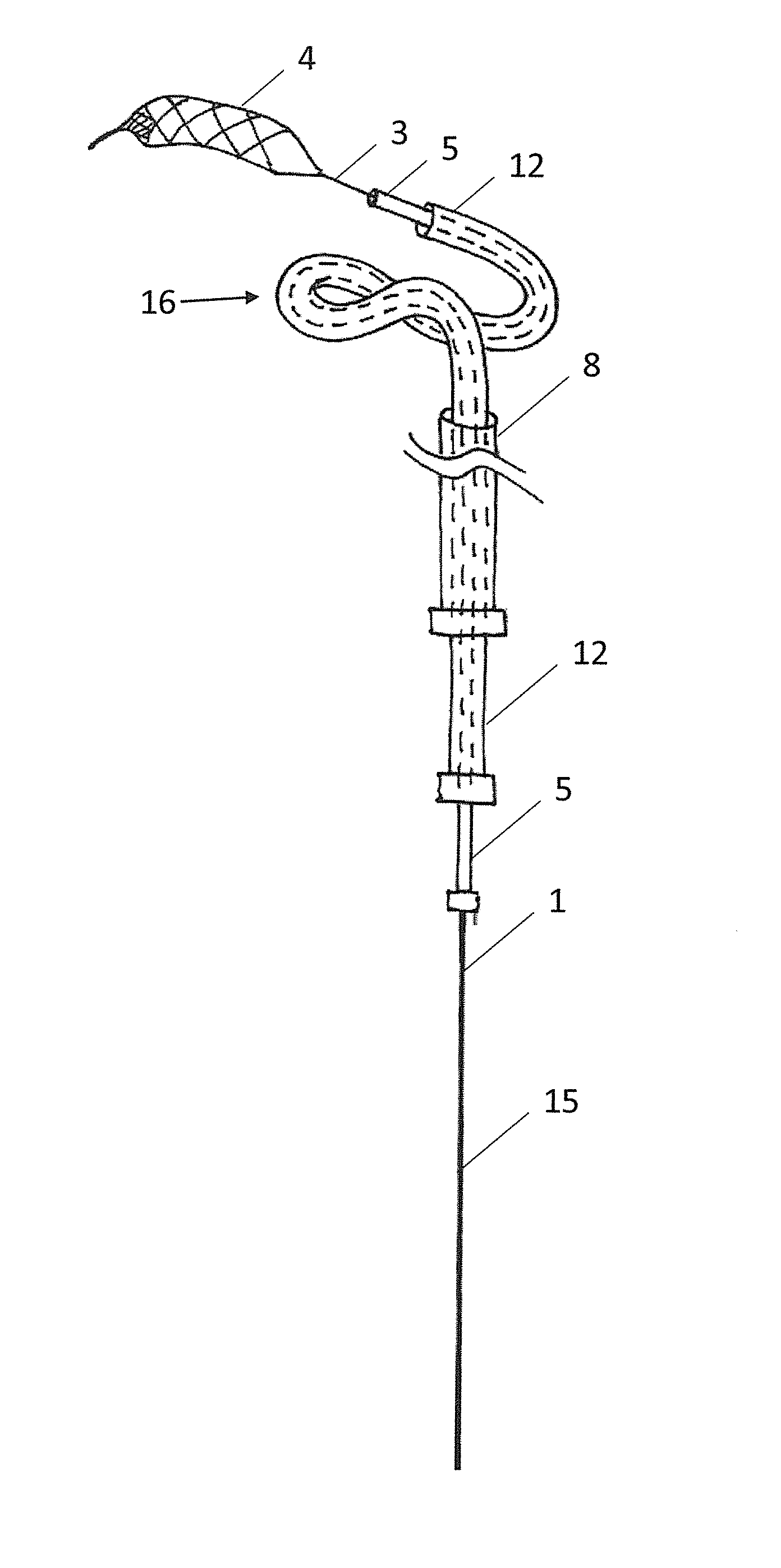
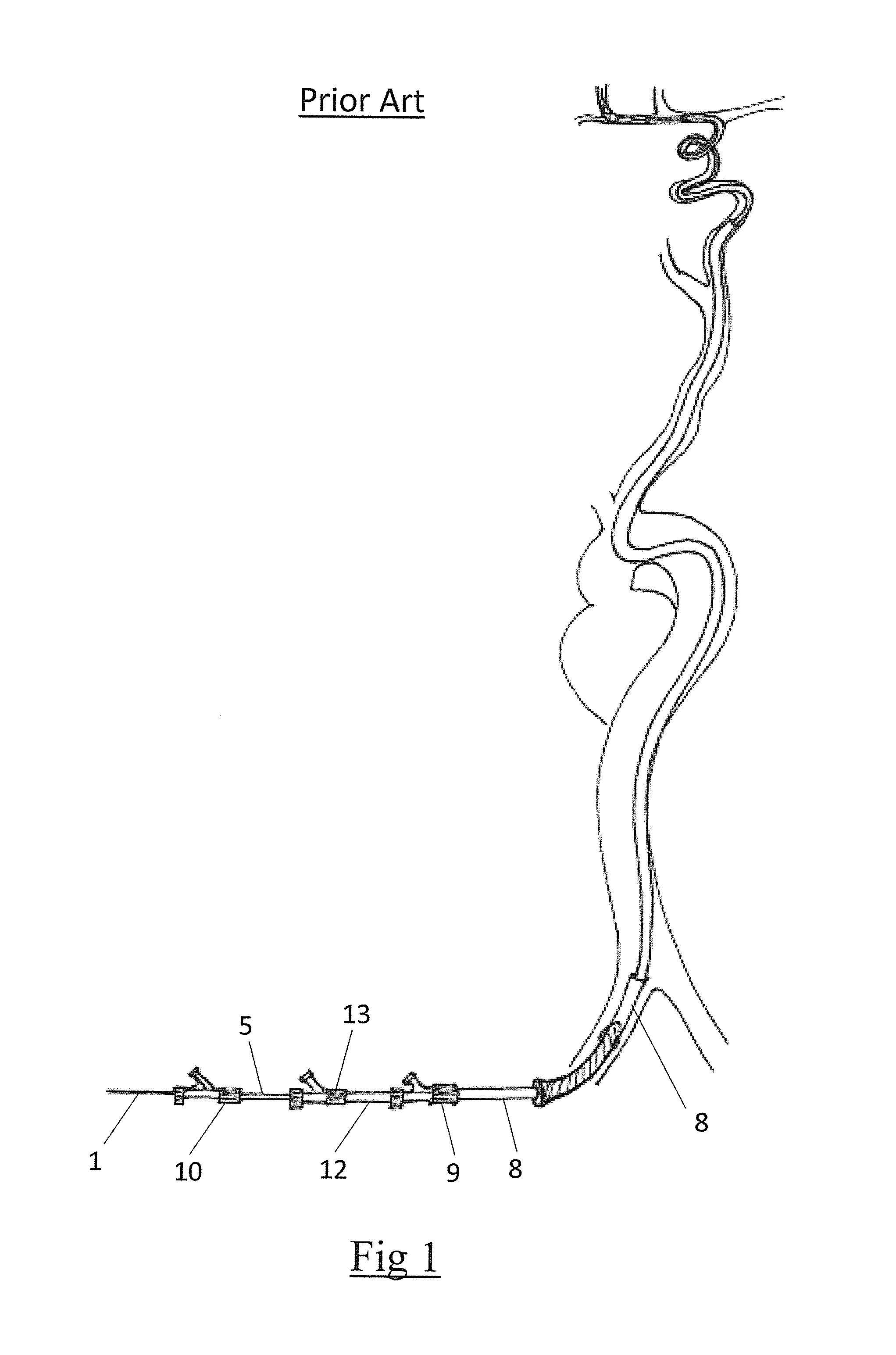
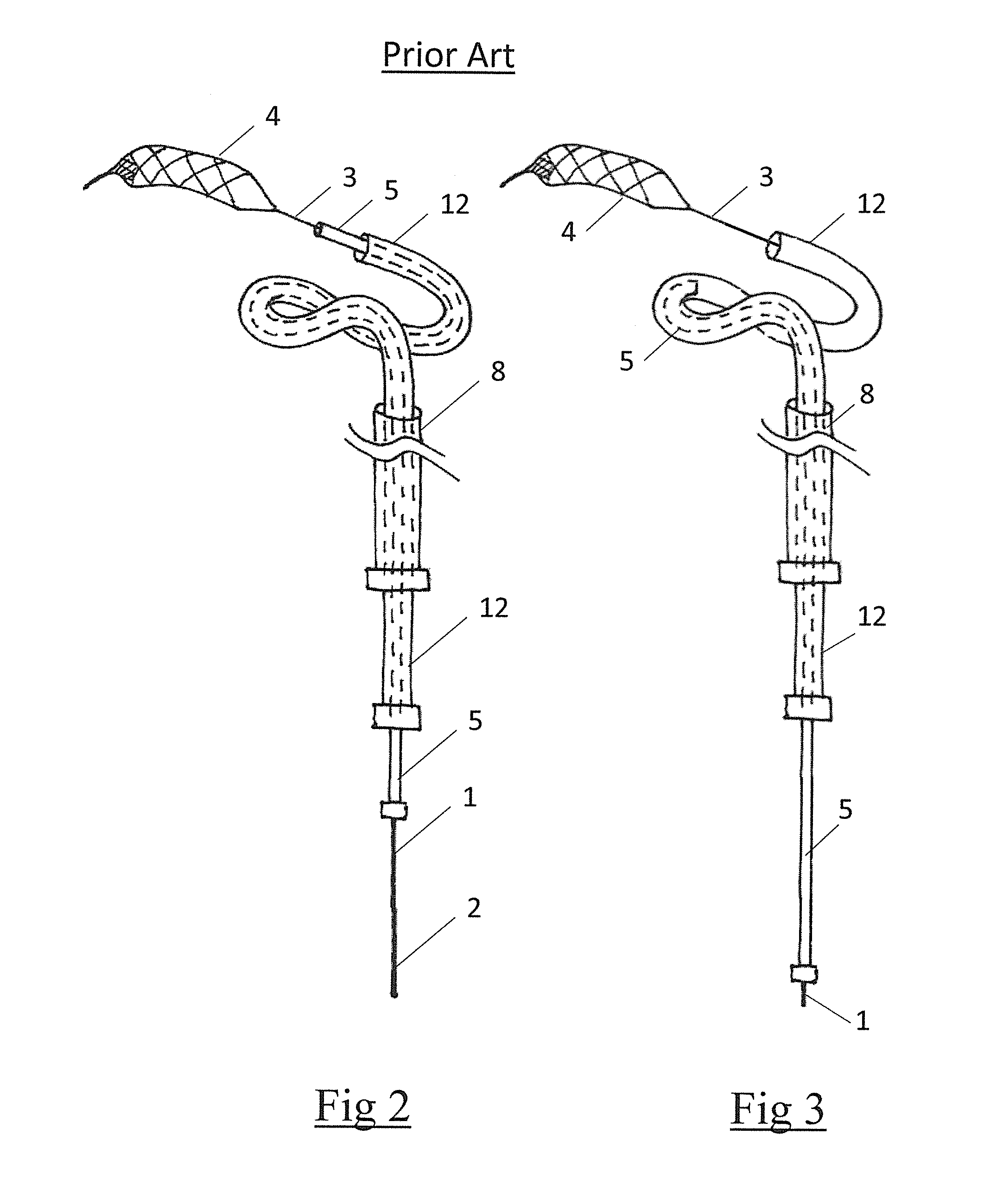
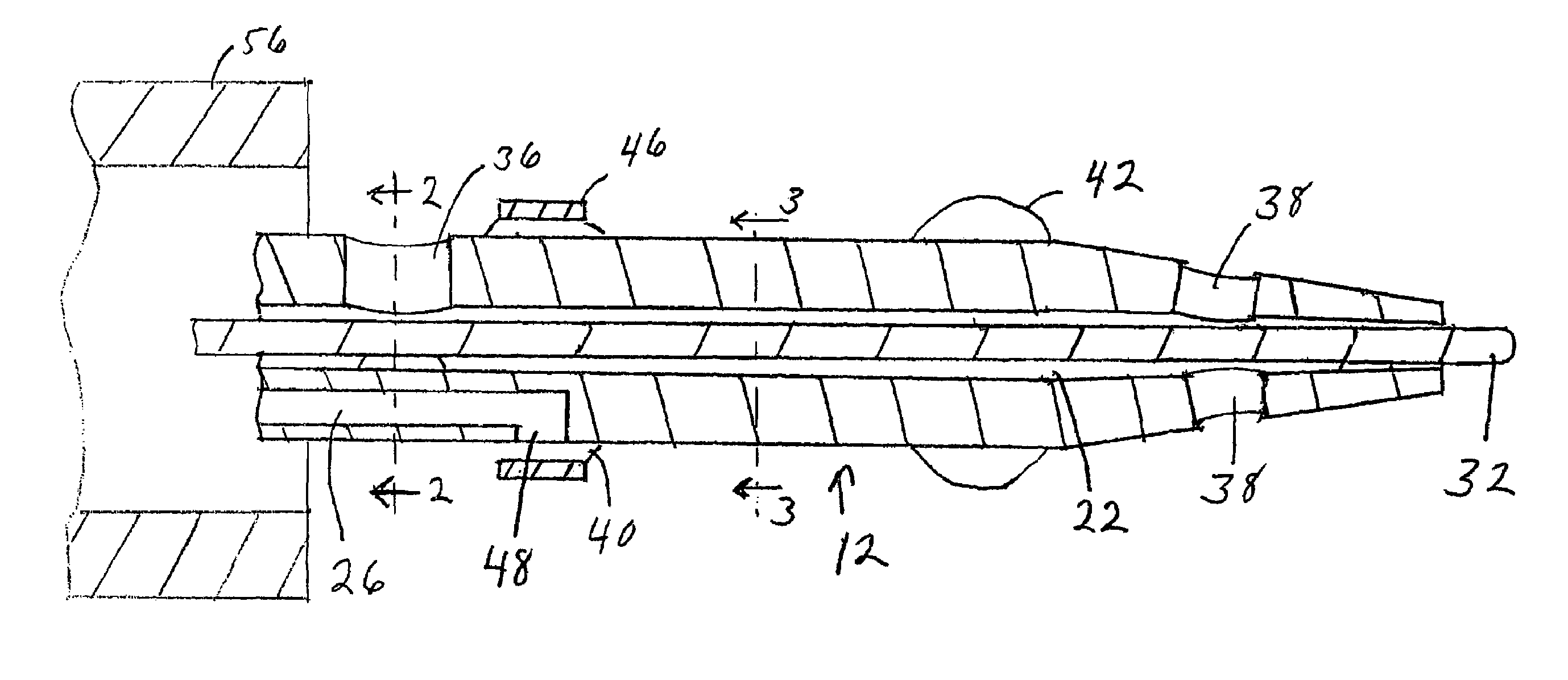
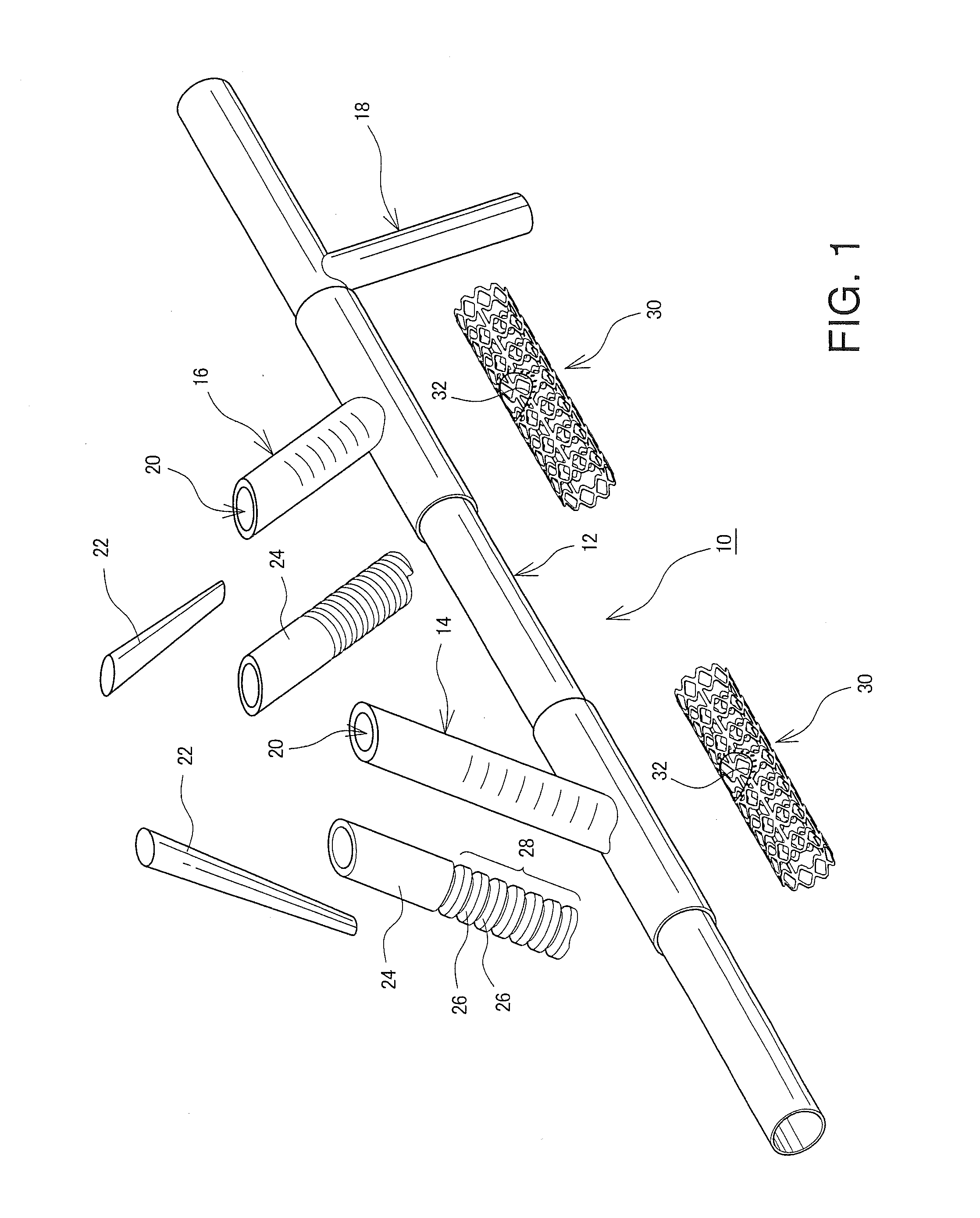
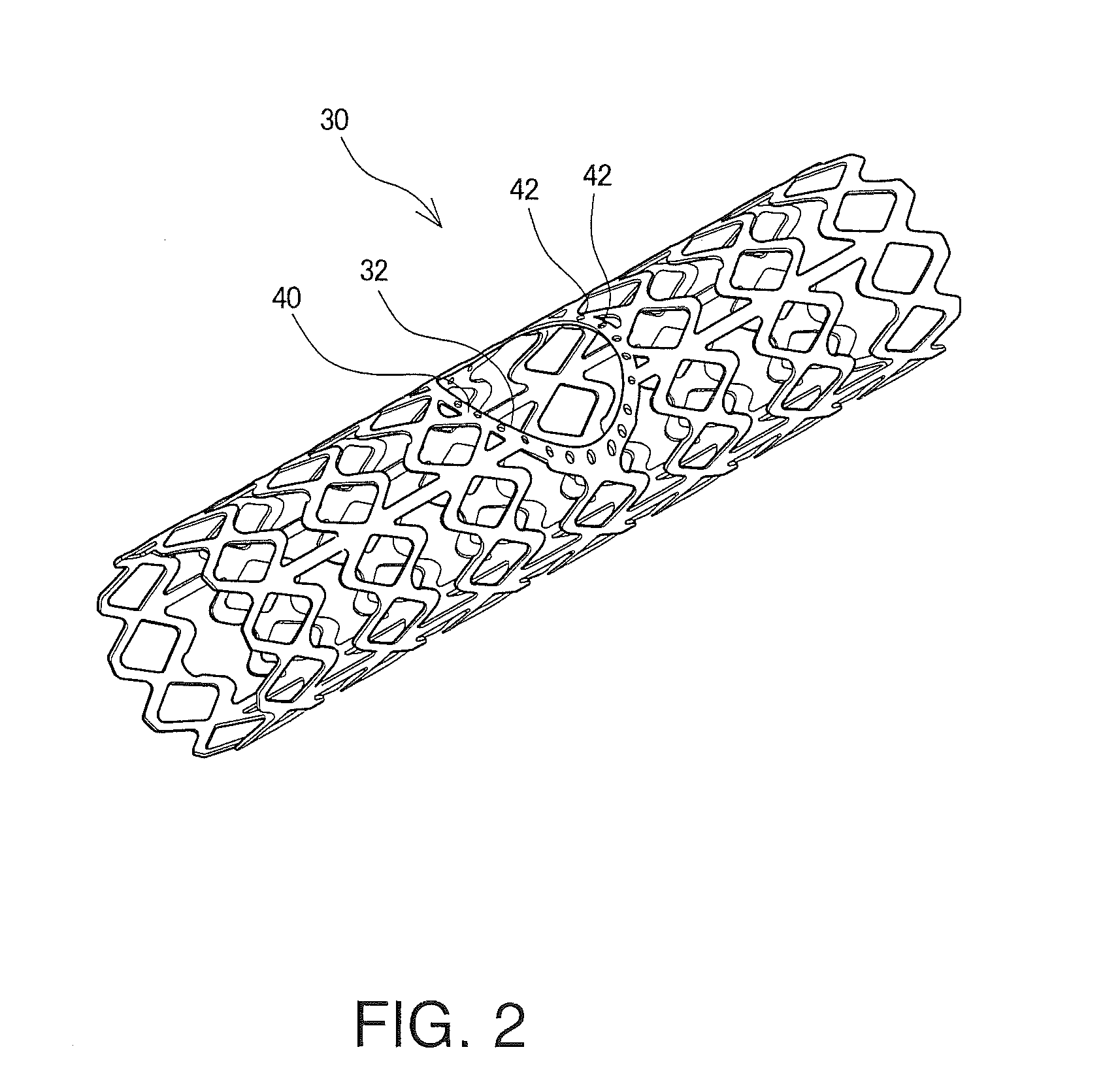
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Blood vessel spasm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood vessel spasms occur when small vessels in the body, usually in the extremities such as toes and fingers, narrow and constrict, preventing blood flow to the affected region of the body.
