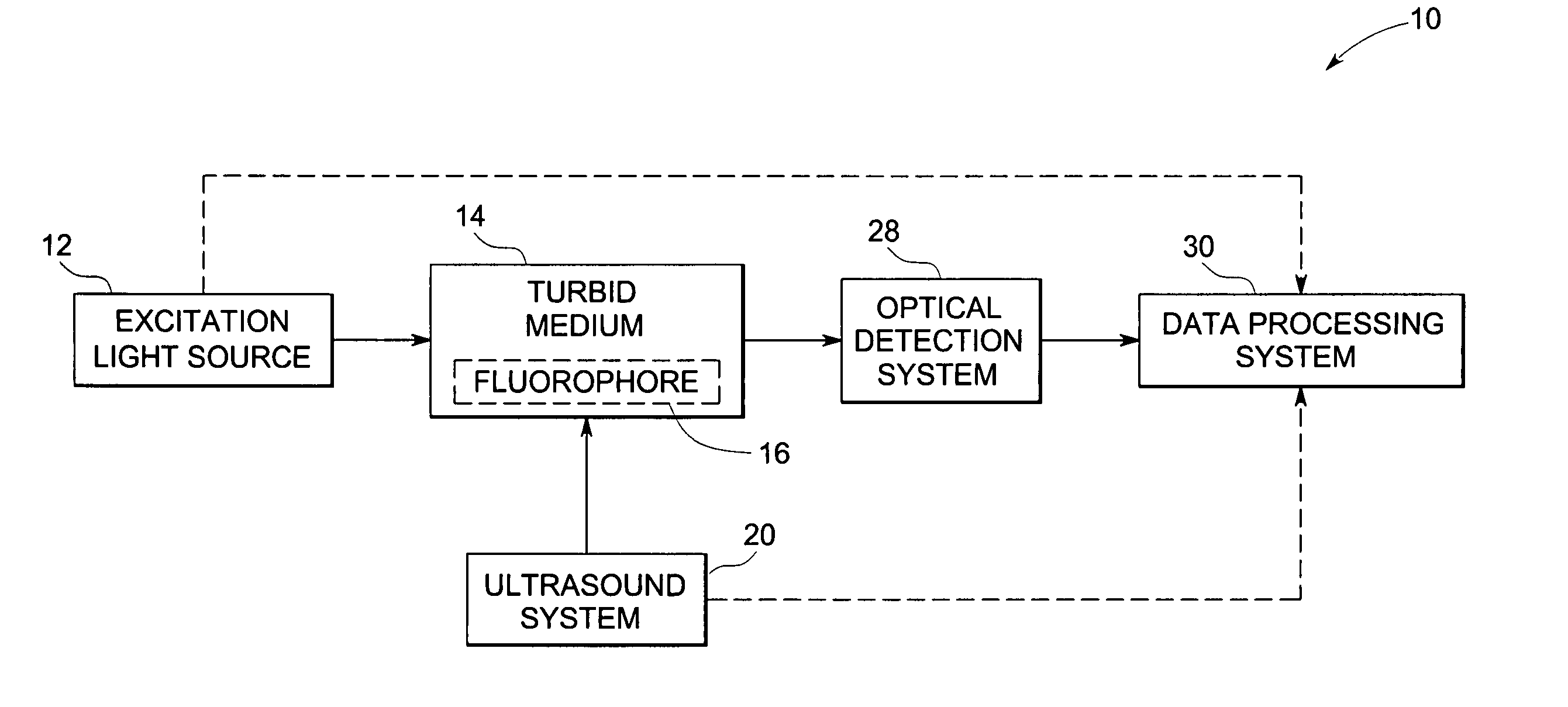
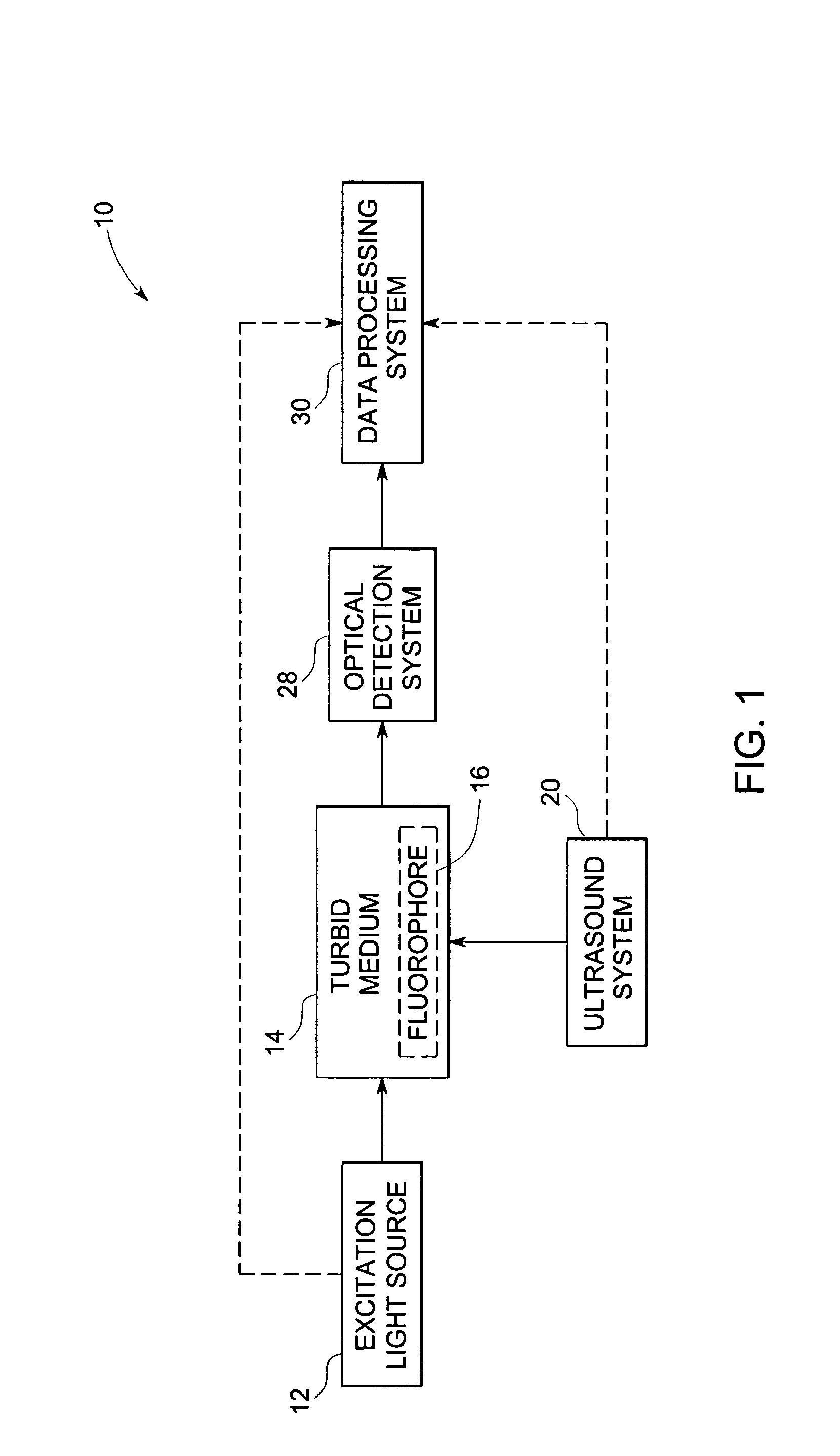
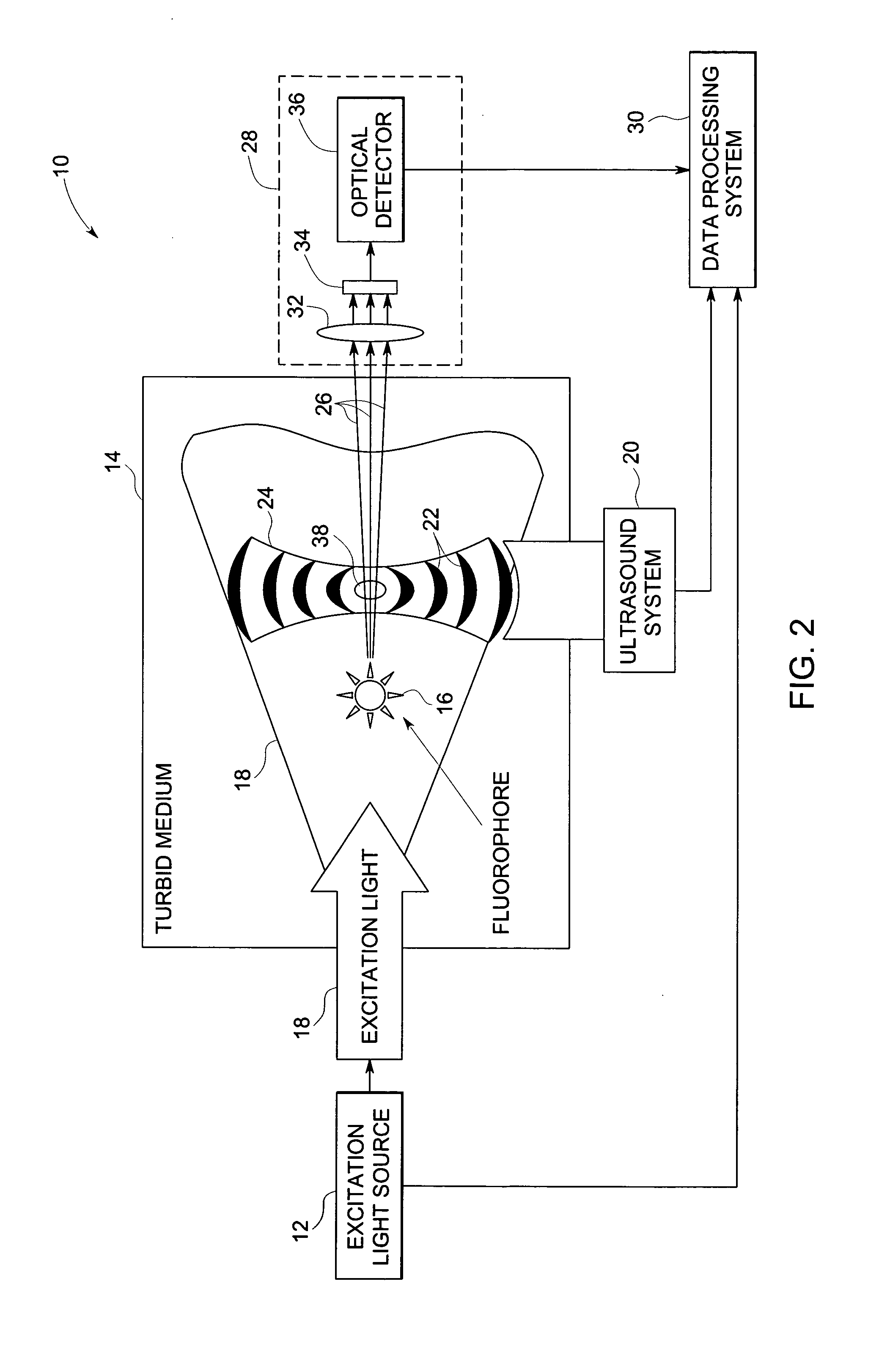
Method and system for ultrasonic tagging of fluorescence
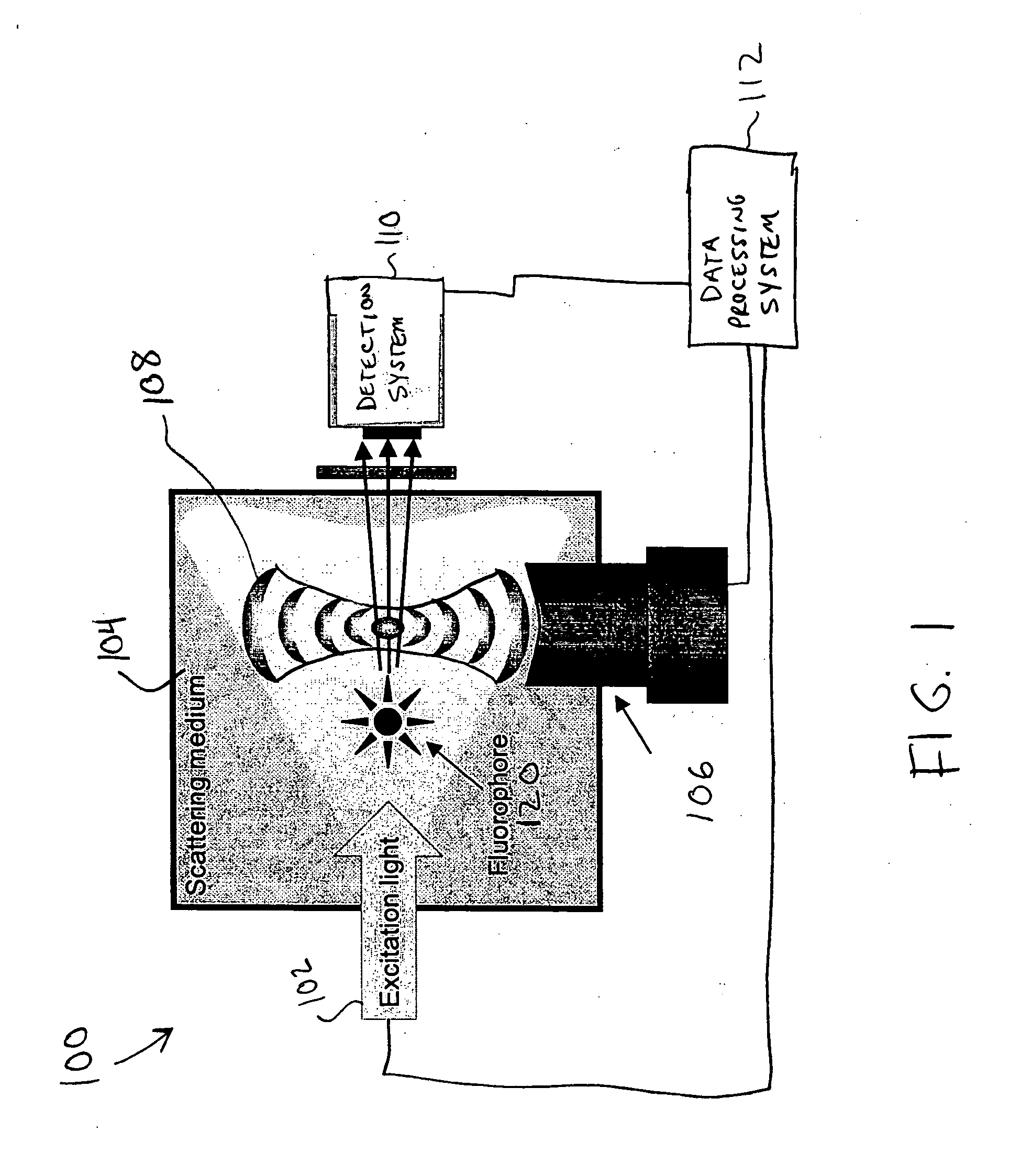
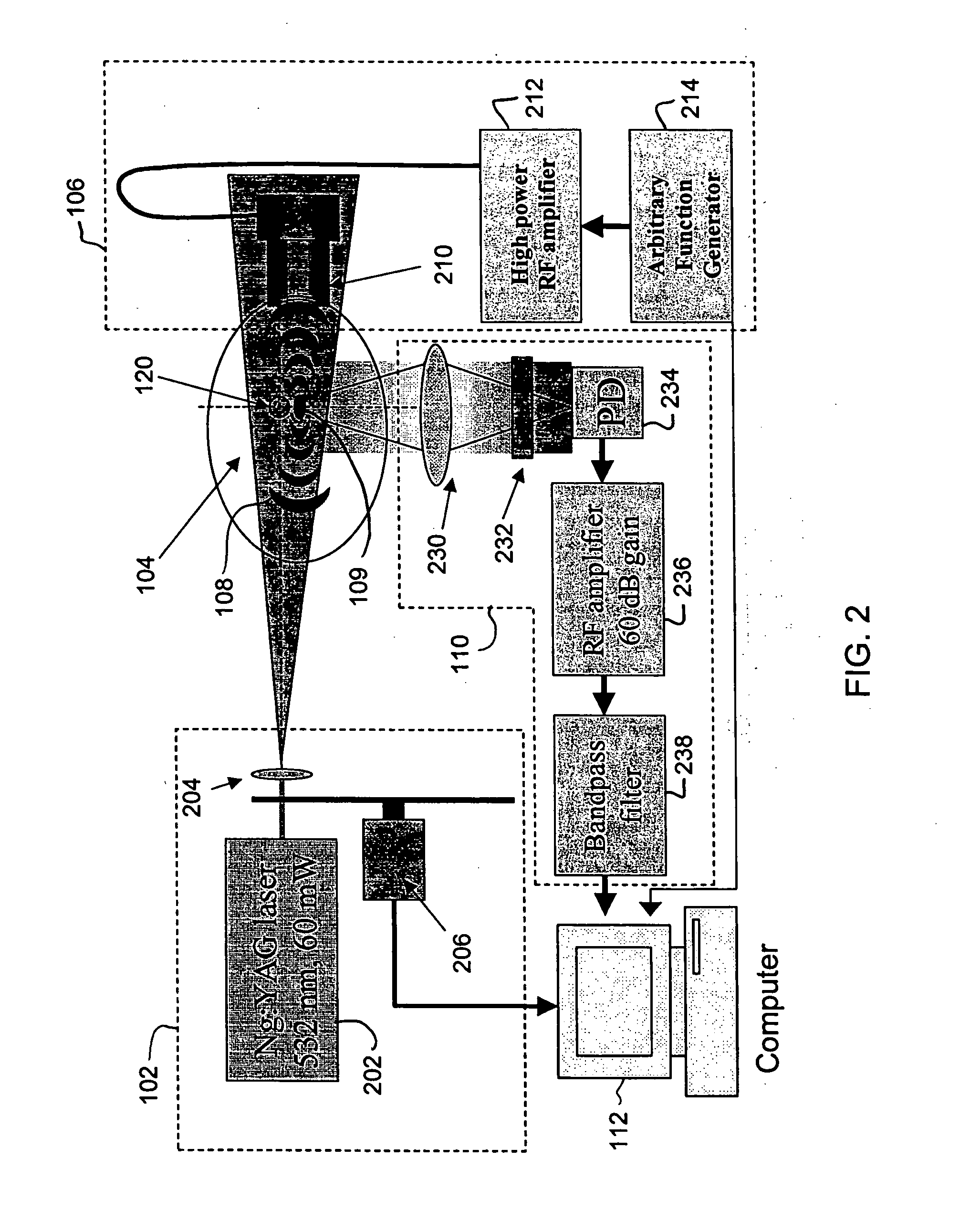
InactiveUS20050107694A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce computing timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsSonificationFluorescence
A method and system for localization of fluorescence in a scattering medium such as a biological tissue are provided. In comparison to other optical imaging techniques, this disclosure provides for improved spatial resolution, decreased computational time for reconstructions, and allows anatomical and functional imaging simultaneously. The method including the steps of illuminating the scattering medium with an excitation light to excite the fluorescence; modulating a portion of the emitted light from the fluorescence within the scattering medium using an ultrasonically induced variation of material properties of the scattering medium such as the refractive index; detecting the modulated optical signal at a surface of the scattering medium; and reconstructing a spatial distribution of the fluorescence in the scattering medium from the detected signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
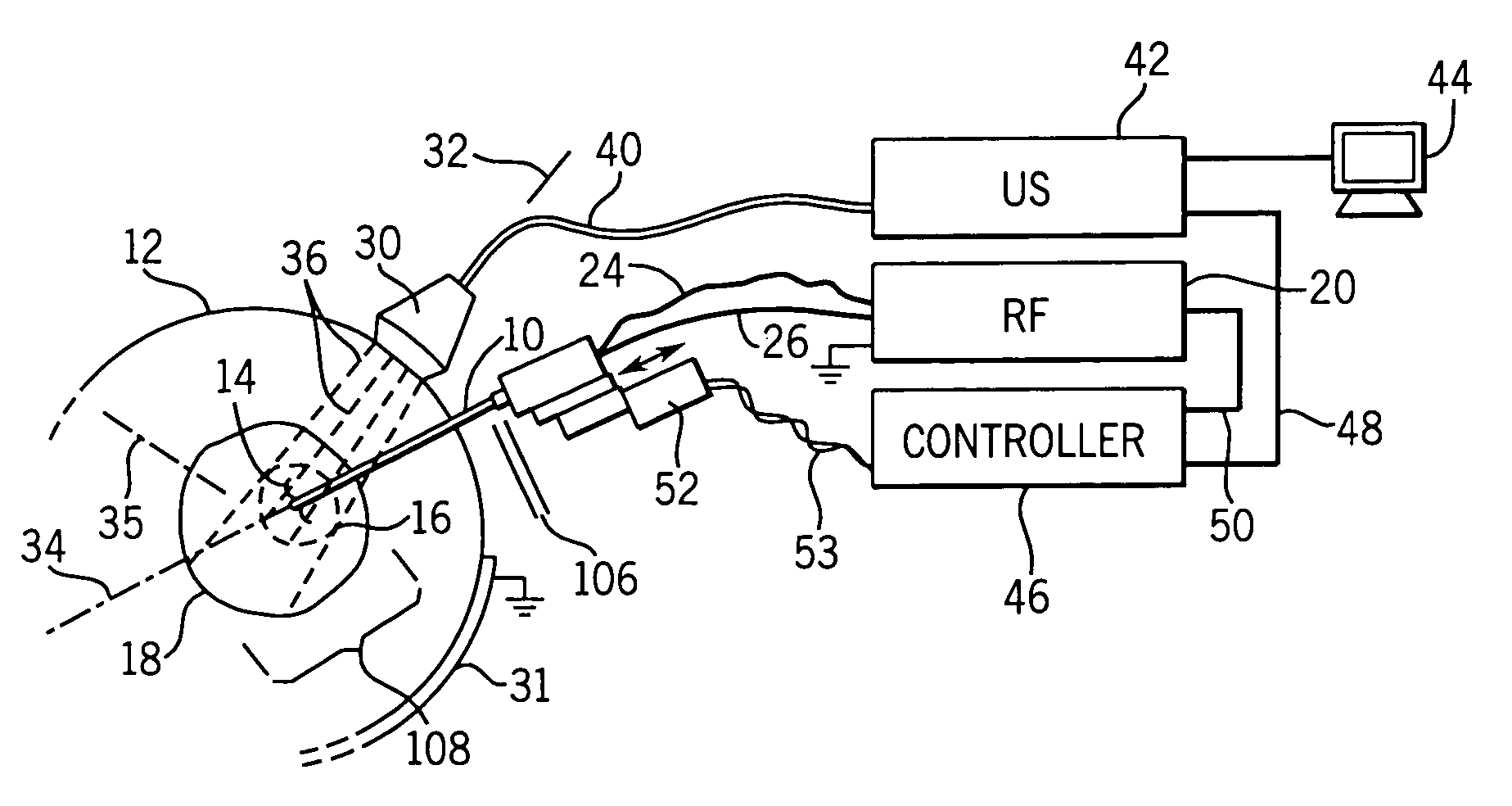
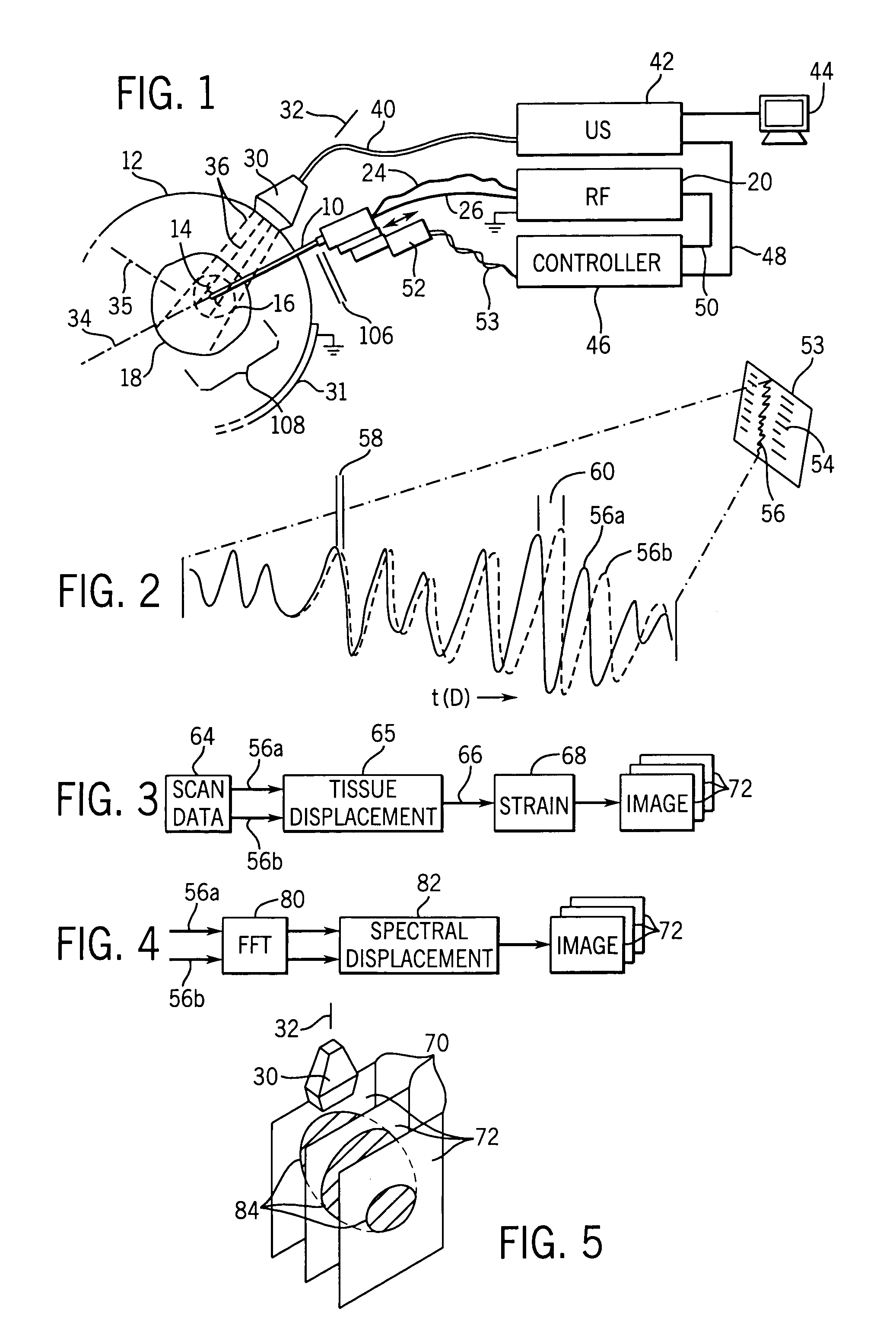
Elastographic imaging of in vivo soft tissue
ActiveUS7166075B2Stabilize against lateral slippageThe process is simple and effectiveWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionNuclear medicineRf ablation
