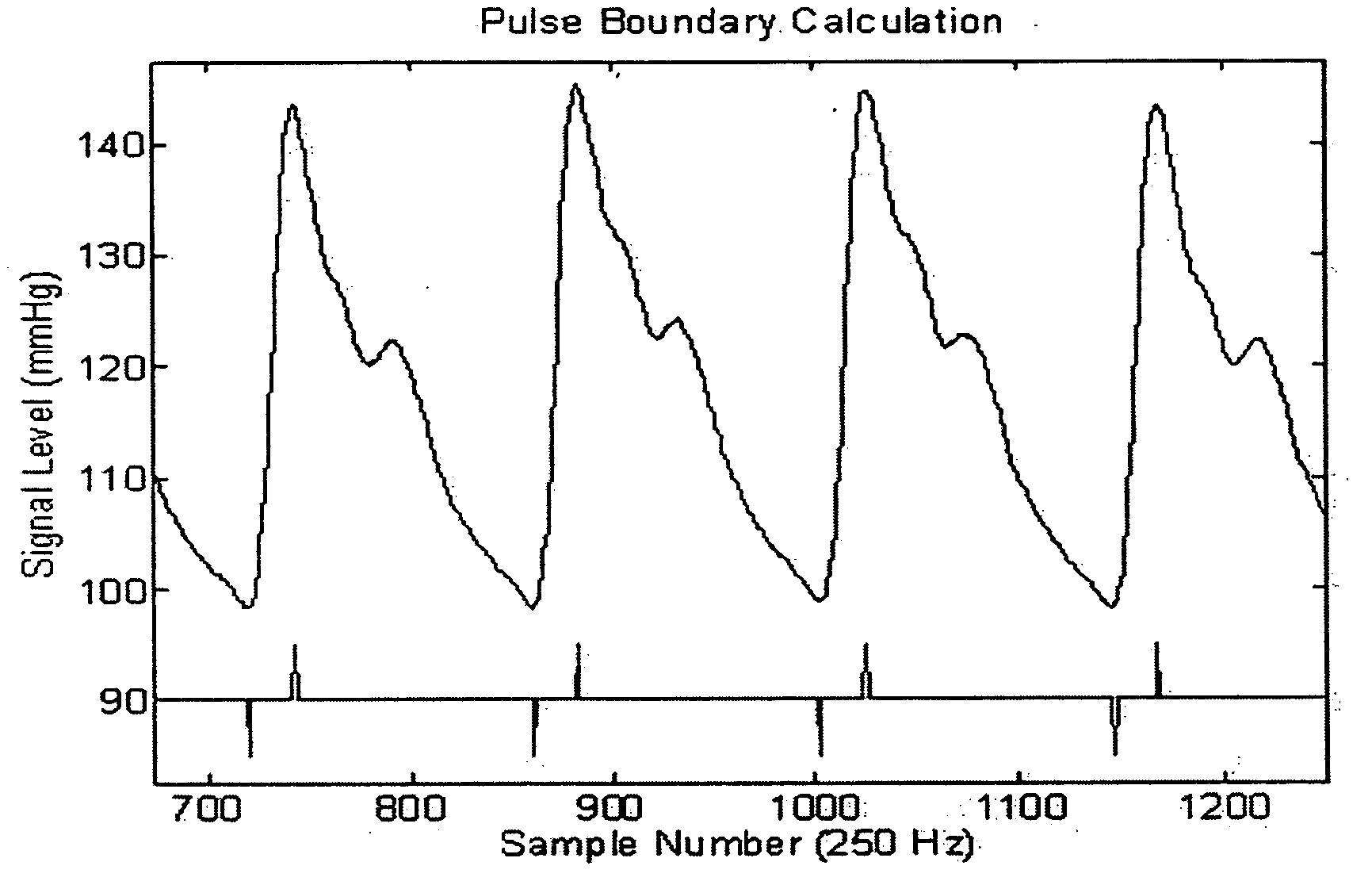
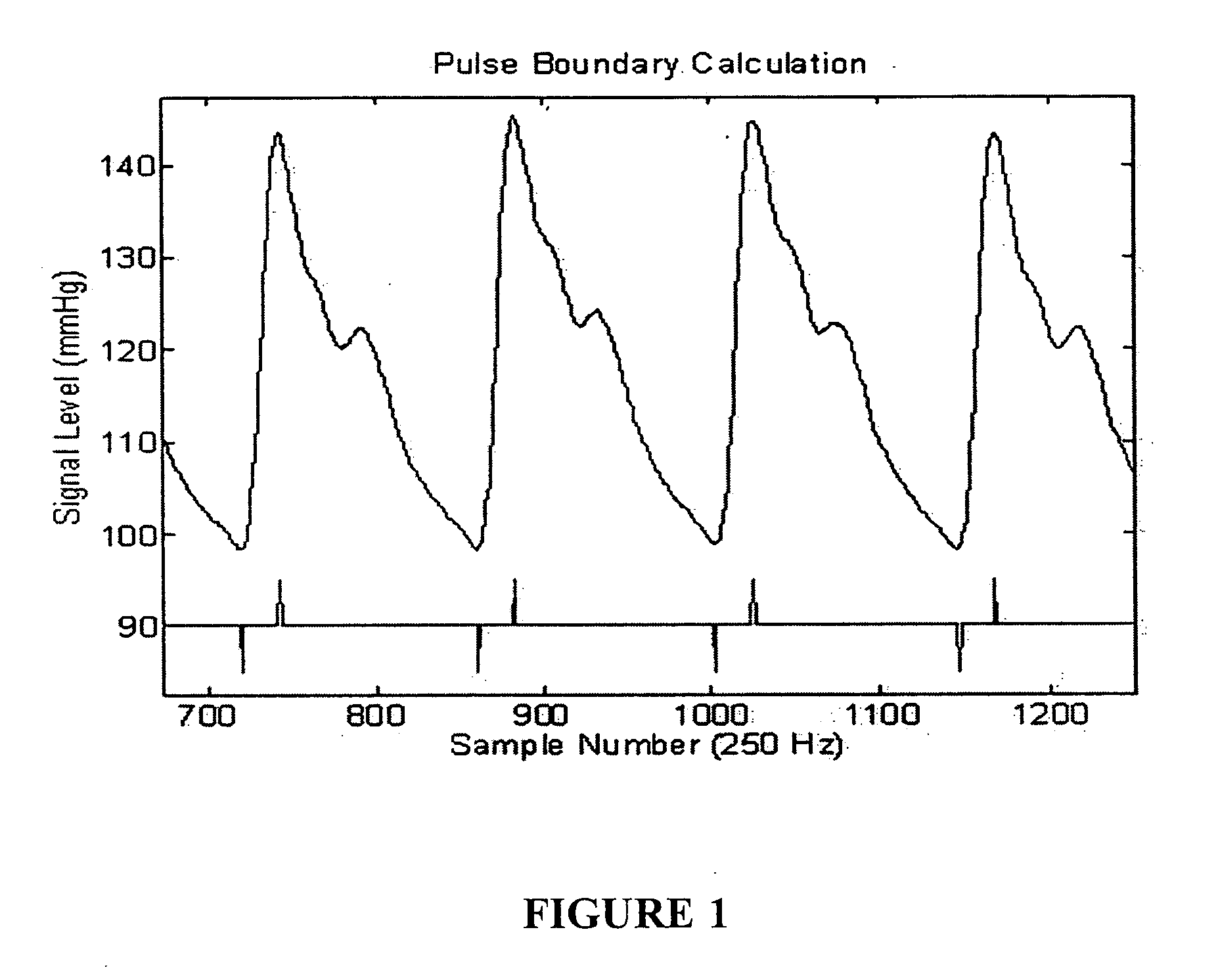
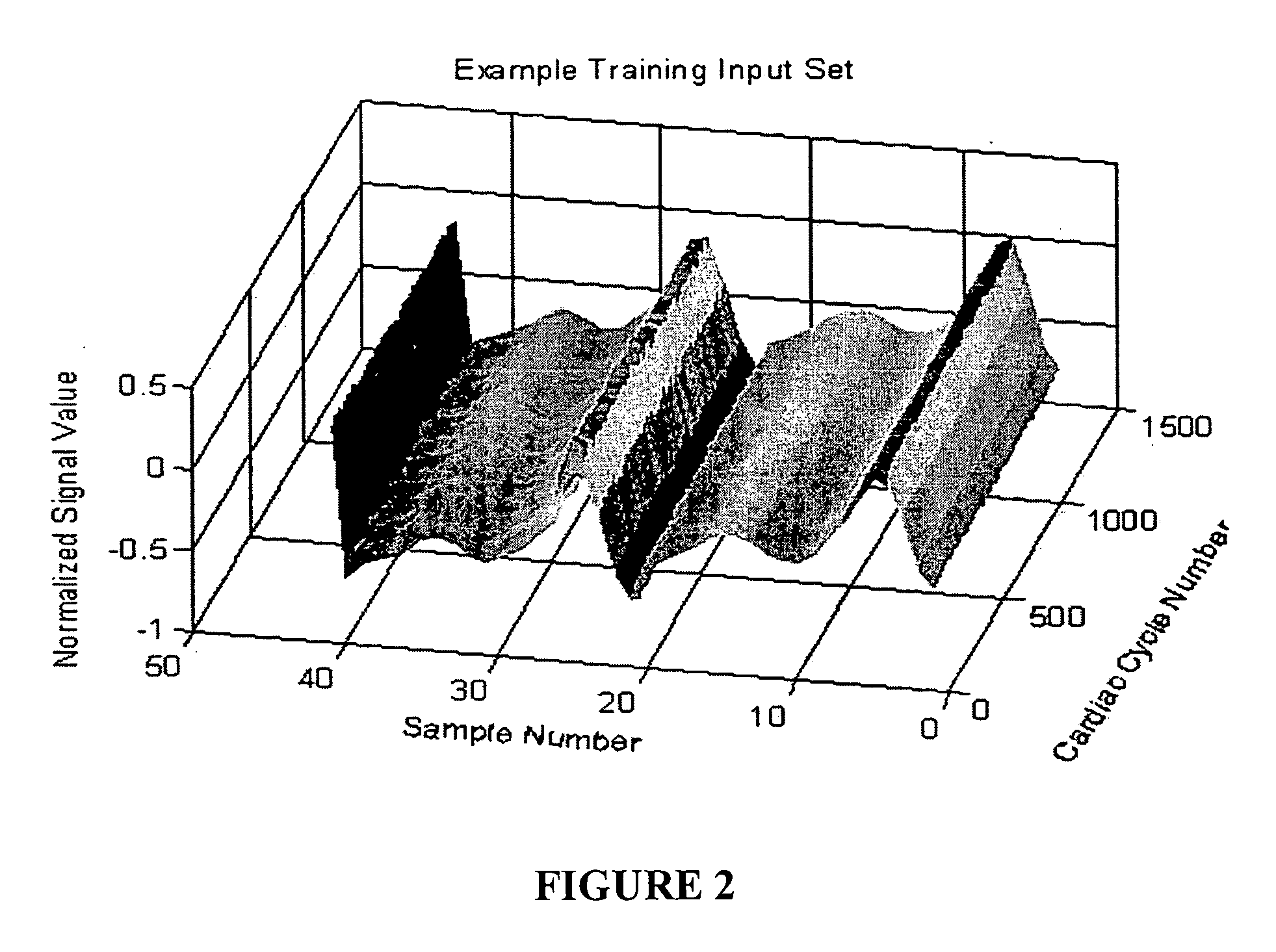
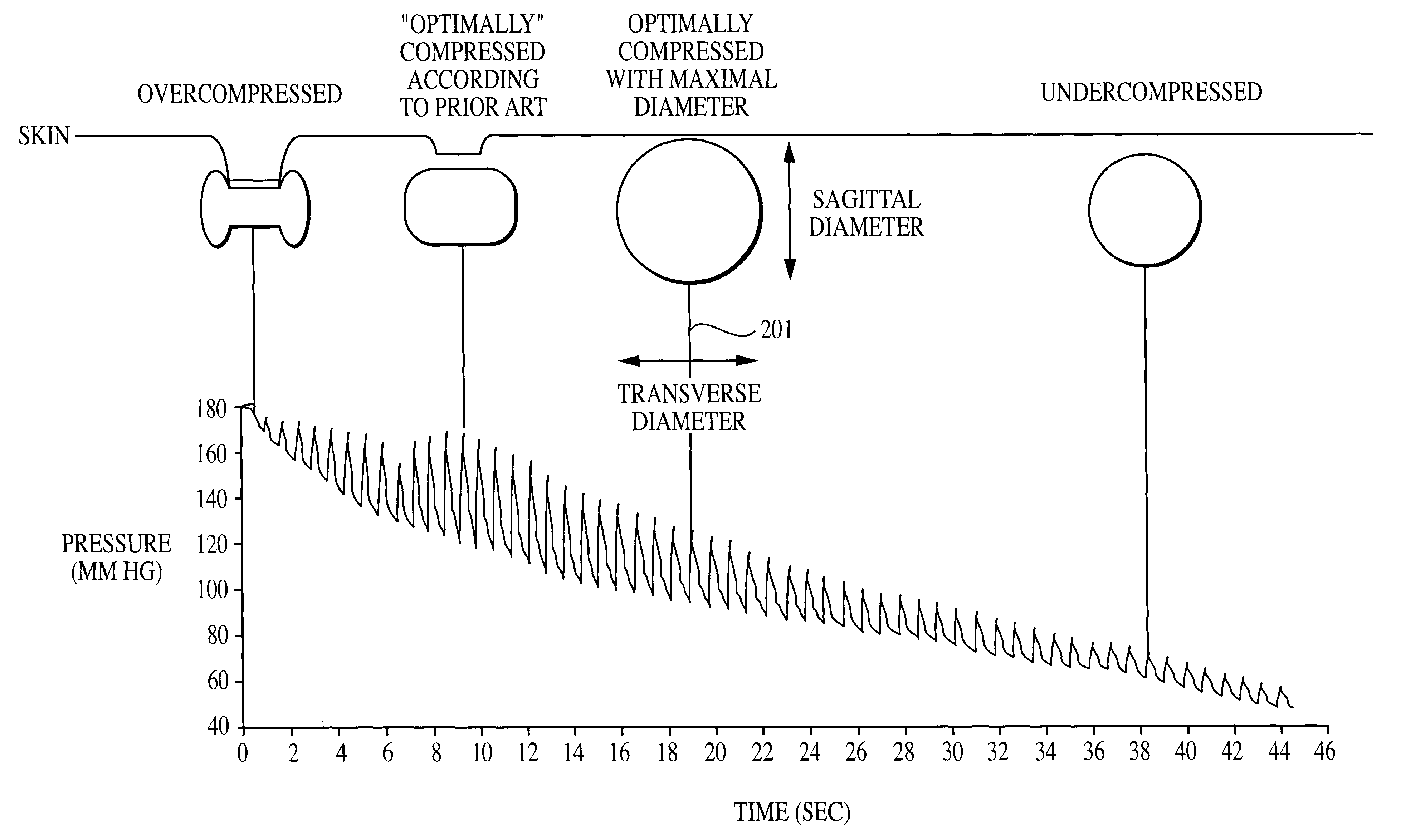
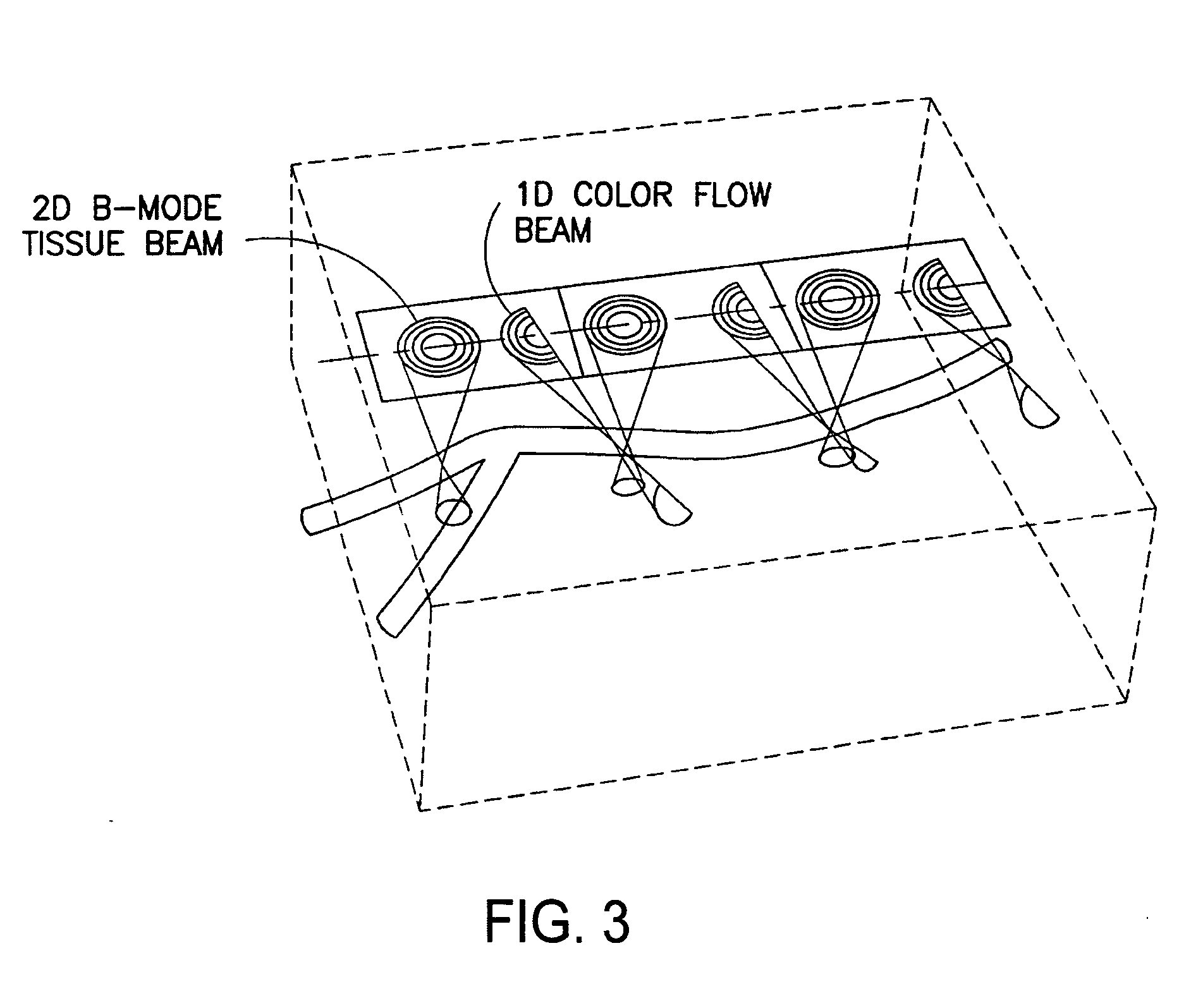
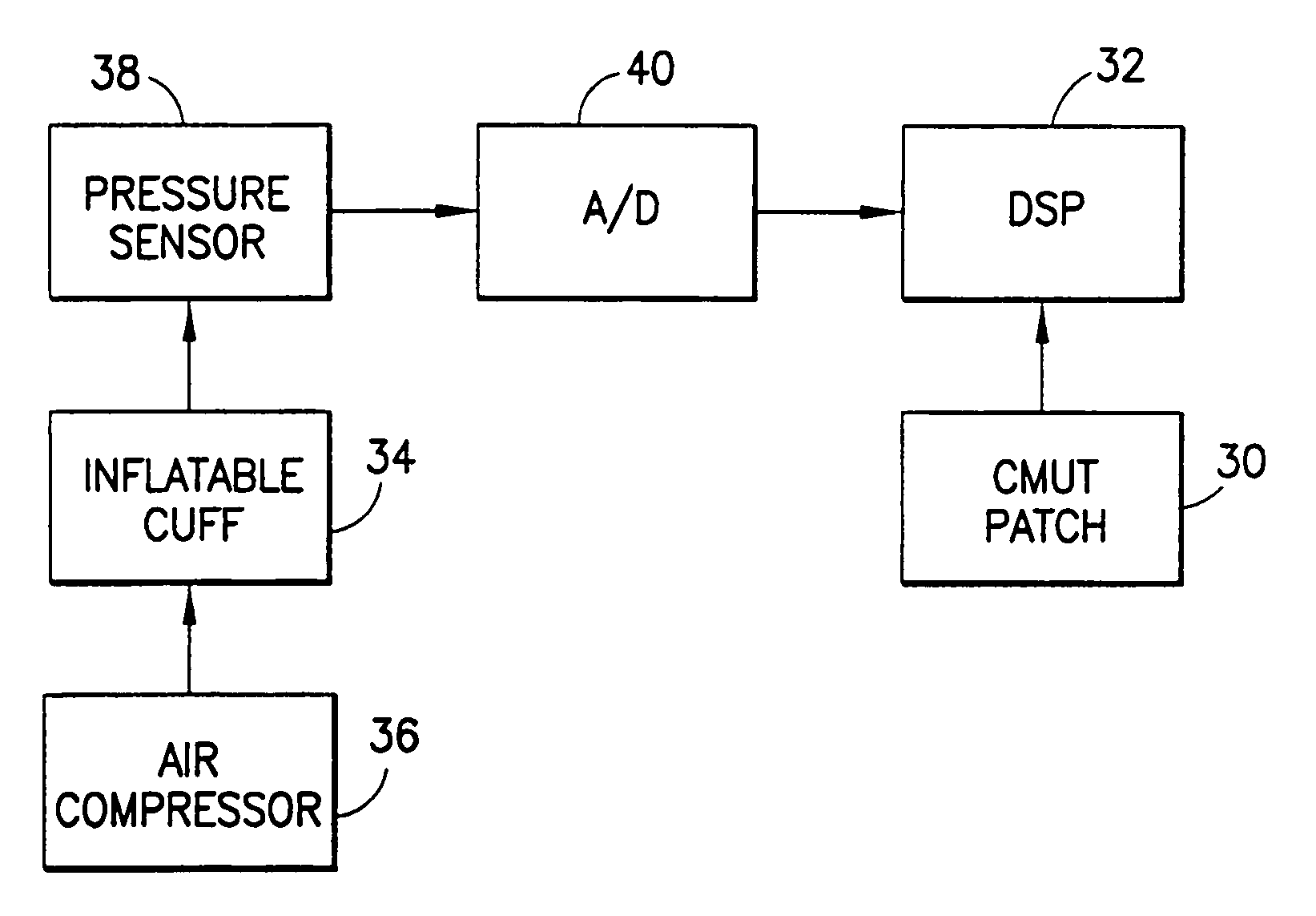
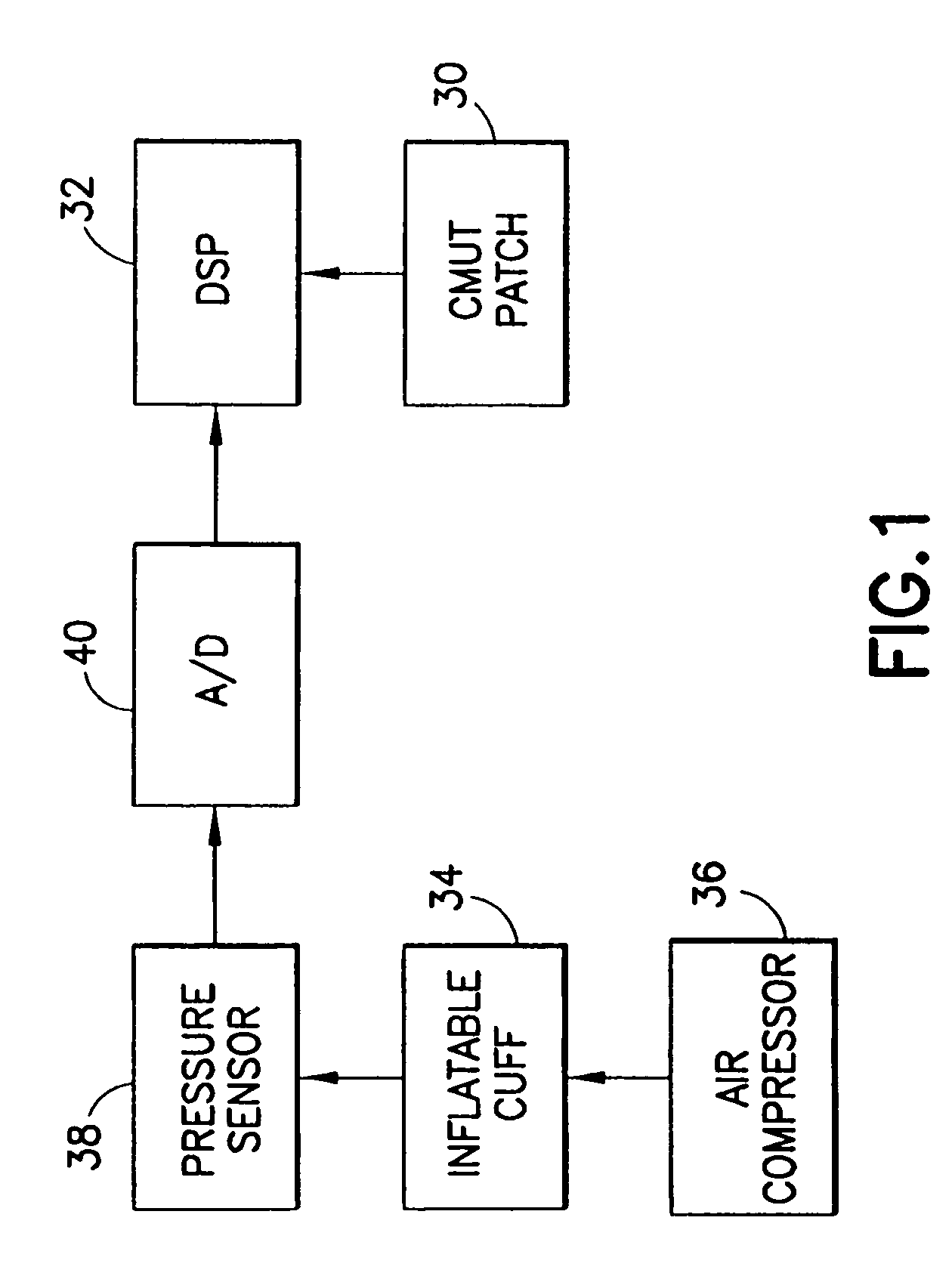
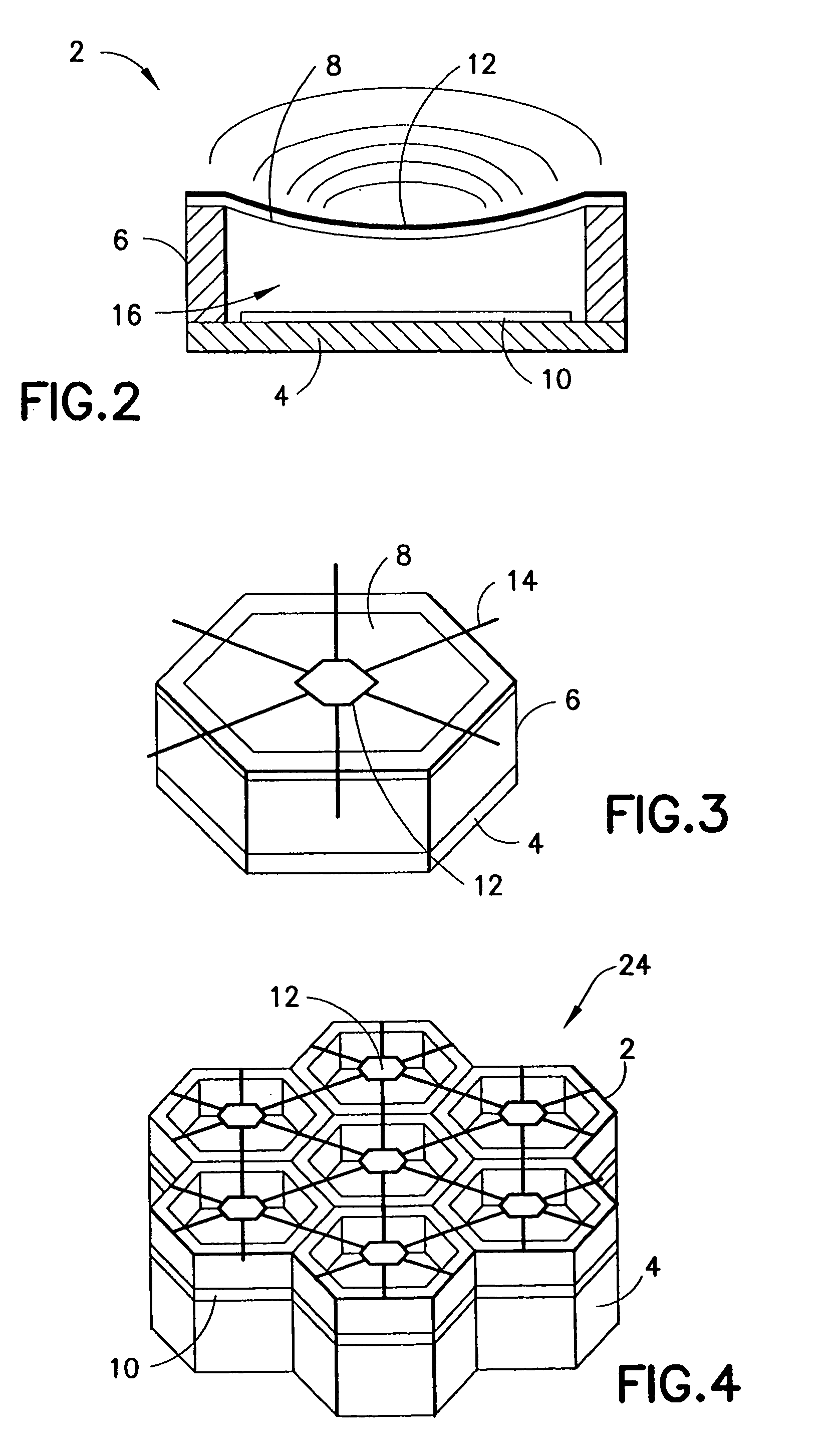
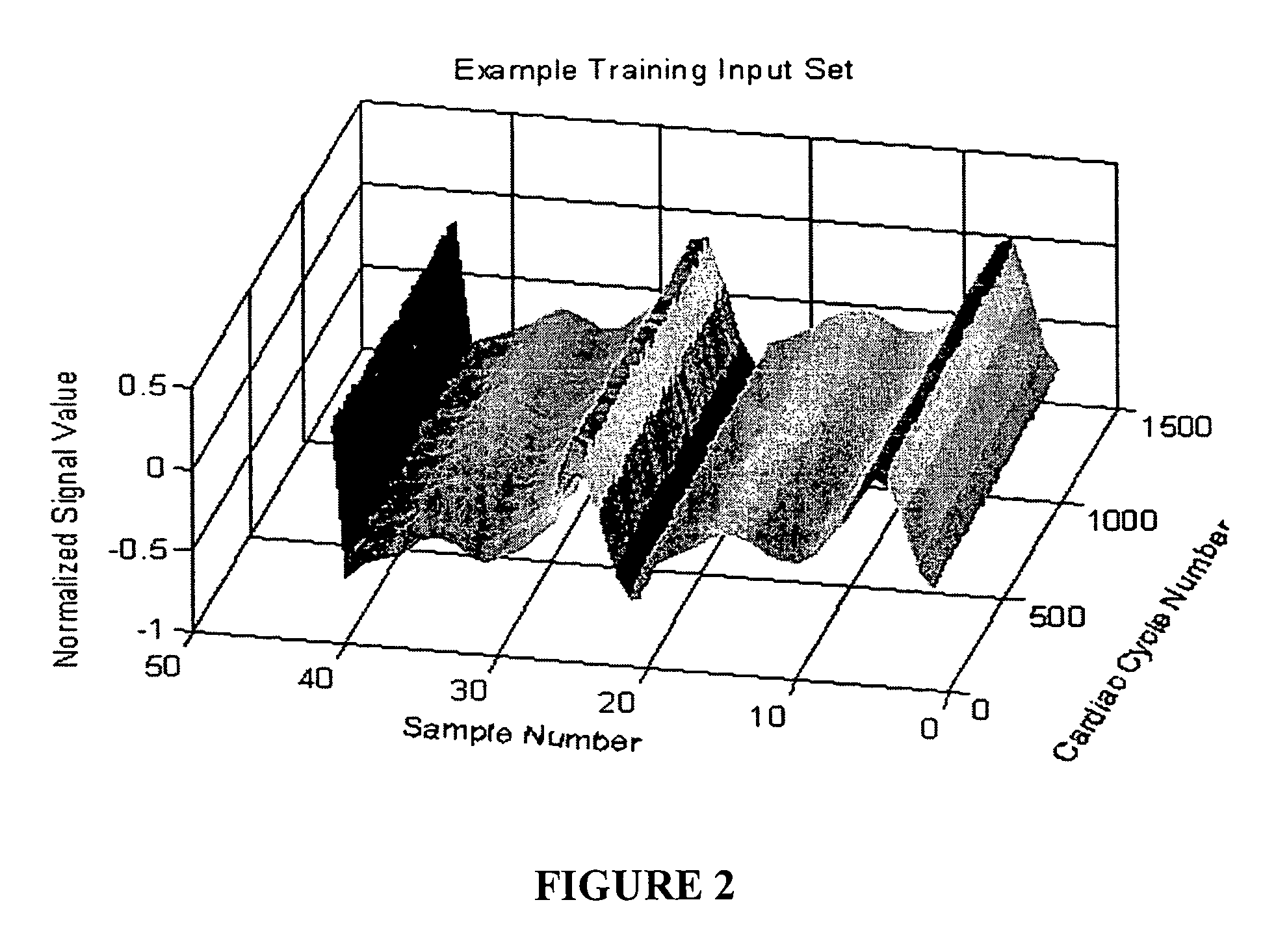
Patents
Literature
346results about "Blood pressure measurement devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
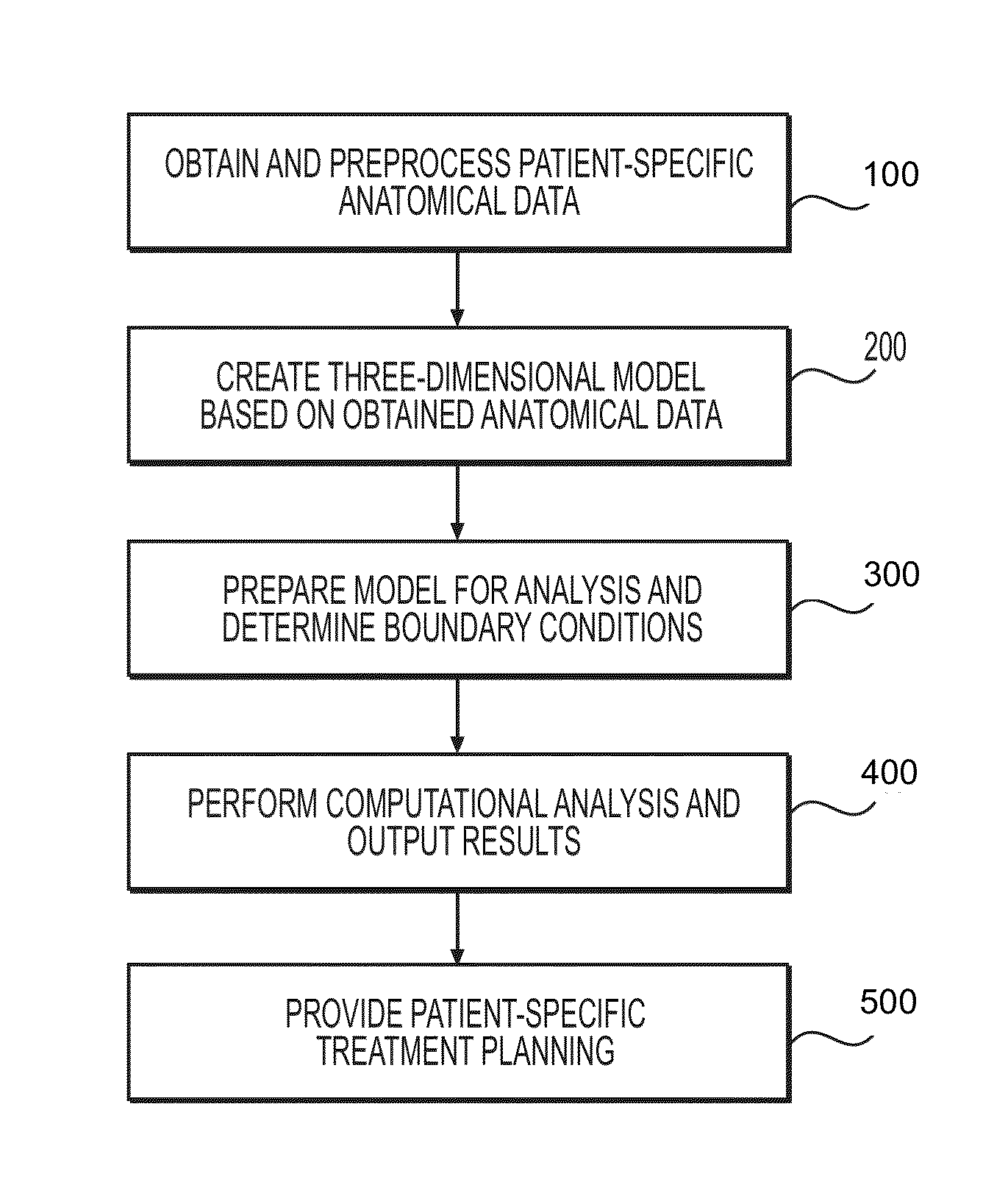
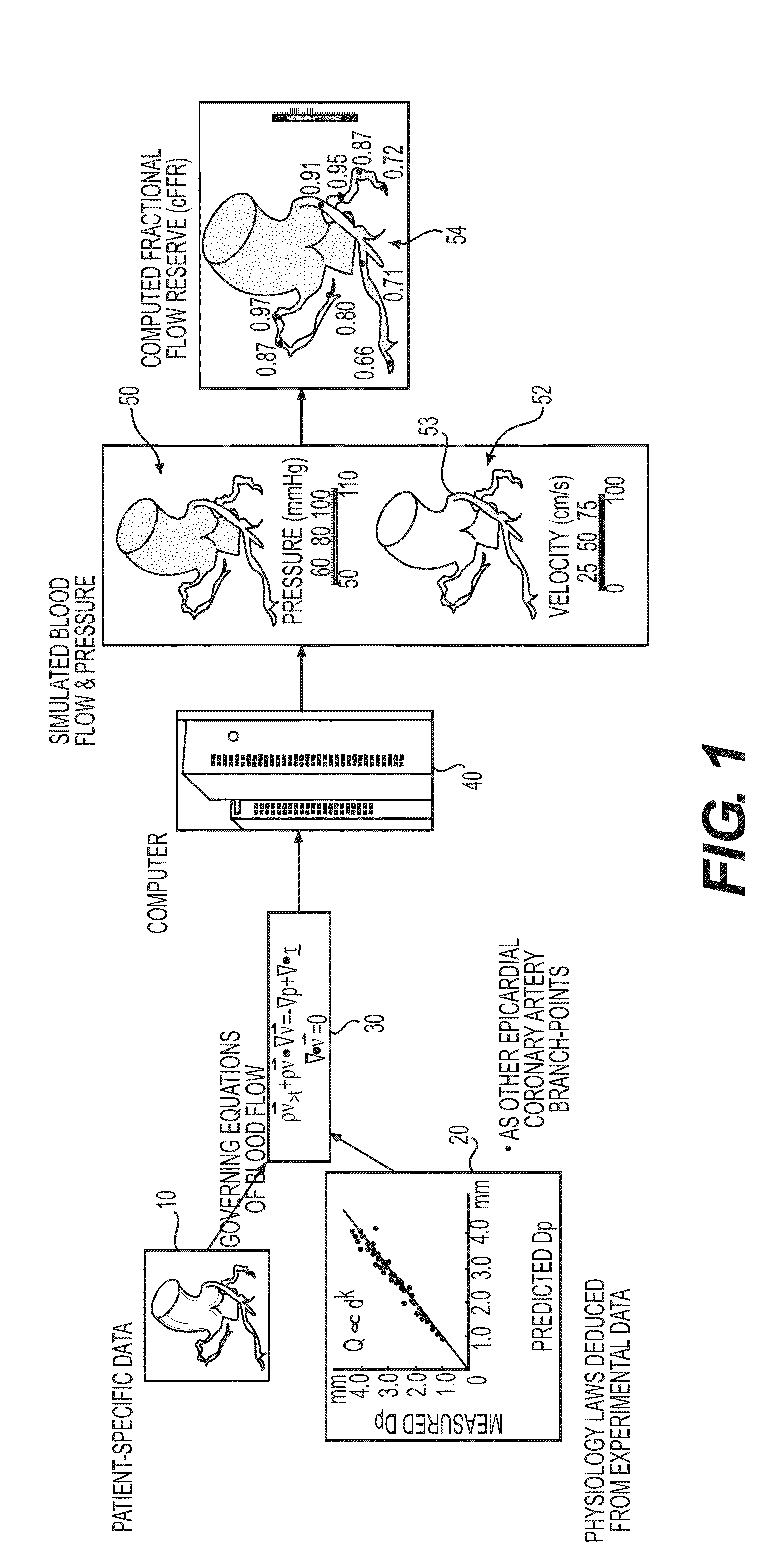
Method and system for patient-specific modeling of blood flow
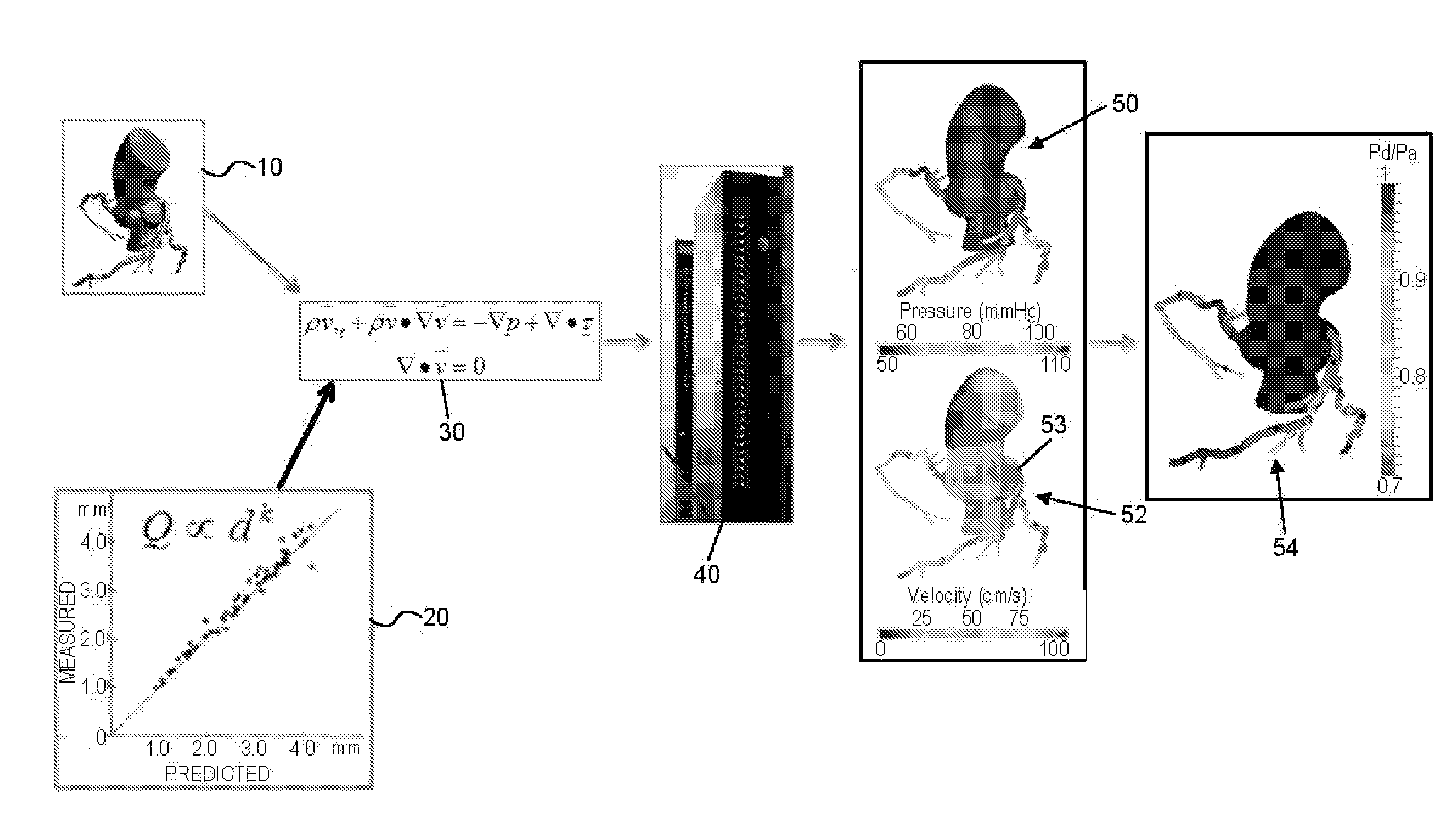
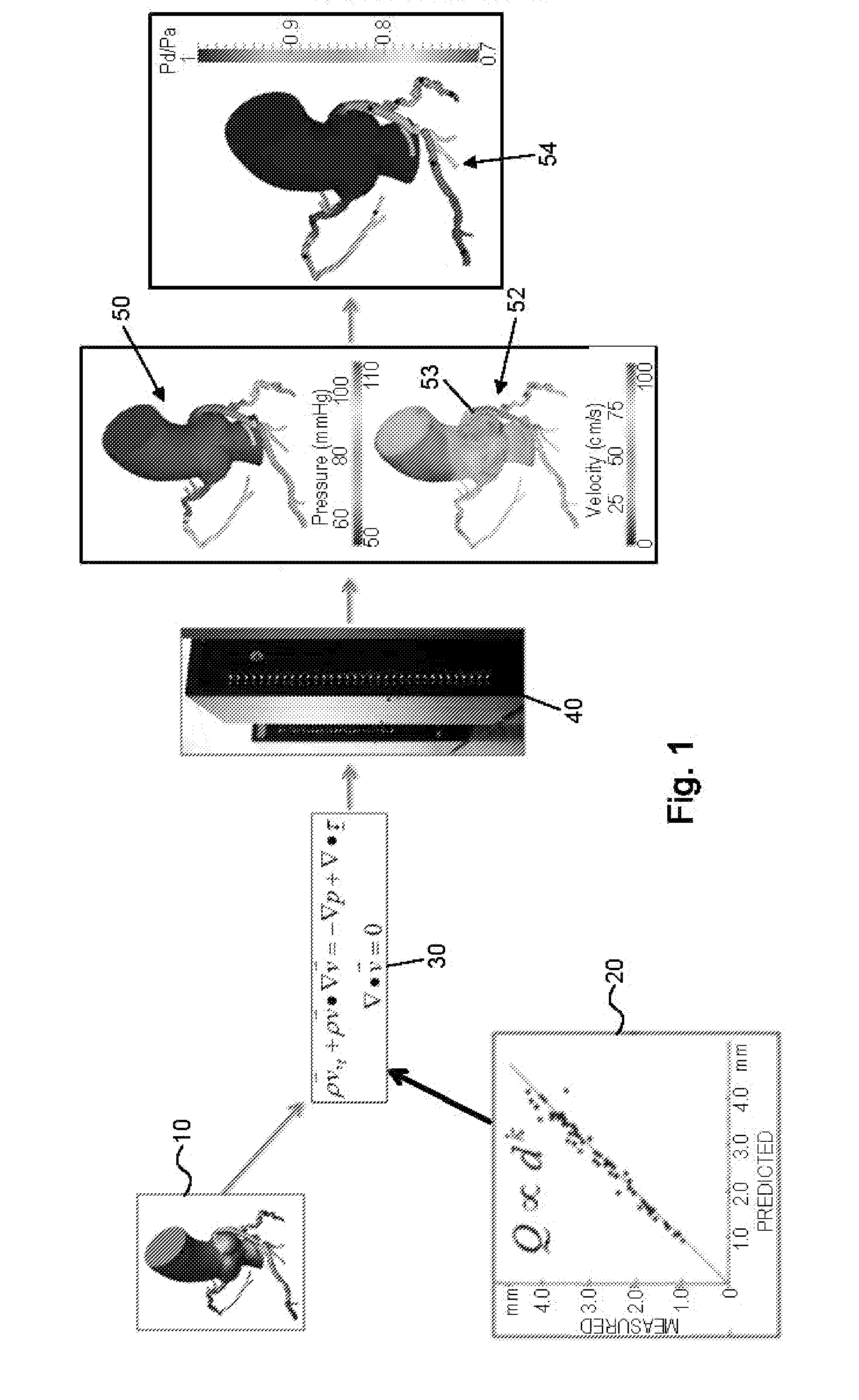