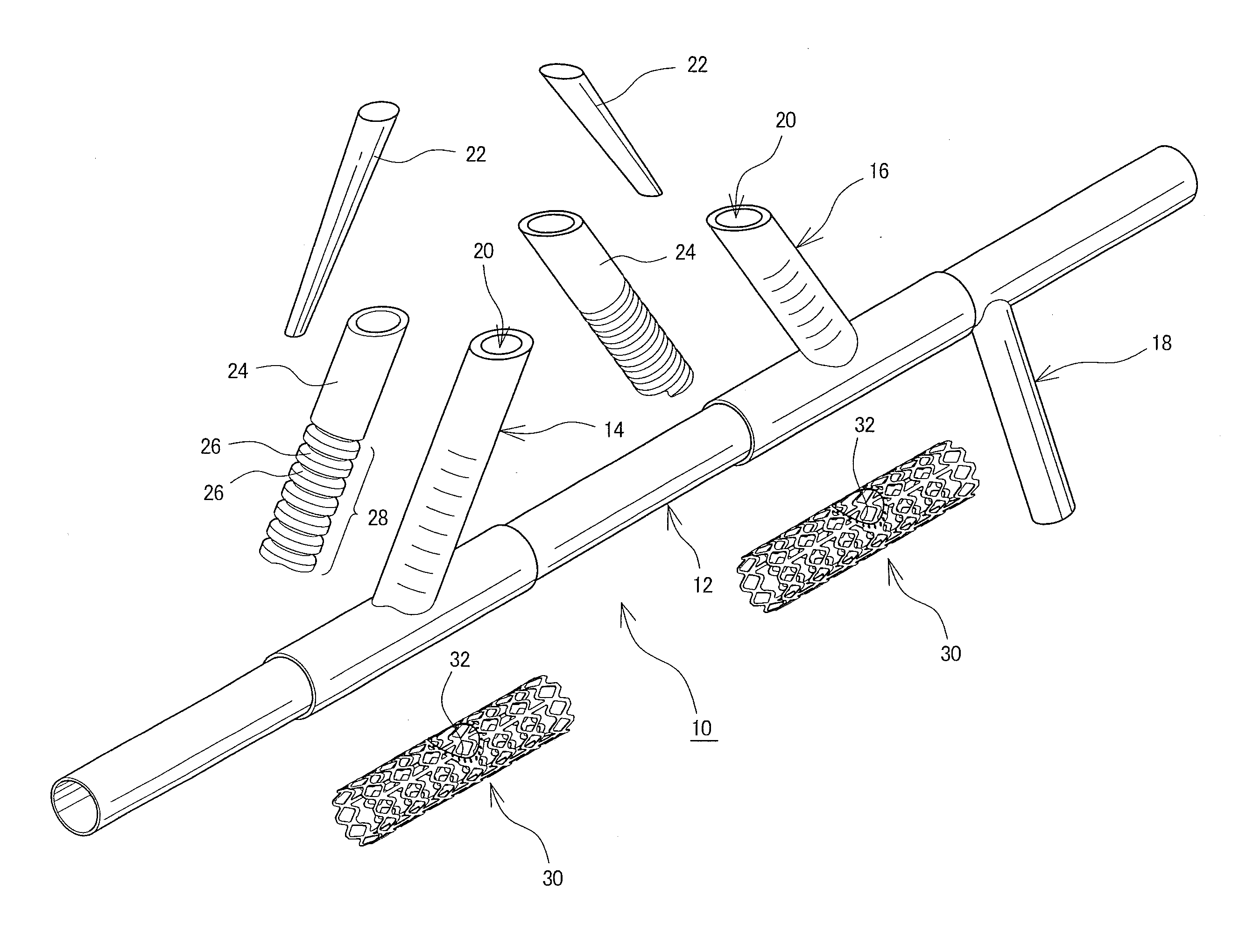
Vein dissector, cauterizing and ligating apparatus for endoscopic harvesting of blood vessels
Owner:TERUMO KK
Devices for creating passages and sensing blood vessels
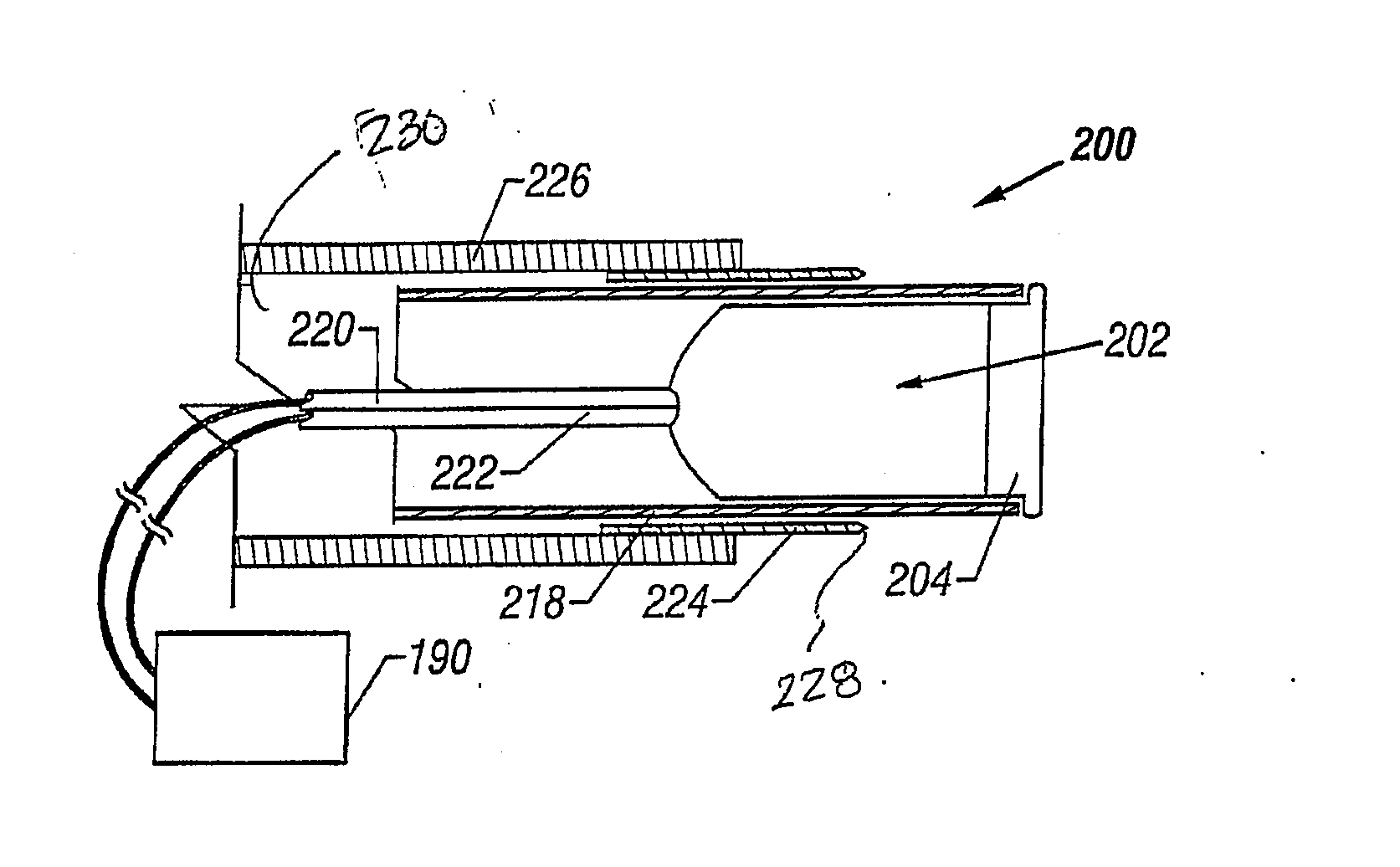
InactiveUS20090143678A1Great pressurizationStentsBronchoscopesBlood vessel spasmObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices and methods are disclosed for creating passages in tissue and detecting blood vessels in and around the passages. The devices may be used to create channels for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). In addition, the devices may be used to sample tissue during biopsy or other medical procedures where perforating a blood vessel could result in injury to a patient.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
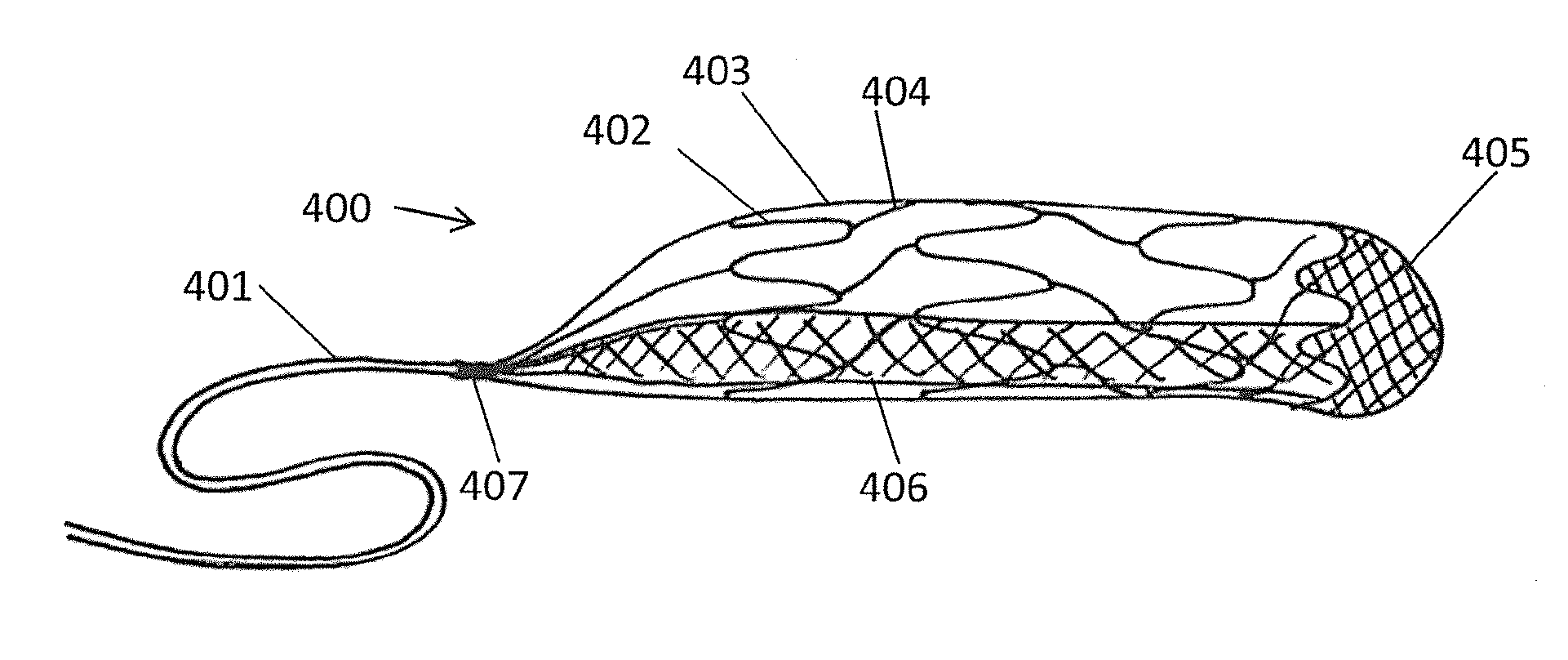
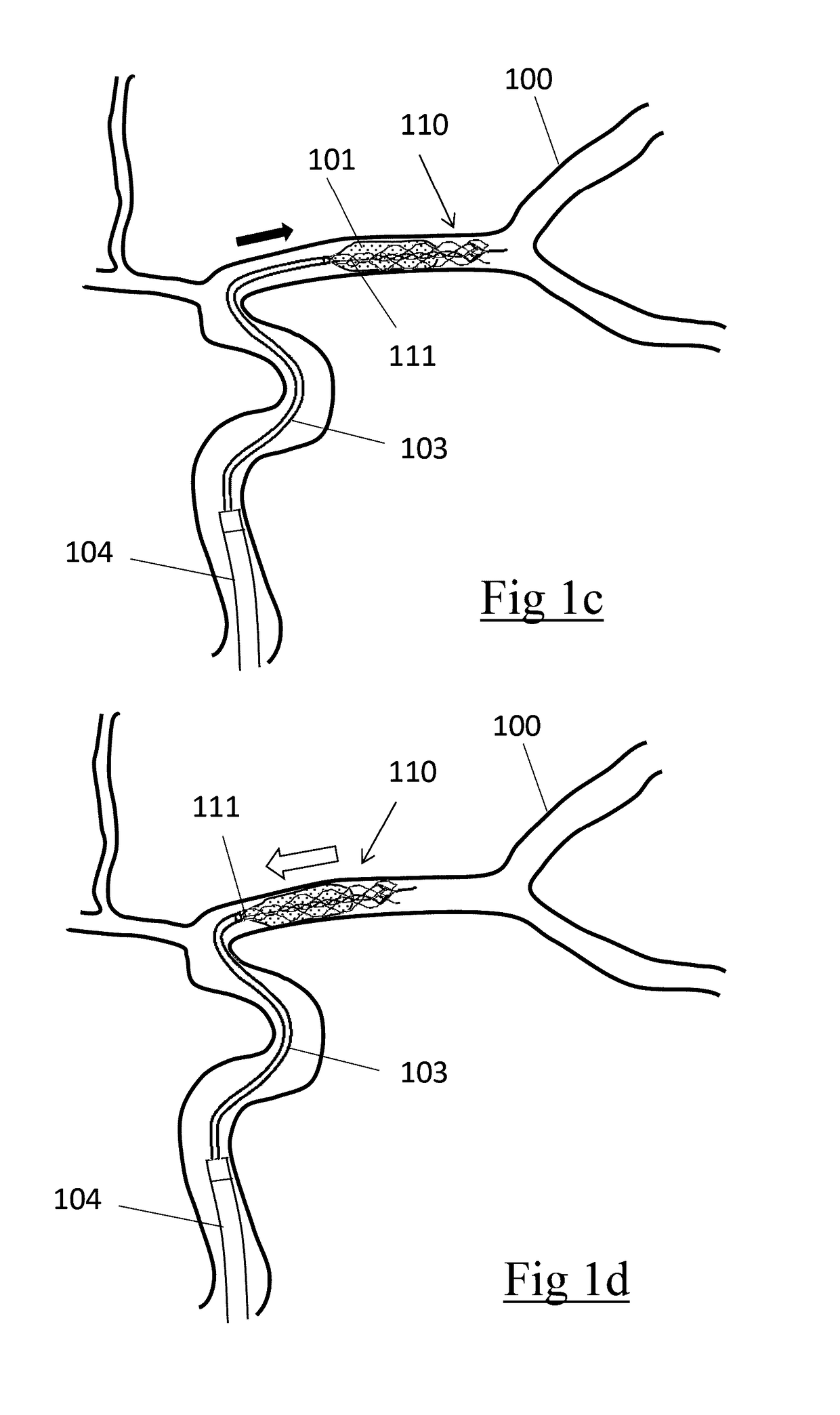
Implant which is intended to be placed in a blood vessel
This implant comprises an endoprosthesis having an axis which can be spontaneously deployed in a radial manner between a compressed configuration and a dilated configuration. The implant comprises at least one radial runner which comprises a separation surface which extends radially with respect to an outer surface of the endoprosthesis and a member which can be deployed away from the axis. The runner is arranged so as to delimit a confinement housing which extends between the separation surface and the outer surface and a radial spacer which is defined by the separation surface and the deployable member. When the implant is retained in a state of radial compression, the maximum radial width of the housing is less than the maximum radial width of the spacer which is not equal to zero.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
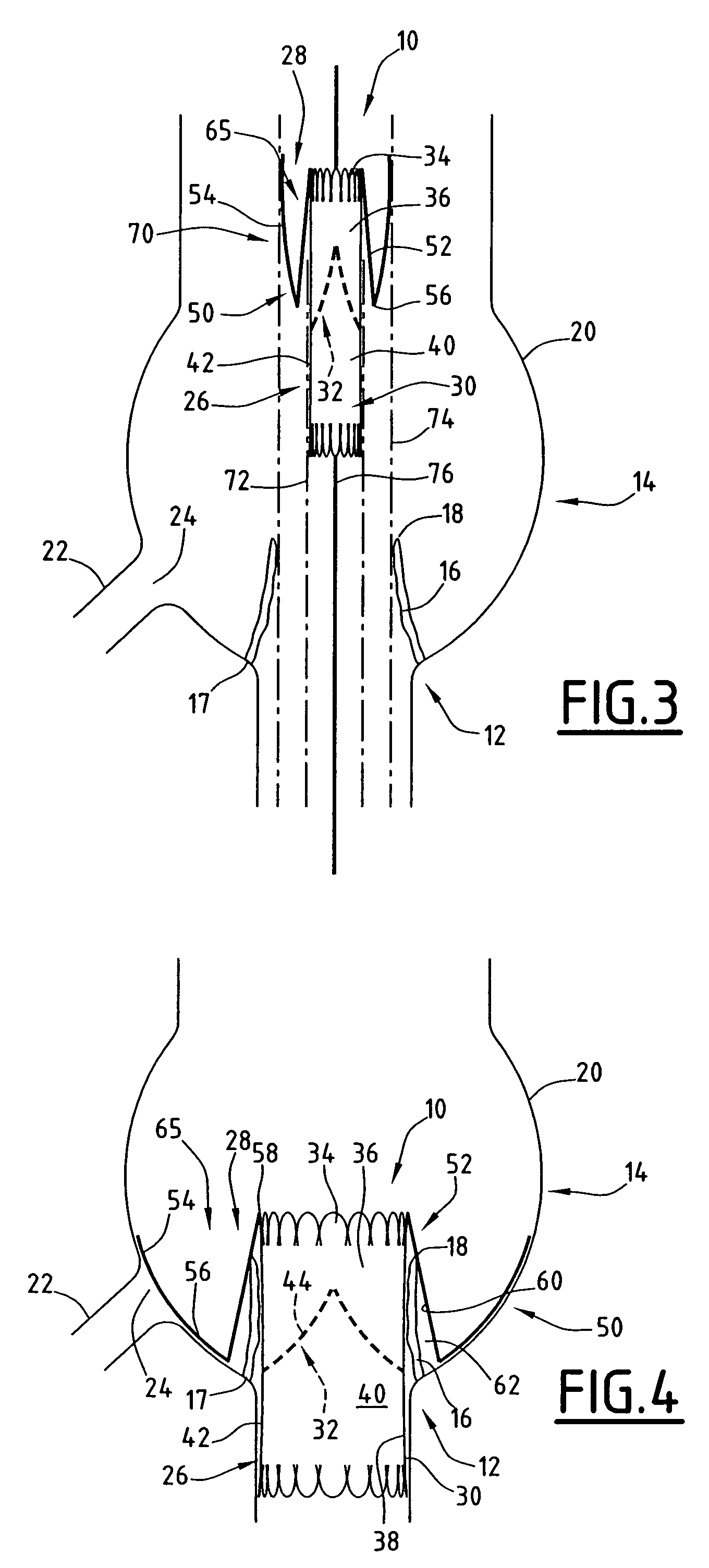
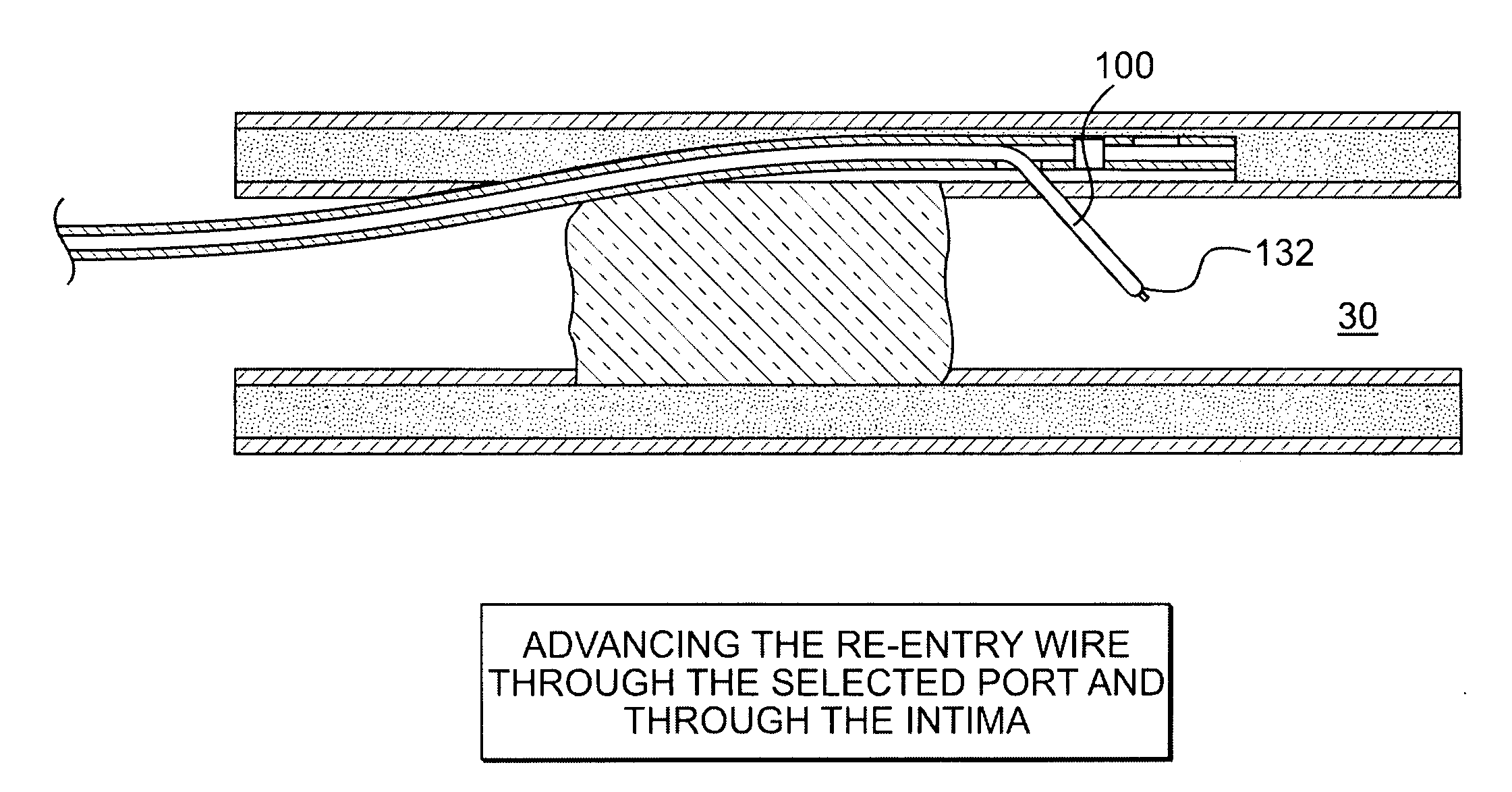
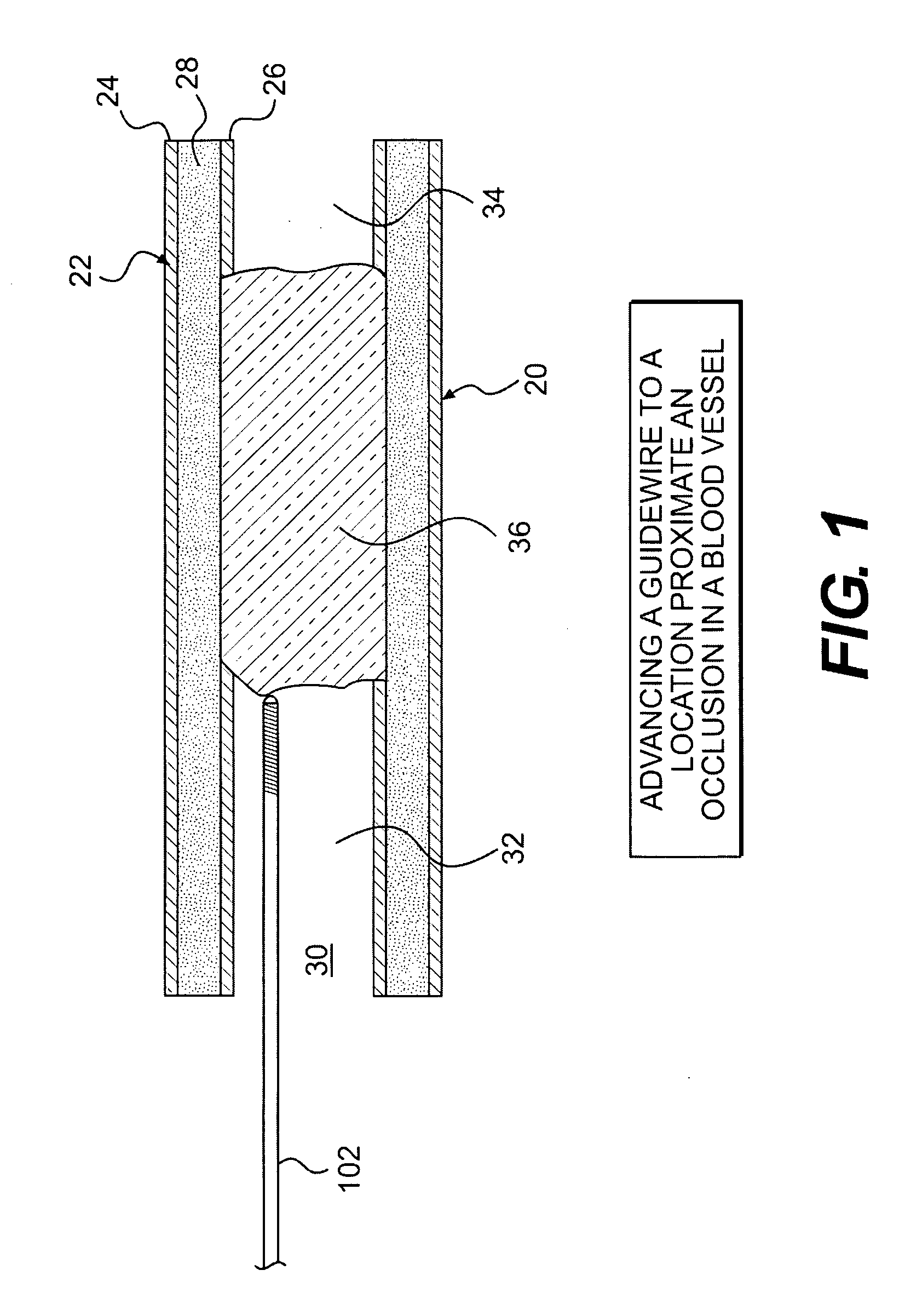
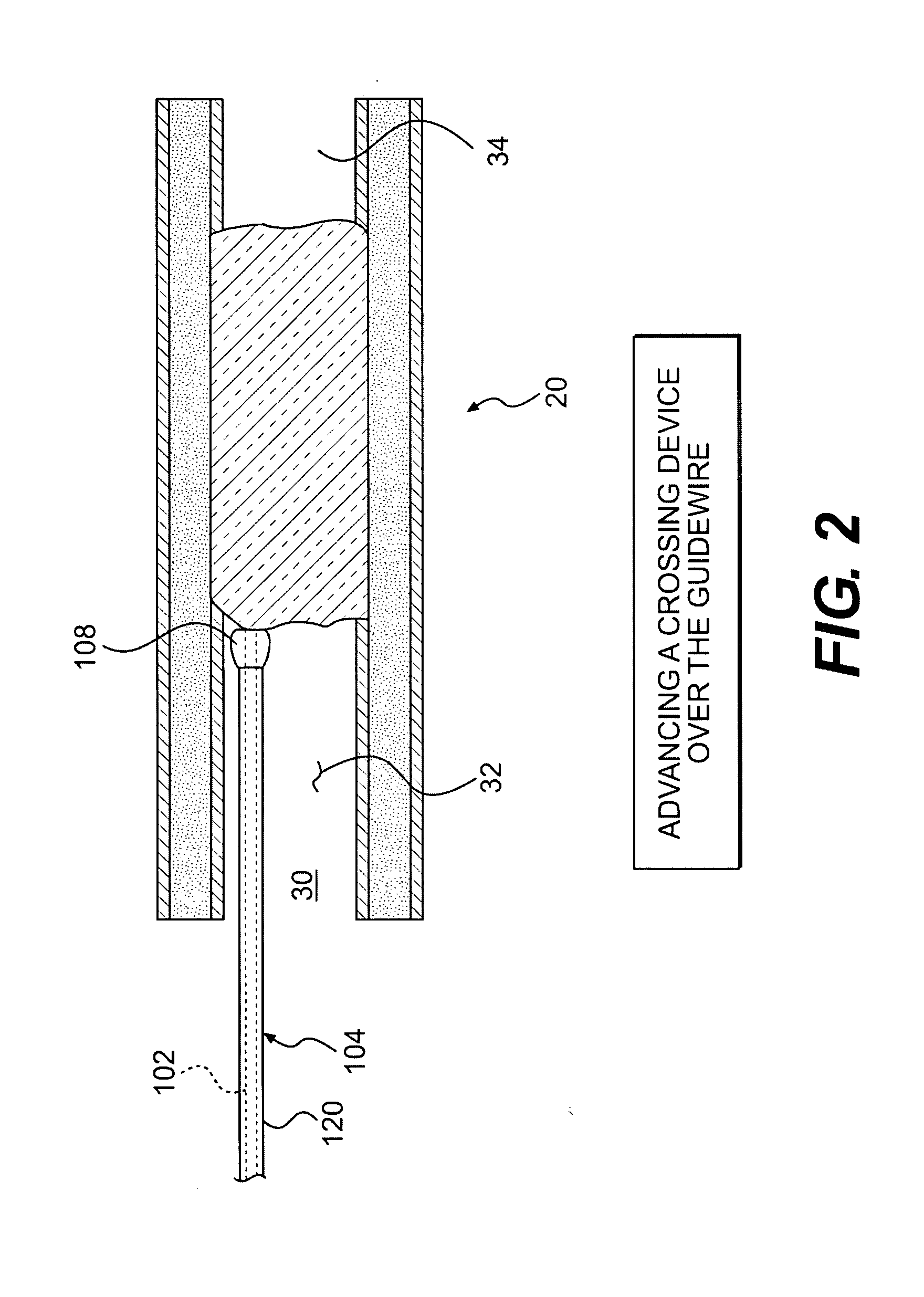
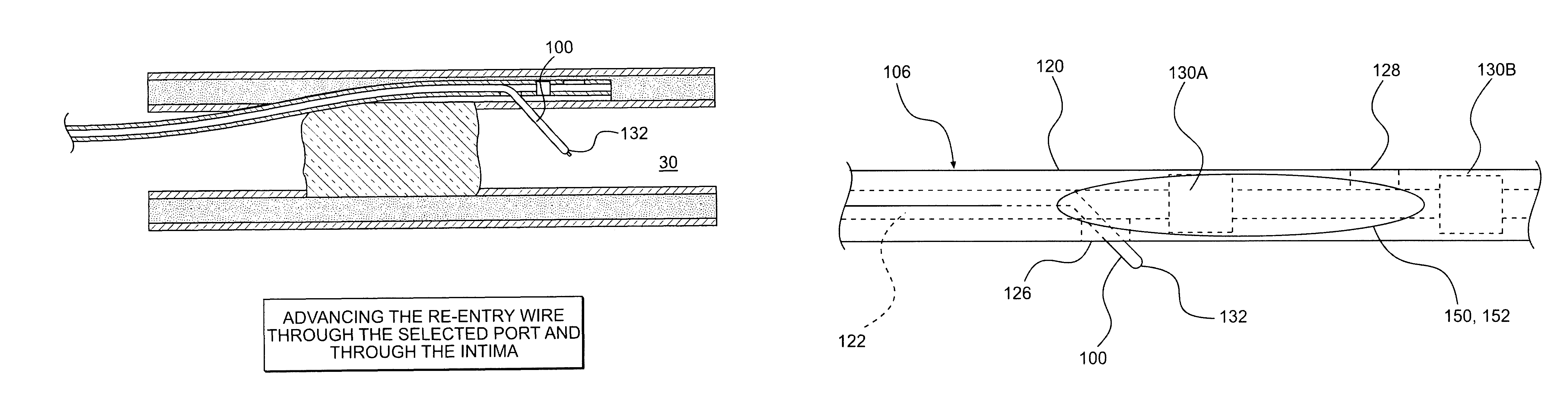
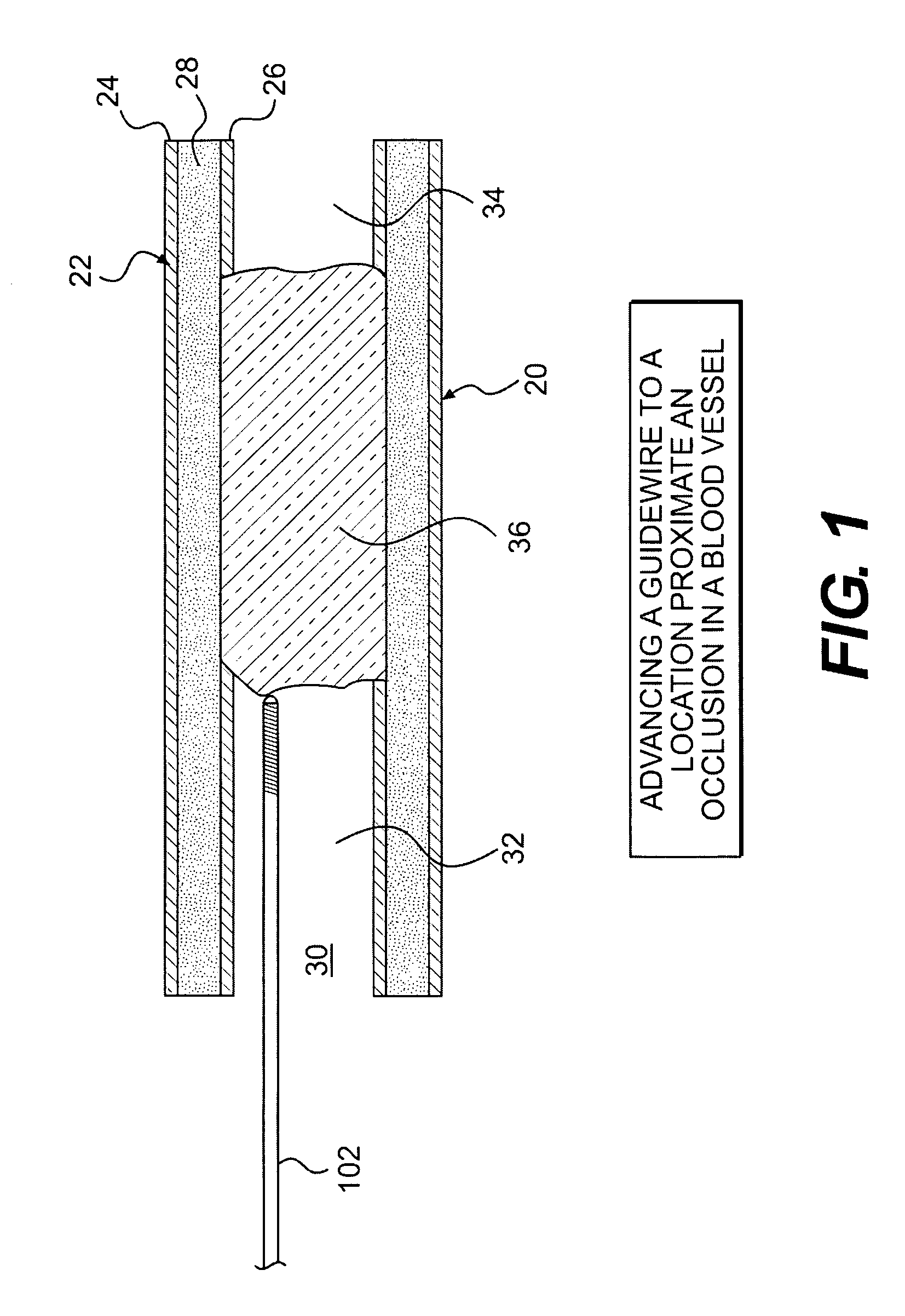
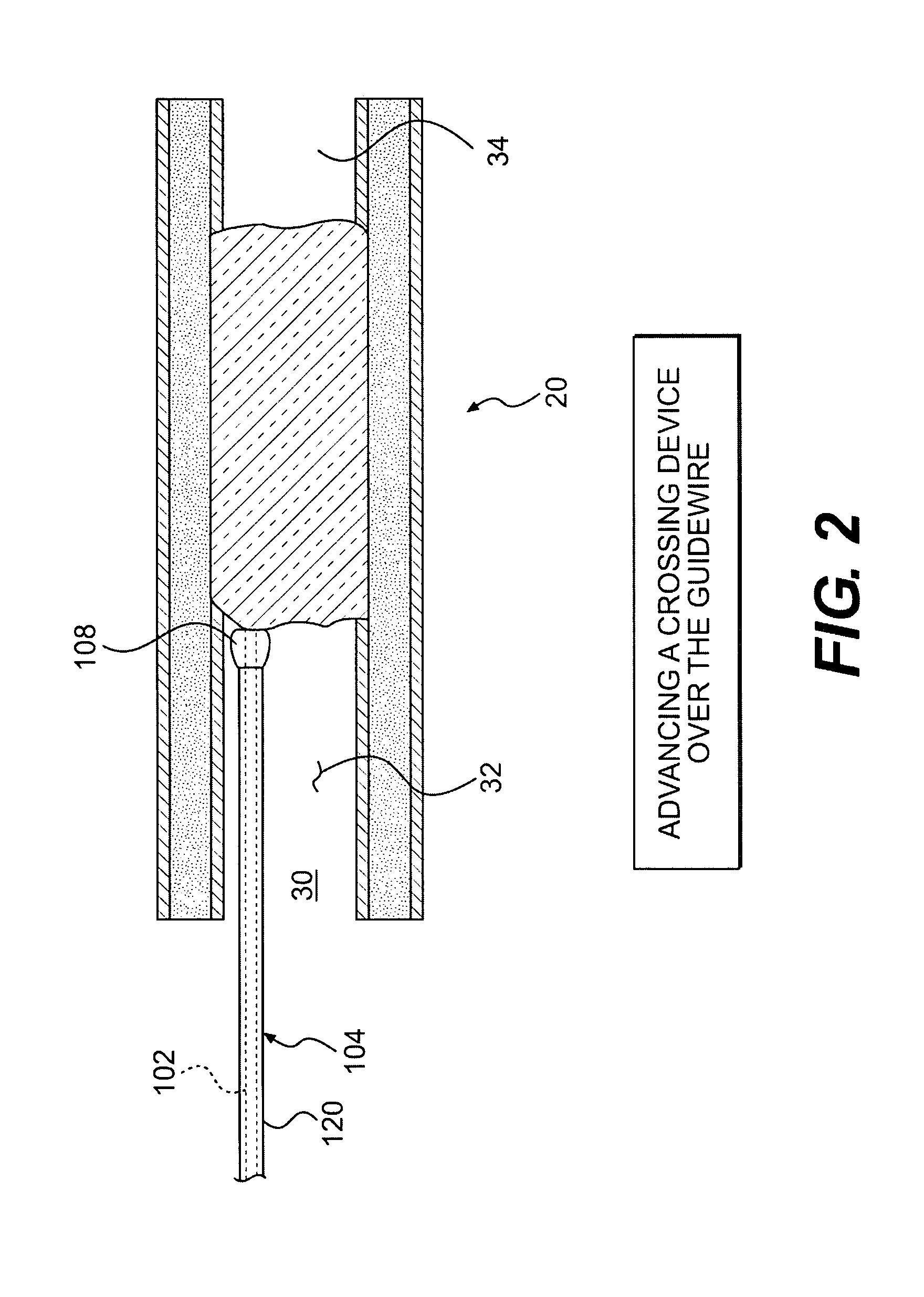
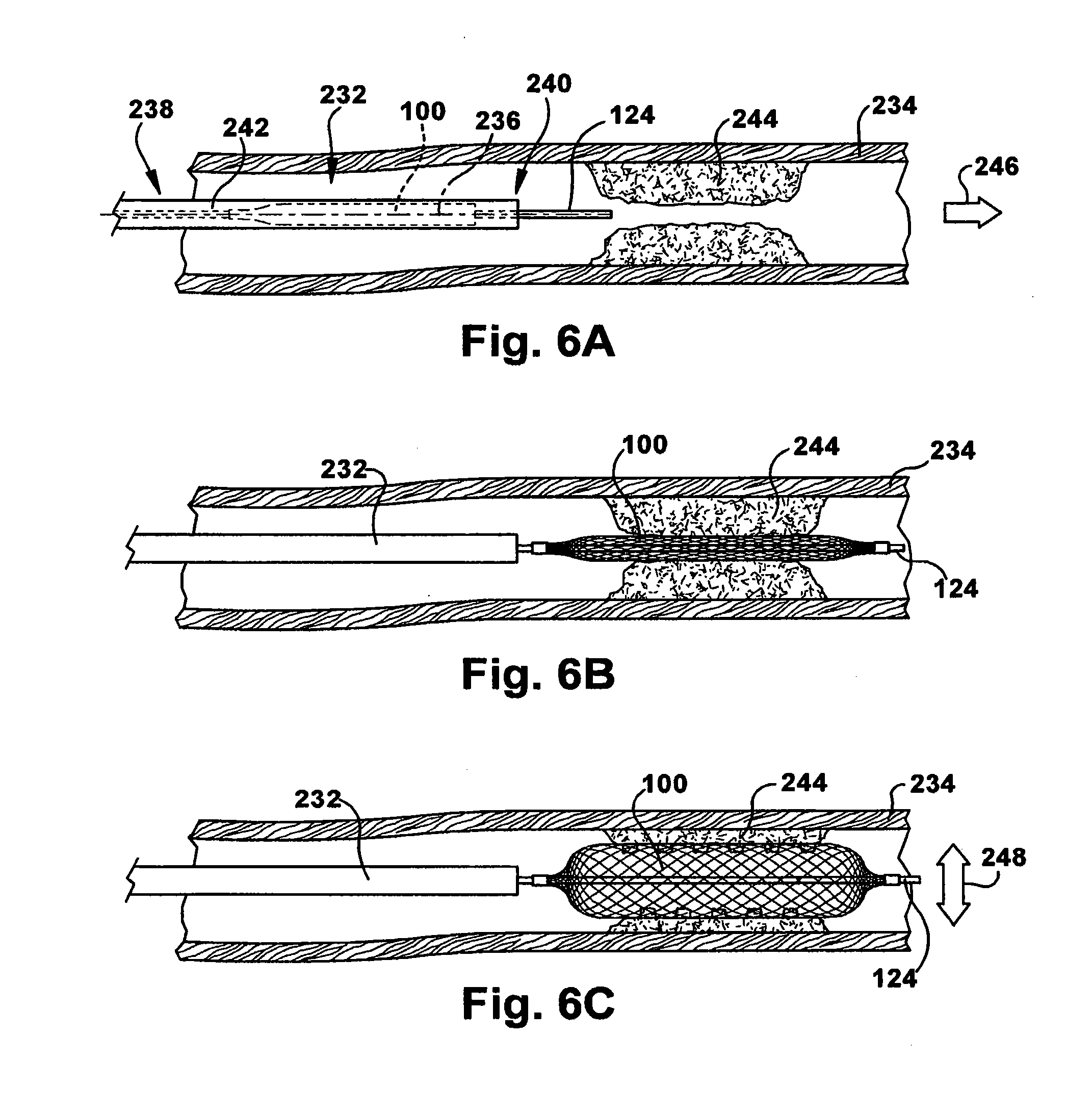
Crossing occlusions in blood vessels