Elastographic images provide visualization in two or three dimensions of RF ablation lesions to guide in the ablation process. Compression may be applied using the RF probe. A similar technique may be applied to in vivo imaging of soft tissue without ablation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
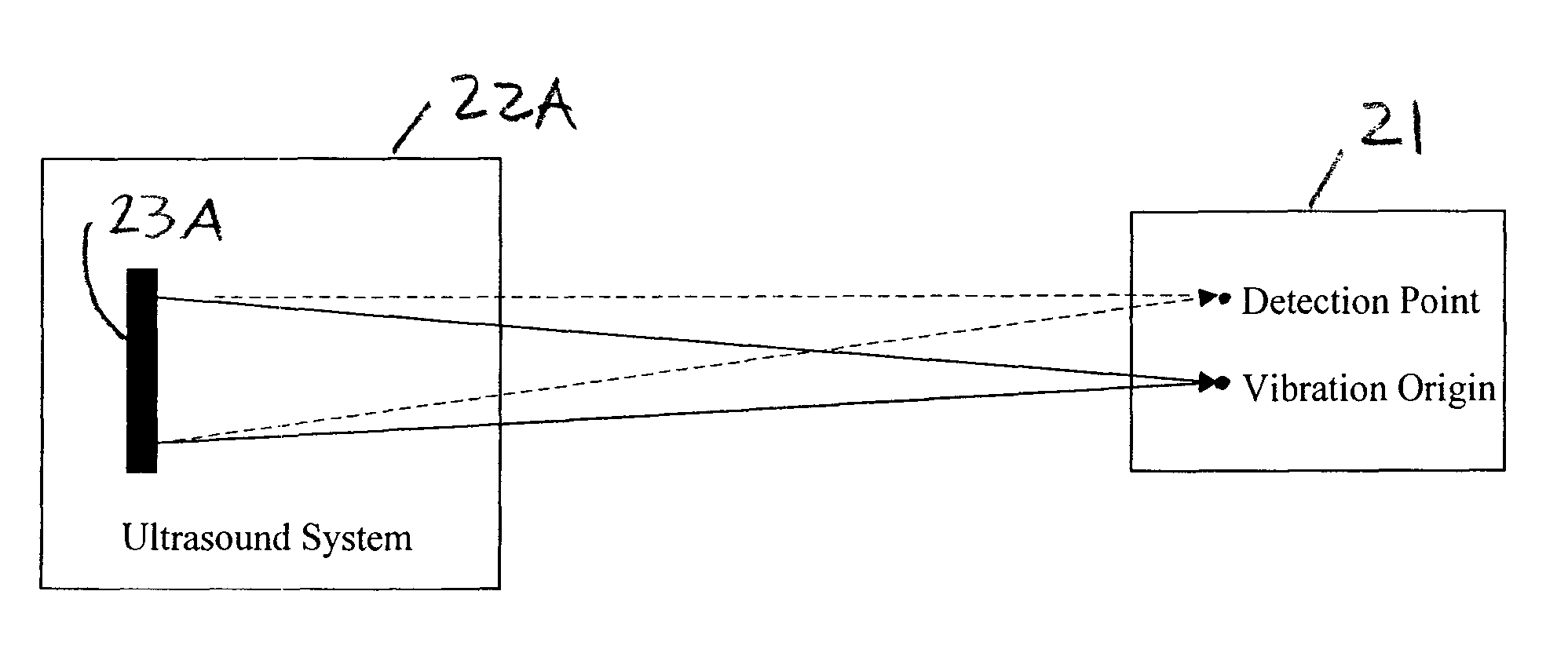
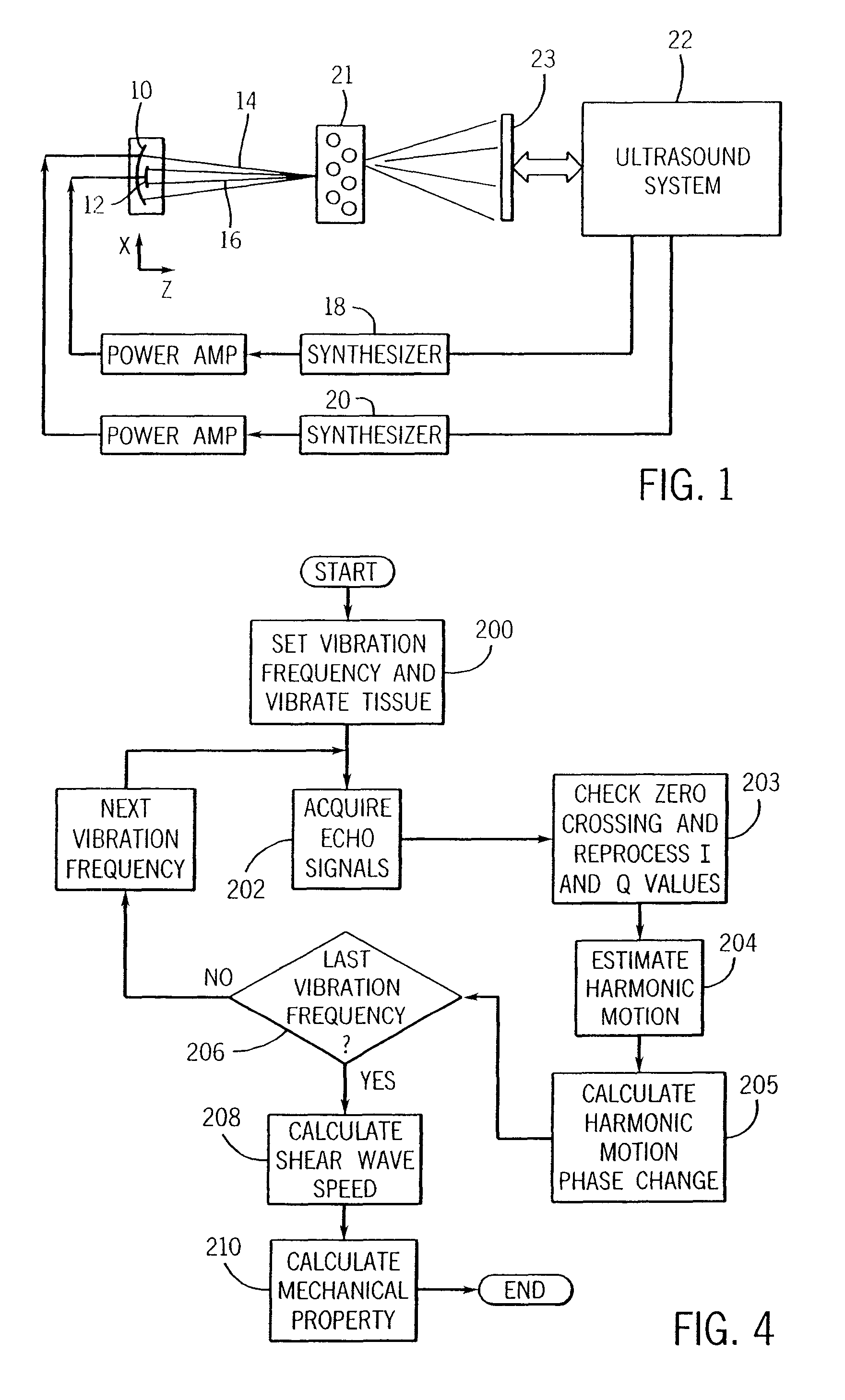
Ultrasound vibrometry
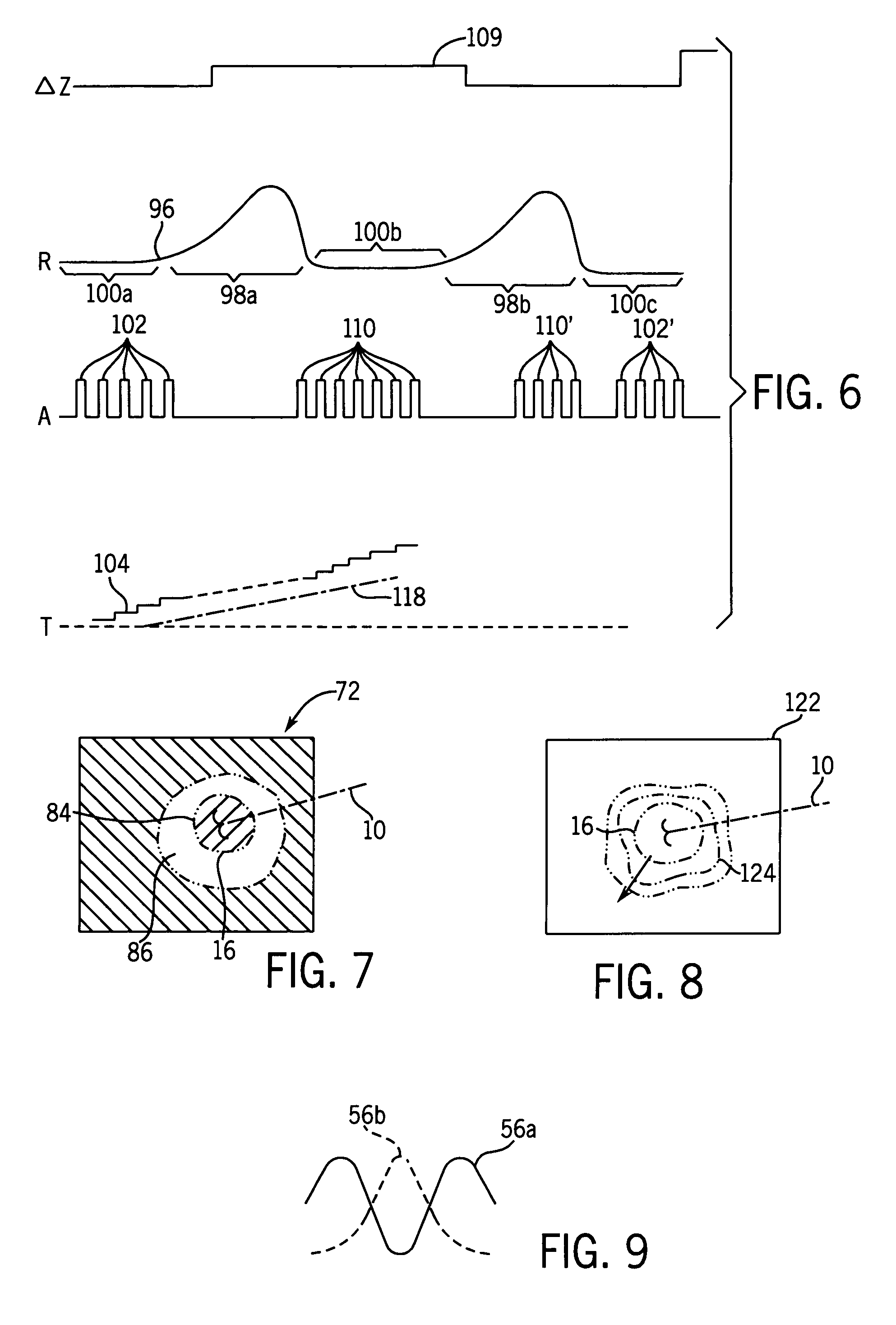
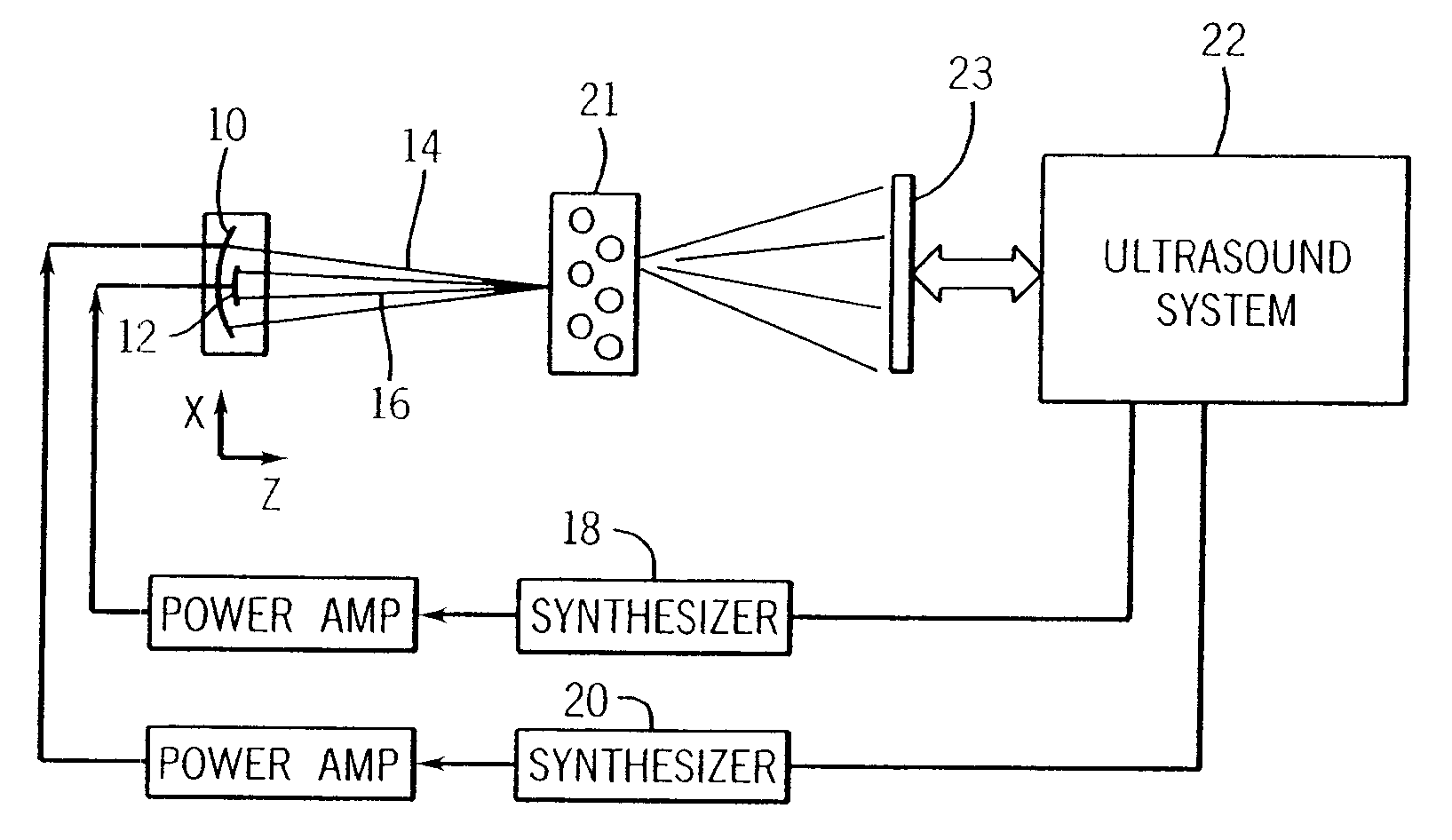
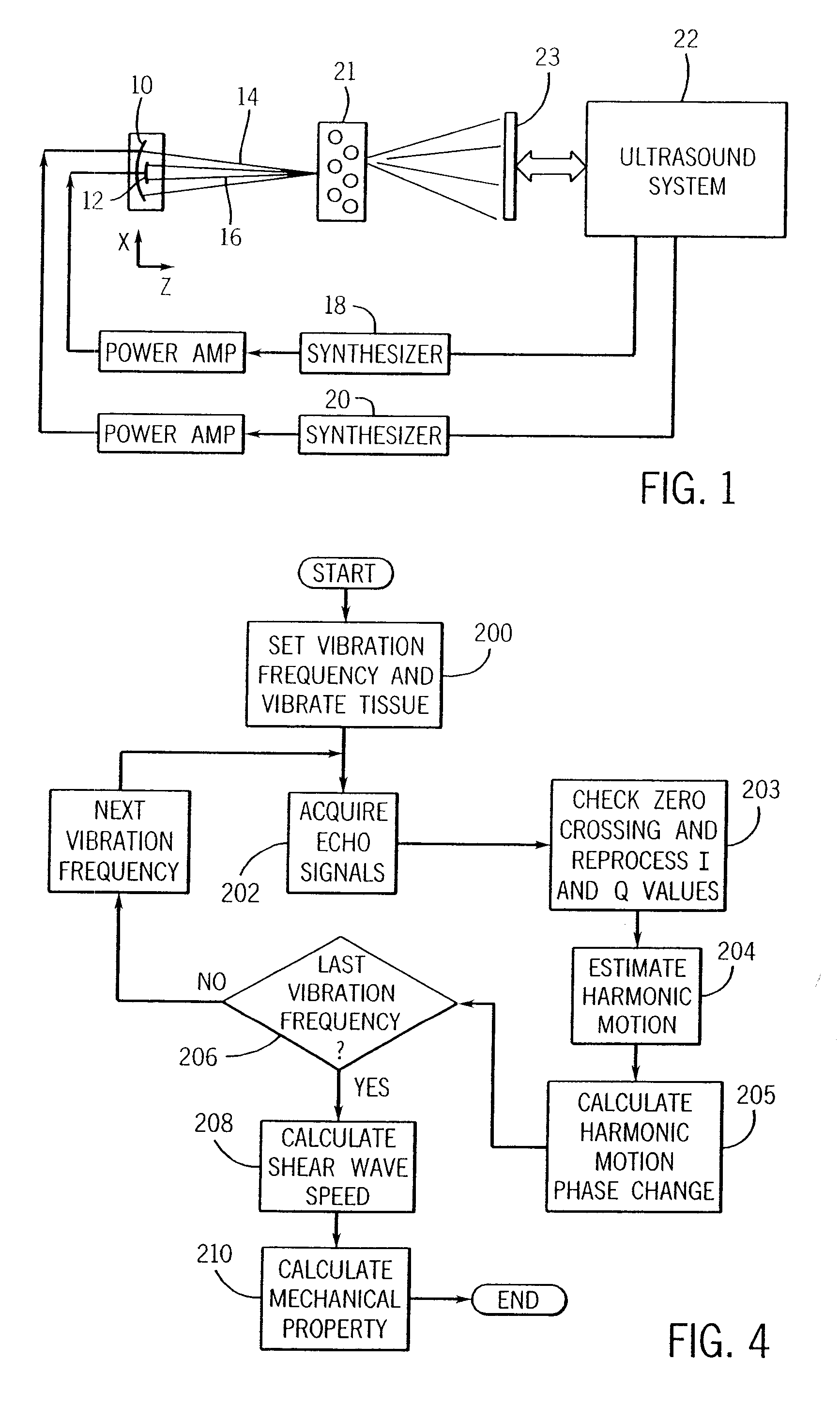
ActiveUS20070038095A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSonificationMechanical property
A method for measuring a mechanical property of a subject includes using an ultrasonic transducer to apply ultrasonic vibration pulses to a vibration origin in the subject in an on-off time sequence in order to impart a harmonic motion at a prescribed frequency to the subject, and when the vibration pulses are off, using the same transducer to apply ultrasonic detection pulses to a motion detection point and to receive echo signals therefrom in order to sense the harmonic motion on the subject at the motion detection point. From the harmonic signal information, a harmonic signal is detected and a characteristic such as amplitude or phase of the detected harmonic signal is measured. The mechanical property is calculated using the measured characteristic using for example a wave speed dispersion method.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Noninvasive tissue assessment
InactiveUS20050113691A1Reduce measurement errorSufficient pressureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFrequency spectrumPost operative
