Patents
Literature
195 results about "Doppler ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Doppler ultrasound is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves to measure the amount of blood flow through your arteries and veins, usually those that supply blood to your arms and legs.
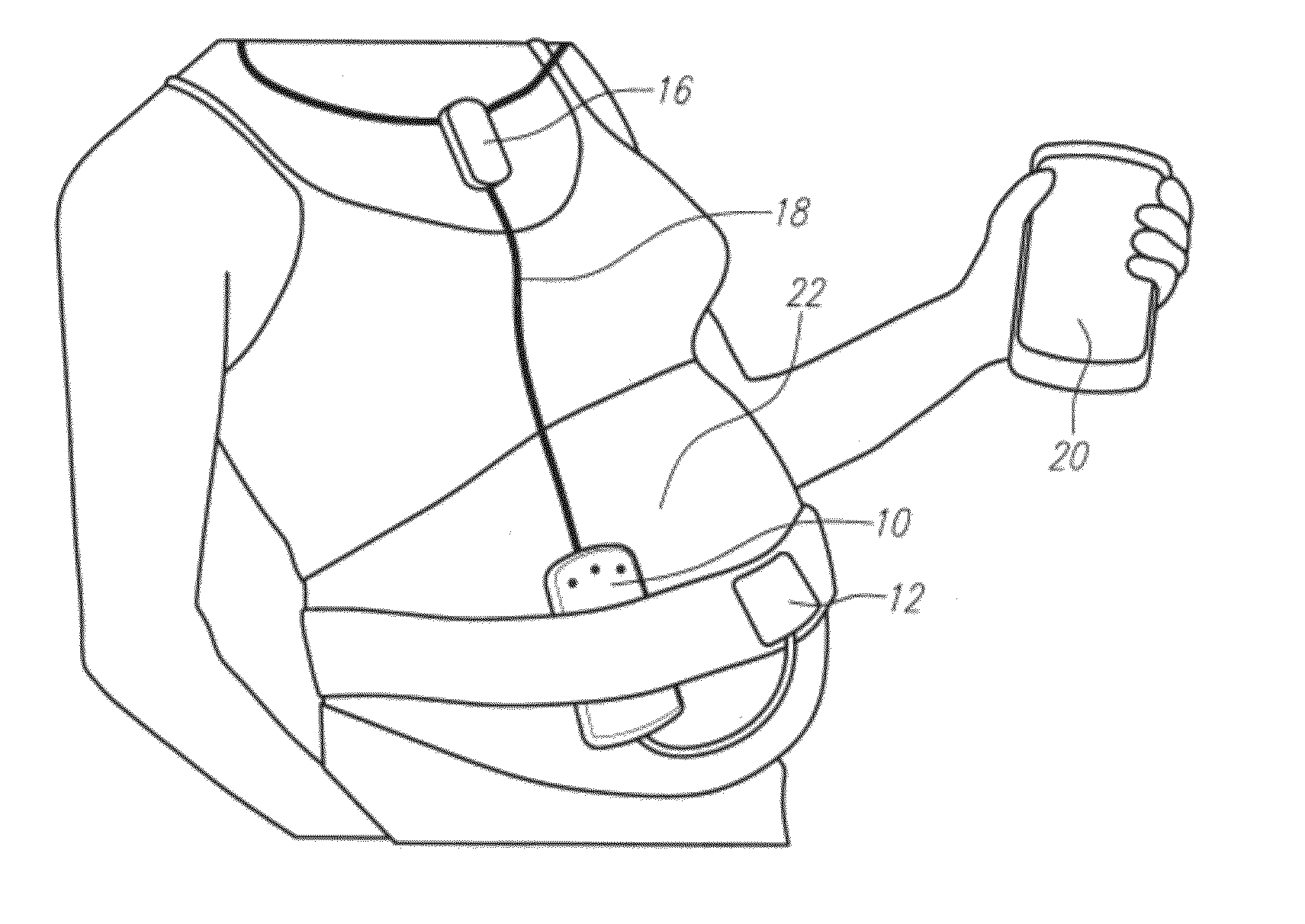
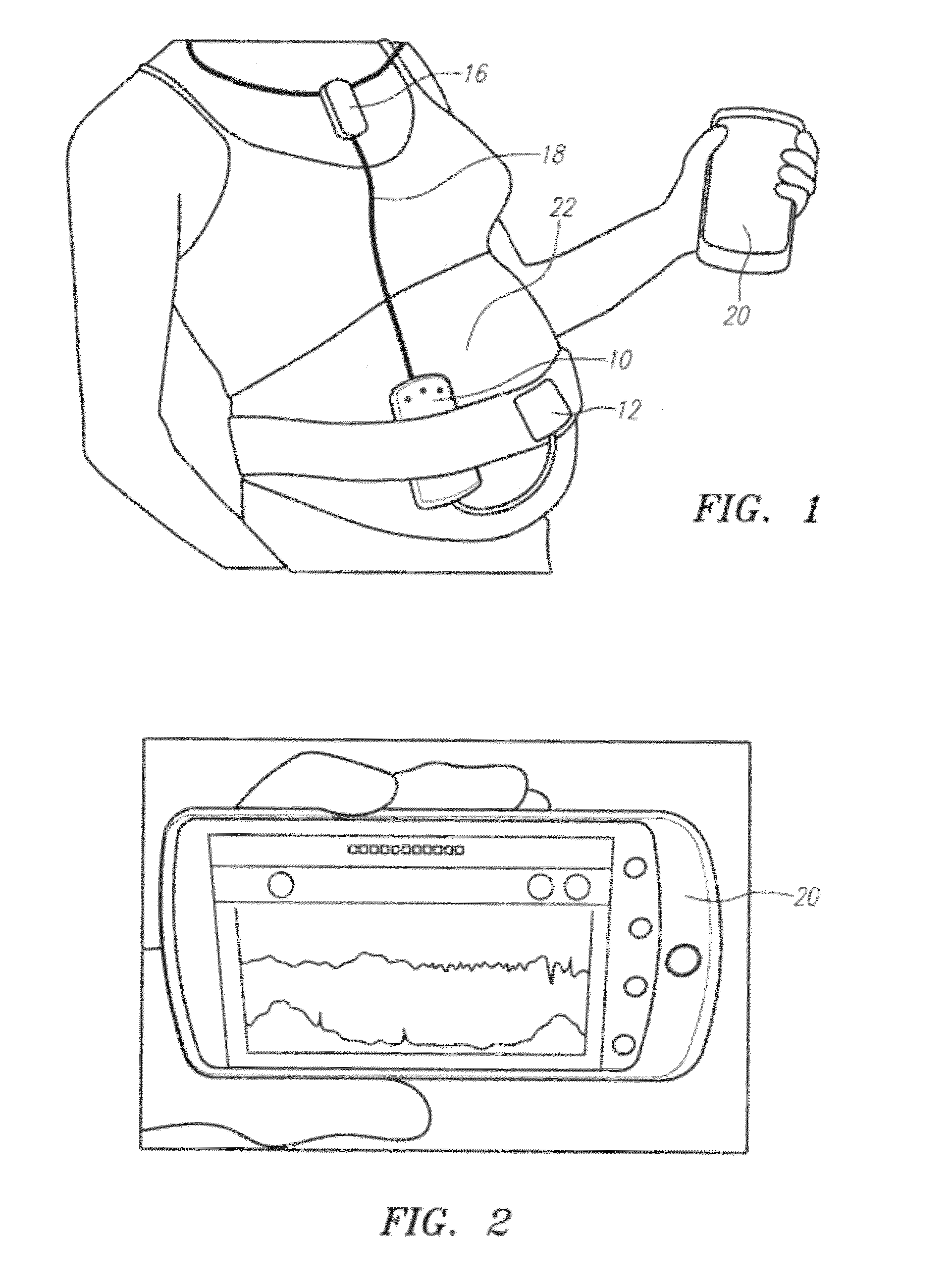
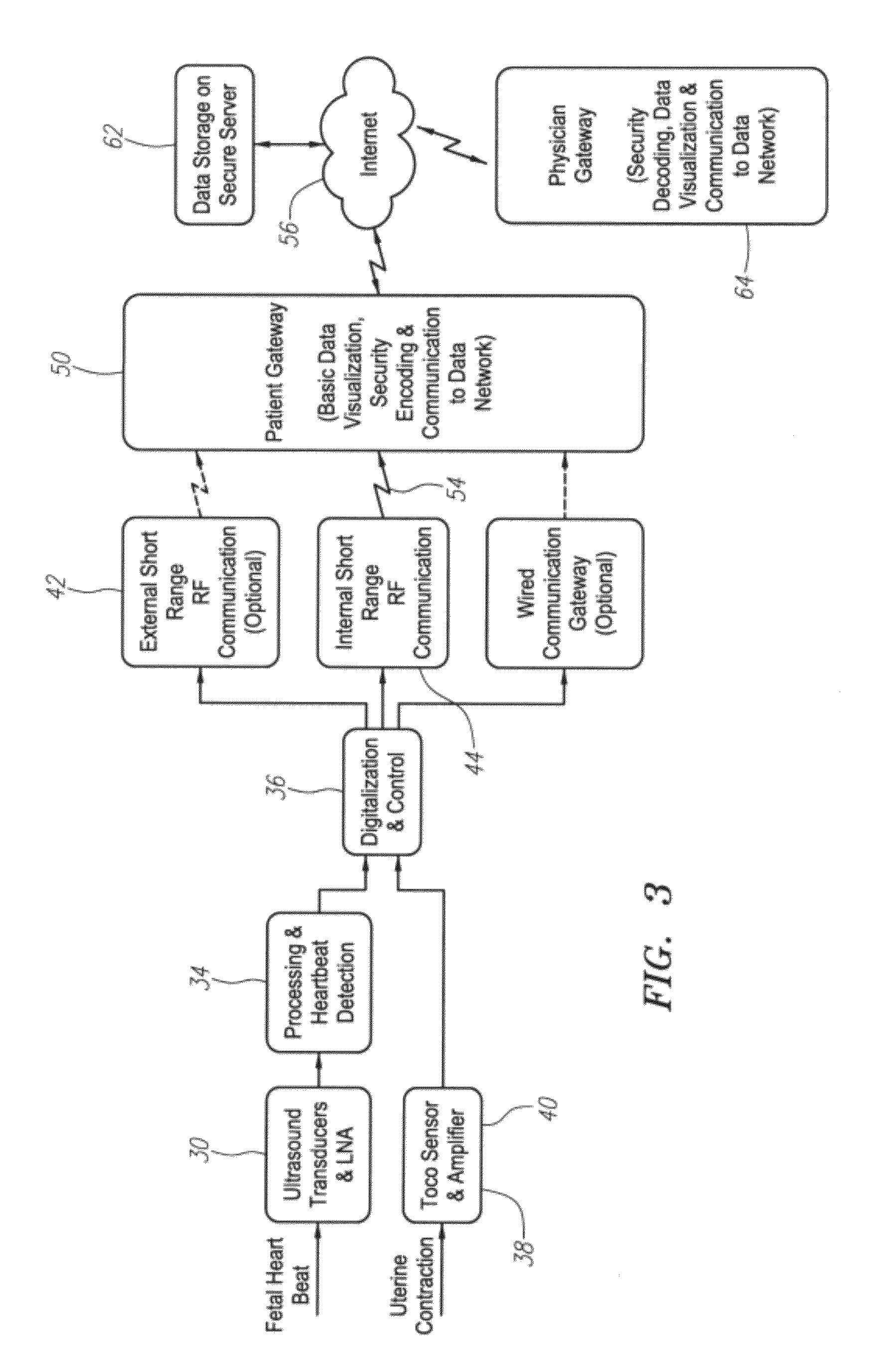
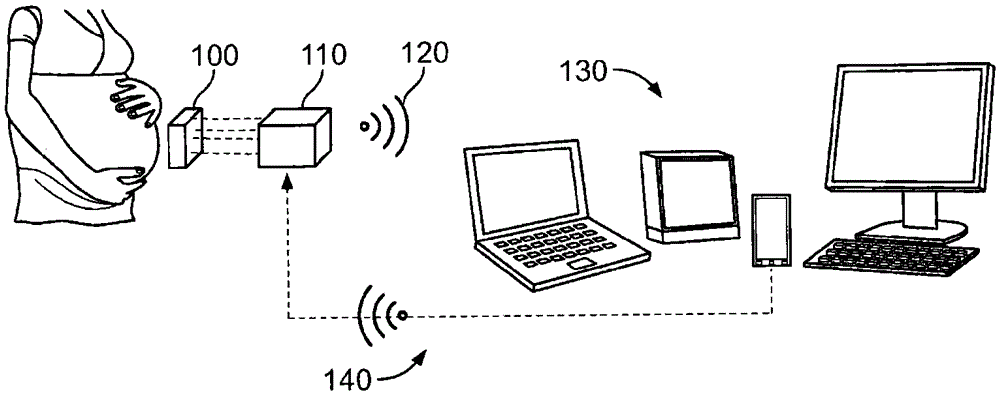
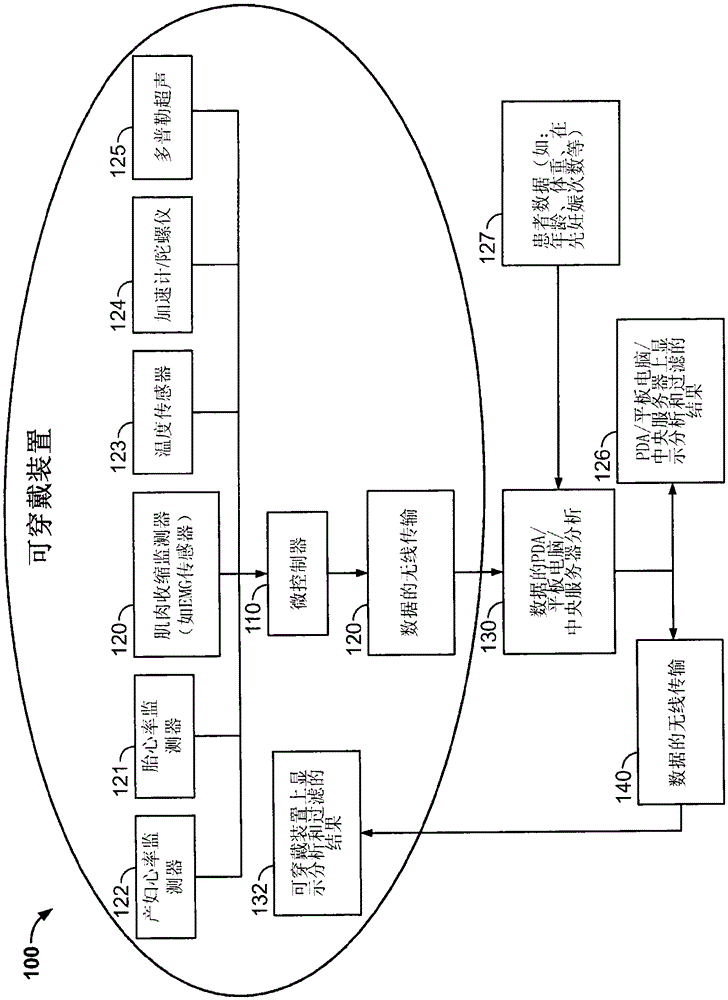
Wireless fetal monitoring system
InactiveUS20120232398A1Low costPoor outcomeElectromyographyHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesEngineeringPatient monitor
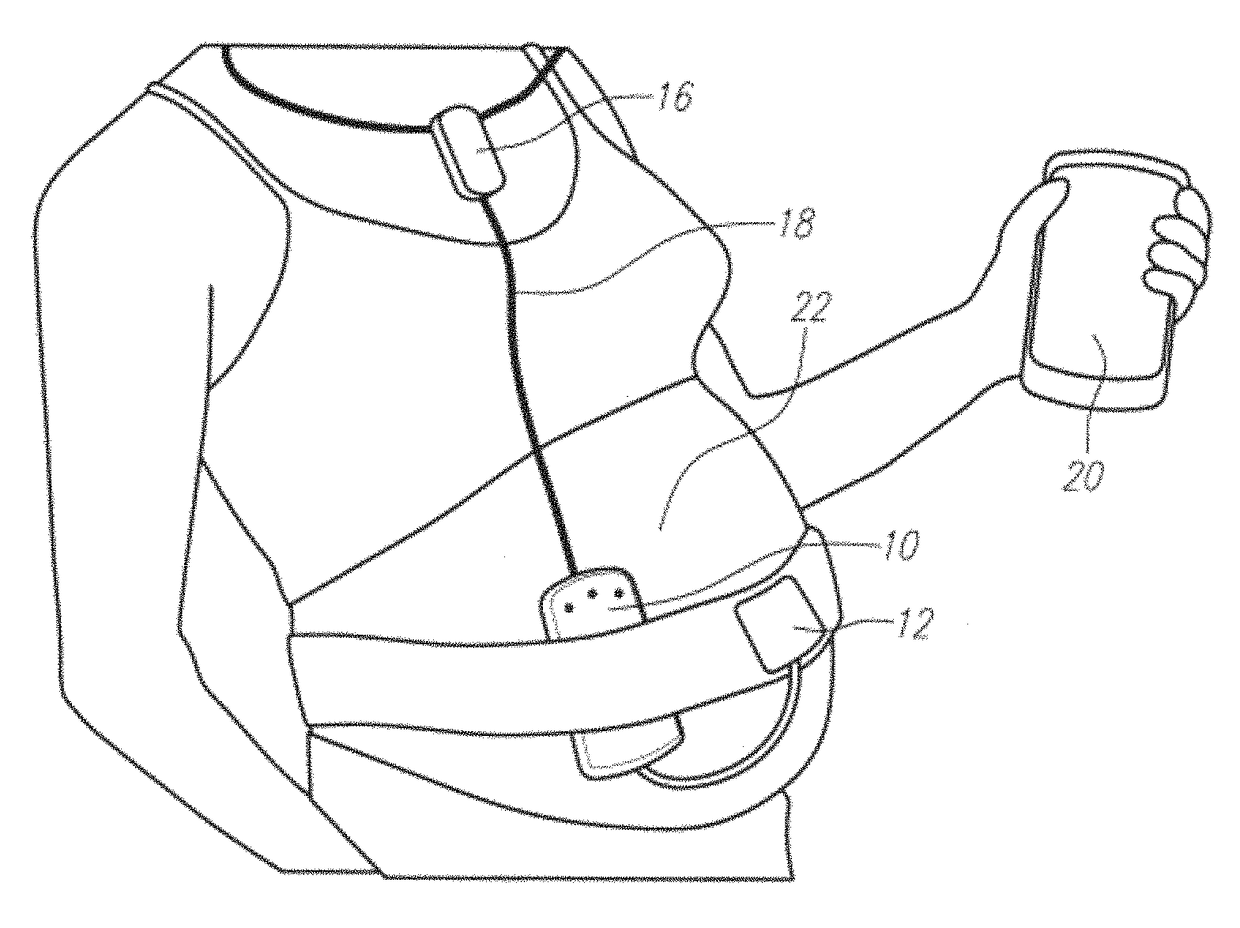
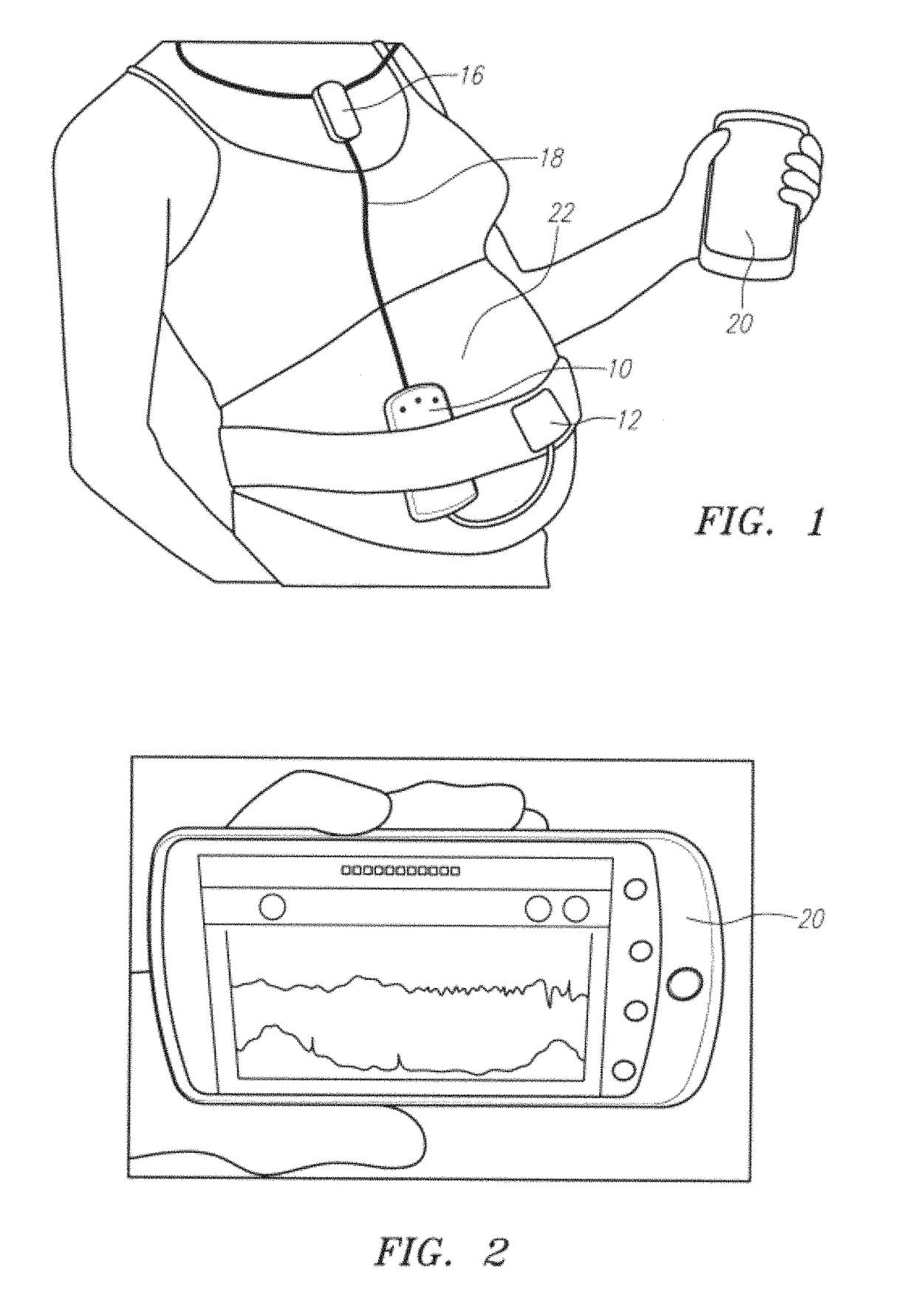
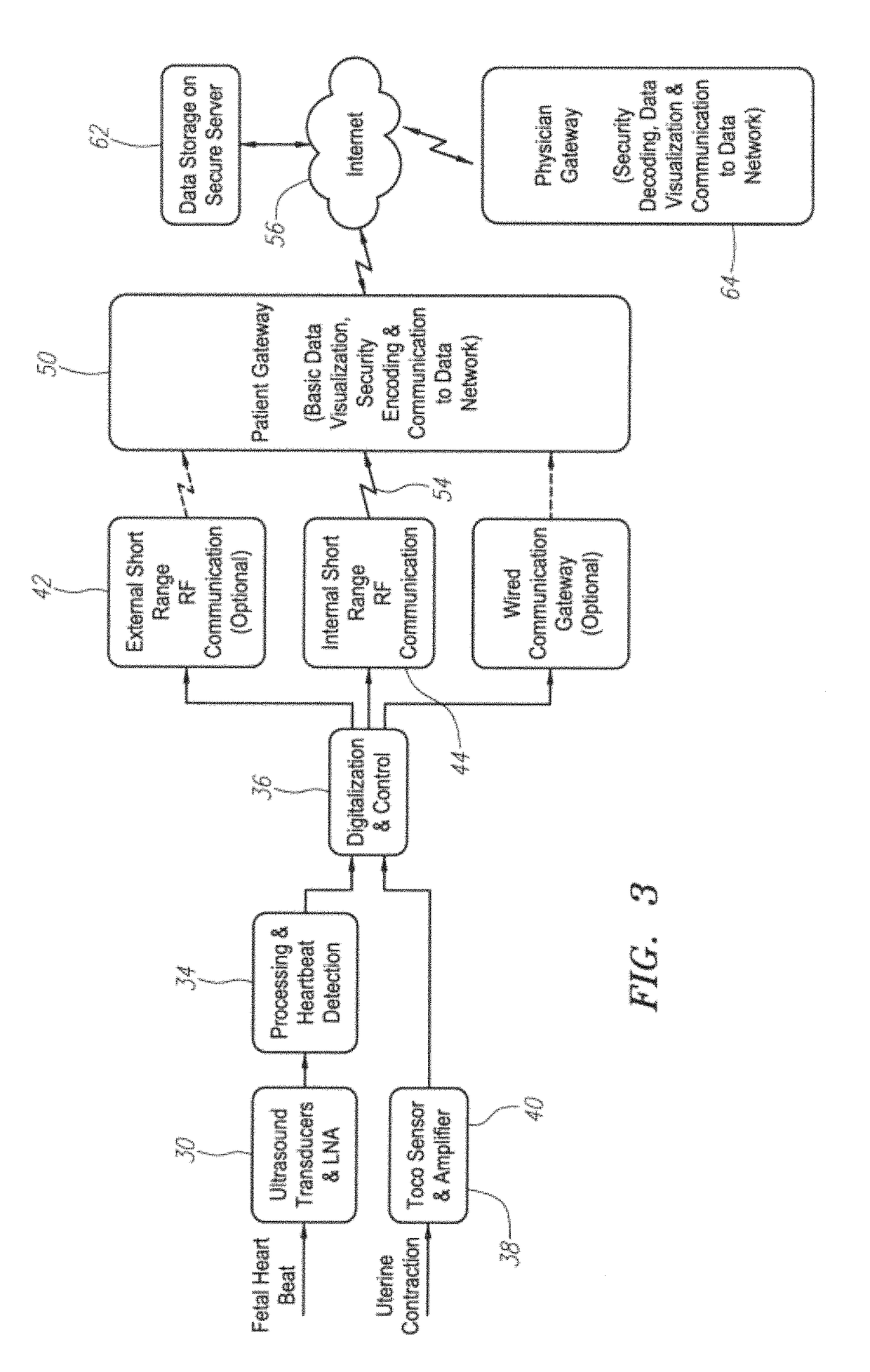
A wireless fetal and maternal monitoring system includes a fetal sensor unit adapted to receive signals indicative of a fetal heartbeat, the sensor optionally utilizing a Doppler ultrasound sensor. A short-range transmission unit sends the signals indicative of fetal heartbeat to a gateway unit, either directly or via an auxiliary communications unit, in which case the electrical coupling between the short-range transmission unit and the auxiliary communications unit is via a wired connection. The system includes a contraction actuator actuatable upon a maternal uterine contraction, which optionally is a EMG sensor. A gateway device provides for data visualization and data securitization. The gateway device provides for remote transmission of information through a data communication network. A server adapted to receive the information from the gateway device serves to store and process the data, and an interface system to permits remote patient monitoring.