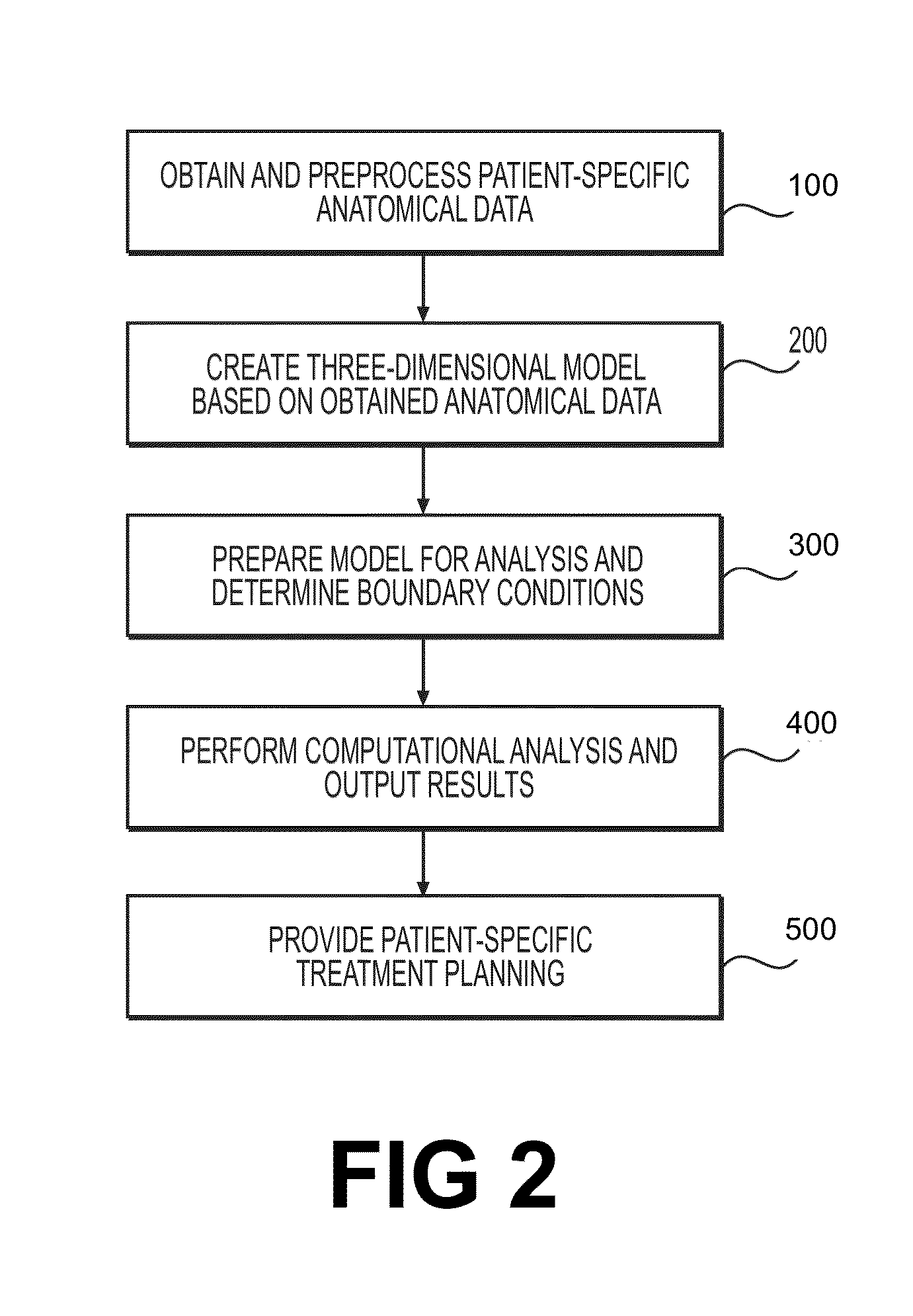
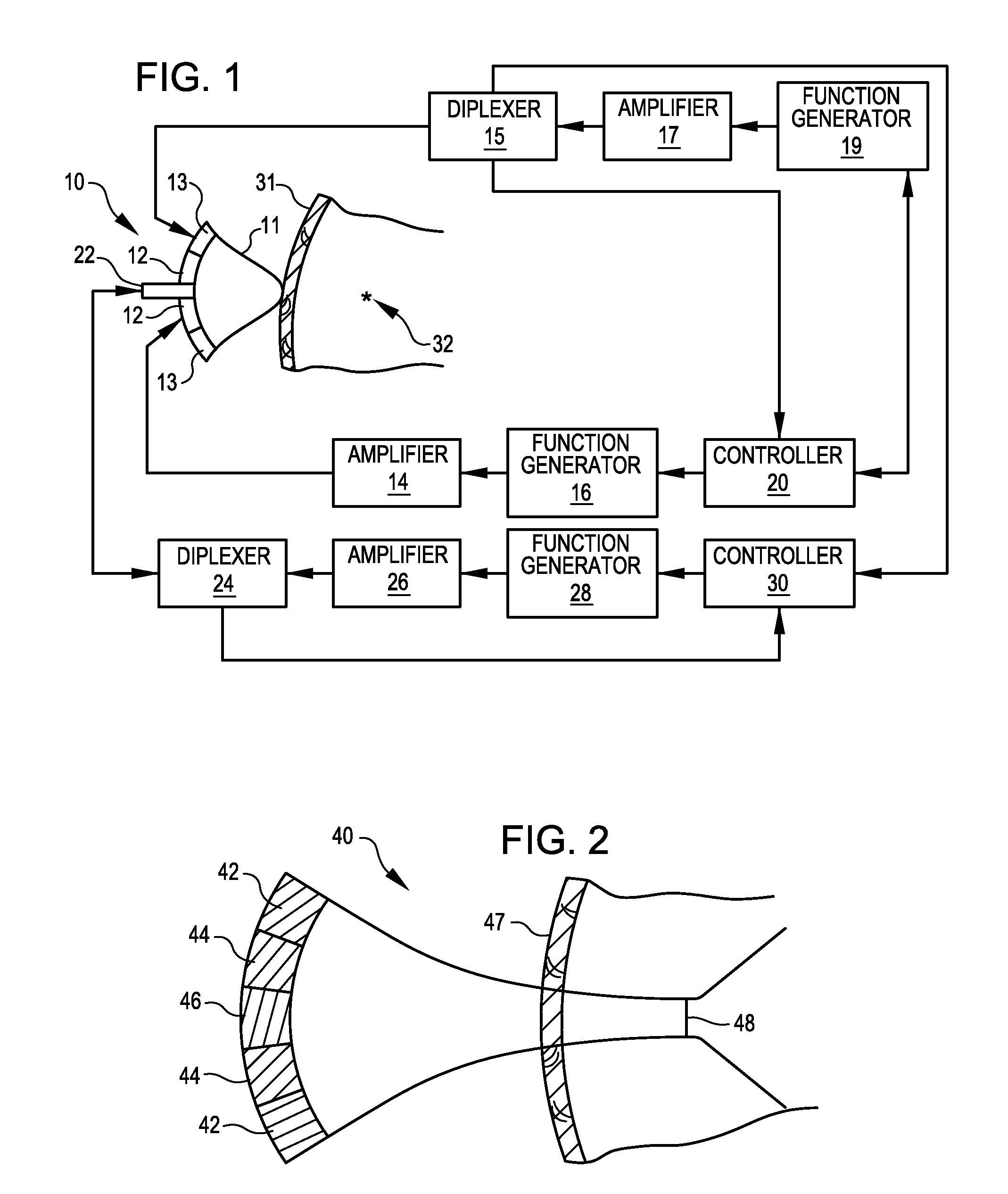
Embodiments include a system for determining cardiovascular information for a patient. The system may include at least one computer system configured to receive patient-specific data regarding a geometry of the patient's heart, and create a three-dimensional model representing at least a portion of the patient's heart based on the patient-specific data. The at least one computer system may be further configured to create a physics-based model relating to a blood flow characteristic of the patient's heart and determine a fractional flow reserve within the patient's heart based on the three-dimensional model and the physics-based model.
