Patents
Literature
205results about How to "Eliminate high frequency noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
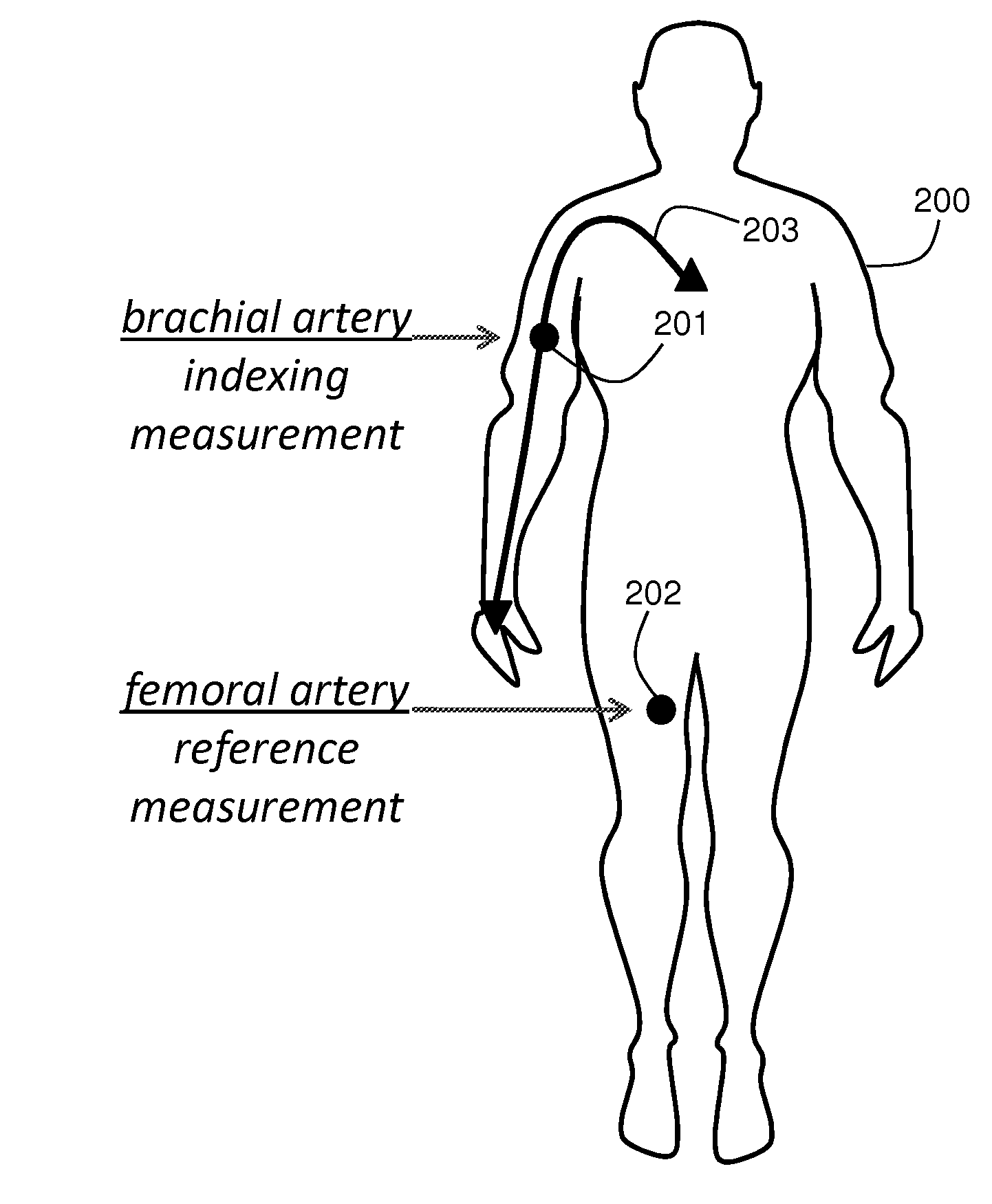
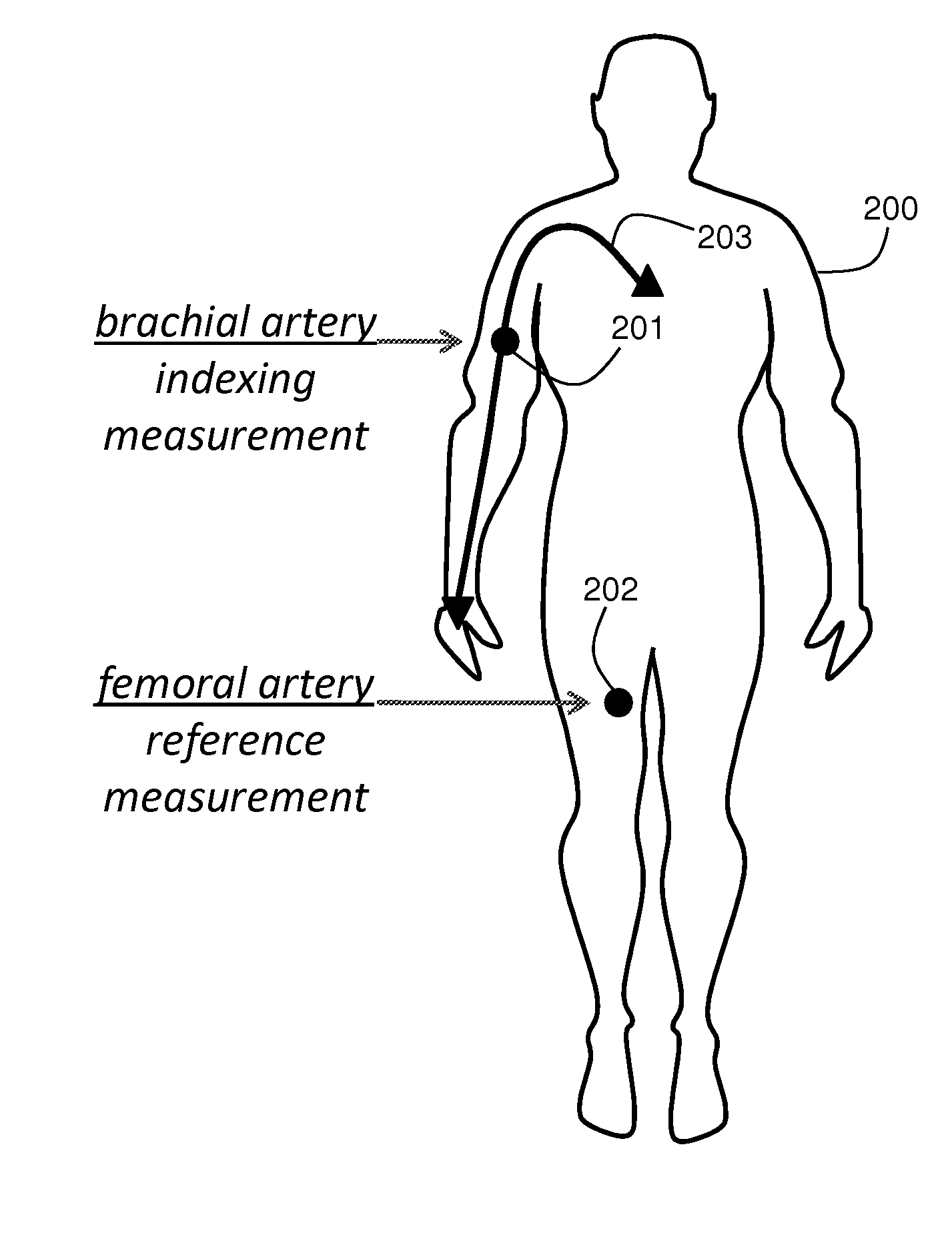
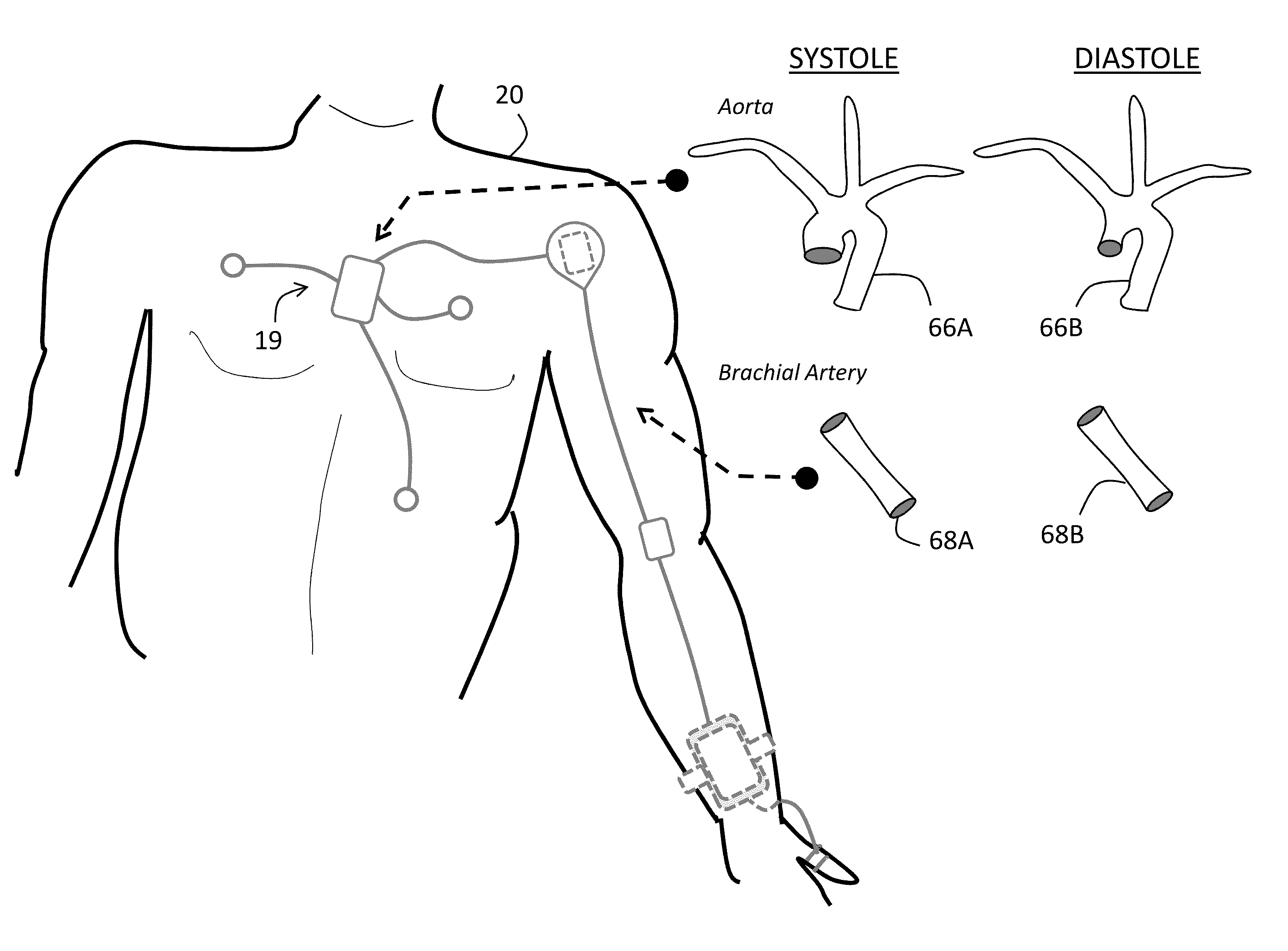
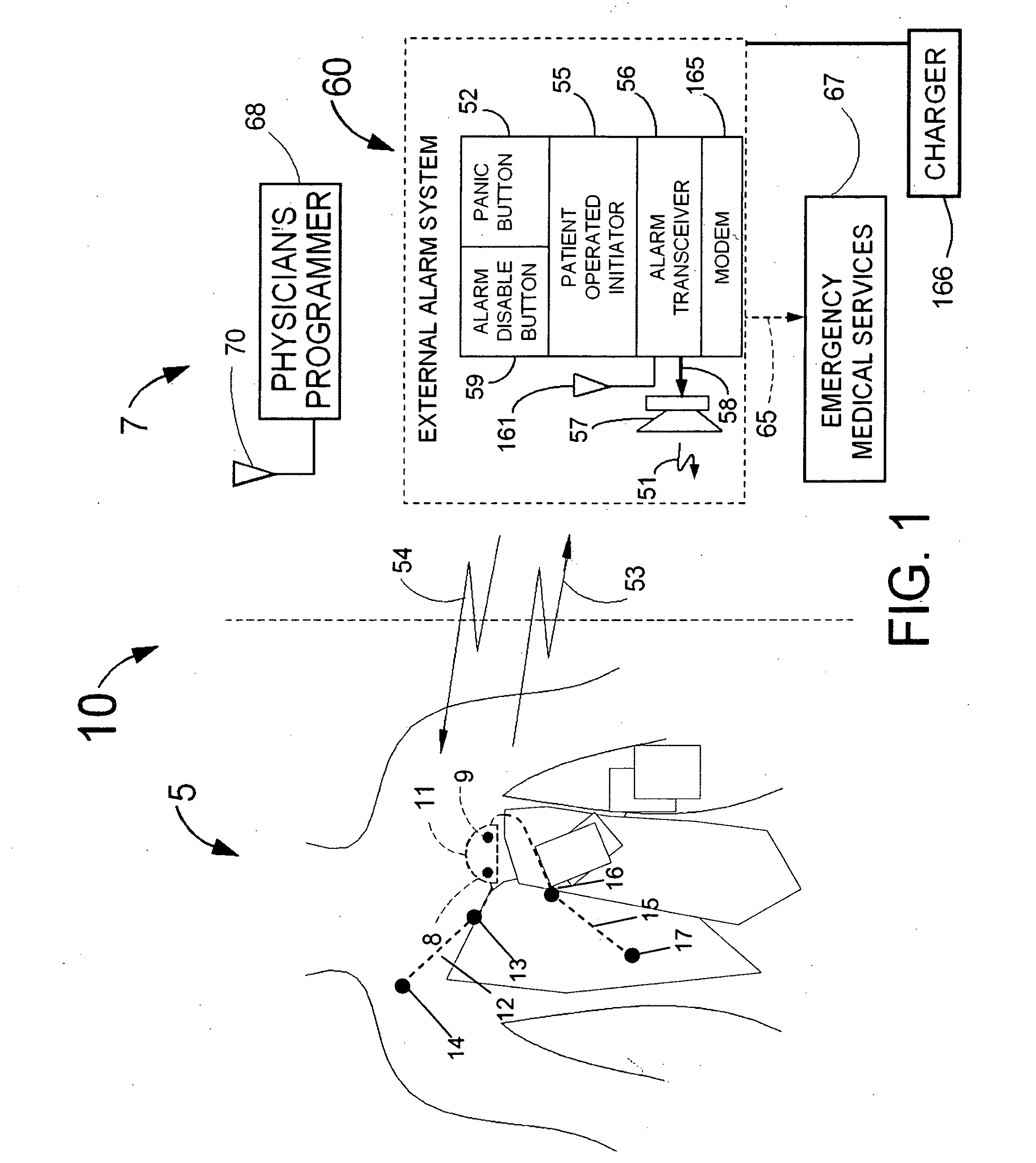
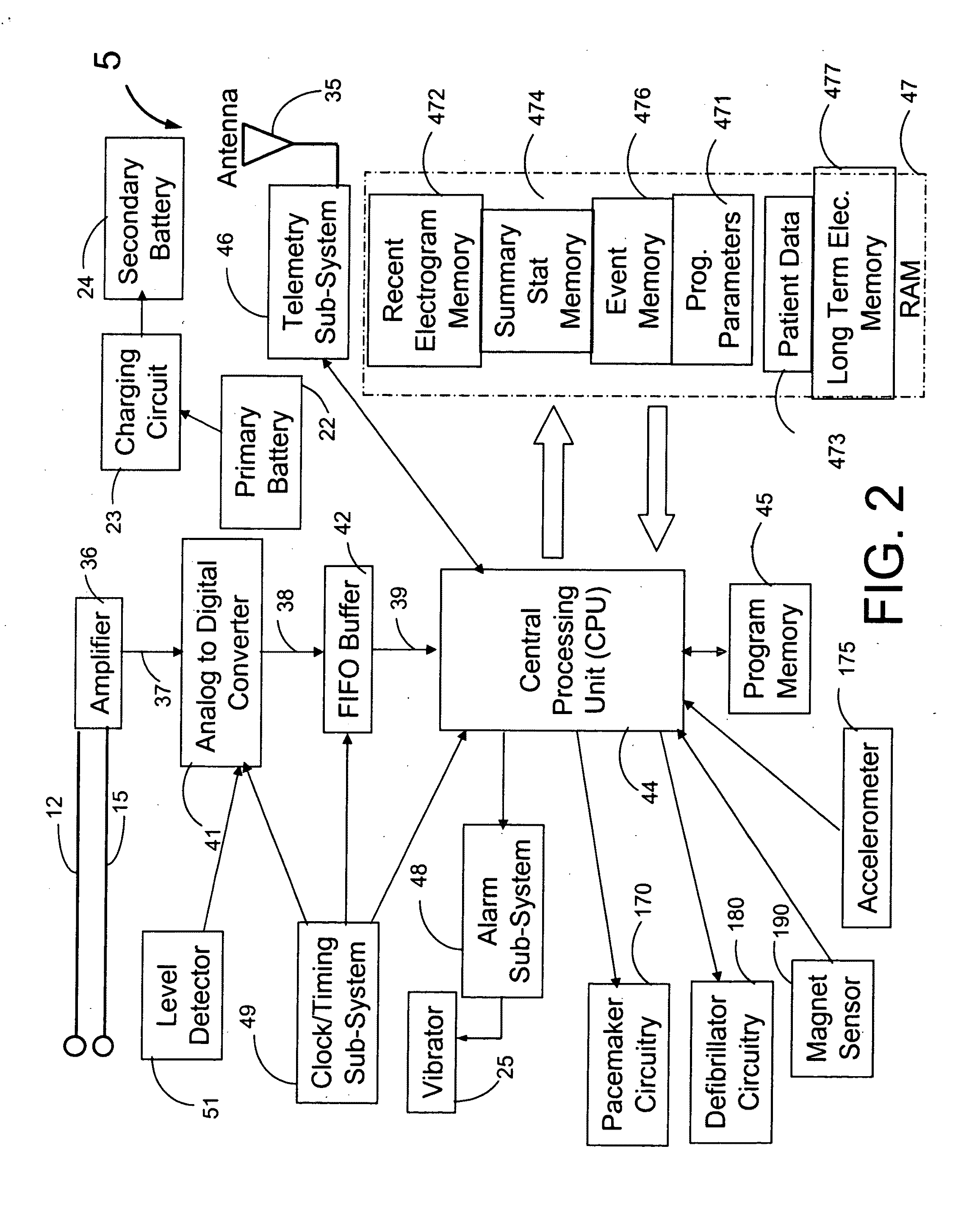
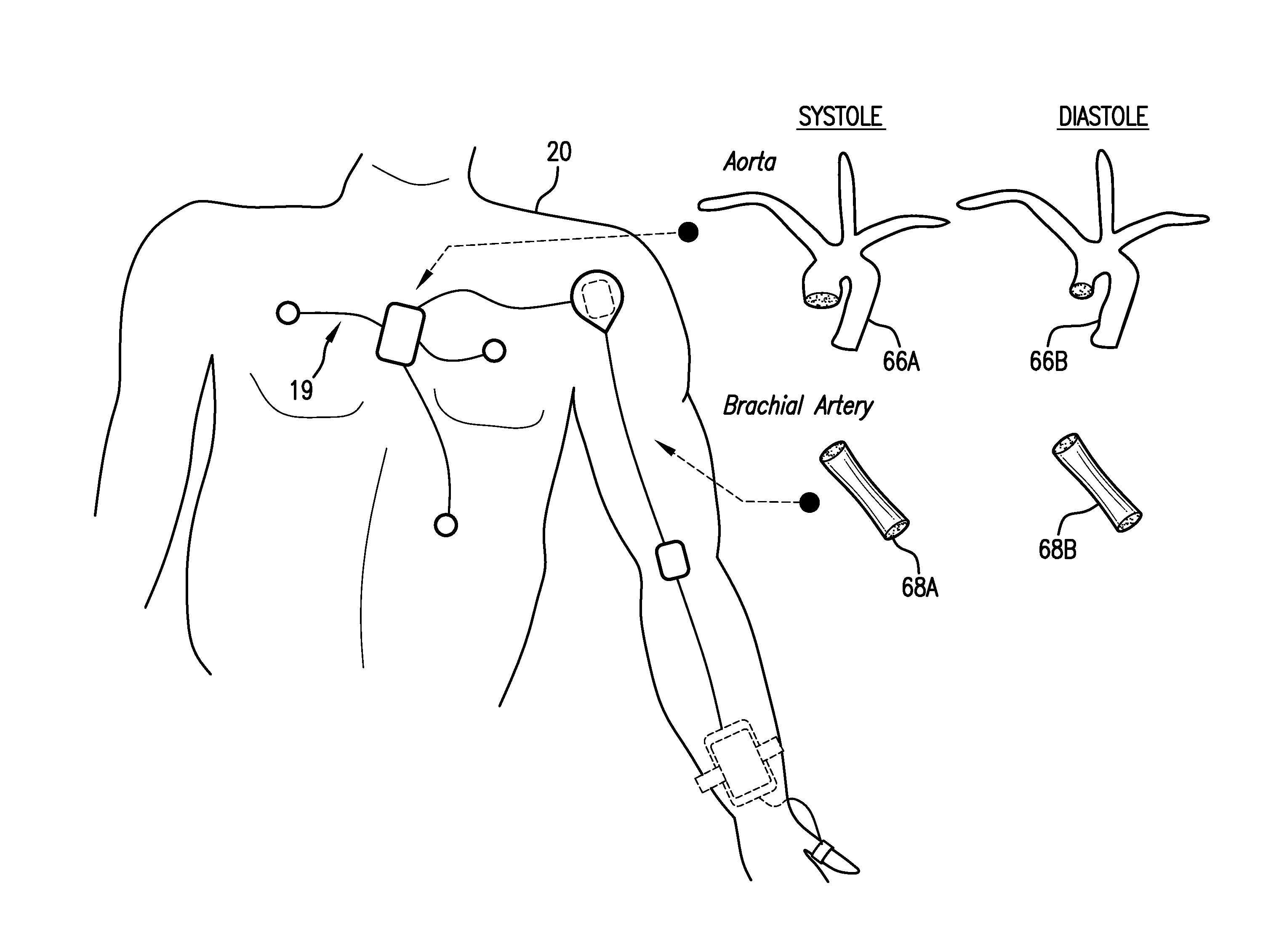
BODY-WORN SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CONTINUOUS NON-INVASIVE BLOOD PRESSURE (cNIBP)
ActiveUS20100160794A1Good curative effectImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyCatheterContinuous measurementAccelerometer
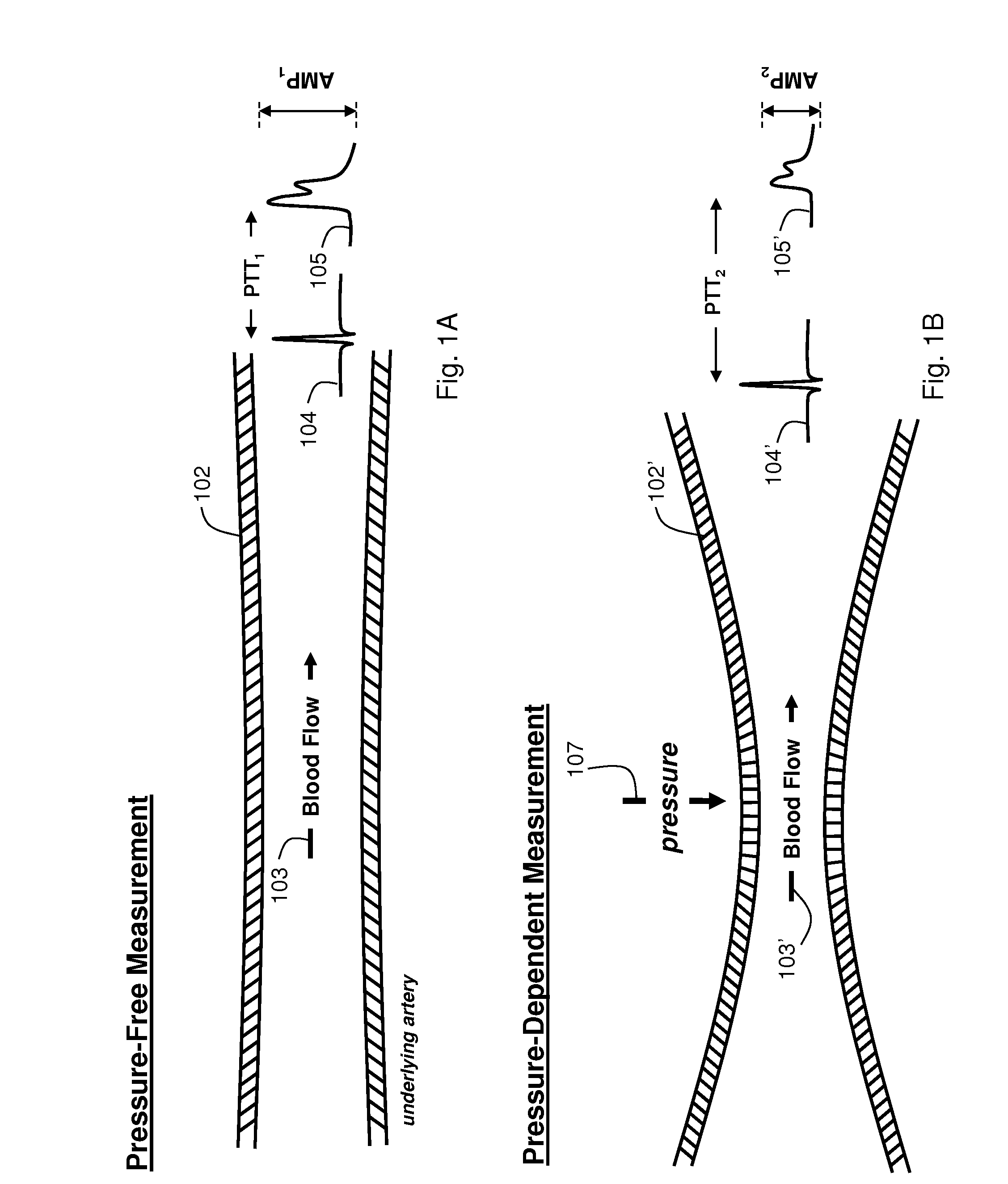
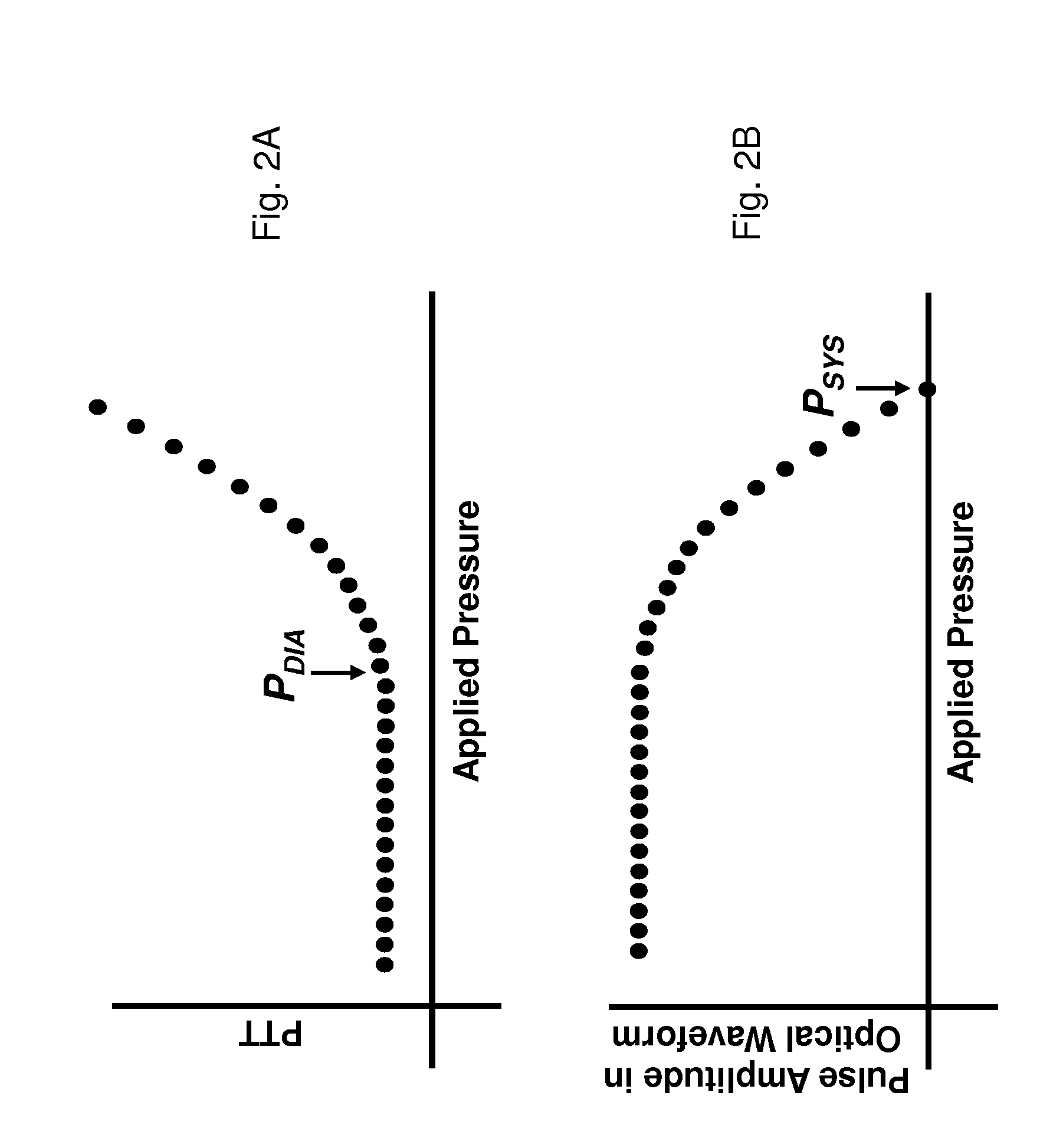
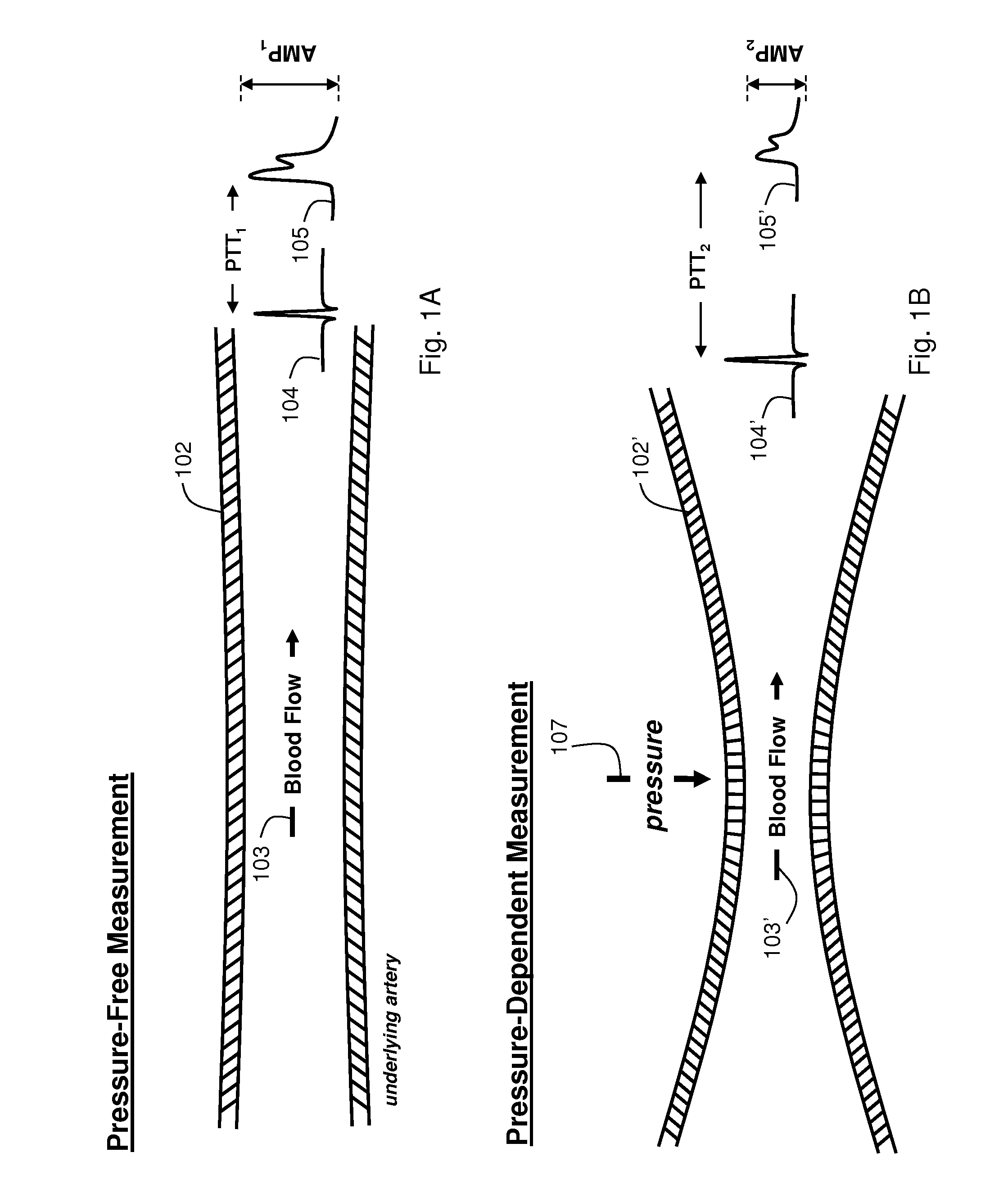
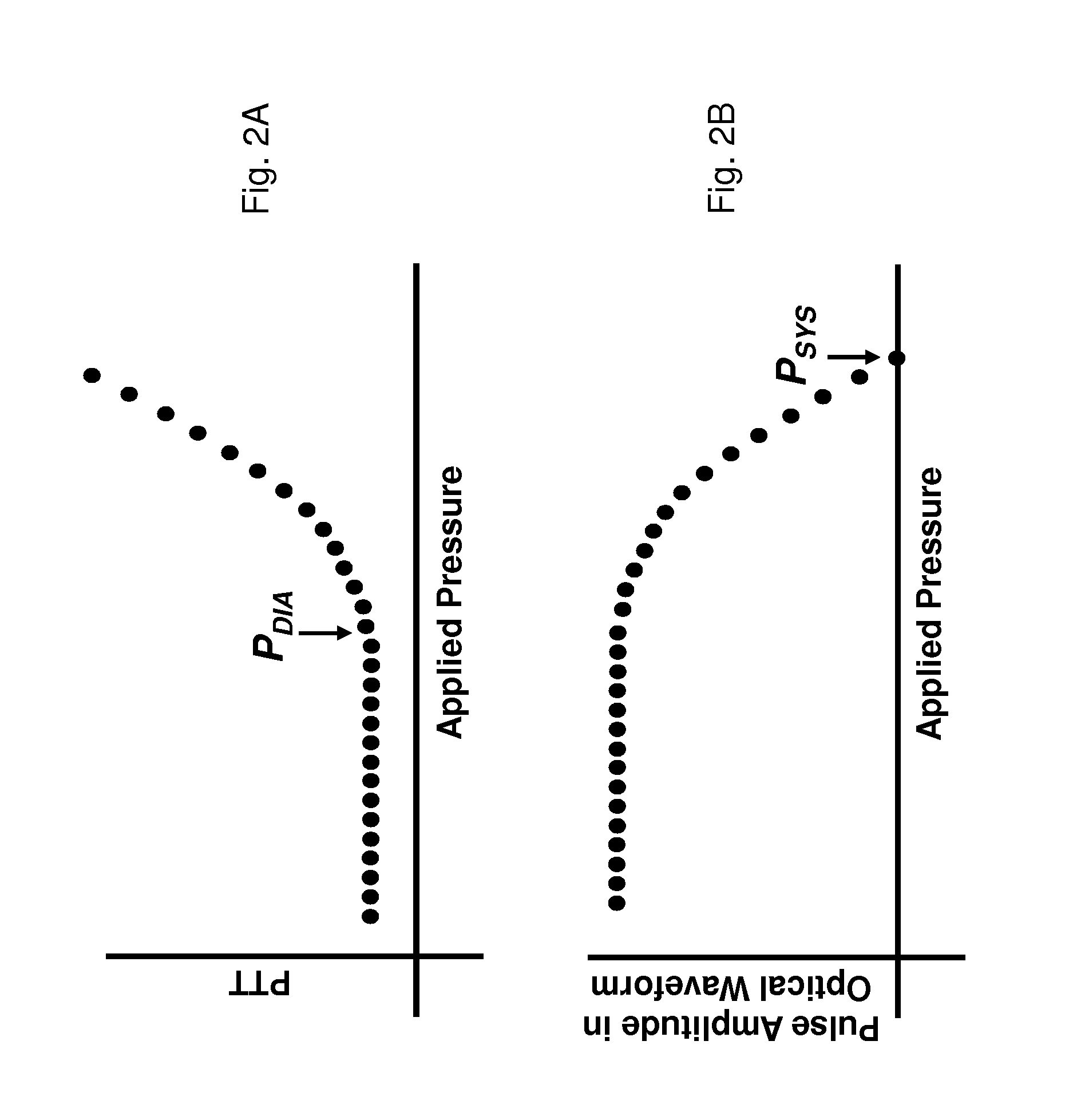
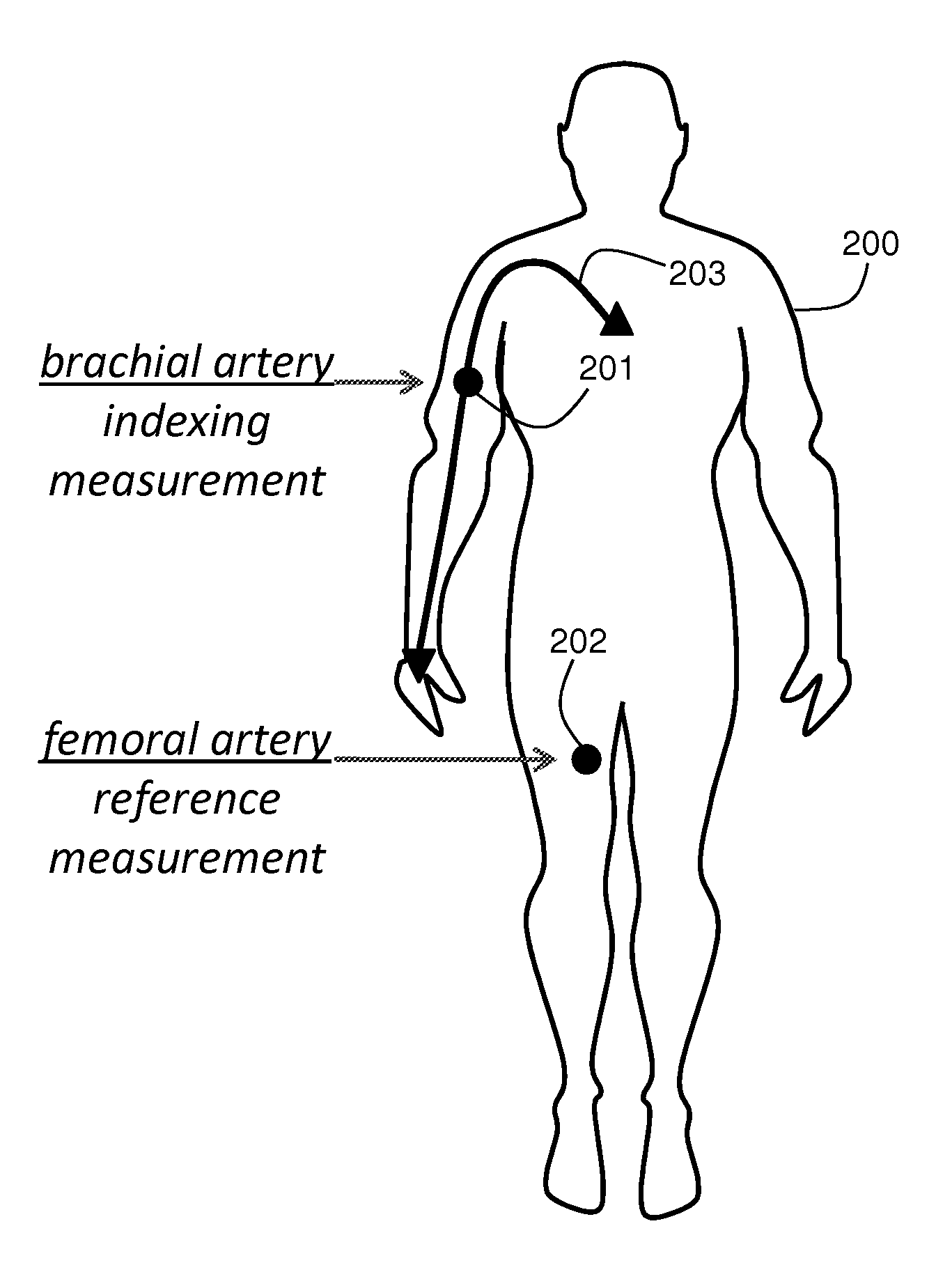
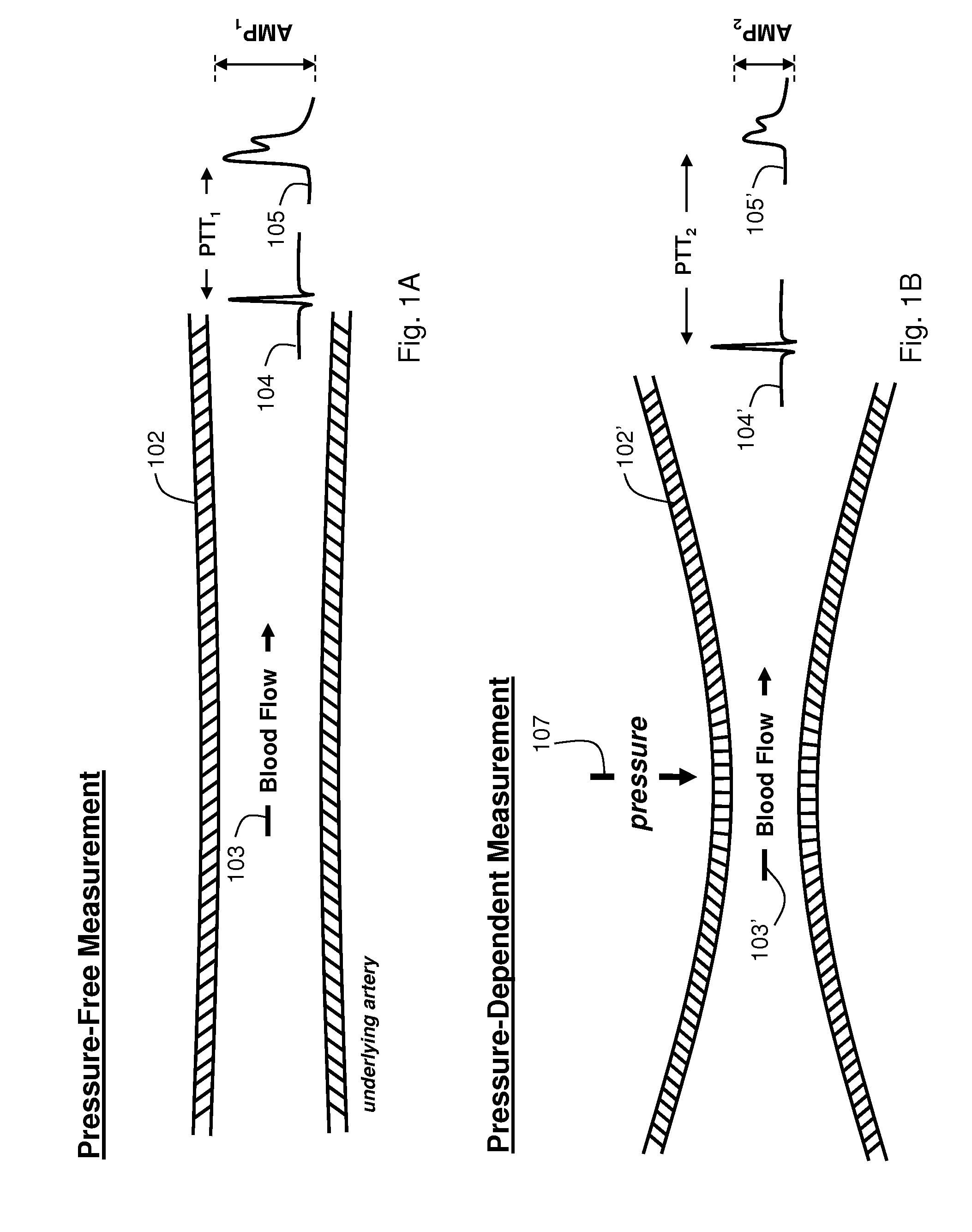
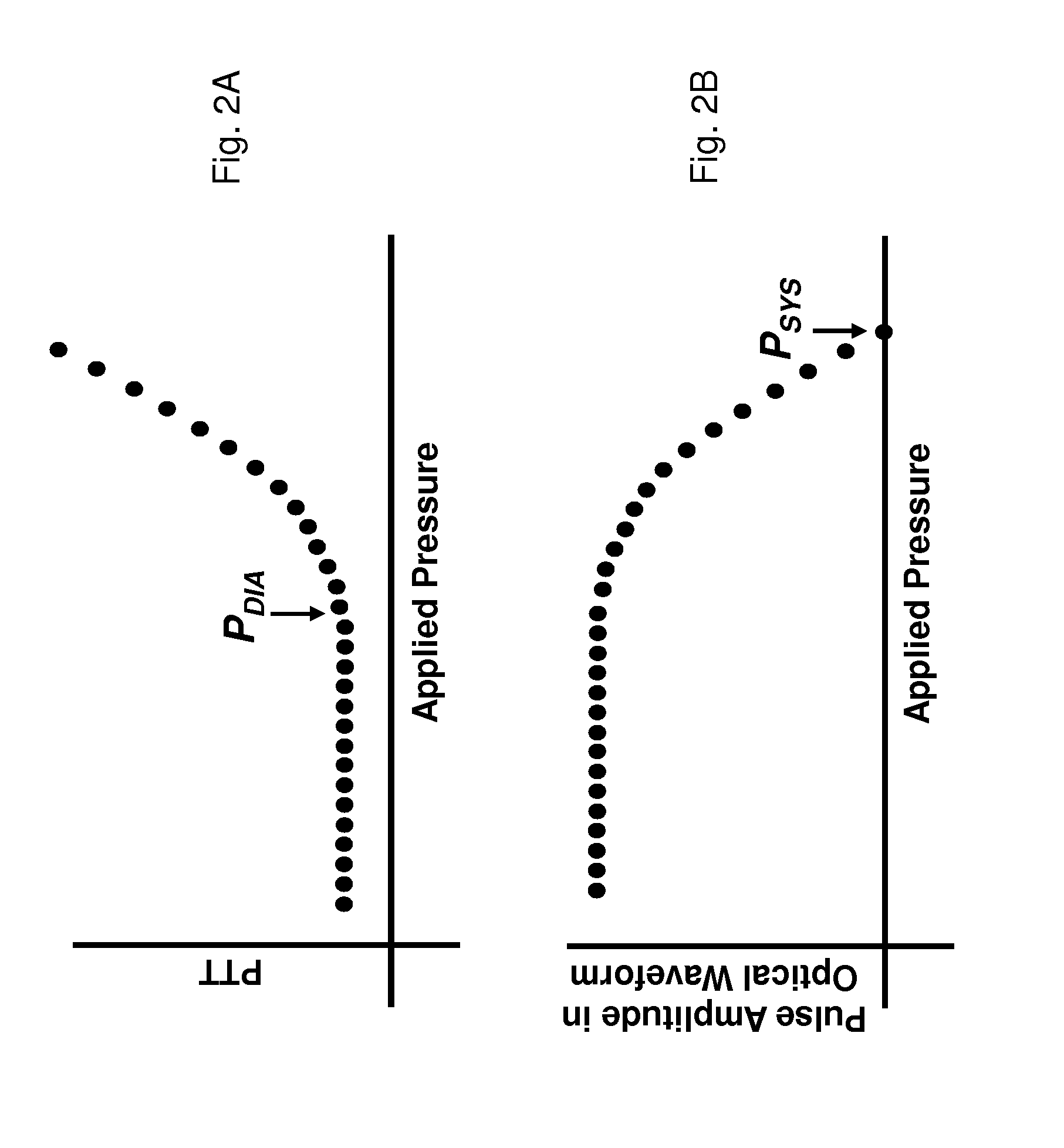
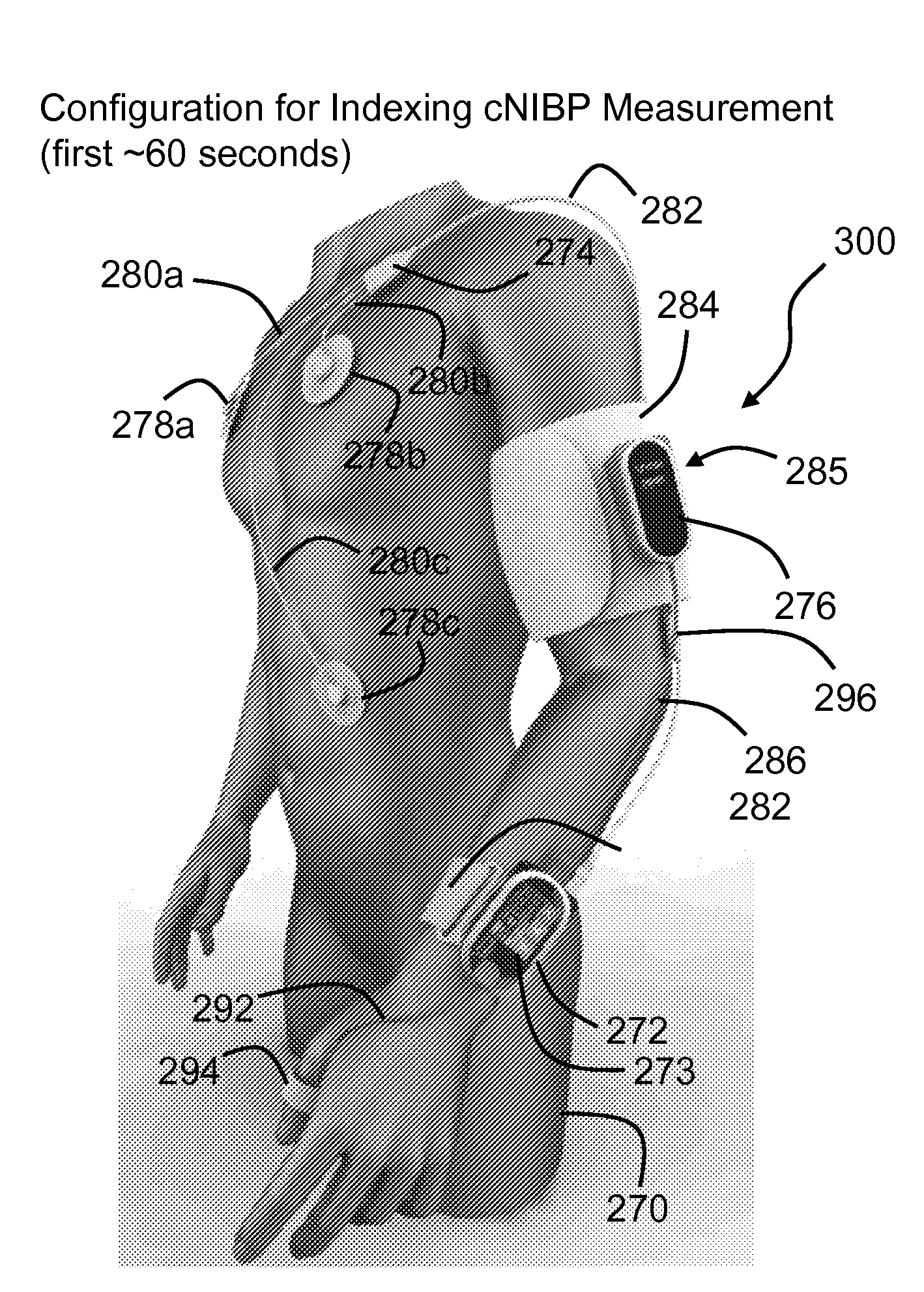
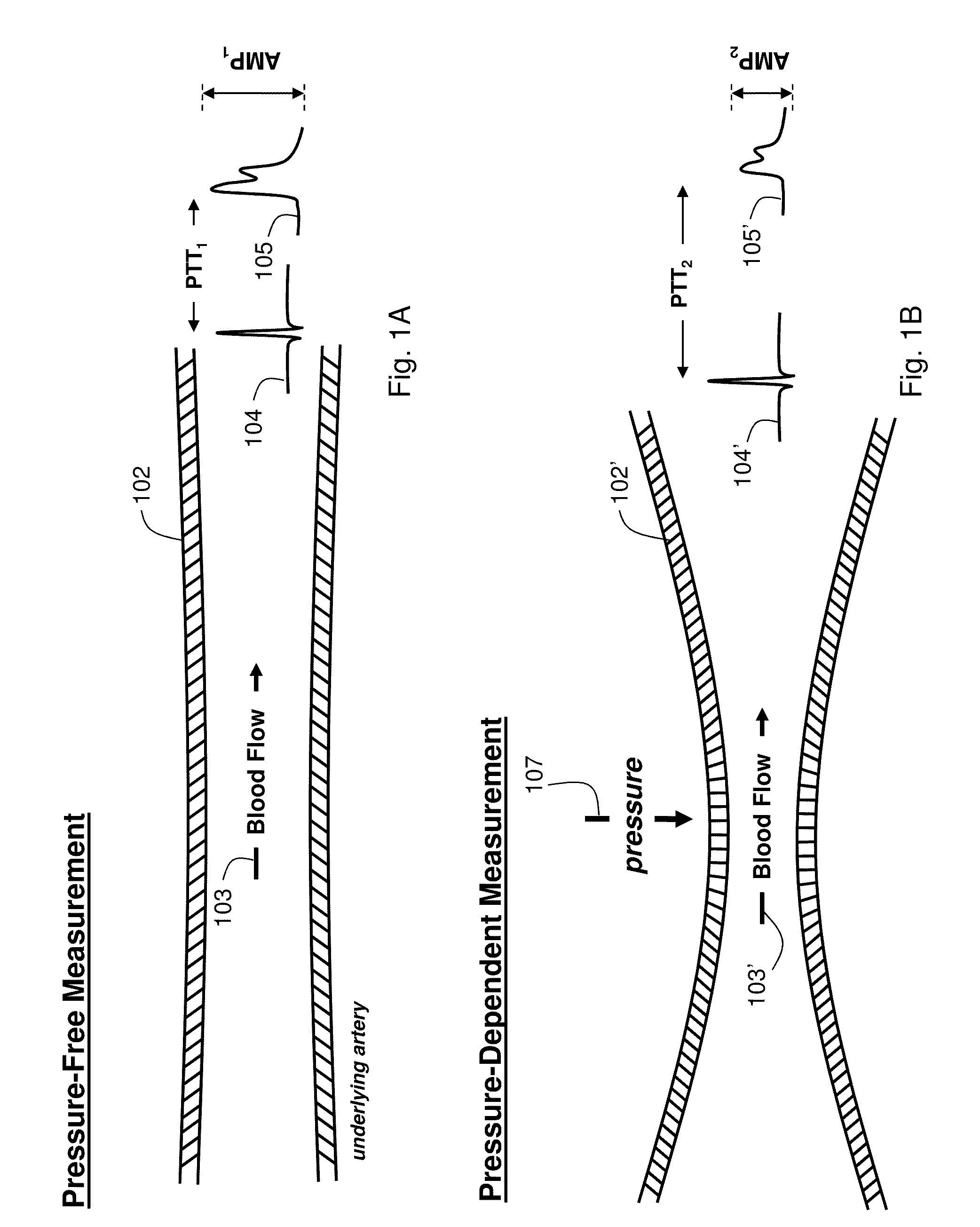
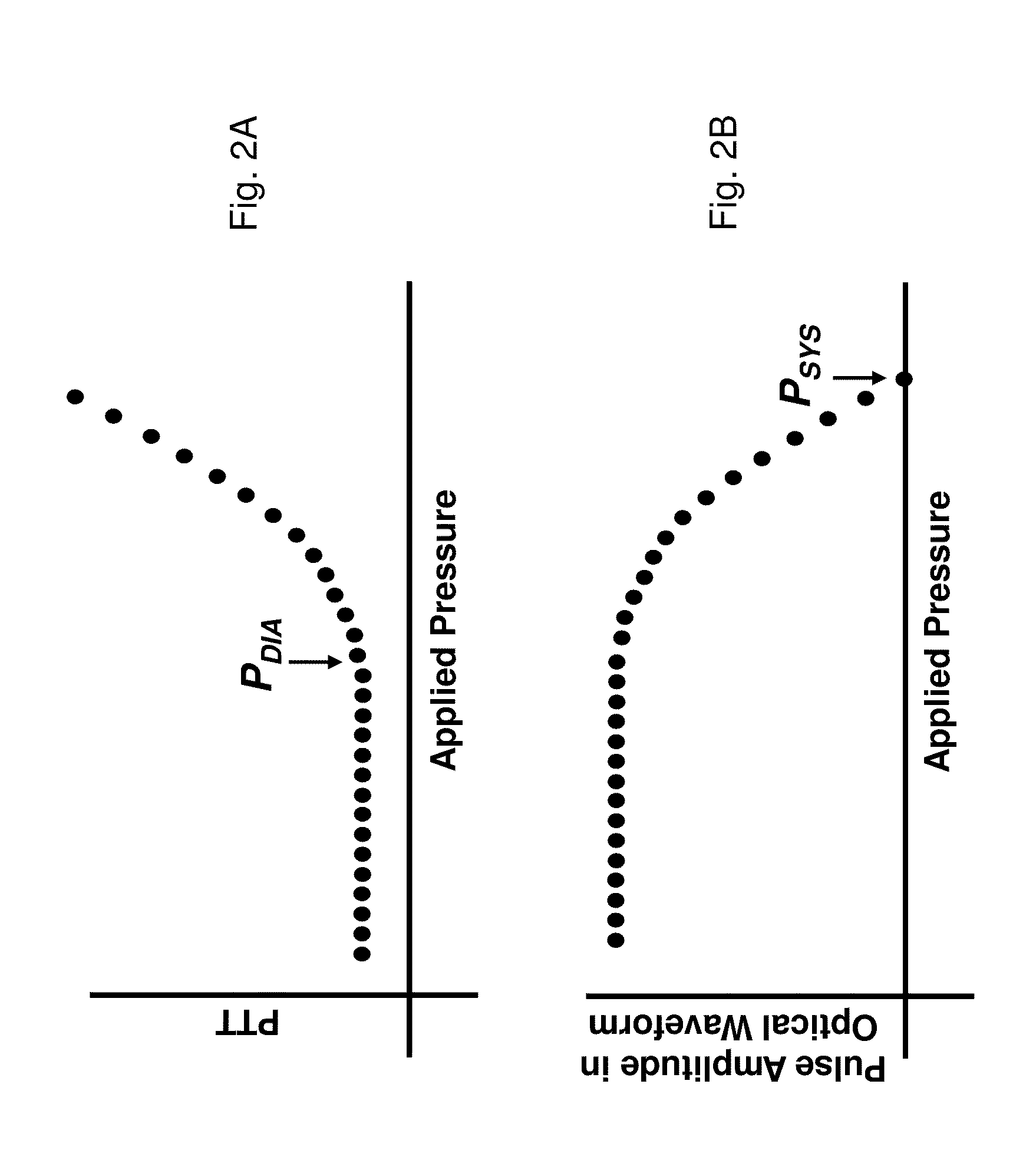
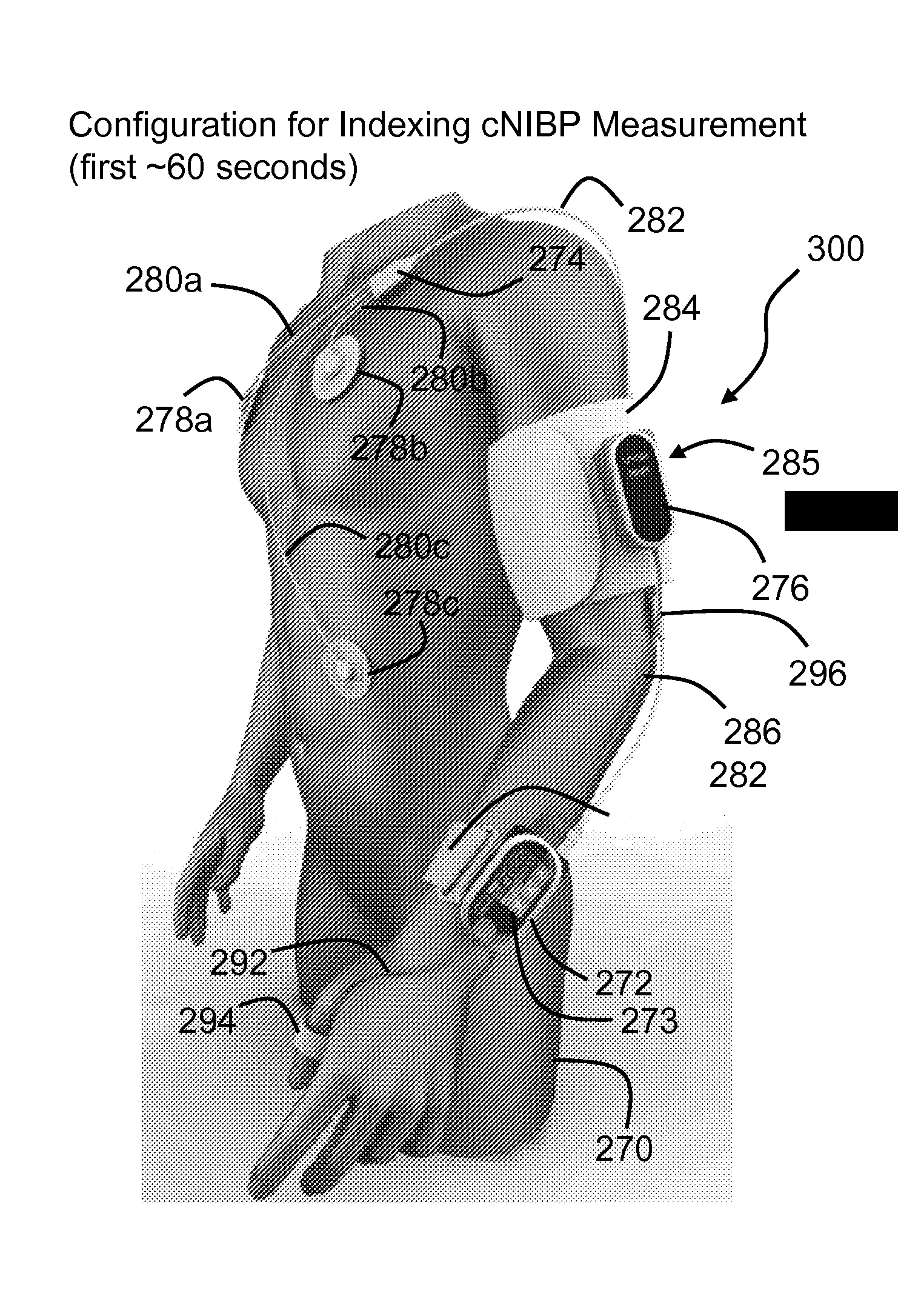
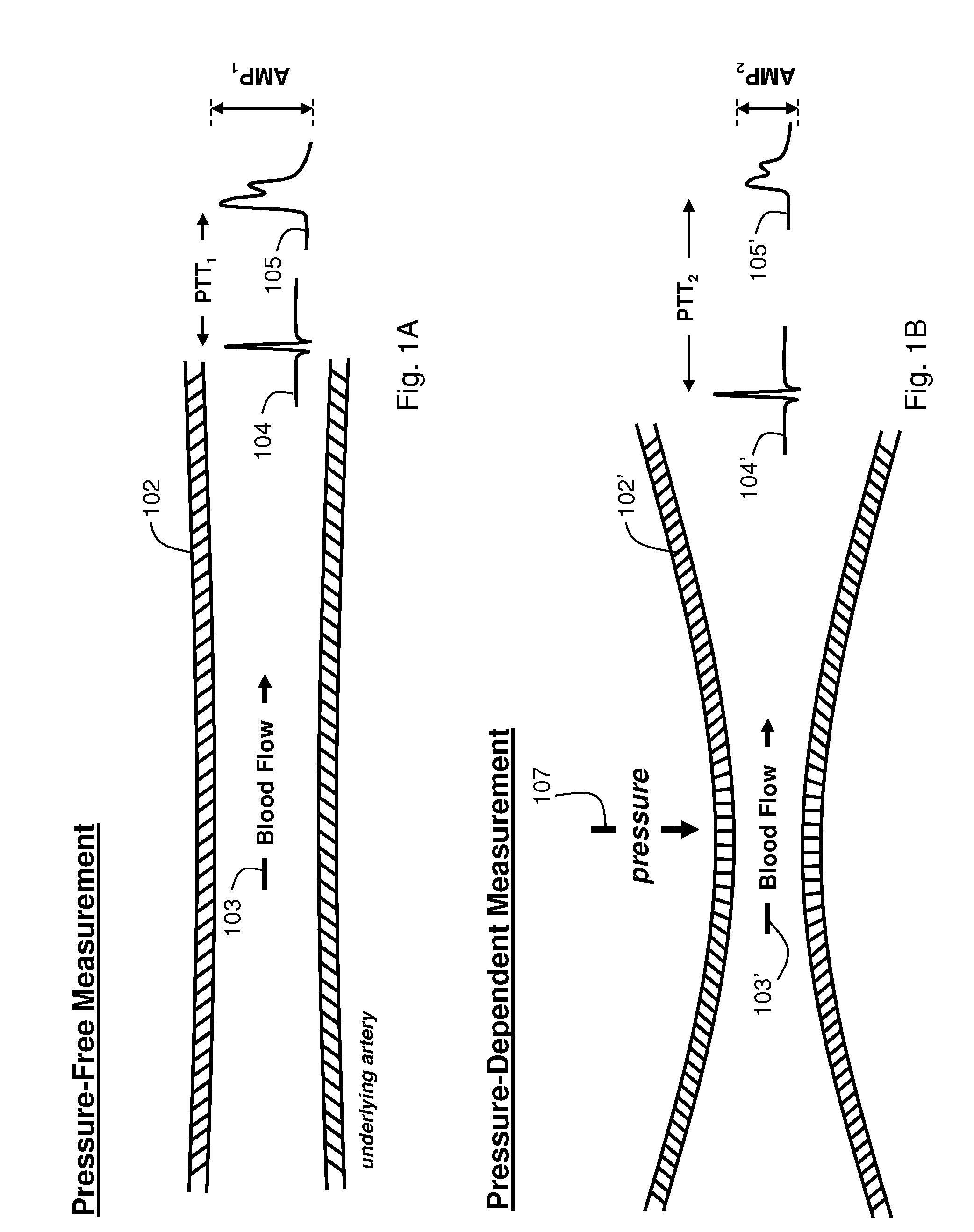
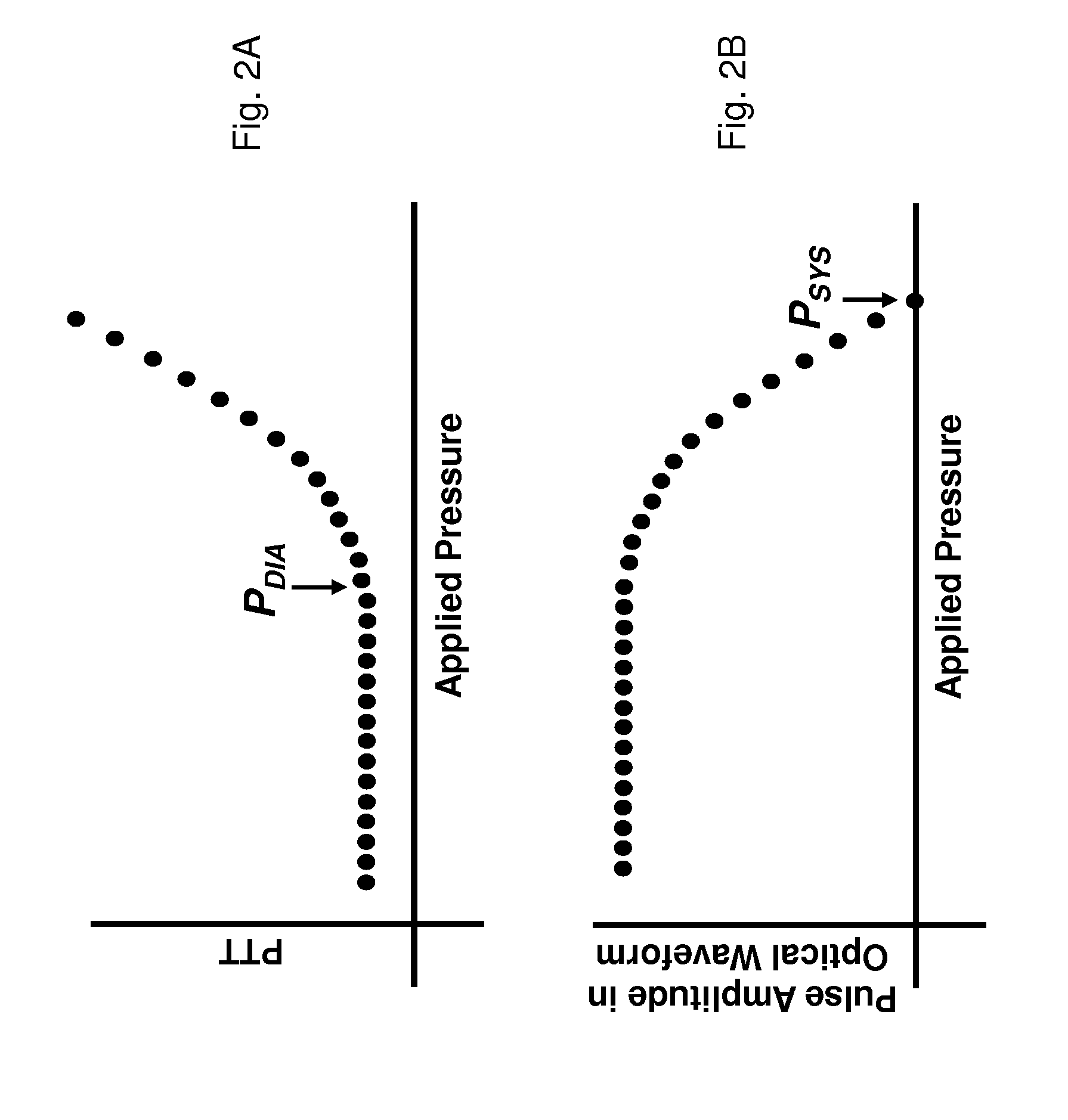
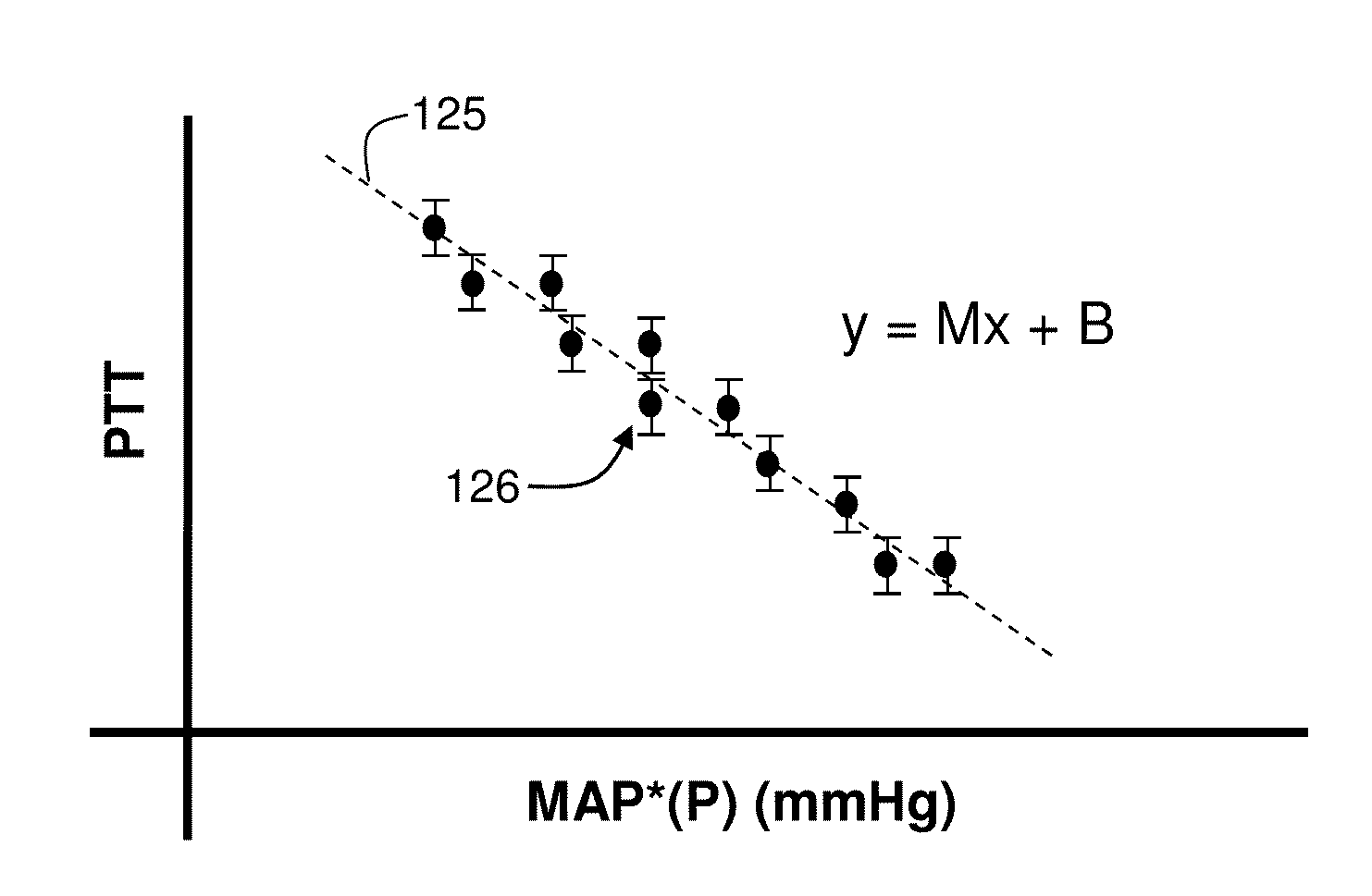
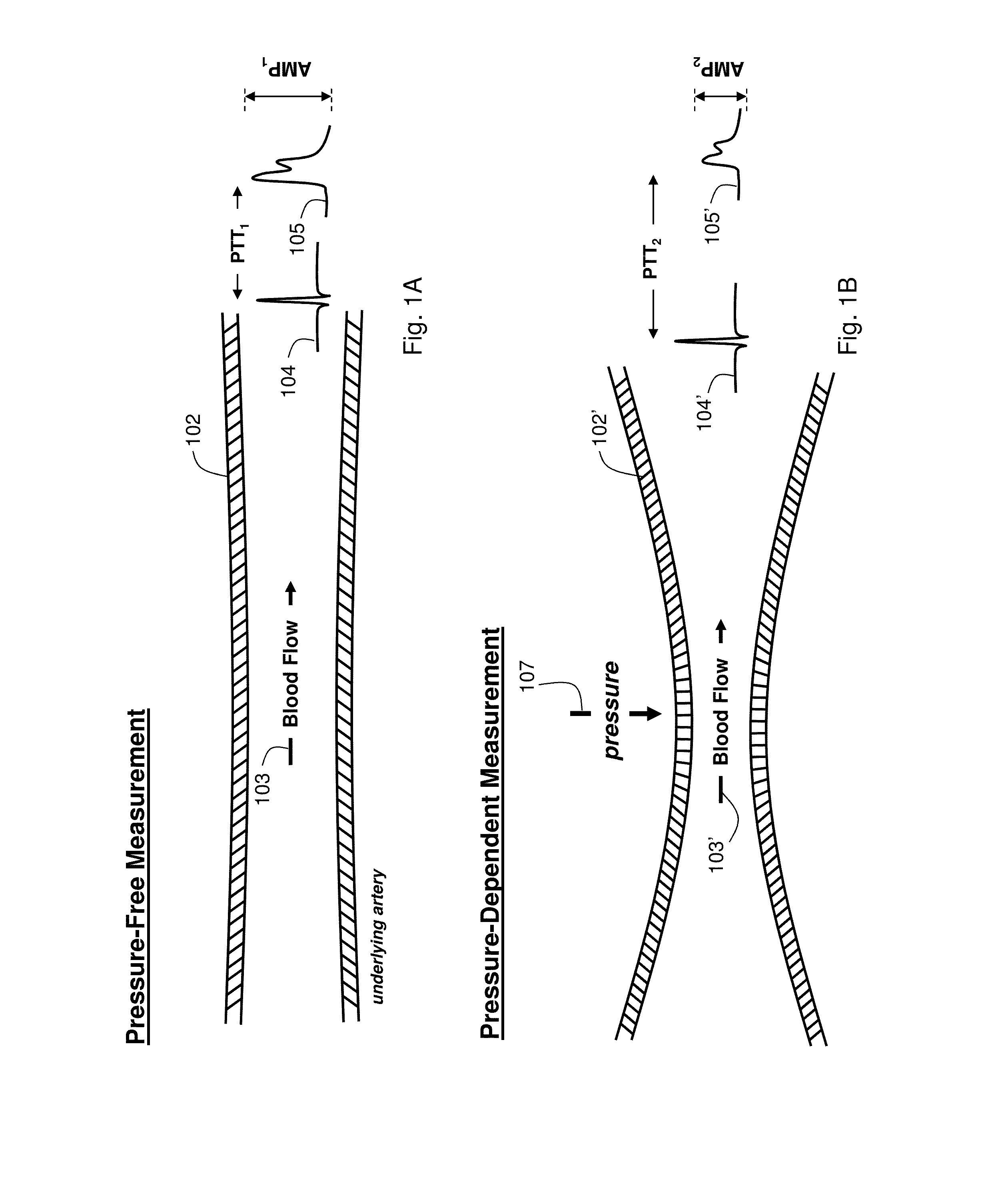
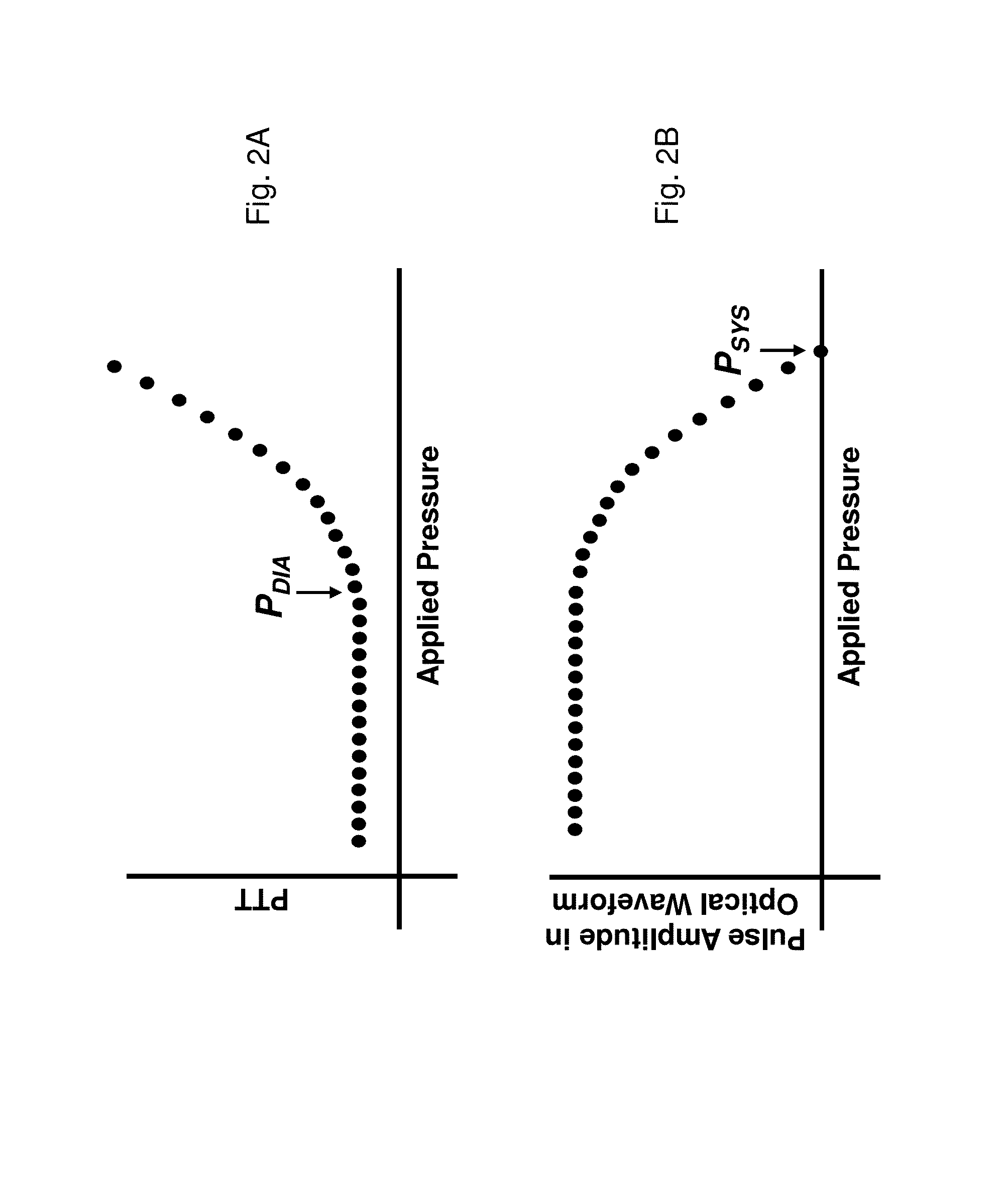
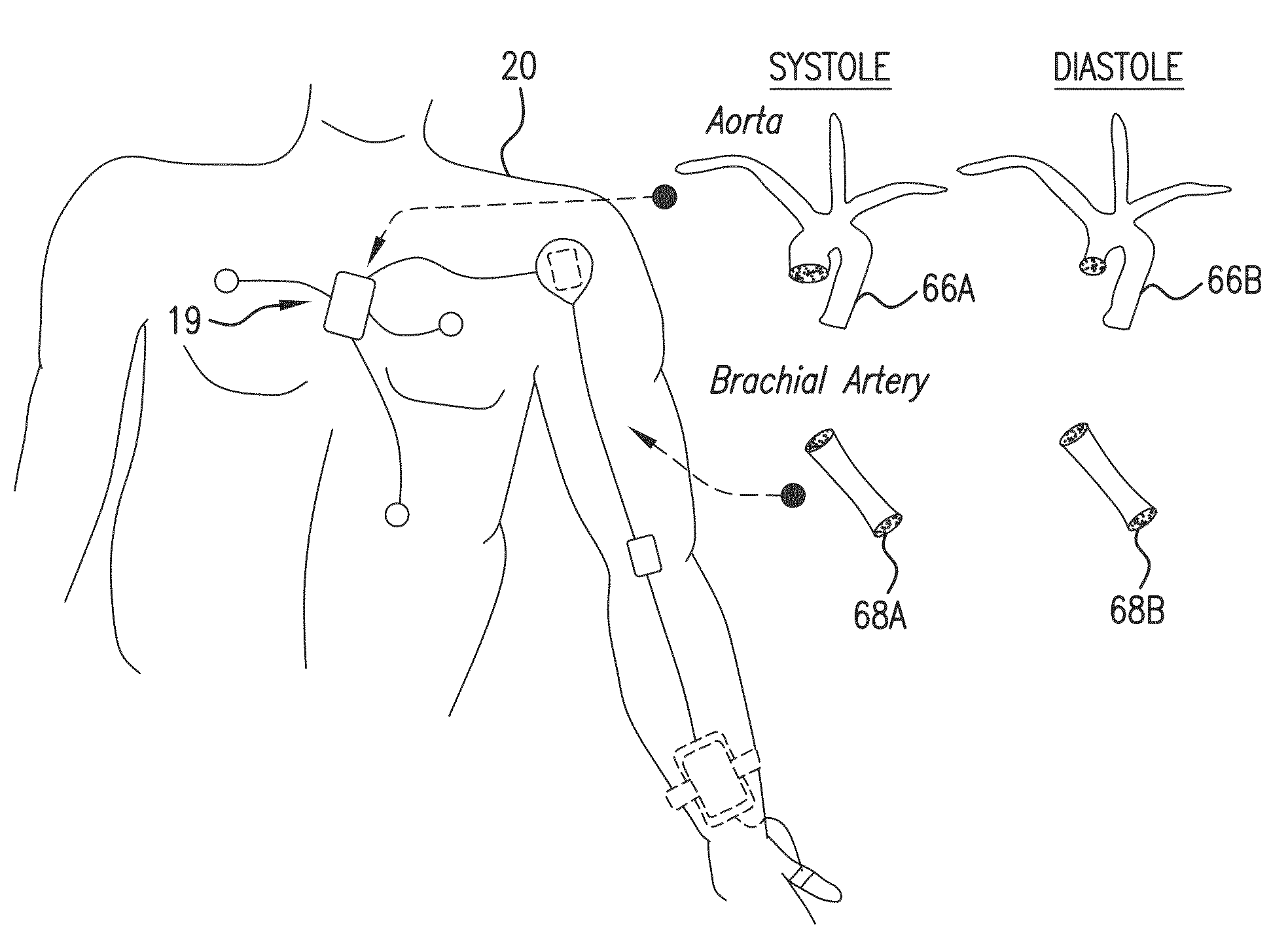
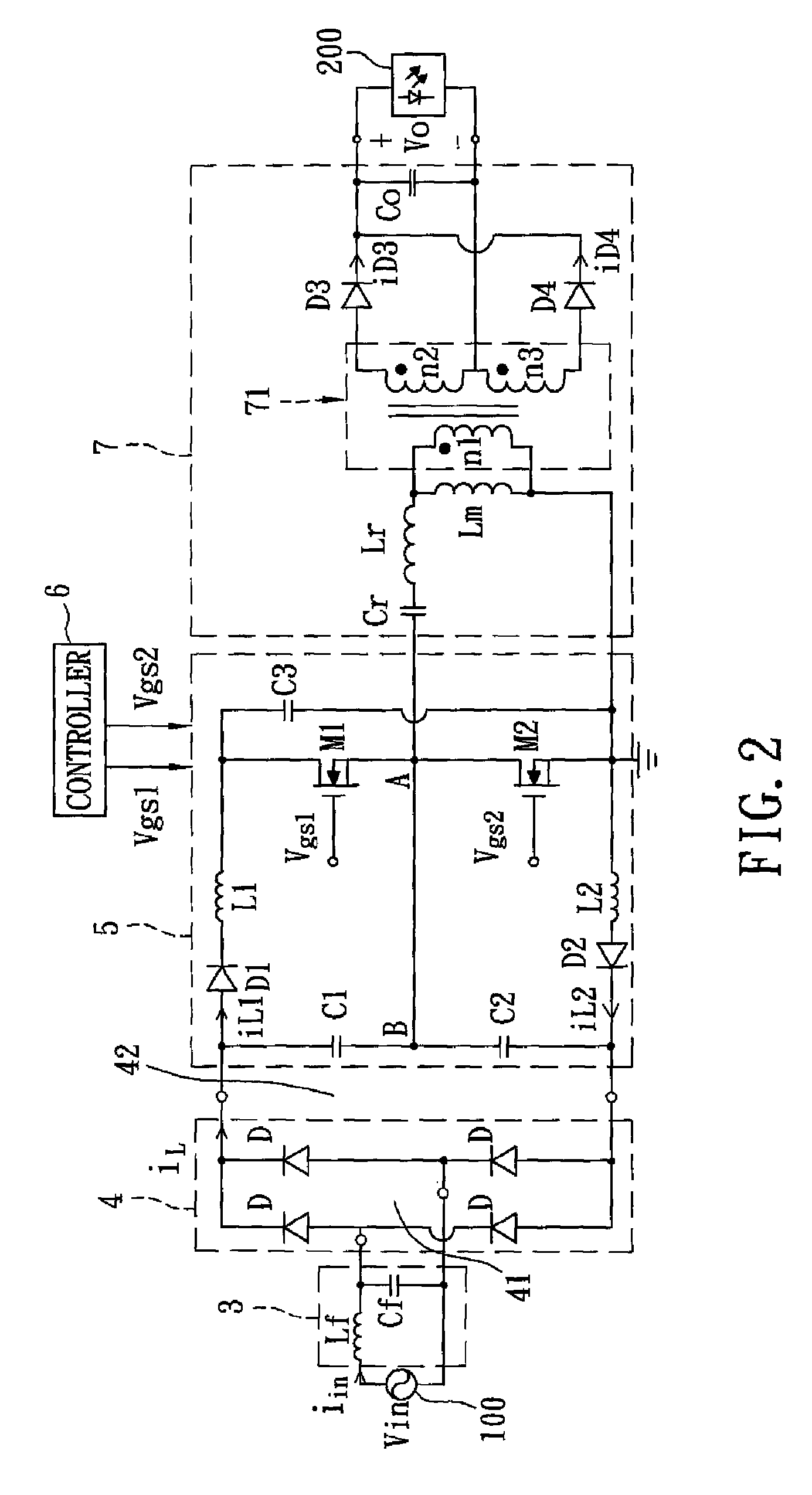
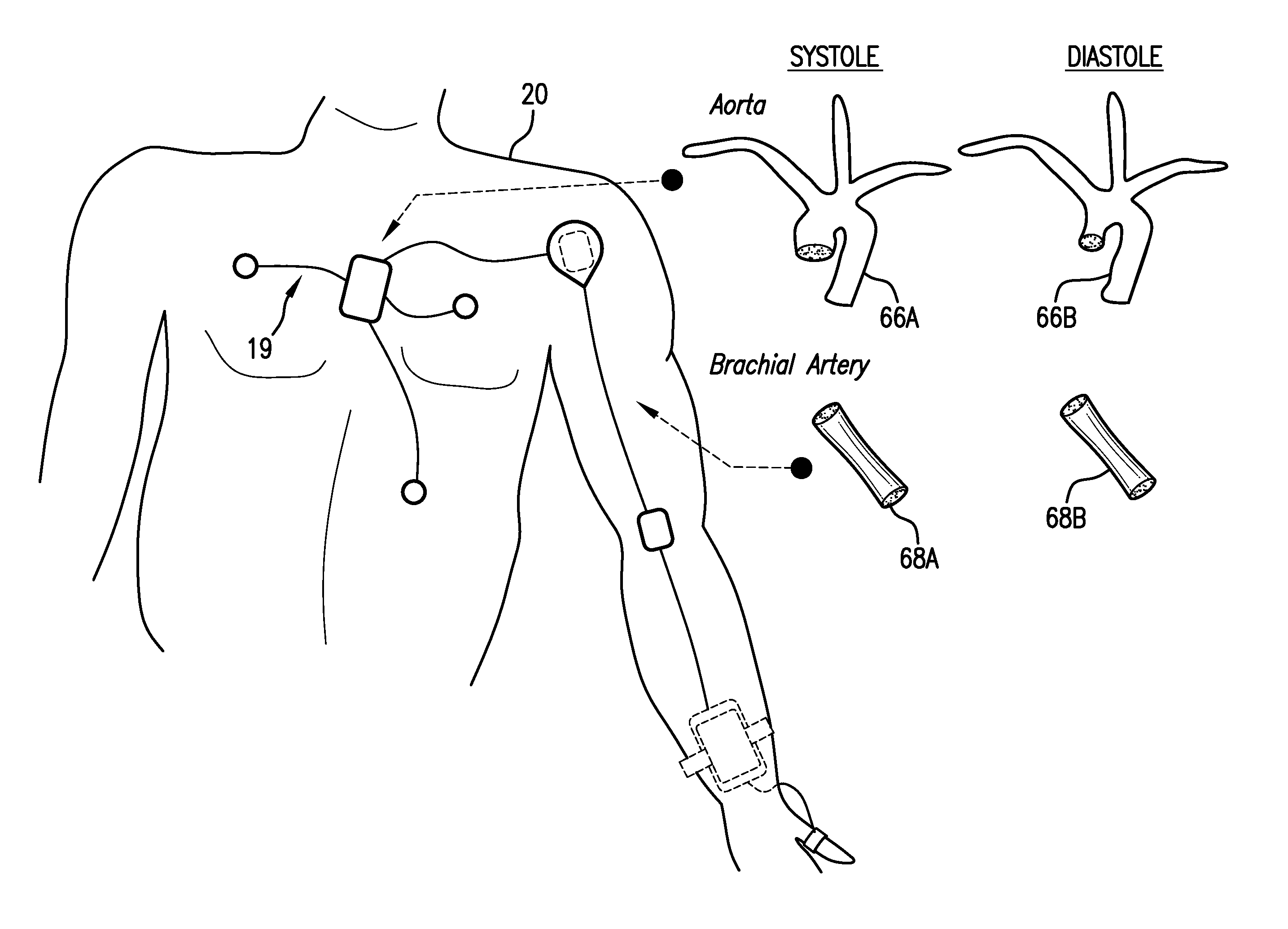