Owner:GARY & MARY WEST HEALTH INST
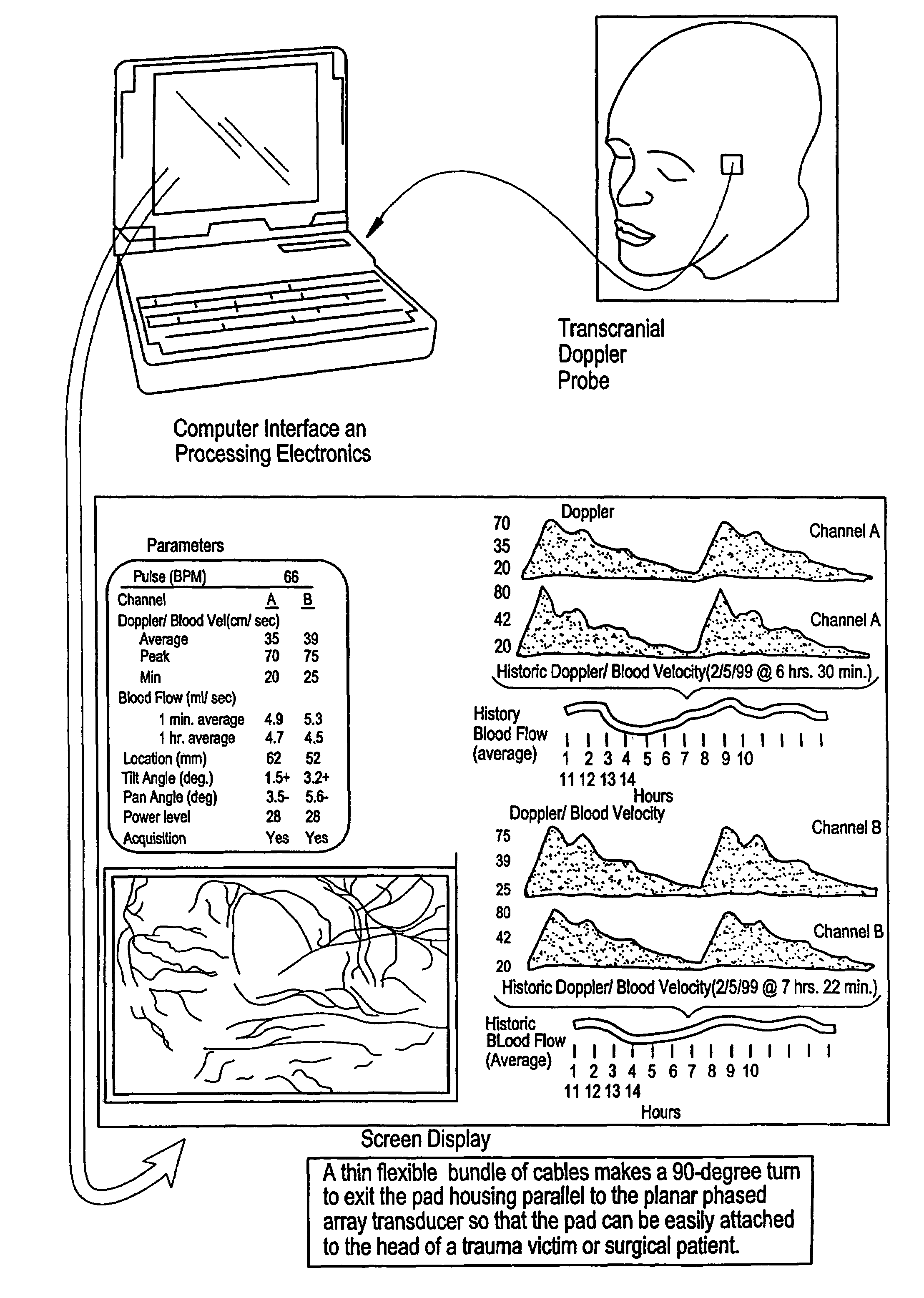
Transmitter patterns for multi beam reception
InactiveUS7399279B2High resolutionSmall sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsThinned arrayDisplay device
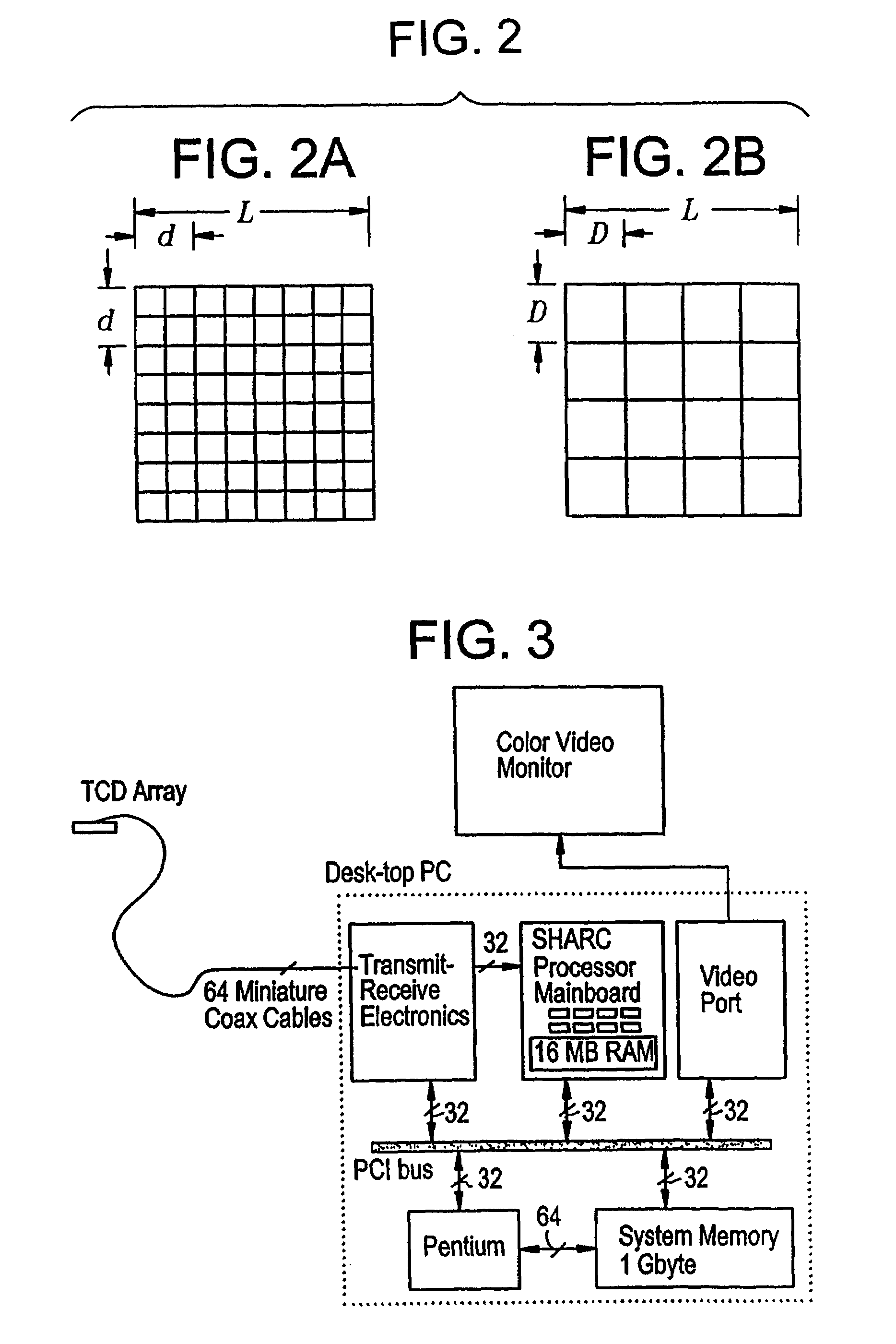
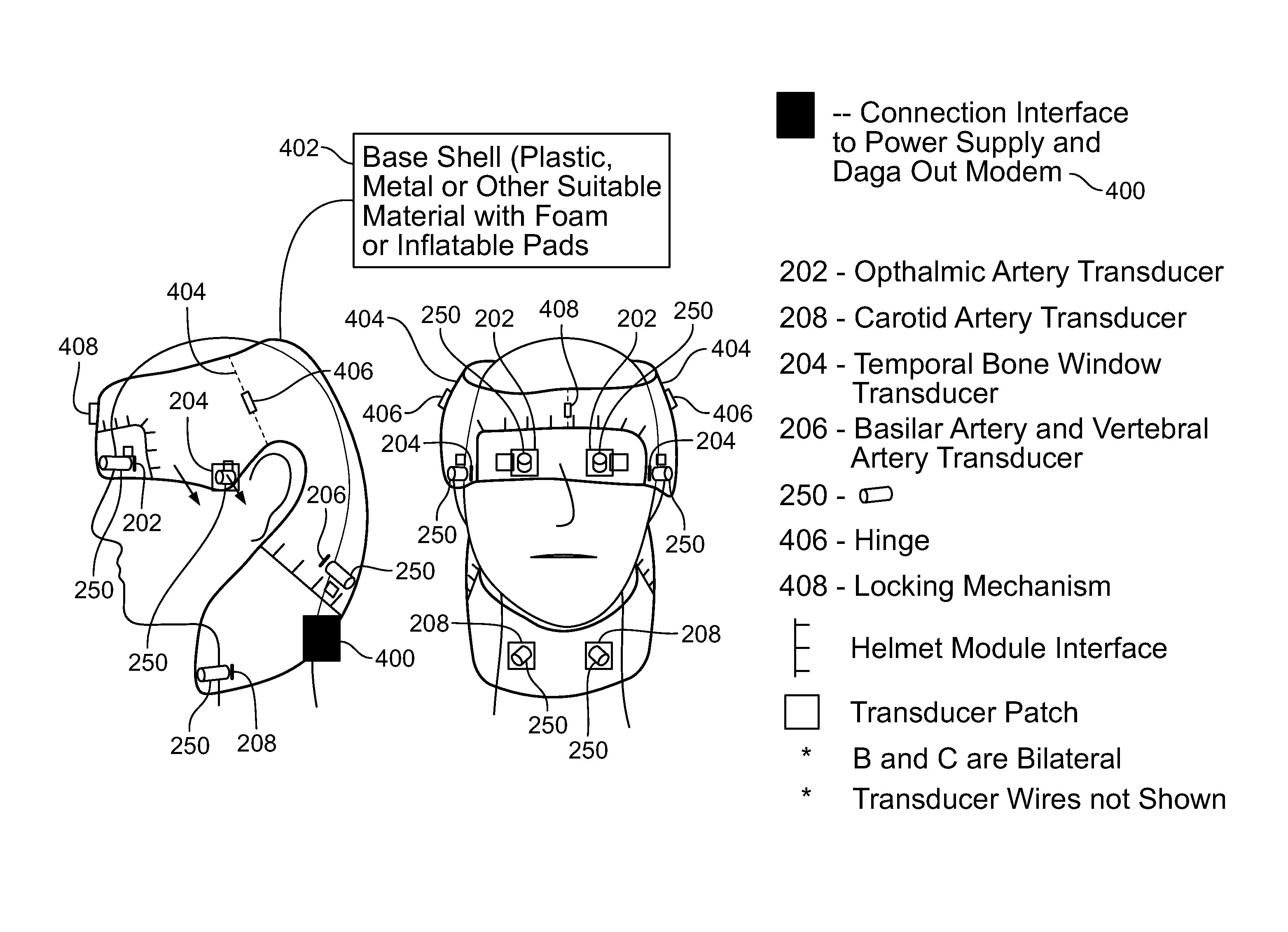
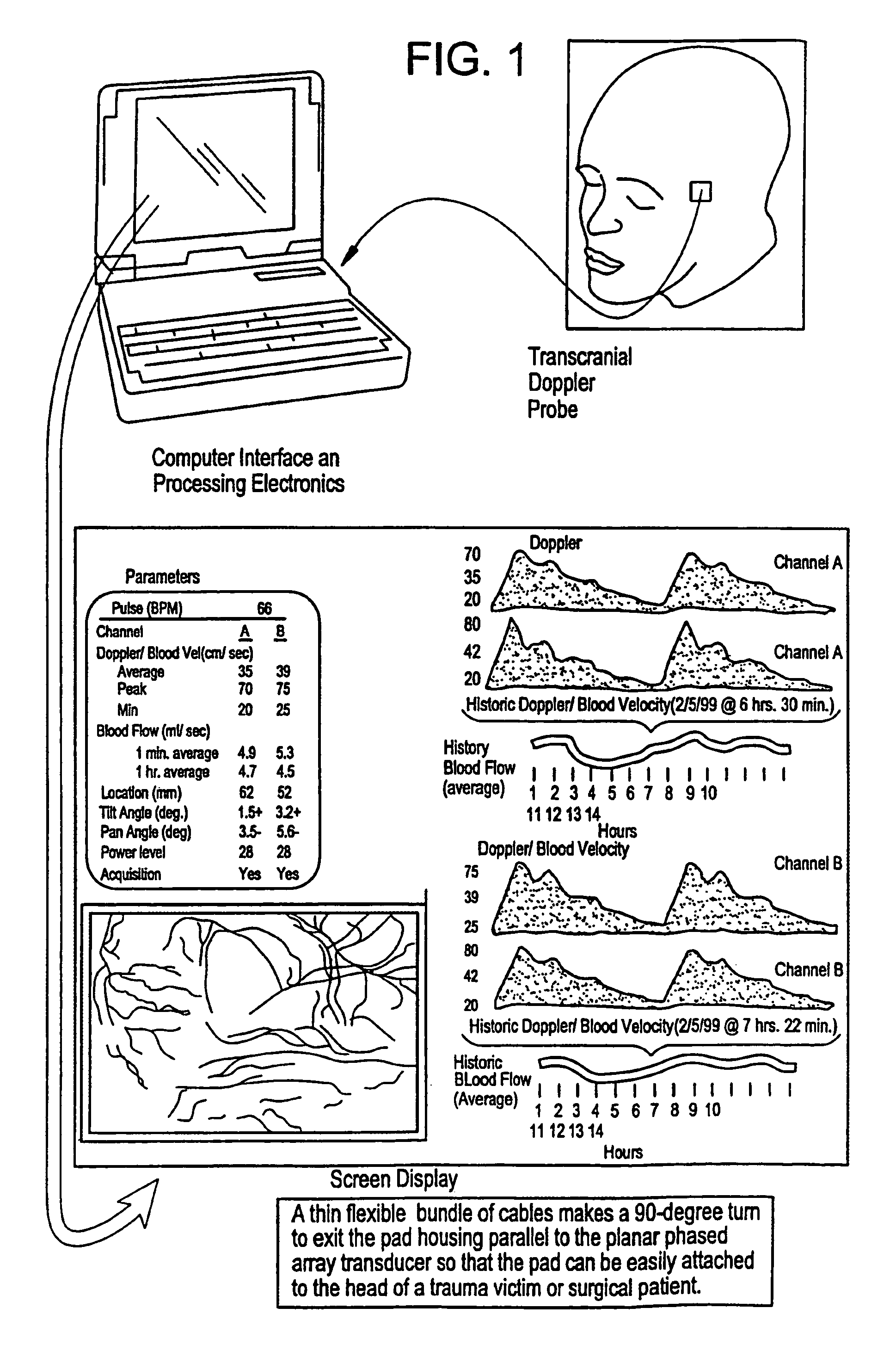
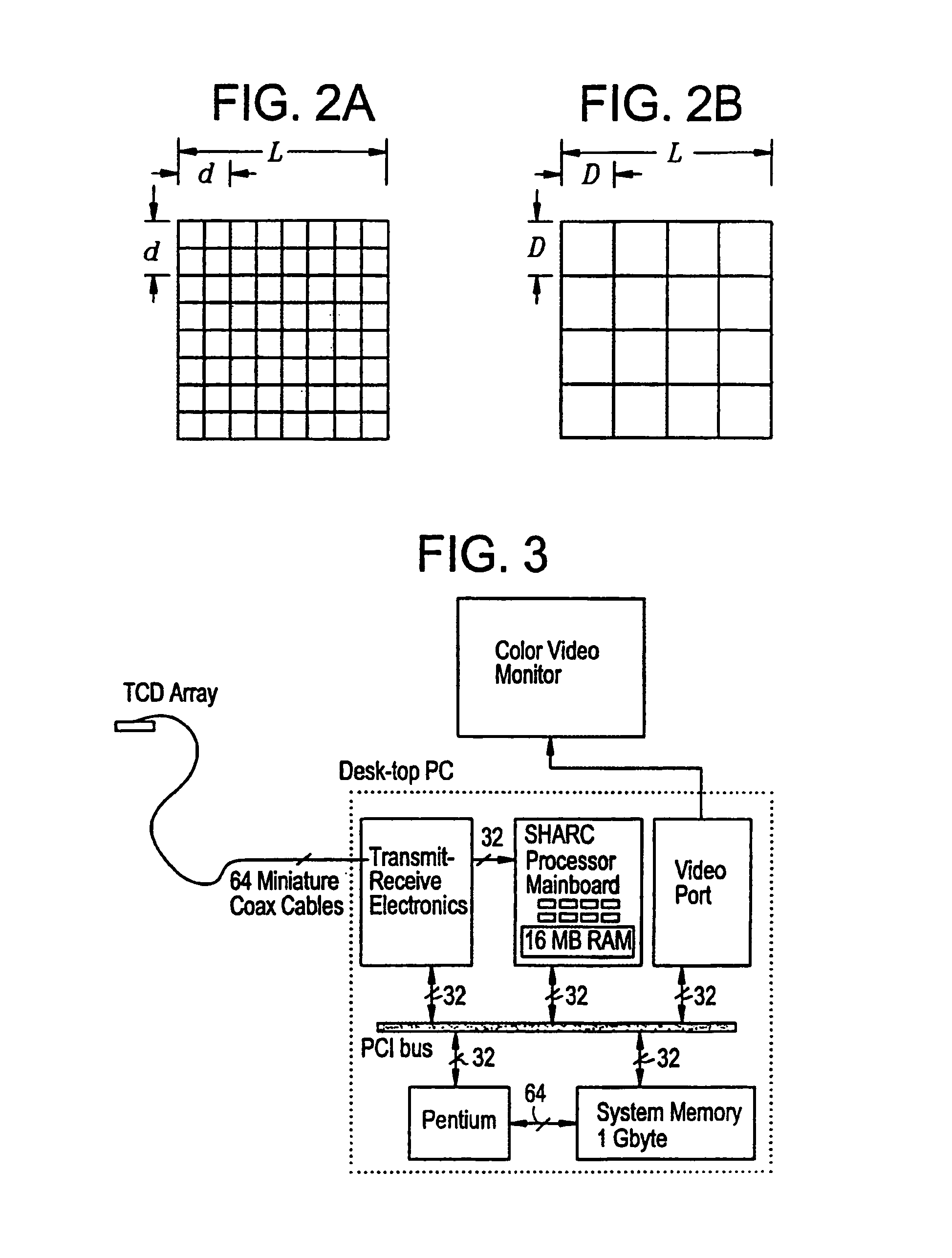
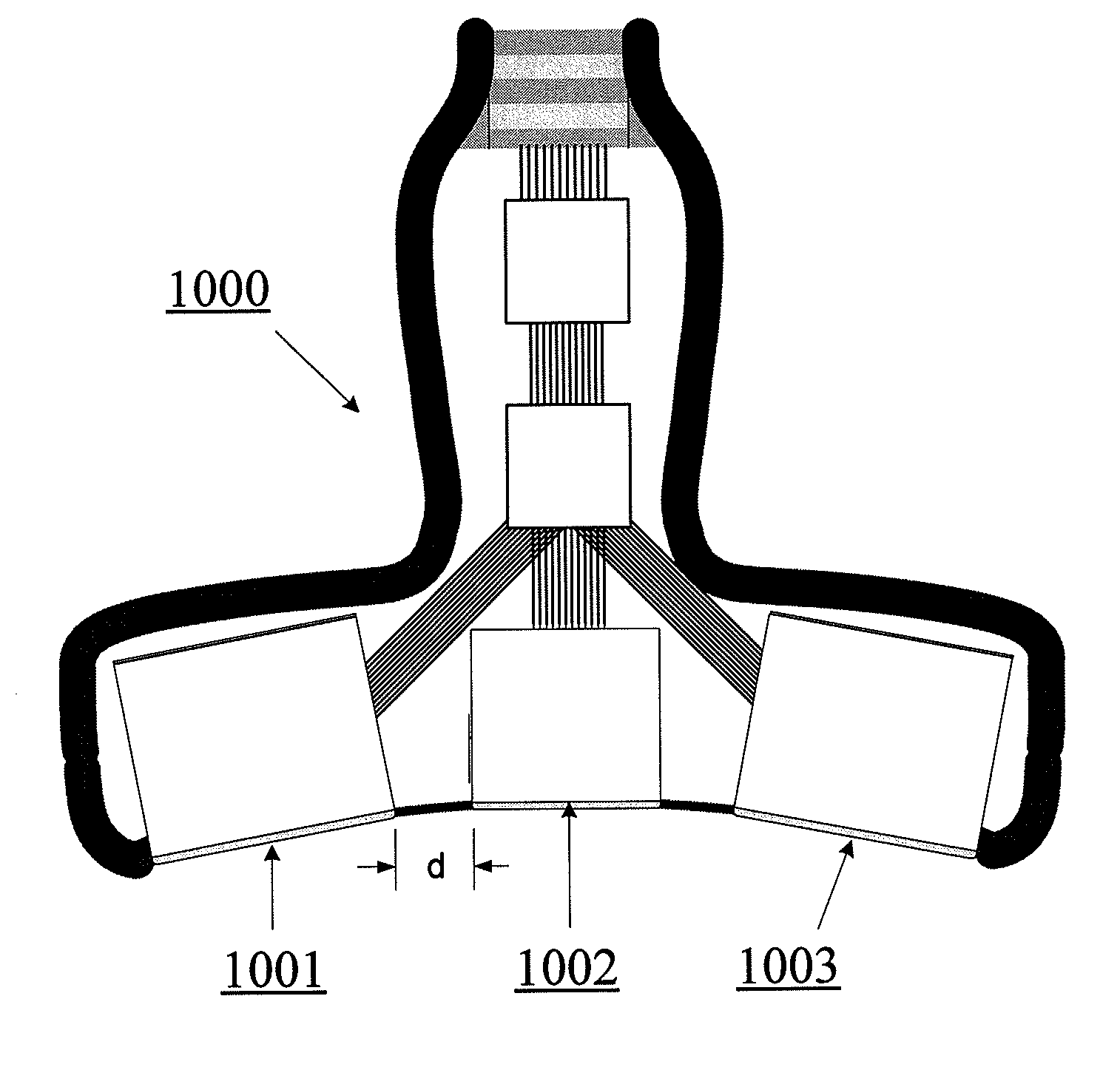
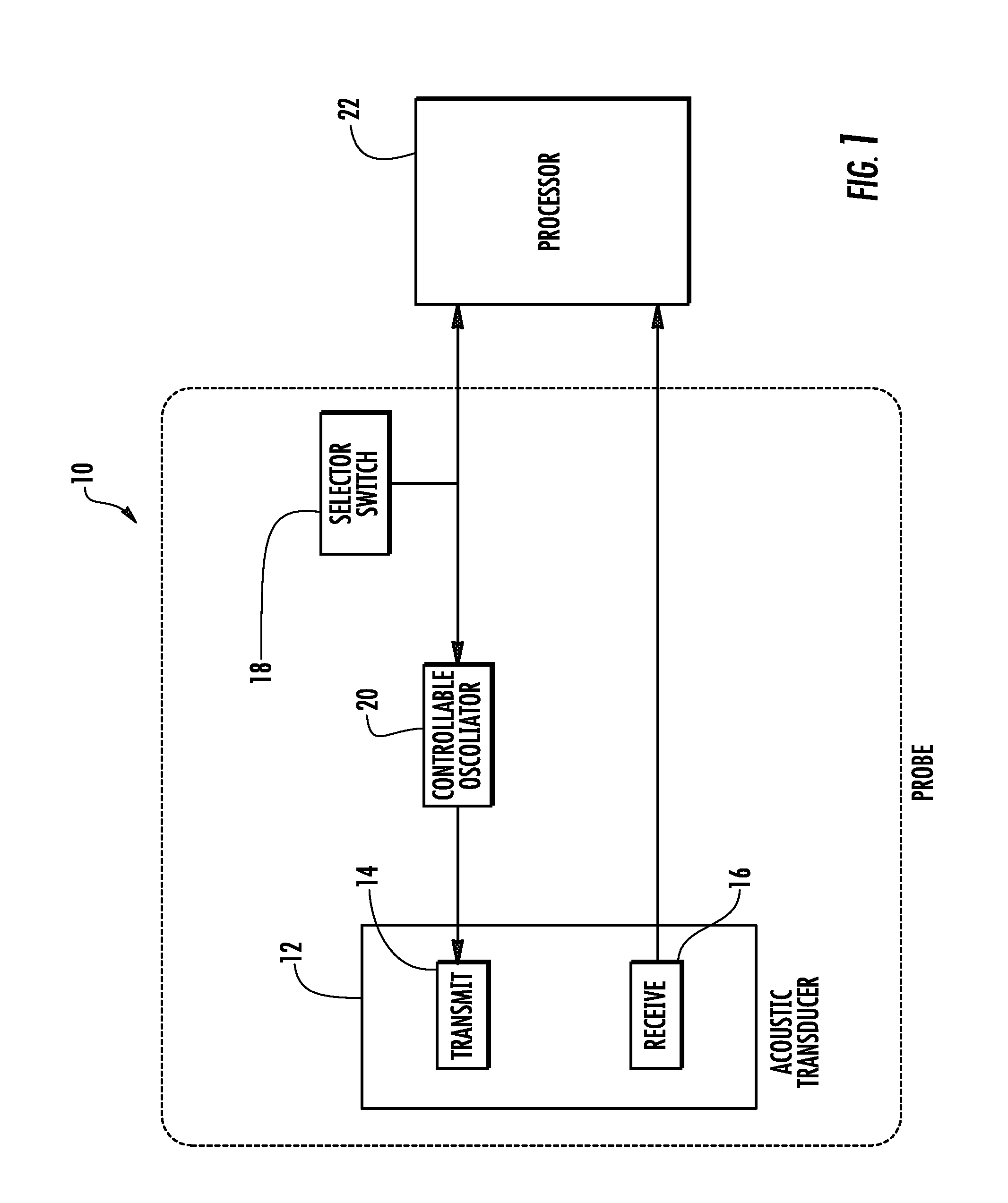
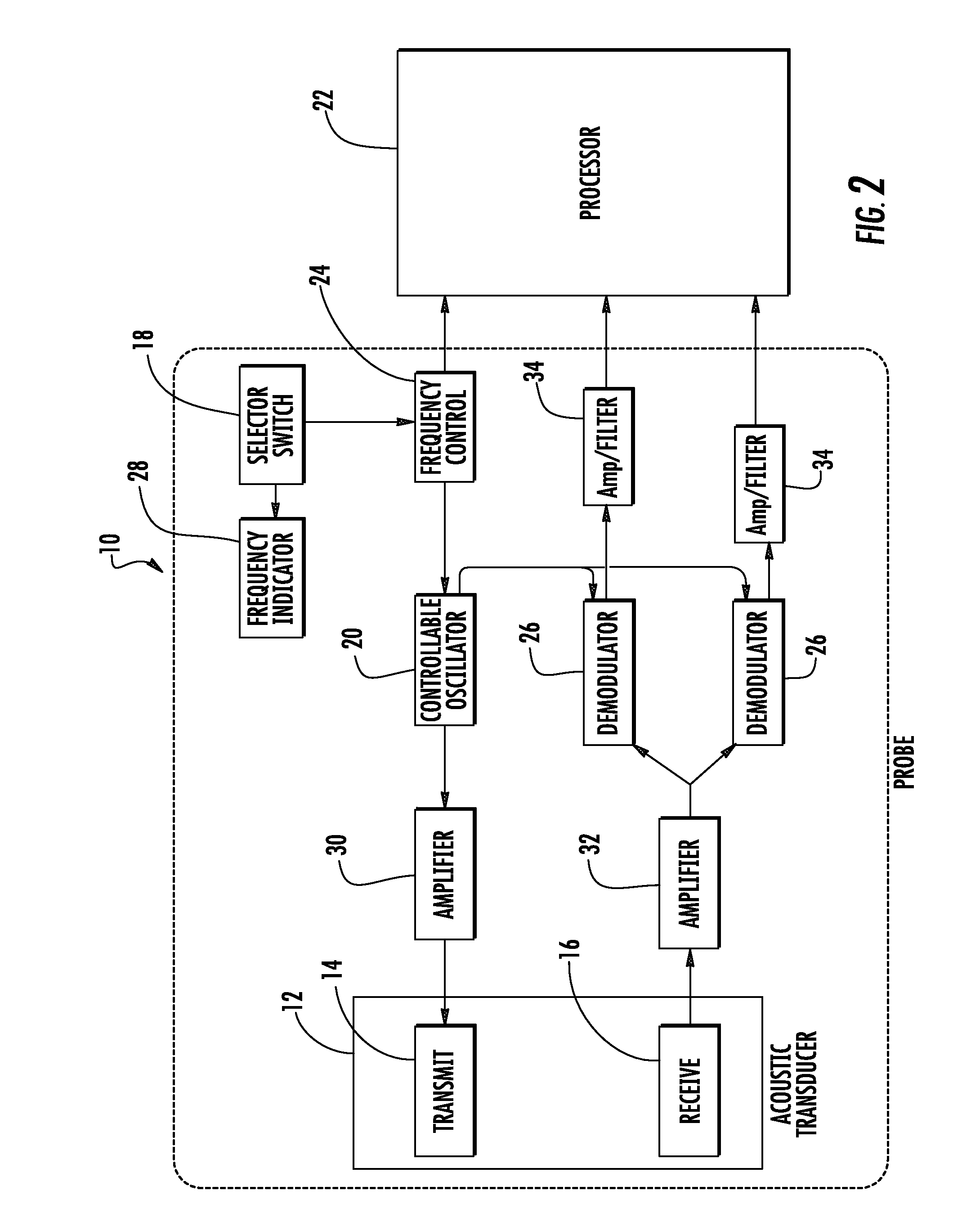
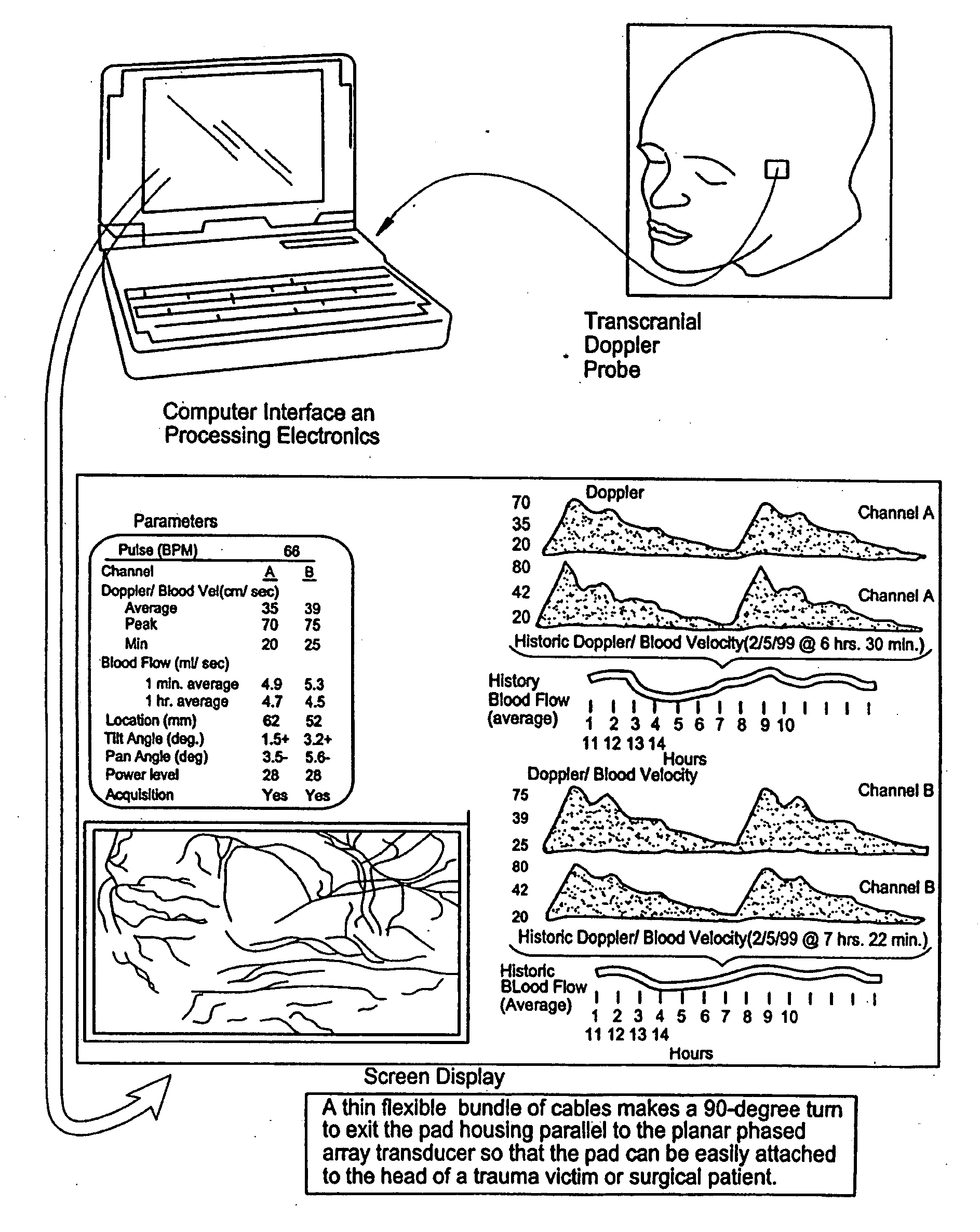
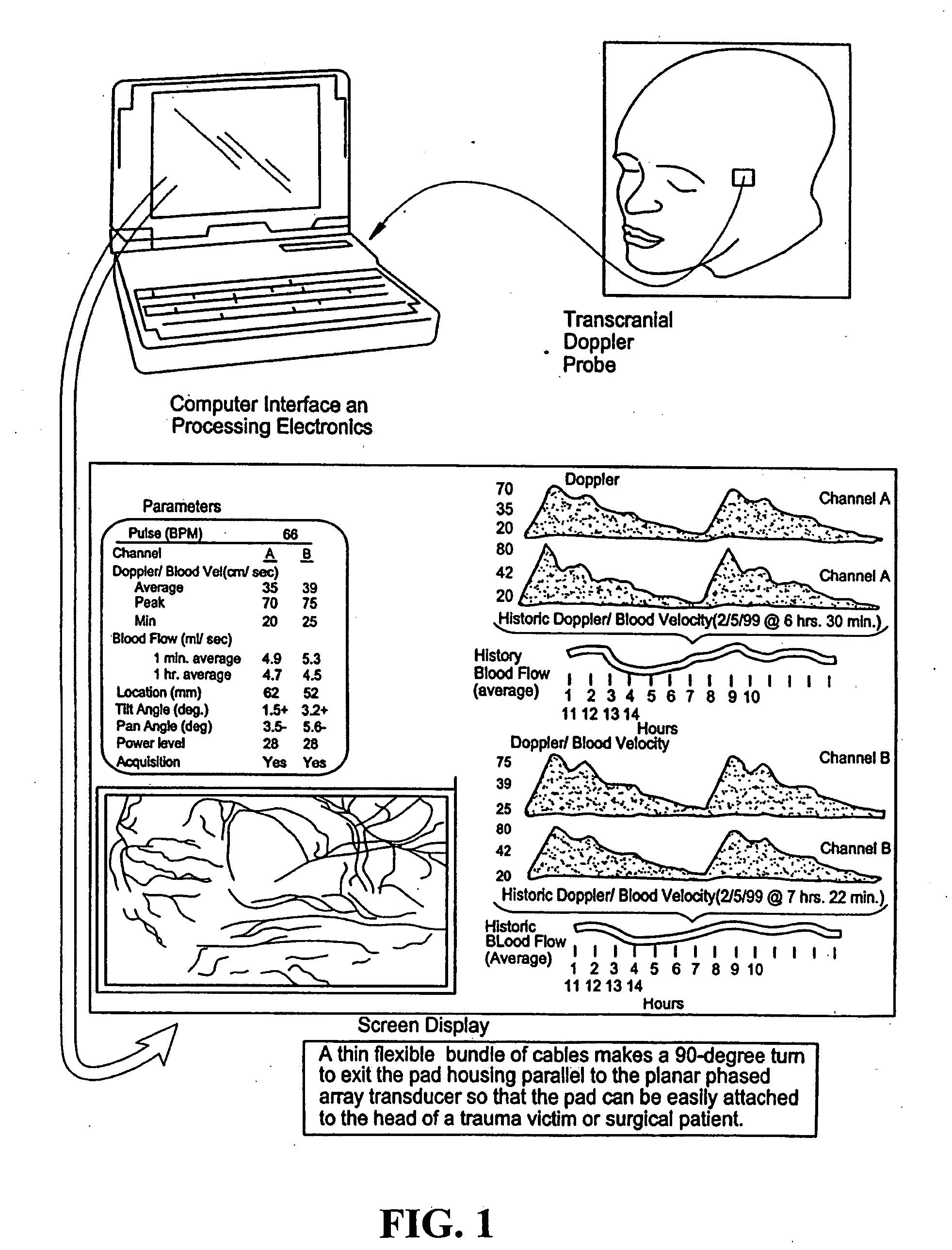
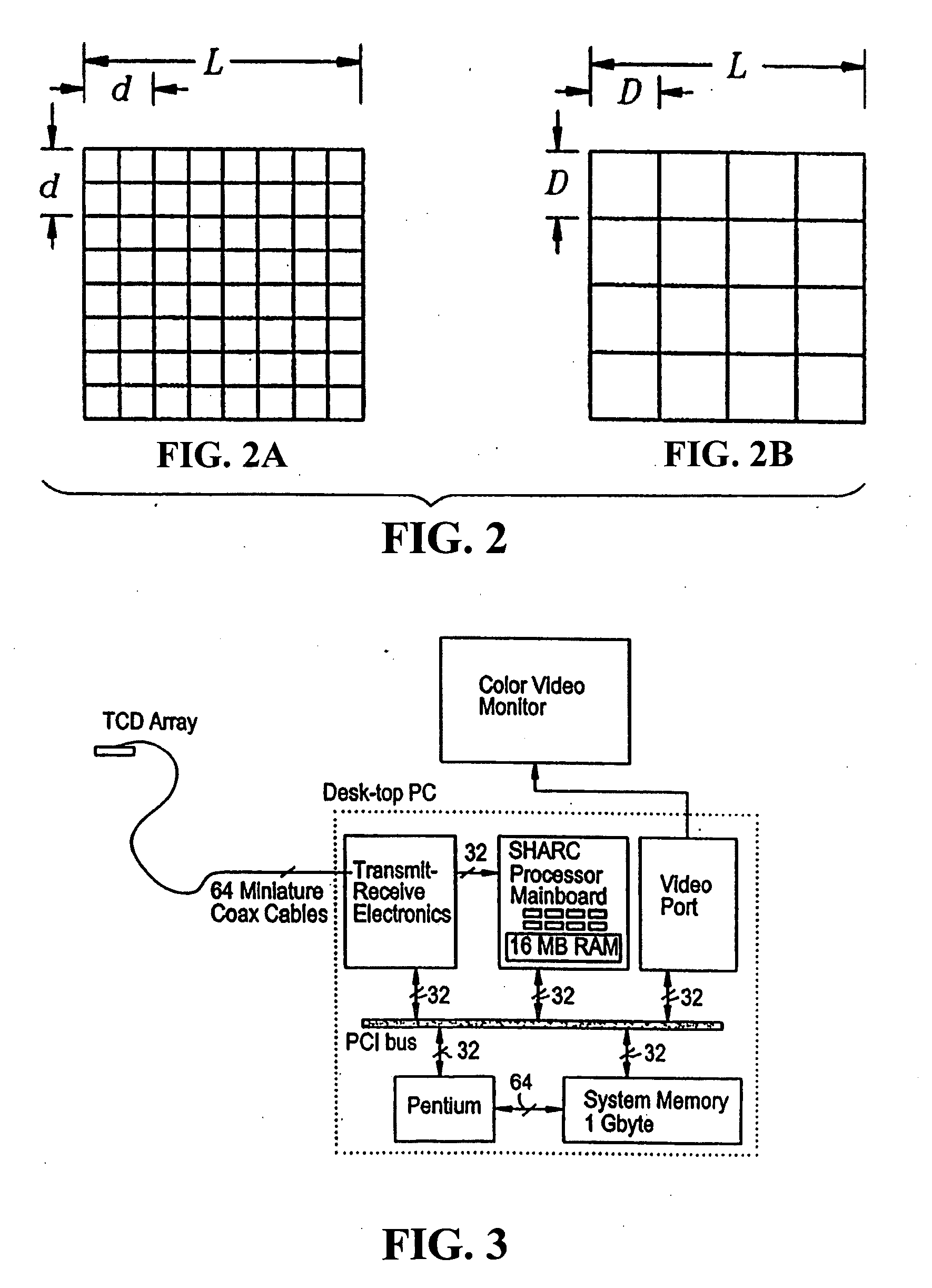
Provided herein is a method for use in medical applications that permits (1) affordable three-dimensional imaging of blood flow using a low-profile easily-attached transducer pad, (2) real-time blood-flow vector velocity, and (3) long-term unattended Doppler-ultrasound monitoring in spite of motion of the patient or pad. The pad and associated processor collects and Doppler processes ultrasound blood velocity data in a three dimensional region through the use of a planar phased array of piezoelectric elements. The invention locks onto and tracks the points in three-dimensional space that produce the locally maximum blood velocity signals. The integrated coordinates of points acquired by the accurate tracking process is used to form a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and provide a display that can be used to select multiple points of interest for expanded data collection and for long term continuous and unattended blood flow monitoring. The three dimensional map allows for the calculation of vector velocity from measured radial Doppler.A thinned array (greater than half-wavelength element spacing of the transducer array) is used to make a device of the present invention inexpensive and allow the pad to have a low profile (fewer connecting cables for a given spatial resolution). The full aperture is used for transmit and receive so that there is no loss of sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) or dynamic range. Utilizing more elements (extending the physical array) without increasing the number of active elements increases the angular field of view. A further increase is obtained by utilizing a convex non-planar surface.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
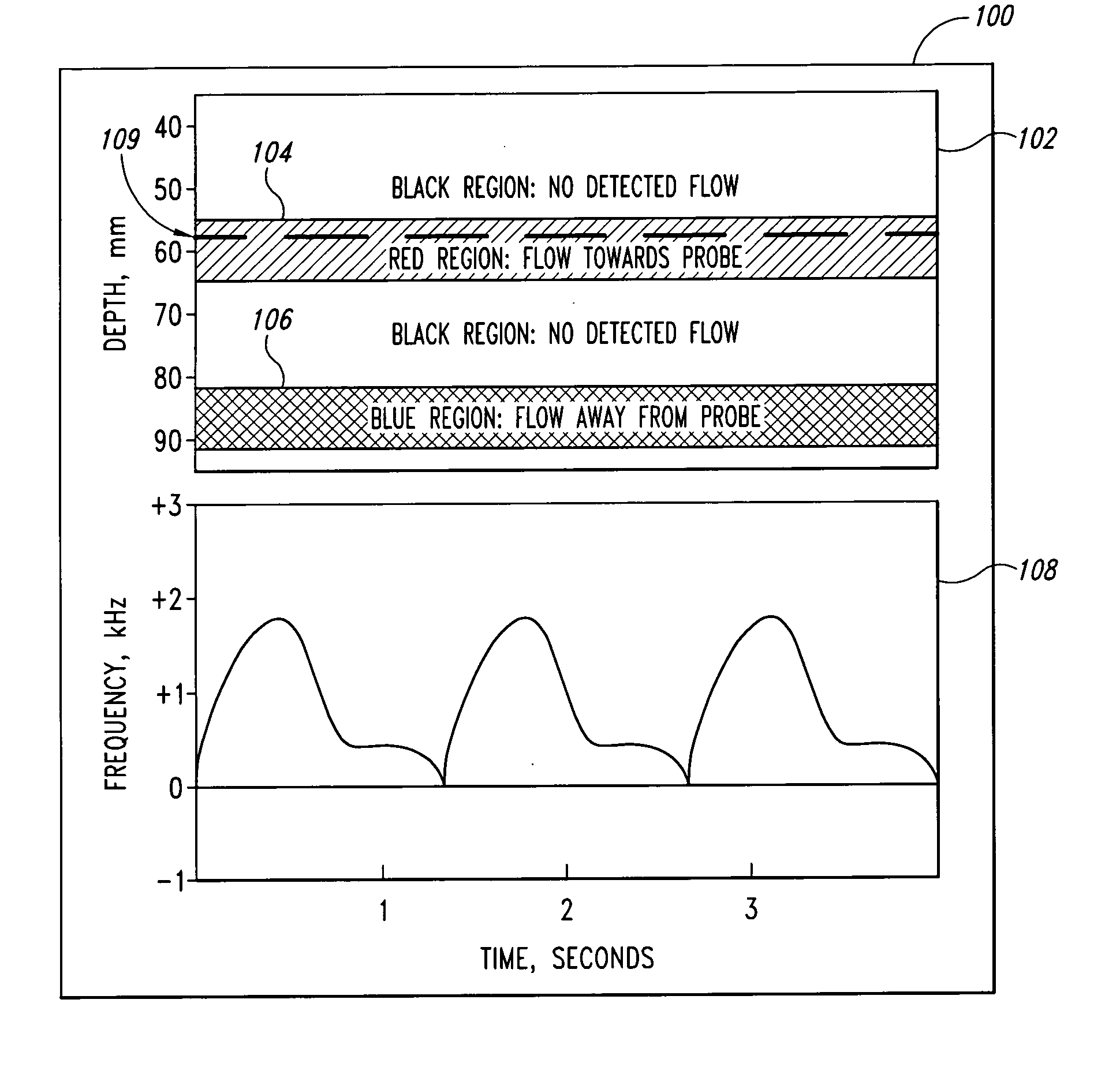
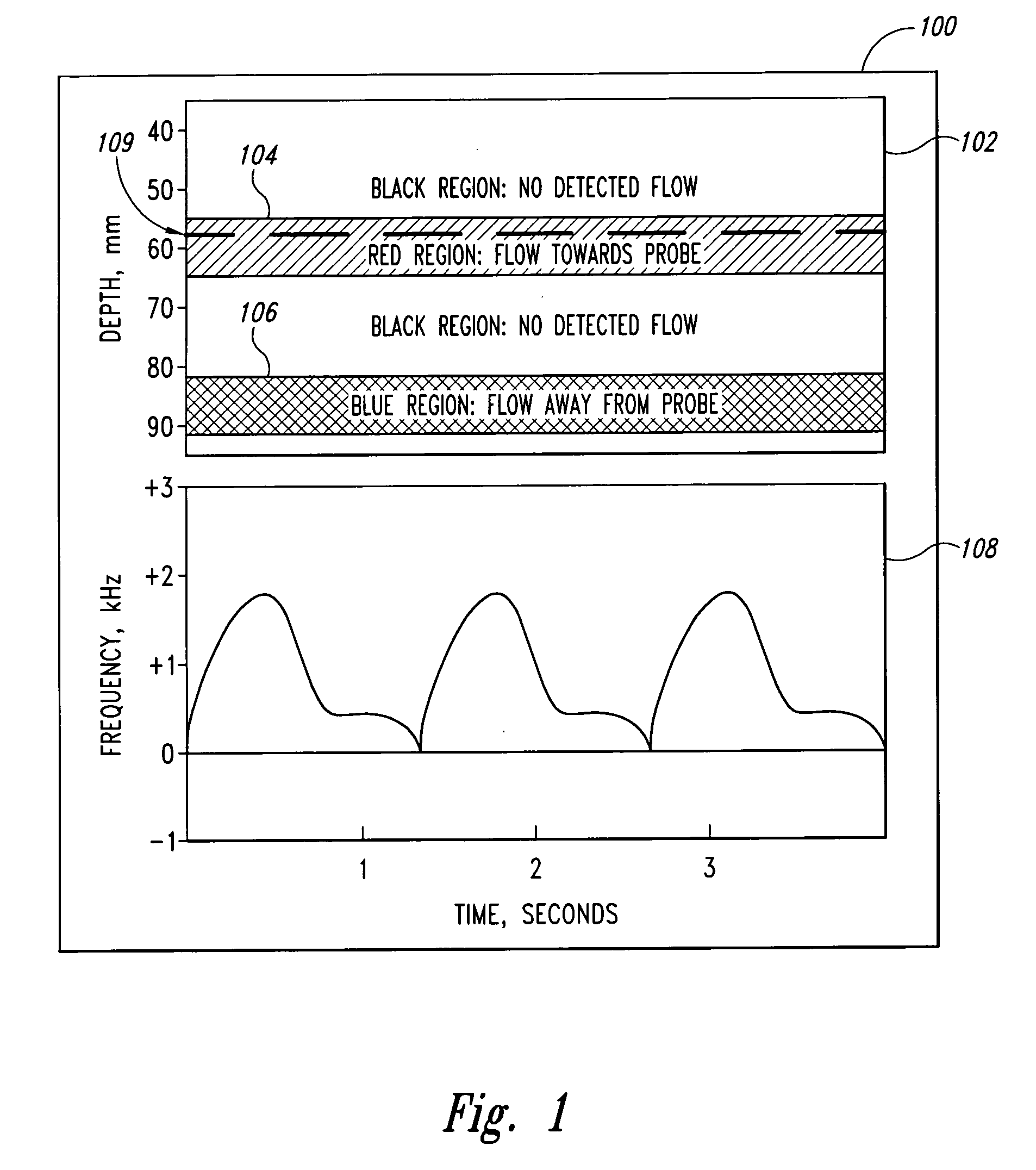
Doppler ultrasound method and apparatus for monitoring blood flow
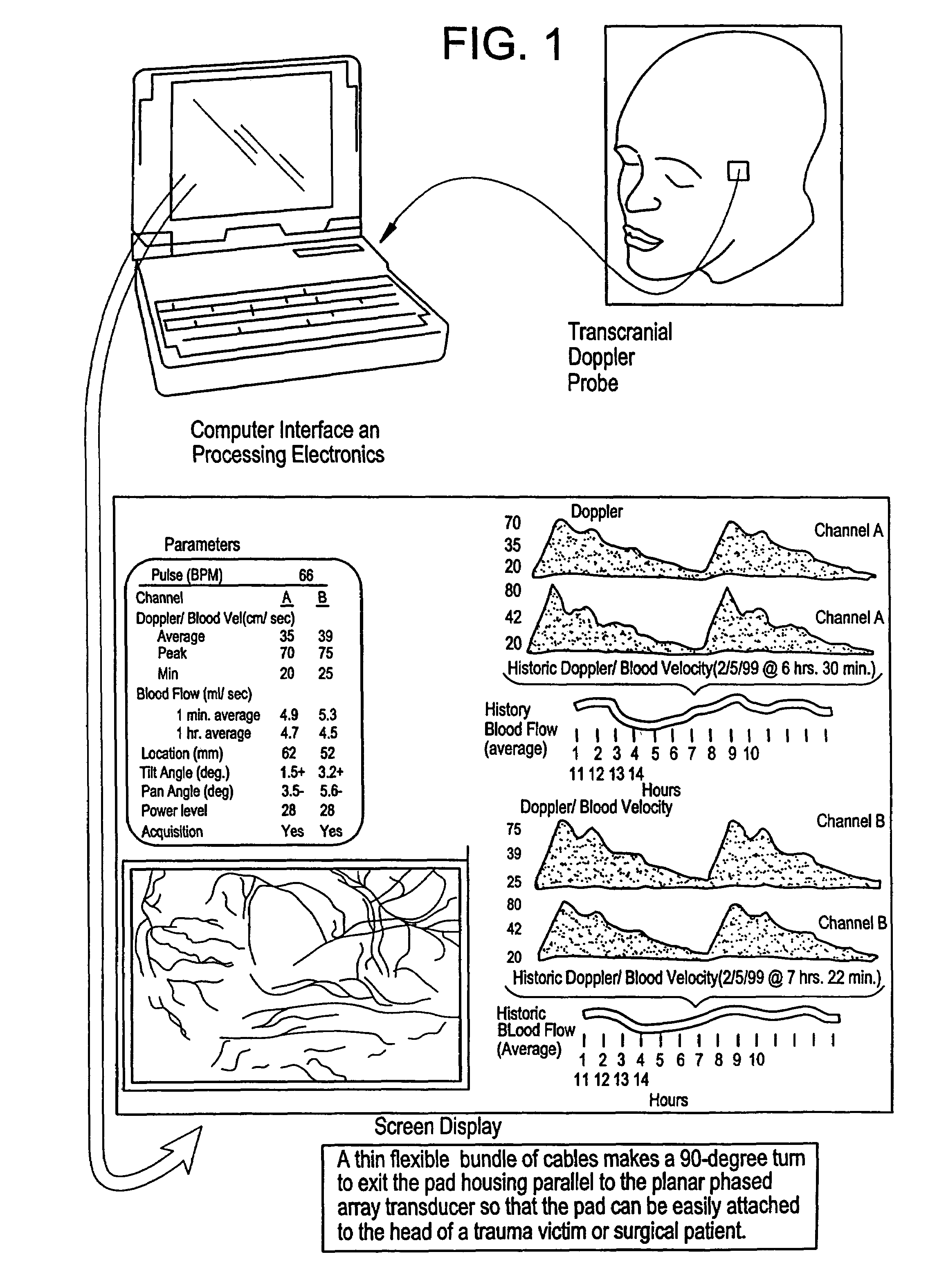
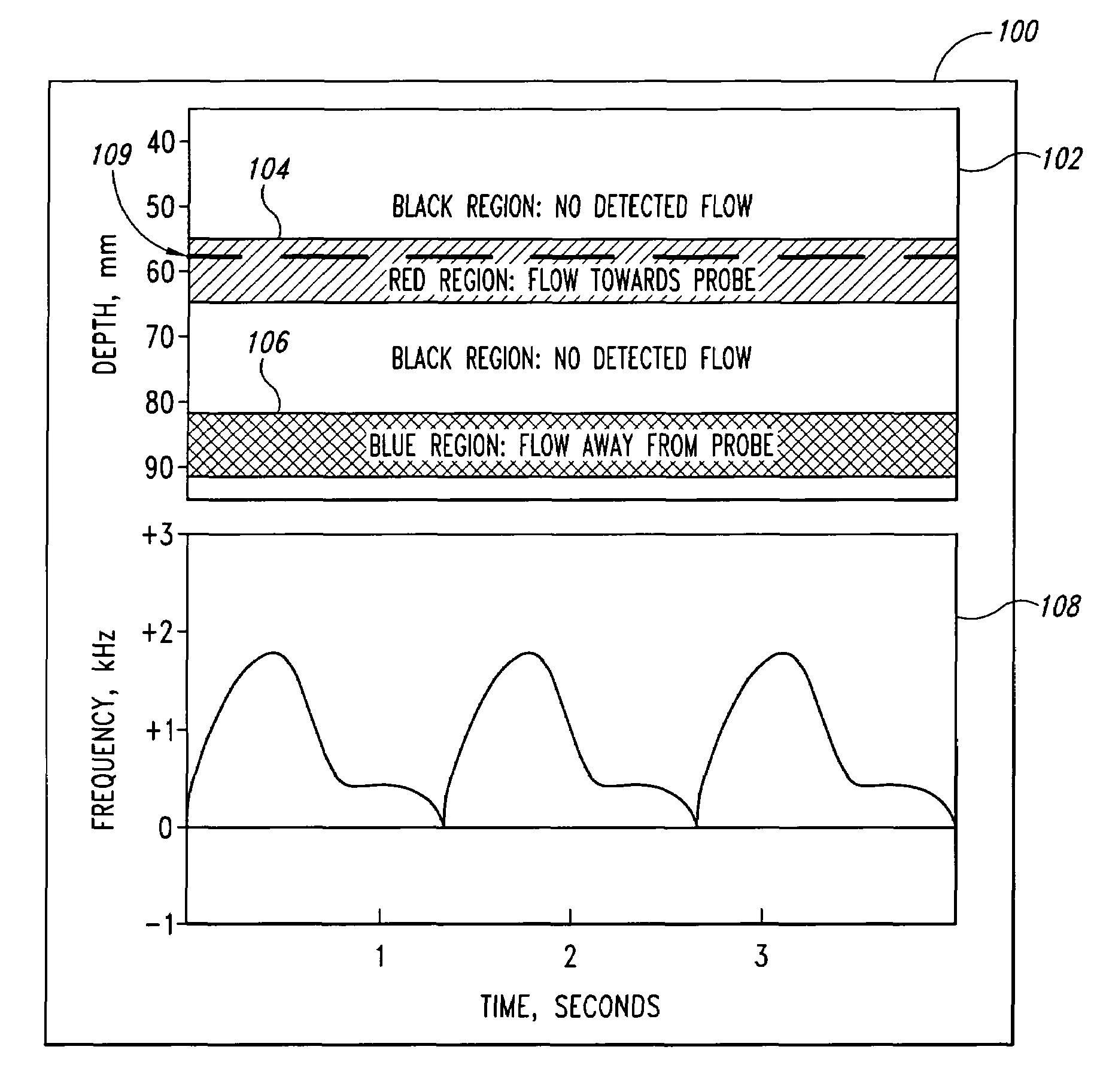
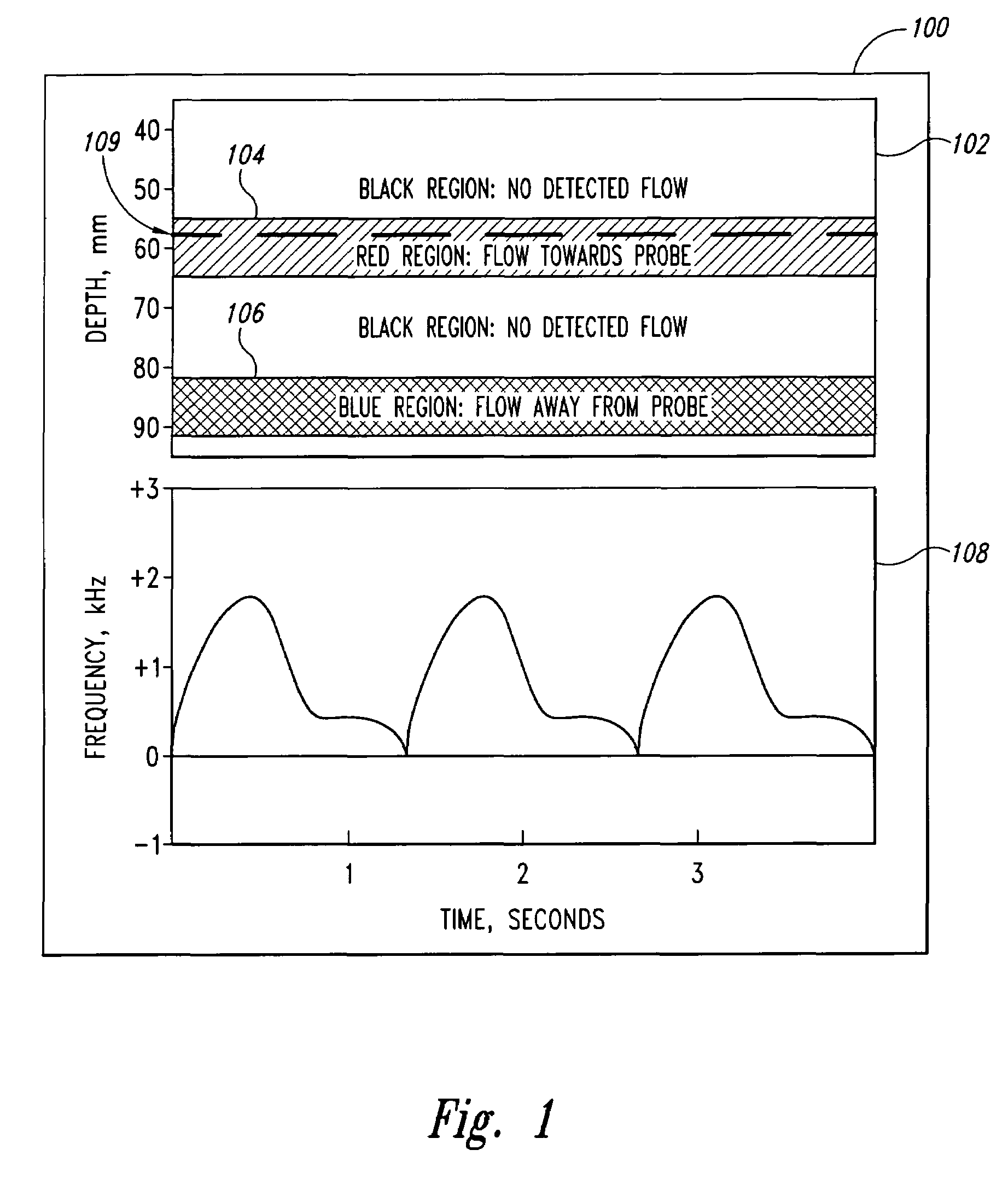
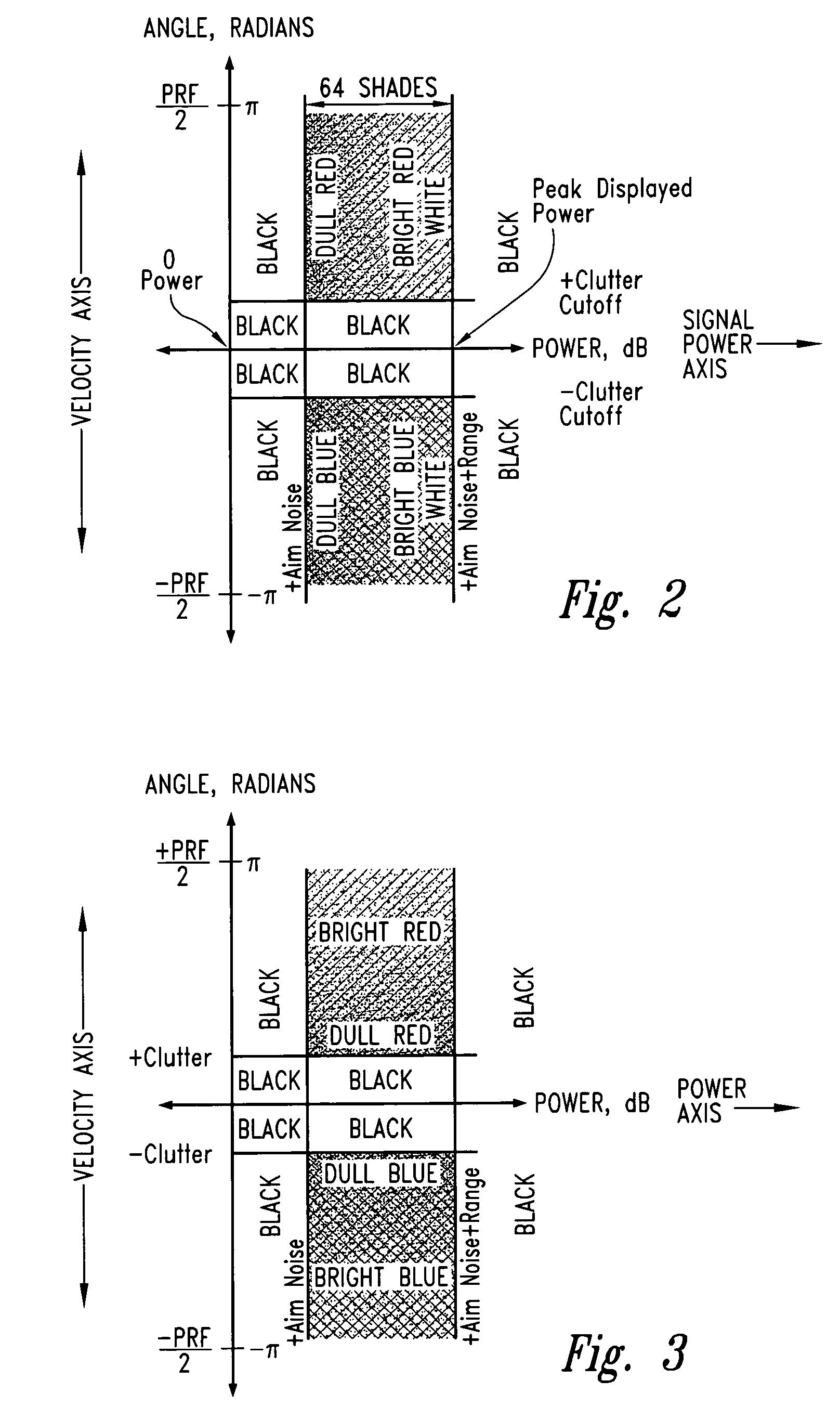
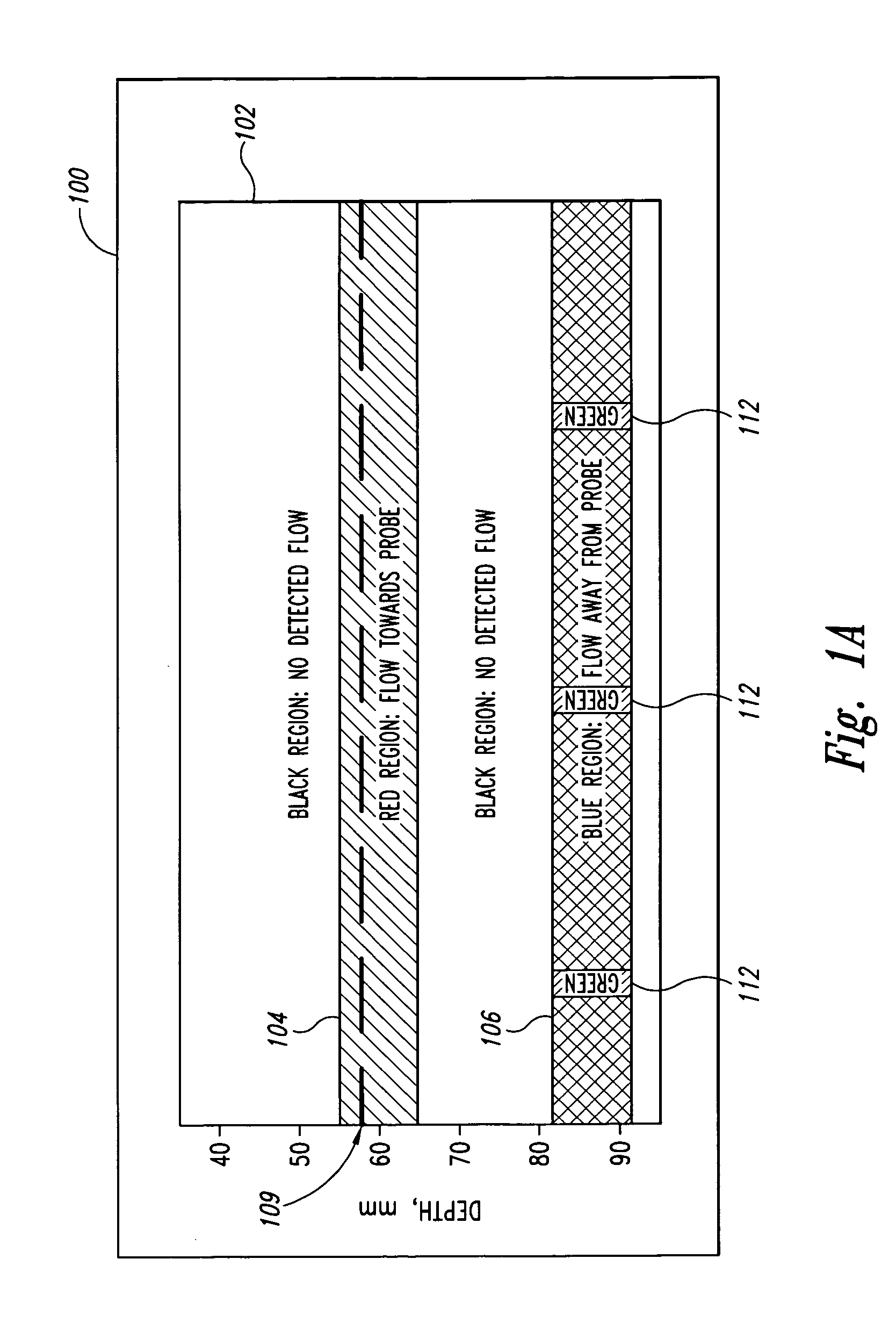
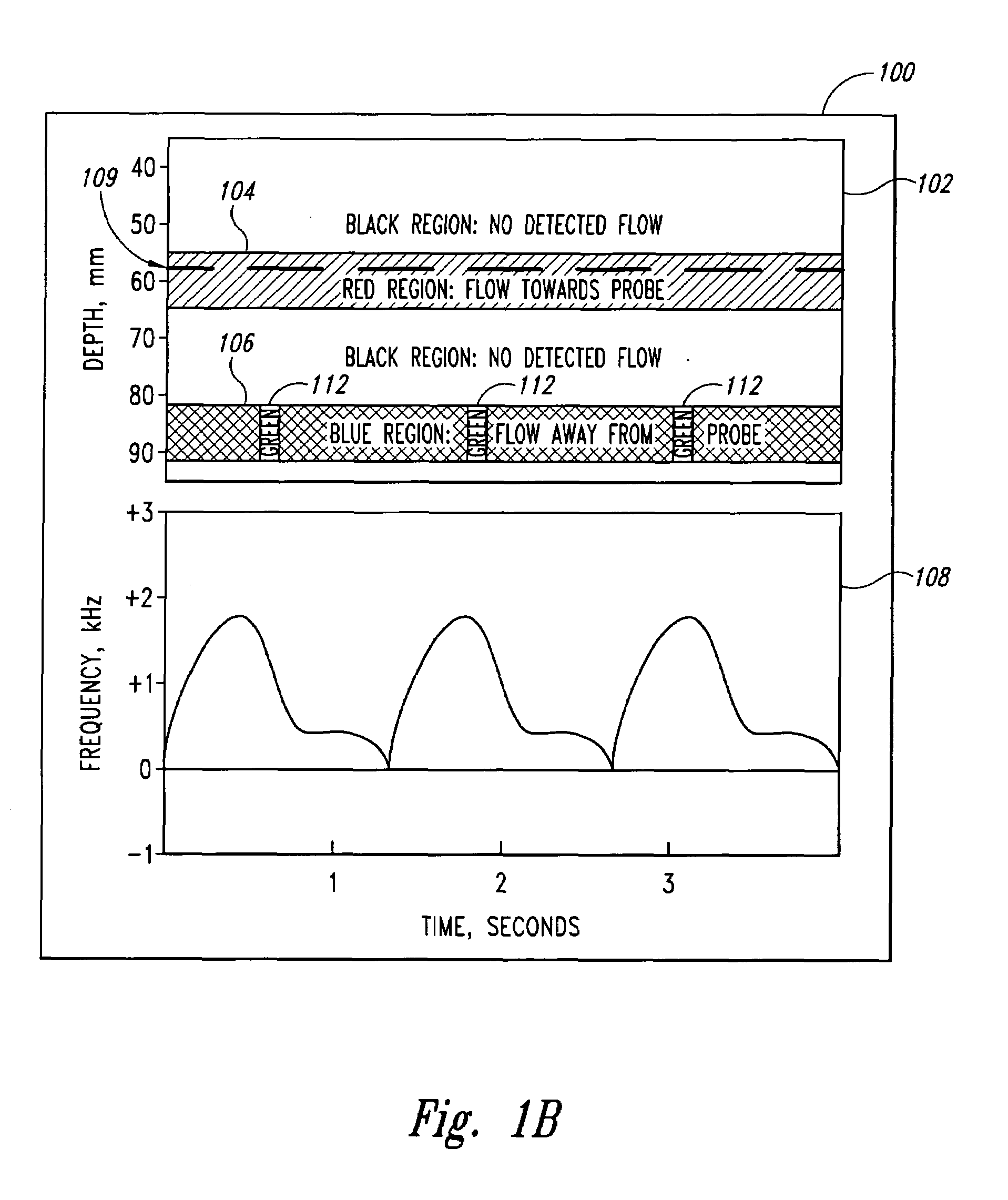
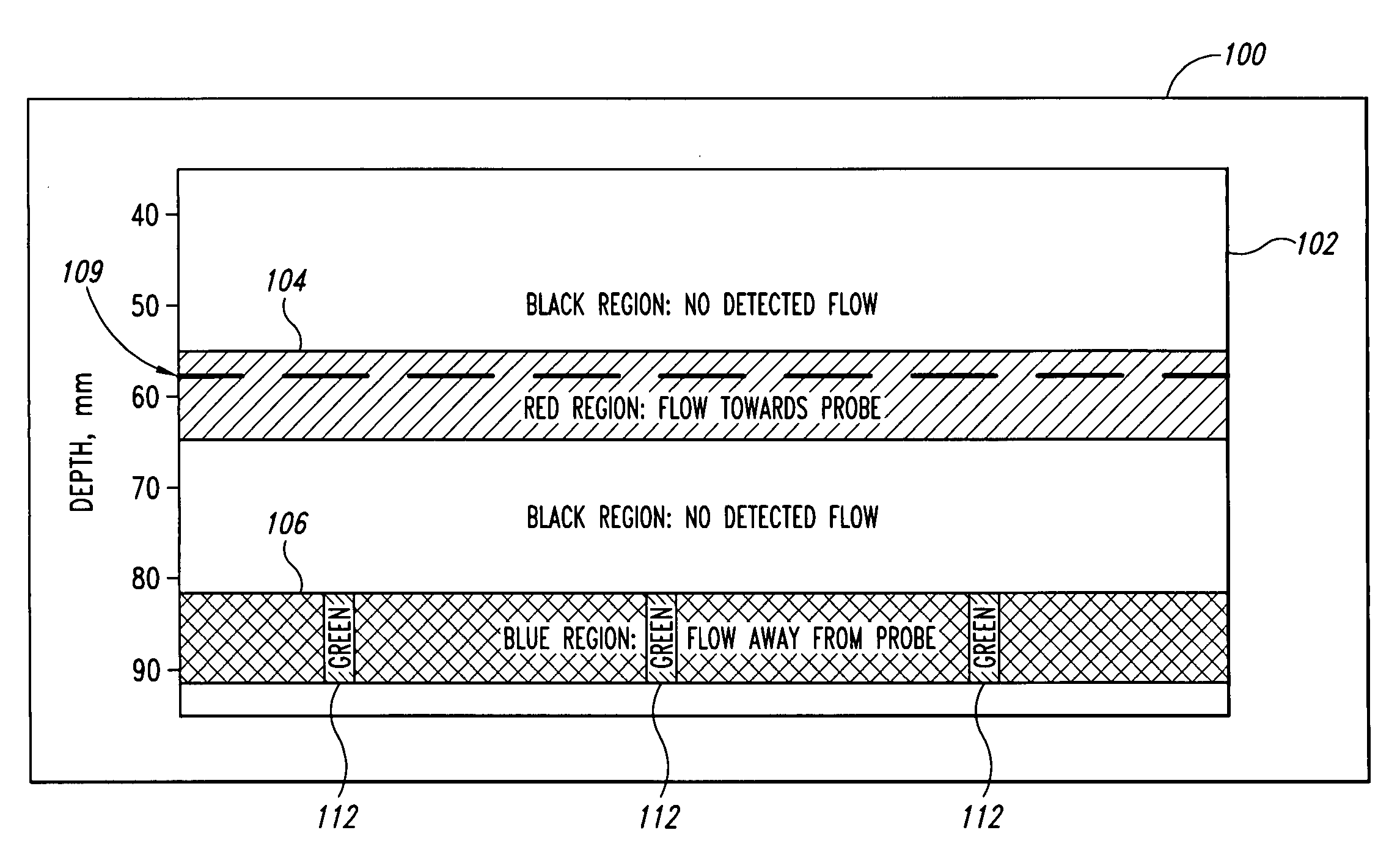
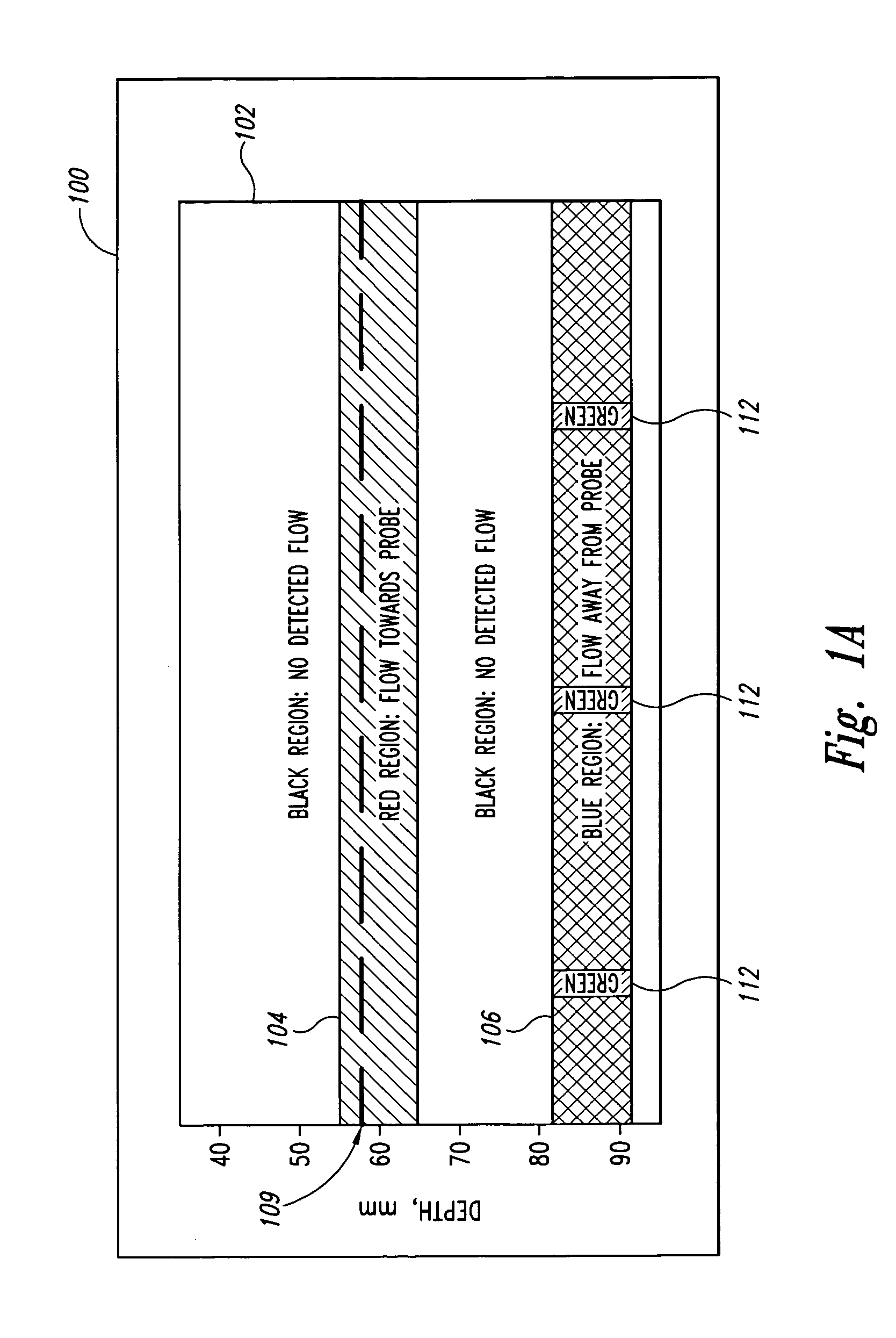
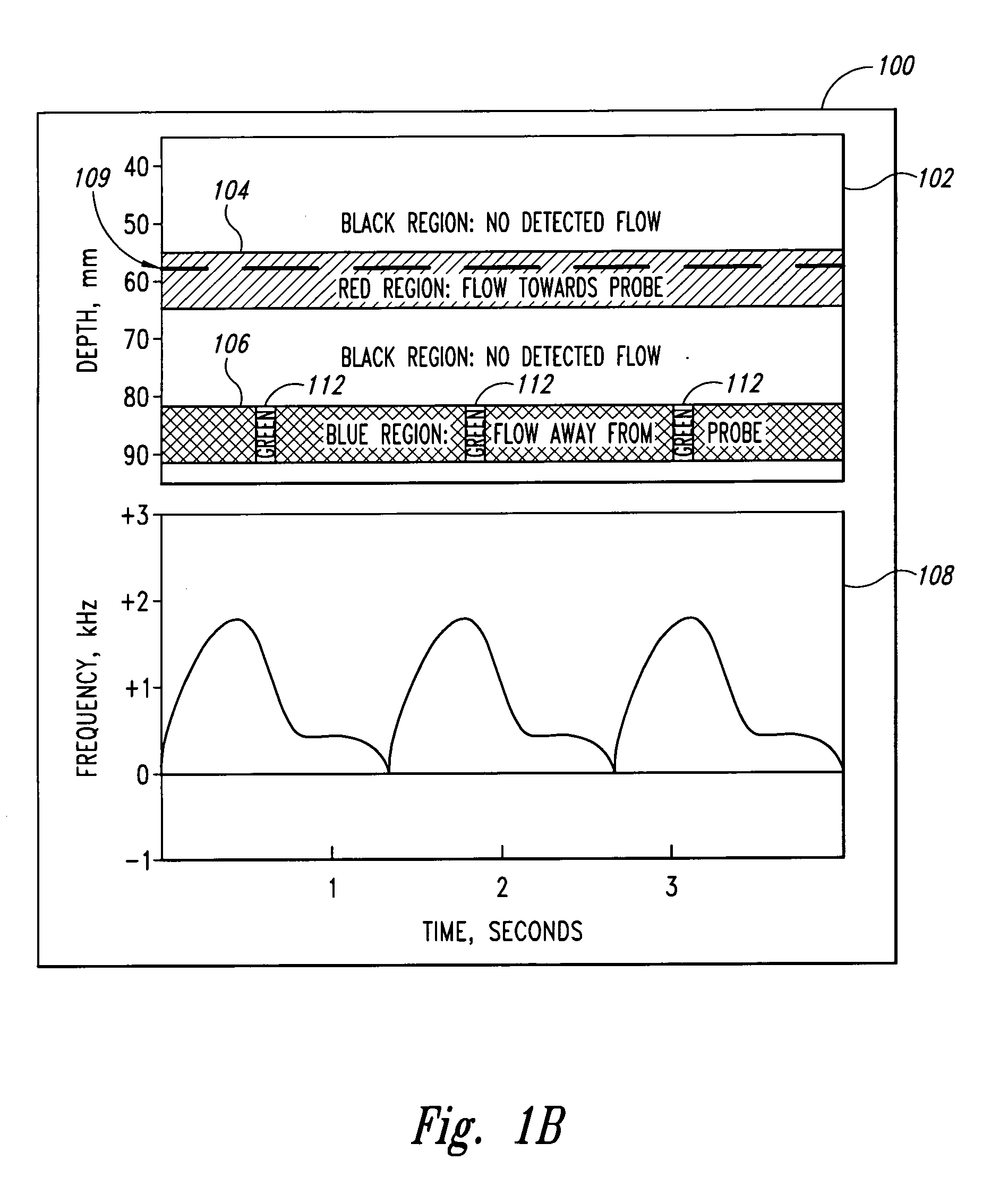