Owner:HEARTFLOW
Systems and methods for making noninvasive physiological assessments
InactiveUS6875176B2Improve accuracySensitive highOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryDiseaseNon invasive
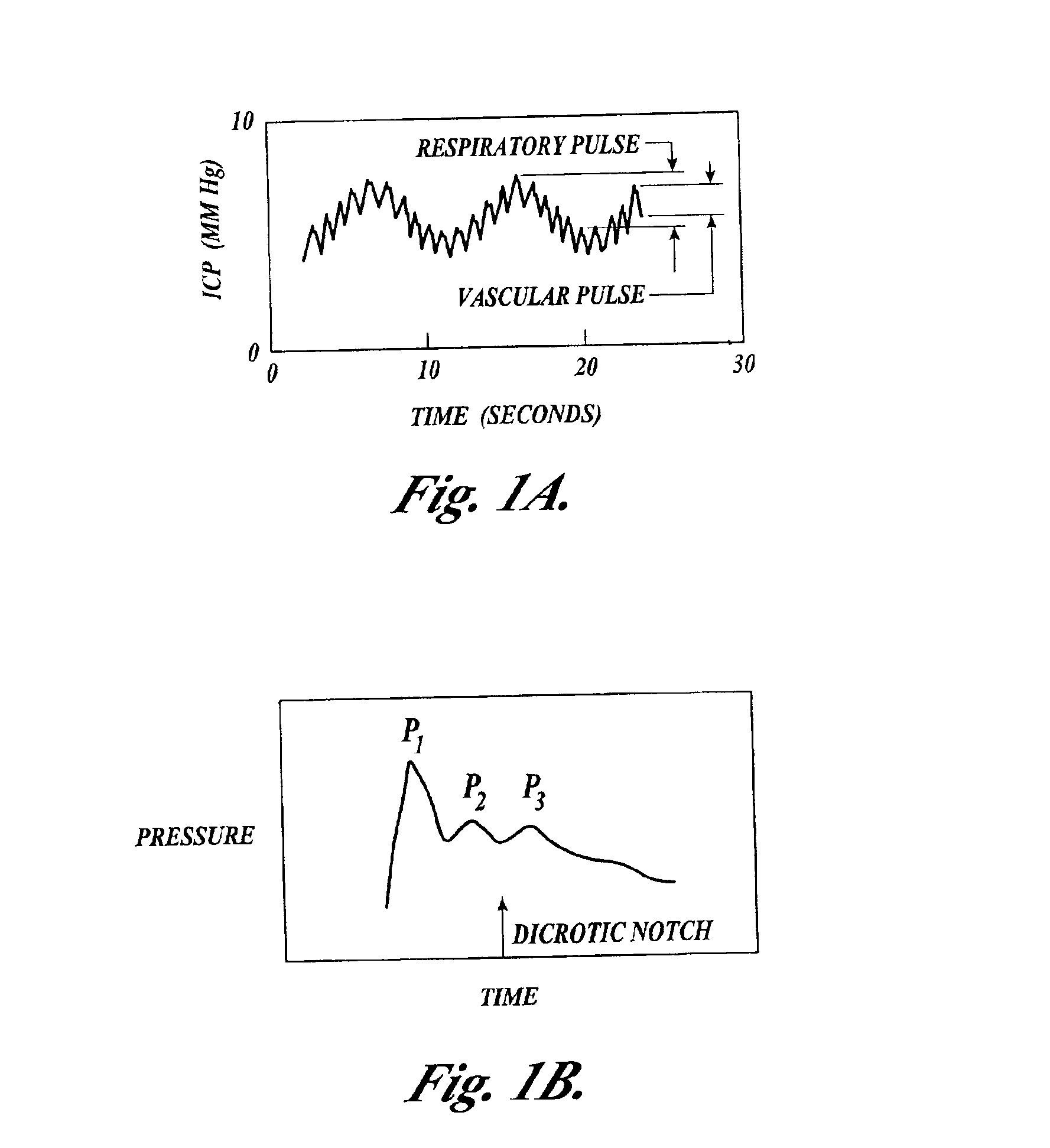
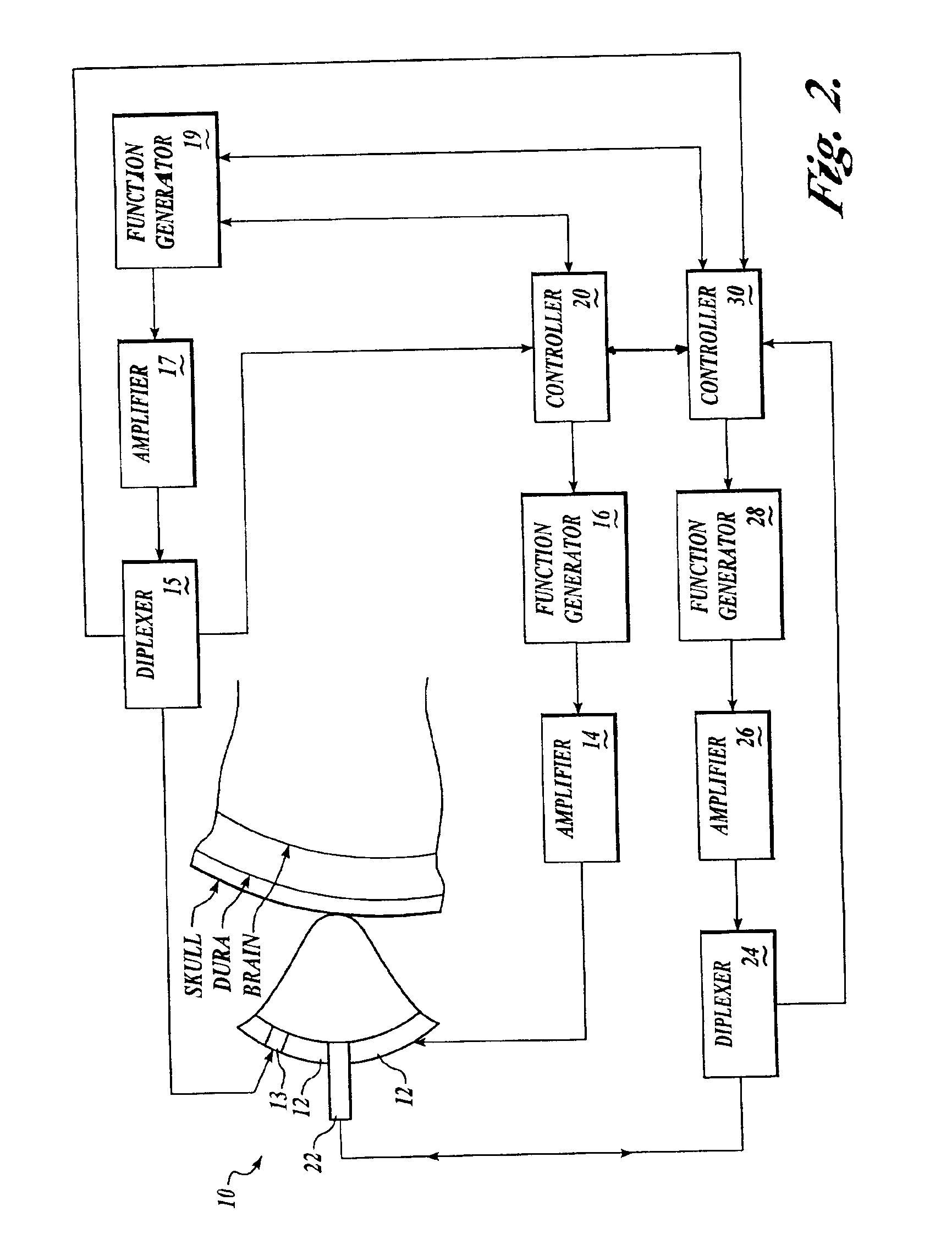
Systems and methods for assessment of tissue properties, noninvasively, by acquiring data relating to at least one aspect of intrinsic and / or induced tissue displacement, or associated biological responses, are provided. Data relating to tissue displacement and associated biological changes may be acquired by detecting acoustic properties of tissue using ultrasound interrogation pulses, preferably in a scatter or Doppler detection mode. Based on this data, tissue properties are assessed, characterized and monitored. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include non-invasive assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties. Methods and systems for localizing physiological condition(s) and / or biological response(s), such as pain, by targeting and selectively probing tissues using the application of focused ultrasound are also provided.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Systems and methods for non-invasive detection and monitoring of cardiac and blood parameters
InactiveUS20060100530A1Easy to detectEffective assessmentBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterData acquisitionNon invasive
Methods and systems for long term monitoring of one or more physiological parameters such as respiration, heart rate, body temperature, electrical heart activity, blood oxygenation, blood flow velocity, blood pressure, intracranial pressure, the presence of emboli in the blood stream and electrical brain activity are provided. Data is acquired non-invasively using ambulatory data acquisition techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Apparatus and methods for monitoring physiological data during environmental interference
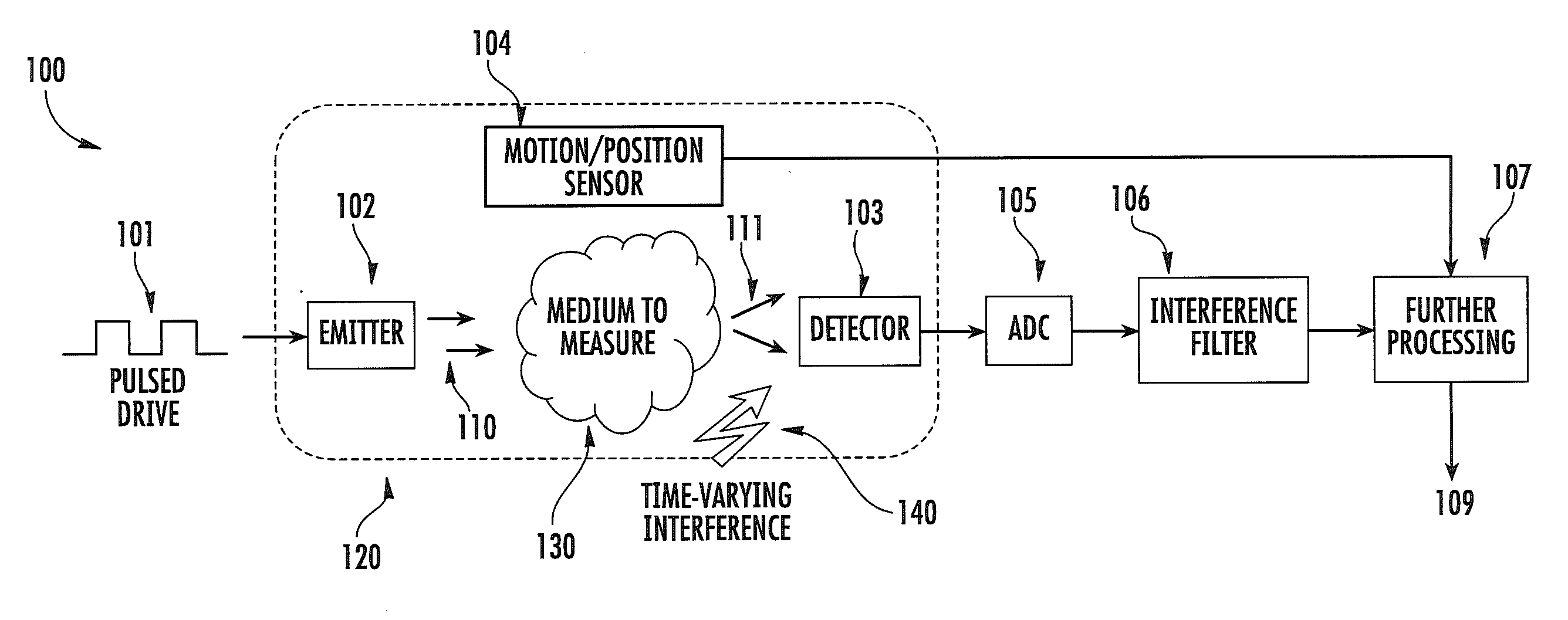
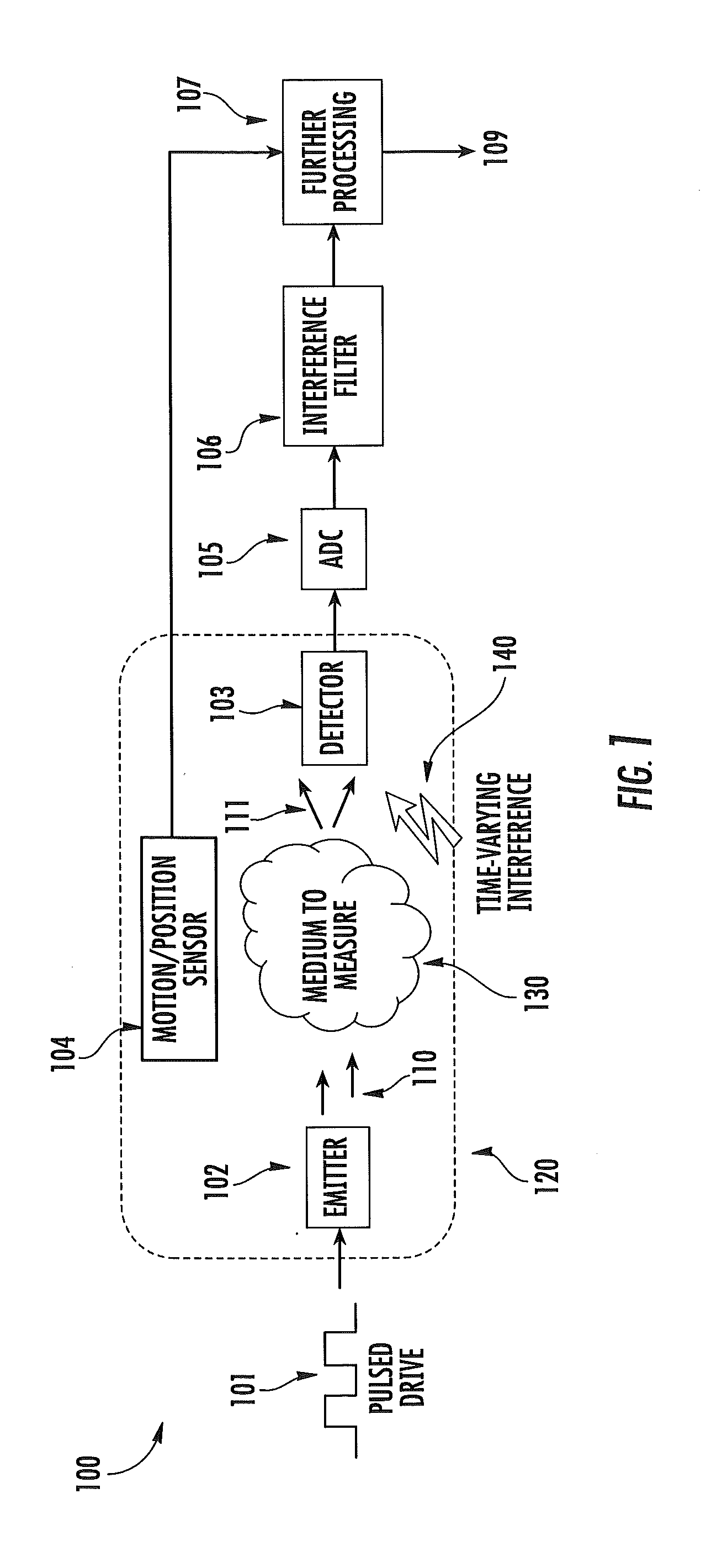
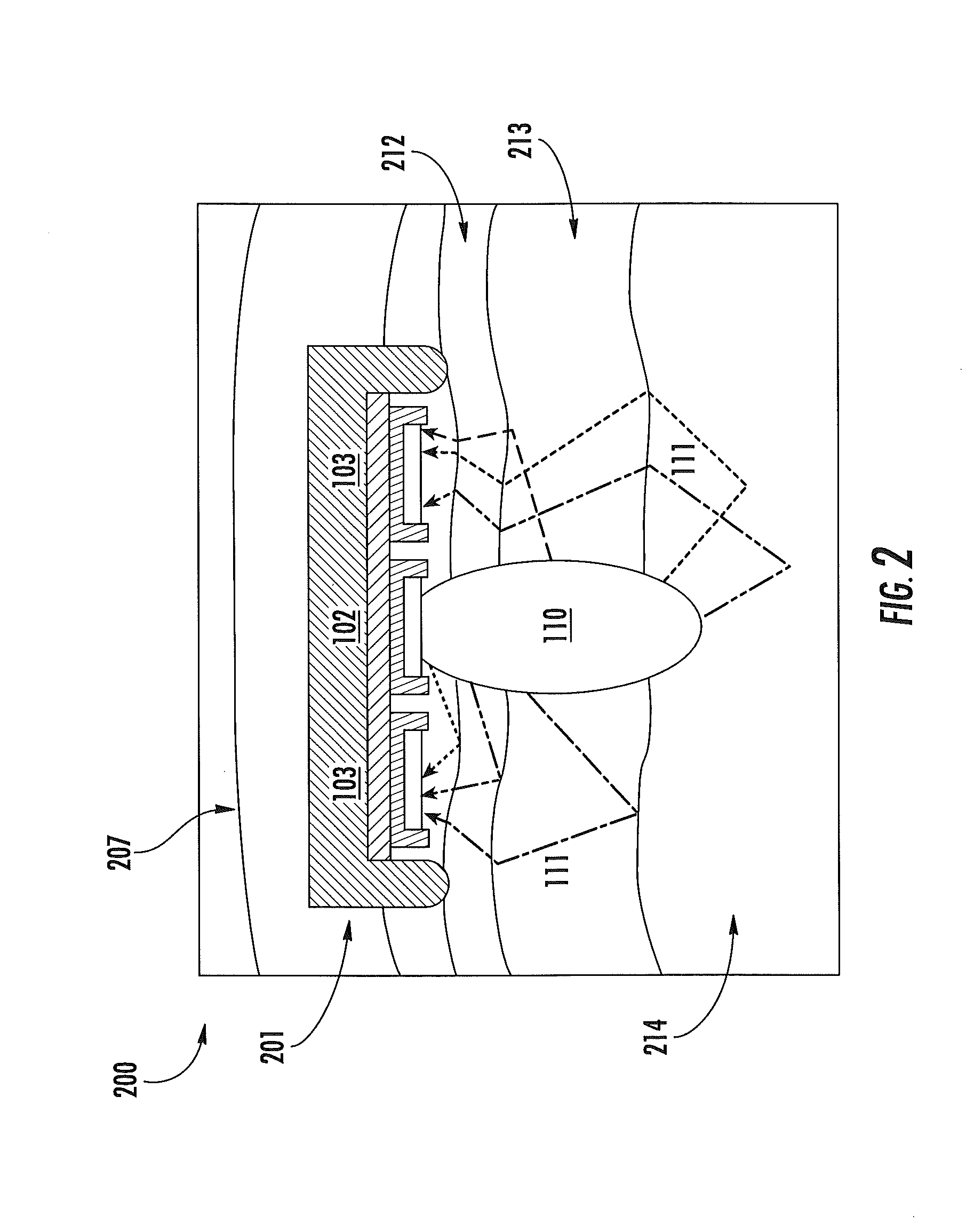
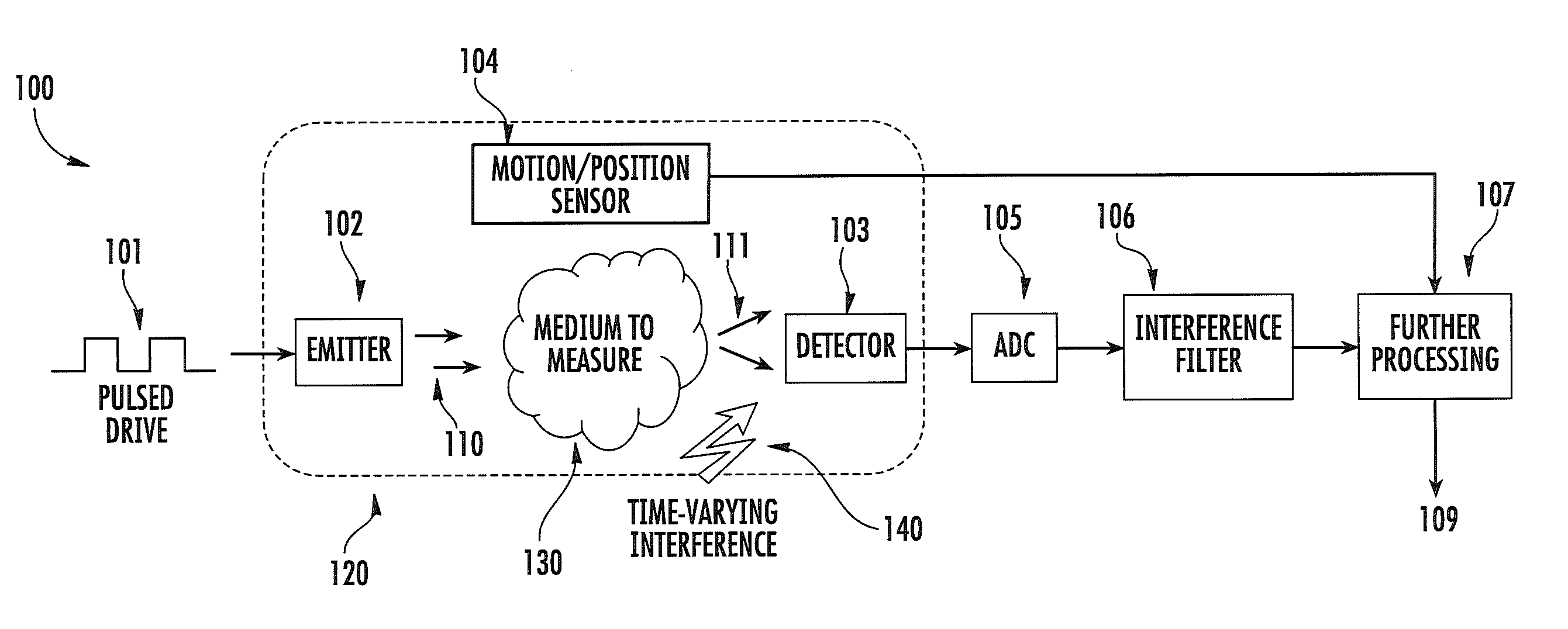
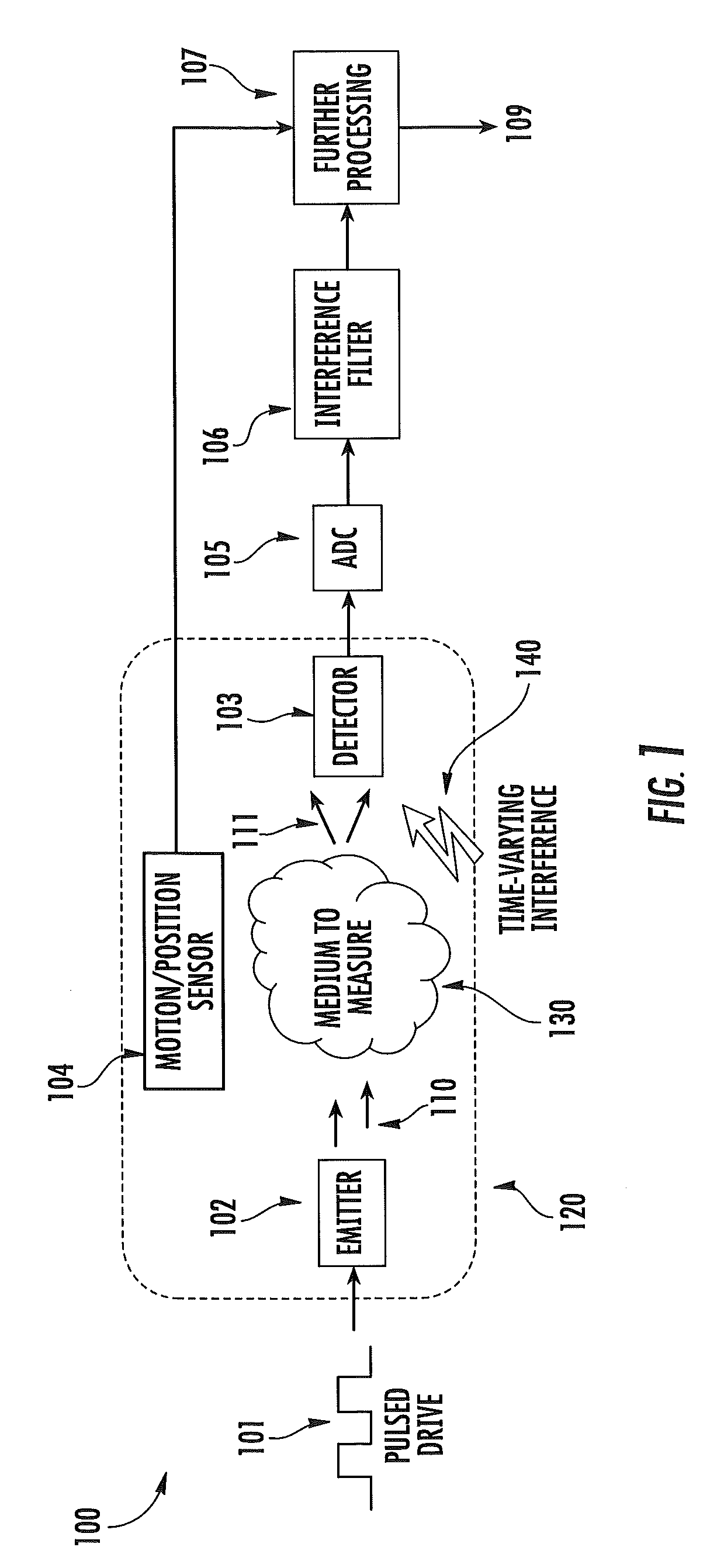
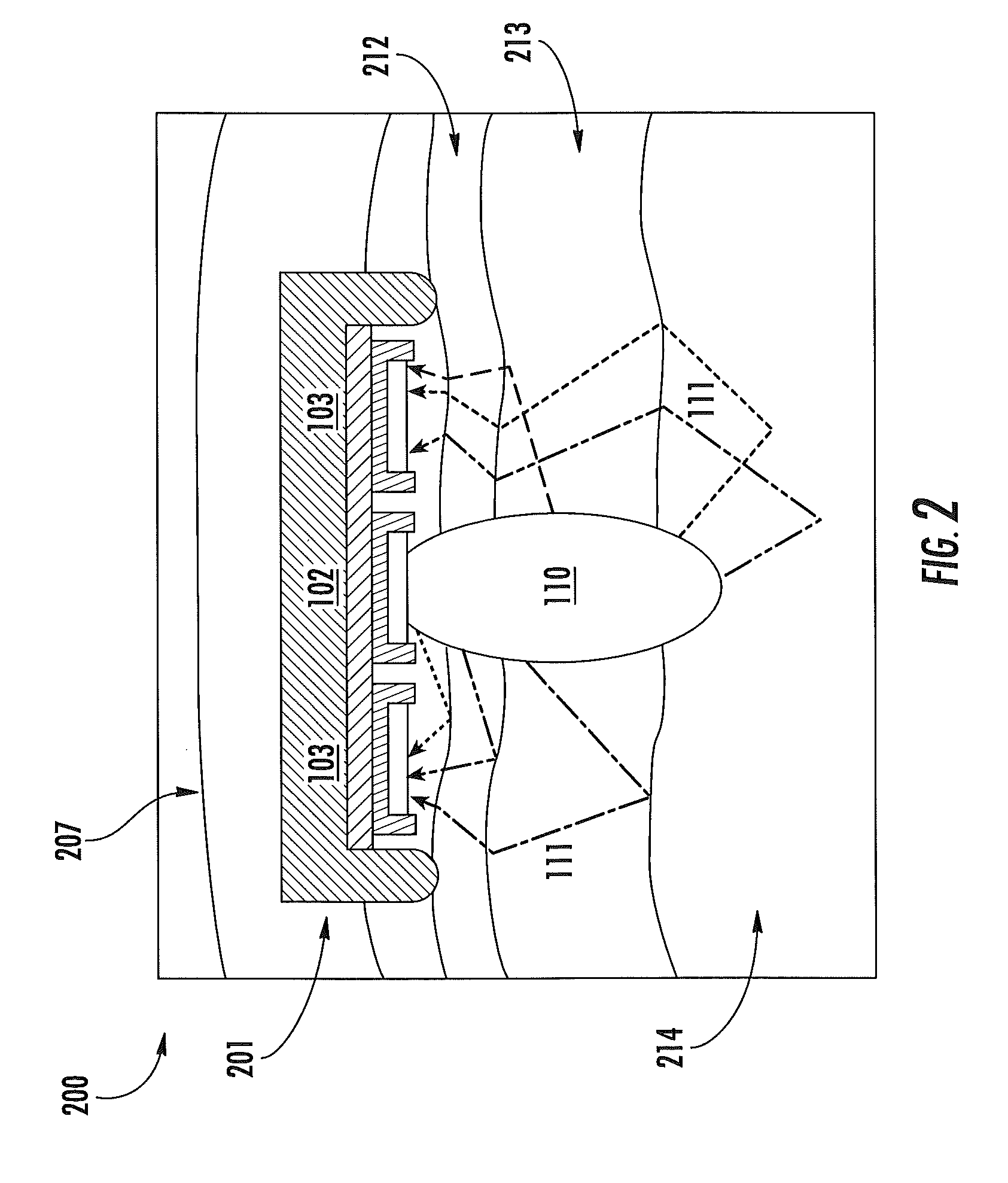
ActiveUS20120197093A1Easy to keepMaximize collectionHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal changeEngineering