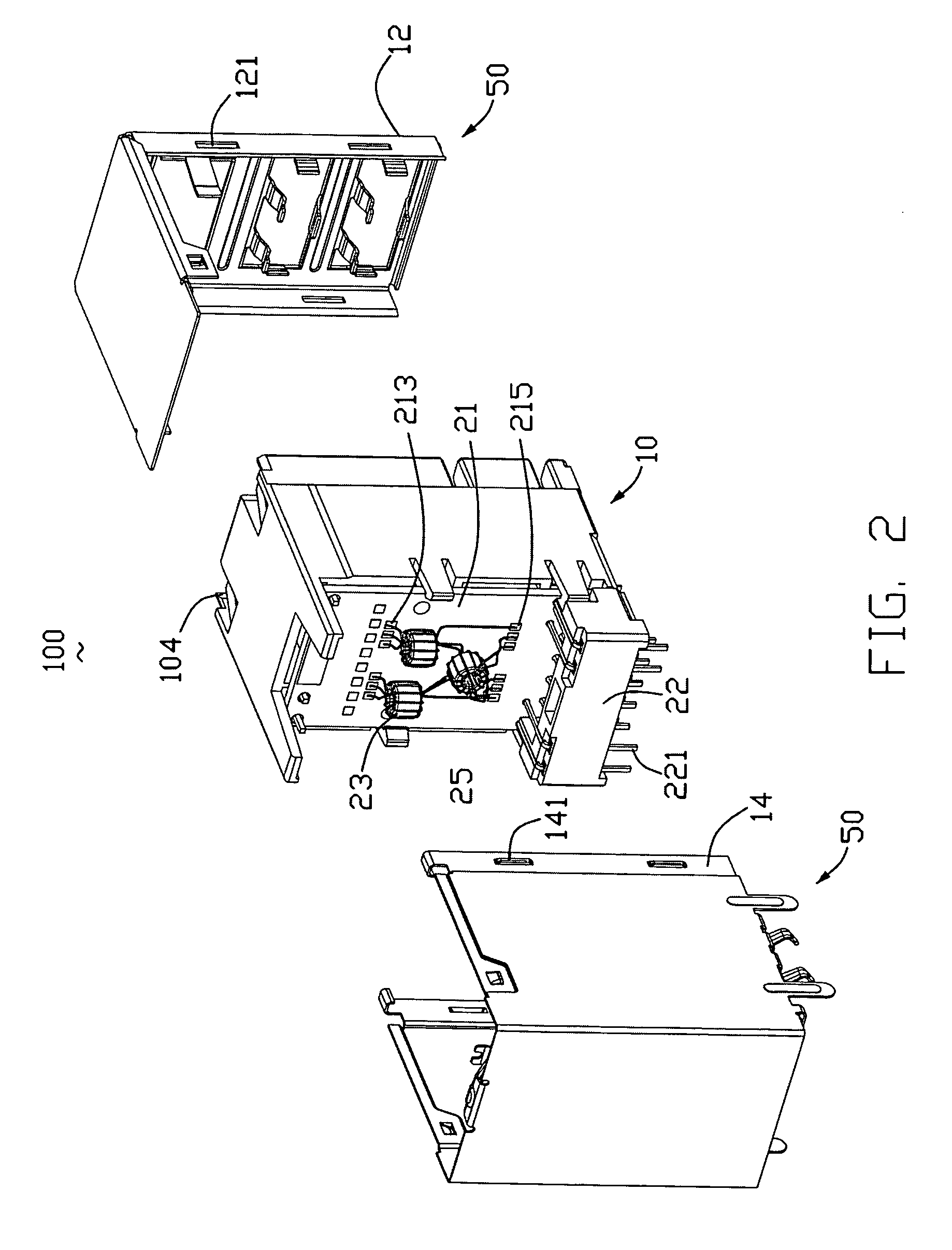
The present invention provides a technique for continuous measurement of blood pressure based on pulse transit time and which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘Composite Method’, is carried out with a body-worn monitor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of body-worn sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body-worn monitor and measure time-dependent ECG, PPG, accelerometer, and pressure waveforms. The disposable sensors can include a cuff that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, three or more electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), three or more accelerometers, a temperature sensor, and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to the patient's thumb.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
BODY-WORN SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CONTINUOUS NON-INVASIVE BLOOD PRESSURE (cNIBP)
ActiveUS20100160798A1Slow inflation speedHigh sensitivityElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementAccelerometer
The present invention provides a technique for continuous measurement of blood pressure based on pulse transit time and which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘Composite Method’, is carried out with a body-worn monitor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of