A pulse Doppler ultrasound system and associated methods are described for monitoring blood flow. A graphical information display includes simultaneously displayed depth-mode and spectrogram displays. The depth-mode display indicates the various positions along the ultrasound beam axis at which blood flow is detected. These positions are indicated as one or more colored regions, with the color indicating direction of blood flow and varying in intensity as a function of detected Doppler ultrasound signal amplitude or detected blood flow velocity. The depth-mode display also includes a pointer whose position may be selected by a user. The spectrogram displayed corresponds to the location identified by the pointer. Embolus detection and characterization are also provided.
Owner:SPENTECH
System and method for grading microemboli monitored by a multi-gate doppler ultrasound system
InactiveUS7771358B2Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSignal classificationPlasma viscosity
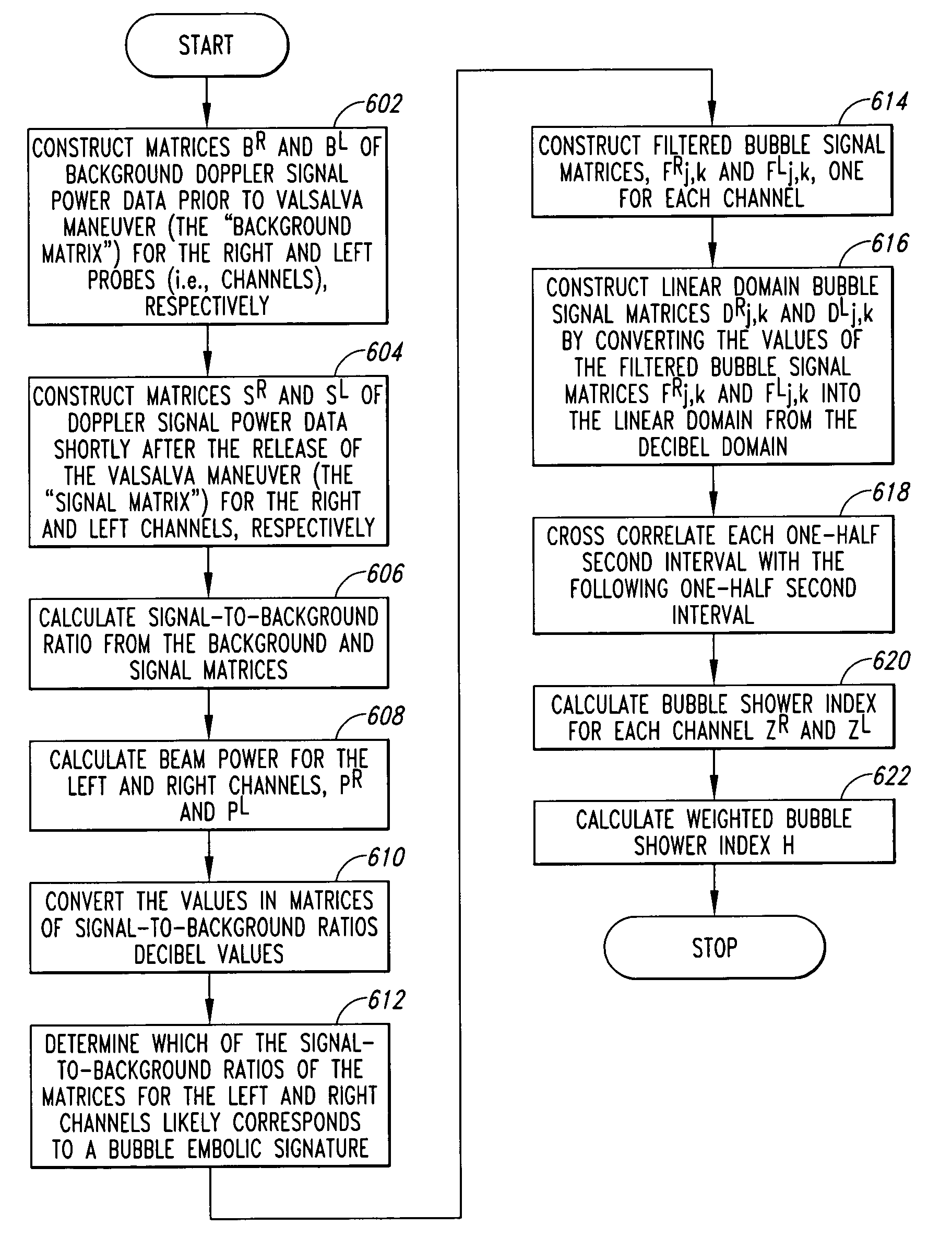
Systems and methods for grading signals from microemboli in blood flow monitored using a Doppler ultrasound system. Signals from microemboli in blood flow are graded by calculating a value related to a power for the signals from microemboli in blood flow and categorizing the signals into one of at least two grades based on the calculated value. Alternatively, signals can be categorized by assessing a power value for the microemboli in blood flow during a period of monitoring. In response to the power value being greater than or equal to a threshold value, the microemboli in blood flow are categorized based on the power value, and in response to the power value being less than the threshold value, a number of microemboli are counted during at least a portion of the period of monitoring and the microemboli are categorized based on the number.
Owner:SPENTECH
Emboli detection in the brain using a transcranial doppler photoacoustic device capable of vasculature and perfusion measurement
InactiveUS20140194740A1Rapid determinationQuick classificationBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionBrain vasculatureTriage
A device, method, and system for detecting emboli in the brain is disclosed. A transcranial Doppler photoacoustic device transmits a first energy to a region of interest at an internal site of a subject to produce an image and blood flow velocities of a region of interest by outputting an optical excitation energy to said region of interest and heating said region, causing a transient thermoelastic expansion and produce a wideband ultrasonic emission. Detectors receive the wideband ultrasonic emission and then generate an image of said region of interest from said wideband ultrasonic emission. A Doppler ultrasound signal will also be deployed to image the region of interest. Doppler presents changes in velocity to map blood flow. Additionally, a dye can be given to visualize the brain vasculature and a perfusion measurement can be made in various regions of the brain along with the transcranial Doppler and the photoacoustic screening. Systems are taught using resultory medical data for better triage within an enhanced stroke ecosystem.
Owner:CEREBROSONICS L L C
Device and method for mapping and tracking blood flow and determining parameters of blood flow
InactiveUS7534209B2Small sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationDisplay device