The present disclosure is directed a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method may include providing a first intravascular device having a distal portion and at least one aperture and positioning the distal portion of the first intravascular device in the vascular wall. The method may further include providing a reentry device having a body and a distal tip, the distal tip having a natural state and a compressed state and inserting the distal tip, in the compressed state, in the distal portion of the first intravascular device. The method may further include advancing the distal tip, in the natural state, through the at least one aperture of the first intravascular device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Clot retrieval device for removing occlusive clot from a blood vessel
ActiveUS20150164523A1Prevent distal egressReduce radial forceDilatorsExcision instrumentsDistal portionBlood vessel spasm
Owner:NEURAVI
Noninvasive treatment of blood vessels
InactiveUS20120330197A1Good effectHighly focusedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyVascular diseaseBlood vessel spasm
A non-invasive method and system for using ultrasound energy for the treatment of conditions resulting from vascular disorders is provided. In one embodiment, an image-treatment approach can be used to locate the blood vessel to be treated and then to ablate it non-invasively, while also monitoring the progress of the treatment. In another embodiment, a transducer is configured to deliver ultrasound energy to the regions of the superficial tissue (e.g., skin) such that the energy is deposited at the particular depth at which the vascular malformations are located below the skin surface. The ultrasound transducer can be driven at a number of different frequency regimes such that the depth and shape of energy concentration can match the region of treatment.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
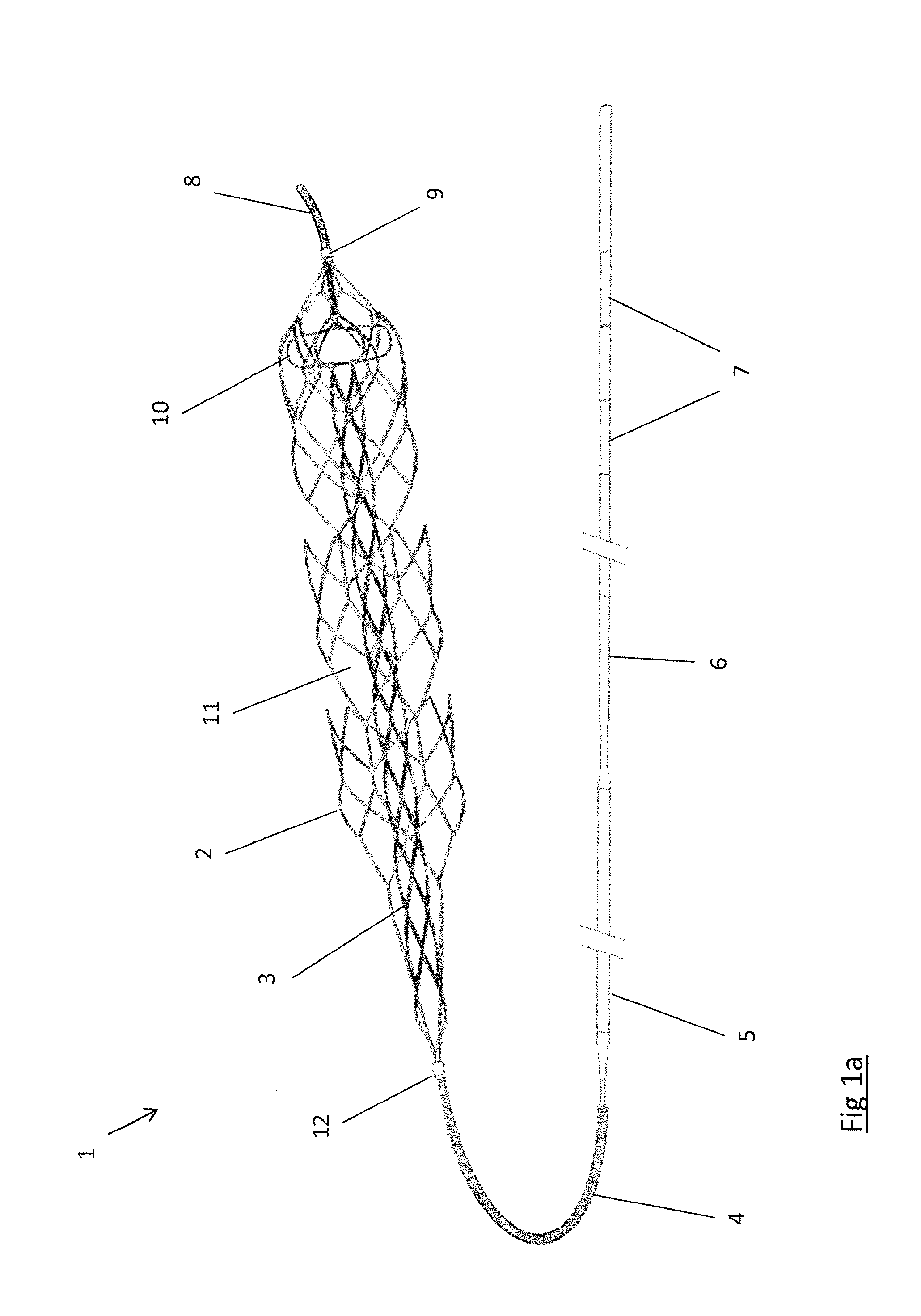
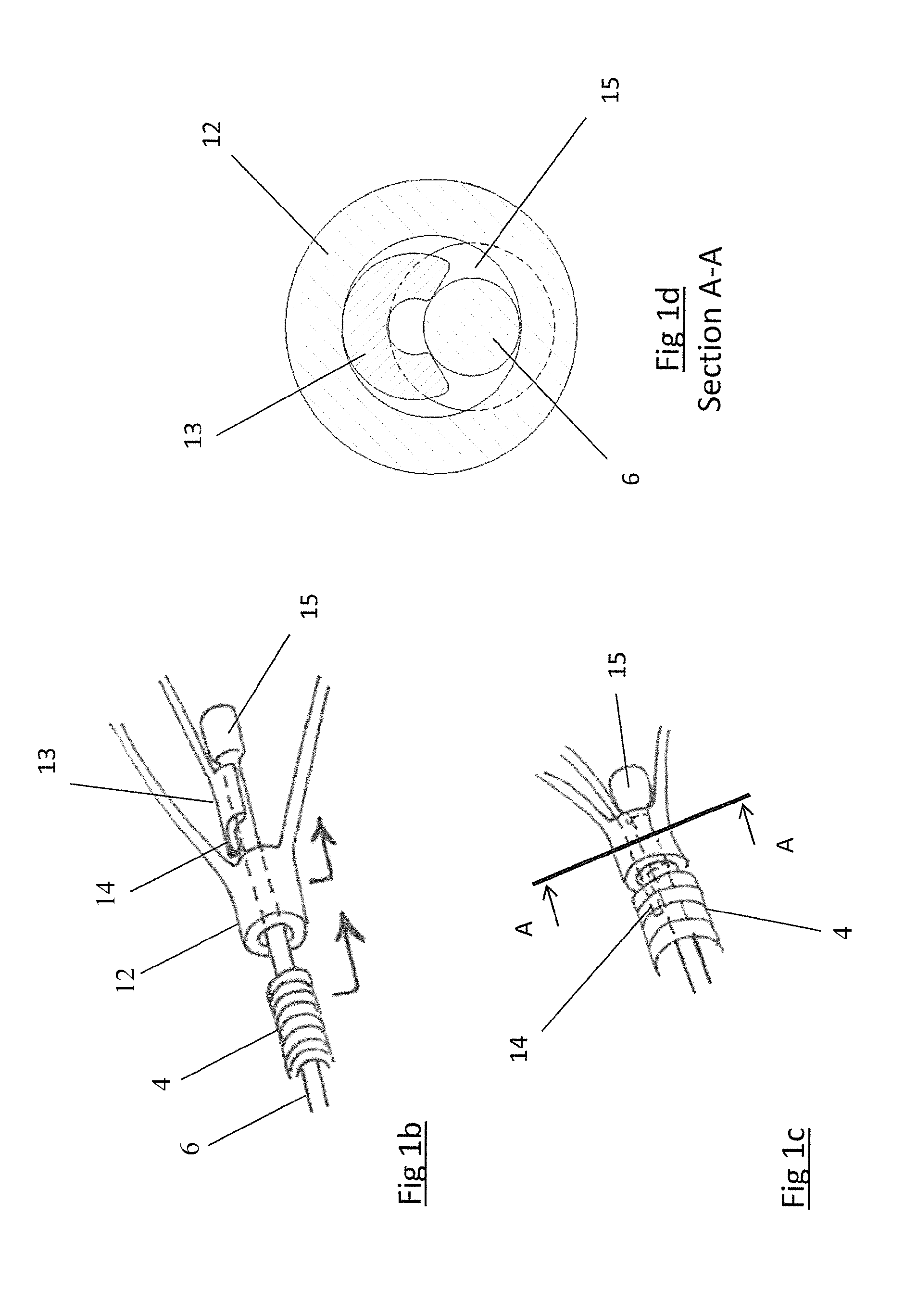
Method for engrafting a blood vessel
A method for deploying an endoluminal prosthesis by introducing into a bifurcated vessel a sheath introducer having therein a bifurcated graft with a primary and contralateral limb. The contralateral limb being radially retained independent of the sheath introducer. The graft being positionable by an insertion catheter. When the graft is in position within the vessel, a retaining device about the contralateral limb is broken and the graft takes the shape of the vessel.