Apparatus and methods for attenuating environmental interference are described. A wearable monitoring apparatus includes a housing configured to be attached to the body of a subject and a sensor module that includes an energy emitter that directs energy at a target region of the subject, a detector that detects an energy response signal—or physiological condition—from the subject, a filter that removes time-varying environmental interference from the energy response signal, and at least one processor that controls operations of the energy emitter, detector, and filter.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
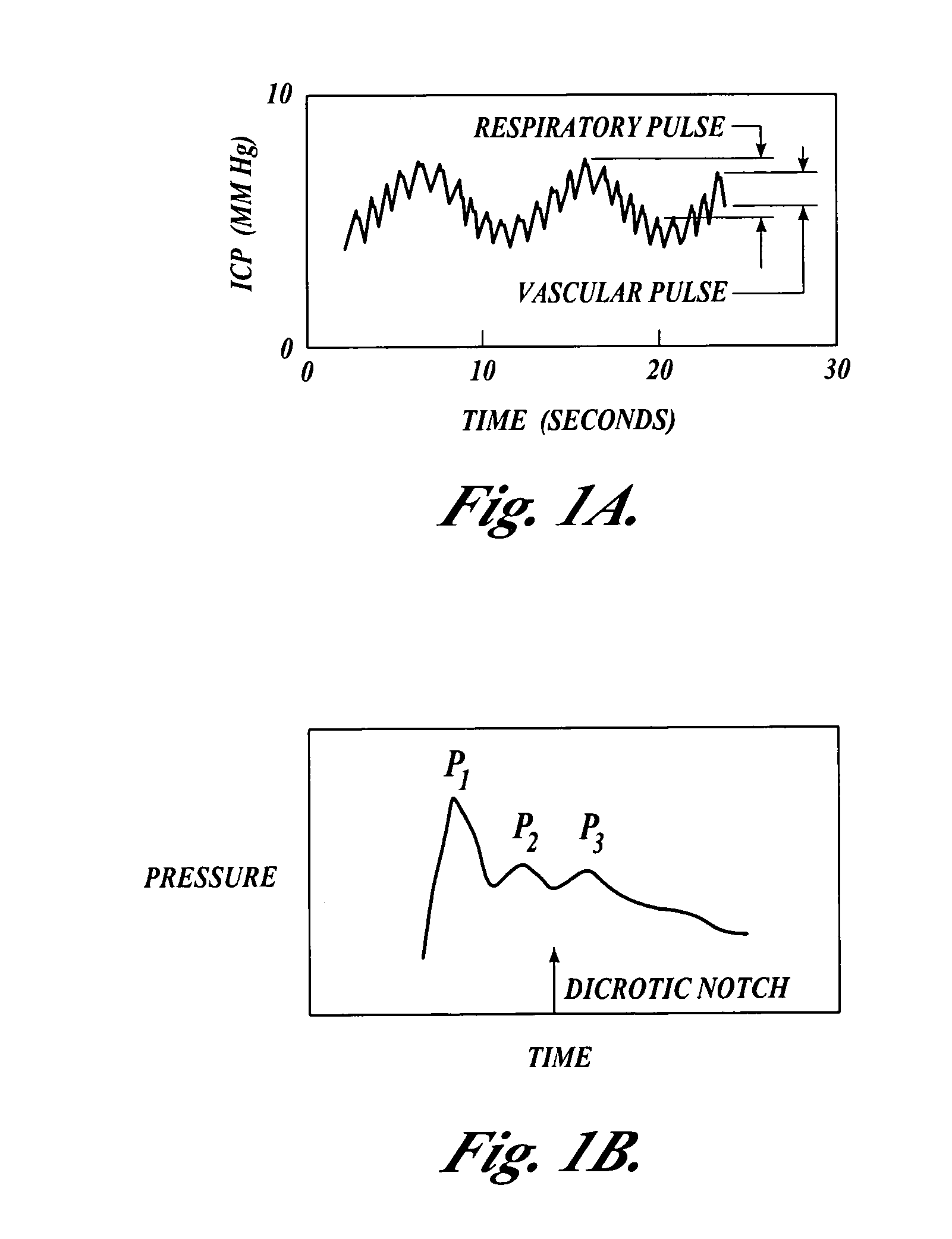
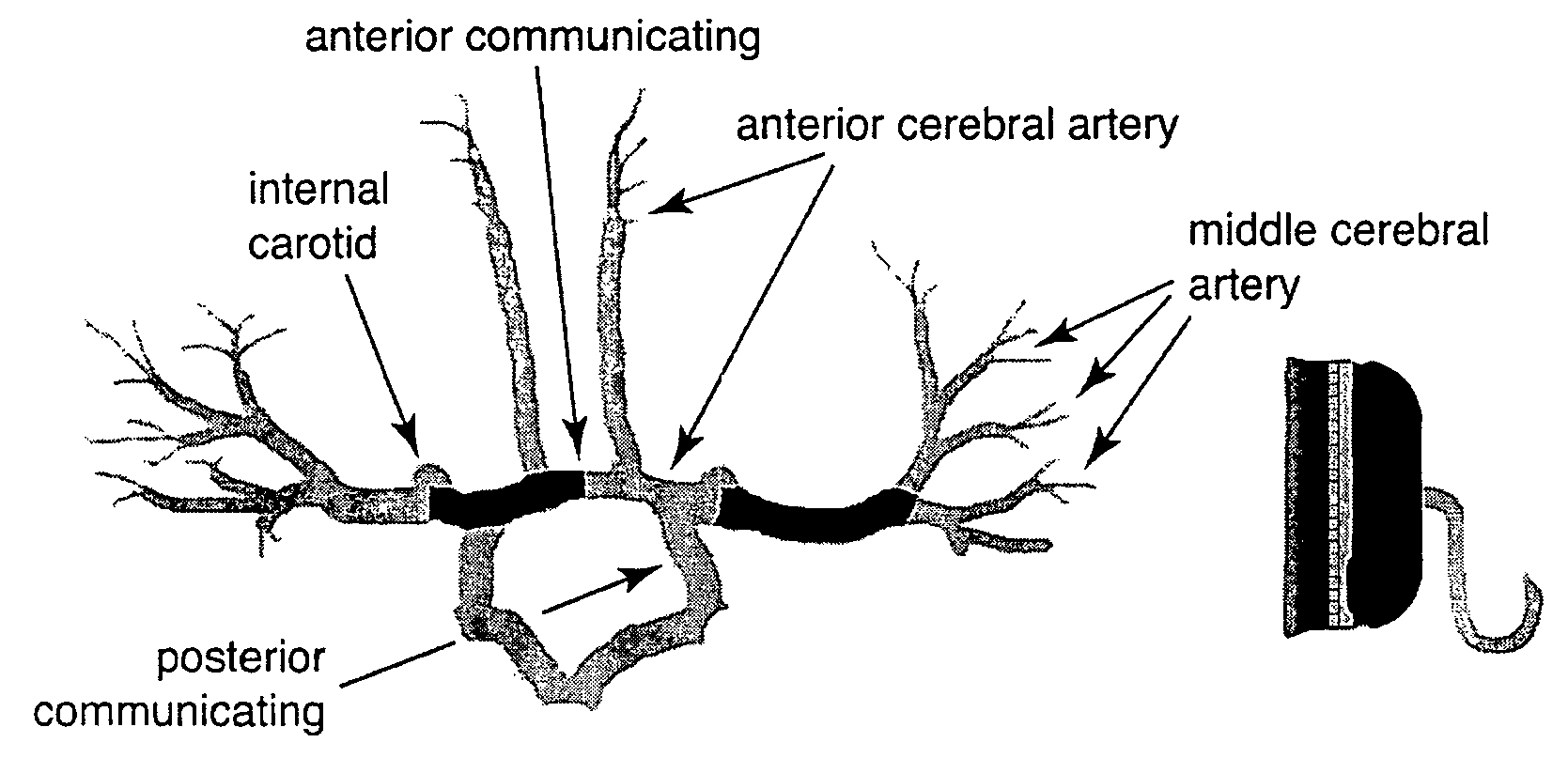
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
InactiveUS20050015009A1Accurate assessmentAccurate monitoringMedical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and apparatus for the noninvasive determination of arterial blood pressure
InactiveUS6514211B1Blood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsUltrasonic sensorTransmural pressure
Owner:TENSYS MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
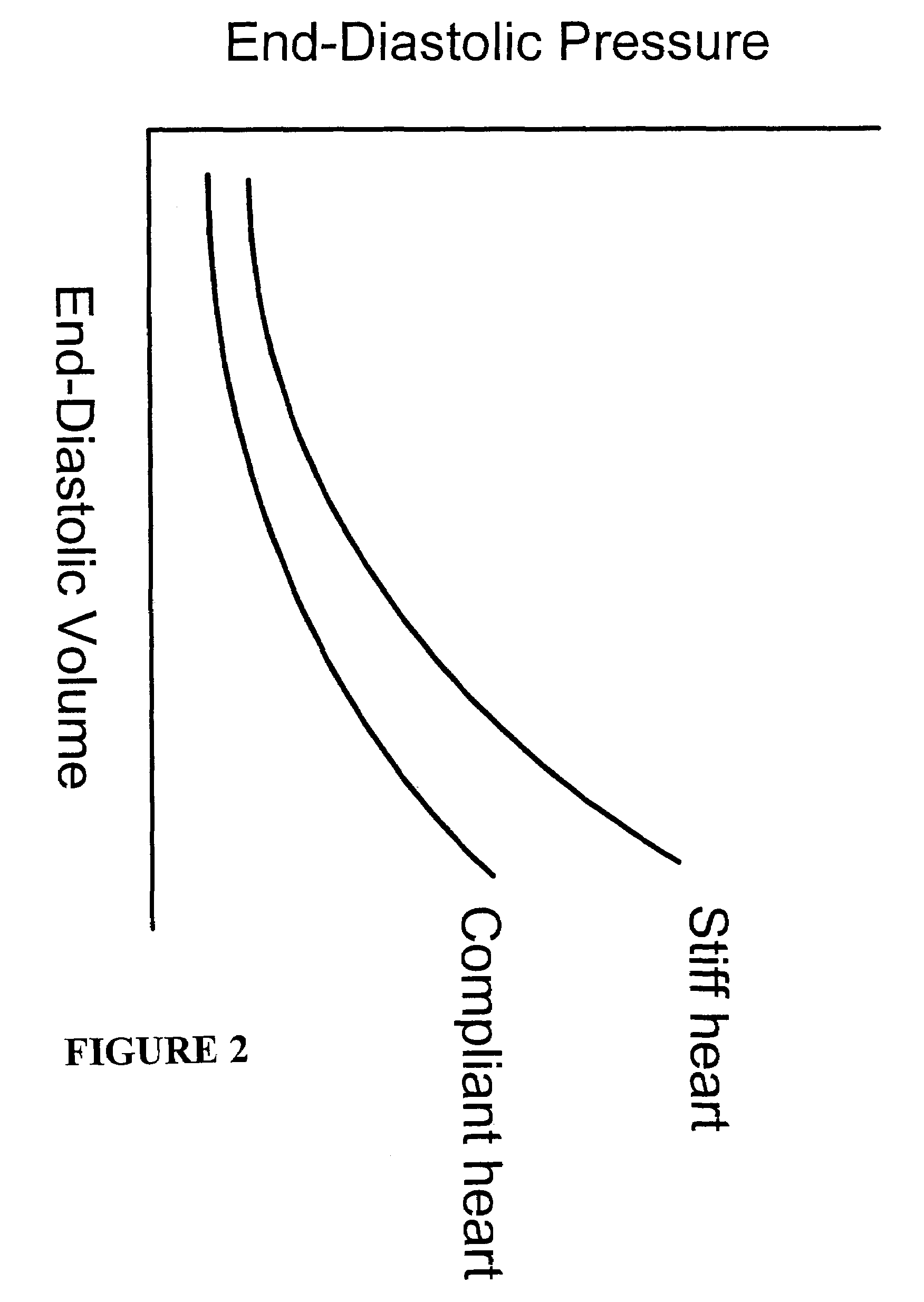
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
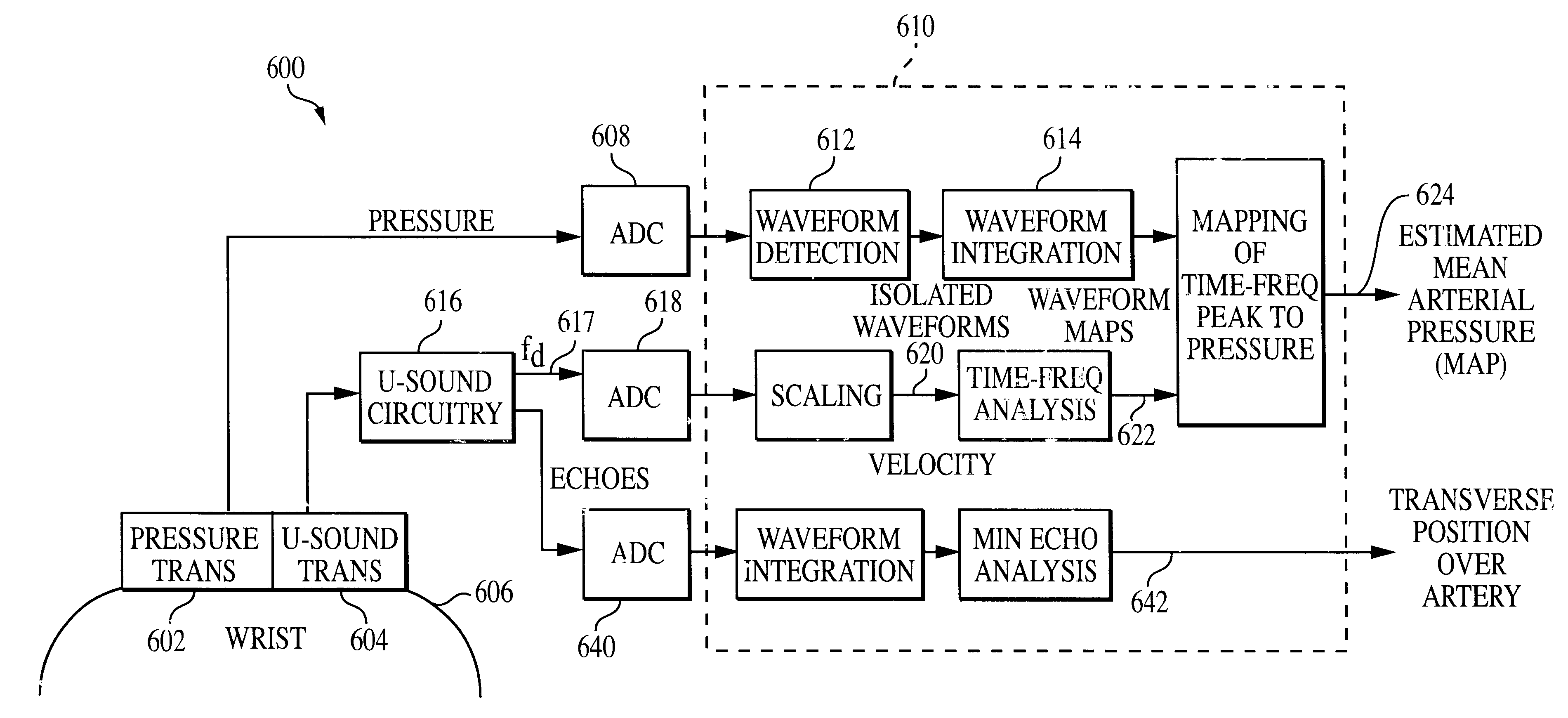
Method and apparatus for the noninvasive assessment of hemodynamic parameters including blood vessel location
InactiveUS20020055680A1Blood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsUltrasonic sensorTherapeutic Devices
A method and apparatus for determining the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of a subject during tonometric conditions. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises one or more pressure and ultrasound transducers placed over the radial artery of a human subject's wrist, the latter transmitting and receiving acoustic energy so as to permit the measurement of blood velocity during periods of variable compression of the artery. In another aspect of the invention, a wrist brace useful for measuring blood pressure using the aforementioned apparatus is disclosed. In yet another aspect of the invention, backscattered acoustic energy is used to identify the location of the blood vessel of interest, and optionally control the position of measurement or treatment equipment with respect thereto.