body-worn sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body-worn monitor and measure time-dependent ECG, PPG, accelerometer, and pressure waveforms. The disposable sensors can include a cuff that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, three or more electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), three or more accelerometers, a temperature sensor, and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to the patient's thumb.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Filtering intensity decision method, moving picture encoding method, and moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS20040179620A1Quality improvementEliminate high frequency noisePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDecoding methodsDecision methods
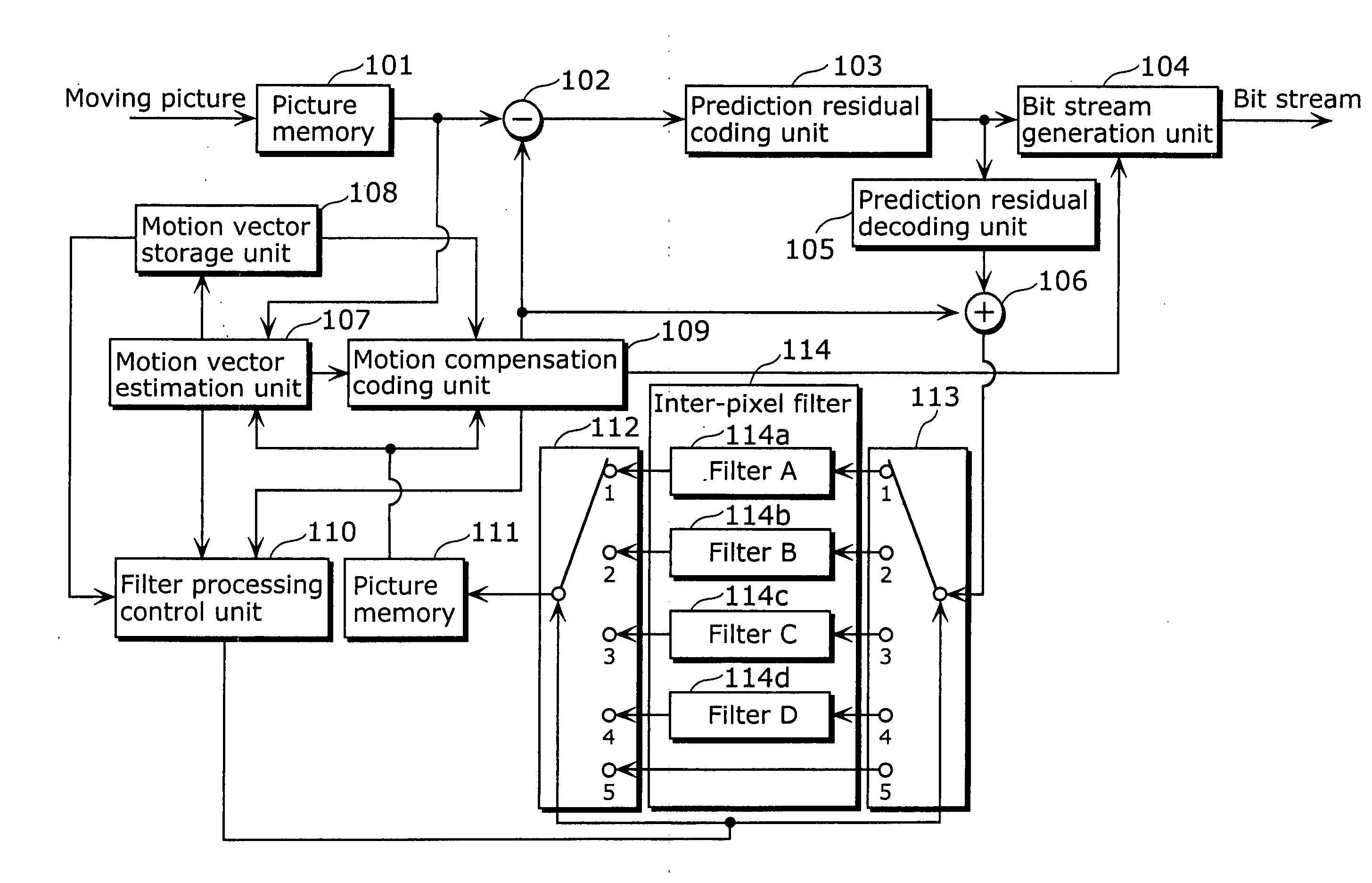
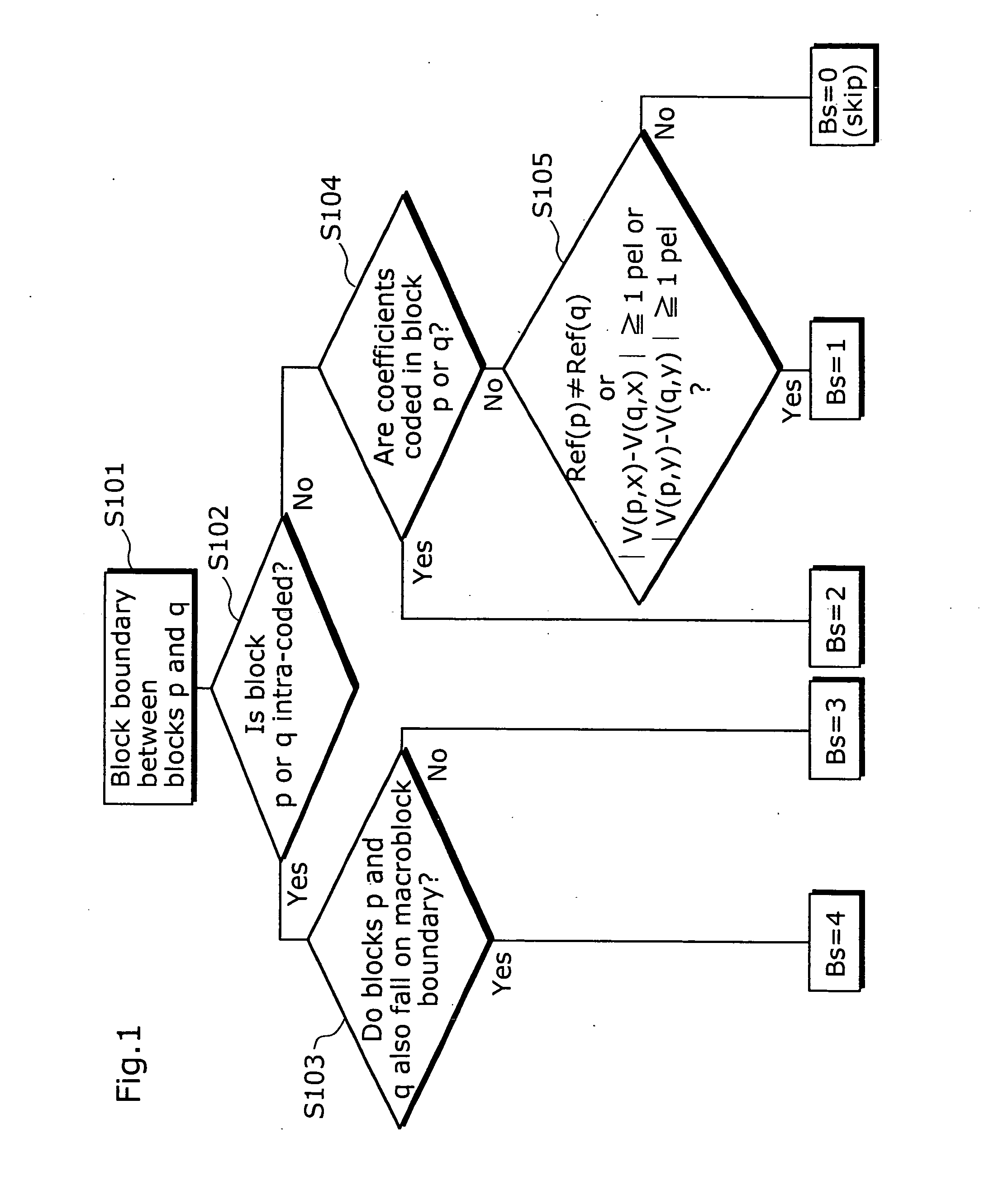
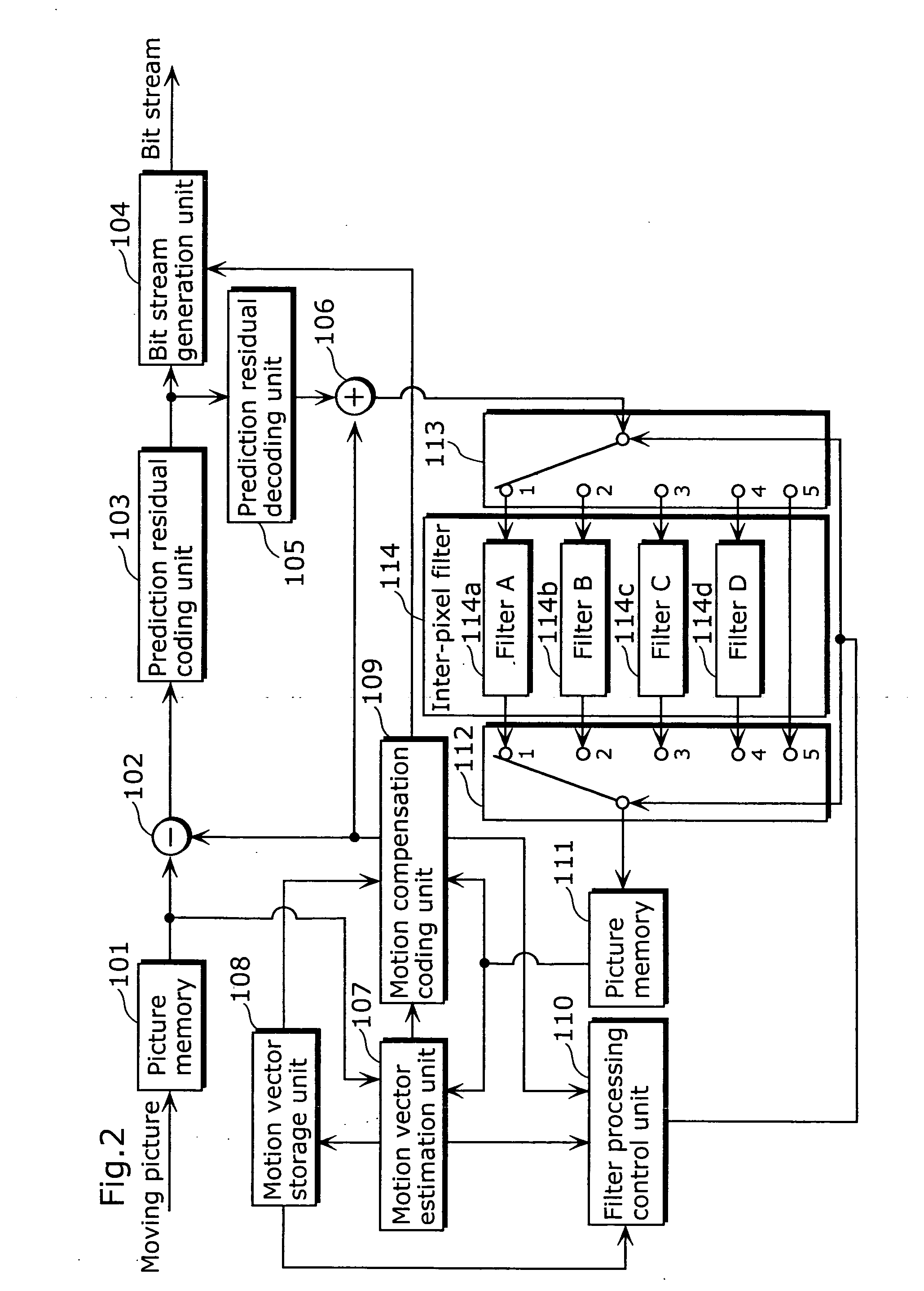
A moving picture coding apparatus includes (i) an inter-pixel filter (114) having the following filters for filtering decoded image data so as to remove block distortion which is high frequency noise around block boundaries: a filter A114a, a filter B114b, a filter C114c, a filter D114d, each having a different filtering strength, and (ii) a filter processing control unit (110) for determining a filtering strength of the inter-pixel filter (114).