Owner:WORLD MEDICAL MFG
Apparatus for suturing a blood vessel
InactiveUS7041119B2Accurate operationShort amount of timeSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleDistal portion
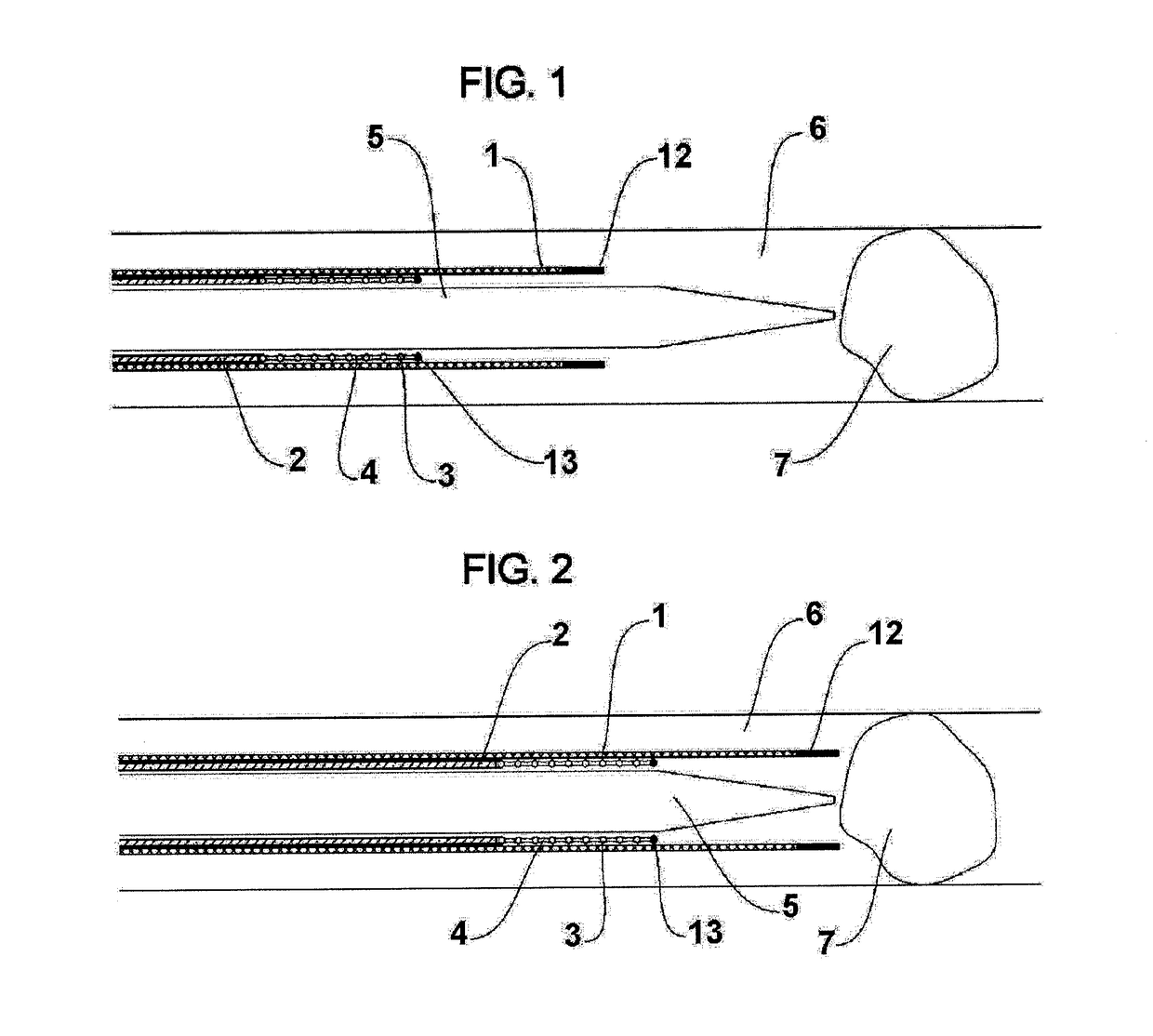
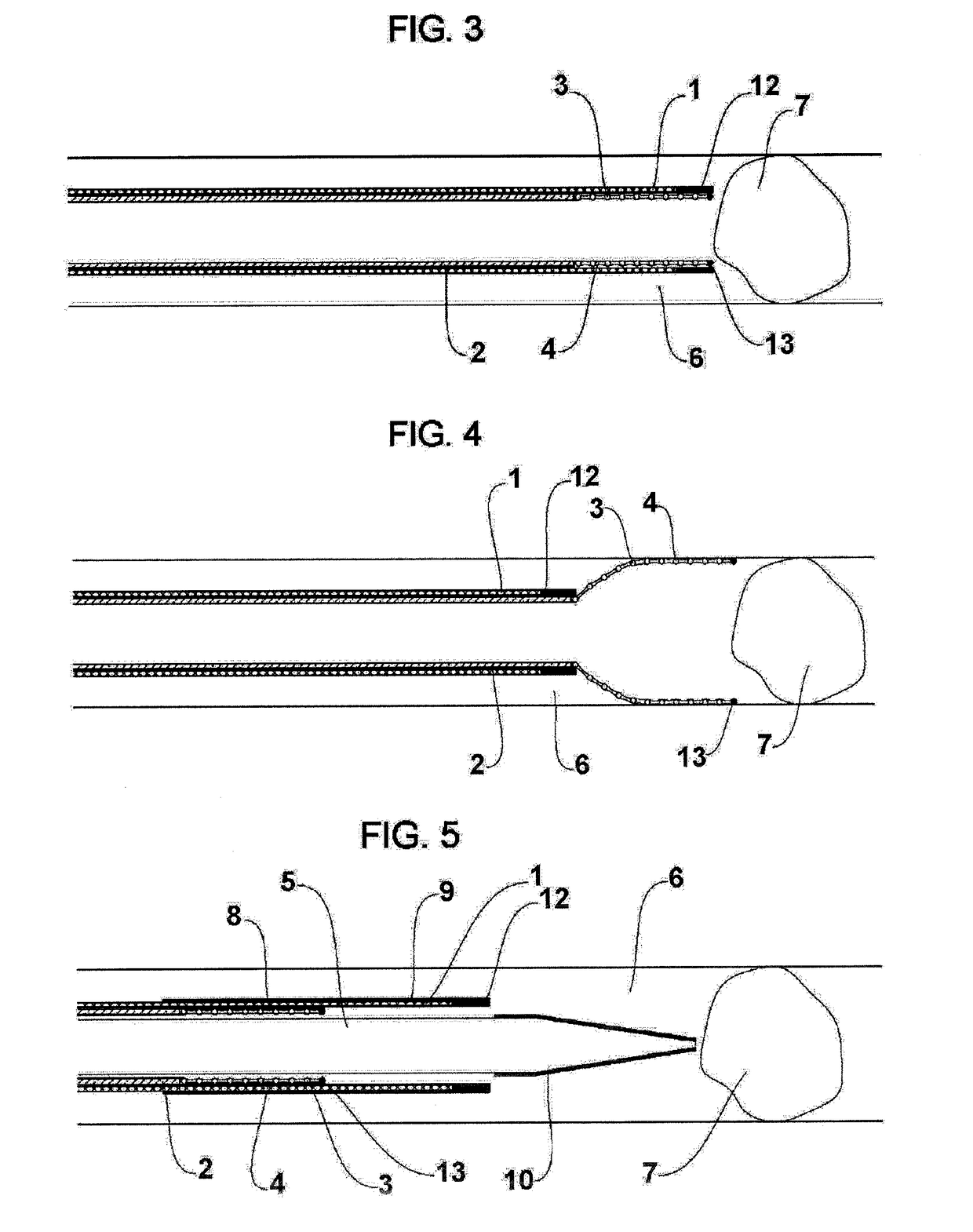
A vascular suturing device is disclosed which includes an elongated tubular body defining opposed proximal and distal end portions and having a longitudinal axis extending therethrough, the body including an inner tubular member, an outer tubular member and a central tubular member disposed between the inner and outer tubular members. The inner tubular member and the central tubular member are mounted for movement relative to the outer tubular member about the longitudinal axis of the body for sequentially driving a pair of suture needles through the wall of a blood vessel to close an incision formed therein. A vascular dilator having a tapered distal tip portion is supported within the inner tubular member and is dimensioned to extend beyond the distal end of the inner tubular member for positioning the suturing device at the incision in the wall of the blood vessel. The dilator is configured to direct blood flow from the distal portion of the dilator to a location remote from the blood vessel for observation to confirm the location of the device.
Owner:GREEN DAVID T
Linear material for blood vessel stent and blood vessel stent utilizing same
InactiveUS7070615B1Good antithrombotic propertiesImprove physical functionStentsSurgeryCoronary arteriesBlood vessel spasm
Owner:KYOTO MEDICAL PLANNING
Stent device for anastomoses of blood vessels and other tubular organs
A method for connecting two blood vessels or other tubular organs in end-to-end fashion and a stent therefor including a central portion that may be expanded, nipples at opposite ends of the central portion and a lumen passing through the central portion and the nipples. The nipples may be of different cross-sectional sizes or funnel-shaped to enable the stent to be used in attaching two vessels or organs of different diameters.