Methods and apparatus for non-invasively assessing physiological hard of soft tissue of human and other species are described. In a preferred embodiment, tissue is vibrationally stimulated in vivo through a frequency spectrum. The tissue reacts against the stimulus and the reaction is preferably measured and recorded. Based on analytical algorithms or comparisons with previously taken measurements, changes within the tissue can be detected and used for diagnostic purposes. Further embodiments describe the usage of the device and methods for in vivo intra-operative and post-operative implant evaluations and as a therapeutic tool.
Owner:RICE UNIV
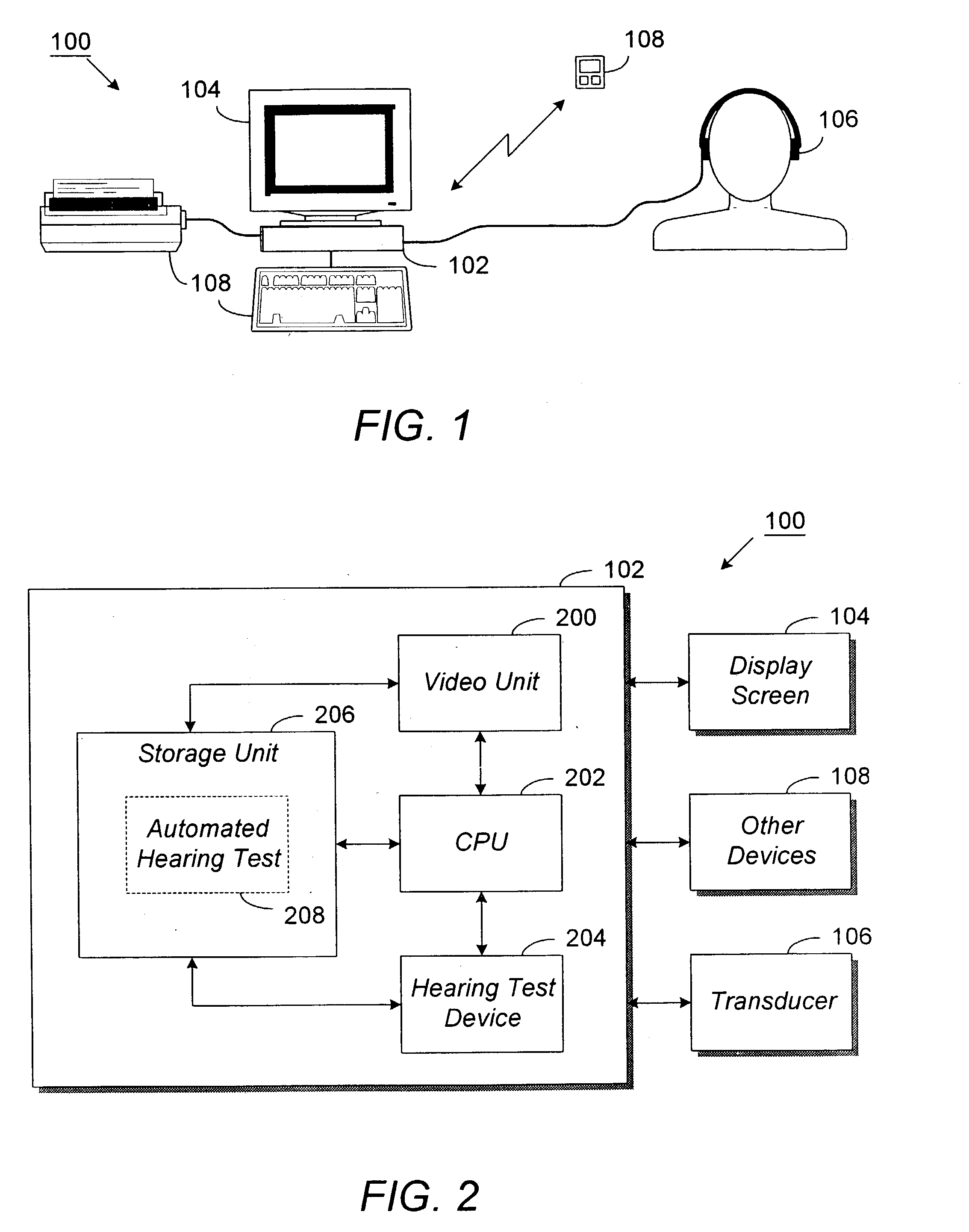
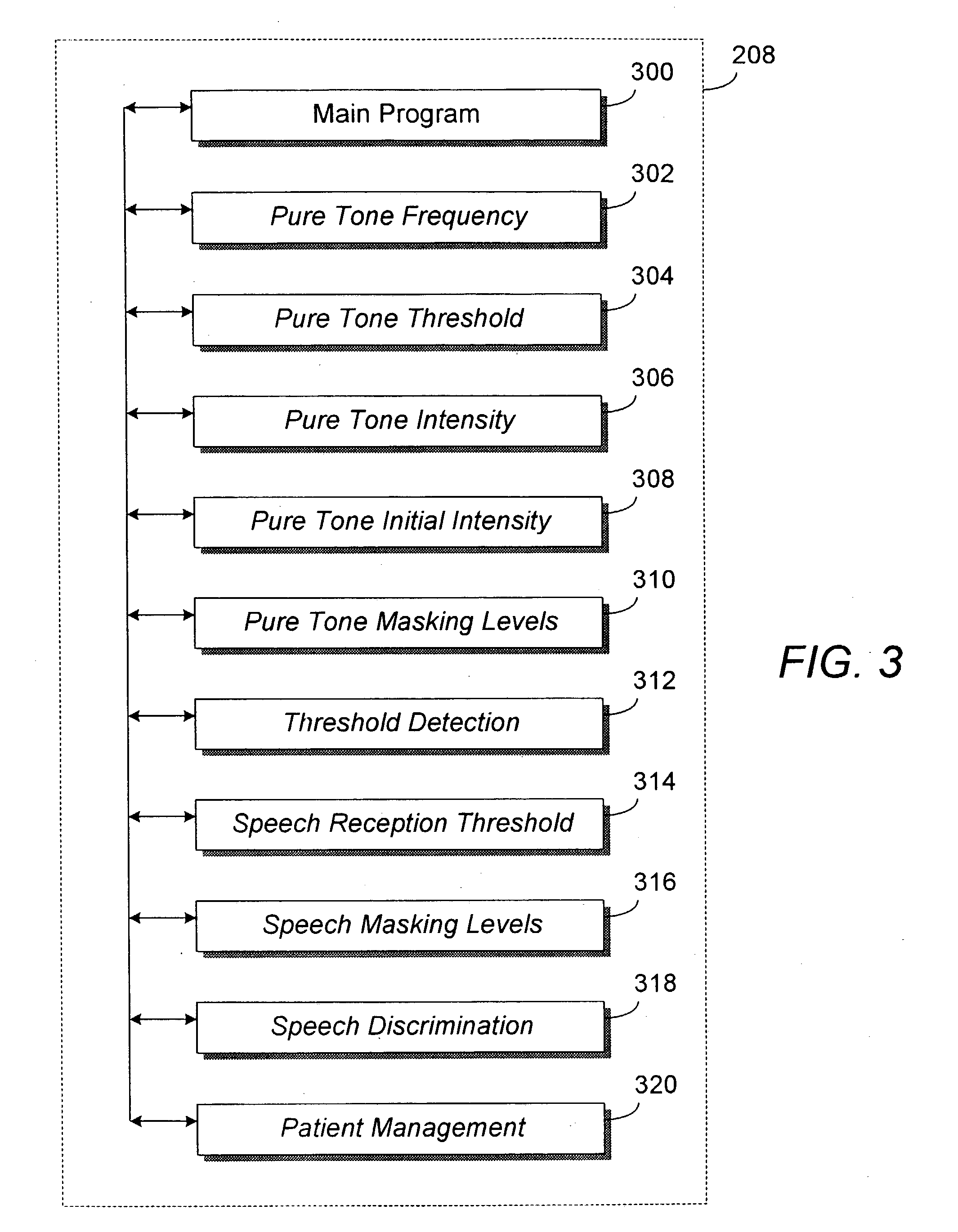
Automated diagnostic hearing test
InactiveUS20040006283A1Diagnostics using vibrationsBone conduction transducer hearing devicesAcoustic reflexSpeech reception threshold
Method and system are disclosed for automated testing of a patient's hearing. The automated hearing test allows the patient to quickly and accurately test his own hearing with minimal or no assistance from an audiologist or other hearing health professionals. The test prompts and instructs the patient for inputs and responses as needed as needed. The patient can select one or several tests to be performed, including air and bone conduction testing with masking, speech reception threshold, speech discrimination, and tympanogram / acoustic reflex testing. Multiple languages are supported. Data obtained from one test may be used for another test or another iteration of the same test to calculate masking levels. The automatic hearing test also detects ambient noise and can compensate for it in the test results. If a contingency occurs, the automated hearing test is configured to page the operator for assistance.