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Power amplifier and radio wave transmitter having the same
ActiveUS20100266066A1Eliminate high frequency noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsPower controllerHigh frequency power
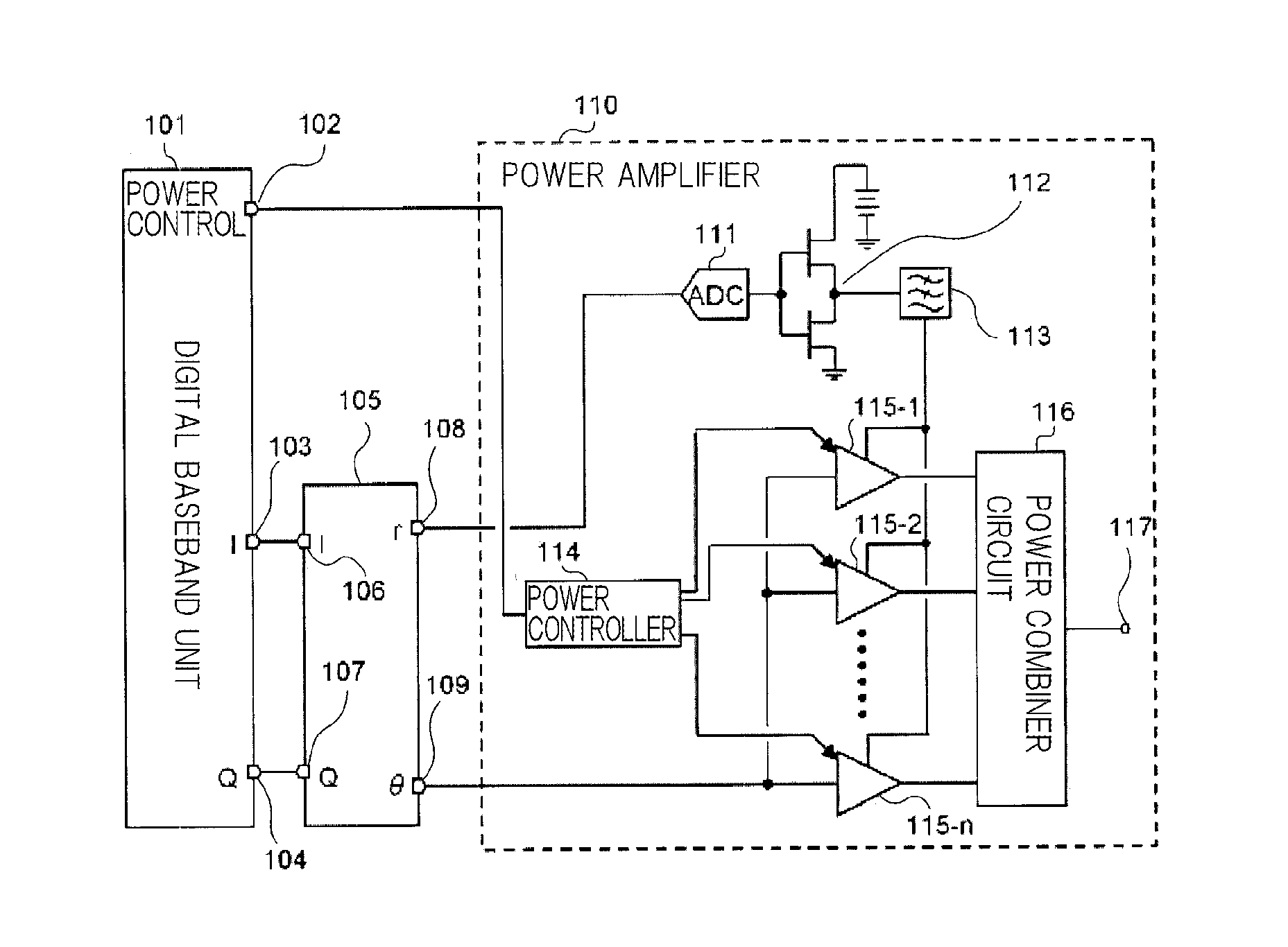
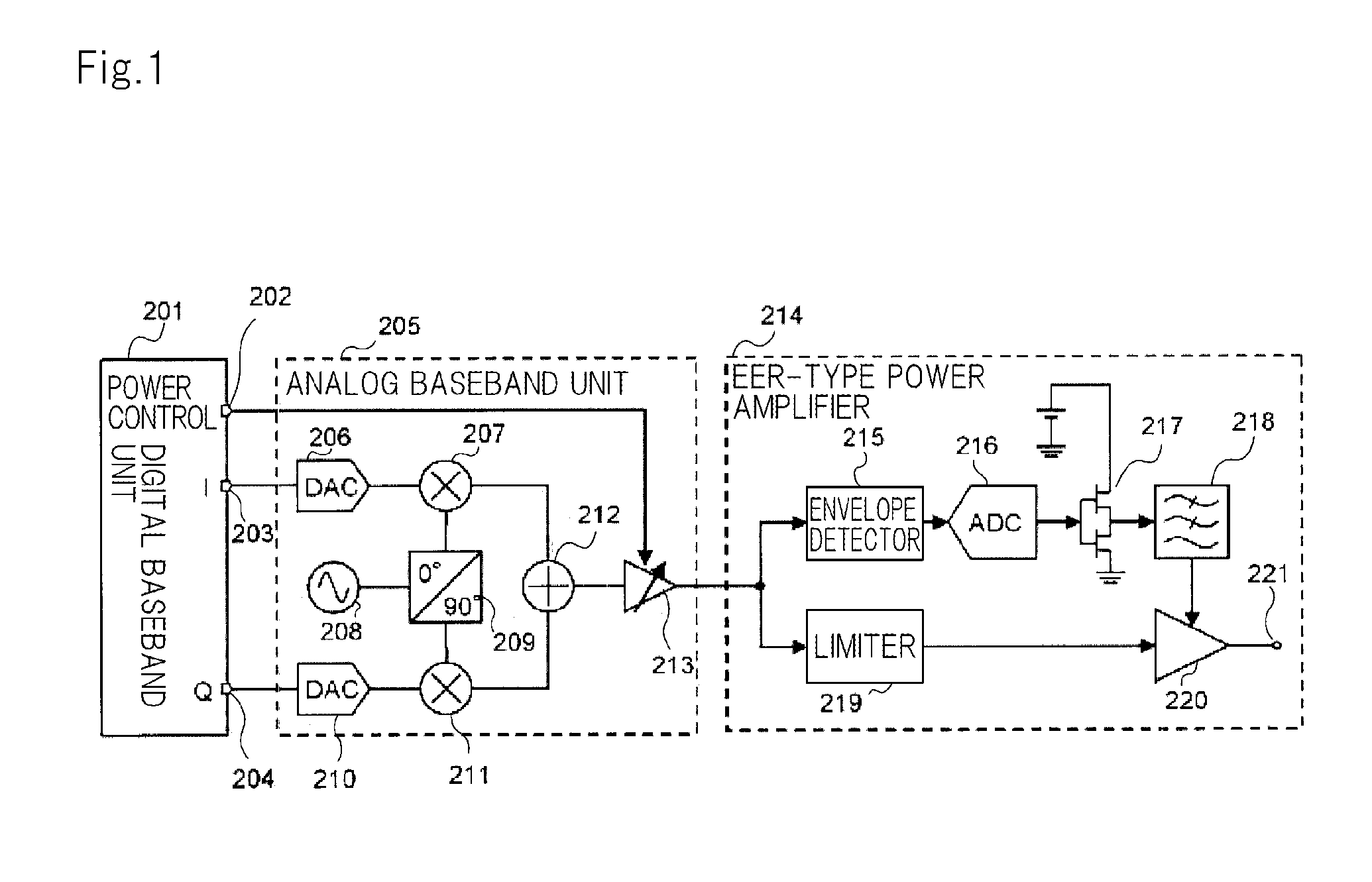
A power amplifier (10) comprises: an A / D converter (11) for converting, to a time discrete signal, an envelope signal included in a high-frequency modulated signal and including only an amplitude modulated component of the high-frequency modulated signal; a switching amplifier (12) for amplifying the output signal of the A / D converter (11); a low-pass filter (13) for removing high frequency noise from the output signal of the switching amplifier (12); a plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n) for receiving the output signal of the low-pass filter (13) as a power supply and for amplifying a carrier signal included in the high-frequency modulated signal; and a power controller (14) for adjusting the average power of the output signal of the power amplifier (10) by controlling the total gains of the plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n).
Owner:NEC CORP
BODY-WORN SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CONTINUOUS NON-INVASIVE BLOOD PRESSURE (cNIBP)
ActiveUS20100160795A1Good curative effectImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsPhysical therapyOptical transducers
The present invention provides a technique for continuous measurement of blood pressure based on pulse transit time and which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘Composite Method’, is carried out with a body-worn monitor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of body-worn sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body-worn monitor and measure time-dependent ECG, PPG, accelerometer, and pressure waveforms. The disposable sensors can include a cuff that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, three or more electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), three or more accelerometers, a temperature sensor, and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to the patient's thumb.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
BODY-WORN SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CONTINUOUS NON-INVASIVE BLOOD PRESSURE (cNIBP)
ActiveUS20100160797A1Good curative effectImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementAccelerometer
The present invention provides a technique for continuous measurement of blood pressure based on pulse transit time and which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘Composite Method’, is carried out with a body-worn monitor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of body-worn sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body-worn monitor and measure time-dependent ECG, PPG, accelerometer, and pressure waveforms. The disposable sensors can include a cuff that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, three or more electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), three or more accelerometers, a temperature sensor, and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to the patient's thumb.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
BODY-WORN SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CONTINUOUS NON-INVASIVE BLOOD PRESSURE (cNIBP)
ActiveUS20100160796A1Good curative effectImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsPhysical therapyOptical transducers
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for measuring continuous non-invasive blood pressure (cNIBP)
ActiveUS8602997B2Good curative effectImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsOptical transducersPhotodiode
The present invention provides a technique for continuous measurement of blood pressure based on pulse transit time and which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘Composite Method’, is carried out with a body-worn monitor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of body-worn sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body-worn monitor and measure time-dependent ECG, PPG, accelerometer, and pressure waveforms. The disposable sensors can include a cuff that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, three or more electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), three or more accelerometers, a temperature sensor, and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to the patient's thumb.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