Owner:EIDOSMED LLC
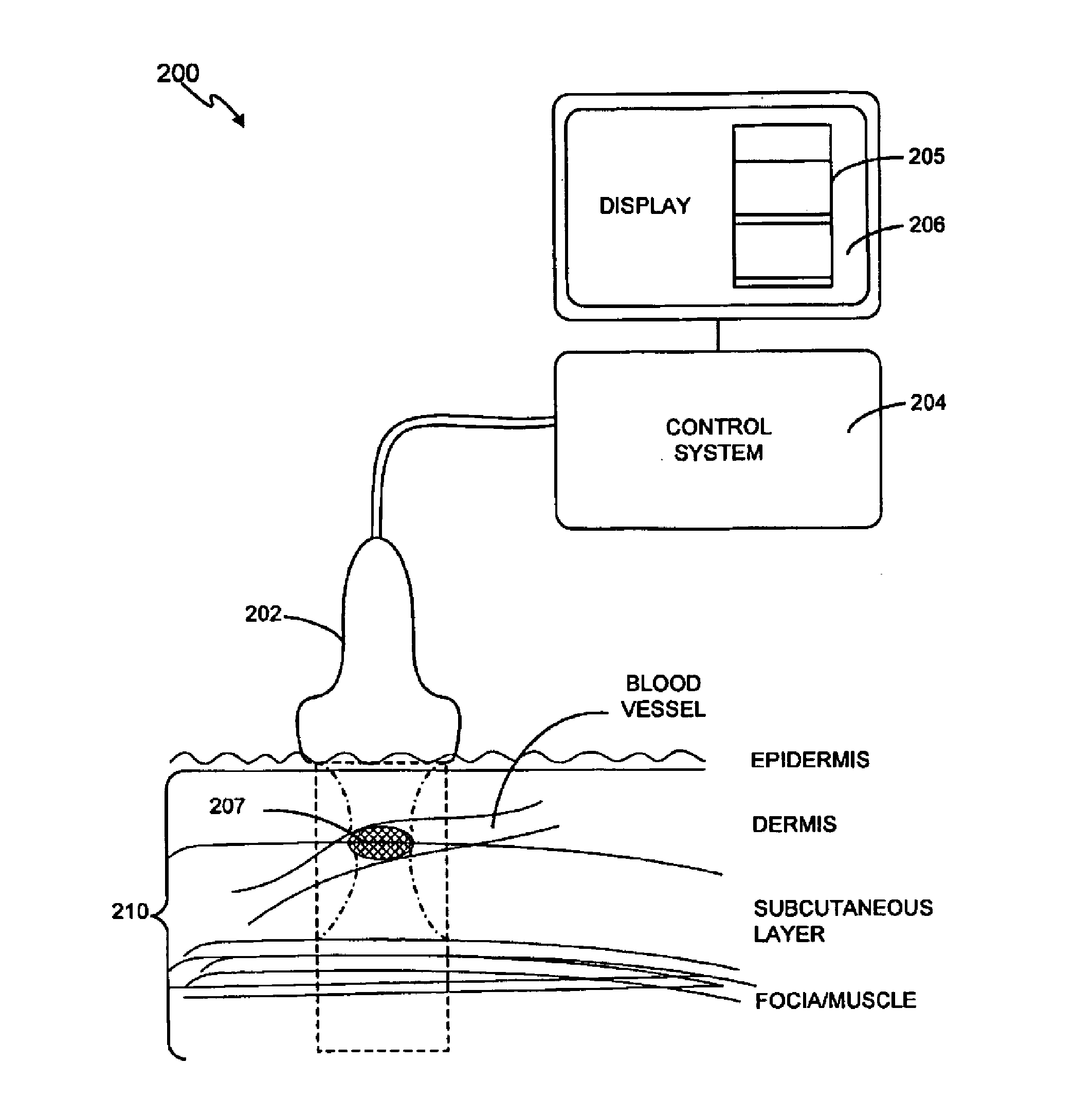
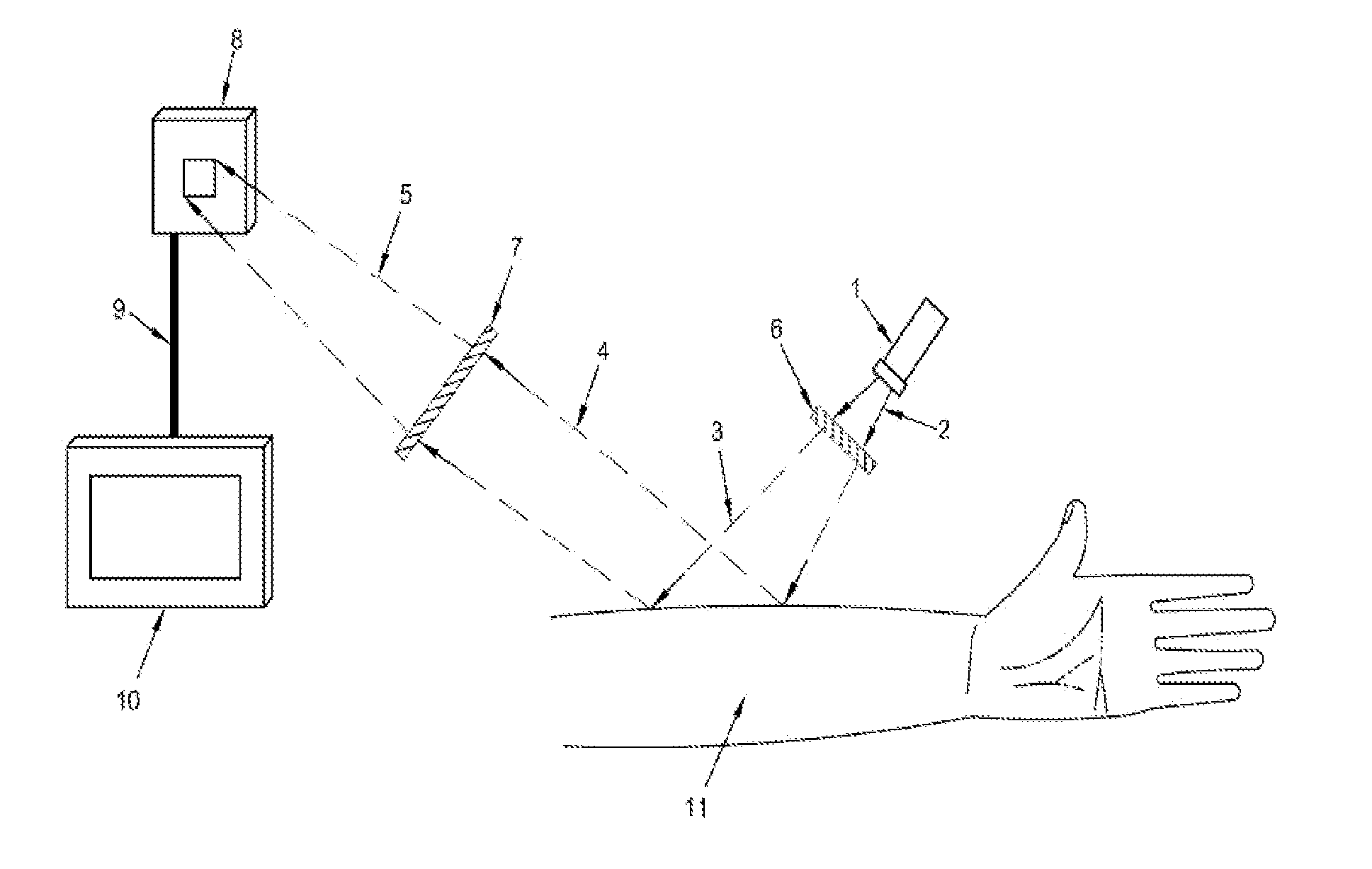
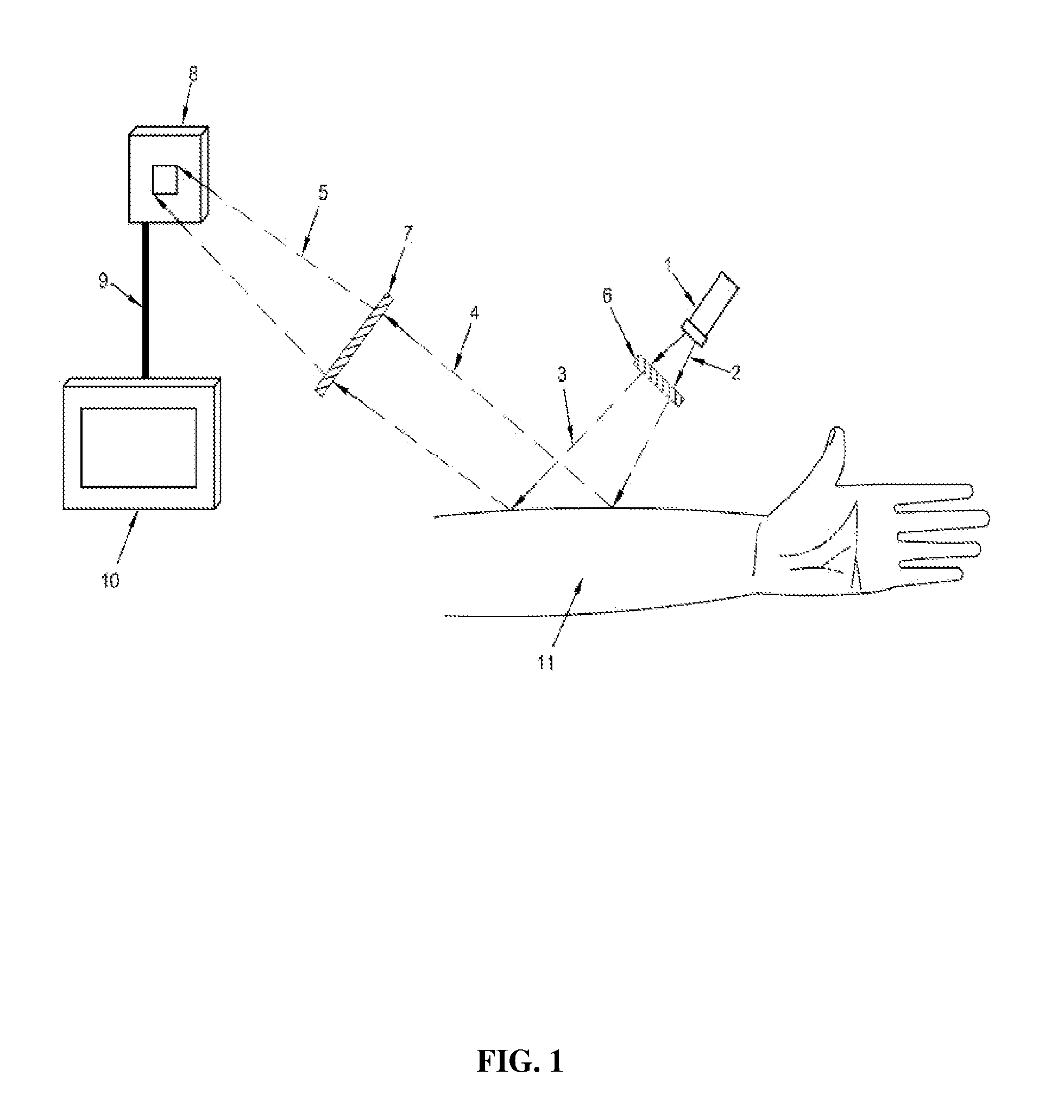
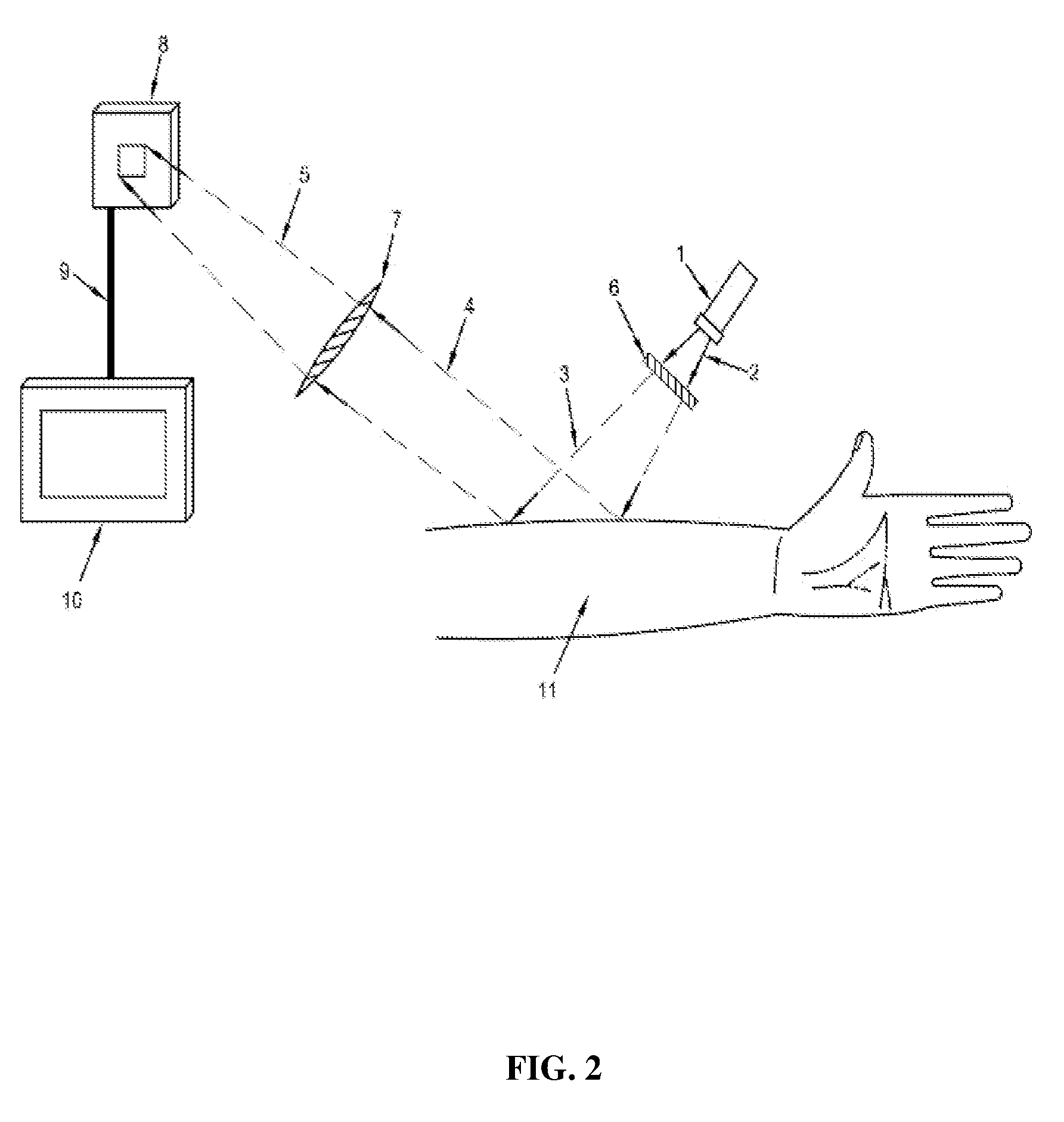
Subcutanous Blood Vessels Imaging System
InactiveUS20090018414A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioClear presentationDiagnostics using lightSensorsAnatomical structuresVein
A real time imaging system is described which displays subcutaneous veins whereby facilitating diagnosis, inspection and easy intravenous access for administration of drugs. The imaging system comprises an infrared source (1), a pinhole focusing unit (7), an infrared Focal Plane Array (8), and a display unit (10). The infrared source (1) emits infrared light which penetrates and is subsequently scattered differently at different layers and depths of the anatomical structure (11) while substantially being absorbed by the blood vessels. Reflected light (4) from the anatomical structure (11) contains the imaging information of the subcutaneous blood vessels of the anatomical structure (11) which is then focused by said pinhole focusing unit (7) upon said infrared Focal Plane Array (8). The image captured by said infrared Focal Plane Array is then displayed on the display unit (10).
Owner:TOOFAN MEHRDAD
Device and method for opening blood vessels by pre-angioplasty serration and dilatation of atherosclerotic plaque
ActiveUS8323243B2Safely and accurately dilated and stretchedDilated more evenly and smoothlyBalloon catheterCannulasBlood vessel spasmPercutaneous angioplasty
An intravascular device can comprise a carrier and an expansion apparatus. The device can be used for intravascular treatment of atherosclerotic plaque. The carrier can be reversibly expandable and collapsible within a vessel and can have ribbon strips extending between opposite ends in a longitudinal direction of the carrier. The ribbon strips can each be formed with a plurality of elongated protrusions thereon. The expansion apparatus can be used to actuate the ribbon strips each with the plurality elongated protrusions to pierce a luminal surface of the plaque with lines or patterns of microperforations which act as serrations for forming cleavage lines or planes in the plaque.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
Clot retrieval system for removing occlusive clot from a blood vessel
A clot retrieval device comprising an elongate shaft having a proximal end and a distal end and a clot retrieval element at the distal end of the elongate shaft. A proximal end of the elongate shaft of the clot retrieval device is adapted for retraction of a first catheter over the clot retrieval device elongate shaft. A second catheter is advanced to or adjacent to the distal end of the clot retrieval device shaft to enable enhanced aspiration adjacent to the clot retrieval element.
Owner:NEURAVI
Arterial obstruction treatment kit
A kit for performing angioplasty or stenting in a blood vessel, composed of at least two components. One of the components includes a first catheter providing a blood bypass flow path and carrying a blocking balloon and a blood vessel dilation device. Another one of the components includes a second catheter having an imperforate wall enclosing an axial lumen and having an open distal end, a hollow tube surrounding, and movable longitudinally with respect to, the second catheter, and a second blocking balloon carried by the hollow tube.
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT +1
Clot retrieval device for removing clot from a blood vessel
A clot removal device for removing clot from a body vessel comprises an expandable structure and an elongate member. The expandable structure has a constrained delivery configuration, an expanded clot engaging deployed configuration, and an at least partially constrained clot pinching configuration. At least a portion of the expandable structure is configured to engage clot in the expanded deployed configuration and to pinch clot on movement from the deployed configuration to the clot capture configuration. The expandable structure may comprise a main body portion and a clot pinching structure and a diameter of the clot pinching structure is less than a diameter of the main body portion. The clot pinching structure may be substantially tubular and of spiral form.
Owner:NEURAVI
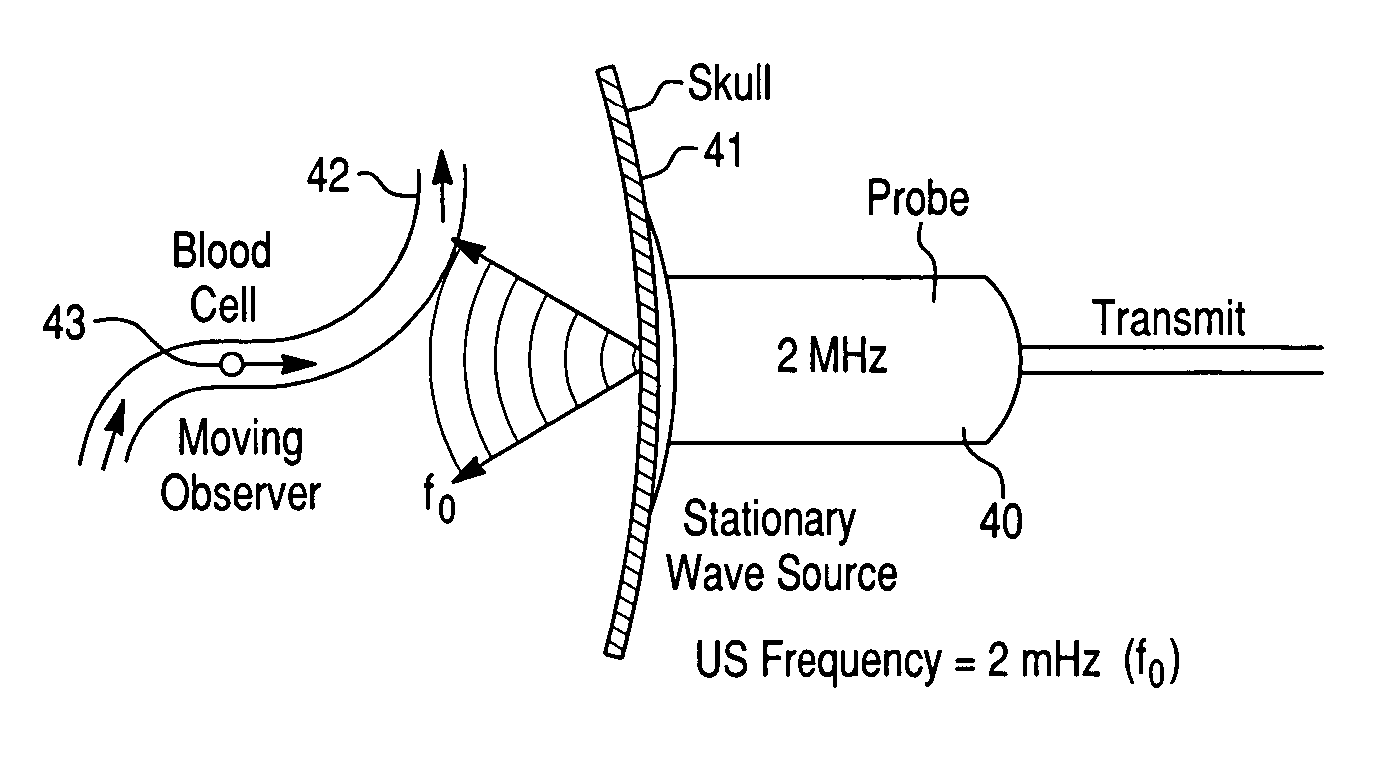
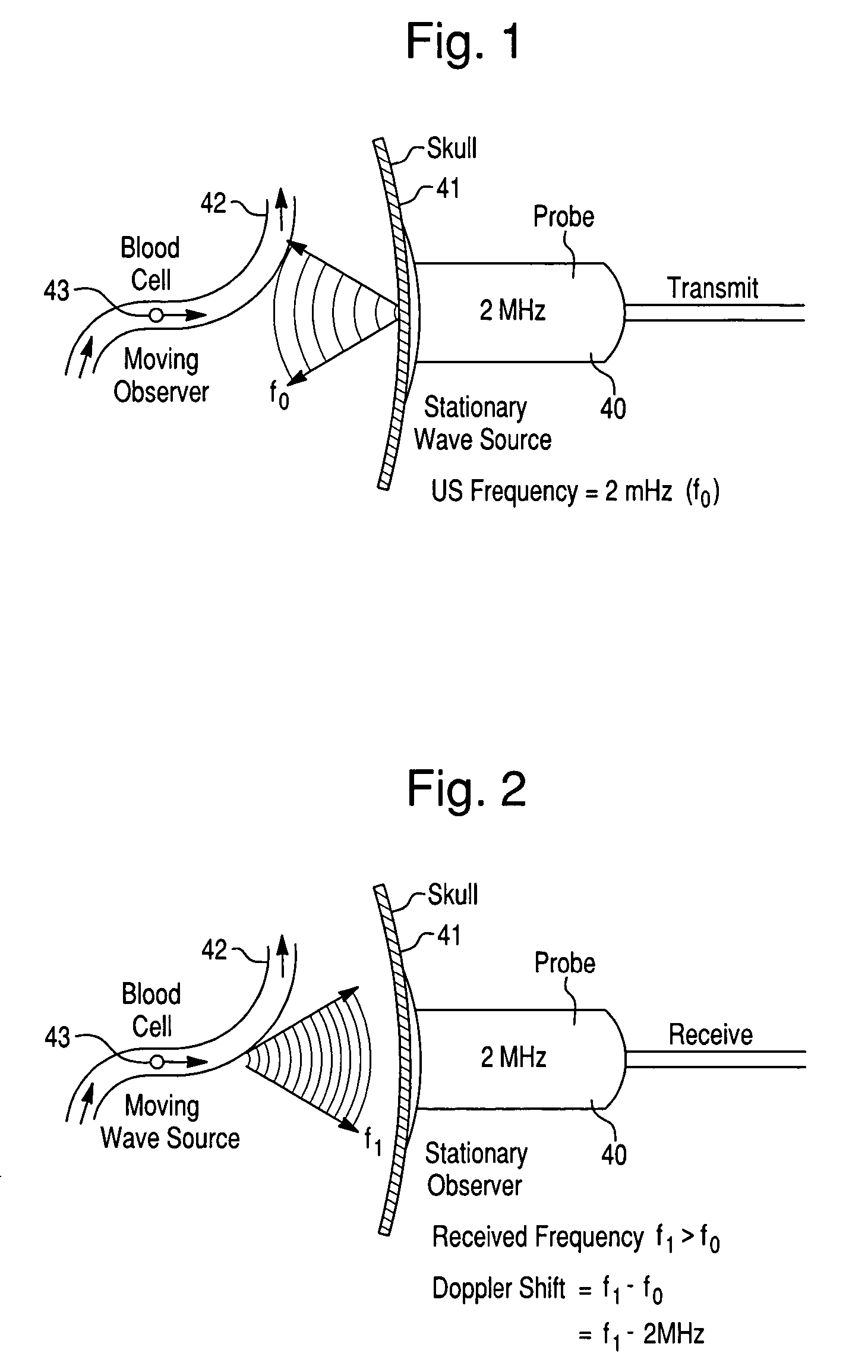
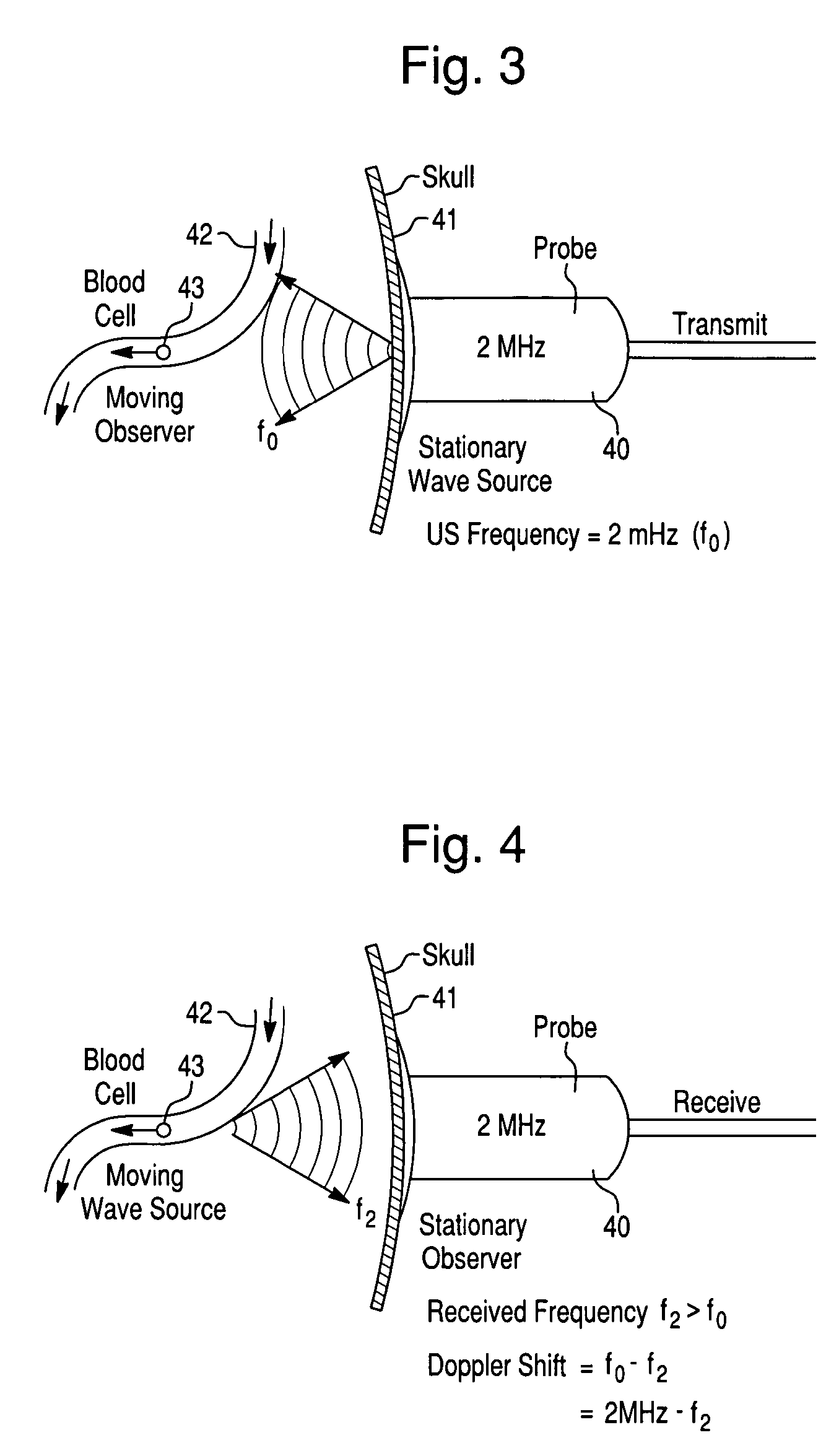
Systems and methods for investigating intracranial pressure
InactiveUS7104958B2Rapid and inexpensive to performEfficient deliveryHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesCatheterClinical trialBlood vessel
The invention relates to systems and methods for assessing blood flow in single or multiple vessels and segments, for assessing vascular health, for conducting clinical trials, for screening therapeutic interventions for effect, for assessing risk factors, for evaluating intracranial pressure and for analyzing the results in a defined manner. The invention enables direct monitoring of therapies, substances and devices on blood vessels, especially those of the cerebral vasculature. Relevant blood flow parameters include mean flow velocity, systolic acceleration, and pulsatility index. Measurement and analysis of these parameters, and others, provides details regarding the vascular health of individual and multiple vessels and a global analysis of an individual's overall vascular health. The invention can track the onset, progression and treatment efficacy in an individual experiencing increased intracranial pressure, or can help identify underlying vulnerabilities of the vascular system to normal pressures, associated with and manifested as hydrocphalus or dementia.