Owner:TYMPANY +1
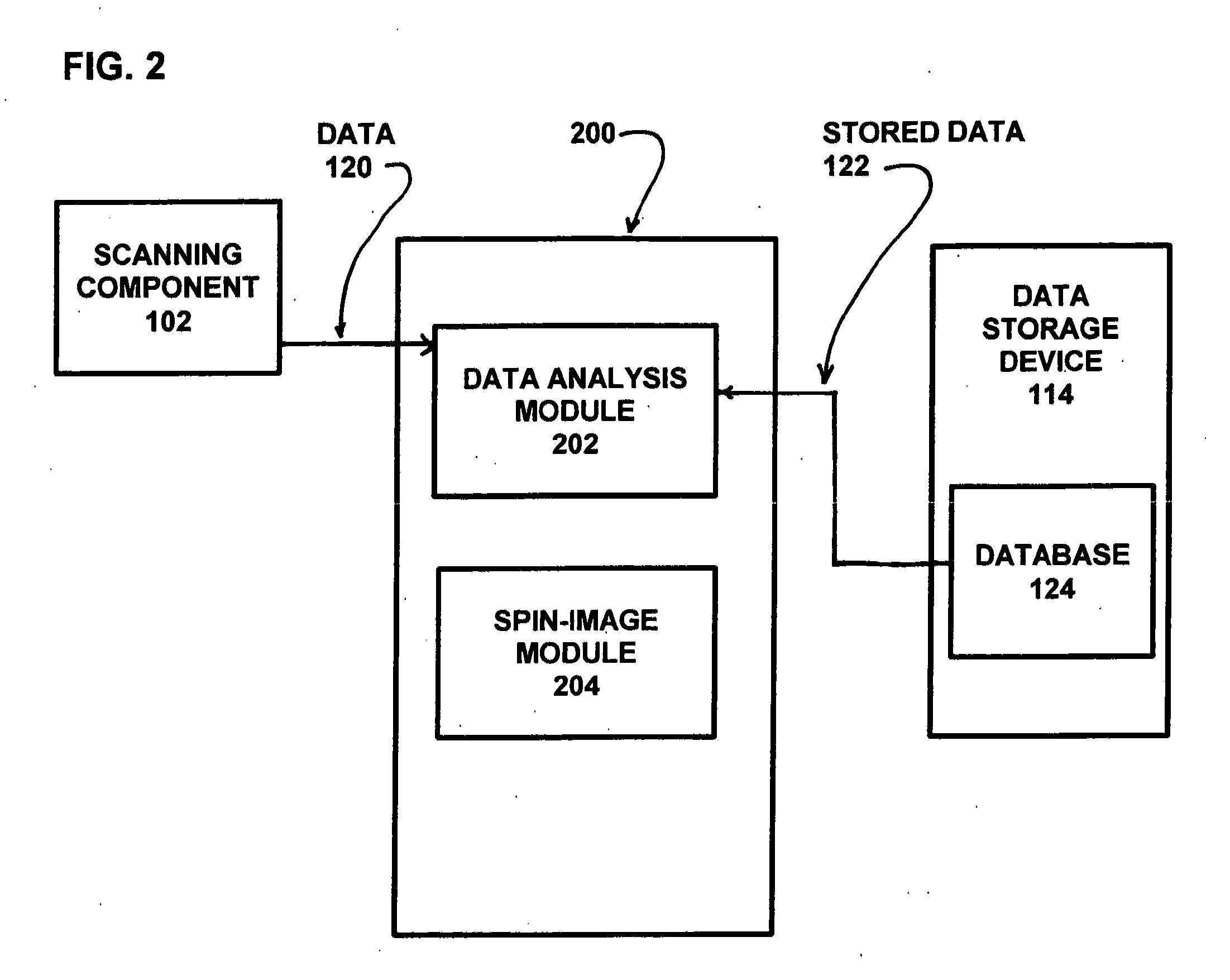
Surface data acquisition, storage, and assessment system
ActiveUS20120330447A1Quicker pose estimationImprove processing speedProgramme controlImage enhancementData acquisitionComputer science
A surface data acquisition, storage, and assessment system for detecting and quantifying similarities or differences between stored data and data collected from a scan. The system operates utilizing a method that decreases the time required for calculating a pose estimate thus increasing its performance making it more practical for applications that require real-time operations. In a preferred embodiment the system comprises one or more sensing components for scanning and measuring surface features of an object for determining the identity of the object, and determines differences between data obtained from two or more scans.
Owner:ECTOSCAN SYST LLC
Noninvasive tissue assessment
InactiveUS7435232B2Reduce measurement errorUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFrequency spectrumNon invasive
Methods and apparatus for non-invasively assessing physiological hard of soft tissue of human and other species are described. In a preferred embodiment, tissue is vibrationally stimulated in vivo through a frequency spectrum. The tissue reacts against the stimulus and the reaction is preferably measured and recorded. Based on analytical algorithms or comparisons with previously taken measurements, changes within the tissue can be detected and used for diagnostic purposes. Further embodiments describe the usage of the device and methods for in vivo intra-operative and post-operative implant evaluations and as a therapeutic tool.
Owner:RICE UNIV
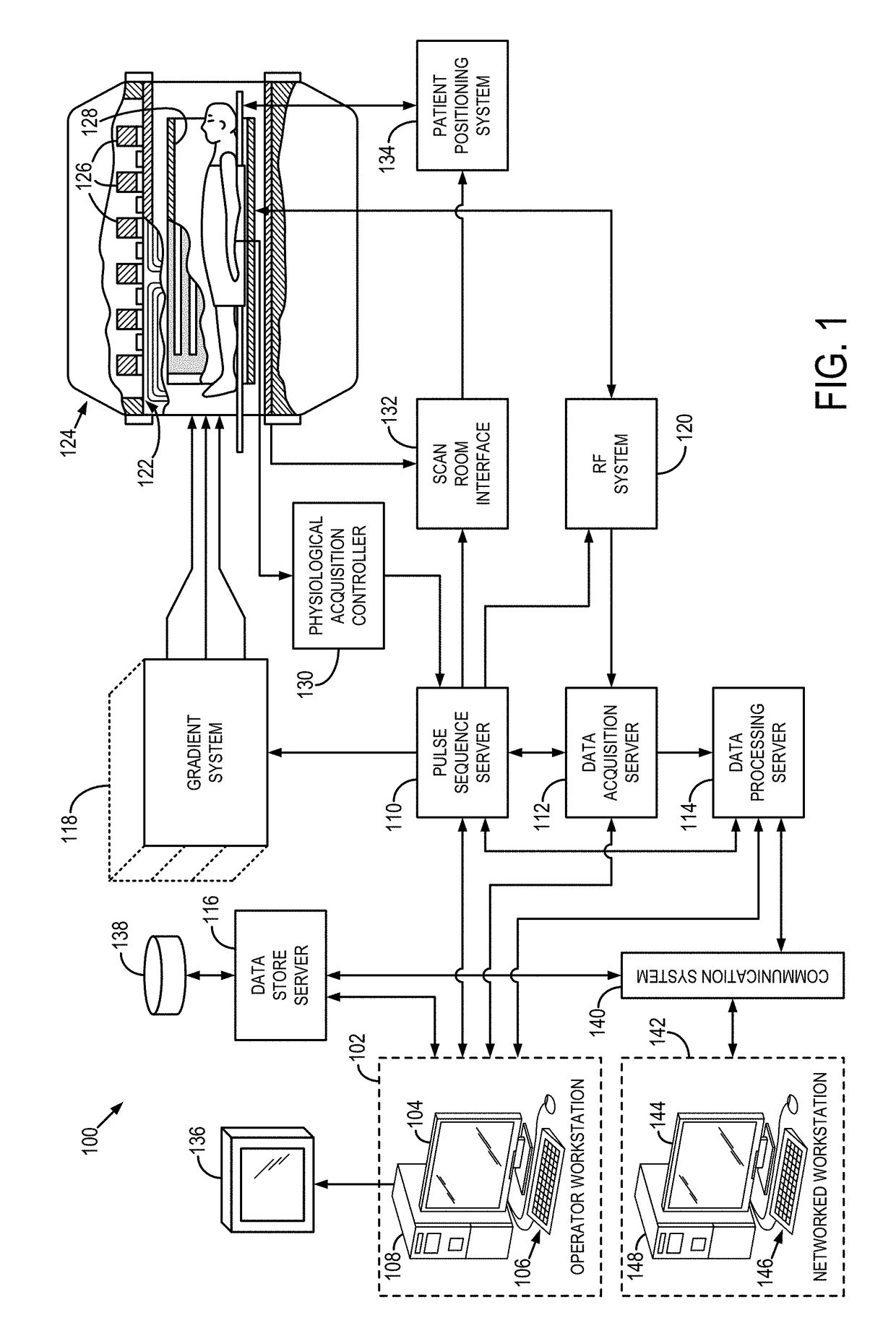
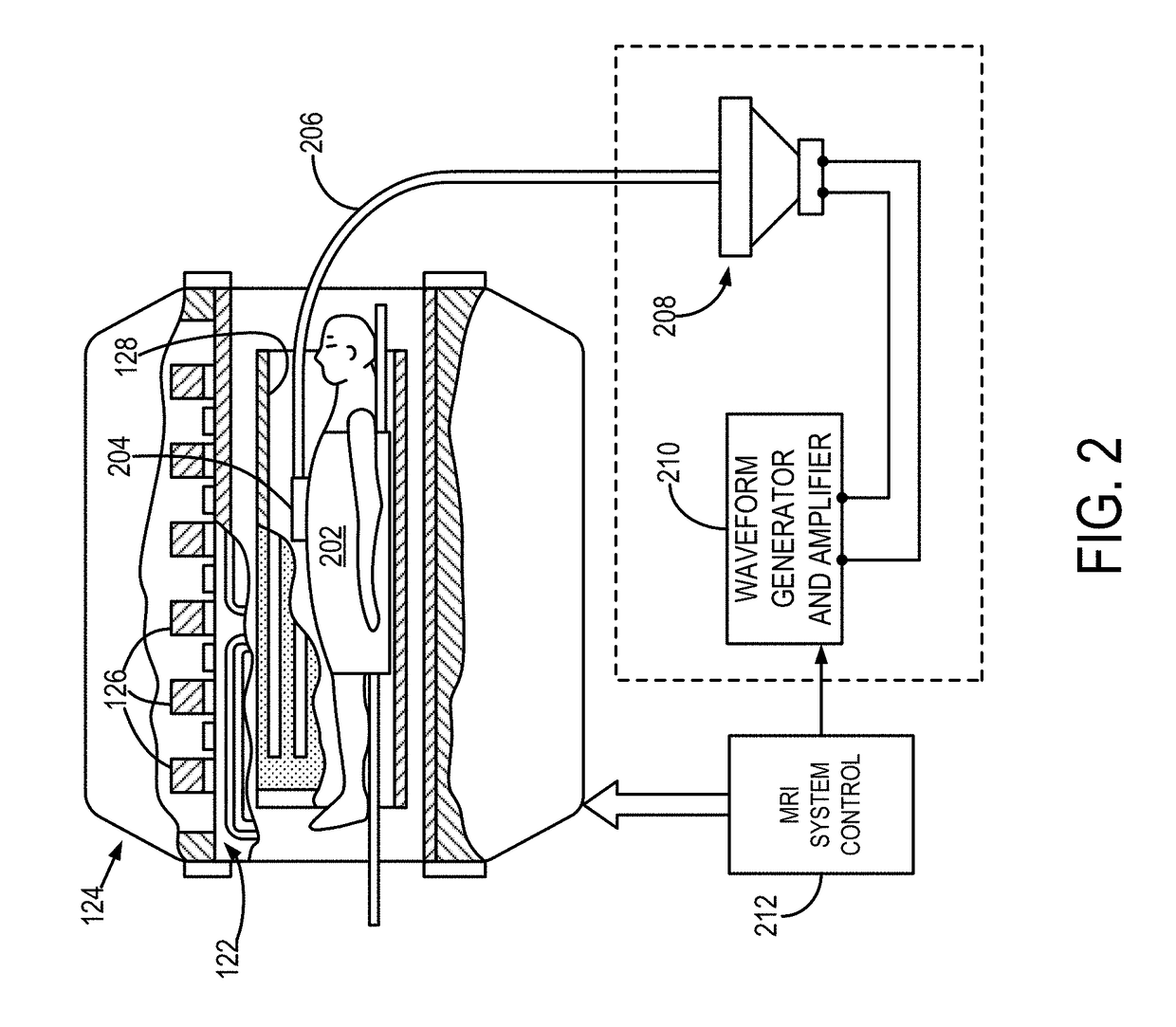
System and method for generating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS) using magnetic resonance elastography
The present disclosure relates to a system and method for non-invasively determining NAFLD activity scores (NAS) in patients using mechanical properties determined through magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) imaging. The non-invasively determined NAS score is then used to diagnose NFALD and NASH patients.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Ultrasound vibrometry
ActiveUS7753847B2Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSonificationHarmonic
A method for measuring a mechanical property of a subject includes using an ultrasonic transducer to apply ultrasonic vibration pulses to a vibration origin in the subject in an on-off time sequence in order to impart a harmonic motion at a prescribed frequency to the subject, and when the vibration pulses are off, using the same transducer to apply ultrasonic detection pulses to a motion detection point and to receive echo signals therefrom in order to sense the harmonic motion on the subject at the motion detection point. From the harmonic signal information, a harmonic signal is detected and a characteristic such as amplitude or phase of the detected harmonic signal is measured. The mechanical property is calculated using the measured characteristic using for example a wave speed dispersion method.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method of utilising measurements of threshold of pain
InactiveUS20100036280A1Diagnostics using vibrationsDiagnostics using pressureSympathetic toneIdentical stimulus
A method of determining the sympathetic tone and / or level of stress and / or level or warning system sensitivity includes the steps of: measuring an applied stimulation at a threshold value of the stimulation in one or more sympathetic tone-neutral points and measuring an applied stimulation at the same threshold value in one or more sympathetic tone-dependent points. The invention further relates to a system for applying and measuring a stimulation, and the use of a system for applying and measuring a stimulation for determining the sympathetic tone including the steps of: measuring an applied stimulation at a threshold value of the stimulation at one or more sympathetic tone-neutral points and measuring an applied stimulation at the same threshold value of the stimulation at one or more sympathetic tone-dependent points.