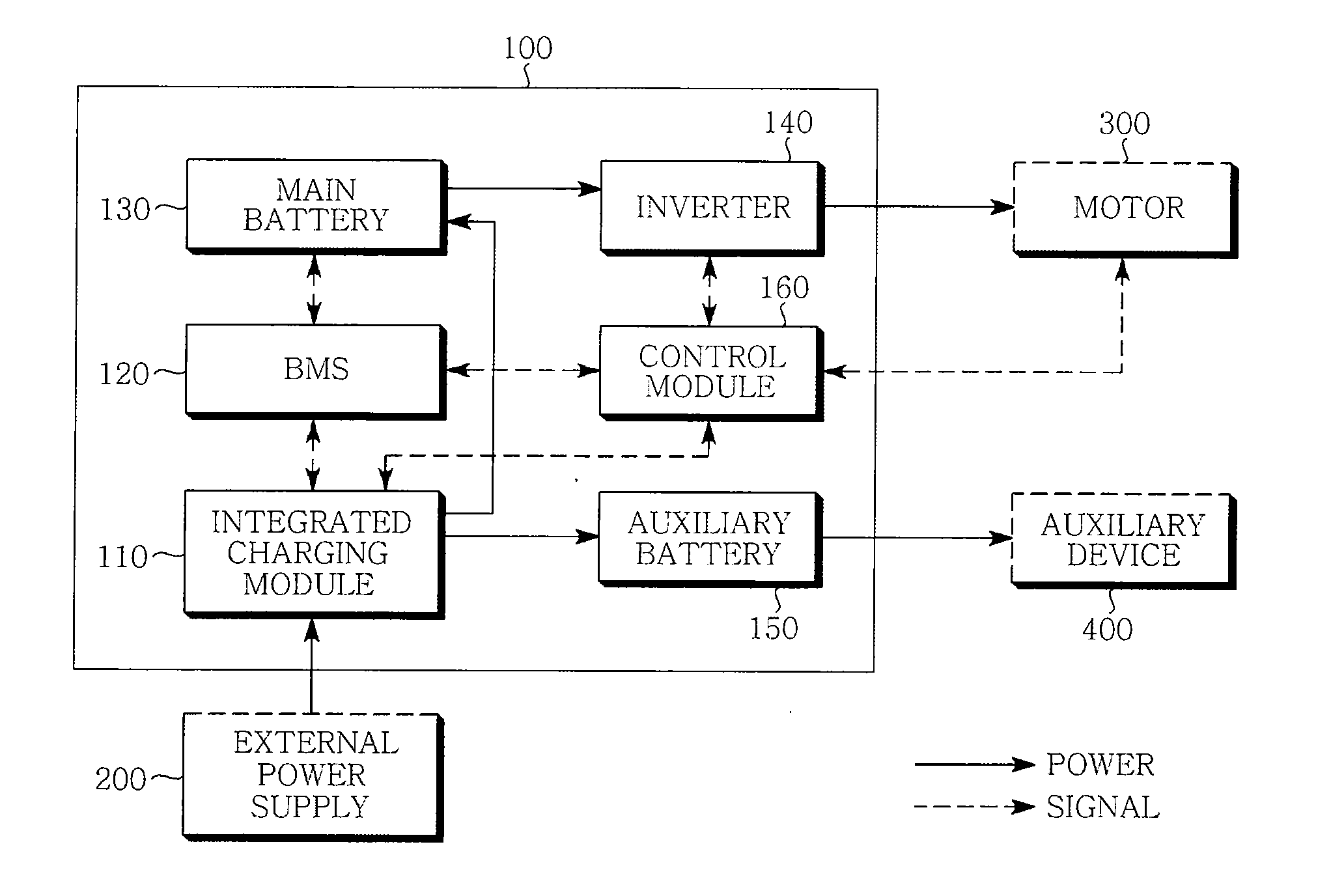
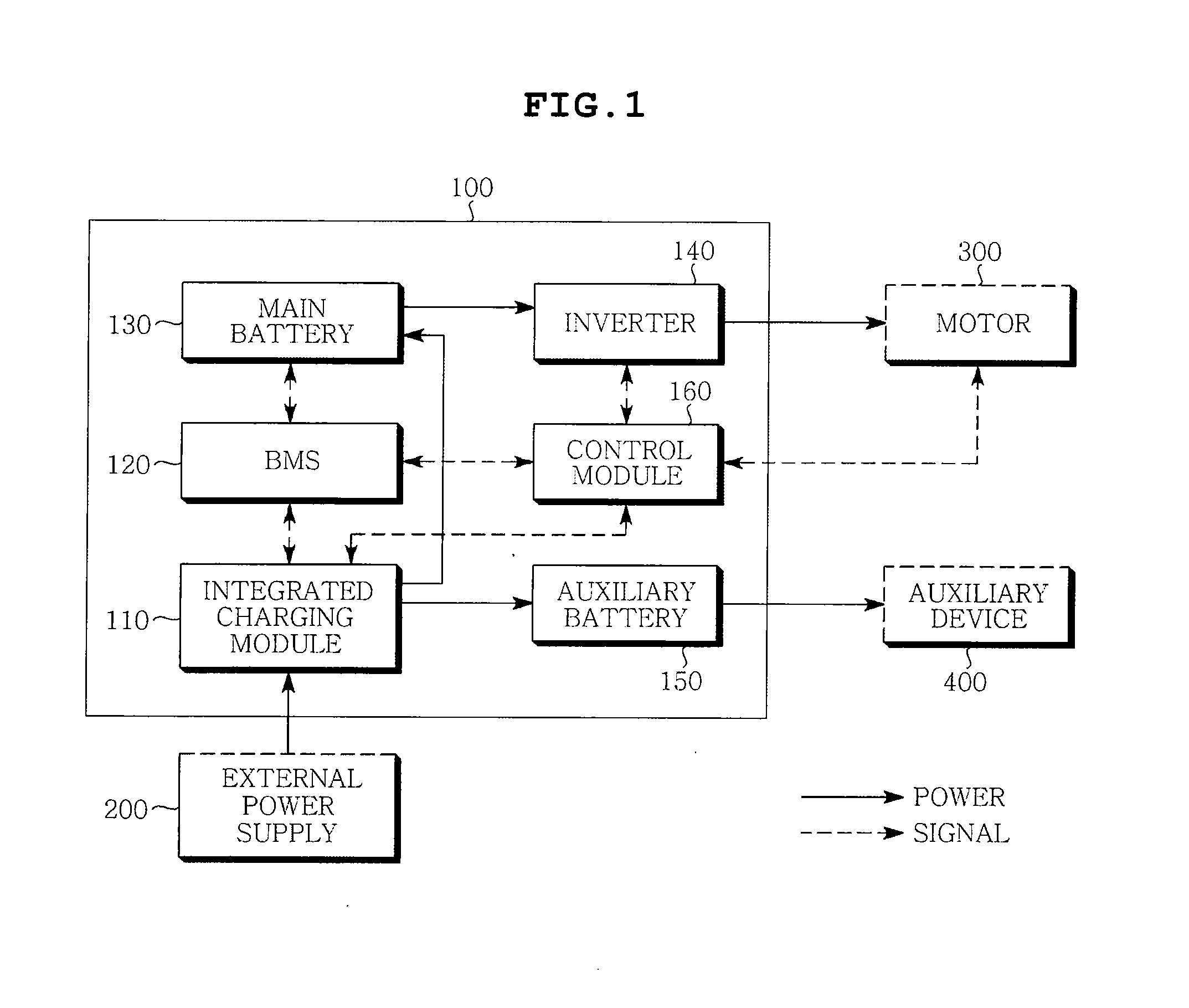
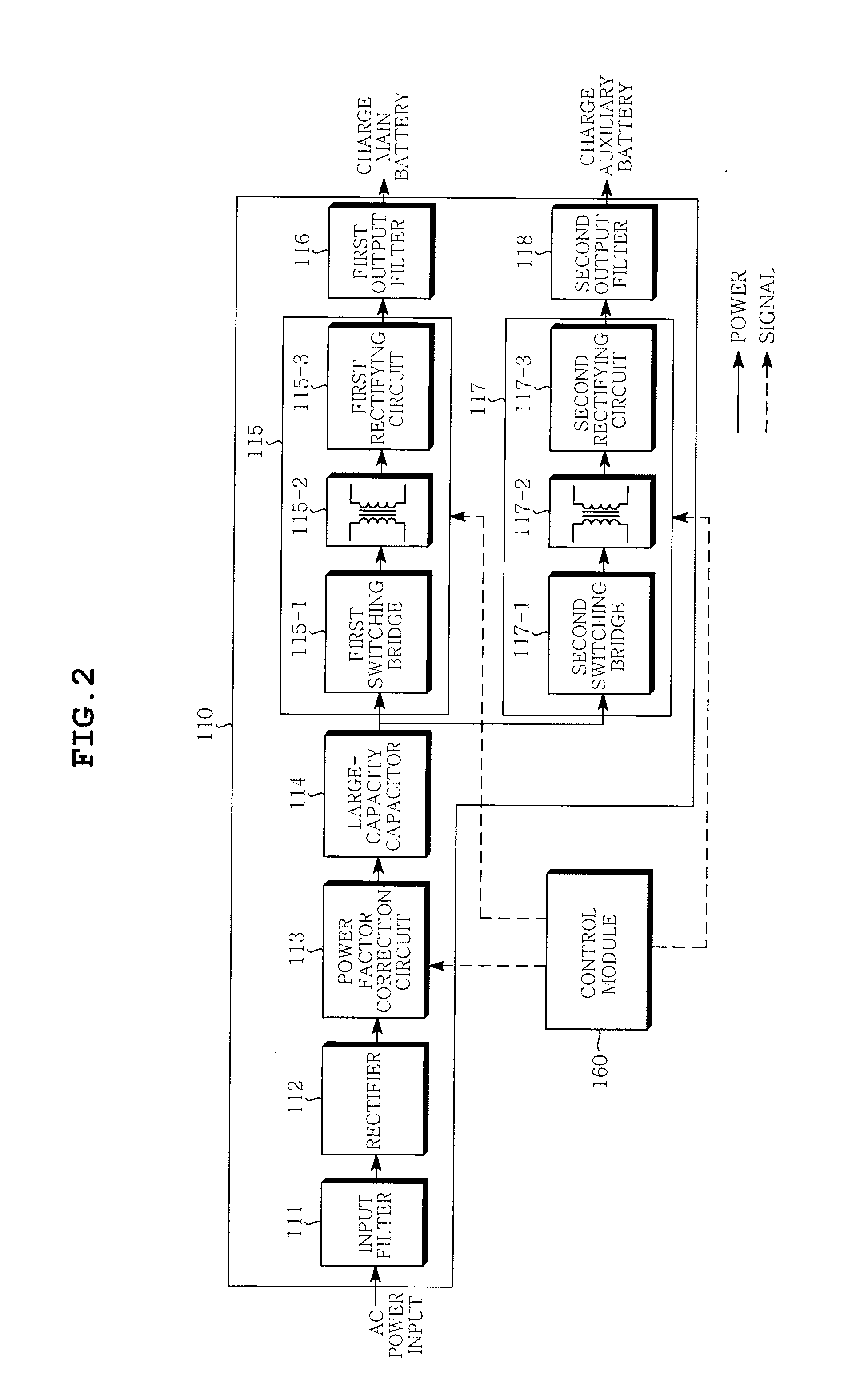
Integrated charging device for electric vehicle
InactiveUS20120049794A1Eliminate high frequency noiseRemove noiseBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectrical batteryEngineering
Disclosed herein is an integrated charging module device for an electric vehicle. The integrated charging module device for an electric device includes: a main battery supplying power for driving an electric vehicle; an auxiliary battery supplying power for driving an auxiliary device within the electric vehicle; an integrated charging module converting external power into a first DC voltage to be charged in the main battery and a second DC voltage to be charged in the auxiliary battery; and a control module controlling the charging of the main battery and the auxiliary battery. The present invention includes the integrated charging modules for charging the main battery and the secondary battery, thereby making it possible to increase the efficiency of the spatial arrangement in a vehicle and simplifying the cooling system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
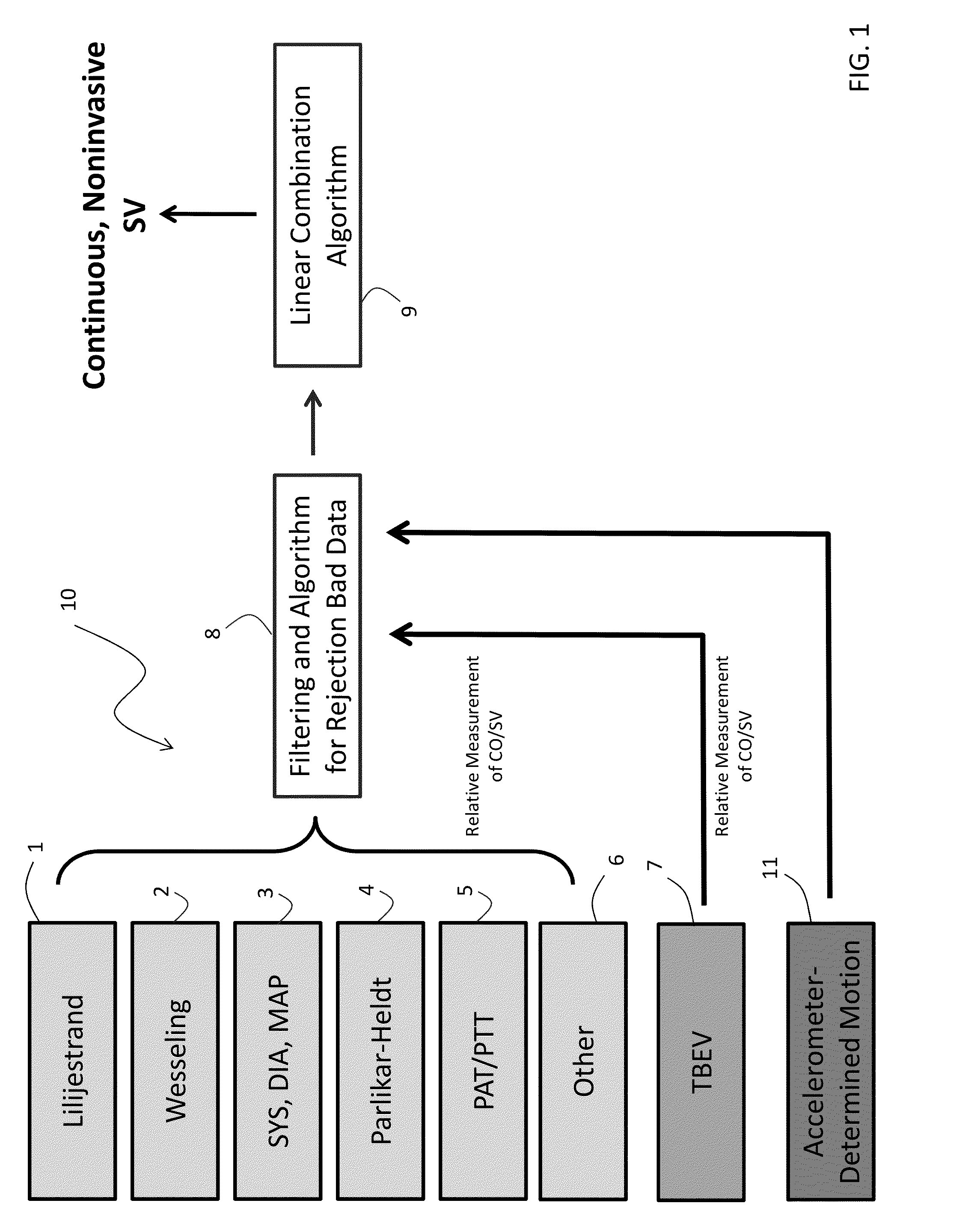
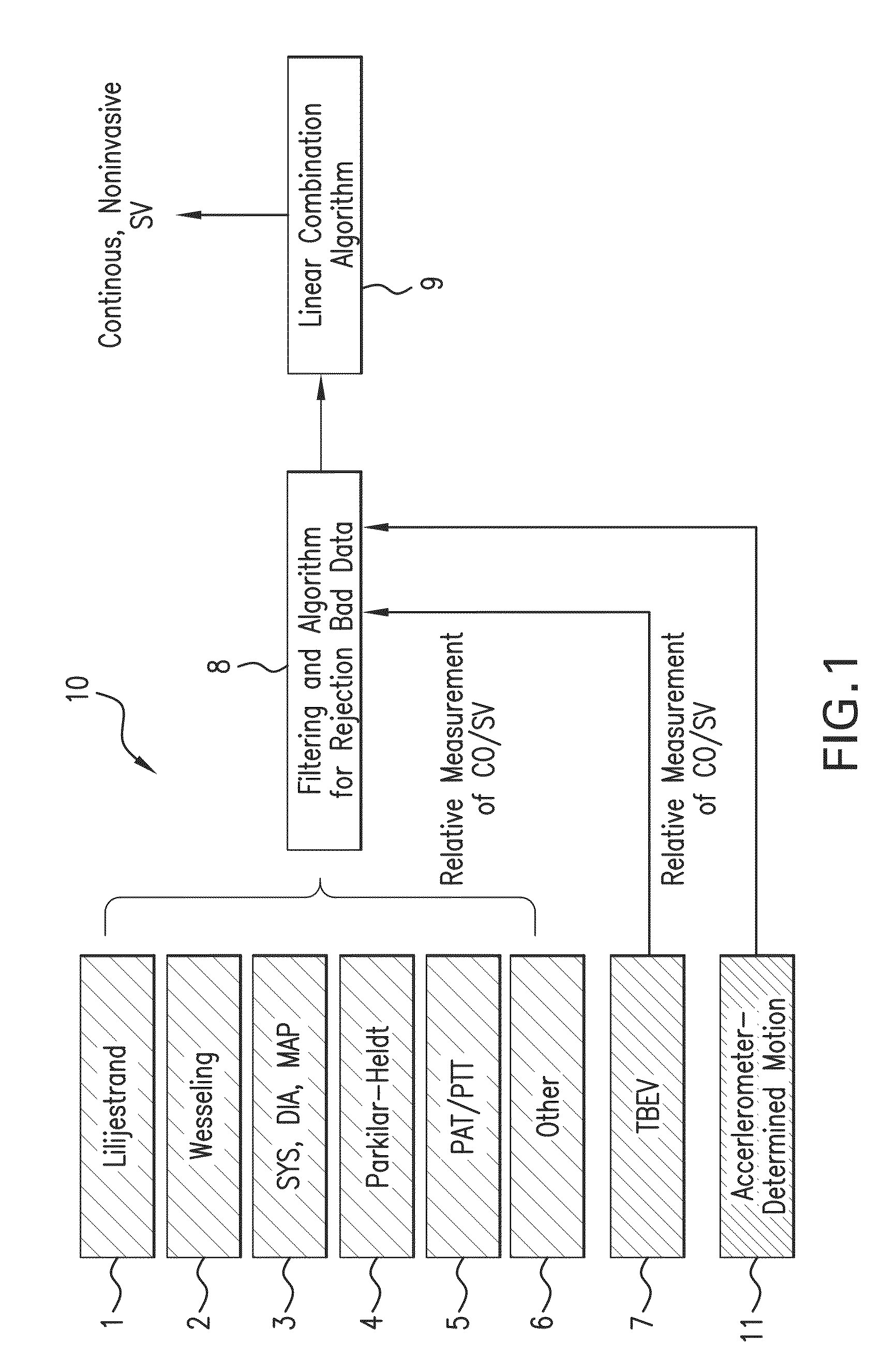
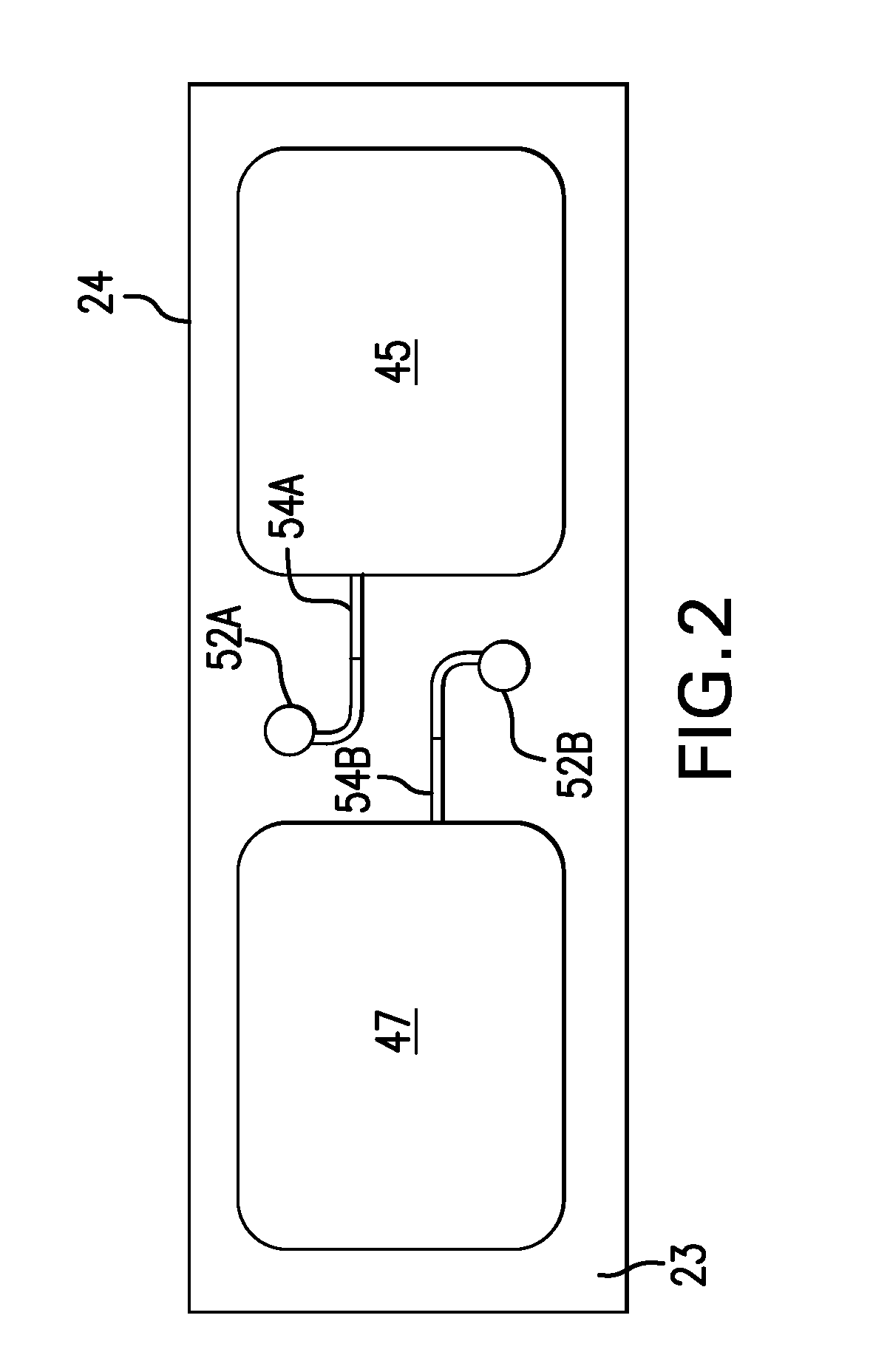
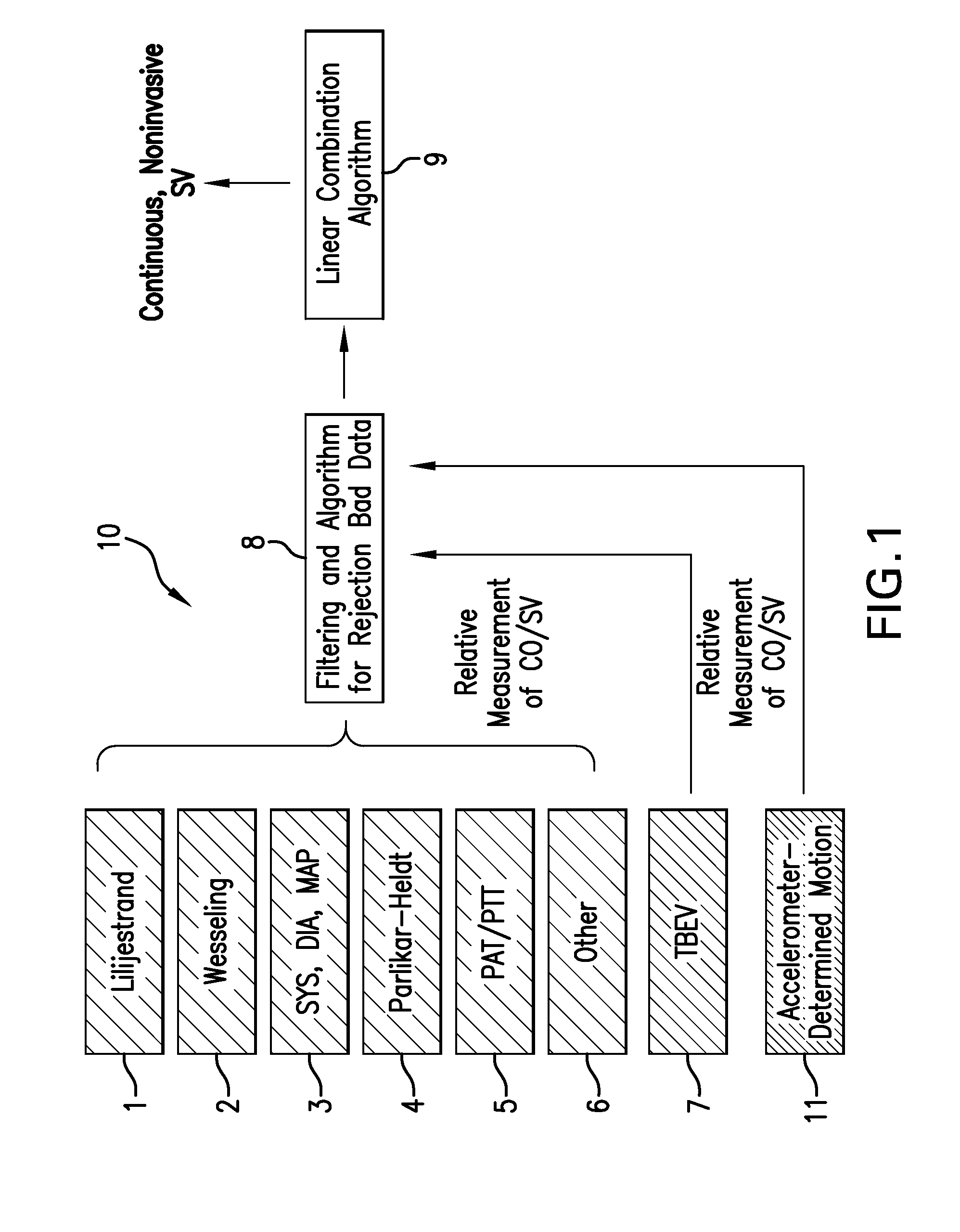
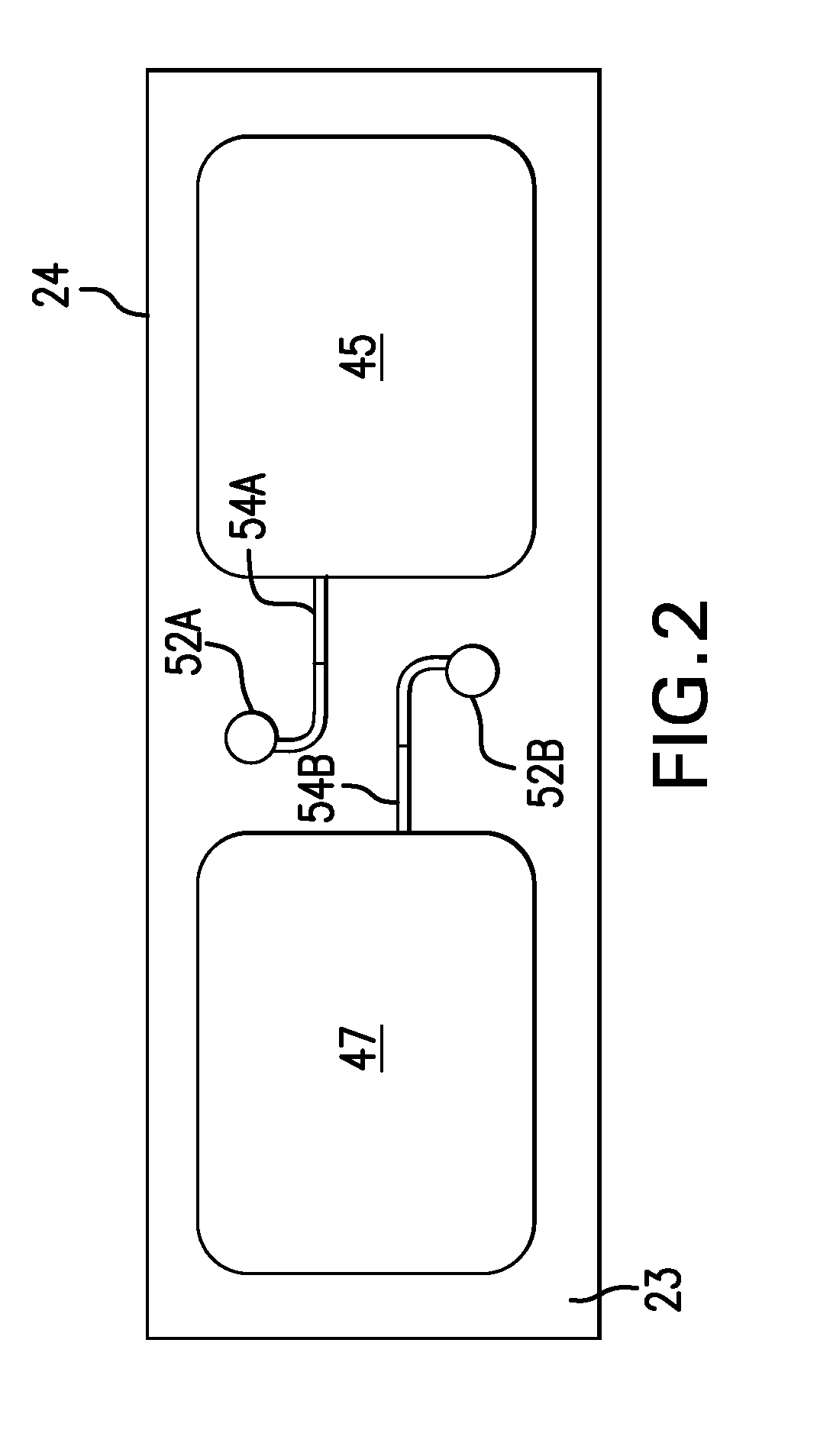
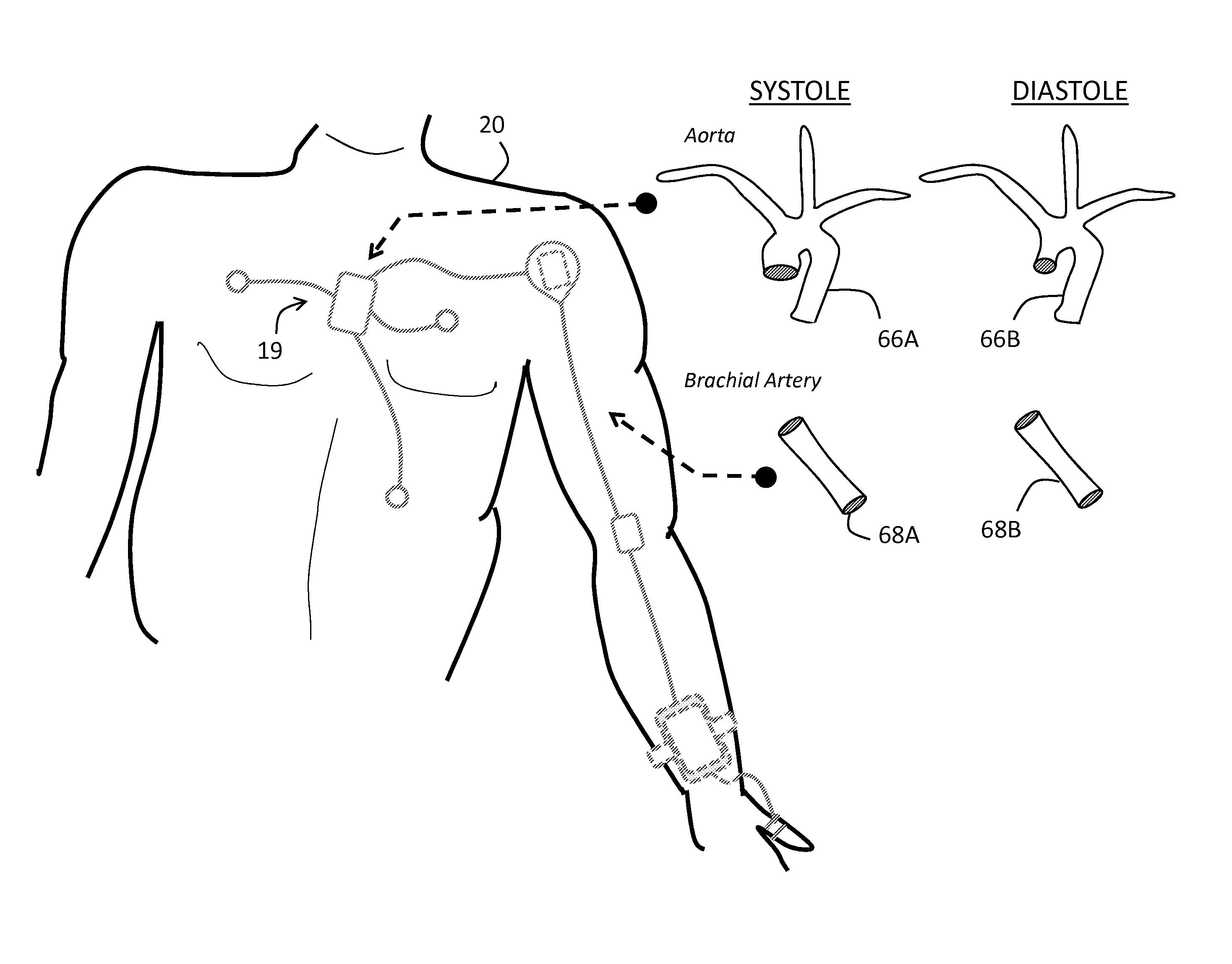
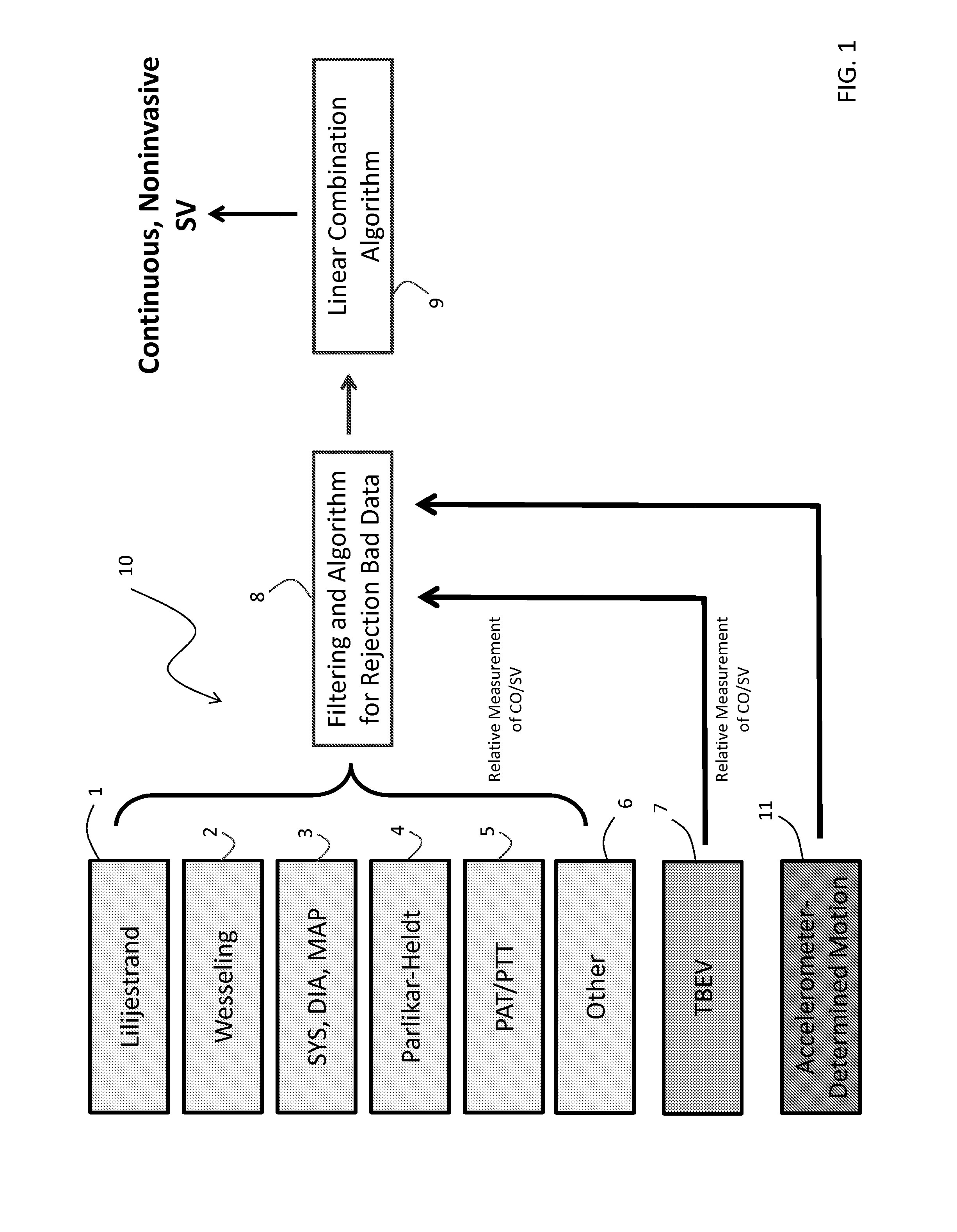
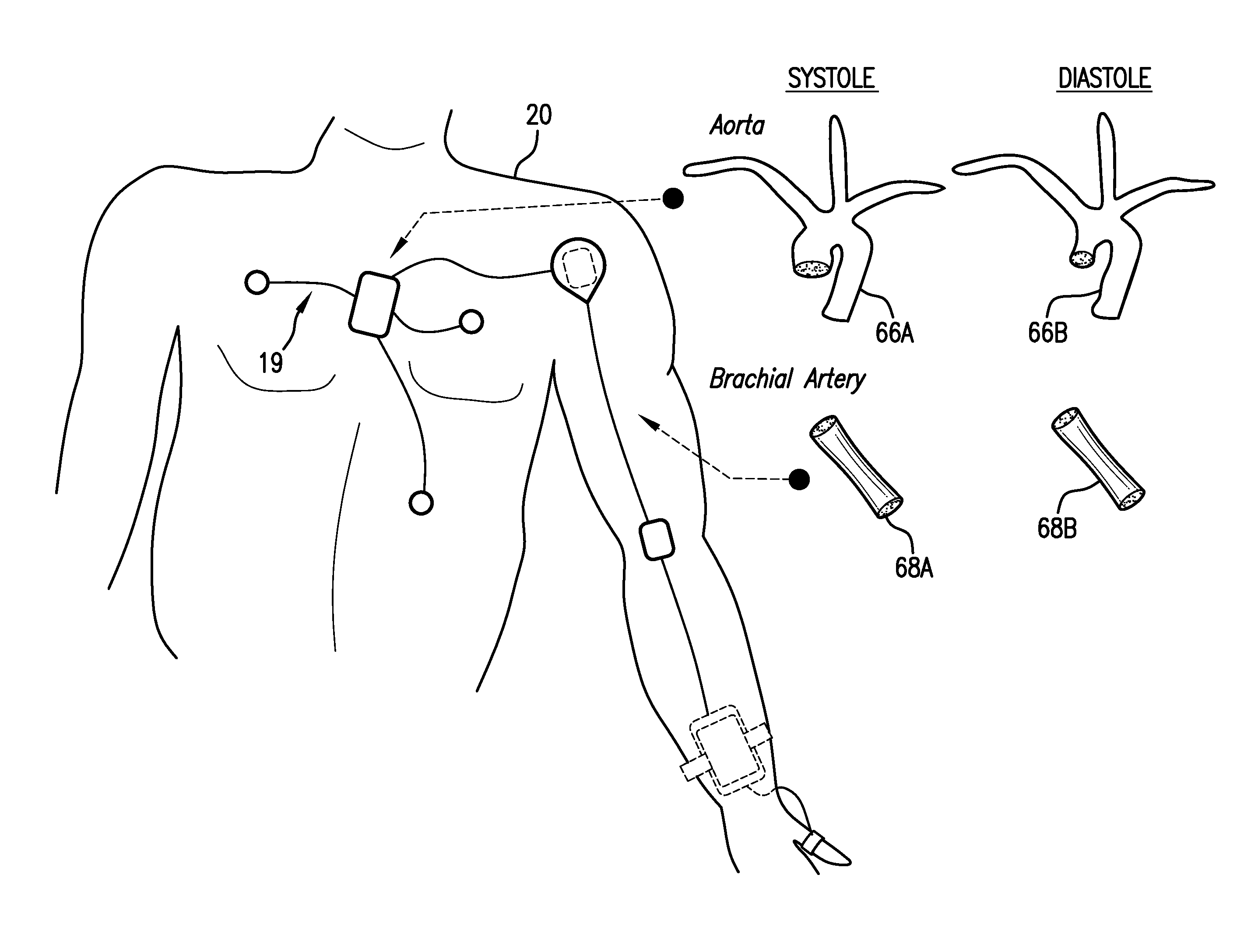
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249431A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure
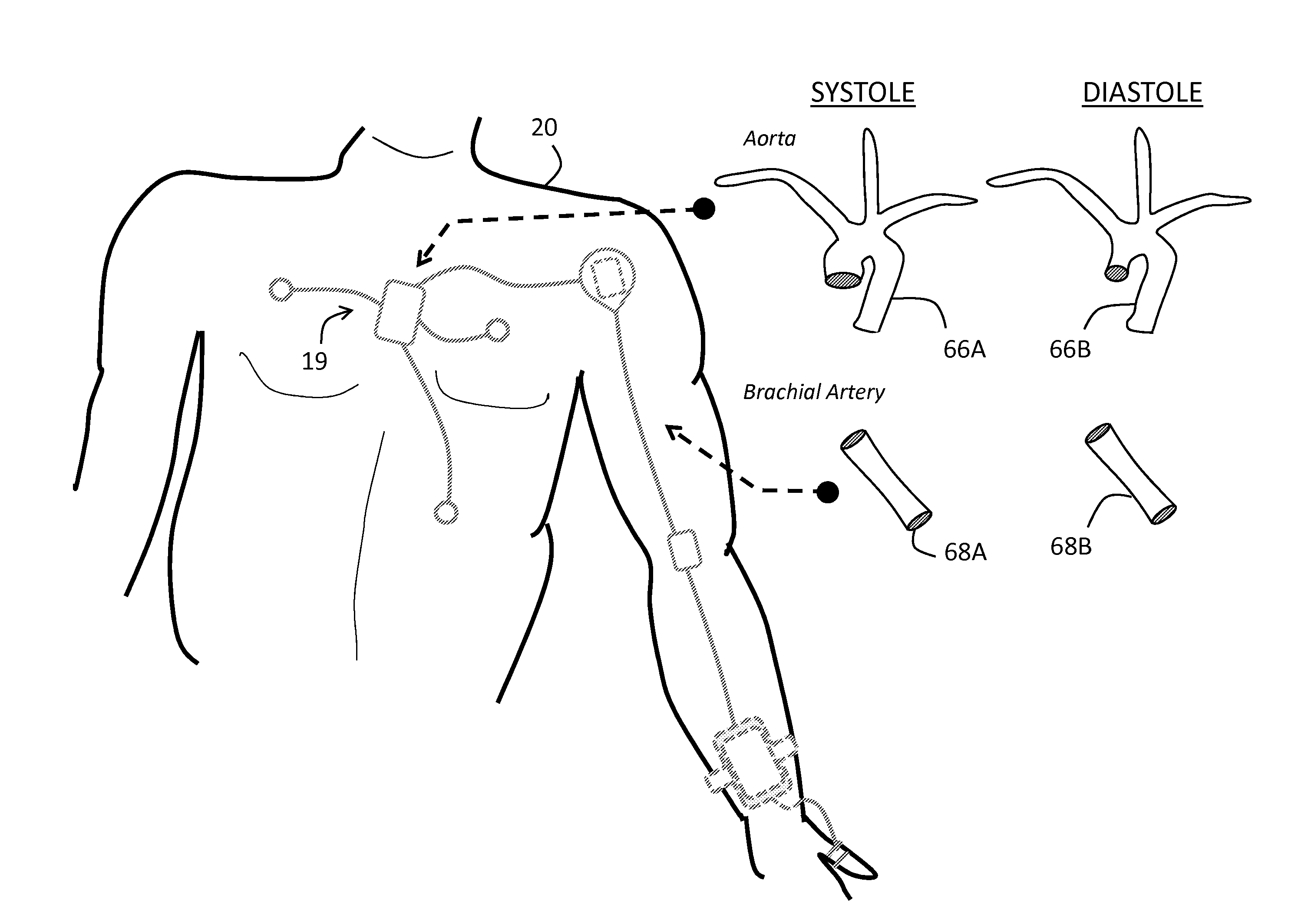
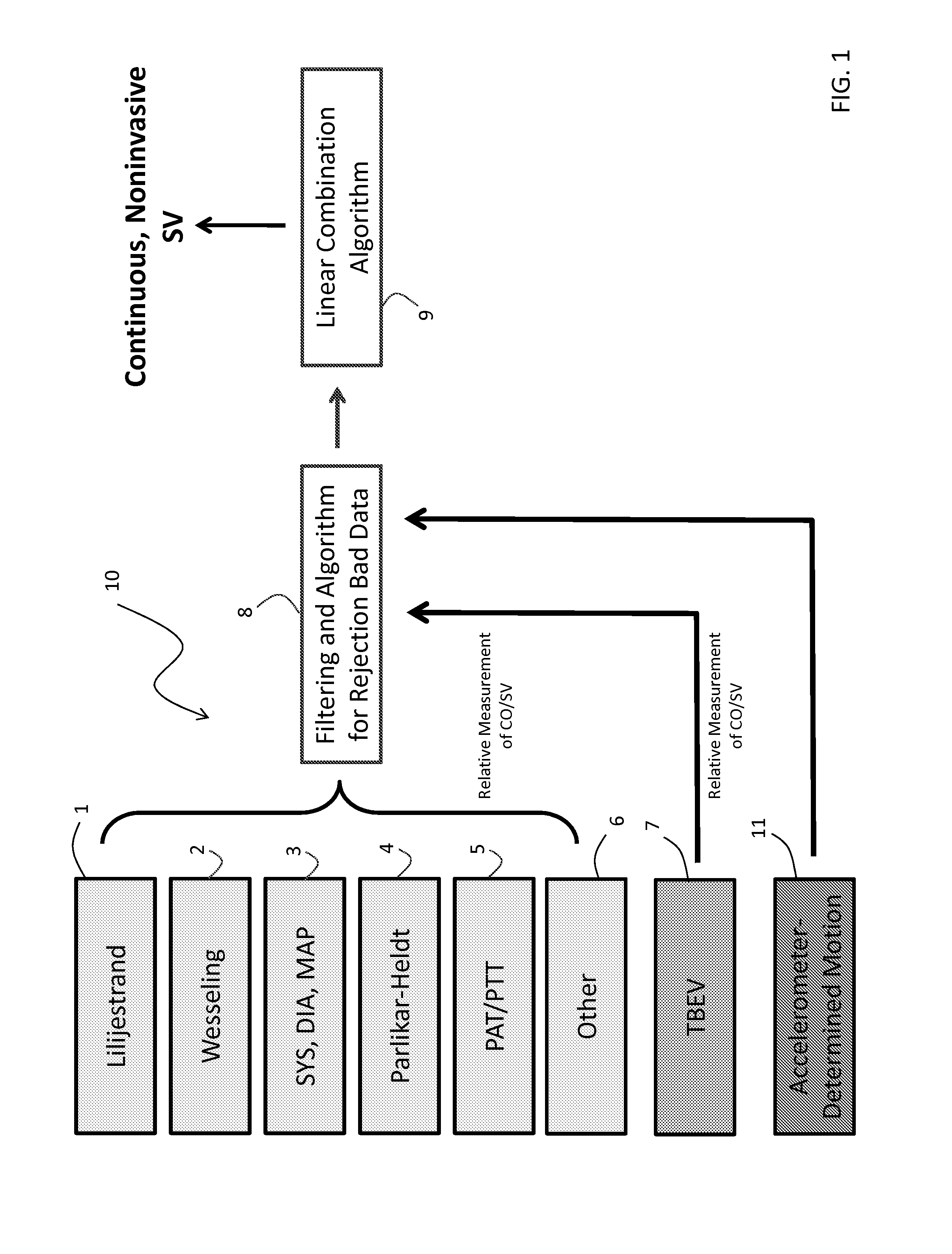
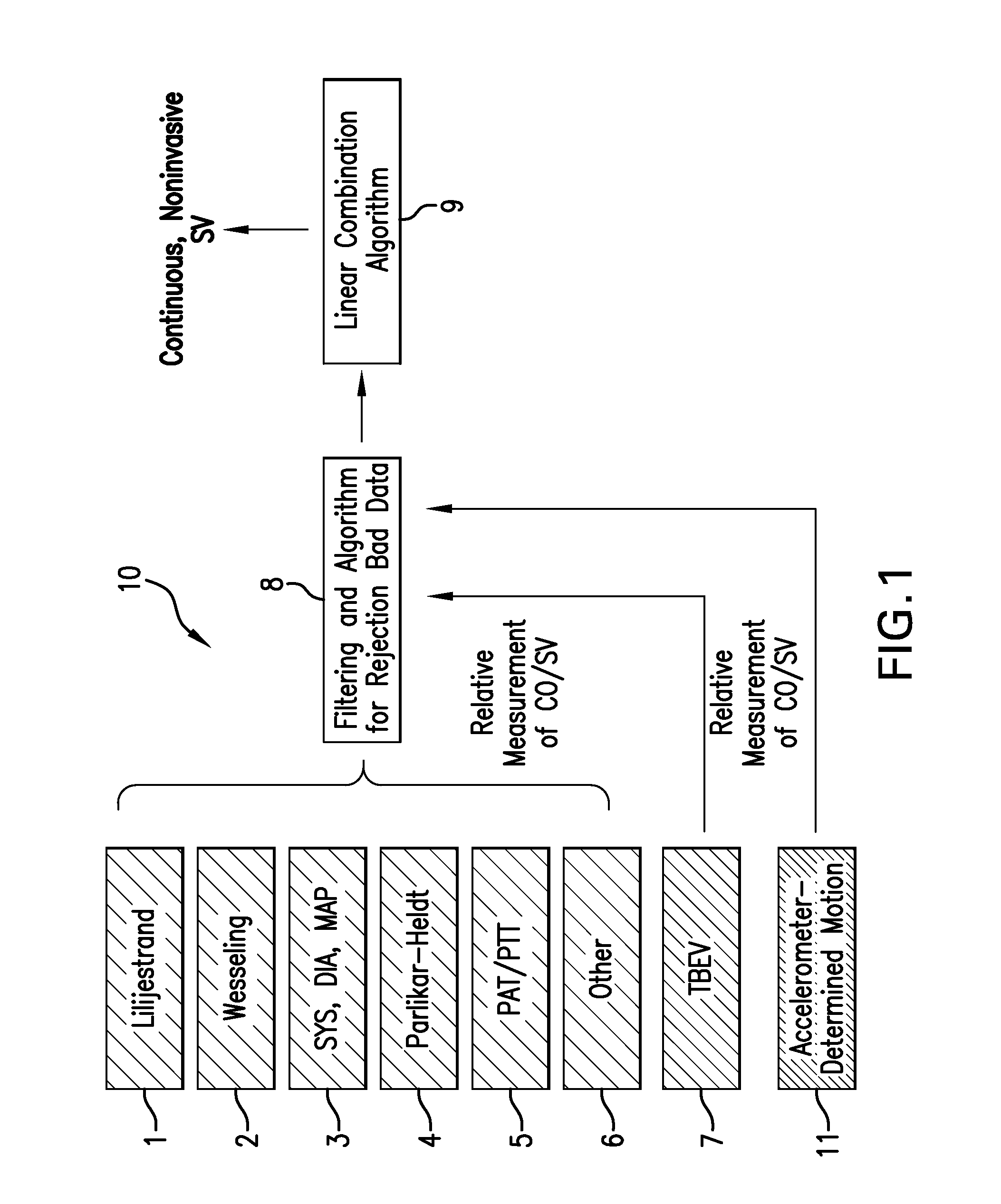
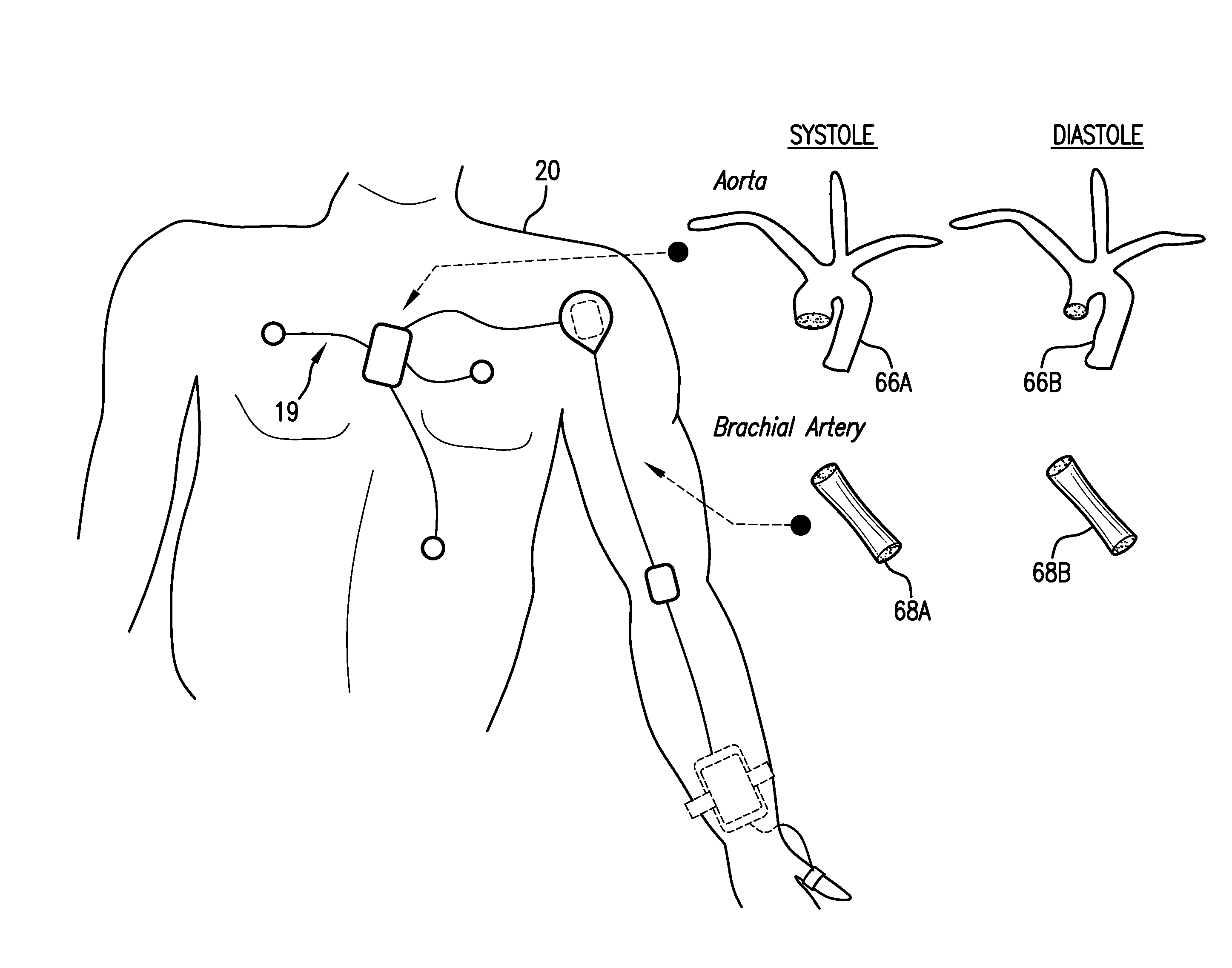
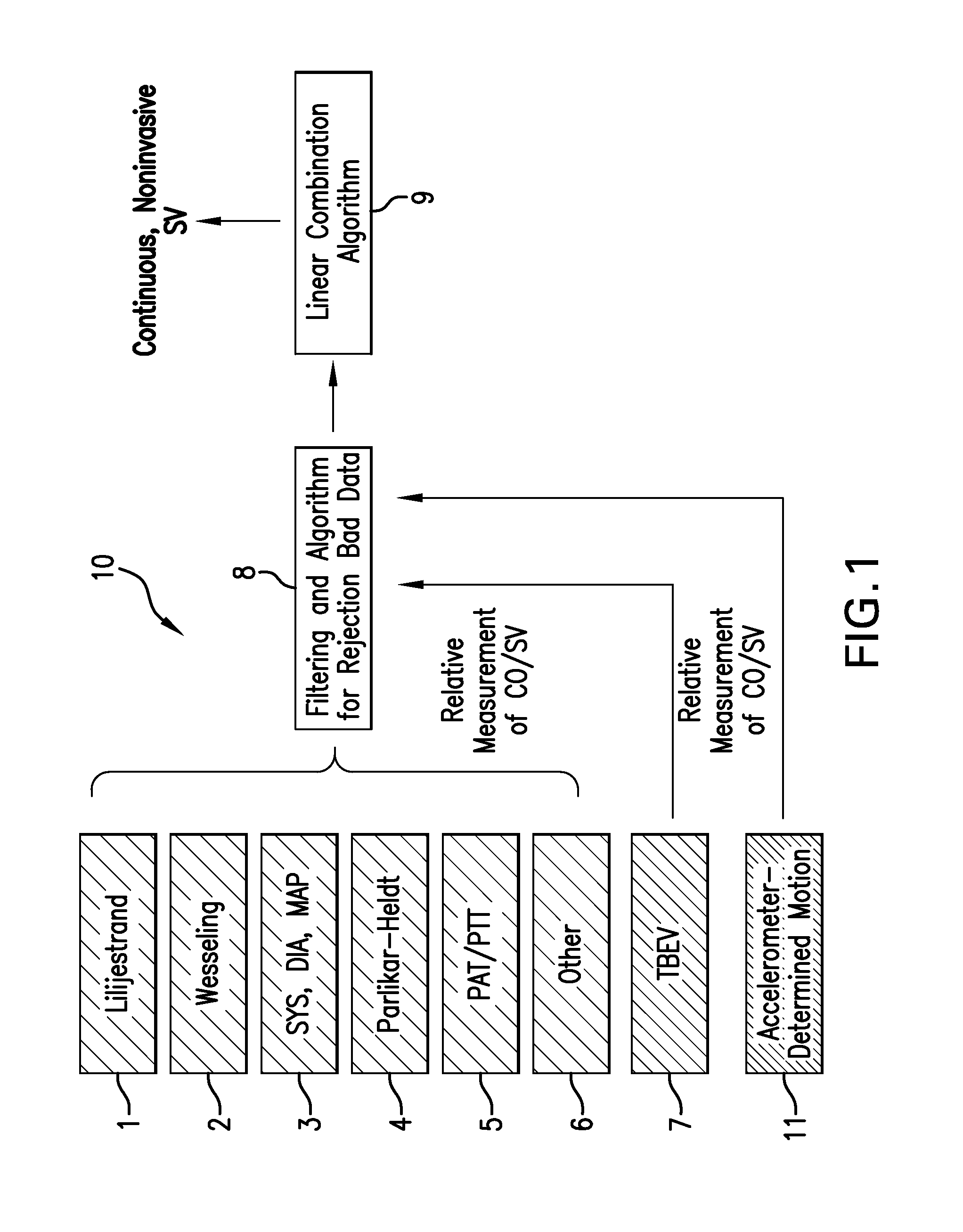
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS9364158B2Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
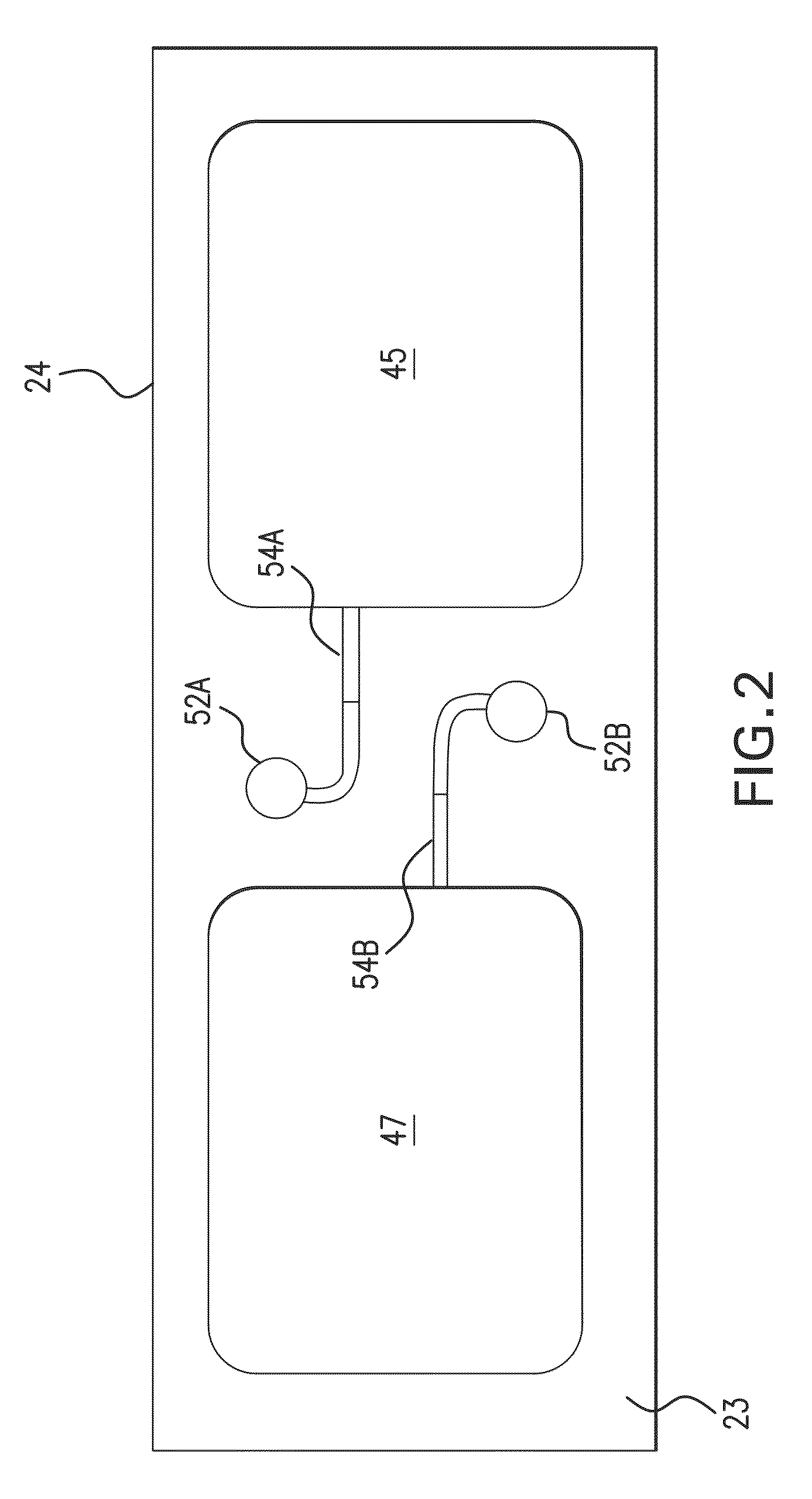
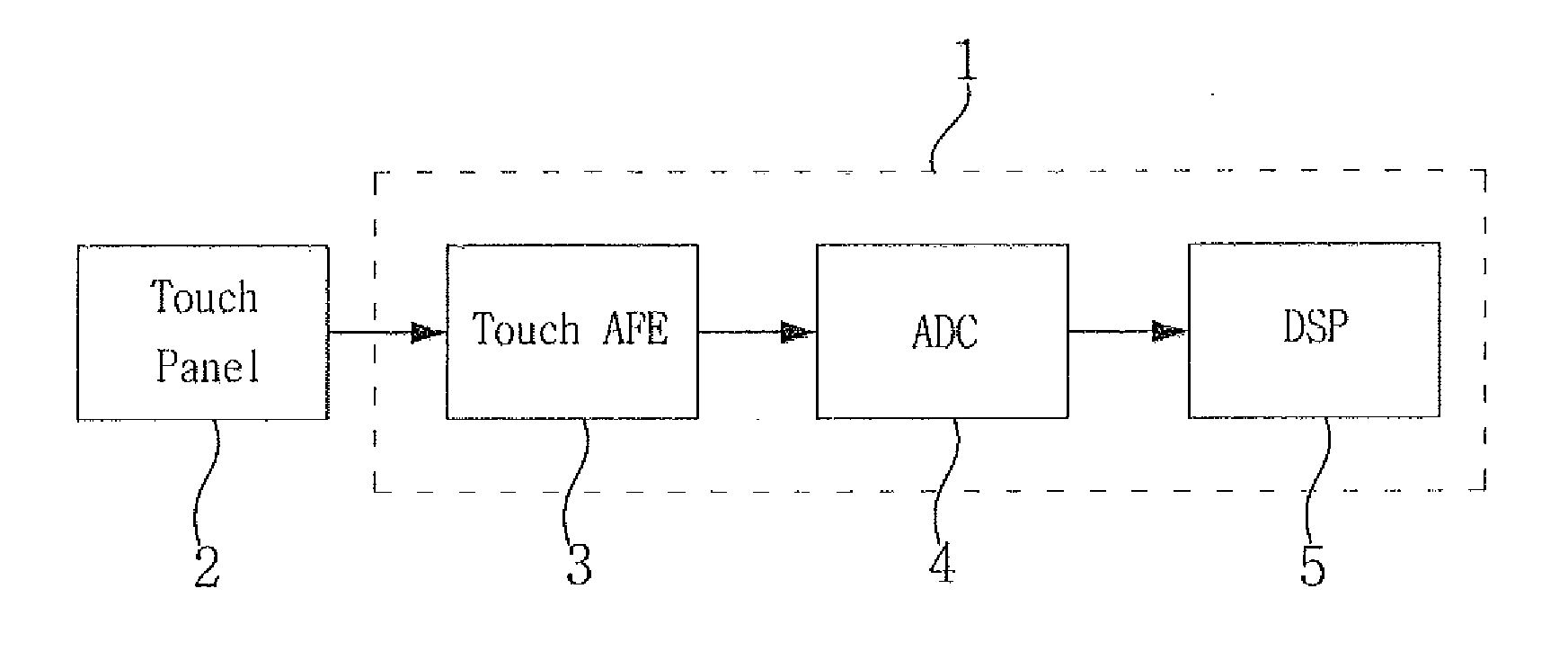
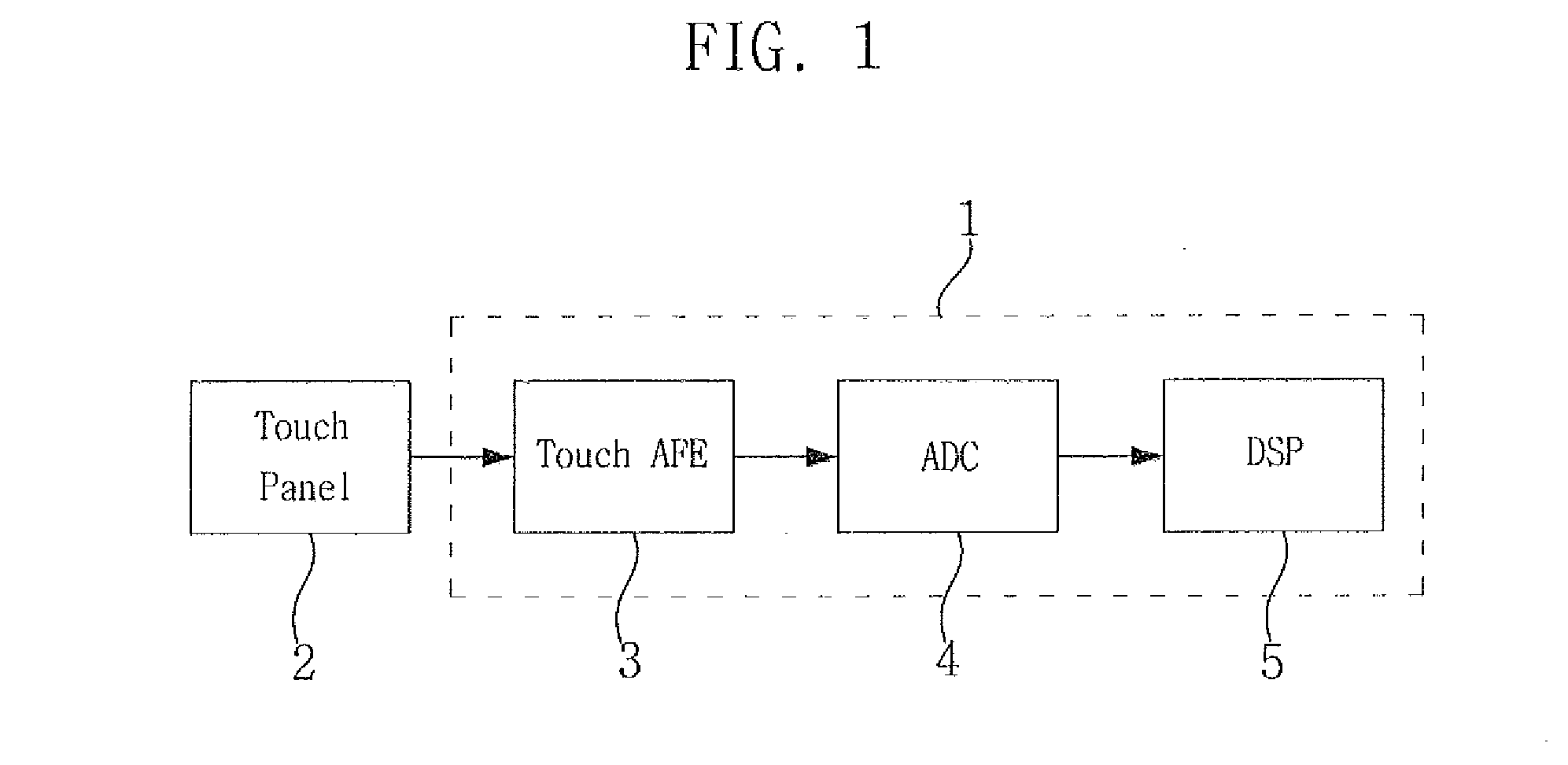
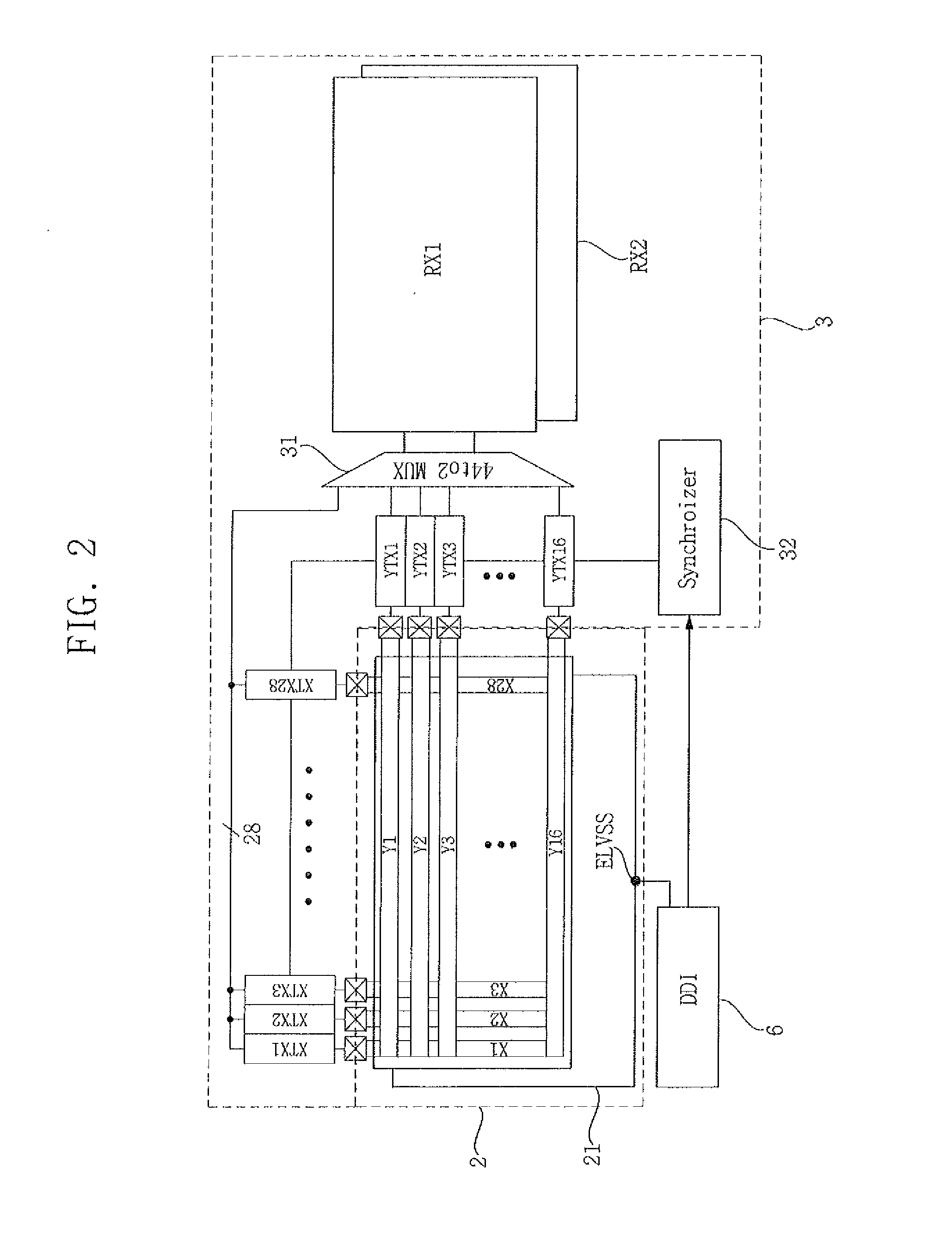
Touch analog front end and touch sensor controller having the same
ActiveUS20160124544A1Eliminate low frequency noiseDoubling sensitivity of a touch inputDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceIntegrator
A touch analog front-end (AFE) for a touch sensitive screen may include a transmitter configured to charge a touch panel and a receiver configured to sense the touch panel. The receiver may include a charge-to-voltage (C2V) converter configured to convert a change of capacitance received from the touch panel into a voltage signal, a correlated double sampling (CDS) block configured to convert the voltage signal into a differential signal and to sample each of the positive and the negative signals of the differential signal, and an integrator configured to accumulate a difference between the sampled positive and negative signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
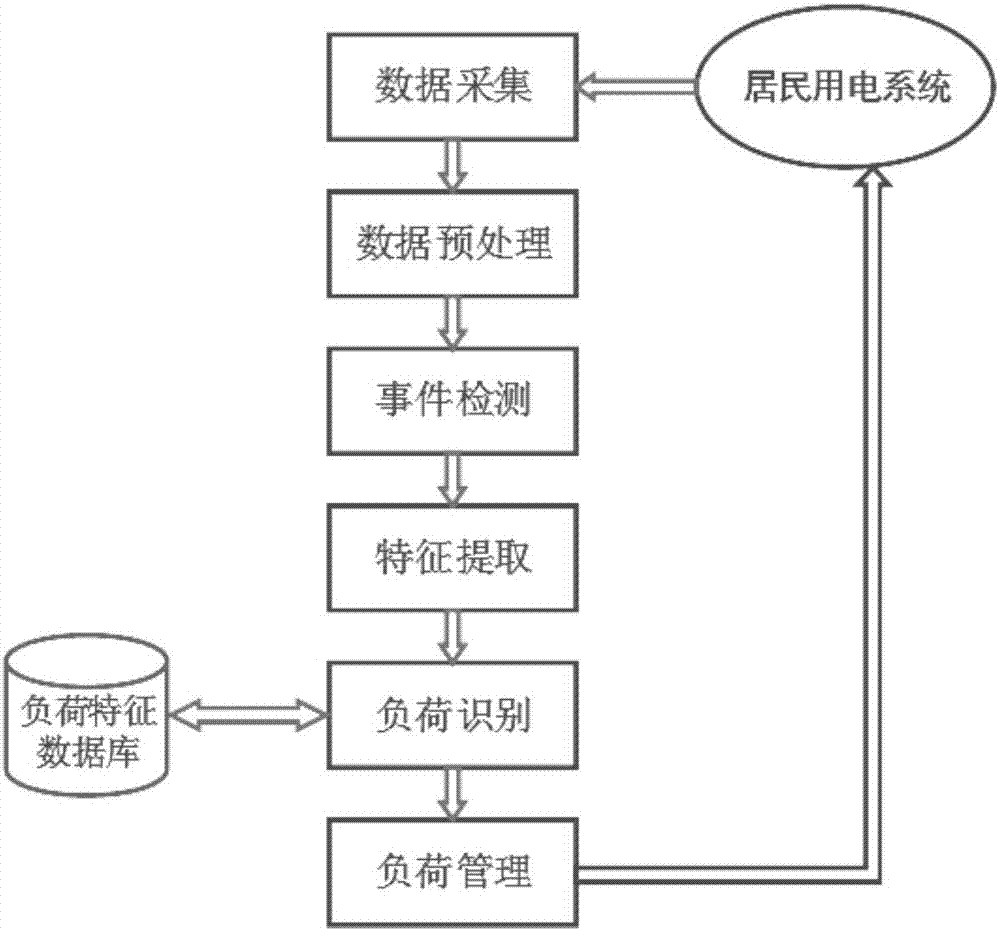
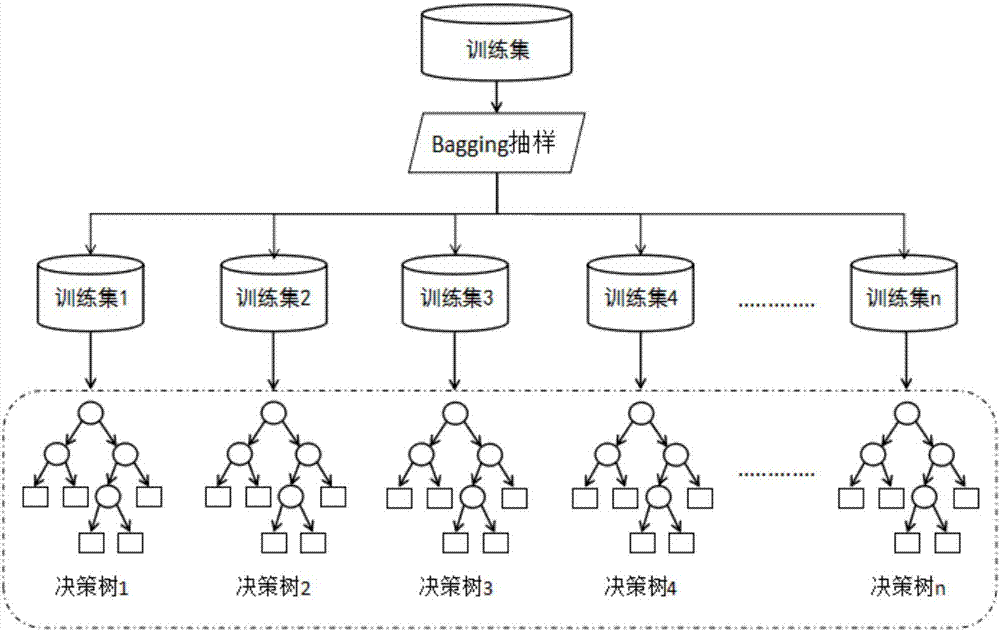
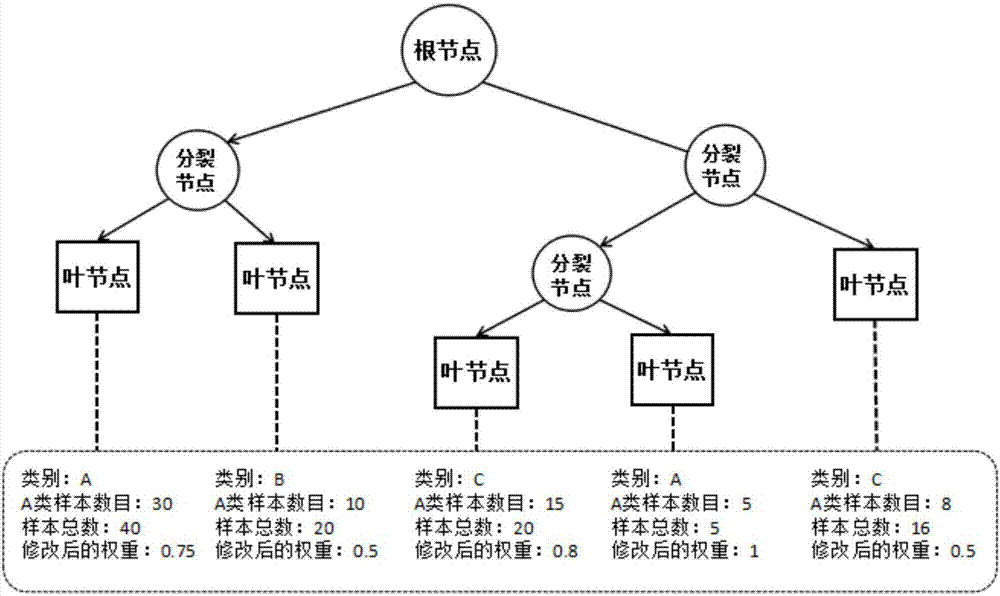
Random forest-based non-invasive home appliance identification method
InactiveCN107273920AGood anti-noise performanceSimplify the modeling processCharacter and pattern recognitionTime integral measurementNon invasiveVoltage
The invention discloses a random forest-based non-invasive home appliance identification method, which aims to monitor a family internal power utilization condition without invading an interior of a family user, and is high in identification speed and high in accuracy. According to the adopted technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of establishing a load feature database; taking load features stored in the feature database as an original training set, and generating N training sub-sets in the original training set; combining N generated decision trees into a random forest; finishing a training process of the random forest through optimization of weights of different decision tree leaf nodes; detecting an electric appliance switching event by utilizing a secondary detection algorithm to obtain starting and ending time of event occurrence, and separating out current and voltage signals of a switched electric appliance from a bus signal, thereby obtaining the load features from separated data; and finally inputting the load features as input parameters to the trained random forest, and finishing electric appliance identification through voting.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