Provided herein is a method for use in medical applications that permits affordable three-dimensional imaging of blood flow using a low-profile easily-attached transducer pad, real-time blood-flow vector velocity, and long-term unattended Doppler-ultrasound monitoring in spite of motion of the patient or pad. The pad and associated processor collects and Doppler processes ultrasound blood velocity data in a three dimensional region through the use of a planar phased array of piezoelectric elements. The invention locks onto and tracks the points in three-dimensional space that produce the locally maximum blood velocity signals. The integrated coordinates of points acquired by the accurate tracking process is used to form a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and provide a display that can be used to select multiple points of interest for expanded data collection and for long term continuous and unattended blood flow monitoring. The three dimensional map allows for the calculation of vector velocity from measured radial Doppler.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
System and method for grading microemboli monitored by a multi-gate doppler ultrasound system
Systems and methods for grading signals from microemboli in blood flow monitored using a Doppler ultrasound system. Signals from microemboli in blood flow are graded by calculating a value related to a power for the signals from microemboli in blood flow and categorizing the signals into one of at least two grades based on the calculated value. Alternatively, signals can be categorized by assessing a power value for the microemboli in blood flow during a period of monitoring. In response to the power value being greater than or equal to a threshold value, the microemboli in blood flow are categorized based on the power value, and in response to the power value being less than the threshold value, a number of microemboli are counted during at least a portion of the period of monitoring and the microemboli are categorized based on the number.
Owner:SPENTECH
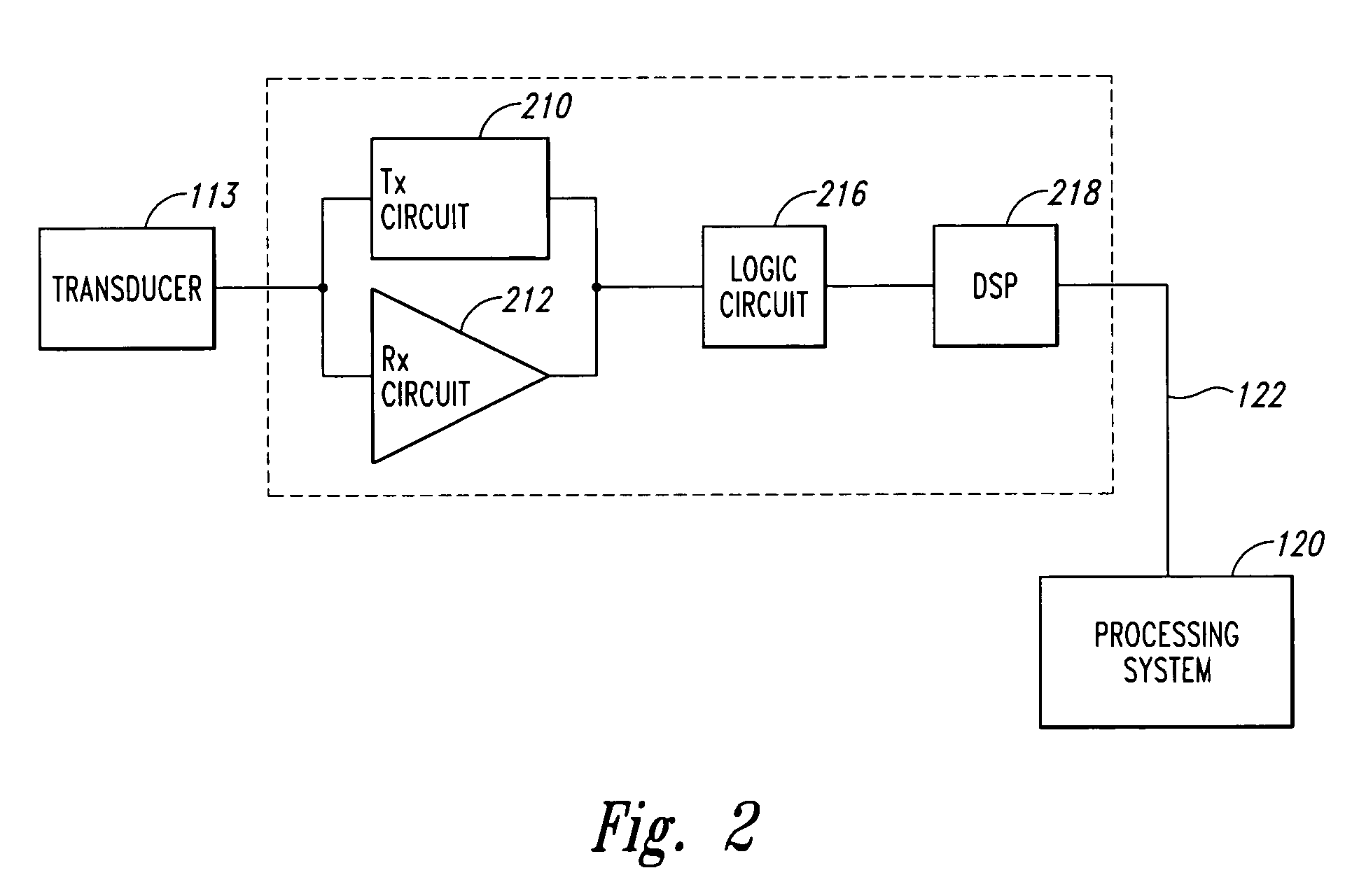
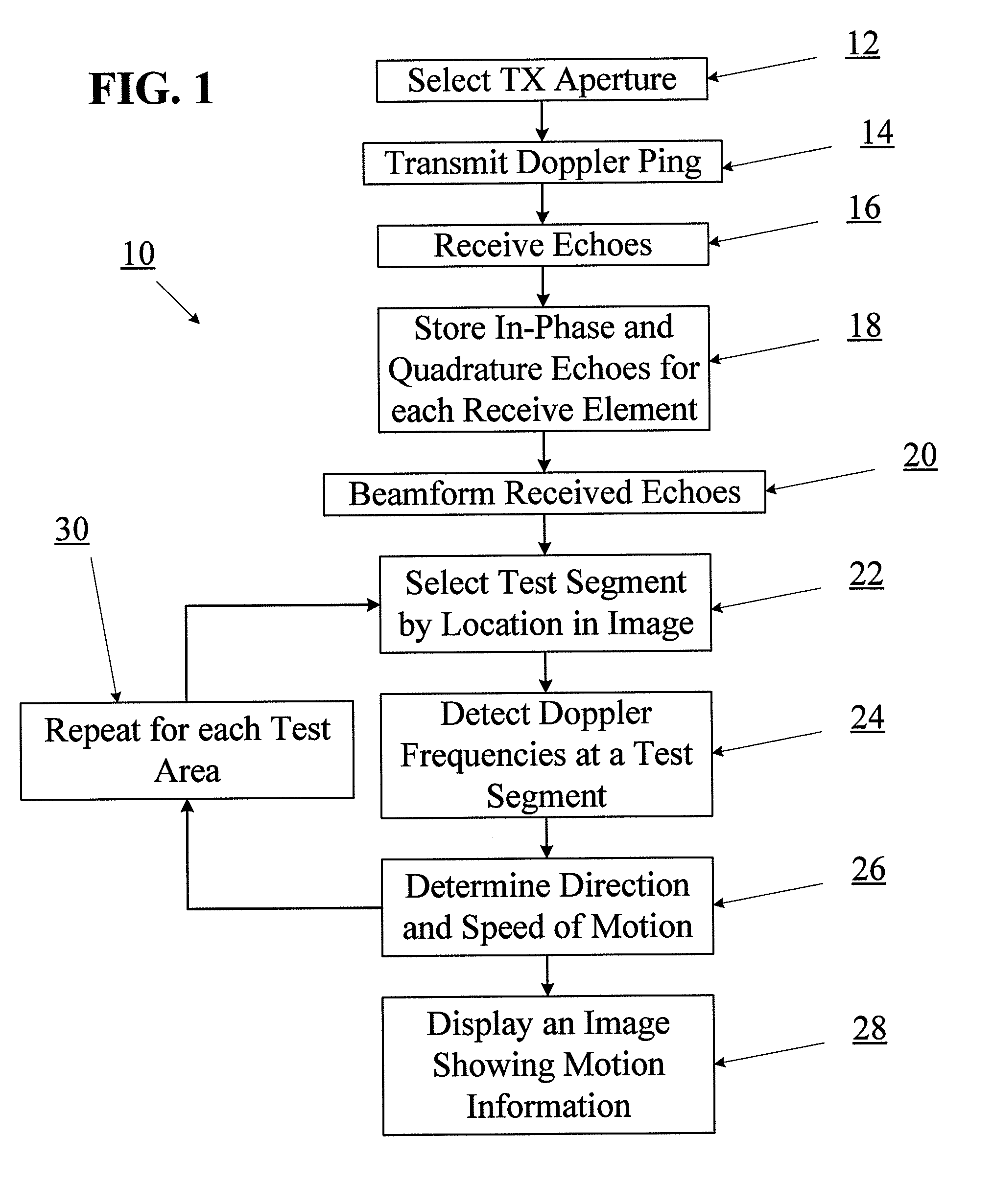
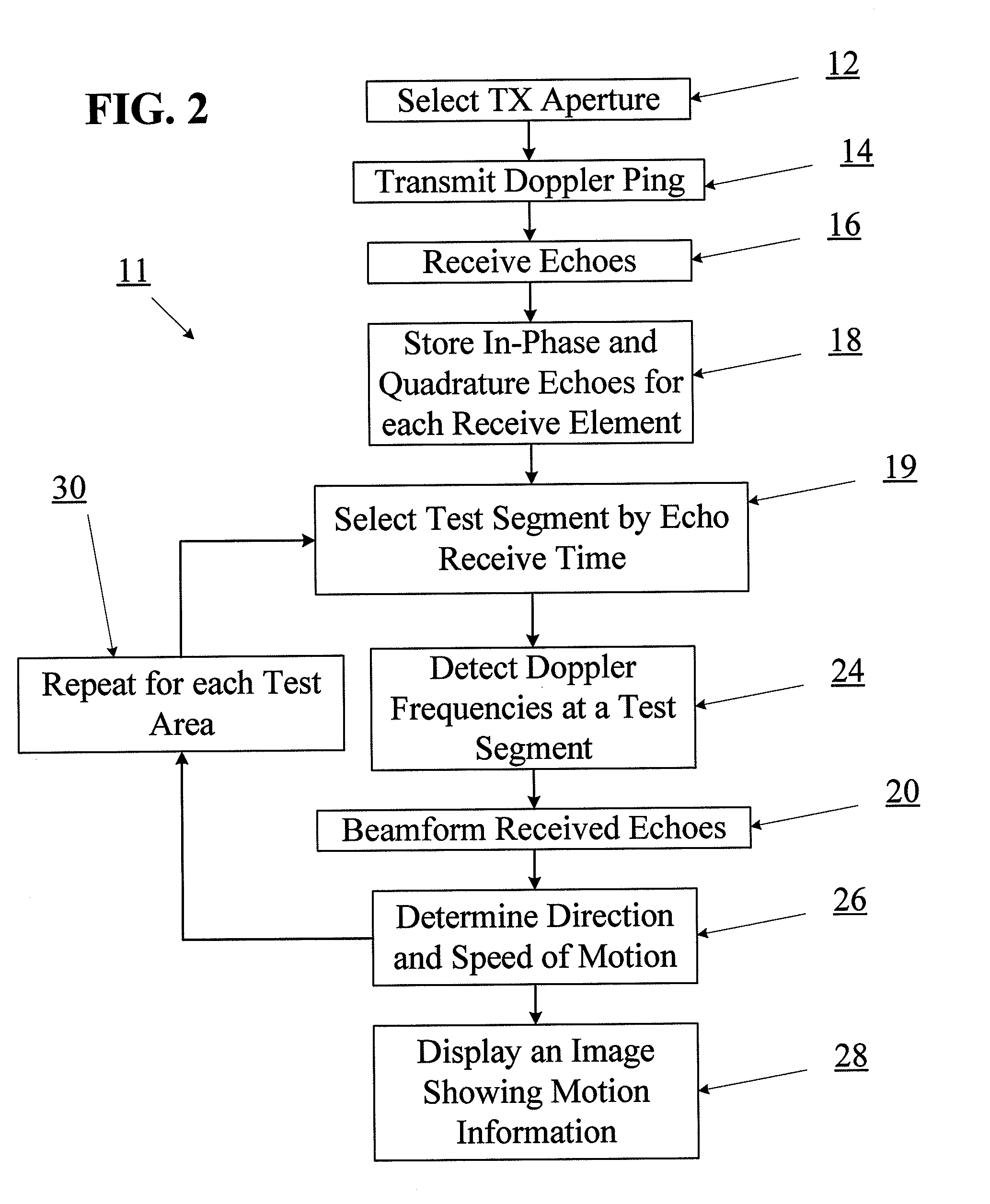
Motion detection using ping-based and multiple aperture doppler ultrasound
ActiveUS20130144166A1High resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDoppler Ultrasound ImagingSonification
A method of full-field or “ping-based” Doppler ultrasound imaging allows for detection of Doppler signals indicating moving reflectors at any point in an imaging field without the need to pre-define range gates. In various embodiments, such whole-field Doppler imaging methods may include transmitting a Doppler ping from a transmit aperture, receiving echoes of the Doppler ping with one or more separate receive apertures, detecting Doppler signals and determining the speed of moving reflectors. In some embodiments, the system also provides the ability to determine the direction of motion by solving a set of simultaneous equations based on echo data received by multiple receive apertures.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
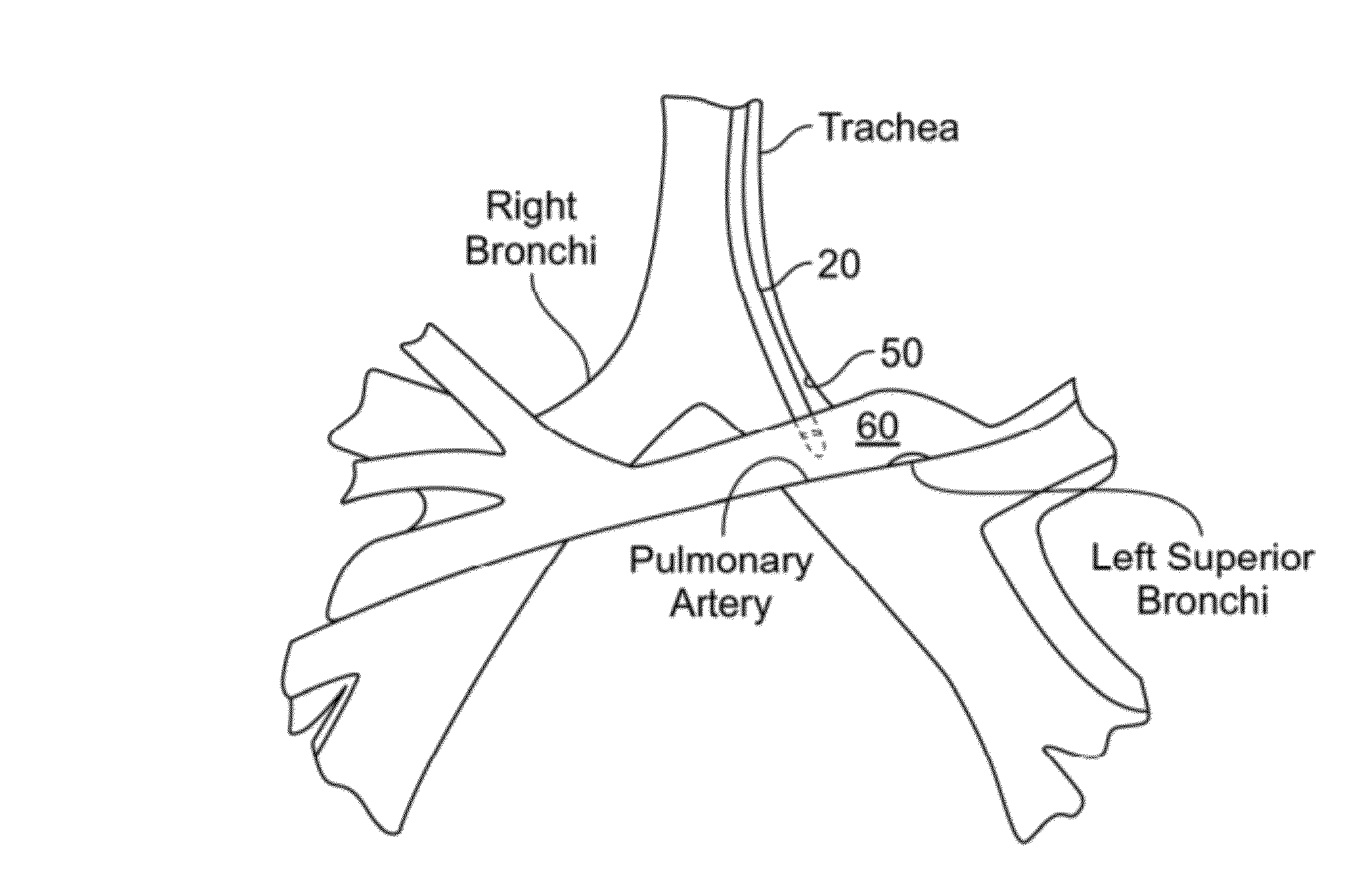
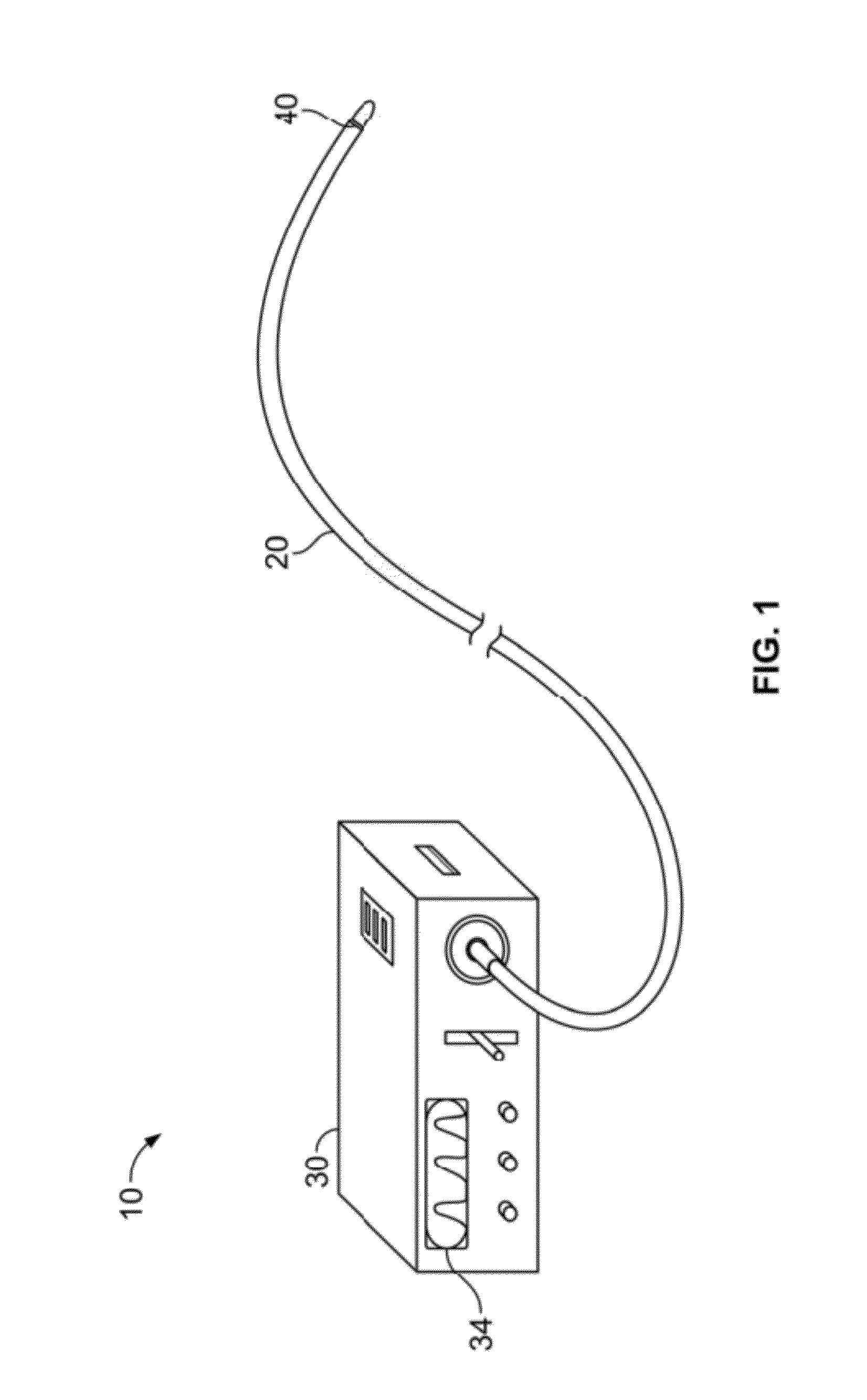