Owner:TENSYS MEDICAL INC
Apparatus and methods for monitoring physiological data during environmental interference
ActiveUS8888701B2Easy to keepMaximize collectionHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesRespiratory organ evaluationTemporal changeEngineering
Apparatus and methods for attenuating environmental interference are described. A wearable monitoring apparatus includes a housing configured to be attached to the body of a subject and a sensor module that includes an energy emitter that directs energy at a target region of the subject, a detector that detects an energy response signal—or physiological condition—from the subject, a filter that removes time-varying environmental interference from the energy response signal, and at least one processor that controls operations of the energy emitter, detector, and filter.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
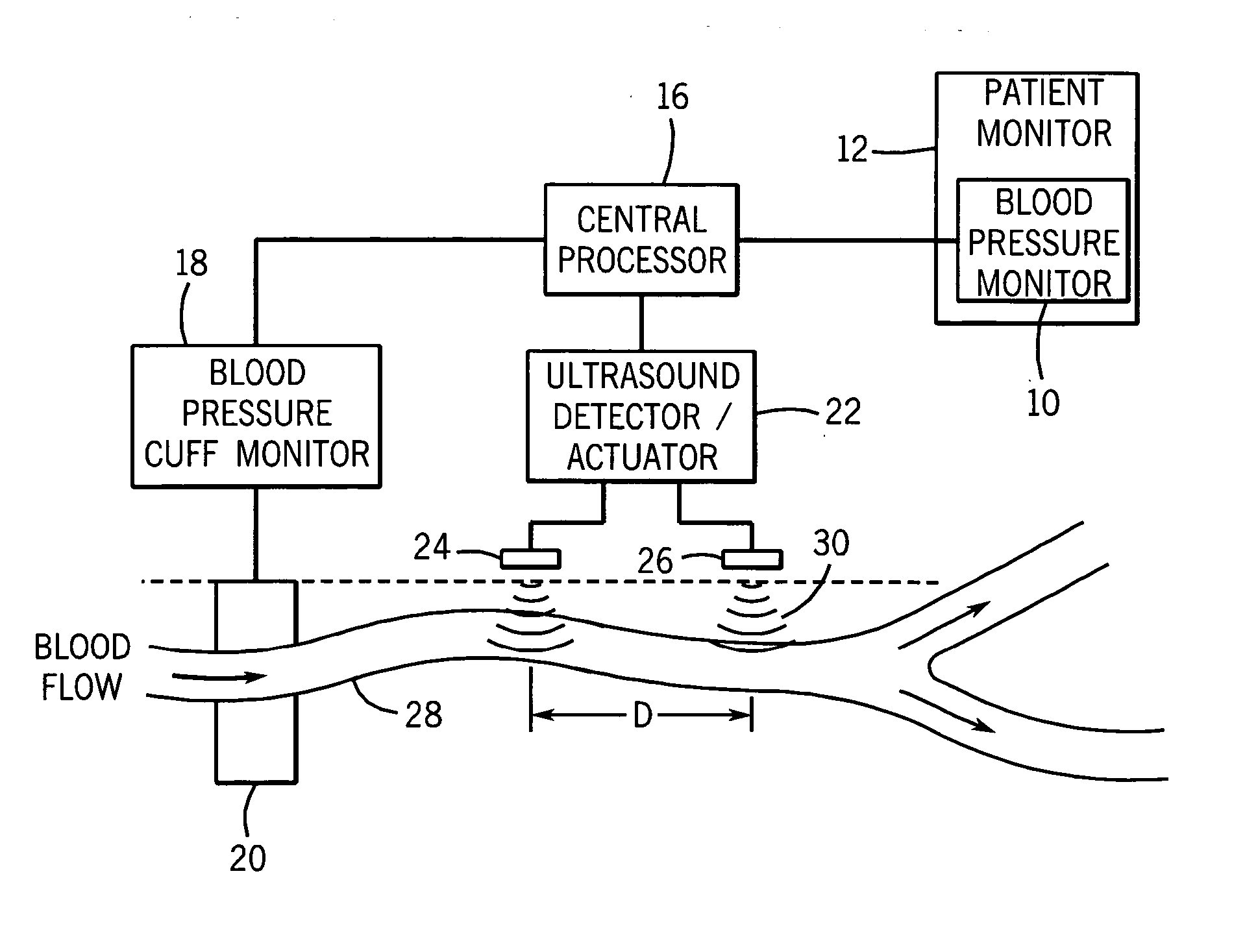
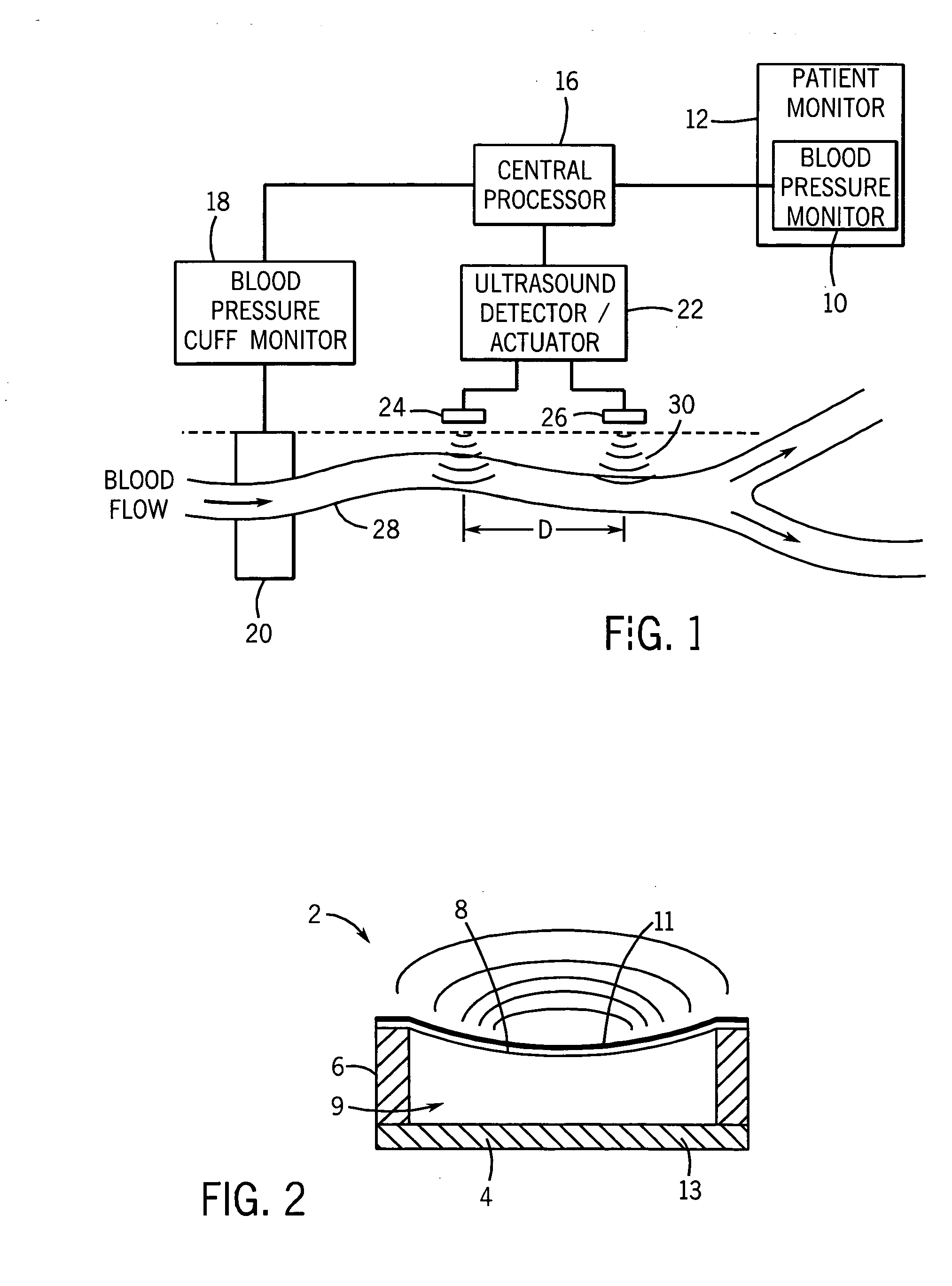
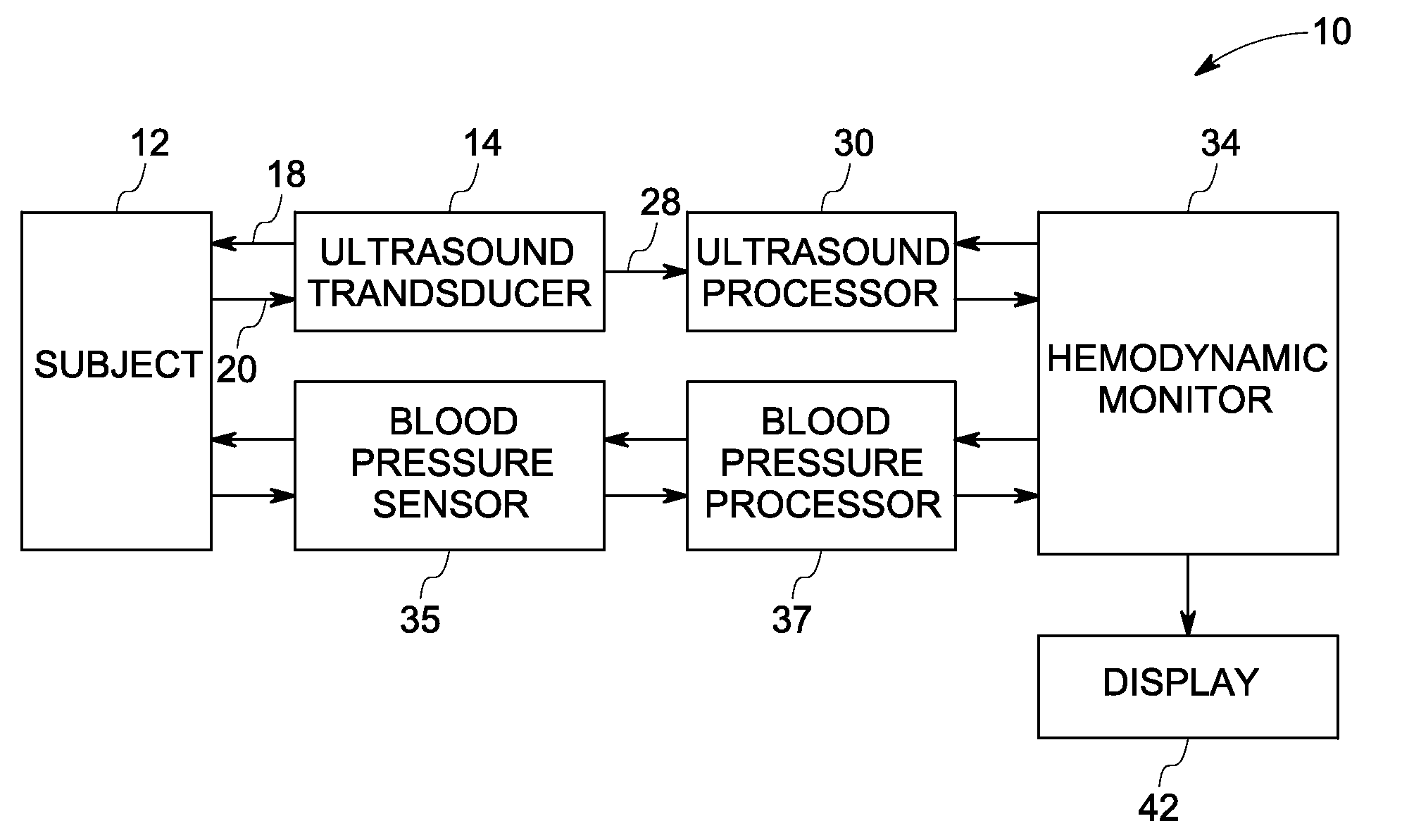
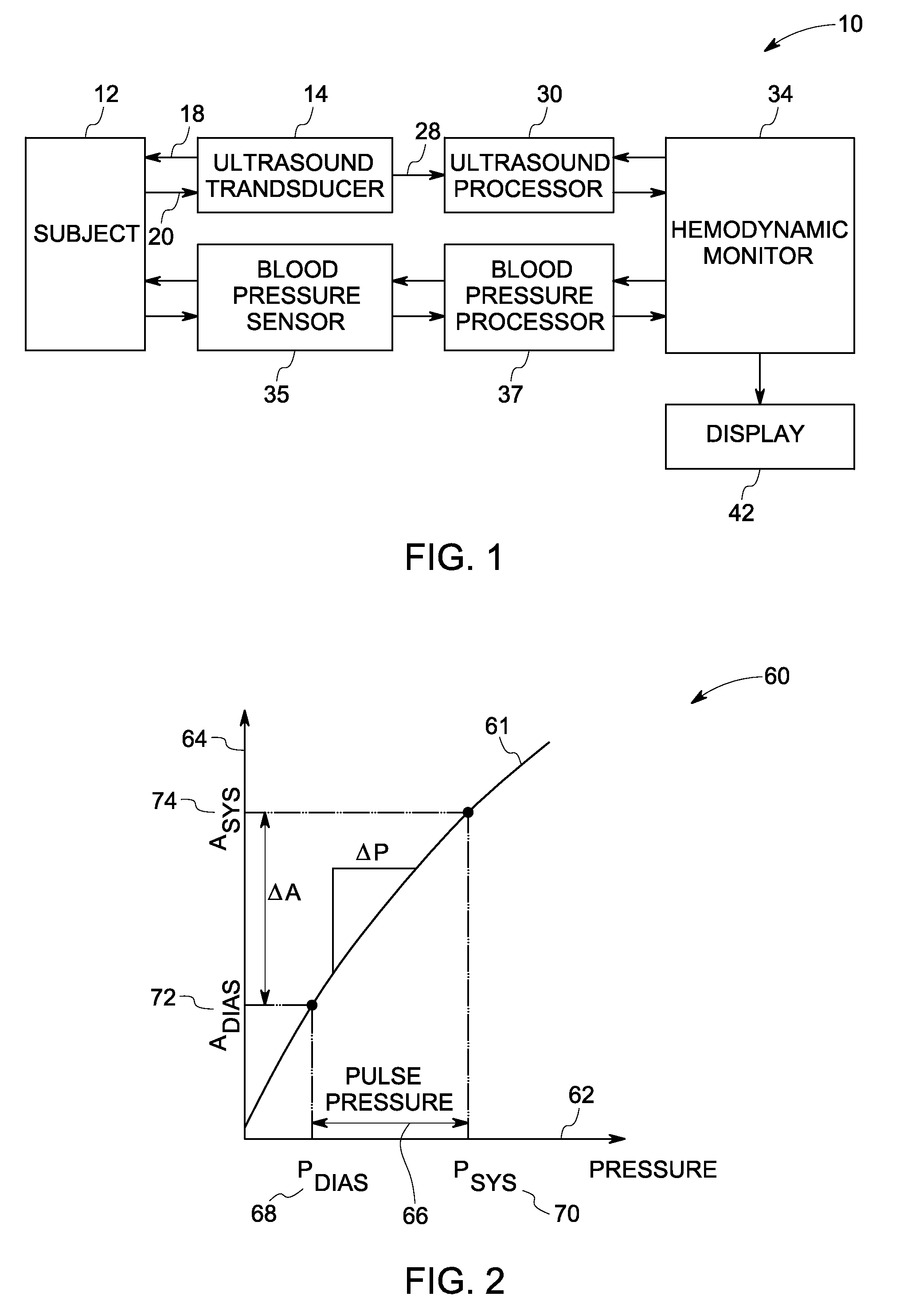
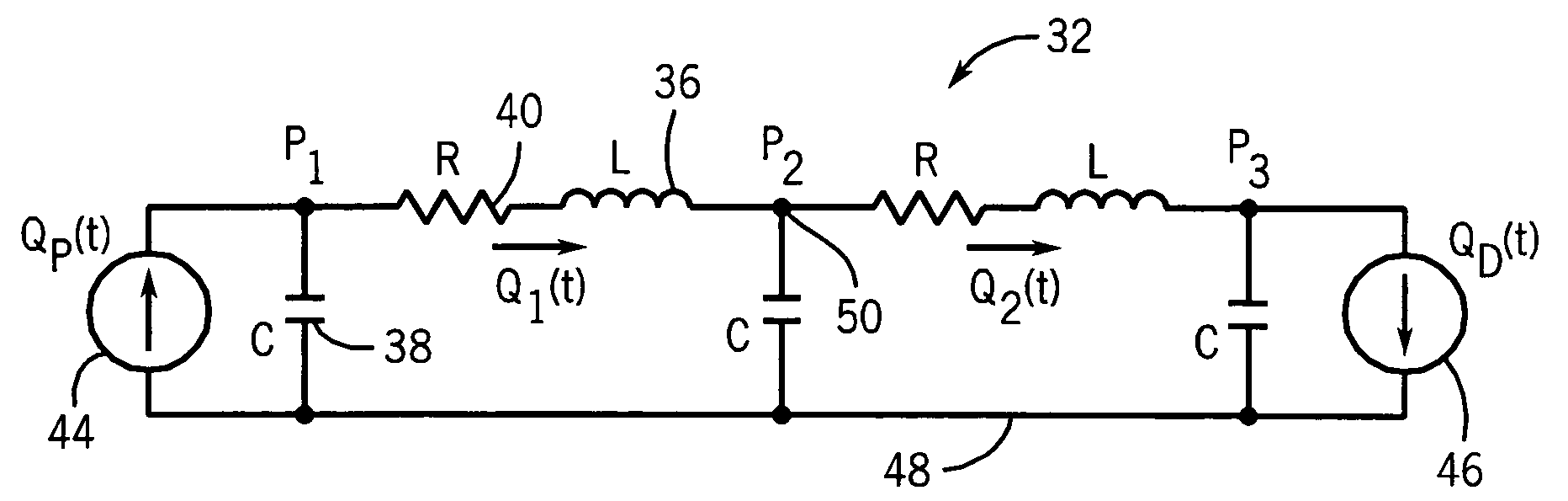
Continuous, non-invasive technique for determining blood pressure using a transmission line model and transcutaneous ultrasound measurements
ActiveUS20060211942A1Good estimateImprove accuracyBlood flow measurement devicesPerson identificationState variableBlood pressure
A method and technique for the continuous, non-invasive measurement of blood pressure. The blood pressure measurement technique of the present invention utilizes ultrasound measurements to determine the diameter of the blood vessel in which the blood pressure is being measured as well as the flow rate of blood at both an input point and an output point along the blood vessel. The system utilizes a transmission line model to relate various blood vessel measurements with electrical components. The transmission line model, in combination with data management techniques including state variable representations and Kalman filtering, is used to develop a blood pressure measurement in real time.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
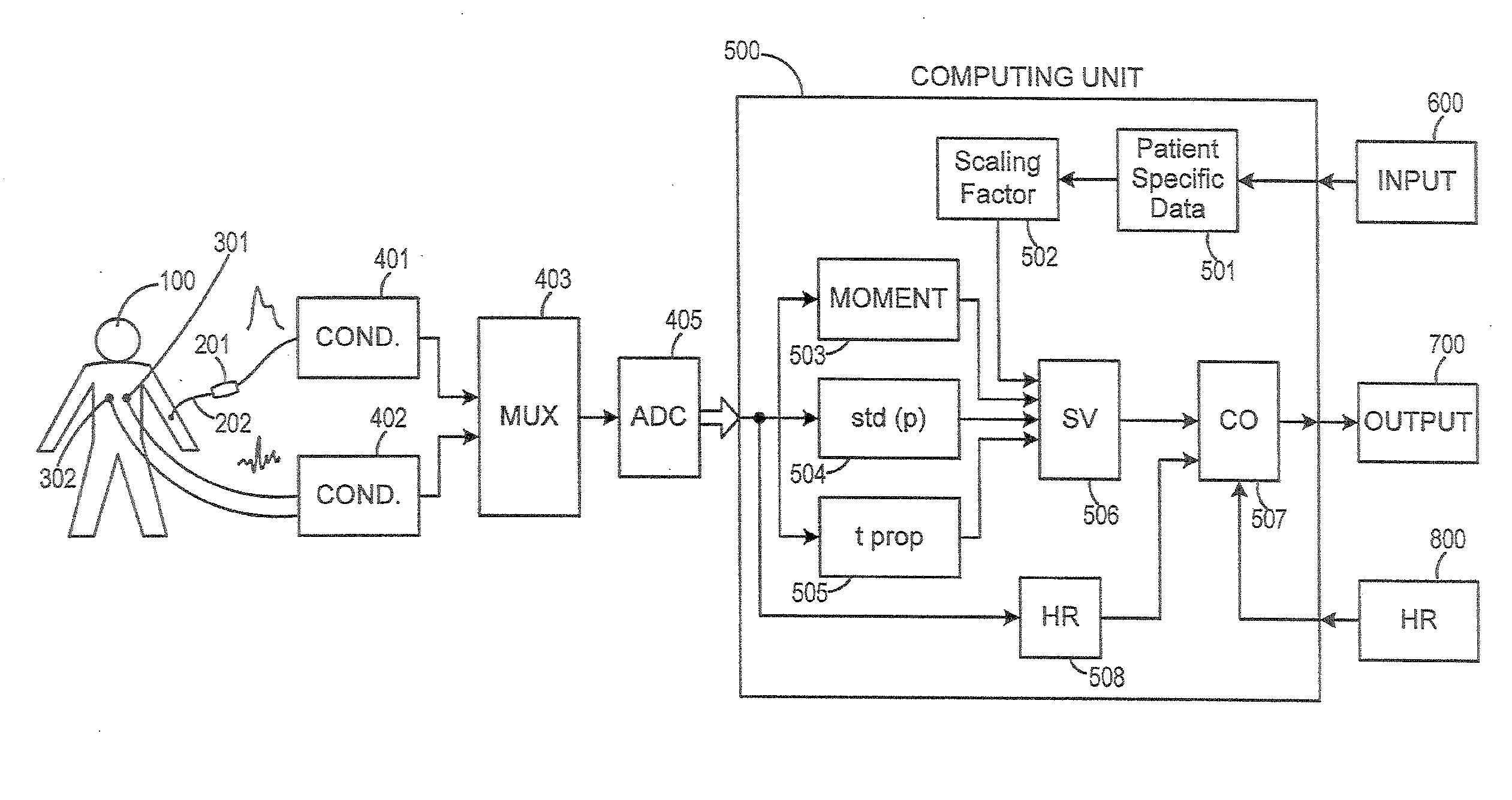
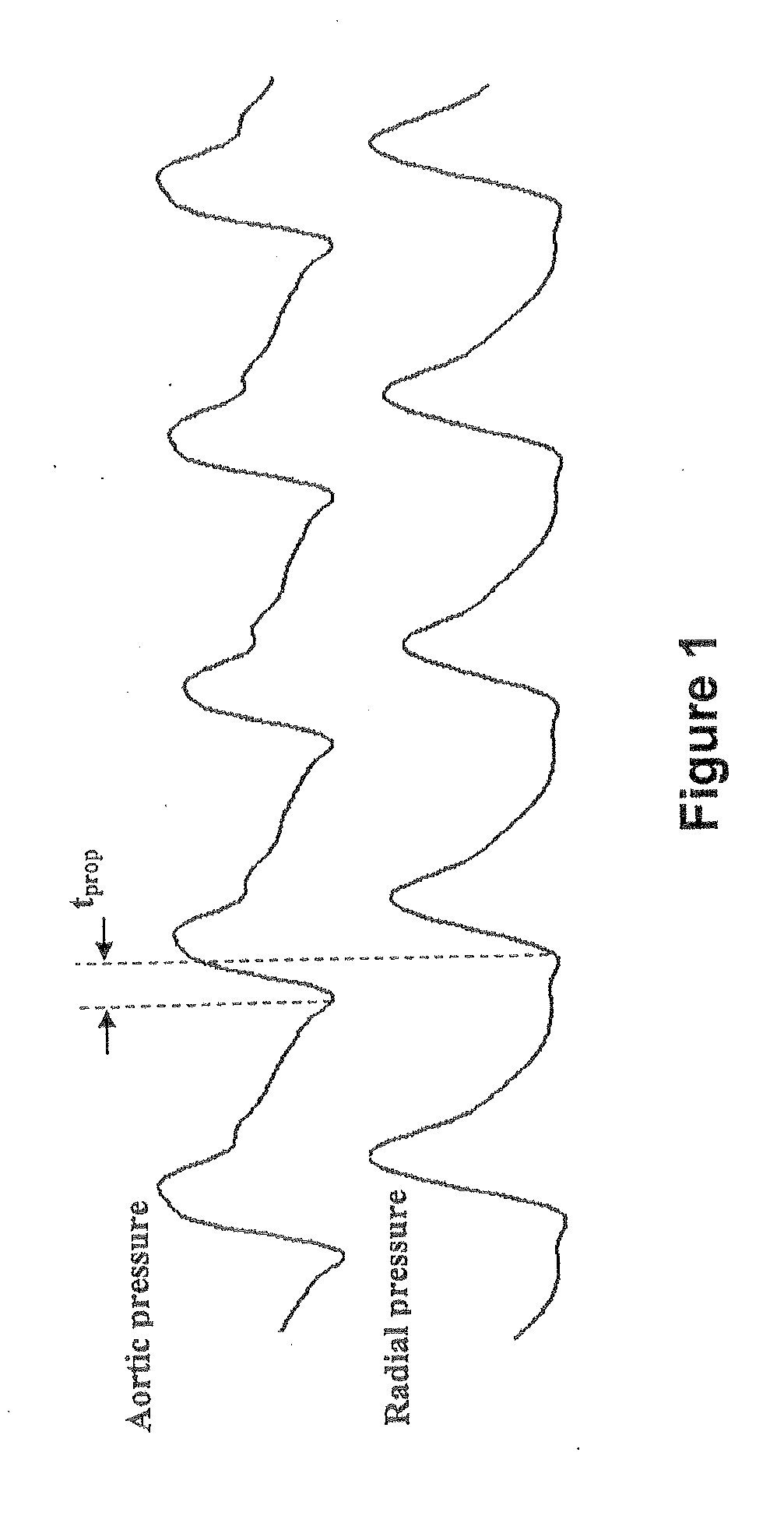
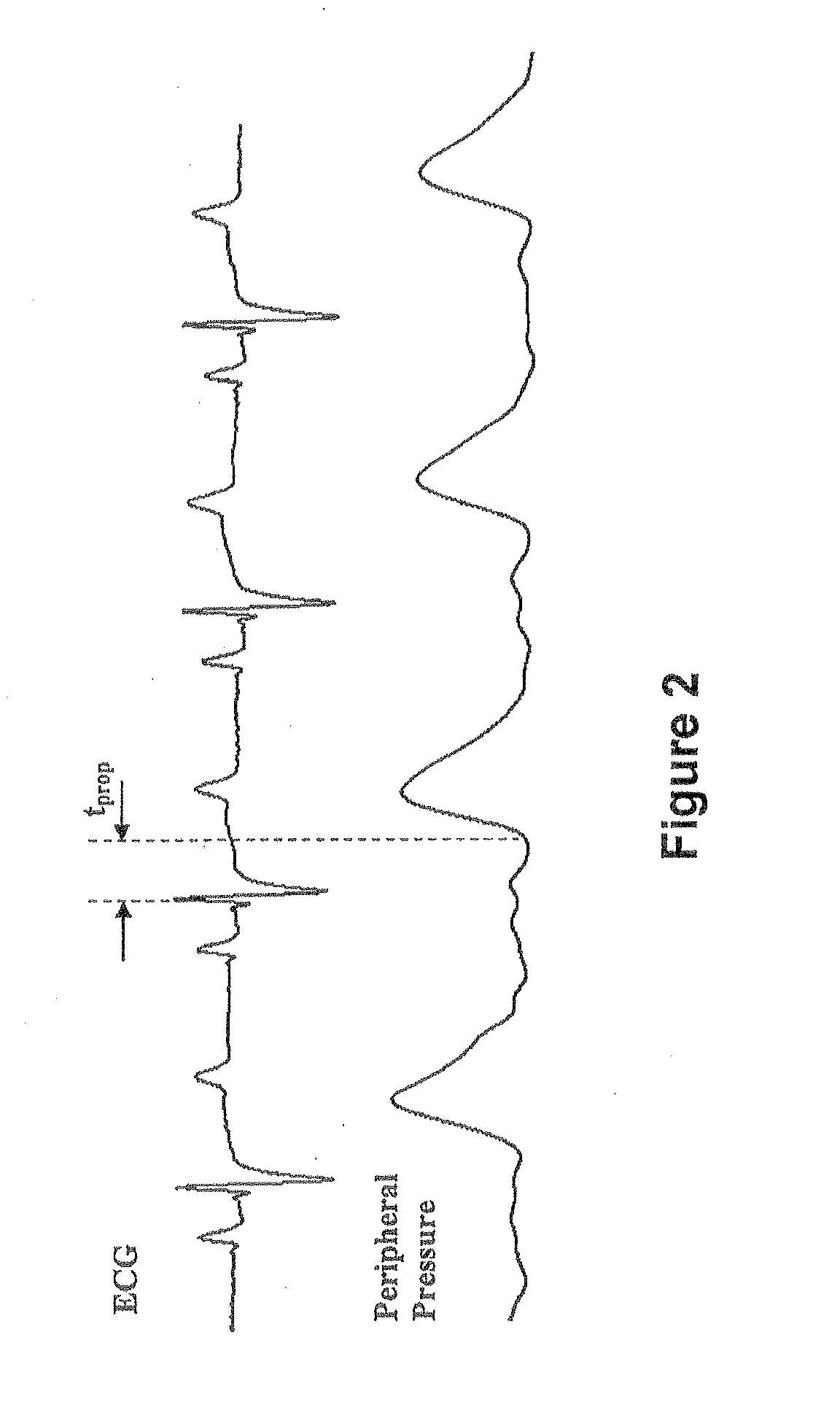
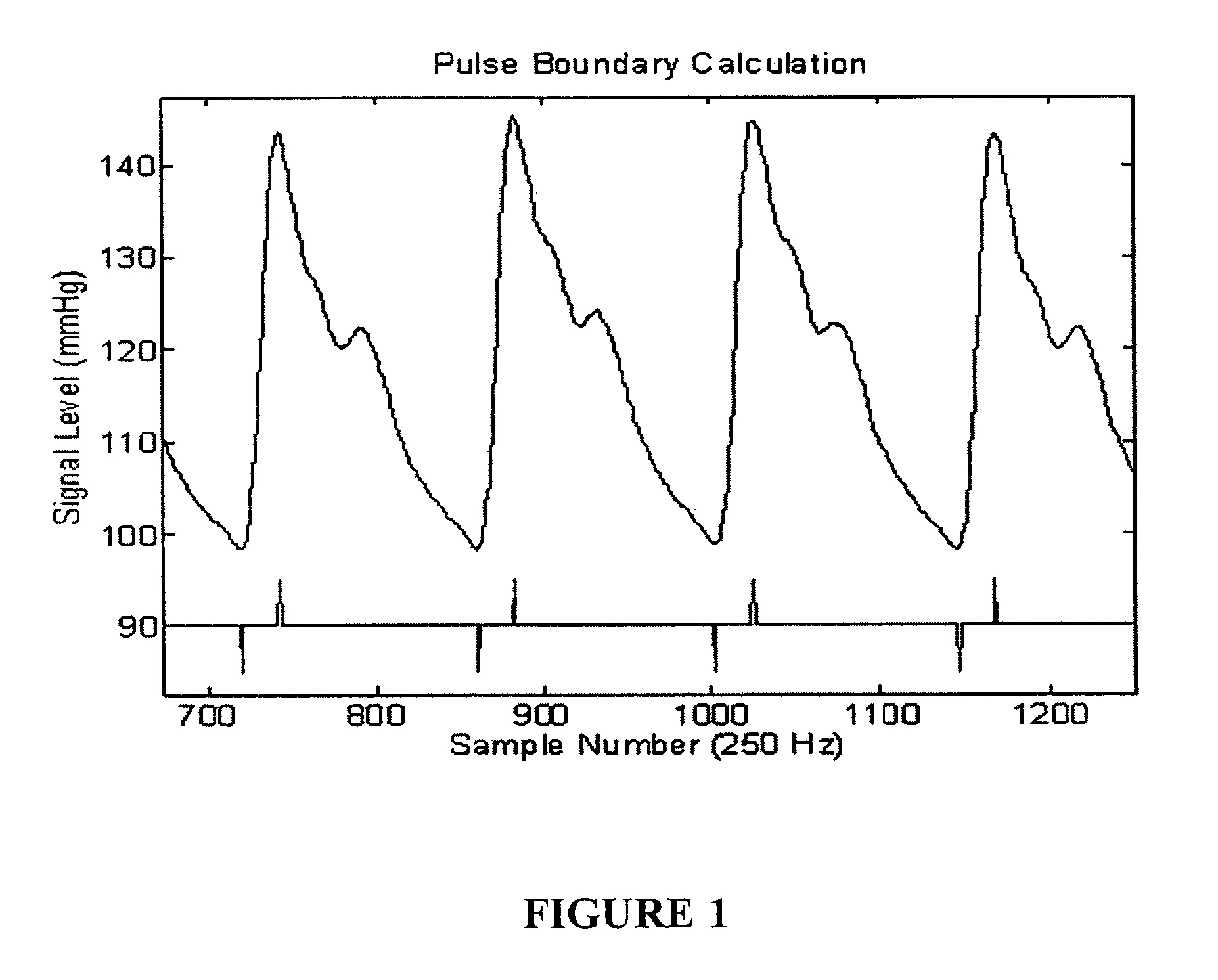
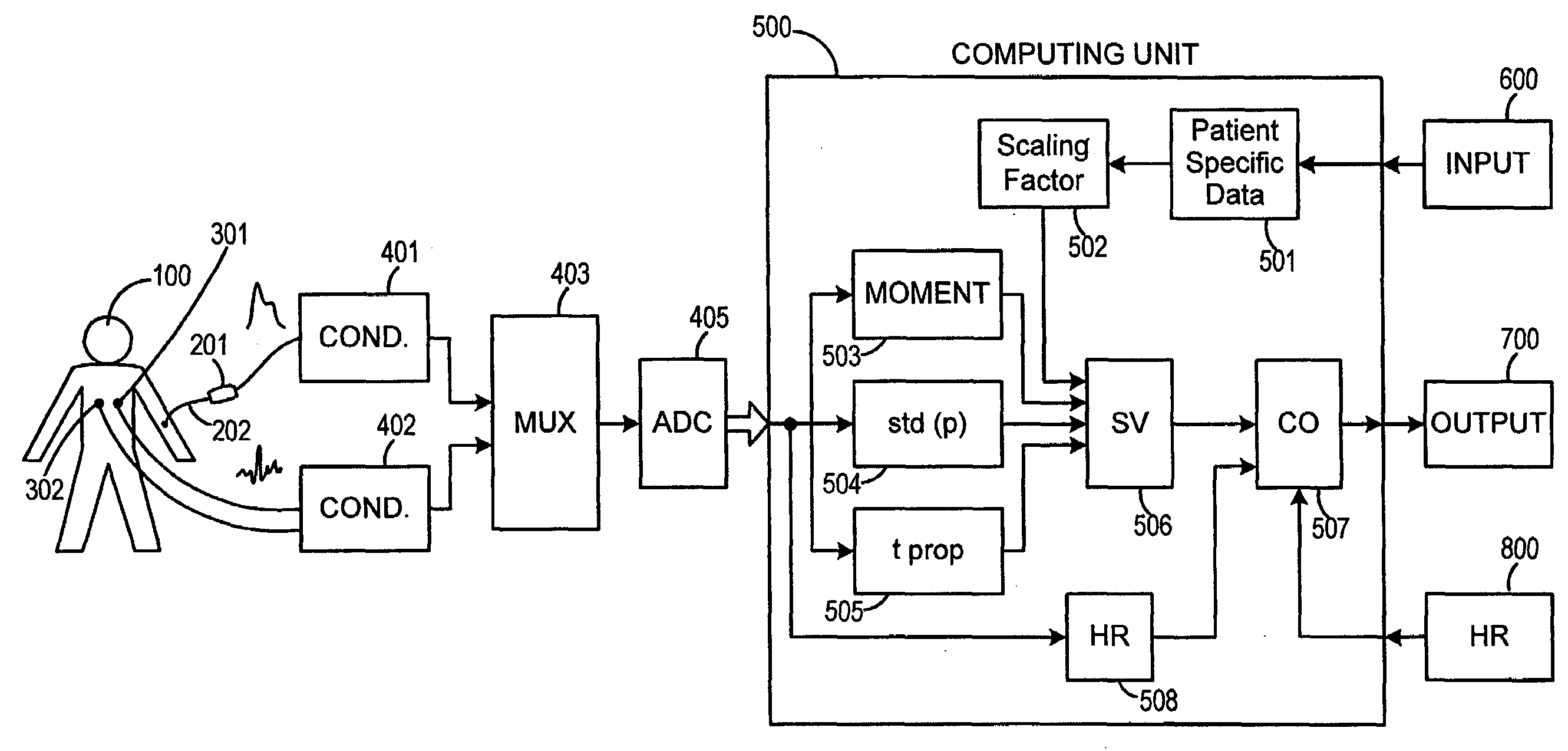
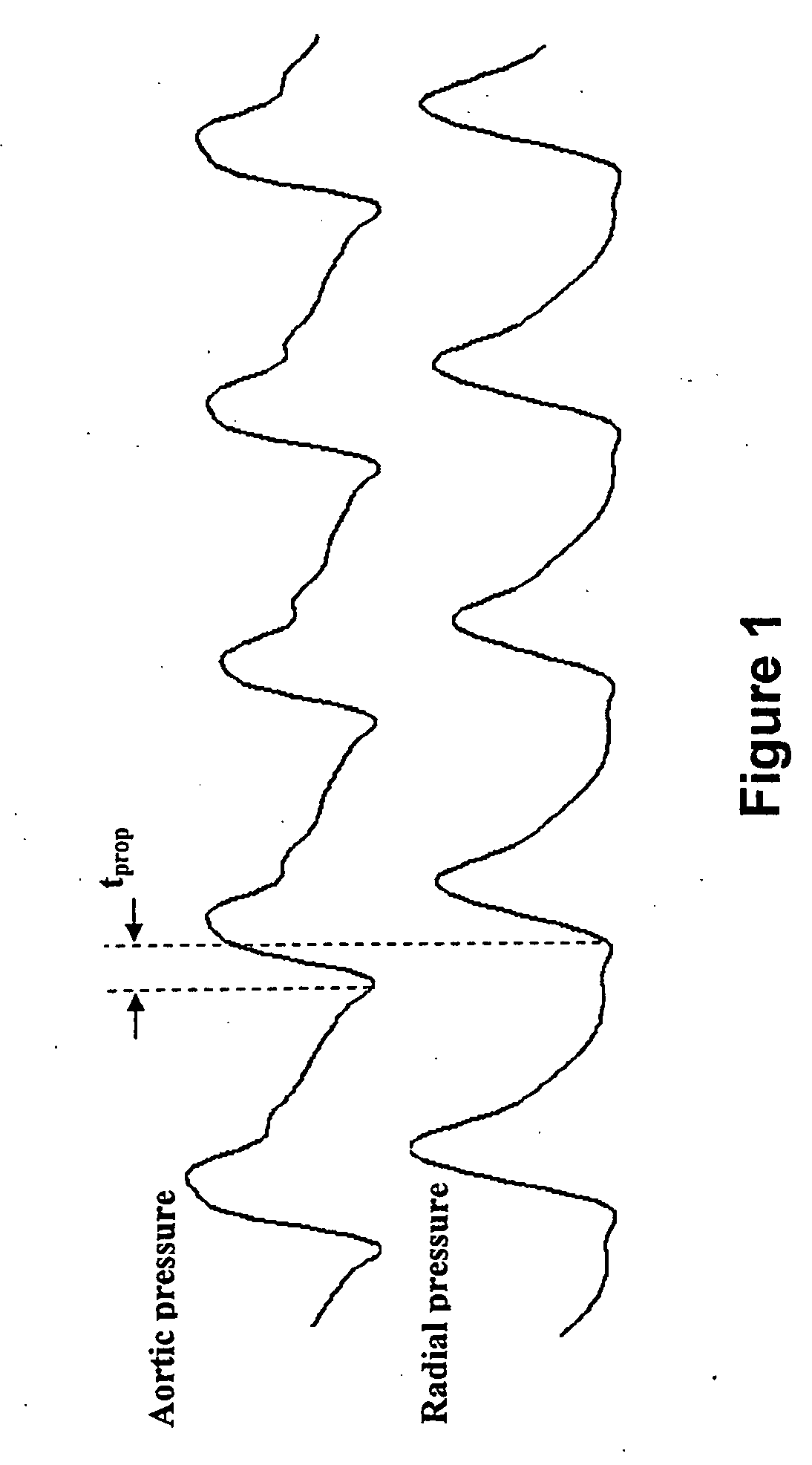