Owner:NEW HEALTH SCI
Device and method for opening blood vessels by pre-angioplasty serration and dilatation of atherosclerotic plaque
ActiveUS20090240270A1Safely and accurately dilated and stretchedDilated more evenly and smoothlyBalloon catheterCannulasBlood vessel spasmPercutaneous angioplasty
A device and method for intravascular treatment of atherosclerotic plaque perforates the plaque with microperforations by small sharp spikes to act as serrations for forming cleavage lines or planes in the plaque. In preferred embodiments, expansion may be obtained by mechanical apparatus, expansion balloon, or balloon-assisted deployment. The plaque treatment enables a subsequent balloon angioplasty to be performed without creating substantial dissections and at low balloon pressure so as to avoid injury to the arterial wall. The plaque treatment may include dilatation of the plaque at low pressure, sufficiently that no subsequent balloon angioplasty is needed. The plaque preparation may be followed by applying one or a few ring tacks to secure the compressed plaque with minimal emplacement of foreign material.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
Crossing occlusions in blood vessels
The present disclosure is directed a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method may include providing a first intravascular device having a distal portion and at least one aperture and positioning the distal portion of the first intravascular device in the vascular wall. The method may further include providing a reentry device having a body and a distal tip, the distal tip having a natural state and a compressed state and inserting the distal tip, in the compressed state, in the distal portion of the first intravascular device. The method may further include advancing the distal tip, in the natural state, through the at least one aperture of the first intravascular device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for increasing blood flow through an obstructed blood vessel
ActiveUS20110270178A1Increase blood flowStentsBalloon catheterBlood vessel spasmIncreased blood flow
A method of increasing blood flow through an obstructed blood vessel includes providing an expandable member substantially made of a mesh having a plurality of interstices. The expandable member is inserted into the blood vessel, positioned within the blood vessel with the proximal member end upstream of the distal member end and the member body located radially adjacent at least a portion of an obstruction, and expanded to bring at least a portion of the member body into contact with the obstruction. An outward radial force is exerted on the obstruction to dislodge at least one fragment from the obstruction and to enhance blood flow through the blood vessel past the obstruction. The at least one fragment is passed through at least one interstice of the member body in the radial direction, and is selectively retained within the expandable member.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Device and method for endovascular treatment for causing closure of a blood vessel
ActiveUS20080188843A1Reduce power densityReduce temperature peaksCatheterSurgical instrument detailsEndovascular treatmentLaser light
An endovascular laser treatment device for causing closure of a blood vessel uses an optical fiber adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel. An inner sleeve is arranged around a distal portion of the optical fiber core such that both distal ends of the inner sleeve and the optical fiber core form an enlarged light emitting face. The enlarged emitting face provides substantially lower power density while providing the same amount of total energy during a treatment session. An outer sleeve arranged around the inner sleeve acts as a spacer to position the light emitting face away from an inner wall of the blood vessel. The enlarged light emitting face and the outer sleeve acting as a spacer reduces the possibility of thermal run-away and device damage, and reduce the possibility of vessel perforations, leading to less bruising, post-operative pain and other clinical complications. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a spacer comprises an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve both arranged around a distal portion of the core to prevent the laser light from traveling laterally and to position the light emitting face away from an inner wall of the vessel. The inner sleeve can be a heat resistive material such as ceramic and the outer sleeve can be, for example, a metallic sleeve to provide structural integrity and strength to the distal section of the treatment device.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Devices for creating passages and sensing for blood vessels