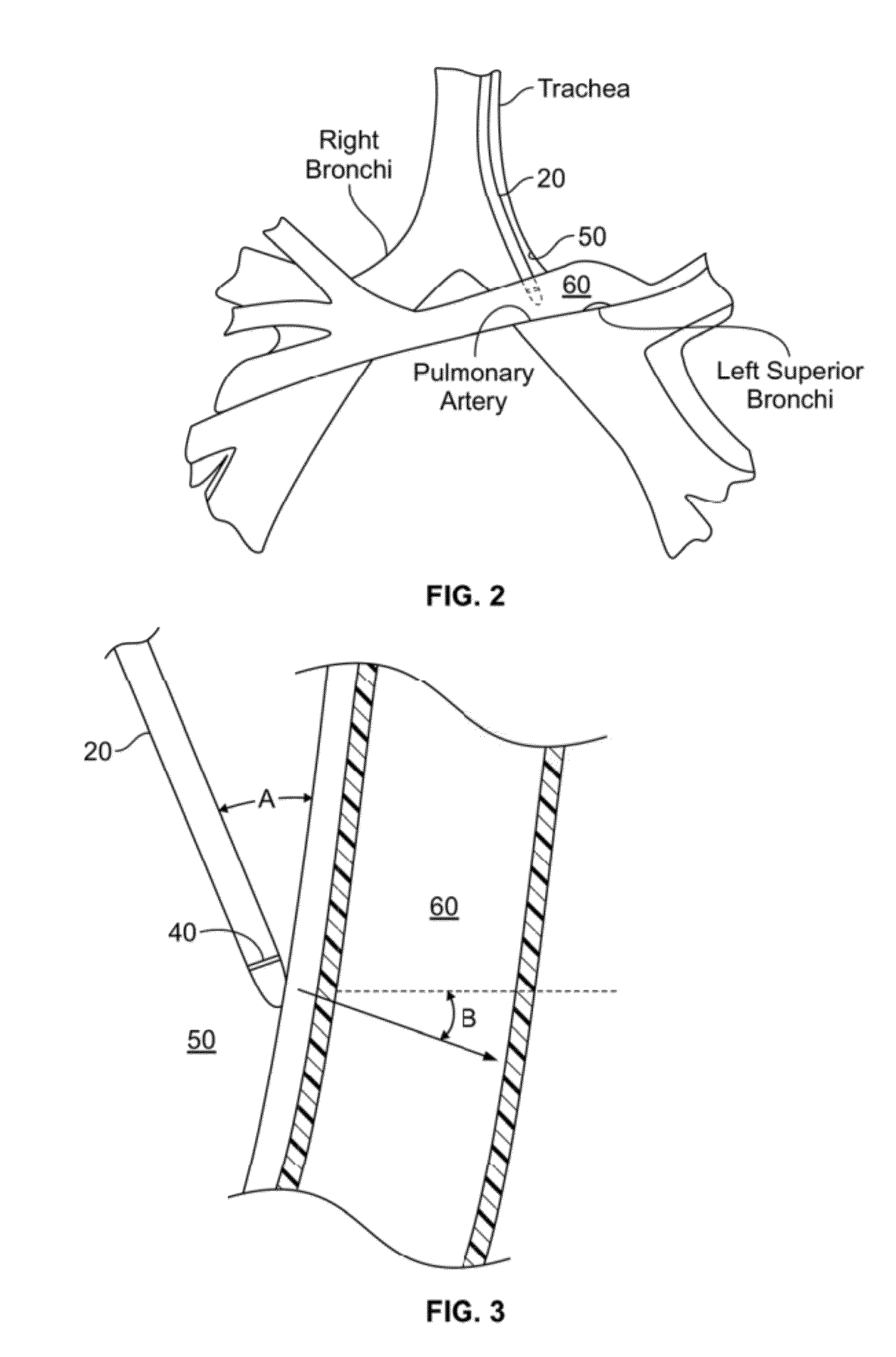
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
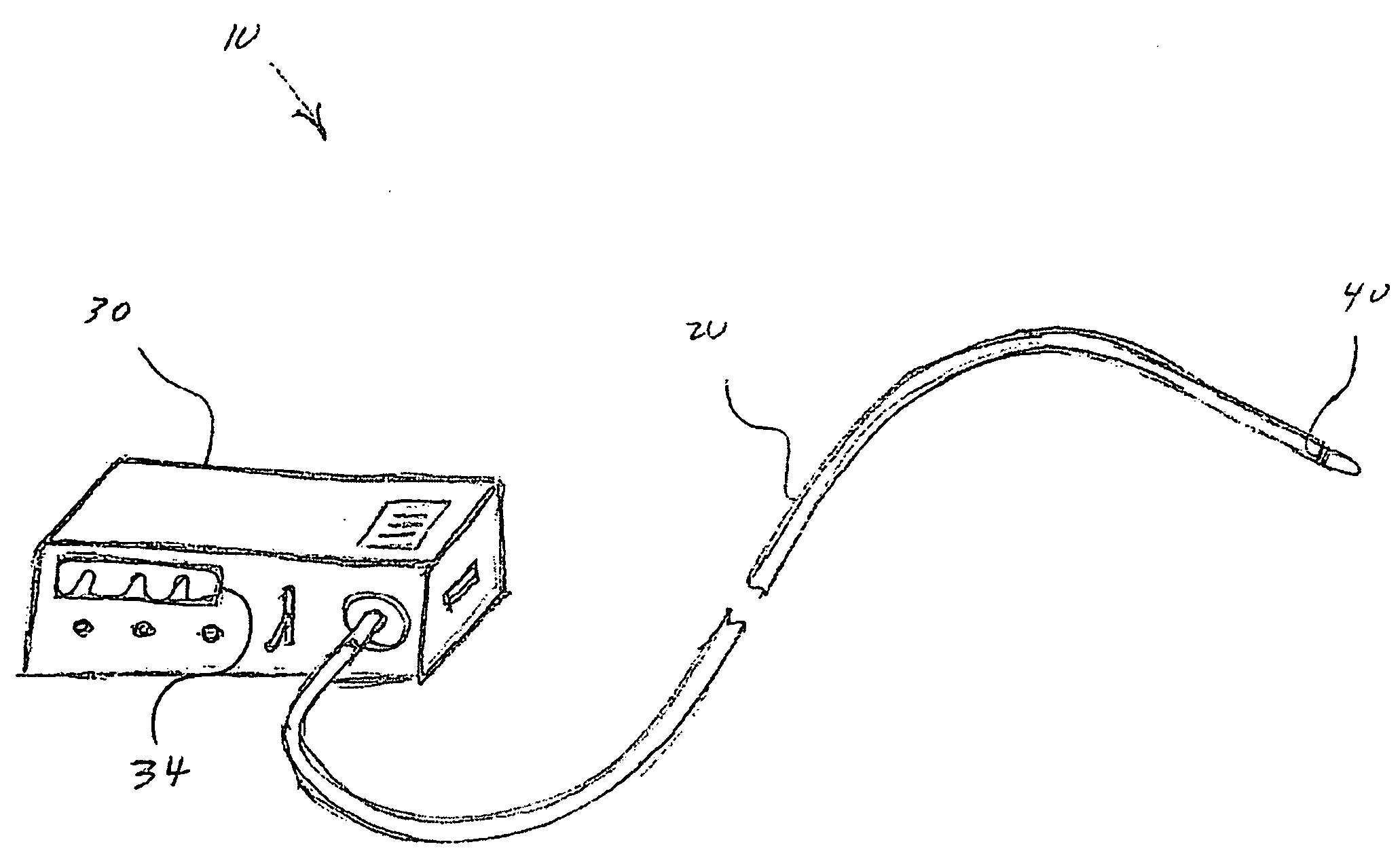
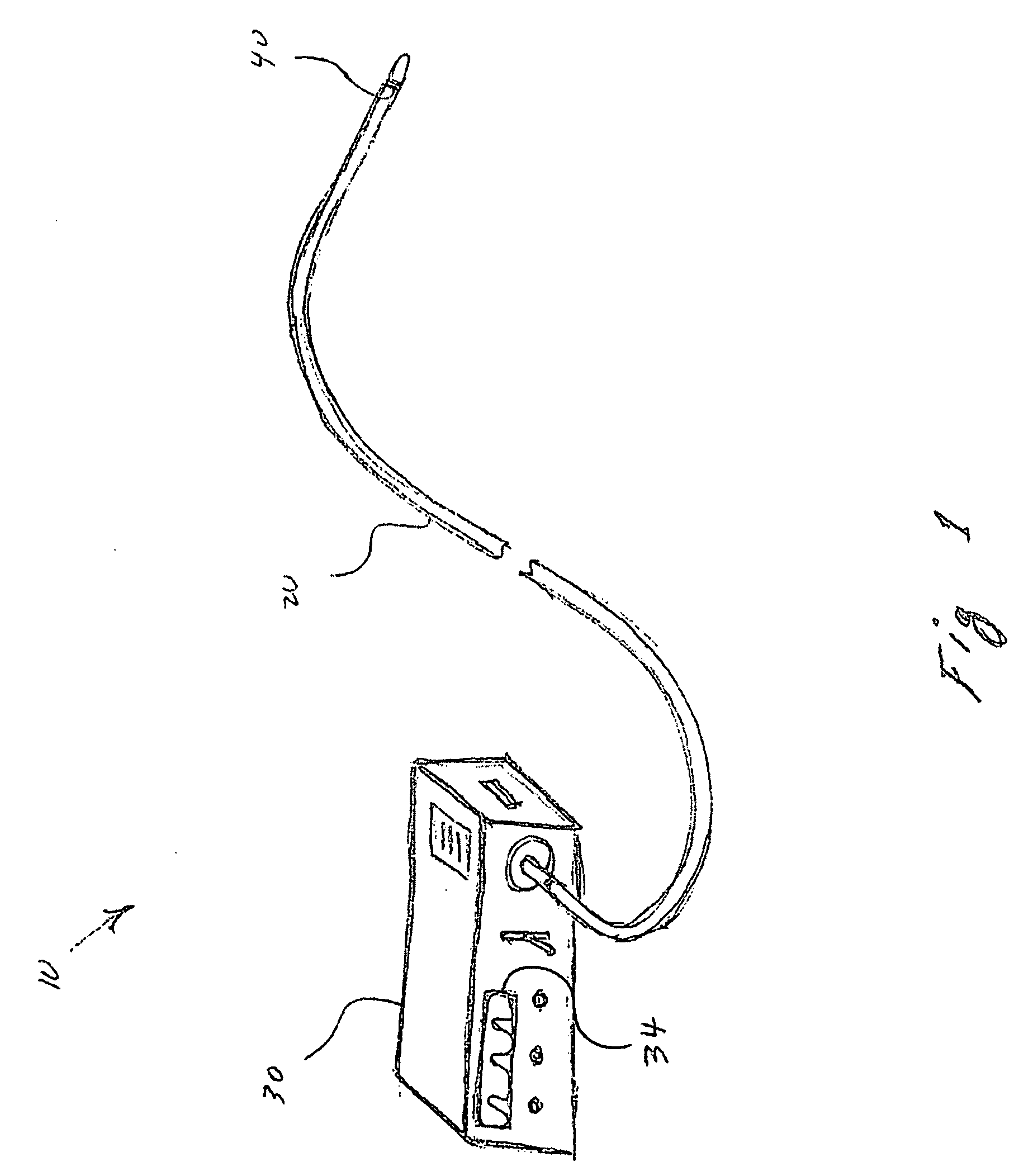
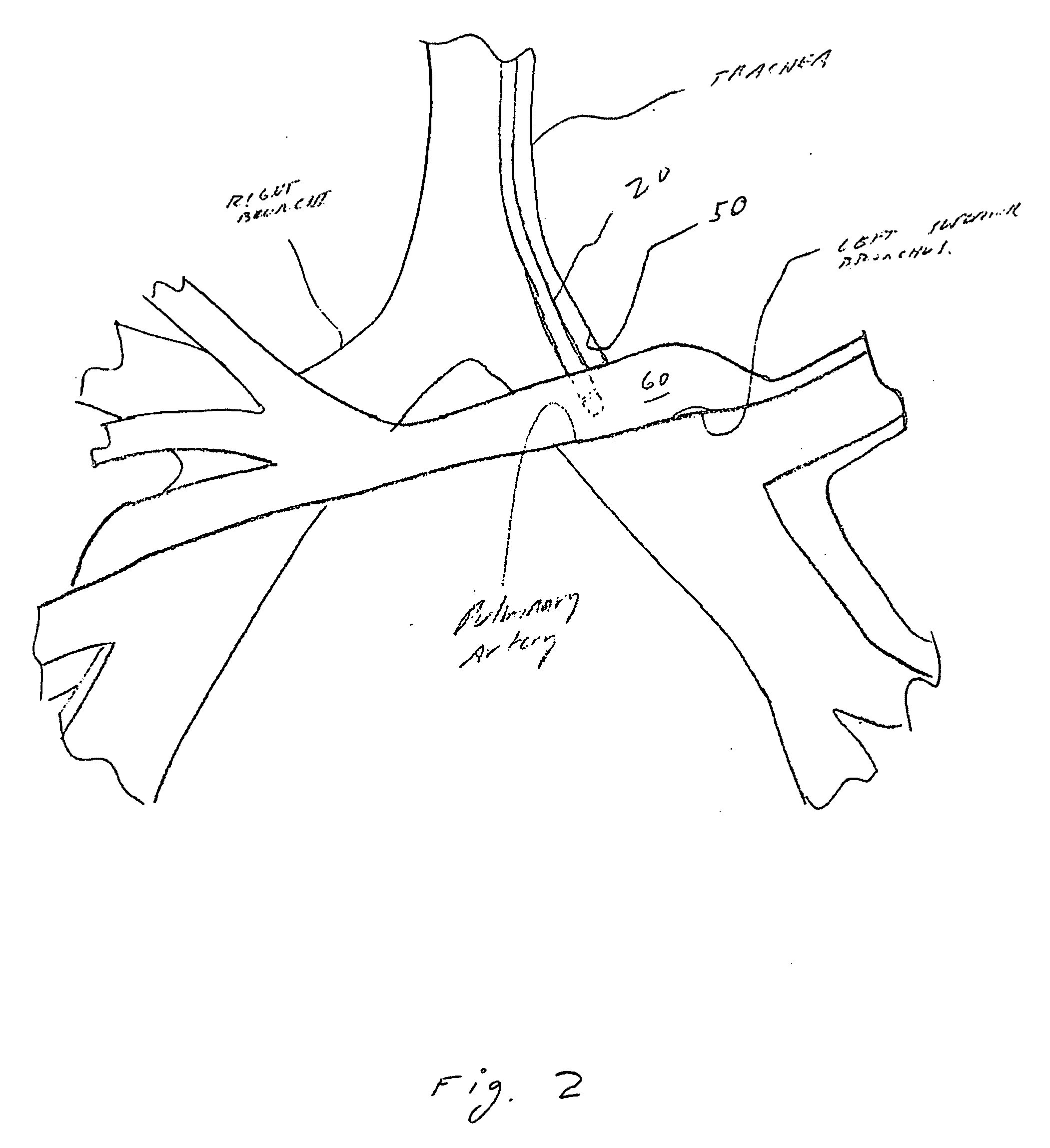
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Doppler ultrasound method and apparatus for monitoring blood flow and hemodynamics
InactiveUS7128713B2Blood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSonificationPulsed doppler
A pulse Doppler ultrasound system and associated methods are described for monitoring blood flow and hemodynamics. The Doppler ultrasound system includes an ultrasound probe to emit ultrasound signals and detect reflected signals therefrom and further includes a processor coupled to the ultrasound probe and operable to process the detected reflected signals and calculate therefrom blood flow data for a plurality of locations at time intervals, the processor further operable to identify locations at which blood flow having a hemodynamic characteristic is present based on the blood flow data calculated for a plurality of the time intervals. A user interface coupled to the processor provides blood flow information based on the blood flow data, the blood flow information representative of detected blood flow and the presence of the hemodynamic characteristic.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for automatic location of blood flow with Doppler ultrasound
InactiveUS7425198B2Improve actionUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic modalitiesSonification
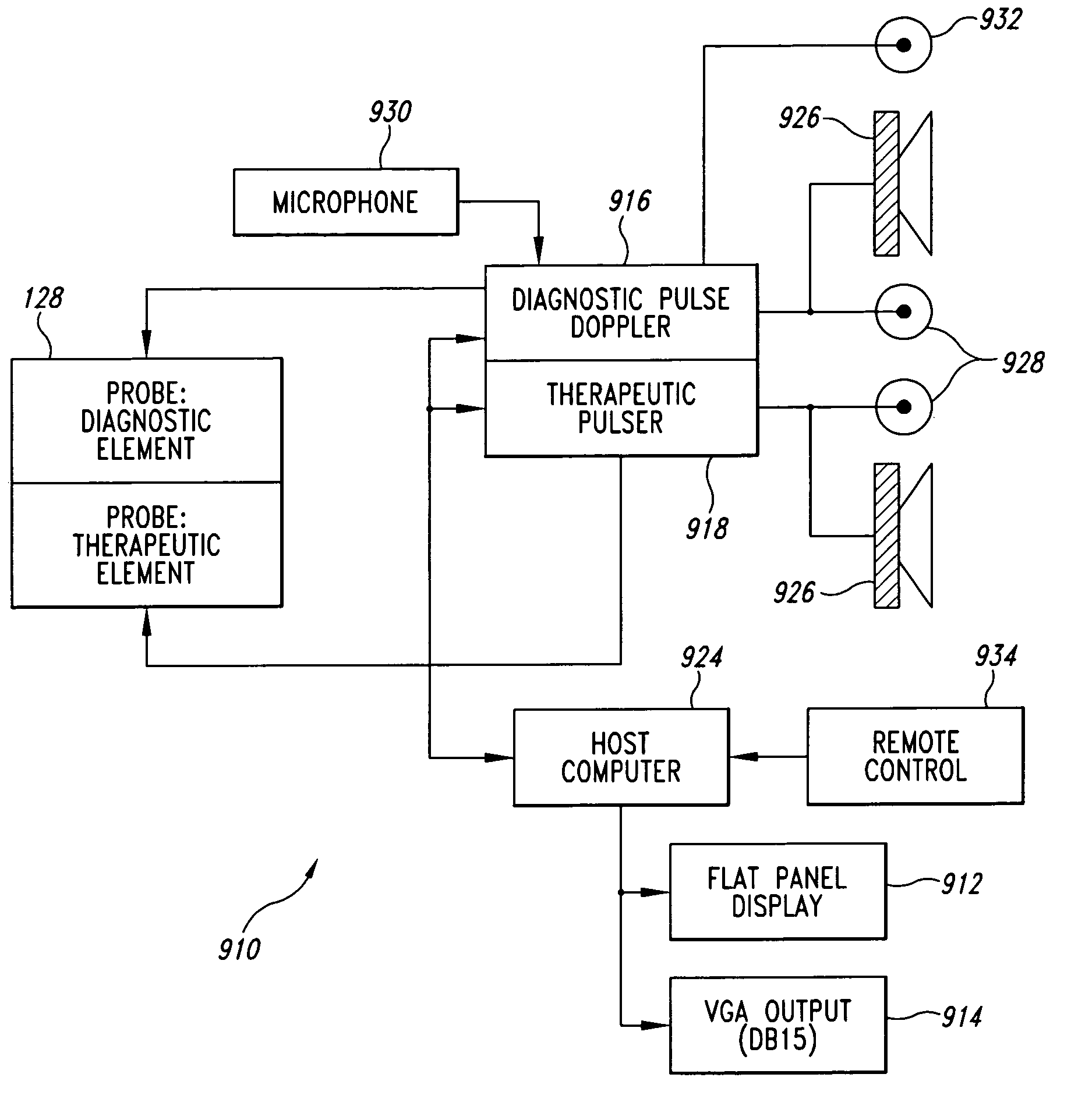
A method and apparatus for combining therapeutic pulsed or continuous-wave ultrasound with diagnostic pulsed ultrasound are described. In both a therapeutic mode and in a diagnostic mode, the ultrasound is administered from a single probe to a patient suffering from thrombosis. The ultrasound can have the same or different frequency ranges in the diagnostic and therapeutic modes. The pulsed or continuous-wave ultrasound in the therapeutic mode enhances a lysing effect of a thrombolytic agent. The pulsed ultrasound in the diagnostic mode allows monitoring of blood flow to locate a thrombus, to determine an optimal window to administer the therapeutic pulsed ultrasound, and to detect when recanalization has occurred. If an operator attends the device, a graphical display operates during the diagnostic mode to display an image representative of the blood flow.
Owner:SPENTECH
Imaging system
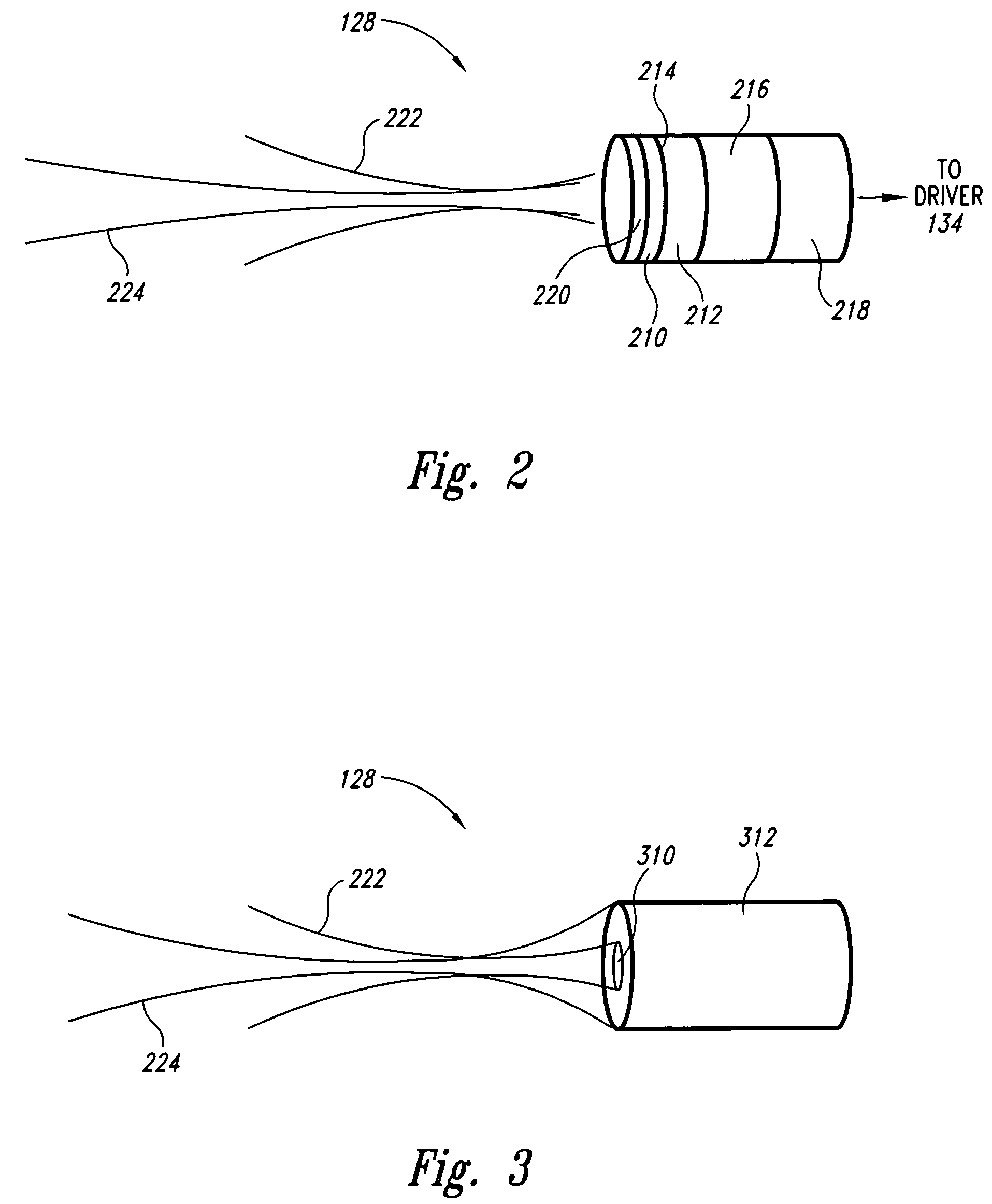
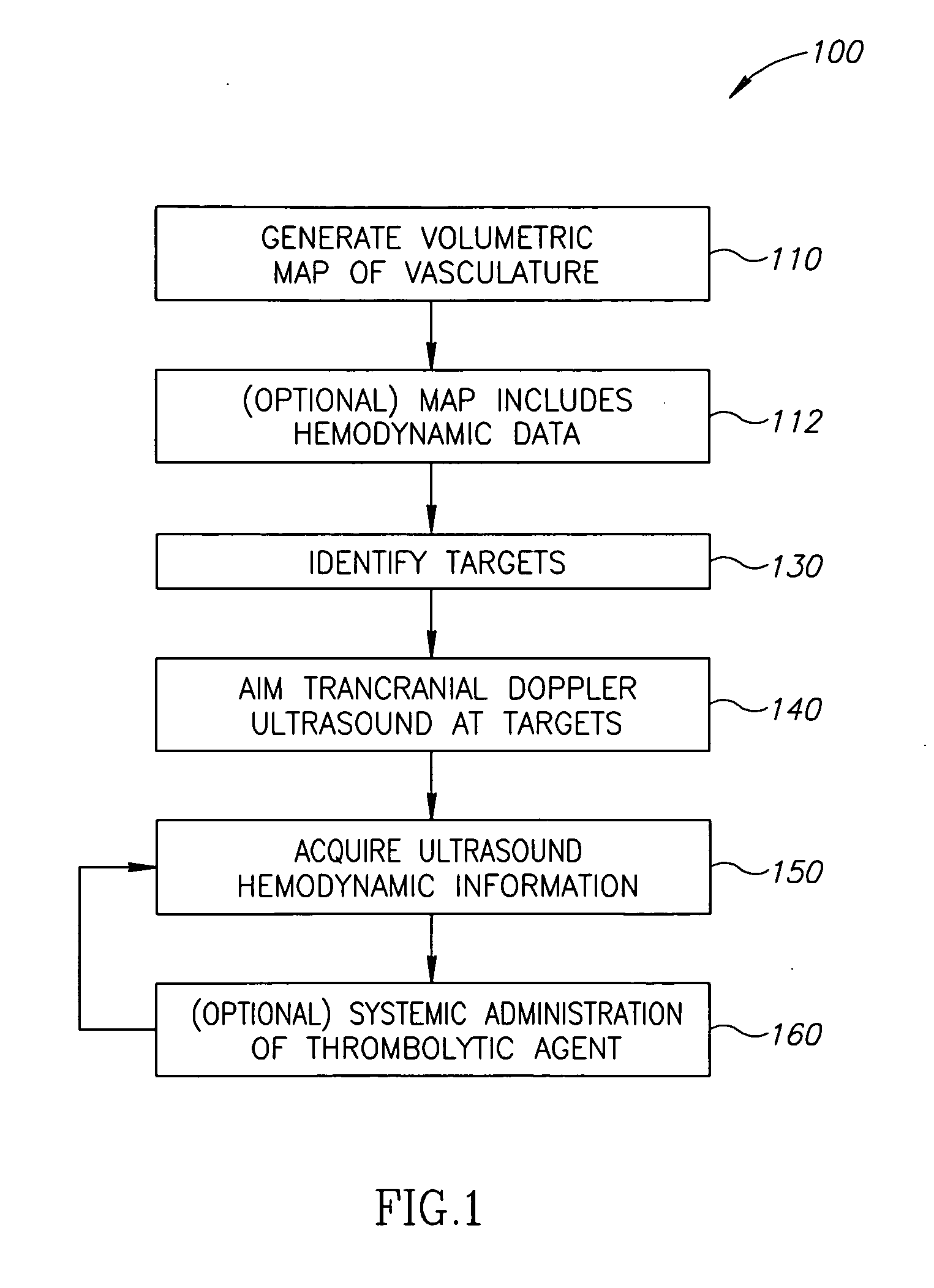
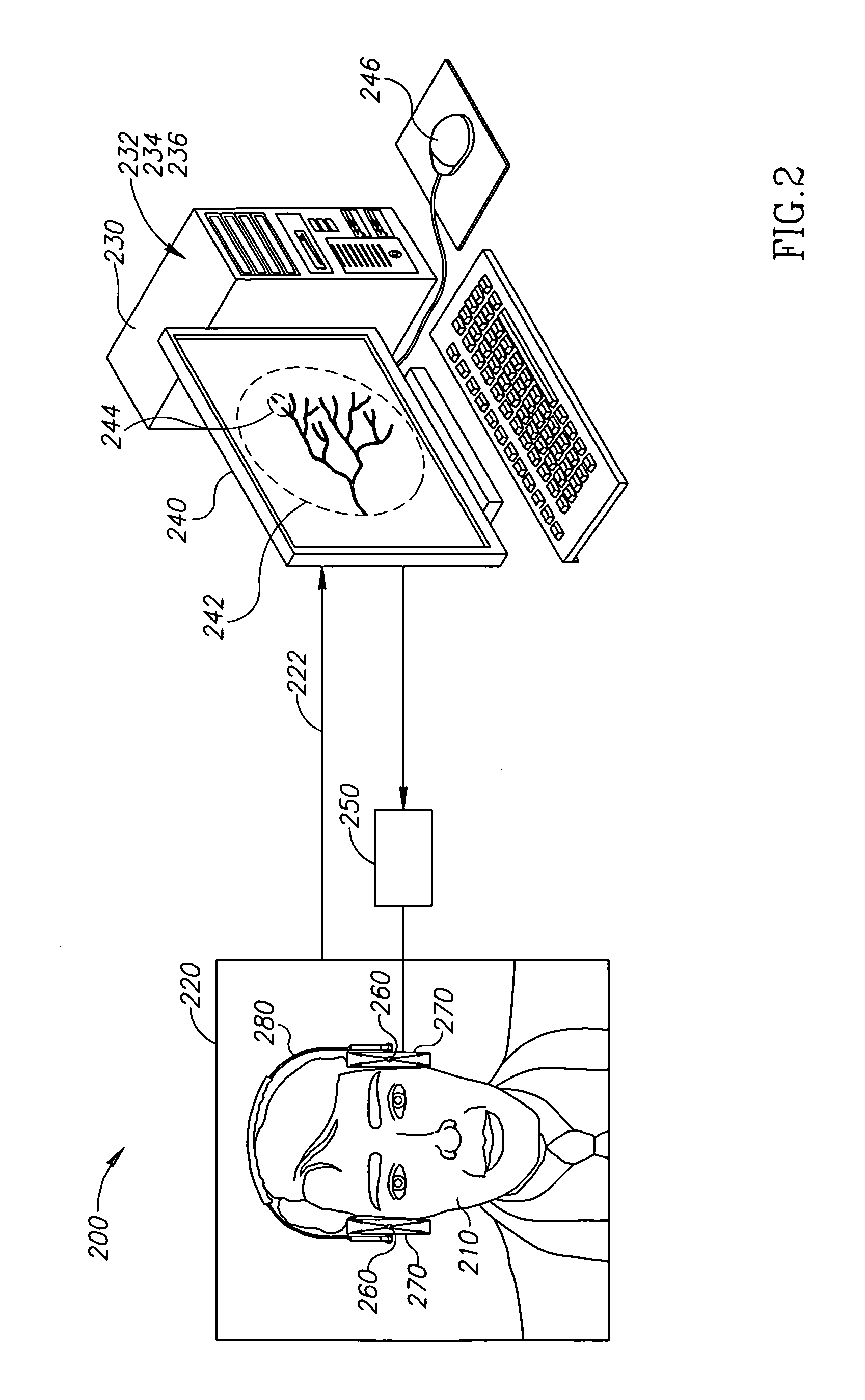
InactiveUS20100016707A1Increase speedImprove accuracyBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound imagingTransducer
A medical diagnostic system, the system comprising:a) a non-ultrasound imaging module configured to generate a volumetric vascular map;b) a controller configured to translate a 3D position co-ordinate from the map into an aiming instruction;c) a Doppler ultrasound unit adapted to aim a transducer responsive to the aiming instruction; andd) a registration module configured to register a position of the transducer with respect to the volumetric map.