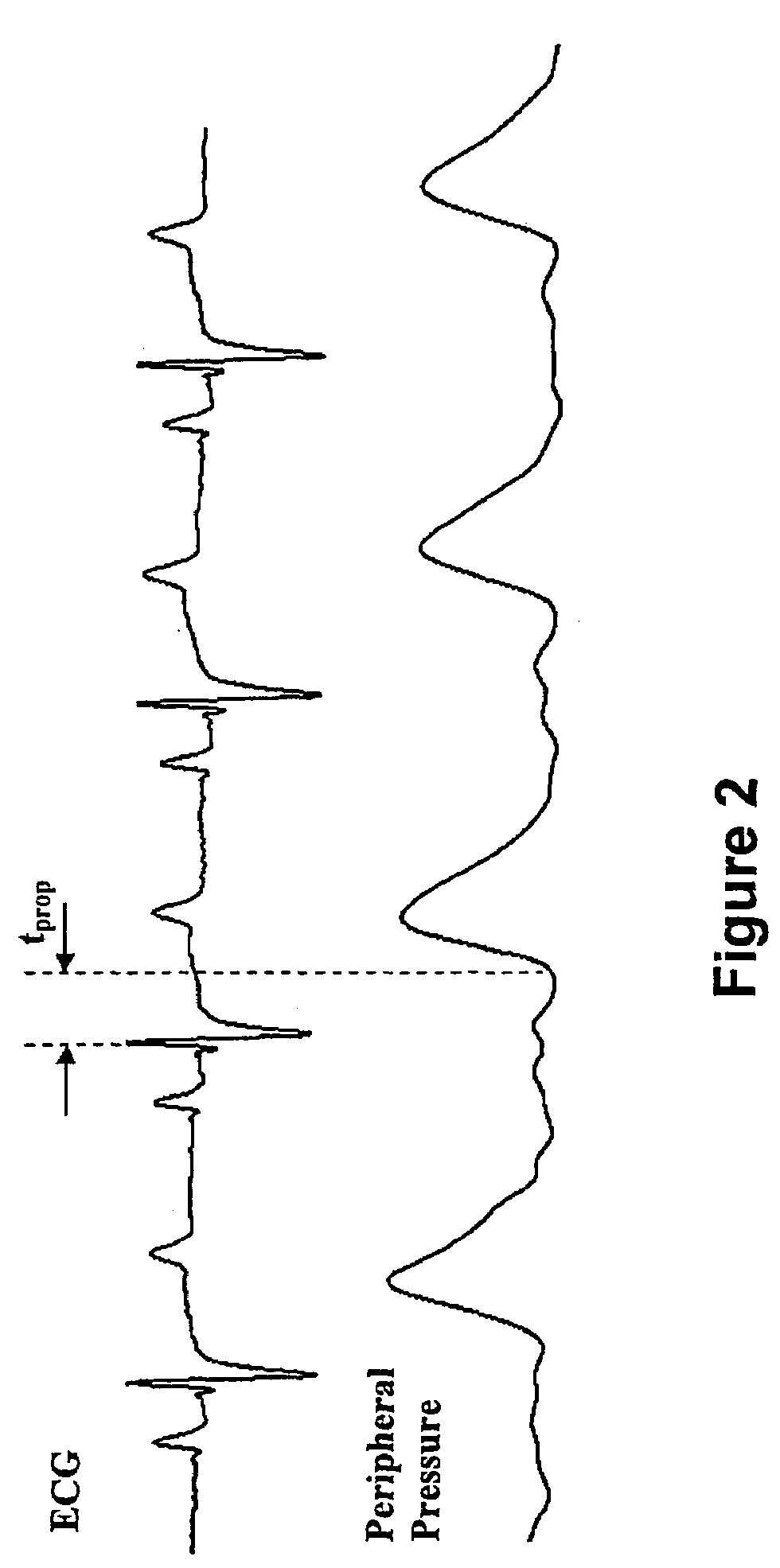
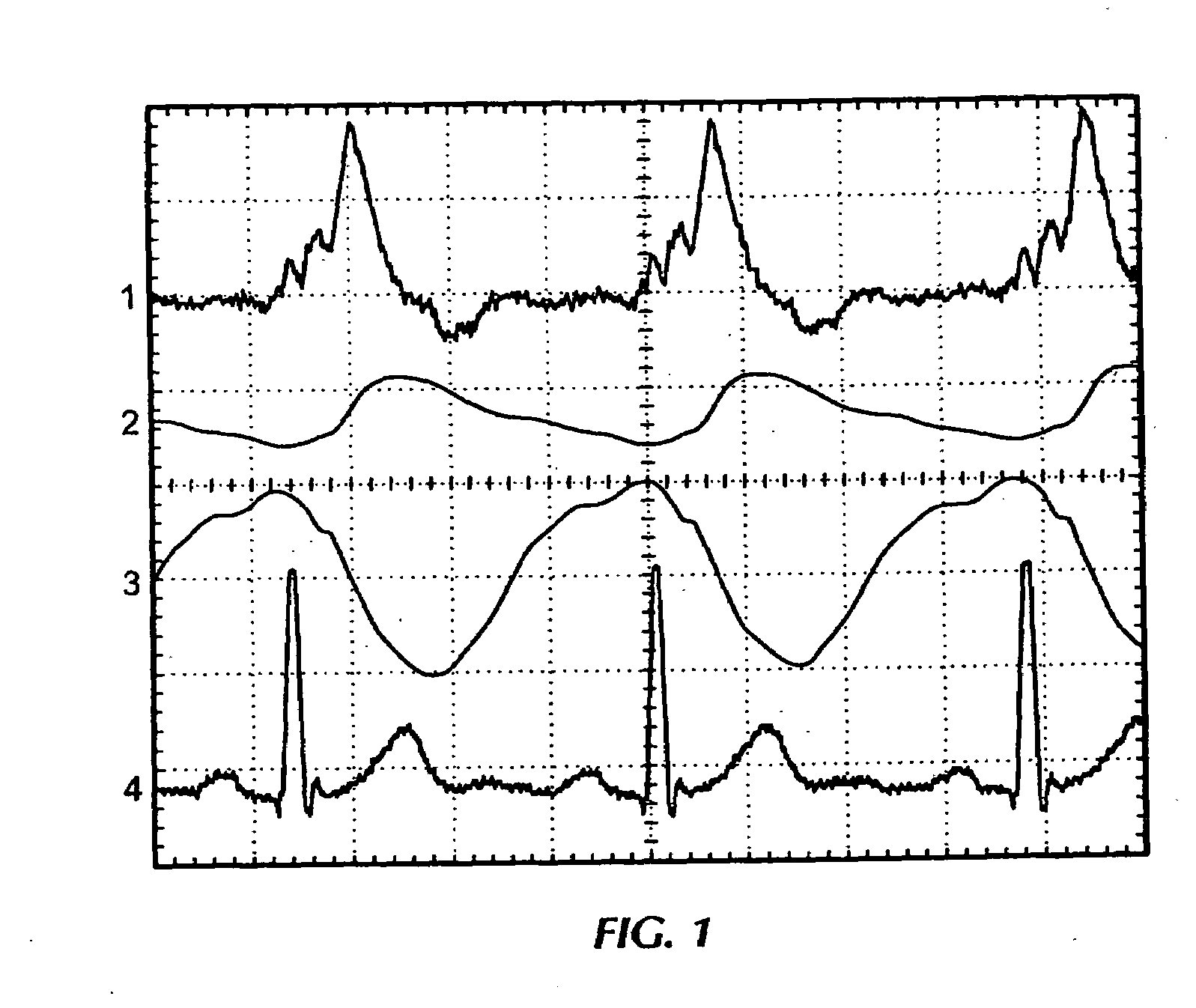
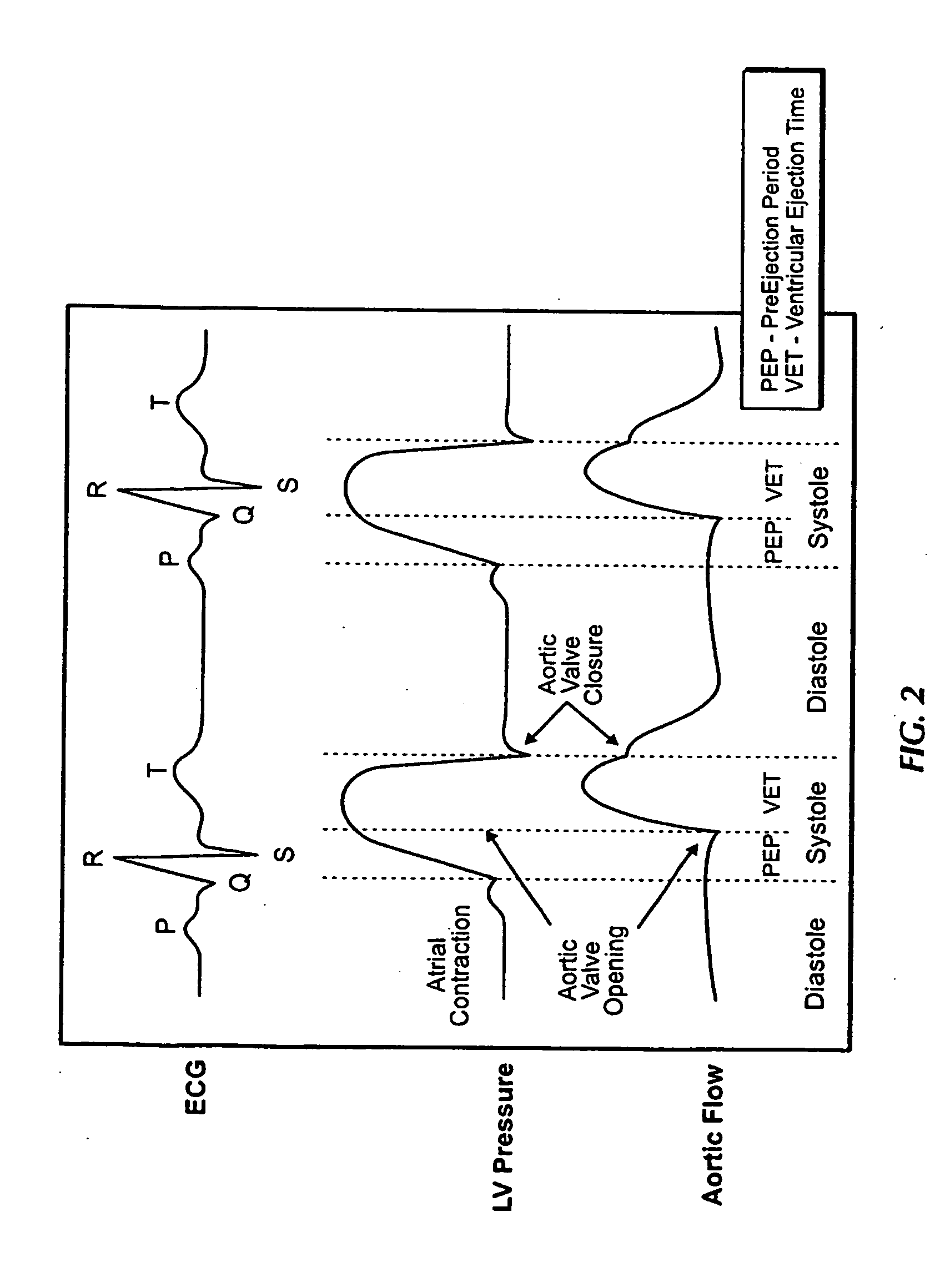
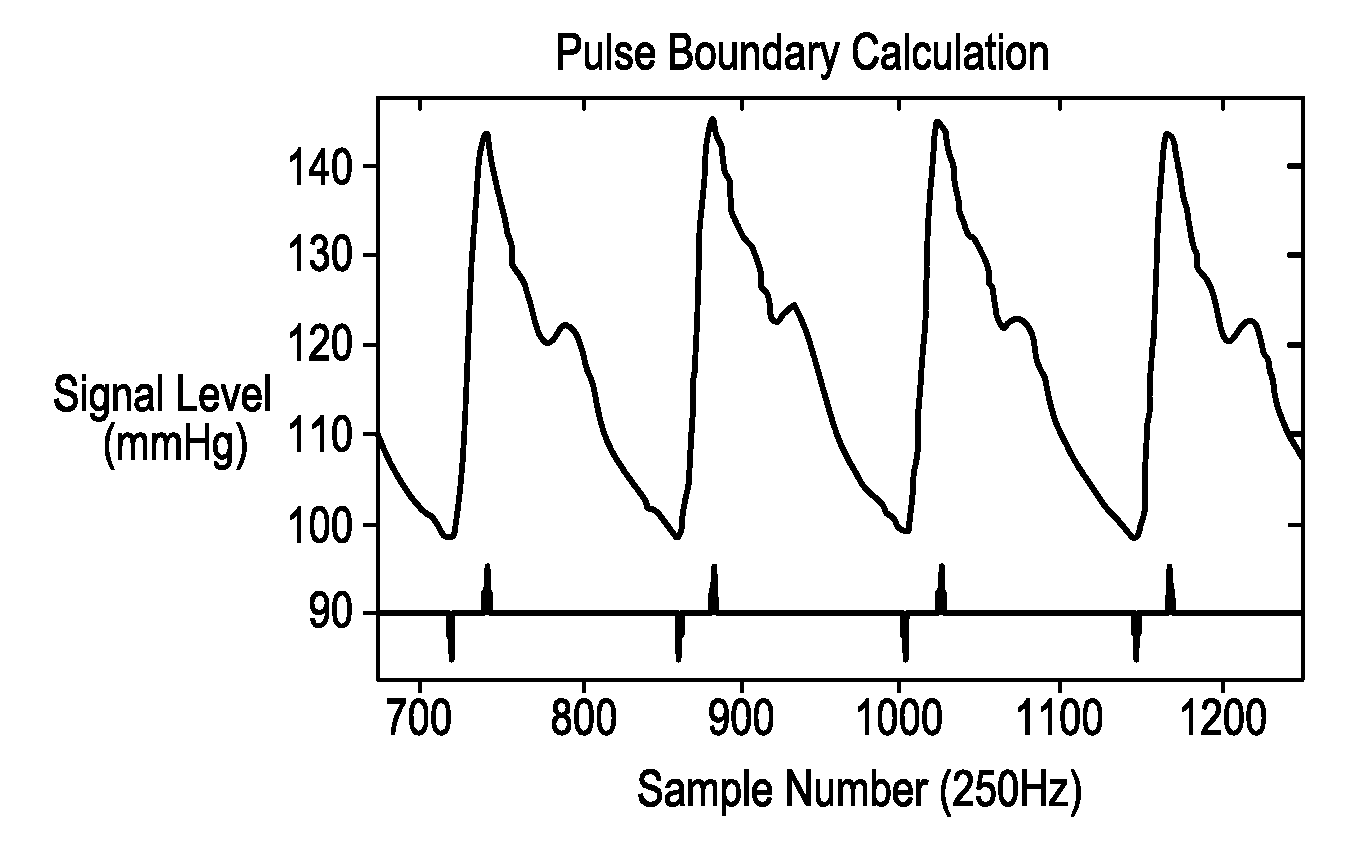
Method and Apparatus for Continuous Assessment of a Cardiovascular Parameter Using the Arterial Pulse Pressure Propagation Time and Waveform
InactiveUS20080015451A1ElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesCardiac cycleArterial pulse pressure
A method and apparatus for determining a cardiovascular parameter including receiving an input signal corresponding to an arterial blood pressure measurement over an interval that covers at least one cardiac cycle, determining a propagation time of the input signal, determining at least one statistical moment of the input signal, and determining an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter using the propagation time and the at least one statistical moment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for the noninvasive determination of arterial blood pressure
InactiveUS6471655B1Blood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsTransmural pressureUltrasonic sensor
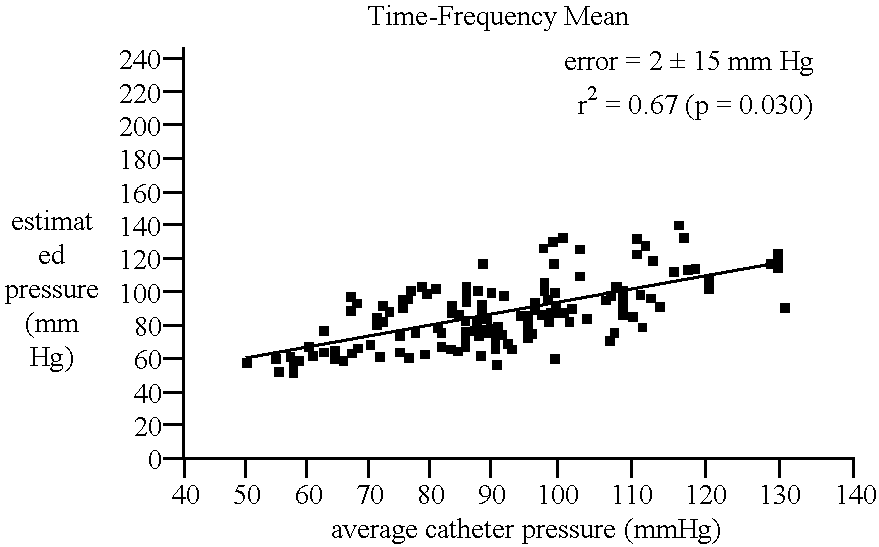
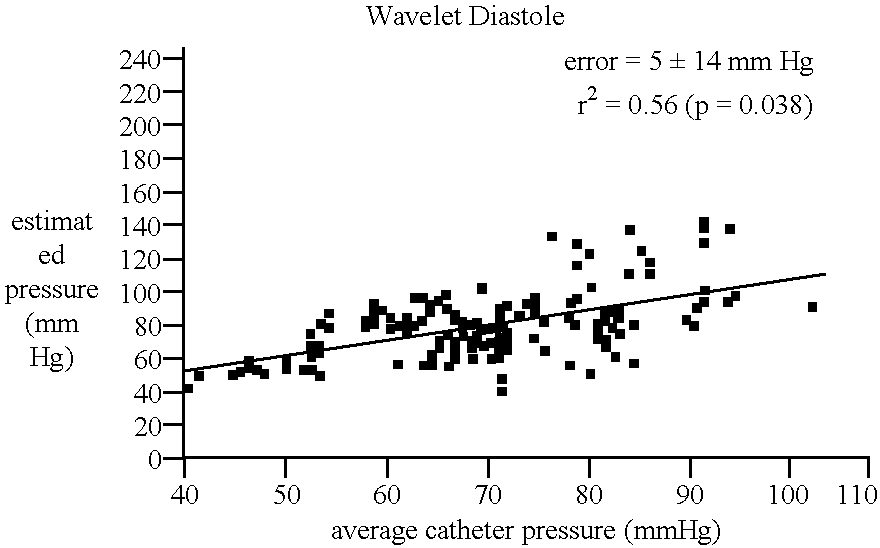
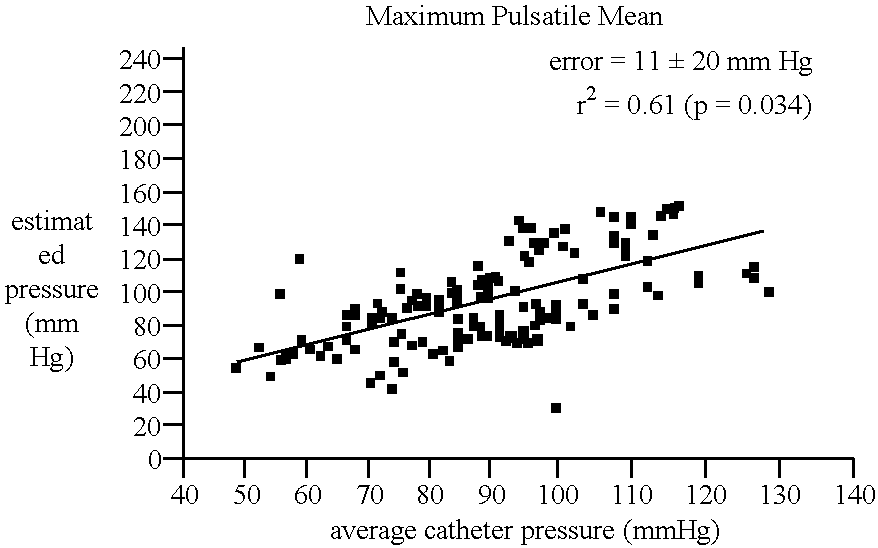
A method and apparatus for determining the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of a subject during tonometric conditions. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises one or more pressure and ultrasound transducers placed over the radial artery of a human subject's wrist, the latter transmitting and receiving acoustic energy so as to permit the measurement of blood velocity during periods of variable compression of the artery. During compression, the ultrasound velocity waveforms are recorded and processed using time-frequency analysis. The time at which the mean time-frequency distribution is maximal corresponds to the time at which the transmural pressure equals zero, and the mean pressure read by the transducer equals the mean pressure within the artery. In another aspect of the invention, the ultrasound transducer is used to position the transducer over the artery such that the accuracy of the measurement is maximized. In yet another aspect of the invention, a wrist brace useful for measuring blood pressure using the aforementioned apparatus is disclosed.