InactiveUS20110306997A9Great pressurizationIncision instrumentsSurgical needlesBlood vessel spasmObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices and methods are disclosed for creating passages in tissue and detecting blood vessels in and around the passages. The devices may be used to create channels for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). In addition, the devices may be used to sample tissue during biopsy or other medical procedures where perforating a blood vessel could result in injury to a patient.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
Appliance for cannulation of a blood vessel
InactiveUS20040215142A1Guaranteed supplyBlood trauma can be minimizedBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesMedicineBlood vessel spasm
The present invention relates to an appliance for cannulation of a blood vessel with a cannula which, after introduction into the vessel, is in fluidic communication with the vessel. At least one means is also provided to permit a controlled division of the blood into a first subsidiary stream which leaves the vessel through the cannula, and a second subsidiary stream which continues to flow through the vessel.
Owner:NOVALUNG
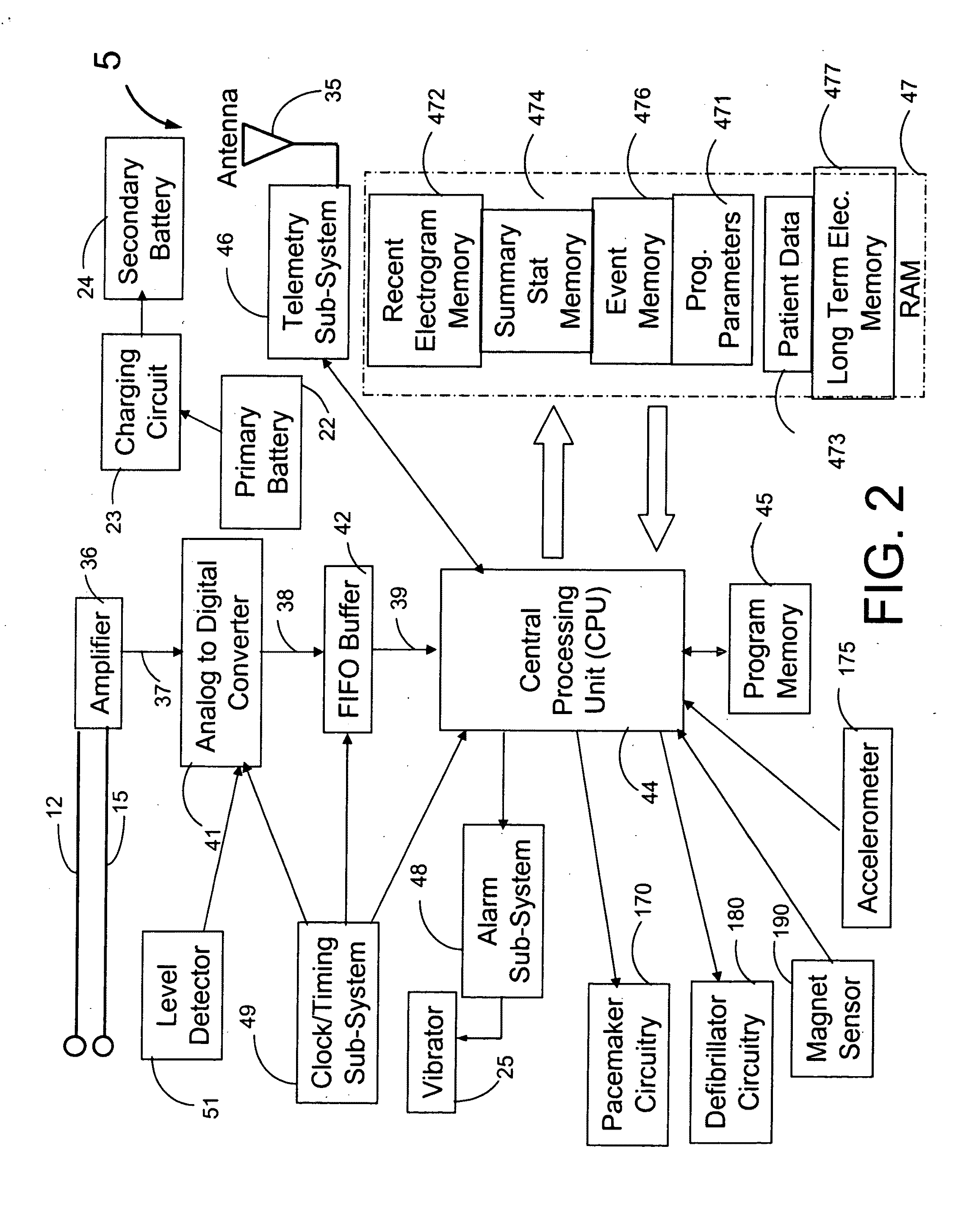
Heart rate correction system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
ActiveUS20110040199A1Strong specificityEliminate high frequency noiseElectrocardiographySensorsBlood vessel spasmAcute ischemia
A device for detecting a cardiac event is disclosed. Detection of an event is based on a test applied to a parameter whose value varies according to heart rate. Both the parameter value and heart rate (RR interval) are filtered with an exponential average filter. From these filtered values, the average change in the parameter and the RR interval are also computed with an exponential average filter. Before computing the average change in the parameter, large changes in the parameter over short times, which may be caused by body position shifts, are attenuated are removed, so that the average change represents an average of small / smooth changes in the parameter's value that are characteristic of acute ischemia, one of the cardiac events that may be detected. The test to detect the cardiac event depends on the heart rate, the difference between the parameter's value and its upper and lower normal values, and its average change over time, adjusted for heart rate changes. The upper and lower normal parameter values as a function of heart rate are determined from long term stored data of the filtered RR values and parameter values. Hysteeresis related data and transitory deviations from normal (e.g. vasospasm related data) are excluded from the computation of normal upper and lower parameter bounds.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Clot retrieval device for removing occlusive clot from a blood vessel
A clot retrieval device for removal of occlusive clot from a blood vessel comprises a clot engaging element 700 having a constrained delivery configuration and an expanded deployed configuration. In the expanded configuration peripheral portions are laterally spaced-apart and the clot engaging section 700 extends between the peripheral portions. The device 700 may have two superimposed wave patterns provided by a large amplitude curve 723 and shorter pitch sinusoidal patterns 721, 722. A wave shape varies the contact pressure between a clot and the device along the length of the device, reducing the compression of the clot by the device at some locations. The device can elongate when placed under tension which aids elongation of the clot during dislodgement.
Owner:NEURAVI
System and Method for Placing a Coronary Stent at the Ostium of a Blood Vessel
A system and method are provided that use a balloon / stent catheter for placing a stent at the ostium of a blood vessel. Included is a barrier member that is attached to the catheter at a location proximal the balloon. In use, the barrier member is reconfigured, prior to insertion of the balloon / stent portion of the catheter through the ostium. With this reconfiguration, a barrier (array) is established that limits advancement of the catheter into the blood vessel to ensure proper placement of the stent at the ostium.
Owner:SCHATZ RICHARD A
Thrombectomy device, system and method for extraction of vascular thrombi from a blood vessel
ActiveUS20170303949A1Minimizes fractureImprove efficiencyDiagnosticsDilatorsBlood vessel spasmDilator
A thrombectomy device including a delivery catheter; a tapered dilator catheter configured to be movably disposed within the delivery catheter; and an expandable aspiration funnel configured to be movably disposed within the delivery catheter in a retracted position and at least partially outside the delivery catheter in an extended position, the funnel comprising a non-permeable covering, a diameter of a distal end of the funnel being greater in the extended position than in the retracted position, the funnel being configured to adapt its shape and length to a surrounding blood vessel such that the funnel lengthens as it narrows to retain a thrombus within the funnel. The invention also includes methods of using the device.