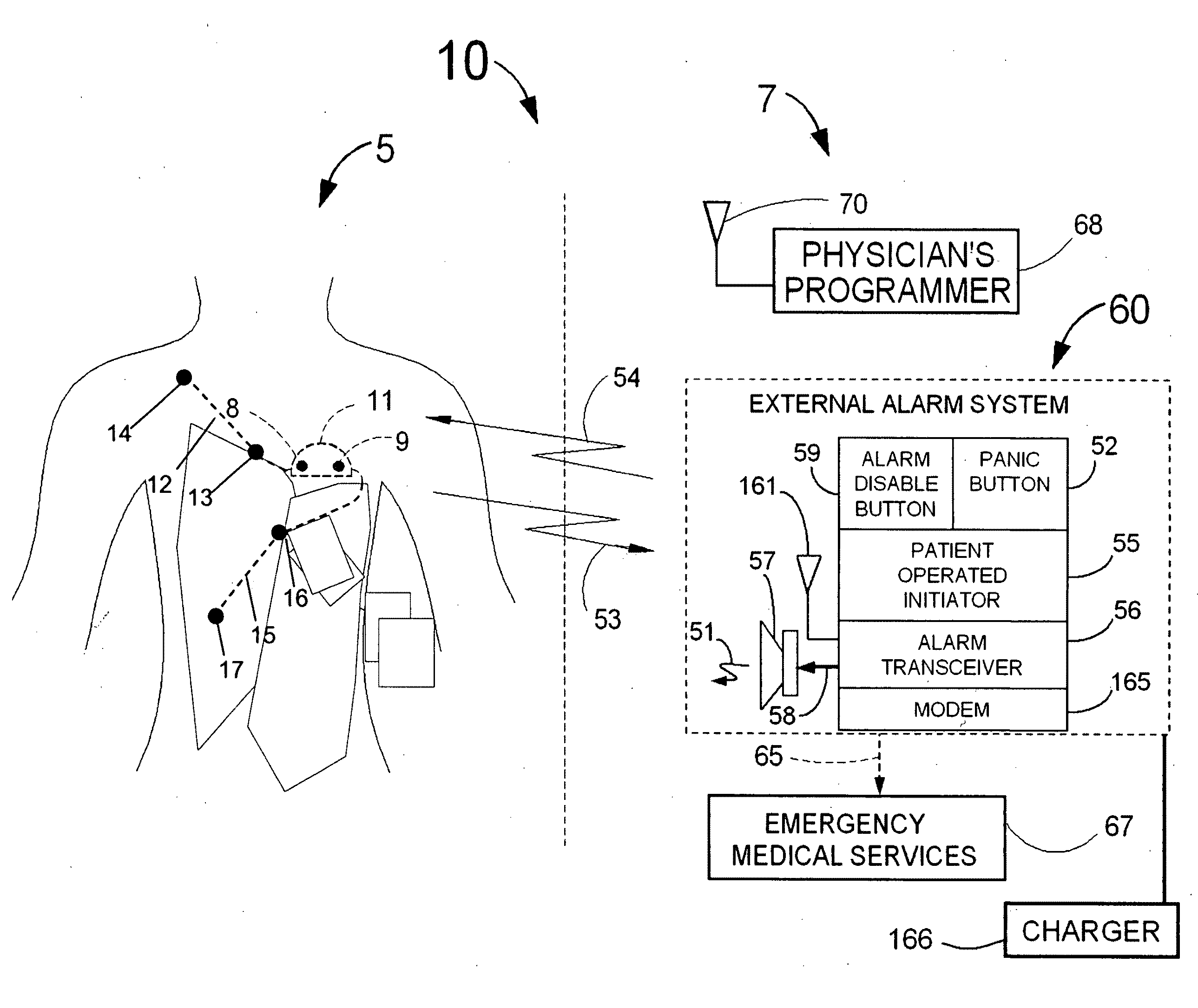
Heart rate correction system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
ActiveUS20110040199A1Strong specificityEliminate high frequency noiseElectrocardiographySensorsBlood vessel spasmAcute ischemia
A device for detecting a cardiac event is disclosed. Detection of an event is based on a test applied to a parameter whose value varies according to heart rate. Both the parameter value and heart rate (RR interval) are filtered with an exponential average filter. From these filtered values, the average change in the parameter and the RR interval are also computed with an exponential average filter. Before computing the average change in the parameter, large changes in the parameter over short times, which may be caused by body position shifts, are attenuated are removed, so that the average change represents an average of small / smooth changes in the parameter's value that are characteristic of acute ischemia, one of the cardiac events that may be detected. The test to detect the cardiac event depends on the heart rate, the difference between the parameter's value and its upper and lower normal values, and its average change over time, adjusted for heart rate changes. The upper and lower normal parameter values as a function of heart rate are determined from long term stored data of the filtered RR values and parameter values. Hysteeresis related data and transitory deviations from normal (e.g. vasospasm related data) are excluded from the computation of normal upper and lower parameter bounds.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
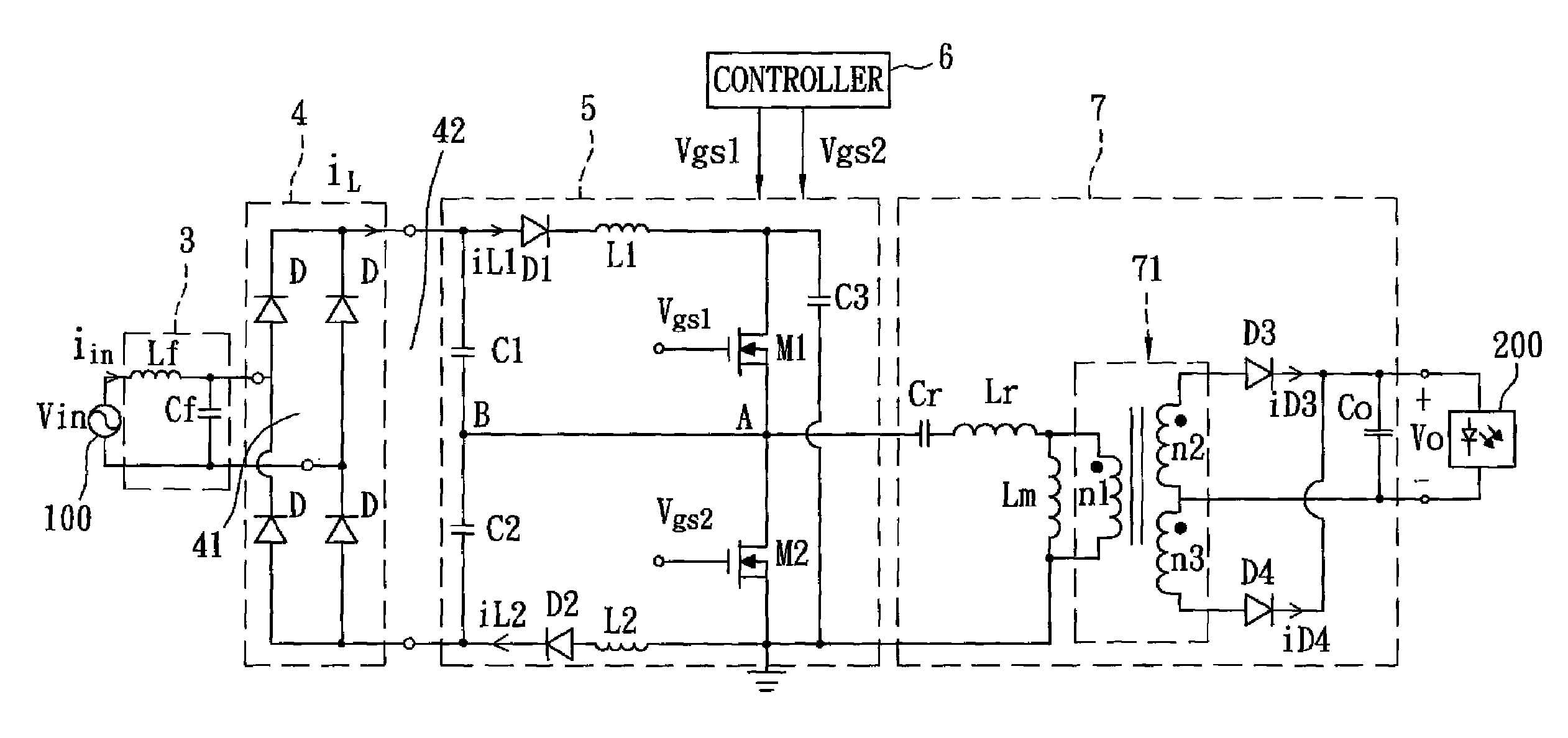
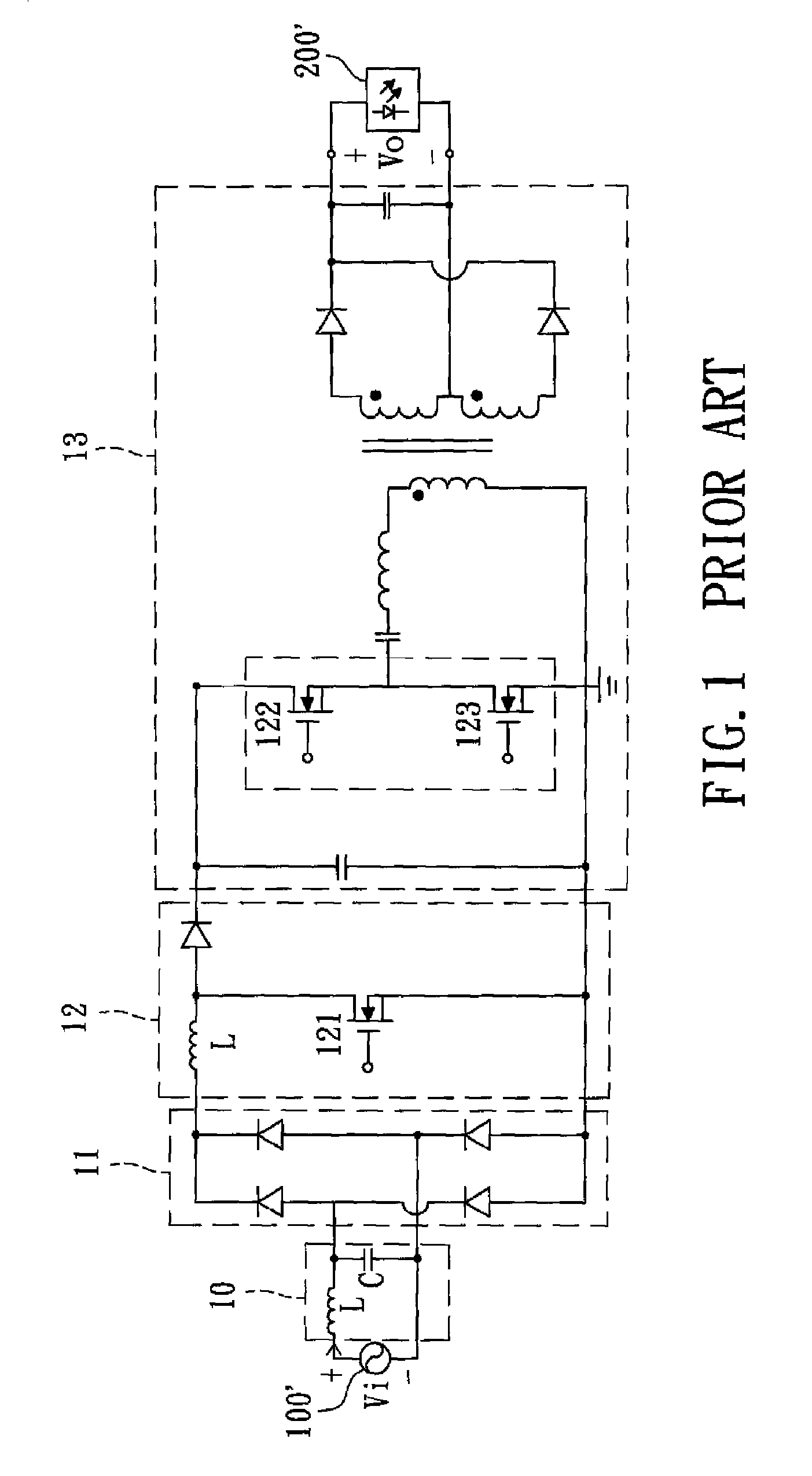
AC-to-DC power converting device
InactiveUS8854839B2Eliminate high frequency noiseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringInductance
An AC-to-DC power converting device includes: a filter for filtering an external AC input voltage; a rectifier for rectifying the AC input voltage filtered by the filter to output a rectified voltage; a power factor corrector for receiving the rectified voltage from the rectifier to generate a boosted voltage; and a step-down converter for receiving the boosted voltage from the power factor corrector to output a DC output voltage. The power factor corrector includes first and second capacitors connected in series across an output side of the rectifier, a series connection of a first diode, a first inductor, a third capacitor, a second inductor and a second diode coupled to the output side of the rectifier, and first and second switches connected in series across the third capacitor. A common node between the first and second capacitors is coupled to a common node between the first and second switches.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
InactiveUS20140249434A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
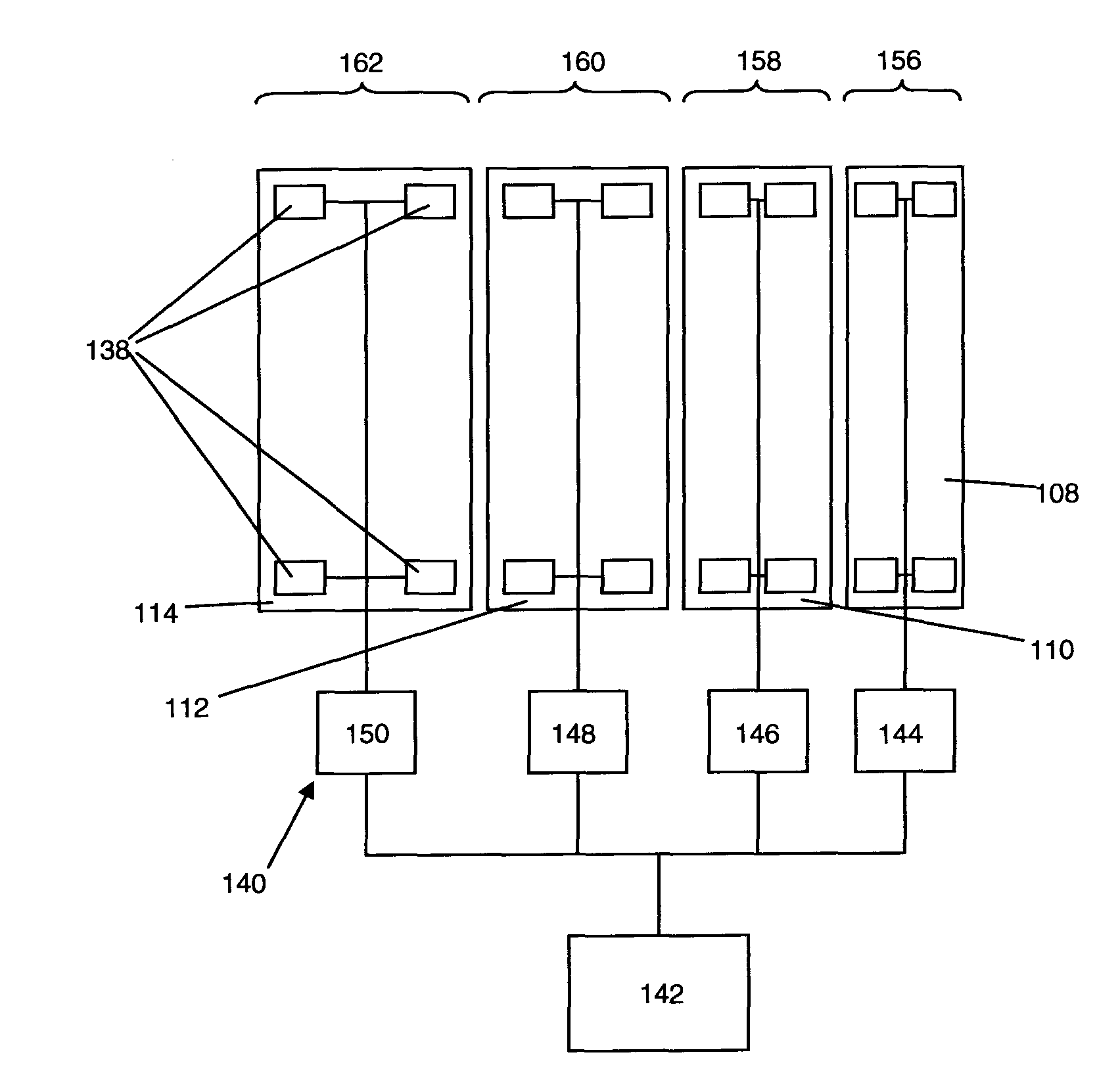
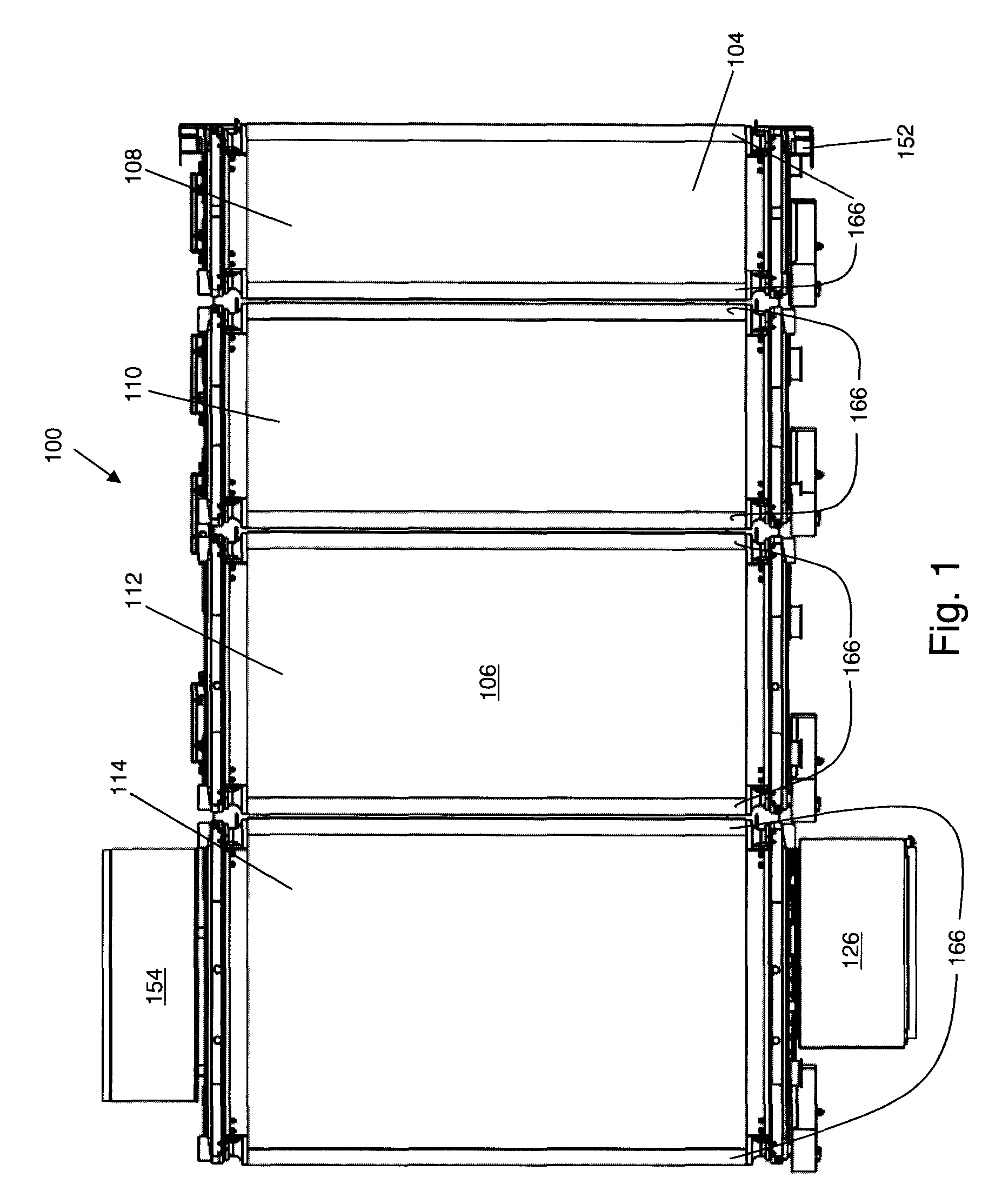
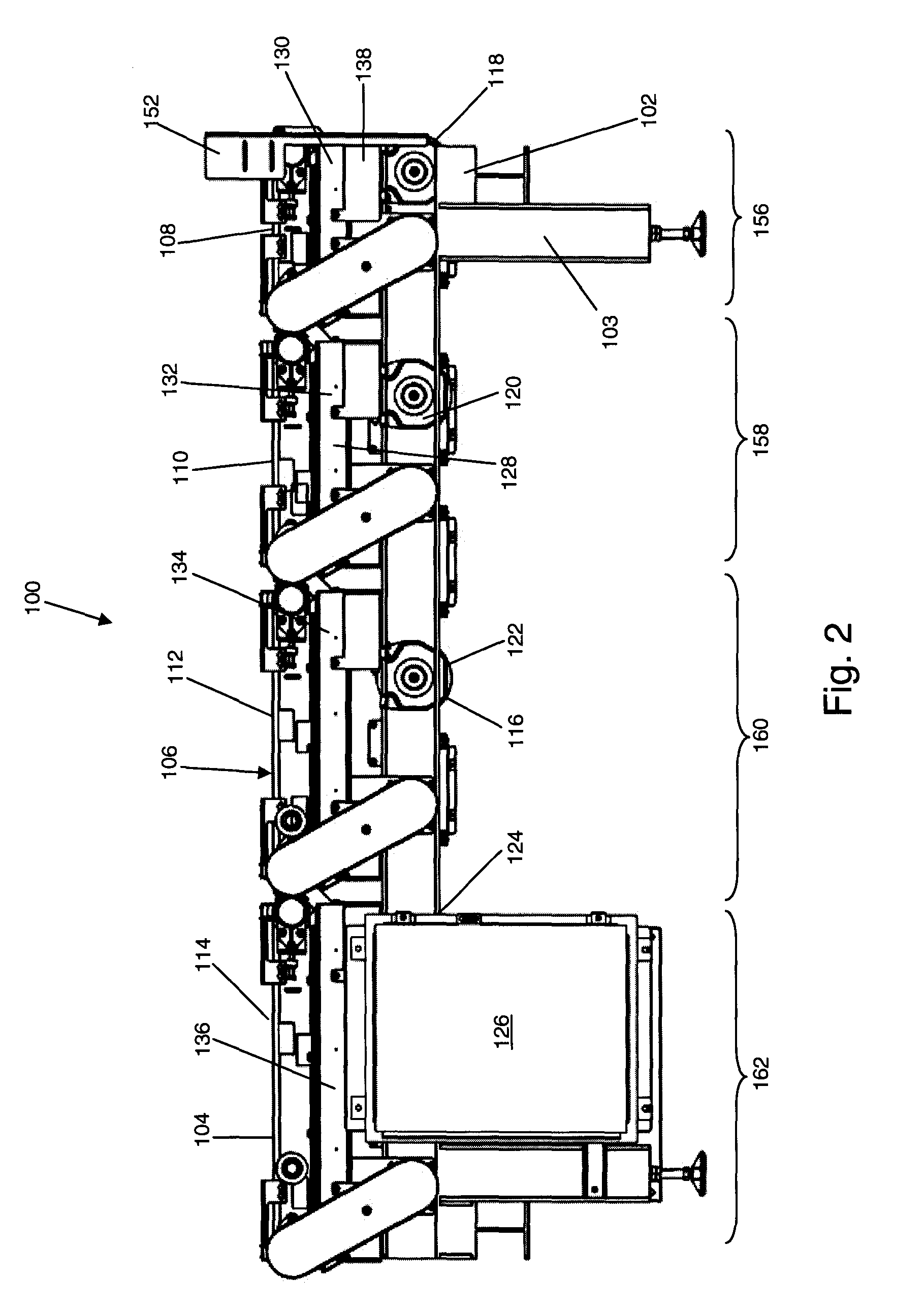
Multiple conveyor and scale weighing apparatus
ActiveUS7279645B1Reduce errorsEliminate high frequency noiseWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowSpecial purpose weighing apparatusConveyor beltMaster processor
The weighing apparatus may have a plurality of conveyor belts, a plurality of physical scales, a plurality of logical scales and a master processor. The master processor may receive weight results from the plurality of physical and logical scales and may determine a net weight of said package. The weighing apparatus may also include a plurality of slave processors.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO INC
Apparatus for and method of measuring blood pressure
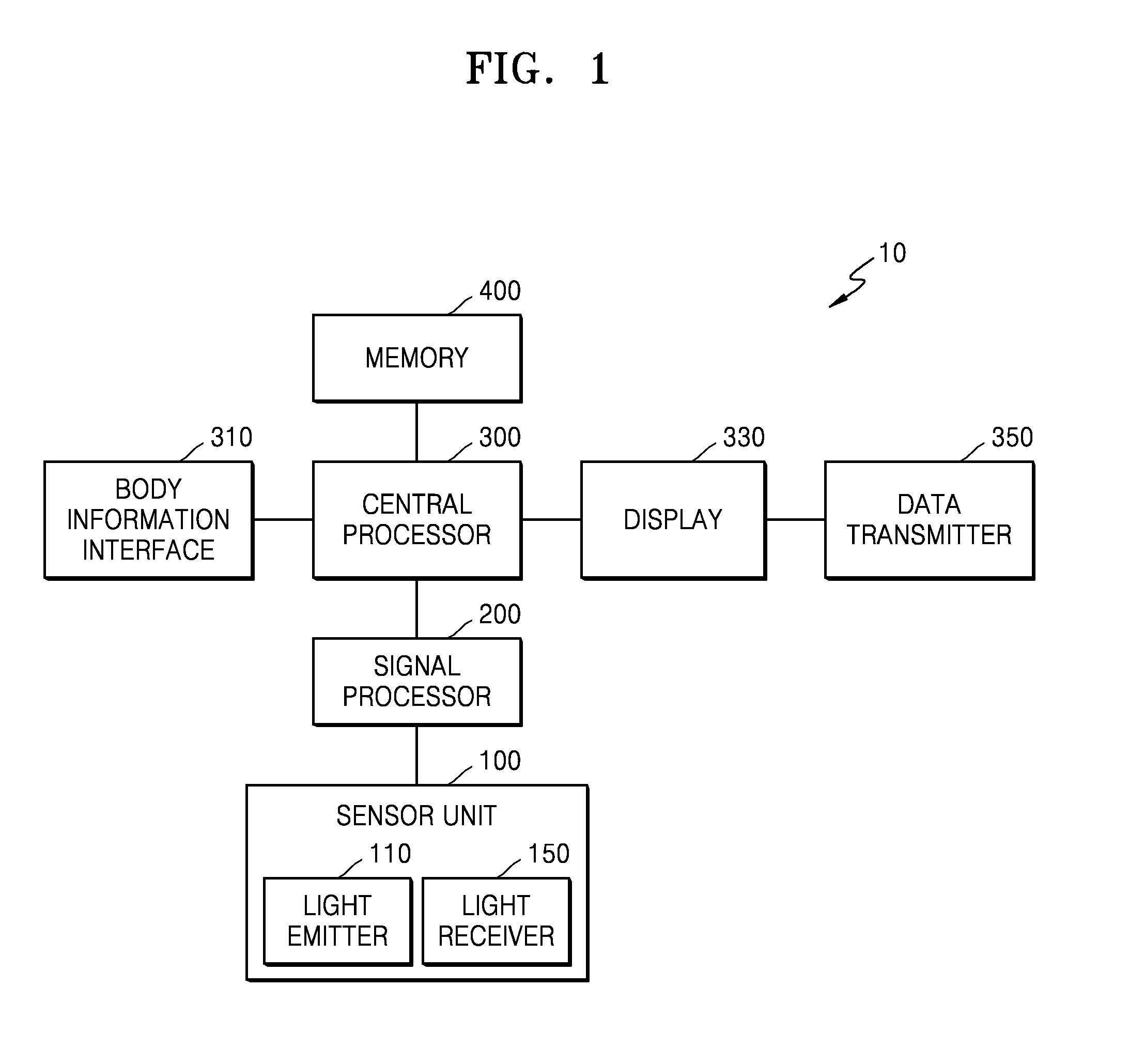
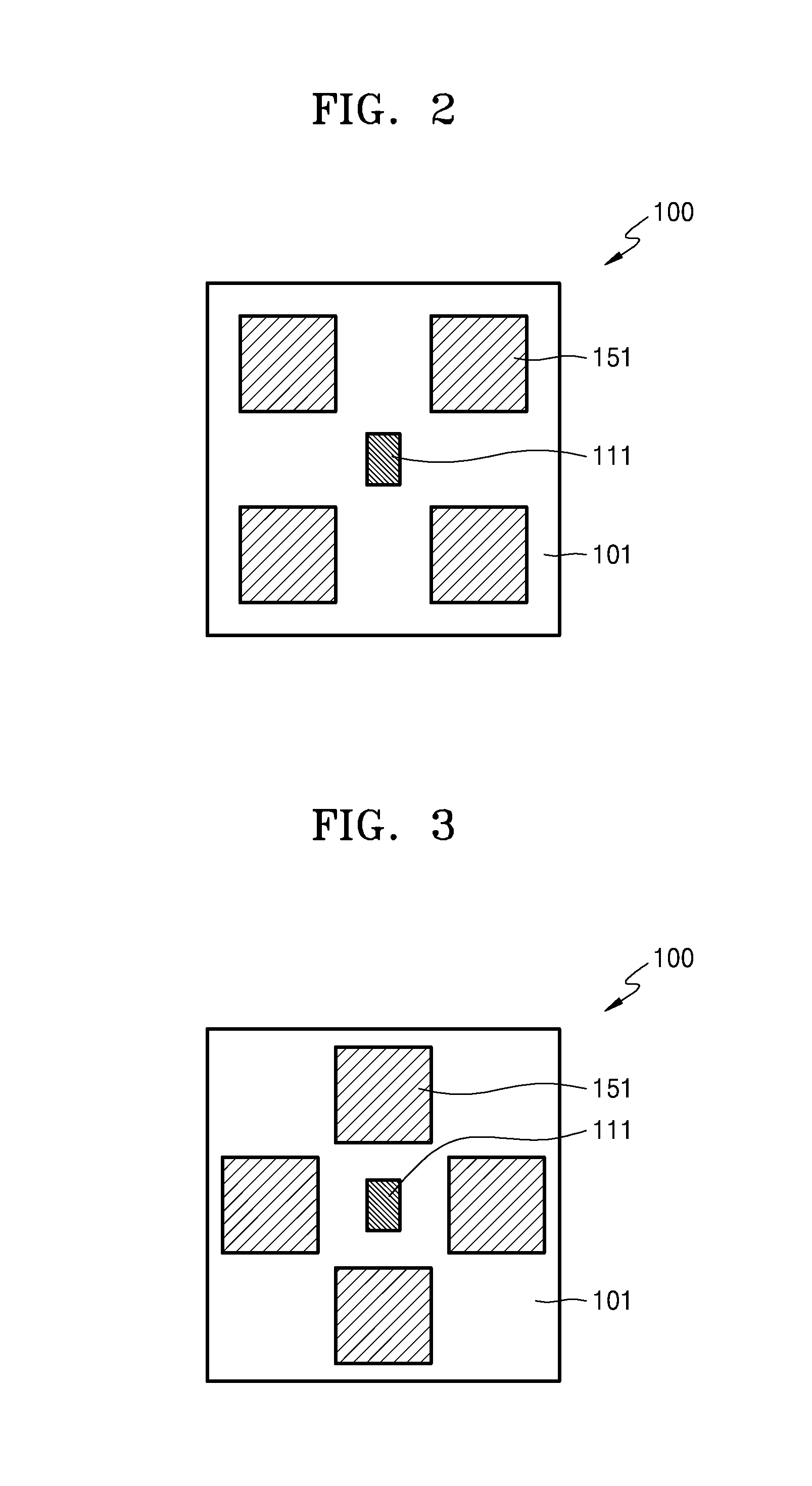
ActiveUS20160256116A1Remove high-frequency noiseEliminate high frequency noiseDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using lightBiomedical engineeringBody segment