Owner:KETER MEDICAL
Doppler ultrasound method and apparatus for monitoring blood flow and hemodynamics
InactiveUS20050033174A1Rapid positioningIncrease intensityBlood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSonificationPulsed doppler
A pulse Doppler ultrasound system and associated methods are described for monitoring blood flow and hemodynamics. The Doppler ultrasound system includes an ultrasound probe to emit ultrasound signals and detect reflected signals therefrom and further includes a processor coupled to the ultrasound probe and operable to process the detected reflected signals and calculate therefrom blood flow data for a plurality of locations at time intervals, the processor further operable to identify locations at which blood flow having a hemodynamic characteristic is present based on the blood flow data calculated for a plurality of the time intervals. A user interface coupled to the processor provides blood flow information based on the blood flow data, the blood flow information representative of detected blood flow and the presence of the hemodynamic characteristic.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
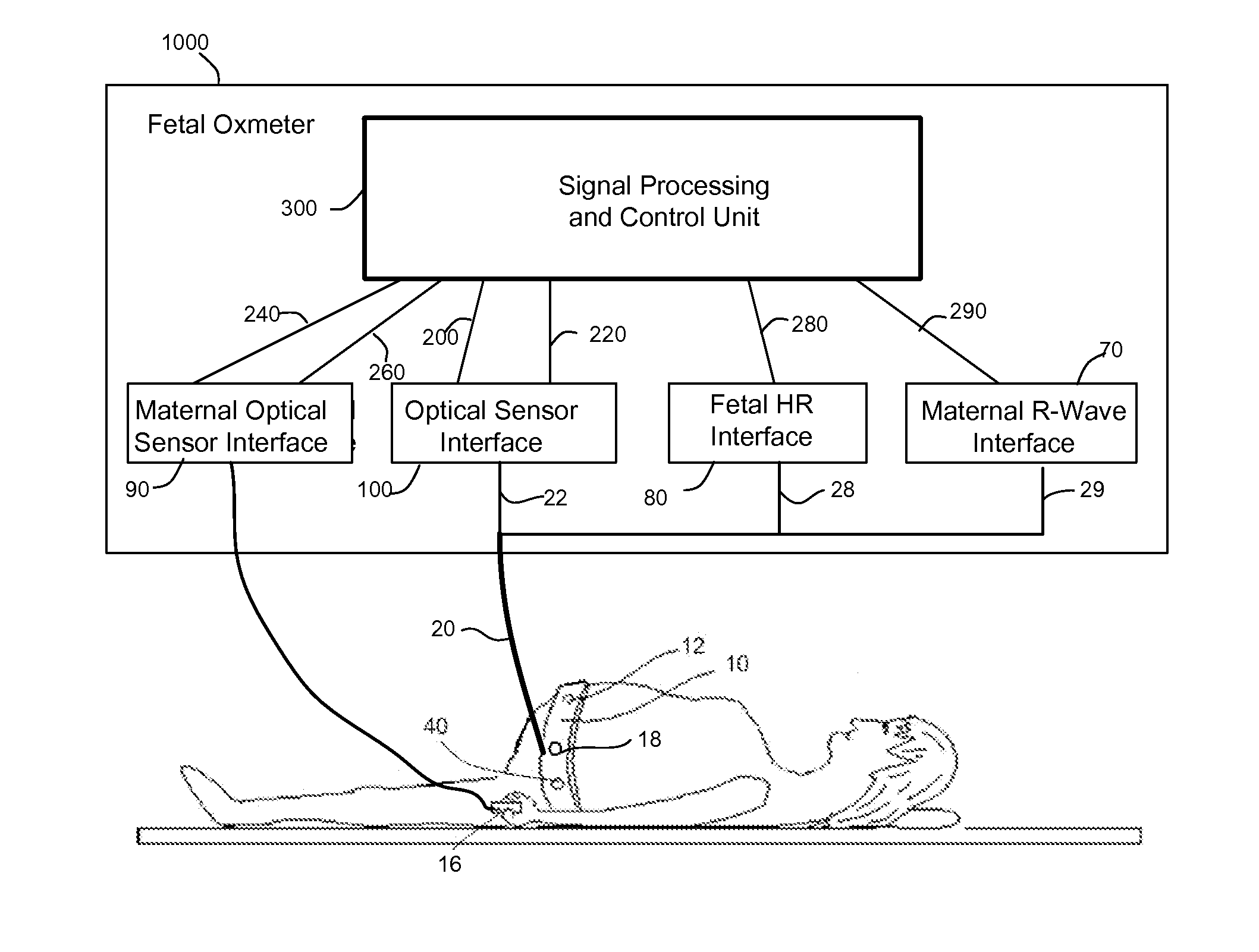
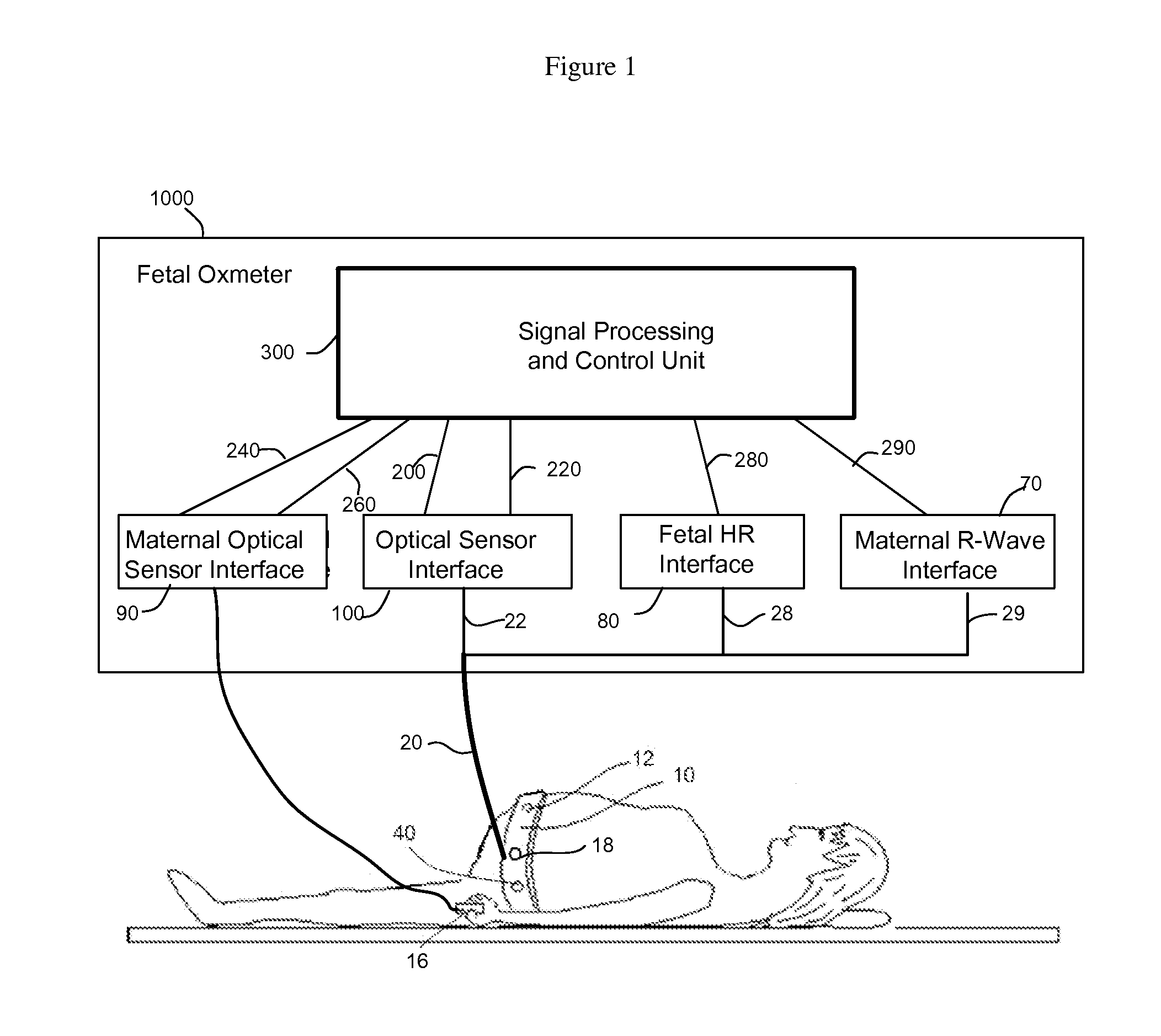
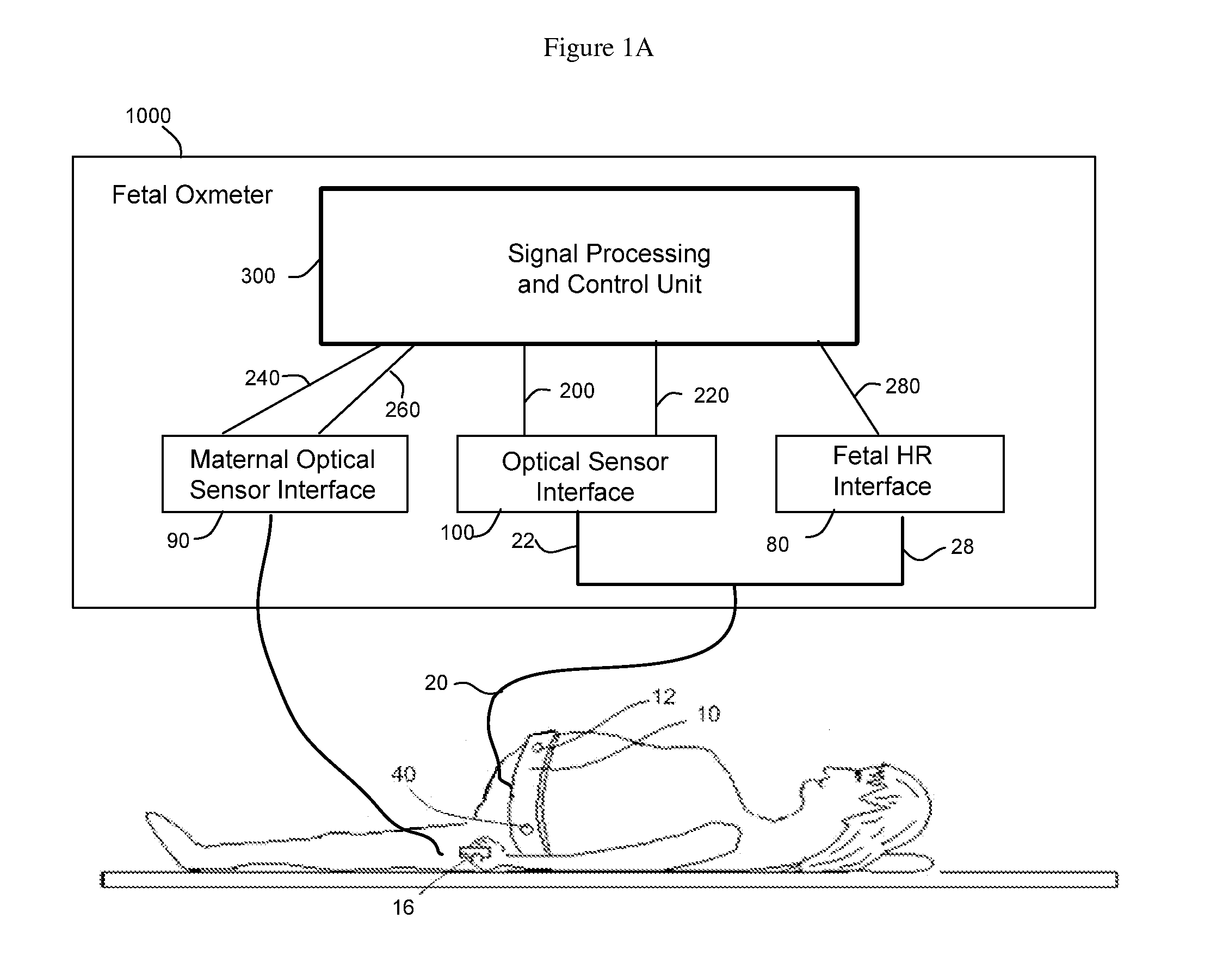
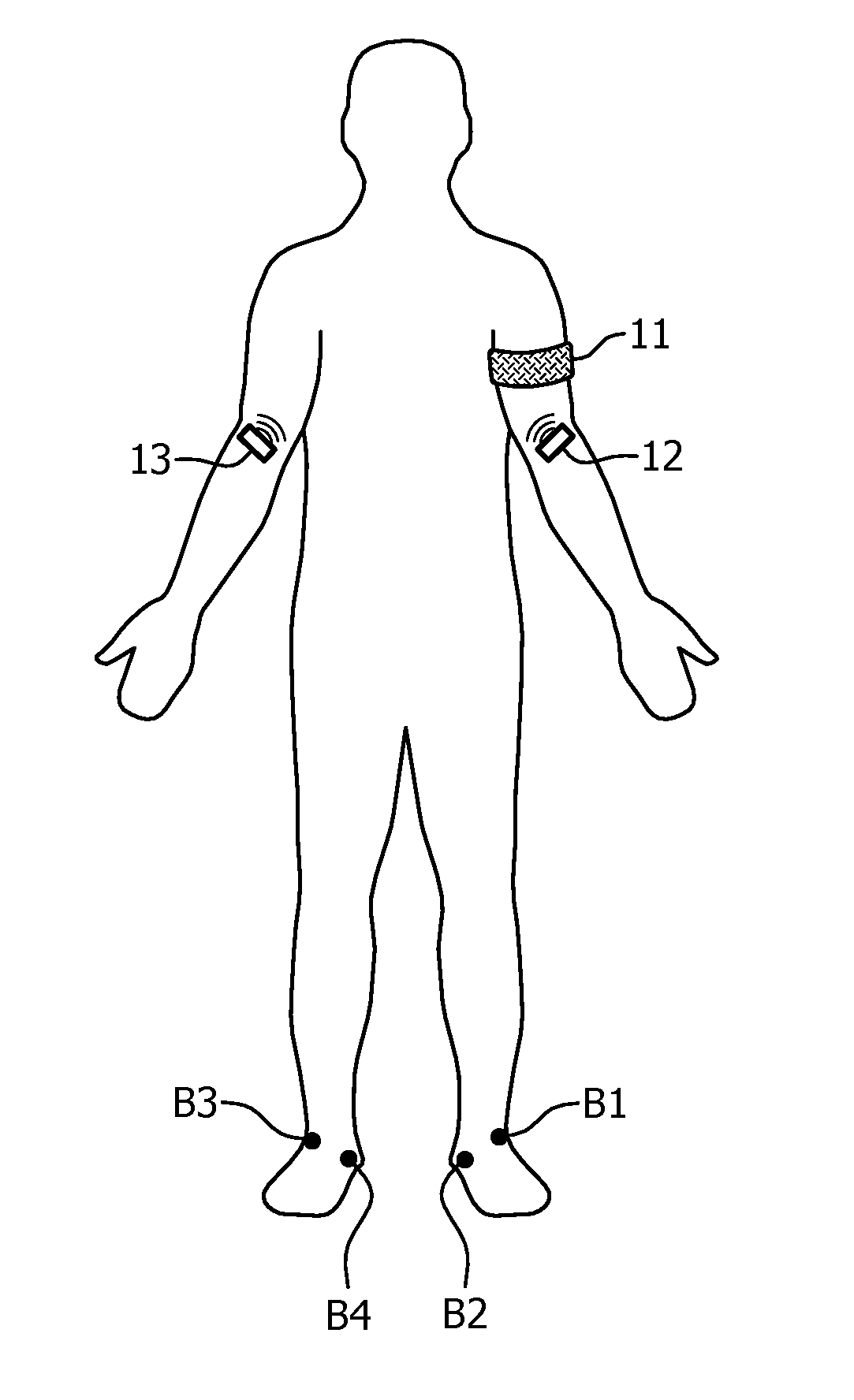
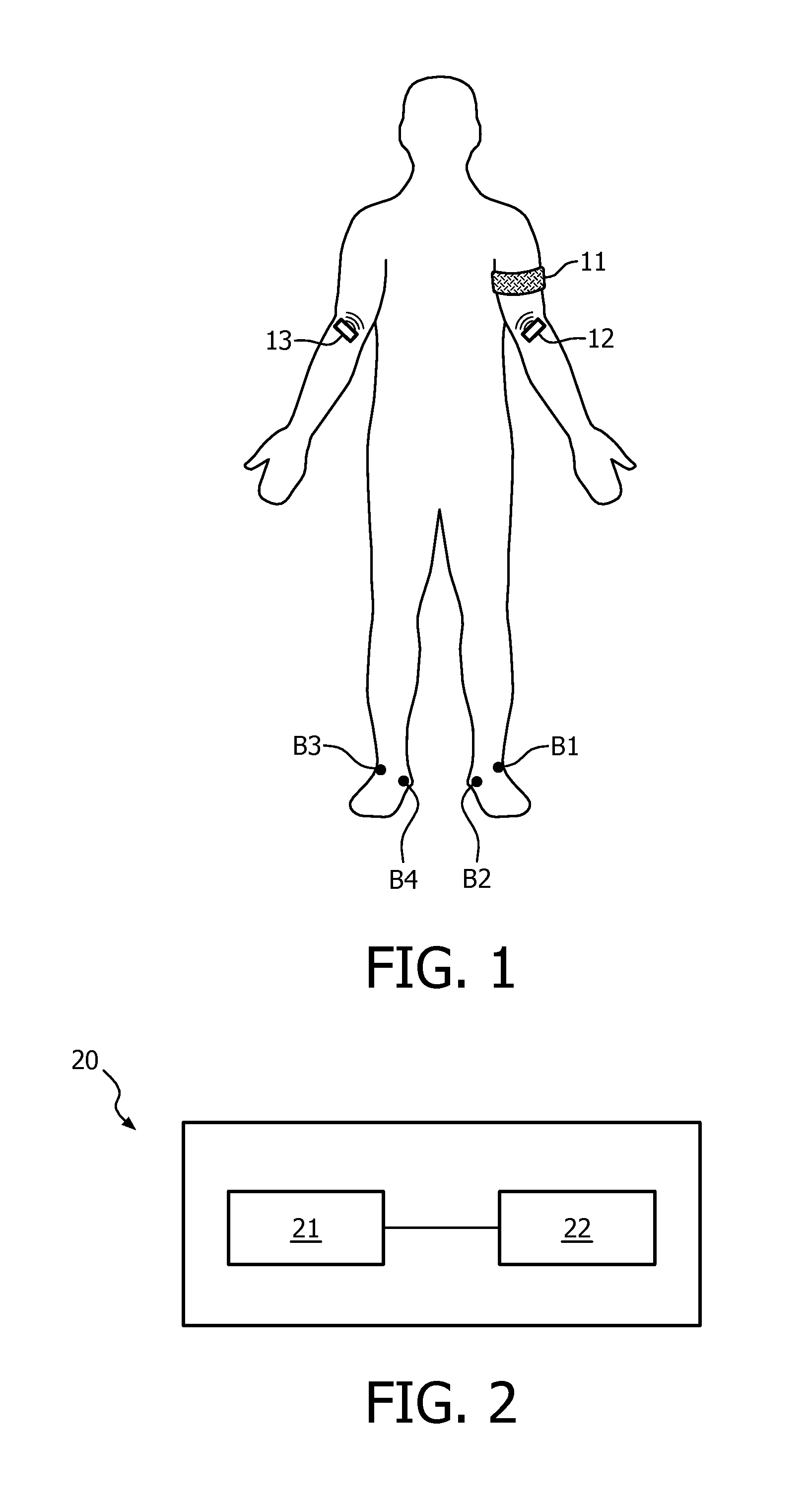
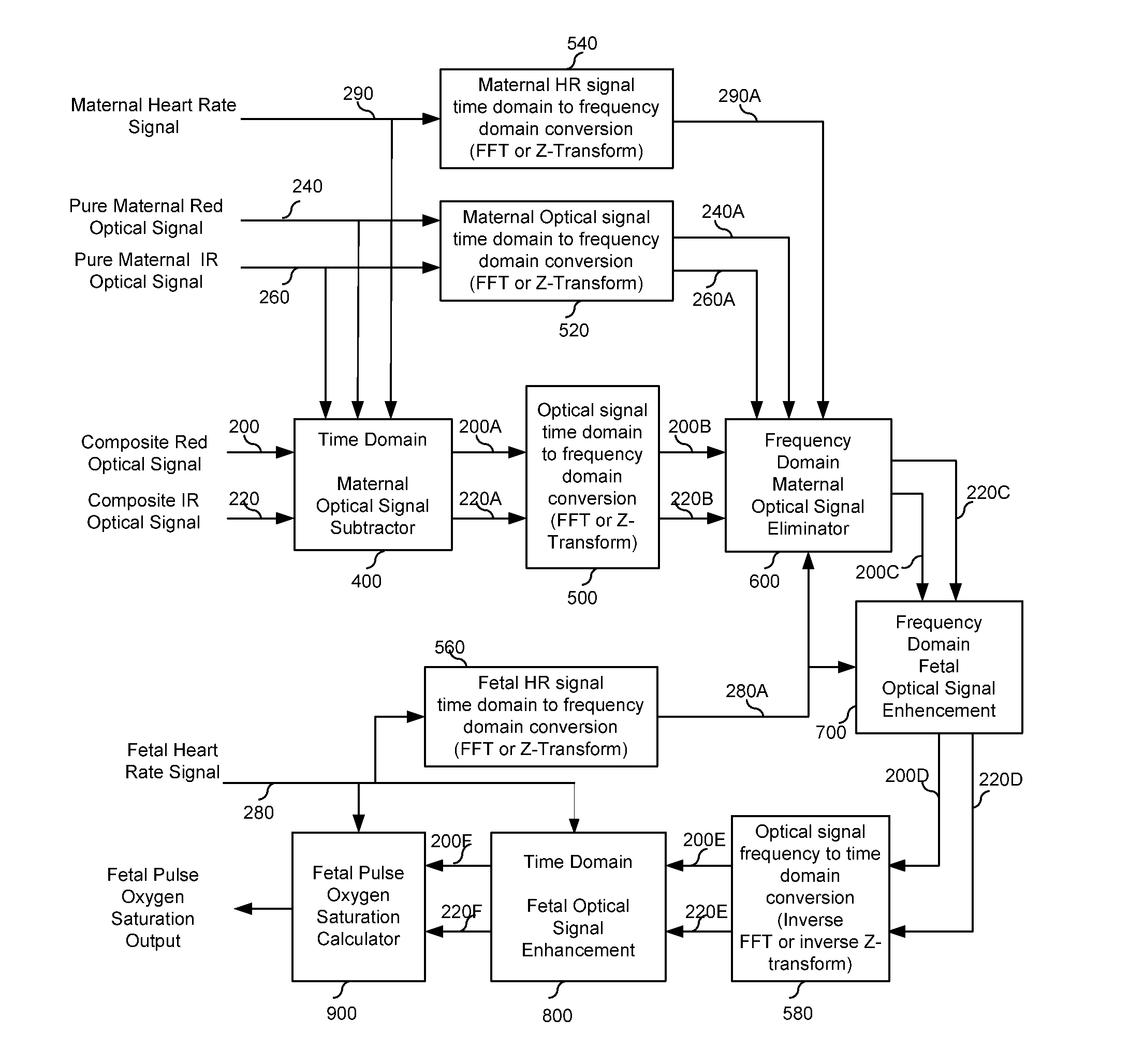
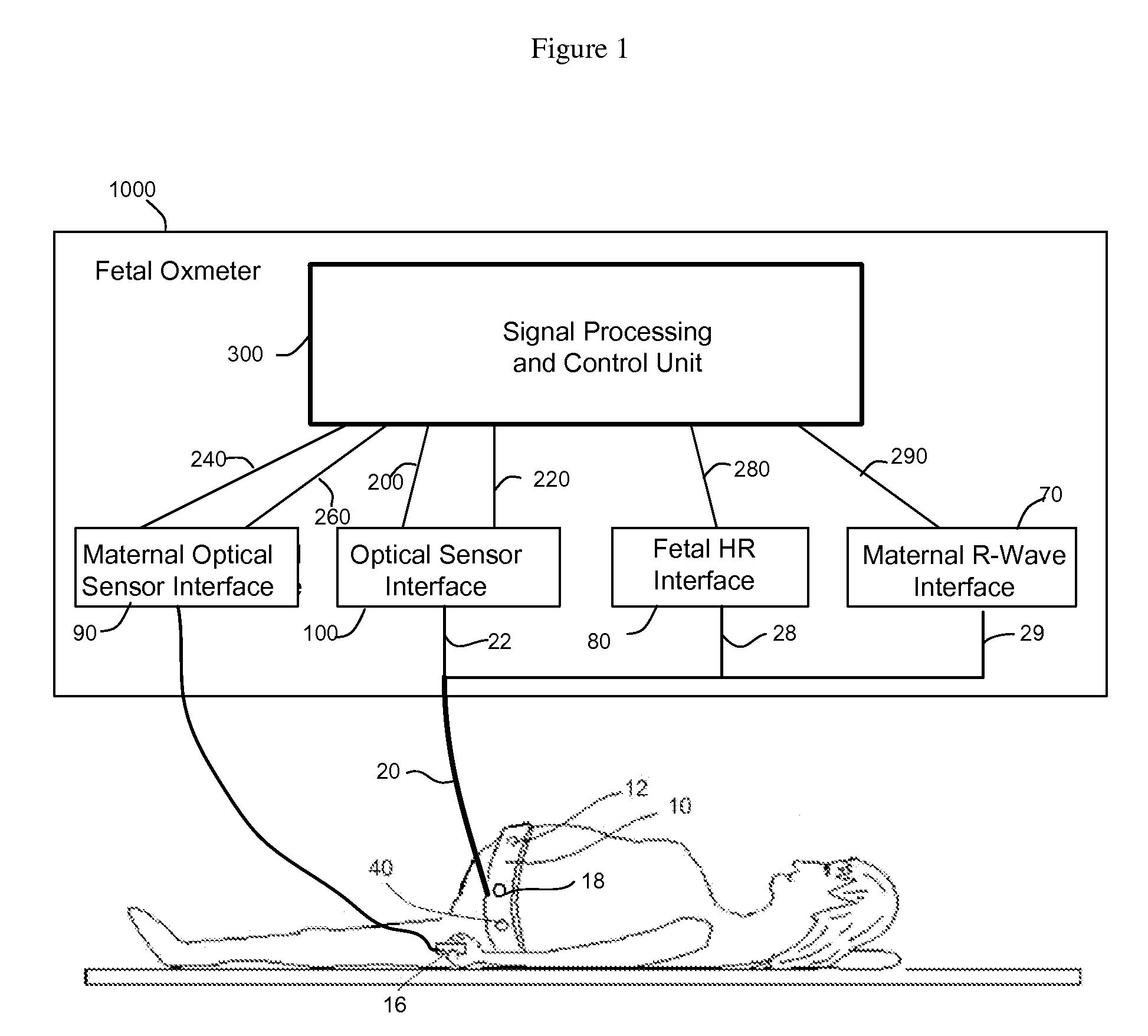
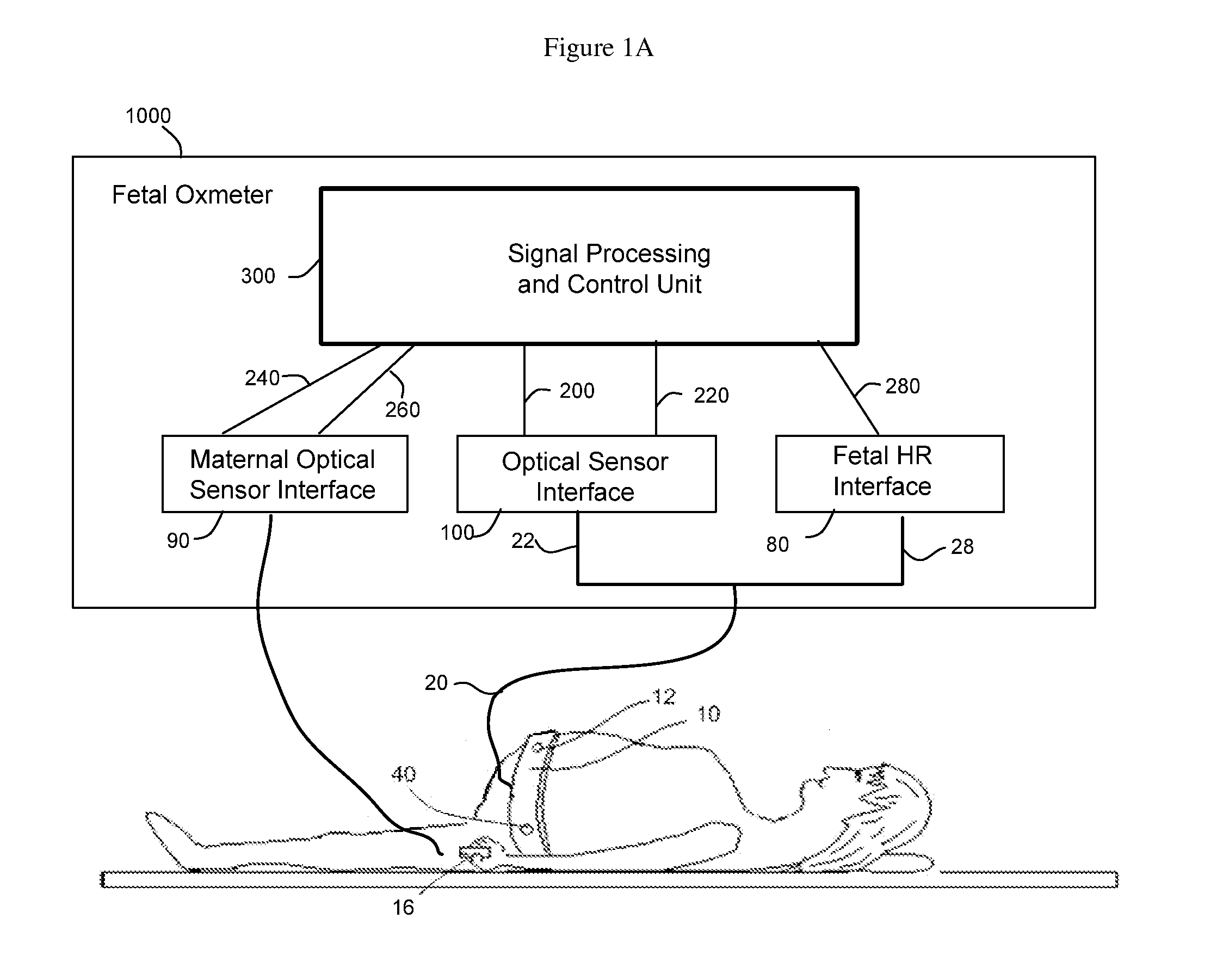
Method and Apparatus for Non-invasive Fetal Oximetry
ActiveUS20110218413A1Improve accuracyHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringObstetricsFetal heart rate
Method and apparatus to non-invasively measure fetal blood oxygen saturation levels. Optical sensors capable of producing and detecting multiple wavelengths of tissue penetrating light are placed on the surface of the maternal abdomen, and the light beams directed to pass through at least a portion of the uterus containing the fetus. The fetal heart rate is monitored by Doppler ultrasound, and pure maternal optical signal related to maternal arterial blood flow are also measured. The optical sensors collect composite signals containing both maternal and fetal hemoglobin absorption spectral data and modulated by their respective pulsatile blood flows. The composite signals processed in the time domain and frequency domain, the pure maternal pulsatile optical signal used to extract the maternal contribution to the composite signal, and the fetal pulsatile signal is used to lock onto and extract the fetal contribution to the composite signal, and a fetal blood oxygen level deduced.