Owner:TENSYS MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic continuous, non-invasive blood pressure monitoring
Ultrasound is used to provide input data for a blood pressure estimation scheme. The use of transcutaneous ultrasound provides arterial lumen area and pulse wave velocity information. In addition, ultrasound measurements are taken in such a way that all the data describes a single, uniform arterial segment. Therefore a computed area relates only to the arterial blood volume present. Also, the measured pulse wave velocity is directly related to the mechanical properties of the segment of elastic tube (artery) for which the blood volume is being measured. In a patient monitoring application, the operator of the ultrasound device is eliminated through the use of software that automatically locates the artery in the ultrasound data, e.g., using known edge detection techniques. Autonomous operation of the ultrasound system allows it to report blood pressure and blood flow traces to the clinical users without those users having to interpret an ultrasound image or operate an ultrasound imaging device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
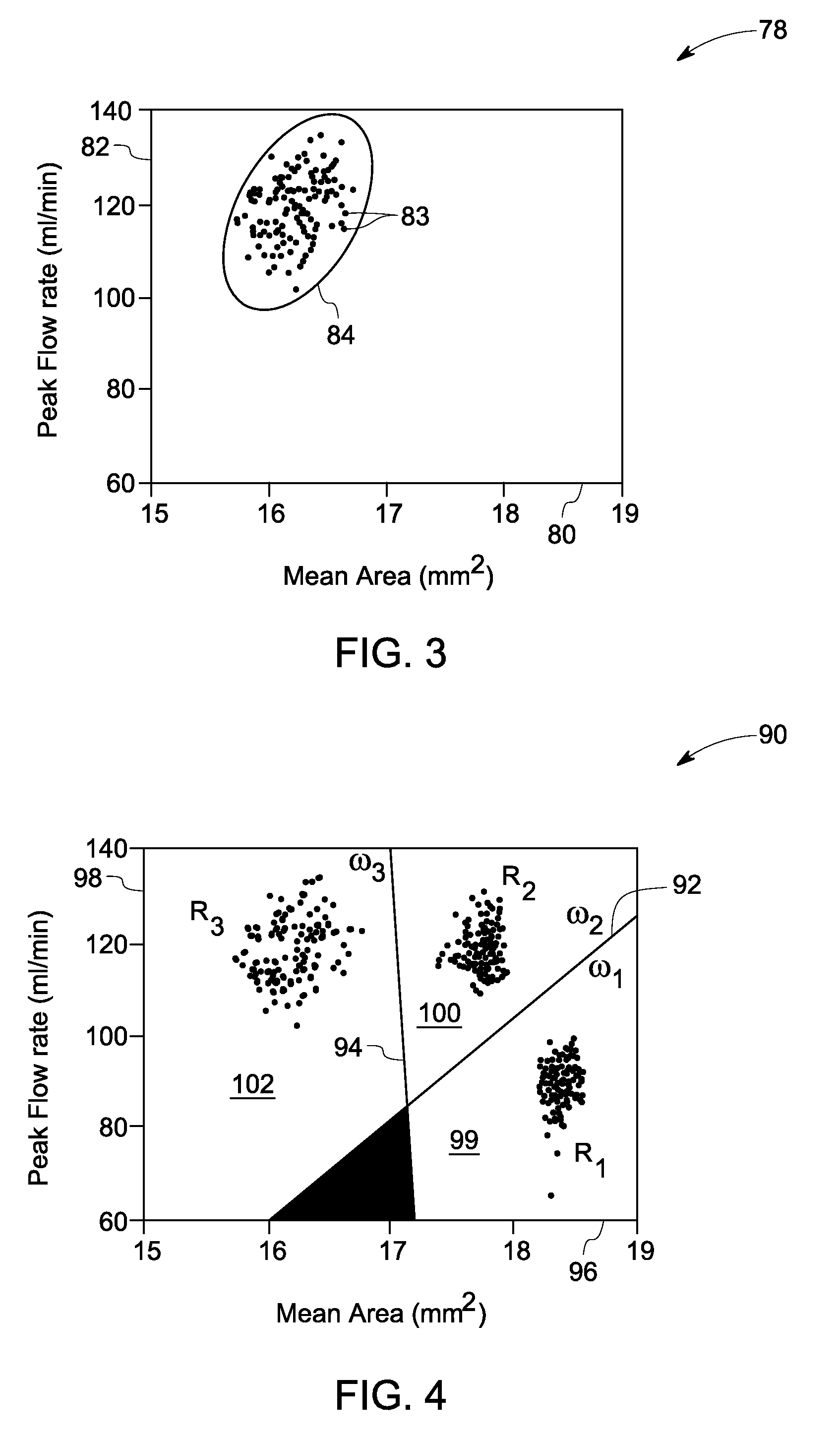
System and method for monitoring hemodynamic state
A method for continuous non-invasive hemodynamic state monitoring in a subject is provided. The method includes acquiring continuous ultrasound data via an ultrasound transducer attached to the subject. The method also includes estimating continuous arterial waveforms based upon the acquired ultrasound data. The method further includes deriving hemodynamic parameters for each cardiac cycle from the arterial waveforms. The method also includes defining a current hemodynamic state of the subject by setting limits on one or more hemodynamic parameters based upon the variation of these parameters over an initial period of time. The method further includes continuously monitoring a hemodynamic state of the subject. The method further includes comparing a current state for one or more hemodynamic parameters of the subject to previously determined limits for the one or more hemodynamic parameters, and either outputting a trigger signal or alarm to a hemodynamic state monitor in an event that a change is detected in the current state of the one or more hemodynamic parameters or converting the arterial parameters into a continuous estimate of the arterial blood pressure in an event that a change is not detected.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
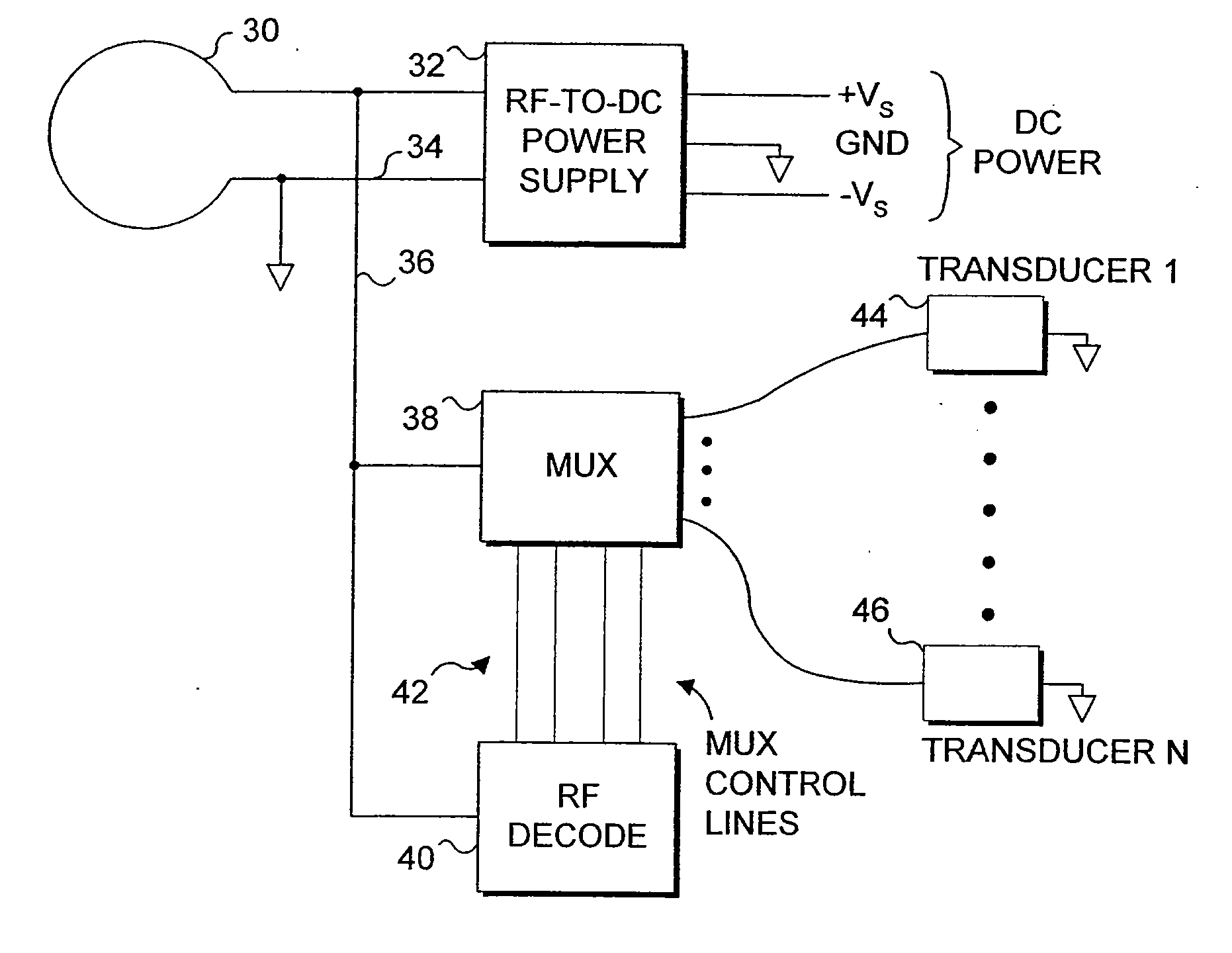
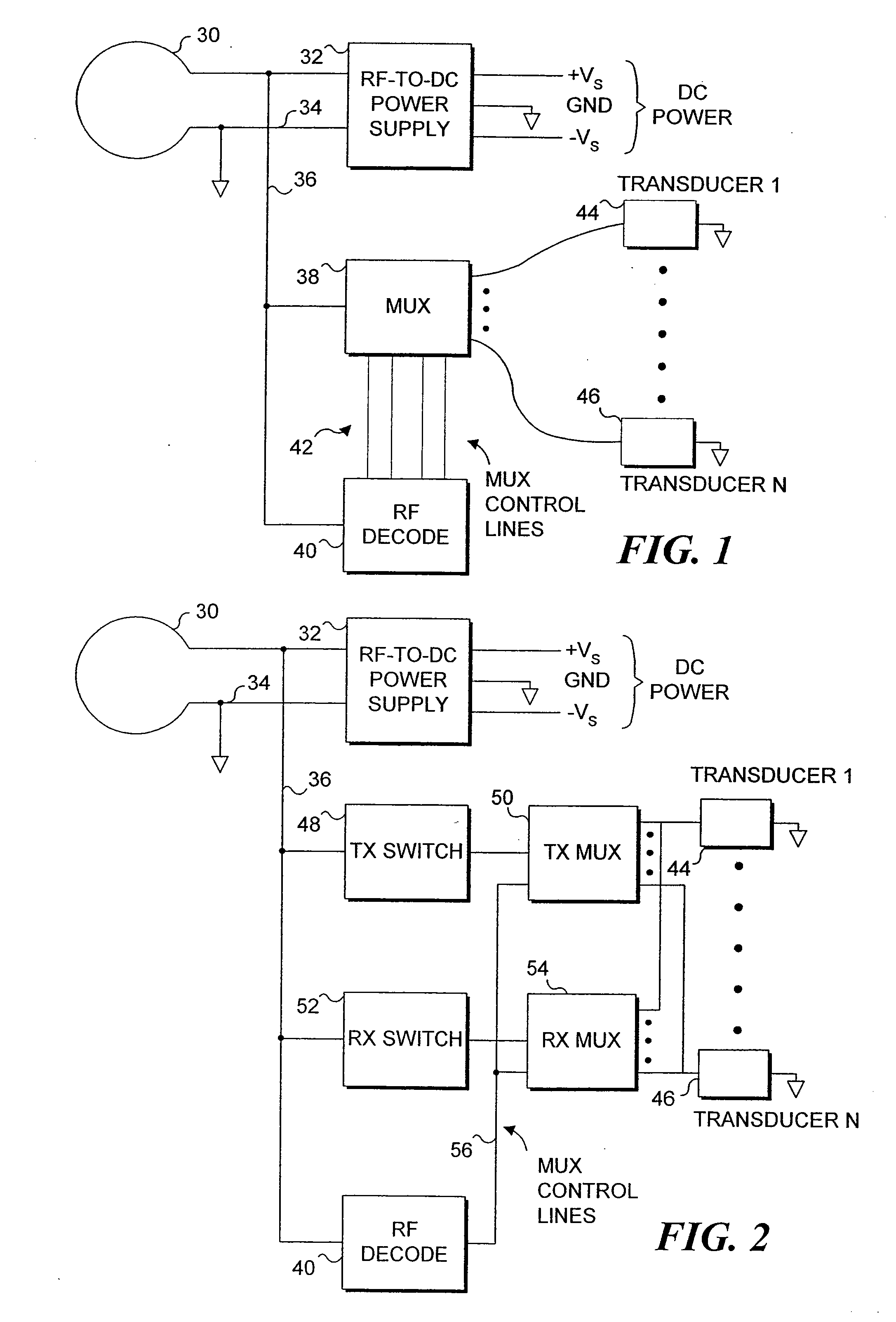
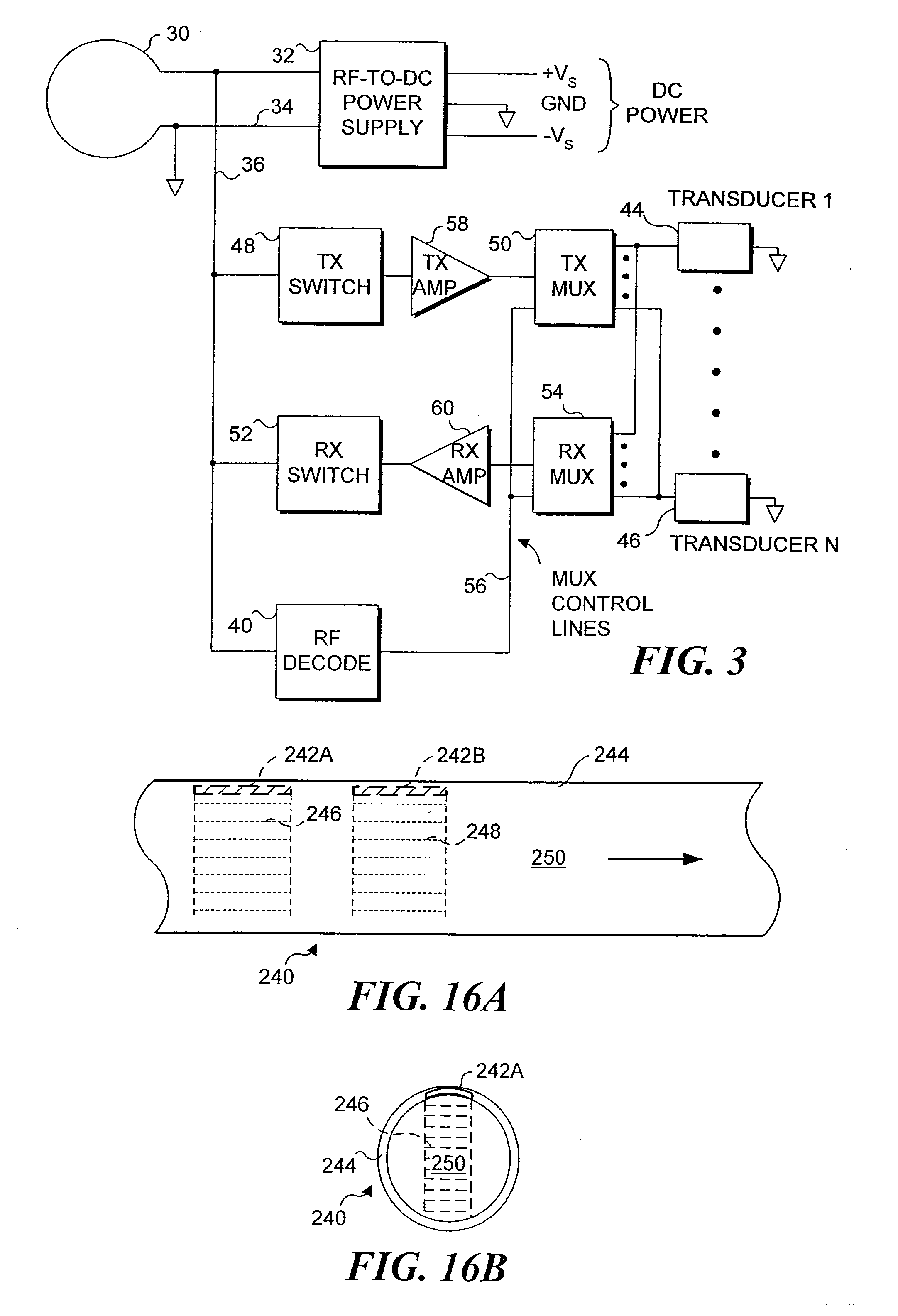
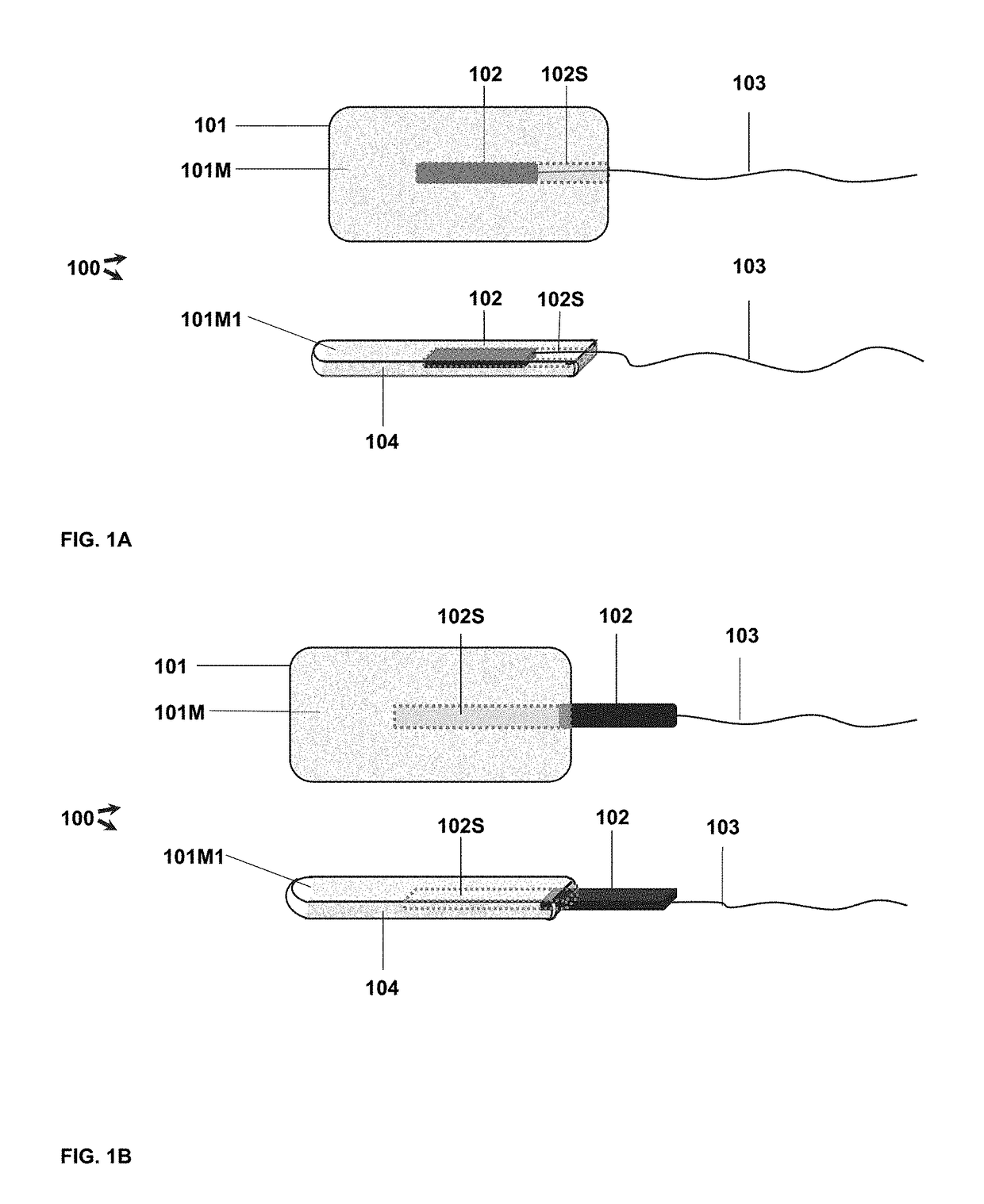
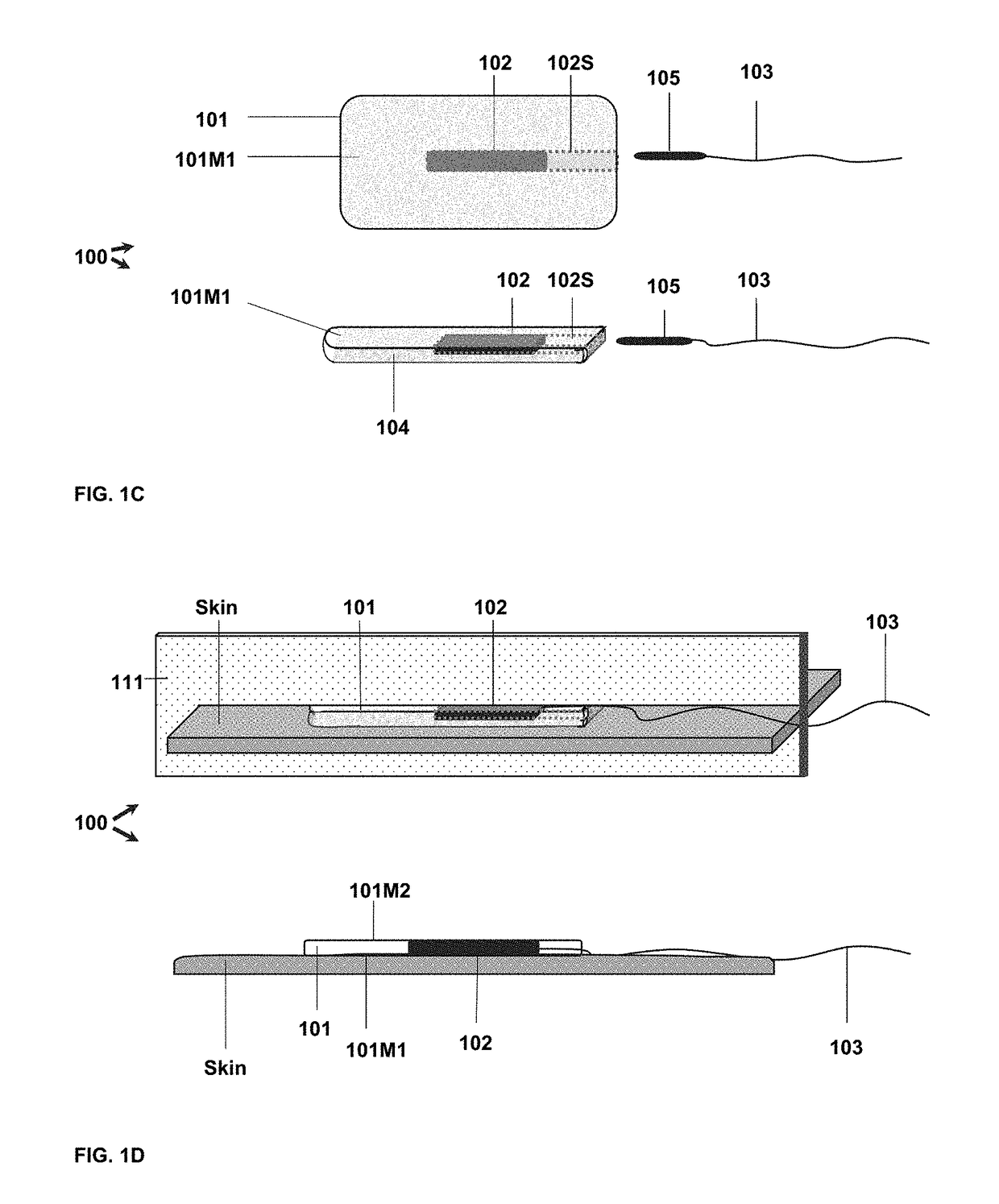
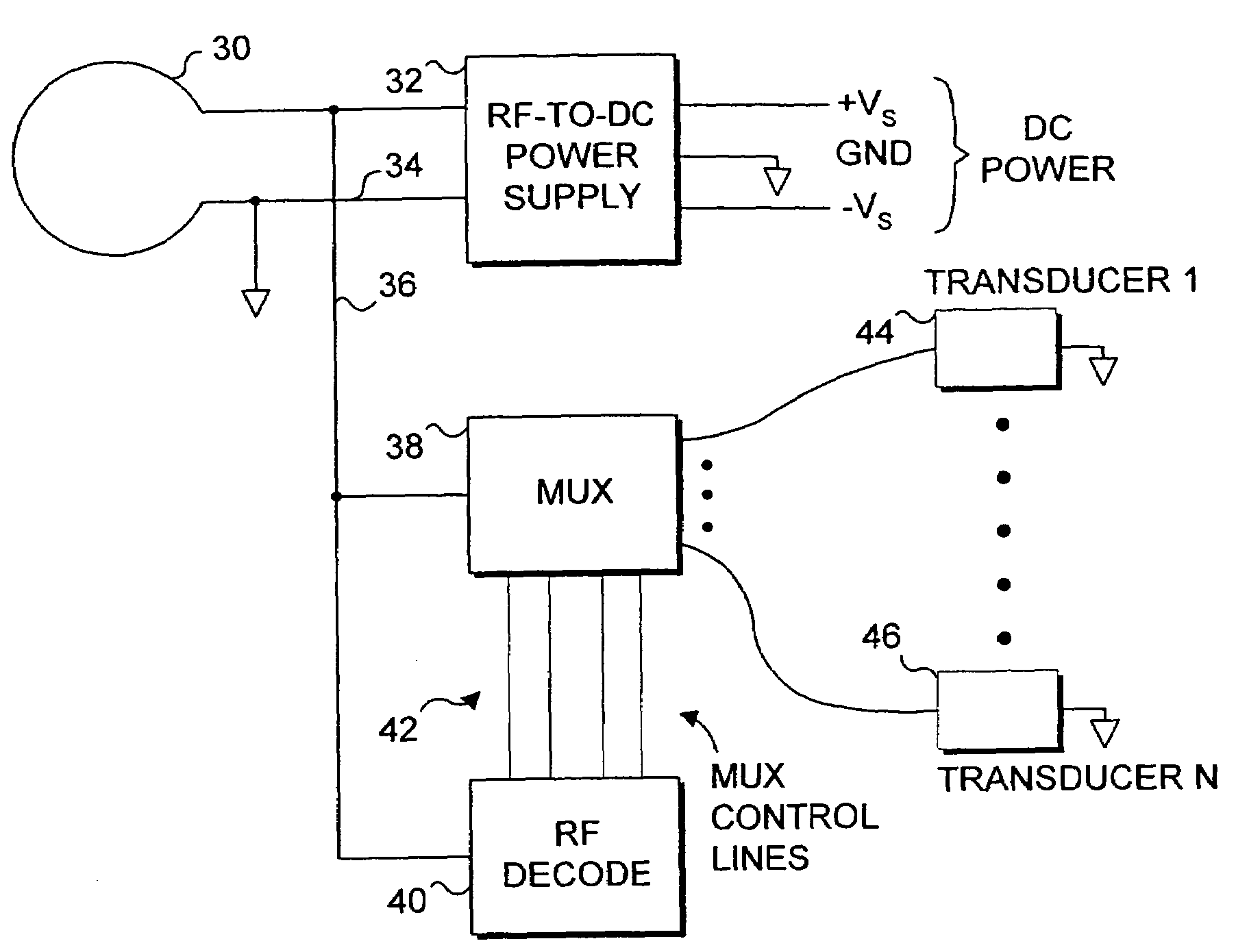
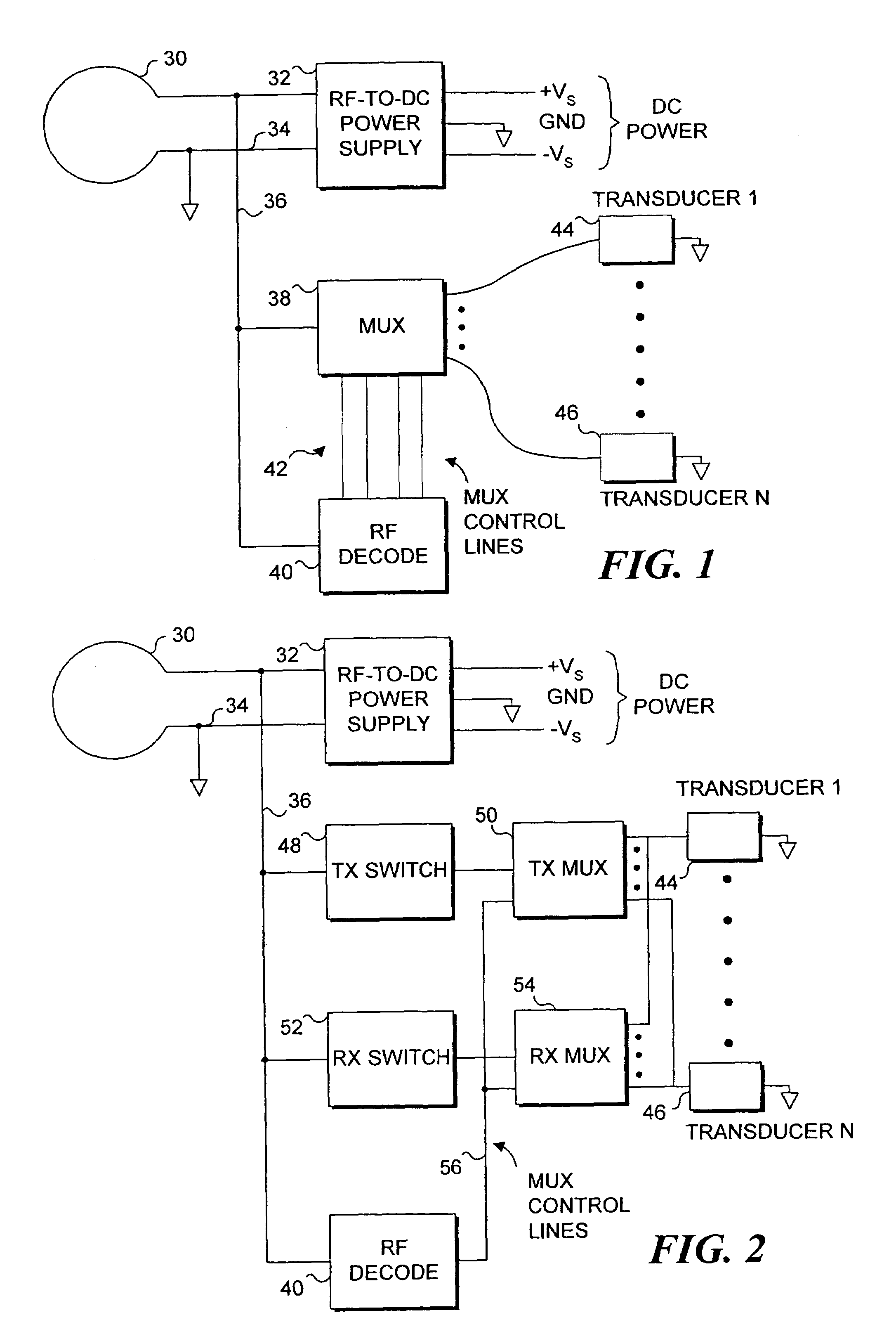
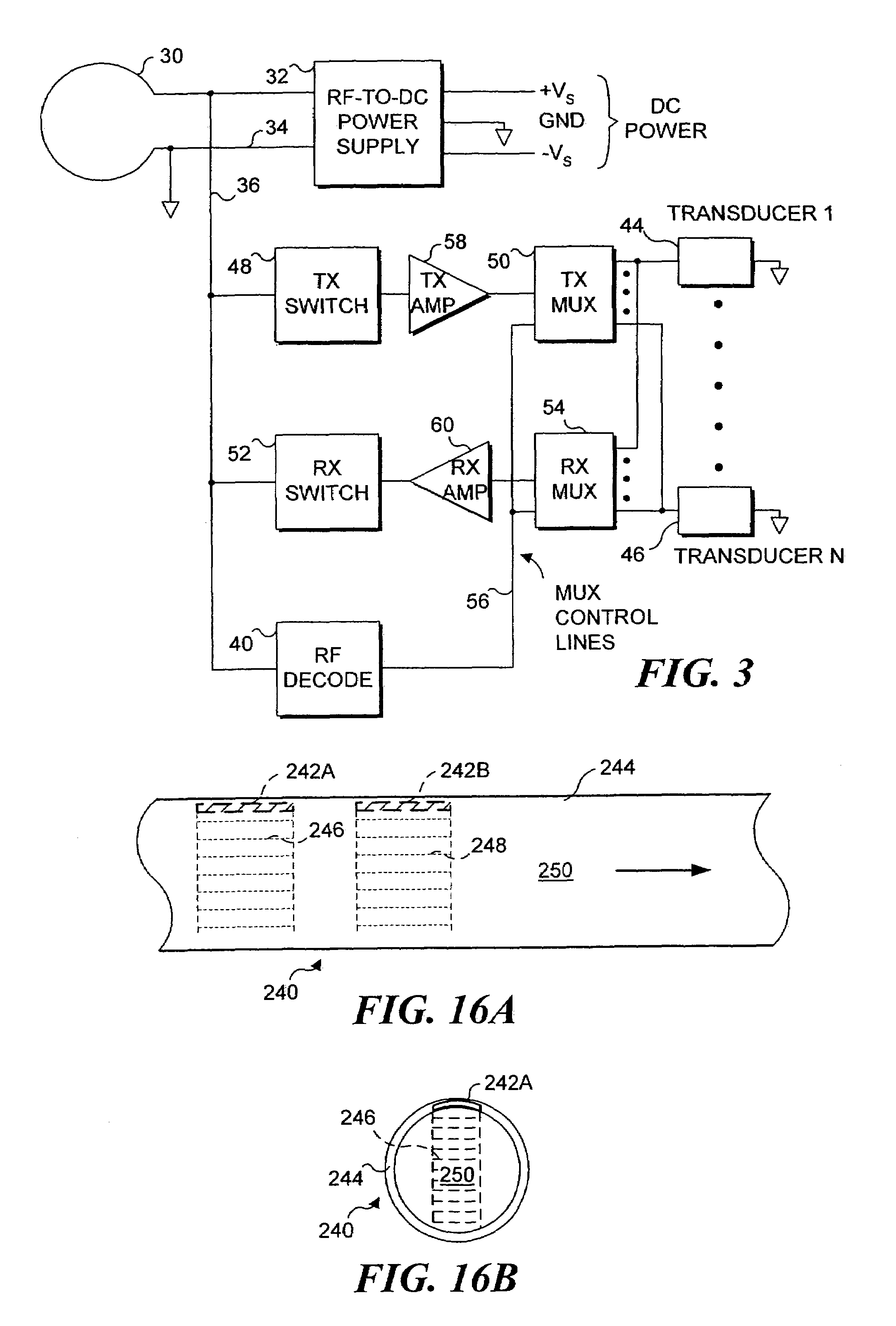
Endoluminal implant with therapeutic and diagnostic capability
InactiveUS20070112344A1Useful lifeExtended service lifeElectrotherapyOther blood circulation devicesCouplingTransducer
An apparatus includes an endoluminal implant, a RF coupling coil coupled to the endoluminal implant and a therapeutic transducer electrically coupled to the RF coupling coil and physically coupled to the endoluminal implant. The RF coupling coil supplies electrical power to the therapeutic transducer. The therapeutic transducer has a capability for delivering therapeutic energy to a lumen disposed within the endoluminal implant in response to signals coupled via the RF coupling coil.
Owner:CARDIOMETRIX
Methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively
InactiveUS7547283B2Medical data miningDiagnostics using vibrationsSound sourcesCentral sulcus artery
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided, wherein a non-linear relationship is used to determine ICP based on one or more variable inputs. The first variable input relates to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel and / or blood flow, such as acoustic backscatter from an acoustic transducer having a focus trained on a cranial blood vessel, flow velocity in a cranial blood vessel, and the like. Additional variables, such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), may be used in combination with a first variable input relating to one or more properties of a cranial blood vessel, such as flow velocity of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to derive ICP using a non-linear relationship. Methods and systems for locating target areas based on their acoustic properties and for acoustic scanning of an area, identification of a target area of interest based on acoustic properties, and automated focusing of an acoustic source and / or detector on a desired target area are also provided. Acoustic transducer assemblies are described.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
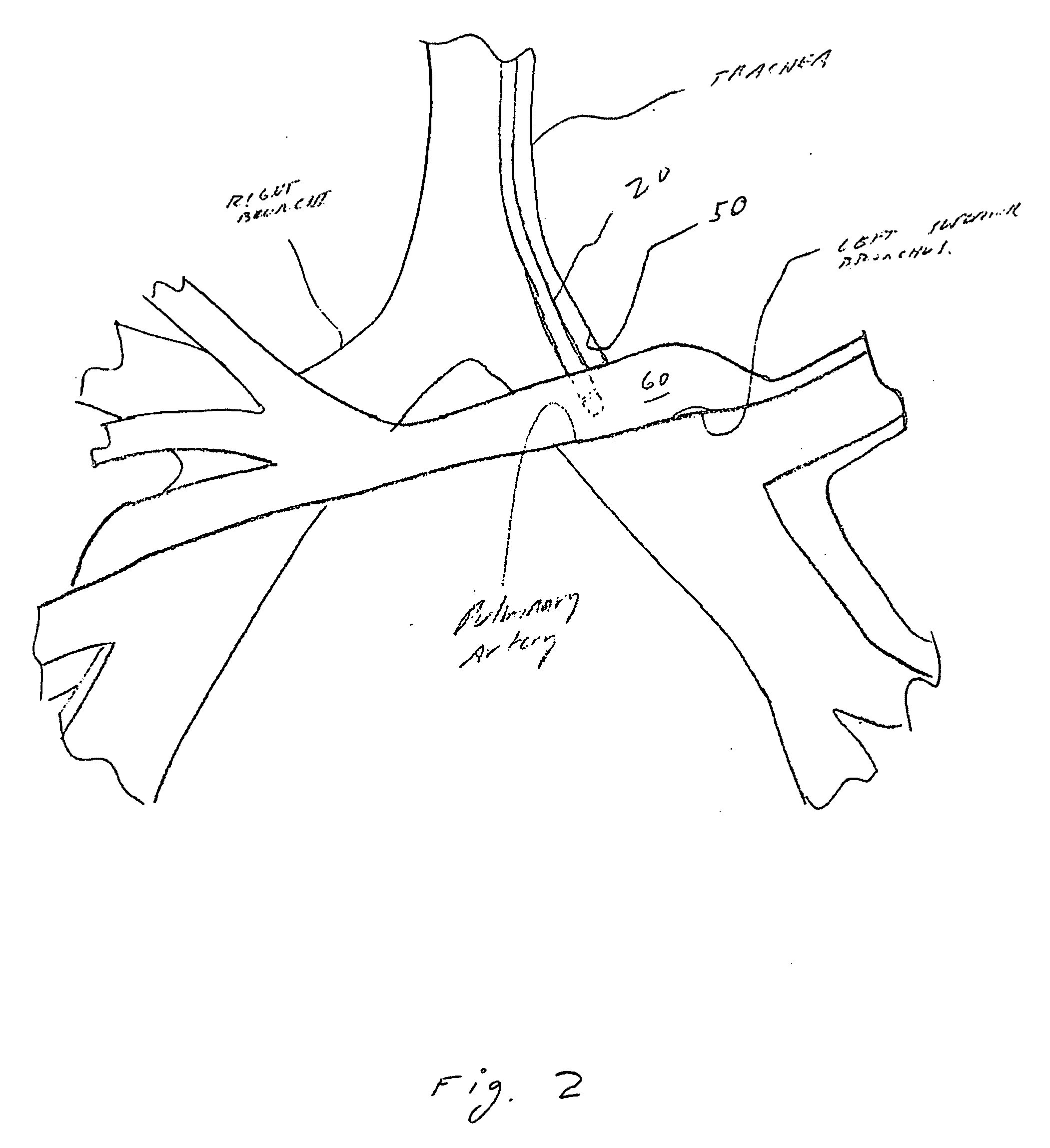
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Method and apparatus for continuous assessment of a cardiovascular parameter using the arterial pulse pressure propagation time and waveform
ActiveUS20080033305A1ElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesCardiac cycleArterial pulse pressure
A method and apparatus for determining a cardiovascular parameter including receiving an input signal corresponding to an arterial blood pressure measurement over an interval that covers at least one cardiac cycle, determining a propagation time of the input signal, determining at least one statistical moment of the input signal, and determining an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter using the propagation time and the at least one statistical moment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Tracking cardiac forces and arterial blood pressure using accelerometers
ActiveUS20180020931A1Easy to detectSimplifies separationElectrocardiographyElectromyographyAccelerometerNon invasive