Owner:ULL METER AS
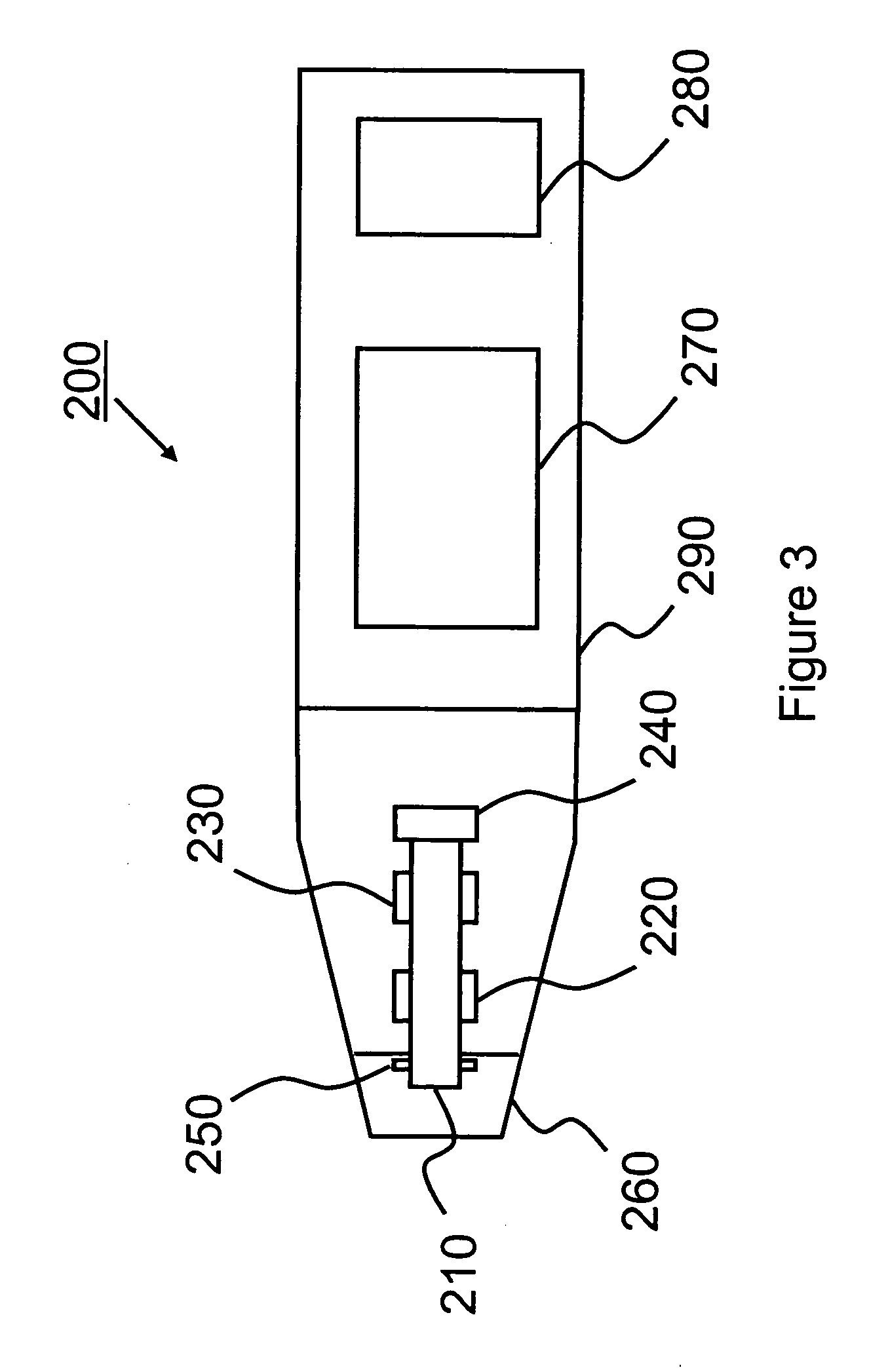
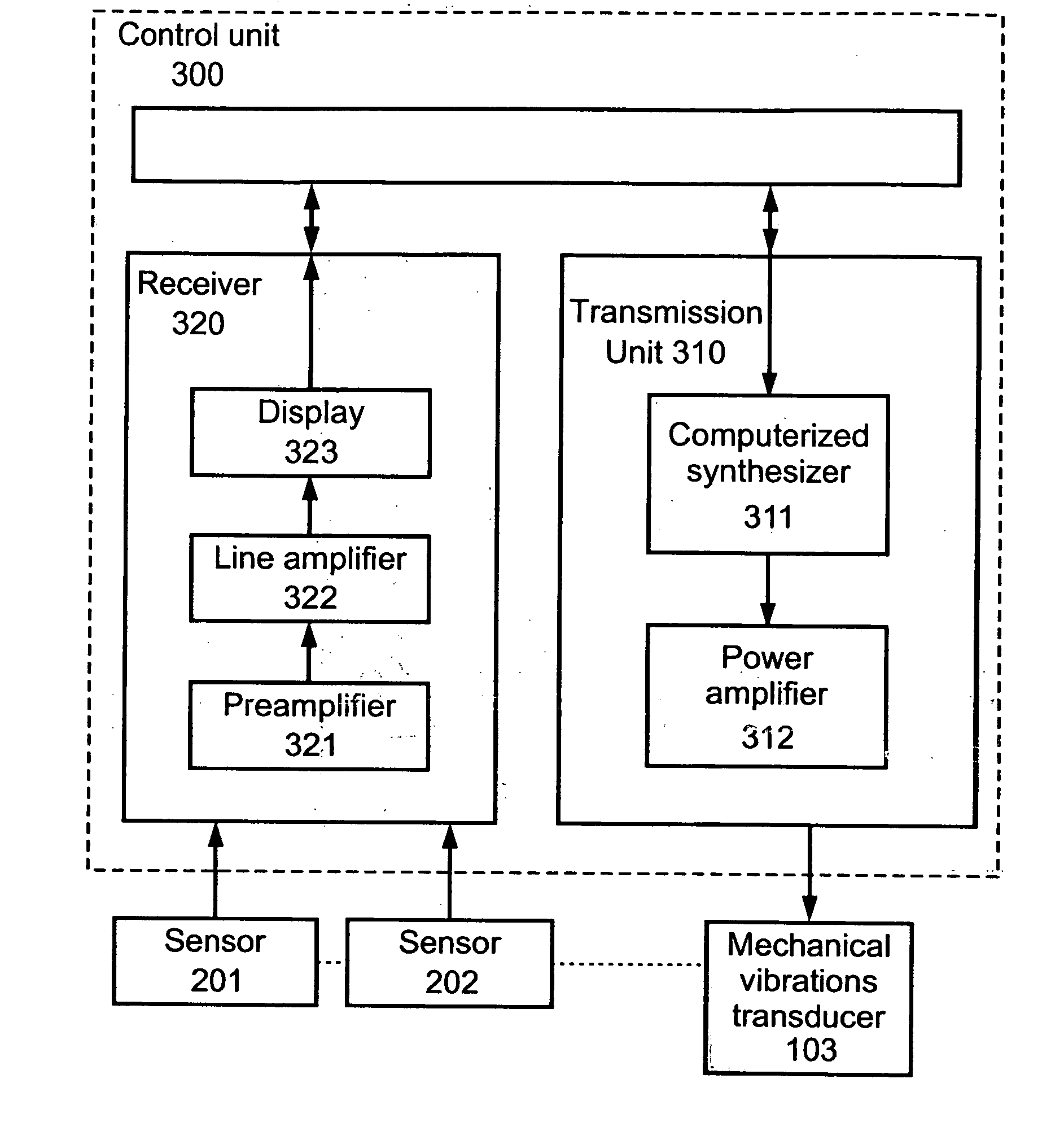
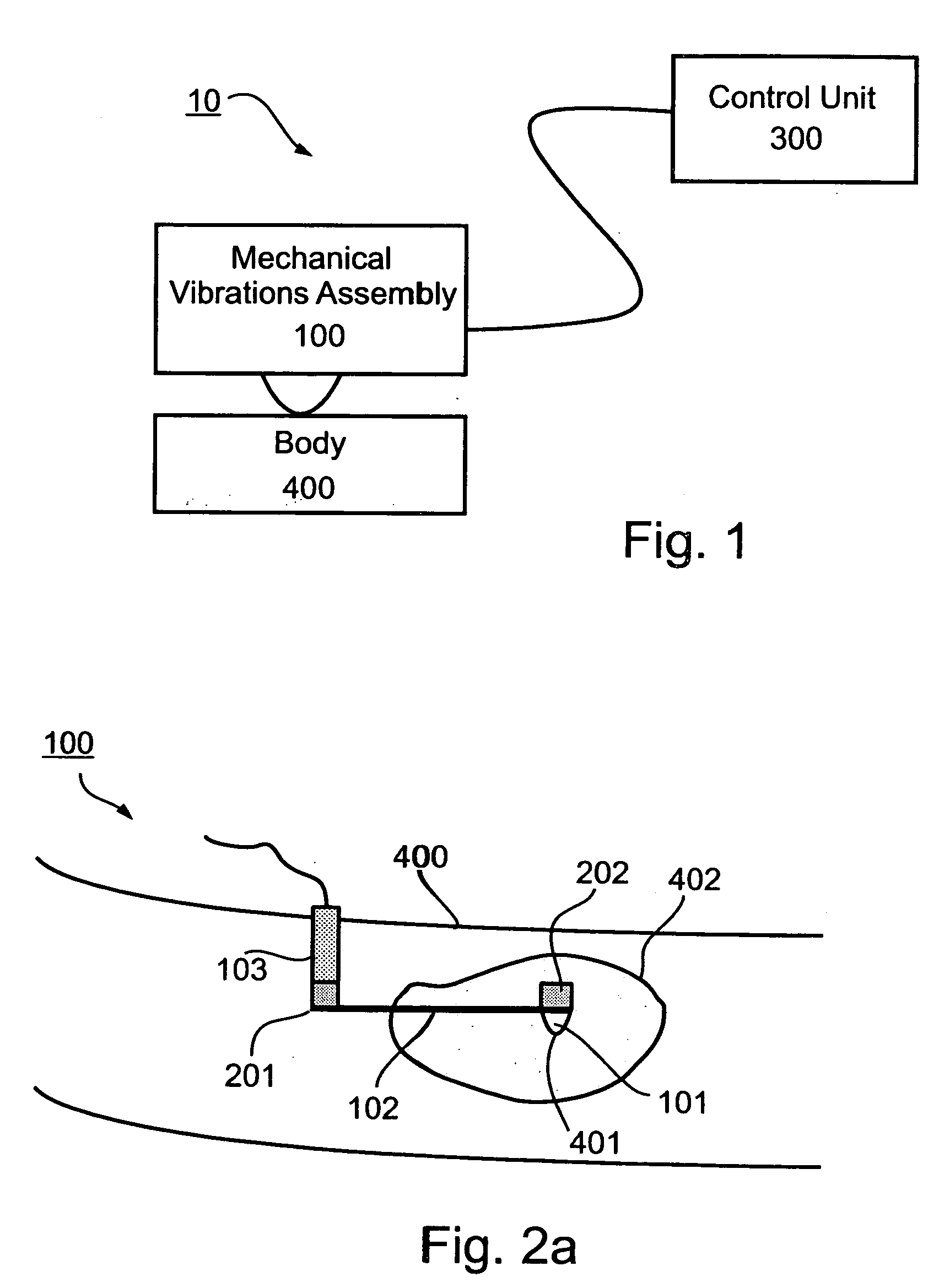
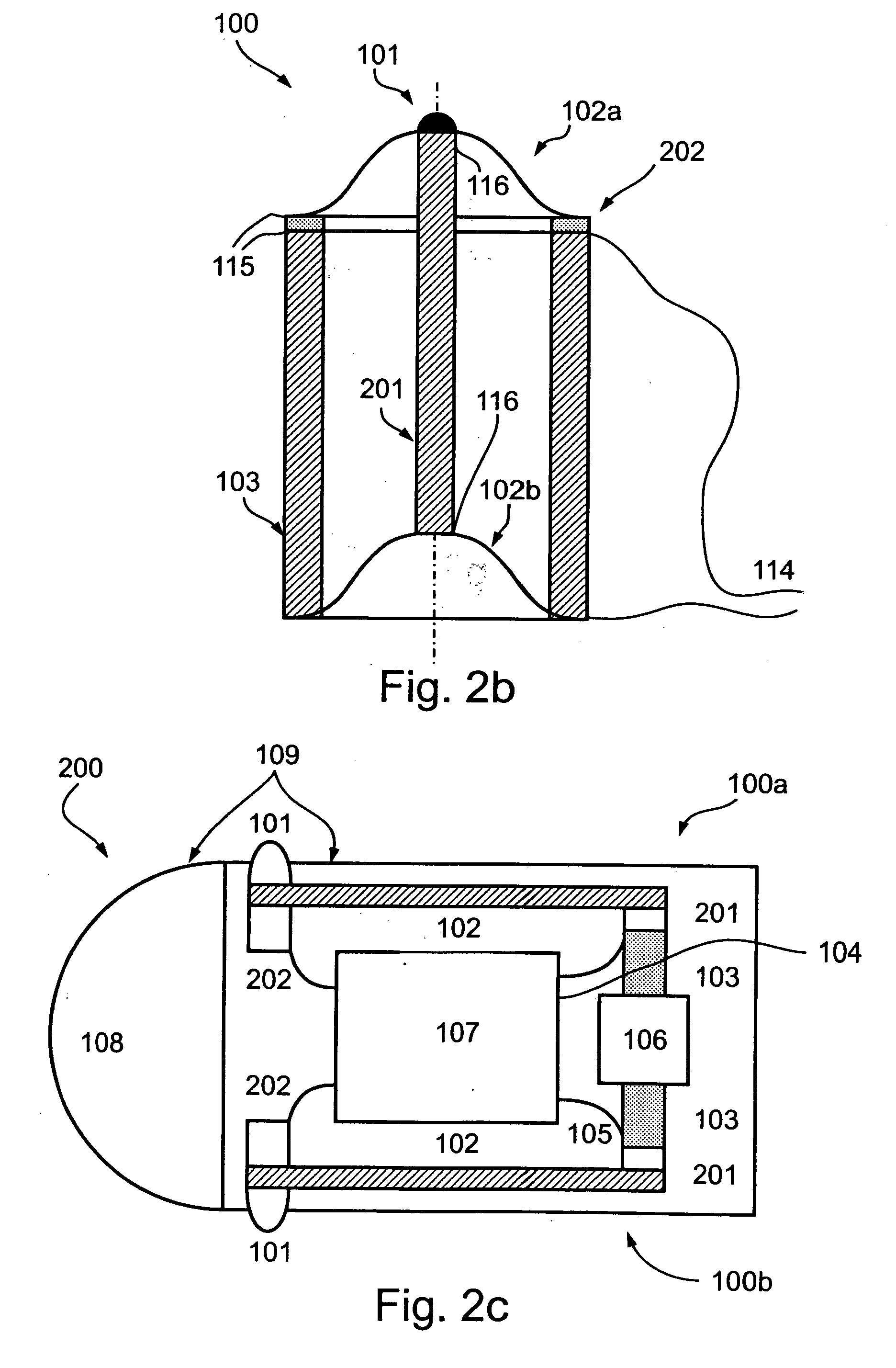
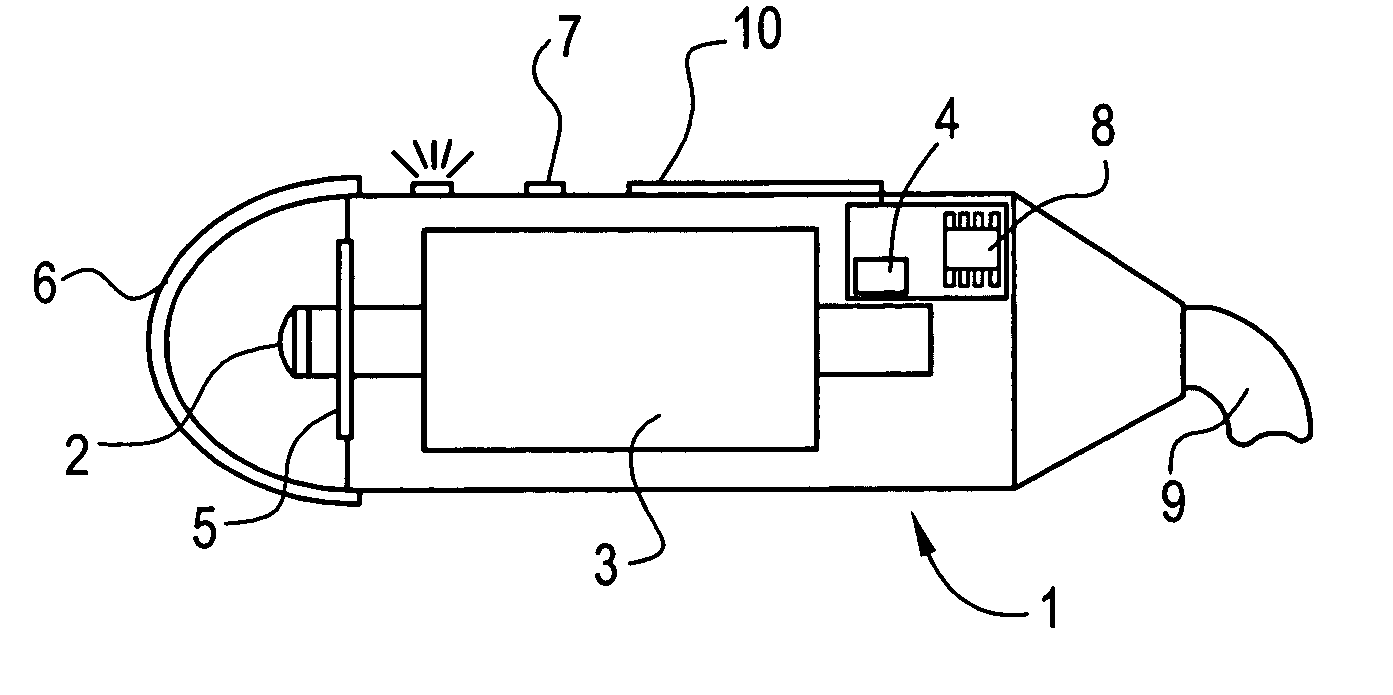
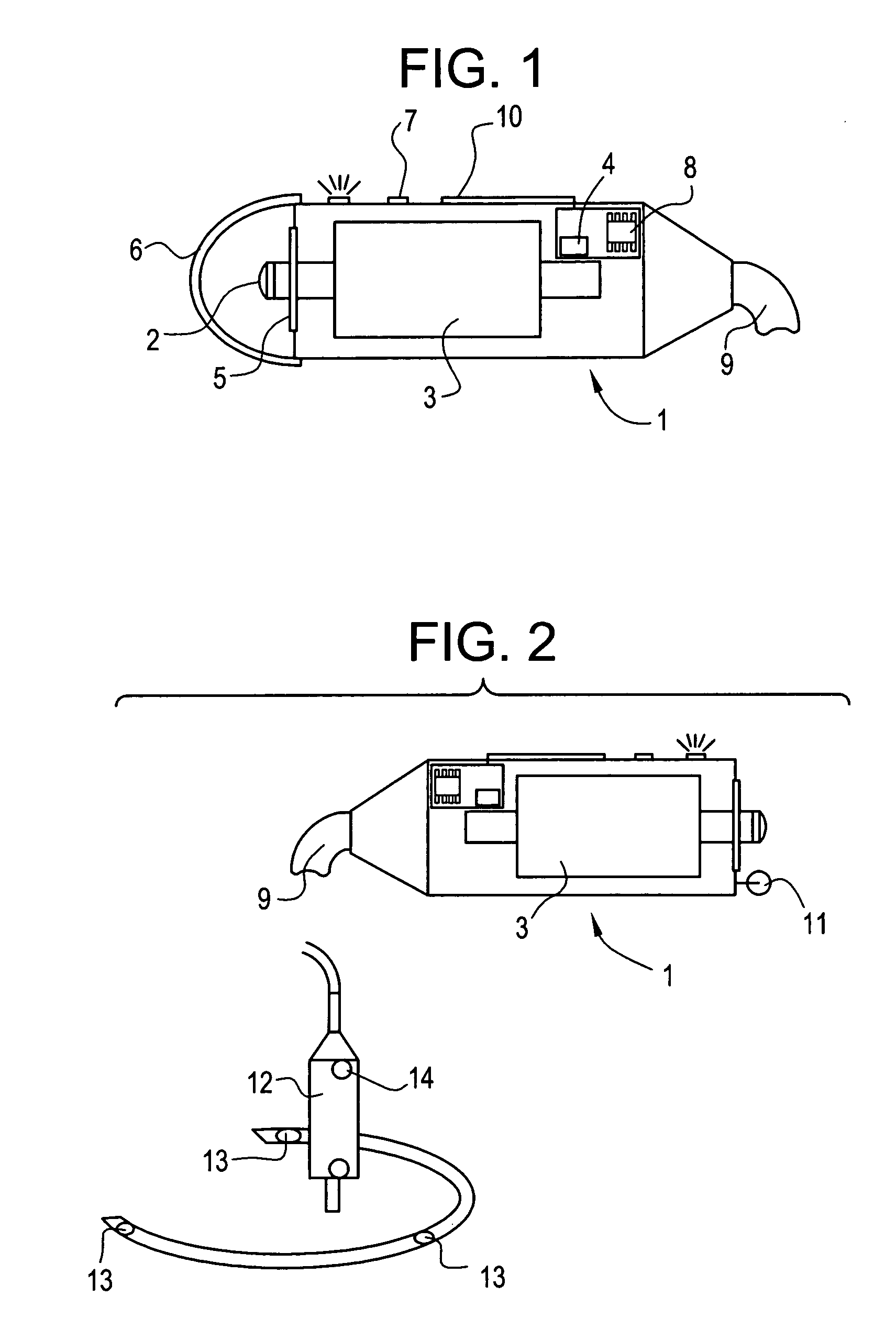
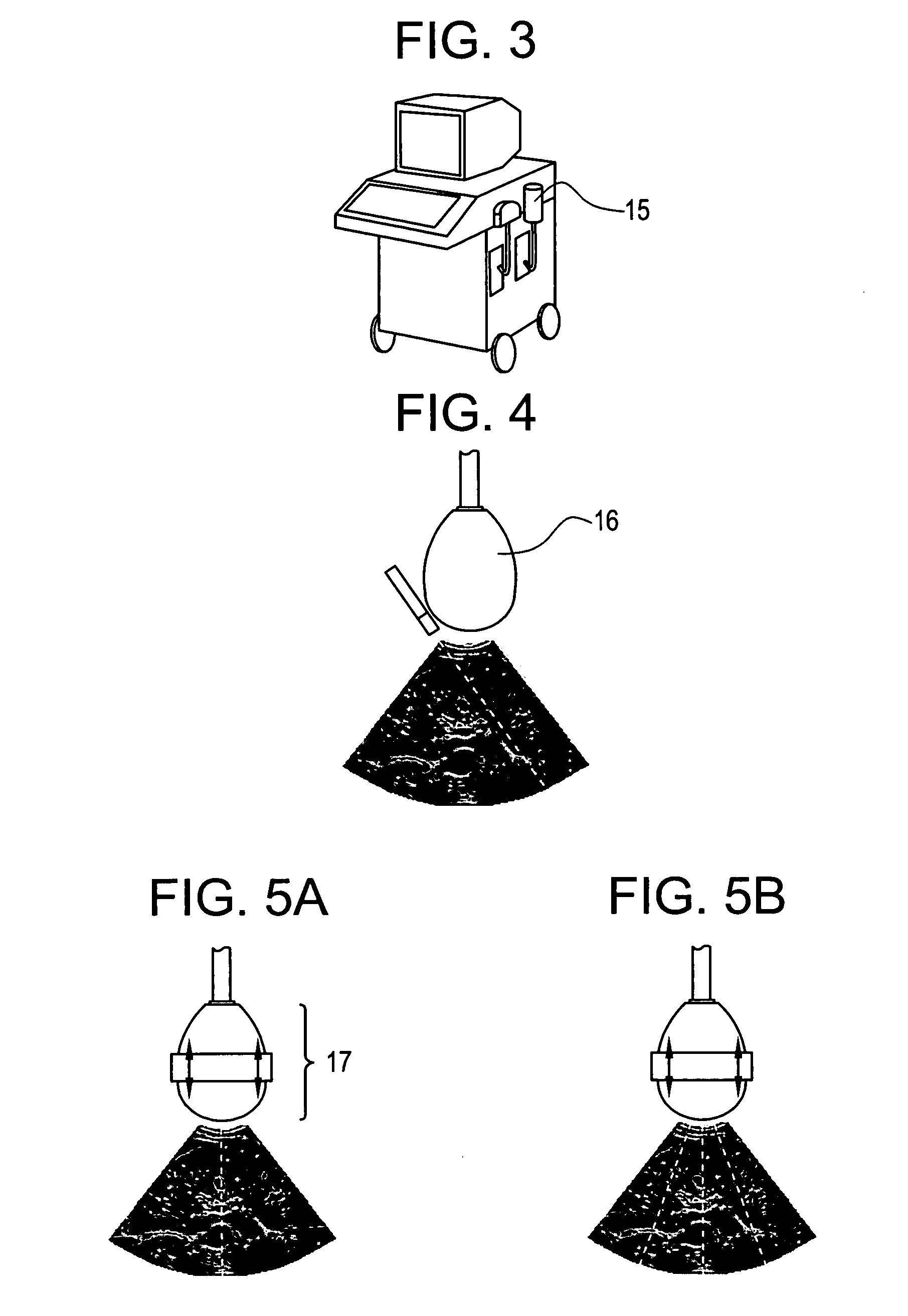
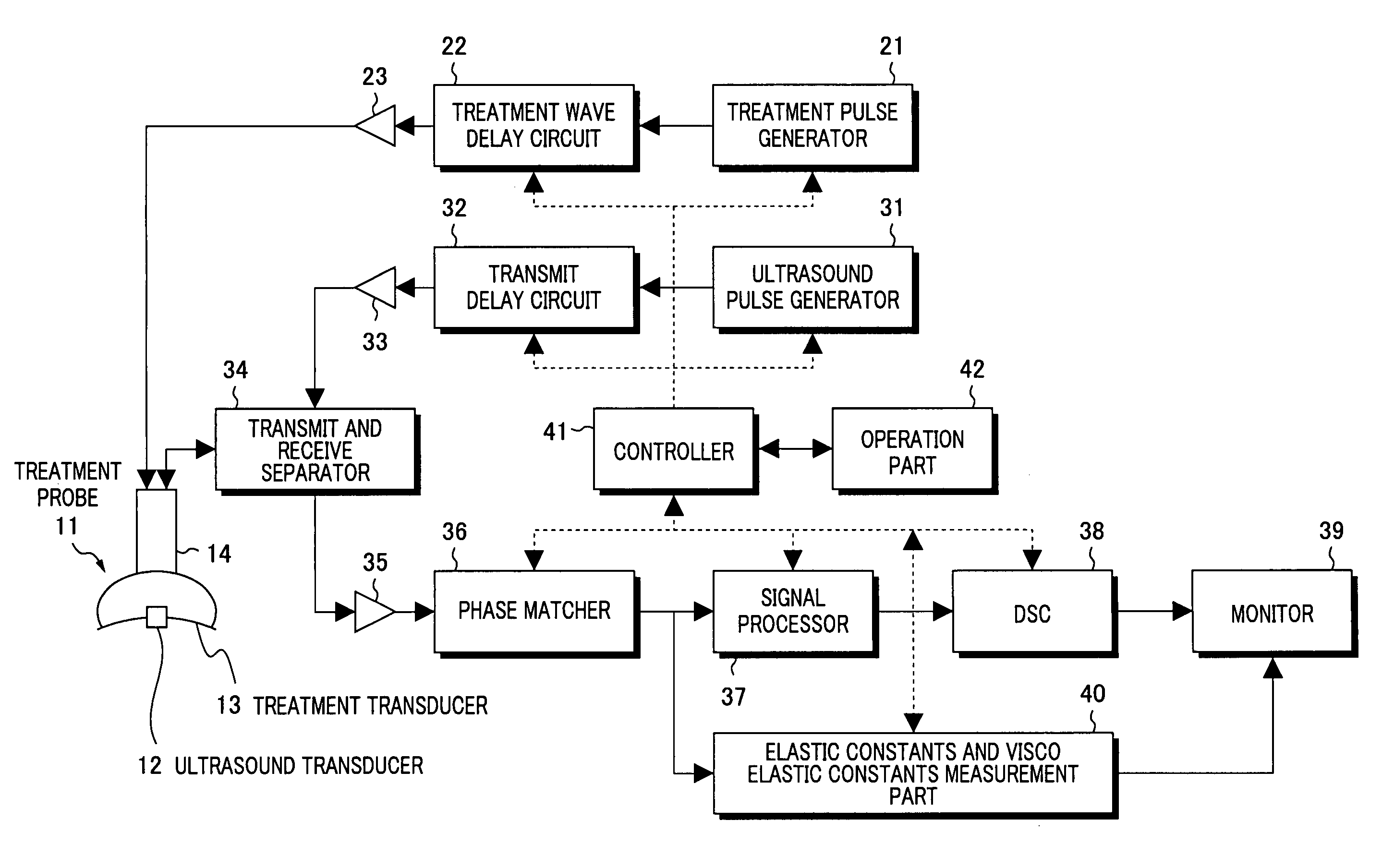
Device and method for measuring the elasticity of a human or animal organ
ActiveUS20050203398A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostics using vibrationsUltrasonic sensorAnimal Organs
A device for measuring elasticity of a human or animal organ or viscoelastic media having an ultrasonic signal after ultrasonic illumination including at least one sensor including an ultrasonic transducer, at least one position sensor, an actuator to trigger the device connected by wire link to an electric power source, and a controlled electrodynamic actuator attached to the ultrasonic transducer that generates a transitory low-frequency impulse having a frequency range between about 1 Hz and about 5000 Hz.
Owner:ECHOSENS SA
Clinical apparatuses
ActiveUS20060173319A1High measurement accuracySimple calculationDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusEngineering
Owner:SUMI CHIKAYOSHI
System for analysing the skin and associated method
ActiveUS20120172685A1Low costJeopardize lifeMedical imagingDiagnostics using lightSkin cancer screeningDigital image
A system for analyzing at least one characteristic of the skin (1) and by extension hair, via optics (7, 4) and image processing (4, 5) elements notably include a consumer electronics device (4). The method for analyzing at least one characteristic of the skin notably includes a step wherein at least one digital image is acquired via a consumer electronics device. According to a first aspect, the method notably aims at applications in the field of cosmetics or that of skin cancer screening, and according to a second aspect in the field of assisting with diagnosis of allergies.
Owner:LOREAL SA
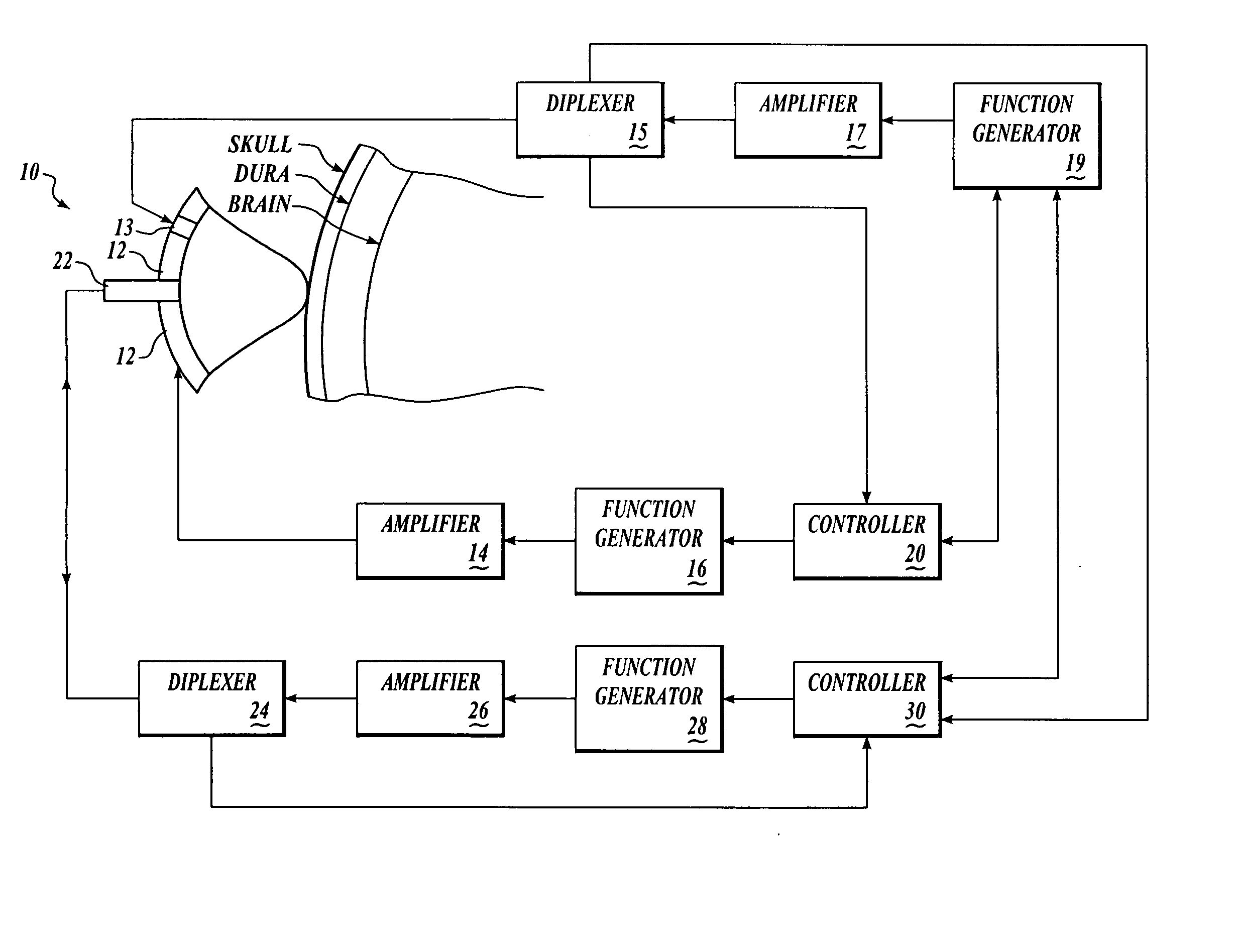
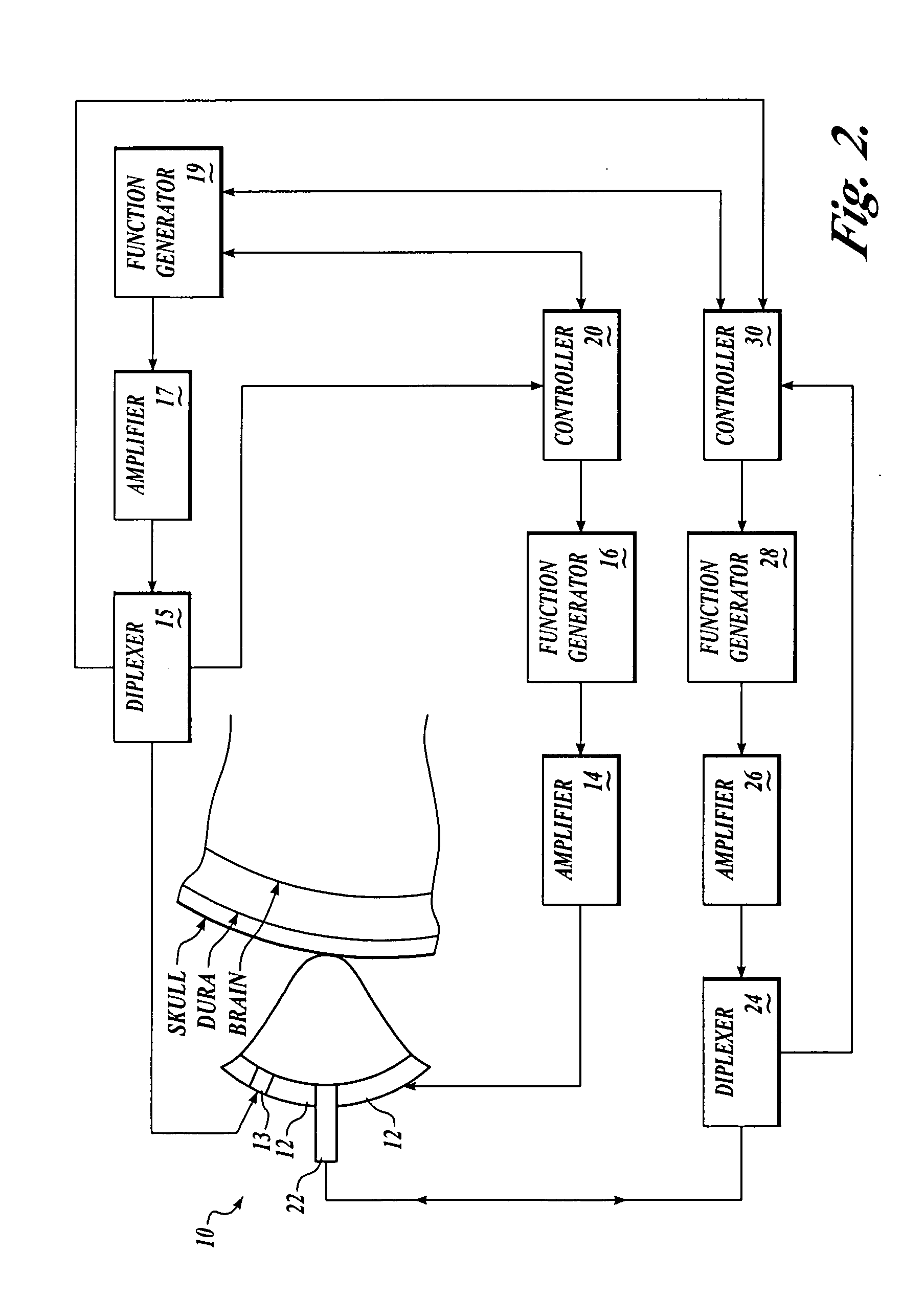
Methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively
InactiveUS7547283B2Medical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Identification Techniques and Device for Testing the Efficacy of Beauty Care Products and Cosmetics
ActiveUS20110054355A1Low costProcedure can be fast and accurateDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using vibrationsMedicineSkin surface
A method for testing the effect of a skin care product includes measuring a mechanical property of skin tissue using nonlinear stochastic system identification, applying the product to the skin, repeating the measurement of the mechanical property after the application of the product, and comparing the before and after measurements to quantify the effect of the product.Measuring the mechanical property of the skin can include placing a probe against a surface of the skin, perturbing the skin with the probe using a stochastic sequence, and measuring the response of the skin to the perturbation. Perturbing the skin can include indenting the skin with the probe, extending the skin with the probe, and sliding the probe across the skin surface. The mechanical property may be indicative of skin compliance, skin elasticity, skin stiffness, or skin damping. The mechanical property can be dependent on perturbation depth and may be measured at a plurality of anatomical locations.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and a device for imaging a visco-elastic medium
ActiveUS20100168566A1Track variation in necrosisTrack variationUltrasound therapyDiagnostics using vibrationsAcousticsMechanical engineering
Owner:SUPER SONIC IMAGINE
Driving device for vibration-type actuator and medical system using same
InactiveUS20130334989A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsAudio power amplifierActuator
A driving device for a vibration-type actuator of the present invention is a driving device for driving a vibration-type actuator disposed in a magnetically shielded room. The driving device includes a linear amplifier is configured to receive a signal based on a driving waveform for driving the vibration-type actuator and output a driving voltage to be applied to the vibration-type actuator.