Owner:ANACONDA BIOMED SL
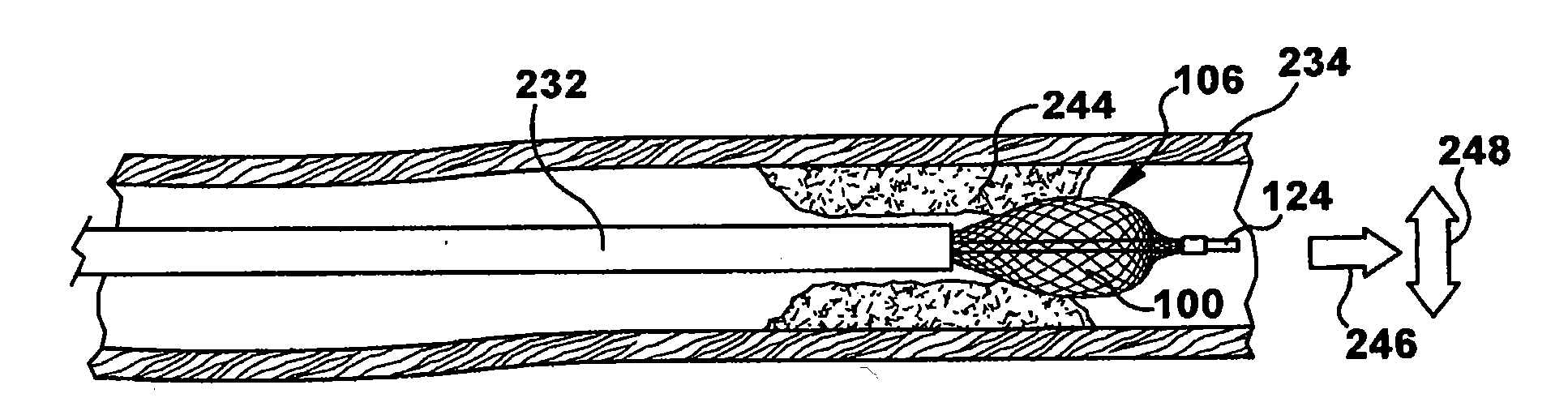
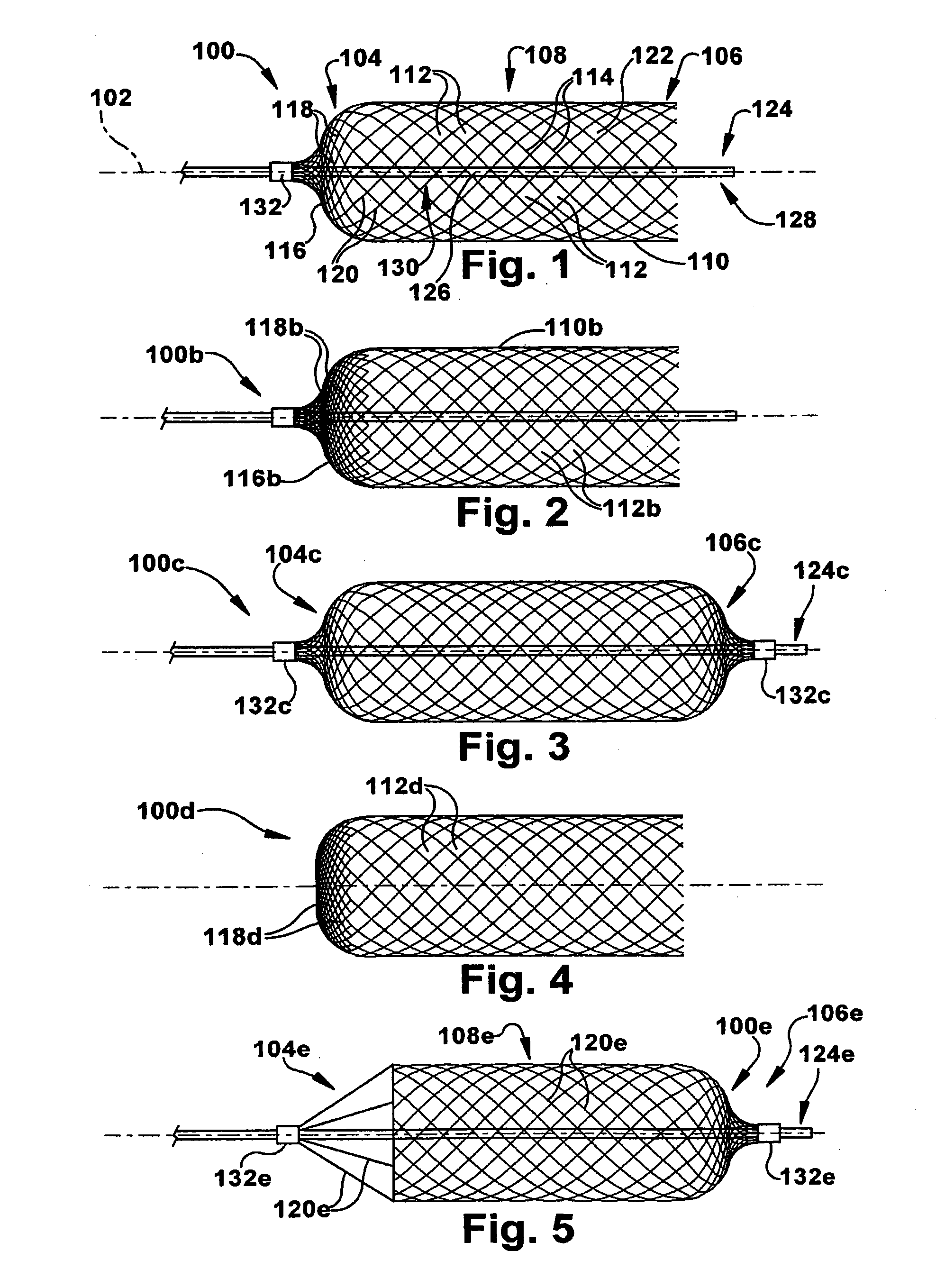
Expandable Prostheses for Treating Atherosclerotic Lesions Including Vulnerable Plaques
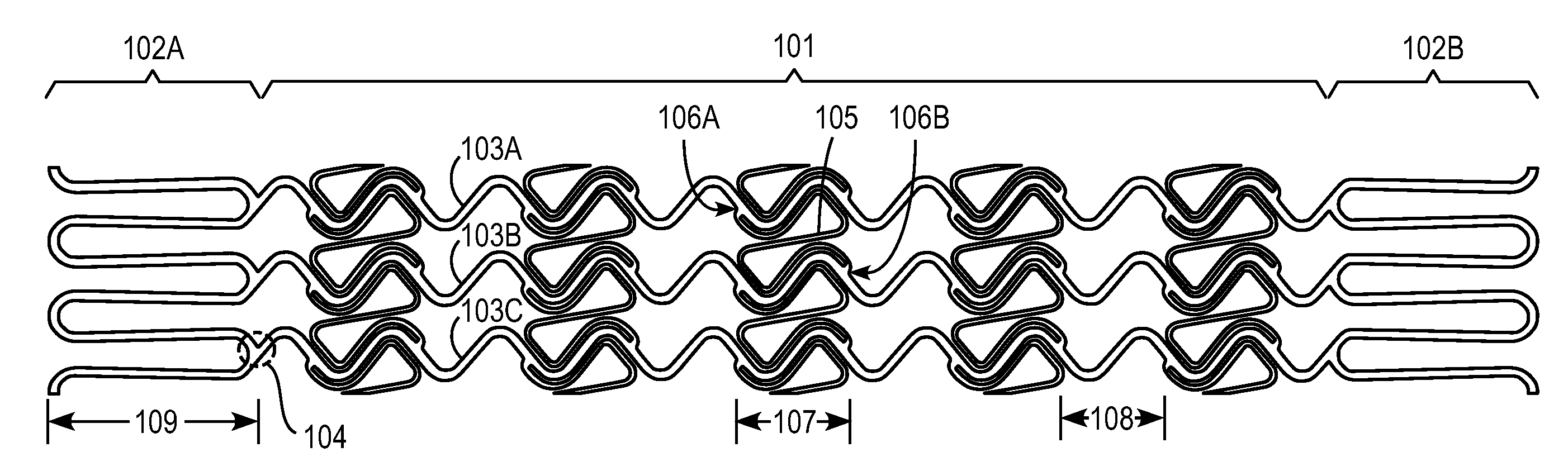
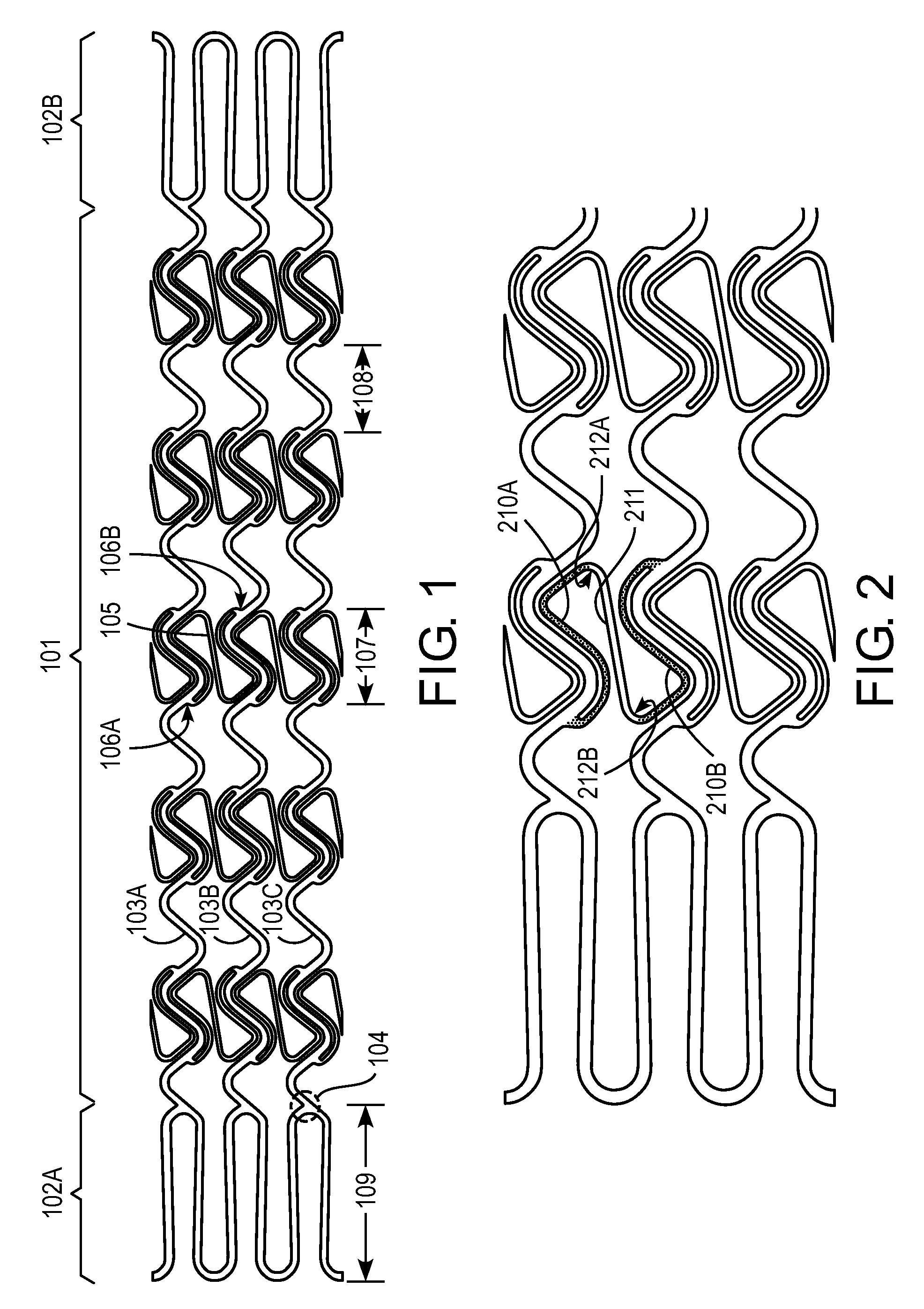
The invention provides expandable tubular prostheses that are designed for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions, such as vulnerable plaques, and that are characterized by no foreshortening, optimal radial force and accuracy of deployment. In the treatment of vulnerable plaque, the device may be expanded in a blood vessel so that its central section at least partially contacts a vulnerable plaque lesion and / or the blood vessel wall in close proximity to the vulnerable plaque lesion. The invention also provides more general methods of treating atherosclerosis and promoting endothelialization using the prostheses of the invention.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
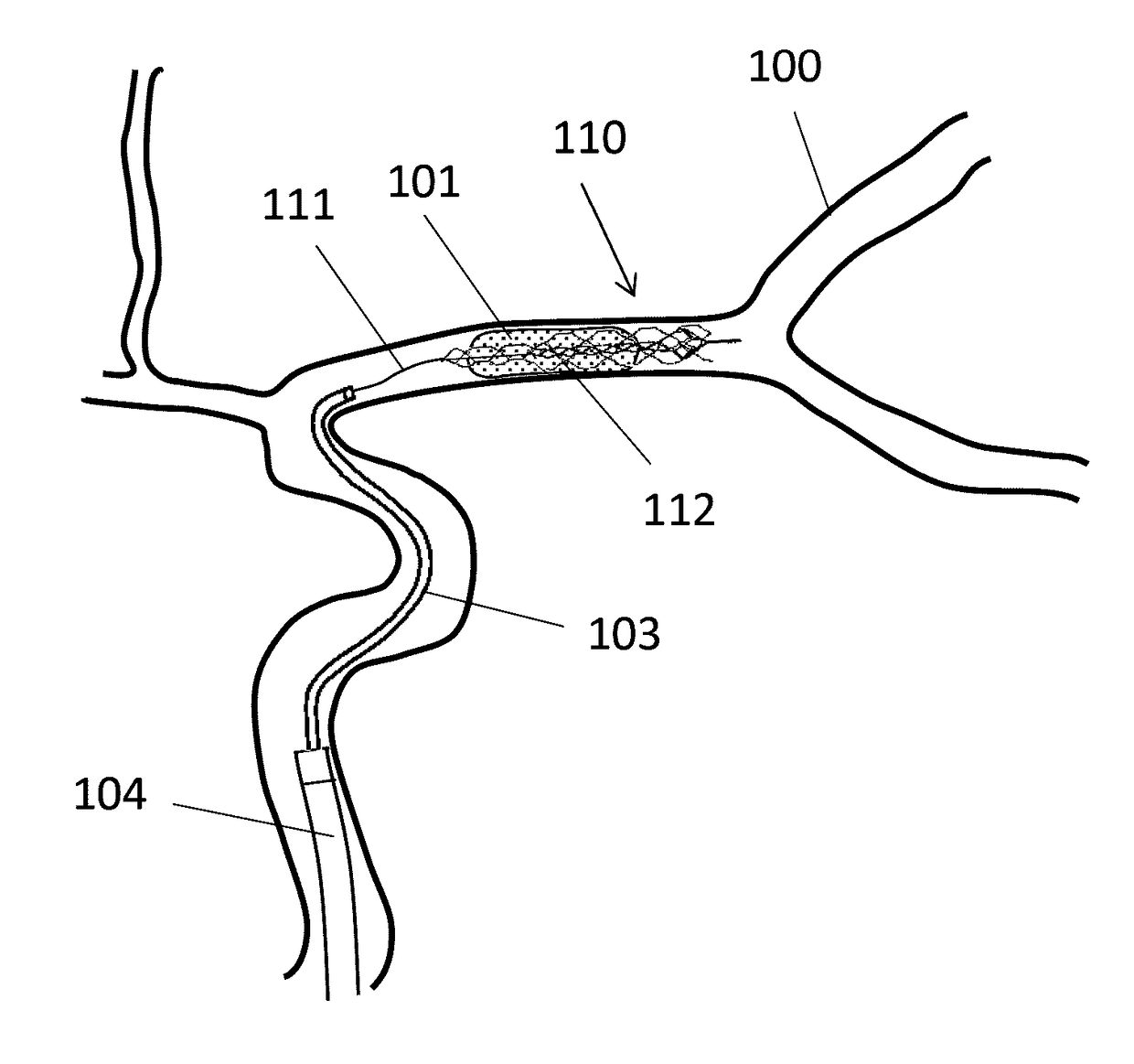
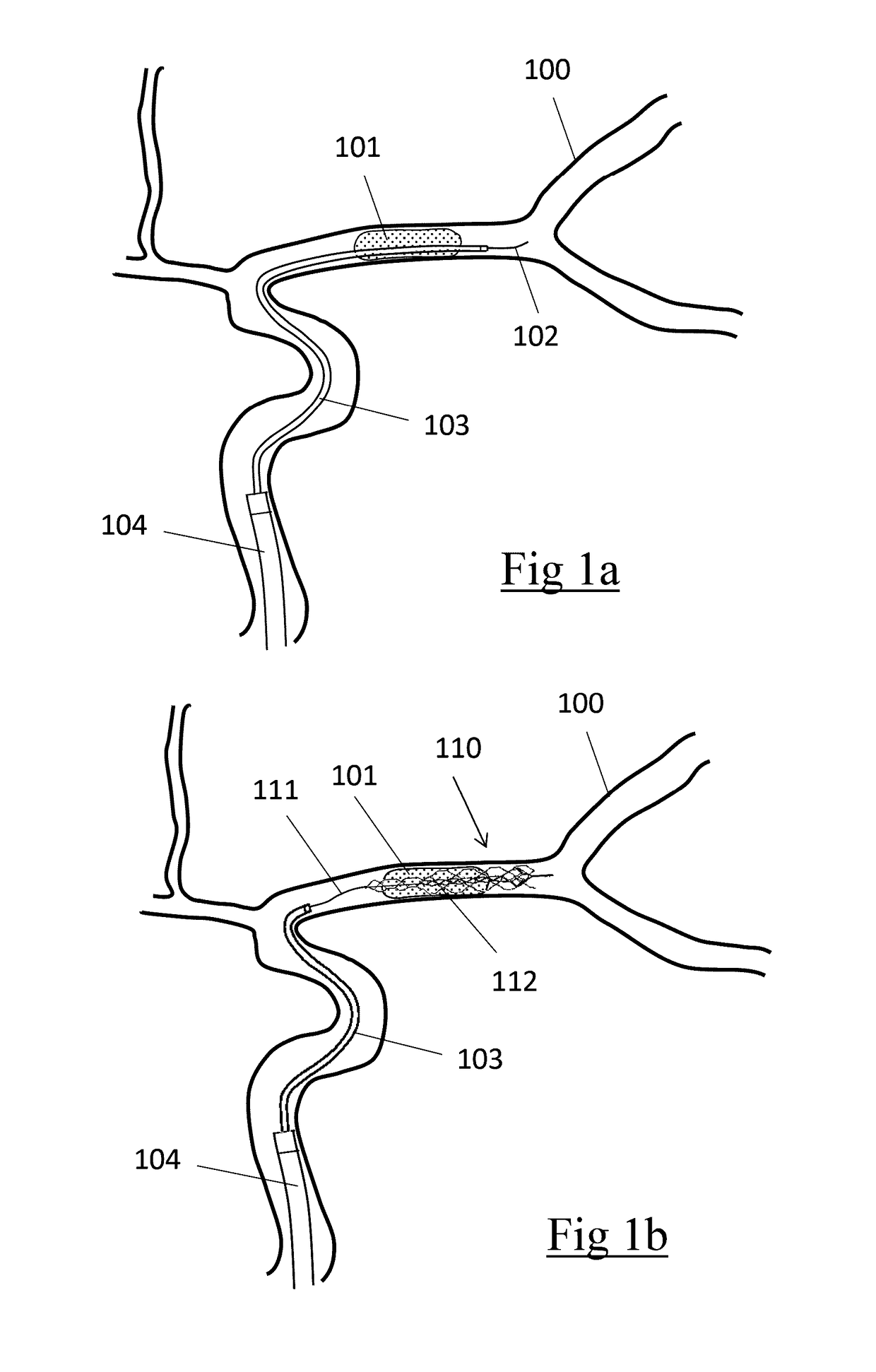
Device for the removal of thrombi from blood vessels
The invention relates to an assembly comprising a support (1, 3, 4) for intervertebral prostheses and intervertebral prostheses (2) that are provided with different widths and are composed of two final plates (21, 22) with a ventral flange (23, 24) and an intermediate joint core (20). The support (1, 3, 4) is equipped with a base plate (10, 30, 40) which encompasses holes (12, 32, 42) for accommodating one of the intervertebral prostheses (2) and is larger than the maximum width of the intervertebral prostheses (2). A couple of steps (17) are embodied on at least one longitudinal edge (13) of the hole (12, 32, 42).; The facing sides (18) of said couple of steps (17) are disposed at a specific distance from each other so as to center the flange (24) of an intervertebral prosthesis (2) that is inserted into the hole (12, 32, 42), thus making it possible to insert intervertebral prostheses (2) having different widths into the holes (12, 32, 42) and retain the same in a centered position in the holes (12, 32, 42) regardless of the actual width thereof.
Owner:PHENOX
Instrument for extroverting blood vessel
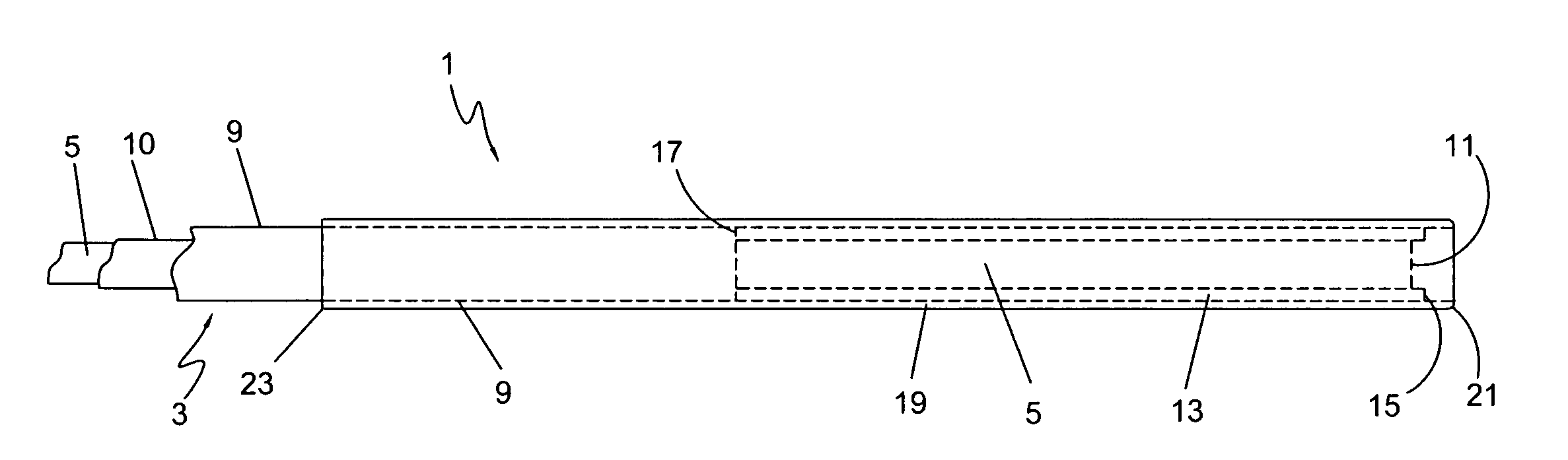
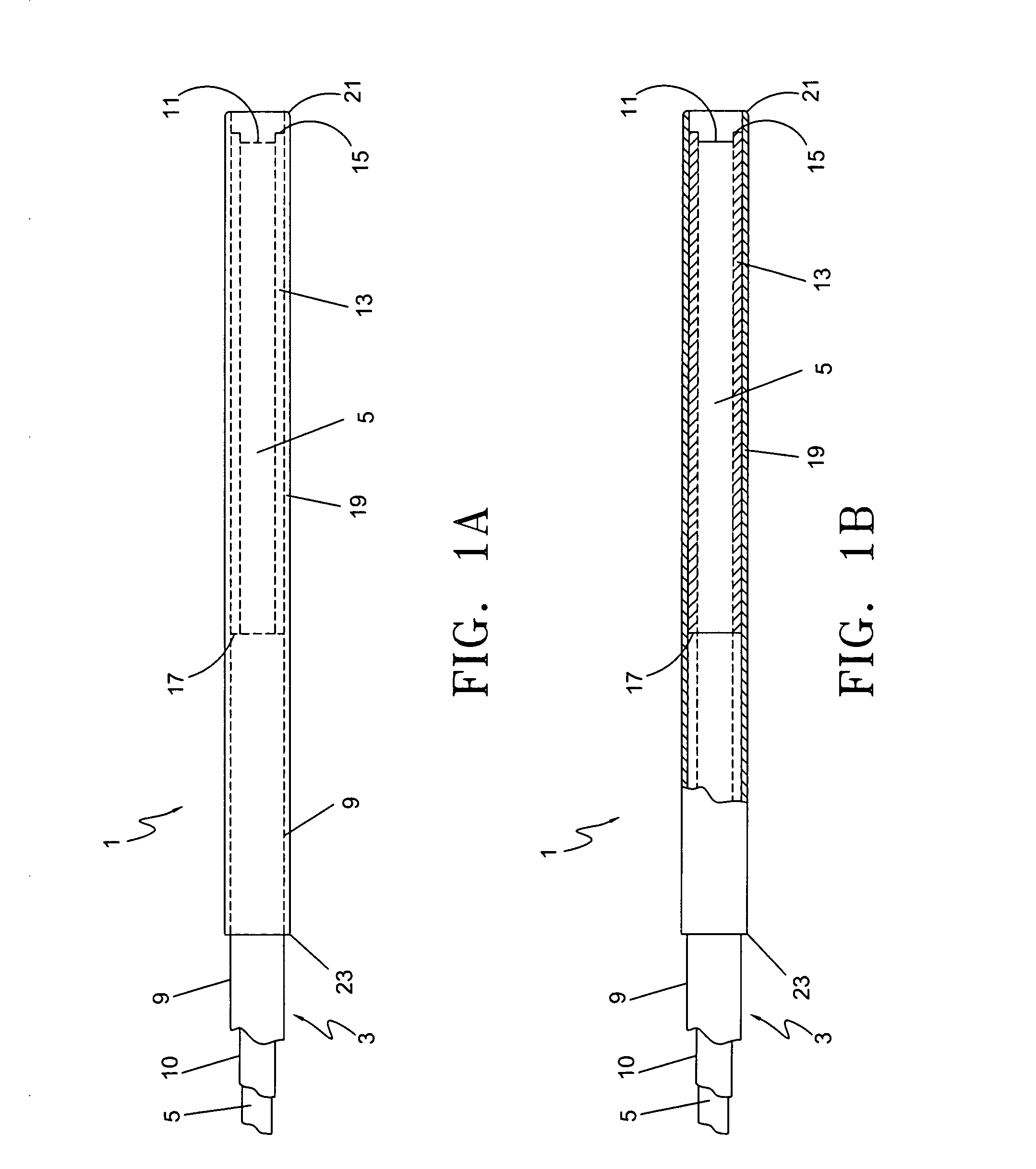
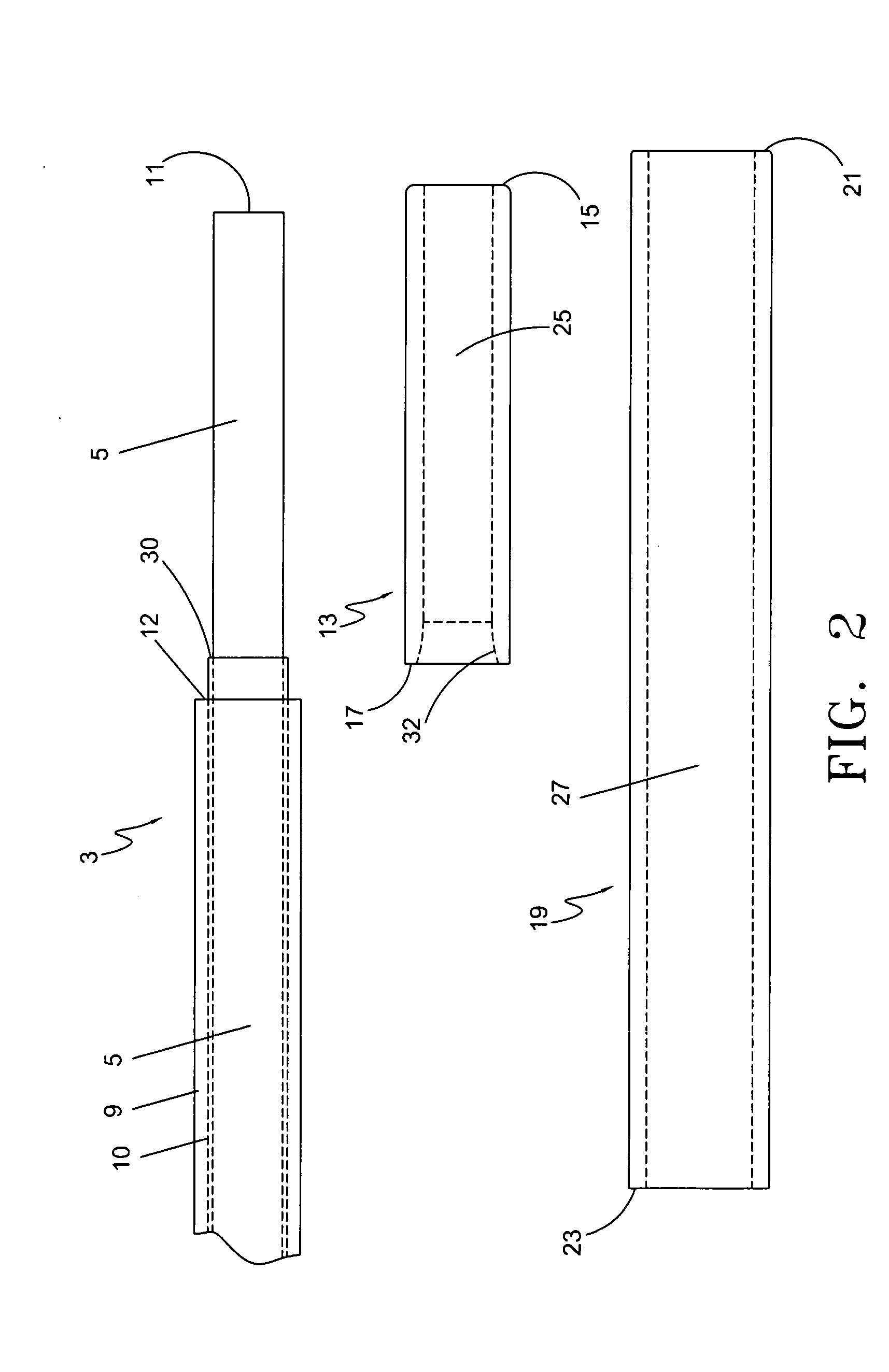
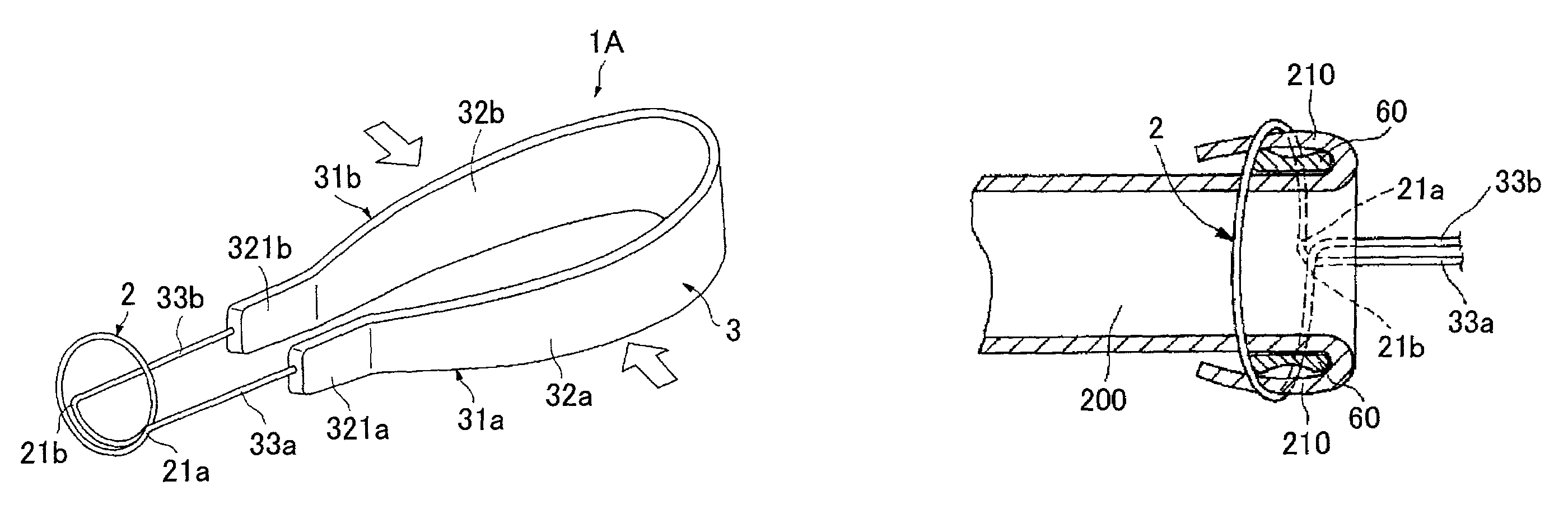
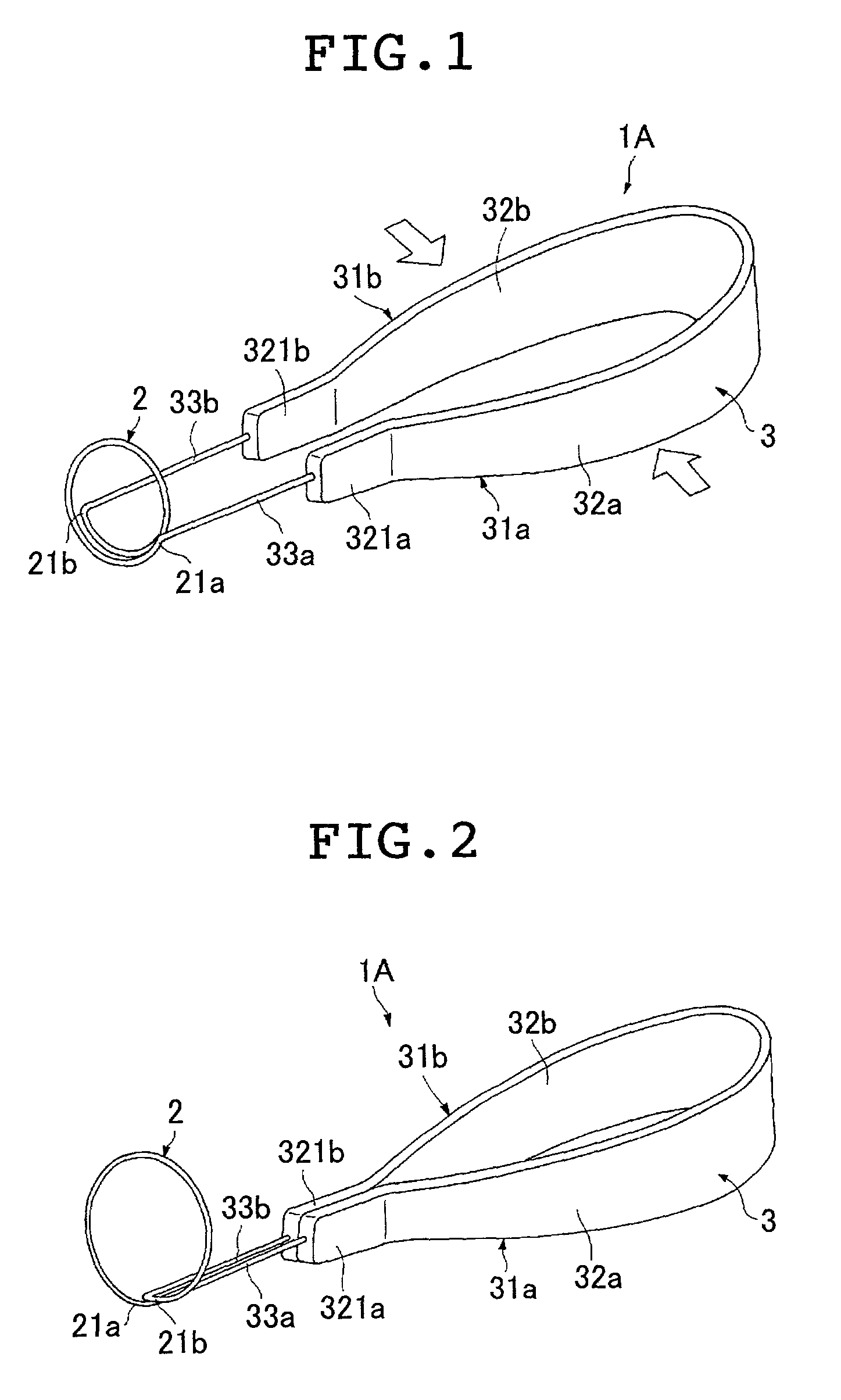
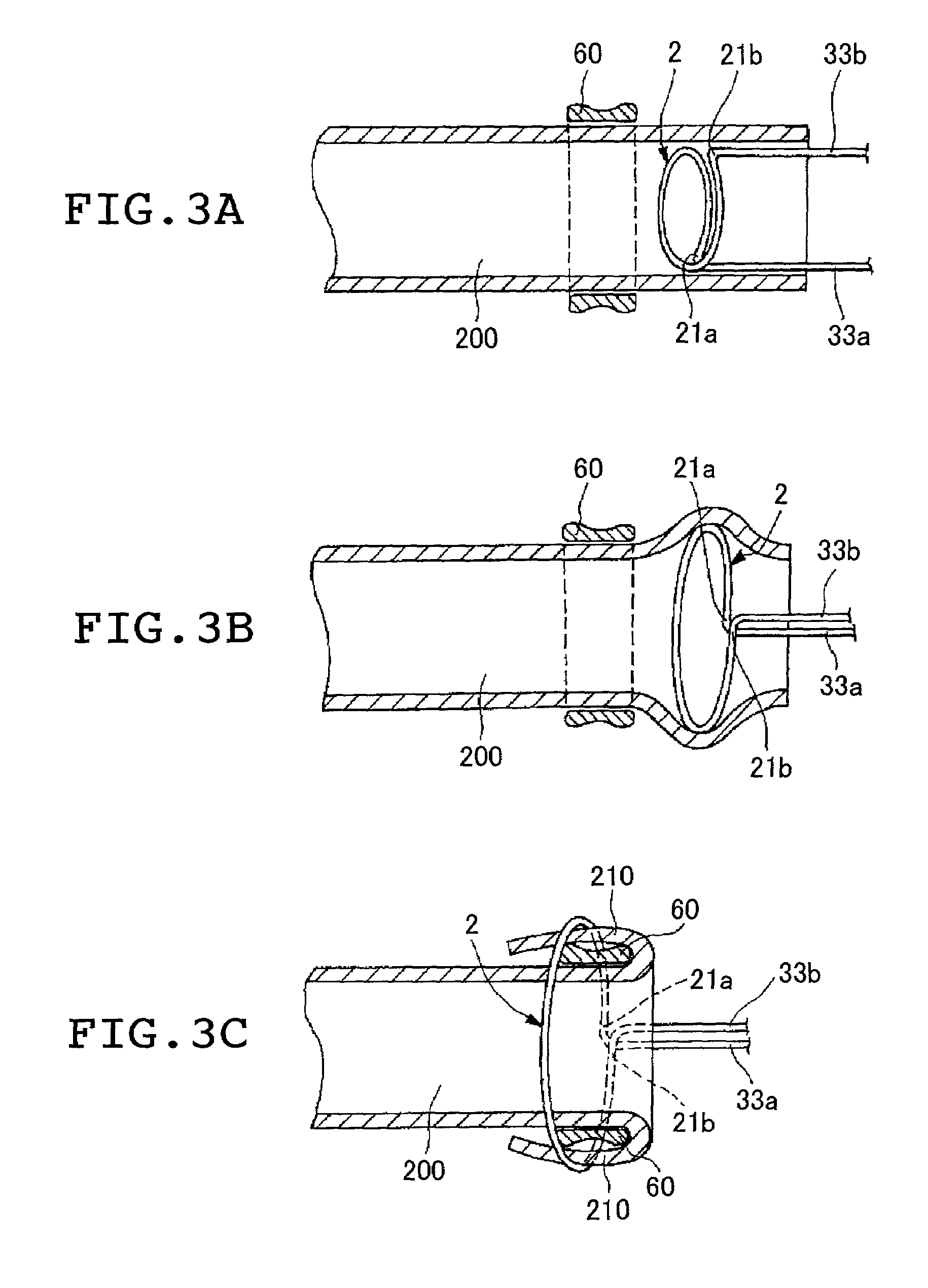
InactiveUS6979337B2Easily perform extroversion operationShort timeSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsInjury blood vesselBlood vessel spasm
A blood vessel extroverting instrument used to turn an end of a blood vessel inside out. The instrument has a contact portion to be brought into contact with an end of a blood vessel, a supporting portion on which the contact portion is supported, and an operating mechanism for increasing and reducing the diameter of the contact portion. At least two portions of the end of the blood vessel in the radial direction can be simultaneously expanded and / or reversed by operating the operating mechanism. Therefore the blood vessel extroverting instrument provided by the present invention is capable of easily turning an end of a blood vessel inside out in a short time without damaging the blood vessel.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Artificial blood vessel
InactiveUS20130103137A1Avoid closingPrevents closure of the artificial blood vesselStentsMedical devicesHuman bodyBlood vessel spasm
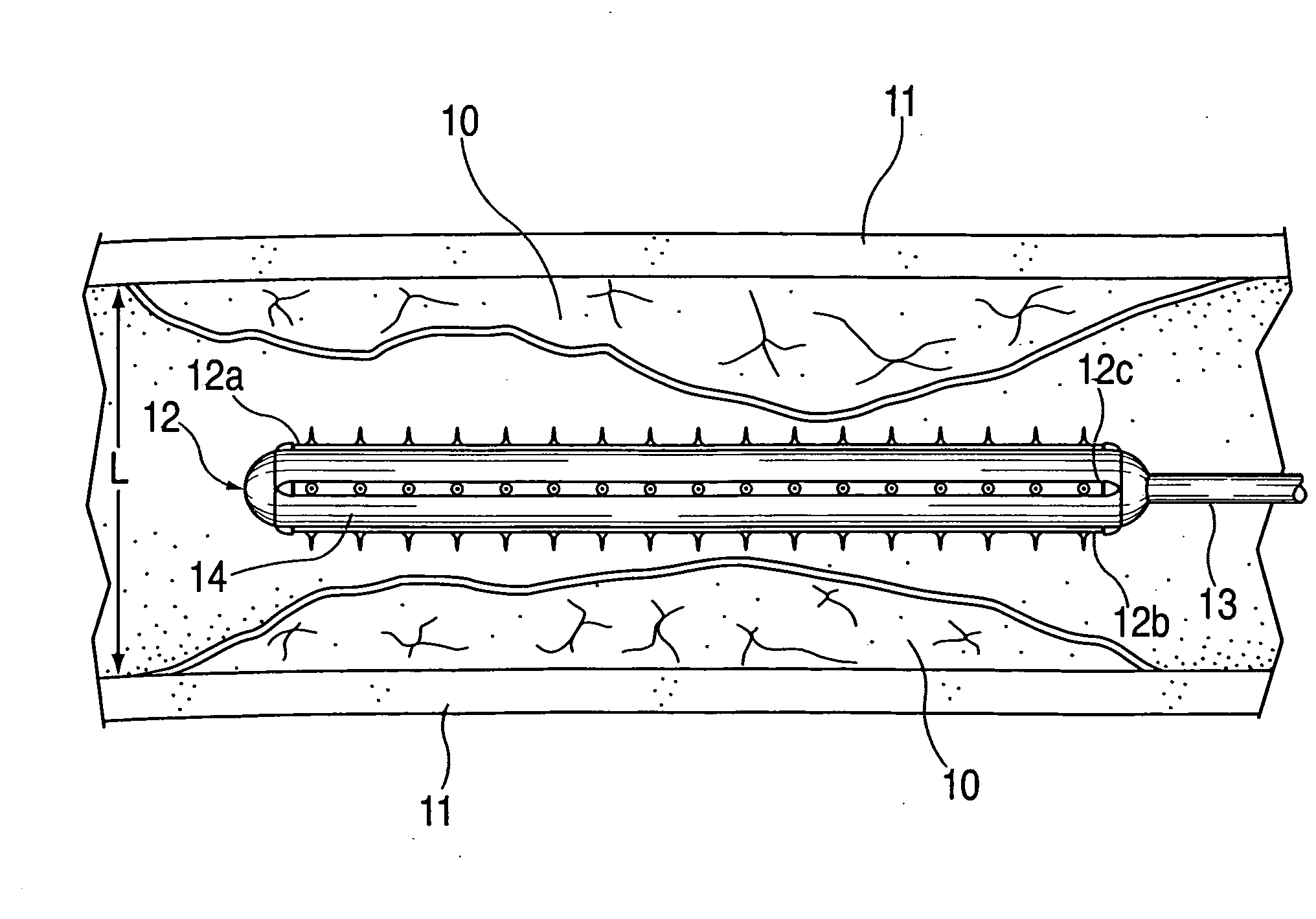
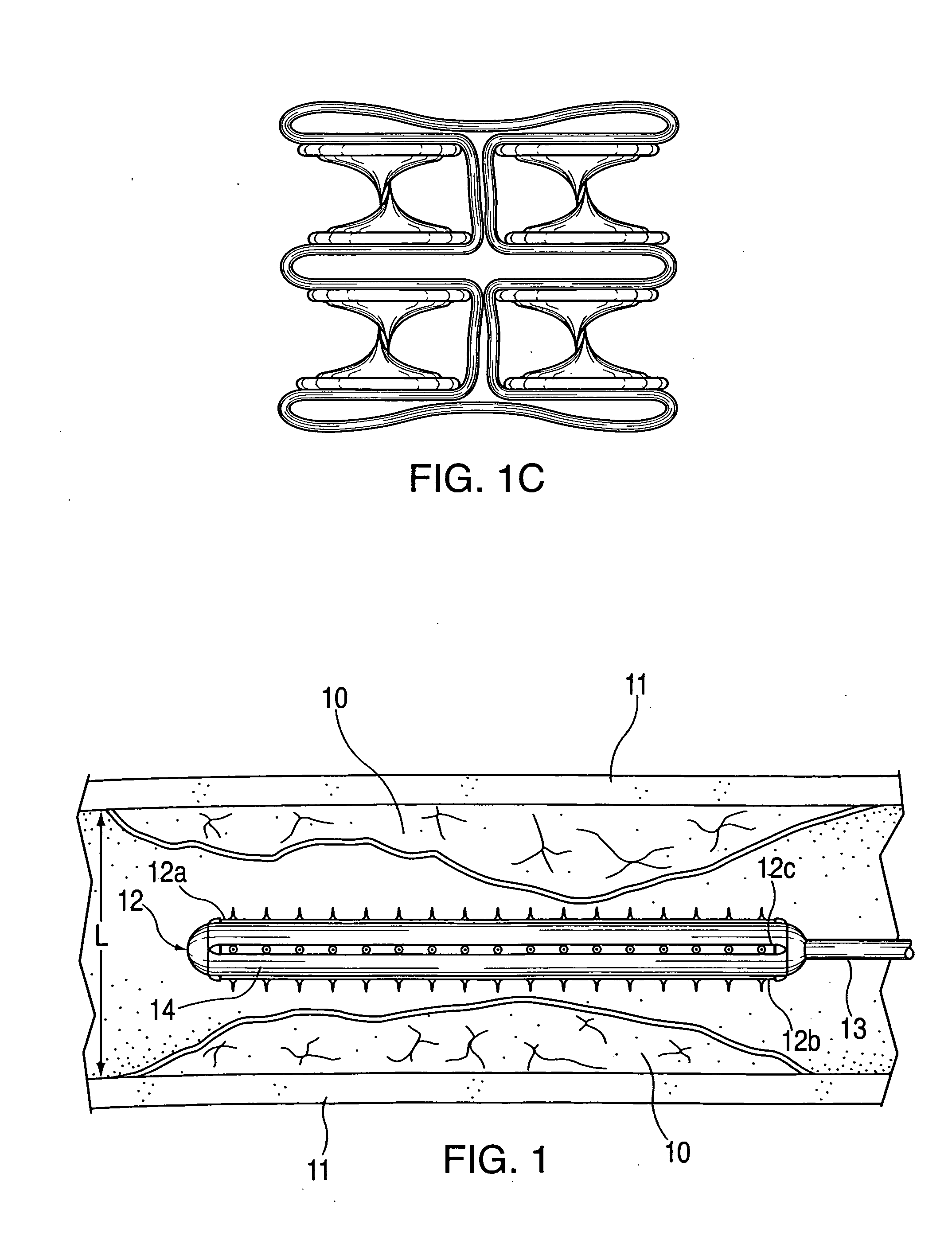
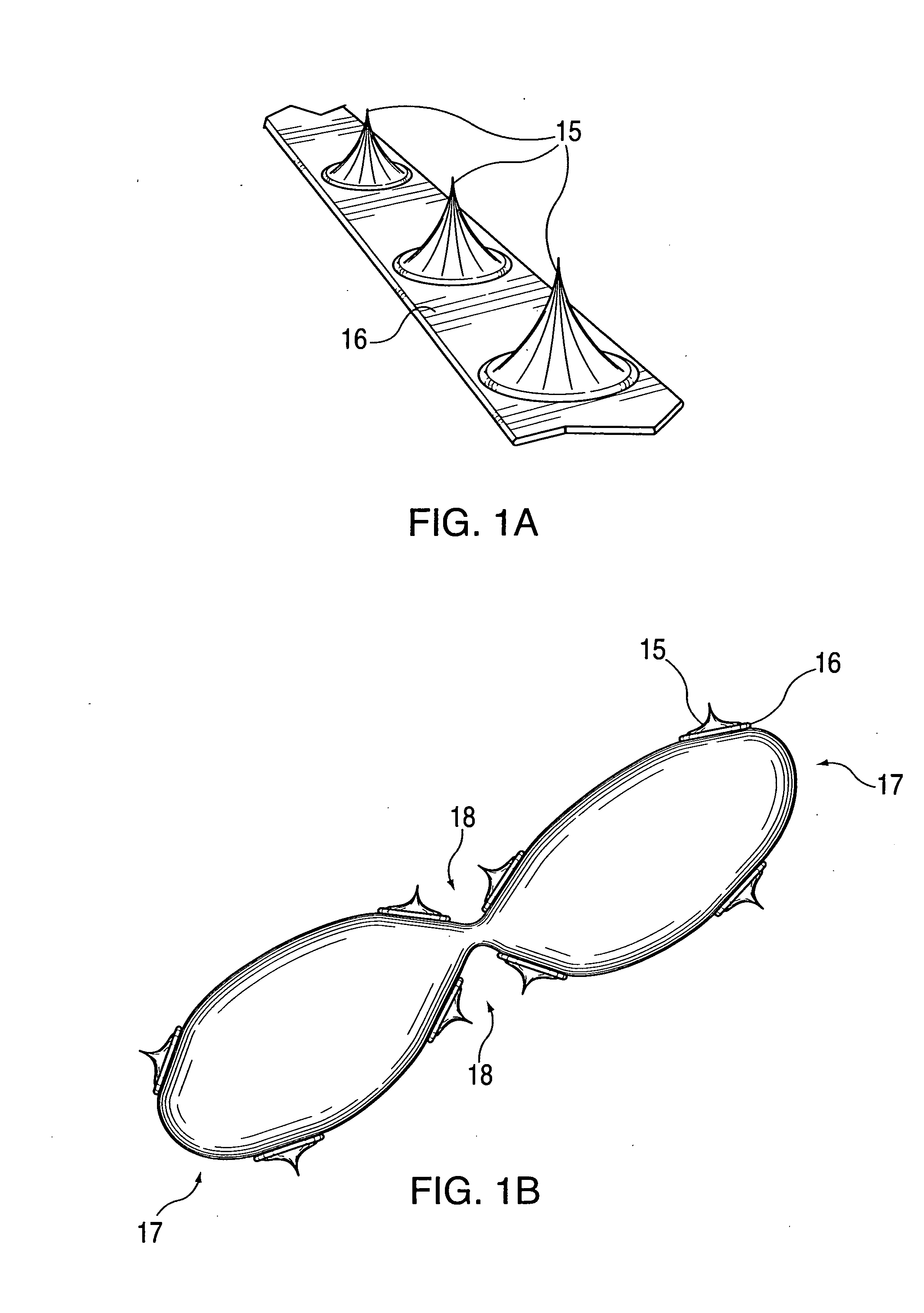
An artificial blood vessel has a trunk portion which forms a part of the blood vessel and also has branch portions which are branched from the trunk portion. The branch portions are provided with access ports into which a needle, for discharging liquid out of a human body or introducing the liquid into the human body, is inserted. Tubular reinforcement members integrated with the blood vessel wall of the trunk portion are disposed at positions of the trunk portion, the positions being those from which the branch portions are branched, and at portions adjacent to the positions of the trunk portion. A lateral force at the time of needle insertion is borne by the reinforcement member, and this prevents the trunk portion from deforming. Thus, the configuration prevents the artificial blood vessel from deforming due to a force applied when a needle for discharging liquid from a human body or introducing the liquid into the human body is inserted into an access port of the artificial blood vessel.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com