Modular, miniaturized cardiovascular sensors, systems, methods, and wearable devices for the non-obtrusive evaluation, monitoring, and high-fidelity mapping of cardiac mechanical and electromechanical forces and central arterial blood pressure are presented herein. The sensor manufacturing process is also presented. Using accelerometers, the sensors register body-surface (preferably torso-surface) movements and vibrations generated by cardiac forces. The sensors may contain single-use or reusable components, which may be exchanged to fit different body sizes, shapes, and anatomical locations; they may be incorporated into clothing, bands, straps, and other wearable arrangements. The invention presents a practical, noninvasive solution for electromechanical mapping of the heart, which is useful for a wide range of healthcare applications, including the remote monitoring of heart failure status and the guidance of cardiac resynchronization therapy. Exercise and cardiovascular fitness tracking applications are also presented.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Endoluminal implant with therapeutic and diagnostic capability
InactiveUS7427265B1Useful lifeExtended service lifeElectrotherapyOther blood circulation devicesCouplingTransducer
An apparatus includes an endoluminal implant, a RF coupling coil coupled to the endoluminal implant and a therapeutic transducer electrically coupled to the RF coupling coil and physically coupled to the endoluminal implant. The RF coupling coil supplies electrical power to the therapeutic transducer. The therapeutic transducer has a capability for delivering therapeutic energy to a lumen disposed within the endoluminal implant in response to signals coupled via the RF coupling coil.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and system for monitoring a health condition
A system and method for monitoring a health condition are disclosed. The system includes a patient management application, a data store and a monitoring device. The monitoring device includes an optical sensor, a Doppler sensor, and a computing device adapted to provide health parameter values including oxygen saturation of the blood, blood flow, blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output.
Owner:CARDIO ART TECH
Apparatus and method for non-invasive, in-vivo, thoracic radio interrogation
InactiveUS20090240133A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsRadio equipmentRadio reception
A radio apparatus and method for non-invasive, thoracic radio interrogation of a subject for the collection of hemodynamic, respiratory and / or other cardiopulmonary related data from the subject includes a antenna positionable proximally to the subject, a radio transmitter transmitting an unmodulated radio interrogation signal of a predetermined fixed frequency at a safe level of about 1 milliwatt or less from the antenna into the subject and a radio receiver capturing through the antenna, reflections of the transmitted radio interrogation signal returned from the subject. A Doppler component of the reflections contains the data that can be extracted from the captured reflections.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
Systems and methods for determining intracranial pressure non-invasively and acoustic transducer assemblies for use in such systems
Systems and methods for determining ICP based on parameters that can be measured using non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques are provided. Systems for acquiring acoustic data from a desired target site in a subject's body using various types of acoustic source and detector elements are also provided, including single use acoustic source / detector combinations are also provided. Acoustic arrays for use with these systems may include multiple capacitive micro-machined ultrasound transducer (cMUT) elements, and may include a combination of different types of acoustic arrays. Methods of targeting localized sites within a broad target area based on acoustic data having various properties are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and system for image processing to determine patient-specific blood flow characteristics
Embodiments include a system for determining cardiovascular information for a patient. The system may include at least one computer system configured to receive patient-specific data regarding a geometry of the patient's heart, and create a three-dimensional model representing at least a portion of the patient's heart based on the patient-specific data. The at least one computer system may be further configured to create a physics-based model relating to a blood flow characteristic of the patient's heart and determine a fractional flow reserve within the patient's heart based on the three-dimensional model and the physics-based model.
Owner:HEARTFLOW
Integrated heart monitoring device and method of using same
InactiveUS20080249379A1Accurate measurementNo human intervention requiredElectrotherapyBlood flow measurement devicesElectricityBlood flow
A device for monitoring the heart of a patient including a housing, a computing device, an optical sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a distance from the optical sensor to a vessel carrying blood, as well a diameter of the vessel, a Doppler sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a velocity of the blood through the vessel, and an ECG sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a plurality of electrical stimuli that cause the heart to pump. The computing device uses signals from the optical sensor, the Doppler sensor, and the ECG sensor to compute parameters including oxygen saturation of the blood, blood flow, blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output.
Owner:CARDIO ART TECH
Continuous, non-invasive technique for determining blood pressure using a transmission line model and transcutaneous ultrasound measurements
ActiveUS7621876B2Good estimateImprove accuracyBlood flow measurement devicesPerson identificationState variableBlood pressure
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
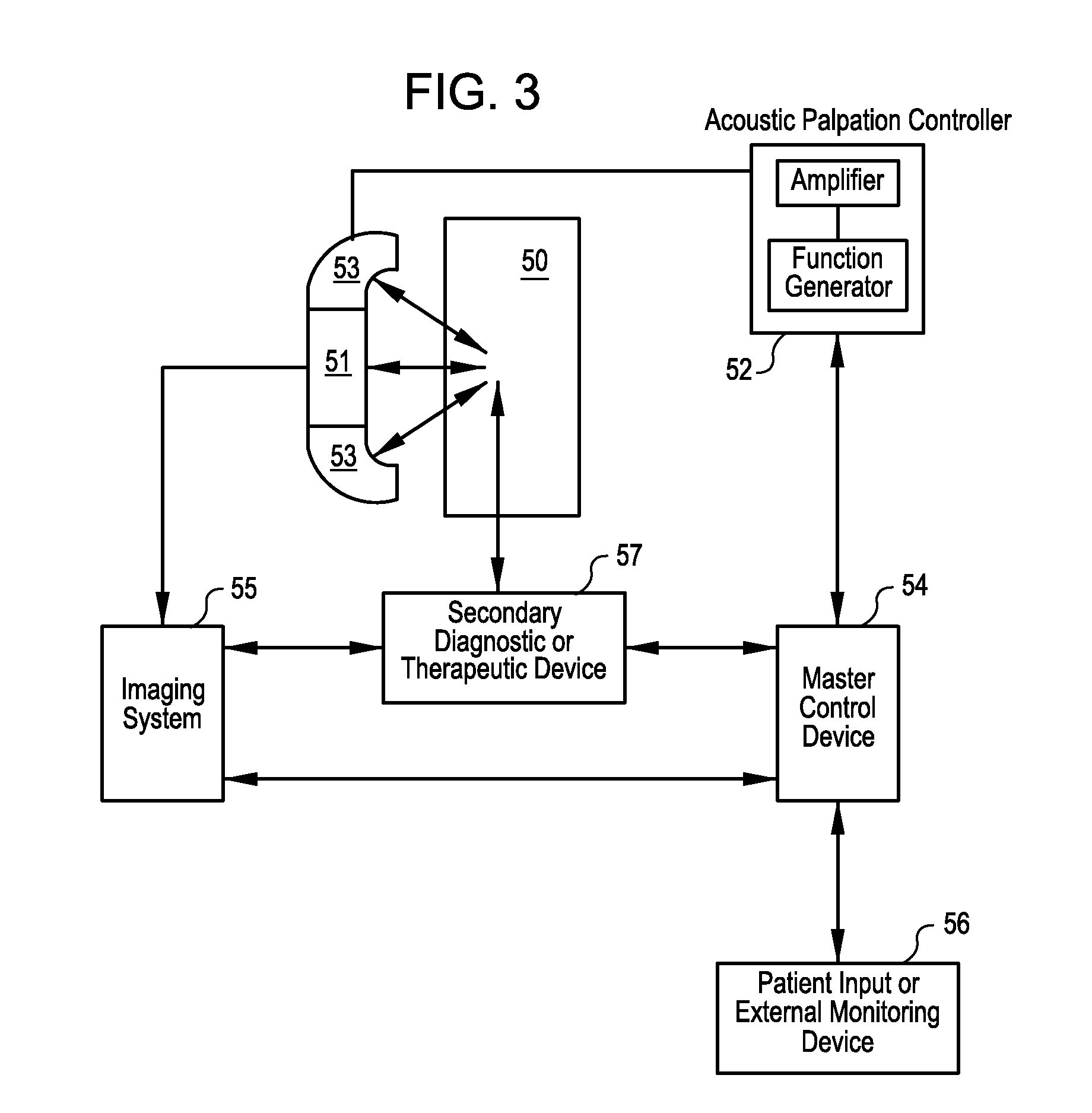
Acoustic palpation using non-invasive ultrasound techniques to identify and localize tissue eliciting biological responses
InactiveUS20100087728A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce exposureUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
Methods and systems for identifying and spatially localizing tissues having certain physiological properties or producing certain biological responses, such as the sensation of pain, in response to the application of intense focused ultrasound (acoustic probing or palpation) are provided. In some embodiments, targeted acoustic probing may be guided or visualized using imaging techniques such as ultrasound imaging or other types of non-invasive imaging techniques.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com