Owner:CANON KK
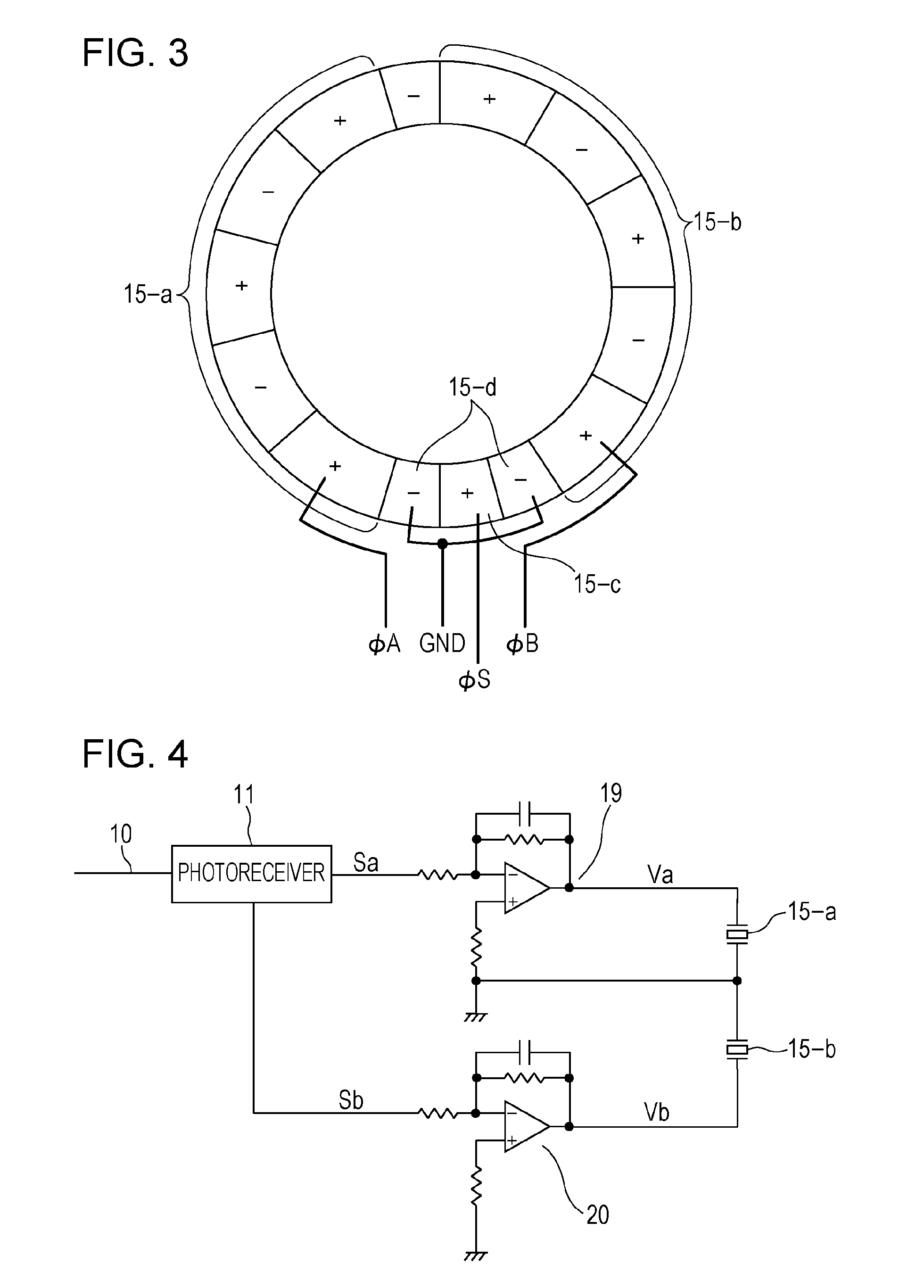
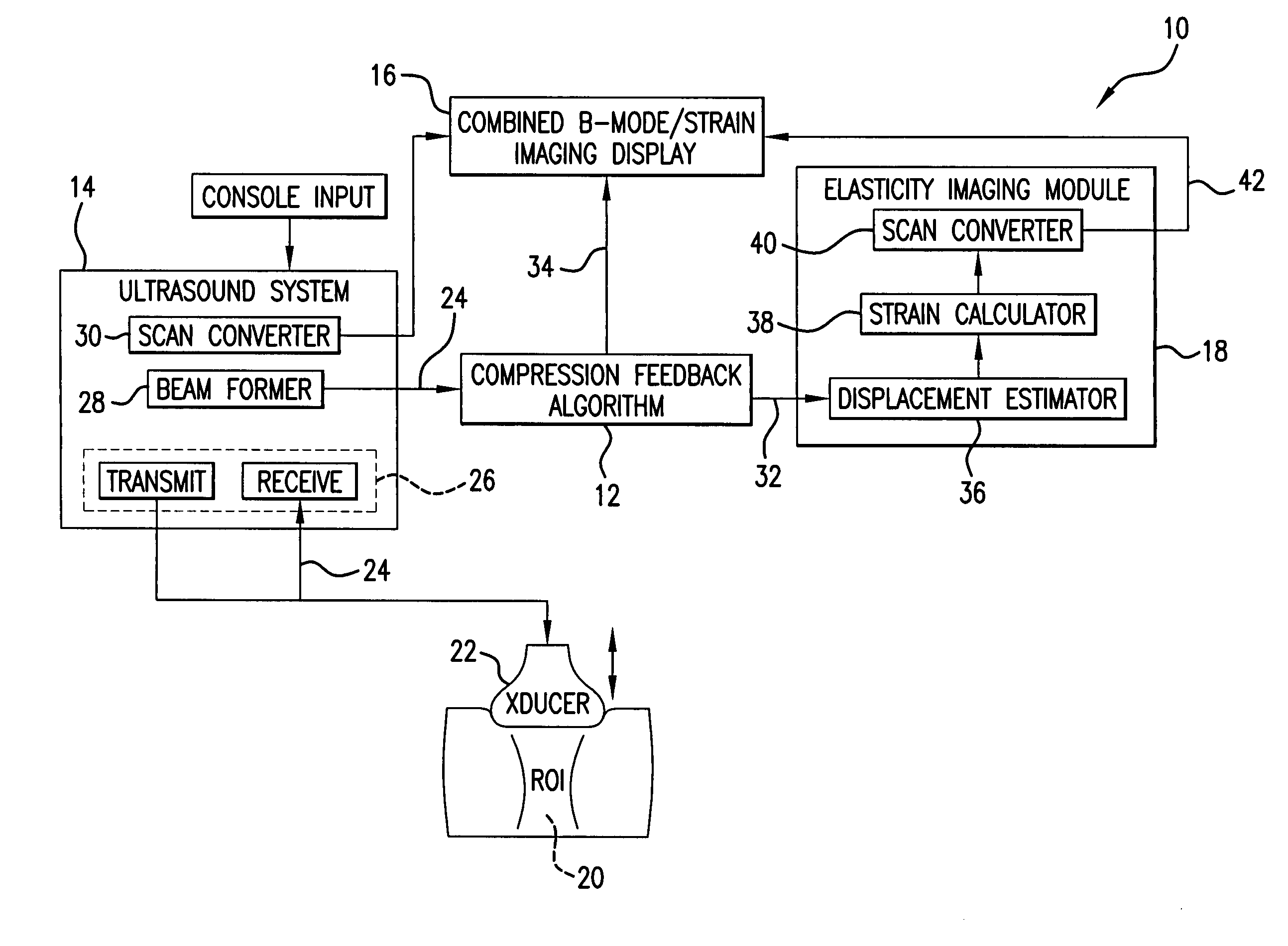
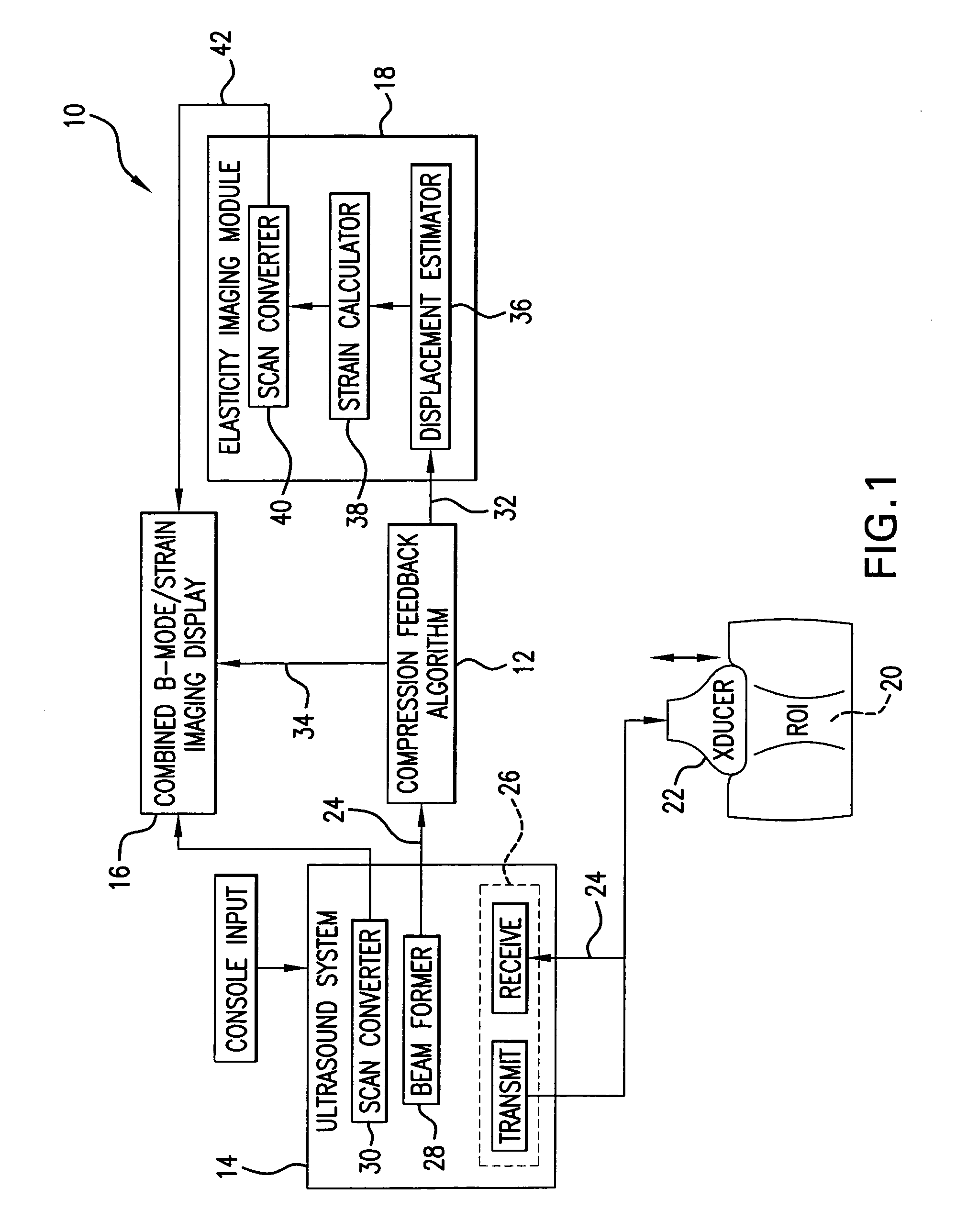
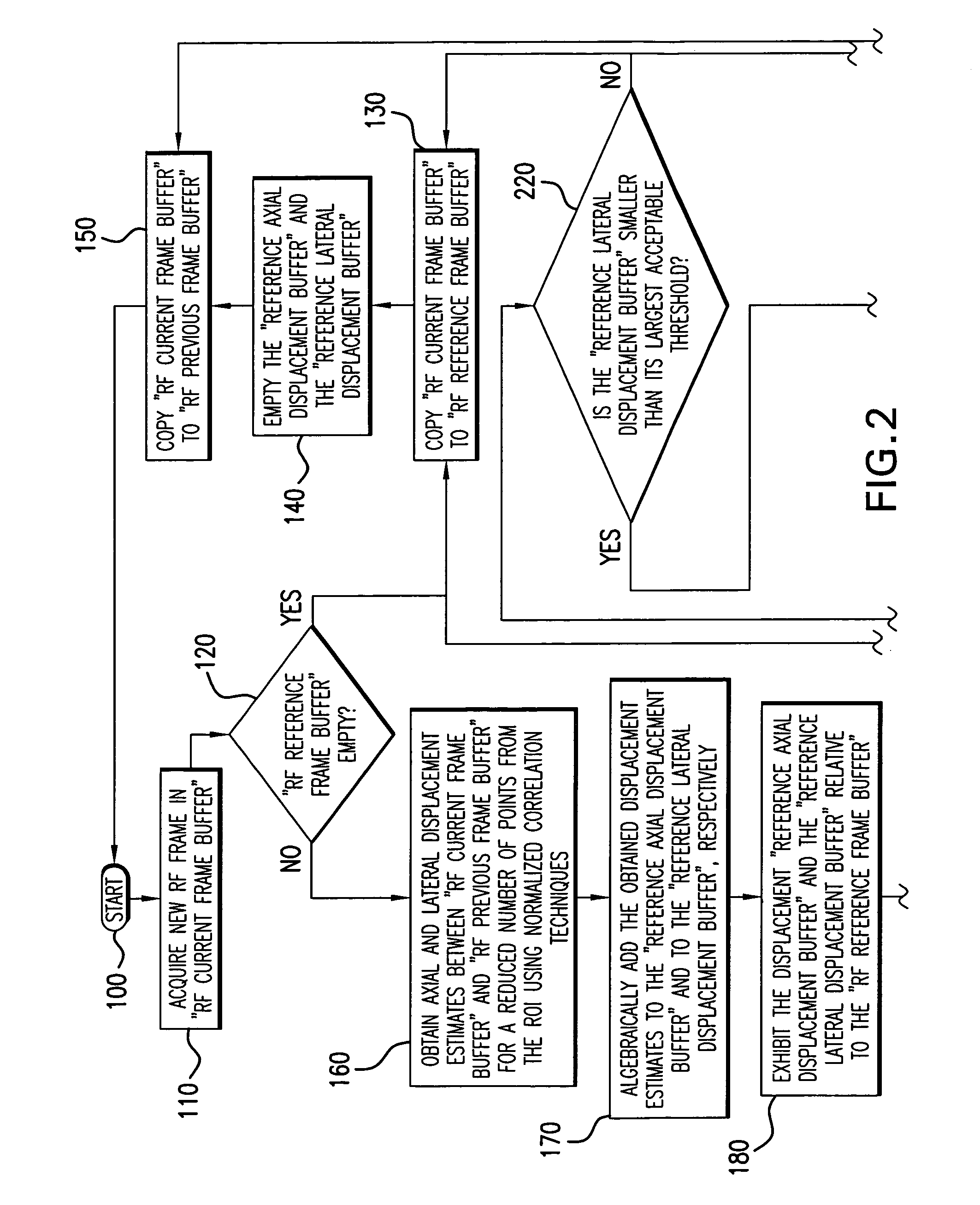
Method and apparatus for elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20070093716A1Wave based measurement systemsDiagnostics using vibrationsUltrasound imagingElastography
A computational efficient algorithm for compression analysis of free-hand static elasticity imaging performed using medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment offers tissue compression quality and quantity feedback to the operator. The algorithm includes a criterion for automatic selection of the most advantageous pre- and post-compression frame pairs delivering elasticity images of optimal dynamic ranges (DR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The use of the algorithm in real time eases operator training and reduces significantly the amount of artifact in the elasticity images while lowering the computational burden.
Owner:ALOKA CO LTD
System and method for imaging based on ultrasonic tagging of light
ActiveUS20060058685A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsUltrasonic beamLight irradiation
A technique is provided for imaging based on localization of fluorescence in a medium. The technique includes illuminating the medium with an excitation light to excite fluorescence, scanning the medium at a plurality of locations via an ultrasonic beam, modulating a portion of the emitted light from the fluorescence via the ultrasonic beam at each of the plurality of locations, differentially detecting the modulated light at a boundary of the medium, and reconstructing an image from the detected signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for detection, characterization and imaging of heterogeneity using shear wave induced resonance
InactiveUS20110130660A1Ultrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical resonanceAcoustics
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided. Systems for acquiring acoustic data from a desired target site in a subject's body using various types of acoustic source and detector elements are also provided, including single use acoustic source / detector combinations are also provided. Acoustic arrays for use with these systems may include multiple capacitive micro-machined ultrasound transducer (cMUT) elements, and may include a combination of different types of acoustic arrays. Methods of targeting localized sites within a broad target area based on acoustic data having various properties are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Medical apparatus, use and methods
InactiveUS7648471B2Maximize contact areaMove quicklyElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesTransducerBiomedical engineering
In accordance with one embodiment, a vibratory transducer has an armature suspended in a magnetic field. The armature has a plurality of electrical conductive paths to provide electrical current flow in said armature to react with said magnetic field and cause movement in the armature controlled by variation in the electrical current flow. A contact surface is secured to the armature, with a surface area for frictionally coupling to a corresponding surface area of a patient for example. Movement of the vibratory transducer induces movement in the patient, and the transducer can produce movement in the contact surface in at least two dimensions simultaneously. In one embodiment the contact surface is flat, while in alternative embodiments the contact surface is incorporated in a toroidal structure so as to surround part of the patient. Medical application can include treatment of bone fractures, oedema, and in elastography, amongst other applications.