An apparatus for and a method of measuring blood pressure are provided. The apparatus includes a sensor configured to radiate light to a body part, and detect a light signal that is changed due to the body part. The apparatus further includes a signal processor configured to determine a bio signal based on the light signal; and a central processing unit configured to determine a blood pressure based on the bio signal and a blood pressure estimation algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249440A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249433A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
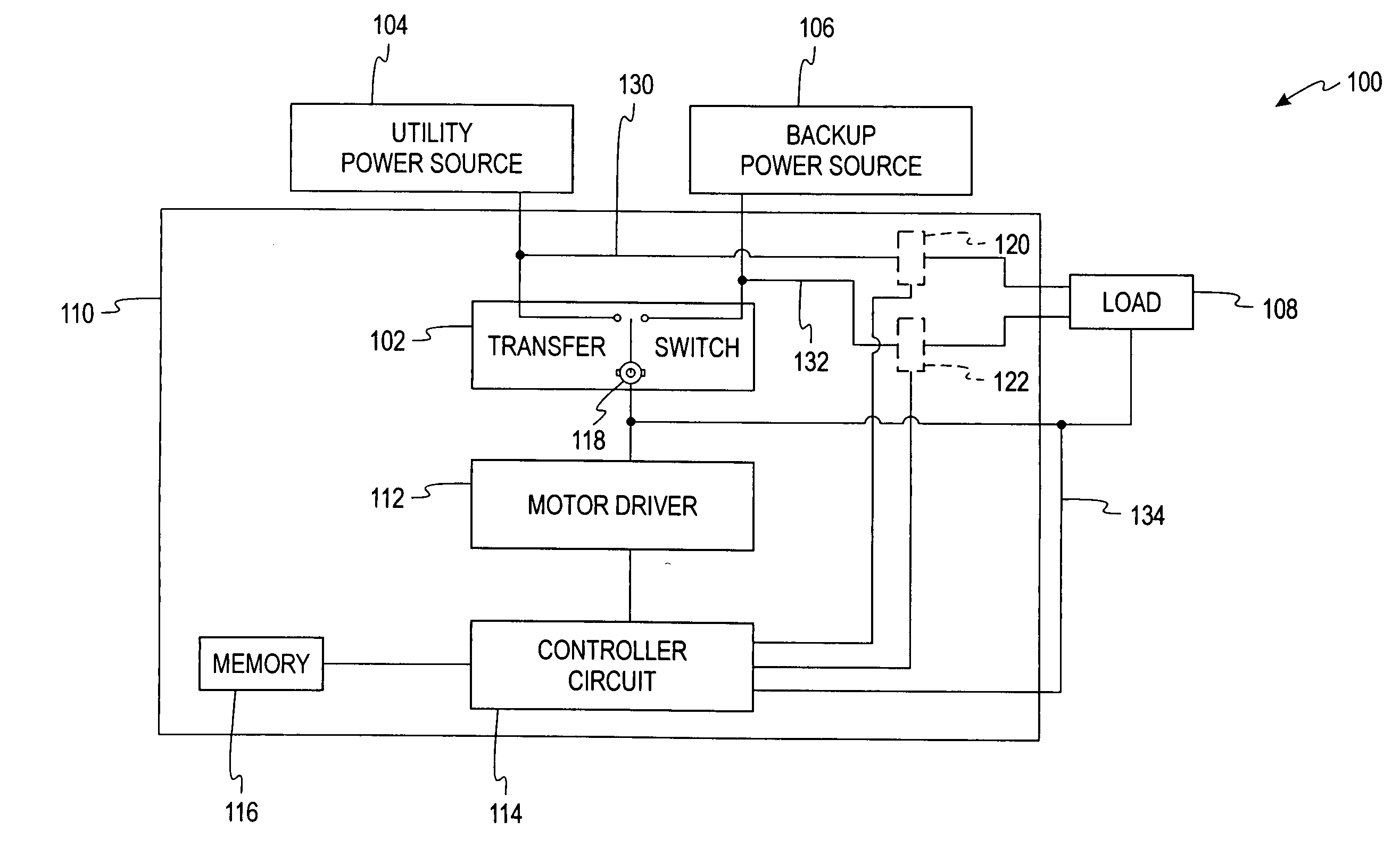
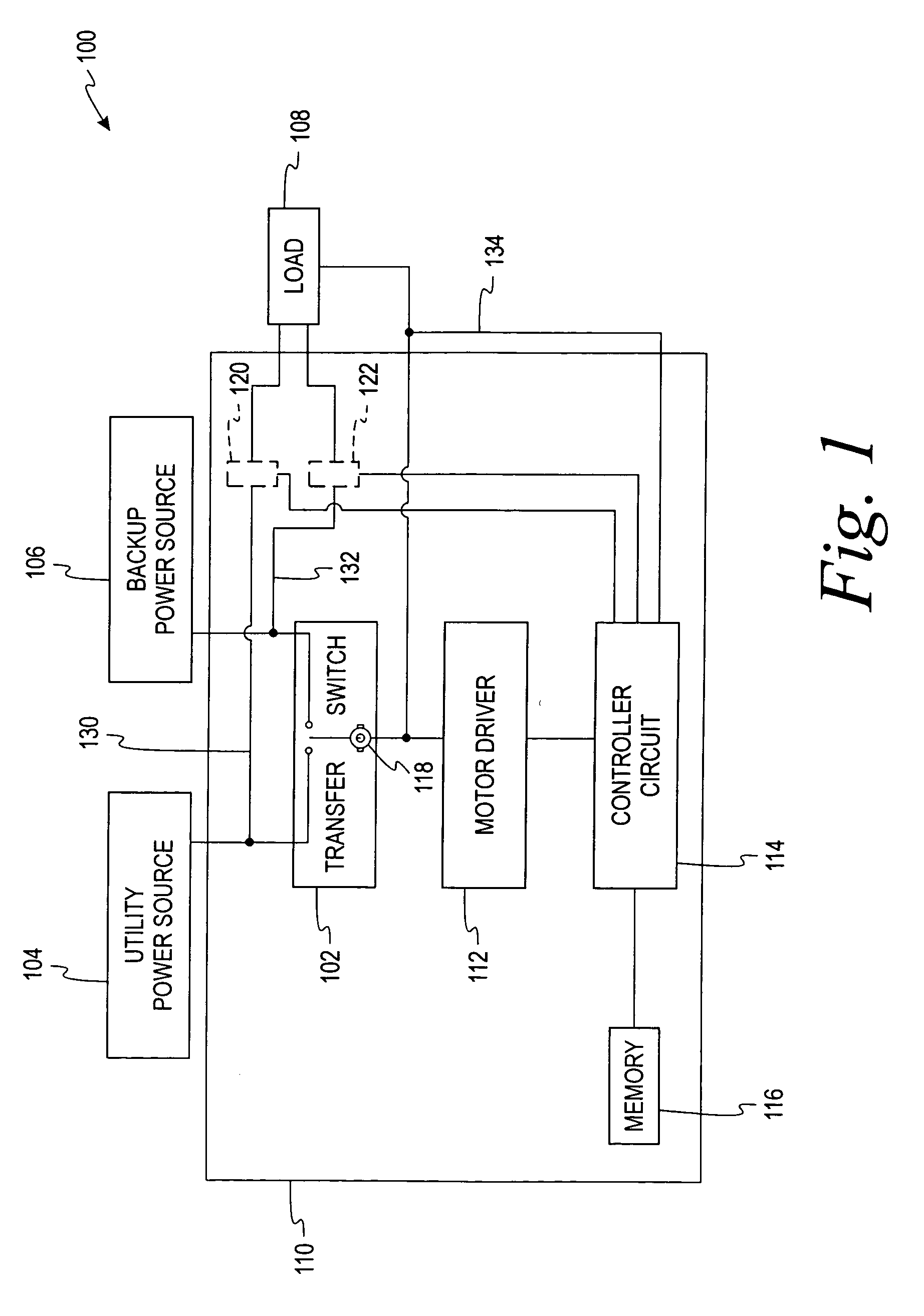
Apparatus and method for controlling a transfer switch mechanism
ActiveUS20080100248A1Eliminate high frequency noiseElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersTransfer switchEngineering
A controller for an automatic transfer switch mechanism in an electrical distribution panel, which automatically determines motor phase by monitoring the back EMF voltage of the motor when no power is applied to the motor as defined by a pulse width modulation circuit. Phase comparisons of the voltage on the line and load sides of the transfer switch mechanism determine the position of the transfer switch mechanism.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
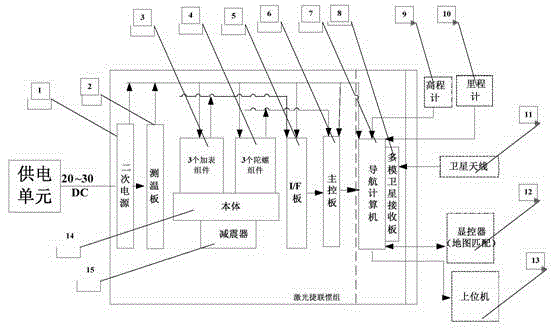
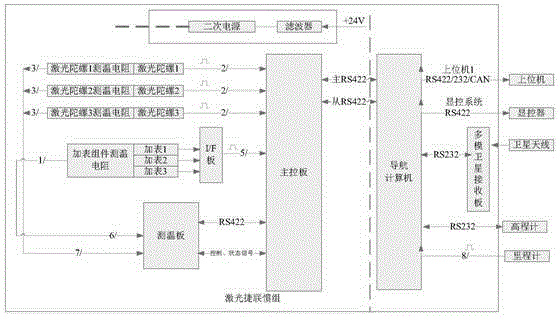
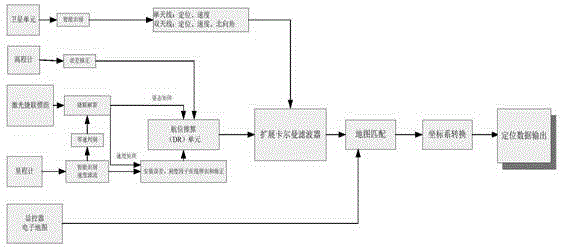
Vehicle positioning device based on laser gyroscope strapdown inertial measurement unit
ActiveCN104154916AEliminate latch-upEffectively remove high frequency noiseNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeEngineering
The invention, aiming to enhance a rapid maneuvering capability and an object targeting precision of a weapon system and satisfy requirements of a quick response, a high precision, a strong independence and a good reliability of the system on a vehicle positioning device, provides the vehicle positioning device based on a laser gyroscope strapdown inertial measurement unit. The vehicle positioning device includes: a laser strapdown inertial measurement unit in which a laser gyroscope is employed, an odometer assembly used for measuring a running speed and a running distance of a vehicle on ground, an elevation meter used for obtaining an altitude by measuring an atmosphere pressure of a level of the vehicle, a multimode satellite system which is compatible with single antenna and double antennas, and a display controlling apparatus assembly used for carrying out an intelligent match between positioning information of the vehicle positioning device and a road network electronic map. By means of advantages of being high in precision, stable in performance, wide in dynamic range, short in response time and high in reliability of the laser gyroscope, a positioning and orienting function which is high in precision, strong in independence and good in reliability is achieved through methods, such as a gyroscope demodulation technology, a multi-information fusion technology and the like, on the basis of a digital filter.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACE LAUNCH TECH +1
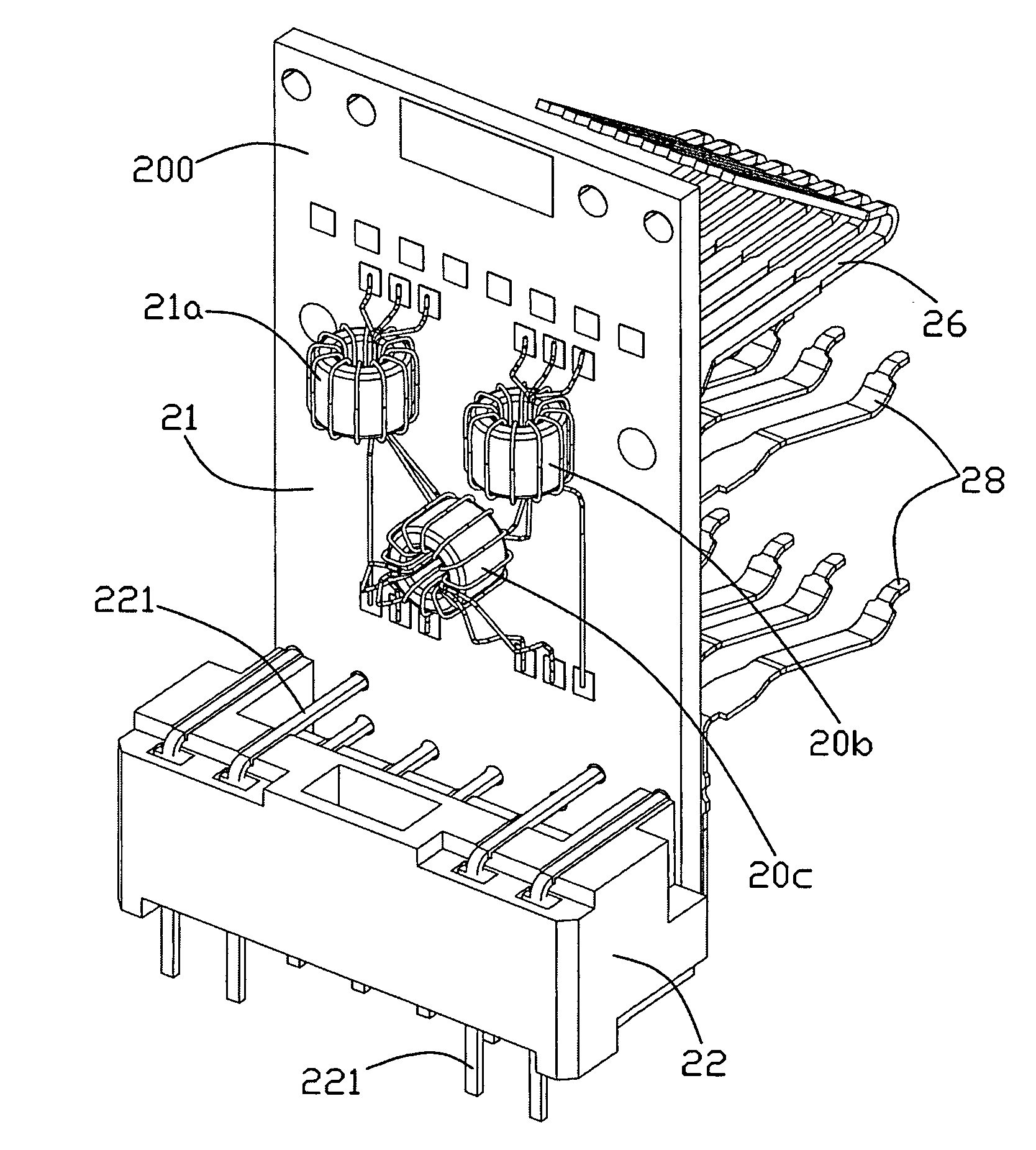
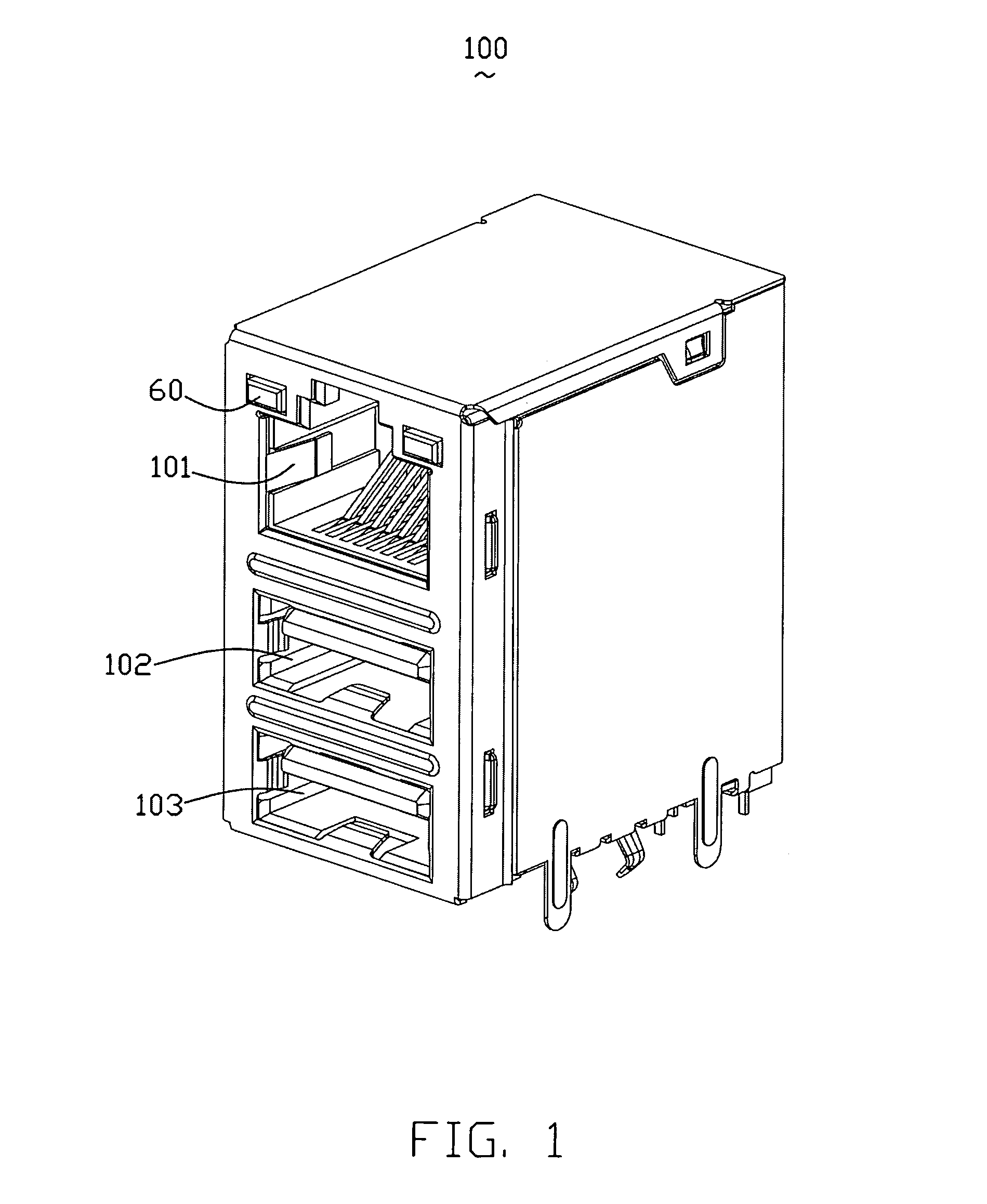
Modular jack having an improved magnetic module
InactiveUS7670183B2Eliminate high frequency noiseLow costCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesEngineeringToroidal coil
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249435A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Multi-person through-wall time varying breathing signal detection method based on VMD
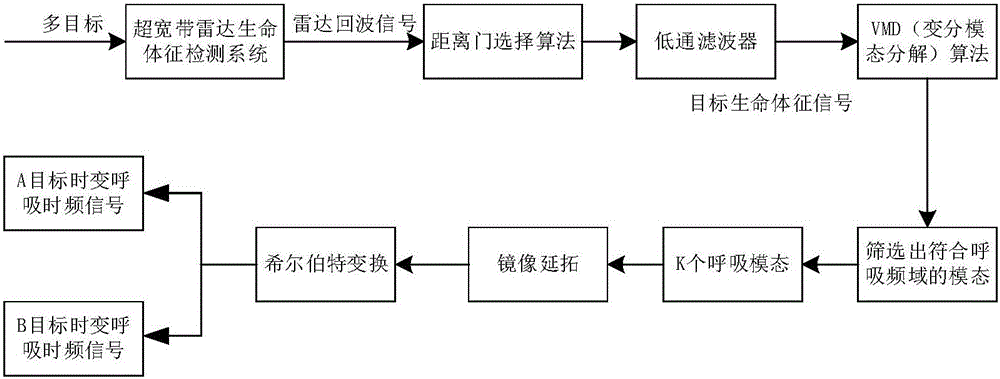
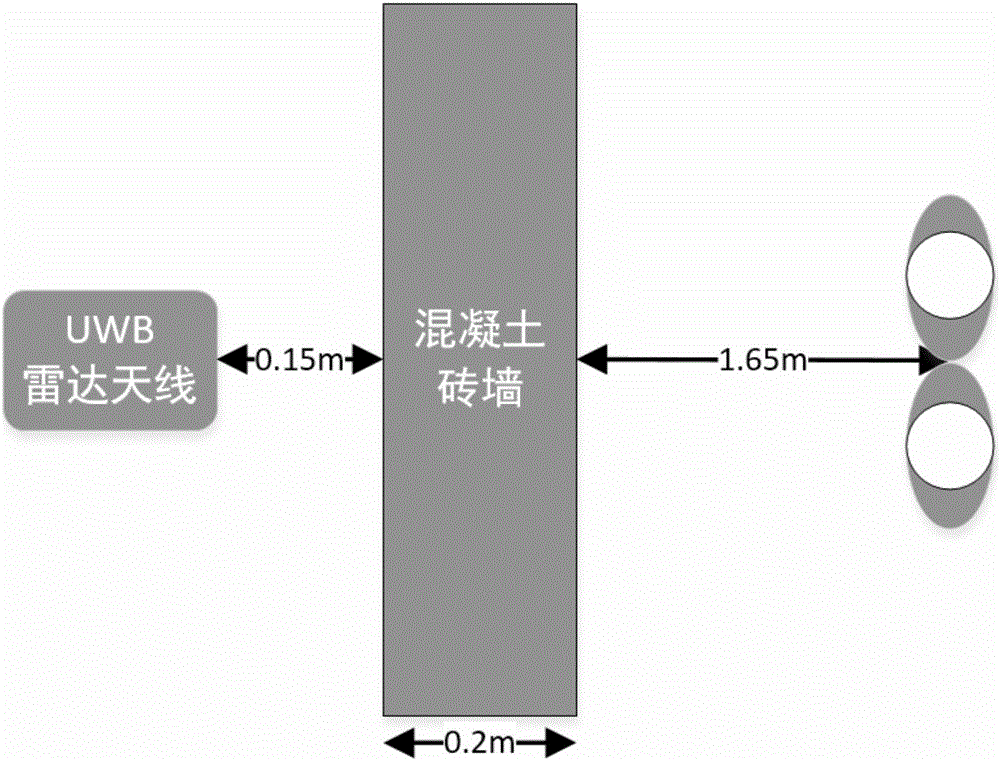
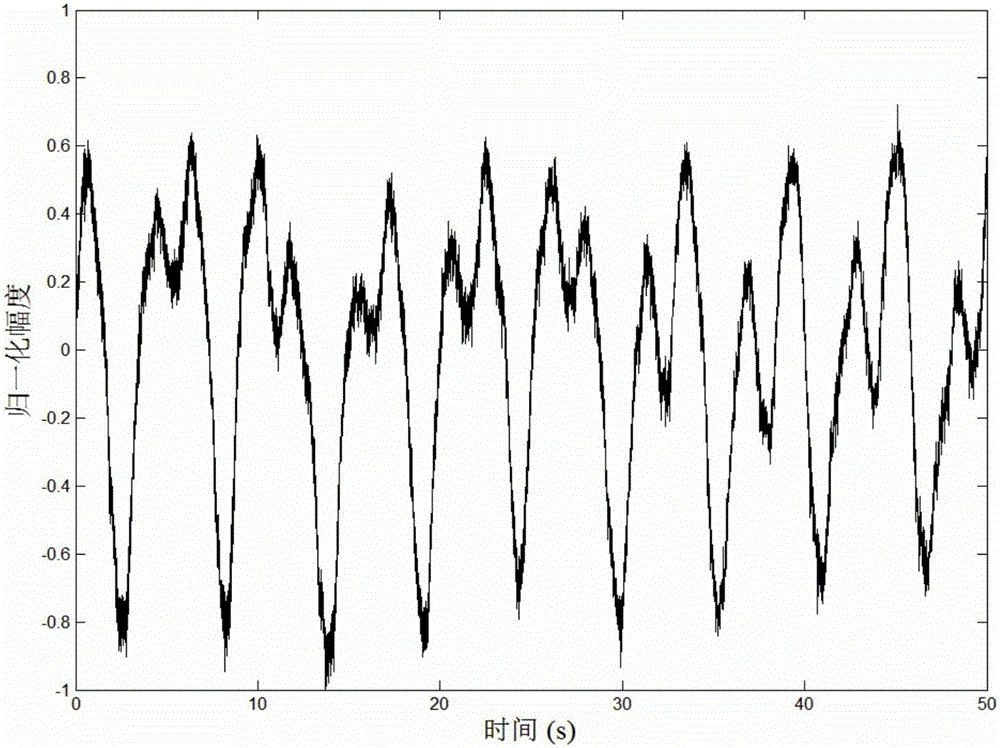
ActiveCN106019271ARealize synchronous trackingEliminate distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a multi-person through-wall time varying breathing signal detection method based on VMD, comprising the steps of: an ultra wide band emission antenna emitting narrow pulse, through human thoracic cavity micro-doppler vibration, echo being received by a receiving antenna, and performing slow time sampling on ultra wide band radar echo to obtain a through-wall human body echo signal matrix; calculating the variance of each distance door through a distance door selection algorithm, the one with a largest variance being a distance door where a multi-person target exists, and employing a low pass filter to eliminate high frequency interference and superfluous frequency components; utilizing