Owner:BEIJING WEITEXING TECH CO LTD
Doppler ultrasound method and apparatus for monitoring blood flow
InactiveUS20050075568A1Rapid positioningIncrease intensityBlood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesGraphicsSonification
A pulse Doppler ultrasound system and associated methods are described for monitoring blood flow. A graphical information display includes simultaneously displayed depth-mode and spectrogram displays. The depth-mode display indicates the various positions along the ultrasound beam axis at which blood flow is detected. These positions are indicated as one or more colored regions, with the color indicating direction of blood flow and varying in intensity as a function of detected Doppler ultrasound signal amplitude or detected blood flow velocity. The depth-mode display also includes a pointer whose position may be selected by a user. The spectrogram displayed corresponds to the location identified by the pointer. Embolus detection and characterization are also provided.
Owner:SPENTECH
Wireless fetal monitoring system
InactiveUS9717412B2Poor outcomePatient benefitOrgan movement/changes detectionElectromyographyEngineeringPatient monitor
A wireless fetal and maternal monitoring system includes a fetal sensor unit adapted to receive signals indicative of a fetal heartbeat, the sensor optionally utilizing a Doppler ultrasound sensor. A short-range transmission unit sends the signals indicative of fetal heartbeat to a gateway unit, either directly or via an auxiliary communications unit, in which case the electrical coupling between the short-range transmission unit and the auxiliary communications unit is via a wired connection. The system includes a contraction actuator actuatable upon a maternal uterine contraction, which optionally is a EMG sensor. A gateway device provides for data visualization and data securitization. The gateway device provides for remote transmission of information through a data communication network. A server adapted to receive the information from the gateway device serves to store and process the data, and an interface system to permits remote patient monitoring.
Owner:GARY & MARY WEST HEALTH INST
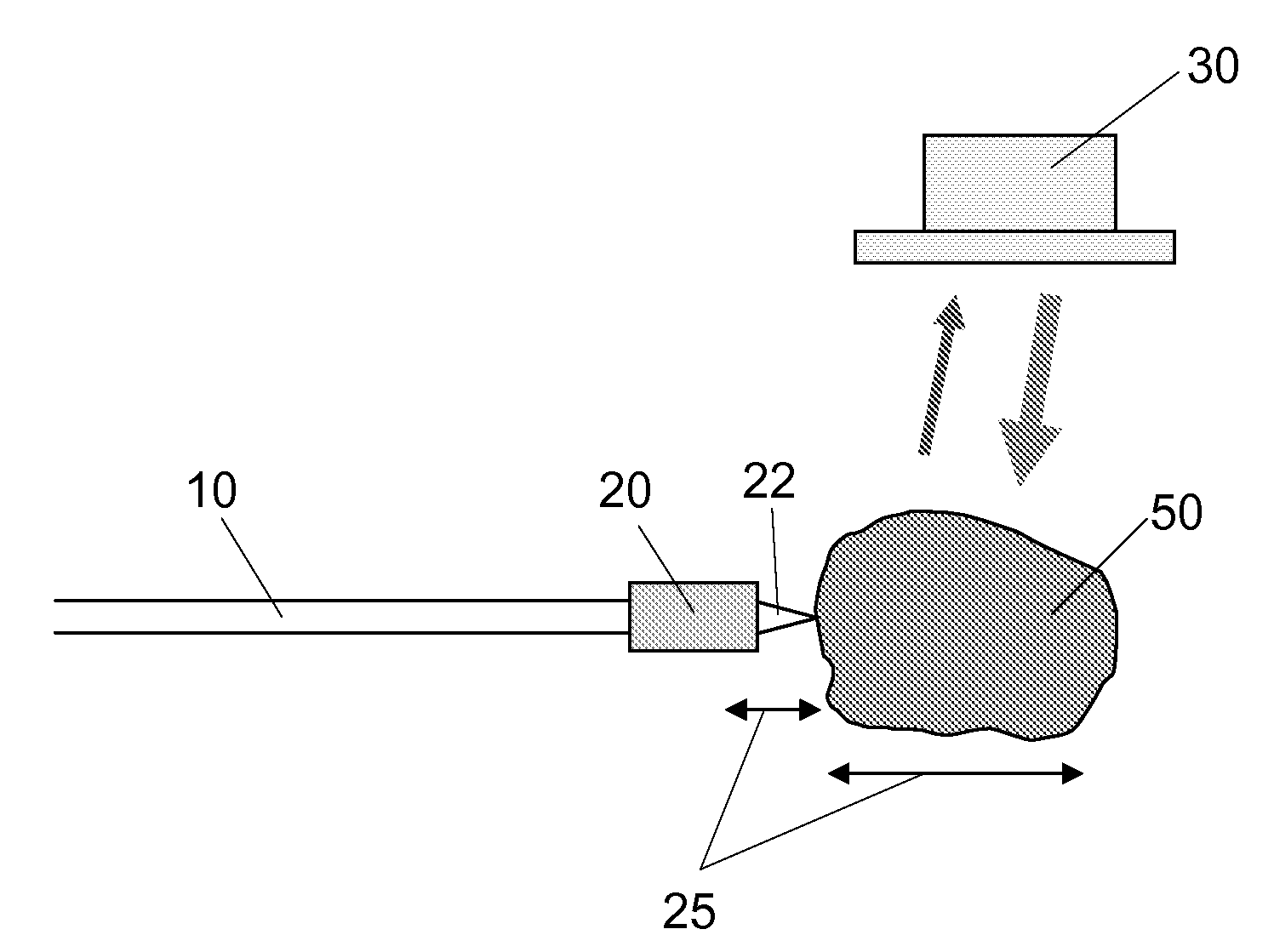
Tracheostomy apparatus
Tracheostomy apparatus includes a needle with a doppler ultrasound transducer mounted within it close to its patient end and connected to a monitor. Two electrodes are insulated from one another on the external surface of the needle close to its patient end. The electrodes are also connected to the monitor. The needle supports a catheter on its outer surface. As the needle is inserted through tissue overlying the trachea, the ultrasound transducer detects the presence of any nearby blood vessels and gives an audible indication on the monitor. The monitor also responds to a rise in impedance between the electrodes indicative of entry of the end of the needle into the trachea so that the needle can be removed to leave the catheter in place. A guide is then inserted through the catheter and the path into the trachea is enlarged with a dilator sufficiently to receive a tracheostomy tube.
Owner:SMITHS GRP PLC
Dual frequency doppler ultrasound probe
An ultrasonic Doppler probe is provided for use in connection with non-invasive Doppler imaging of fluid flow within the human body. The Doppler probe can be selectively operated at more than one frequency during the course of a Doppler imaging examination thereby enhancing the resolution of the image obtained while also increasing the effective depth of the image. The probe of the present invention employs piezo-electric materials for the formation of acoustic transmitting and receiving transducers that are positioned within the probe to allow the probe to be selectively operated at a number of different frequencies spanning no more than one octave in frequency range.
Owner:UNETIXS VASCULAR INC
Devices and methods for tracking blood flow and determining parameters of blood flow
InactiveUS20080269609A1Small sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationThinned array
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Method and Apparatus for Hemodynamic Monitoring Using Combined Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Measurement
ActiveUS20110137173A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionMeasurement deviceBlood flow
Combined blood flow and blood pressure measurements are used for the calculation of central vascular blood flow parameters. Blood flow measurements may be made simultaneously with arterial pressure measured either centrally or peripherally and central venous pressure for the monitoring of human subjects. A combined blood flow and blood pressure measurement device for hemodynamic monitoring may include a Doppler ultrasound probe utilizing a continuous wave or pulse wave ultrasound beam for the measurement of blood flow in the aorta, combined with arterial pressure measurement, or signal input from a suitable pressure transducer system from one of either the radial, brachial, dorsalis pedis or femoral artery. The ultrasound probe may comprise either an esophageal or suprasternal ultrasound probe, while the blood pressure measurement may be either an electronic transducer blood pressure sphygmomanometer on the arm, or a finger cot infrared light optical pulse detector.
Owner:DELTEX MEDICAL
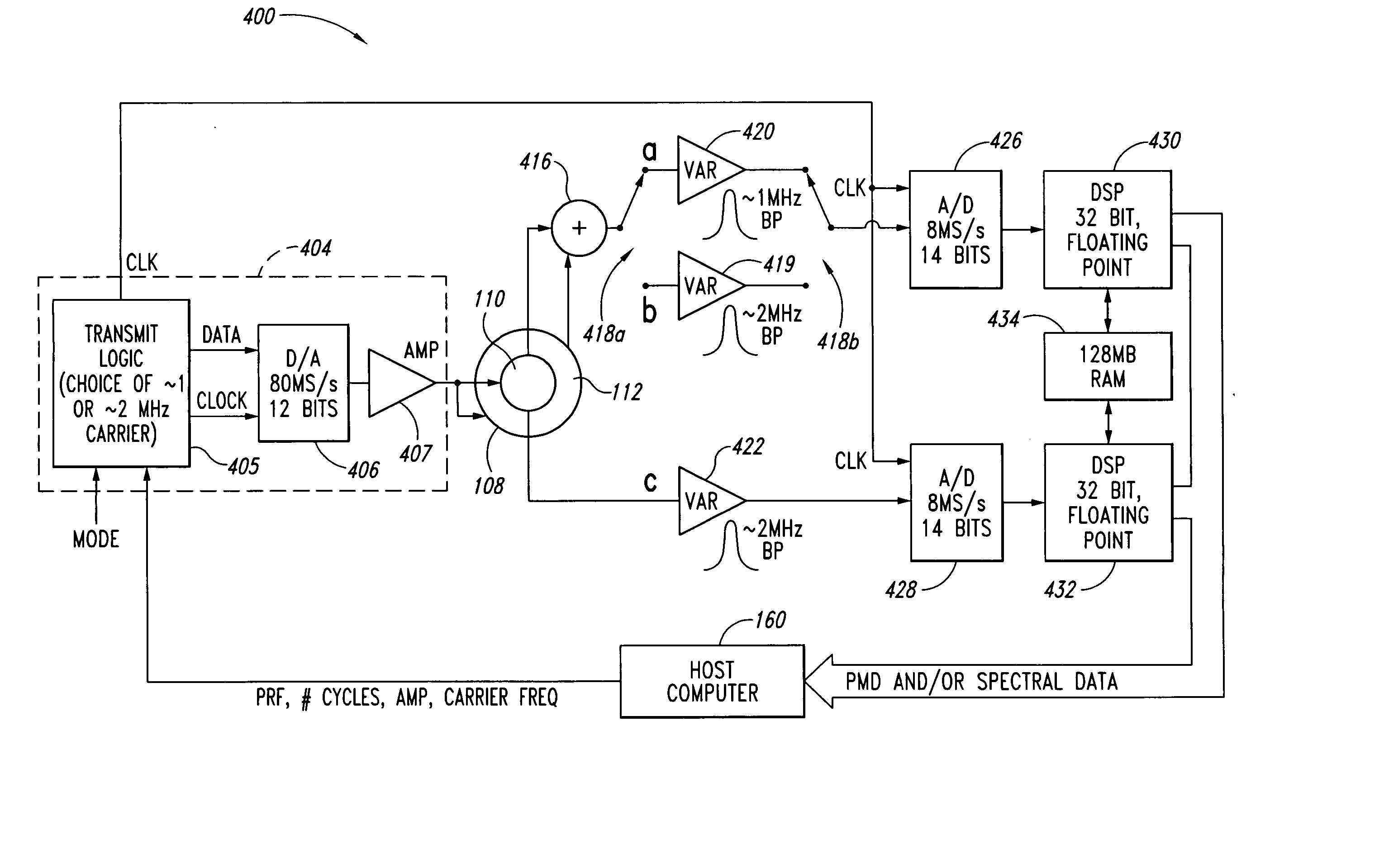
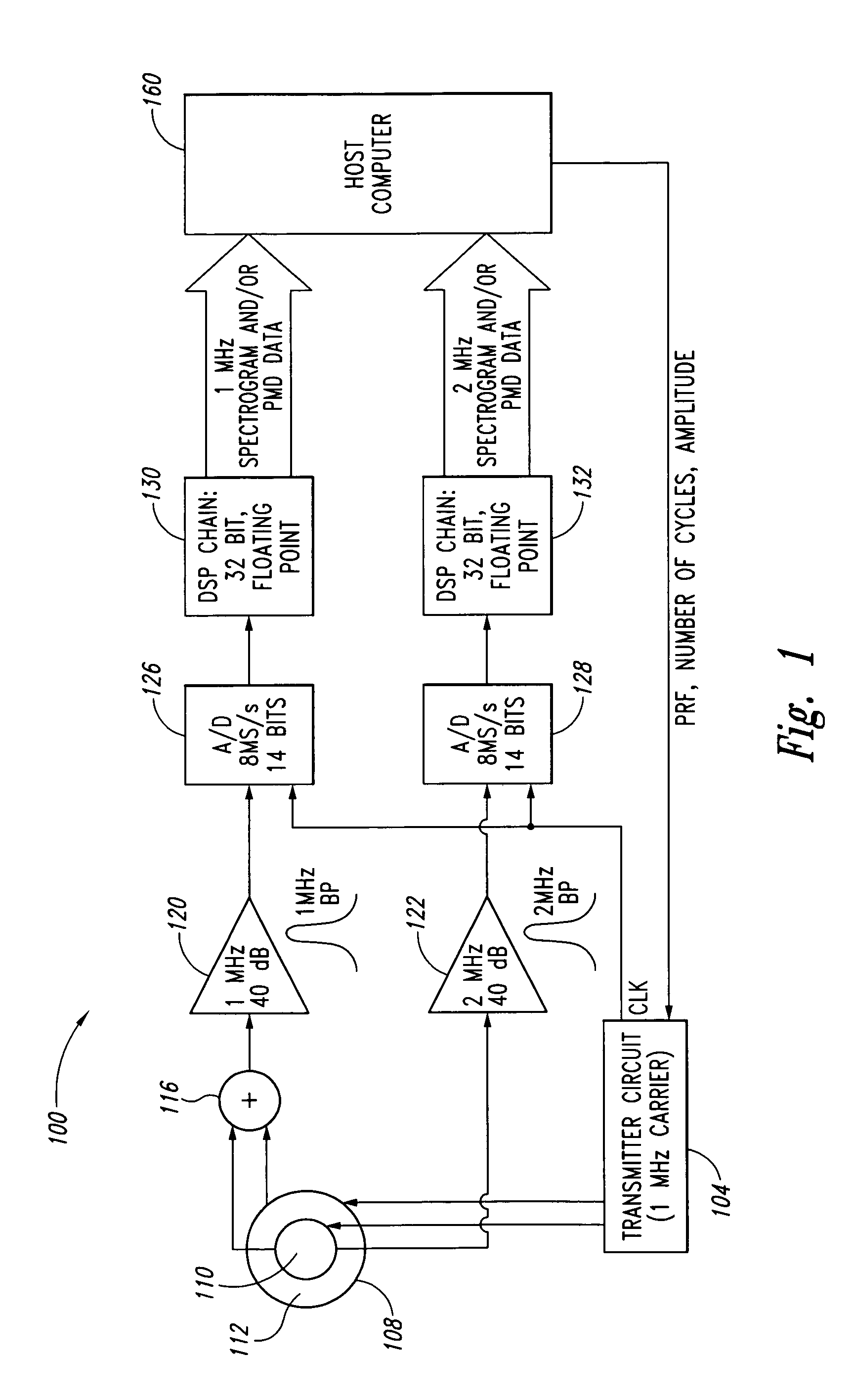
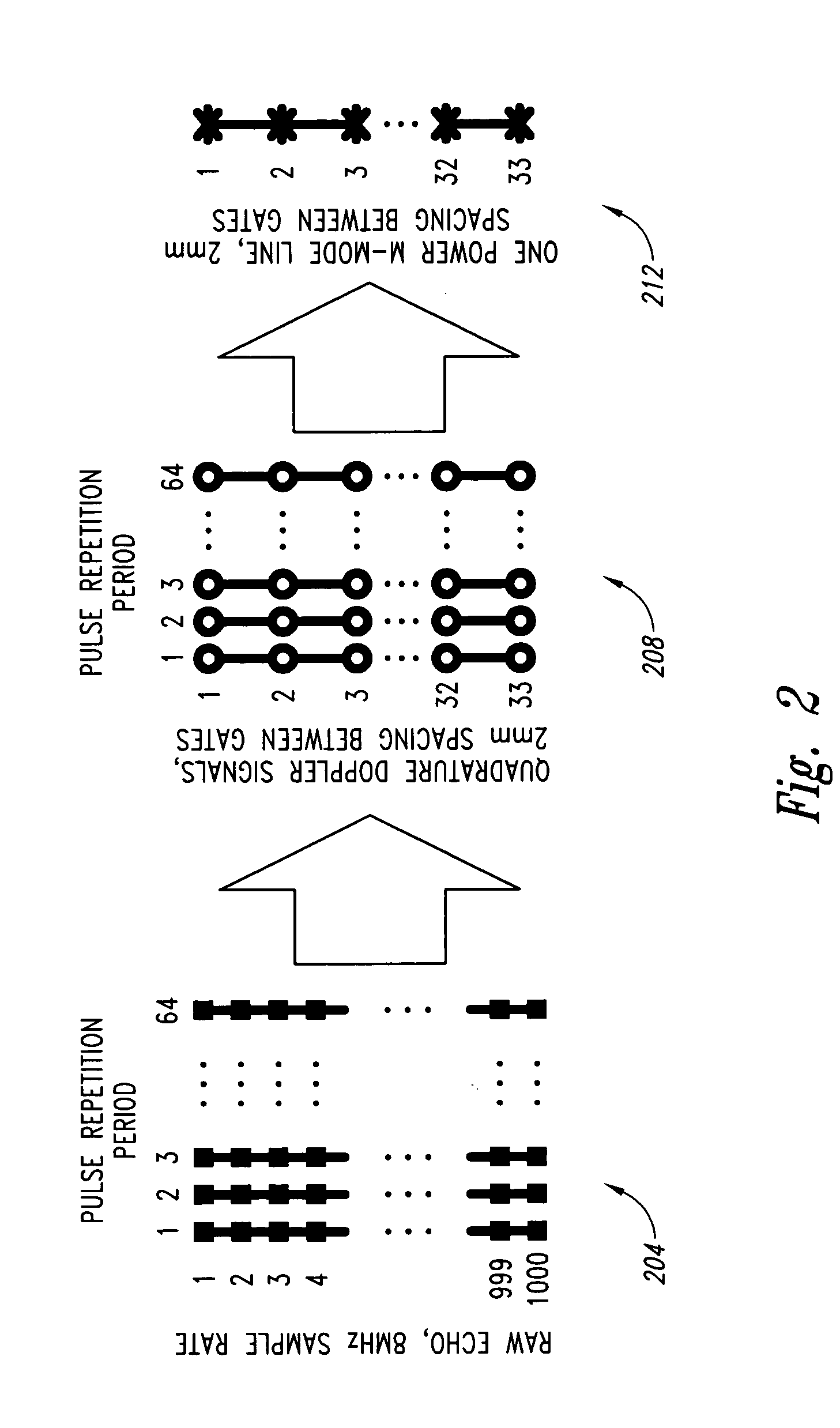
Doppler ultrasound processing system and method for concurrent acquisition of ultrasound signals at multiple carrier frequencies, embolus characterization system and method, and ultrasound transducer
A Doppler ultrasound signal processing system for processing reflected ultrasound signals detected by an ultrasound transducer for multiple carrier frequencies concurrently. Additionally, an embolus characterization system and method, and an ultrasound transducer are included as well.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Method and device for recognizing tissue structure using doppler effect
InactiveUS20090292204A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound imagingTransducer
An apparatus, method and system comprising an imaging tool for imaging an interventional device and its target organ using Doppler ultrasound are disclosed. The apparatus comprises an imaging tool and an interventional medical device; in some embodiments the imaging tool itself may be an interventional device or may comprise components of the interventional device. The imaging tool comprises a vibratory transducer and a vibratable element. The vibratory transducer is energized to generate a vibration motion in the vibratable element at first imaging frequency, which in turn is capable of oscillating a target organ at a second imaging frequency, the imaging frequencies being detectable by an ultrasound imaging system with Doppler mode. In certain applications the vibratory transducer may be energized to vibrate at a therapeutic frequency to effect treatment of the target organ, for example to clear a lumenal or vascular stenosis or to penetrate a vascular occlusion.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
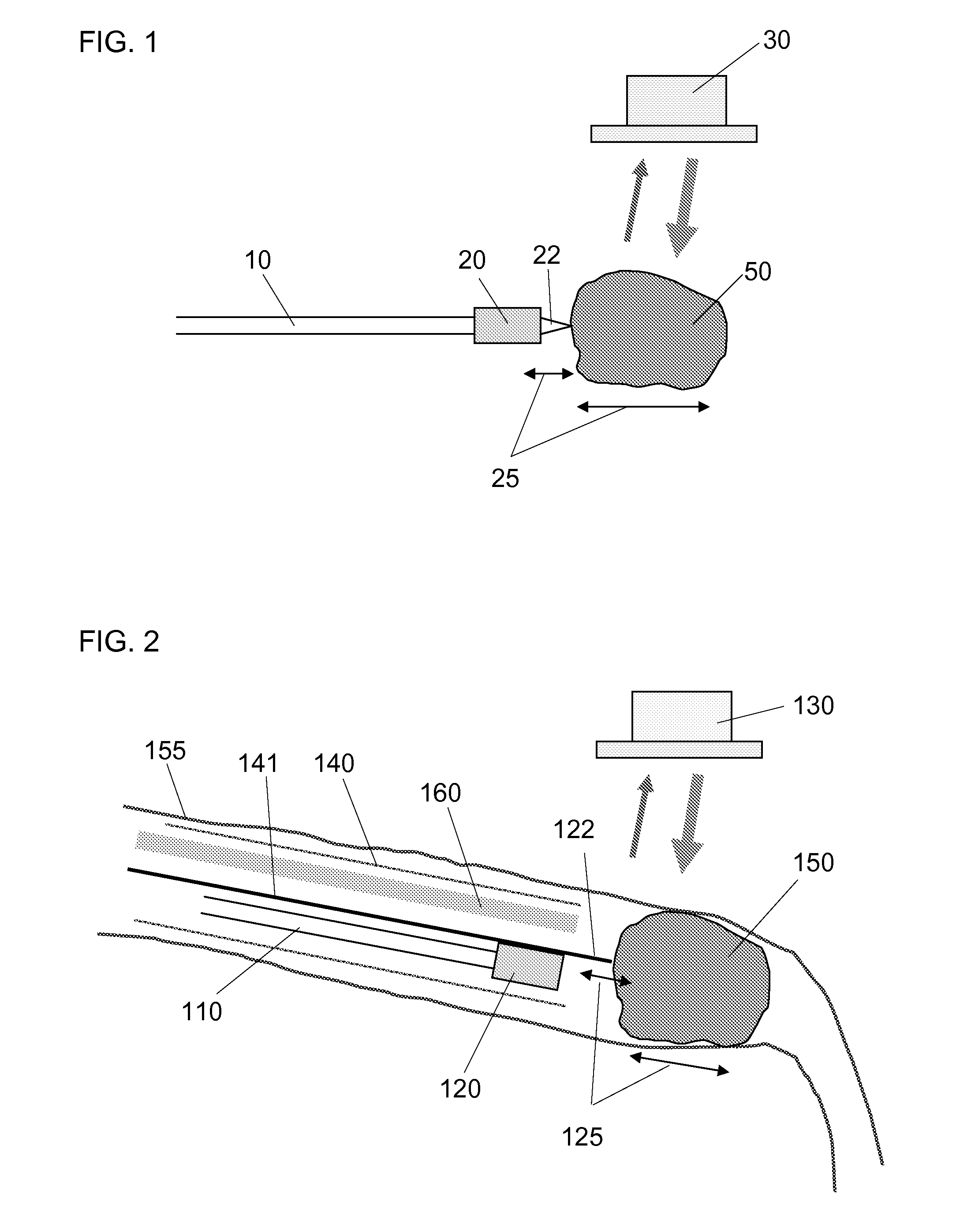
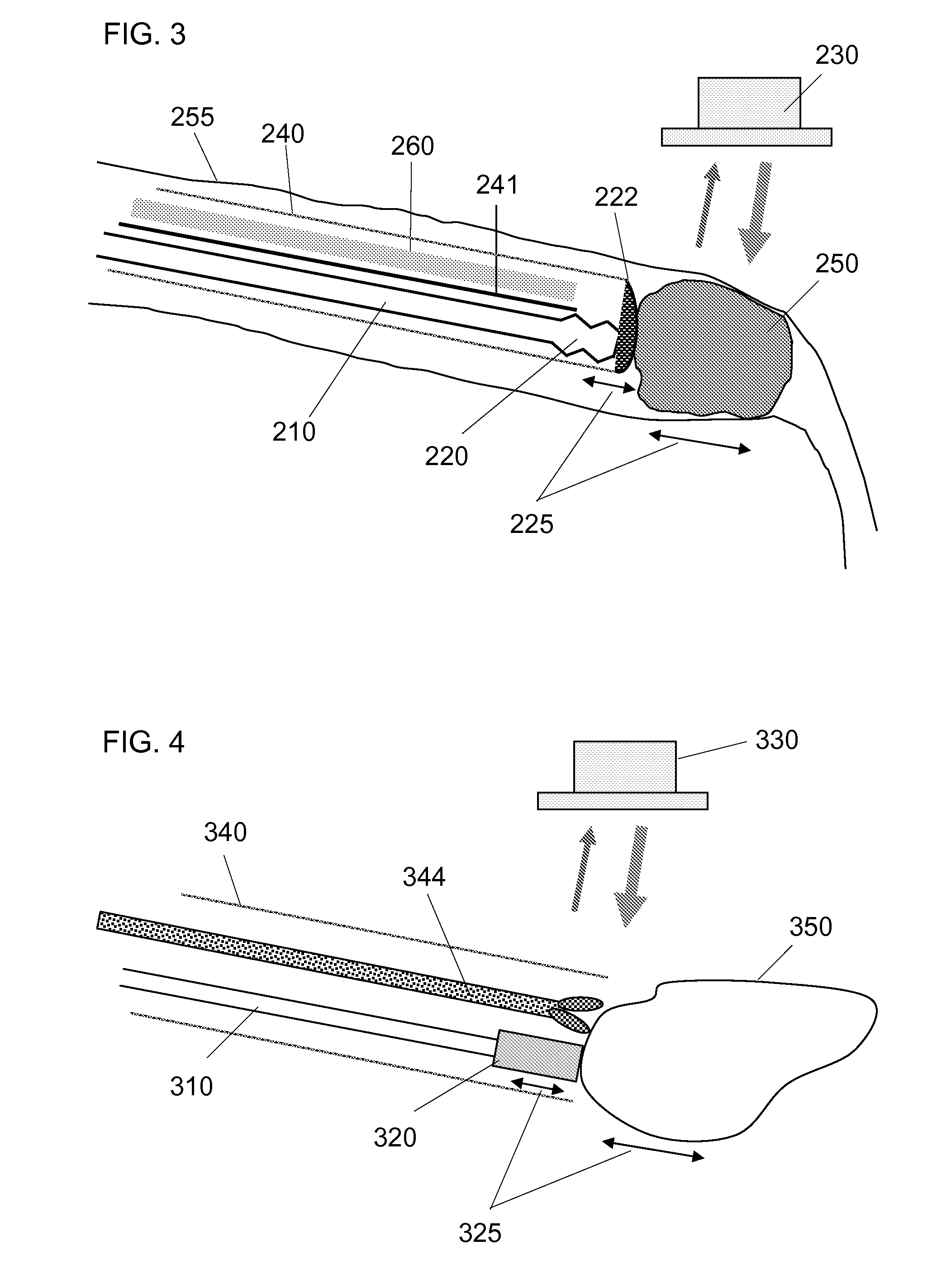
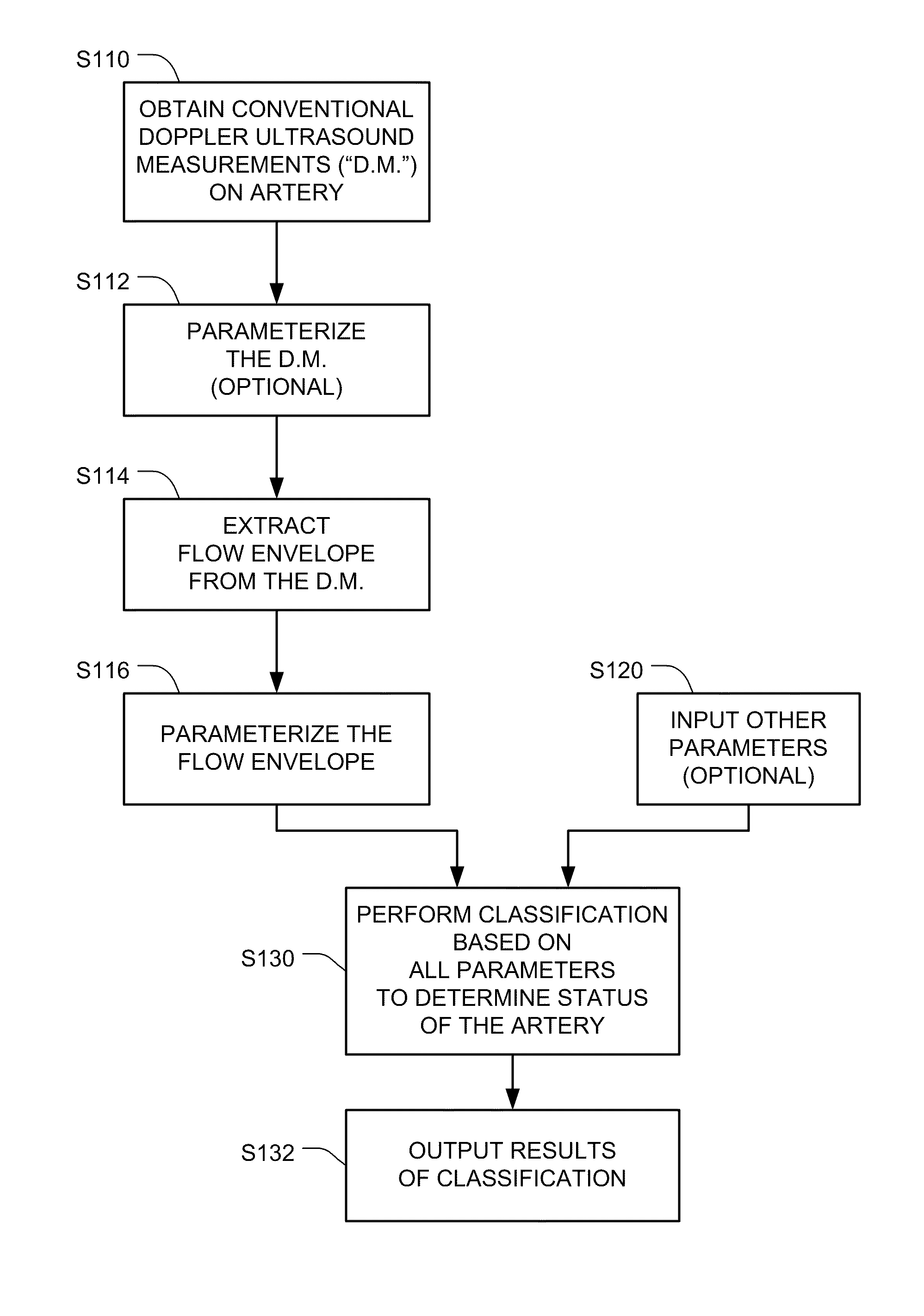
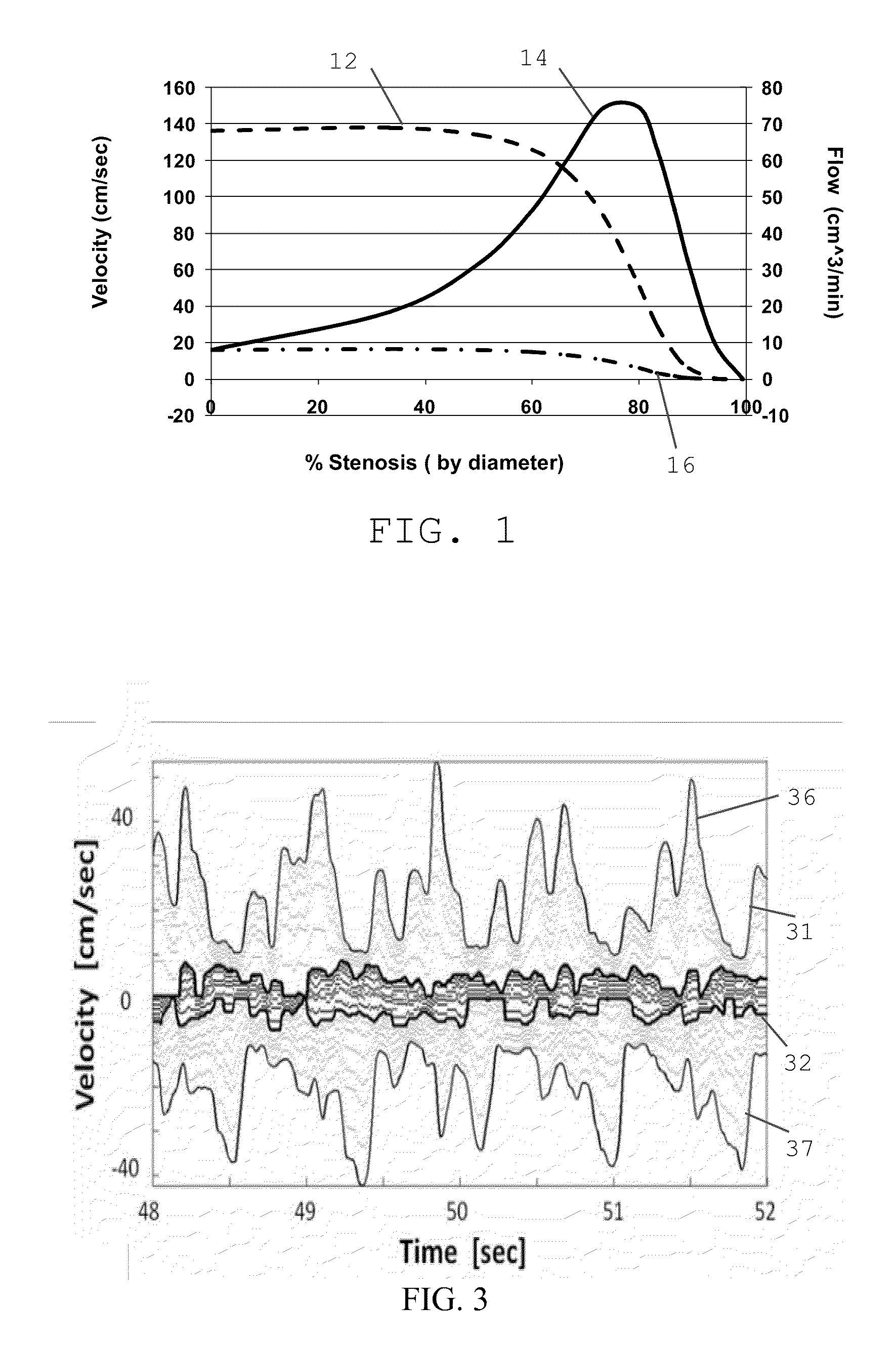
Detecting a stenosis in a blood vessel
InactiveUS20100274133A1Raise the possibilityBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationBlood vessel spasm
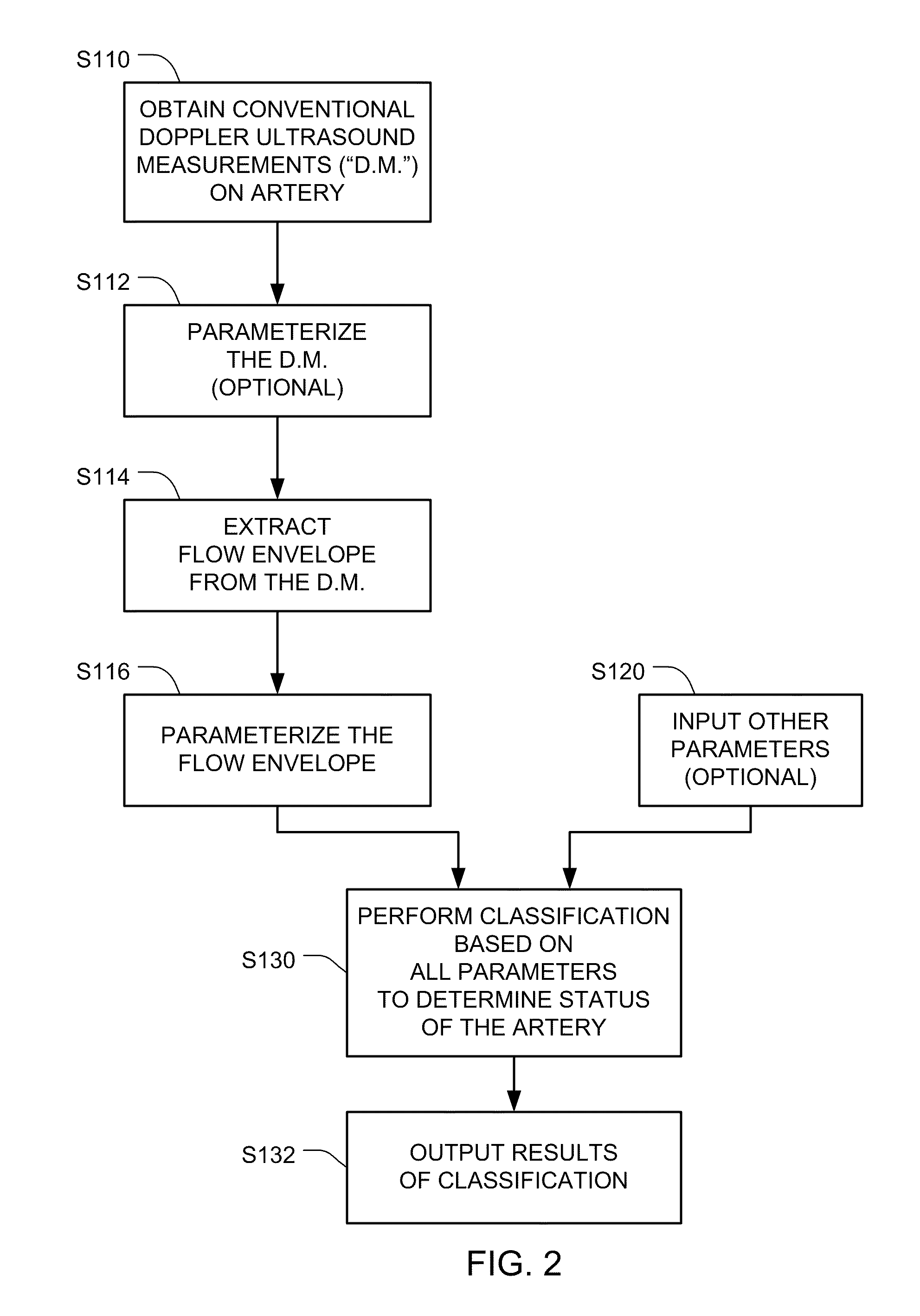
Doppler ultrasound may be used to detect stenosis in a blood vessel using a variety of approaches. In one approach, the flow envelope is extracted from the Doppler ultrasound measurements, and the extracted flow envelope is parameterized. Classification is then done based on those parameters (and optionally other parameters), to determine whether a stenosis exists. A second approach uses Doppler data that is acquired in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction of blood flow, and detects artifacts that are consistent with turbulences that usually appear downstream from stenoses.