Owner:MERLEX CORP PTY LTD
Portable Pulmonary Injury diagnostic Devices And Methods
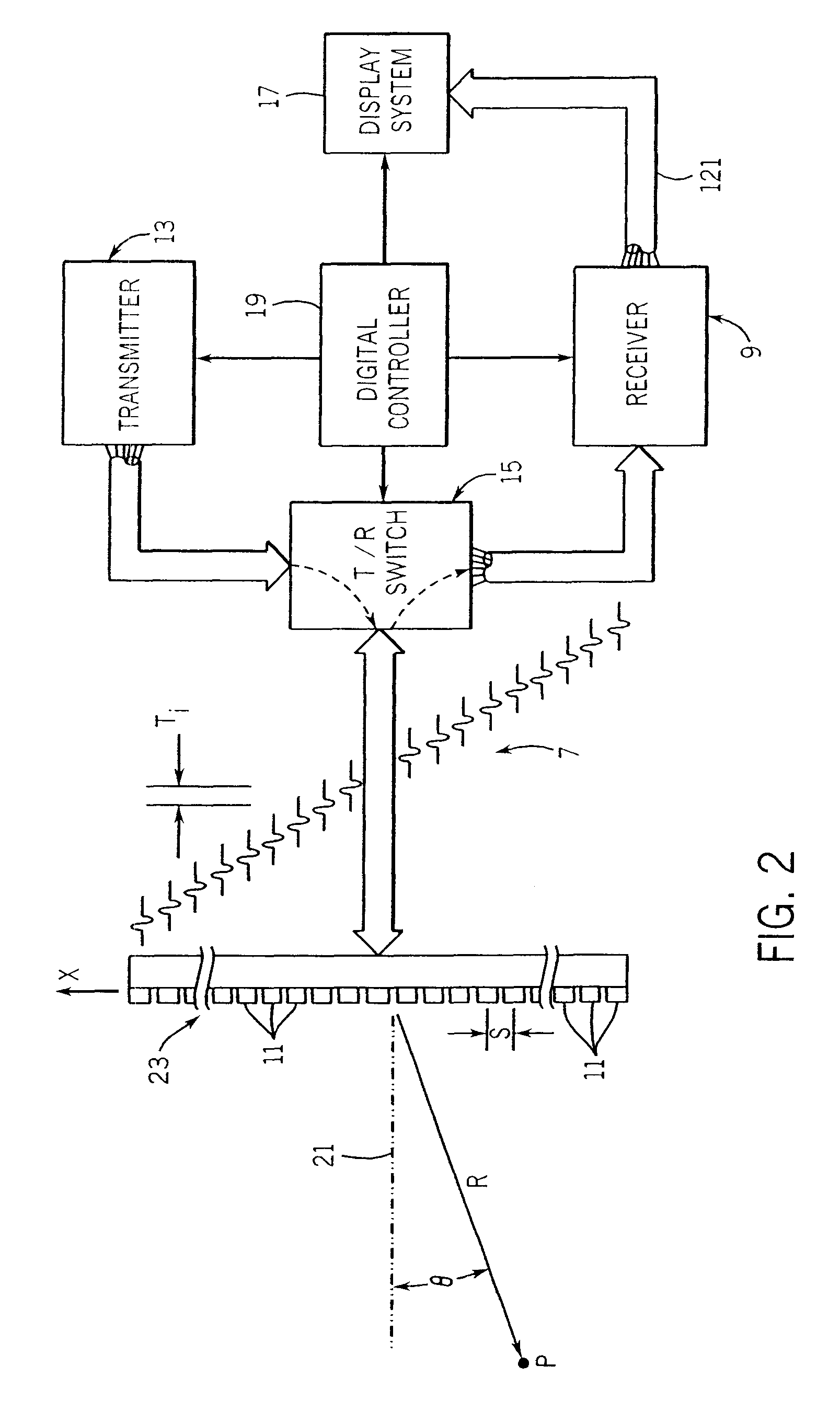
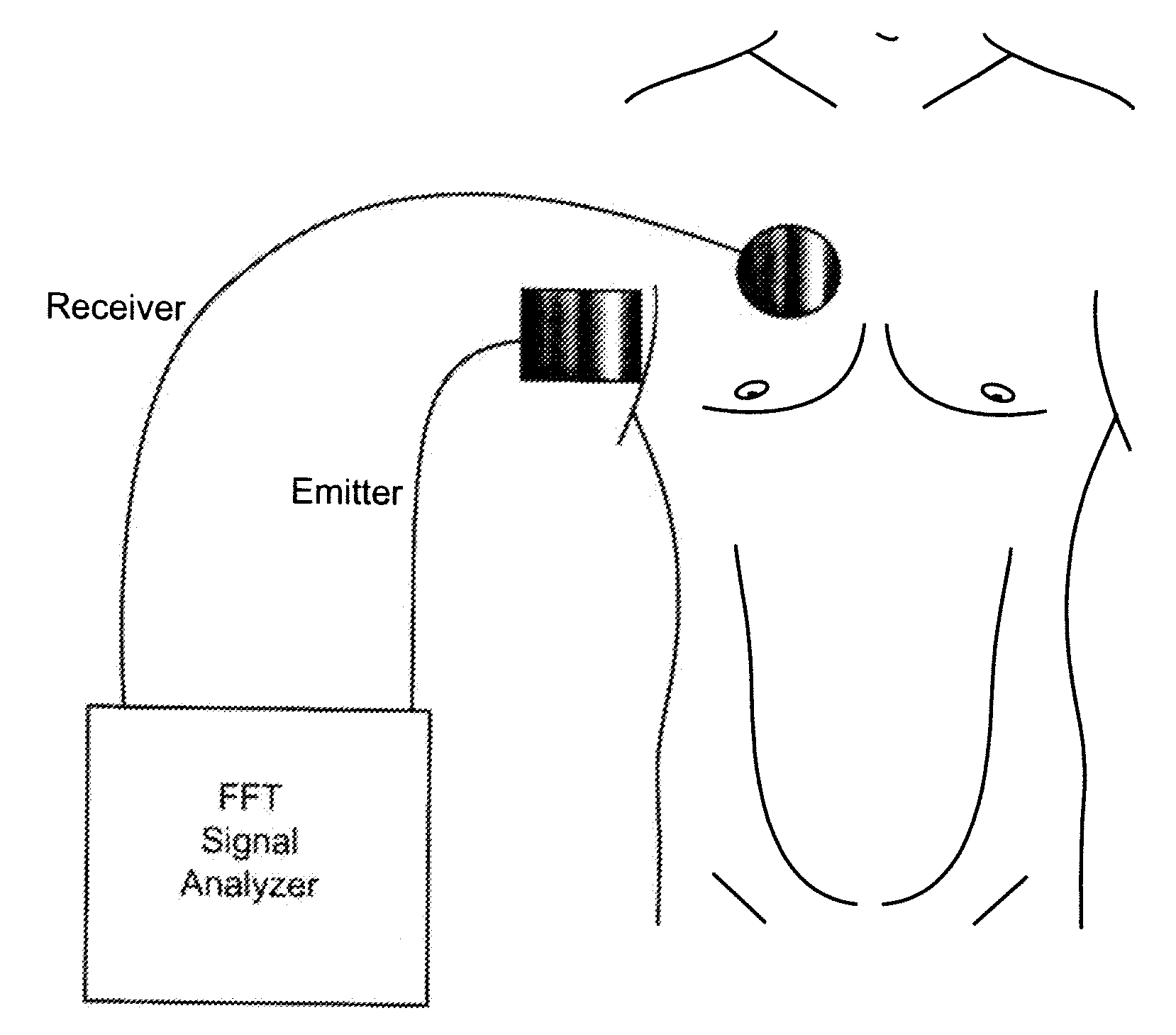
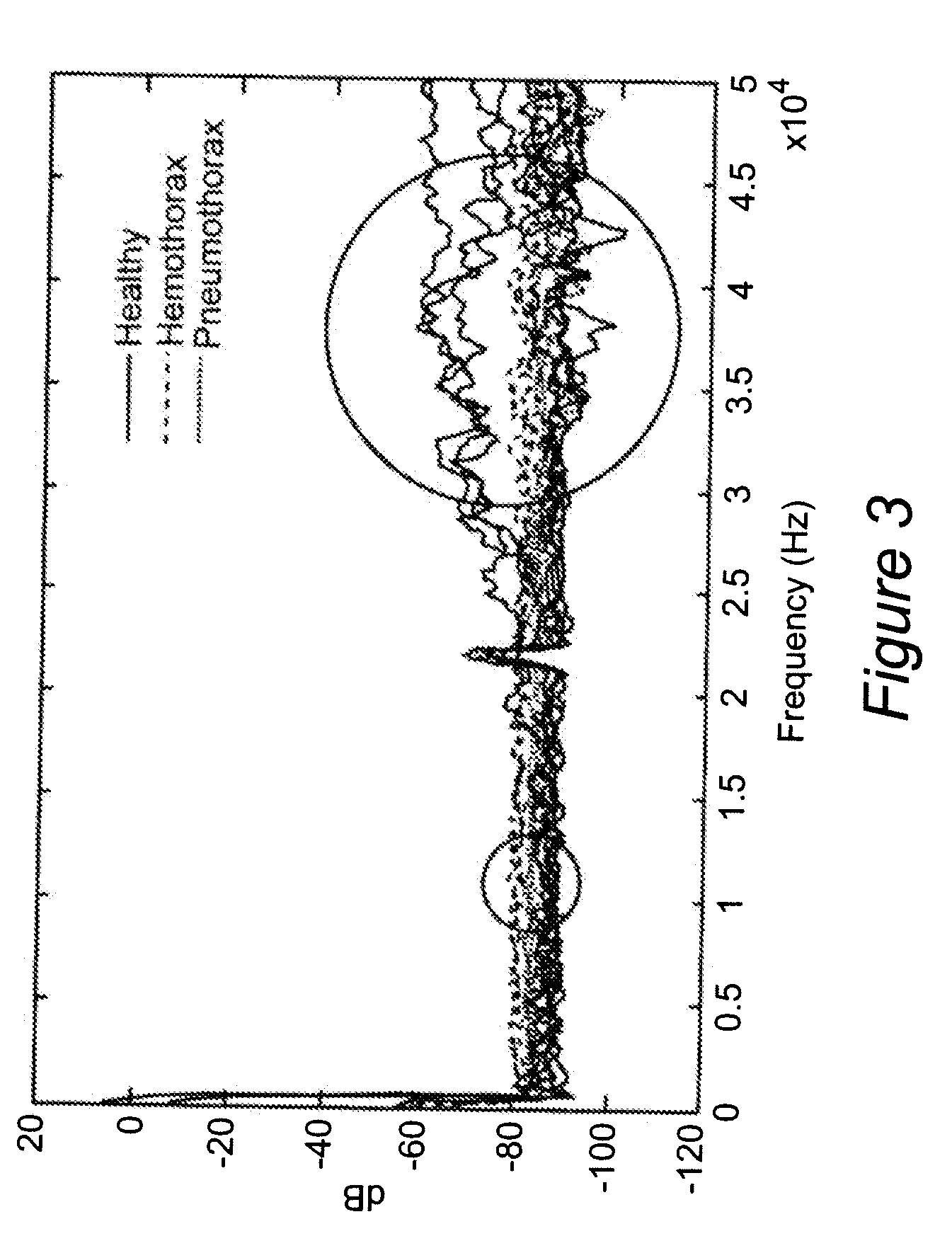
InactiveUS20090149748A1Increase chances of survivalMinimal experienceDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound attenuationMedicine
Lung injury such as pneumothorax now can be diagnosed reliably, portably and quickly. Vibro-acoustic waves are sent through the chest and the resulting wave is measured. By analyzing attenuation characteristics determined by the geometry of the chest structures, a determination can be made of whether the patient's pleural space is healthy, contains air (pneumothorax) or contains fluid (hemothorax).
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
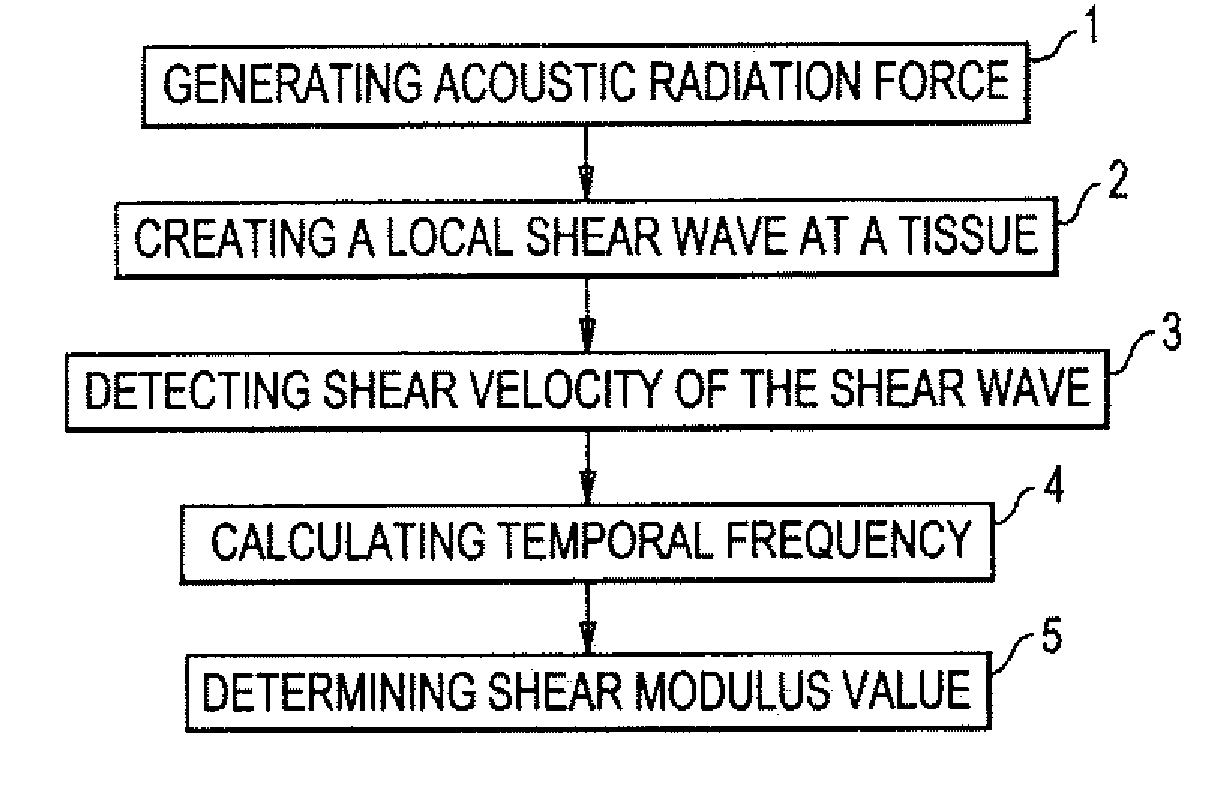
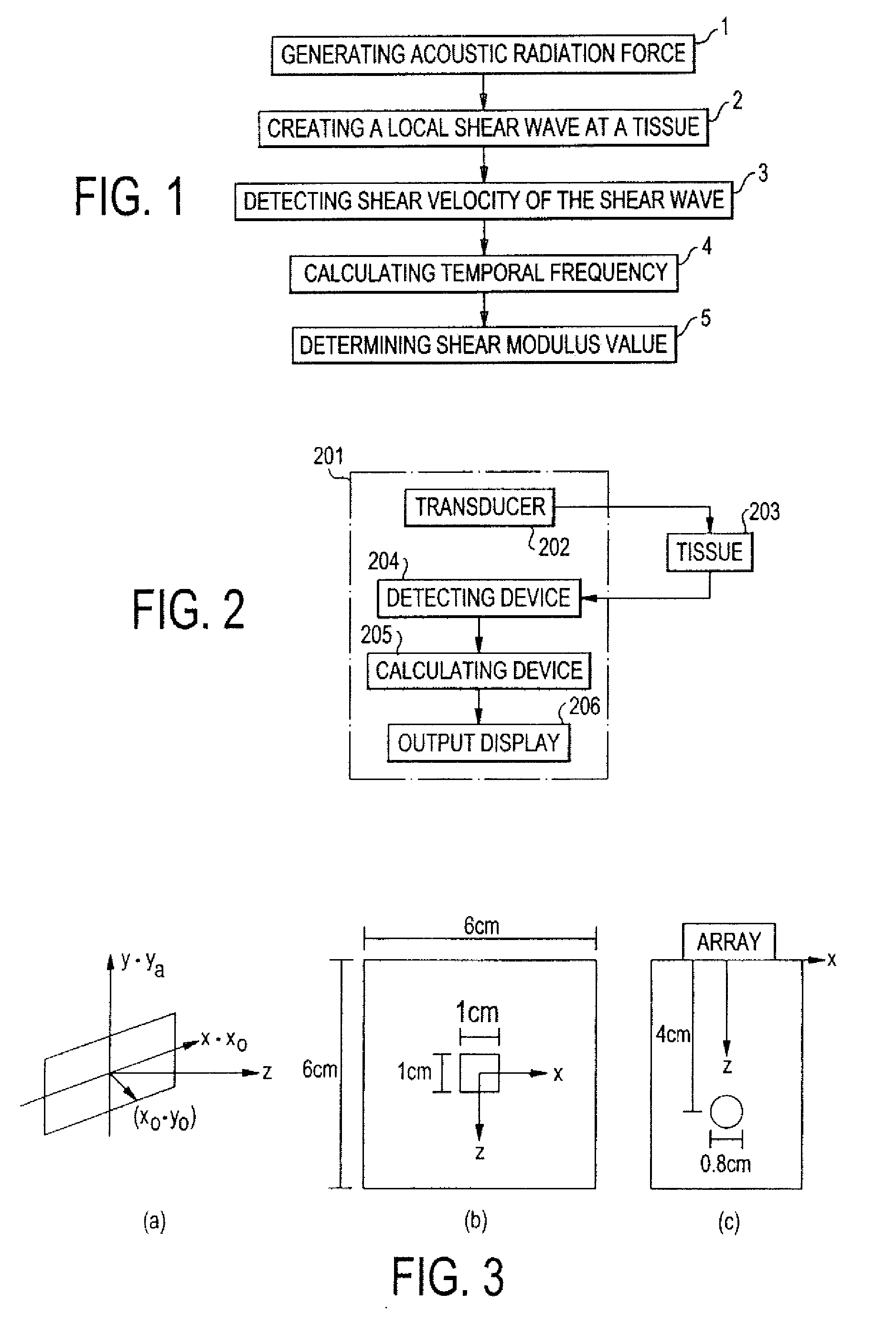
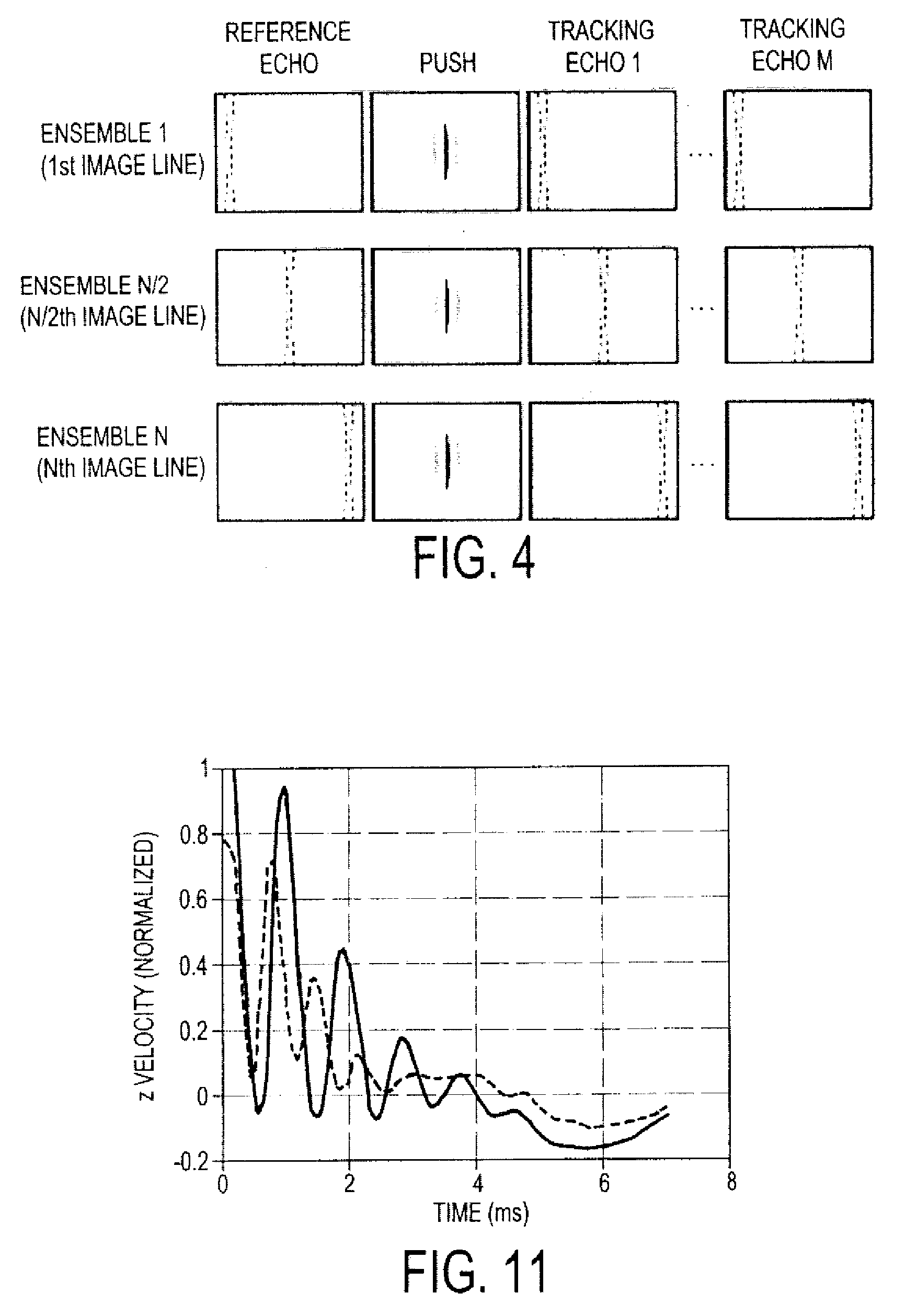
Shear modulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulse acoustic radiation force approximation
ActiveUS20090056453A1Quantitative measurement of the shear modulus of the tissueVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidShear modulusSonification
A method for determining a shear modulus of an elastic material with a known density value is provided. In this method, a spatially modulated acoustic radiation force is used to initially generate a disturbance of known spatial frequency or wavelength. The propagation of this initial displacement as a shear wave is measured using ultrasound tracking methods. A temporal frequency is determined based on the shear wave. The shear modulus of the elastic material at the point of excitation may be calculated using the values of the spatial wavelength, material density, and temporal frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com