a VMD algorithm to perform mode decomposition on filtered signals, and iterating sub-signals to obtain effective information meeting the number and frequency band of breathing; and performing Hilbert transformation and time frequency treatment to obtain dynamic instantaneous information including smooth breathing characteristics. The method can effectively eliminate interference harmonic wave of different breathing components, remove metope interference, and enhance weak breathing signals, and has the characteristics of strong interference immunity and accurate time varying tracking characteristics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor sensorless control method based on expansion state observer
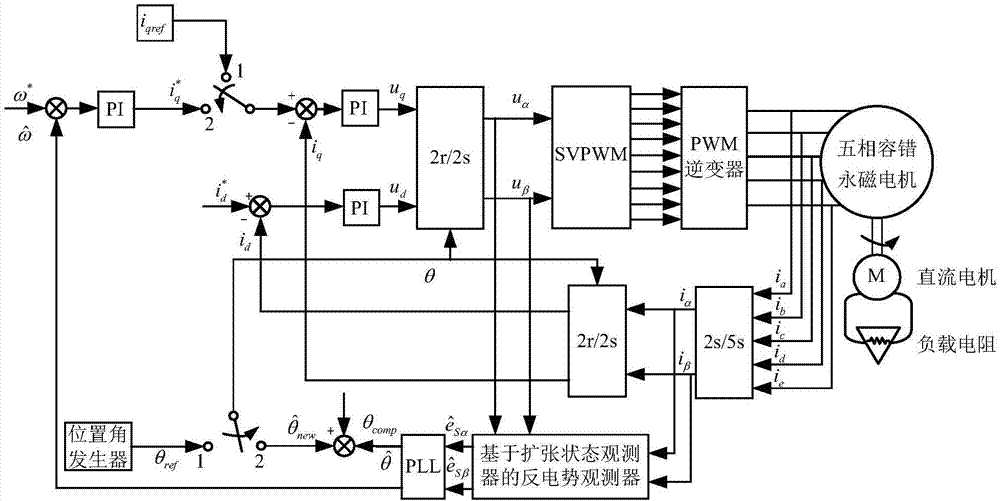
ActiveCN107134964ASolve the problem of zero speed startObservation of back EMFElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlState variableState observer
The invention discloses a novel five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor sensorless control method based on an expansion state observer. According to the method, the counter potential in the current state equation under a two-phase stationary coordinate system acts as interference quantity, correct estimation of the disturbance quantity can be realized without the differential and filtering link of the state variable, and the rotating speed and the rotor position of the motor can be obtained by using a phase-locked loop observer according to the observed counter potential. Meanwhile, a rotor position error compensation link changing along with the rotating speed of the motor is designed based on selection of the observer parameters so that novel five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor sensorless control based on the ESO can be realized. According to the designed novel counter potential observer, the observer is simple in gain selection method and has great adaptability and robustness for the rotating speed and load change of the motor so that use of the filter can be avoided, and reliable operation of the five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet synchronous motor sensorless system can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
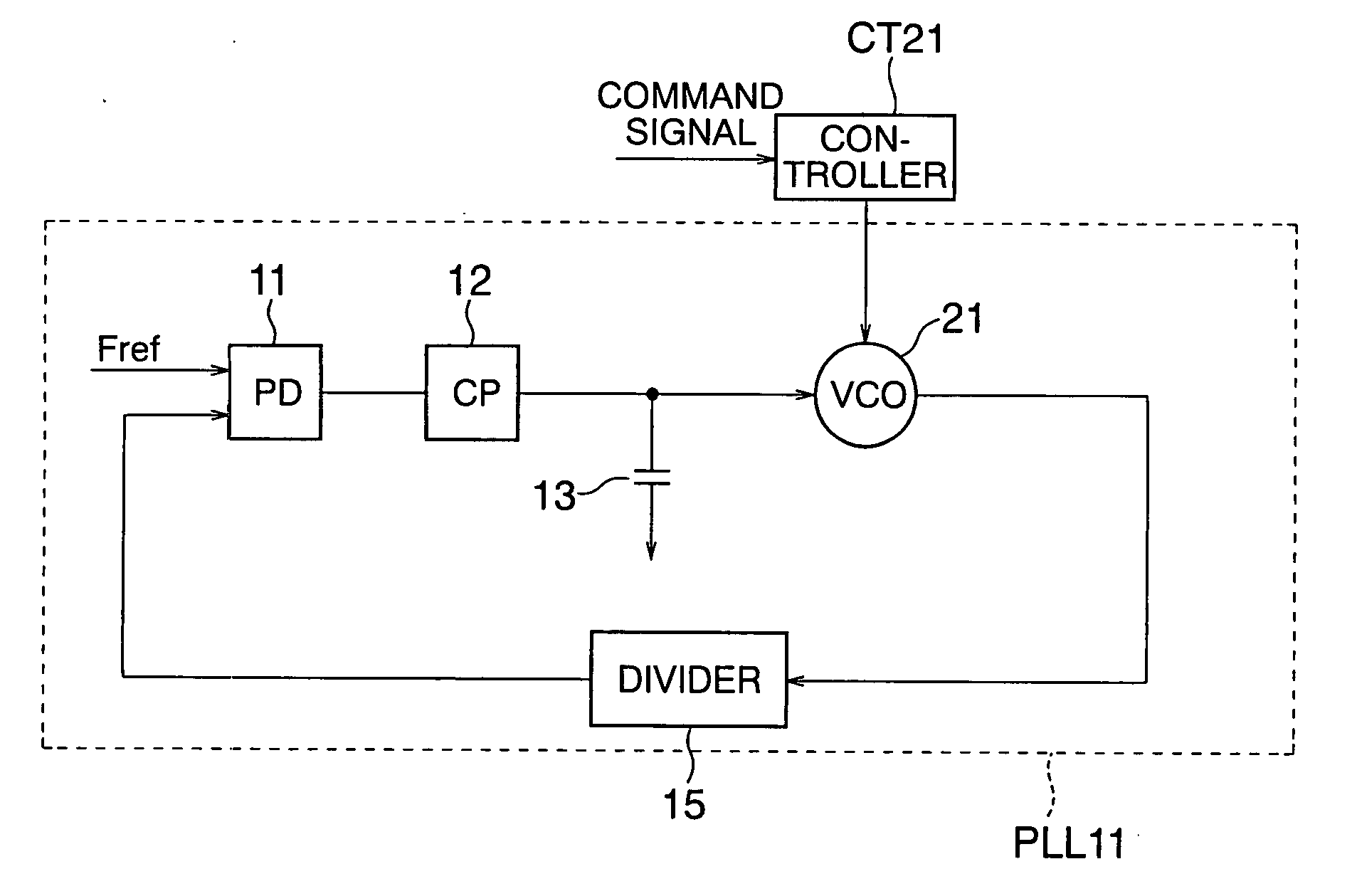
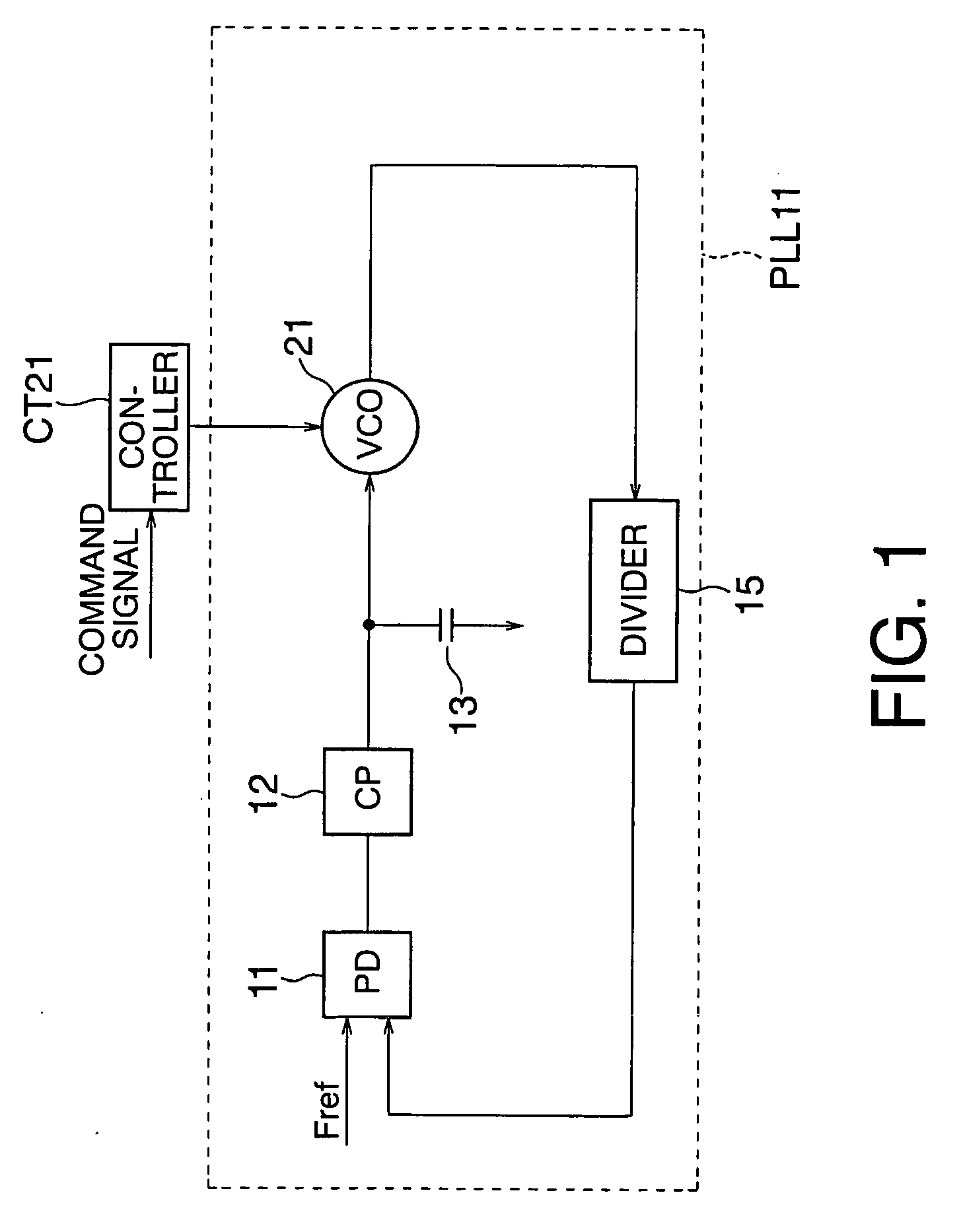
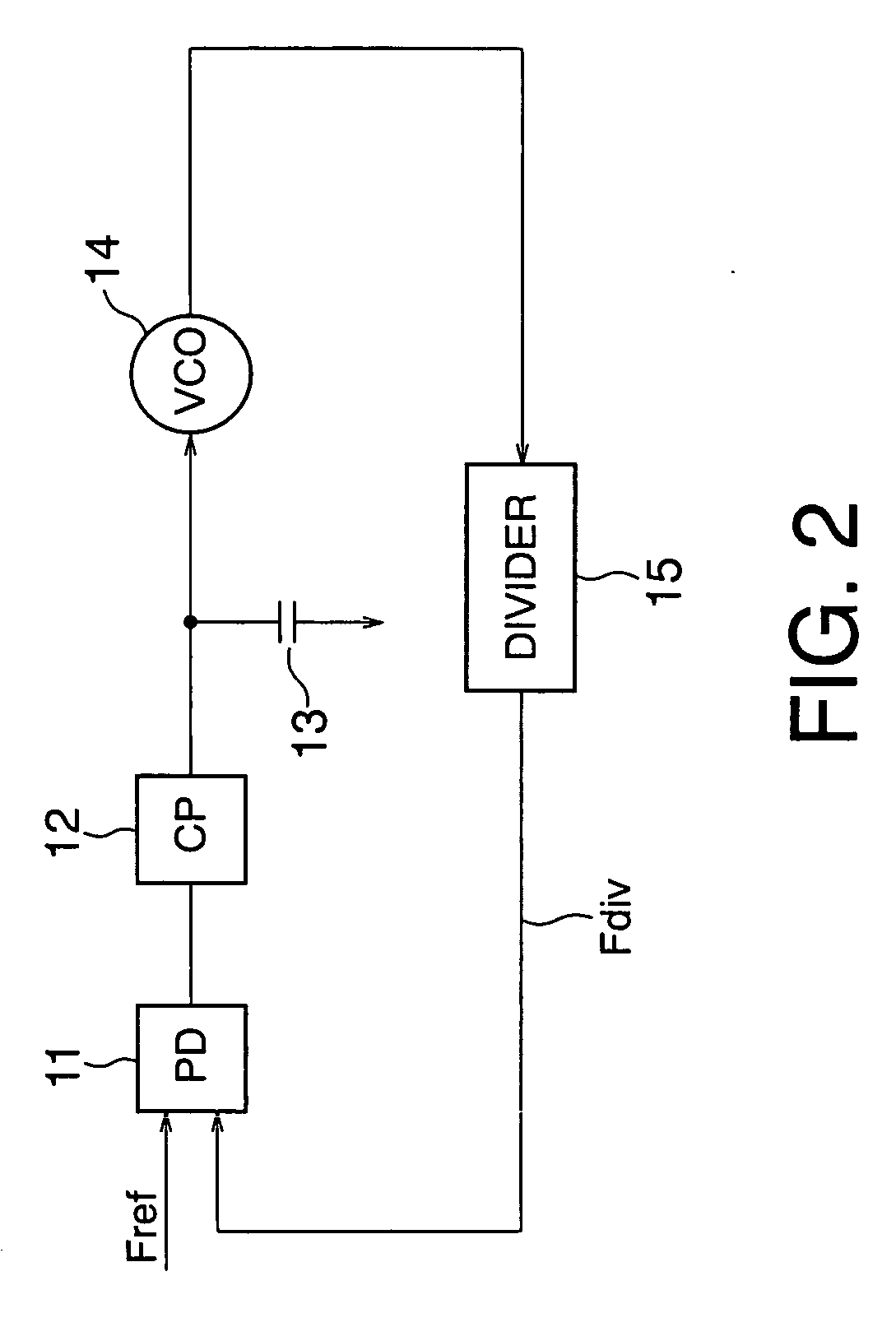
Frequency synthesizer
InactiveUS20060158264A1Remove high-frequency noiseEliminate high frequency noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitancePhase locked loop circuit
According to the present invention, there is provided a frequency synthesizer comprising: a phase locked loop circuit which receives a reference signal having a reference frequency and a first signal having a first frequency, compares phases of the reference signal and first signal, applies a control voltage based on a phase comparison result to an input terminal of a voltage controlled oscillator to generate a second signal having an oscillation frequency and output the second signal from an output terminal, and supplies the second signal to a divider to divide the frequency of the second signal and output the first signal; and a controller which generates and supplies a control signal to the voltage controlled oscillator, wherein the voltage controlled oscillator has an arrangement in which a coil and variable capacitance are connected in parallel between the input terminal and output terminal, and one of a plurality of capacitances is selectively connected between the input terminal and output terminal by a switch in parallel with the variable capacitance, and ON / OFF of the switch is controlled by the control signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249441A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
InactiveUS20140249432A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Analog continuous time statistical processing
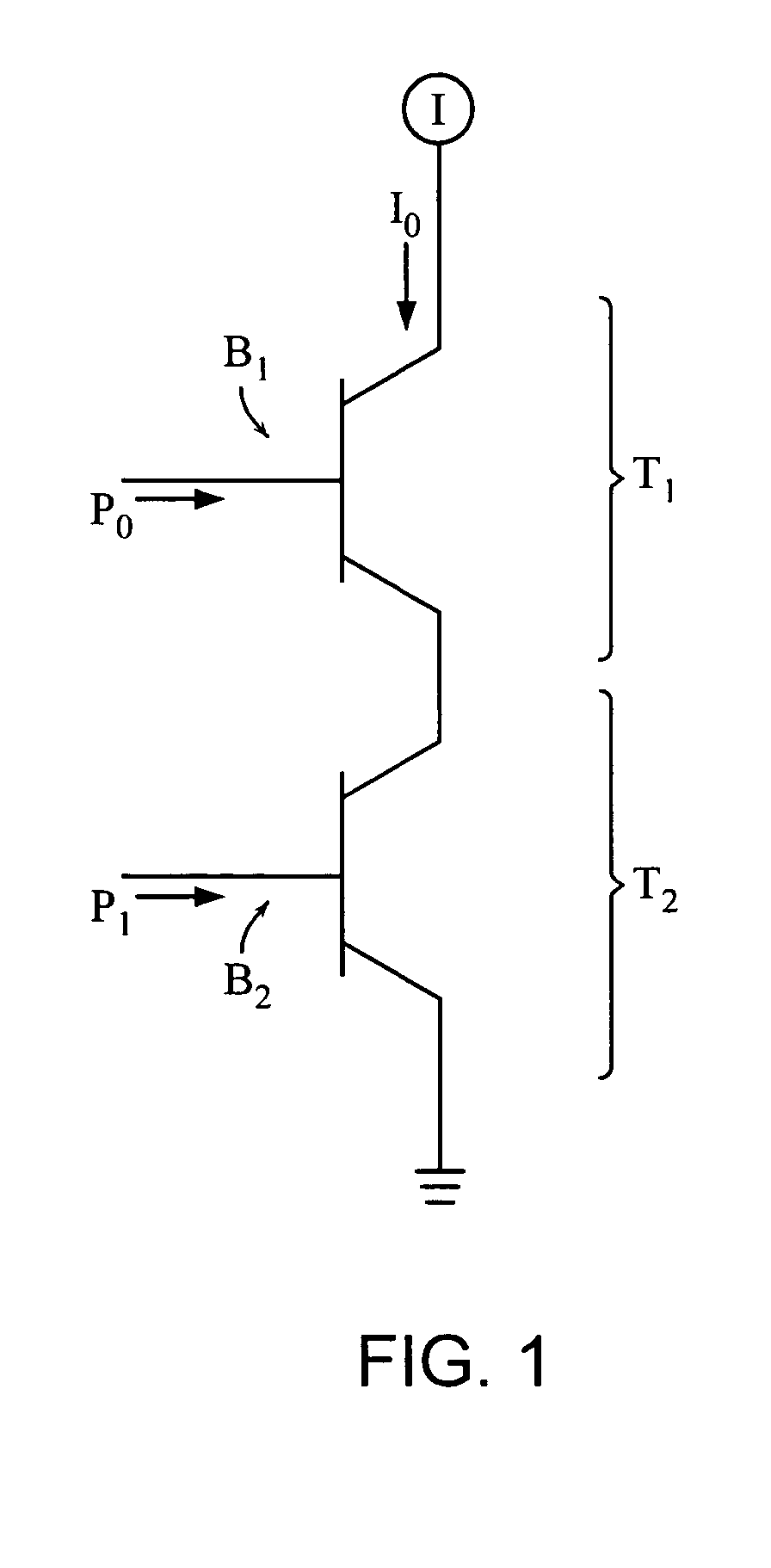
ActiveUS7209867B2Improve processing speedAvoid electricityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceOther decoding techniquesDigital signal processingLogic gate
Methods and apparatus for applications such as signal processing, analysis, and coding / decoding replace digital signal processing elements with analog components. By combining soft logic gates and filters, the functionality of complex finite state machines can be implemented.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com