Owner:ECHOSENSE
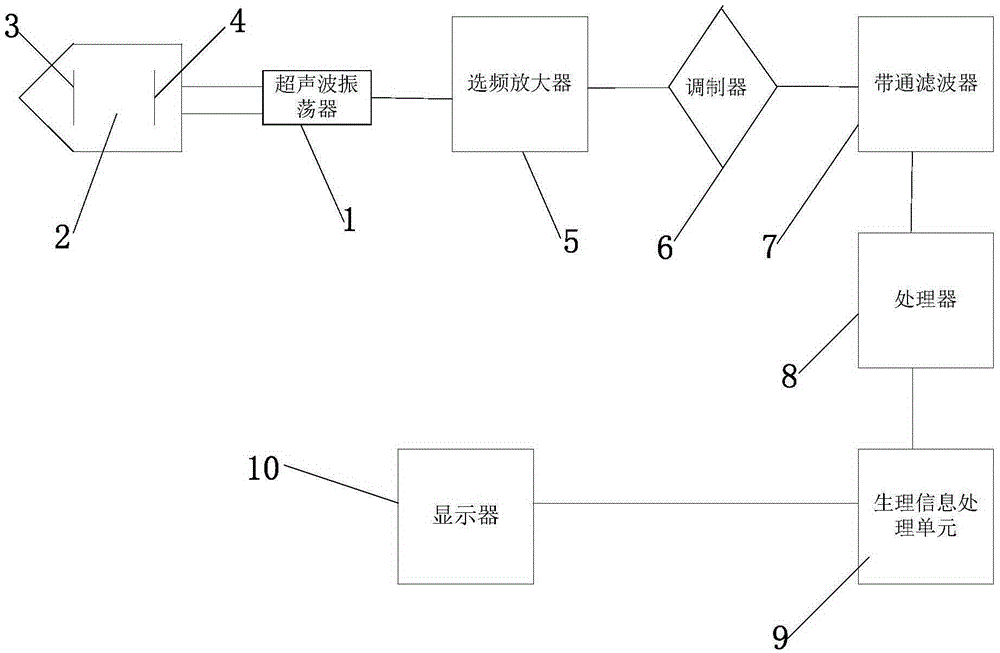
Method for recognizing ultrasonic spectrum enveloped peaks by combining cardiac sound
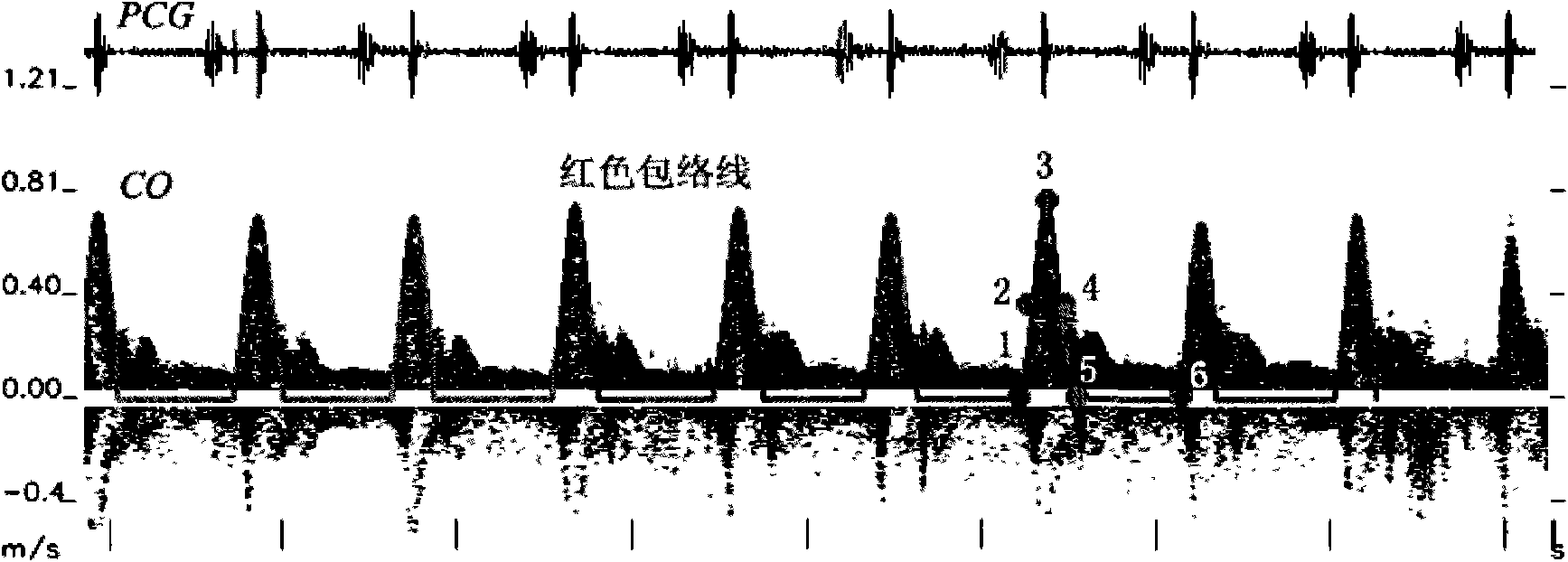
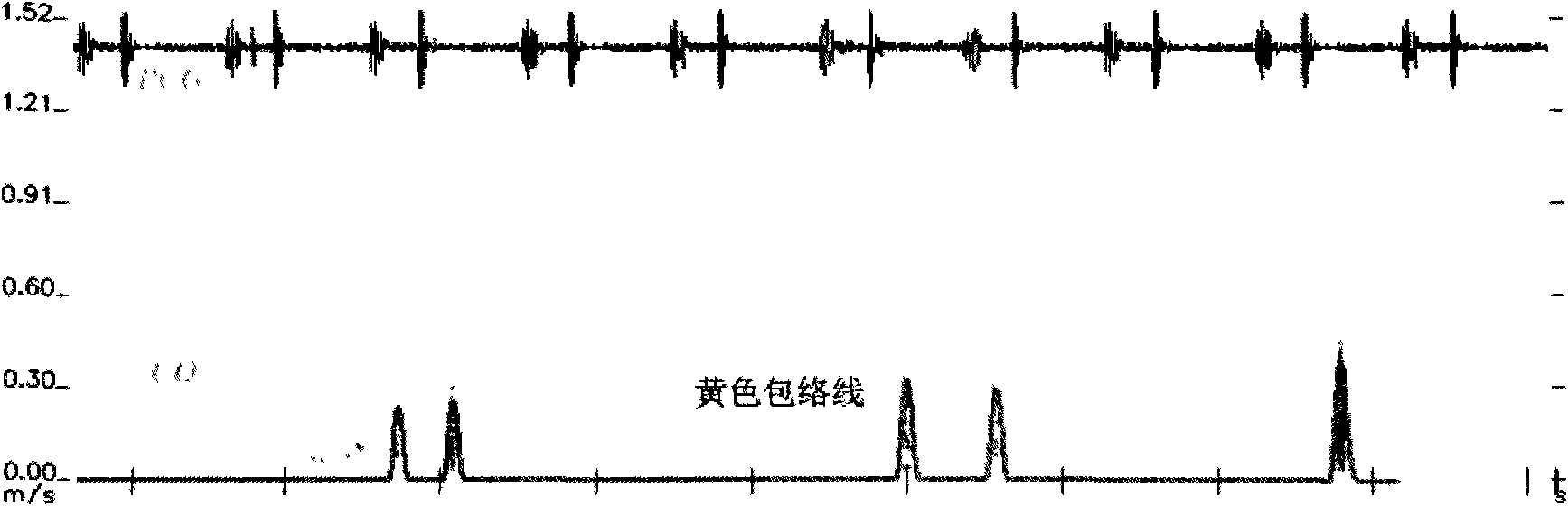
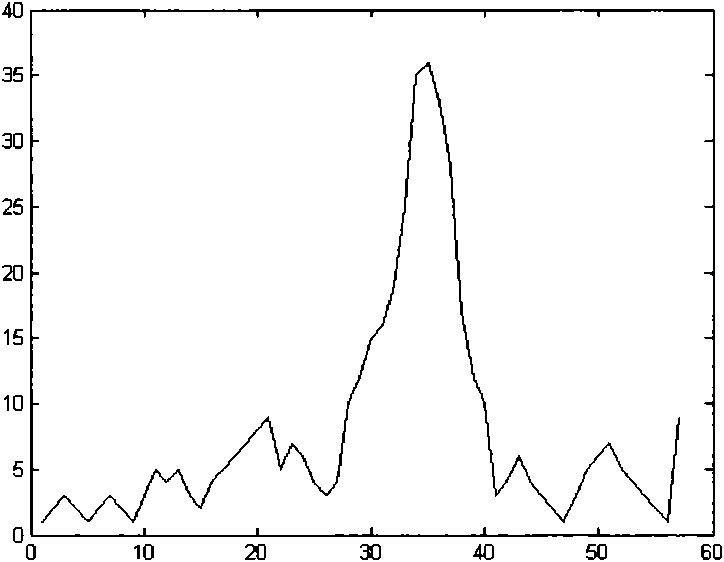
ActiveCN101779966AEfficient extractionImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHuman bodyAcoustics
The invention provides a method for recognizing ultrasonic spectrum enveloped peaks by combining cardiac sound, which comprises the following steps: synchronously acquiring cardiac output signals and cardiac sound signals in relevant positions of human bodies by simultaneously adopting a Doppler ultrasonic probe and a cardiac sound probe, and inputting the cardiac output signals and the cardiac sound signals into a computer for processing; combining the cardiac output signals and the cardiac sound signals by the computer to automatically analyze effective peaks, and enveloping the effective peaks; and then, computing cardiac output parameters and cardiac sound parameters. The invention can more effectively extract real peaks, simultaneously can acquire relevant parameters capable of reflecting cardiac functions by computing effective enveloped peaks, can effectively acquire multiple parameters of spectrum enveloped peaks, and can really reflect basic physical conditions and changes of cardiac functions of human bodies.
Owner:SHANGHAI 3F ELECTRONICS
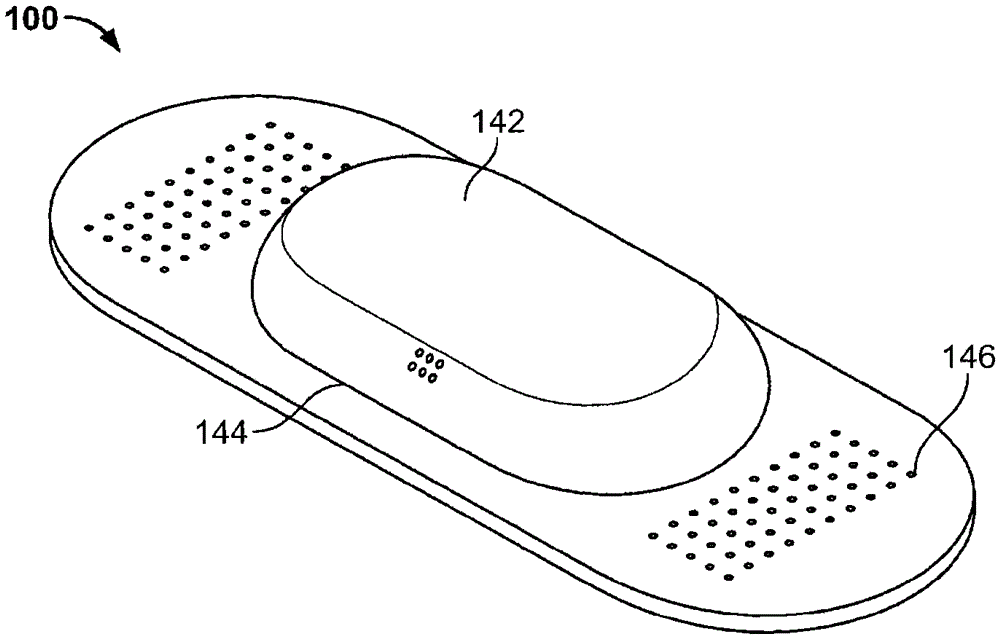
Wireless pregnancy monitor
A apparatus for automatically detecting a pregnancy status of a patient include a patch for adhering to human skin, a uterine contraction sensor, such as electromyography (EMG), coupled to the patch with at least two electrodes, and an inertial sensor for sensing fetal movement, or fetal heart rate (FHR) sensor, such as fetal EKG or a Doppler ultrasound. An electronic circuit is coupled to the patch, the EMG sensor and the inertial sensor, and / or FHR sensor. The circuit provides an output based on a uterine contraction signal from the EMG sensor (or the Doppler ultrasound) correlated in time to a fetal movement, and / or fetal heart rate. The apparatus may include a thermometer to aid in automatically providing an indication of a pregnancy complication or ovulation status of the patient, based on the output.
Owner:R·S·盖思特
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
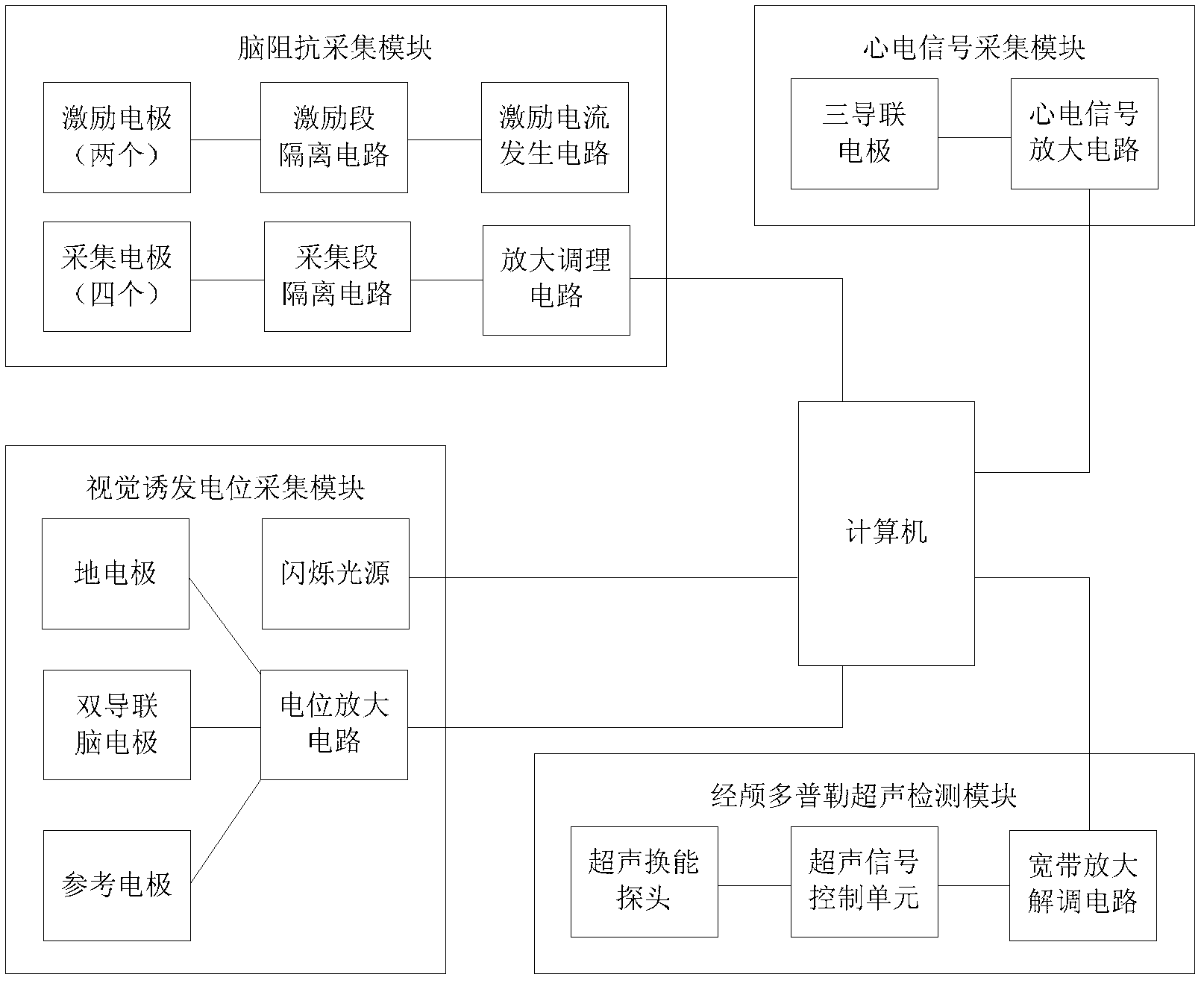
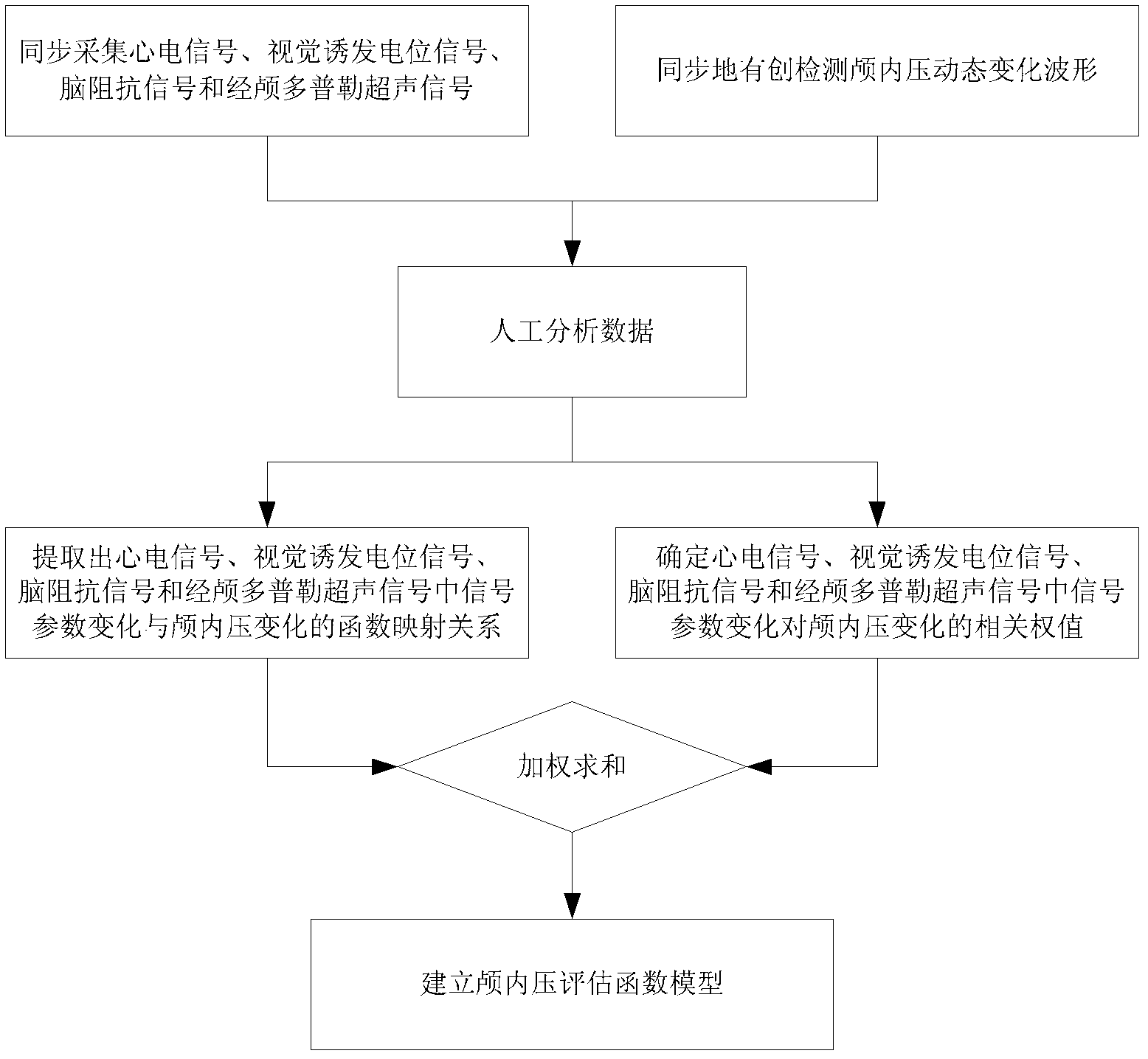
Multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device
InactiveCN102429651AHigh precisionGood clinical applicabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSonification
The invention provides a multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-establishing an intracranial pressure evaluation function model for recording a function mapping relation between the change of the intracranial pressure and the changes of an electrocardiosignal, a visual evoked potential signal, a brain impedance signal and a transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal and setting in a computer; and synchronously acquiring the electrocardiosignal, the visual evoked potential signal, the brain impedance signal and the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal into a computer and inputting the signals serving as the intracranial pressure evaluation function model to obtain the dynamic change process waveform of the intracranial pressure of an inspected object by performing multi-parameter and multi-direction operation. Due to the adoption of the method, invasive intracranial pressure detection is avoided; the device for implementing the method is easy to obtain; and meanwhile, various physiological and pathological signal parameters causing the change of the intracranial pressure are considered comprehensively in the intracranial pressure evaluation function model, so that the intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method has higher clinical detection accuracy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Method, device and system for determining the open/closed switch moment of an artery of interest under a changing pressure
ActiveUS20140148702A1Overcome limitationsHigh feasibilityBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationSonificationTransducer
The method of determining the open / closed switch moment of an artery of interest under a changing pressure comprises: detecting a first Doppler ultrasound signal from the blood flow in the artery of interest using a first Doppler ultrasound transducer, which is placed on the artery of interest in one limb which is provided with a cuff that is capable of being inflated or deflated to provide the changing pressure to the artery of interest; detecting a second Doppler ultrasound signal from the blood flow in a reference artery using a second Doppler ultrasound transducer, the reference artery being in any one of the other three limbs; deriving a third signal from the first Doppler ultrasound signal and the second Doppler ultrasound signal, the third signal indicating the degree of synchronism between the first Doppler ultrasound signal and the second Doppler ultrasound signal; and out-putting a fourth signal to indicate the artery of interest is closed or reopened at the moment when the third signal satisfies a predefined condition. By utilizing the second ultrasound signal as a reference and deriving a signal indicating the synchronization property between the two ultrasound signals, the open / closed status of the artery of interest under a changing pressure can be determined more stably and more reliably regardless of the detailed condition of the patient.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for non-invasive fetal oximetry
ActiveUS8275436B2Improve accuracyHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsObstetricsFetal heart rate
Method and apparatus to non-invasively measure fetal blood oxygen saturation levels. Optical sensors capable of producing and detecting multiple wavelengths of tissue penetrating light are placed on the surface of the maternal abdomen, and the light beams directed to pass through at least a portion of the uterus containing the fetus. The fetal heart rate is monitored by Doppler ultrasound, and pure maternal optical signal related to maternal arterial blood flow are also measured. The optical sensors collect composite signals containing both maternal and fetal hemoglobin absorption spectral data and modulated by their respective pulsatile blood flows. The composite signals processed in the time domain and frequency domain, the pure maternal pulsatile optical signal used to extract the maternal contribution to the composite signal, and the fetal pulsatile signal is used to lock onto and extract the fetal contribution to the composite signal, and a fetal blood oxygen level deduced.
Owner:BEIJING WEITEXING TECH CO LTD
Method and system for measuring pulse wave propagation speed
ActiveCN105310724ASimple methodEasy to operateBlood flow measurement devicesHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesHuman bodyDoppler ultrasonics
The invention discloses a method and system for measuring pulse wave propagation speed. The method includes: measuring and recording artery pulse wave of a certain part of a human body by using Doppler ultrasound to obtain a Doppler ultrasonic signal strength-time map, measuring a time difference Delta t between a main peak descending branch end and a re-pulse wave start on the time map, calculating an artery total length L from a main artery root to a pulse wave measurement site according to the height H of a testee, pulse wave propagation speed S of the testee on this artery measurement section being equal to a ratio of L to Delta t. The invention provides a novel method of measuring artery pulse wave speed by using the method of measuring pulse wave signals using Doppler ultrasound, in the hope of providing theoretical and technical basis for further clinical application. In addition, the method is simple, operating is convenient, measuring accuracy is higher, and clinical level is partly increased.
Owner:江苏合心医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com